Patents
Literature
101 results about "Living tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Termite acoustic detection
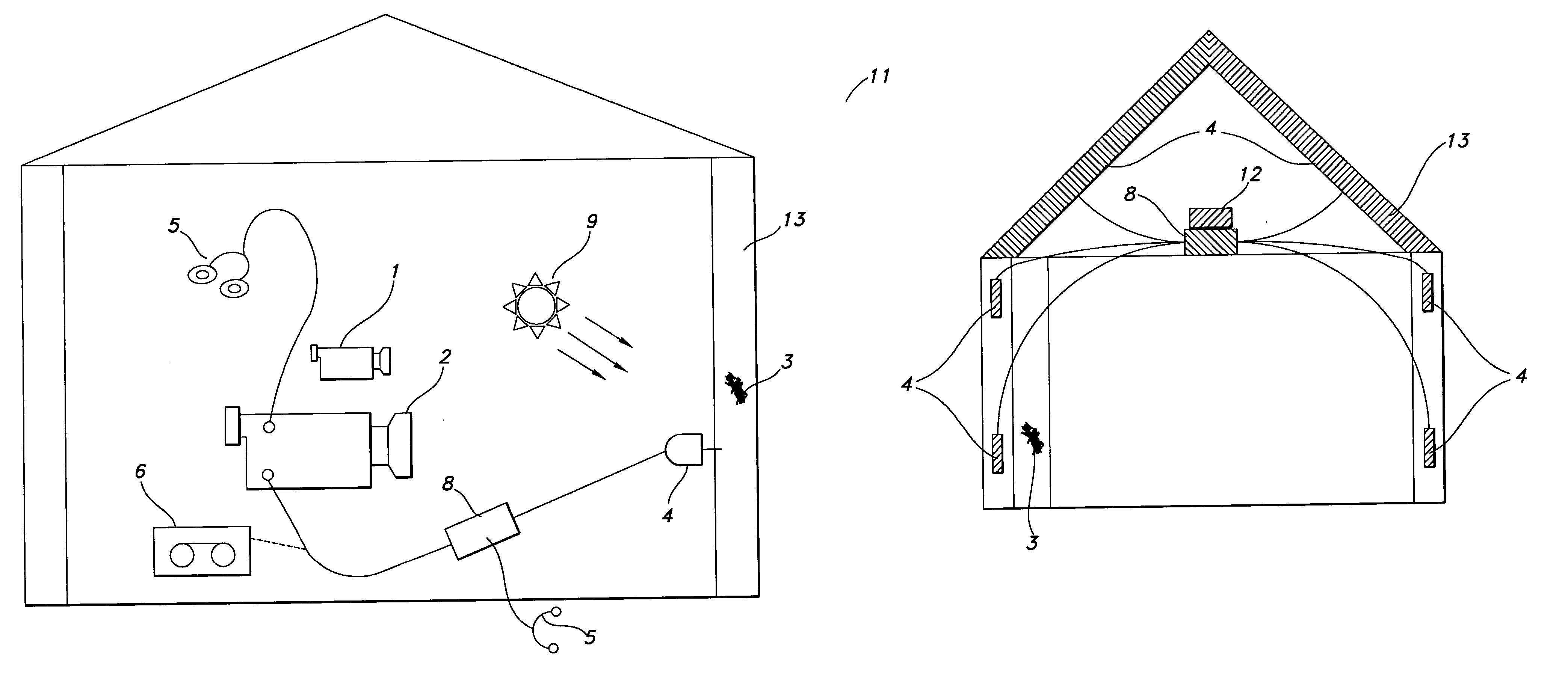
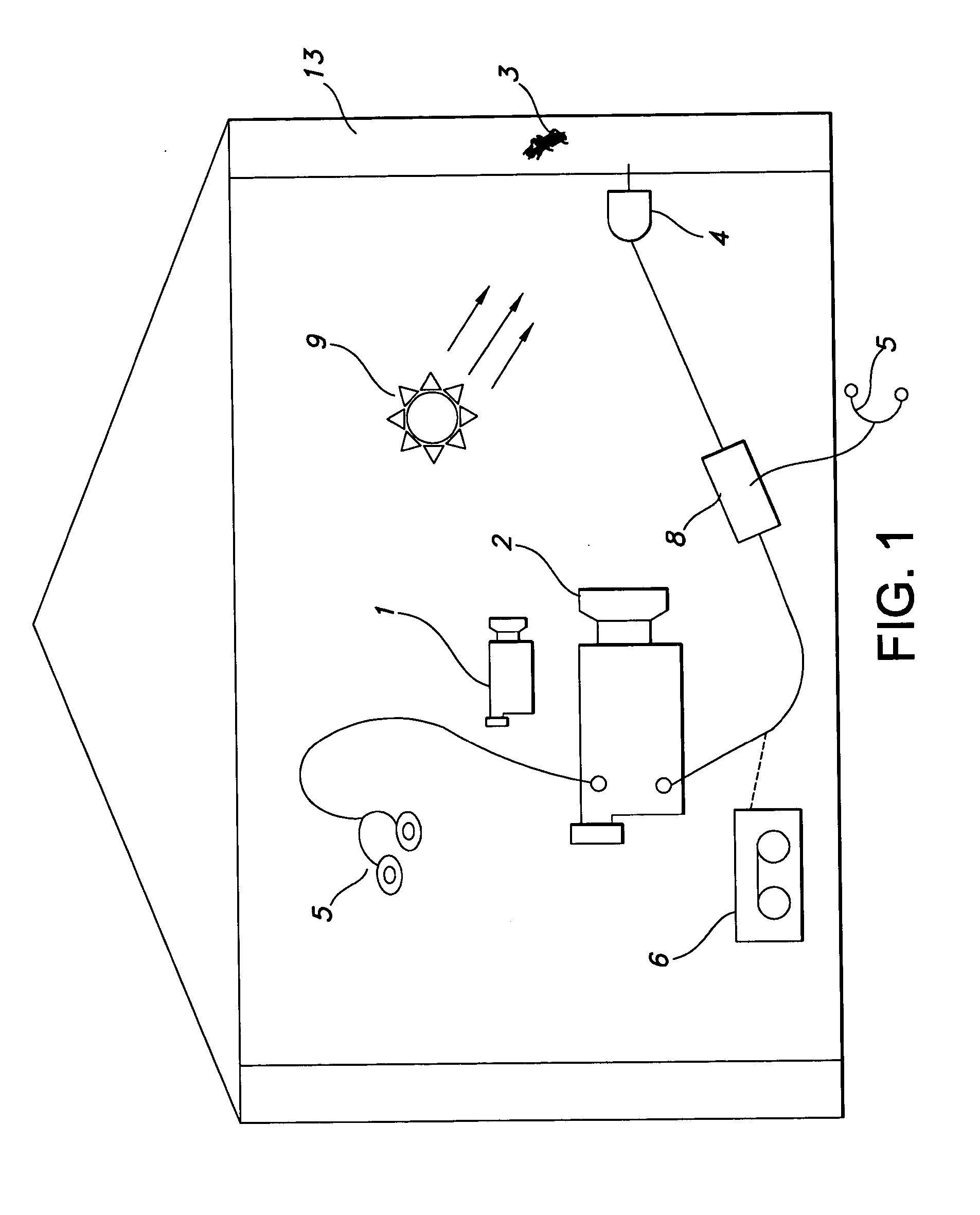
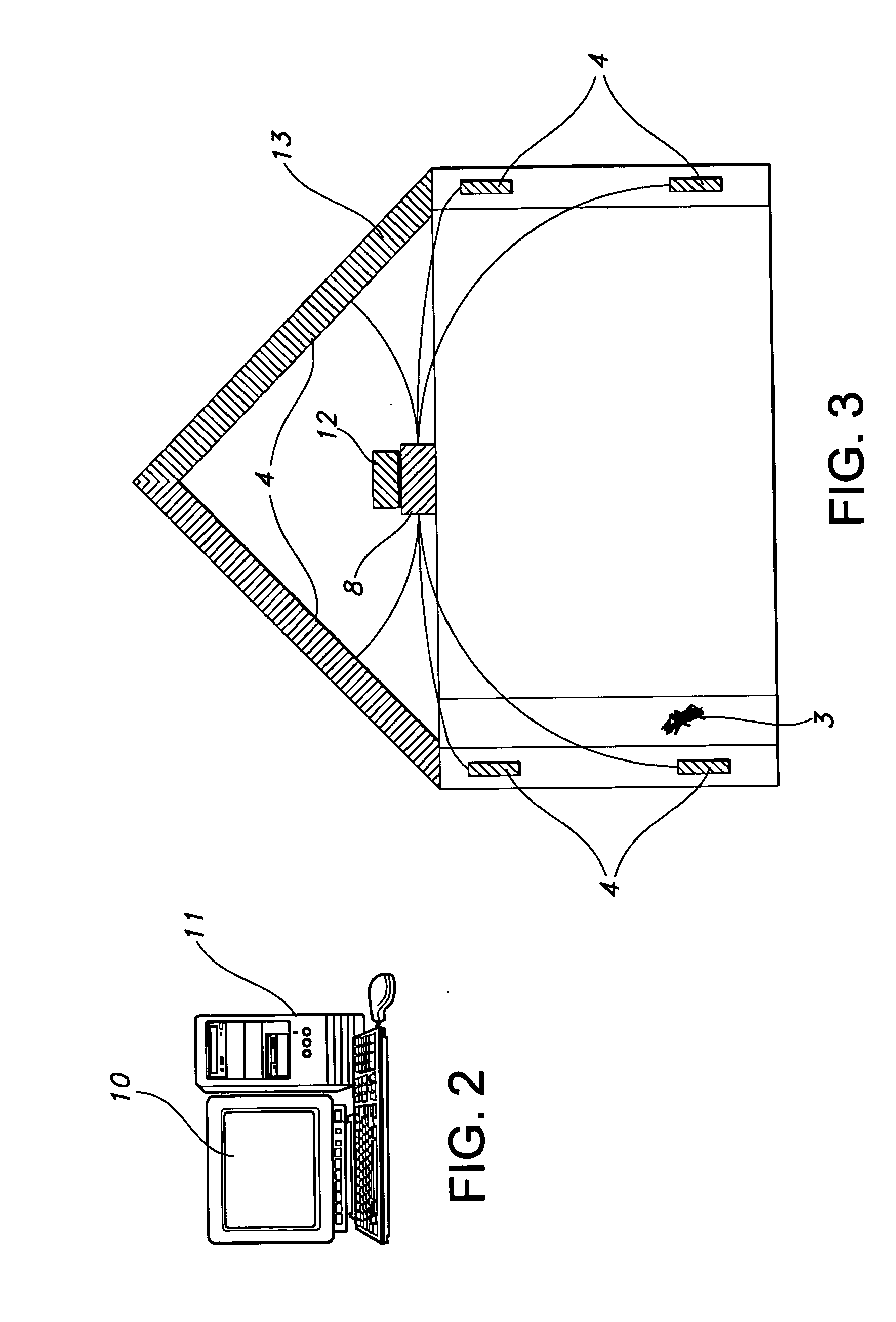
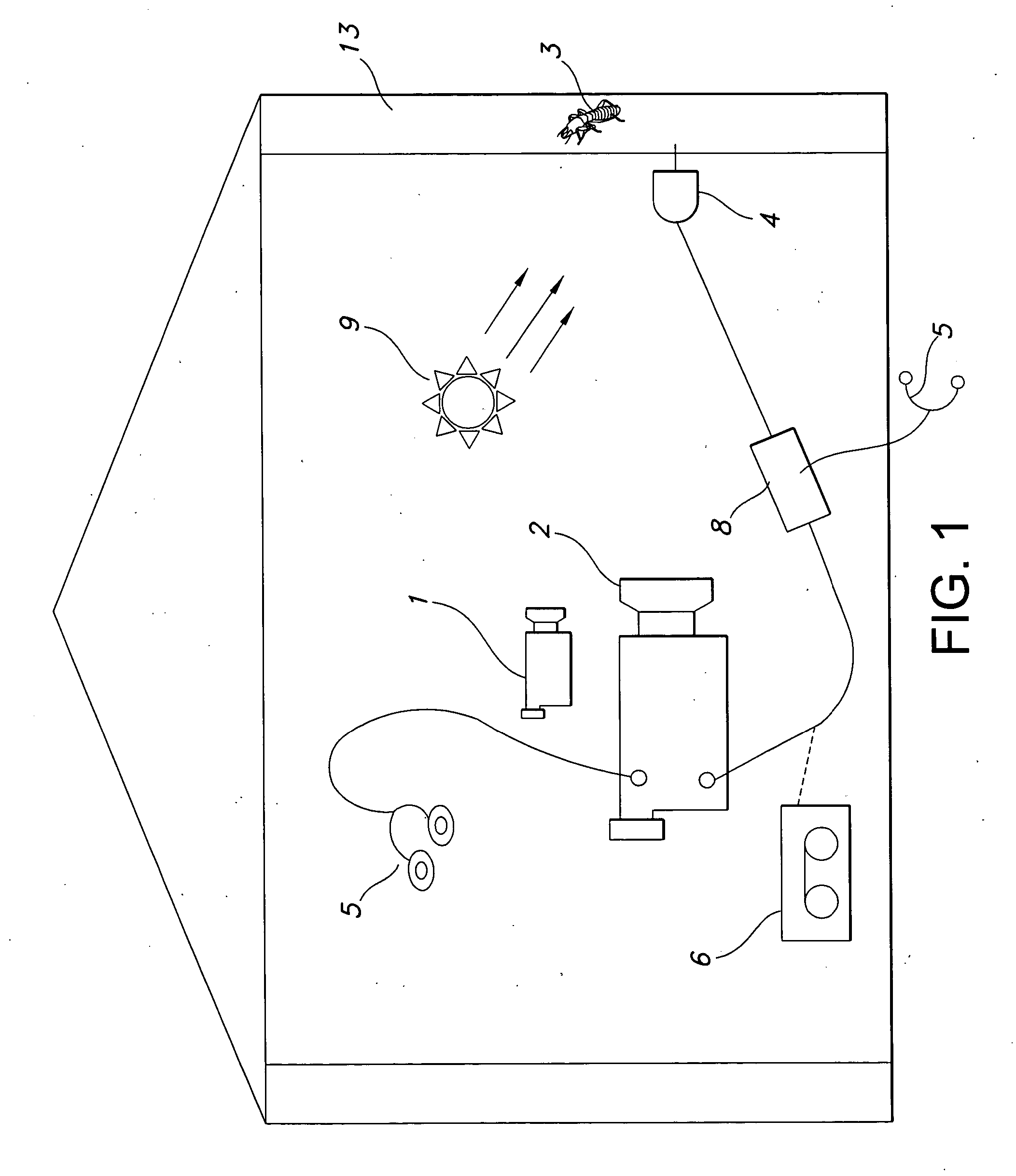
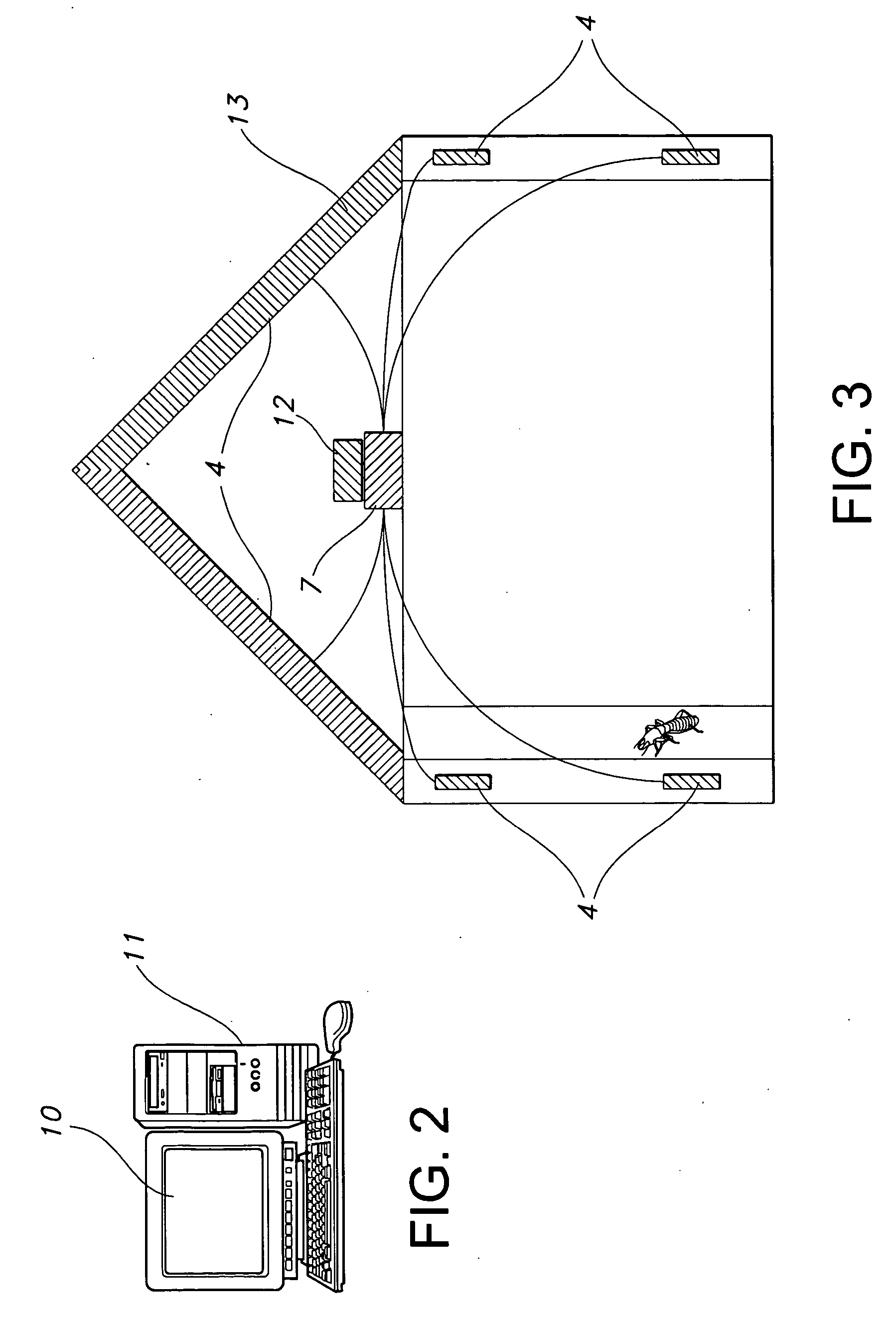
InactiveUS20060028345A1Reduce harmReduce the amount requiredSound producing devicesBurglar alarmMicrocomputerAccelerometer
A method and system for detecting the presence of subterranean termites, involving use of a thermal imaging camera to scan the structure before installation of an acoustic sensor in order to quickly locate potential areas of subterranean termite infestation, and an acoustic sensor in the form of an accelerometer or the disclosed innovative acoustic sensors having a bandwidth of at least 100 Hz to 15 kHz to detect noises made by the subterranean termites. Information collected by the acoustic sensor may be transmitted to a portable mini-computer (pocket PC) for confirmation and to a central operations center for inclusion in a comprehensive database of termite data and information. A method and system for detecting the presence of dry-wood termites concealed in a structure, involving use of a heat source to warm up the wooden structure of interest and then using a thermal imaging camera to scan the structure for suspicious dry-wood infestation, followed by the use of an acoustic sensor and pattern recognition software to more precisely and accurately locate potential area of dry-wood termite infestation. Additionally, structural damage can be evaluated by the methods discussed herein, including live trees. Additionally, the method can be used to manipulate termite infestation behavior.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSISSIPPI
Water amusement system with elevated structure
InactiveUS7785207B2Self-acting watering devicesArtificial flowers and garlandsLiving treeEngineering
A water amusement system may include a composite tree and an elevated structure. A composite tree may include a base having an artificial trunk portion. The base may be coupled to the surface. Living plants may be coupled to the base. Portions of the living plants may form branches of the composite tree. In some embodiments, the living plants are living trees. The system may include at least one structure coupled to the base. At least one of the structures may function to contain one or more persons above the surface. The water amusement system may include a water amusement ride coupled to the base. The water amusement ride may include an access point configured to allow participants to access the water amusement ride from the structure.
Owner:WATER RIDE CONCEPTS
Tree with covering apparatus
Owner:WATER RIDE CONCEPTS
Composite tree
InactiveUS20070033867A1Artificial flowers and garlandsSelf-acting watering devicesLiving treeNutrient
A composite tree may include a base having an artificial trunk portion. Living plants may be coupled to the base. Portions of the living plants may form branches of the composite tree. In some embodiments, the living plants are living trees. The base may include one or more openings. A first portion of at least one of the living plants may be coupled in one of the openings such that a second portion of the living plant extends from the opening to form a branch of the composite tree. A first portion of the living plant may include at least a portion of the root system of the living plant. In some embodiments, a composite tree may include one or more systems forming and / or coupled to the composite tree. Systems may perform various functions (e.g., providing heat and / or nutrients to a living plant).
Owner:WATER RIDE CONCEPTS
Thematic tree system
InactiveUS20070051037A1Artificial flowers and garlandsSelf-acting watering devicesLiving treeRoot system
A composite tree may include a base having an artificial trunk portion. Living plants may be coupled to the base. Portions of the living plants may form branches of the composite tree. In some embodiments, the living plants are living trees. The base may include one or more openings. A first portion of at least one of the living plants may be coupled in one of the openings such that a second portion of the living plant extends from the opening to form a branch of the composite tree. A first portion of the living plant may include at least a portion of the root system of the living plant. In some embodiments, at least two sets of branch portions may be configured to removably couple to the base. At least one set of branch portions may have a different theme.
Owner:WATER RIDE CONCEPTS
Tree with elevated structure
InactiveUS20070051036A1Self-acting watering devicesArtificial flowers and garlandsLiving treeStructure system
An elevated structure system may include a composite tree and an elevated structure. A composite tree may include a base having an artificial trunk portion. The base may be coupled to a surface. Living plants may be coupled to the base. Portions of the living plants may form branches of the composite tree. In some embodiments, the living plants are living trees. The base may include one or more openings. A first portion of at least one of the living plants may be coupled in one of the openings such that a second portion of the living plant extends from the opening to form a branch of the composite tree. The system may include at least one structure coupled to the base. At least one of the structures may function to contain one or more persons above the surface.
