Patents
Literature
37 results about "Transcription Repressor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
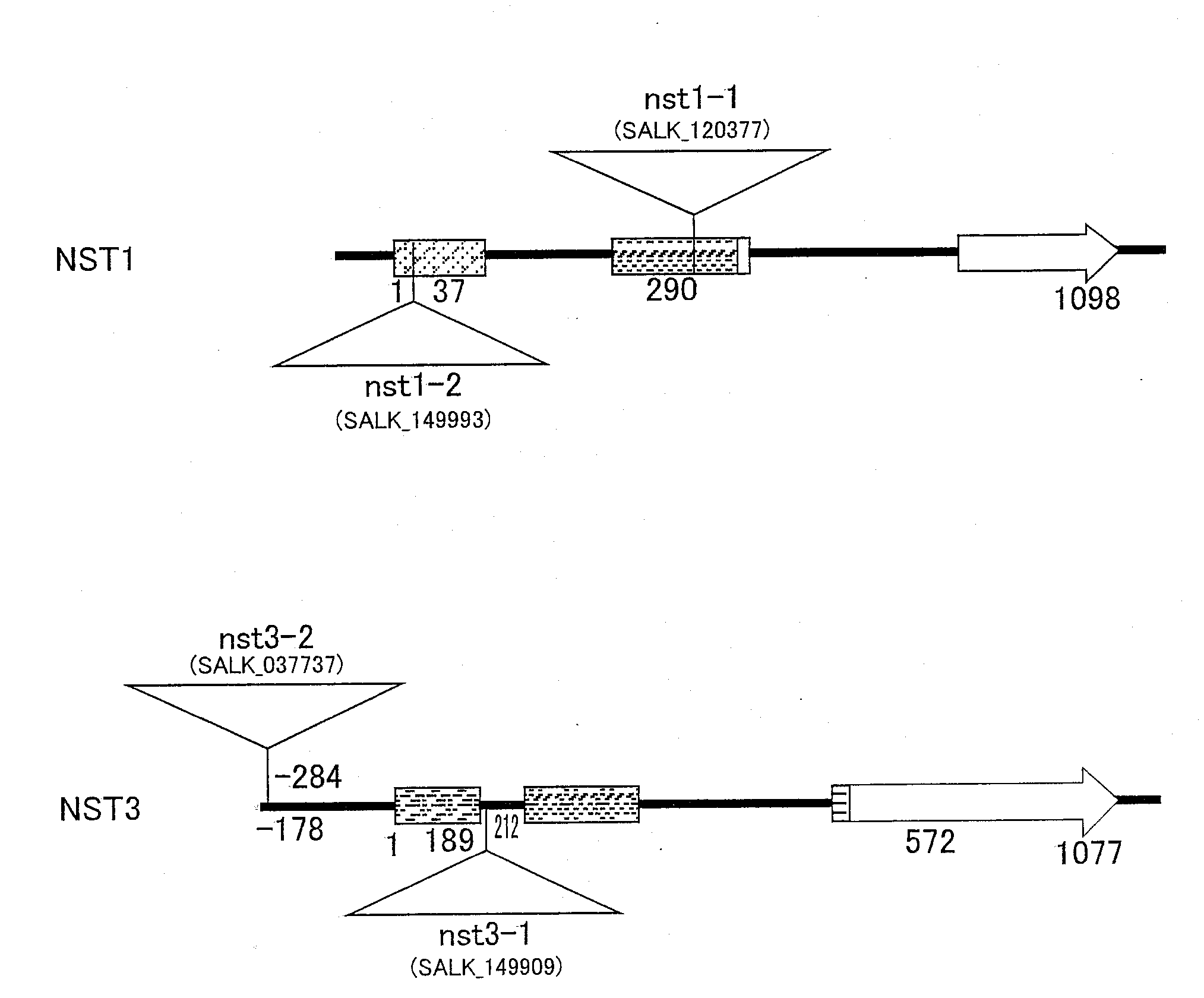
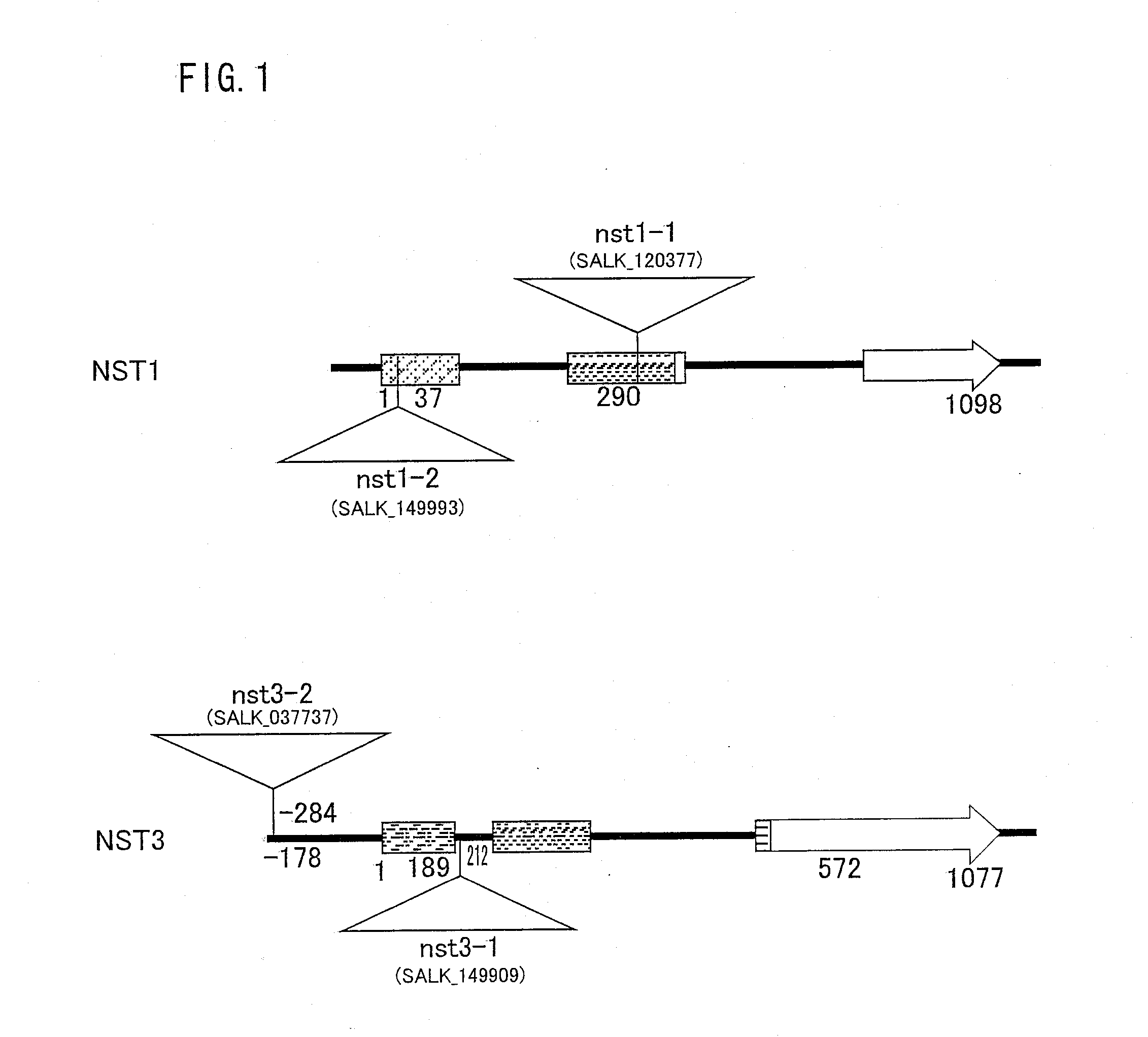
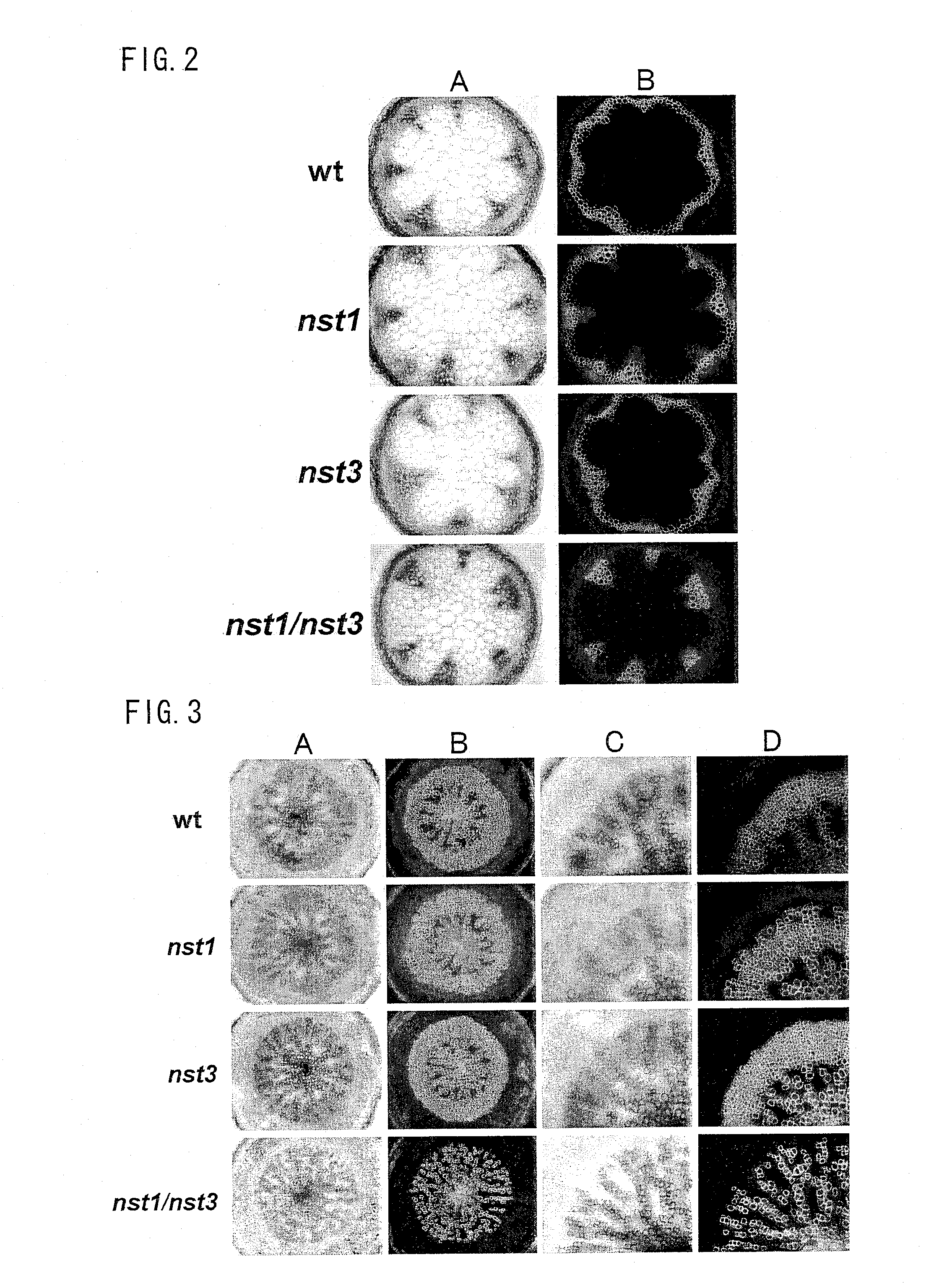
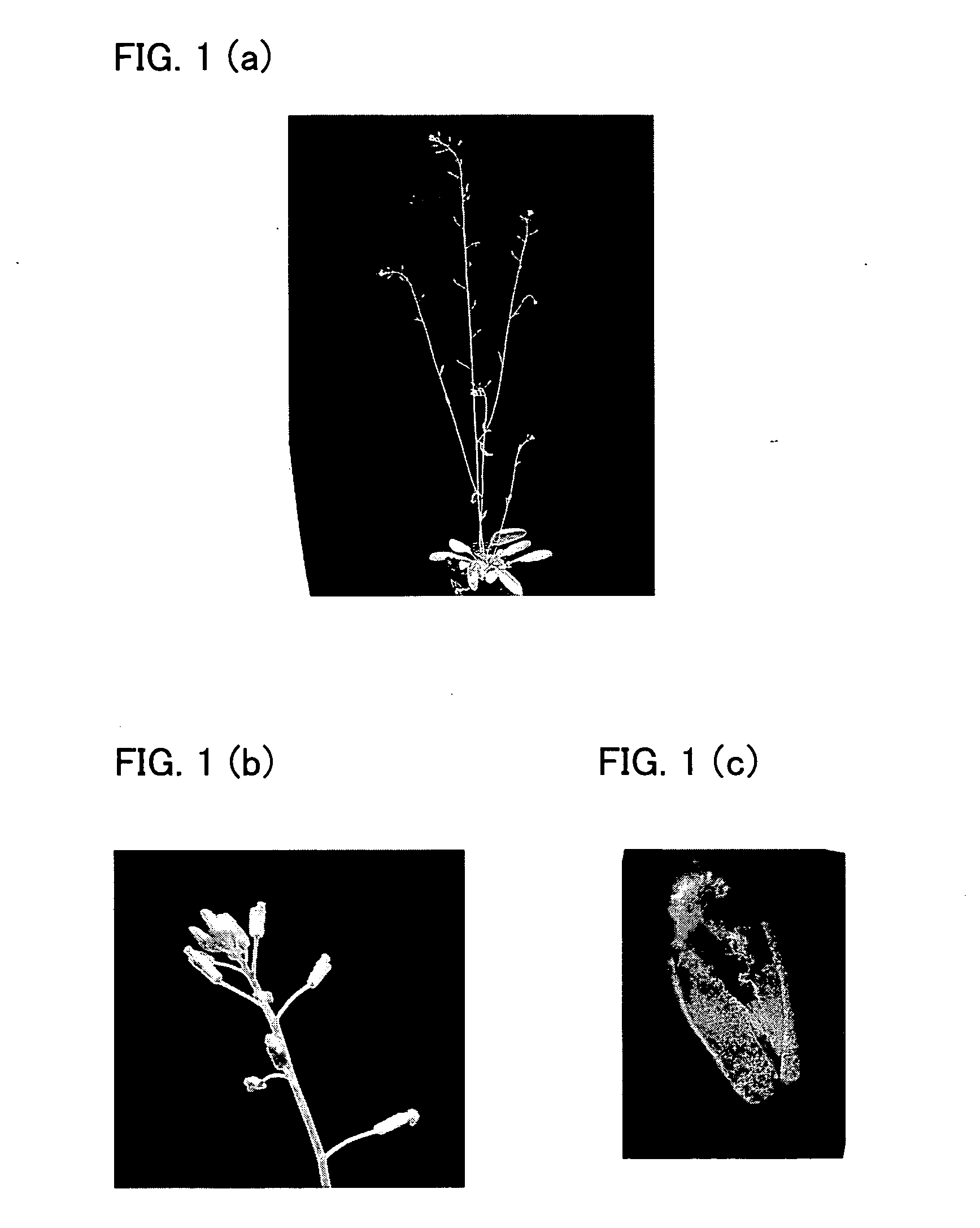
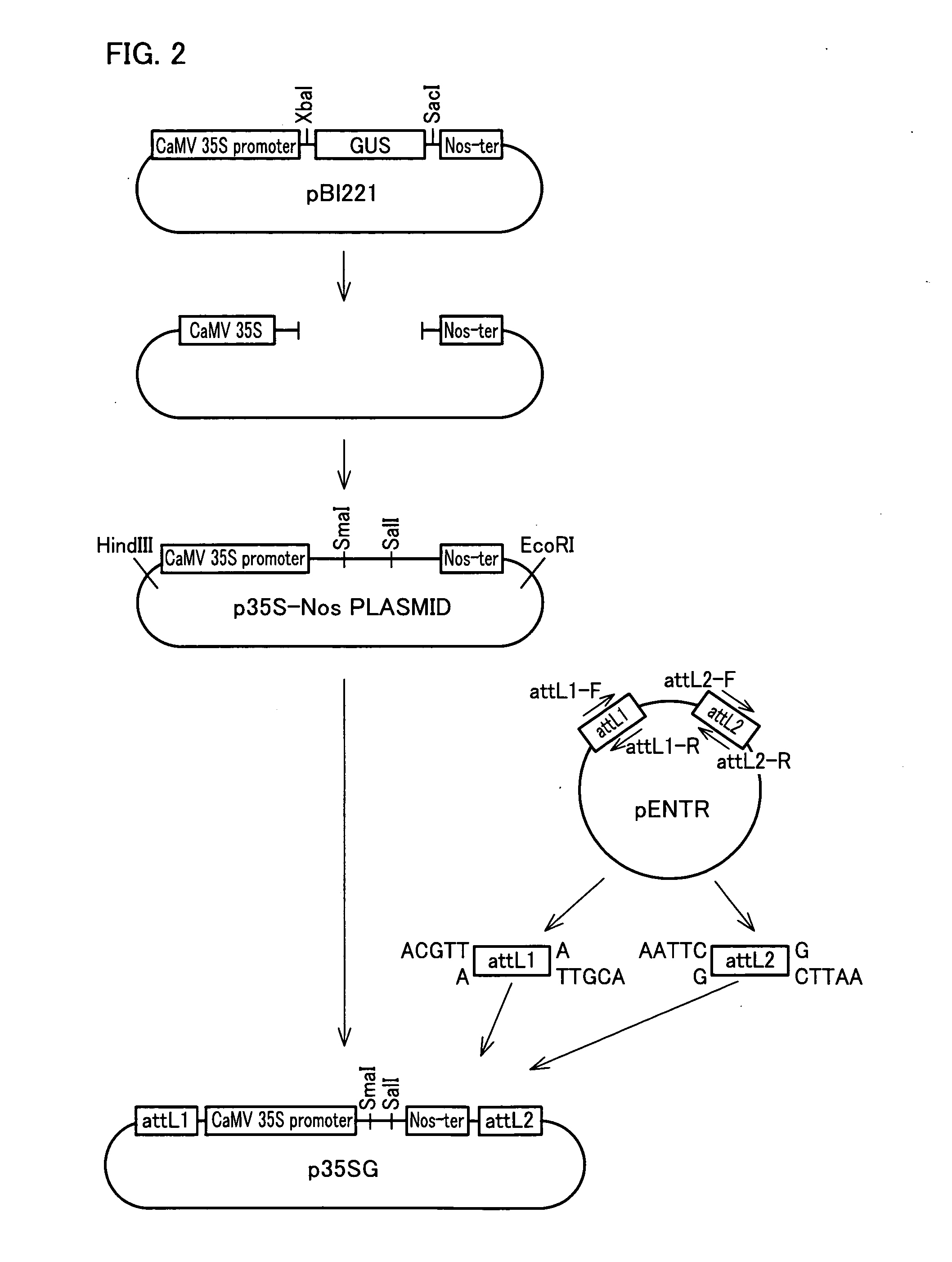
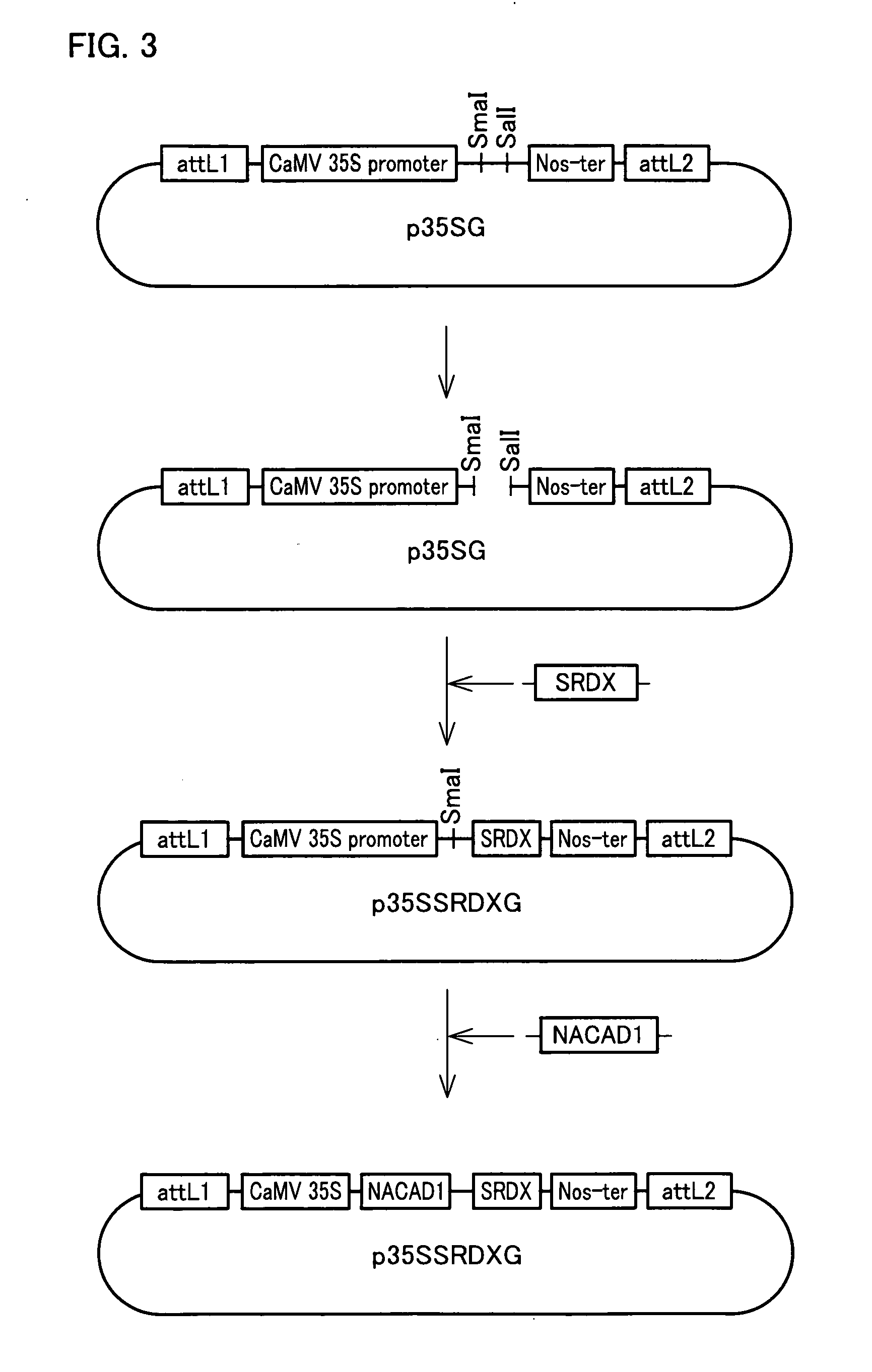
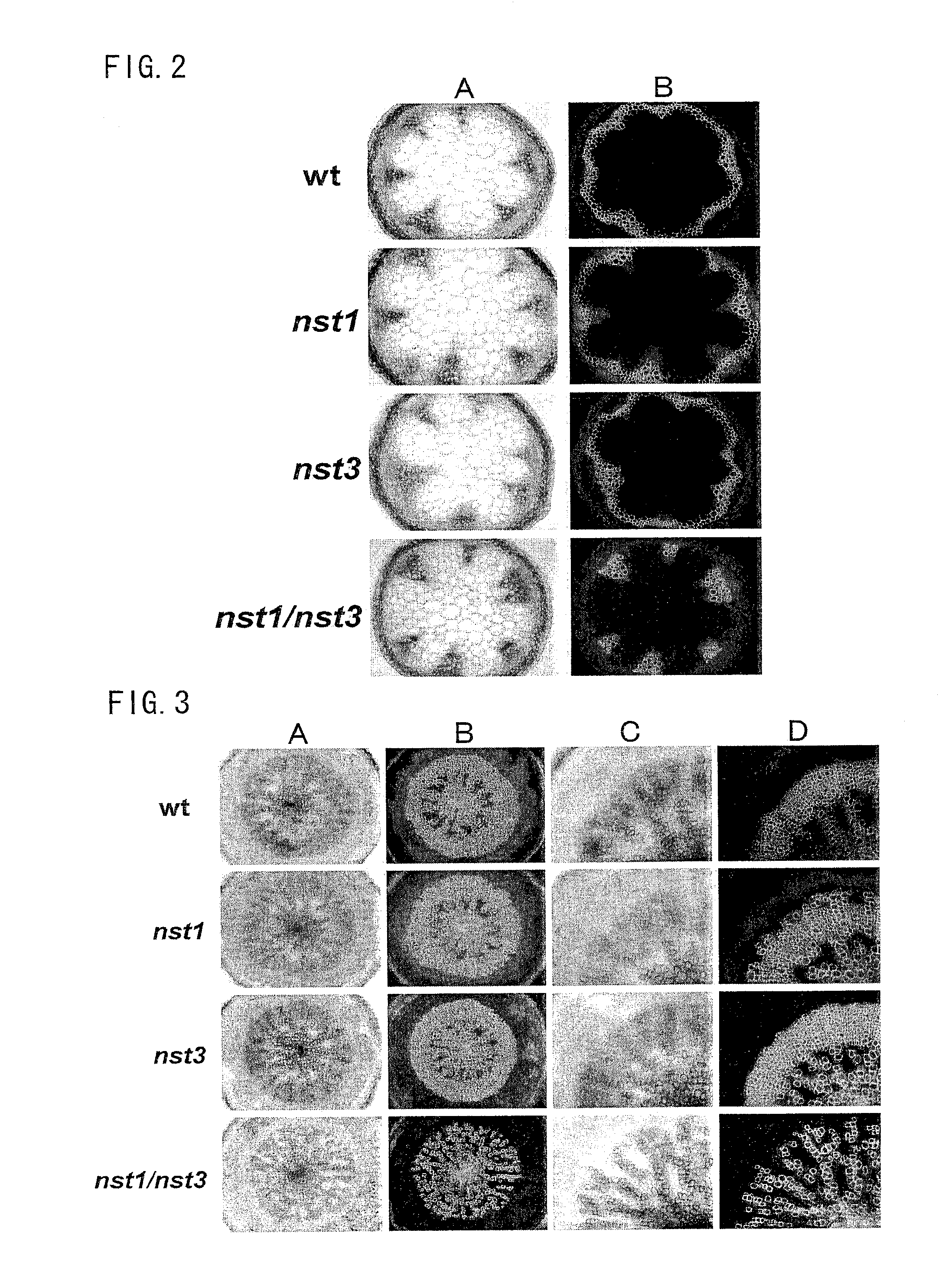
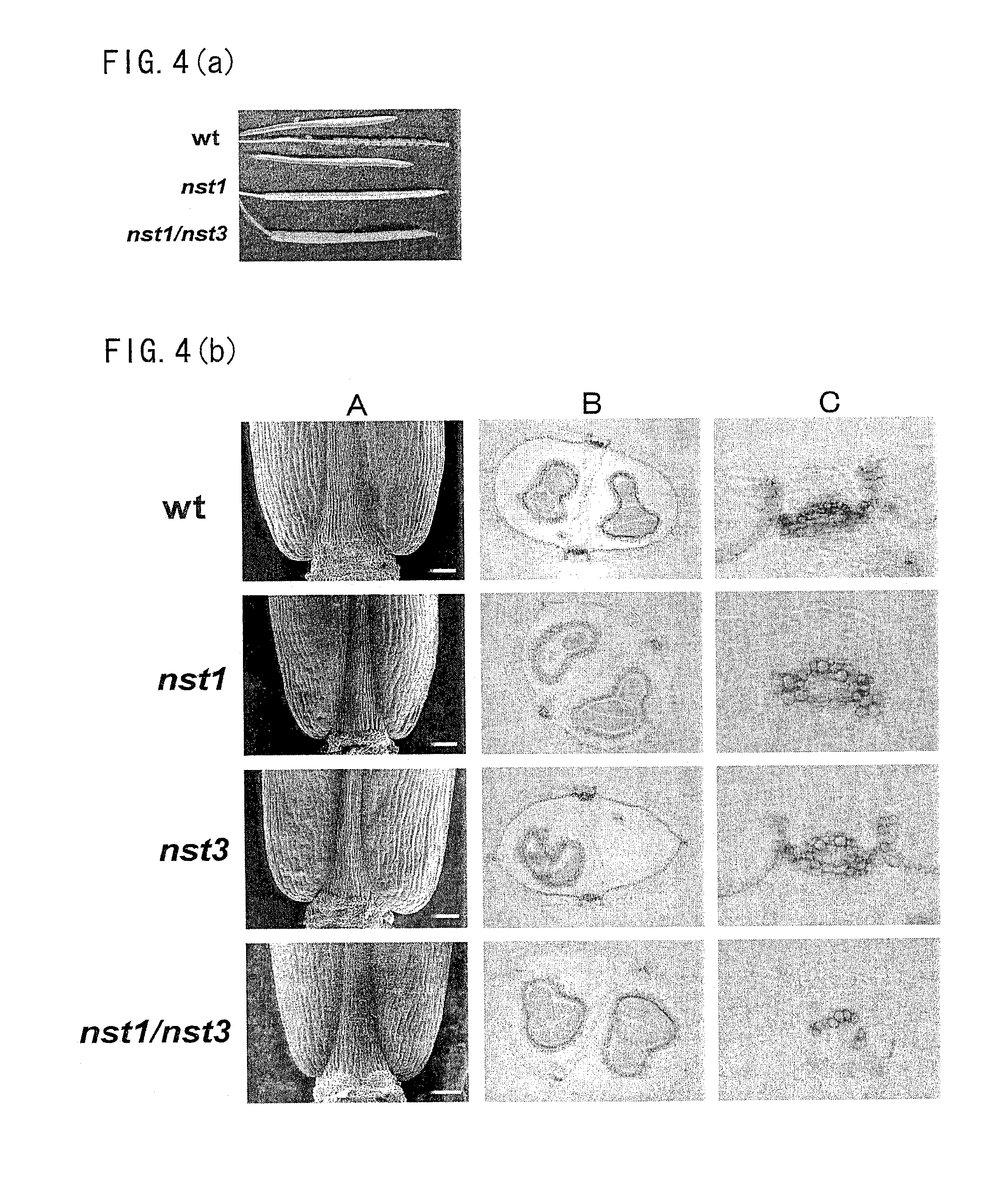
Plant having reduced lignin and cellulose contents without reducing glucan content, method of producing the same and utilization thereof
InactiveUS20090019605A1Reduce the amount of solutionSuppress transcriptionBryophytesSugar derivativesCelluloseNucleotide
By inhibiting the function of a transcription factor that promotes transcription of a gene associated with the amounts of lignin and cellulose, a plant in which the amounts of lignin and cellulose are reduced without reducing the amount of glucan is produced. In this plant, glucan in the obtained cell wall components is in the state of highly easily undergoing saccharification. In this plant, moreover, natural dehiscence of pods is suppressed. A method of inhibiting the transcription factor includes a method in which a chimeric gene between a transcription factor gene and a polynucleotide that encodes a functional peptide capable of converting the transcription factor into a transcription repressor is introduced into a plant cell so that a chimeric protein in which the transcription factor is fused with the functional peptide is produced in a plant cell, and a method of inhibiting the expression of the transcription factor, such as knockout method or RNAi method. Thus, a plant in which the amounts of lignin and cellulose are reduced without reducing the amount of glucan is provided.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Producing process of sterile plants, plants obtained by the process, and use of the plants
