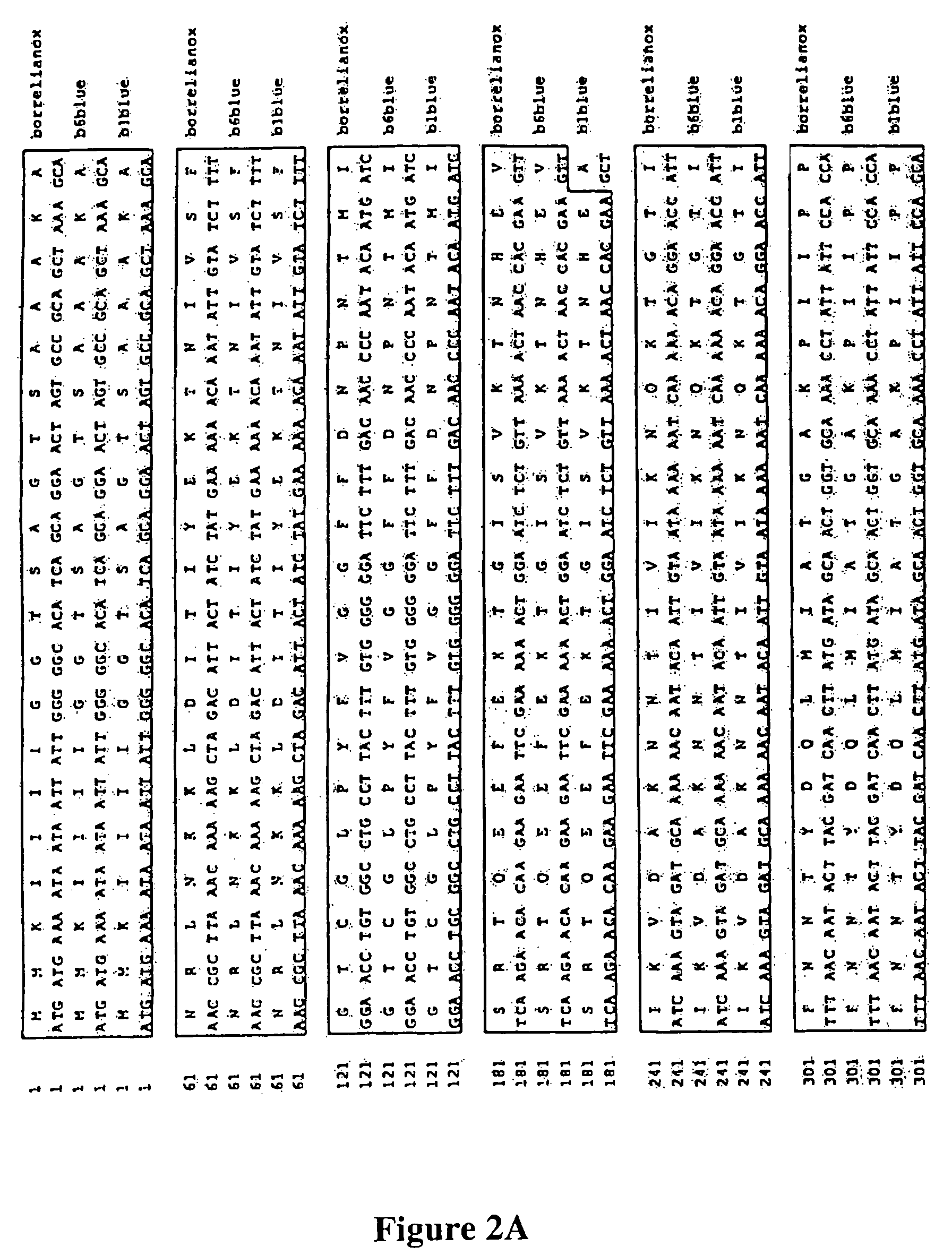
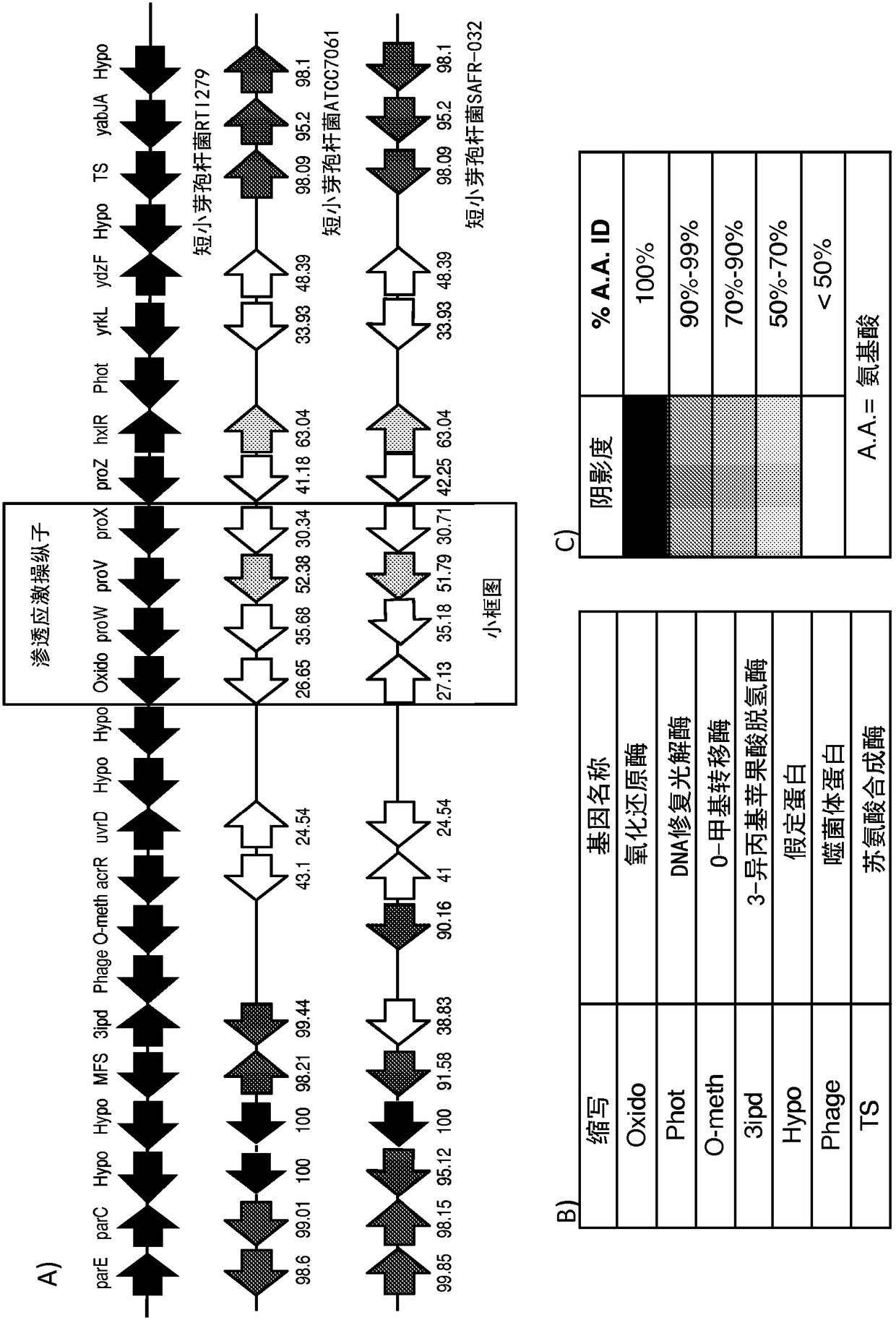
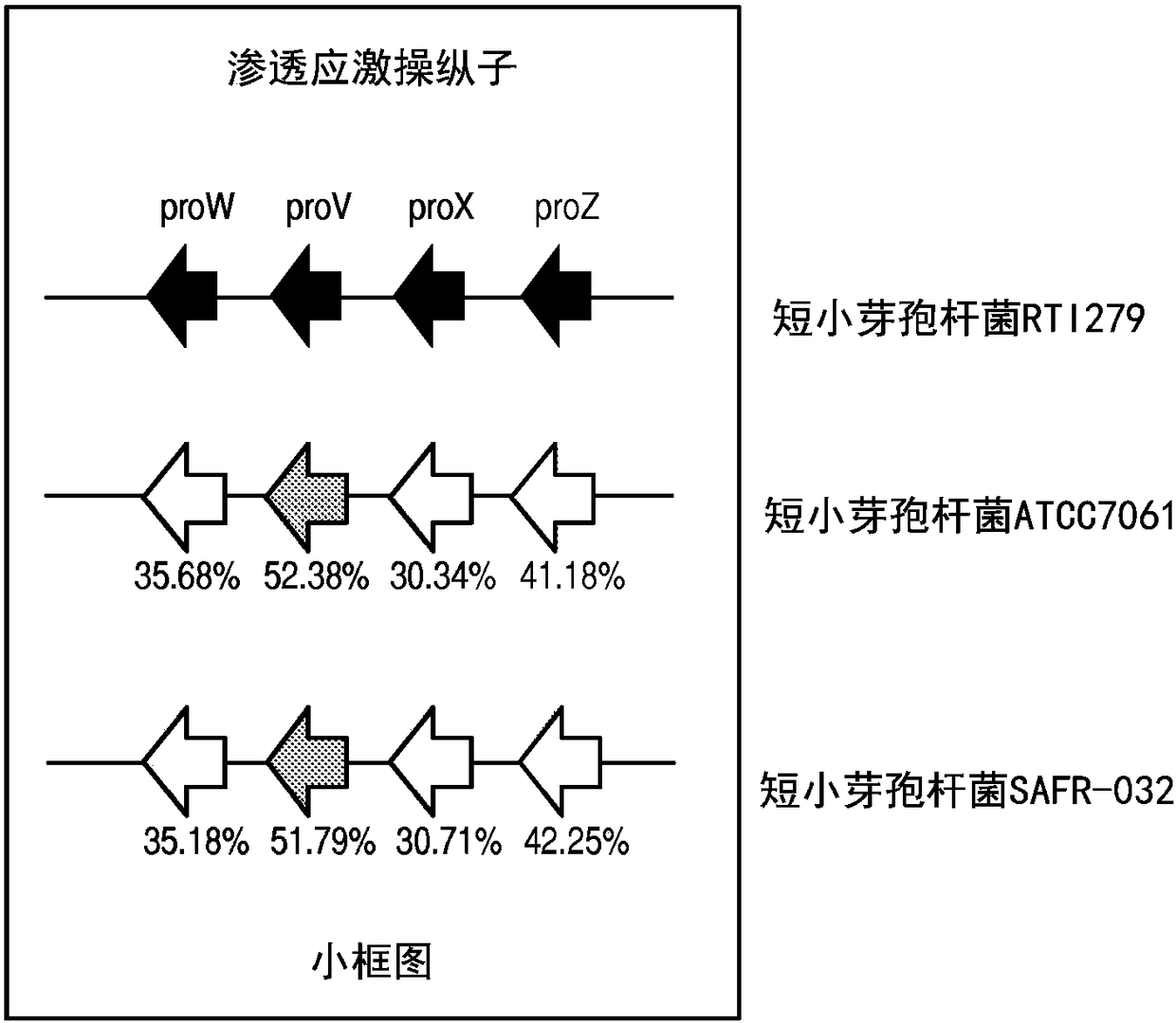
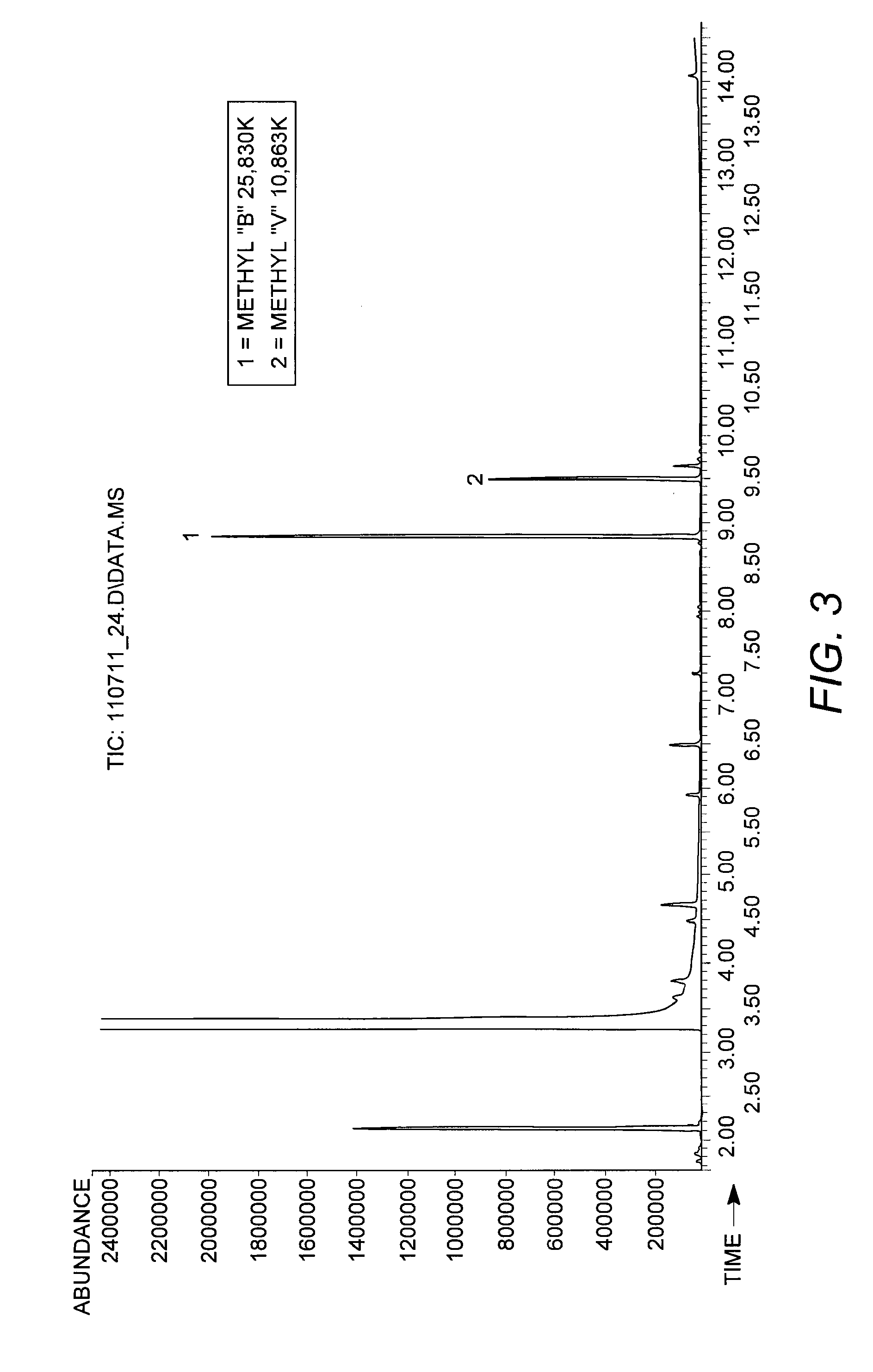
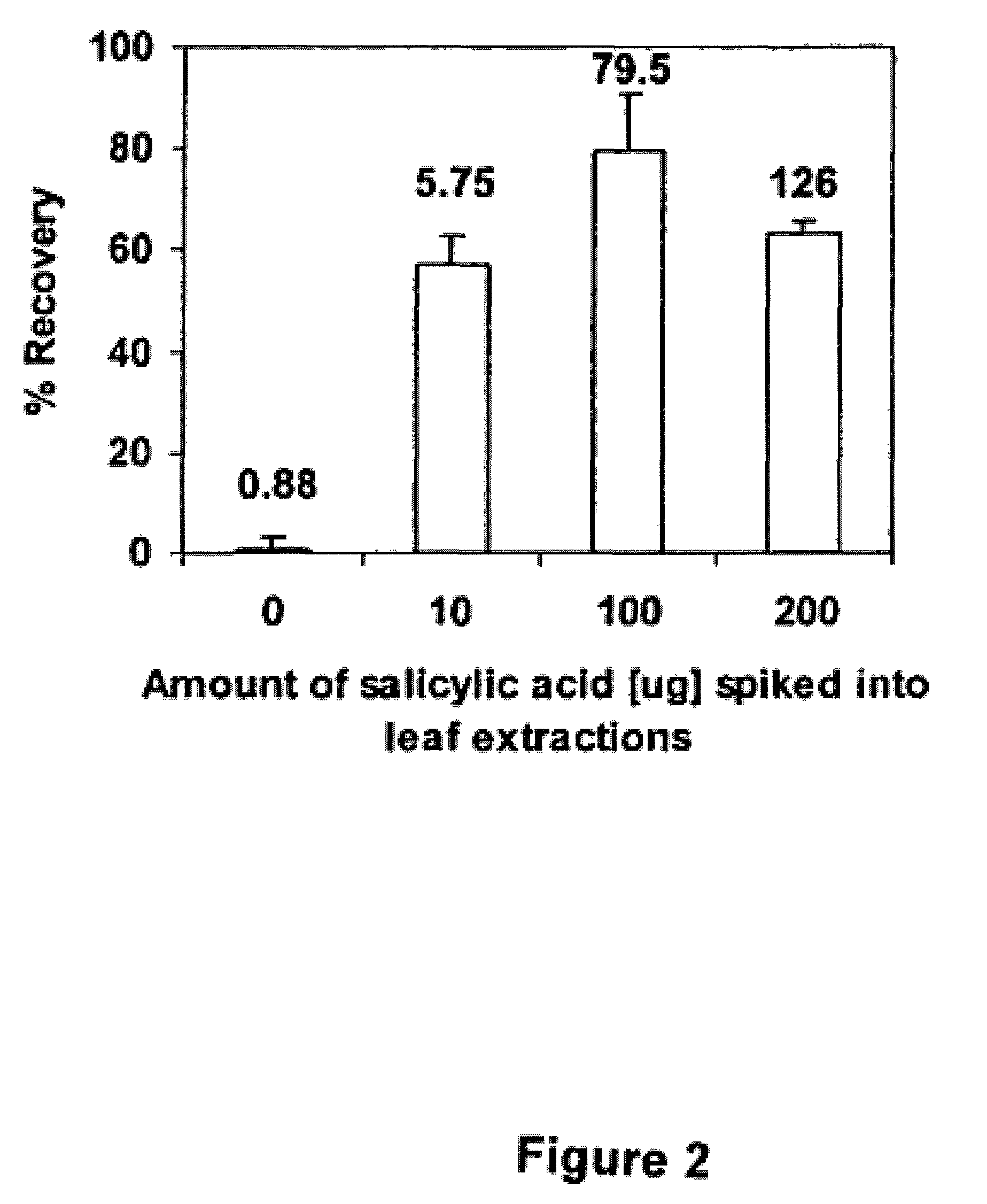
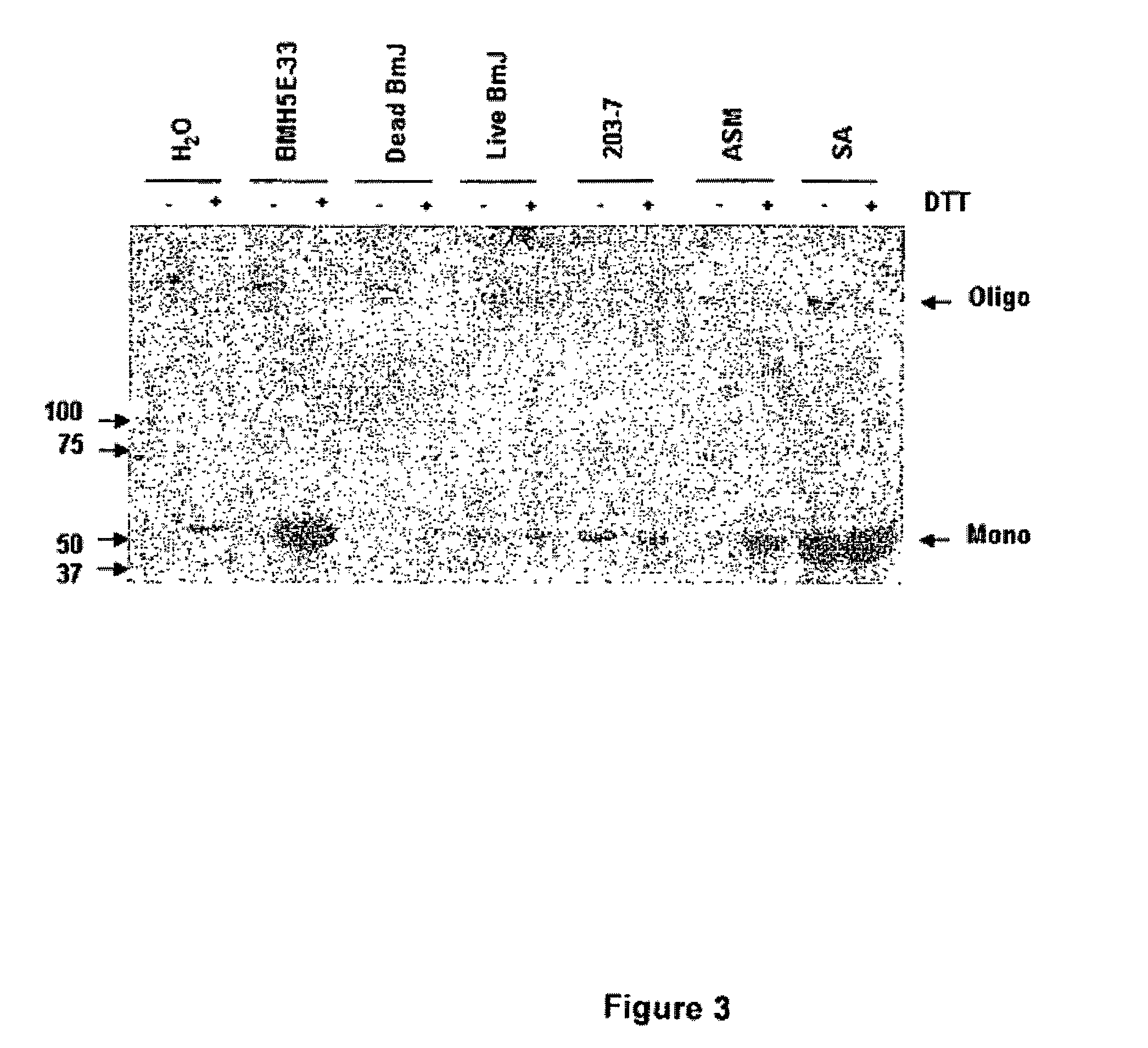
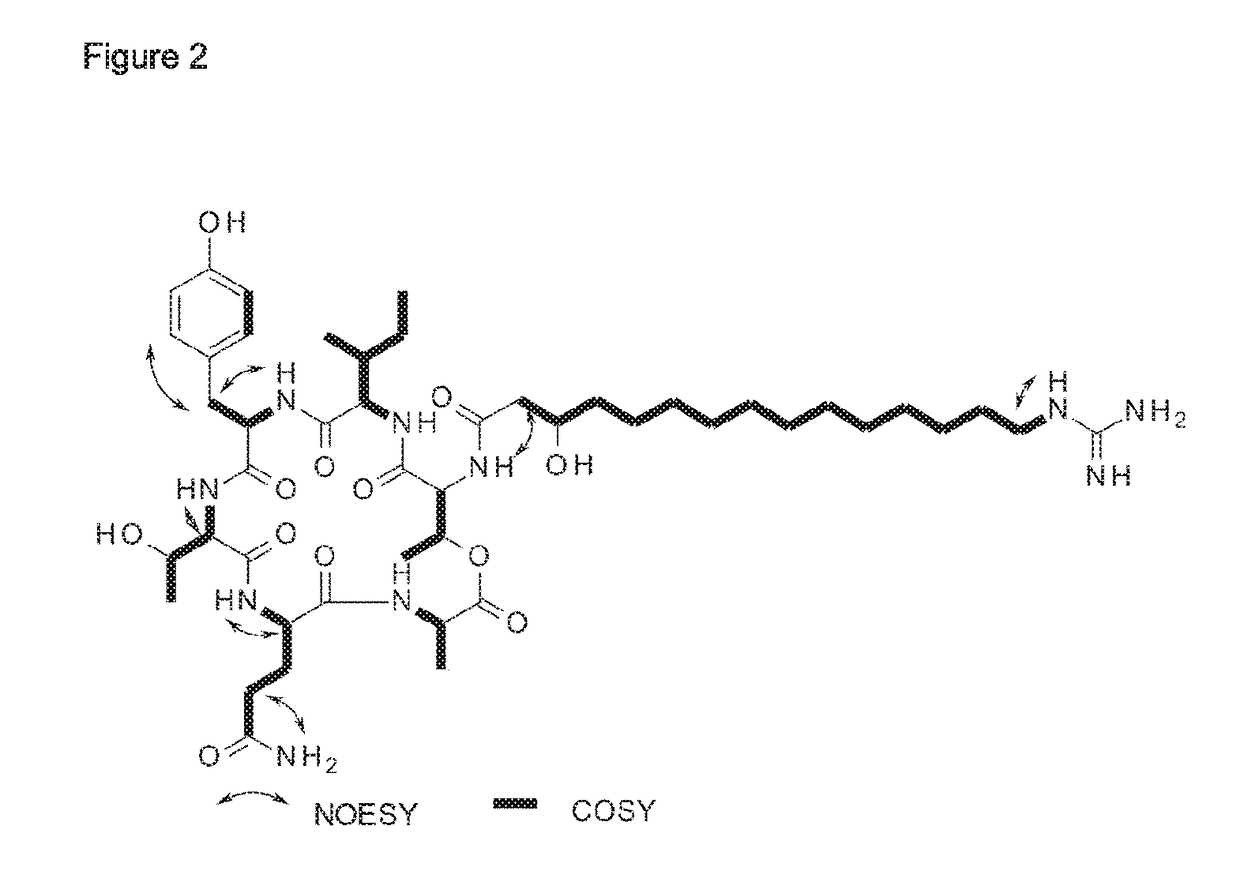
Patents
Literature
94 results about "Bacillus isolates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacillus isolates have a variety of biotechnological applications.
Method for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal system
There are provided novel synthetic stool preparations comprising bacteria isolated from a fecal sample from a healthy donor. The synthetic stool preparations are used for treating disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including dysbiosis, Clostridium difficile infection and recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, prevention of recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection, treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticular disease, and treatment of food poisoning such as salmonella. Methods of preparation and methods of use of the synthetic stool preparations are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH +2
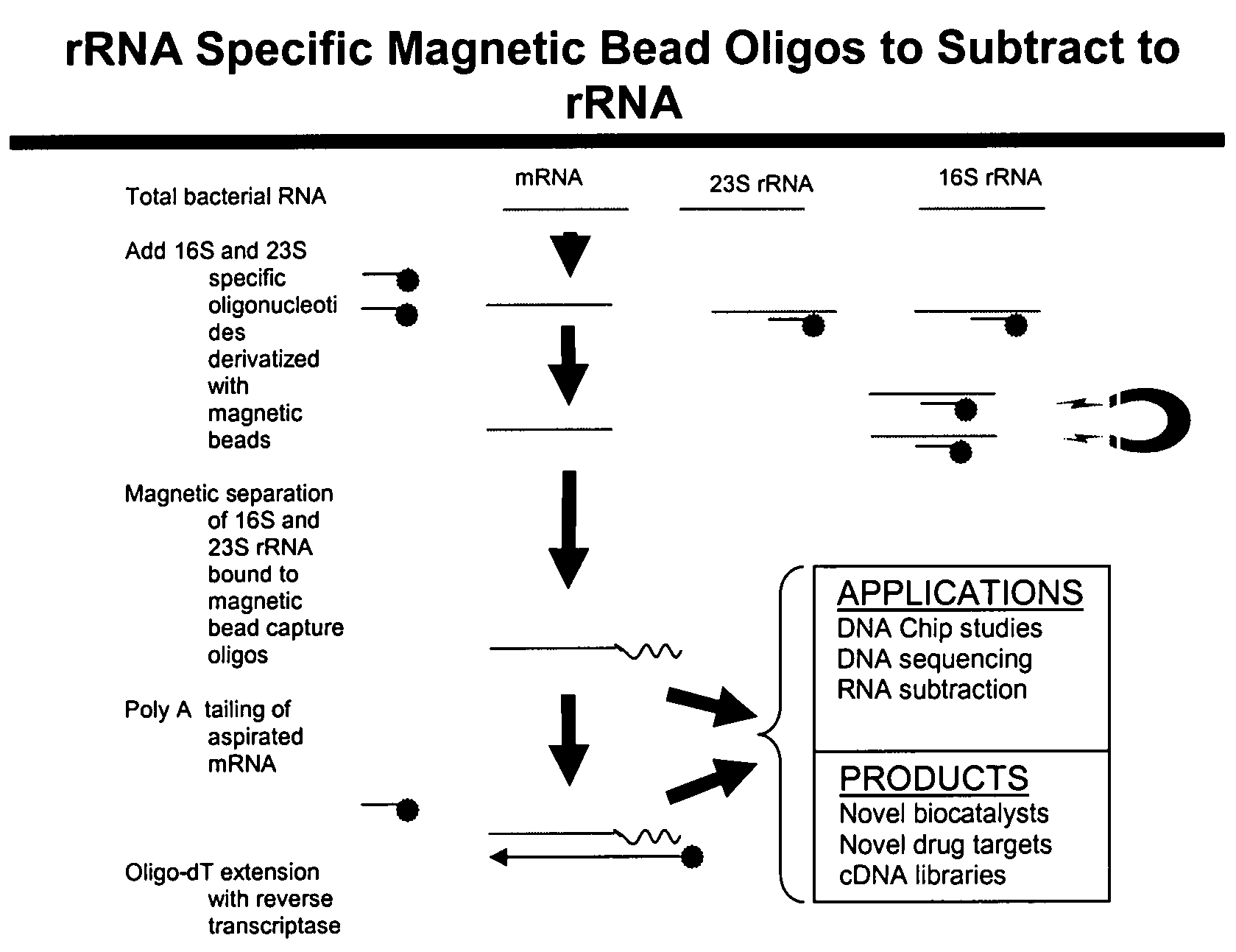
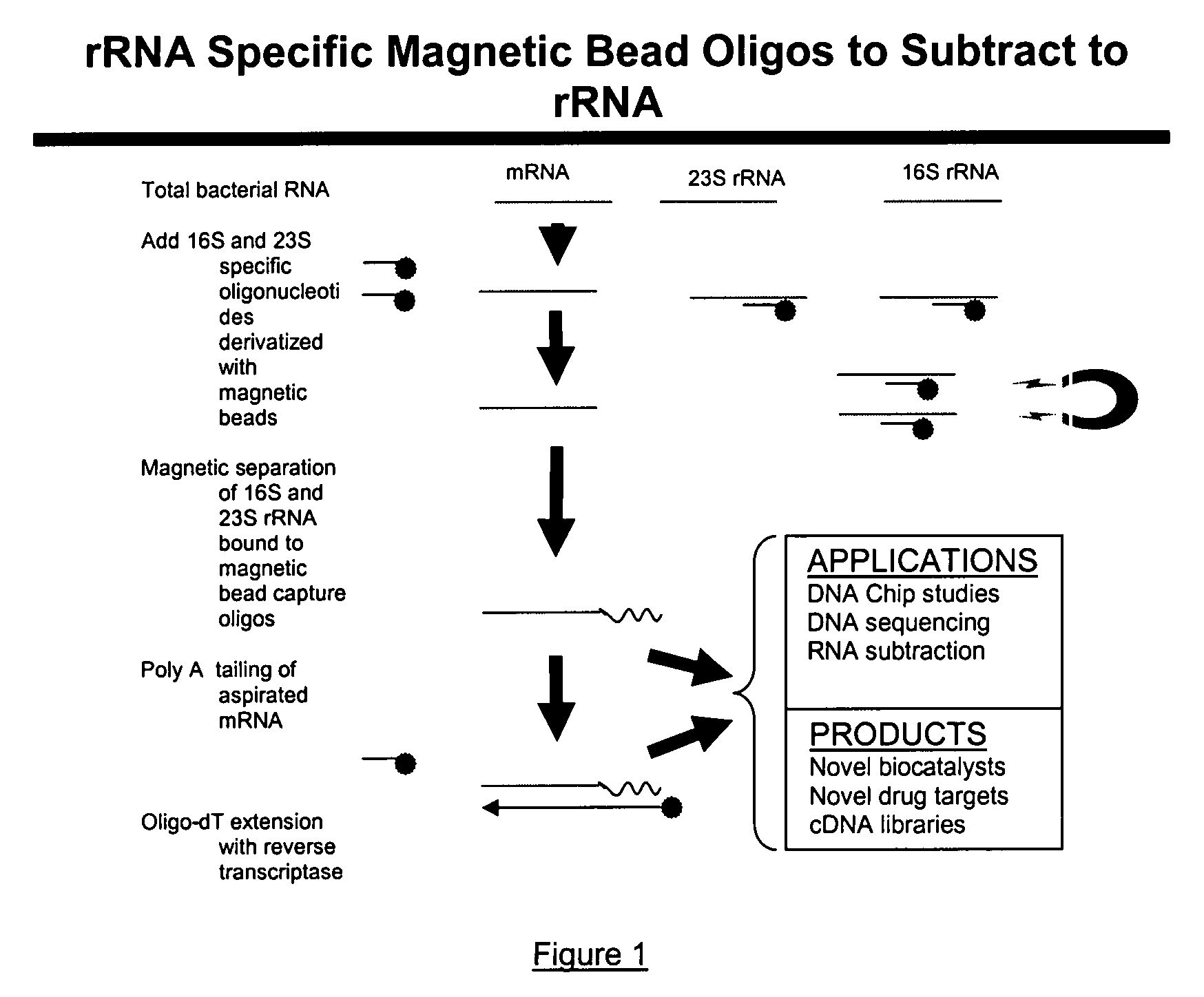
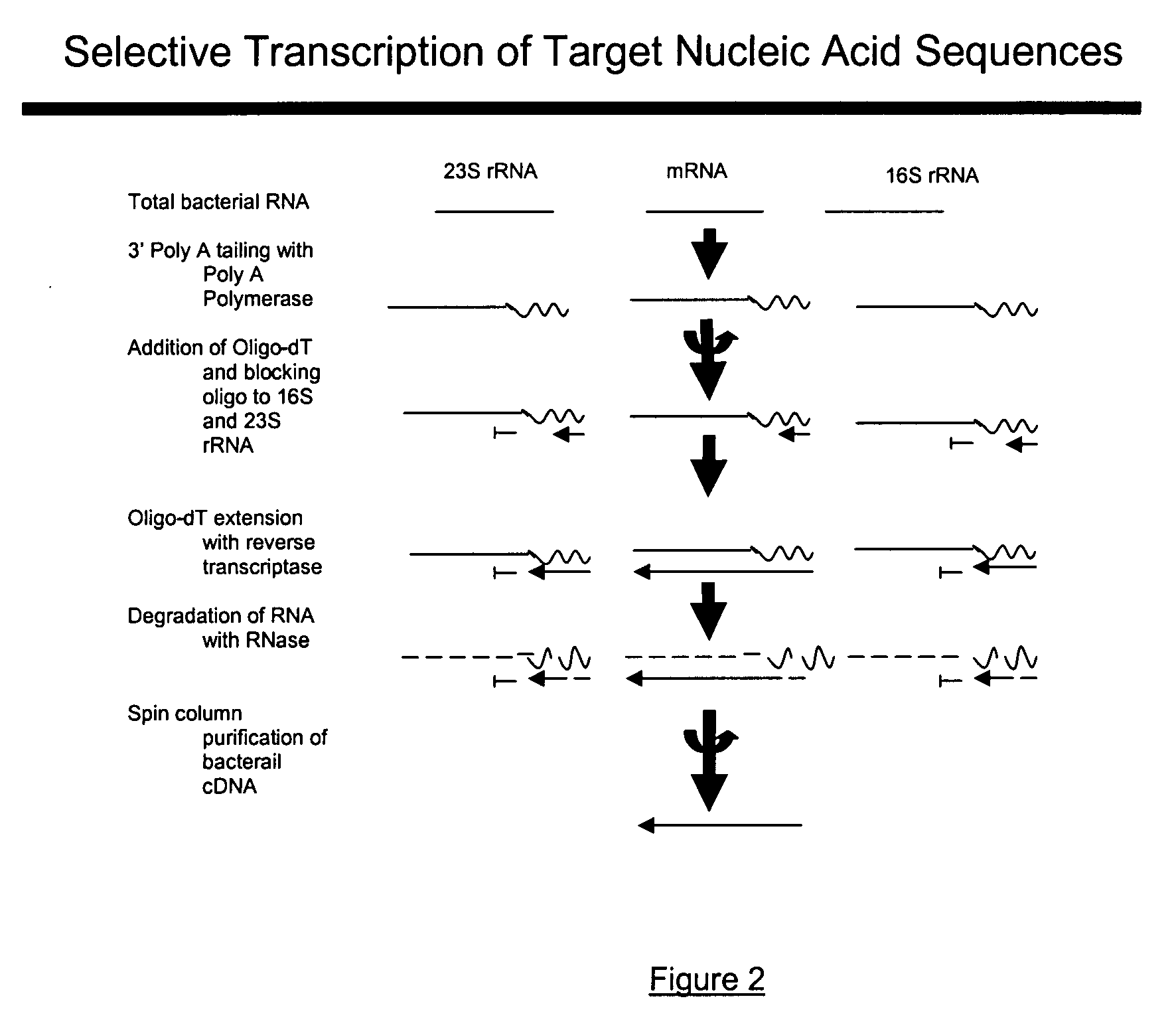
Methods and kits for negative selection of desired nucleic acid sequences
