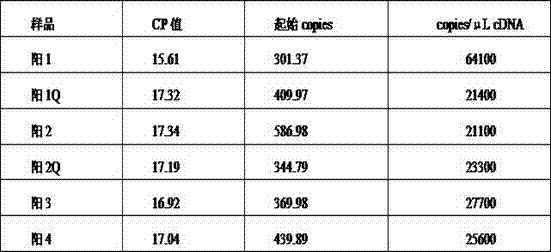
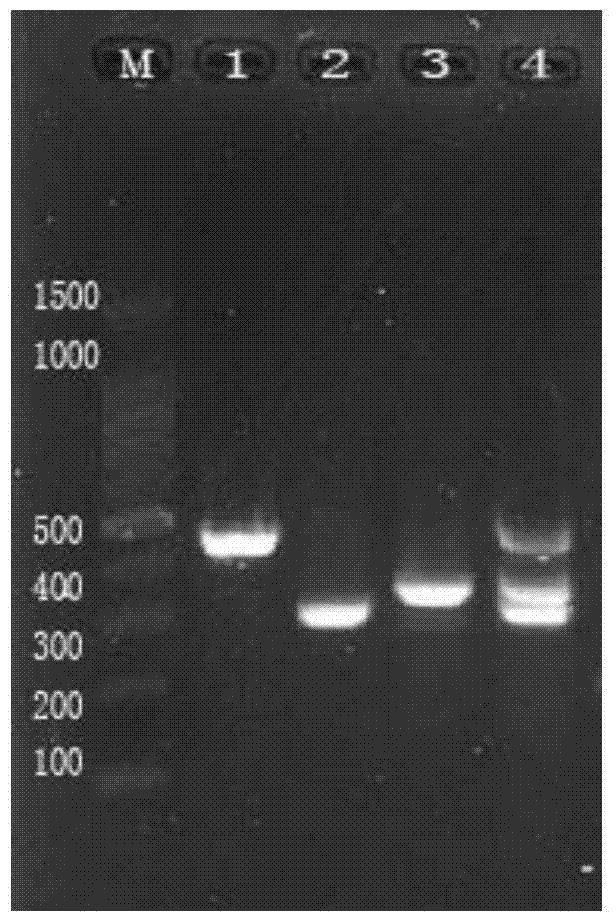
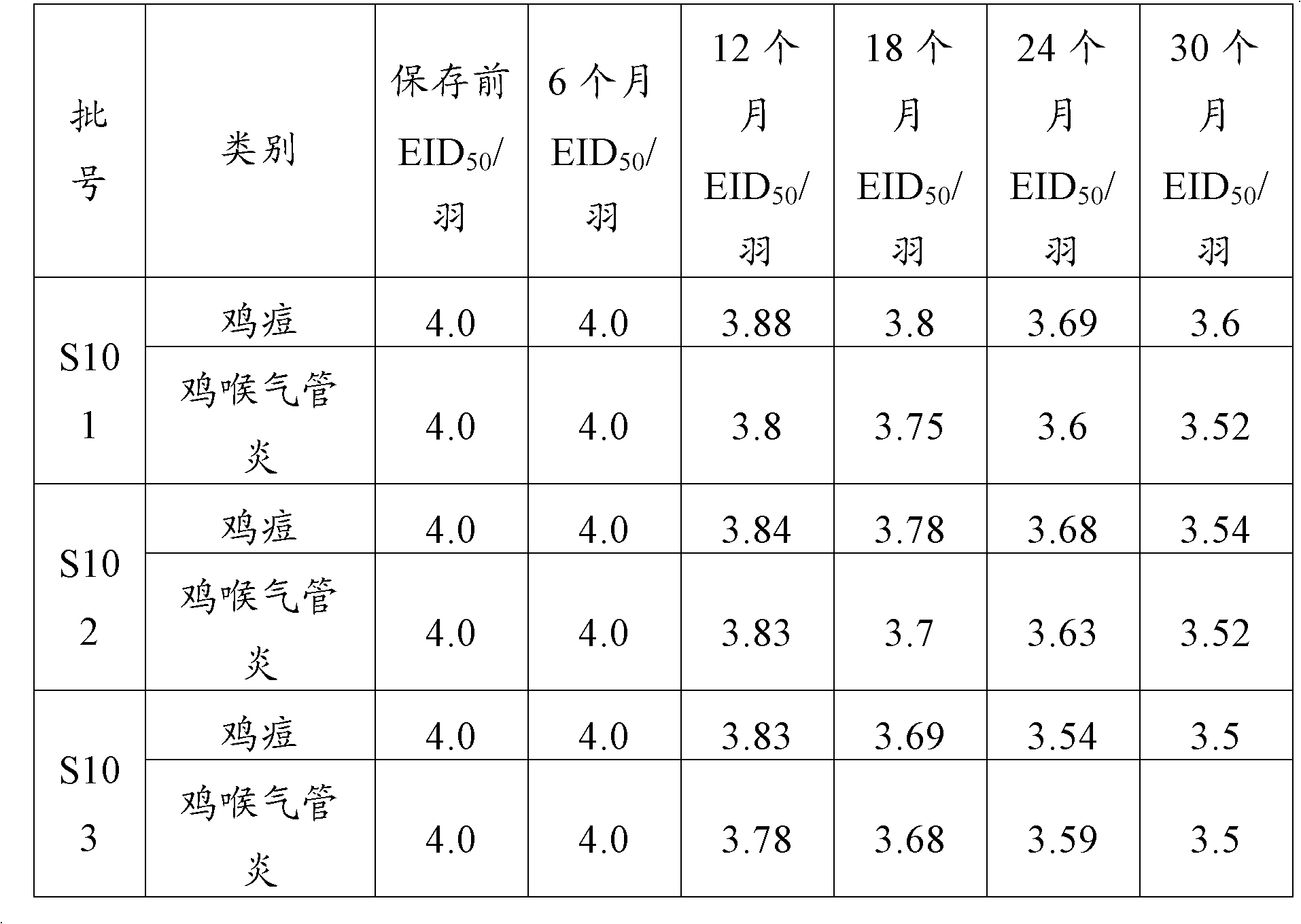
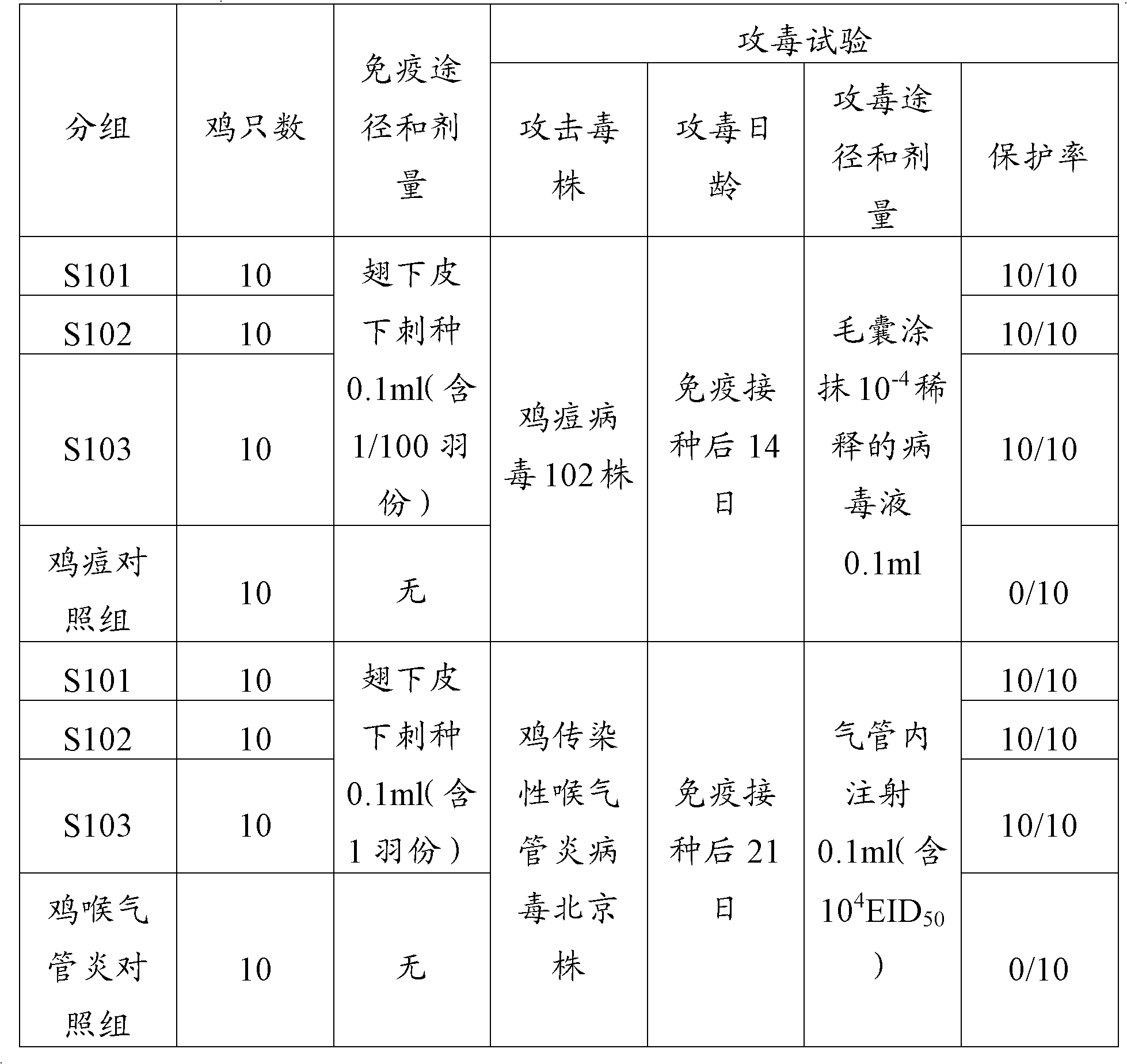Patents
Literature
50 results about "Laryngotracheitis virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Infectious laryngotracheitis (ILT) is an important respiratory disease of chickens and annually causes significant economic losses in the poultry industry world-wide. ILT virus (ILTV) belongs to alphaherpesvirinae and the Gallid herpesvirus 1 species. The transmission of ILTV is via respiratory and ocular routes.
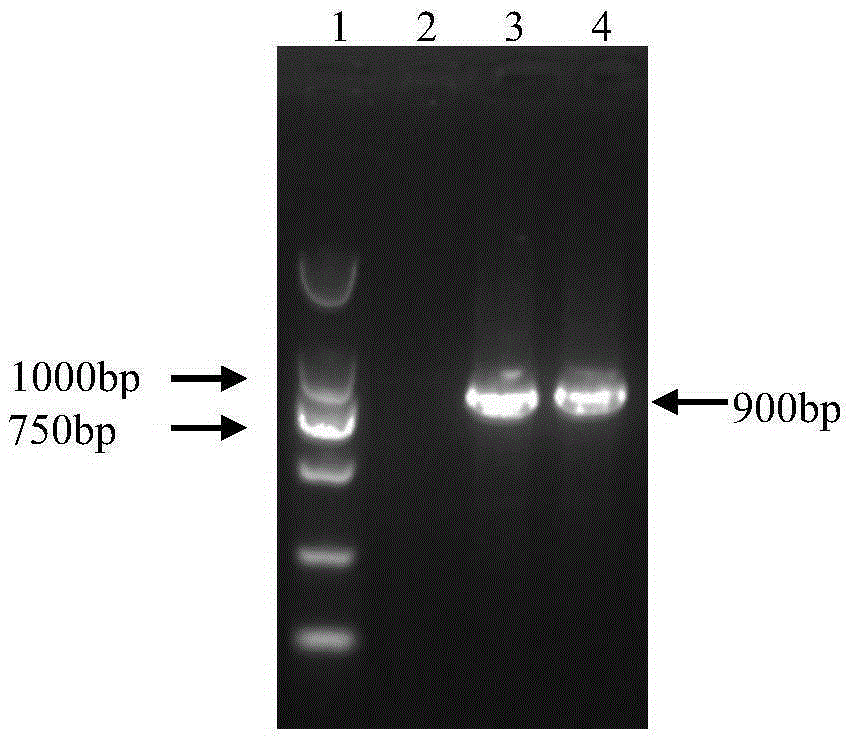
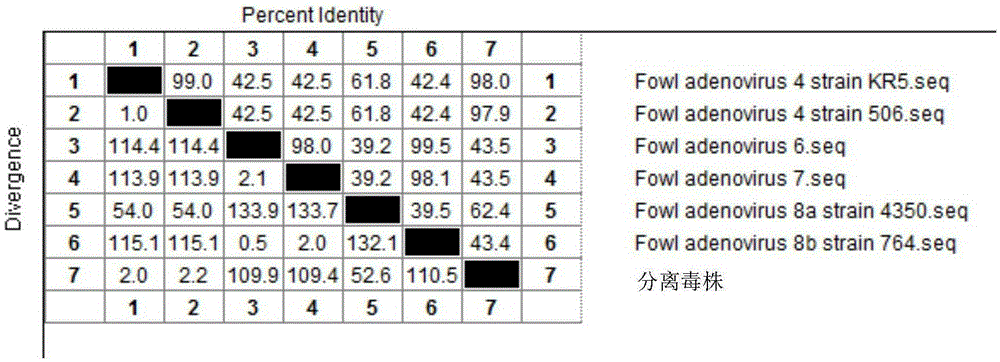
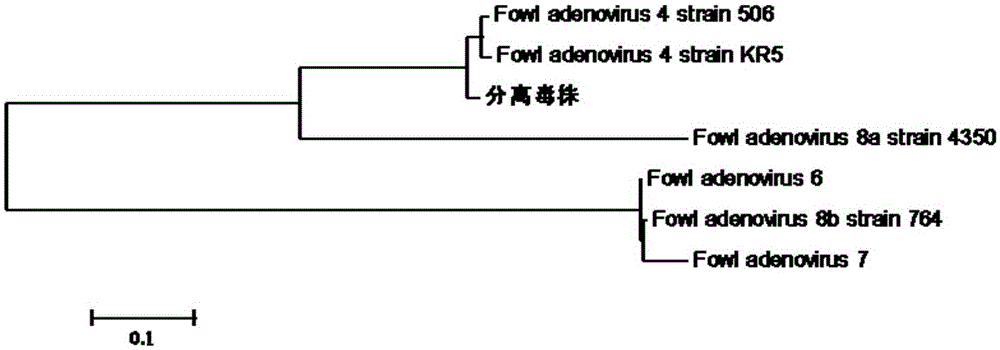
I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 strain and application thereof
ActiveCN105368795AImprove featuresImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisInfected cellLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention aims at providing an I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 strain, which is preserved with preservation number of CCTCC No. V201541. The I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 YBAV-4 strain disclosed by the invention is excellent in specificity and immunogenicity; a specific precipitation line does not appear in specific positive serum chicken SPF chicken serum such as infected cell sap and egg drop syndrome resisting virus, chicken infectious bursal disease virus, Newcastle disease virus, chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus, chicken Marek's disease virus, avian influenza and the like, while an obvious specific precipitation line appears in I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 specific serum. The strain disclosed by the invention, as a vaccine strain which is good in manufacturing effect, is capable of preventing chicken hydropericardium syndrome, and the strain is applicable to identification of virus serotype and investigation on epidemiology.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
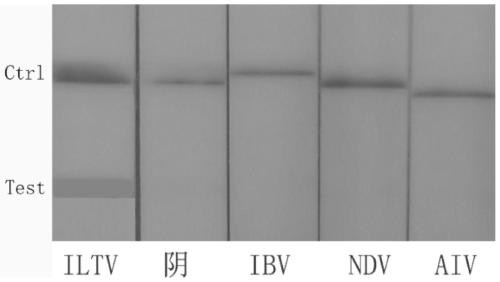
Primer and probe combination for RAA-LFD detection of chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus and application of primer and probe combination
PendingCN110257562AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention relates to the technical field of biological detection, and particularly discloses a primer and probe combination for RAA-LFD detection of chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus and application of the primer and probe combination. The primer comprises an upstream primer and a downstream primer, wherein the sequence of the upstream primer is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and the sequence of the downstream primer is shown as SEQ ID No. 2; and the probe sequence is shown in SEQ ID No. 11. The primer and probe combination provided by the invention is used for detecting chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus, and the corresponding RAA-LFD method is simple, rapid, convenient, reliable, strong in specificity, high in sensitivity and accuracy, and is more suitable for clinical field detection.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
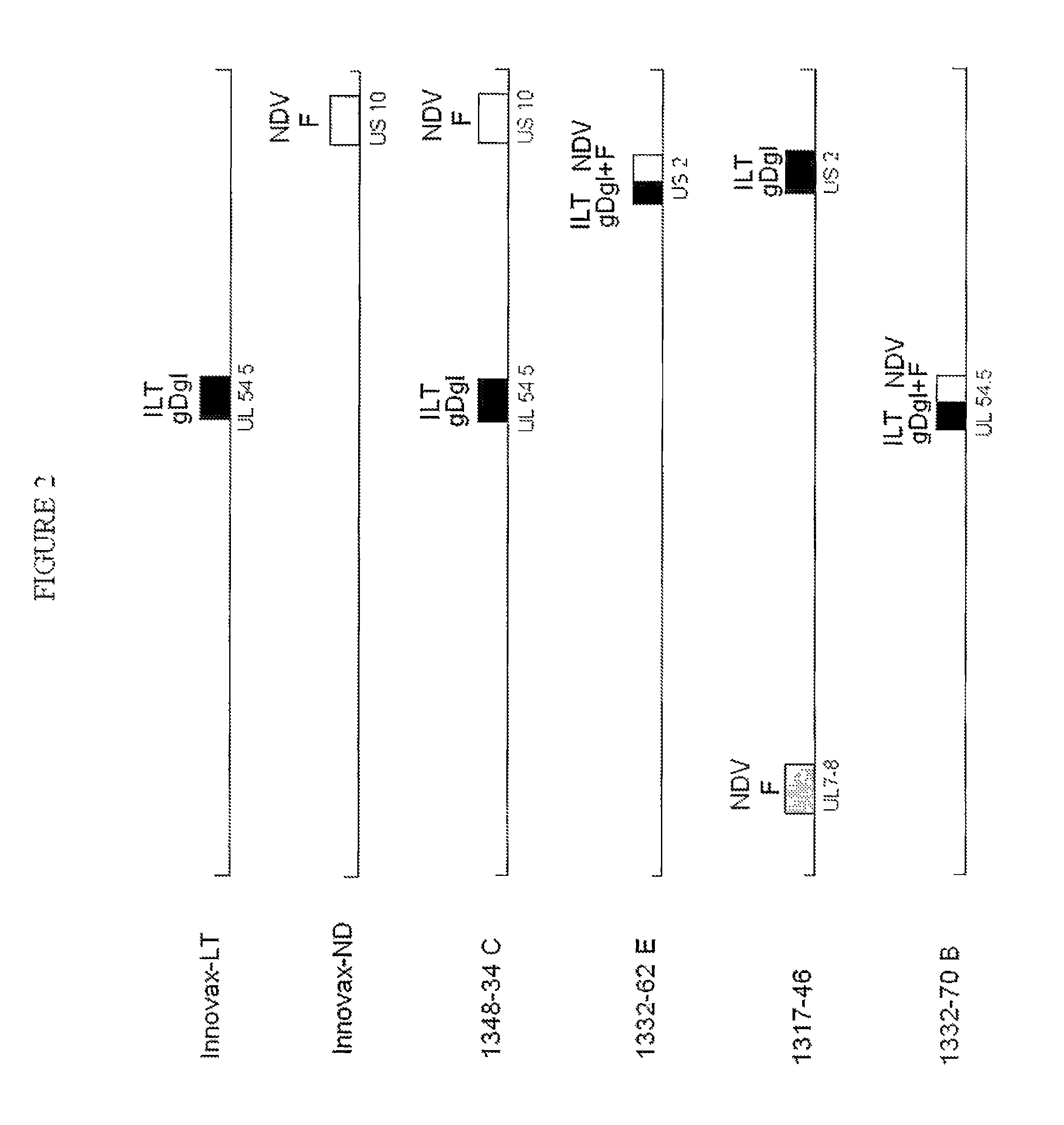
