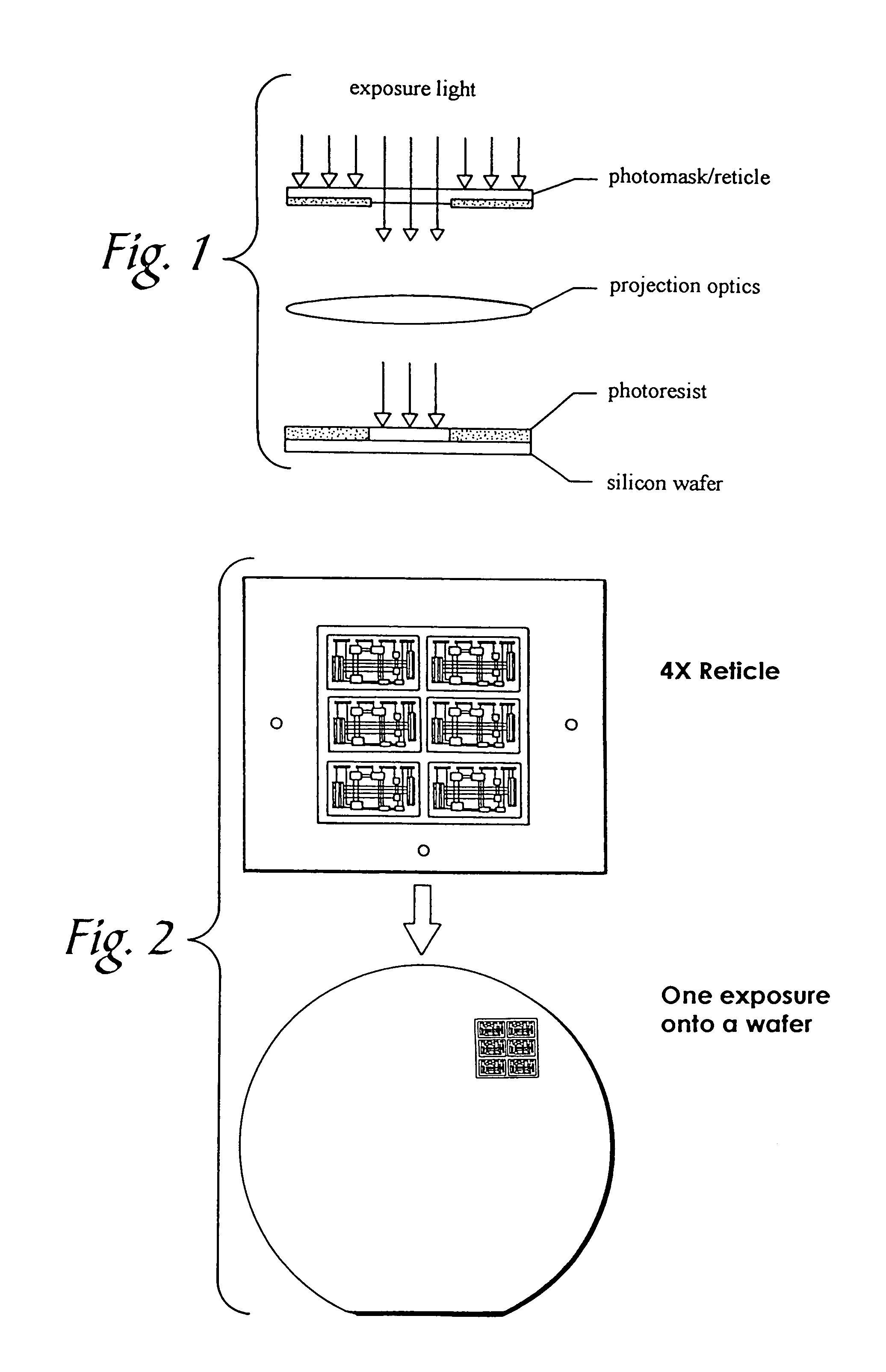
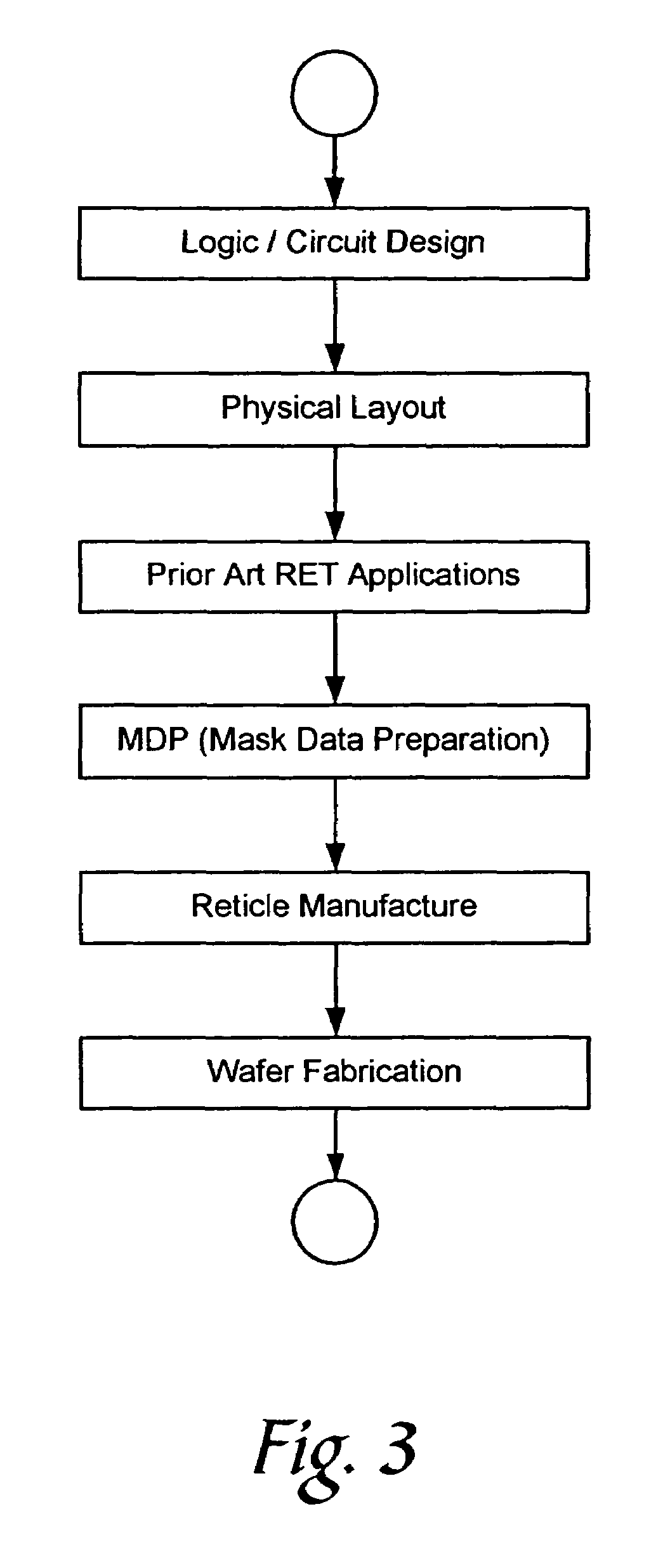
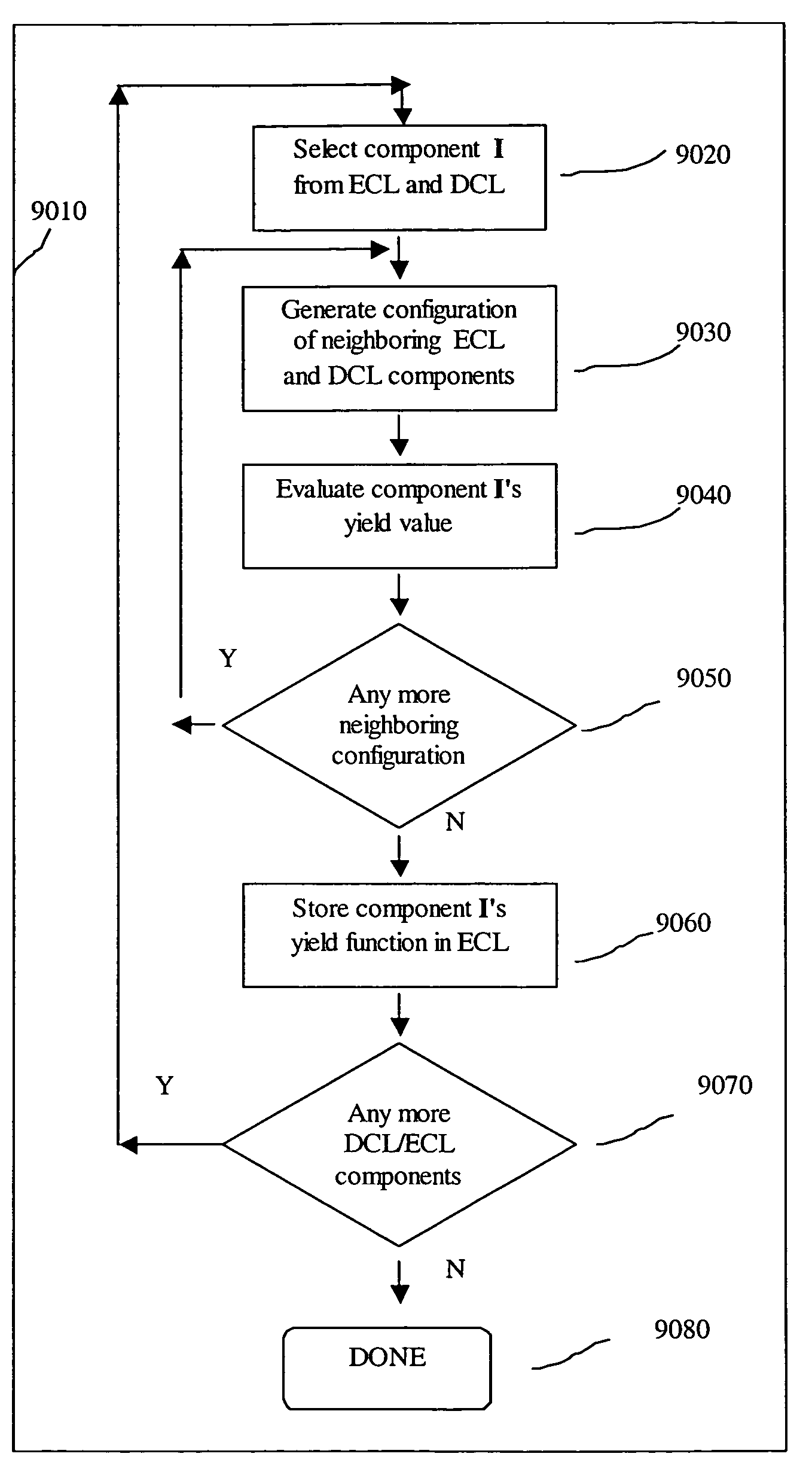
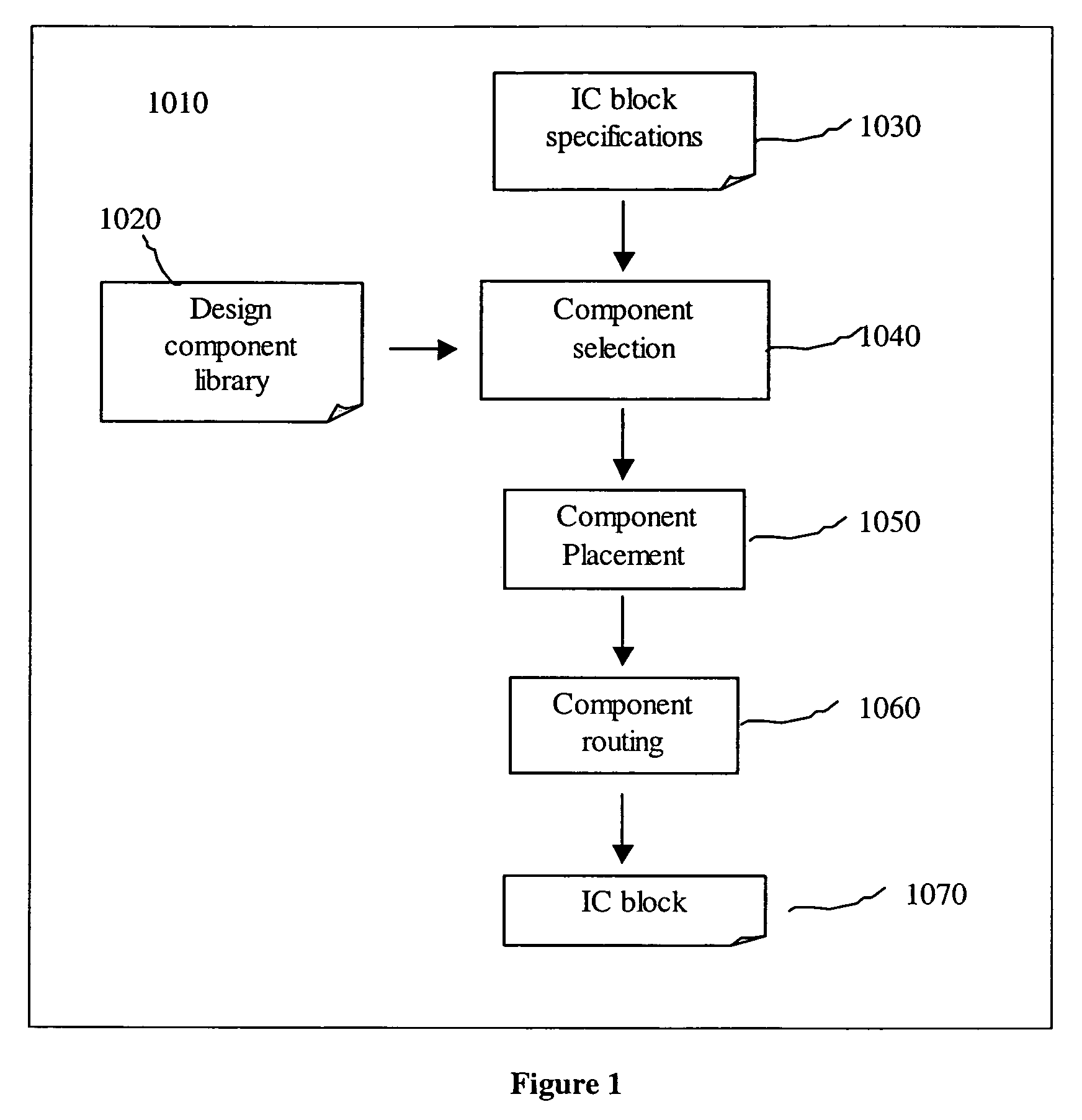
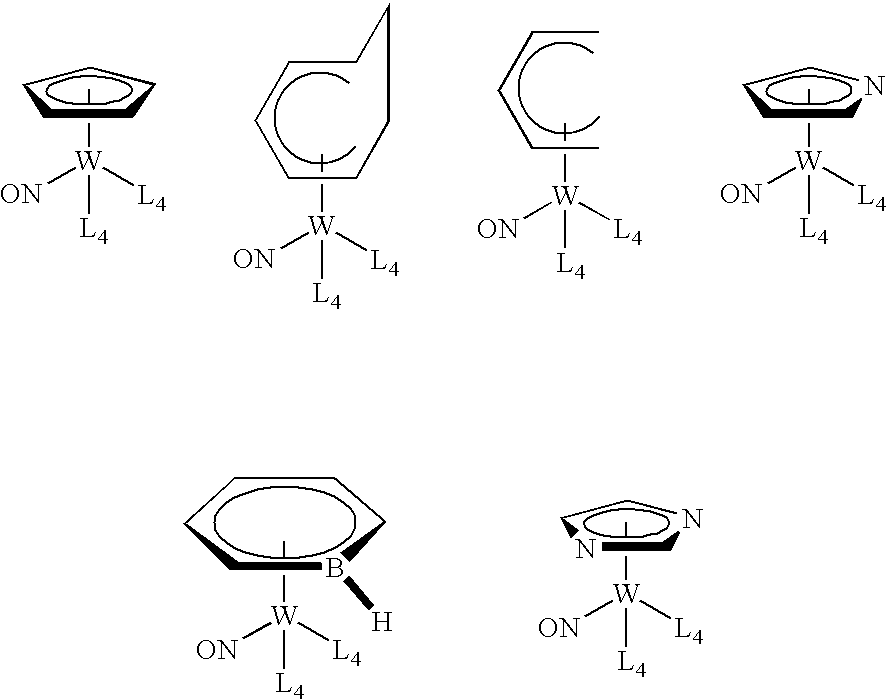Patents
Literature
860 results about "Integrated circuit manufacturing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
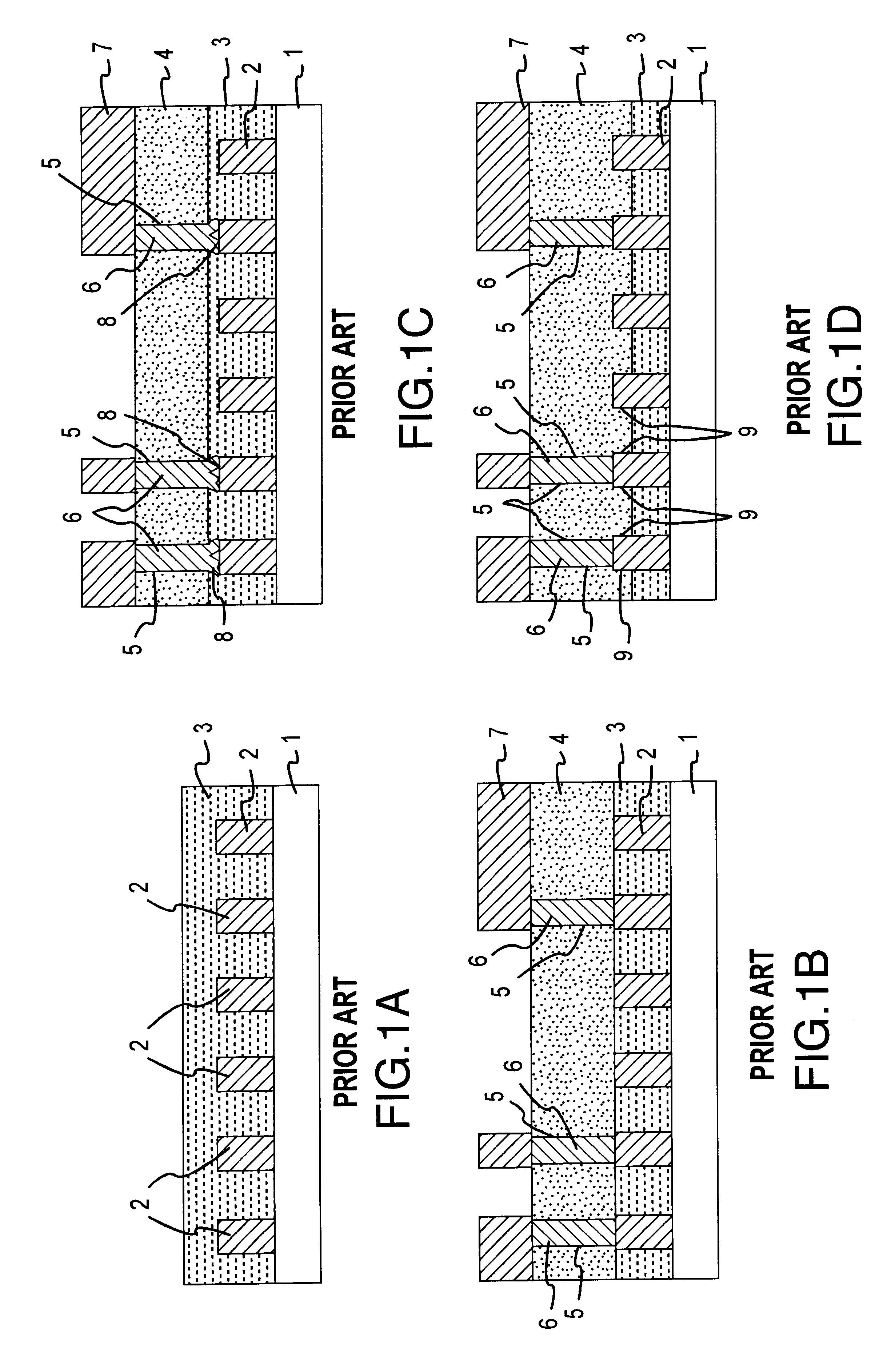
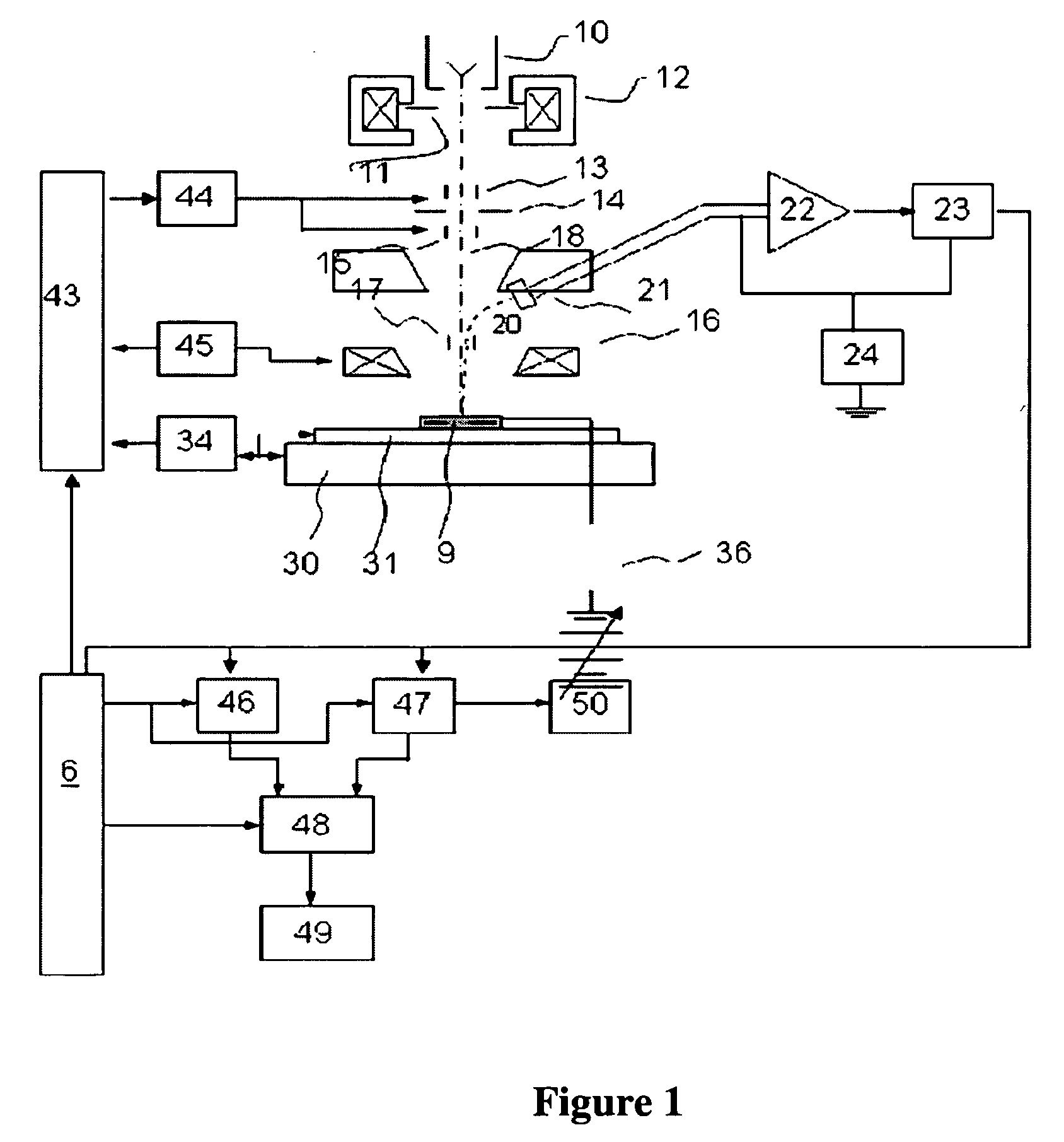
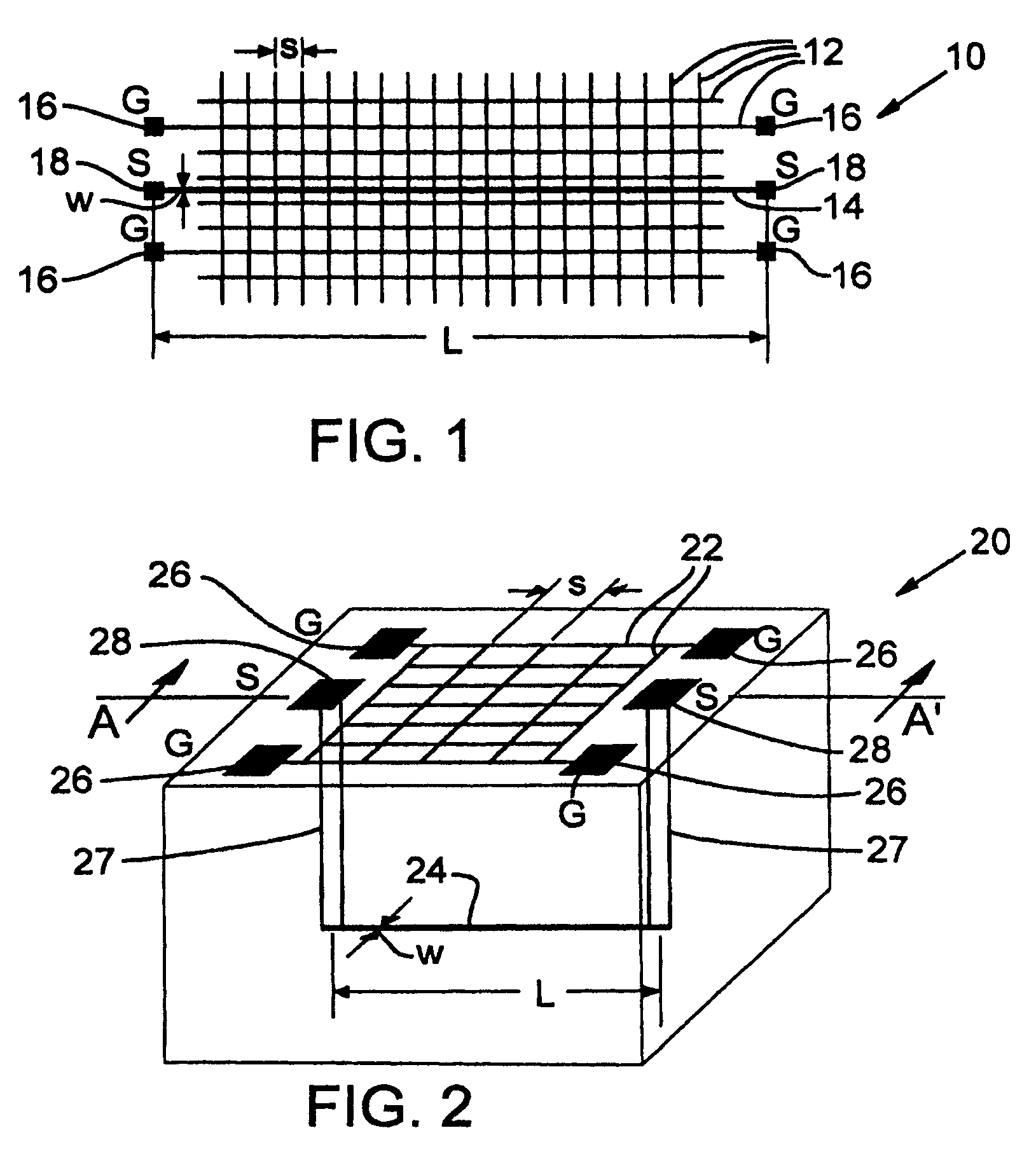
System and Method for Integrated Circuit Manufacturing
ActiveUS20150278429A1Photomechanical apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationMask inspectionIntegrated circuit manufacturing
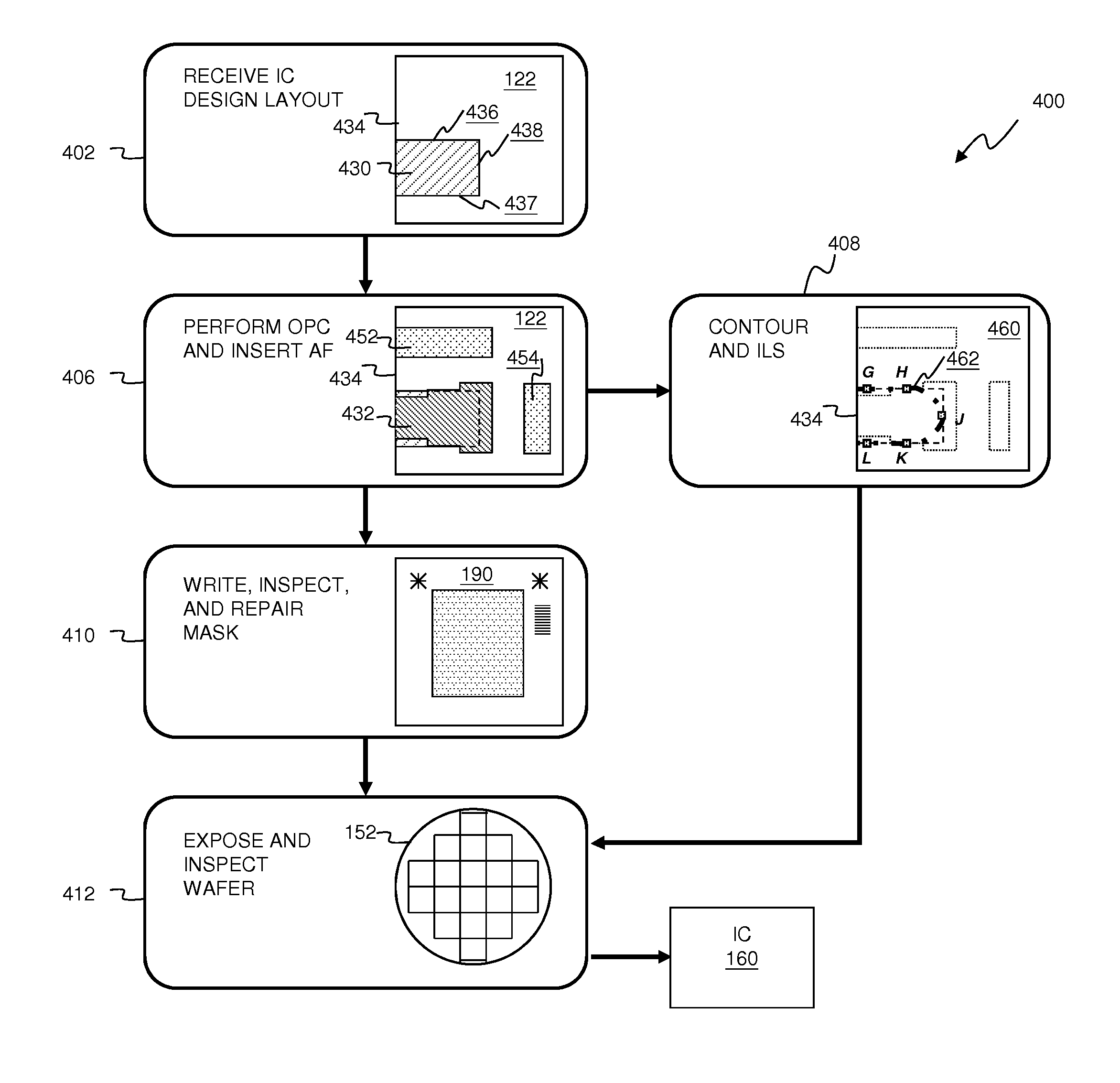
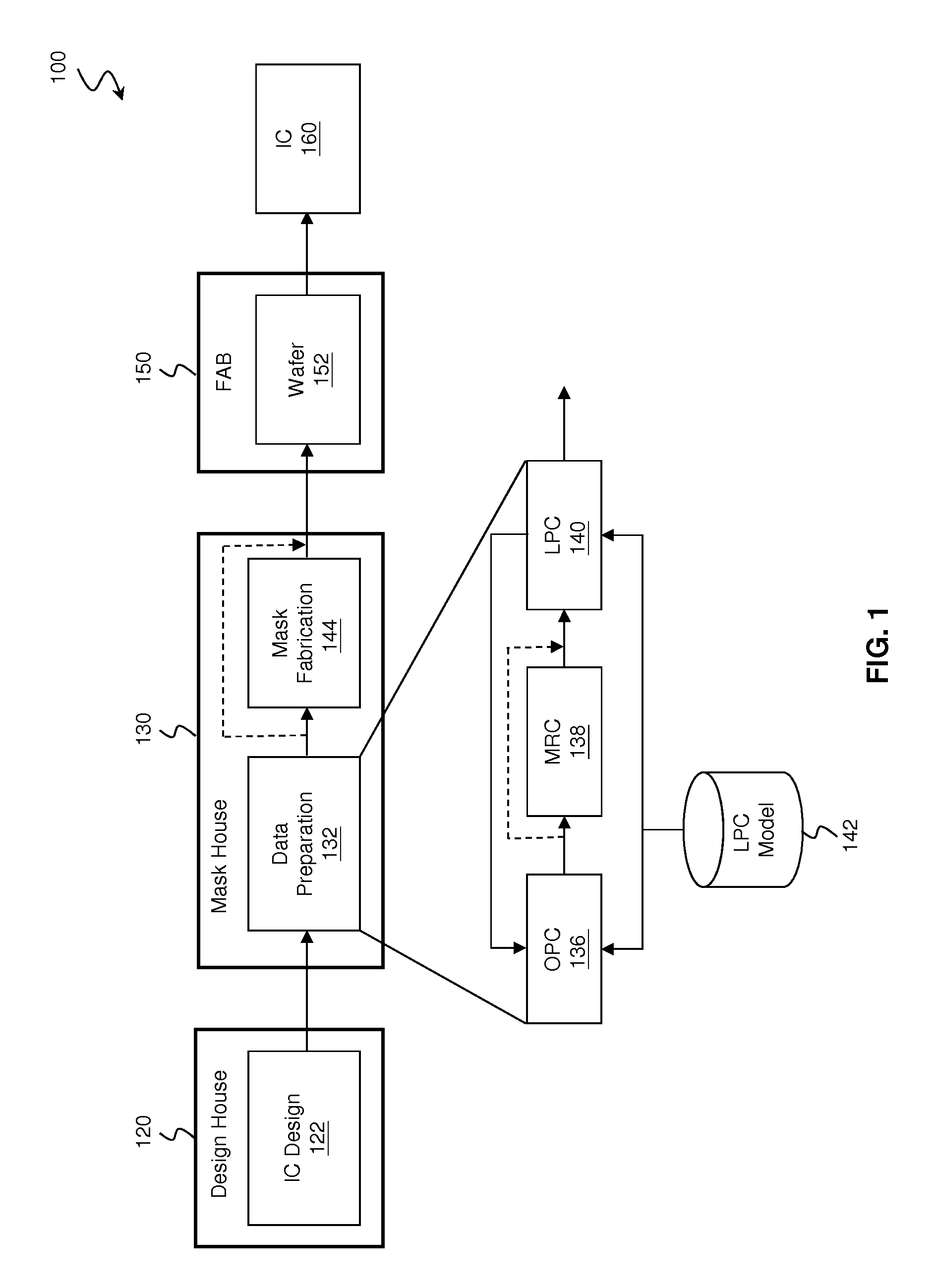
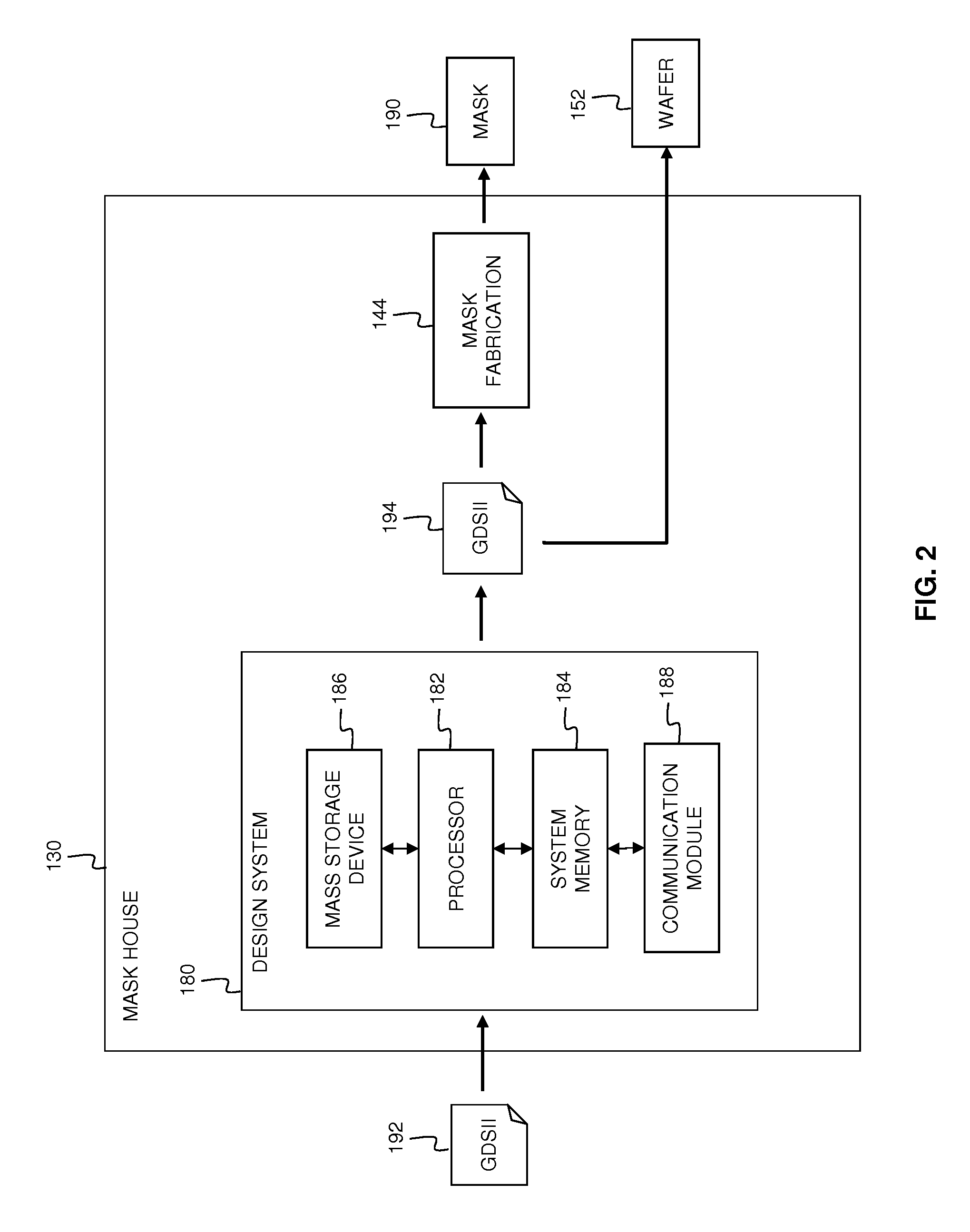
Provided is an integrated circuit (IC) manufacturing method. The method includes receiving a design layout of an IC, the design layout having a main feature; performing a process correction to the main feature thereby generating a modified main feature; using a computer, generating a simulated contour of the modified main feature, the simulated contour having a plurality of points; generating a plurality of assistant data in computer readable format, wherein each assistant data includes at least one process performance factor associated with one of the points; and keeping the simulated contour and the assistant data for use by a further process stage, such as mask making, mask inspection, mask repairing, wafer direct writing, wafer inspection, and wafer repairing.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Interconnect with low dielectric constant insulators for semiconductor integrated circuit manufacturing
InactiveUS6187672B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistIntegrated circuit manufacturing
