Patents
Literature
100 results about "Dorsal roots" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
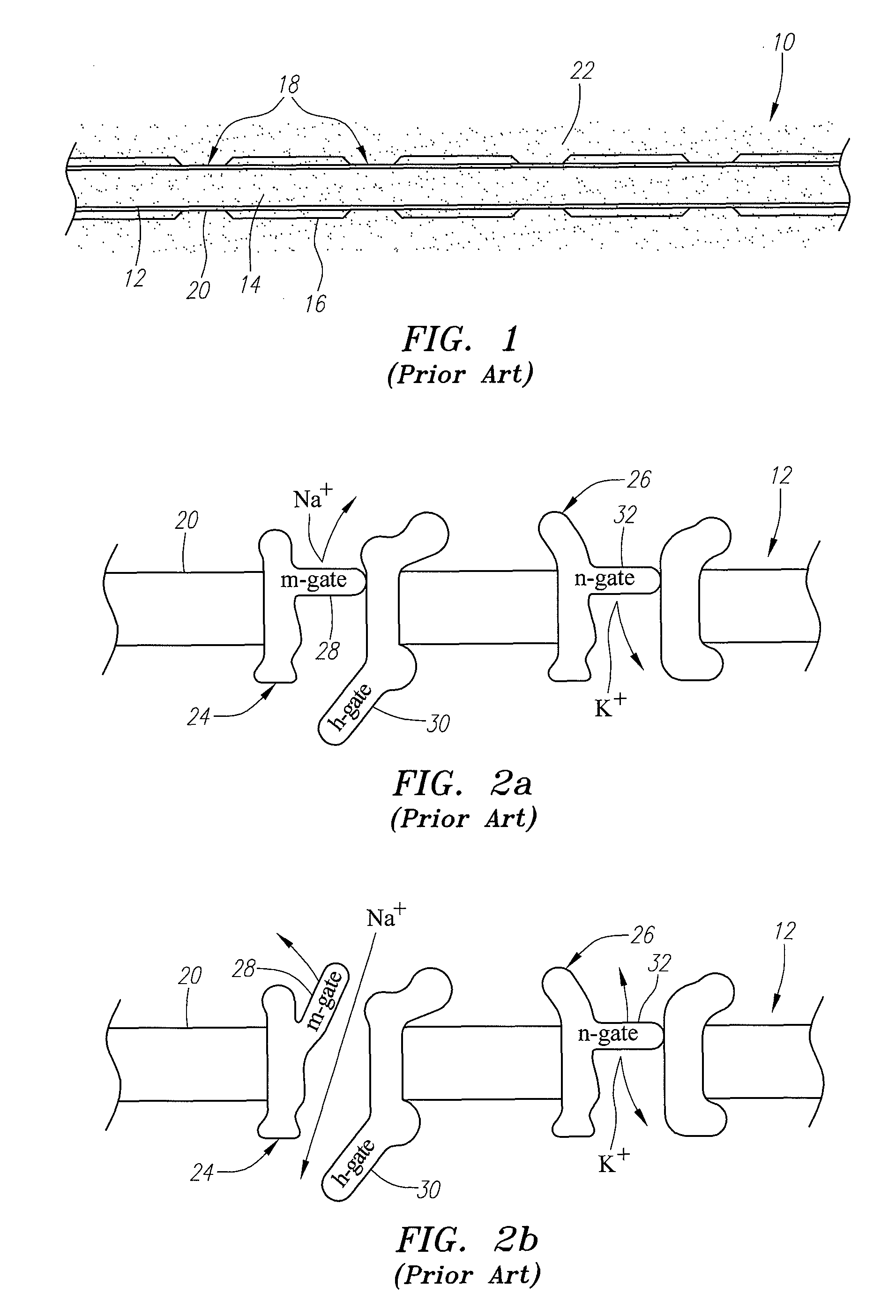
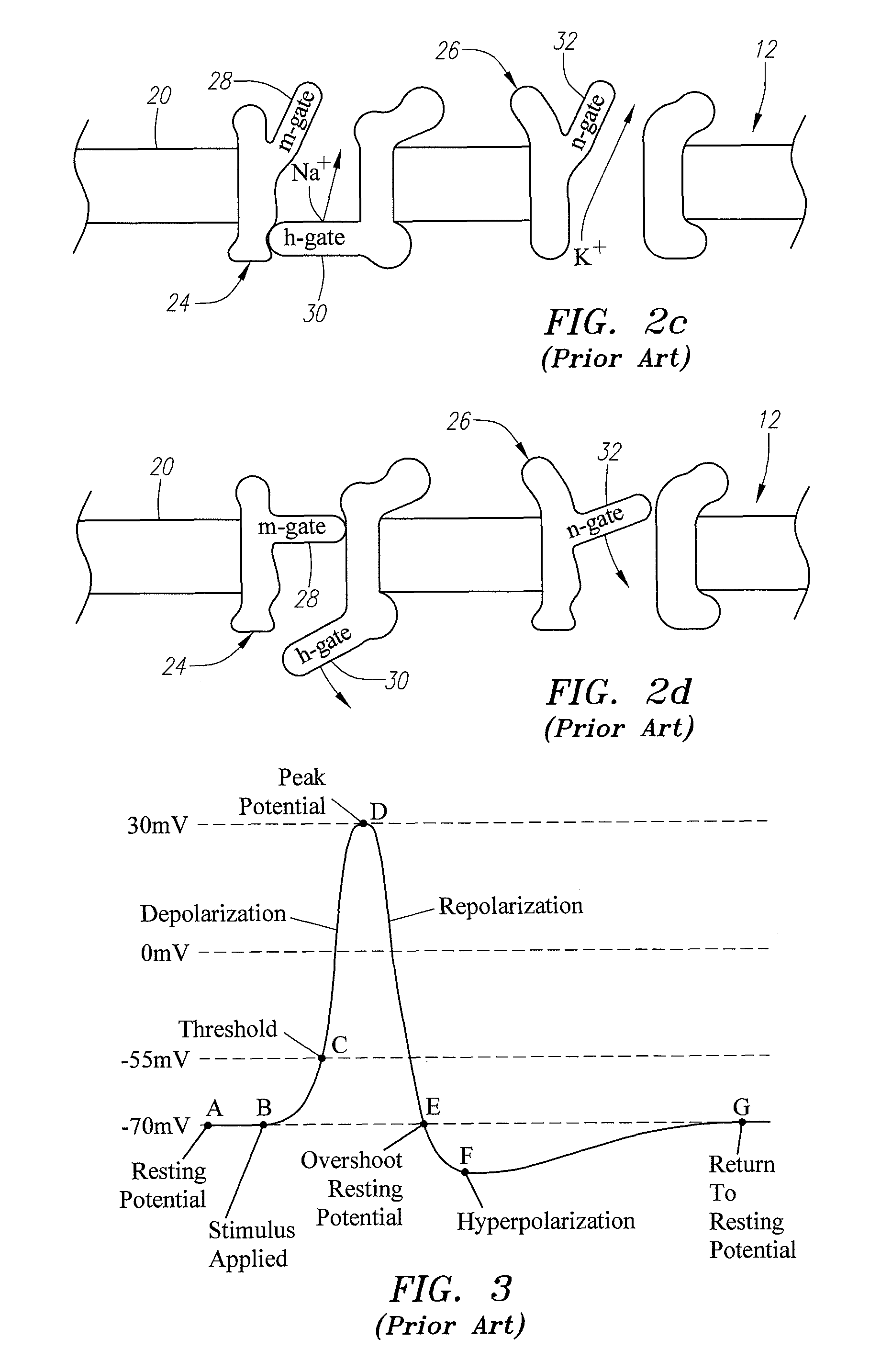
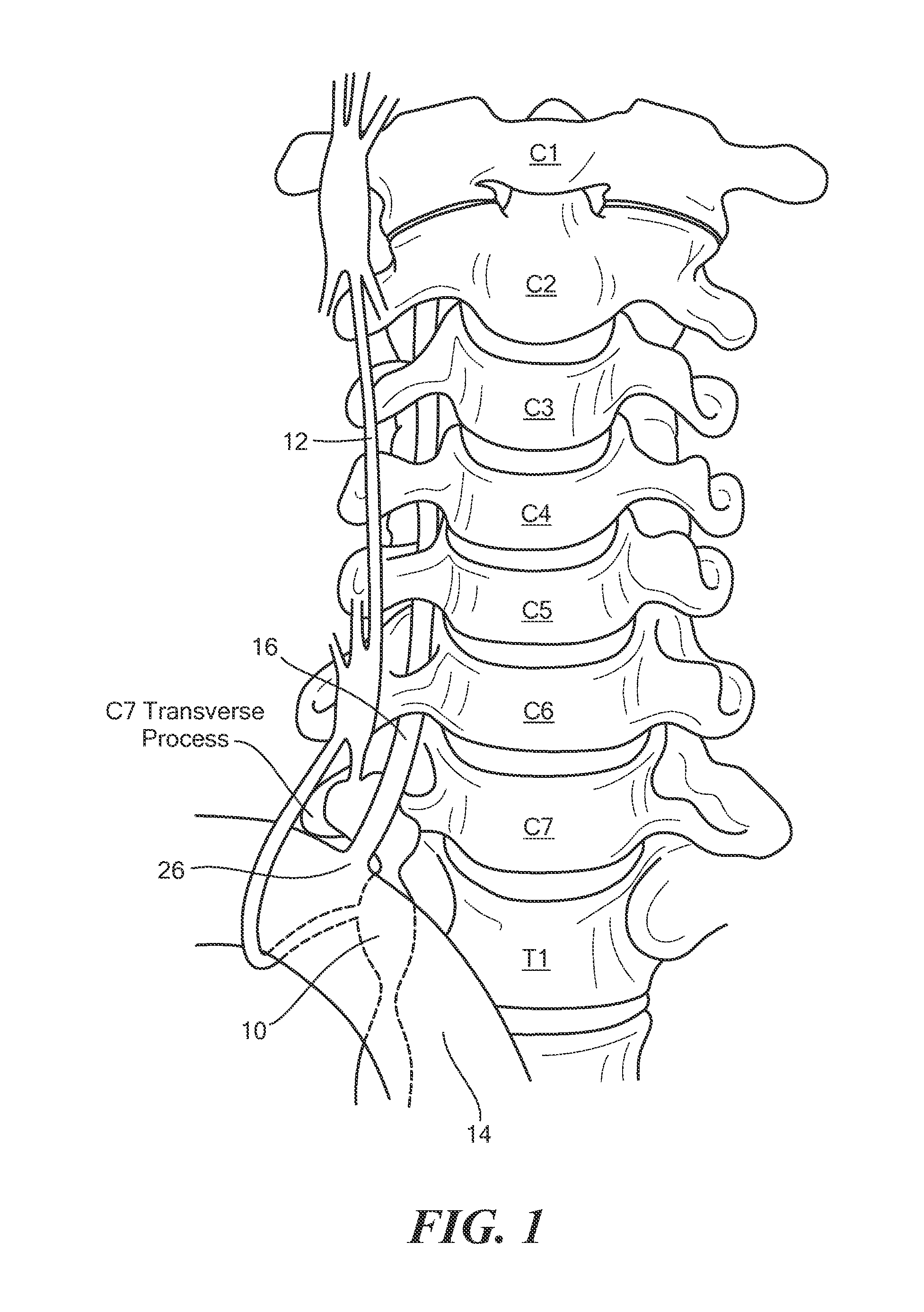
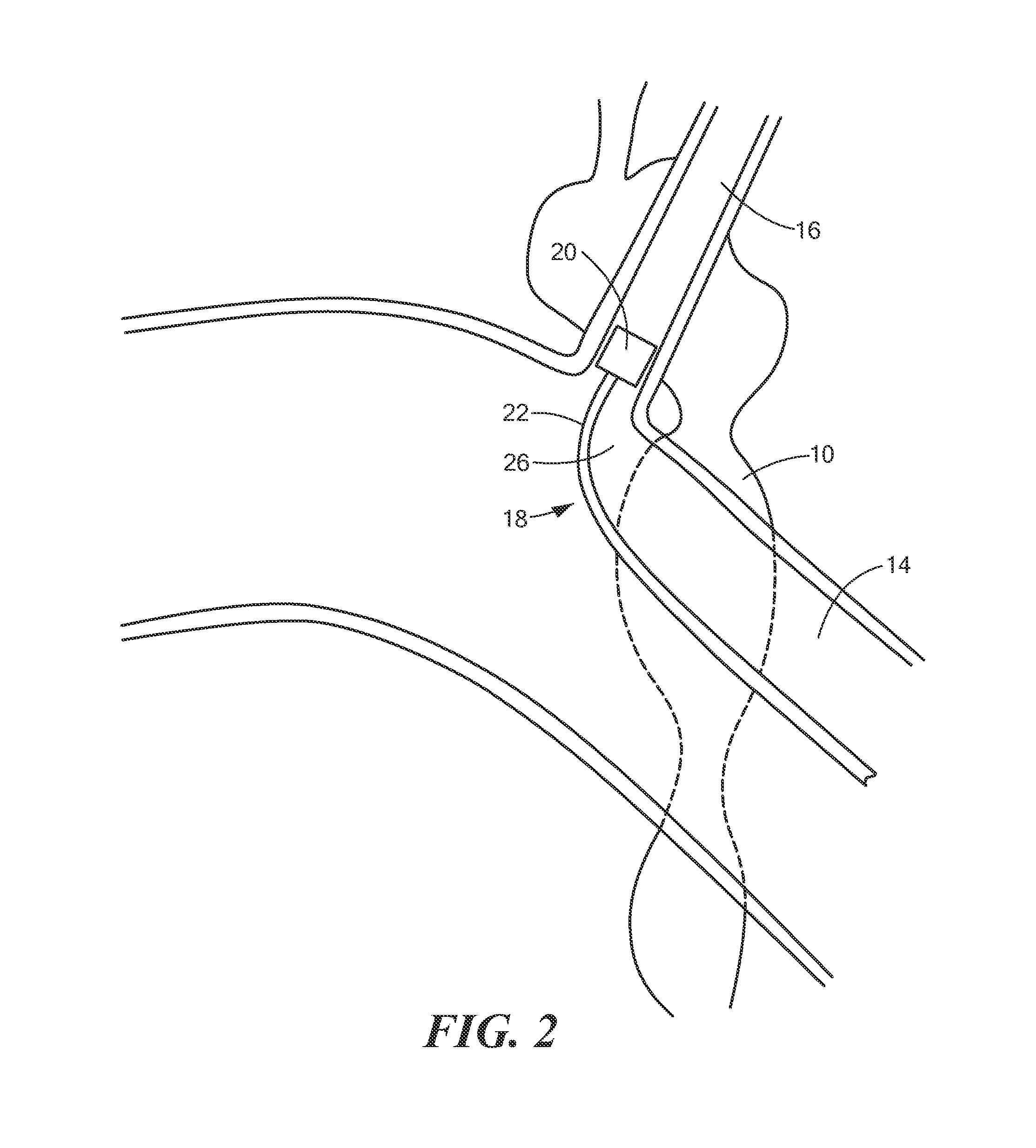
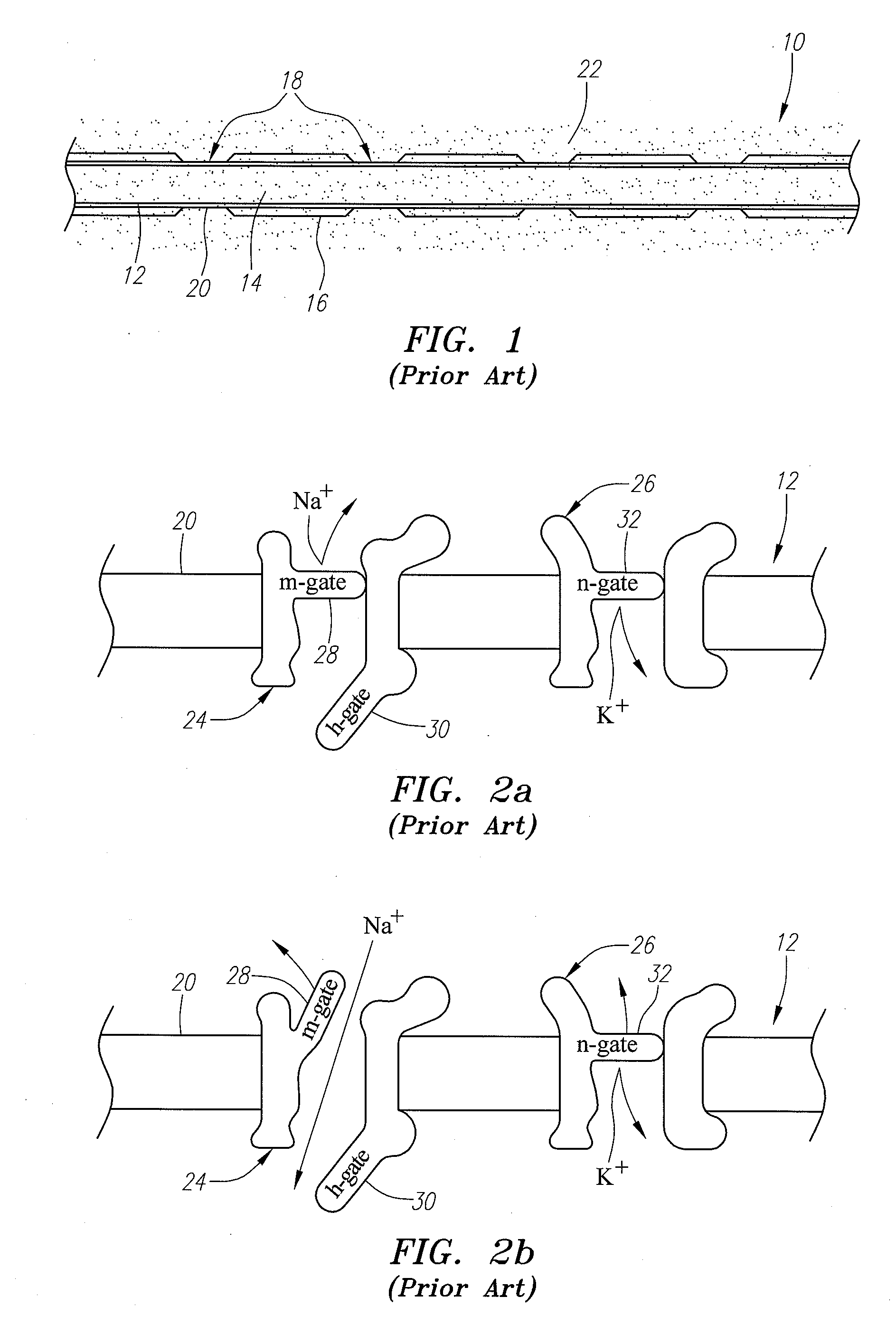
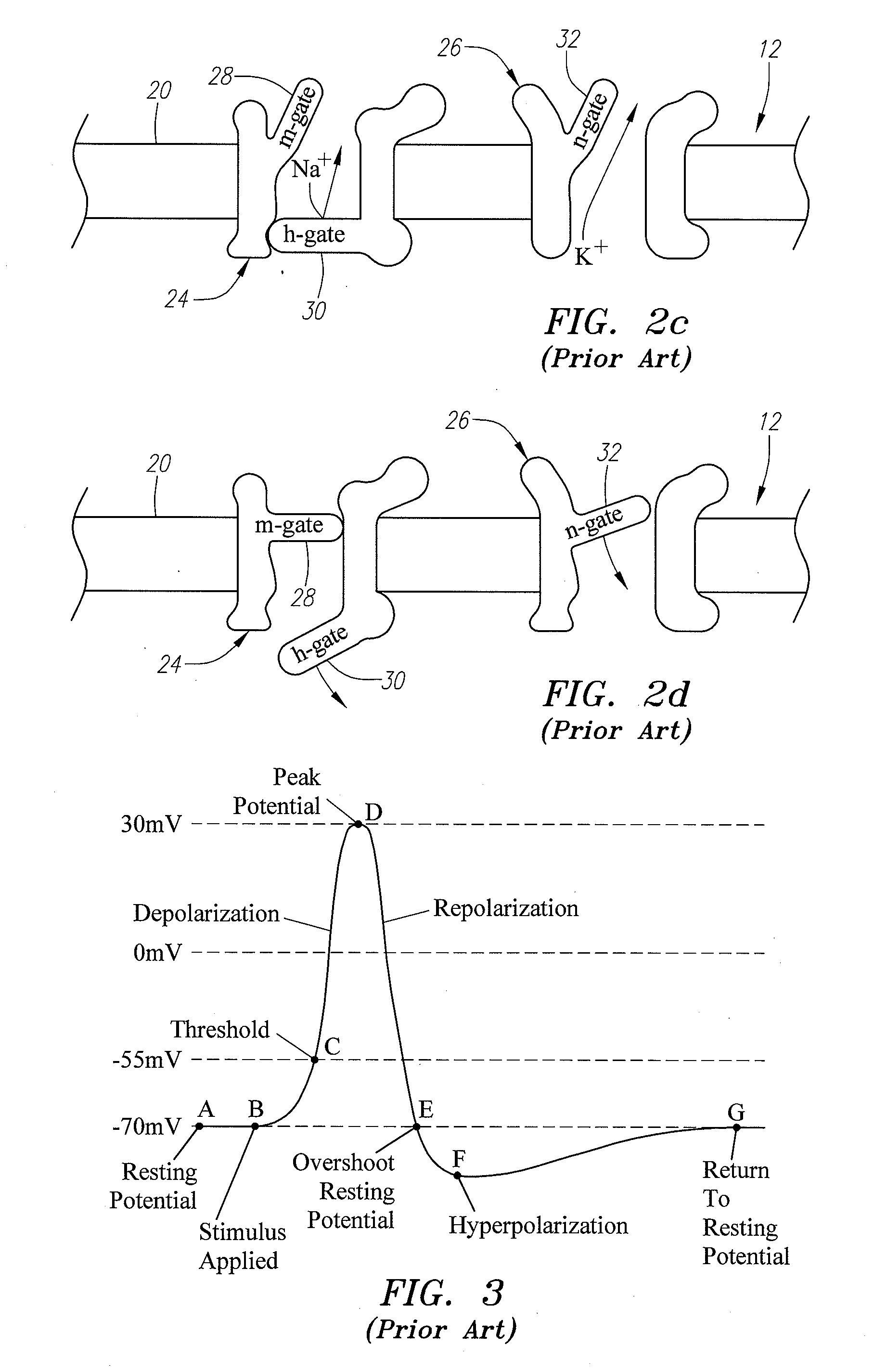
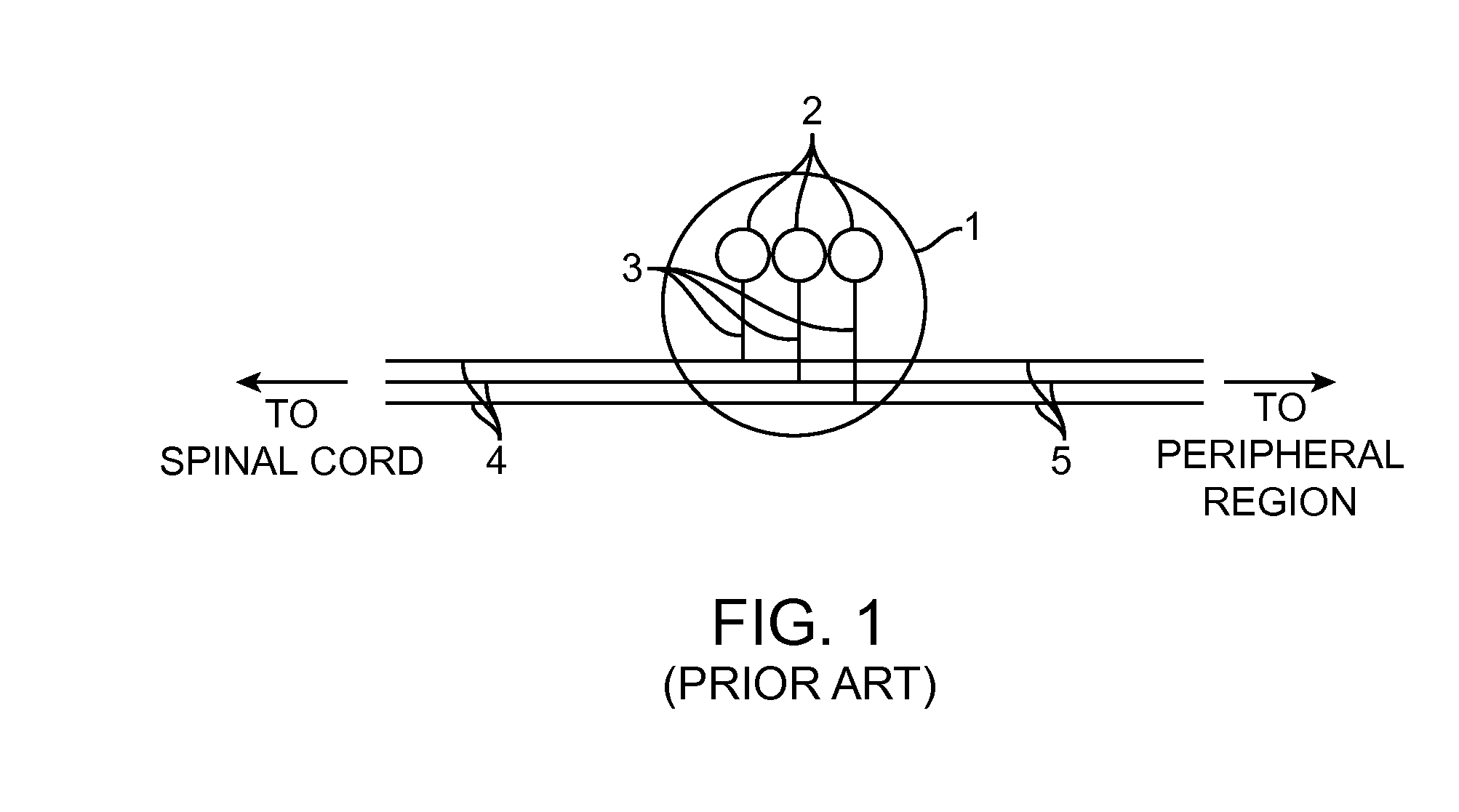
Dorsal root. n. Either of the two roots of a spinal nerve, consisting of sensory fibers and arising from the posterior section of the spinal cord.
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
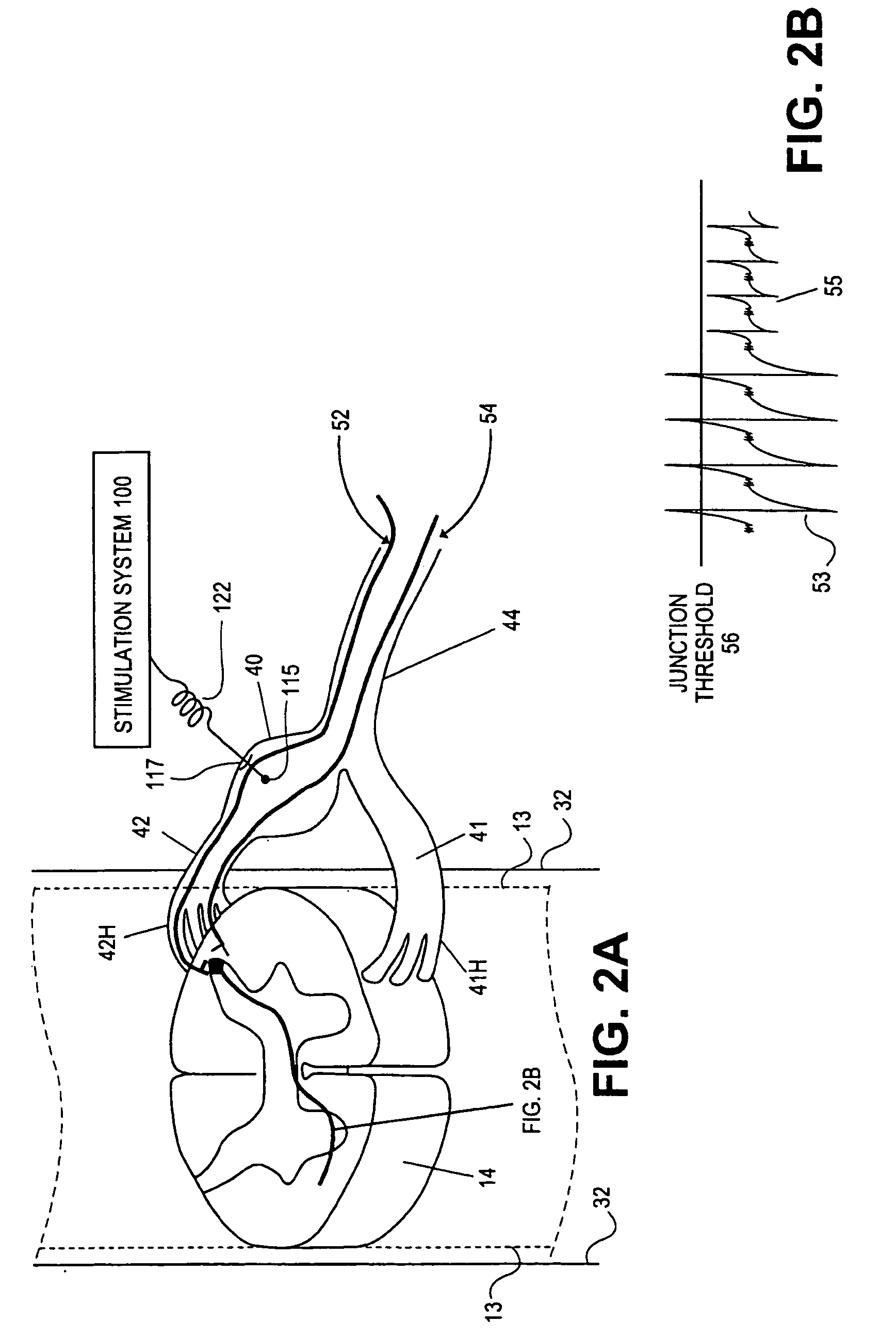
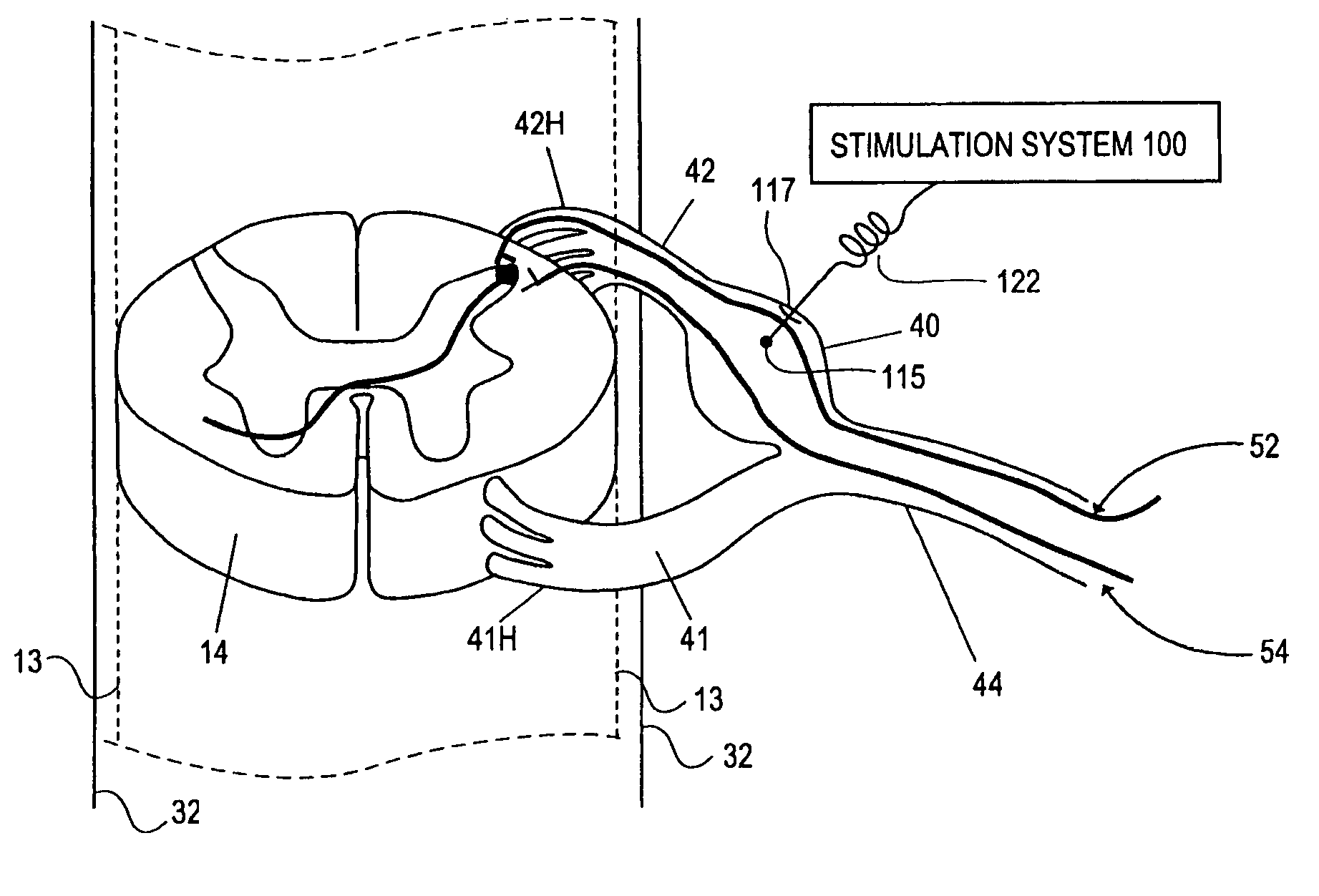
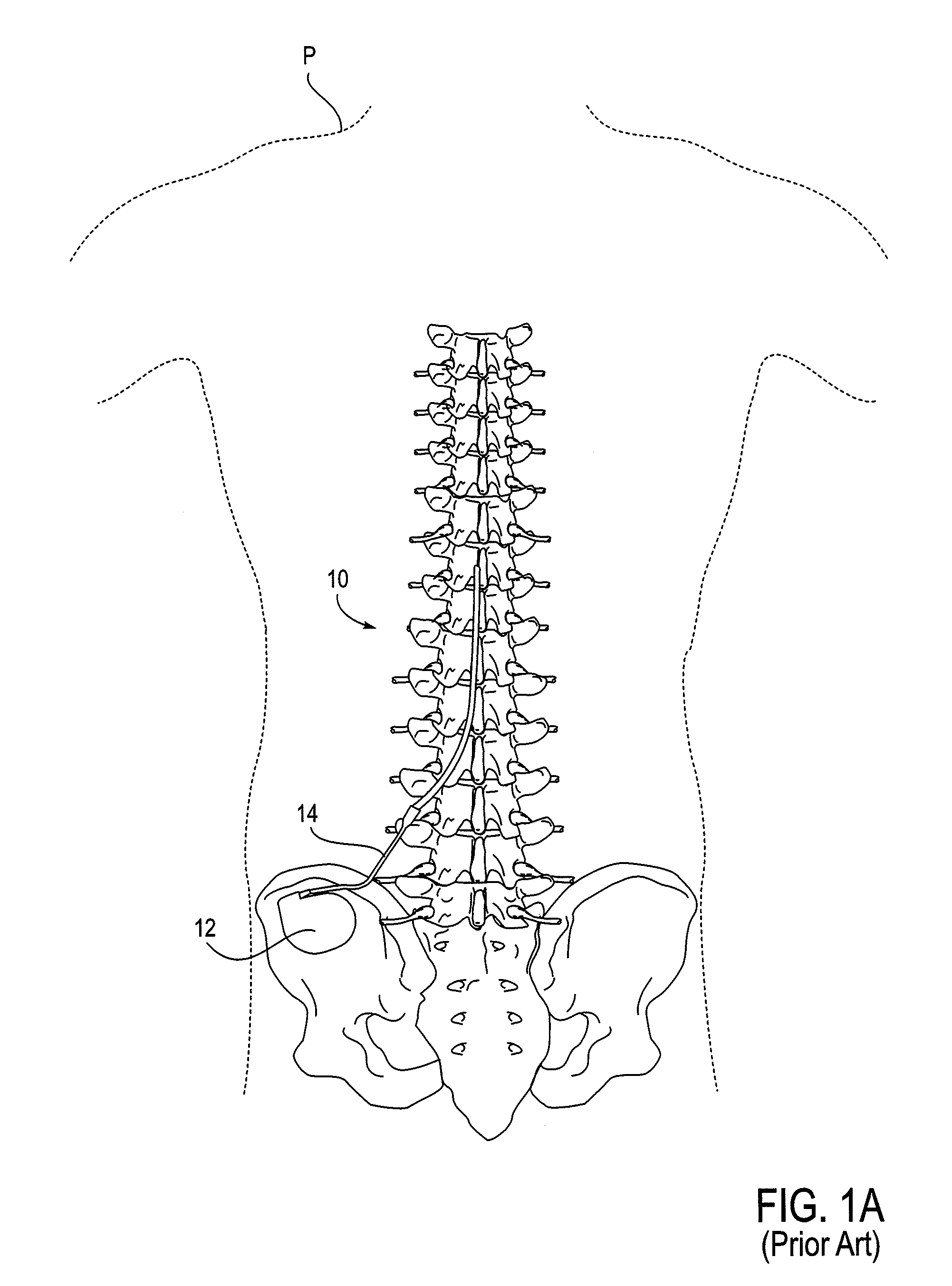
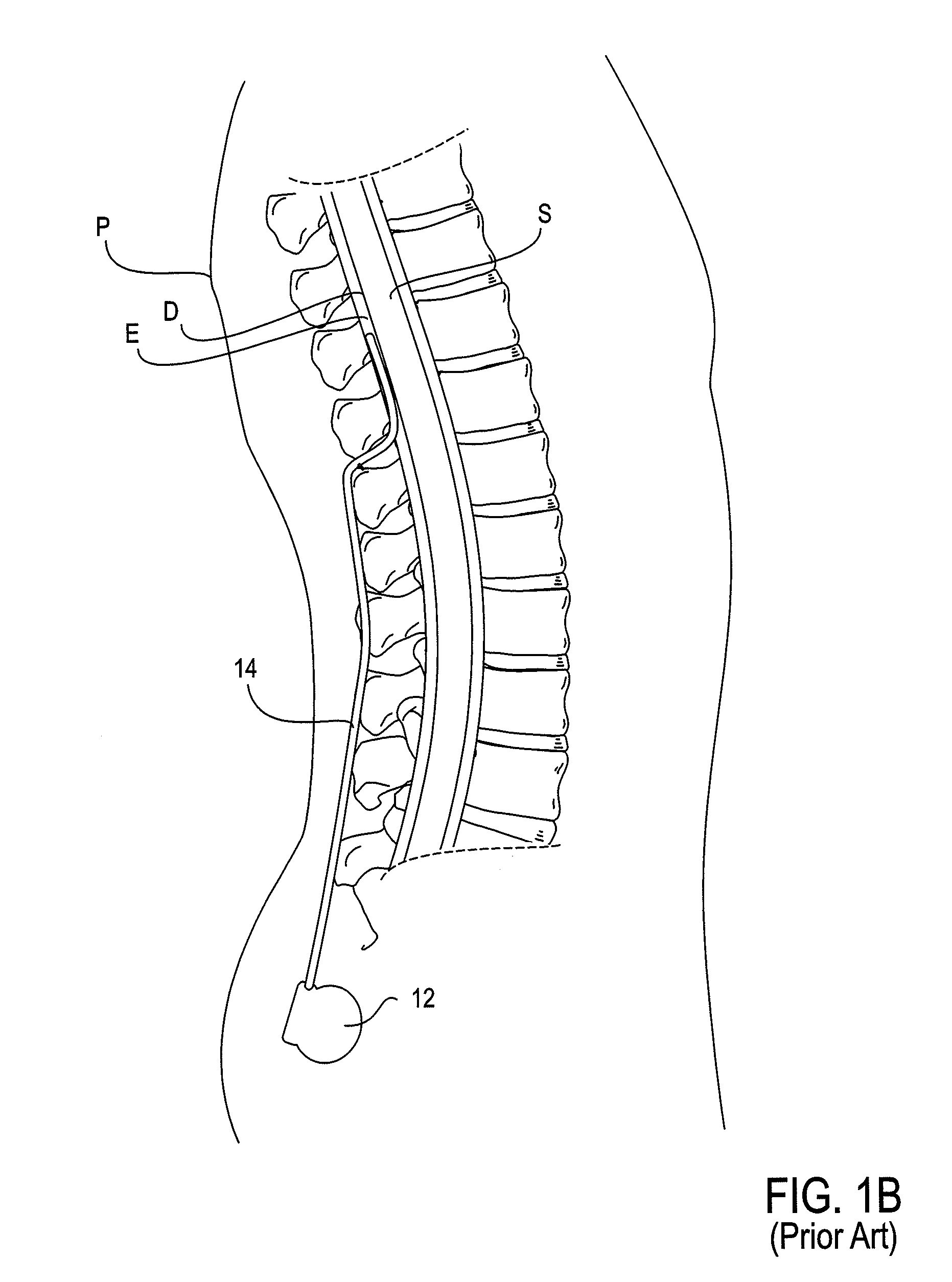
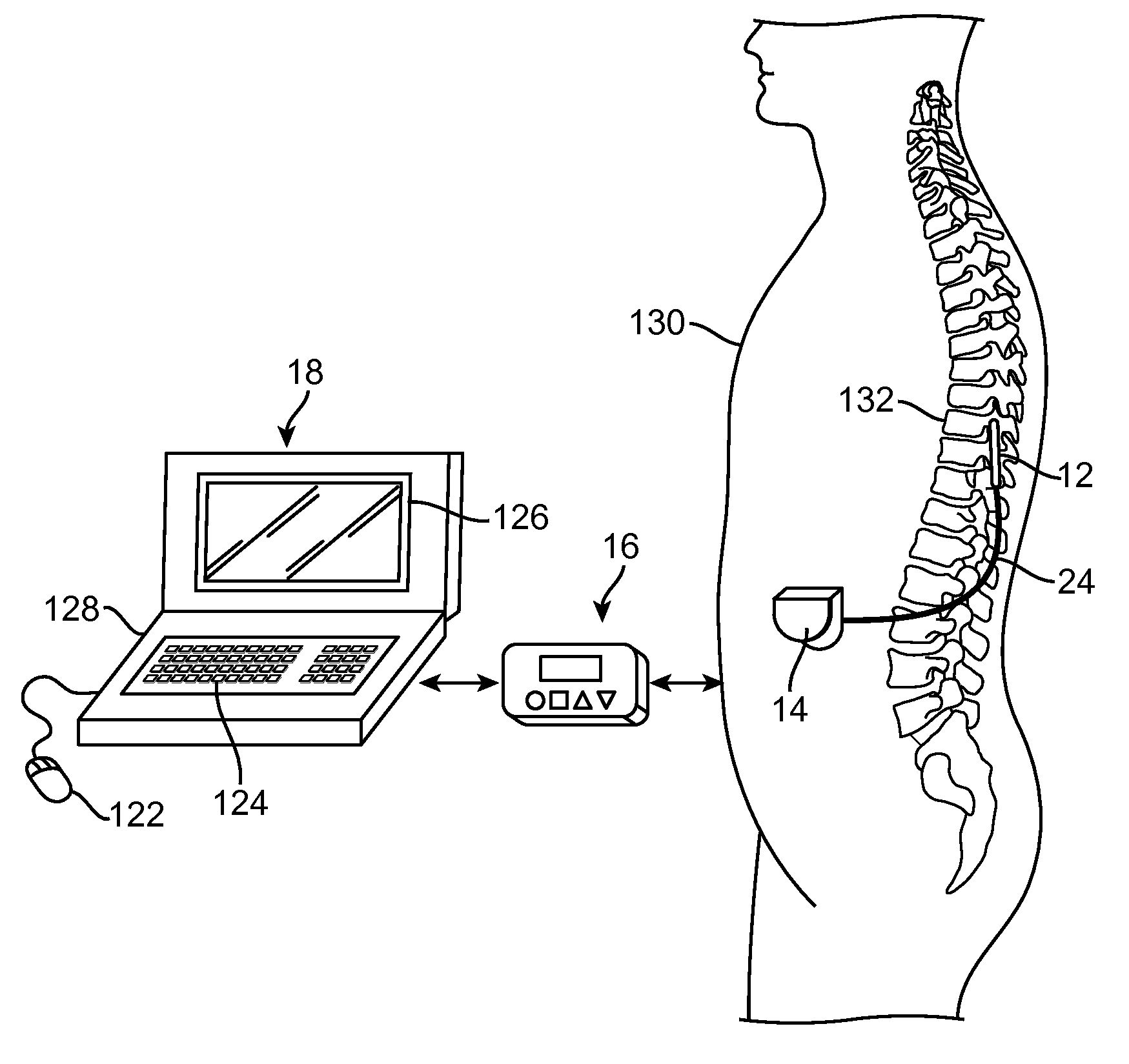
Methods for stimulating a nerve root ganglion
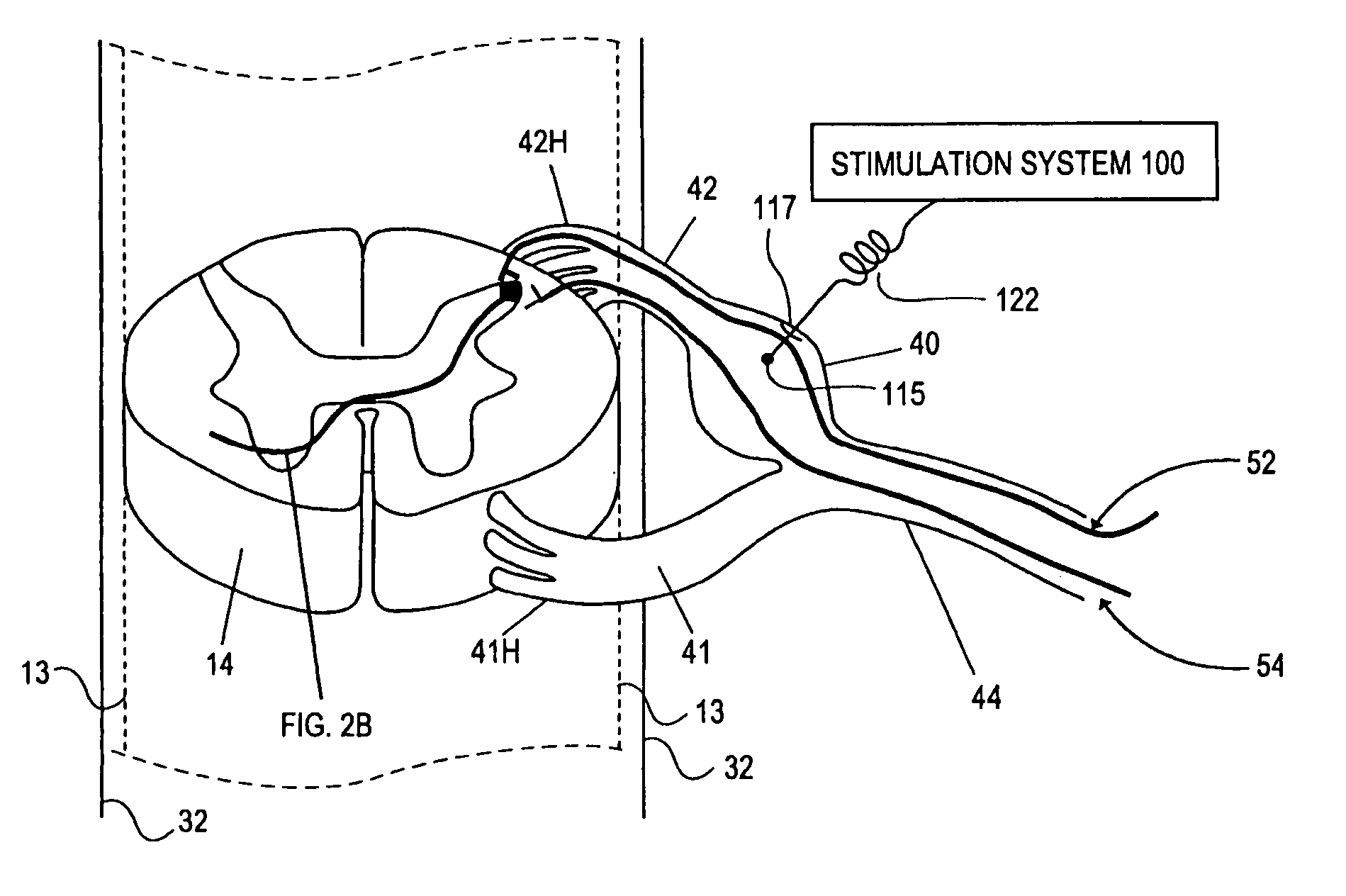
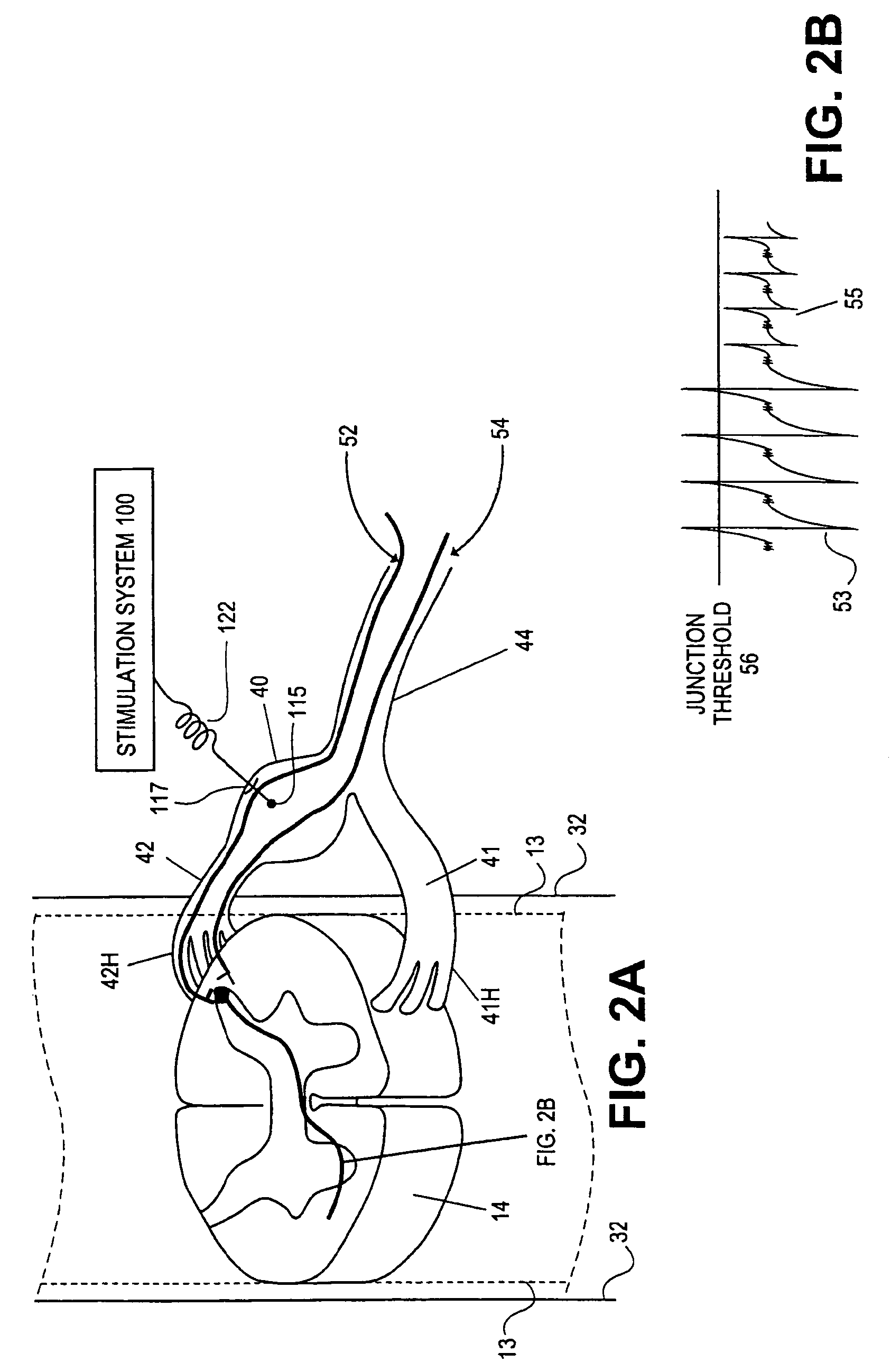
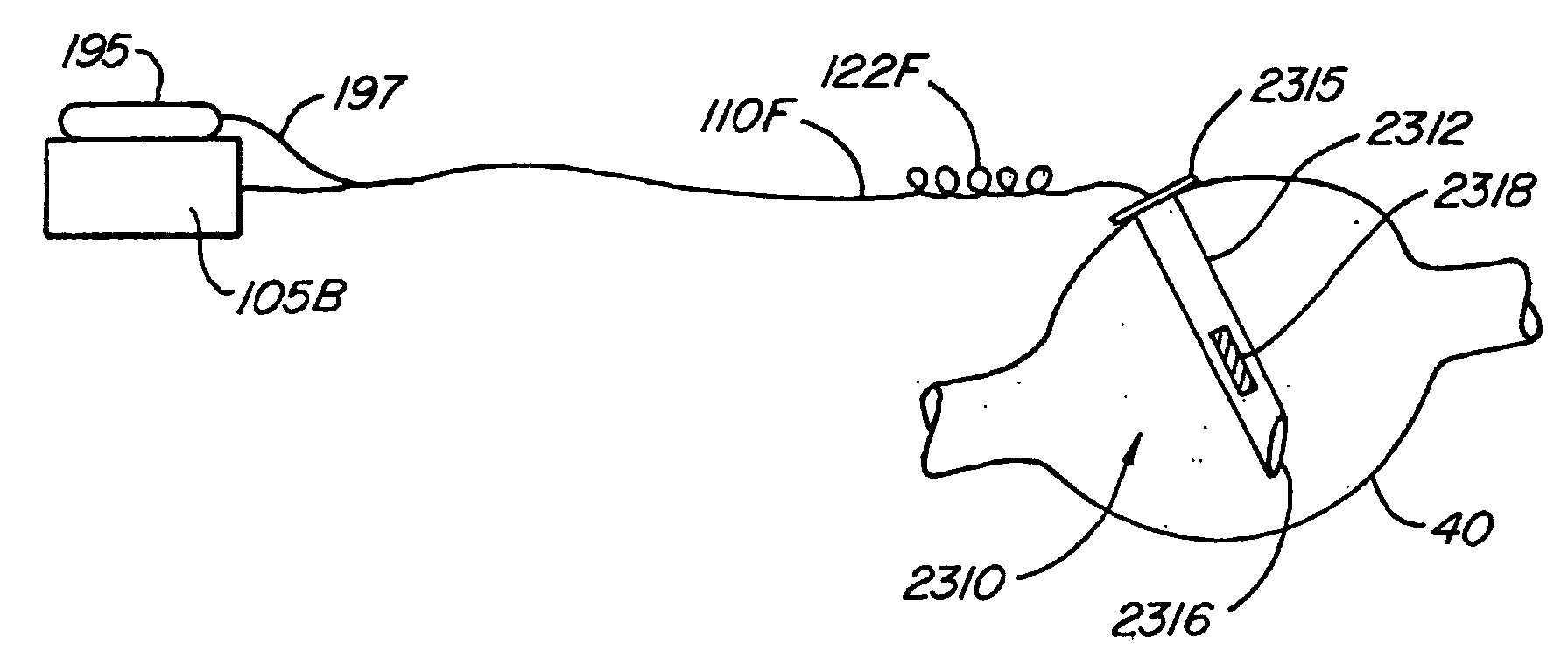
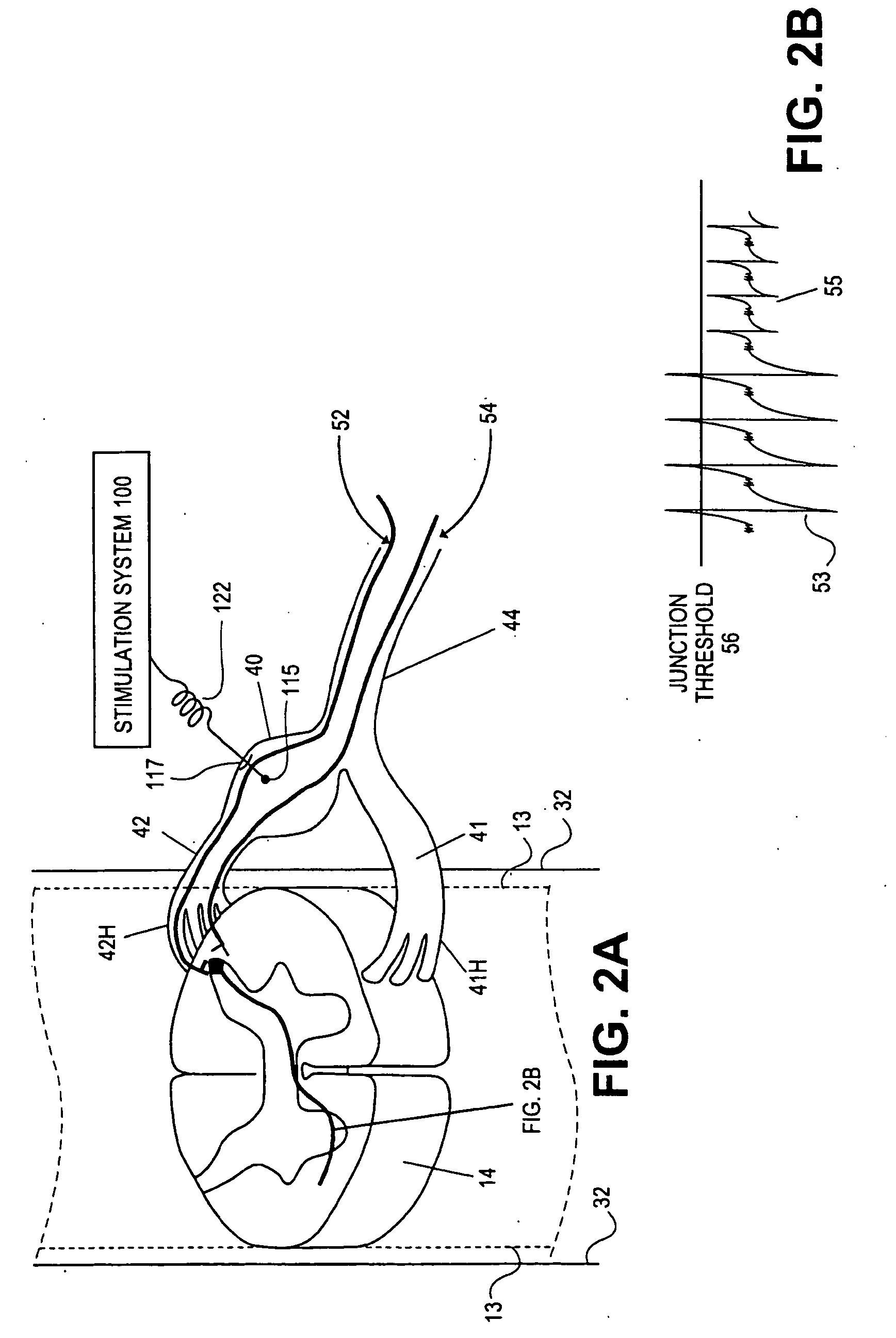
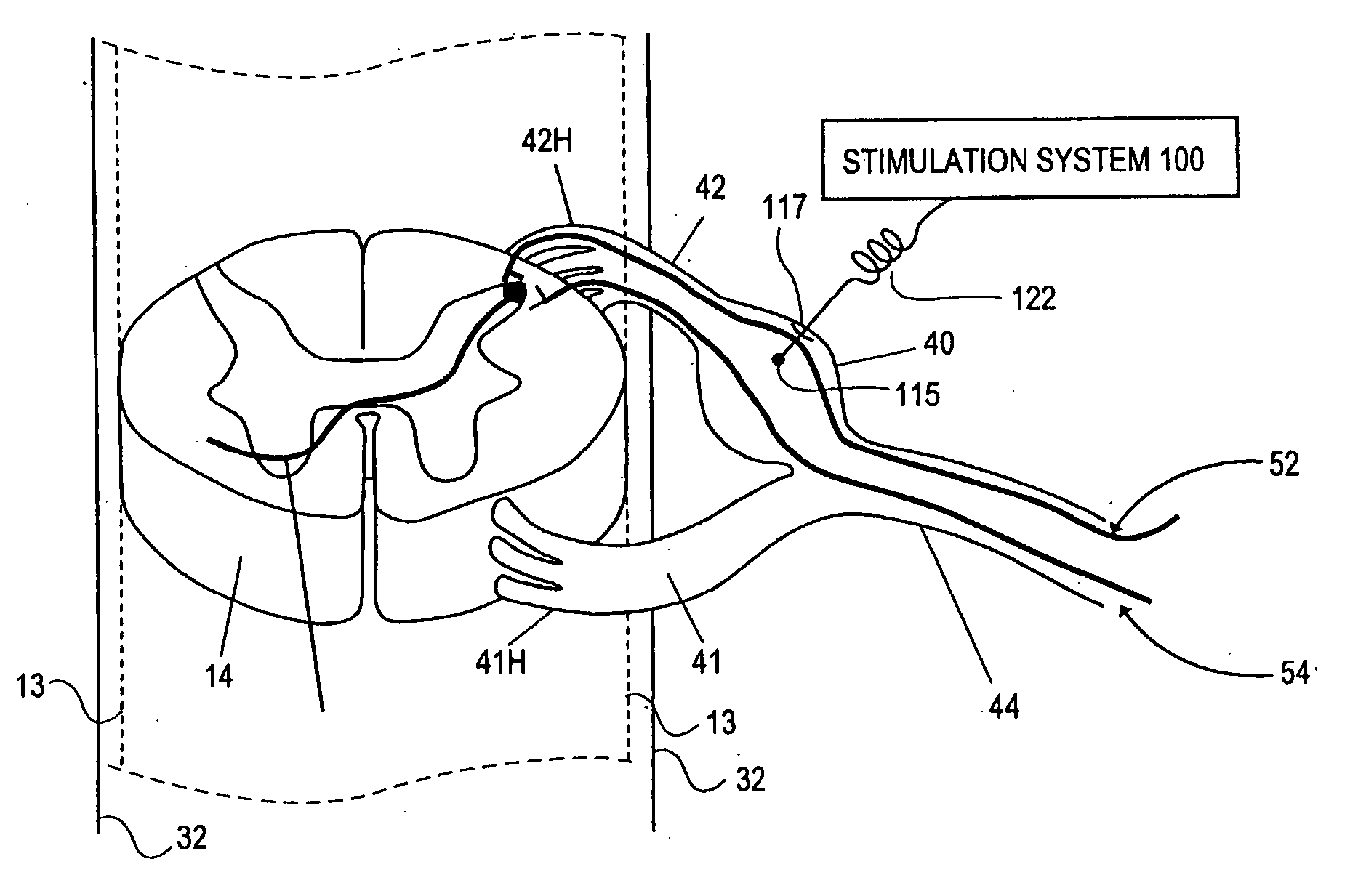
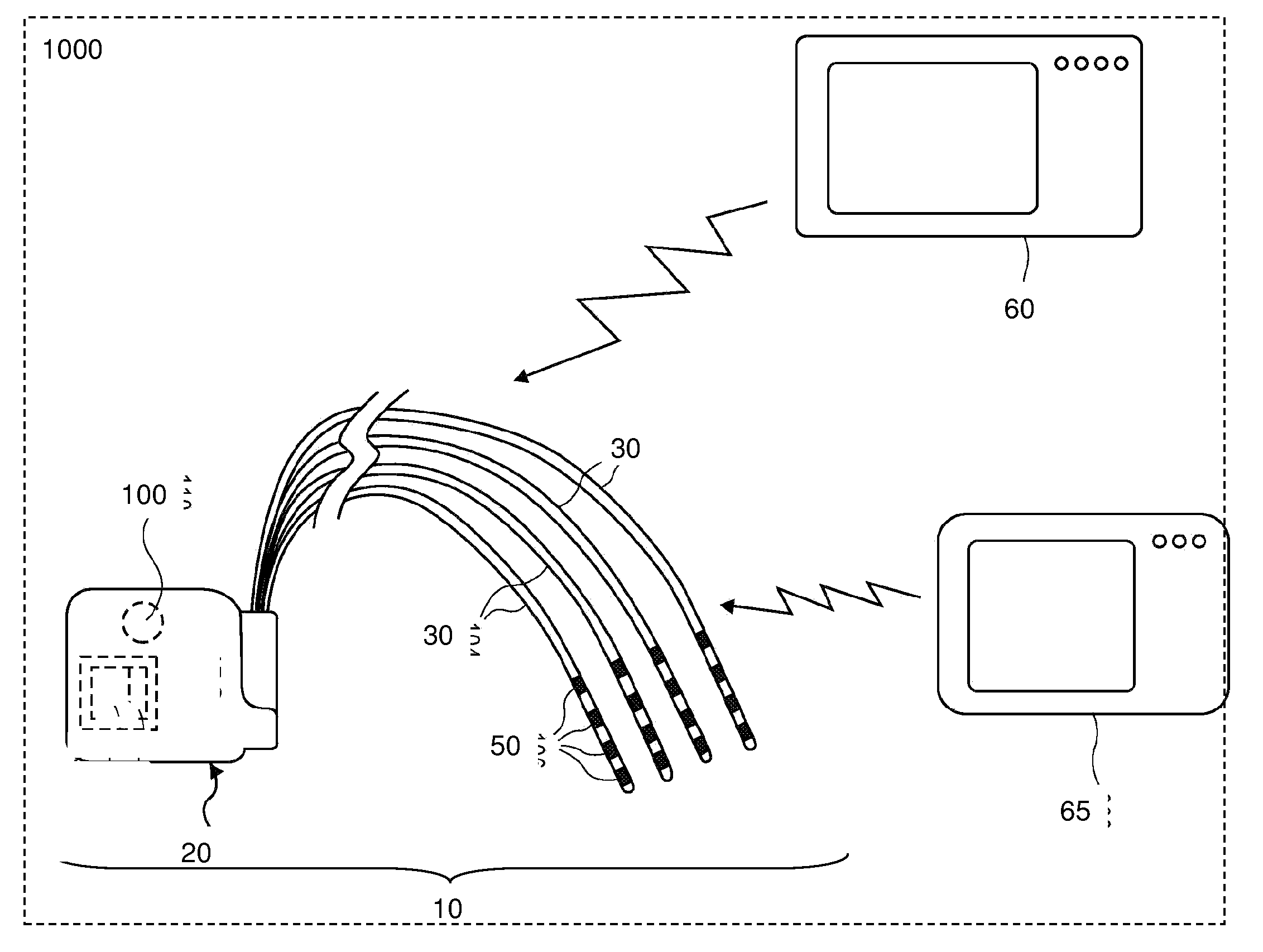
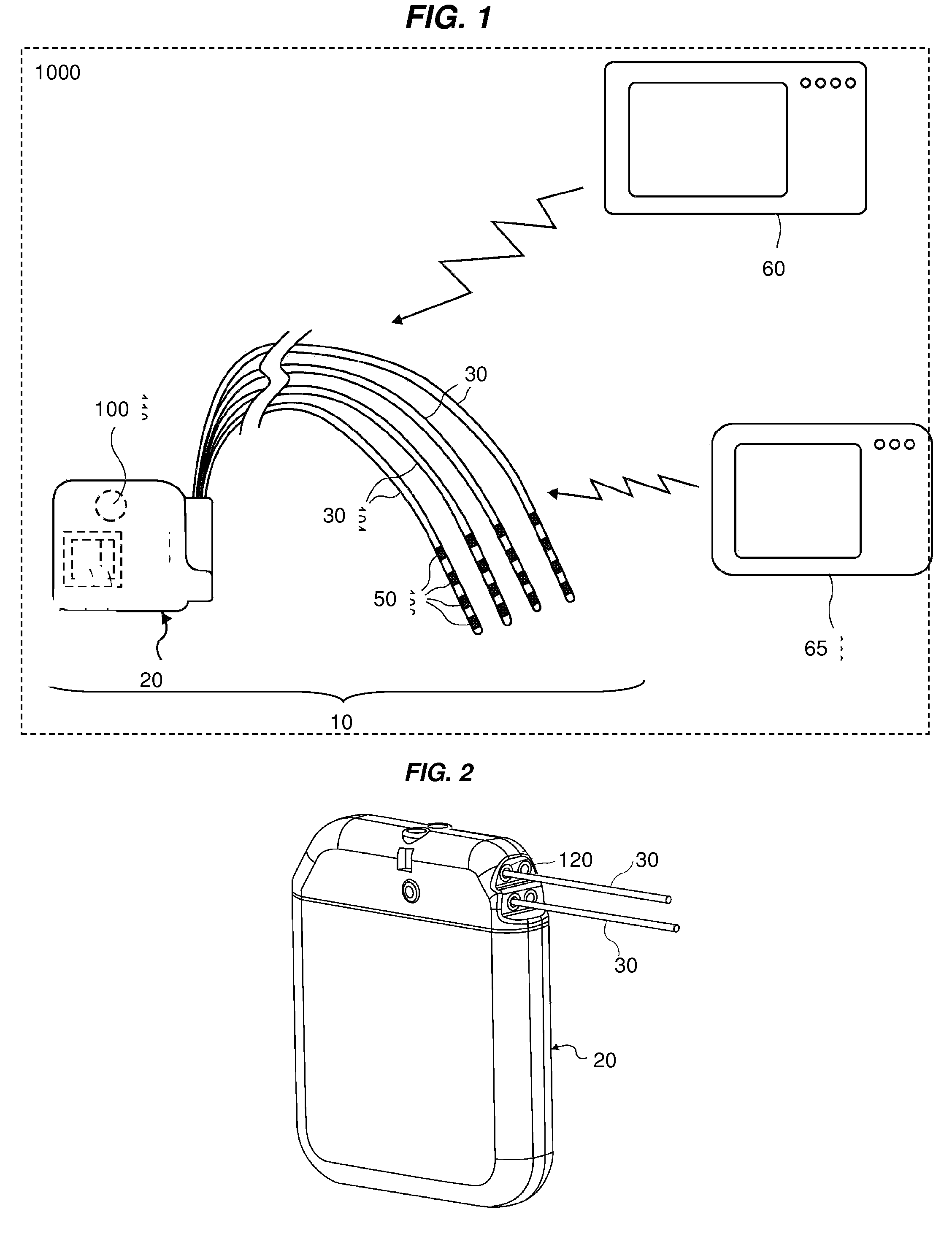
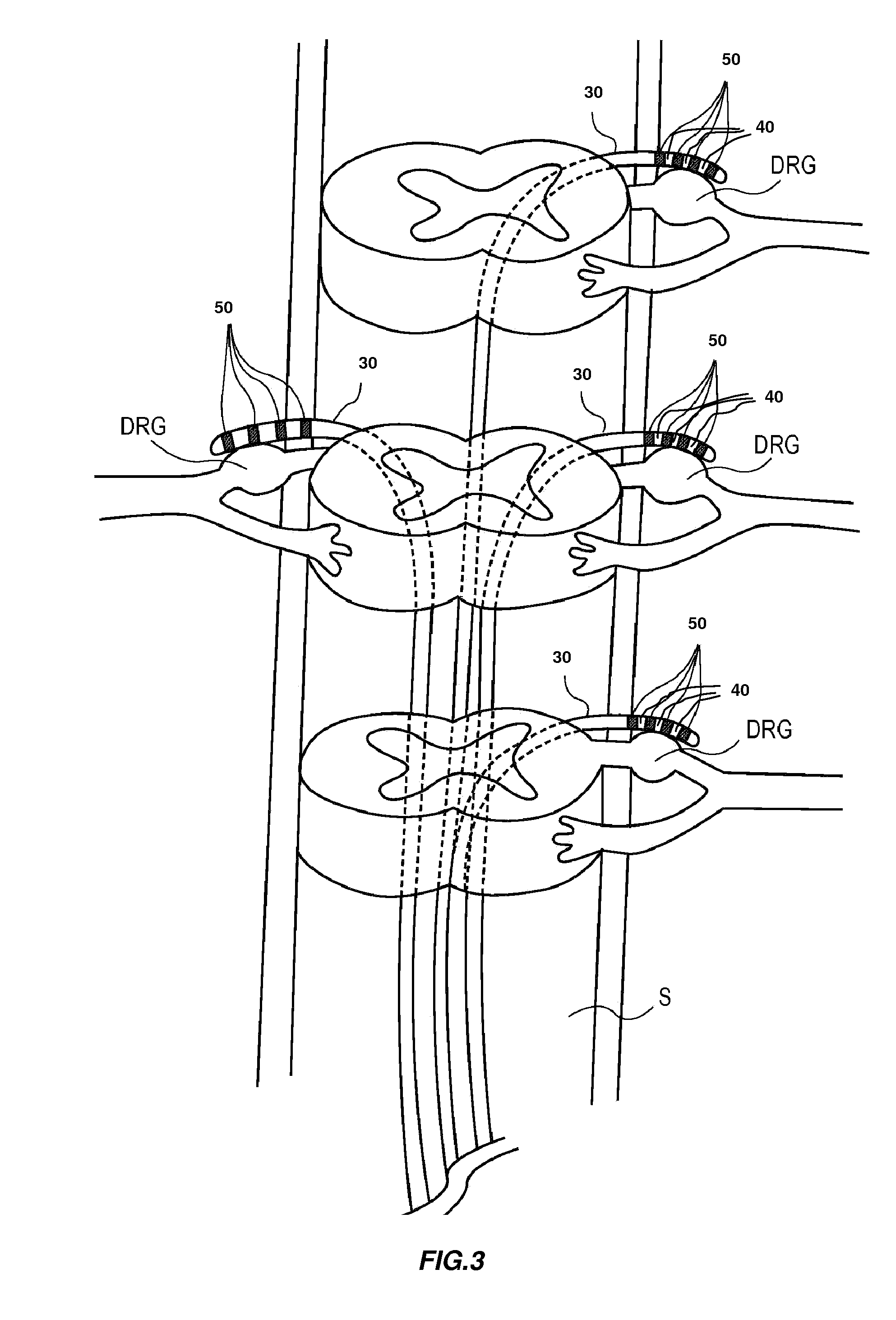
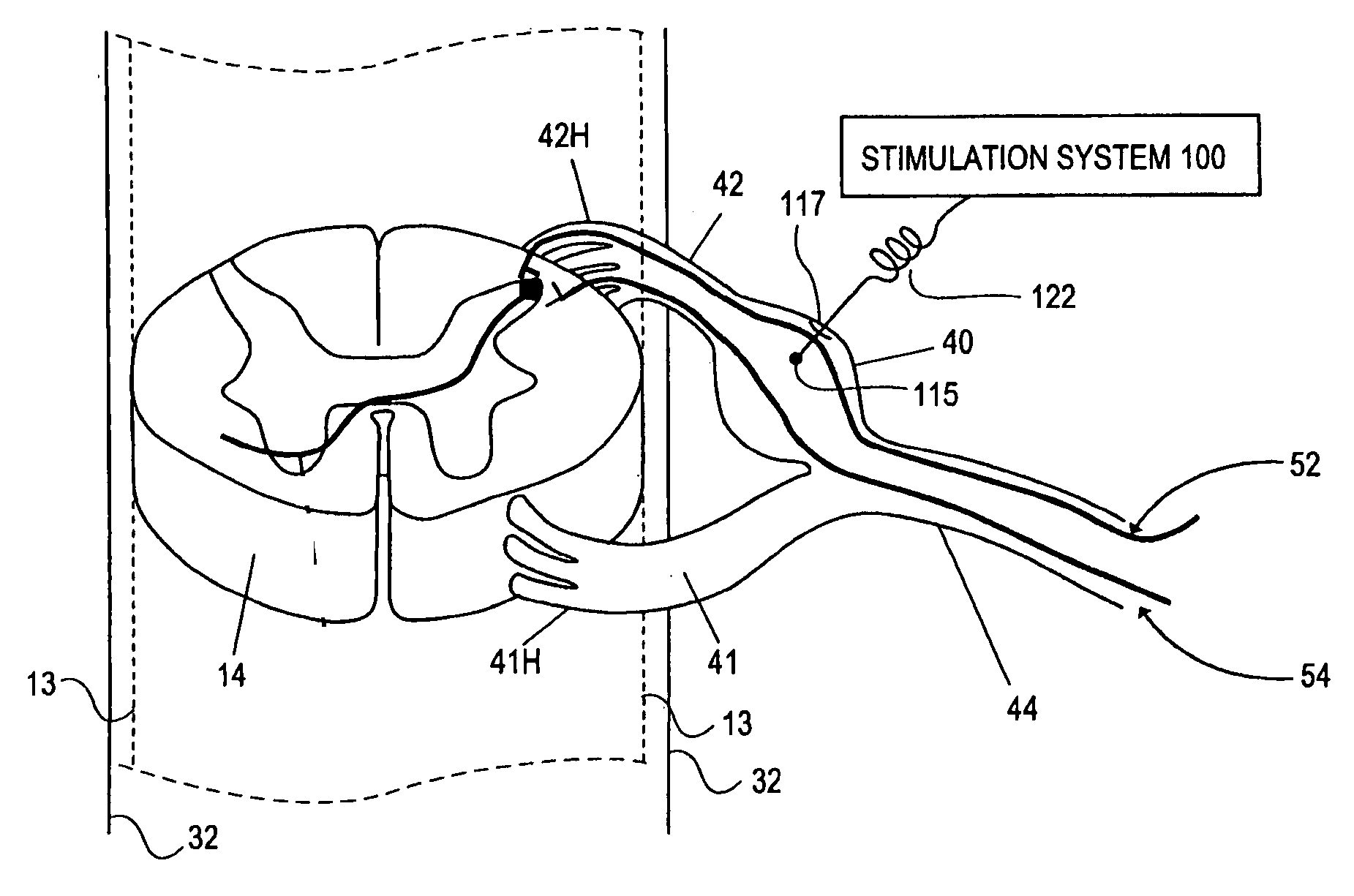
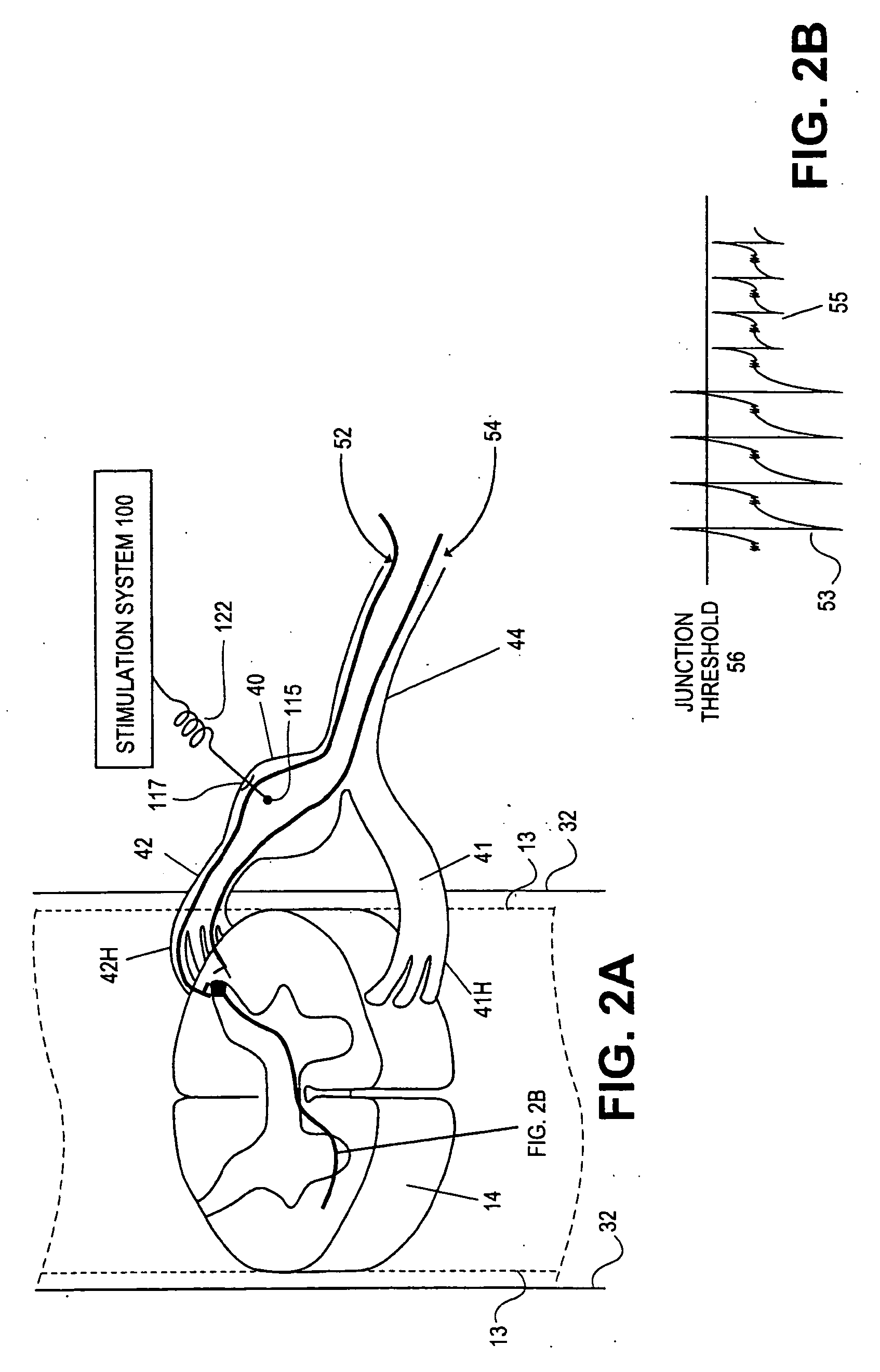
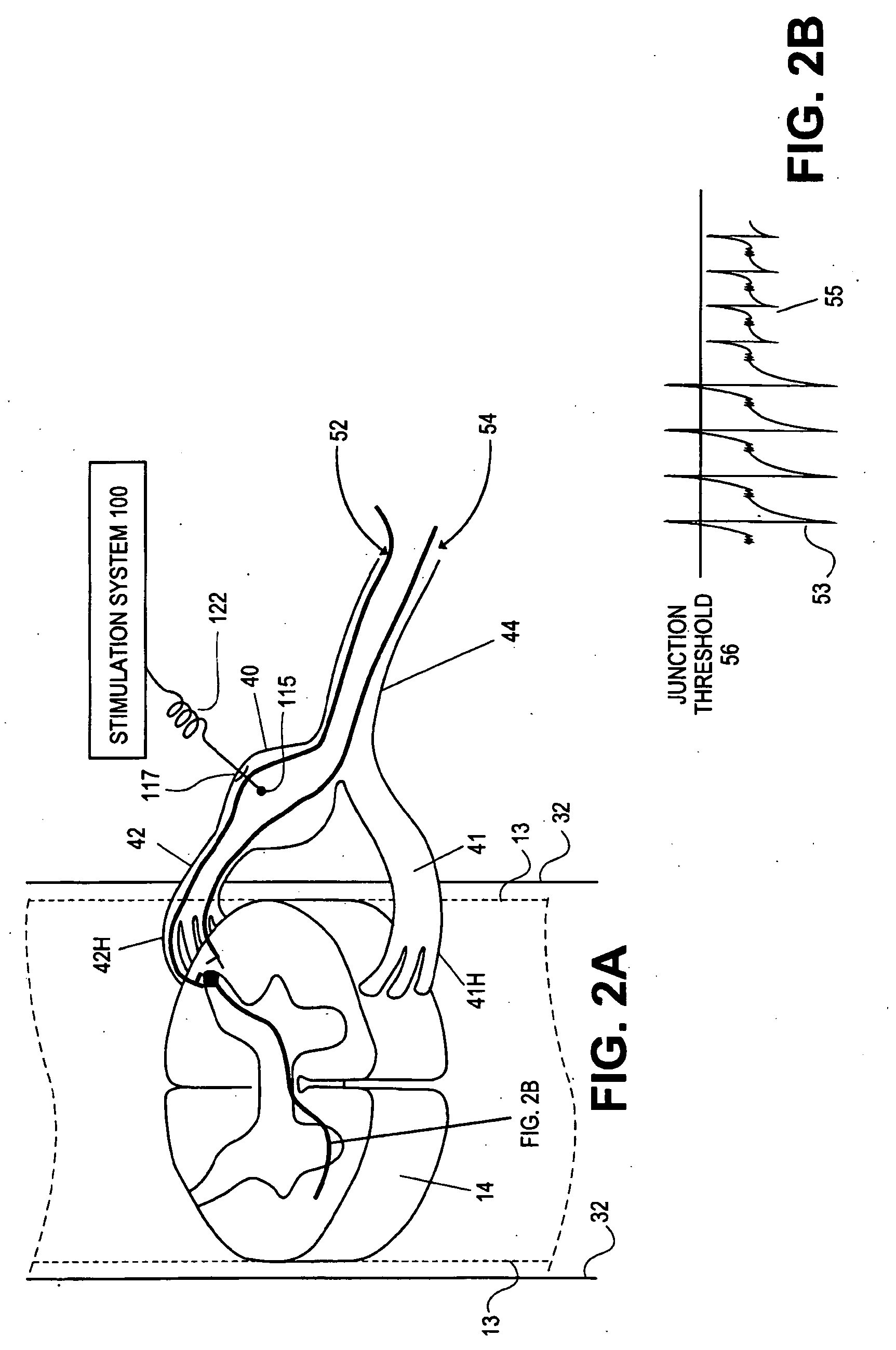
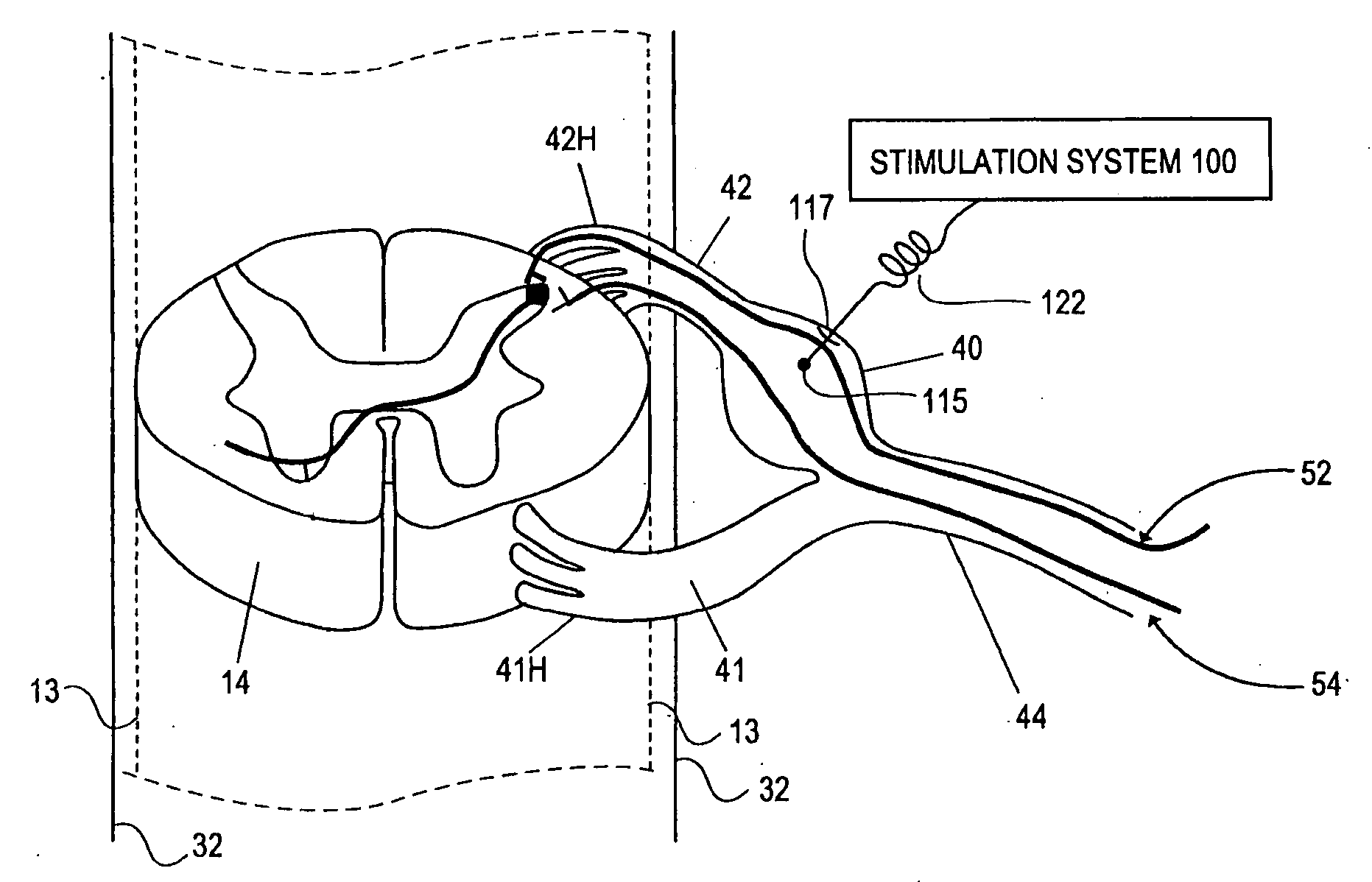
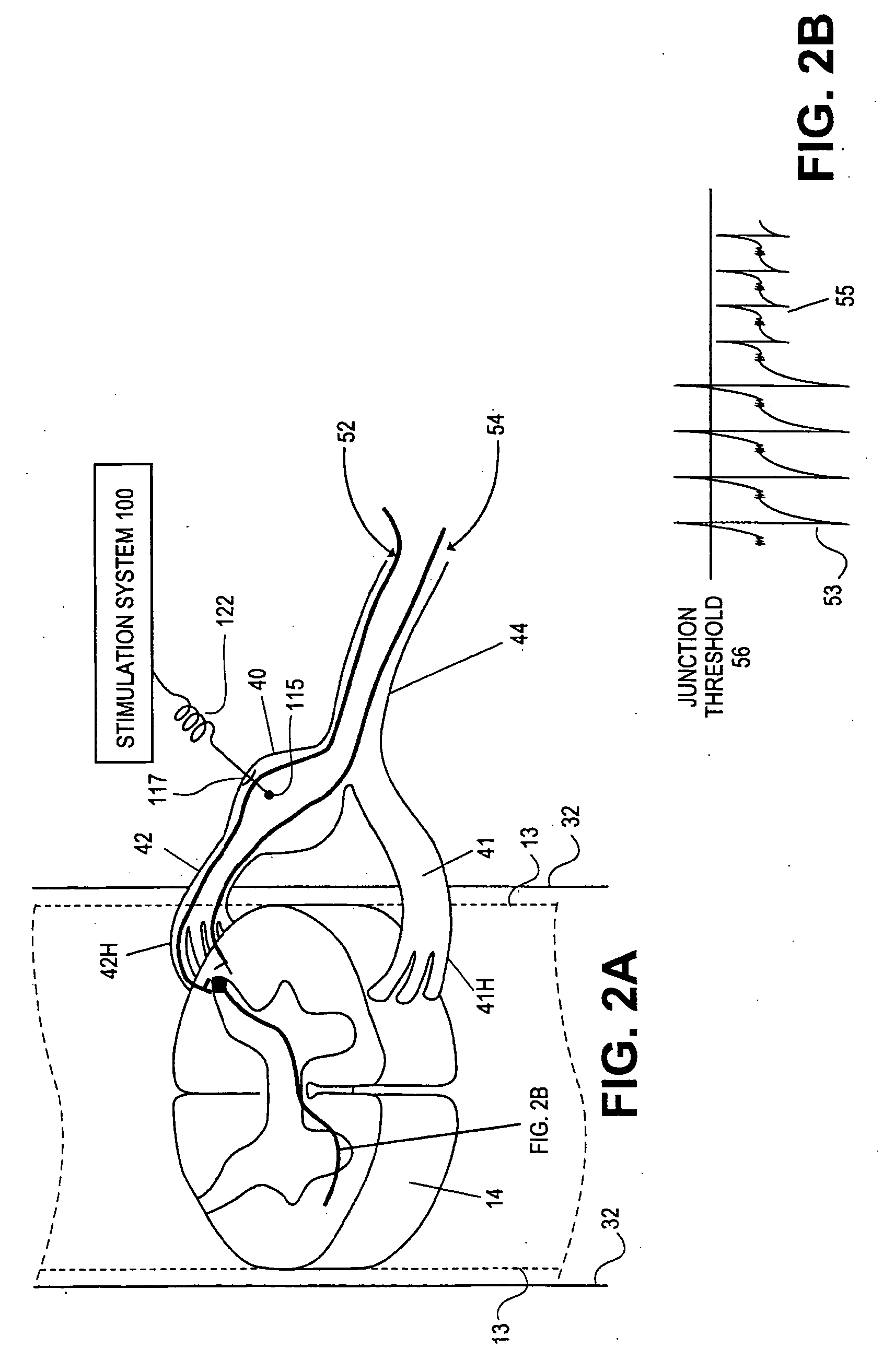
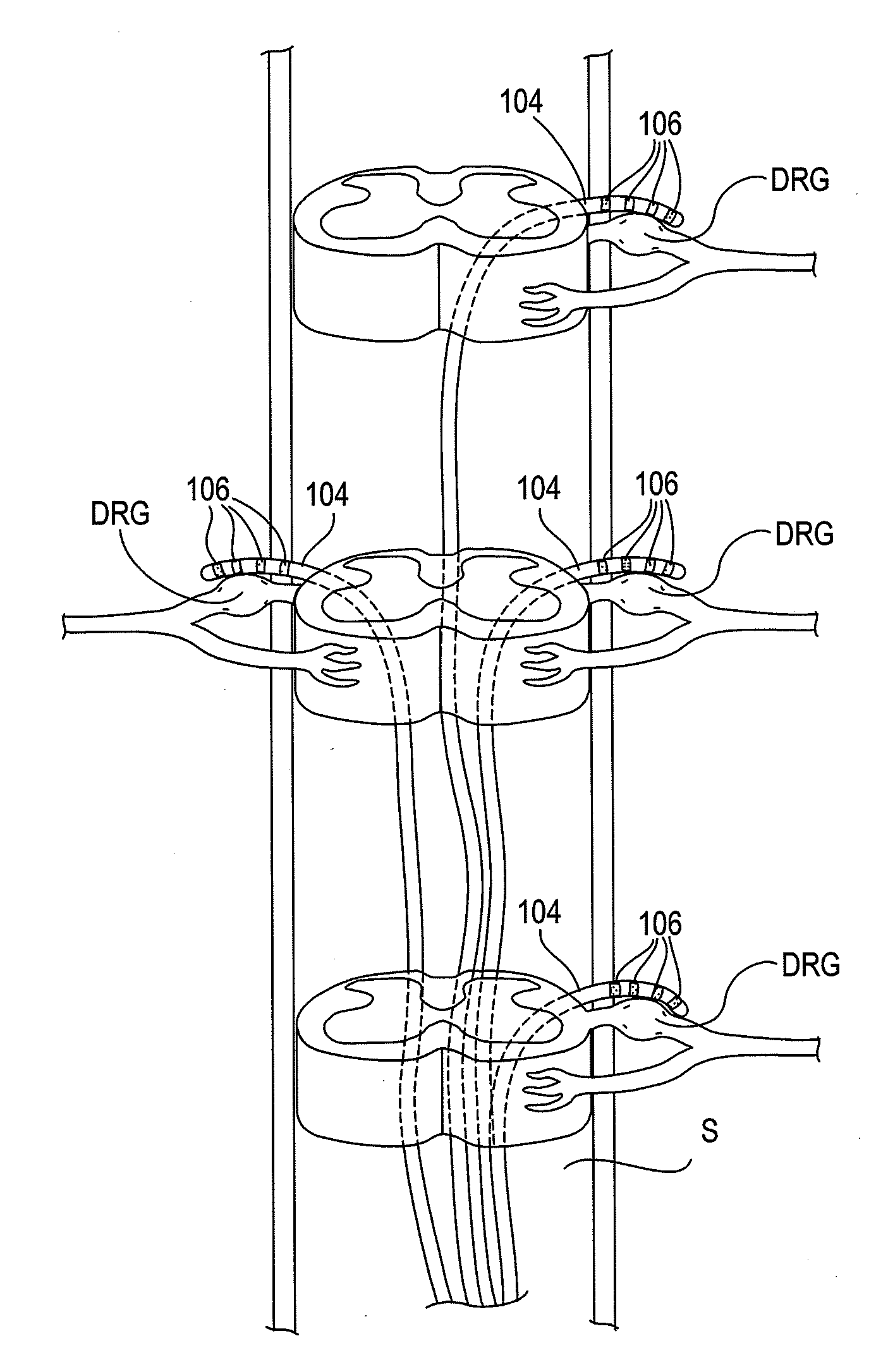
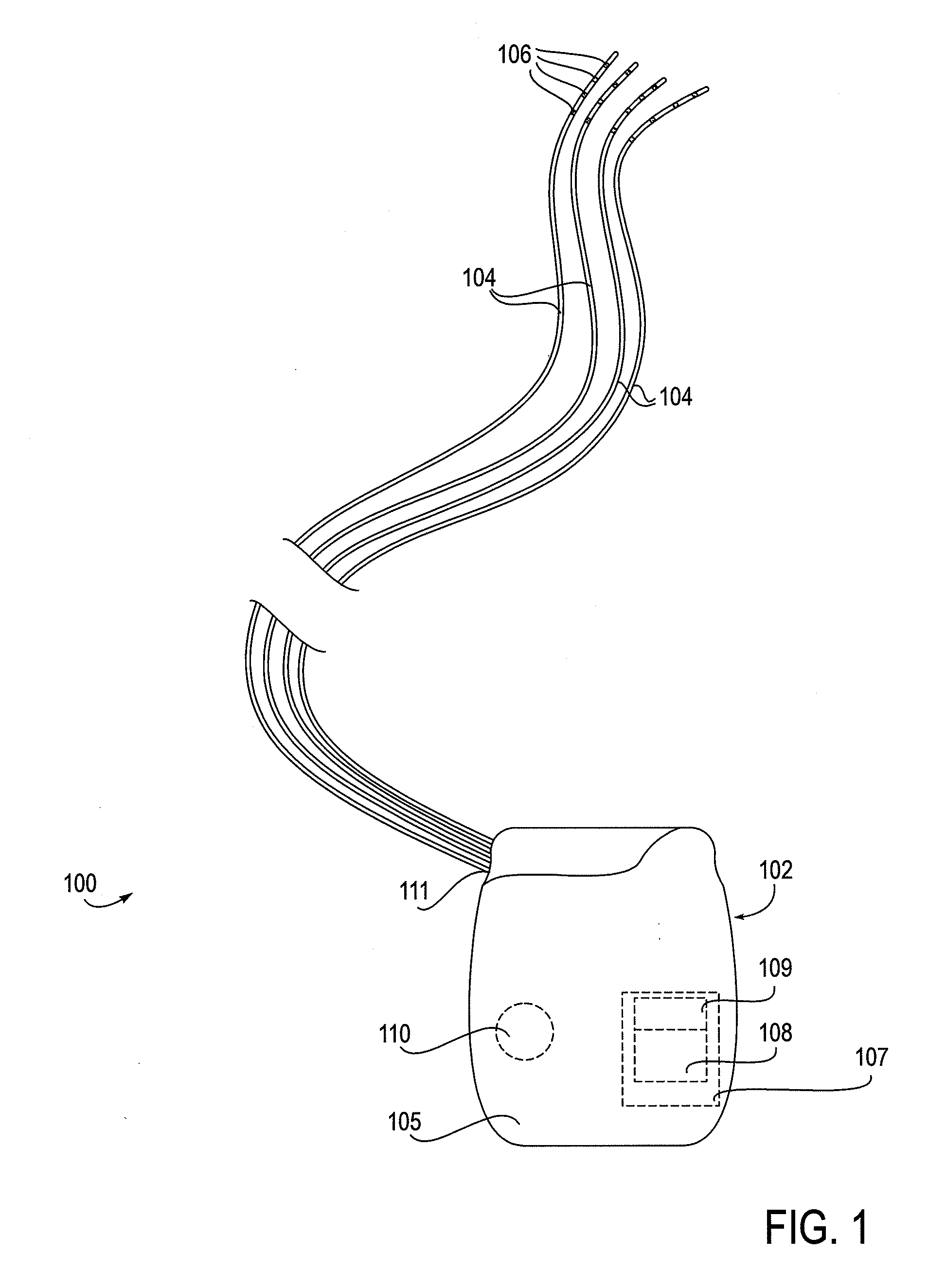
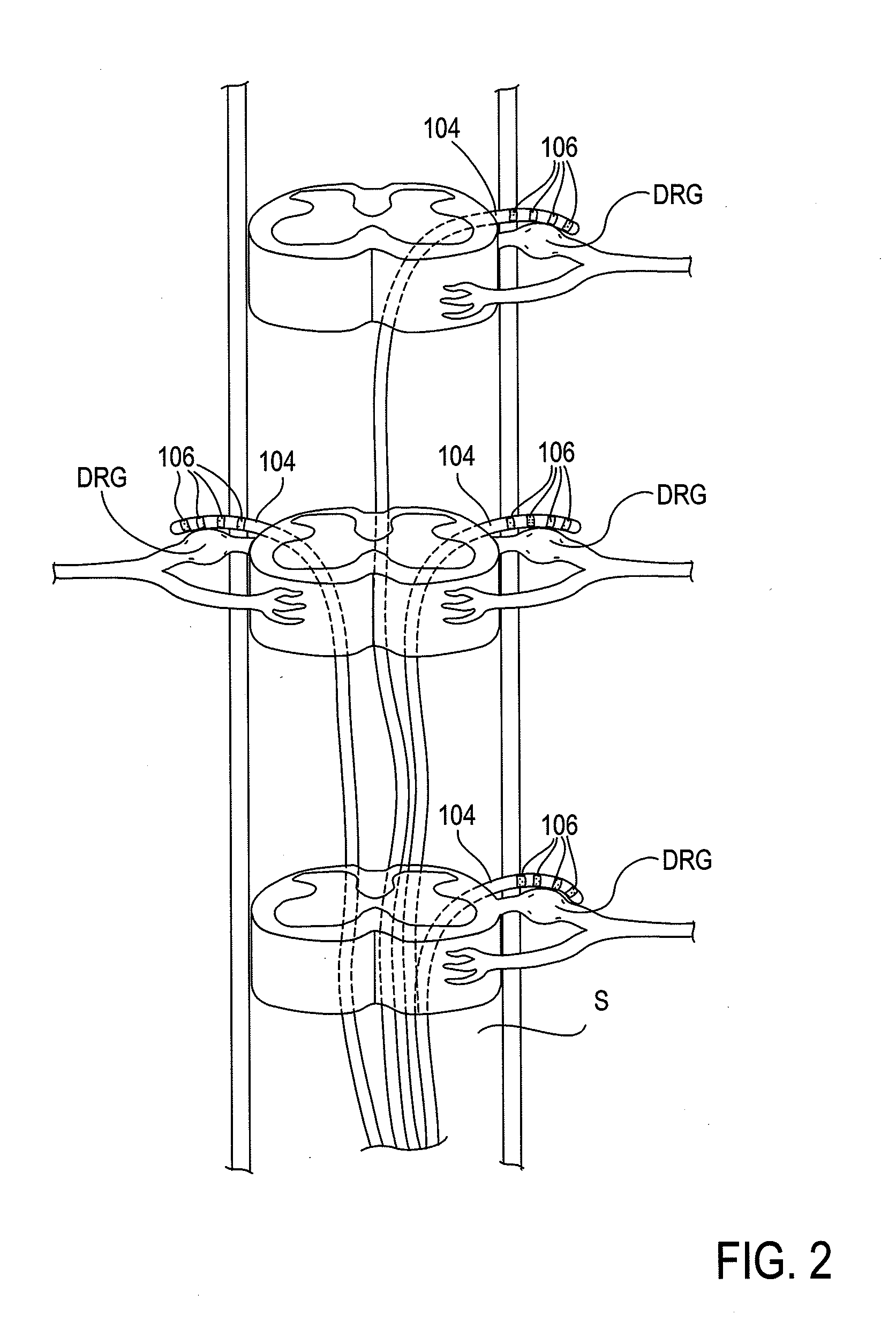
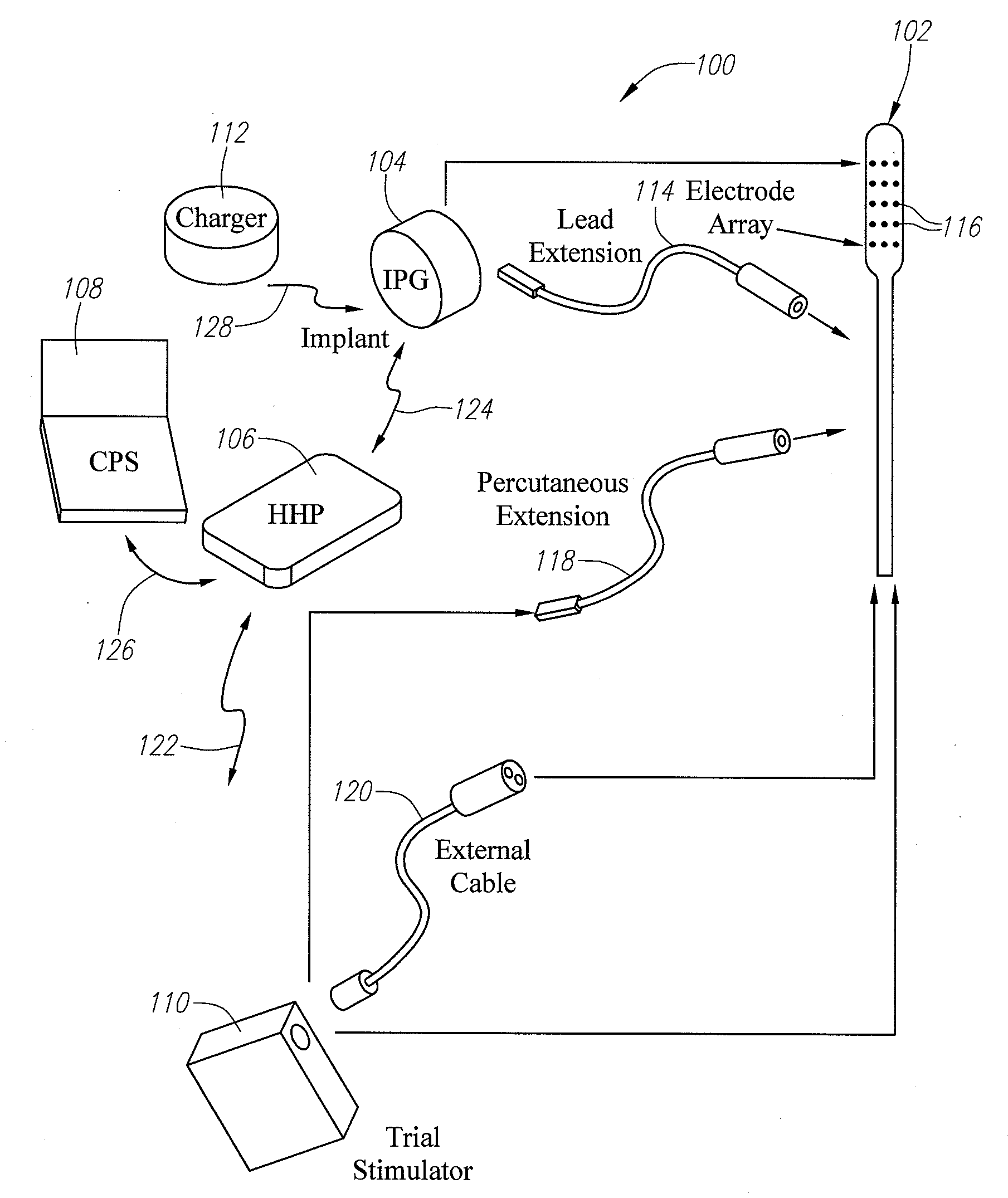
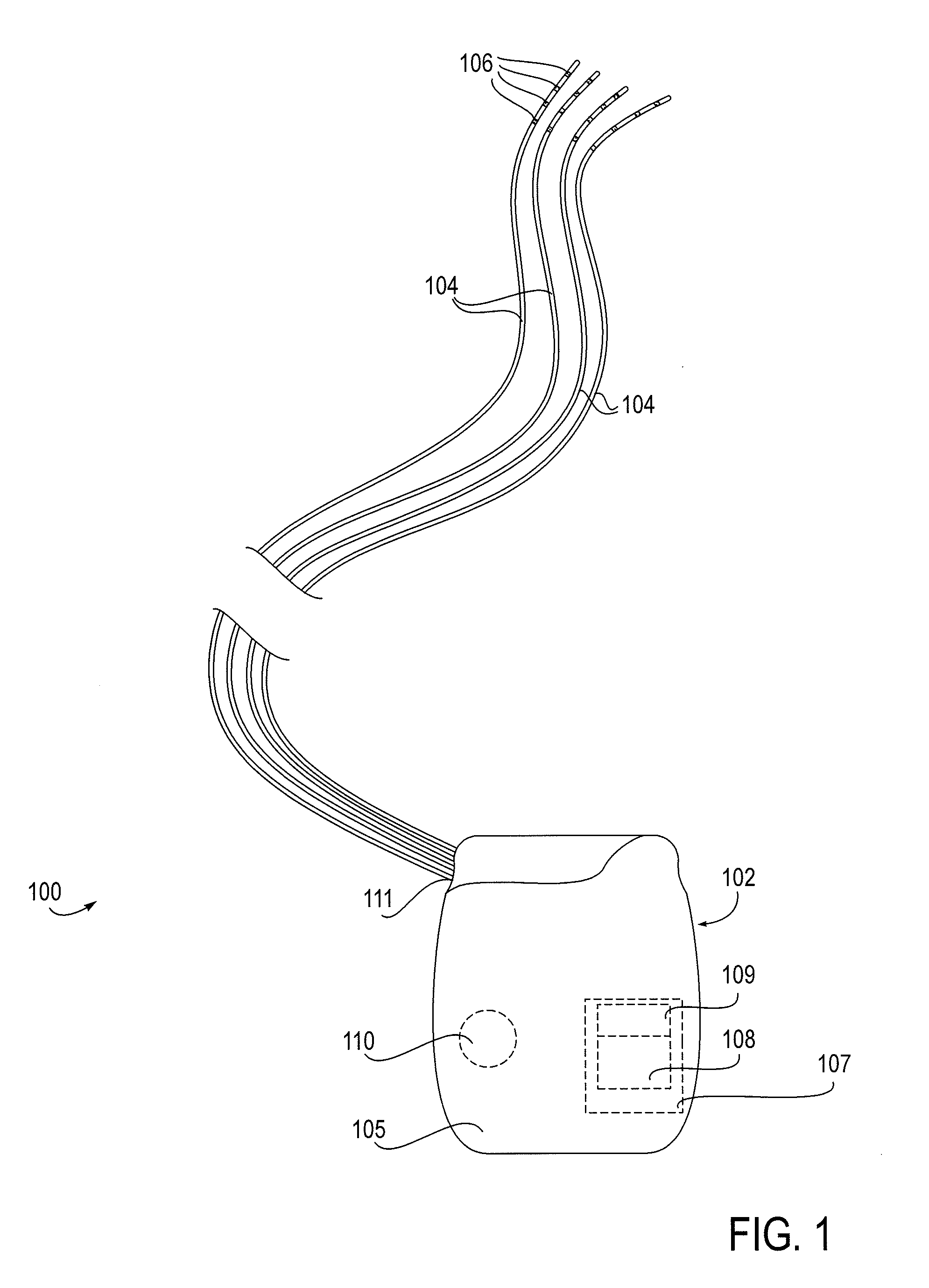
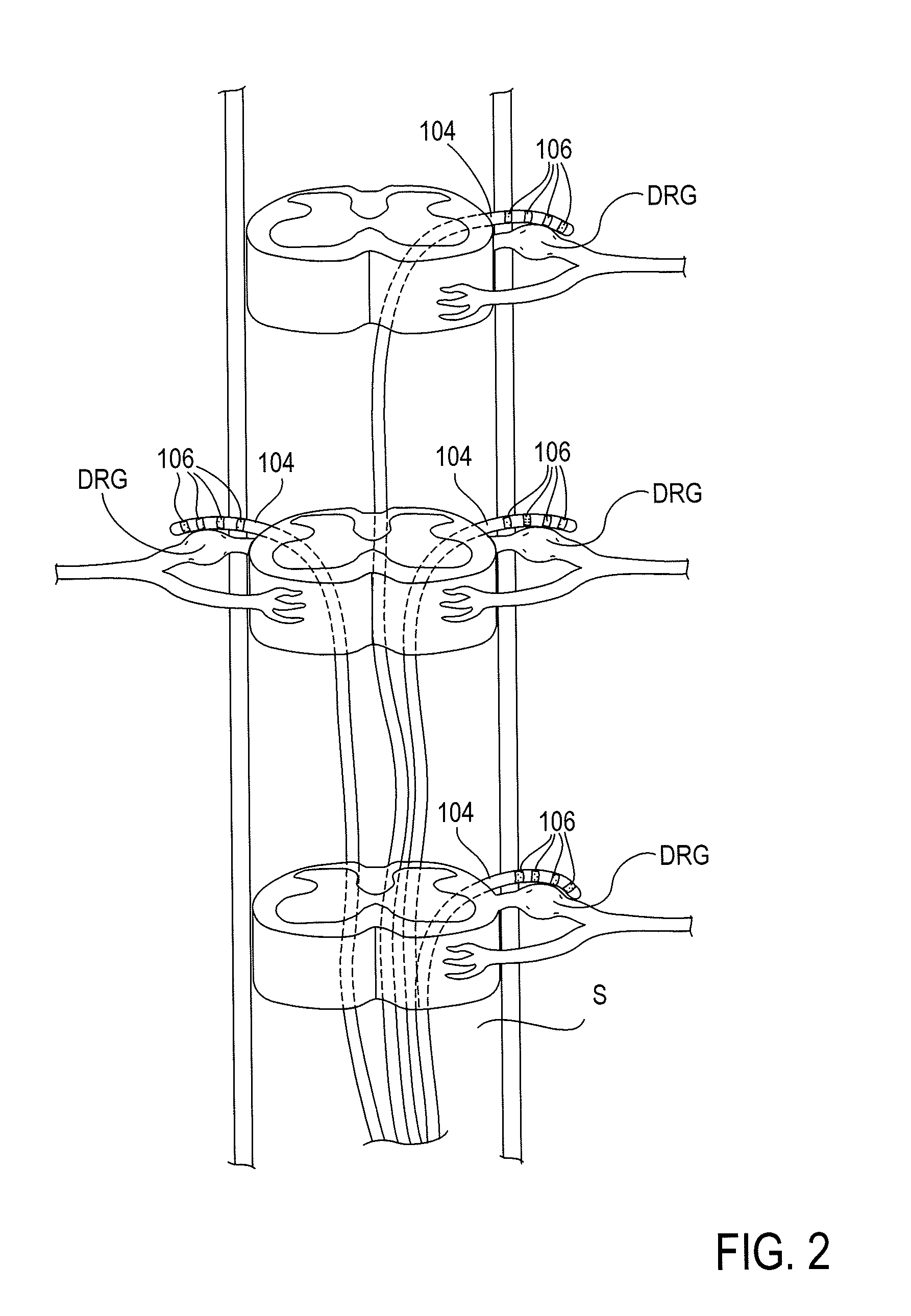
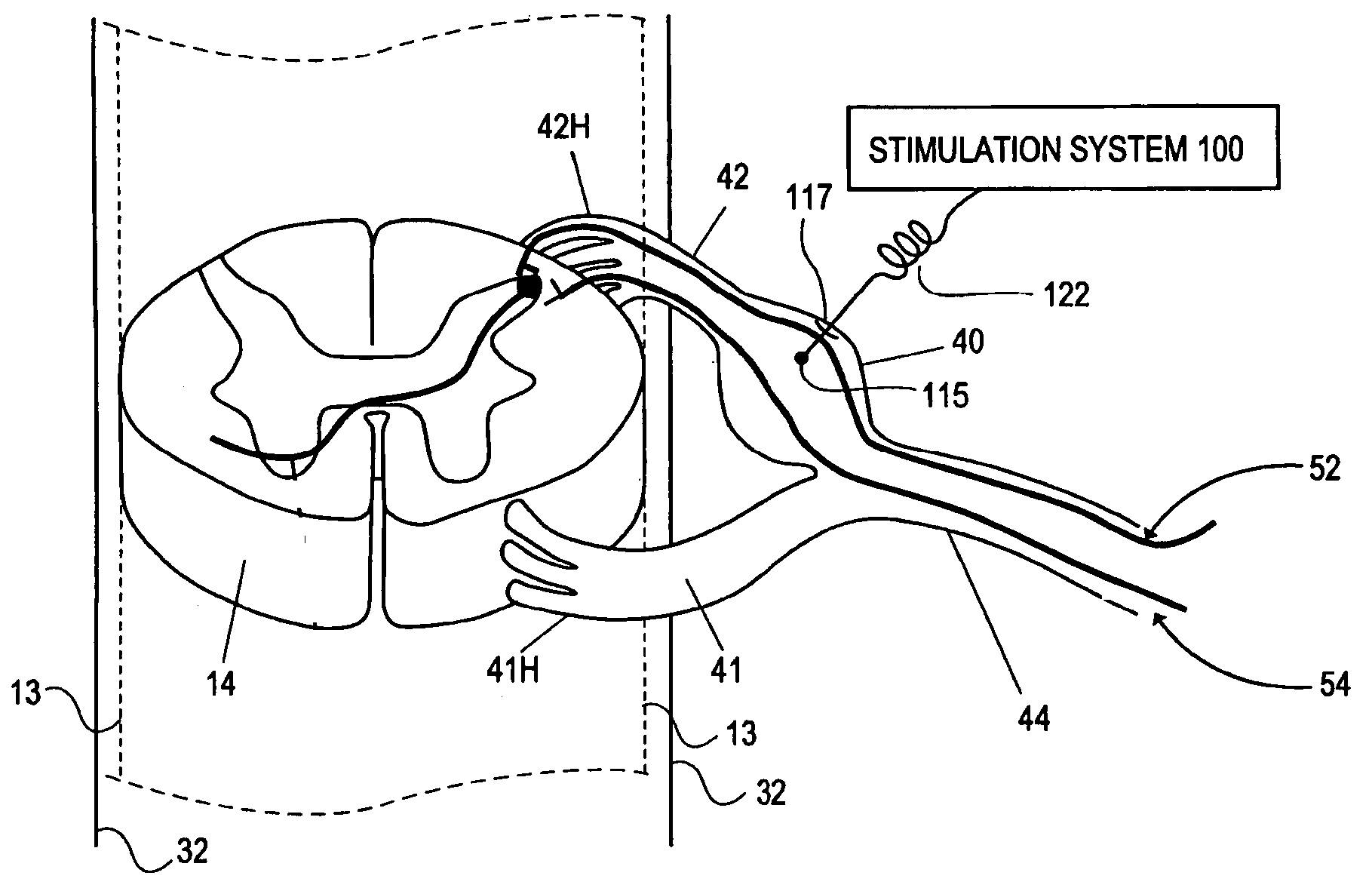
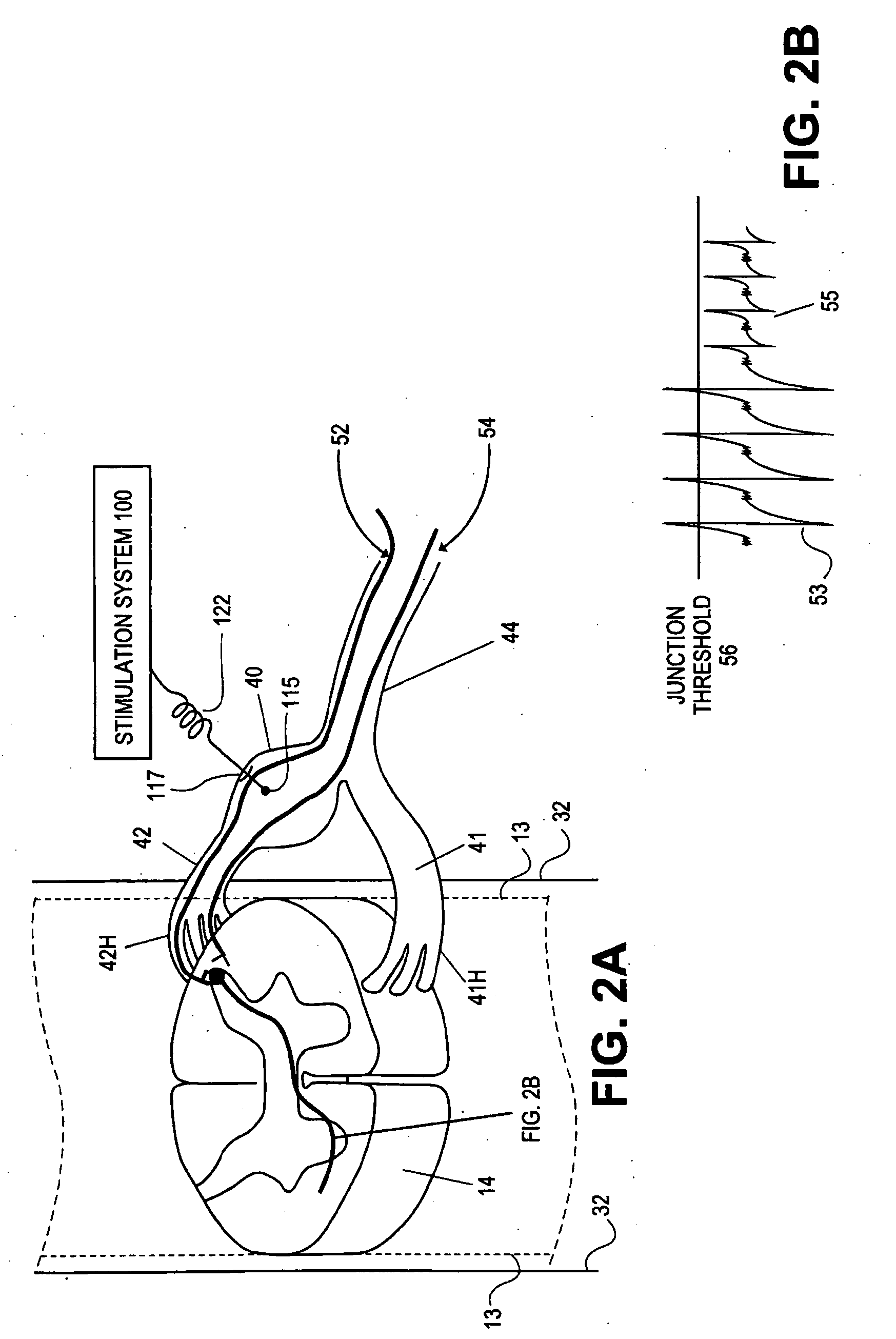
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Methods and systems for modulating neural tissue
Some embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for modulating neural tissue including systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of targeted neural tissue. Targeted neural tissue may include one or more ganglia including those of the spinal nerves in the dorsal root and the sympathetic chain. Methods also include implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
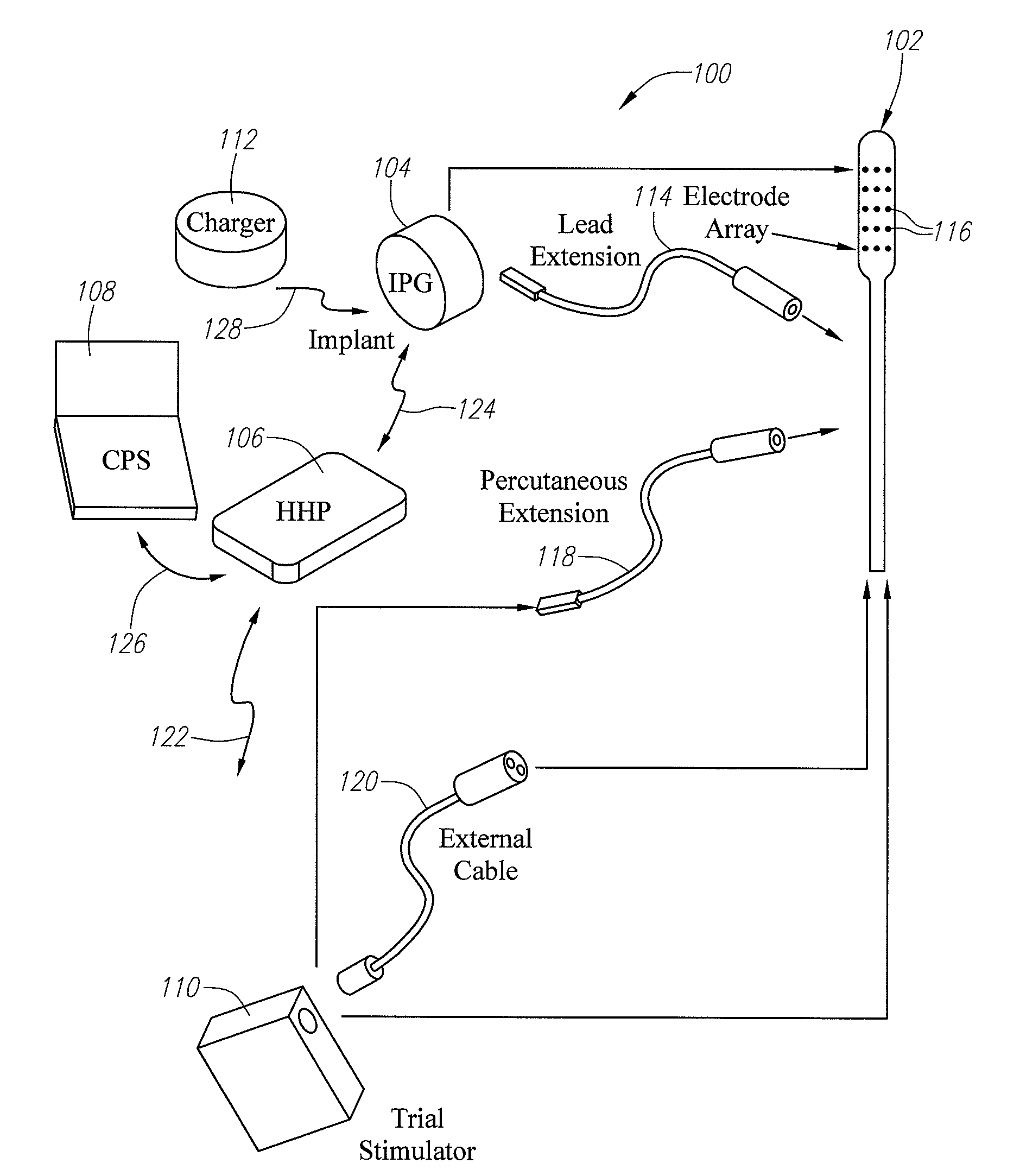
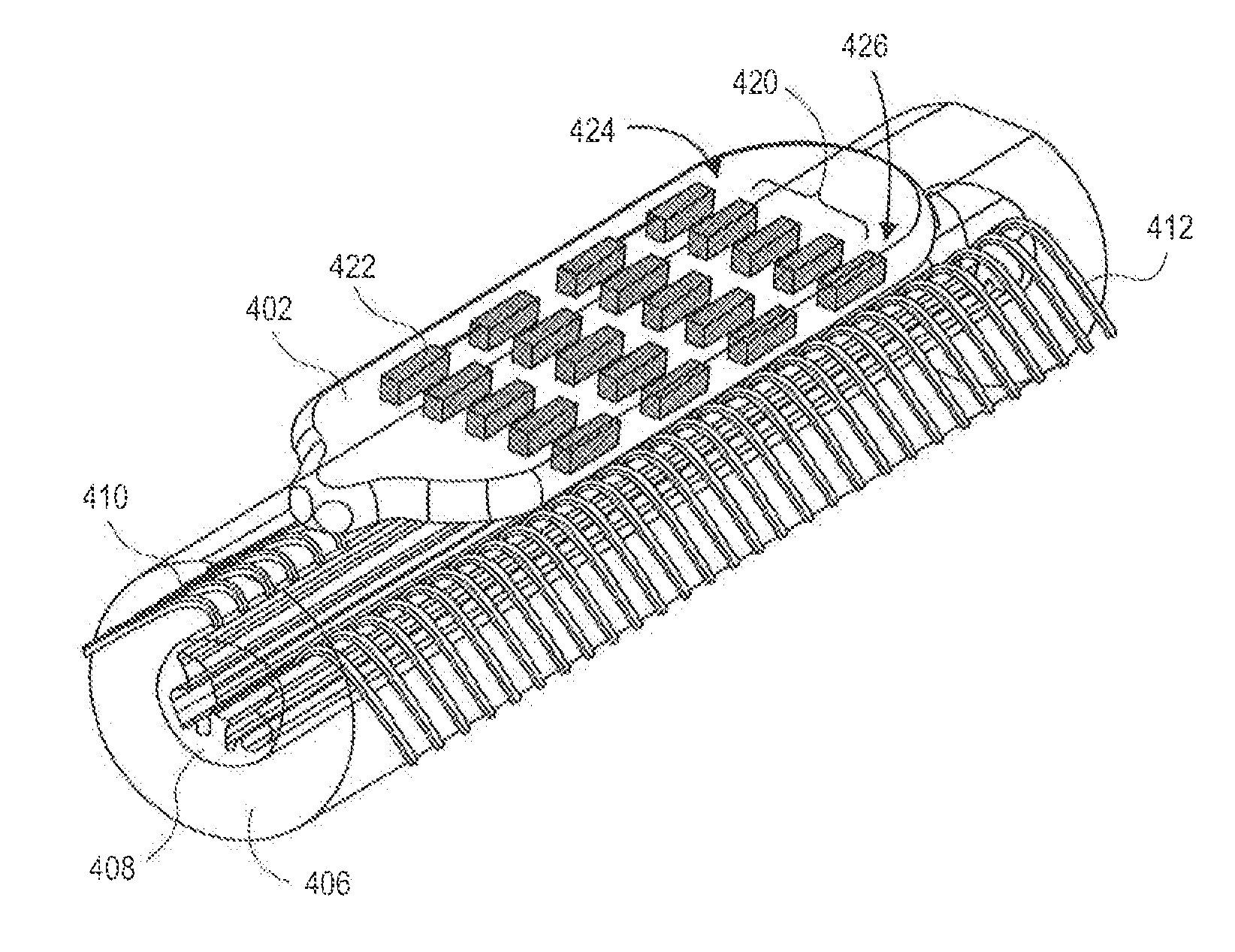
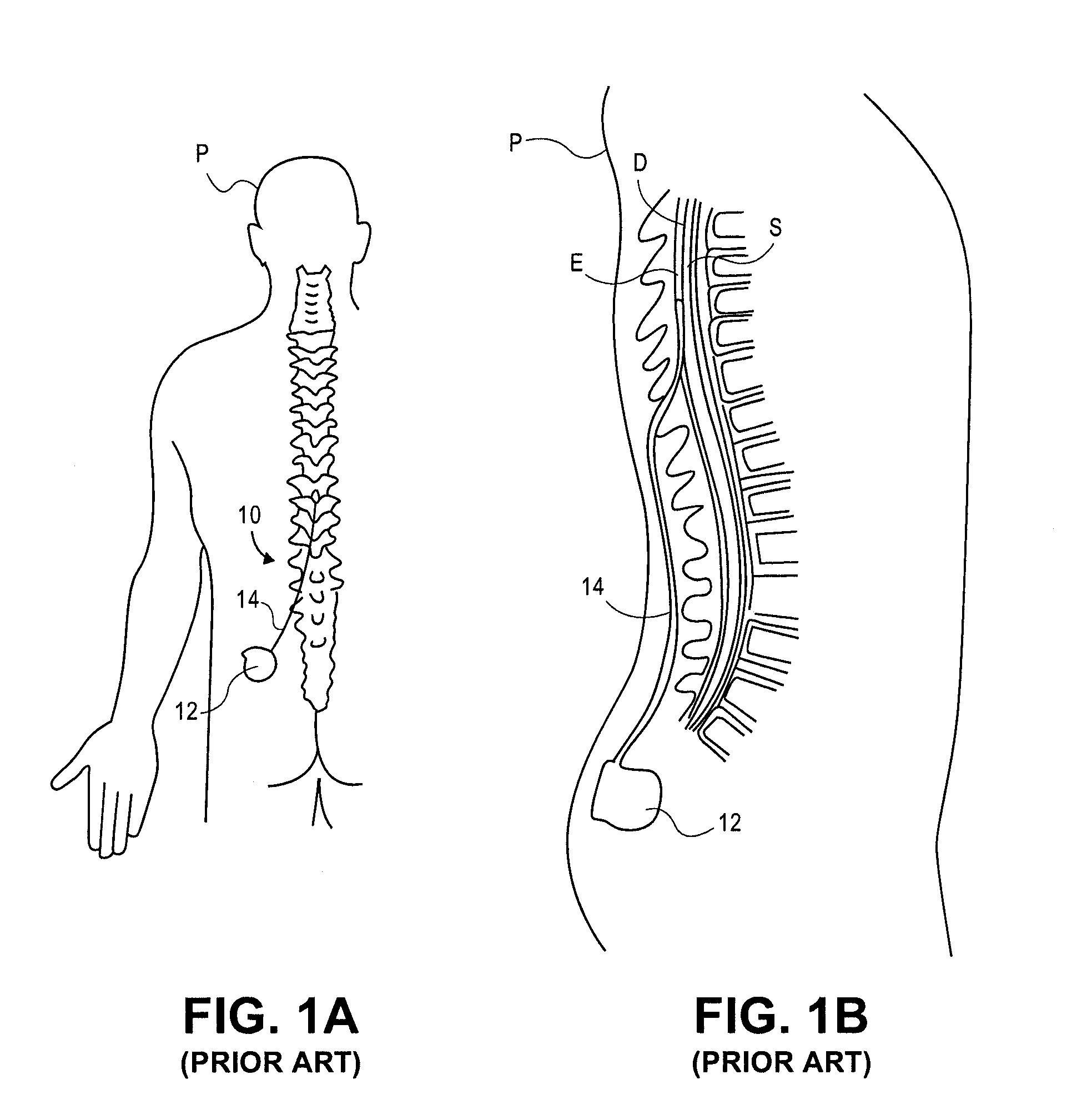
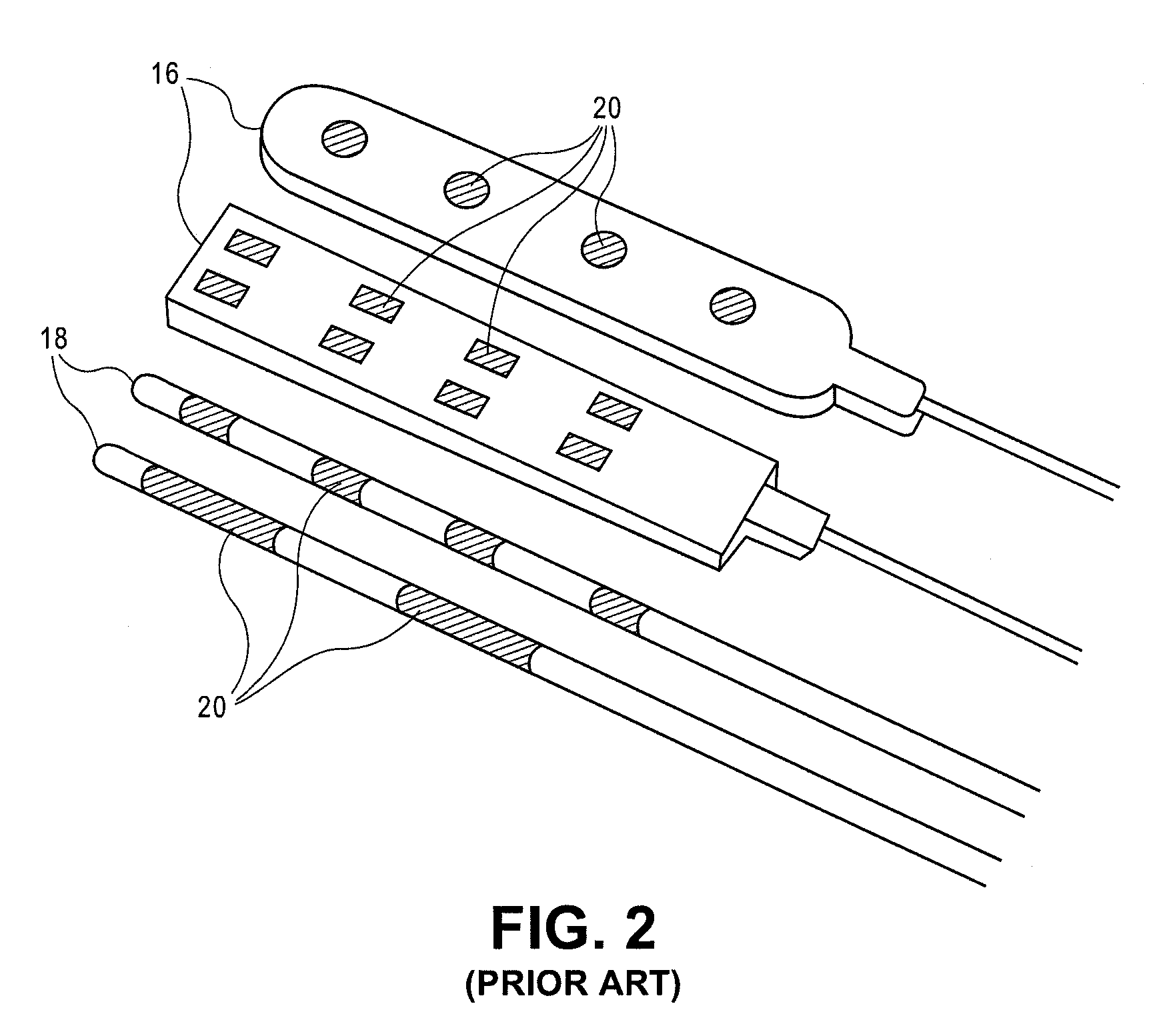
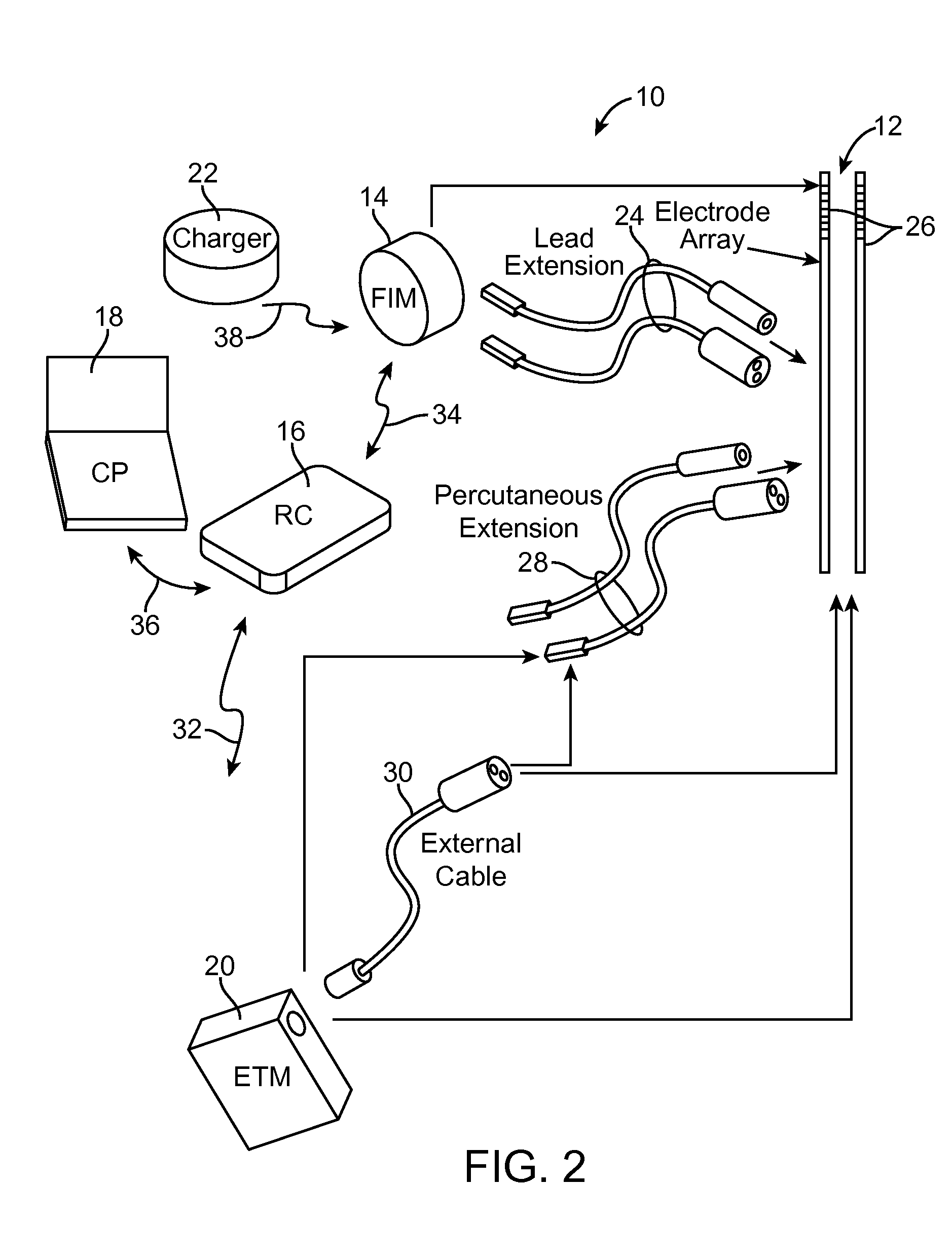
Implantable flexible circuit leads and methods of use
InactiveUS20080140152A1Easy to manufactureStrong specificitySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesDielectricFlexible circuits
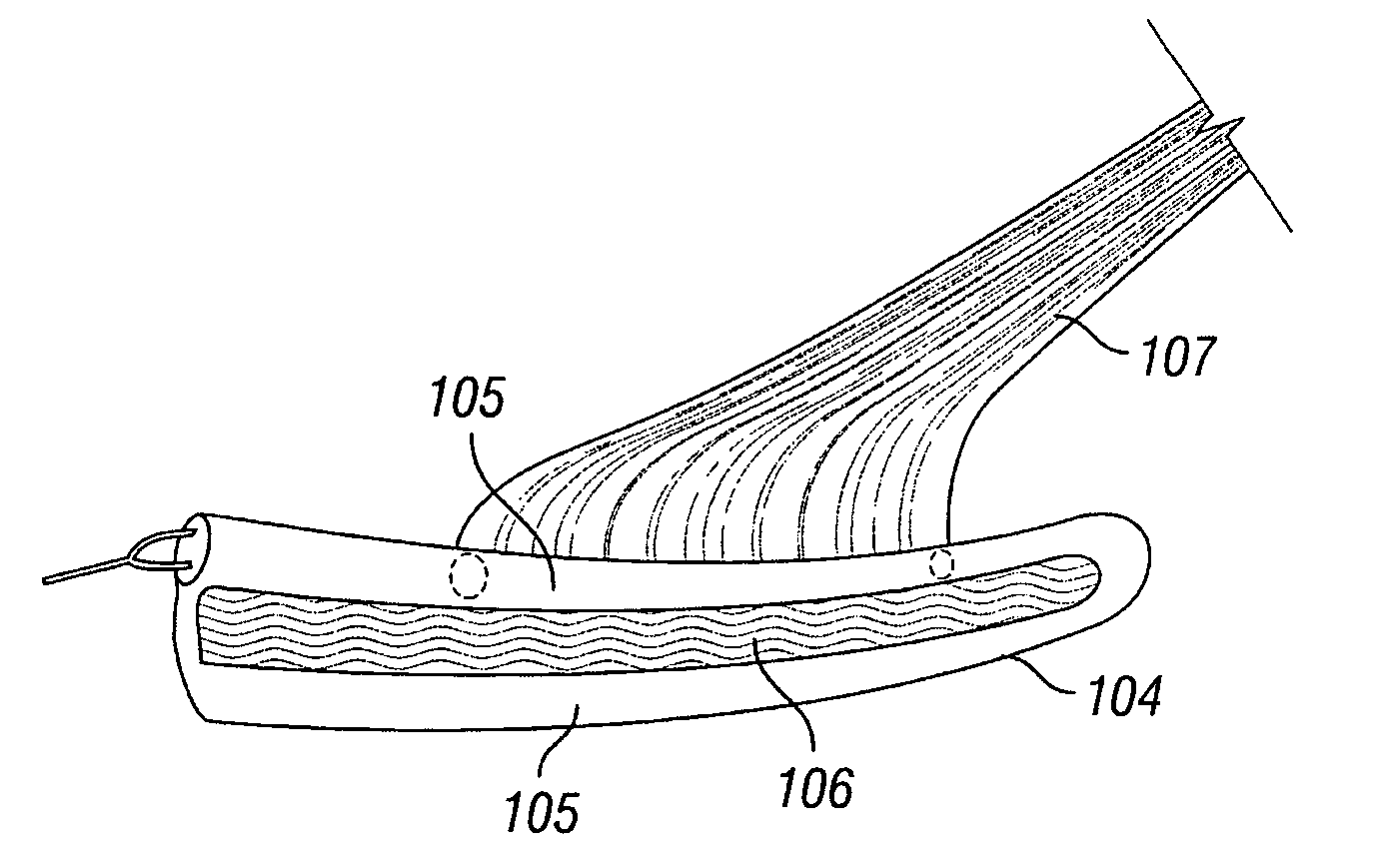
