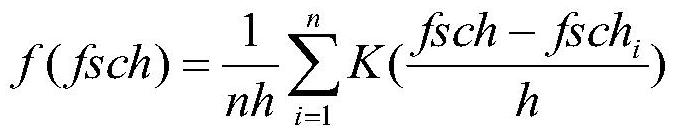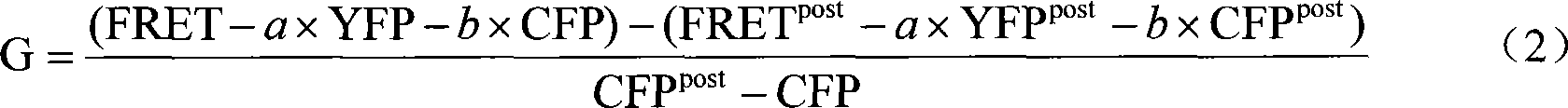Patents
Literature
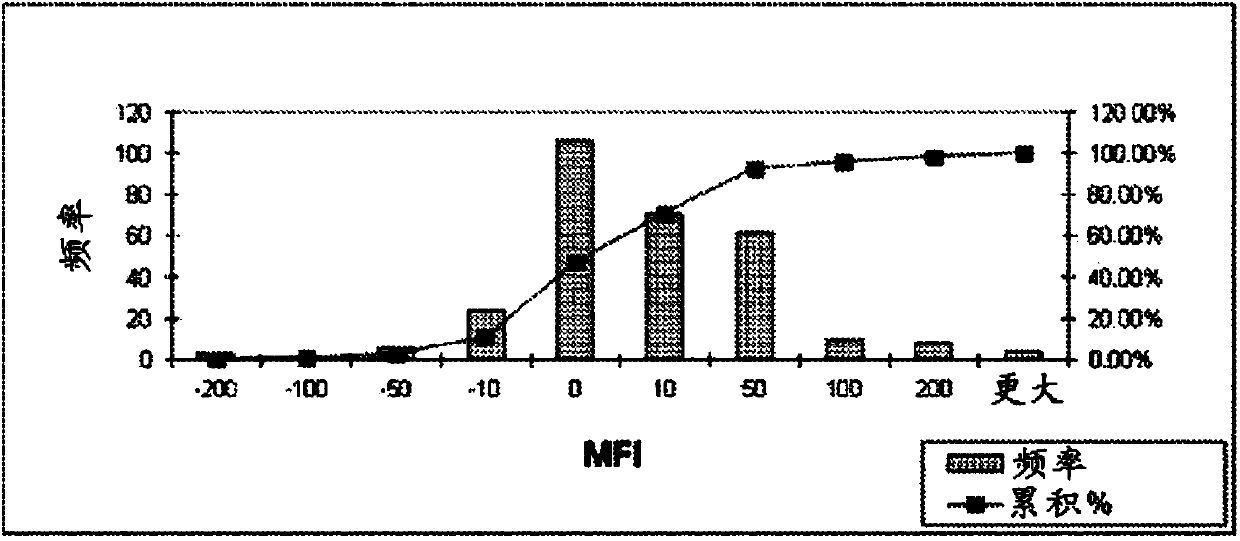
79 results about "Mean fluorescence intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
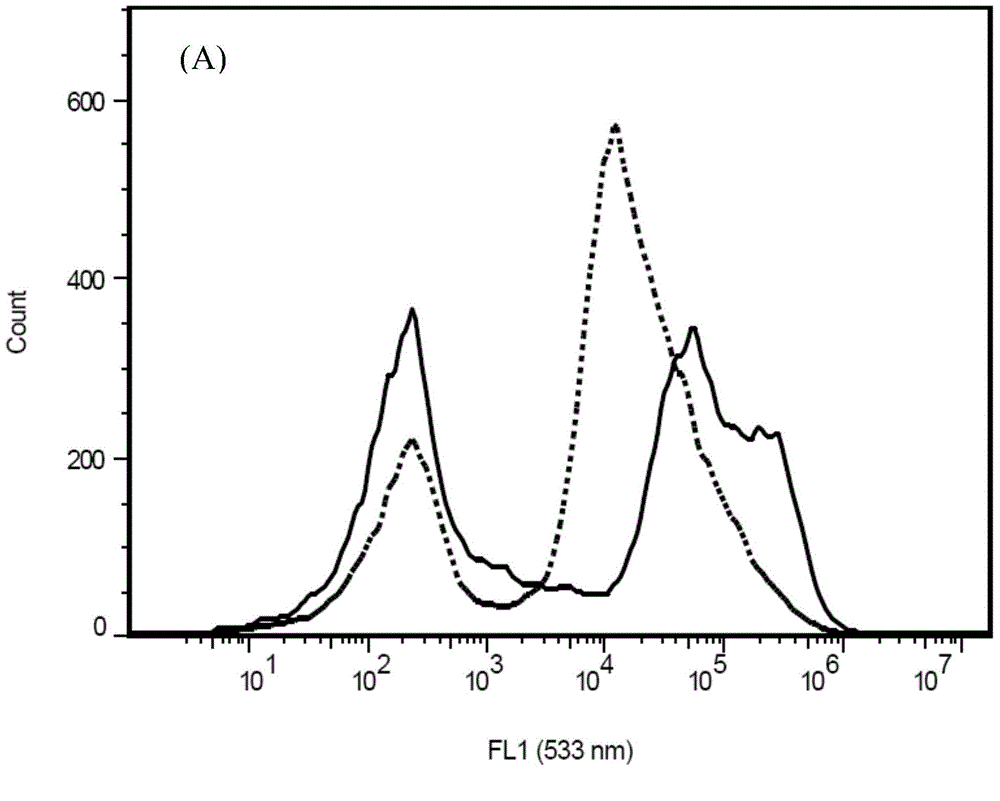
It is the mean of the fluorescence intensity in the fluorescence channel that you choose (FITC, PE, PerCP, etc.). It's value depends on the corresponding parameters you chose (you can change the intensity of each channel).
Synchronous quantum dot fluorescence immunological detection method and kit of multiple small molecular compounds
InactiveCN102411050AHigh detection throughputHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceImmune complex depositionMicrosphere
The invention provides an indirect competitive quantum dot fluorescence immunological detection method for synchronously detecting multiple small molecular compounds and detection kit, wherein the immunological detection method is a liquid phase immunological detection method which uses an encoded microsphere as a solid phase carrier and a quantum dot as a fluorescent marker and is used for competitive specificity reactions of a small molecular compound antigen. c Firstly, a captured antigen is covalently bound to the surface of the encoded microsphere, an indirect competitive fluorescent immune complex of microsphere-captured antigen-detected antibody-second antibody-quantum dot is formed in a filter film plate reaction hole through capturing the antigen, detecting the antibody and binding the second antibody specificity, and then the indirect competitive fluorescent immune complex flows across a suspension chip or a detection region of a flow analysis system one by one under the restraint of the sheath fluid, recognizes different encoded microspheres and detects the fluorescent intensity (or average fluorescence intensity) of the quantum dot to complete the detection. A plurality of small molecule compounds in the same sample can be synchronously detected, and one or more small molecule compounds in different samples can also be detected. The invention has the advantages of fast speed and high flux.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
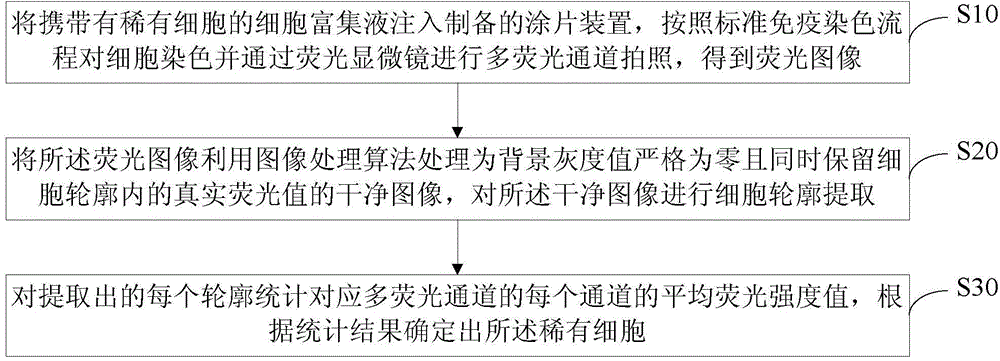
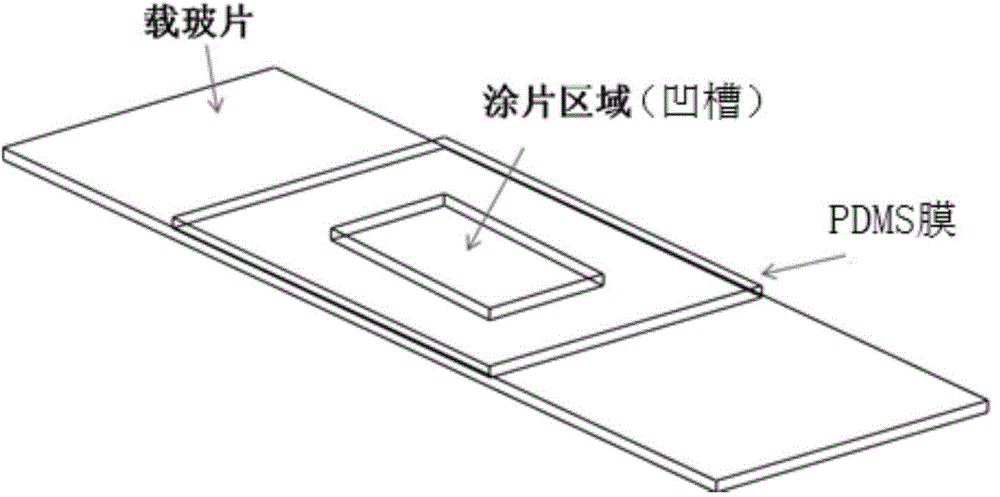
Method and system for automatically recognizing rare cells
InactiveCN106190945APreserve True Fluorescence ValuesLow impact on contour extractionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMean fluorescence intensityFluorescence microscope
The present invention relates to a method and a system for automatically recognizing rare cells. The method comprises: injecting a cell enrichment liquid carrying rare cells into a prepared coating-slice device, staining the cells according to a standard immunostaining process, and carrying out multi-fluorescence channel shooting through a fluorescence microscope to obtain a fluorescence image; treating the fluorescence image into a clean image strictly having a background gray value of zero and retaining the true fluorescence value in the cell contour, and carrying out cell contour extraction on the clean image; and carrying out statistics on the average fluorescence intensity value of various extracted contour channels corresponding to the multi-fluorescence channel, and determining the rare cells according to the statistics results. According to the present invention, the obtained fluorescence image is treated to strictly achieve the background gray value of zero while the true fluorescence value in the cell contour is retained, such that the influence of the background noise on the cell contour extraction is minimized; and for the fluorescence image obtained through the multi-fluorescence channel, the cells are confirmed and recognized from more parameters so as to improve the staining recognizing of the rare cells.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
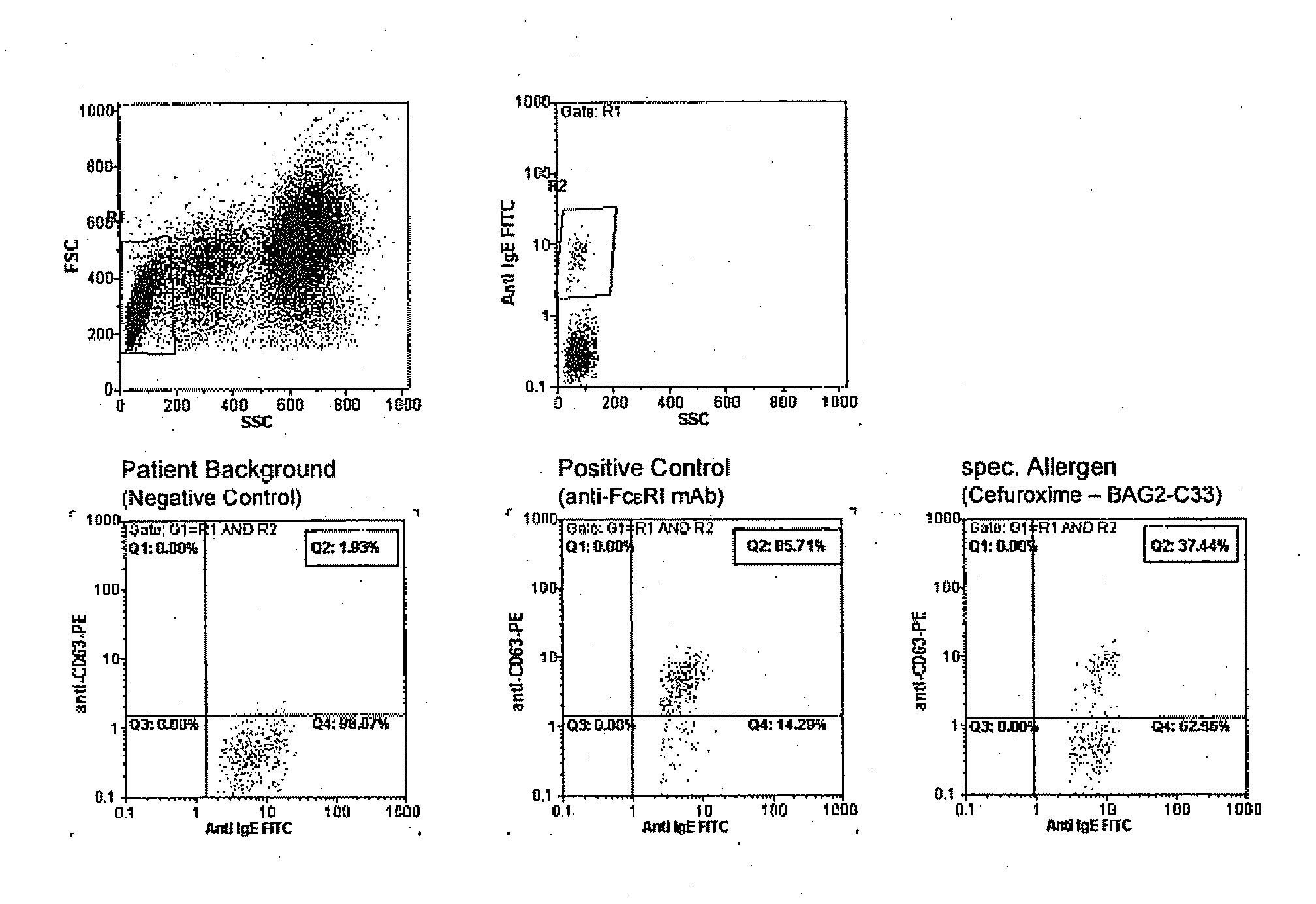
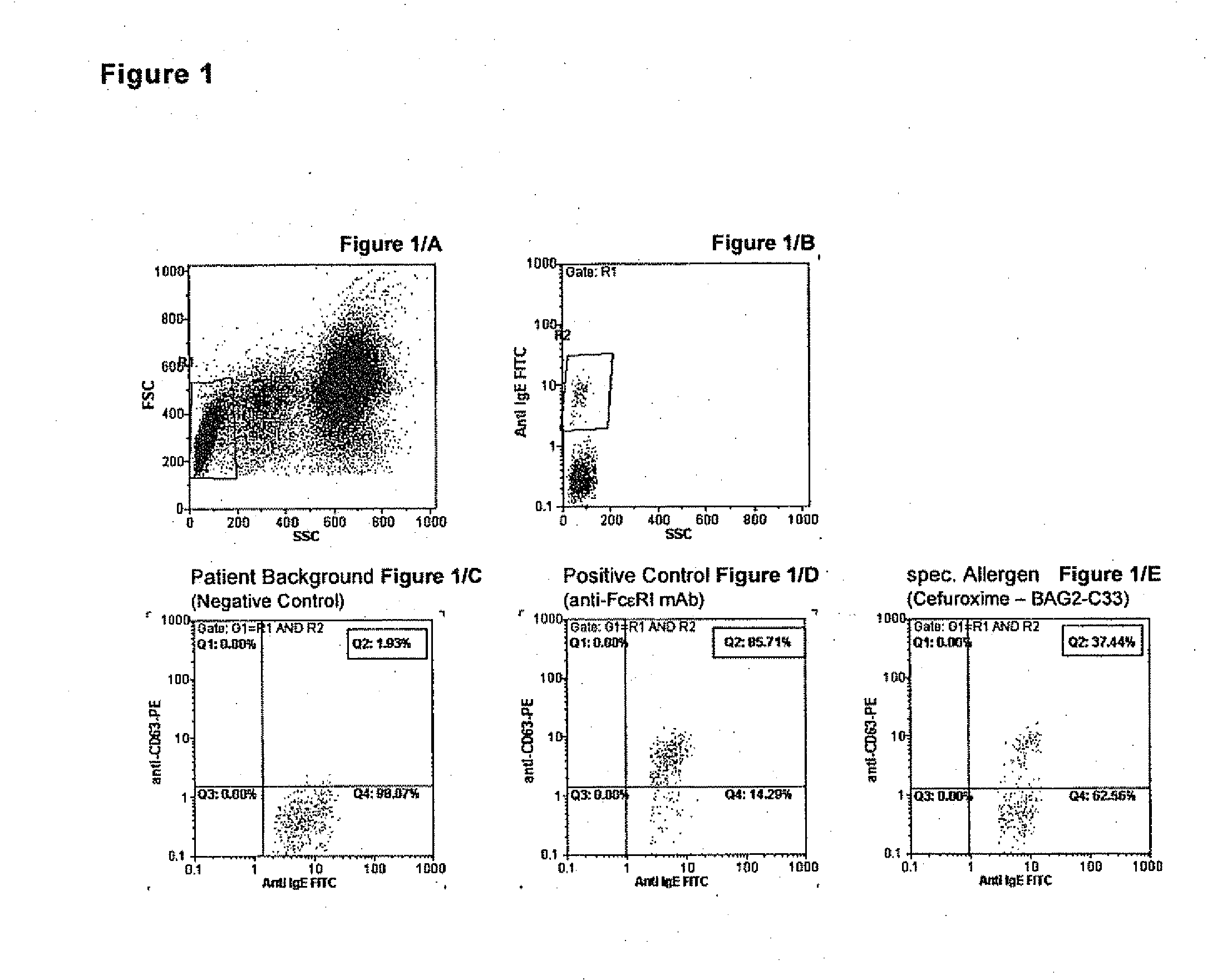
Allergy test based on flow cytometric analysis
ActiveUS20100221756A1Disease diagnosisBiological testingMean fluorescence intensityMedian Fluorescence Intensity
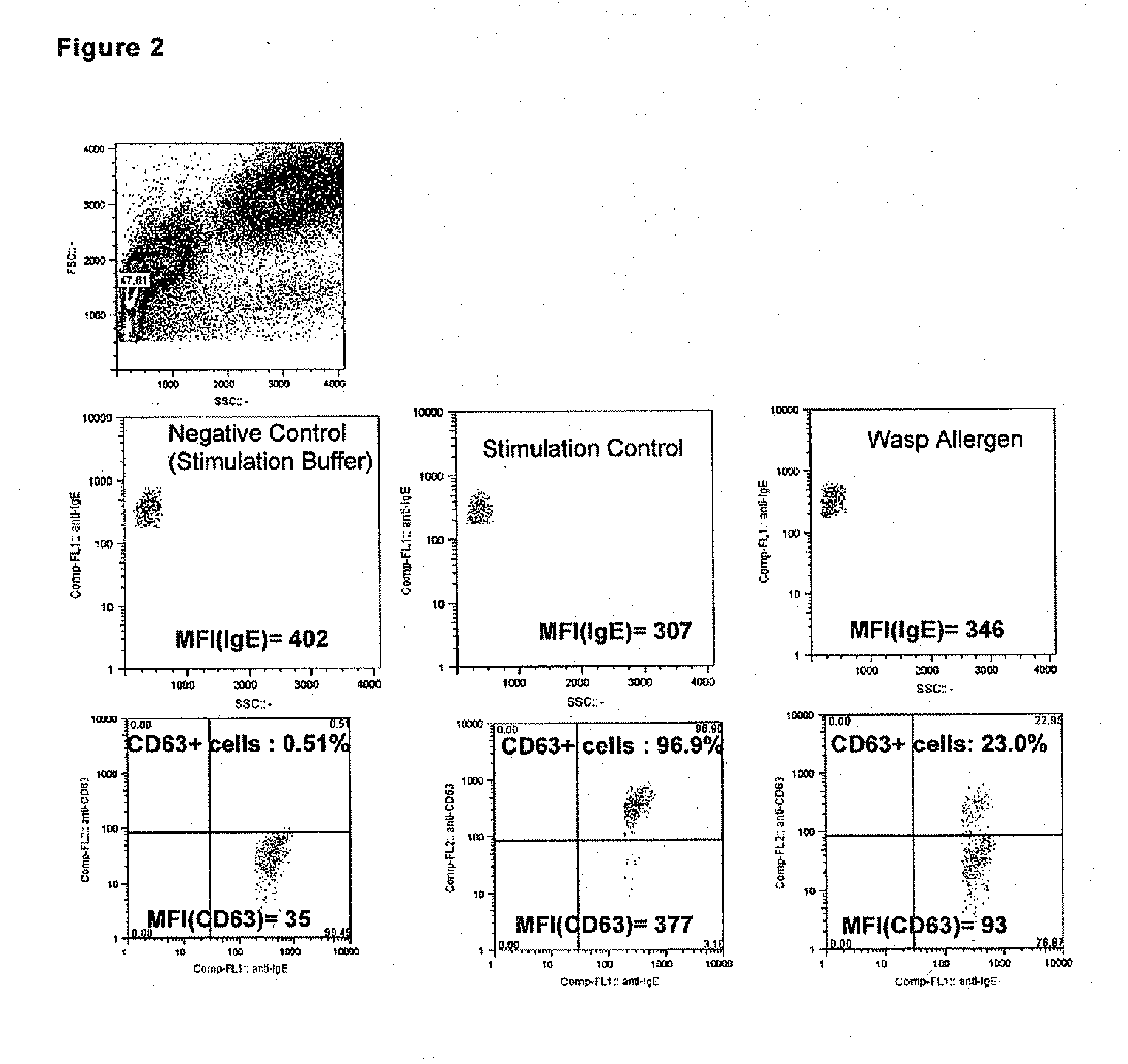
The invention pertains to a method for the determination of basophil activation induced by a test substance by flow cytometric measurement of the changes of the mean or median fluorescence intensities (WI) of the basophilic FcεRI receptor present on the cell surface of basophils (MFI-FcεRI) and / or the IgE antibodies bound to the FcεRI receptor (MFI-IgE), and the CD63 antigen exposed on the cell surface of basophils after their activation (MFI-CD63), by means of a mixture of anti-CD63, anti-FcεRI or anti-IgE, and anti-CCR3 antibodies each labelled with a distinct fluorophore, of which at least one antibody acts as a basophil selection marker and at least two antibodies act as basophil activation markers, and bringing the mean fluorescence intensities of the activation markers in correlation to obtain an Activation Index. These methods combining the measurement of an early (such as IgE, FcεRI or CD203c) and a late basophil activation marker (such as CD63), respectively, provide a markedly improved clinical sensitivity in allergy diagnosis over existing methods which consider only one activation marker, such as CD203c or CD63, expressed in percentage of basophil activation. It is also an aspect of the present invention to provide an ex-vivo allergy provocation test comprising the above-mentioned flow cytometric measurement and analysis of the results as well as a test kit for carrying out the test in-vitro.
