Patents
Literature
58 results about "Fc binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)-binding polypeptide variants, dimeric Fc binding proteins and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20070148164A1Increase free energyReduced binding affinityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesFc bindingNeonatal Fc receptor
The compositions and methods of the present invention are based, in part, on our discovery that an effector function mediated by an Fc-containing polypeptide can be altered by modifying one or more amino acid residues within the polypeptide (by, for example, electrostatic optimization). The polypeptides that can be generated according to the methods of the invention are highly variable, and they can include antibodies and fusion proteins that contain an Fc region or a biologically active portion thereof.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Methods of purifying Fc region containing proteins
ActiveUS20070072307A1Efficient removalDecrease and prevent nonspecific adherenceImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPeptide preparation methodsProtein GFc binding
The present application provides methods of purifying polypeptides having a Fc region, for example, antibodies or antibody fusions, by adsorbing the polypeptides to a Fc binding agent, such as, for example, Protein A or Protein G, followed by a wash with a divalent cation salt buffer to remove impurities and subsequent recovery of the adsorbed polypeptides. The present application also features methods of eluting the purified polypeptide as well as the incorporation of the methods within a purification train. Kits comprising components for carrying out the methods and instructions for use are also provided.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
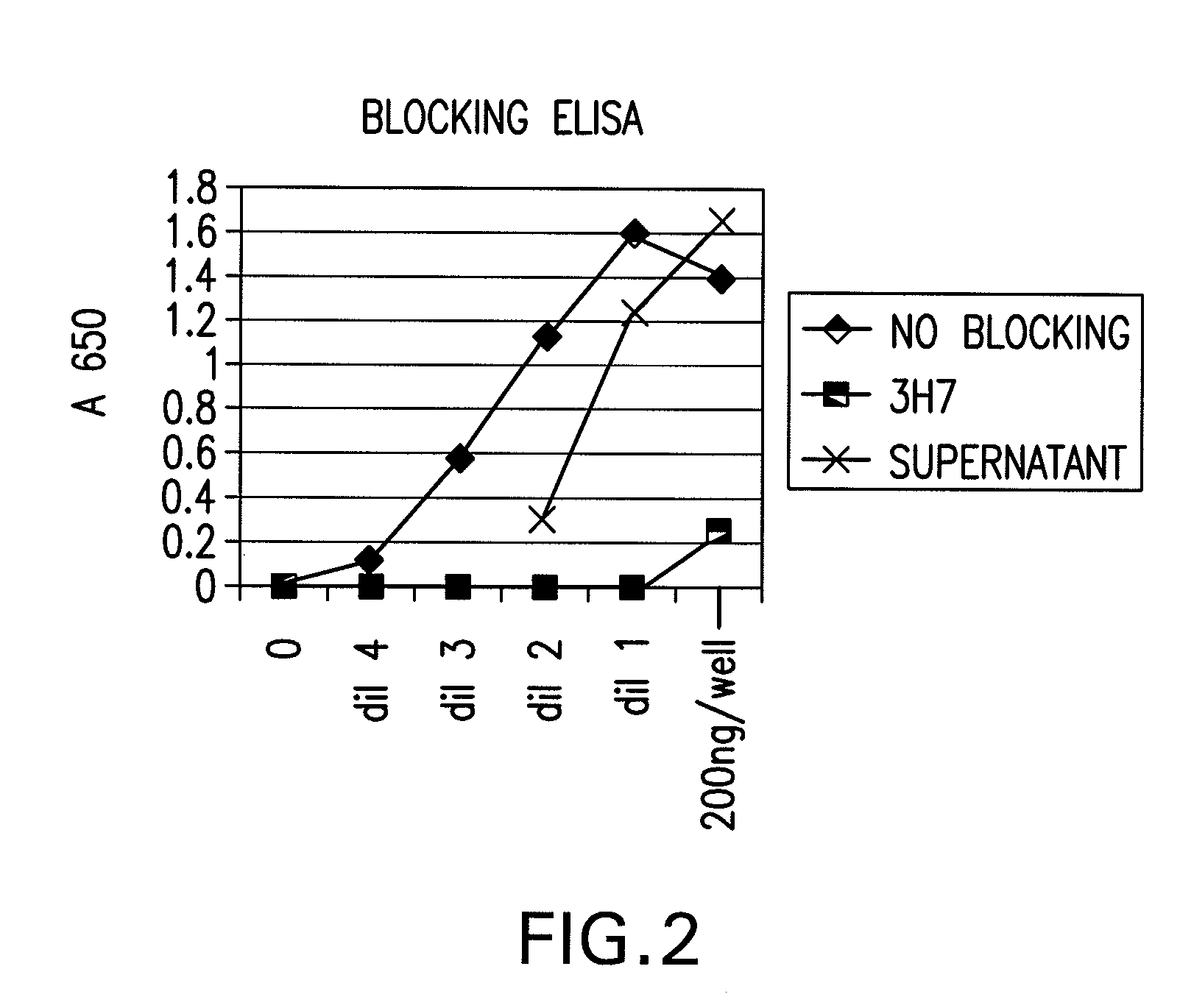
