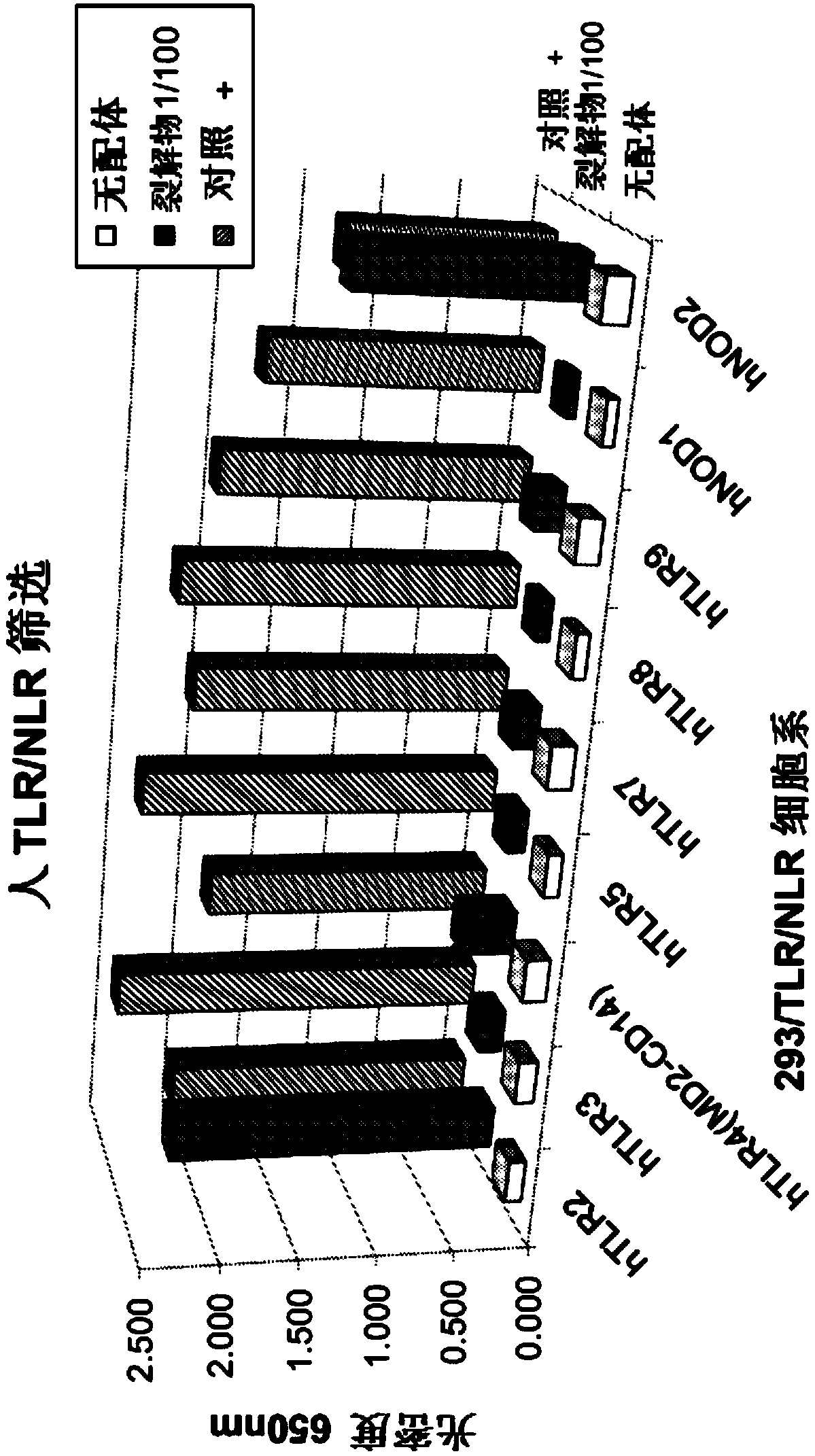
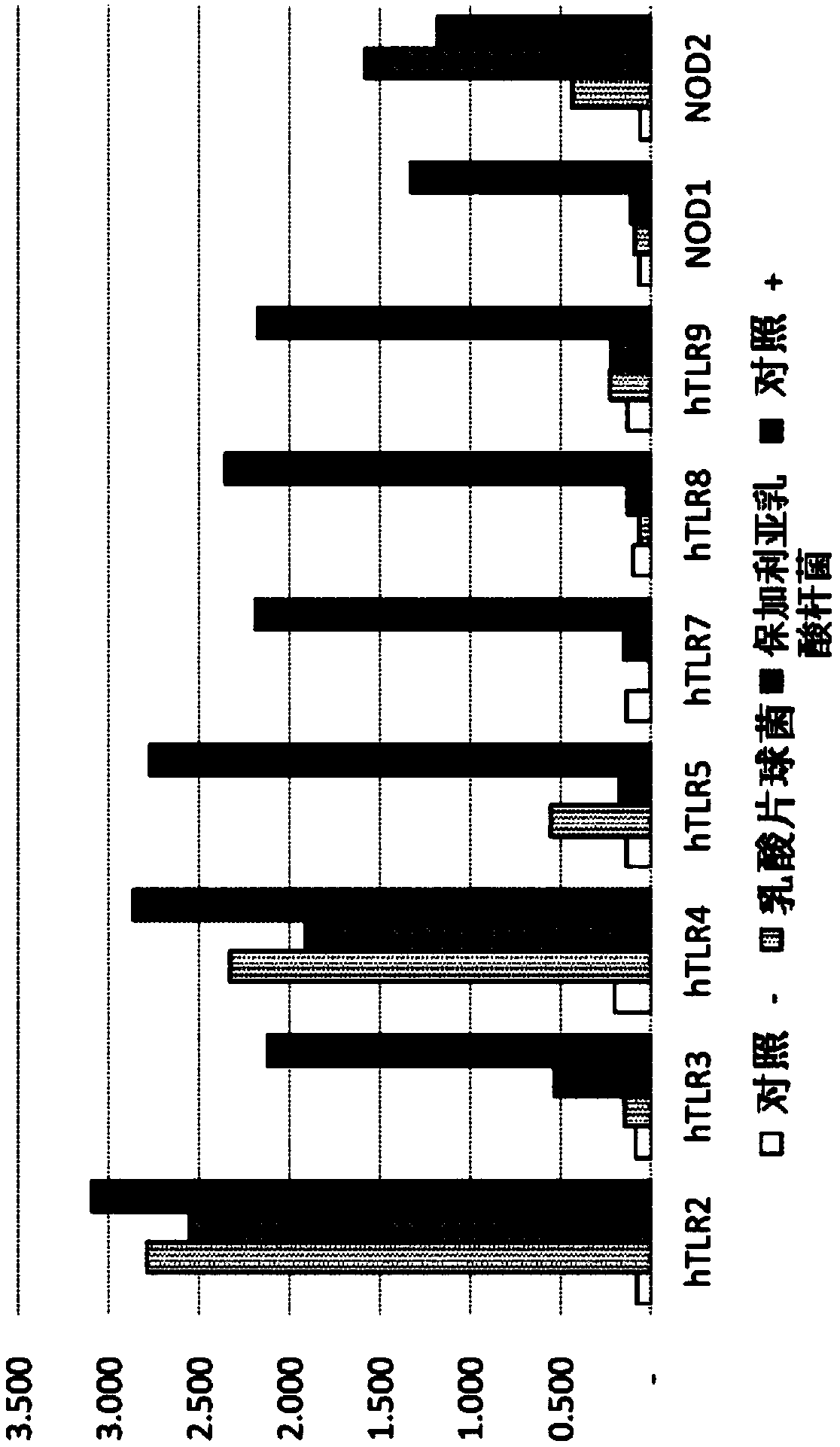
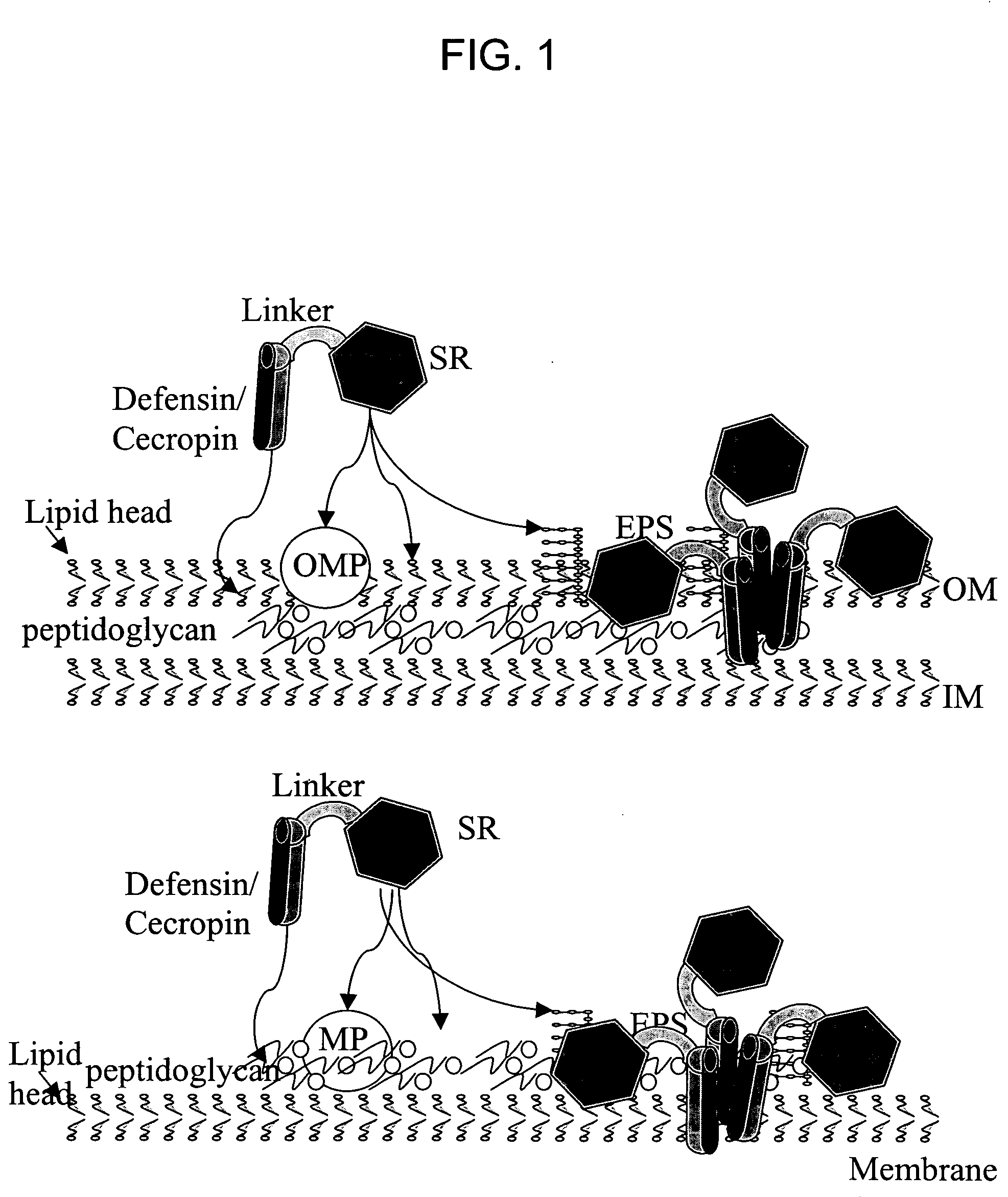
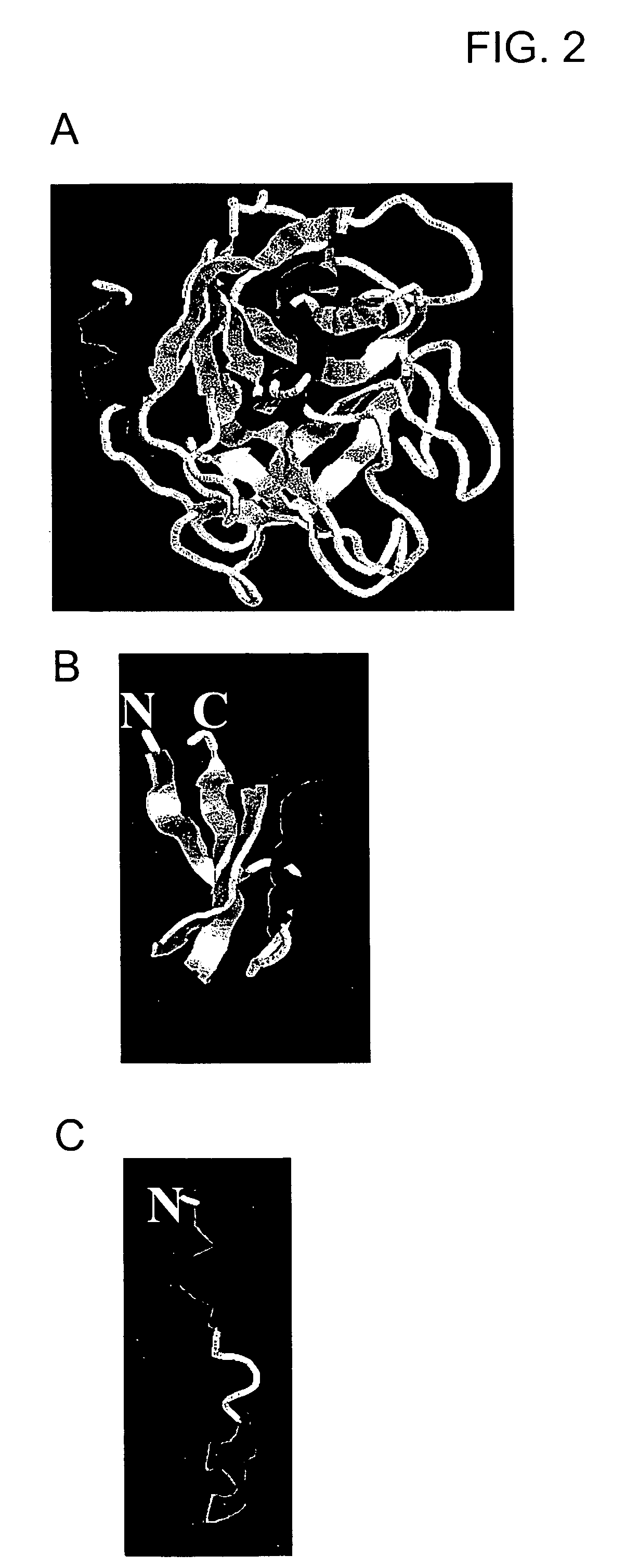
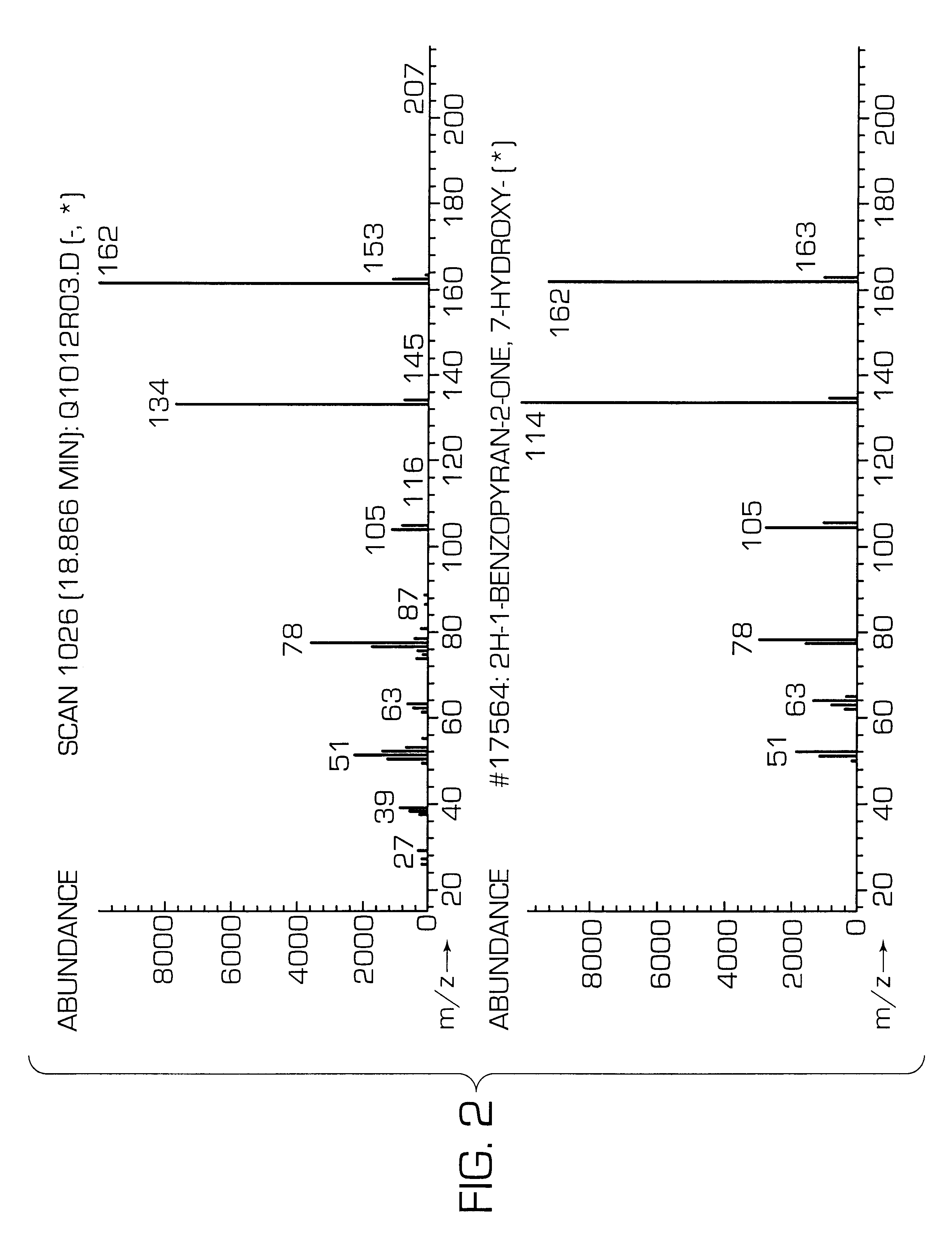
Patents
Literature
64 results about "Bacterial lysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial Cell Lysis. CelLytic products are a family of protein extraction reagents specifically formulated to lyse and extract cellular proteins based on the type of expression system. CelLytic proprietary formulations for bacterial cell lysis are available in a range of products specific to your protein extraction needs including solubilizing...
Cellular Constituents From Bacteroides, Compositions Thereof, and Therapeutic Methods Employing Bacteroides or Cellular Constituents Thereof
A cellular constituent is lysed from, produced by and / or isolated from one or more bacteria from the genus Bacteroides, and the cellular constituent, a derivative thereof, and / or one or more bacteria from the genus Bacteroides, or a modified form thereof, is employed in compositions and methods for modulating an inflammatory response. Such methods include methods of treating, delaying the onset of or reducing the symptoms of one or more inflammatory conditions / diseases, including corporal or gastrointestinal inflammation, for example, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Crohn's Disease, or colitis, and / or associated diseases such diabetes, asthma, multiple sclerosis, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, gingivitis, atopic diseases, for example, hay fever, food allergies, eczema, rhinitis, dermatitis, conjunctivitis, atopic syndrome and keratosis pelaris, ocular inflammatory disease, strokes, cardiovascular disease, depression, atherosclerosis and hypertension, and comprise administering a composition comprising one or more natural and / or modified bacteria of the genus Bacteroides, and / or a cellular constituent lysed from, produced by, or isolated from one or more natural and / or modified bacteria from the genus Bacteroides, or a derivative thereof.
