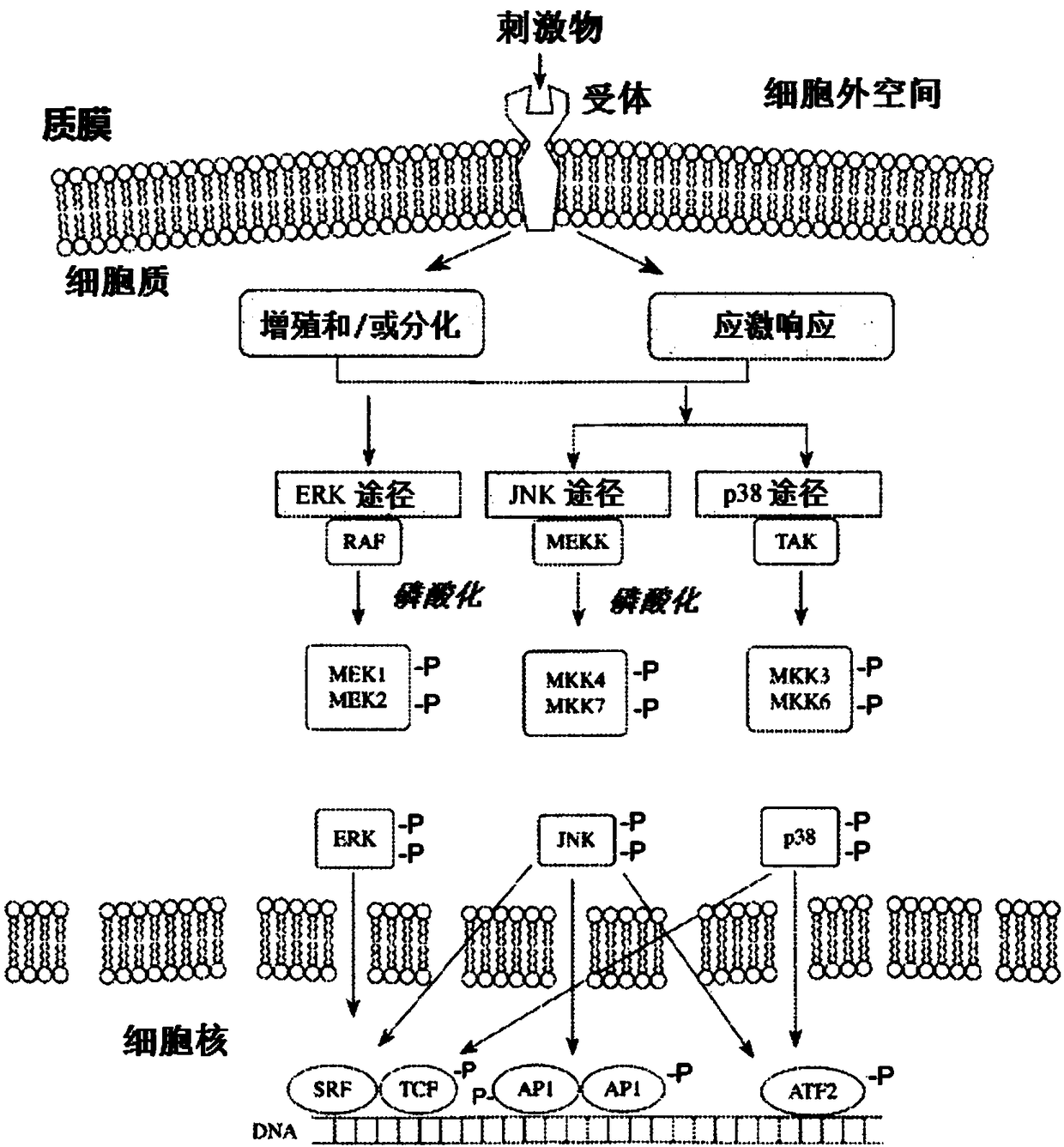
Control of cellular redox levels
An oxidative and bacterial technology, applied in the direction of extracellular fluid diseases, medical raw materials derived from bacteria, antibacterial drugs, etc., can solve problems such as sepsis, excessive cell activation response, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0183] Example 1: Preparation of active ingredients for TLR agonist compositions
[0184] Examples of how to formulate the compositions include the following procedures.
[0185] active ingredient. The active ingredients are derived from bacterial fermentation and cell isolation processes as described below. Lactobacillus delbrueckii, ssp. bulgaricus (referred to herein as L. bulgaricus) is the organism used in this example, but the bacterial organism can be any Gram-positive or Gram-positive Negative bacteria or both.
[0186] Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp bulgaricus contains 1.5% casein hydrolyzate, 1% yeast extract, 3% lactose, 0.2% sodium acetate, 0.02% sodium formate, 0.01% disodium 5-inosinate , 0.01% manganese sulphate, 0.05% magnesium sulphate and 0.05% polysorbate 80, pH 6.4 growth medium for fermentation. The inoculated medium was incubated at 37°C until the fermentation reached steady growth, as determined by metabolic arrest. The broth was cooled to 4°C and ha...