Owner:WATER RIDE CONCEPTS
Water amusement system with elevated structure
InactiveUS20070033868A1Self-acting watering devicesArtificial flowers and garlandsLiving treeEcology
A water amusement system may include a composite tree and an elevated structure. A composite tree may include a base having an artificial trunk portion. The base may be coupled to the surface. Living plants may be coupled to the base. Portions of the living plants may form branches of the composite tree. In some embodiments, the living plants are living trees. The system may include at least one structure coupled to the base. At least one of the structures may function to contain one or more persons above the surface. The water amusement system may include a water amusement ride coupled to the base. The water amusement ride may include an access point configured to allow participants to access the water amusement ride from the structure.
Owner:WATER RIDE CONCEPTS
Water amusement system with trees
InactiveUS20070051039A1Artificial flowers and garlandsSelf-acting watering devicesLiving treeEnvironmental geology
A water amusement system may include a composite tree and an elevated structure. A composite tree may include a base having an artificial trunk portion. The base may be coupled to a surface. Living plants may be coupled to the base. Portions of the living plants may form branches of the composite tree. In some embodiments, the living plants are living trees. The water amusement system may include a water amusement ride coupled to the base. The water amusement ride may include an access point configured to allow participants to access the water amusement ride from the structure. The access point may be positioned adjacent to the base.
Owner:WATER RIDE CONCEPTS
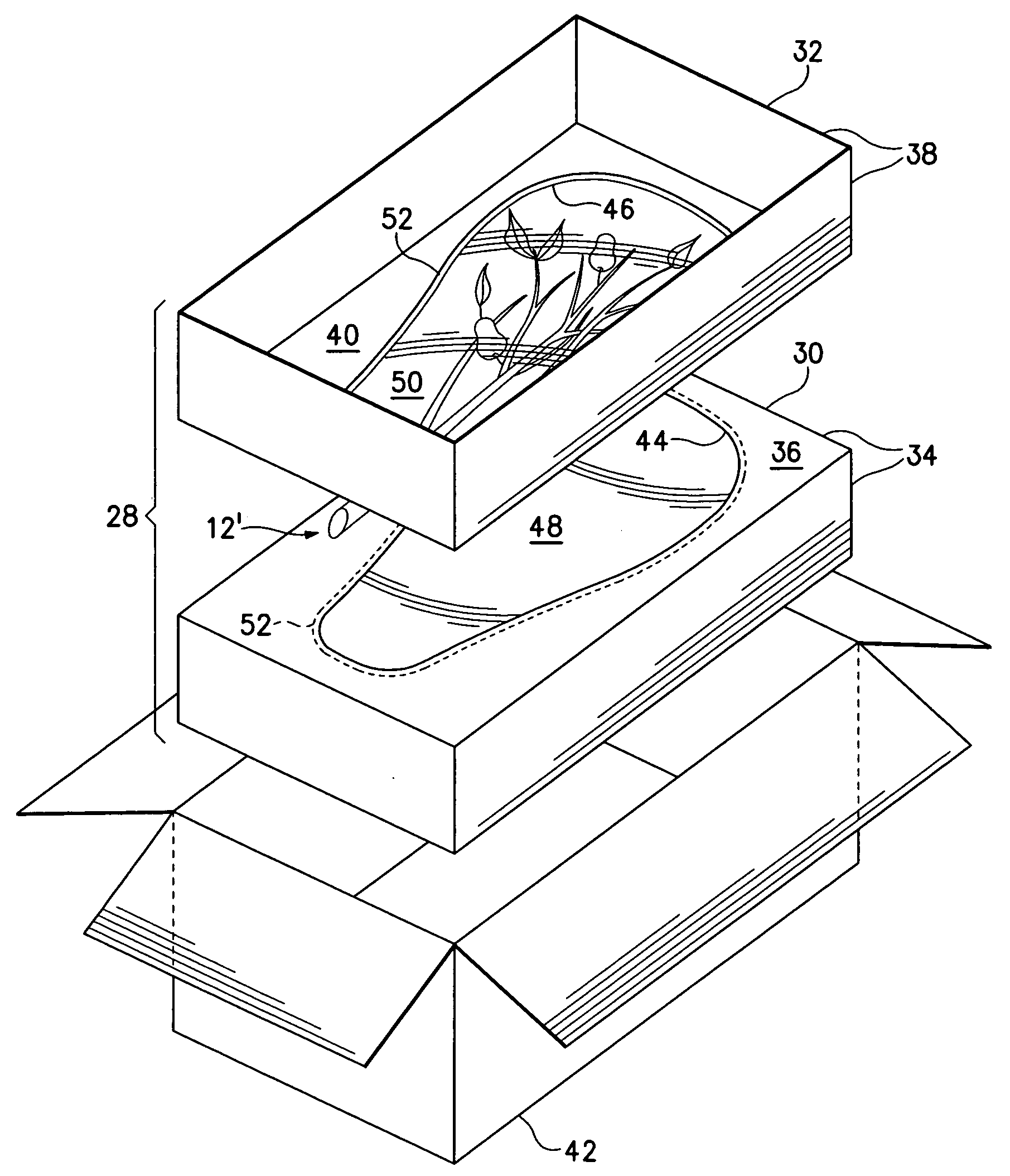
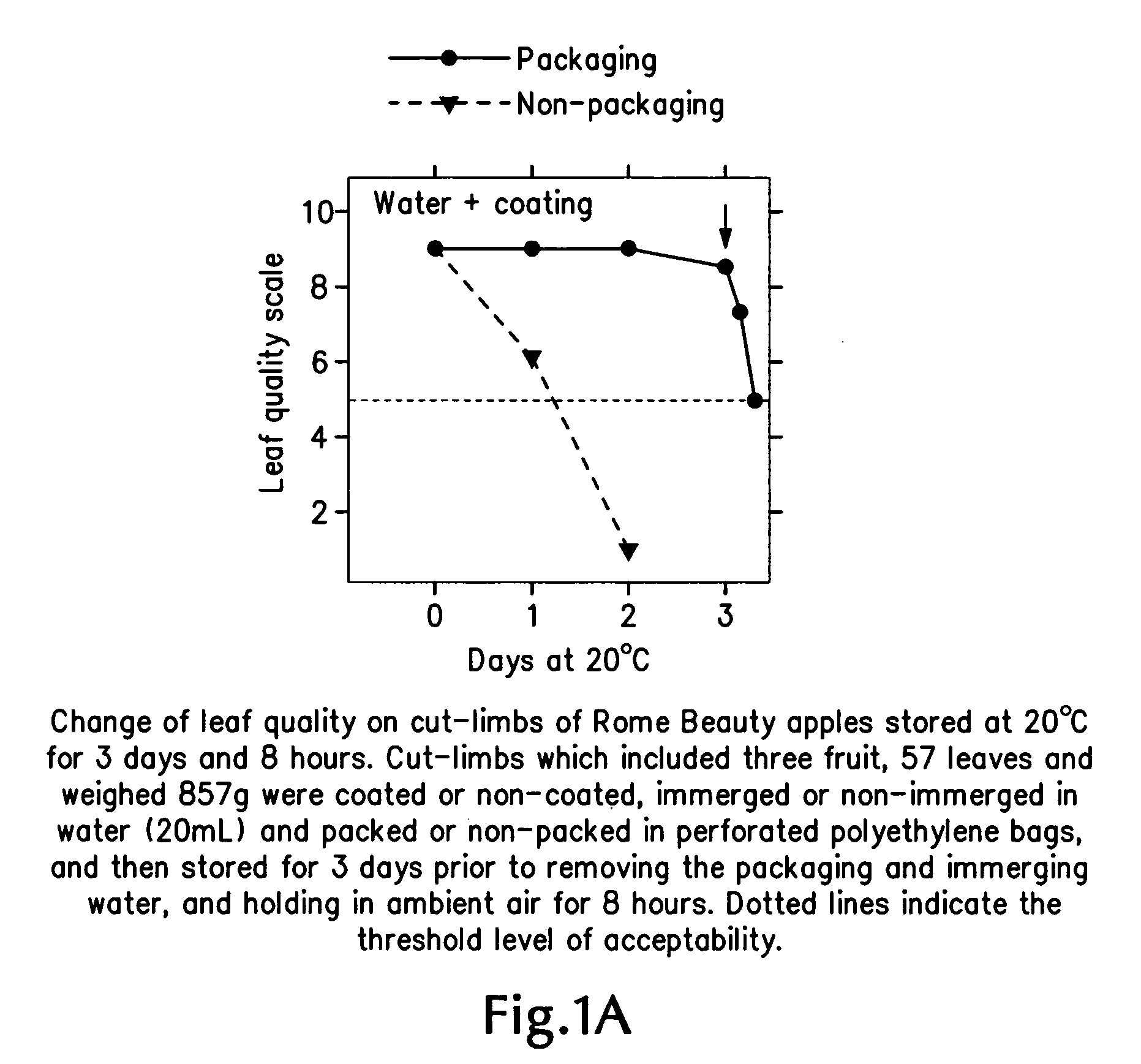
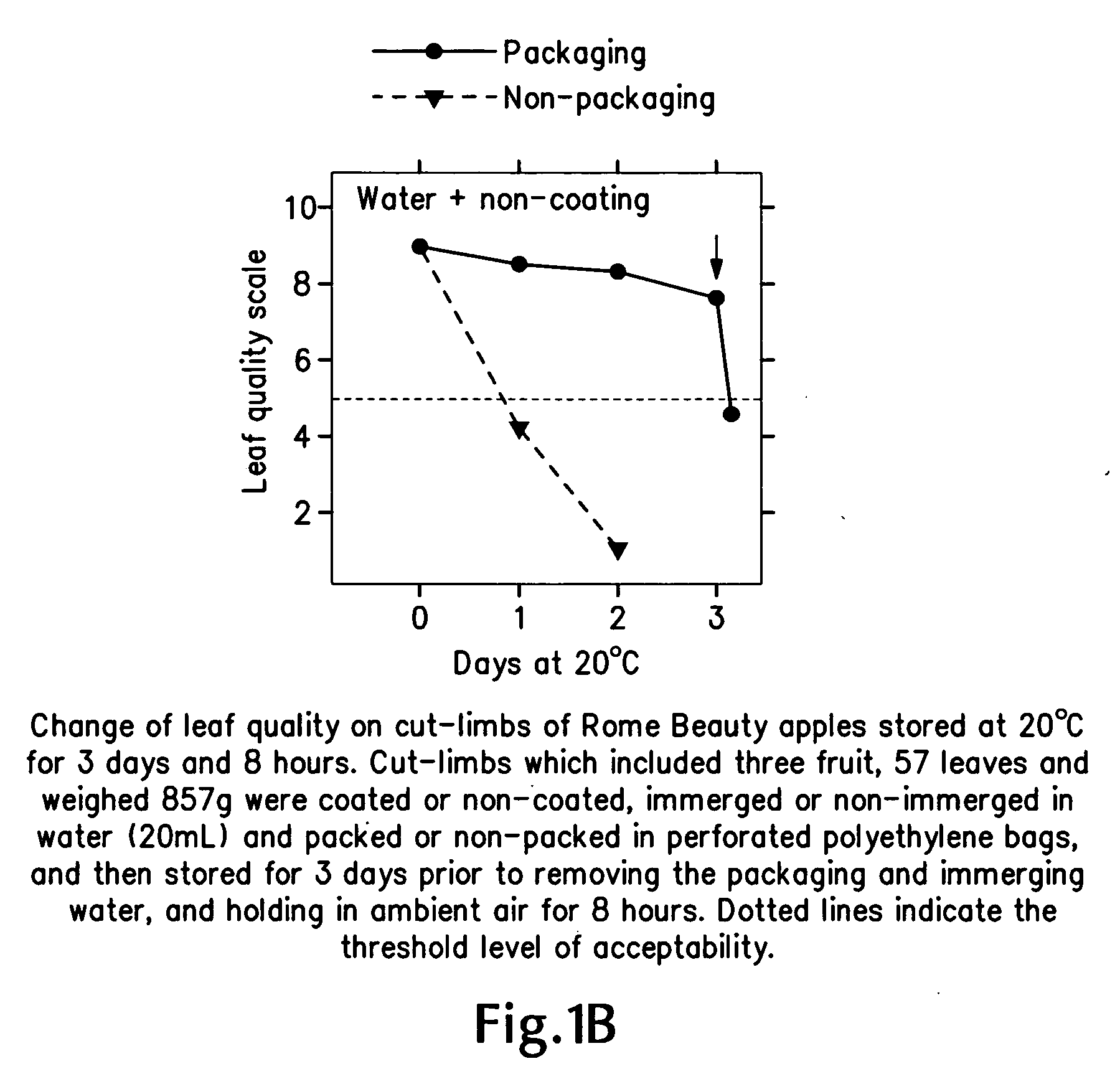
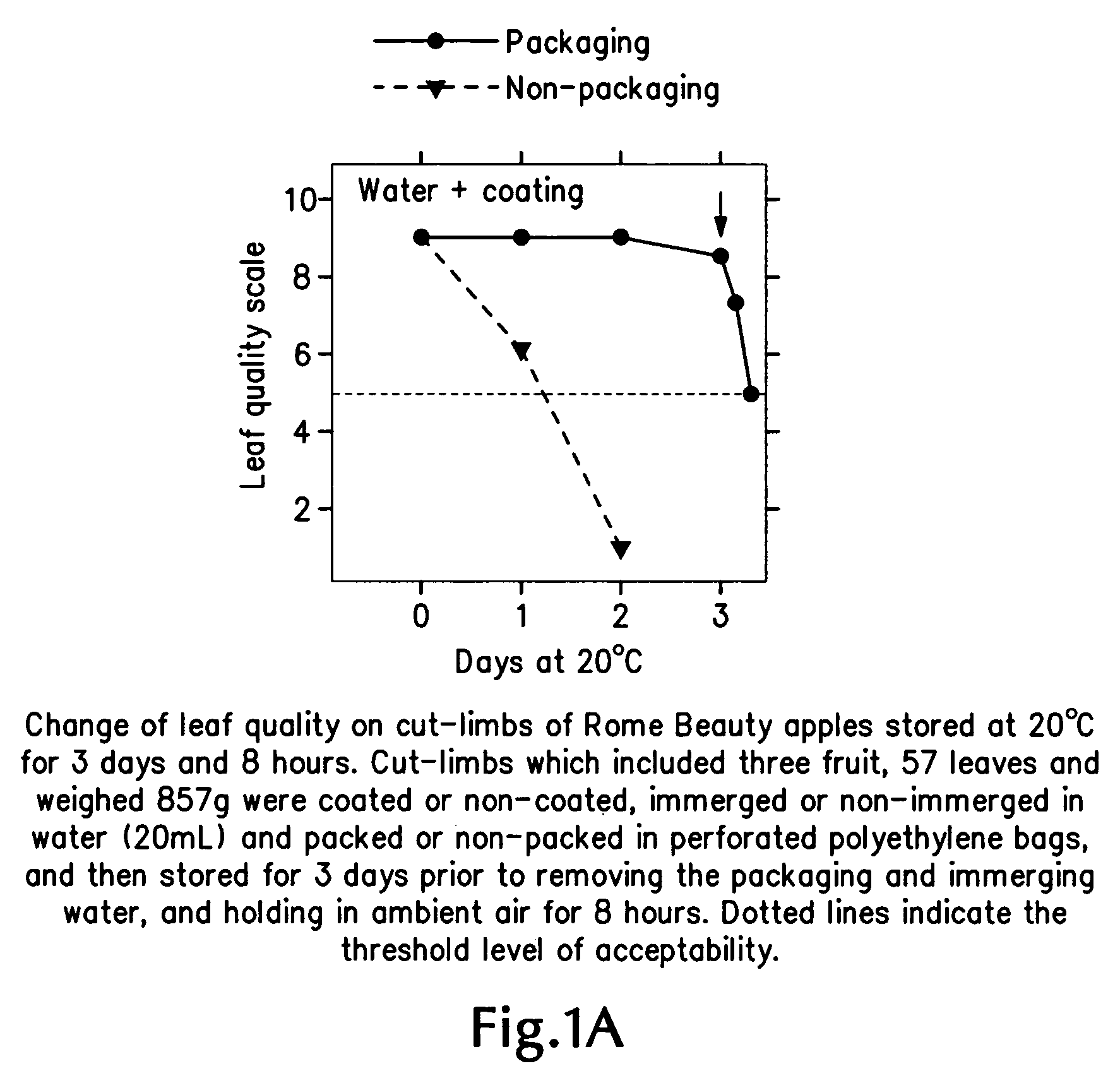
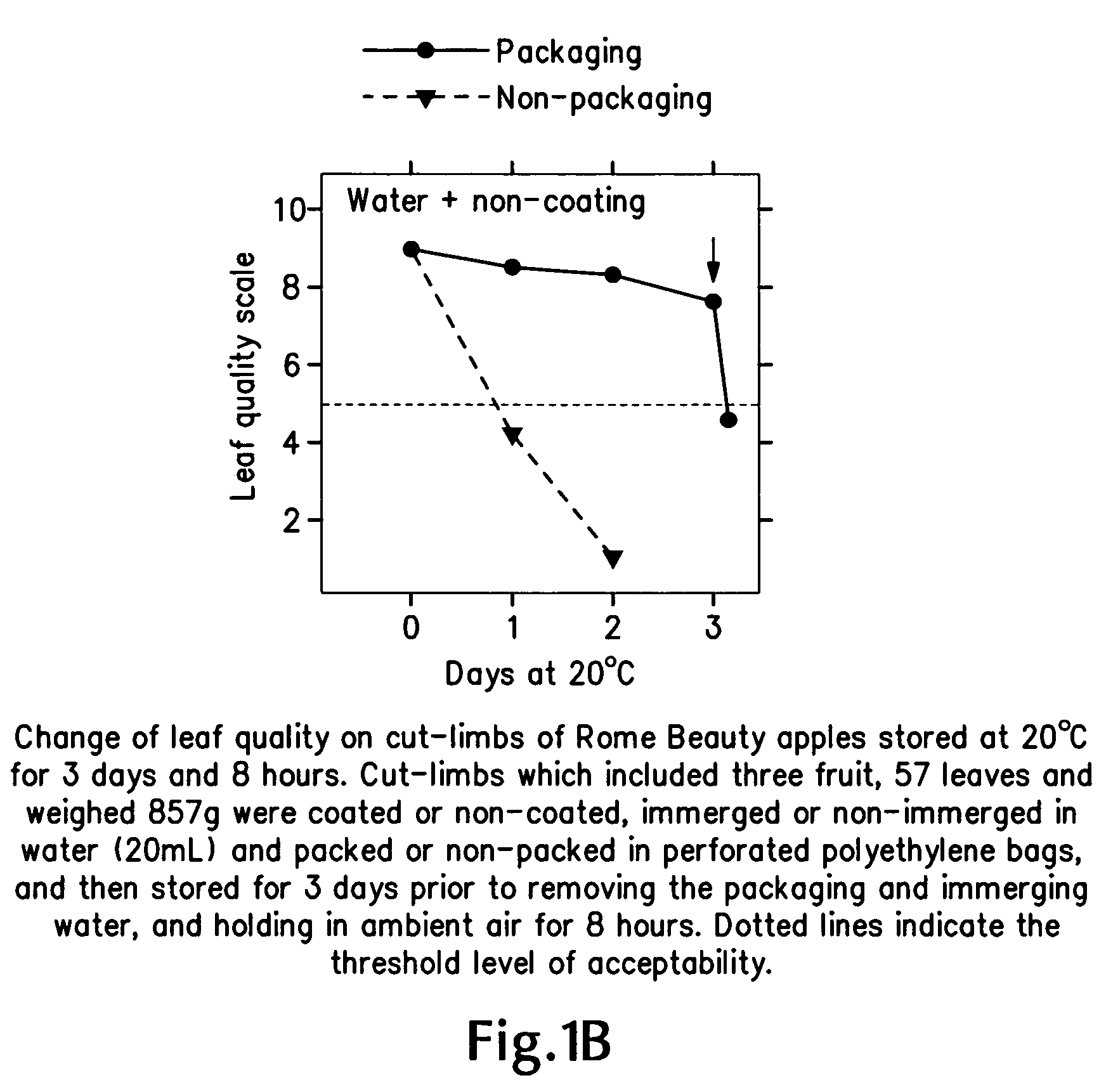
Perishable-fruit-bearing cut-limb preservation and distribution method, coating and shipping container therefor
InactiveUS20080310991A1Extended service lifeEdible oils/fats ingredientsWax coatingsFruit treeLiving tree
A method of preserving fruit-bearing cut-limbs from cutting at an orchard to receiving by a remote consumer includes cutting a live, fruit-bearing limb off a fruit tree in an orchard; and bagging the cut limb with perforated film substantially to seal the limb therein substantially continuously from the time of cutting at the orchard to the time of receiving by the remote consumer. After the cutting and before the bagging, the method can include dipping the cut end of the limb in a solution of water substantially continuously from cutting at the orchard to receiving by the remote consumer and / or coating the cut limb including the fruit and leaves thereon using a moisture-retentive agent. A perishable-fruit distribution method includes cutting an intact fruit- and leaf-bearing limb from a live tree in an orchard; treating the cut-limb to extend the useful life of the intact fruit and leaf thereon; placing the treated cut-limb with the intact fruit and leaf thereon in a shipping container; and delivering the treated, containerized cut-limb with the intact fruit and leaf thereon within the shipping container to a consumer remote from the orchard. A coating and a shipping container also are described and claimed.