Owner:MOORE RES ENTERPRISES
Bacterial vector systems
InactiveUS20060068469A1Efficient rapid deliveryFusion with DNA-binding domainBacteriaGene deliveryGene targets
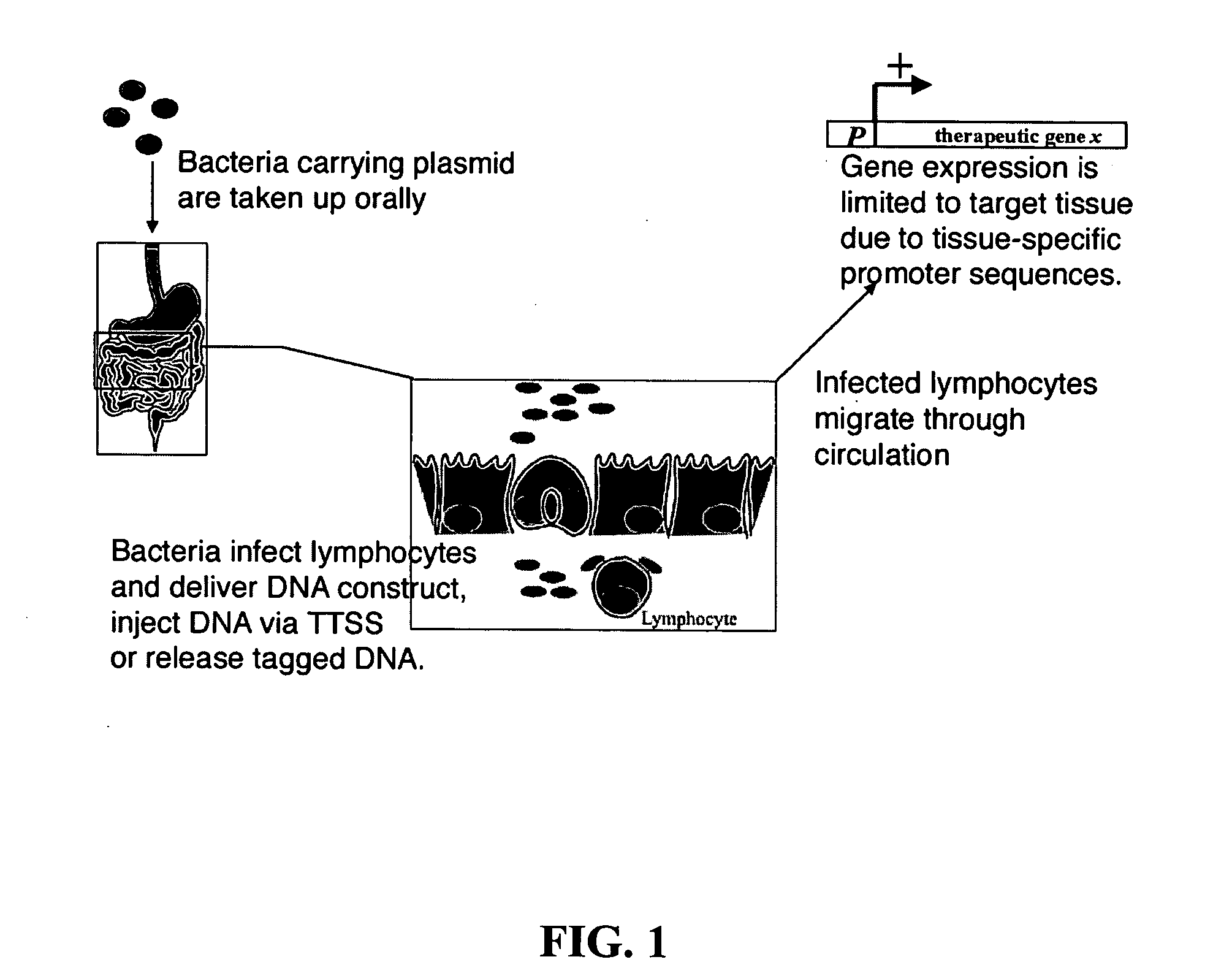
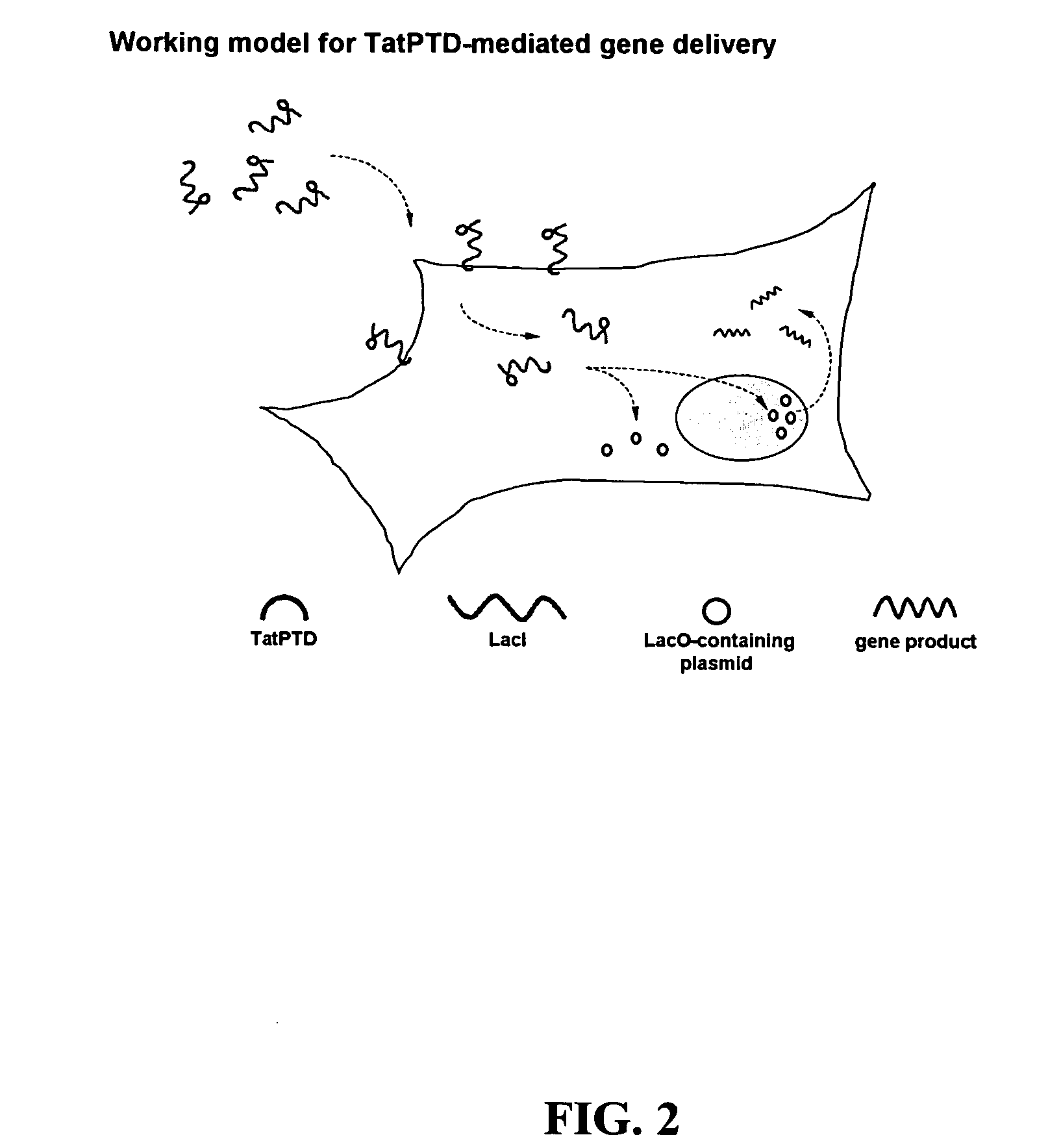
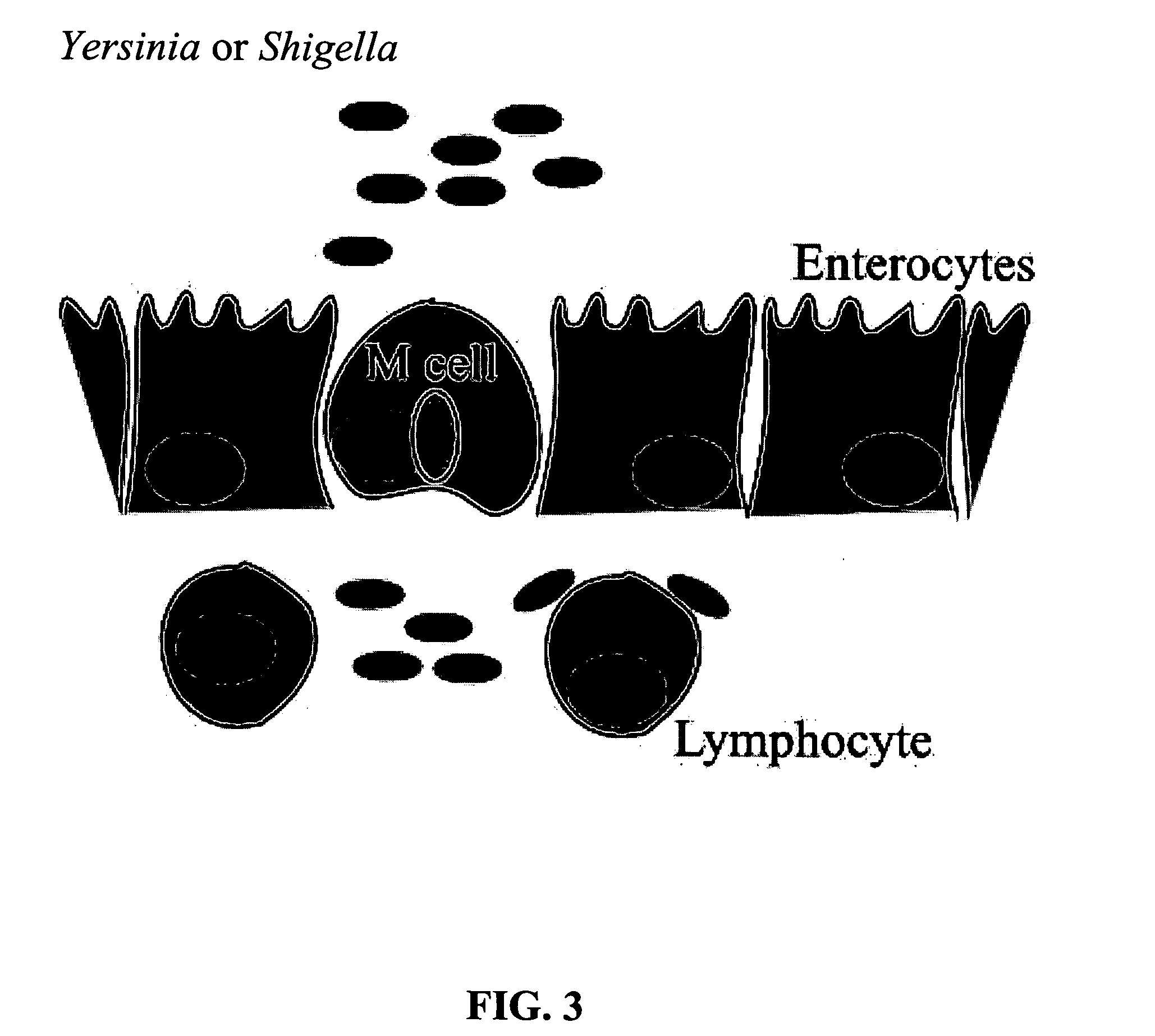
The present invention provides bacterial vectors and fusion proteins containing a TTSS polypeptide, compositions of such fusion proteins including polynucleotides, and methods of delivering one or more genes into a target cell that involve contacting the cell with a composition that includes such a fusion protein. Compositions and methods of gene delivery that involve a bacterium and a TAT, Antp, or HSV VP22 polypeptide are also disclosed. The invention also concerns methods of delivering one or more genes into a target cell utilizing a bacterium capable of becoming internalized within the cell, wherein the bacterium includes one or more genes targeted for delivery to the cell, a gene encoding an RNA polymerase, and a gene that causes lysis of the bacterium.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Selective isolation of bacterial mRNA
The invention provides methods and compositions for selectively isolating total bacterial mRNA. The general method comprises contacting a bacterial lysate comprising total bacterial mRNA and nonisolated bacterial polysomes with an exogenous enzyme under conditions wherein the enzyme selectively modifies the mRNA to form modified mRNA, and isolating the modified mRNA. In particular embodiments, the enzyme is selected from a poly(A) polymerase, a RNA ligase and a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Depending on the enzyme, the modified mRNA may have any of a variety of modifications, such as a 3' tail, particularly a poly(A) tail, a specific sequence tag, a detectably labeled nucleotide, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for treatment of microbial infections
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for treatment of microbial infections and for the enhancement of resistance to infection. The invention comprises administration of an effective amount of bacterial lysate compositions for the treatment of pathological conditions of microbial infections. The present invention can also be used to enhance the immune system to prevent infections by the administration of an effective amount of the compositions.
Owner:IMMUNOLOGY LAB
Control of cellular redox levels
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for regulating redox status and / or reducing oxidative stress in a subject, the methods and compositions comprising TLR agonists comprising bacterial lysates and / or lysate fractions. Also disclosed are compositions and methods comprising bacterial lysates and / or lysate fractions formulated or administered in combination with one or more other therapeutic or pharmaceutical agents.
