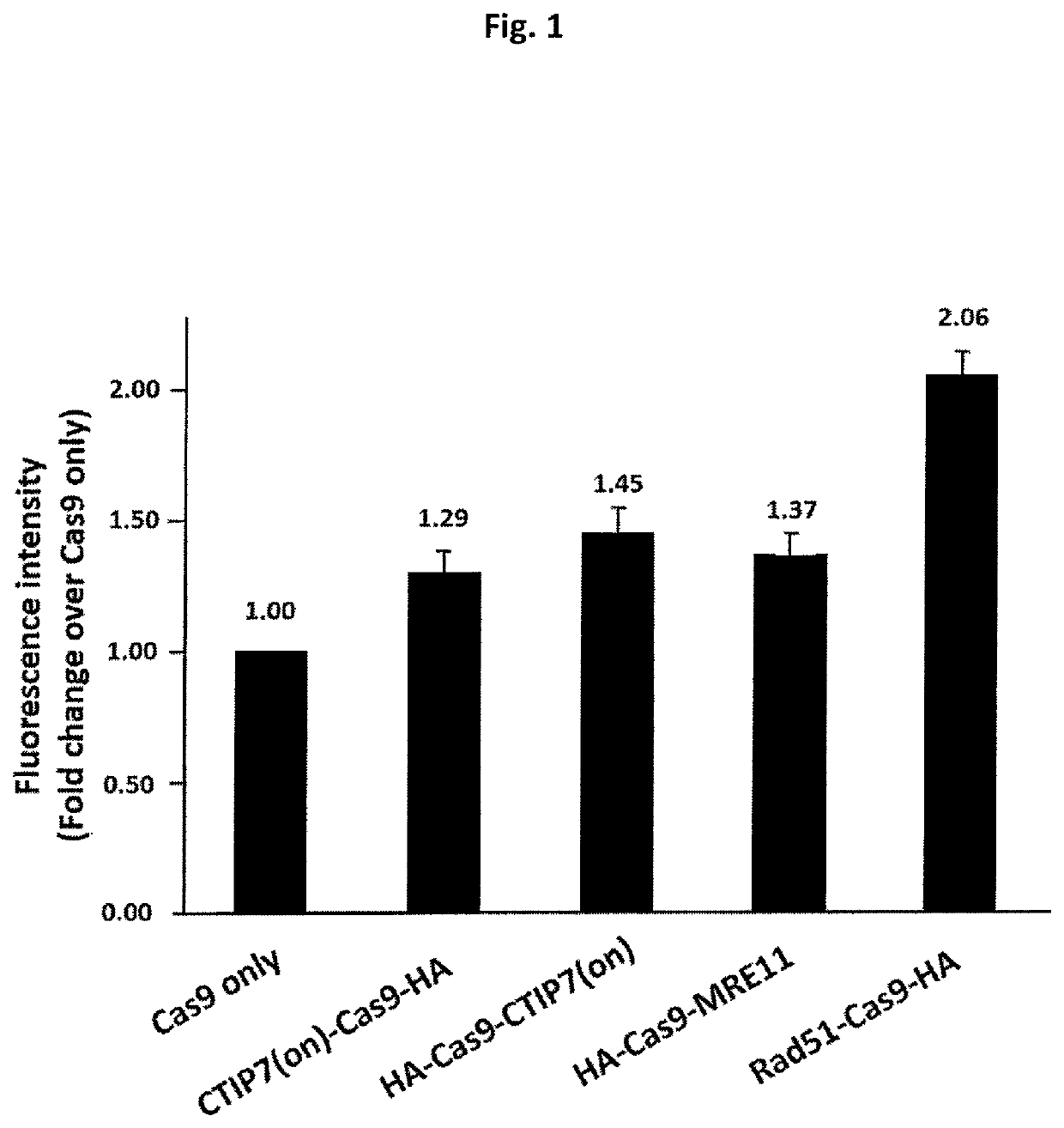
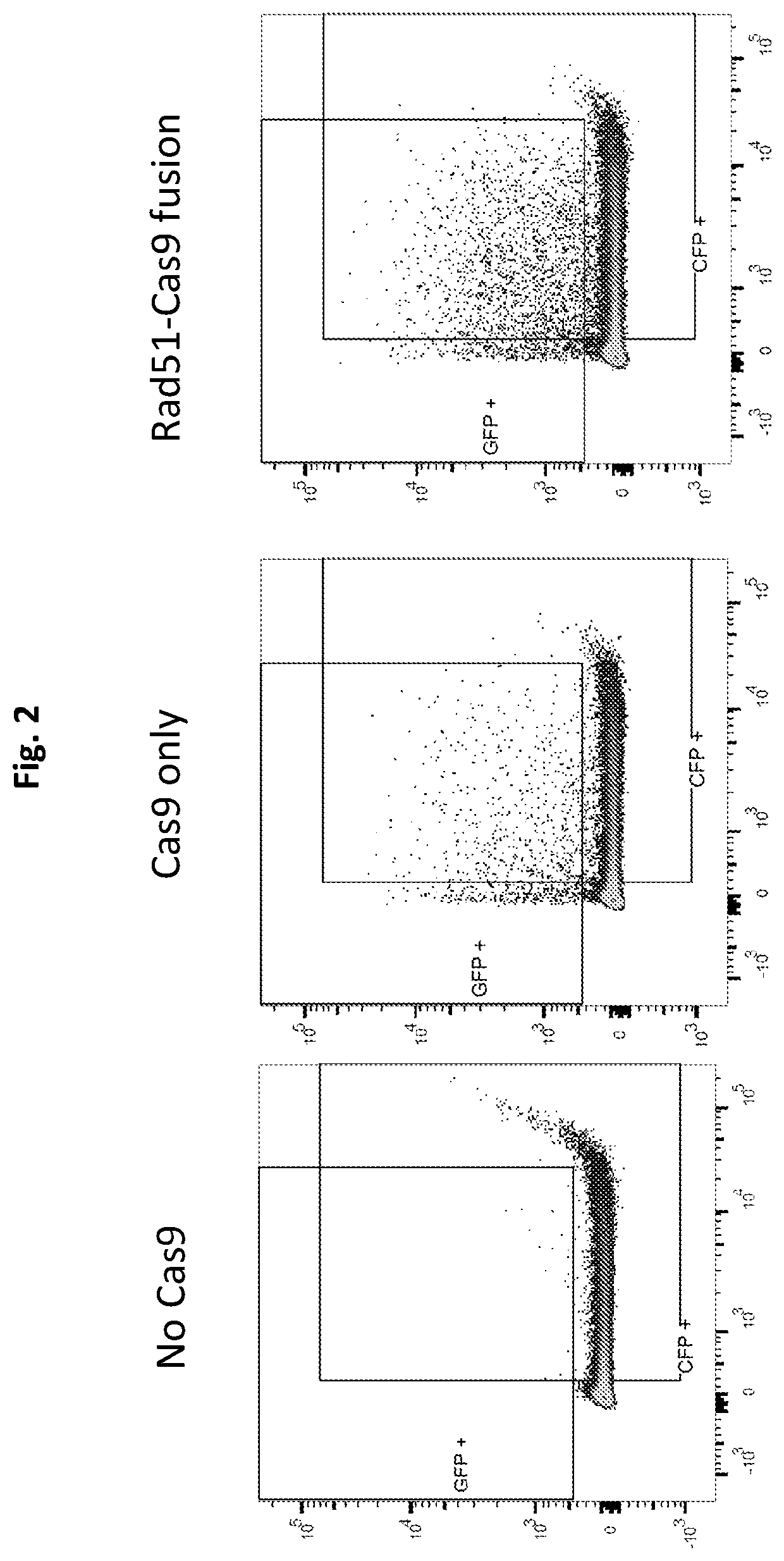
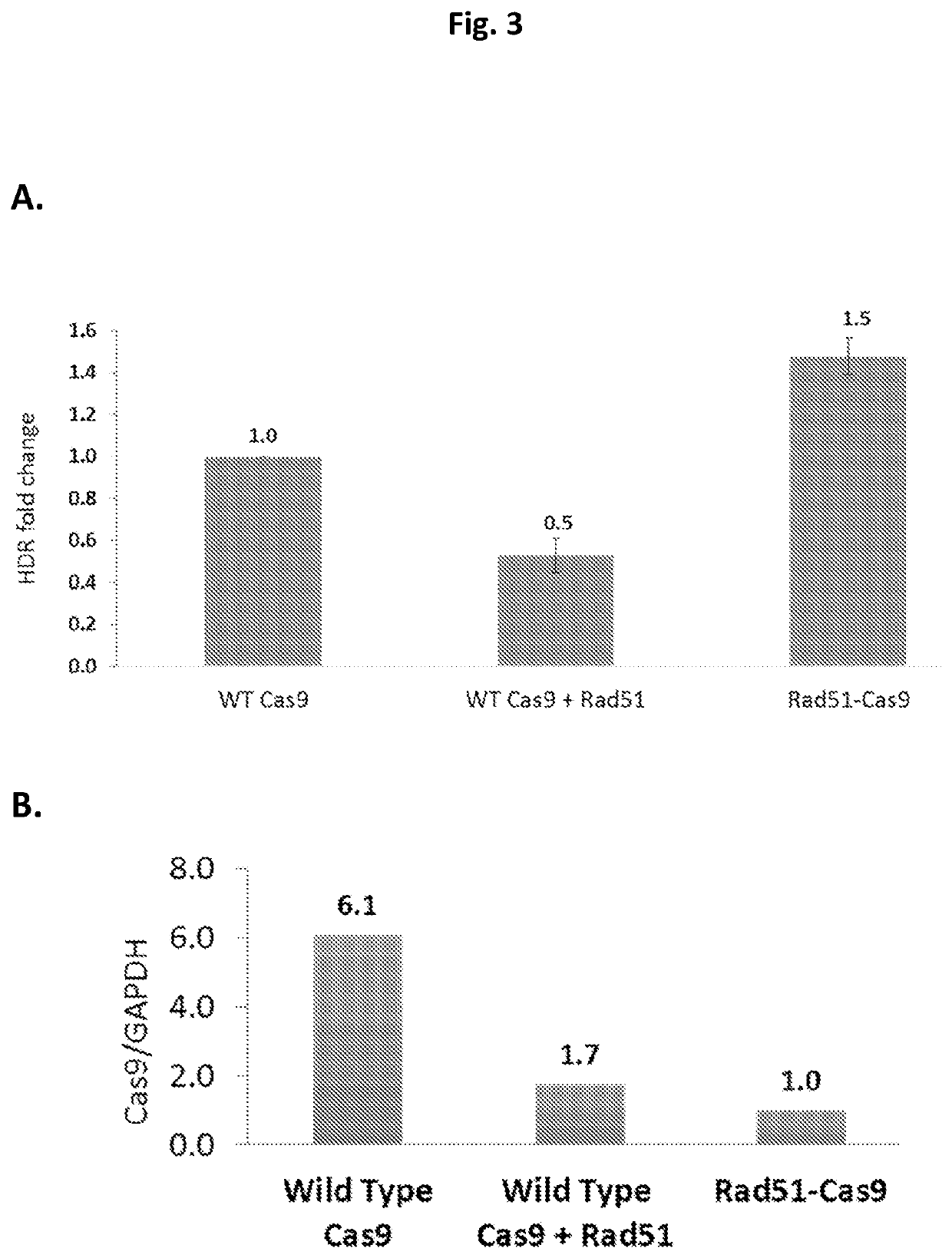
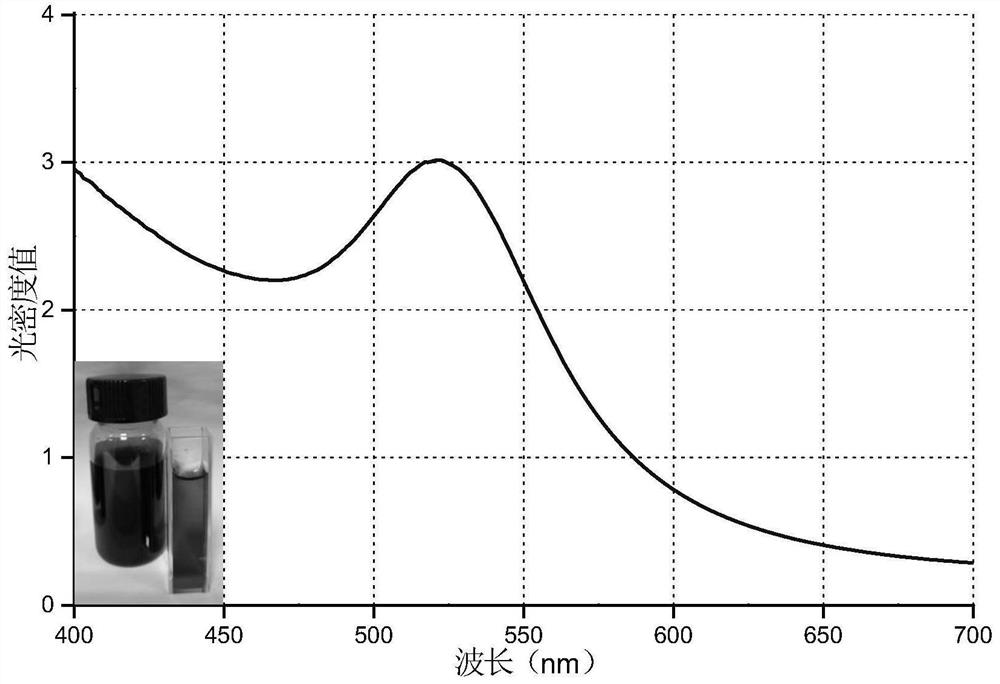
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Dna breaks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Somatic human cell line mutations
ActiveUS20170009256A1Even mixtureDifferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAGenomic mutationDna breakage
The invention provides for a method of producing a mutant somatic human cell line of cells comprising a genomic mutation of interest (MOI) at a predefined genomic site of interest (GOI) in close proximity to a genomic target site, which comprises: a) providing a guide RNA (gRNA) comprising a tracrRNA in conjunction with crRNA including an oligonucleotide sequence that hybridizes with the target site; b) providing an RNA-guided endonuclease which catalyzes the DNA break at the target site upon hybridizing with the gRNA; c) introducing the gRNA into the cells in the presence of the endonuclease to obtain a repertoire of cells comprising a variety of genomic mutations at the target site; d) selecting a cell from said repertoire which comprises a MOI; wherein the cell is haploid for the genomic locus of the target site; and e) expanding the cell to obtain the mutant cell line. The invention further provides for a mutant human somatic cell line obtainable by such method; and libraries of mutant human somatic cell lines of isogenic cells with a variety of genomic mutations at different predefined genomic target sites.