Devices, systems and methods are provided for stimulation of tissues and structures within a body of a patient. In particular, implantable leads are provided which are comprised of a flexible circuit. Typically, the flexible circuit includes an array of conductors bonded to a thin dielectric film. Example dielectric films include polyimide, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) or other biocompatible materials to name a few. Such leads are particularly suitable for stimulation of the spinal anatomy, more particularly suitable for stimulation of specific nerve anatomies, such as the dorsal root (optionally including the dorsal root ganglion).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
Methods for stimulating a nerve root ganglion
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Stimulation leads, delivery systems and methods of use
InactiveUS20100179562A1Minimizing complicationMinimize side effectsSpinal electrodesDiagnosticsSide effectMedicine
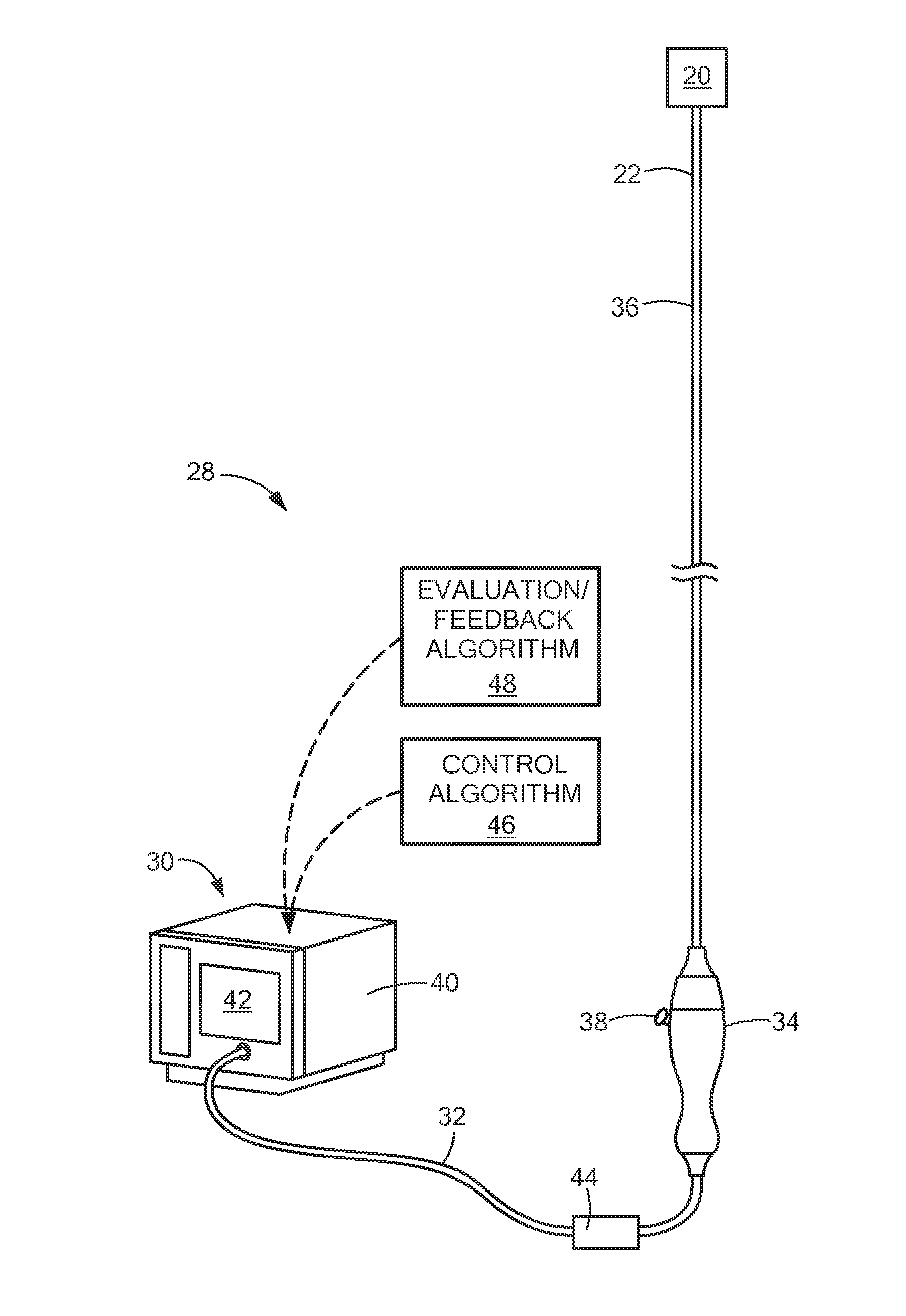
Devices, systems and methods are provided for accessing and treating anatomies associated with a variety of conditions while minimizing possible complications and side effects. This is achieved by directly neuromodulating a target anatomy associated with the condition while minimizing or excluding undesired neuromodulation of other anatomies. Typically, this involves stimulating portions of neural tissue of the central nervous system, wherein the central nervous system includes the spinal cord and the pairs of nerves along the spinal cord which are known as spinal nerves. In particular, some embodiments of the present invention are used to selectively stimulate portions of the spinal nerves, particularly one or more dorsal root ganglions (DRGs), to treat chronic pain while causing minimal deleterious side effects such as undesired motor responses.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
Short duration pre-pulsing to reduce stimulation-evoked side-effects
A method and neurostimulation system of providing therapy to a patient is provided. At least one electrode is placed in contact with tissue of a patient. A sub-threshold, hyperpolarizing, conditioning pre-pulse (e.g., an anodic pulse) is conveyed from the electrode(s) to render a first region of the tissue (e.g., dorsal root fibers) less excitable to stimulation, and a depolarizing stimulation pulse (e.g., a cathodic pulse) is conveyed from the electrode(s) to stimulate a second different region of the tissue (e.g., dorsal column fibers). The conditioning pre-pulse has a relatively short duration (e.g., less than 200 μs).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Neurostimulation system
Some embodiments of the present invention provide neurostimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide neurostimulation systems adapted for selective neurostimulation of one or more nerve root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Directed delivery of agents to neural anatomy
InactiveUS20120310140A1Effective pain managementAdequate pain reliefSpinal electrodesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseAutomatic control