Owner:伊丽莎白麦克纳
Compositions and methods for the treatment of Pierce's disease
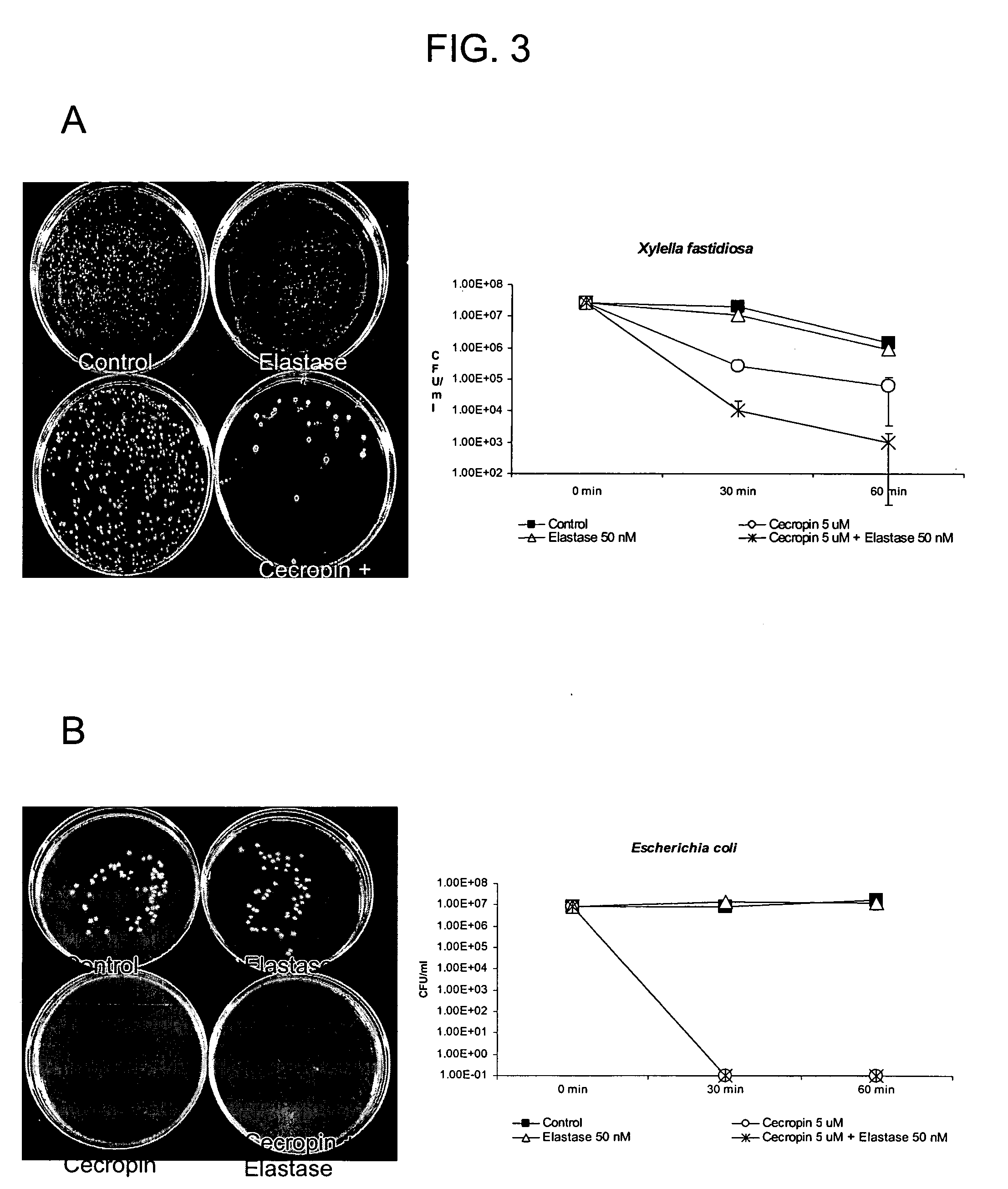
InactiveUS20050257285A1Efficient killingHigh protein concentrationBacteriaHydrolasesProphylactic treatmentTransgene
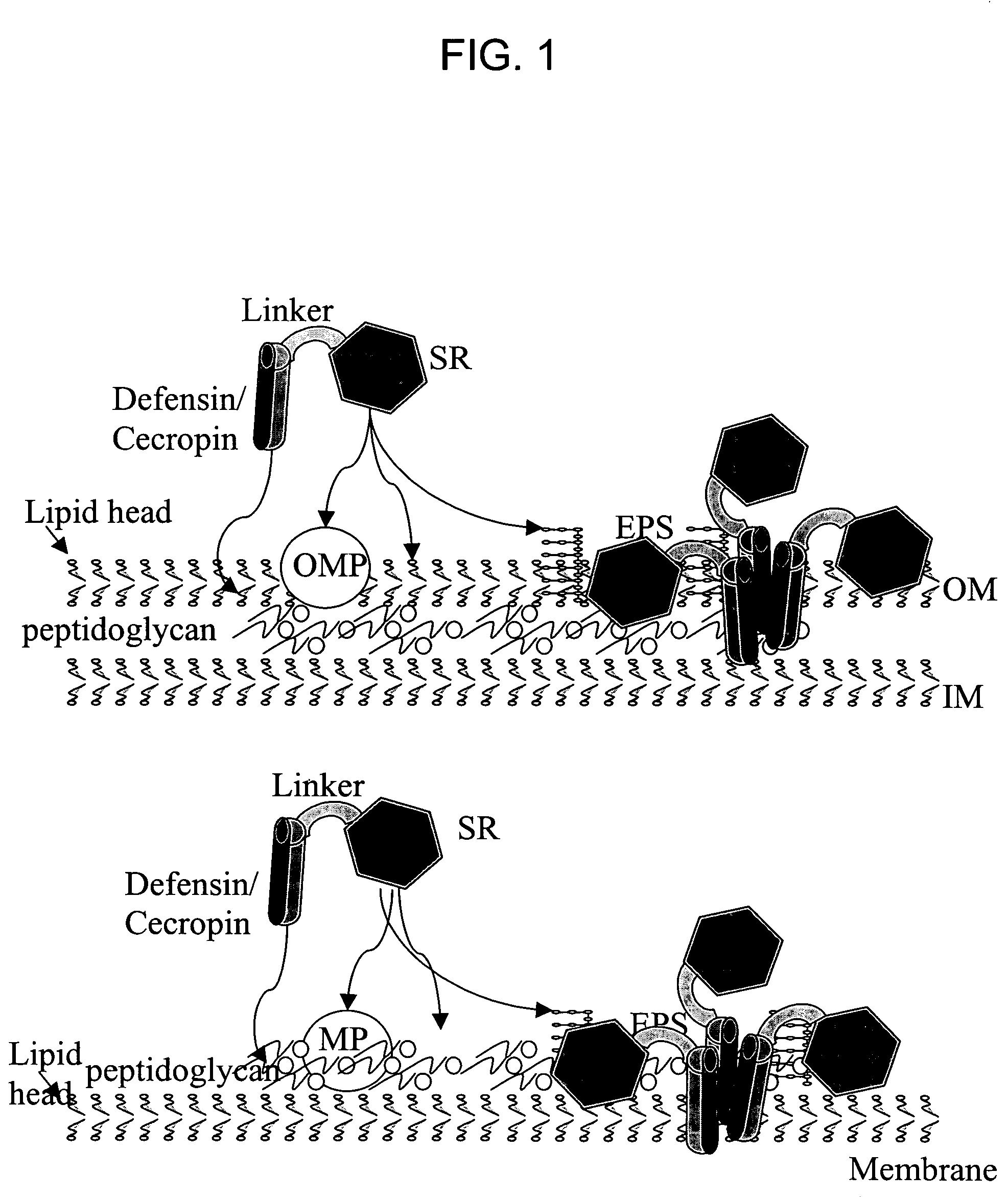
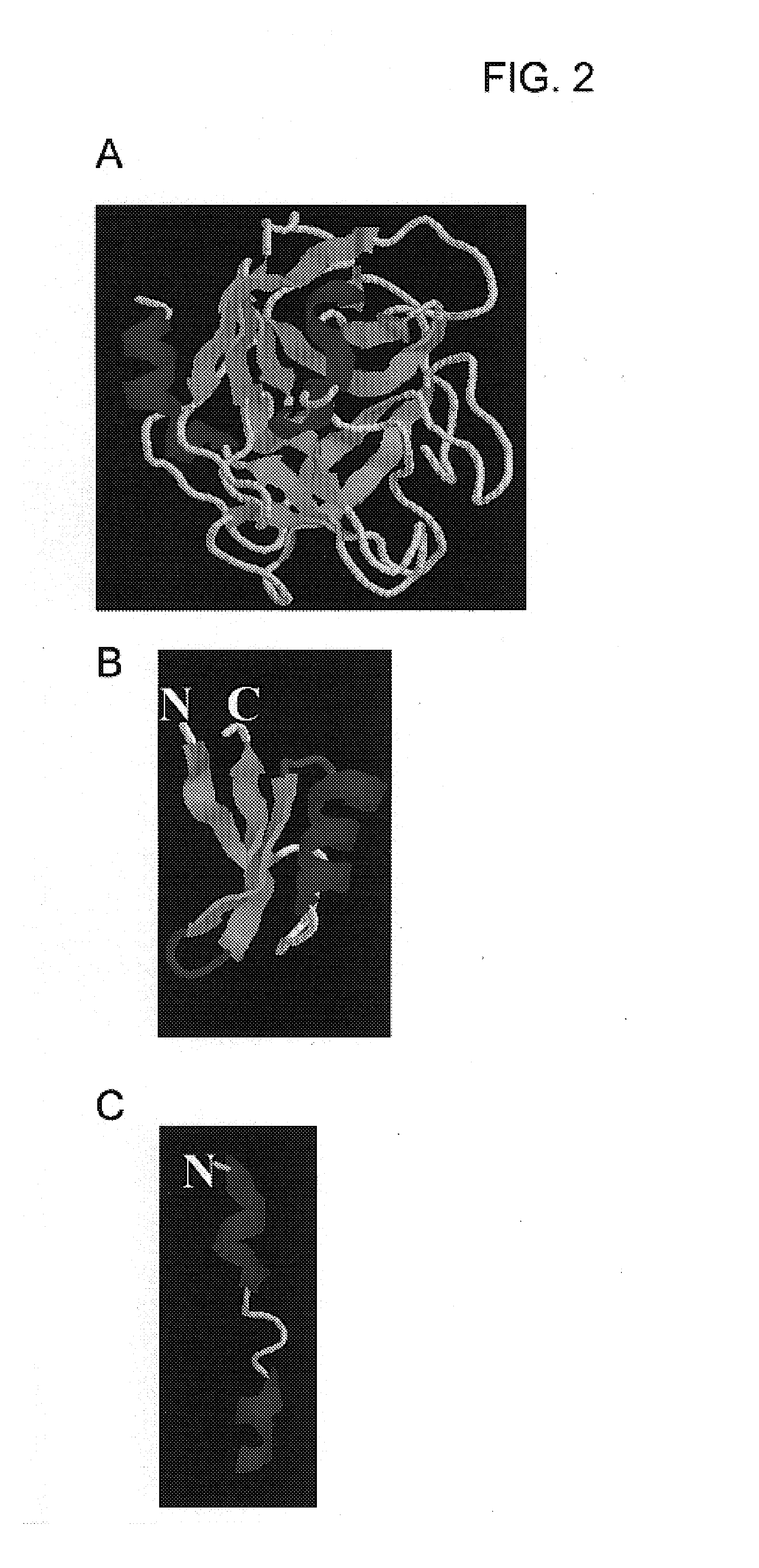
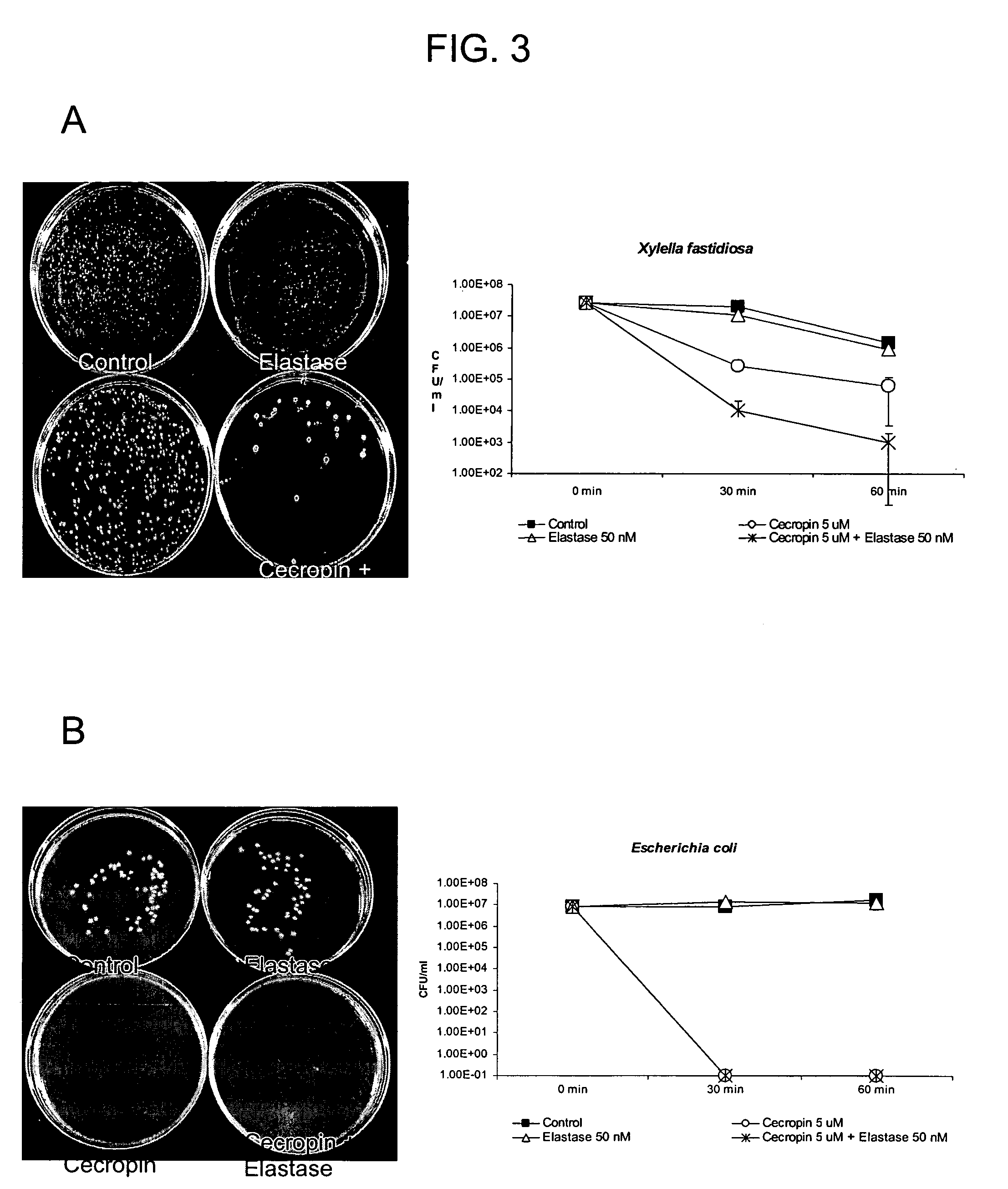
Chimeric anti-microbial proteins, compositions, and methods for the therapeutic and prophylactic treatment of plant diseases caused by the bacterial pathogen Xylella fastidiosa are provided. The anti-microbial proteins of the invention generally comprise a surface recognition domain polypeptide, capable of binding to a bacterial membrane component, fused to a bacterial lysis domain polypeptide, capable of affecting lysis or rupture of the bacterial membrane, typically via a fused polypeptide linker. In particular, methods and compositions for the treatment or prevention of Pierce's disease of grapevines are provided. Methods for the generation of transgenic Vitus vinefera plants expressing xylem-secreted anti-microbial chimeras are also provided.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Controlled lysis of bacteria
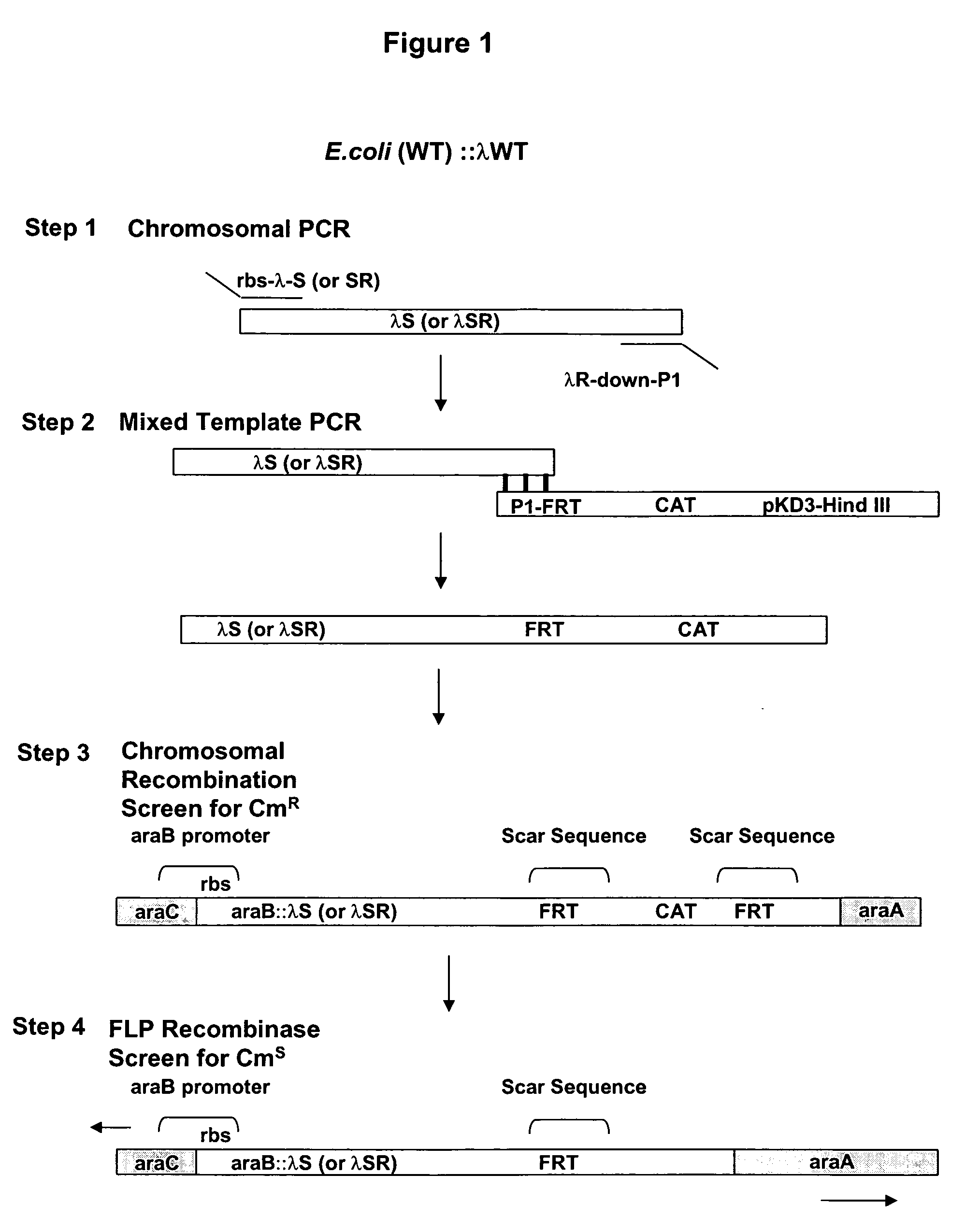
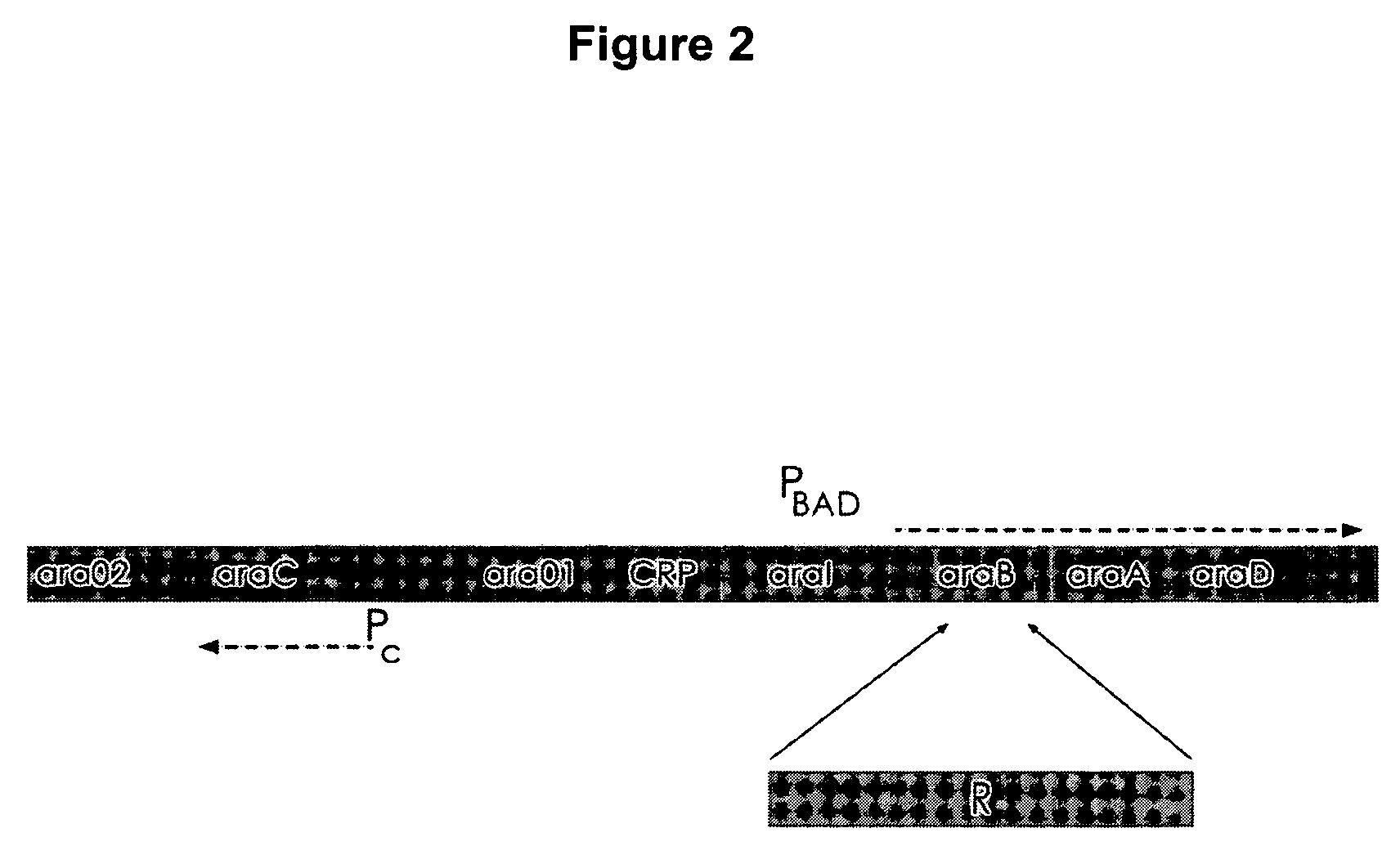
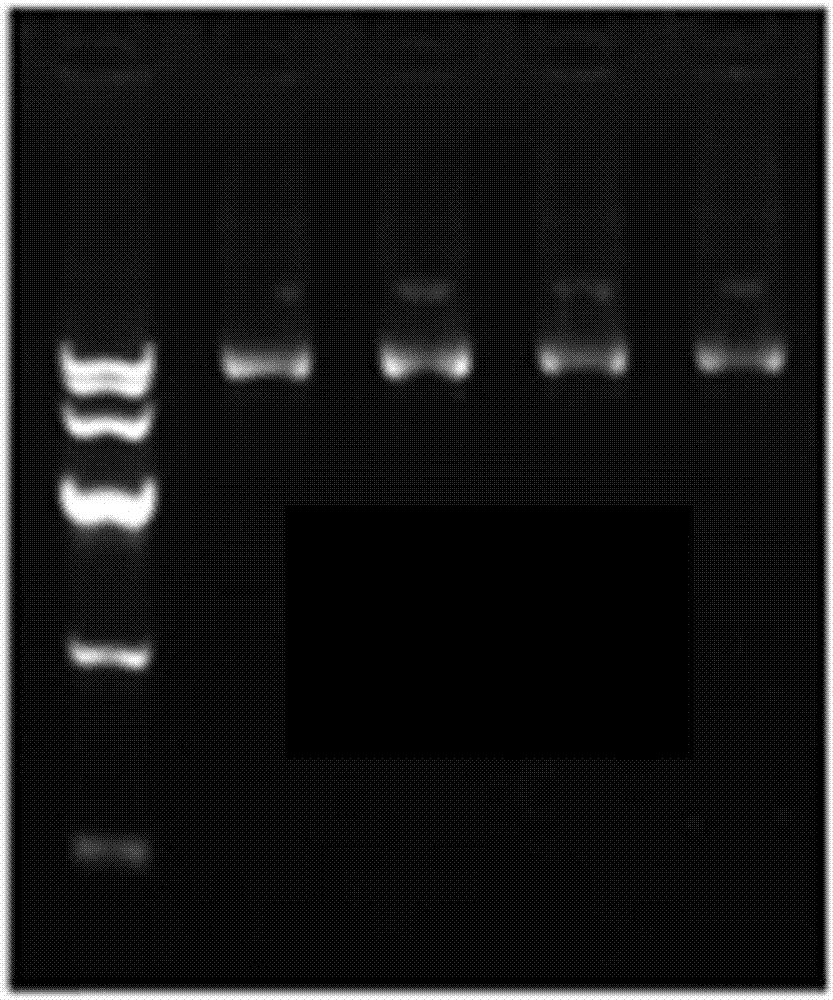
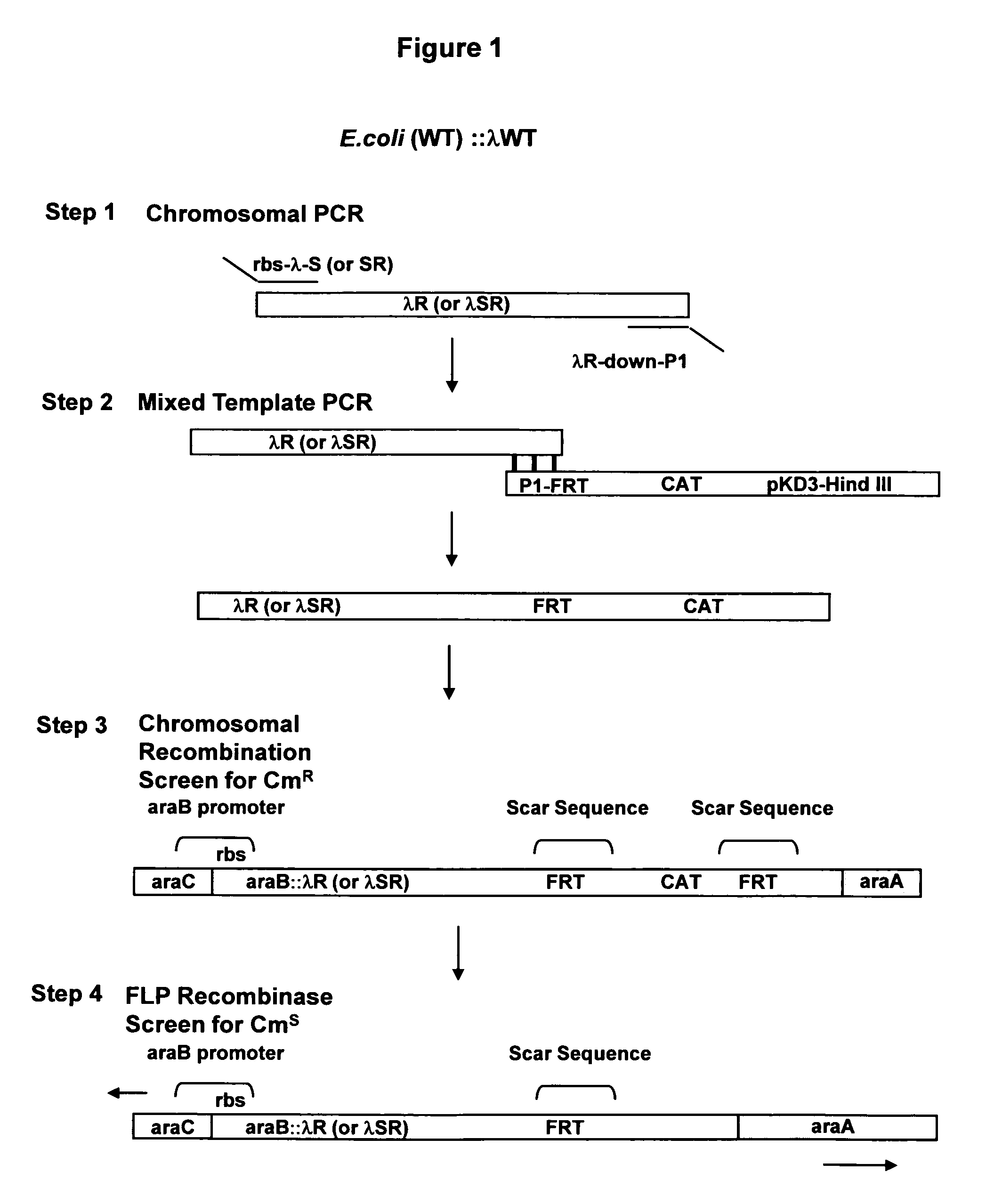
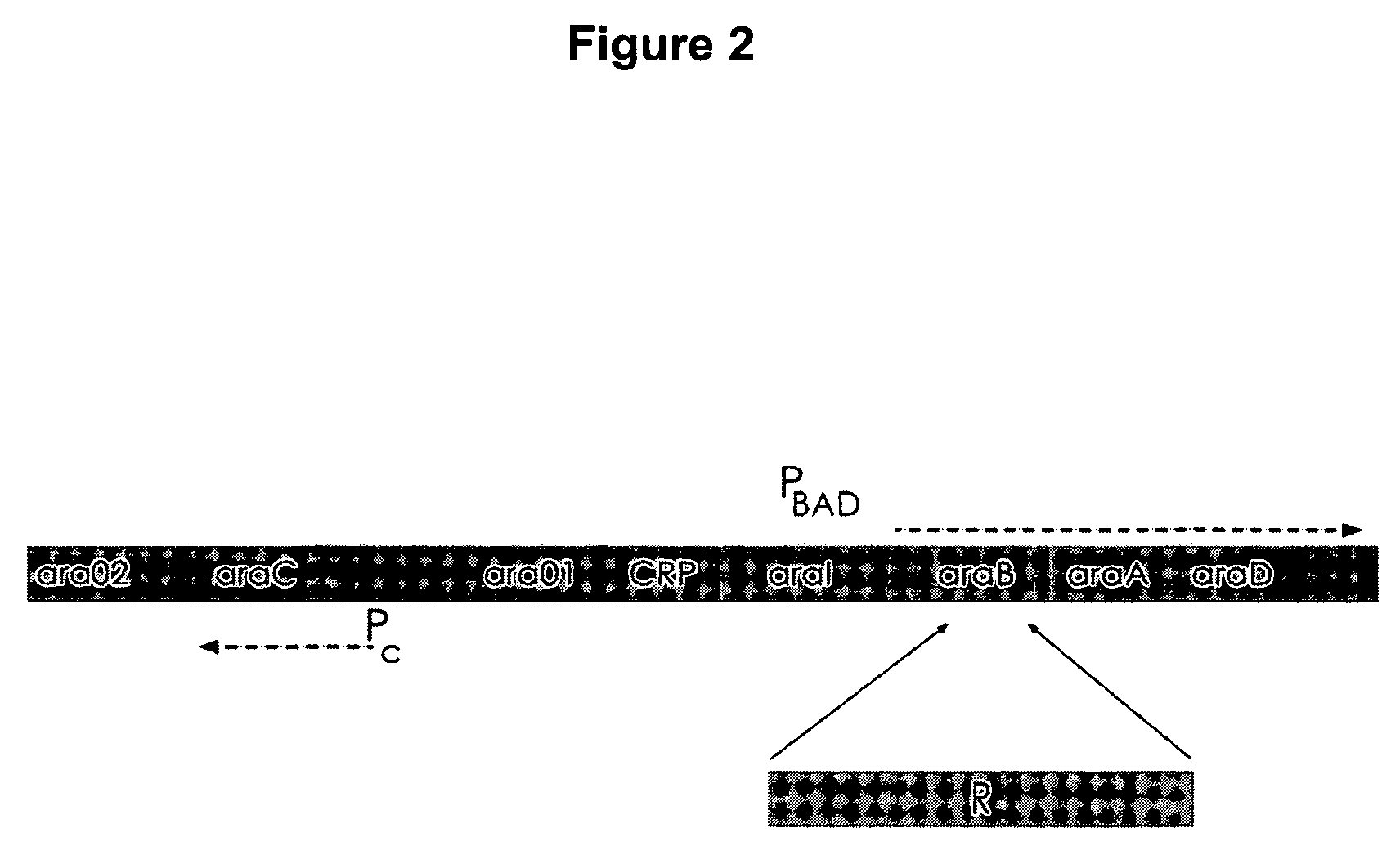
