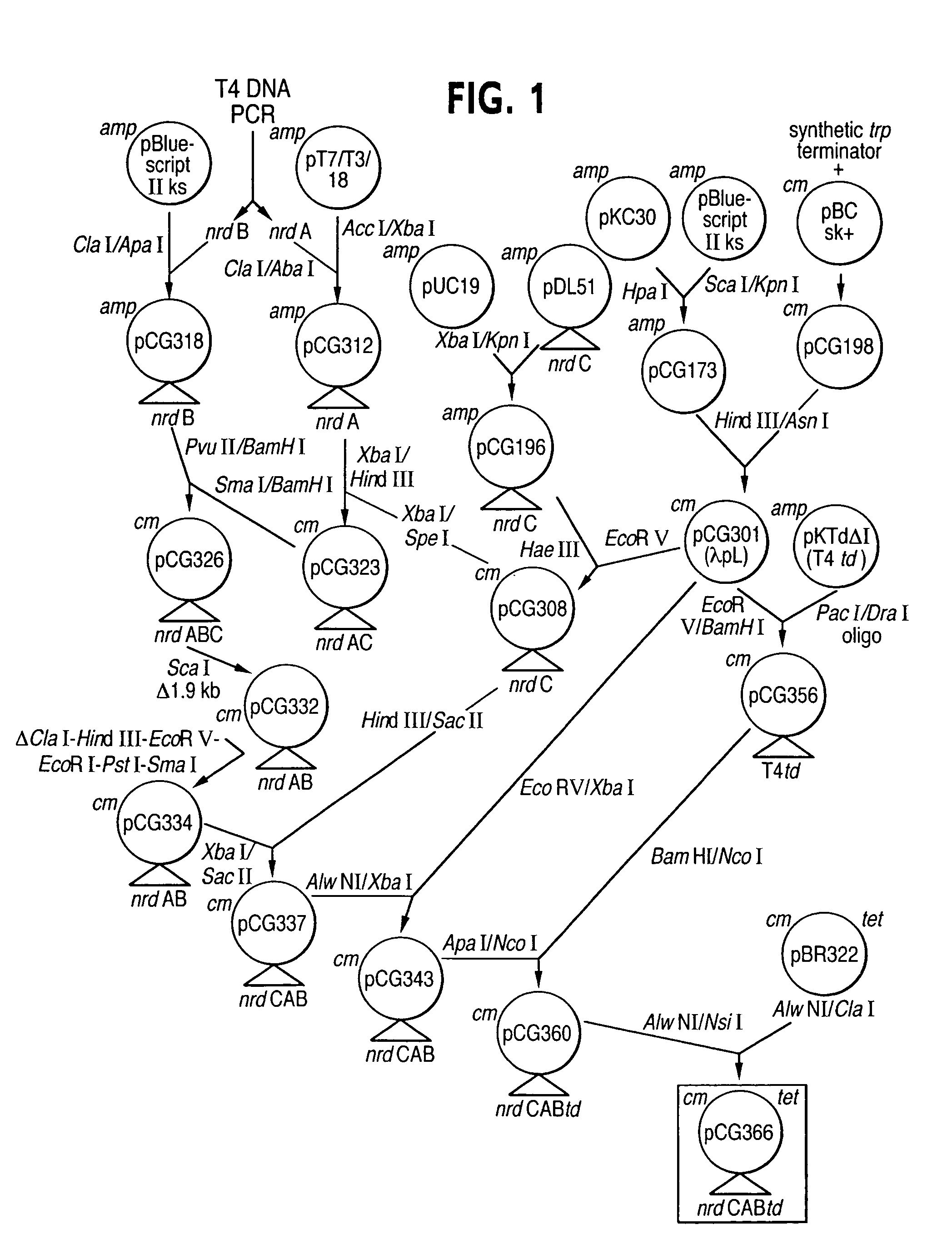
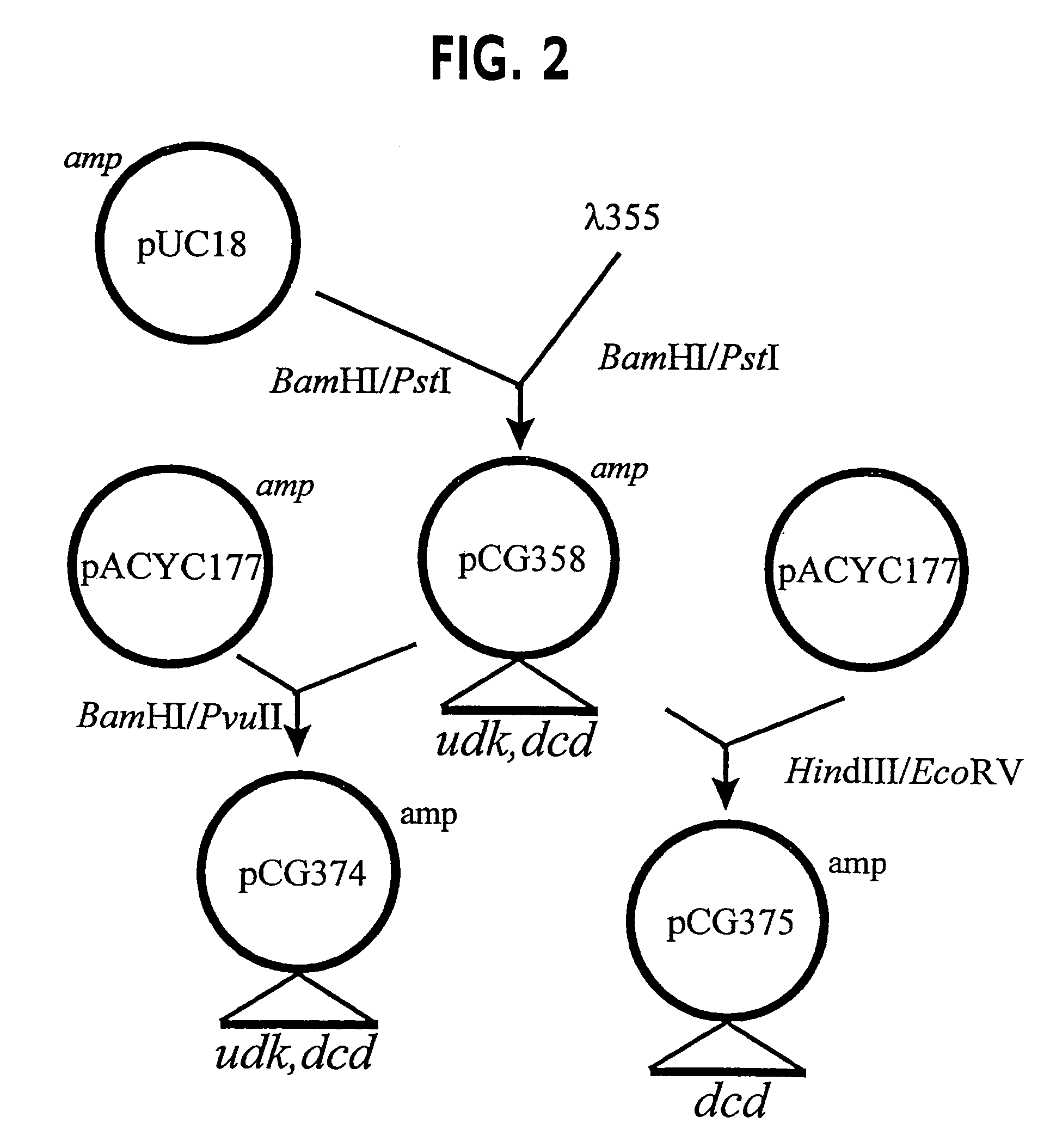
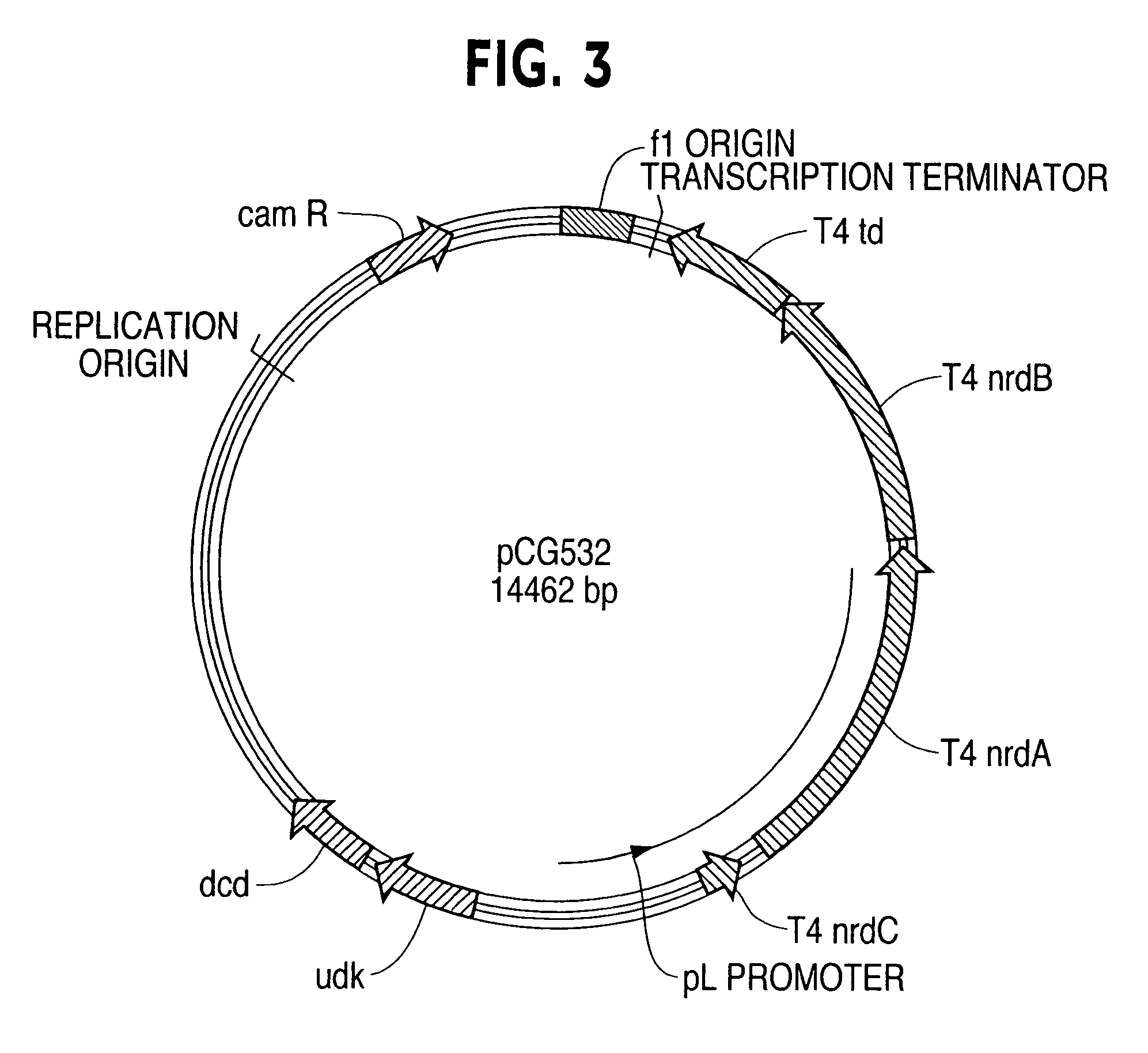
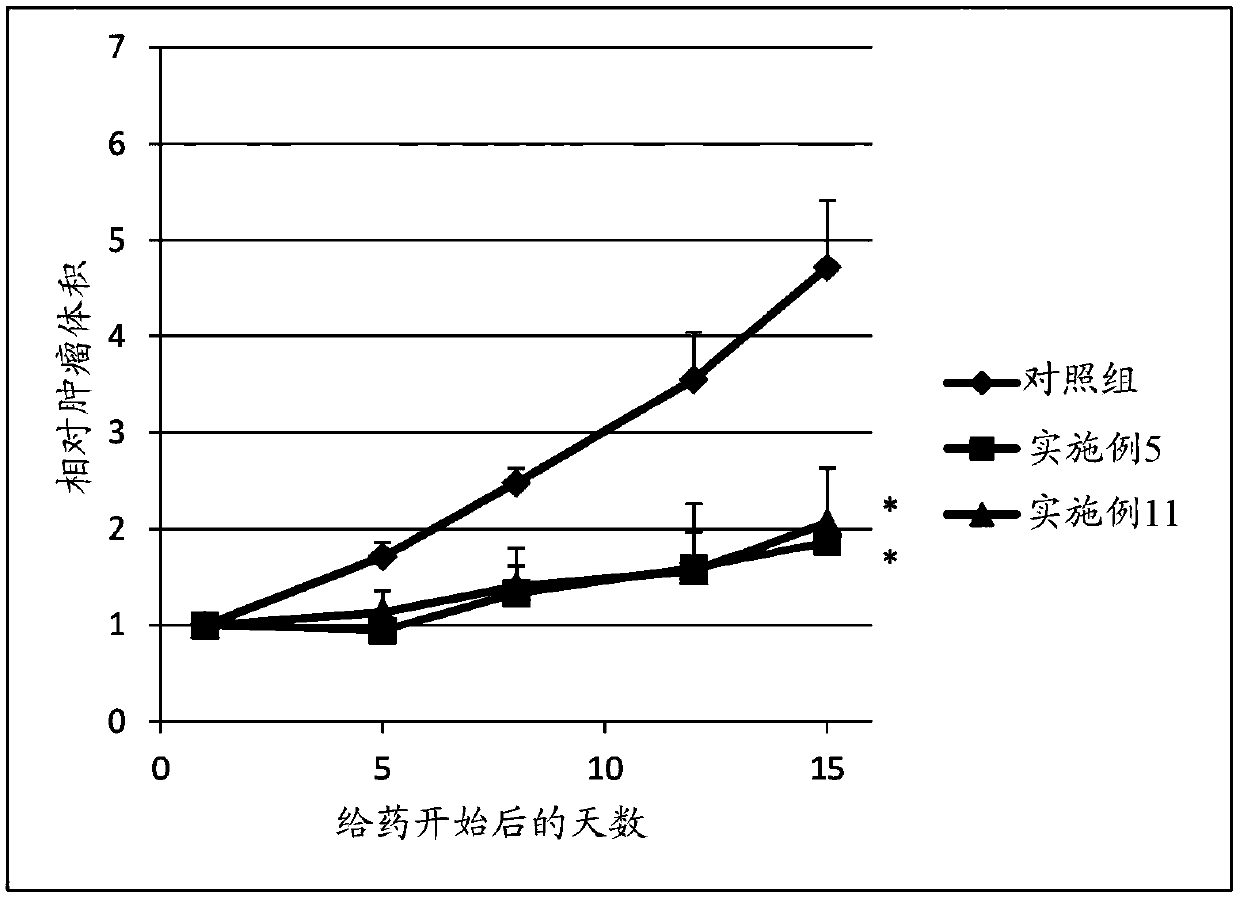
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Ribonucleotide reductase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
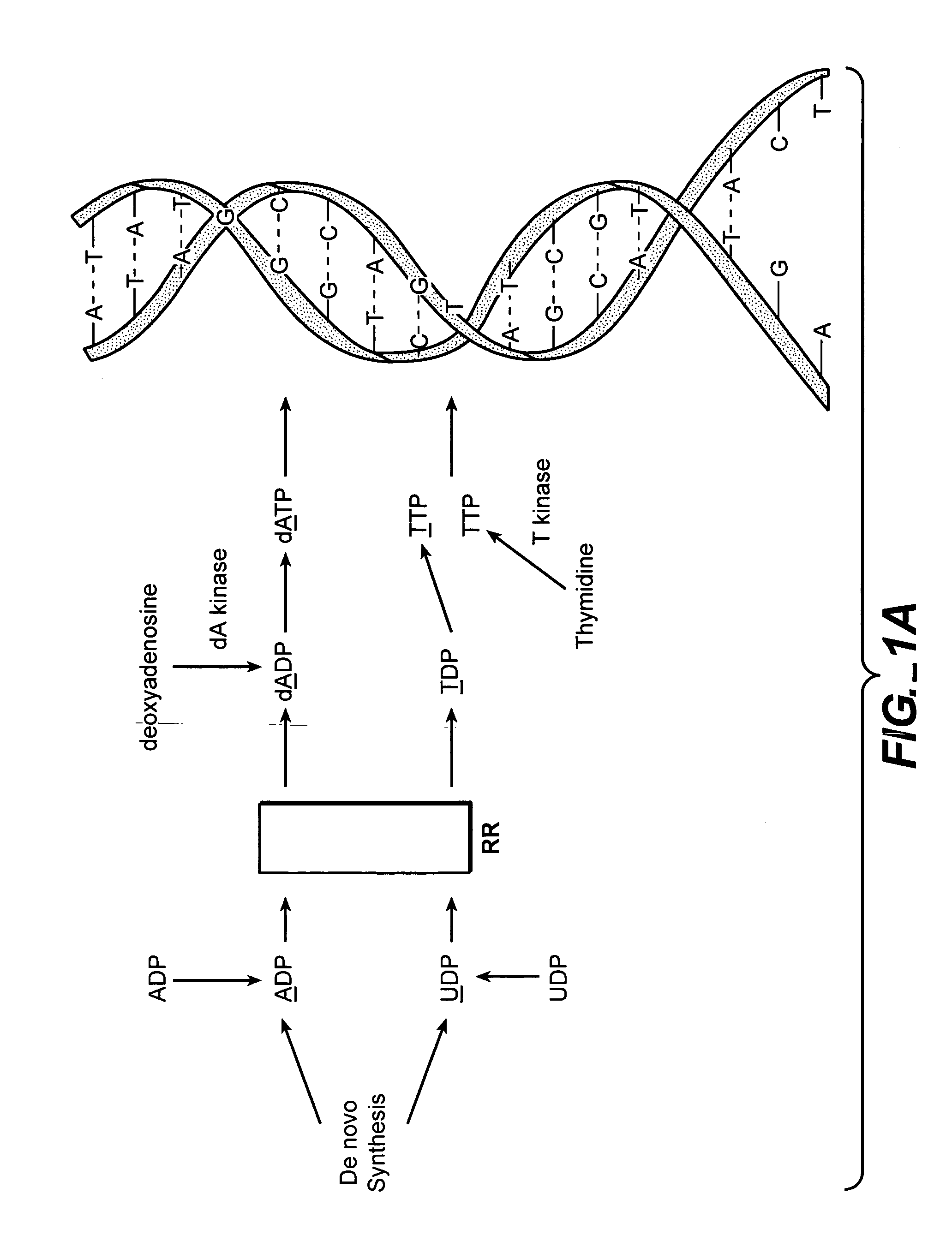
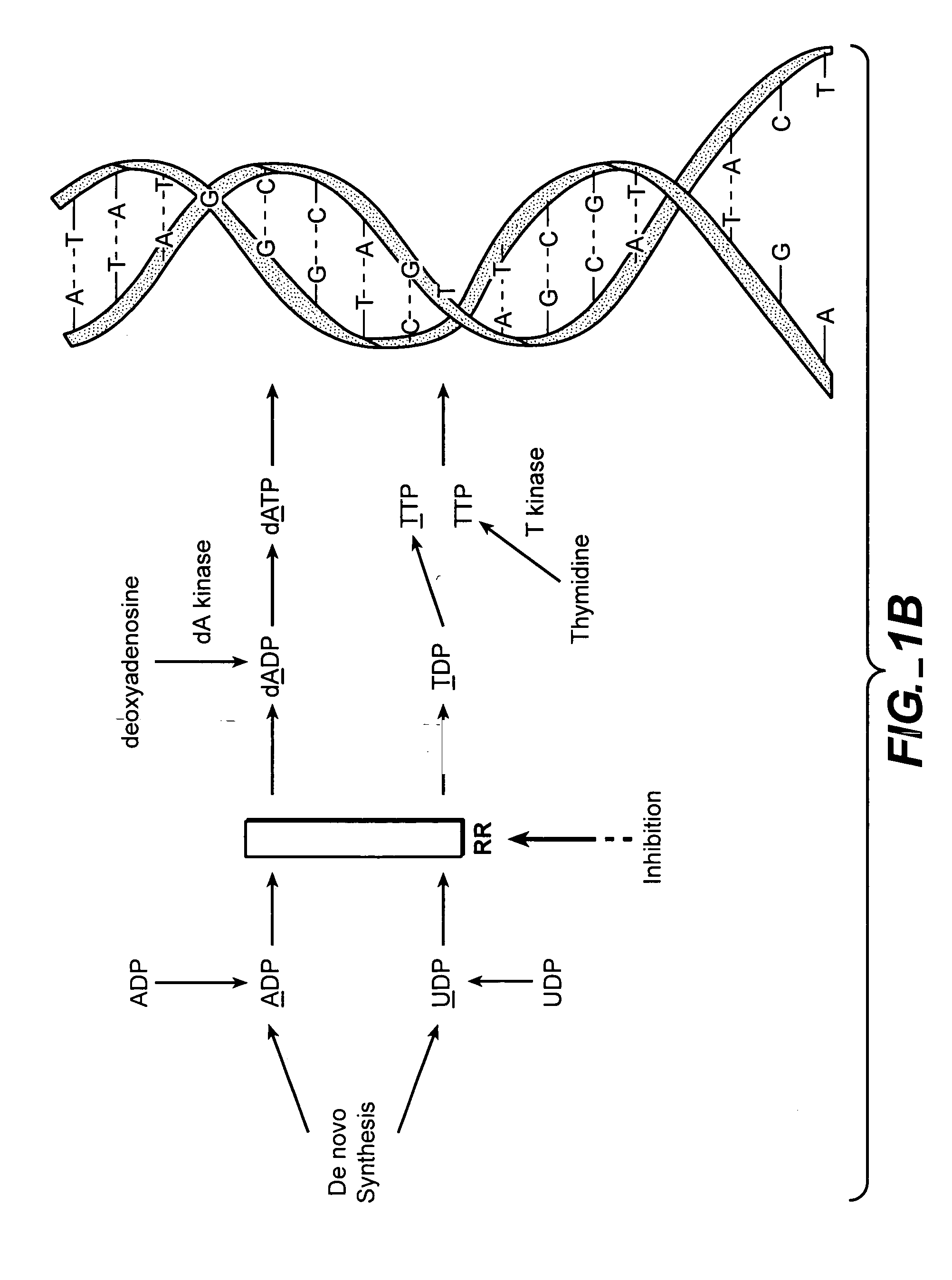
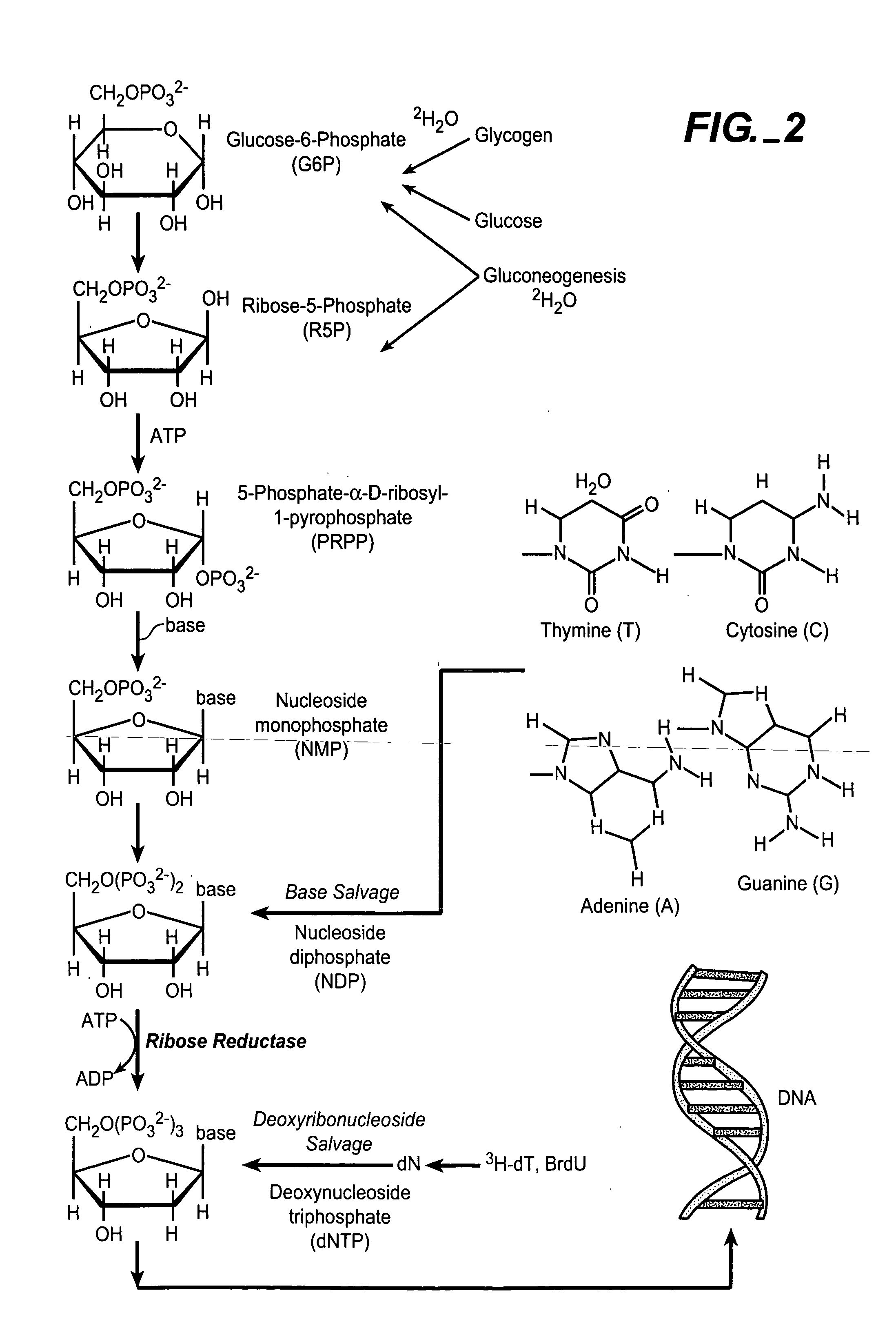
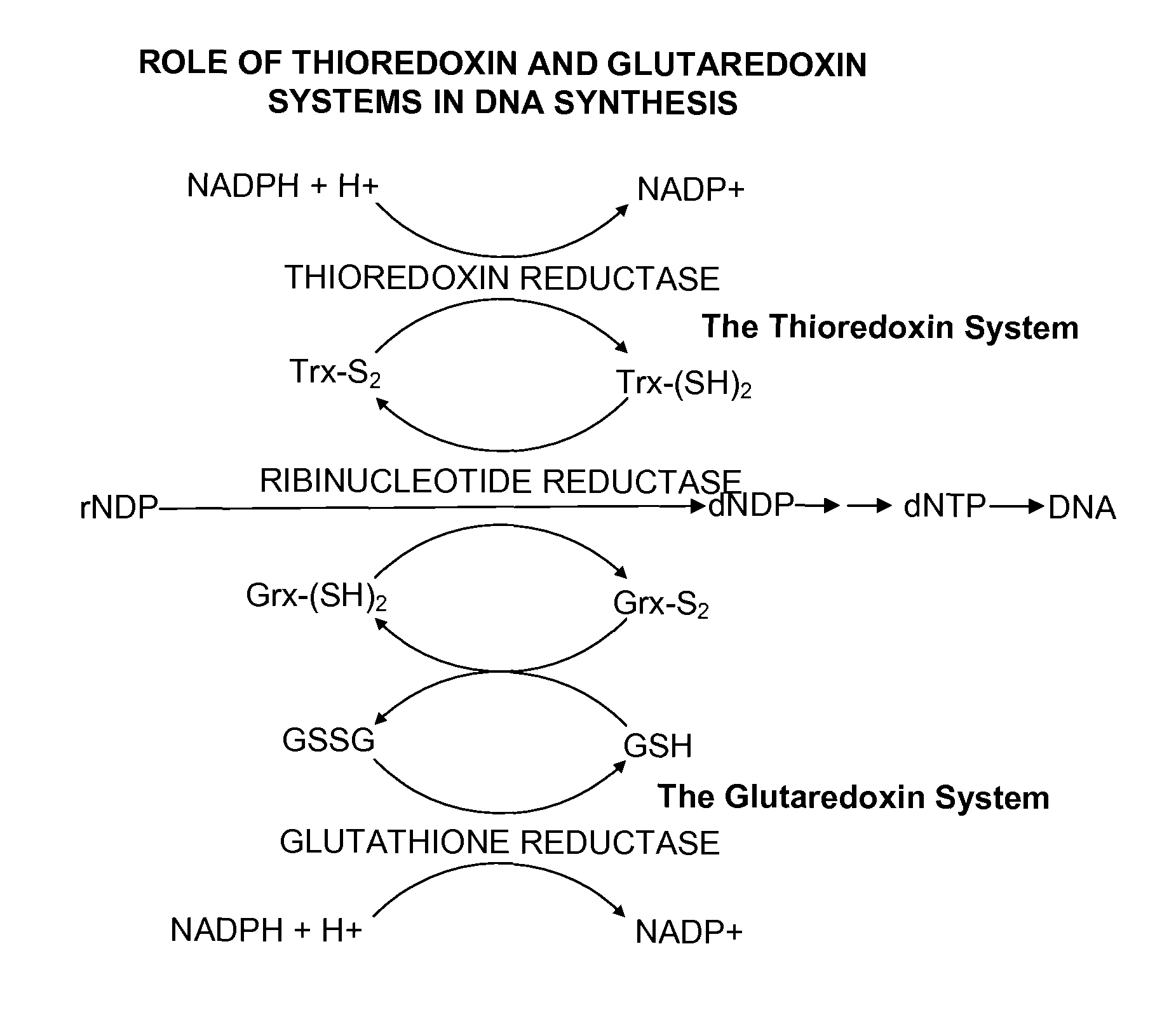
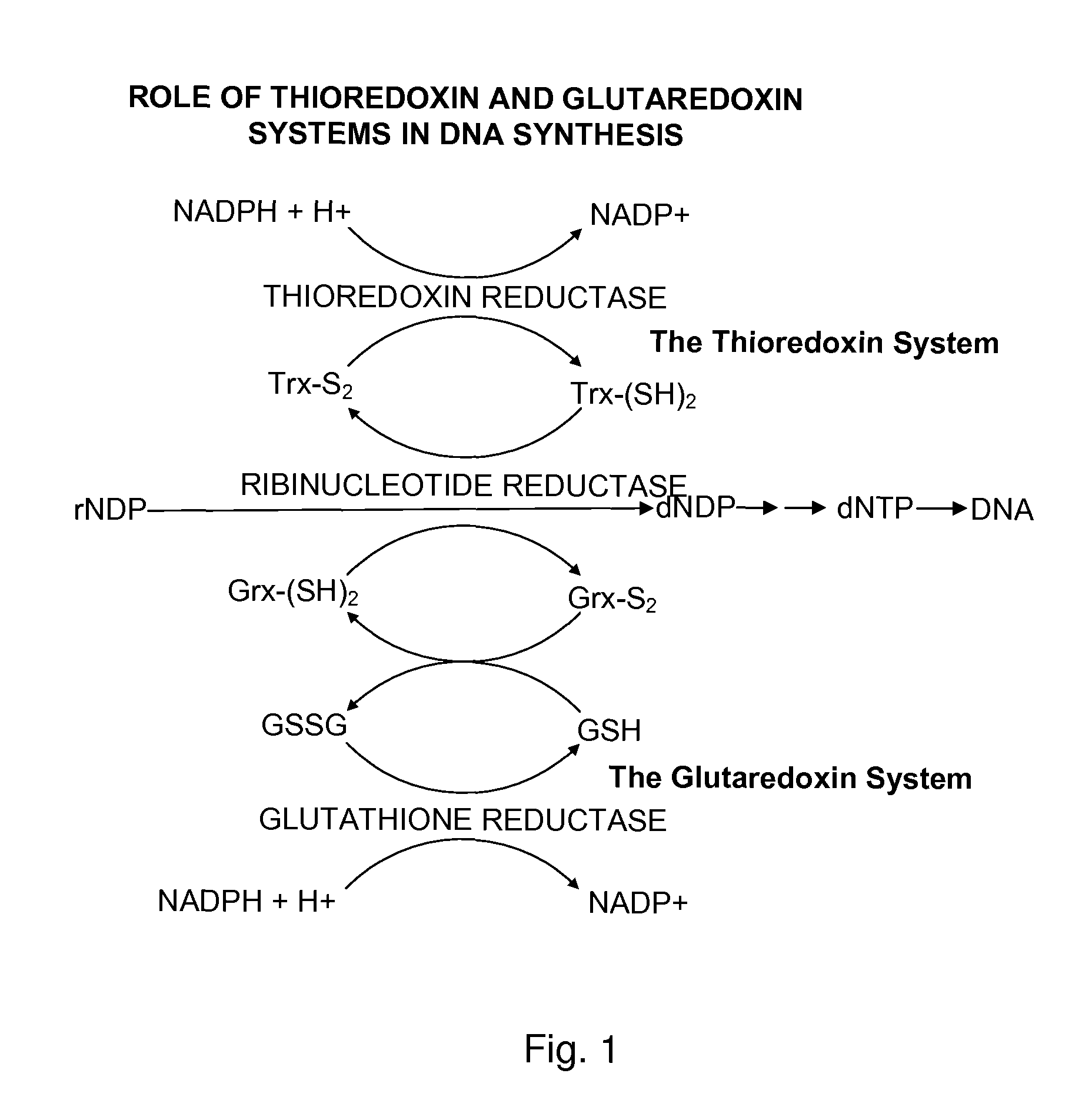
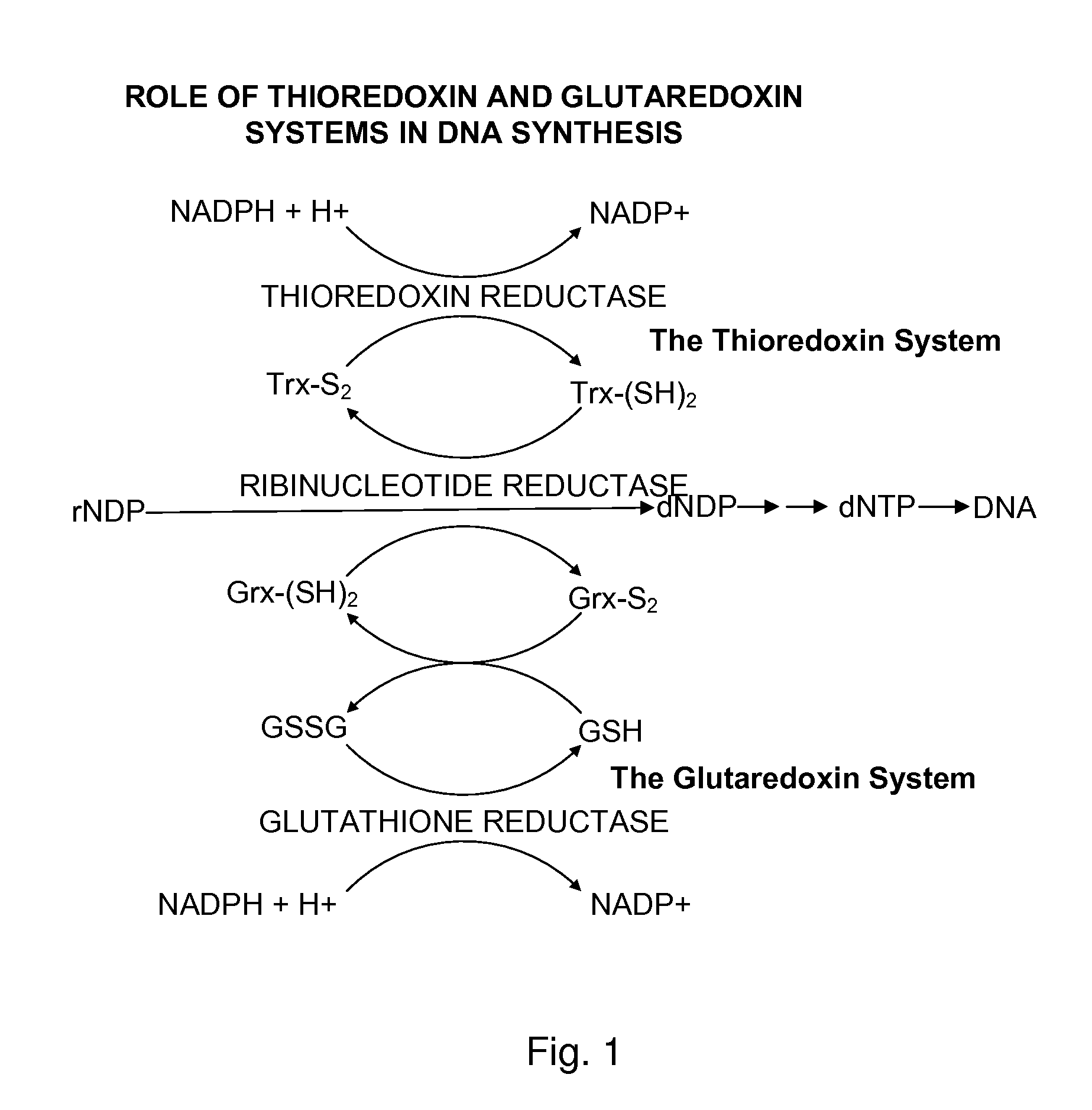
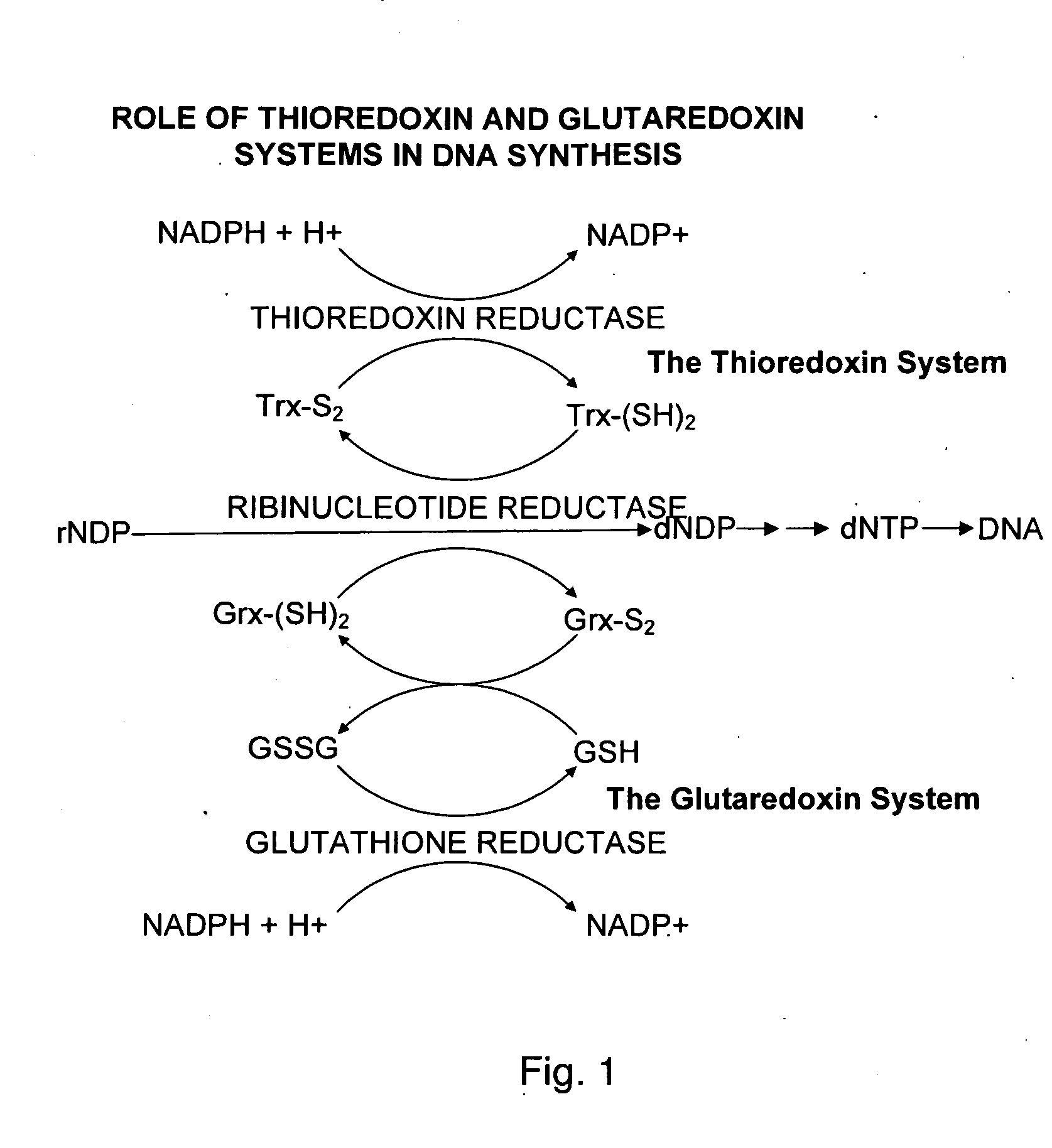
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), also known as ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase (rNDP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides. It catalyzes this formation by removing the 2'-hydroxyl group of the ribose ring of nucleoside diphosphates. This reduction produces deoxyribonucleotides. Deoxyribonucleotides in turn are used in the synthesis of DNA. The reaction catalyzed by RNR is strictly conserved in all living organisms. Furthermore, RNR plays a critical role in regulating the total rate of DNA synthesis so that DNA to cell mass is maintained at a constant ratio during cell division and DNA repair. A somewhat unusual feature of the RNR enzyme is that it catalyzes a reaction that proceeds via a free radical mechanism of action. The substrates for RNR are ADP, GDP, CDP and UDP. dTDP (deoxythymidine diphosphate) is synthesized by another enzyme (thymidylate kinase) from dTMP (deoxythymidine monophosphate).
In vivo measurement of the relative fluxes through ribonucleotide reductase vs. deoxyribonucleoside pathways using isotopes
InactiveUS20050255509A1Increase salvageHigh activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionRate-determining stepDeoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis
The methods of the present invention allow for the measurement of ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity, an important enzyme in the de novo DNA synthesis pathway. Ribonucleotide reductase converts all four ribonucleotides to their deoxy form and is a rate-controlling step in this pathway. Biosynthetic pathways of deoxyribonucleotides (dN) have received considerable attention in the context of anti-proliferative chemotherapy. Inhibitors of various steps in dN biosynthesis, including inhibitors of RR are among the most useful chemotherapeutic agents in cancer, viral infections, and other therapeutic uses. DNA synthesis from the dN salvage pathway is also an important component to DNA replication. The relative contributions from RR vs. salvage pathways are critical to the actions and effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents that act on nucleoside metabolic pathways. Until now, however, it has not been possible to study these metabolic processes in vivo. Disclosed within are methods of measuring RR activity in vivo and in vitro which find use, among other things, in drug discovery, development, and approval.