The present invention is directed generally to systems, devices and methods for direct delivery of agents, e.g., pharmaceutical agents, to target spinal and neuronal anatomies, e.g., the dorsal root ganglia (DRG), for the treatment of various disorders, particularly pain and pain related disorders, such as chronic itch, sensory disorders, multiple sclerosis, post-herpetic neuralgia and the like. The system, devices and methods of the invention encompass the agents to be delivered to the target anatomy alone or in combination with electrical stimulation. The delivery device and systems and methods as disclosed herein place the distal end of the delivery element, which comprises at least one agent delivery structure, and optionally at least one electrode, in close proximity, or in contact with or next to the target spinal anatomy, e.g., DRG. A variety of agents can be delivered using the device, including sodium channel blockers, biologics, neuroinflammatory modulators, toxins etc., to selectively neuromodulate the neurons. Agent delivery and / or electrical stimulation can be automated and / or can be controlled automatically or by a pre-determined program, or by a patient control pump (PCA).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
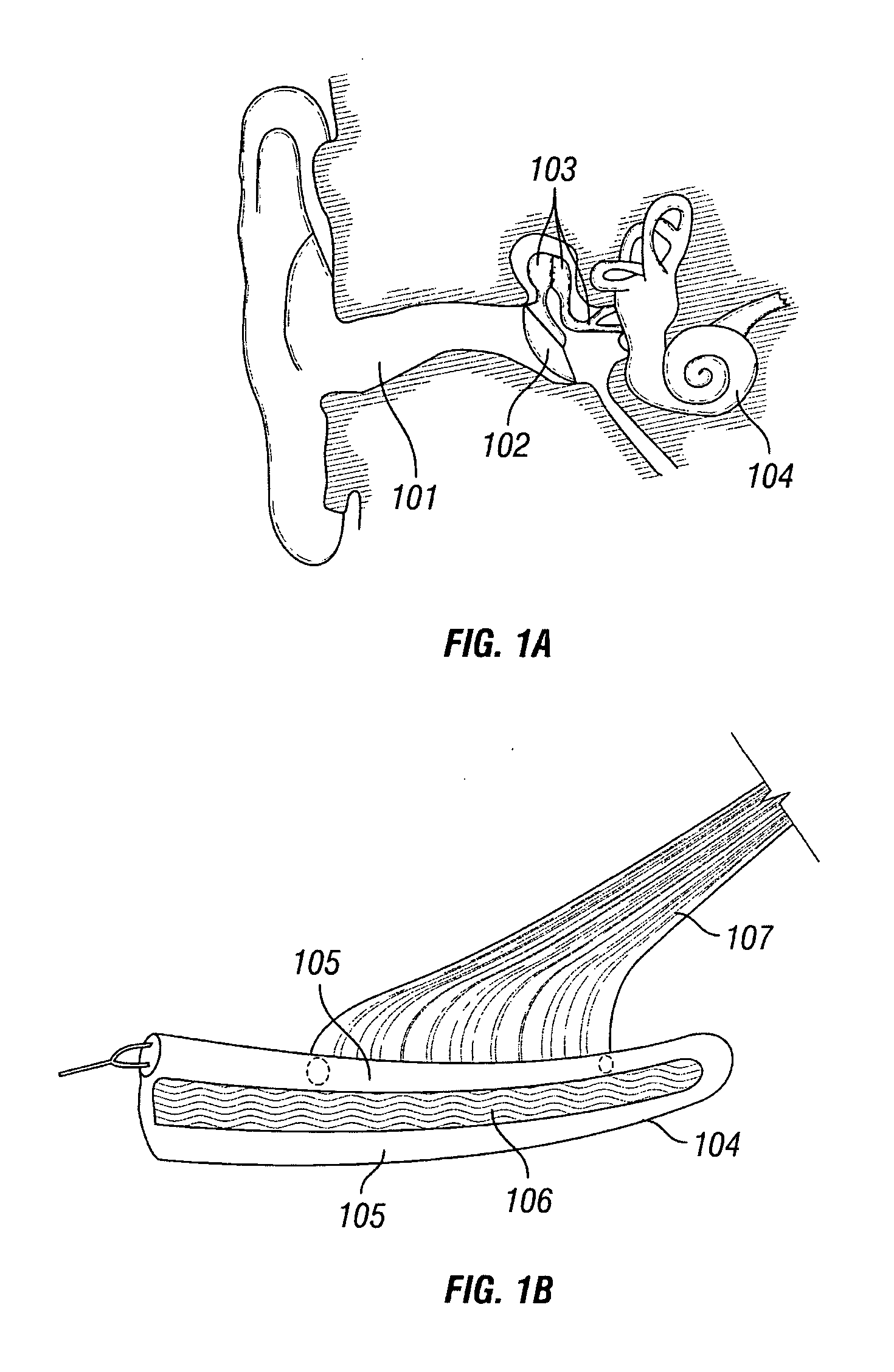
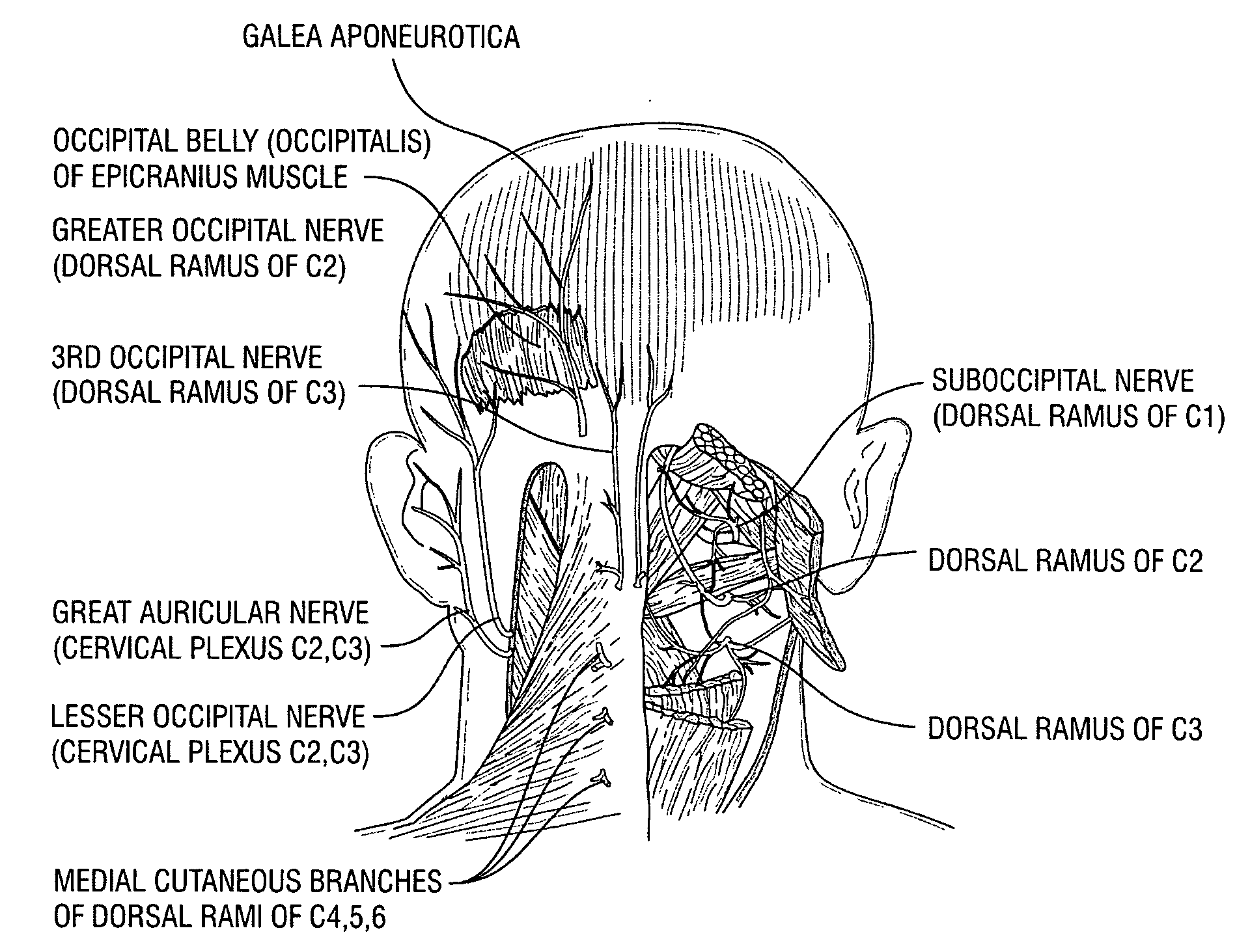
Peripheral nerve stimulation to treat auditory dysfunction
A system and / or method for treating auditory dysfunction by somatosensory system stimulation. The system and / or method comprises a probe and a device to stimulate the probe. The probe has a stimulation portion implanted in communication with a predetermined peripheral nerve site. The stimulation portion of the probe may be implanted in contact with a peripheral nerve dorsal root ganglia, cranial nerve or dermatome area, for example C2 dermatome area or a trigeminal dermatome area. The stimulation portion may be a laminotomy, paddle, surgical, or multiple electrode lead. The device to stimulate the probe may be implanted subcutaneously or transcutaneously.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
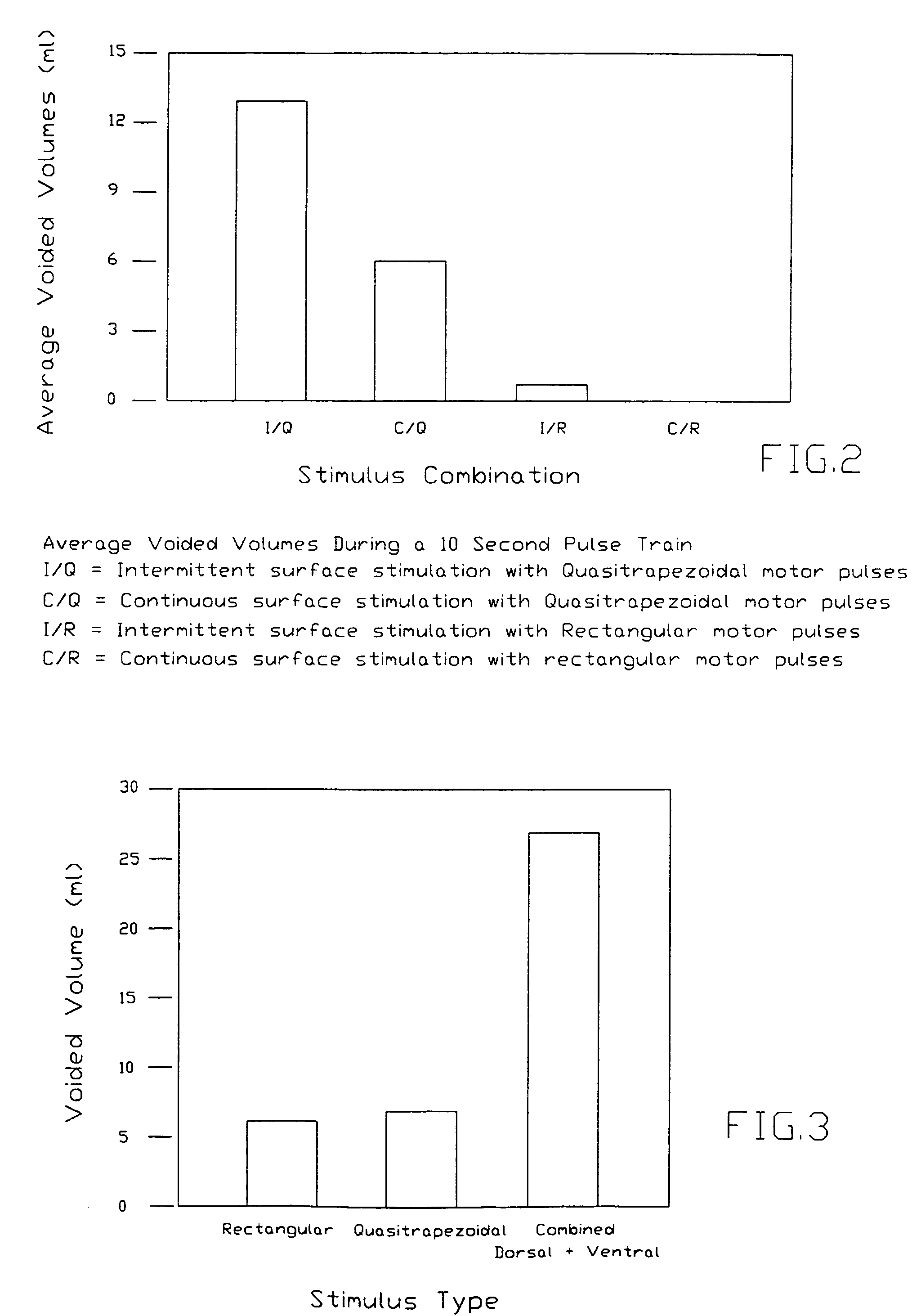
Combined stimulation of ventral and dorsal sacral roots for control of bladder function
InactiveUS7142925B1Efficiently voidingSelectively controlling activationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationBladder functionVentral Roots
Methods and apparatuses for controlling bladder discharge in a patient are described. The method includes coupling a first electrode to a sacral ventral root of the patient and coupling a second electrode to a sacral dorsal root of the patient. The method may be applied to spinal cord injured patients without dorsal root section.
Owner:AXON ENG
Implantable flexible circuit leads and methods of use