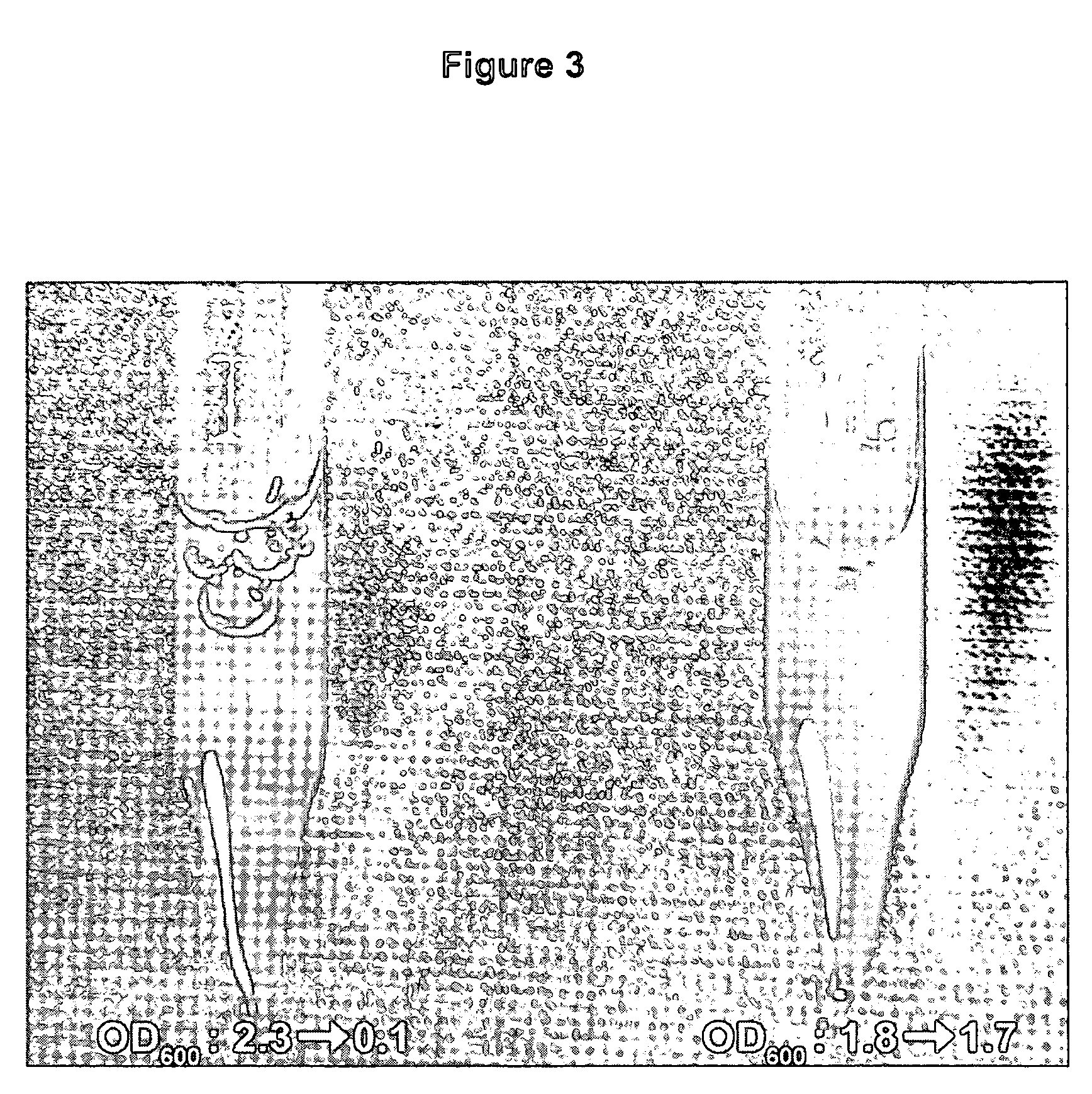
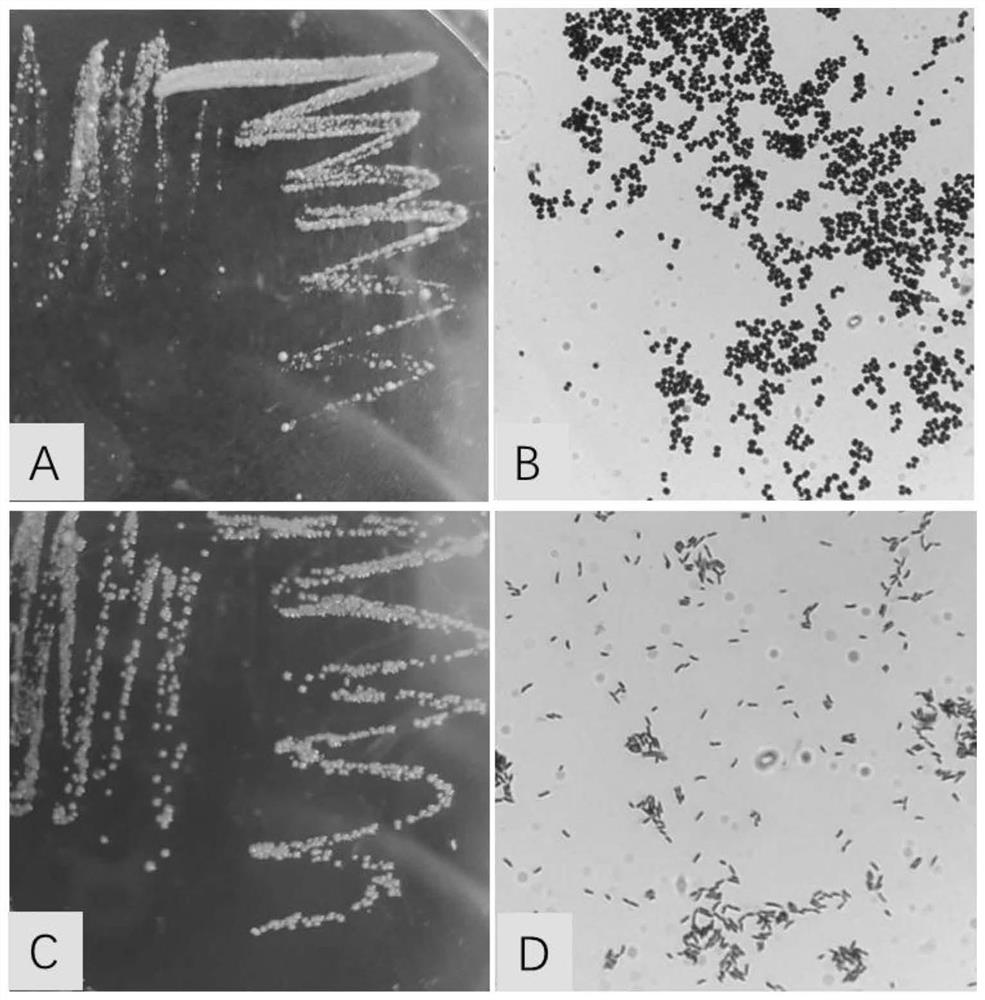
The present invention relates to the simple, gentle, and efficient extraction of biological material from Escherichia coli (E. coli). The use of E. coli in research laboratories depends on the ability to prepare lysates to isolate the desired products under investigation. The present invention includes methods and engineered E. coli strains that are capable of rapid controlled lysis or herein “autolysis”. The XJa strains were made from JM109 and the XJb strains from BL21 by insertion of the λ R or (λ RS) lytic endolysin gene to replace the tightly regulated araB gene. Thus, arabinose becomes a non-metabolizable inducer and the controlled autolysis phenotype is induced by the PBAD promoter by the presence of saturating arabinose. Upon induction of the bacteriophage λR endolysin, the E. coli remains intact but is efficiently lysed after one freeze-thaw cycle. The present invention is usable with many different buffer systems and is flexible in this regard. The controlled autolysis phenotype shows increrased yields and purity of extracted protein compared to detergent based lysis or traditional sonication lysis methods. The present invention is useful for routine protein expression or nucleic acid extraction and also for high-through-put manipulation involving protein or nucleic acid from E. coli.