A method is provided for forming an improved interconnect structure on a semiconductor body. A first metal layer is deposited on the semiconductor body. A sacrificial layer having a height is deposited on the first metal layer. The sacrificial layer and the metal layer are patterned to form separate metal lines with the sacrificial layer remaining on said metal lines. A low-k material is then deposited to fill the gaps between metal lines and to cover the sacrificial layer. The low-k material is then removed to a level within the height of the sacrificial layer. The sacrificial layer is then removed. A protective layer is deposited on top of the metal lines and the low-k material. A dielectric layer is deposited over the protective layer. The protective layer protects the low-k material from attack by chemicals utilized by subsequent process steps to etch vias in the dielectric layer, to strip photo-resist, and to clean the vias. The protective layer is then selectively etched away to make contact between a via plug and the metal lines.
Owner:NEWPORT FAB
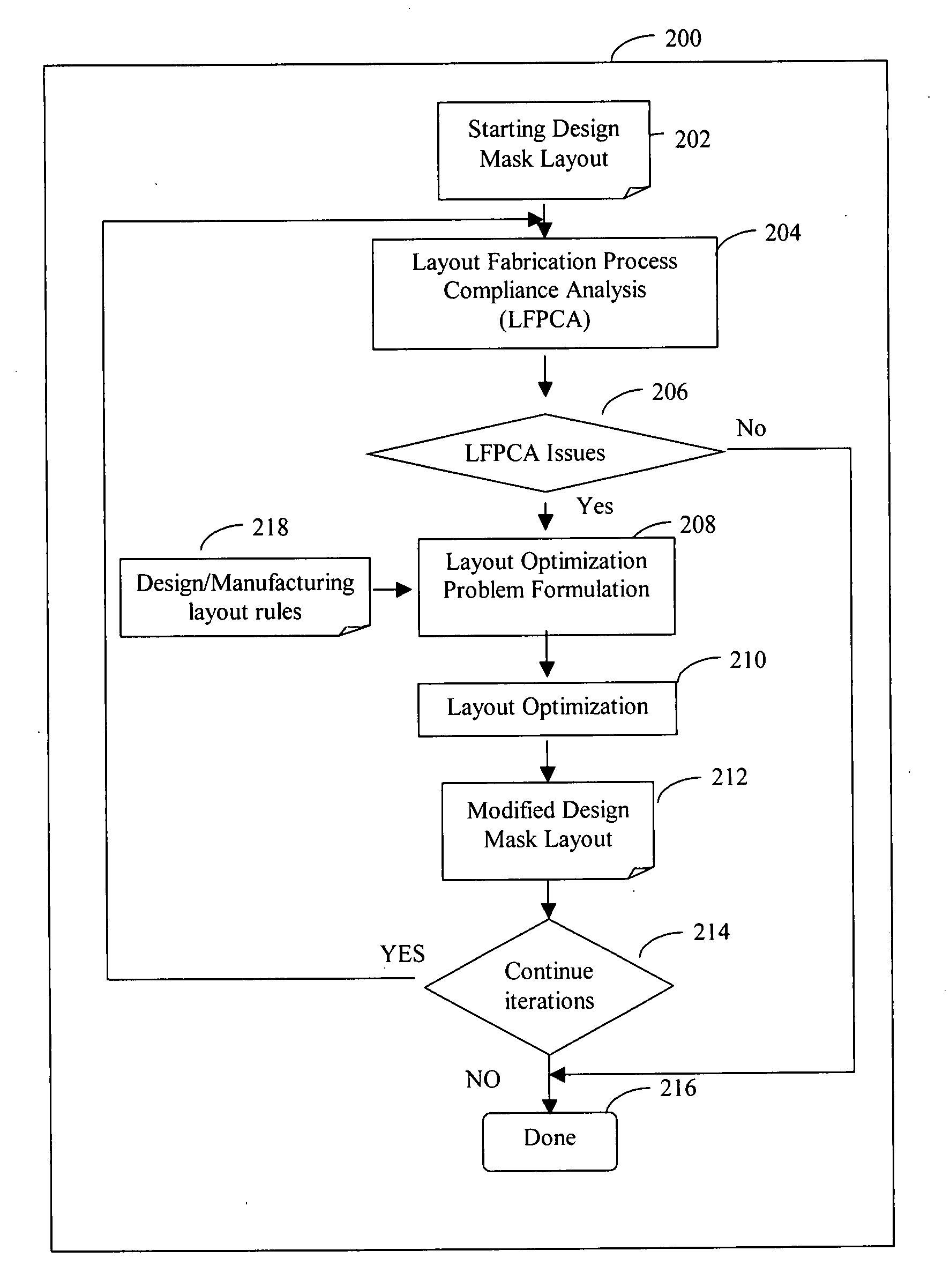
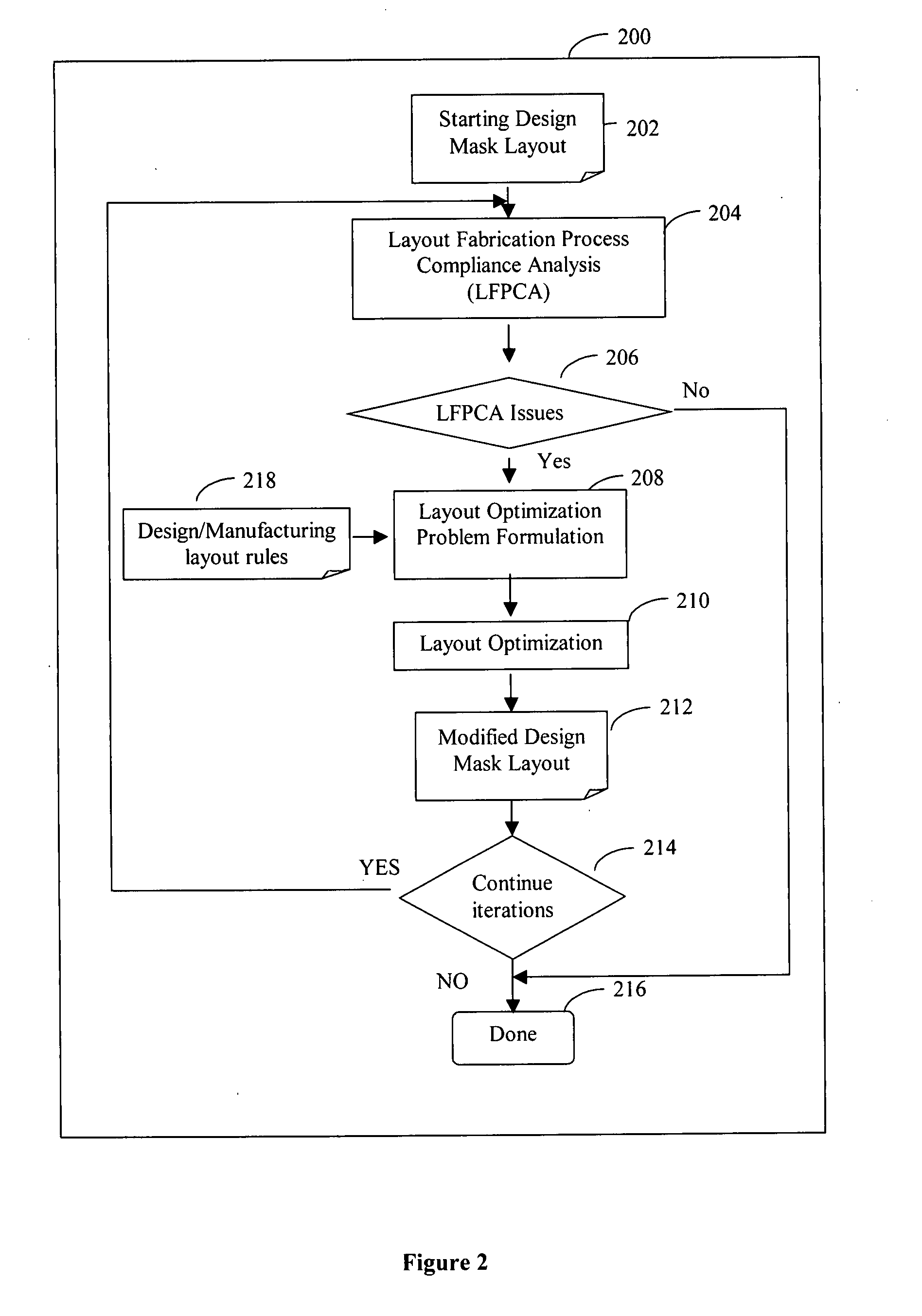
System and method of maximizing integrated circuit manufacturing yield with fabrication process simulation driven layout optimization
InactiveUS20080046846A1Maximizing manufacturing yieldYield maximizationCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationIntegrated circuit manufacturingEngineering
A system and a method of maximizing the manufacturing yield of integrated circuit (“IC”) design using IC fabrication process simulation driven layout optimization is described. An IC design layout is automatically modified through formulation of a layout optimization problem utilizing the results of layout fabrication process compliance analysis tools. The modification of layout is performed adaptively and iteratively to make an IC layout less susceptible to yield issues while maintaining design rule correctness and minimal circuit performance impact.