Owner:BUHLMANN LAB AG
Quantum-dot-based method for carrying out in-situ and real-time detection on heavy metal ions in cells
ActiveCN102998291ADoes not affect normal growthRealize real-time in-situ detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceCanine kidneyFluorescence
The invention discloses a quantum-dot-based method for carrying out in-situ and real-time detection on heavy metal ions in cells. The method comprises the following steps of: A. preparing a carboxymethyl chitosan-CdTe quantum dot solution with certain concentration; B. digesting canine kidney cells overgrowing in a T25 cell culture flask bottle into a unicellular suspension, inoculating into a cell culture dish, and culturing; C. adding the carboxymethyl chitosan-CdTe quantum dot solution into the culture dish, and hatching for a period of time, thereby obtaining the canine kidney cells marked with fluorescence; and D. adding a DMEM (dulbecco's modified eagle medium) nutrient solution containing heavy metal ions with gradient concentration and unknown concentration respectively in washed cells in the culture dish, hatching together with the cells, detecting the average fluorescent intensity of the cells respectively by a flow cytometry, and drawing a standard curve through the changes of the cell fluorescent intensity, so that the concentration of the heavy metal ions in the cells can be calculated. The method is simple and convenient to operate; the fluorescence of marked cells can be quenched regularly as the increase of heavy metal ions, and the real-time and in-situ detection on the outer source heavy metal ions in the cells is realized.
Owner:武汉市疾病预防控制中心 +1
Kit for detecting specificity platelet antoantibody by combination of monoclonal antibody and nano-microspheres
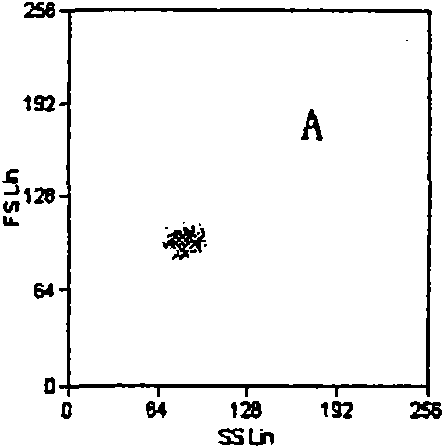
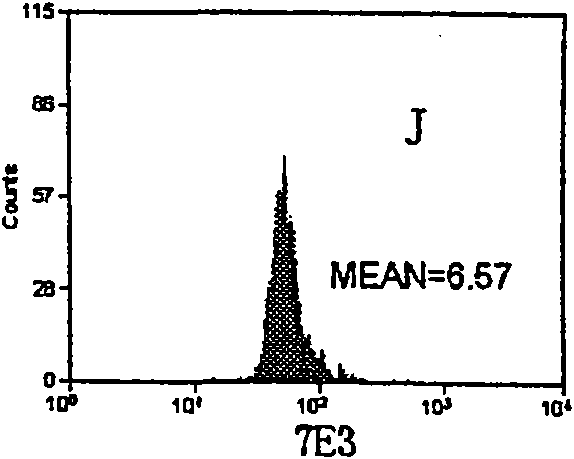
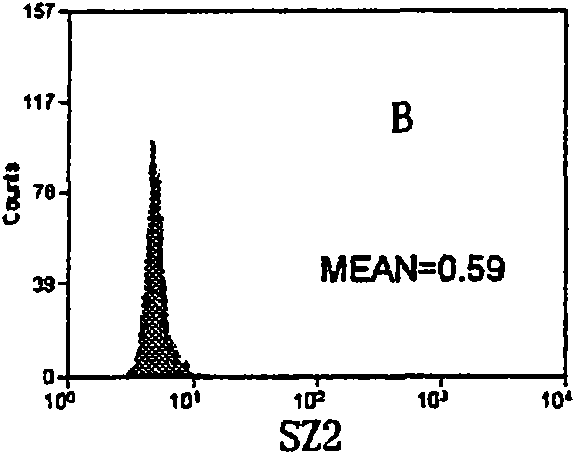
InactiveCN101713782ASmall saturation capacity changeUse less bloodFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrosphereMean fluorescence intensity
The invention relates to a set of a kit for detecting specificity platelet antoantibody by the combination of monoclonal antibody and nano-microspheres. The kit comprises each 3 ml of four types of monoclonal antibody-polystyrene nano-microspheres PBS solution, 6 ml goat-anti-human polyclonal antibody and PBS solution, wherein the four types of the monoclonal antibody-polystyrene nano-microspheres PBS solution are sealed by bovine serum albumin and are respectively connected with a monoclonal antibody SZ-2, a monoclonal antibody SZ-22, a monoclonal antibody SZ-21, a monoclonal antibody 7E3, and the concentration of polystyrene nano-microspheres is 2 mg / ml; the goat-anti-human polyclonal antibody is connected with fluorescein isothiocyanate and with the concentration of the goat-anti-human polyclonal antibody is 15 mug / ml. A detection process of the specificity platelet antoantibody comprises the following steps of: oscillating monoclonal antibody--microspheres and platelet lysis buffer sample for incubation; washing by PBS; adding the goat-anti-human polyclonal antibody connected with the fluorescein isothiocyanate; washing, re-suspending by the PBS; detecting on a flow cytometry to obtain average fluorescence intensity values of the four types of the nano-microspheres respectively; and confirming whether the specificity platelet antoantibody is positive or not according to a ratio of the obtained values to a basic contrast value of that of a healthy person, in order to provide foundation for early diagnosis of ITP. The detection has the advantages of simple process, high sensitivity and good specificity.
Owner:苏州苏大赛尔免疫生物技术有限公司 +1
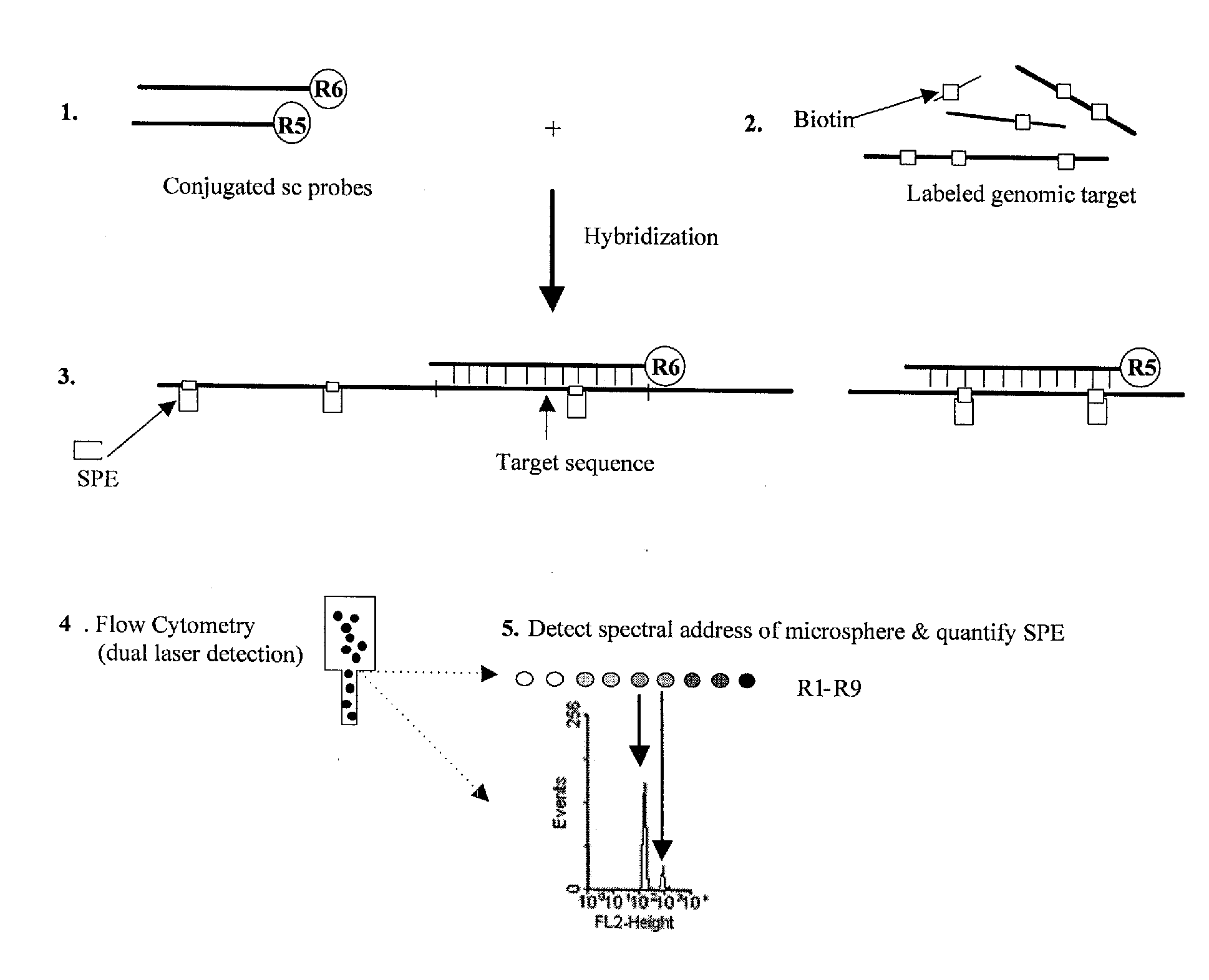
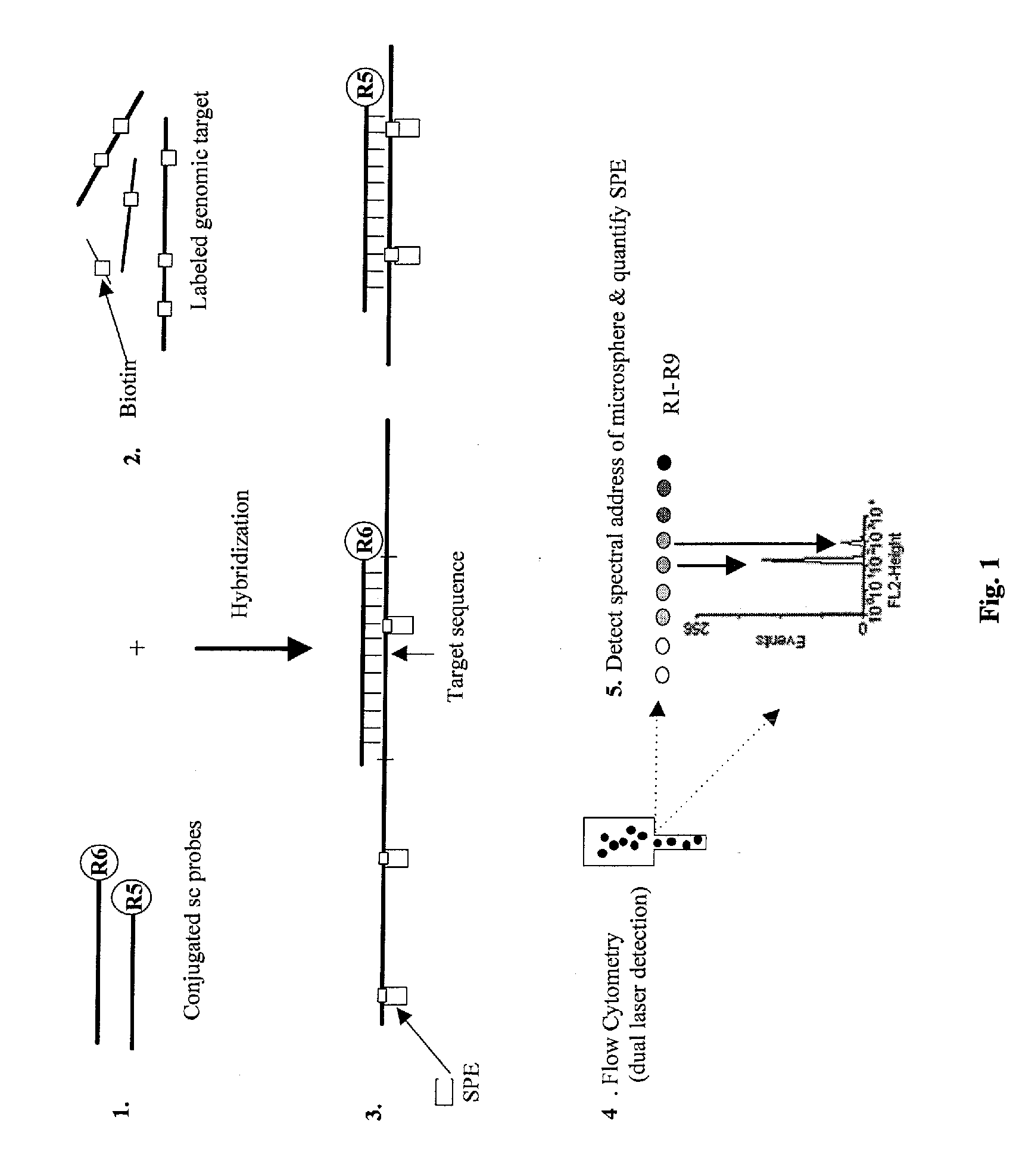
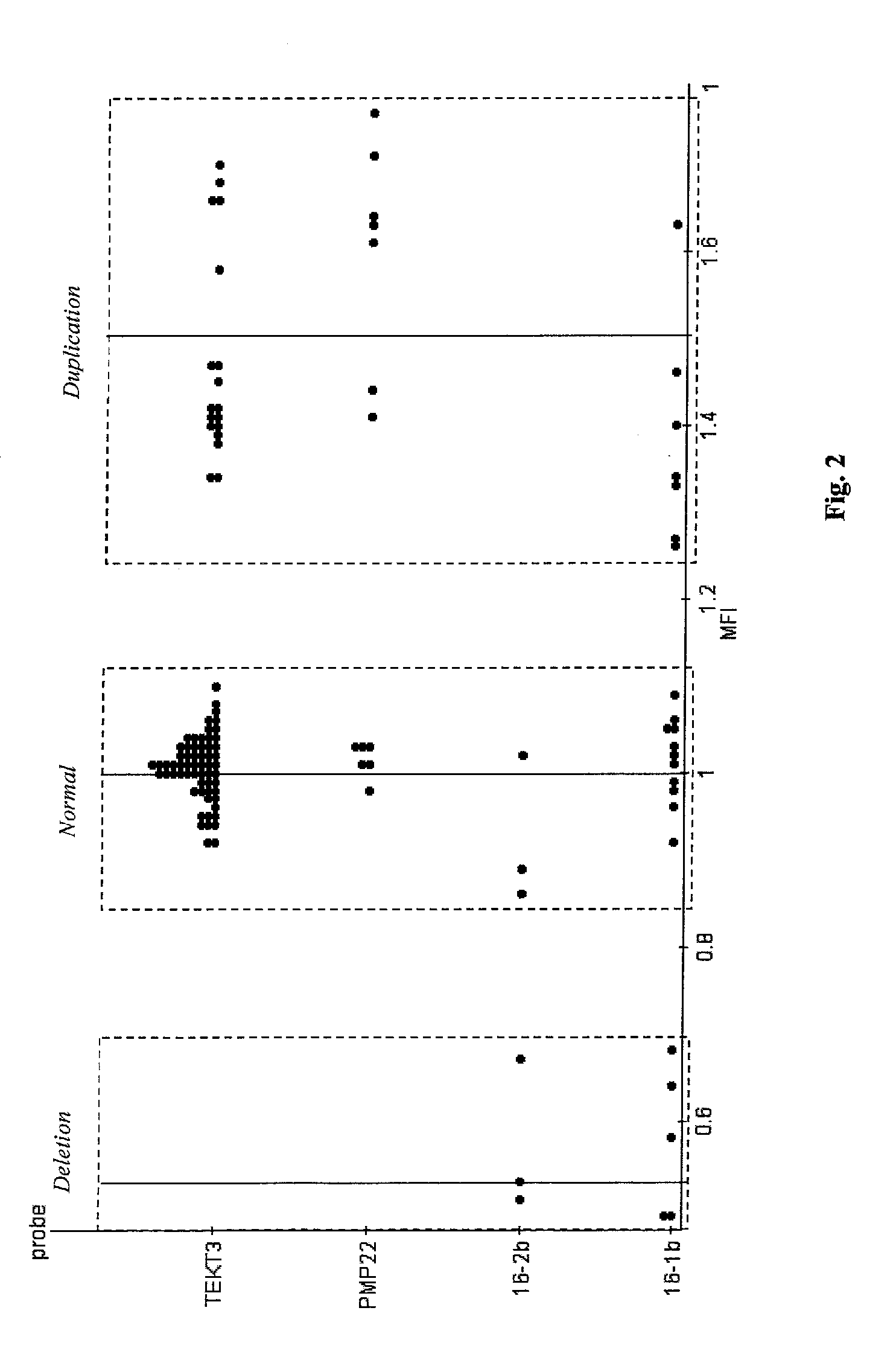
Quantification of microsphere suspension hybridization and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090136918A1Improve accuracyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseBiotin-streptavidin complex