Owner:ZYMO RES CORP
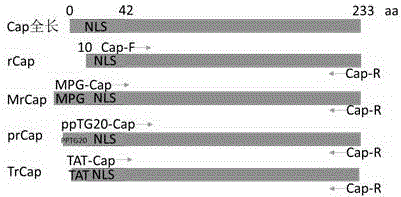
Gene encoding recombinant porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein and application thereof
The present invention provides a gene encoding a recombinant porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein and application thereof. The present invention aims to obtain a soluble recombinant PCV2 Cap protein, and adopts a PCR method for fusion of MPG and NLS partially deleted Cap protein N-terminal gene to construct a new gene; and then the new gene is cloned into an E. coli expression vector pET28a to obtain a recombinant plasmid; the recombinant plasmid is transformed into E. coli BL21 to obtain recombinant engineering bacteria; the recombinant engineering bacteria is subjected to induced expression by IPTG to obtain the soluble recombinant PCV2 Cap protein. SDS-PAGE and Western-blot identification shows that most of the recombinant protein MrCap is present in the bacterial lysis supernatant and is soluble; and the recombinant protein MrCap has high immunogenicity and immunoreactivity, and lays foundation for the development of a PCV2 antibody detection kit and subunit vaccines.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Bacterial cleavage of only organic C-N bonds of carbonaceous materials to reduce nitrogen content
A microbial process is provided for selective cleavage of only organic C-N bonds while leaving C-C bonds intact which may be used for reducing the nitrogen content of nitrogen-containing organic carbonaceous materials. Microorganisms of Pseudomonas ayucida have been found which have the ability of selective cleavage of organic C-N bonds. A particularly preferred microorganism is Pseudomonas ayucida strain ATCC No PTA-806. Other microorganisms useful in the cleavage of organic C-N bonds are Aneurinibacillus sp, Pseudomonas stutzeri, Yokenella sp. and Pseudomonas nitroreducens.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Method for synthesizing ferulic acid through enzyme method
InactiveCN104818300ASimple processMild reaction conditionsTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
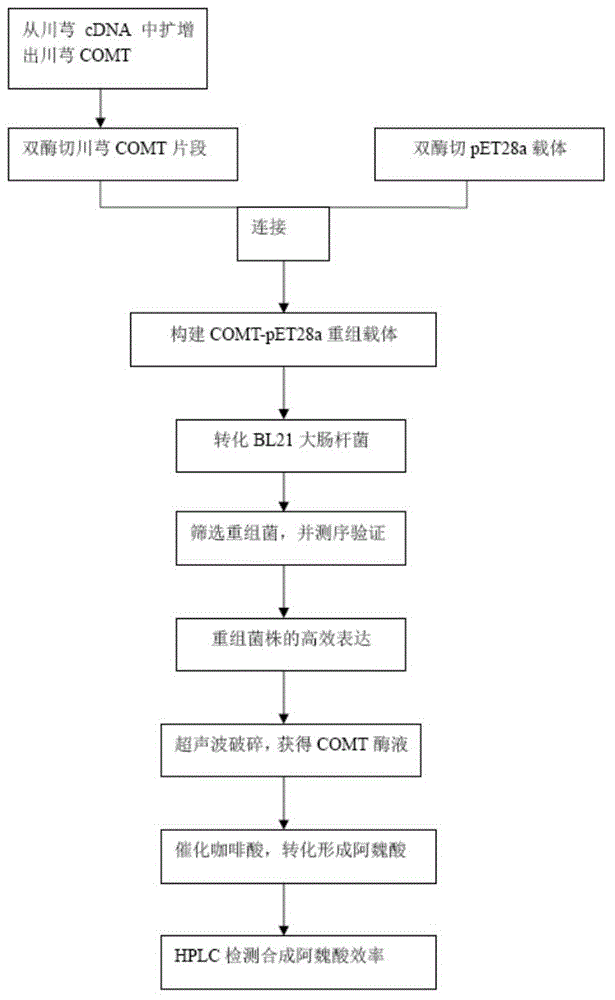
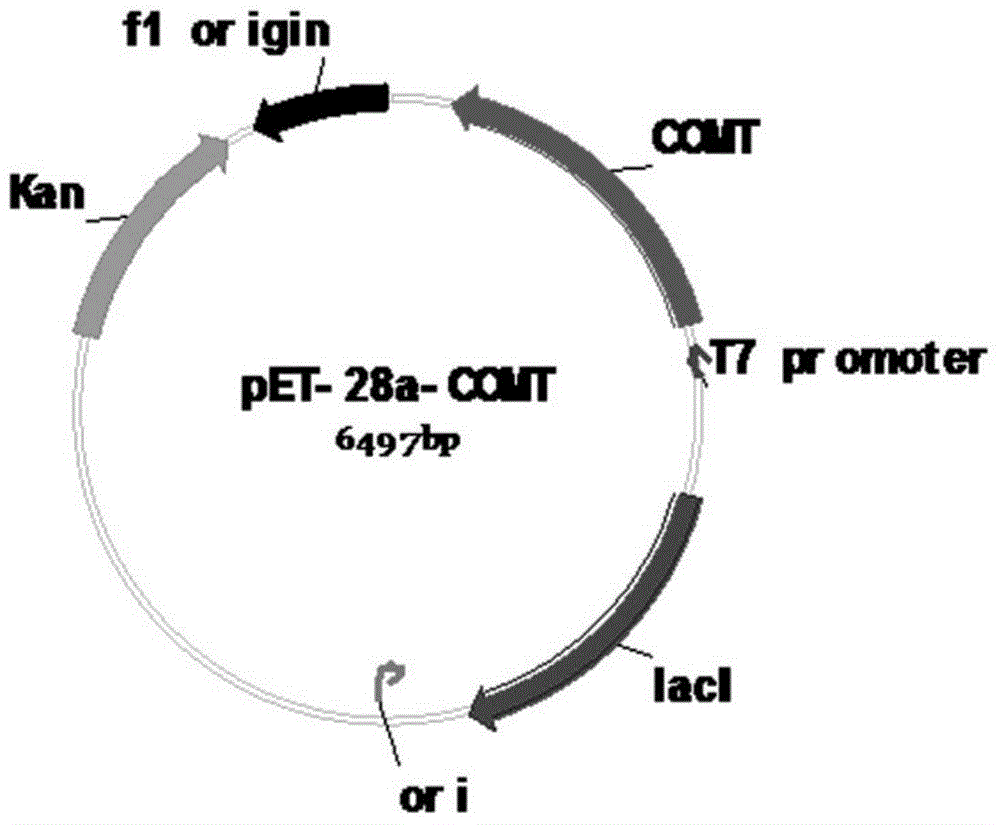
The present invention discloses a method for synthesizing ferulic acid through an enzyme method, wherein the methyl on S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) is transferred onto caffeic acid so as to finally form the product ferulic acid. The method comprises: a) highly expressing ligusticum chuanxiong hort caffeic acid-O methyltransferase(COMT) through fermentation of escherichia coli, collecting bacteria through centrifugation, re-suspending the bacteria with a Tris-HCl buffer solution, and carrying out ultrasonic bacterial lysis to obtain a mixed enzyme solution containing the ligusticum chuanxiong hort COMT; and b) transferring the methyl provided by SAM to the caffeic acid through the ligusticum chuanxiong hort COMT obtained in the step a), and finally converting into the ferulic acid. The method of the present invention has advantages of simple process, mild reaction condition, high conversion efficiency, low conversion cost, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of effecting lysis of acid-fast bacteria and method of performing gene amplification or detection therewith
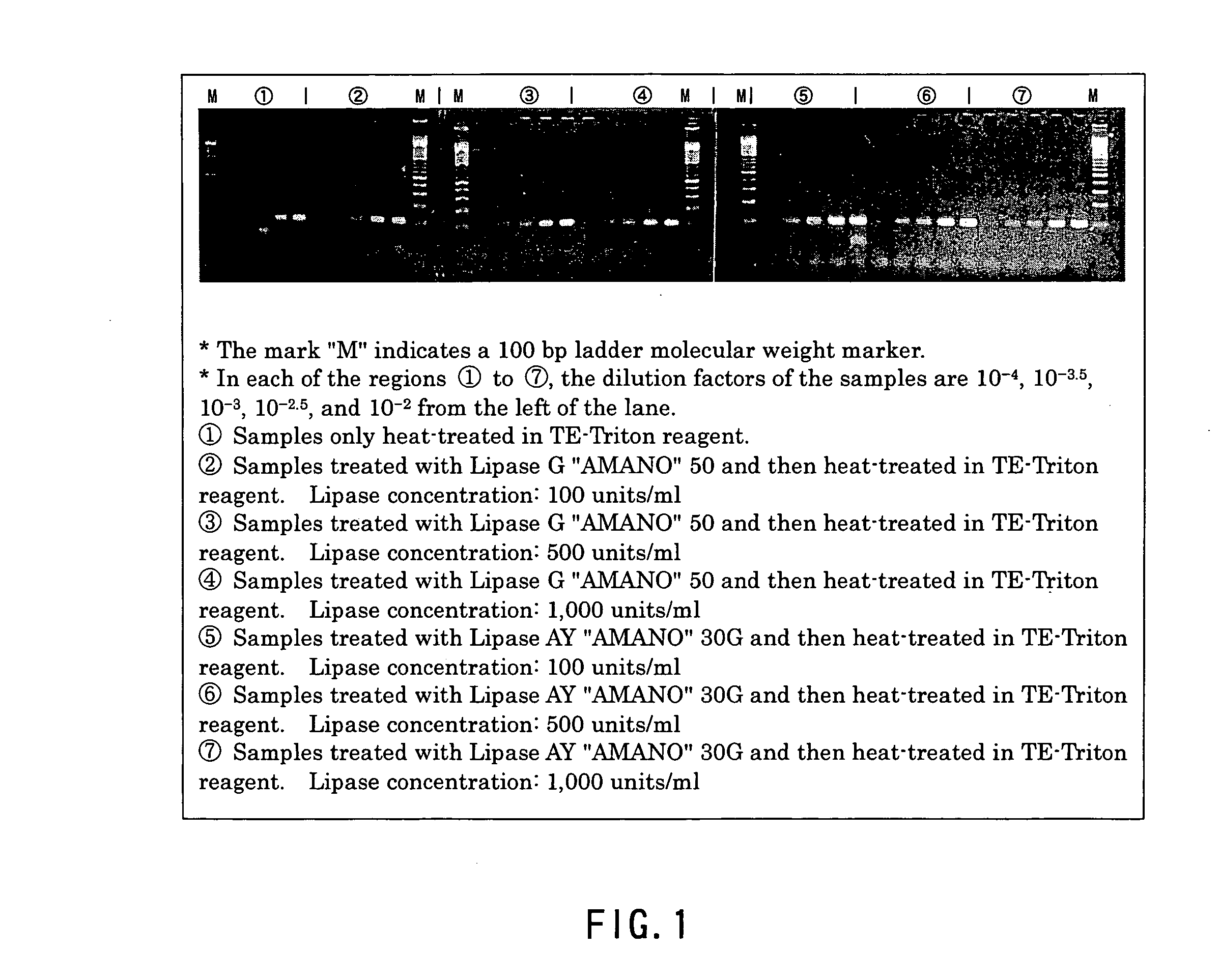
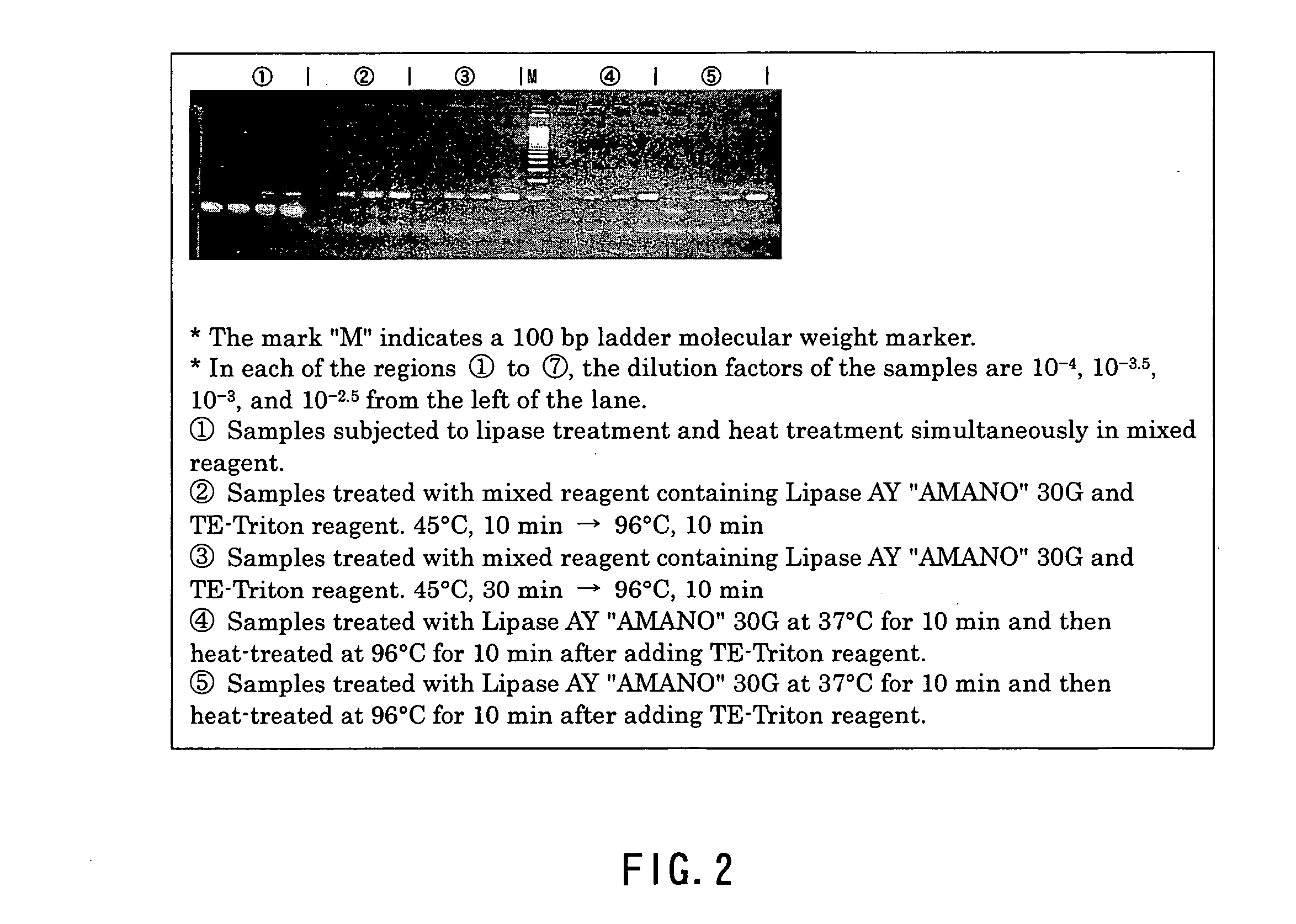
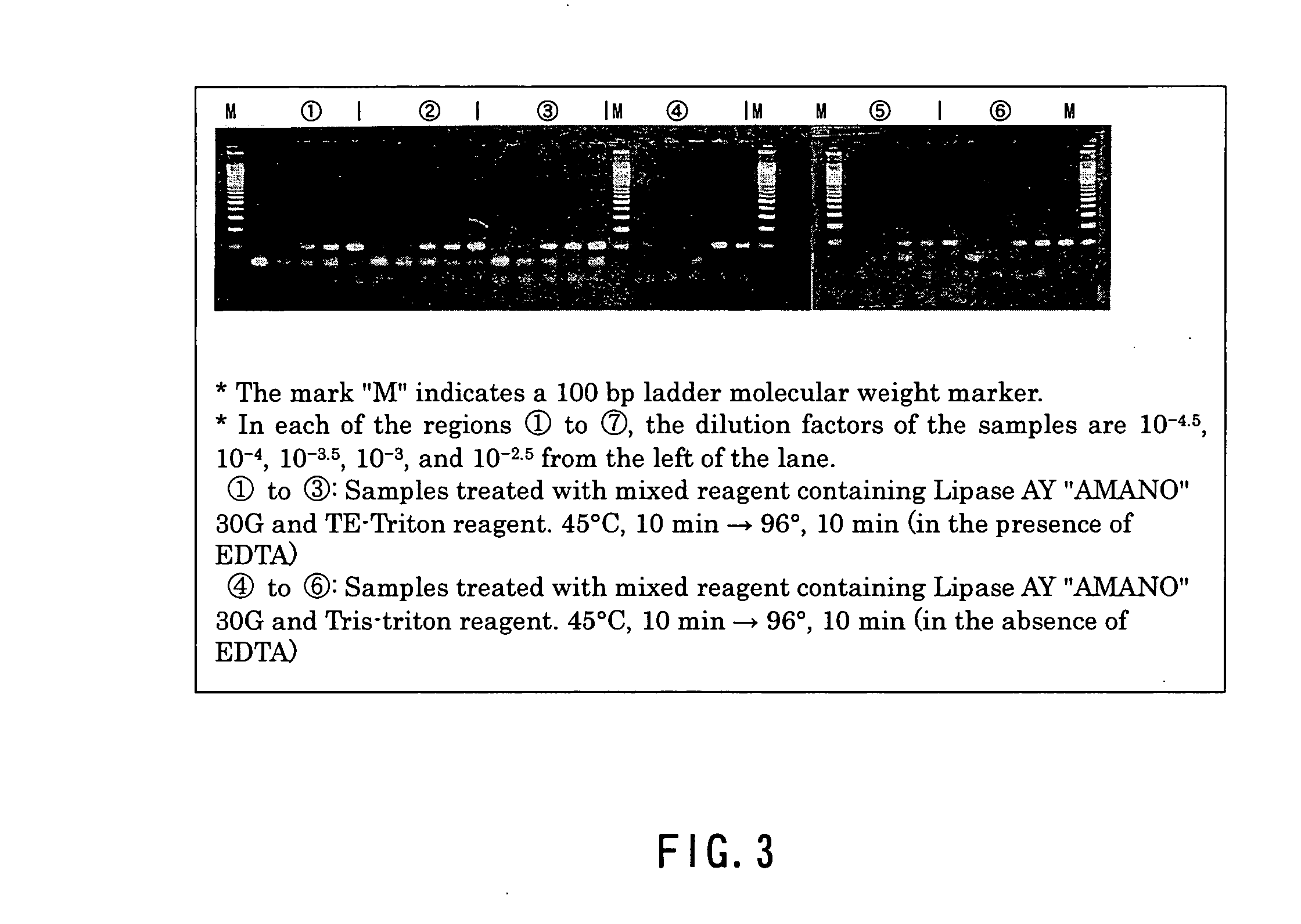
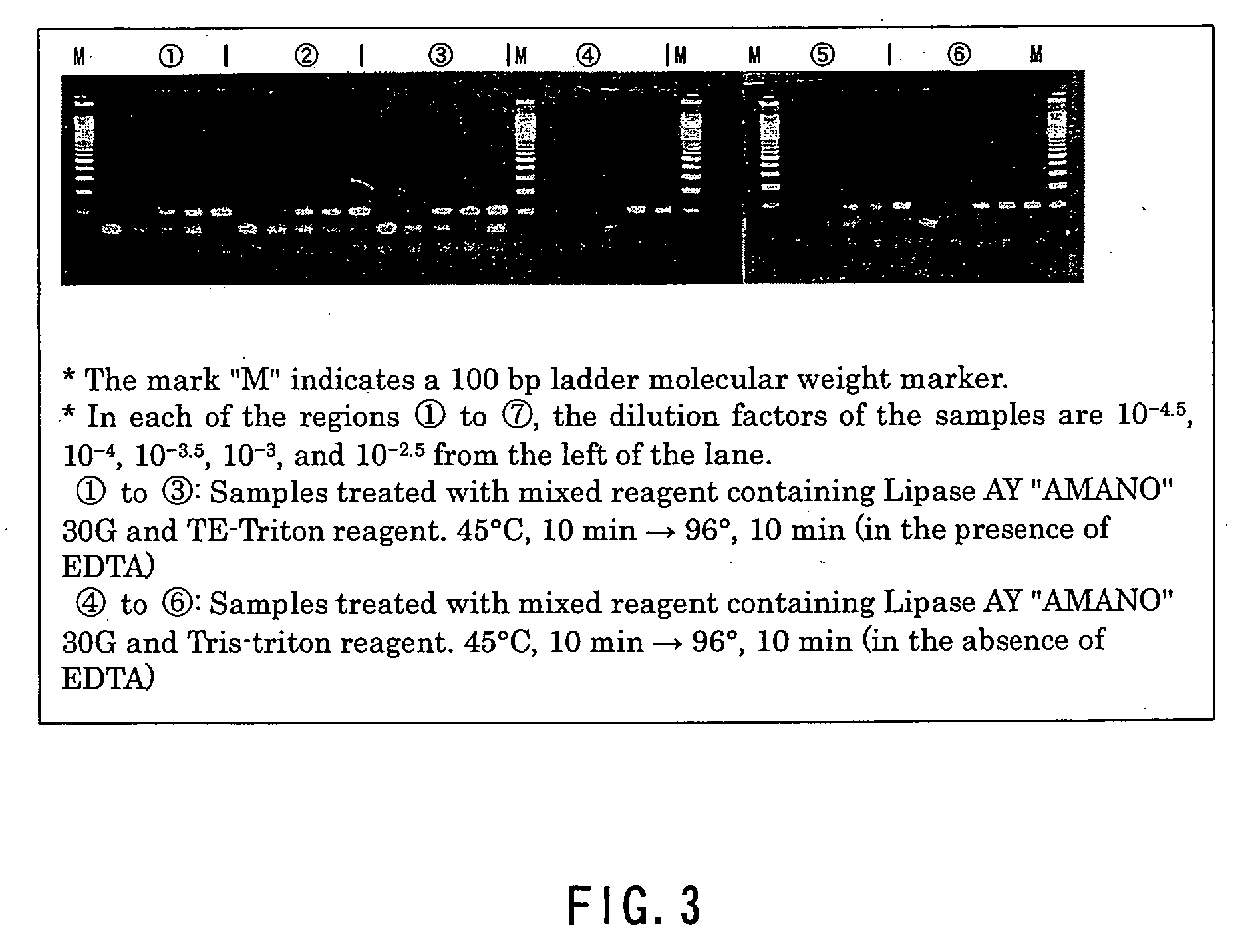
InactiveUS20050181363A1Little riskCarry-out safelyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisAcid-fastPolyethylene glycol
A method of effecting lysis of acid-fast bacteria, comprising heating acid-fast bacteria in a liquid containing a non-ionic surfactant at a temperature of below the boiling point of the liquid. This method enables accomplishing secure lysis of acid-fast bacteria in a simple manner within a short period of time without the use of special apparatus and agent and enables extracting genes. The heating is preferably conducted at 96° C. for 10 min. As the nonionic surfactant, use can be made of a d-sorbitol fatty acid ester, a polyoxyethylene glycol sorbitan alkyl ester, a polyoxyethylene glycol p-t-octylphenyl ether or the like. The pH value of the liquid is preferably 8, and the liquid preferably contains EDTA. It is also preferred that before the heating, the acid-fast bacteria be treated with lipase.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Method of effecting lysis of acid-fast bacteria and method of performing gene amplification or detection therewith
InactiveUS20070178508A1Keep for a long timeBumping of the liquid is preventedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisAcid-fastPolyethylene glycol
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Method and device for continuously removing cell/bacterial lysis floccules
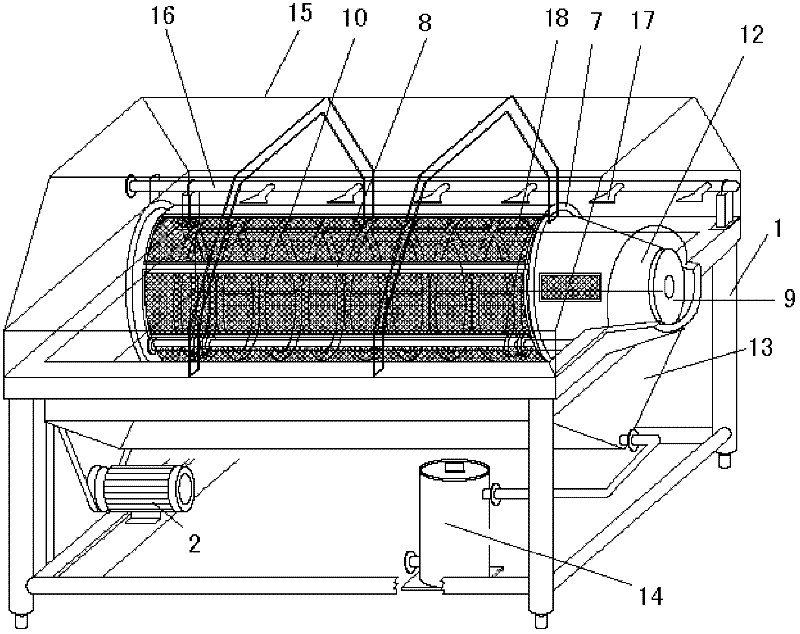
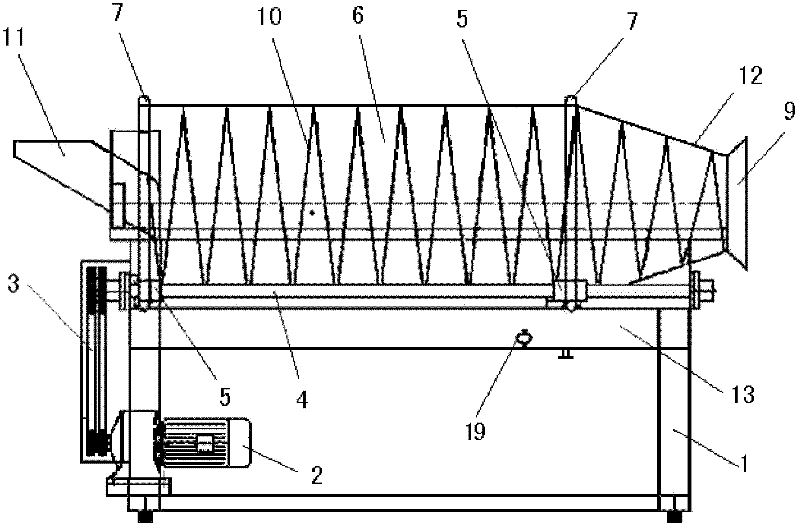
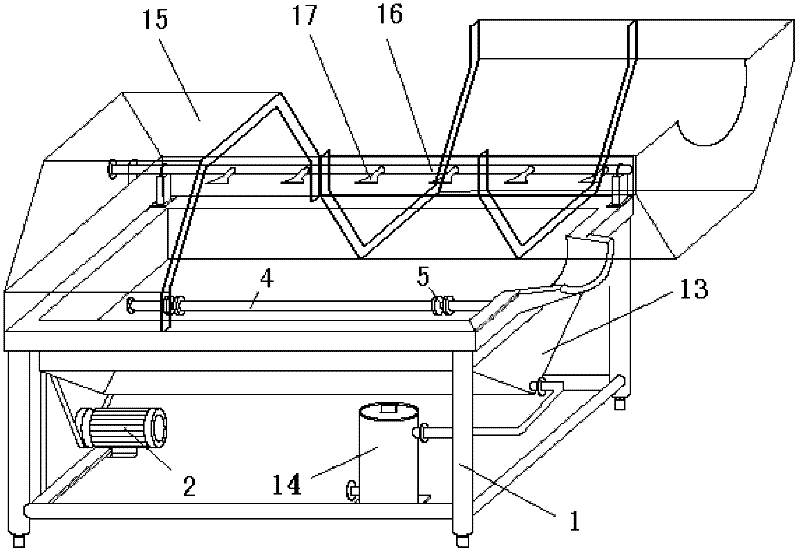
InactiveCN102240474AReduce breakageAvoid spillingMoving filtering element filtersEngineeringBacterial lysis
The invention relates to a method and device for continuously removing cell / bacterial lysis floccules. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) arranging a solid-liquid separation device, wherein the solid-liquid separation device comprises a motor and a roller driven by a transmission mechanism, the roller is internally provided with blades extending forwards in a spiral shape, a screen is arranged outside the roller, a collection bed is arranged below the roller, and the liquid outlet of the collection bed is connected with a downstream deep bed filter by virtue of a liquid pump; 2) starting a motor to drive the roller to rotate, feeding a lysis solution containing solid floccules into the roller while the lysis solution spirally advances under the driving of the blades, and carrying out solid-liquid separation; and 3) causing a liquid to flow into the collection bed by virtue of the screen, and taking the solid floccules out of the roller by virtue of the blades. In the invention, the lysis solution is advanced under the actions of the blades and the screen while the solid-liquid separation is carried out, the liquid flows into the collection bed by virtue of the roller, and dehydrated solid floccules can be discharged from a solid collection hole, thus the method and device provided by the invention can be widely applied to a production process for continuously removing cell / bacterial lysis floccules in a large scale.