Owner:CHEW MARKO P +1
Apparatus of antenna with heat slug and its fabricating process
ActiveUS20060071308A1Simple structureEasy to makeAntenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringDual band antenna
An apparatus of antenna with heat slug and its fabricating process are provided, in which the antenna with heat slug can be realized with a single sheet or double sheets of metal. A dual-band antenna module with a mask cover is taken as an example to realize the apparatus. Each single sheet of metal can be achieved by simply cutting and bending a metal plate. Thereby, it is a simple and low-cost fabricating process. In the known fabricating process of integrated circuit, the heat slug and the antenna can be combined in a module at the same step. Therefore, integrating the antenna with heat slug in a fabricating process needs not to develop a new process.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
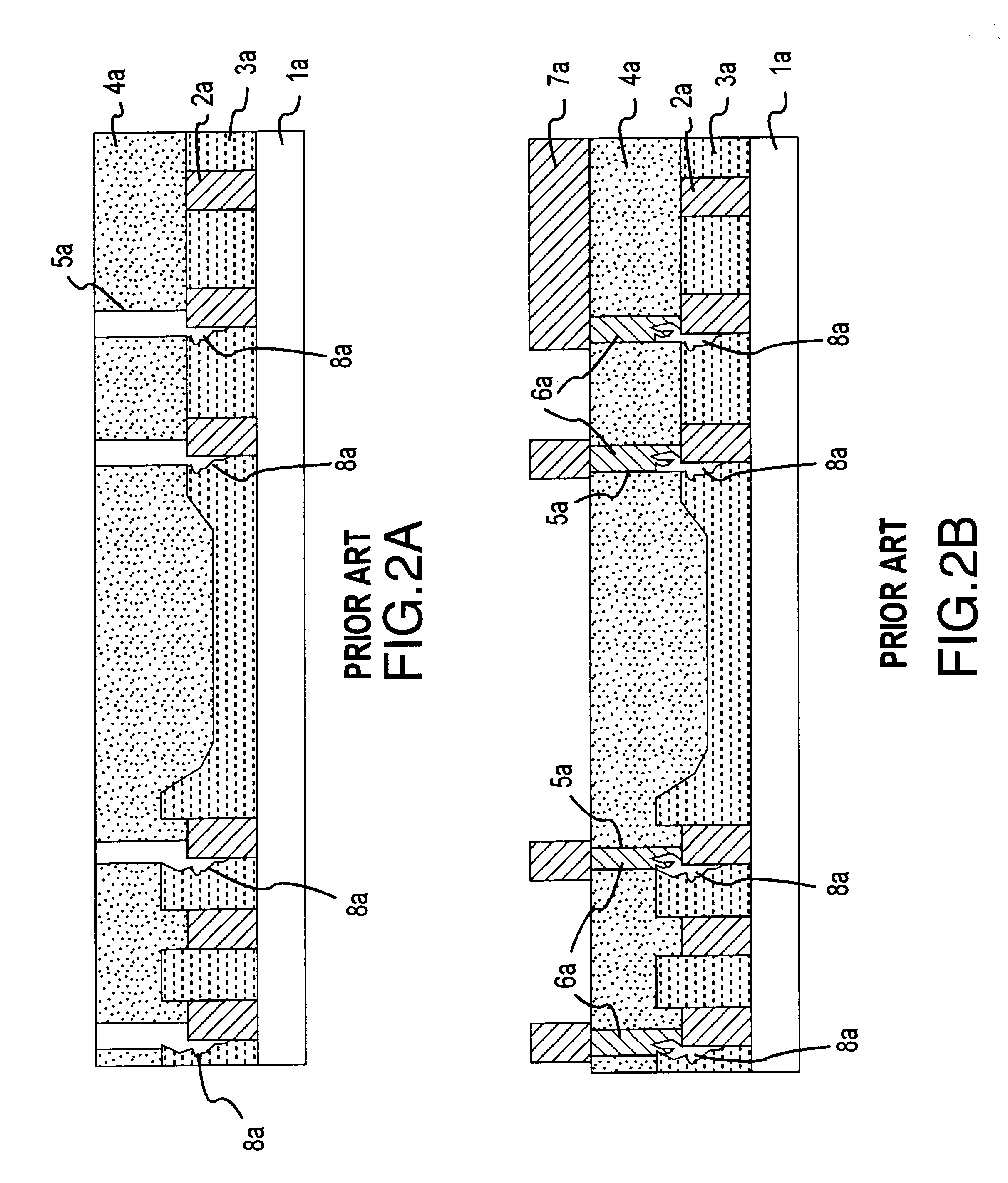
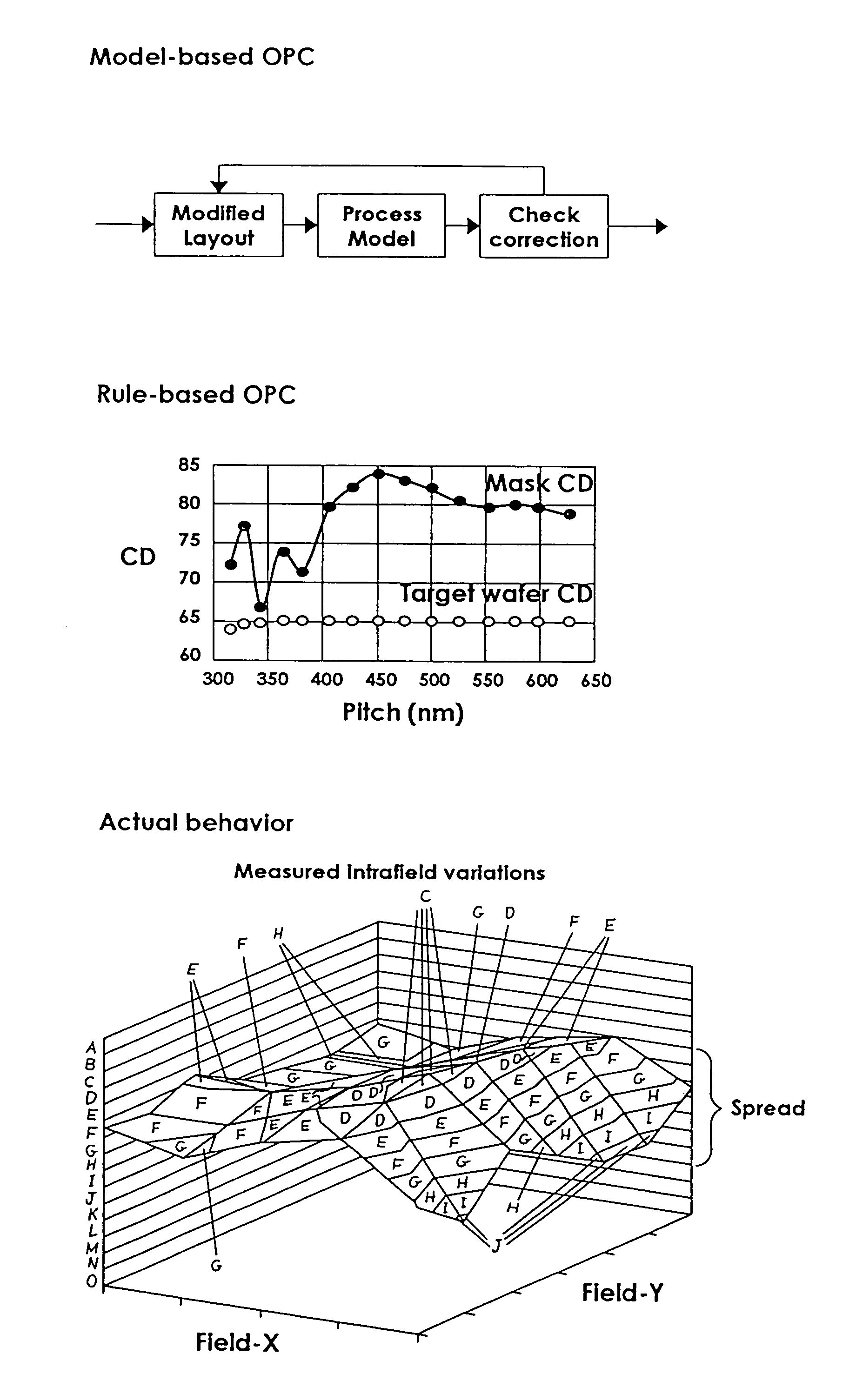
System and method for reducing patterning variability in integrated circuit manufacturing through mask layout corrections
ActiveUS7318214B1Improve accuracyImprove fidelityPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentIntegrated circuit manufacturingEngineering
The present invention provides a system and method of modifying the mask layout shapes of an integrated circuit layout design to compensate for reticle field location-specific systematic CD variations resulting from mask writing process variations, lens imperfections in lithographic patterning, and photoresist process variations. Called PLC (Process-optimized Layout Compensation), each set of compensation rules according to the present invention is specifically tailored for a particular mask-writer-patterning-tools-and-resist-process combination, and are performed on a reticle-wide basis. Furthermore, for each geometric shape in the mask layout, the amount of modification is determined based on a categorization of the type of the shape, the specific location in the reticle field the particular shape falls in, its context (i.e., surrounding patterns, orientation, etc.), as well as certain photoresist parameters to be used in the patterning process.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
System and method of maximizing integrated circuit manufacturing yield with context-dependent yield cells
InactiveUS7739627B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationIntegrated circuit manufacturingSignal integrity
Owner:CHEW MARKO P +1
System and method for lithography process monitoring and control
InactiveUS20060000964A1Highly precise moveable platformSolid-state devicesPhotomechanical apparatusIntegrated circuit manufacturingLithography process
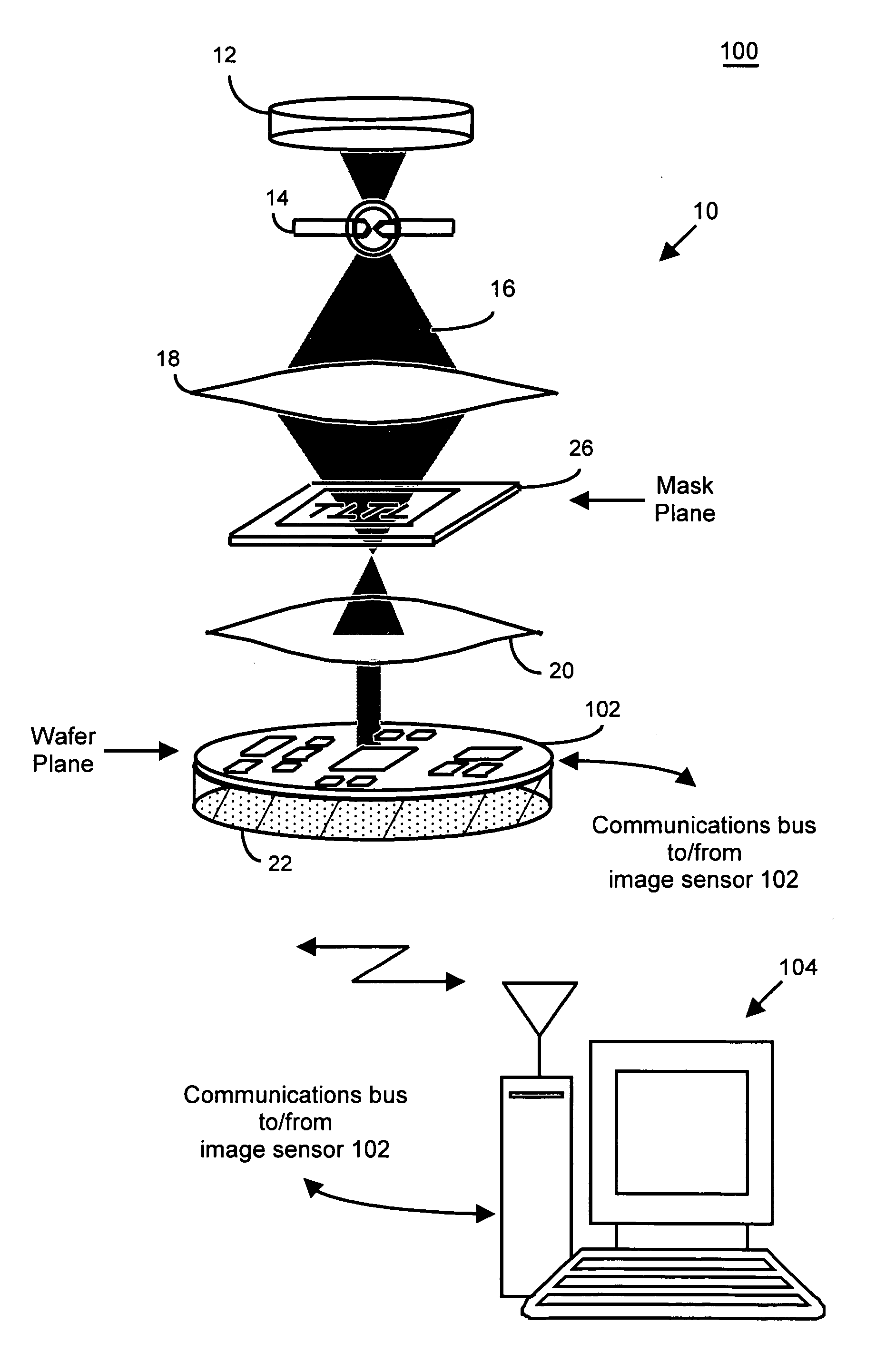
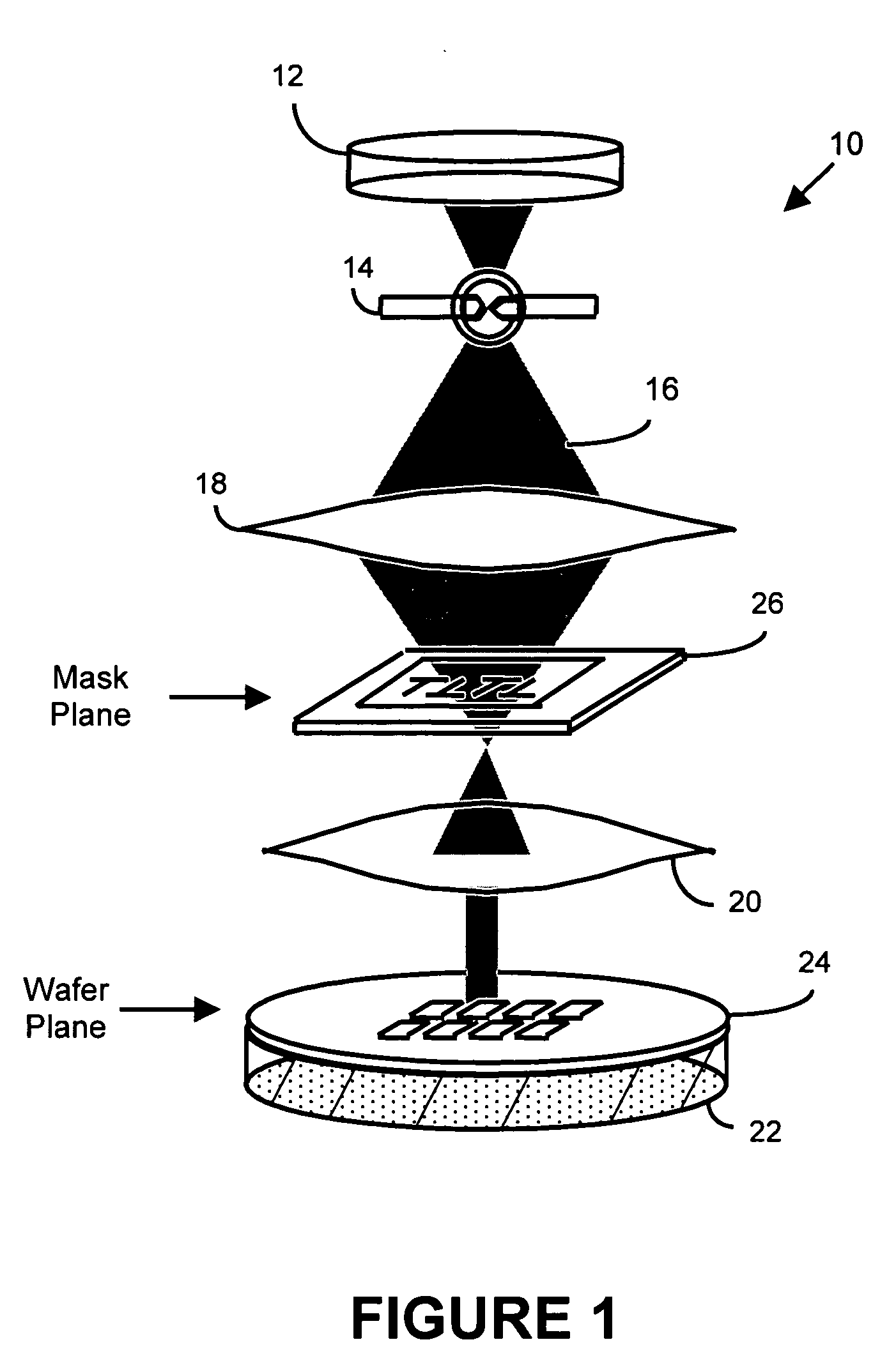
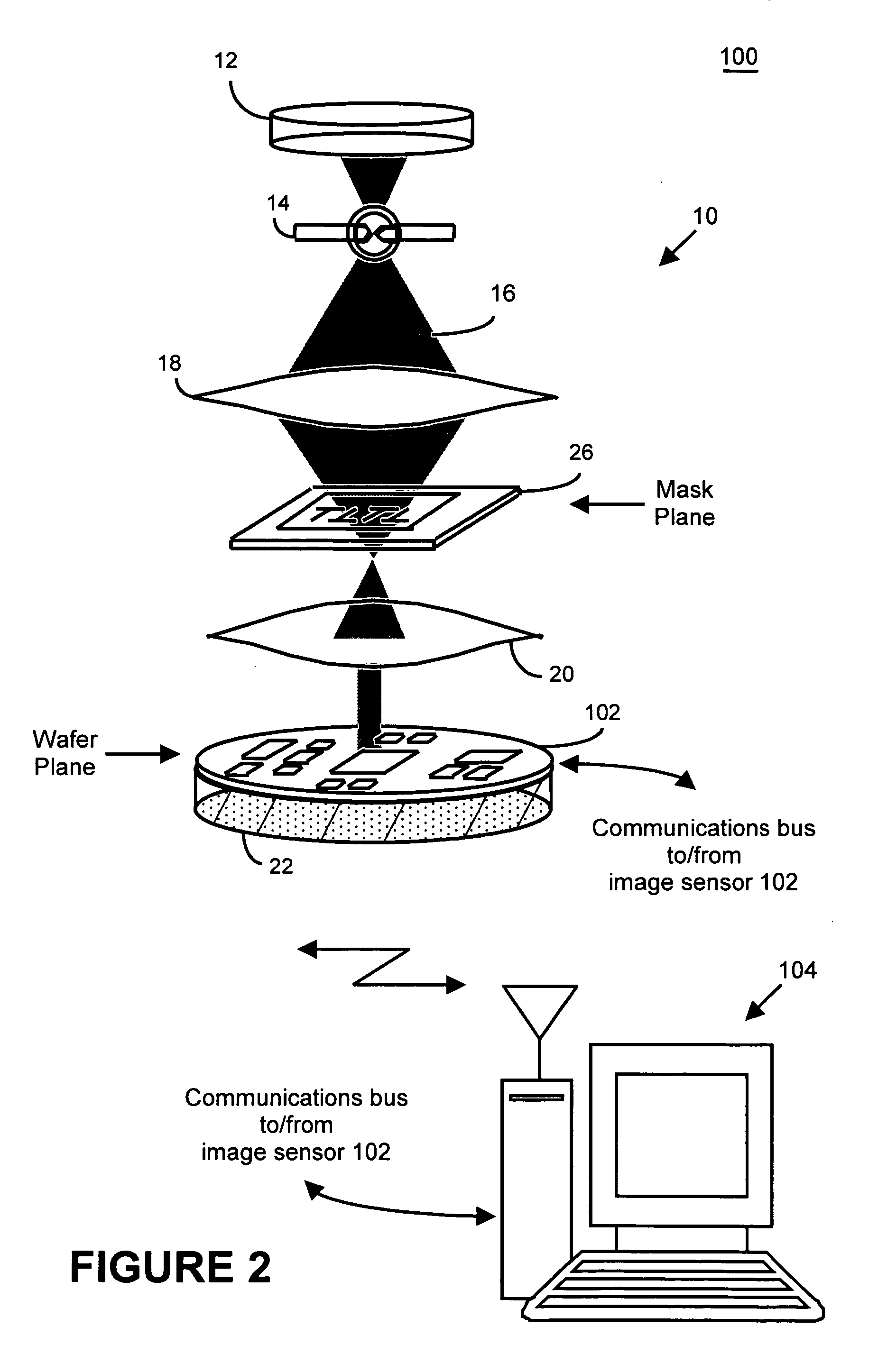
In one aspect, the present invention is a technique of, and a system and sensor for measuring, inspecting, characterizing and / or evaluating optical lithographic equipment, methods, and / or materials used therewith, for example, photomasks. In one embodiment, the system, sensor and technique measures, collects and / or detects an aerial image produced or generated by the interaction between the photomask and lithographic equipment. An image sensor unit may measure, collect, sense and / or detect the aerial image in situ—that is, the aerial image at the wafer plane produced, in part, by a product-type photomask (i.e., a wafer having integrated circuits formed during the integrated circuit fabrication process) and / or by associated lithographic equipment used, or to be used, to manufacture of integrated circuits. In this way, the aerial image used, generated or produced to measure, inspect, characterize and / or evaluate the photomask is the same aerial image used, generated or produced during wafer exposure in integrated circuit manufacturing. In another embodiment, the system, sensor and technique characterizes and / or evaluates the performance of the