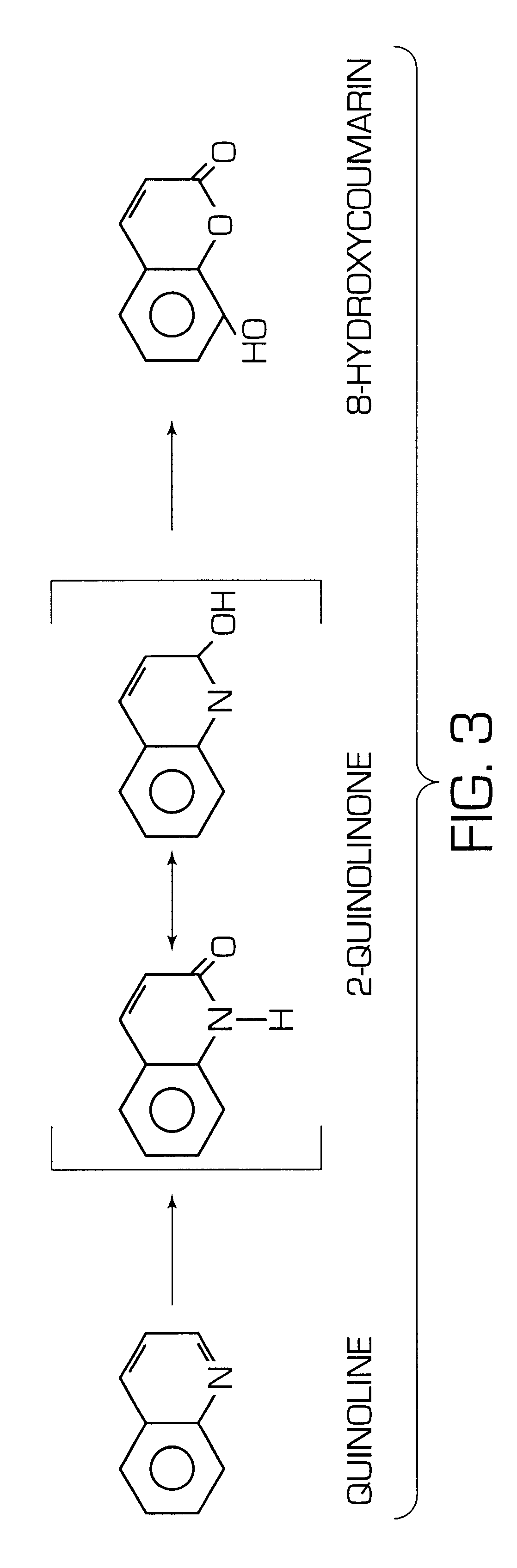
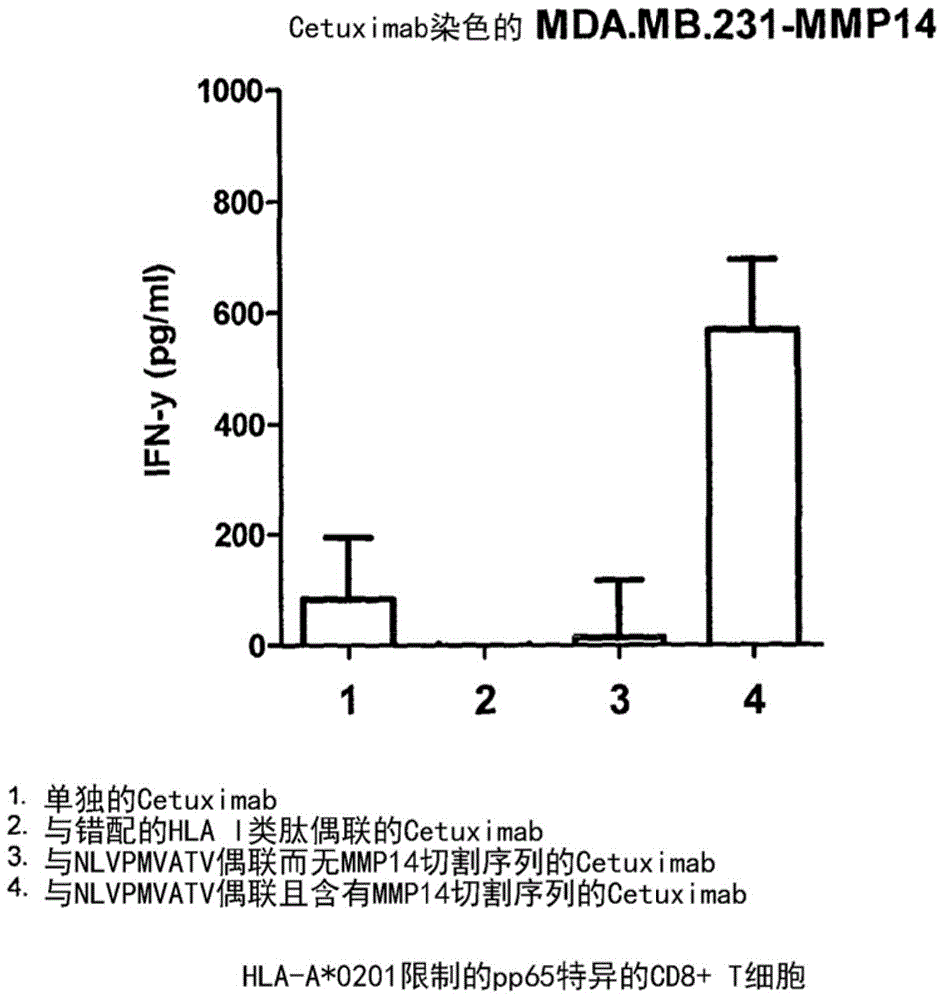
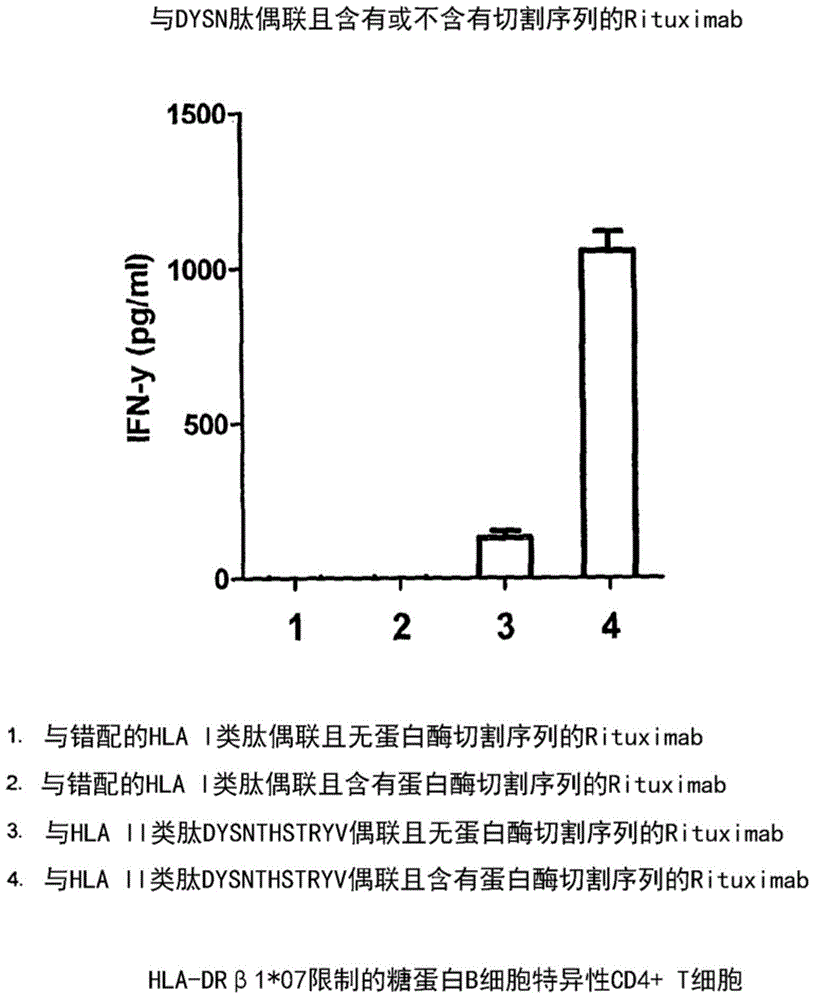
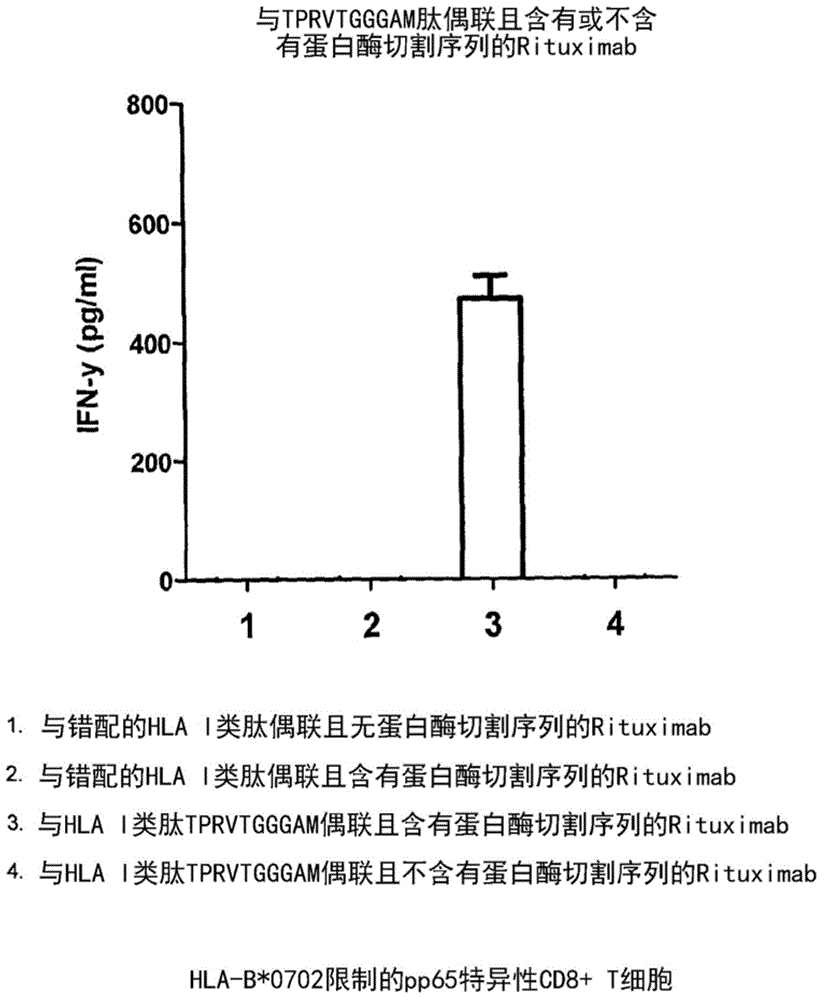
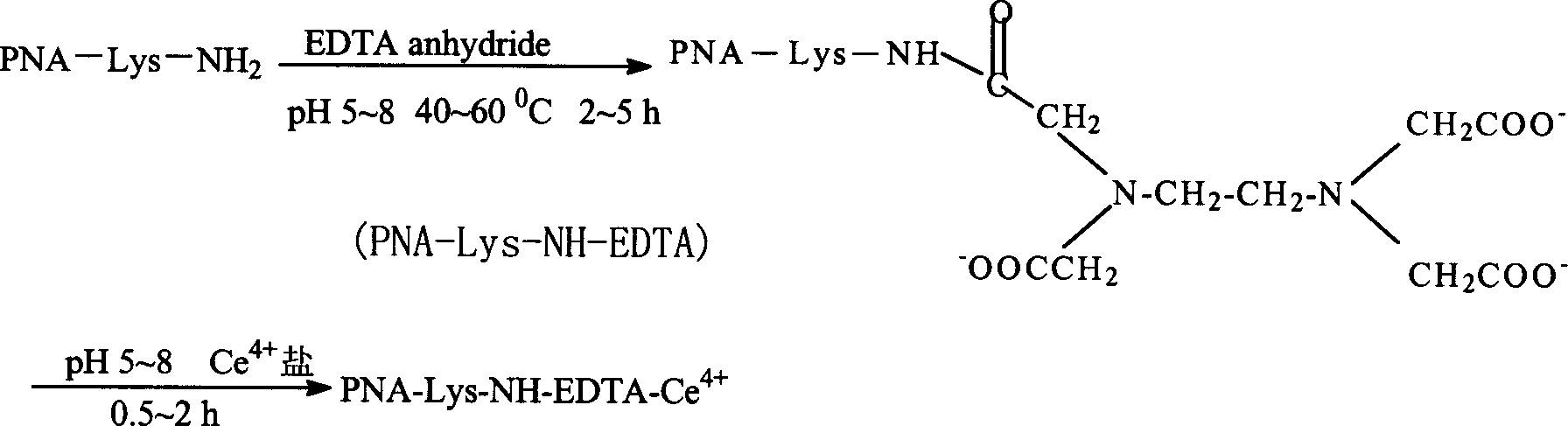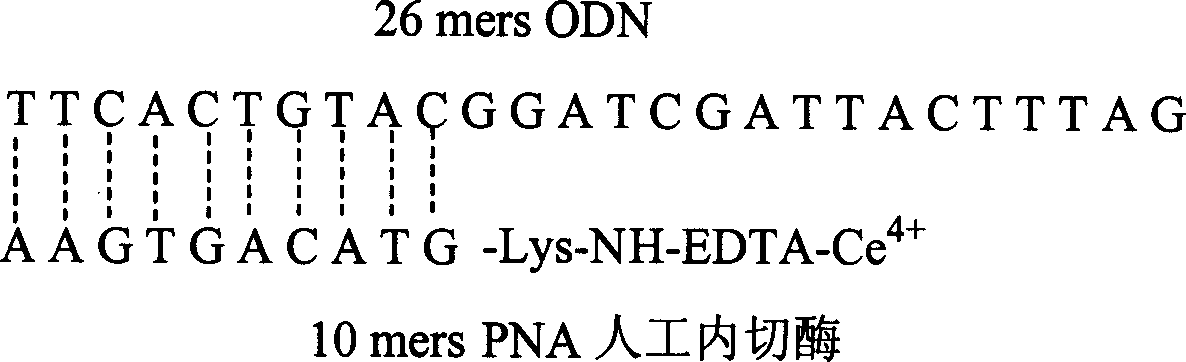Patents
Literature
68 results about "Selective cleavage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
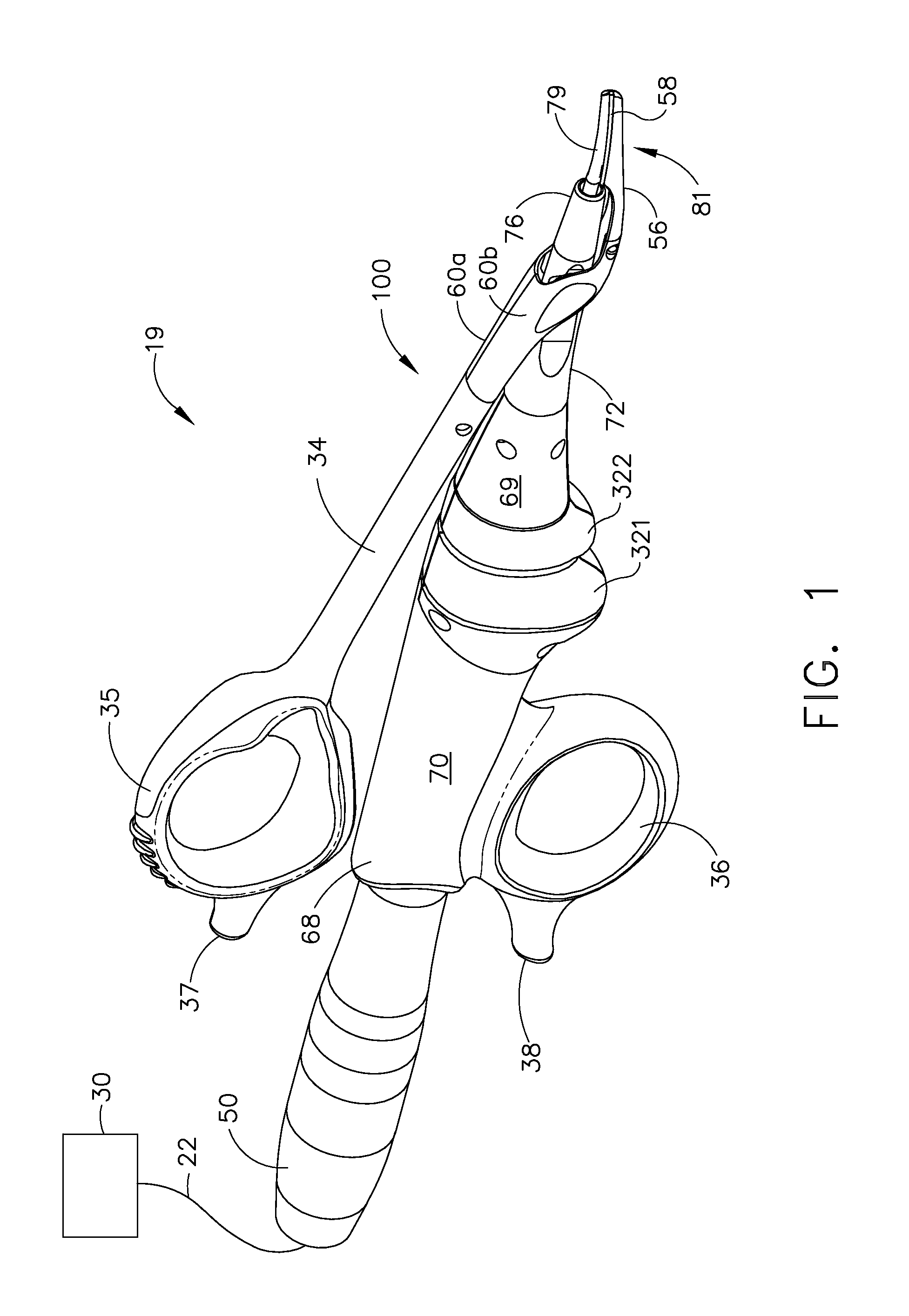
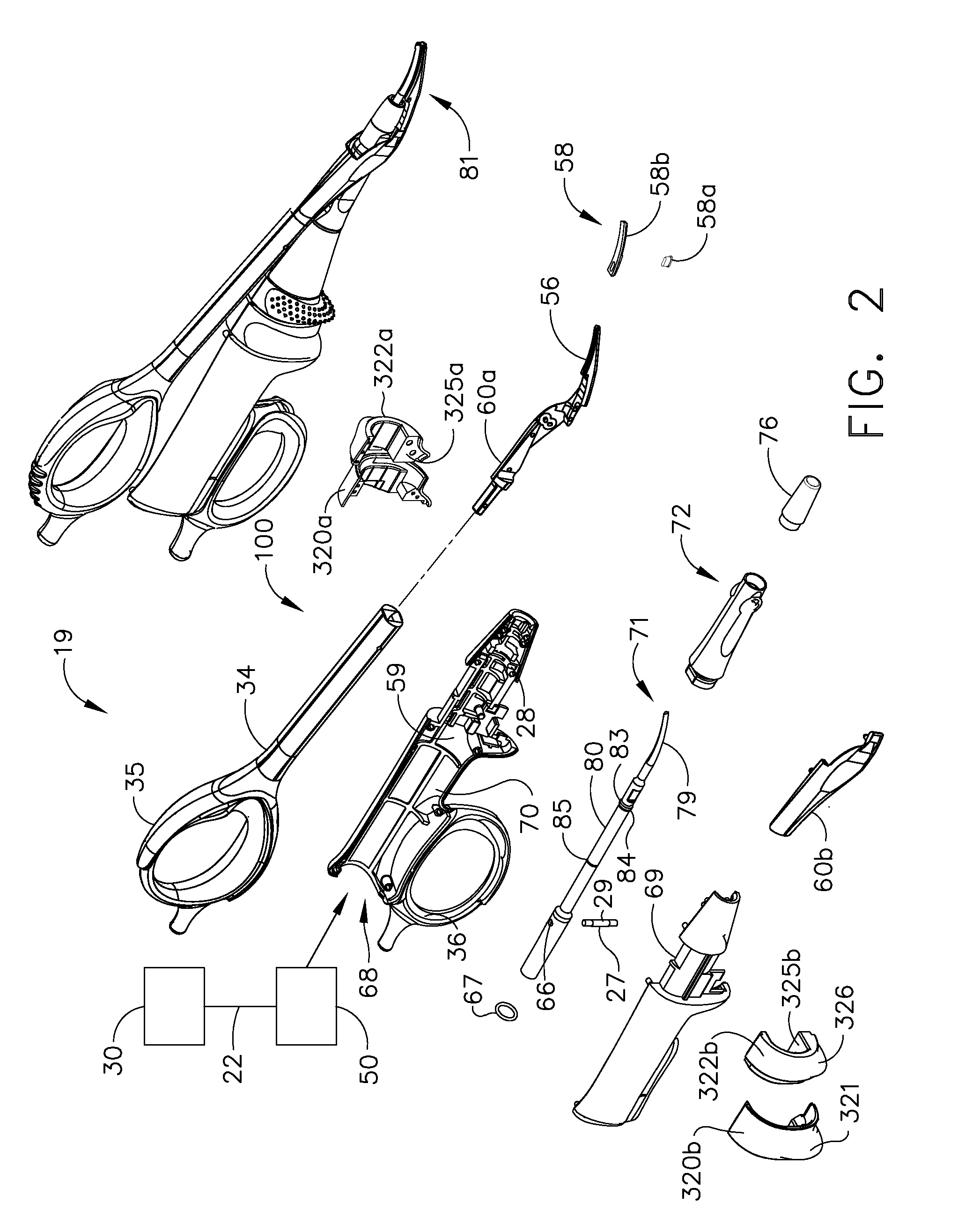
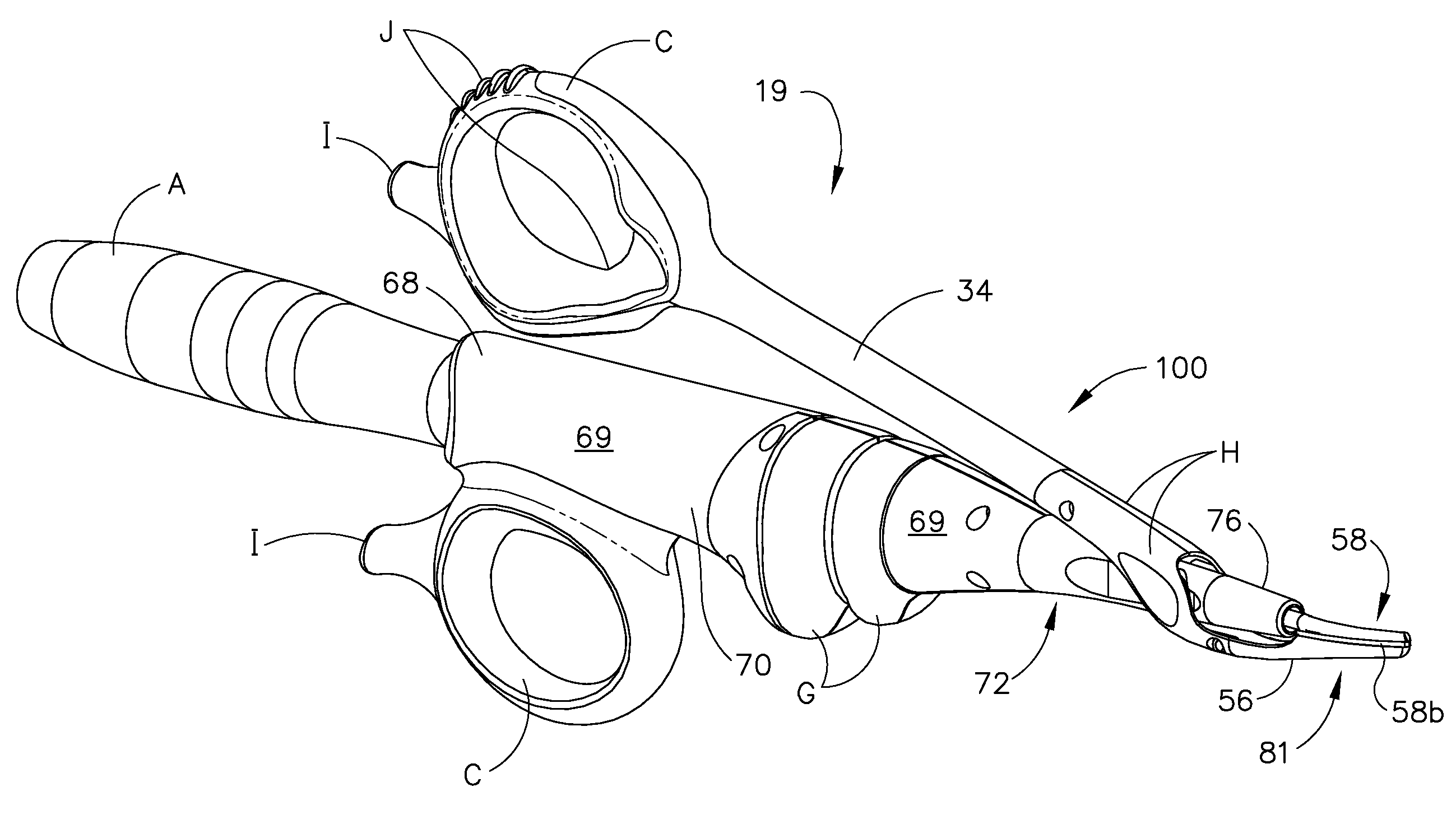
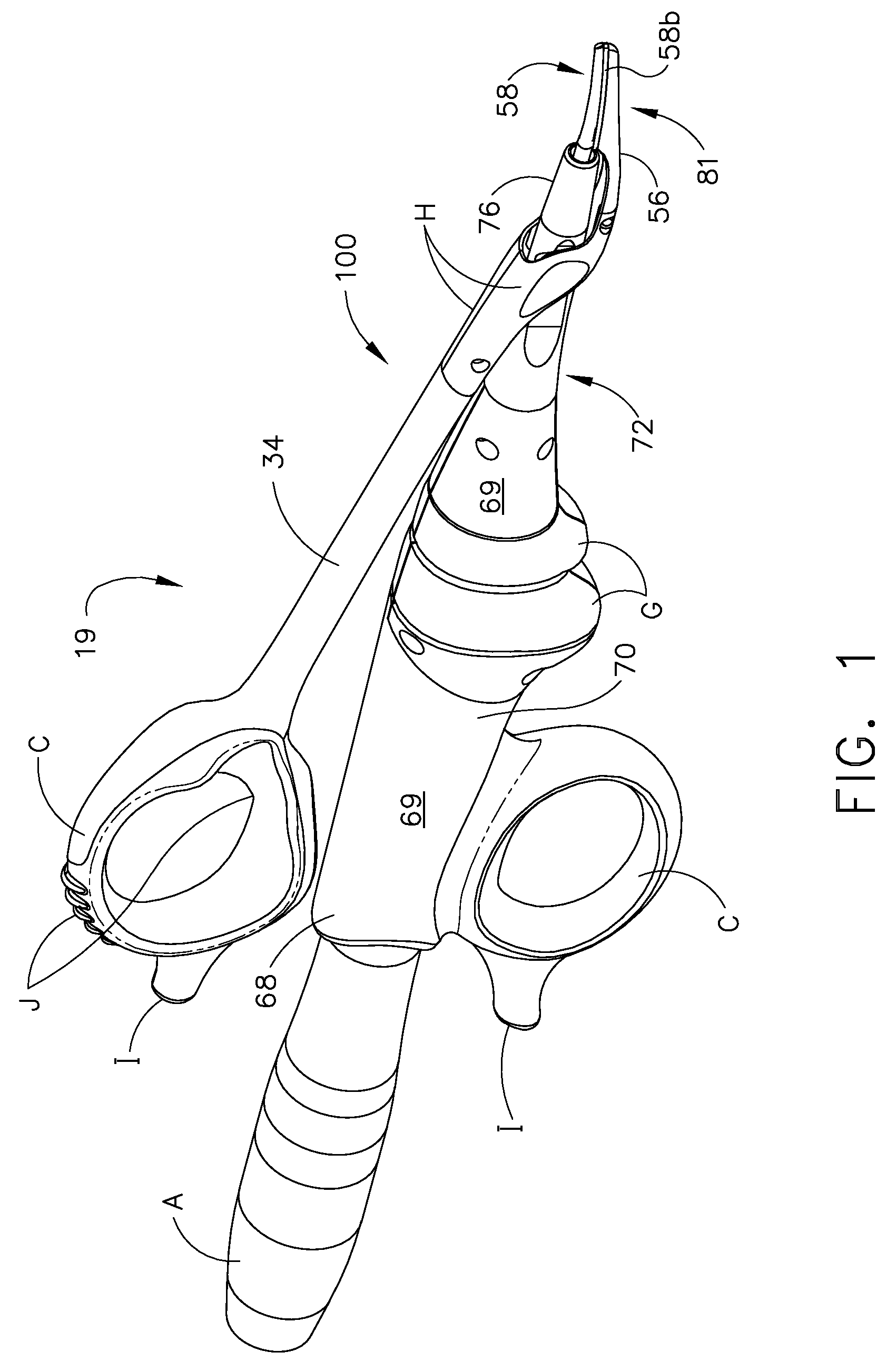
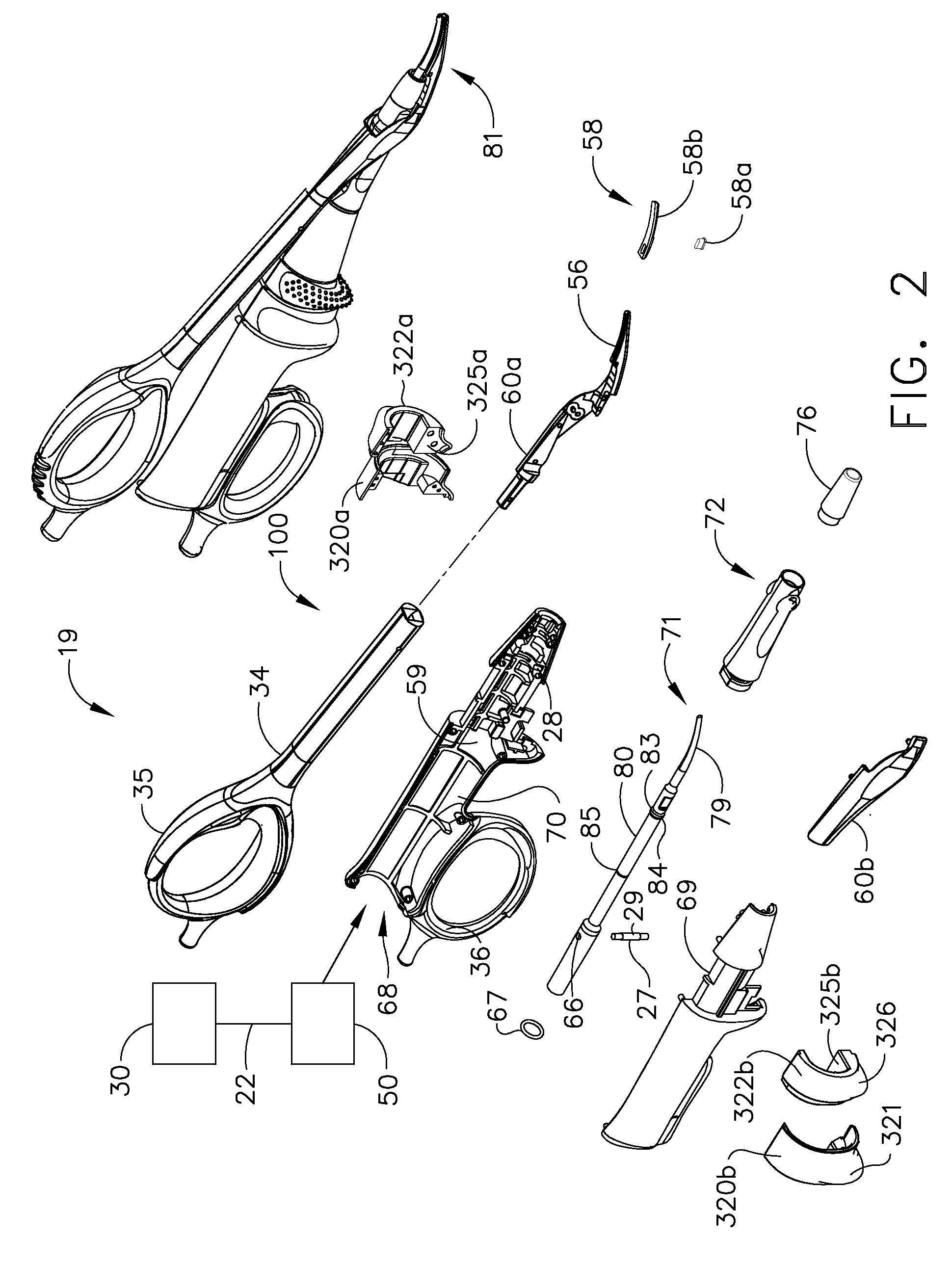
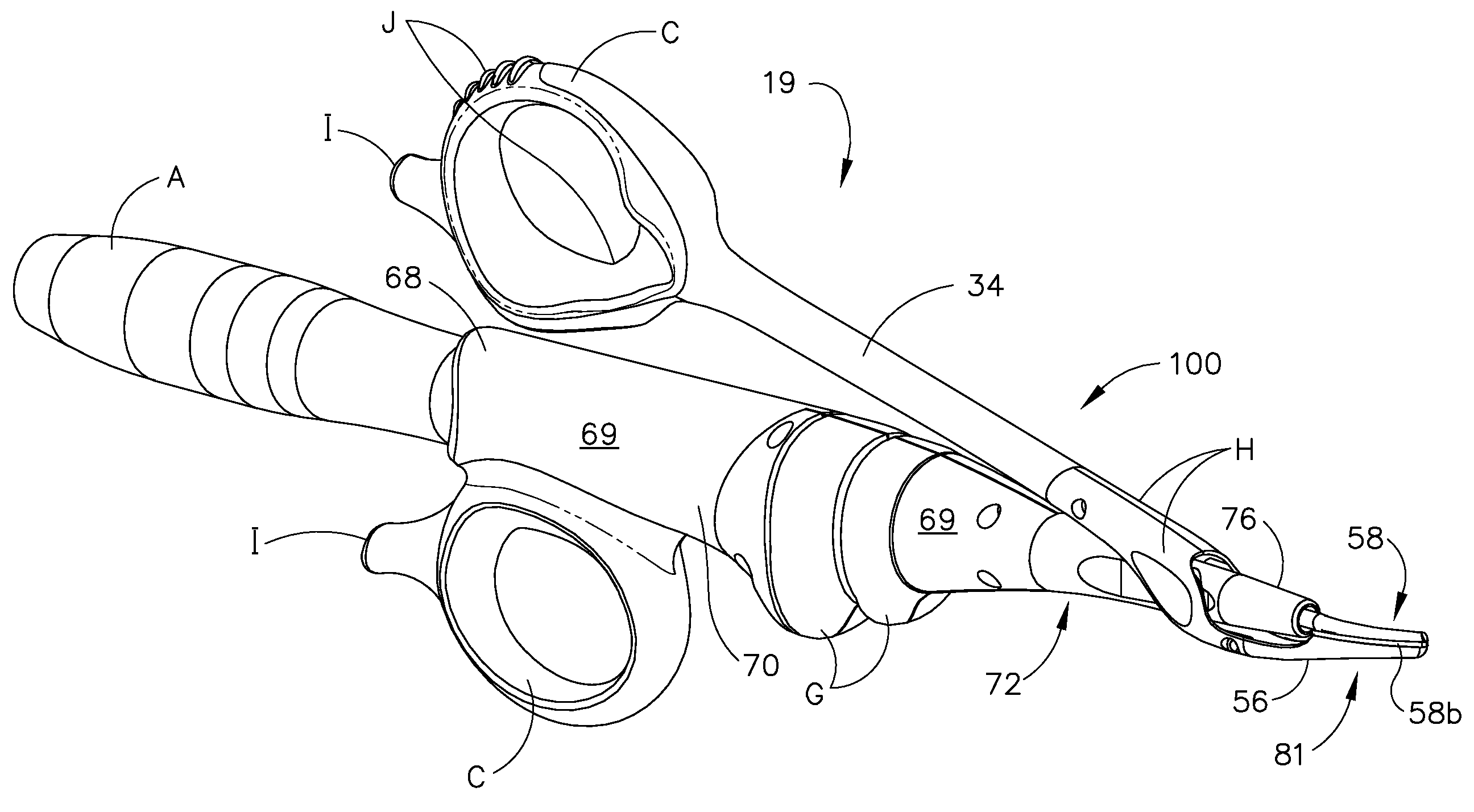
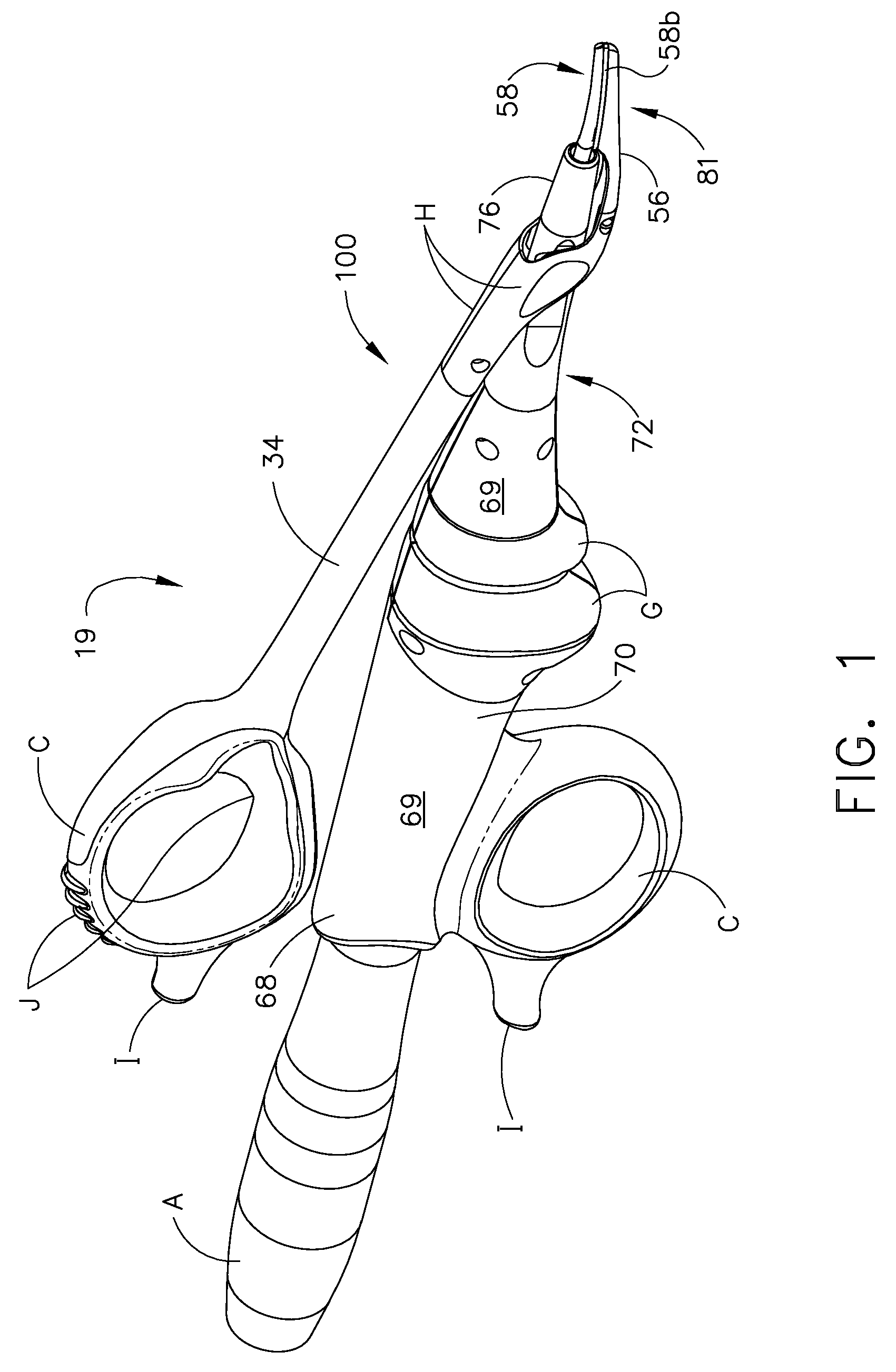
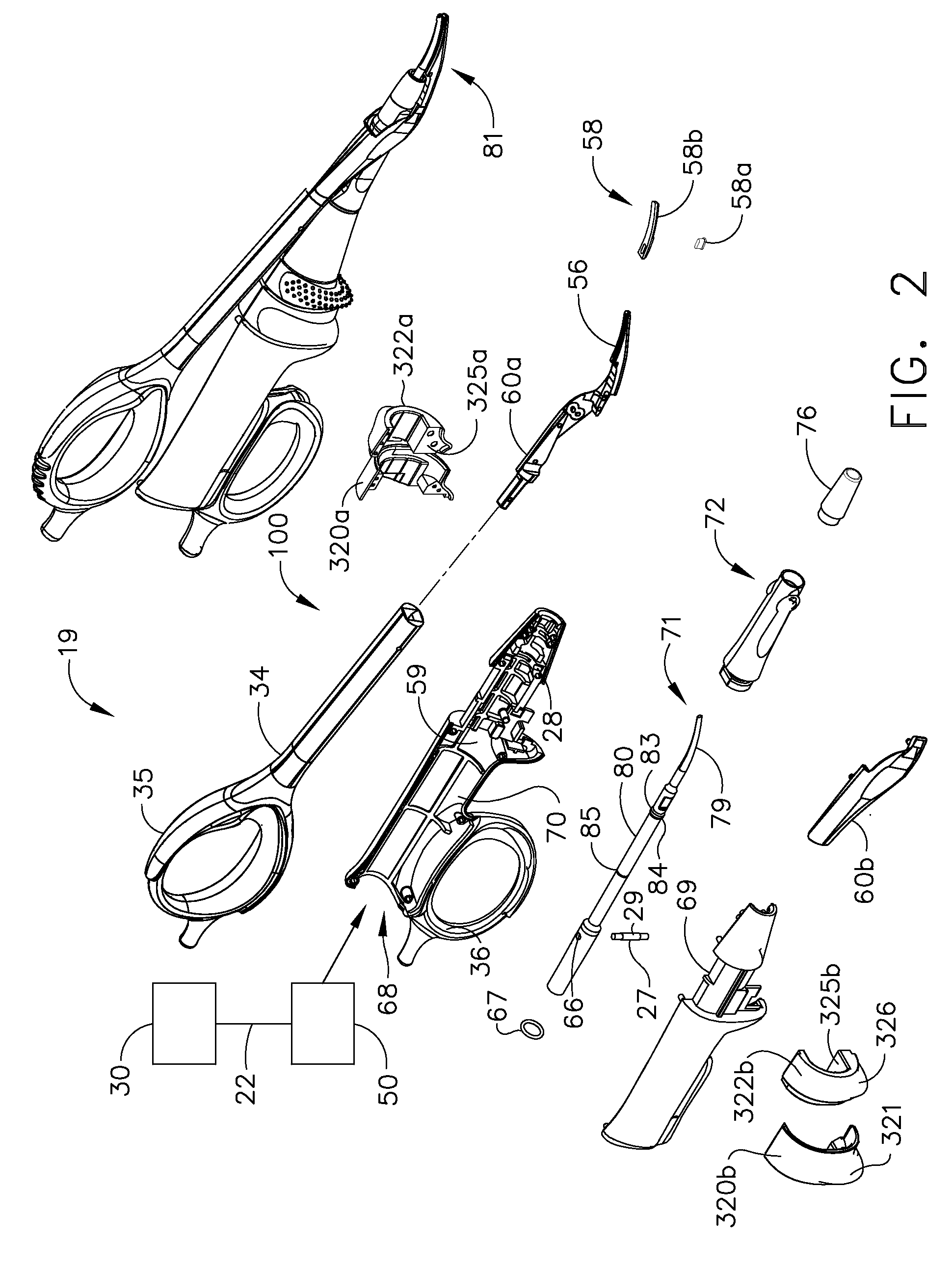
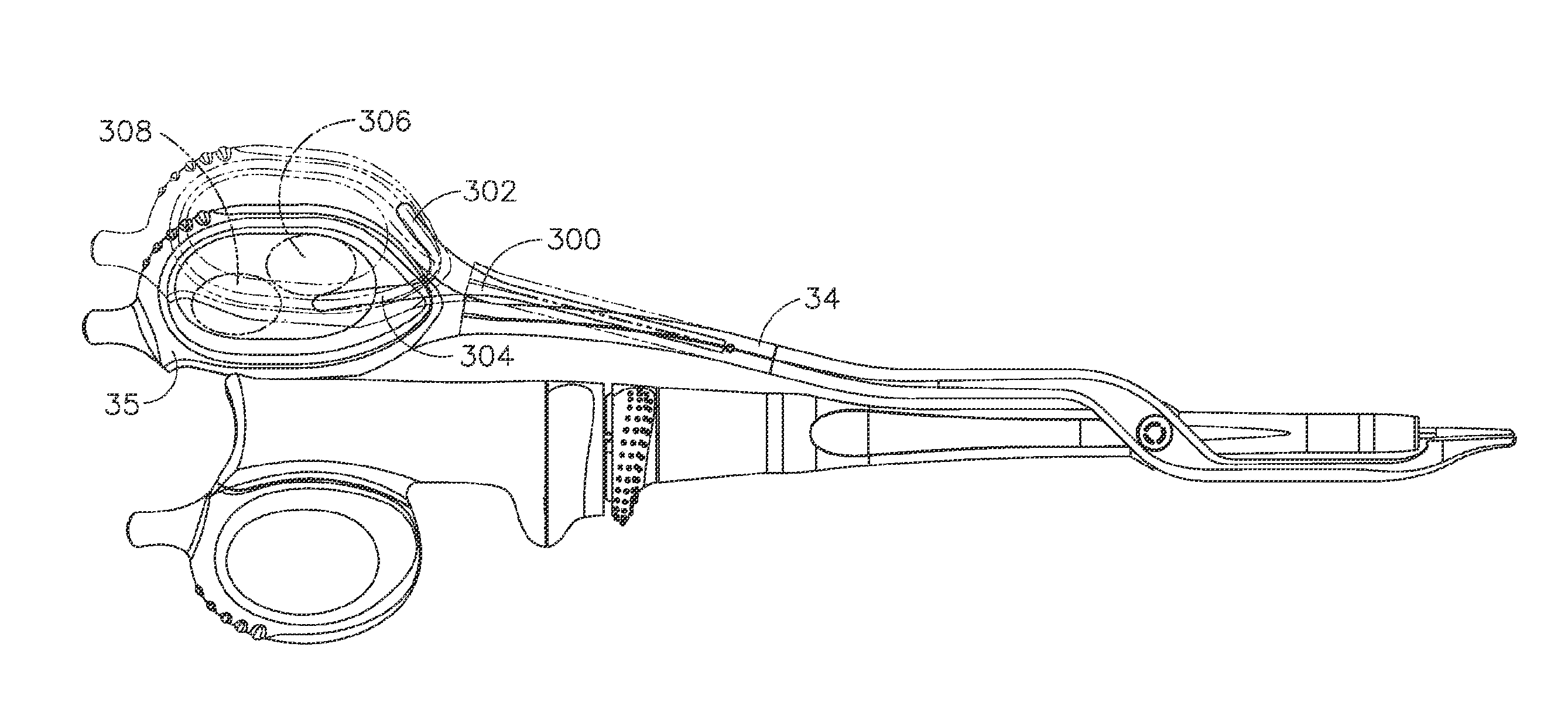
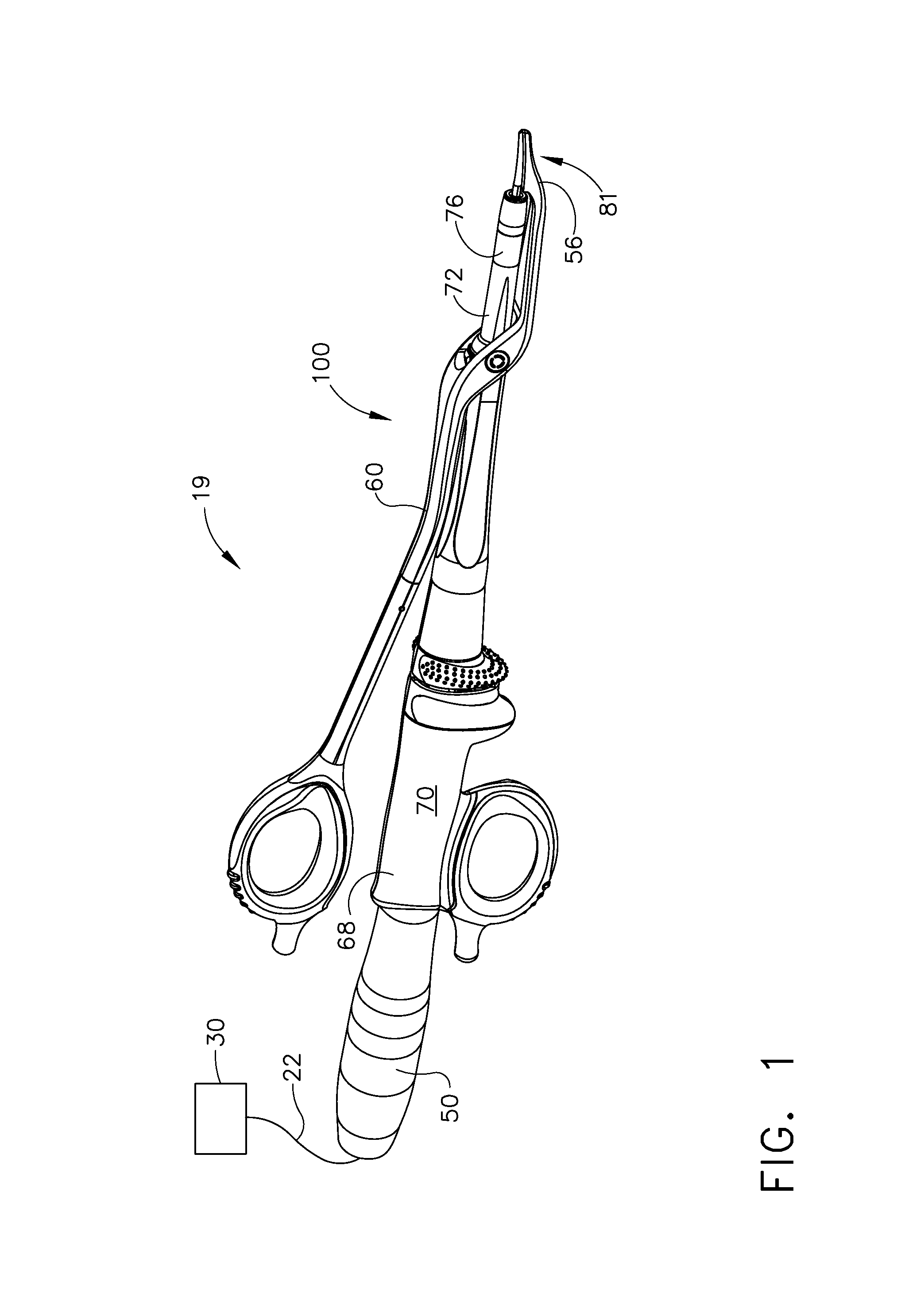
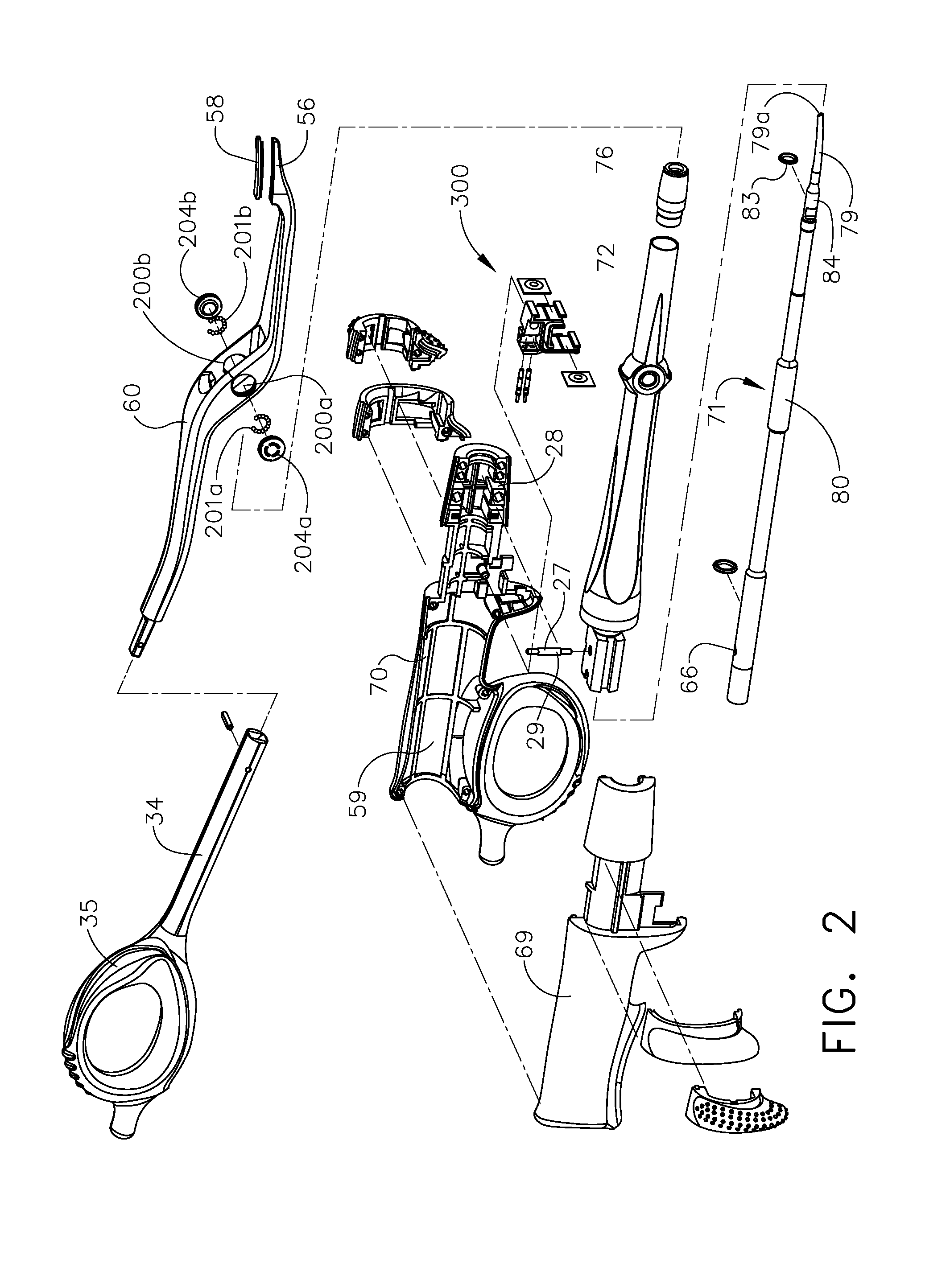
Ultrasonic device for cutting and coagulating
InactiveUS20070191713A1Improve wear resistanceLoad moreUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBack cuttingBiological activation
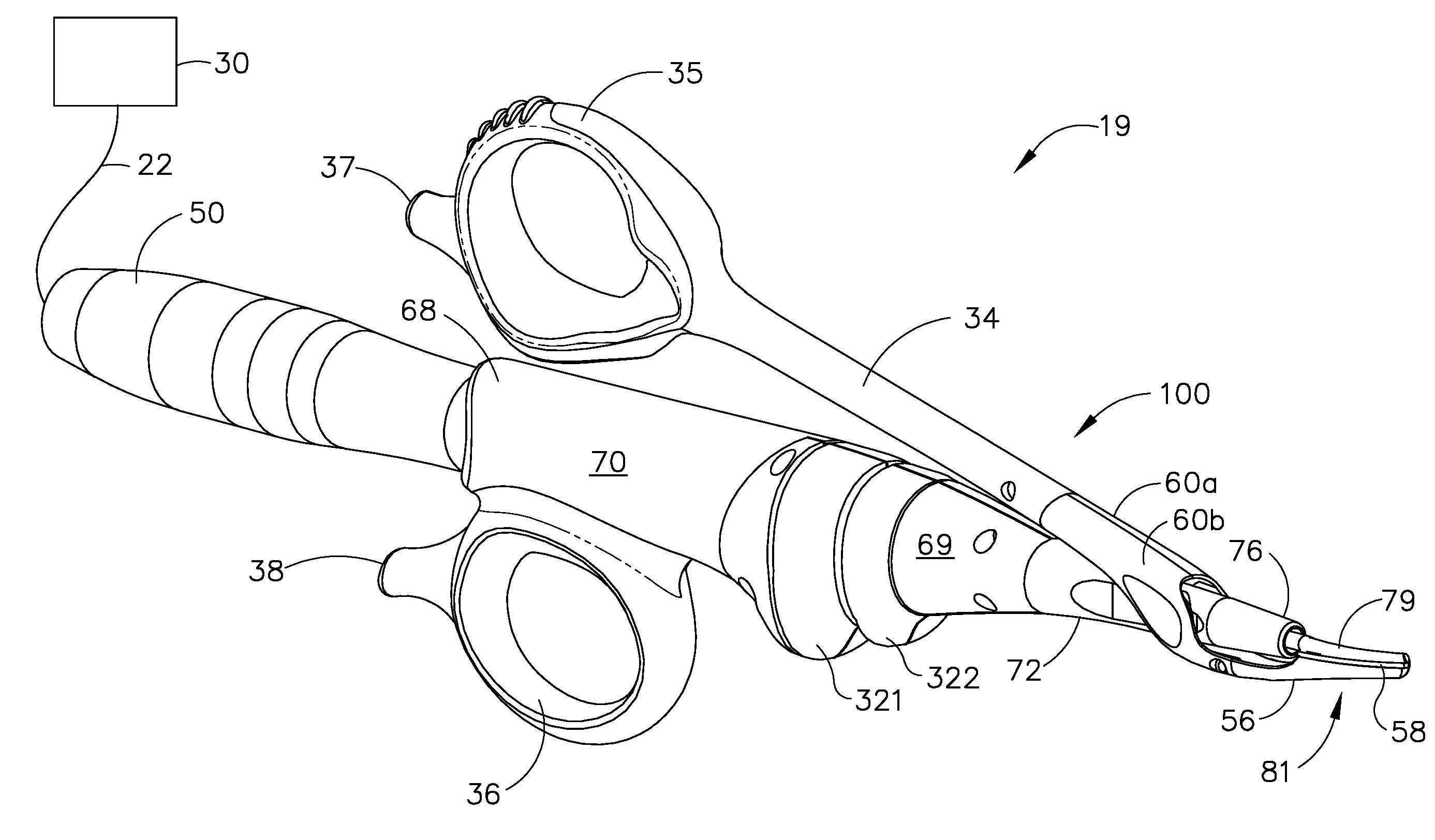
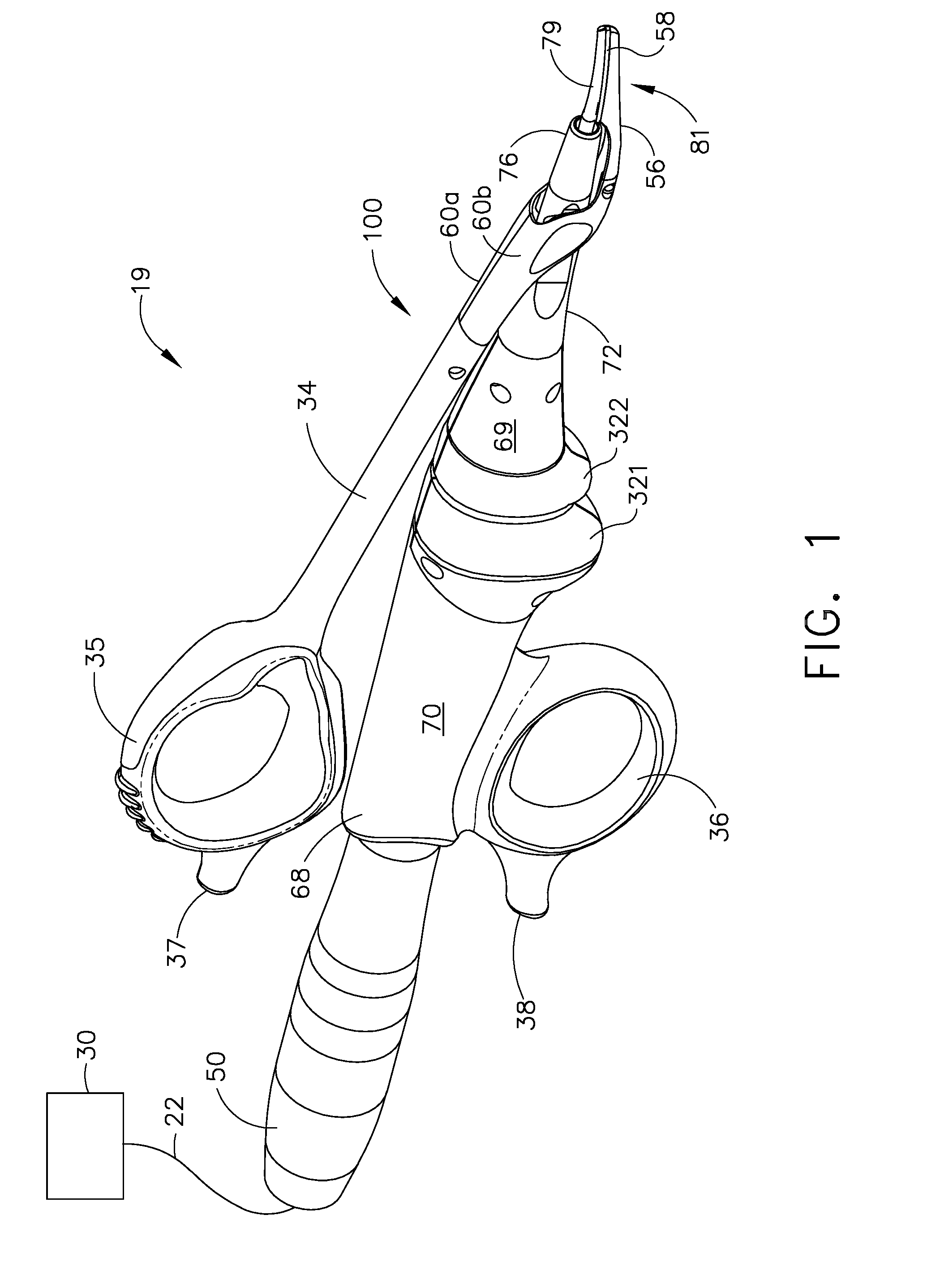
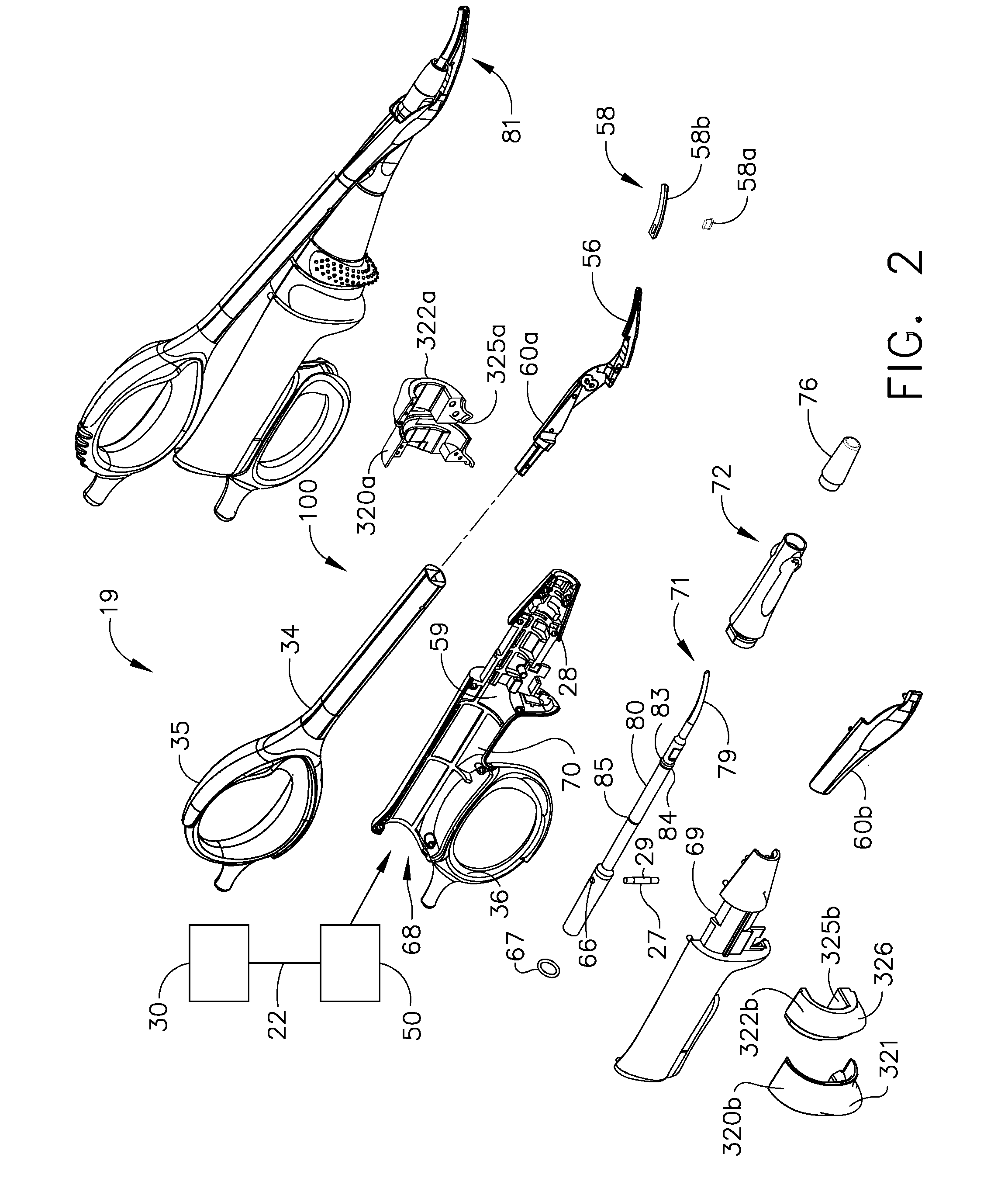
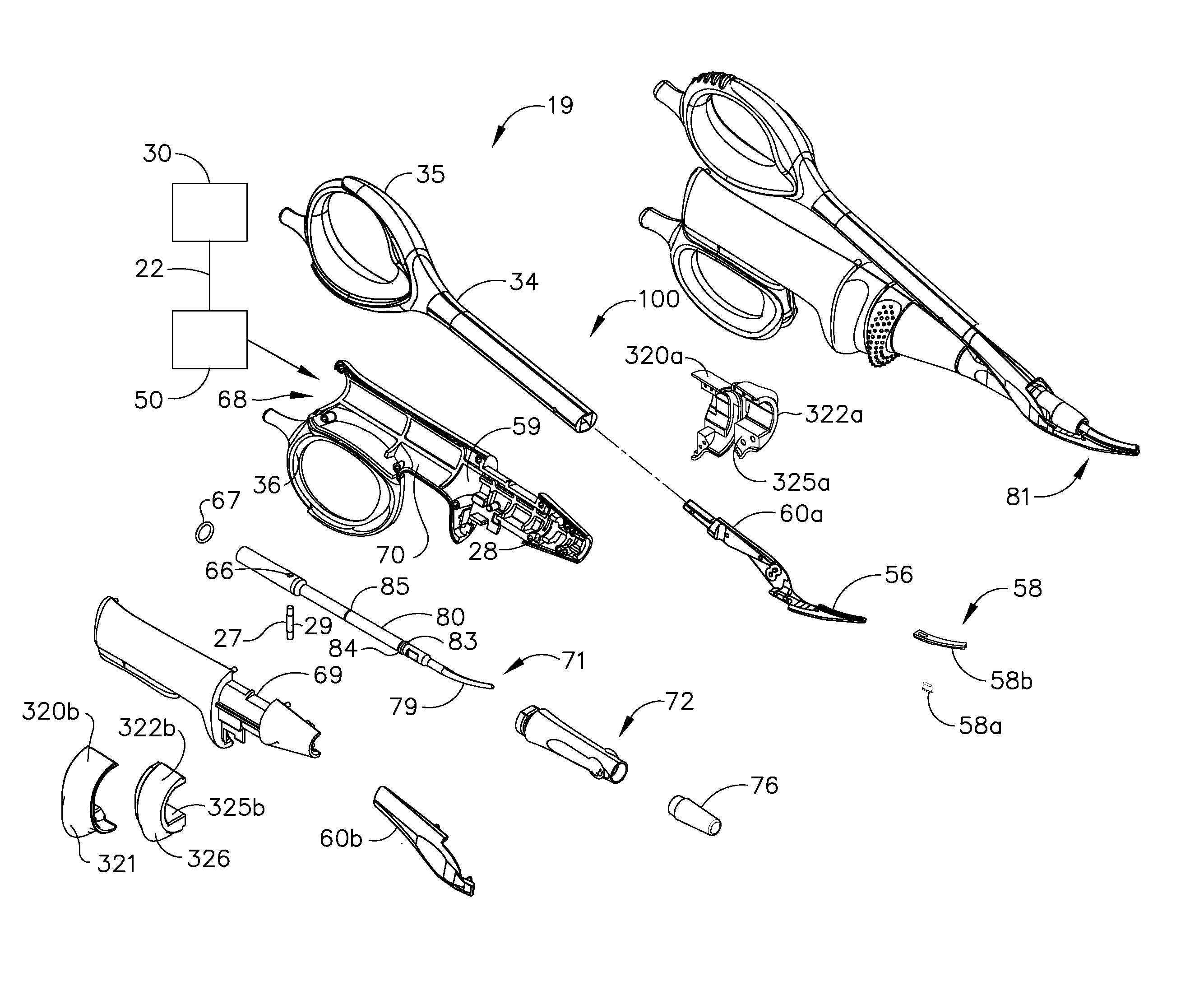
An ultrasonic clamp coagulator assembly that is configured to permit selective cutting, coagulation, and fine dissection required in fine and delicate surgical procedures. The assembly includes a clamping mechanism, including a clamp arm cam-mounted at the distal portion of the instrument, which is specifically configured to create a desired level of tissue clamping forces. The balanced blade provides a functional asymmetry for improved visibility at the blade tip and a multitude of edges and surfaces, designed to provide a multitude of tissue effects: clamped coagulation, clamped cutting, grasping, back-cutting, dissection, spot coagulation, tip penetration and