Owner:格兰柏生化科技有限公司
Kit and method for extracting plasmid DNAs by one step
The invention discloses a kit and a method for extracting plasmid DNAs by one step, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The invention adopts the technical scheme as follows: the kit for extracting the plasmid DNAs by one step comprises a lysing reagent, a rinsing solution and an eluting buffer solution, wherein the lysing reagent comprises lysozyme, RNase A and a lysing buffer solution. On the basis of the optimized lysing buffer solution and a synergistic lysozyme and RNase A rapid lysing method, one-step bacterial lysis, namely application to a column, is achieved, the plasmid extracting cycle is shortened to 5min, the supercoiled plasmid content is 90% or above, the experimental efficiency is improved, and high-quality plasmids are provided for a subsequent experiment; the kit and the method have the characteristics of high efficiency, rapidness and simplicity.
Owner:GENFINE BIOTECH BEIJING CO LTD
Controlled lysis of bacteria
The present invention relates to the simple, gentle, and efficient extraction of biological material from Escherichia coli (E. coli). The use of E. coli in research laboratories depends on the ability to prepare lysates to isolate the desired products under investigation. The present invention includes methods and engineered E. coli strains that are capable of rapid controlled lysis or herein “autolysis”. The XJa strains were made from JM109 and the XJb strains from BL21 by insertion of the λ R or (λ SR) lytic endolysin gene to replace the tightly regulated araB gene. Thus, arabinose becomes a non-metabolizable inducer and the controlled autolysis phenotype is induced by the PBAD promoter by the presence of saturating arabinose. Upon induction of the bacteriophage λR endolysin, the E. coli remains intact but is efficiently lysed after one freeze-thaw cycle. The present invention is usable with many different buffer systems and is flexible in this regard. The controlled autolysis phenotype shows increased yields and purity of extracted protein compared to detergent based lysis or traditional sonication lysis methods. The present invention is useful for routine protein expression or nucleic acid extraction and also for high-through-put manipulation involving protein or nucleic acid from E. coli.
Owner:ZYMO RES CORP
Application of pyroptosis-associated protein GSDMD (Gasdermin-D) for preparing bacterial ghost vaccine
ActiveCN109303916AAvoid damageInfection controlAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHumoral immune reactionOrganism
The invention discloses application of pyroptosis-associated protein GSDMD (Gasdermin-D) for preparing a bacterial ghost vaccine. A bacteriolysis plasmid containing a pyroptosis-associated protein GSDMD coding gene is constructed and is converted into salmonella enteritidis; under the induction of gum sugar, bacteria are split to successfully obtain a salmonella novel bacterial ghost vaccine. An experiment proves that GSDMD mediated bacteriolysis has an extremely long persistent period, and a splitting rate is 99.9985% or more. After a novel bacterial ghost immune mouse prepared by the invention is adopted, an organism can be stimulated to generate powerful humoral immunity and cellular immunity; protective immunity response is induced; an experiment animal can be protected so as to resistsalmonella infection. The salmonella bacterial ghost vaccine prepared by the invention has a good immune protection effect.
Owner:HARBIN WEIKE BIOTECH DEV
Kit for rapidly extracting gram-negative bacterium genome DNA and extraction method
ActiveCN112391384AReduce extraction timeLow efficiencyDNA preparationAgainst vector-borne diseasesMagnetic beadSuperparamagnetism
The invention discloses a kit for rapidly extracting gram-negative bacterium genome DNA. The kit comprises a working solution A, a working solution B, a magnetic bead binding solution, a working solution C and a working solution D. The extraction method using the kit is simple, and mainly comprises the following four steps: bacterial lysis, magnetic bead adsorption, washing and elution. Monodisperse and superparamagnetic silicon oxide nano magnetic beads are adopted, other required reagents are conventional non-toxic reagents, the cost is low, the experiment safety is improved, and an extracted gram-negative bacterium genome DNA fragment is good in integrity, high in yield, high in purity and suitable for downstream molecular biology experiments such as PCR detection, nucleic acid hybridization and DNA library construction.
Owner:甘肃省科学院传感技术研究所
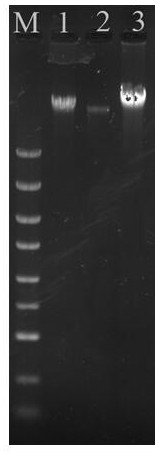
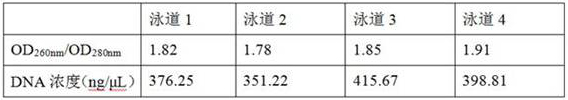
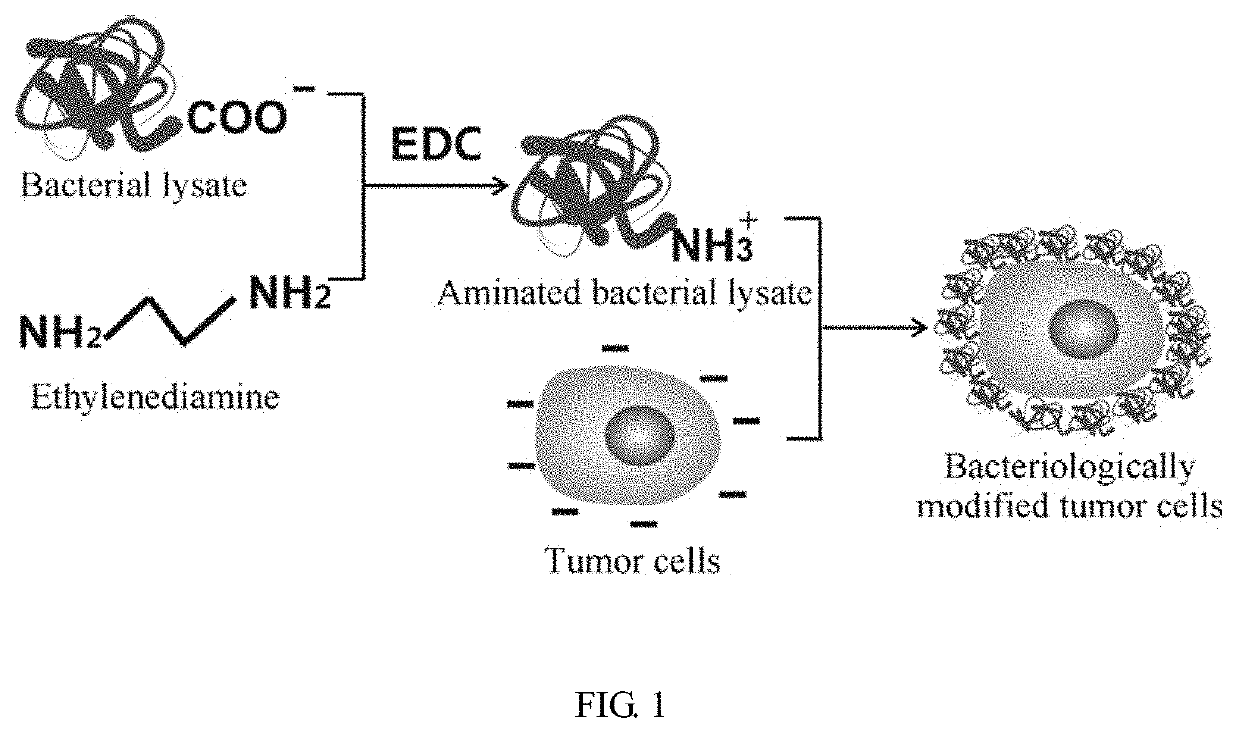
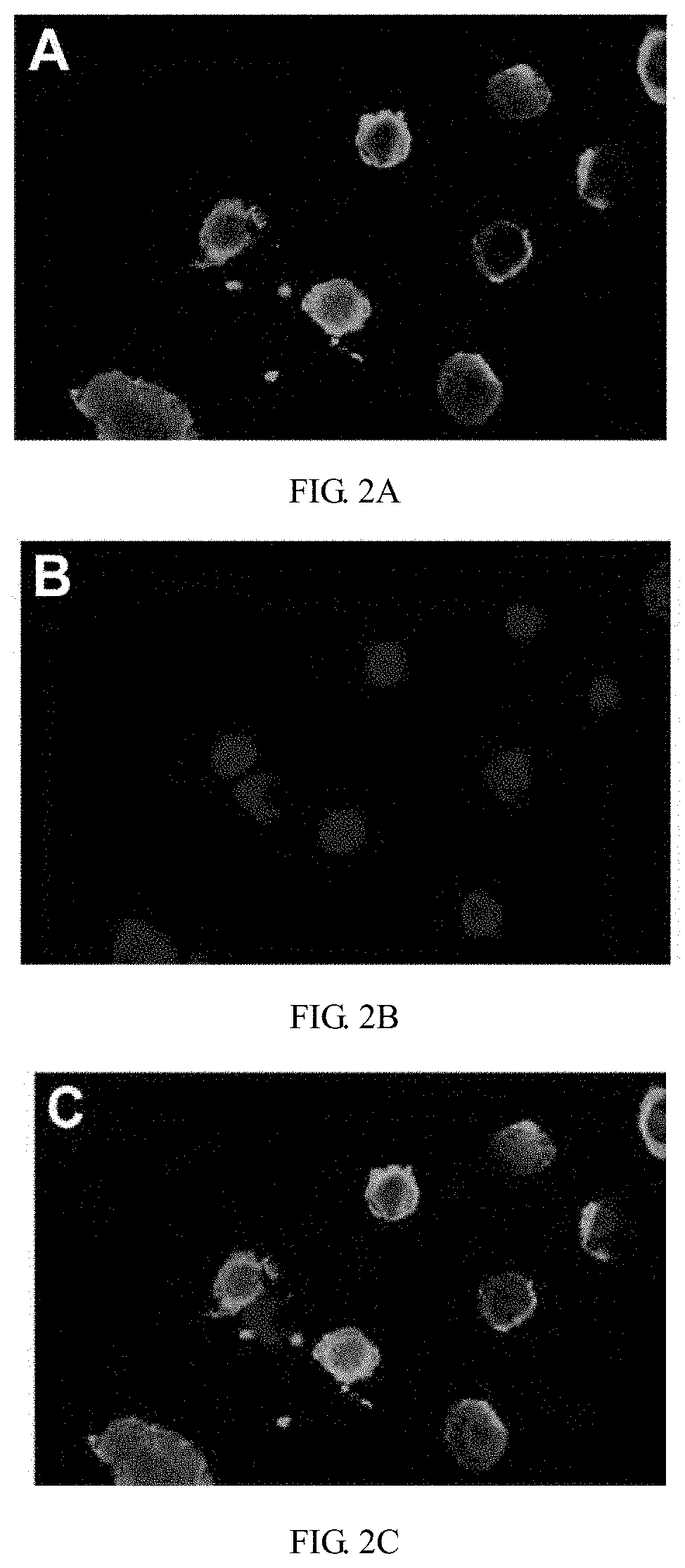
Bacteriologically-modified whole-cell tumor vaccine and method of making same
Disclosed are a bacteriologically-modified whole-cell tumor vaccine and a method of making the same. The method includes: lysing bacteria at logarithmic growth phase to obtain a bacterial lysate; mixing the bacterial lysate with an excessive amino compound solution to aminate the bacterial lysate in the presence of EDC; mixing the aminated bacterial lysate with the tumor cells for a certain period of time to produce bacteriologically-modified tumor cells; and inactivating the bacteriologically-modified tumor cells to produce the bacteriologically-modified whole-cell tumor vaccine. The bacteriologically-modified whole-cell tumor vaccine has been demonstrated to have desirable therapeutic effect in tumor model mice.
Owner:HAINAN MEDICAL UNIV
Special bacterial genome DNA extraction kit and method for septicemia
InactiveCN107746843AQuality improvementExclude influenceDNA preparationHuman DNA sequencingPurification methods
The invention discloses a special bacterial genome DNA extraction kit and method for septicemia. The kit consists of a buffer solution GPA, a buffer solution GRB, a bacterial lysis solution DA, a bacterial lysis solution DB, a buffer solution DC, a washing solution PE, an eluent EB and protease K. According to the extraction kit and method provided by the invention, red / white cells are separated by virtue of the buffer solution GRB, so that the influence and interference of human genome can be removed to the greatest extent; bacterial cells are cracked and broken by virtue of SDS and the protease K, and protein is degraded, so that bacterial genome DNA is released; and by virtue of a silica gel column separation and purification method, the bacterial genome DNA with high quality can be obtained.