The present invention pertains to a method to isolate, separate, enrich or amplify a targeted nucleotide polymer such as mRNA through selective reverse transcription of the targeted polymer into cDNA from a sample comprising of chemically identical or similar polynucleotide polymers such as rRNA. The enrichment of the targeted nucleic acid such as mRNA is accomplished by blocking the reverse transcription of undesired rRNA while allowing unrestricted reverse transcription of the targeted polymer. The invention also embodies that the cleavage of the non-targeted nucleic acid such as rRNA bound to an oligonucleotide through enzymatic activity (RNase H). The invention further embodies methods and kits to accomplish the utility of the invention through the following steps 1) 3′ tailing of chemically identical or similar nucleotide polymers in a sample that includes bacterial mRNA 2) a 3′ tail capable of binding to a oligo-dN primer 3) at least one oligonucleotide capable of preventing the extension of oligo-dN bound to at least one non-targeted nucleotide polymers by a DNA polymerase such as a reverse transcriptase without restricting conversion of bacterial mRNA into cDNA 4) where the non-targeted molecule is prevented as a template for cDNA synthesis by enzymatic cleavage (RNase H) of template (rRNA)-oligonucleotide hybrid 5) where the reverse transcriptase is physically blocked by the oligonucleotide bound to the non-targeted nucleic acids such as rRNA 5) purification of the selectively transcribed cDNA. In further embodiments of the present invention, methods and composition to enable the study of bacterial transcriptomics-an analysis of genes expressed by a bacterial infection of a host, an isolated bacterial culture or a bacterial community, such as recovered from soil, intestine, mouth, biofilm, water etc are also included for use in DNA-chip or sequencing analyses.
