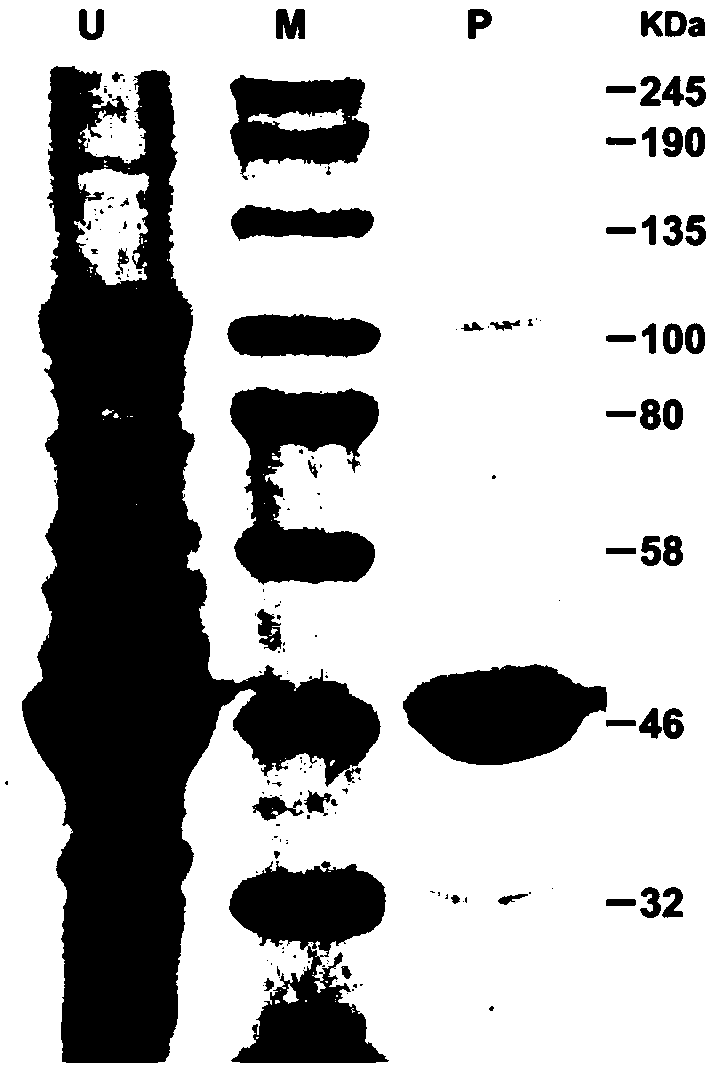Patents
Literature
97 results about "O-methyltransferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
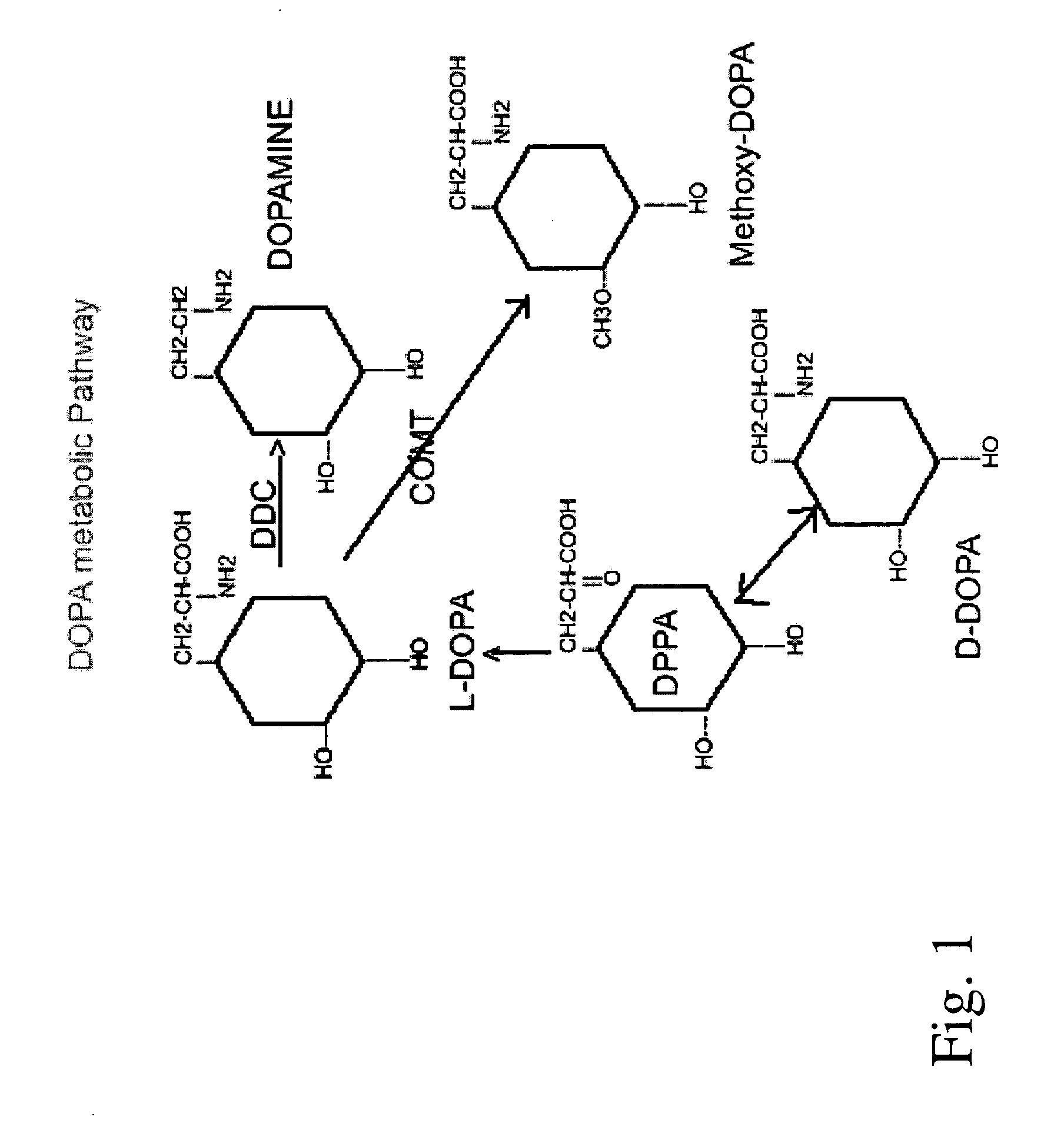
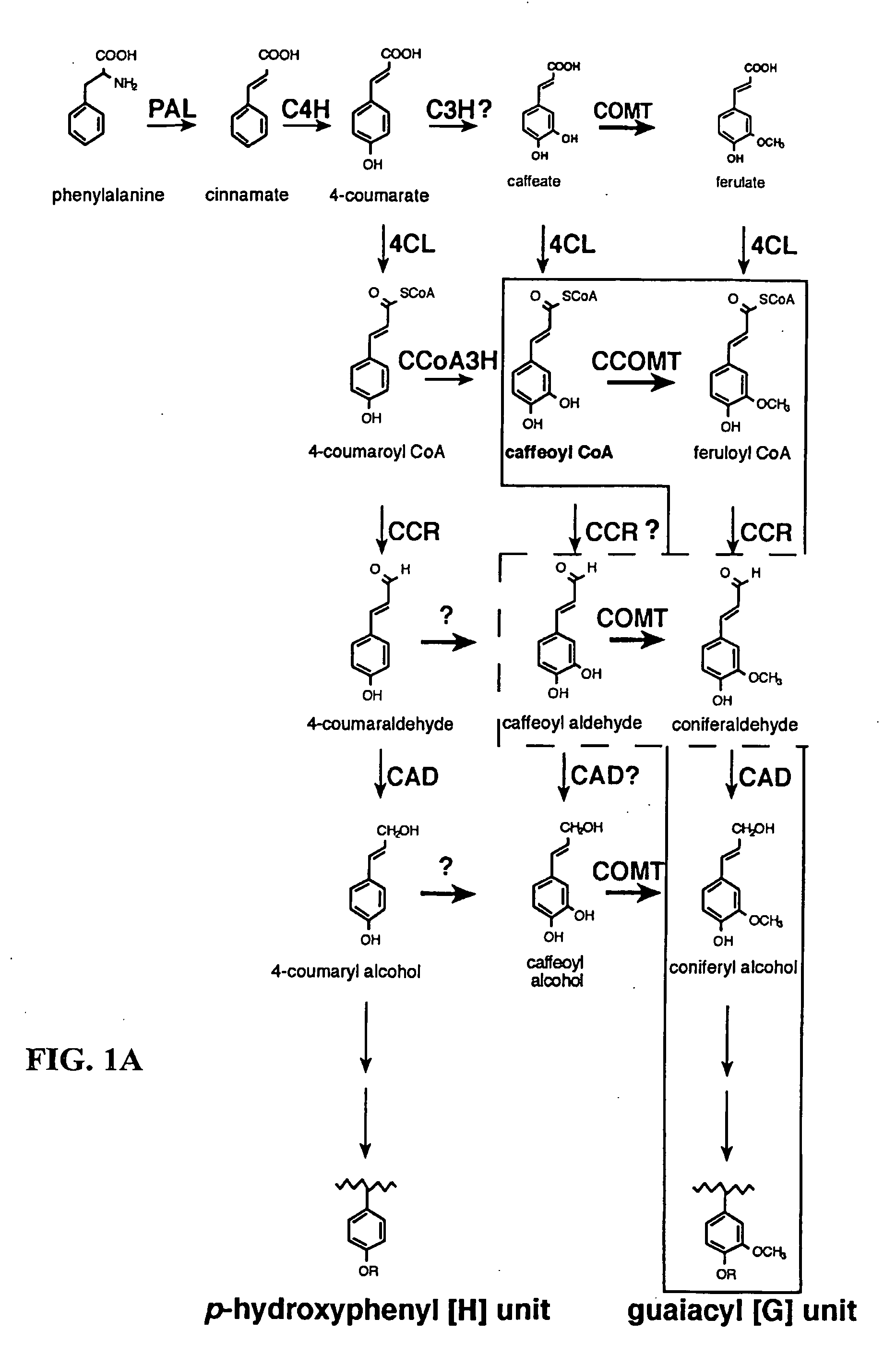
An O-methyltransferase (OMT) is a type of methyltransferase enzyme transferring a methyl group on a molecule.
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS7094606B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationACC oxidaseGenetic Change
Owner:CIBUS
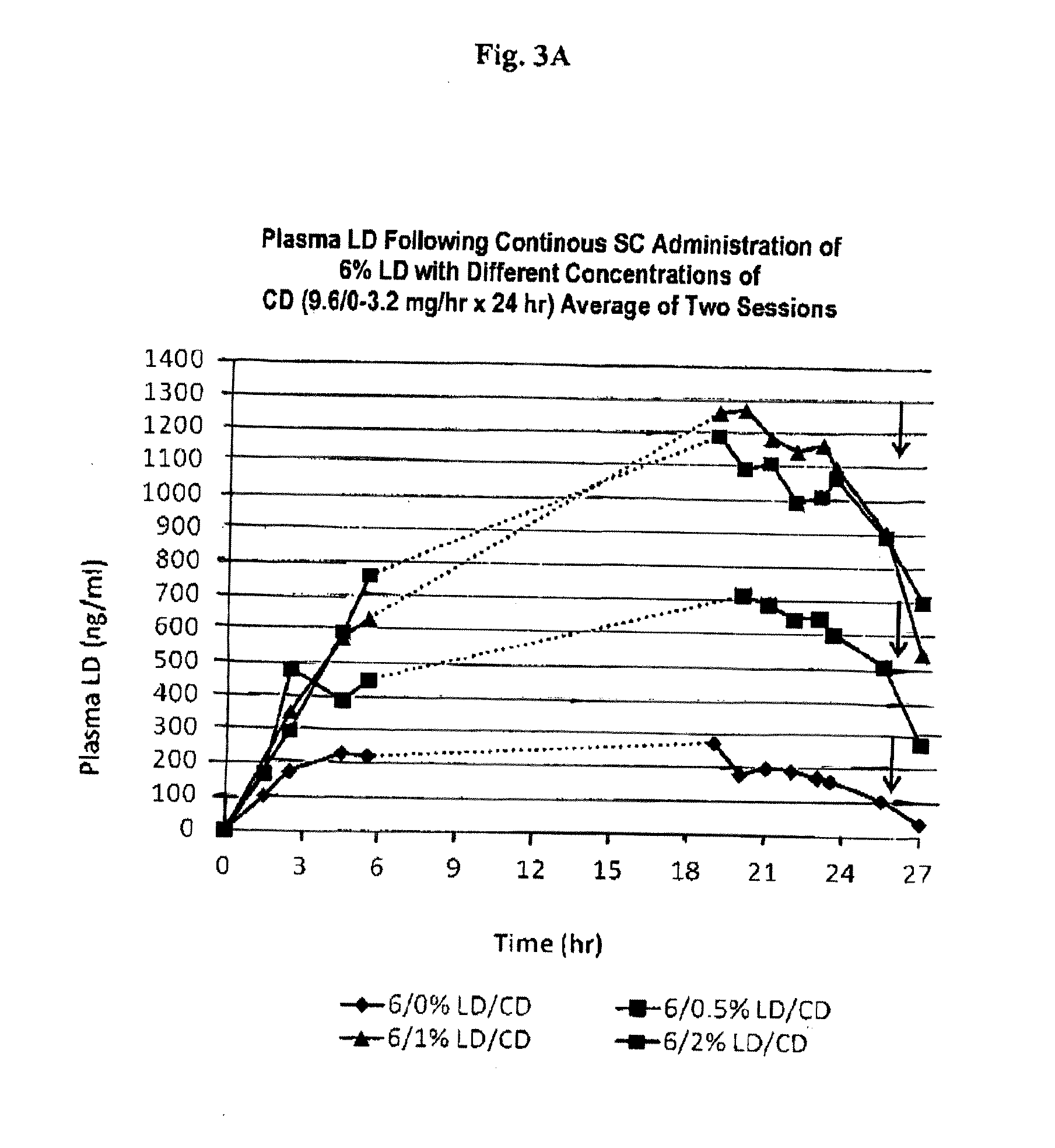
Continuous Administration of L-Dopa, Dopa Decarboxylase Inhibitors, Catechol-O-Methyl Transferase Inhibitors and Compositions for Same
ActiveUS20140051755A1Effectively treating movementImprove efficiencyBiocideNervous disorderTolcaponeCarbidopa
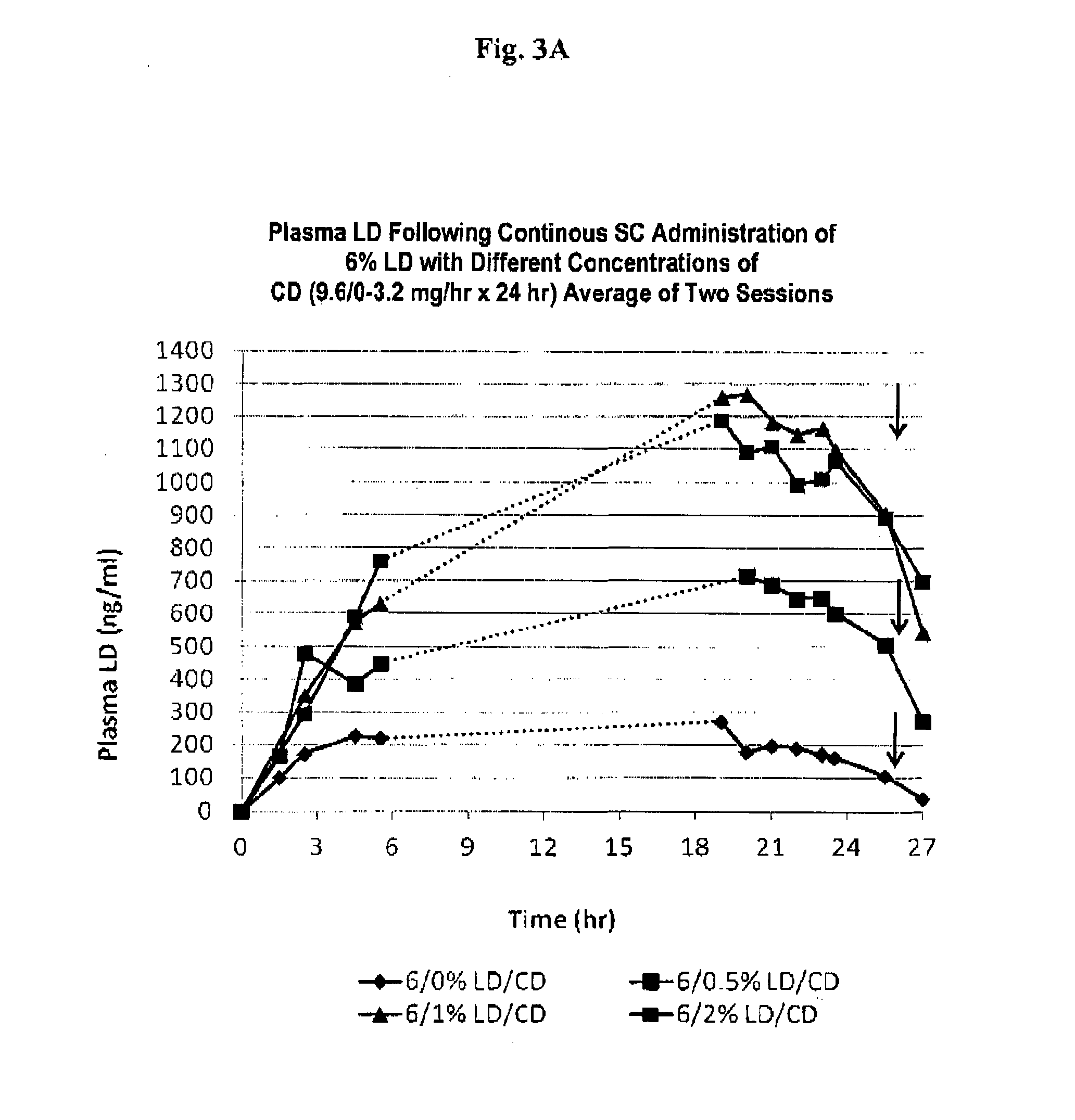
Provided herein, in part, is a method of treating a neurological or movement disorder in a patient in need thereof, comprising subcutaneously administering to said patient a pharmaceutically acceptable composition comprising levodopa and optionally carbidopa and optionally entacapone or tolcapone, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein said composition is administered substantially continuously, and compositions that can be used in the disclosed methods.