A novel suspension hybridization assay was used to determine nucleic acid copy number by flow cytometry. The assay was validated with low copy (lc) products ranging in length from 100 to 2304 bp conjugated to spectrally-distinct polystyrene microspheres. In the example provided herein, these conjugated microspheres were used as multiplex hybridization probes to detect homologous sequences in genomic DNA extracted from cytogenetic cell pellets and labeled with biotin-dUTP. Hybridization was detected with phycoerythrin-labeled streptavidin and analyzed by flow cytometry. Copy number differences were distinguishable by comparing the mean fluorescence intensities of test probes with a diploid reference probe in genomic DNA of patient samples and abnormal cell lines. The assay is capable of distinguishing a single allele and three alleles at a test locus from a biallelic reference sequence, regardless of chromosomal context. The assay is an improvement on previous methods which require prior amplification of locus-specific target DNA because, lc probes provide adequate specificity and sensitivity for accurate copy number determination of homologous targets. Because of its high sensitivity and accuracy, the assay is useful for determination of nucleic acid copy number for a variety of applications, including determination of genomic copy number in humans, animal models of disease and in solution, measurement of transcript levels, forensic DNA analysis, and quality control analysis in agriculture.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
Method for rapidly and nondestructively detecting astaxanthin in C.zofingiensis cells
ActiveCN104964957AEasy to handleSimplify detection stepsFluorescence/phosphorescenceAstaxanthinLinear regression
The invention provides a method for rapidly and nondestructively detecting astaxanthin in C.zofingiensis cells. The method comprises the following steps of (1) re-suspending algal cells collected from a known C.zofingiensis suspension sample to regulate the known C.zofingiensis suspension sample into heavy suspension with cell density of 6*10(5) to 2*10<6>CFU / mL by virtue of de-ionized water or a phosphate buffer solution, detecting the average fluorescence intensity of the heavy suspension in an FL1 channel or an FL2 channel by virtue of a flow cytometer, and performing linear regression on a log value of the content of astaxanthin in the known C.zofingiensis suspension sample and a log value of the corresponding measured average fluorescence intensity in the FL1 or FL2 channel to obtain a standard curve; (2) preparing a sample to be detected: re-suspending algal cells collected from C.zofingiensis suspension to be detected to regulate the C.zofingiensis suspension to be detected into algal cell heavy suspension to be detected with cell density of 6*10(5) to 2*10<6>CFU / mL by virtue of de-ionized water or a phosphate buffer solution; (3) detecting the average fluorescence intensity of the sample to be detected in the FL1 channel or the FL2 channel by virtue of the flow cytometer, and calculating the content of astaxanthin in the sample to be detected according to the standard curve obtained in step (1). The method has the characteristic of high detection efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Tem8 antibodies and methods of use
InactiveUS20170114133A1High activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsAntigen Binding FragmentMean fluorescence intensity
The present invention provides, inter alia, isolated monoclonal and polyclonal anti-tumor endothelial marker 8 (TEM8) antibodies or antigen binding fragments thereof that (a) bind to TEM8 membrane antigen in its native form occurring on the surface of a tumor cell; (b) may be internalized by a tumor cell; (c) bind strongly to tumor cells but not or only minimally to cells which lack expression of TEM8; and (d) are characterized in that the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the antibody or an antigen binding fragment thereof against a mammalian cell line expressing TEM8 is at least two times higher than the MFI against the mammalian cell line not expressing TEM8 at antigen saturation. Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) including an antigen binding fragment of such antibodies, modified antibodies, compositions, pharmaceutical compositions, and kits including the antibodies according to the present invention, and methods of use are also provided.
Owner:BIOMED VALLEY DISCOVERIES INC
Method for quantitatively detecting protein concentration by flow cytometer
ActiveCN105717033ASmall reaction systemQuantitatively accurateIndividual particle analysisBiological testingLower limitMicrosphere
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting protein concentration by a flow cytometer, and specific protein concentration is detected by the combination of fluorescence immunological magnetic microspheres and flow cytometric detection. The method comprises the specific steps: preparing a fluorescence detection antibody; preparing fluorescence immunological magnetic microspheres and calibrating magnetic microspheres; making a standard article working curve, and acquiring actual protein concentration through unknown sample average fluorescence strength. The flow cytometry and the fluorescence immunological magnetic microspheres are combined for detecting protein concentration; specific protein molecular concentration is detected by using the method, a reaction system is small, measuring is more accurate, a detection lower limit is pg / ml level, specificity and sensitivity are high, operating is more convenient and quick, operating steps are simpler, incubation is direct without stepwise incubation and washing so that reaction time is shortened, detection results are obtained within a shorter time, and quantitating is more accurate.