Recombinant non-pathogenic marek's disease virus constructs encoding infectious laryngotracheitis virus and newcastle disease virus antigens
ActiveUS8932604B2Stable, safe, and efficacious immunogenic compositionsImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideInfectious bronchitis virusBorna disease virus
Recombinant multivalent non-pathogenic Marek's Disease virus constructs that encode and express both Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus and Newcastle Disease virus protein antigens, and methods of their use in poultry vaccines.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Recombinant non-pathogenic marek's disease virus constructs encoding infectious laryngotracheitis virus and newcastle disease virus antigens
ActiveUS20130101619A1Stable, safe, and efficacious immunogenic compositionsImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBorna disease virusNewcastle disease virus NDV
The present invention discloses novel recombinant multivalent non-pathogenic Marek's Disease virus constructs that encode and express both Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus and Newcastle Disease virus protein antigens, and methods of their use in poultry vaccines.
Owner:INTERVET INC
RPA primer for detecting chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus and its detecting method
ActiveCN107287353AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInfectious laryngotracheitisDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses a RPA primer for detecting chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus. The nucleotide sequence of the RPA primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2; the RPA primer is strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, and accurate in detection result. The invention further provides a RPA method for detecting the chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus. The detecting method is easy to operate, low in equipment requirement, strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, and accurate and reliable in detection result; the detecting method provides a low-cost, fast and specific field diagnosis method for effectively detecting and diagnosing the chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
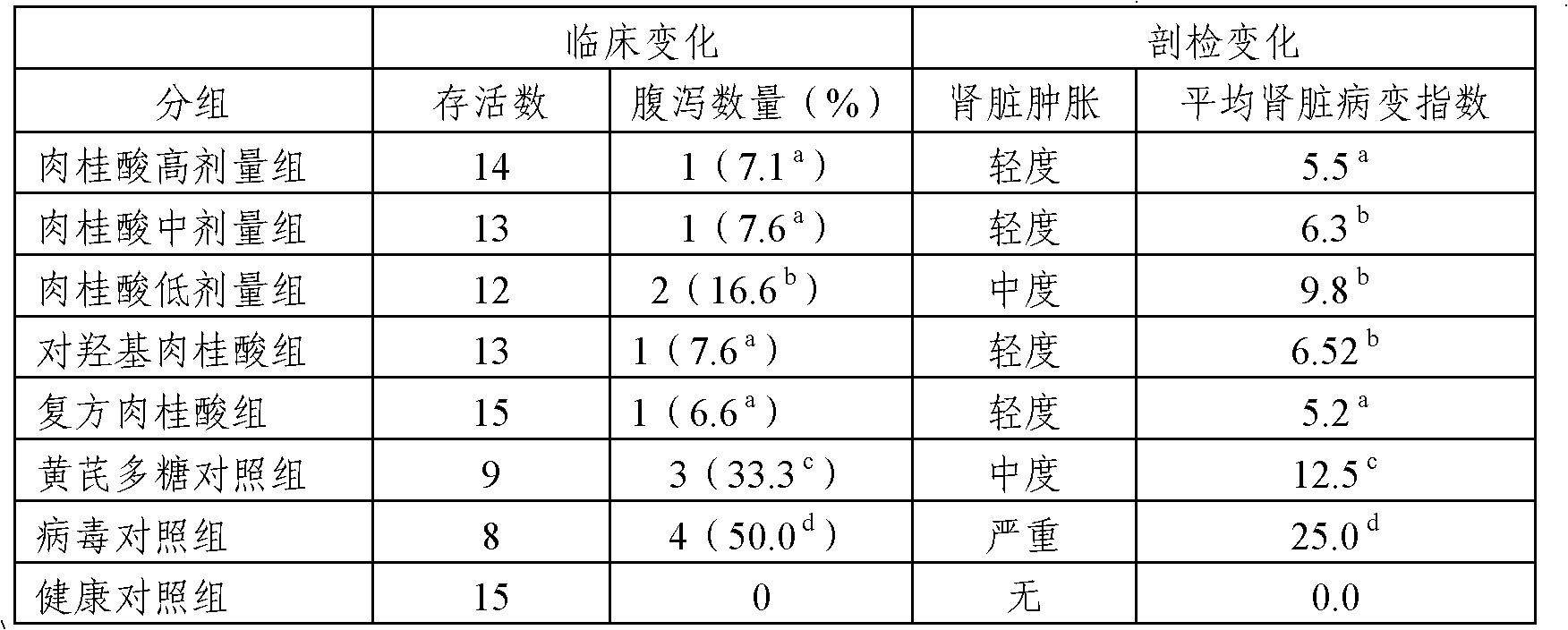
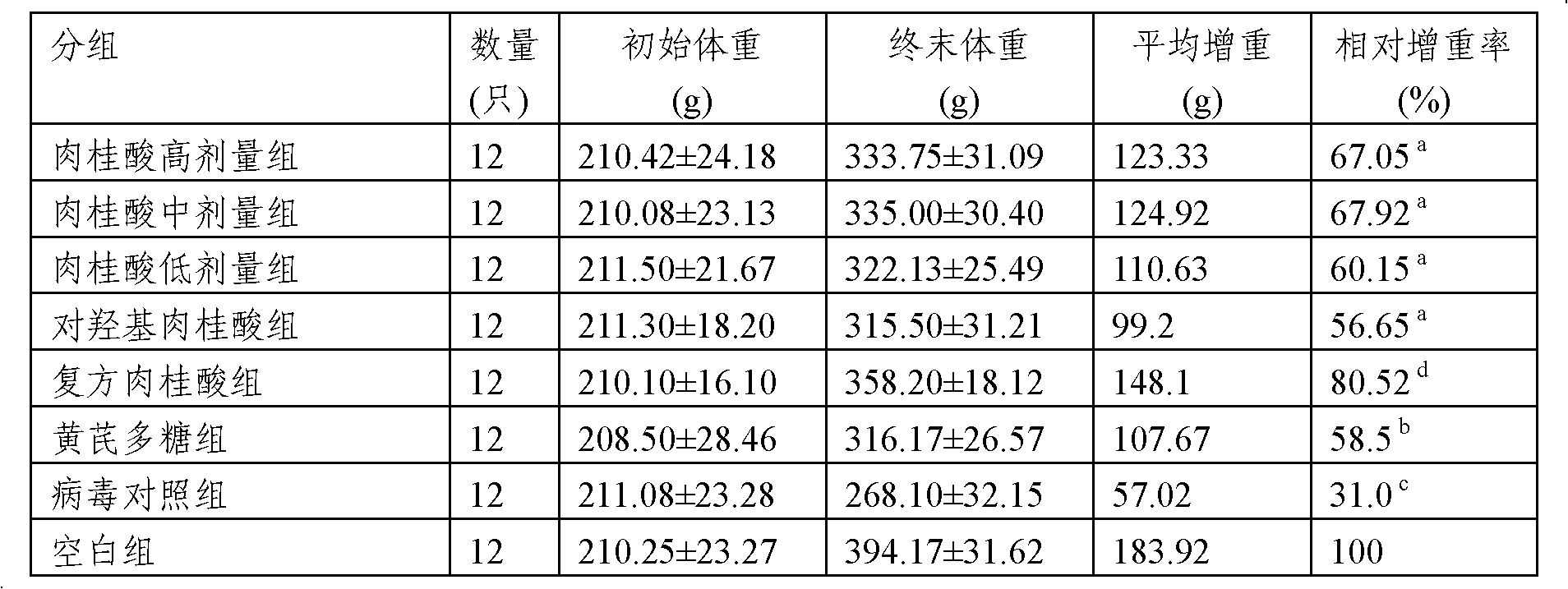
Application of cinnamic acid in preparation of drugs for preventing and treating livestock and poultry virus infection
ActiveCN102600120AImprove survival rateIncrease production capacityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsBird fluMortality rate
The invention relates to application of cinnamic acid in the preparation of drugs for preventing and treating livestock and poultry virus infection. Cinnamic acid has an activity resisting to poultry virus diseases, and can effectively prevent and treat infections of a bird flu H9 subtype virus, a bird flu H5 subtype virus, an infectious bursal disease virus LX strain, a nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus and an avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus, so that the death rate of diseased chickens is reduced, the survival rate of the poultry is effectively increased and the parturition performance of the poultry is effectively improved.