Owner:SOWLAY MOHANKUMAR R
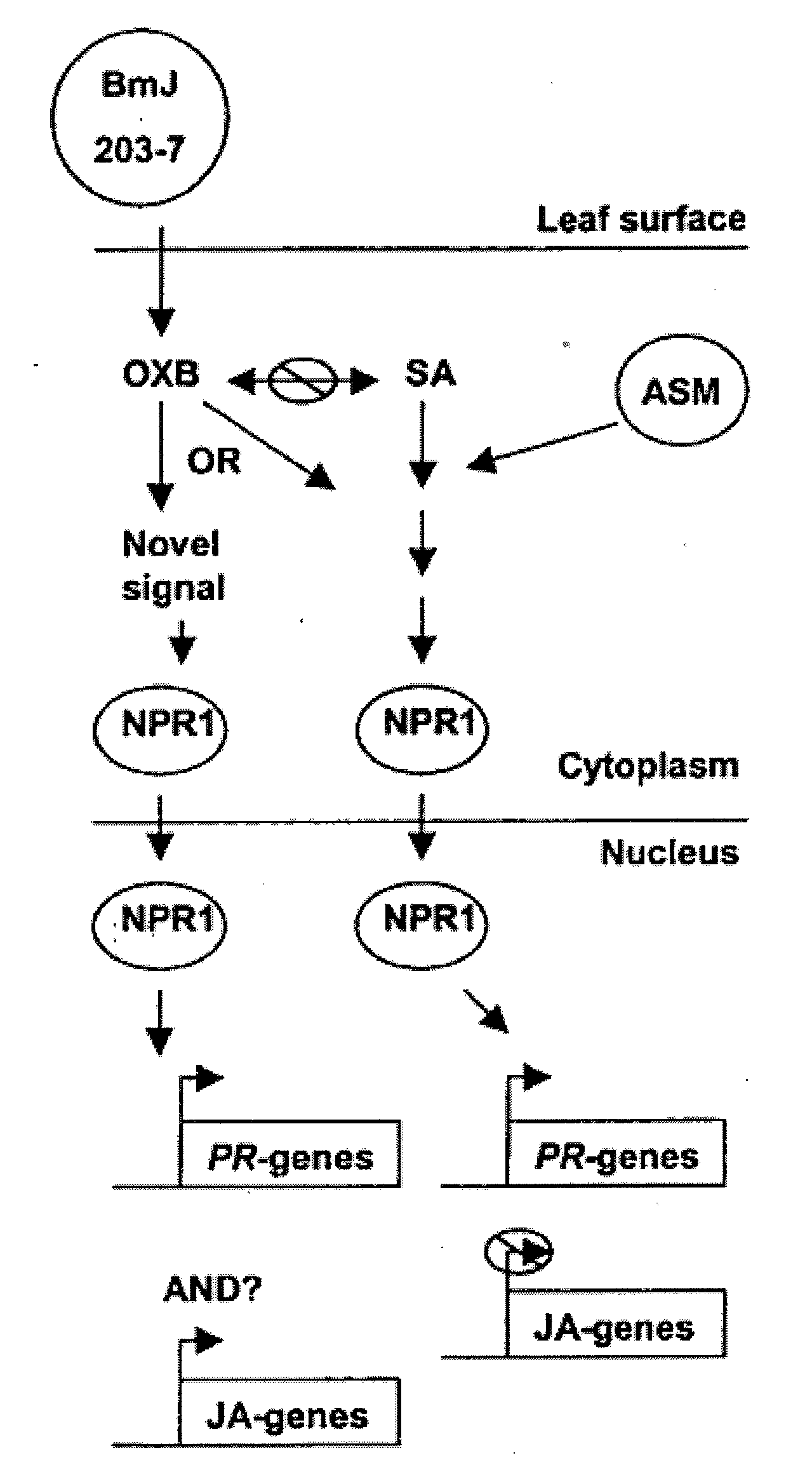
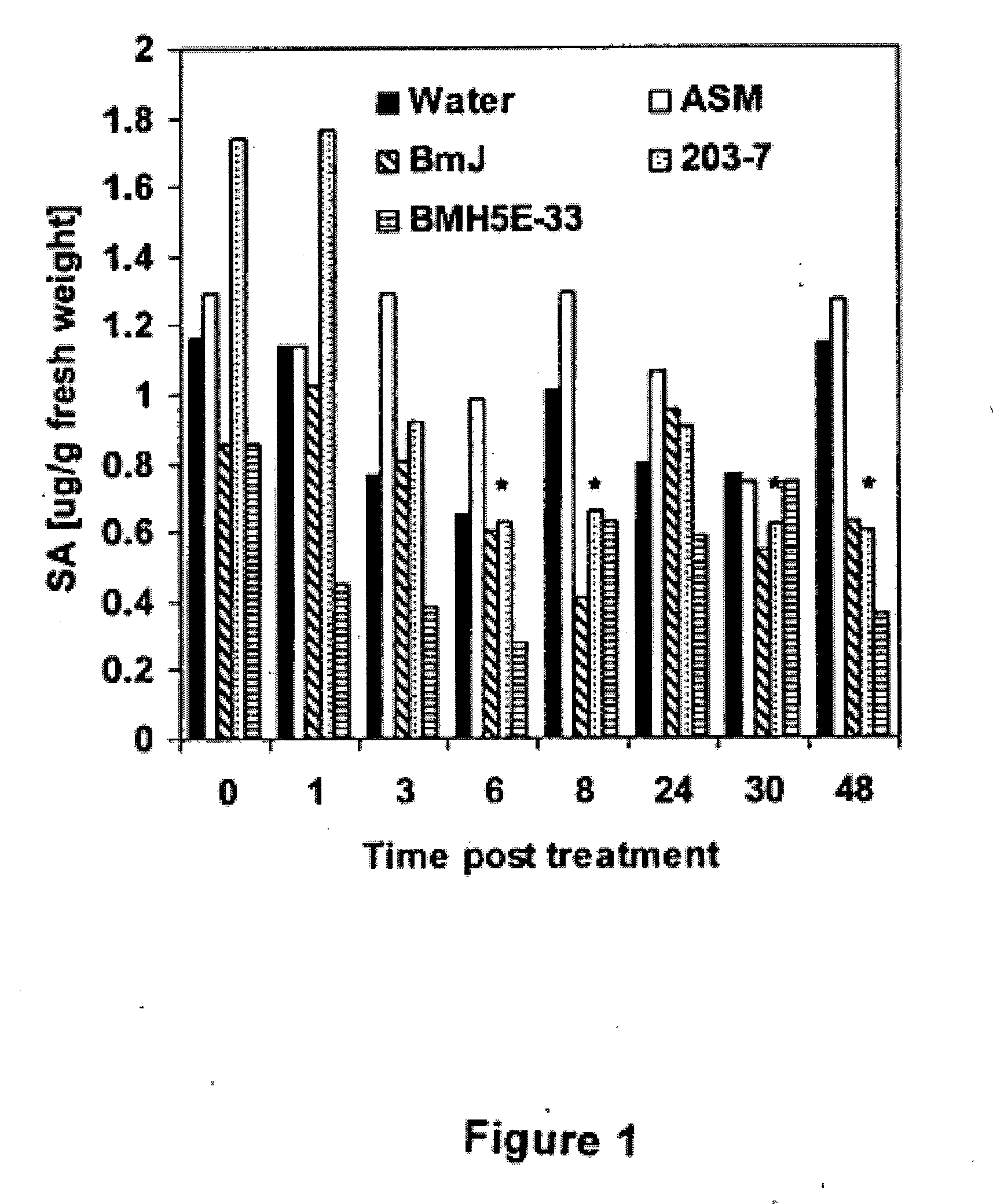
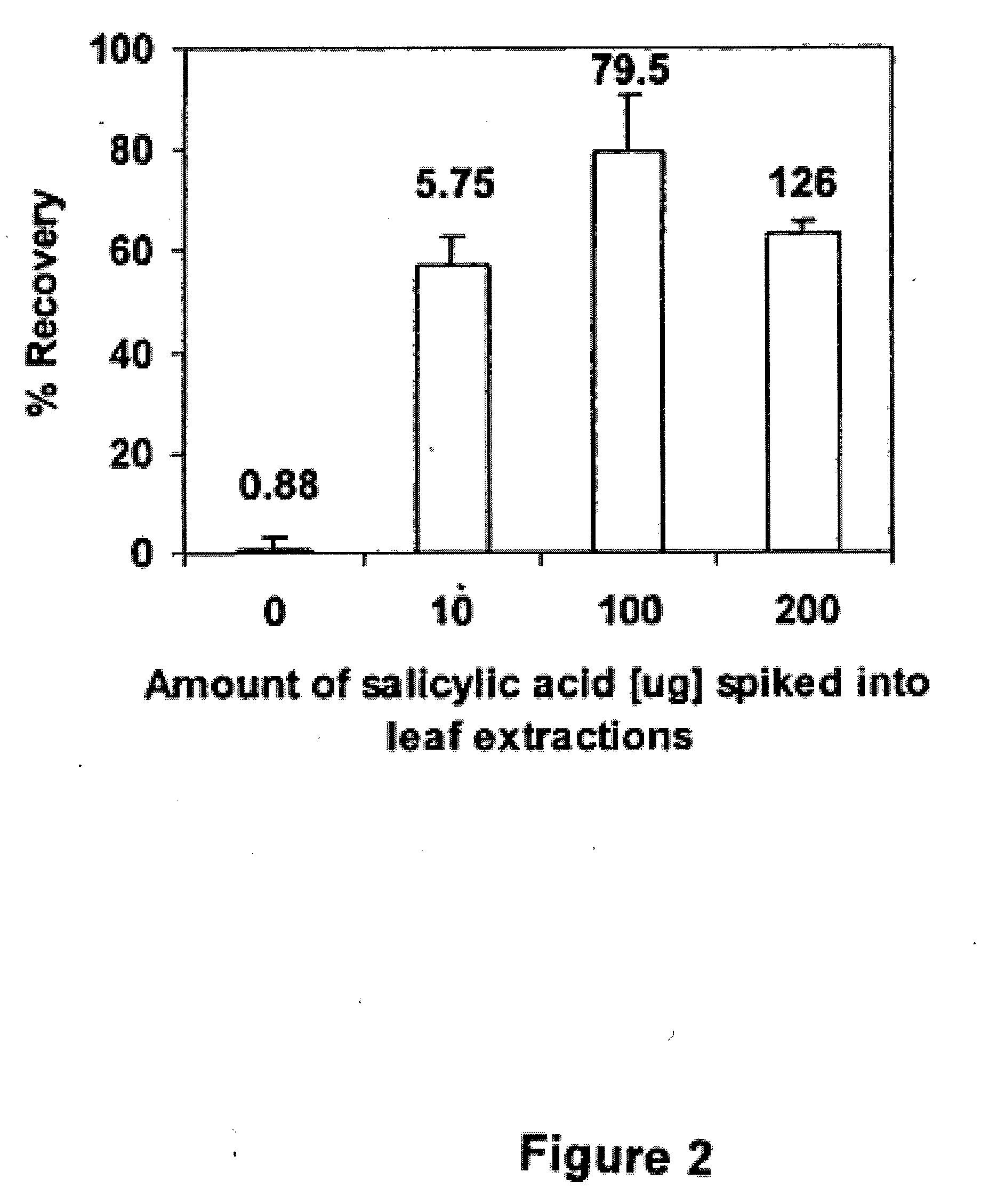
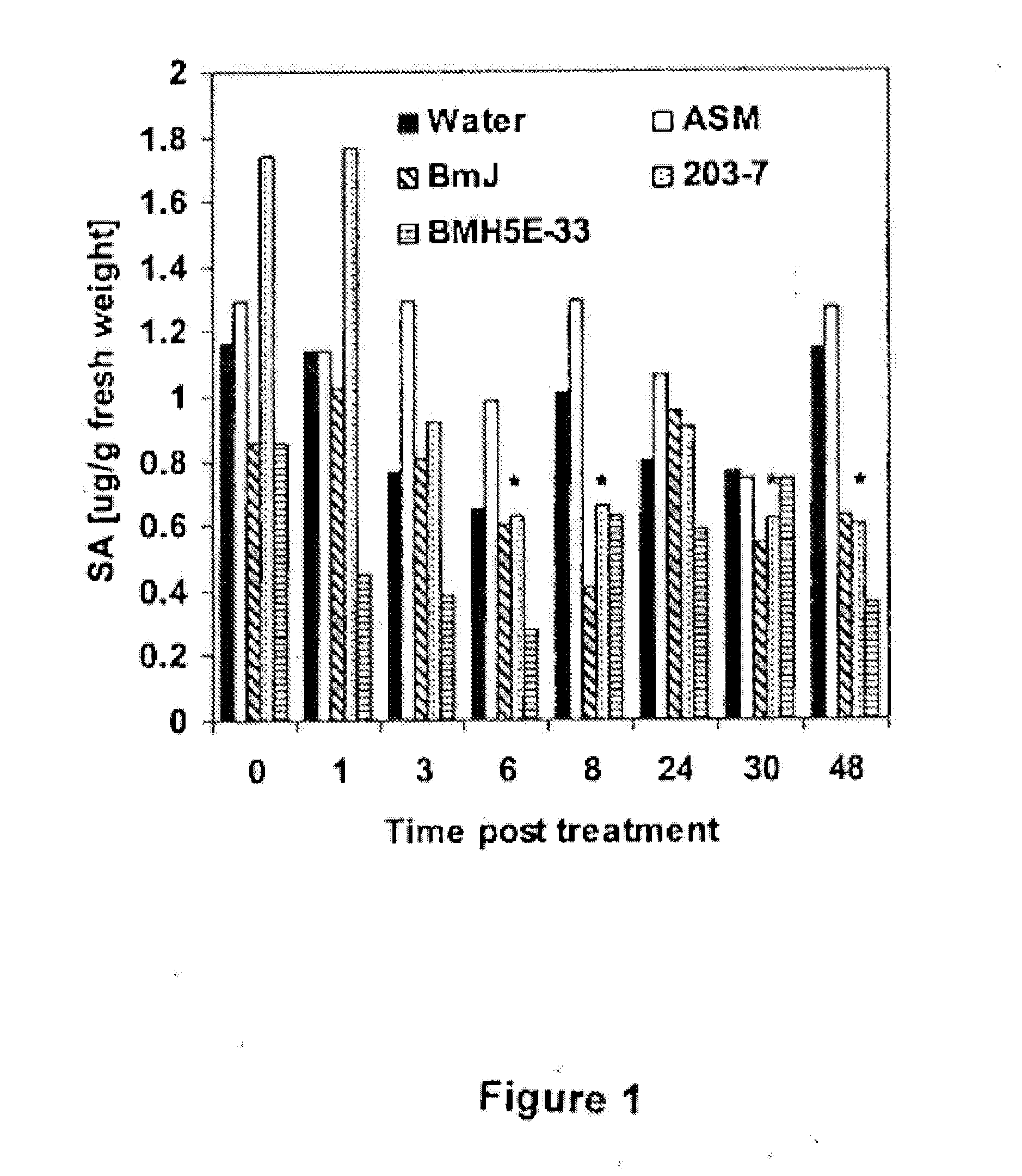
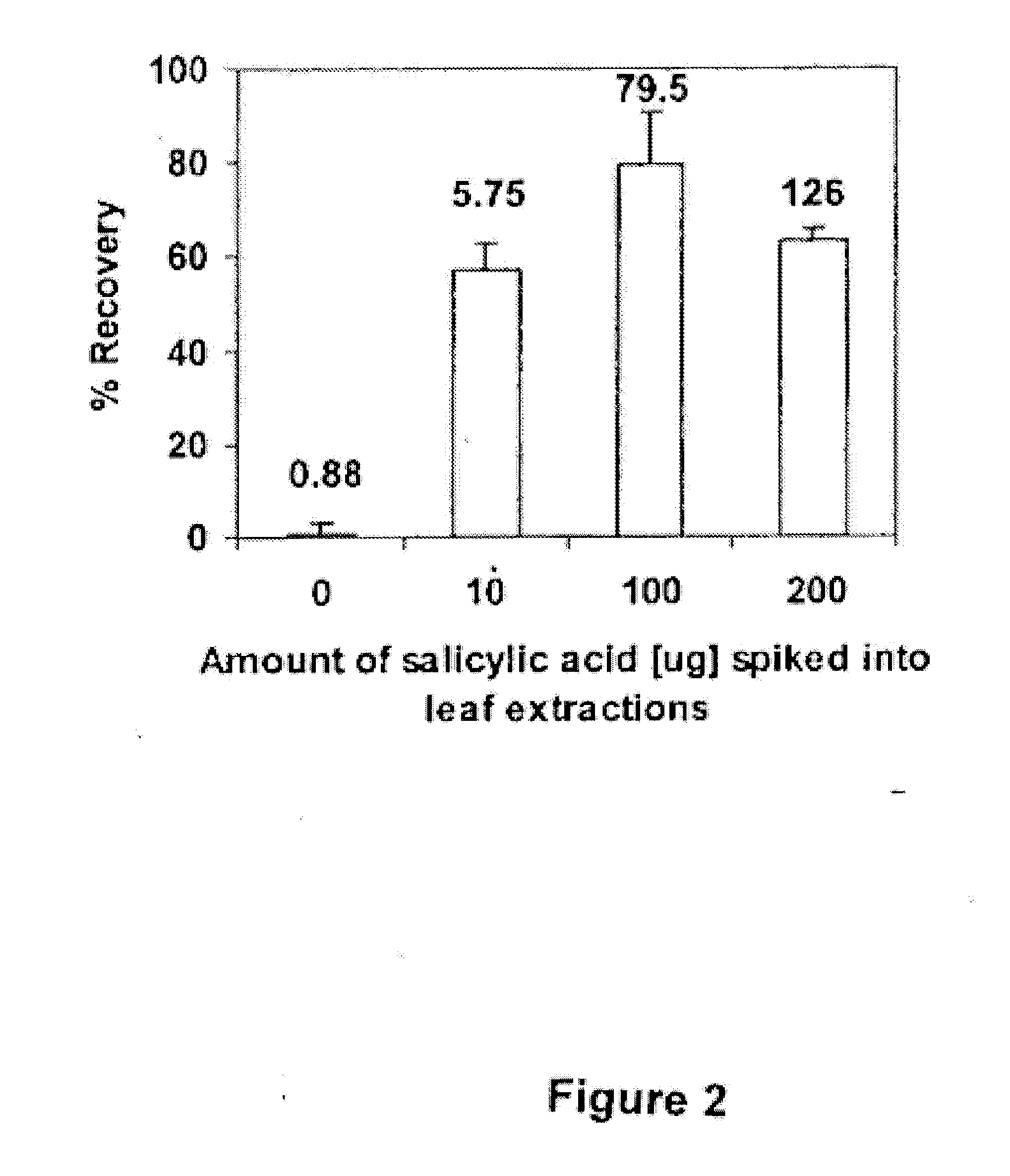
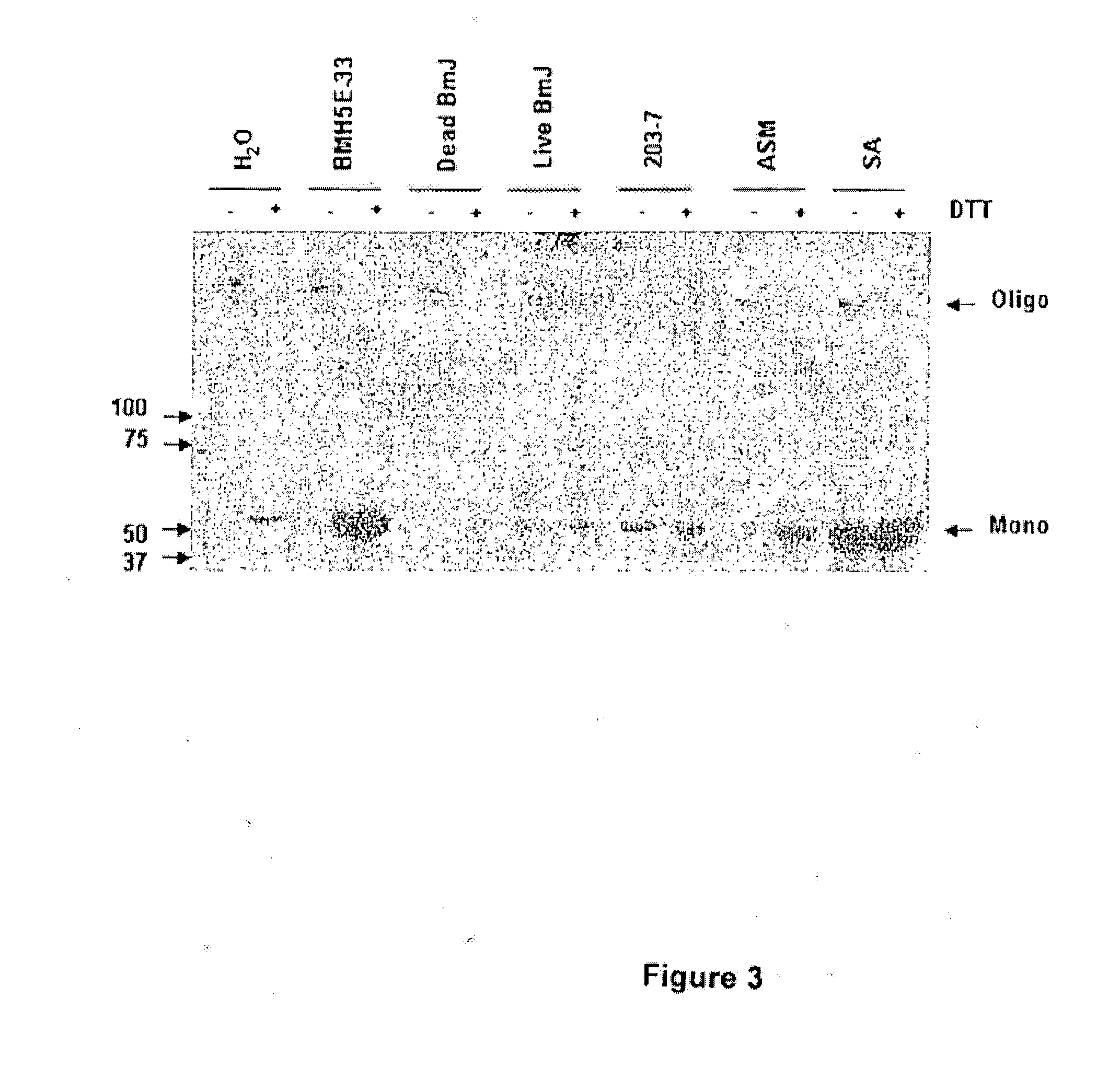
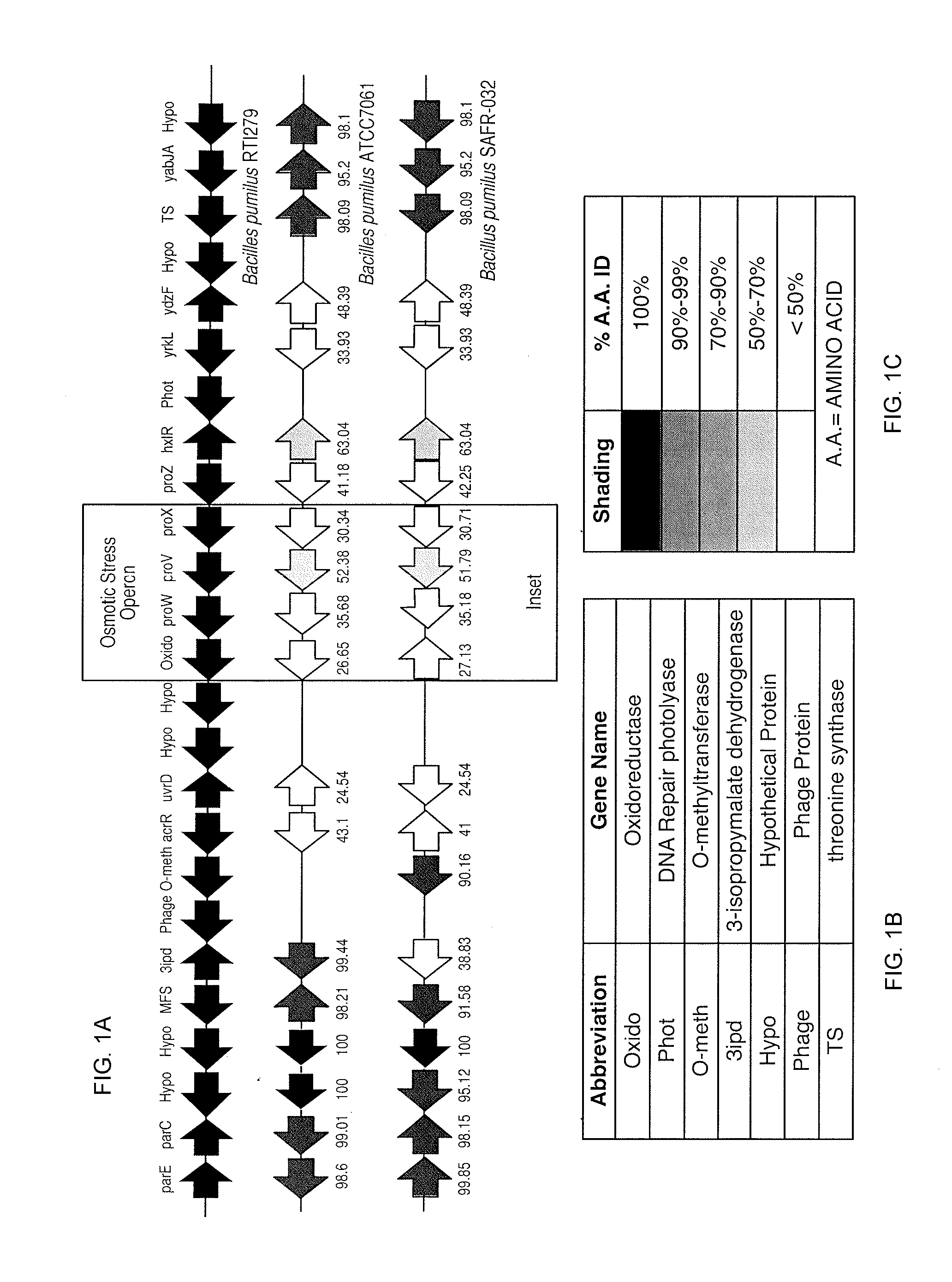
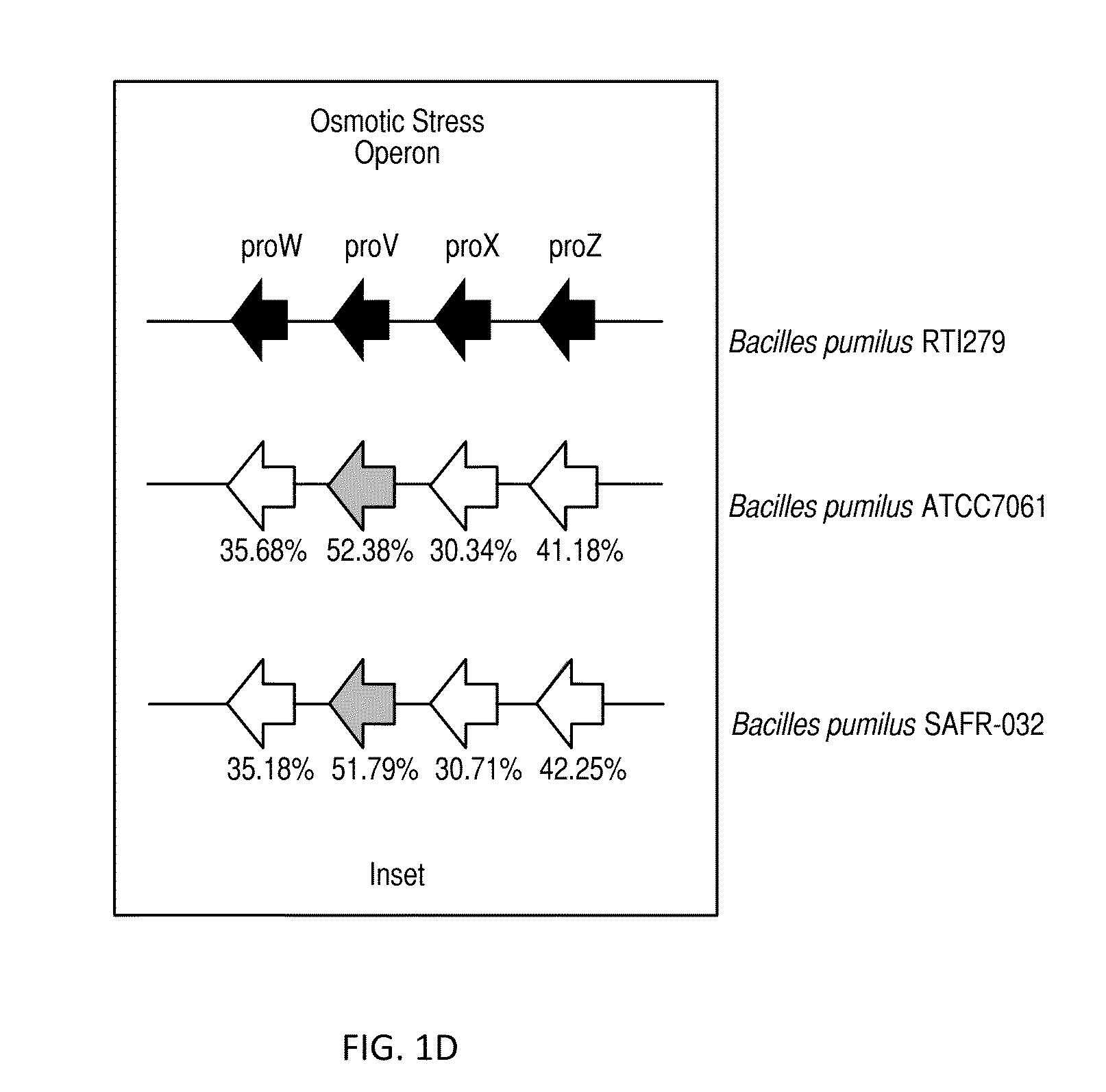
Bacillus isolates and methods of their use to protect against plant pathogens
ActiveUS20100092442A1Promote plant growthBiocideAnimal repellantsSystemic acquired resistanceBacillus isolates
Methods of inducing systemic acquired resistance to infection in a plant by applying a composition comprising a Bacillus control agent to said plant wherein said plant is capable of producing defense proteins.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20050042606A9Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesGenomic SegmentMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Bacillus isolates and methods of their use to protect against plant pathogens and virus transmission
ActiveUS20120003197A1Easy to usePreventing and reducing virus infectionBiocideBacteria material medical ingredientsDiseaseSpore
Methods of inducing systemic acquired resistance to infection in a plant are provided. The methods comprise applying a composition comprising a Bacillus control agent to said plant wherein said plant is capable of producing defense proteins. Also provided are, methods for controlling one or more plant diseases, methods for preventing plant virus transmission, methods for preventing and / or treating soil-borne plant pathogens using the Bacillus control agent of the present invention, and methods of generating bacterial spores. In addition, synergistic biocontrol combinations and methods of using the same are provided.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Novel Anammox Bacterium Isolate
ActiveUS20110180476A1Ammonia reductionReduce ammonia levelsBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesMicrobacterium
Disclosed is an isolated bacterial strain Candidatus Brocadia caroliniensis strain, having Accession Deposit Number NRRL B-50286. The strain is capable of oxidizing ammonium and releasing di-nitrogen gas.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Bacteria and method for improving plant health and growth
InactiveUS20160227789A1Improve disease resistanceGood for healthBiocideBacteriaBacillus megateriumBacterial composition
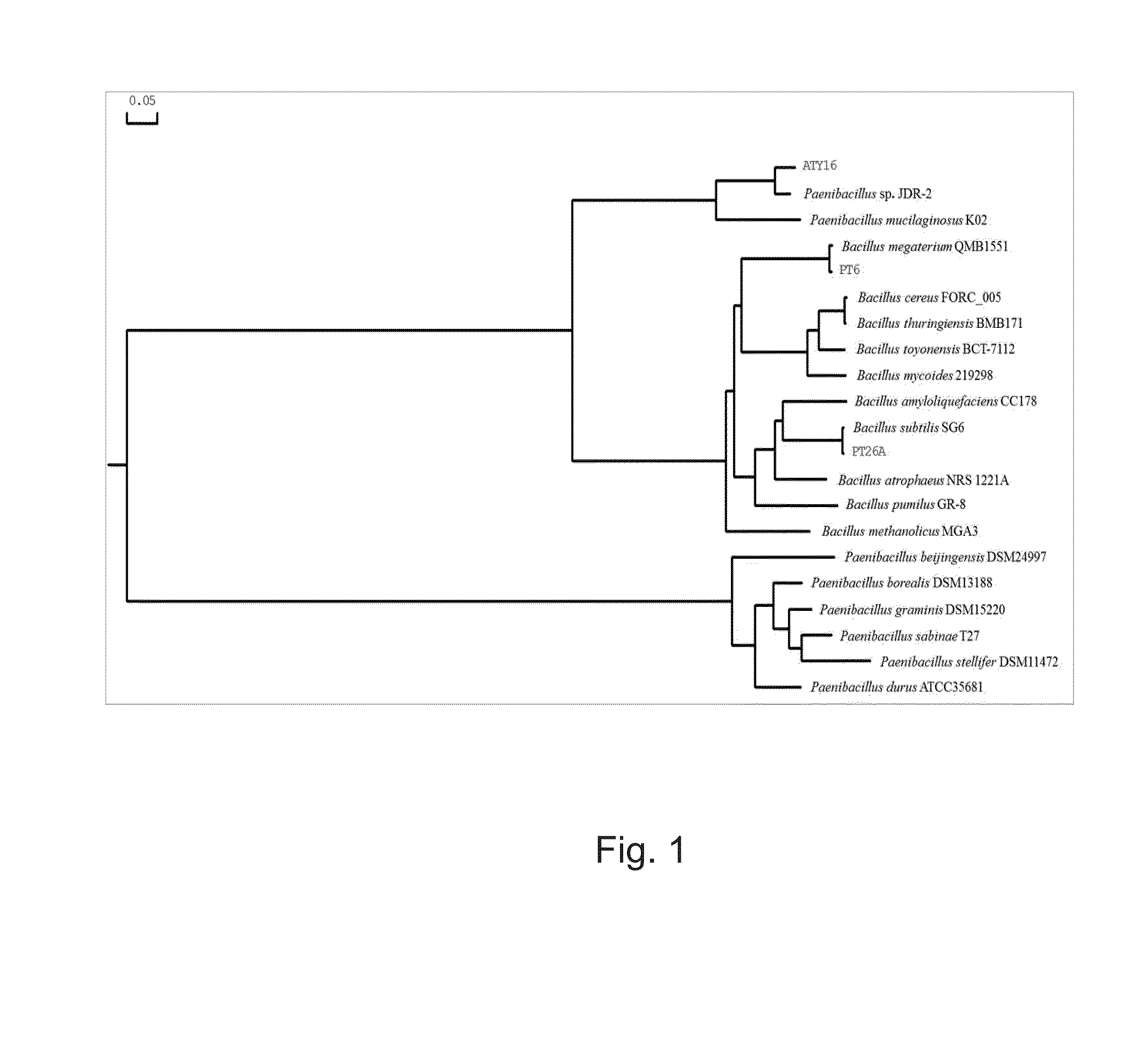
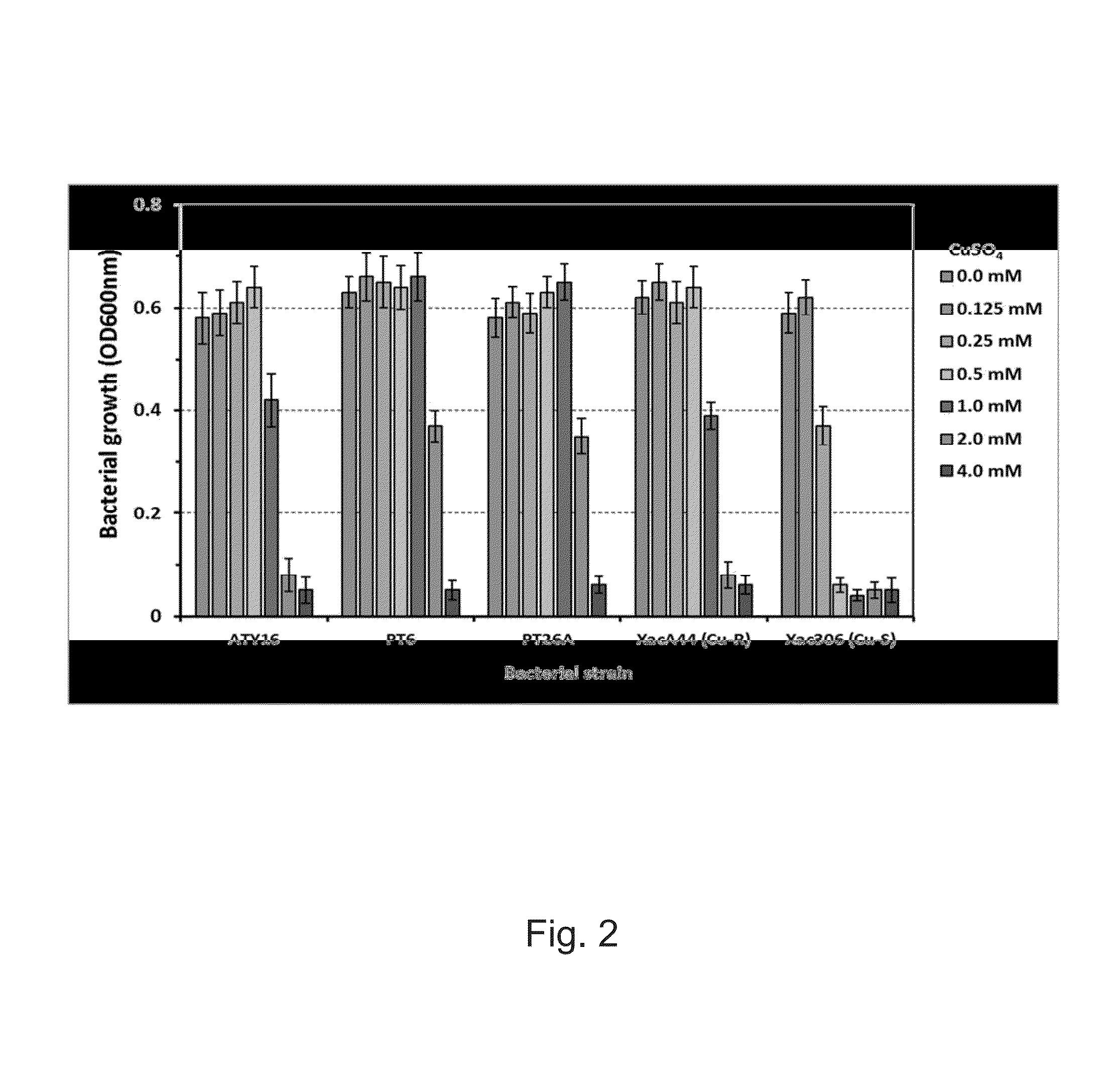
This application describes and claims a method of improving the health and vigor of a plant, comprising administering to the plant an effective amount of a bacterial composition which comprises a botanically compatible vehicle and an isolated bacterial strain selected from the group consisting of Bacillus megaterium PT6, Bacillus subtilis PT26A, Paenibacillus sp. ATY16, and any combination thereof. Improvement in health and vigor is one or more of the following: a) improved resistance to disease; b) improved ability to defend against disease; c) reduction of disease symptoms; d) faster growth; e) improved crop productivity; f) improved crop quality; g) improved seed germination; h) improved seedling emergence; or any combination thereof. Isolated bacterial strains and mixtures of bacteria are provided, as well as compositions comprising the isolated bacterial strains.