InactiveUS9314618B2Easy to manufactureStrong specificitySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringDielectricAnatomical structures
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
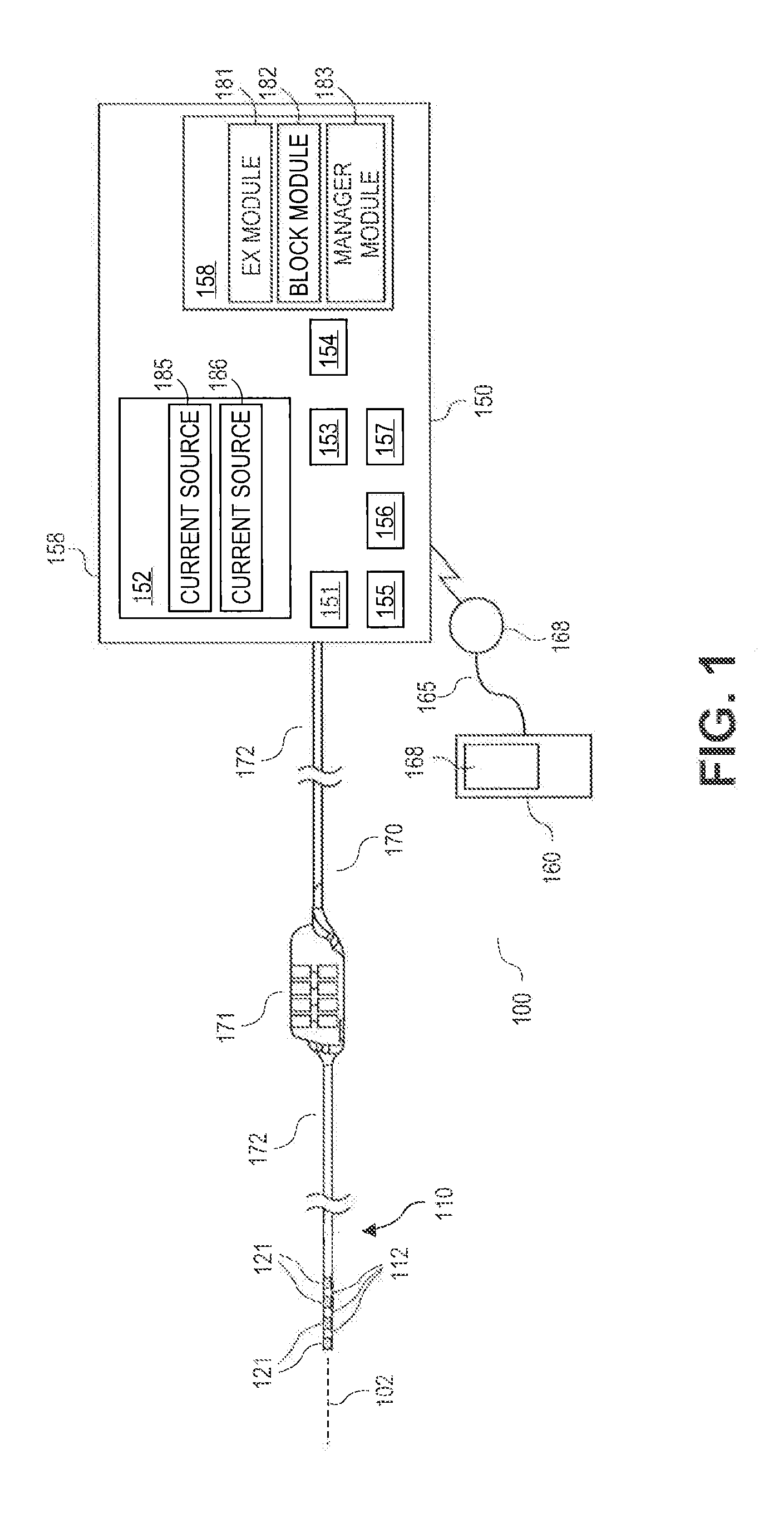
Pulse generator for high impedance electrodes
Some embodiments of the present invention provide a pulse generator for high impedance electrodes as well as stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of targeted neural tissue. Targeted neural tissue may include one or more dorsal root ganglia with an electrode implanted on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:KIM DANIEL H +2
Peripheral nerve stimulation to treat auditory dysfunction
A system and / or method for treating auditory dysfunction by somatosensory system stimulation. The system and / or method comprises a probe and a device to stimulate the probe. The probe has a stimulation portion implanted in communication with a predetermined peripheral nerve site. The stimulation portion of the probe may be implanted in contact with a peripheral nerve dorsal root ganglia, cranial nerve or dermatome area, for example C2 dermatome area or a trigeminal dermatome area. The stimulation portion may be a laminotomy, paddle, surgical, or multiple electrode lead. The device to stimulate the probe may be implanted subcutaneously or transcutaneously.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Stimulation components
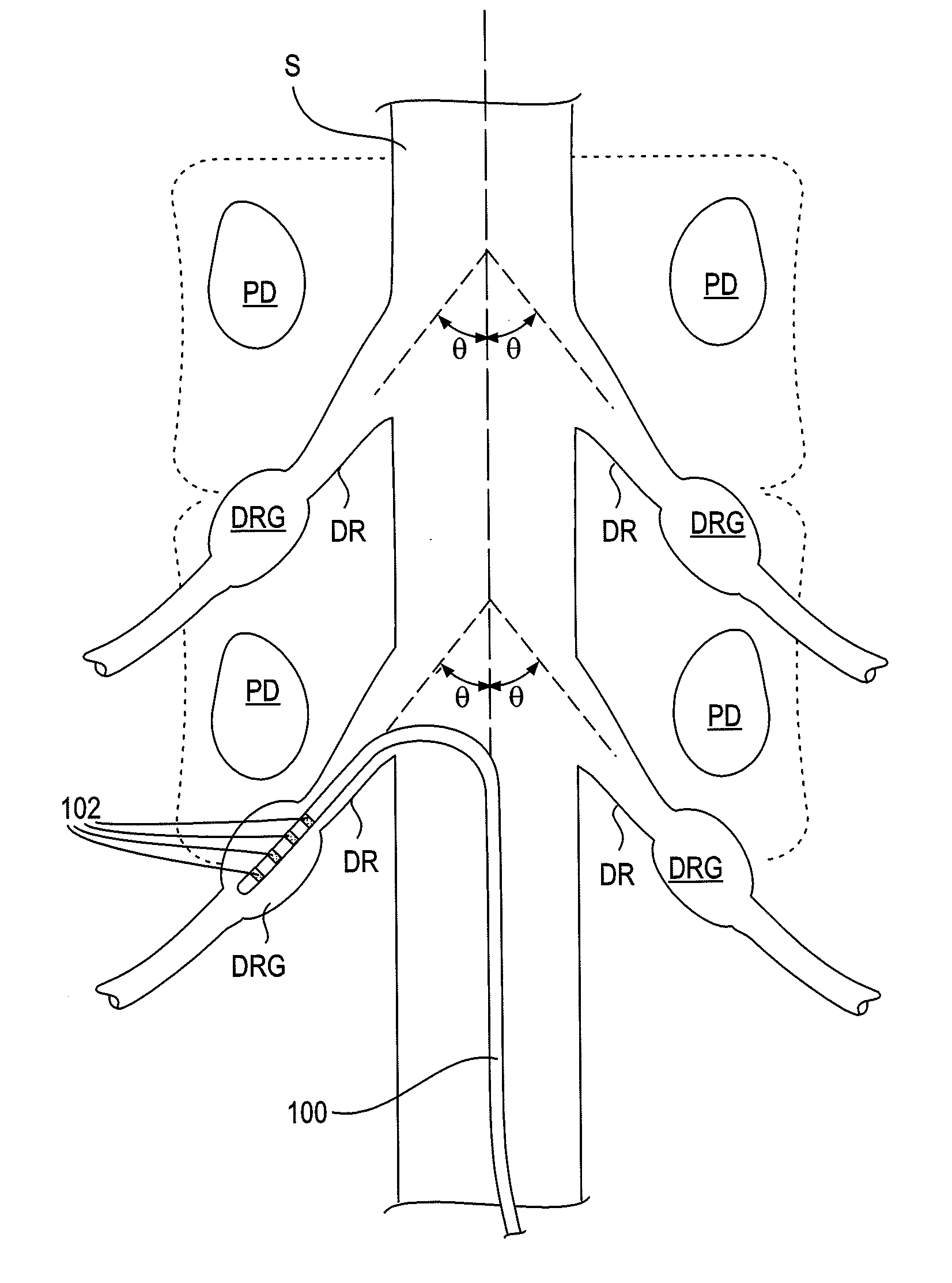
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for stimulating a dorsal root ganglion
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
System and method for dorsal root block during spinal cord stimulation
InactiveUS20160158551A1Eliminate side effectsSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationNerve fiber bundleMedicine
A system and method are provided to mitigate excitation of non-target regions of nerve fibers during spinal cord stimulation (SCS) of nervous tissue of a patient. The method and system deliver an SCS excitation waveform to an excitation electrode located proximate to a dorsal column (DC), the SCS excitation waveform shaped to excite a nerve fiber target region (TR) within the DC. The method and system also deliver a blocking waveform to a blocking electrode located proximate to the DR, the excitation waveform shaped to at least partially induce hyperpolarization into a nerve fiber non-target region (NTR) within the DR.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
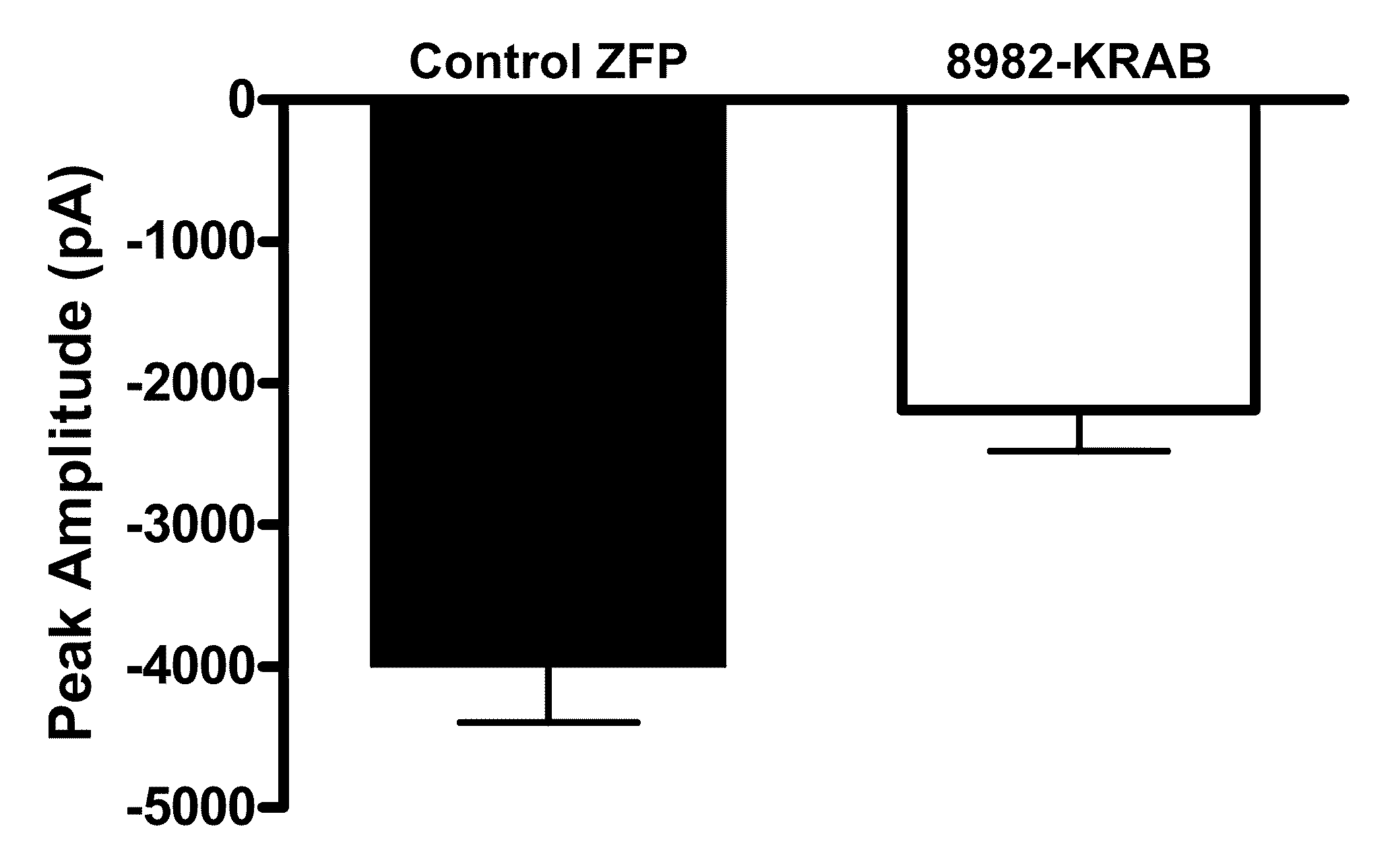
Treatment of chronic pain with zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS20090215878A1Suppress gene expressionModulate physiological processes correlatedOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNormal levelPain patient
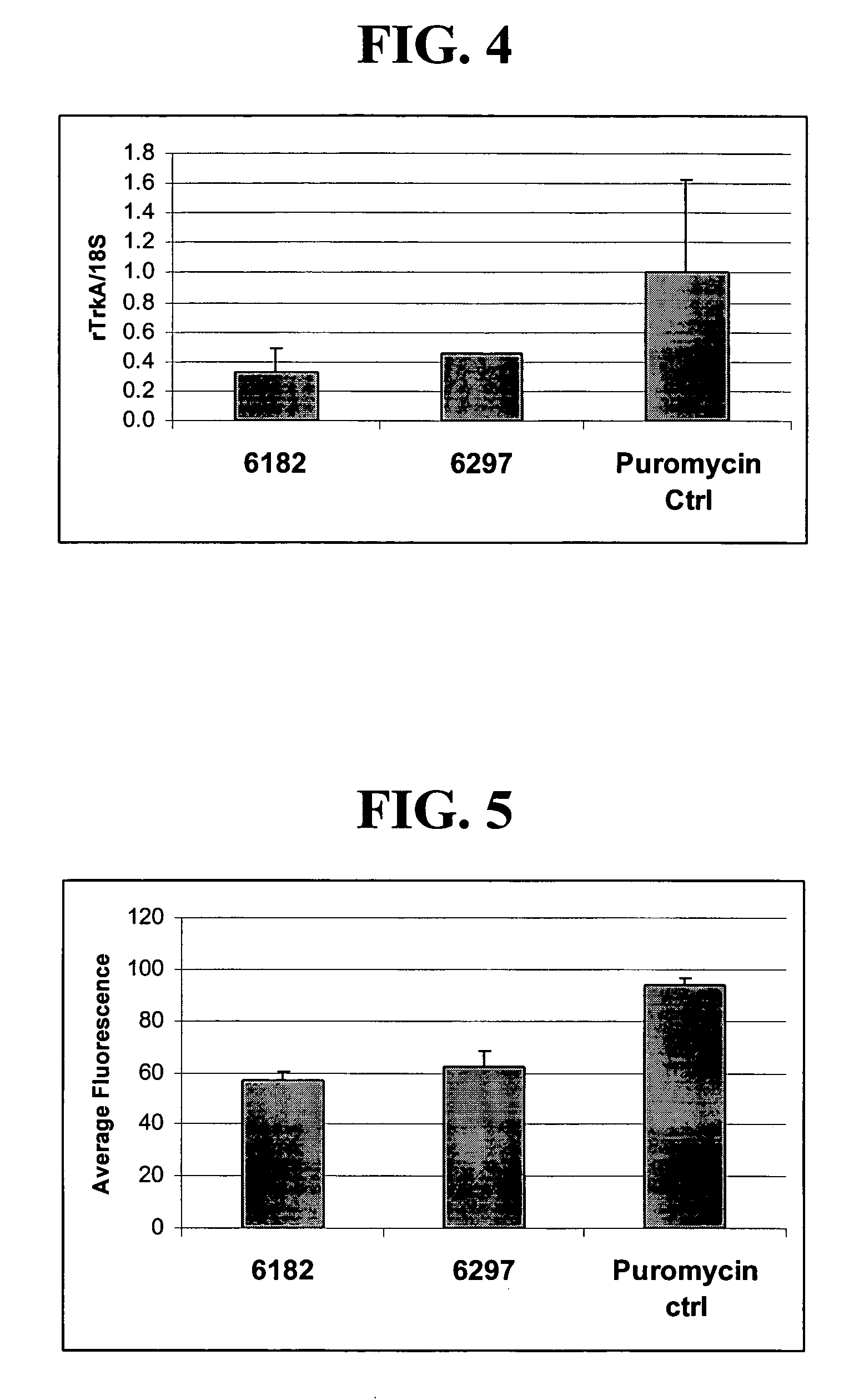
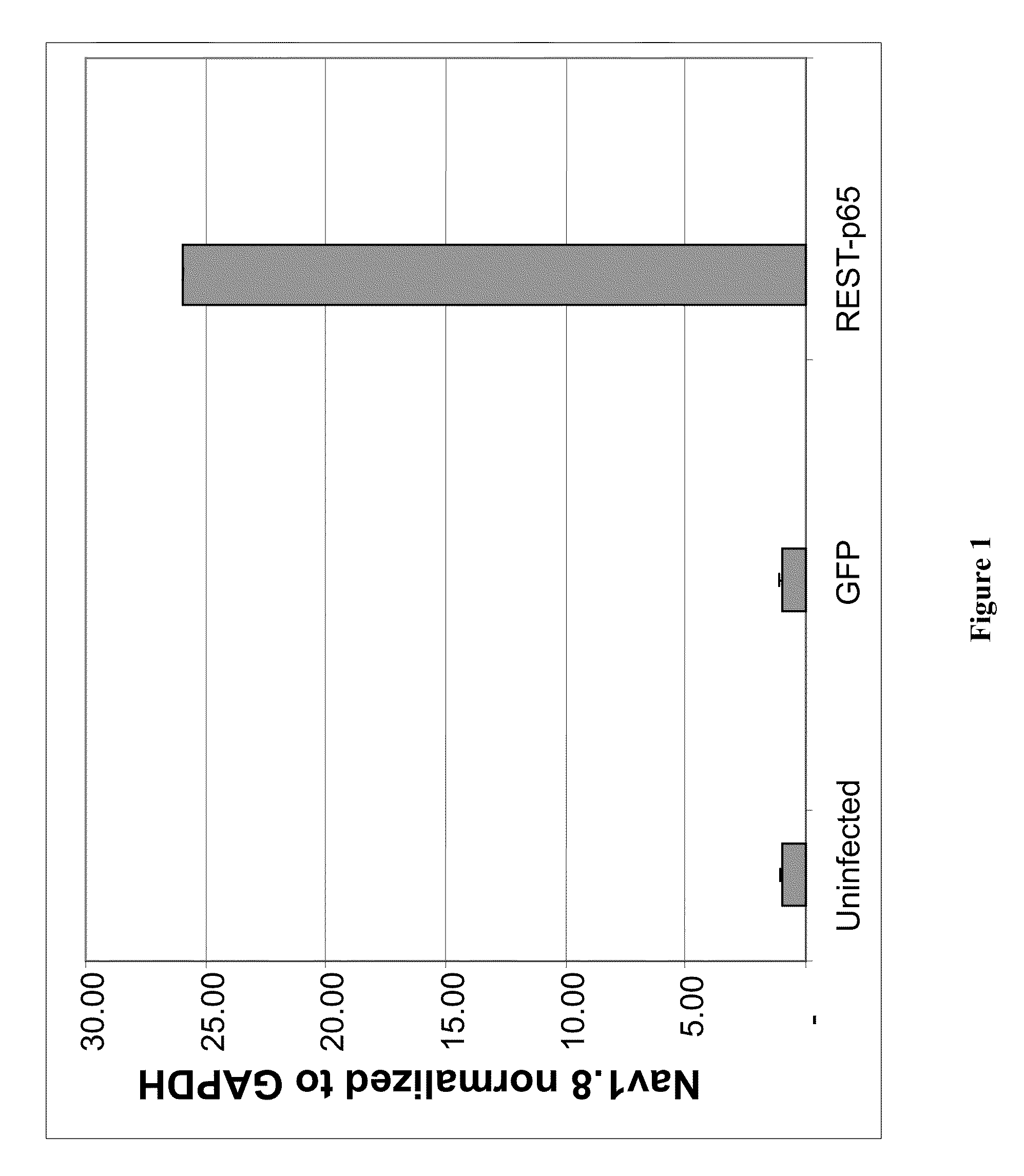