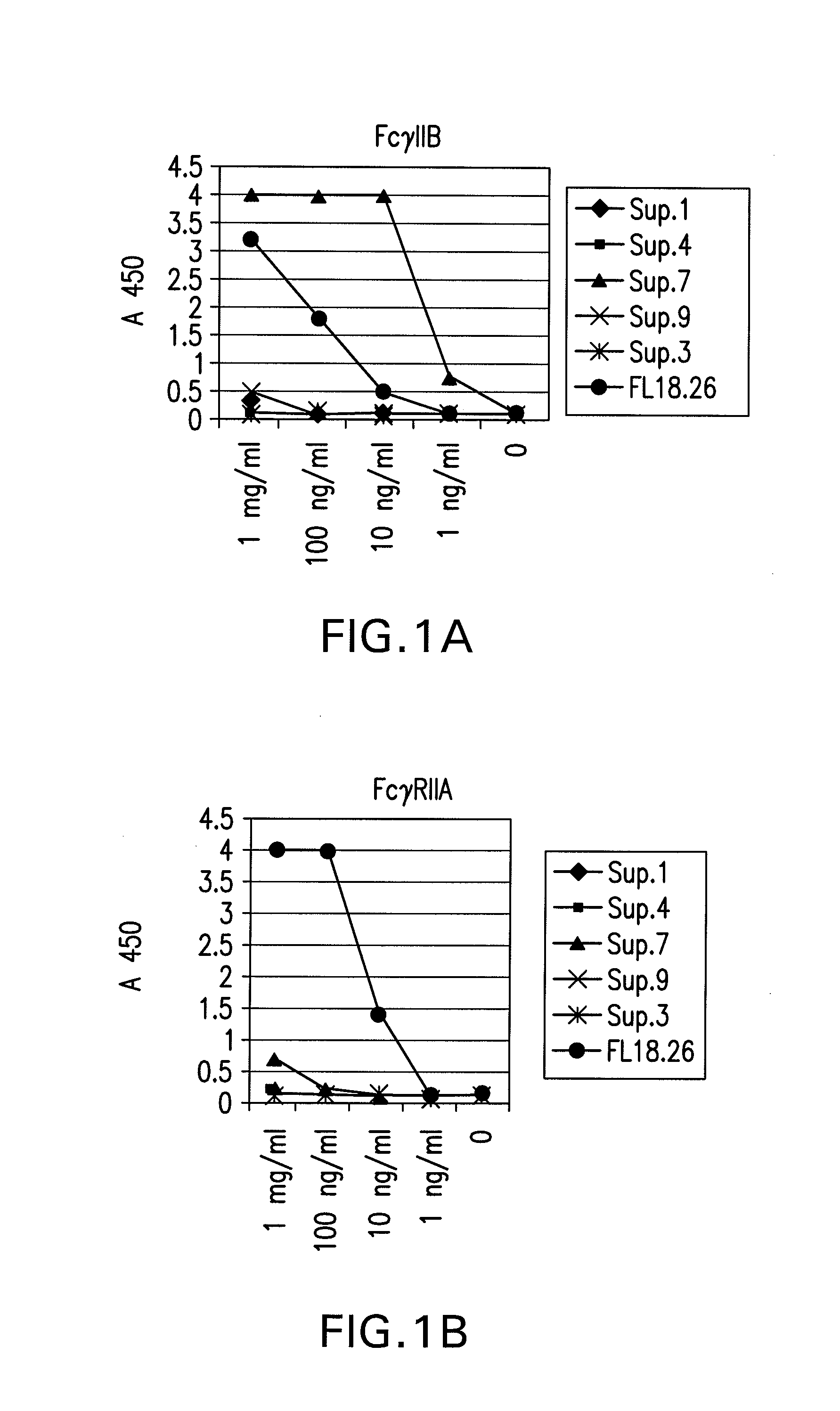
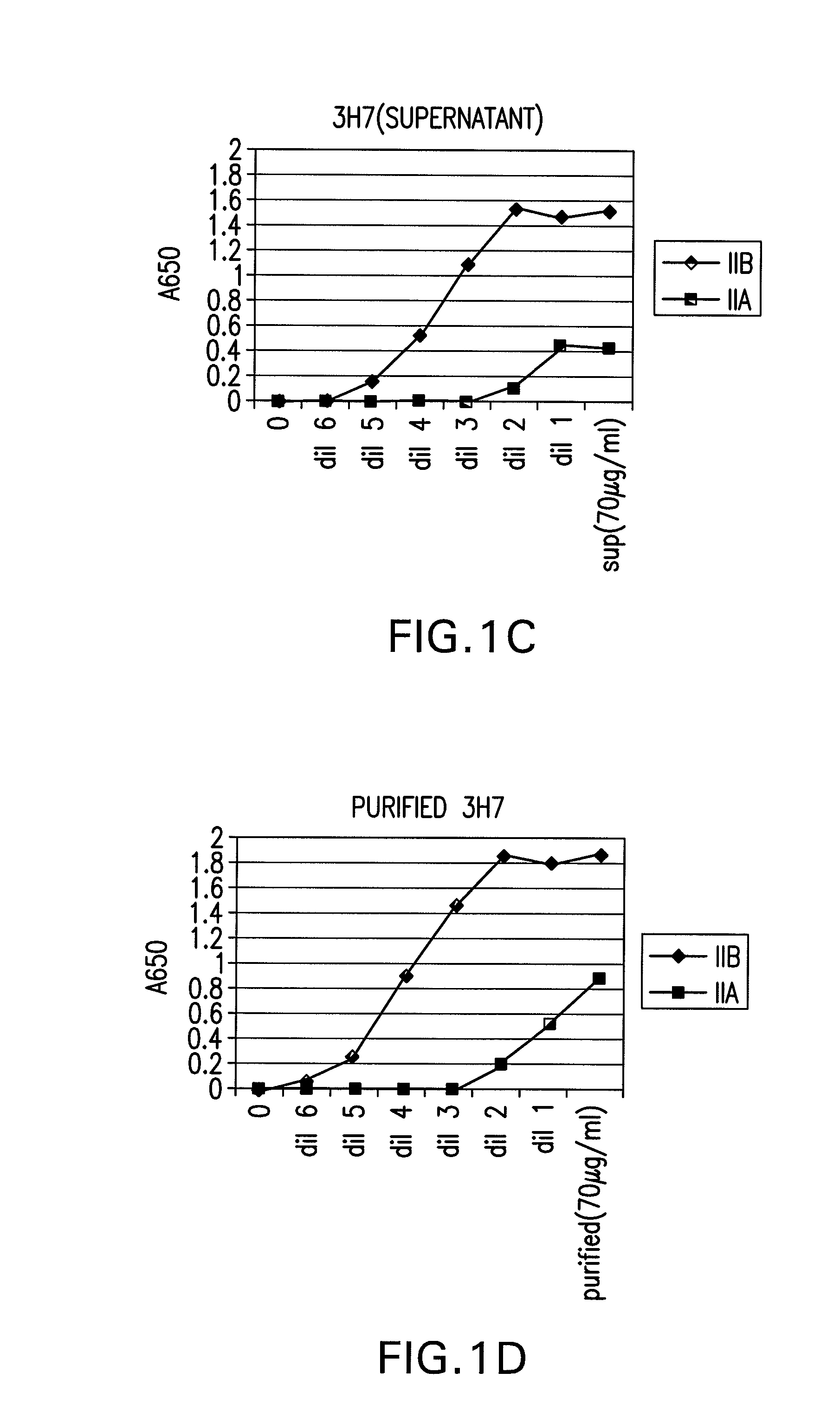
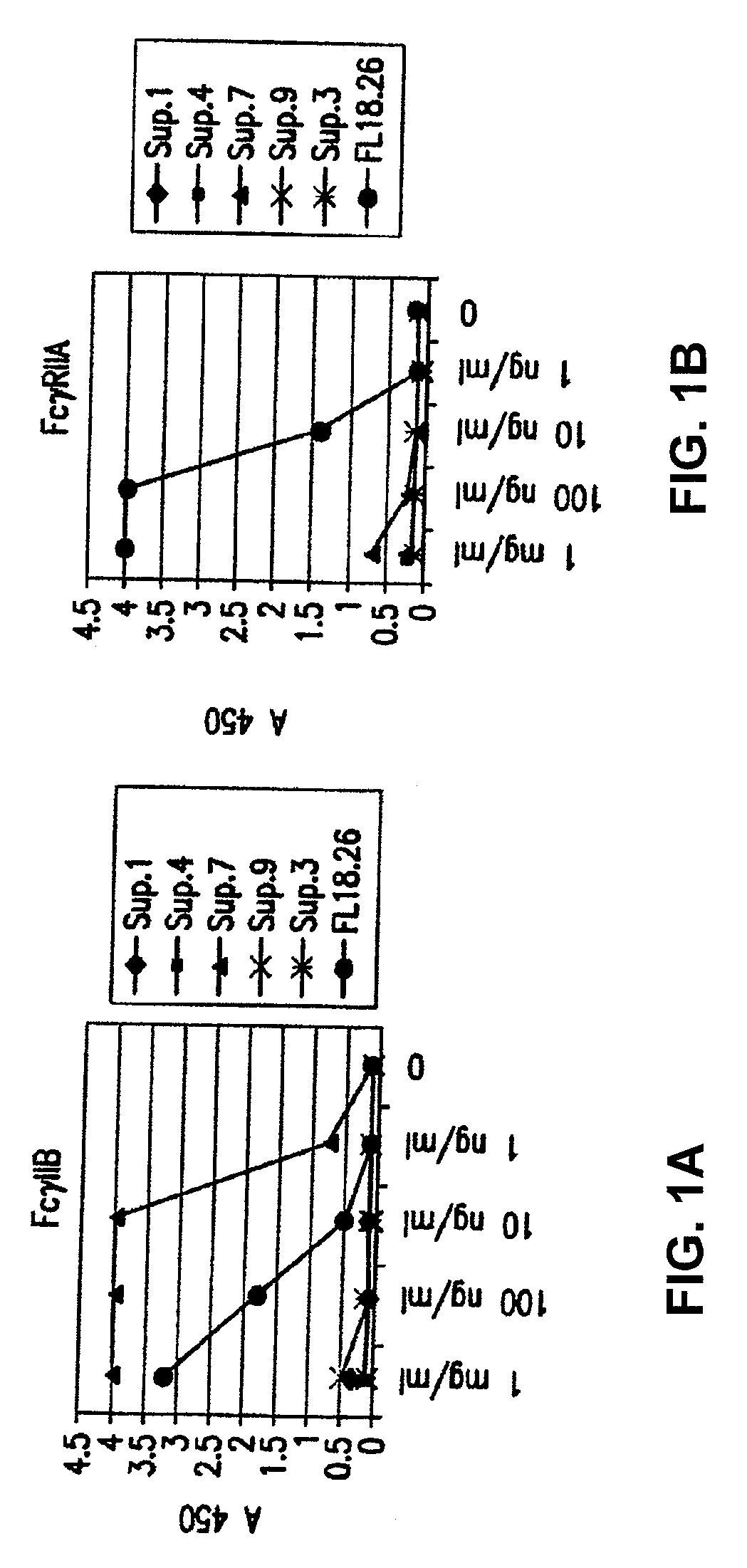
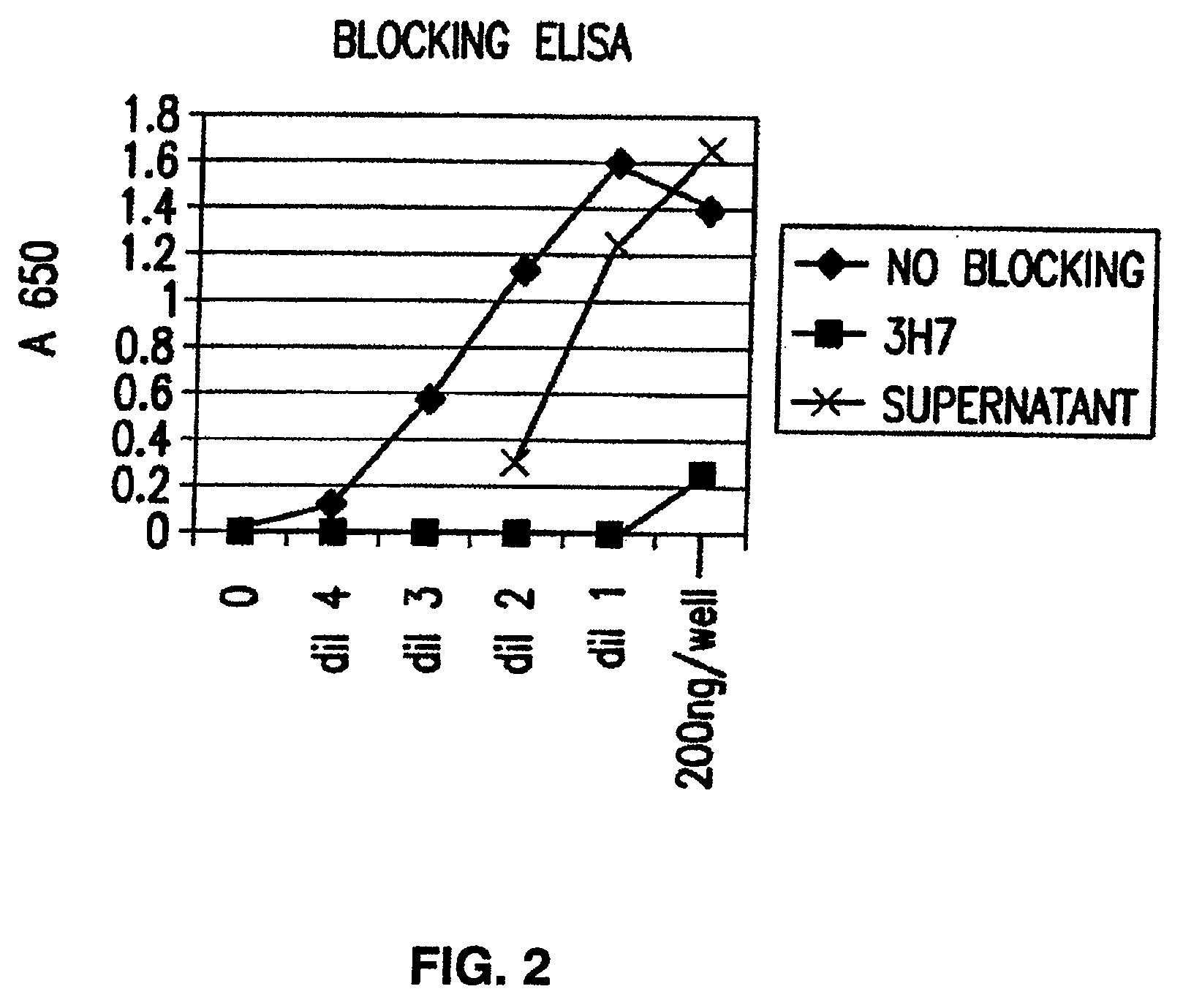
FcGammaRIIB Specific Antibodies and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090074771A1Strong therapeutic activityEnhancing antibody-mediated effector functionAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsTolerabilityImmune complex deposition
The present invention relates to antibodies or fragments thereof that specifically bind FcγRIIB, particularly human FcγRIIB, more particularly the extracellular domain of FcγRIIB with greater affinity than said antibodies or fragments thereof bind FcγRIIA, particularly human FcγRIIA, and block the Fc binding site of FcγRIIB. The present invention also encompasses the use of an anti-FcγRIIB antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, as a single agent therapy for the treatment, prevention, management, or amelioration of a cancer, preferably a B-cell malignancy, particularly, B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, an autoimmune disorder, an inflammatory disorder, an IgE-mediated allergic disorder, or one or more symptoms thereof. The present invention also encompasses the use of an anti-FcγRIIB antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, in combination with other cancer therapies. The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising an anti-FcγRIIB antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, in amounts effective to prevent, treat, manage, or ameliorate a cancer, such as a B-cell malignancy, an autoimmune disorder, an inflammatory disorder, an IgE-mediated allergic disorder, or one or more symptoms thereof. The invention further provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the antibodies of the invention with a vaccine composition. The