optical lithographic equipment, for example, the optical sub-system of such equipment. In this regard, in one embodiment, an image sensor unit measures, collects, senses and / or detects the aerial image produced or generated by the interaction between lithographic equipment and a photomask having a known, predetermined or fixed pattern (i.e., test mask). In this way, the system, sensor and technique collects, senses and / or detects the aerial image produced or generated by the test mask—lithographic equipment in order to inspect, evaluate and / or characterize the performance of the lithographic equipment.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
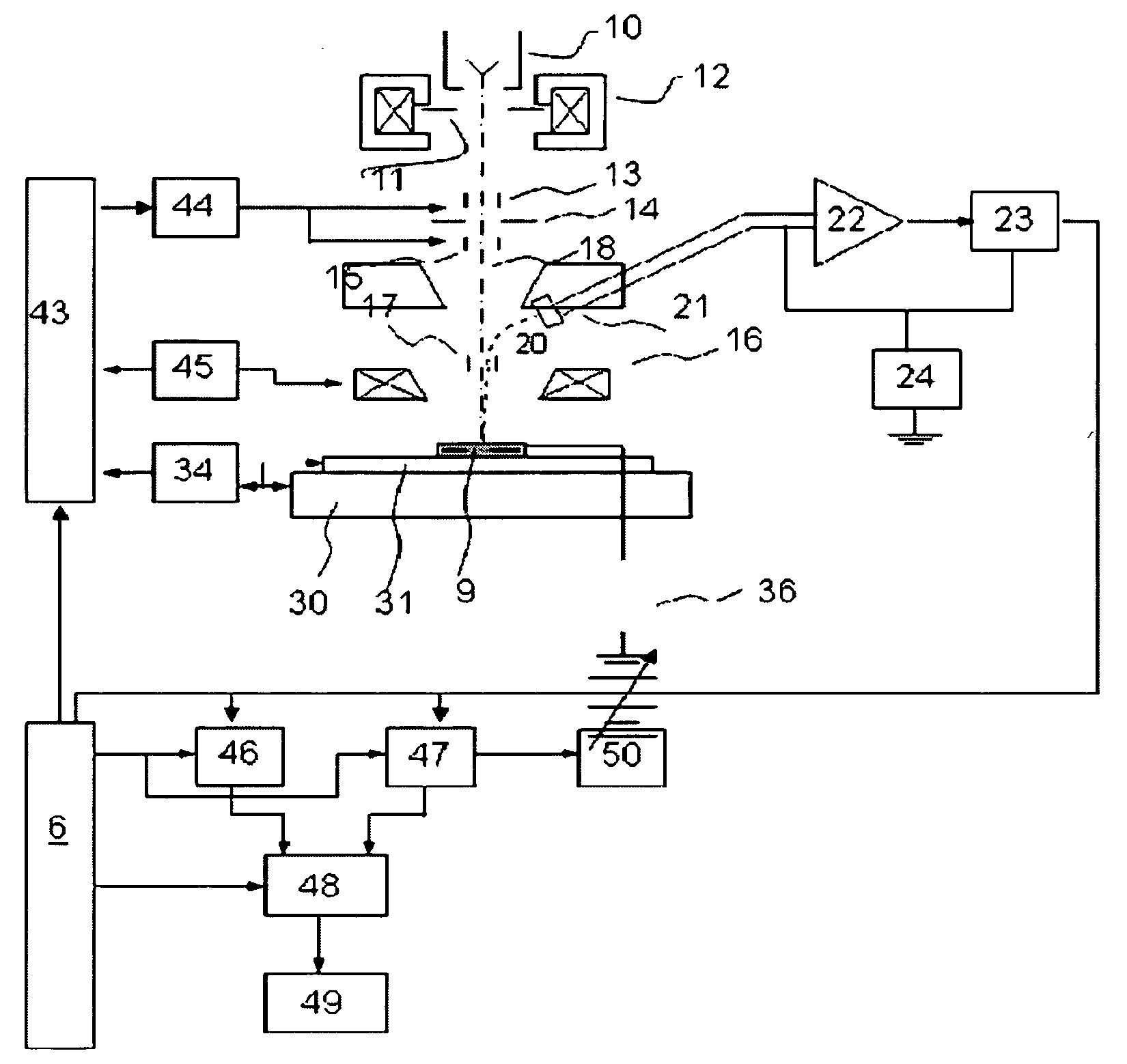
Method for determining abnormal characteristics in integrated circuit manufacturing process
A method for determining abnormal characteristics in integrated circuit manufacturing process is disclosed. The method comprises obtaining a charged particle microscope image of a sample test structure, wherein the sample including a reference pattern and a test pattern; measuring gray levels of the reference pattern and the test pattern; calculating a standard deviation from a distribution of the gray levels of the reference pattern measured; and determining the abnormal characteristics of the test pattern based on the gray levels measured and the standard deviation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
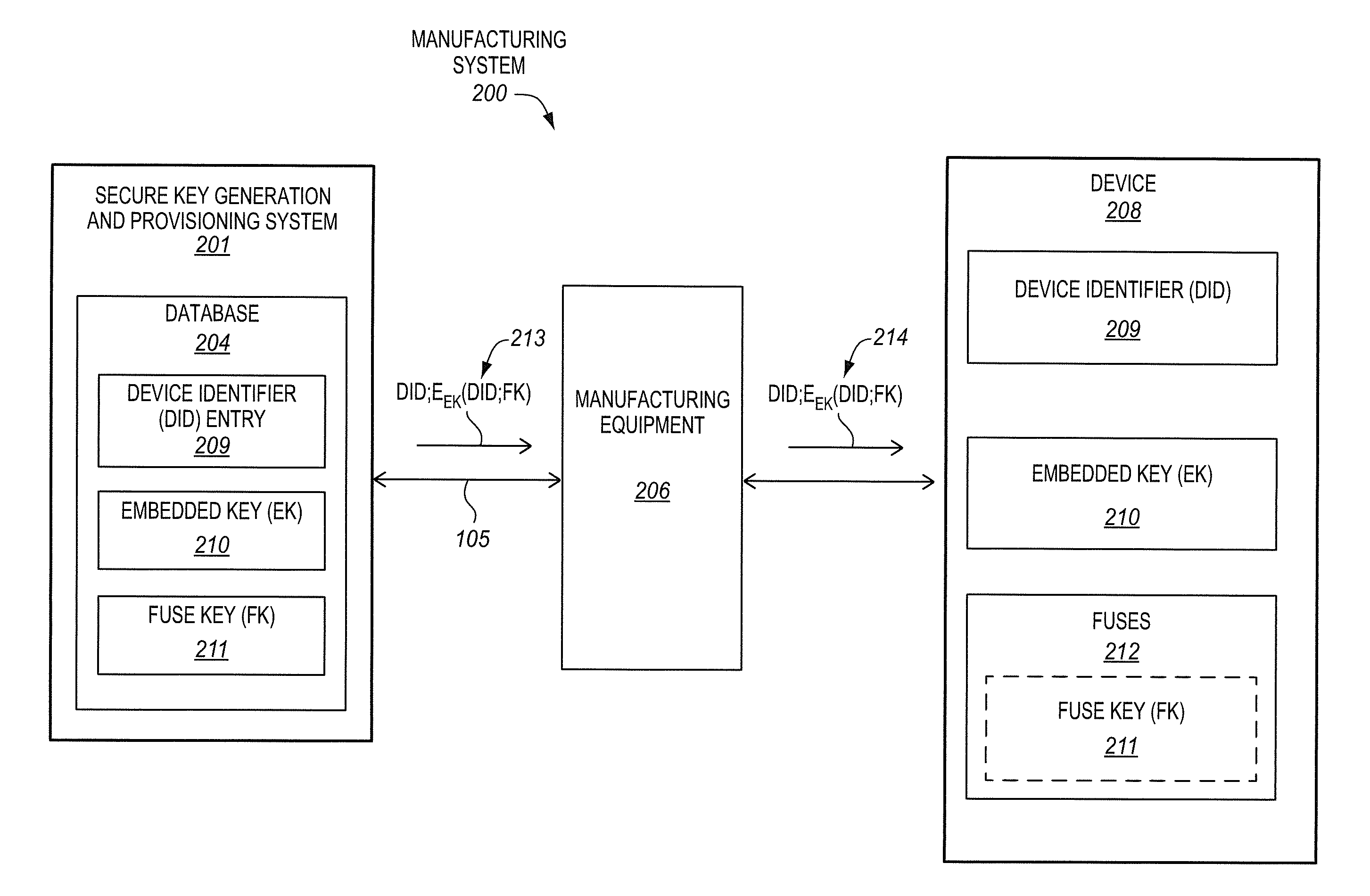
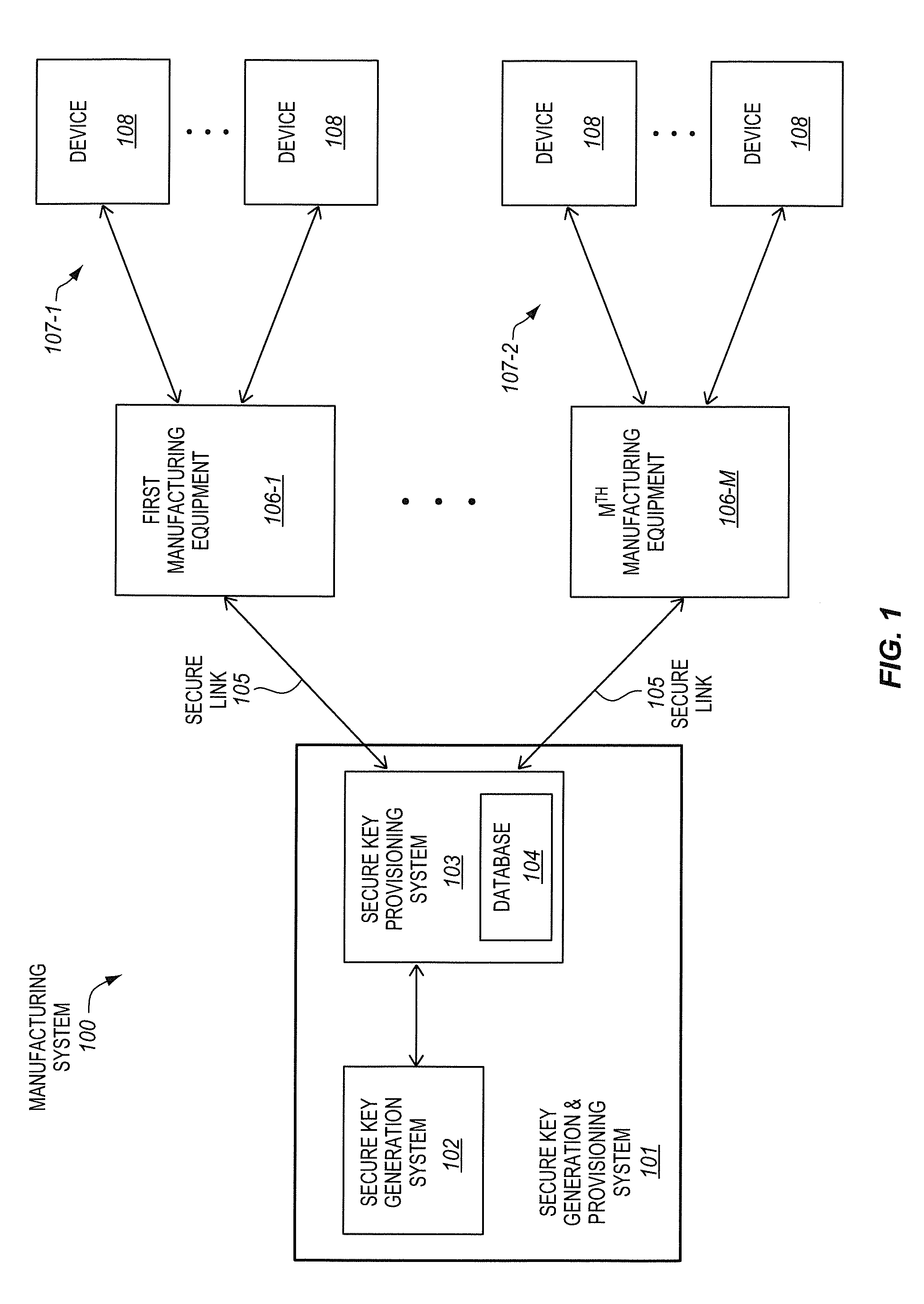
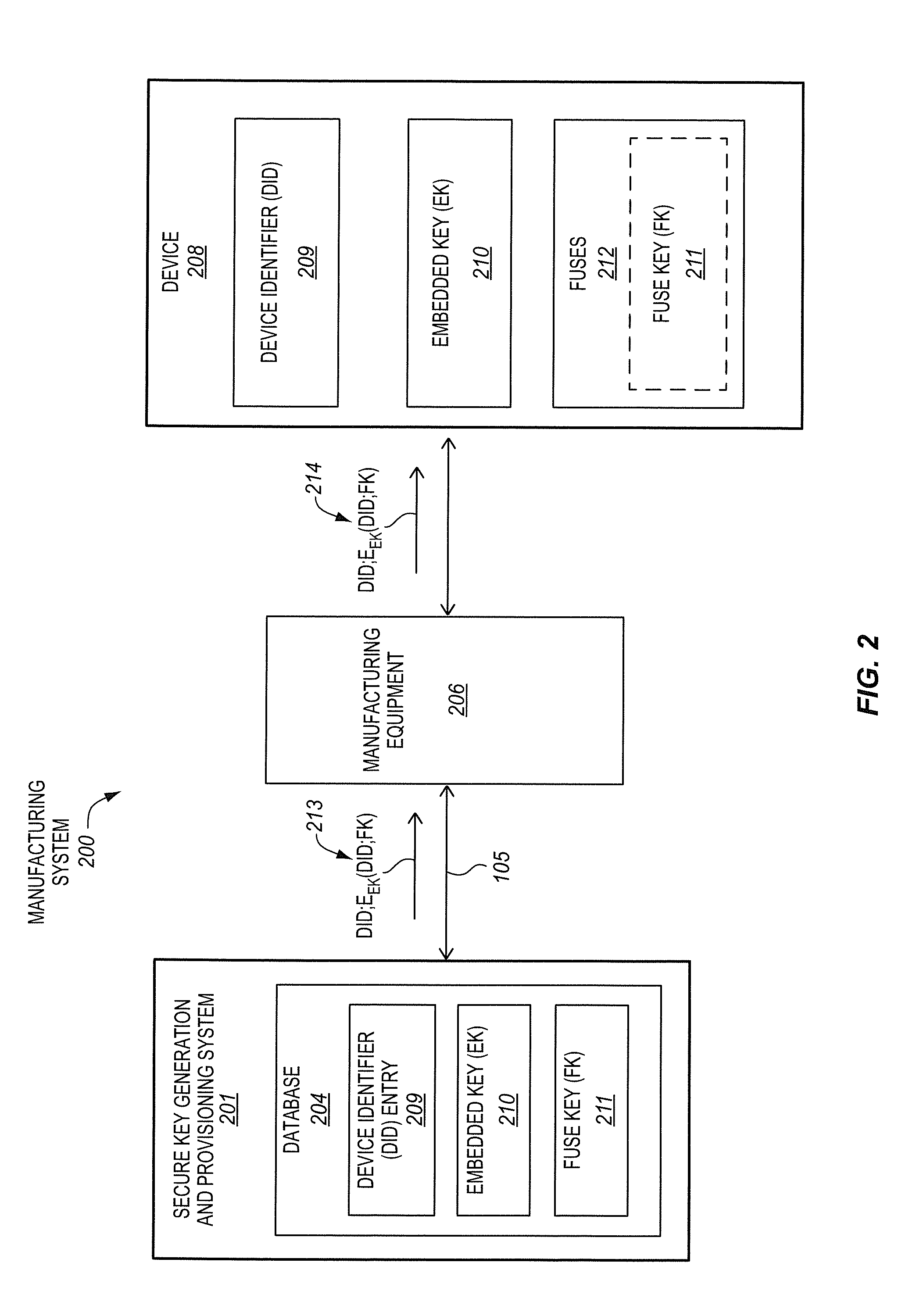
Secure provisioning of secret keys during integrated circuit manufacturing
ActiveUS20140093074A1Internal/peripheral component protectionSecuring communicationComputer hardwareIntegrated circuit manufacturing
A method, of an aspect, includes challenging a set of Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) cells, of an integrated circuit device, and receiving a set of PUF bits from the PUF cells in response. A PUF key is generated based on the set of PUF bits. An encryption of the PUF key with an embedded key is output from the integrated circuit device. The integrated circuit device receives an encryption of a fuse key with the PUF key. Fuses of the integrated circuit device are programmed with at least one of the fuse key and the received encryption of the fuse key with the PUF key. Other methods, apparatus, and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
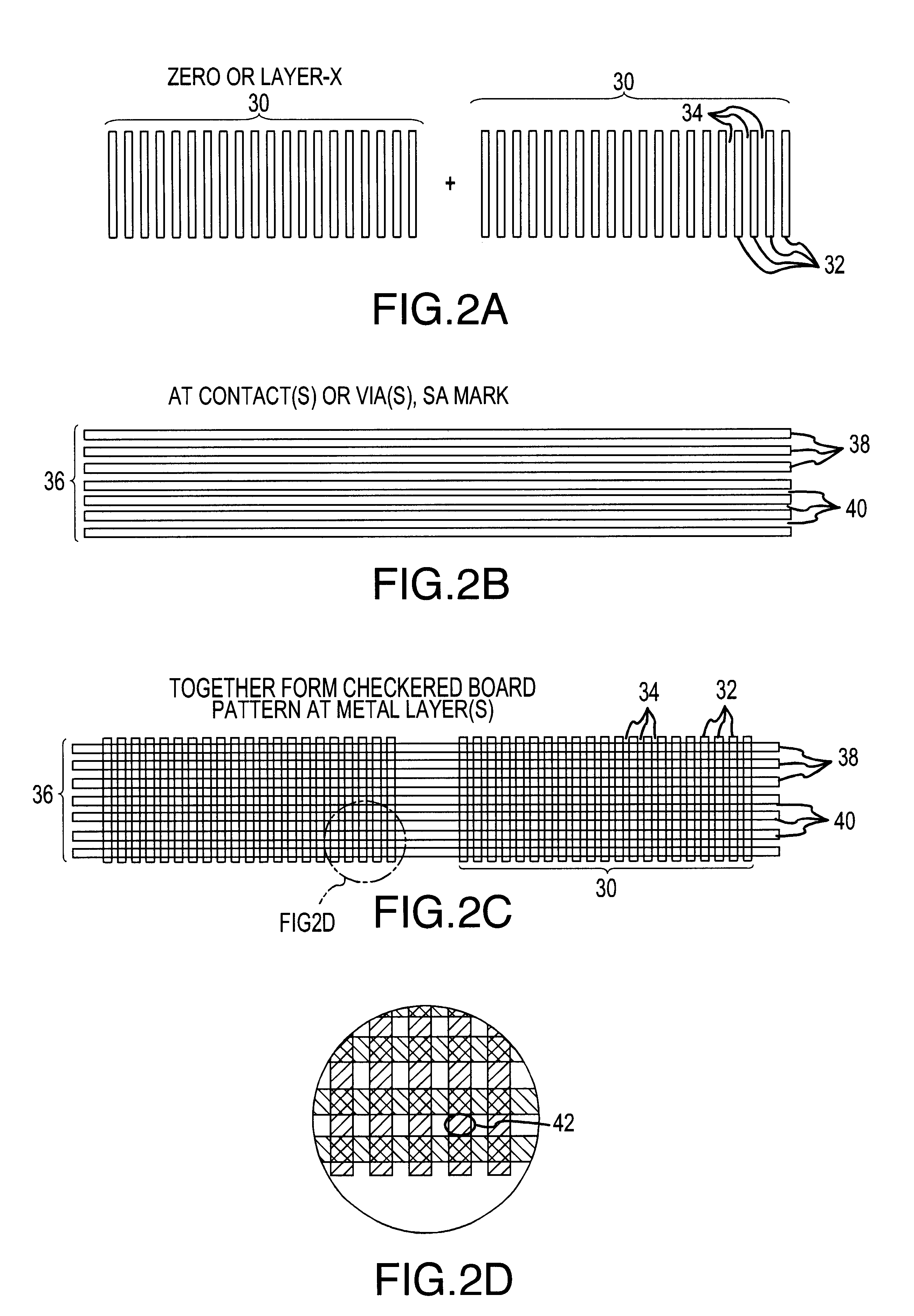
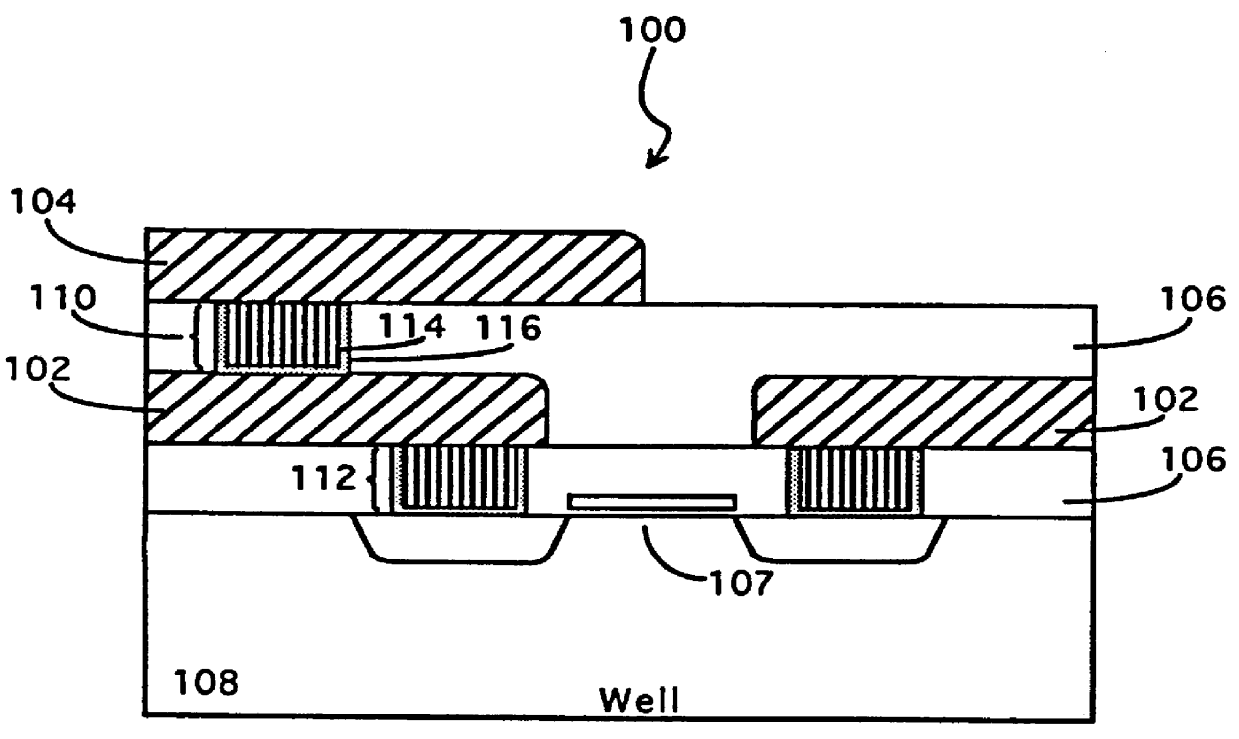
Method for creating and preserving alignment marks for aligning mask layers in integrated circuit manufacture
InactiveUS6261918B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
A method for creating and preserving alignment marks used for aligning mask layers in integrated circuit formation including the steps of creating a first set of marks within a reference layer to form a basic alignment mark, creating a second set of marks overlapping the first set of marks and positioned perpendicular to the first set of marks in the same reference layer to form a preservation pattern, and etching the reference layer to form a substantially checkerboard-type pattern where portions of the first set of marks are recessed within a thickness of the reference layer. After creating the checkerboard-type pattern formed from the first and second marks, a first metal a layer may be deposited to fill in any recesses contained within the pattern. CMP follows without damaging the segmented portions of the first set of marks which lie recessed within a thickness of the reference layer. Finally, the preserved portions of the first set of marks are aligned with pattern marks for a second metal layer.
Owner:NEWPORT FAB
Plug or via formation using novel slurries for chemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS6046099AOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntegrated circuit manufacturingPotassium ferricyanide