Owner:承德普润生物制药有限公司
Multi-fluorescent immunoassay method for rapidly distinguishing 6 types of poultry respiratory pathogens
ActiveCN106191319AAvoid crossbreedingGuaranteed temperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotin-streptavidin complexMycoplasma synoviae
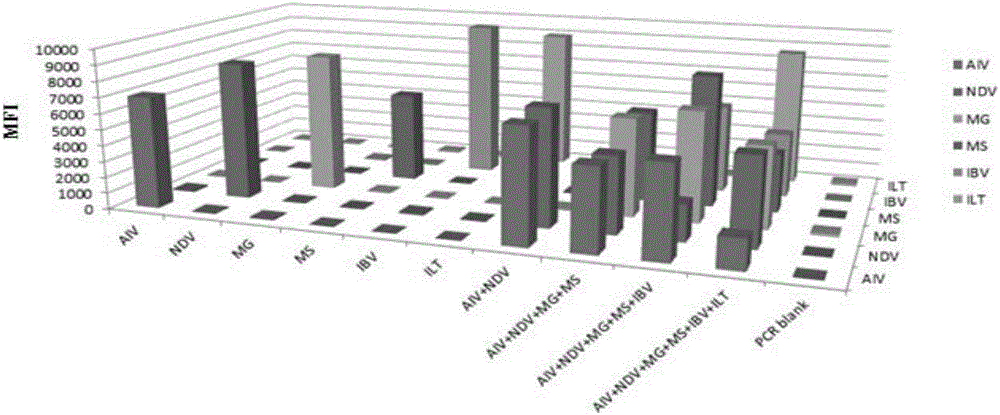
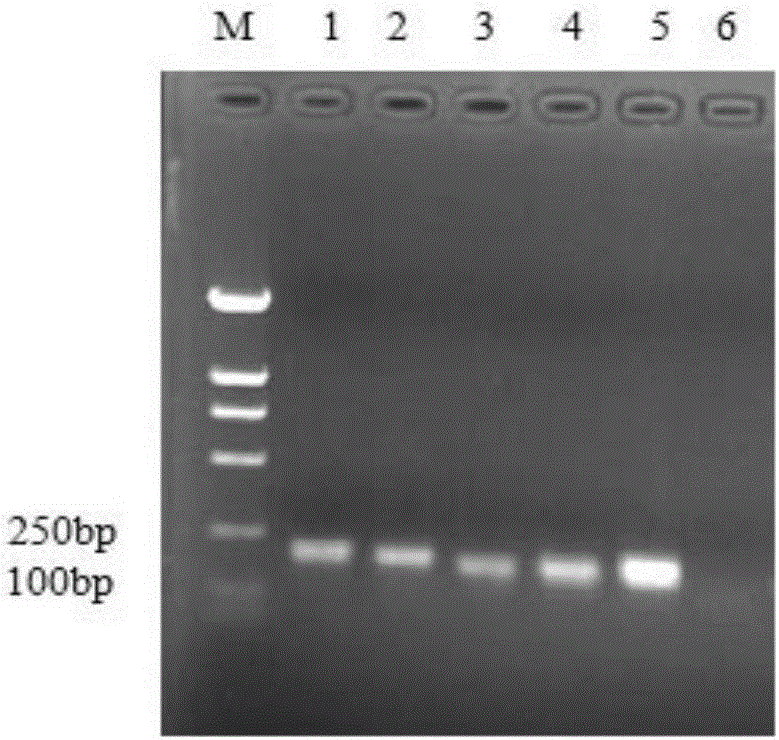
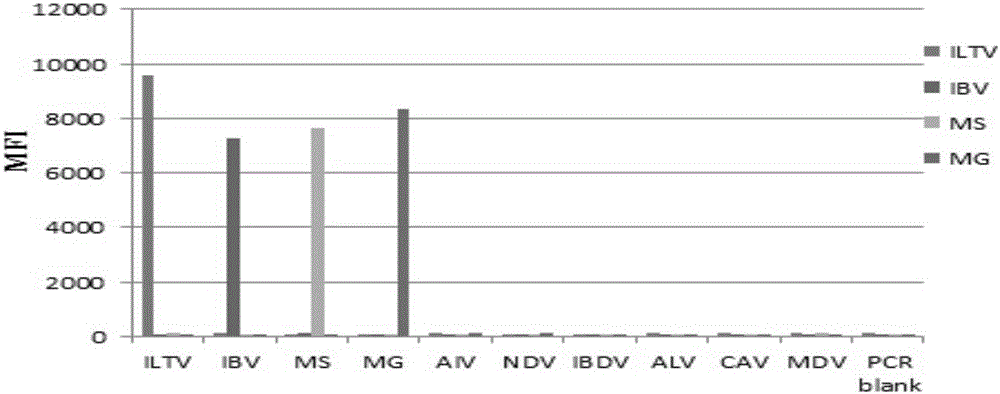
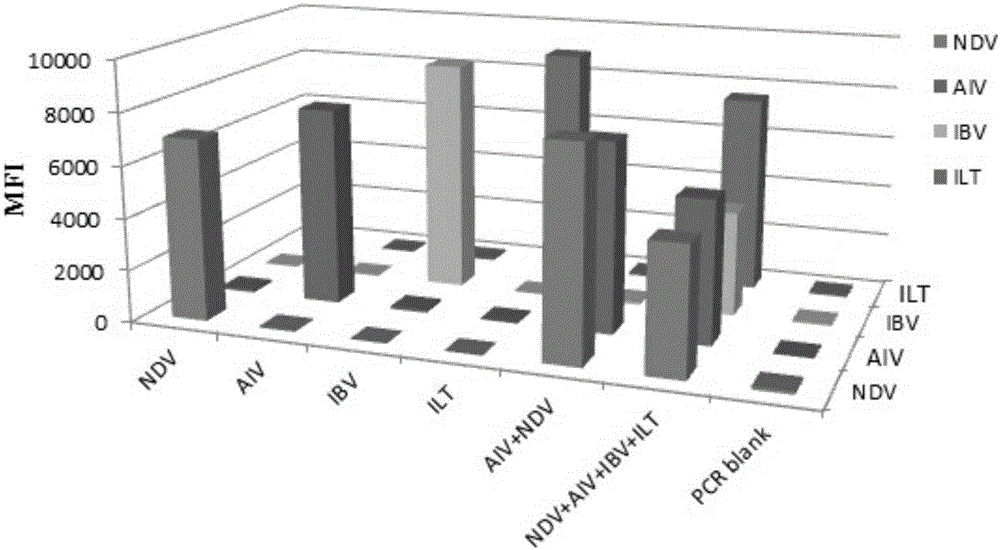
The invention discloses a multi-fluorescent immunoassay method for rapidly distinguishing 6 types of poultry respiratory pathogens. The multi-fluorescent immunoassay method is simple to operate; a target amplified fragment is obtained through a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); then an amplified product, fluorescence coded microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized; an MFI (Mean Fluorescence Intensity) value is read through a detector to distinguish viruses of different types. According to the method disclosed by the invention, avian influenza viruses, chicken infectious bronchitis viruses, chicken Newcastle disease viruses, chicken infectious laryngotracheitis viruses, mycoplasma gallisepticum and mycoplasma synoviae can be accurately detected at the same time; the multi-fluorescent immunoassay method has high specificity, high sensitivity and good repeatability. Compared with a traditional detection method, the method disclosed by the invention realizes simultaneous detection of a plurality of types of different target molecules in the same sample; the use amount of the sample is less; the method is simple and rapid to operate and the detection cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
Infectious laryngotracheitis recombinant virus strain for expressing Newcastle disease virus F protein and establishment and application of strain
ActiveCN108611328AGood immune effectFast immune protectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism preservationMicroorganism
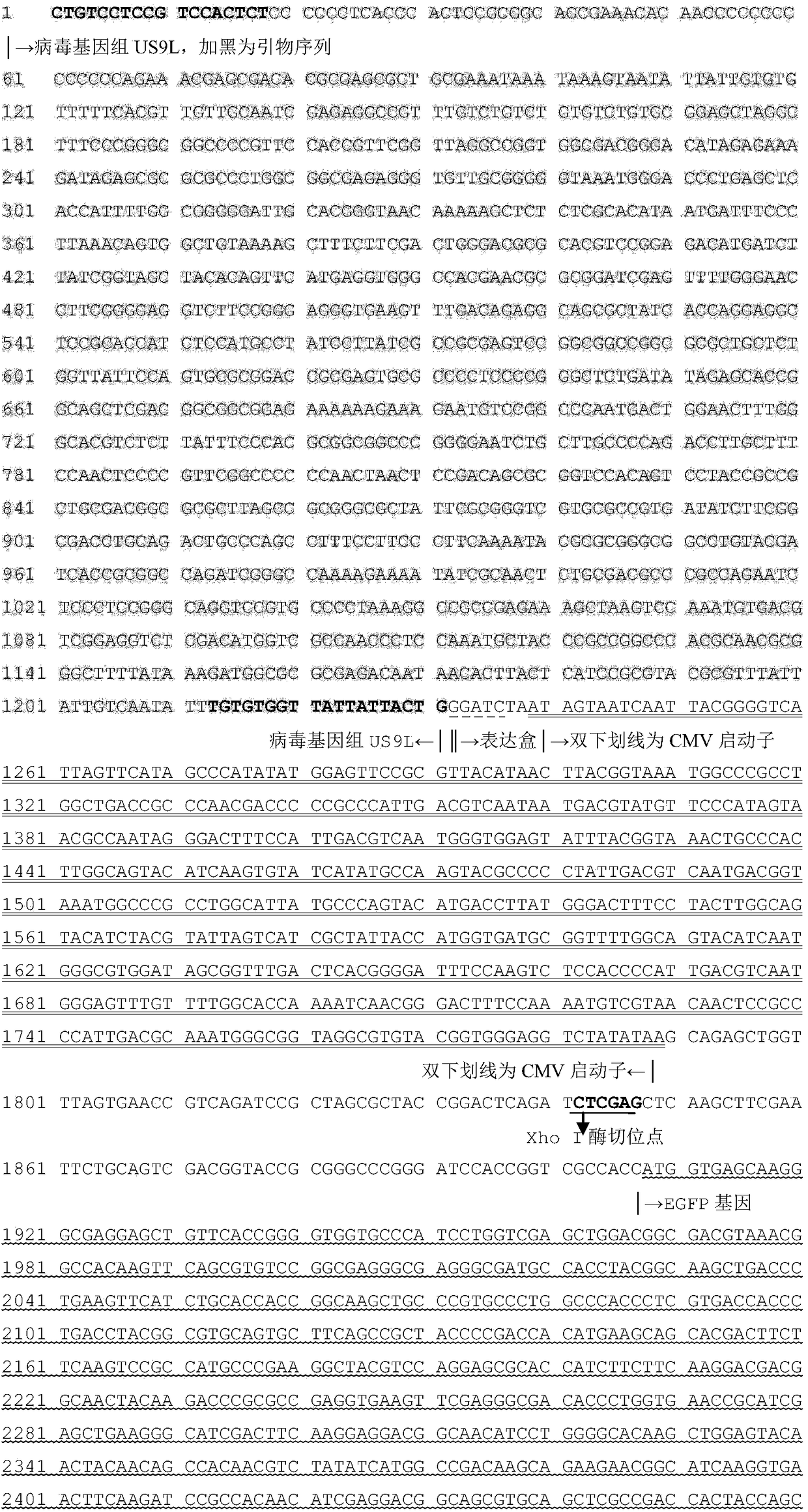
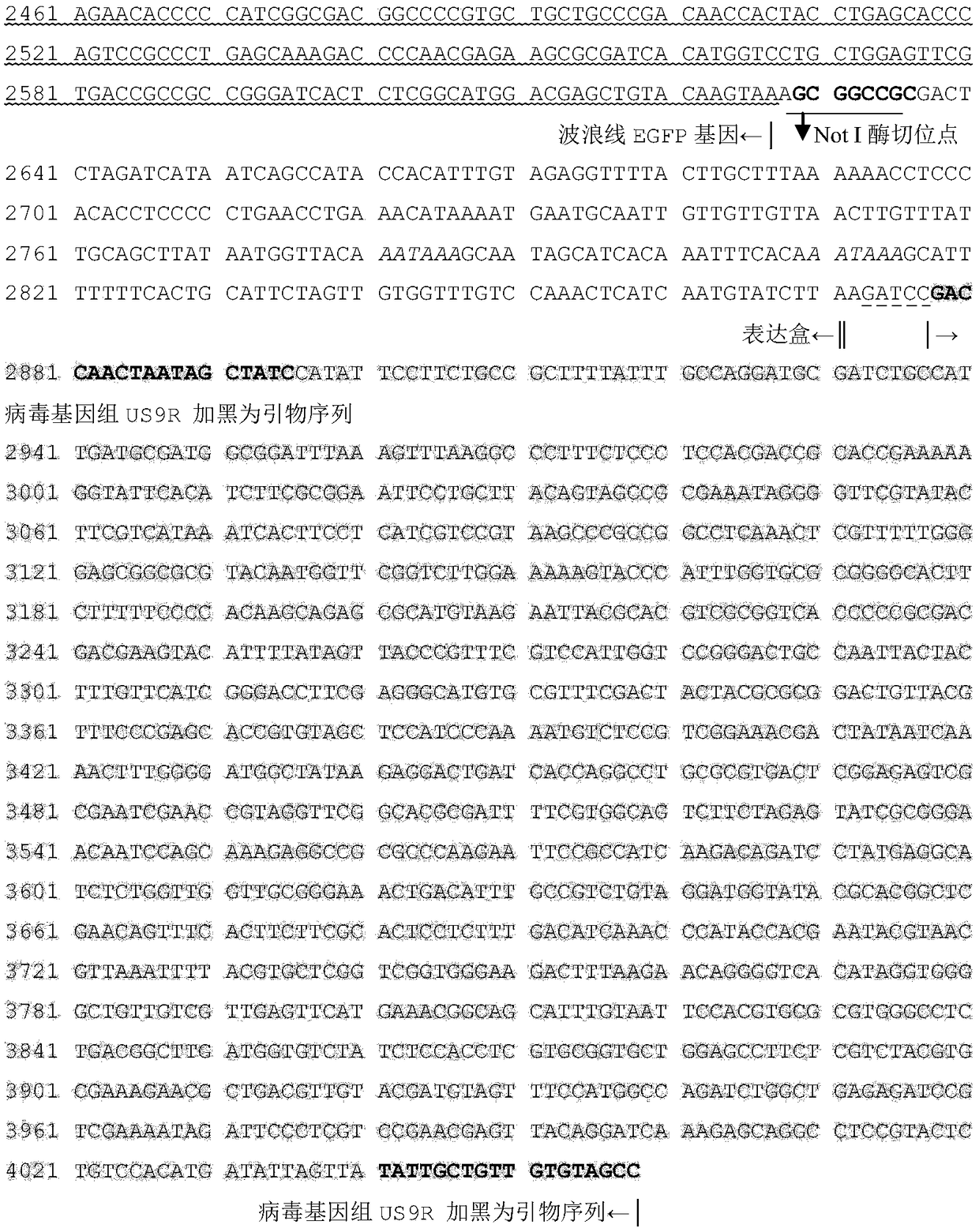
The invention discloses an infectious laryngotracheitis recombinant virus strain for expressing a Newcastle disease virus F protein and establishment and the application of the strain and relates to the field of recombinant virus vaccines. Aiming at problems of recombinant virus establishment and the application of an exogenous immunogenic gene with a nonobligatory gene US9 locus of an ILTV (Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus), the invention provides an infectious laryngotracheitis recombinant virus strain which is named as rILTV US9-NDV-F, the microorganism preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.14738, and the virus strain is an infectious laryngotracheitis recombinant virus which is established by replacing a US9 gene of the infectious laryngotracheitis recombinant virus by the Newcastle disease virus F protein, establishing an acquirement deficiency US9 gene and by inserting an NDV-F (Newcastle Disease Virus-F Protein) expression box into a corresponding position of the gene,and is used for recombining the Newcastle disease virus F protein. The recombinant infectious laryngotracheitis recombinant virus strain disclosed by the invention is used for preparing vaccines forpreventing infectious laryngotracheitis and other chicken infectious diseases.