Embodiment 2
[0190] Example 2: TLR Screening Assays
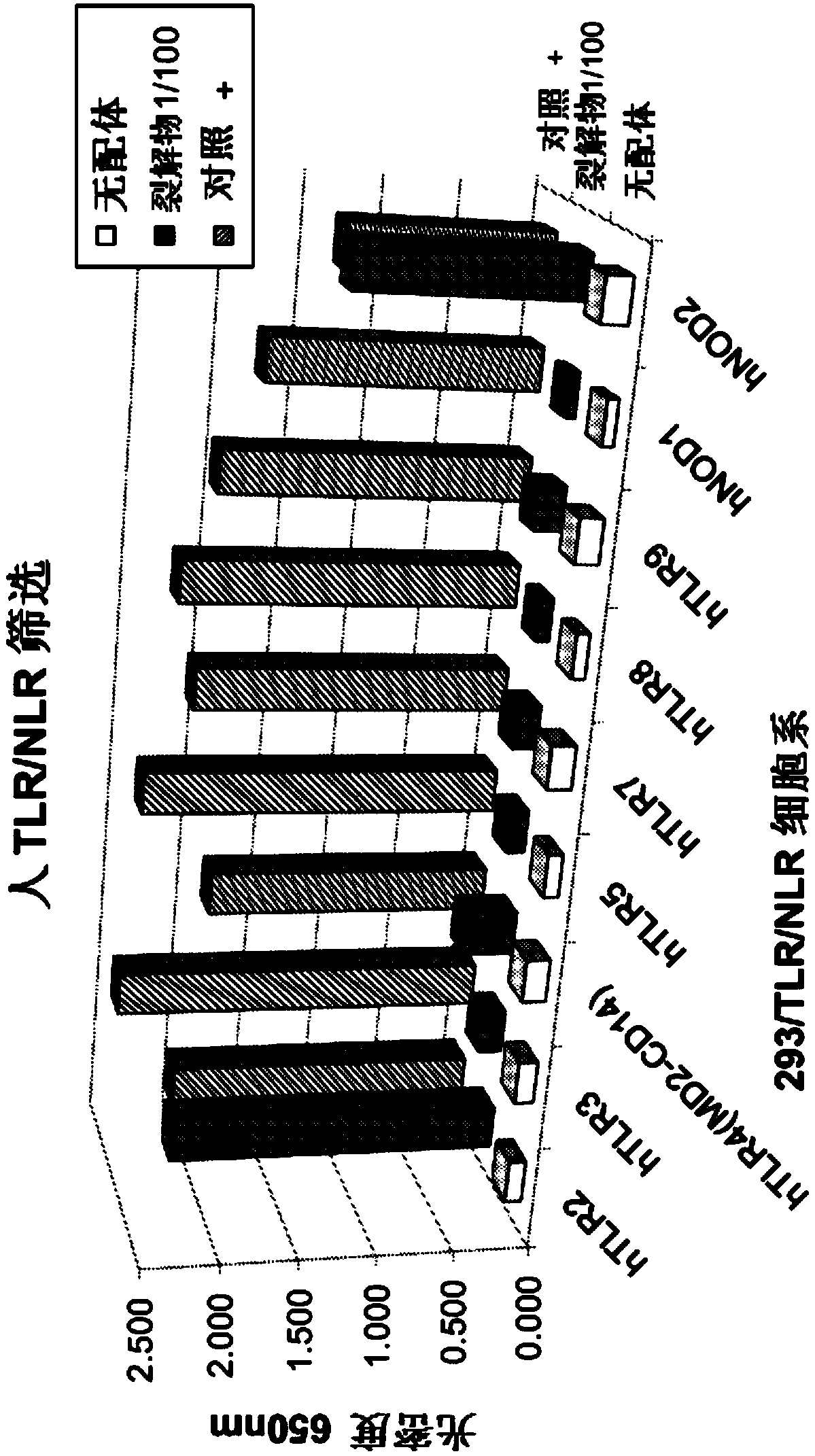
[0191] Toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulation was tested by assessing NF-κB activation in HEK293 cells expressing a given TLR or Nod-like receptor (NLR). In seven different human TLRs (TLR2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8 and 9 (Invivogen, San Diego, CA)) and in two different human NLRs (TLRs containing a nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain The activity of the samples was tested on proteins 1 and 2 (NOD1 and NOD2)). Each ligand was tested on TLR or NLR cells at a final concentration of 1 / 100 stock solution and compared to a control ligand as described below. This step was repeated three times.
[0192] The control ligands, control cell lines and samples used in the examples are shown in Table 1.
[0193] Table 1: Control Ligand and Control Cell Line Information for Ligand Screening Tests
[0194]
[0195]
[0196] usual procedure. TLR stimulation in the screen was tested by assessing NF-κB activation in HEK293 cells expressing a given TLR...