Owner:NEURODERM
Compositions and methods of using D-DOPA to treat Parkinson's disease
InactiveUS20060241183A1Improve bioavailabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmacologyCatechol
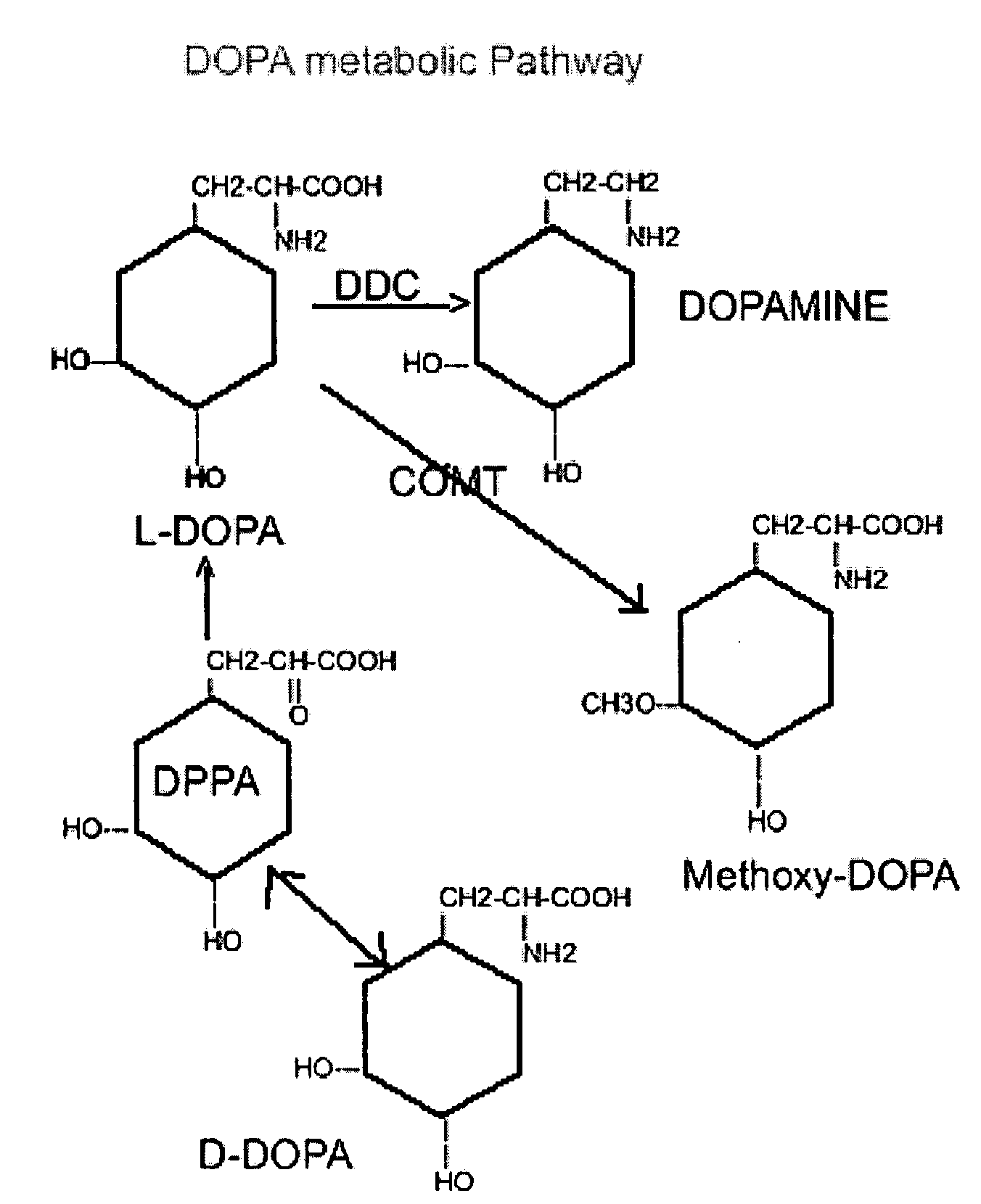
A method of treating Parkinson's disease by administering the racemic mixture of D,L-DOPA in combination with both peripheral amino acid decarboxylase and catechol, O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors in pharmaceutically acceptable salts forms and effective doses for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Alternatively, D-DOPA is administered in combination with both peripheral amino acid decarboxylase and catechol, O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors in pharmaceutically acceptable salts forms and effective doses for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:AMAR INT
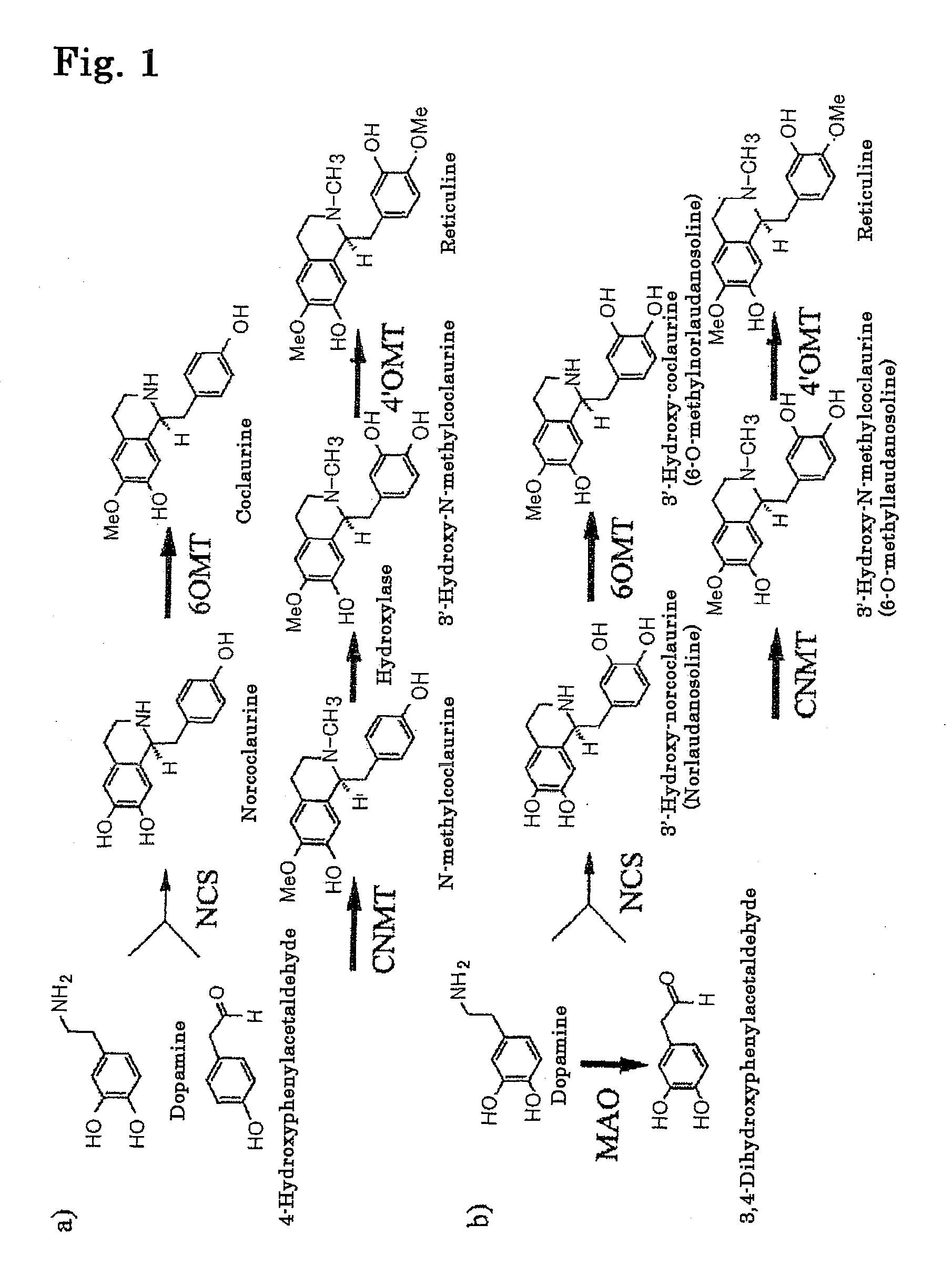
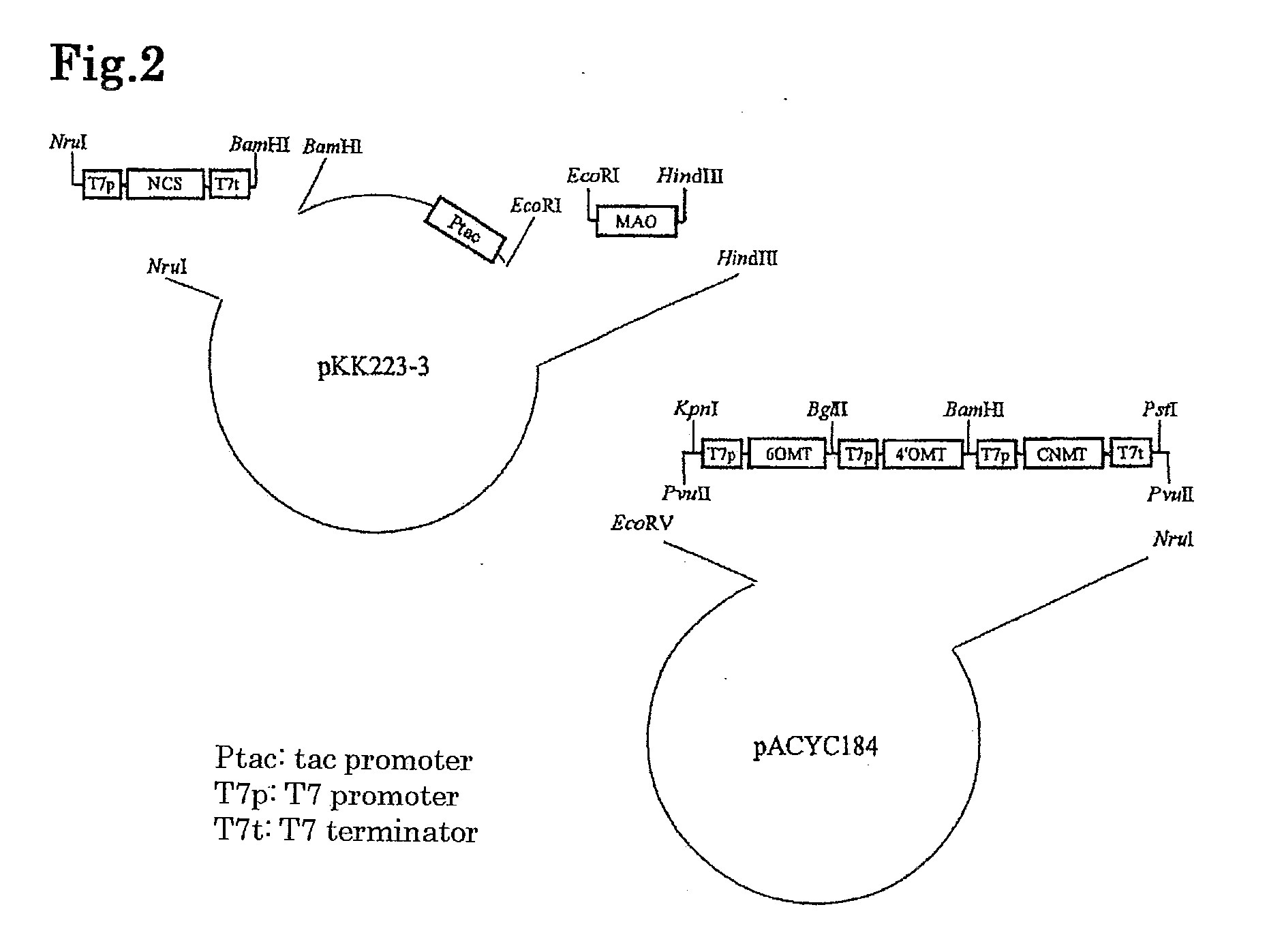
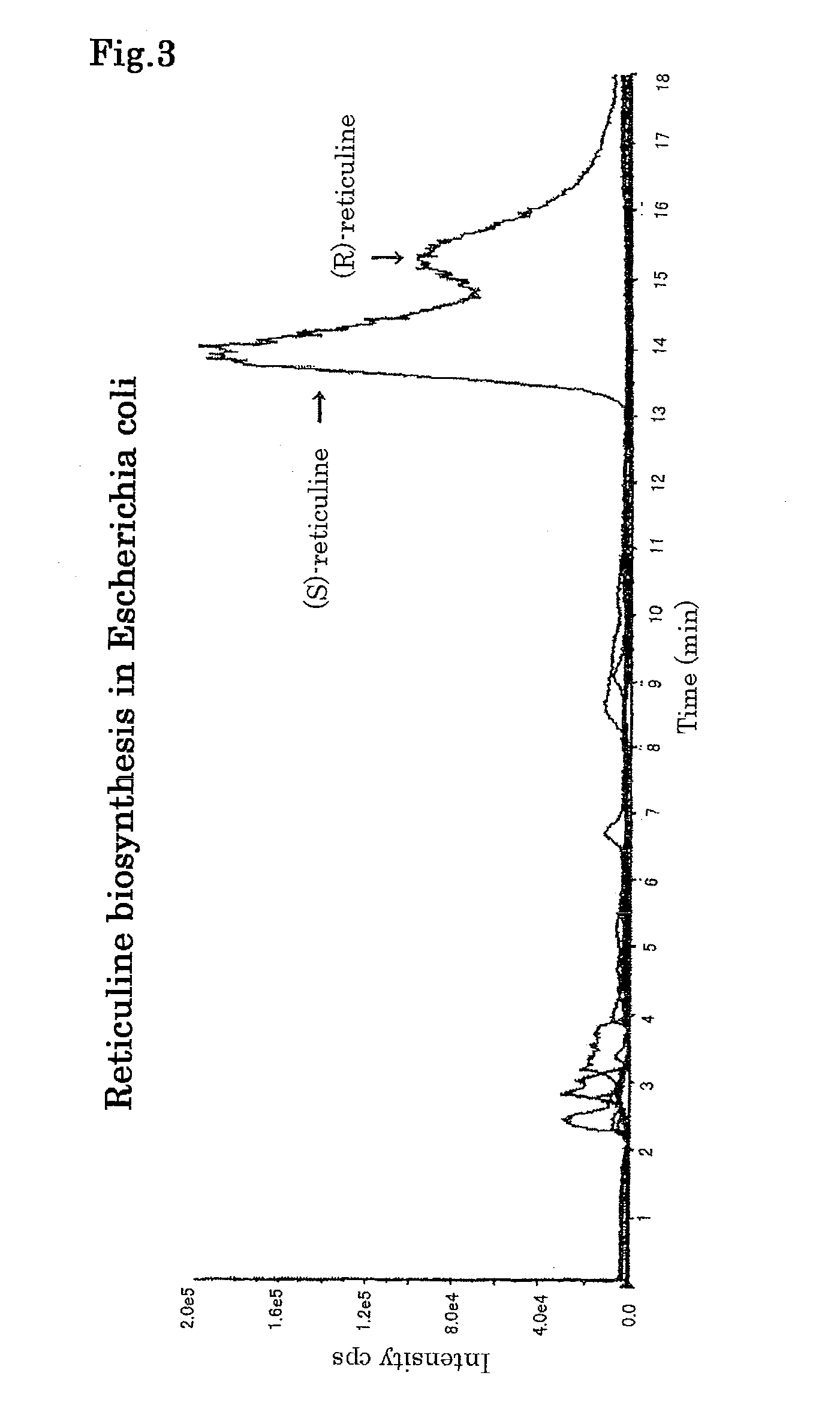
Method for producing alkaloids
ActiveUS20100184166A1Improve efficiencyMicroorganismsFermentationCoclaurine N-methyltransferaseDopamine
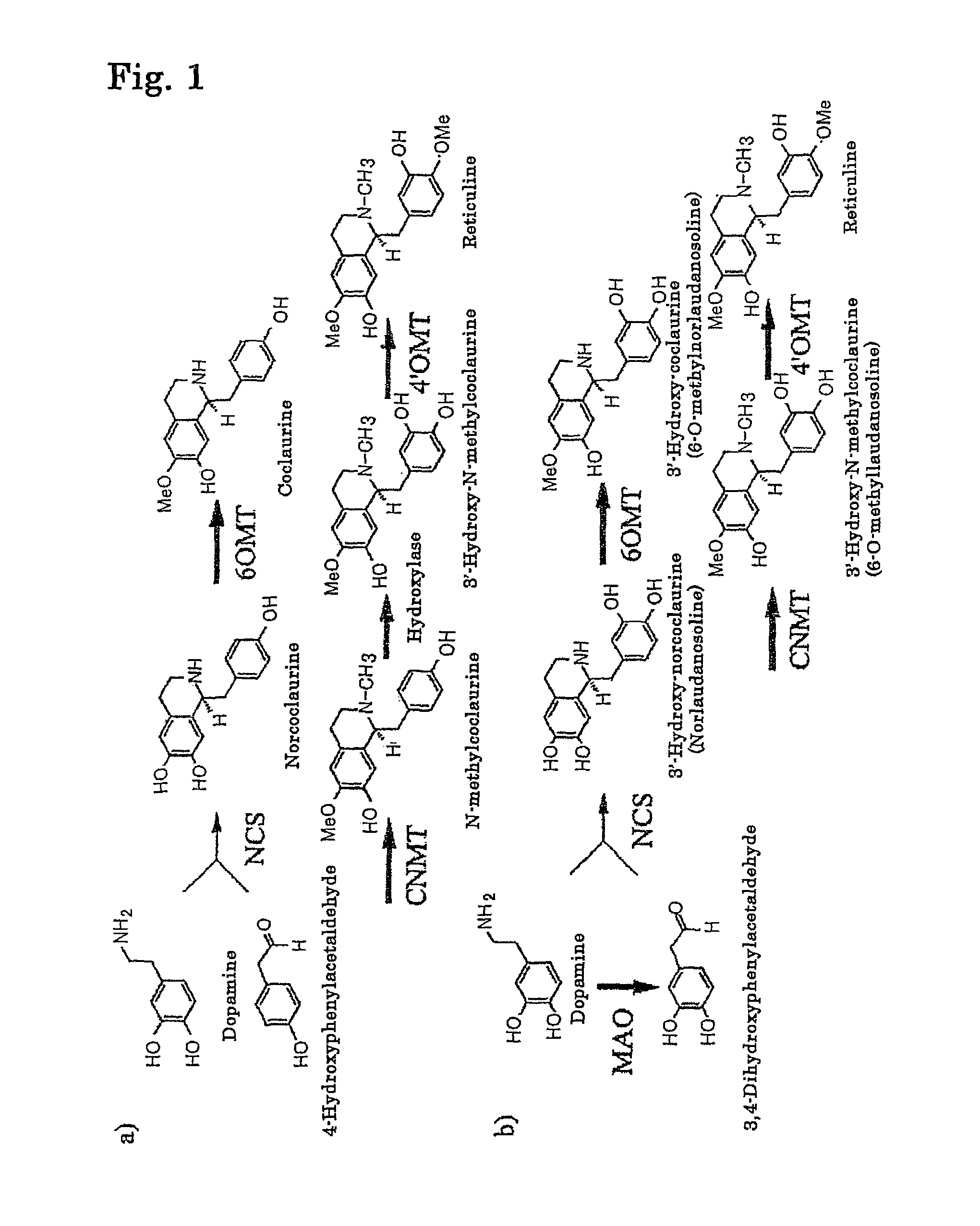
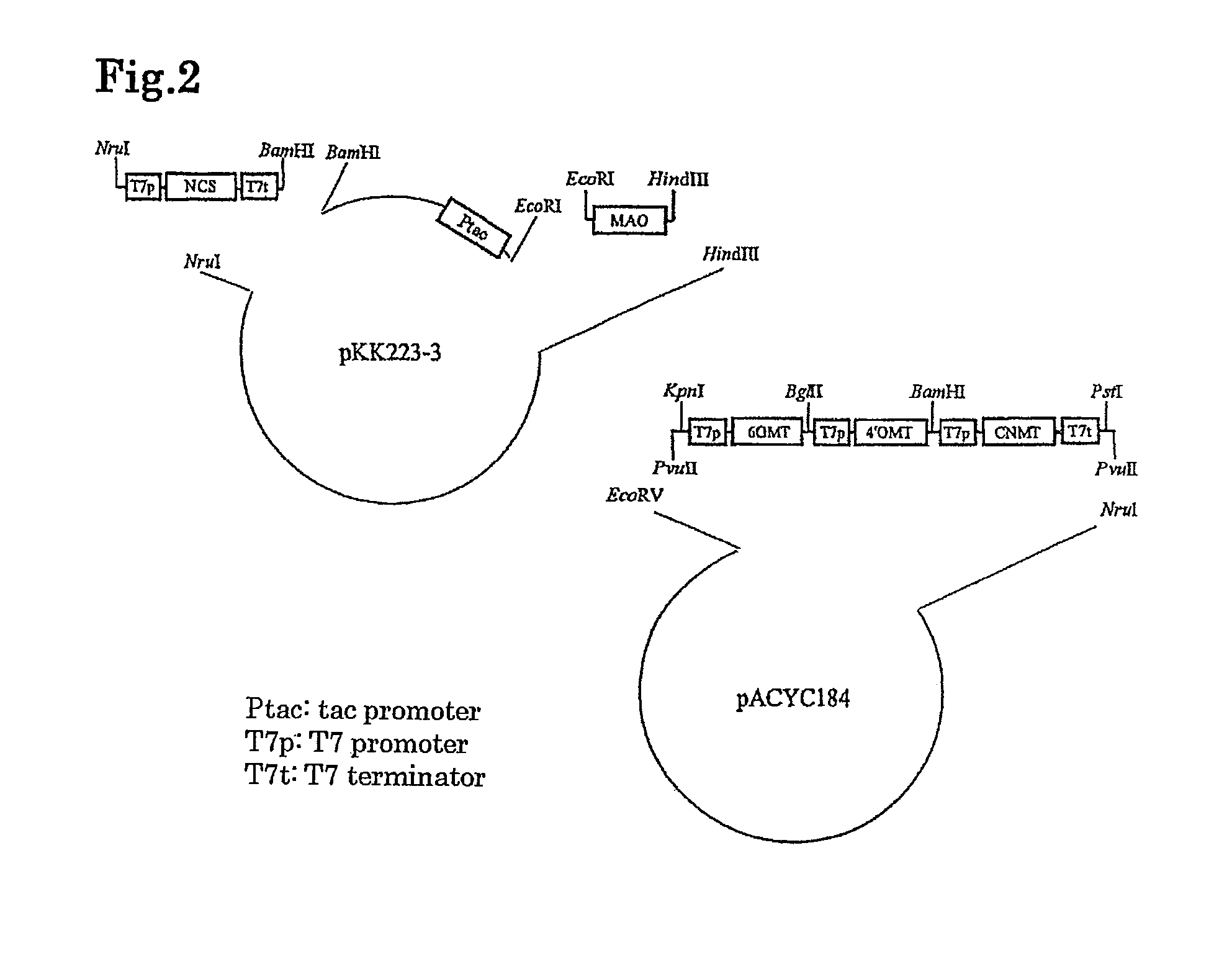
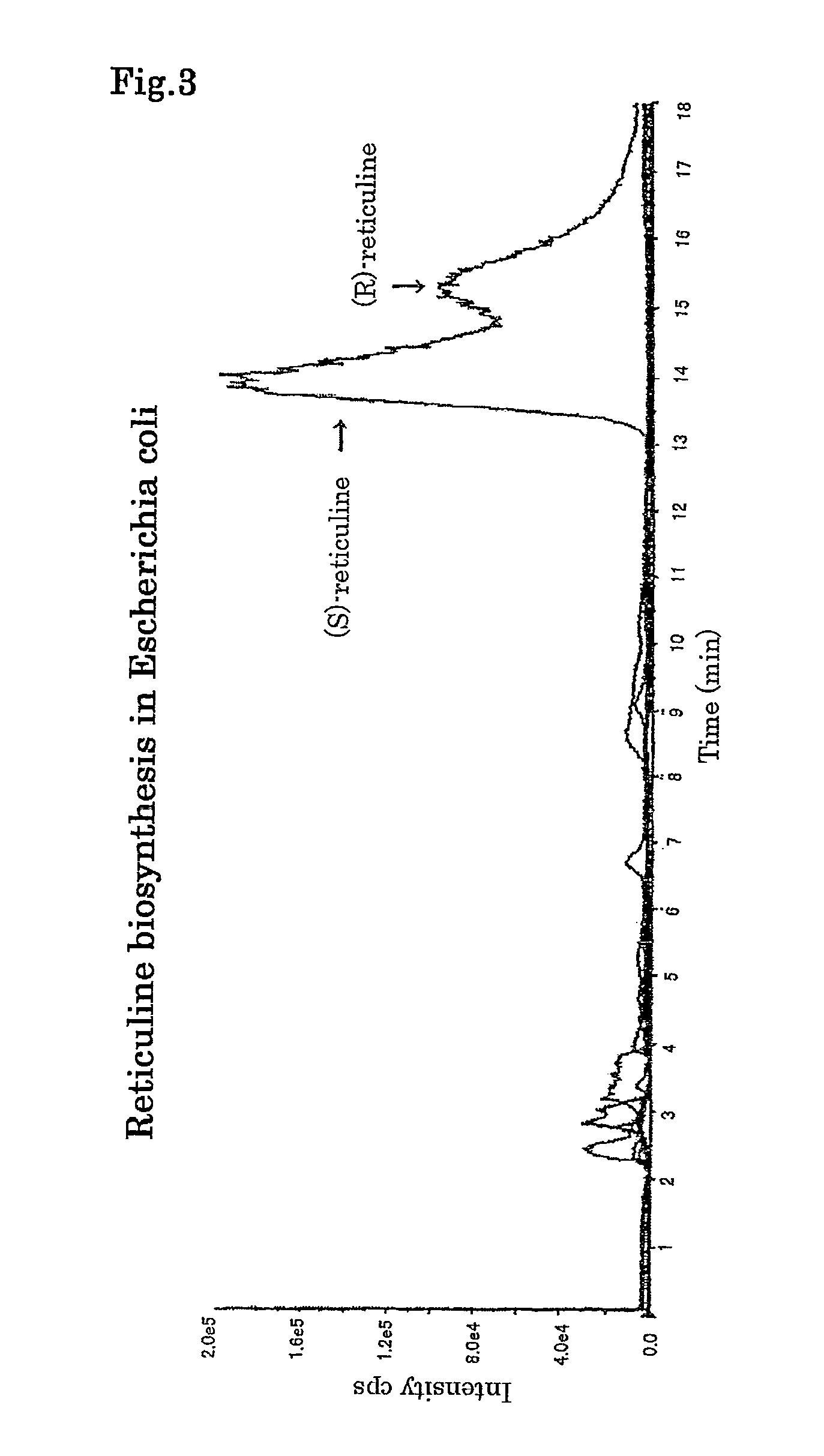
The present invention provides a method for producing an alkaloid, for example, reticuline, comprising providing dopamine as a substrate for a series of actions of monoamine oxidase, norcoclaurine-6-O-methyltransferase, coclaurine-N-methyltransferase and 3′-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine-4′-O-methyltransferase.