Owner:HARBIN WEIKE BIOTECH DEV
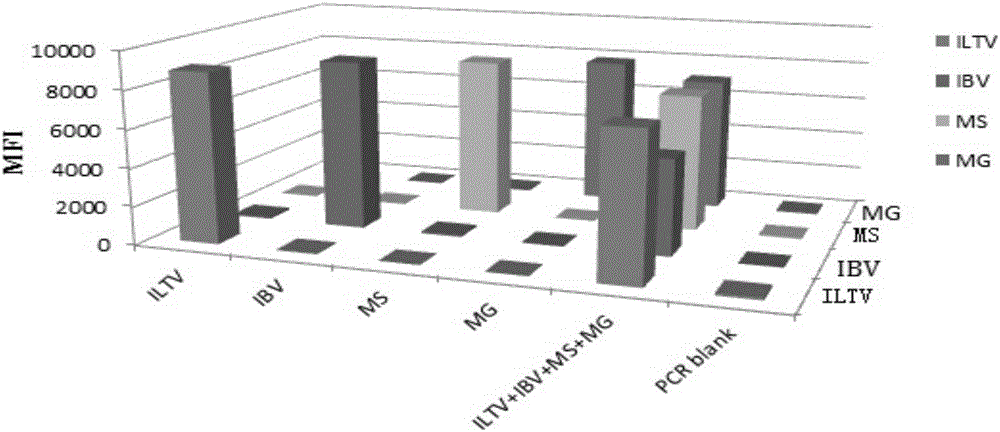
Multiple fluoroimmunoassay method capable of quickly differentiating infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV), infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), myeoplasma gallisepticum (MG) and mycoplasma synoviae (MS) and reagent
ActiveCN106011313AReduce dosageAvoid crossbreedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMycoplasma synoviaeFluorescence
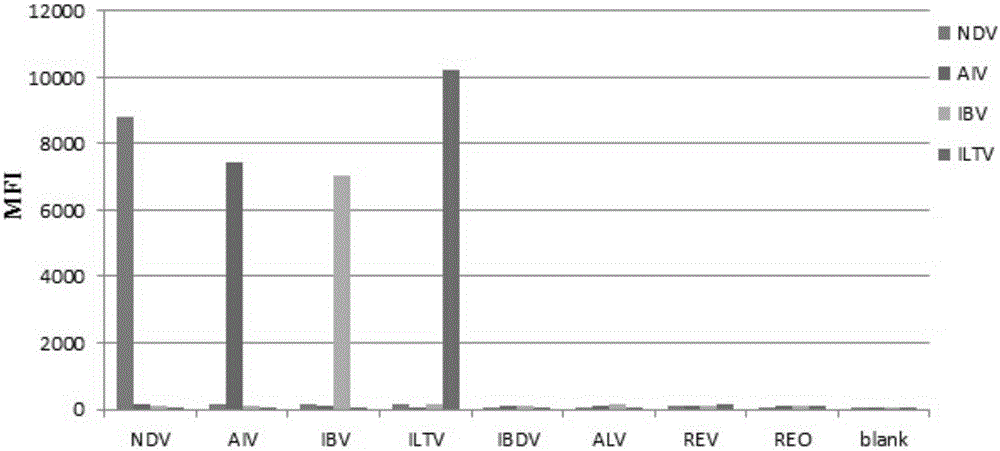
The invention discloses a multiple fluoroimmunoassay method capable of quickly differentiating infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV), infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), myeoplasma gallisepticum (MG) and mycoplasma synoviae (MS) and a reagent. The method is simple to operate, a target amplified fragment is obtained through polymerase chain reaction (PCR); an amplified product, fluorescence coded microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized, a mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) value is read through a detector, and pathogens of different types are differentiated. According to the method, avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus, infectious bronchitis virus, myeoplasma gallisepticum and mycoplasma synoviae can be accurately detected simultaneously, and the method is high in specificity and sensitivity and good in repeatability. Compared with a conventional detection method, the method can be used to simultaneously detect various target molecules in an identical sample, the sample usage amount is small, the method is simple and quick to operate, and the detection cost can be greatly reduced. The method is good in flexibility, and the varieties of detected pathogens can be increased or decreased as required on the basis.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
Gene chip and kit for infectious bronchitis viruses and/or infectious laryngotracheitis viruses
ActiveCN104293979AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesInfectious bronchitisInfectious laryngotracheitis
The invention discloses a gene chip and a kit for infectious bronchitis viruses and / or infectious laryngotracheitis viruses. The gene chip and detection kit disclosed by the invention can accurately and effectively detect infectious bronchitis viruses and / or infectious laryngotracheitis viruses, and are strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, short in time consuming and rapid in detection, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection method for avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus
InactiveCN107099617AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceLaryngotracheitis virus
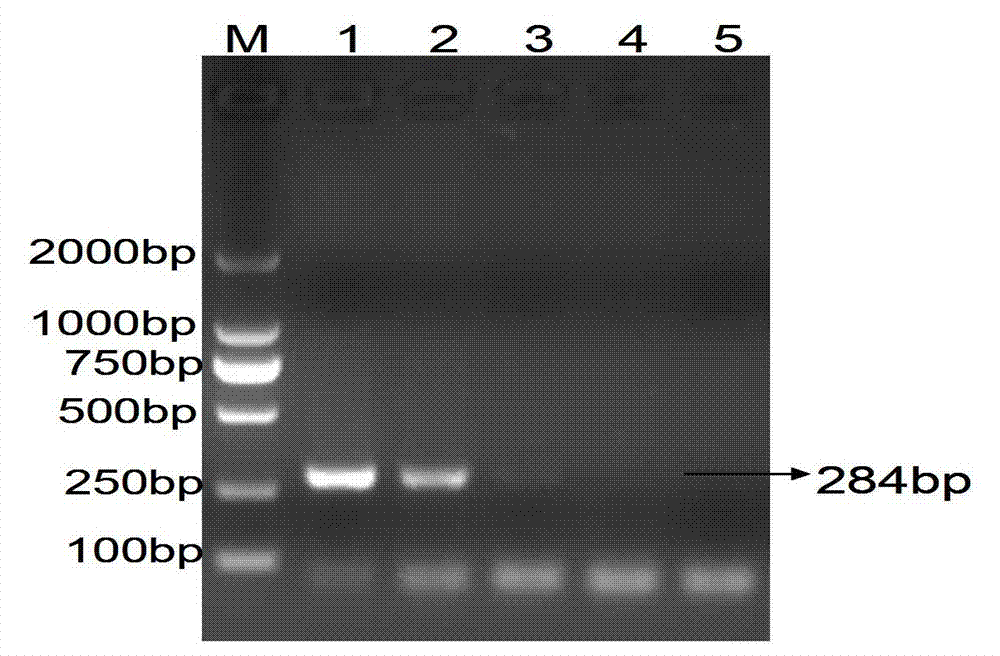
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (real-time PCR) detection method for an avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus, relating to the molecular biology field. The real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection method aims to the gB gene of the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus to design and synthesize a pair of primers, namely PF: 5'-CAATGGCTTCGGAGAAAGAG-3' and PR: 5'-GGCAATCCTGATCCCATCTA-3'. By PCR amplification and standard product preparation, a fluorescence quantification PCR method for detecting the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus is constructed; the specificity is stronger; the sensitivity is high; the operation is simple and fast; the real-time detection is performed on the PCR progress; the qualitative and quantitative analysis can be performed on each cycle; and the constructed fluorescence quantification PCR method for the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus can be used for detecting the virus content in tissue.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Kit for detecting infectious laryngotracheitis virus, newcastle disease virus and infectious bronchitis virus
ActiveCN104232802AEfficient detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesInfectious bronchitis virusNewcastle disease virus NDV
The invention discloses a kit for detecting infectious laryngotracheitis virus, newcastle disease virus and infectious bronchitis virus. The kit disclosed by the invention is capable of correctly and effectively detecting the infectious laryngotracheitis virus, the newcastle disease virus and the infectious bronchitis virus, and is strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, short in time, rapid in detection and good in application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
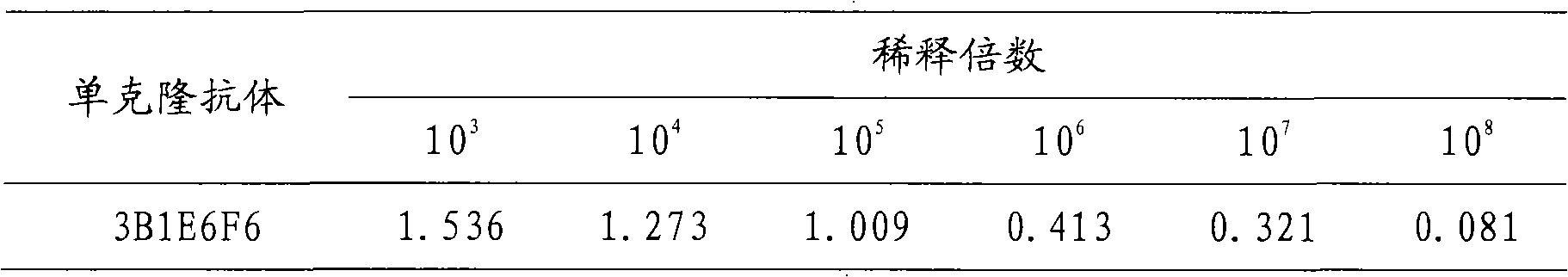
Monoclonal antibody of chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus gJ protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody of chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus gJ protein and application thereof. The monoclonal antibody is screened to obtain a hybridoma cell strain (3B1E6F6) which can stably secrete the anti-gJ protein monoclonal antibody, wherein the preservation number of the microbe is China general microbiological culture collection (CGMCC) No. 4337. The monoclonal antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell strain can be reacted with the ILTV WG (laryngotracheitis virus WG) virulent strain and can not be reacted with the other correlated pathogenies of the birds. The monoclonal antibody of the invention can be used for detecting the chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus, and laying a foundation for building a fast, simple and exact diagnosis method and distinguishing the infectious laryngotracheitis wild toxicity infection from the recombinant vaccine immunity.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