InactiveUS20110099664A1Suppress transcriptionReliable and easy to produceOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationDouble-floweredPlant cell
Transcription of a gene associated with formation of floral organs is suppressed to produce a sterile plant. A plant cell is transfected with a chimeric gene that includes (i) a coding gene of a transcription factor that promotes expression of a gene associated with formation of floral organs, and (ii) a polynucleotide that encodes a functional peptide that converts an arbitrary transcription factor into a transcription repressor, and a chimeric protein in which the transcription factor is fused with the functional peptide is expressed in the plant cell. The expression of the gene associated with formation of floral organs is dominantly suppressed by the chimeric protein, and as a result a male sterile plant is produced that cannot properly form pollen. The chimeric protein also suppresses expression of a gene associated with dehiscence of anther, and as a result a plant is produced in which dehiscence of anther is suppressed. Further, the chimeric protein suppresses expression of target genes of a transcription factor associated with formation of stamen and pistil, and as a result a double flowered plant is produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Nephropathy-associated gene
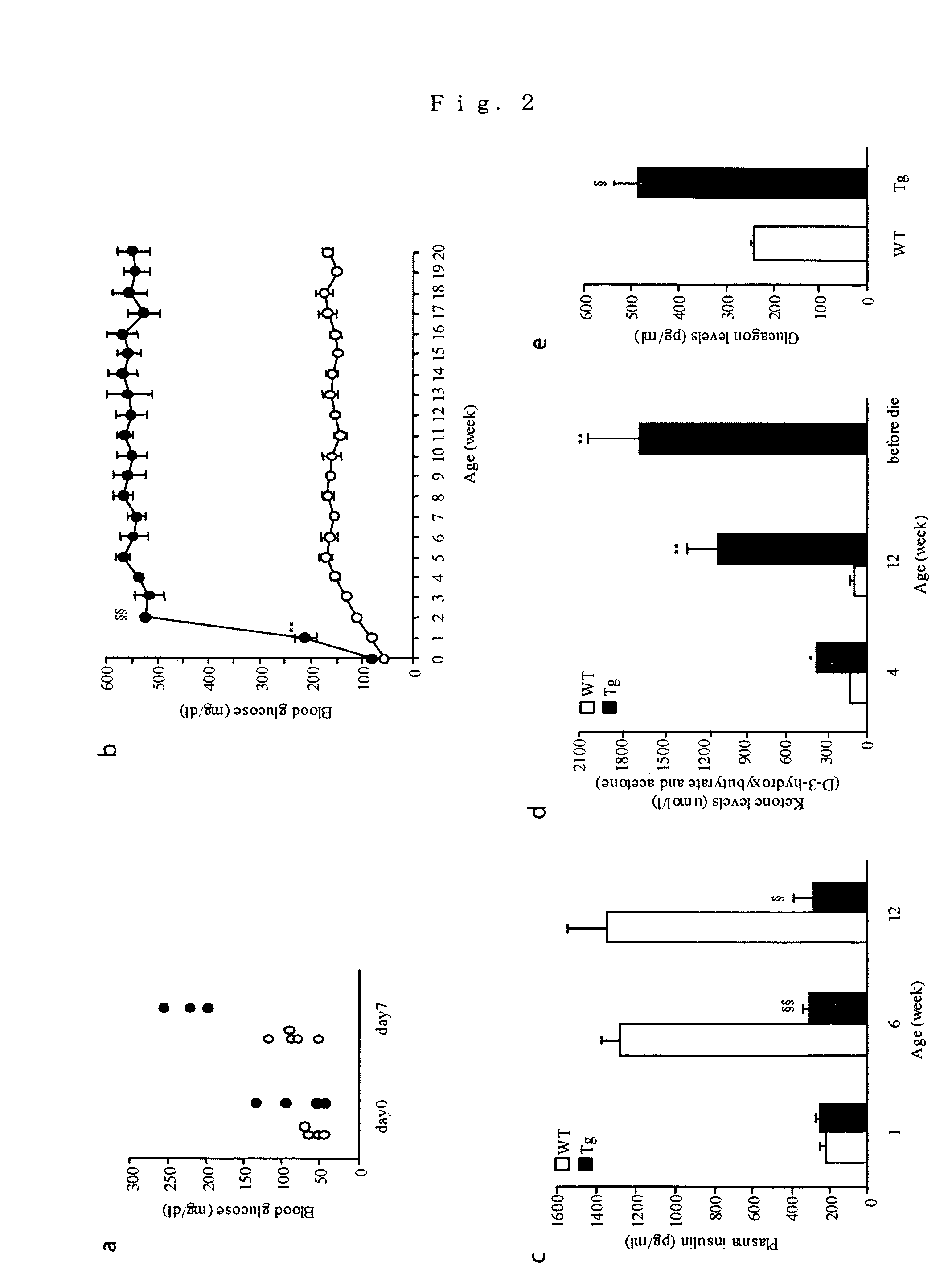
A nephropathy-associated gene which encodes a transcription repressor; and a nonhuman transgenic animal suffering from nephropathy which is constructed by transferring the above gene and allows the observation of increases in urinary volume, urinary albumin and urinary NAG, pyelectasis, enlargement in kidney tubule and glomerular swelling at the early stage and the following sclerosis.