Owner:KINEMED
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
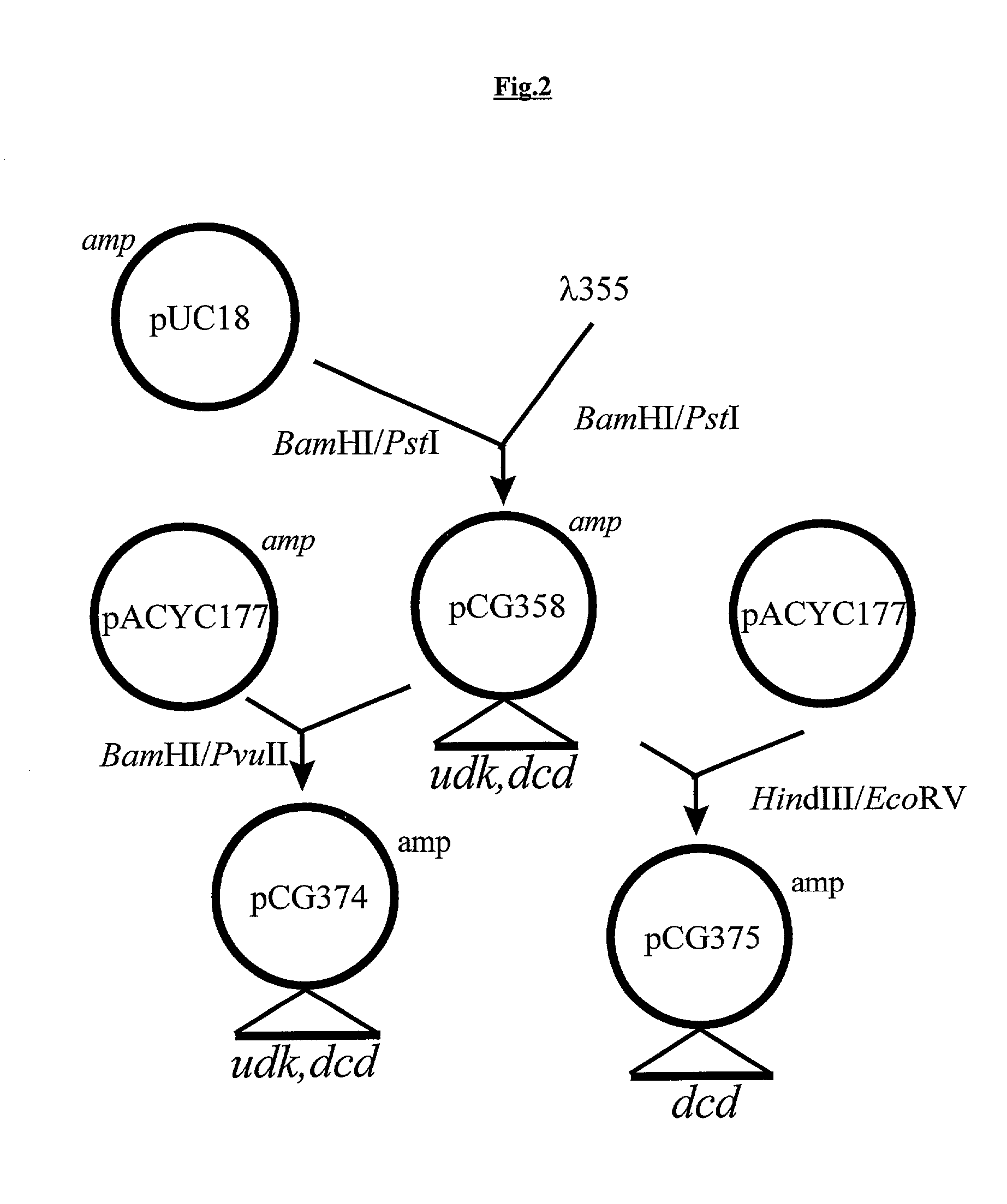
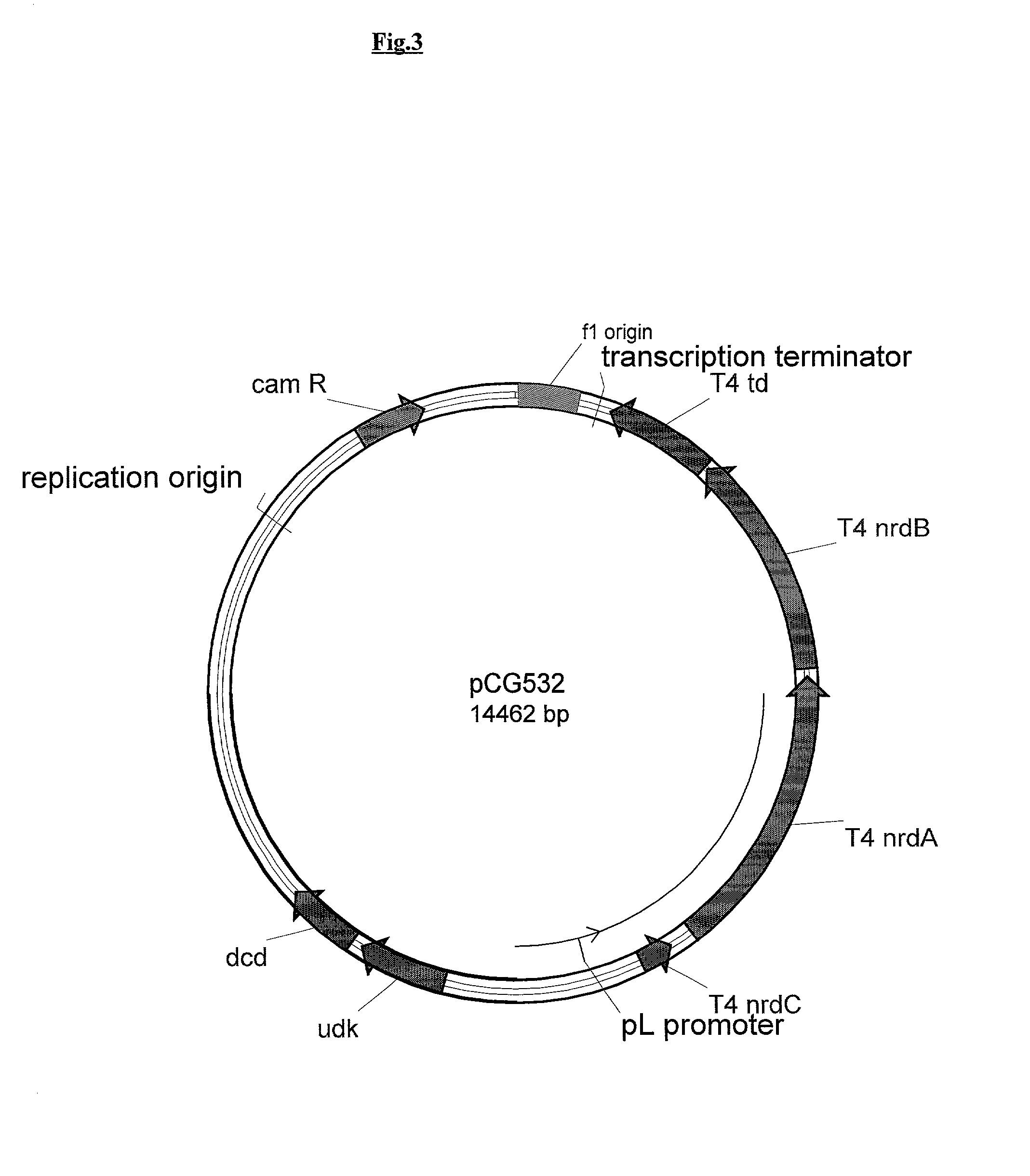
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin. In preferred embodiments, constructs further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, host cells comprising constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
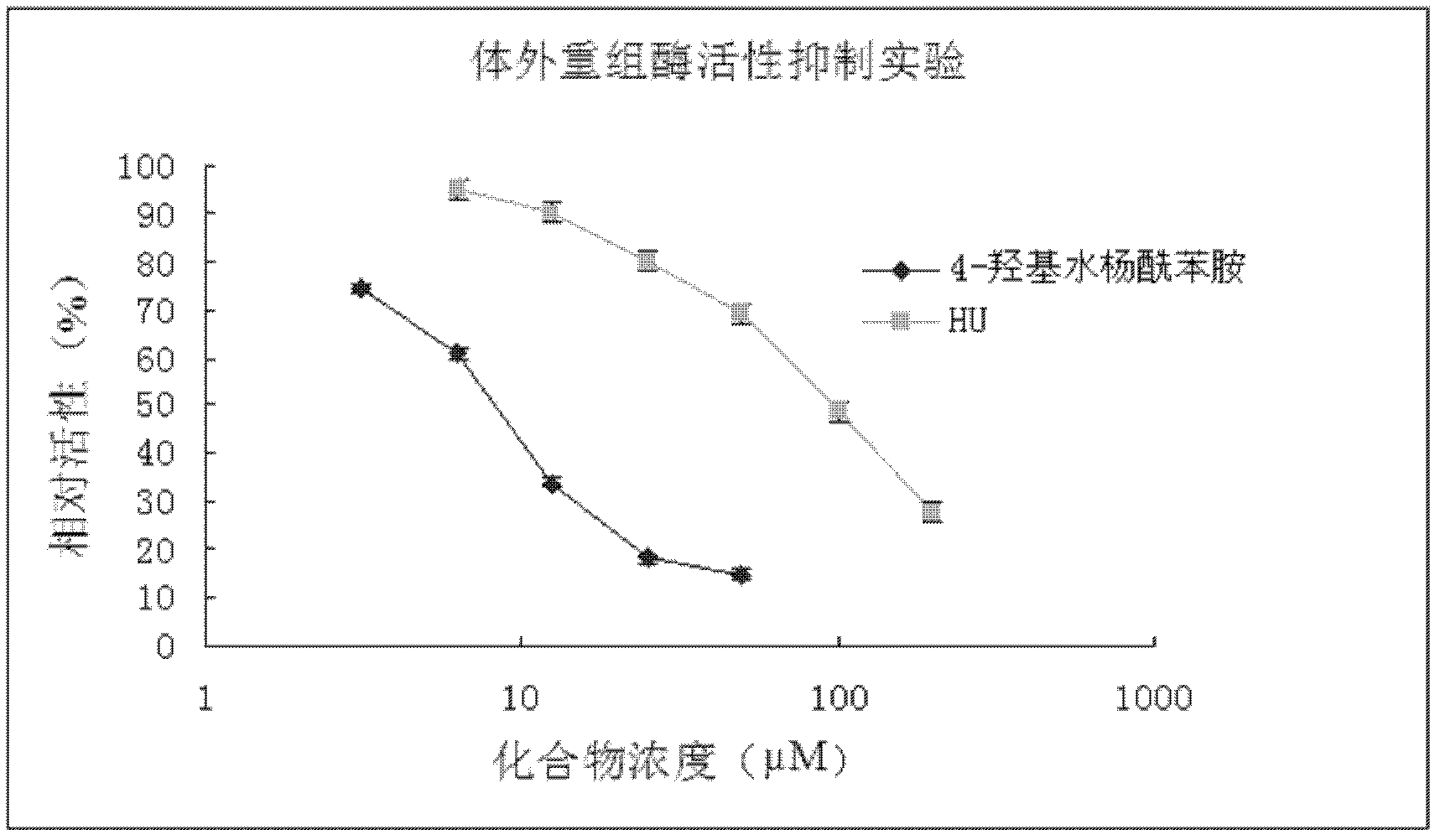
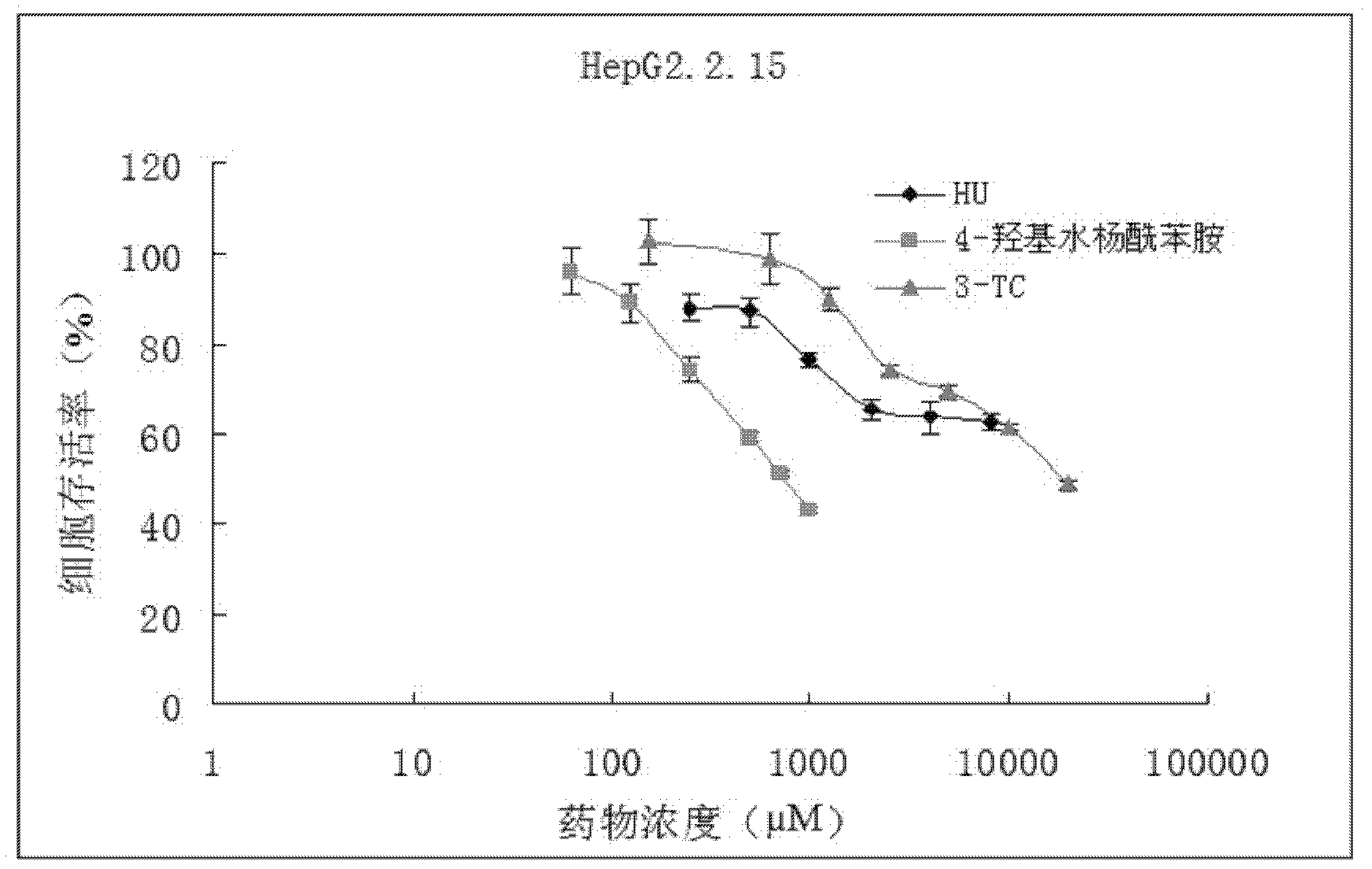
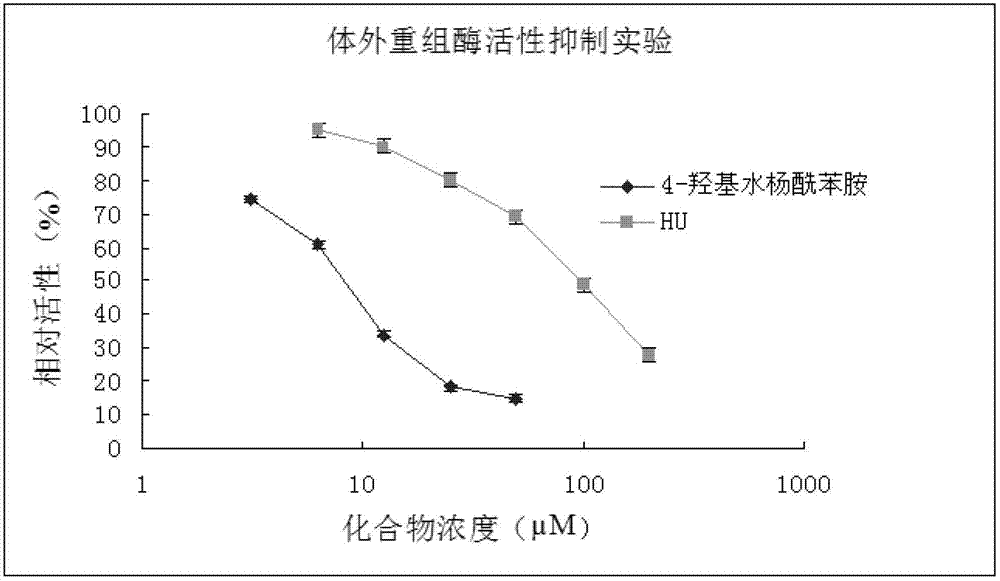
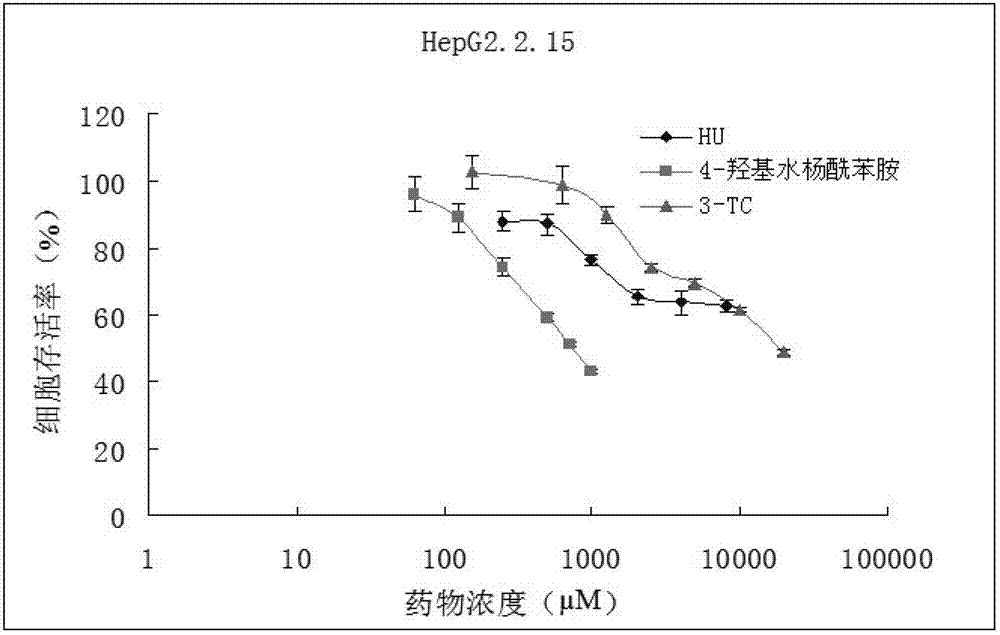
Application of 4-hydroxy salicylamide in preparing medicament for preventing and treating hepatitis and resisting tumor
ActiveCN102379881AHigh RR enzyme inhibitory activityPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemMyeloid leukemiaChronic myeloid leukaemia
The invention provides novel application of 4-hydroxy salicylamide in the field of pharmacy. The compound is an inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase (RR), and can achieve the aims of inhibiting replication of HBV and treating hepatitis, in particular the hepatitis B by inhibiting activity of RR enzyme to block synthesis of dNTPs (deoxynucleotide triphosphates) required by hepatitis B virus (HBV)replication, achieve the aim of preventing and treating liver cancer by inhibiting the activity of RR of liver cancer cells, including the RR activity activated by HBV to inhibit proliferation of liver cancer cells, and achieve the aim of treating various tumors by inhibiting the RR. The 4-hydroxy salicylamide can be used for preventing and treating hepatitis B, liver cancer, oropharyngeal epithelioma, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, chronic myeloid leukemia and other tumors, and has important application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
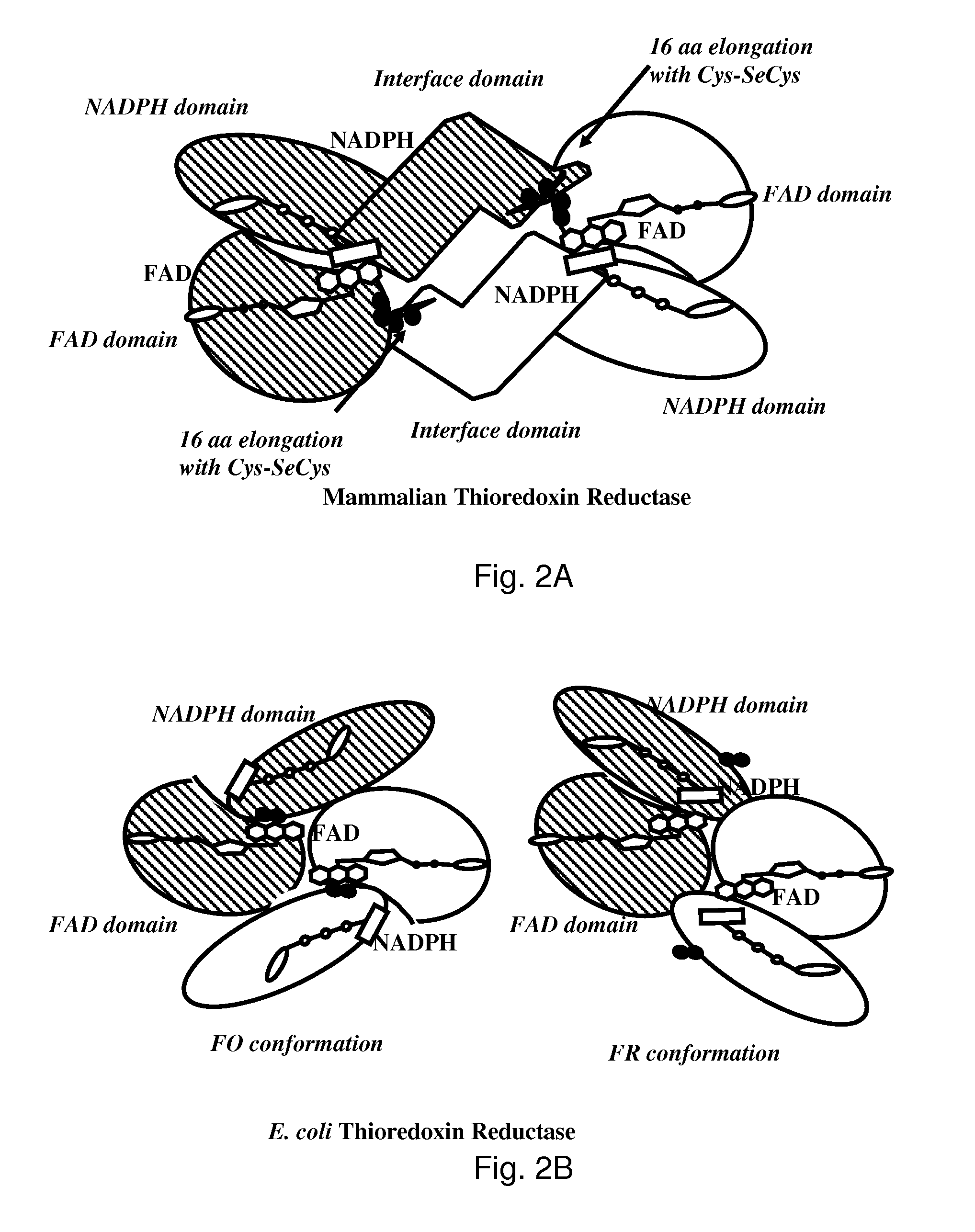
Bacterial thioredoxin reductase inhibitors and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS8592468B2Prevent bacterial growthImprove understandingAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesEscherichia coli
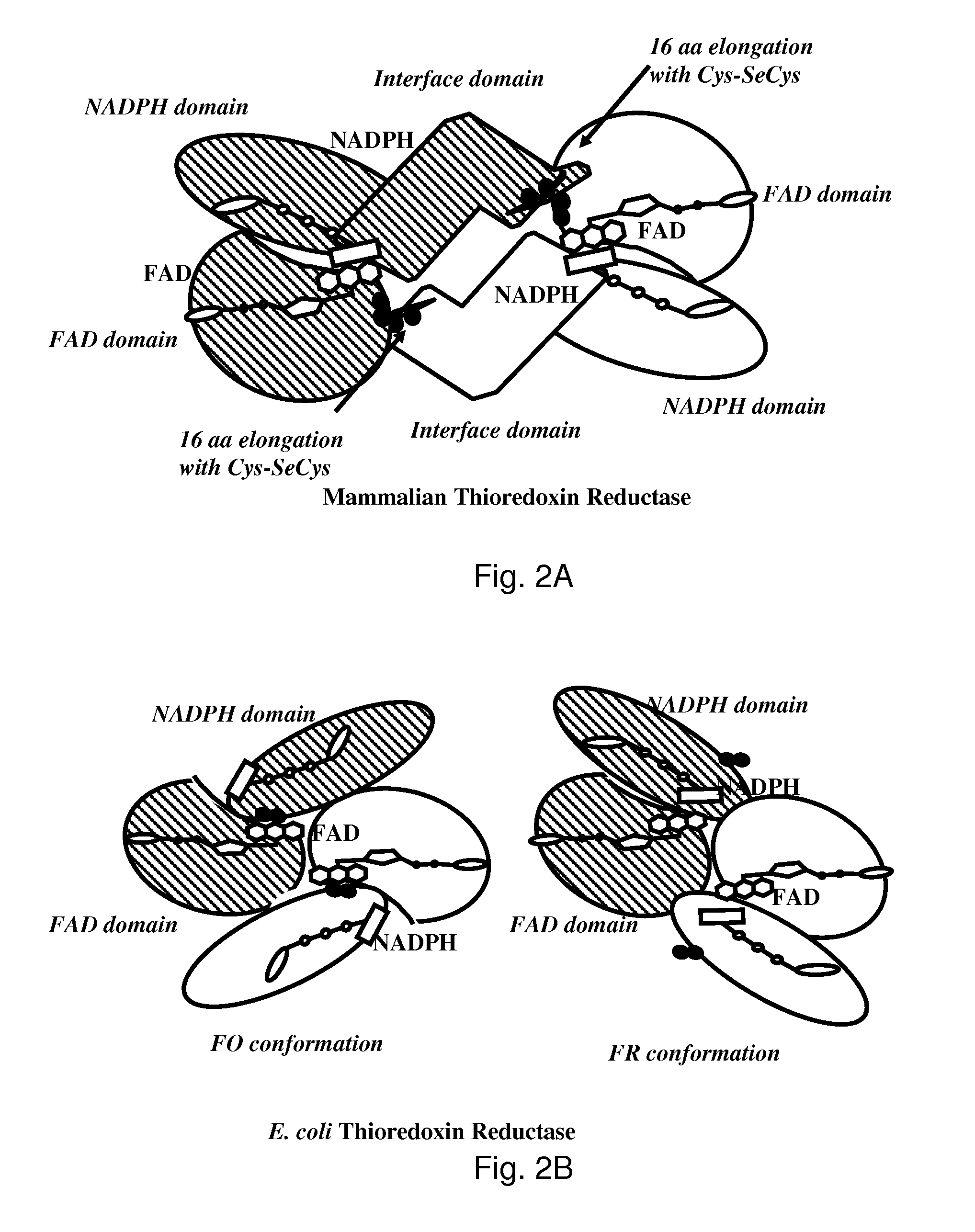
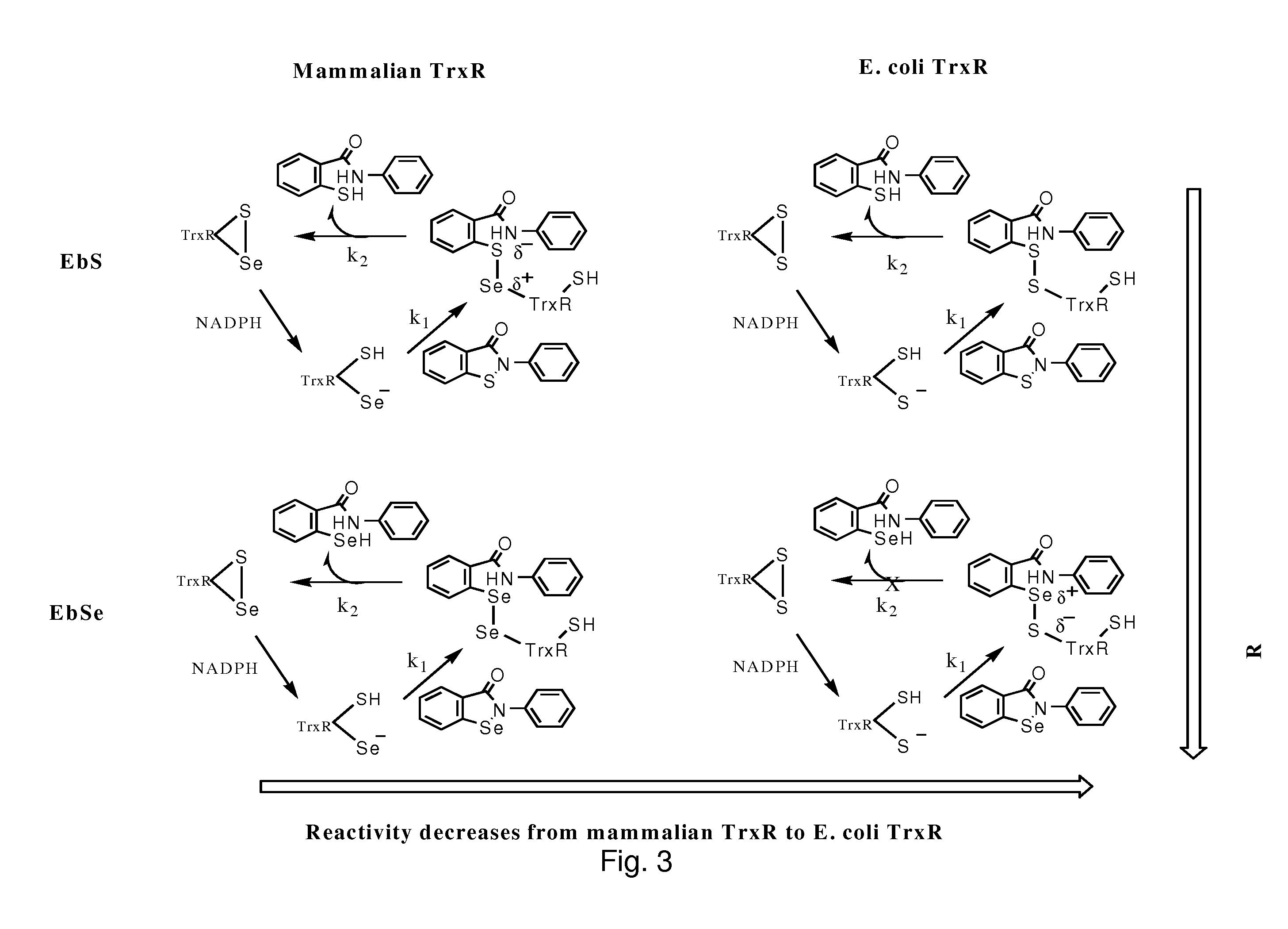
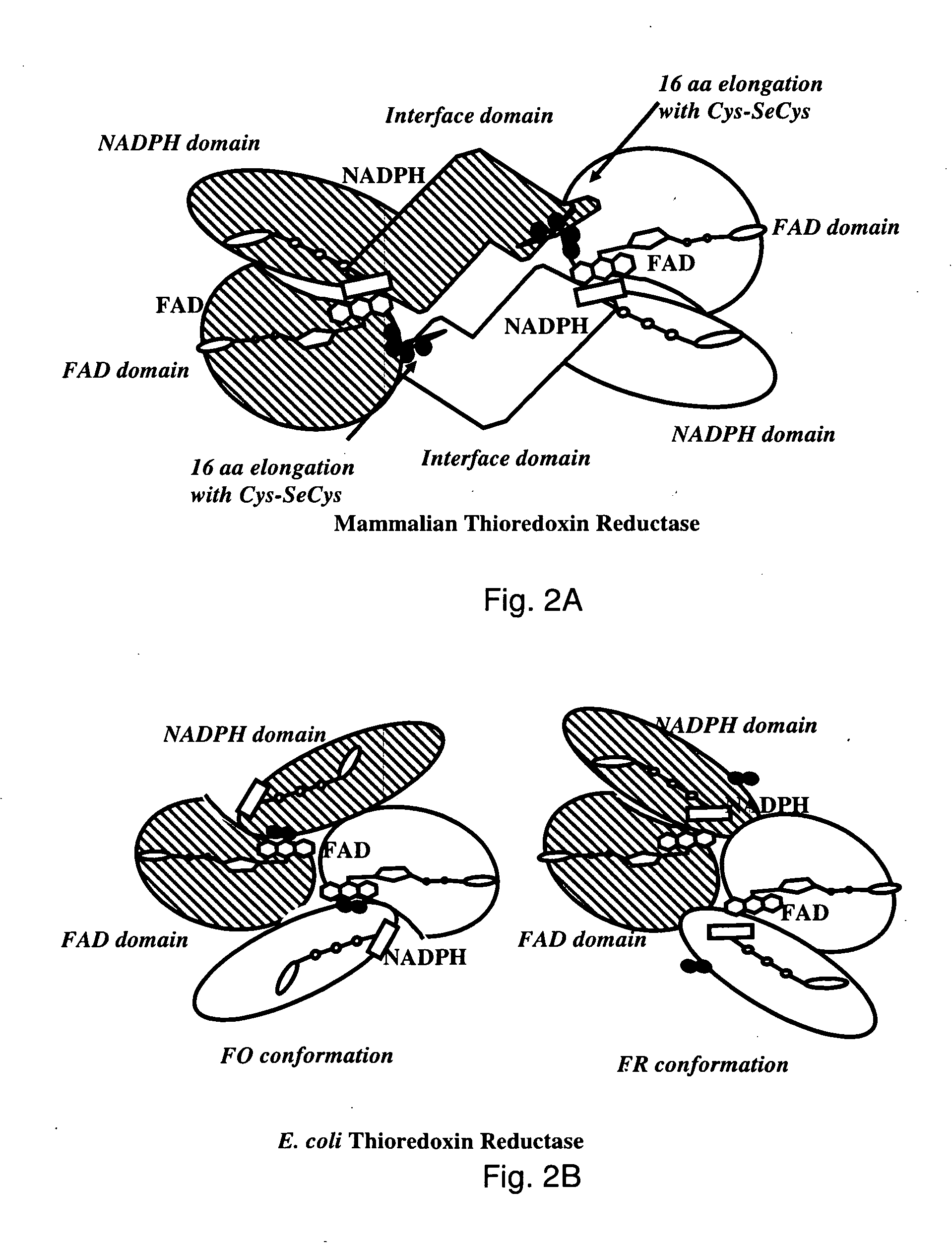
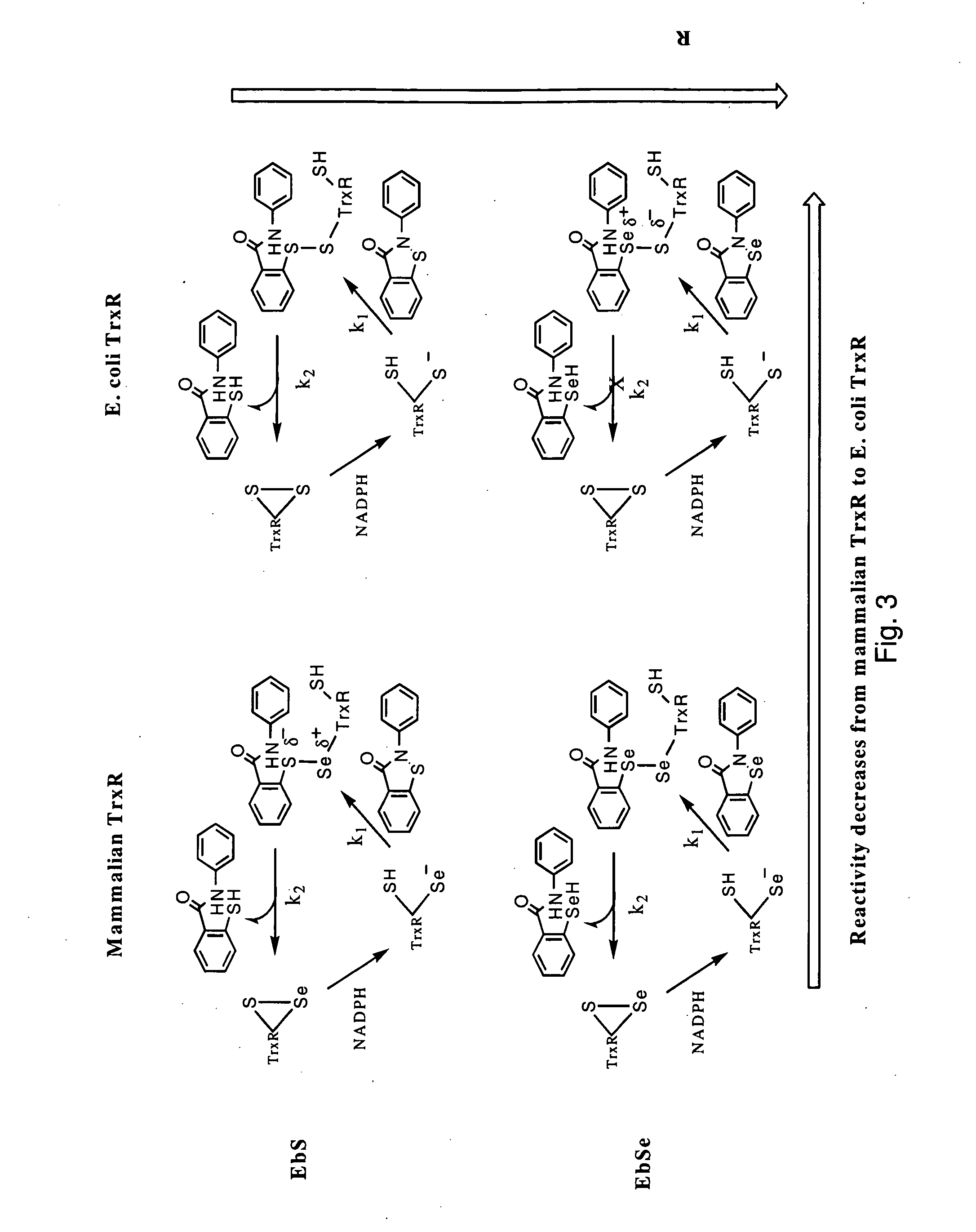
The mechanism of action of Ebselen differentiates between bacterial and mammalian thioredoxin reductase (TrxR). It displays fast oxidation of mammalian Trx and via the NADPH-TrxR catalyzed turnover of ebselen selenol with hydrogen peroxide, and therefore are mammalian antioxidants. Ebselen, and its diselenide, are strong competitive inhibitors of E. coli TrxR with Ki of 0.14 μM and 0.46 μM, respectively. E. coli mutants lacking glutathione reductase or glutathione were much more sensitive to inhibition by ebselen. Since either glutaredoxin or thioredoxin systems are electron donors to ribonucleotide reductase, ebselen targets primarily glutathione and glutaredoxin-negative bacteria, a class which includes major pathogens. Ebselen, and similar compounds are therefore useful as antibacterial agents, even for multiresistant strains. Two major pathogenic bacteria, which previously had not been known to be sensitive to ebselen, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tuberculosis) and Helicobacter pylori (stomach ulcer and cancer), were shown to be excellent targets. Helicobacter pylori was also sensitive to ebsulfur.
Owner:THIOREDOXIN SYST AB
HSV with a Musashi promoter regulating γ34.5 and ribonucleotide reductase expression
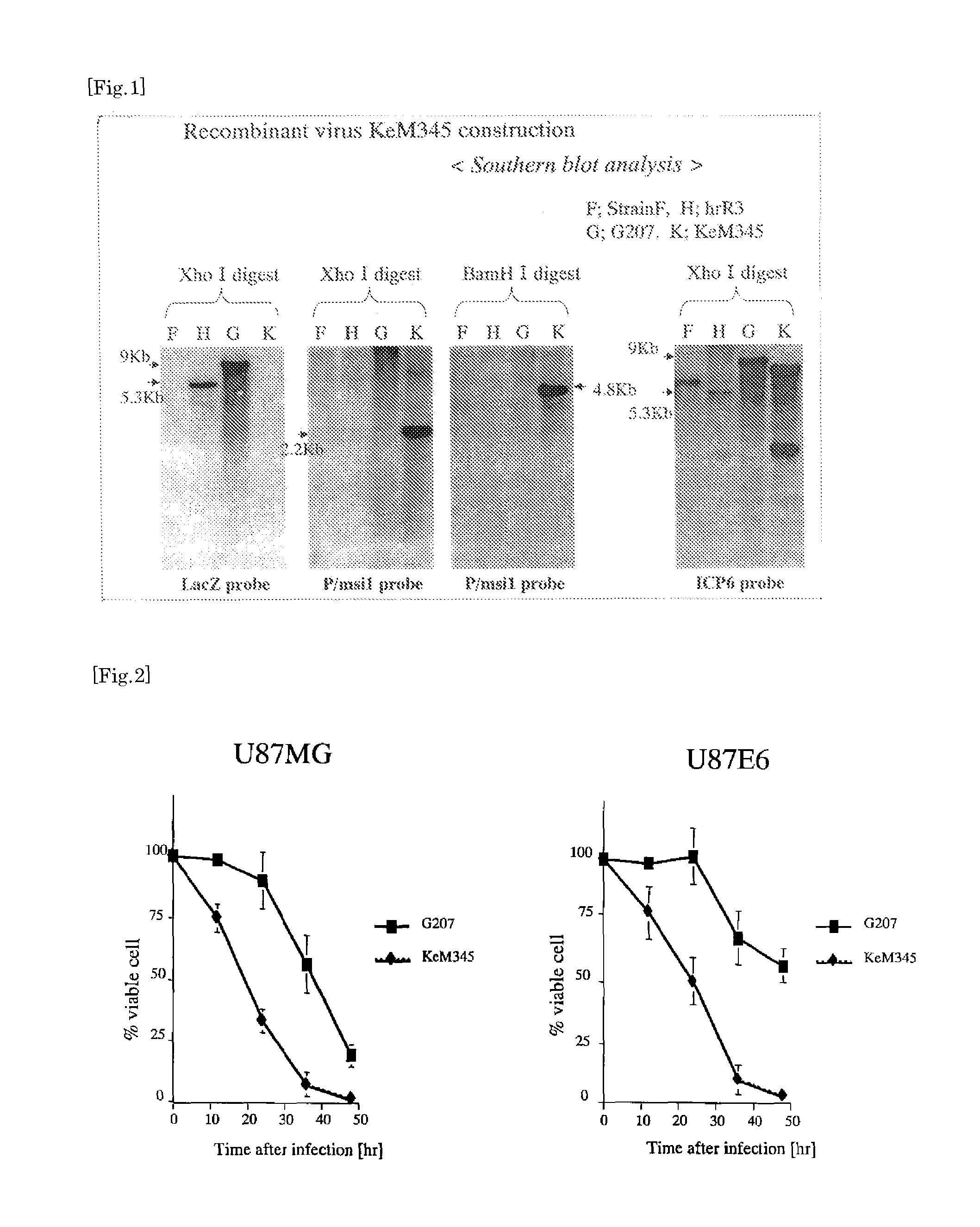
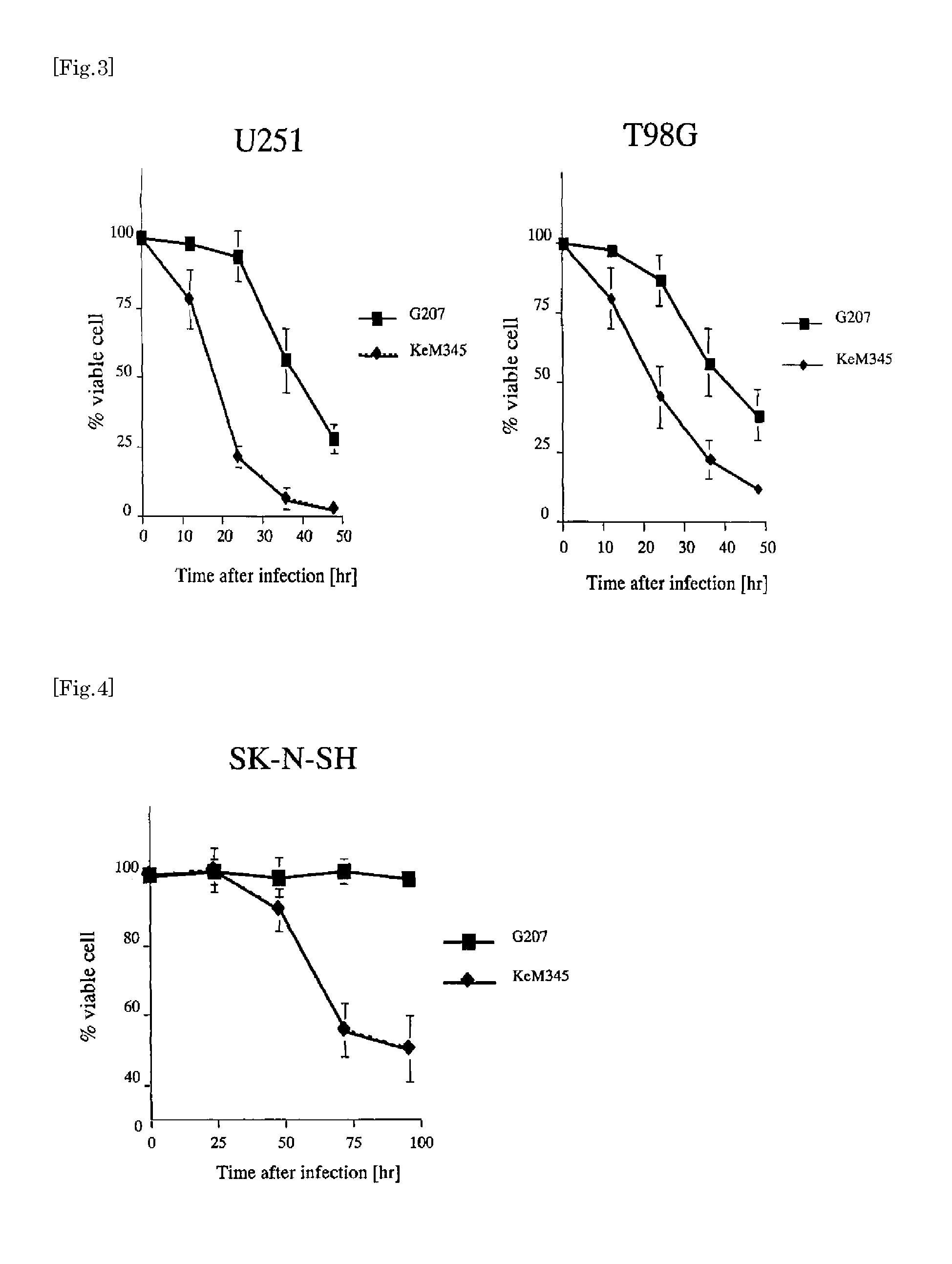
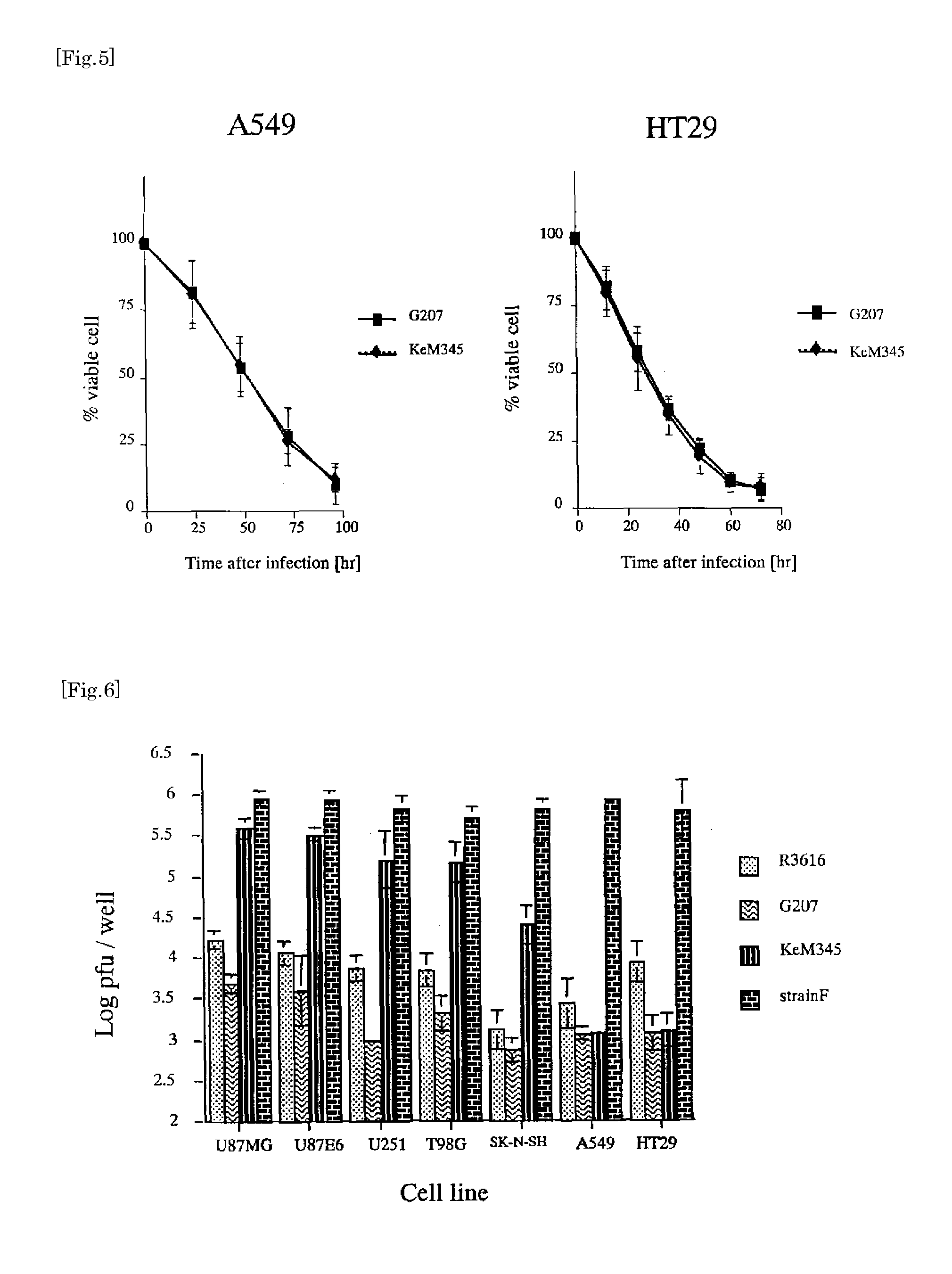