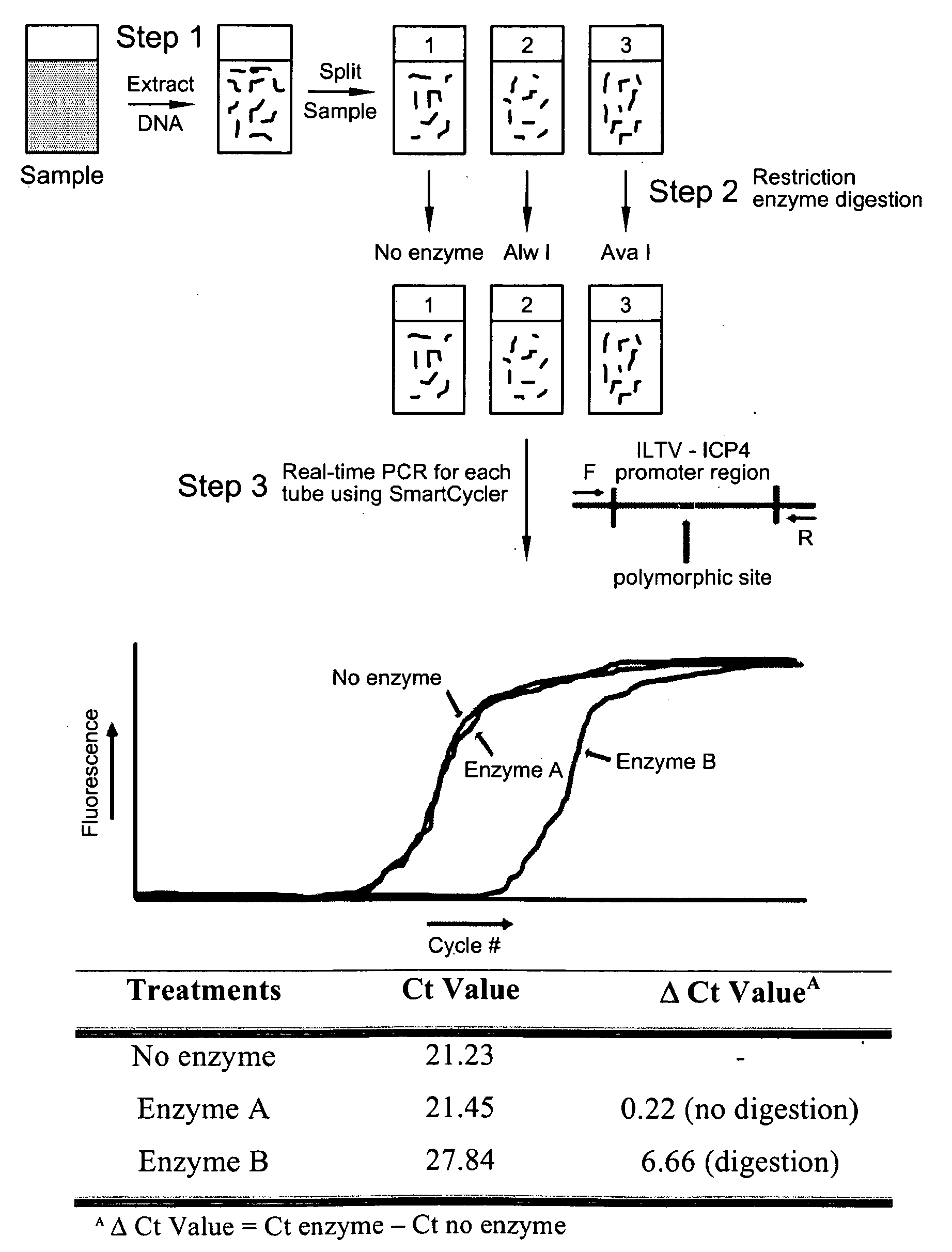
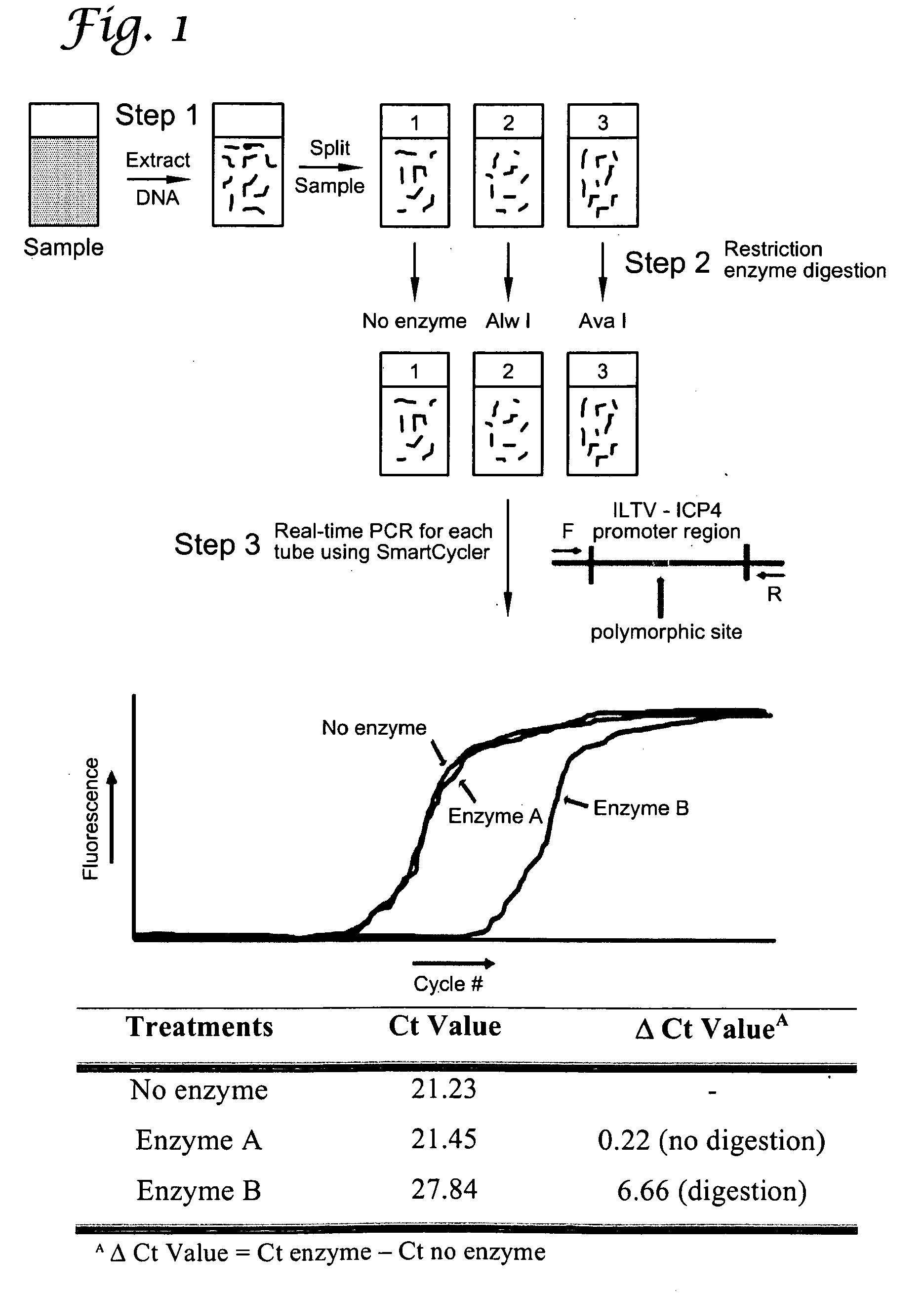
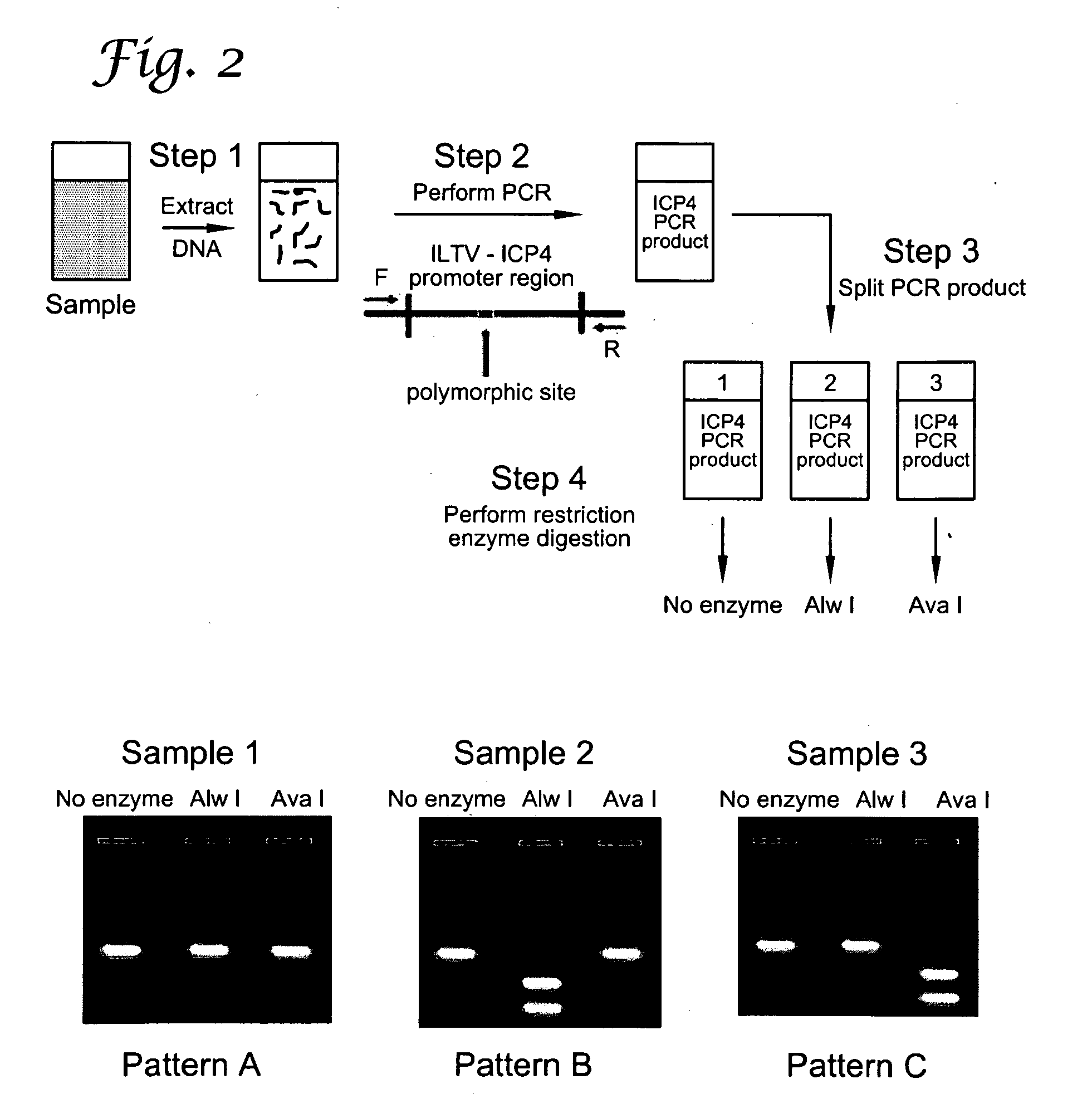
Reverse restriction fragment length polymorphism assay and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100196881A1Microbiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionTerminal restriction fragment length polymorphism
The present invention presents a Reverse Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RRFLP) method for the detection of the presence of an informative restriction enzyme site in a nucleotide sequence. The method includes digesting a sample with the informative restriction enzyme; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on the digested sample with an oligonucleotide primer pair that flanks the informative restriction enzyme site; determining the Ct value of the sample; comparing the Ct value of the sample to the Ct value from a control sample; and calculating a ΔCt value, wherein a ΔCt value is the Ct value of the sample minus the Ct value of a control; and wherein a ΔCt value ≧+1 indicates that the informative restriction enzyme sites is present in the nucleotide sequence. The present invention includes the application of the RRFLP method for detection of the infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV).
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer pair for identifying H9 subtype avian influenza virus and application thereof
InactiveCN103667519AStrong specificityRapid detection meansMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLaryngotracheitis virusEpidemiologic survey
The invention discloses a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer pair for identifying an H9 subtype avian influenza virus (AIV) and application thereof. The PCR primer pair disclosed by the invention is composed of two single chain deoxyribonucleic acids (DNAs), wherein the two single chain DNAs are single chain DNAs shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 in a sequence table. The HA gene of the H9 subtype AIV in a sample can be subjected to specific amplification, and the length of a target segment is 425bp. The method is free of cross reaction on H3, H4, H5 and other subtype AIVs, and a newcastle disease virus, avian infectious bronchitis, an infectious bursal disease virus, an infectious laryngotracheitis virus and the like; the minimum detectable quantity of virus allantoic fluid is 1*10<4.25>EID50 / 100mu L. Compared with the conventional methods such as a hemagglutination inhibition test of the virus and the like, the accordance rate of the identification result is 100%. A rapid, specific and sensitive detection means is provided for identification of the H9 subtype AIV. The PCR primer pair can be applied to rapid diagnosis of a disease caused by the H9 subtype AIV, and has a good application prospect in the aspects of clinical diagnosis and epidemiological investigation.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
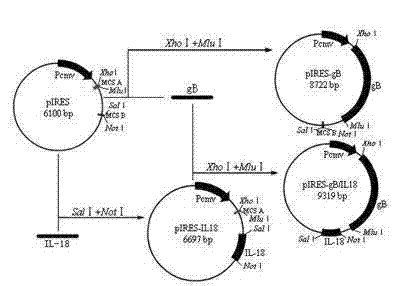
Eukaryotic coexpression vector of gB gene of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus and chicken interleukin-18 gene
InactiveCN102220368AAvoid the problem of disproportionate intakeImprove commission efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionImmune effectsInfectious laryngotracheitis
The invention discloses a eukaryotic coexpression vector of a gB gene of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus and a chicken interleukin-18 gene. The eukaryotic coexpression vector is constructed by respectively or simultaneously inserting the gB gene of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) and the chicken interleukin 18 (IL-18) gene into a eukaryotic coexpression vector (p1RES), wherein a fragment of the gB gene of the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus is inserted between the restriction sites XhoI and M1uI of an MCSA (Multiple Cloning Site A) at the downstream of a promoter and a fragment of the chicken interleukin-18 gene is inserted between the restriction sites Sa1I and NotI of an MCSB (Multiple Cloning Site B) to obtain the coexpression plasmid pIRES / gB / IL18. According to the eukaryotic compression vector disclosed by the invention, after a nucleic acid vaccine immune organism is obtained, the expressed gB glycoprotein can stimulate the organism to have an immune protection function on the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus; the expressed chicken interleukin 18 can give play to the obvious immune adjustment; and the immune effect is enhanced through the synergistic effect of the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus and the chicken interleukin 18.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU HOUYI PHARMA