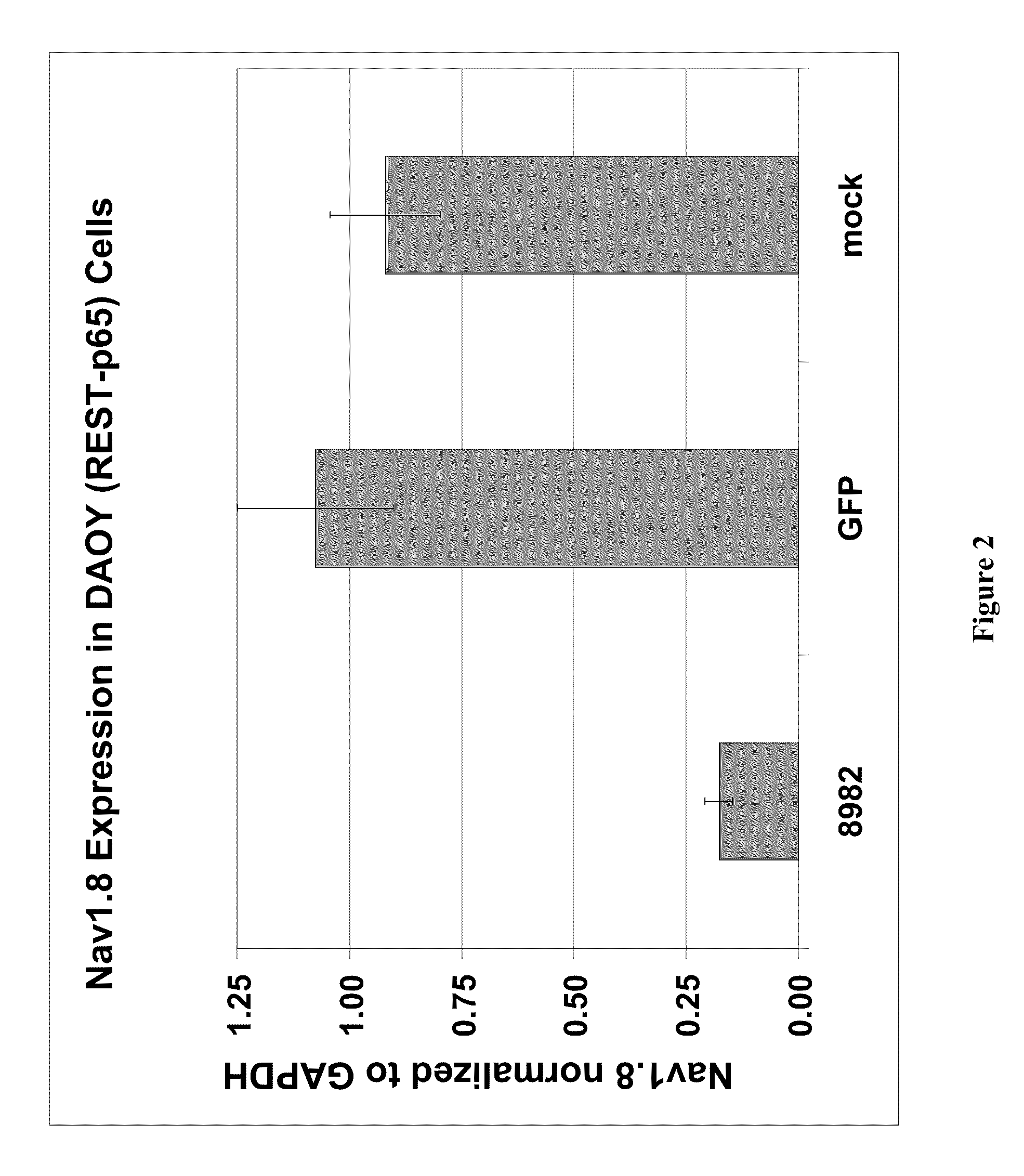
A variety of zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) and methods utilizing such proteins are provided for use in treating chronic pain. ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes that are aberrantly expressed in subjects having chronic pain are described. In addition, ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes expressed at normal levels in subjects experiencing chronic pain, modulation of whose expression results in decreased pain perception, are also provided. For example, genes that are over-expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of pain patients (e.g., Nav1.8) can be repressed.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
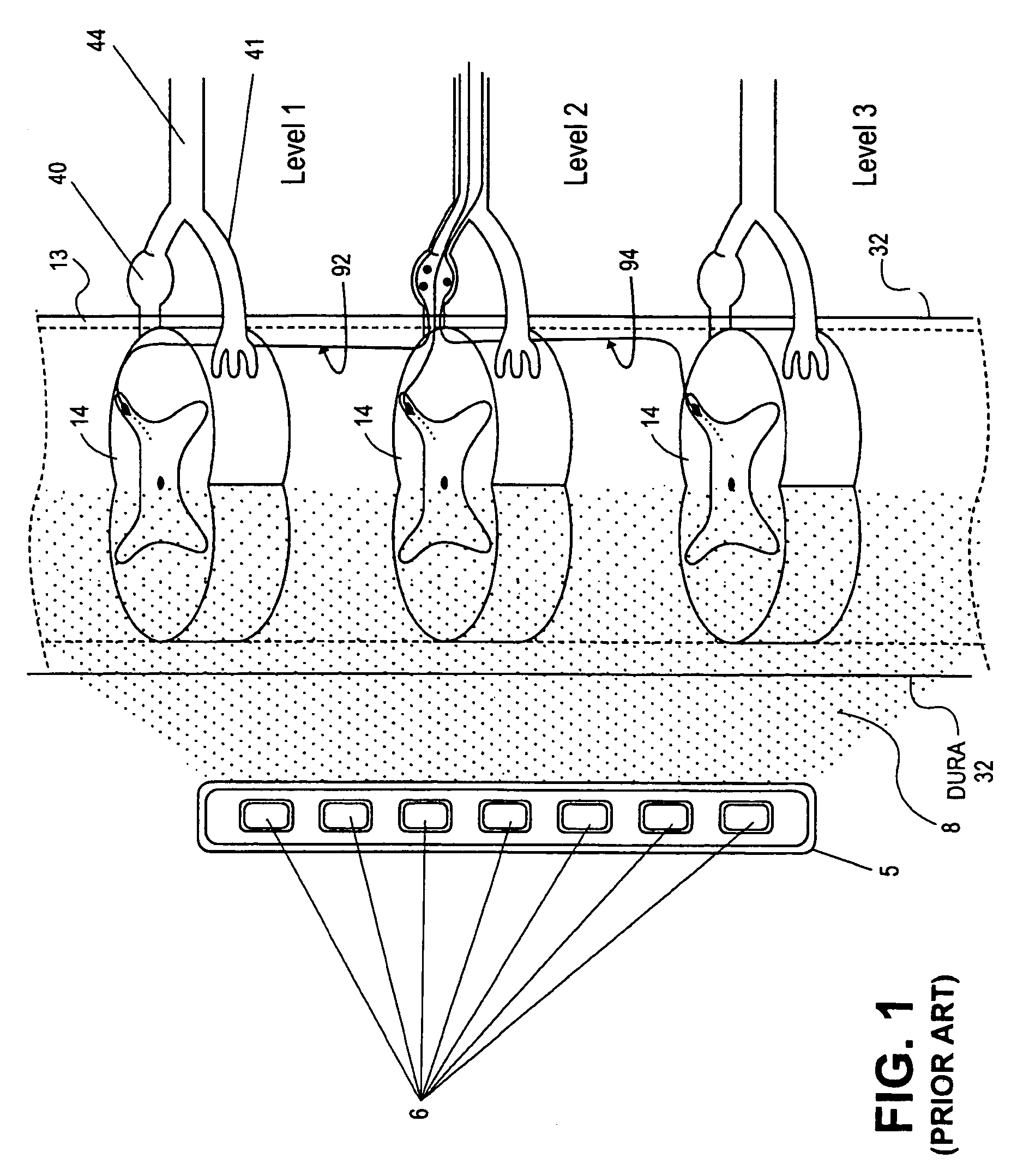
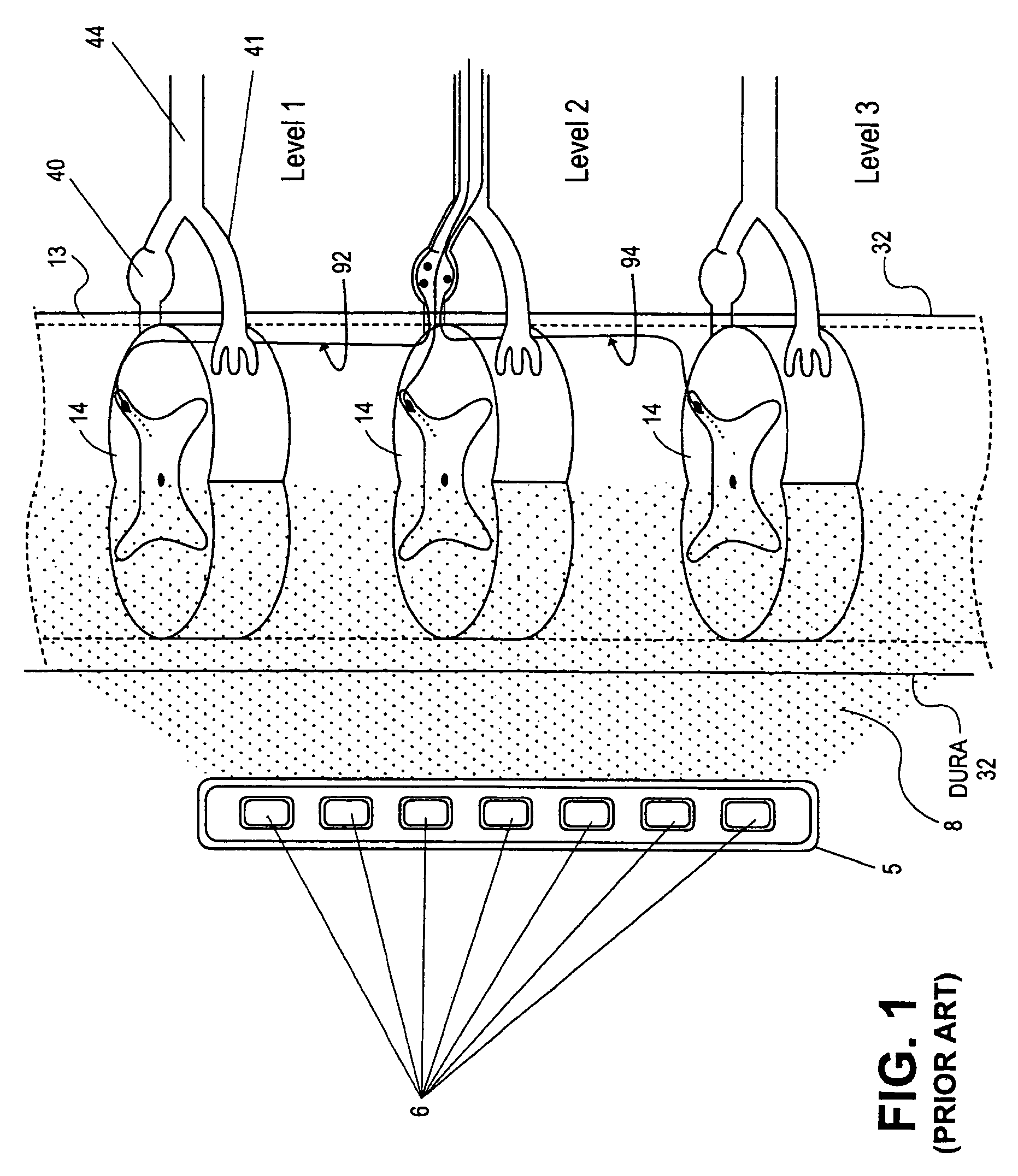
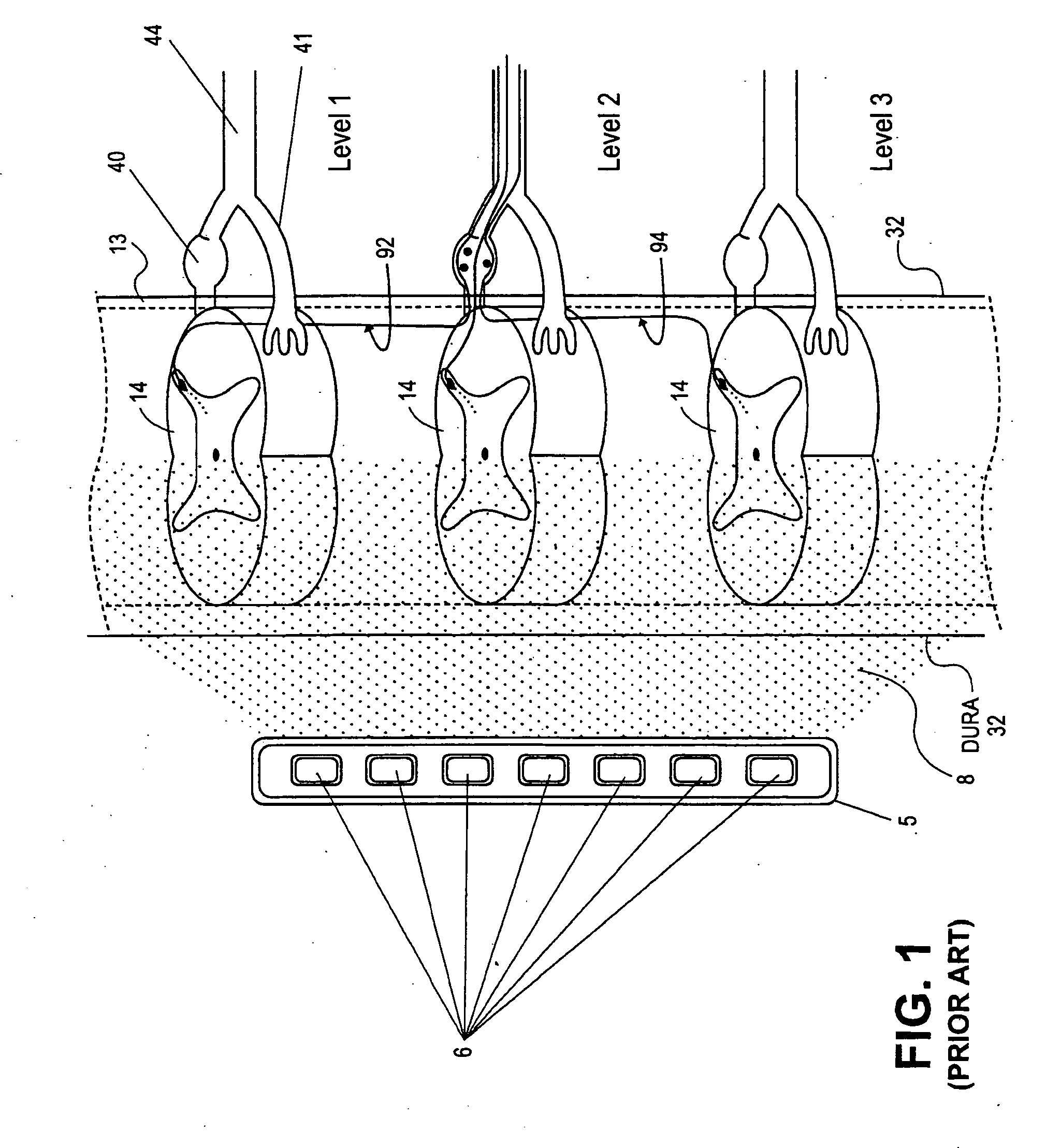
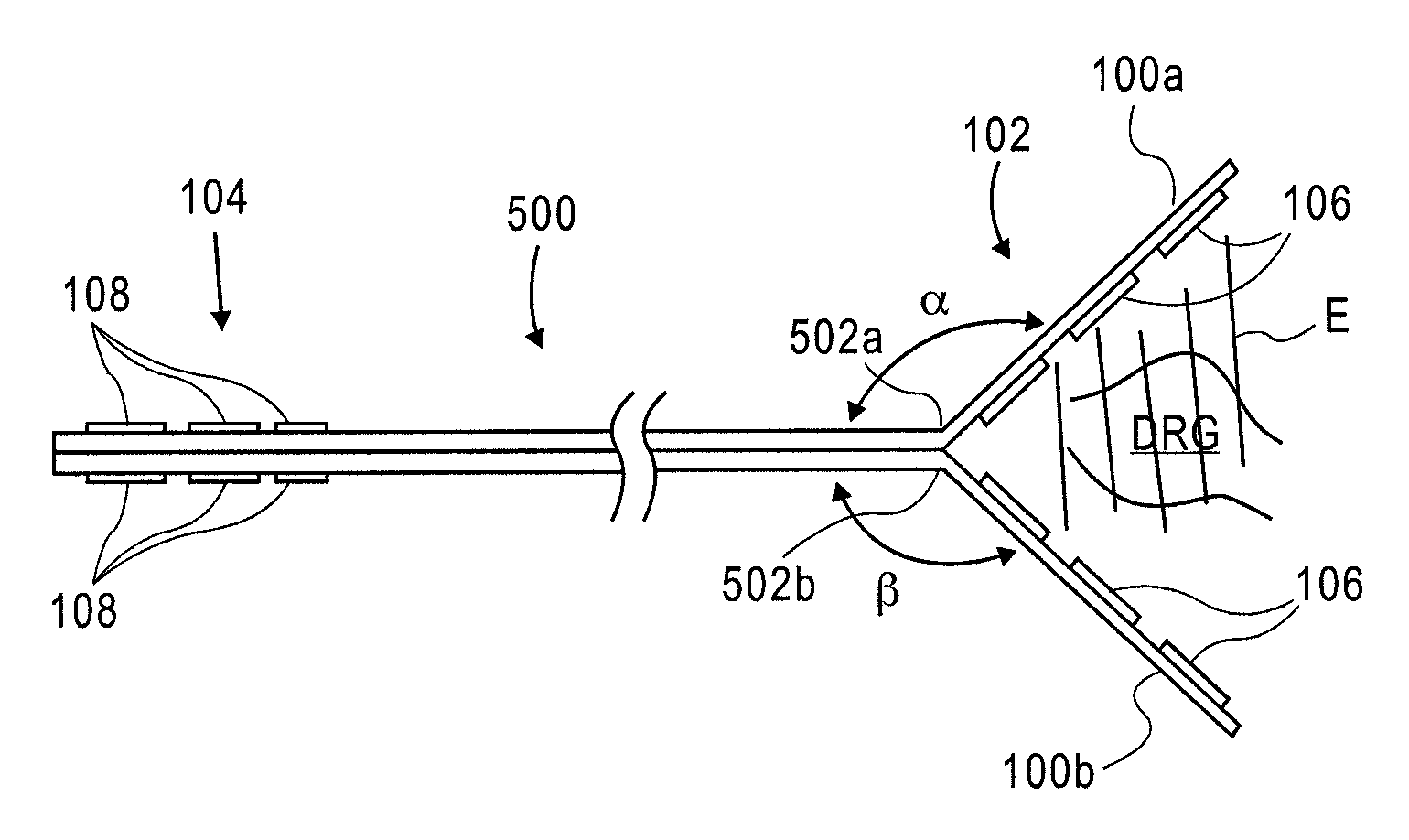
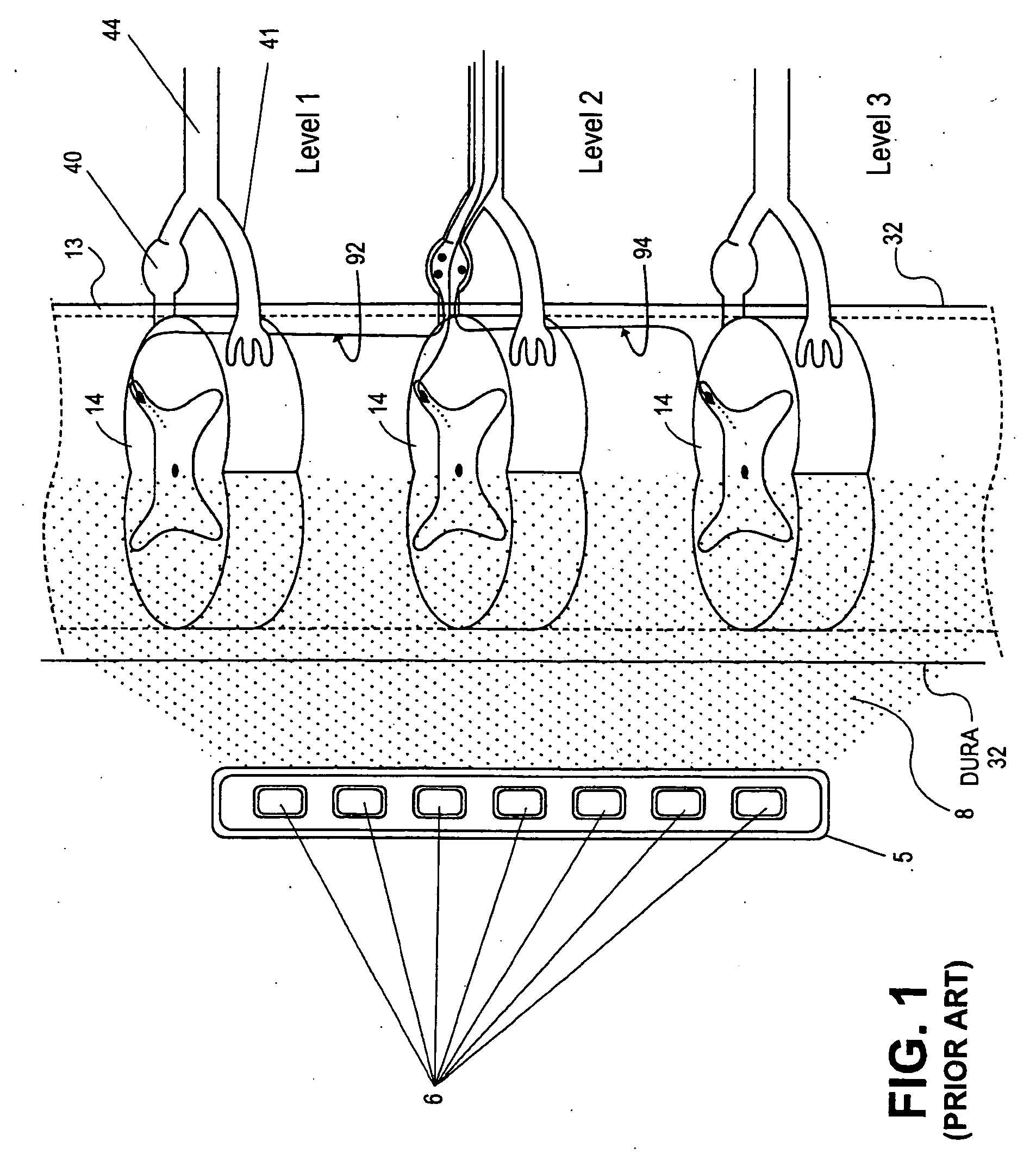
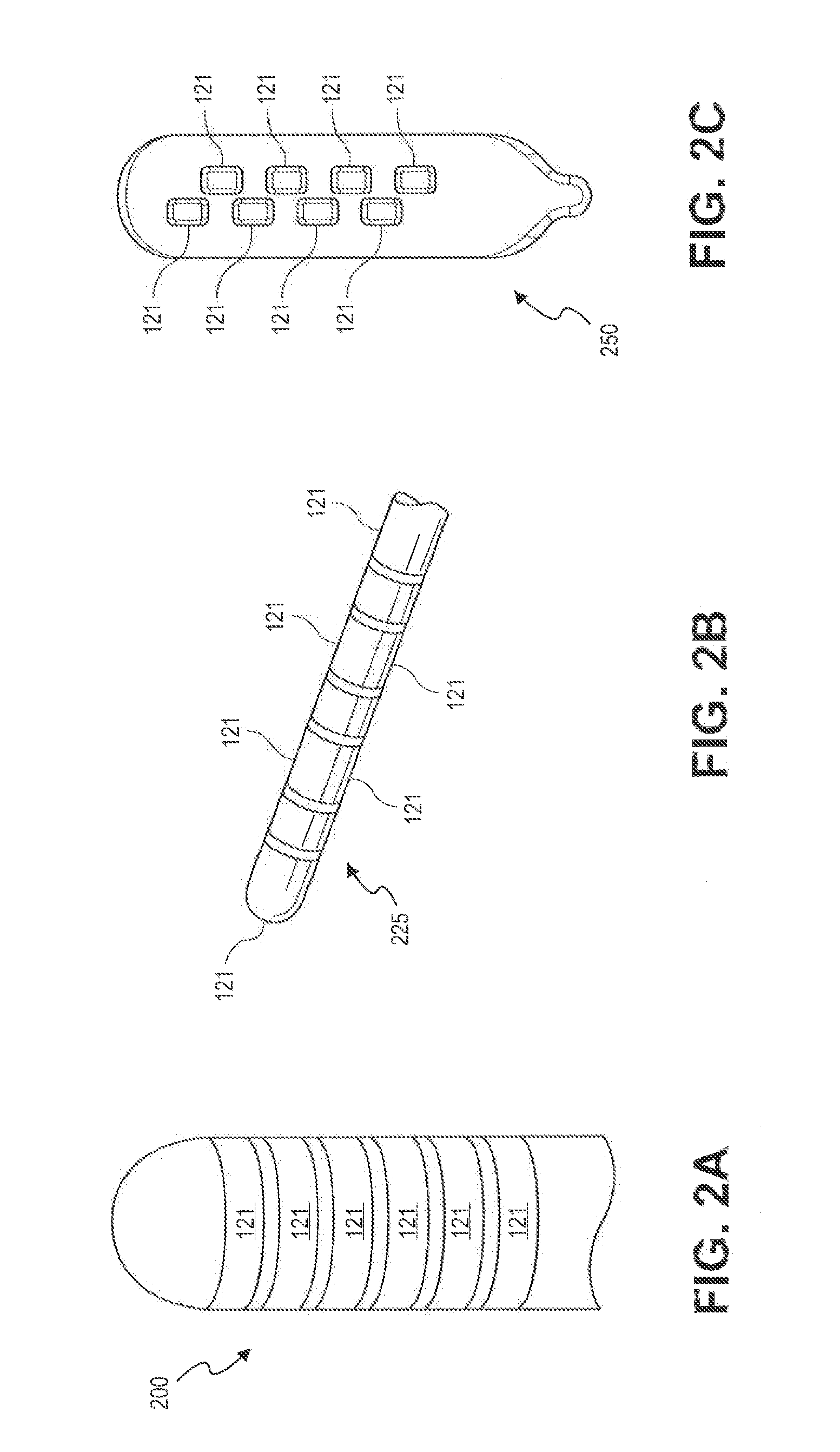
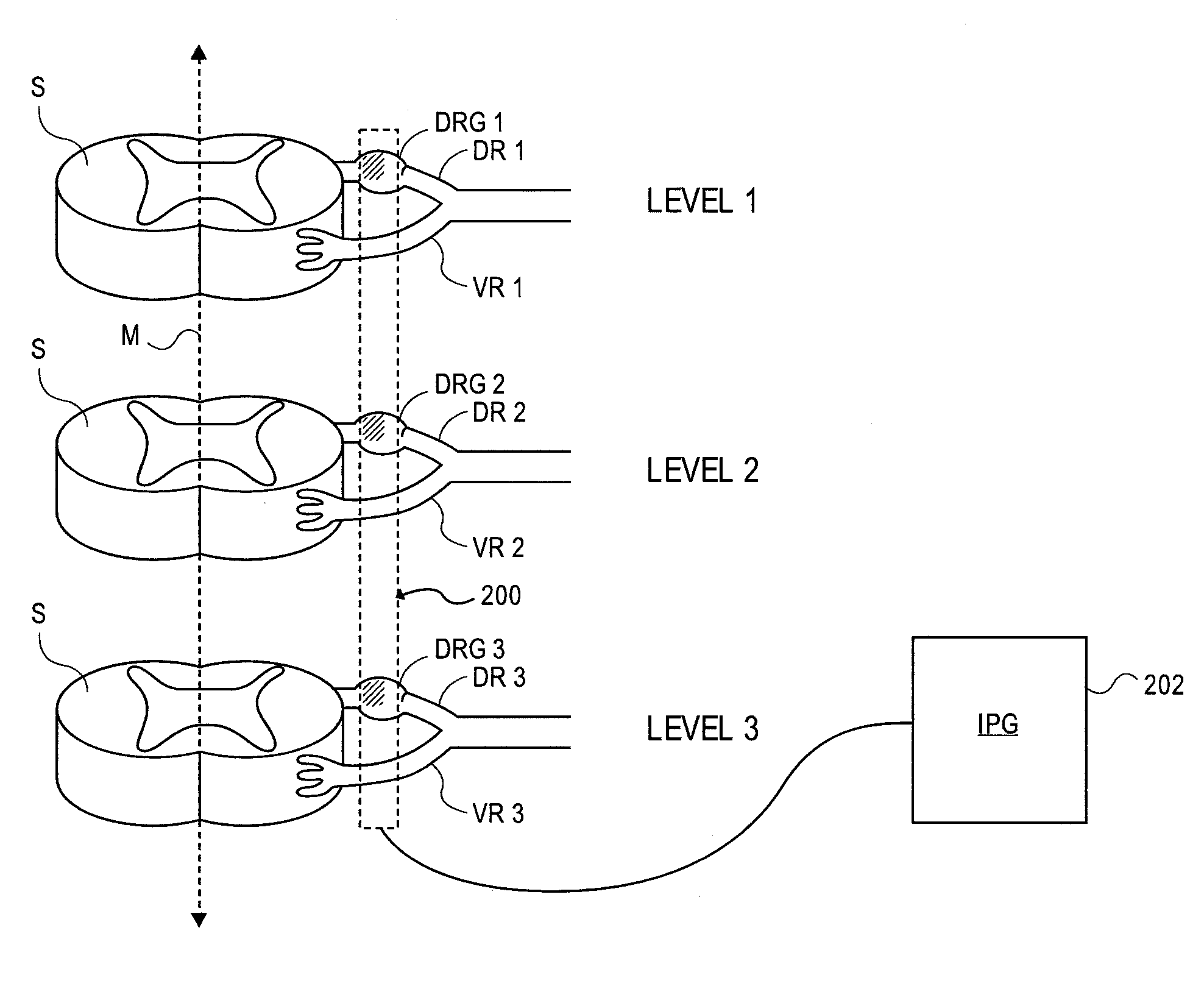
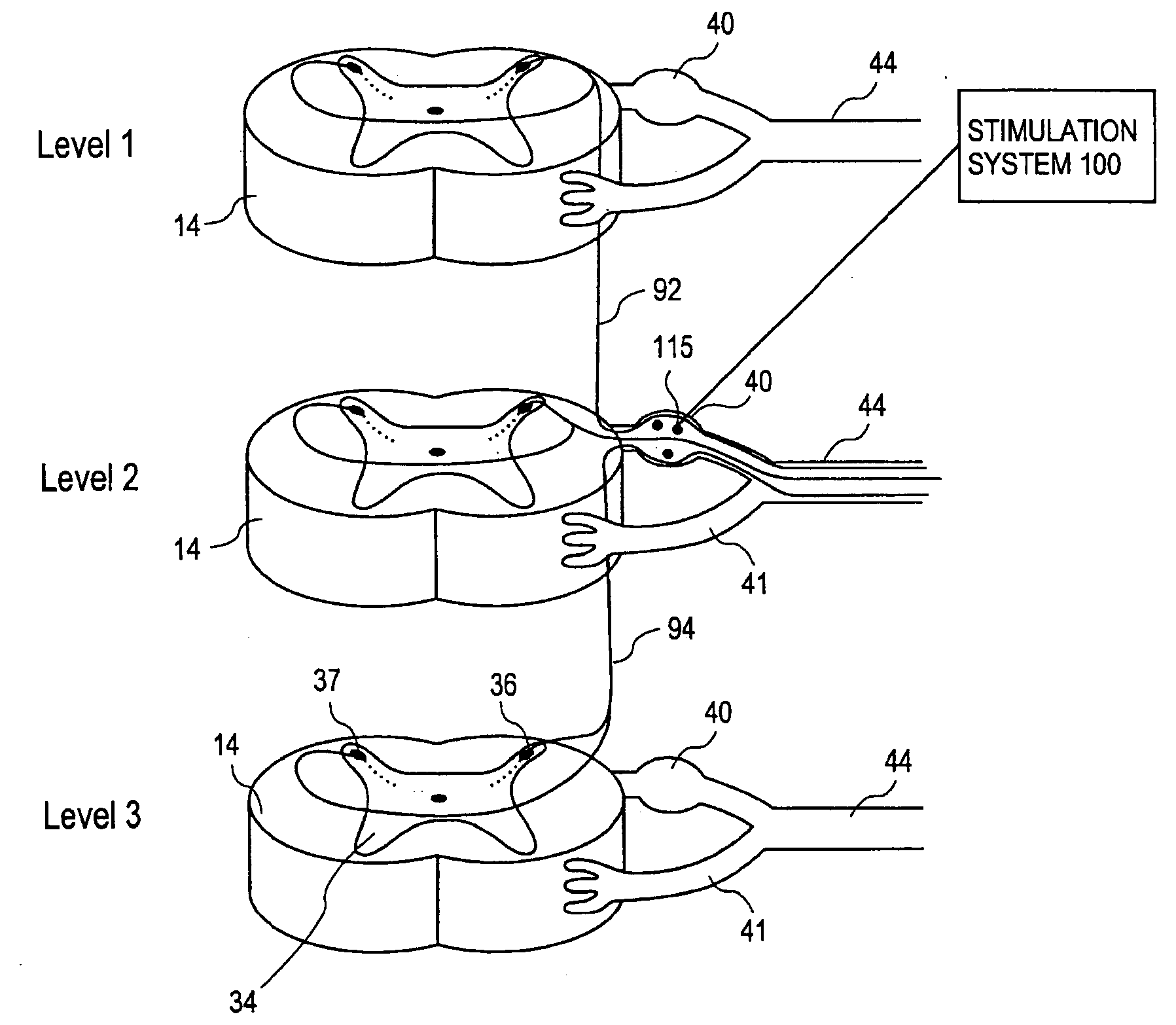
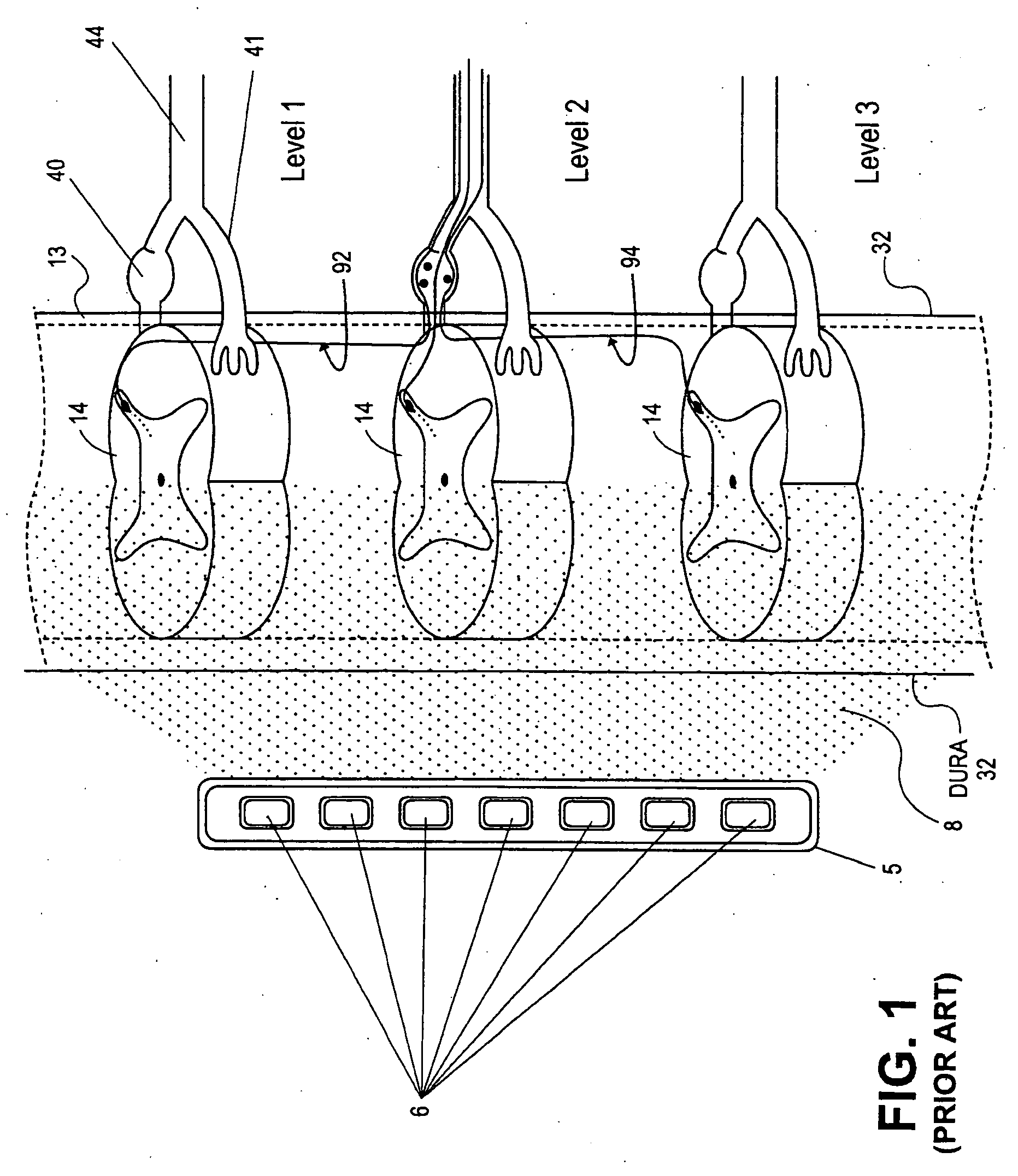
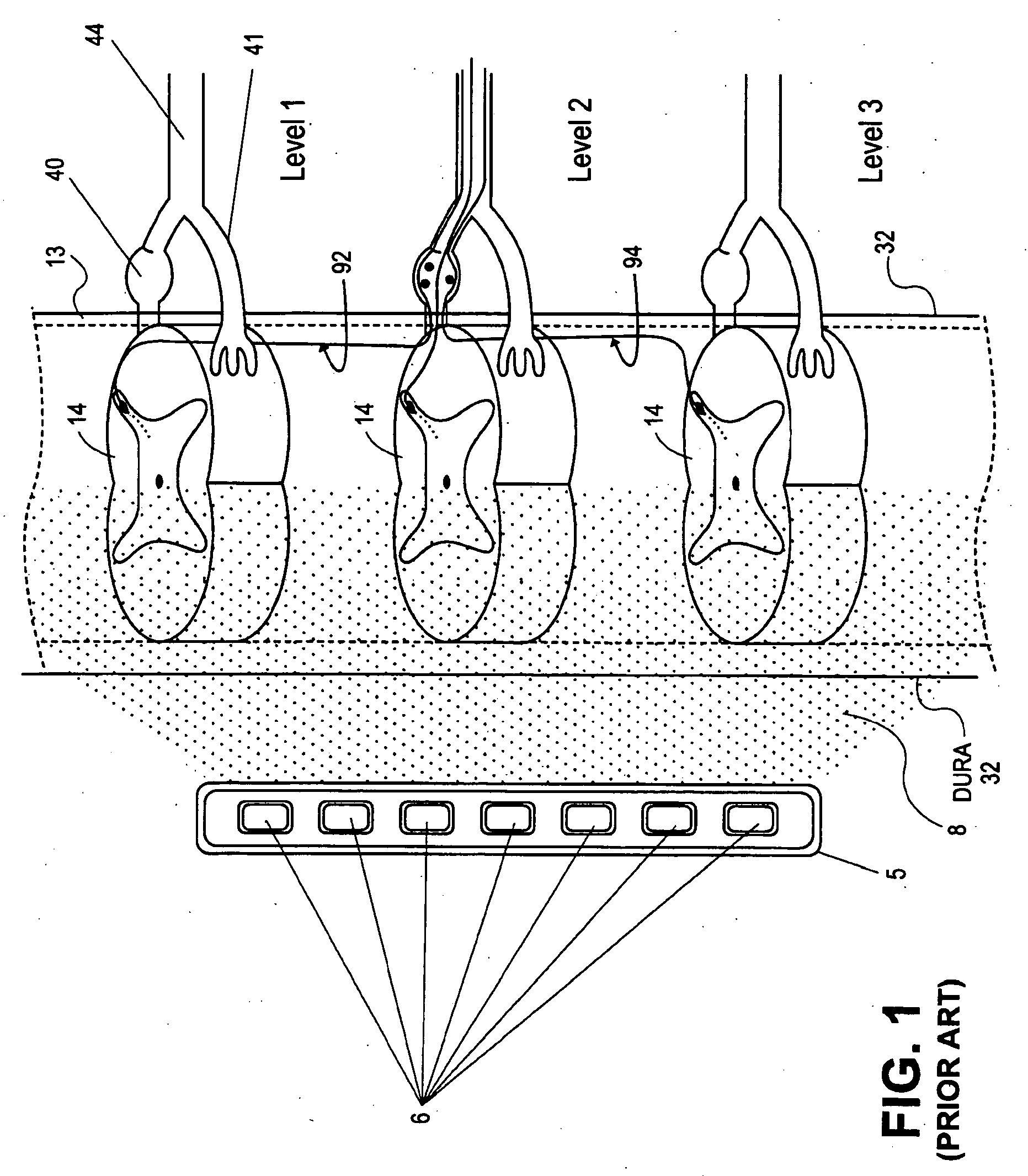
Grouped leads for spinal stimulation
InactiveUS20080147156A1Effective treatment of painReduces deleterious side effectSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesAnatomical structuresSpinal column
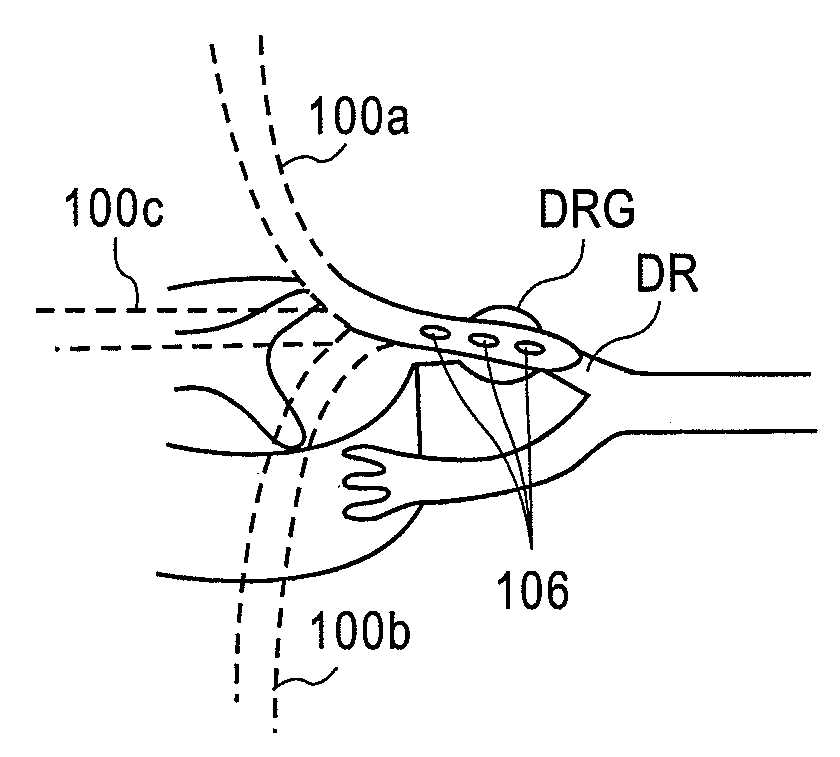
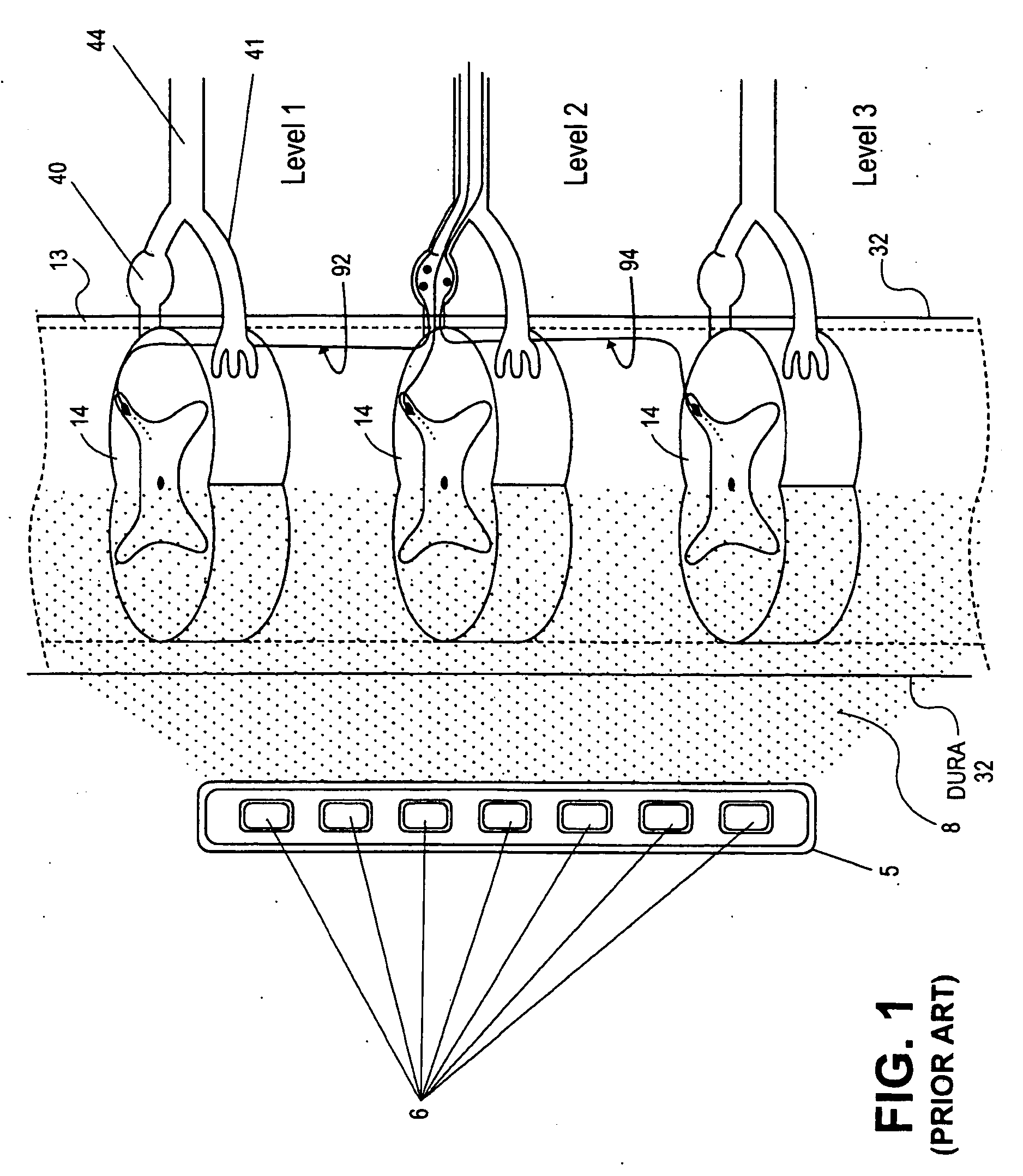
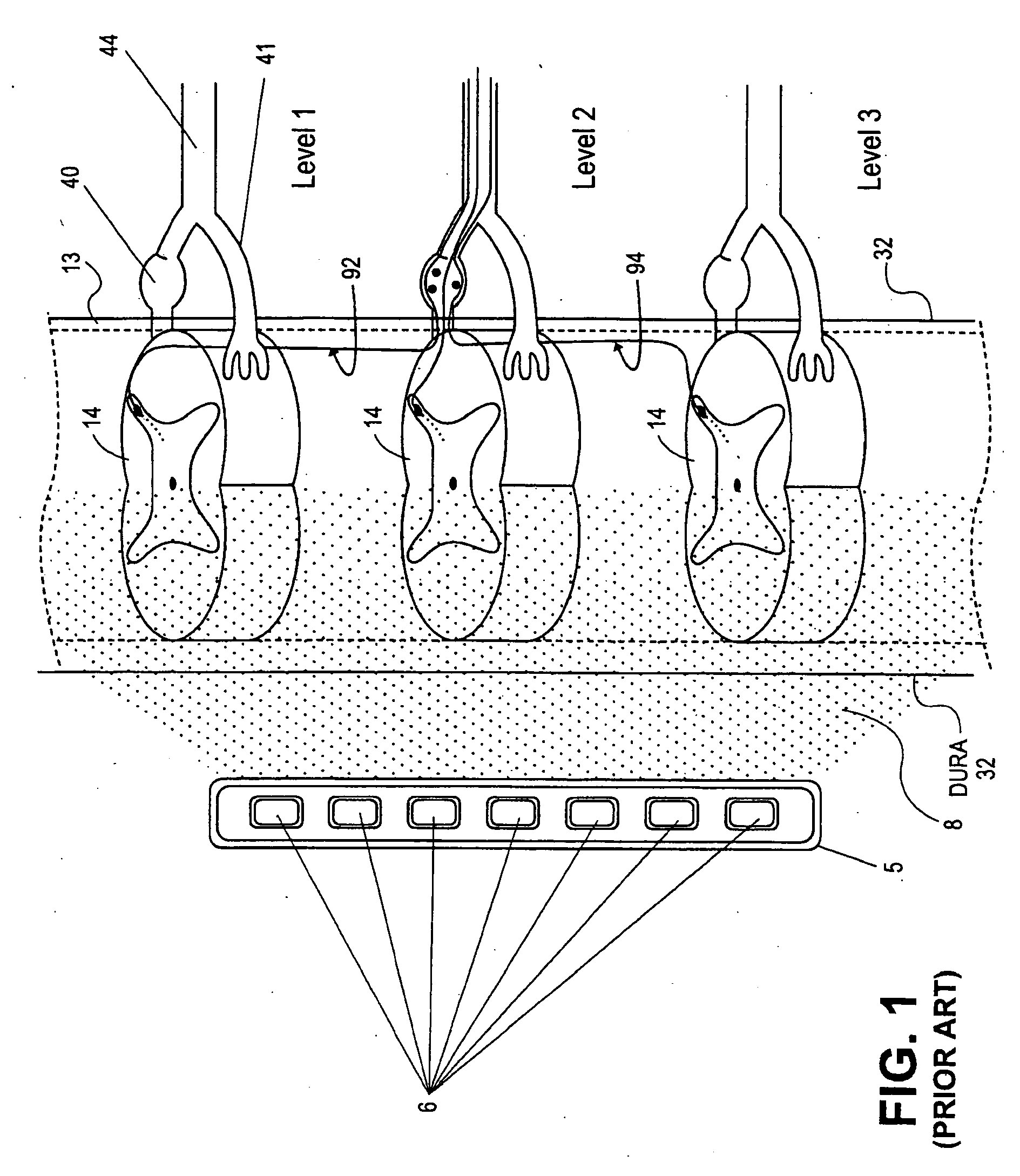
Devices, systems and methods are provided for simultaneously stimulating the spinal anatomy at various target locations, such as spinal levels, along the spinal cord. In some embodiments, the devices, systems and methods stimulate the various spinal levels at specific nerve anatomies, such as the dorsal root DR or more specifically the dorsal root ganglion DRG. Optionally, the devices, systems and methods may be used to stimulate a single DRG or other anatomies.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
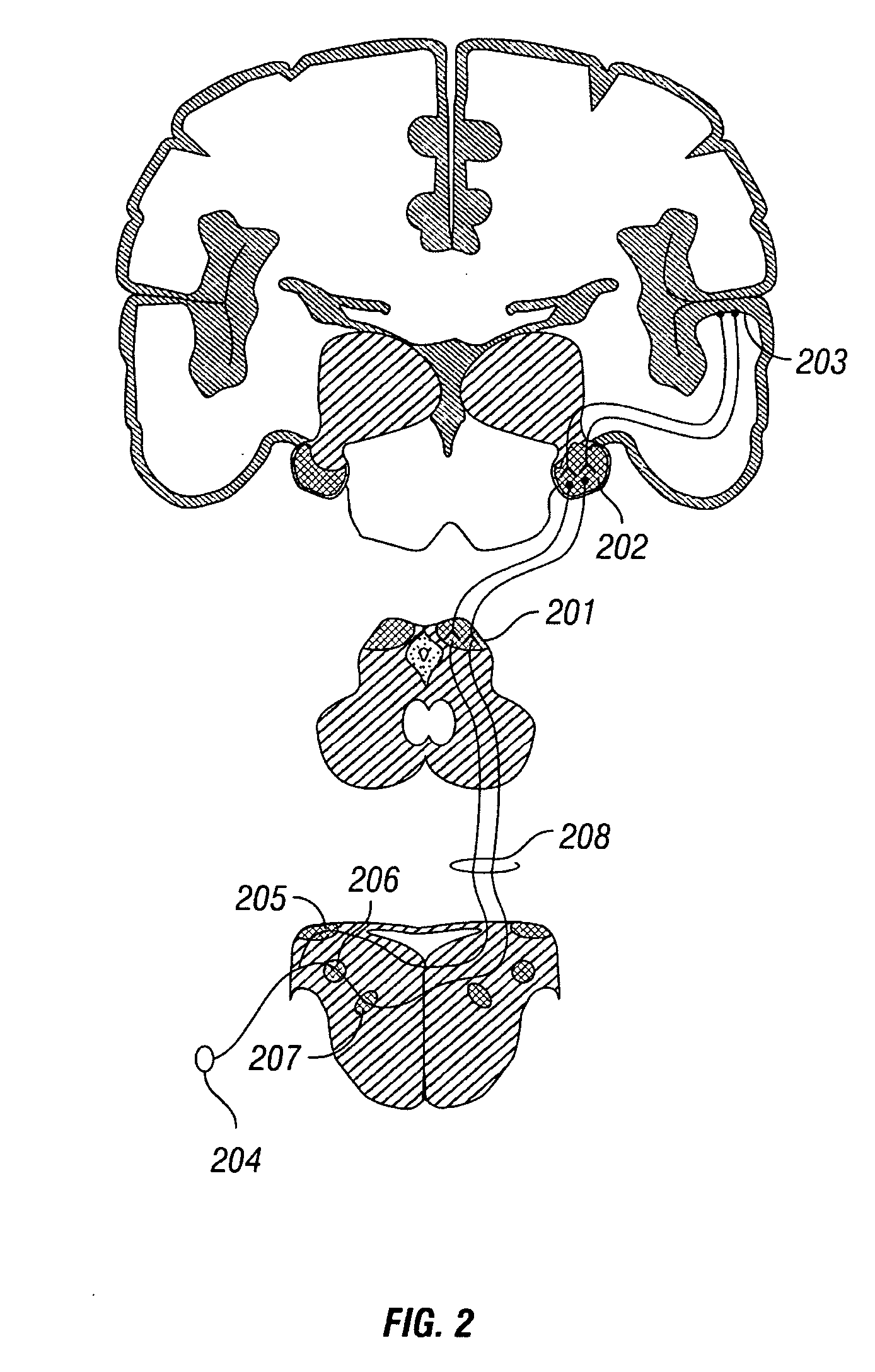
Spinal neuromodulation and associated systems and methods
Methods for treating a patient using therapeutic spinal neuromodulation and associated devices, systems, and methods are disclosed herein. One aspect of the present technology is directed to methods including modulating nerves of one or more targeted organs proximate one or more dorsal root ganglia, stellate ganglia, vertebral ganglia, or cervical ganglia of the nerves using an intravascularly-positioned therapeutic element. One or more measurable physiological parameters corresponding to at least one condition associated with sympathetic activity in the targeted organs and / or central sympathetic activity in the patient can thereby be reduced.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Selective stimulation to modulate the sympathetic nervous system