tip scoring. The assembly also features hand activation configured to provide an ergonomical grip and operation for the surgeon. Hand switches are placed in the range of the natural axial motion of the user's index or middle fingers, whether gripping the surgical instrument right-handed or left handed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Tissue pad for an ultrasonic device for cutting and coagulating
InactiveUS20100094323A1Improve wear resistanceLoad moreLaminationLamination apparatusActuatorDissection
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Ultrasonic device for cutting and coagulating
ActiveUS8328834B2Improve wear resistanceLoad moreSurgical scissorsSurgical forcepsSurgical departmentBiomedical engineering
An ultrasonic clamp coagulator assembly that is configured to permit selective cutting, coagulation, and fine dissection required in fine and delicate surgical procedures. The assembly includes a housing, a curved blade assembly and a first shroud and a second shroud.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Ultrasonic device for cutting and coagulating
ActiveUS20090099582A1Improve wear resistanceLoad moreSurgical scissorsSurgical forcepsSurgical departmentBiomedical engineering
An ultrasonic clamp coagulator assembly that is configured to permit selective cutting, coagulation, and fine dissection required in fine and delicate surgical procedures. The assembly includes a housing, a curved blade assembly and a first shroud and a second shroud.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
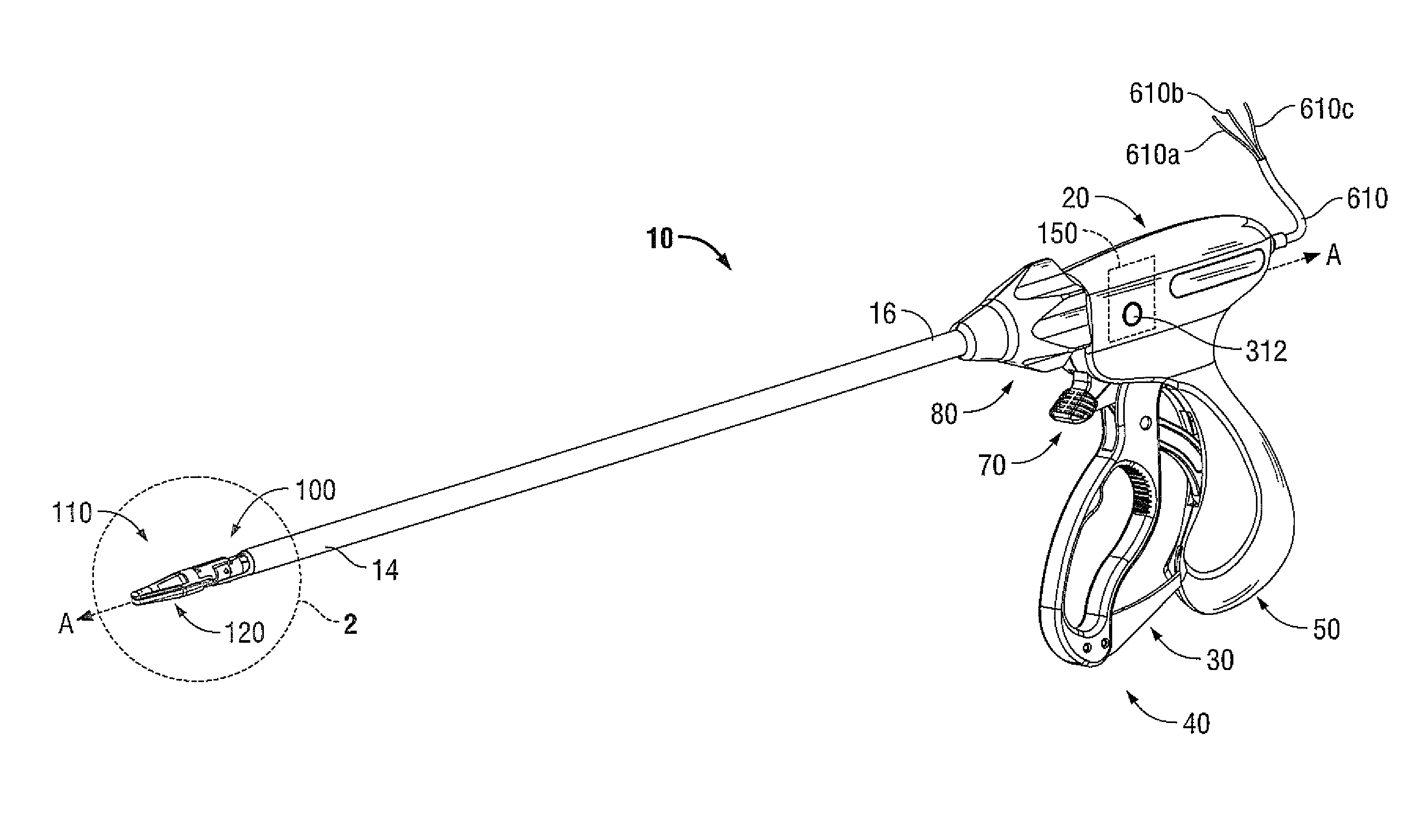
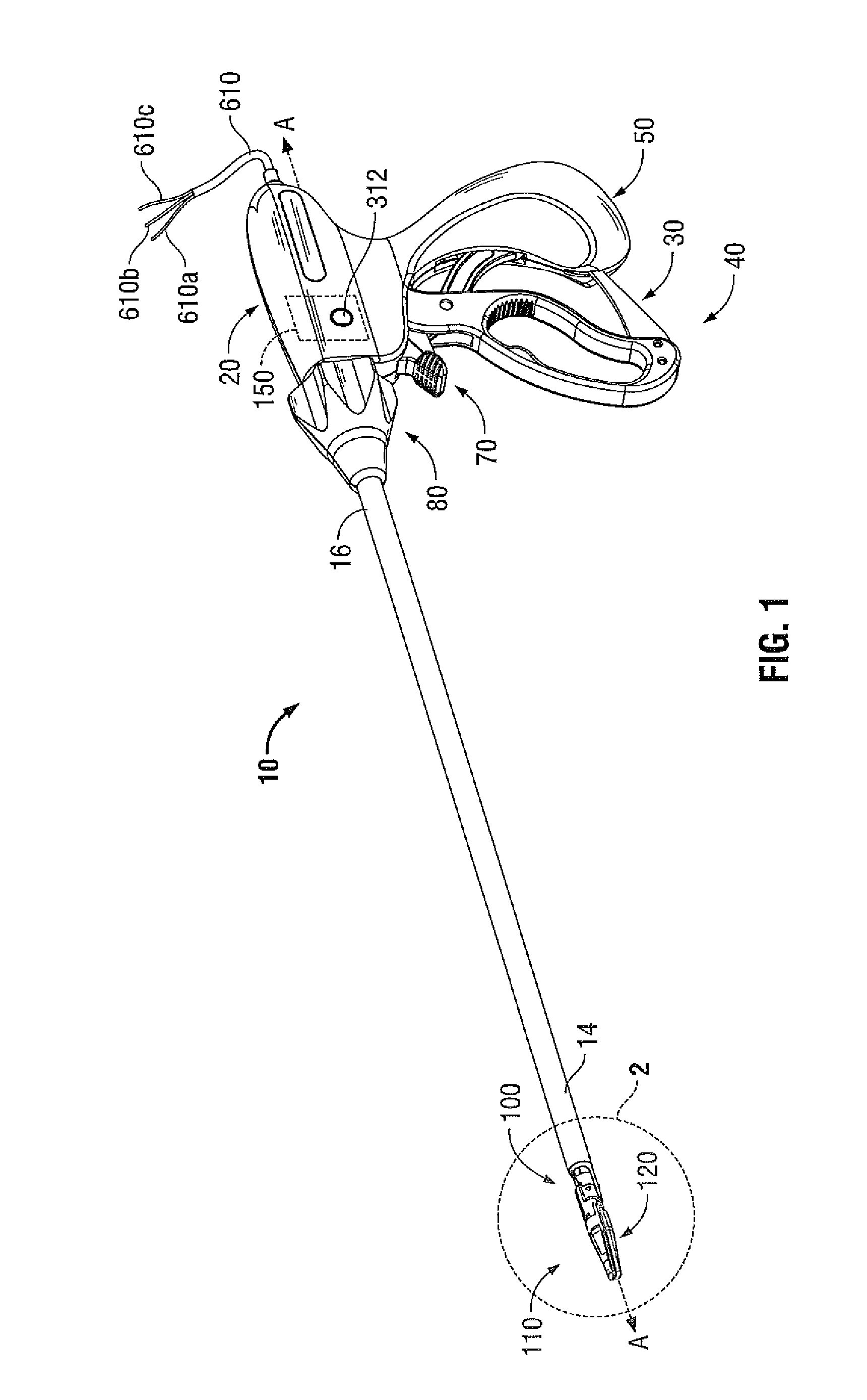
Apparatus with Multiple Channel Selective Cutting