Gene chip and kit for detecting Newcastle disease virus, avian infectious bronchitis virus and avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus
ActiveCN104232803AEfficient detectionStrong specificityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNewcastle disease virus NDVLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention discloses a gene chip and kit for detecting a Newcastle disease virus, an avian infectious bronchitis virus and an avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus. The gene chip and the kit disclosed by the invention can accurately and effectively detect the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus, the Newcastle disease virus and the avian infectious bronchitis virus, and are strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, short in time consumption, fast in detection and good in application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Avian infectious laryngotracheitis-fowl pox combined active vaccine
ActiveCN103182080AExtended storage timeReduce side effectsAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsFiberInfectious laryngotracheitis
The avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus and fowl pox virus are cultured by using chicken whole embryo fibroblasts. Particularly, the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus is successfully cultured by using the chicken whole embryo fibroblasts, the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus and the fowl pox virus cultured by using the chicken whole embryo fibroblasts are obtained, and a combined freeze-drying active vaccine after a proper freeze-drying protectant is added. The combined freeze-drying active vaccine can be inoculated for immunization in a subalar and subcutaneous inoculation manner, so that side effects of the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus can be alleviated, immune operations can be simplified, stress response can be reduced and production cost can be lowered. At the same time, the freeze-drying protectant prepared by a novel formula can effectively prolong storage time of the active vaccine and provide convenience for storing and transporting the products.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Construction method of recombinant adenovirus with capacity of fusion expression of gene TM-1 and gene gD, recombinant adenovirus and application
InactiveCN107603958AHighly conservativeLow variabilityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsInfectious laryngotracheitisShuttle vector
The invention discloses a construction method of a recombinant adenovirus with capacity of fusion expression of a gene TM-1 and a gene gD, the recombinant adenovirus and an application. The gene TM-1of mycoplasma gallisepticum and the gene gD of infectious laryngotracheitis are cloned into a shuttle vector pDC315-EGFP, cells HEK293 are transfected with the shuttle vector constructed successfully,an adenovirus backbone vector pBHGlox (delta)E1 and 3cre simultaneously, so that the shuttle vector and the adenovirus backbone vector are homologously recombined in the 293 cell line by a Cre / loxP recombinase system, the recombinant adenovirus pBH-TM-1-gD containing the target genes is obtained by packaging, and the recombinant adenovirus with high titer is obtained after amplification. The combined effect and relevant mechanism of the gene TM-1 and the gene gD on the two contagious respiratory diseases, namely, the mycoplasma gallisepticum infection and the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus under the mediation of the adenovirus are evaluated.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
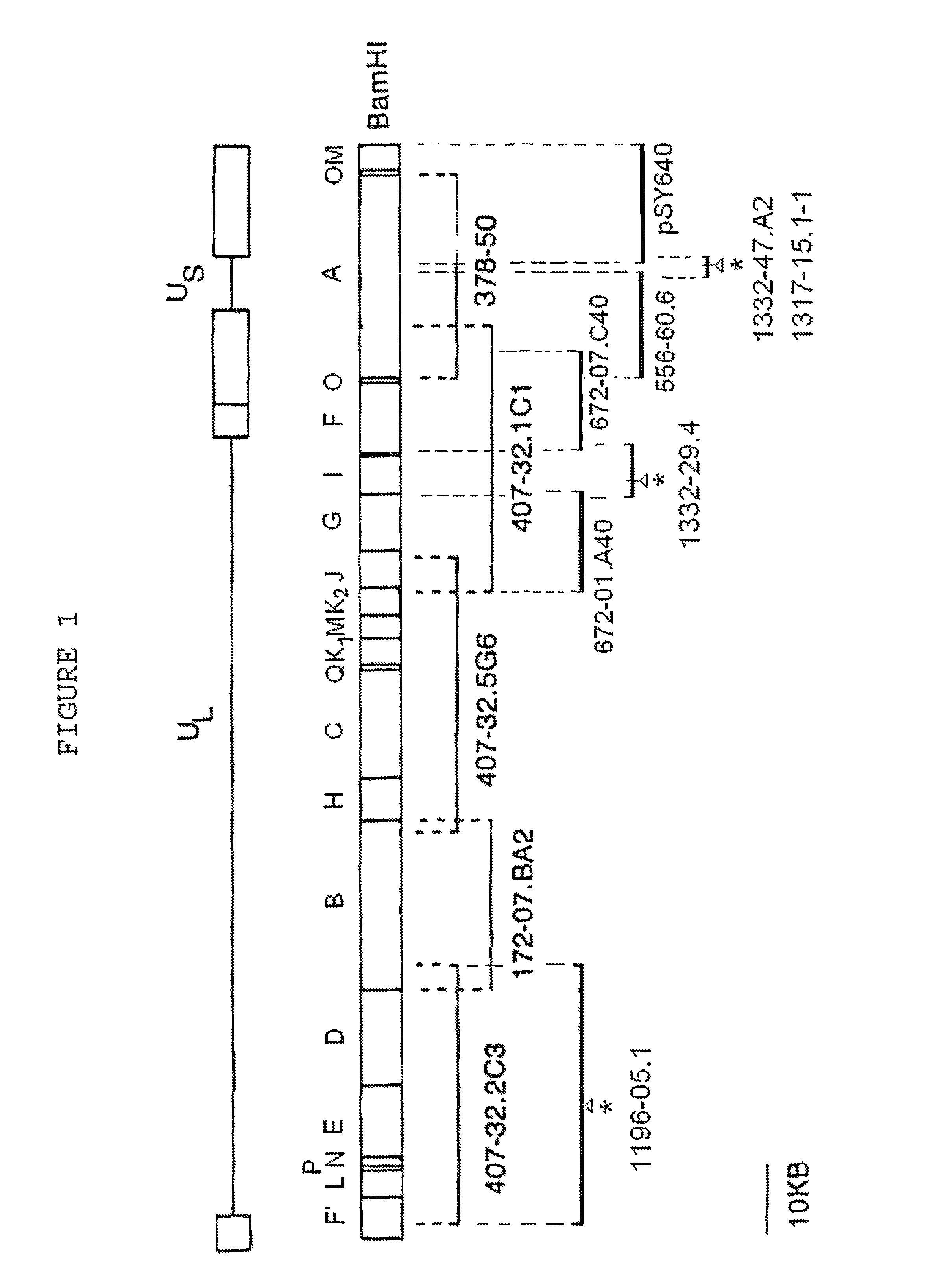
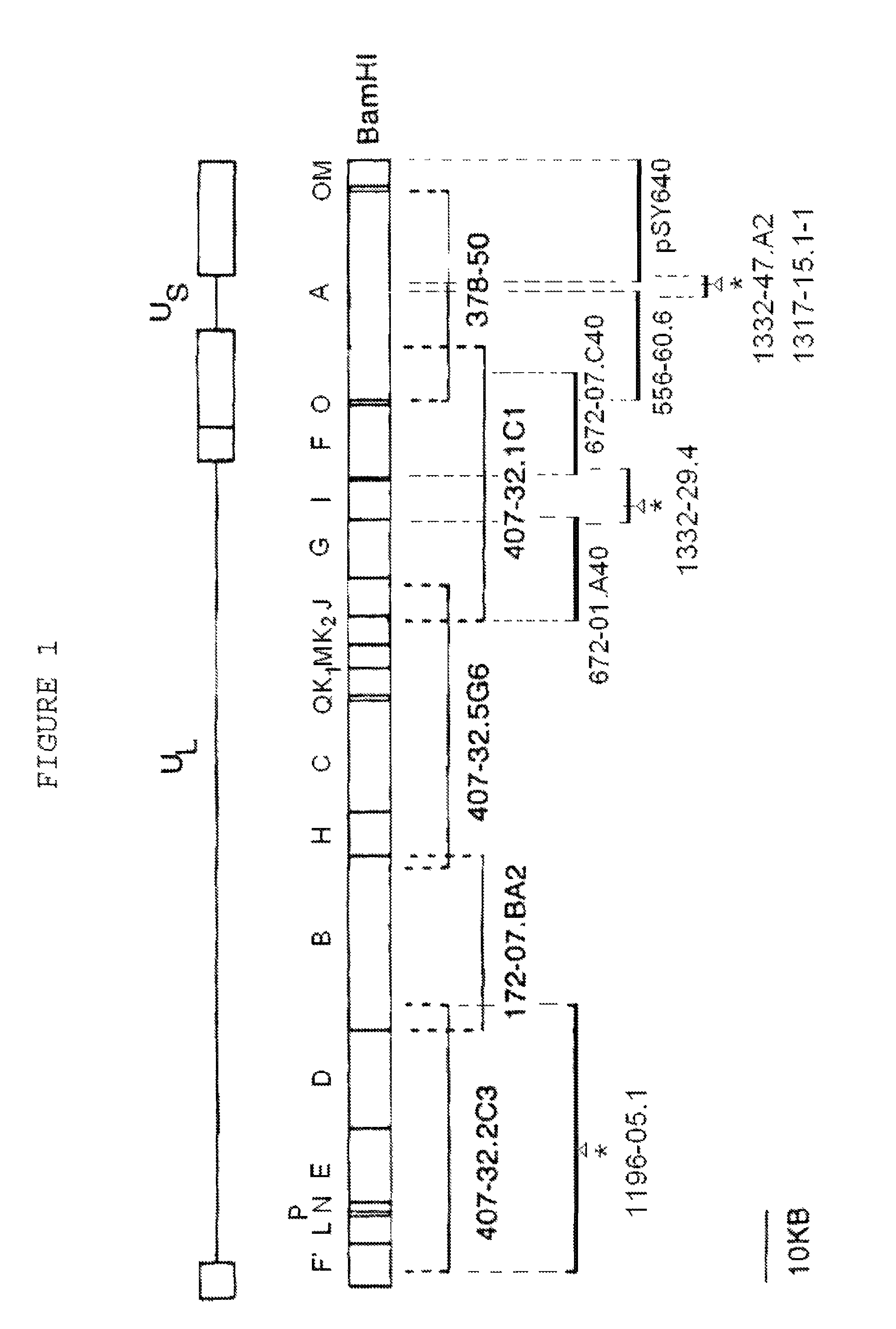
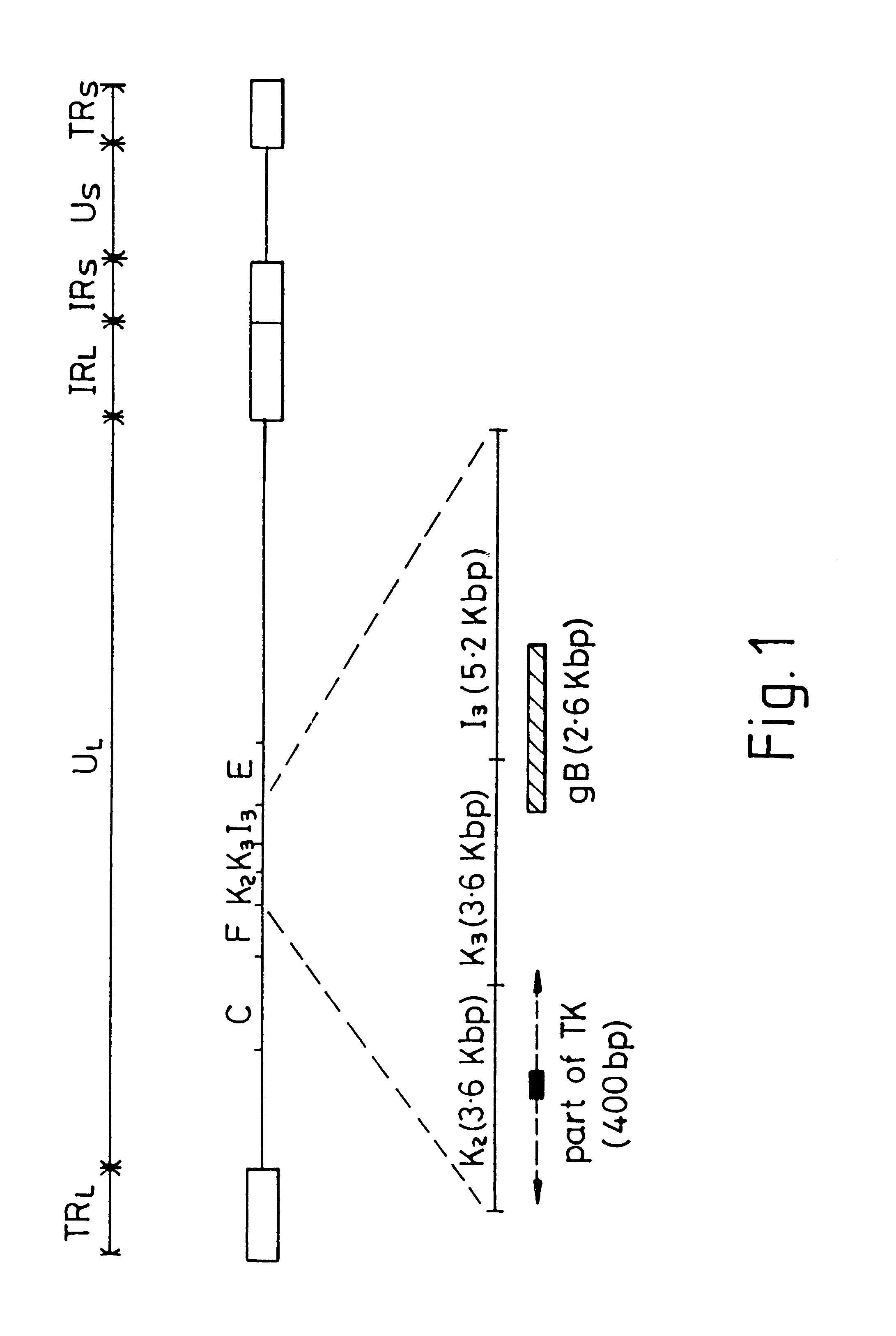
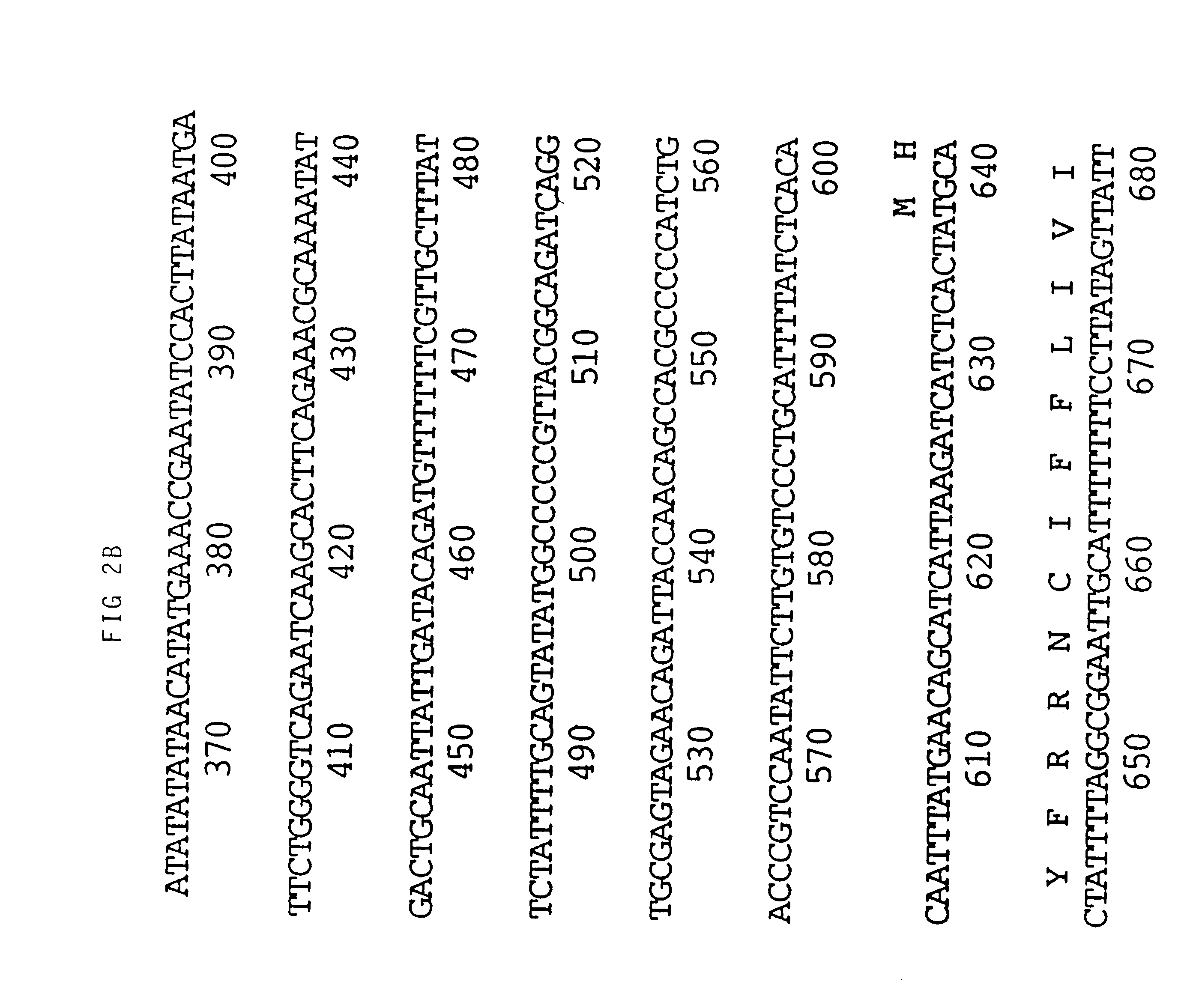
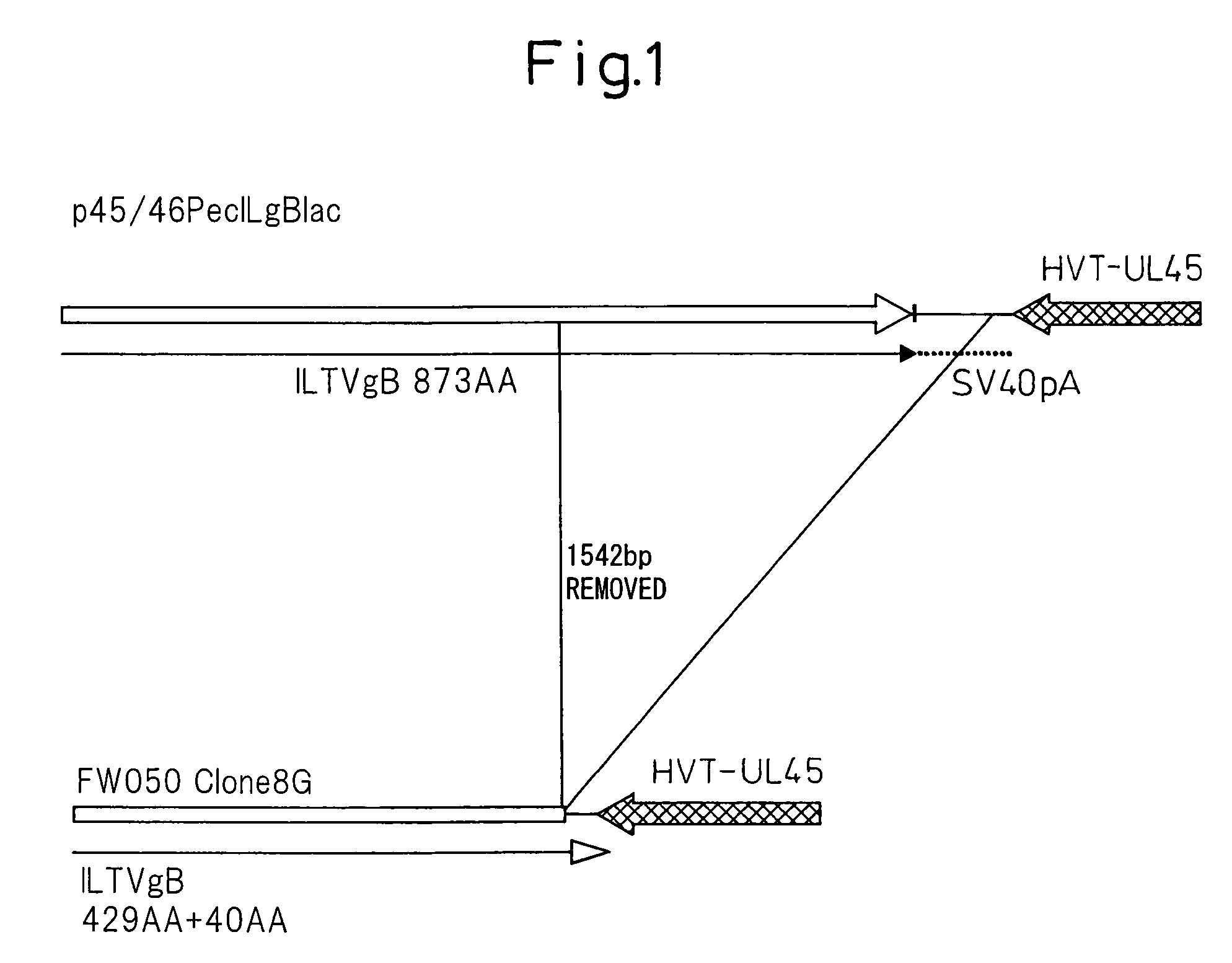
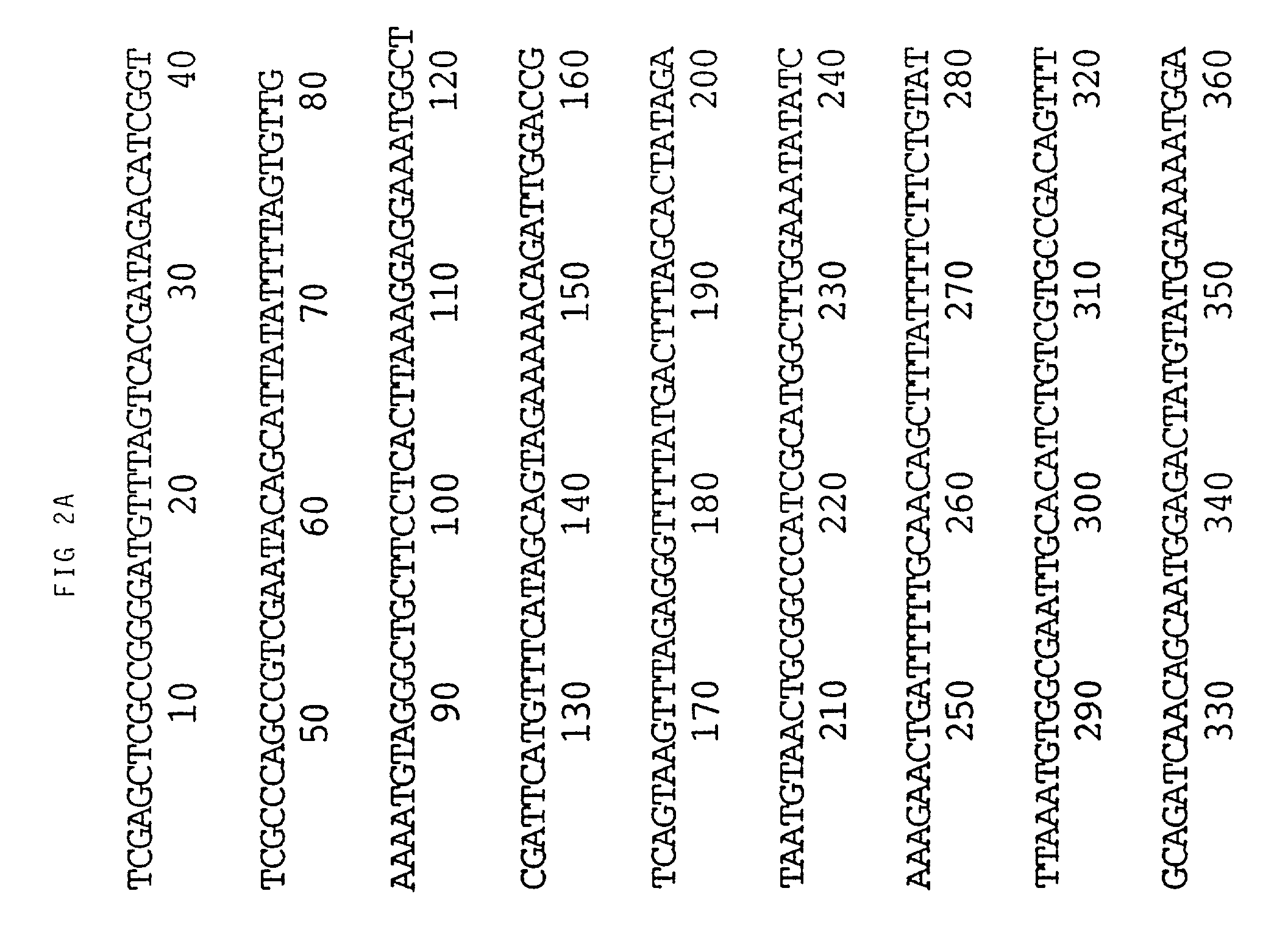
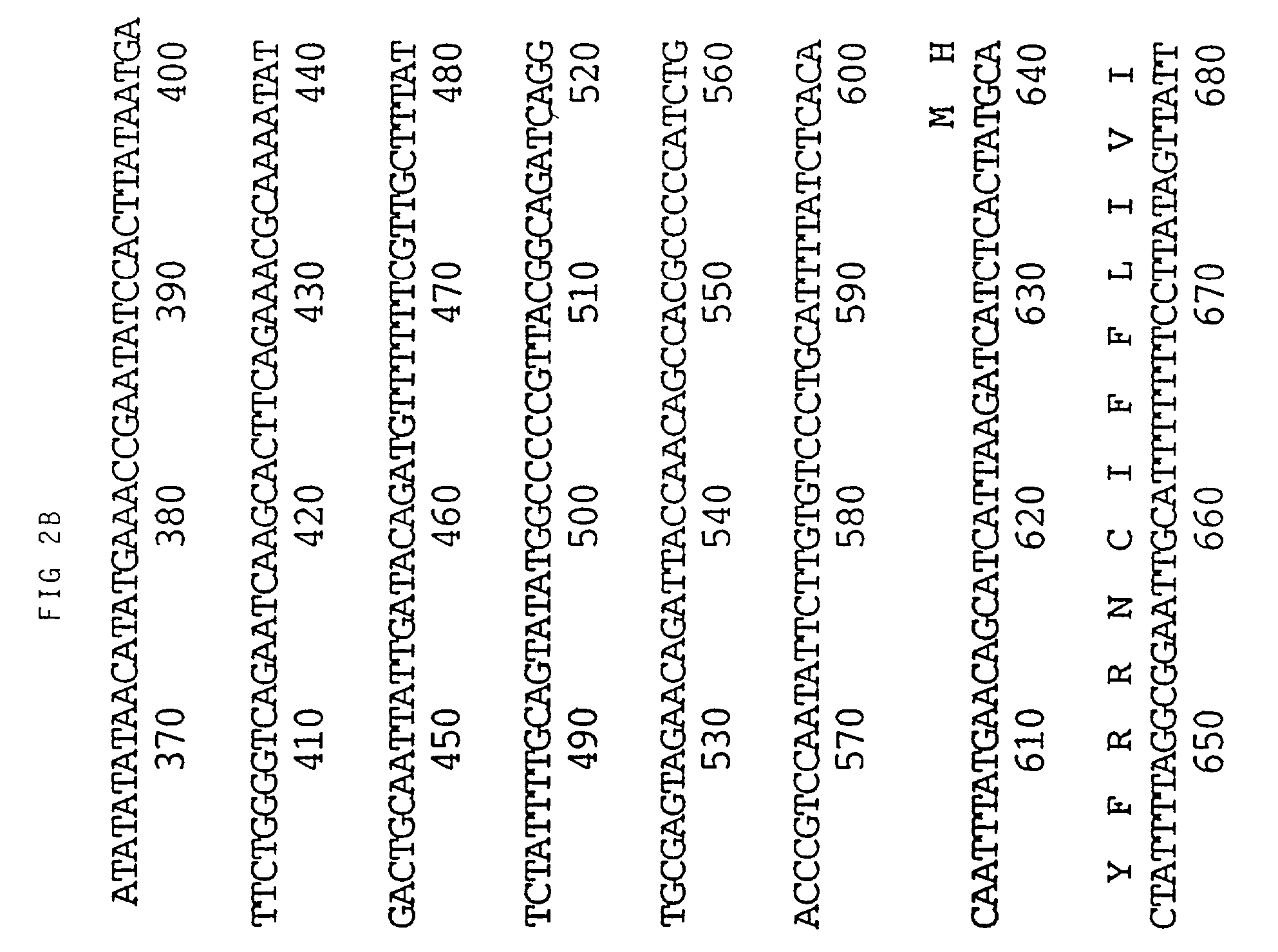
Viral nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6204045B1Improved vaccineOrganic active ingredientsFungiHeterologousLaryngotracheitis virus
Various genes of herpes virus of turkeys (HVT), Marek's disease virus (MDV) and infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) have been identified as non-essential regions (and candidates for insertion sites for foreign genes) and / or as antigen-encoding regions. The former include the HVT homologue of the HSV (herpes simplex virus) gC gene, the TX (thymidine kinase) region of MDV or ILTV, ORF3 of ILTV (as defined herein), the ribonucleotide reductase (large subunit) gene of ILTV, MDV or HVT and the ribonucleotide reductase (small subunit) gene of MDV. The antigen-encoding regions include the HVT homologues of the HSV gB, gC and gH genes, the ILTV homologue of HSV gB, ORF2 of ILTV, and the HVT homologue of the HSV-1 immediate early genes IE-175 and IE-68. Manipulation of these genes allows vaccines to be prepared comprising attenuated virus or virus carrying heterologous antigen-encoding sequences.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
Recombinant herpesvirus and uses thereof
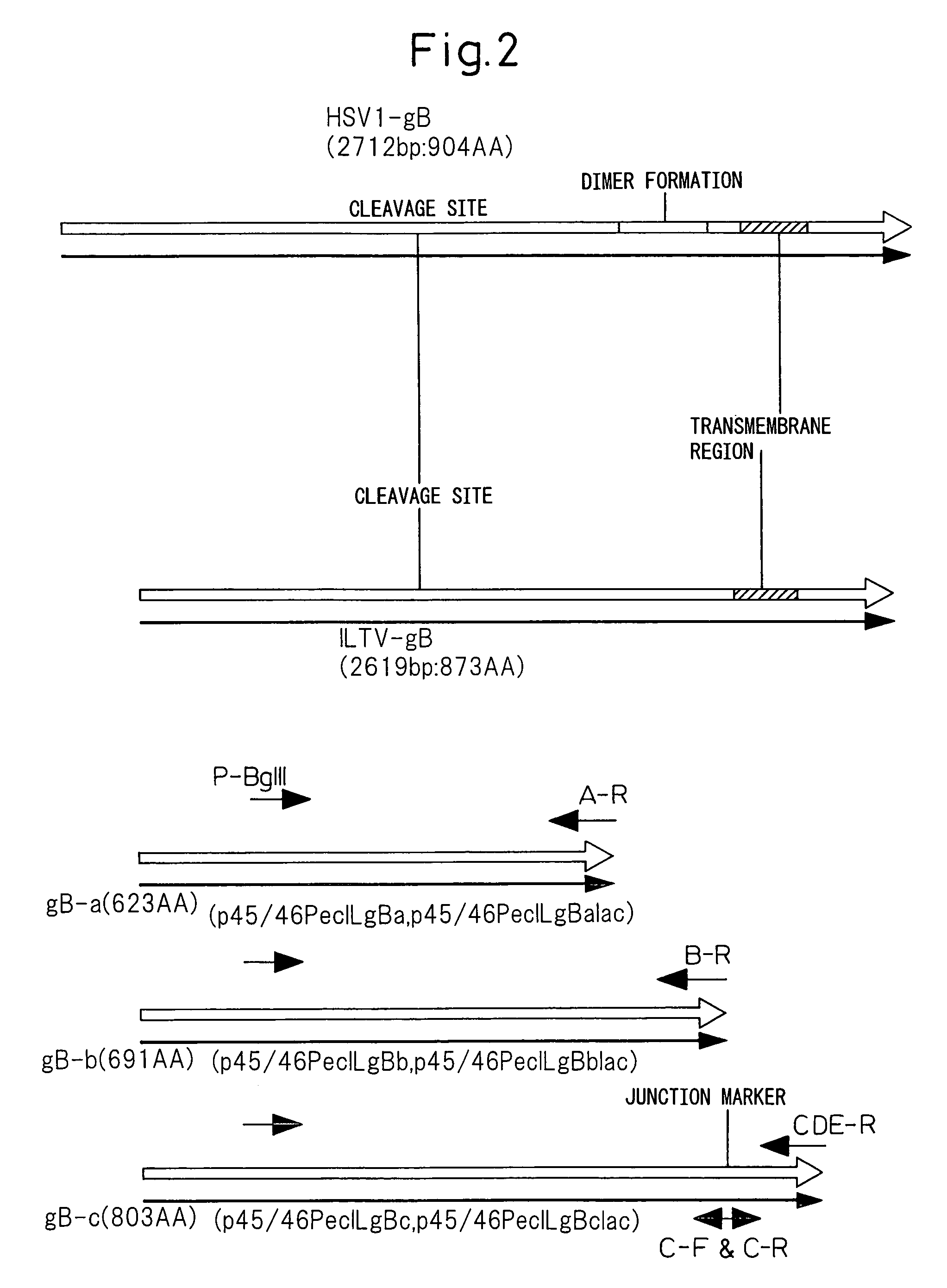