Novel slurries for the chemical mechanical polishing of thin films used in integrated circuit manufacturing. A tungsten slurry of the present invention comprises an oxidizing agent, such as potassium ferricyanide, an abrasive such as silica, and has a pH between two and four. The tungsten slurry of the present invention can be used in a chemical mechanical planarization process to polish back a blanket deposited tungsten film to form plugs or vias. The tungsten slurry can also be used to polish copper, tungsten silicide, and titanium nitride. A second slurry, which is a 9:1 dilution of the tungsten slurry is ideal for chemical mechanical polishing of titanium nitride films. A third slurry of the present invention comprises a fluoride salt, an abrasive such as silica and has a pH< / =8. The third slurry can be used to polish titanium films.
Owner:INTEL CORP
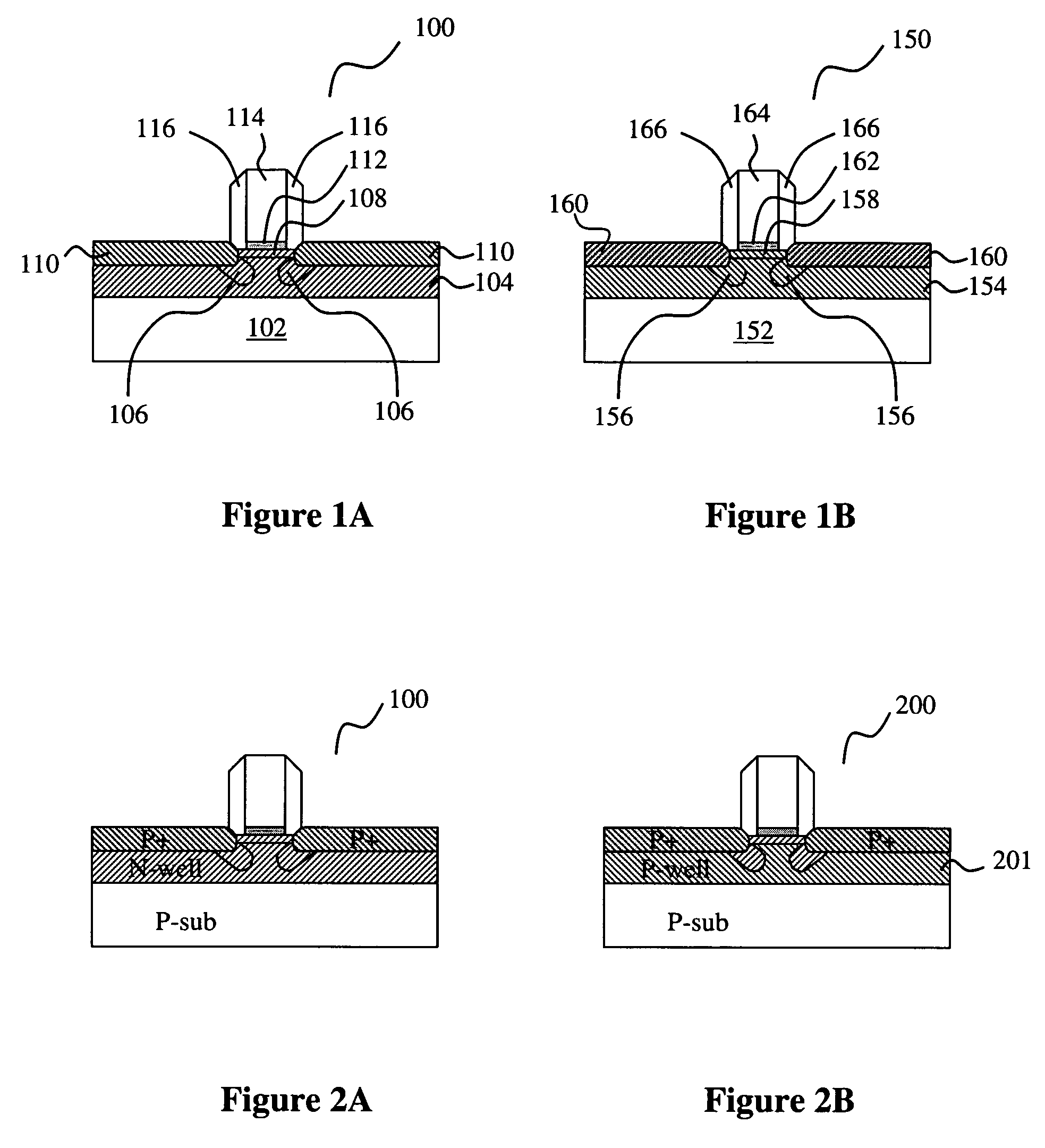
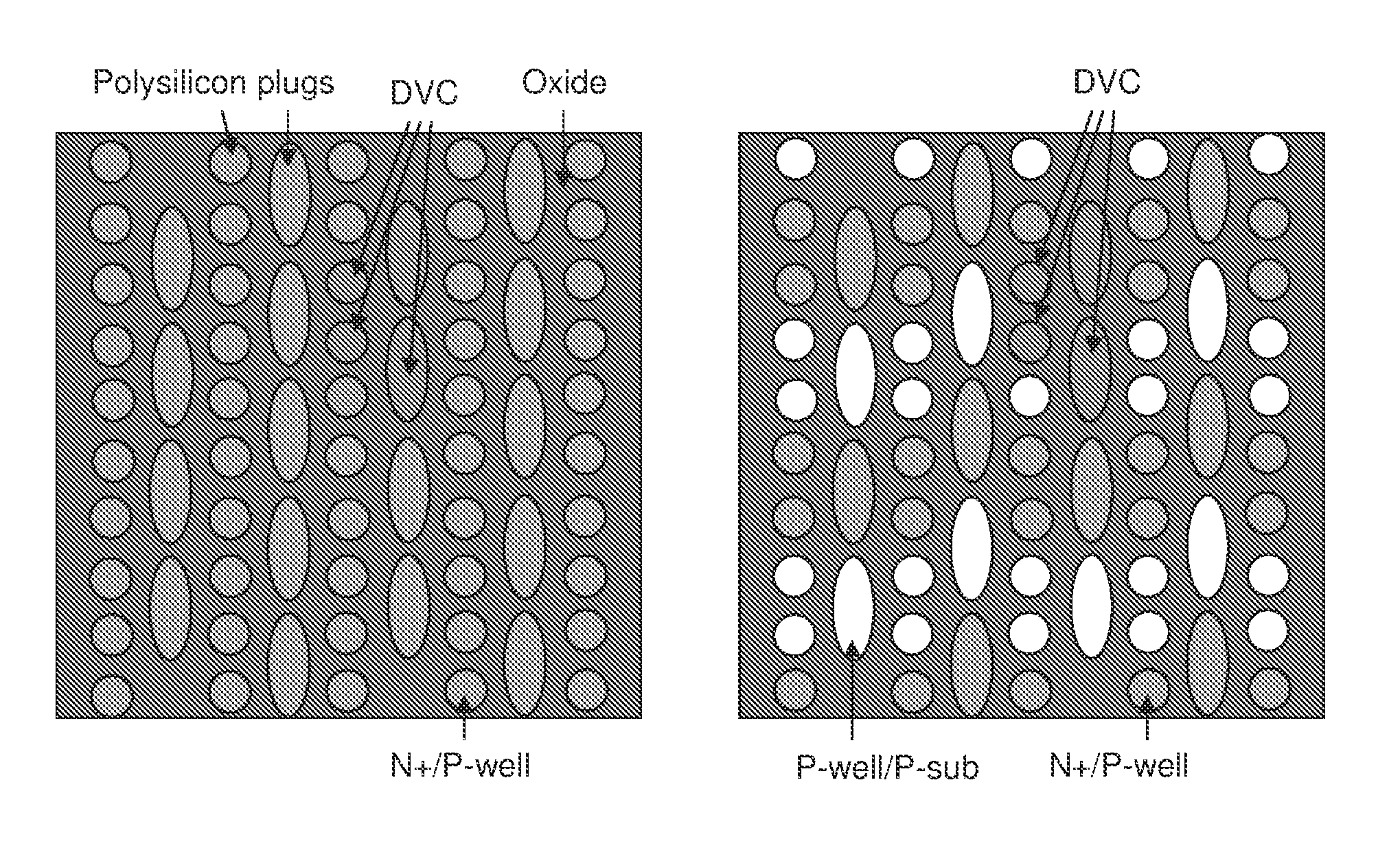
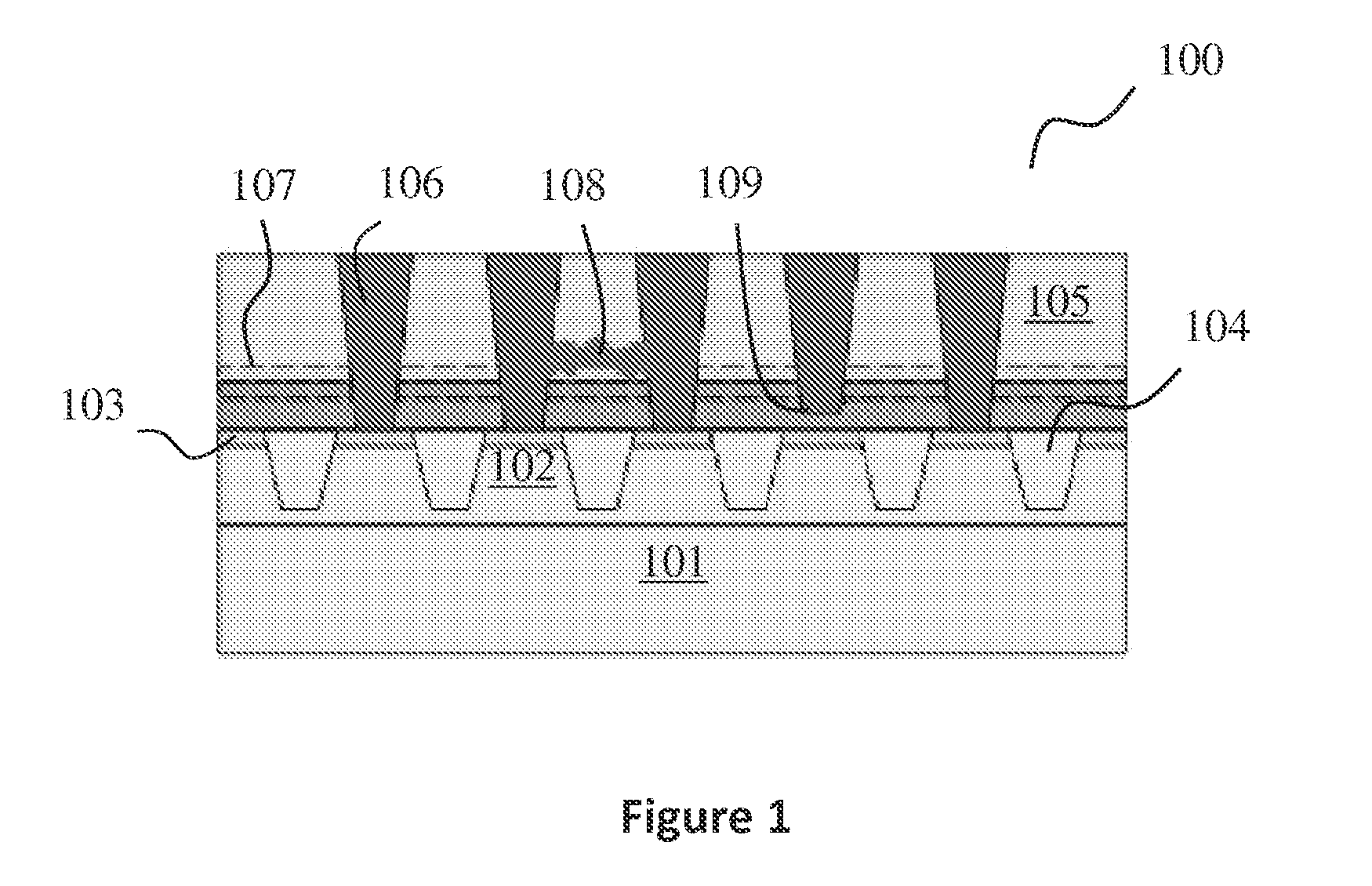
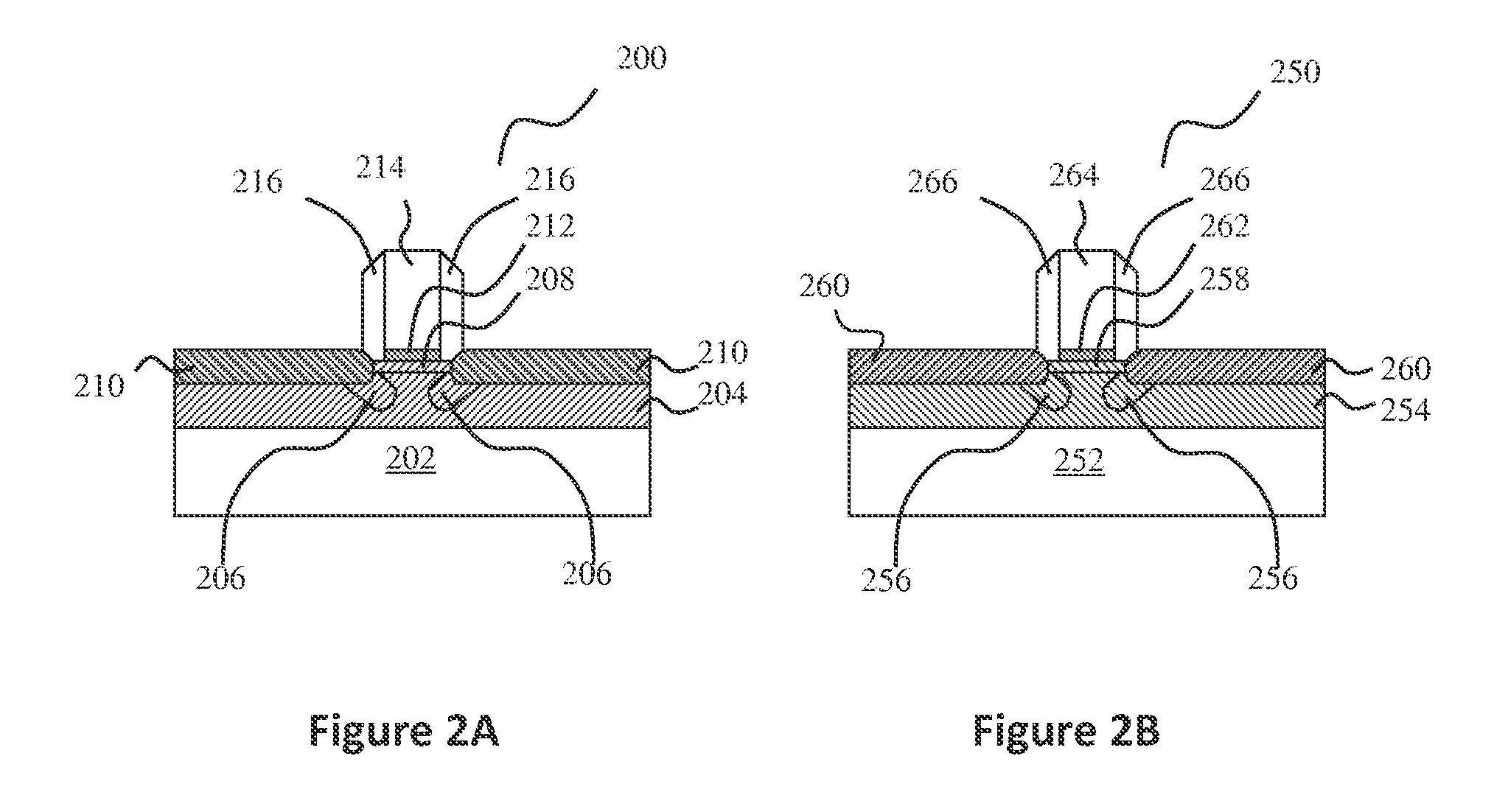
Structure and method for determining a defect in integrated circuit manufacturing process
ActiveUS8089297B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementIntegrated circuit manufacturingEngineering
The present invention discloses a structure and method for determining a defect in integrated circuit manufacturing process, wherein the structure comprises a plurality of normal active areas formed in a plurality of first arrays and a plurality of defective active areas formed in a plurality of second arrays. The first arrays and second arrays are interlaced, and the defect is determined by monitoring a voltage contrast from a charged particle microscope image of the active areas.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
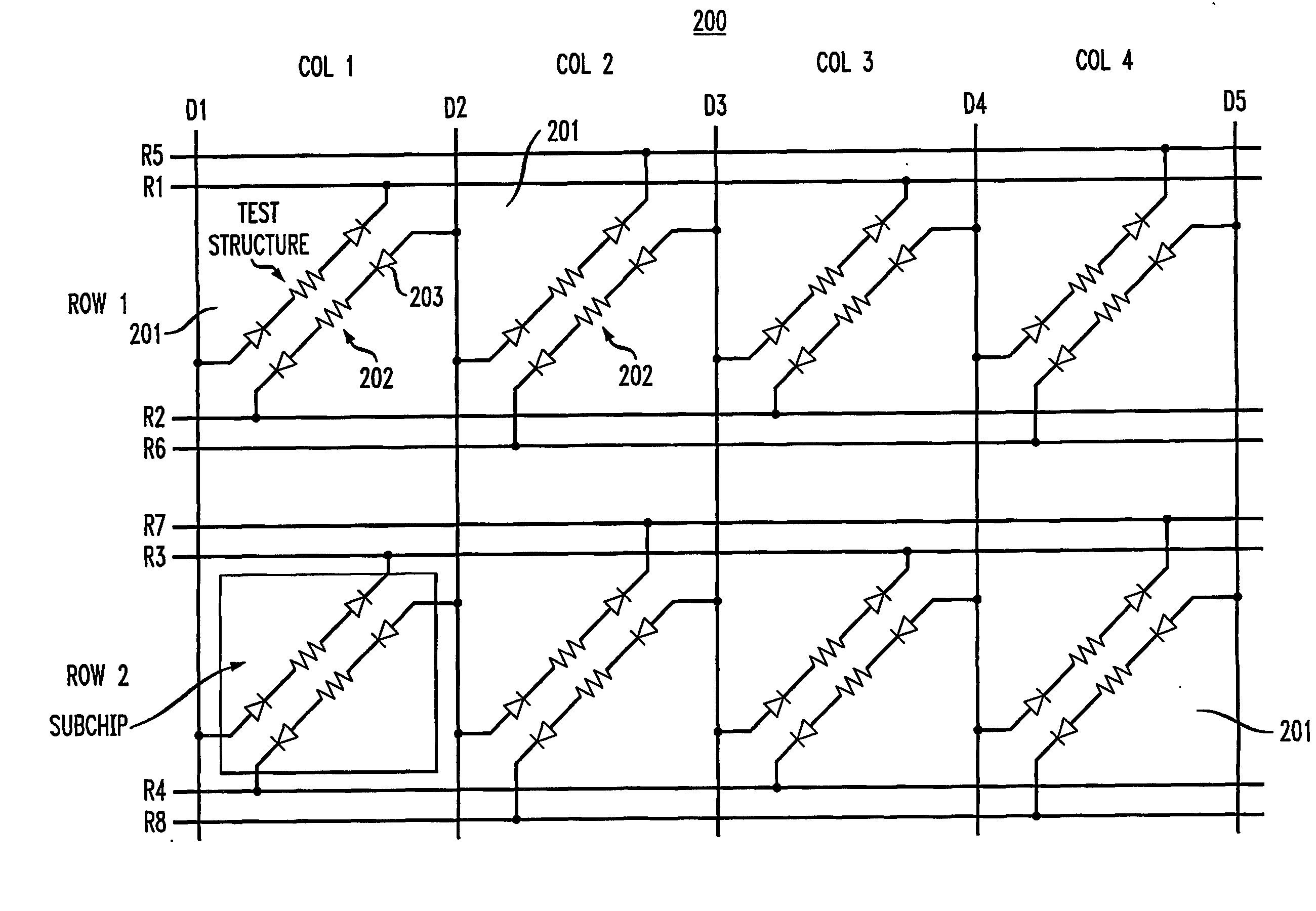
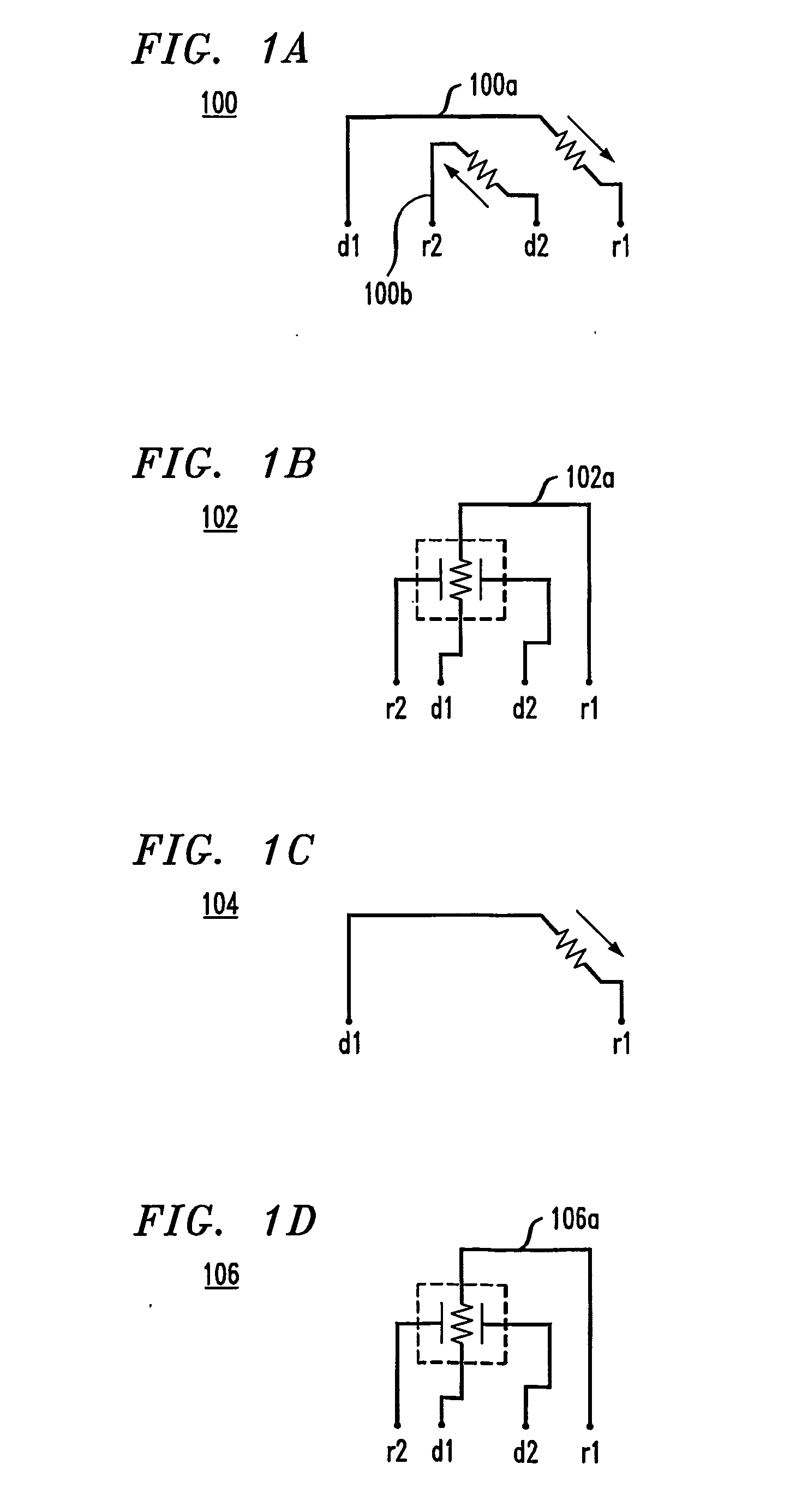
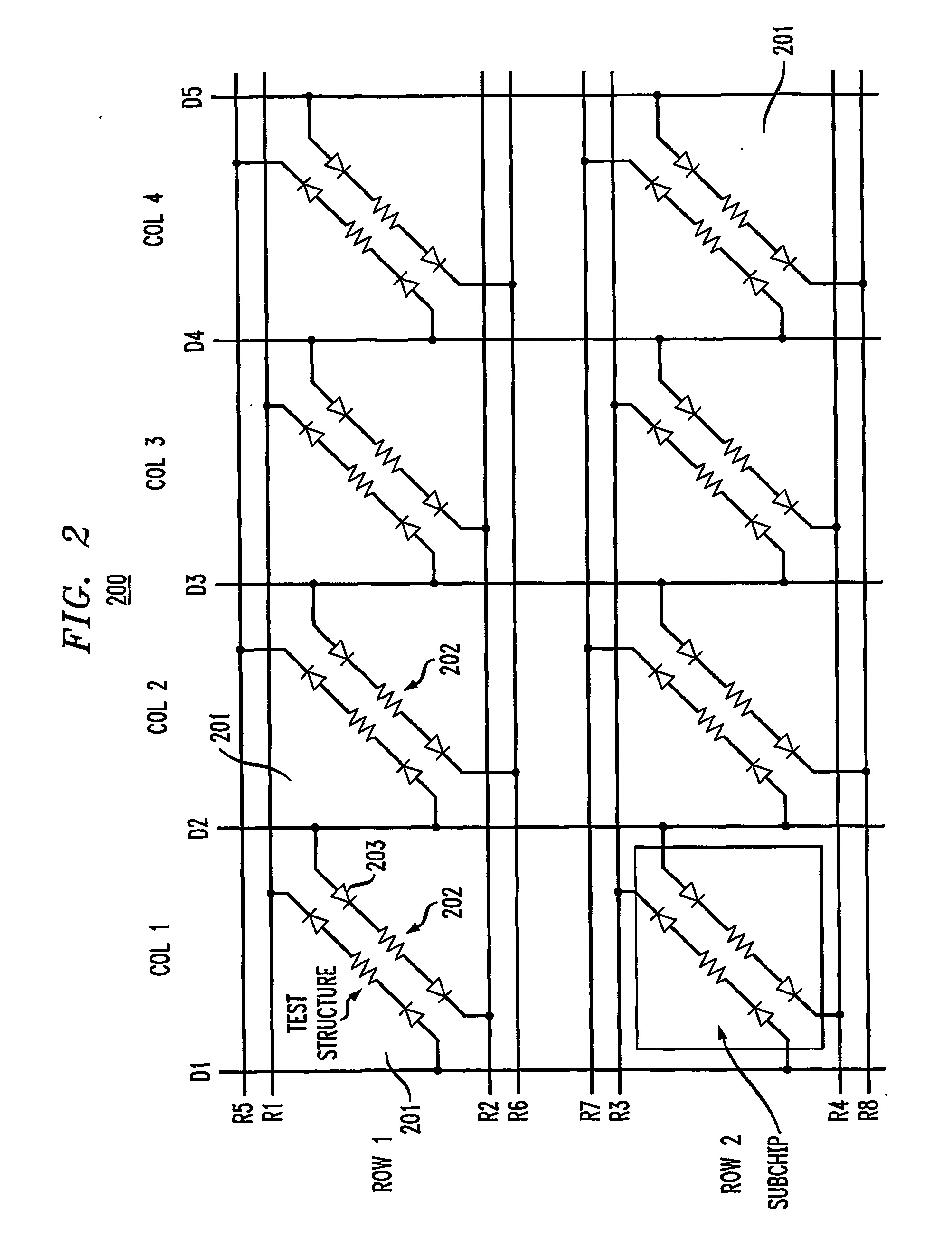
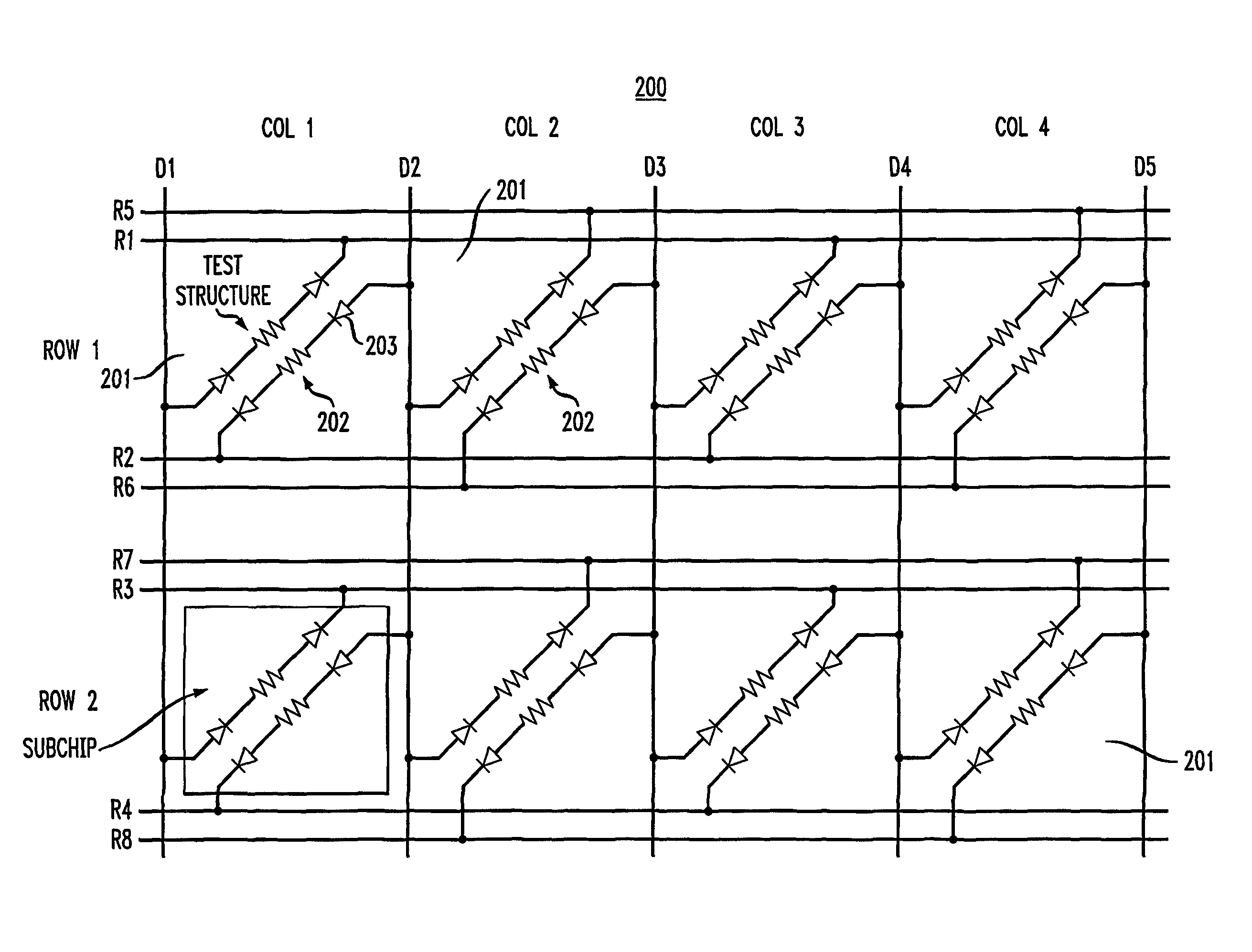
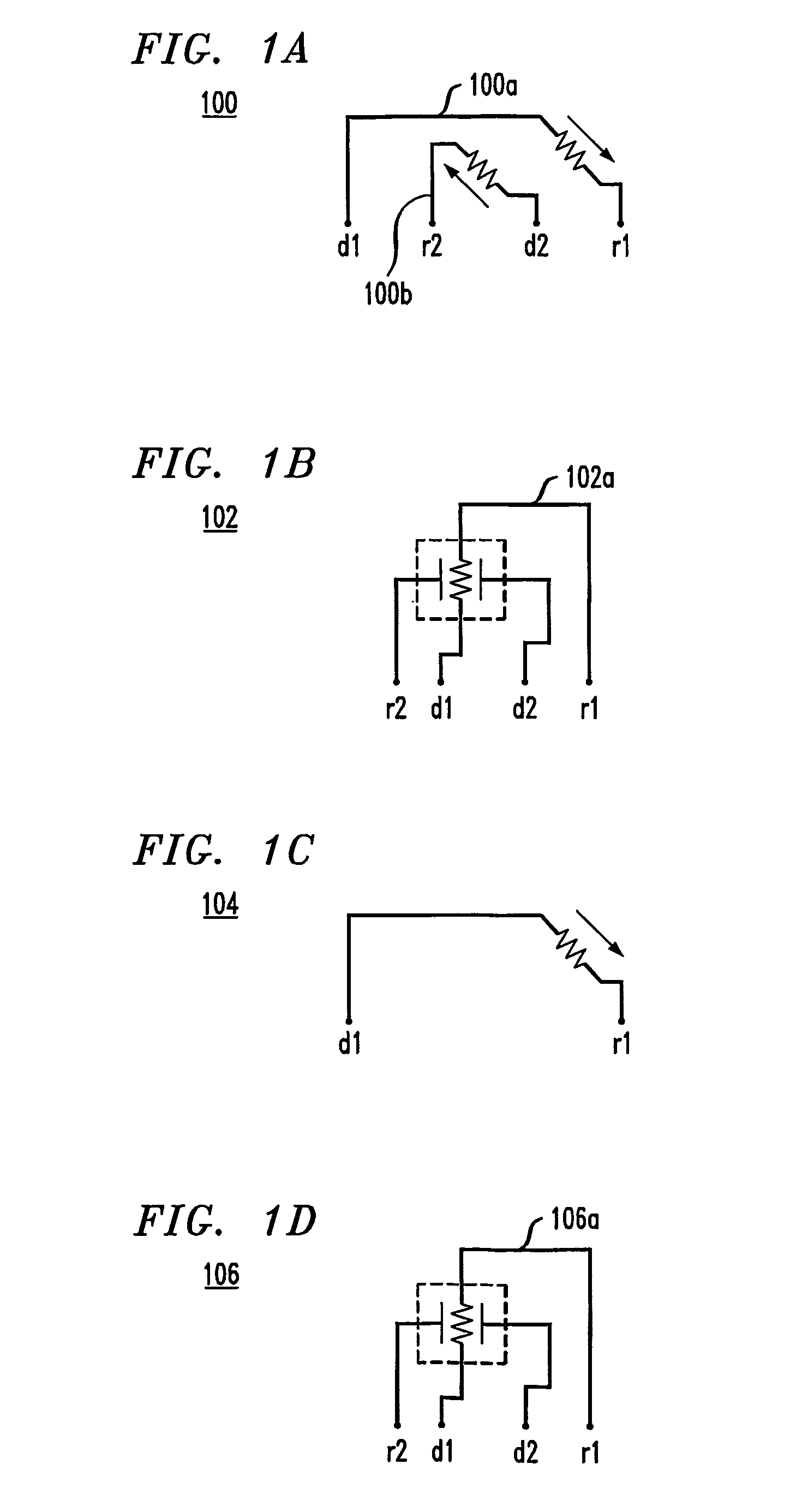
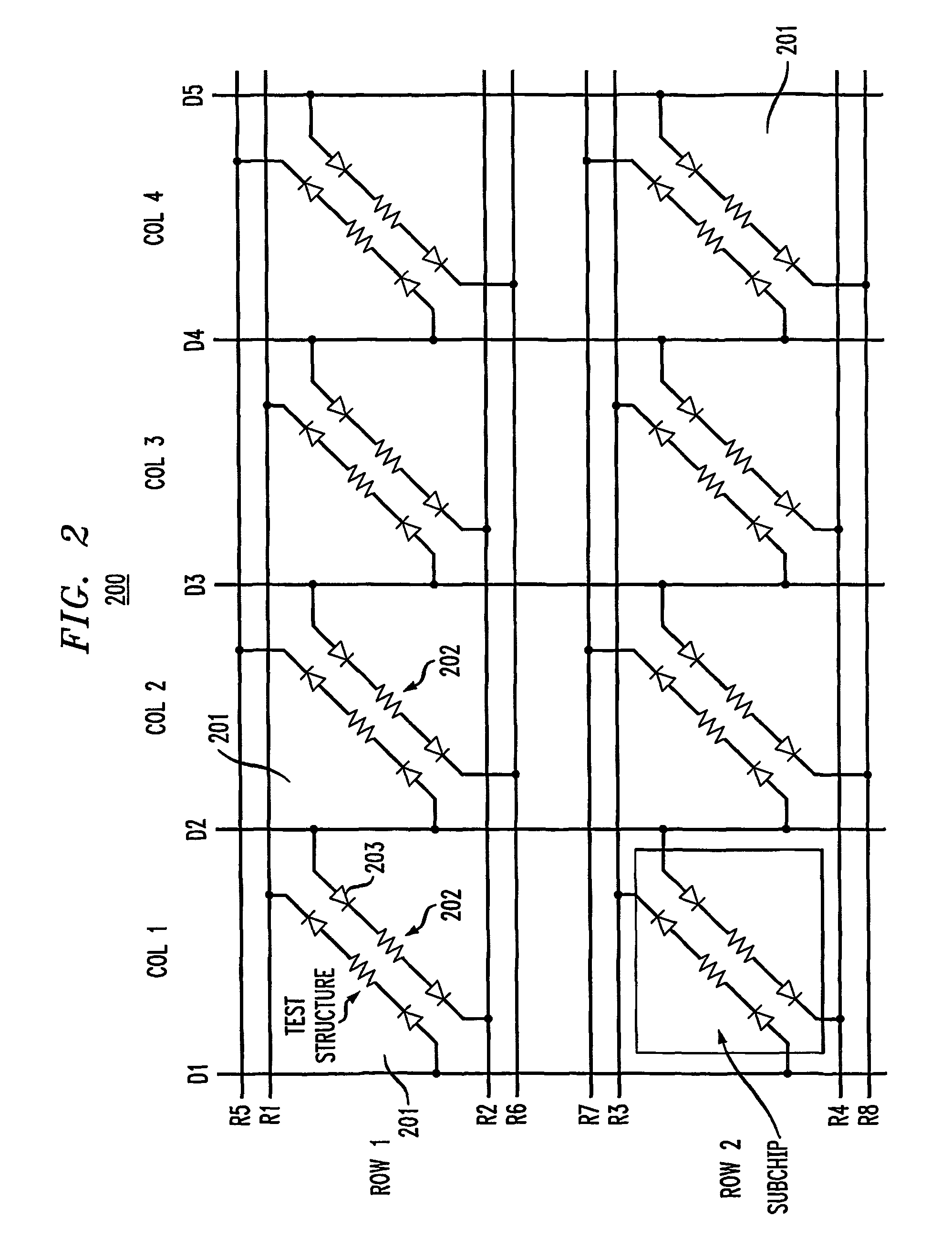
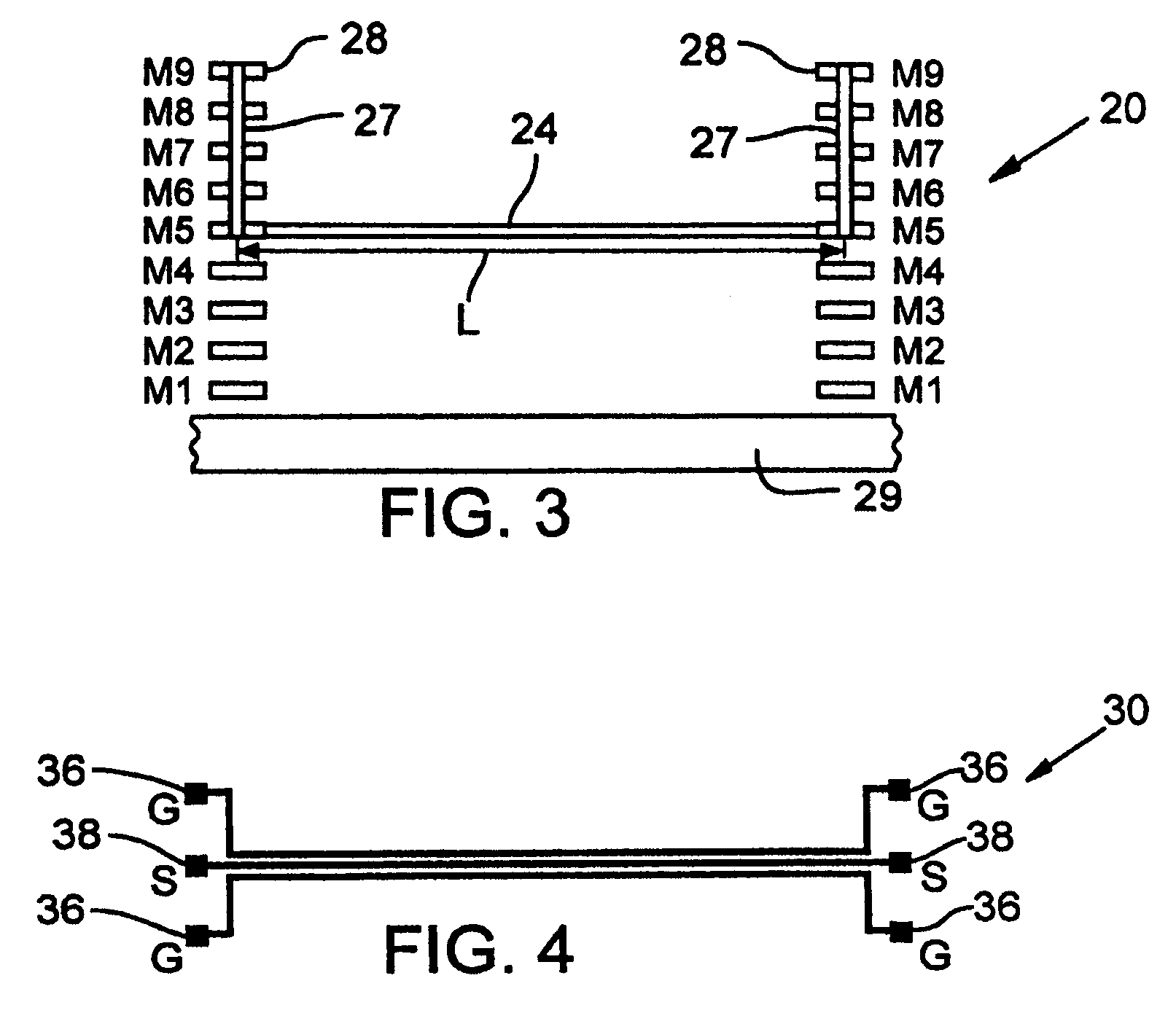
Method and configuration for connecting test structures or line arrays for monitoring integrated circuit manufacturing
ActiveUS20090037131A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceIntegrated circuit manufacturingEngineering
A test chip comprises at least one level having an array of regions. Each region is capable of including at least one test structure. At least some of the regions include respective test structures. The level has a plurality of driver lines that provide input signals to the test structures. The level has a plurality of receiver lines that receive output signals from the test structures. The level has a plurality of devices for controlling current flow. Each test structure is connected to at least one of the driver lines with a first one of the devices in between. Each test structure is connected to at least one of the receiver lines with a second one of the devices in between, so that each of the test structures can be individually addressed for testing using the driver lines and receiver lines.
Owner:PDF SOLUTIONS INC
Method and configuration for connecting test structures or line arrays for monitoring integrated circuit manufacturing
ActiveUS8178876B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsIntegrated circuit manufacturingEngineering
A test chip comprises at least one level having an array of regions. Each region is capable of including at least one test structure. At least some of the regions include respective test structures. The level has a plurality of driver lines that provide input signals to the test structures. The level has a plurality of receiver lines that receive output signals from the test structures. The level has a plurality of devices for controlling current flow. Each test structure is connected to at least one of the driver lines with a first one of the devices in between. Each test structure is connected to at least one of the receiver lines with a second one of the devices in between, so that each of the test structures can be individually addressed for testing using the driver lines and receiver lines.