A forceps includes an end effector assembly and one or more cutting blades. The end effector assembly defines a longitudinal axis and has a pair of jaw members selectively positionable relative to one another about a pivot. One or more of the jaw members includes an electrically conductive tissue engaging surface adapted to connect to an electrosurgical energy source. One or more of the jaw members includes two or more blade channels defined therein and extending therealong. The one or more cutting blades are selectively movable within one or more of the two or more blade channels.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
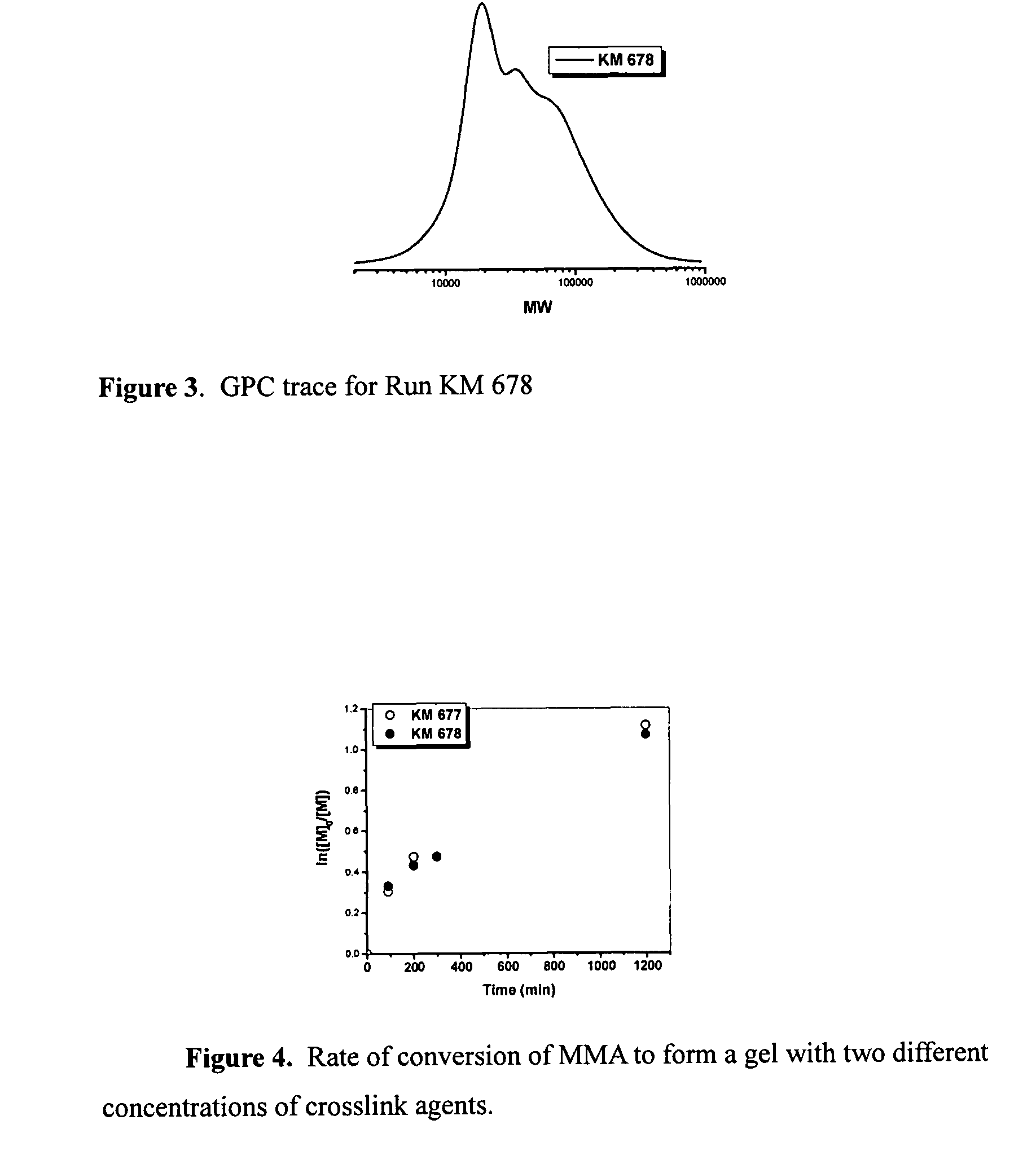
Preparation of functional gel particles with a dual crosslink network
ActiveUS8367051B2Improve surface propertiesAvoid rapid degradationPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsCrosslinked polymersReactive agent
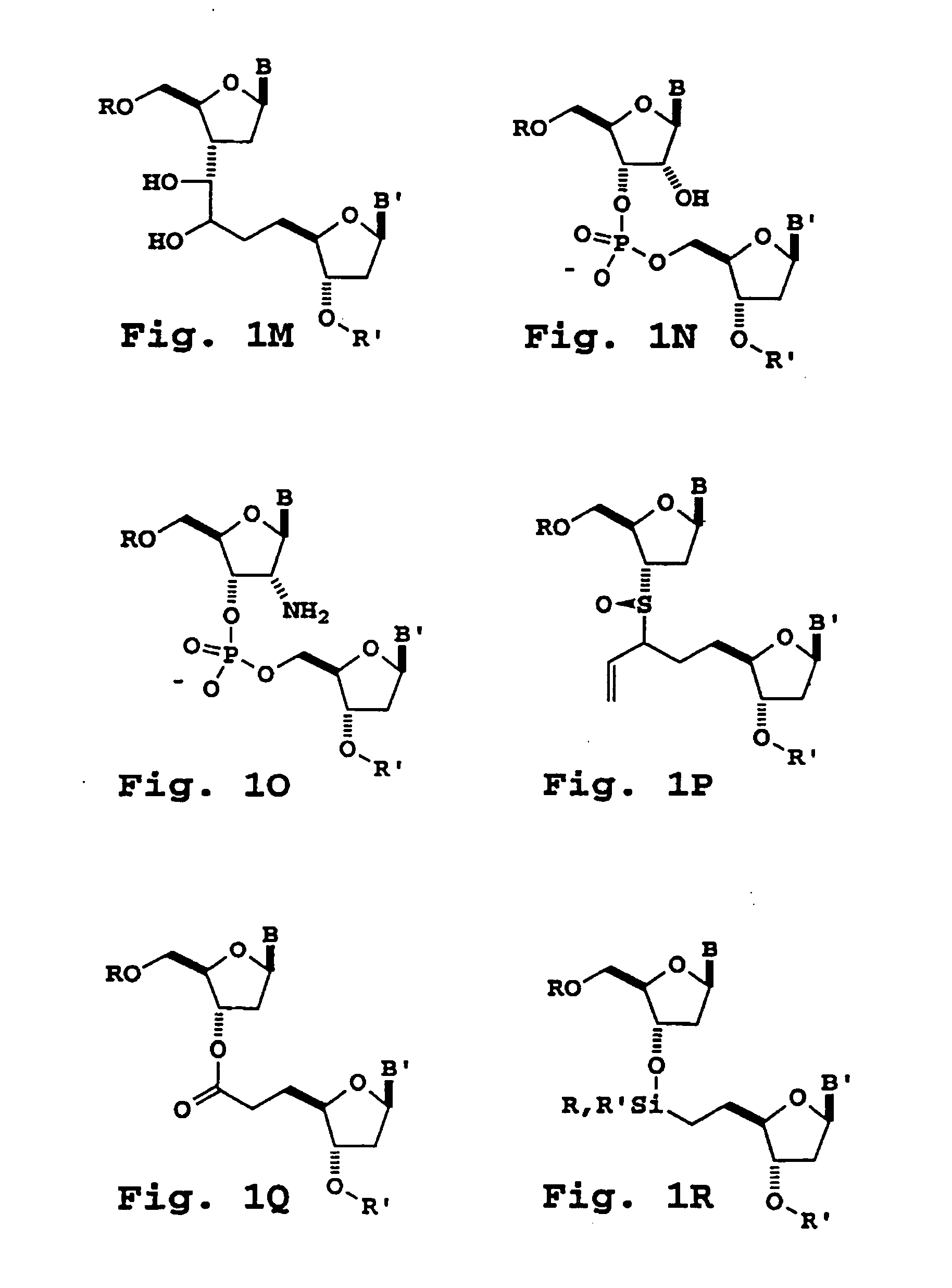
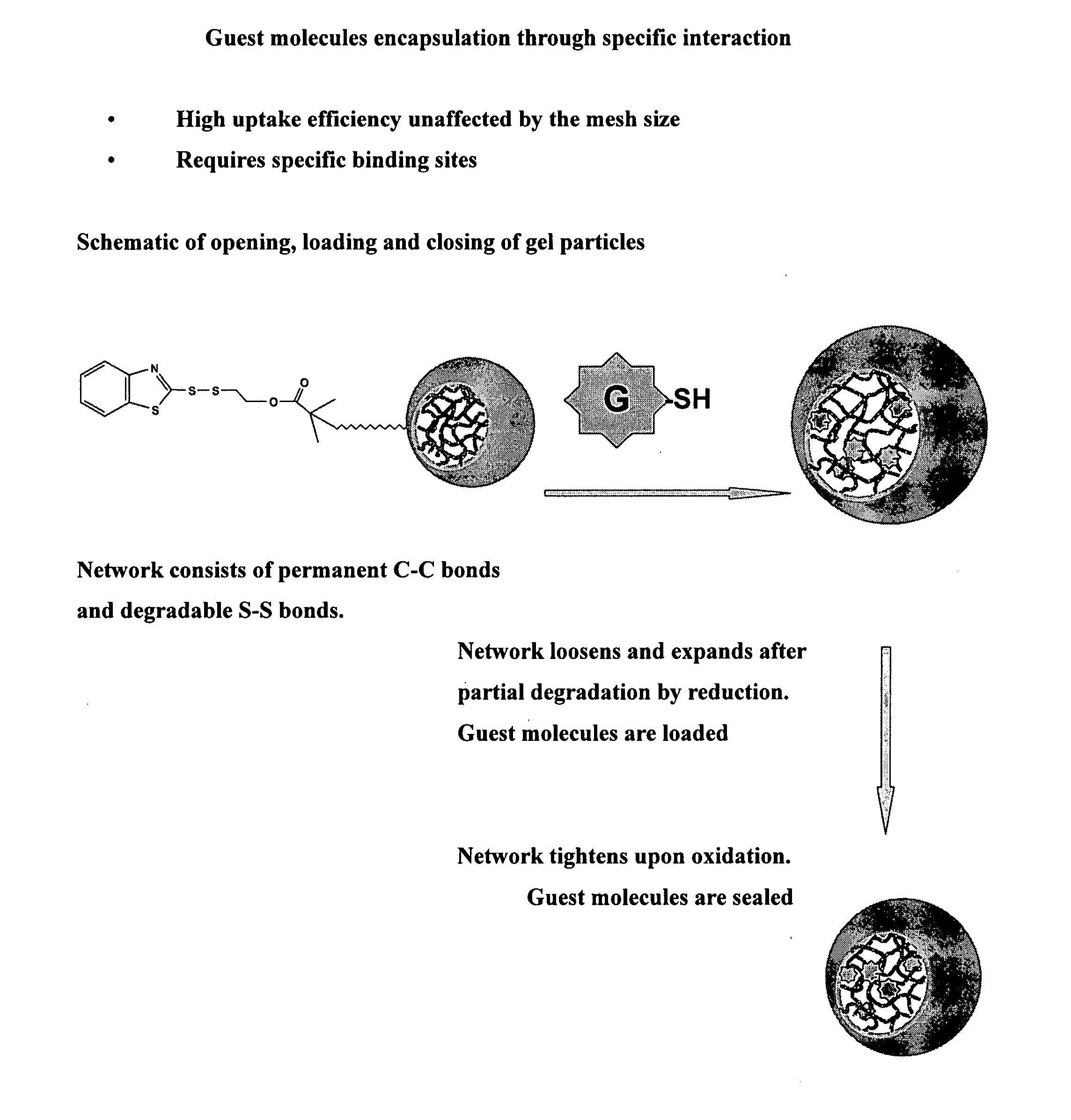
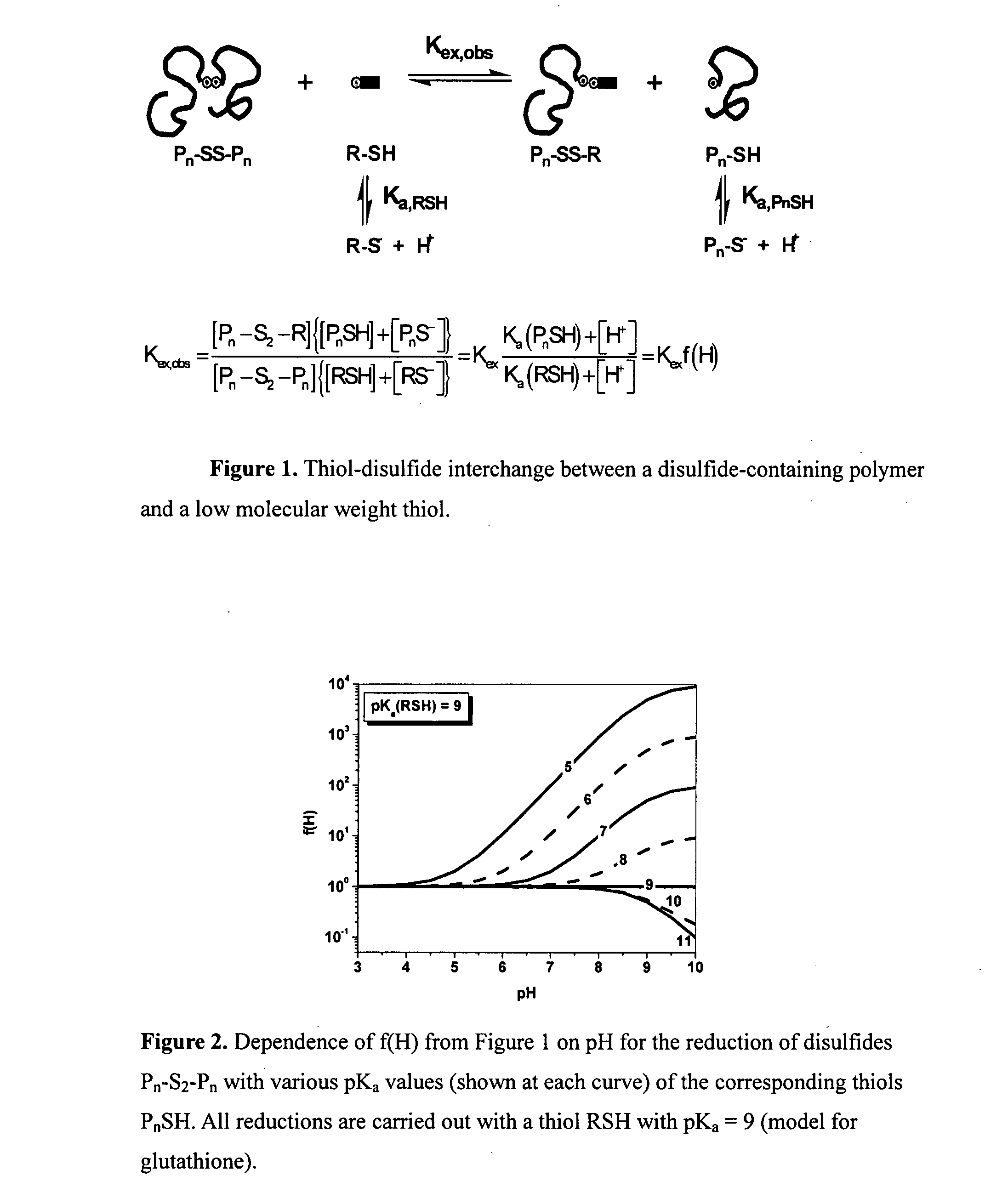
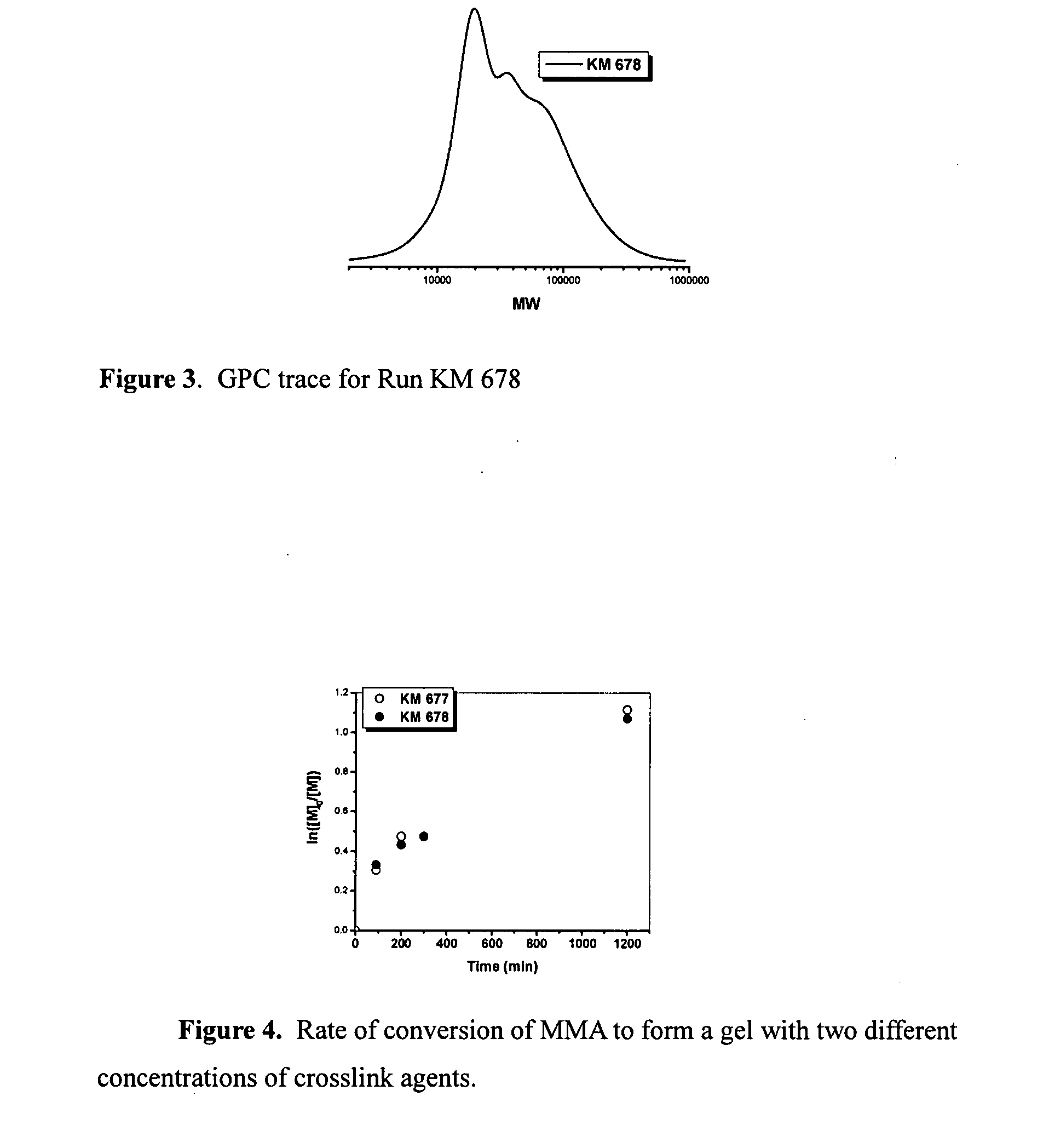
Functional gel particle formed from a crosslinked polymeric network including a fraction of stable crosslinks and a second fraction of cleavable crosslinks are disclosed. Functional compounds may be chemically or physically encapsulated within and / or released from the gel particle by selective cleavage of the cleavable crosslinks. The functional compounds may be delivered and released to a pre-selected target site. Peripheral or other accessible functionality on the surface of the gel particle allows attachment of a surface reactive agent, thereby modifying one or more surface properties of the gel particle. Processes of preparing the gel particles and processes of delivering the functional compounds to a target site are also disclosed.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Apparatus with multiple channel selective cutting