invention further provides methods of treating cancer and / or regulating immune complex-mediated cell activation by administering the antibodies of the invention to enhance an immune response. The invention also provides methods of breaking tolerance to an antigen by administering an antigen-antibody complex and an antibody of the invention.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
FcGammaRIIB Specific Antibodies and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090076251A1Strong therapeutic activityEnhancing antibody-mediated effector functionImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsTolerabilityAutoimmune responses
The present invention relates to antibodies or fragments thereof that specifically bind FcγRIIB, particularly human FcγRIIB, more particularly the extracellular domain of FcγRIIB with greater affinity than said antibodies or fragments thereof bind FcγRIIA, particularly human FcγRIIA, and block the Fc binding site of FcγRIIB. The present invention also encompasses the use of an anti-FcγRIIB antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, as a single agent therapy for the treatment, prevention, management, or amelioration of a cancer, preferably a B-cell malignancy, particularly, B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, an autoimmune disorder, an inflammatory disorder, an IgE-mediated allergic disorder, or one or more symptoms thereof. The present invention also encompasses the use of an anti-FcγRIIB antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, in combination with other cancer therapies. The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising an anti-FcγRIIB antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, in amounts effective to prevent, treat, manage, or ameliorate a cancer, such as a B-cell malignancy, an autoimmune disorder, an