Intercellular labeling of ligand-receptor interactions
a technology of ligand receptor and intercellular labeling, which is applied in the field of immune system, can solve the problems of inability to achieve effective determination and tracking of these interactions in the context of living animals, and achieve the effect of facilitating purification and isolation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
ular Labeling Mediated by CD40 / CD40L Interaction
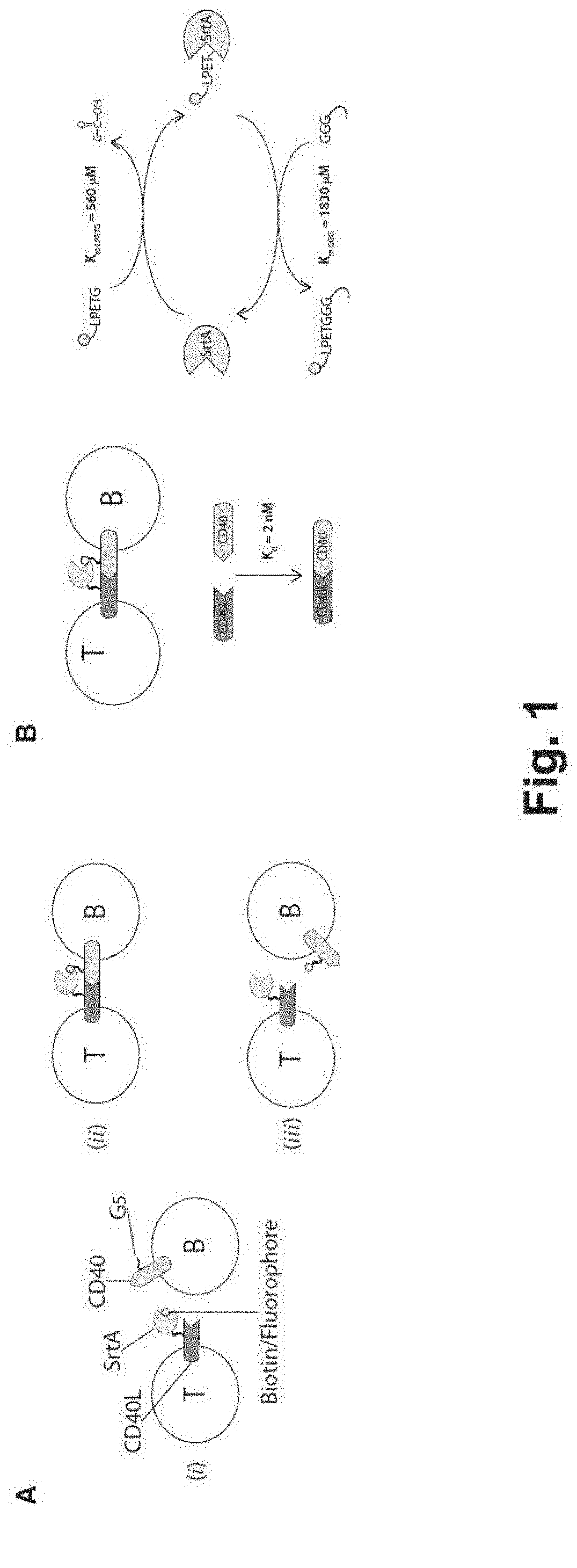
[0185]To track intercellular interactions between ligand and receptor molecules expressed at the plasma membrane of cells, ligand and receptor pairs were engineered by genetic fusion so that one of the interacting partner expressed S. aureus SortaseA (SrtA) enzyme at its extracellular portion and the other one presented 5 extracellular N-terminal glycine residues (FIG. 1A). A triple mutated version of SrtA enzyme (P94S-D160N-K196T) with improved catalytic properties as described by Chen et al. PNAS, 2011 (FIG. 1B) was employed. Upon ligand-receptor interaction, and in presence of a biotinylatated or fluorescently labeled SrtA substrate as the short peptide LPETG (SEQ ID NO: 2), spatial proximity allows the labeled substrate to be transferred from the SrtA-engineered ligand to the N-terminus glycine of the receptor.