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Excisional devices having selective cutting and atraumatic configurations and methods of using same
InactiveUS7029451B2Not to damageSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical deviceSelective cleavage
Surgical devices include a selectively cutting and atraumatic distal tip that is configured to assume a first configuration in which cutting surface or surfaces thereof are effective to cut tissue and a second configuration in which the cutting surface or surfaces thereof are ineffective to cut tissue.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
Device for cutting glass substrate and its method
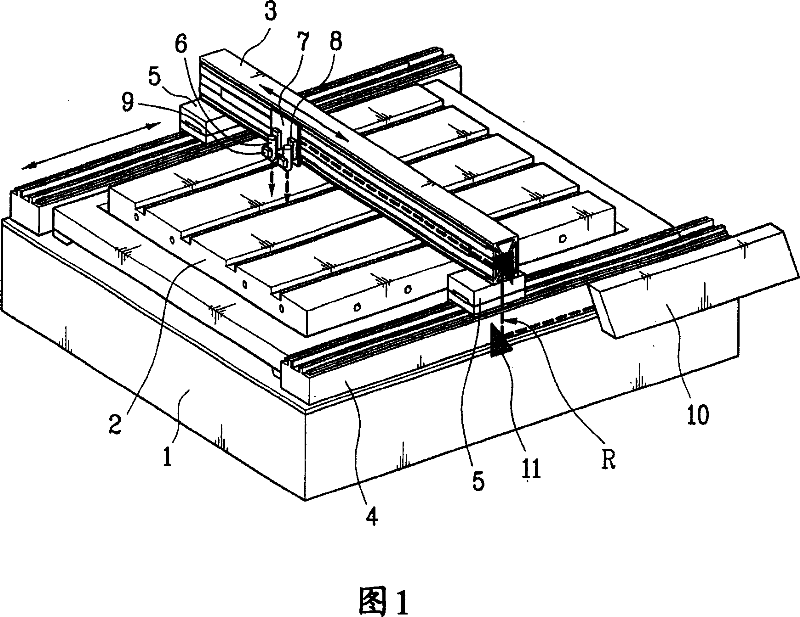
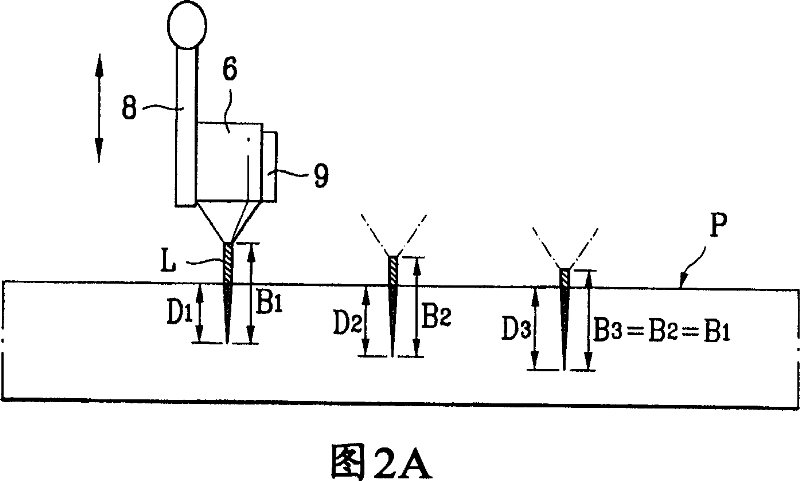
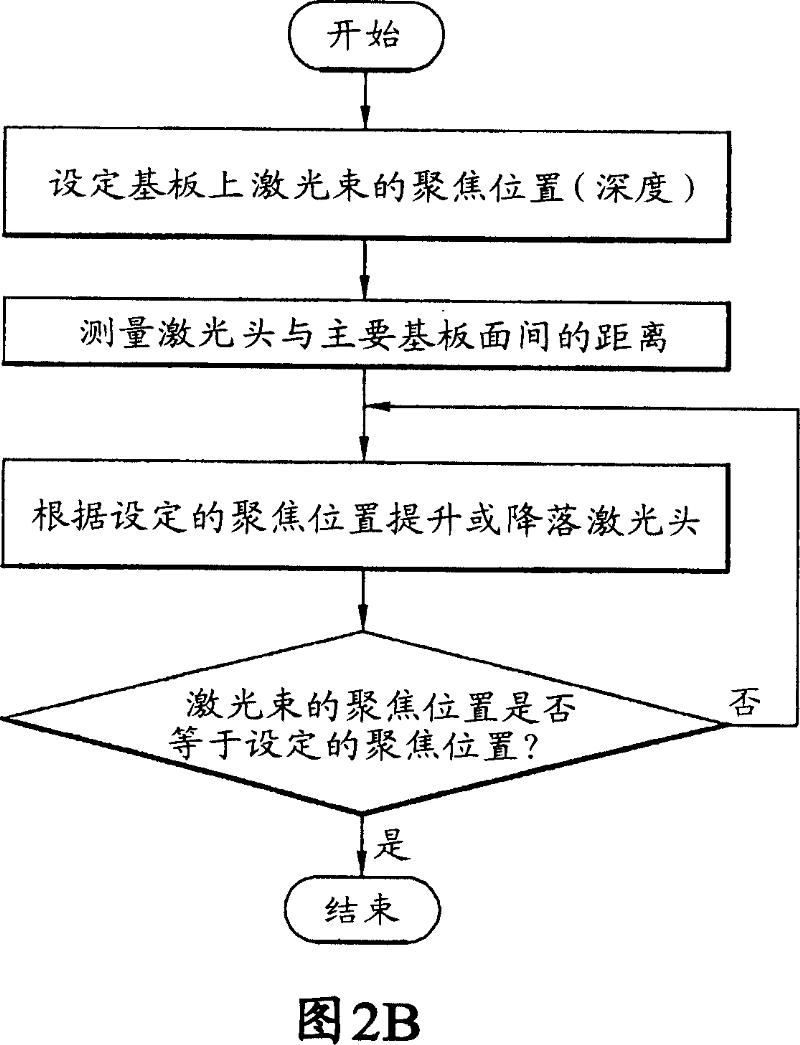
ActiveCN101031383AControl the depth of cutPackaging toiletriesPackaging cosmeticsCutting glassUltraviolet
An apparatus for cutting a nonmetallic substrate (P) and method thereof are disclosed. The present invention is suitable for cutting upper and lower substrates (P) simultaneously or for cutting either an upper or lower substrate selectively in a manner of controlling a cutting depth by adjusting a focus position of a short wavelength laser beam in cutting various nonmetallic substrates (P) such as a glass substrate for fabricating a flat panel display such as TFT-LCD, PDP, OLED, etc. The present invention includes a laser beam generator (10) generating a UV short wavelength laser beam, a torch (6) applying the short wavelength laser beam to a specific location on the nonmetallic substrate to be cut, a focus moving means (8) for varying a focus location of the laser beam in a depth direction of the substrate, and a relative object moving means (3, 4) for allowing the substrate and the laser beam to make a relative movement to cut the substrate.