Owner:FERMELANTA INC
Method for treatment of parkinson's disease
The present invention provides a method for treatment of a neurological or movement disorder, e.g., Parkinson's disease, in an individual in need thereof, by parenteral administration of a composition comprising carbidopa and levopoda, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and concomitant oral administration of a catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibitor, e.g., entacapone or tolcapone.
Owner:NEURODERM
Intermediate for preparing a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor
ActiveUS9126988B2Improve securityExtension of timeNervous disorderOrganic chemistryParkinson's diseaseCatechol
There is disclosed a methylated intermediate which may be demethylated to provide an inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase useful in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Also disclosed are methods of making and using said intermediate.
Owner:BIAL PORTELA & CA SA
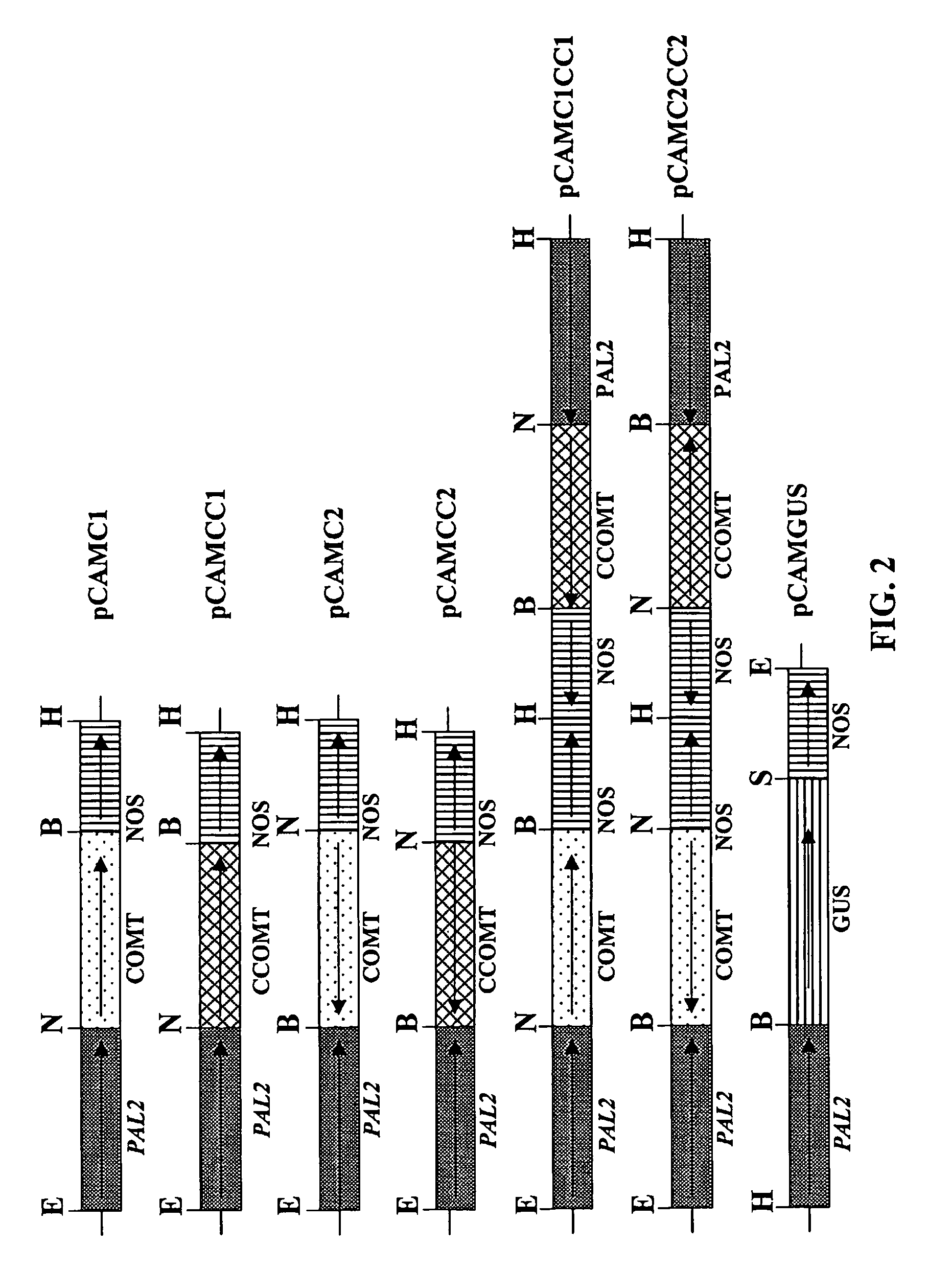
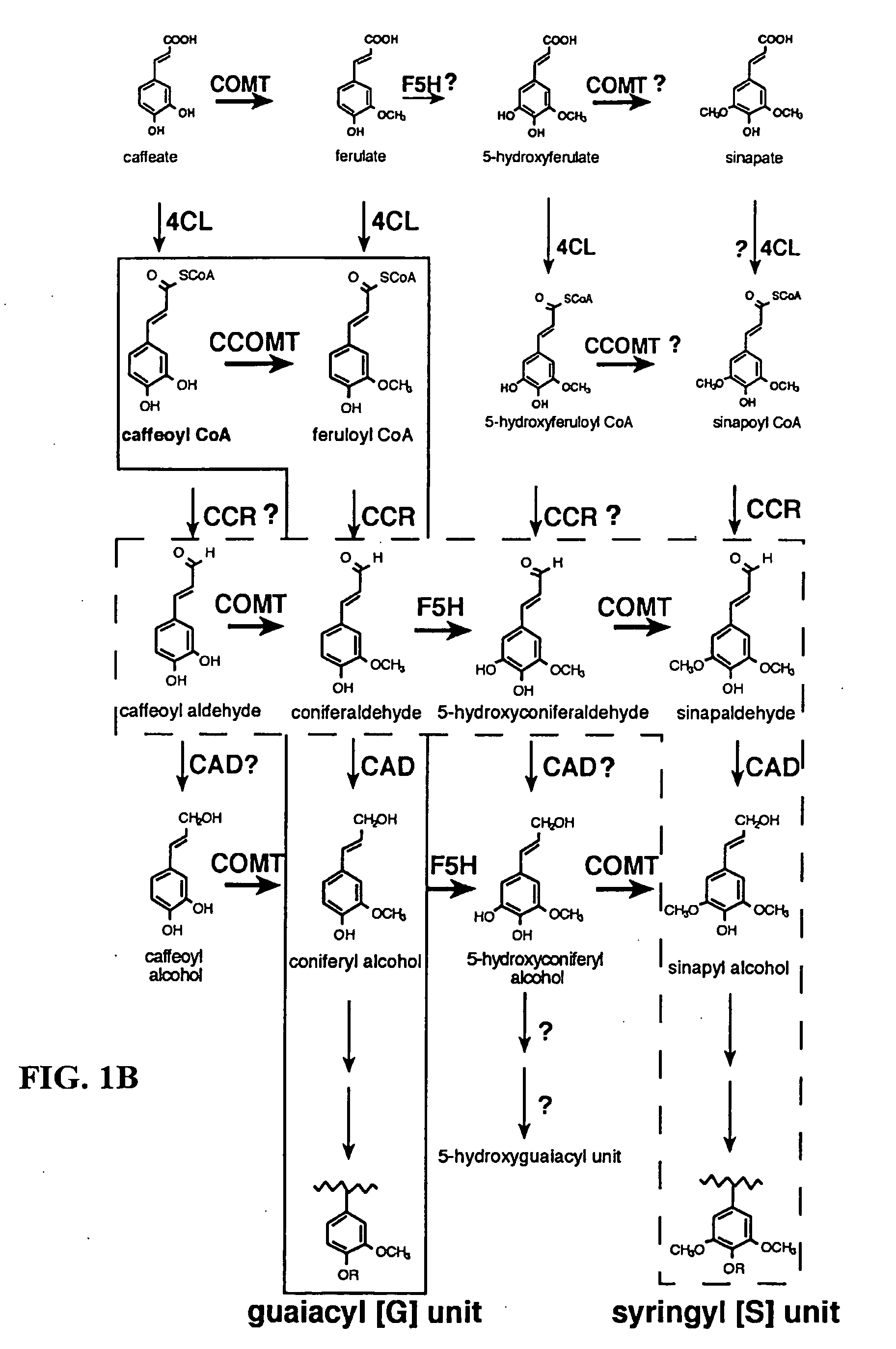
Method for modifying lignin composition and increasing in vivo digestibility of forages
InactiveUS7888553B2Improve digestibilityTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationOpen reading frame
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Transgenic sweet sorghum with altered lignin composition and process of preparation thereof
The present invention provides a sweet sorghum plant characterized by altered lignin content and / or altered lignin composition compared to a wild plant and this is achieved by manipulating the expression of caffeoylCoA-O-methyltransferae (CCoAOMT) in particular and optionally caffeic acid-O-methyltranferase (COMT) in sweet sorghum by incorporation of a construct comprising an isolated DNA sequence represented by SEQ ID NO 2 and optionally SEQ ID NO 1.
Owner:NAGARJUNA ENERGY
Method for producing alkaloids
The present invention provides a method for producing an alkaloid, for example, reticuline, comprising providing dopamine as a substrate for a series of actions of monoamine oxidase, norcoclaurine-6-O-methyltransferase, coclaurine-N-methyltransferase and 3′-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine-4′-O-methyltransferase.
Owner:FERMELANTA INC
Method for modifying lignin composition and increasing in vivo digestibility of forages
InactiveUS20090044294A1Improve digestibilityLow lignin contentTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationOpen reading frame
Methods for transforming forage legumes or woody plants with a DNA construct comprising at least one open reading frame encoding for a caffeoyl CoA 3-O-methyltransferase enzyme or a Medicago sativa caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase enzyme or a fragment thereof in either a sense or antisense orientation under a lignification-associated tissue specific promoter have been found, resulting in the down-regulation of the corresponding homologous gene either through antisense inhibition or sense suppression, as well as reduced lignin content and modified lignin composition in the transgenic plants. The expression of the caffeoyl CoA 3-O-methyltransferase transgene produces an increased syringyl lignin to guaiacyl lignin ratio in the transformed plant, and greatly improved forage digestibility.
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Continuous administration of l-dopa, dopa decarboxylase inhibitors, catechol-o-methyl transferase inhibitors and compositions for same
ActiveUS20140249229A1Improve efficiencyReduce the daily dosage of levodopaBiocideNervous disorderTolcaponeCarbidopa
Provided herein, in part, is a method of treating a neurological or movement disorder in a patient in need thereof, comprising subcutaneously administering to said patient a pharmaceutically acceptable composition comprising levodopa and optionally carbidopa and optionally entacapone or tolcapone, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein said composition is administered substantially continuously, and compositions that can be used in the disclosed methods.
Owner:NEURODERM
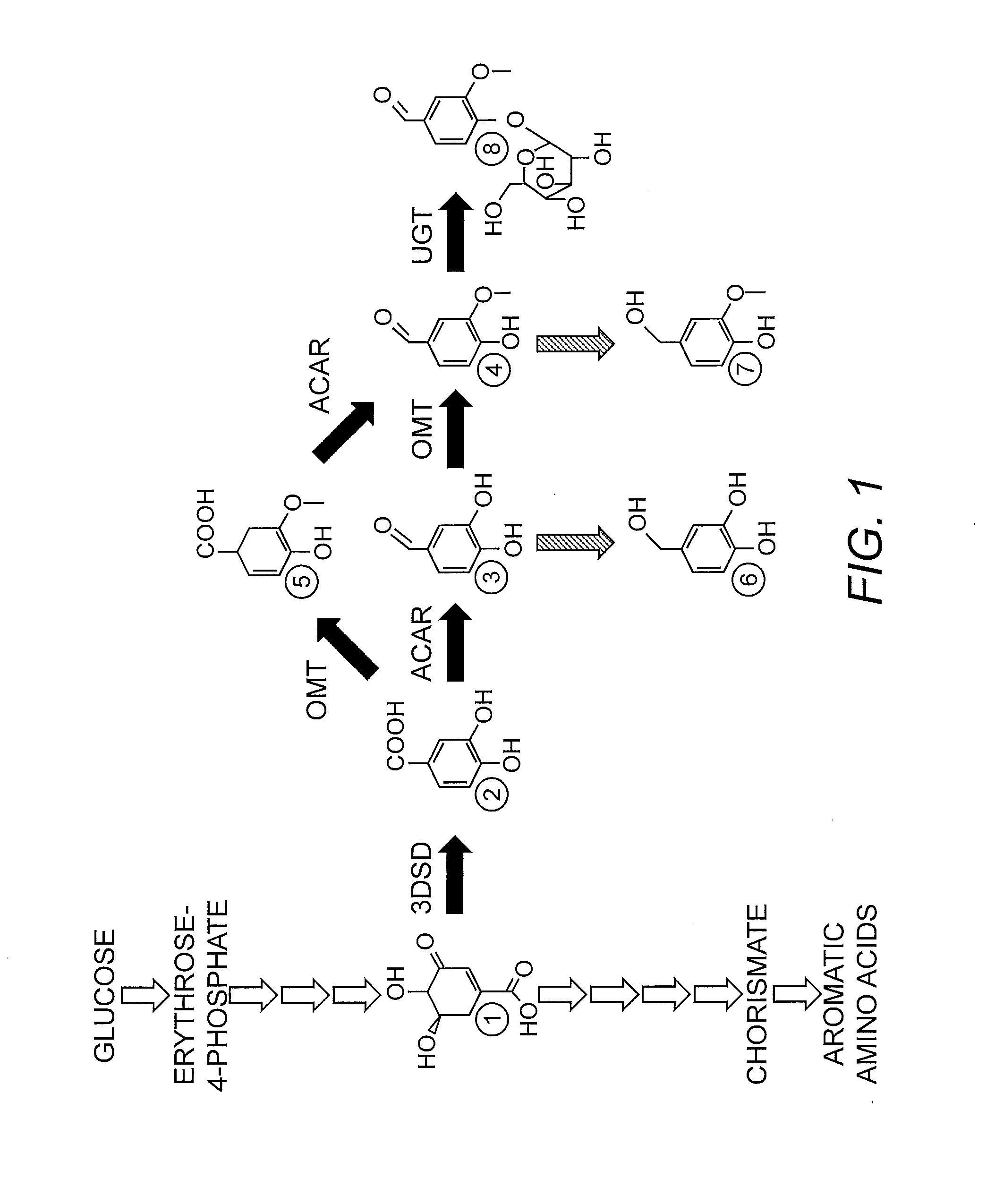