Owner:INADA AKARI +1
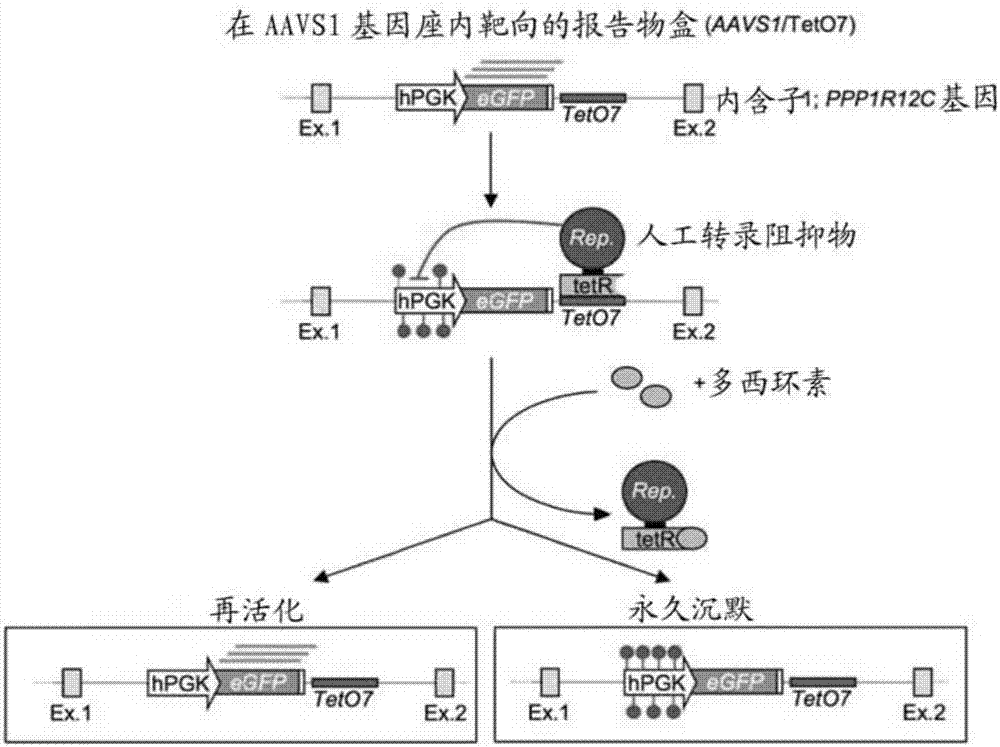
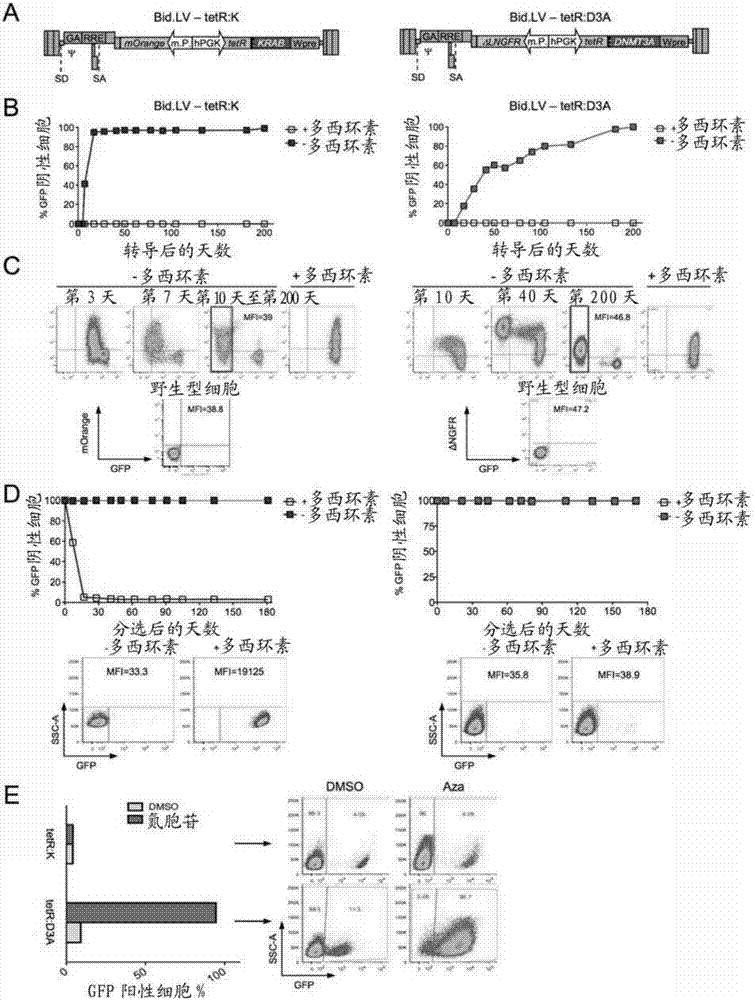
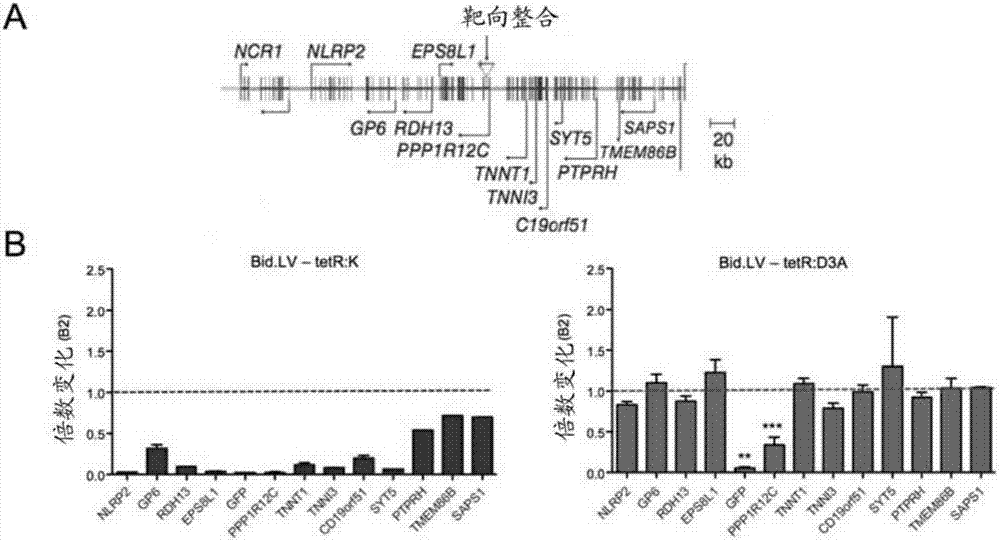
Permanent Epigenetic Gene Silencing
PendingUS20190032049A1Alternative splicing of a target gene may be alteredFusion with DNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideTranscription Repressor
A product comprising two or more artificial transcription repressors (ATRs), or polynucleotides encoding therefor, selected from groups (a), (b), (c) or (d): (a) an ATR comprising a DNA-binding domain operably linked to a KRAB domain or homologue thereof; (b) an ATR comprising a DNA-binding domain operably linked to a DNMT3A, DNMT3B or DNMT1 domain or homologue thereof; (c) an ATR comprising a DNA-binding domain operably linked to a DNMT3L domain or homologue thereof; and (d) an ATR comprising a DNA-binding domain operably linked to a SETDB1 domain or homologue thereof, wherein at least two of the ATRs are selected from different groups (a), (b), (c) or (d).
Owner:OSPEDALE SAN RAFFAELE SRL +1
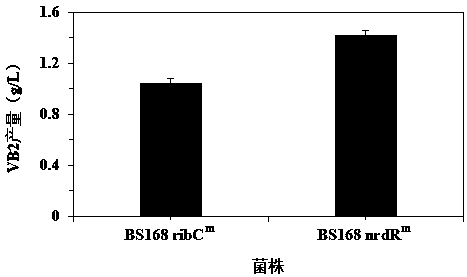
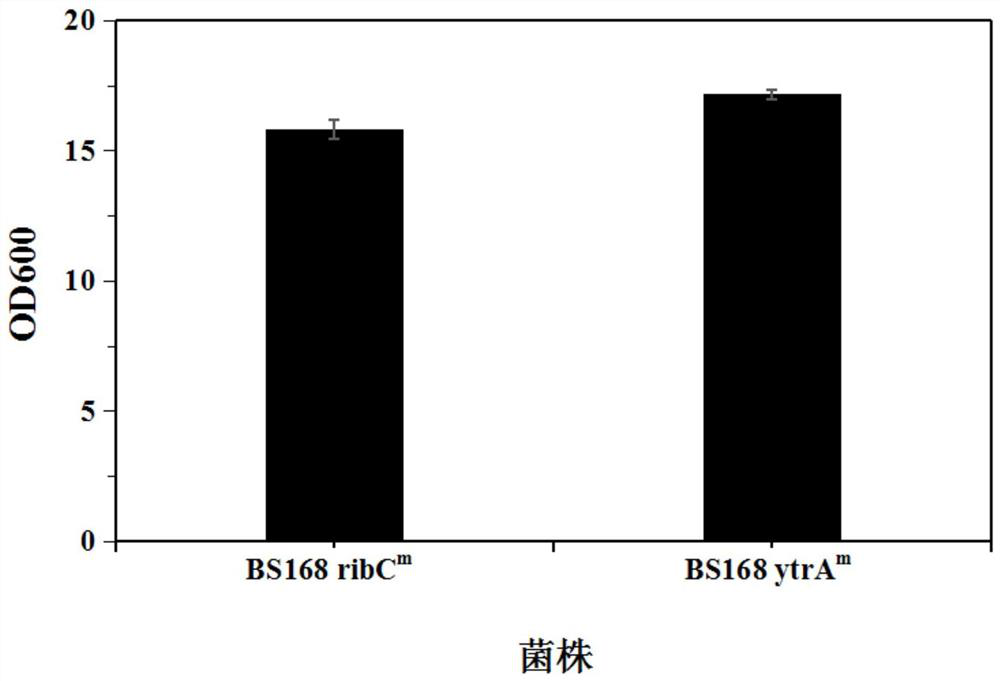
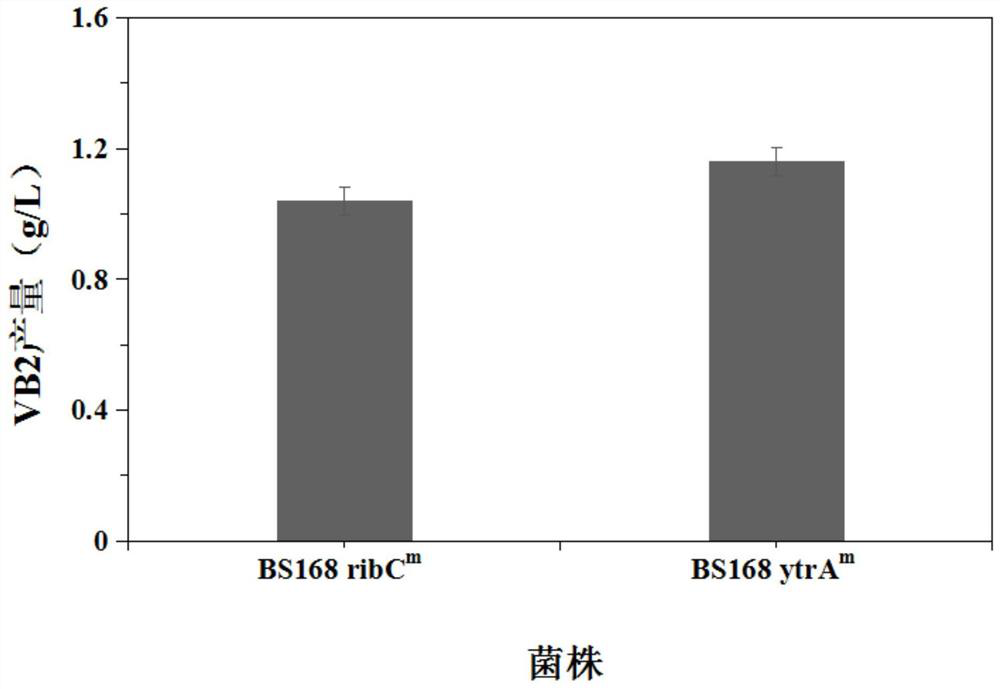
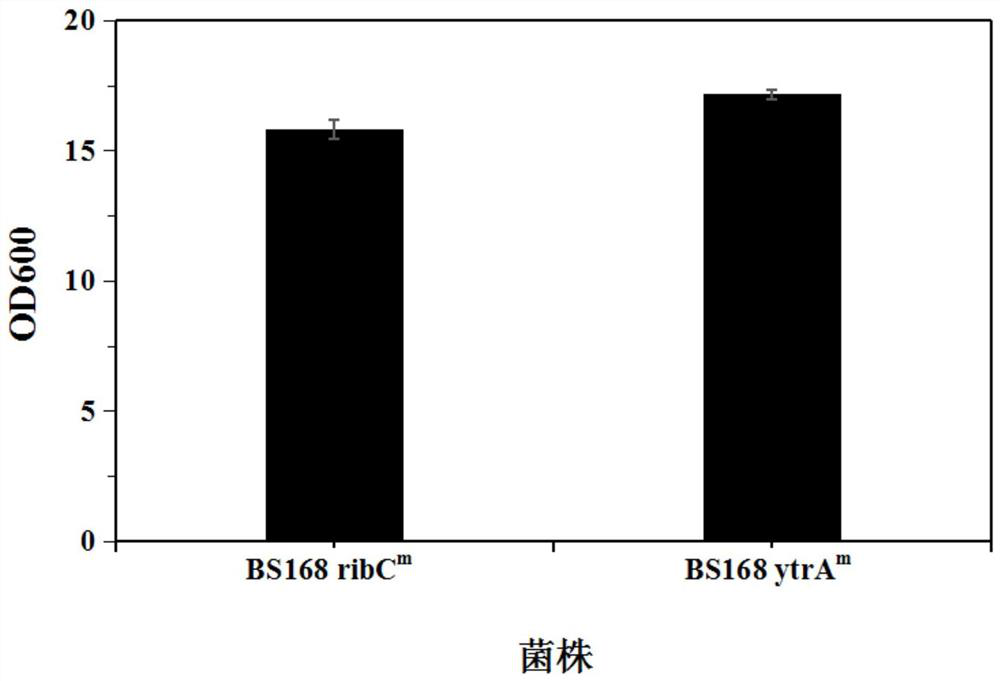
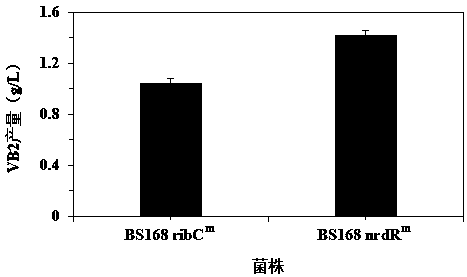
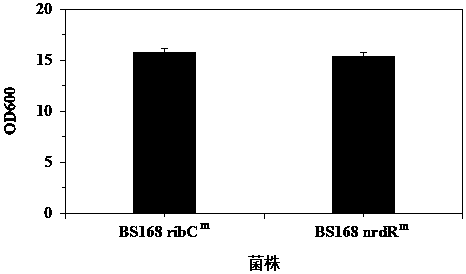
Ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant, mutation gene and application of ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant and mutation gene to preparation of vitamin B2
The invention discloses a ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant, a mutation gene and an application of the ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant andthe mutation gene to preparation of vitamin B2. The amino acid sequence of the mutant is subjected to the following mutation relative to the sequence as shown in SEQID No.3; and an amino acid at the26th site is replaced with H. For the nucleotide fixed point mutation that the amino acid at the 26th site, coded in the ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor gene on a bacillus subtilis chromosome is replaced with H, a genetic engineering bacterium is obtained, and the capacity for producing the vitamin B2 is greatly improved. The ribonucleoside reductase transcription inhibition factor mutant has great application and extension value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of producing sterile plant, plant obtained by using the same and use thereof
Transcription of a gene associated with formation of floral organs is suppressed to produce a sterile plant. A plant cell is transfected with a chimeric gene that includes (i) a coding gene of a transcription factor that promotes expression of a gene associated with formation of floral organs, and (ii) a polynucleotide that encodes a functional peptide that converts an arbitrary transcription factor into a transcription repressor, and a chimeric protein in which the transcription factor is fused with the functional peptide is expressed in the plant cell. The expression of the gene associated with formation of floral organs is dominantly suppressed by the chimeric protein, and as a result a male sterile plant is produced that cannot properly form pollen. The chimeric protein also suppresses expression of a gene associated with dehiscence of anther, and as a result a plant is produced in which dehiscence of anther is suppressed. Further, the chimeric protein suppresses expression of target genes of a transcription factor associated with formation of stamen and pistil, and as a result a double flowered plant is produced.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
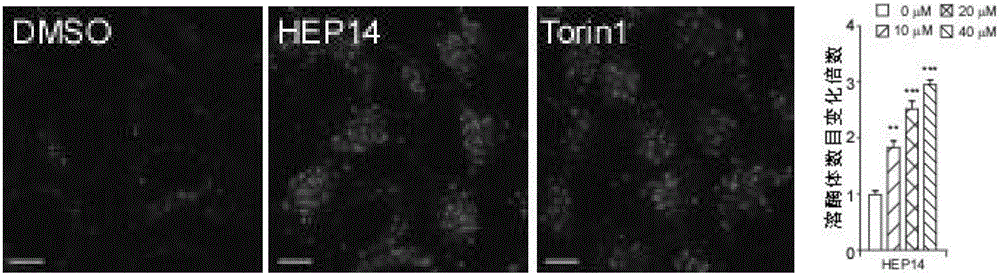
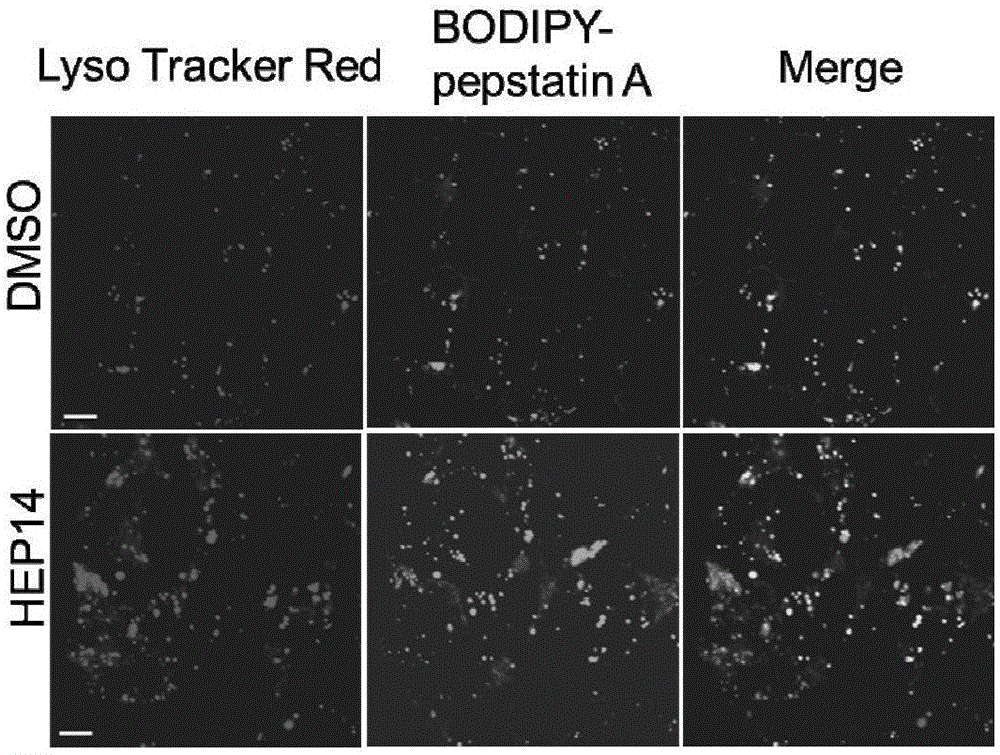
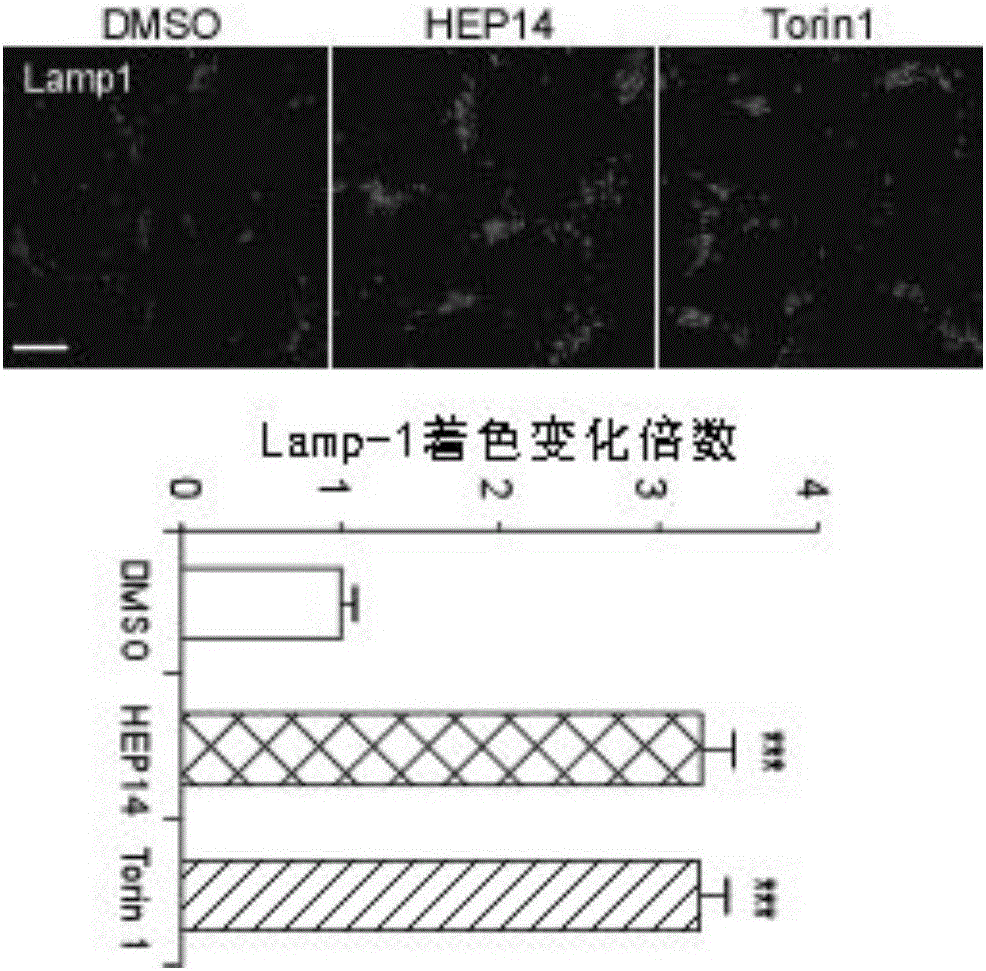
Ingenol and application of derivative of ingenol in enhancement of generation of lysosome
ActiveCN106619600AInterfering with metabolic balanceNervous disorderEster active ingredientsFunctional disturbanceDisease