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090047671A1Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
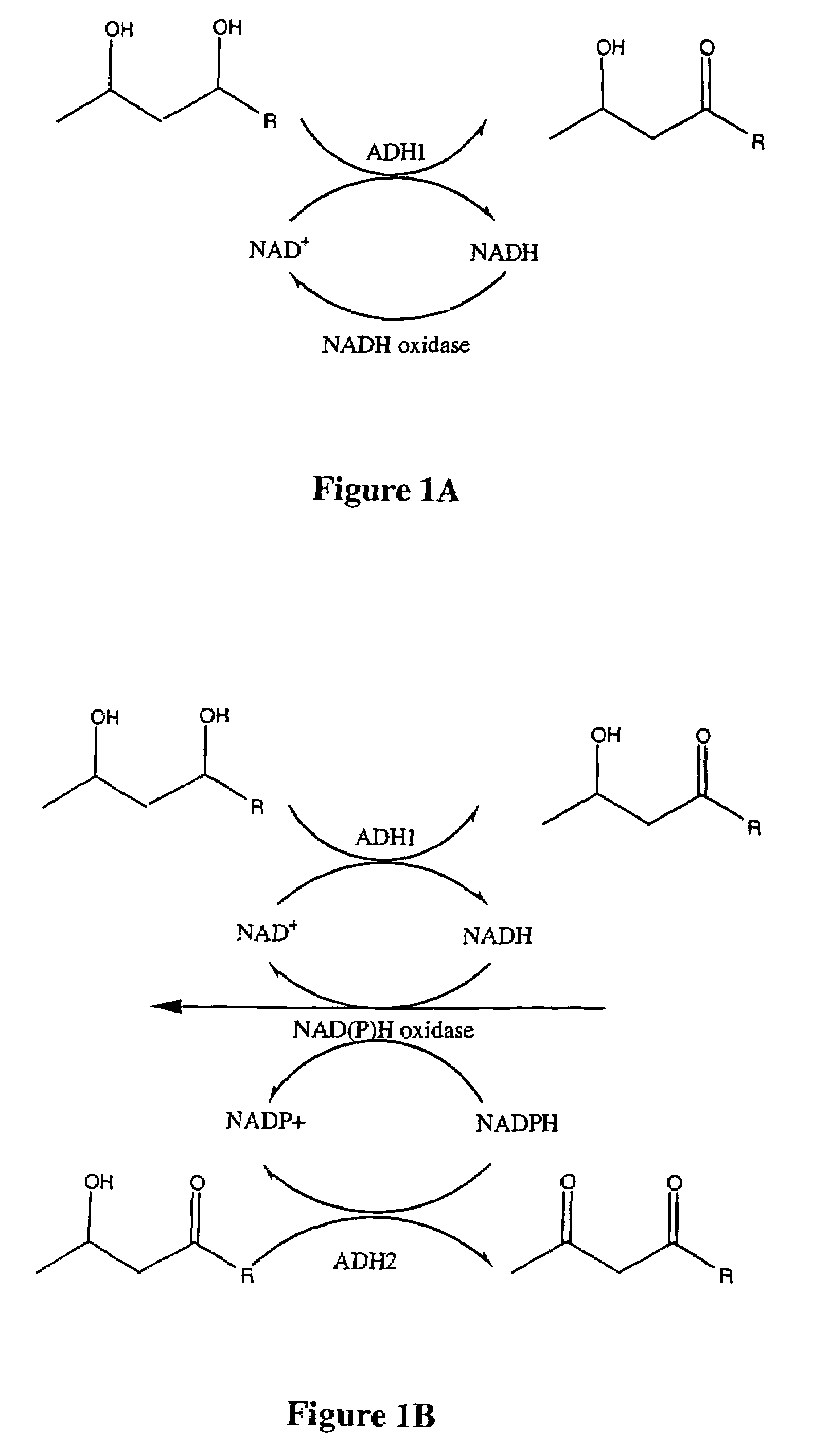
Methods and compositions for NAD(P)(H) oxidases
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods comprising NAD(P)H oxidases, particularly bacterial oxidases, nucleic acids, recombinant plasmid vectors and recombinant proteins therein encoded, and host cells comprising the oxidases and nucleic acids. The present invention also comprises an isolated bacterial oxidase that oxidizes both NADH and NADPH. Methods for producing the enzymes and enzymatic reactions comprising use of NAD(P)H oxidases and products of such reactions are also disclosed.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Bacterial sucrose synthase compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6682918B1Low backgroundImproving immunogenicityClimate change adaptationTransferasesSucrose synthase activitySucrose synthetase
The present invention provides isolated and purified polynucleotides that encode bacterial polypeptides that participate in the utilization of sucrose. Isolated bacterial sucrose synthase compositions and methods of use are provided. Processes for altering sucrose synthase activity, altering the starch and / or sucrose content of bacterial and / or plant cells, methods of identifying sucrose synthase-encoding nucleic acid segments, and compositions comprising sucrose synthase peptides and antibodies are also disclosed.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Microbial compositions for use in combination with soil insecticides for benefiting plant growth
Compositions and methods are provided for benefiting plant growth. The compositions contain isolated bacterial or fungal strains having properties beneficial to plant growth and development that can provide beneficial growth effects when delivered in a liquid fertilizer in combination with a soil insecticide to plants, seeds, or the soil or other growth medium surrounding the plant or seed. The beneficial growth effects include one or a combination of improved seedling vigor, improved root development, improved plant health, increased plant mass, increased yield, improved appearance, improvedresistance to osmotic stress, improved resistance to abiotic stresses, or improved resistance to plant pathogens. The isolated bacterial strains include those of the Bacillus species including speciessuch as Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:FMC CORP
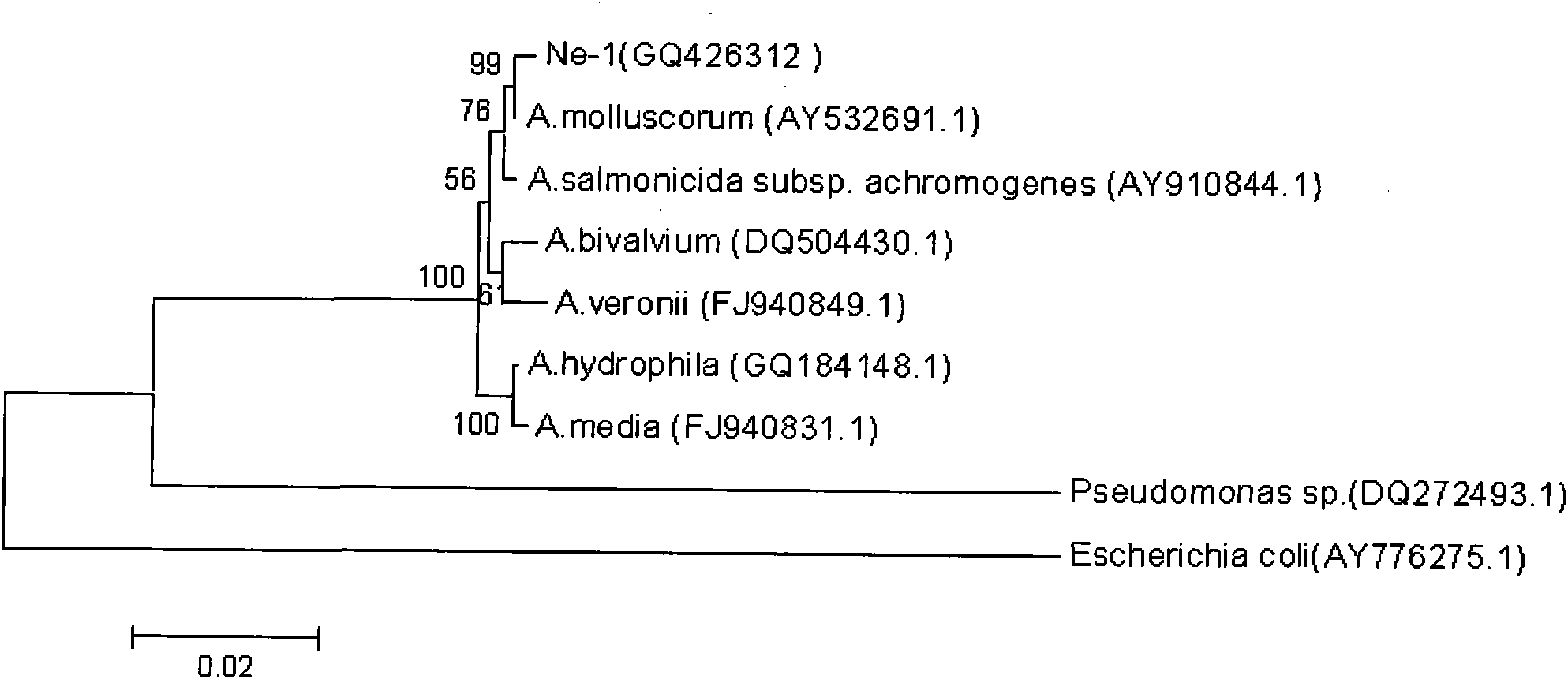
Method for separating Aeromonas molluscorum producing tetrodotoxin from Takifugu fasciatus tissue and fermentation culture method of Aeromonas molluscorum as well as detection method of produced tetrodotoxin