Owner:王博
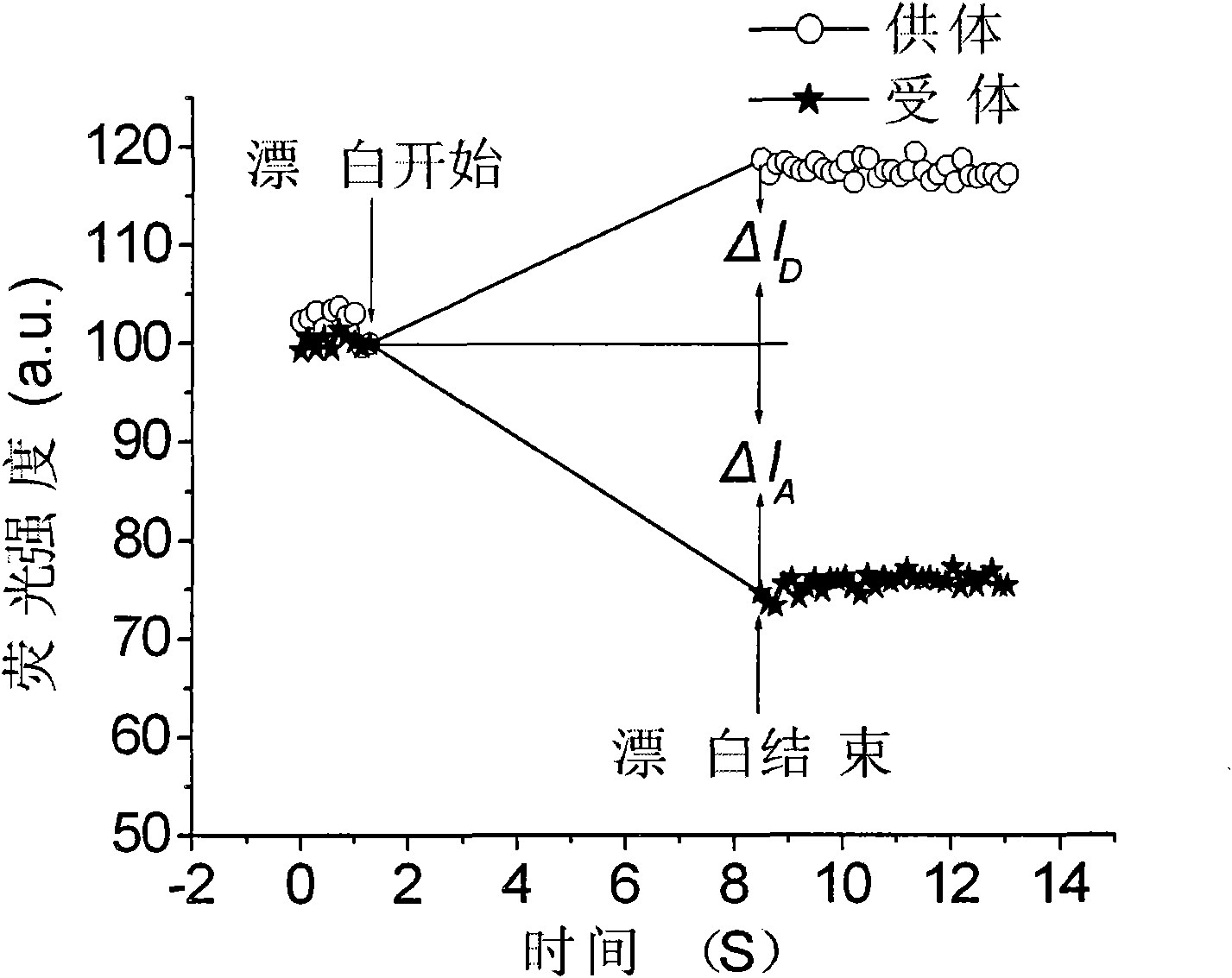
Photobleaching-based method for quantitatively measuring fluorescence resonance energy efficiency
InactiveCN101581669ASolve the damageAvoid damageFluorescence/phosphorescenceResonanceMean fluorescence intensity
The invention relates to a method for measuring conversion efficiency of fluorescence resonance energy, in particular to a photobleaching-based method for quantitatively measuring fluorescence resonance energy efficiency. In the method, the fluorescence resonance energy efficiency is calculated by acquiring the average fluorescence intensity of a donor channel and donee channel before and after the photobleaching in living cells transfected with donor-donee pair with a laser confocal microscopy before and after the photobleaching of the donor. The method can effectively solve the problem that the living cells are damaged seriously by the conventional photobleaching method of donee due to the overlong time of photobleaching. By the method, FRET efficiency can be obtained quantitatively by only bleaching small part of donee so as to quantitatively monitor the interactions between the proteins of the living cells. Because of the short time only in the order of seconds, the method can reduce the damages to the living cells considerably.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-liquid-phase gene chip detection primer, kit and method for quickly distinguishing 5 respiratory pathogens of mouse
ActiveCN107312873AAvoid crossbreedingGuaranteed temperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotin-streptavidin complexFluorescence
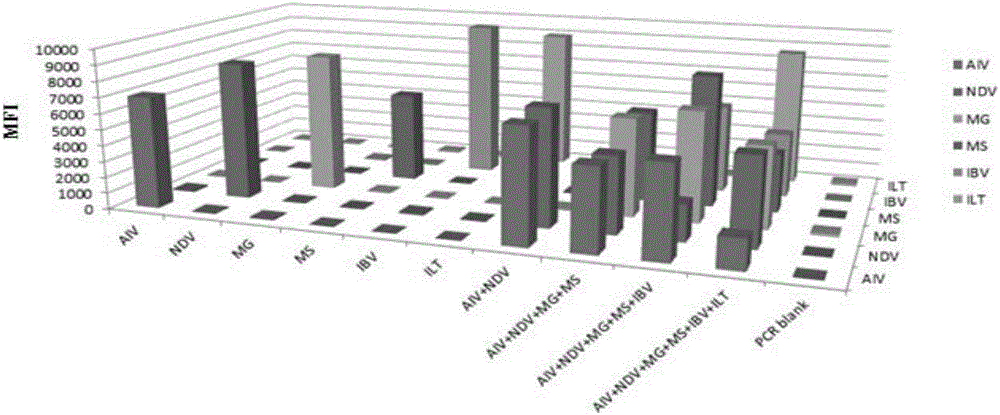
The invention discloses a multi-liquid-phase gene chip detection primer, kit and method for quickly distinguishing 5 respiratory pathogens of a mouse. The multi-liquid-phase gene chip detection primer is easy to operate; a target amplified fragment is obtained through PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); an amplified product, fluorescence coded microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized; an MFI (Mean Fluorescence Intensity) value is read through a detector so as to distinguish different types of viruses. The method disclosed by the invention can detect a pneumonia virus, a hantaan virus, a sendai virus, a lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and mycoplasma pulmonis of the mouse at the same time, and is high in specificity, high in sensitivity and high in repetitiveness. Compared with the conventional detection method, the method disclosed by the invention realizes simultaneous detection of various different target molecules in the same sample; the sample use amount is small; the operation is simple and quick; the detection cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
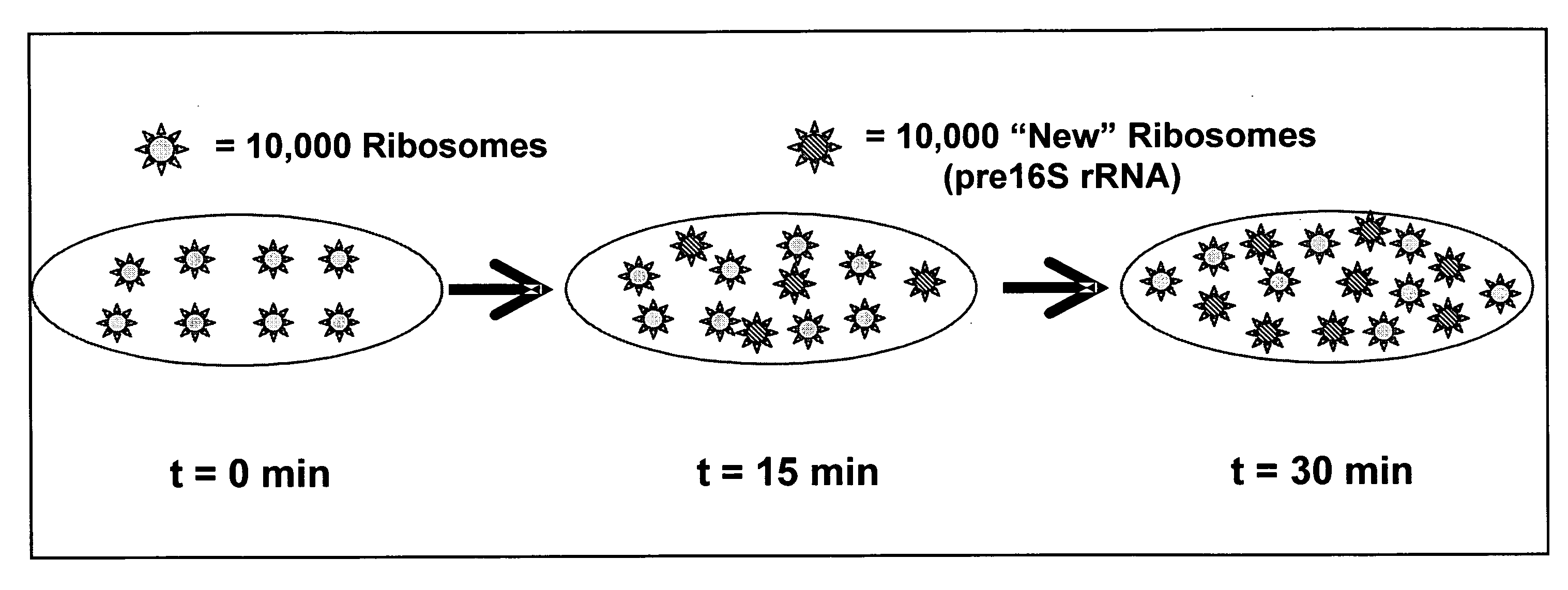
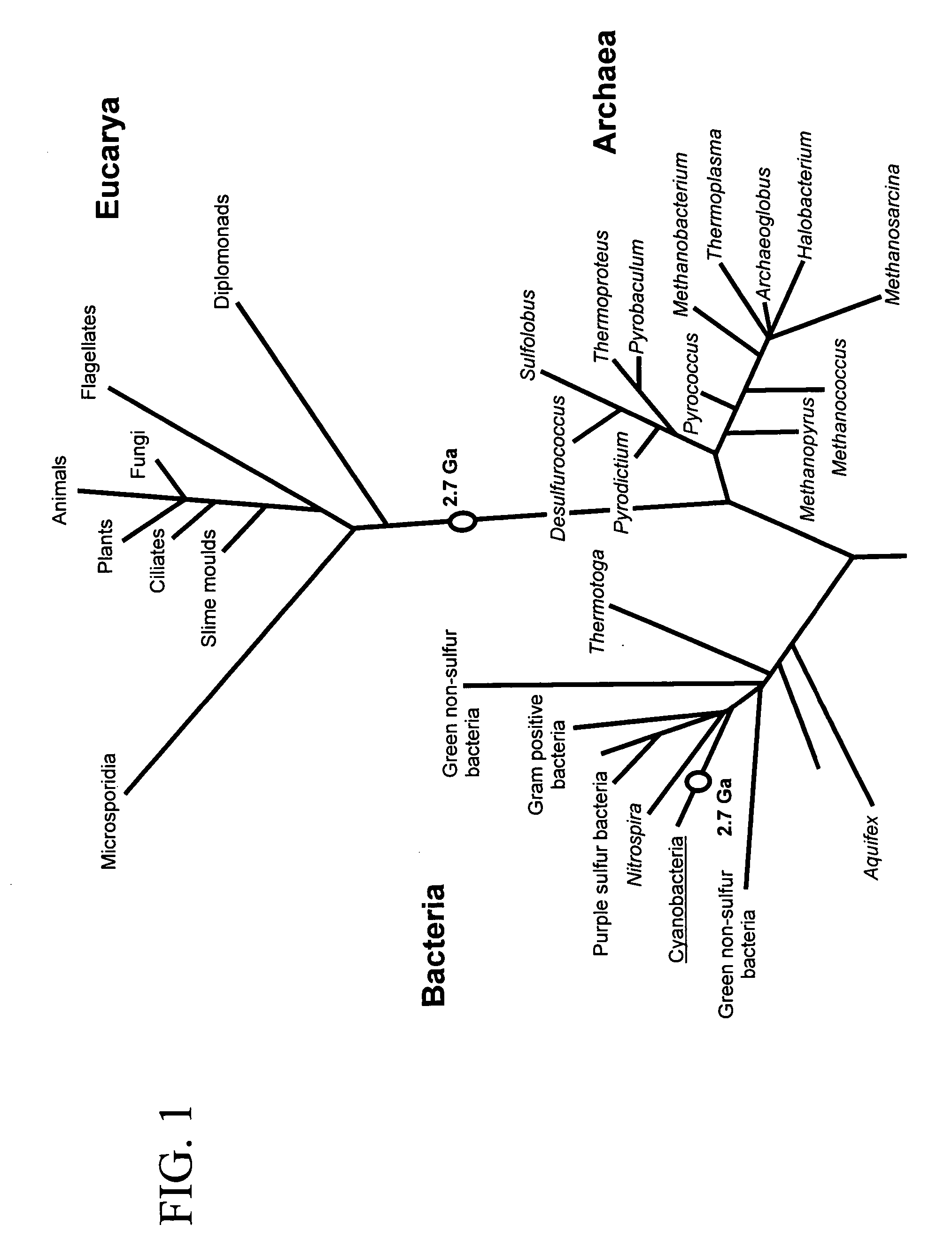
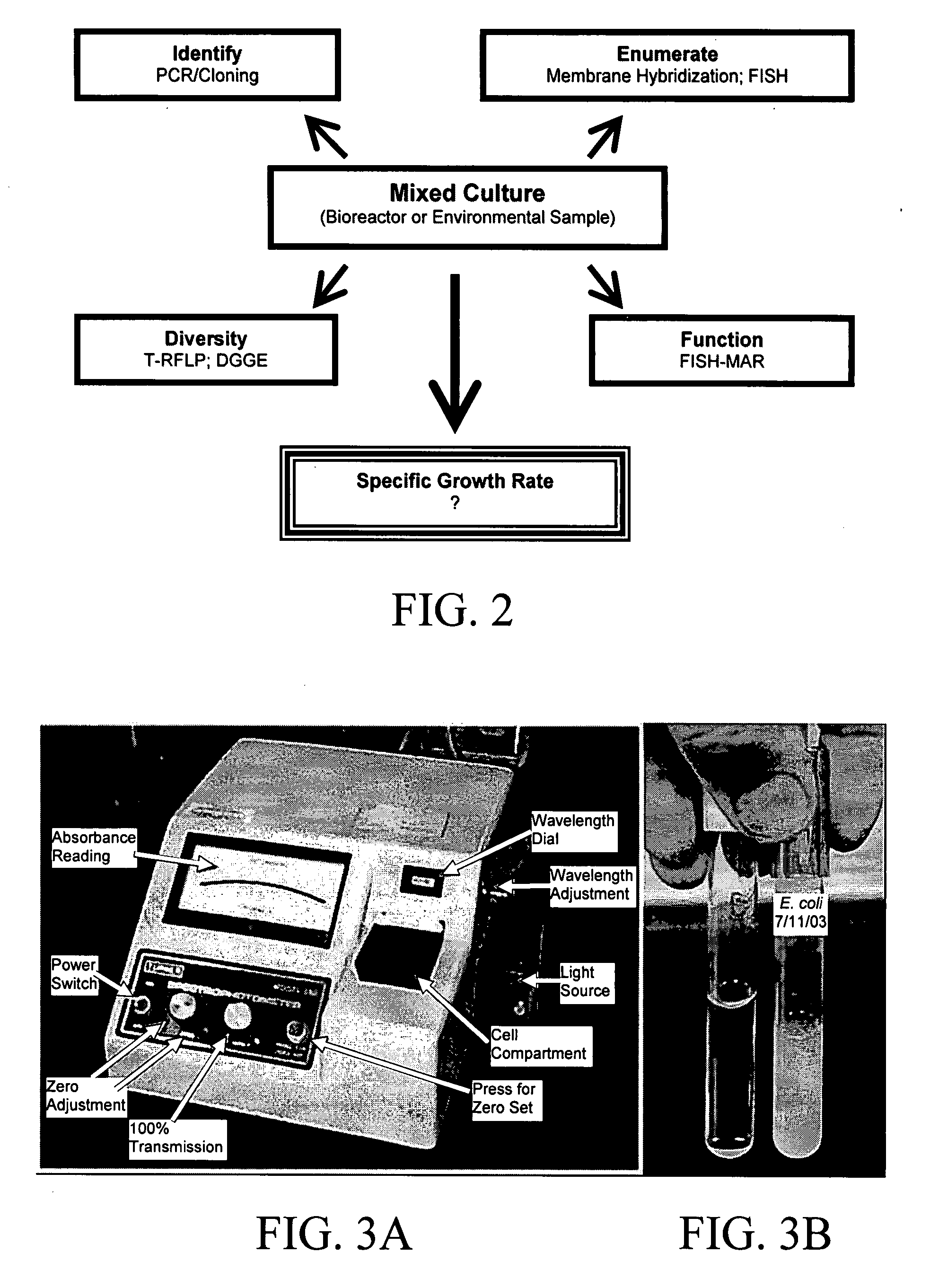
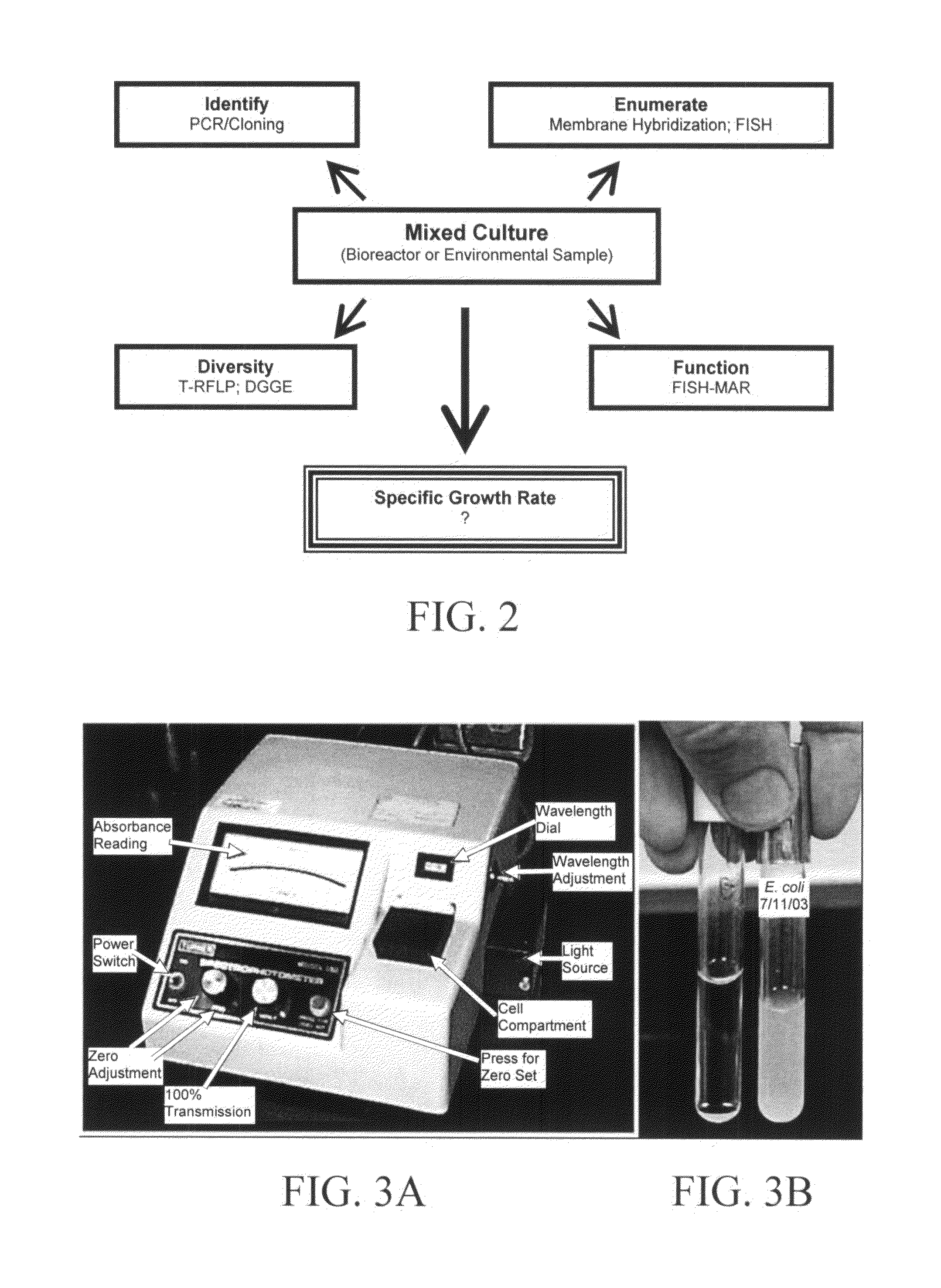
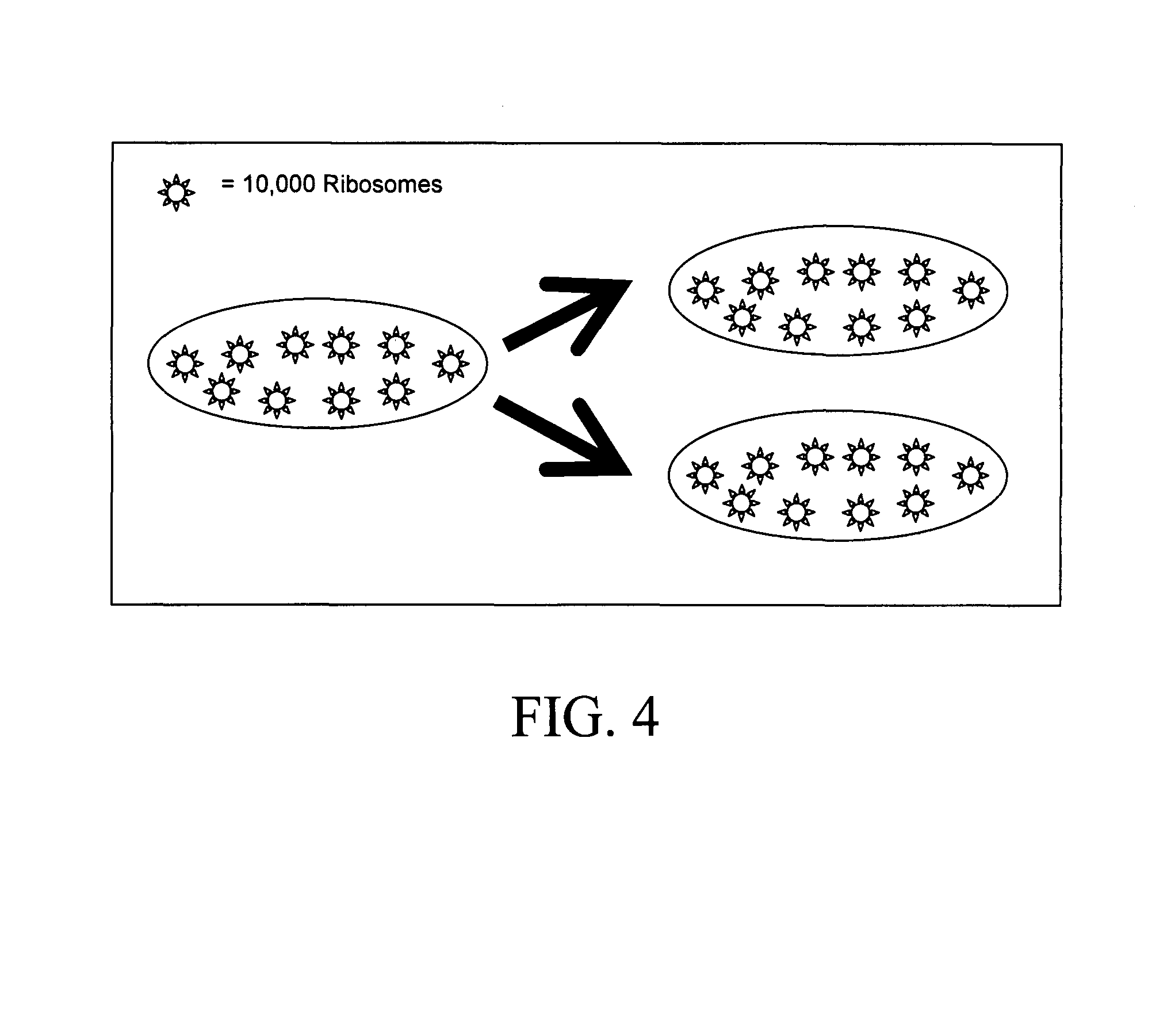
Method for determining the specific growth rate of distinct microbial populations in a non-homogeneous system
InactiveUS20080009011A1Quick measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceHomeland security
The present invention pertains to a molecular biology-based method and kit for measuring the specific growth rate (or cell doubling time) of distinct microbial populations. The method and kit can be used to analyze mixed culture samples that have been exposed to chloramphenicol or other protein synthesis inhibitors for defined times. In a preferred embodiment, the method of the invention (also referred to herein as FISH-RiboSyn) is an in situ method that utilizes fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with probes that target: (1) the 5′ or 3′ end of precursor 16S rRNA; or (2) the interior region of both precursor 16S rRNA and mature 16S rRNA. Images can be captured for a defined exposure time and the average fluorescent intensity for individual cells can be determined. The rate of increase of the whole cell fluorescent intensity is used to determine the specific growth rate. The method of the invention can be attractive for rapidly measuring the specific growth rate (or cell doubling time) of distinct microbial populations within a mixed culture in industries such as environmental systems (water and wastewater treatment systems), bioremediation (optimization of conditions for microbial growth), public health (identification of rapidly growing infectious microbes), and homeland security (identification of rapidly growing bioterrorism agents).