Owner:PDF SOLUTIONS INC
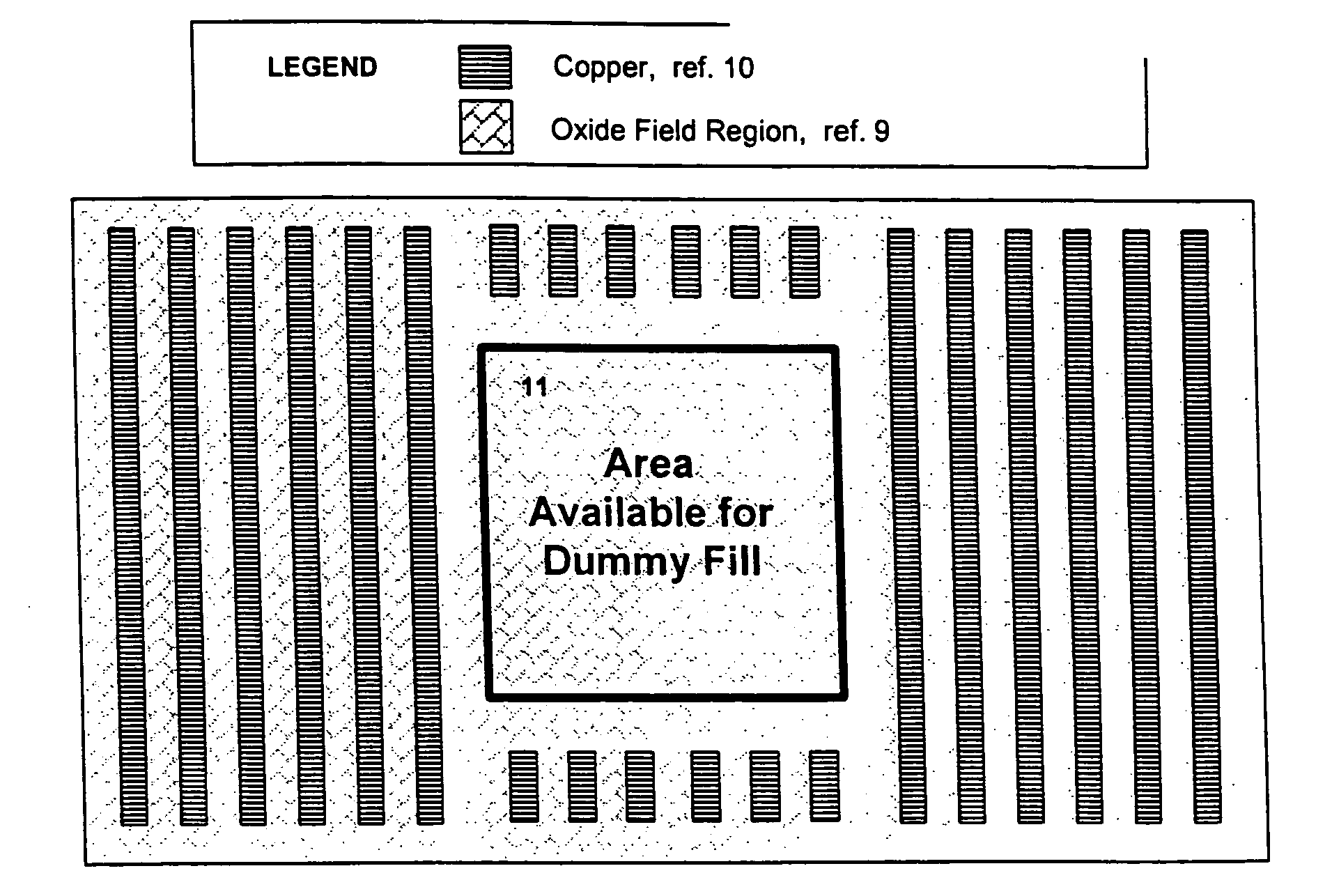
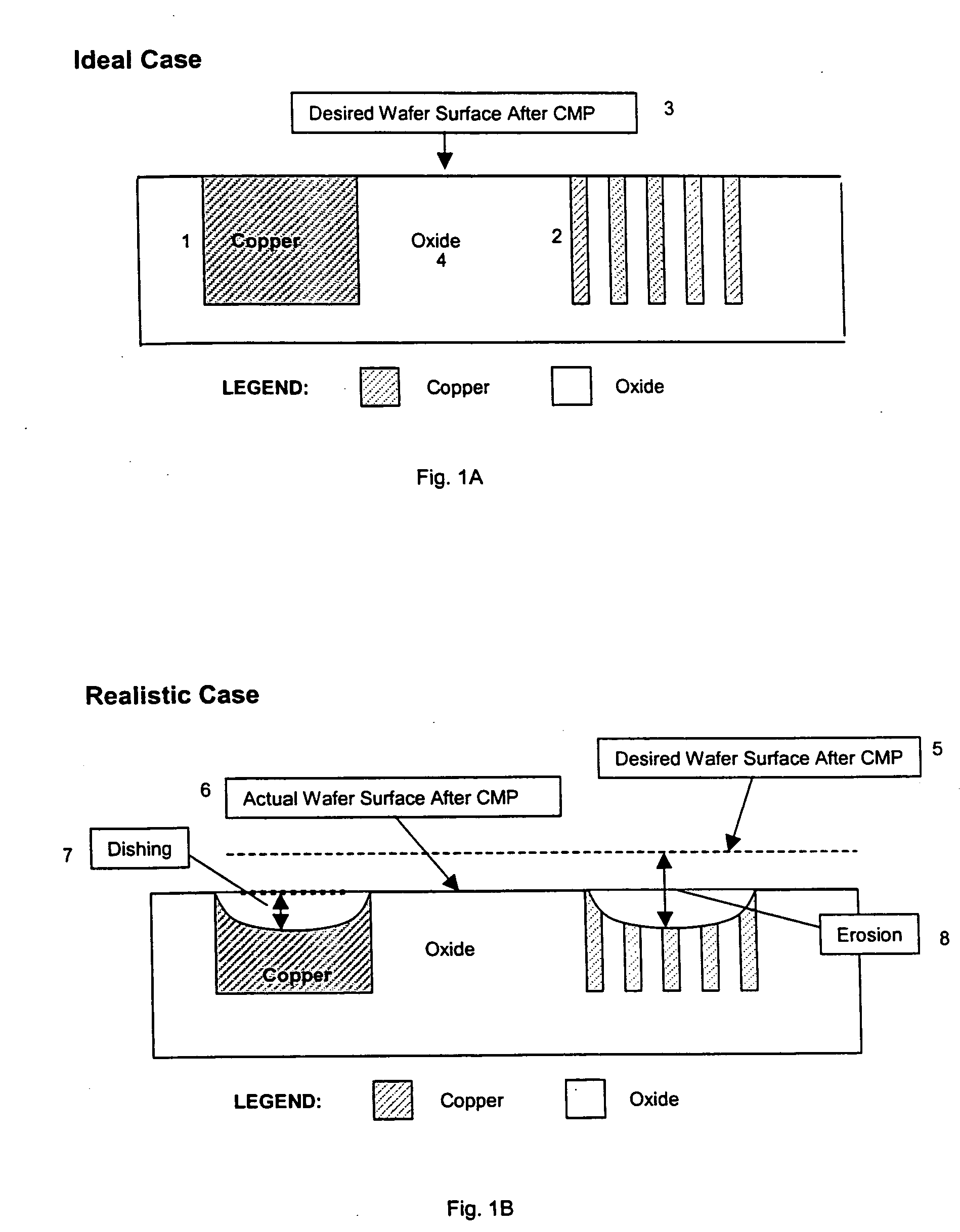
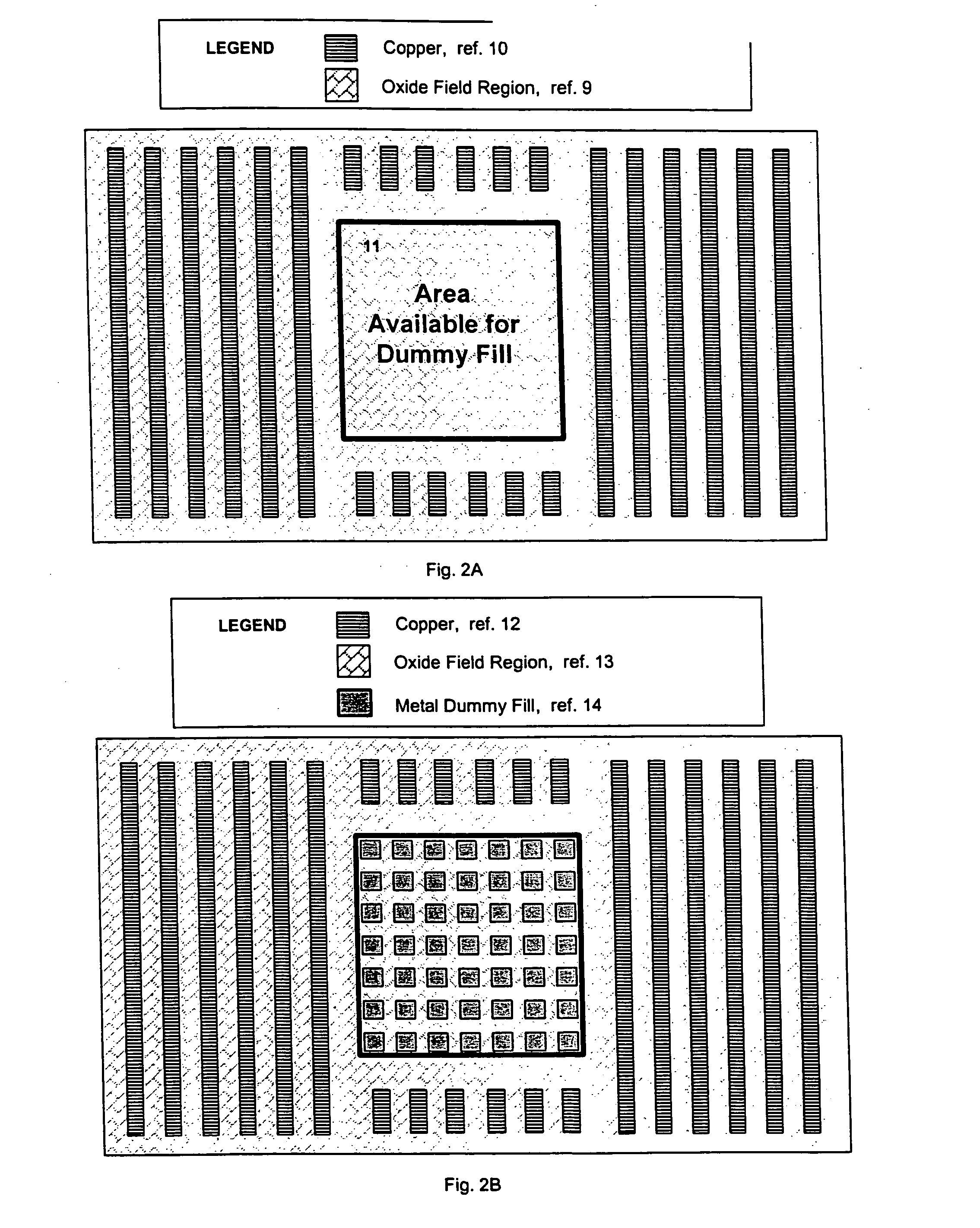
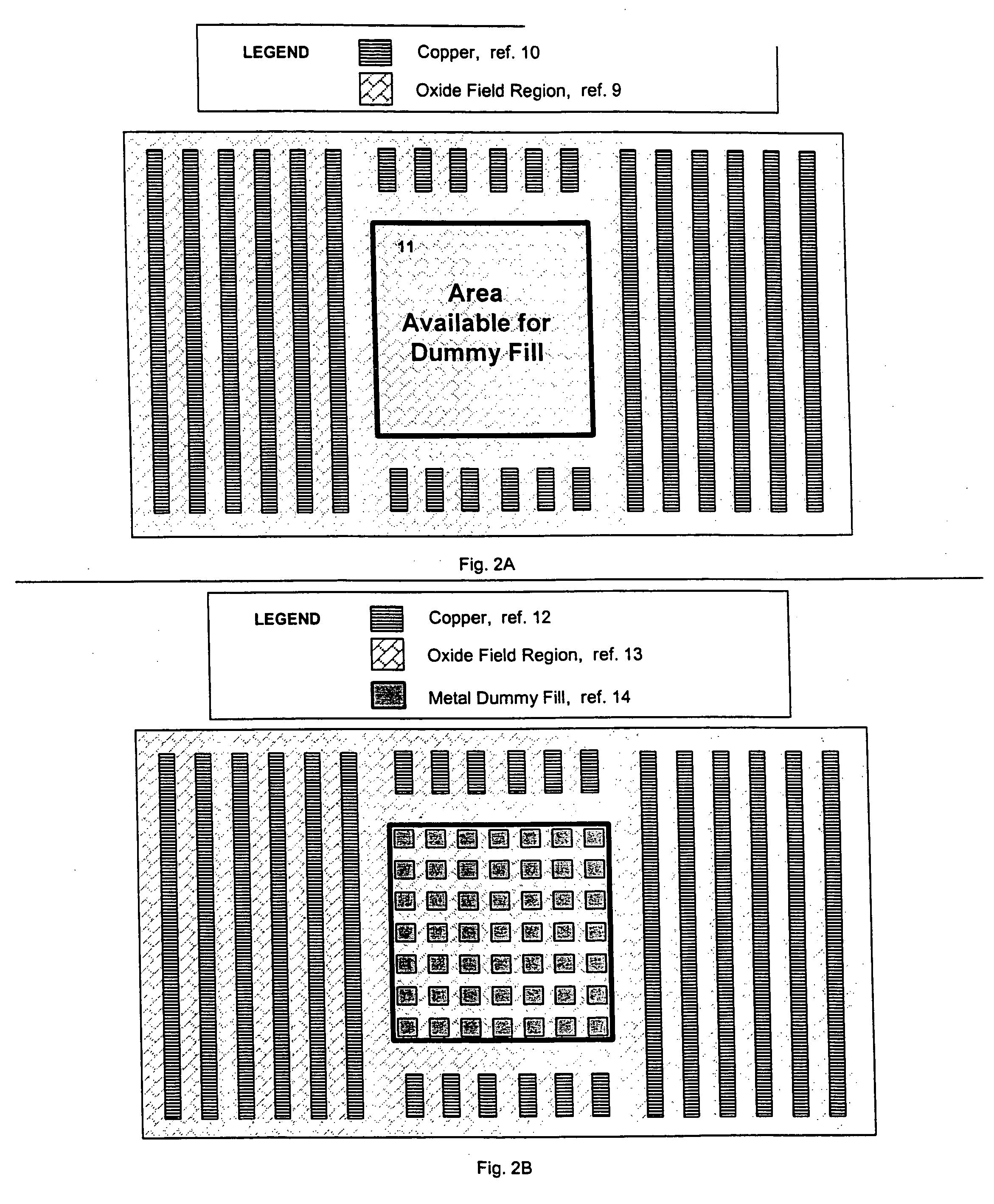
Dummy fill for integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050037522A1Minimize full-chip film thickness variationImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuit manufacturingIntegrated circuit layout
A method and system are described to reduce process variation as a result of the electrochemical deposition (ECD), also referred to as electrochemical plating (ECP), and chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) processing of films in integrated circuit manufacturing processes. The described methods use process variation and electrical impact to direct the insertion of dummy fill into an integrated circuit.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
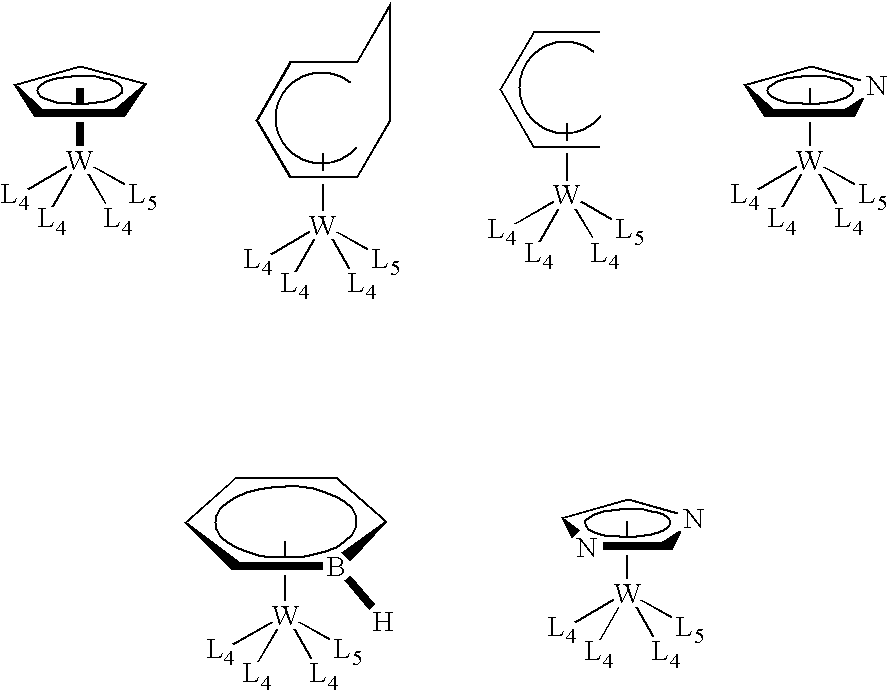
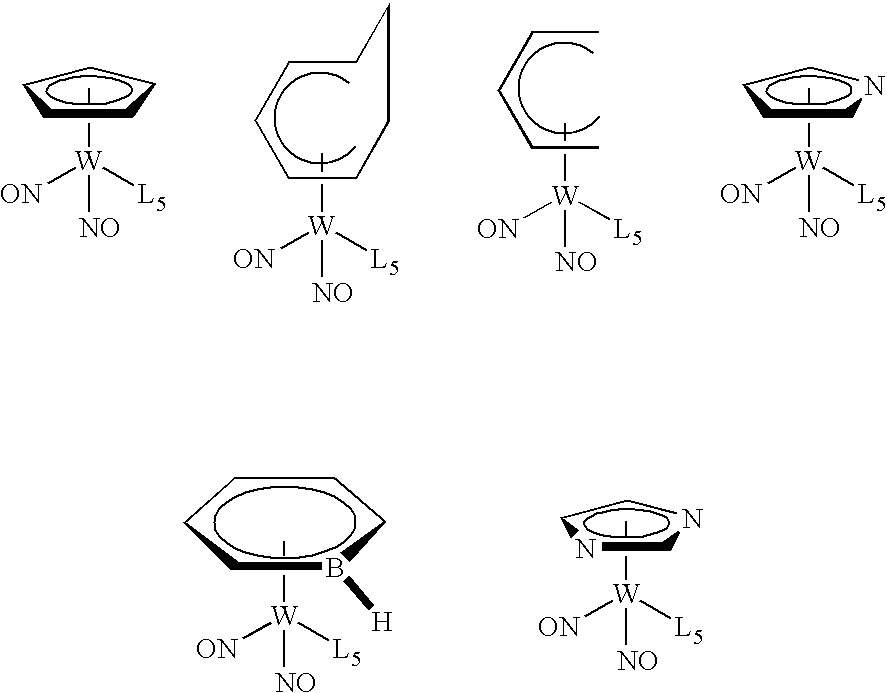
Organometallic compounds, processes for the preparation thereof and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20080081127A1Improve responseReduce usageGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuit manufacturingElectron donor
This invention relates to organometallic compounds represented by the formula (L1)yM(L2)z-y wherein M is a Group 5 metal or a Group 6 metal, L1 is a substituted or unsubstituted anionic 6 electron donor ligand, L2 is the same or different and is (i) a substituted or unsubstituted anionic 2 electron donor ligand, (ii) a substituted or unsubstituted cationic 2 electron donor ligand, or (iii) a substituted or unsubstituted neutral 2 electron donor ligand; y is an integer of 1, and z is the valence of M; and wherein the sum of the oxidation number of M and the electric charges of L1 and L2 is equal to 0.; a process for producing the organometallic compounds; and a method for depositing a metal and / or metal carbide / nitride layer, e.g., a tungsten, tungsten nitride, tungsten carbide, or tungsten carbonitride layer, on a substrate by the thermal or plasma enhanced dissociation of the organometallic precursor compounds, e.g., by CVD or ALD techniques. The metal and / or metal carbide layer is useful as a liner or barrier layer for conducting metals and high dielectric constant materials in integrated circuit manufacturing.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Dummy fill for integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050051809A1Speed up the processHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuit manufacturingIntegrated circuit layout
A method and system are described to reduce process variation as a result of the electrochemical deposition (ECD), also referred to as electrochemical plating (ECP), and chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) processing of films in integrated circuit manufacturing processes. The described methods use process variation and electrical impact to direct the insertion of dummy fill into an integrated circuit.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
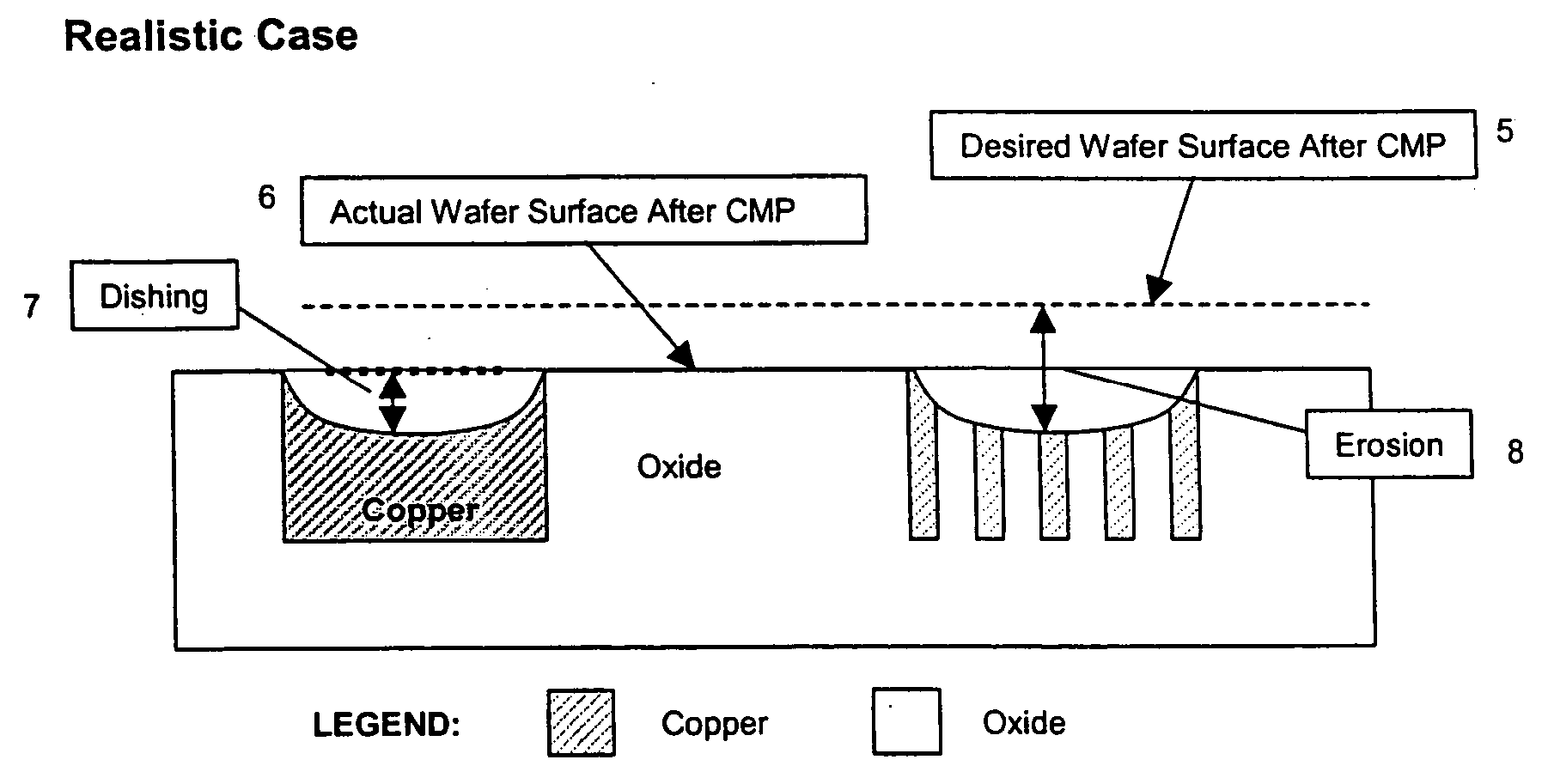
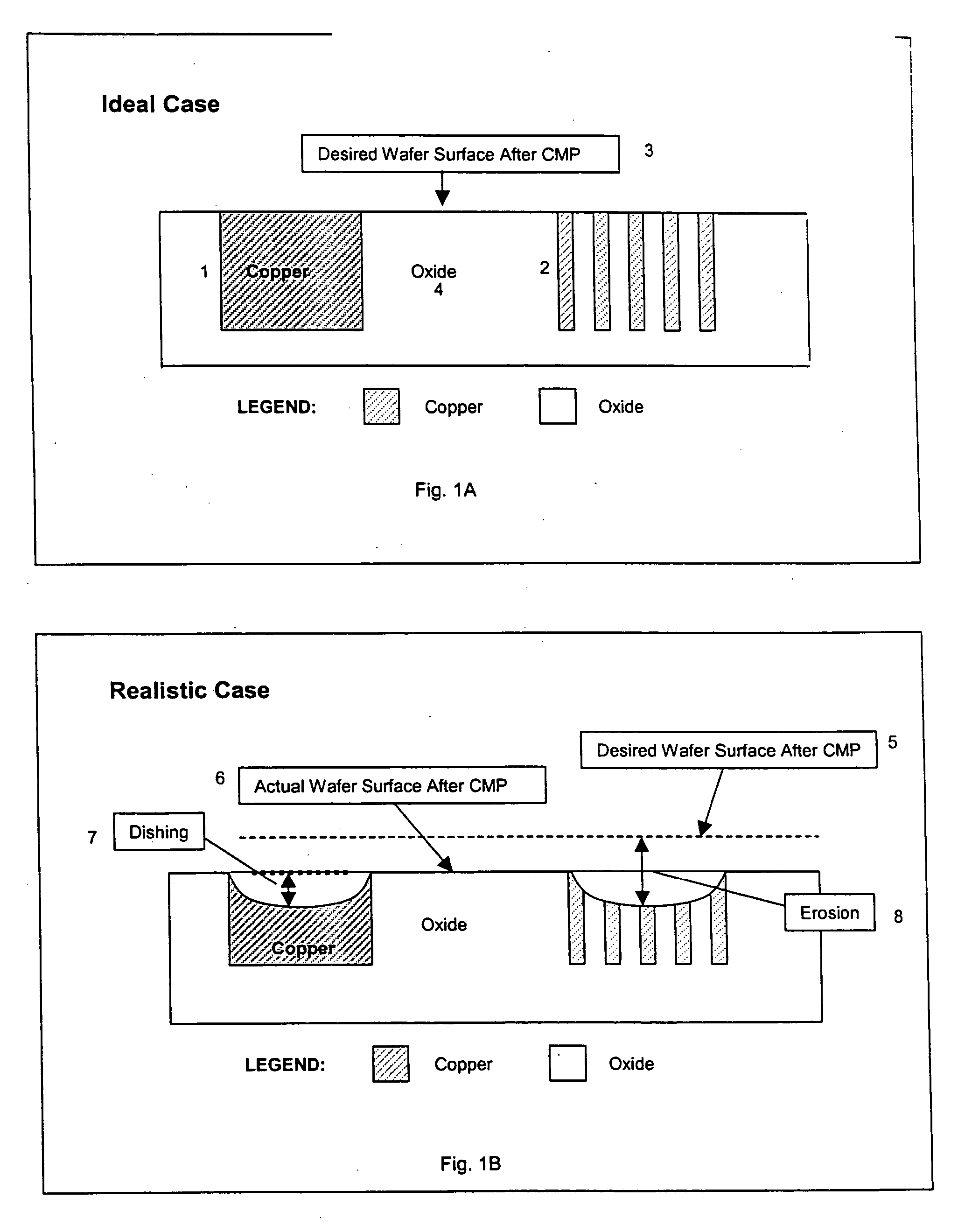
Thermal spray coatings for semiconductor applications
InactiveUS20100272982A1Erosion is goodImproved corrosion resistant coatingLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingThermal sprayingIntegrated circuit manufacturing
This invention relates to thermal spray coatings on a metal or non-metal substrate. The thermal spray coating comprises a partially or fully stabilized ceramic coating, e.g., yttria stabilized zirconia coating, and has sufficiently high thermodynamic phase stability to provide corrosion and / or erosion resistance to the substrate. This invention also relates to methods of protecting metal and non-metal substrates by applying the thermal spray coatings. The coatings are useful, for example, in the protection of integrated circuit manufacturing equipment, internal chamber components, and electrostatic chuck manufacture.