ActiveUS7538201B2Shortening the gB geneEfficient processSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsLaryngotracheitis virusA-DNA
A recombinant herpesvirus (excluding infectious laryngotracheitis virus) having a DNA that encodes a polypeptide comprising 429 amino acids at the amino terminal end of a protein encoded by the gB gene of infectious laryngotracheitis virus or a polypeptide in which one or a plurality of amino acids have been deleted, added, or substituted in said polypeptide.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Multiplex fluorescence immunoassay primer, kit and method for rapidly distinguishing four respiratory pathogens
ActiveCN106086241AAccurate detectionReduce dosageMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotin-streptavidin complexDisease
The invention discloses a multiplex fluorescence immunoassay primer, kit and method for rapidly distinguishing four respiratory pathogens. Operation is easy, a target amplified fragment is obtained through a PCR, then an amplified product, fluorescence coded microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized, an MFI value is read through a detector, and viruses of different types are distinguished. The method can be used for accurately detecting chicken new castle disease viruses, avian influenza viruses, chicken infectious bronchitis viruses and chicken infectious laryngotracheitis viruses at the same time, and is high in specificity, high in sensitivity and good in repeatability. Compared with a traditional detection method, the method can detect multiple different target molecules in the same sample at the same time, the use quantity of samples is small, operation is easy and rapid, and the detection cost can be greatly reduced. The flexibility is good, and the varieties of detected pathogens can be increased or decreased on the basis according to requirements.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
Liquid-phase chip method used for detecting infectious laryngotracheitis virus
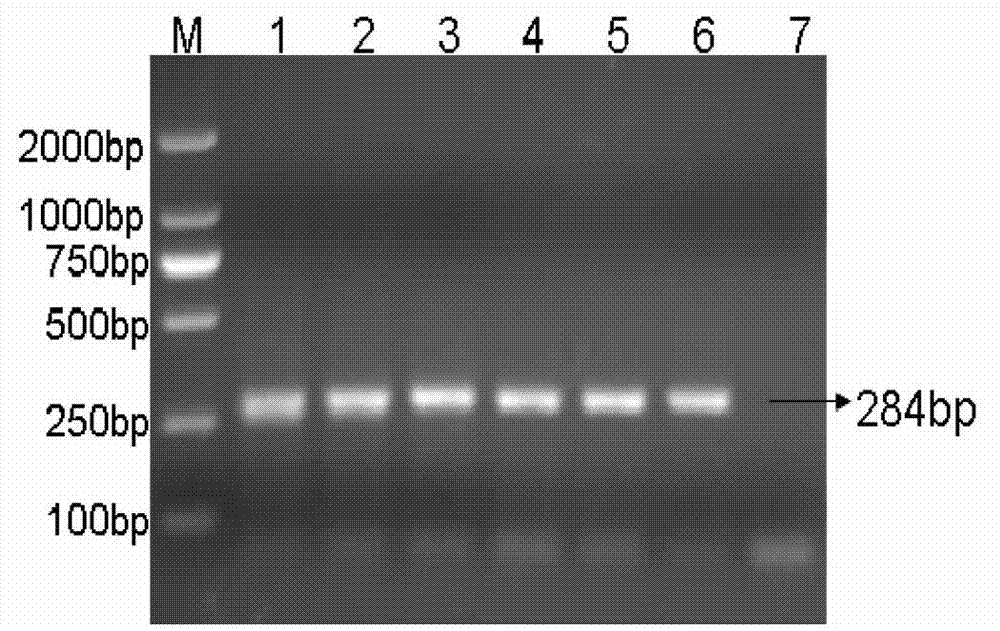
InactiveCN102851395ADetection fitHigh speedNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementInfectious laryngotracheitisLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention provides a liquid-phase chip method used for detecting infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV). Through comparison and analysis upon ILTV TK genome sequence, conserved regions are found, and specific primers and a probe of the ILTV are designed. The nucleotide sequences are respectively represented by SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, and SEQ ID NO.3. The primers above are used for carrying out PCR amplification upon ILTV DNA, and the probe is coupled with microspheres. A PCR amplification product and the probe coupled on fluorescent microspheres are subjected to hybridization. Through the detection upon fluorescence values, the liquid-phase chip method used for detecting ILTV is established. The detection method provided by the invention has the advantages of accurate detection, high sensitivity, and high specificity. The method is simple and fast.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Gene chip and kit for detecting Newcastle disease virus and/or chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus
ActiveCN104328215AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNewcastle disease virus NDVLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention discloses a gene chip and a kit for detecting Newcastle disease virus and / or chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus. The gene chip and the kit can detect the chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus and the Newcastle disease virus accurately and effectively. The gene chip and the kit are strong in specificity, are high in sensitivity, are less in time consumption, are quick in detection and have a good application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method of avian infectious laryngotracheitis live vaccine using cell line
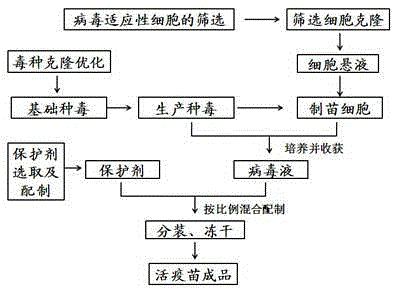
InactiveCN105267961AReduce immune side effectsQuality improvementAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesCell freeInfectious laryngotracheitis
A method of an avian infectious laryngotracheitis live vaccine using a cell line includes: replacing chick embryos with the cell line to proliferate avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus liquid, and performing cell line culturing, cloning and purifying, passage, culturing, cloning and culturing of a viral strain, preparing of vaccines, collecting of vaccine preparation virus liquid, subpackaging, freeze-drying and the like. The avian infectious laryngotracheitis live vaccine is produced using passage cells, the production cost is lowered, vaccine immunity side effect is reduced, inter-batch difference is diminished, quality stability of the vaccine is guaranteed, and basis is laid for the large-scale culturing of the virus. Experiments show that bright, round, and vividly outlined cells free of intra-cell impurity can be obtained by only three times of cloning, while an existing method needs seven times of cloning, the cloning time of the present method is shortened, and high activity and high cloning rate are given to cloning.