Owner:TOP ENG CO LTD
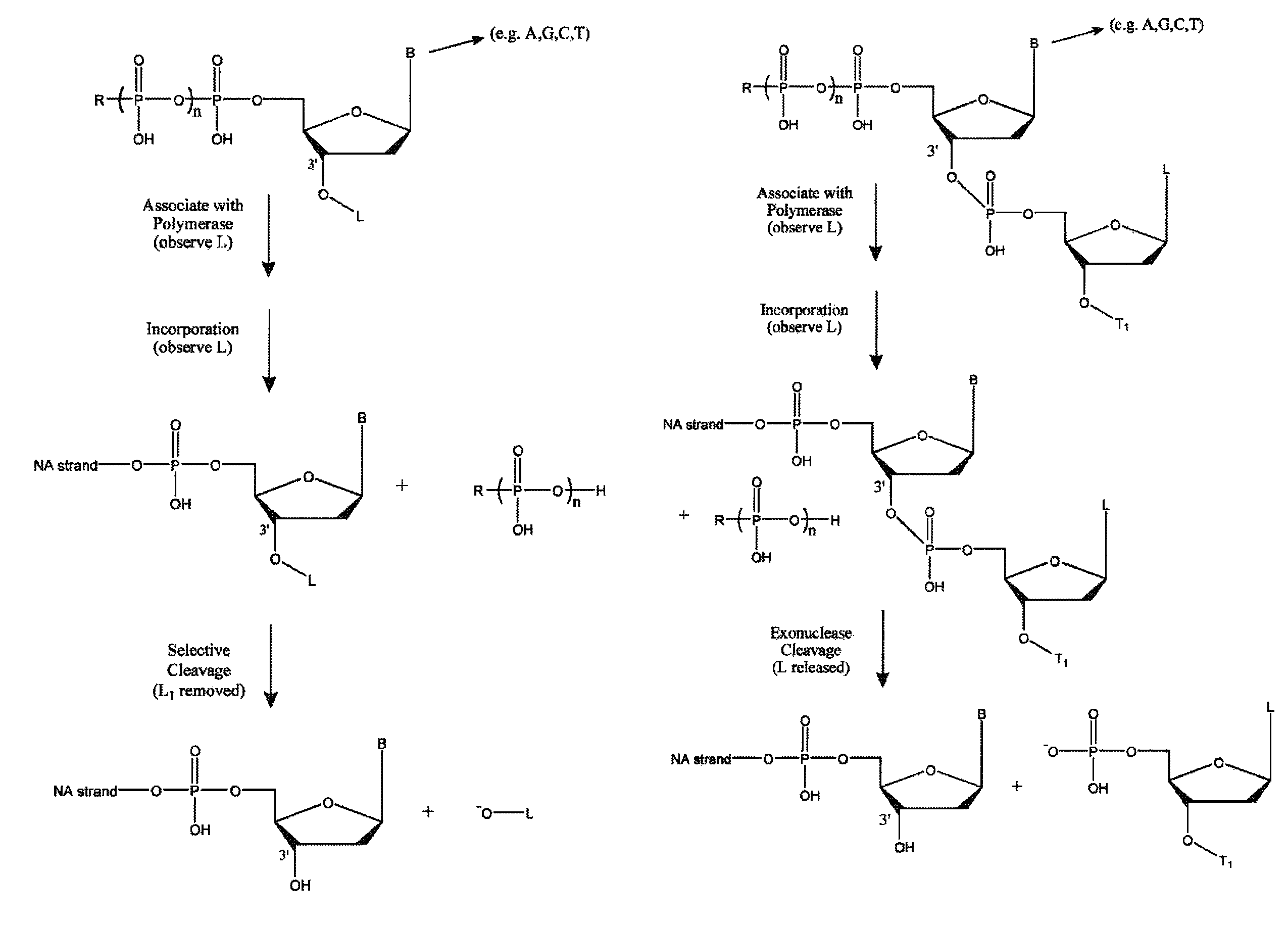
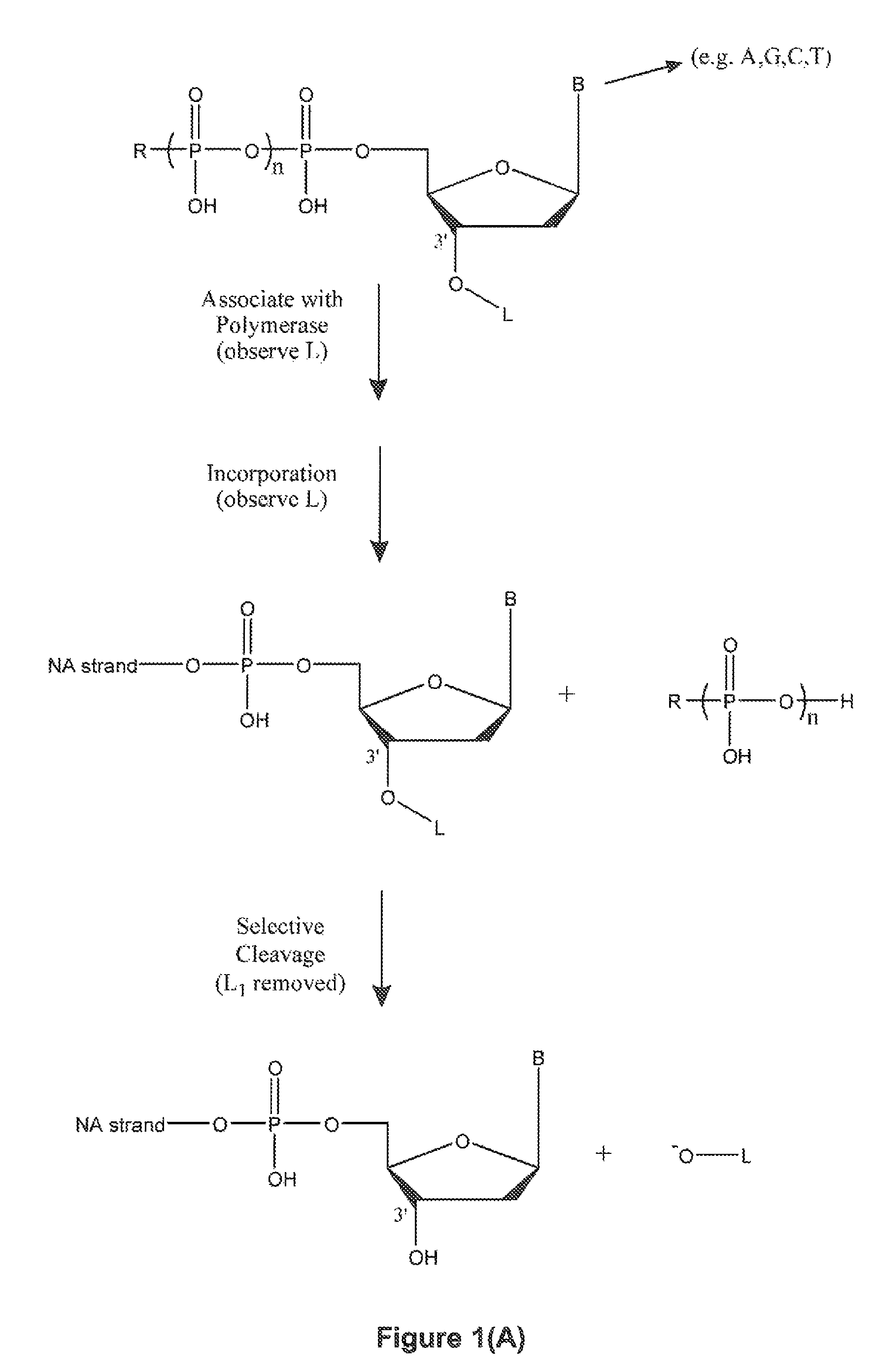
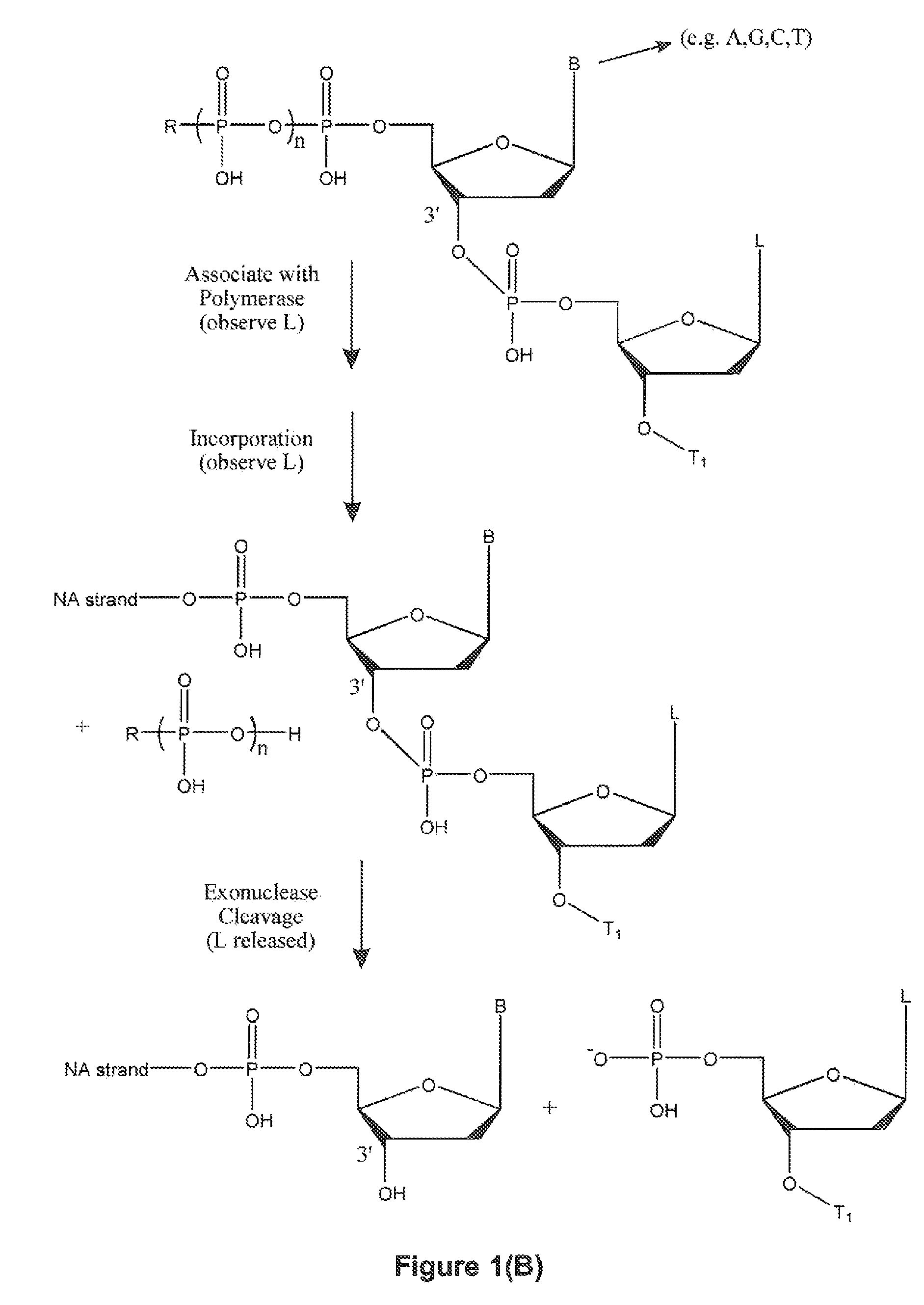
Single molecule sequencing with two distinct chemistry steps
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Liquid crystal display device, optical element, method of fabricating the liquid crystal display device and method of making the optical element
InactiveUS6852374B2Improve performanceImprove productivityLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsActinic RaysAtomic group
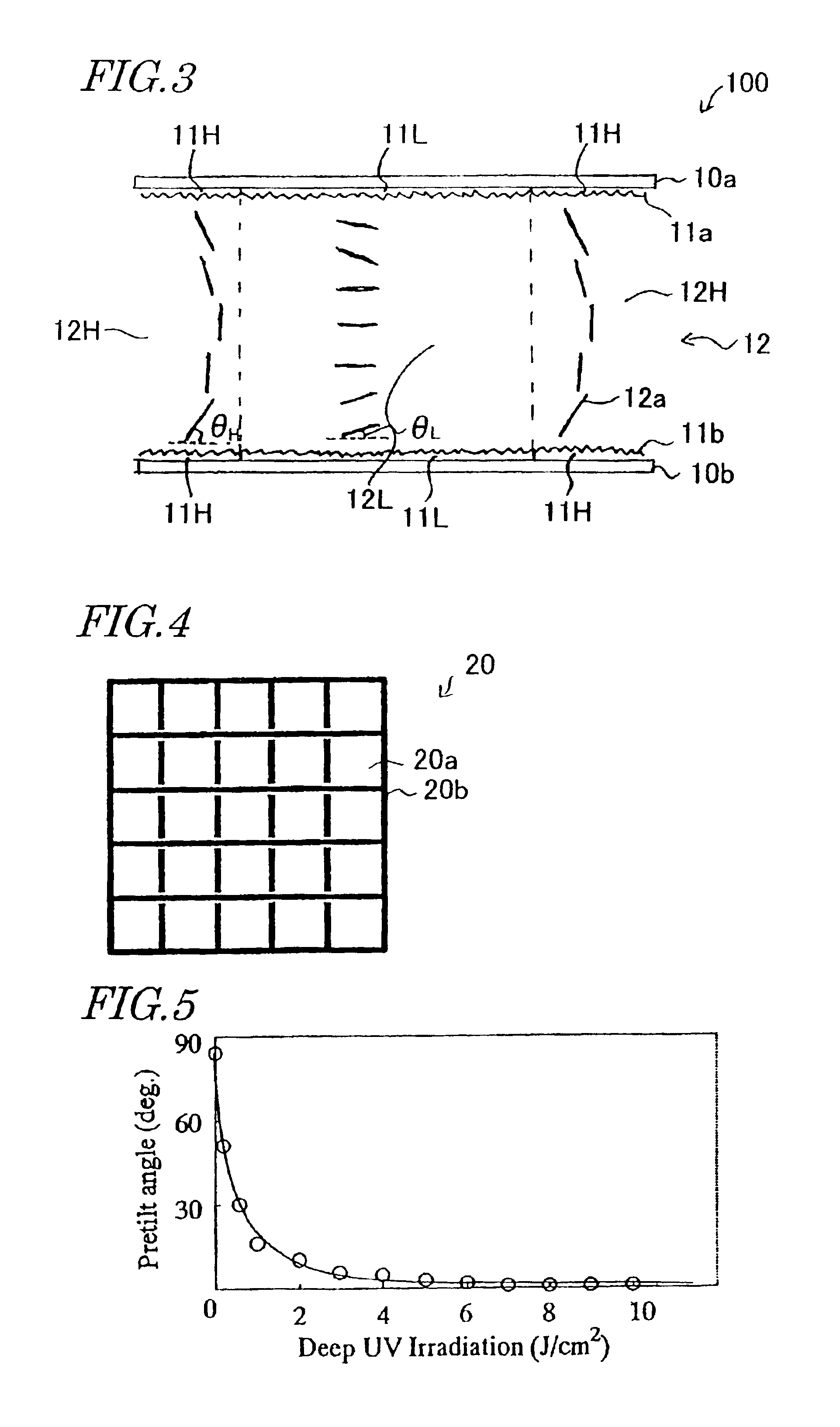
A liquid crystal display device includes two substrates, a liquid crystal layer sandwiched between the substrates and two alignment films, each being provided on one surface of associated one of the substrates so as to face the liquid crystal layer. The device defines multiple picture elements. At least one of the two alignment films is made of a polymer material that includes a main chain, an atomic group having a bond that is selectively cut when exposed to an actinic ray and a side chain bonded to the main chain via the atomic group. The polymer material with the side chain can give a pretilt angle of greater than 85 degrees but 90 degrees or less to liquid crystal molecules. The polymer material without the side chain can give a pretilt angle of 2 degrees to 15 degrees to the liquid crystal molecules.
Owner:SHARP KK
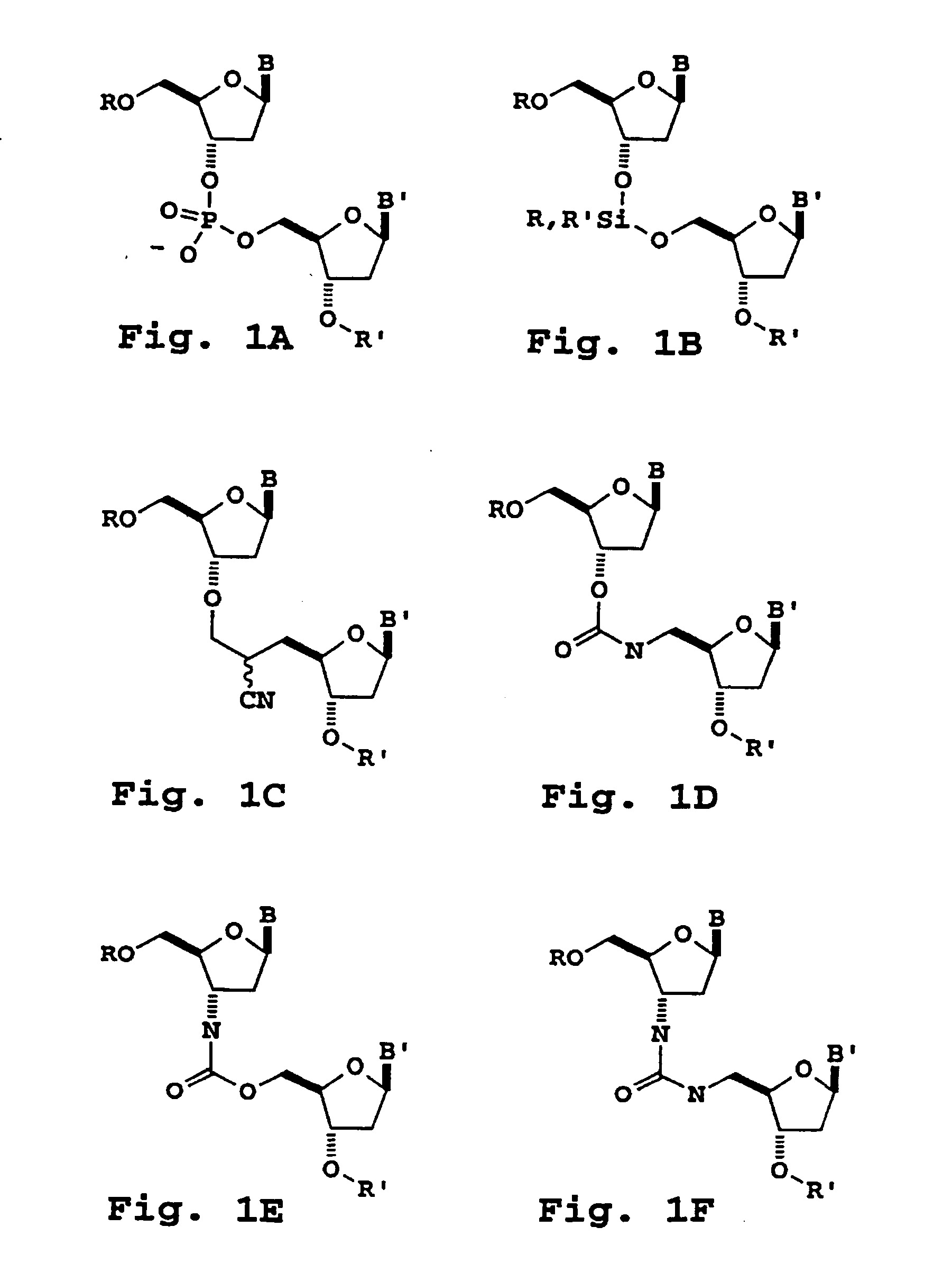
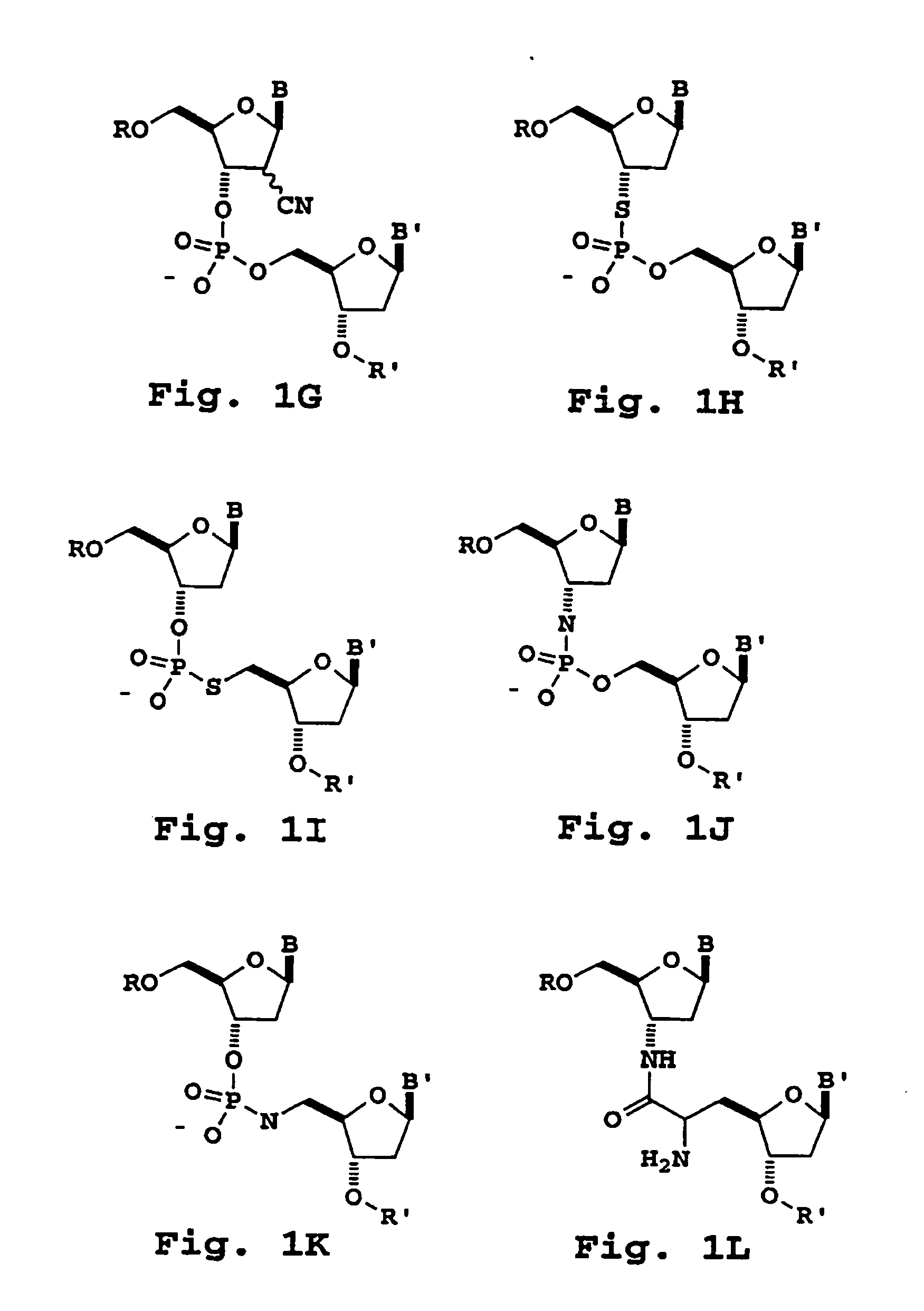
Primers useful for sizing nucleic acids
InactiveUS6949633B1Amount of new and usefulNew and useful and size informationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersBase pair
The present invention provides modified oligonucleotide primers designed to incorporate a cleavable moiety so that a 3′ portion of the primer (linked to an extension product) can be released from an upstream 5′ portion of the primer. Upon selective cleavage of the cleavable site, primer extension products that contain about five or fewer base pairs of the primer sequence are released, to provide more useful sizing and sequence information per fragment than extension products containing the entire primer.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Ultrasonic device for cutting and coagulating
An ultrasonic clamp coagulator assembly that is configured to permit selective cutting, coagulation, and fine dissection required in fine and delicate surgical procedures. The assembly includes a clamping mechanism, which is specifically configured to provide for variable tissue clamping forces.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
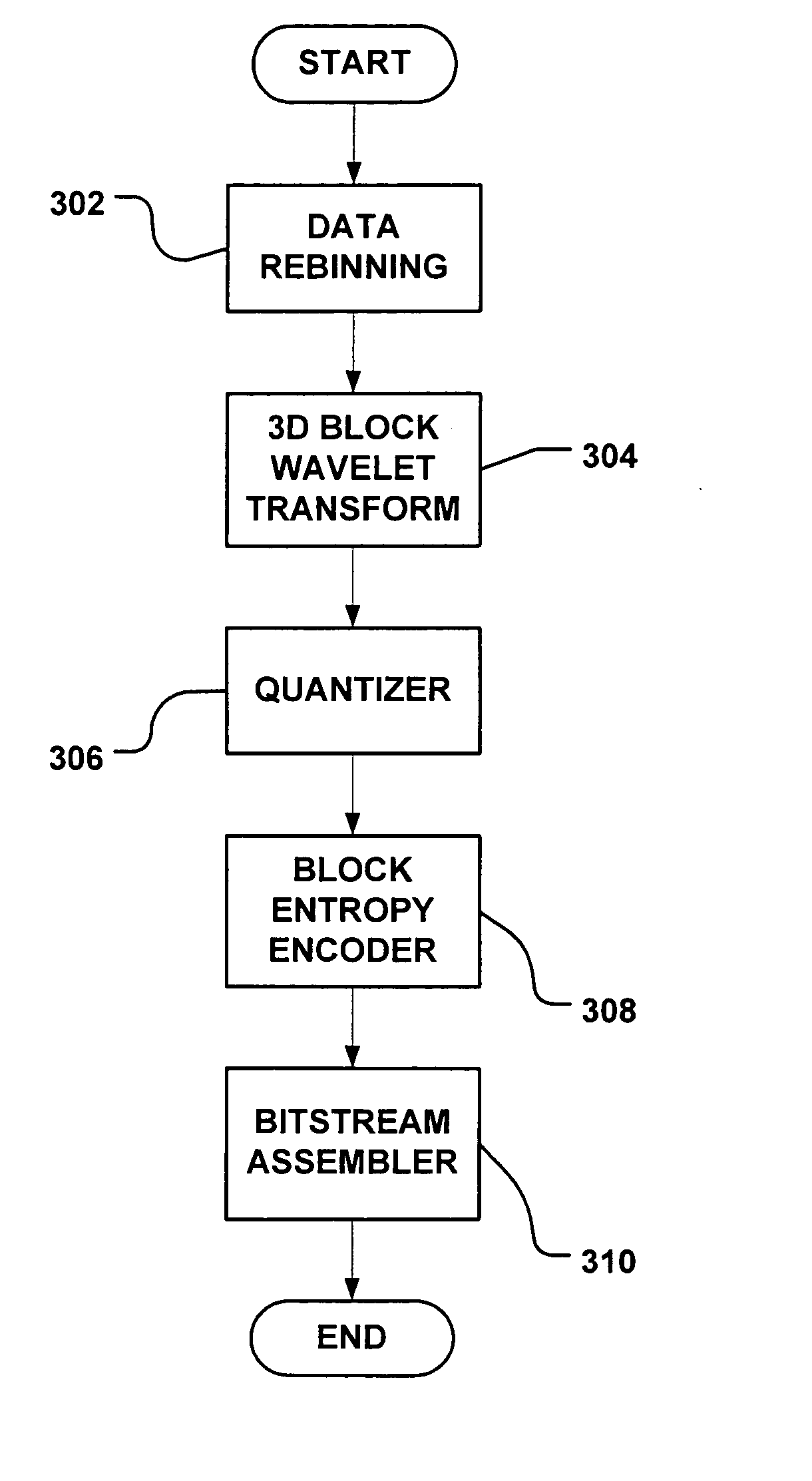
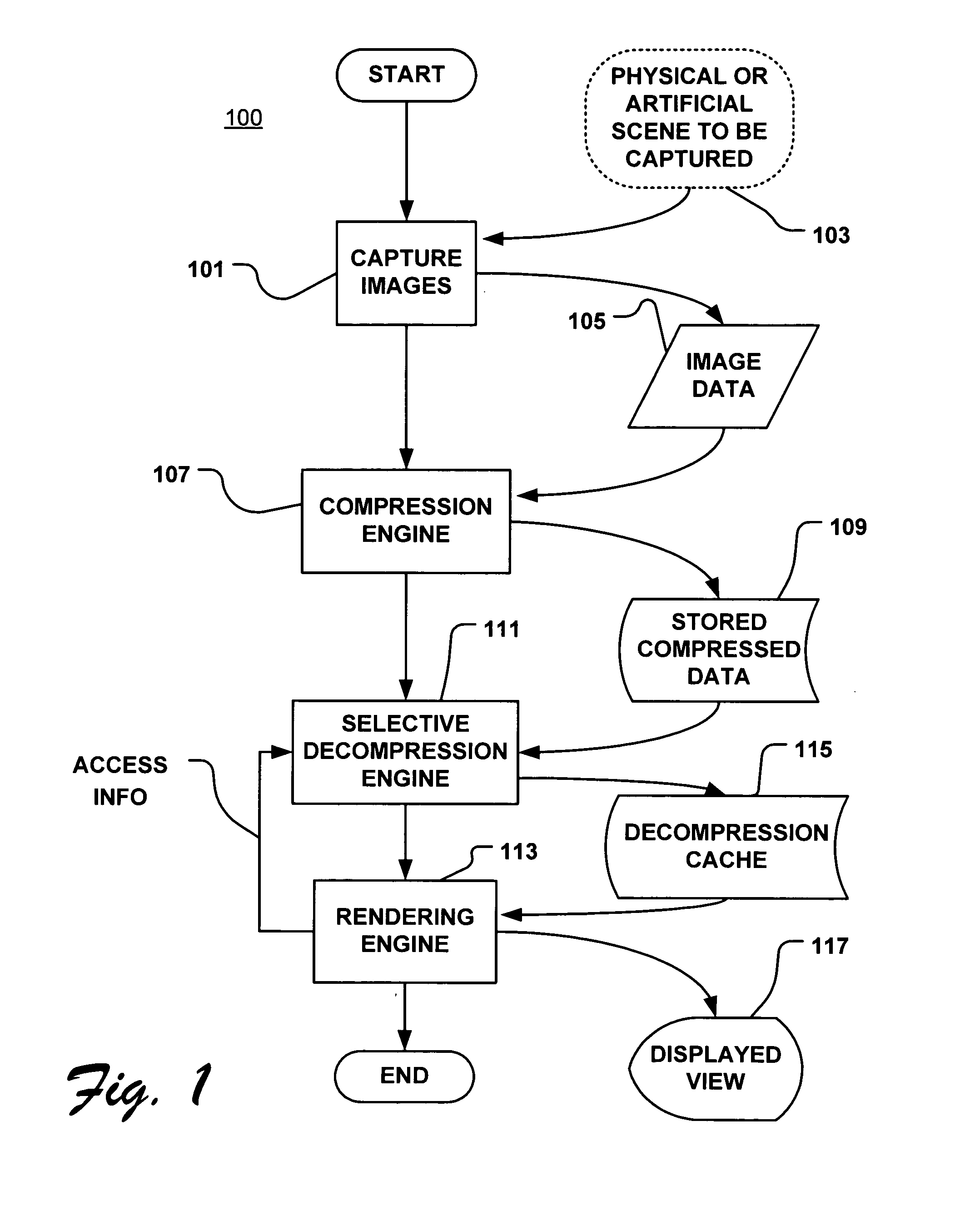
Rebinning methods and arrangements for use in compressing image-based rendering (IBR) data
InactiveUS20050031214A1Increase the compression ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modification2d arrayJPEG
Rebinning methods and arrangements are provided that significantly improve the 3D wavelet compression performance of the image based rendering data, such as, e.g., concentric mosaic image data. Through what is essentially a selective cutting and pasting process the image data is divided into stripes that are then used to form a set of multi-perspective panoramas. The rebinning process greatly improves the performance of the cross shot filtering, and thus improves the transform and coding efficiency of 3D wavelet codecs. While the region of support after rebinning may cease to be rectangular in some cases, a padding scheme and an arbitrary shape wavelet coder can be implemented to encode the result data volume of the smart rebinning. With an arbitrary shape wavelet codec, the rebinning outperforms MPEG-2 by 3.7 dB, outperforms direct 3D wavelet coder by 4.3 dB, and outperforms a reference block coder (RBC) by 3.2 dB on certain tested concentric mosaic image scenes. Hence, the rebinning process nearly quadruples the compression ratio for selected scenes. Additional methods and arrangements are provided that include selectively dividing the image data into slits and rebinning the slits into a huge 2D array, which is then compressed using conventional still image codecs, such as, JPEG.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Oligonucleotide sizing using cleavable primers
InactiveUS20060040282A1Increase volumeQuantity maximizationMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual molecule manipulationOligonucleotide primersOligonucleotide
The present invention provides modified oligonucleotide primers designed to incorporate a cleavable moiety so that a 3′ portion of the primer (linked to an extension product) can be released from an upstream 5′ portion of the primer. Upon selective cleavage of the cleavable site, primer extension products that contain about five or fewer base pairs of the primer sequence are released, to provide more useful sizing and sequence information per fragment than extension products containing the entire primer.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Electrosurgical devices and methods for selective cutting of tissue
Methods and devices for cutting or coagulating. A device comprises a) an elongate member having a distal end, b) at least one foot member extending from the distal end of the elongate member, said foot member having a upper surface and a lower surface, c) an electrically and thermally insulating covering formed on at least the lower surface of the foot member and d) at least one electrode on the upper surface of the foot member. In operation, the at least one electrode is energized so as to cause cutting or coagulation of tissue located above the upper surface(s) of the foot member(s) while not causing substantial damage to tissue located below the lower surface(s) of the foot member(s).
