Method of effecting lysis of acid-fast bacteria and method of performing gene amplification or detection therewith
a technology of acid-fast bacteria and lysis method, which is applied in the field of lysing acid-fast bacteria, can solve the problems of insufficient lysis method, complicated operation, and longer treatment period, and achieve the effects of easy and fast lysing, safe operation, and low risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1-1
(Example 1-1, Comparative Example 1)
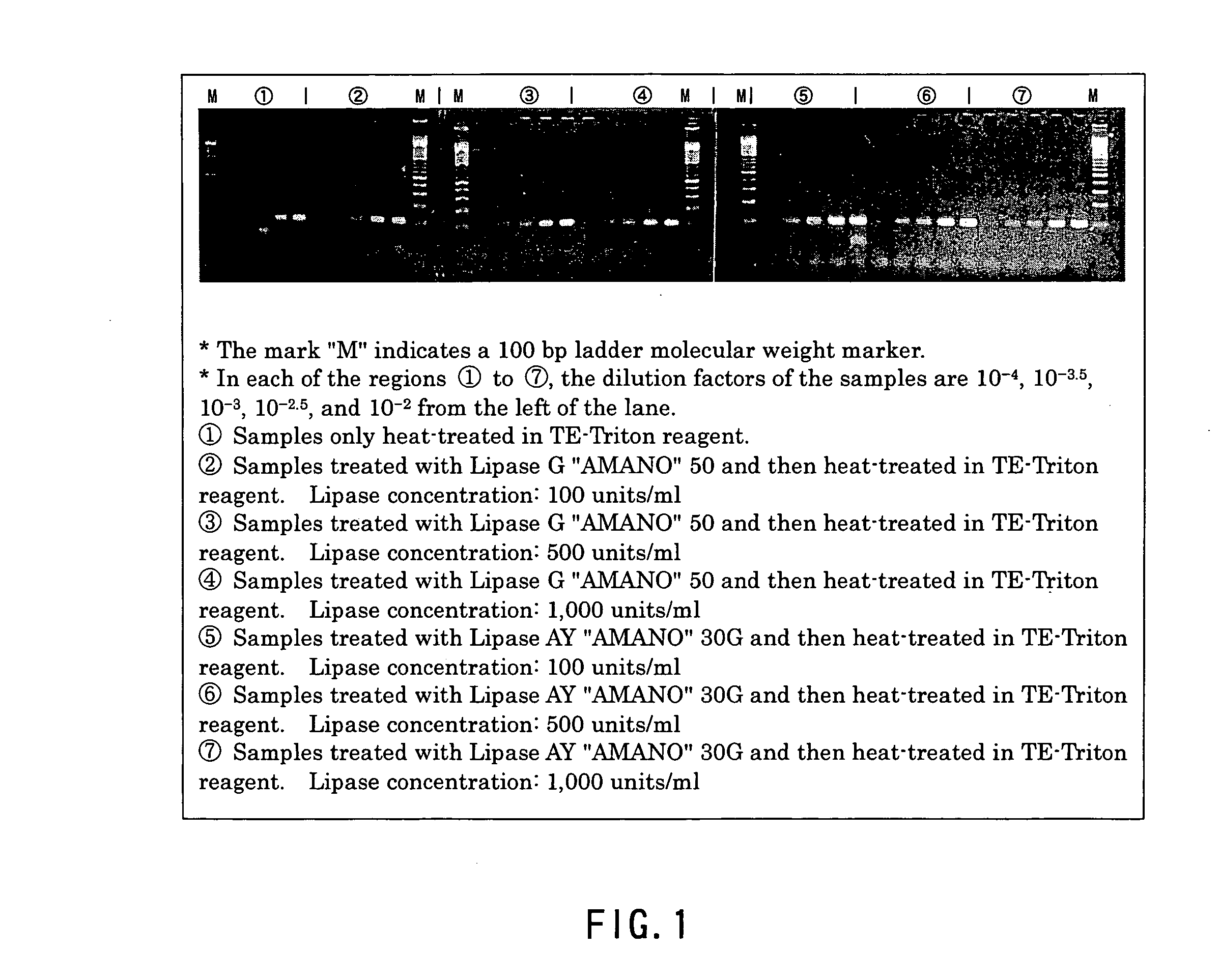
[0036] A clinical isolate of a tubercule bacillus was cultured in a product named MycoBroth (Kyokuto Pharmaceutical Industrial Co., Ltd.) at 37° C. until a turbidity corresponding to #1 of the McFarland turbidity standard was obtained. Then, the culture was diluted with phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) so as to achieve a series of 10-fold dilutions (102-fold to 105-fold), thus preparing test solutions containing the tubercule bacillus. Subsequently, 100 μl of the test solutions with the above-described concentrations were poured into screw capped tubes, respectively, and then centrifuged (10000 g, 15 minutes) to prepare pellets. The pellets obtained from the respective test solutions were used as samples to be subjected to a lysis reaction. On the other hand, a product named Triton X-100 (Nacalai Tesque, Inc.) was dissolved in TE buffer (10 mM EDTA and 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0) so that its concentration became 3 wt % to prepare a lysis reagent solution, an...