Owner:OREGON STATE OF
Dendrobium candidum planting method
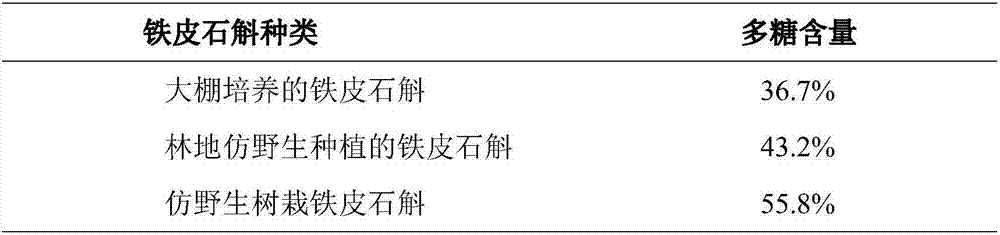
A dendrobium candidum planting method specifically includes the steps that dendrobium candidum seedlings are planted on tree species with longitudinal grooves in the surface of bark; before planting, the roots of the dendrobium candidum seedlings dip in a solid nutrient solution prepared through a high-water-absorbent material and a Jin Weiguo effective foliar fertilizer produced by the America Grow More Inc; during planting, the dendrobium candidum seedlings are bound on trunks through binding strips manufactured through shading nets so that the dendrobium candidum seedlings can be attached to the trunks. According to the method, the trunks serve as epiphytes, tress are used for shading, plastic greenhouses and other infrastructure do not need to be built, substrates are not used, cost is reduced by nearly a half, and environment is not influenced. Meanwhile, dendrobium candidum products cultivated through live trees are more ecological, higher in polysaccharide content and higher in quality. Dendrobium candidum is planted on the trees, does not occupy fertile farmland suitable for grains and does not occupy forest land suitable for the trees, and comprehensive benefits of the forest land can be better achieved. Most importantly, the live trees are planted in the wild, restoration of wild populations is facilitated, and sustainable development is achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEIHUJIAN BIOTECH LTD
Termite acoustic detection
InactiveUS20070096928A1Accurate detectionProvide quicklySound producing devicesBurglar alarmMicrocomputerAccelerometer
A method and system for detecting the presence of subterranean termites, involving use of a thermal imaging camera to scan the structure before installation of an acoustic sensor in order to quickly locate potential areas of subterranean termite infestation, and an acoustic sensor in the form of an accelerometer or the disclosed innovative acoustic sensors having a bandwidth of at least 100 Hz to 15 kHz to detect noises made by the subterranean termites. Information collected by the acoustic sensor may be transmitted to a portable mini-computer (pocket PC) for confirmation and to a central operations center for inclusion in a comprehensive database of termite data and information. A method and system for detecting the presence of dry-wood termites concealed in a structure, involving use of a heat source to warm up the wooden structure of interest and then using a thermal imaging camera to scan the structure for suspicious dry-wood infestation, followed by the use of an acoustic sensor and pattern recognition software to more precisely and accurately locate potential area of dry-wood termite infestation. Additionally, structural damage can be evaluated by the methods discussed herein, including live trees. Additionally, the method can be used to manipulate termite infestation behavior.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSISSIPPI
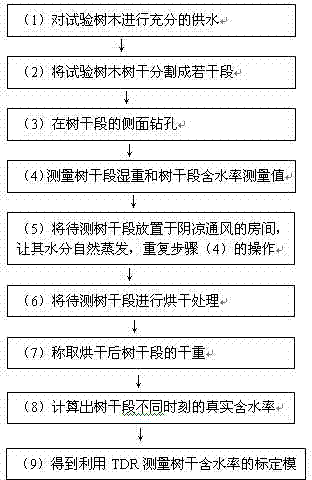
Calibration method for measuring tree trunk moisture content by time domain reflectometry (TDR)
InactiveCN102539271AWell formedEasy to calculateWeighing by removing componentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSoil scienceLiving tree
The invention provides a calibration method for measuring the tree trunk moisture content by a time domain reflectometry (TDR). According to the method, the TDR and a scale are respectively utilized for continuously measuring the tree trunk section moisture content (moisture content measuring value) and the wet weight, in addition, a baking method is adopted for obtaining the dry weight of the tree truck section, the measured dry weight and wet weight data of the tree truck section can be utilized for calculating the corresponding moisture containing weight during the tree trunk moisture content measurement by using the TDR in each time, the corresponding moisture content (real value) can be calculated according to the timber water content definition, and the quantitative relationship between the real water content and the corresponding moisture content measuring value data according to the obtained real water content of the tree trunk section and the corresponding moisture content measuring value data, so a calibration model for measuring the tree trunk moisture content by using the TDR is obtained. According to the calibration model, the TDR can be utilized for carrying out in-situ dynamic monitoring on the moisture content of the live tree trunk, so the tree trunk moisture content measuring process is simplified, and in addition, the measuring precision is improved.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Method for cultivating dendrobe
InactiveCN1748455AGuaranteed healthy growthPromote reproductionHorticulture methodsLiving treeNutrient solution
The dendrobe cultivating method is to fix live dendrobe on plant of live tree stem and bamboo or stump with bark, irrigate, apply nutritious liquid and provide shady and cool environment for dendrobe to grow. The said method provides moist growth environment, reduce disease and ensure healthy growth of dendrobe. In addition, the present invention can utilize space fully to lower the dendrobe cultivating cost.
Owner:刘俊
Cultivation method of rhizoma paridis yunnanensis
ActiveCN103181285AAdaptableImprove survival rateFertilising methodsHorticultureSocial benefitsLiving tree
The invention discloses a cultivation method of a rhizoma paridis yunnanensis. The method uses local wild seedlings as seedlings to perform artificial cultivation; wild excavation and artificial cultivation of the rhizoma paridis yunnanensis are combined with each other organically, so that not only is the maximized medicinal value of wild medicinal materials kept, but also the ratio of living tree is improved; growing cycles are shortened; and growing investment risks are reduced. The cultivation method of the rhizoma paridis yunnanensis has the advantages of simple operation, facilitation of popularization, high yield, low risks, and the like; a new optimum scheme is provided for the artificial and large scale cultivation of the rhizoma paridis yunnanensis; and the method has better economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:曲靖促创科技有限公司
Dendrobium bonsai manufactured by planting dendrobium on stone or tree stump
InactiveCN102077745AGuaranteed survivalEasy to fixSpecial ornamental structuresHorticultureLiving treeTree stump
The invention discloses a dendrobium bonsai manufactured by planting a dendrobium on a stone or tree stump. The rock and tree stump dendrobium bondai is formed by selecting the stone or tree stump with water absorptivity and other bonsai molding materials, arranging the molding materials into a basin according to different shapes, planting the living tree stump in the basin with soil and fixing a dendrobium seedling onto the molding materials. The bonsai directly shows the special growing environment of the dendrobium on the stone or the tree, exhibits the visual effect of strong life, demonstrates a life legend on the stone, is highly ornamental and is an innovative means for vividly publicizing and graphically displaying the dendrobium medicinal material which is a plant to die.
Owner:廖晓康
Method for planting dendrobium officinale on living tree
InactiveCN106982724AHigh outputReduce land costCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationDiseaseCollection period
The invention relates to a method for planting dendrobium officinale on a living tree. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, selecting a planting site, 2, selecting and processing the living tree used for planting the dendrobium officinale, 3, selecting and processing nursery stocks, 4, planting is conducted and 5, after-planting management. The method takes full use of natural forest resources, saves the land cost and improves the yield of a standing forest, by controlling water in the planting site, pests, diseases and other aspects, the dendrobium officinale growing on the living tree is obtained, the problem that the collection period is short is solved, and the reliability and safety of the products are ensured; naturalized dendrobium officinale tissue culture seedlings vigorous in growth and developed in root system are selected as the nursery stocks, then the nursery stocks are planted on the living tree, and the survival rate is high; materials are easy to obtain, the production cost is low, the operation is simple and convenient, and the method has good economic and social and ecological benefits.
Owner:恩施土家族苗族自治州林科所
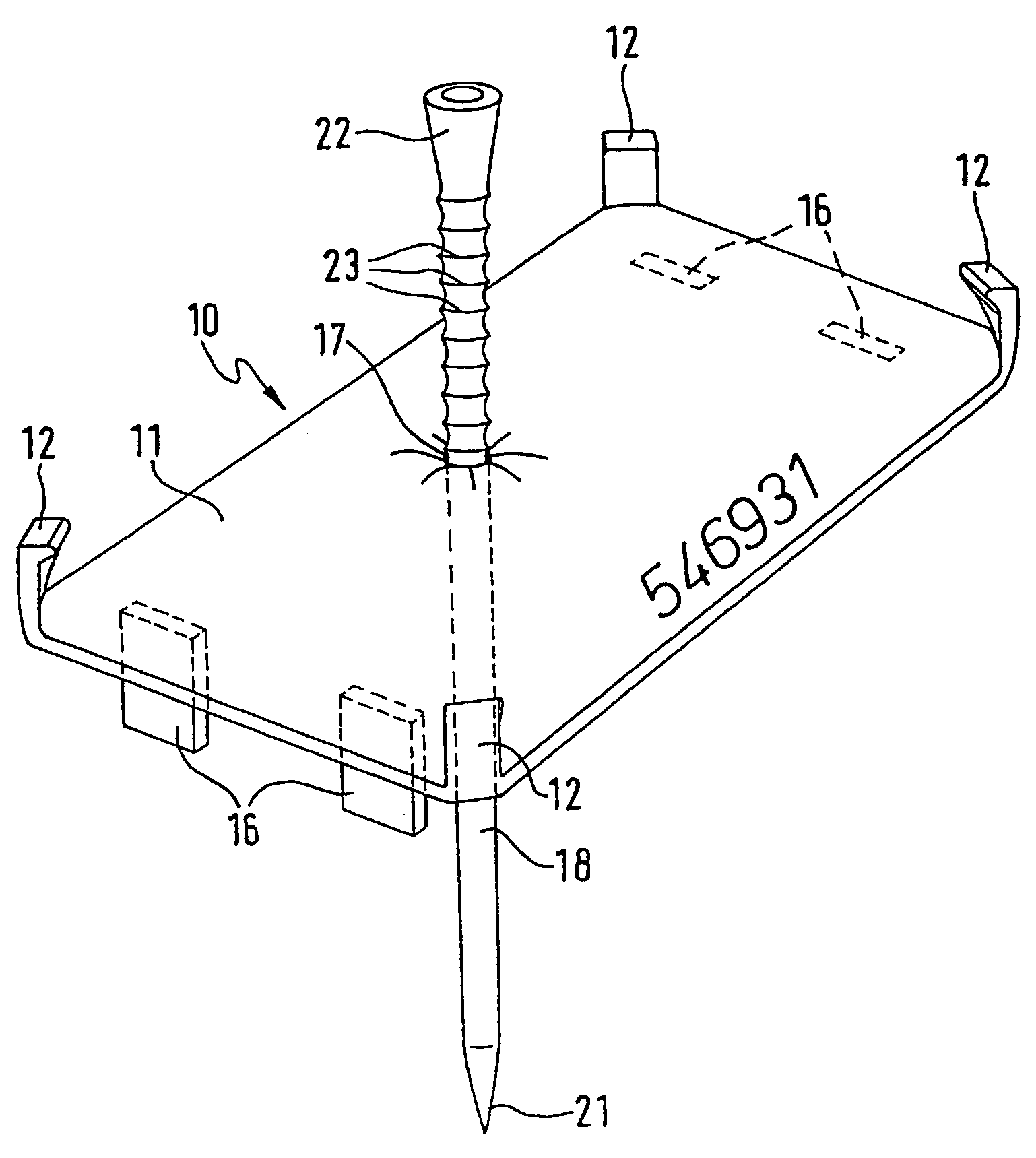
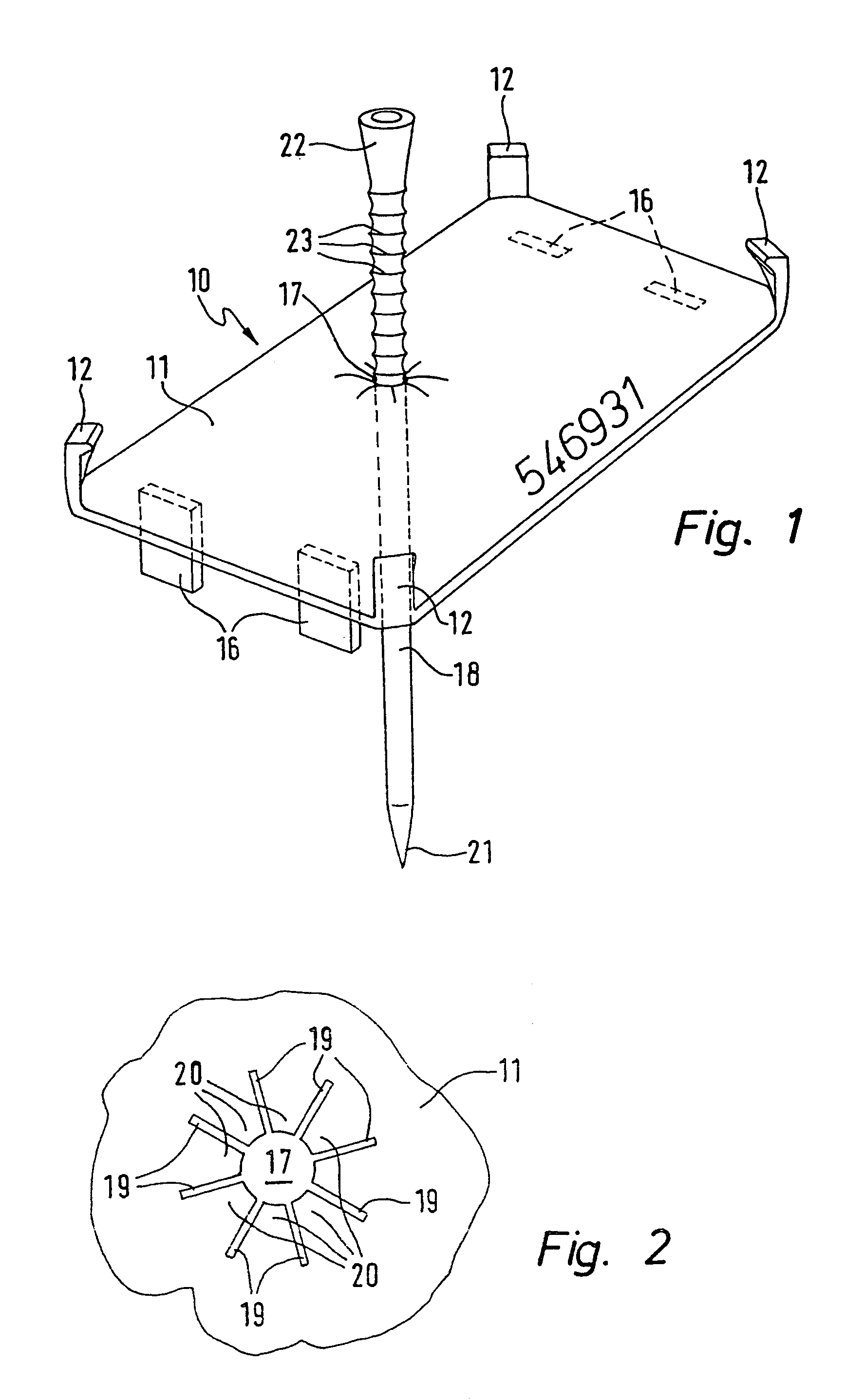
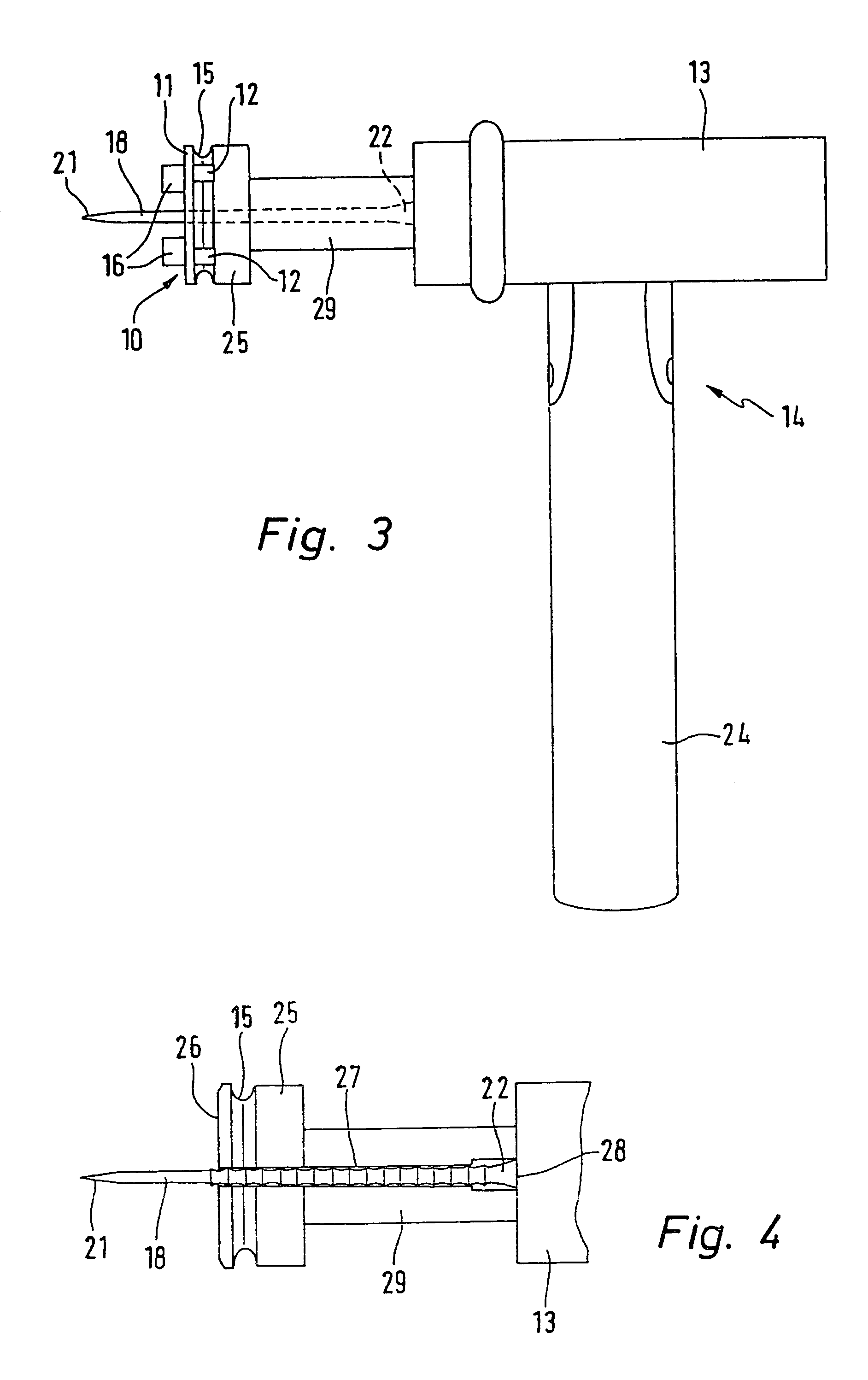
Marker tag for tree trunks and an applicator hammer for the application of same to tree trunks
A marker tag for tree trunks is provided with a flat element bearing indicia adapted to clip onto an applicator hammer. A nail extends perpendicularly through the flat element and is able to slide in a passage opening in the flat element preferably subject to the action of a clamping force and only able to be slid on application of a force. After driving the nail provided with the marker tag into a living tree trunk the trunk continues to increase in diameter and accordingly pushes the marker tag along the nail so that after a certain number of years it is stripped off and drops to the ground.