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Quick detection method for in-situ fluorescent staining of livestock meat spoilage bacteria
InactiveCN102866140AQuick checkExtended shelf lifeFluorescence/phosphorescencePsychological statusSpoilage bacteria
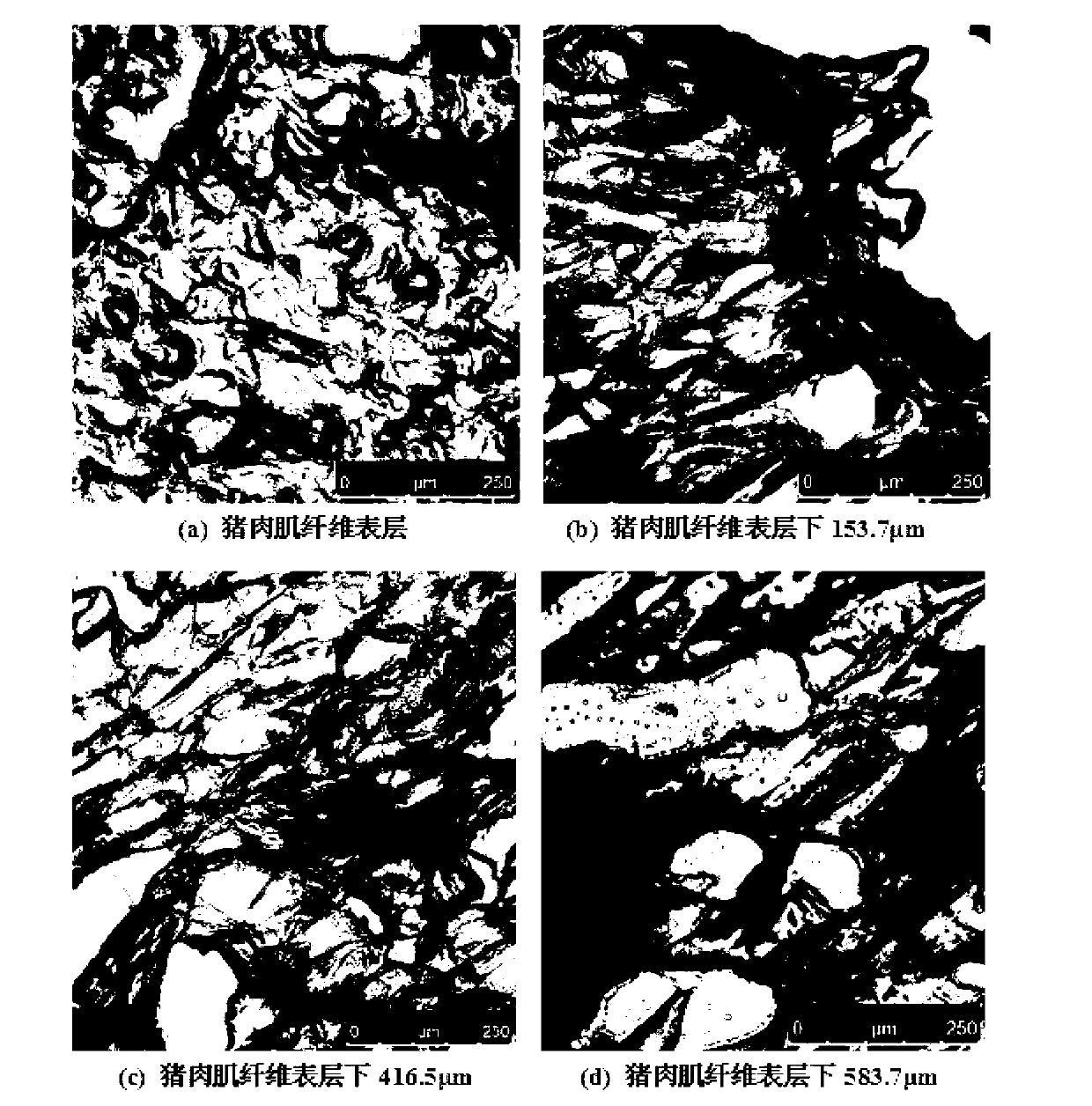
The invention relates to a quick detection method for in-situ fluorescent staining of livestock meat spoilage bacteria. Spoilage bacterium living bodies are subjected to in-situ fluorescent staining by fluorescent dye, shot images are processed by tomography through a confocal scanning laser microscope, and average fluorescent strength is calculated to represent relative cell quantity of unit area of a section of pork tissue. The quick detection method is easy to operate, high in detection speed and free of harmfulness and capable of detecting livestock spoilage bacteria within a short time on the premise of not damaging psychological status, and thus distribution and impregnation situations of spoilage bacteria in pork tissue and dynamic change of the spoilage bacteria can be observed and tracked in rail time. In addition, the quick detection method has direct practical significance in further researching spoilage mechanism of livestock meat deeply so as to control the spoilage bacteria pointedly, prolong shelf life of meat, guarantee quantity safety of meat and care health of customers.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Multi-fluorescent immunoassay method for rapidly distinguishing 6 types of poultry respiratory pathogens
ActiveCN106191319AAvoid crossbreedingGuaranteed temperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotin-streptavidin complexMycoplasma synoviae
The invention discloses a multi-fluorescent immunoassay method for rapidly distinguishing 6 types of poultry respiratory pathogens. The multi-fluorescent immunoassay method is simple to operate; a target amplified fragment is obtained through a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); then an amplified product, fluorescence coded microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized; an MFI (Mean Fluorescence Intensity) value is read through a detector to distinguish viruses of different types. According to the method disclosed by the invention, avian influenza viruses, chicken infectious bronchitis viruses, chicken Newcastle disease viruses, chicken infectious laryngotracheitis viruses, mycoplasma gallisepticum and mycoplasma synoviae can be accurately detected at the same time; the multi-fluorescent immunoassay method has high specificity, high sensitivity and good repeatability. Compared with a traditional detection method, the method disclosed by the invention realizes simultaneous detection of a plurality of types of different target molecules in the same sample; the use amount of the sample is less; the method is simple and rapid to operate and the detection cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
Multiple fluorescence immunoassay method for detecting mycoplasma gallisepticum and mycoplasma synoviae
InactiveCN106222256AAvoid crossbreedingGuaranteed temperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotin-streptavidin complexMycoplasma synoviae
The invention discloses a multiple fluorescence immunoassay method for detecting mycoplasma gallisepticum and mycoplasma synoviae. The multiple fluorescence immunoassay method has the advantages that the operation is simple; a target amplified fragment is obtained through PCR (polymerase chain reaction), then the amplified fragment, fluorescent encoding microspheres, and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized, and an MFI (mean fluorescence intensity) value is read through a detection instrument, so as to distinguish different types of pathogens; the mycoplasma gallisepticum and mycoplasma synoviae can be simultaneously detected and identified; the specificity is strong, the sensitivity is high, the repeatability is good, and the like; multiple types of molecules with different purposes in the same sample can be simultaneously detected; the flexibility is good, and the type of to-be-detected pathogens can be increased or decreased on the basis according to requirements.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
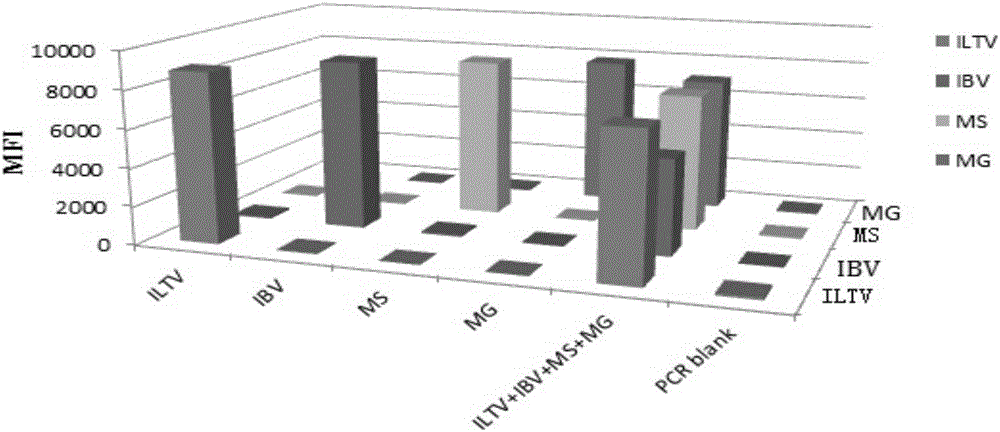
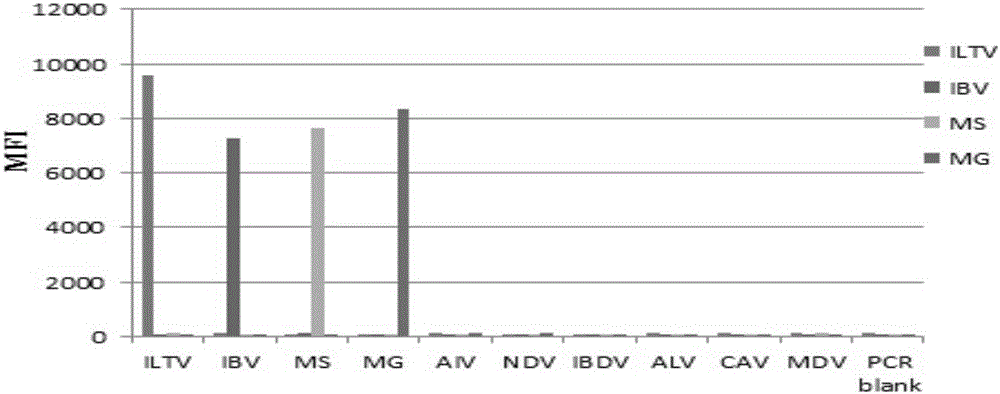
Multiple fluoroimmunoassay method capable of quickly differentiating infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV), infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), myeoplasma gallisepticum (MG) and mycoplasma synoviae (MS) and reagent
ActiveCN106011313AReduce dosageAvoid crossbreedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMycoplasma synoviaeFluorescence
The invention discloses a multiple fluoroimmunoassay method capable of quickly differentiating infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV), infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), myeoplasma gallisepticum (MG) and mycoplasma synoviae (MS) and a reagent. The method is simple to operate, a target amplified fragment is obtained through polymerase chain reaction (PCR); an amplified product, fluorescence coded microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized, a mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) value is read through a detector, and pathogens of different types are differentiated. According to the method, avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus, infectious bronchitis virus, myeoplasma gallisepticum and mycoplasma synoviae can be accurately detected simultaneously, and the method is high in specificity and sensitivity and good in repeatability. Compared with a conventional detection method, the method can be used to simultaneously detect various target molecules in an identical sample, the sample usage amount is small, the method is simple and quick to operate, and the detection cost can be greatly reduced. The method is good in flexibility, and the varieties of detected pathogens can be increased or decreased as required on the basis.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
Precise quantification method of HBV (hepatitis B virus) cccDNA (covalent closed circular DNA)
InactiveCN106636466ASolve the problem of false positive interferenceRealize closed tube operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlMicroparticle
The invention relates to a precise quantification method of HBV (hepatitis B virus) cccDNA (covalent closed circular DNA). The precise quantification method of the HBV cccDNA comprises steps as follows: the copy number of a sample is quantitatively controlled within 10,000 copes through nucleic acid; primers and probes of cccDNA and rcDNA are designed and detected with a double-gap method; digital PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed; analysis parameters are adjusted in digital PCR instrument analysis software, 1 / 2-1 / 3 of the average fluorescence intensity of positive particles in positive control holes is set as a positive threshold, the to-be-detected sample is analyzed and the copy number of cccDNA in the sample is calculated using software of the digital PCR instrument, and false positive caused by non-specific amplification is eliminated. The method solves the false positive interference problem of double-gap method and the PCR method for rcDNA; compared with other digital PCR detection methods for cccDNA, the method has the advantages that specific DNA enzyme is not required to treat the sample, closed pipe operation is realized, the cross-pollution risk is reduced, and the operation process is simplified.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Primer group, kit and method for detecting six mouse viruses by multiple immunity fluorescence