Owner:MICROSURGICAL TECH INC
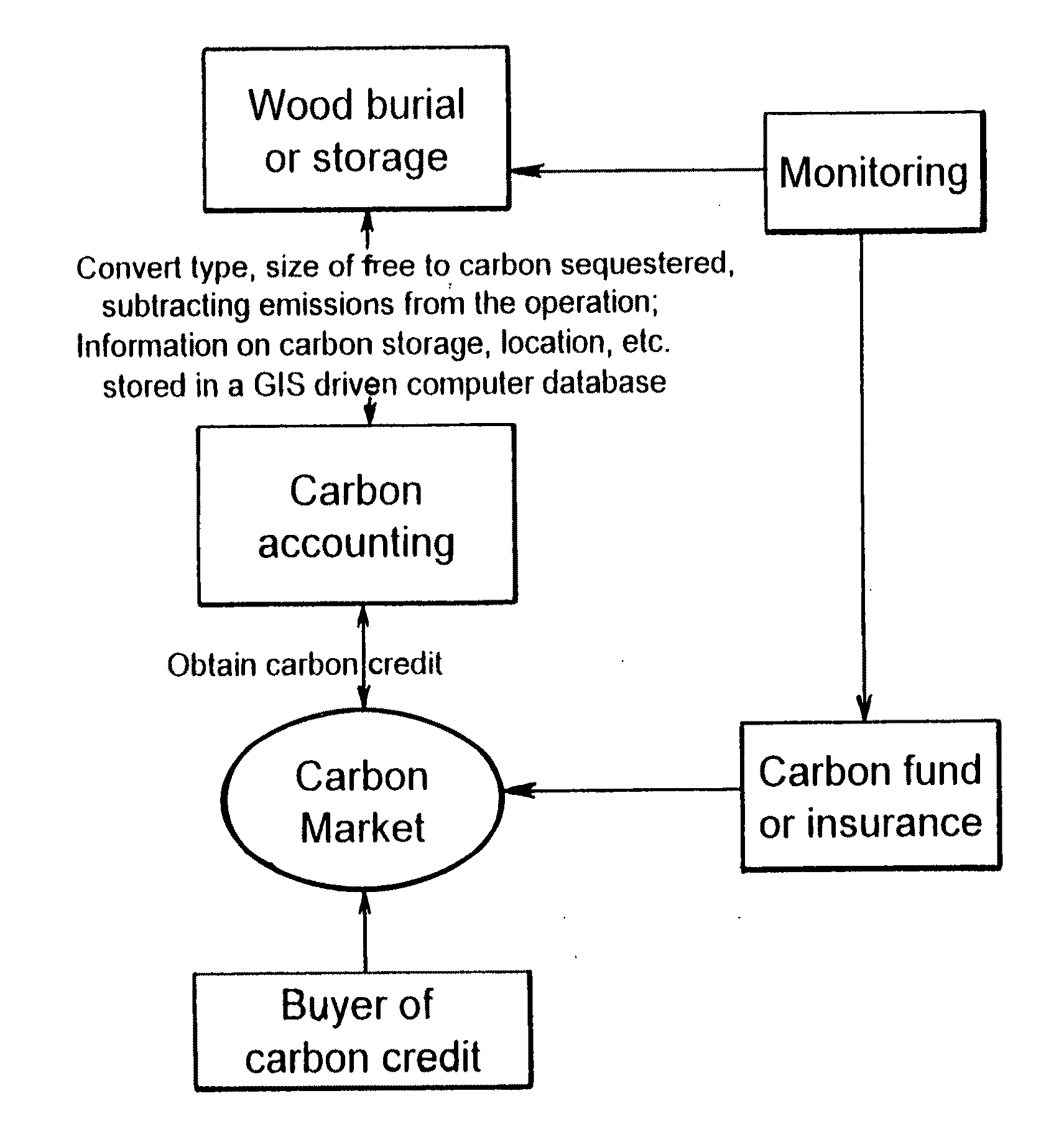
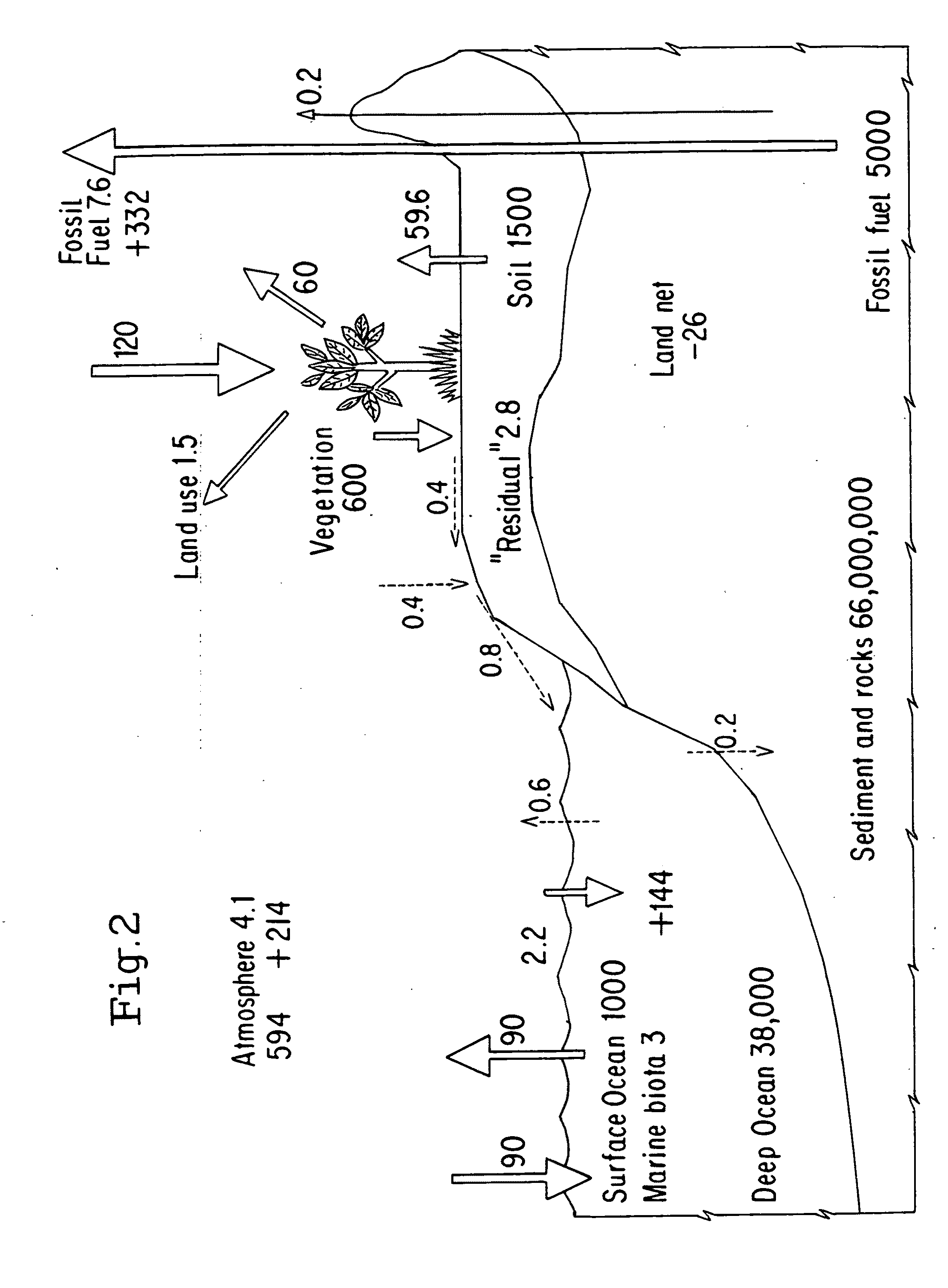
Carbon sequestration via wood burial and storage
InactiveUS20100145716A1Reduce decompositionLow techHydrogen sulfidesDispersed particle separationAbove groundLiving tree
To mitigate global climate change, a portfolio of strategies will be needed to keep the atmospheric CO2 concentration below a dangerous level. Here a carbon sequestration strategy is proposed in which certain dead or live trees are harvested via collection or selective cutting, then buried in trenches or stowed away in above-ground shelters. The largely anaerobic condition under a sufficiently thick layer of soil will prevent the decomposition of the buried wood. Because a large flux of CO2 is constantly being assimilated into the world's forests via photosynthesis, cutting off its return pathway to the atmosphere forms an effective carbon sink.
Owner:ZENG NING
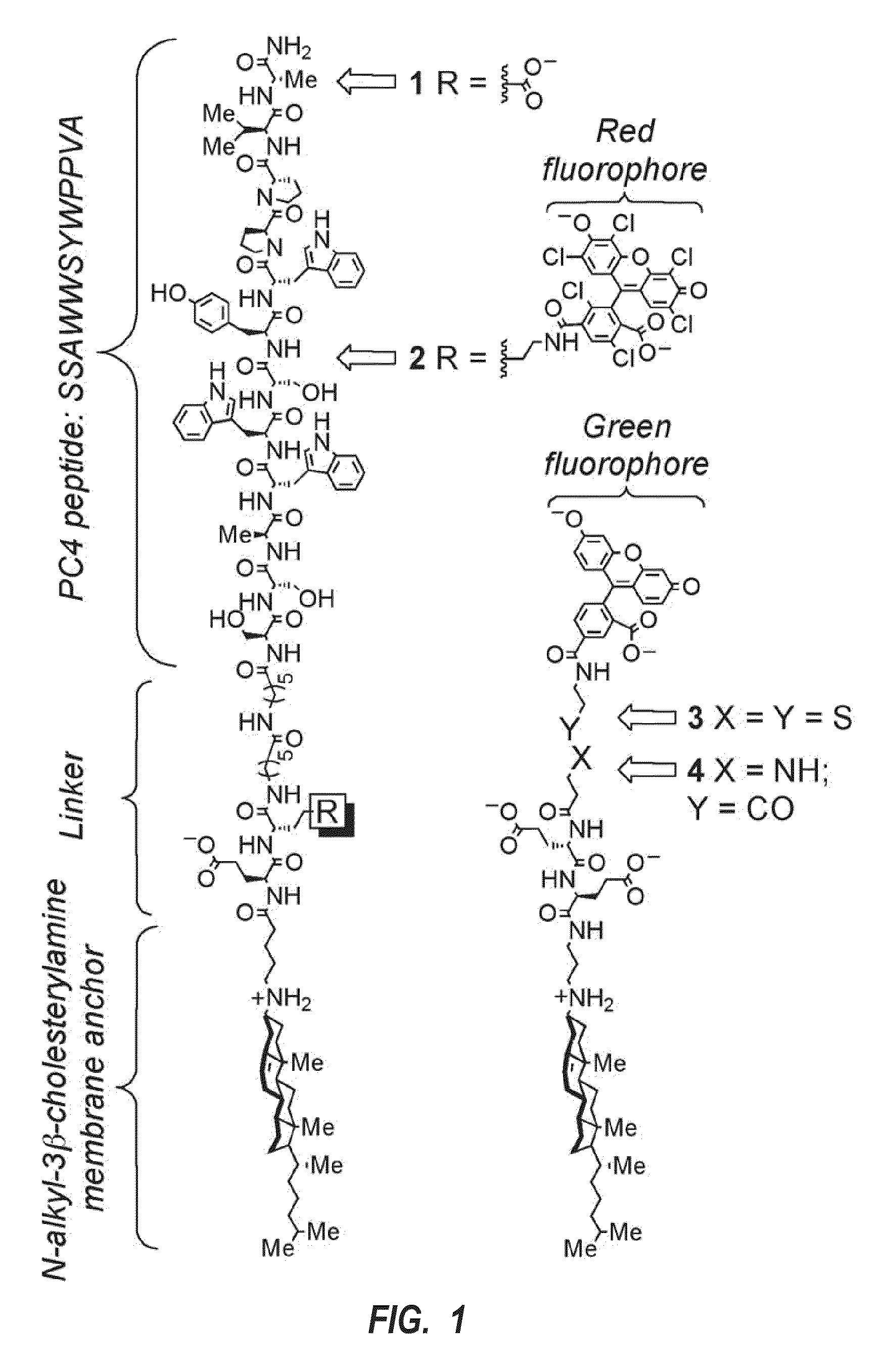
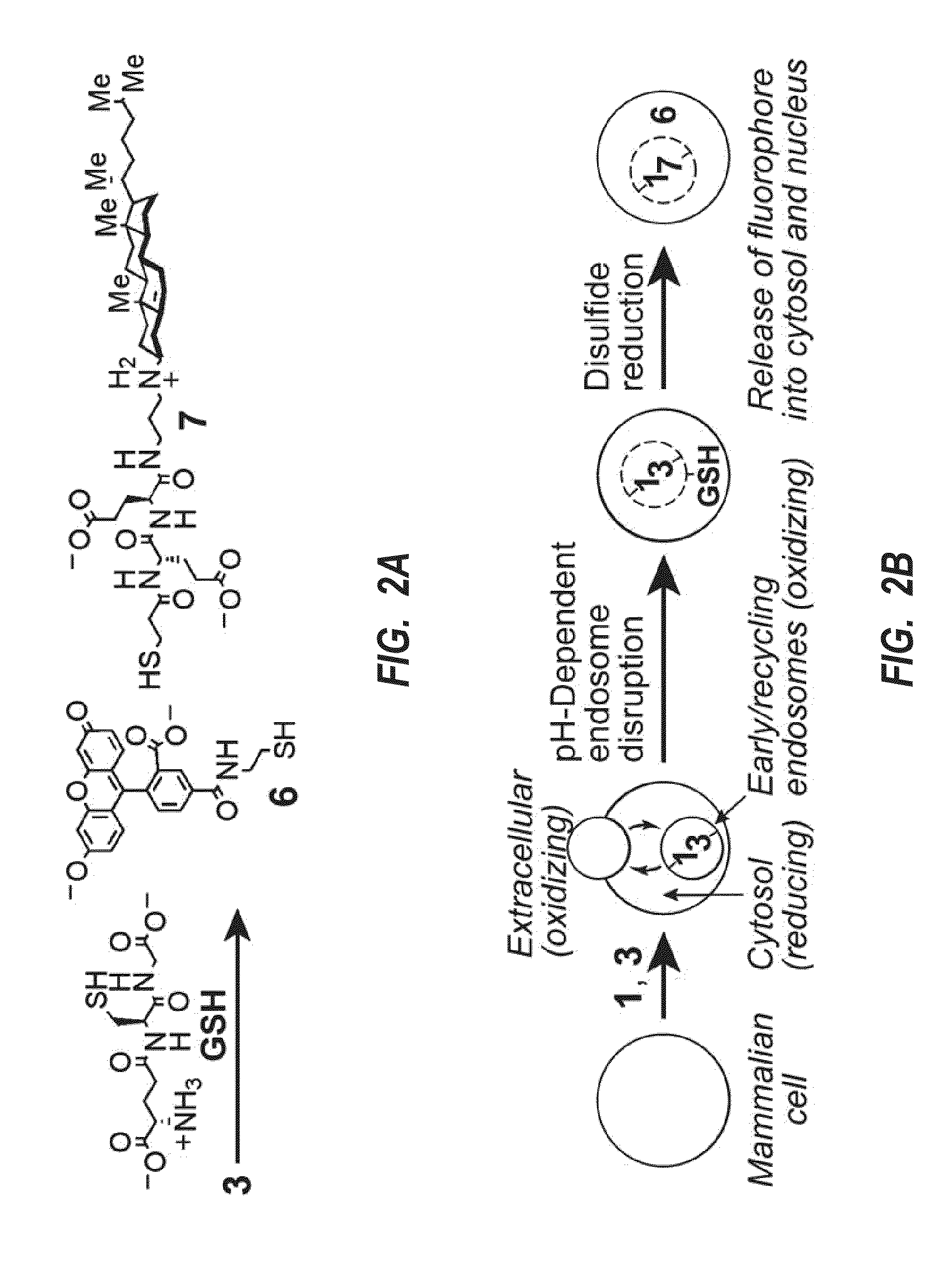
Disruptors of early/recycling endosomes
A delivery system for introducing a cargo molecule into cytosol of a living cell can include: a first membrane binding element linked to an endosomal compartment disrupting element through a first linker having one or more anionic moieties; and a second membrane binding element linked to an exogenous cargo molecule through a second linker having one or more anionic moieties, the second linker having a region that is selectively cleavable, wherein the first and second membrane binding elements both induce endocytosis into an early / recycling endosome and the endosomal compartment disrupting element destabilizes the early / recycling endosome such that the exogenous cargo molecule is released from the second membrane binding element and into the cytosol of the living cell.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
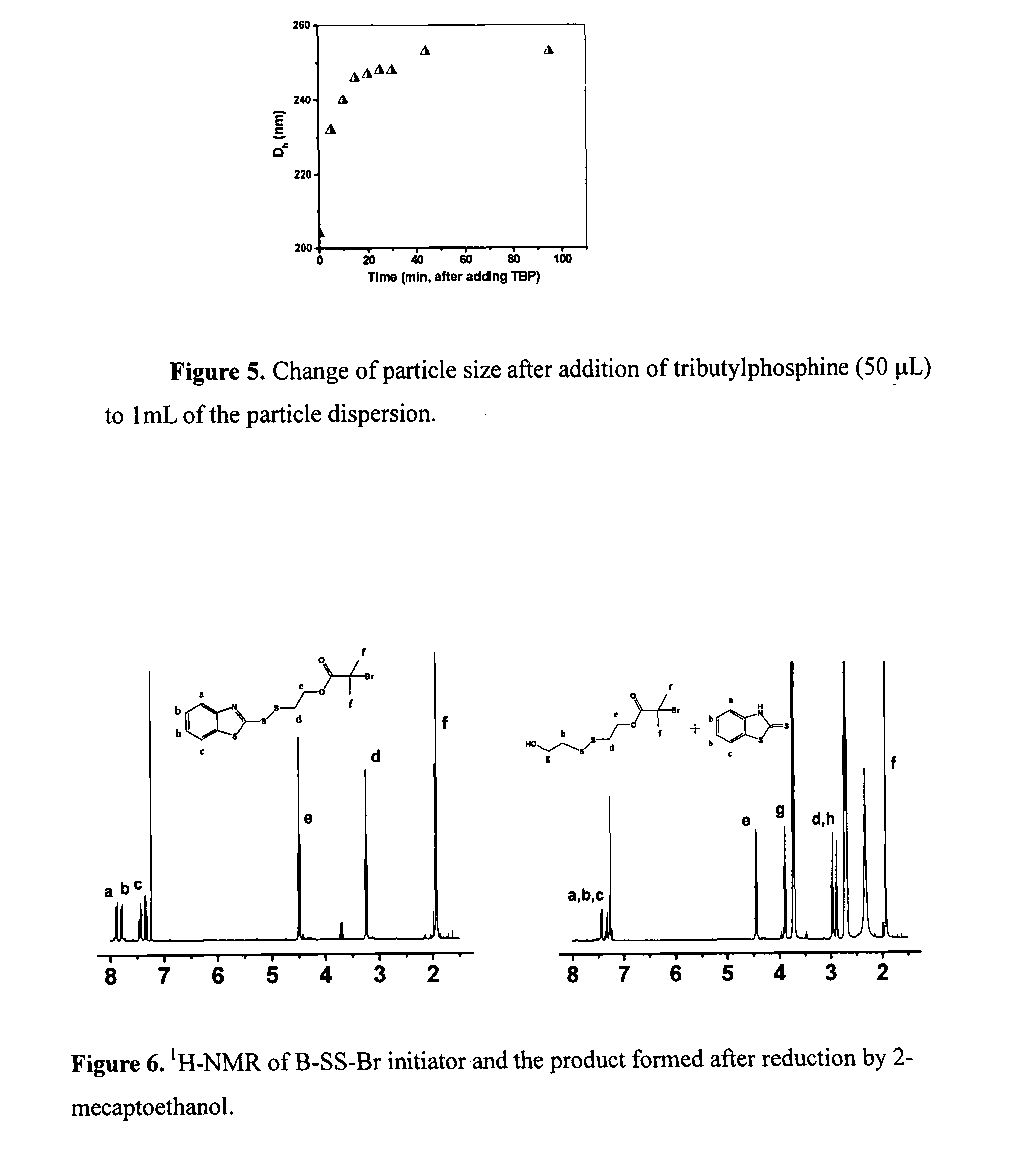
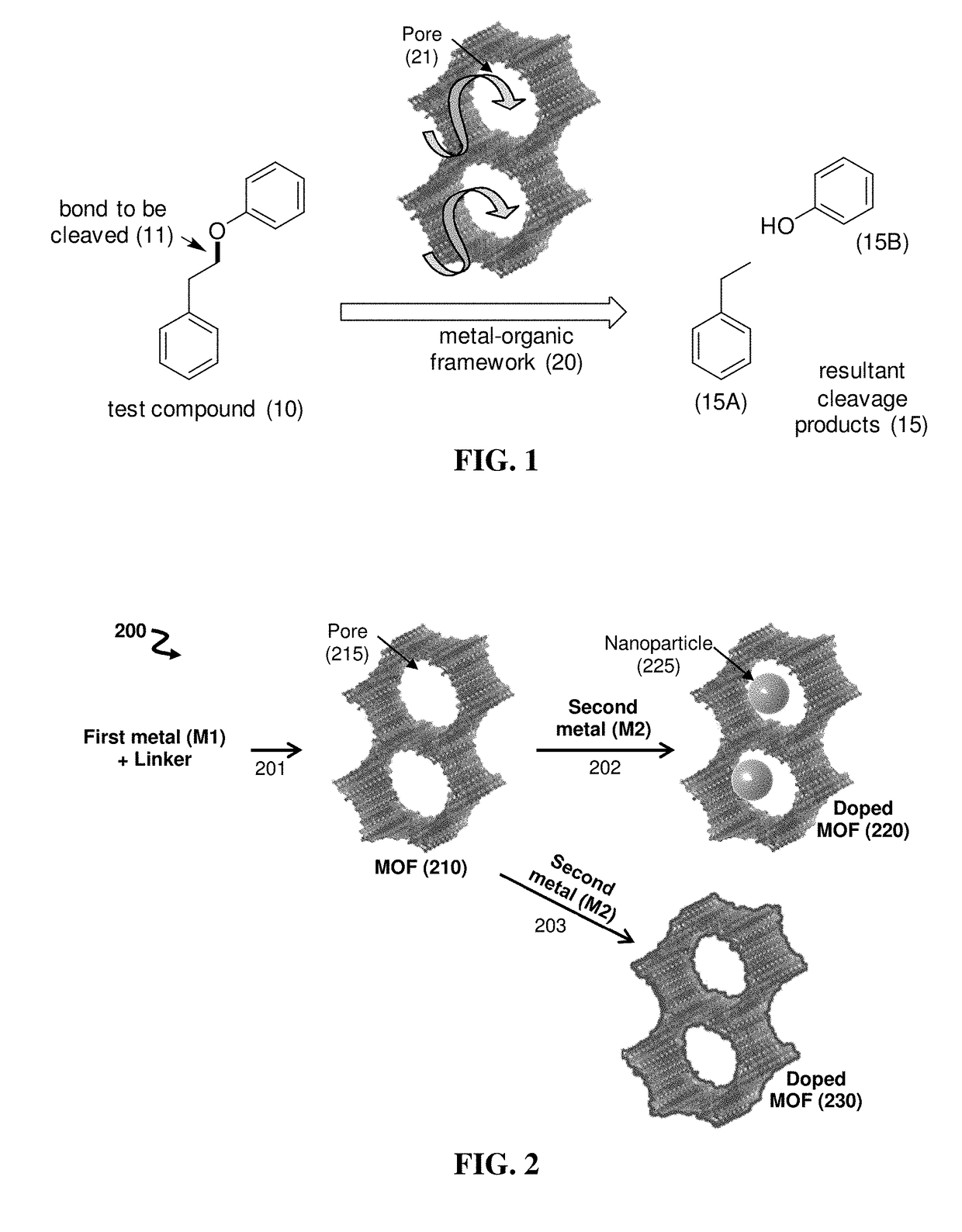
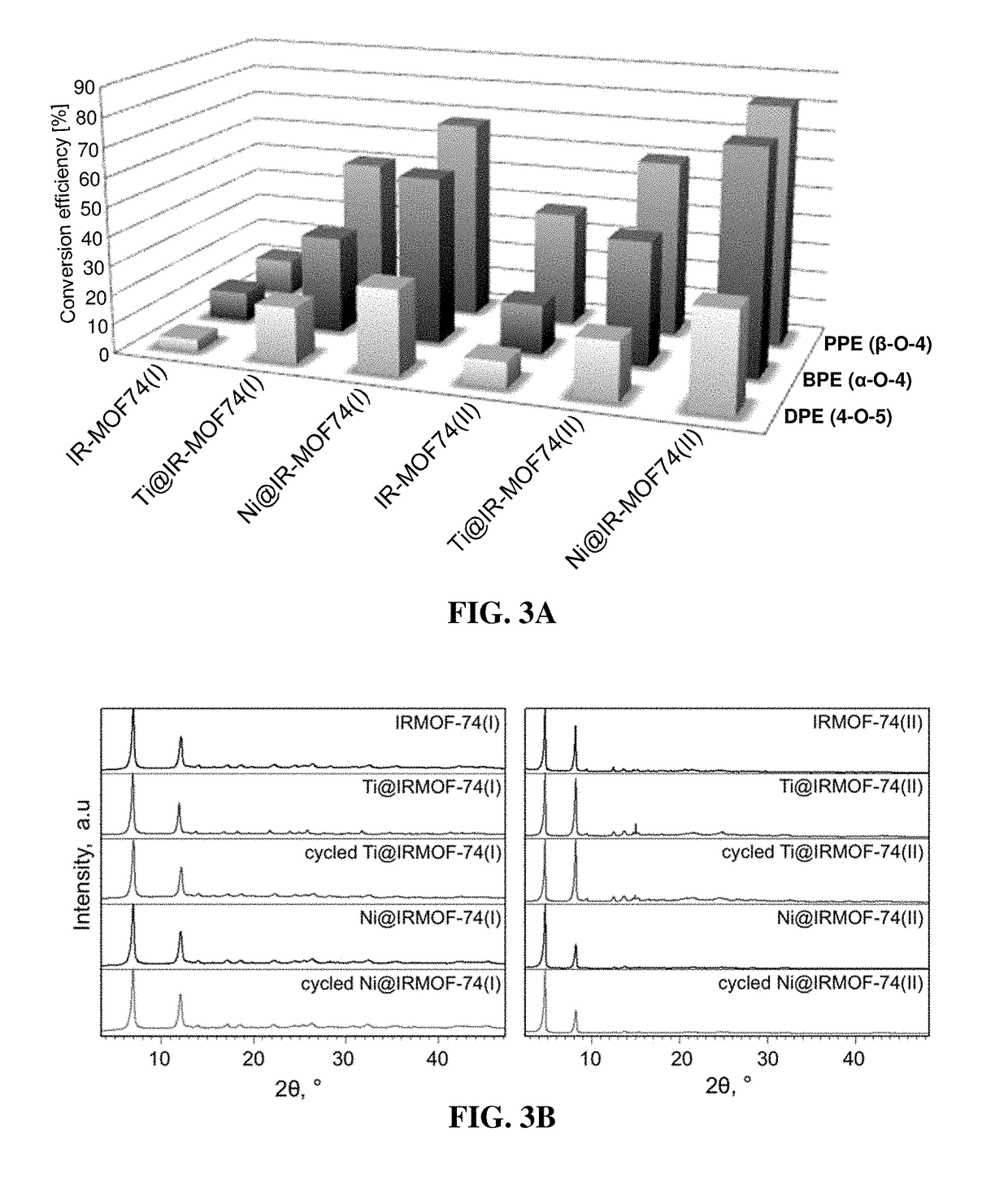
Metal-organic framework catalysts for selective cleavage of aryl-ether bonds
ActiveUS9718748B1Organic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsArylBond cleavage
The present invention relates to methods of employing a metal-organic framework (MOF) as a catalyst for cleaving chemical bonds. In particular instances, the MOF results in selective bond cleavage that results in hydrogenolyzis. Furthermore, the MOF catalyst can be reused in multiple cycles. Such MOF-based catalysts can be useful, e.g., to convert biomass components.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Preparation of functional gel particles with a dual crosslink network
ActiveUS20100143286A1Improve surface propertiesAvoid rapid degradationCosmetic preparationsPowder deliveryCrosslinked polymersReactive agent
Functional gel particle formed from a crosslinked polymeric network including a fraction of stable crosslinks and a second fraction of cleavable crosslinks are disclosed. Functional compounds may be chemically or physically encapsulated within and / or released from the gel particle by selective cleavage of the cleavable crosslinks. The functional compounds may be delivered and released to a pre-selected target site. Peripheral or other accessible functionality on the surface of the gel particle allows attachment of a surface reactive agent, thereby modifying one or more surface properties of the gel particle. Processes of preparing the gel particles and processes of delivering the functional compounds to a target site are also disclosed.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Selective cutting one shot
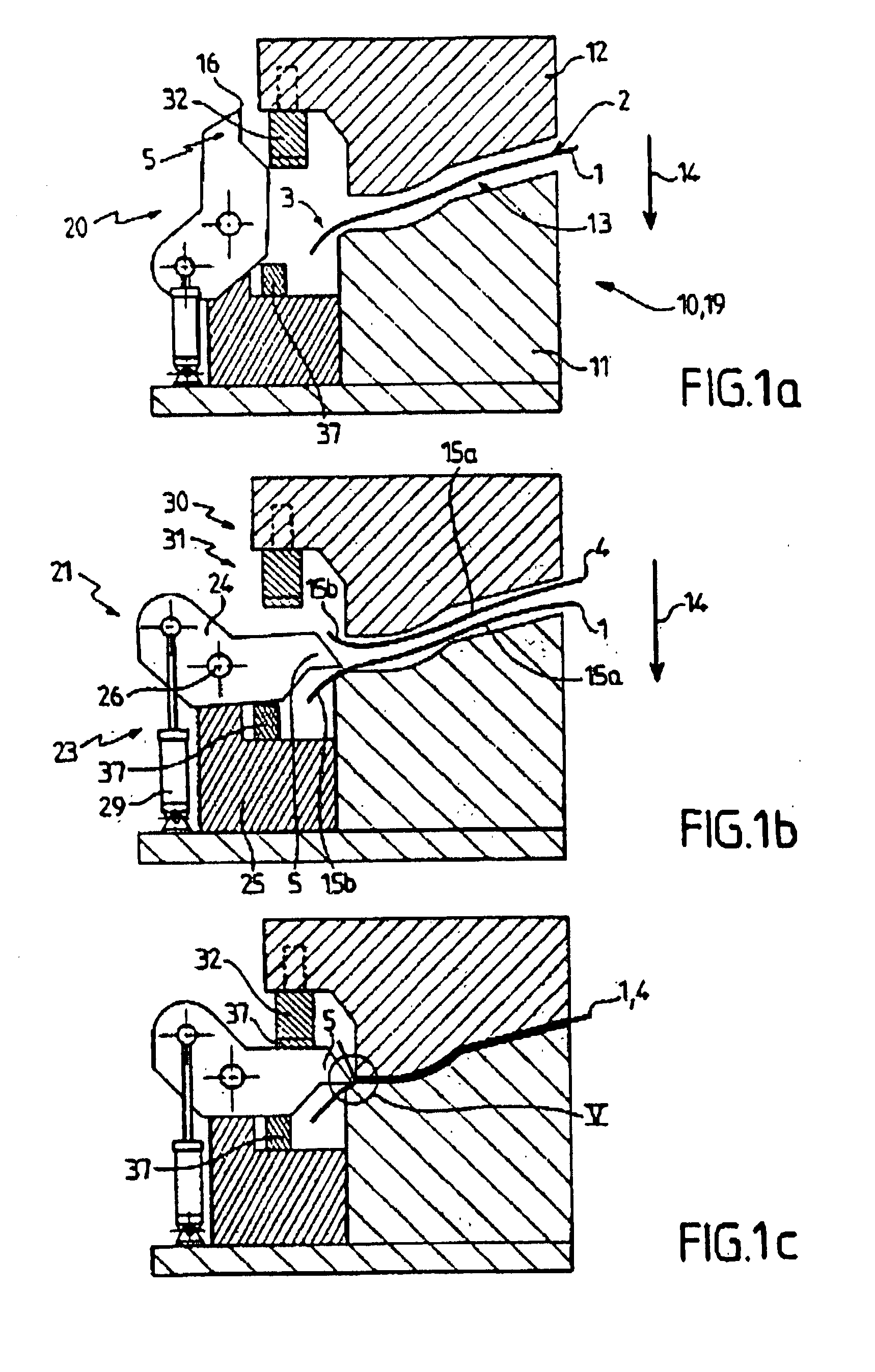
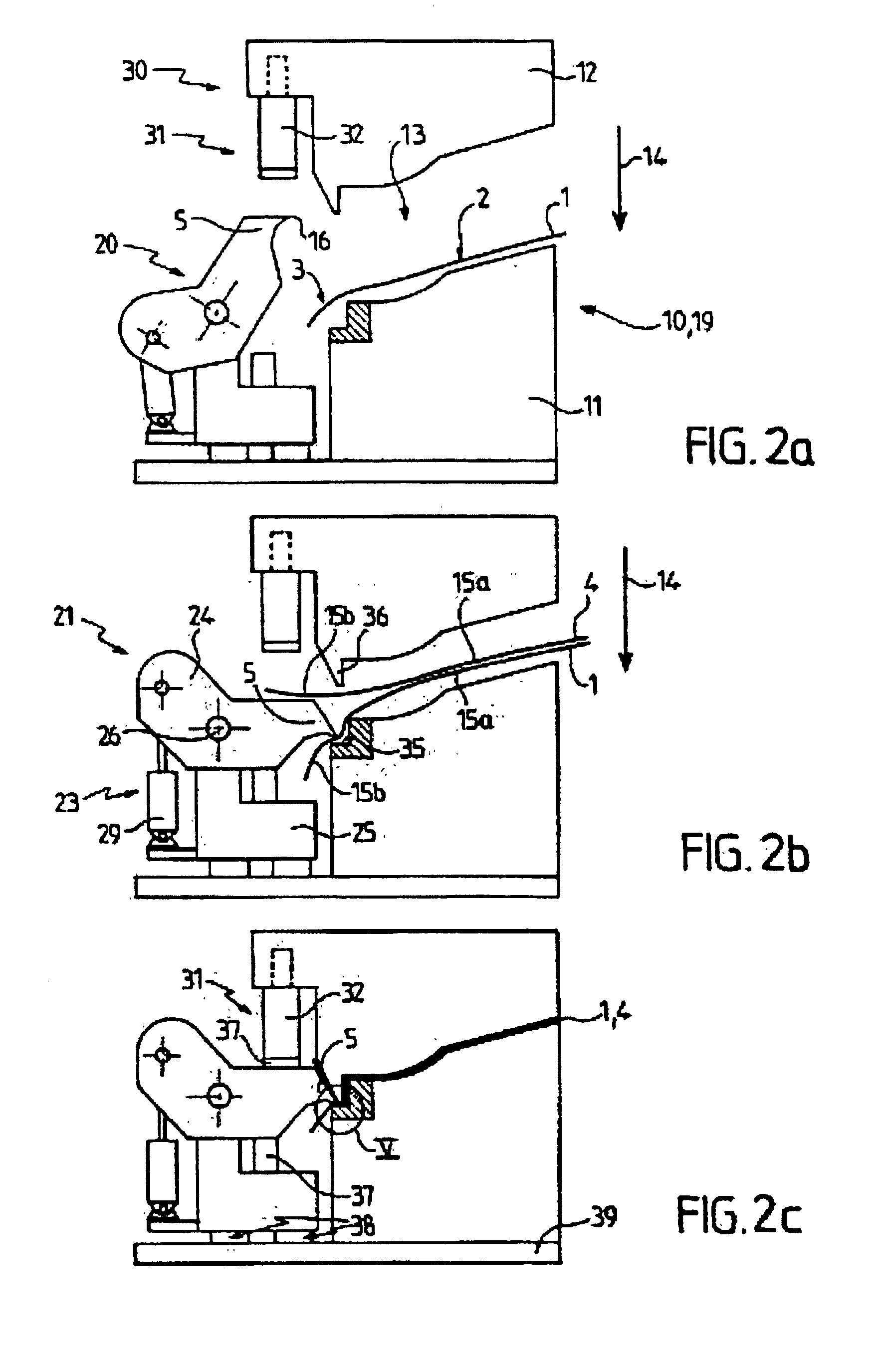
The invention relates to a process and a device for forming a planiform piece intended, in particular, for the interior fittings of motor vehicles, in which a layer of support material (1) is covered, at least on one of its faces (2) and in the area of a portion (3), at least, of its contour, or so-called portion to be bordered, with a cladding sheet (4) and said support (1) is cut along said portion to be bordered (3) in such a way that said cladding (4) projects from said support (1) in the area of said portion. According to the invention, a cutting tool (5) is pre-positioned between said cladding (4) and said support (1) along said portion to bordered (3) said cutting is effected with said cutting tool (5), when the support (1) is covered by the cladding (4).