Owner:LATSCHBACHER
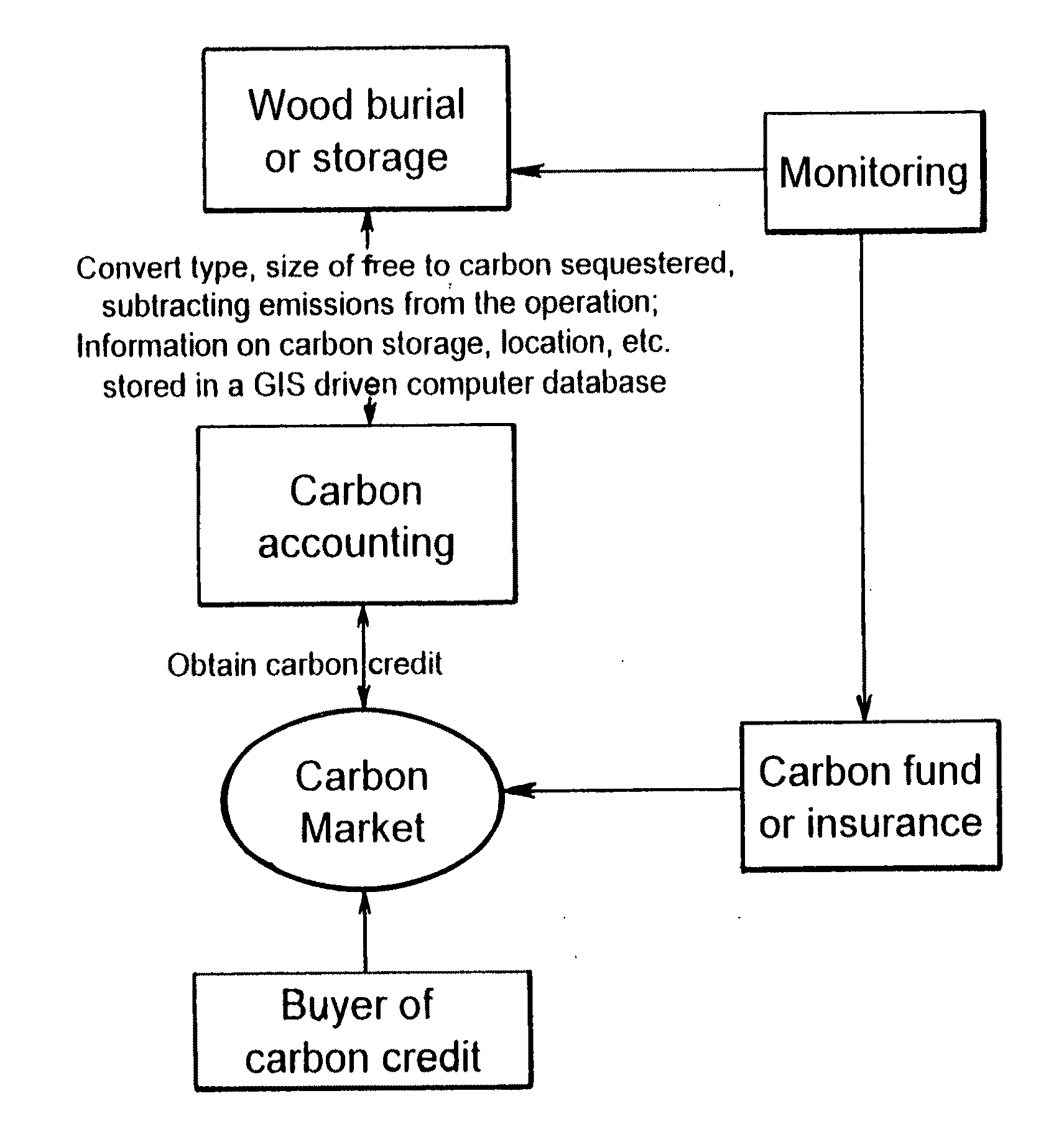
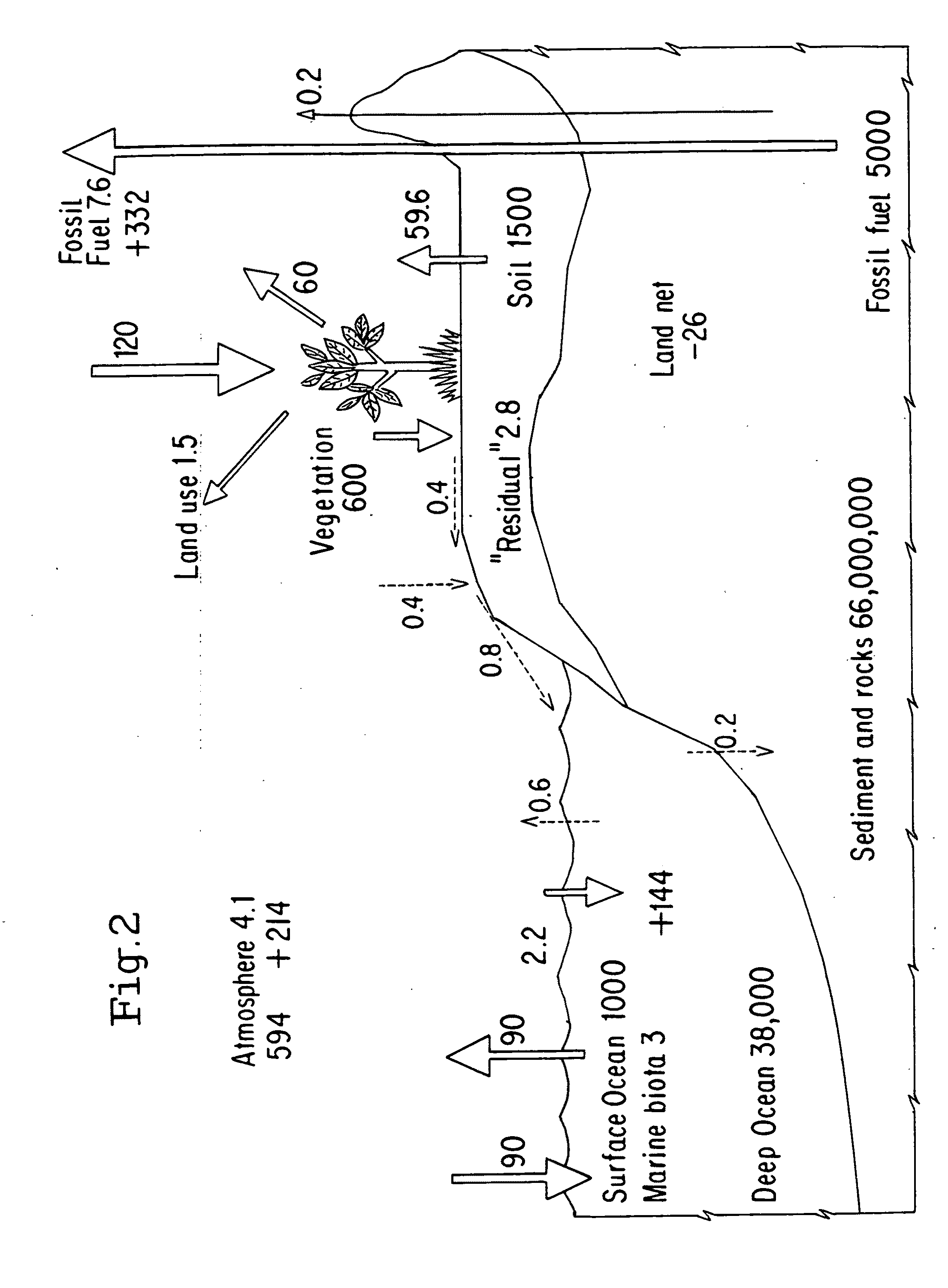
Carbon sequestration via wood burial and storage
InactiveUS20100145716A1Reduce decompositionLow techHydrogen sulfidesDispersed particle separationAbove groundLiving tree
To mitigate global climate change, a portfolio of strategies will be needed to keep the atmospheric CO2 concentration below a dangerous level. Here a carbon sequestration strategy is proposed in which certain dead or live trees are harvested via collection or selective cutting, then buried in trenches or stowed away in above-ground shelters. The largely anaerobic condition under a sufficiently thick layer of soil will prevent the decomposition of the buried wood. Because a large flux of CO2 is constantly being assimilated into the world's forests via photosynthesis, cutting off its return pathway to the atmosphere forms an effective carbon sink.
Owner:ZENG NING
Live tree epiphytic cultivating method of dendrobium officinale
InactiveCN106332760ANo pests or diseases occurredImprove food safetyBiocideDead animal preservationLiving treeInsect pest
The invention is applicable to the field of plant cultivating technology improvement, and provides a live tree epiphytic cultivating method of dendrobium officinale. The method comprises the following steps of A, selecting natural environment; B, selecting an attachment host; C, performing young seedling domestication, wherein a substrate for planting is shown as the accompanying drawing; D, selecting and processing epiphytic seedlings; E, planting young seedling; F, performing temperature and illumination regulation; G, performing branch trimming and weeding; H, preventing and controlling plant diseases and insect pests; I, performing harvesting. The dendrobium officinale basically has no plant diseases and insect pests; the use of pesticides is not needed; the edible safety of the dendrobium officinale is greatly improved. The nutrition value of the cultivated dendrobium officinale is most similar to that of wild dendrobium officinale; the medicinal value is high.
Owner:LIUZHOU HONGJI AGRI TECH
Crawler type tree mover
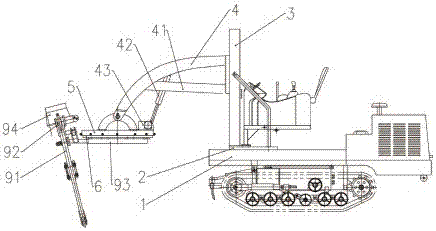
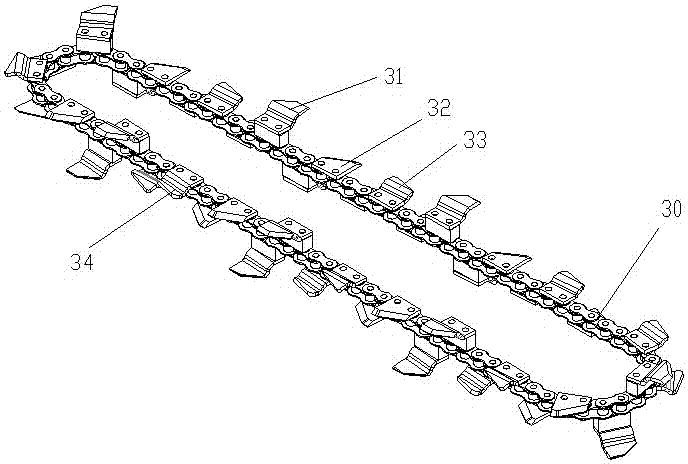
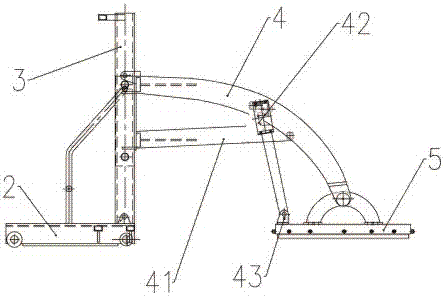
ActiveCN106900485AThe scope of application of the slope is expandedGood technical effectForestryLiving treeAgricultural engineering
The invention relates to the field of manufacturing of living tree transplanting work machines in agriculture and forestry machines, and discloses a crawler type tree mover. The crawler type tree mover comprises a walking rack, a movable base, a door type suspension support, a rotary support and a chain tool assembly. The movable base and the rack are in sliding connection, and the door type suspension support assembly and the movable base are fixedly connected. The crawler type tree mover has a digging work posture omnibearing adjusting function, the slope application range of the mover on nursery gardens or transplanting parcels is effectively widened, the mover can be suitable for ecological utilization and other environments of living tree transplanting digging work of hill and hummock slope nursery gardens and urban corner parcels.
Owner:ANHUI SANPU MACHINERY
Perishable-fruit-bearing cut-limb preservation and distribution method, coating and shipping container therefor
Owner:OREGON STATE OF
Chinese chestnut branch embedding grafting method
InactiveCN104737828AEffective protectionReduce lossesGraftingCultivating equipmentsFruit treeLiving tree
Provided is a Chinese chestnut branch embedding grafting method. When stock or young trees reach the grafting standard, grafting is performed, and the grafting method includes the steps of scion grafting, two-incision grafting, management performed on the current grafting year and pruning of live tree columns. Because the cortical layers of seedlings of nursery land and the cortical layers of the young trees which are planted newly are thin, the branch embedding grafting method can effectively protect the critical layers of branches and trunks, and the method is simple, practical and high in survival rate. Through the method, coppice shoots, generated after grafting, of the branches and the trunks can be removed in time or bud picking is performed as soon as possible, loss of tree liquid nutrient is reduced, and grafted buds can grow healthily and strongly. The method is particularly suitable for cultivating grafting seedlings in the nursery land and being used in a Chinese chestnut orchard where the young trees are newly planted, and the method can also be used for grafting of the branches and the trunks, with thin critical layers, of adult Chinese chestnut trees and grafting seedling cultivation of other fruit trees.
Owner:迁西县职业技术教育中心
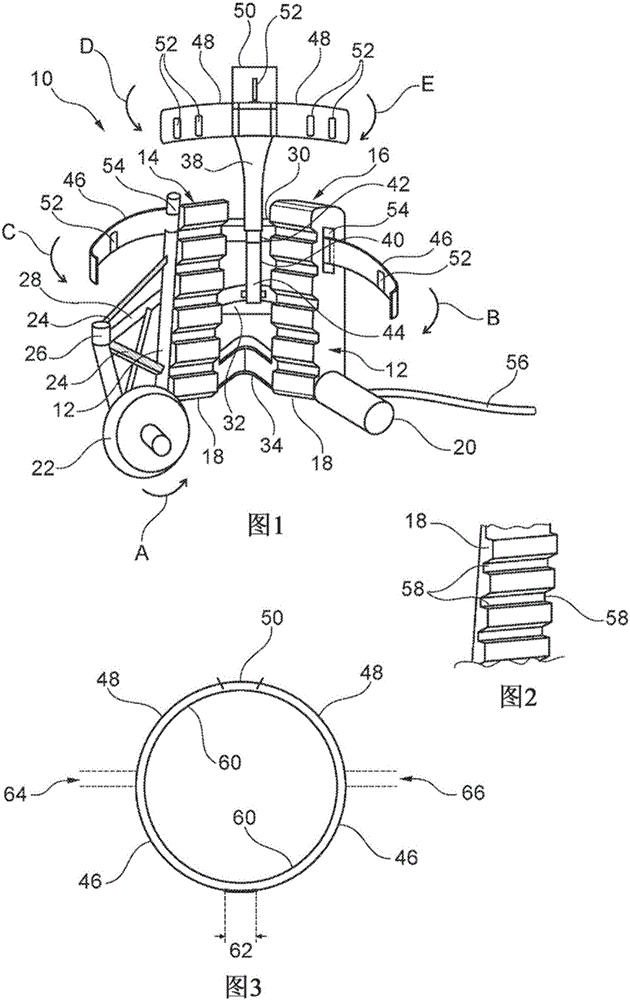
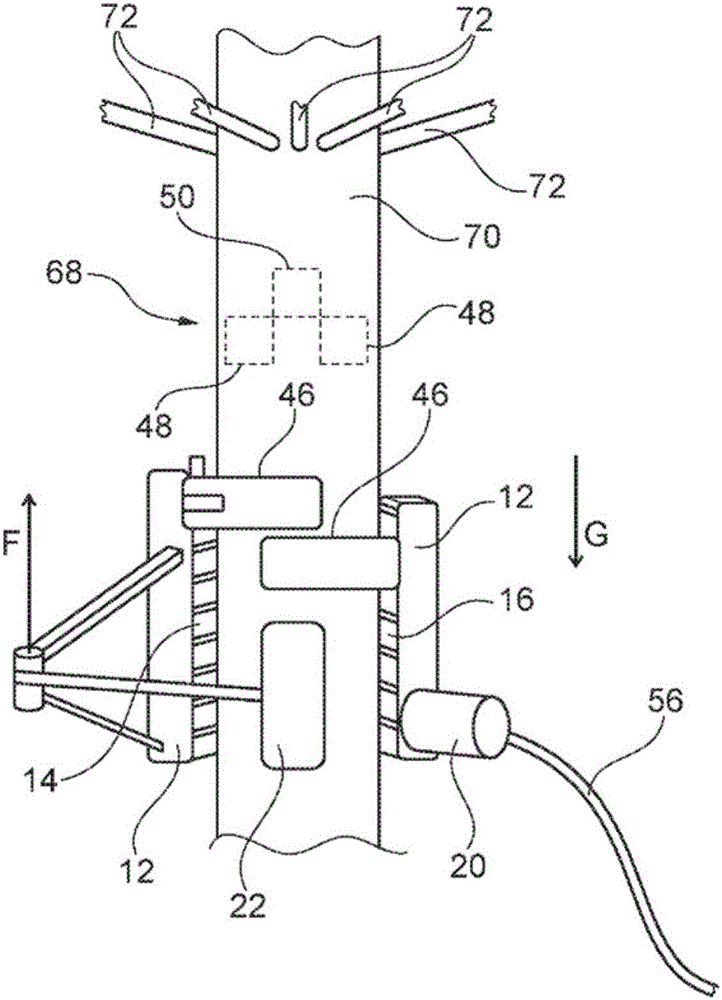
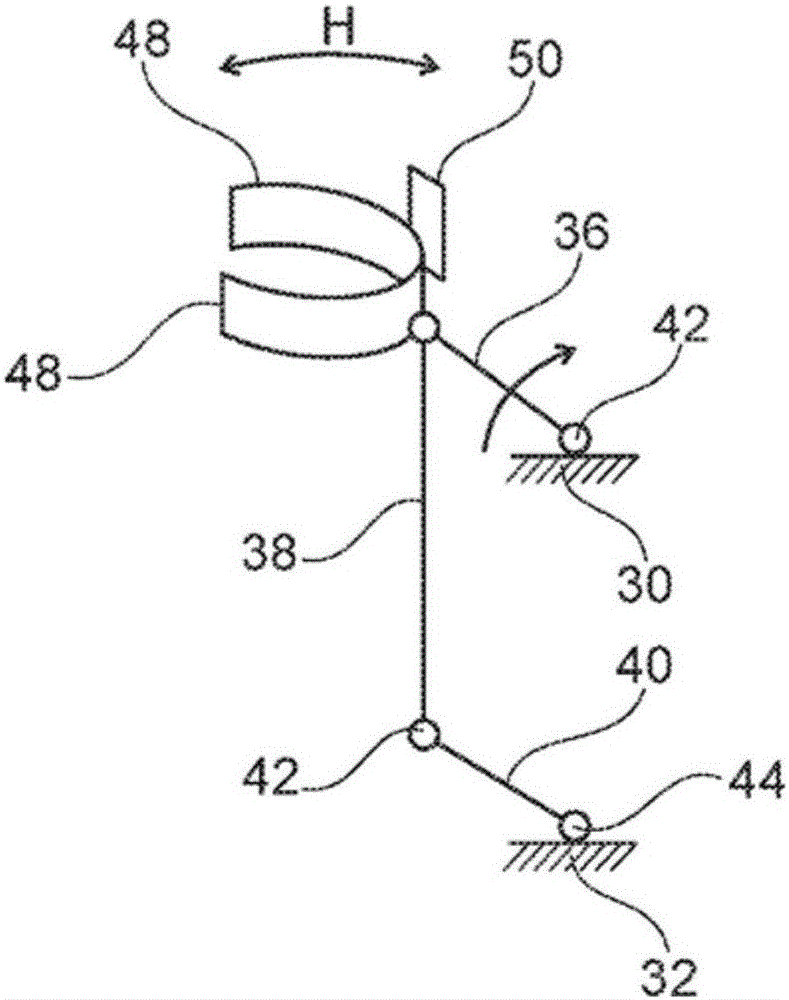
Machine for debranching living trees
Described is a machine (10) for debranching living trees. The machine can move up and down the tree autonomously by means of a drive mechanism and has an upper cutting unit comprising three blades (48, 50) and below the upper cutting unit a lower cutting unit comprising two blades (46). The in total five blades (46, 48, 50) are arranged so that they cover the full girth of the tree. The two blades (46) in the lower cutting unit are horizontally offset so that their end portions can overlap. To move the machine (10) along the tree trunk there are two belt drives which press against the tree and are both driven by a single hydraulic motor (20). The upper cutting unit with its three blades (48, 50) can move horizontally as a whole, so that when the machine (10) is moved and encounters thicker or slightly bent parts of the tree trunk it can give way in order to prevent the bark from being damaged by the blades (46, 48, 50).
Owner:ADVALIGNO GMBH
Method for cultivating phellinus igniarius by using wild living tree stumps
InactiveCN103493685AIndividual bigTo satisfy the market's needsHorticultureLiving treeLand resources
Disclosed is a method for cultivating phellinus igniarius by using wild living tree stumps. The method includes the steps that first, mother seeds, stock seeds and cultivation seeds are manufactured through a traditional method; second, mulberry seedlings are cultivated, 100-1000mu of mulberry trees are planted, and 1 / 5 of mulberry bark is cut away with a knife when the diameter of the mulberry trees reaches 10cm according to the standard of enabling the mulberry trees to grow as well as preventing the mulberry trees from dying; third, when surface drying occurs to the xylem of the positions where the bark is cut away, holes with the depth of 5.5-6cm are punched through a hollow punch or electric drill, the space between every two holes is made to be 16-18cm, and then the holes are inoculated with phellinus igniarius strains and sealed by yellow mud; phellinus igniarius fruit can be picked within as long as 10 years through one time of inoculation till the mulberry trees die of aging and rot. By means of the method for cultivating the phellinus igniarius by using the wild living tree stumps, forest land resources can be fully utilized for cultivating phellinus igniarius products, the method is simple and easy to realize, the produced phellinus igniarius products are large in size and can be artificially cultivated in quantity, and therefore market demands can be fully met.
Owner:贵州省施秉县民生天麻科技有限公司
Method for planting dendrobium officinale in imitated wild conditions
InactiveCN107242124AIncrease productionReduced germination rateCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationLiving treeSeedling
The invention discloses a method for planting dendrobium officinale in imitated wild conditions. The method comprises the following steps of choosing natural environment, choosing living trees for epiphytic seedlings, choosing the epiphytic seedlings, planting, fertilizing, preventing and controlling pests, pruning branches and harvesting. According to the method for planting dendrobium officinale in the imitated wild conditions, the wild environment suitable for the growth of dendrobium officinale is selected, an epiphytic mode with the living trees is adopted, higher-yield dendrobium officinale is obtained in the space with the same area, and the cost is greatly saved; meanwhile, the environment is similar to wild climate environment, so that the content of polysaccharide in dendrobium officinale is higher, and the quality is higher.
Owner:XILIN DAYINZI DENDROBIUM OFFICINALE PLANTING & SALES FARMERS SPECIALIZED COOP
Non-destructive method and test kit for the detection of infestation of live trees by invasive wood boring insect species
The invention disclosed is a method and test kit for the non-destructive detection of infestation of live conifer trees by invasive wood boring insects having a specific established fungal associate. The method involves identifying an infested tree, providing a probe for collecting viable fungal spore samples and matching the spore sample with a known insect.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN IN RIGHT OF CANADA AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT RESOURCES CANADA CANADIAN FOREST SERVICE
Method for cultivating Agrocybe aegerita with alive stumpage
InactiveCN101366347AGuaranteed not to dieExtended growing seasonFungiHorticultureComing outPesticide residue
The invention provides a method for cultivating Agrocybe chaxingu on living trees. The method comprises the following steps of separating and culturing mother seeds and cultivating Agrocybe chaxingu on living trees. After dibbling, mycelia are subjected to field planting, extend and twist together under the supply of the own moisture and nutrition of trees, and the Agrocybe chaxingu comes out under the climatic conditions of proper external temperature and humidity. The Agrocybe chaxingu obtained through the method is the same as natural wild Agrocybe chaxingu in color, fragrance, taste and health care effect. Whether the Agrocybe chaxingu is fresh or dried, the Agrocybe chaxingu has no pesticide residue, thereby meeting the requirements of natural foods. People can benefit from the trees subjected to dibbling after planting once if only the trees are not hewn at will or die for lack of water.
Owner:徐瑞安
Method for preparing rattan mildew proofing medicament
InactiveCN104430646ASteps to change anti-mildew treatmentCause harmBiocideFungicidesLiving treeAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a method for preparing a rattan mildew proofing medicament and relates to the technical field of production of rattan-woven products. The method comprises the specific steps: weighing all raw material ingredients for preparing the mildew proofing medicament according to a weight ratio, and mixing the raw material ingredients together; placing the mixed raw material ingredients into a vessel, adding water, decocting, boiling with intense fire firstly, then, decocting for 20-30 minutes with soft fire, and filtrating to remove decoction dregs, so as to obtain medicated liquid, wherein the volume of water added accords with that 6kg of medicated liquid is prepared from 1 kg of mixed raw material ingredients; removing macromolecular substances from the medicated liquid by adopting a nanofiltration technology, thereby preparing the rattan mildew proofing medicament. According to the method, the mildew proofing process for living trees is simple, and the traditional mildew proofing methods are broken through; after living rattan is subjected to mildew proofing, the rattan can be directly used for weaving the rattan-woven products, the steps of carrying out mildew proofing on the rattan in the traditional rattan weaving processes are thoroughly changed, the mildew proofing effect is greatly improved, and the utilization ratio of drugs is greatly increased compared with that of the traditional methods; the mildew proofing medicament is non-toxic and cannot cause any injury to human bodies.