inflammatory disorder, an IgE-mediated allergic disorder, or one or more symptoms thereof. The invention further provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the antibodies of the invention with a vaccine composition. The invention further provides methods of treating cancer and / or regulating immune complex-mediated cell activation by administering the antibodies of the invention to enhance an immune response. The invention also provides methods of breaking tolerance to an antigen by administering an antigen-antibody complex and an antibody of the invention.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Methods of purifying anti a beta antibodies
InactiveUS20070082367A1Efficient removalDecrease and prevent nonspecific and adherenceAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGreek letter betaProtein G
The present application provides methods of purifying Aβ binding proteins having a Fc region, for example, anti-Aβ antibodies or antibody fusions, by adsorbing the Aβ binding protein to a Fc binding agent, such as, for example, Protein A or Protein G, followed by a wash with a divalent cation salt buffer to remove impurities and subsequent recovery of the adsorbed Aβ binding protein. The present application also features methods of eluting the purified Aβ binding protein as well as the incorporation of the methods within a purification train. Kits comprising components for carrying out the methods and instructions for use are also provided.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
Mutated Immunoglobulin-Binding Polypeptides
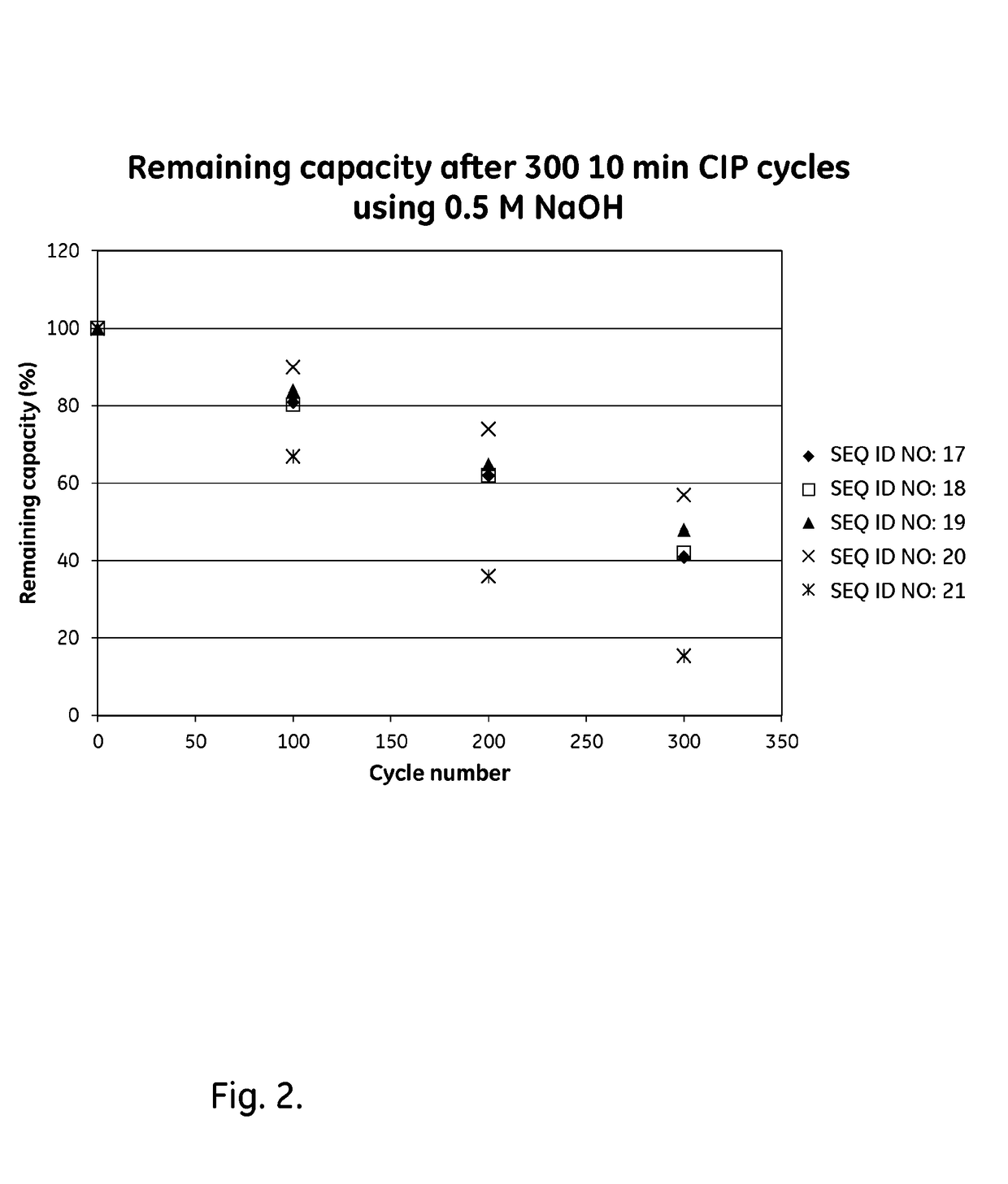
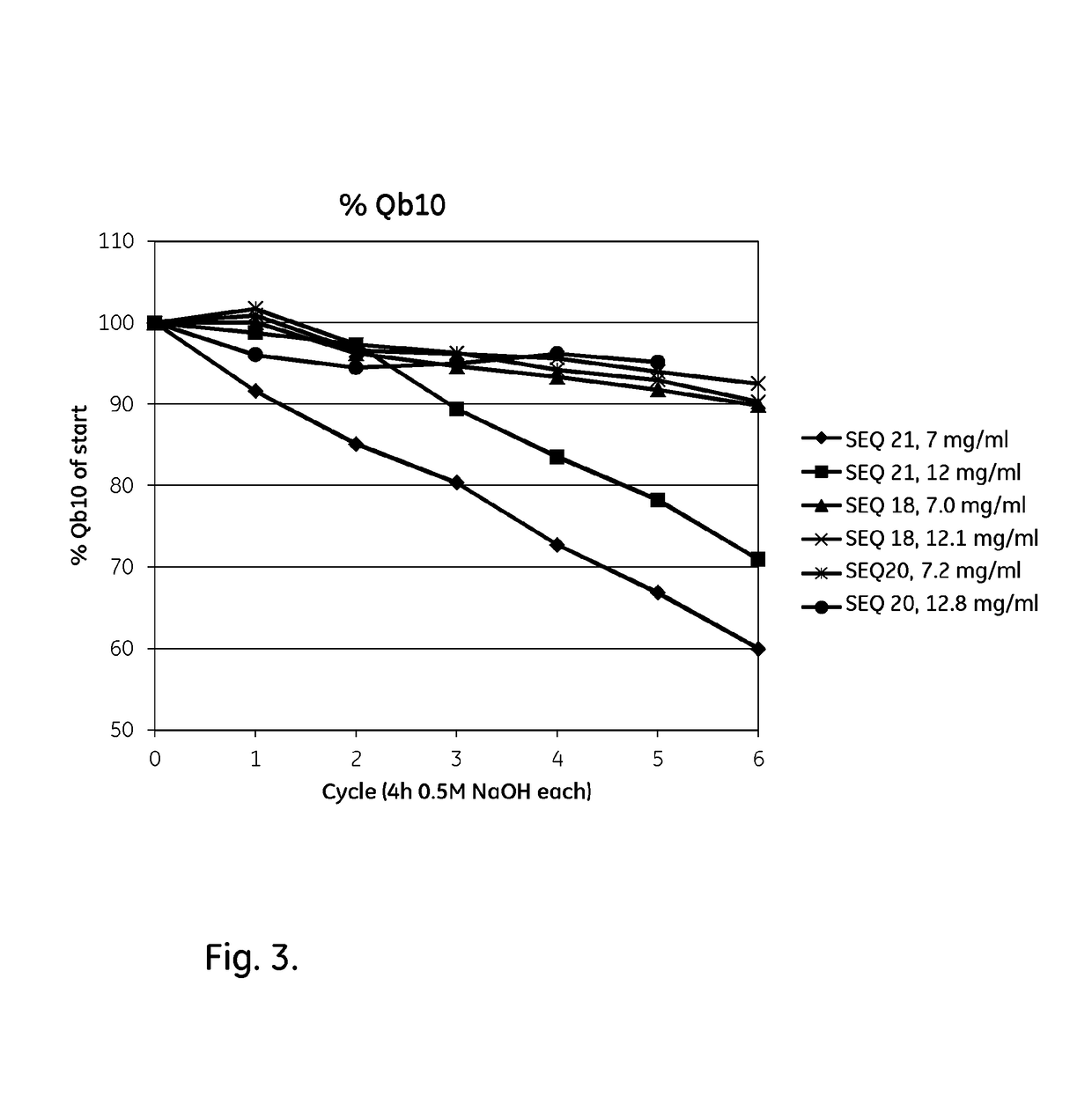
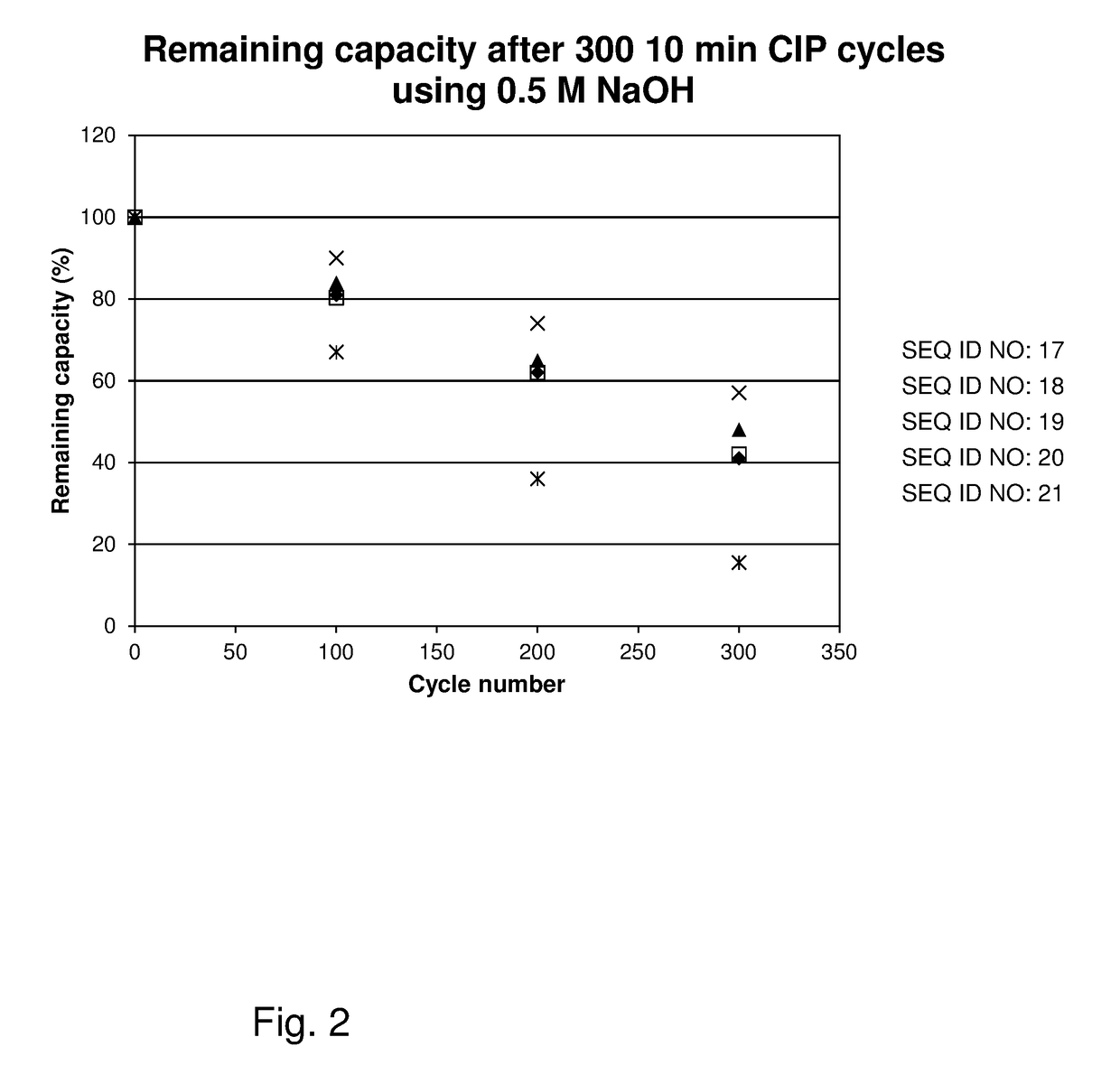
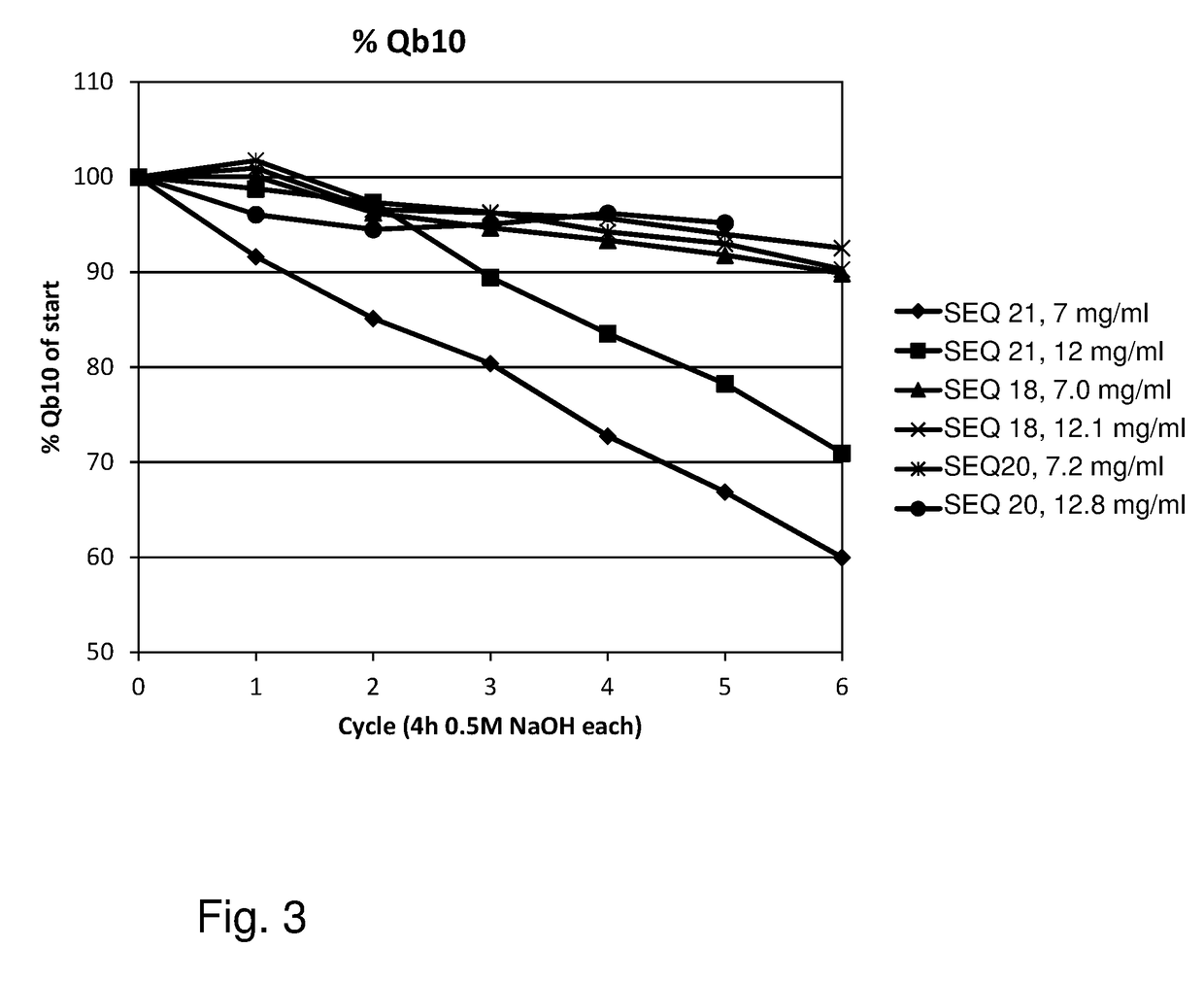
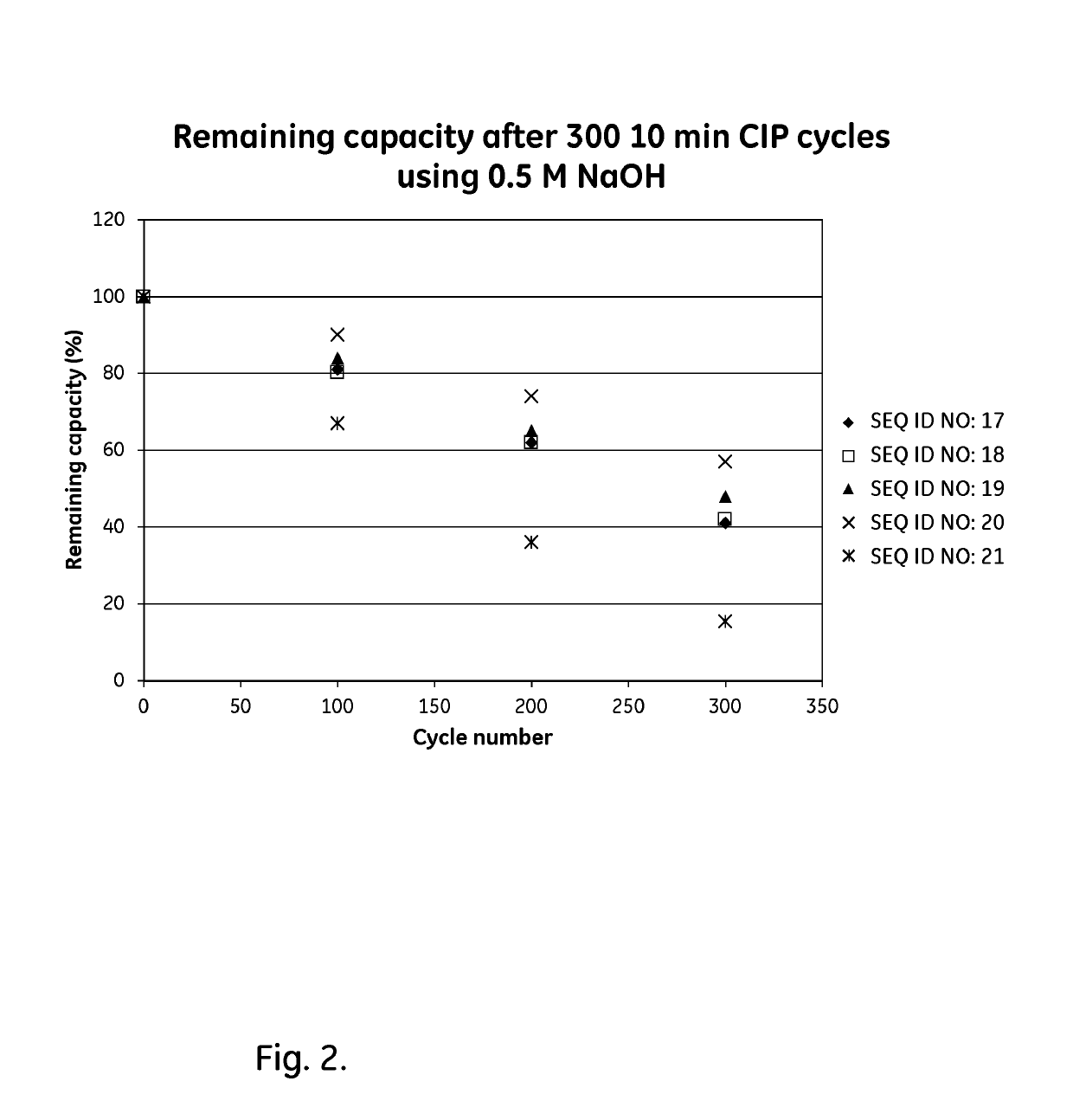
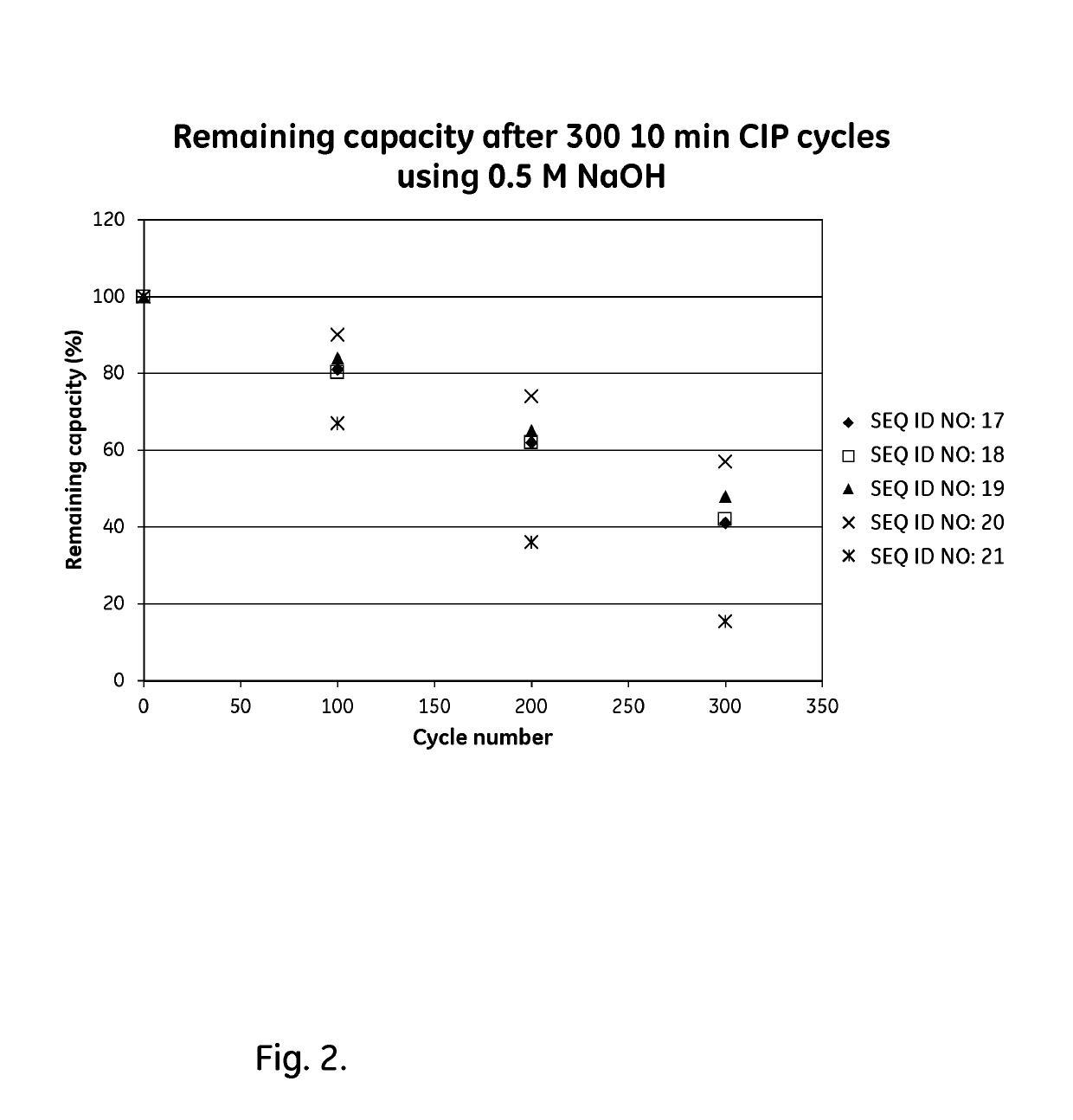
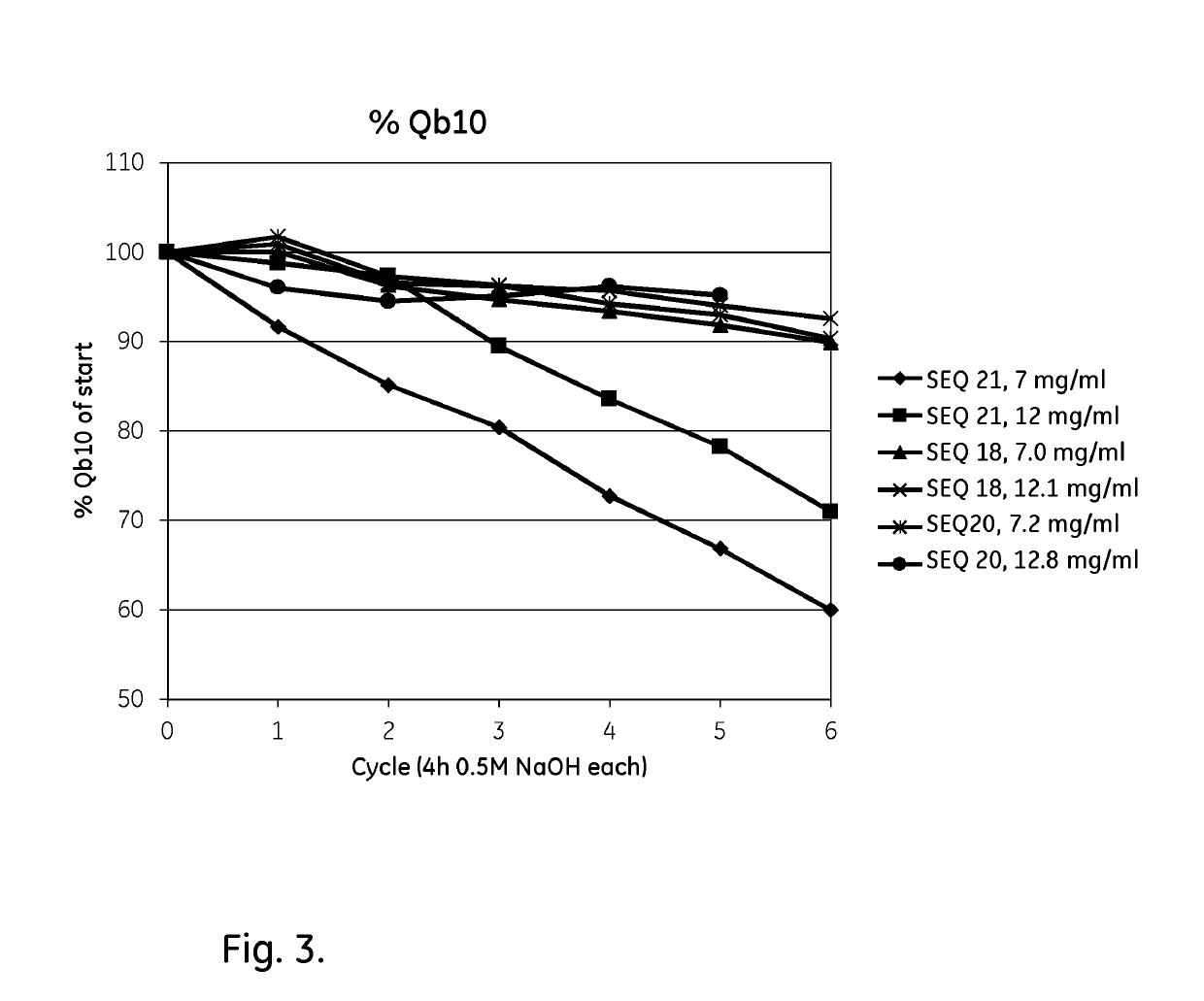