ActiveCN106636474AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotin-streptavidin complexMicrosphere
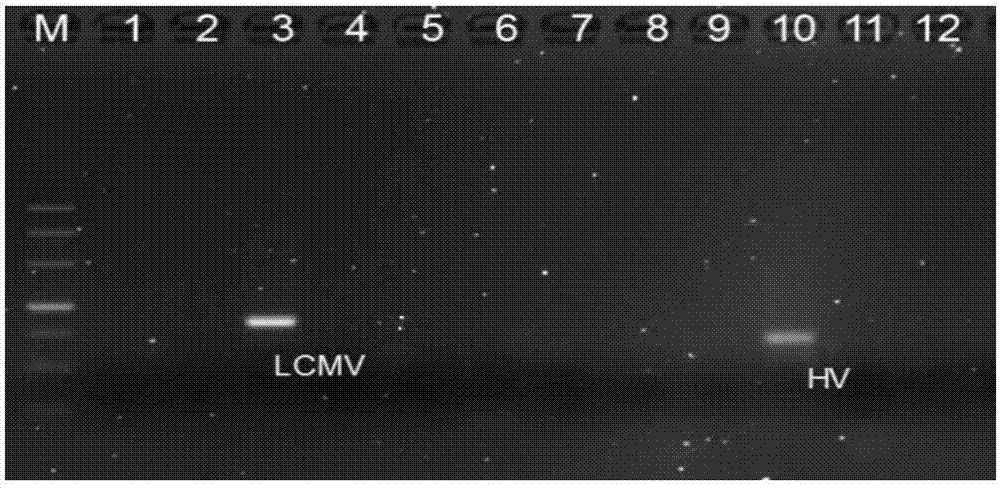
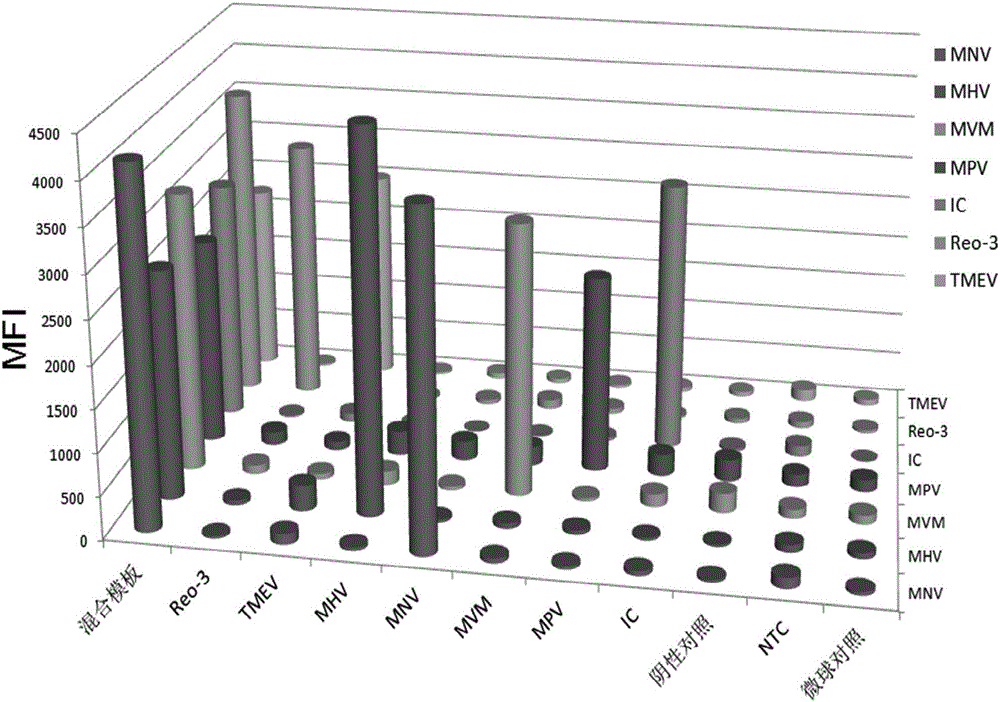
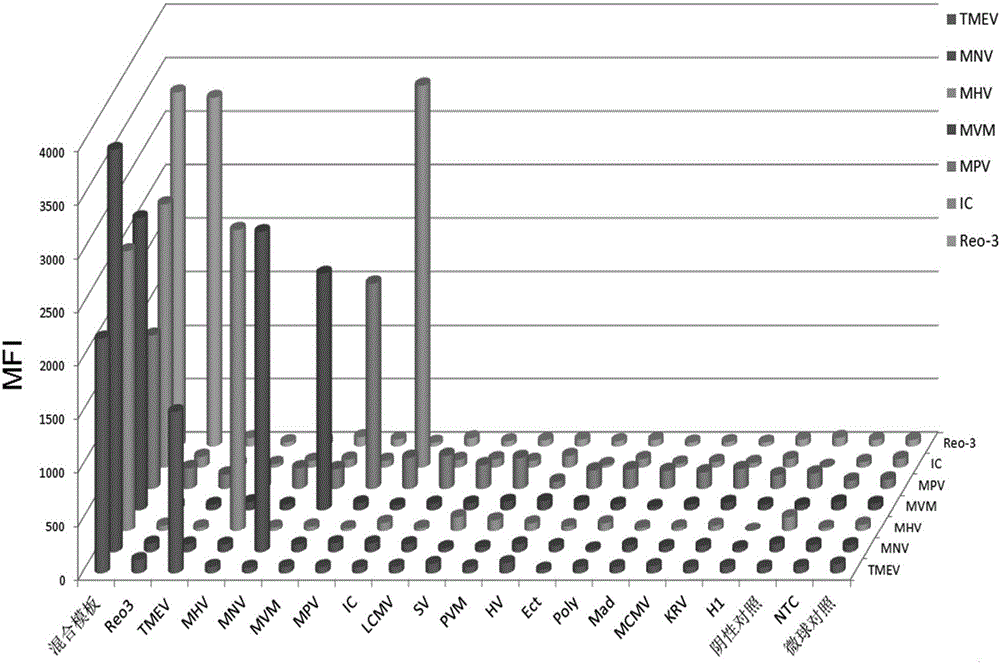
The invention discloses a primer group, a kit and a method for detecting six mouse viruses by multiple immunity fluorescence. The primer group is designed by the aid of multiple RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) technologies and Luminex liquid chip technologies and can simultaneously detect six high-infection viruses such as TMEV, MHV, MNV, Reo-3, MVM and MPV of mice. By the aid of the primer group, target amplification products are acquired through specific PCR, the amplification products, fluorescence encoding microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized, and different types of viruses are distinguished when a mean fluorescence intensity value is read by a Luminex detector. The method has the advantages of rapidness, high efficiency, high specificity and sensitivity, good repeatability and the like and can be applied to quality monitoring, epidemiological investigation and early warning of test mice. The primer group is good in flexibility, and varieties detecting the viruses can be increased and decreased as required on the basis.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
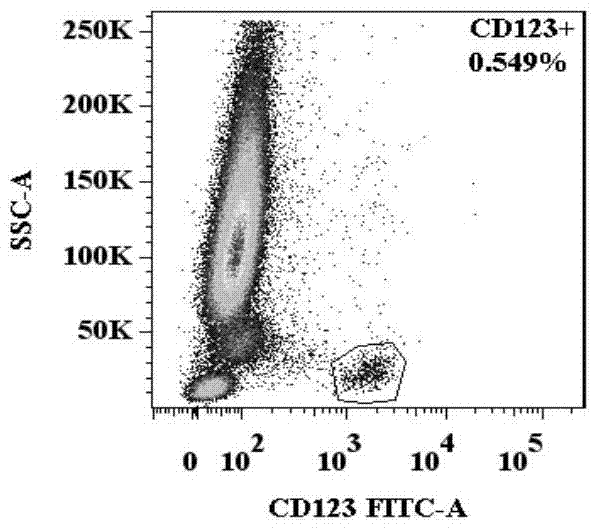
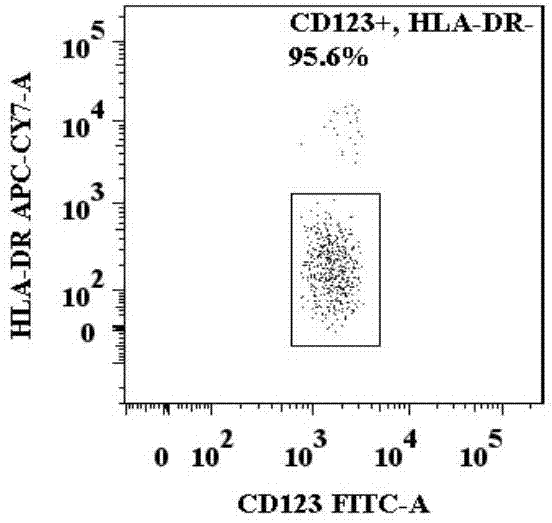
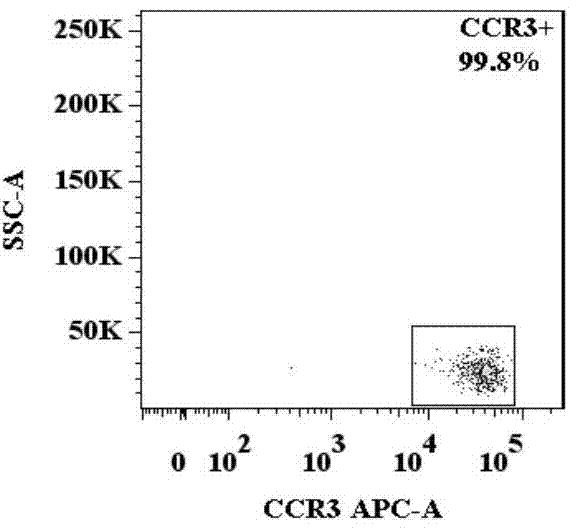
Basophilic granulocyte activation and degranulation identification method
ActiveCN104777303AGood repeatabilityReduce mistakesDisease diagnosisIndividual particle analysisRed blood cellTest sample
The invention provides a basophilic granulocyte activation and degranulation identification method. The basophilic granulocyte activation and degranulation identification method comprises the following steps that test samples are numbered in sequence, and flow type sample feeding pipes required by testing are marked; a required anti-human CD123, anti-human CCR3, anti-human HLA-DR, anti-human CD203c and / or anti-human CD63 fluorescence labeling flow type antibody combination is added into each flow type sample feeding pipe; mixed whole blood is added into the marked flow type pipes, and shading incubation is conducted at the indoor temperature; red blood cell lysate is added into each sample pipe, and shading incubation is conducted at the indoor temperature again; supernatant is removed in a centrifugal mode after incubation; detection is conducted by means of a flow cytometry, and the number of basophilic granulocytes and the average fluorescence intensity are analyzed. According to the basophilic granulocyte activation and degranulation identification method, 80%-100% of the basophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood can be distinguished from other types of cells under the condition that the basophilic granulocytes do not need to be separated or purified, the basophilic granulocyte activation and / or degranulation state can be identified, whole blood of no more than 100 microlitres is needed by each sample to be tested, and the repeatability is good.
Owner:HPY BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for determining the specific growth rate of distinct microbial populations in a non-homogeneous system
InactiveUS7771941B2Quick measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementHomeland securityBioremediation
The present invention pertains to a molecular biology-based method and kit for measuring the specific growth rate (or cell doubling time) of distinct microbial populations. The method and kit can be used to analyze mixed culture samples that have been exposed to chloramphenicol or other protein synthesis inhibitors for defined times. In a preferred embodiment, the method of the invention (also referred to herein as FISH-RiboSyn) is an in situ method that utilizes fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with probes that target: (1) the 5′ or 3′ end of precursor 16S rRNA; or (2) the interior region of both precursor 16S rRNA and mature 16S rRNA. Images can be captured for a defined exposure time and the average fluorescent intensity for individual cells can be determined. The rate of increase of the whole cell fluorescent intensity is used to determine the specific growth rate. The method of the invention can be attractive for rapidly measuring the specific growth rate (or cell doubling time) of distinct microbial populations within a mixed culture in industries such as environmental systems (water and wastewater treatment systems), bioremediation (optimization of conditions for microbial growth), public health (identification of rapidly growing infectious microbes), and homeland security (identification of rapidly growing bioterrorism agents).
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
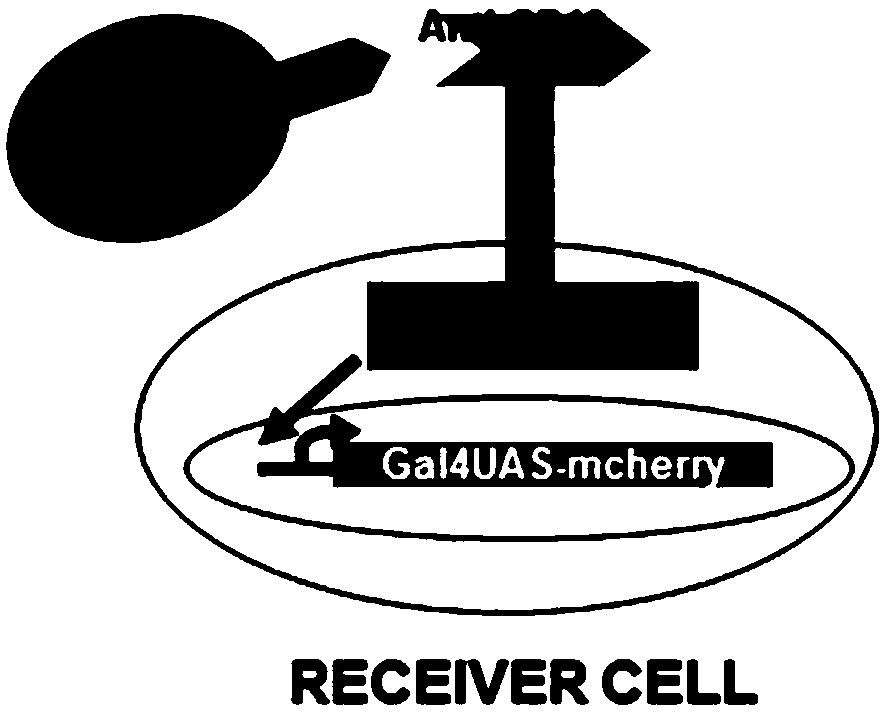
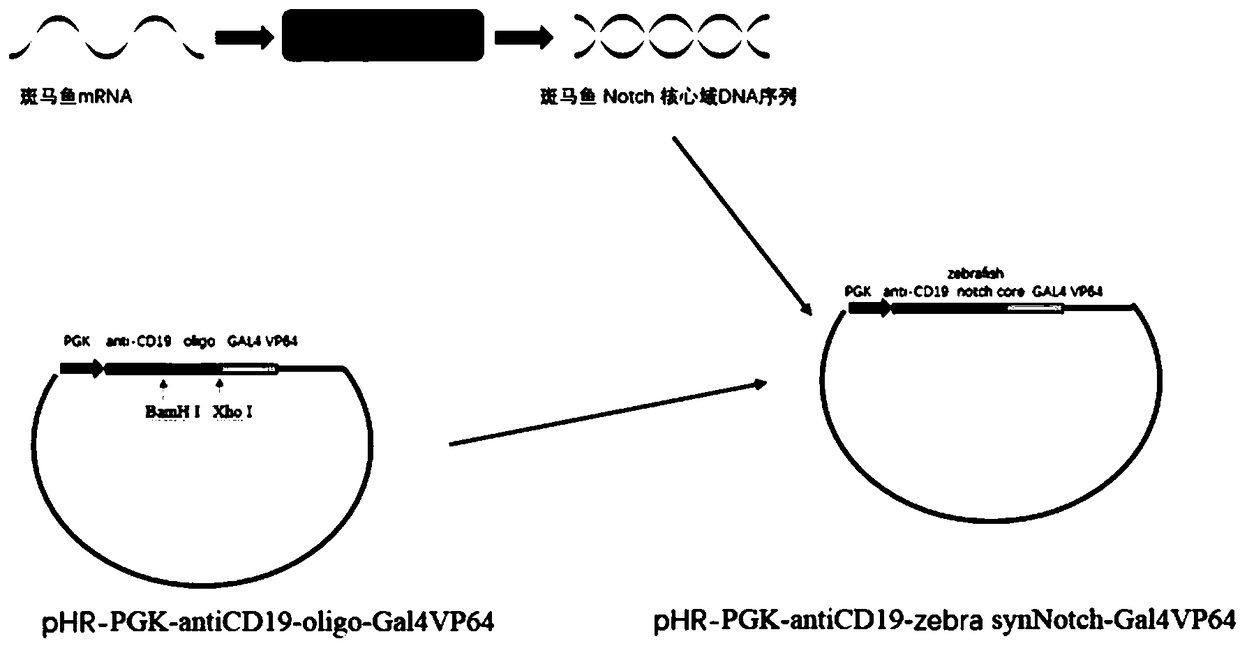
Novel SynNotch synthetic acceptor and coding gene thereof
ActiveCN109180805AEfficient activationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationMean fluorescence intensityNucleotide
The invention discloses a novel SynNotch synthetic acceptor and a coding gene thereof. The novel SynNotch synthetic acceptor contains anti-CD19scFV, a zebra fish Notch core segment and a GAL-VP64 segment, the amino acid sequence of the novel SynNotch synthetic acceptor is represented by SEQ ID NO.5, and the corresponding nucleotide sequence of the coding gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.4. According to a SynNotch system modified by virtue of the novel SynNotch synthetic acceptor, a downstream gene can be relatively efficiently expressed. Compared with an original SynNotch acceptor system, theaverage fluorescence intensity for regulating and controlling the expression of a Mcherry fluorescent protein of the modified SynNotch system can be increased by 4.9 times. According to the modified SynNotch acceptor, the application range of SynNotch can be expanded, a novel application prospect is provided for the cell modification, and the novel SynNotch synthetic acceptor has potential important economic values and significances.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
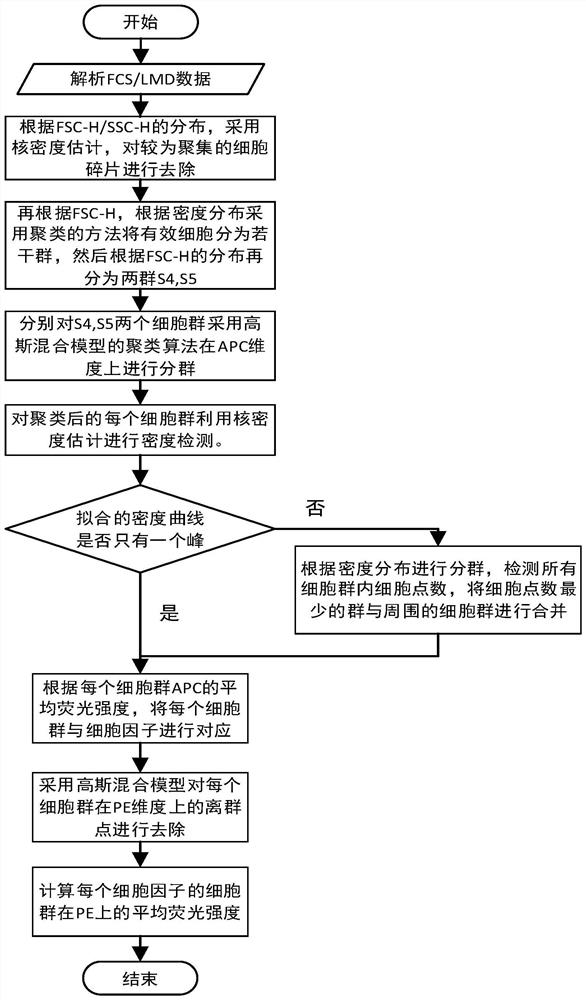
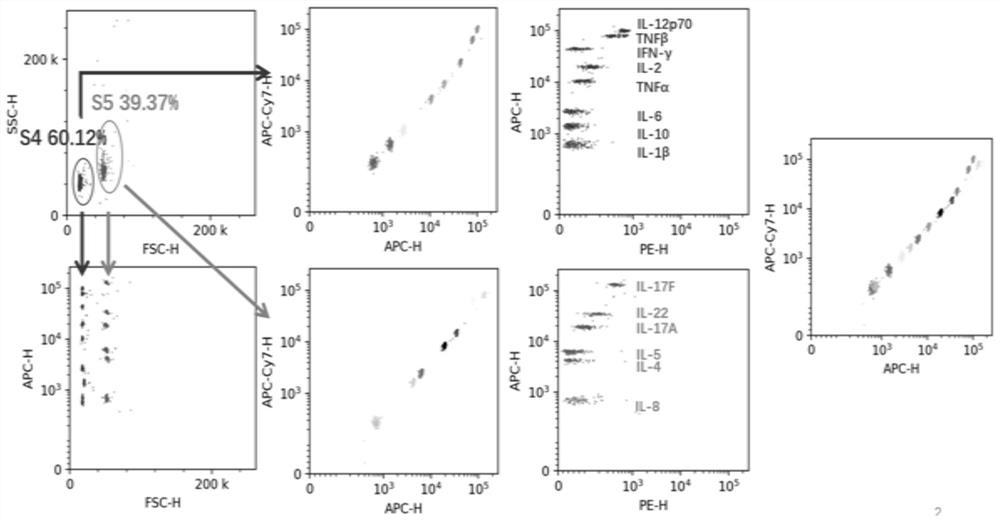
Multi-factor cell factor automatic analysis method
ActiveCN113188981AAccurate grip and separationAccurate Fluorescence IntensityIndividual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceMean fluorescence intensityCytokine
The invention relates to a multi-factor cell factor automatic analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of extracting flow cytometry data in an FCS format or LMD format file; removing cell debris from the FSC-Hs of all the cells; dividing the effective cells into a plurality of cell populations, and re-dividing a plurality of cell populations into two cell populations; dividing the two cell populations into a plurality of cell populations with the same number as the detected cell factors; carrying out peak number detection of a nuclear density probability density function curve on the fluorescence intensity of all cell antibodies APC in each cell population; continuously grouping the cell population; combining the cell population with the cell count less than 60 with the cell population with the nearest distance; enabling each cell population to correspond to the detected cell factors; carrying out outlier detection on the fluorescence intensity of the PE antibodies of all cells in each cell population, and removing outliers; and calculating the average fluorescence intensity of the cell population PE antibody of each cell factor. The method can effectively remove noise interference and intensity fluctuation to obtain accurate fluorescence intensity of the cell population.