Embodiment 3
[0198] Example 3: Effect of Process Variables on Changes in TLR Signaling
[0199] By observing the effect of certain process changes on TLR signaling, it was noted that TLR signaling patterns may be altered.
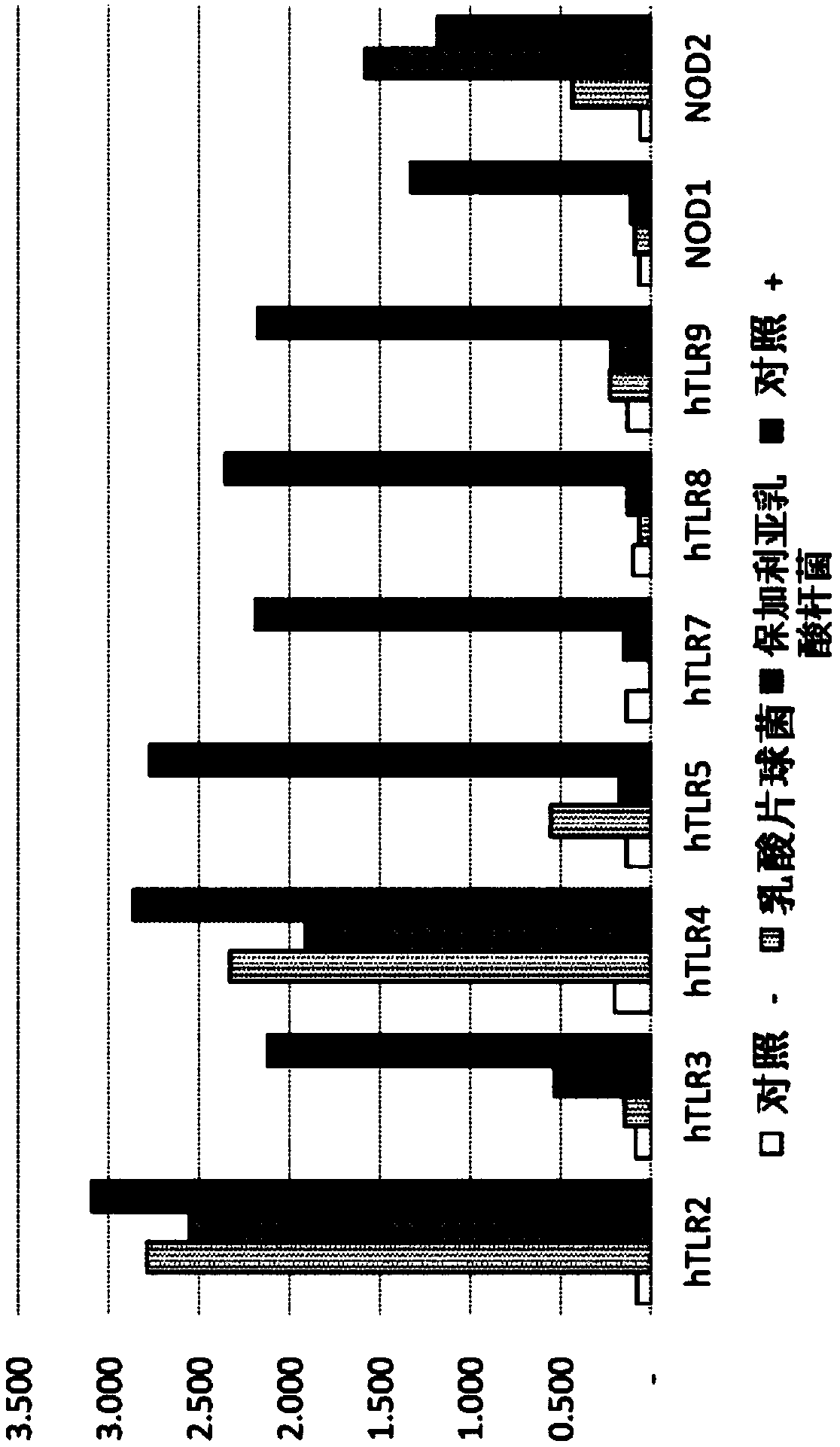
[0200] image 3 Differences in cell morphology with TLR signaling of Gram-positive organisms are shown. Lysates from Pediococcus acidilactici (a coccus organism) produced higher TLR4 and lower NOD2 signals compared to the bacillus organism L. bulgaricus, which (P acidilactici) was only slightly higher than the TLR2 signal produced by L. bulgaricus. NOD2 activation was significantly reduced in P. acidilactici, reflecting the lower muramyl peptides found in cocci.
[0201] Such as Figure 4 It was shown that TLR signaling patterns are also affected by the time of culture harvest of Bacillus coagulans lysates. Bacillus coagulans was incubated at 45° C. and 250 rpm using shake flasks containing standard yeast extract / glucose medium with a pH value of 6.5. The harvest ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com