Owner:HORIZON DISCOVERY
Methods and means to modify a plant genome
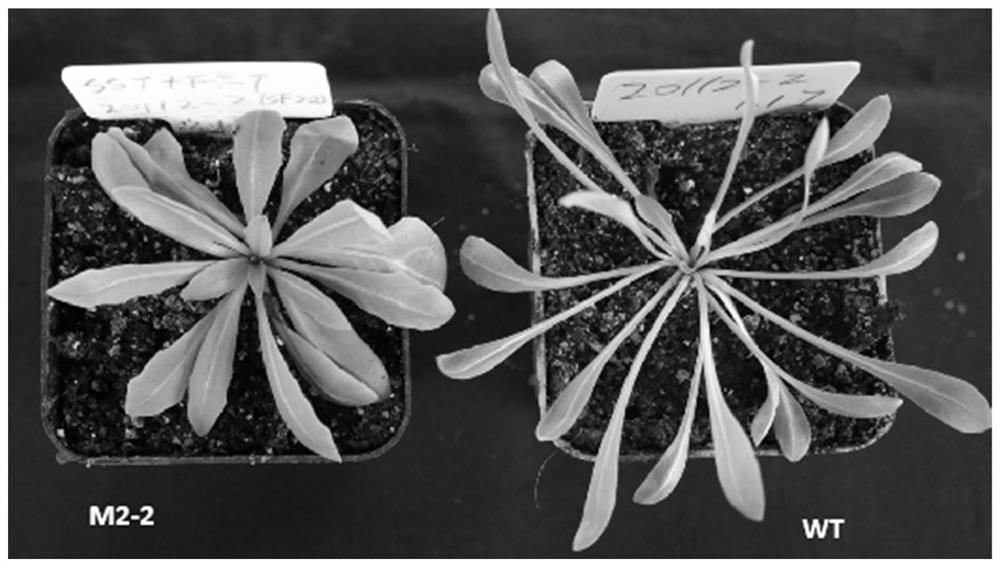
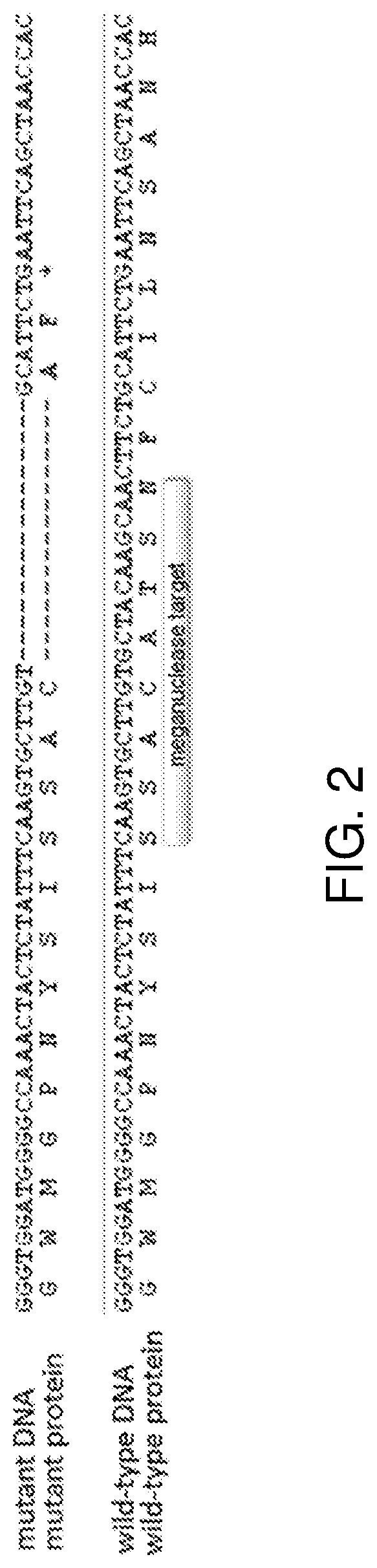
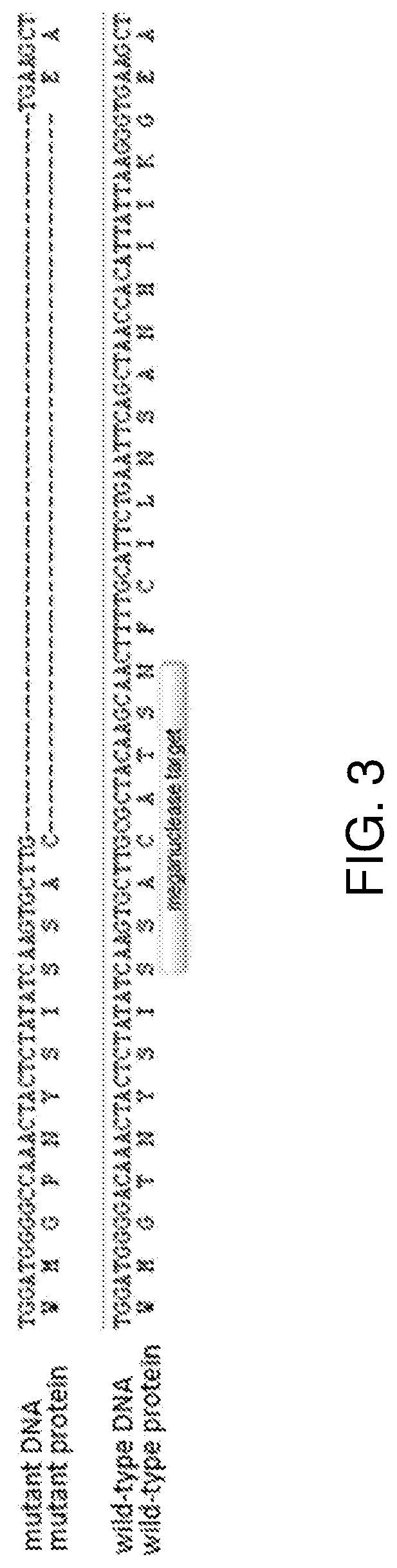
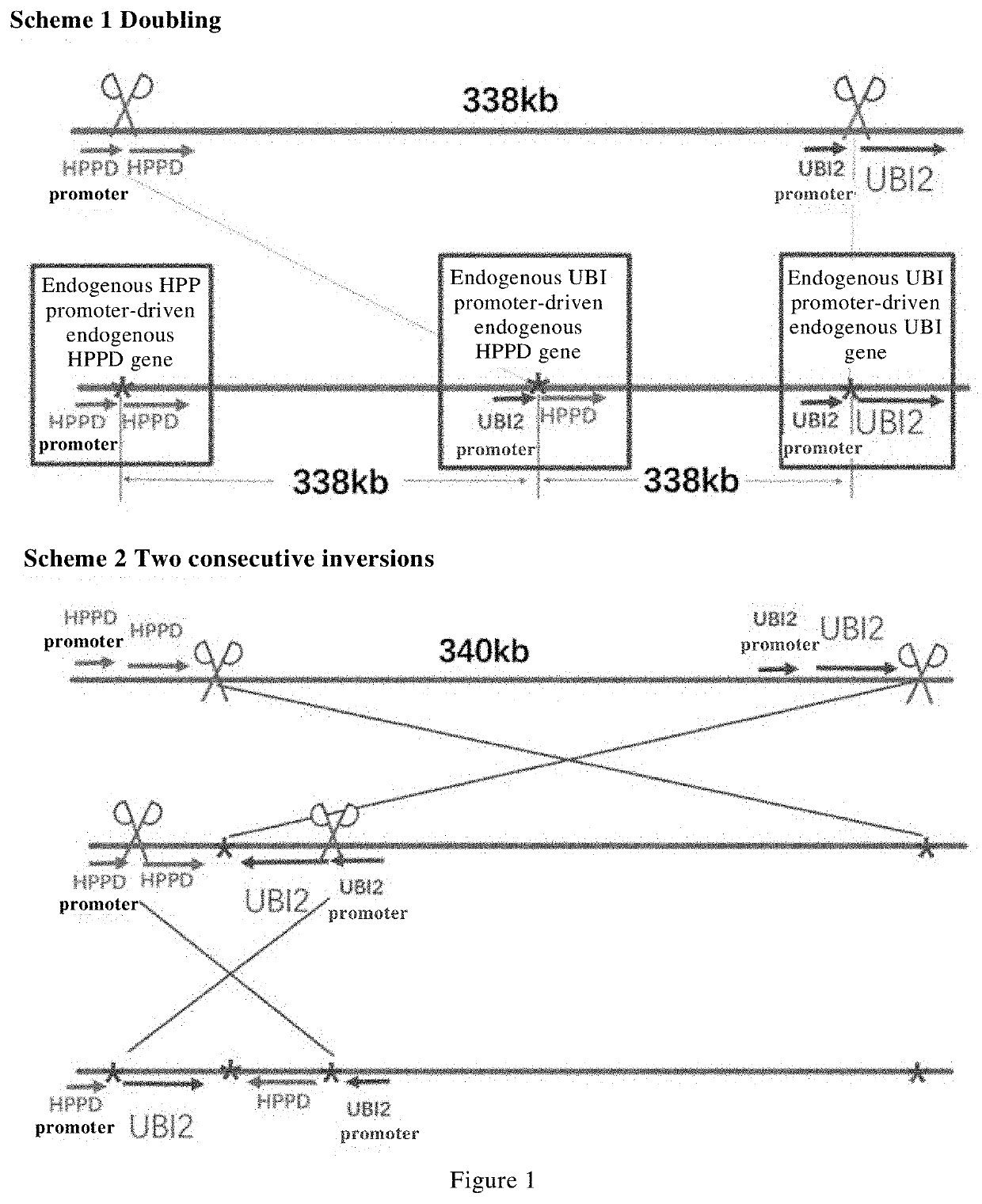
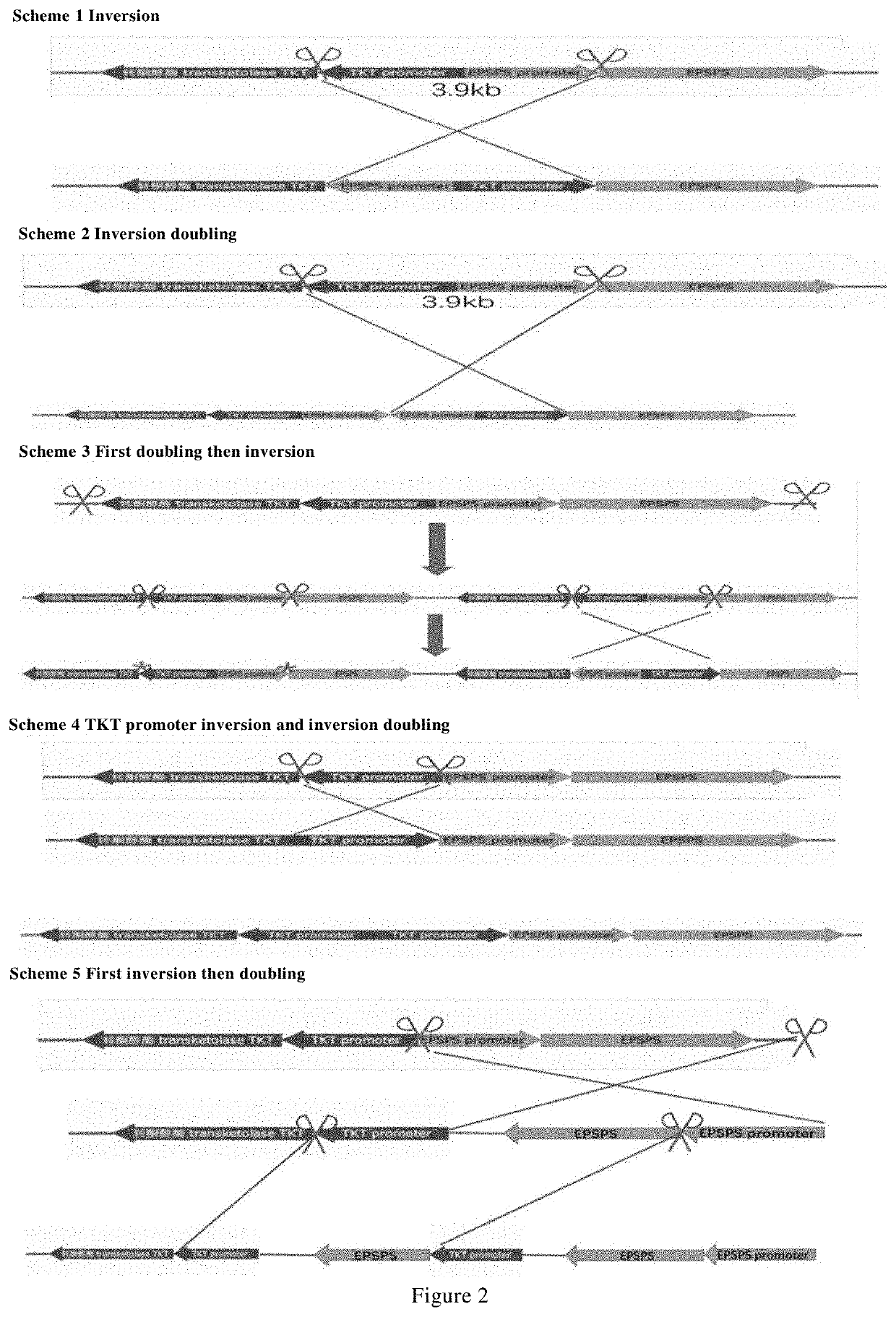
ActiveUS20150167009A1Mutant preparationOther foreign material introduction processesDna breaksDouble-Strand DNA Breaks
Methods and means are provided to modify in a targeted manner the genome of a plant in close proximity to an existing elite event using a double stranded DNA break inducing enzyme. Also provided are plants, in particular cotton plants showing tolerance to a field dose of at least IX of at least one HPPD inhibitor, and methods for making such plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Inhibitors of endo-exonuclease activity for treating cancer
InactiveUS7115665B1Increase concentrationPrevent proliferationBiocideNitro compound active ingredientsDna breakageSerum ige
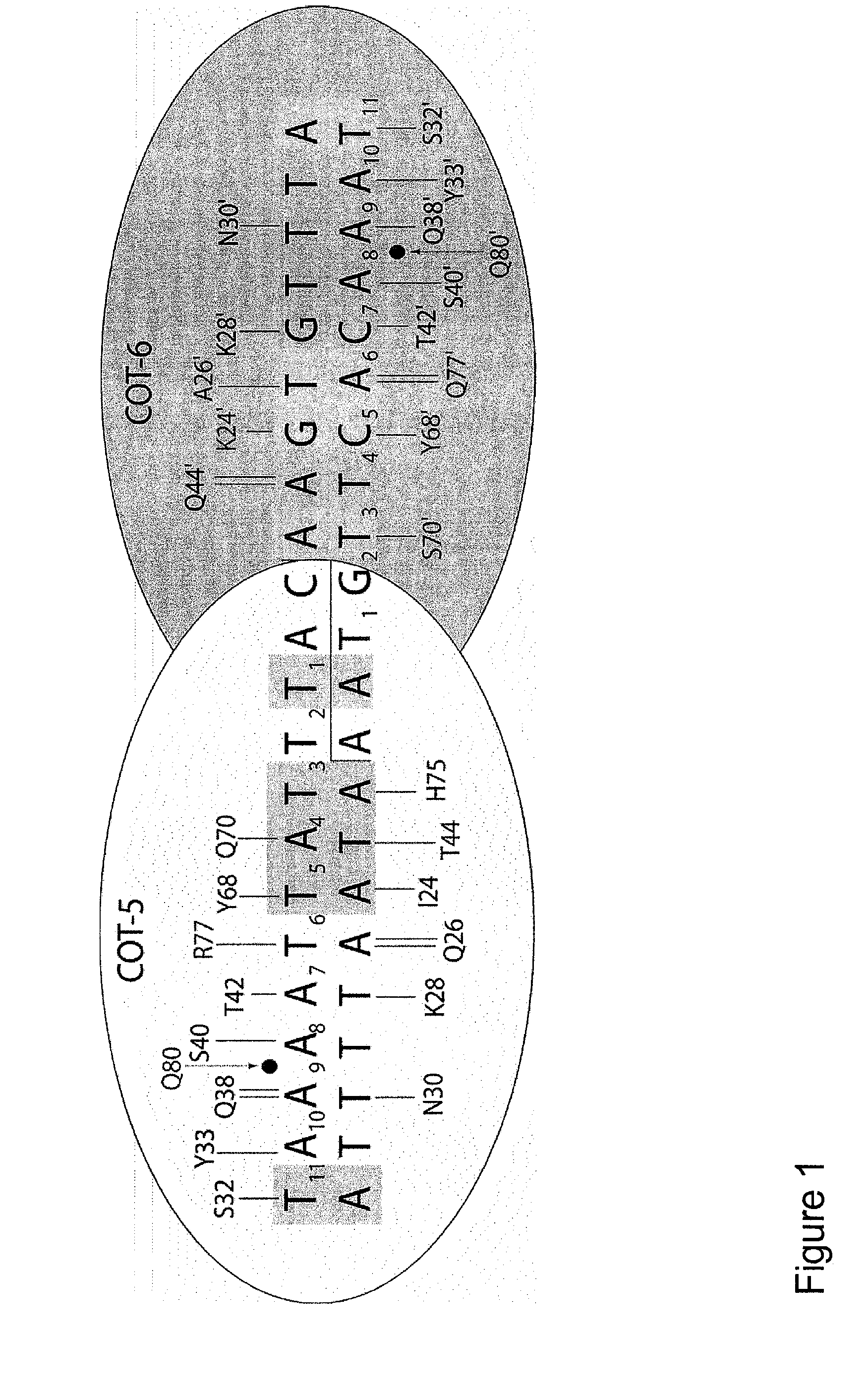
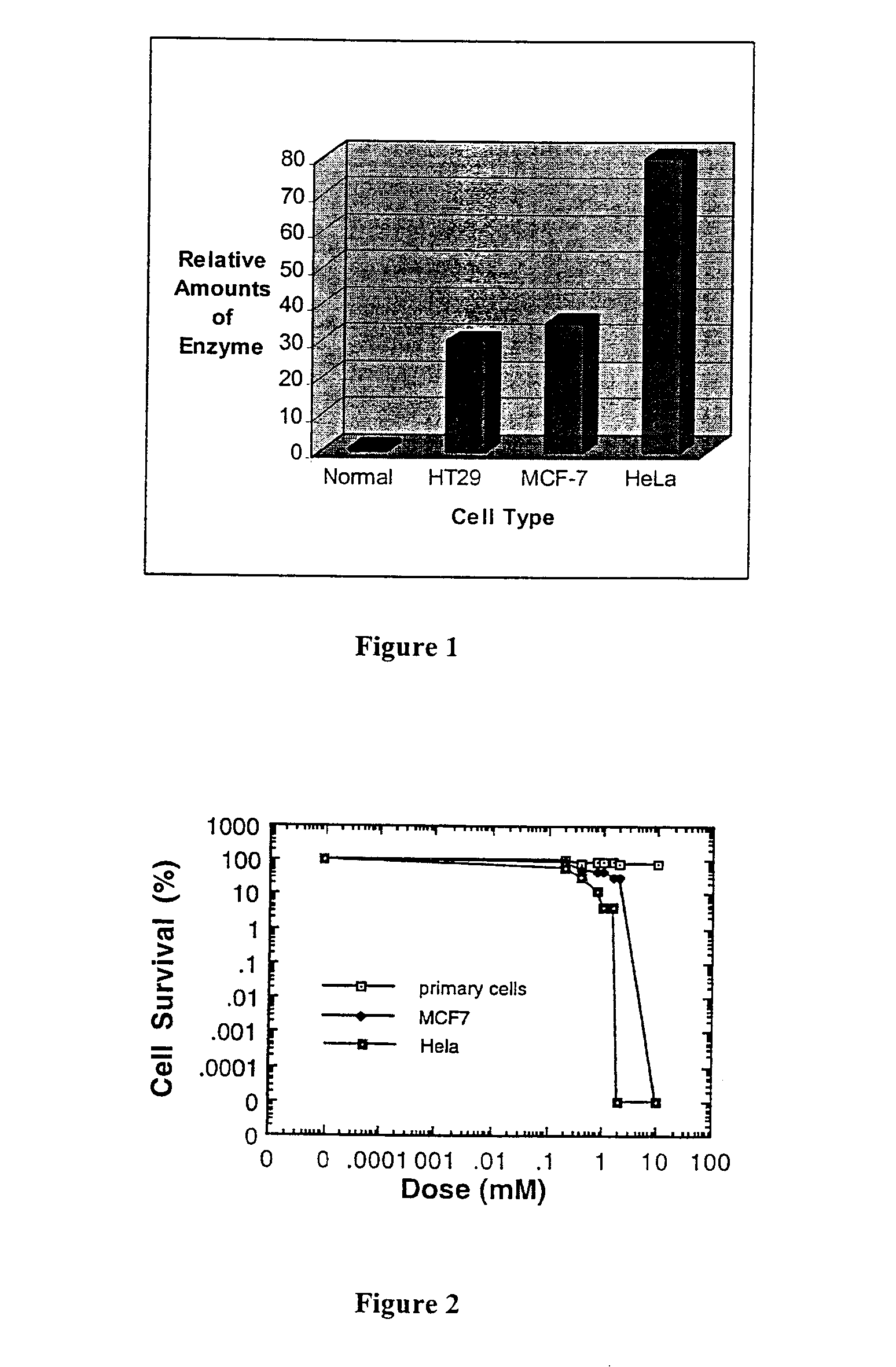
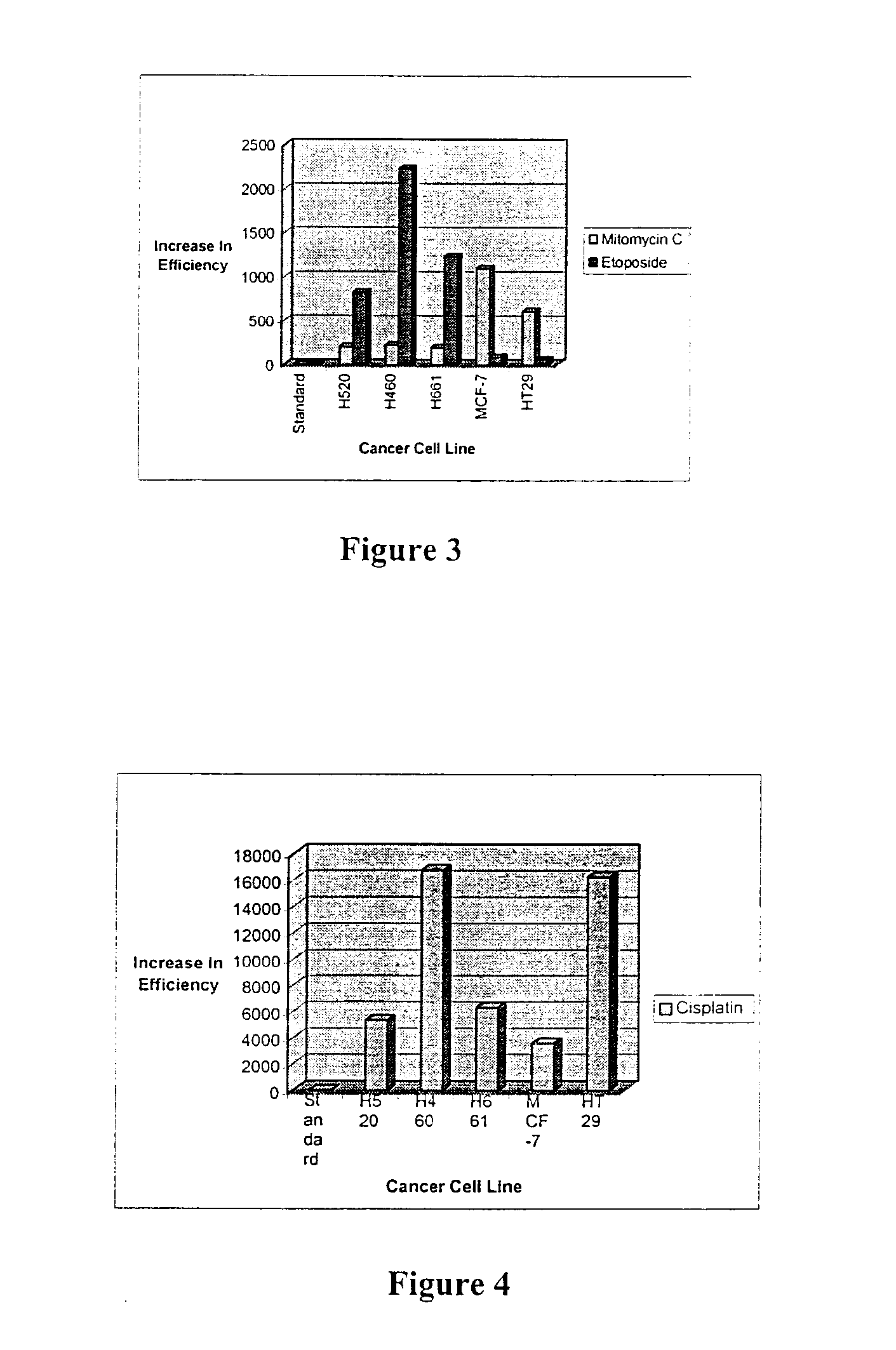
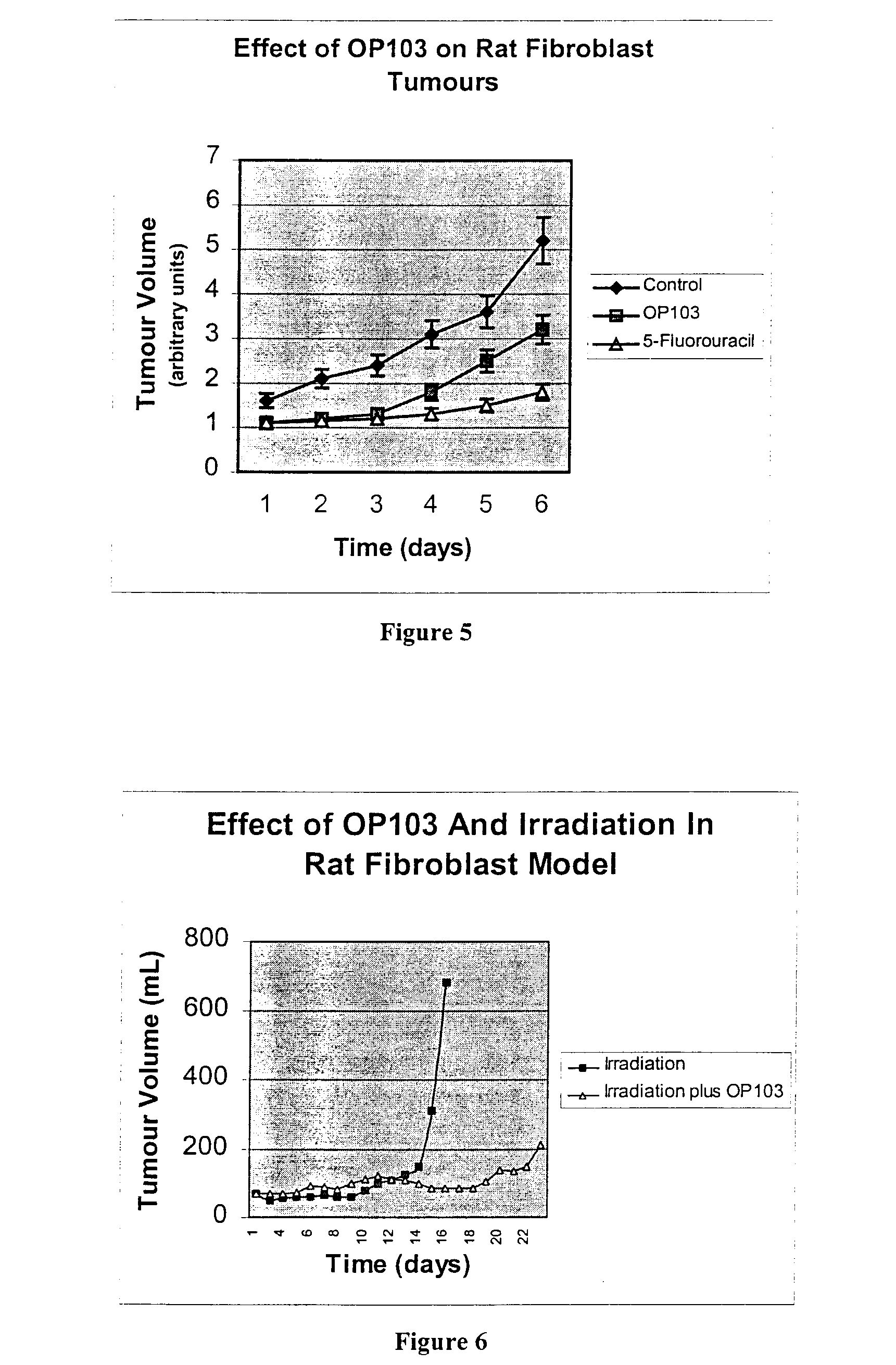
The present invention relates to the treatment of cancer with compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease. Endo-exonuclease has been shown to be necessary for the repair of damaged DNA. Compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have been shown to be particularly effective for treating cancer when used in combination with drugs that induce DNA breaks such as cisplatin and mitomycin C. These compounds have a synergistic effect when used in combination for inhibiting tumour growth. The invention includes pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting tumour growth comprising a compound that inhibits endo-exonuclease activity. These pharmaceutical compositions preferably include compounds that induce DNA breaks. The invention includes methods of treating cancer with these pharmaceutical compositions and uses of these compositions to treat cancer. The preferred compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have low toxicity. One such compound is pentamidine. The invention also includes a method for diagnosing cancer and monitoring its progression. This aspect of the invention involves isolating serum from a patient; measuring the concentration of endo-exonuclease in said serum and determining whether said concentration is above a predetermined mean.
Owner:ONCOZYME PHARMA
Method for removing residual DNA in hydrophobia vaccine product by utilizing ultrasound combined with EDTA solution
ActiveCN101780276AEffective removal of contentBreak through the quality bottleneckAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsAntigenHybrid protein