The invention discloses ingenol and application of a derivative of ingenol in enhancement of generation of lysosome. The application specifically comprises optional application of HEP14 or the derivative thereof in the following applications: induction of generation of the lysosome; preparation of drugs for induction of generation of the lysosome; and preparation of drugs for treating and / or preventing lysosome functional disturbance related diseases. HEP14 can activate PKC alpha and PKC delta, on one hand, transcription factors TFEB are activated through two parallel signal pathways, and on the other hand, transcription inhibitors are inactivated and are finally used as 'molecular switches' to control generation of the lysosome. Activation of PKC causes inactivation of GSK3 beta, then transfer of TFEB dephosphorylation to cell nucleus is caused, meanwhile, PKC which is in an activated state can further activate MAPK kinase JNK2 and p38 and phosphorylate ZKSCAN3, and ZKSCAN3 can be transferred to cytoplasm from cell nucleus. HEP14 does not affect activity of mTORC1, therefore, cell metabolism balance is not disturbed, and the ingenol is a perfect drug for treating lysosome related diseases possibly.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
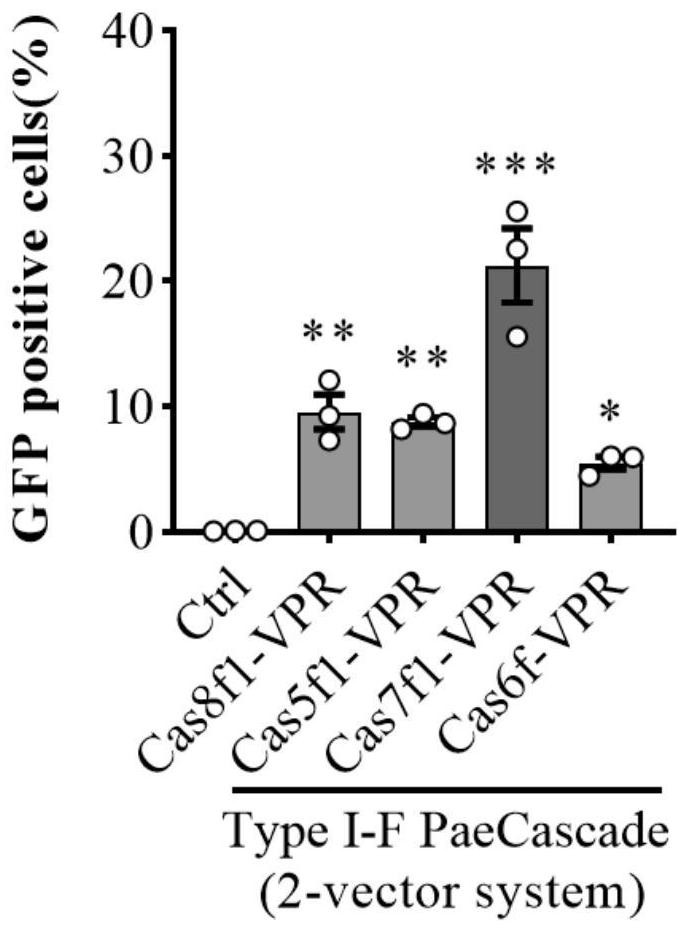
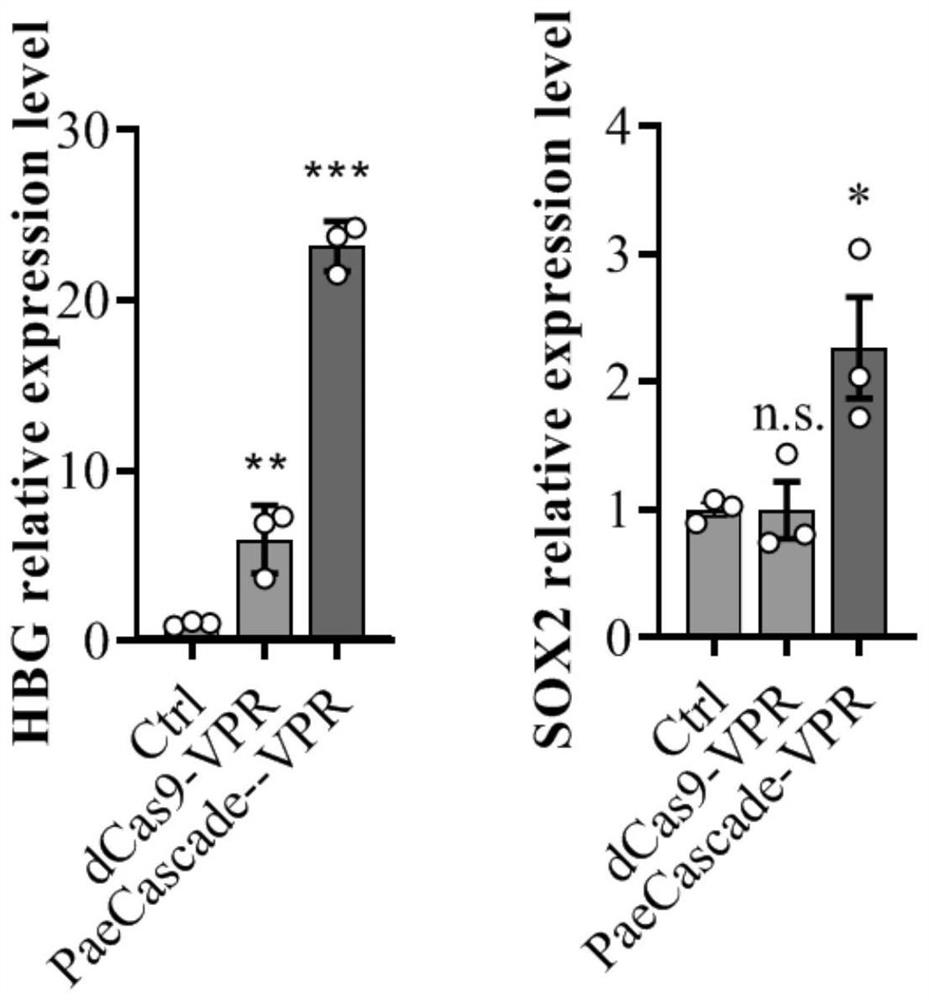
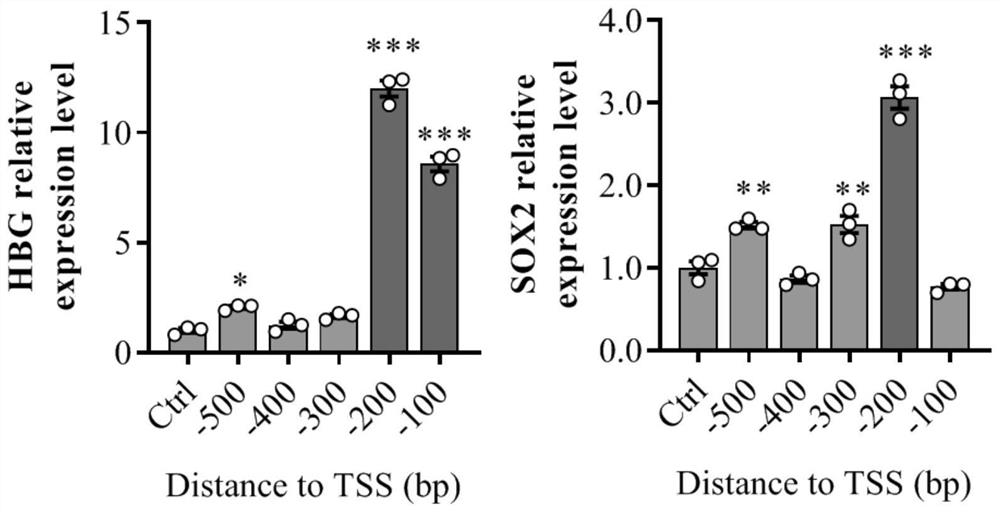
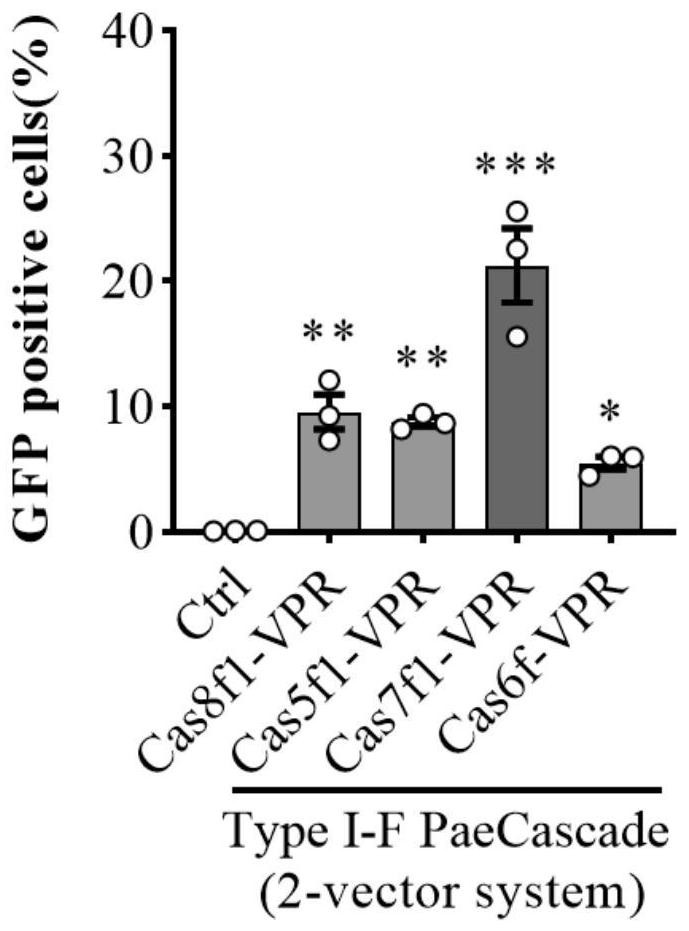
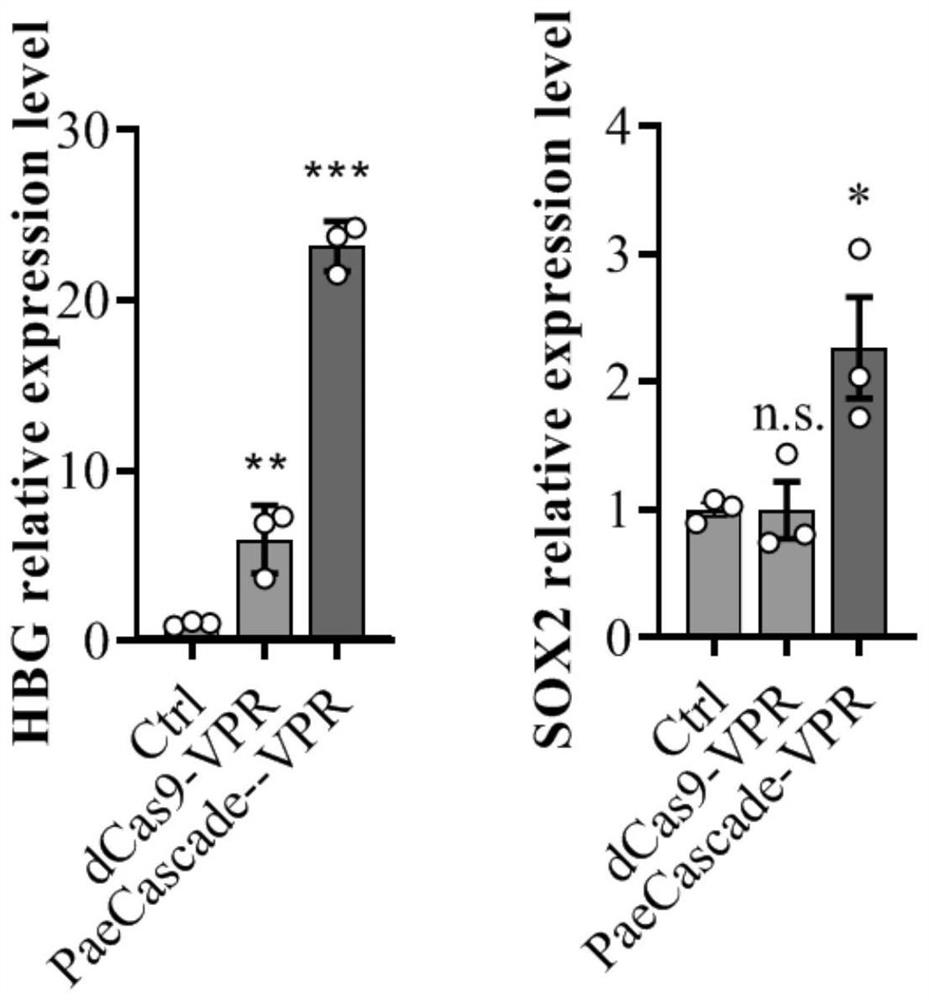
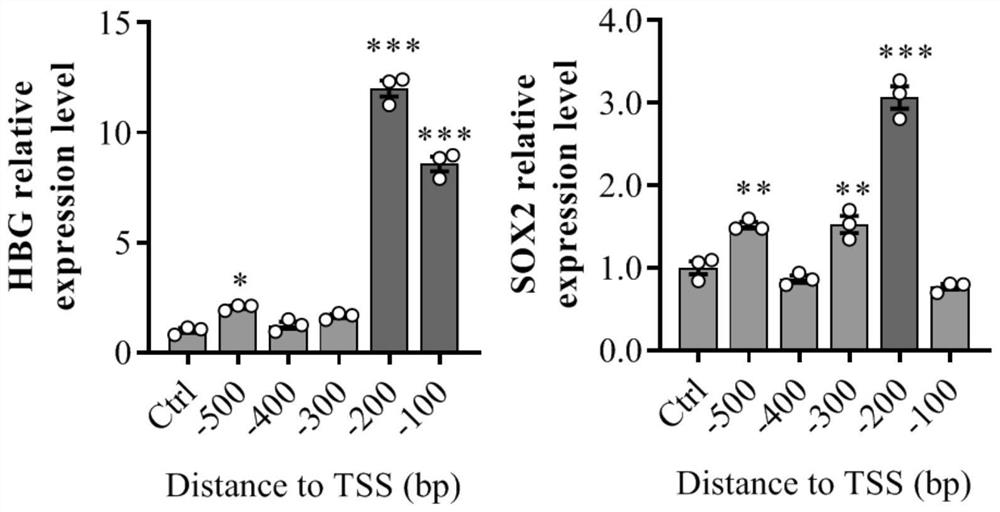
Gene expression regulation and control method and system based on Type I-F CRISPR/ Cas
ActiveCN111979240AHave binding activityHigh expressionHydrolasesStable introduction of DNARegulation of gene expressionTranscription Repressor
The invention discloses a gene expression regulation and control method and system based on Type I-F CRISPR / Cas. The first study shows that a Cascade compound, such as a PaeCascade compound, belonging to a Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system can be efficiently combined with a target site in a mammalian cell; and meanwhile, the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system is subjected to mammalian expression system optimization, so that a transcription activation factor or a transcription inhibition factor can be efficiently recruited to the target site in the mammalian cell, and a transcription activation system anda transcription inhibition system are successfully constructed. The application of the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system in the aspect of gene regulation and control of the mammalian cell becomes possible,and a necessary tool is provided for gene transcription regulation and control based on the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
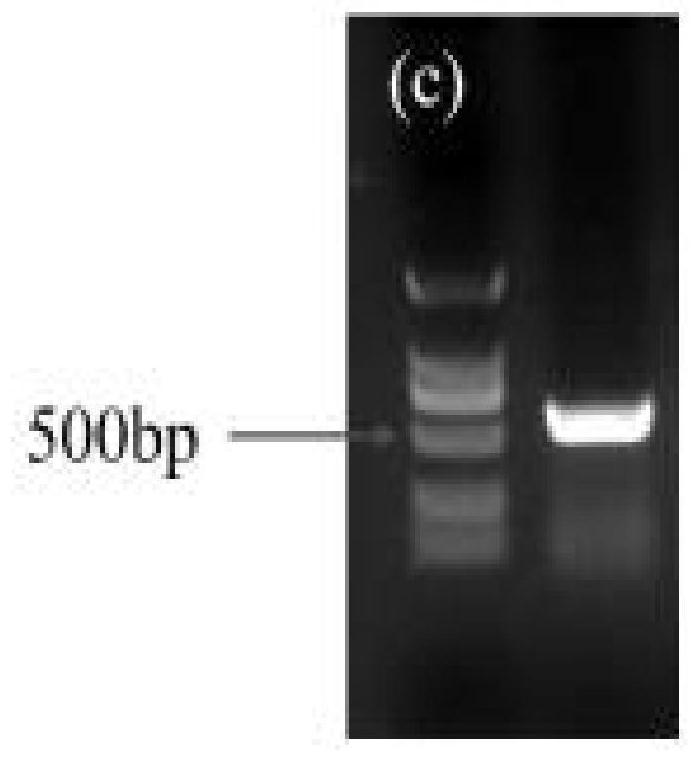
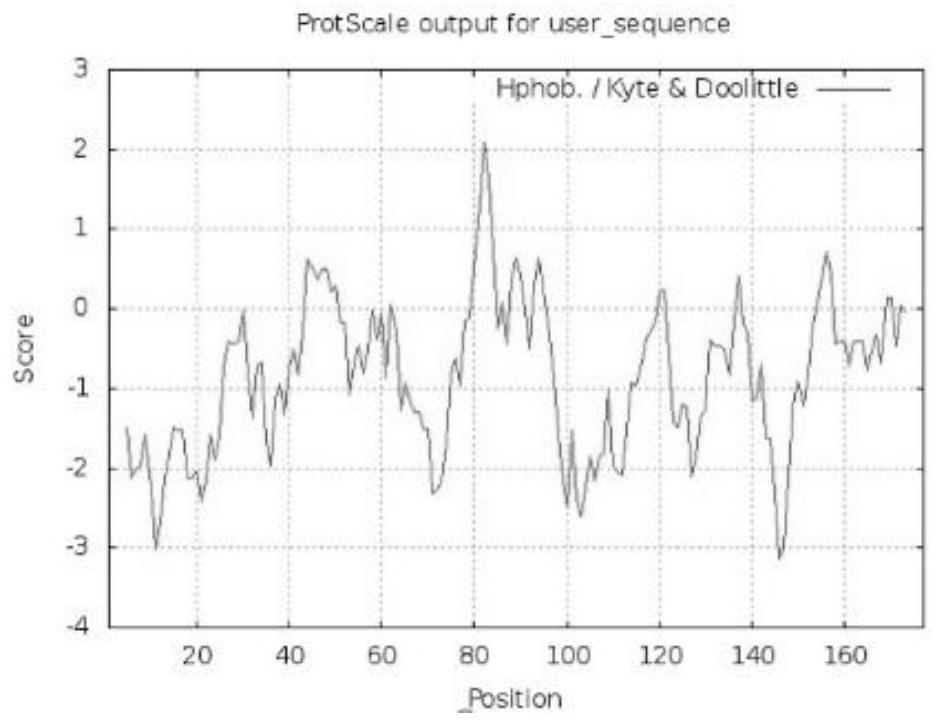
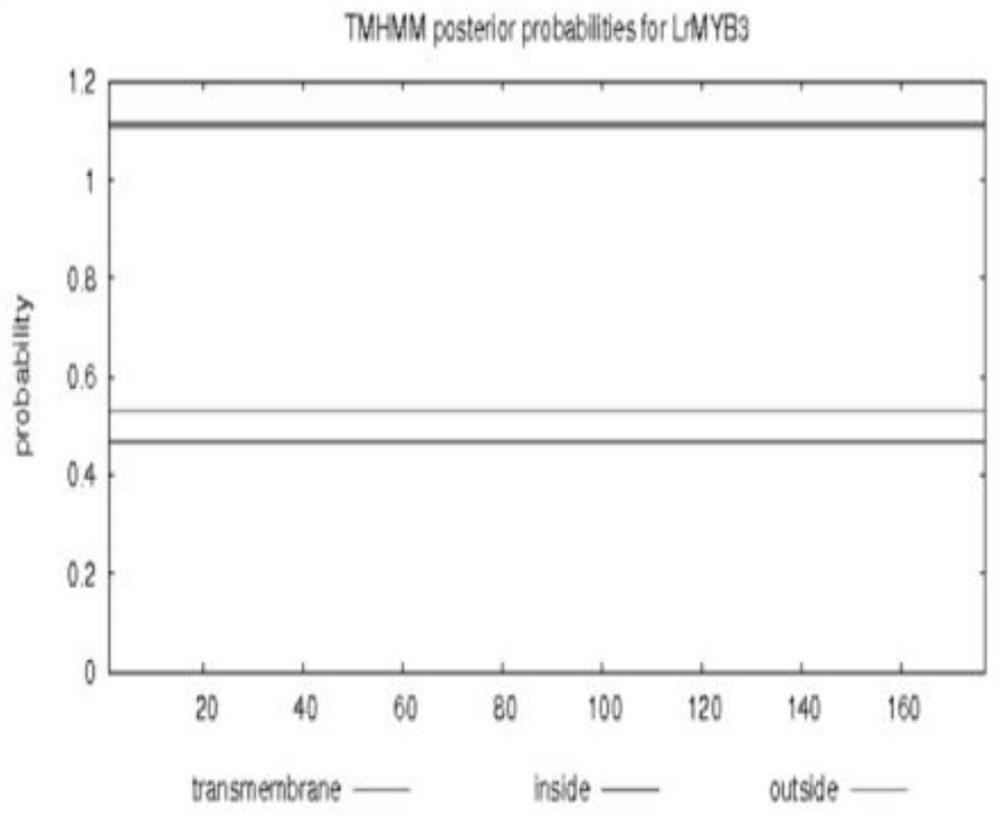
MYB transcription inhibition factor LrMYB3 related to lycium ruthenicum anthocyanin synthesis and application thereof
The invention discloses an MYB transcription inhibition factor LrMYB3 related to lycium ruthenicum anthocyanin synthesis and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to transcriptome data of lycium ruthenicum, the MYB transcription inhibition factor LrMYB3 participating in anthocyanin synthesis is screened and cloned according to annotation results and expression quantity differences of MYB transcription factors, and belongs to a R2R3 type MYB transcription factor. Multiple sequence alignment and evolutionary tree analysis show that the transcription inhibition factor belongs to a FaMYB1-like transcription inhibition factor. QRT-PCR analysis shows that: the LrMYB3 is expressed in each tissue of the lycium ruthenicum, and the expression level is gradually increased along with ripening of the lycium ruthenicum. Subcellular localization and transcriptional activity detection experiments show that the LrMYB3 is a transcription factor which is localized in a cell nucleus and has no activation function.
Owner:WOLFBERRY SCI INST NINGXIA ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
GntR family transcription inhibitor mutant, mutant gene and application of the mutant gene to preparation of vitamin B2
ActiveCN112225785AIncreased ability to produce vitamin B2BacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideTranscription Repressor