Owner:PRAXAIR ST TECH INC
Composition and process for ashless removal of post-etch photoresist and/or bottom anti-reflective material on a substrate
InactiveUS20060063687A1Non-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent mixture composition preparationDielectricIntegrated circuit manufacturing
An aqueous-based composition and process for removing photoresist and / or bottom anti-reflective coating (BARC) material from a substrate having such material(s) thereon. The aqueous-based composition includes a quaternary ammonium base, at least one co-solvent, and optionally a chelator. The composition achieves high-efficiency removal of photoresist and / or BARC material in the manufacture of integrated circuitry without adverse effect on metal species on the substrate, such as copper, and without damage to SiOC-based dielectric materials employed in the semiconductor architecture.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
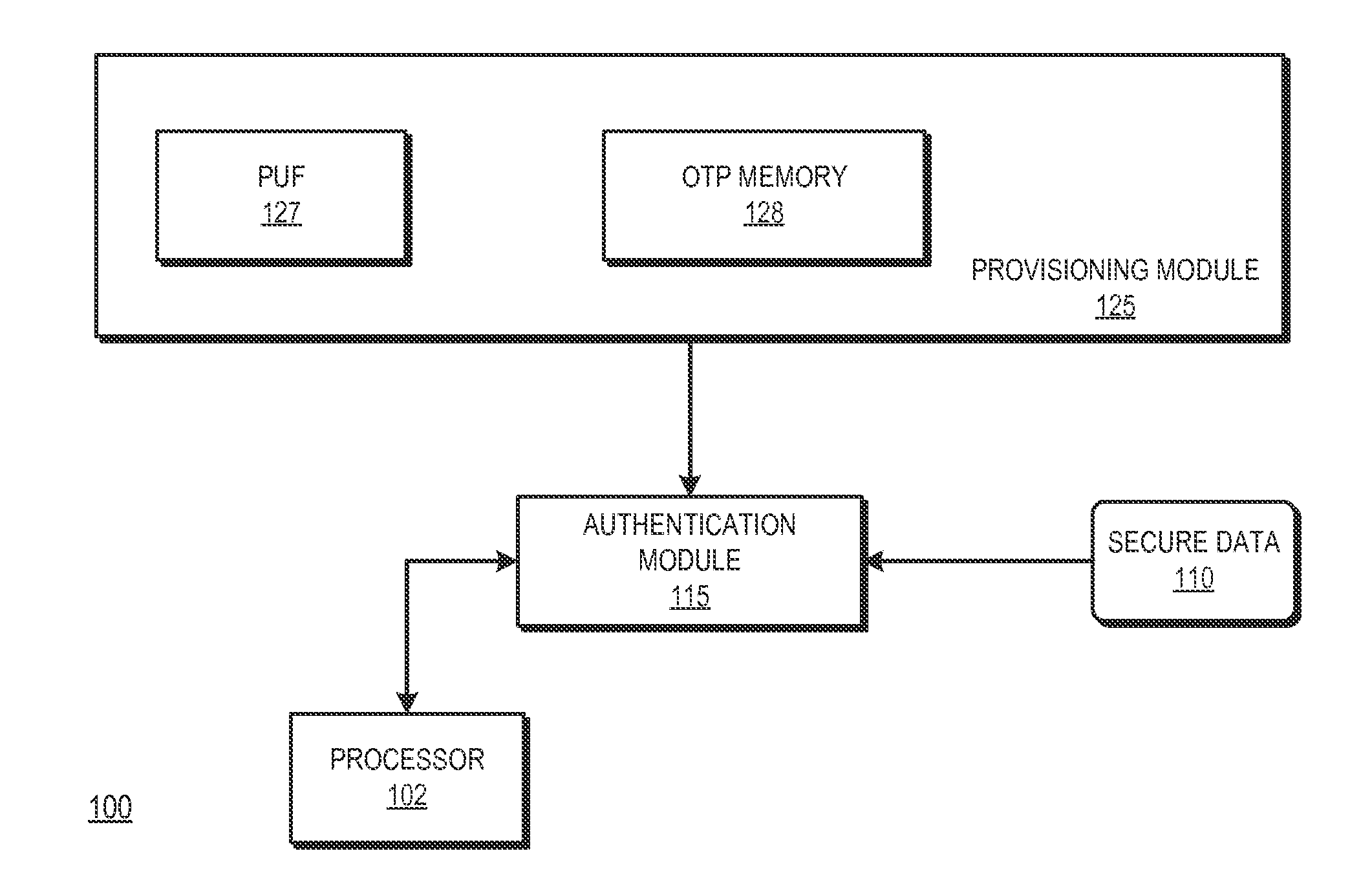
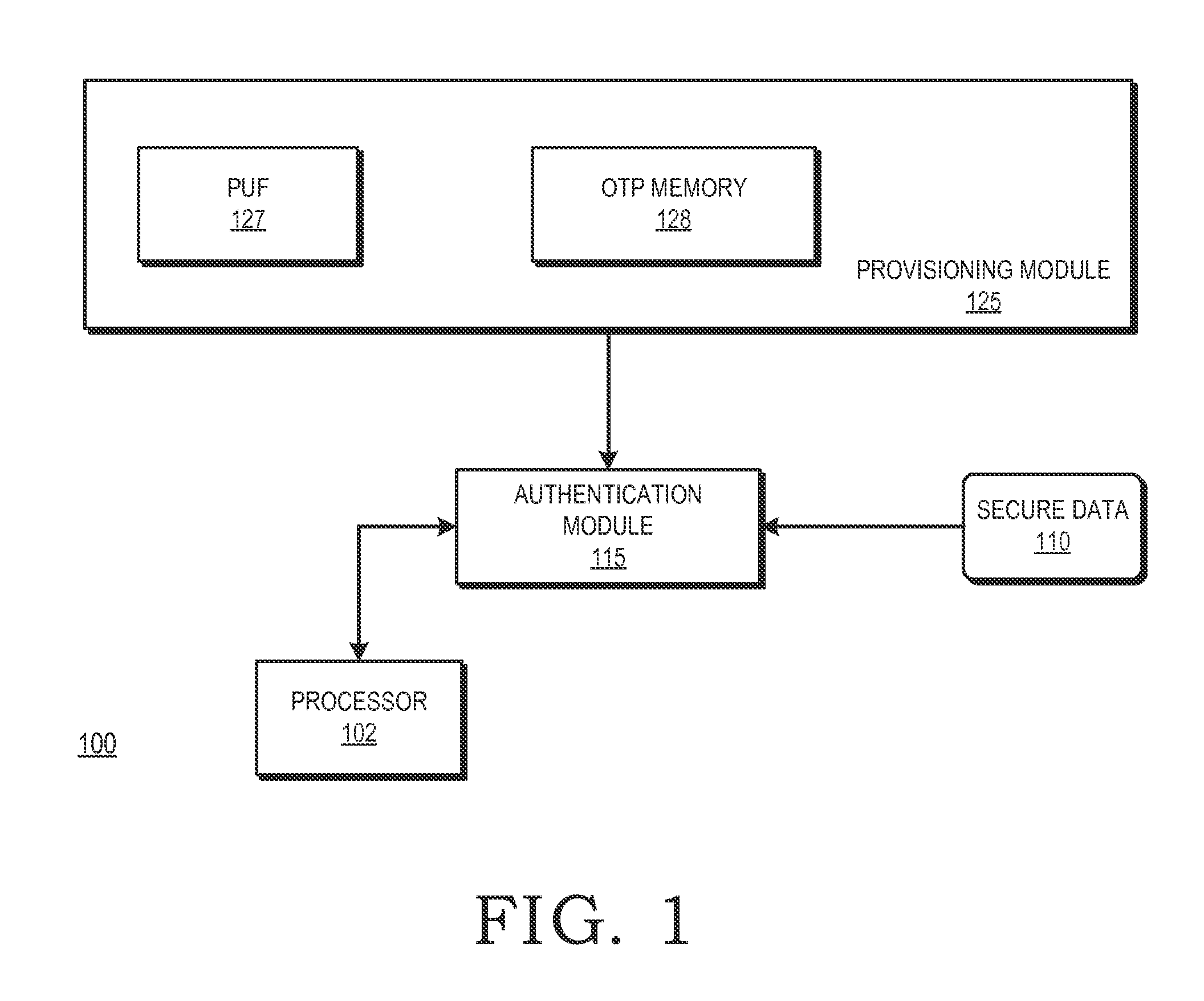
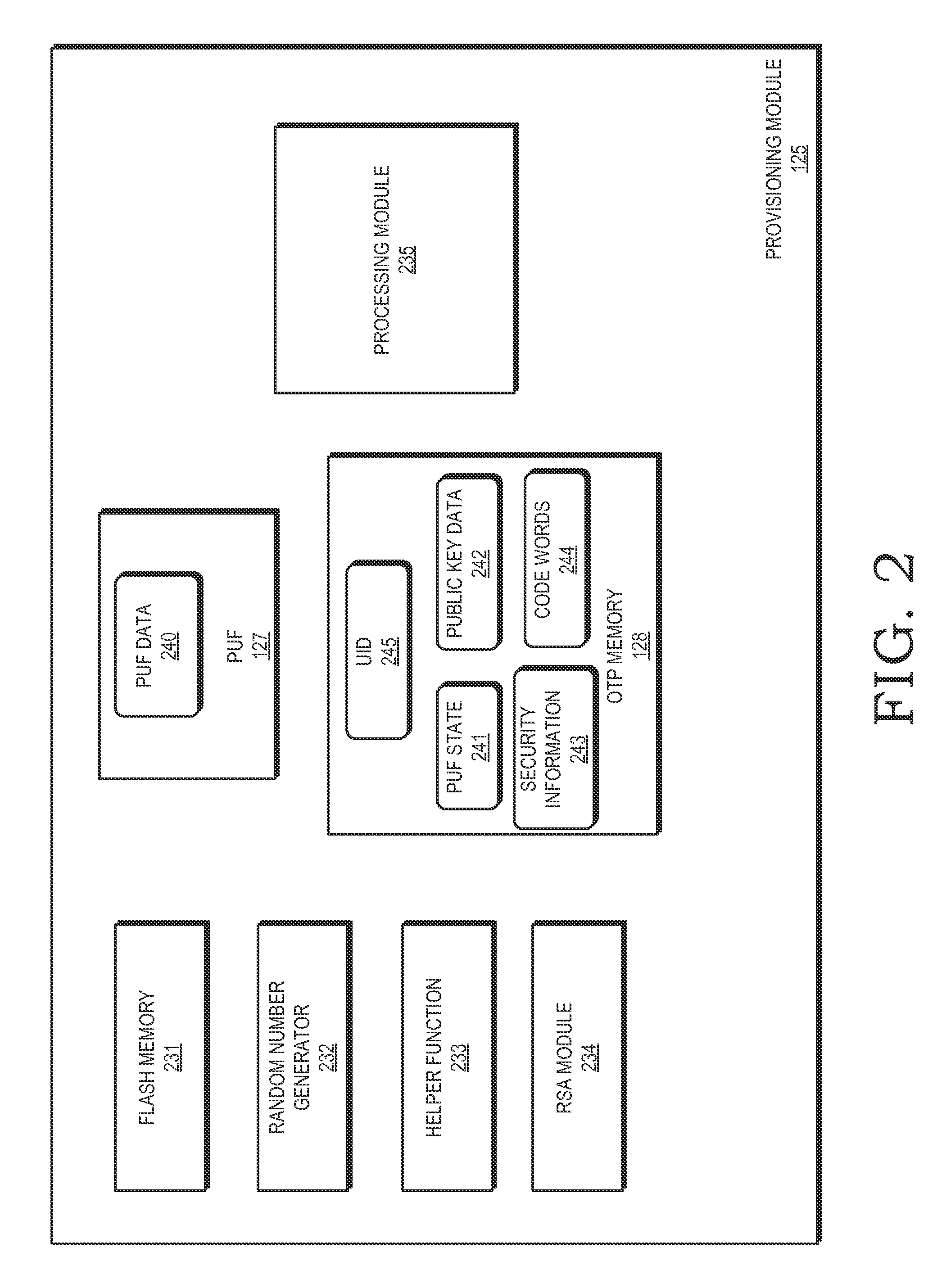
Integrated circuit provisioning using physical unclonable function
InactiveUS20150143130A1Volume/mass flow measurementUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareIntegrated circuit manufacturing
A one-time programmable (OTP) memory of an integrated circuit is provisioned based on identifier data generated by a physical unclonable function (PUF) of the integrated circuit. The identifier data is used as part of cryptographic operations to secure provisioning of security information at an OTP memory of at the integrated circuit. Because of the physical characteristics of the PUF and its incorporation in the integrated circuit, the identifier information is unique to the integrated circuit. Accordingly, the provisioned security information is also unique to the integrated circuit. The OTP memory can therefore be securely provisioned at later stages of the integrated circuit manufacturing and configuration process, such as after the integrated circuit has been packaged or attached to a printed circuit board.
Owner:VIXS SYSTEMS INC
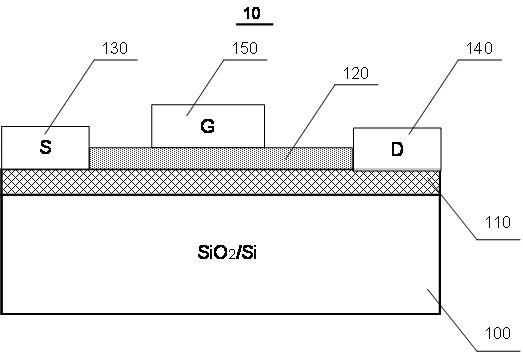
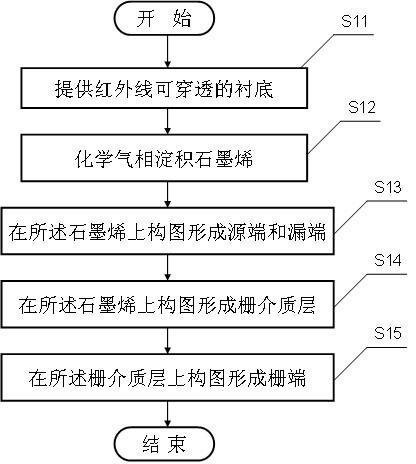
Preparation method of graphene field effect transistor
InactiveCN102184858AHigh sensitivityReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingInfraredIntegrated circuit manufacturing
The invention belongs to the technical field of field effect transistors, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a graphene field effect transistor. The method comprises the steps of: providing a substrate through which infrared rays can penetrate; carrying out chemical vapor deposition on graphene to form a graphene channel layer; constructing a pattern on the graphene channel layer to form a grid medium layer; and constructing a pattern on the grid medium layer to form a grid end, wherein the graphene channel layer generates a photoconductive effect operatively under the radiation of the infrared rays so as to lead the electric characteristic of the graphene field effect transistor to be changed. In the preparation method, the technique is simple in process and is compatible with an integrated circuit manufacturing technique, the prepared field effect transistor has the advantages that the sensitivity is high, the power consumption is low, the infrared detection function is ultra-light and ultra-stable, the infrared absorbing belt is wide and the adjustability can be achieved according to the practical application needs.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
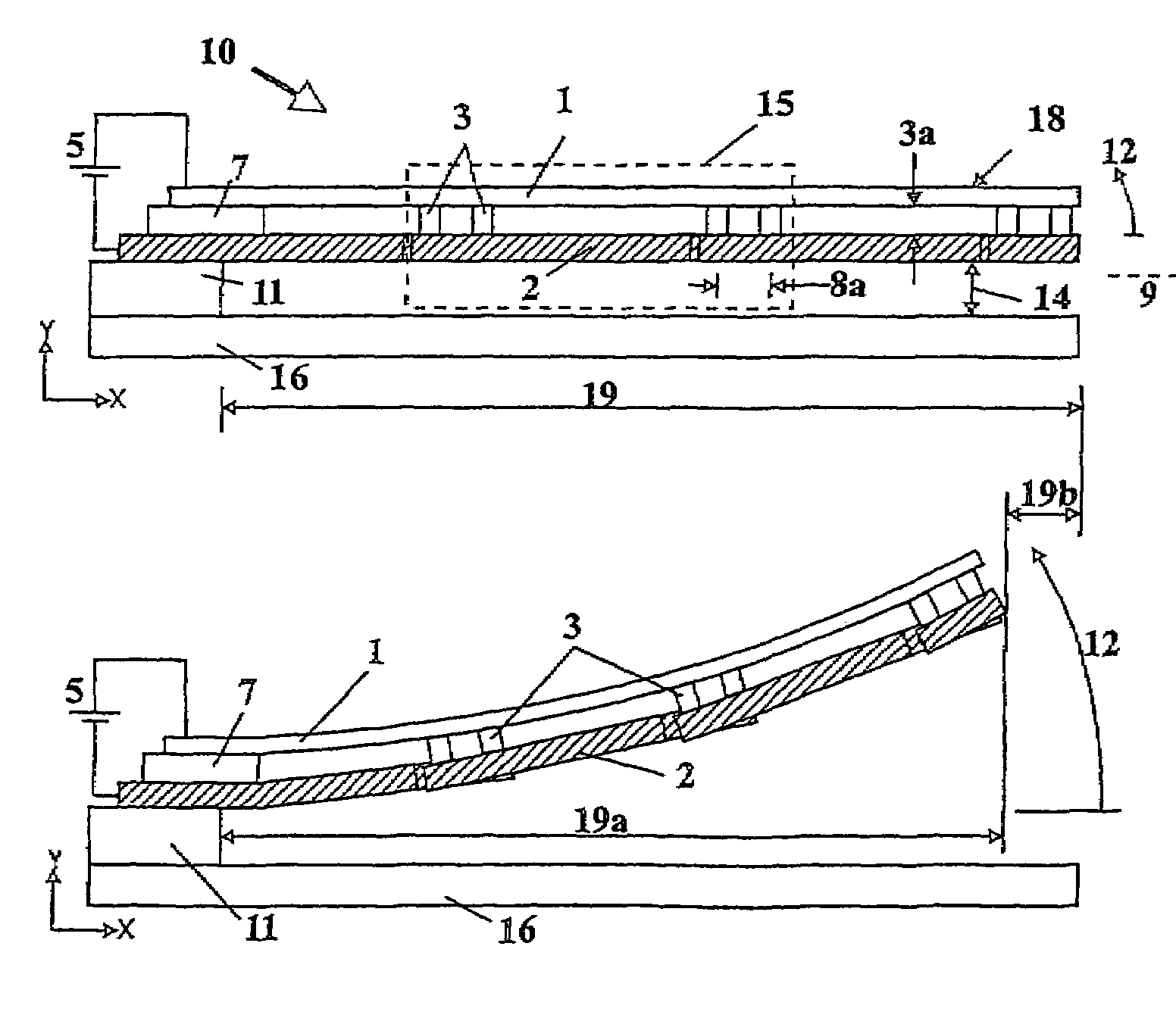
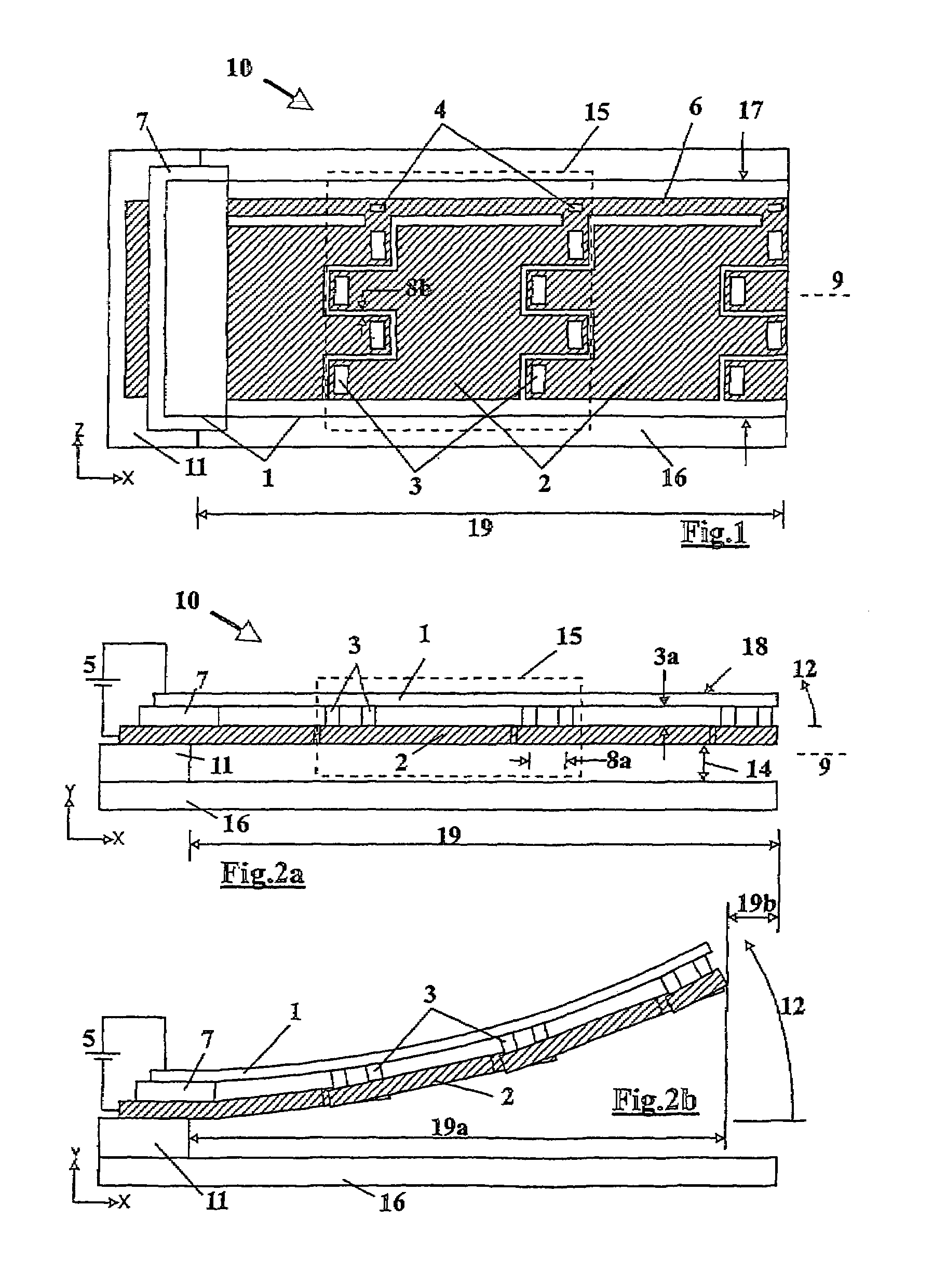
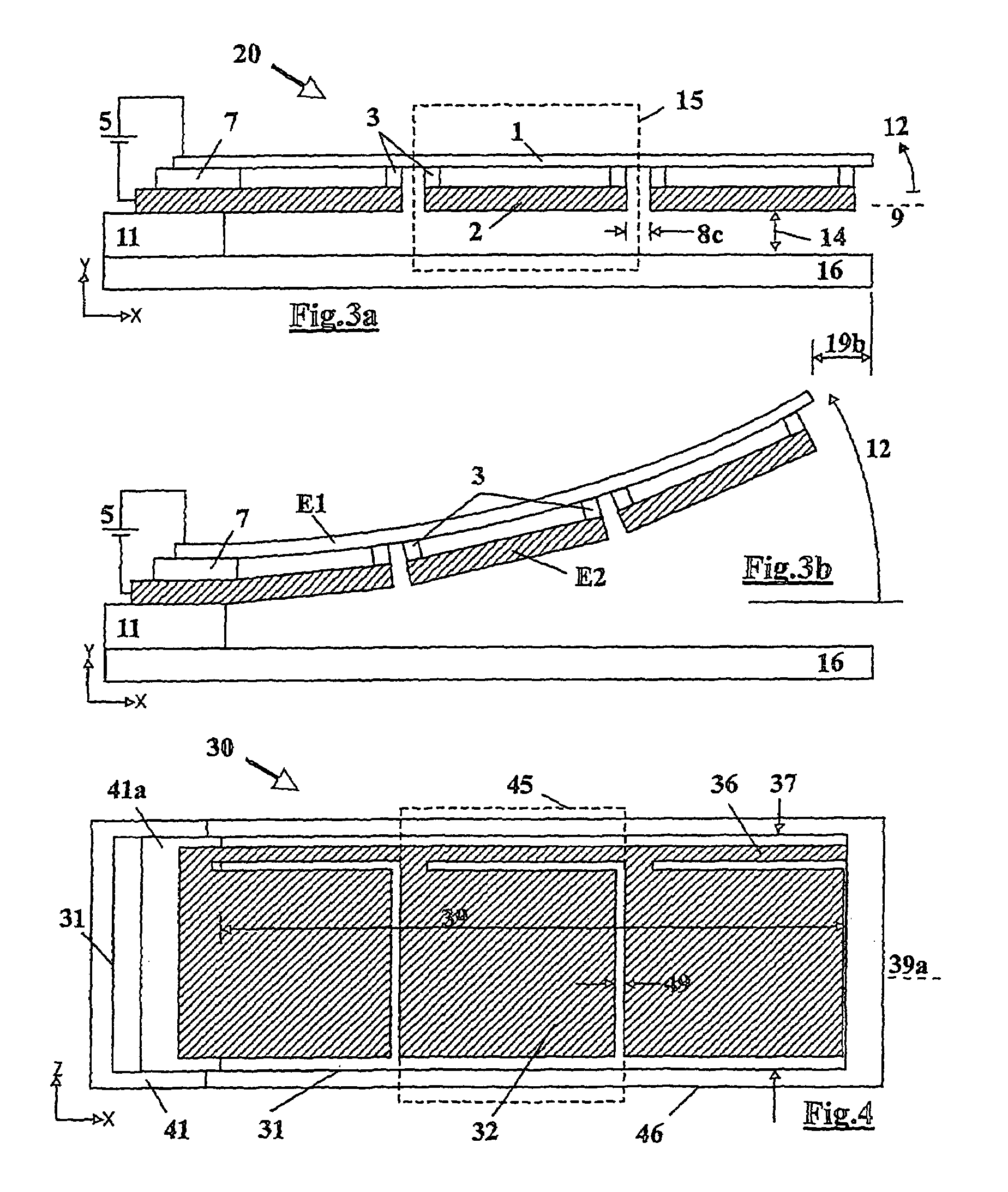
Electrostatic device
InactiveUS7196599B2Improve voltage characteristicsImprove balanceCapacitor with electrode distance variationElectrostatic motorsIntegrated circuit manufacturingEngineering
An electrostatic device (10) includes a first flexible electrode (1) on which a plurality of second electrodes (2) are mounted so as to move with the first electrode (1). Upon the application of an electrical charge, the or each second electrode (2) causes deflection of the first electrode (1) which deflection is enhanced by the movement of the second electrode therewith. A variety of different designs of the device are possible to provide movement of the first electrode in a plurality of directions and also different types of in and out of plane movement, including rotation and twisting. The structure enables the device to operate at voltage levels compatible with integrated circuits and for the device to be manufactured using integrated circuit manufacturing techniques.
Owner:DABBAJ RAD H
System and method for removal of photoresist in transistor fabrication for integrated circuit manufacturing
In a technique for fabricating an integrated circuit to include an active device structure which supports an electrical interconnect structure, a photoresist layer is used prior to forming an electrical interconnect structure on the active device structure. The photoresist and related residues are removed by exposing the photoresist and exposed regions of the active device structure to one or more reactive species that are generated using a gas mixture including hydrogen gas, as a predominant source of the reactive species, in a plasma source such that the photoresist and residues are continuously exposed to hydrogen-based reactive species. An associated system architecture is described which provides for a substantial flow of hydrogen gas in the process chamber.
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
Process for forming features of 50 nm or less half-pitch with chemically amplified resist imaging
InactiveUS20040265747A1High resolutionElimination of blurSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntegrated circuit manufacturingActivation energy
Lithographic imaging of 50 nm (or less) half-pitch features in chemically amplified resists (commonly used in the manufacture of integrated circuits) is enabled by the use of reduced temperature post-exposure processing and low activation energy chemically amplified resists. The post-exposure processing preferably involves ambient to moderately elevated temperature and the presence of a deprotection reaction-dependent co-reactant (e.g., water).