example 1-2
(Example 1-2, Comparative Example 2)
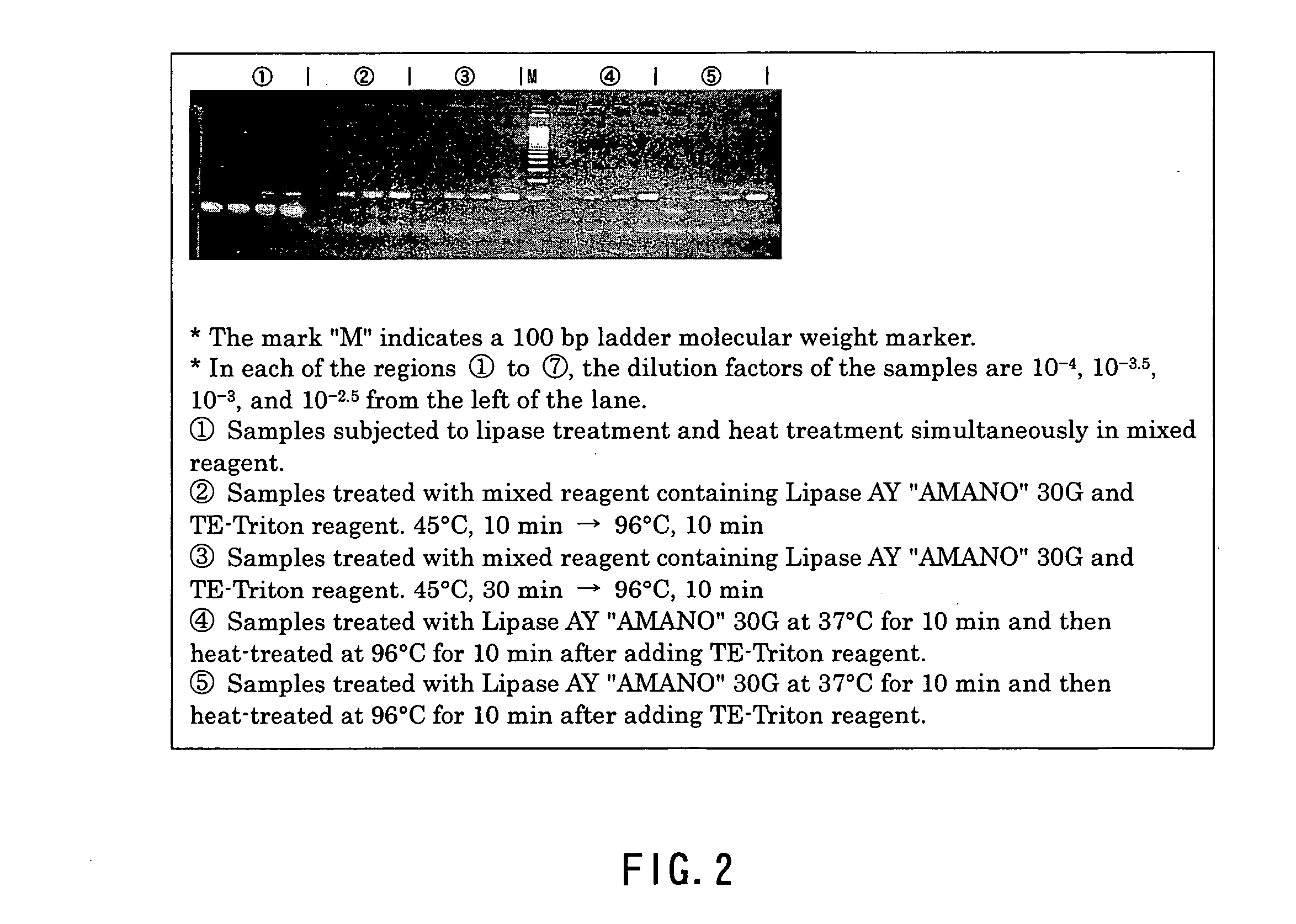
[0040] A clinical isolate of a tubercule bacillus was cultured in a product named MycoBroth (Kyokuto Pharmaceutical Industrial Co., Ltd.) at 37° C. until a turbidity corresponding to #1 of the McFarland turbidity standard was obtained. Then, the culture was diluted with a non-tuberculous sputum that had been homogenized with a product named SUPTAZYME (Kyokuto Pharmaceutical Industrial Co., Ltd.) so as to achieve a series of 10-fold dilutions (100-fold to 1010-fold). The resultant diluents were used as samples. On the other hand, a product named Triton X-100 (Nacalai Tesque, Inc.) was dissolved in TE buffer (10 mM EDTA and 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0) so that its concentration became 3 wt % to prepare a lysis reagent solution, and the lysis reagent solution was sterilized by high-pressure steam in an autoclave.