Owner:安徽阜南县万家和工艺品有限公司
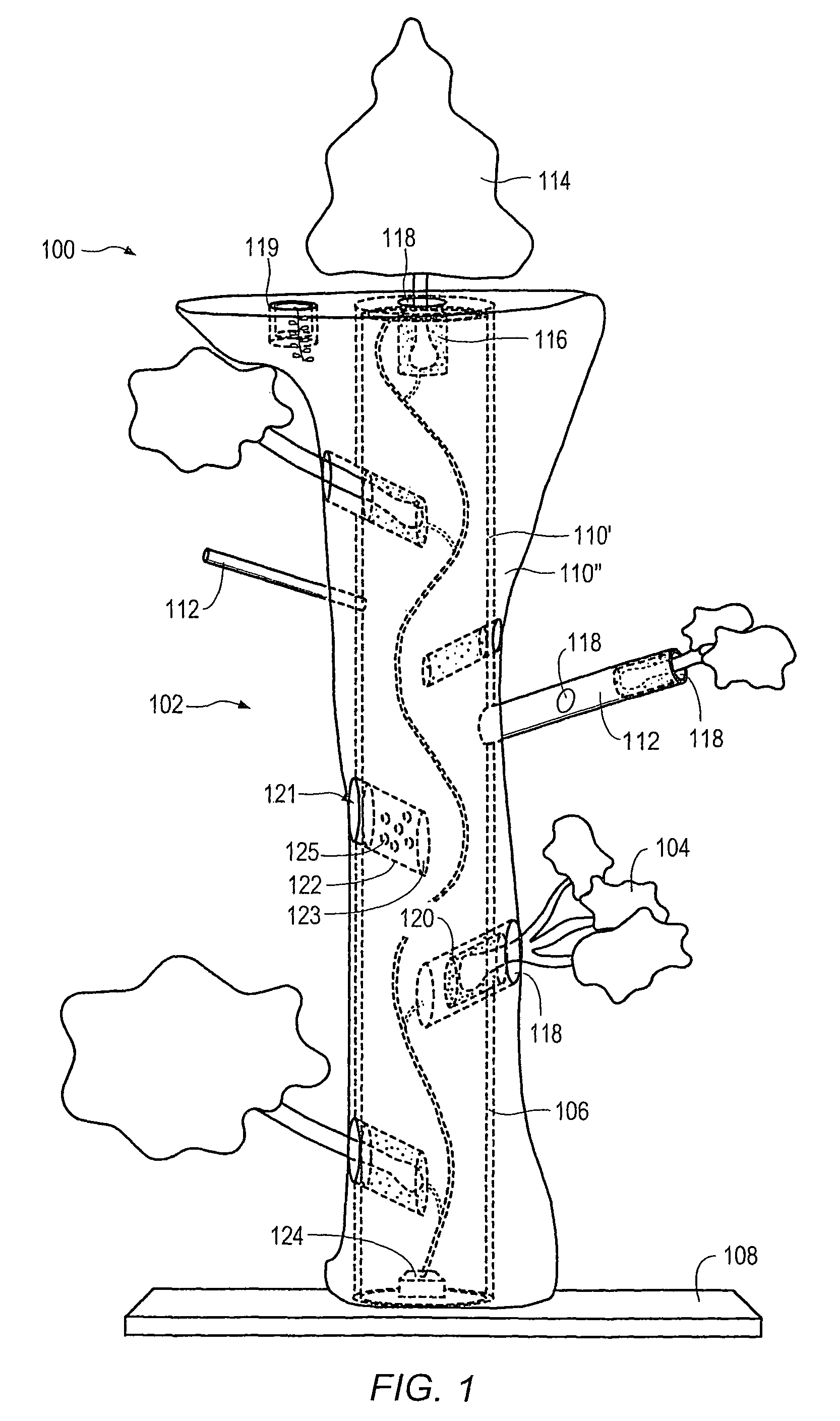
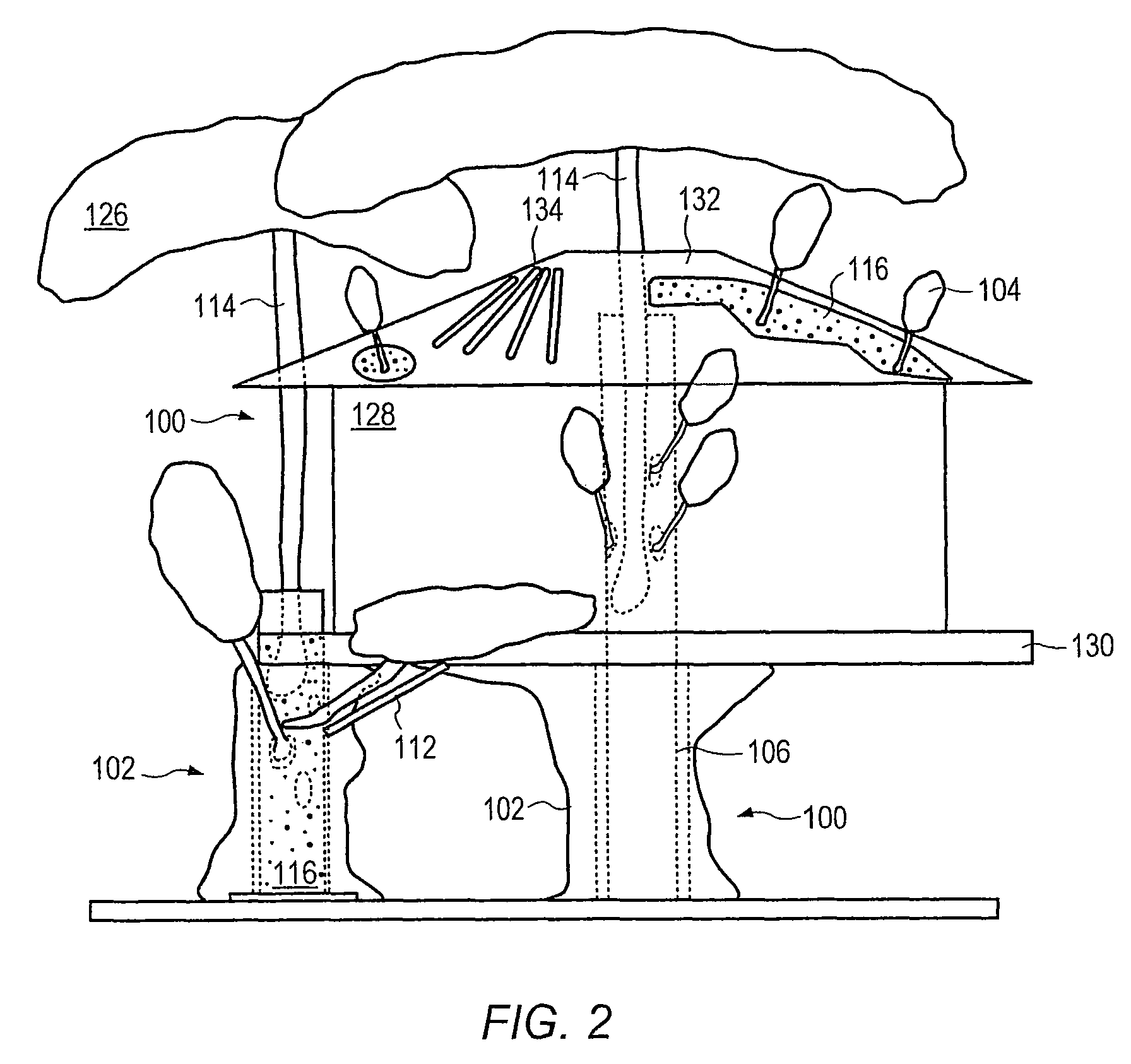
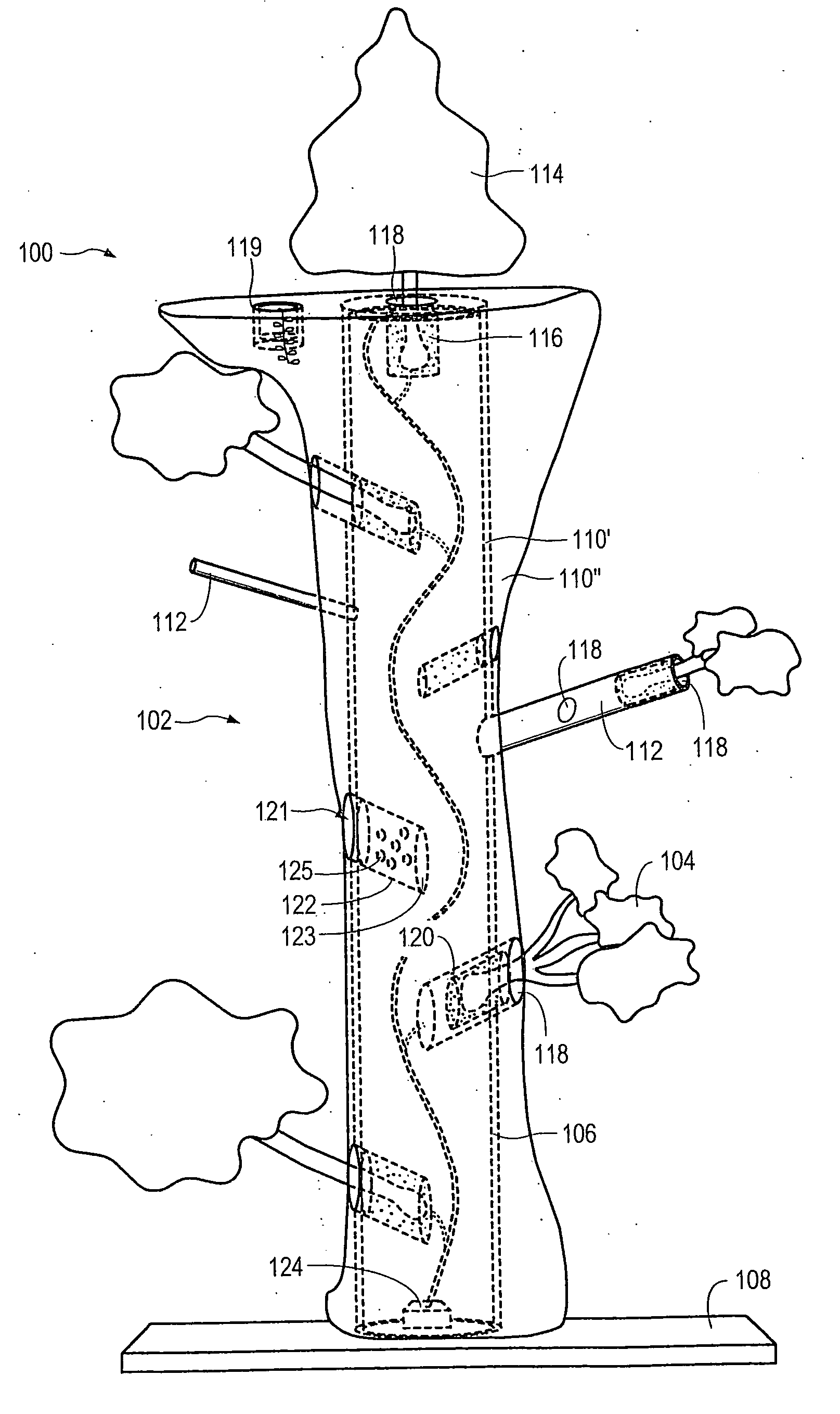
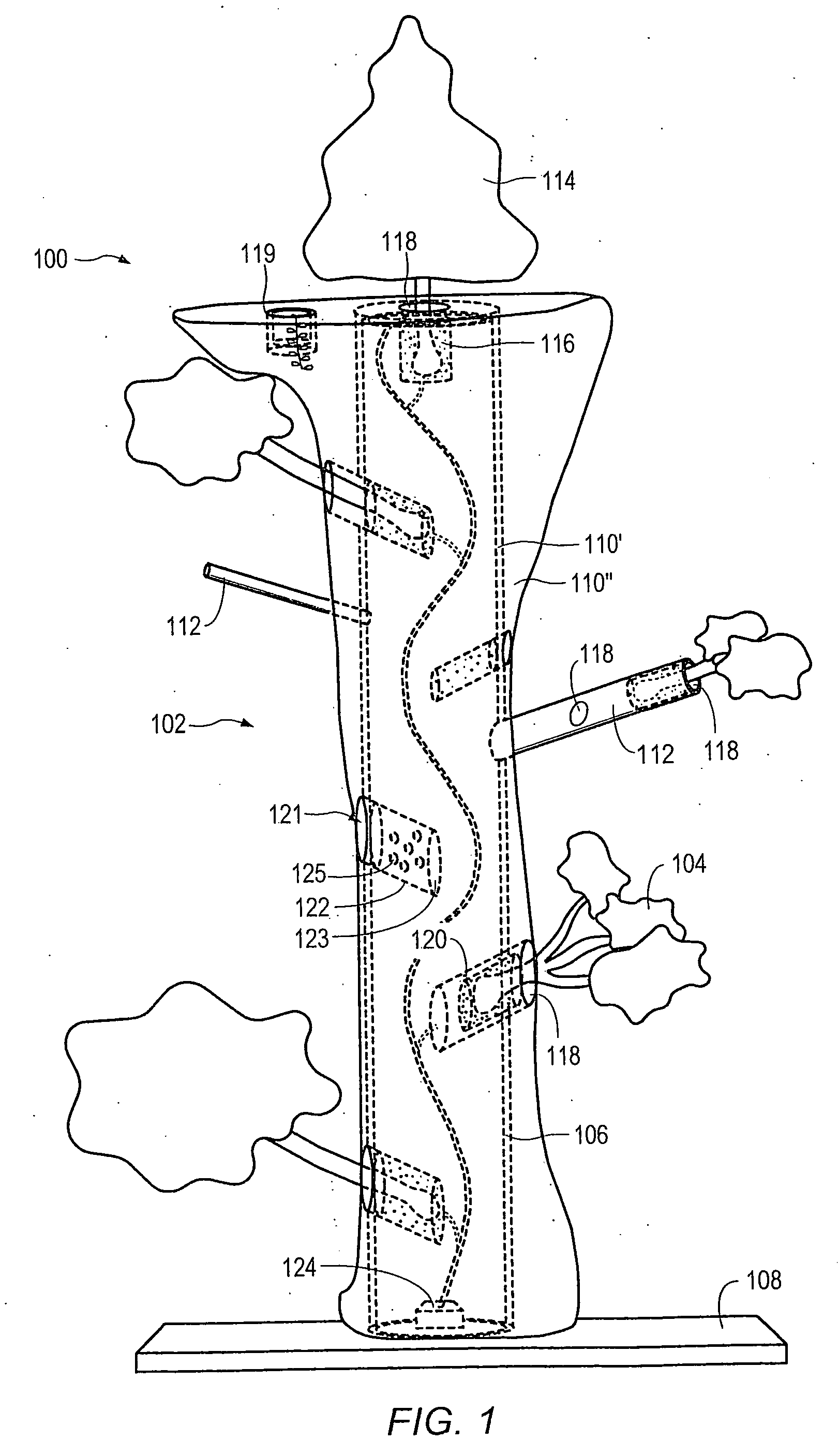
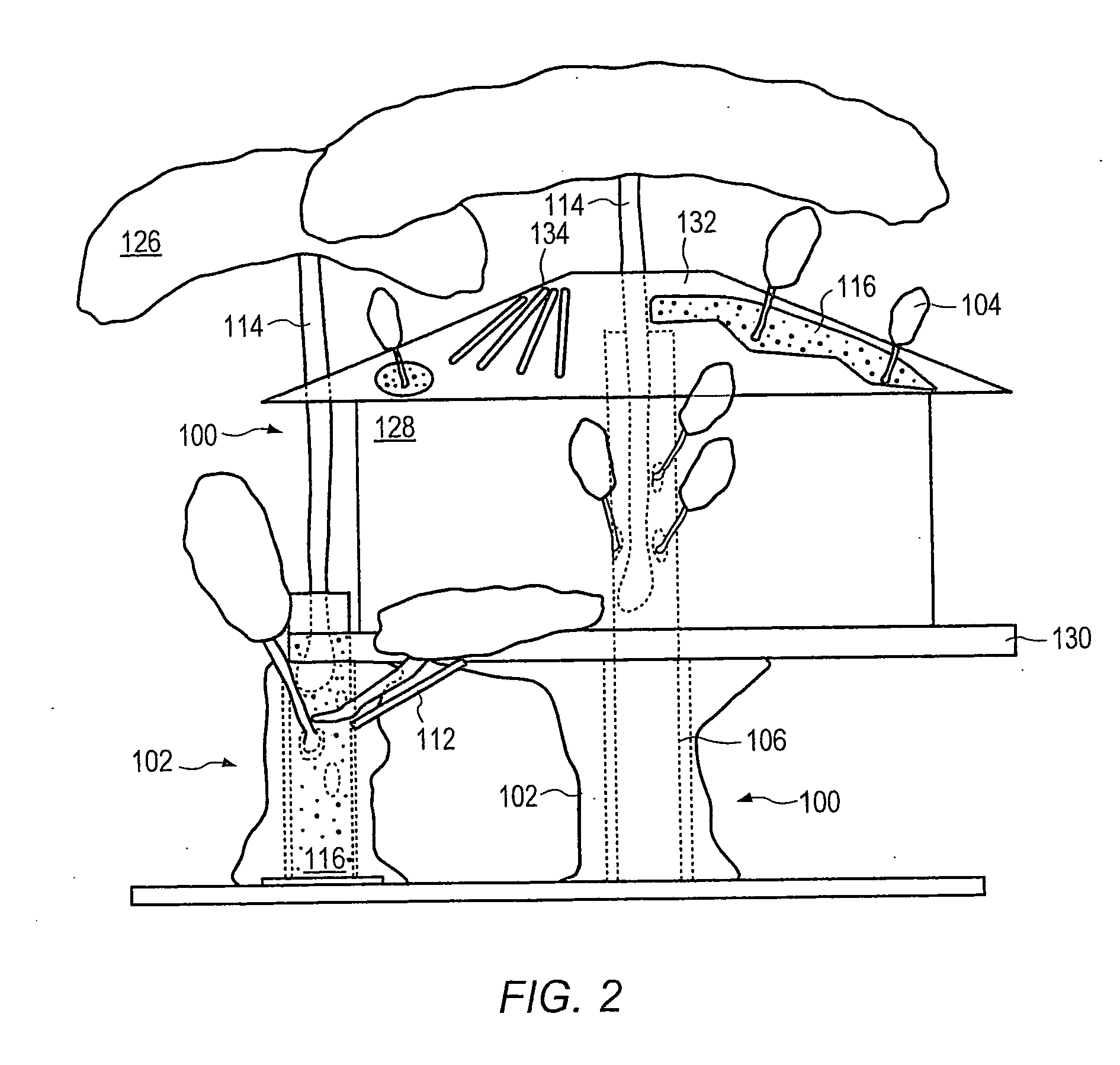
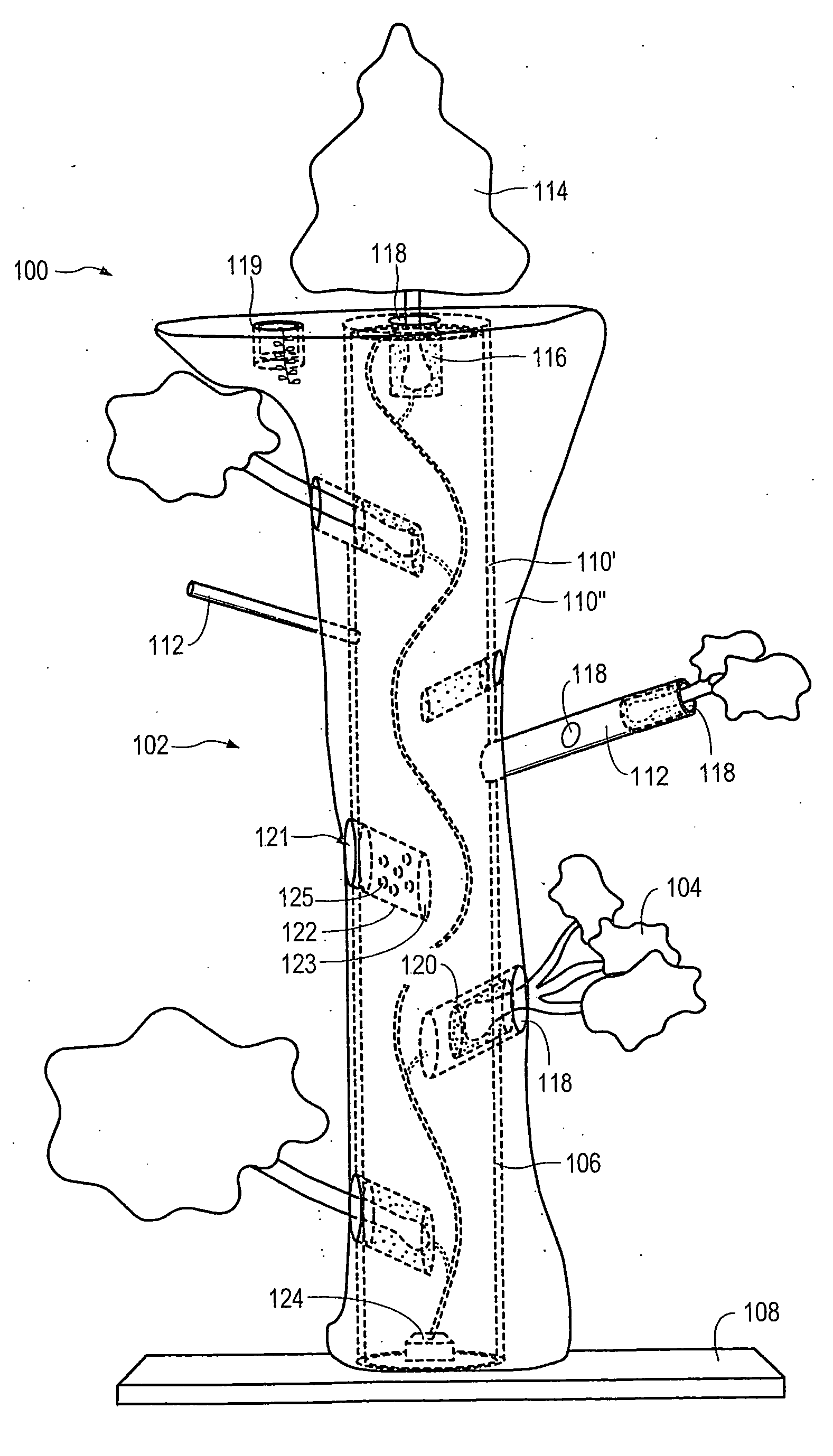
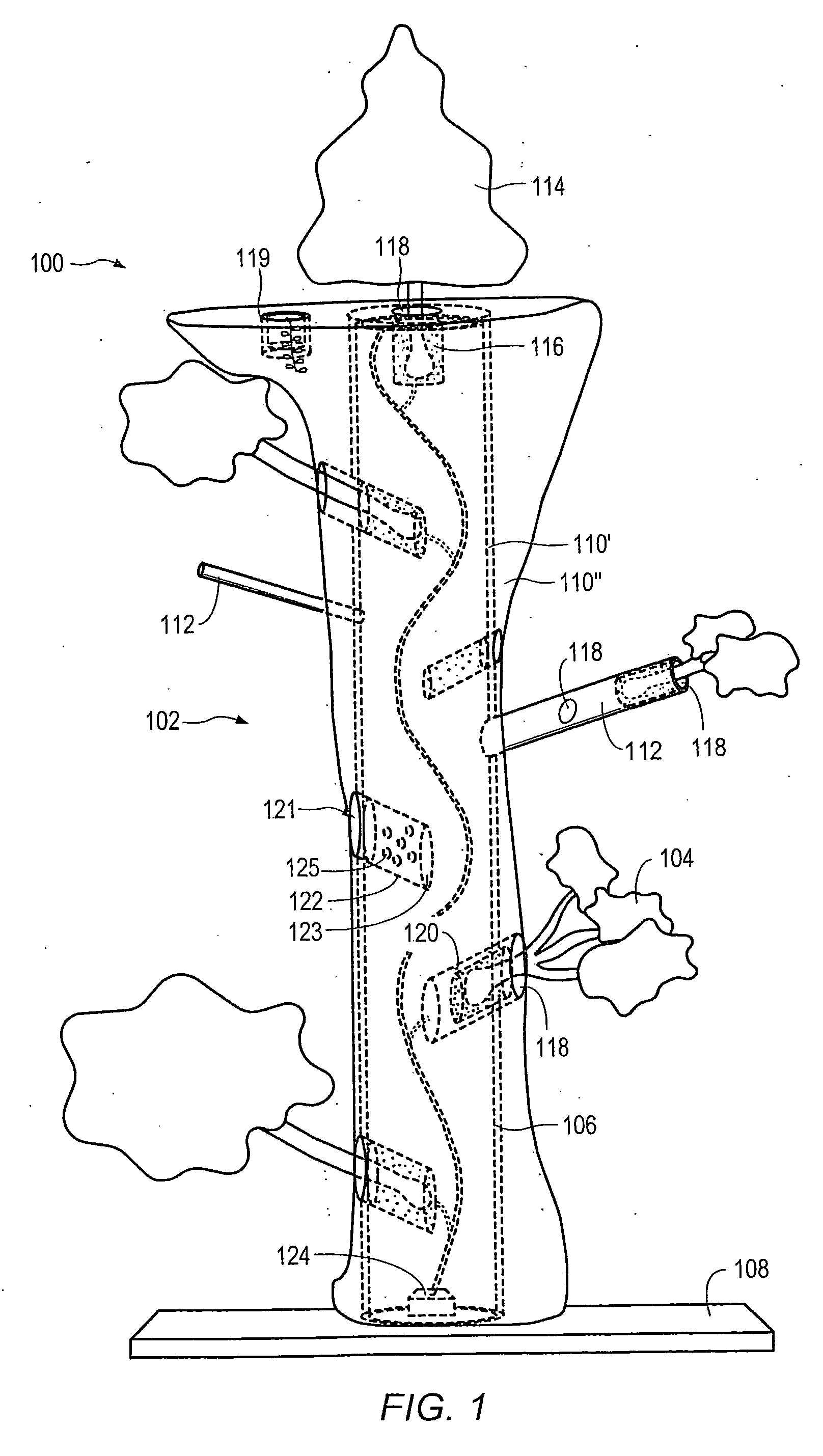
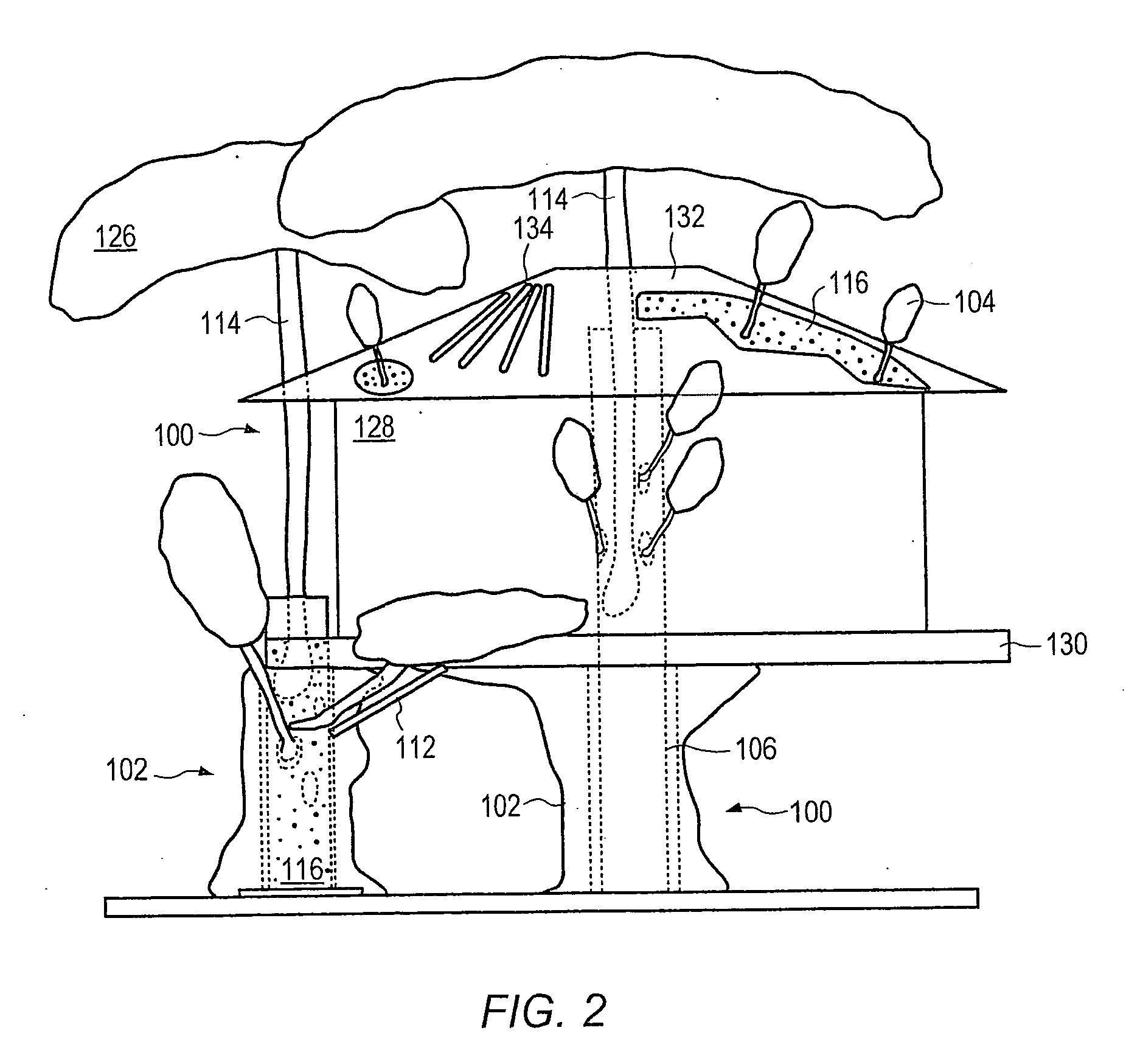
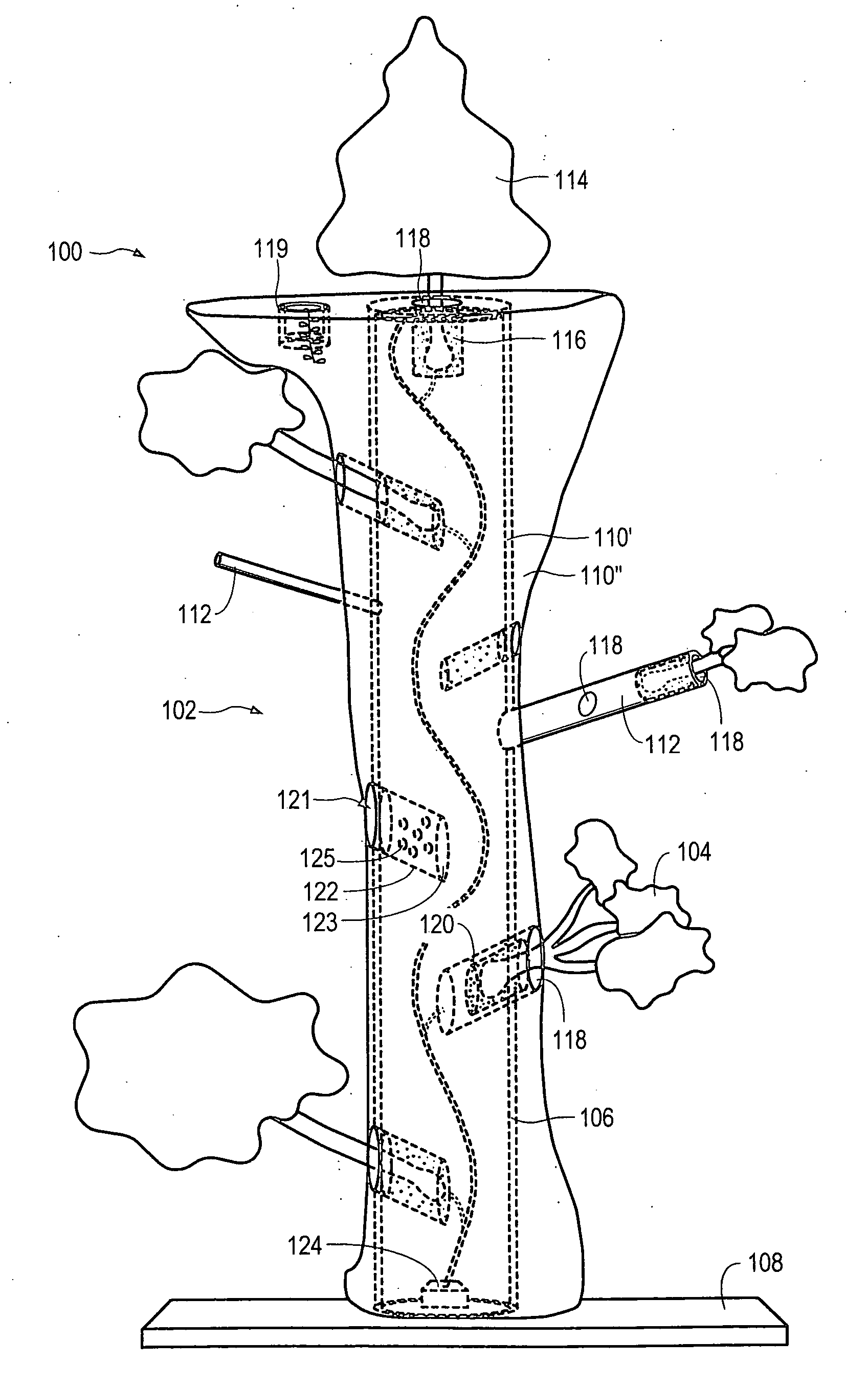
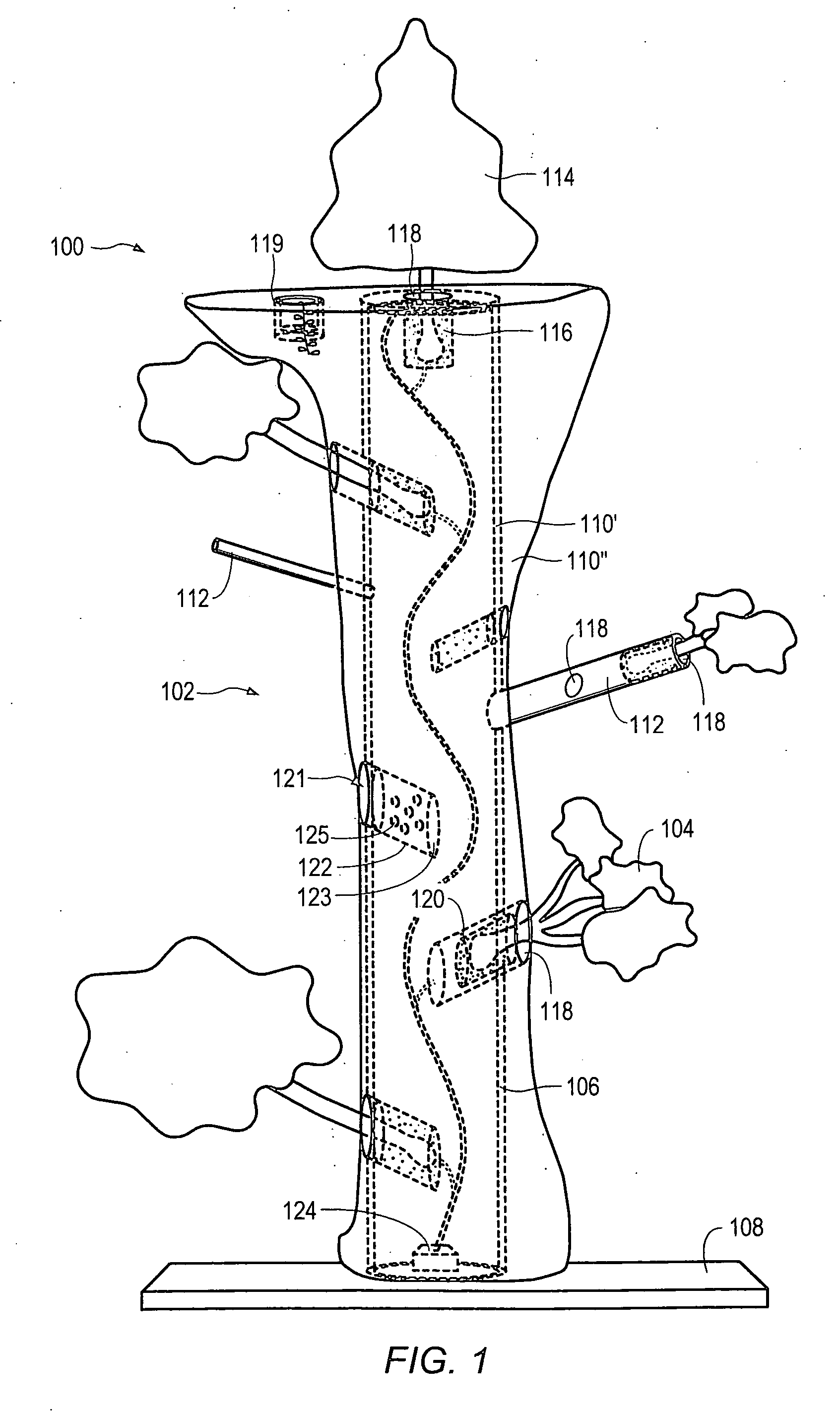
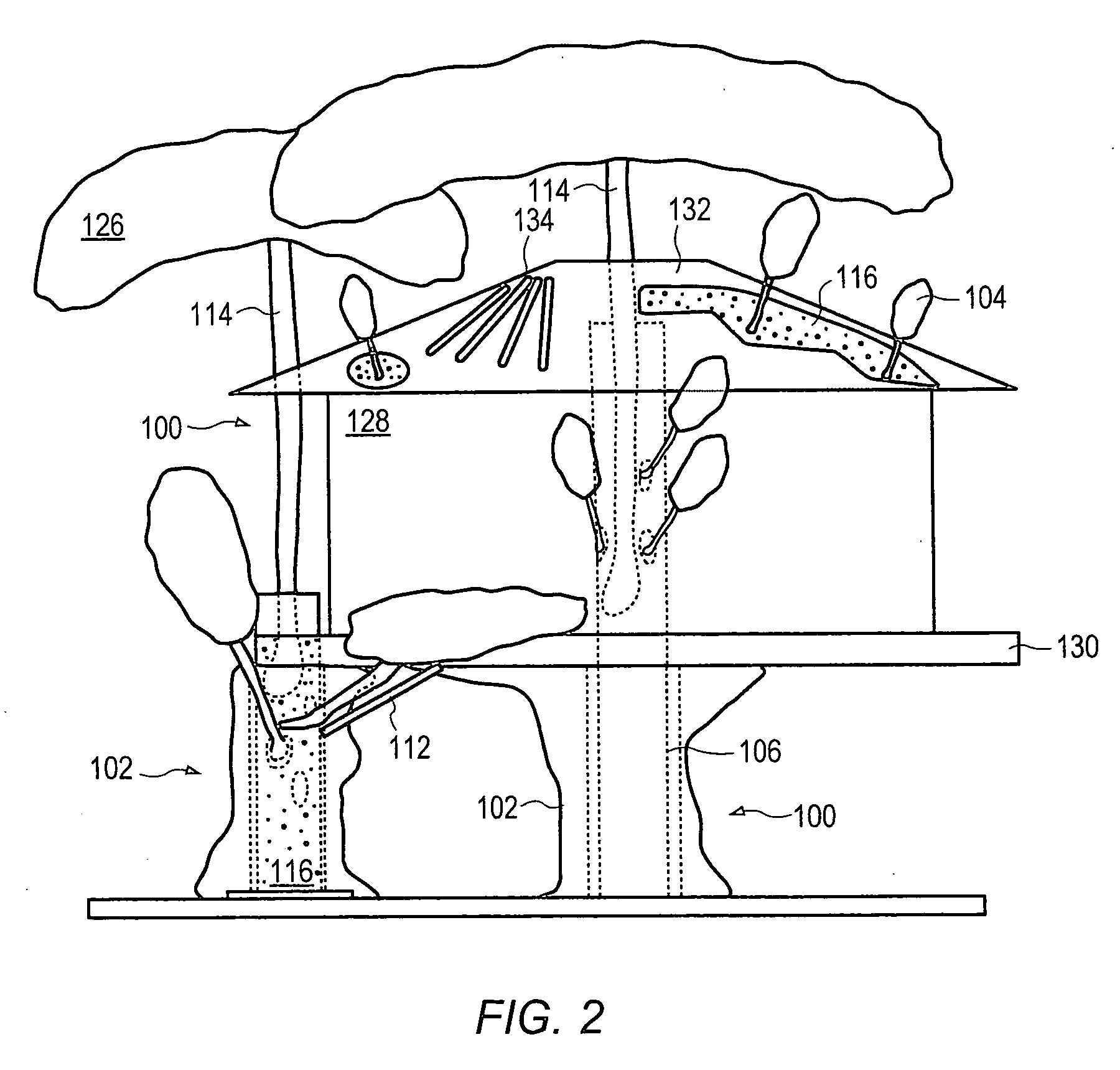
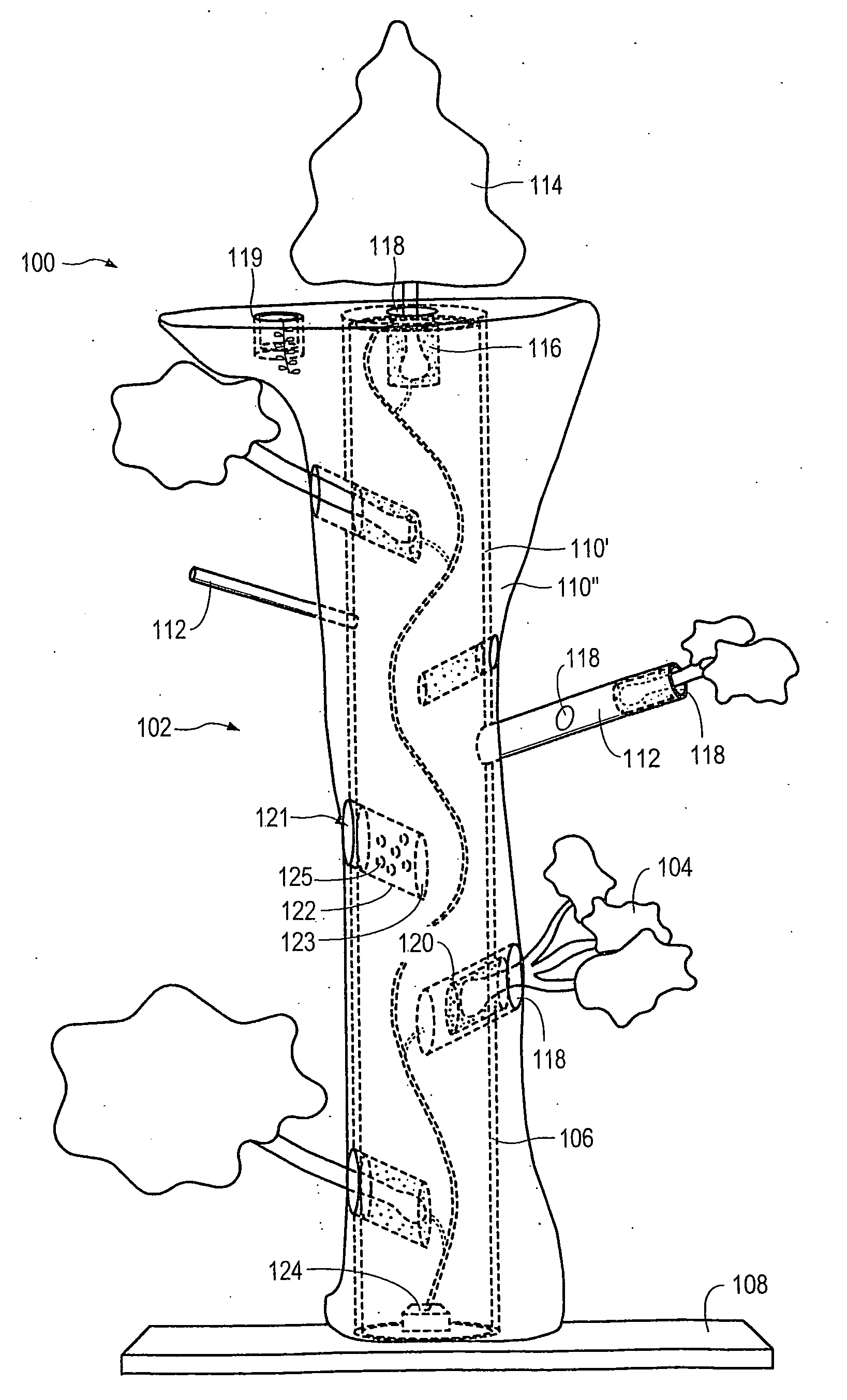
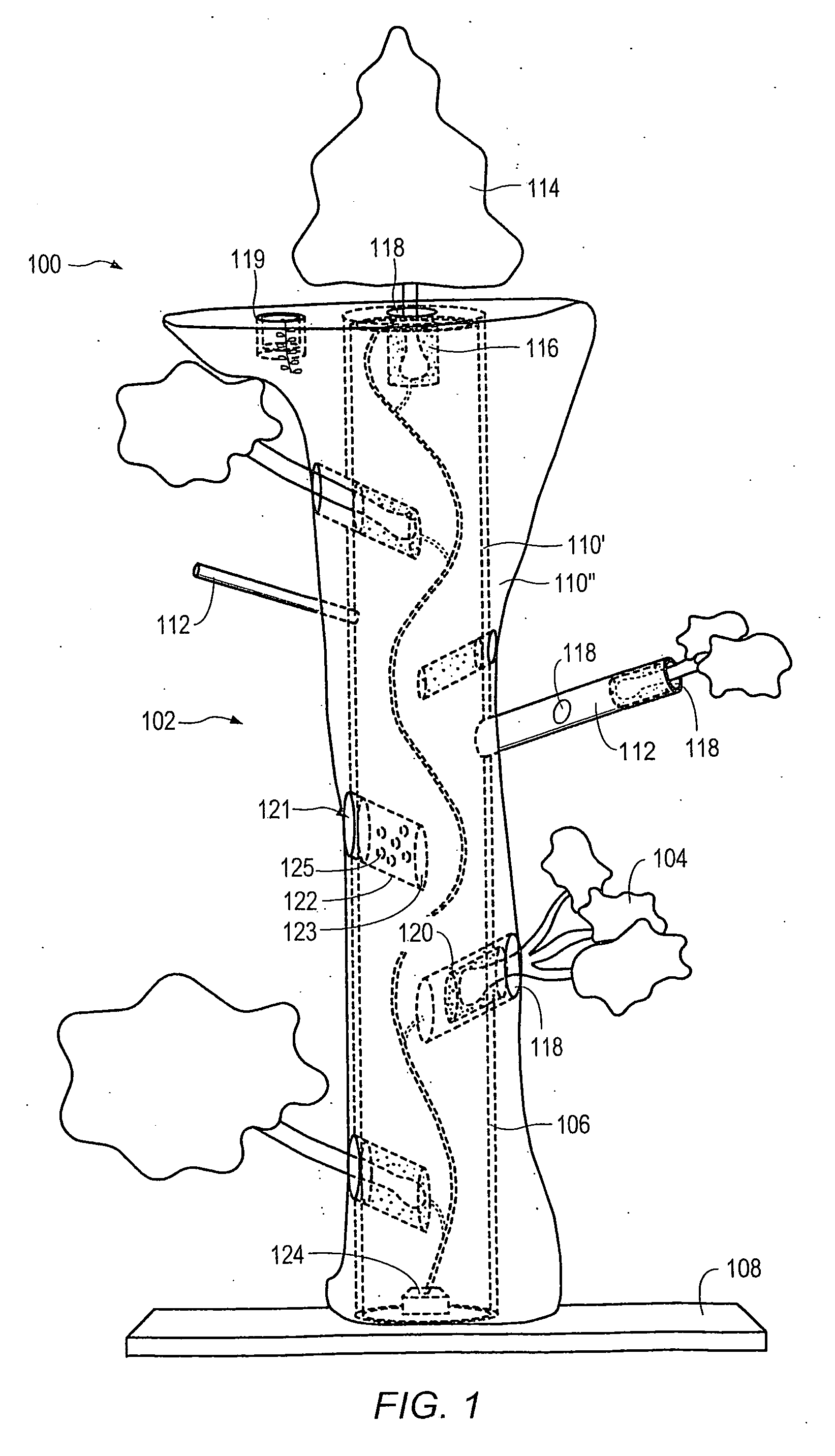
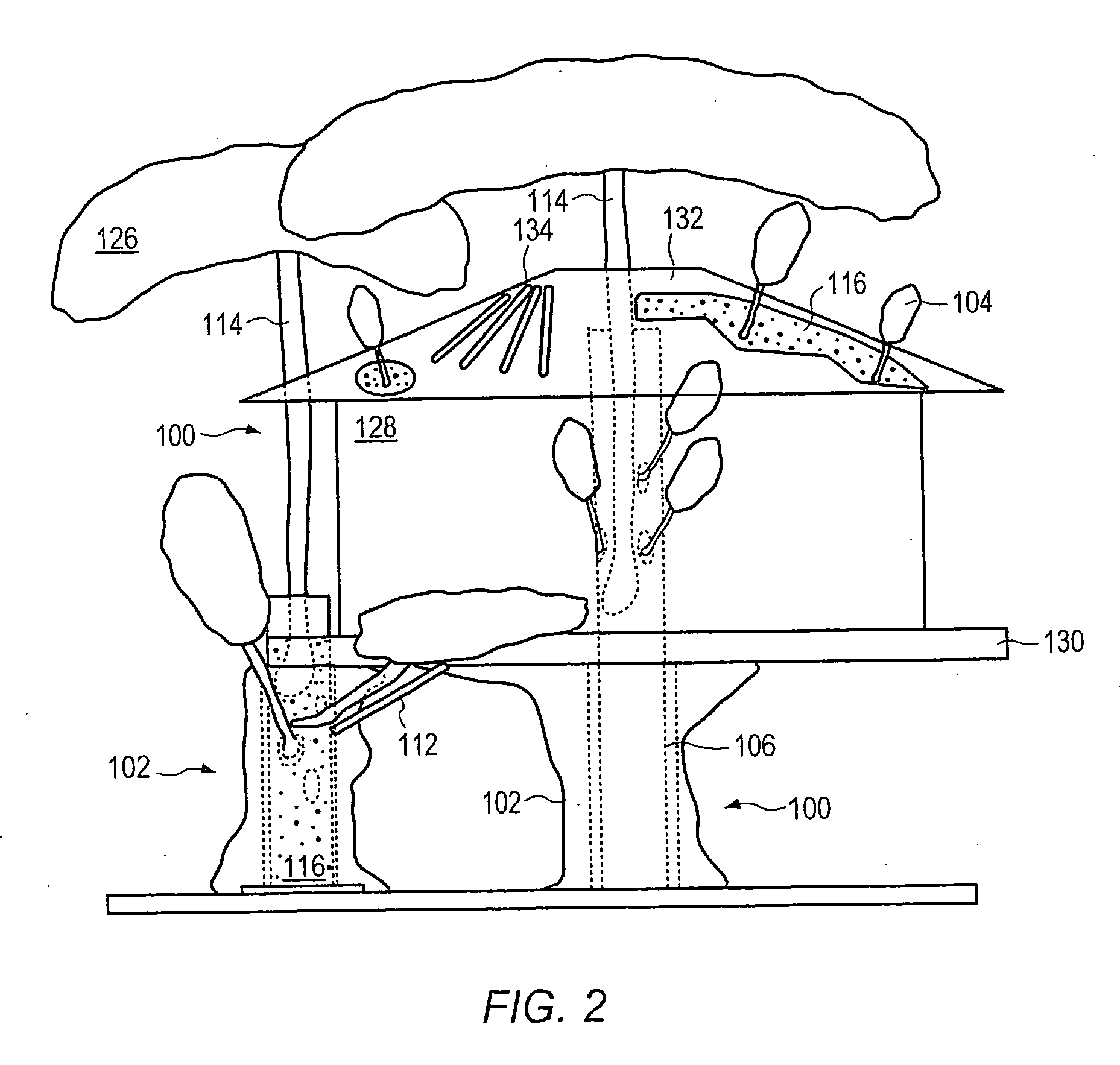
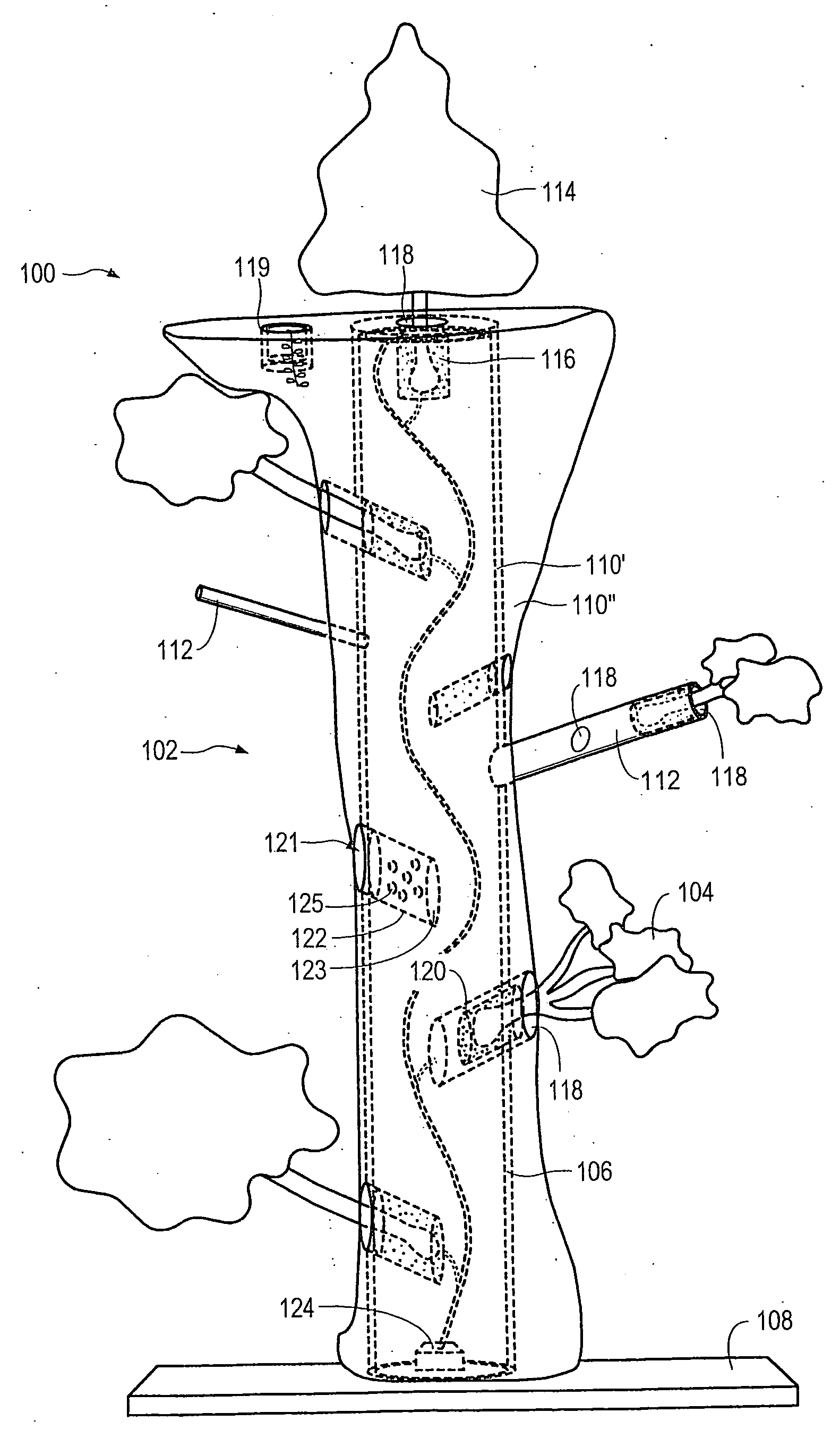
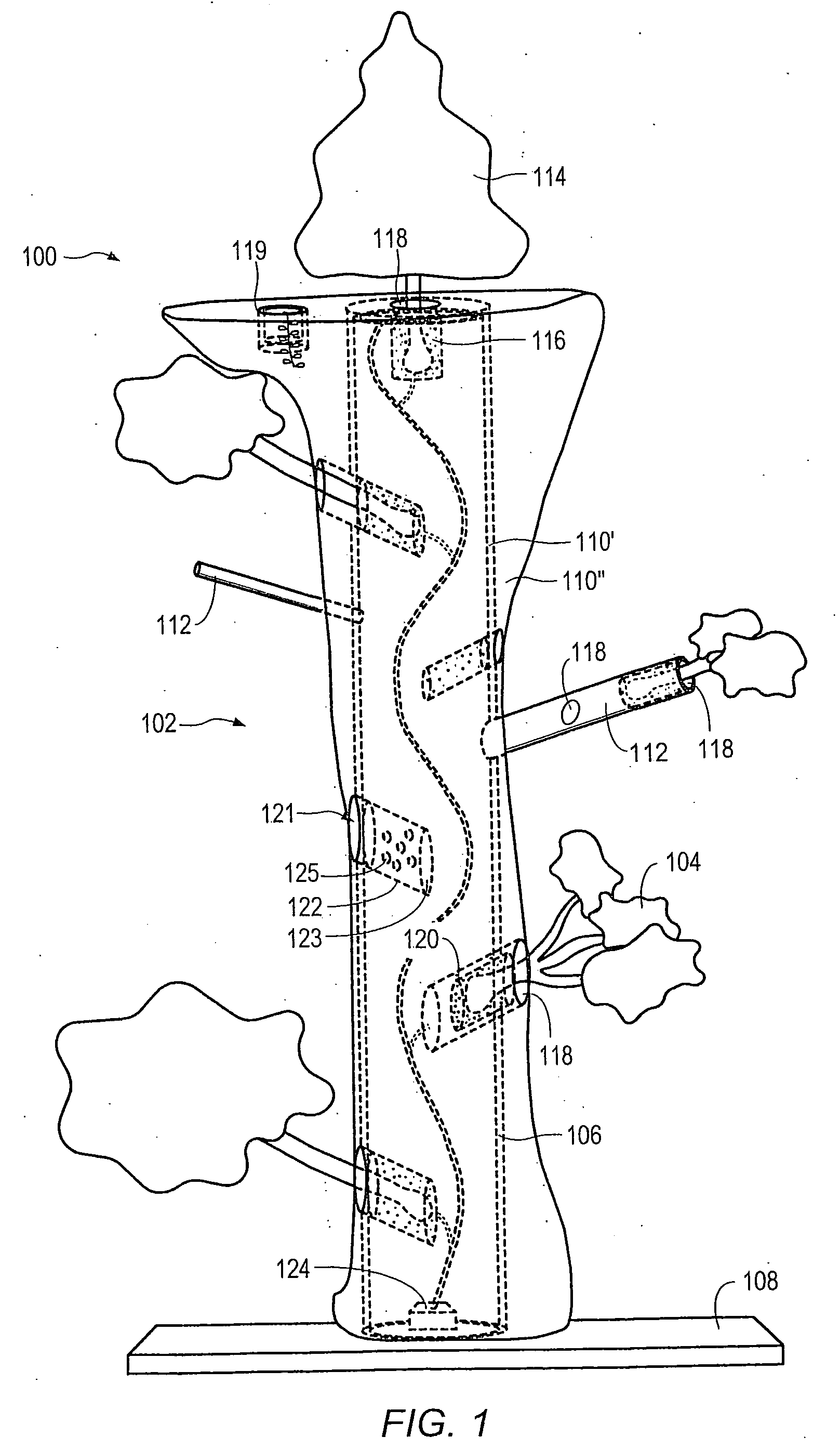
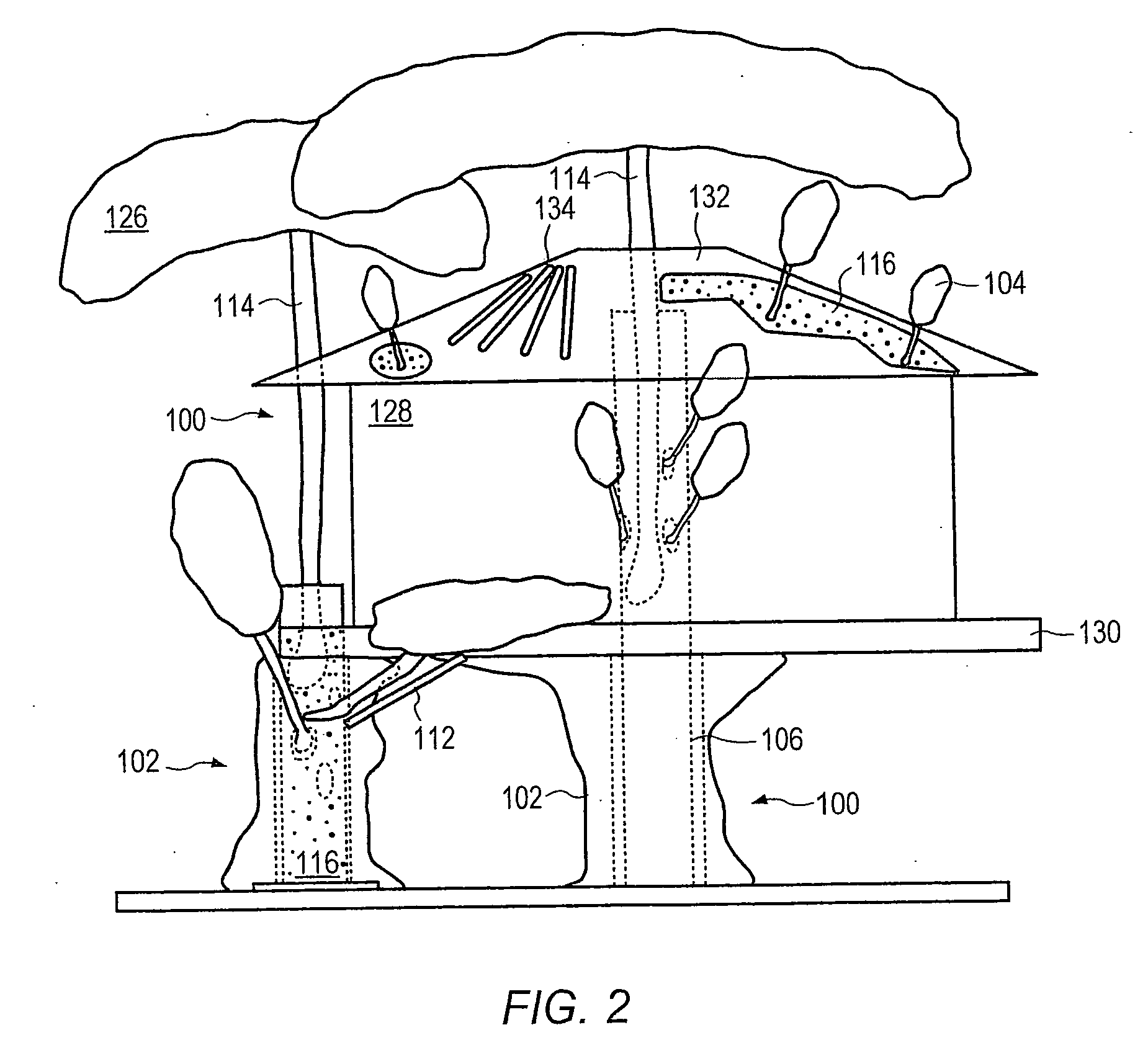
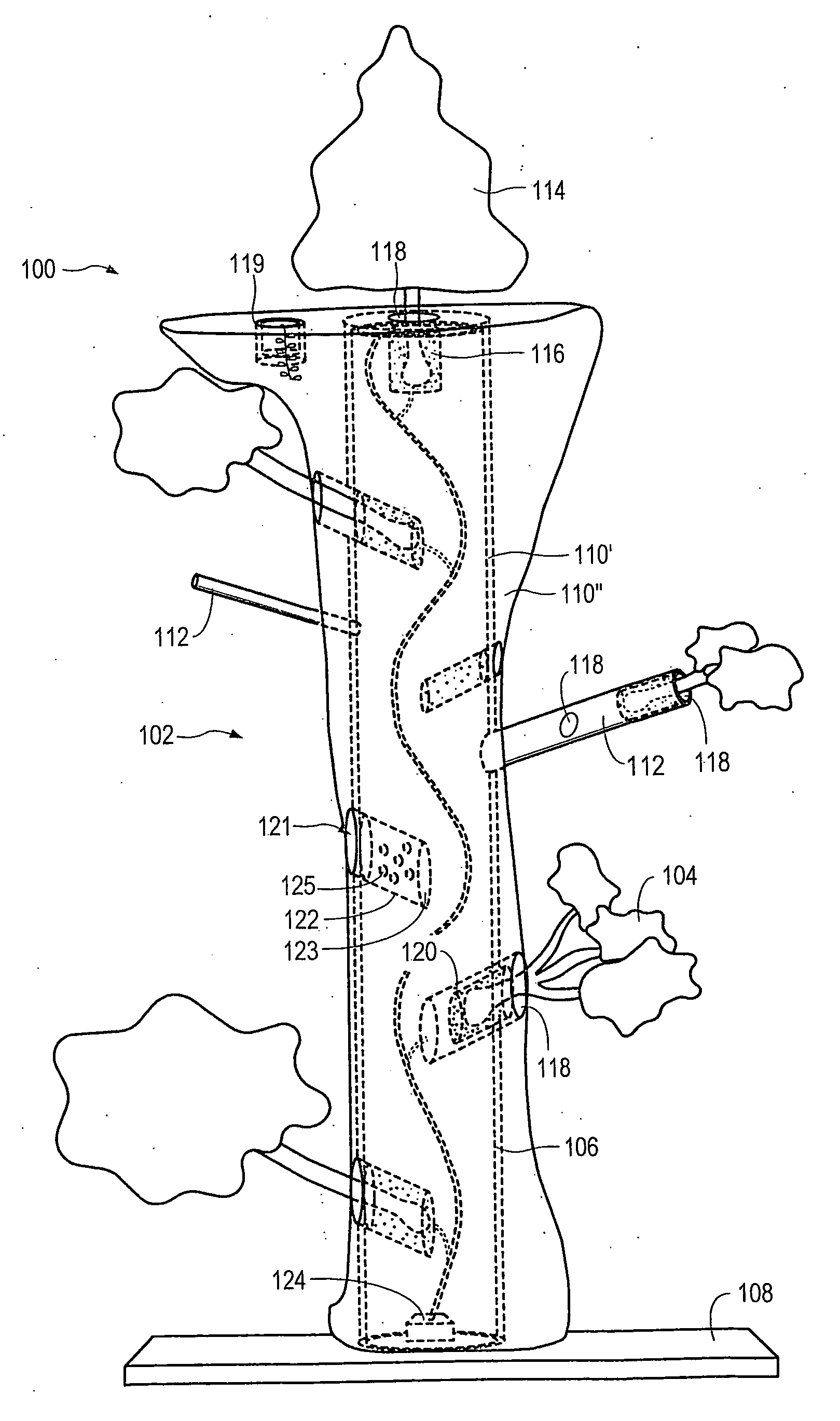
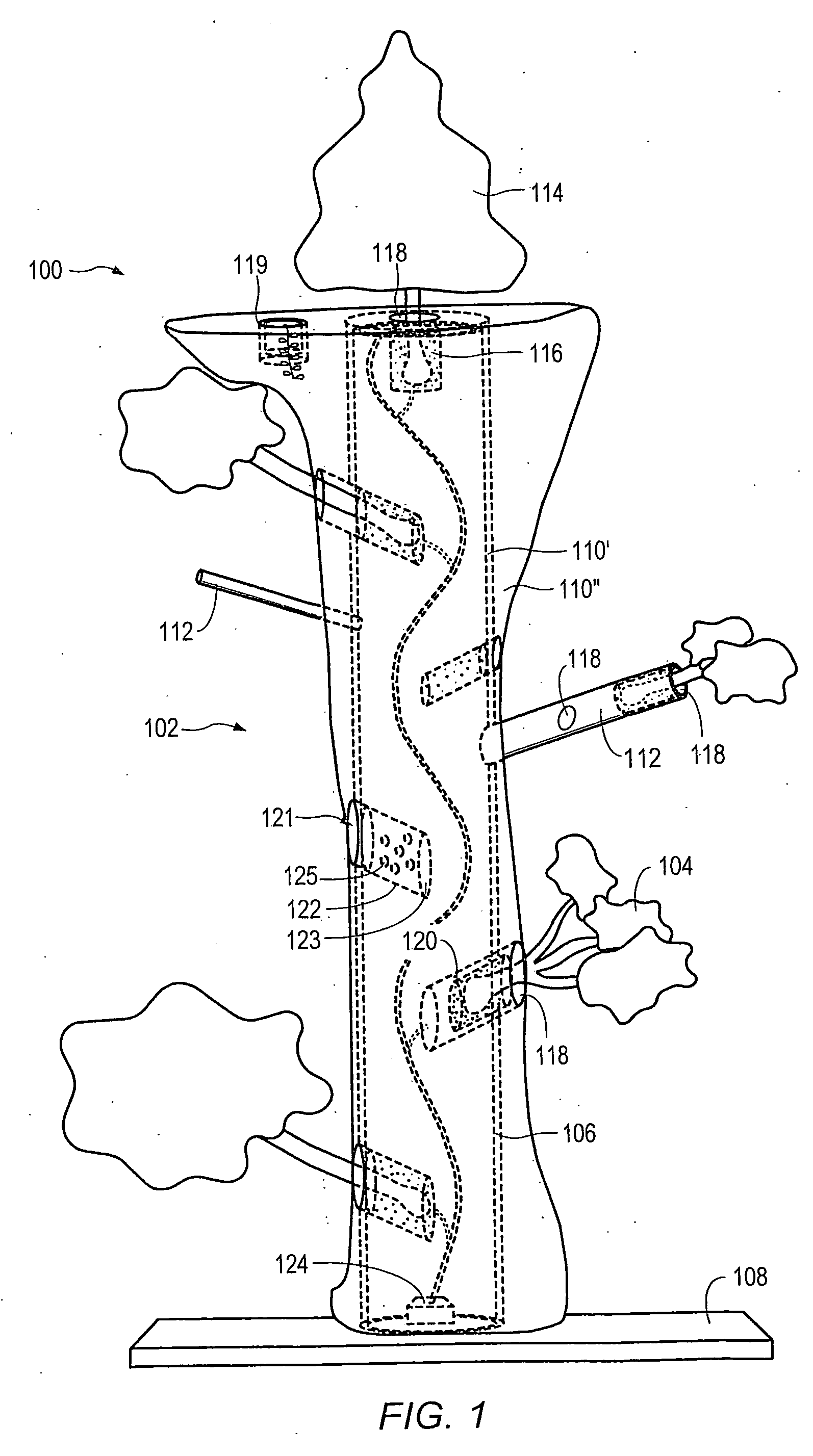
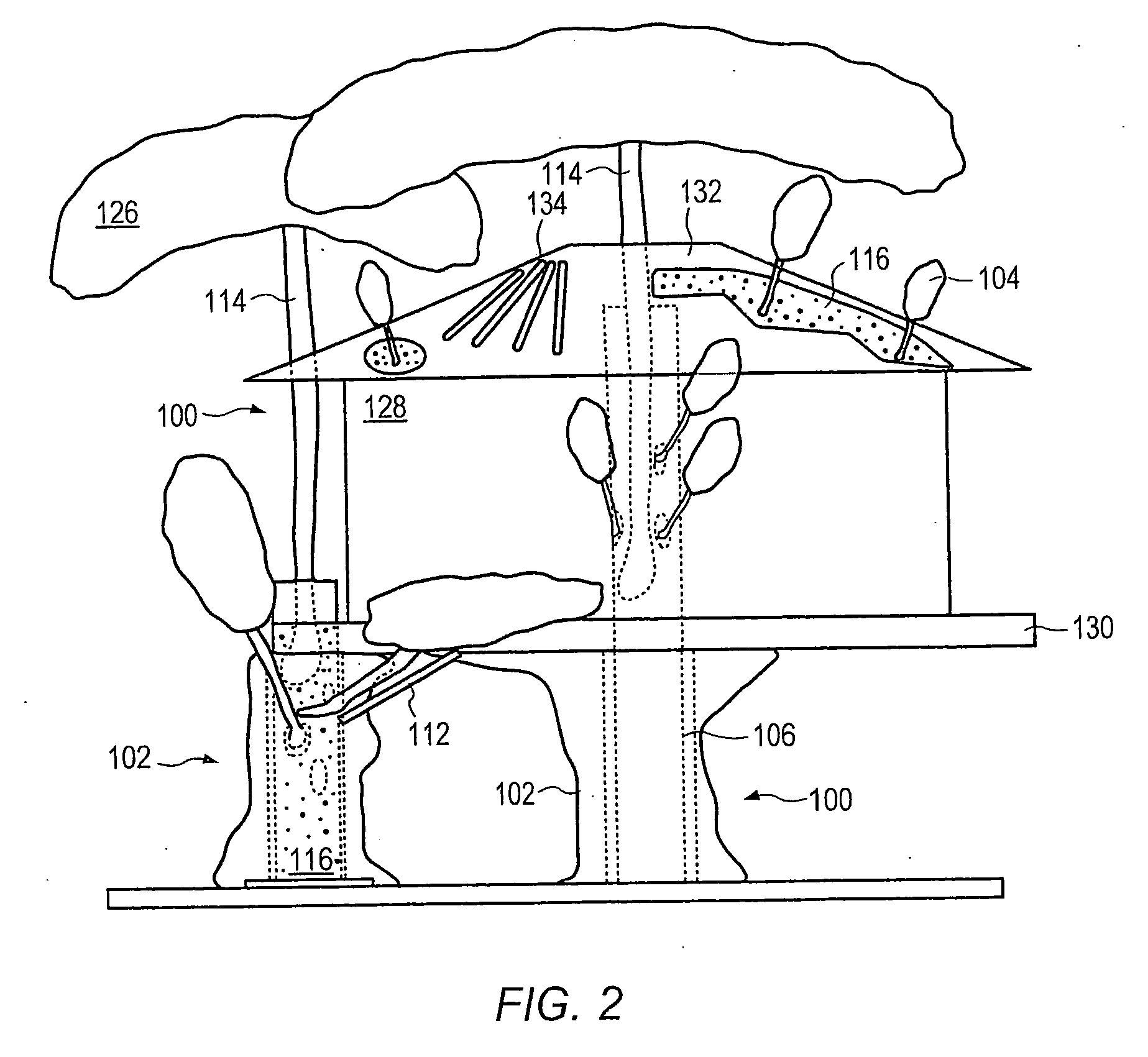