The present invention provides a recombinant HSV having the ability to specifically kill tumor cells such as human glioma cells in vivo, useful and safe for treating human glioma, etc. and that can easily put to clinical use. A new recombinant HSV, KeM345, is constructed by inserting a γ34.5 gene transcription unit, which is expressed by Musashi1 promoter, into a ribonucleotide reductase gene site of the genome of a herpes simplex virus (HSV) previously attenuated, by means of homologous recombination and obtained as a purified strain. Since KeM345 is a recombinant virus itself, it can not only induce viral proliferation by being transmitted to culture cells but can also induce viral replication equivalent to that of wild-type HSV, showing an excellent cytotoxic effect (cytolytic ability) selectively upon a malignant glioma.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Protein capable of promoting chloroplast development and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102477090APromote photosynthesisIncrease productionViruses/bacteriophagesPlant peptidesRibonucleotide reductaseBiotechnology
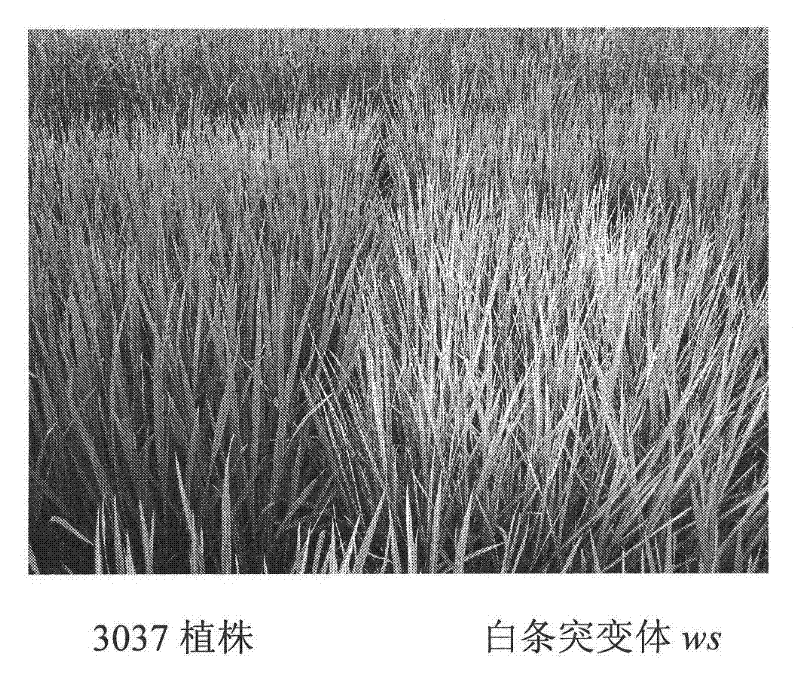
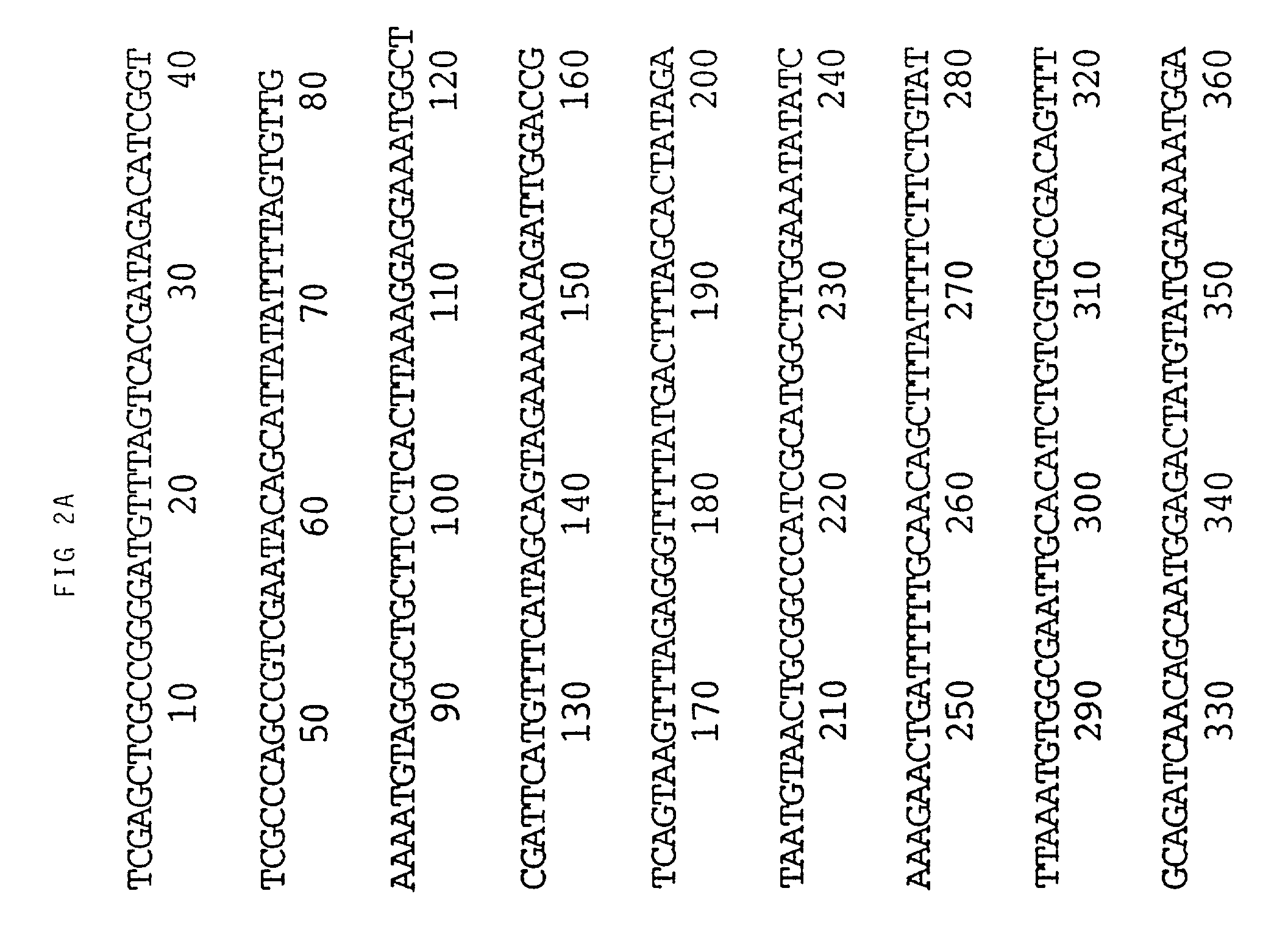
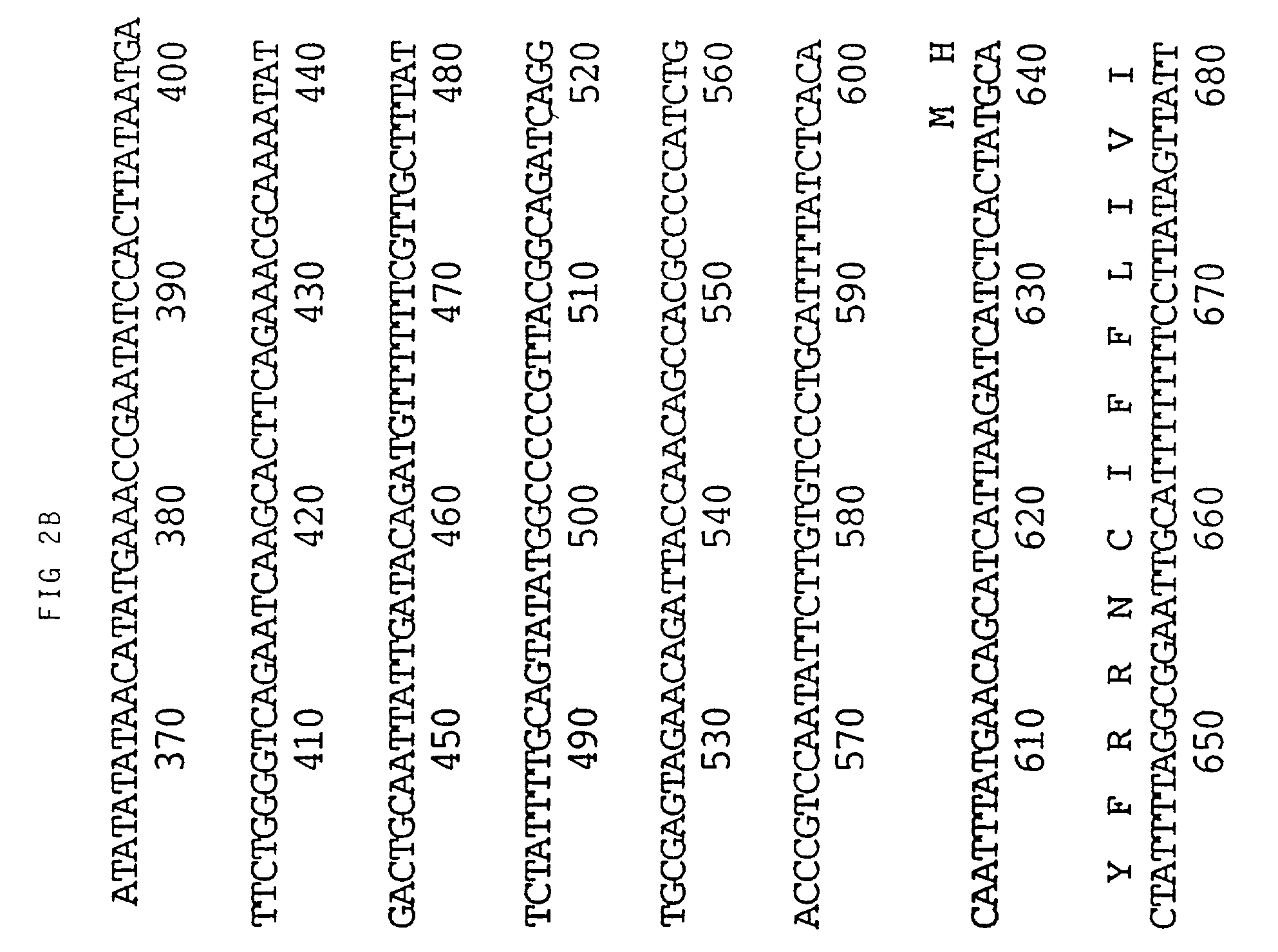
The invention discloses a rice protein capable of promoting chloroplast development and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein is one of 1) a protein formed by amino acid residue sequences of the SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table or 2) a protein which is formed after one or more amino acid residues in the amino acid residue sequences of the SEQ ID No.2 in the sequence table are substituted and / or deleted and / or added and has the same activities as the amino acid residue sequences of the SEQ ID No.2. The gene is used for coding the small subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, and the development of rice chloroplast is affected after the gene is mutated so that white stripes are distributed on the rice leaves in the vein direction.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
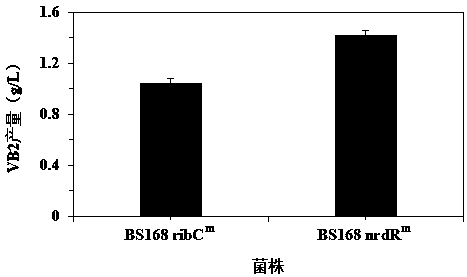
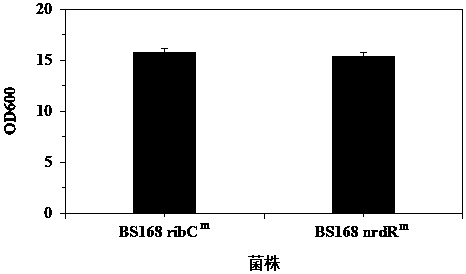
Ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant, mutation gene and application of ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant and mutation gene to preparation of vitamin B2
The invention discloses a ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant, a mutation gene and an application of the ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant andthe mutation gene to preparation of vitamin B2. The amino acid sequence of the mutant is subjected to the following mutation relative to the sequence as shown in SEQID No.3; and an amino acid at the26th site is replaced with H. For the nucleotide fixed point mutation that the amino acid at the 26th site, coded in the ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor gene on a bacillus subtilis chromosome is replaced with H, a genetic engineering bacterium is obtained, and the capacity for producing the vitamin B2 is greatly improved. The ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant has great application and extension value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Bacterial thioredoxin reductase inhibitors and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS20110288130A1Prevent bacterial growthImprove understandingAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesEscherichia coli
Owner:THIOREDOXIN SYST AB