The invention discloses a GntR family transcription inhibitor mutant, a mutant gene and an application of the mutant gene to preparation of vitamin B2. The amino acid sequence of the mutant has the following mutation relative to the sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3: the 89th amino acid is replaced with M. The 89th amino acid encoding nucleotide in the GntR family transcription inhibitor gene on the chromosome of bacillus subtilis is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis to encode the amino acid M. The vitamin B2 production capacity of the obtained genetically engineered bacterium is greatly improved, and growth of the bacterium is facilitated, so that high application and popularization values are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method and application of bacilli for efficiently metabolizing glycerol
ActiveCN108588108AIncrease metabolic rateIncrease consumption rateStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisGlycerol
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and microorganism, and particularly relates to a preparation method and application of bacilli for efficiently metabolizing glycerol. According to the method, a molecular biology technology is used; a transcription inhibition factor gene ccpC is knocked out in bacillus licheniformis to obtain a bacillus licheniformis engineering strain WX-02 delta ccpC with the ccpC being deleted, and the glycerol metabolizing speed of the bacillus licheniformis is obviously improved. The glycerol consumption speed of the WX-02 delta ccpC in different culture mediums is at least improved by 18.38 percent through being compared with that of an original bacterium of the bacillus licheniformis; the improvement value can reach 32.67 percent tothe highest degree. When the strain is used in a poly gamma-glutamic acid fermentation culture medium, the yield of the poly gamma-glutamic acid can be obviously improved and is at least improved by10.7 percent; the improvement value can reach 17.4 percent to the highest degree. The result shows that the genetic engineering transformation method has important effect on improving the glycerol metabolizing effect; the efficiency of synthesizing bio-based chemicals by the glycerol is improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
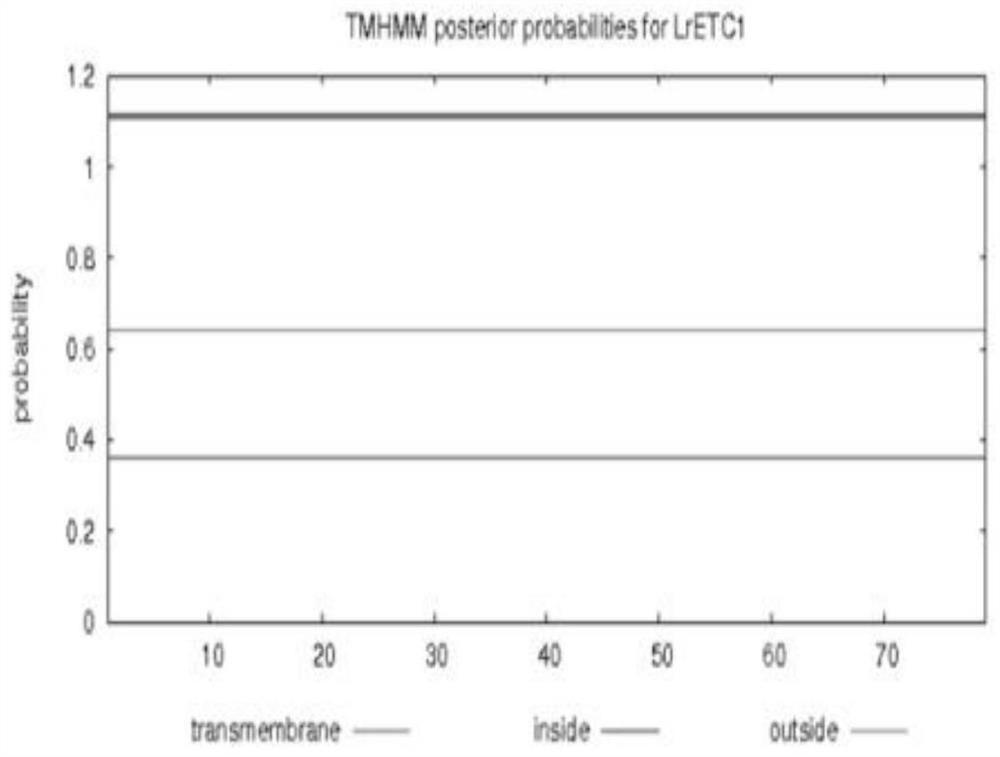
MYB transcription inhibition factor LrETC1 related to lycium ruthenicum anthocyanin synthesis and application thereof
ActiveCN113444731AMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesSequence databaseTranscription Repressor
The invention discloses an MYB transcription inhibition factor LrETC1 related to lycium ruthenicum anthocyanin synthesis and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the invention, the MYB transcription inhibition factor LrETC1 participating in the anthocyanin synthesis is screened and cloned, the total cDNA of the gene is 240bp, and 79 amino acids are encoded; protein sequence database analysis shows that the transcription factor belongs to R3 type MYB; and multiple sequence alignment and evolutionary tree analysis show that the transcription inhibition factor belongs to AtCPC-like transcription inhibition factors, and is a transcription factor which is located in a cell nucleus and does not have an activation function. A LrETC1 transgenic arabidopsis thaliana strain is obtained through agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation, compared with a wild type, seed coats of seeds are light brown, arabidopsis thaliana seedlings are free of pigment accumulation under the stress condition of high sucrose concentration, and the expression level of related structural genes is remarkably reduced.
Owner:WOLFBERRY SCI INST NINGXIA ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Permanent epigenetic gene silencing
A product comprising two or more artificial transcription repressors (ATRs), or polynucleotides encoding therefor, selected from groups (a), (b), (c) or (d): (a) an ATR comprising a DNA-binding domain operably linked to a KRAB domain or homologue thereof; (b) an ATR comprising a DNA-binding domain operably linked to a DNMT3A, DNMT3B or DNMT1 domain or homologue thereof; (c) an ATR comprising a DNA-binding domain operably linked to a DNMT3L domain or homologue thereof; and (d) an ATR comprising a DNA-binding domain operably linked to a SETDB1 domain or homologue thereof, wherein at least two of the ATRs are selected from different groups (a), (b), (c) or (d).