ActiveUS20170334954A1Improved alkaline stabilityImprove stabilityHybrid immunoglobulinsSolid sorbent liquid separationArginineFc binding
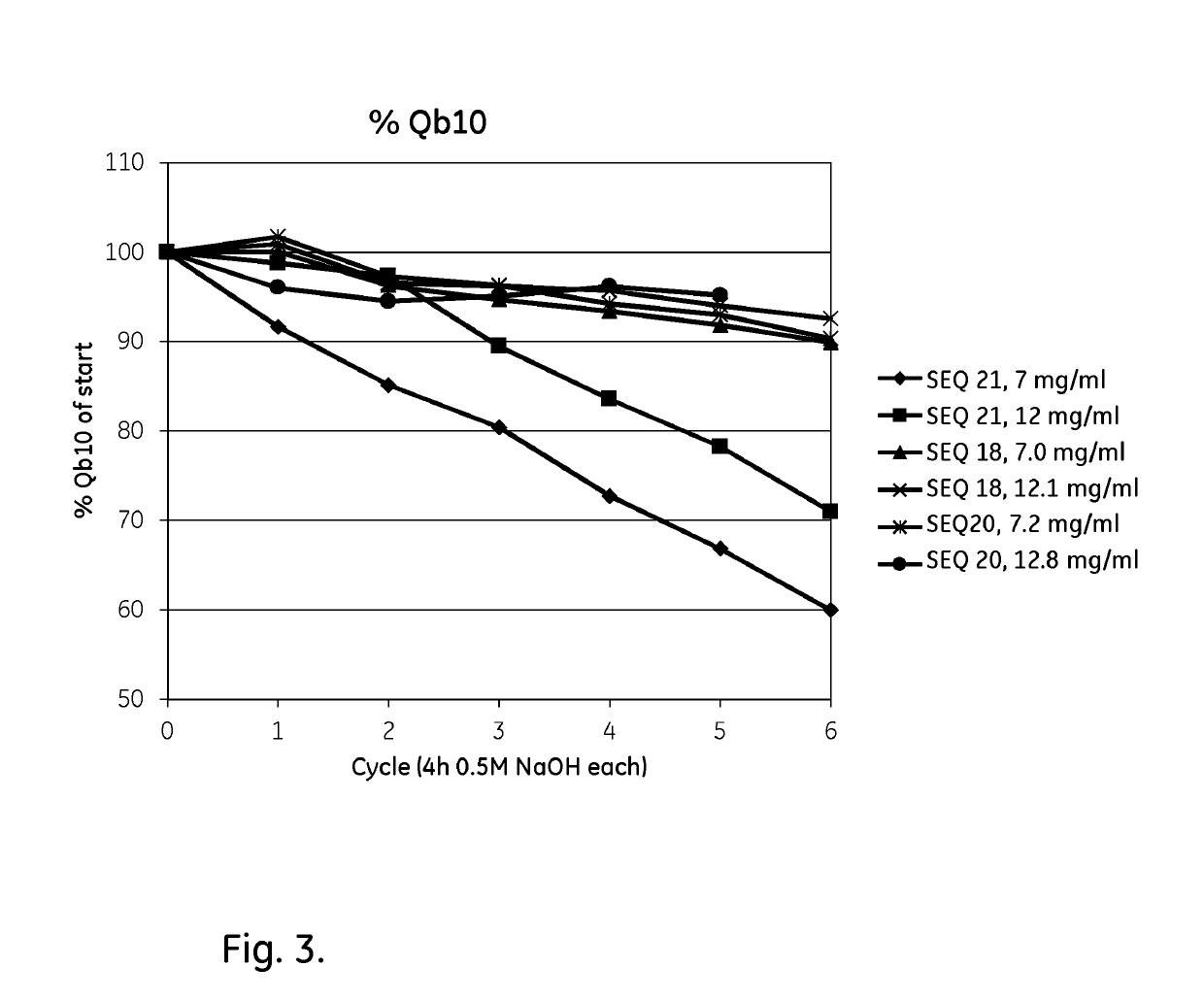
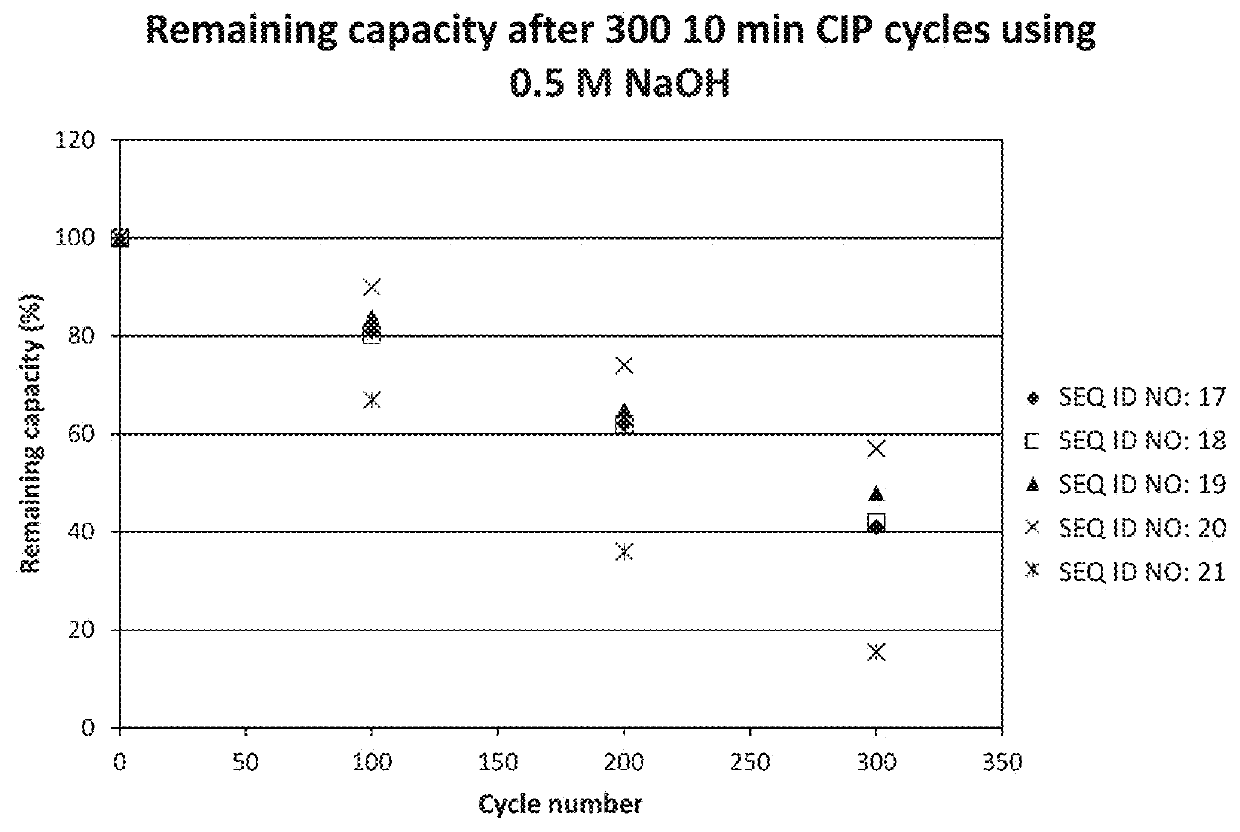
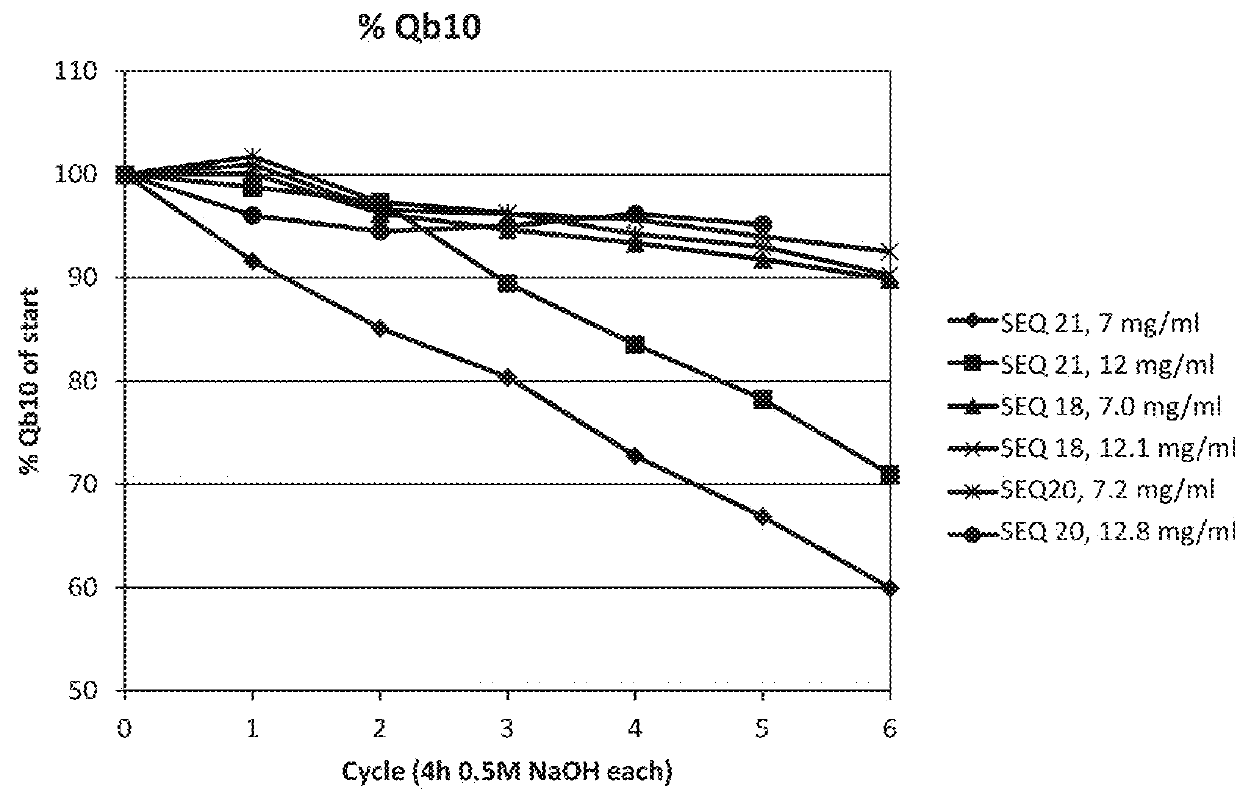
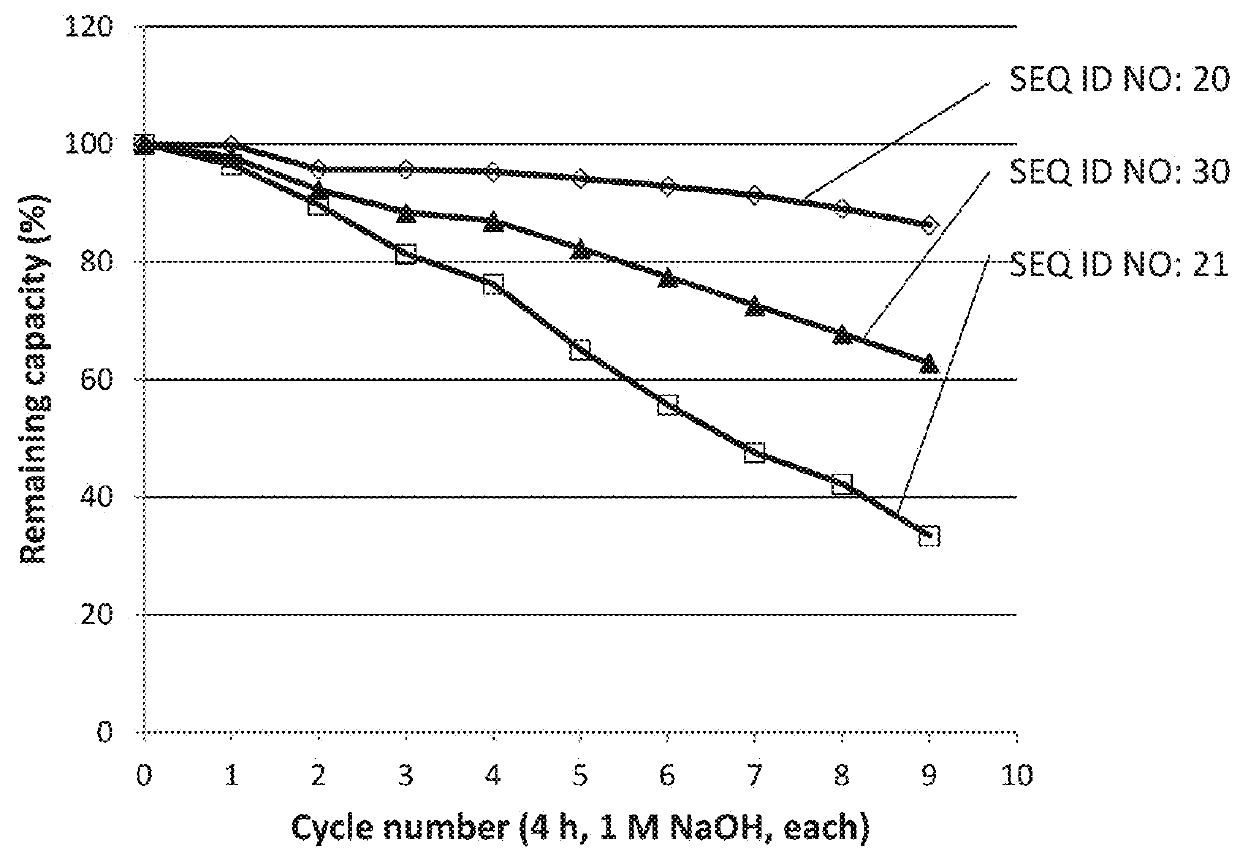
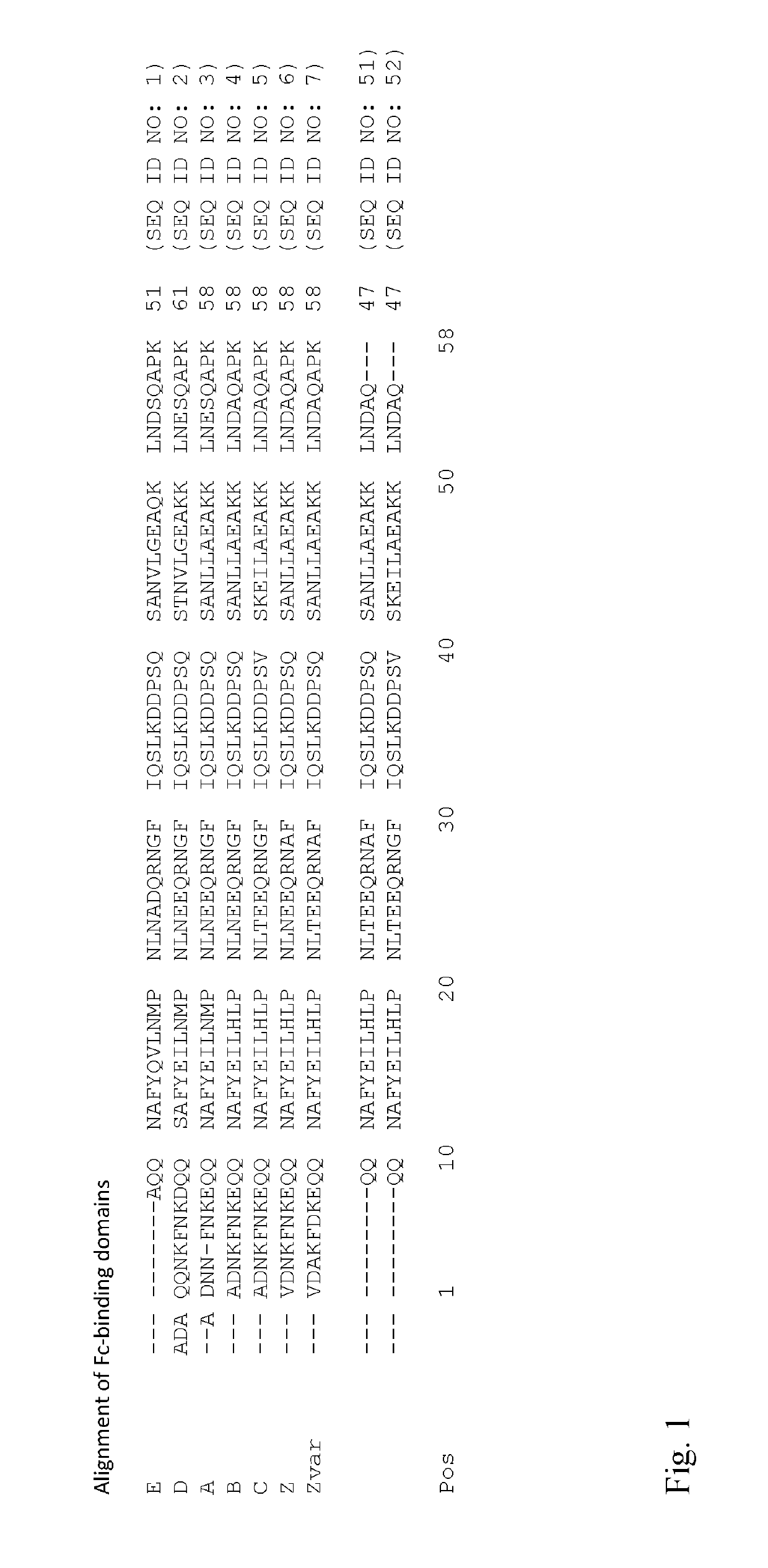
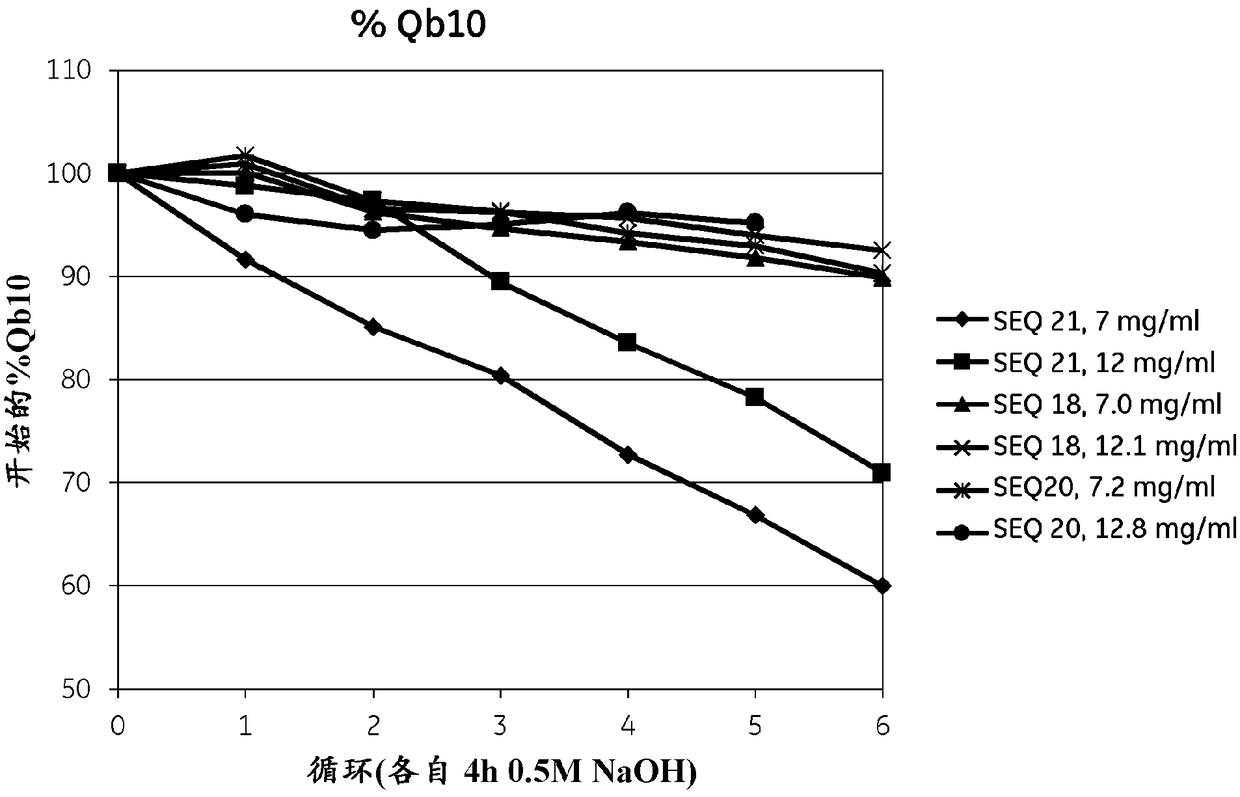
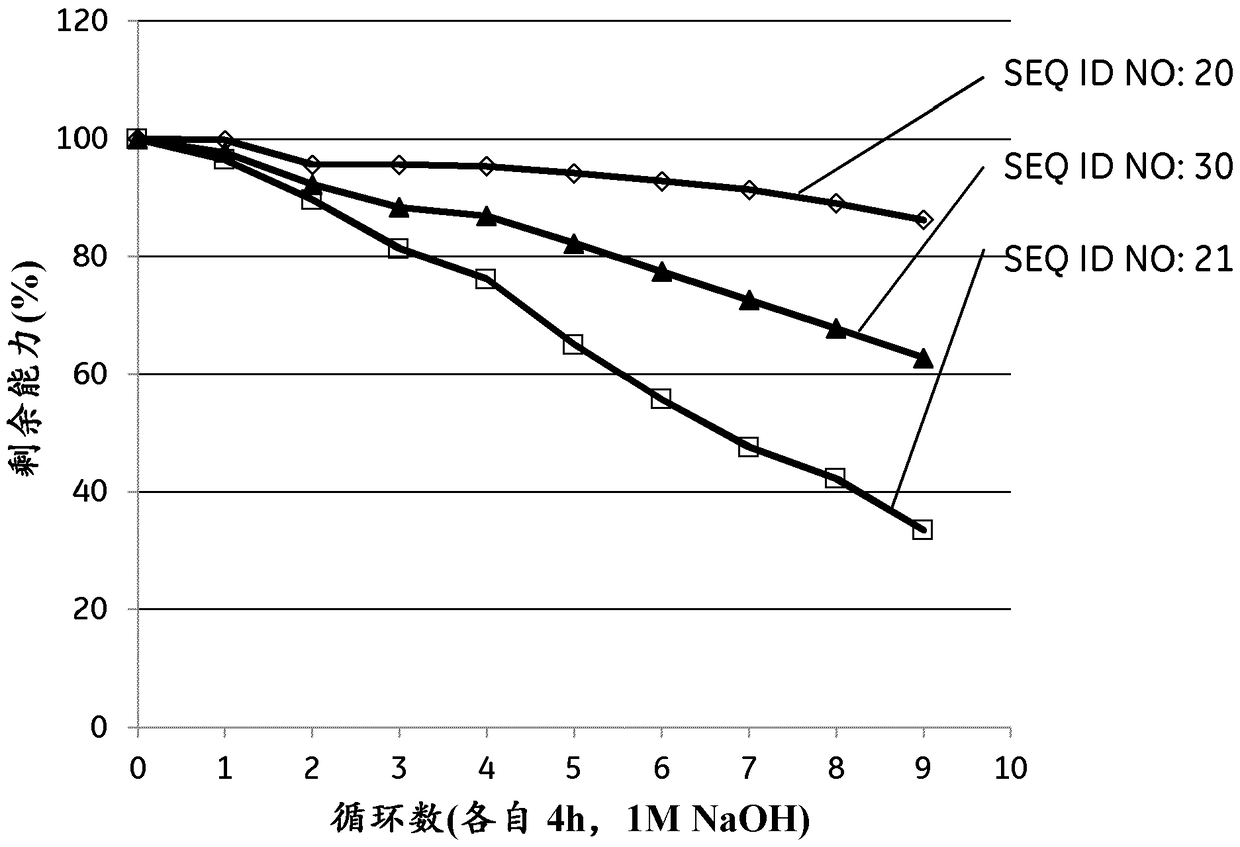
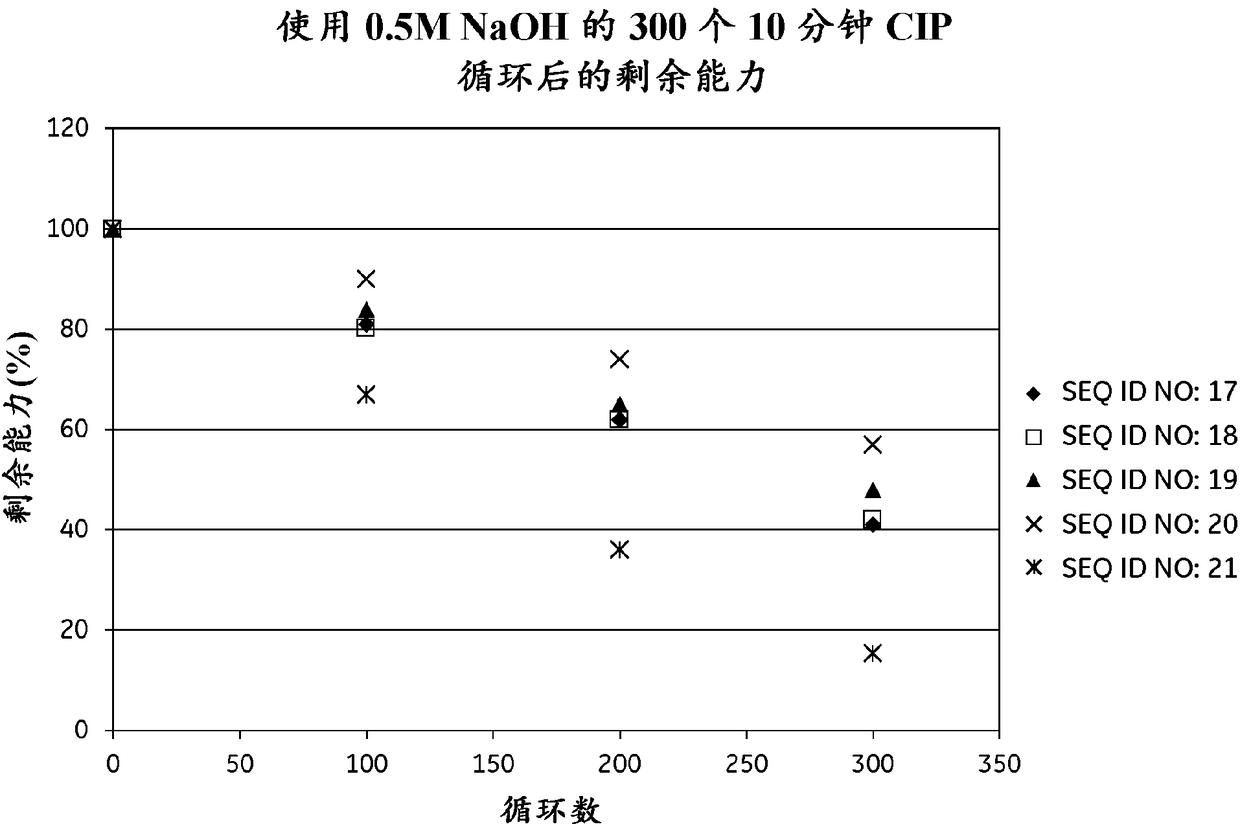
An Fc-binding polypeptide of improved alkali stability, comprising a mutant of an Fc-binding domain of Staphylococcus Protein A (SpA), as defined by SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 5, SEQ ID NO:6, SEQ ID NO:7, SEQ ID NO:22, SEQ ID NO 51 or SEQ ID NO 52 wherein at least the asparagine or serine residue at the position corresponding to position 11 in SEQ ID NO:4-7 has been mutated to an amino acid selected from the group consisting of glutamic acid, lysine, tyrosine, threonine, phenylalanine, leucine, isoleucine, tryptophan, methionine, valine, alanine, histidine and arginine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)-binding polypeptide variants, dimeric Fc binding proteins and methods related thereto
InactiveCN101124245AImprove stabilityEnhance binding interactionSerum immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsFc bindingDrug biological activity
The compositions and methods of the invention are based in part on our discovery that effector functions mediated by Fc-containing polypeptides can be altered by modifying one or more amino acid residues in the polypeptide (by, eg, electrostatic optimization). Polypeptides that can be produced according to the methods of the invention are highly variable and they can include antibodies and fusion proteins comprising Fc regions or biologically active portions thereof.