Bacterial thioredoxin reductase inhibitors and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS20090005422A1Reduced thioredoxinPrevent bacterial growthAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The mechanism of action of Ebselen differentiates between bacterial and mammalian thioredoxin reductase (TrxR). It displays fast oxidation of mammalian Trx and via the NADPH-TrxR catalyzed turnover of ebselen selenol with hydrogen peroxide, and therefore are mammalian antioxidants. Ebselen, and its diselenide, are strong competitive inhibitors of E. coli TrxR with Ki of 0.14 μM and 0.46 μM, respectively. E. coli mutants lacking glutathione reductase or glutathione were much more sensitive to inhibition by ebselen. Since either glutaredoxin or thioredoxin systems are electron donors to ribonucleotide reductase, ebselen targets primarily glutathione and glutaredoxin-negative bacteria, a class which includes major pathogens. Ebselen, and similar compounds are therefore useful as antibacterial agents, even for multiresistant strains. Two major pathogenic bacteria, which previously had not been known to be sensitive to ebselen, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tuberculosis) and Helicobacter pylori (stomach ulcer and cancer), were shown to be excellent targets. Helicobacter pylori was also sensitive to ebsulfur.
Owner:THIOREDOXIN SYST AB
Application of 4-hydroxy salicylanilide to preparation of medicament for preventing and treating hepatitis B
InactiveCN102920688AEnhance killing activityHigh RR enzyme inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemRibonucleotide reductaseMedicine
The invention provides new application of 4-hydroxy salicylanilide in the field of pharmacy. 4-hydroxy salicylanilide is an inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase (RR) and inhibits the enzyme activity of RR, so that the compounding of dNTPs required by reproduction of HBV is blocked, and the aims of inhibiting reproduction of HBV, treating hepatitis and particularly treating hepatitis B are fulfilled. The 4-hydroxy salicylanilide can be used for preventing and treating the hepatitis B and has a significant application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
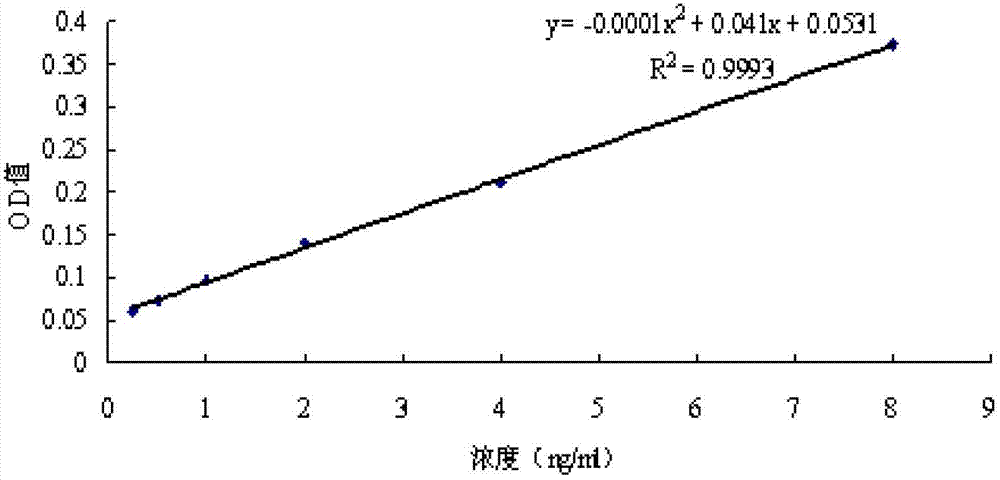
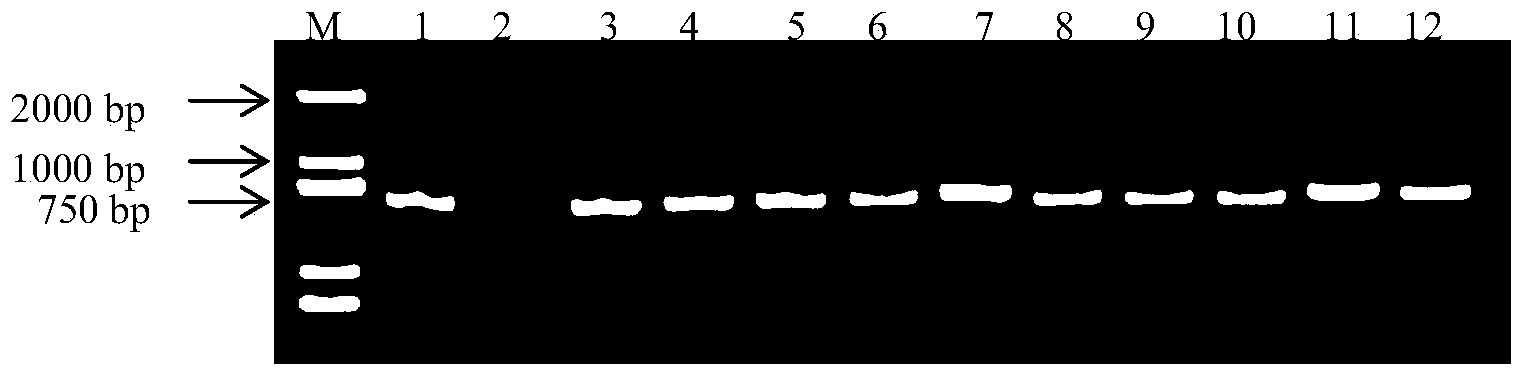
Method for detecting exogenous gene copy number in transgenic tobacco
InactiveCN104032007AMeet screening needsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesRibonucleotide reductase
The invention discloses a method for detecting an exogenous gene copy number in transgenic tobacco. A real-time fluorescent quantitation PCR technology is utilized to simply, rapidly and accurately detect the exogenous gene copy number in transgenic tobacco. The invention discloses a pair of primers consisting of DNA molecules shown in (1) and (2), namely (1) a DNA molecule shown in SEQ ID No.3; and (2) a DNA molecule shown in SEQ ID No.4. A single-copy endogenous gene ribonucleotide reductase gene (RNR2) of the tobacco is selected as a reference gene, and the exogenous gene copy number in transgenic tobacco is detected through a SYBR GreenI real-time fluorescent quantitation PCR technology. The method disclosed by the invention provides a new thought for copy number analysis of the transgenic tobacco, and the screening requirement for excellent transformation plants in genetic engineering is met.
Owner:GUANGXI VETERINARY RES INST
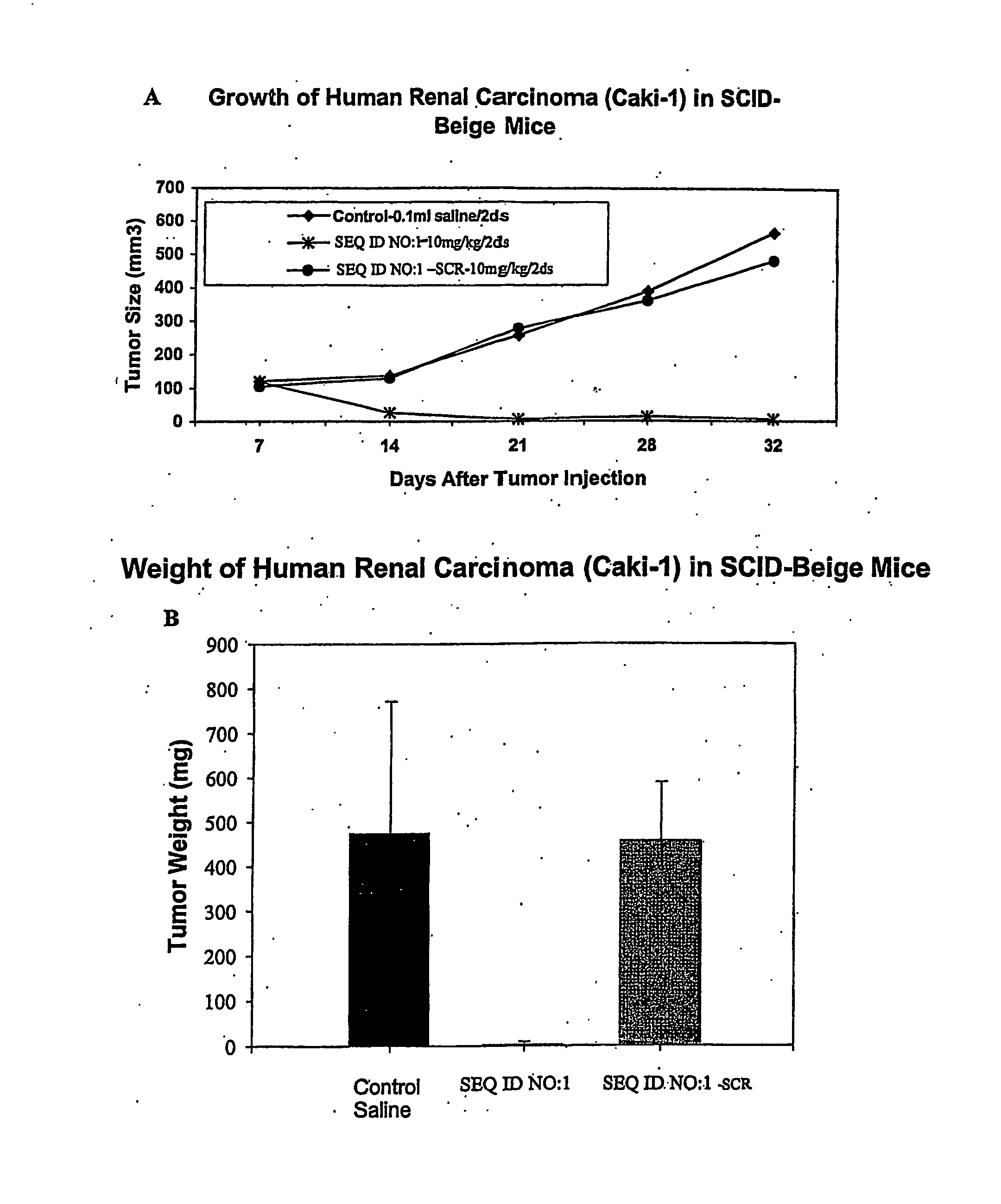
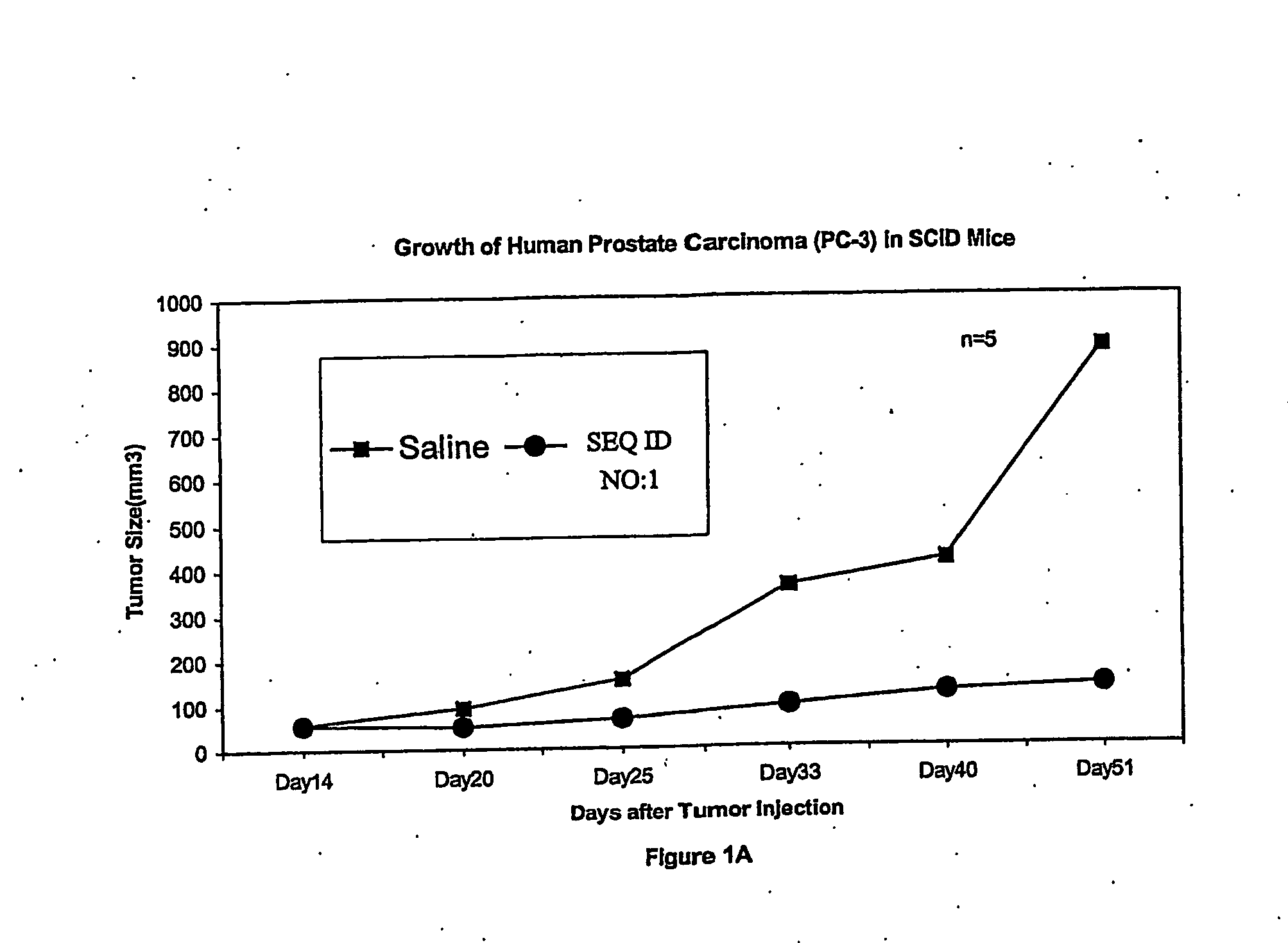
Antisense Oligonucleotides Directed to Ribonucleotide Reductase R1 and Uses Thereof in the Treatment of Cancer
The present invention provides antisense oligonucleotides directed to a mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R1 gene and combinations of the antisense oligonucleotides with one or more chemotherapeutic agents for use in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:LORUS THERAPEUTICS
Antisense oligonucleotides directed to ribonucleotide reductase r2 and uses thereof in the treament of cancer
The present invention provides antisense oligonucleotides directed to a mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R2 gene and combinations of the antisense oligonucleotides with one or more chemotherapeutic agents for use in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:LORUS THERAPEUTICS