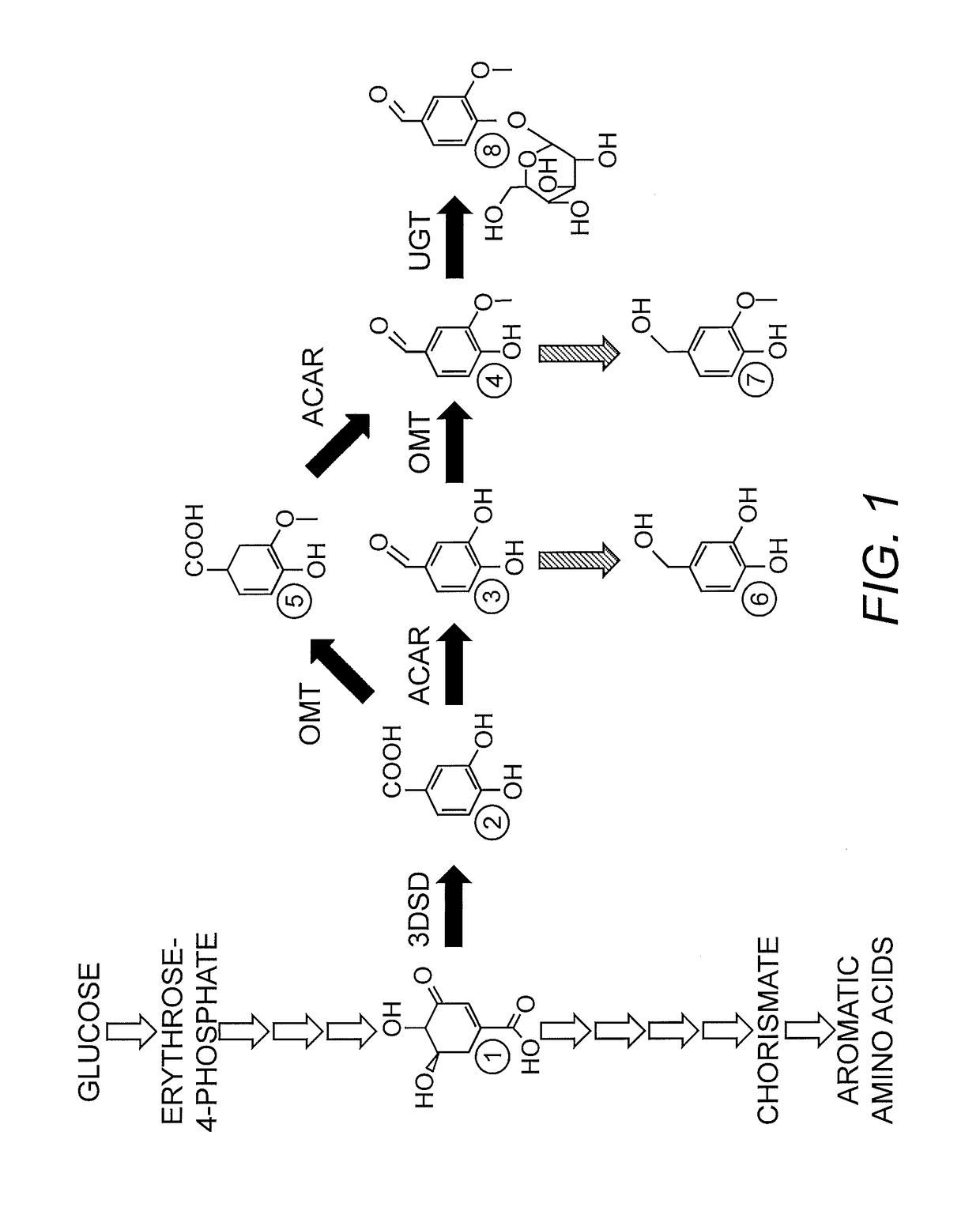
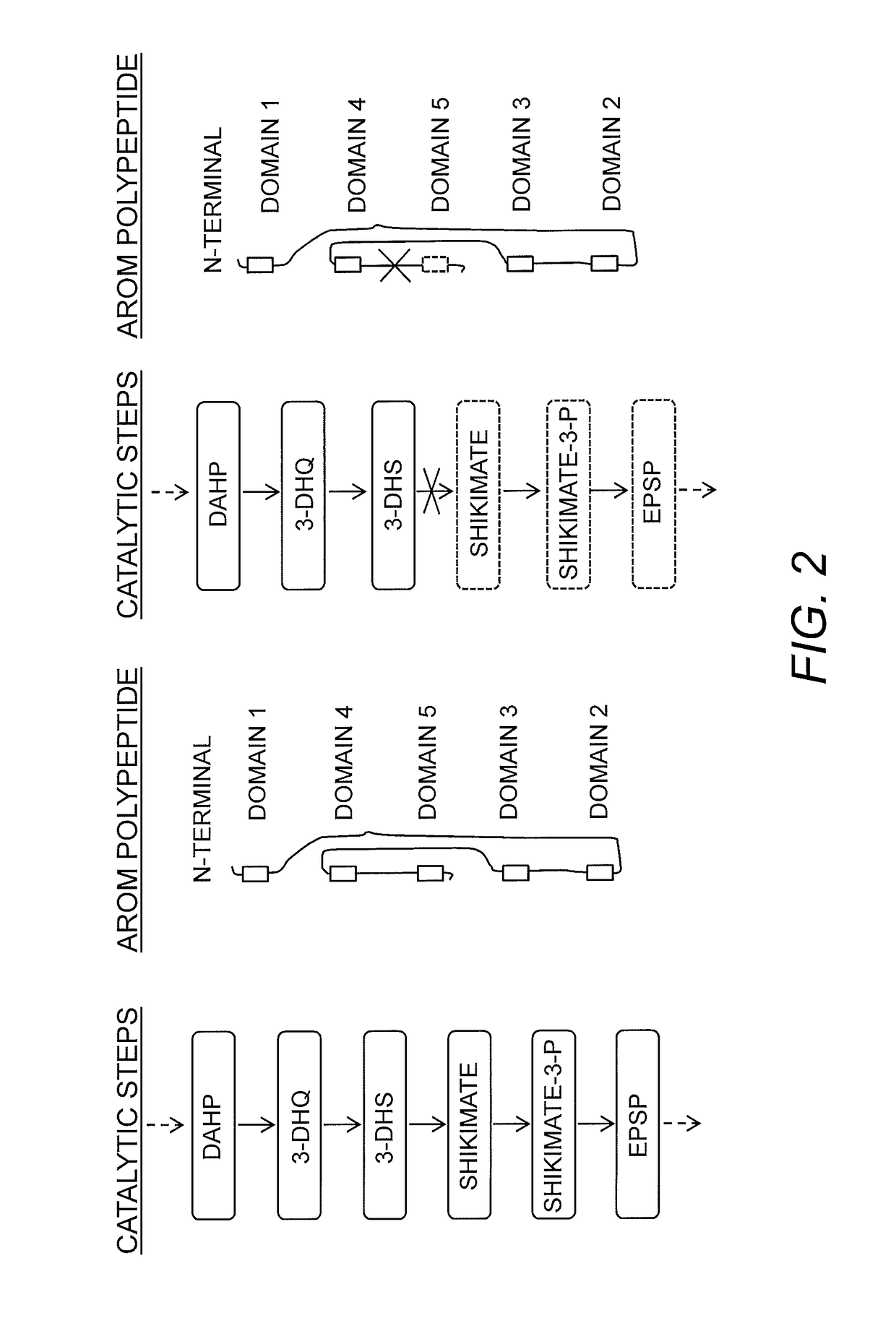
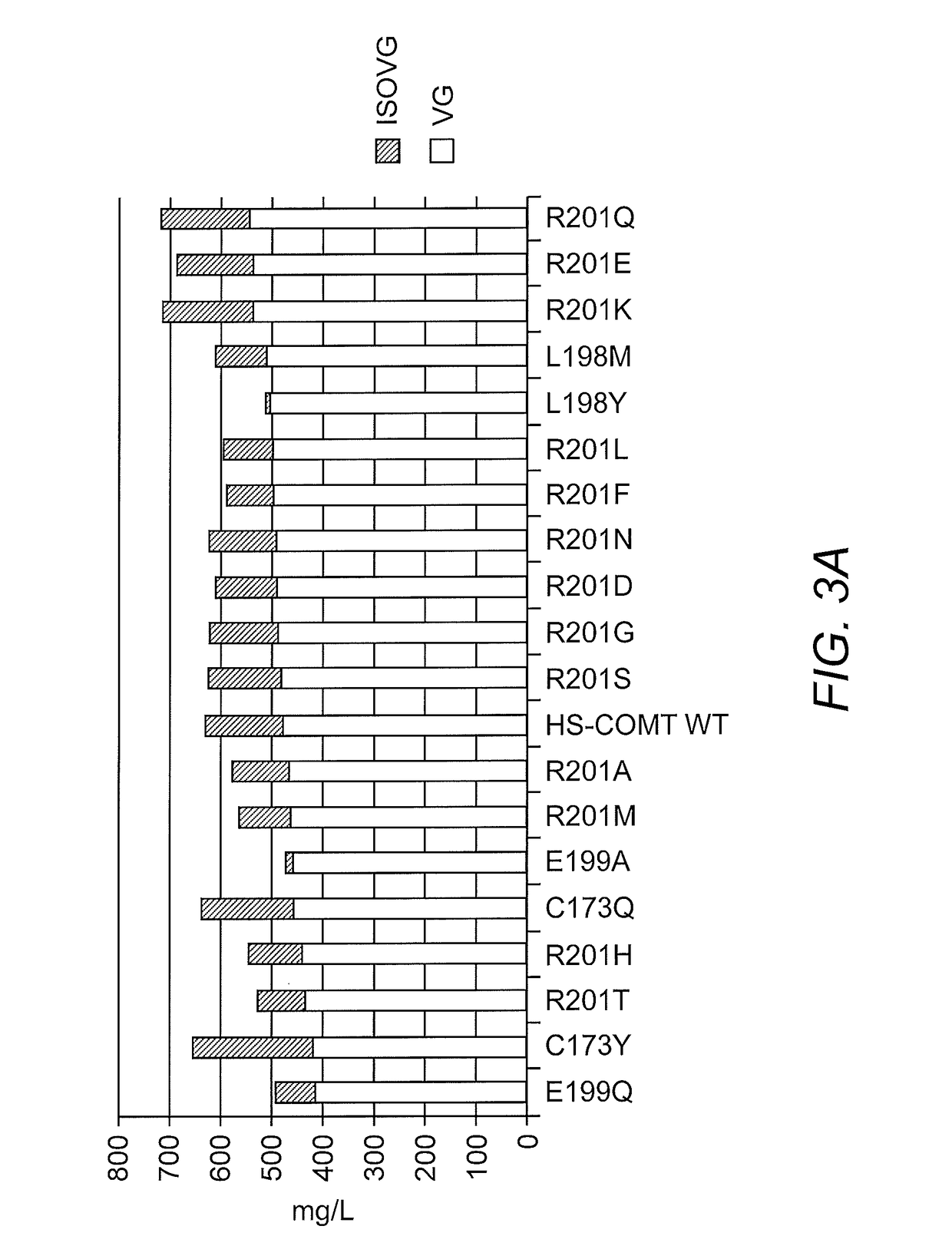
Compositions and methods for the biosynthesis of vanillan or vanillin beta-d-glucoside
Recombinant microorganisms, plants, and plant cells are disclosed that have been engineered to express a mutant AROM polypeptide and / or mutant catechol-O-methyltransferase polypeptide alone or in combination with one or more vanillin biosynthetic enzymes or UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs). Such microorganisms, plants, or plant cells can produce vanillin or vanillin beta-D-glucoside.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES +1
Chemical compound useful as intermediate for preparing a catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibitor
ActiveUS20140350057A1Improve securityExtension of timeBiocideNervous disorderChemical compoundProcaterol
There is disclosed a methylated intermediate which may be demethylated to provide an inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase useful in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Also disclosed are methods of making and using said intermediate.
Owner:BIAL PORTELA & CA SA
Engineering bacteria for generating gentamicin C1a and constructing method of engineering bacteria
ActiveCN102586146AHigh C1a contentClear genetic backgroundBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicromonospora echinosporaGentamicin C2b
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and relates to engineering bacteria for mainly generating gentamicin C1a and a constructing method of the engineering bacteria. 6'-C-O-methyltransferase gntK in micromonospora echinospora of gentamicin generated bacteria is damaged by using a gene blocking technology, so that the synthesis of gentamicin C1, C2 and C2a is blocked and gentamicin C1a and small part of gentamicin C2b are mainly generated. The contents of the C1A, the C2, the C2a and C1 in an original strain are 6.5 percent, 45.3 percent, 20.1 percent and 27.1 percent respectively; and the contents of the C1a and the C2b in a blocked strain are 94.0 percent and 6.0 percent respectively. According to the constructing method, the gntK gene in the micromonospora echinospora is damaged by a method of deleting in the architecture to inactivate, including the construction of gntK gene blocking plasmid, conversion of the blocking plasmid into the micromonospora echinospora, screening of a double-exchange strain and analysis of a fermentation product. The engineering bacteria constructed by the constructing method provided by the invention have no resistant marker; and through continuous passage, the yield of the gentamicin C1a is very stable.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
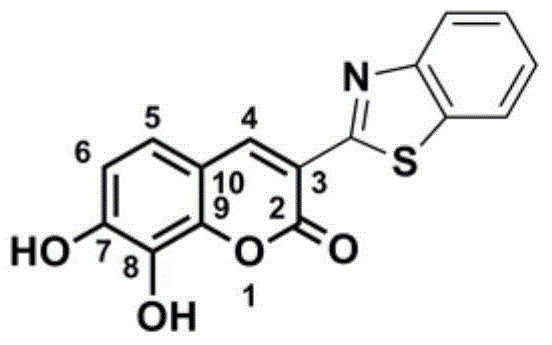
Specific probe substrate of catechol-O-methyltransgerase and application thereof
ActiveCN103193746AExoactive advantageConvenient sourceOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug metabolismQuantitative determination
The invention provides a specific probe substrate of catechol-O-methyltransgerase and application thereof. The specific probe substrate is a 7,8-dihydroxycoumarin compound and can be used for determination of activity of COMT enzyme in mammalian tissue and cells from different sources. The determination comprises the following concrete steps: selecting a coumarin compound having hydroxyl groups at positions 7 and 8 as a highly specific probe substrate; carrying out a COMT catalyzed reaction of the specific probe substrate in virtue of a COMT in-vitro incubation system; and determining the activity of COMT enzyme in each biological sample and each cell through quantitative detection of a product generation amount per unit time. The specific probe substrate can be used for quantitative evaluation of the activity of COMT enzyme in biological samples of different species and from different individual sources and quantitative determination of the activity of COMT enzyme in different-source-derived animal tissue cell culture fluids and prepared cell products, so assessment of capability of the important drug metablic enzyme COMT in disposition of drugs can be realized.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Radix scutellariae flavone phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid O-methyltransferase gene and vector construction and application thereof