Owner:OSPEDALE SAN RAFFAELE SRL +1
Fusion Molecules of Rationally-Designed DNA-Binding Proteins and Effector Domains
InactiveUS20140010797A1Reduced activityFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesTranscription RepressorRegulator gene
Targeted transcriptional effectors (transcription activators and transcription repressors) derived from meganucleases are described. Also described are nucleic acids encoding same, and methods of using same to regulate gene expression. The targeted transcriptional effectors can comprise (i) a meganuclease DNA-binding domain lacking endonuclease cleavage activity that binds to a target recognition site; and (ii) a transcription effector domain.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Plant having reduced lignin and cellulose contents without reducing glucan content, method of producing the same and utilization thereof
InactiveUS8183432B2Reduce the amount of solutionSuppress transcriptionBryophytesSugar derivativesCelluloseTranscription Repressor
By inhibiting the function of a transcription factor that promotes transcription of a gene associated with the amounts of lignin and cellulose, a plant in which the amounts of lignin and cellulose are reduced without reducing the amount of glucan is produced. In this plant, glucan in the obtained cell wall components is in the state of highly easily undergoing saccharification. In this plant, moreover, natural dehiscence of pods is suppressed. A method of inhibiting the transcription factor includes a method in which a chimeric gene between a transcription factor gene and a polynucleotide that encodes a functional peptide capable of converting the transcription factor into a transcription repressor is introduced into a plant cell so that a chimeric protein in which the transcription factor is fused with the functional peptide is produced in a plant cell, and a method of inhibiting the expression of the transcription factor, such as knockout method or RNAi method. Thus, a plant in which the amounts of lignin and cellulose are reduced without reducing the amount of glucan is provided.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
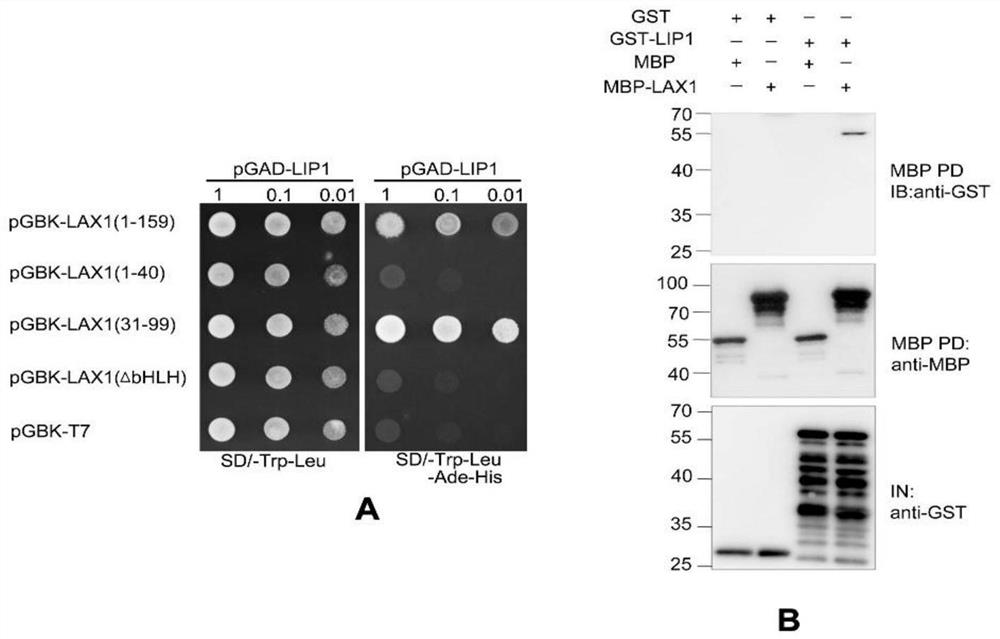
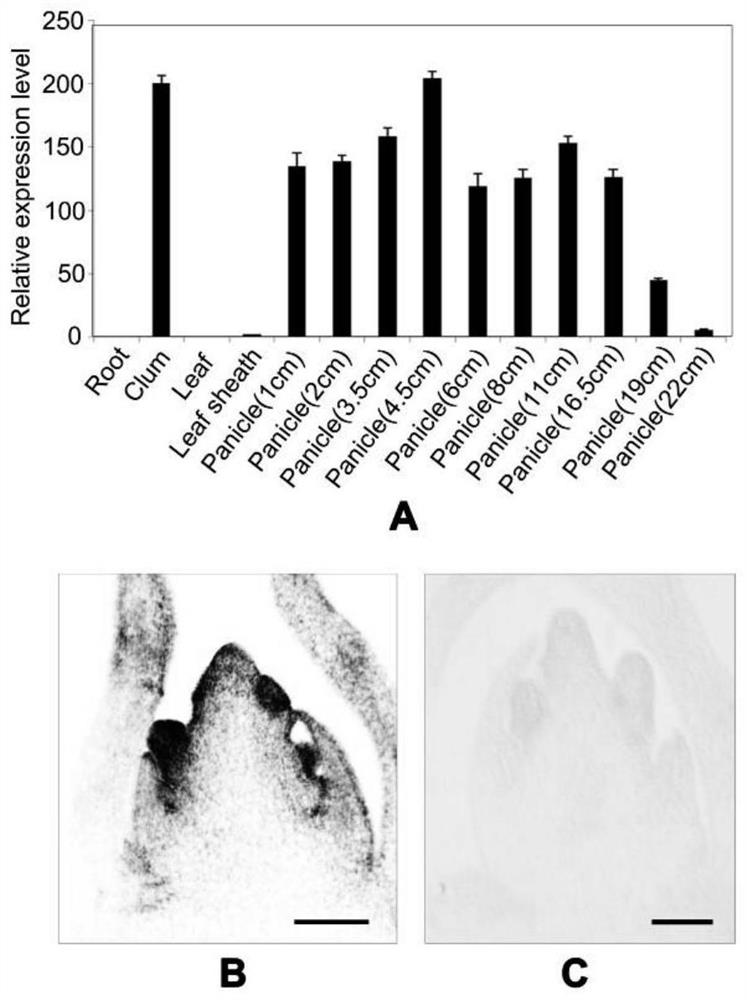
Function and application of transcription inhibitor LIP1 for regulating and controlling rice yield
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a function and application of a transcription inhibitor LIP1 for regulating and controlling rice yield. A cloned LIP1 protein gene interacts with a LAX1 gene, and is expressed in the later developing stage of the meristem of a lateral spikelet and inhibits the transcriptional activity of the LAX1 protein by interaction with the LAX1. The deletion or space-time ectopic expression of the LIP1 gene functions can change the space-time activity of the LAX1 protein and influence formation of rice spikelet. The spatio-temporal expression of the LIP1 defines the activation range of LAX1 in spikelet lateral meristem, and ensures formation of rice lateral spikelet so as to control the yield. By utilizing the cloned LIP1 gene and the encoding protein thereof, the space-time activity of LAX1 can be changed by regulating and controlling the expression activity of the LIP1 gene through a gene manipulation means, so that the formation of spikelet is regulated and controlled, and important significance is achieved on genetic improvement of rice yield traits.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Fusion Molecules of Rationally-Designed DNA-Binding Proteins and Effector Domains
InactiveUS20150315556A1Reduced activityFusion with DNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA-binding domainTranscription Repressor
Owner:DUKE UNIV
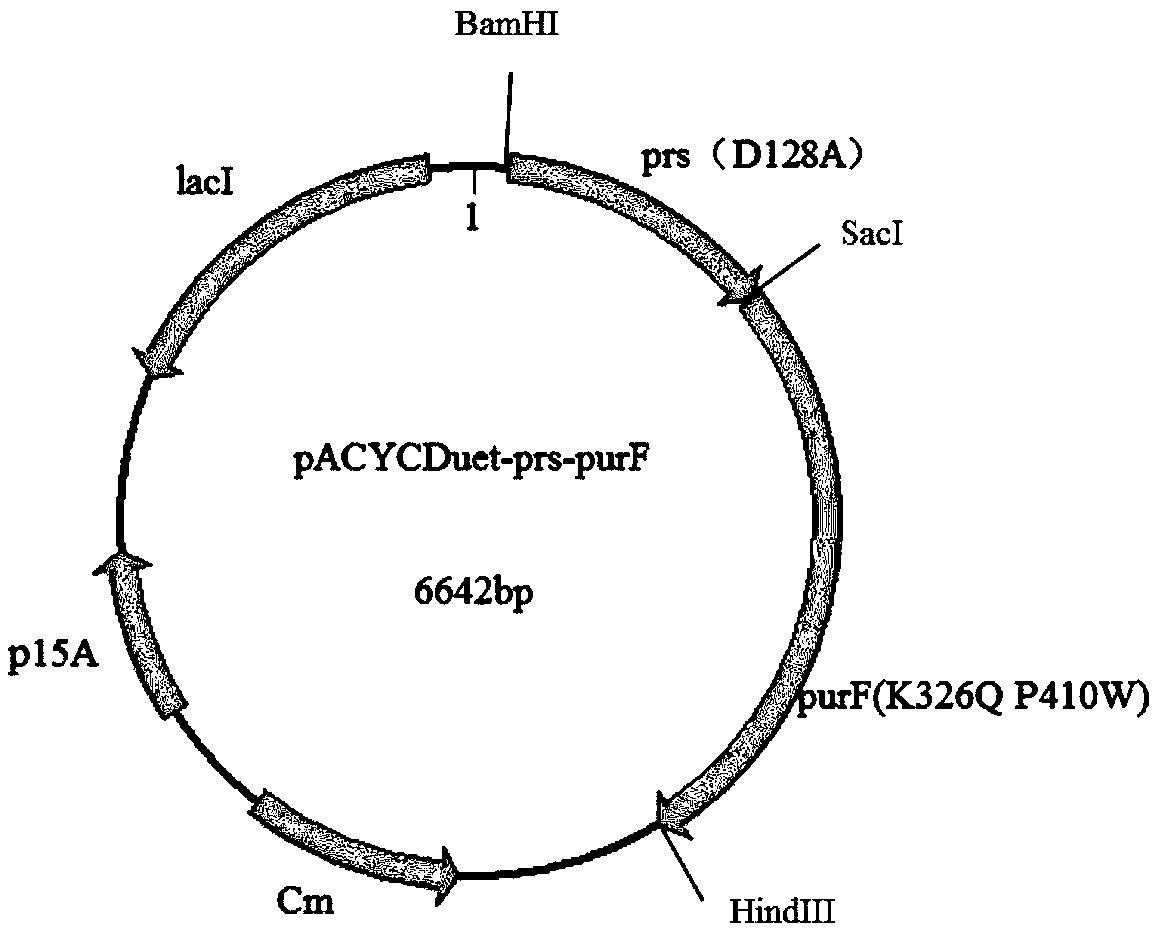
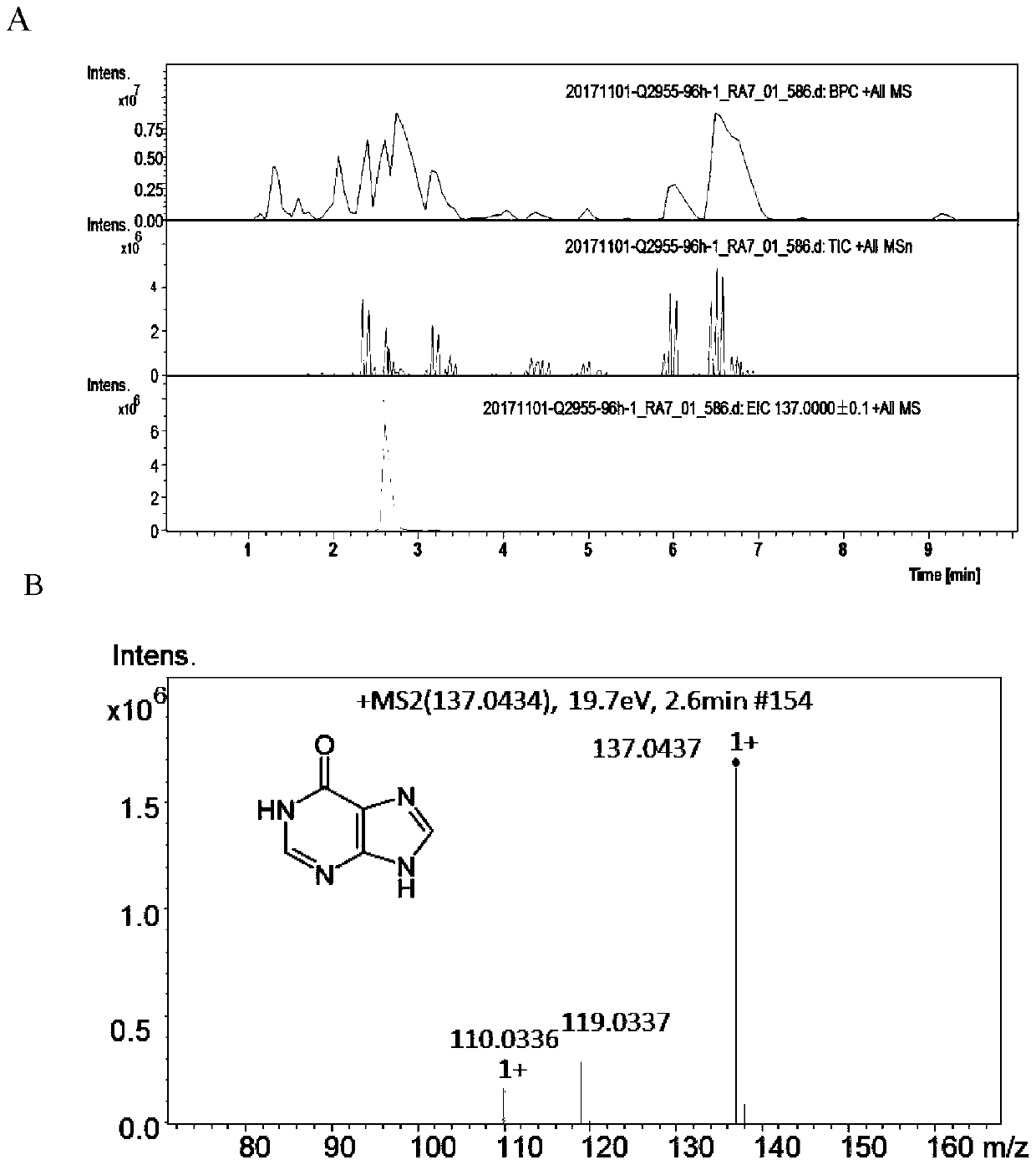
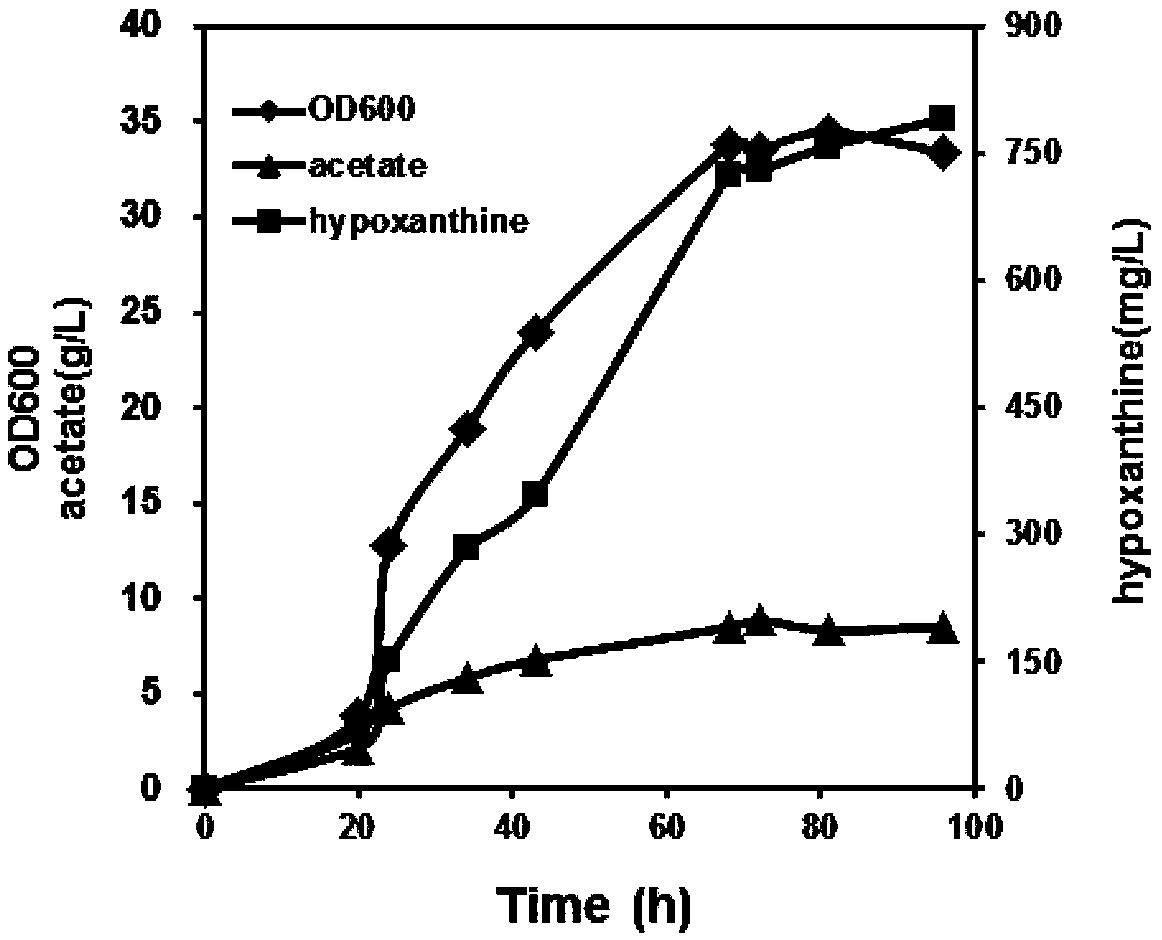
Recombinant strain for synthesizing hypoxanthine and construction method and application of recombinant strain
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for synthesizing hypoxanthine and a construction method and application of the recombinant strain, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant strain, escherichia coli is used as an original strain, a transcription repressor protein gene purR, a phosphogluconate anhydrase gene edd, an adenylosuccinic acid synthetase gene purA and an inosinic acid dehydrogenase gene guaB on an escherichia coli genome are respectively knocked out, and besides, D128A mutated PRPP synthetase gene prs and K326Q as well as a P410W double-mutated PRPP transamidase gene purF are subjected to overexpression. Besides, the invention further provides a preparation method of the recombinant strain and a method for producing the hypoxanthine through the recombinant strain. The efficient biosynthesis of the hypoxanthine in engineering escherichia coli is realized for the first time. The recombinant strain is suitable for production of the hypoxanthine through fermentation.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A gene expression regulation method and regulation system based on type I-F CRISPR/Cas
ActiveCN111979240BHave binding activityHigh expressionHydrolasesStable introduction of DNARegulation of gene expressionTranscription Repressor