InactiveUS20120277839A1Minimizing and excluding undesired neuromodulationReduces and eliminates undesired side effectSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesAnatomical structuresMedicine
Systems, methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of a variety of medical conditions by directly neuromodulating a target anatomy associated with the condition while minimizing or excluding undesired neuromodulation of other anatomies. Typically, the target anatomy includes one or more dorsal root ganglia, dorsal roots, dorsal root entry zones, or portions thereof. Such target stimulation areas are utilized due in part to their effect on the sympathetic nervous system.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Short duration pre-pulsing to reduce stimulation-evoked side-effects
A method and neurostimulation system of providing therapy to a patient is provided. At least one electrode is place in contact with tissue of a patient. A sub-threshold, hyperpolarizing, conditioning pre-pulse (e.g., an anodic pulse) is conveyed from the electrode(s) to render a first region of the tissue (e.g., dorsal root fibers) less excitable to stimulation, and a depolarizing stimulation pulse (e.g., a cathodic pulse) is conveyed from the electrode(s) to stimulate a second different region of the tissue (e.g., dorsal column fibers). The conditioning pre-pulse has a relatively short duration (e.g., less than 200 μs).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
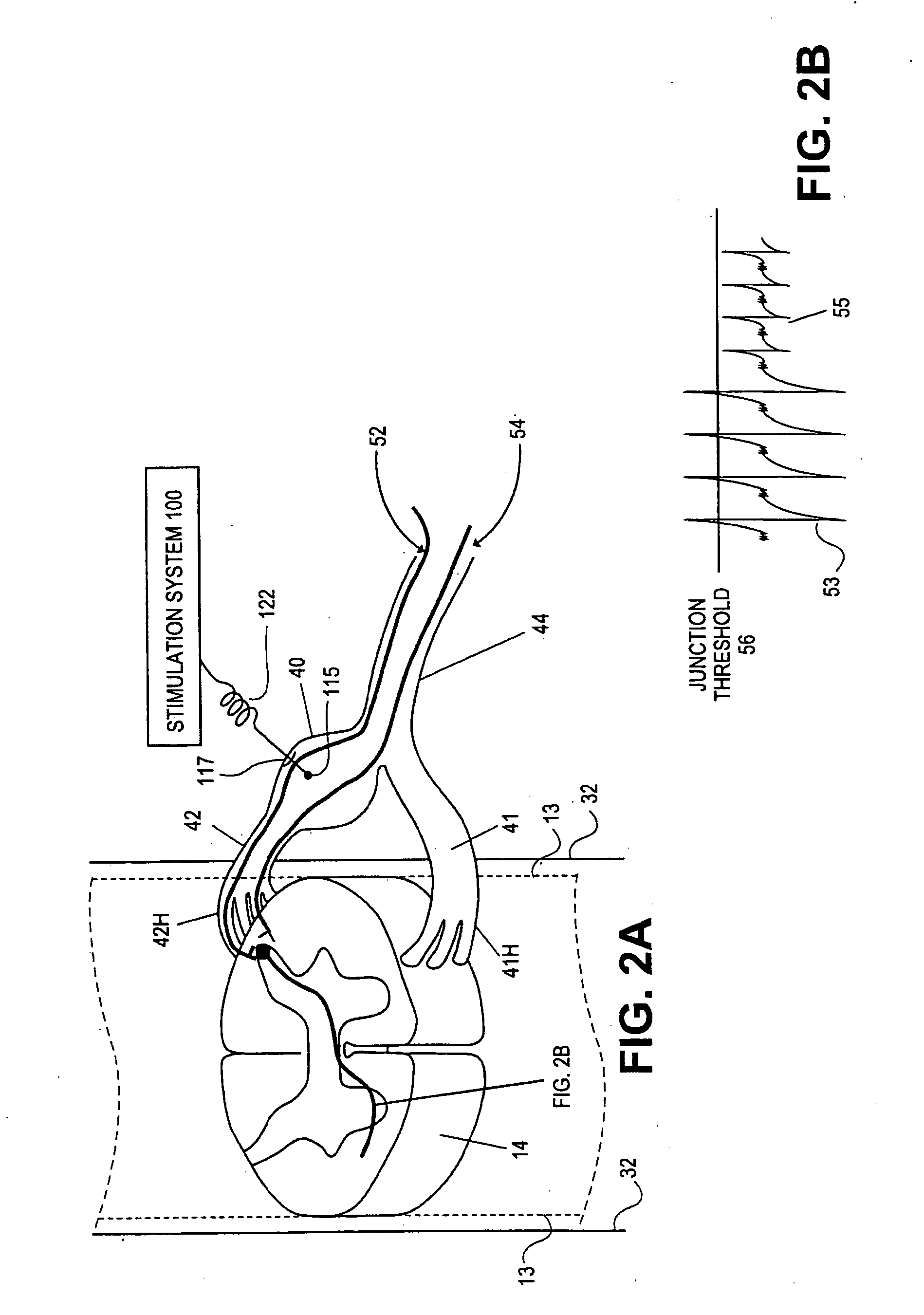
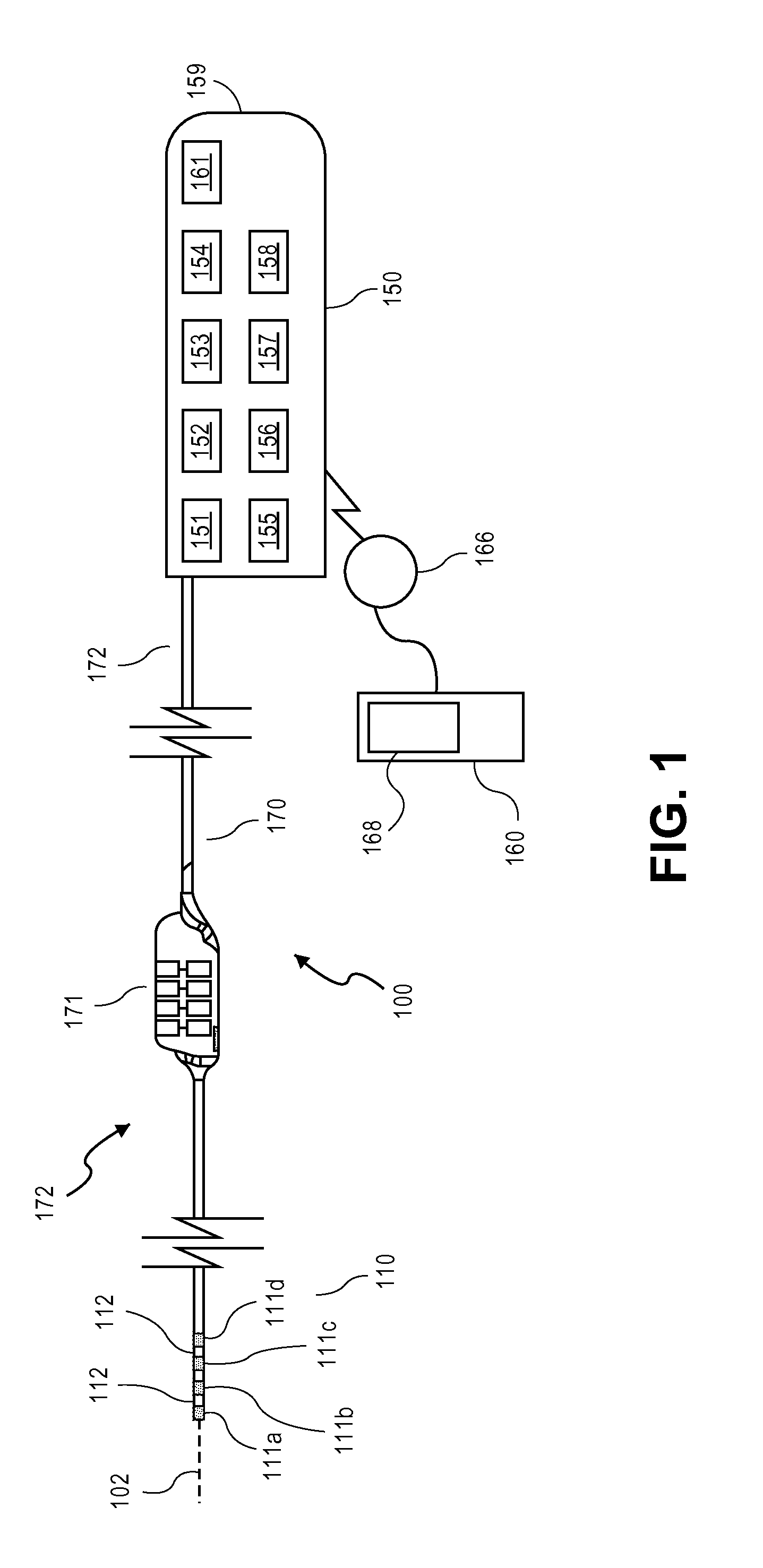
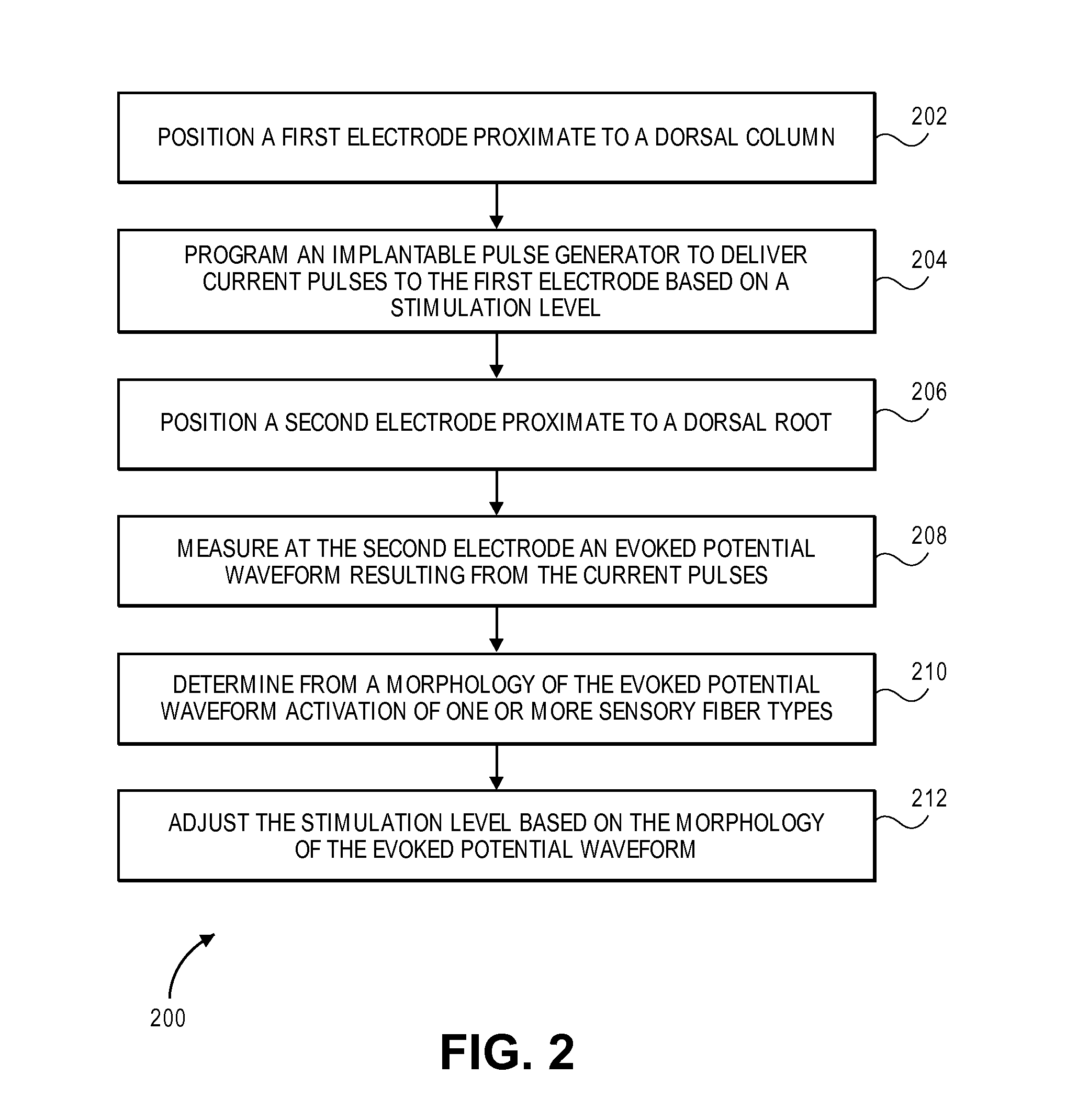
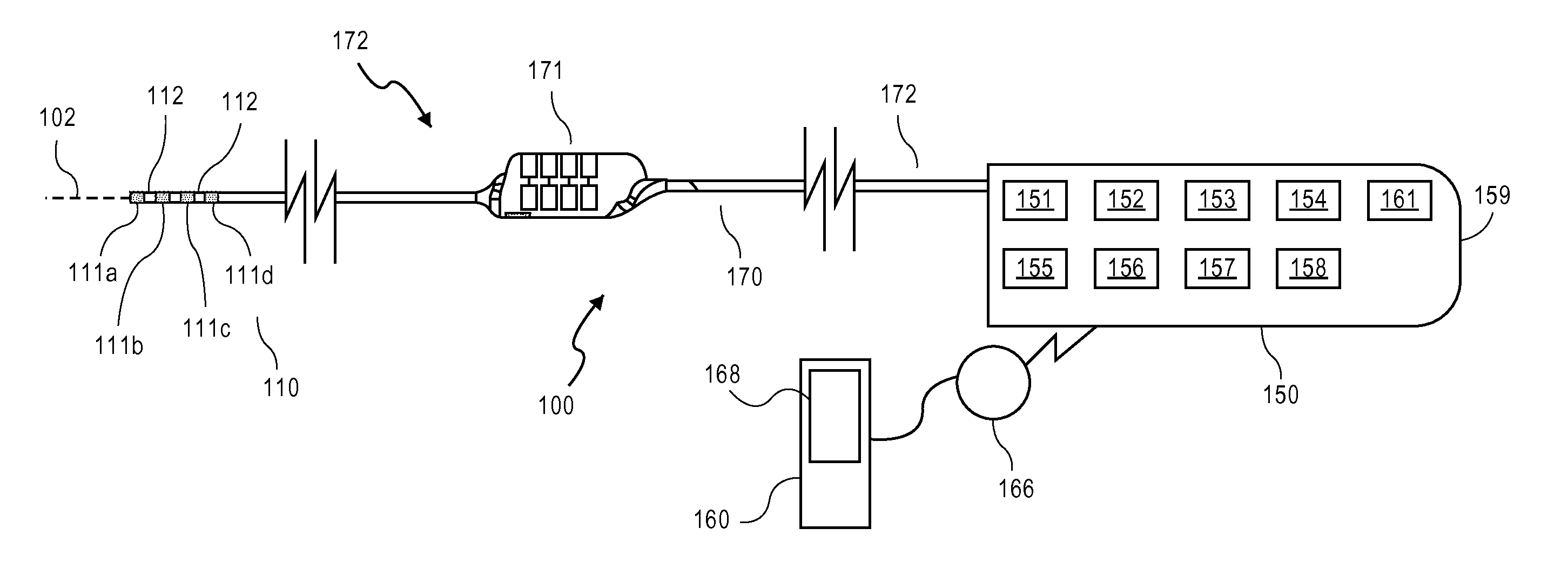
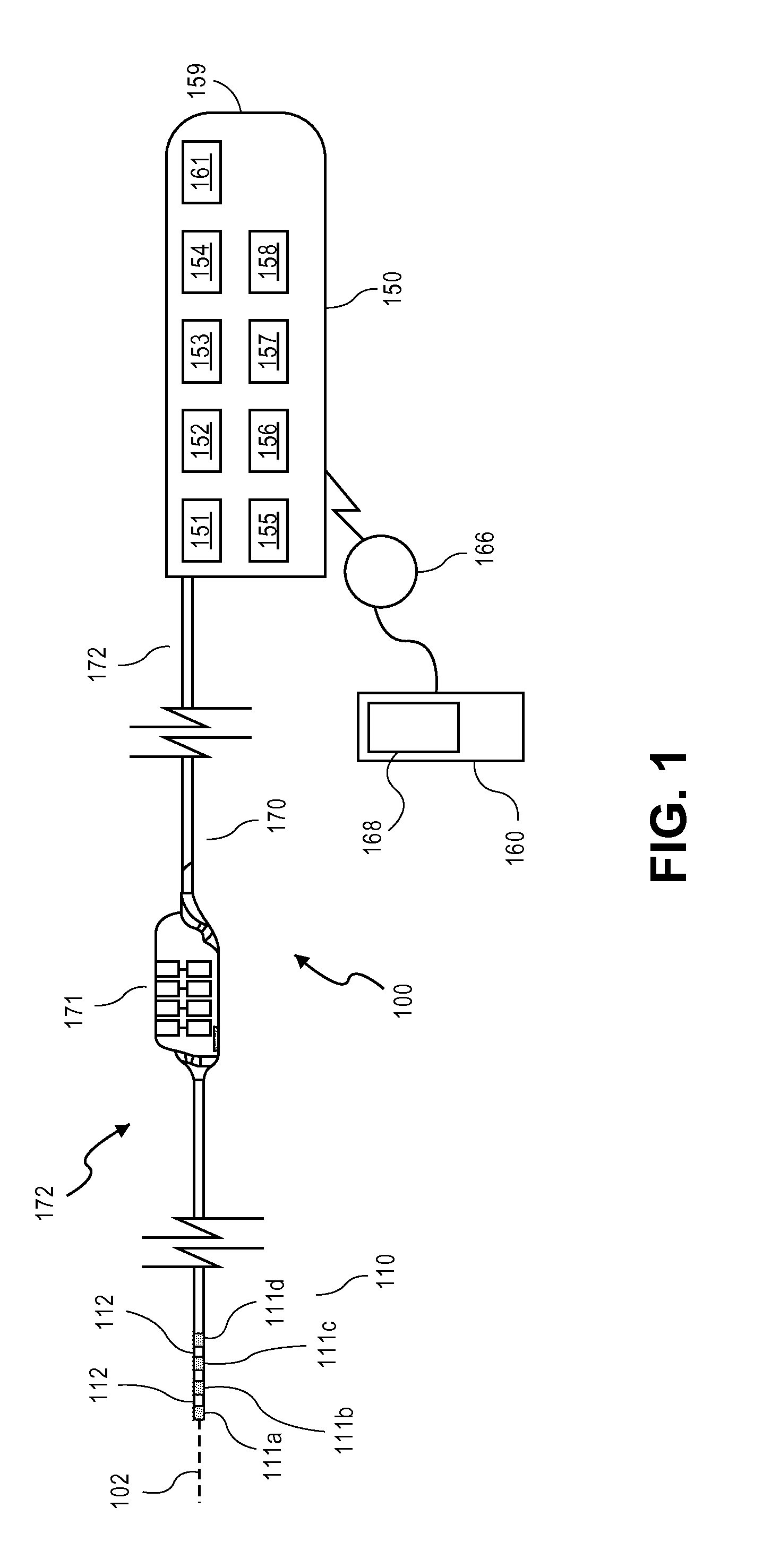
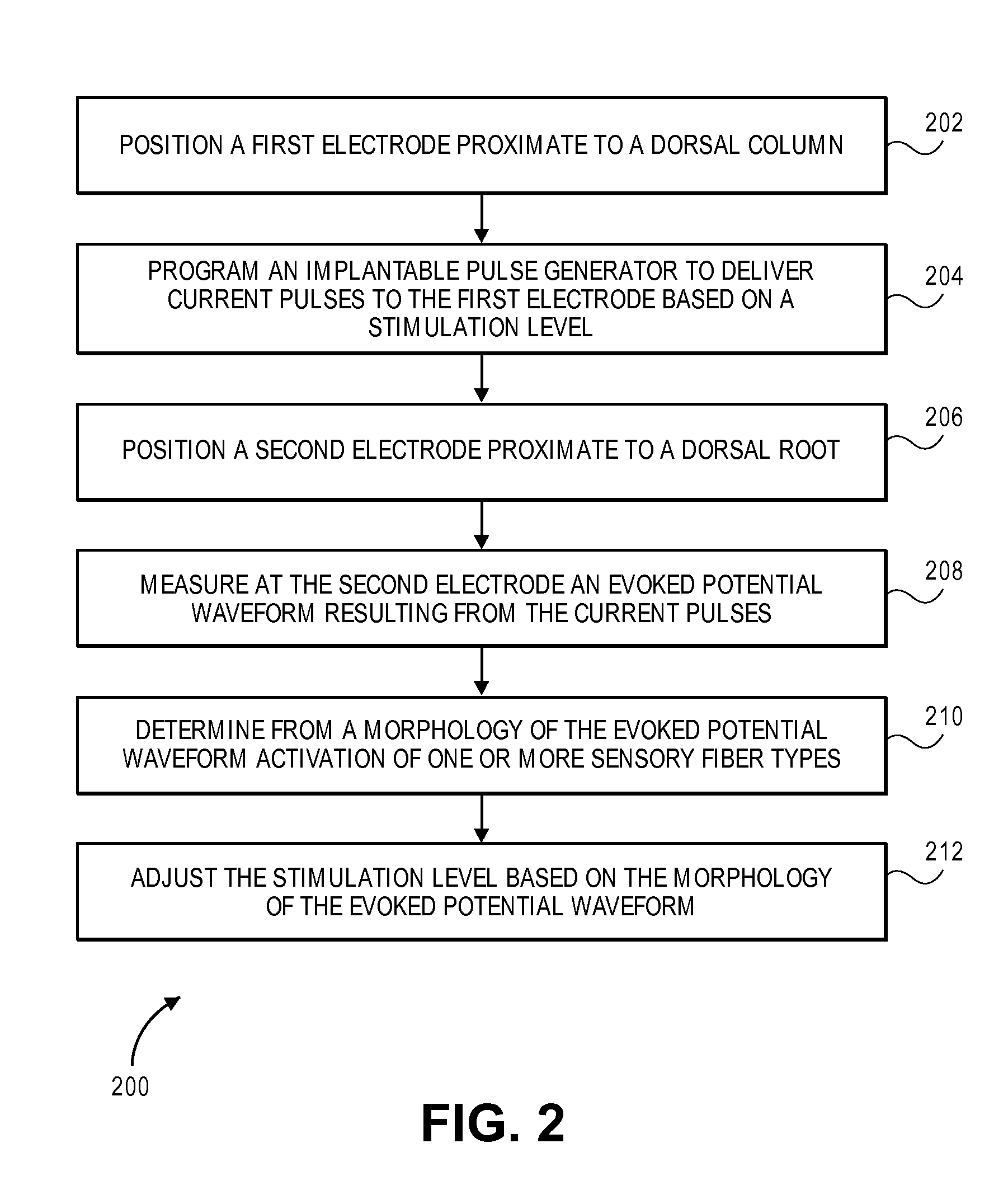
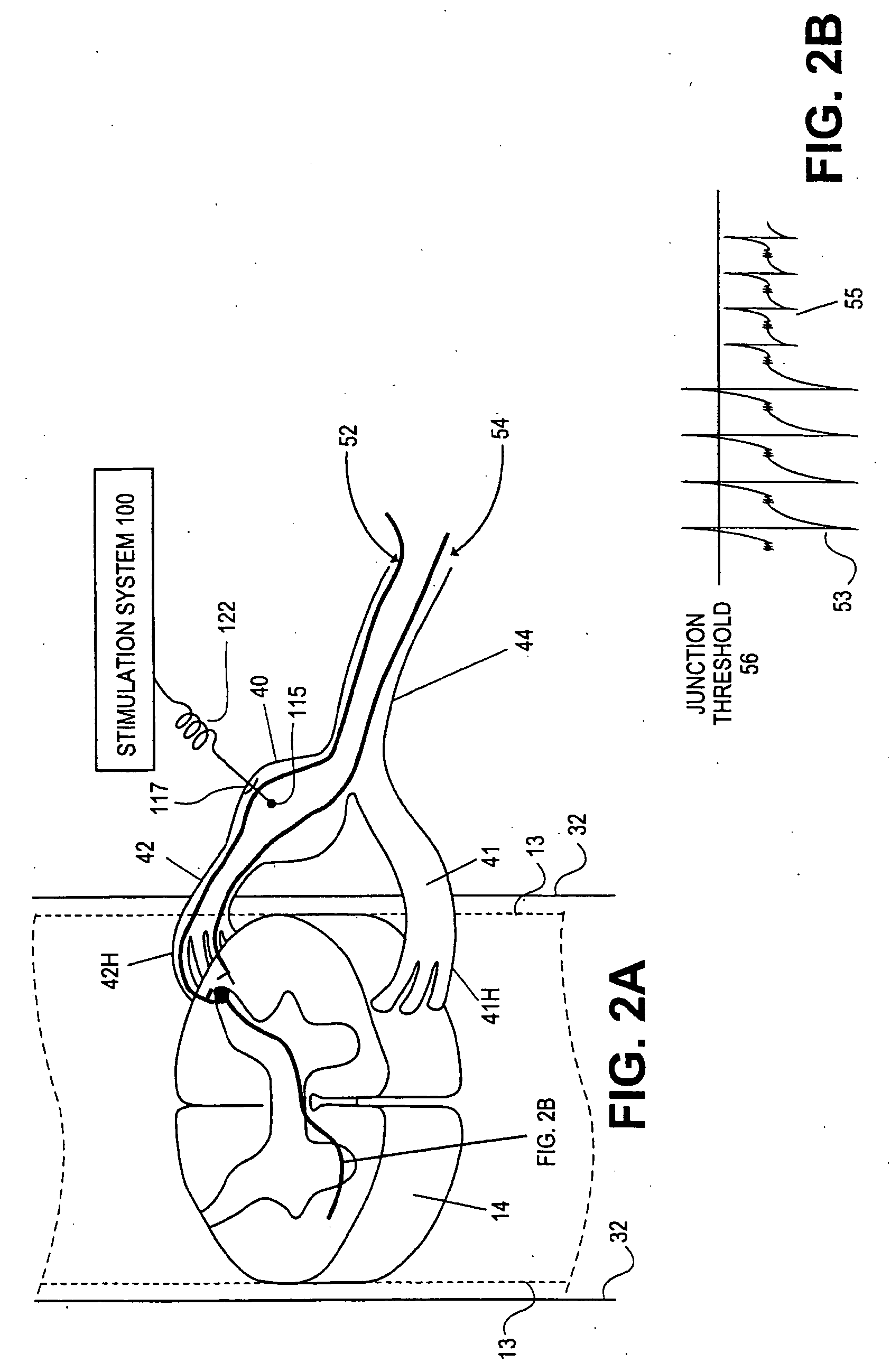
Systems and methods for recording evoked responses from neurostimulation
Systems and methods for closed loop spinal cord stimulation are provided. The systems and methods position a first electrode proximate to a dorsal column. The first electrode is electrically coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The systems and methods further program the IPG to deliver excitation pulses to the first electrode based on a stimulation level. The excitation pulses are emitted from the first electrode. The systems and methods further position a second electrode proximate to a dorsal root. The second electrode is electrically coupled to the IPG. The systems and methods further measure at the second electrode a first evoked potential waveforms resulting from the excitation pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for recording evoked responses from neurostimulation