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Bacterial cleavage of only organic C-N bonds of carbonaceous materials to reduce nitrogen content
A microbial process is provided for selective cleavage of only organic C-N bonds while leaving C-C bonds intact which may be used for reducing the nitrogen content of nitrogen-containing organic carbonaceous materials. Microorganisms of Pseudomonas ayucida have been found which have the ability of selective cleavage of organic C-N bonds. A particularly preferred microorganism is Pseudomonas ayucida strain ATCC No PTA-806. Other microorganisms useful in the cleavage of organic C-N bonds are Aneurinibacillus sp, Pseudomonas stutzeri, Yokenella sp. and Pseudomonas nitroreducens.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Re-directed immunotherapy
The invention provides an agent for preventing or treating a condition characterised by the presence of unwanted cells, the agent comprising: (i) a targeting moiety that is capable of targeting to the unwanted cells; and (ii) a T cell antigen, wherein the T cell antigen can be released from the targeting moiety by selective cleavage of a cleavage site in the agent in the vicinity of the unwanted cells.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BIRMINGHAM
Device for protecting selective cutting machines against overload
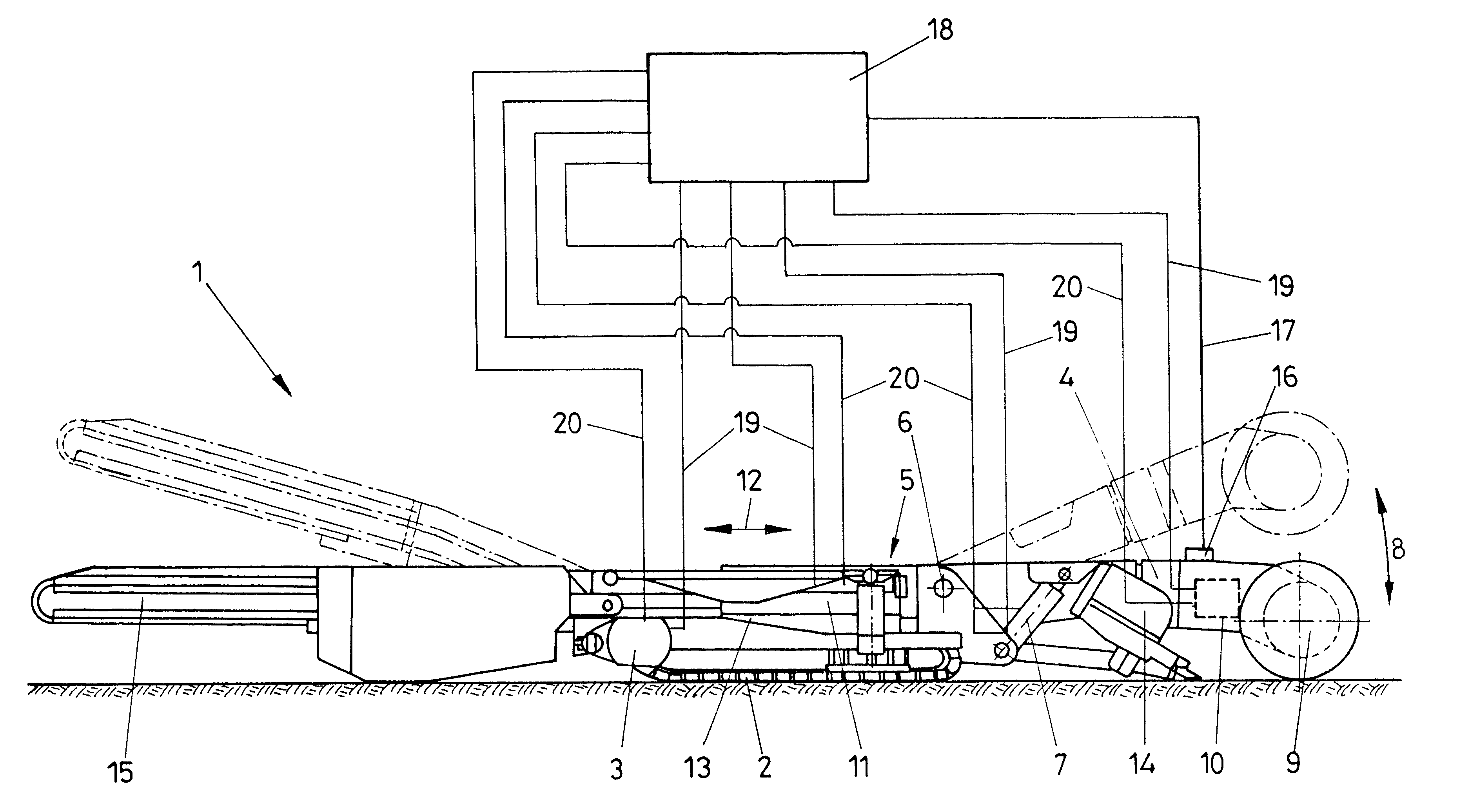
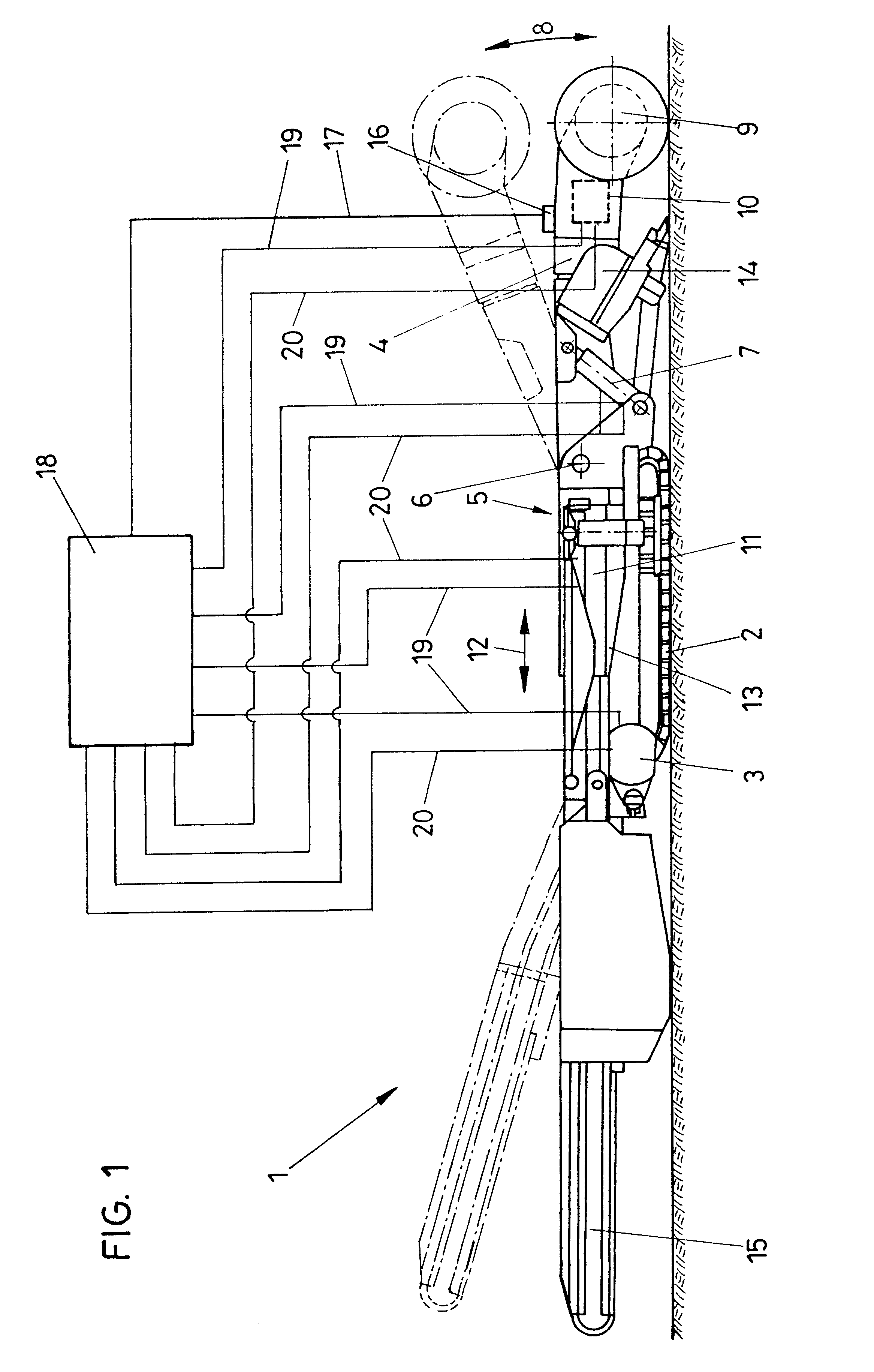
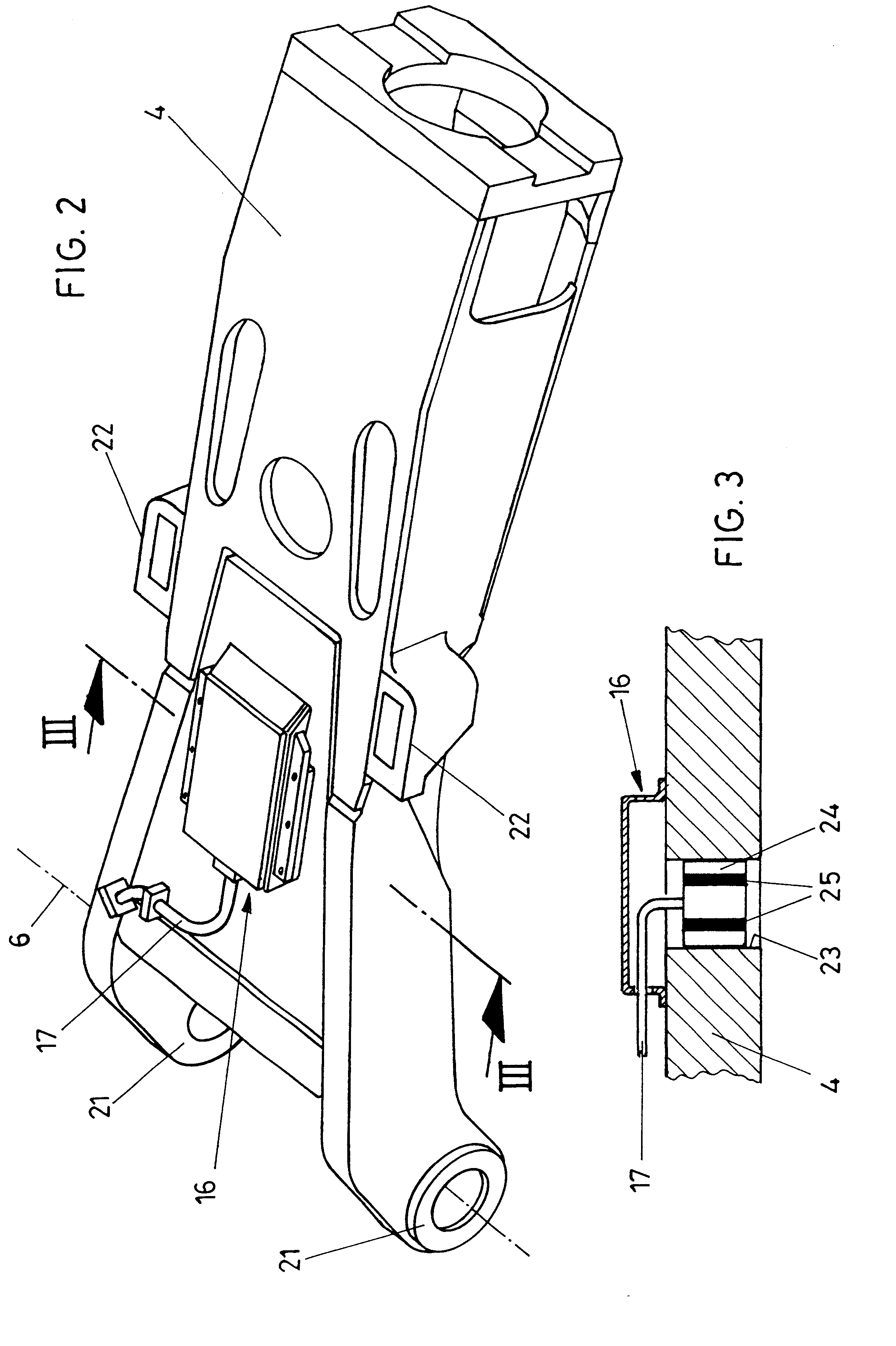
The invention relates to a device for protecting selective cutting machines against overload, in which the selective cutting machine has cutting tools, in particular cutting rollers, rotatably supported on a pivotable cantilevered arm, and both the cutting tools and the cutting arm are connected to separate drive mechanisms. At least one strain or deformation measuring sensor is disposed on the pivotable cantilevered arm, and its signals are delivered to an evaluation circuit; the evaluation circuit is connected via control lines at least to the drive mechanisms of the cutting arm and the cutting tool.
Owner:VOEST ALPINE BERGTECHNIK GMBH
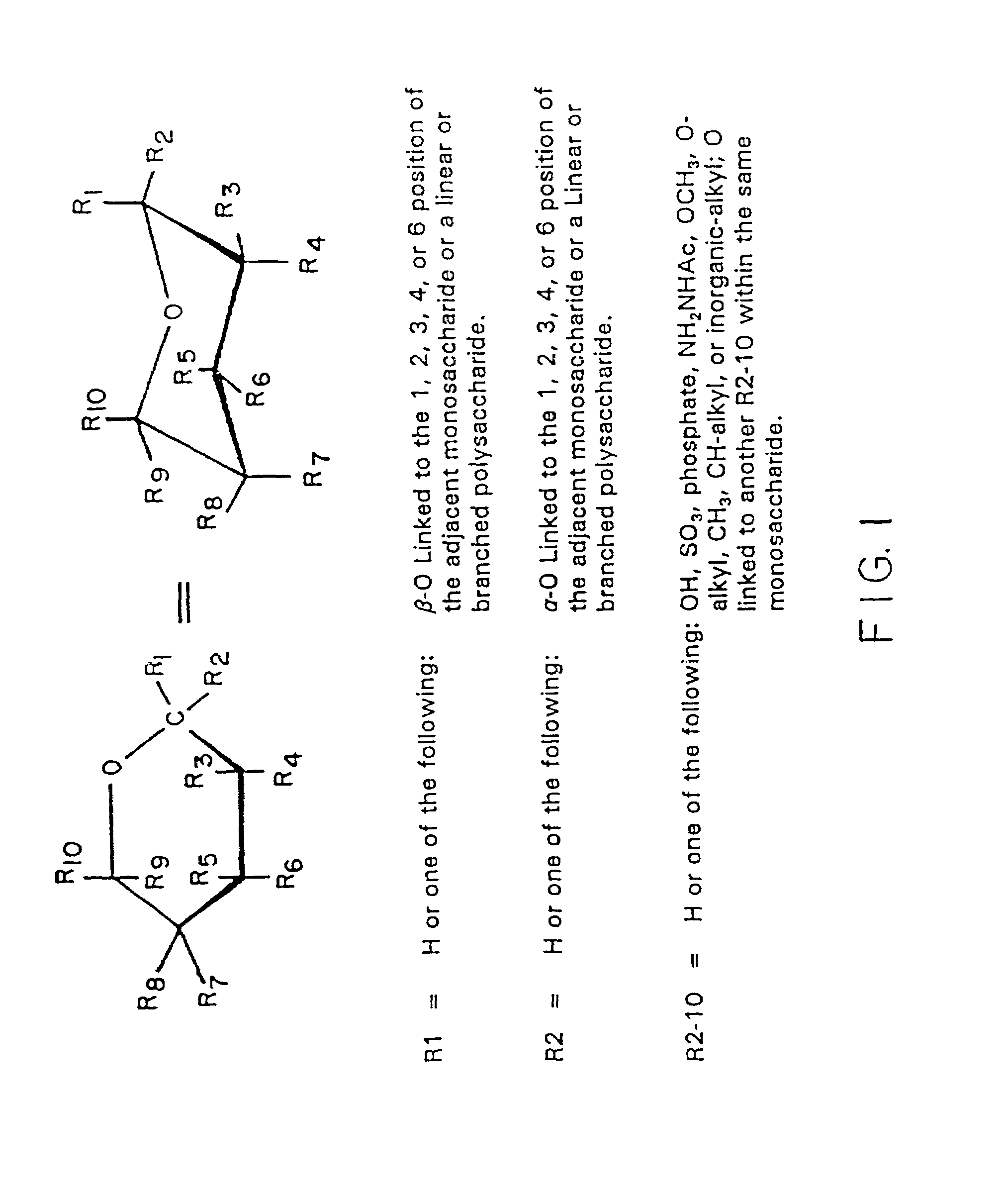
Isolation and composition of novel glycosidases
Substantially pure glycosidases capable for cleaving selected glycosidic bonds have been described including glycosidases isolated from Xanthomonas and recombinant glycosidases. Substrate specificity of isolated enzymes have been identified for GlcNacβ1-x, Galα1-3R, Galα1-6R, Galβ1-3R, Fucα-2R, Fucα1-3R, Fucα1-4R, Manα1-2R, Manα1-3R, Manα1-6R, Manβ1-4R, Xylβ1-2R, Glcβ1-4R, and Galβ1-4R providing improved capability for selectively cleaving a glycosidic linkage in a carbohydrate substrate and for forming modified carbohydrates.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Apparatus, system and method for mechanical, selective plant removal in mature and establishing crops including turfgrasses
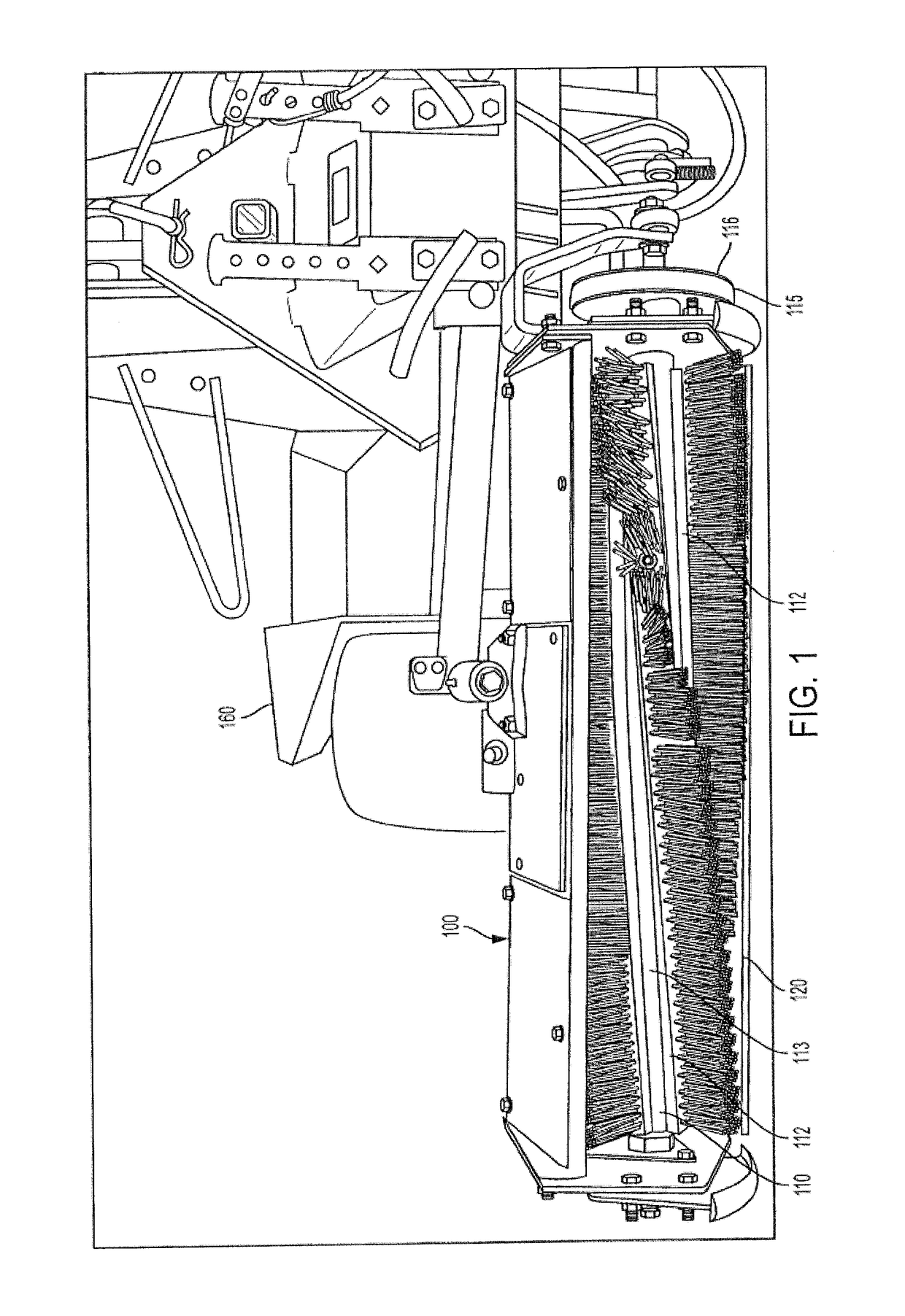
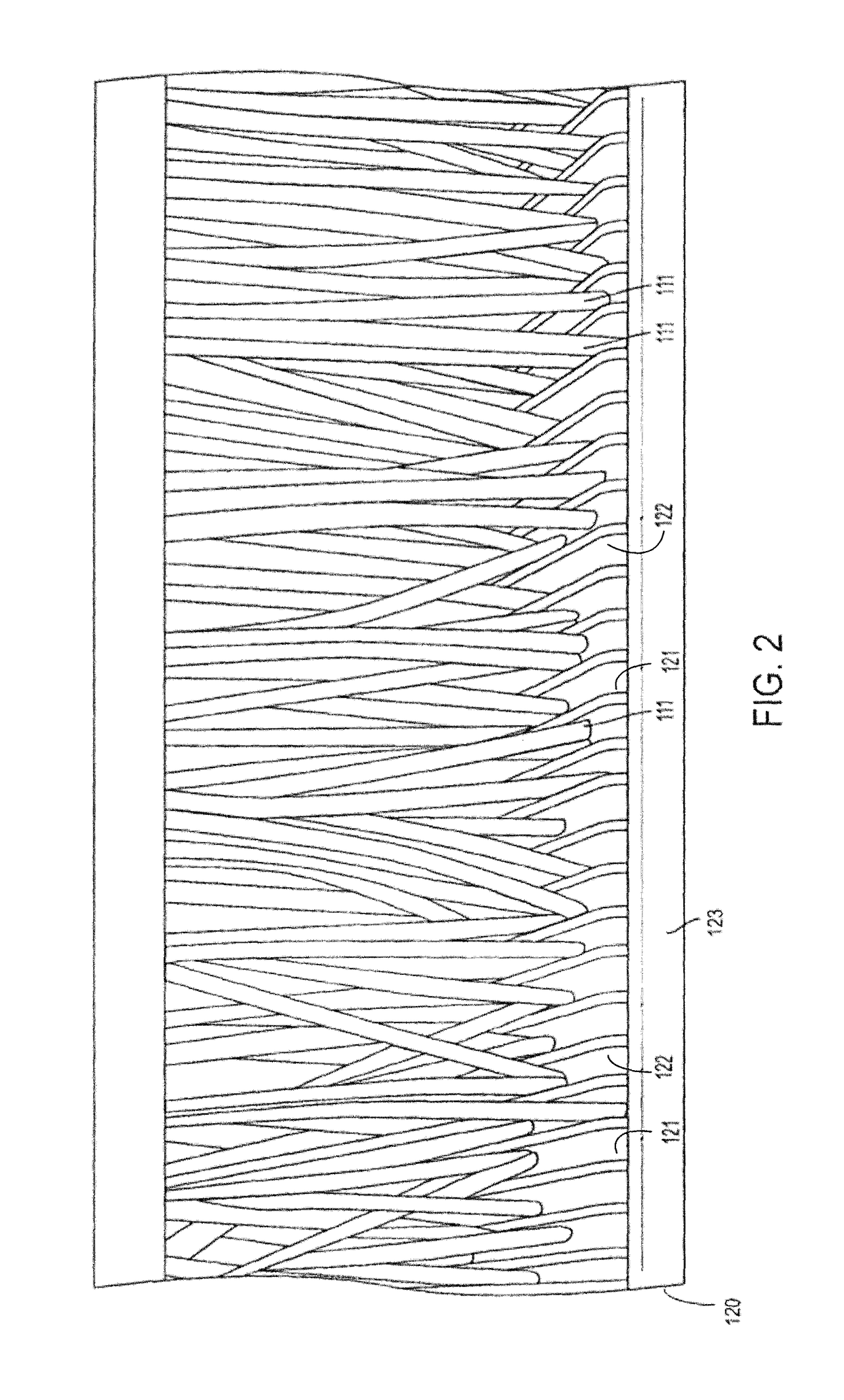
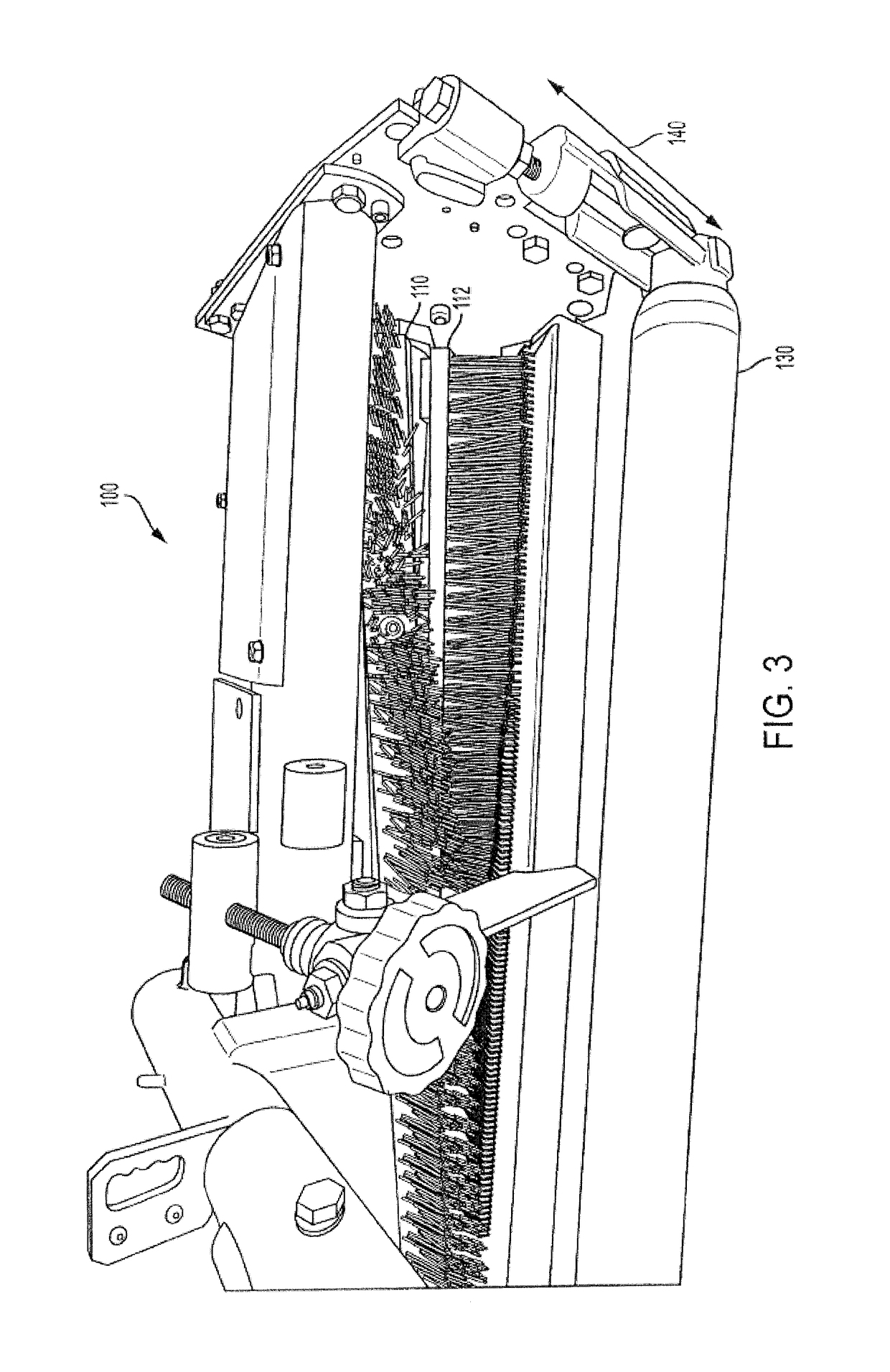
ActiveUS10194649B2Reducing weedImprove wear resistanceHops/wine cultivationTurf growingBristleEngineering
An apparatus for applying a desired amount of mechanical abrasion to plants and selective cutting of undesirable plant material. The apparatus includes a base, a brush and an elevation device for maintaining the base at desirable height. The base has a first longitudinal axis and a plurality of grooves, the grooves being oriented approximately perpendicular to the first longitudinal axis. The brush has a second longitudinal axis and a plurality of bristles and / or blades extending outwardly from the second longitudinal axis. The brush is attached to the apparatus such that the second longitudinal axis is substantially parallel to the first longitudinal axis and the brush is rotatable about the second longitudinal axis. The brush is spaced from the base such that the plurality of bristles engage the plurality of grooves. The base is adjustable enabling the operator to move the base closer or further from the rotating brush / blades.