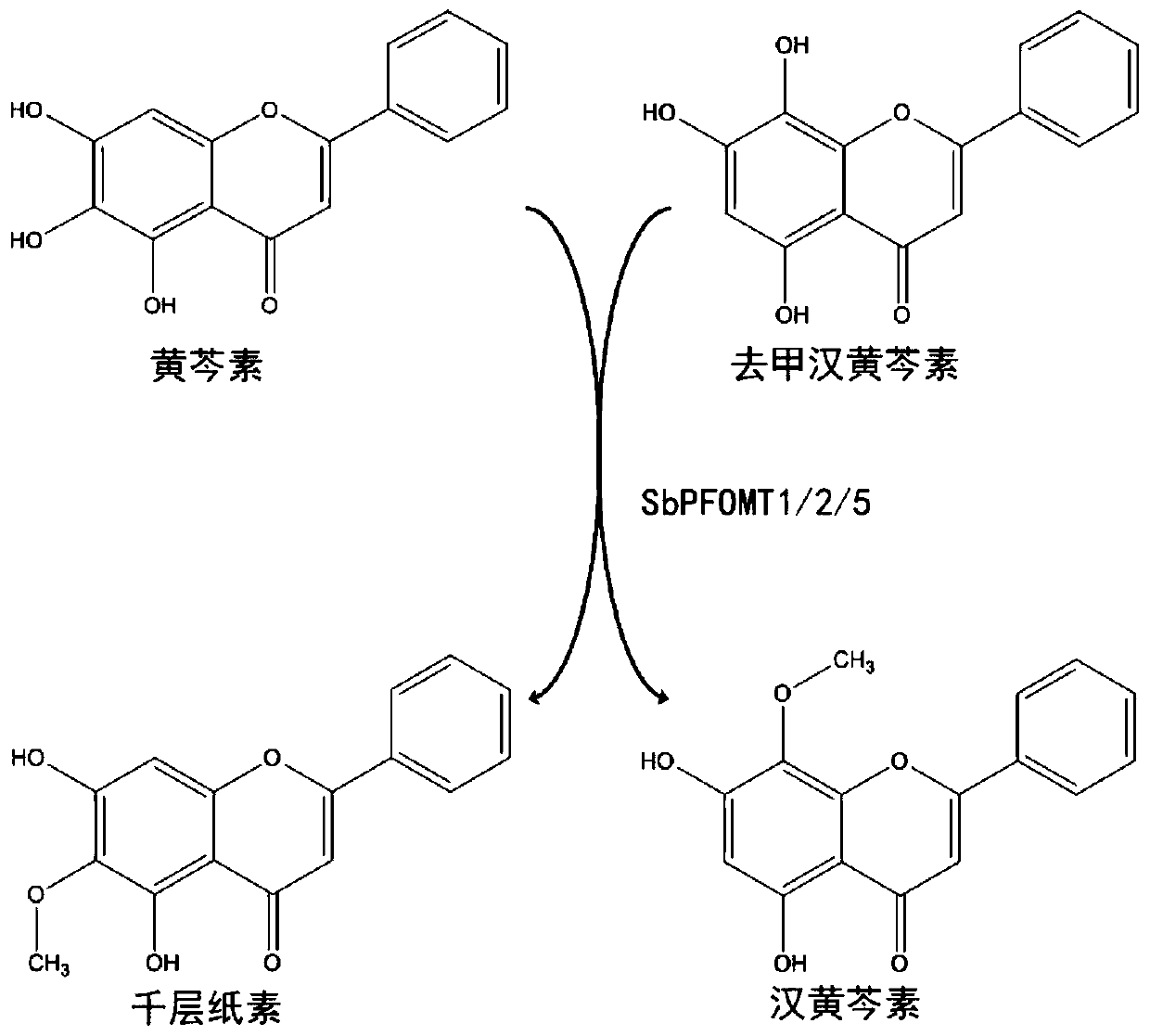
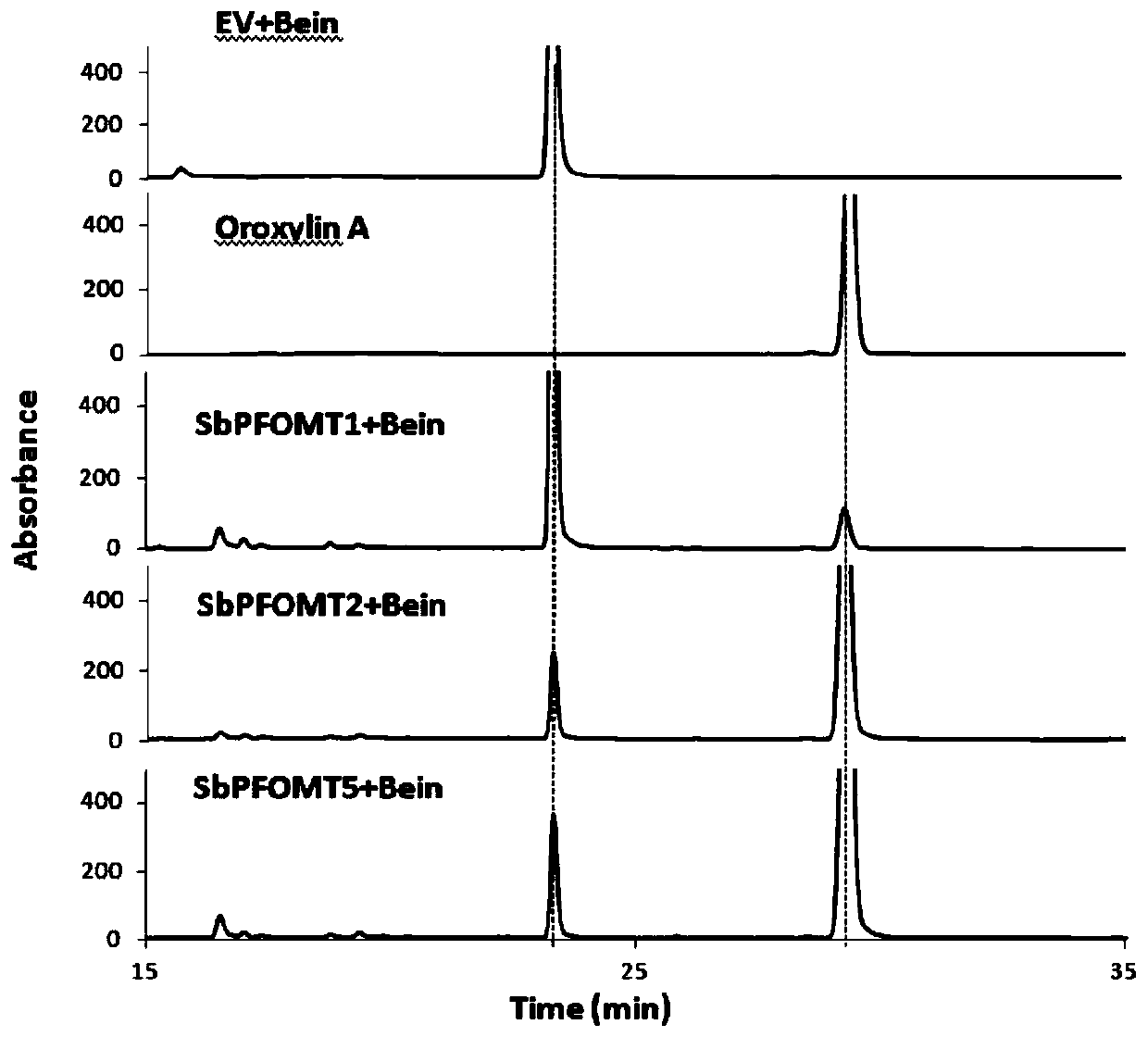
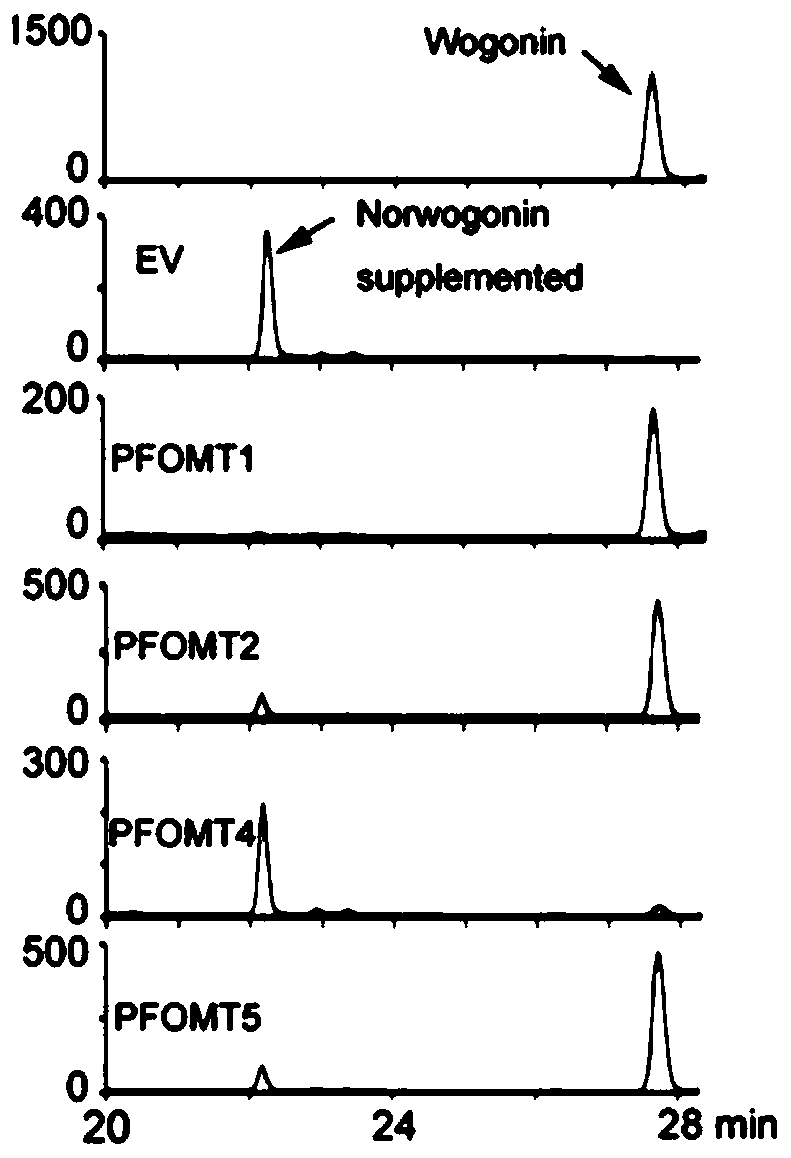
The invention provides a radix scutellariae flavone phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid O-methyltransferase gene. The radix scutellariae flavone phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid O-methyltransferase genecomprises at least one of SbPFOMT1, SbPFOMT2 and SbPFOMT5 genes, the gene sequence of the SbPFOMT1 is as shown in SEQID No.1, the gene sequence of the SbPFOMT2 is as shown in SEQID No.3, and the genesequence of the SbPFOMT5 is as shown in SEQID No.5; and a primer composition amplifying the gene, protein coded by the gene, a recombinant vector, a recombinant microorganism, a host cell, a transgenic cell line, transgenic plant tissue or a transgenic plant constructed by the gene, and an application of the recombinant vector, the recombinant microorganism, the host cell, the transgenic cell line, the transgenic plant tissue or the transgenic plant are provided. The methylation process of wogonin and similar flavonoid is analyzed, 3 flavone phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid O-methyltransferasegenes SbPFOMT1, SbPFOMT2 and SbPFOMT5 are obtained for the first time and cloned, besides, the function of enzymes coded by the gene is verified in an exogenous plant and a microorganism body, a theoretical basis is provided for methylation of wogonin and similar flavonoid in mass production, and a firm basis is also established for industrial production of other pertinent flavonoid compounds.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENSHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN
Metarhizium anisopliae o-methyltransferase and application thereof
The invention provides an o-methyltransferase with a wide range of substrates, and can be applied to oxygen methyl transfer in a biosynthesis process of an organic compound. An experiment proves the catalytic activity of the o-methyltransferase, and shows that the o-methyltransferase can be applied to a plurality of substrates. The invention further provides a synthesis method for a hydroquinone lactone compound. The hydroquinone lactone compound is obtained by transforming an o-methyltransferase gene and a hydroquinone lactone synthetic gene into yeast cells, carrying out fermentation cultivation and extracting a product.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
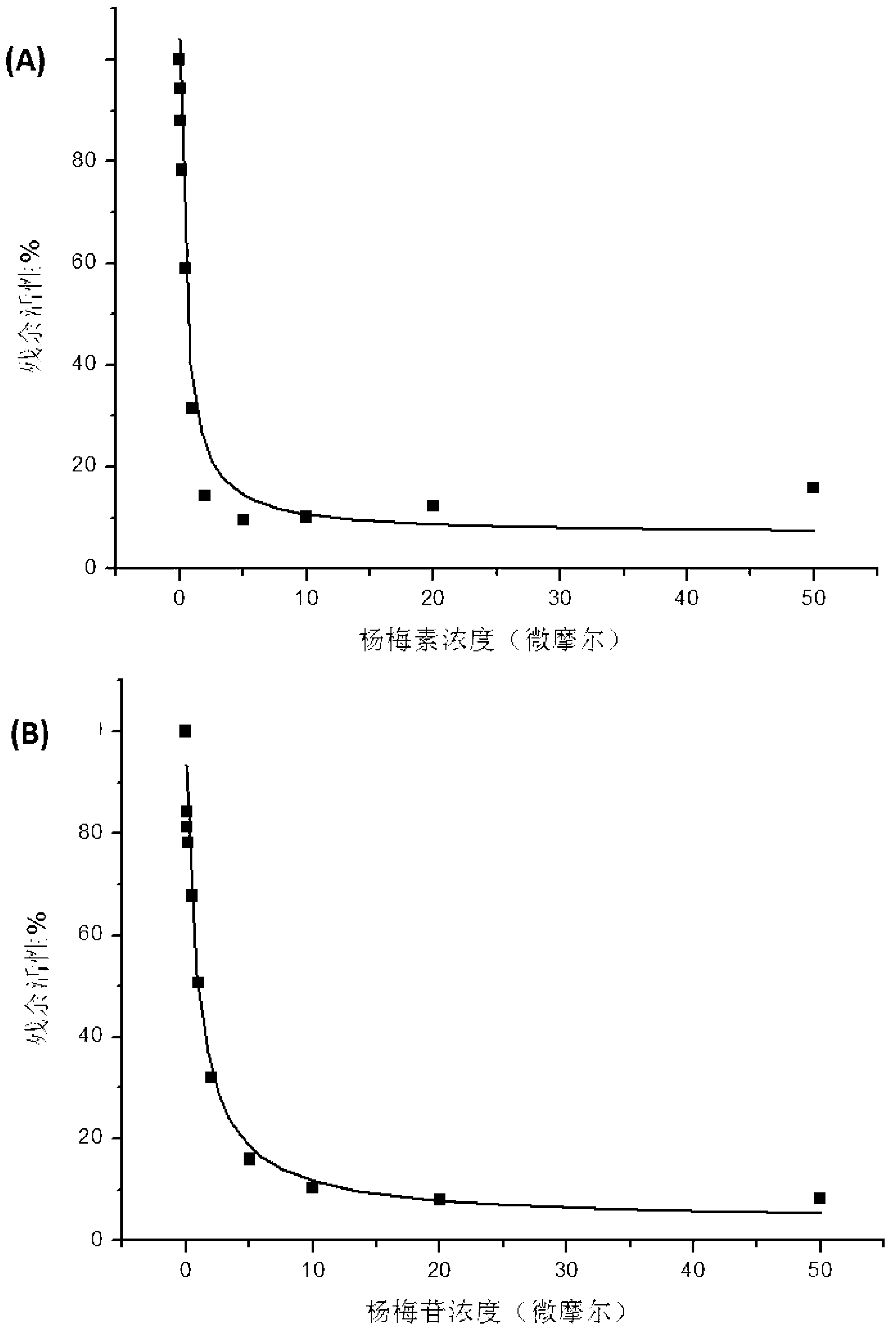
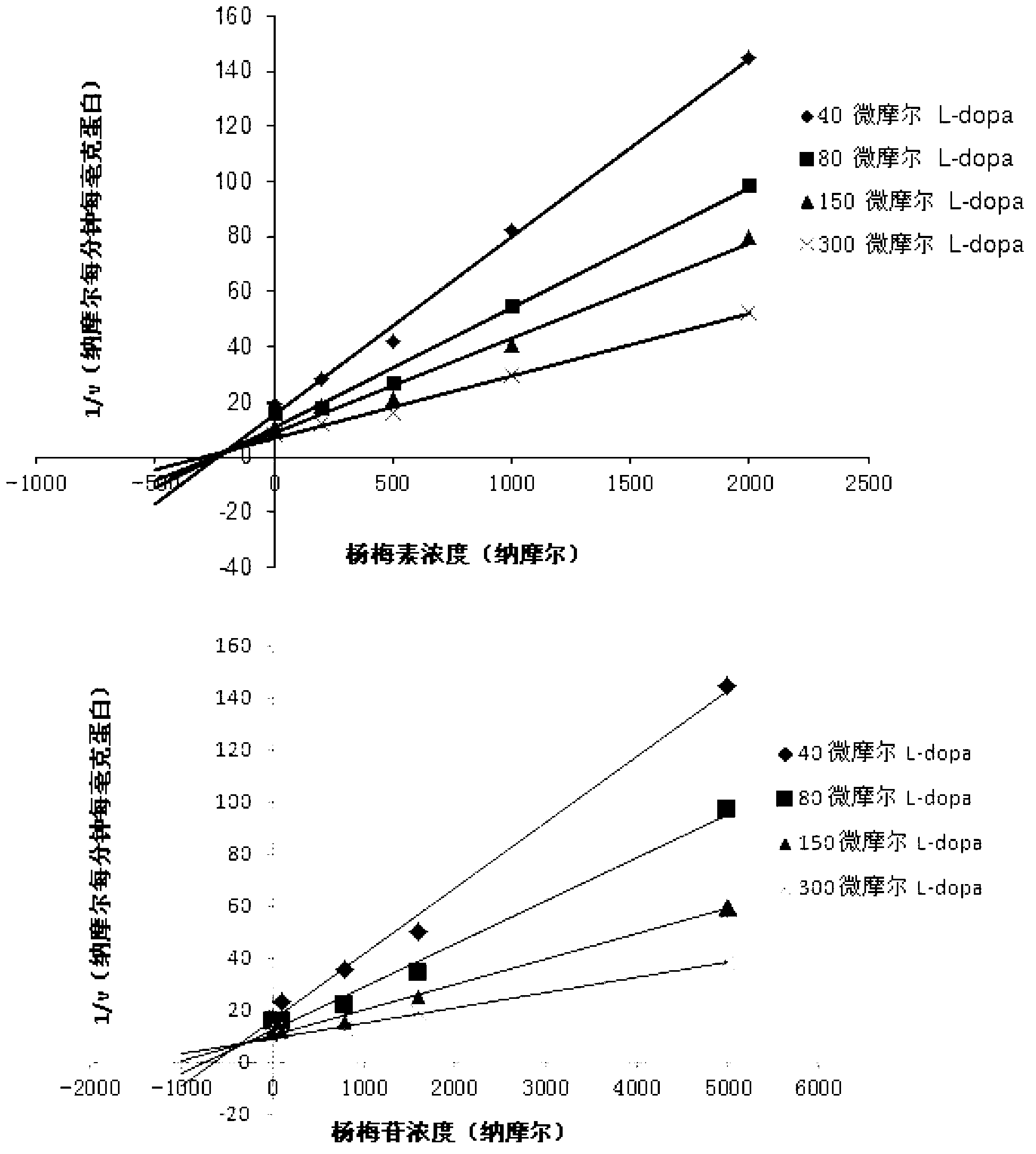
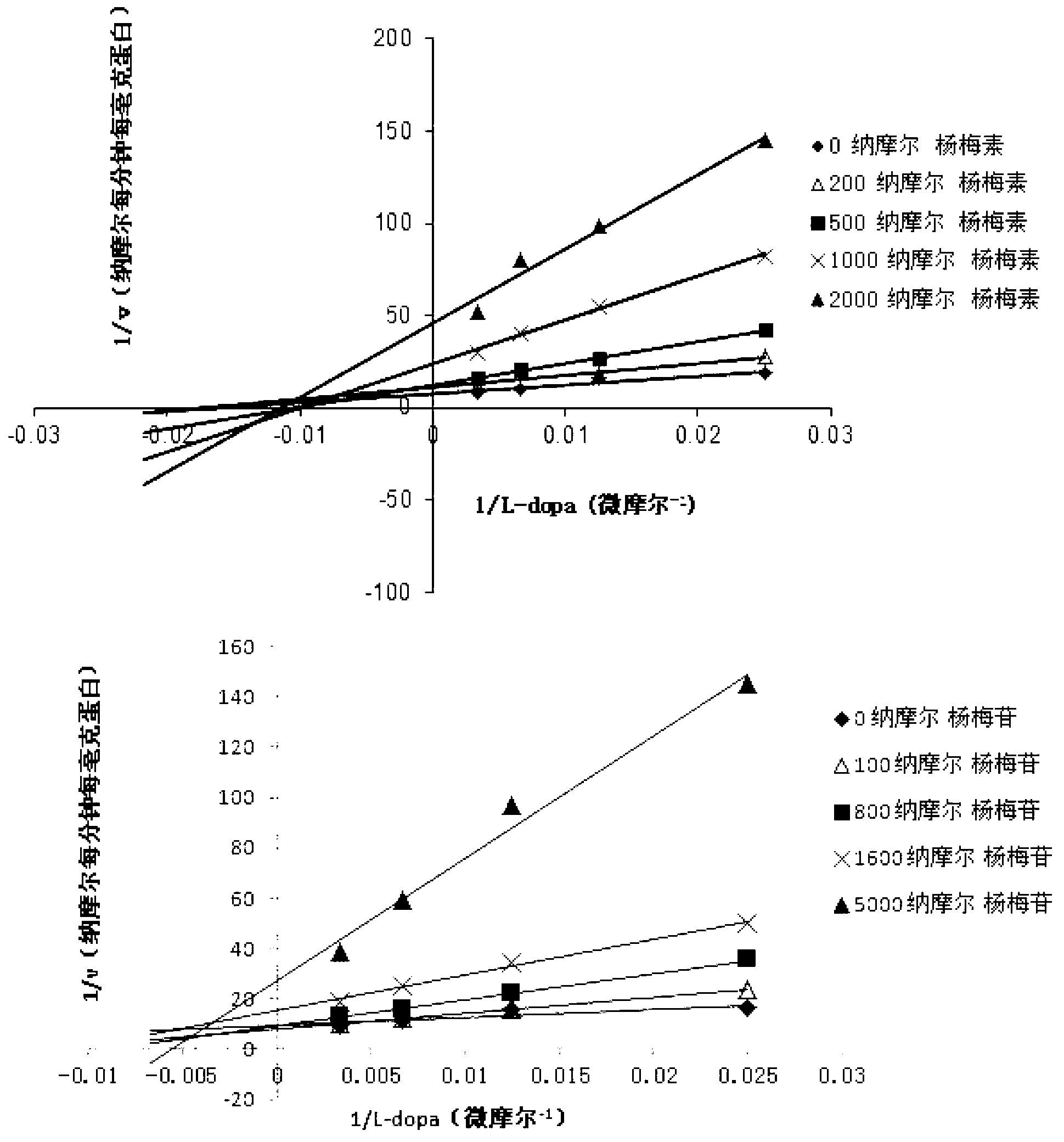
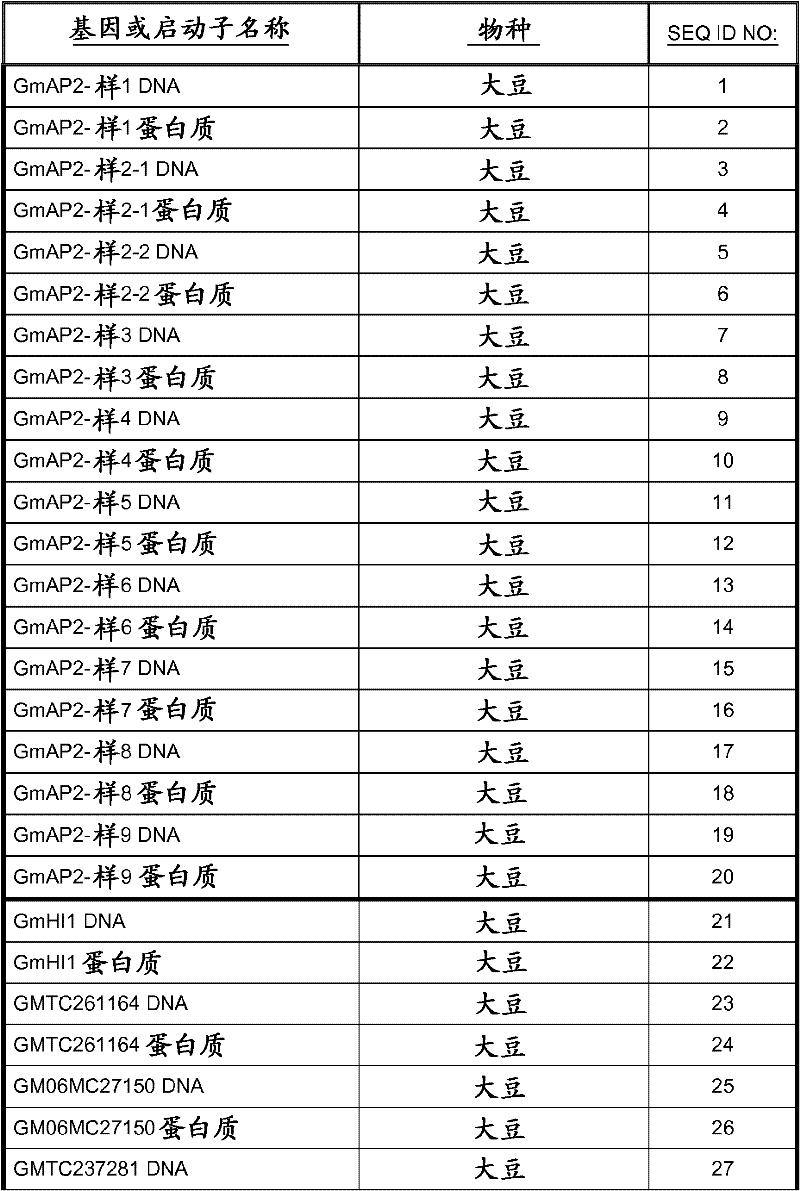
Medicine composition containing myricetrin or/and myricetin and application of medicine composition in preparation of medicine used for treating Parkinson
InactiveCN103211832AEnhance anti-inflammatoryImproves antioxidant activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderLiver and kidneyAglycone
The invention relates to a medicine composition of myricetrin or / and myricetin aglycone thereof and levodopa or of levodopa and carbidopa and an application of myricetrin or / and myricetin aglycone thereof as a synergist in preparation of a medicine used for treating Parkinson. In vitro activity determination finds that IC50 of myricetrin and myricetin inhibiting catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) can be a micromole-nanomole scale. Rat overall pharmacokinetic study finds that blood concentration of levodopa can be increased after myricetrin and myricetin aglycone thereof and levodopa are used jointly; and myricetrin and myricetin aglycone thereof are high in safety, no obvious toxicity is produced to main visceral organ cells of a human body, and no active intermediate is produced by virtue of metabolism activation and further no damage done to organs such as liver and kidney is initiated, so that the myricetrin and myricetin aglycone thereof have a good application prospect in adjuvant therapy of Parkinson.