Owner:IBM CORP
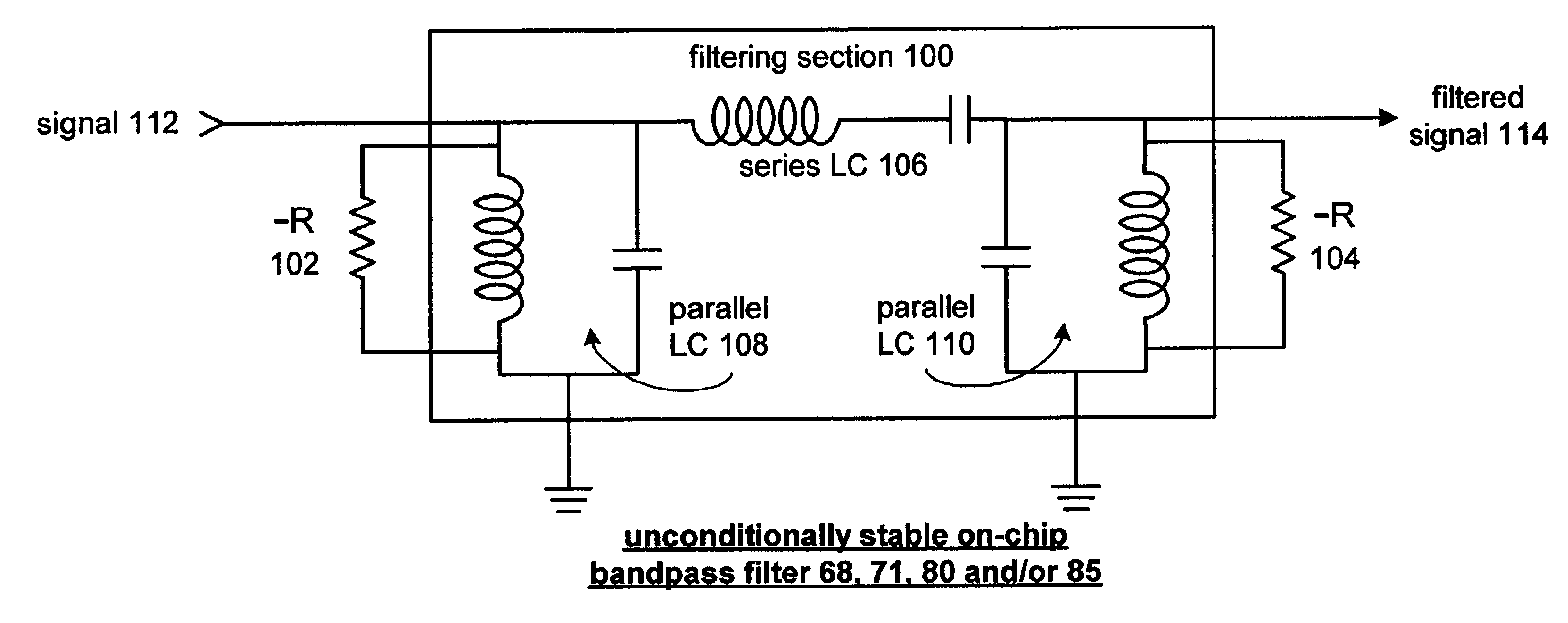
Unconditionally stable on-chip filter and applications thereof
InactiveUS6944435B2Reduced passive lossesEasy to useMultiple-port networksBalance-unbalance networksElectrical resistance and conductanceCMOS
An unconditionally stable on-chip filter includes a filtering section and at least one negative resistance module. The filtering section is operably coupled to filter a signal and includes realizable integrated circuit passive components. The at least one negative resistance module is operably coupled to compensate for integrated circuit losses of the filtering section. The realizable integrated circuit passive components have values that are robust, in comparison to parasitic values, have minimal integrated circuit real estate, and provide realizable values for various integrated circuit manufacturing processes including CMOS technology.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Air-gap grapheme transistor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102074584ALow dielectric constantSmall overall permittivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIntegrated circuit manufacturingAND gate
The invention belongs to the technical field of carbon integrated circuit manufacturing, in particular relates to an air-gap grapheme transistor and a manufacturing method thereof. In the method, gate electrodes and gate medium grow on a silicon base and then source and drain graphics are formed; grapheme is transformed to the formed source and drain graphics so as to separate the grapheme from the gate medium; and the air-gap is used to separate the grapheme from the gate medium so as to eliminate the growth process of a buffer layer on the grapheme, thus high mobility of carriers in the grapheme is retained maximally, and deterioration for the surface properties of the grapheme is reduced, thereby further improving electrical properties of grapheme devices.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
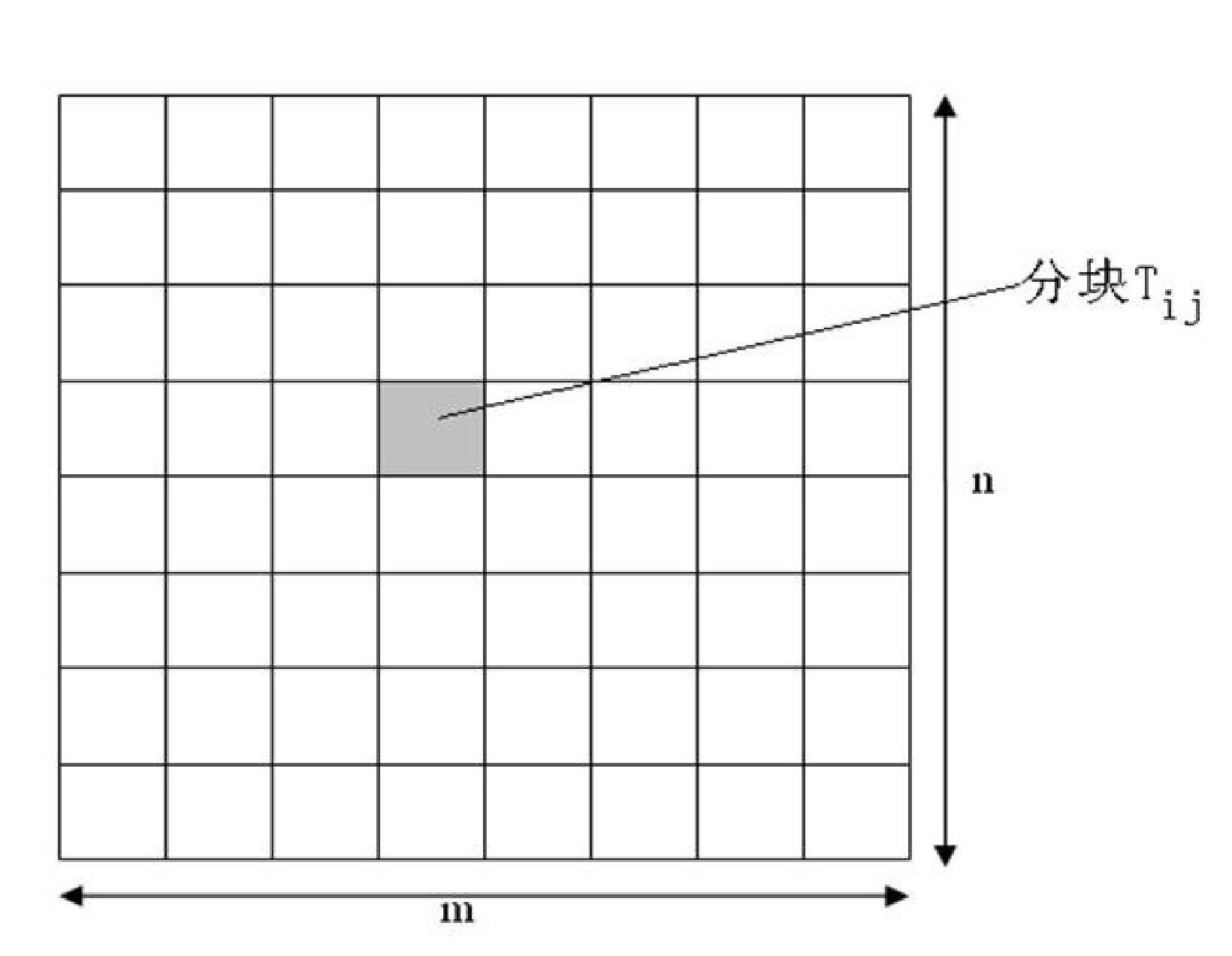
Test structures and method for interconnect impedance property extraction
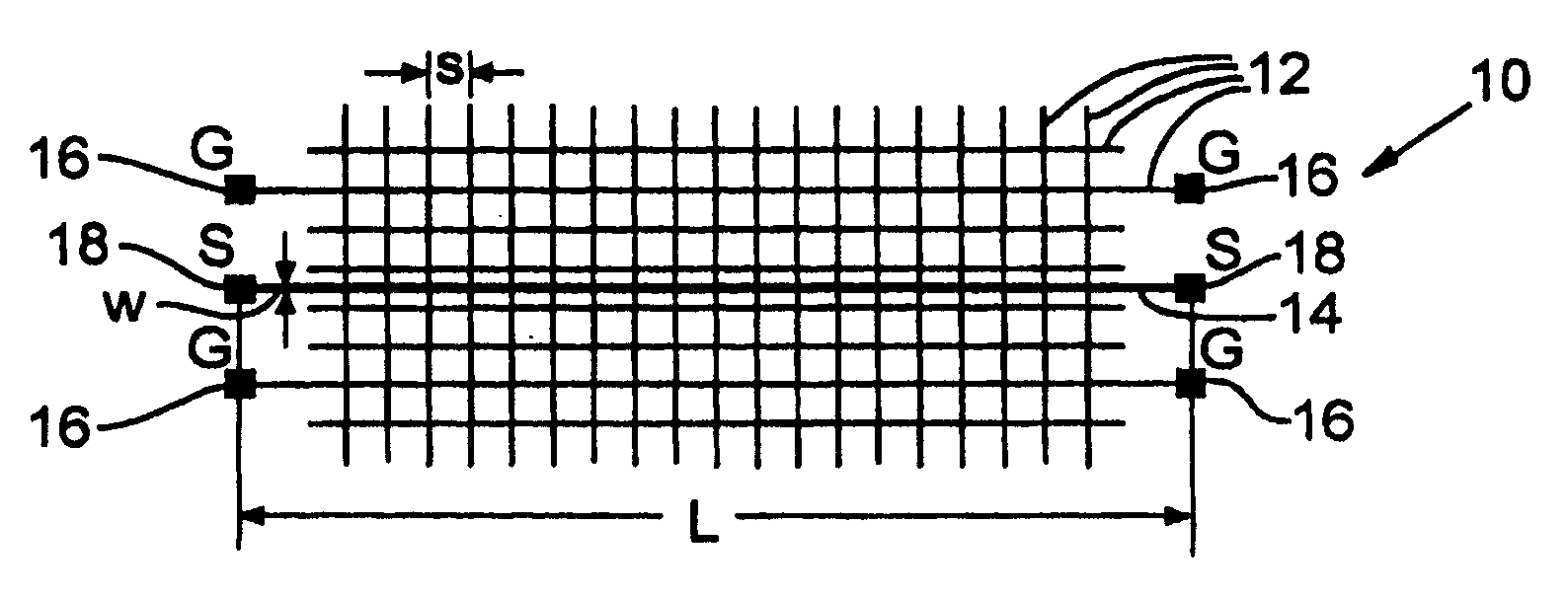
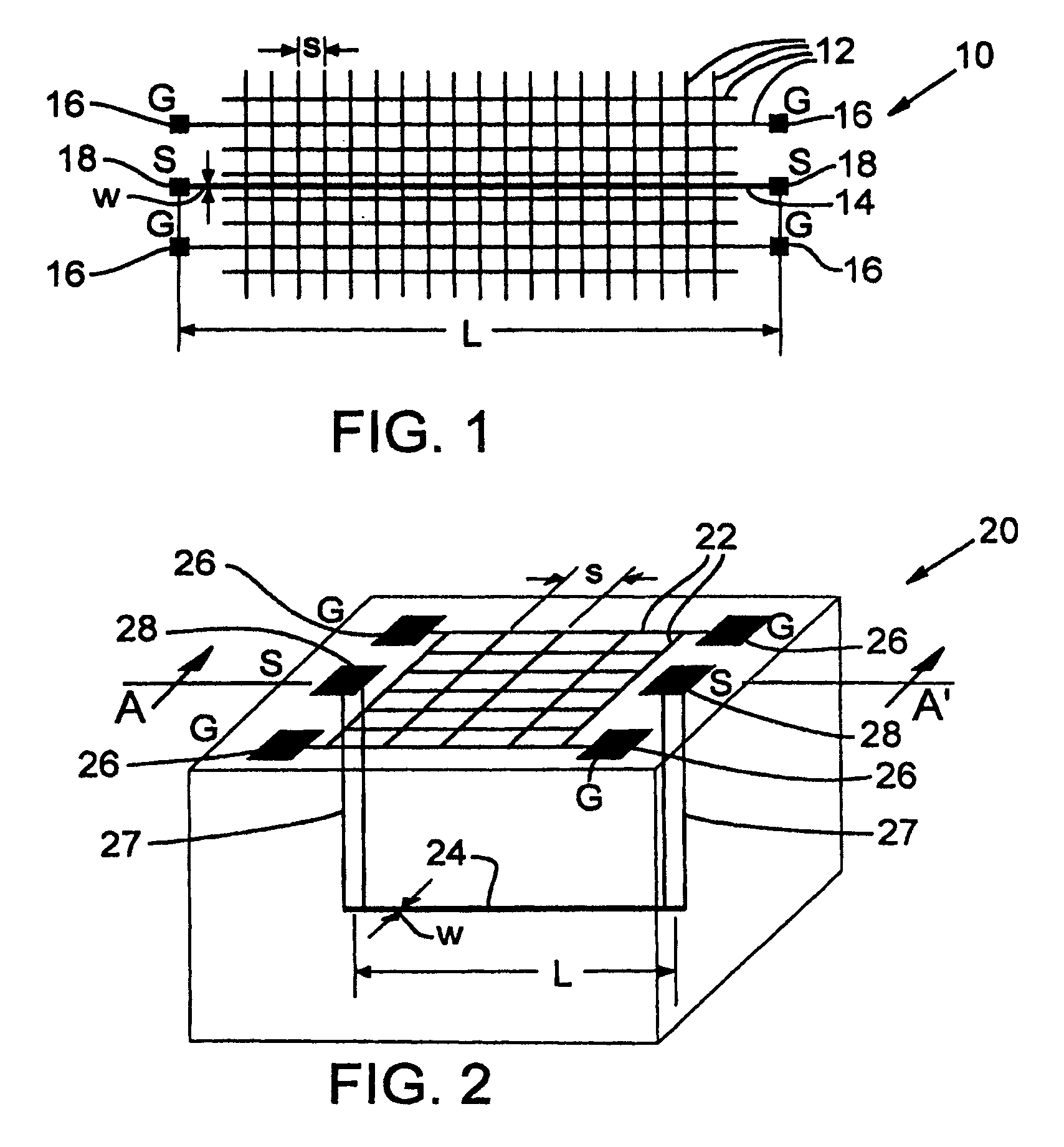
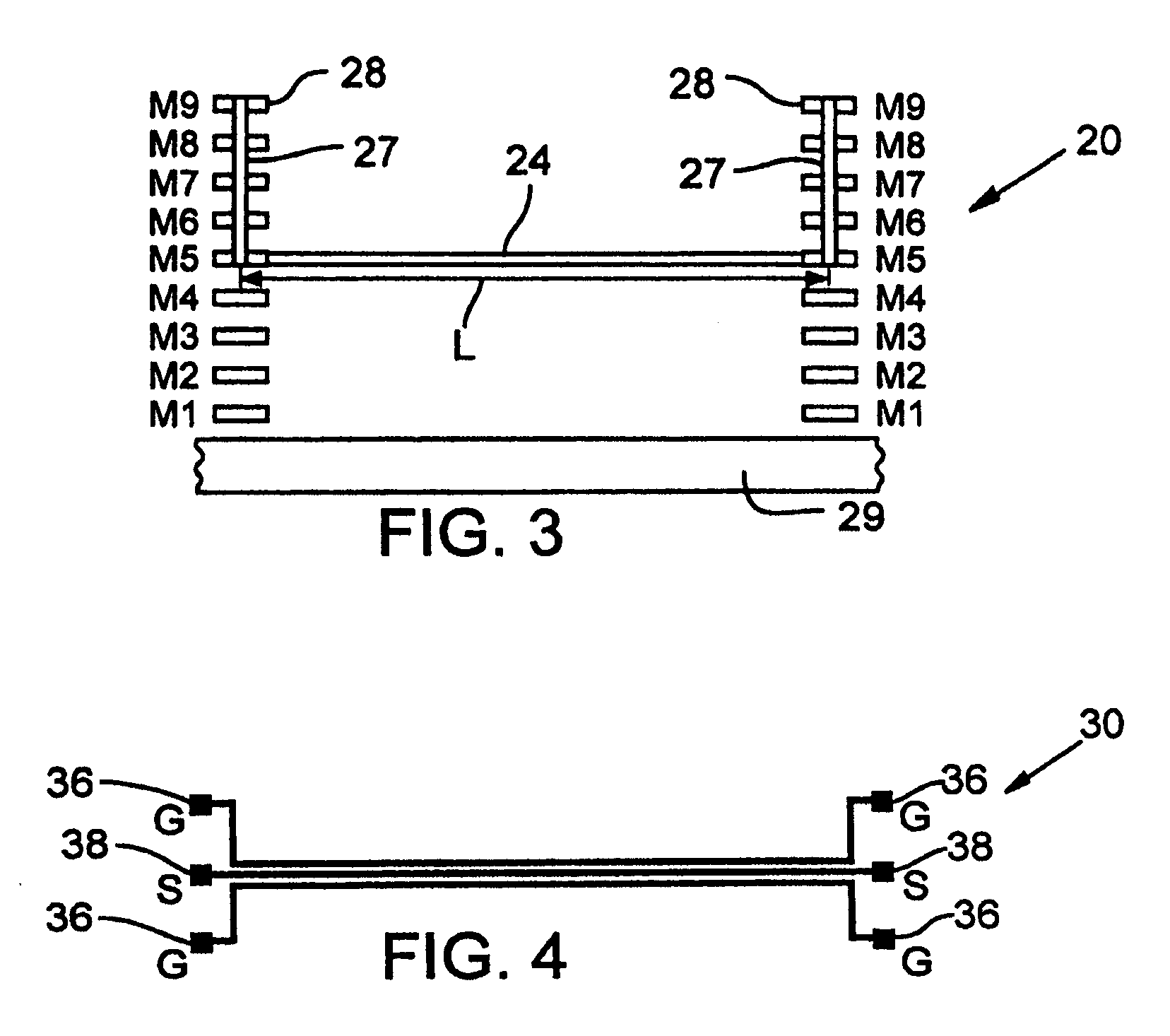
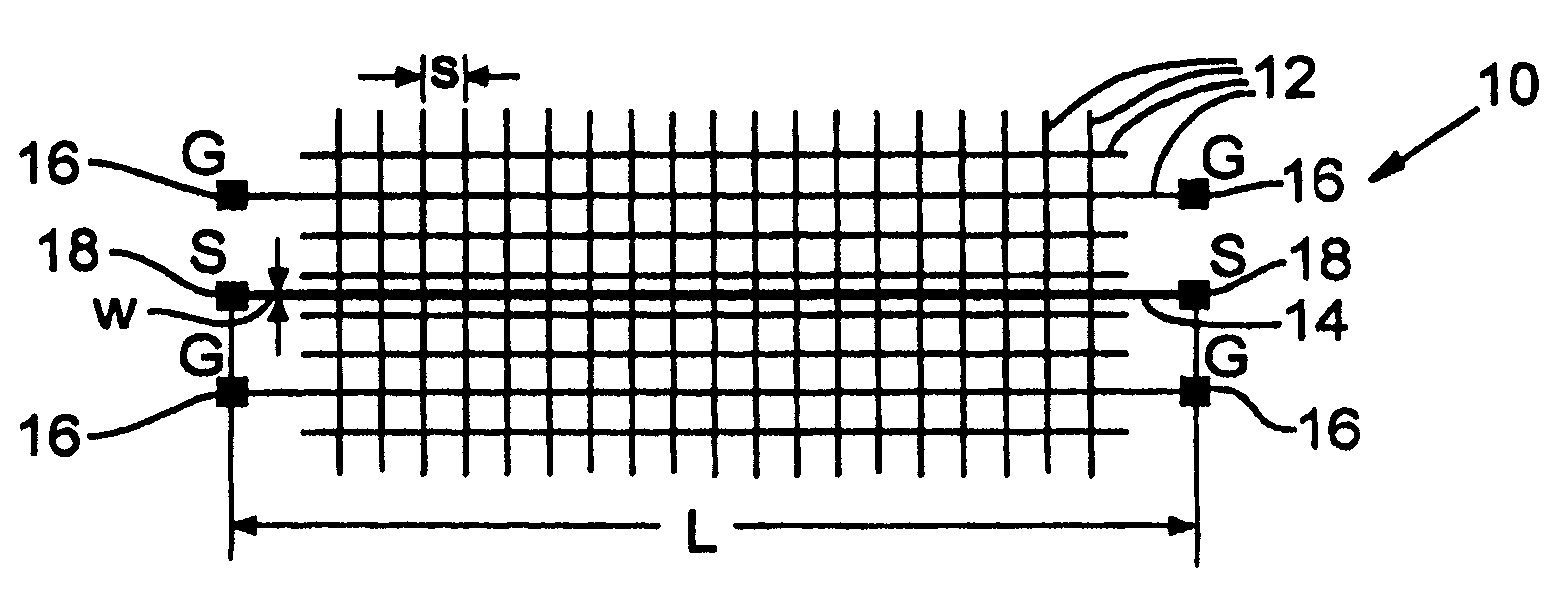
ActiveUS20060022678A1Easy to understandResistance/reactance/impedenceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGrounding gridGrid density
A method and test structures are disclosed for characterizing interconnects of an integrated circuit. The method provides a set of test structures and determines a unit impedance property of each test structure, desirably using S-parameter measurements. A reference impedance data set is then formulated that characterizes the impedance of an integrated circuit manufacturing technology and that can be used to characterize the impedance of interconnects of the chip made by the technology. Each test structure desirably comprises a ground grid and a signal line, and is characterized by values of a set of predetermined attributes such as layer location of the respective ground grid, grid density, layer association, width and length of the respective signal line.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Test structures and method for interconnect impedance property extraction
ActiveUS7340703B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGrounding gridData set
A method and test structures are disclosed for characterizing interconnects of an integrated circuit. The method provides a set of test structures and determines a unit impedance property of each test structure, desirably using S-parameter measurements. A reference impedance data set is then formulated that characterizes the impedance of an integrated circuit manufacturing technology and that can be used to characterize the impedance of interconnects of the chip made by the technology. Each test structure desirably comprises a ground grid and a signal line, and is characterized by values of a set of predetermined attributes such as layer location of the respective ground grid, grid density, layer association, width and length of the respective signal line.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
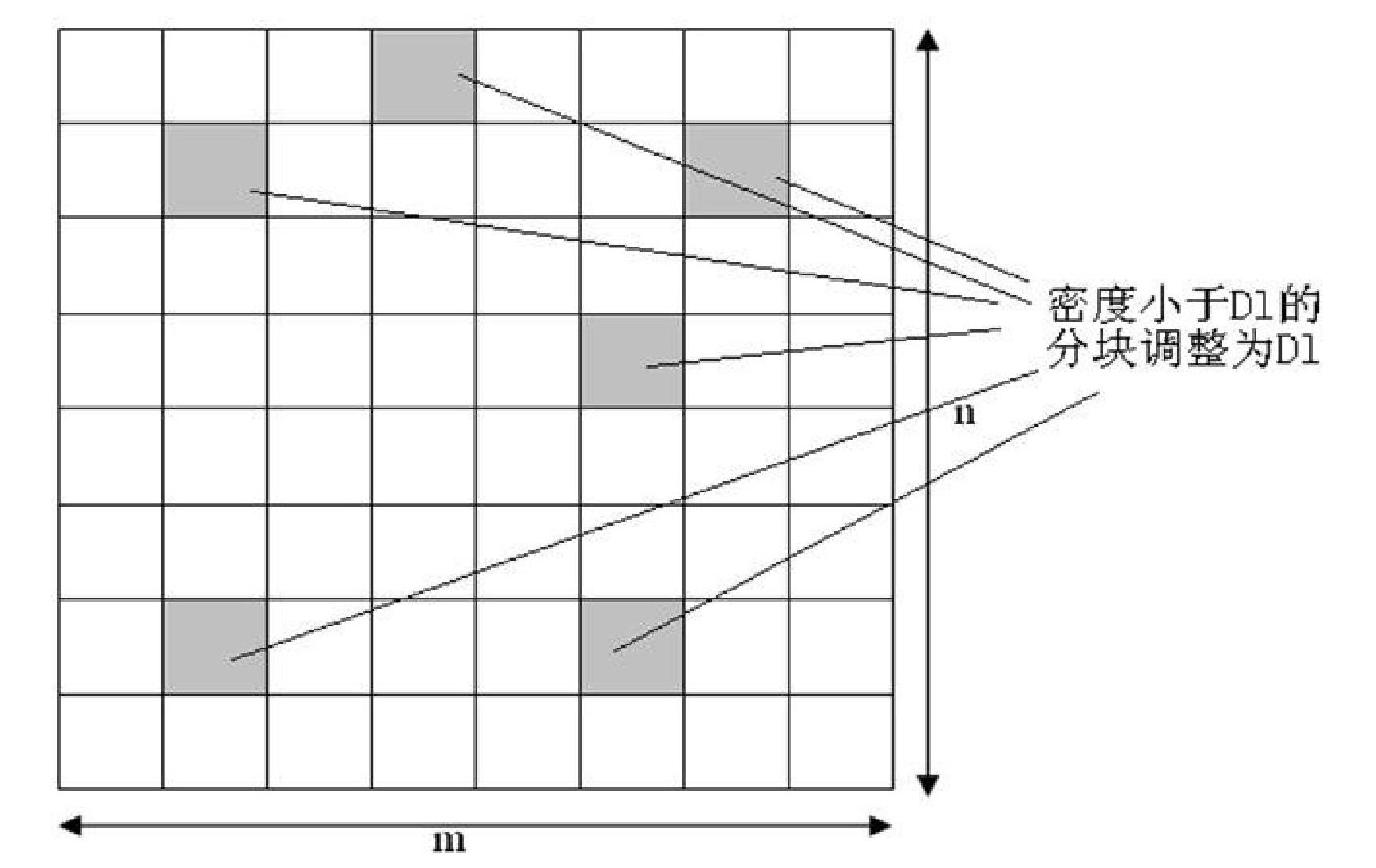
Preprocessing method using redundancy metal filling for realizing layout density uniformity
ActiveCN102117348AHomogenize Global DensitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial data processing applicationsLower limitPretreatment method
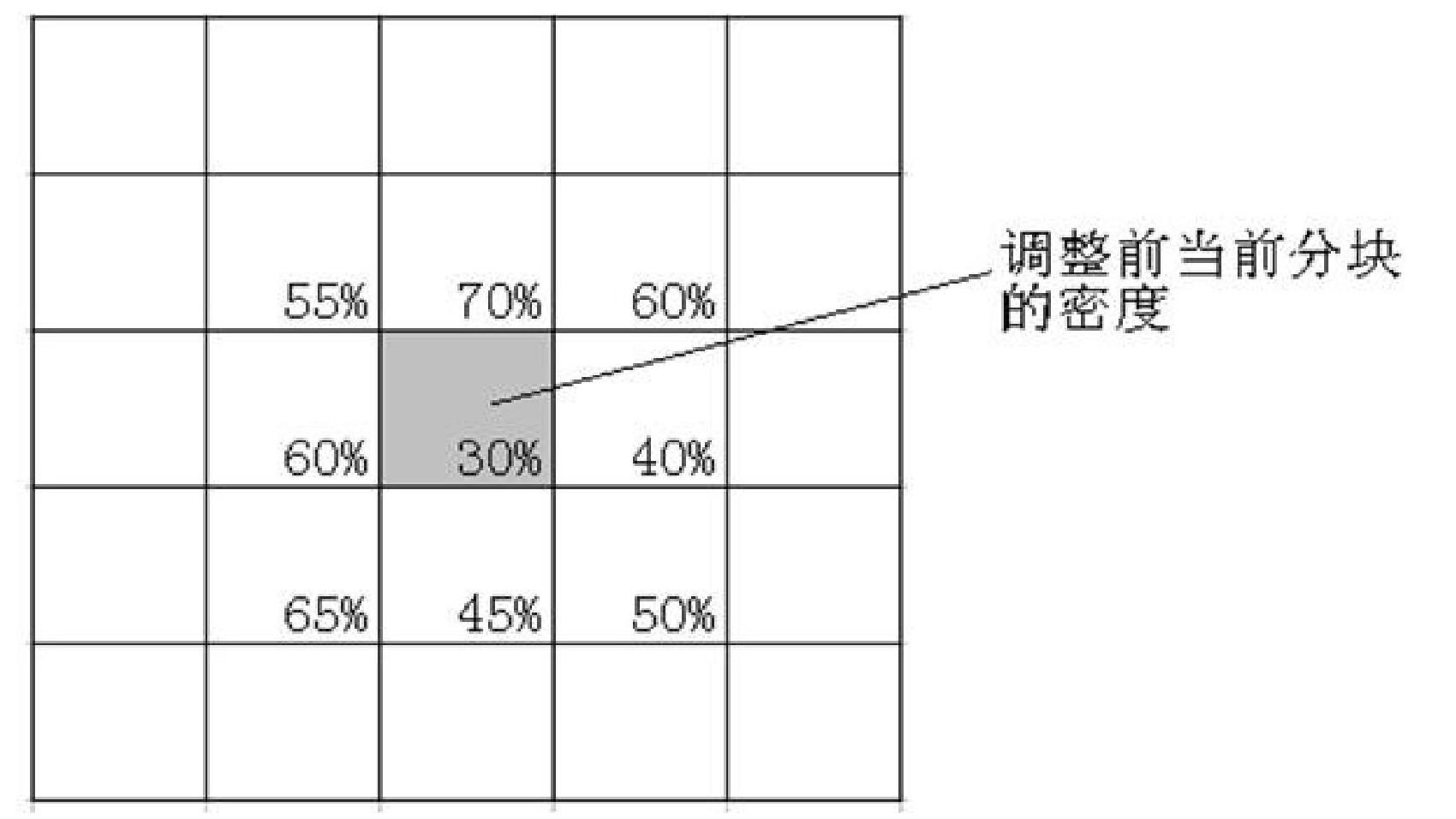
The invention relates to a preprocessing method using redundancy metal filling for realizing layout density uniformity, belonging to the technical field of integrated circuit manufacturing process and layout design. The method can determine the density of each block by a design rule check rule through a pre-setting the block density lower limit and pre-setting the allowable density undulating quantity and then dividing the layout into blocks having the same size. For the method, the density of each block is adjusted to be above the density lower limit, and then the density difference between each block and the adjacent blocks is limited within the preset allowable undulating quantity range, so that the density difference among different blocks is reduced, the uniformity of the metal wire density on the layout is improved, better smoothness is realized and chip quality is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com