[0041] Then, 50 μl of the above-described lysis reagent solution was added to the respective samples (100 μl), and a lysis treatment was carried...
example 1-3
(Example 1-3, Comparative Example 3)
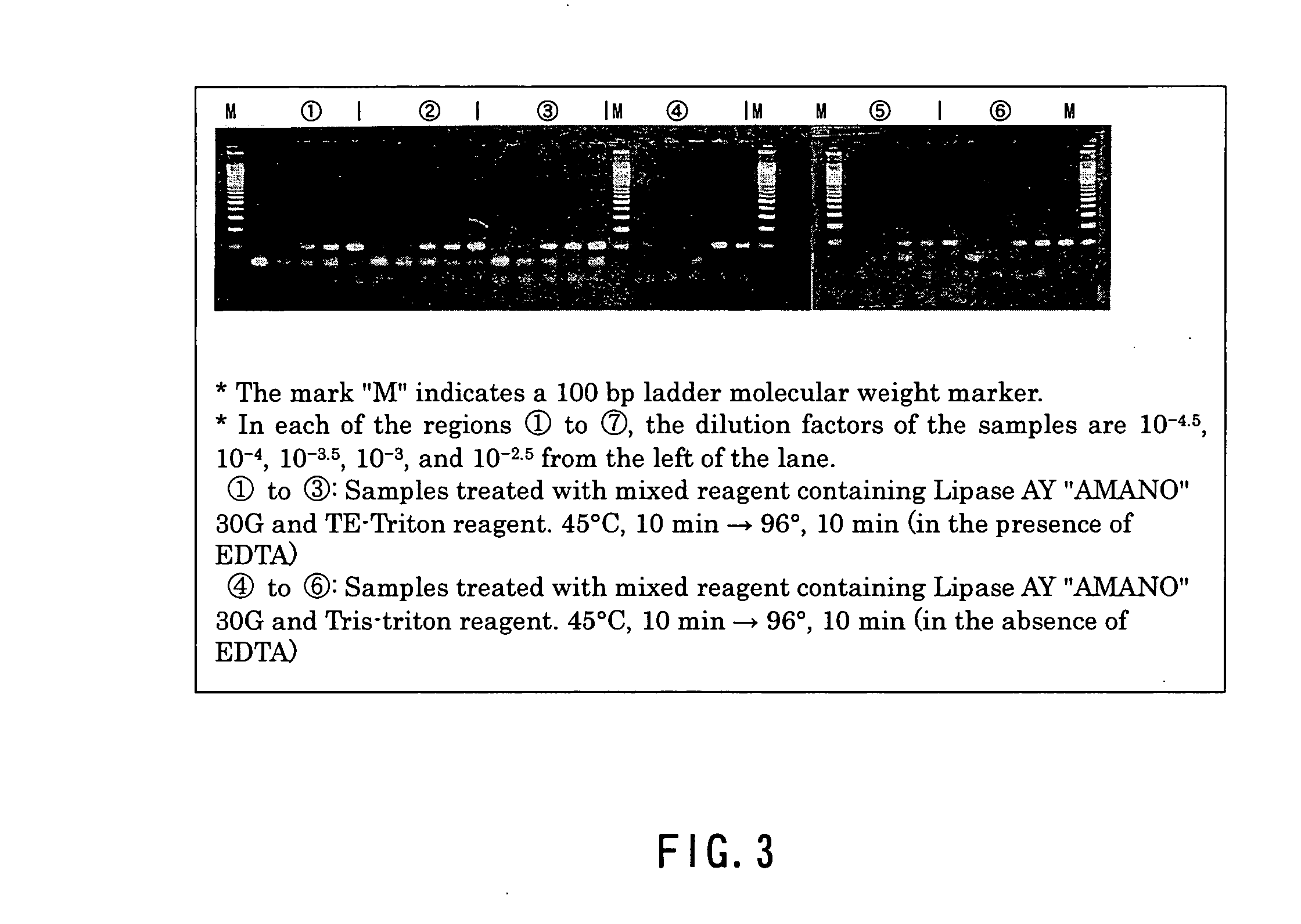
[0044] 90 sputum specimens collected from patients were homogenized and sterilized by the NALC-NaOH method (“New Guideline for Tubercle Bacillus Test 2000” edited by The Japanese Society for Tuberculosis). Then, 100 μl of each of the treated sputum specimens was centrifuged at 13,000 g for 10 minutes. After removing the supernatant, the precipitate (pellet) was collected. On the other hand, a product named Triton X-100 (Nacalai Tesque, Inc.) was dissolved in TE buffer (10 mM EDTA and 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0) so that its concentration became 1 wt % to prepare a lysis reagent solution, and the lysis reagent solution was used after being sterilized by high-pressure steam in an autoclave. Specifically, 50 μl of the sterilized lysis reagent solution was added to the pellets obtained from the respective specimens to suspend the pellets. Then, a lysis treatment was carried out by heating the suspensions at 96° C. for 10 minutes in a heating block. On the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com