Owner:无锡艾德美特生物科技有限公司
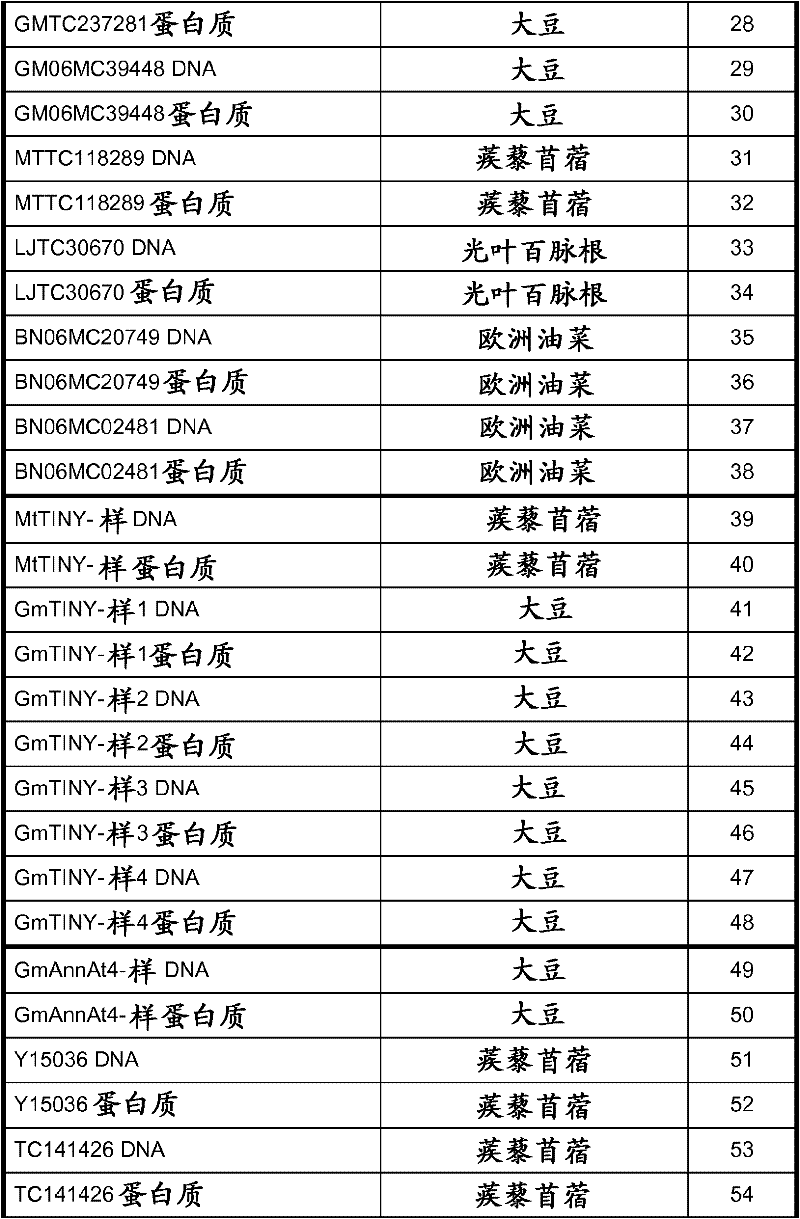
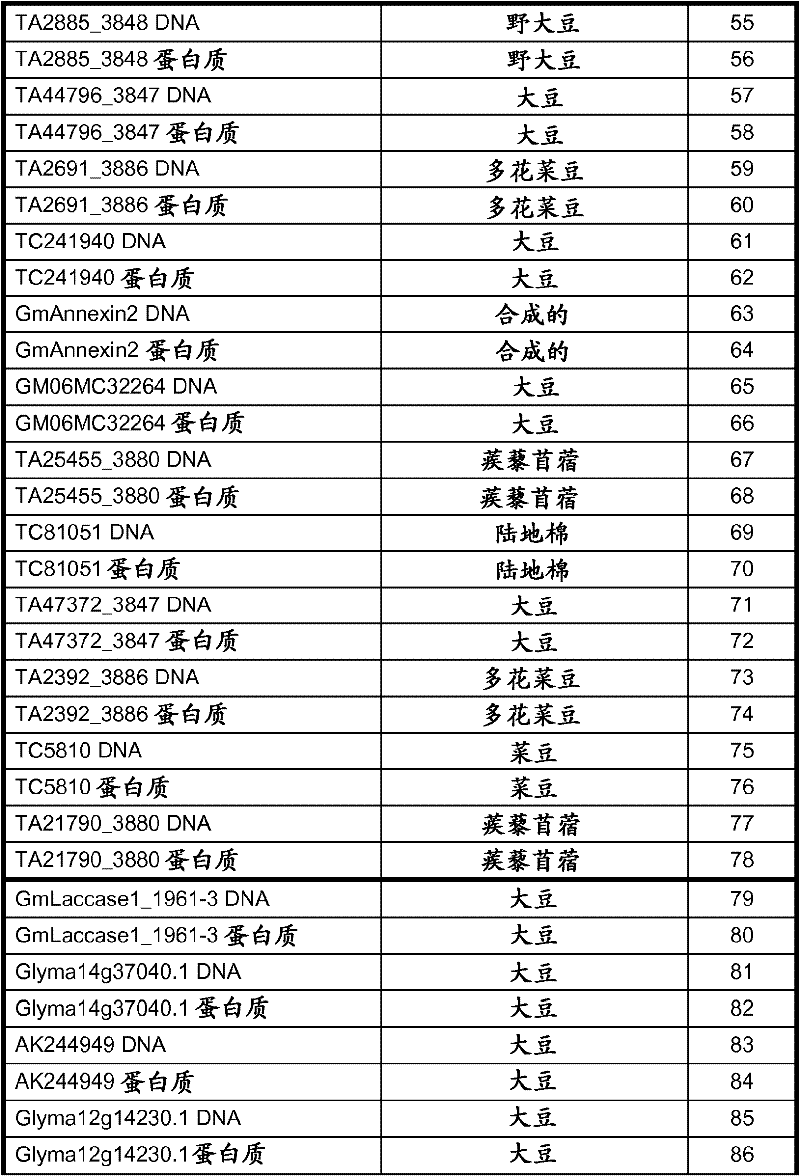
Nematode-resistant transgenic plants
InactiveCN102482682AIncrease productionClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionNematodeNucleotide
The invention provides nematode-resistant transgenic plants and seed that express polynucleotides encoding AP2 / EREBP transcription factors, harpin-induced proteins, TlNY-like transcription factors, annexins, laccases, isoflavone 7-0-methyltransferases, anthocyanidin 3-glucoside rhamnosyltransferases, hsr201 -like, or AUX / IAA proteins. The invention also provides methods of producing transgenic plants with increased resistance to plant parasitic nematodes and expression vectors for use in such methods.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
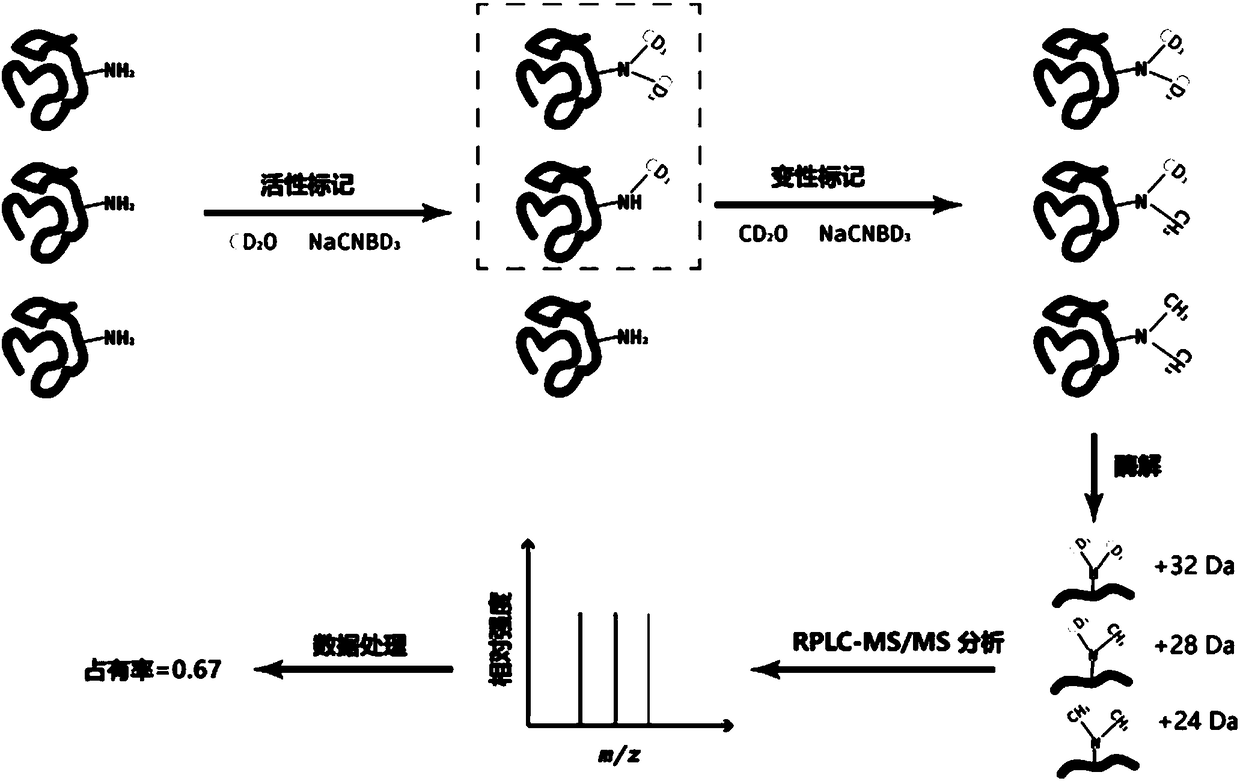
Mass spectrum detection method for interaction between active protein and small molecule
ActiveCN108508125ARealize detectionAchieve confirmationComponent separationBiological testingChemical labelingProtein target
The invention provides a mass spectrum detection method for interaction between an active protein and a small molecule. According to the method, in-vivo covalent chemical labeling is performed on a protein while the active state is maintained; and the site and the intensity of the interaction between a small molecule and the protein are judged through the difference in the labeling efficiency before and after the interaction between the specific amino acid position on the protein and the small molecule. According to the present invention, with the mass spectrum detection method, the protein inhibitor candidate small molecule can be subjected to high-throughput screening, and the potential protein target of the specific small molecule can be subjected to large-scale identification analysis;and through the large-scale identification analysis of the Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)-small molecule interaction and the ATP-binding protein in the complex system biological system, the method has accuracy and high efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
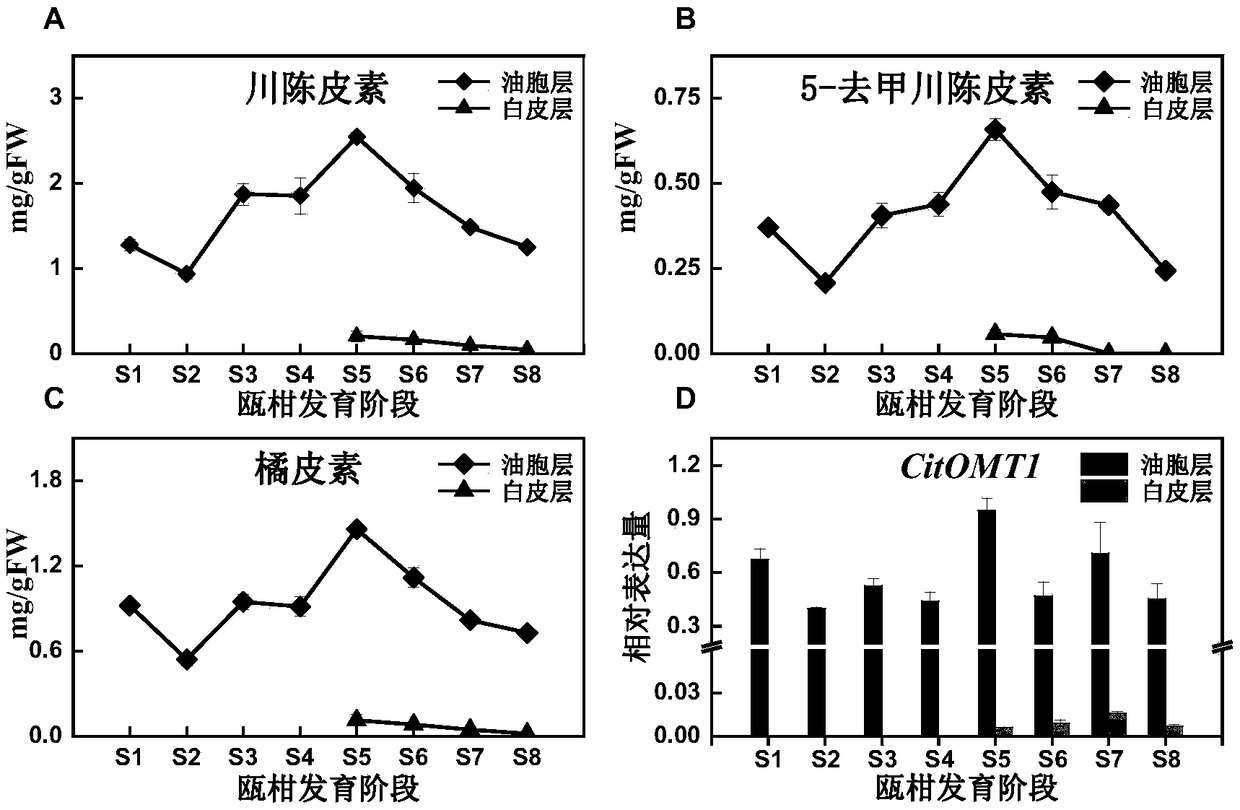
O-methyltransferase participating in citrus peel flavone synthesis and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN109321543ASimple reaction conditionsTransferasesGenetic engineeringHomoeriodictyolChrysoeriol
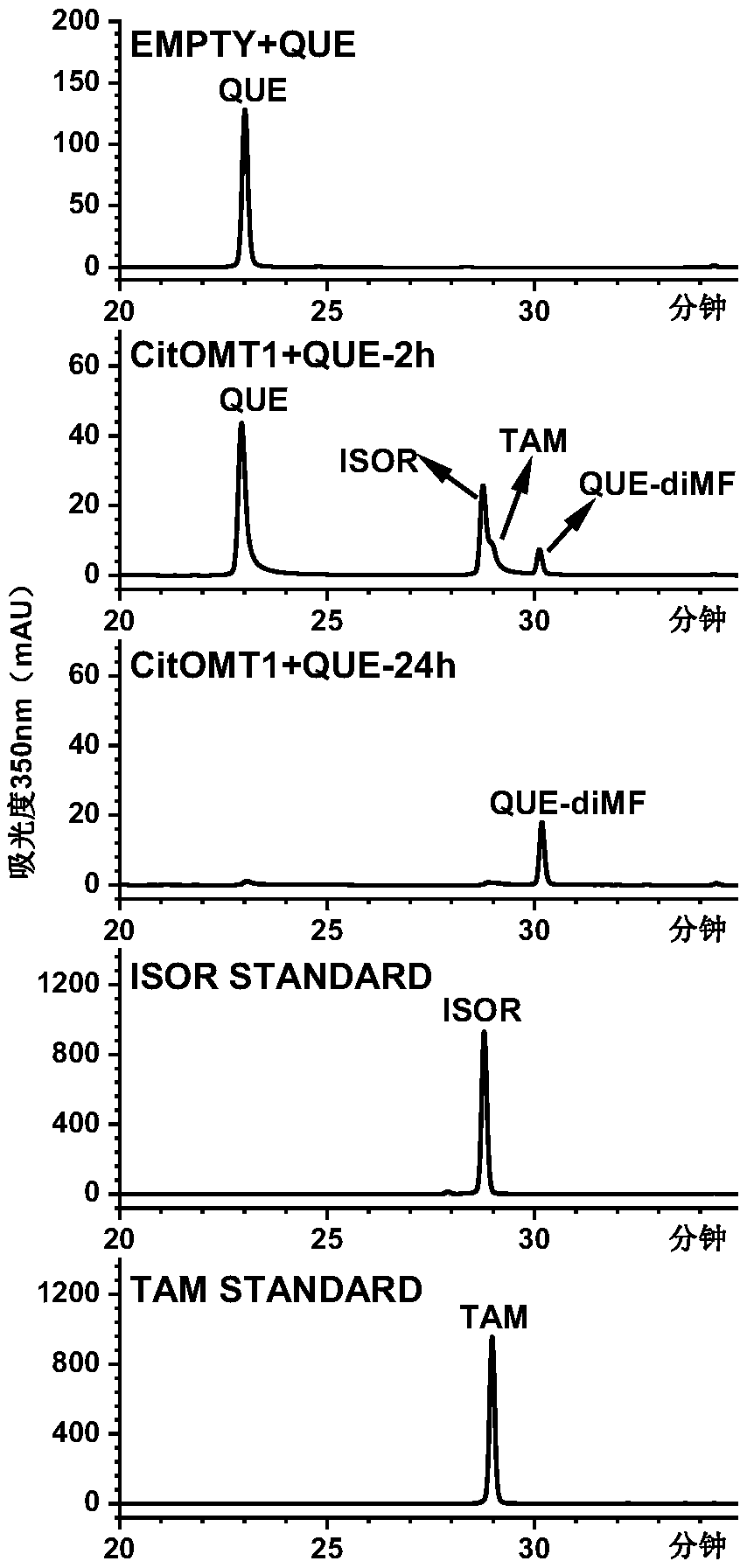
The invention provides O-methyltransferase participating in citrus peel flavone synthesis and a coding gene and application thereof. The expression level of CitOMT1 is positively correlated with the accumulation of polymethoxylated flavones in a fruit development process of Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima; in vitro enzyme activity assays indicate that the O-methyltransferase can be applied to catalyze specific site methylation of flavones, in particular to catalyze quercetin to produce quercetin 3',4' dimethyl ester, catalyze luteolin to produce chrysoeriol, catalyze eriodictyol to produce hesperidin and homoeriodictyol, catalyze baicalein to produce oroxylin A, and catalyze 7,8-dihydroxyflavone to produce 7-hydroxy-8-methoxy flavone. The enzyme activity assays have simple reaction conditions, do not require additional metal ions, and have high application value and research prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
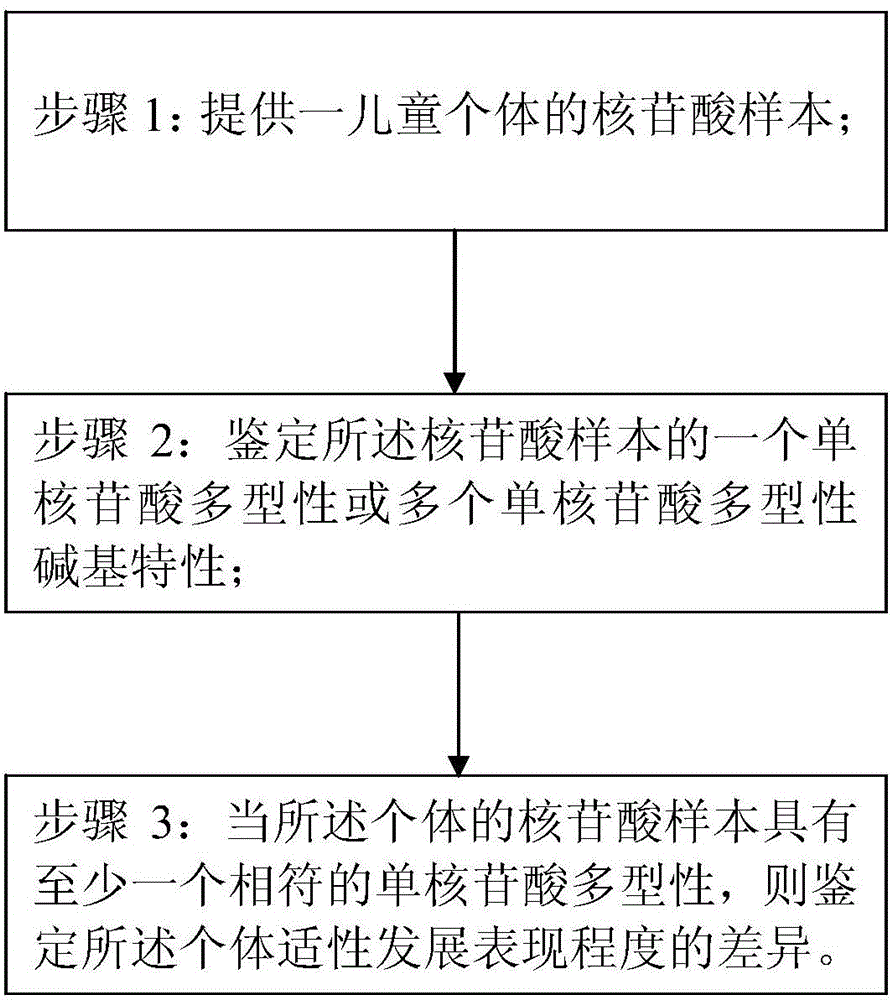
Children's gene evaluation and detection method
The invention discloses a children's gene evaluation and detection method. The method is used for judging children adaptive education by detecting catechol-O-methyltransferase gene, synaptosome associated gene, brain-derived neurotrophic gene, hydroxytryptamine receptor gene, short memory regulation gene, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor gene, morphine receptor gene, developmental reading dyslexia susceptibility gene, dyslexia susceptibility candidate gene, fork head box P2 gene, contactin-associated protein gene, neuregulin gene, synaptosome associated gene and dopamine beta hydroxylase gene. Individual adaptability development performance degree is judged or evaluated by identifying whether single nucleotide polymorphism in nucleotide samples of children individuals is associated with the above genes or not to serve as application evaluation data in acquired learning.
Owner:GENE TARGET TECH
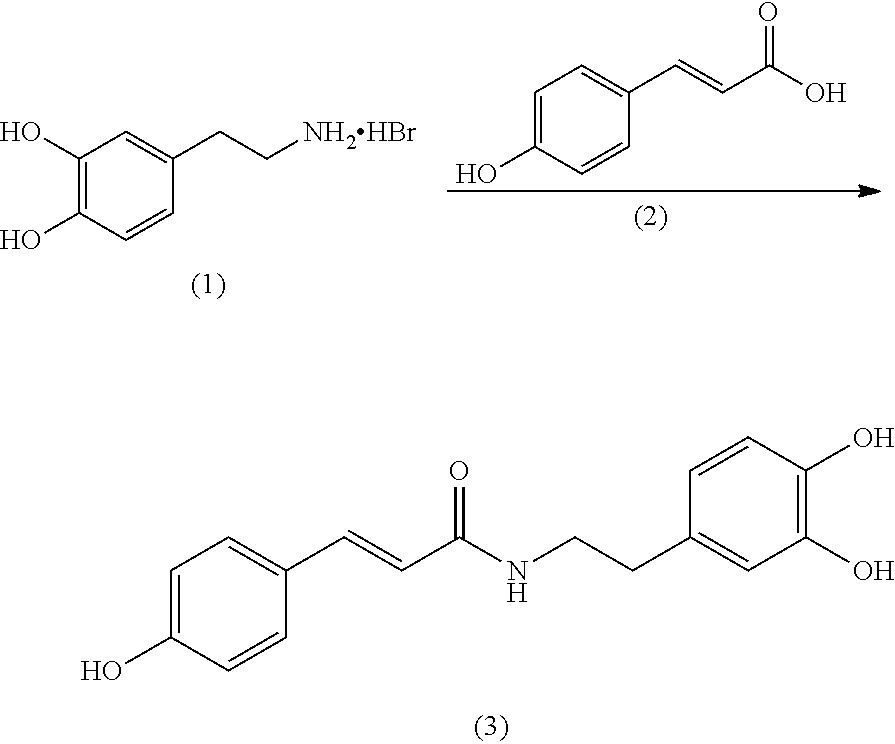
Increasing bioavailability of n-coumaroyldopamine through co-administration with a catechol-o-mehtyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor
InactiveUS20140107050A1Decrease body fatGood for weight lossBiocideOrganic chemistryProcaterolO-methyltransferase
The present invention is directed to a composition including N-Coumaroyldopamine and a catechol-o-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor for promoting weight loss in a user.