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin or a uridine kinase gene and / or a dCTP deaminase gene. In preferred embodiments the constructs comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, the host cells comprise constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
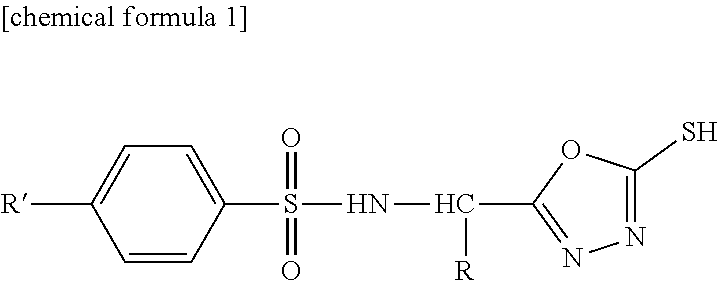
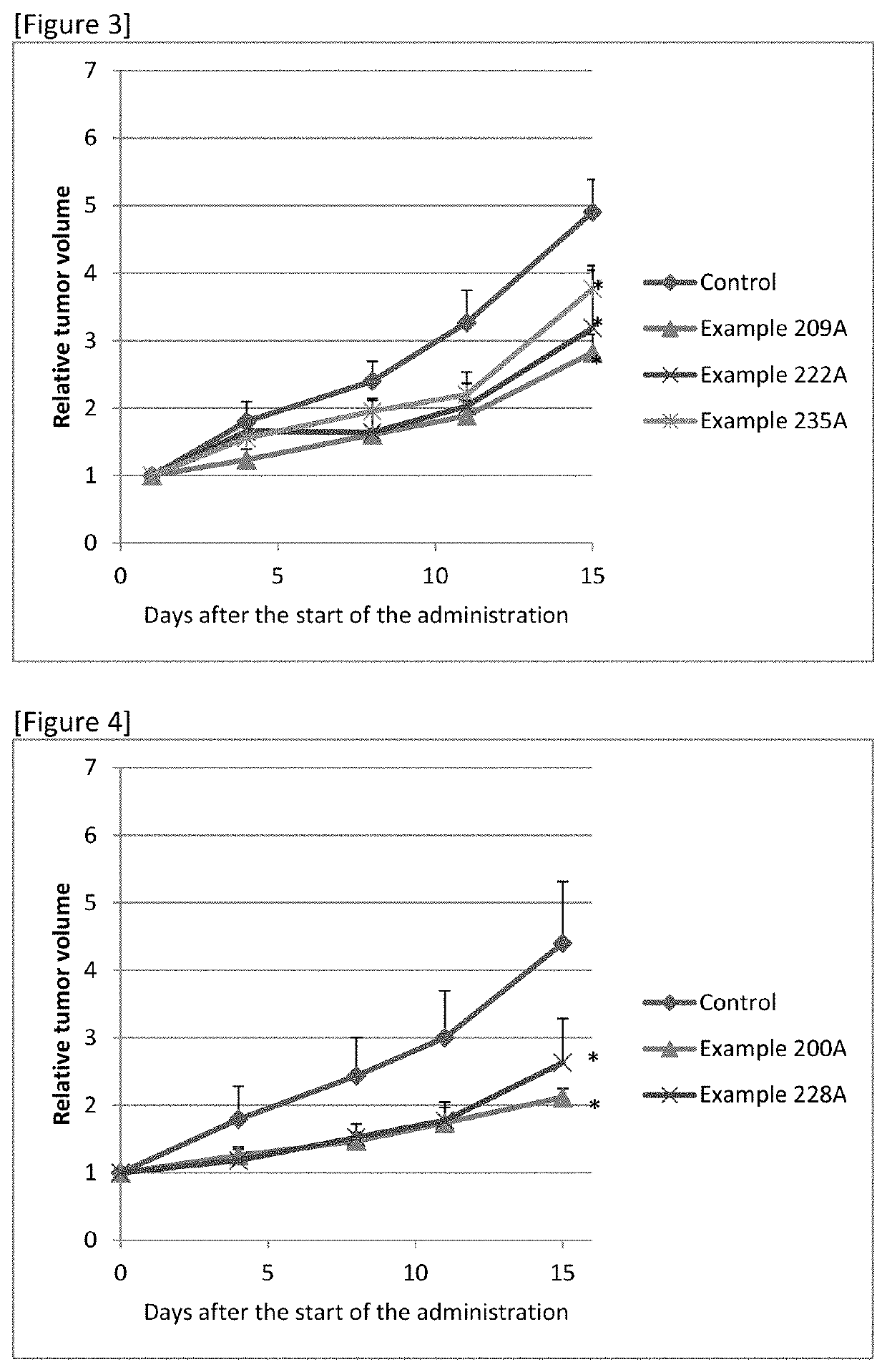
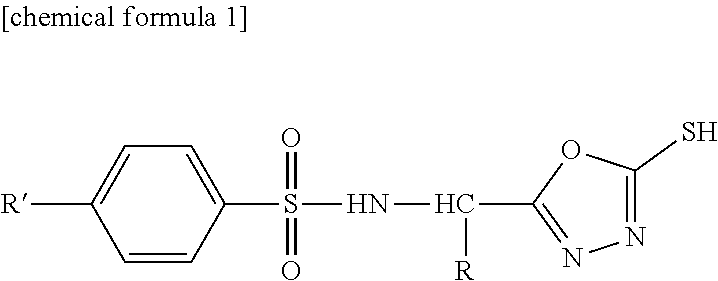
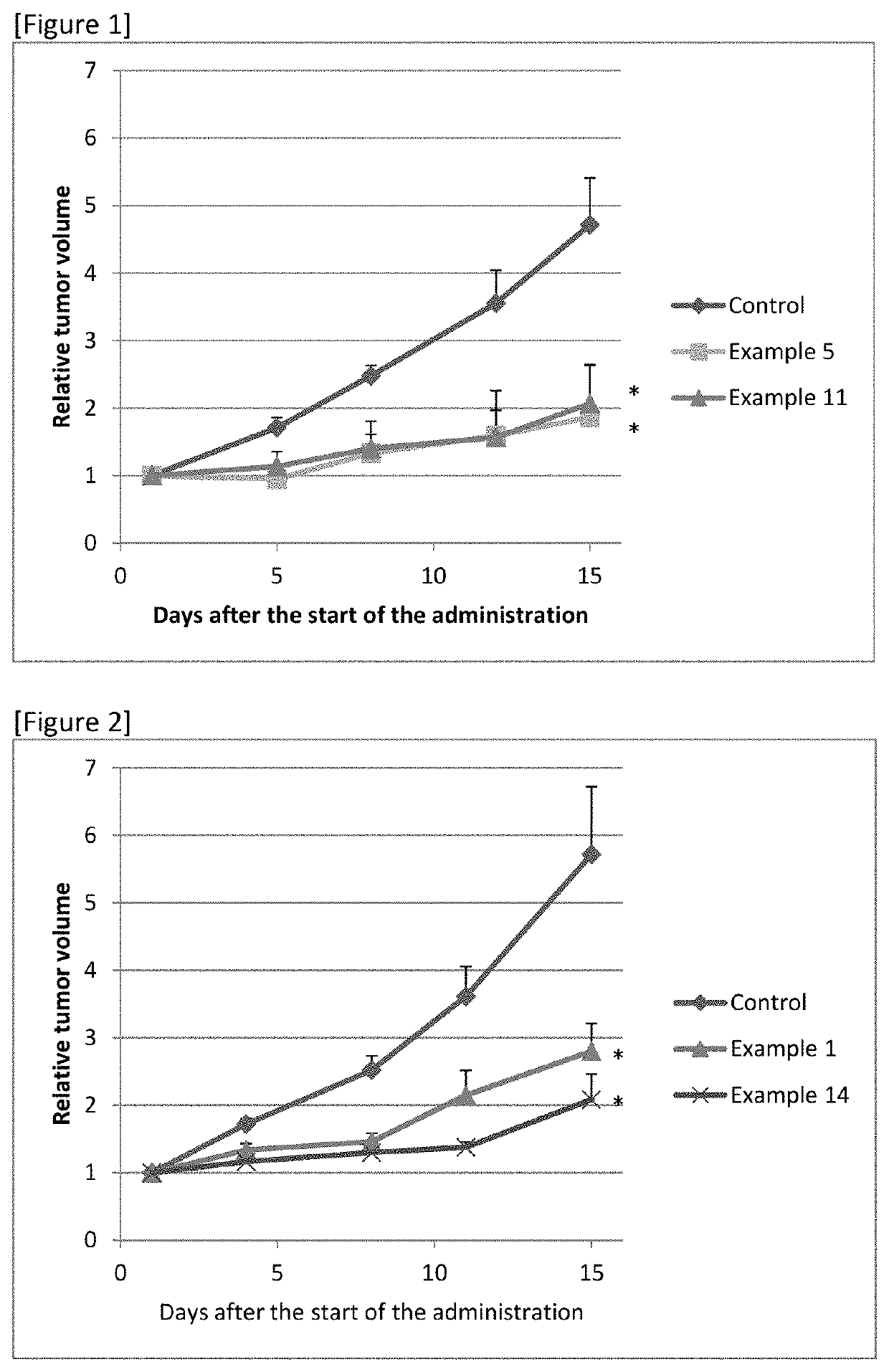
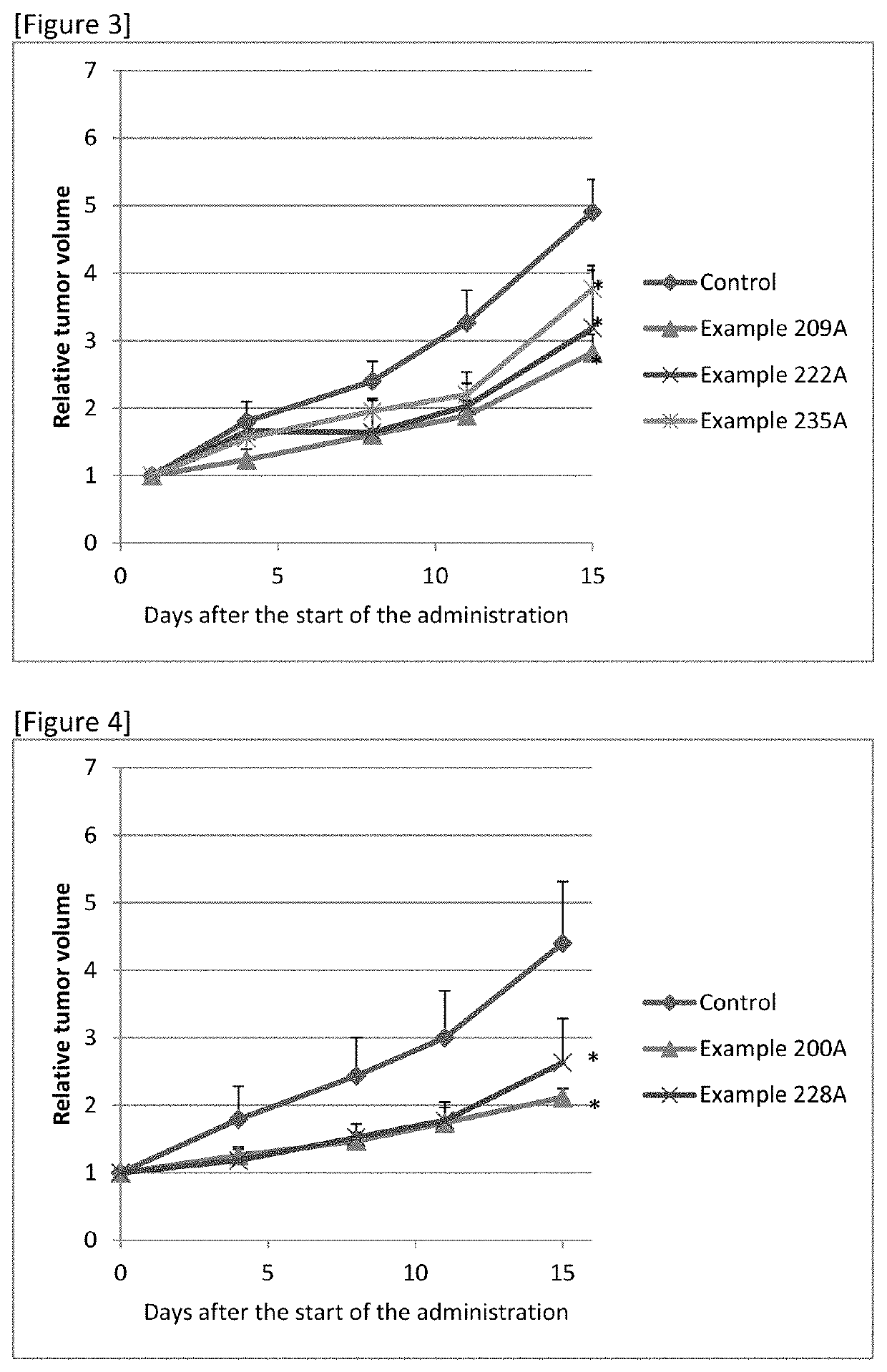
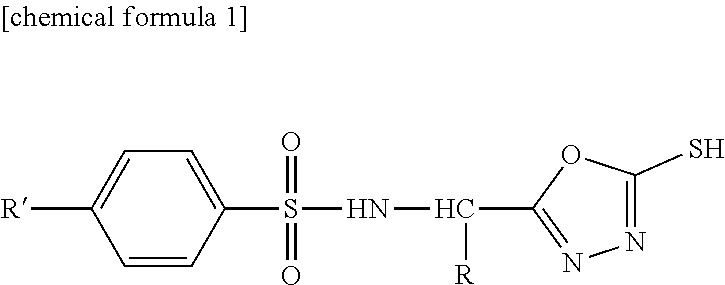
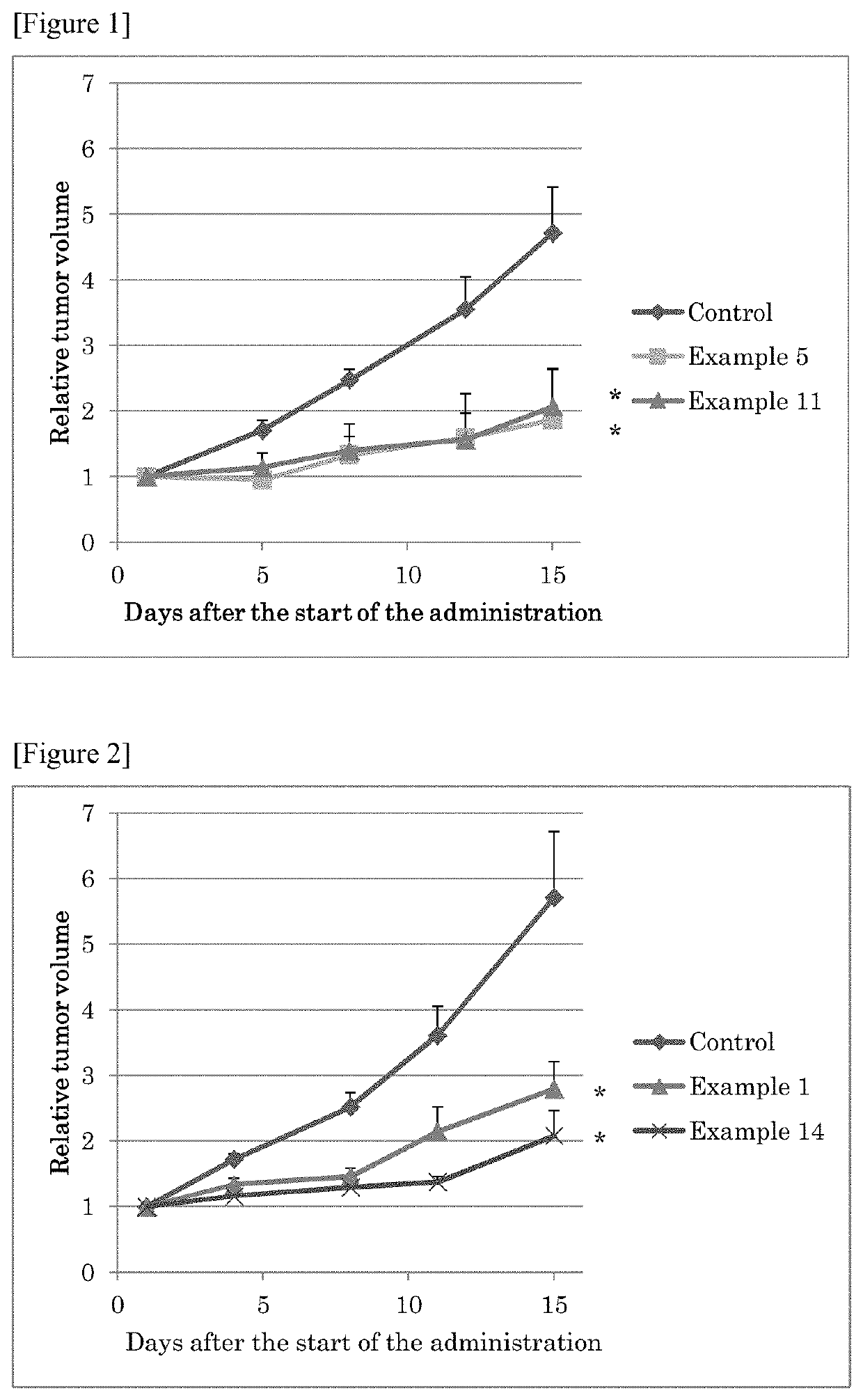
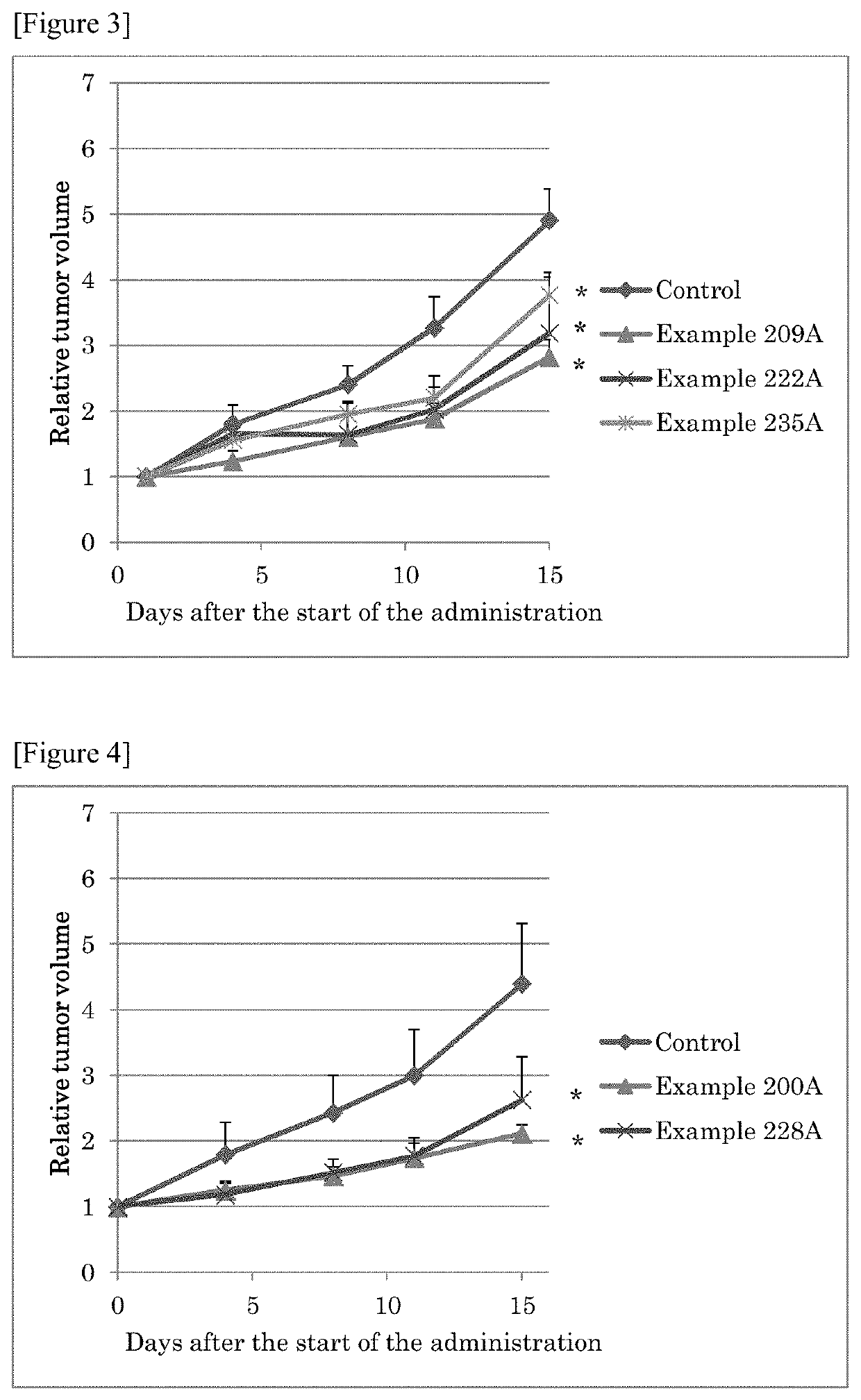
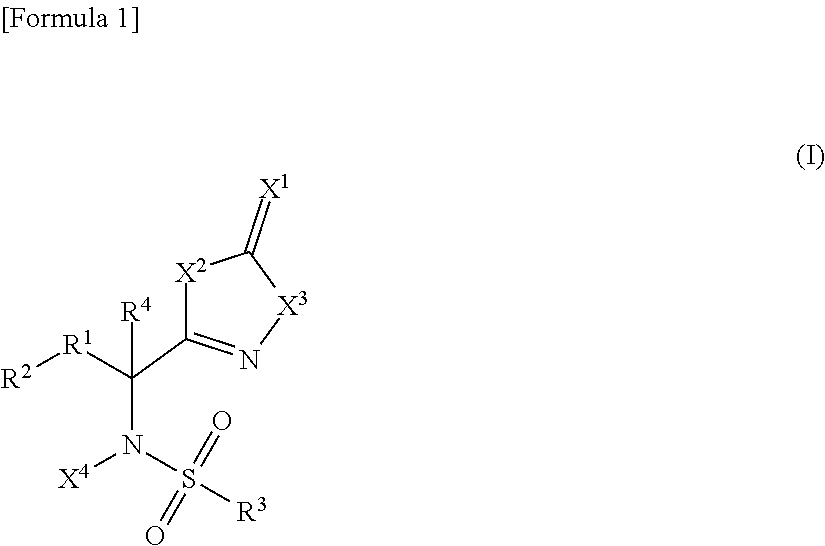
Sulfonamide compound or salt thereof
ActiveCN109563057AExcellent RNR inhibitory activityExhibit proliferation inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryRibonucleotide reductaseNucleotide
Provided are: a novel sulfonamide compound having ribonucleotide reductase inhibitory activity or a salt thereof; and a pharmaceutical composition which contains this sulfonamide compound or a salt thereof as an active ingredient. A compound represented by formula (I) or a salt thereof. (In the formula, X1 represents an oxygen atom or the like; X2 represents an oxygen atom; X3 represents -NH-; X4represents a hydrogen atom or the like; R1 represents -C(R11)(R12)- or the like; R11 and R12 may be the same or different and each represents a hydrogen atom or the like; R2 represents an optionally substituted C6-C14 aromatic hydrocarbon group or the like; R3 represents an optionally substituted C6-C14 aromatic hydrocarbon group or the like; and R4 represents a hydrogen atom or the like.)
Owner:TAIHO PHARMA CO LTD
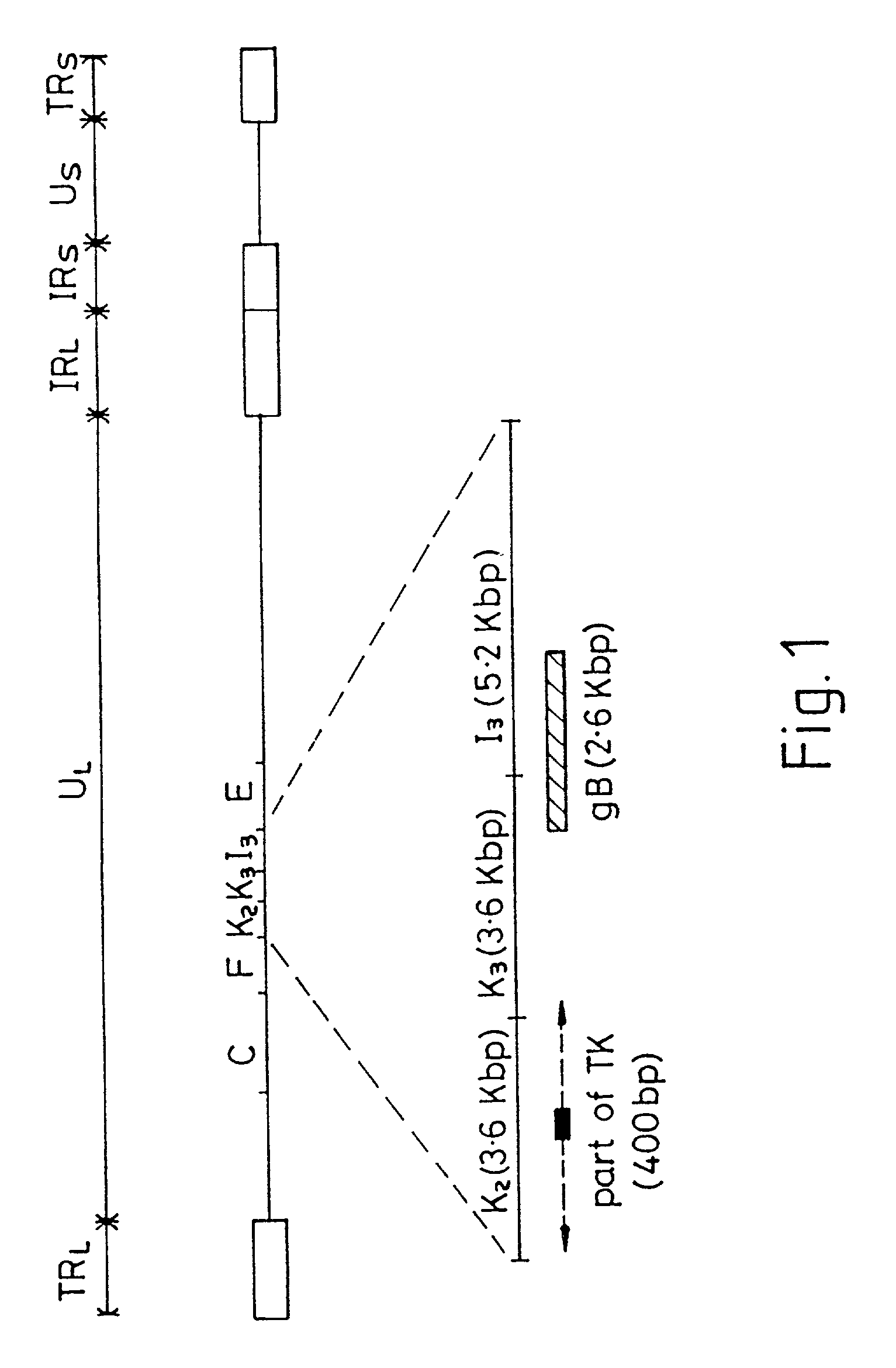
Viral nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6204045B1Improved vaccineOrganic active ingredientsFungiHeterologousLaryngotracheitis virus
Various genes of herpes virus of turkeys (HVT), Marek's disease virus (MDV) and infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) have been identified as non-essential regions (and candidates for insertion sites for foreign genes) and / or as antigen-encoding regions. The former include the HVT homologue of the HSV (herpes simplex virus) gC gene, the TX (thymidine kinase) region of MDV or ILTV, ORF3 of ILTV (as defined herein), the ribonucleotide reductase (large subunit) gene of ILTV, MDV or HVT and the ribonucleotide reductase (small subunit) gene of MDV. The antigen-encoding regions include the HVT homologues of the HSV gB, gC and gH genes, the ILTV homologue of HSV gB, ORF2 of ILTV, and the HVT homologue of the HSV-1 immediate early genes IE-175 and IE-68. Manipulation of these genes allows vaccines to be prepared comprising attenuated virus or virus carrying heterologous antigen-encoding sequences.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
Sulfonamide Compound or Salt Thereof
ActiveUS20200157066A1Excellent RNR-inhibiting activityInhibition effectOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsNucleotideBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention provides a novel sulfonamide compound having a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitory activity or a salt thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same as an active ingredient.A compound represented by Formula (I) [wherein, X1 represents an oxygen atom or the like; X2 represents an oxygen atom; X3 represents —NH—; X4 represents a hydrogen atom or the like; R1 represents —C(R11)(R12)— or the like; R11 and R12 are the same or different and each represents a hydrogen atom or the like; R2 represents an optionally substituted C6-C14 aromatic hydrocarbon group or the like; R3 represents an optionally substituted C6-C14 aromatic hydrocarbon group or the like; R4 represents a hydrogen atom or the like] or a salt thereof.