Owner:天津深析智能科技发展有限公司
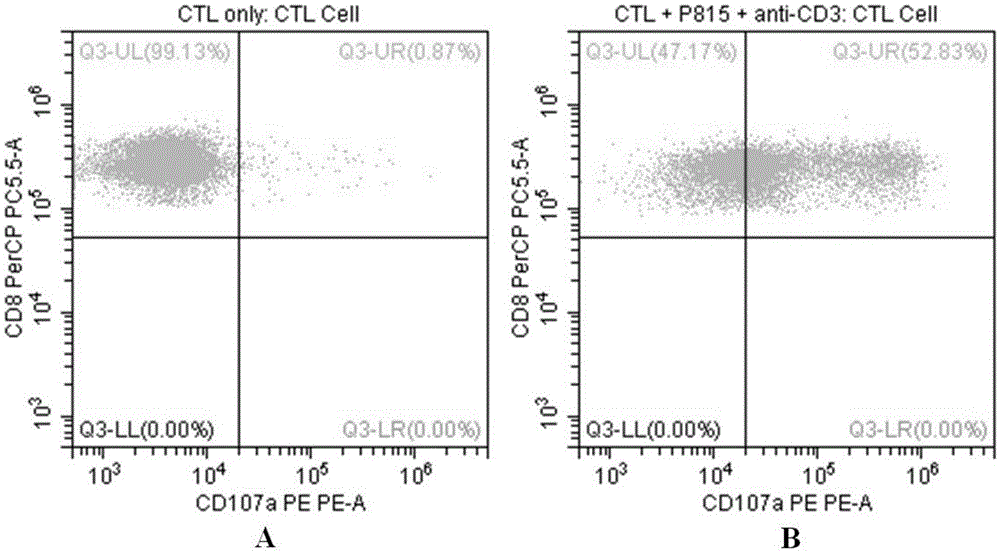
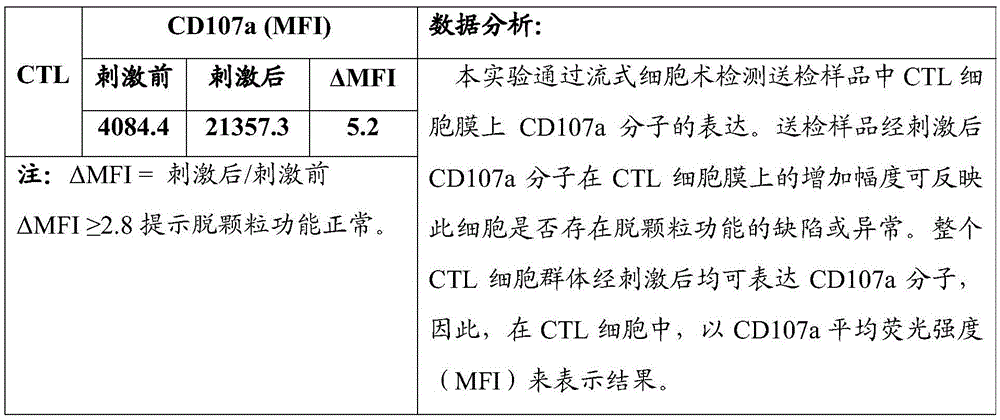
Flow-cytometry detecting method of cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte degranulation
ActiveCN105547971AQuick checkImprove throughputIndividual particle analysisCell-mediated cytotoxicityMean fluorescence intensity
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a flow-cytometry detecting method of cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte degranulation. The flow-cytometry detecting method includes the steps that cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte degranulation is excited through the antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic effect, the ratio of the average fluorescence intensity of vesicle-membrane-protein markers CD107a in cytotoxic T lymphocytes after exciting to the average fluorescence intensity before exciting is detected through flow cytometry to evaluate the degranulation function of the cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and if the ratio is larger than or equal to 2.8, the degranulation function is normal. The flow-cytometry detecting method of cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte degranulation is rapid in detection, large in flux, high in accuracy and small in human-factor influence. As key technology details such as natural irritant selecting, the effector target cell ratio and the incubating time are optimized and limited, the stable and normative technical process is built.
Owner:倍科为(天津)生物技术有限公司
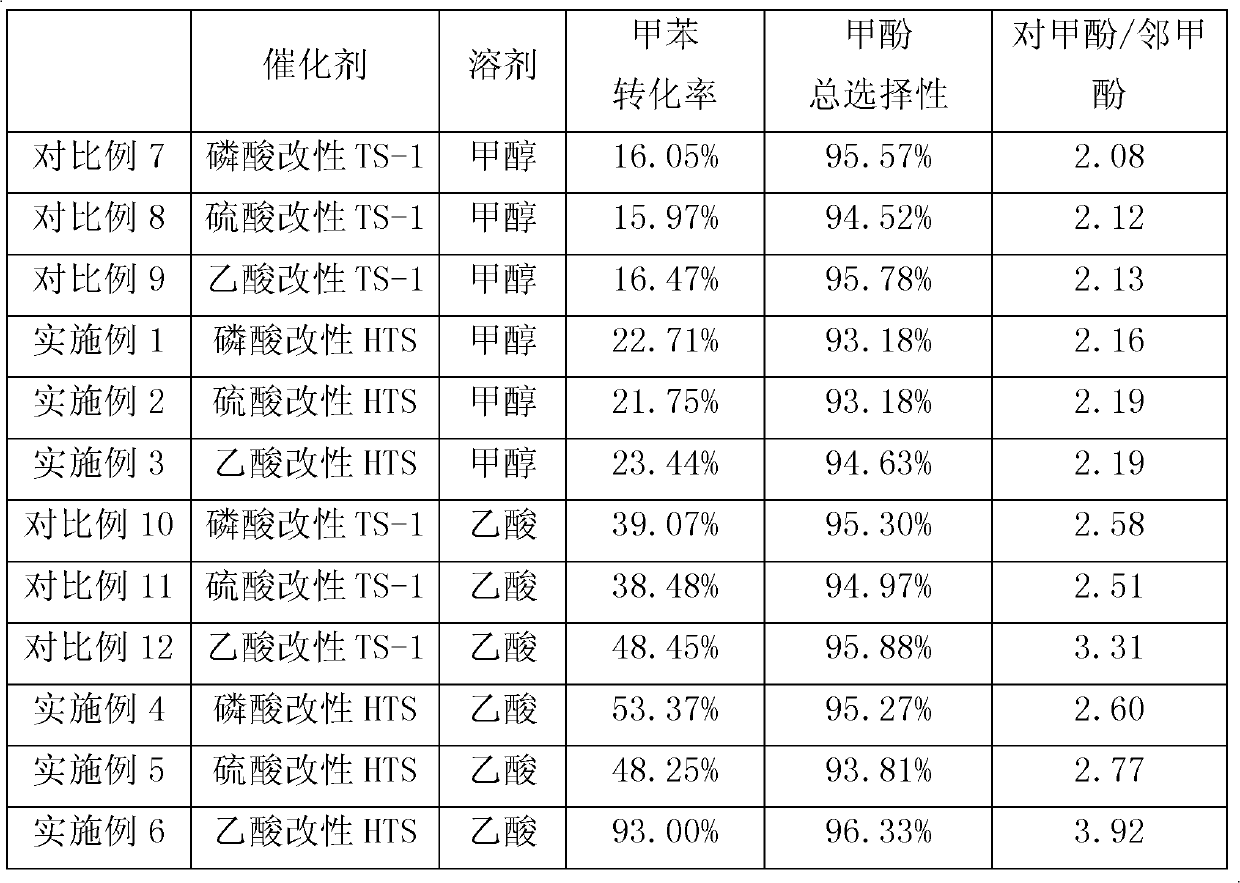
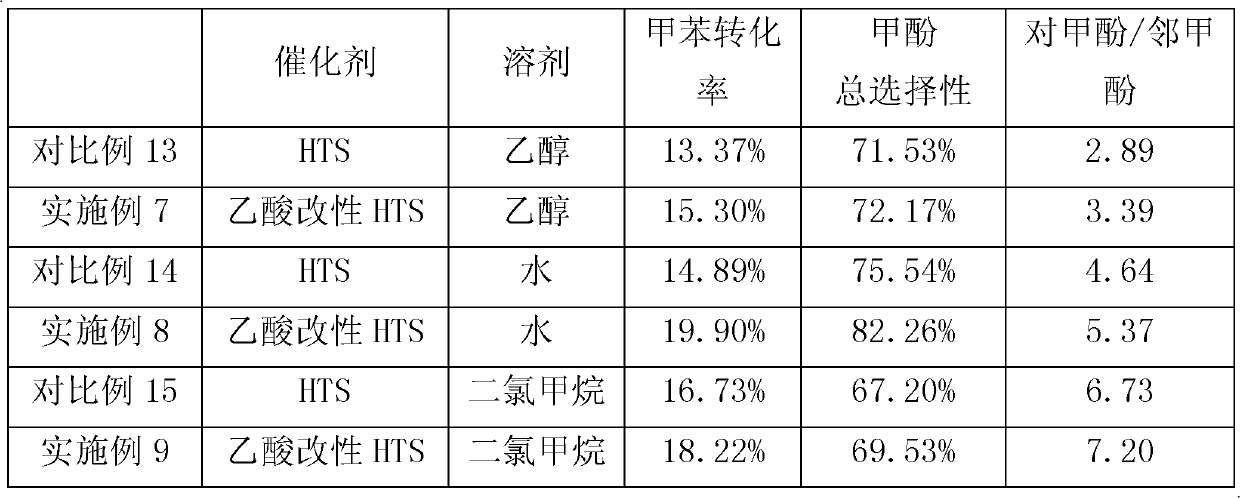
Method for preparing methylphenol by hydroxylating methylbenzene
ActiveCN103373903AGood choiceImprove conversion rateOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationMolecular sieveMean fluorescence intensity
The invention relates to a method for preparing methylphenol by hydroxylating methylbenzene. The method comprises the following step of: carrying out a contact reaction on the methylbenzene, a solvent, hydrogen peroxide and a catalyst under the hydroxylating reaction condition, wherein the catalyst contains a titanium-silicon molecular sieve in an MFI (Mean Fluorescence Intensity) structure. The method is characterized in that the titanium-silicon molecular sieve in the MFI structure is obtained through acid treatment. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high transformation ratio and good product selectivity and can obtain more para-products.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
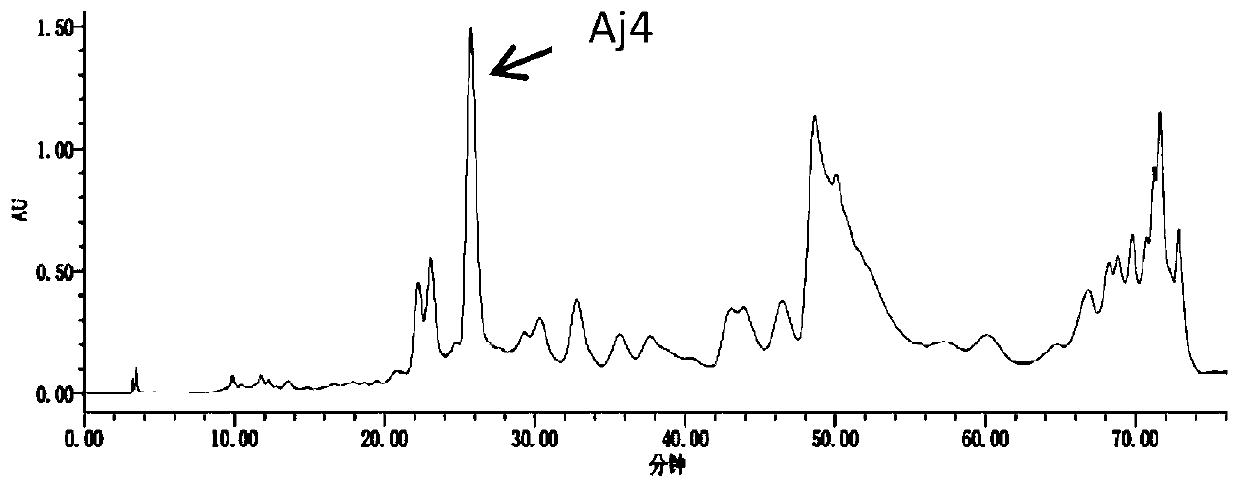
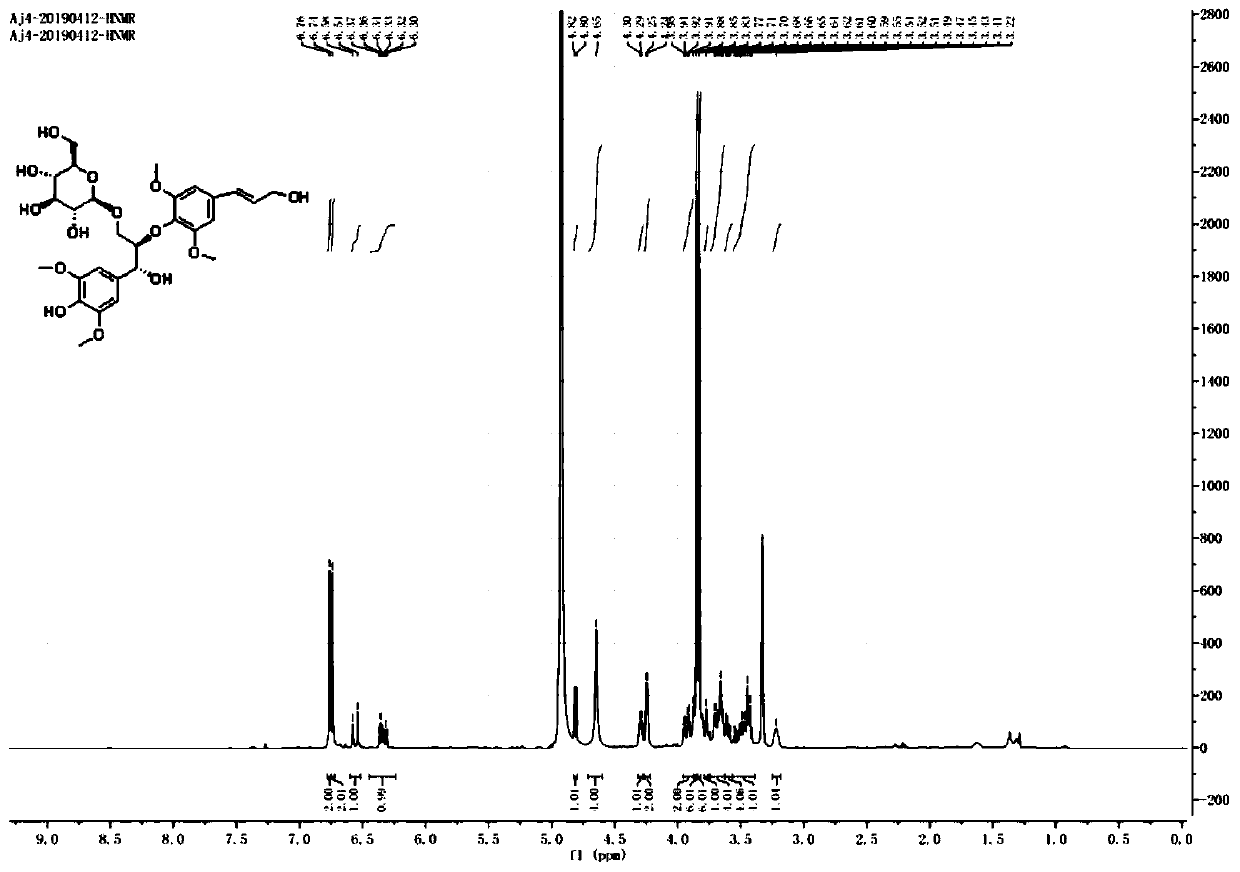
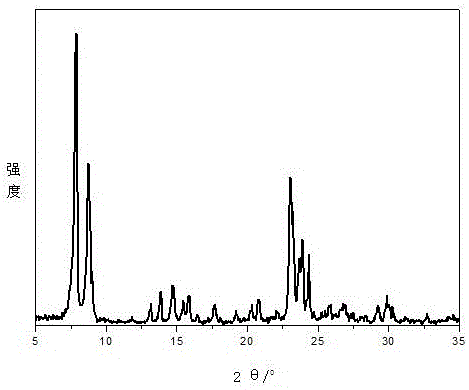
Preparation method of cortex albiziae neolignan monomeric compound
ActiveCN110563781ASugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationFluorescenceMean fluorescence intensity
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cortex albiziae neolignan monomeric compound and belongs to the technical field of biochemistry. The prepared compound can effectively treat FFAs-induced lipid metabolism disorder and fatty degeneration and can reduce the lipid droplet area by about 3 times at the administration concentration of 20 [mu] M 24 h after administration; the compound cansignificantly enhance cell viability of HUVEC and significantly promote self replication of cells so as to promote proliferation of endothelial cell HUVEC. The cell viability can reach 242.233% in control at the administration concentration of 40 [mu] M 24 h after administration. The prepared compound can remarkably inhibit HG-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) of the HUVEC cells and reduce the average flurescence intensity of an HG group to 176.36% from 818.37%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing cyclohexanone oxime under catalytic action of molecular sieve
InactiveCN105693551AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsOximes preparationMolecular sieveMean fluorescence intensity
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing cyclohexanone oxime catalyzed by molecular sieves. The catalyst has an MFI topological structure, and the molar ratio of Si / Ti is 20-200, the molar ratio of Si / B is 50-200, and the molar ratio of Si / Al is It is a molecular sieve of 50~300, and catalyzes cyclohexanone, ammonia and hydrogen peroxide liquid phase method to prepare cyclohexanone oxime. It is characterized in that, compared with the TS-1 molecular sieve with the same MFI topology, the catalyst of the present invention simultaneously introduces heteroatoms B and Al atoms into the MFI molecular sieve framework through crystallization synthesis, which is effective in catalyzing the ammoximation reaction of ketone compounds Among them, on the basis of maintaining a considerable level of activity and selectivity of the traditional TS-1 molecular sieve, it shows the effect of significantly improving the catalyst life. The further mechanism of action shows that due to the introduction of heteroatoms B and Al atoms into the framework of TS-1 molecular sieve, the obtained catalyst has the effect of significantly reducing the residual hydrogen peroxide in the system and obviously inhibiting the loss of Ti in the active center framework, resulting in a longer catalyst life. Significantly increased.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for detecting nitrofuran metabolites in animal-derived food through liquid-phase chip