Owner:REDEFINE NUTRITION
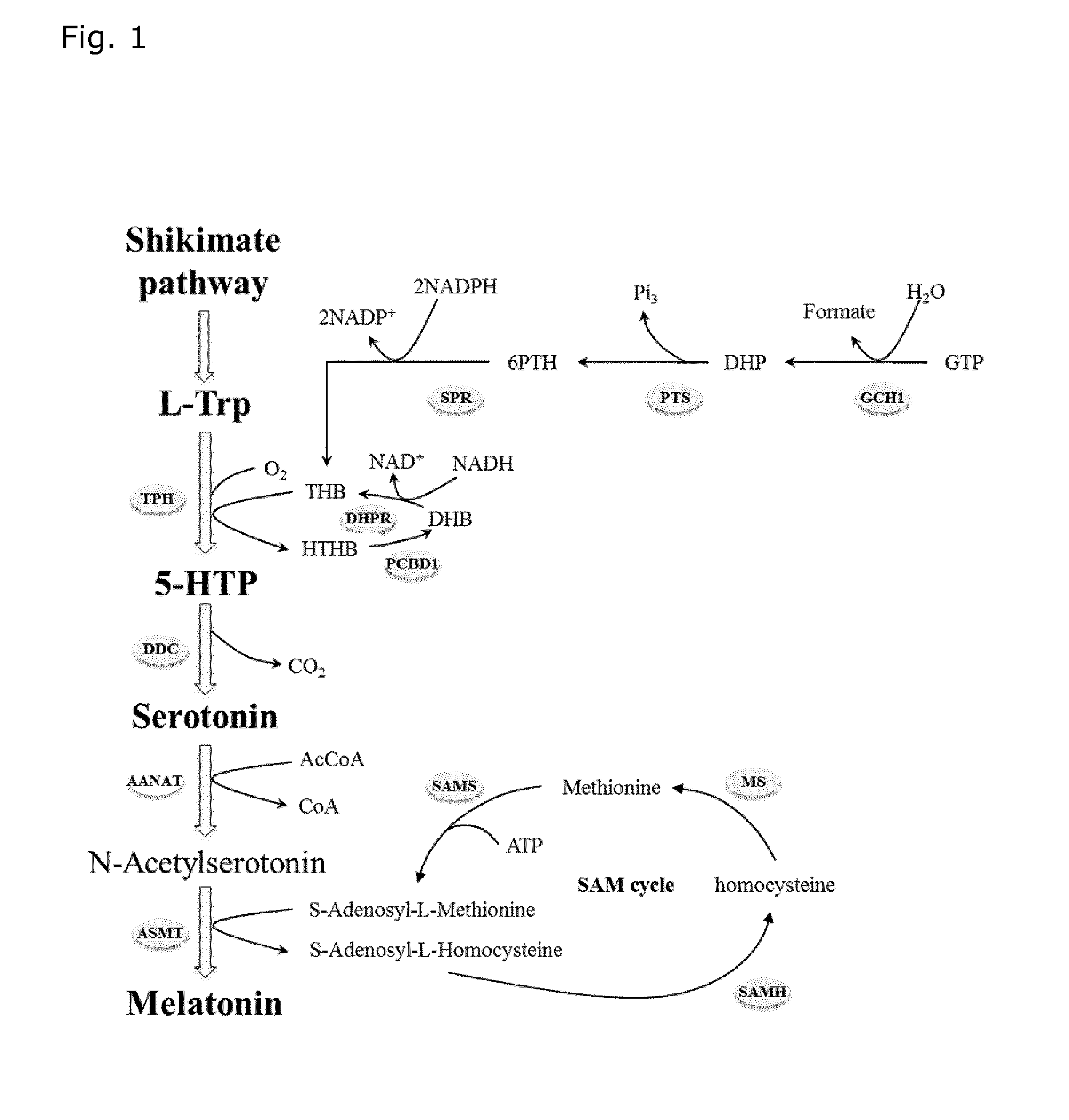
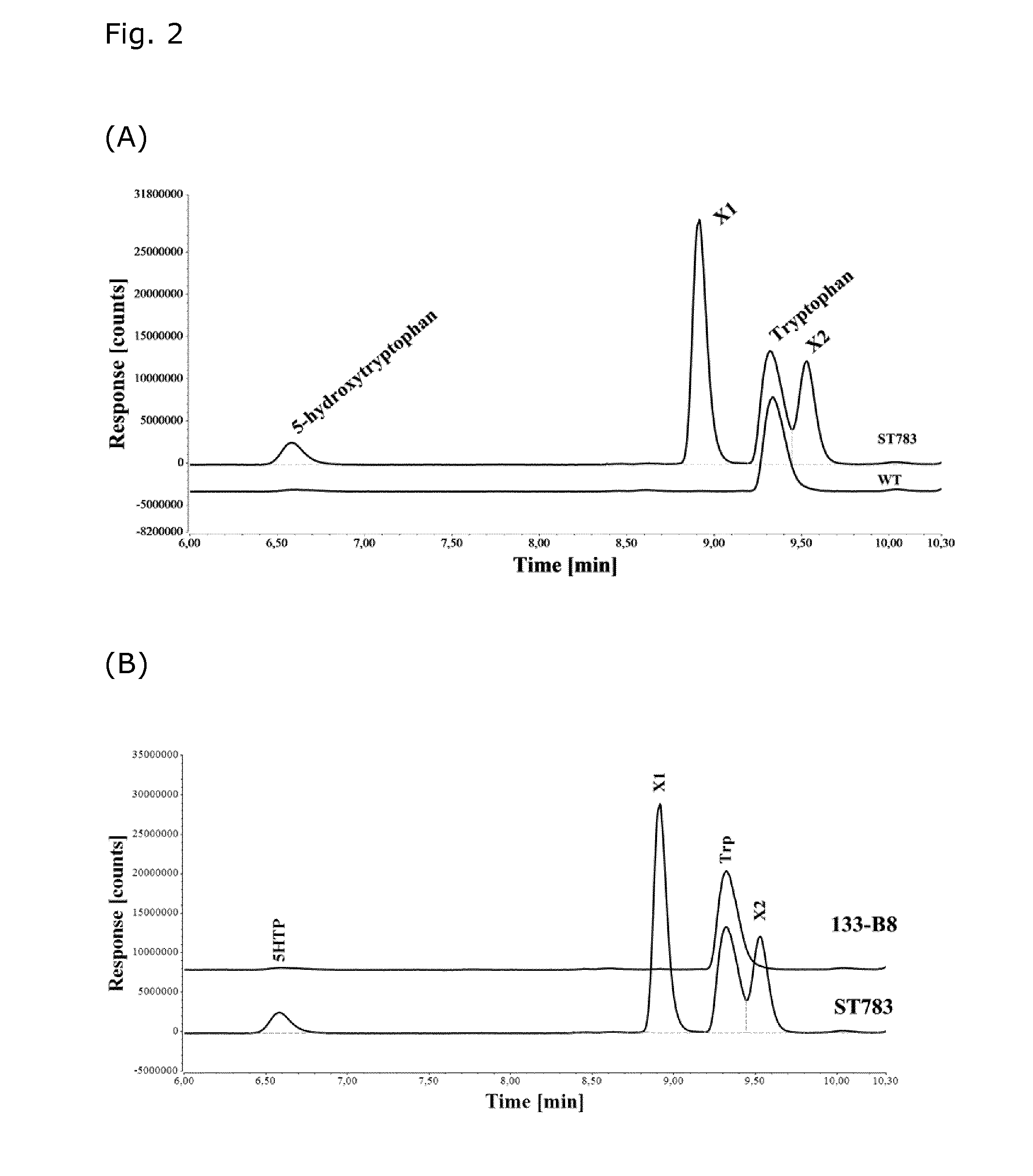
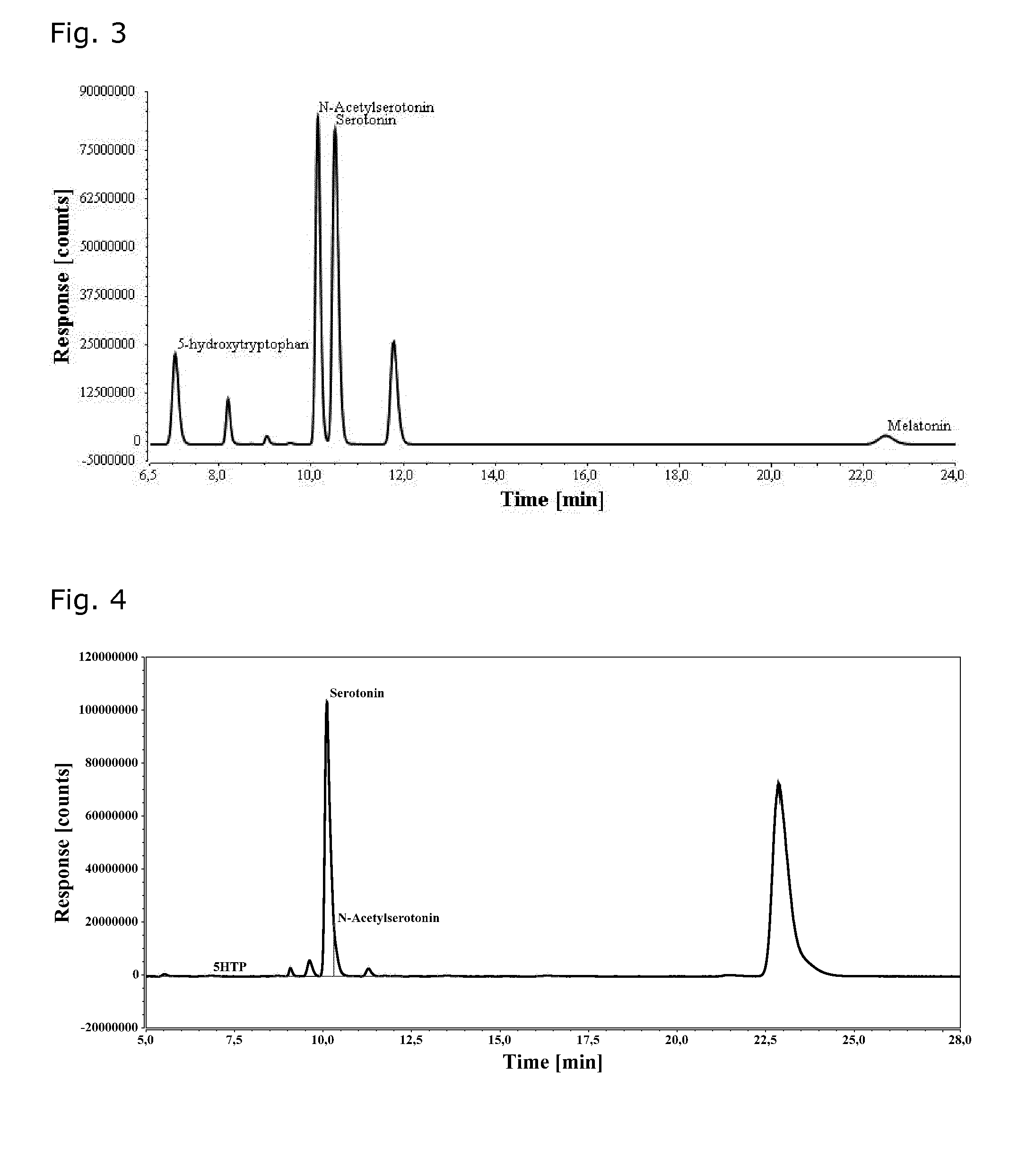
Microorganisms for efficient production of melatonin and related compounds
Recombinant microbial cells and methods for producing 5HTP, melatonin and related compounds using such cells are described. More specifically, the recombinant microbial cell may comprise exogenous genes encoding one or more of an L-tryptophan hydroxylase, a 5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan decarboxylyase, a serotonin acetyltransferase, an acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase; and means for providing tetrahydrobiopterin (THB), and can be further genetically modified to enrich one or more of tryptophan, S-adenosyl-L-methinonine and acetyl coenzyme A. Related sequences and vectors for use in preparing such recombinant microbial cells are also described.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
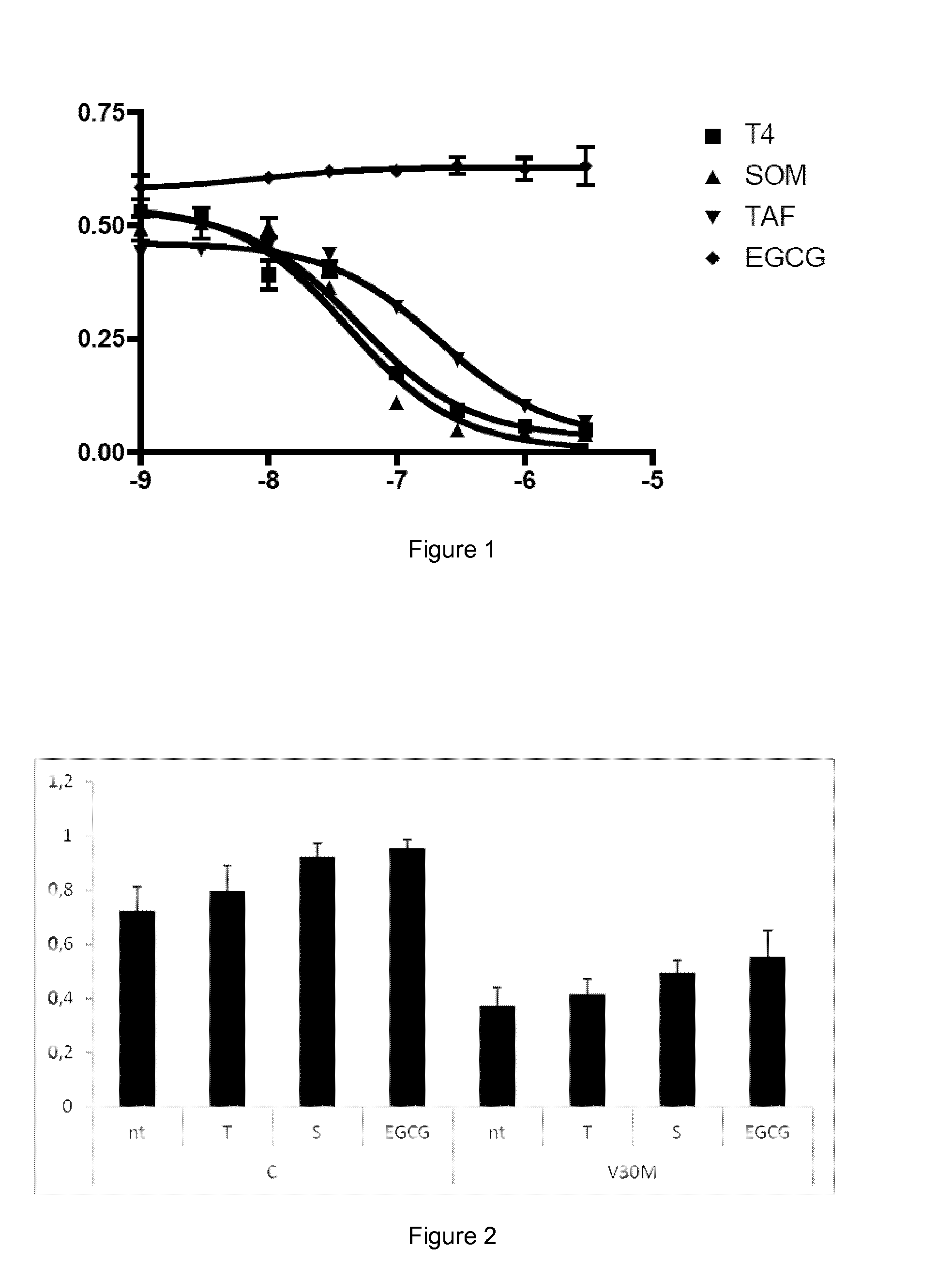
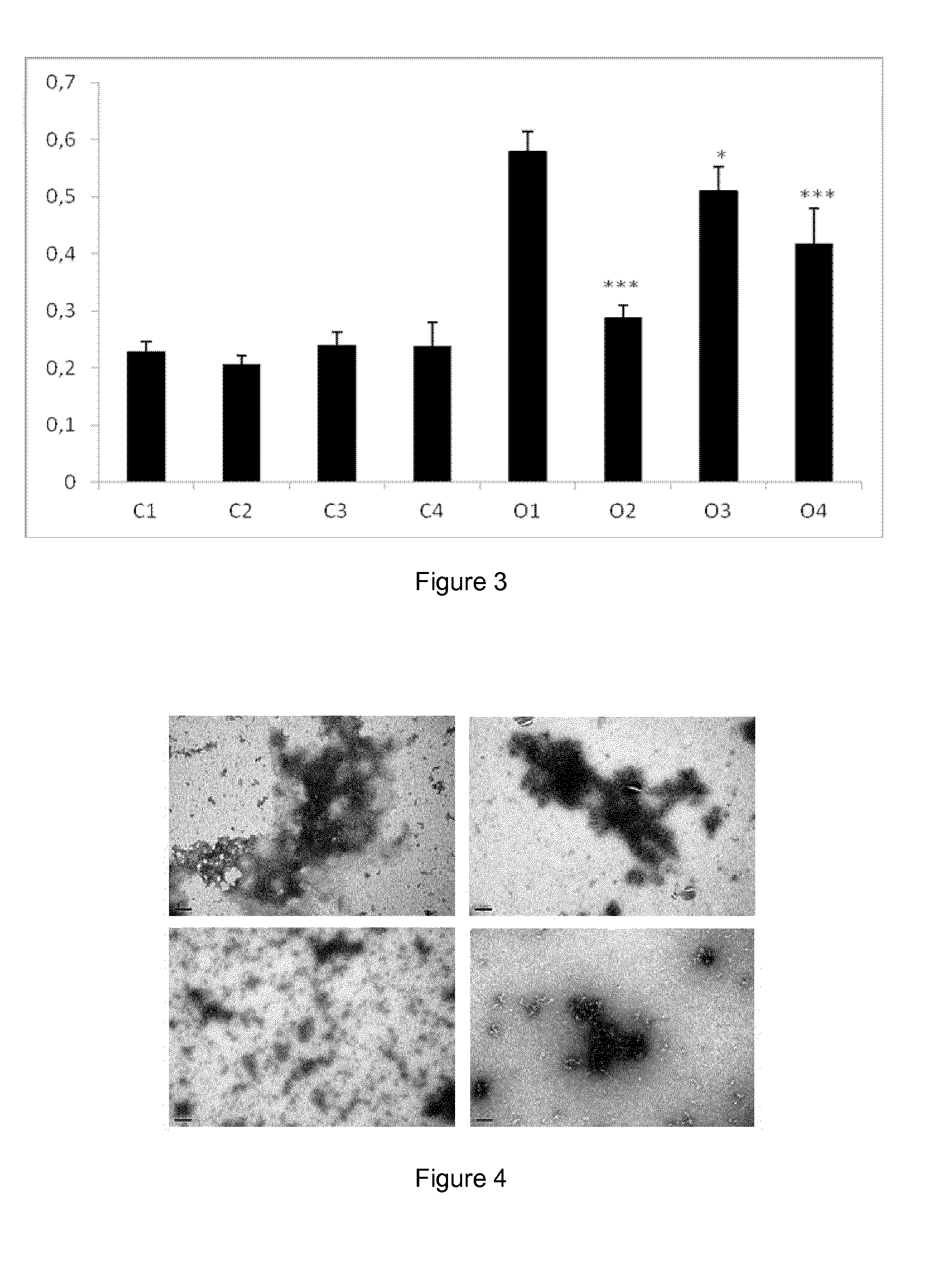
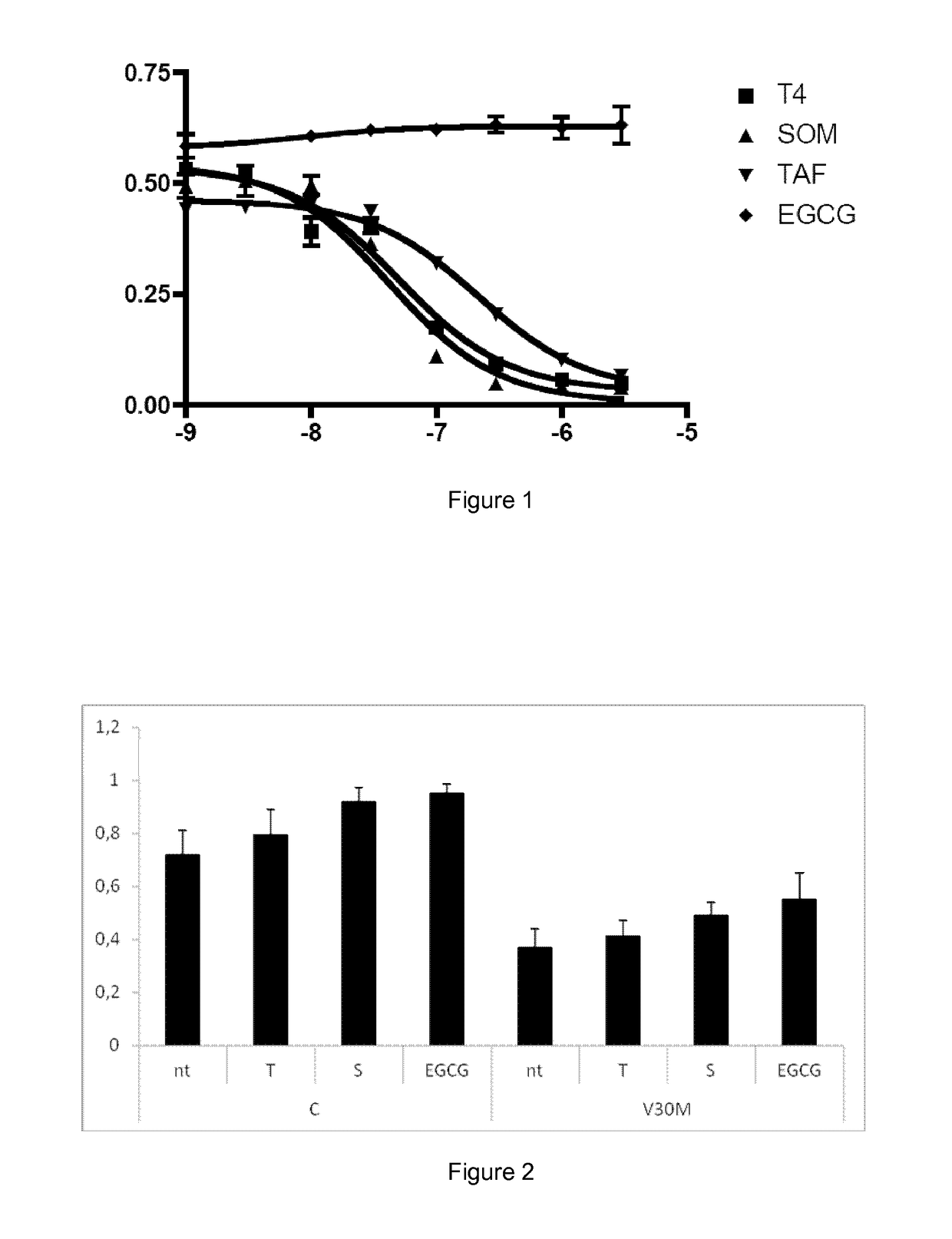
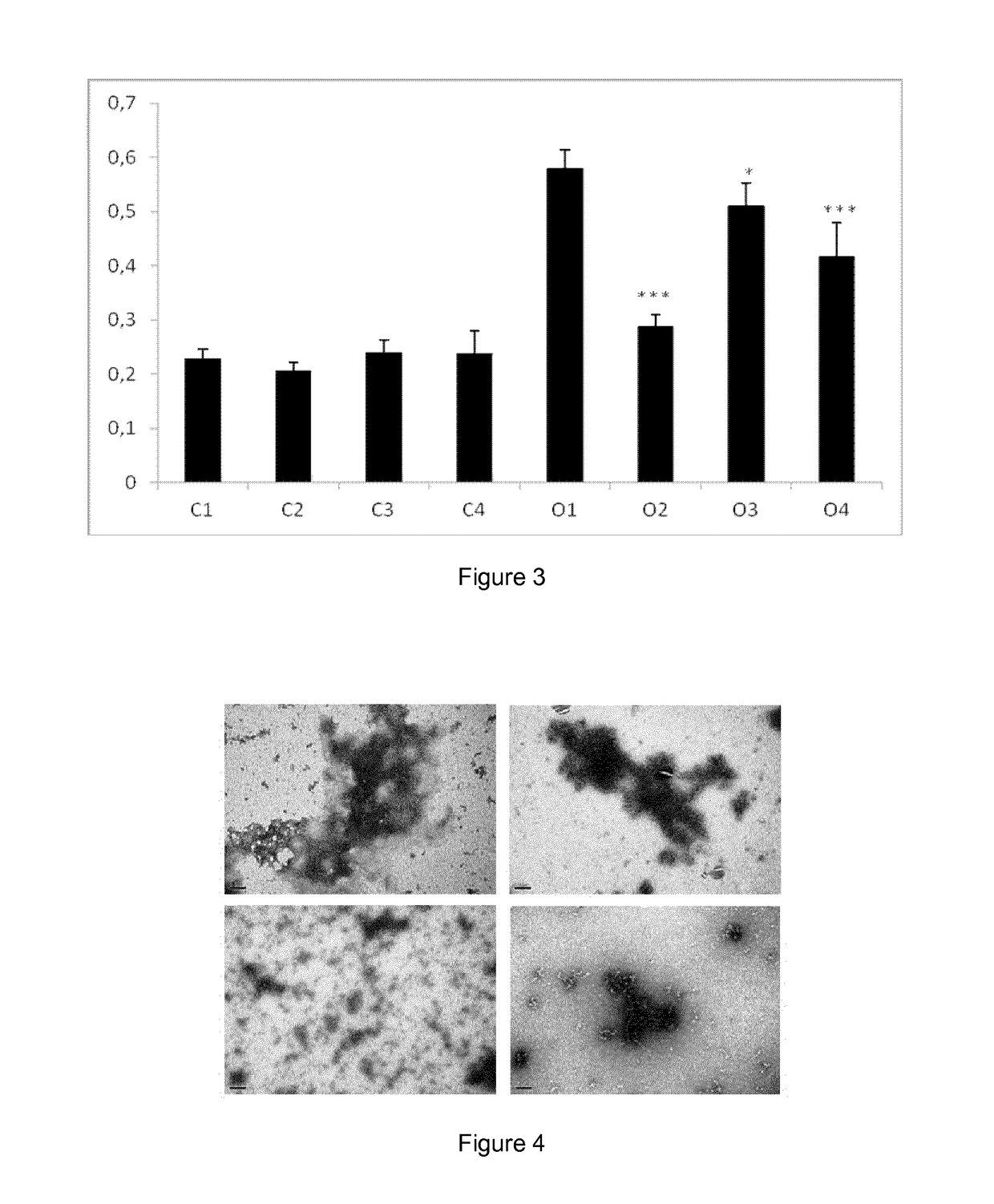
New therapy for transthyretin-associated amyloidosis
ActiveUS20140296188A1Acceptable safety profileImprove bioavailabilityBiocideNervous disorderBenzoxazoleGallate
It is provided a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor for use in the prevention and / or treatment of trans-thyretin-associated amyloidosis. It is also provided a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor for use in the prevention and / or treatment of transthyretin-associated amyloidosis in combination therapy with another COMT inhibitor, a benzoxazole derivative, iododiflunisal, diflunisal, resveratrol, tauroursodeoxycholic acid, doxocycline, or epigallocatechin-3-gallate.