The invention provides a method for removing residual DNA in a hydrophobia vaccine product by utilizing ultrasound combined with EDTA solution. The method solves the problems that a method for extracting hydrophobia vaccine through concentration, purification and the like can only remove dissociative DNA in a certain percentage and cannot remove host DNA combined with antigen protein and clinical adverse reactions commonly occur. The method has main points of: adding the EDTA solution into hydrophobia vaccine concentrate; performing ultrasonic treatment on the hydrophobia vaccine by using ultrasonic wave to make the host DNA broken more easily under the action of the ultrasound; and removing the host DNA through chromatography and purification. The method has the advantages that: on the premise of ensuring the valence of the vaccine, the quality of a vaccine product is improved, mass hybrid protein and the host DNA are removed so that the residual DNA content of the vaccine product is less than 100 pg / dose, and the quality problem in the hydrophobia vaccine industry at present is solved.
Owner:LIAONING YISHENG BIOLOGY PHARMACY
Methods and means to modify a plant genome
Methods and means are provided to modify in a targeted manner the genome of a plant in close proximity to an existing elite event using a double stranded DNA break inducing enzyme. Also provided are plants, in particular cotton plants showing tolerance to a field dose of at least 1× of at least one HPPD inhibitor, and methods for making such plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Inhibitors of endo-exonuclease activity for treating cancer
InactiveUS20060276548A1Increase concentrationPrevent proliferationBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsMitomycin CCisplatin
The present invention relates to the treatment of cancer with compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease. Endo-exonuclease has been shown to be necessary for the repair of damaged DNA. Compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have been shown to be particularly effective for treating cancer when used in combination with drugs that induce DNA breaks such as cisplatin and mitomycin C. These compounds have a synergistic effect when used in combination for inhibiting tumour growth. The invention includes pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting tumour growth comprising a compound that inhibits endo-exonuclease activity. These pharmaceutical compositions preferably include compounds that induce DNA breaks. The invention includes methods of treating cancer with these pharmaceutical compositions and uses of these compositions to treat cancer. The preferred compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have low toxicity. One such compound is pentamidine. The invention also includes a method for diagnosing cancer and monitoring its progression. This aspect of the invention involves isolating serum from a patient; measuring the concentration of endo-exonuclease in said serum and determining whether said concentration is above a predetermined mean.