Systems and methods for closed loop spinal cord stimulation are provided. The systems and methods position a first electrode proximate to a dorsal column. The first electrode is electrically coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The systems and methods further program the IPG to deliver excitation pulses to the first electrode based on a stimulation level. The excitation pulses are emitted from the first electrode. The systems and methods further position a second electrode proximate to a dorsal root. The second electrode is electrically coupled to the IPG. The systems and methods further measure at the second electrode a first evoked potential waveforms resulting from the excitation pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
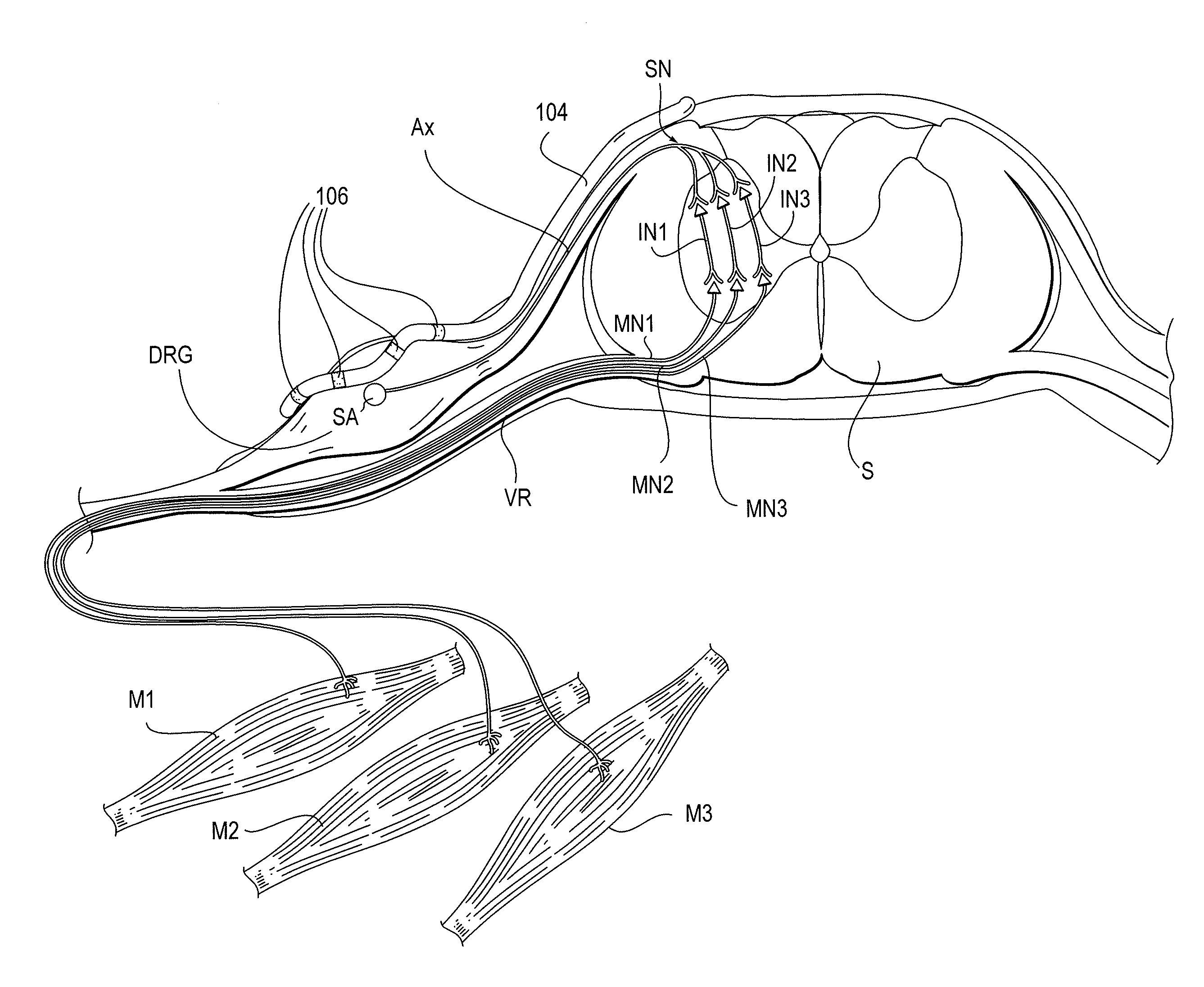
Electrical stimulation method for modulation on sensory information around dorsal root ganglia
A method of treating a patient with an ailment, comprises delivering first energy to a dorsal root ganglia (DRG), thereby modulating the DRG, and delivering second energy to at least one of a central neural axon extending from the DRG and a peripheral neural axon extending from the DRG, thereby modulating the at least one of the central neural axon and the peripheral neural axon.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Devices, systems and methods for the targeted treatment of movement disorders
Devices, systems and methods are provided for the targeted treatment of movement disorders. Typically, the systems and devices are used to stimulate one or more dorsal root ganglia while minimizing or excluding undesired stimulation of other tissues, such as surrounding or nearby tissues, ventral root and portions of the anatomy associated with body regions which are not targeted for treatment. The dorsal root ganglia are utilized in particular due to their specialized role in movement. It is in these areas that sensory fibers are isolated from motor fibers. Sensory fibers are involved in a variety of reflexes that are involved in movement control, and these reflexes can be utilized in the treatment of various movement disorders. Thus, by stimulating sensory fibers in these areas, fundamental reflexes can be affected to lessen the symptoms of movement disorders.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
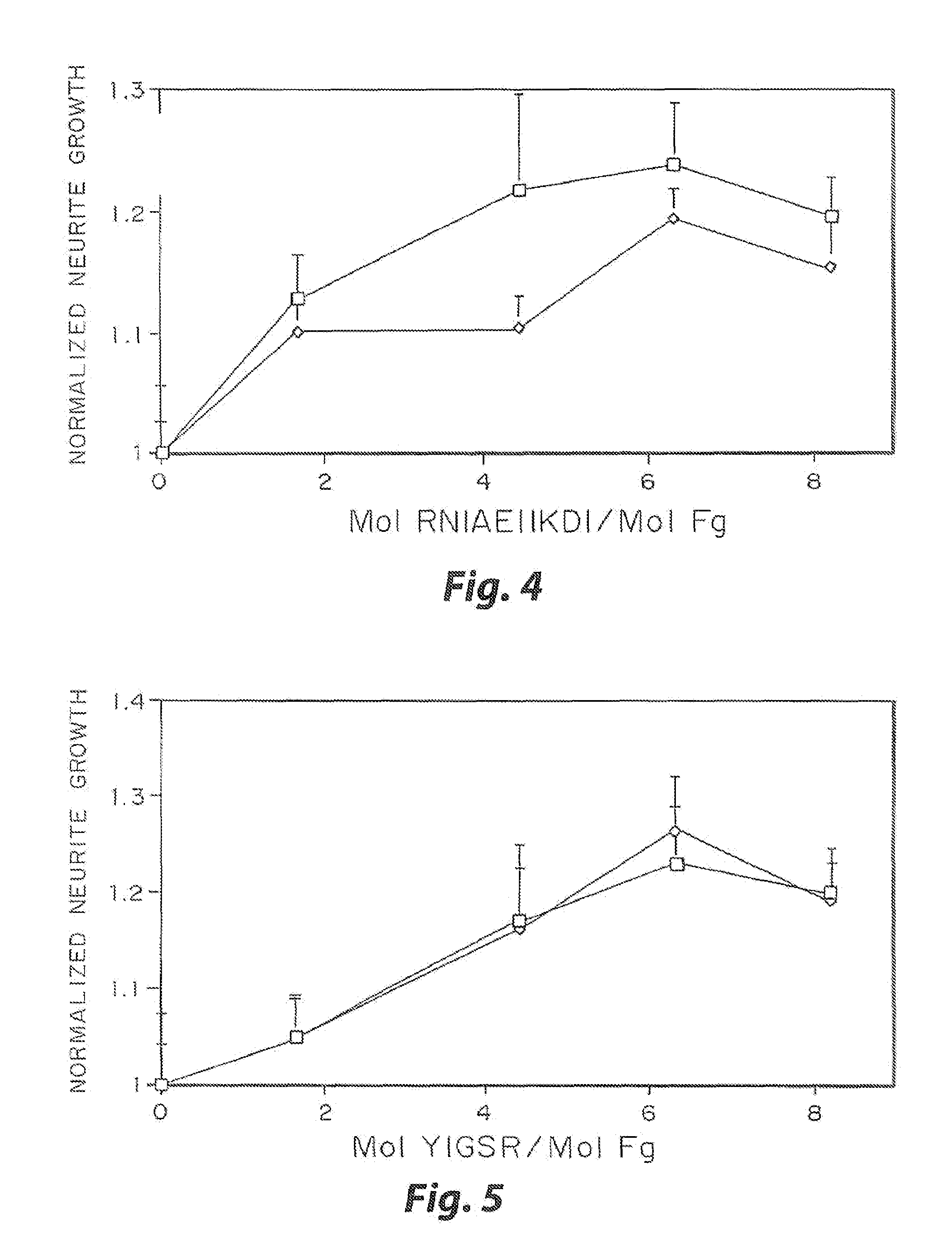
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering: fibrin formulations with peptides
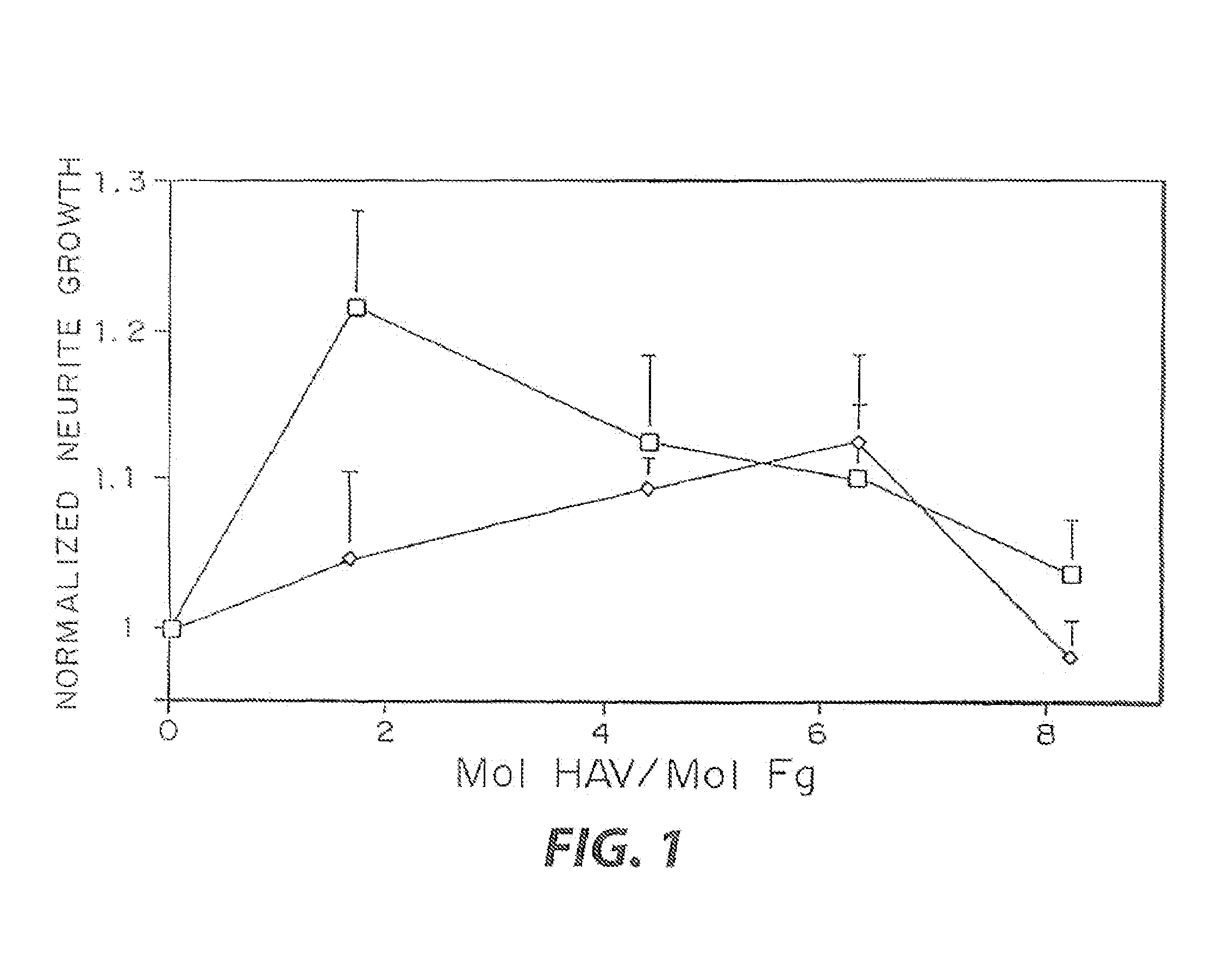
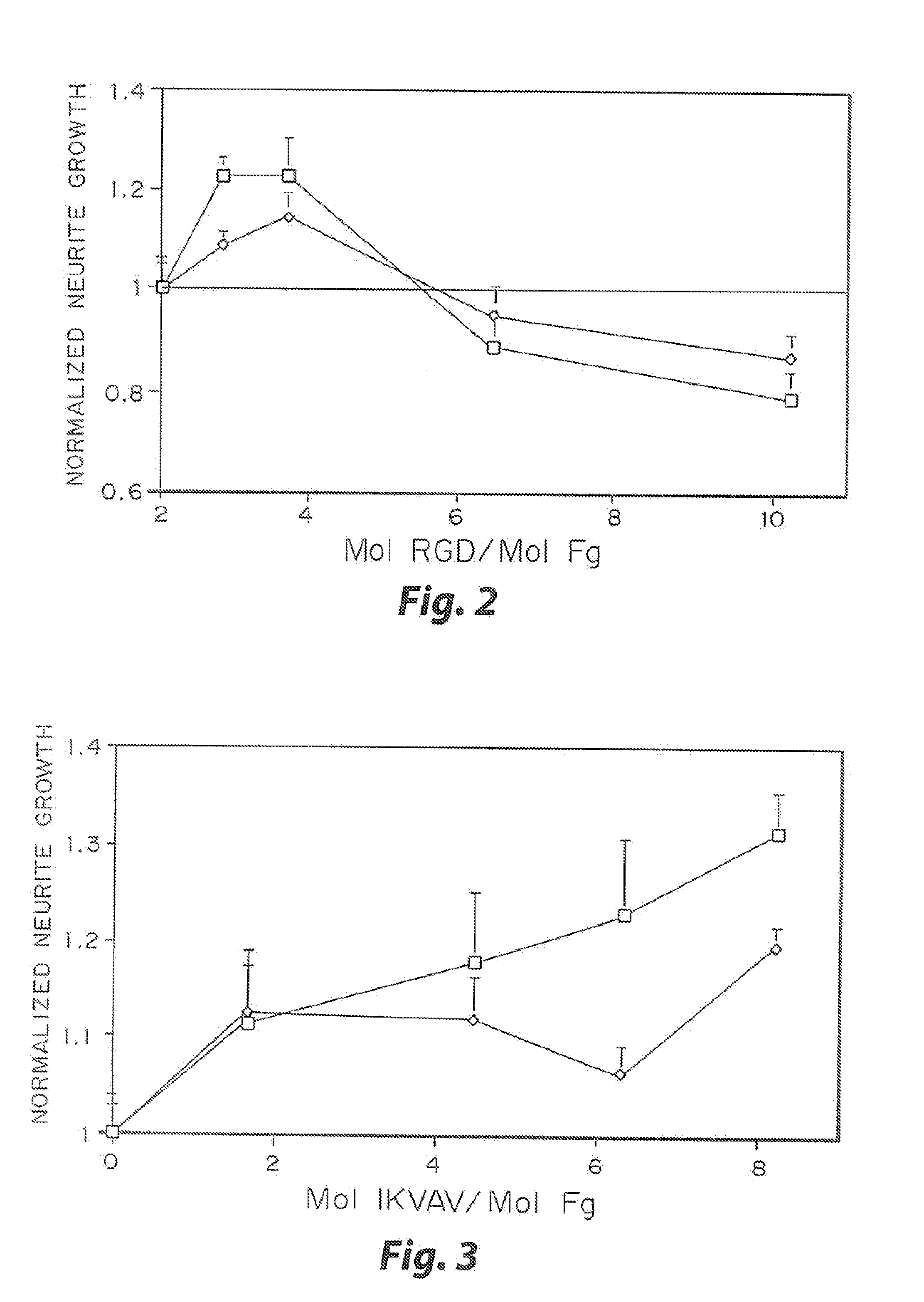
InactiveUS7241730B2Efficacious platformEnhanced andPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesCell Surface ProteinsADAMTS Proteins