Owner:BIOGEN IDEC MA INC
FcGammaRIIB Specific Antibodies and Methods of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20090092610A1Enhance immune responseImprove responseImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCell activationImmune complex deposition
The present invention relates to antibodies or fragments thereof that specifically bind the extracellular domain of FcγRIIB, particularly human FcγRIIB, and block the Fc binding site of human FcγRIIB. The invention provides methods of treating cancer and / or regulating immune complex-mediated cell activation by administering the antibodies of the invention to enhance an immune response. The invention also provides methods of breaking tolerance to an antigen by administering an antigen-antibody complex and an antibody of the invention.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Separation matrix
ActiveUS20170327534A1Improved alkaline stabilityImprove stabilityOther chemical processesImmunoglobulins against bacteriaCross-linkMicrometer
The invention relates to a separation matrix comprising at least 11 mg / ml Fc-binding ligands covalently coupled to a porous support, wherein:a) the ligands comprise multimers of alkali-stabilized Protein A domains, andb) the porous support comprises cross-linked polymer particles having a volume-weighted median diameter (d50,v) of 56-70 micrometers and a dry solids weight of 55-80 mg / ml.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
FcγRIIB specific antibodies and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS8968730B2Enhance immune responseImprove responseImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCell activationImmune complex deposition
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Immunoglobulin Fc polypeptides
ActiveUS8679493B2Reduced affinity and binding abilityReduced affinity to and ability to bindCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
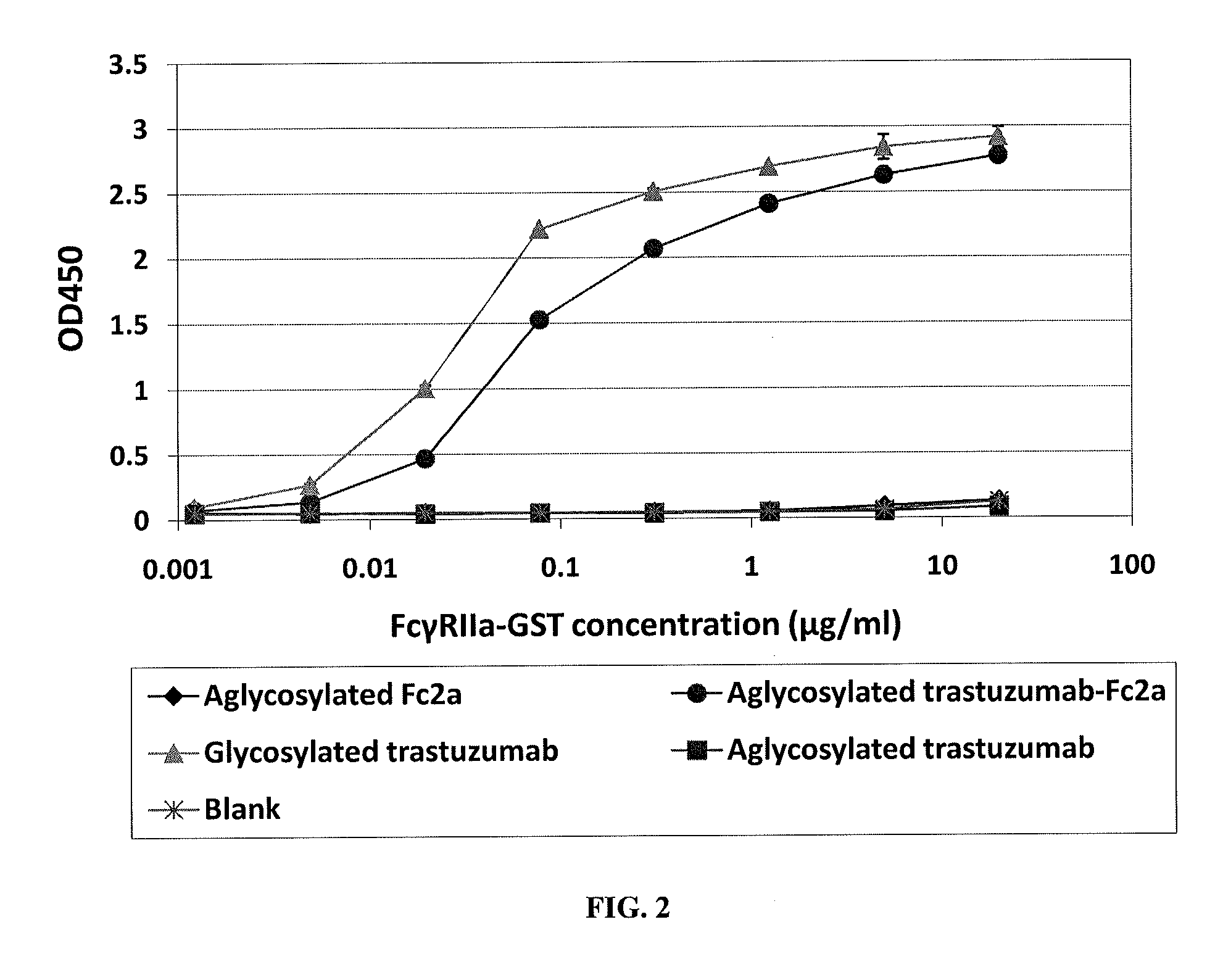
Methods and compositions involving polypeptides having an aglycosylated antibody Fc domain. In certain embodiments, polypeptides have an aglycosylated Fc domain that contains one or more substitutions compared to a native Fc domain. Additionally, some embodiments involve an Fc domain that is binds some Fc receptors but not others. For example, polypeptides are provided with an aglycosylated Fe domain that selectively binds FcγRI at a level within 2-fold of a glycosylated Fc domain, but that is significantly reduced for binding to other Fc receptors. Furthermore, methods and compositions are provided for promoting antibody-dependent cell-mediated toxicity (ADCC) using a polypeptide having a modified aglycosylated Fc domain and a second non-Fc binding domain, which can be an antigen binding region of an antibody or a non-antigen binding region. Some embodiments concern antibodies with such polypeptides, which may have the same or different non-Fc binding domain.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
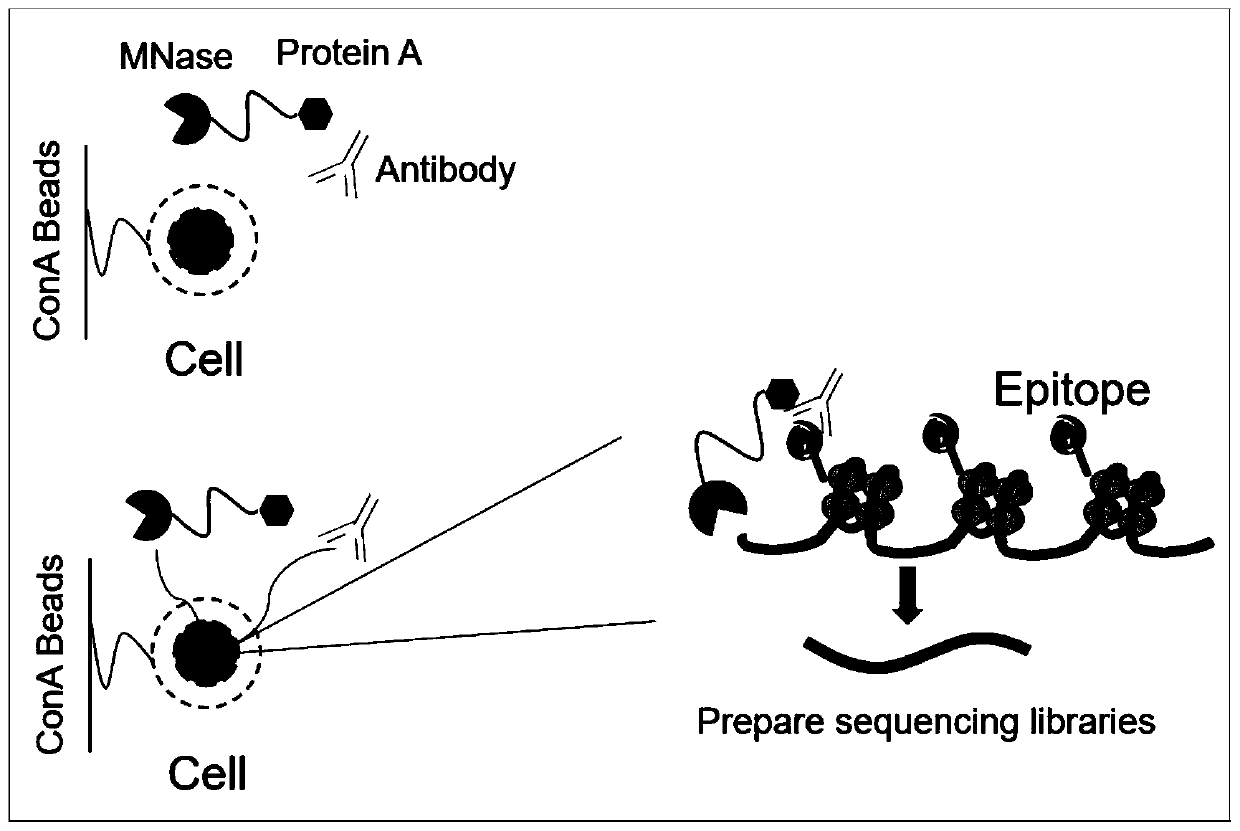
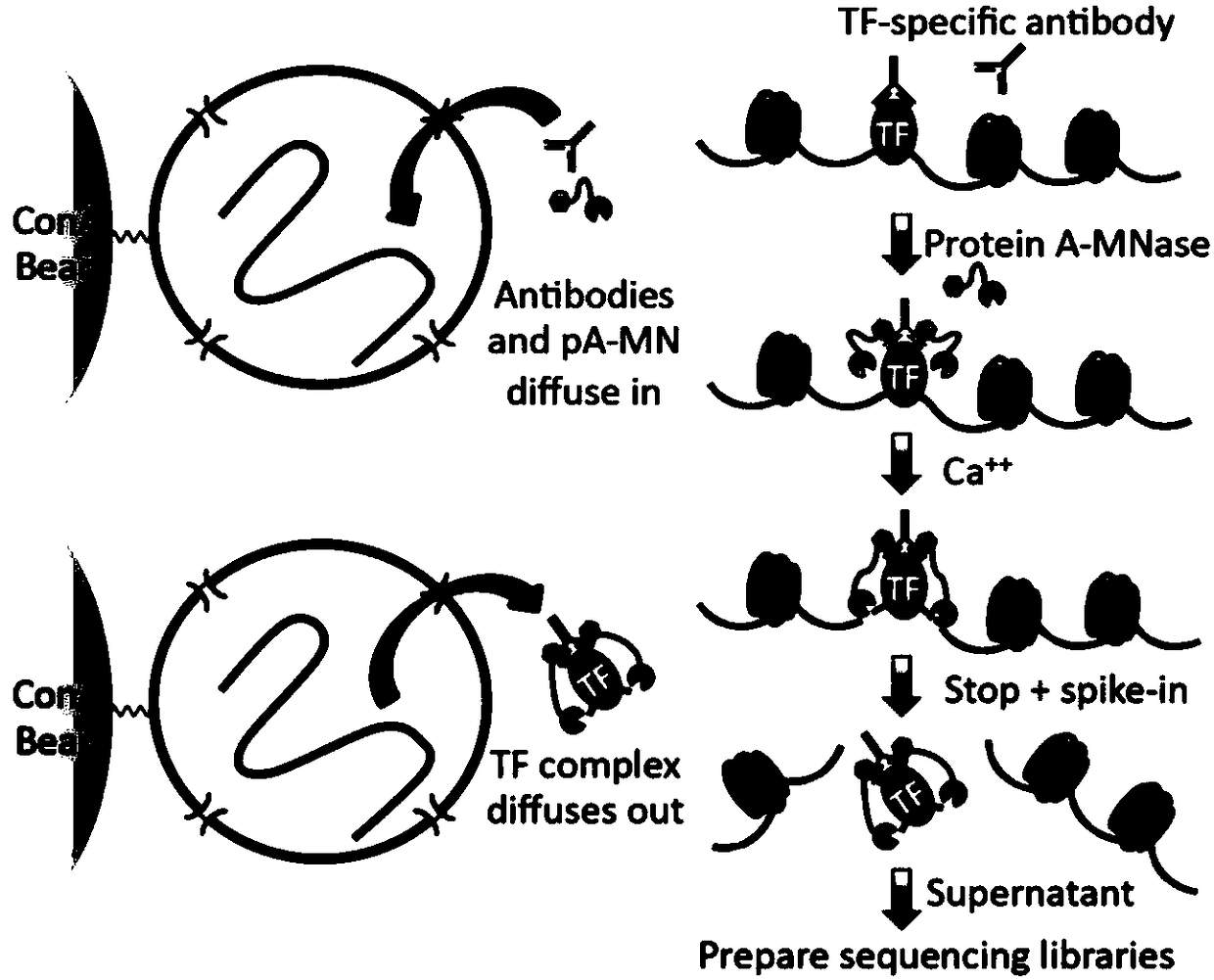
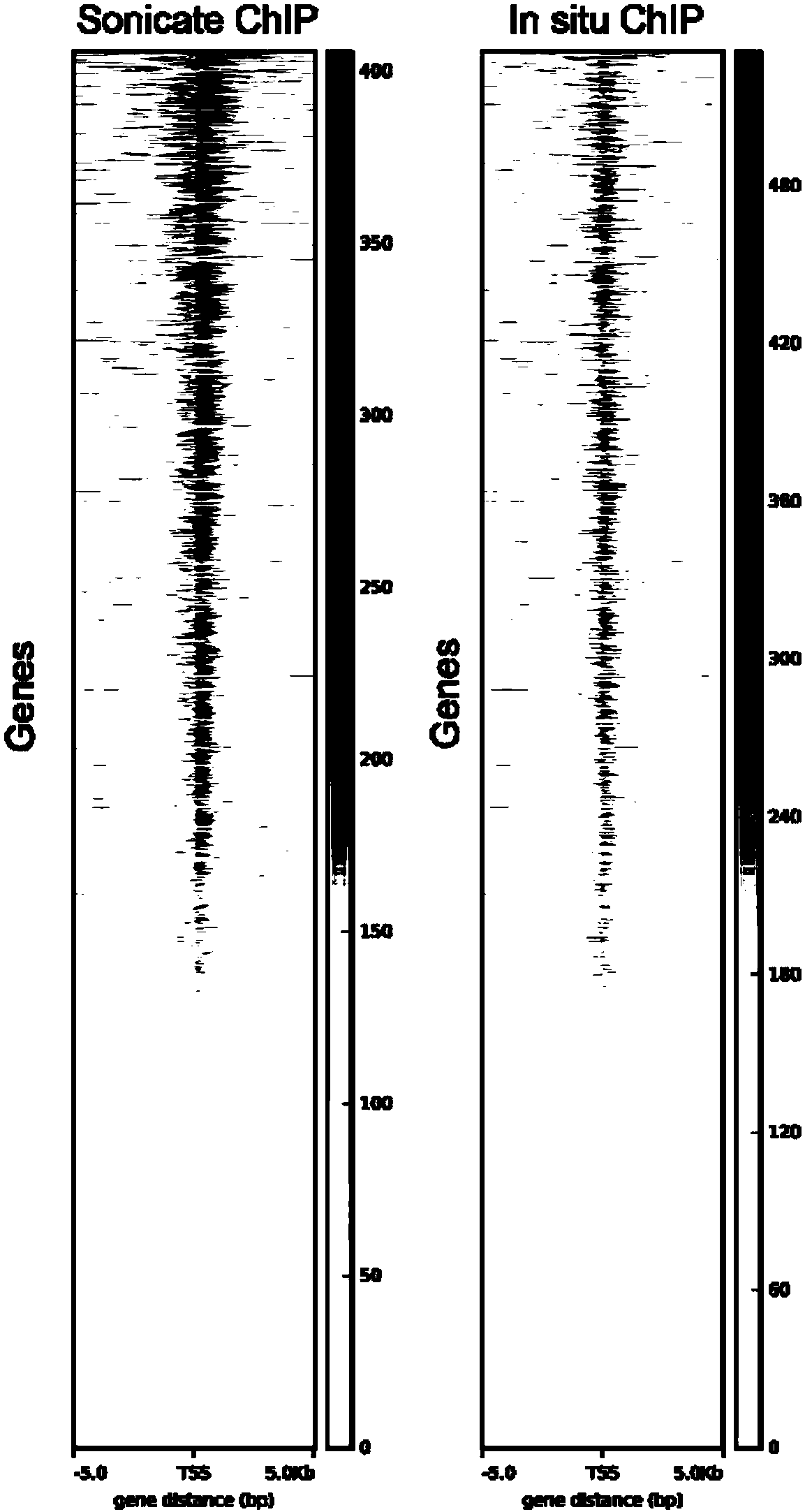
Fusion protein used for single-cell ChIP-seq library preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN110372799AImprove accuracySimplify the experimental processPolypeptide with affinity tagMicrobiological testing/measurementTn5 transposaseFc binding
The invention relates to a fusion protein used for single-cell ChIP-seq library preparation and application thereof. The fusion protein comprises Tn5 transposase and an Fc binding protein; a kit comprises the fusion protein and other auxiliary detection reagents; a method uses the fusion protein or the kit for ChIP-seq detection. The fusion protein, the kit and the method can improve the library building efficiency and lower the library background in the ChIP-seq detection process, so that the accuracy of the ChIP-seq detection method can be improved, and the experimental flow of ChIP-seq canbe simplified.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Separation Matrix
ActiveUS20190119318A1Improved alkaline stabilityImprove stabilityOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationCross-linkMicrometer
The invention relates to a separation matrix comprising at least 11 mg / ml Fc-binding ligands covalently coupled to a porous support, wherein: a) the ligands comprise multimers of alkali-stabilized Protein A domains, and b) the porous support comprises cross-linked polymer particles having a volume-weighted median diameter (d50,v) of 56-70 micrometers and a dry solids weight of 55-80 mg / ml.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Separation method
ActiveUS20180094024A1Improve stabilityOther chemical processesImmunoglobulins against bacteriaArginineFc binding
The invention relates to a method of isolating an immunoglobulin, comprising the steps of:a) providing a separation matrix comprising multimers of immunoglobulin-binding alkali-stabilized Protein A domains covalently coupled to a porous support,b) contacting a liquid sample comprising an immunoglobulin with the separation matrix,c) washing said separation matrix with a washing liquid,d) eluting the immunoglobulin from the separation matrix with an elution liquid, ande) cleaning the separation matrix with a cleaning liquid,wherein the alkali-stabilized Protein A domains comprise mutants of a parental Fc-binding domain of Staphylococcus Protein A (SpA), as defined by, or having at least 80% such as at least 90%, 95% or 98% identity to, SEQ ID NO 51 or SEQ ID NO 52, wherein the amino acid residues at positions 13 and 44 of SEQ ID NO 51 or 52 are asparagines and wherein at least the asparagine residue at position 3 of SEQ ID NO 51 or 52 has been mutated to an amino acid selected from the group consisting of glutamic acid, lysine, tyrosine, threonine, phenylalanine, leucine, isoleucine, tryptophan, methionine, valine, alanine, histidine and arginine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Separation matrix
ActiveUS10513537B2Improve stabilityOther chemical processesSerum immunoglobulinsCross-linkMicrometer
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