The invention relates to a method for separating Aeromonas molluscorum producing tetrodotoxin from Takifugu fasciatus tissues and a fermentation culture method of the Aeromonas molluscorum as well as a detection method of the produced tetrodotoxin. The method for separating the Aeromonas molluscorum producing the tetrodotoxin from the Takifugu fasciatus tissues comprises a bacteria separation method, a bacteria identification method, a bacteria fermentation culture method, a competitiveness ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) detection method and an LC-MS (Liquid Chromatograph-mass Spectrometry) detection method of the tetrodotoxin produced by the Aeromonas molluscorum, and the like. In the invention, by separating bacteria from Takifugu fasciatus ovaries and adopting a TCBS (Thiosulfate Citrate Bile (salt) Sucrose (agar)) culture medium for screening, the Aeromonas molluscorum capable of producing the tetrodotoxin is separated from blowfish bodies for the first time; the separated bacteria is identified by adopting a 16 SrDNA method; the competitiveness ELISA detection method and the LC-MS detection method are both firstly adopted for the tetrodotoxin produced by the separated Aeromonas molluscorum; and the produced tetrodotoxin and tetrodotoxin extracted from the blowfish bodies are determined to be the same substance; in addition, the separated Aeromonas molluscorum can massively separate the tetrodotoxin from the bacteria after being cultured.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Bacillus isolates and methods of their use to protect against plant pathogens and virus transmission
ActiveUS8524222B2Preventing and reducing virus infectionEasy to useBiocideBacteriaDiseaseBacteroides
Methods of inducing systemic acquired resistance to infection in a plant are provided. The methods comprise applying a composition comprising a Bacillus control agent to said plant wherein said plant is capable of producing defense proteins. Also provided are, methods for controlling one or more plant diseases, methods for preventing plant virus transmission, methods for preventing and / or treating soil-borne plant pathogens using the Bacillus control agent of the present invention, and methods of generating bacterial spores. In addition, synergistic biocontrol combinations and methods of using the same are provided.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Pha-producing bacteria
ActiveUS20120301933A1Reduce pollutionPromote recoveryBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicrobiologyBacterial strain
Owner:ORIGIN MATERIALS OPERATING INC
Preparation method of hybrid hydrolase formulation for promoting methane yield from fermentation
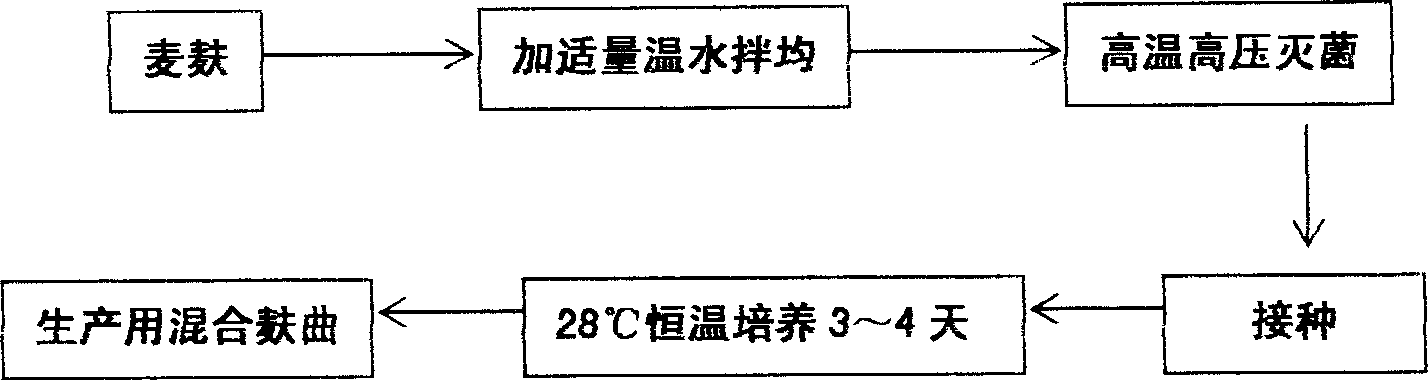
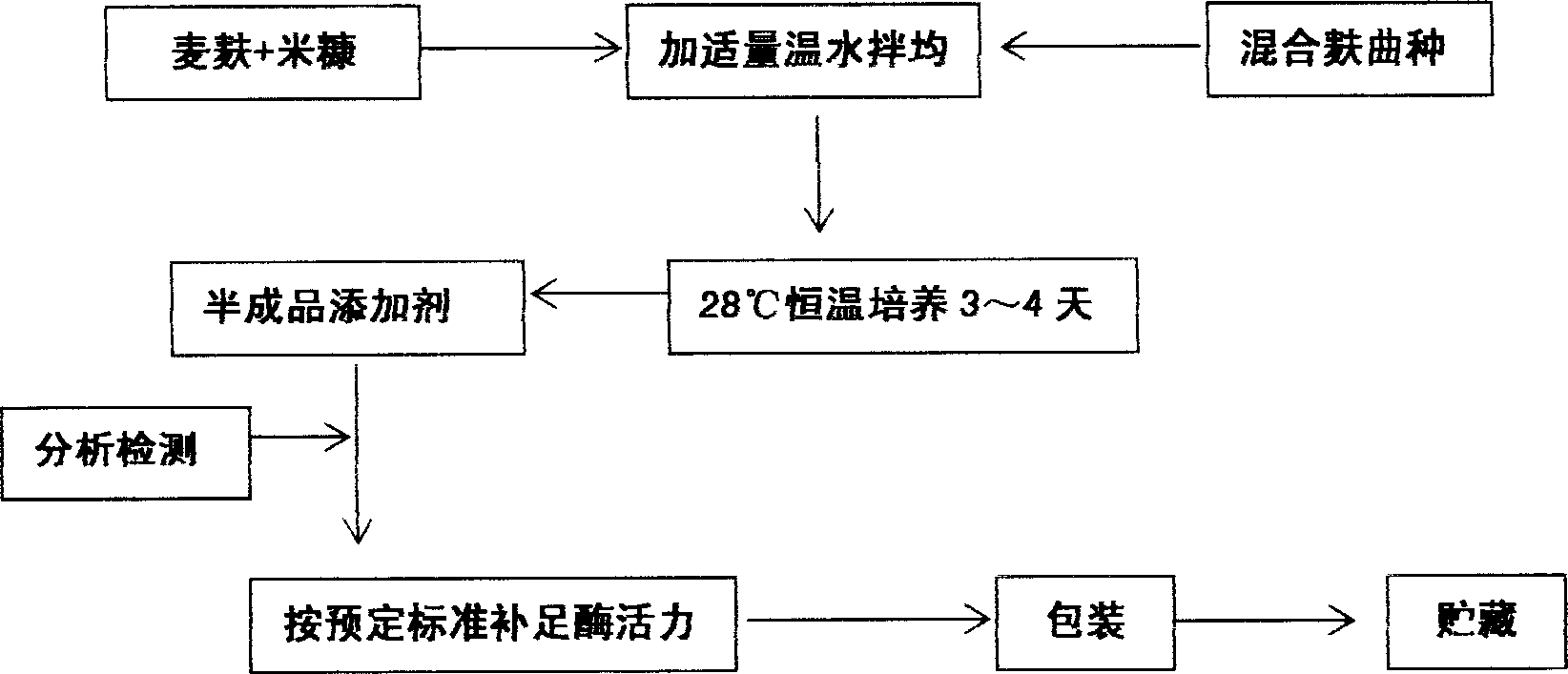
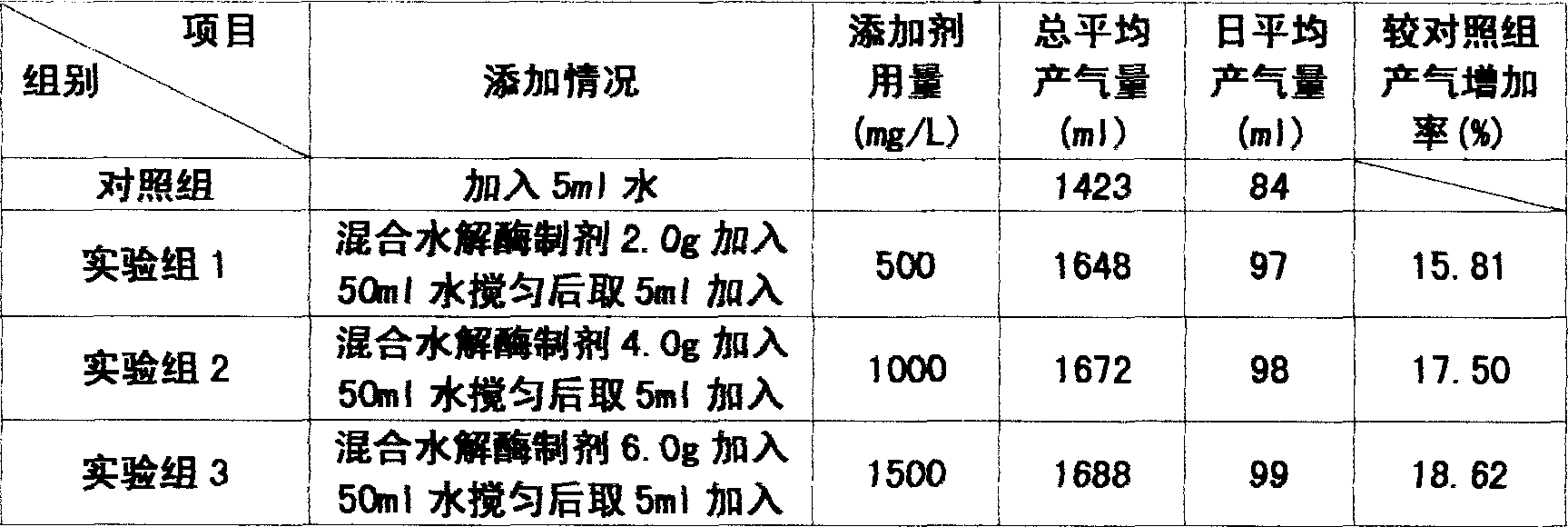
InactiveCN1884509AIncrease fermentation gas productionPromote degradationHydrolasesMicroorganismsBiotechnologyMethane yield