Heparin-binding regions of several proteins, such as neural cell adhesion molecule, fibronectin, laminin, midkine, and anti-thrombin III have been shown to promote neurite extension on two-dimensional surfaces. The effect of heparin-binding peptides on neurite extension through three-dimensional matrices was investigated by culturing embryonic chick dorsal root ganglia (DRG) within fibrin gels containing chemically attached heparin-binding peptide (HBP). The length of neurites within fibrin gels containing cross-linked HBP was increased by more than 70% over extension through fibrin gels containing no peptide. The HBP sequence of antithrombin III was incorporated into the fibrin gel as the C-terminal domain of a bidomian, chimeric peptide; the N-terminal second domain of this peptide contained the ∀2-plasmin inhibitor substrate for Factor XIIIa. Factor XIIIa, a transglutaminase, was used to chemically attach the HBP-containing chimeric peptide to the fibrin gels during polymerization. The amount of HBP cross-linked into the fibrin gels was determined, after degradation by plasmin using gel permeation chromatography, to be approximately 8 moles of peptide per mole fibrinogen. A peptide (HBP), where the cross-linking glutamine was replaced with glycine, showed no increase in extension in comparison with fibrin gels. The additional of heparin to the gel percursors resulted in no increase in neurite extension in comparison with fibrin gels. HBPs promote neurite extension by binding to cell surface proteoglycans on the DRG.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Methods and systems for modulating neural tissue
Some embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for modulating neural tissue including systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of targeted neural tissue. Targeted neural tissue may include one or more ganglia including those of the spinal nerves in the dorsal root and the sympathetic chain. Methods also include implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Stimulation systems
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:KIM DANIEL H +2
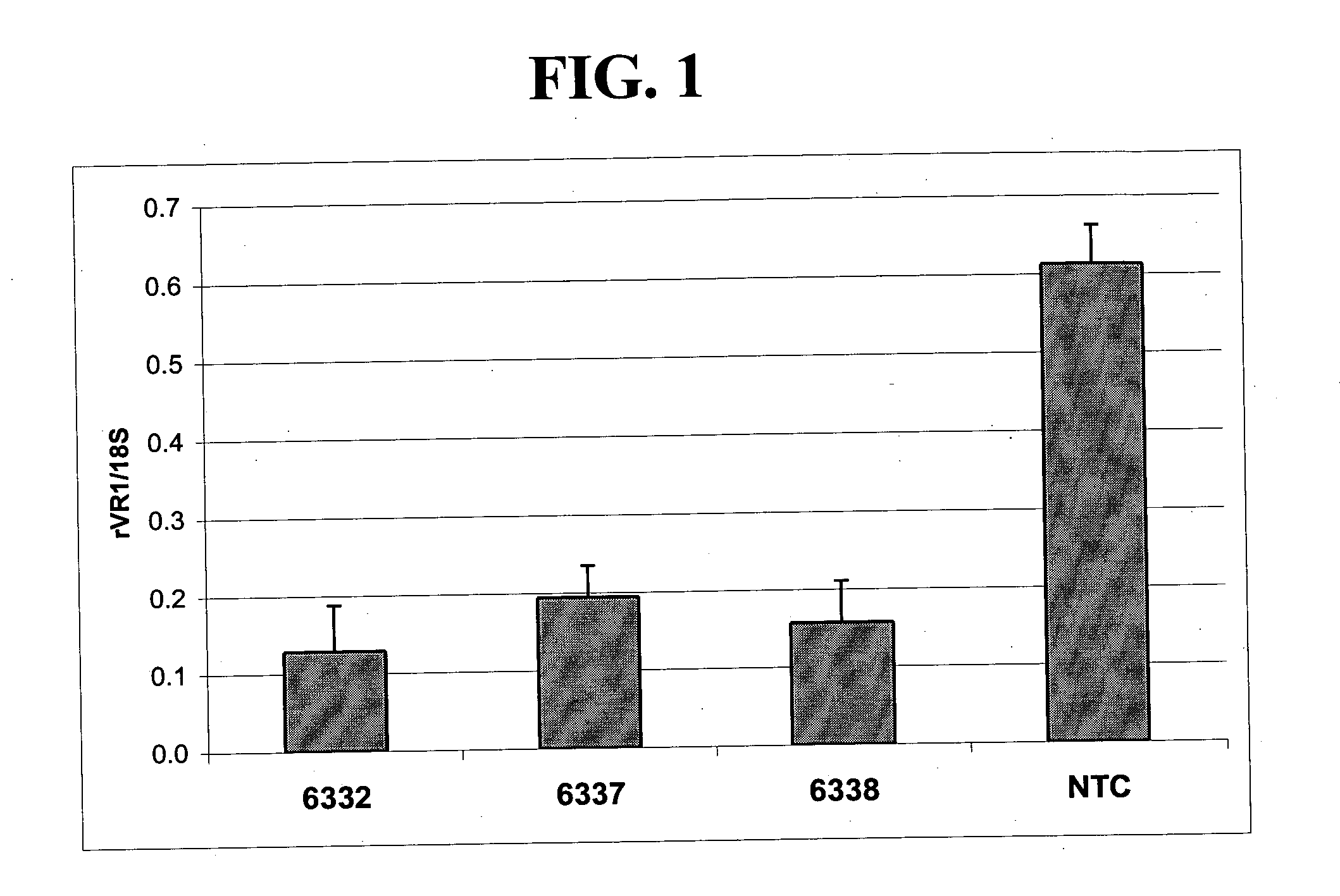
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS20050245476A1Easy to produceNervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainNAV1Dorsal roots
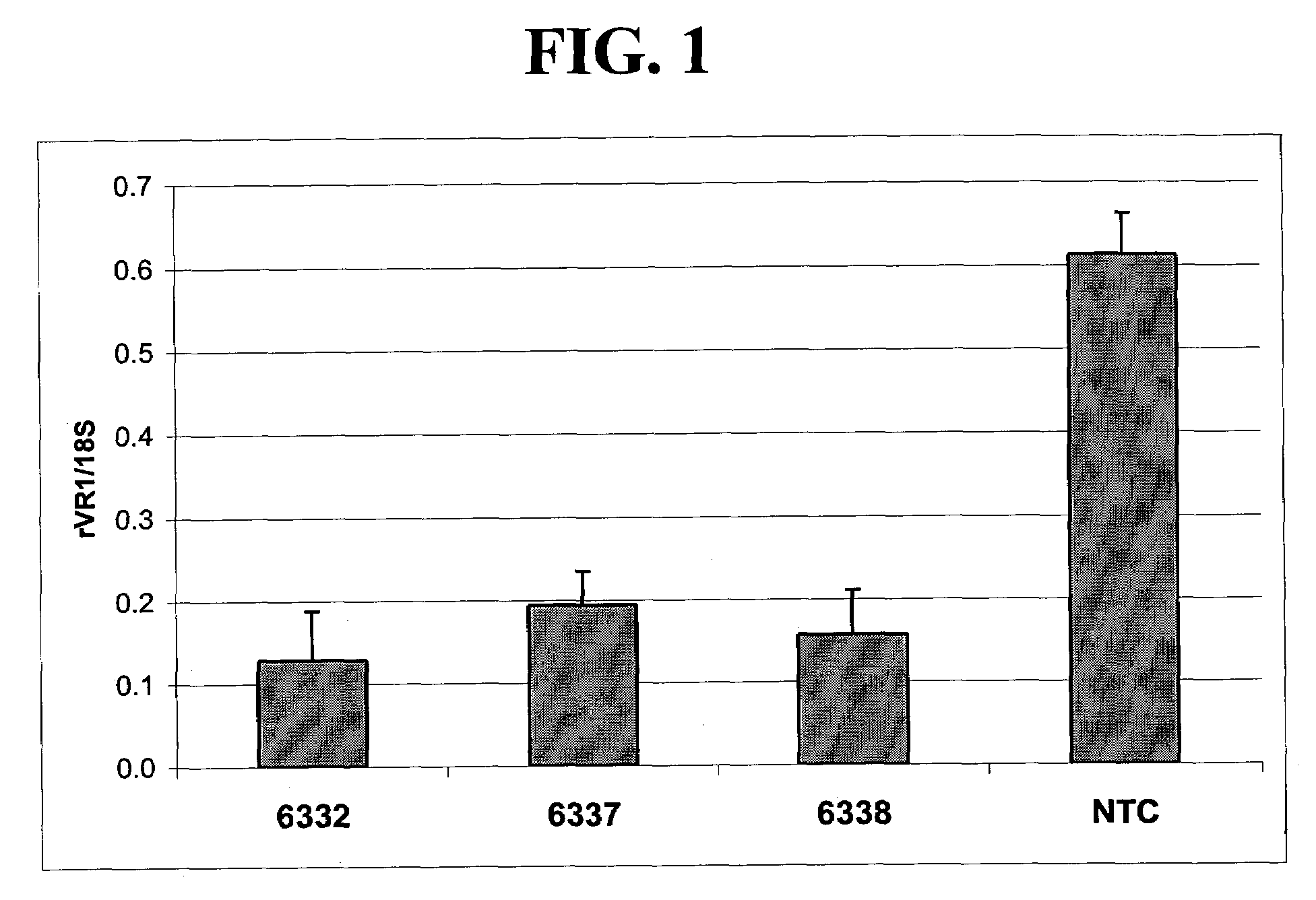
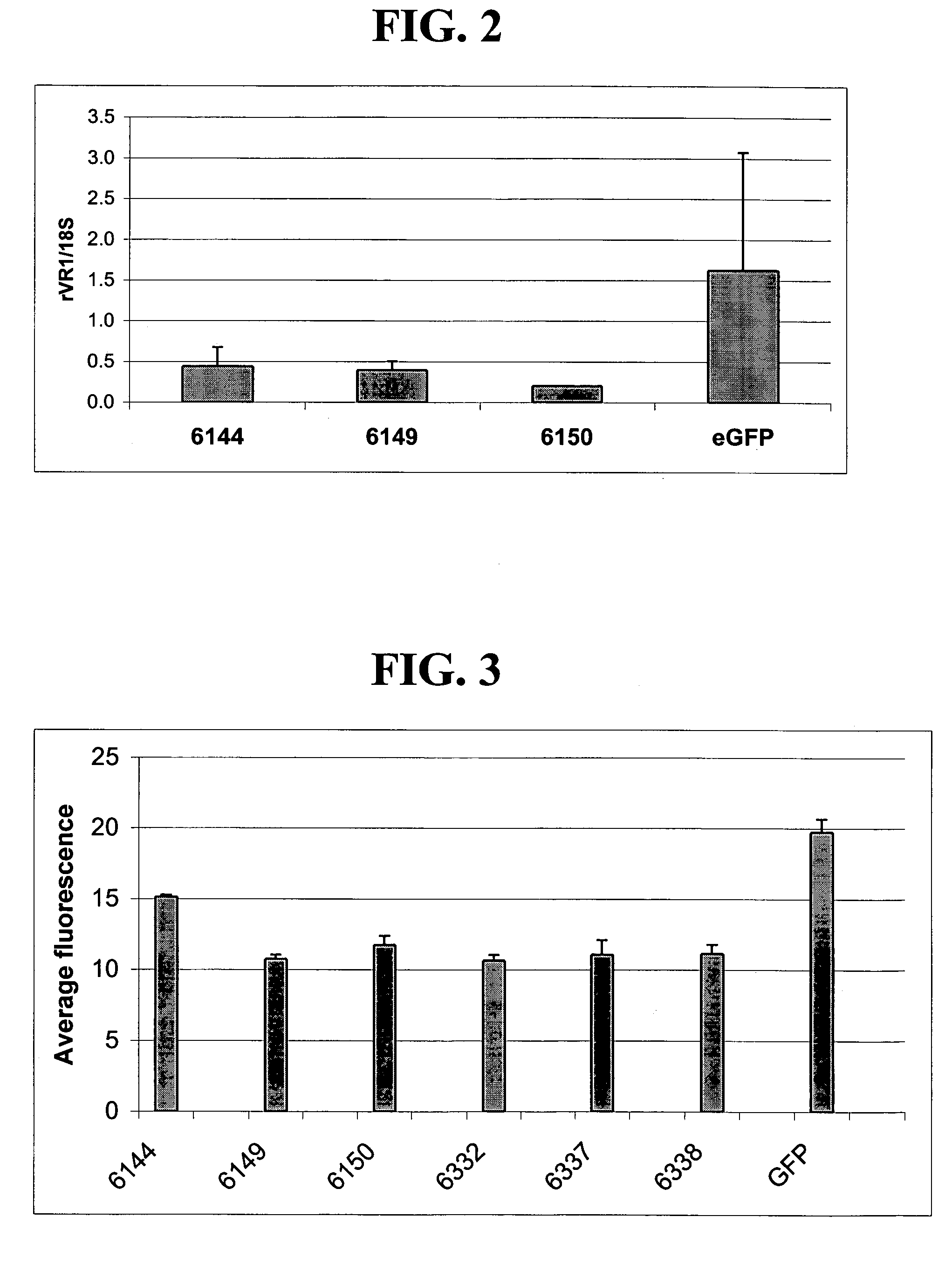
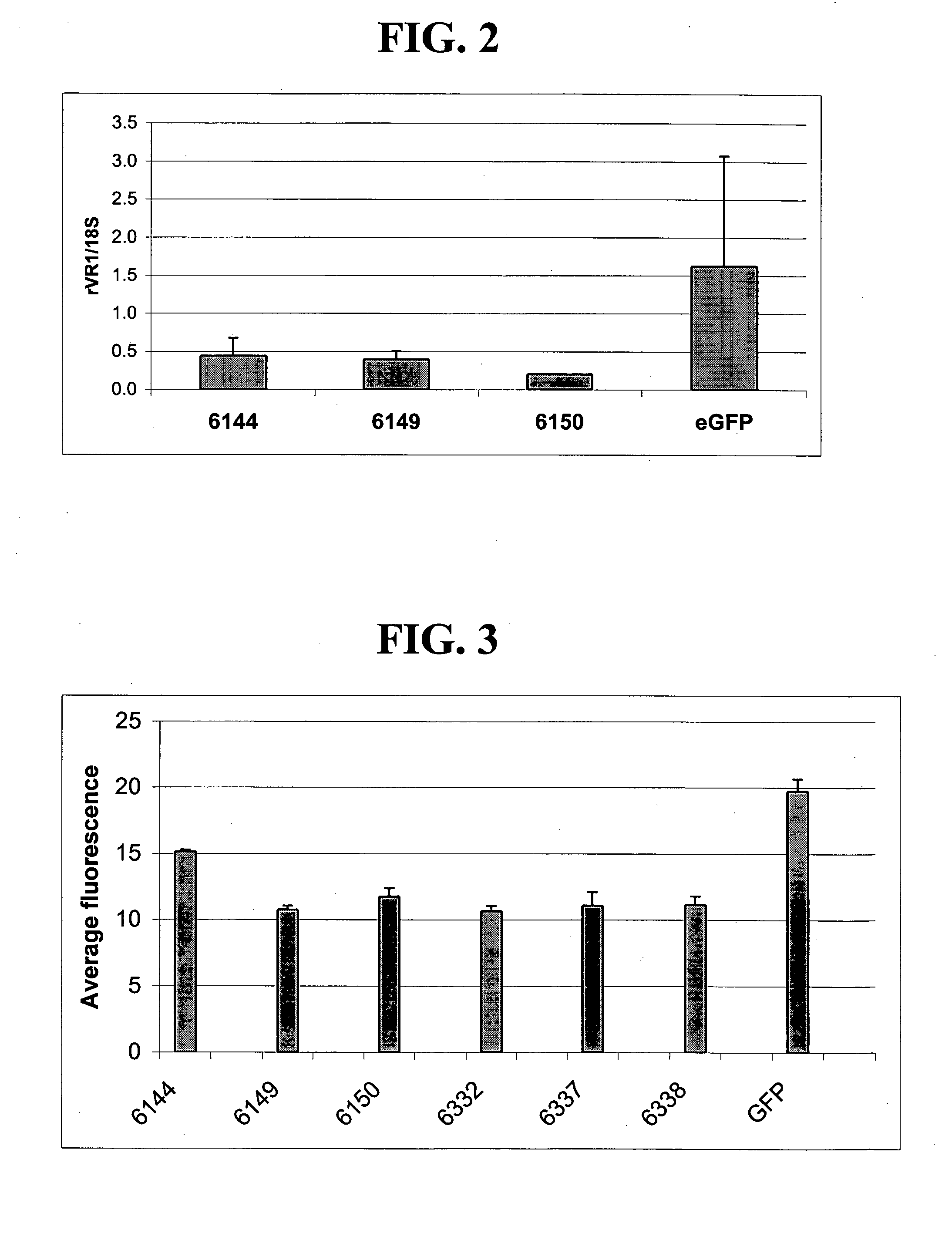
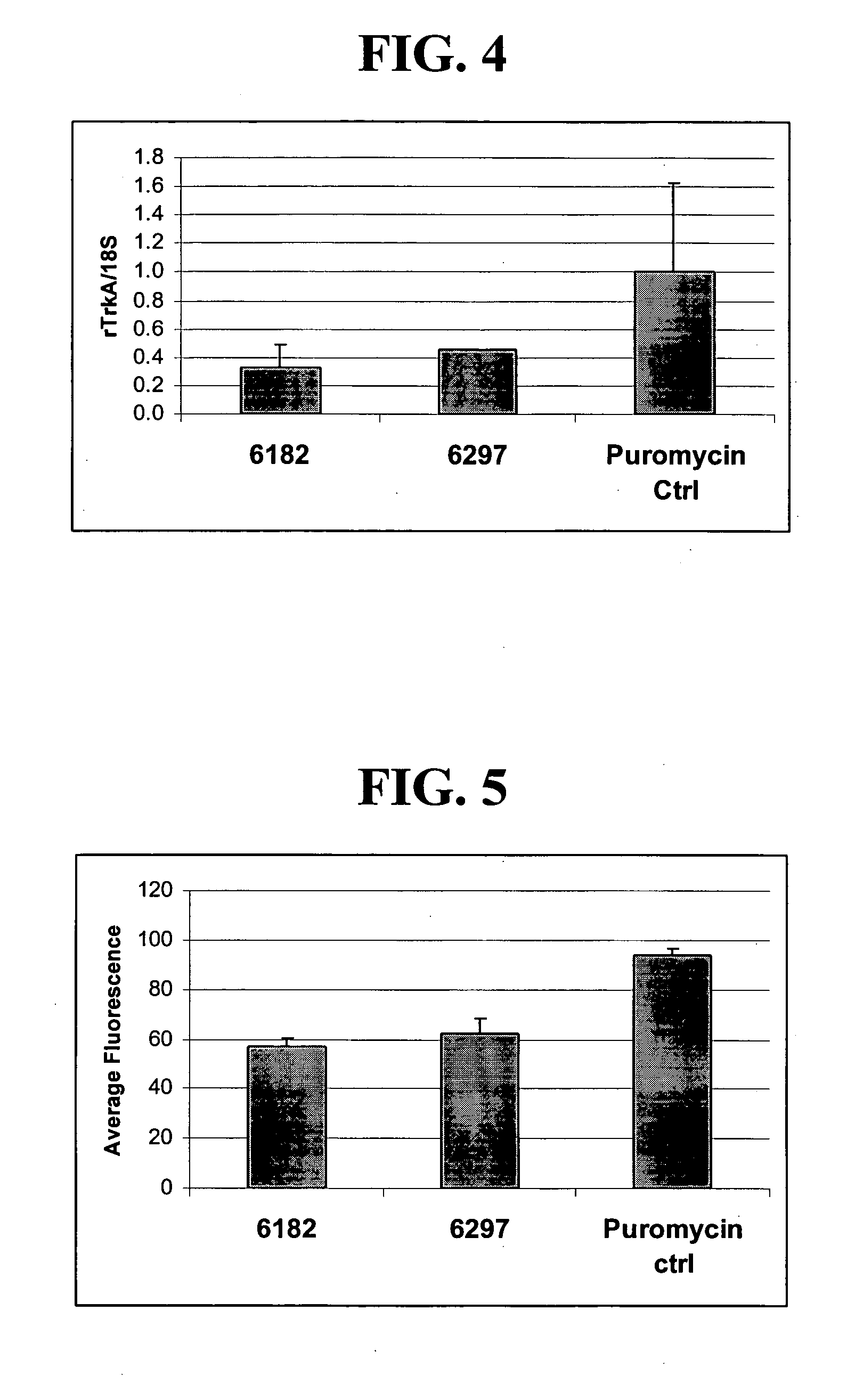
A variety of zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) and methods utilizing such proteins are provided for use in treating neuropathic pain. ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes that are aberrantly expressed in subjects having neuropathic pain are described. In addition, ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes expressed at normal levels in subjects experiencing neuropathic pain, modulation of whose expression results in decreased pain perception, are also provided. For example, genes that are over-expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of pain patients (e.g., VR1, TRKA and / or Nav1.8) can be repressed, whereas genes that are under-expressed in the same populations can be activated.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com