Owner:ONCOZYME PHARMA
Methods and compositions for assessing germline risk of cancer
ActiveUS10718774B2Change is minimalMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMolecular phenotypePhosphorylation
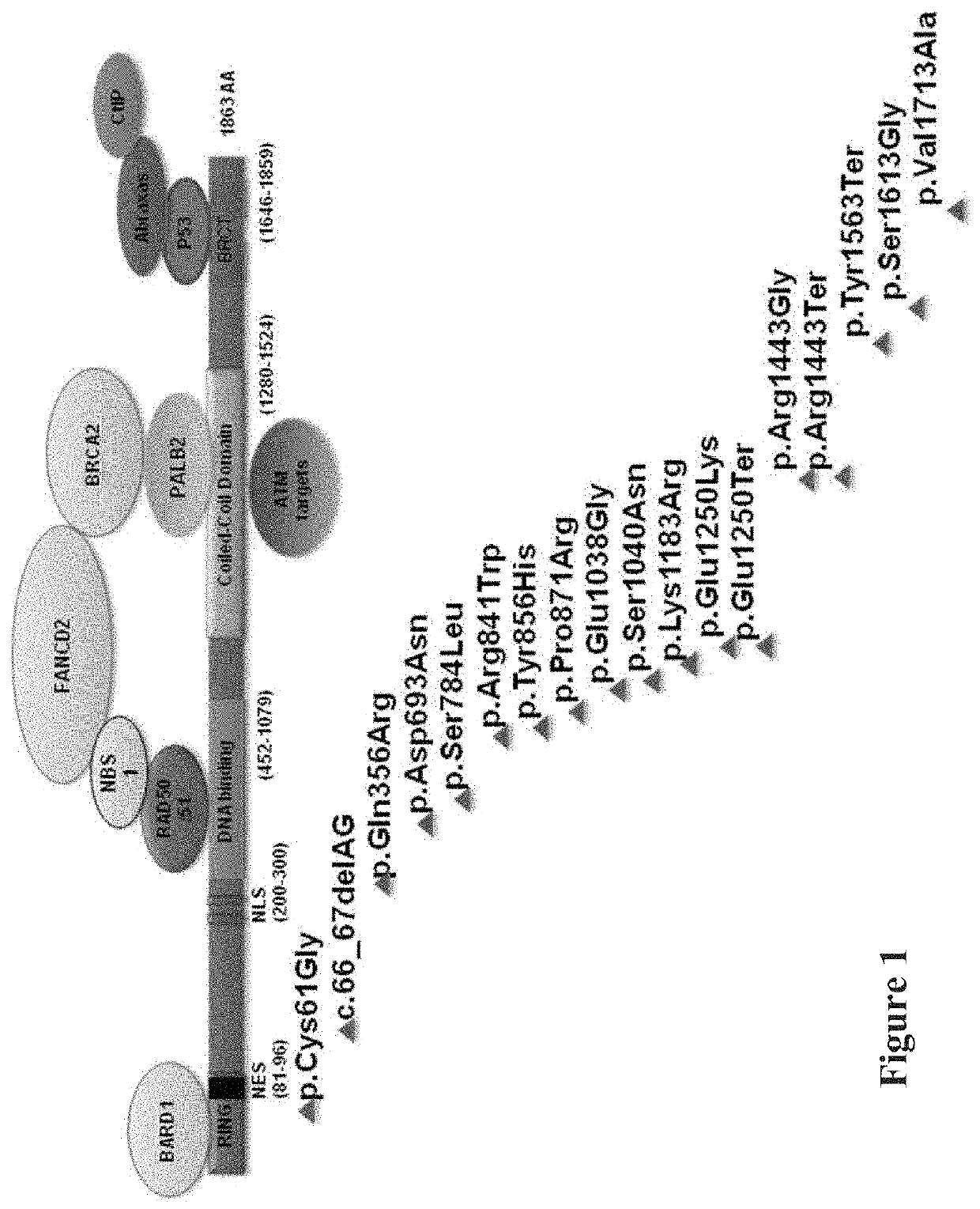
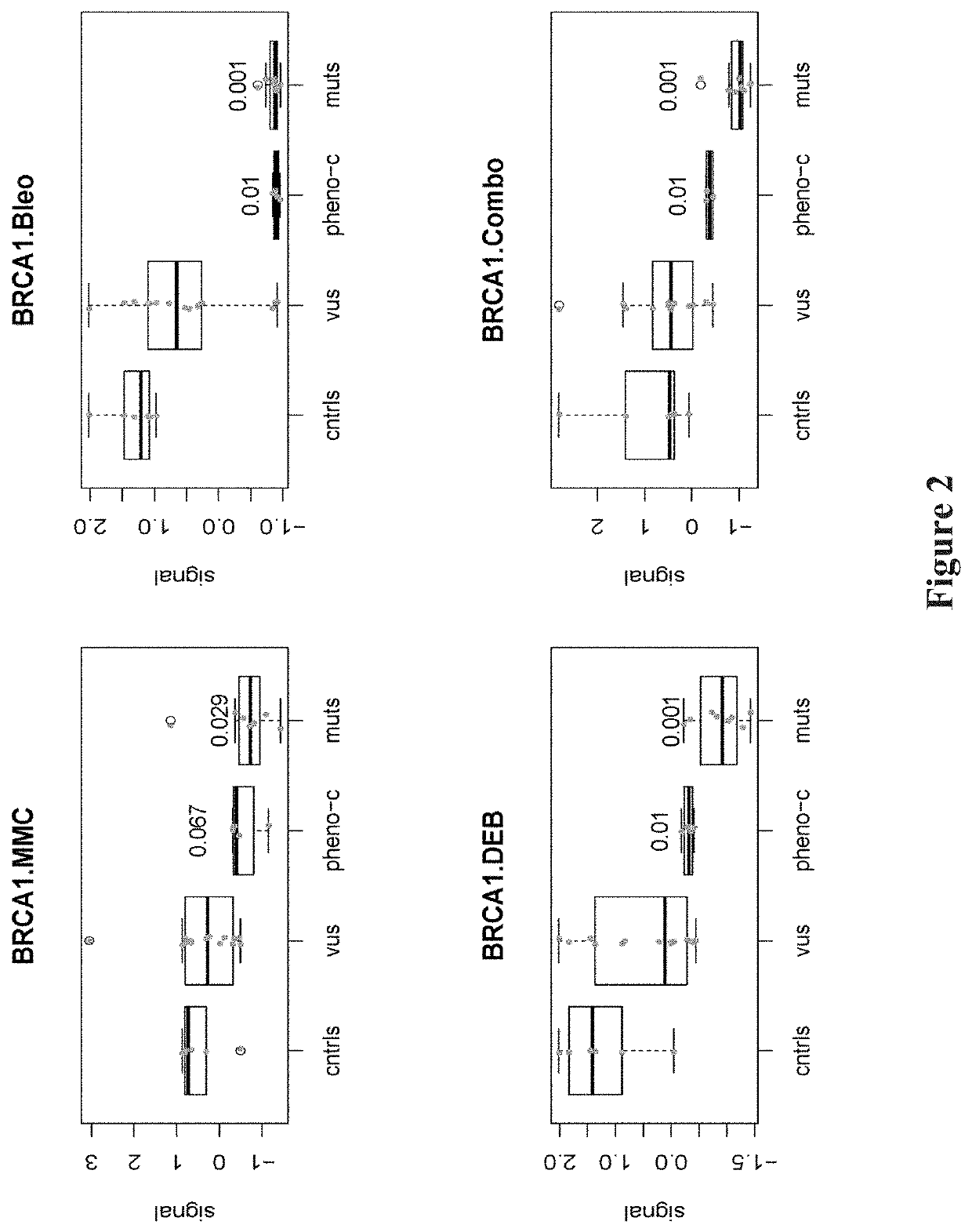
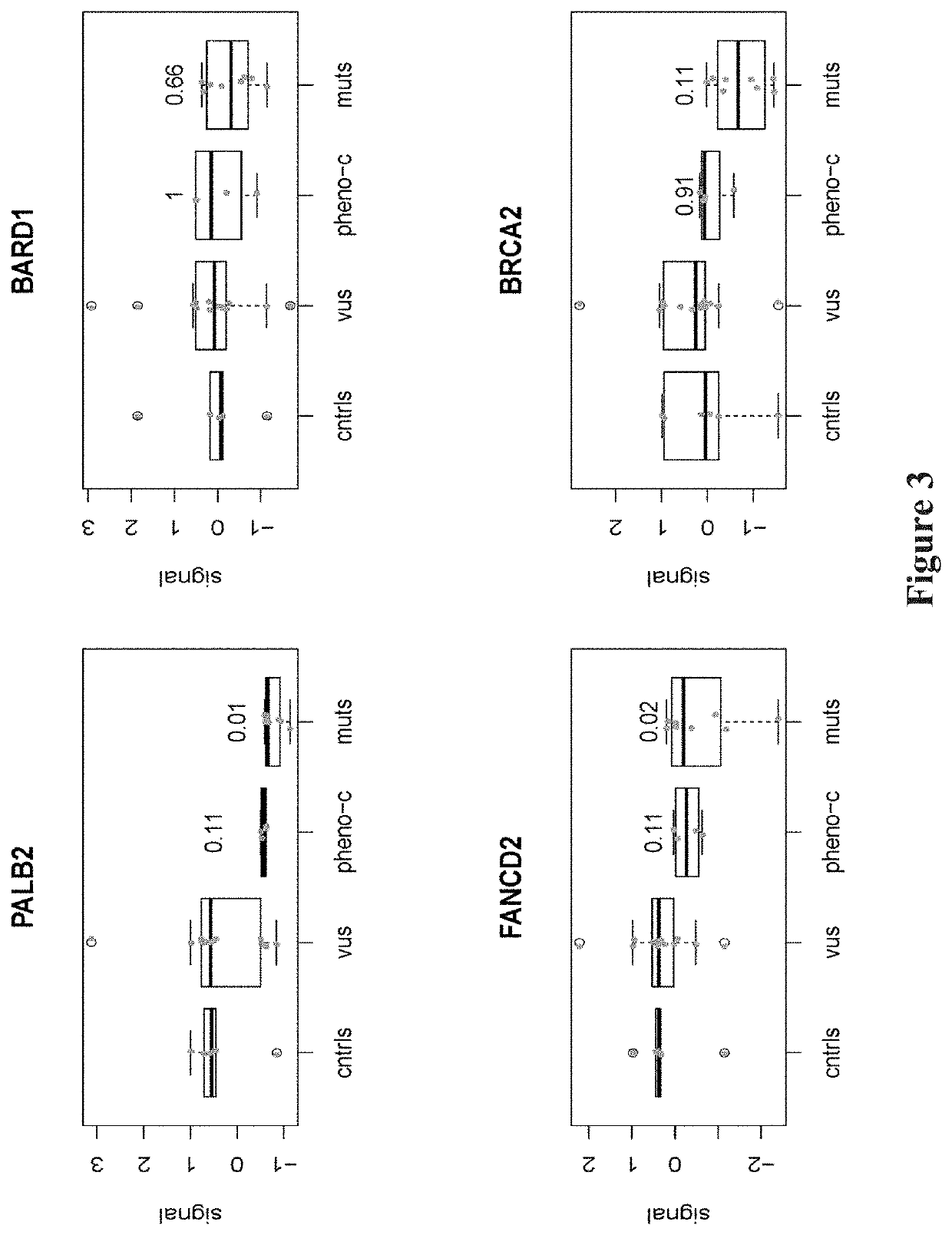
Heritable mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 and other genes in the DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway increase risk of breast, ovarian and other cancers. In response to DNA breaks, the proteins encoded by these genes bind to each other and are transported into the nucleus to form nuclear foci and initiate homologous recombination. Flow cytometry-based functional variant analyses (FVAs) were developed to determine whether variants in BRCA1 or other DSB repair genes disrupted the binding of BRCA1 to its protein partners, the phosphorylation of p53 or the transport of the BRCA1complex to the nucleus in response to DNA damage. Each of these assays distinguished high-risk BRCA1 mutations from low-risk BRCA1 controls. Mutations in other DSB repair pathway genes produced molecular phenocopies with these assays. FVA assays may represent an adjunct to sequencing for categorizing VUS or may represent a stand-alone measure for assessing breast cancer risk.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
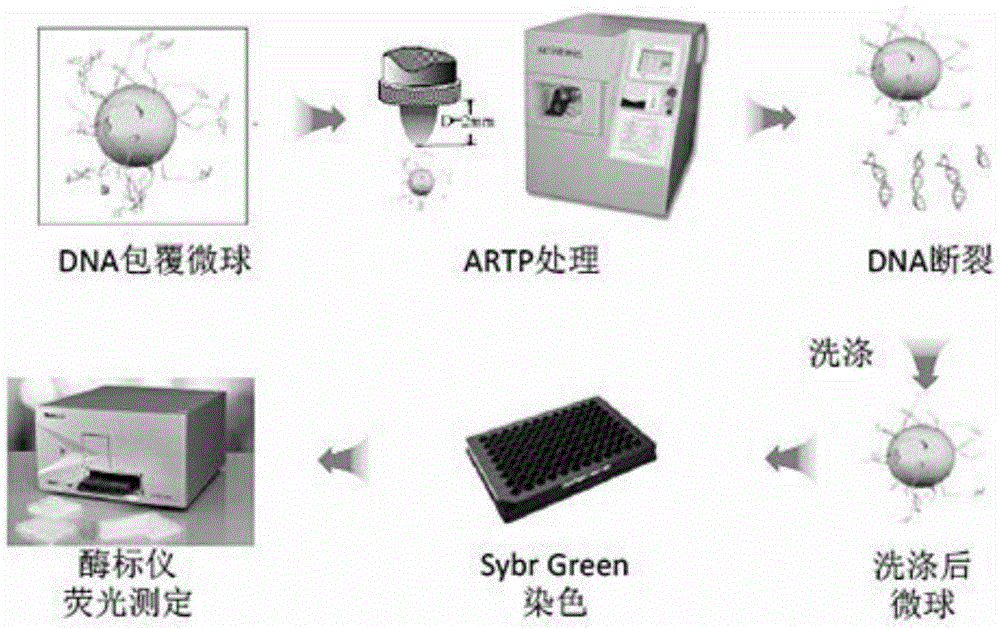
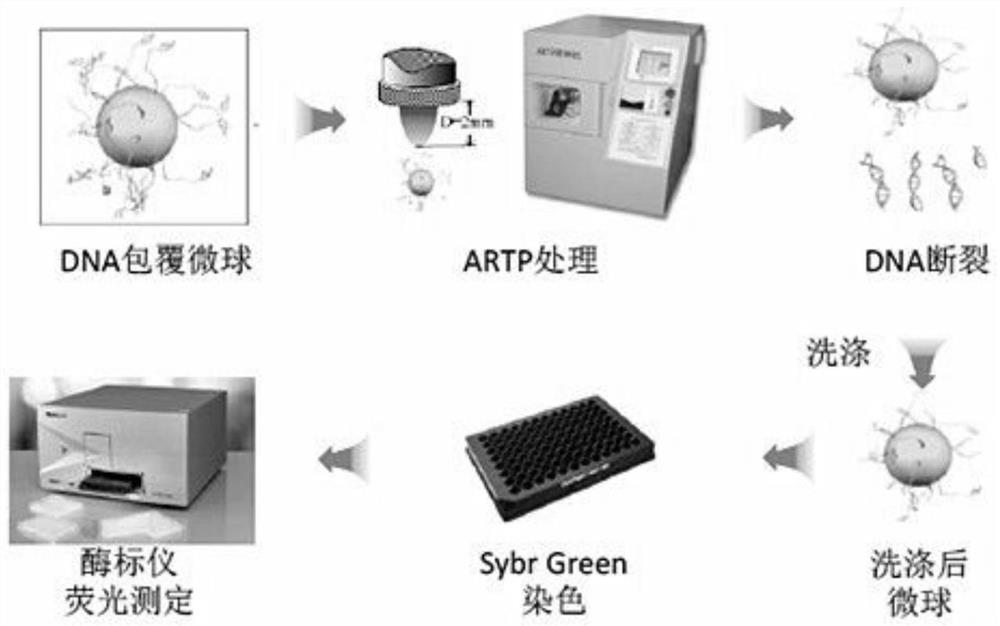
Method for rapid detection of in vitro DNA break damage strength by plasma
The invention relates to a method for rapid detection of in vitro DNA break damage strength by plasma, and the method is used for determining the damage strength of plasma mutagenesis methods including atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) on DNA. The method includes the steps of: 1) treating DNA coated microspheres by plasma mutagenesis method, and setting a control group without plasma treatment; 2) performing washing, and then dyeing the DNA coated microspheres with a dye; 3) determining the fluorescence value of the dyed DNA coated microspheres by a fluorescence detector; and 4) calculating the DNA relative content of the control group and the plasma mutagenesis treated microspheres according to the fluorescence value, and judging the gene damage strength of plasma. The invention utilizes DNA coated microspheres to establish a rapid detection method for in vitro DNA damage strength so as to realize direct and effective evaluation of plasma caused damage strength to DNA.