InactiveCN103884837AEasy to operateEnable high-throughput detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiotin-streptavidin complexMetabolite
The invention provides a method for detecting nitrofuran metabolites in animal-derived food through a liquid-phase chip. The method comprises the steps of coupling four microspheres with different numbers with artificial antigens for nitrofuran metabolites such as AHD, SEM, AOZ and AMOZ to obtain coupled microspheres; performing biotin reaction on four AHD, SEM, AOZ and AMOZ monoclonal antibodies and a BNHS (biotin-hydroxysuccinimide) solution to obtain a biotin antibody; performing reaction on the nitrofuran metabolites, the coupled microspheres, the biotin antibody and streptavidin-phycoerythrin (SA-PE) to obtain liquid to be detected; finally detecting a mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) value of the reaction liquid, and performing data analysis. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously detecting the AHD, SEM, AOZ and AMOZ in the animal-derived food according to the specificity; furthermore, the whole process is simple to operate and is economical, practical, quick and accurate, and high-flux detection can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
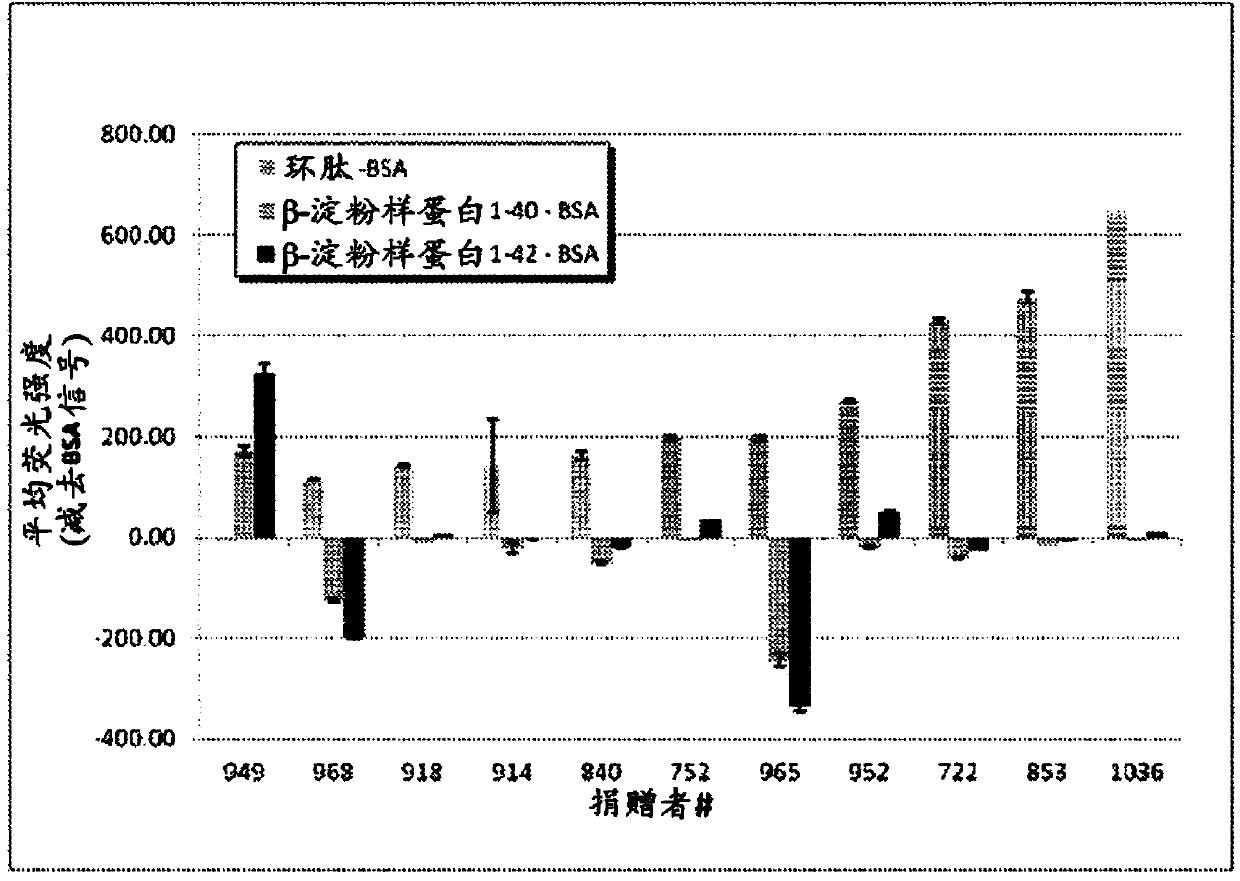
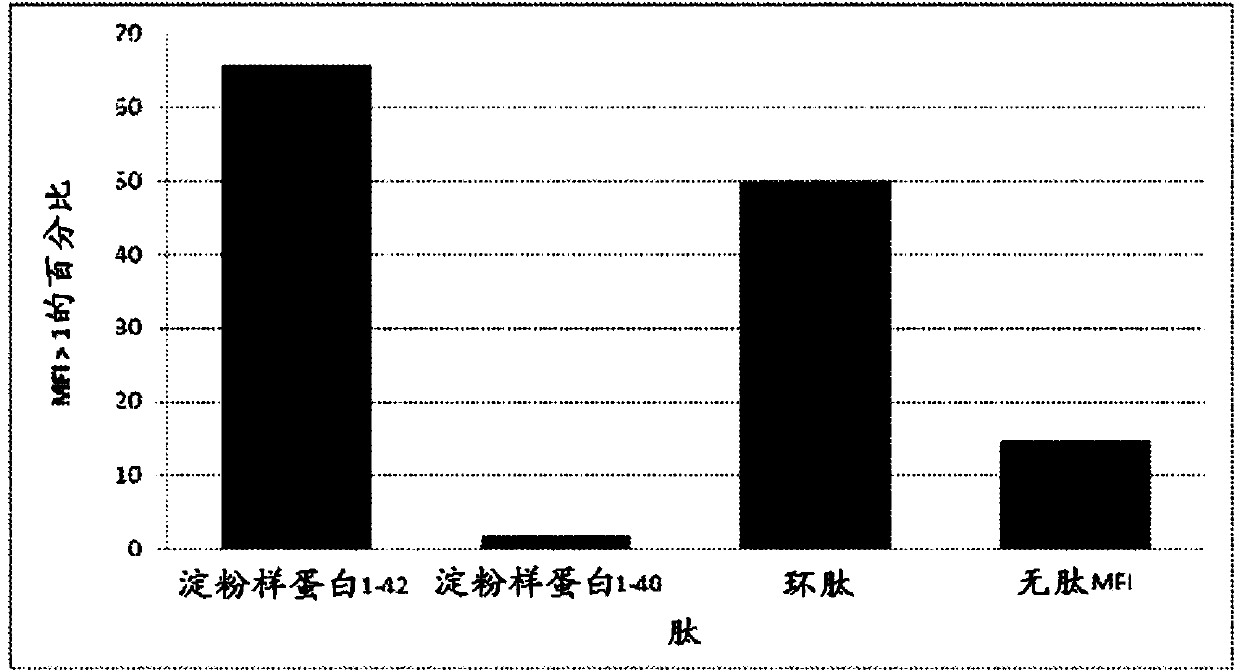
Compositions and methods for treating alzheimer's disease
The present disclosure provides for a hyperimmune preparation comprising human polyclonal antibodies or fragments thereof specific to a cyclic peptide having an amino acid sequence comprising SNK. The cyclic peptide may comprise an amino acid sequence GSNK (SEQ ID NO: 1 ), SNKG(SEQ ID NO: 2), GSNKG (SEQ ID N0:3), CSNKG (SEQ ID NO: 4), CGSNKGC (SEQ ID NO: 5), CGSNKGG (SEQ ID NO: 6), or CCGSNKGC (SEQ ID NO: 7). The antibodies in the hyperimmune preparation may have a titer ranging from about 200 to about 400 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). In one embodiment, greater than about 80% of the antibodies in the hyperimmune preparation are IgG. The fragments of the antibodies are Fab, F(ab')2, scFv, disulfide linked Fv, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:CANGENE U S +1
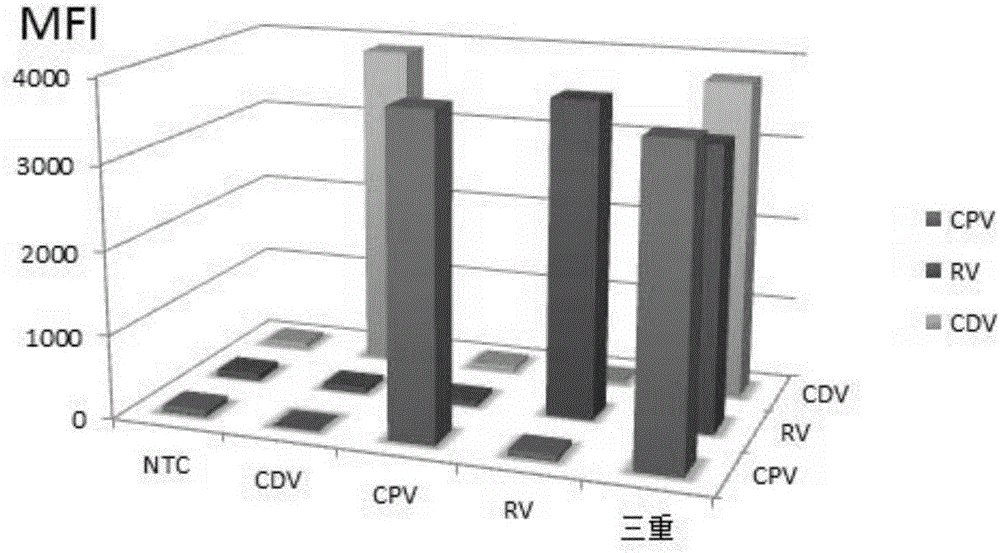
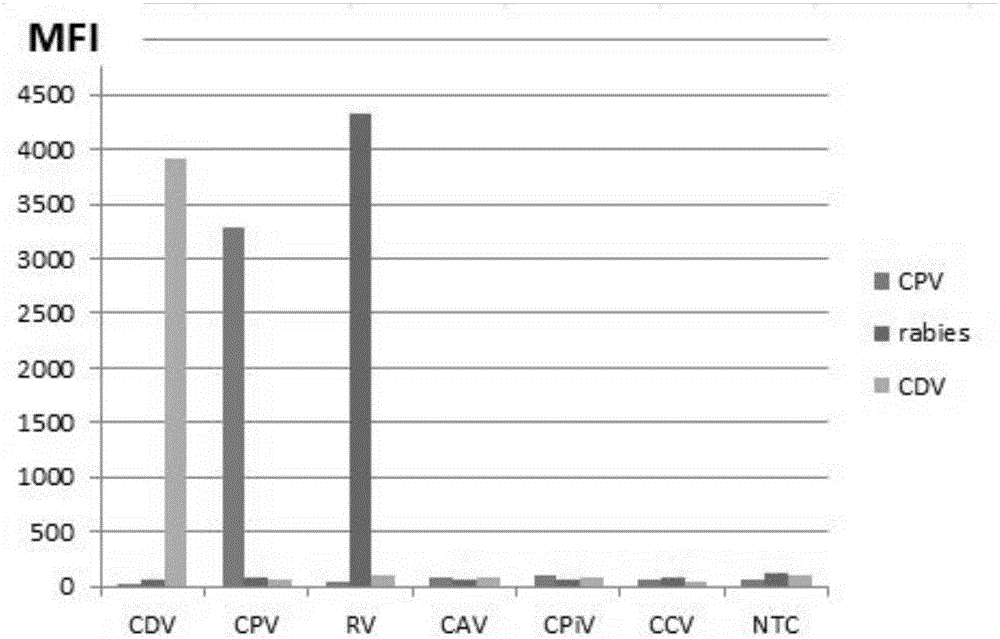
Multiple-FIA (fluorescence immunoassay) method and kit for quickly distinguishing CDV (canine distemper virus), CPV (canine parvovirus) and RV (rabies virus)
ActiveCN106319091AAccurate detectionReduce dosageMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicrosphereFluorescence
The invention discloses a multiple-FIA (fluorescence immunoassay) method and kit for quickly distinguishing CDV (canine distemper virus), CPV (canine parvovirus) and RV (rabies virus). The operation is simple, a target amplified fragment is obtained through a PCR (polymerase chain reaction), then an amplification product, fluorescence coded microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized, the MFI (mean fluorescence intensity) value is read through a detector, and different types of pathogens are distinguished. The method can be used for detecting and distinguishing the CDV, CPV and RV simultaneously, has the advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity, good repeatability and the like and can realize simultaneous detection of various different target molecules in the same sample. The method is good in flexibility, and the type of detected pathogens can be increased or decreased on the basis as required.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
Method for measuring three-way fluorescent resonance energy displace microscope G parameter
InactiveCN101042345ASmall standard errorGood precisionFluorescence/phosphorescenceSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy transferMean fluorescence intensity
This invention relates to one three-channel fluorescence calibration energy transfer microscope G parameter test method, which comprises the following steps: a, testing three-channel fluorescence vibration energy transfer microscope filter parameters; b using three channel vibration energy to transfer microscope to test CFP-YFP protein even intensity in the YFP and FRET channel; c, computing the G parameter. This invention measures the G parameters with small standard error with good accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com