Owner:TAIHO PHARMA CO LTD
Pyrimidines antimetabolic chemotherapeutical medicine curative effect prognose reagent kit and application thereof
InactiveCN1975388AThe detection method is simpleReliable test resultsFluorescence/phosphorescenceRibonucleotide reductaseCurative effect
The invention discloses a regent box to detect the expressing level in the tumor organize of the ribonucleotide reductase M1, RRM1. It can detect the malignancy sufferer who can resist on the metabolizing medicine curing.
Owner:GUANGDONG GENERAL HOSPITAL
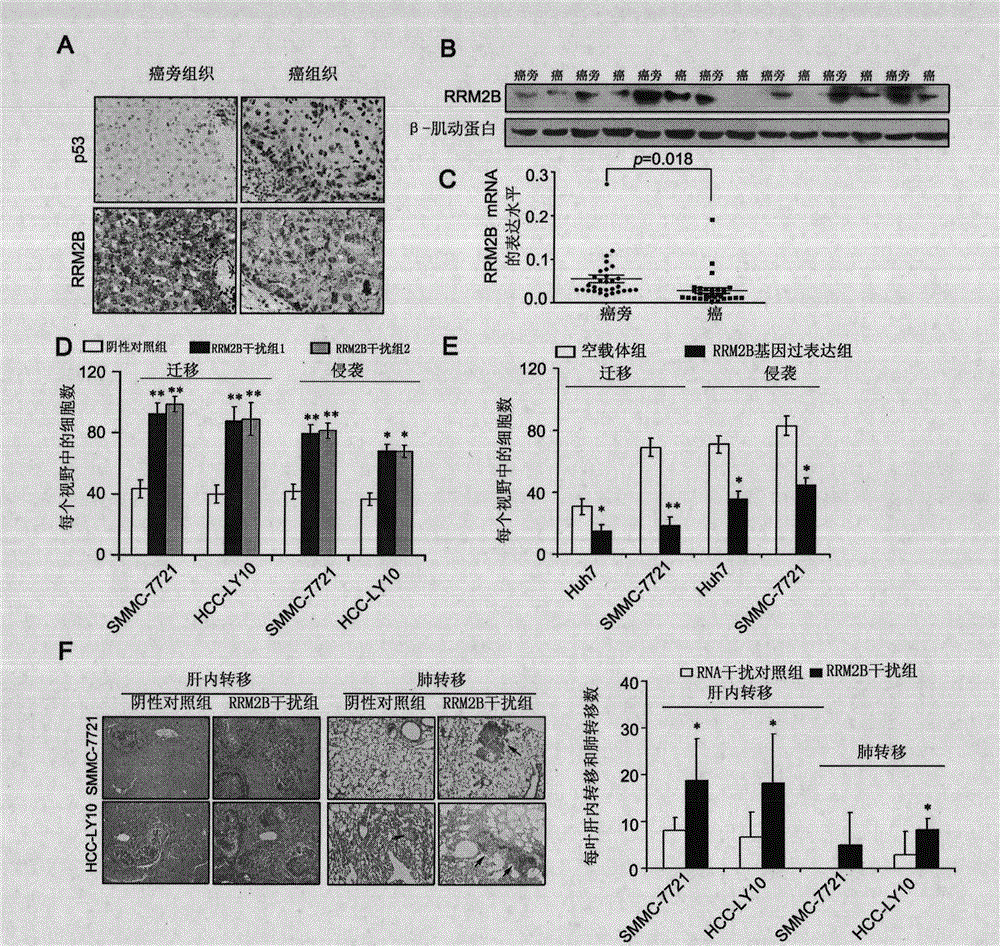
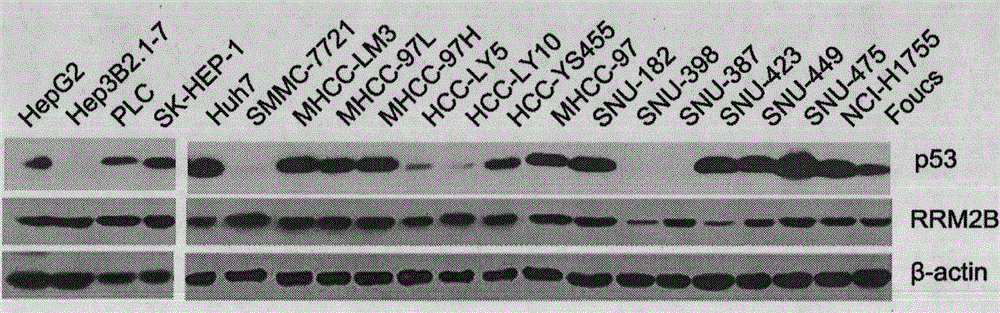
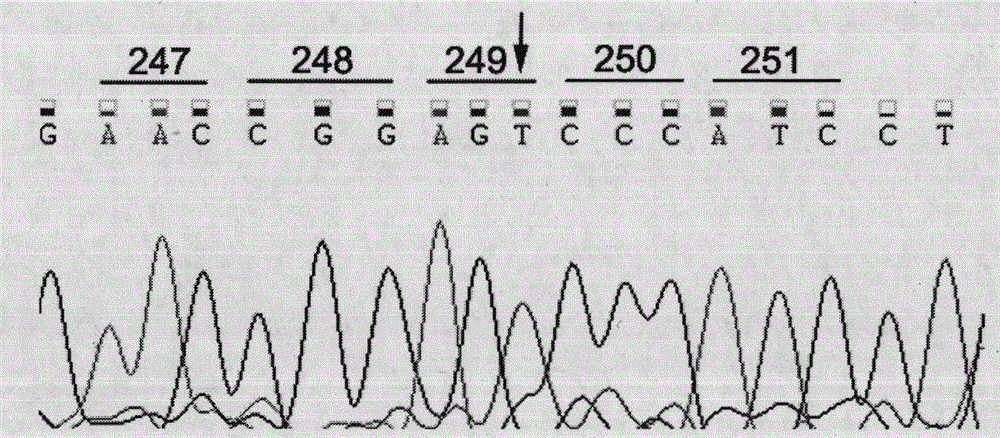
Application of RRM2B gene or protein thereof in metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
ActiveCN104630338APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementRibonucleotide reductaseLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses application of RRM2B gene or protein thereof in metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma, and particularly provides application of detection reagents of ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit M2B (RRM2B) gene or protein thereof, as well as the RRM2B gene or protein thereof for preparing kits for diagnosing metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Furthermore, the RRM2B has an inhibiting effect on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma, and a new approach is provided to diagnosis and treatment of metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
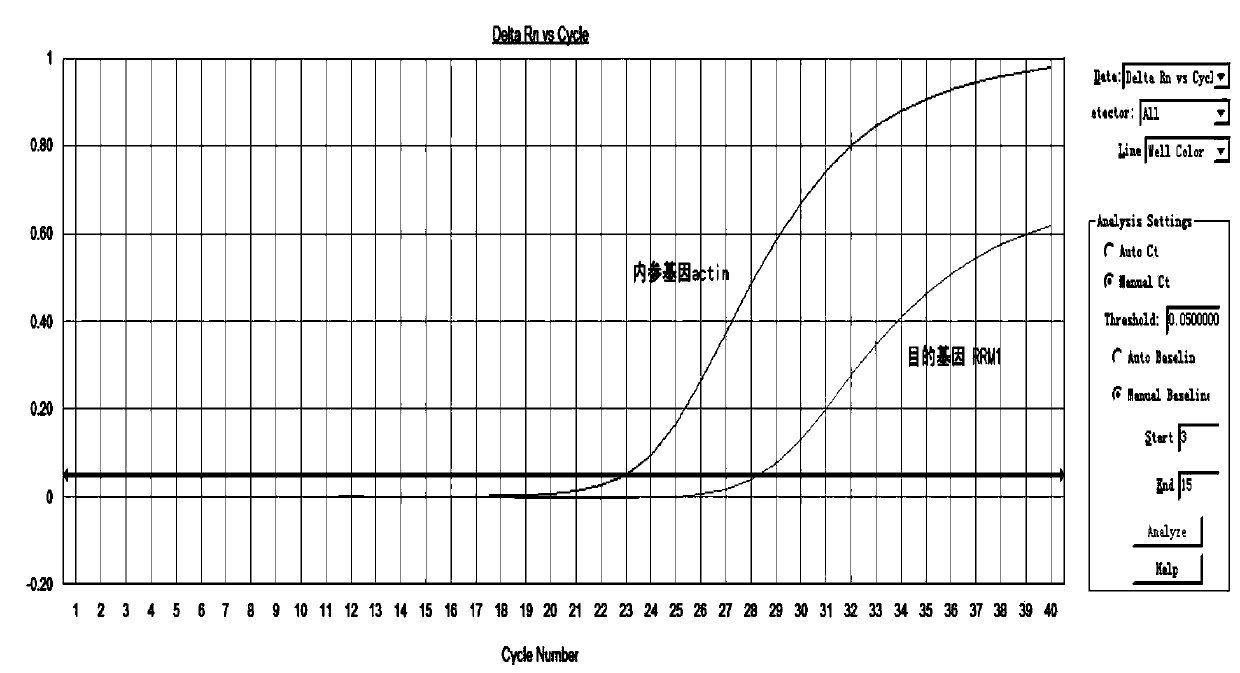
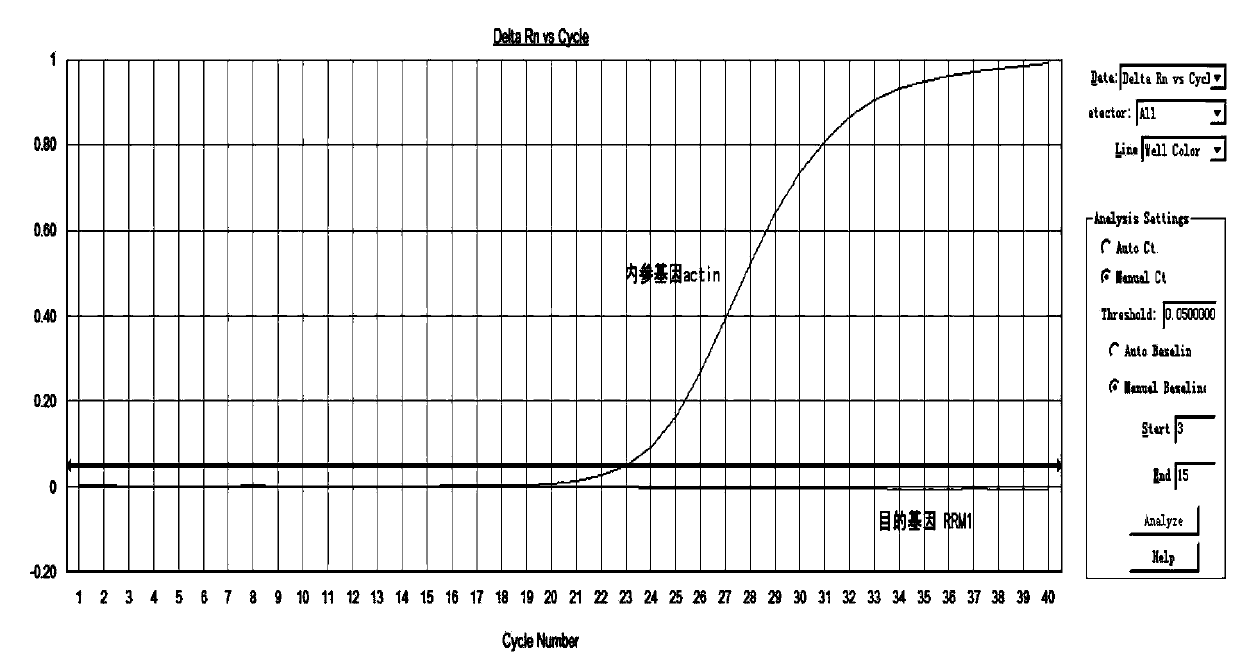
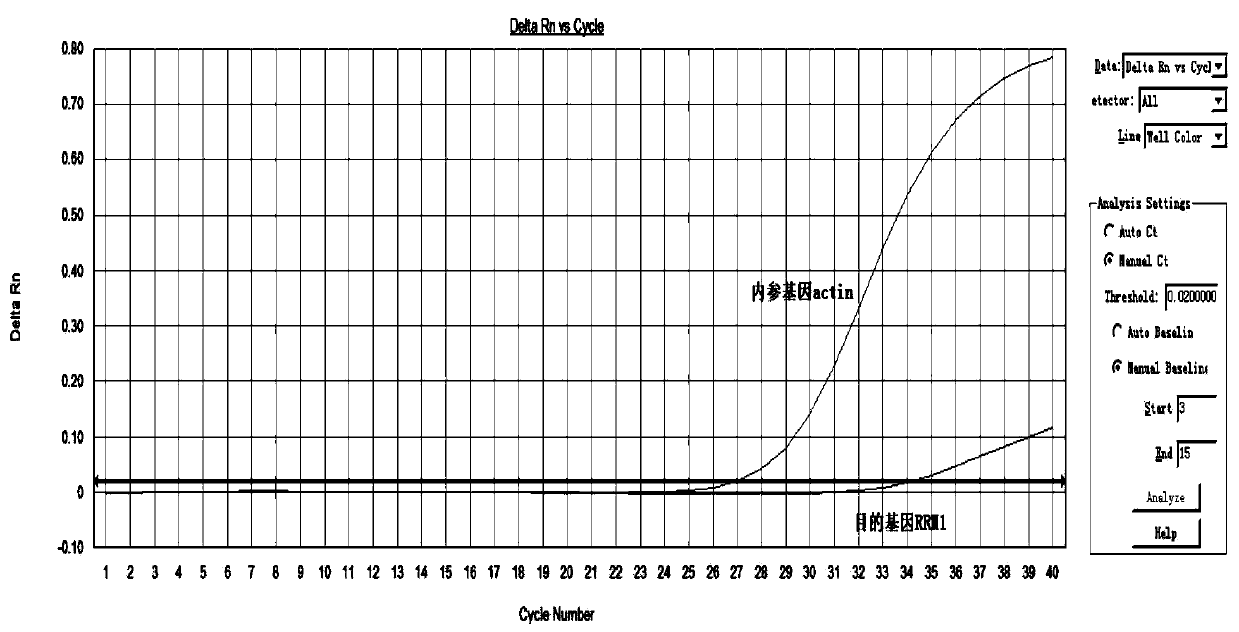
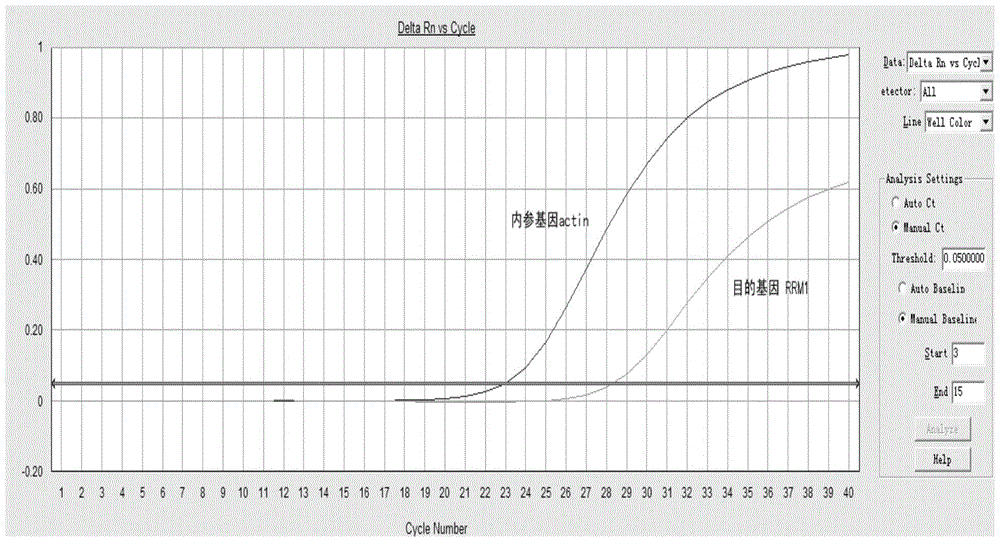
Method, kit, primer and probe for detecting relative expression quantity of RRM1 (ribonucleotide reductase M1) mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid)
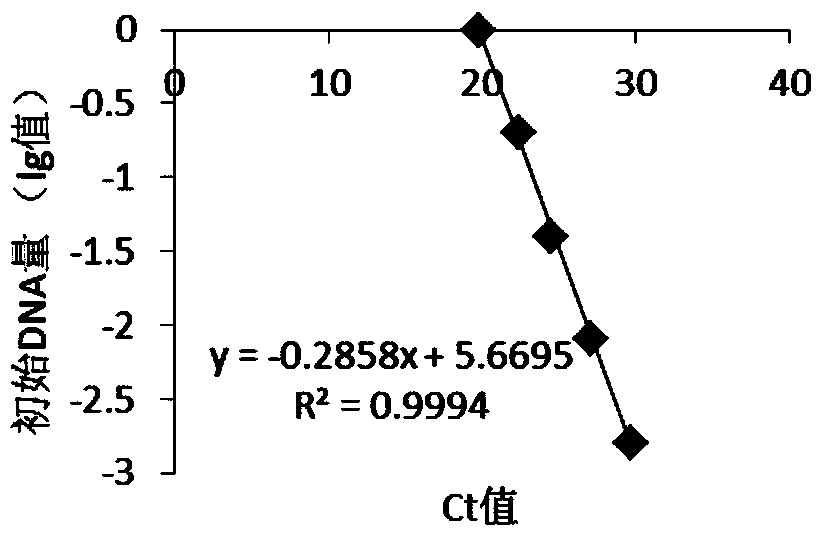
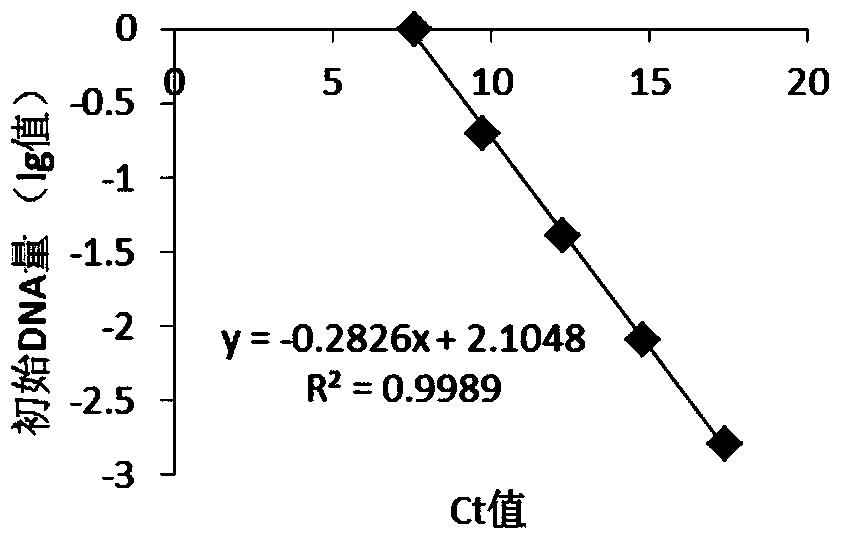
ActiveCN103589786AImprove detection accuracyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRibonucleotide reductaseFluorescence
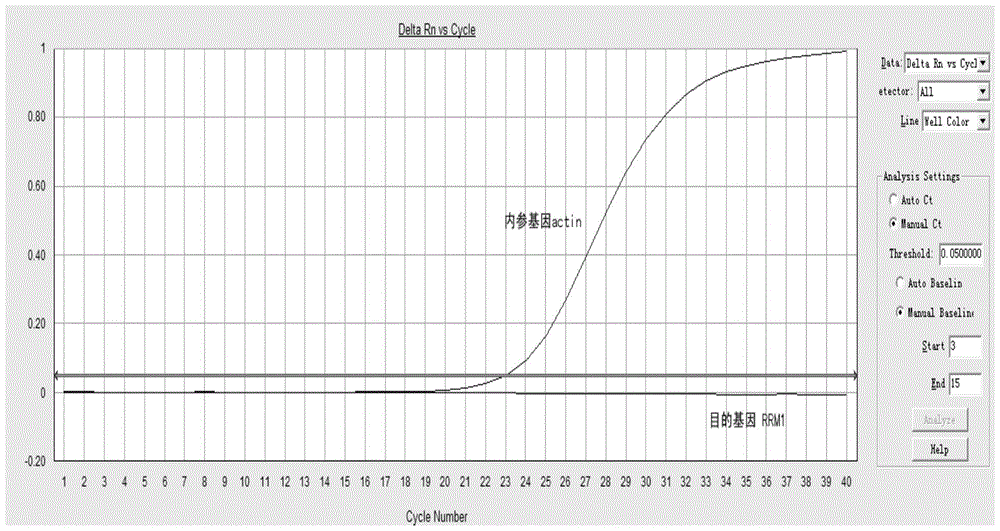
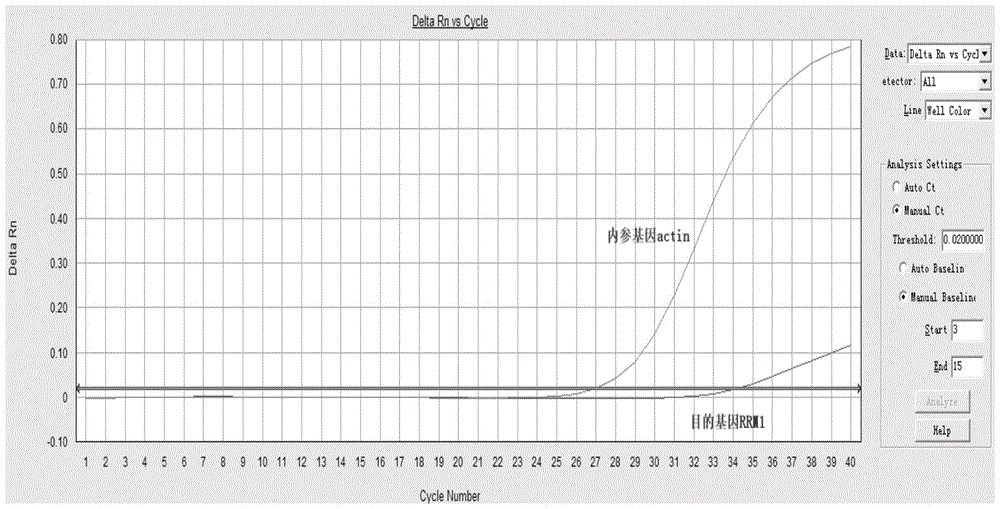
The invention provides a method for quantitatively detecting the relative expression quantity of RRM1 (ribonucleotide reductase M1) mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) in a sample. In the method, the relative expression quantity of RRM1mRNA in the sample can be quantitatively detected by use of the real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology. The invention provides a primer and a probe for quantitatively detecting the relative expression quantity of RRM1 mRNA in the sample, wherein the primer and the probe comprise upstream and downstream primers RRM1-F / RRM1-R and a probe RRM1-Probe for detection as well as upstream and downstream primers Actin-F / Actin-R and a probe Actin-Probe for a house-keeping gene actin. The invention also provides a kit for quantitatively detecting the relative expression quantity of RRM1 mRNA in the sample. By calculating the ratio of the expression quantity of RRM1 in the sample obtained by the method to the normal base of a healthy person, obtained by statistics, the relative expression quantity of RRM1 mRNA is obtained, the detection time can be effectively saved, and the detection accuracy is improved.