Owner:SOM INNOVATION BIOTECH
Therapy for transthyretin-associated amyloidosis
ActiveUS9610270B2Acceptable safety profileStrong inhibitory activityNervous disorderKetone active ingredientsBenzoxazoleGallate
It is provided a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor for use in the prevention and / or treatment of transthyretin-associated amyloidosis. It is also provided a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor for use in the prevention and / or treatment of transthyretin-associated amyloidosis in combination therapy with another COMT inhibitor, a benzoxazole derivative, iododiflunisal, diflunisal, resveratrol, tauroursodeoxycholic acid, doxocycline, or epigallocatechin-3-gallate.
Owner:SOM INNOVATION BIOTECH
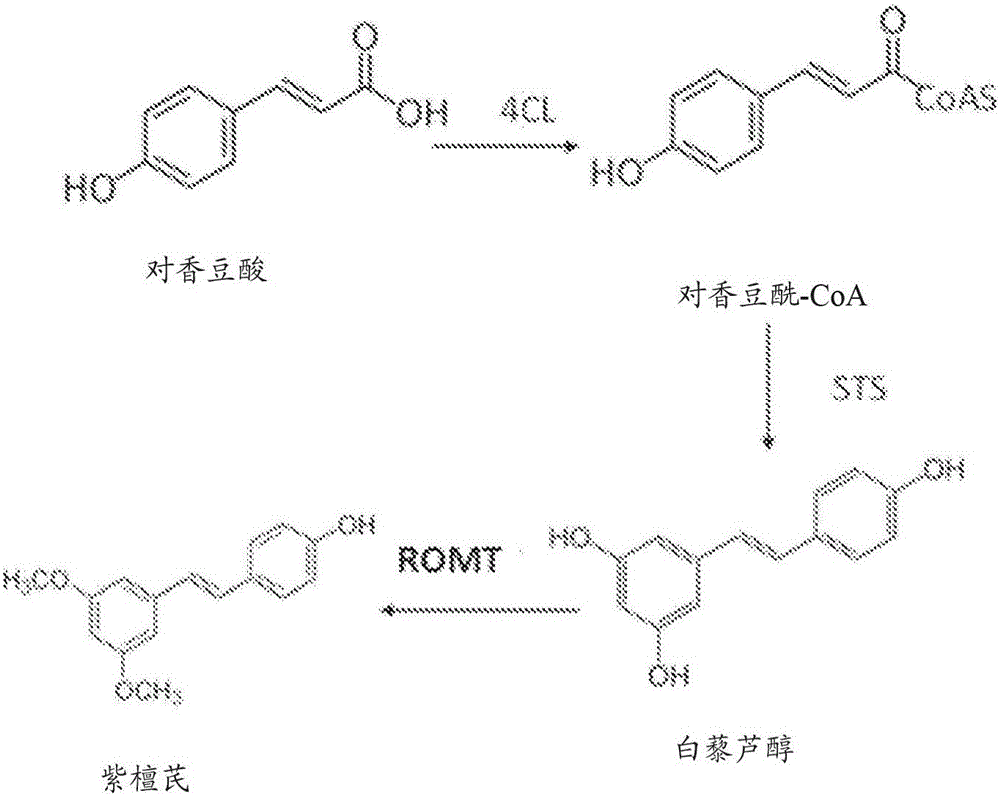
Methods of using O-methyltransferase for biosynthetic production of pterostilbene
ActiveCN106102454ASolve the technical problem of generating pterostilbenePromote generationBryophytesNervous disorderStilbene synthaseP-Coumaric acid
A biosynthetic method of making pterostilbene including expressing a 4- coumaratexoenzyme A ligase (4CL) in a cellular system, expressing a stilbene synthase (STS) in the cellular system, expressing a resveratrol O-methyltransferase (ROMT) in the cellular system, feeding p-coumaric acid to the cellular system, growing the cellular system in a medium, and producing pterostilbene.
Owner:CONAGEN INC
Compositions and methods for the biosynthesis of vanillan or vanillin beta-D-glucoside
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES +1
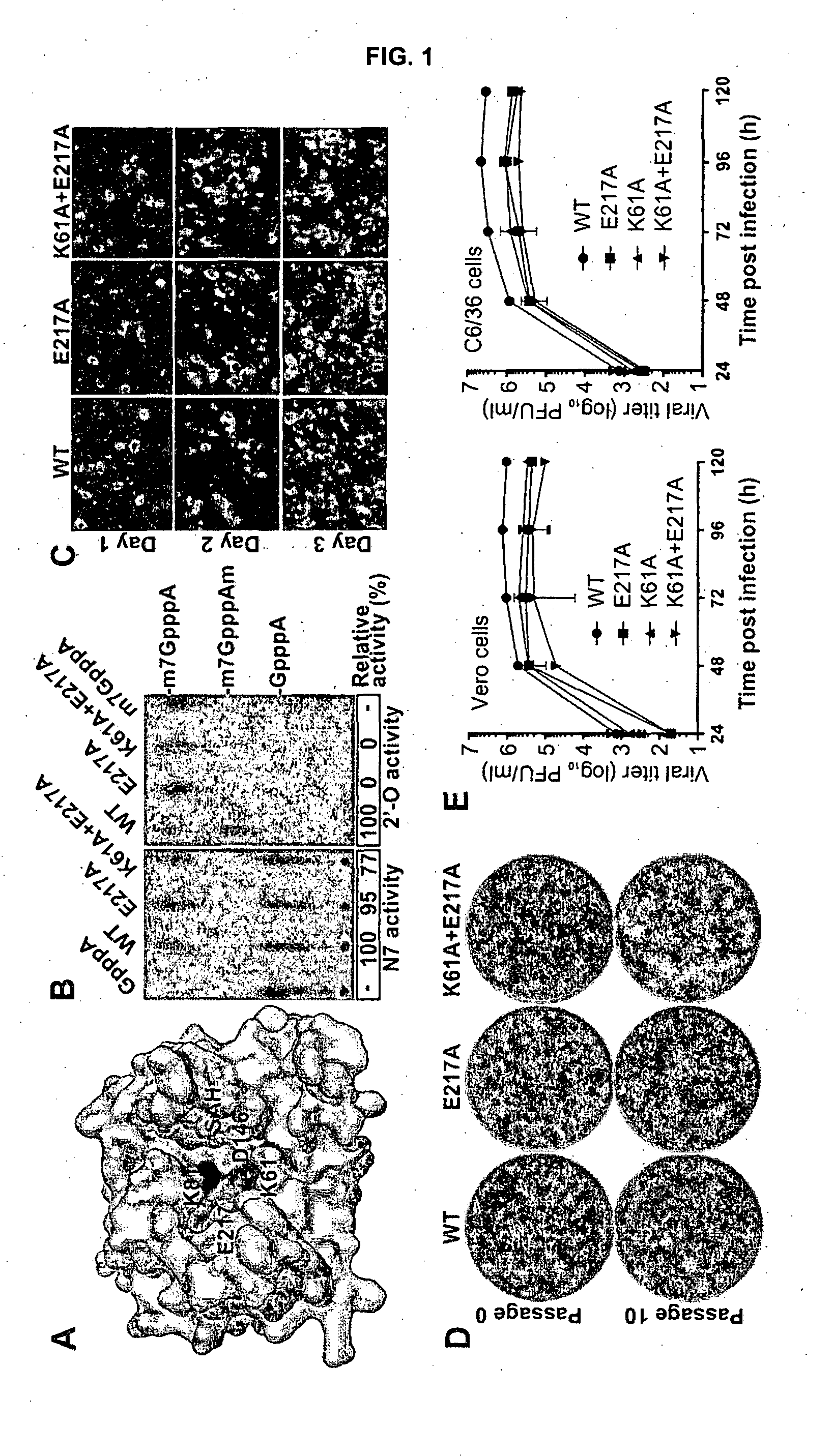
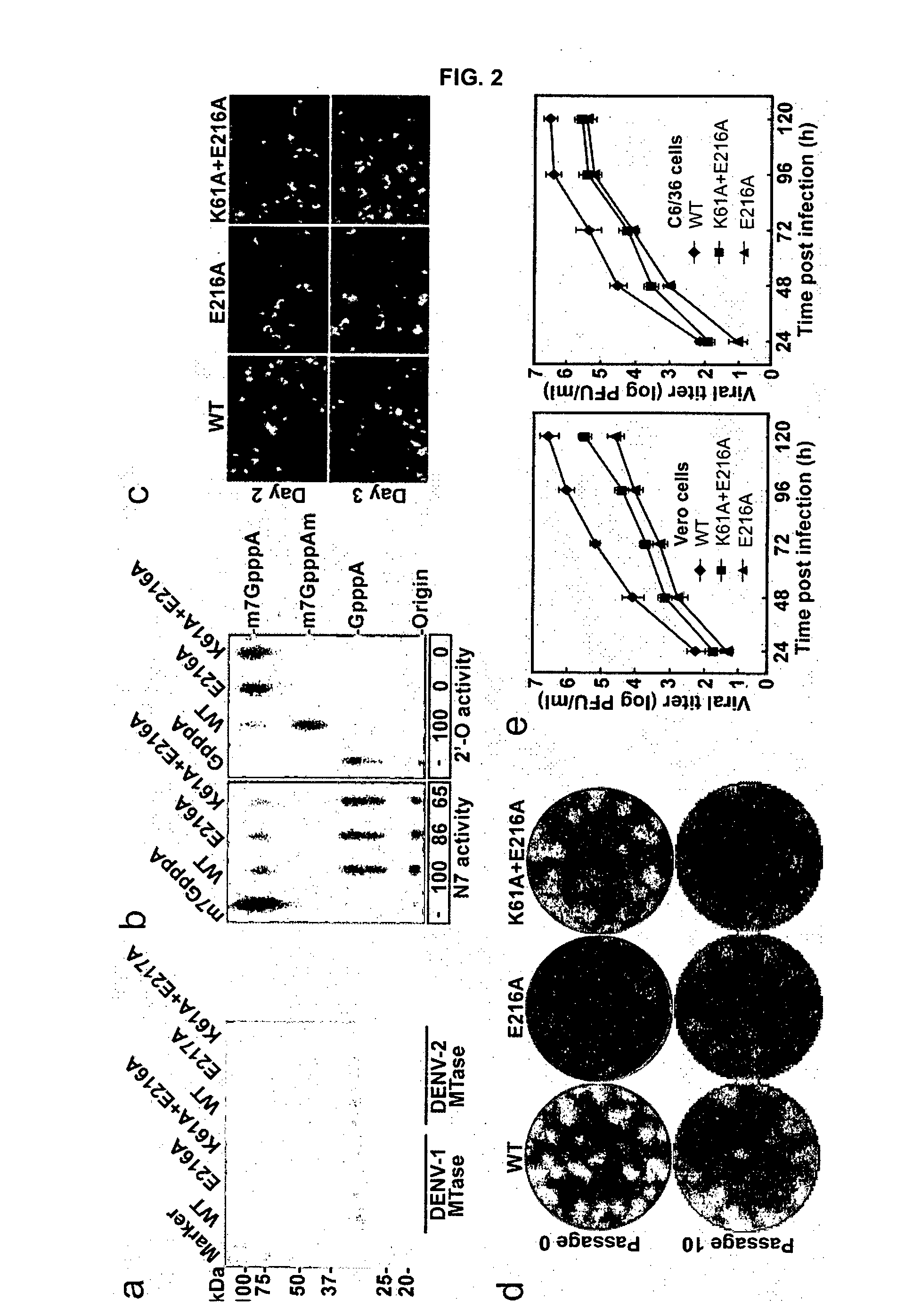
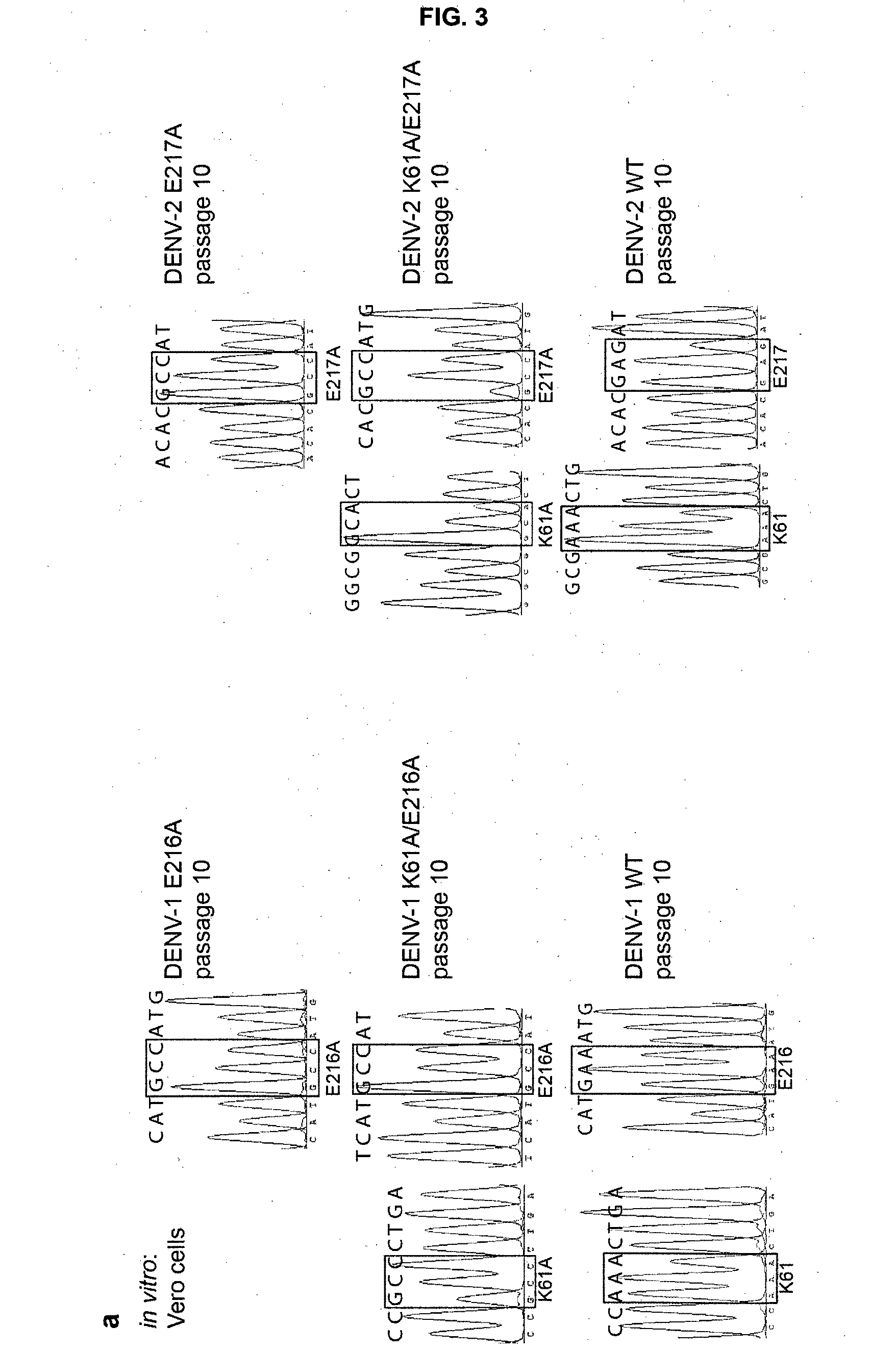
Novel attenuated dengue virus strains for vaccine application
InactiveUS20150231226A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsVaccinationNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention discloses a method of eliciting an immune response and a method of vaccination comprising administration of a mutated flavivirus. The mutated flavivirus comprises at least one mutation in a nucleic acid sequence encoding for the non-structural protein 5 of the flavivirus sequence resulting in inactivation of the 2′O-methyltransferase.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Specific fluorescent probe for catechol-O-methyltransgerase (COMT) and application thereof
ActiveCN106467739ANot easy to interfereReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh fluxMutant
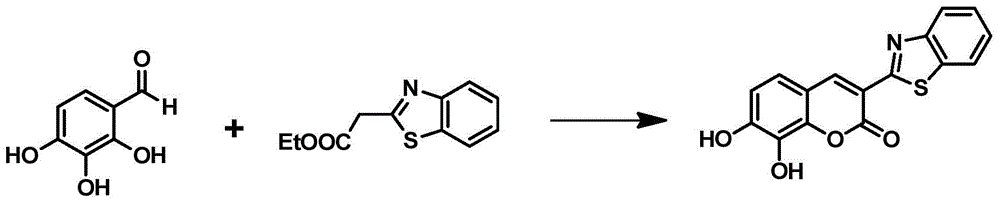
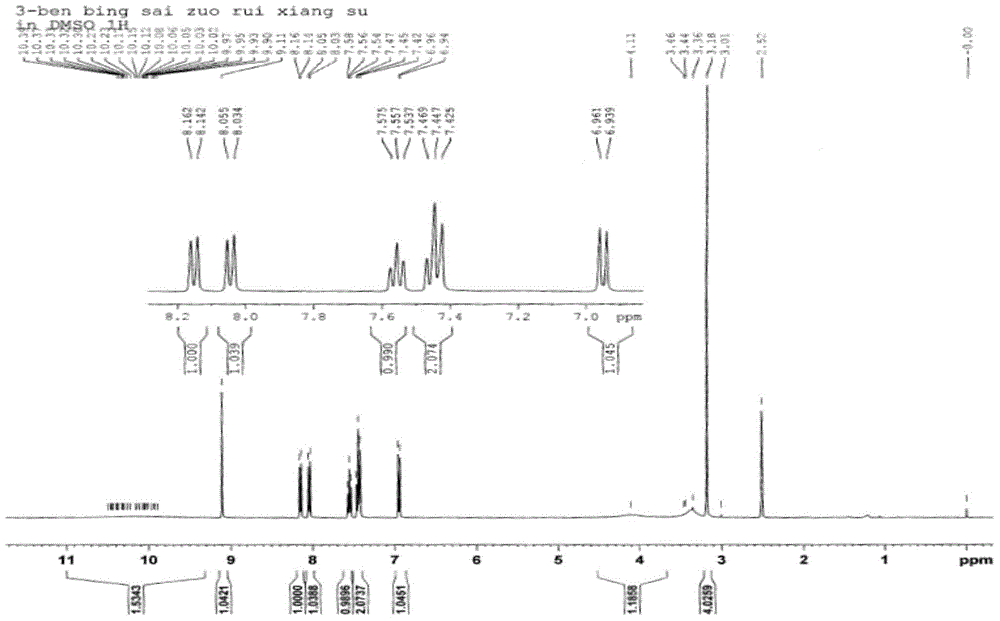
The invention provides a specific fluorescent probe for COMT and application thereof. A specific probe substrate provided by the invention is 3-benzothiazole-7,8-dihydroxycoumarin (3-BTD); the substrate can be specifically catalyzed by COMT to produce an 8-methoxy product and presents a fluorescence signal at a position of 520 nm; and the activity of COMT can be quantitatively determined by detecting changes of fluorescence intensity. The probe is applicable to quantitative assessment of the activity of COMT in biological samples from different sources, in-vitro rapid screening of inhibitors for COMT and evaluation of the inhibitory capability of the inhibitors. A method provided by the invention can be used for quantitative assessment of the actual activity of COMT in a variety of in-vitro biological samples and realizes rapid screening of inhibitors and quantitative assessment of the inhibitory capability of the inhibitors; the method is also applicable to evaluation of the catalytic activity of COMT of different species and COMT mutants with different amino acid sequences, so the method can assess the capability of COMT in metabolization of catechol drugs; and the method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high accuracy, good environment interference resisting capability, convenience in high-flux detection and inhibitor screening, etc.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com