The method for preparation of hydrolytic enzyme preparation used for improving gas-producing rate of marsh gas fermentation belongs to preparation of supplementary exoenzyme used for marsh gas fermentation. The invention is to provide a method for preparation of hydrolytic enzyme preparation used for improving gas-producing rate of marsh gas fermentation, which has the production bacteria with the following enzymatic vitality index: selecting wheat bran and rice bran as mixed culture medium, obtaining mixed bran seeds by pedigree breed two-stage enlargement culture of the bacteria with solid method, fermenting for 3-4 days at 28 DEG after evenly mixed, sampling and analyzing every enzymatic vitality index, adding commodity enzyme preparation to reach enzymatic vitality index, and airing until the humidity is lower than 5%. The enzymatic vitality index of the prolease in the said mixed bran seeds is not more than 2000+-5% mug tyrosine / g / min. The bacteria can be obtained by bacteria and fungus separated from different environment. The test proves that when hydrolytic enzyme preparation is input into the methane tank fermentation raw materials, the rate of dissolution and degradation of the marsh gas fermentation raw materials can be improve, and the gas-producing rate of marsh gas fermentation, TS and VS gas-production potential and methane content in marsh gas can be increased.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Microbial compositions for use in combination with soil insecticides for benefiting plant growth
Compositions and methods are provided for benefiting plant growth. The compositions contain isolated bacterial or fungal strains having properties beneficial to plant growth and development that can provide beneficial growth effects when delivered in a liquid fertilizer in combination with a soil insecticide to plants, seeds, or the soil or other growth medium surrounding the plant or seed. The beneficial growth effects include one or a combination of improved seedling vigor, improved root development, improved plant health, increased plant mass, increased yield, improved appearance, improved resistance to osmotic stress, improved resistance to abiotic stresses, or improved resistance to plant pathogens. The isolated bacterial strains include those of the Bacillus species including species such as Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:FMC CORP
Bacillus isolates and methods of their use to protect against plant pathogens
Methods of inducing systemic acquired resistance to infection in a plant by applying a composition comprising a Bacillus control agent to said plant wherein said plant is capable of producing defense proteins.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
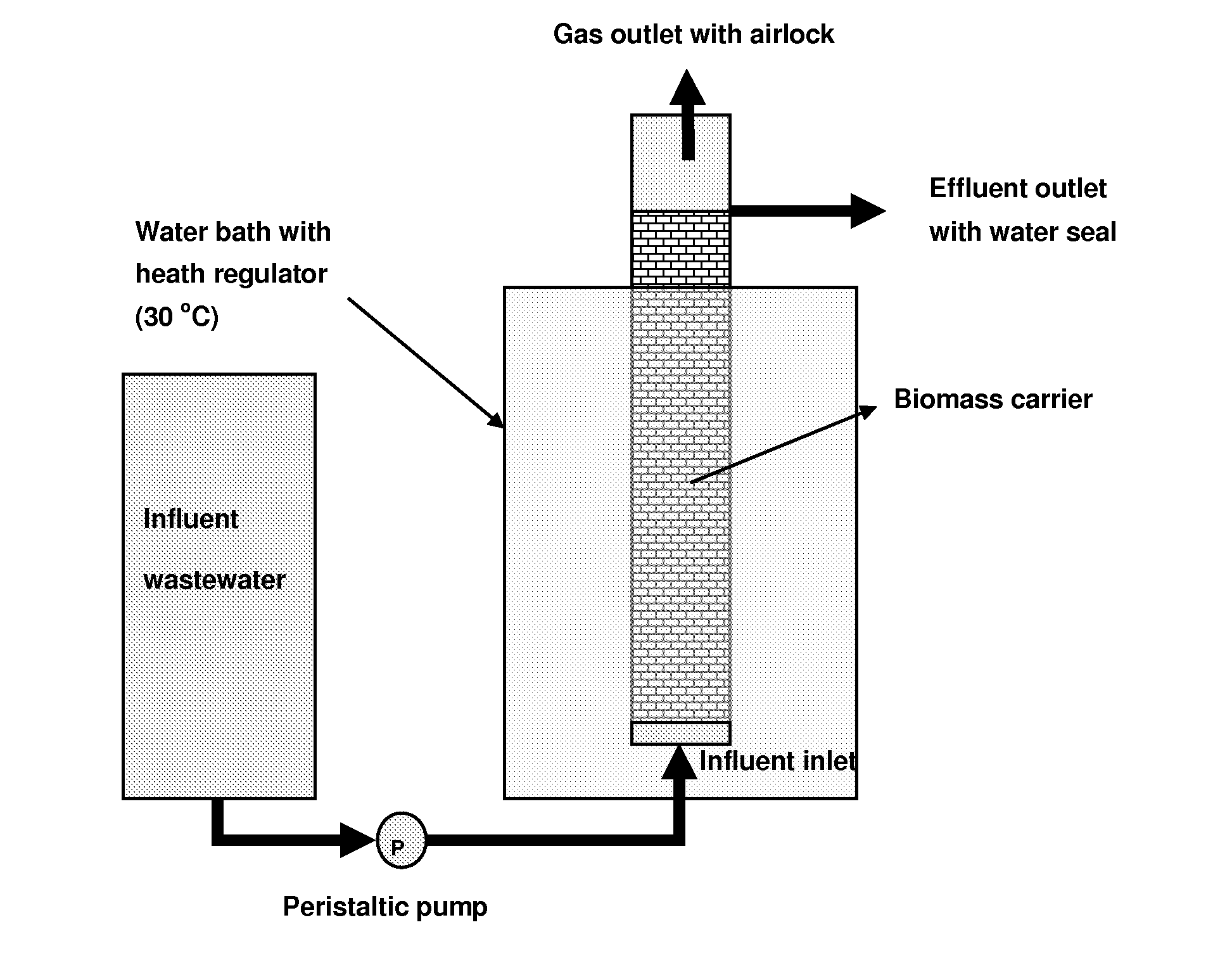
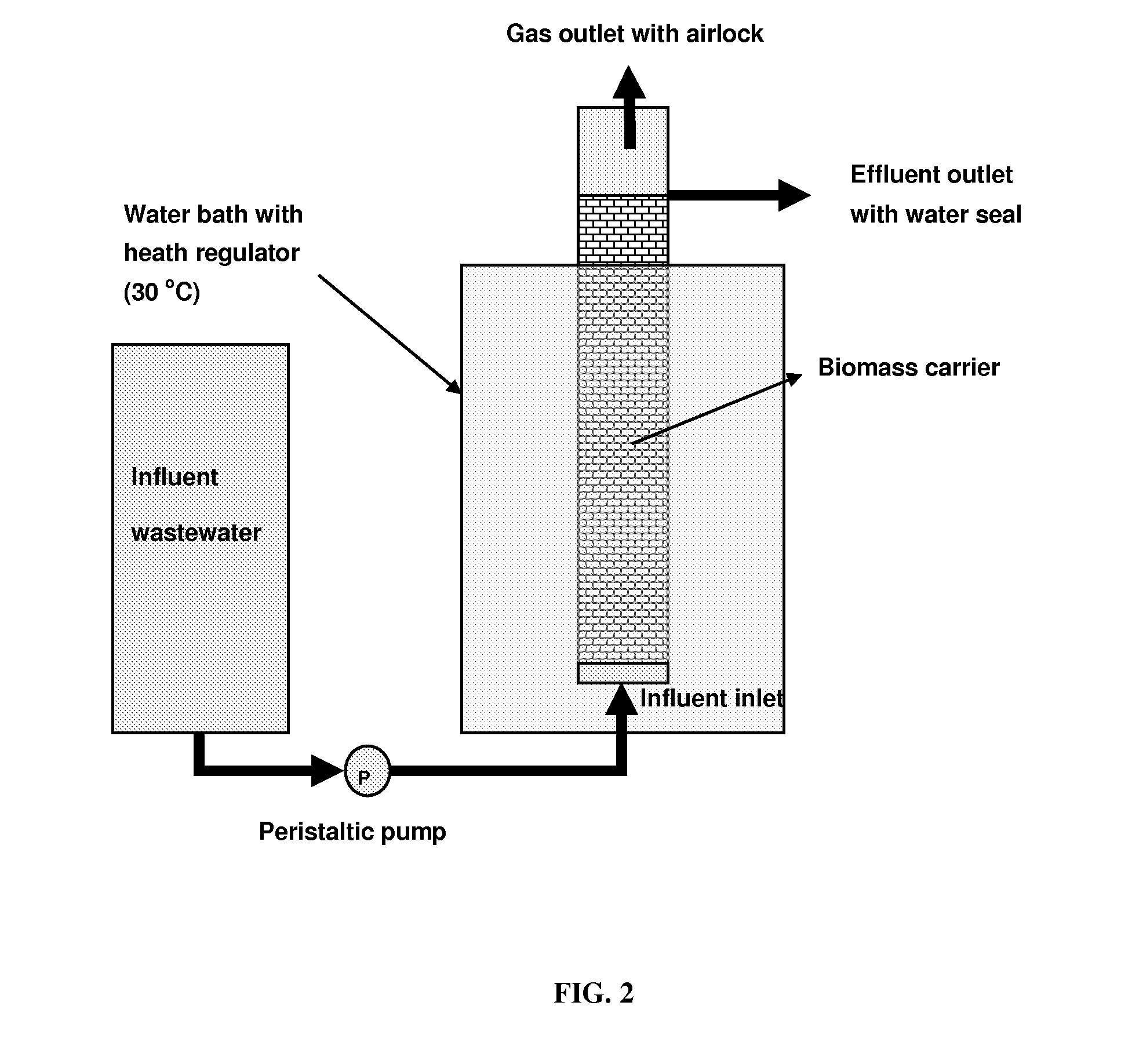
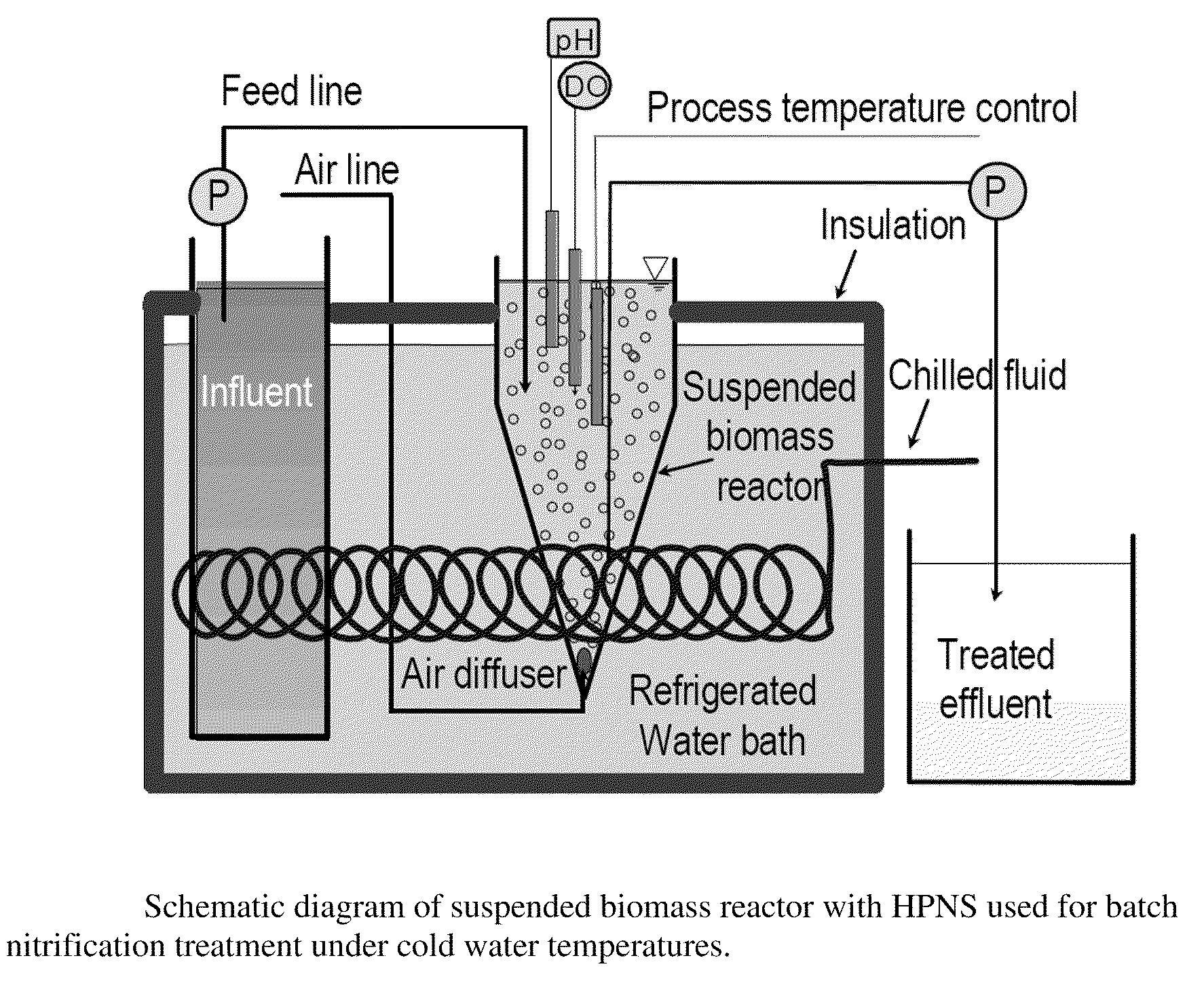
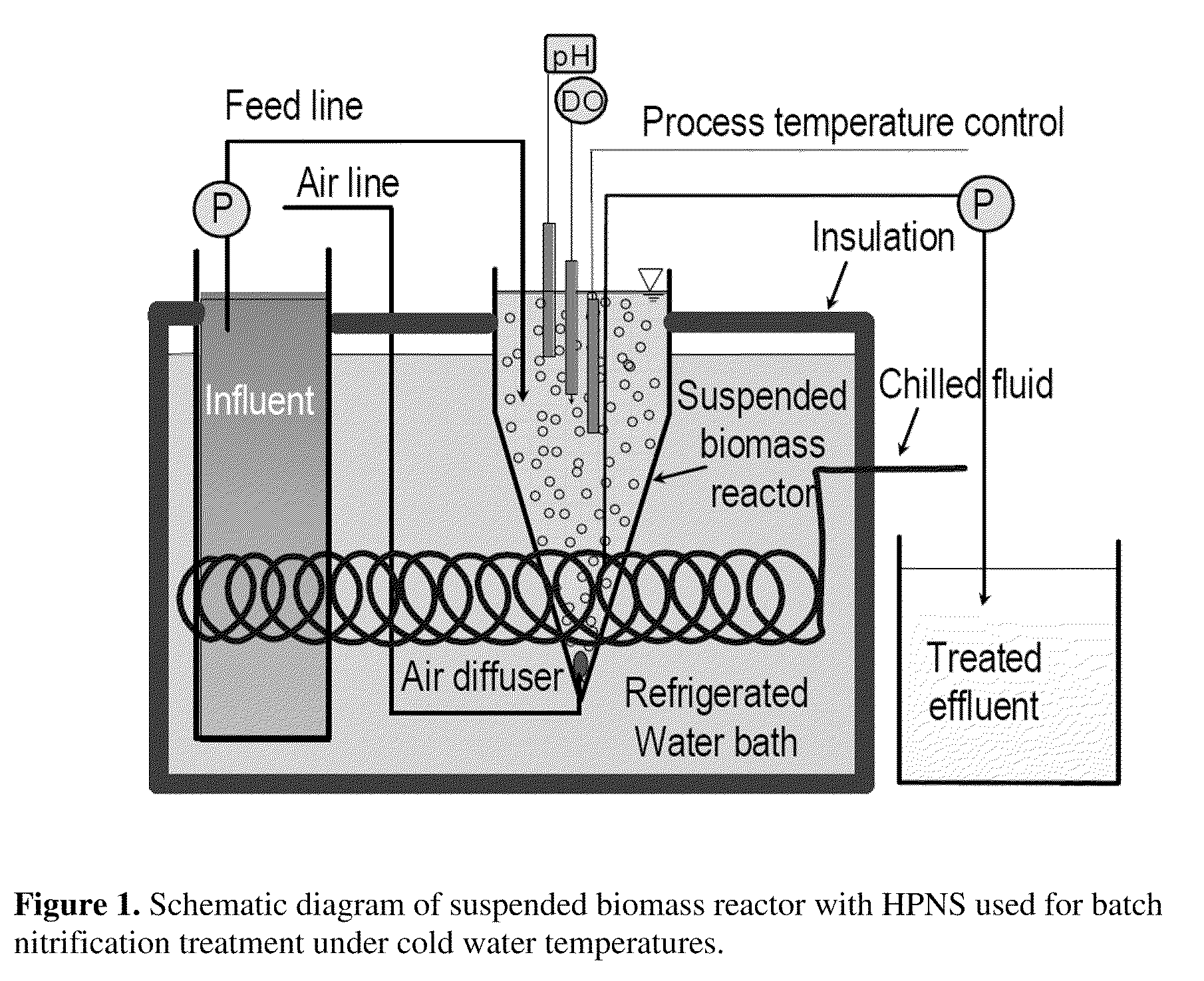
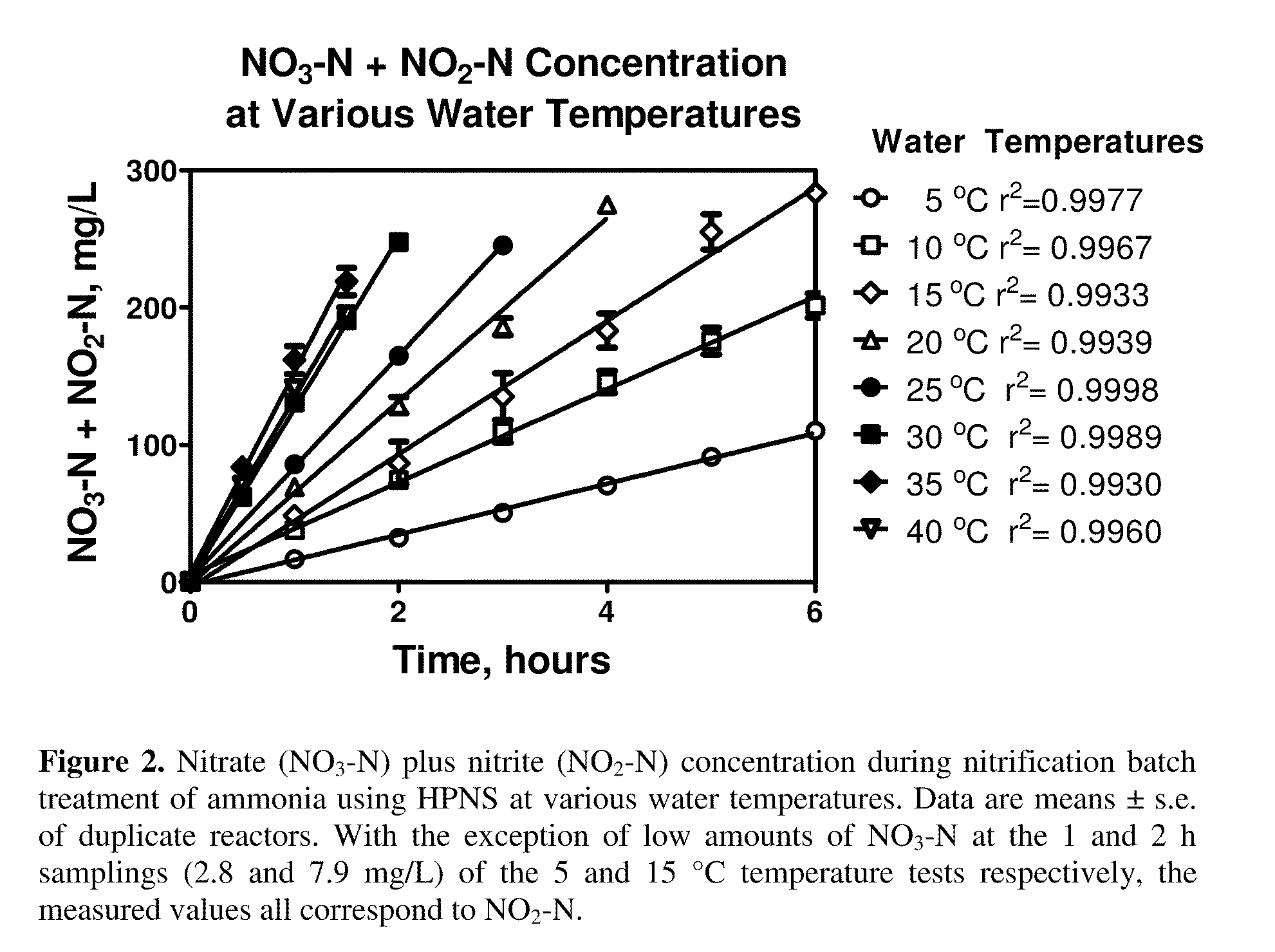
High Performance Nitrifying Sludge For High Ammonium Concentration and Low Temperature Wastewater Treatment