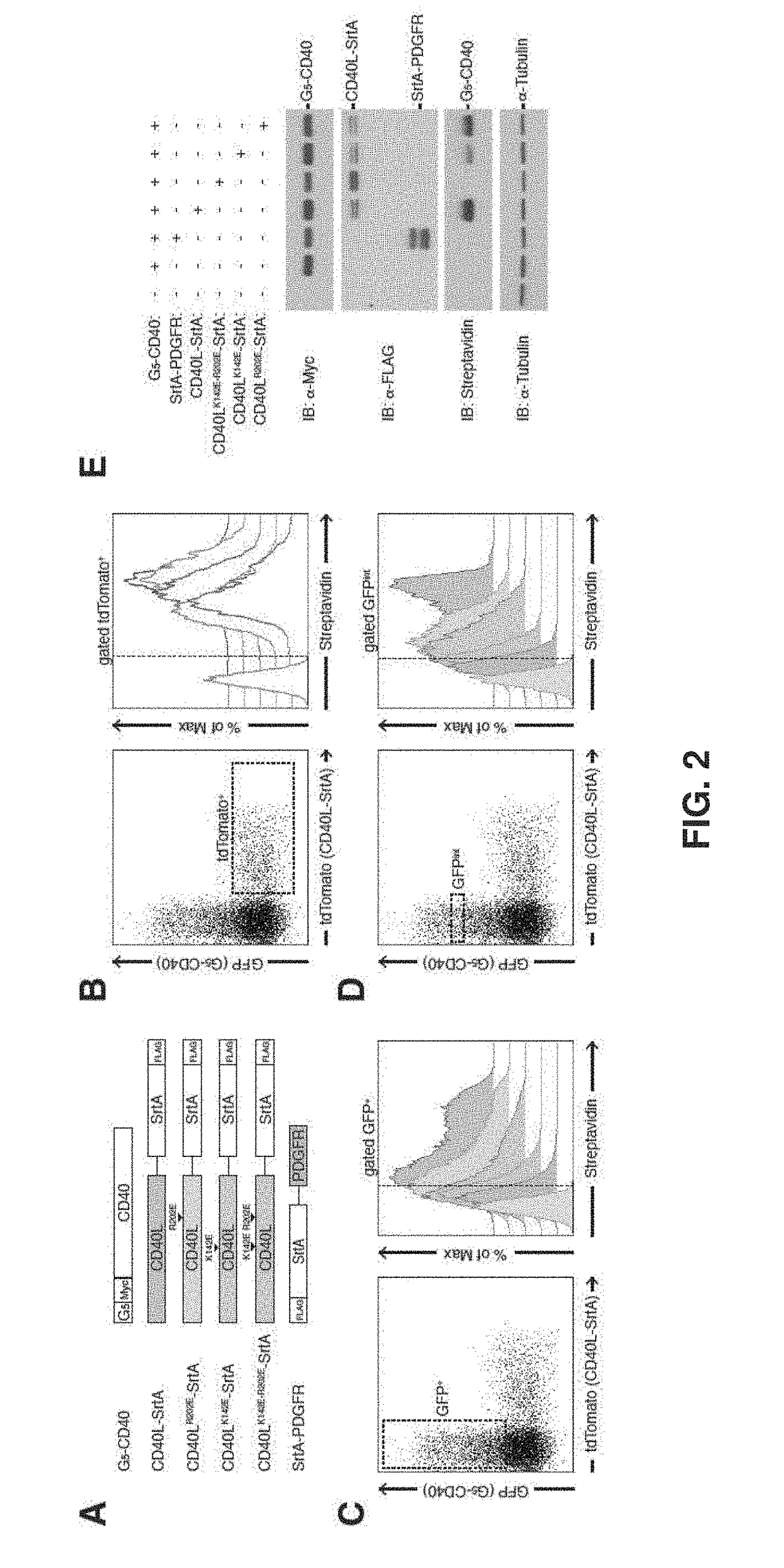
[0186]Briefly, expression vectors carrying G5-myc-CD40 and CD40L-SrtA fusion proteins as shown in FIG. 2A were constructed ...
example 2
ular Labeling Mediated by Various Ligand-Receptor Pair Interaction
[0190]Intercellular labeling mediated by additional ligand-receptor pair interaction (including CD28 / CD80, CTLA4 / CD80, CD28 / CD86, CTLA4 / CD86, PD-1 / PD-L1, PD-1 / PD-L2, and ICOS / ICOSL) was examined following the method described in Example 1 above.