Owner:WUXI TMAXTREE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Human gene correction
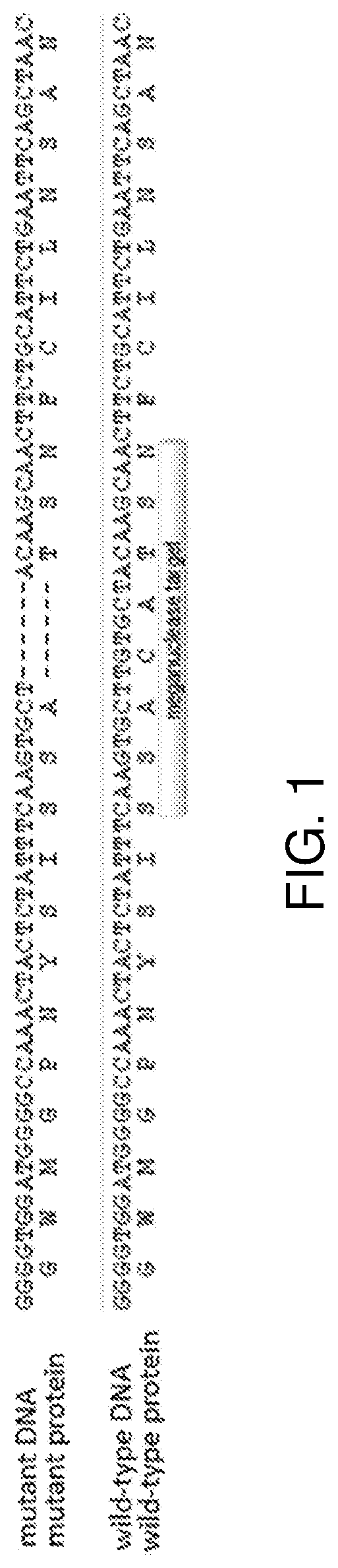
Methods are disclosed for correcting a mutant allele of a gene of interest in a primate cell. The methods include a) introducing a non-naturally occurring targeted nuclease and site-specific nucleotide-binding guide that act together to introduce double-stranded breaks in the mutant allele into the primate cell, wherein: i) the primate cell is undergoing mitotic cell division; ii) the primate cell comprises a genome that is heterozygous for the mutant allele, such that the genome comprises one copy of the mutant allele and one copy of a wild-type allele; iii) single-stranded oligonucleotides homologous to the wild-type allele are not introduced into the primate cell. The methods also include b) allowing the primate cell to activate homology-directed repair of the double-stranded DNA breaks in the mutant allele, thereby correcting the mutant allele using the normal wild-type allele as a repair template and producing a primate cell that is homozygous for the wild-type allele. The primate cell can be a one-cell embryo and / or a human cell.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
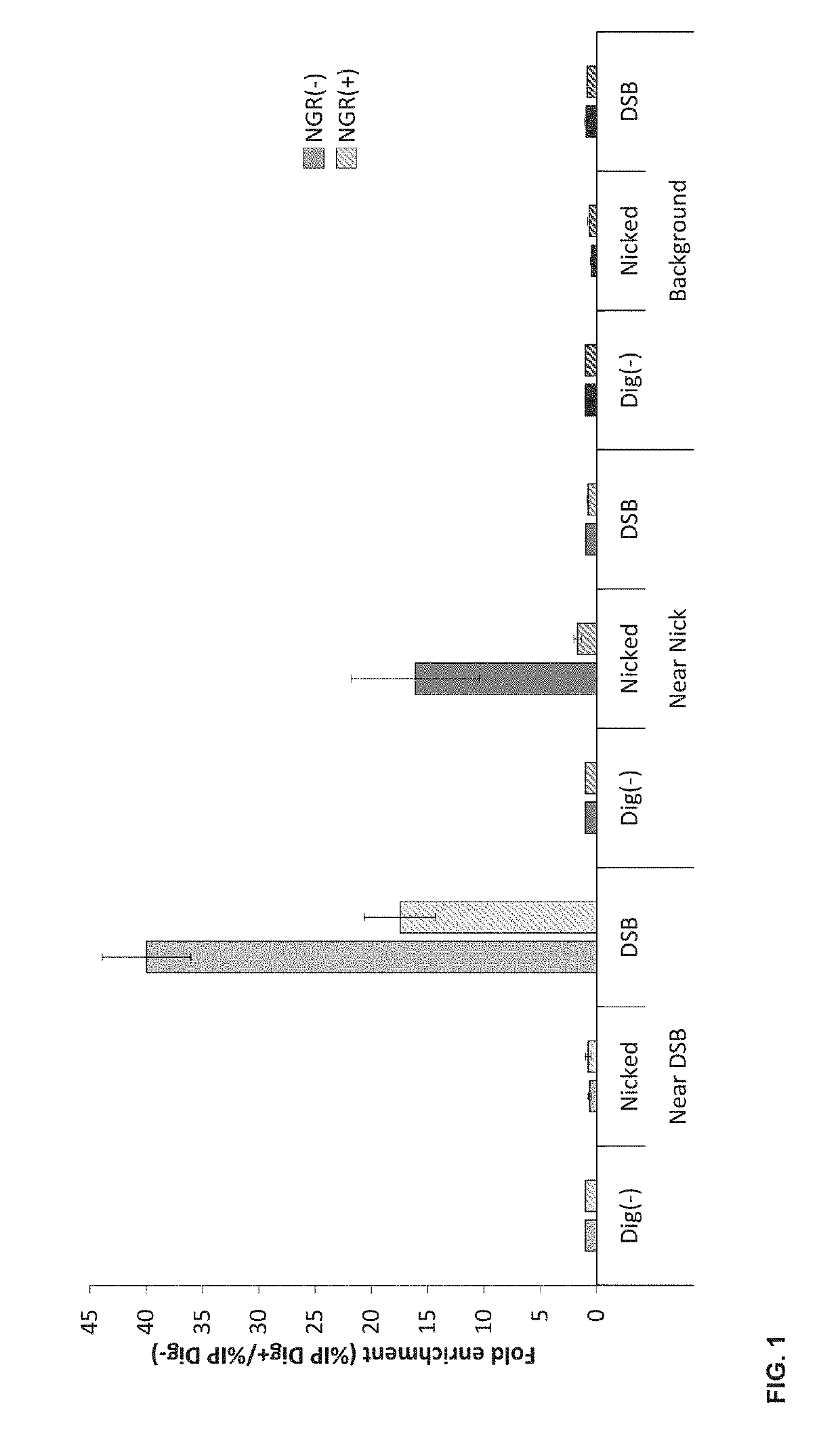
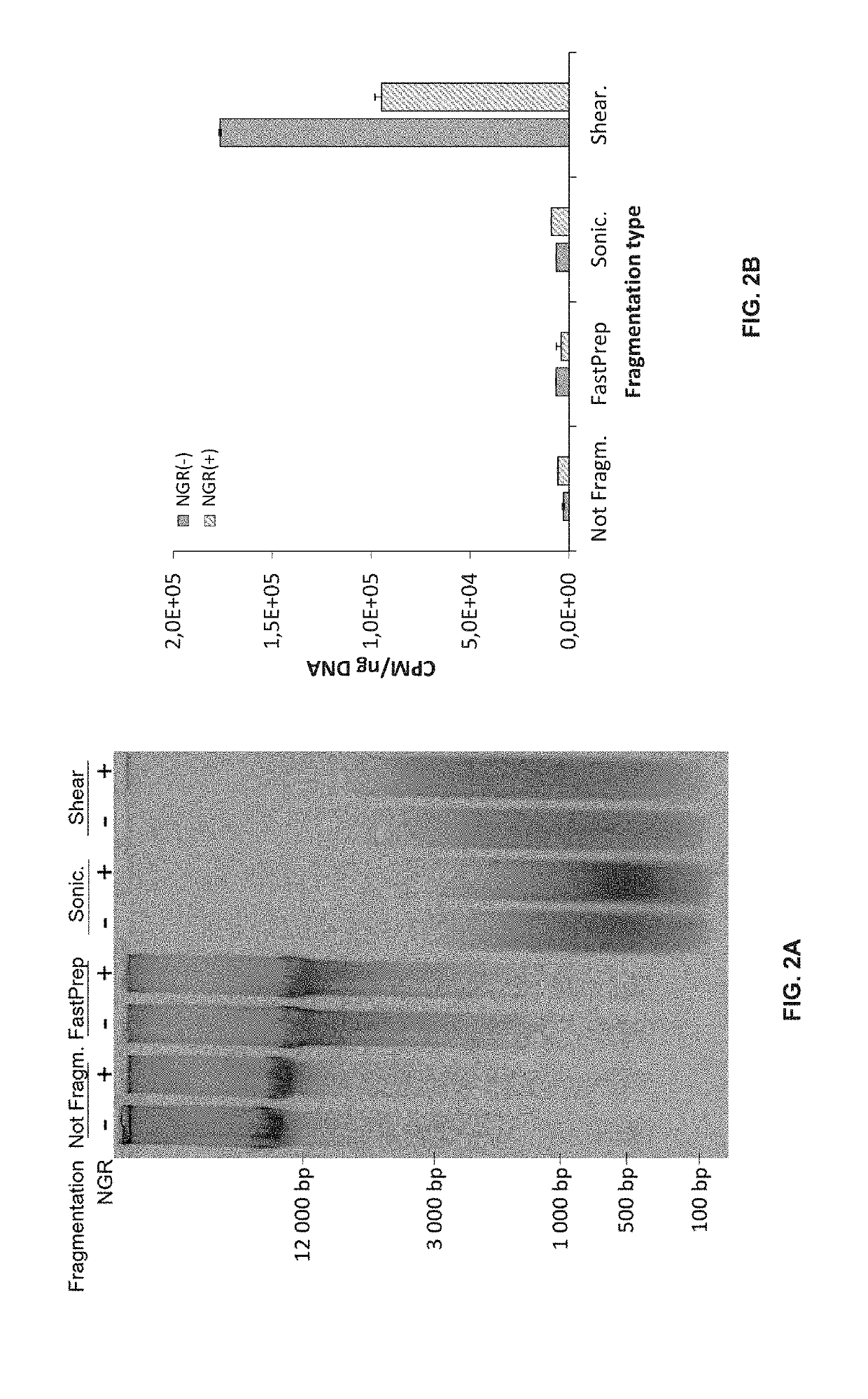
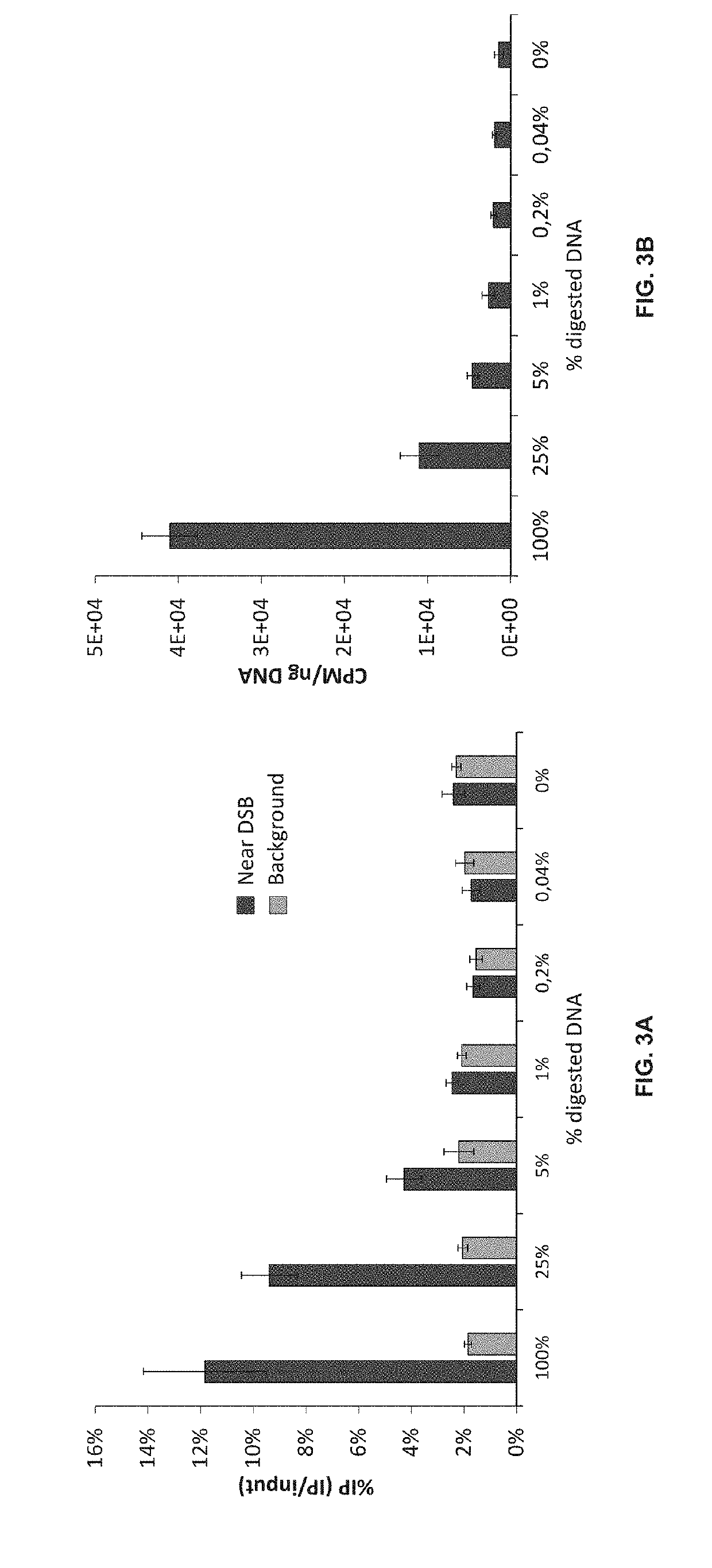
Double-strand DNA break quantification method
The present disclosure provides the quantification of double-strand breaks in DNA molecules using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase using a preliminary step of nick gap and repair. This preliminary step comprising contacting the DNA molecules with both a DNA ligase and a DNA polymerase to repair DNA nicks and remove DNA gaps prior to using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
Selective destruction of cells
PendingUS20200171159A1Increase the number ofImprove fusion rateOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDna breaksCancer research
Owner:CODE PHARMA BV
Cancer vaccine compositions and methods for using same to treat cancer
InactiveUS20200268864A1Good effectEffectively inhibit the growthOrganic active ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsCancer cellDna breaks
The present invention provides a cancer vaccine comprising DNA repair-deficient cancer cells, wherein the cancer cells are contacted with a PARP inhibitor to induce DNA breaks. In another aspect, a method of treating a subject afflicted with a cancer comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a cancer vaccine comprising DNA repair-deficient cancer cells, wherein the cancer cells are contacted with a PARP inhibitor to induce DNA breaks, is provided. The present invention also provides a kit comprising DNA repair-deficient cancer cells modified as described herein, PARP inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and combinations thereof, packaged in a suitable container.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Method for removing residual DNA in hydrophobia vaccine product by utilizing ultrasound combined with EDTA solution
ActiveCN101780276BEffective removal of contentBreak through the quality bottleneckAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsAntigenDna breaks
The invention provides a method for removing residual DNA in a hydrophobia vaccine product by utilizing ultrasound combined with EDTA solution. The method solves the problems that a method for extracting hydrophobia vaccine through concentration, purification and the like can only remove dissociative DNA in a certain percentage and cannot remove host DNA combined with antigen protein and clinicaladverse reactions commonly occur. The method has main points of: adding the EDTA solution into hydrophobia vaccine concentrate; performing ultrasonic treatment on the hydrophobia vaccine by using ultrasonic wave to make the host DNA broken more easily under the action of the ultrasound; and removing the host DNA through chromatography and purification. The method has the advantages that: on the premise of ensuring the valence of the vaccine, the quality of a vaccine product is improved, mass hybrid protein and the host DNA are removed so that the residual DNA content of the vaccine product isless than 100 pg / dose, and the quality problem in the hydrophobia vaccine industry at present is solved.