ActiveUS20110000851A1Ammonia reductionImprove performanceTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaFecesBacterial composition
Compositions of bacteria which are effective for the nitrification of wastewater, particularly at low temperatures, are described. The compositions are comprised of 35 strains or populations of at least partially characterized isolated bacteria. These compositions may be used to treat wastewater contaminated with animal fecal waste and / or ammonia. In use, wastewater is contacted with the bacterial composition of the invention under aerobic conditions and for a period of time effective to oxidize ammonia therein.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite membrane for efficient protein adsorption and separation and preparation method of composite membrane
ActiveCN107413316ALarge specific surface areaImprove adsorption capacitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiltrationReactive site
The invention discloses a bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite membrane for efficient protein adsorption and separation and a preparation method of the composite membrane. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: a bacterial cellulose membrane is mechanically dissociated into bacterial cellulose nanofiber; the surface of the bacterial cellulose nanofiber is modified with an adsorption functional group; the modified bacterial cellulose nanofiber is dispersed in an insoluble solvent, and a stable bacterial cellulose nanofiber suspension is formed by adding a dispersant; the bacterial cellulose nanofiber suspension is laid on the surface of a porous fiber base material with a synchronous ultrasonic filtration method to form a wet-state composite fiber membrane; the residual solvent in the wet-state composite fiber membrane is removed and the bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite membrane for efficient protein adsorption and separation can be obtained. A completely covered continuous two-dimensional net structure formed by the bacterial cellulose nanofiber is arranged on the surface of the composite membrane, meanwhile, a large quantity of adsorption active sites on the surface and high porosity are realized, and quick and effective adsorption of protein is realized, and the adsorption capacity is high.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
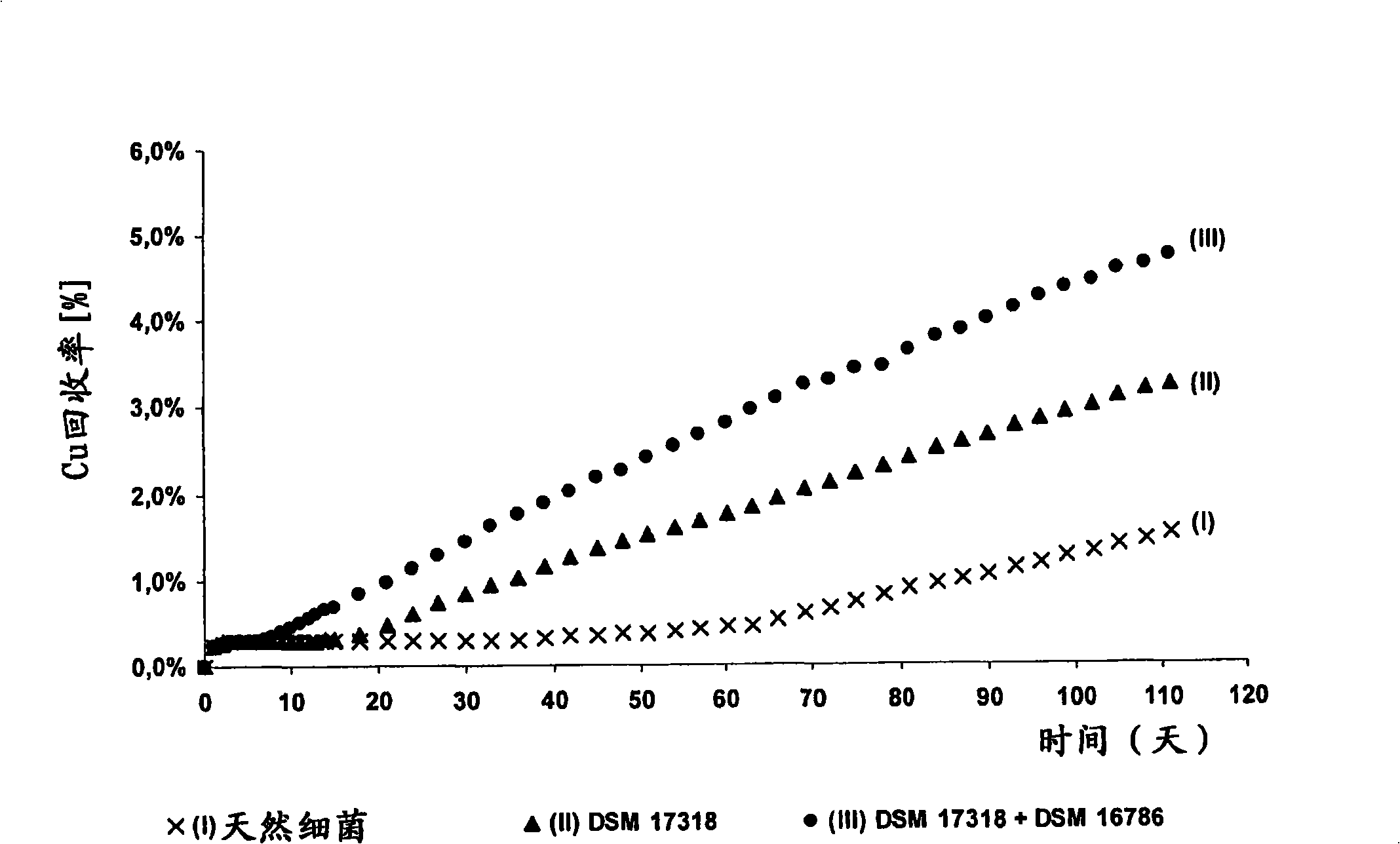
Method for improving biological leaching speed of metallic sulphide ore or concentrate by using leaching liquid containing separated microorganism to inoculate continuously
ActiveCN101260465AHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansTailings dam
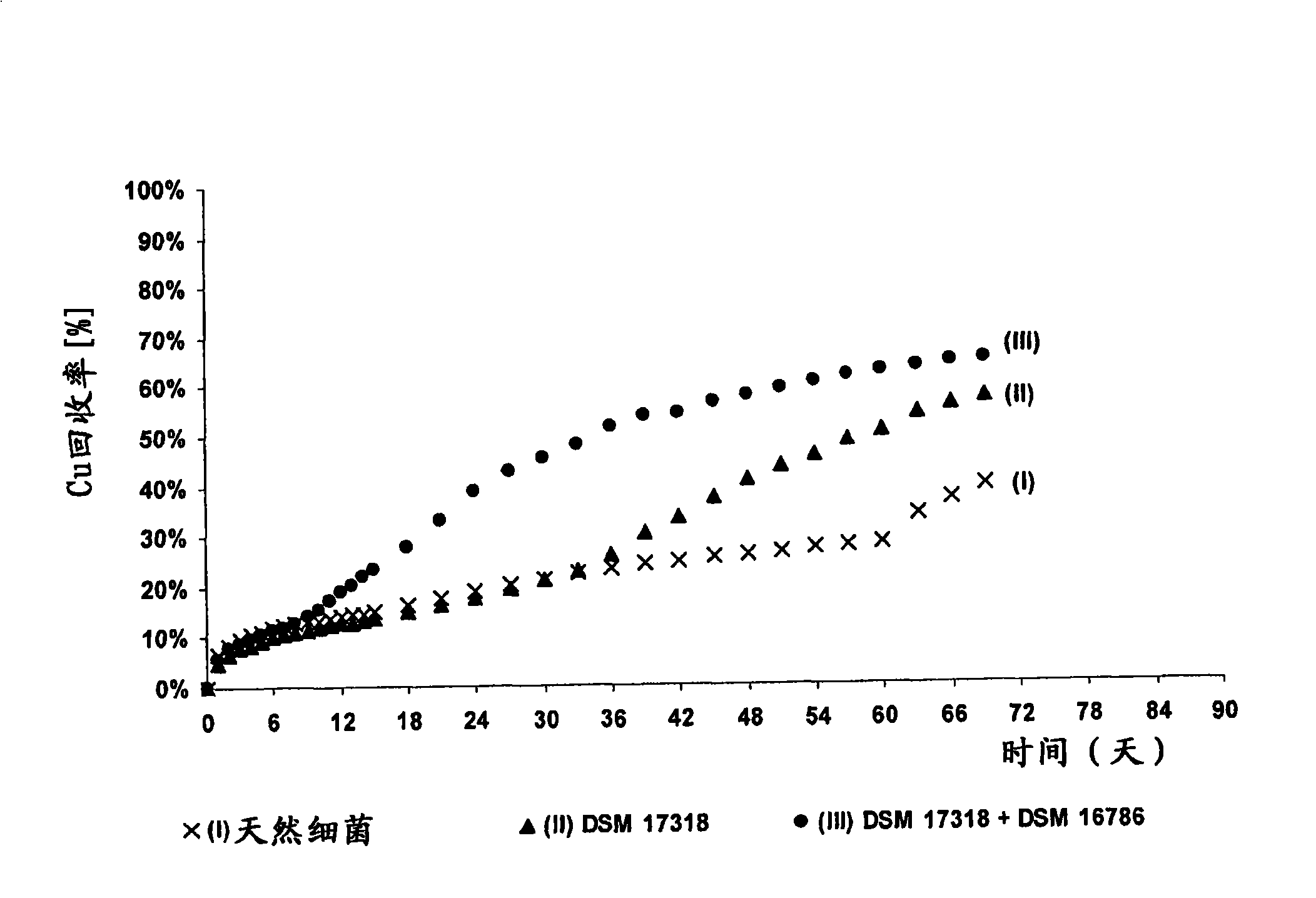