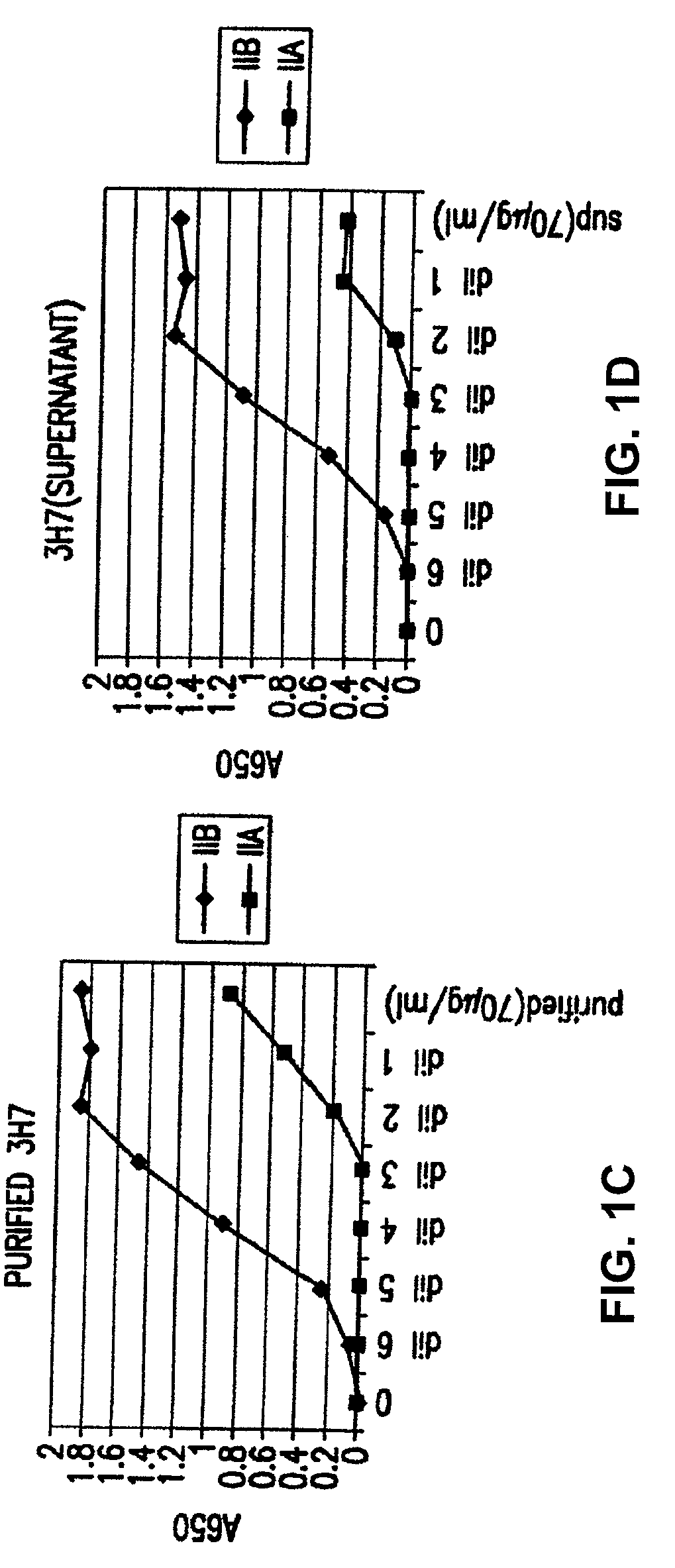
Fc-binding protein, method for producing said protein, and antibody adsorbent using said protein, and methods for purifying and identifying antibody using said adsorbent
ActiveCN105555801AImprove stabilityEfficient manufacturingSugar derivativesBacteriaPurification methodsFc binding
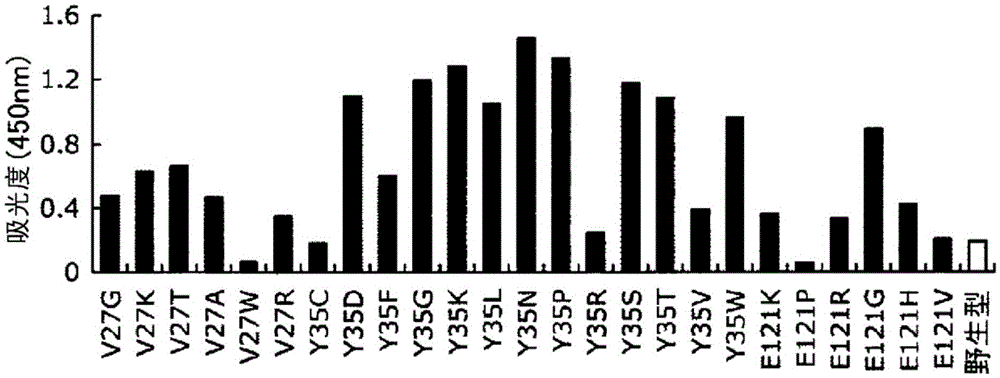
The present invention addresses the first problem of providing an Fc-binding protein having improved stability, especially stability to heat and acid, of the Fc-binding protein, a method for producing this protein, and an antibody adsorbent using this protein. The present invention also addresses the second problem of providing a method that makes it possible to identify the presence or absence of glycosylation of an antibody, and a material to be used in this method. The first problem is solved by an Fc-binding protein having improved stability to heat and acid obtained by substituting amino acid residues at specific positions in the extracellular domain within human Fc[gamma]RIIIa with other specific amino acids, a method for producing this protein, and an antibody adsorbent using this protein. The second problem is solved by using an adsorbent capable of specifically adsorbing an antibody having a sugar chain, the adsorbent being obtained by immobilizing human Fc[gamma]RIIIa on an insoluble carrier.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Multimeric Fc Receptor Polypeptides
ActiveUS20080008700A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFc(alpha) receptorImmune complex deposition
A soluble multimeric protein or polypeptide is disclosed that is able to inhibit interaction of leukocyte Fcgamma receptors (FcgammaR) and immunoglobulin G (IgG). The protein or polypeptide comprises two or more linked Fc binding regions, at least one of which is derived from an FcgammaR type receptor and, particularly, FcgammaRIIa. Also described are polynucleotide molecules encoding the protein or polypeptide and the use thereof in methods of treating a subject for an immune-complex (IC)-mediated inflammatory disease.
Owner:SUPPREMOL GMBH
Fc binding protein and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20130079499A1Improve stabilityStably purifiedSugar derivativesBacteriaFc(alpha) receptorBinding site
Disclosed are: an Fc binding protein having increased stability with respect to heat, acid, and / or alkalinity compared with the wild type; a method for producing same; and a method for specifically isolating protein containing an Fc binding protein binding site using said Fc binding protein as a ligand for affinity chromatography.An Fc binding protein was obtained having increased stability with respect to heat, acid, and / or alkalinity compared with the wild-type human Fc receptor by means of substituting at least one specific amino acid residue in the extracellular domain of the wild-type human Fc receptor with another amino acid residue. The Fc binding protein is useful as a ligand for affinity chromatography for example by immobilizing in a solid phase. Also, when the Fc binding protein is expressed using a host that has been transformed with an expression vector containing a polynucleotide coding for said protein, the amount of produced protein is increased compared with using a wild-type human Fc receptor.
Owner:SAGAMI CHEM RES CENT +1
Improved fc-binding protein, method for producing said protein, antibody adsorbent using said protein, and method for separating antibody using said adsorbent
ActiveUS20170218044A1Improve stabilityEasily accurately separateComponent separationOther chemical processesSorbentAmino acid substitution
Provided are: an Fc-binding protein having improved stability, particularly to heat and acid; a method for producing the protein; an antibody adsorbent using the protein; and a method for separating the antibodies using the adsorbent. Specifically provided are: an Fc-binding protein having improved stability to heat and acid, achieved by substituting an amino-acid residue in a specific position in the extracellular region of human FcyRIIIa with another specific amino acid; a method for producing the protein; an antibody adsorbent using the protein; and a method for separating the antibodies using the adsorbent.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Fusion protein, kit and CHIP-seq detection method
ActiveCN108285494AImprove binding efficiencyImprove cutting efficiencyHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTn5 transposaseFc binding
The invention relates to fusion protein, a kit and a CHIP-seq detection method. The fusion protein comprises Tn5 transposase and Fc binding protein, the kit comprises the fusion protein and other auxiliary detection reagents, and the method is the CHIP-seq detection method by using the fusion protein or the kit. According to the fusion protein, the kit and the method, the library establishment efficiency can be improved in the CHIP-seq detection process, the library background is reduced, the accuracy of the CHIP-seq detection method is improved accordingly, and the experimental process of CHIP-seq is simplified.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
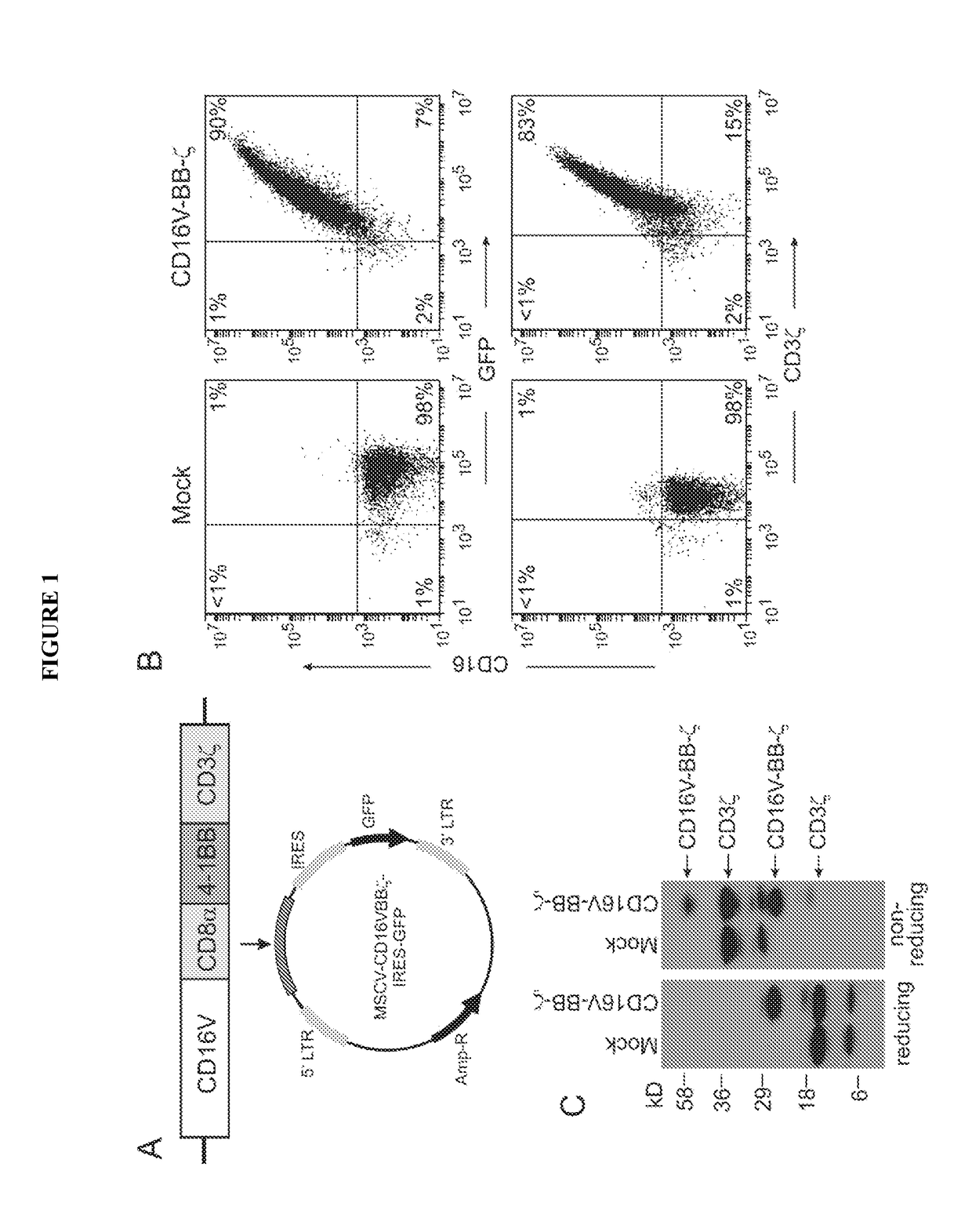
Chimeric receptors and uses thereof in immune therapy
InactiveUS20170281682A1Good curative effectEnhanced ADCC activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammal material medical ingredientsFc bindingCytotoxicity
Disclosed herein are chimeric receptors comprising an extracellular domain with affinity and specific for the Fc portion of an immunoglobulin molecule (Ig), an Fc-binding domain; a transmembrane domain; at least one co-stimulatory signaling domain; and a cytoplasmic signaling domain comprising an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM). Also provided herein are nucleic acids encoding such chimeric receptors and immune cells expressing the chimeric receptors. Such immune cells can be used to enhance antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and / or to enhance antibody-based immunotherapy, such as cancer immunotherapy.