Owner:LIAONING YISHENG BIOLOGY PHARMACY
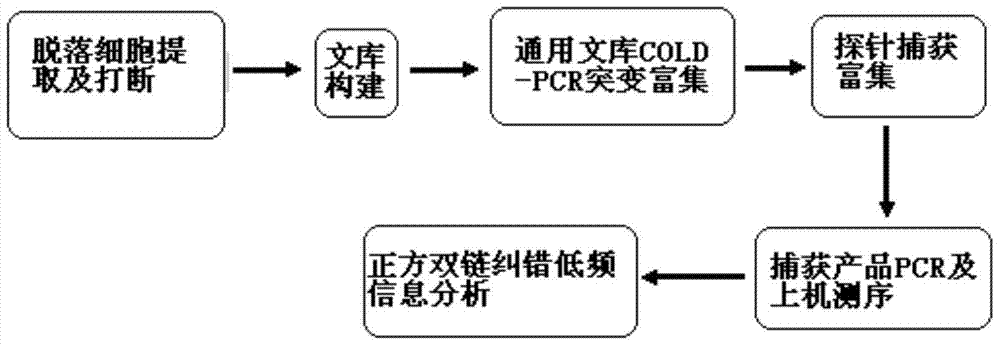
A DNA low-frequency mutation enrichment sequencing method for exfoliated cells
ActiveCN105132407BEfficient and accurate detectionAccurate predictionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationUniversal jointDna breaks
The present invention provides a low-frequency mutation enrichment sequencing method for exfoliated cell DNA, including the extraction of exfoliated cell DNA and DNA fragmentation, sample DNA library construction, general library TT-COLD PCR amplification enrichment, and probe enrichment capture , capture product PCR and on-machine sequencing, positive and negative double-strand error correction low-frequency information analysis steps, specifically TT COLD PCR based on joint universal primers to achieve first-level mutation enrichment and amplification for all types of mutations; design enrichment probe chip For hotspot mutations, replace the probe designed based on the human genome reference sequence hg19 with the probe designed based on the mutant base, and keep the probes at other sites unchanged, and perform the second-level enrichment capture; the two ends of the inserted DNA in the library construction are 12bp The self-sequence is used as a tag for positive and negative double-strand error correction comparison, which improves data utilization and realizes low-frequency accurate detection. It can detect 0.01% low-frequency variation with high specificity.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH
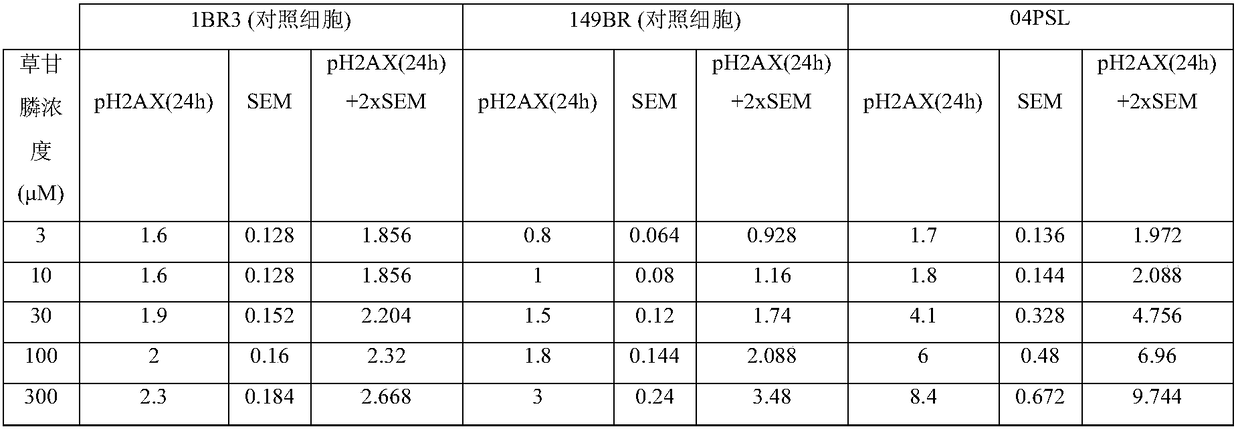
Individual method predictive of the dna-breaking genotoxic effects of chemical or biochemical agents
A process for evaluating the sensitivity of a tissue taken from an individual to the DNA-breaking toxic effect of at least one chemical or biochemical agent, or of a combination of chemical and / or biochemical agents, comprising the following steps: (a) a working concentration is set for said at least one chemical or biochemical agent, or for chemical and / or biochemical agents included in said combination of chemical and / or biochemical agents; (b) cells are taken from a tissue to be evaluated of an individual; (c) said cells are dispersed and / or amplified so as to obtain a cell sample; (d) saidcell sample is brought into contact with said at least one chemical or biochemical agent (or said combination of chemical and / or biochemical agents) in the working concentration thereof defined in step (a), for a predetermined period of time; (e) the number of double-stand breaks of the DNA, and / or a biomarker representing this number, and / or the number of micronuclei is detected, in the knowledge that steps (b), (c), (d) and (e) must be carried out one after the other, and that step (a) must be carried out before step (e).
Owner:ネオリスディアグノスティック +4
Engineered nucleases in plant generation
ActiveUS20200308595A1Reduce contentHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPlant cell
Methods are provided to mutate, in a targeted manner, the genome of a plant cell using a double stranded DNA break inducing enzyme. Also provided are plants, in particular Brassica plants that yield seeds producing oils having a reduced total saturated fatty acid content, and method for making such plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Methods for generating new genes in organism and use thereof
PendingUS20220348950A1Improve the immunityIncrease productionHydrolasesPlant peptidesDna breaksGenetic element
The present invention relates to the technical fields of genetic engineering and bioinformatics, in particular, to a method for creating a new gene in an organism in the absence of an artificial DNA template, and a use thereof. The method comprises simultaneously generating DNA breaks at two or more different specific sites in the organism's genome, wherein the specific sites are genomic sites capable of separating different genetic elements or different protein domains, and the DNA breaks are ligated to each other through non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homologous repair to generate a new combination of the different gene elements or different protein domains that is different from the original genome sequence, thereby creating a new gene. The new gene of the invention can change the growth, development, resistance, yield and other traits of the organism, and has great value in application.
Owner:QINGDAO KINGAGROOT CHEM COMPOUNDS CO LTD
A method for editing gene fusions
ActiveCN113717991BMeeting the Needs of Fusion ResearchOvercome inaccuraciesStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionDna breaksExon
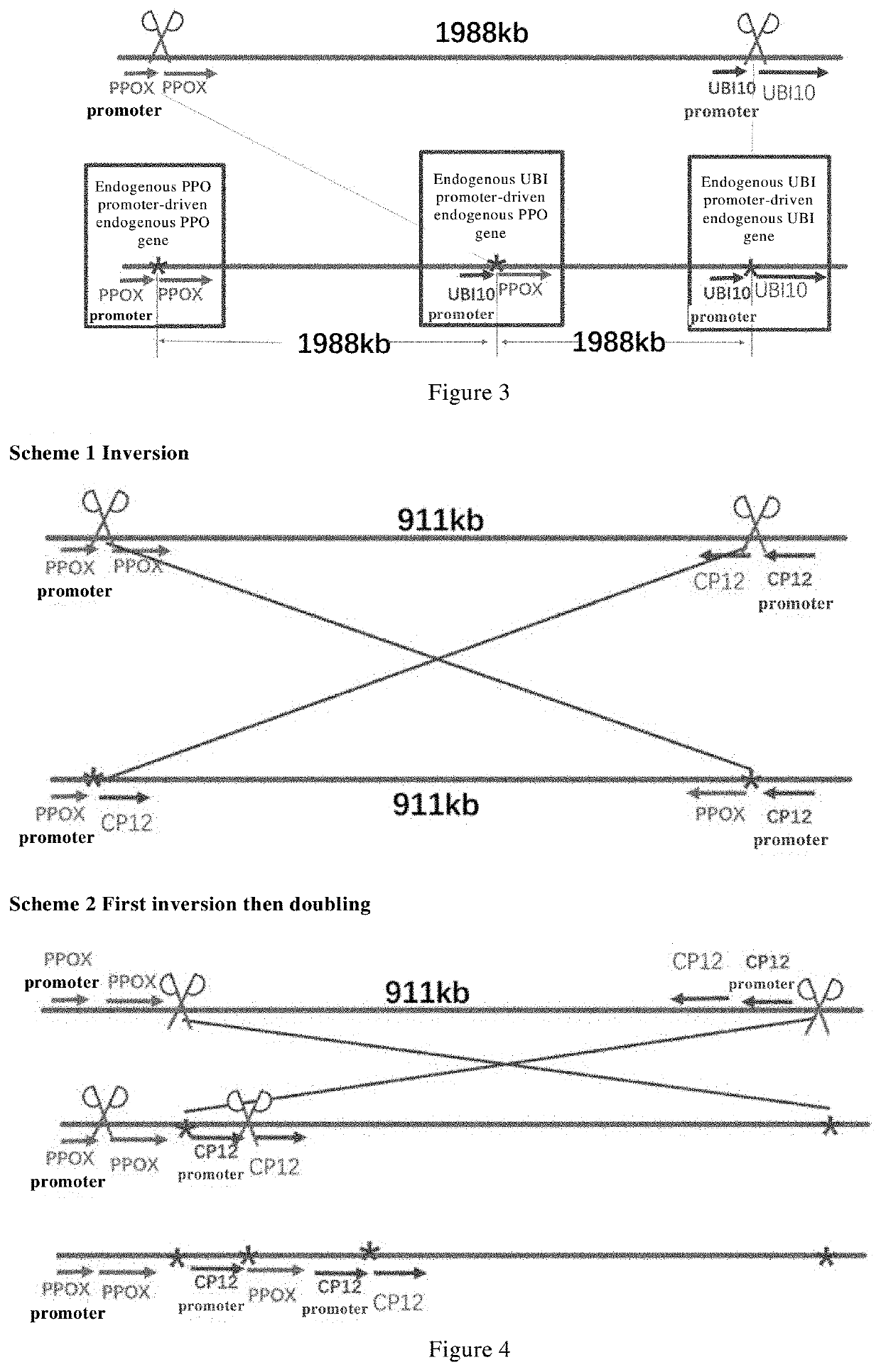
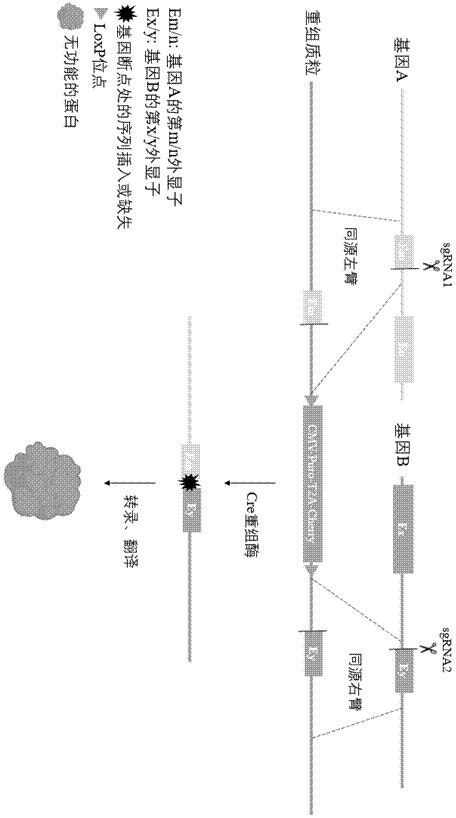
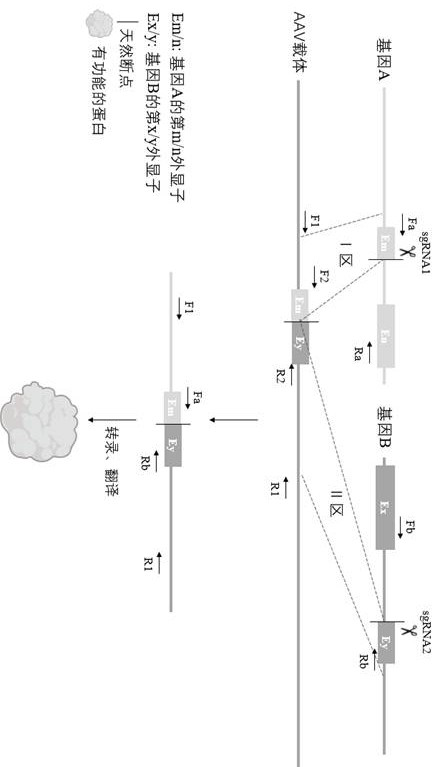
The invention provides a fusion gene editing method, which is characterized in that the editing method includes: (1) designing a sgRNA near the natural breakpoints of the two genes involved in the fusion; (2) designing a recombinant The AAV vector enables homologous recombination repair of two DNA breaks. Using this method can ensure that no matter the natural breakpoint is within an exon, an exon boundary or an intron region, the sequence of the obtained fusion gene is completely consistent with the natural sequence, which overcomes the inaccurate breakpoint sequence of the existing method. question.
Owner:菁良科技(深圳)有限公司
Double-strand DNA break quantification method
ActiveUS20190161792A1Growth inhibitionMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesNucleotideDna breaks
The present disclosure provides the quantification of double-strand breaks in DNA molecules using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase using a preliminary step of nick gap and repair. This preliminary step comprising contacting the DNA molecules with both a DNA ligase and a DNA polymerase to repair DNA nicks and remove DNA gaps prior to using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
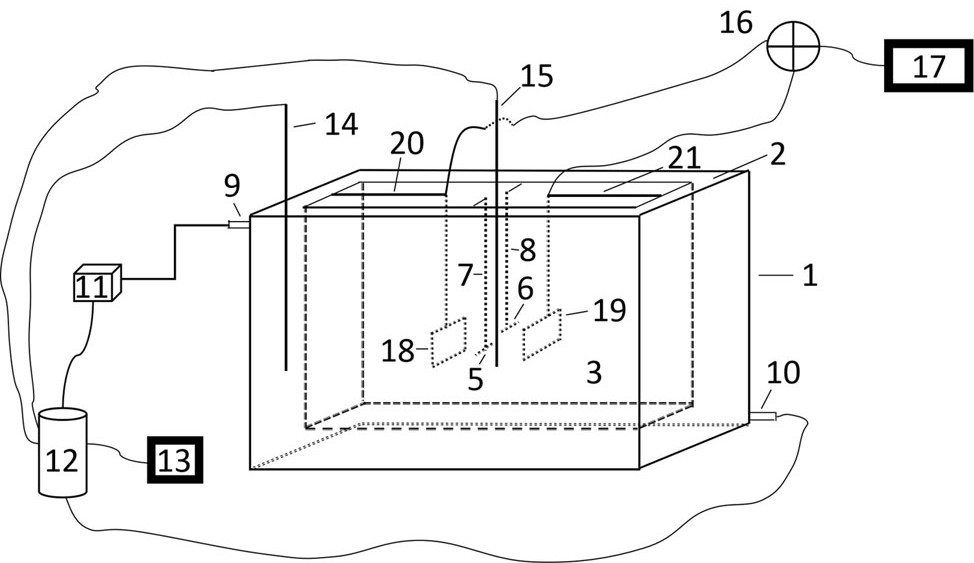
DNA breaking instrument
PendingCN113684125AGood response uniformitySimple structureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlFluid phase
The invention discloses a DNA breaking instrument. According to the DNA breaking instrument, a water tank with a shell layer is mounted on a machine box of the DNA breaking instrument, a temperature control system capable of accurately controlling the temperature is connected to the shell layer of the water tank, L-shaped sample seat assemblies for placing sample tanks are mounted on the front side and the rear side of the water tank, the sample seat assemblies are foldable, when the sample seat assemblies are unfolded, sample tubes in the mounted sample tanks can be suspended in the water tank, microelectrode arrays are installed on the left side and the right side of the machine box through assemblies, and the two microelectrode arrays are connected with a power source and a controller of a liquid phase plasma device; and when the breaking instrument is used, the sample seat assemblies are unfolded, the sample tubes are placed on the sample tanks, water is filled in the water tank, and a centrifugal tube is in contact with the water, so that non-contact liquid-phase plasma of a sample in the sample tube can be broken. The breaking instrument is simple in structure and wide in application, is mainly used for breaking DNA required by sequencing, and can also be used for preparing DNA and DNA terminal protein compounds and the like.
Owner:杭州奥明医学检验实验室有限公司
A rapid method for detecting the damage intensity of DNA fragmentation caused by plasma in vitro
The invention relates to a method for rapid detection of in vitro DNA break damage strength by plasma, and the method is used for determining the damage strength of plasma mutagenesis methods including atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) on DNA. The method includes the steps of: 1) treating DNA coated microspheres by plasma mutagenesis method, and setting a control group without plasma treatment; 2) performing washing, and then dyeing the DNA coated microspheres with a dye; 3) determining the fluorescence value of the dyed DNA coated microspheres by a fluorescence detector; and 4) calculating the DNA relative content of the control group and the plasma mutagenesis treated microspheres according to the fluorescence value, and judging the gene damage strength of plasma. The invention utilizes DNA coated microspheres to establish a rapid detection method for in vitro DNA damage strength so as to realize direct and effective evaluation of plasma caused damage strength to DNA.