Owner:JILIN ADICON CLINICAL LAB
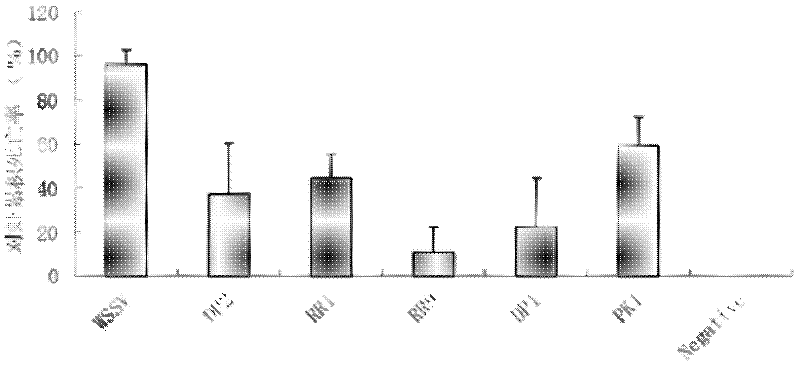
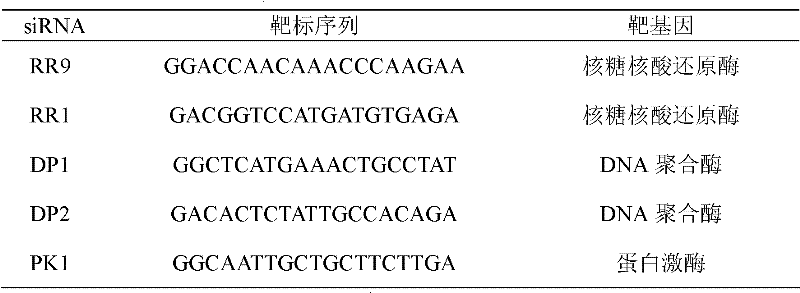
Target spot selecting method for efficiently inhibiting WSSV (White Spot Syndrome Virus)
InactiveCN102646172APrevent proliferationGood antiviral effectSpecial data processing applicationsRibonucleotide reductaseWhite spot syndrome
The invention relates to a target spot selecting method for efficiently inhibiting WSSV (White Spot Syndrome Virus), which comprises the steps of: 1, selecting coded sequences of ribonucleotide reductase and DNA polymerase in a WSSV genome; 2, generating a WSSV-resistant small RNA interference molecule by using software; and 3, screening theoretically efficient WSSV-resistant siRNA (small interfering RNA) according to a siRNA design rule. The small RNA molecule is designed by using the target spot selecting method, thus the selection range of the virus-resistant small RNA molecule can be effectively narrowed, the working efficiency is increased, the research cost is remarkably lowered, and the popularization and the application of an RNA interference technology in the aquatic virus-resistant field are facilitated.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Southernwood 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)- cyclobutenyl 4-diphosphoric acid reductase protein encoding sequence
InactiveCN1995355AIncrease contentIncrease productionOxidoreductasesFermentationRibonucleotide reductaseRibonucleotide synthesis
The invention discloses an arteannuin 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-cyclobutenyl 4-pyrophosphoric acid reductase protein coded sequence in the gene engineering domain, which is characterized by the following: the ribonucleotide sequence possesses 70% consanguinity with 36-1403th in the SEQ ID NO. 1, which an cross the 36-1403th in the SEQ ID NO. 1 under 45-55 deg. c.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Sulfonamide compound or salt thereof
ActiveUS10889555B2Excellent RNR-inhibiting activityInhibitionOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsNucleotideBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention provides a novel sulfonamide compound having a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitory activity or a salt thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same as an active ingredient.A compound represented by Formula (I) [wherein, X1 represents an oxygen atom or the like; X2 represents an oxygen atom; X3 represents —NH—; X4 represents a hydrogen atom or the like; R1 represents —C(R11)(R12)— or the like; R11 and R12 are the same or different and each represents a hydrogen atom or the like; R2 represents an optionally substituted C6-C14 aromatic hydrocarbon group or the like; R3 represents an optionally substituted C6-C14 aromatic hydrocarbon group or the like; R4 represents a hydrogen atom or the like] or a salt thereof.
Owner:TAIHO PHARMA CO LTD
Sulfonamide Compound or Salt Thereof
ActiveUS20200399235A1Excellent RNR-inhibiting activityInhibition effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryNucleotideBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention provides a novel sulfonamide compound having a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitory activity or a salt thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same as an active ingredient.A compound represented by Formula (I) [wherein, X1 represents an oxygen atom or the like; X2 represents an oxygen atom; X3 represents —NH—; X4 represents a hydrogen atom or the like; R1 represents —C(R11)(R12)— or the like; R11 and R12 are the same or different and each represents a hydrogen atom or the like; R2 represents an optionally substituted C6-C14 aromatic hydrocarbon group or the like; R3 represents an optionally substituted C6-C14 aromatic hydrocarbon group or the like; R4 represents a hydrogen atom or the like] or a salt thereof.
Owner:TAIHO PHARMA CO LTD
Cordyceps sinensis ribonucleotide reductase as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103045548AIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideNucleoside diphosphate
The invention relates to ribonucleotide reductase from 'Bailing' producing strain cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis for anabolism of deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate from pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate, a gene coding the ribonucleotide reductase and application of the ribonucleotide reductase. The ribonucleotide reductase has over 90% of homology to the amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1 or SEQ ID No.3; and the coding gene has over 90% of homology to the nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID No.2 or SEQ ID No.4. According to the invention, the metabolic pathway for synthesizing deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate from pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate is studied in details in principle, the cloning DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) comprising the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transferred into engineering bacteria through transduction, transformation and combined transfer, high expressivity of the host deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate is obtained by adjusting the expression of the deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate biosynthesis gene, an effective means of increasing output of the deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate is provided, and a significant application prospect is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Viral nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS20010024817A1Improved vaccineOrganic active ingredientsFungiLaryngotracheitis virusInsertion site
Various genes of herpes virus of turkeys (HVT), Marek's disease virus (MDV) and infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) have been identified as non-essential regions (and candidates for insertion sites for foreign genes) and / or as antigen-encoding regions. The former include the HVT homologue of the HSV (herpes simplex virus) gC gene, the TK (thymidine kinase) region of MDV or ILTV, ORF3 of ILTV (as defined herein), the ribonucleotide reductase (large subunit) gene of ILTV, MDV or HVT and the ribonucleotide reductase (small subunit) gene of MDV. The antigen-encoding regions include the HVT homologues of the HSV gB, gC and gH genes, the ILTV homologue of HSV gB, ORF2 of ILTV, and the HVT homologue of the HSV-1 immediate early genes IE-175 and IE-68. Manipulation of these genes allows vaccines to be prepared comprising attenuated virus or virus carrying heterologous antigen-encoding sequences.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
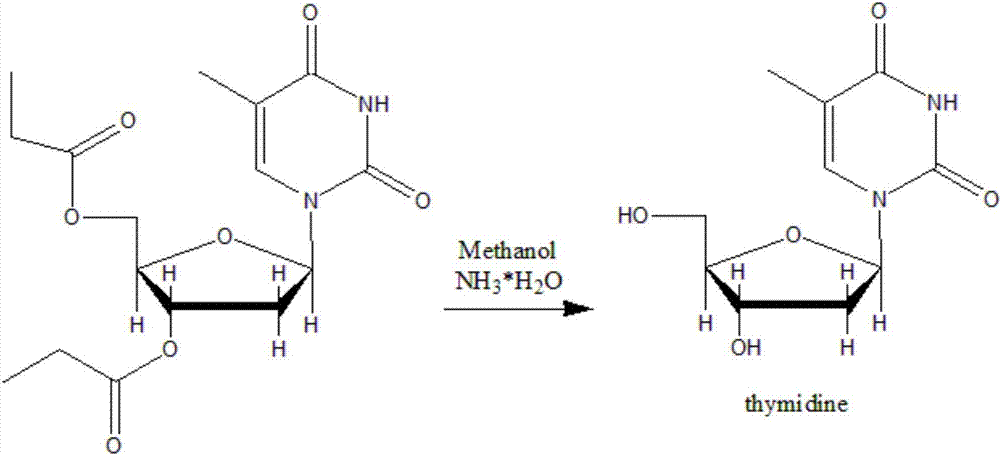
Synthetic method of beta-thymidine
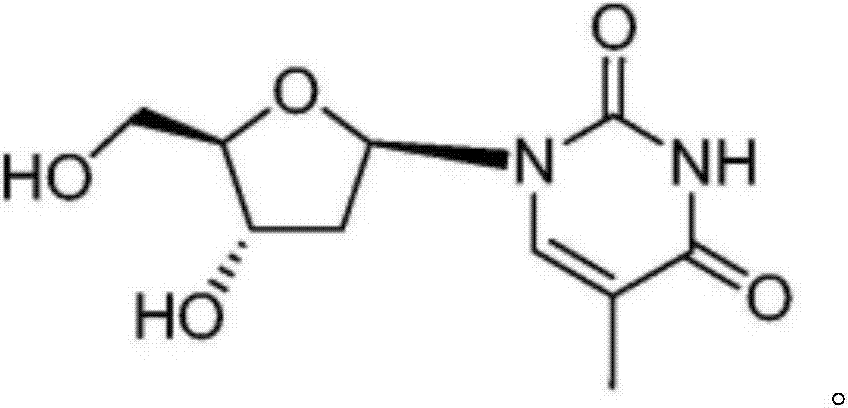
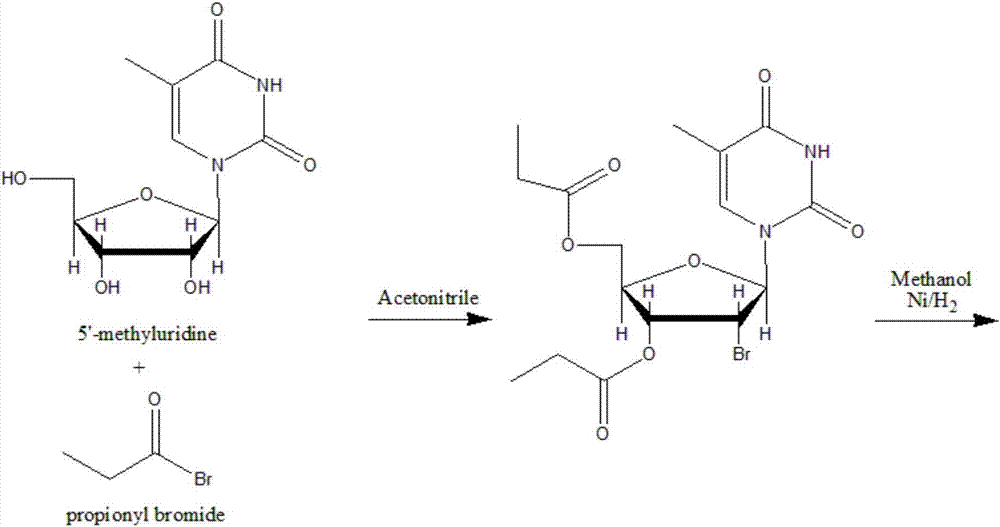
The invention discloses a synthetic method of beta-thymidine. Thymidine is synthesized reversely by adopting enzyme engineering, glucose dehydrogenase, uridine kinase, inkfish pyruvate kinase, ribonucleotide reductase, thymidylate kinase and thymidine kinase are used, 5-methyluridine is used as a raw material, nucleotide is generated through two phosphorylation steps and then is converted into deoxynucleotide, and then the thymidine is generated through two-step dephosphorylation. According to the synthetic method of beta-thymidine disclosed by the invention, the cost is greatly reduced, the production cycle is shortened, the industrial waste is reduced, and the beta-thymidine is non-toxic and environmentally-friendly.
Owner:SUZHOU DUMEI BIOTECH CO LTD
Antitumor Agent
InactiveUS20200405697A1Improve anti-tumor effectAvoid side effectsOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsRibonucleotide reductaseChemical compound
Owner:TAIHO PHARMA CO LTD
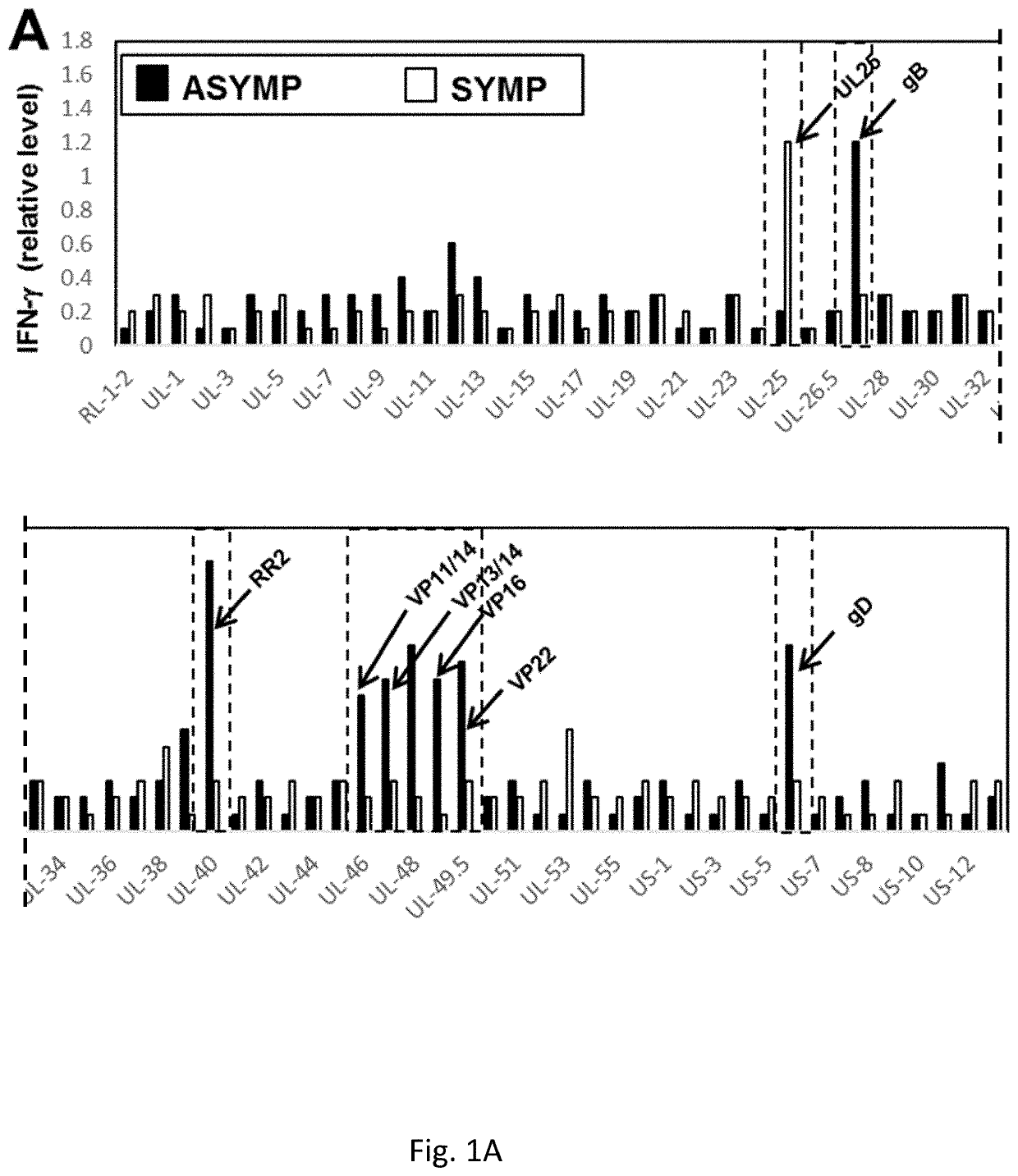
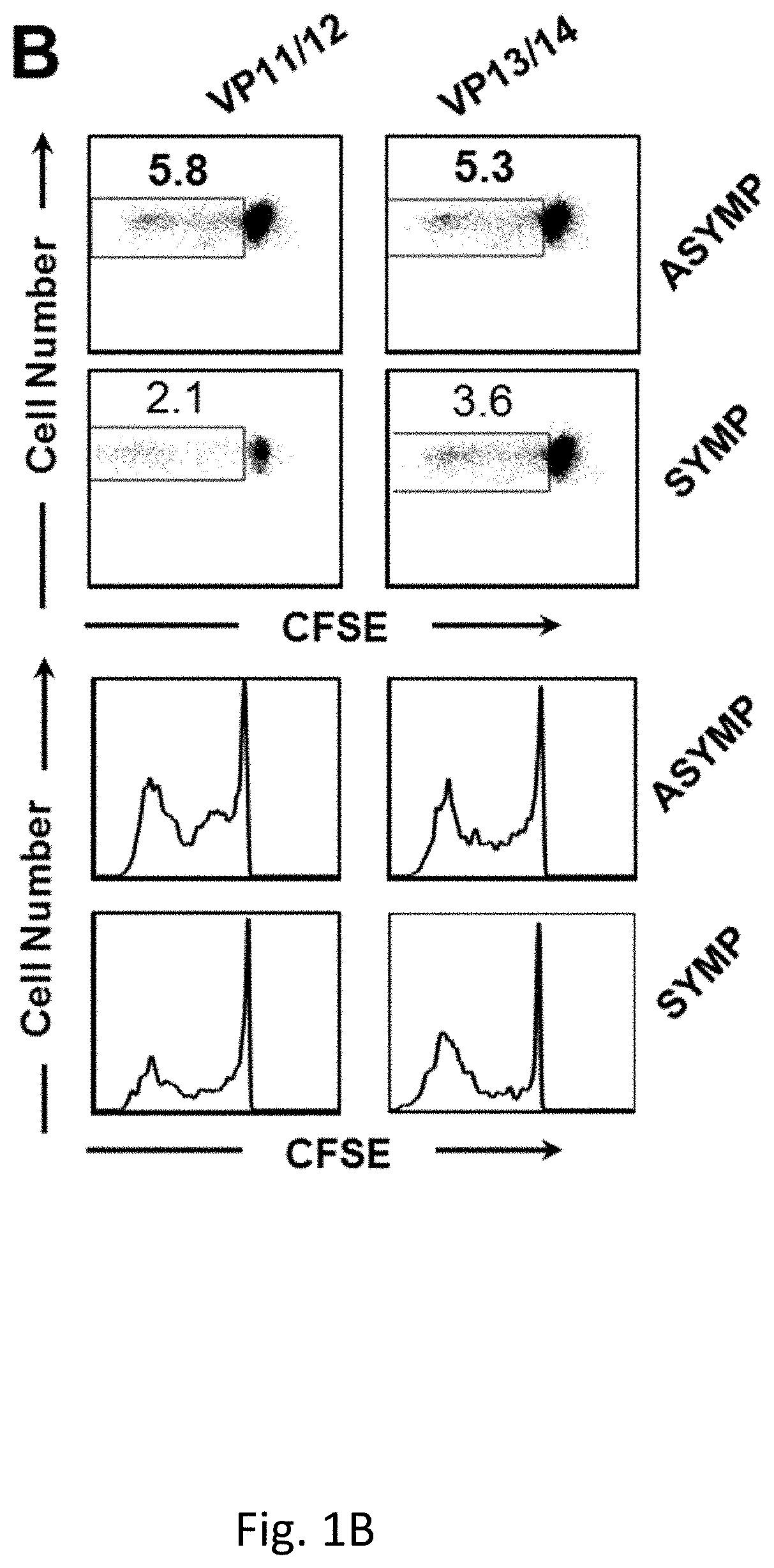
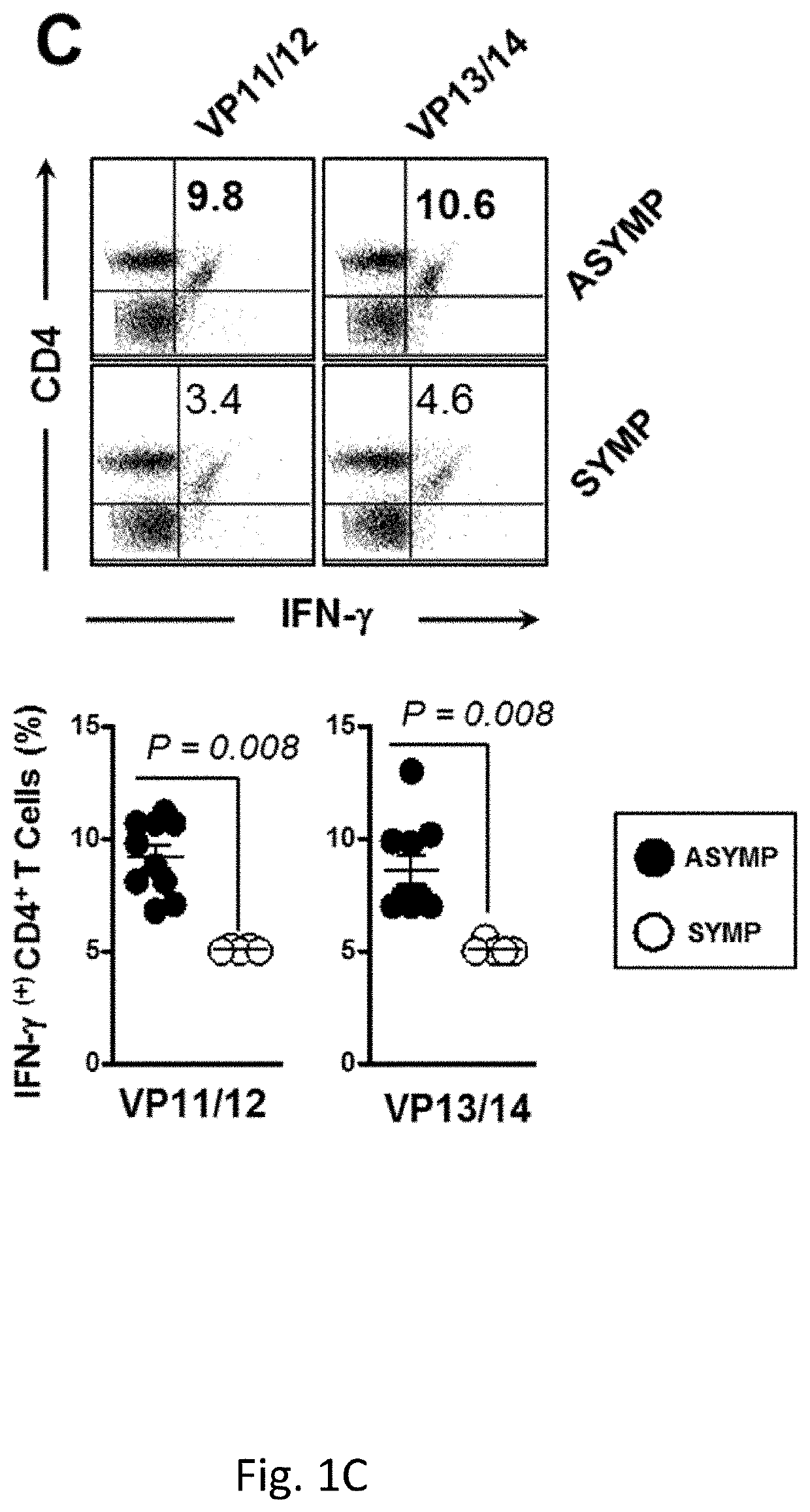
Protection Against Recurrent Genital Herpes by Therapeutic Immunization with Herpes simplex virus type 2 Ribonucleotide Reductase Protein Subunits
The present invention relates to compositions comprising HSV antigens and methods for their use in the treatment or prevention of asymptomatic and symptomatic herpesvirus infection, or recurrence.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method, kit, primers and probes for detecting relative expression of rrm1 mRNA
ActiveCN103589786BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRibonucleotide reductaseFluorescence
The invention provides a method for quantitatively detecting the relative expression quantity of RRM1 (ribonucleotide reductase M1) mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) in a sample. In the method, the relative expression quantity of RRM1mRNA in the sample can be quantitatively detected by use of the real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology. The invention provides a primer and a probe for quantitatively detecting the relative expression quantity of RRM1 mRNA in the sample, wherein the primer and the probe comprise upstream and downstream primers RRM1-F / RRM1-R and a probe RRM1-Probe for detection as well as upstream and downstream primers Actin-F / Actin-R and a probe Actin-Probe for a house-keeping gene actin. The invention also provides a kit for quantitatively detecting the relative expression quantity of RRM1 mRNA in the sample. By calculating the ratio of the expression quantity of RRM1 in the sample obtained by the method to the normal base of a healthy person, obtained by statistics, the relative expression quantity of RRM1 mRNA is obtained, the detection time can be effectively saved, and the detection accuracy is improved.
Owner:JILIN ADICON CLINICAL LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com