Owner:UNUM THERAPEUTICS INC
Fc-BINDING PROTEIN, METHOD FOR PRODUCING SAID PROTEIN, AND ANTIBODY ADSORBENT USING SAID PROTEIN, AND METHODS FOR PURIFYING AND IDENTIFYING ANTIBODY USING SAID ADSORBENT
ActiveUS20160222081A1Increased stability against heatIncreased acidSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAmino acid substitutionFc binding
The present invention addresses the first problem of providing an Fc-binding protein having improved stability, especially stability to heat and acid, of the Fc-binding protein, a method for producing this protein, and an antibody adsorbent using this protein. The present invention also addresses the second problem of providing a method that makes it possible to identify the presence or absence of glycosylation of an antibody, and a material to be used in this method. The first problem is solved by an Fc-binding protein having improved stability to heat and acid obtained by substituting amino acid residues at specific positions in the extracellular domain within human FcγRIIIa with other specific amino acids, a method for producing this protein, and an antibody adsorbent using this protein. The second problem is solved by using an adsorbent capable of specifically adsorbing an antibody having a sugar chain, the adsorbent being obtained by immobilizing human FcγRIIIa on an insoluble carrier.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Magnetic Immunoglobulin-Binding Particles
PendingUS20190339261A1Improve bindingHigh yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGlobin bindingMagnetic bead
The invention discloses an immunoglobulin-binding magnetic bead, comprising a porous matrix and one or more magnetic particles embedded in said matrix, wherein said matrix comprises a porous polymer and at least 10 mg / ml Fc-binding proteinaceous ligands covalently coupled to said porous polymer.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
Engineered immunoglobulin FC polypeptides
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
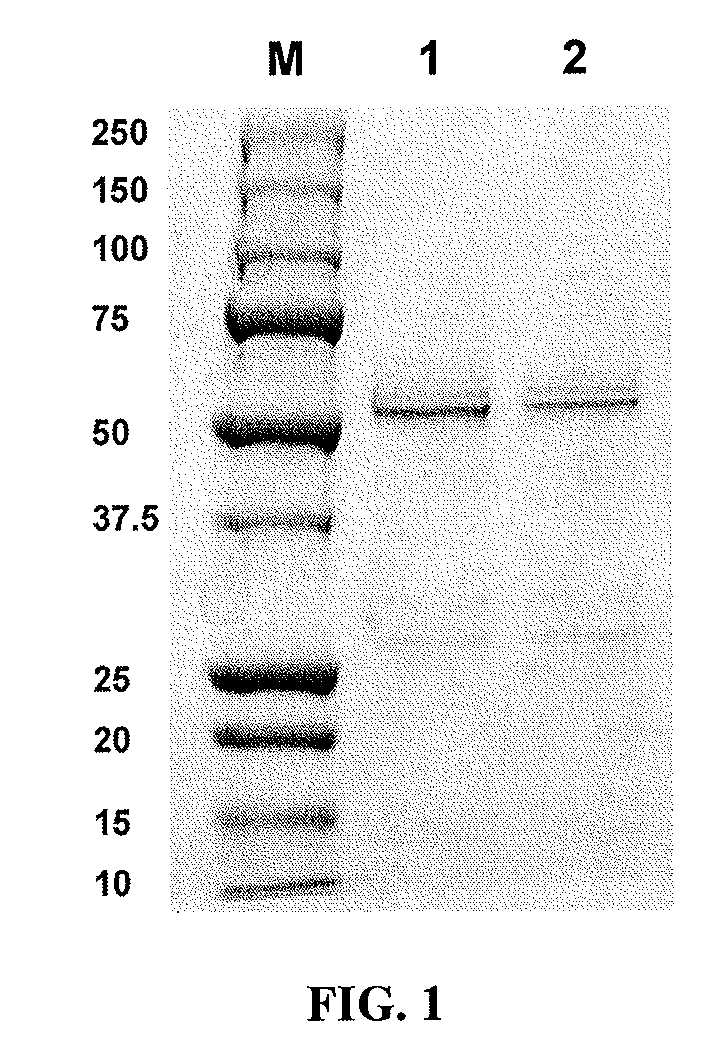
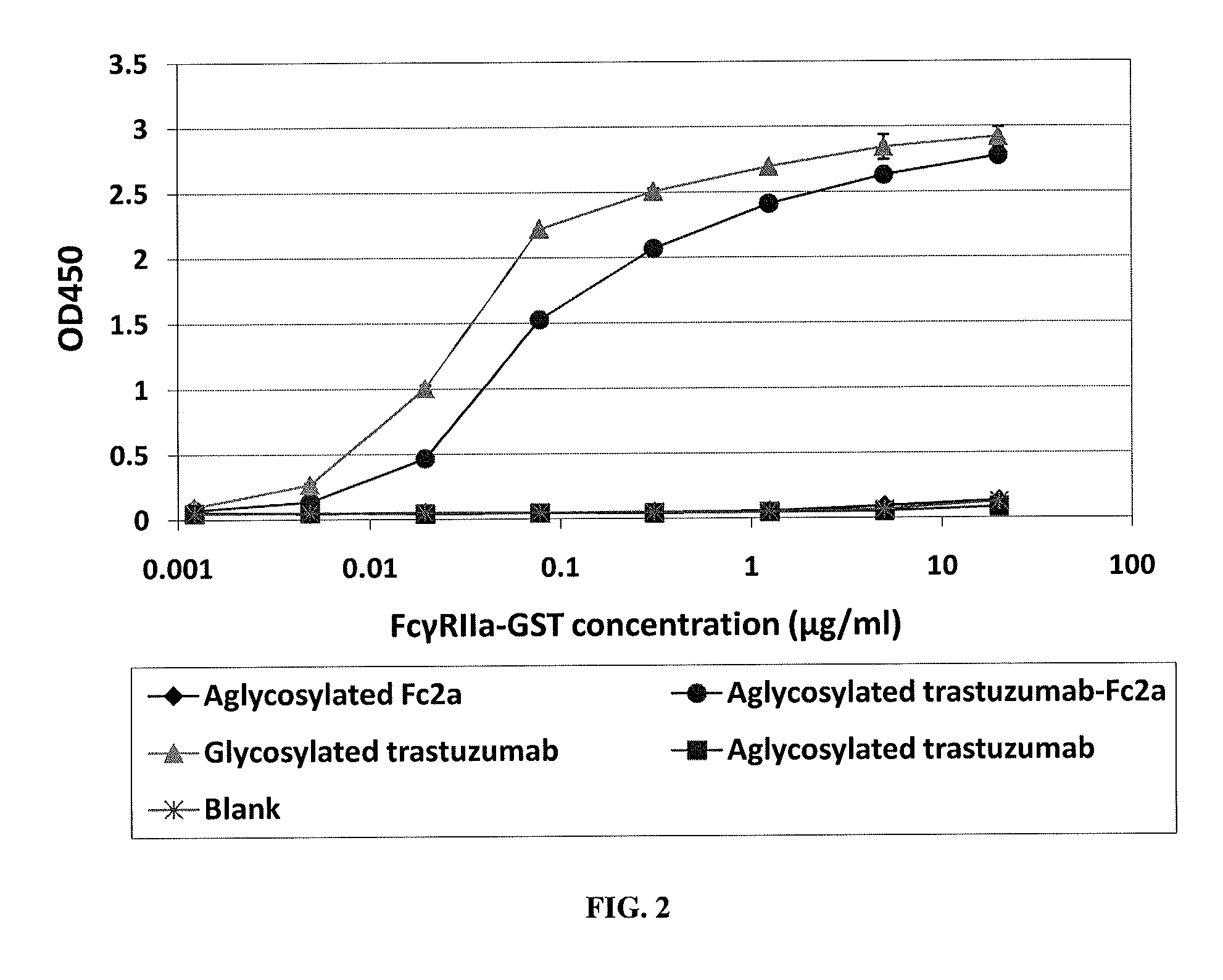
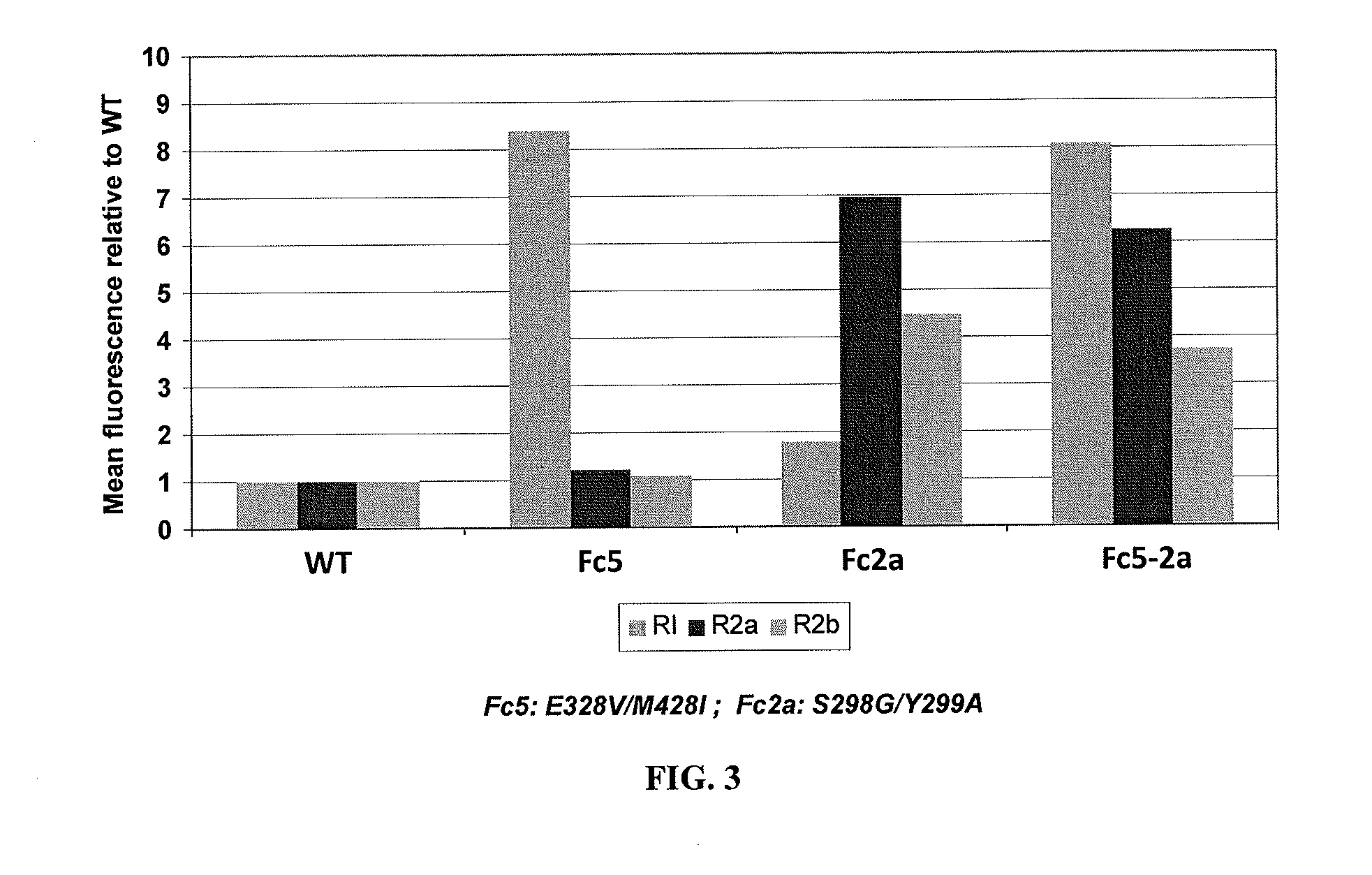
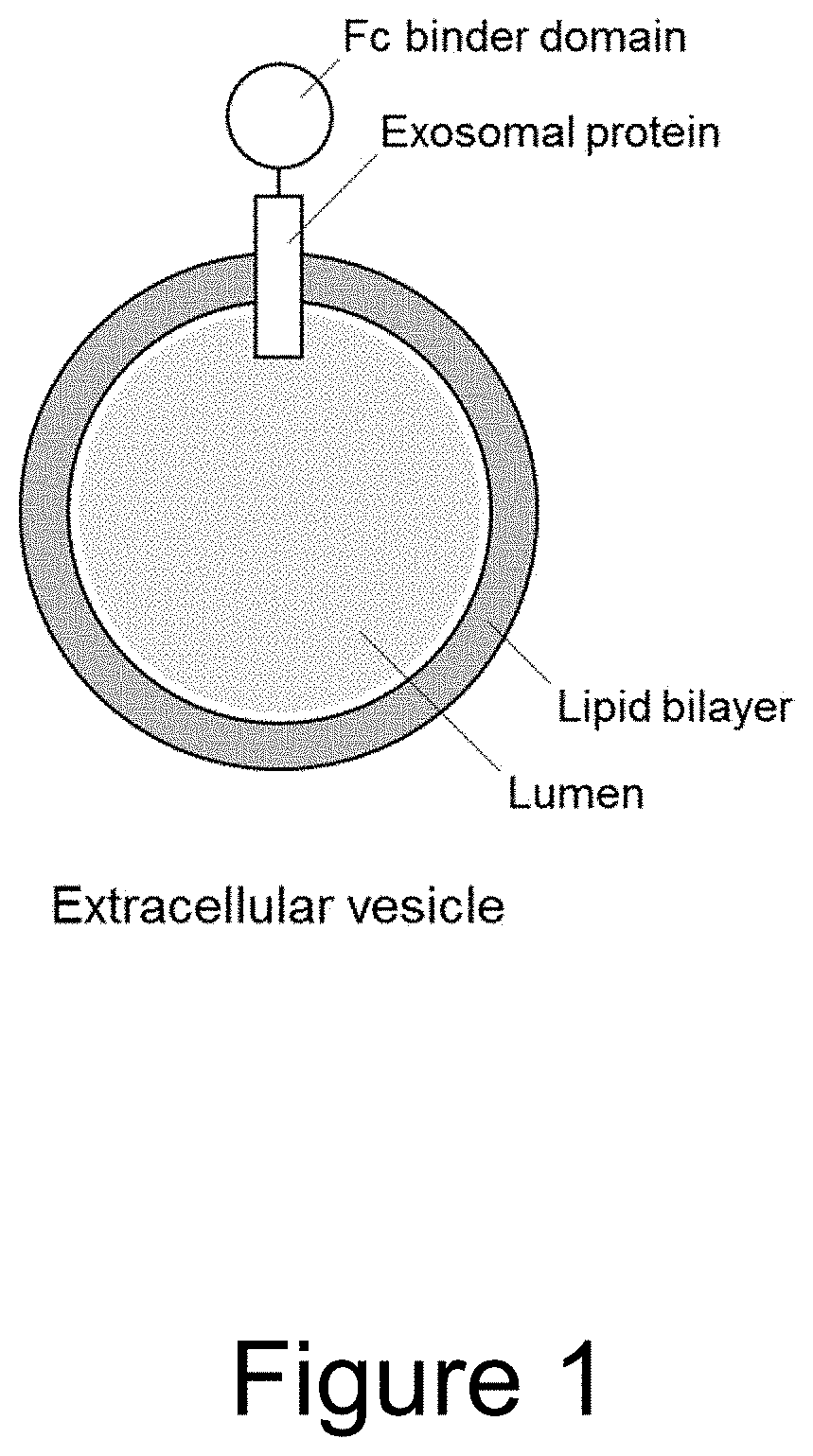
Extracellular vesicle comprising a fusion protein having fc binding capacity
ActiveUS20200109183A1Enhance therapeutic potentialOvercome problemsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsExtracellular vesicleAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention pertains to extracellular vesicle (EV) therapeutics, wherein the EVs are coated with proteins containing Fc domains (such as antibodies) for i.a. targeting and therapeutic applications. The coating of EVs is achieved through inventive protein engineering of EV polypeptides. The present invention thus relates to methods for coating of EVs, EVs per se, as well as pharmaceutical compositions and medical applications of such EVs coated with Fc containing proteins.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Engineered immunoglobulin fc polypeptides
Methods and compositions involving polypeptides having an aglycosylated antibody Fc domain. In certain embodiments, polypeptides have an aglycosylated Fc domain that contains one or more substitutions compared to a native Fc domain. Additionally, some embodiments involve an Fc domain that is binds some Fc receptors but not others. For example, polypeptides are provided with an aglycosylated Fc domain that selectively binds FcγRIIa, but that is significantly reduced for binding to the highly homologous FcγRIIb receptors. Furthermore, methods and compositions are provided for promoting antibody-dependent cell-mediated toxicity (ADCC) using a polypeptide having a modified aglycosylated Fc domain and a second non-Fc binding domain, which can be an antigen binding region of an antibody or a non-antigen binding region. Some embodiments concern antibodies with such polypeptides, which may have the same or different non-Fc binding domain.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Engineered immunoglobulin fc polypeptides displaying improved complement activation
ActiveUS20160297886A1Strongly enhanced CDCKilling of cells targetedImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsFc(alpha) receptorActivation method
Methods and compositions involving polypeptides having an aglycosylated antibody Fc domain are provided. In certain embodiments, polypeptides have an aglycosylated Fc domain that contains one or more substitutions compared to a native Fc domain. Additionally, some embodiments involve an Fc domain that is binds some Fc receptors but not others. For example, polypeptides are provided with an aglycosylated Fc domain that selectively binds Clq, and optionally activating Fc receptors, but that is significantly reduced for binding to the inhibitory FcγRIIb receptor. Furthermore, methods and compositions are provided for promoting complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) using a polypeptide having a modified aglycosylated Fc domain and a second non-Fc binding domain, which can be an antigen binding region of an antibody or a non-antigen binding region. Some embodiments concern antibodies with such polypeptides, which may have the same or a different non-Fc binding domain.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
MULTIMERIC Fc RECEPTOR POLYPEPTIDES INCLUDING A MODIFIED Fc DOMAIN
InactiveUS20100112080A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFc(alpha) receptorDisease
A soluble multimeric polypeptide or protein is disclosed that is able to inhibit interaction of leukocyte Fcγ receptors (FcγR) and immunoglobulin G (IgG). The protein or polypeptide comprises two or more Fc binding regions linked in a head to tail arrangement, at least one of which is derived from an FcγR type receptor, and an Fc domain of an immunoglobulin which has been modified to reduce or prevent binding to the said Fc binding regions and / or to alter effector function. Also described are polynucleotide molecules encoding the polypeptide or protein and the use thereof in methods of treating a subject for an immune-complex (IC)-mediated inflammatory disease.
Owner:SUPPREMOL GMBH
Fc binding fragments comprising a cd137 antigen-binding site
PendingUS20210277134A1Avoiding liver inflammationAdvantageously avoidedImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsInfectious DisorderCD137
The invention relates to specific binding members that bind CD137. The specific binding members comprise a CD137 antigen-binding site located in a constant domain of the specific binding member and find application in the treatment of cancer and infectious diseases, for example.
Owner:F STAR THERAPEUTICS LTD
Mutated immunoglobulin-binding polypeptides
ActiveCN109071612AHighly selective bindingGood alkali stabilitySolid sorbent liquid separationDepsipeptidesArginineFc binding
An Fc-binding polypeptide of improved alkali stability, comprising a mutant of aparental Fc-binding domain of Staphylococcus Protein A (SpA), as defined by SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 5, SEQ ID NO: 6, SEQ ID NO: 7, SEQ ID NO: 22, SEQ ID NO 51 or SEQ ID NO 52, wherein at least the asparagine or serine residue at the position corresponding to position 11 in SEQID NO: 4-7 has been mutated to an amino acid selected from the group consisting of glutamic acid, lysine, tyrosine, threonine, phenylalanine, leucine, isoleucine, tryptophan, methionine, valine, alanine, histidine and arginine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com