[0191]Constructs for expressing the ligand / receptor fusion proteins are illustrated in FIG. 4A. These expression vectors were transfected into HEK293T cells. Cells expressing G5-containing fusion proteins were included with cells expressing the corresponding interaction partner-Srt fusion proteins min in presence of a biotin-LPETGG (SEQ ID NO: 5) peptide. The cells were then washed, stained with Streptavidin and analyzed by flow cytometry. As shown in FIGS. 4B and 4C. A strong labeling of G5-expressing cells was observed when incubated with cells expressing the interacting partner. These results further demonstrate that the cell labelled was mediated by receptor-ligand interact...
example 3
ular Labeling in Primary Murine Lymphocytes
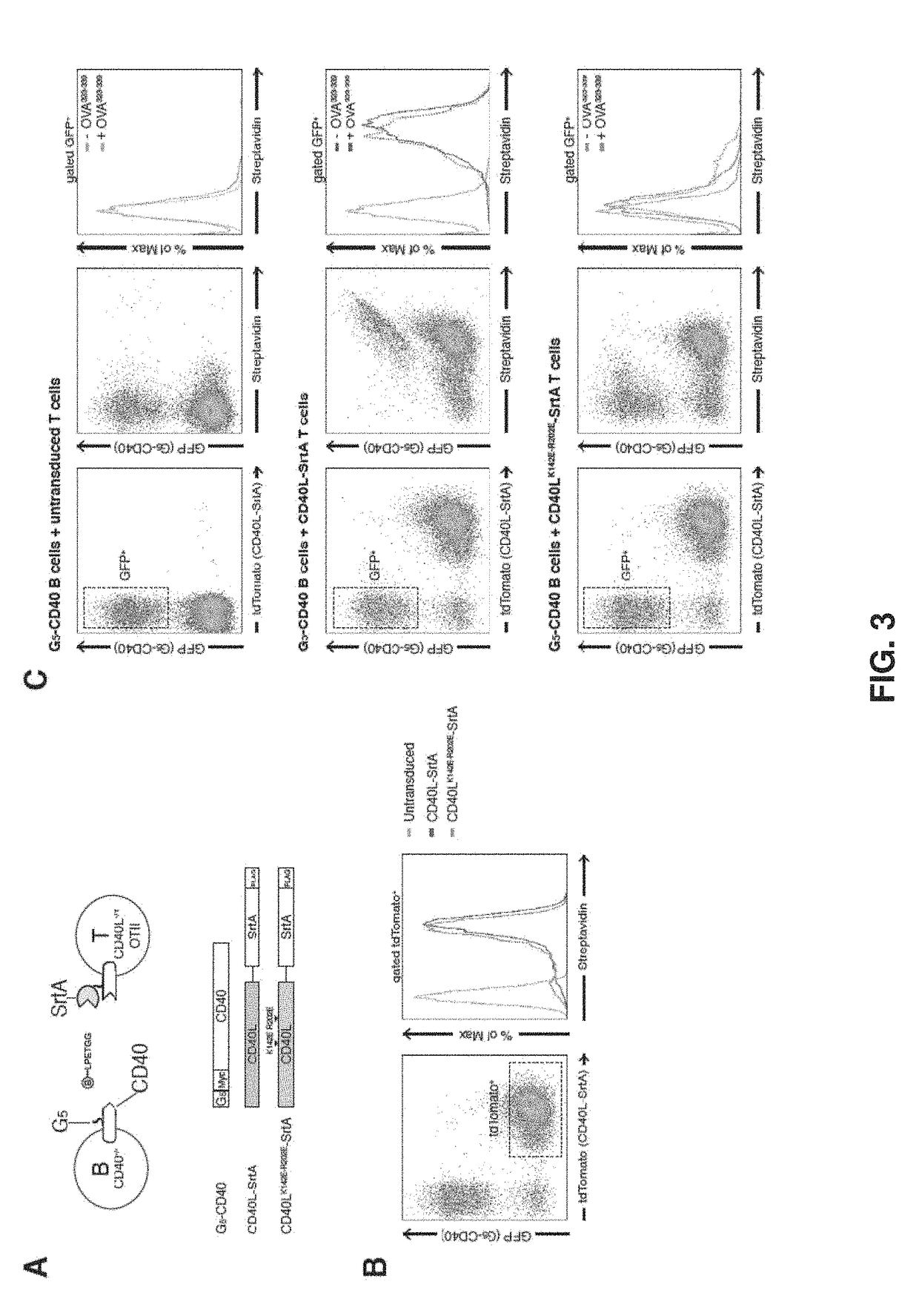
[0192]Intercellular labeling was also tested in primary murine B and T lymphocytes overexpressing SrtA / G5 tagged constructs (FIG. 7). As observed in HEK293T cells, intercellular labeling of G5-CD40 expressing B cells occurs efficiently upon interaction with CD4+T OT-II cells overexpressing CD40L-SrtA, but it is present at a very low level when SrtA-PDGFR is used. When OT-II peptide is added to the co-culture, intercellular labeling is efficiently achieved with both CD40L-SrtA and SrtA-PDGFR expressing CD4+ T cells, indicating that cognate interaction can be tracked also using non interacting molecules (i.e., SrtA-PDFGR).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com