Owner:SWARD LLC
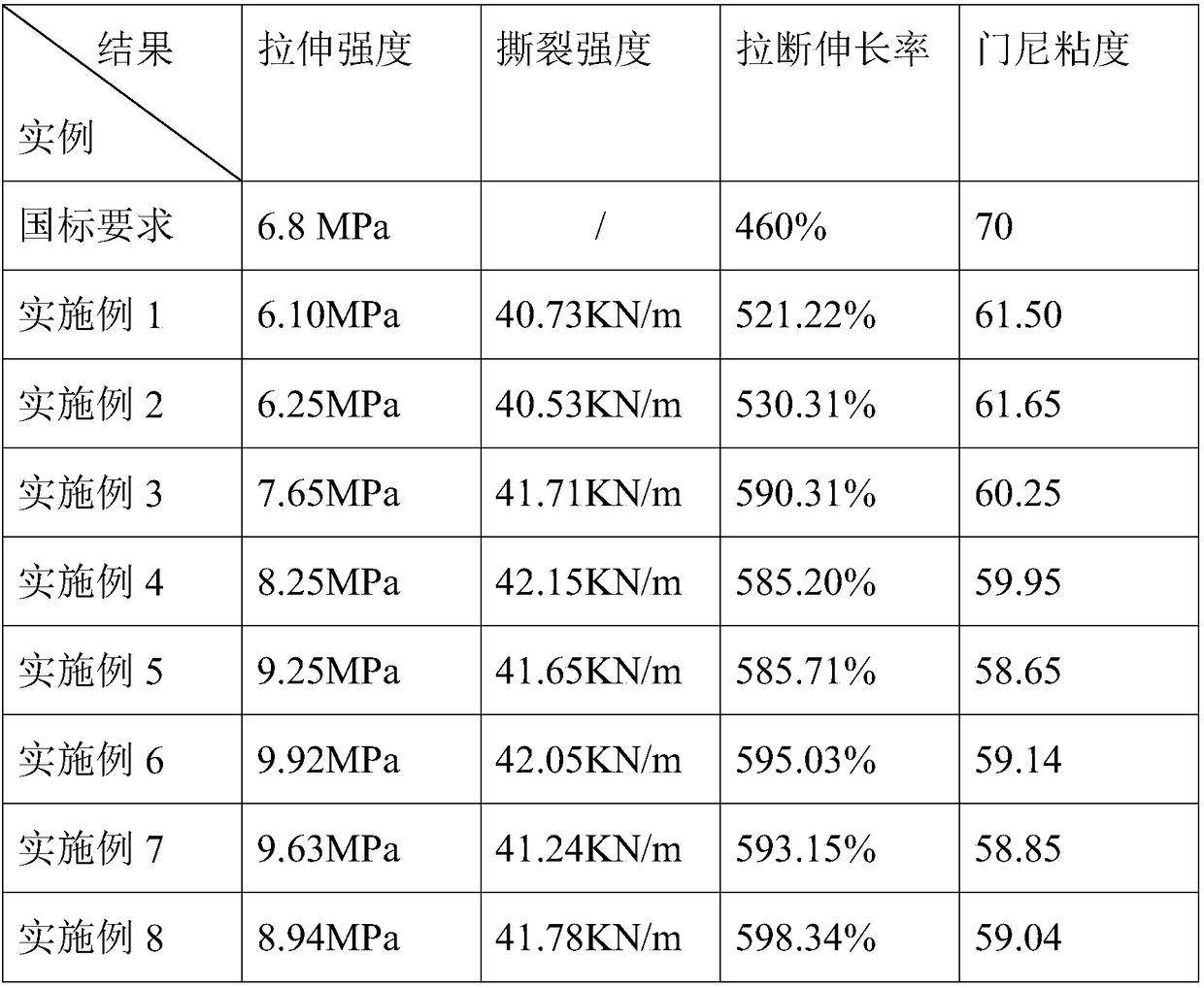
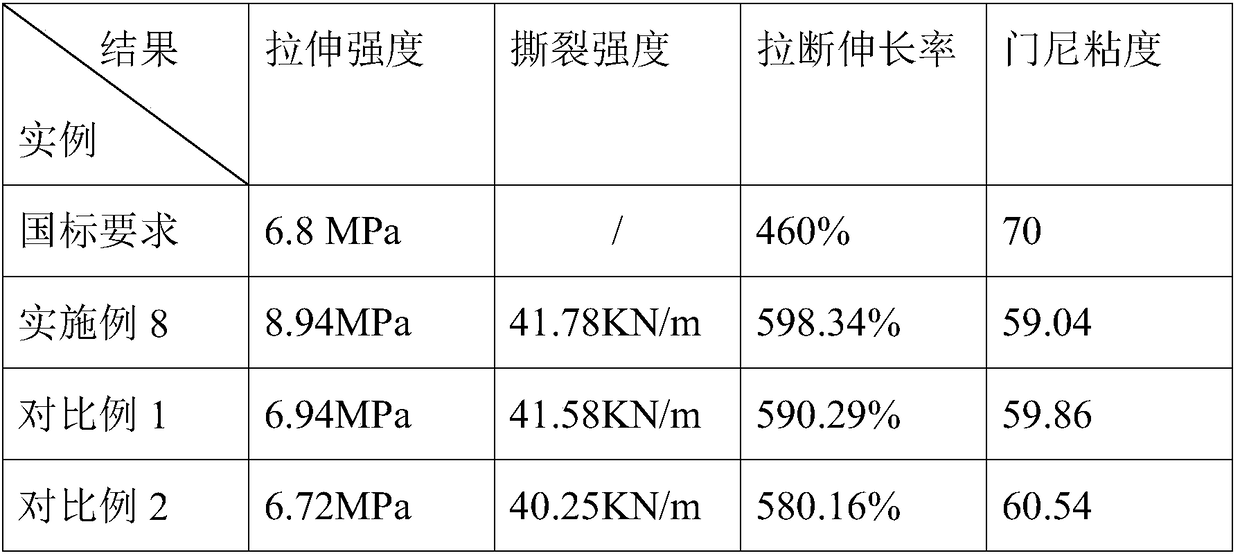
Waste butyl rubber regeneration technology and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108841040AAchieve regenerationConducive to energy saving and environmental protection regenerationPlastic recyclingChemical LinkageVegetable oil
The invention relates to a waste butyl rubber regeneration technology. The following components are used in the waste butyl rubber regeneration technology in parts by weight: 100 parts of waste butylrubber, 2 to 3 parts of vegetable oil, 2 to 3 parts of plant ester, 3 to 4 parts of an efficient water reducer, 2 to 3 parts of a special-effect activating agent and 4 to 6 parts of mineral oil. 0.1 to 0.2 parts of lignin is further added in the technology in parts by weight, and prepared waste butyl rubber has preferable comprehensive performance by controlling the mass ratio of the vegetable oilto the plant ester and the mass ratio of the vegetable oil to the lignin. The invention also provides a preparation method of the waste butyl rubber regeneration technology, the waste butyl rubber isregenerated by using a low temperature continuous mixing and refining method, a continuous regeneration technology is carried out on the waste butyl rubber by using an internal mixer, a double-screwextruder, a rubber filter and a refiner to replace a reaction still under traditional high temperature and high pressure, the selective cleavage of chemical bonds is realized, and then the low-temperature environmental protection regeneration of the waste butyl rubber is realized.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synthetic catalyst for selective cleavage of protein and method for selective cleavage of protein using the same
InactiveUS20020165365A1Highly effectiveKeep for a long timeOrganic active ingredientsHybrid immunoglobulinsProtein targetMetal
The present invention relates to a synthetic catalyst of the following formula (A) which can selectively recognize and cleave a specific protein among a protein mixture, and to a method for selective cleavage of a target protein using the same: <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>(R)(Z)n (A) < / in-line-formula>in which n denotes an integer of 1 or more, R represents a material capable of selectively recognizing and binding a target protein, and Z represents a metal ion-ligand complex.
Owner:TEIJIN SEIKI CO LTD
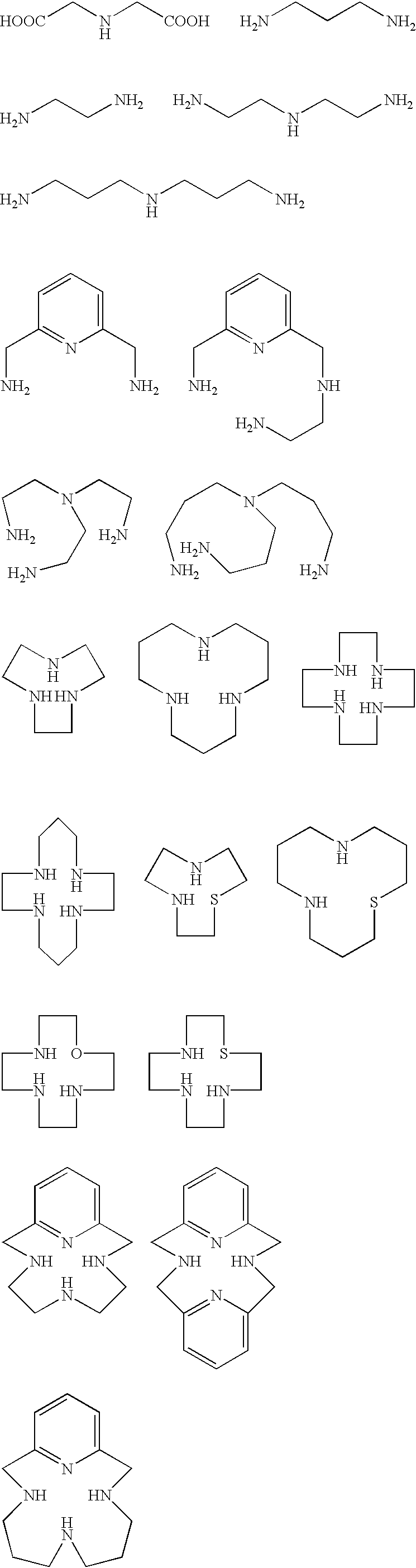
Artificial endo enzyme containing peptide nucleic acid recognition element, and its preparing method and use
The invention provides the artificial inner cut enzyme which can cut phosphodiester bond in nucleic acid selectivitily. The inner cut enzyme contains recognition and cutting details. The recognition details is single strand of peptide nucleic acid which constitutional unit is 6-200 qae glycine. The cutting details is chelating agent of rare earth metal ion which is chelated with metal ion at the ammonia or carbon terminal of single strand of peptide nucleic acid and which has joint between the chelating agent and single strand. the artificial inner cut enzyme can be used implemental enzyme widely in molecular biology, genetic engineering and medical treatment area.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
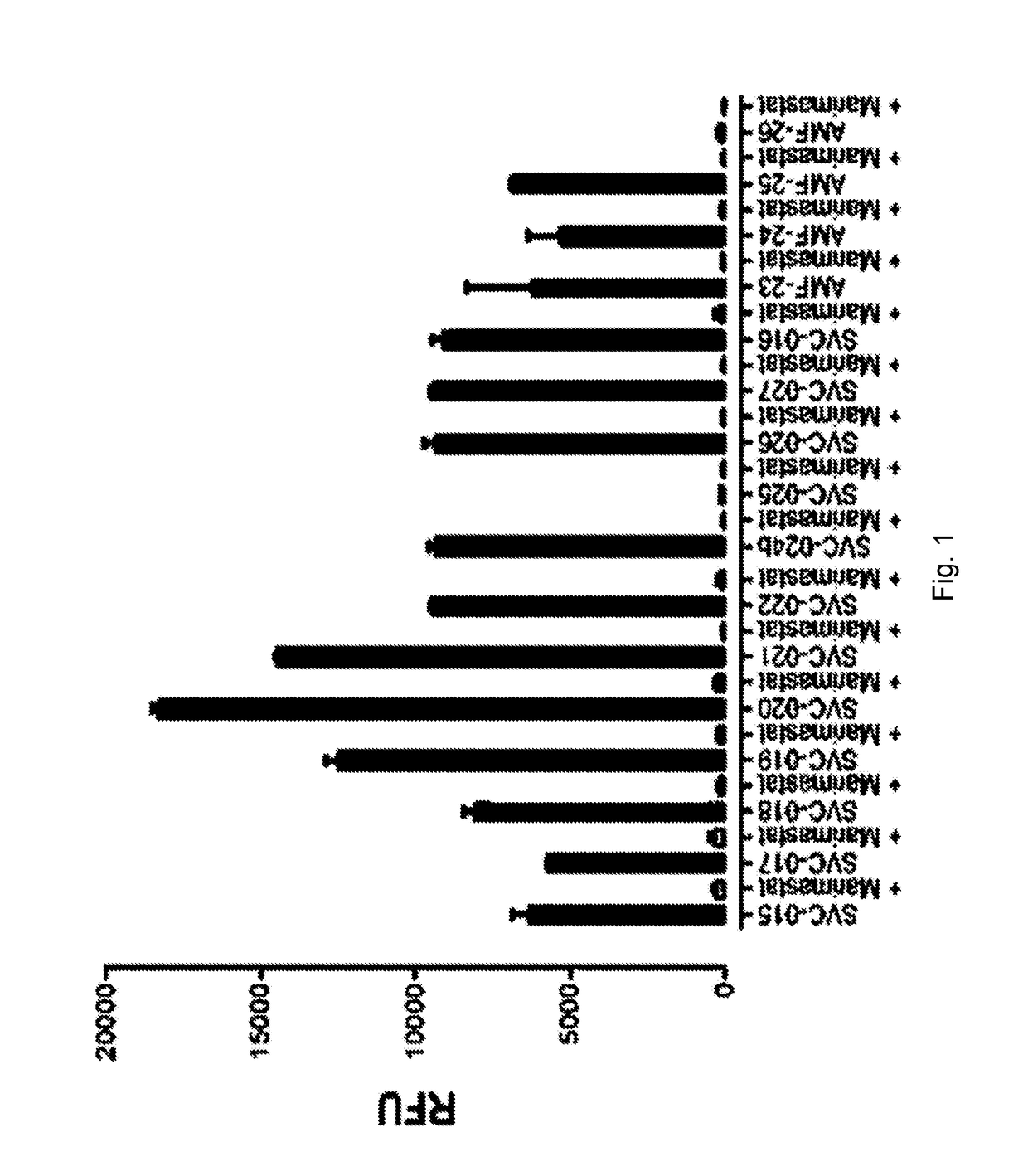
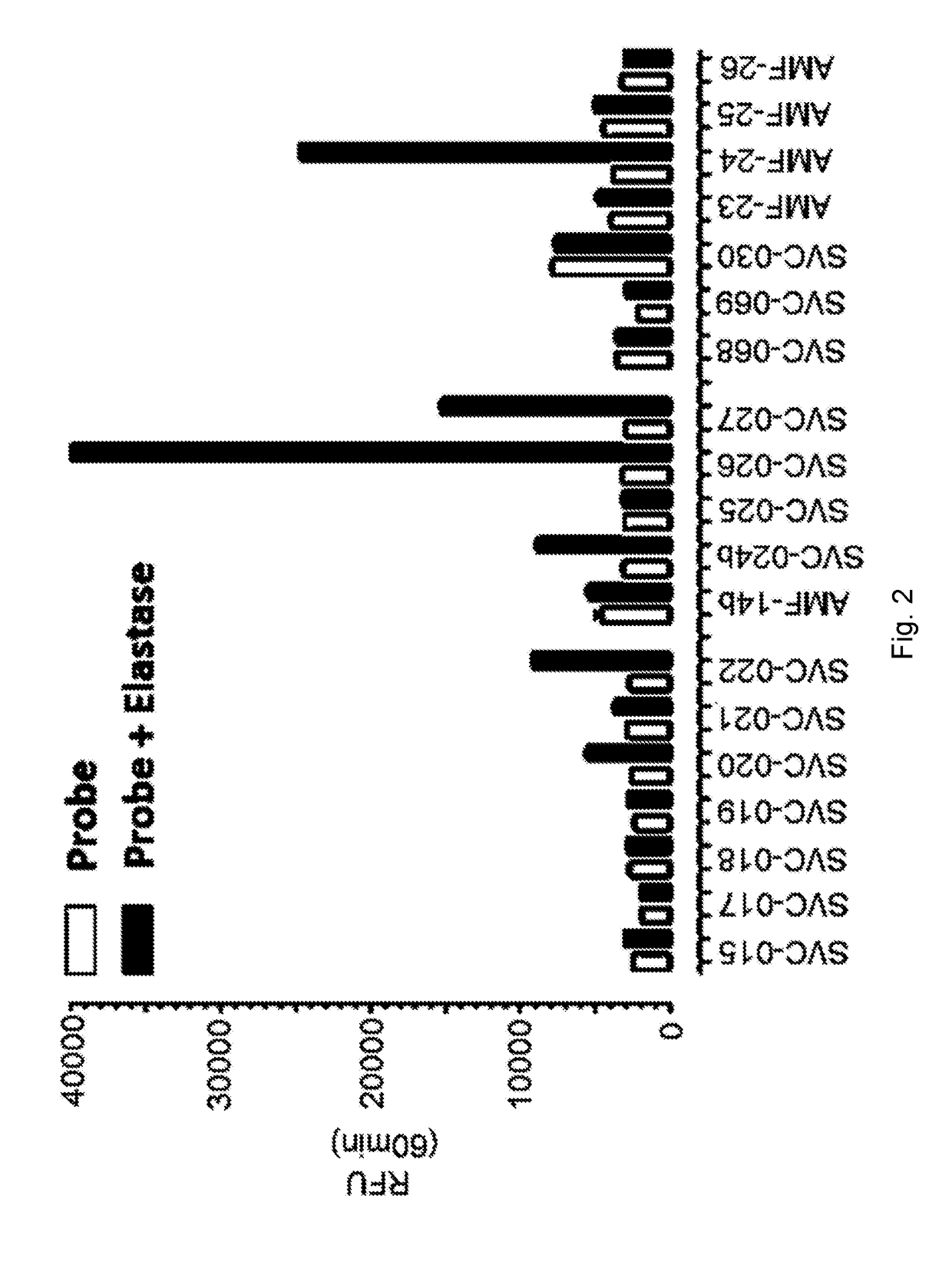
Optical probes for matrix metalloproteinases
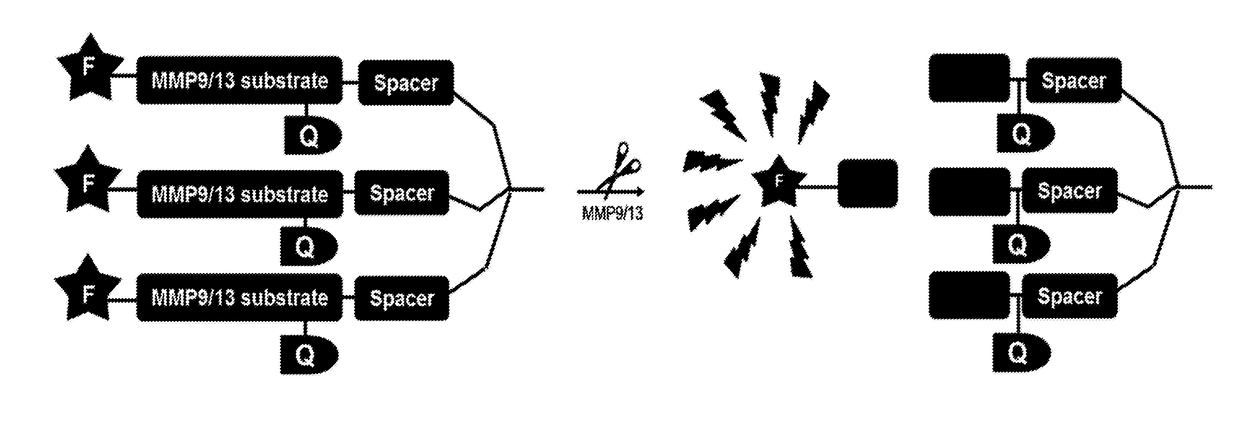
ActiveUS20180085466A1Maximize likelihoodMinimal amountMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPeptide sequenceFluorophore
An optical probe is presented comprising at least one fluorophore connected to at least one quencher by an enzyme cleavable peptide sequence; the or each fluorophore being substantially fluorescently quenched by the at least one quencher when connected to the enzyme cleavable peptide sequence; the or each fluorophore is separated from the at least one quencher when the enzyme cleavable peptide sequence of the at least one probe element is cleaved; and the enzyme cleavable peptide sequence is selectively cleavable by one or more matrix metalloproteinase (MMP). Methods of use of the optical probe are also presented.
Owner:THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com