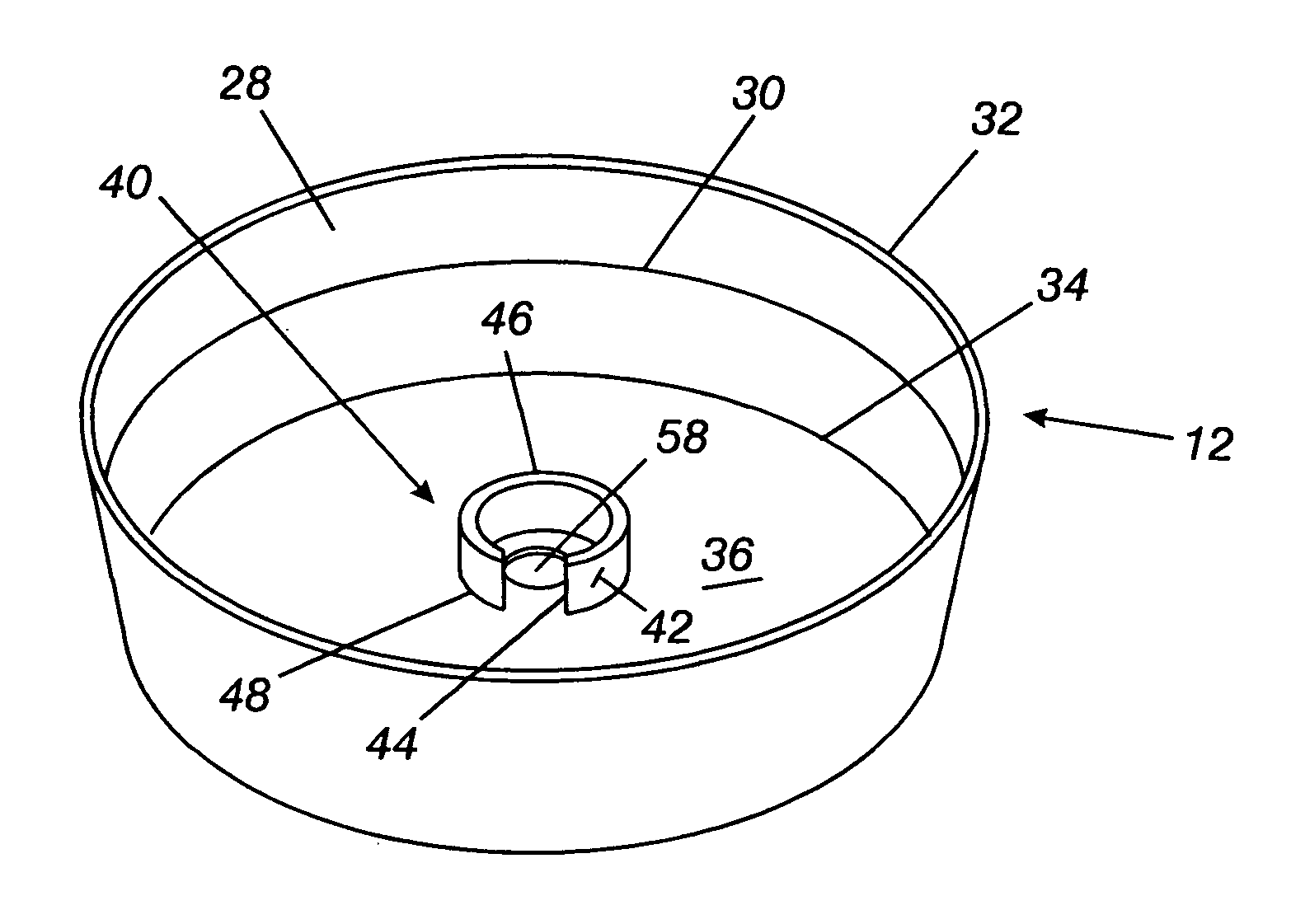
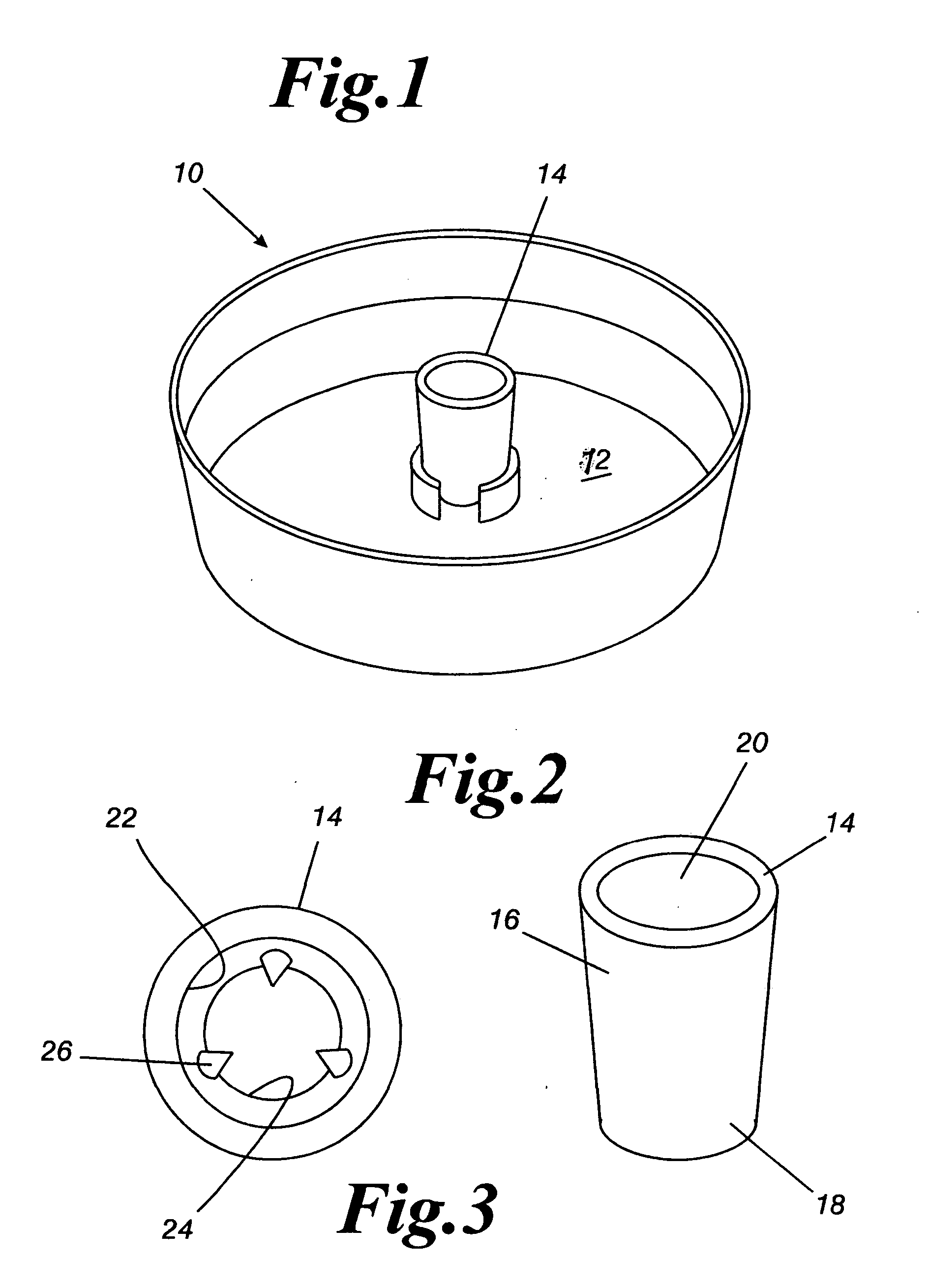
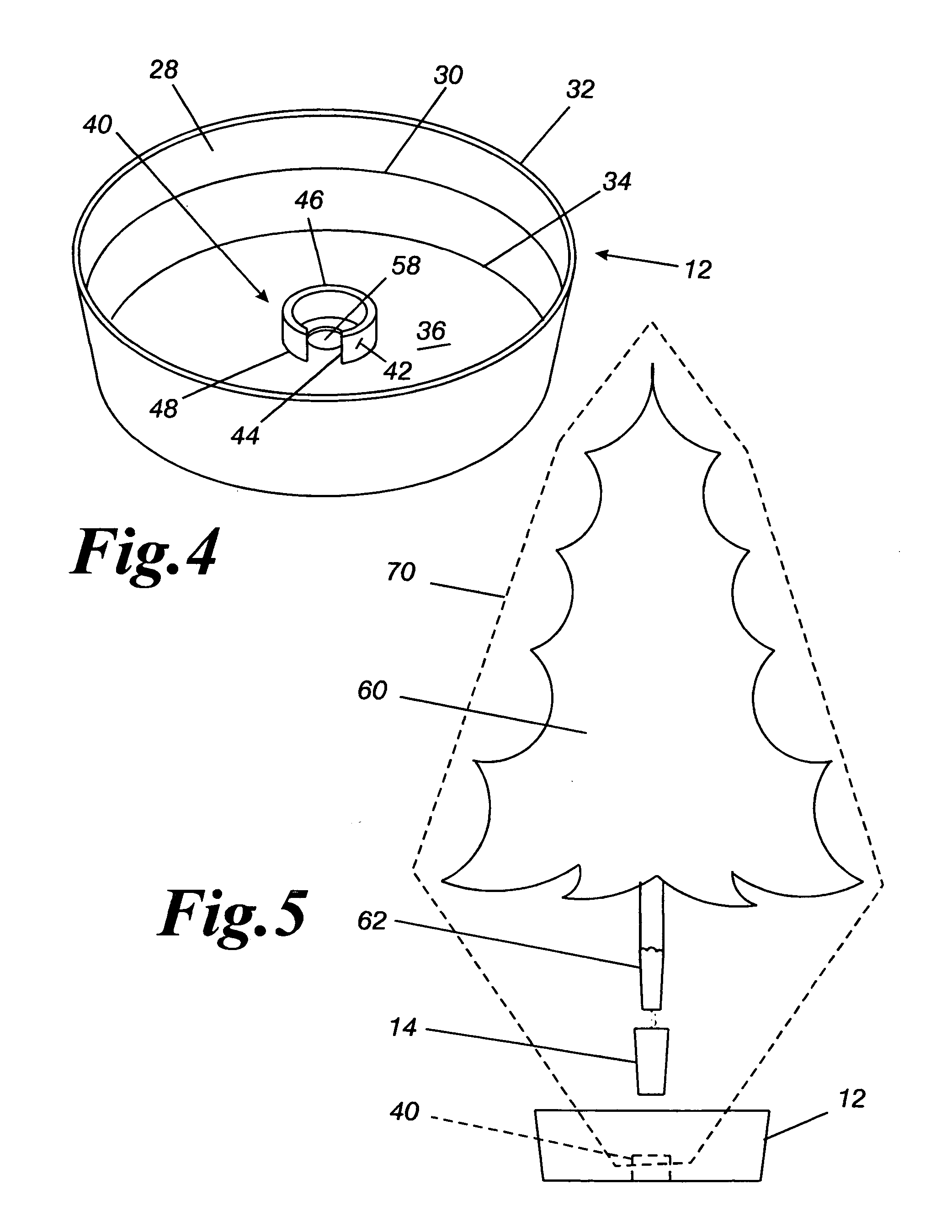
Method for packaging trees with a stand and tree stand apparatus
The invention is both a method of harvesting and mounting a tree and the tree stand itself. The method is for that of harvesting a live tree. On the other hand the tree stand can mount a live tree or an artificial tree. The description is written from the live tree viewpoint. The method comprises: harvesting a tree from the field; trimming the tree; optionally packaging said tree in netting; and mounting a stand on said trimmed tree. The mounting step also includes sliding a tapered sleeve or a bulb-like sleeve onto the base of the tree and jamming or inserting the sleeve with the tree into a corresponding well of the base stand. The