Owner:WUXI TMAXTREE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
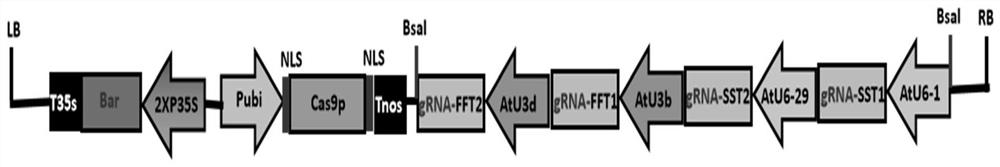
Simultaneous Knockout of 1-sst and 1-fft Genes in Rubbergrass Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System
ActiveCN112266913BEfficient knockoutPrecise knockoutGlycosyltransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention relates to the technical field of rubber grass gene editing, in particular to a method for simultaneously knocking out 1-SST and 1-FFT genes of rubber grass by using a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The sgRNAs specifically targeting the inulin synthase genes 1-SST and 1-FFT provided by the present invention can efficiently guide the endonuclease protein Cas9 to cut at the target site and generate double-stranded DNA breaks, combined with resistance screening and DNA sequencing Accurate and efficient simultaneous knockout of the rubbery inulin synthase genes 1-SST and 1-FFT. The present invention provides a convenient and efficient method for creating a rubber grass inulin synthase gene mutant, which effectively avoids the problems of long period, mutation uncertainty, high screening difficulty and high cost in conventional mutagenesis breeding. Breeding of grass elite germplasm provides a new method.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +2
A fusion protein and a method for homologous recombination using it
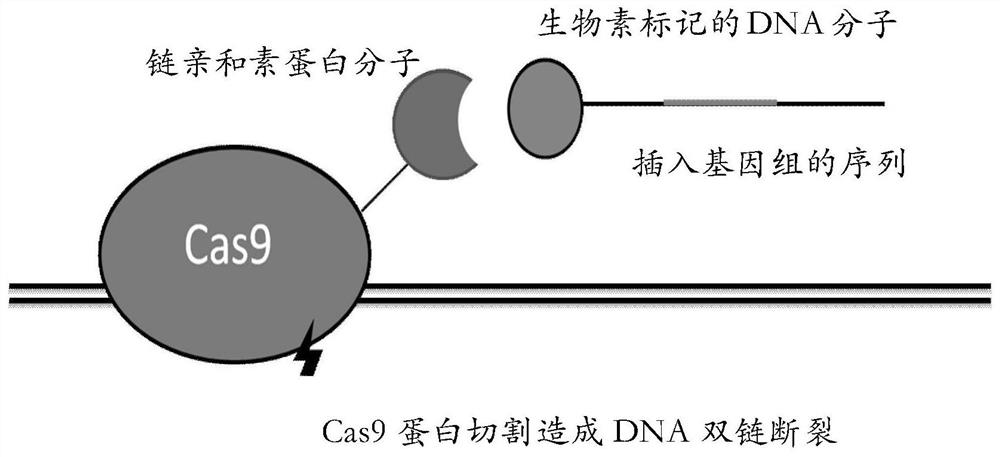
ActiveCN107880132BSignificant progressIncrease local densityNucleic acid vectorHybrid peptidesSingle strandBiotin
The invention relates to a fusion protein, a method for homologous recombination using it and its application in homologous recombination of exogenous DNA molecules into target sequences. The fusion protein of the present invention includes CRISPR protein, TALEN or ZFN protein, biotin-binding protein and linker; it realizes exogenous Efficient and precise insertion of DNA sequences; compared with the traditional CRISPR gene editing technology, the fusion protein of the present invention and the homologous recombination method using it greatly improve the homologous recombination efficiency.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
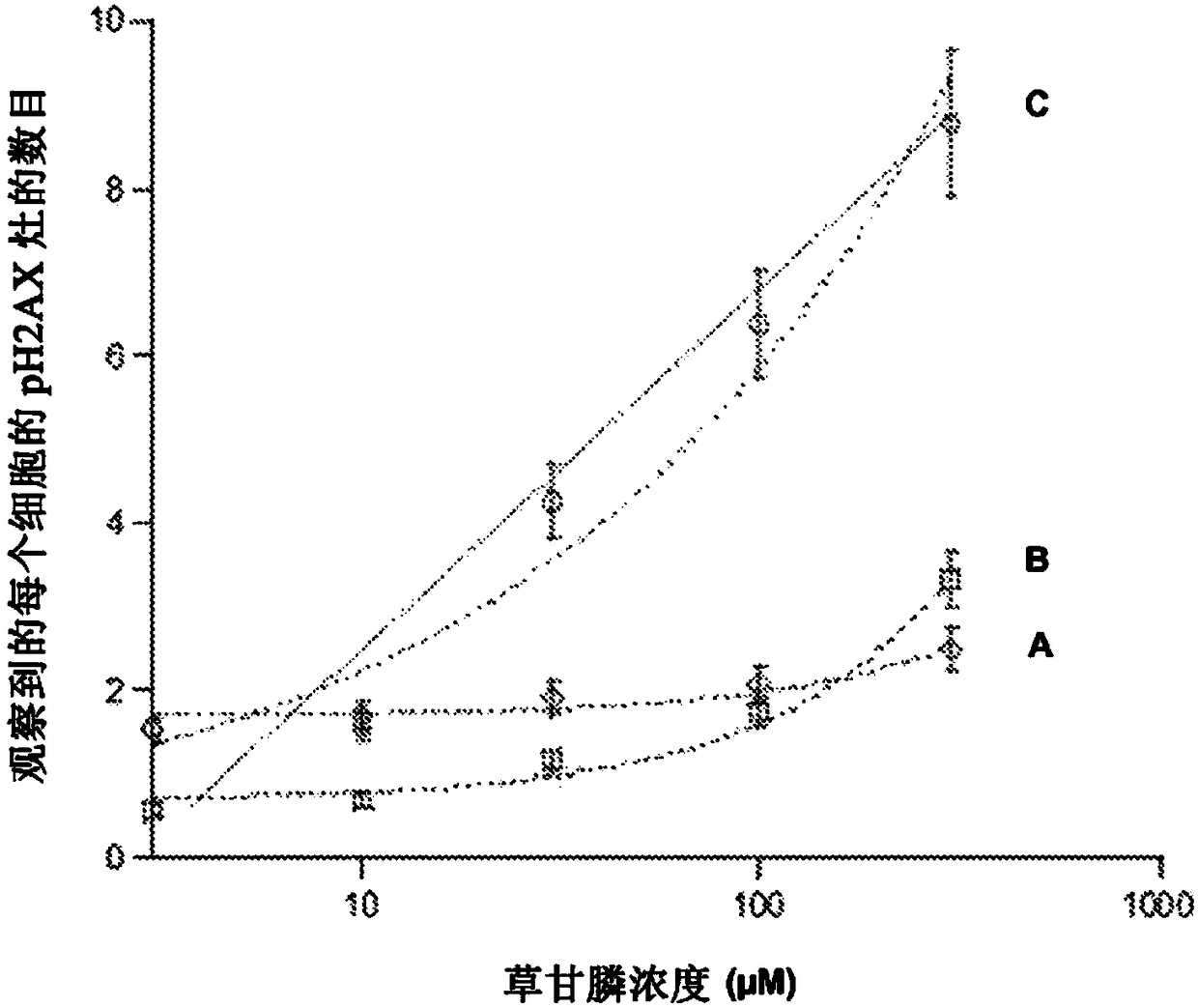
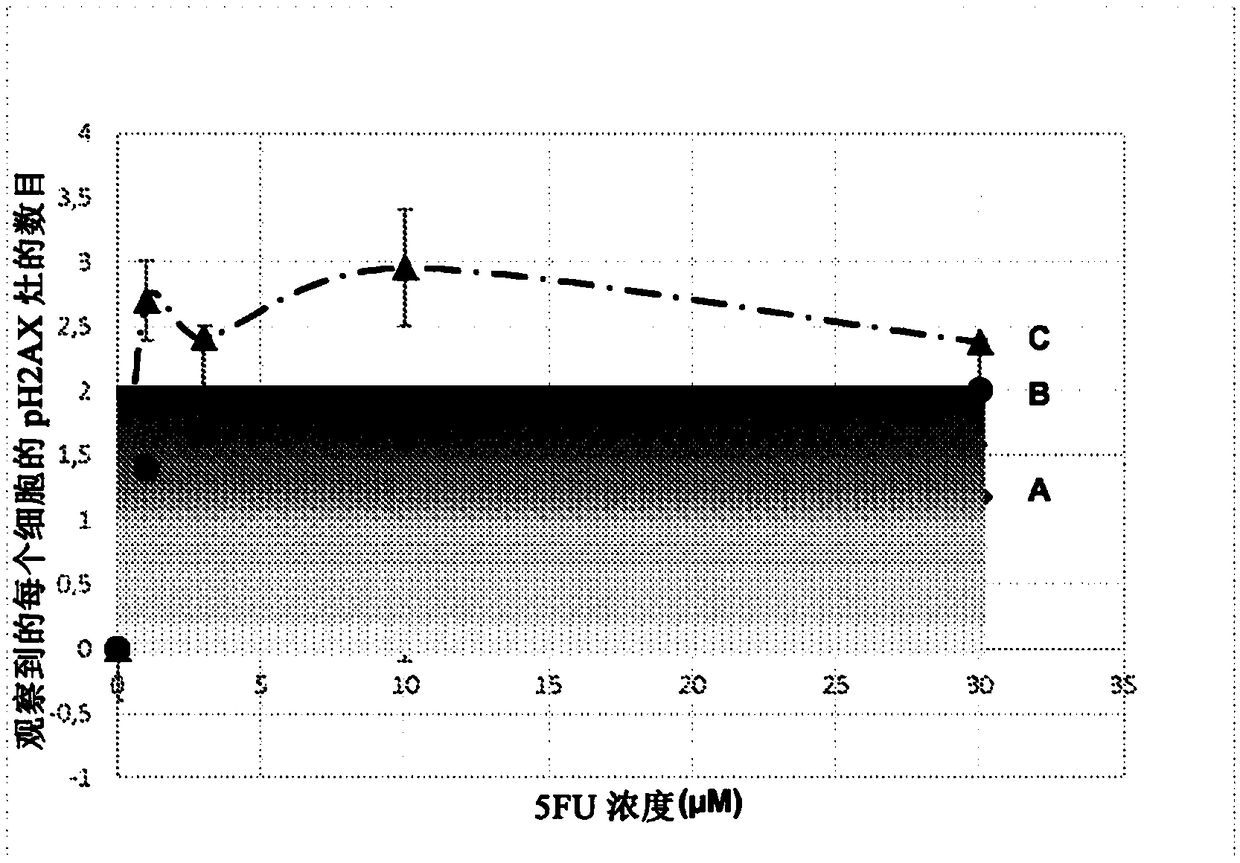
Predictive method for characterizing the sensitivity of a tumour in response to a dna-breaking treatment
A process for evaluating the response of a tumour to a DNA-breaking treatment using a sample of cells from said tumour, in which: (a) a cell sample is prepared from the cells taken from said tumour; (b) said cell sample is subjected to a DNA-breaking treatment characterized by a dose D, (c) the average number of nuclear foci obtained with a marker pH2AX at the observation times t (these average numbers being respectively called NpH2Ax(t)) is determined on said cell sample, said observation times t being the time t=0 min (called tO, state before administration of the dose D) and at least one observation time selected from t = t1, t2, t3 and t4 after administration of the dose D; (d) at least one parameter or score which makes it possible to characterize the response of the sample to said DNA-breaking treatment is determined using at least the average numbers NpH2Ax(t), and in which process t4 is a fixed value which represents the time for which the level of DNA breaks reaches its residual value, t3 is a fixed value which represents the time after which approximately 25% of the double-strand breaks (DSBs) are repaired in control cells from radioresistant patients, t2 is a fixed valuewhich represents the time after which approximately 50% of the DSBs are repaired in control cells from radioresistant patients, t1 is a fixed value which represents the time after which the number ofrecognized DSBs reaches its maximum in control cells from radioresistant patients.
Owner:ネオリスディアグノスティック +4
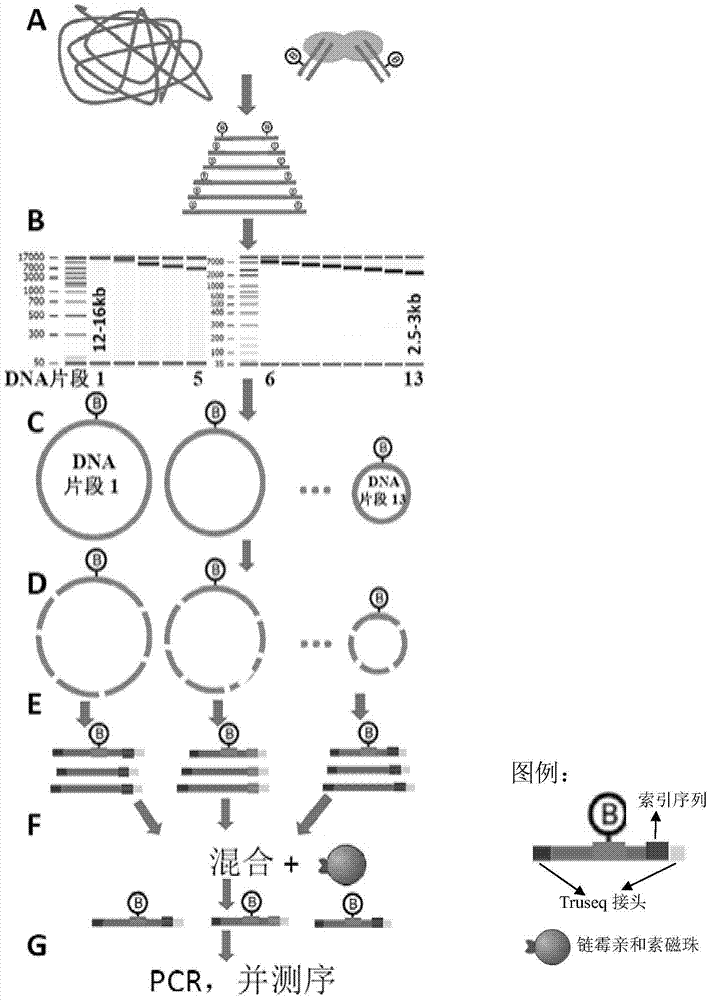
A method for preparing multiple DNA large fragments inserted into a paired-end sequencing library at one time
ActiveCN105002570BReduce demandAvoid wastingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationLinker DNABiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention provides a method for preparing a plurality of large DNA fragments to be inserted into a paired-end sequencing library at one time, comprising the following steps: performing biotin linker labeling after the DNA to be tested is broken; sorting the biotin-labeled DNA fragments into N DNA fragments of different sizes, wherein, 10≤N≤12; the N DNA fragments of different sizes are respectively subjected to circularization treatment to obtain circular DNA, and then the uncircularized linear DNA fragments are removed, and the circular DNA After DNA fragmentation, connect Truseq adapters with different index sequences; mix DNA fragments of different lengths with Truseq adapters and react with streptavidin magnetic beads to enrich biotin-labeled DNA fragments; PCR The biotinylated DNA fragments are amplified and sequenced.