Owner:南通柯侎克生物科技有限公司
Method for isolating nucleic acids from a food sample
ActiveUS20150056624A1Efficient processingIncrease heightSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSolubilityHigh concentration
The method for isolating nucleic acids from a food sample comprising the following steps: a) obtaining a food enrichment culture; b) transferring a portion of the food enrichment culture into a reaction vessel thereby providing a food enrichment sample and providing a water-immiscible phase in contact with the food enrichment culture; c) lysing the food enrichment sample to provide a lysed sample; d) isolating nucleic acids from the lysed sample. Food enrichment culture samples are known to contain high concentrations of organic and / or liposoluble inhibitors. By contacting the enrichment culture sample with a water-immiscible phase before the actual DNA extraction procedure starts, part of the lipophilic inhibitors is expected to cross the phase interface due to an enhanced solubility in the organic phase and thereby become depleted. The water-immiscible phase provided according to the invention interacts directly with the sample material throughout bacteria lysis and DNA extraction thereby optimizing the subsequent DNA purification processes due to the depletion of food-borne inhibitors. This method yields nucleic acids, in particular DNA that is of an improved quality and purity to be used in a subsequent PCR reaction to detect pathogen nucleic acids in the isolated nucleic acids.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Compositions and methods for the treatment of Pierce's disease
InactiveUS7432419B2Efficient killingHigh protein concentrationBacteriaHydrolasesBacteroidesProphylactic treatment
Chimeric anti-microbial proteins, compositions, and methods for the therapeutic and prophylactic treatment of plant diseases caused by the bacterial pathogen Xylella fastidiosa are provided. The anti-microbial proteins of the invention generally comprise a surface recognition domain polypeptide, capable of binding to a bacterial membrane component, fused to a bacterial lysis domain polypeptide, capable of affecting lysis or rupture of the bacterial membrane, typically via a fused polypeptide linker. In particular, methods and compositions for the treatment or prevention of Pierce's disease of grapevines are provided. Methods for the generation of transgenic Vitus vinefera plants expressing xylem-secreted anti-microbial chimeras are also provided.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Preparation method using bacterial lysate as inactivated vaccine adjuvant
PendingCN114028558ABiosafetyImprove immunityRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingBiotechnologyBacilli
The invention relates to a preparation method using bacterial lysate as inactivated vaccine adjuvant. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, respectively putting corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis and rhodococcus equi into an LB culture medium for culturing at 37 DEG C, and harvesting thalli through a centrifugal machine; step 2, diluting each thallus to 8.0* 10<9> cfu / mL by using sterilized normal saline, and crushing the bacterial liquid by using a high-pressure homogenizer; and step 3, after sterility test, mixing the split products of corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis and rhodococcus equi with the two bacteria inactivated by formaldehyde according to a ratio of 1: 1 to obtain the inactivated vaccine added with the adjuvant. The preparation method has the characteristics of safety, high efficiency, strong immune enhancement capability and low cost, and is suitable for producing various bacterial inactivated vaccines.
Owner:ZHANGZHOU PIEN TZE HUANG PHARM +1
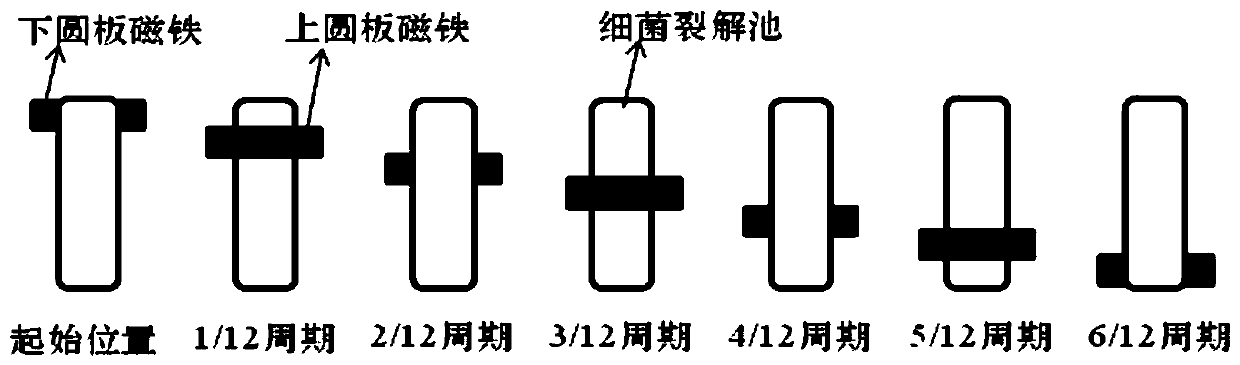
Portable bacterial lysis device based on centrifugal microfluidic technology and using method thereof
InactiveCN110938522AImprove cracking efficiencyIncrease throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacterial lysisCentrifugal microfluidics
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of bacterial lysis devices, discloses a portable bacterial lysis device based on a centrifugal microfluidic technology and a using method thereof. The device comprises upper and lower circular plates, a disc micro-fluidic chip, and a rotating shaft, wherein the disc micro-fluidic chip and the rotating shaft are parallel to each other between theupper and lower circular plates. The rotating shaft passes through the parts, away from the circle centers, of the circulate plates but is not in contact with the circular plates; and the rotating shaft passes through the circle center of the disc micro-fluidic chip. A plurality of magnets are respectively arranged on the circular plates and are uniformly distributed on each circular plate, wherein the magnets are mutually staggered in a vertical position. A plurality of bacteria lysis pools are arranged on the disc micro-fluidic chip. According to the invention, the bacterial lysis efficiencyand the sample treatment flux can be effectively improved; and other operation units can be integrated to realize real-time on-site detection of bacteria. The designed bacterial lysis device is portable, low in cost, easy and convenient to operate; the operation is automatic; and the device is used flexibly. The portable bacterial lysis device can meet different requirements and has the broad application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
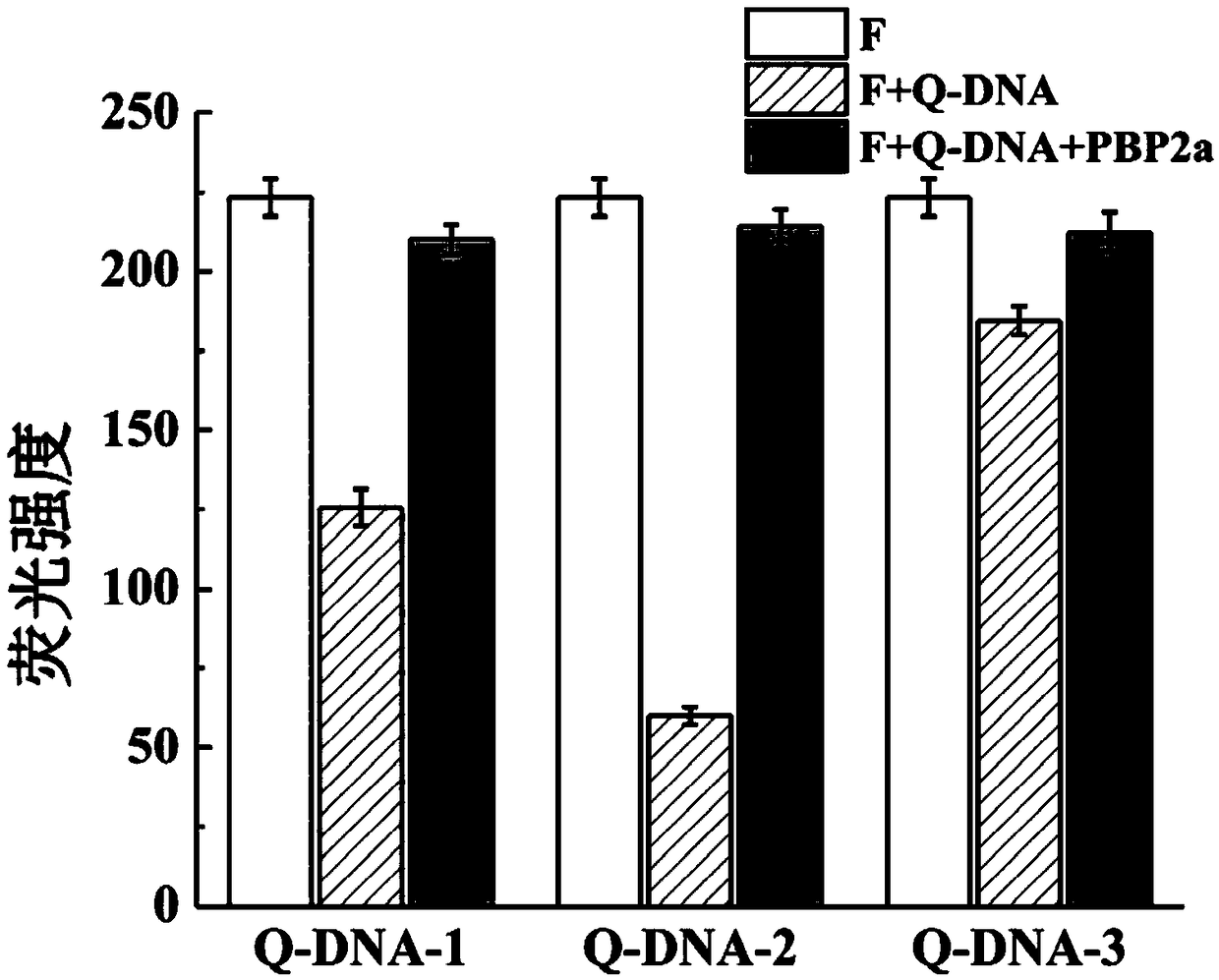
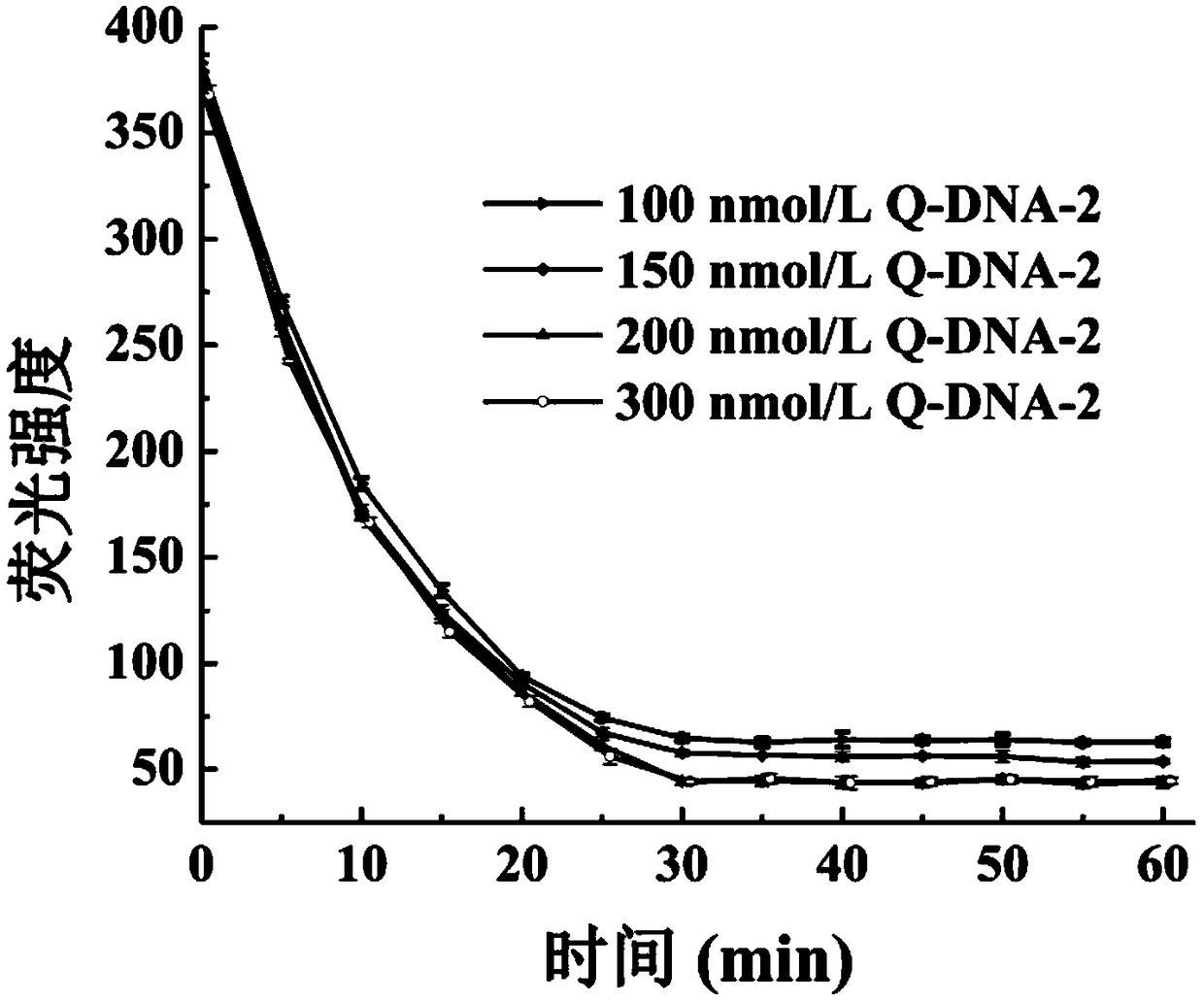
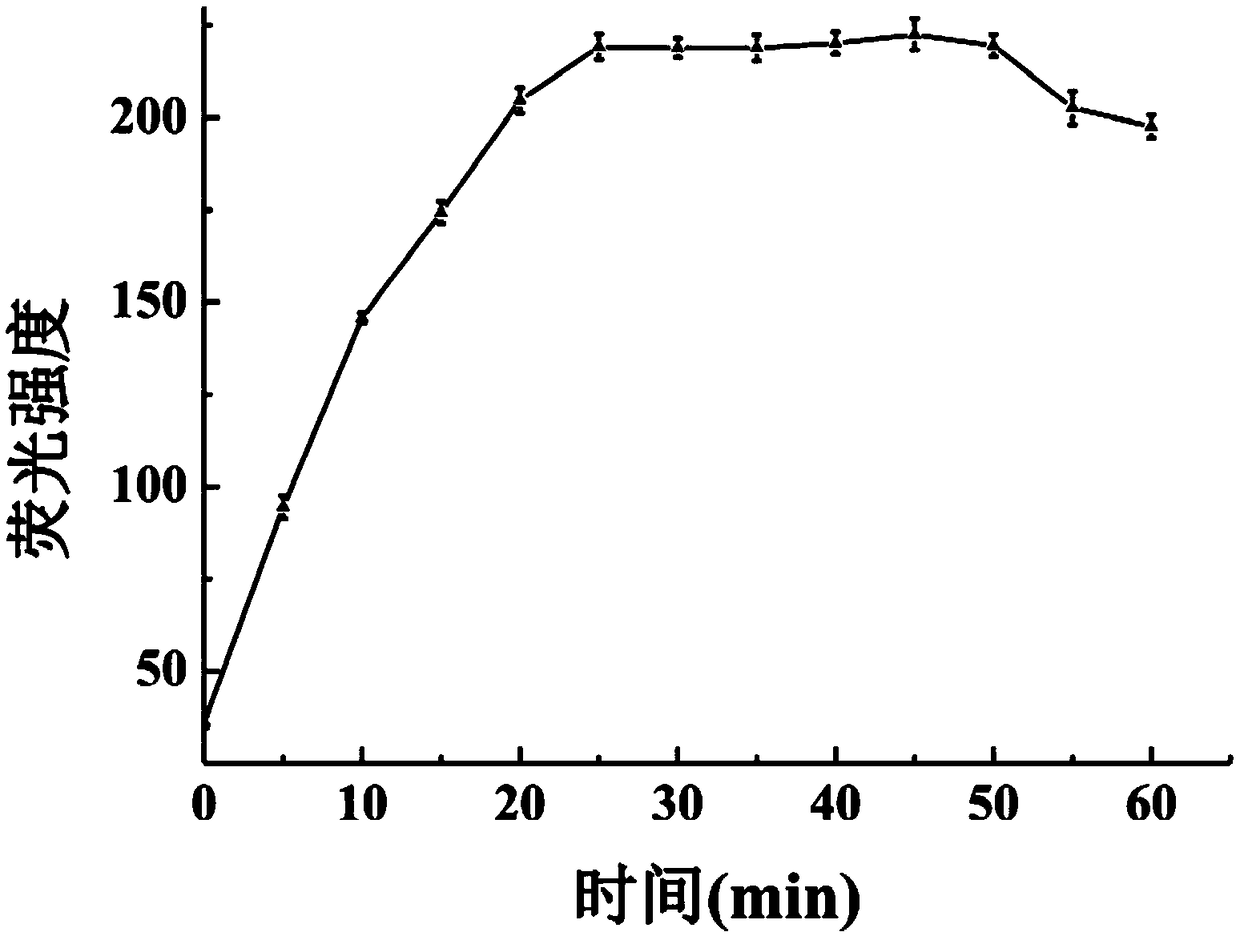
Aptamer based methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus fluorescence detection method
The invention discloses an aptamer based methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus fluorescence detection method and application thereof. The detection method comprises the following steps of (1) sequentially adding IgG antibody coated magnetic nano-particles and a sample to detected in a vessel, and performing uniform mixing and incubation to enable the antibody coated magnetic nano-particles to be fully combined with staphylococcus aureus in the sample; (2) collecting the magnetic nano-particles with an applied magnetic field, performing washing, adding a staphylococcus aureus cracking reagent, performing incubation for a period of time, and collecting a bacterium lysate under the effect of the applied magnetic field; (3) adding the bacterium lysate in a complementary DNA chain hybridof a fluorescence labeled PBP2a protein aptamer and a quencher group labeled aptamer, and performing uniform mixing and incubation; and (4) determining fluorescence changes of the aptamers and the complementary DNA chain hybrid thereof before and after addition of the bacterium lysate, judging whether PBP2a exists or not according to fluorescence change values, and realizing rapid detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus in a clinic sample.
