Method and system for automatically recognizing rare cells
A rare cell and automatic identification technology, applied in the field of biomedical inspection, can solve the problems of too large smear area, weak expression of CTC-specific antibodies, and difficulty in manually finding CTCs, so as to improve the effect of staining and identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
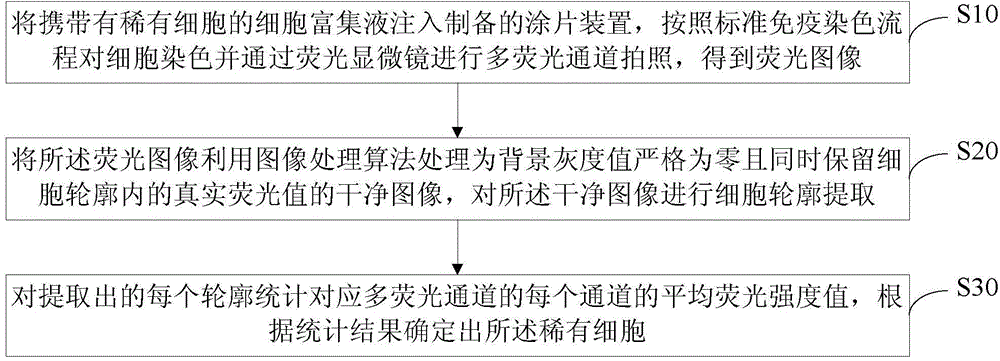
[0041] A schematic flowchart of a method for automatically identifying rare cells provided in this embodiment is shown in figure 1 As shown, it includes: injecting the cell enrichment solution containing rare cells into the prepared smear device, staining the cells according to the standard immunostaining process, and taking pictures of multi-fluorescence channels through a fluorescence microscope to obtain the image acquisition step S10 of the fluorescence image. The fluorescence image is processed into a clean image whose background gray value is strictly zero while retaining the true fluorescence value in the cell outline by using an image processing algorithm, and then the image processing step S20 of extracting the cell outline is performed on the clean image, and each extracted The profile statistics corresponds to the average fluorescence intensity value of each channel of the multi-fluorescent channels and the statistical identification step S30 of determining rare cell...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that, considering that the images obtained when the fluorescence scanning microscope performs multi-channel fluorescence scanning are usually very large, such as larger than 5G, the memory allocated to Matlab calculations is very limited, and it is difficult to process such a large image. The matrix is obviously very slow. Therefore, compared with Embodiment 1, in this embodiment, when performing the aforementioned image processing step S20, the fluorescence image is first divided into several small pictures, such as ensuring that each small picture is not greater than 30M, and Matlab searches for the loop according to the file name. Read in the small images and process them, that is, perform sub-steps such as background processing, binarization, and restore the initial value for each small image, and then splicing the output results of all the processed small images to obtain the corresponding original fluoresc...
Embodiment 3
[0062] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 or embodiment 2 is that after the clean image is obtained, a pseudo-color can be added to the clean image for manual observation. How to add the pseudo-color specifically can refer to the existing related technology implementation, which will not be described in detail here.
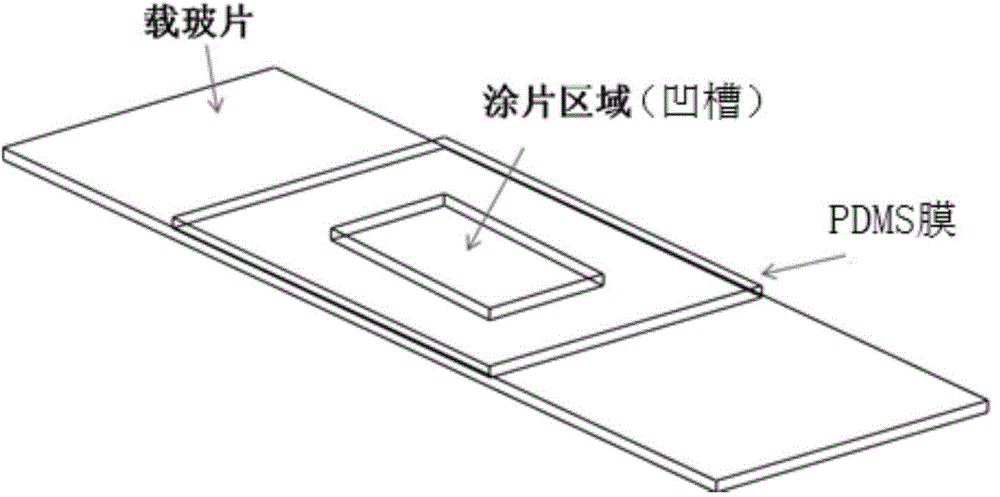
[0063]In summary, the method or system for automatically identifying rare cells provided by the present invention involves immunostaining of rare cells such as circulating tumor cells, image recognition, identification and counting, and by designing grooves in PDMS smears, it avoids rare cells The loss during the staining operation can also facilitate the setting of the scanning area to prevent cells from being missed due to unscanned cells; the background of the cell fluorescence image after background processing in the image recognition part is very clean, the background fluorescence value is strictly zero, and the cell outline The original...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com