Owner:河北远征药业有限公司
Pharmaceutical composition for controlling infectious laryngotracheitis of chicken and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN108310140AGood antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effectReduce moistureHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseInfectious laryngotracheitis
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for controlling infectious laryngotracheitis of chicken and a preparation method and applications thereof, and belongs to the field of veterinary drugs. The pharmaceutical composition comprises following components in parts by weight: 12 to 17 parts of blackberry lily rhizome, 10 to 15 parts of dandelion, 2 to 7 parts of bunge corydalis herb, 3 to 8 parts of borneol, 2 to 9 parts of alum, and 1 to 3 parts of ascorbic acid. Through the cooperation among the raw materials, the antibacterial and anti-inflammation performance of the pharmaceutical composition is strong, the transmission of chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus is inhibited, the disease resistance is enhanced, the antibody generation is promoted, the dead rate is reducedeffectively, the drug resistance is difficult to generate, and the curative effect is quick and excellent.
Owner:绵阳市农业科学研究院
Viral nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS20010024817A1Improved vaccineOrganic active ingredientsFungiLaryngotracheitis virusInsertion site
Various genes of herpes virus of turkeys (HVT), Marek's disease virus (MDV) and infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) have been identified as non-essential regions (and candidates for insertion sites for foreign genes) and / or as antigen-encoding regions. The former include the HVT homologue of the HSV (herpes simplex virus) gC gene, the TK (thymidine kinase) region of MDV or ILTV, ORF3 of ILTV (as defined herein), the ribonucleotide reductase (large subunit) gene of ILTV, MDV or HVT and the ribonucleotide reductase (small subunit) gene of MDV. The antigen-encoding regions include the HVT homologues of the HSV gB, gC and gH genes, the ILTV homologue of HSV gB, ORF2 of ILTV, and the HVT homologue of the HSV-1 immediate early genes IE-175 and IE-68. Manipulation of these genes allows vaccines to be prepared comprising attenuated virus or virus carrying heterologous antigen-encoding sequences.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
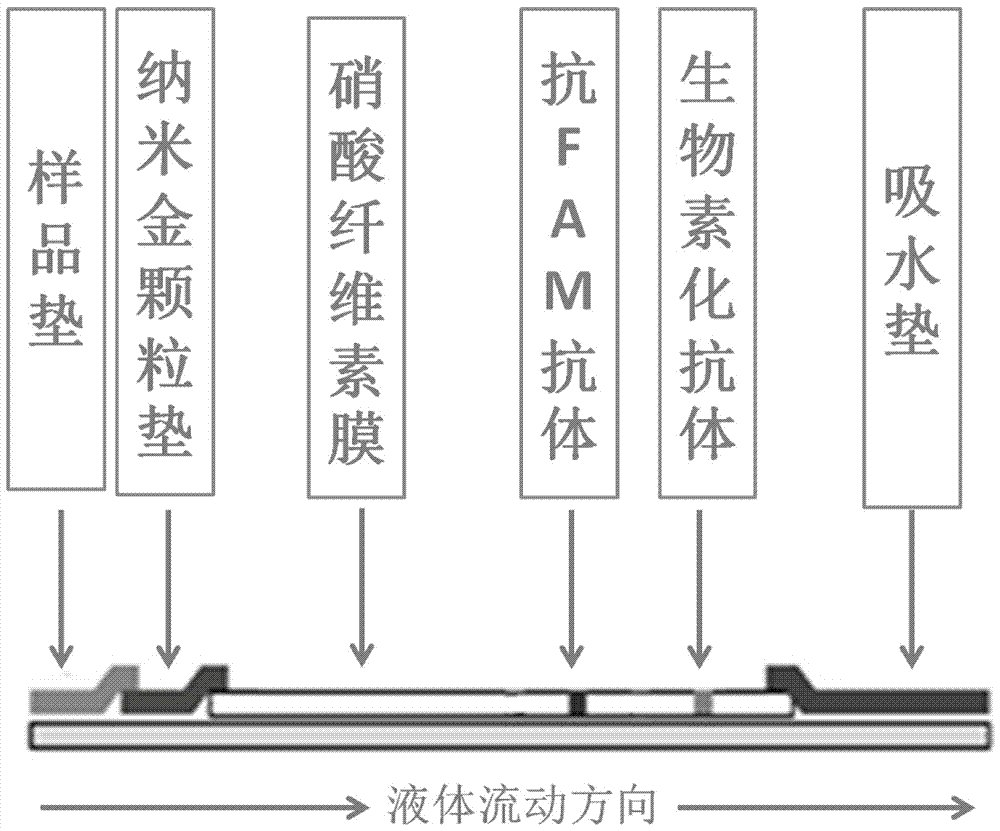
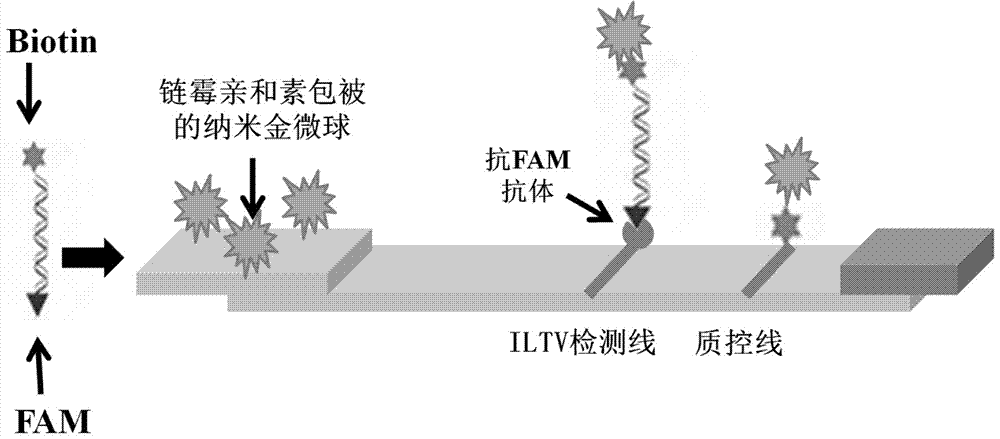
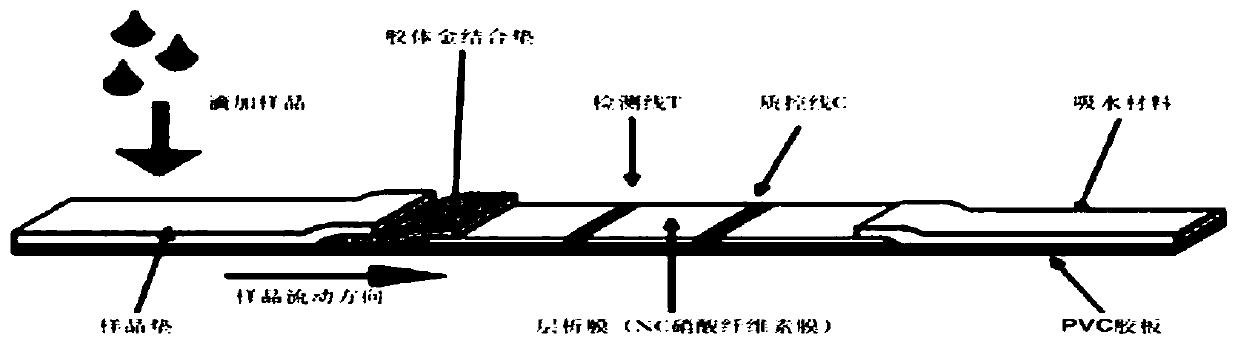
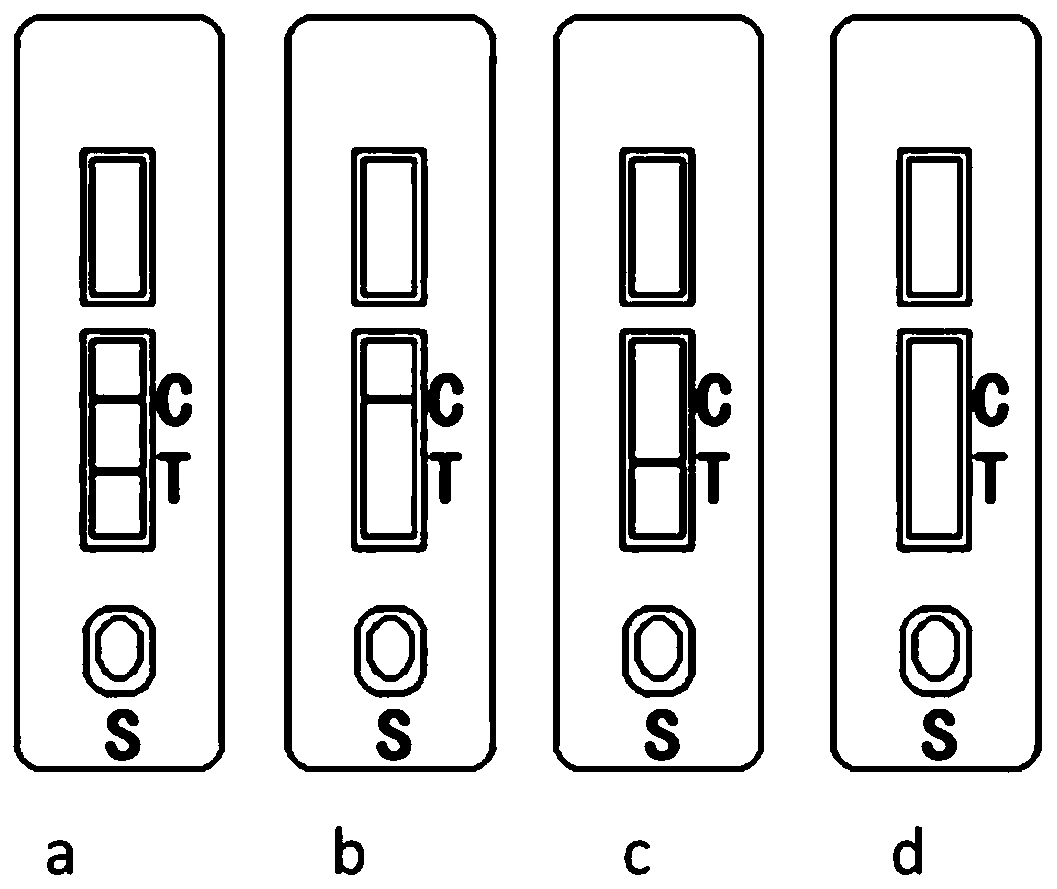
Test strip for detecting infectious laryngotracheitis virus, preparation method, detection method and kit
InactiveCN110146702AEffective prevention and controlWide range of test samplesMaterial analysisNitrocelluloseMonoclonal antibody
The invention discloses a test strip for detecting an infectious laryngotracheitis virus, a preparation method, a detection method and a kit, and relates to the technical field of infectious laryngotracheitis virus detection. The test strip specifically comprises a bottom plate and a water absorption material bonded to the upper edge of the bottom plate. A sample pad, a colloidal gold bond pad anda nitrocellulose film are successively laid on the upper surface of the bottom plate along the chromatographic direction, wherein a T-line and a C-line are set on the nitrocellulose film in advance.The upper edge of the nitrocellulose film and the lower edge of the water absorption material are in lap joint. The lower edge of the nitrocellulose film is bonded to the upper edge of the colloidal gold bond pad. The lower edge of the colloidal gold bond pad is bonded to the upper edge of the sample pad. The T-line is coated with the monoclonal antibody of the infectious laryngotracheitis virus.The test strip for detecting the infectious laryngotracheitis virus has the advantages of high specificity, good repeatability and high sensitivity.
Owner:SICHUAN ANIMAL SCI ACAD
Gene chips and kits for detecting chicken Newcastle disease virus, chicken infectious bronchitis virus and chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus
ActiveCN104232803BEfficient detectionStrong specificityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNewcastle disease virus NDVLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention discloses a gene chip and kit for detecting a Newcastle disease virus, an avian infectious bronchitis virus and an avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus. The gene chip and the kit disclosed by the invention can accurately and effectively detect the avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus, the Newcastle disease virus and the avian infectious bronchitis virus, and are strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, short in time consumption, fast in detection and good in application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Bigeminal multi-epitope vaccine for chicken infectious laryngotracheitis and egg drop syndrome
ActiveCN110092840AImproving immunogenicityAvoid infectionViral antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFiberAdjuvant
The invention relates to a bigeminal multi-epitope vaccine for chicken infectious laryngotracheitis and egg drop syndrome. Specifically, a gene recombination technology is used, 8 antigen epitope polypeptides related to chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus gB, gD, and gE proteins as well as 6 antigen epitope polypeptides related to egg drop syndrome virus Penton and Fiber protein are connected with a molecular adjuvant IL-8, then are connected to a vector, transformed into host bacteria, and prepared by fermentation, purification and emulsification processes to obtain the bigeminal multi-epitope vaccine. The animal experiments show that the vaccine is safe and easy to use, and can induce significant humoral immunity and cellular immune responses in the body, the persistent period ofan antibody is long, and the infection of the infectious laryngotracheitis virus and egg drop syndrome virus can be effectively prevented.
Owner:QINGDAO MINGQIN BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com