Owner:WEIFANG MEDICAL UNIV
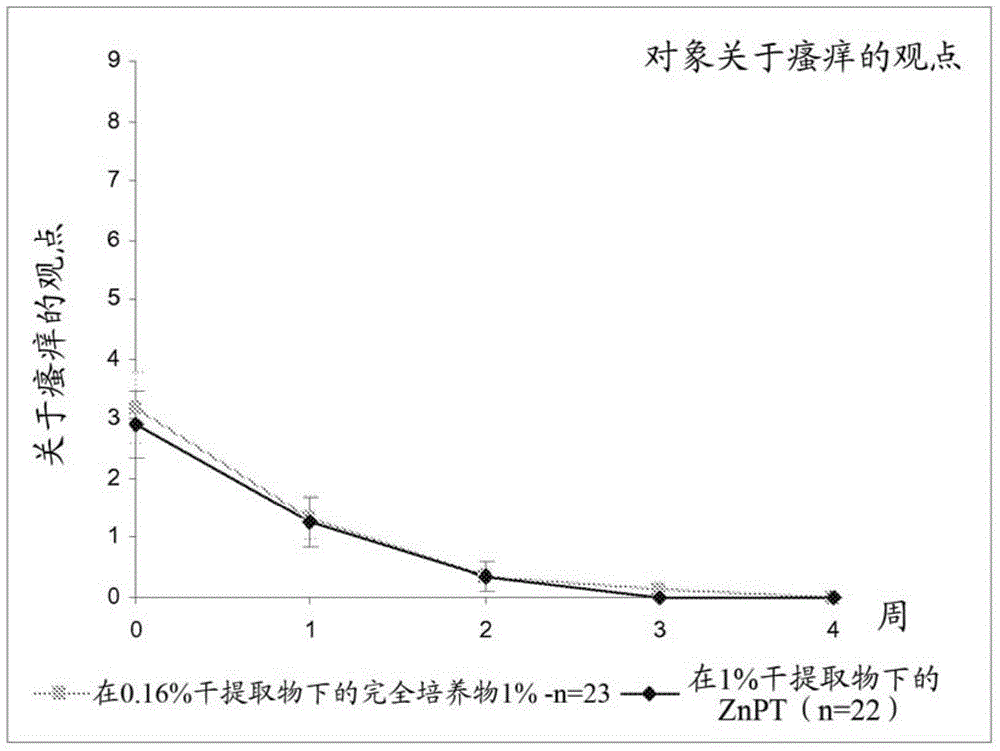
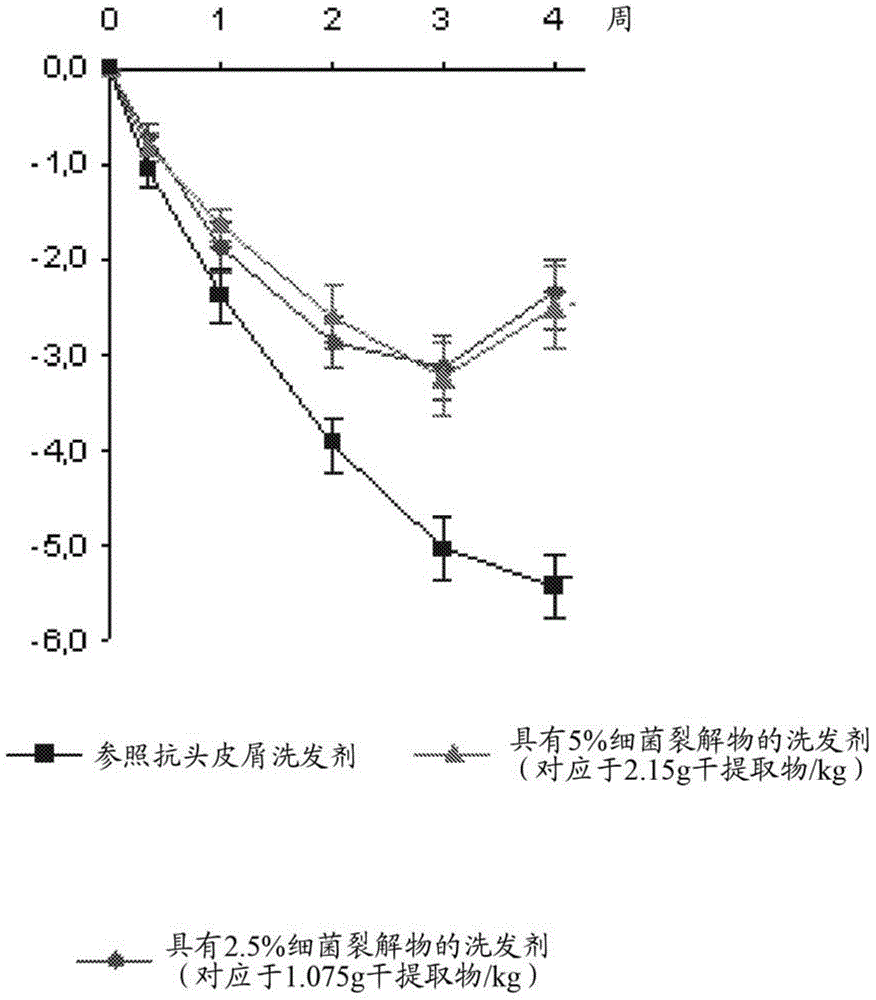
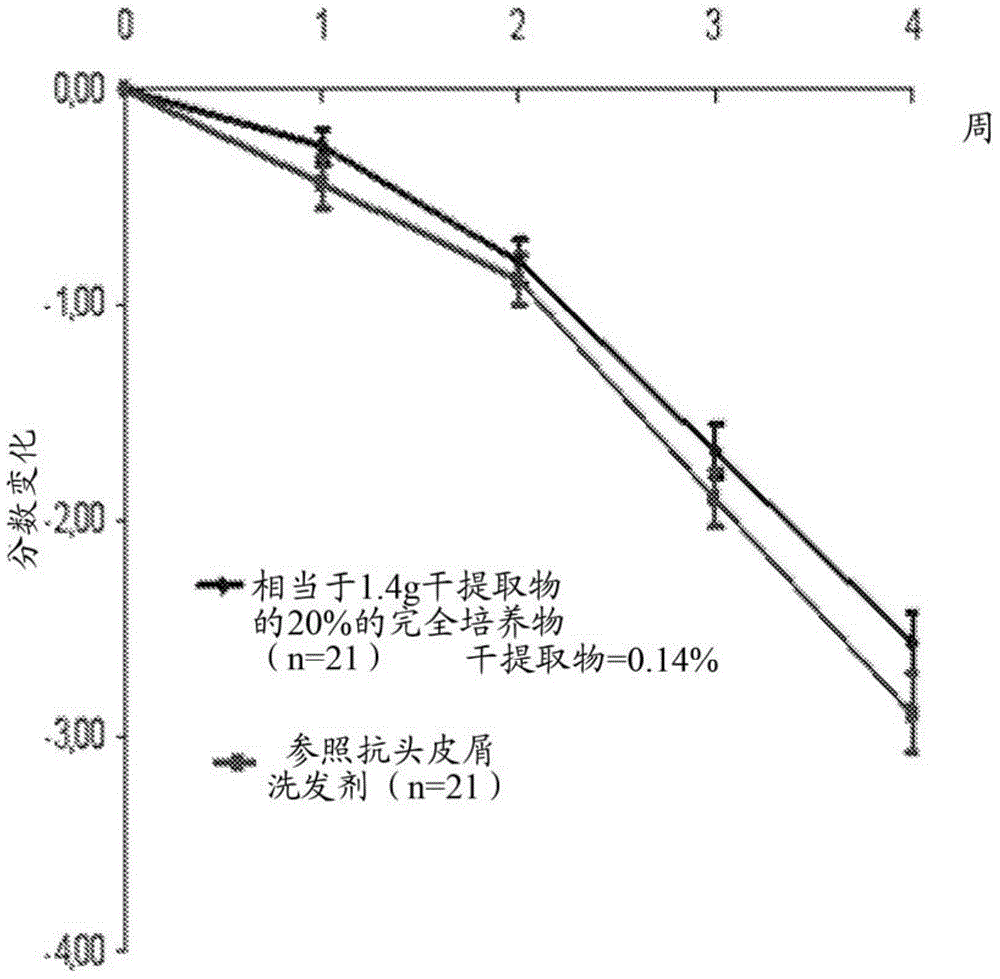
Novel useful active agent for preventing and/or treating dandruff on the scalp
The invention relates to a the cosmetic use of a bacterial lysate pertaining to the Vitreoscilla sp. genus (particularly the Vitreoscilla filiformis species) in a complete fermentation medium, as an active agent for preventing and / or treating dandruff on the scalp, including dandruff on the scalp associated with a prevalence of the pathogenic microorganisms on the scalp and / or an imbalance of the ecoflora of the scalp.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Alpha-1, 3 galactosyl transferase fusion protein and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an alpha-1, 3 galactosyl transferase fusion protein and a preparation method thereof. The alpha-1, 3 galactosyl transferase fusion protein provided by the invention comprises TRX (thioredoxin) and catalyzes the formation of an alpha-galactose epitope. The invention also provides a bacterium for generating the alpha-1, 3 galactosyl transferase fusion protein. The fusion protein provided by the invention completely has the activity of alpha-1, 3 galactosyl transferase, is expressed in a soluble way, further, is higher in expression quantity, occupies above 20% of a soluble bacterial crackate, and has a favorable industrial application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING JING MENG STEM CELL TECH
Method for quickly extracting genome DNA of riemerella anatipestifer, and kit
InactiveCN103614370AHigh purityImprove extraction efficiencyMicroorganism based processesDNA preparationEthylene diamineSulfonate
The invention discloses a method for quickly extracting a genome DNA (Deoxyribo-Nucleic Acid) of riemerella anatipestifer, and a kit. The method comprises the following steps: 1) lysing bacteria; 2) precipitating bacterial proteins; 3) removing the bacterial proteins; 4) precipitating the genome DNA; 5) deionizing; and 6) dissolving the DNA, wherein a bacterial lysis buffer solution used in the step 1) contains 38-42 mM of Tris-acetate having the pH of 7.8, 18-22 mM of sodium-acetate, 0.8-1.2 mM of EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) and 0.8-1.2% of SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfonate). The extraction method provided by the invention is high in extraction efficiency, and the genome DNA of riemerella anatipestifer extracted by the method is high in purity, which lays a strong foundation for subsequent molecular biologicalstudy; and the extraction method is simple and feasible to operate, and high in practicability.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HEALTH GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for isolating nucleic acids from a food sample
ActiveUS10011827B2Efficient processingIncrease heightMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisHigh concentrationSolubility
The method for isolating nucleic acids from a food sample comprising the following steps: a) obtaining a food enrichment culture; b) transferring a portion of the food enrichment culture into a reaction vessel thereby providing a food enrichment sample and providing a water-immiscible phase in contact with the food enrichment culture; c) lysing the food enrichment sample to provide a lysed sample; d) isolating nucleic acids from the lysed sample. Food enrichment culture samples are known to contain high concentrations of organic and / or liposoluble inhibitors. By contacting the enrichment culture sample with a water-immiscible phase before the actual DNA extraction procedure starts, part of the lipophilic inhibitors is expected to cross the phase interface due to an enhanced solubility in the organic phase and thereby become depleted. The water-immiscible phase provided according to the invention interacts directly with the sample material throughout bacteria lysis and DNA extraction thereby optimizing the subsequent DNA purification processes due to the depletion of food-borne inhibitors. This method yields nucleic acids, in particular DNA that is of an improved quality and purity to be used in a subsequent PCR reaction to detect pathogen nucleic acids in the isolated nucleic acids.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Method for preparing lactoferricin and method for applying lactoferricin in bacterial inhibition of foods
InactiveCN102505033AHigh expressionHigh purityFood preservationMicroorganism based processesInclusion bodiesLactoferricin
The invention relates to a method for preparing lactoferricin and a method for applying the lactoferricin in bacterial inhibition of foods. The method for preparing the lactoferricin comprises the following steps of: (i) activating genetic engineering bacteria; (ii) performing bacterial lysis; (iii) separating an inclusion body and performing lysis; (iv) extracting fusion protein and performing acid hydrolysis; and (v) separating by using a chromatographic column. The method is feasible, easy to operate and low in cost; and the lactoferricin prepared by the method can be used for bacterial inhibition of aquatic products. The method for applying the lactoferricin comprises the following steps of: cleaning an aquatic product, and soaking in a solution of the lactoferricin at normal temperature or at the temperature of between 0 and 4 DEG C for 0.5 to 10 hours.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
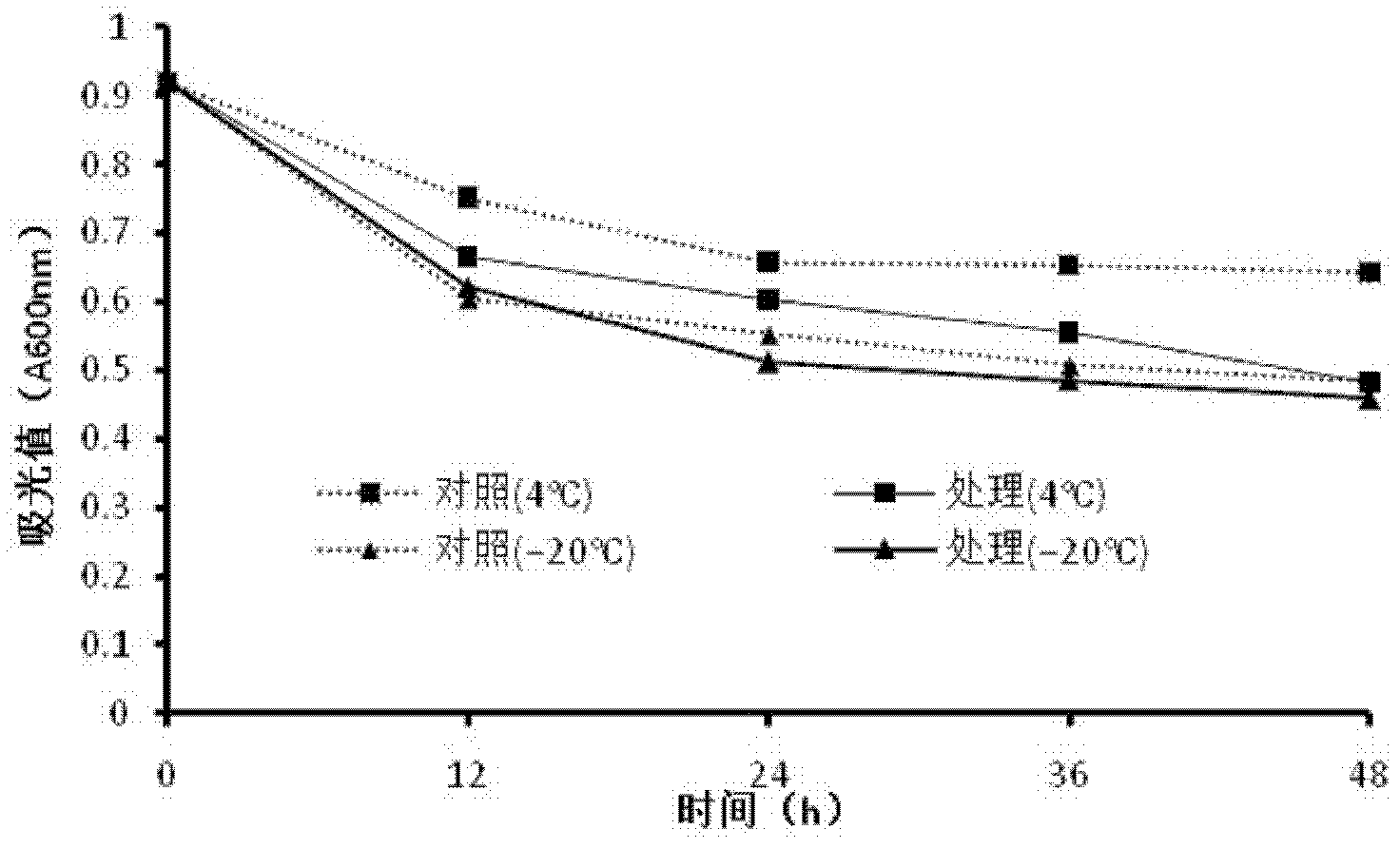
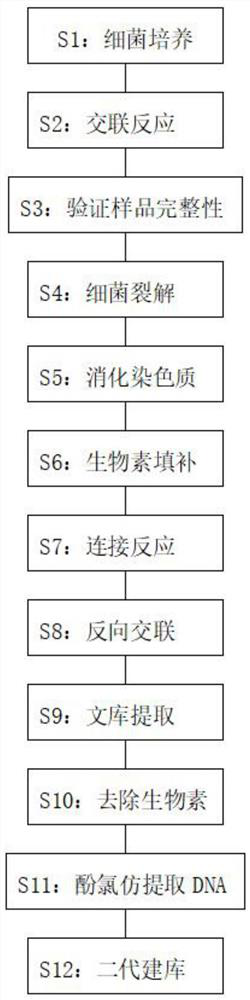
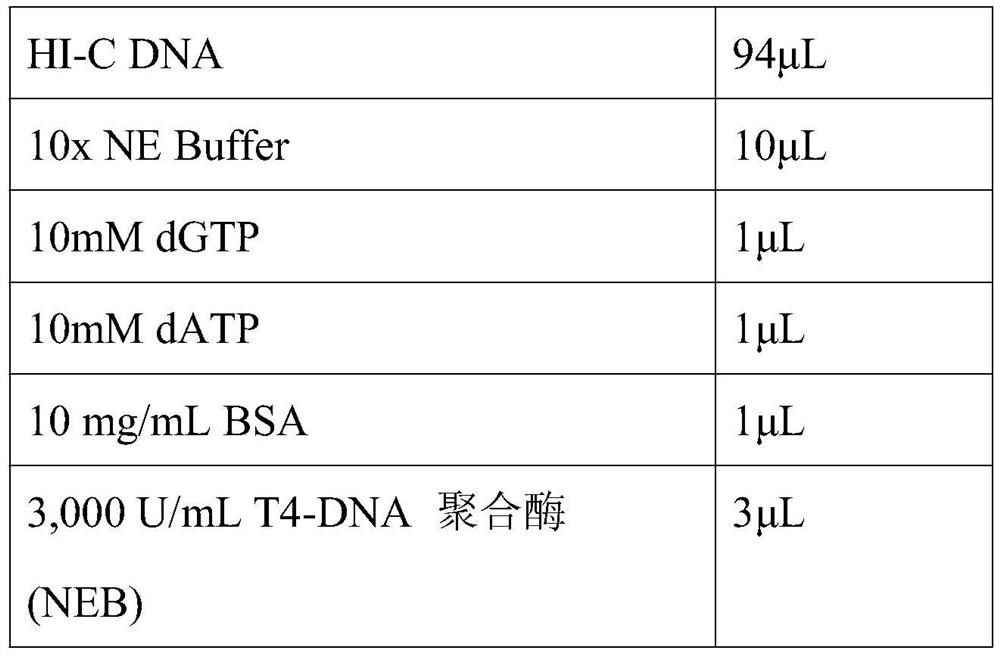
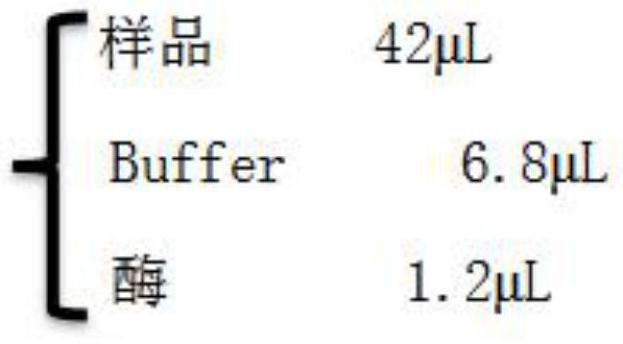
Bacterial HI-C genome and plasmid conformation capturing method
PendingCN113215141APracticalMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationEnzyme digestionRegulation of gene expression
The invention discloses a bacterial HI-C genome and plasmid conformation capturing method. The method comprises the following capturing steps: bacterial culture, cross-linking reaction, sample integrity verification, bacterial lysis, chromatin digestion, biotin filling, ligation reaction, reverse cross-linking, library extraction, biotin removal, phenol chloroform DNA extraction and second generation library establishment. According to the method, DNA and protein are crosslinked together through formaldehyde treatment so as to fix the conformation of the DNA, enzyme digestion, biotin introduction, enzyme linkage and extraction are carried out, then library construction and high-throughput sequencing are carried out on treated nucleic acid, and finally, interaction information between bacterial chromatin fragments and between bacterial chromatin fragments and plasmids can be revealed by analyzing sequencing data. The method can be applied to genome assembly, gene expression regulation research and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com