Owner:深圳中农京跃生物技术有限公司
Compositions and methods for promoting homology directed repair mediated gene editing
ActiveUS20210207119A1Improve efficiencyReduce off-target effectsSugar derivativesHydrolasesGenome editingDna breaks
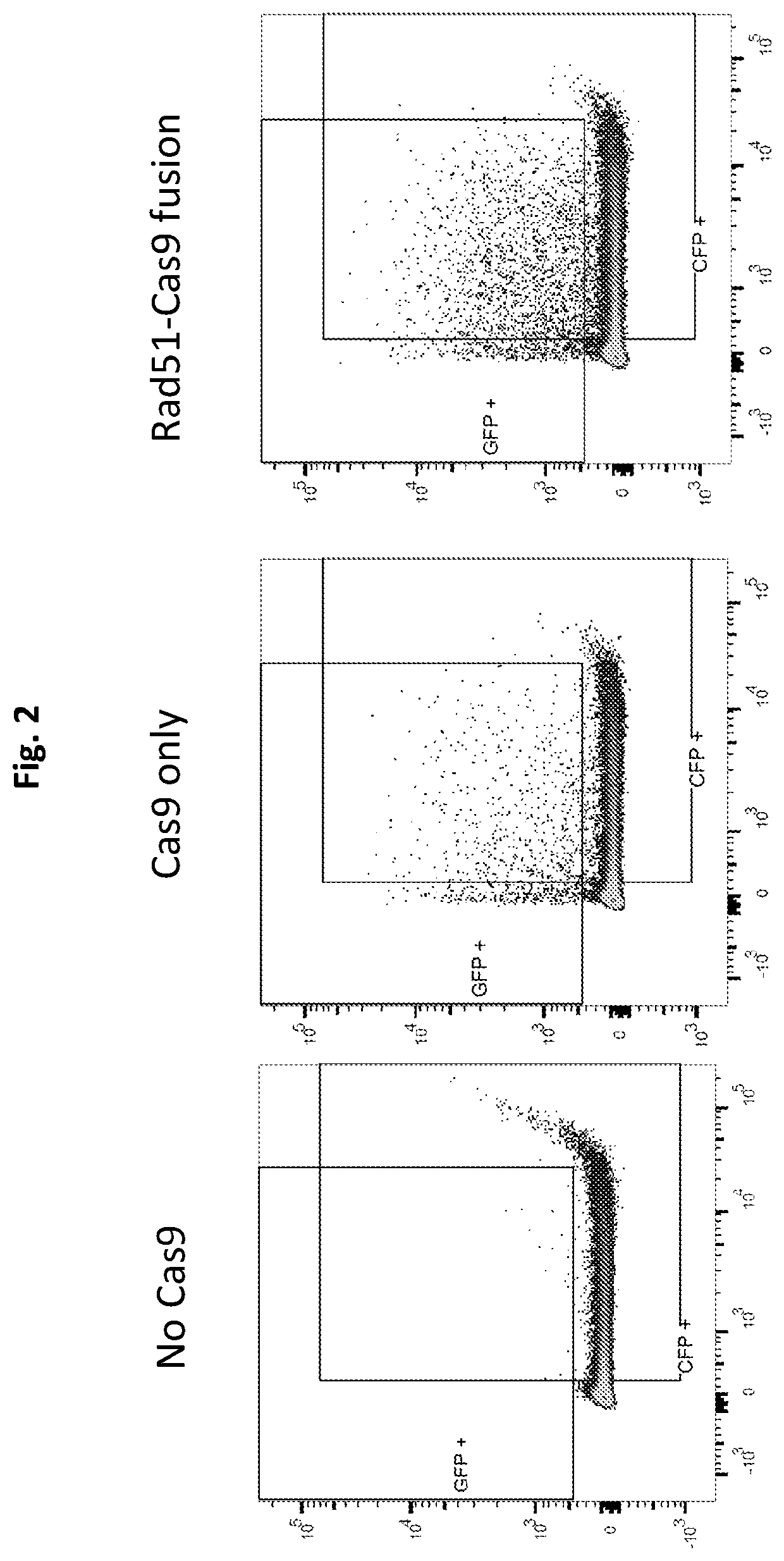
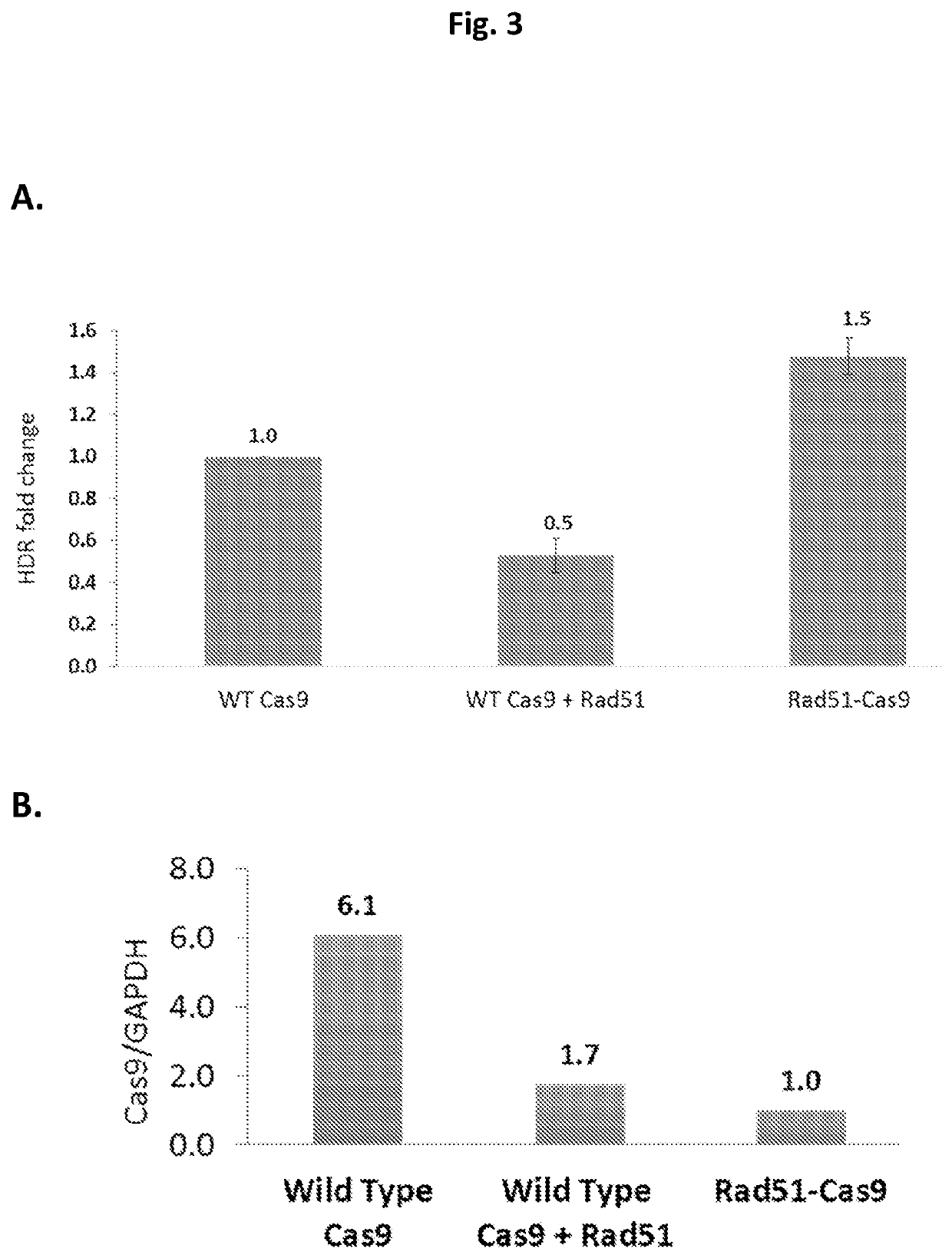
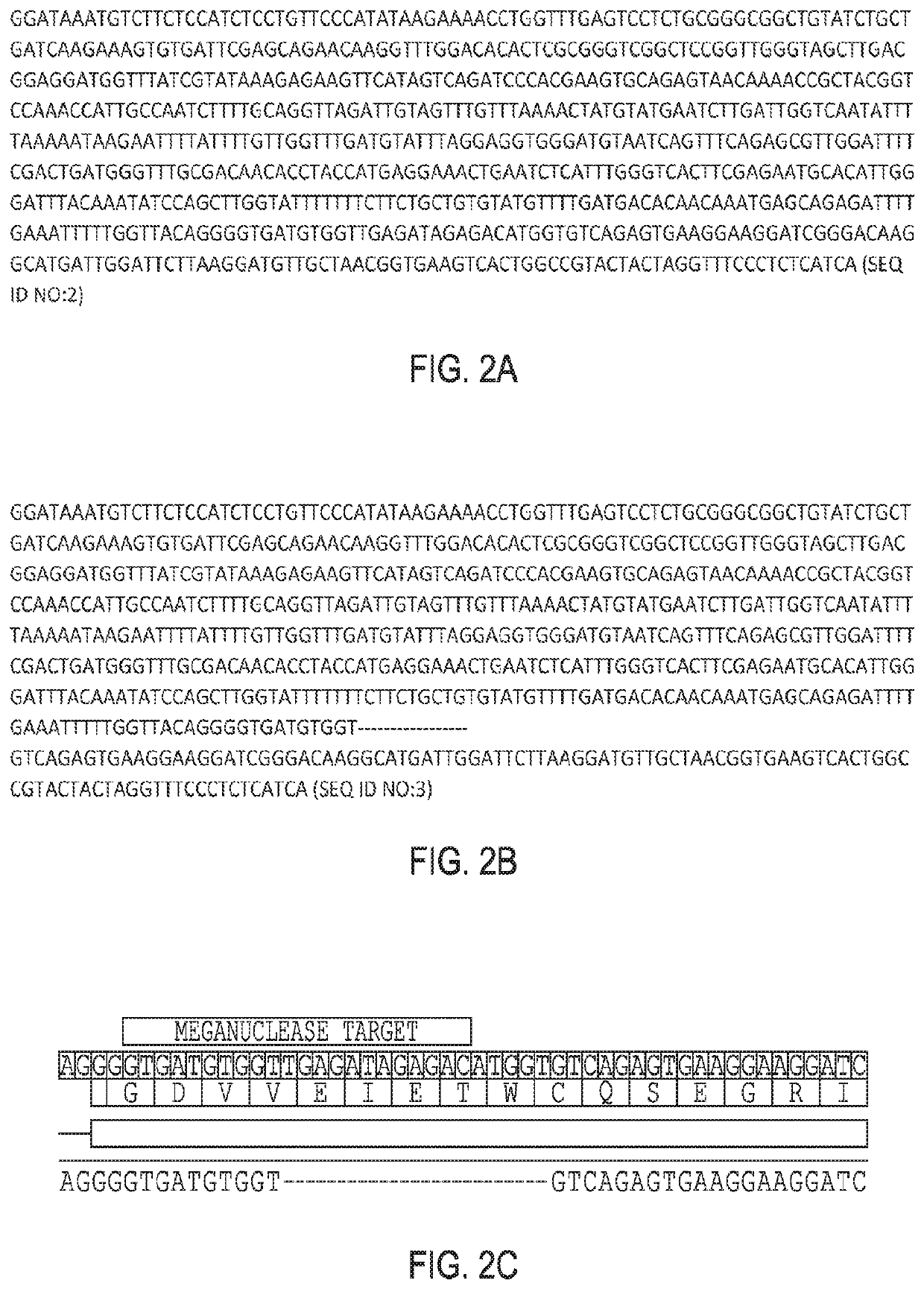
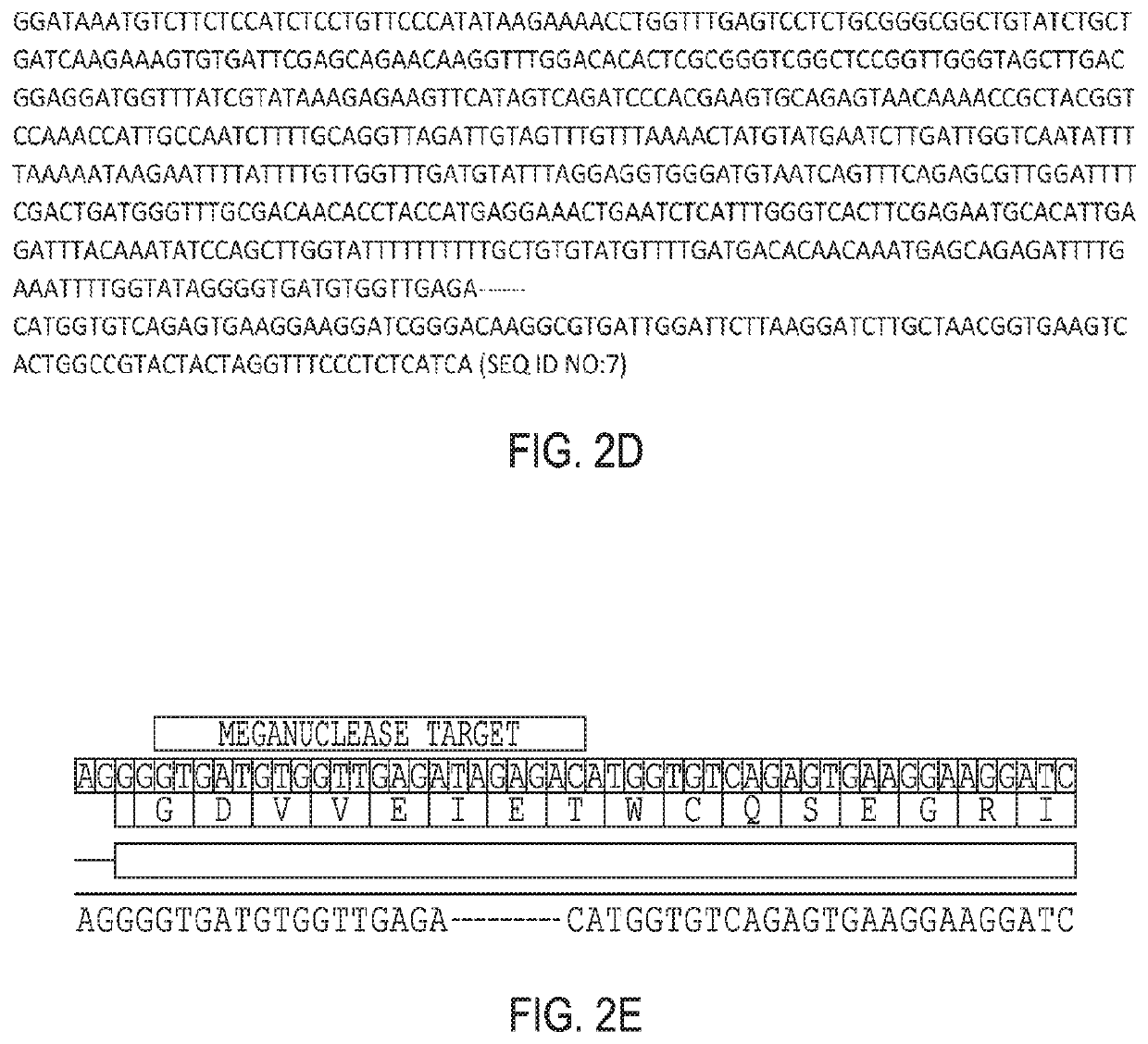
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for increasing the rate of nuclease-mediated site specific insertions of donor DNA sequence to the genome via recombination. More specifically, the method utilizes a non-naturally occurring nuclease-homology directed repair (HDR) protein chimeras for genome editing applications. Physically tethering the activity of a DNA nuclease to an HDR protein results in significant increase in the fraction of nuclease induced DNA breaks that are repaired by homologous recombination and provides higher accuracy and specificity of genome editing.
Owner:EMENDOBIO INC
Engineered nucleases to generate mutations in plants
PendingUS20220064657A1Plant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPlant cell
Methods are provided to mutate, in a targeted manner, the genome of a plant cell using a double stranded DNA break inducing enzyme. Also provided are plants, in particular Brassica plants that yield seeds producing oils having a reduced total saturated fatty acid content, and method for making such plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Engineered nucleases to generate deletion mutants in plants
Methods are provided to mutate, in a targeted manner, the genome of a plant cell using a double stranded DNA break inducing enzyme. Also provided are plants, in particular Brassica plants that yield seeds producing oils having a reduced total saturated fatty acid content, and method for making such plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Compositions and methods for promoting homology directed repair mediated gene editing
ActiveUS11274288B2Improve efficiencyReduce off-target effectsSugar derivativesHydrolasesGenome editingDna breaks
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for increasing the rate of nuclease-mediated site specific insertions of donor DNA sequence to the genome via recombination. More specifically, the method utilizes a non-naturally occurring nuclease-homology directed repair (HDR) protein chimeras for genome editing applications. Physically tethering the activity of a DNA nuclease to an HDR protein results in significant increase in the fraction of nuclease induced DNA breaks that are repaired by homologous recombination and provides higher accuracy and specificity of genome editing.
Owner:EMENDOBIO INC
Gene transporter and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111154808BSmall particle sizeGood dispersionOther foreign material introduction processesMetal particleEmbryo cell
The invention relates to a gene transporter and its preparation method and application. The gene transporter includes nano-metal particles and polyethyleneimine, the gene transporter has a core-shell structure, wherein the nano-metal particles form the core of the gene transporter, and the polyethyleneimine contains molecular weight The first polyethyleneimine with a molecular weight of 20000-30000 and the second polyethyleneimine with a molecular weight of 1500-2000, the first polyethyleneimine and the second polyethyleneimine are interwoven and covered on the surface of the core to form Cover the case. After the gene transporter combines with the plasmid inserted into the exogenous target gene fragment through electrostatic adsorption, it can break through the zona pellucida barrier on the outer layer of the plasma membrane of the embryonic cell and enter the embryonic cell, and promote the breakage of the double-strand DNA of the embryonic cell to generate the exogenous target gene fragment conditions for integration. At the same time, the inventors also found that the gene transporter also has the advantages of small particle size, good dispersibility, high stability, and low toxicity.
Owner:FUYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com