The invention discloses a gene expression regulation method and a gene expression regulation system based on Type I‑F CRISPR / Cas. The present invention shows for the first time that the Cascade complex belonging to the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system, such as the PaeCascade complex, can efficiently bind to the target site in mammalian cells; at the same time, the present invention conducts the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system The mammalian expression system has been optimized so that it can efficiently recruit transcriptional activators or transcriptional repressors to target sites in mammalian cells, and successfully constructed a transcriptional activation system and a transcriptional repression system. The invention makes it possible to apply the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system in the gene regulation of mammalian cells, and provides a necessary tool for gene transcription regulation based on the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
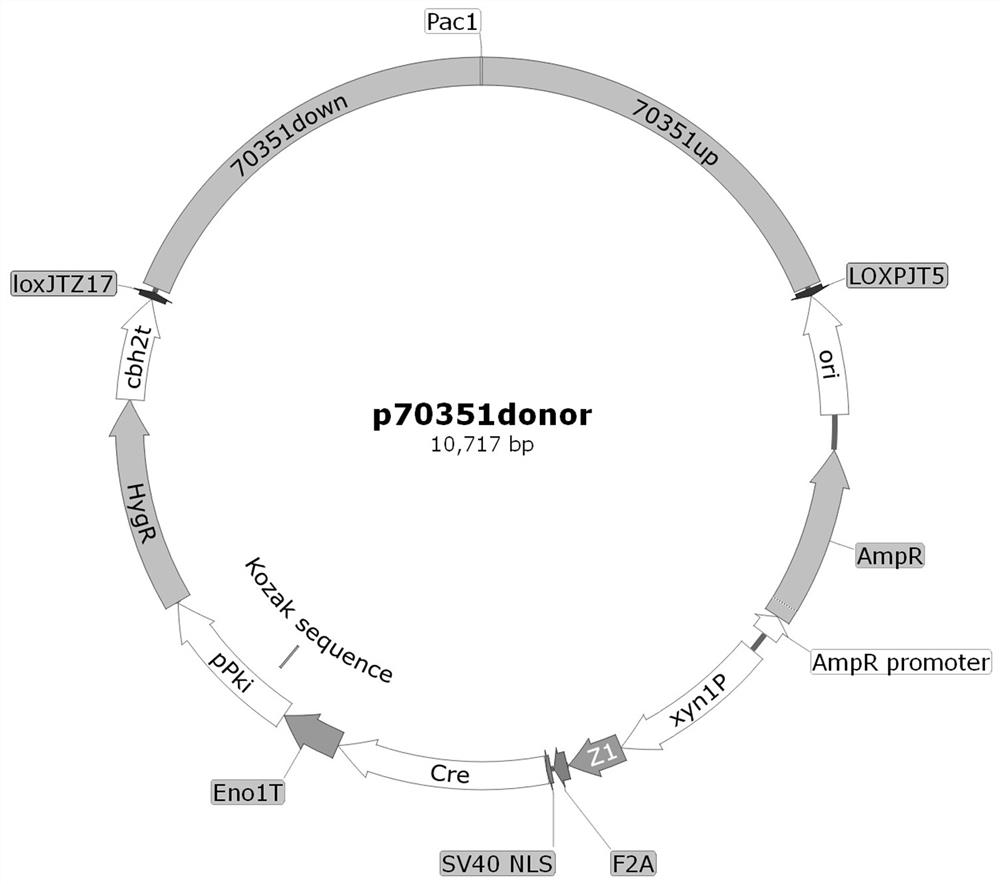
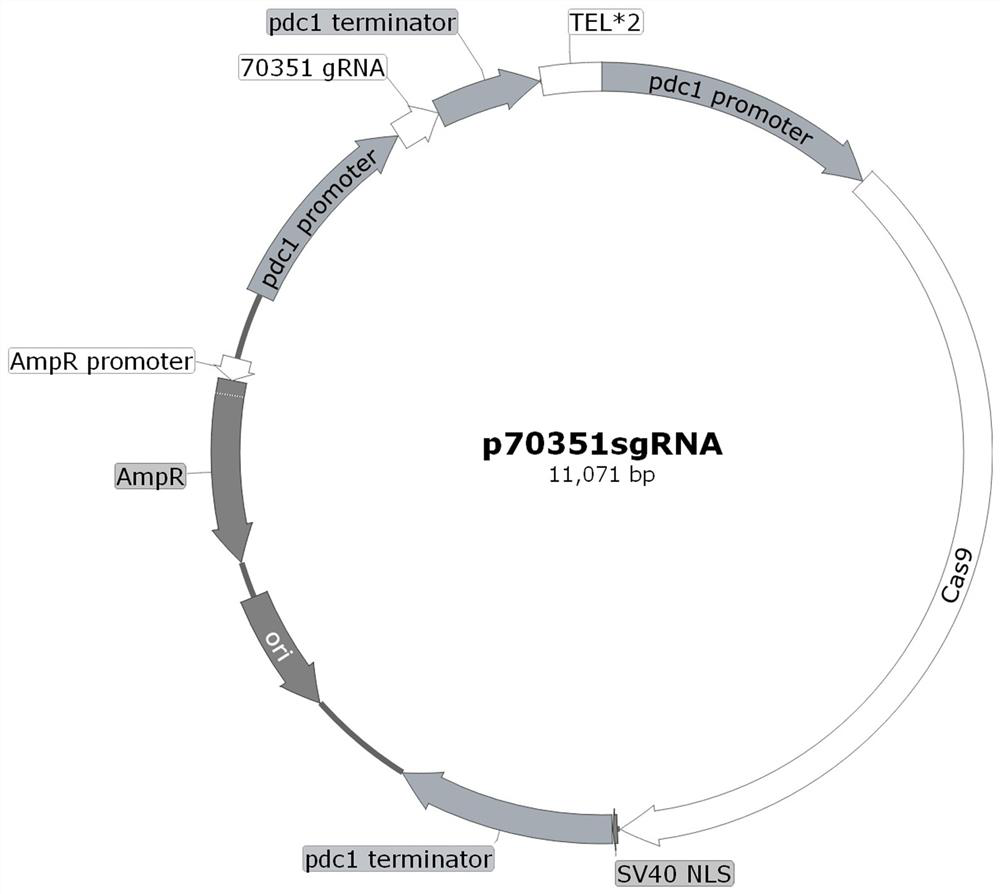
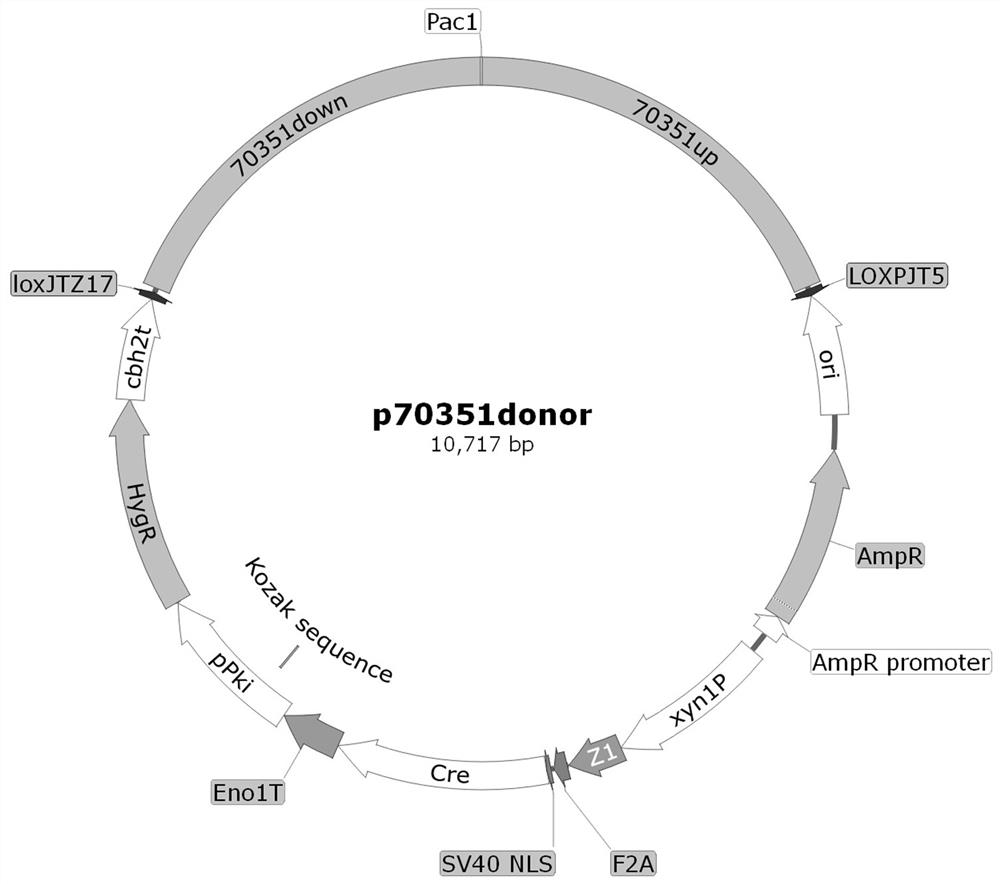
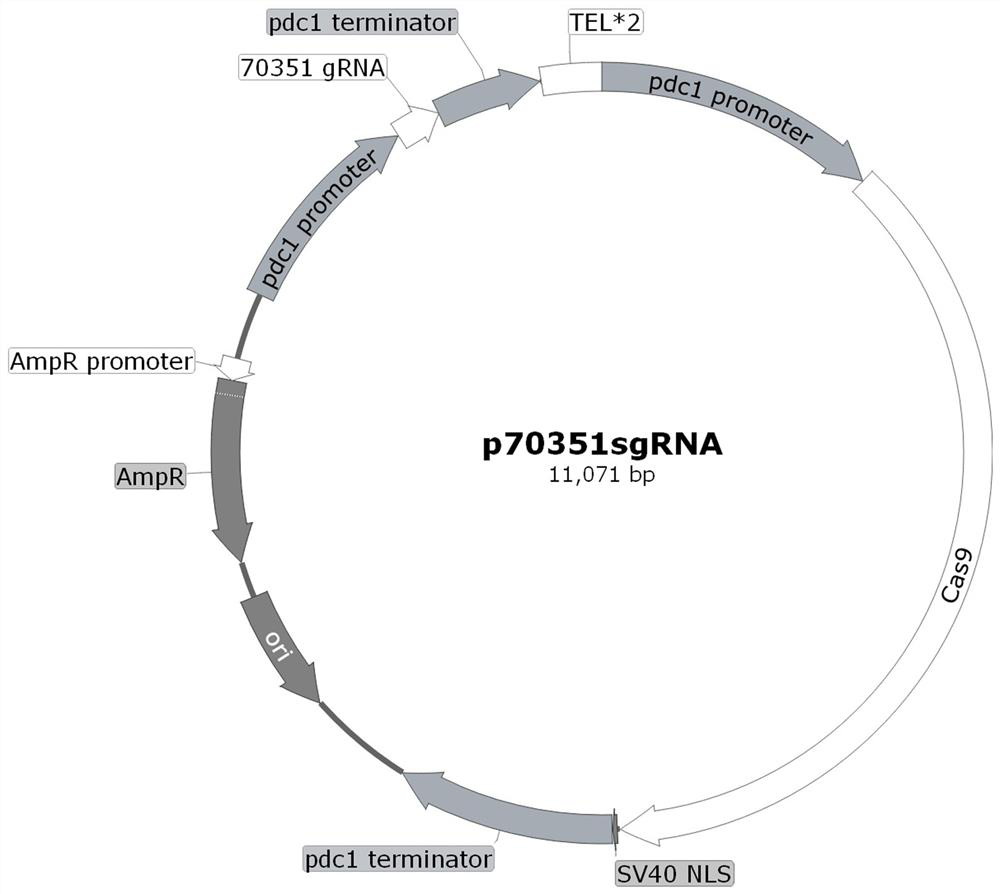
Application of Trichoderma reesei cellulase transcription inhibition factor 70351 and method for improving cellulase expression quantity and enzyme activity
ActiveCN114686459AEfficient use ofIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTranscription Repressor
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural biology, in particular to application of a Trichoderma reesei cellulase transcription inhibition factor 70351 and a method for improving cellulase expression quantity and enzyme activity. The transcriptional inhibition factor 70351 related to cellulase expression provided by the invention has a regulation effect on cellulase activity expression, a knockout plasmid of the gene is constructed and is used for converting host bacteria, and the expression of the transcriptional inhibition factor 70351 is knocked out from the host bacteria, so that the protein expression quantity of the host bacteria and the cellulase activity can be improved. The invention enriches the transcriptional regulation network of the trichoderma reesei cellulase, and provides a new way for improving the yield of the cellulase, reducing the cost of the cellulase and realizing the effective utilization of the cellulose.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
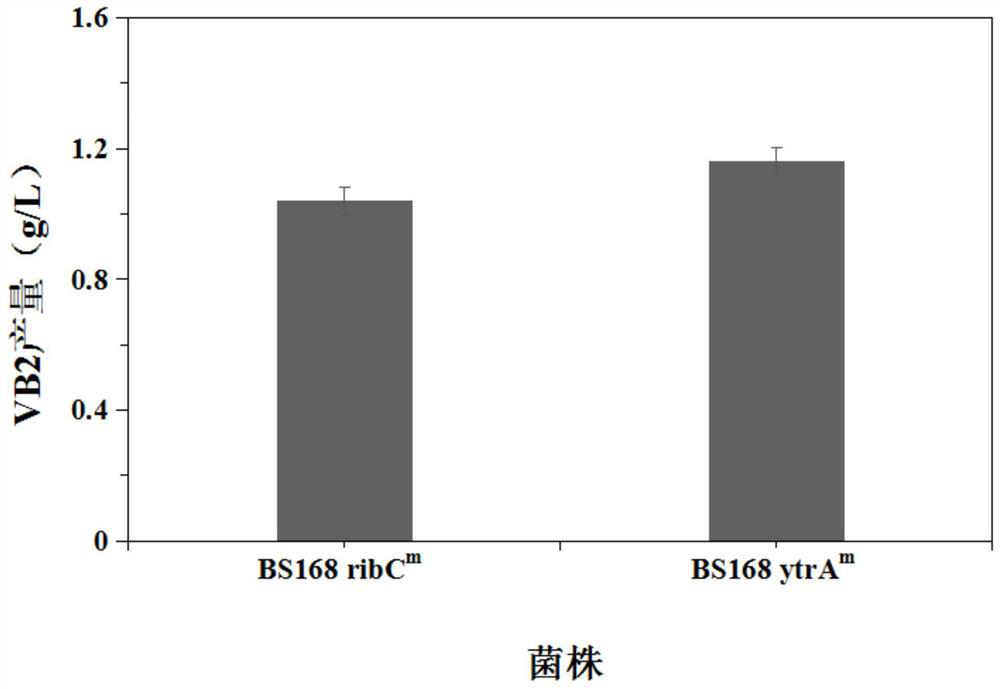
Gntr family transcriptional repressor mutants, mutant genes and their role in the production of vitamin b 2 application in
ActiveCN112225785BIncreased ability to produce vitamin B2BacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideTranscription Repressor
The invention discloses a GntR family transcription inhibitor mutant, a mutant gene and an application thereof in preparing vitamin B2. Wherein the amino acid sequence of the mutant has the following mutations relative to the sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3: the 89th amino acid is replaced by M. The 89th amino acid coding nucleotide in the GntR family transcription repressor gene on the Bacillus subtilis chromosome is subjected to site-directed mutation to encode the amino acid M, and the genetic engineering bacteria obtained have a relatively improved ability to produce vitamin B2 , and is beneficial to the growth of bacteria, so it has great application and promotion value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Fusion molecules of rationally-designed dna-binding proteins and effector domains
InactiveUS20180023065A1Affect specificityAffect activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainDNA-binding domainTranscription Repressor
Targeted transcriptional effectors (transcription activators and transcription repressors) derived from meganucleases are described. Also described are nucleic acids encoding same, and methods of using same to regulate gene expression. The targeted transcriptional effectors can comprise (i) a meganuclease DNA-binding domain lacking endonuclease cleavage activity that binds to a target recognition site; and (ii) a transcription effector domain.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Ribonucleotide reductase transcription inhibitor mutant, mutant gene and its application in the preparation of vitamin b2
The invention discloses a ribonucleotide reductase transcription inhibitor mutant, a mutant gene and its use in the preparation of vitamin B 2 in the application. Wherein the amino acid sequence of the mutant has the following mutation relative to the sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3: the 26th amino acid is replaced by H. The genetically engineered bacteria obtained by replacing the 26th amino acid encoded by the ribonucleotide reductase transcription inhibitor gene on the chromosome of Bacillus subtilis with H by site-directed mutation, which can produce vitamin B 2 The ability has been greatly improved, and it has great application and promotion value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A myb gene regulating cotton fiber elongation and its application
ActiveCN112111500BConfirmed regulationLocation verificationPlant peptidesFermentationOpen reading frameNucleotide
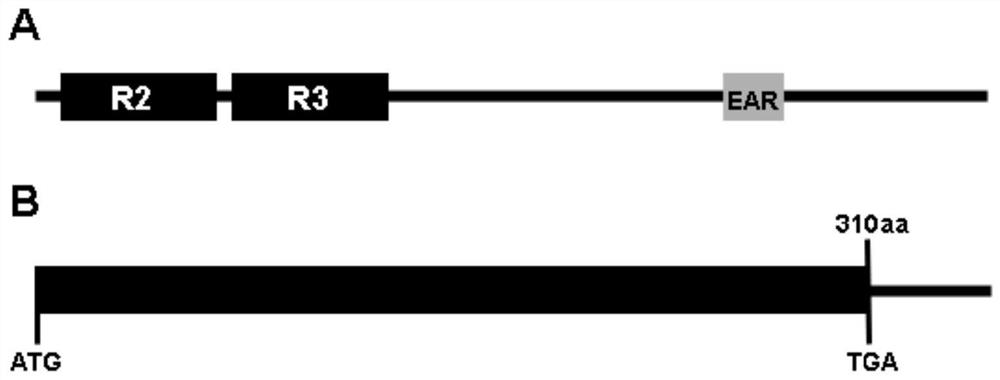
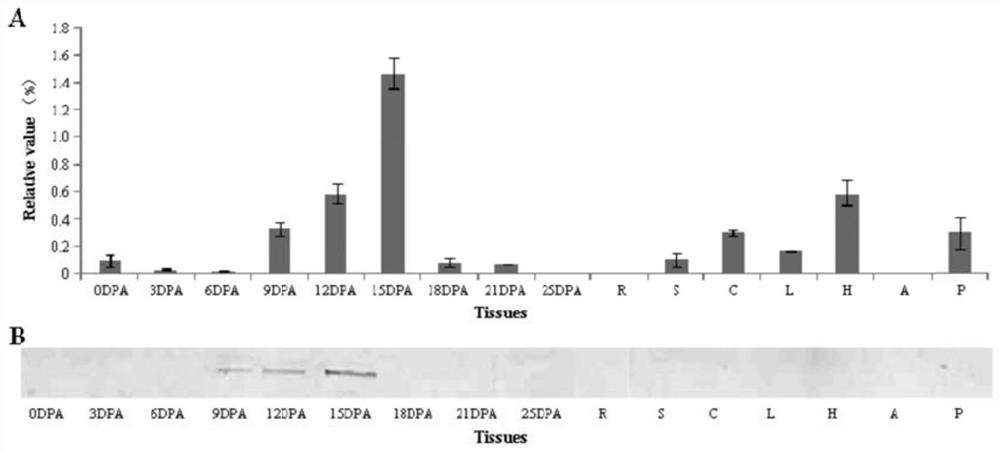
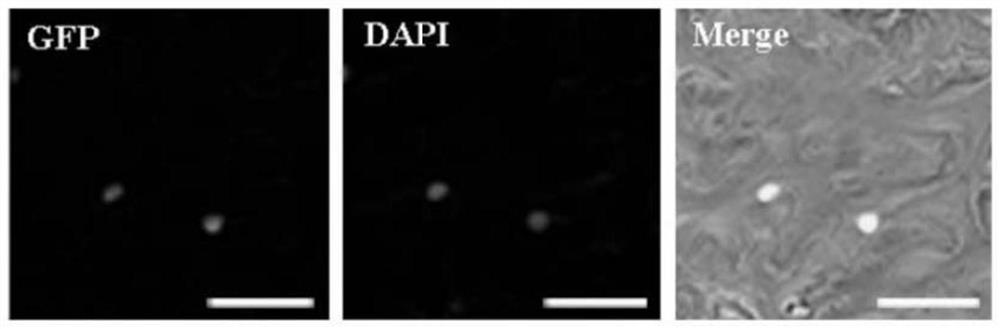