tree stand comprises a base with an upwardly projecting well and a sleeve. The sleeve may be a tapered hollow sleeve, or a bulb-like sleeve. When the bulb-like sleeve is used, wing screws can be employed to secure it to the well.
Owner:FOX CREEK INVESTMENTS
Mildew-resistant processing method for rattan
ActiveCN104476636ASteps to change anti-mildew treatmentSimple anti-mildew treatment processBiocideWood treatment detailsLiving treeMildew
The invention provides a mildew-resistant processing method for rattan, and relates to the technical field of production of rattan-plaited products. The processing process is performed aiming at intravital rattan, and comprises the following concrete steps: 1) injecting a mildew-resistant drug liquid into rattan via rhizome or braches of rattan by employing a transfusion method before rattan is picked; 2) determining the initial time of injecting the mildew-resistant drug liquid; and 3) determining the rattan picking time. The living-tree mildew-resistant processing technology is simple and breaks through a conventional mildew-resistant processing method. After intravital rattan is subjected to mildew-resistant processing, rattan is directly used to prepare rattan-plaited products, the mildew-resistant processing step for rattan in the conventional rattan plaiting technology is thorough changed, the mildew resistant effect is greatly improved, and the drug utilization rate is relatively substantially improved compared with that of the conventional method. The mildew-resistant drug is nontoxic and does not generate any damage to human body.
Owner:安徽阜南县万家和工艺品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com