The invention relates to a MYB gene for regulating the elongation and growth of cotton fibers and its application. The gene is derived from Gossypium hirsutum, and its full-length nucleotide sequence is 1149 bp, without introns, and its open reading frame is 933 bp, encoding a protein with 310 amino acids. This transcription factor has a typical MYB domain and a transcriptional repressor-binding domain (EAR-domain). The present invention verifies the function of the gene in regulating the elongation and development of cotton fibers through genetic transformation. Using RNAi technology to reduce the expression of the gene in cotton fibers can significantly reduce the length of cotton fibers, indicating that the gene is a positive regulator of cotton fiber elongation. The long-developed genes are of great value in the improvement of cotton fiber quality, and can be used for molecular breeding research on cotton fiber quality improvement through hybridization, transgenic and other methods.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Nephropathy-associated gene
A nephropathy-associated gene which encodes a transcription repressor; and a nonhuman transgenic animal suffering from nephropathy which is constructed by transferring the above gene and allows the observation of increases in urinary volume, urinary albumin and urinary NAG, pyelectasis, enlargement in kidney tubule and glomerular swelling at the early stage and the following sclerosis.
Owner:INADA AKARI +1
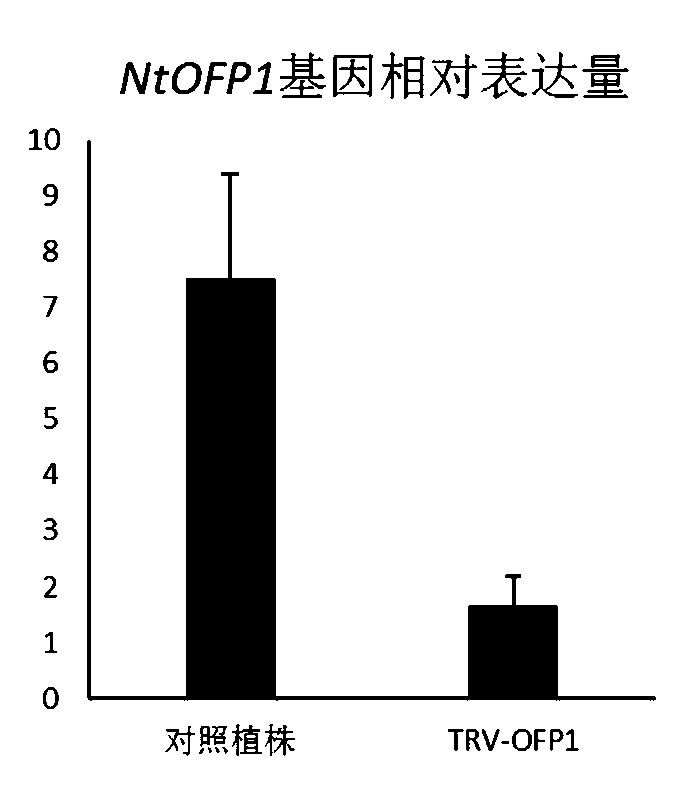
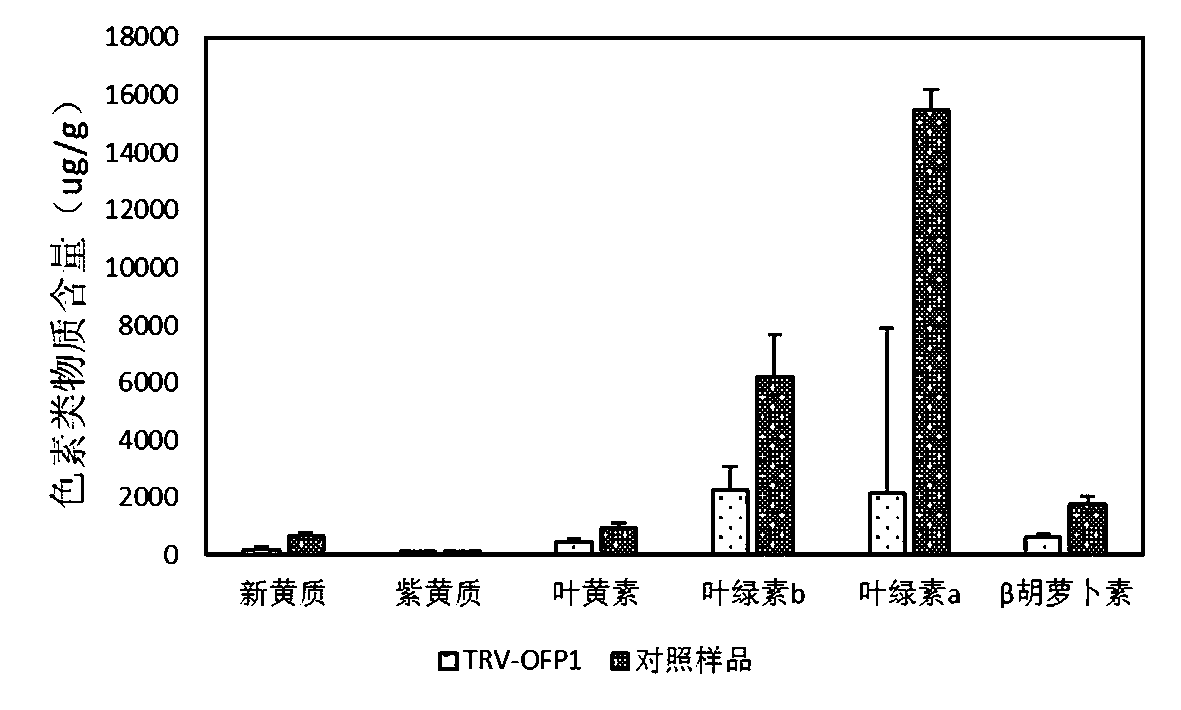
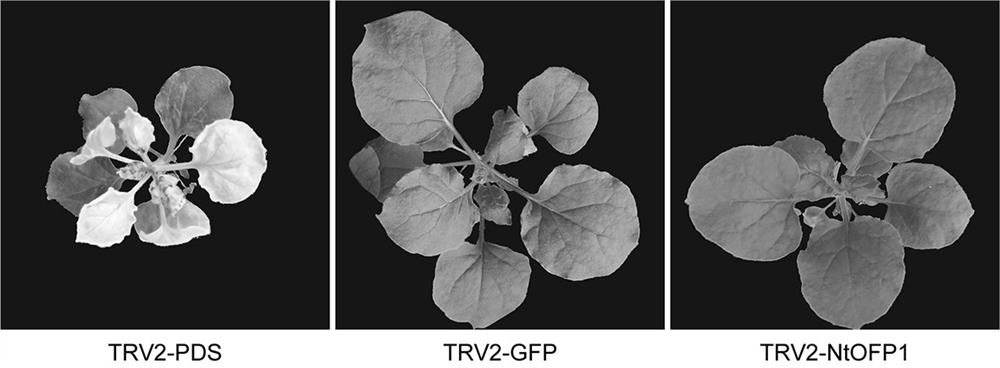
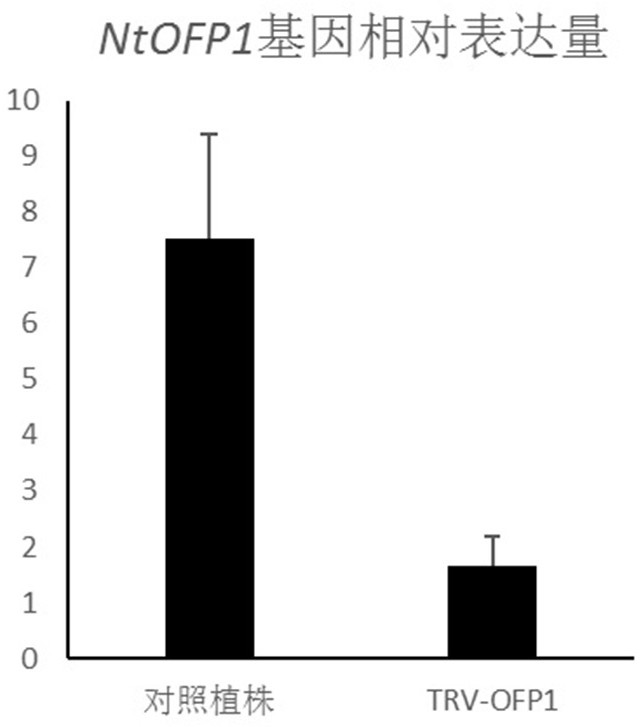
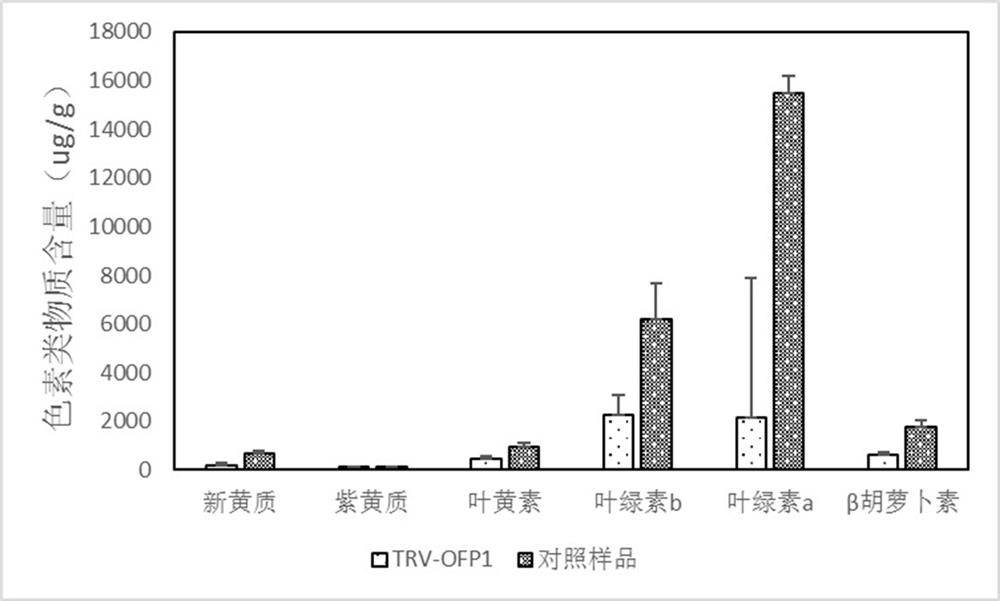
Tobacco transcription repressor protein OFP1 and application thereof
ActiveCN110157717AReduced content of pigmentsPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a tobacco transcription repressor protein OFP1 and application thereof. The tobacco transcription repressor protein OFP1 is composed of 87 amino acid residues, wherein the amino acids from 34 locus to 83 <rd> locus are at a conserved structure domain. The protein is relevant to the contentof pigment substances in plant leaves, and after the expression of the protein is lowered, the content of the pigment substances in the leaves is significantly lowered, wherein the pigment substancesare neoxanthin, violaxanthin, xanthophyll, chlorophyll a / b and beta-carotene. According to the tobacco transcription repressor protein OFP1 and the application thereof, through the preliminary studyon genes of the tobacco transcription repressor protein OFP1, it is found that the genes are highly relevant to the content of pigment substances in tobacco, and after the genes are silenced, the content of the pigment substances in the tobacco is significantly lowered. By utilizing the feature, a new reference can be provided for cultivation of new varieties of tobacco plants.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Deinococcus radiodurans transcription inhibition factor
The invention discloses a Deinococcus radiodurans transcription inhibition factor. The transcription inhibition factor can be combined with an RDRM site-containing DNA damage emergency response and repair gene promoter in Deinococcus radiodurans in vitro. Components of a combination reaction buffer comprise 100-200mM of NaCl, 10-50mM of Tris-HCl 8.0 and 5-10mM of MgCl2, and the reaction temperature is 30DEG C. The transcription inhibition factor can inhibit the transcription expression of the DNA damage emergency response and repair gene in vivo. The transcription inhibition factor has not been reported so far is disclosed in the invention, and is of great significance for researching DNA damage repair.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A method for producing butanol
The present invention comprises a method of bioconverting a fermentable carbon source into n-butanol by a microorganism, wherein said microorganism is deficient in at least one gene or protein involved in the regulation of the four-carbon compound pathway, thereby improving the four-carbon compound pathway, In particular by inactivation of the transcriptional repressor rex.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
Application of Trichoderma reesei cellulase transcription inhibitor 70351 and method for improving cellulase expression and enzyme activity
ActiveCN114686459BEfficient use ofIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTranscription Repressor
The invention relates to the field of agricultural biotechnology, in particular to Trichoderma reesei cellulase transcription inhibitor 70351 application and method of improving cellulase expression and enzymatic activity. The cellulase expression-related transcriptional repressor provided by the present invention 70351 It has a regulatory effect on the expression of cellulase activity. By constructing a knockout plasmid of this gene and transforming it into the host bacteria, the transcriptional repressor is knocked out in the host bacteria. 70351 The expression can improve the protein expression and cellulase activity of the host bacteria. The invention enriches the transcriptional regulation network of Trichoderma reesei cellulase, and provides a new approach for improving the yield of cellulase, reducing the cost of cellulase and realizing effective utilization of cellulose.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Tobacco transcription repressor protein ofp1 and its application
ActiveCN110157717BReduced content of pigmentsPlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumTranscription Repressor
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com