The invention discloses a method for increasing biological lixiviating speed of metal sulphate ore or ore concentrate in waste pile, tailing dam, scrap yard or other on-line processing. The method is charactered in that an acidophilic thiobacillus thiooxidans type isolated microbe and an acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans type isolated microbe process inoculability continuously to ore or ore concentrate in the event that nature microbe is not exist, and microbe total concentration in continuous inoculability flow reaches about 1*10<7> cells / ml to 5.6*10<7> cells / ml. Especially, the invention discloses continuous inoculability microbe as follows: acidophilic thiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318, and acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786, or other nature microbe above 5*10<7> cells / ml concentration. The invention also includes adding oxide (for example, high-iron ion generated on outside), and adding nutriment in forms of ammonium salt, magnesium salt, ferric salt and kali salt, in addition, injecting air containing CO2 continuously for improving bacilli action in biological lixiviating process of ore or ore concentrate.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Bionematicide composition and method for controlling phytopathogenic nematodes using the same
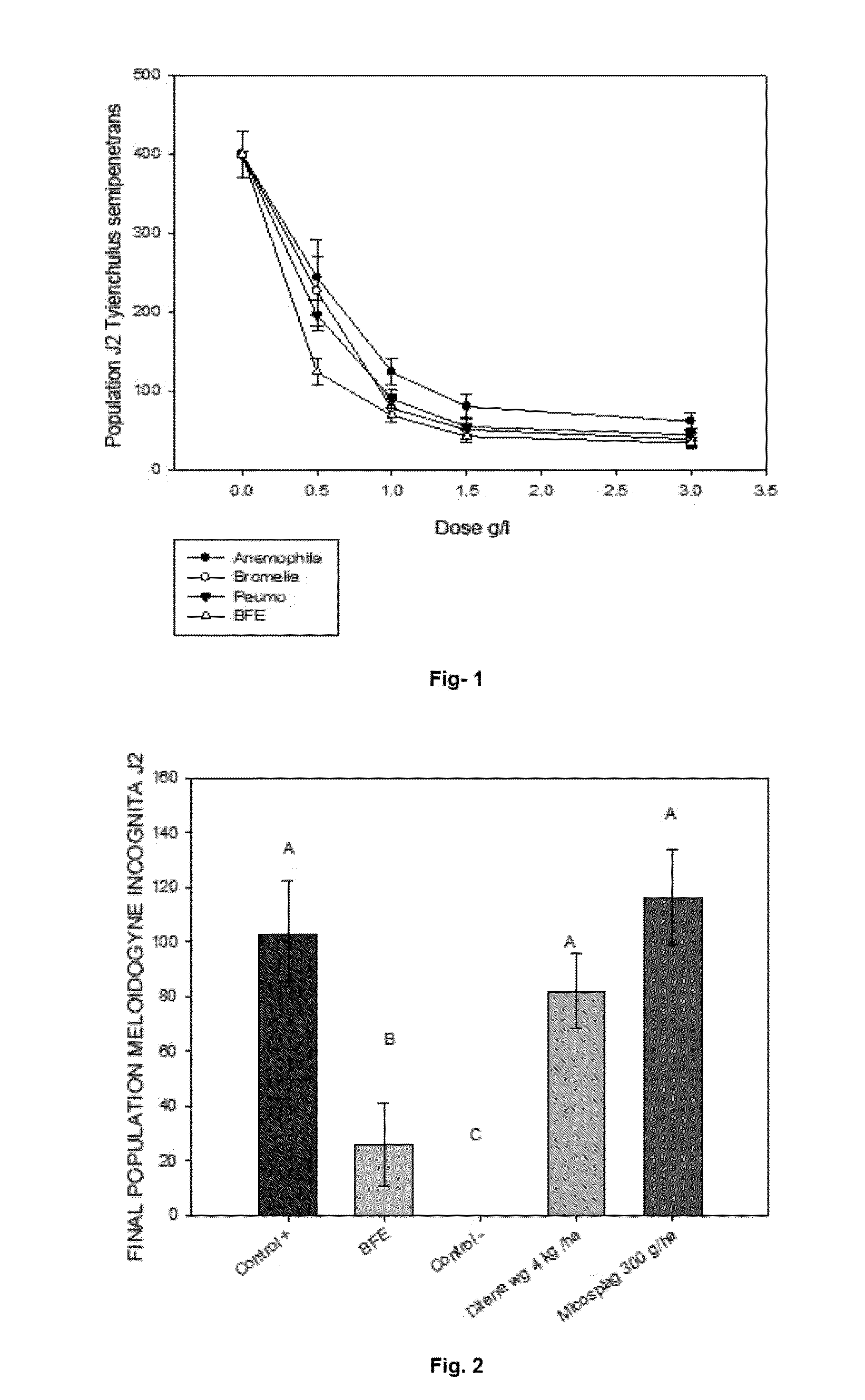
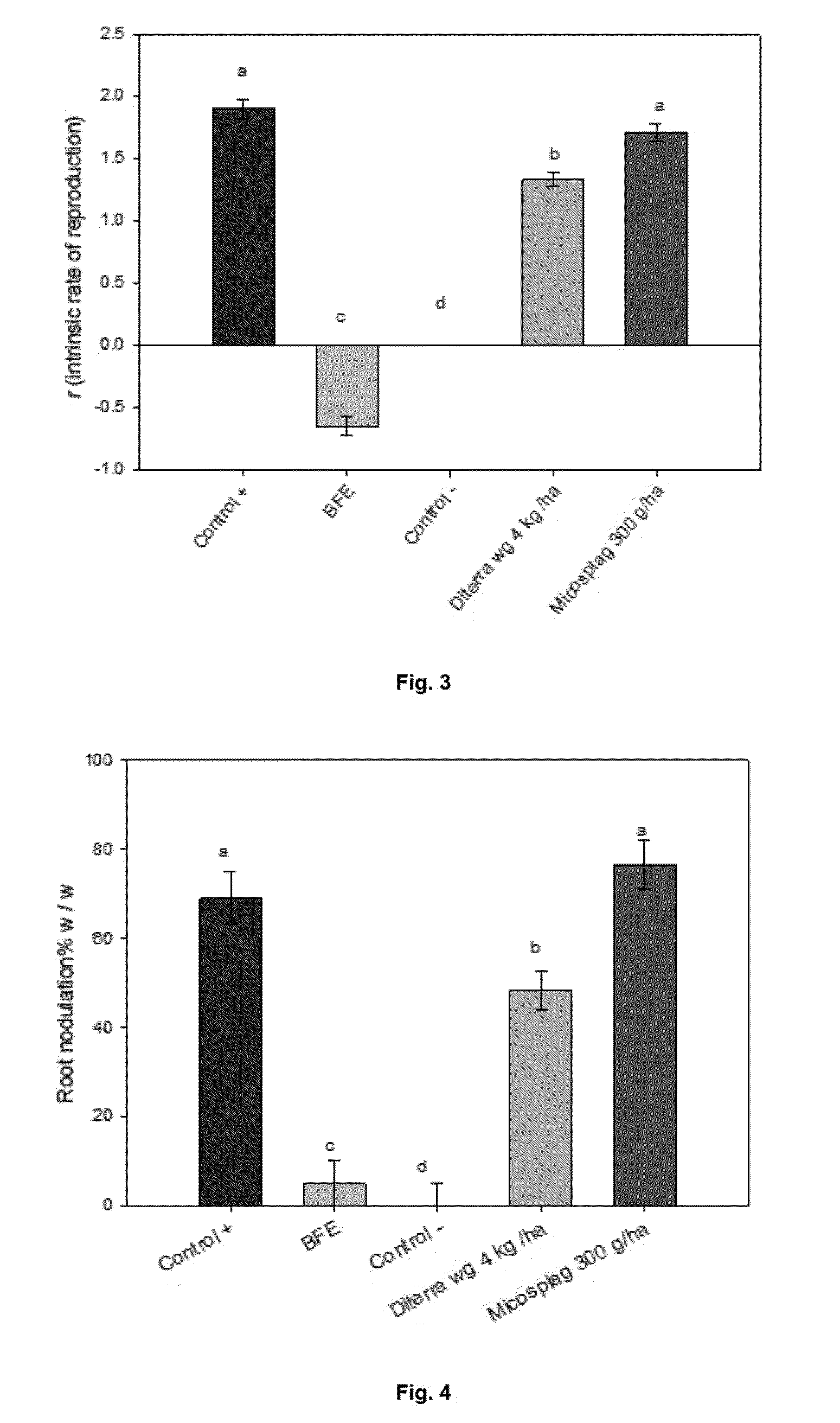
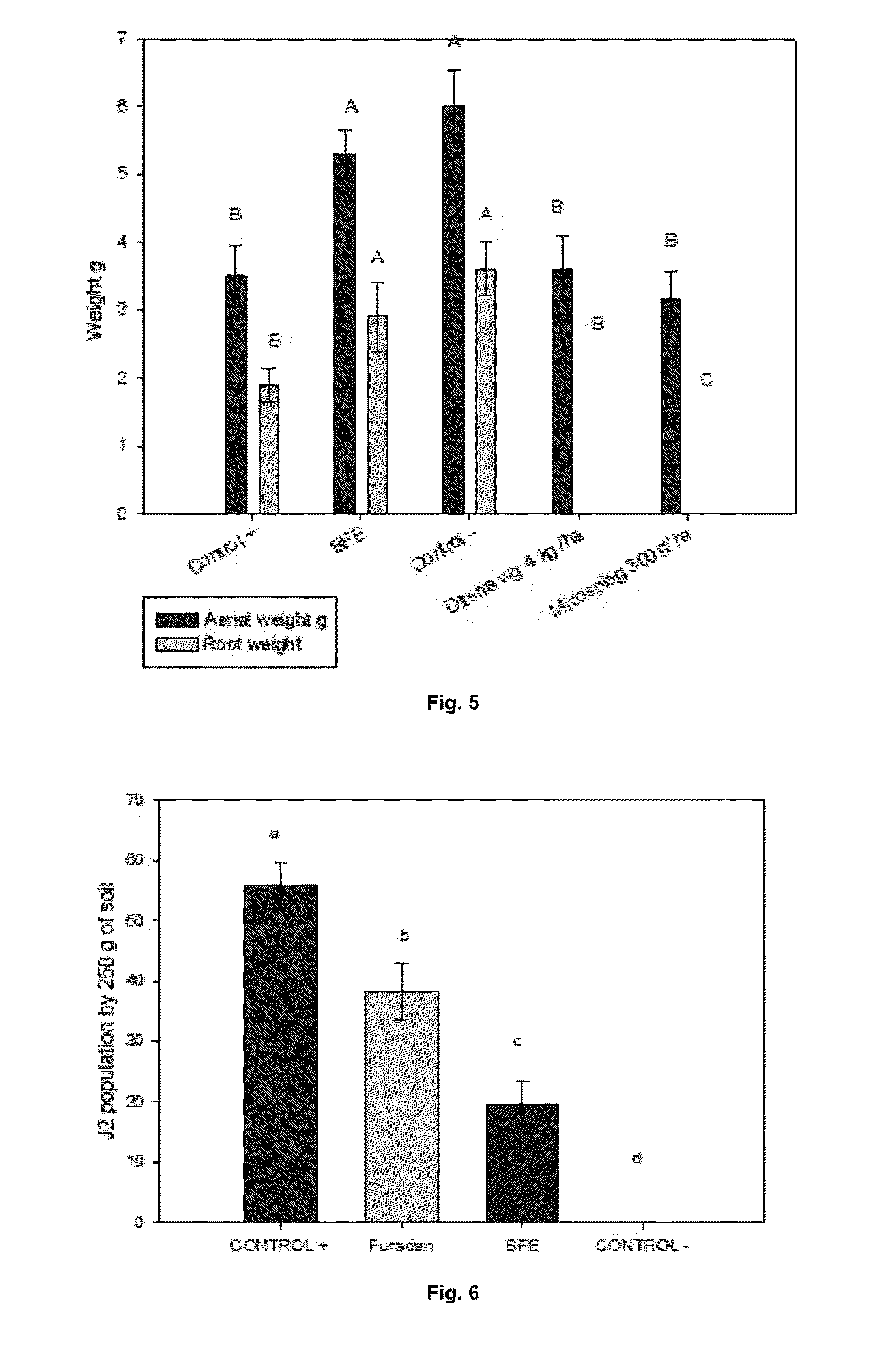
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a bionematicide composition broad spectrum action on phytopathogenic nematodes which comprises one or more bacterial strains isolated from Chilean soil belonging to the genus Bacillus, and the method of use of this composition for the protection of plants against nematode attack.
Owner:BIO INSUMOS NATIVA SPA
Antifungal paenibacillus strains, fusaricidin-type compounds, and their use
The present invention relates to novel isolated bacterial strains, which are members of the genus Paenibacillus, originally isolated from soil and showing antagonistic activity against a broad range of pathogens and being capable of producing antimicrobial metabolites. It was found that the strains Lu16774 and Lu17007 belong to a novel subspecies named Paenibacillus polymyxa ssp. plantarum while the strain Lu17015 belongs to a novel species which is proposed to be Paenibacillus epiphyticus. The present invention also relates to microbial pesticide compositions comprising at least one of such novel bacterial strains, whole culture broth or a cell-free extract or a fraction thereof or at least one metabolite thereof, and / or a mutant of at least one of said novel bacterial strains having all the identifying characteristics of the respective bacterial strain or whole culture broth, cell-free extract, fraction and / or metabolite of the mutant thereof showing antagonistic activity against plant pathogens. The present invention also relates to a method of controlling or suppressing plant pathogens or preventing plant pathogen infections by applying such composition. The present invention also relates to novel fusaricidin-type compounds which are metabolites produced by the strains of the present invention.
Owner:BASF SE
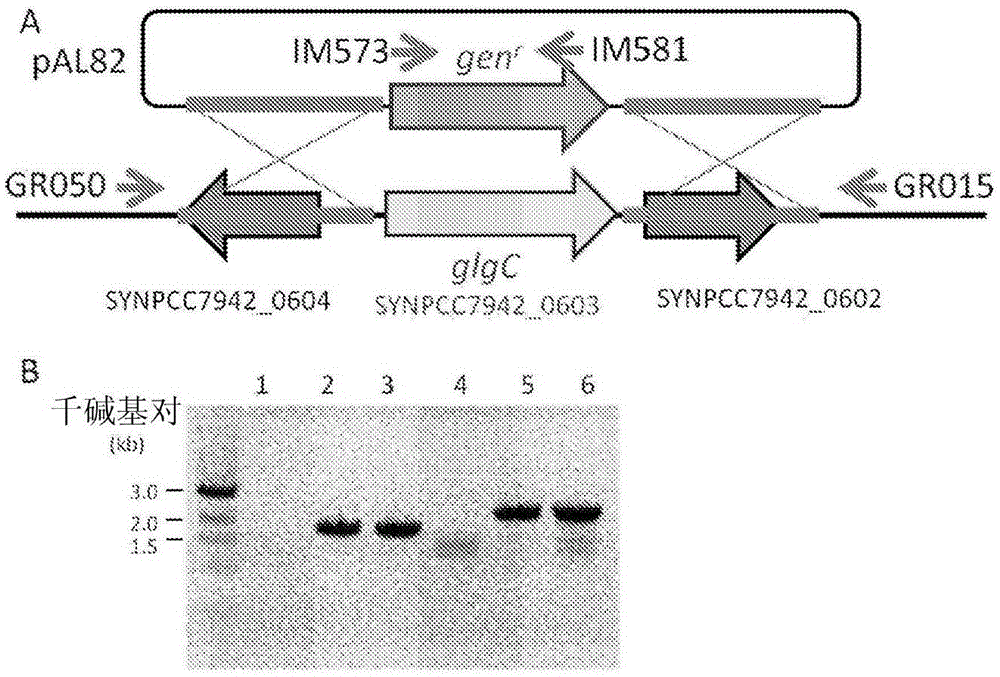
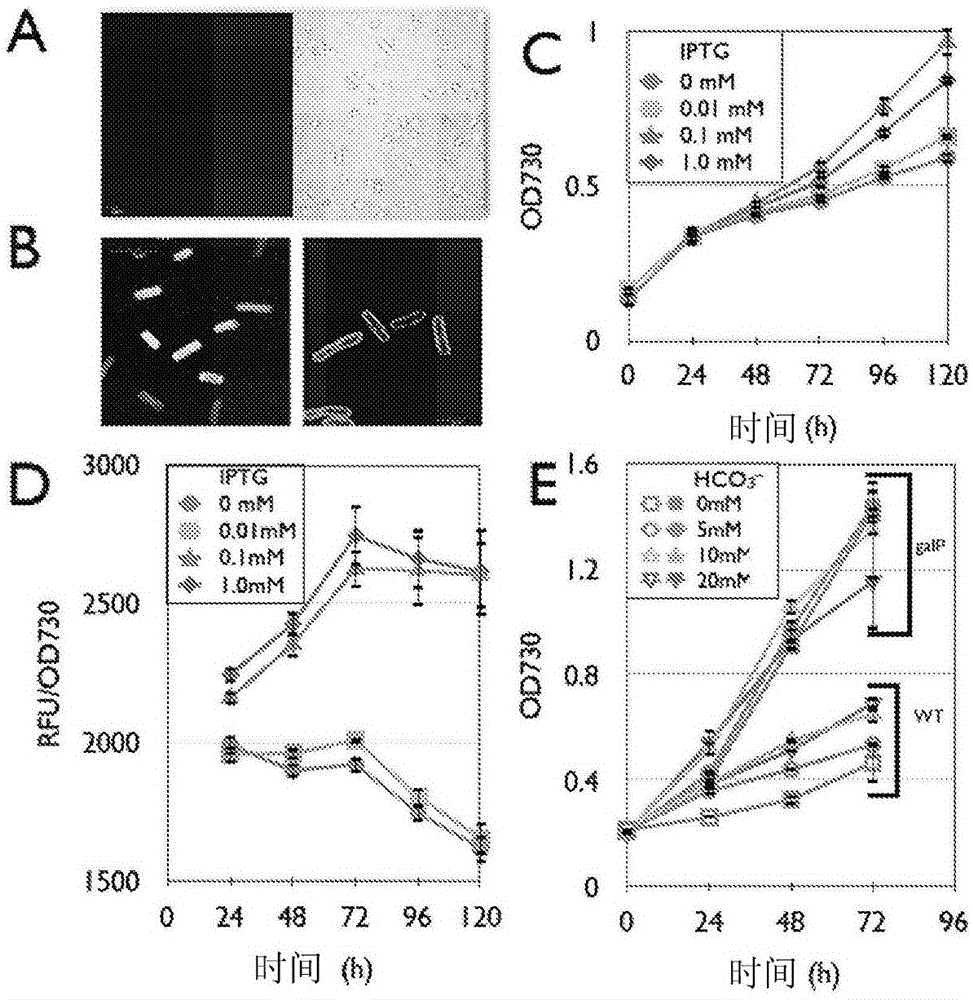
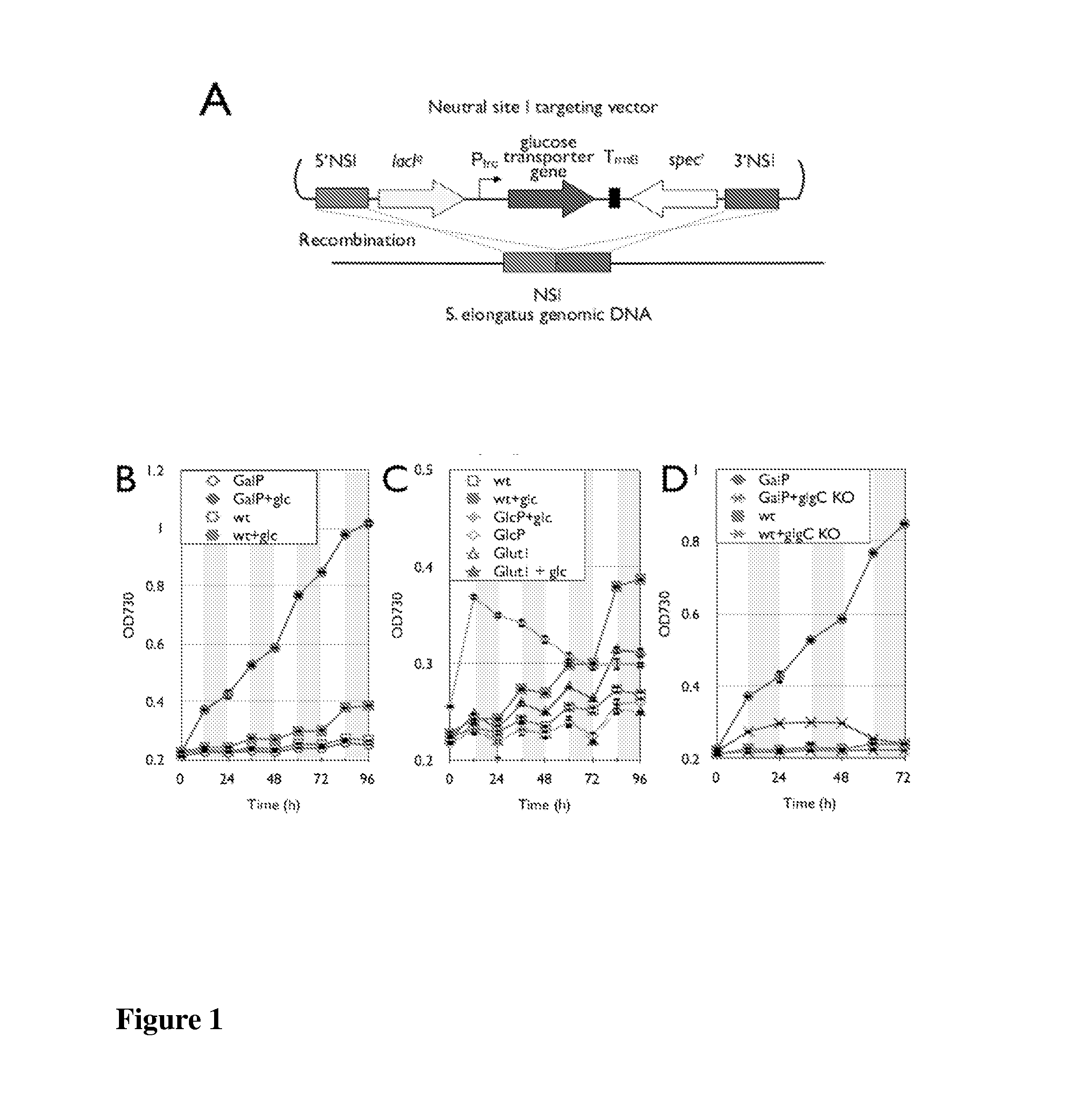
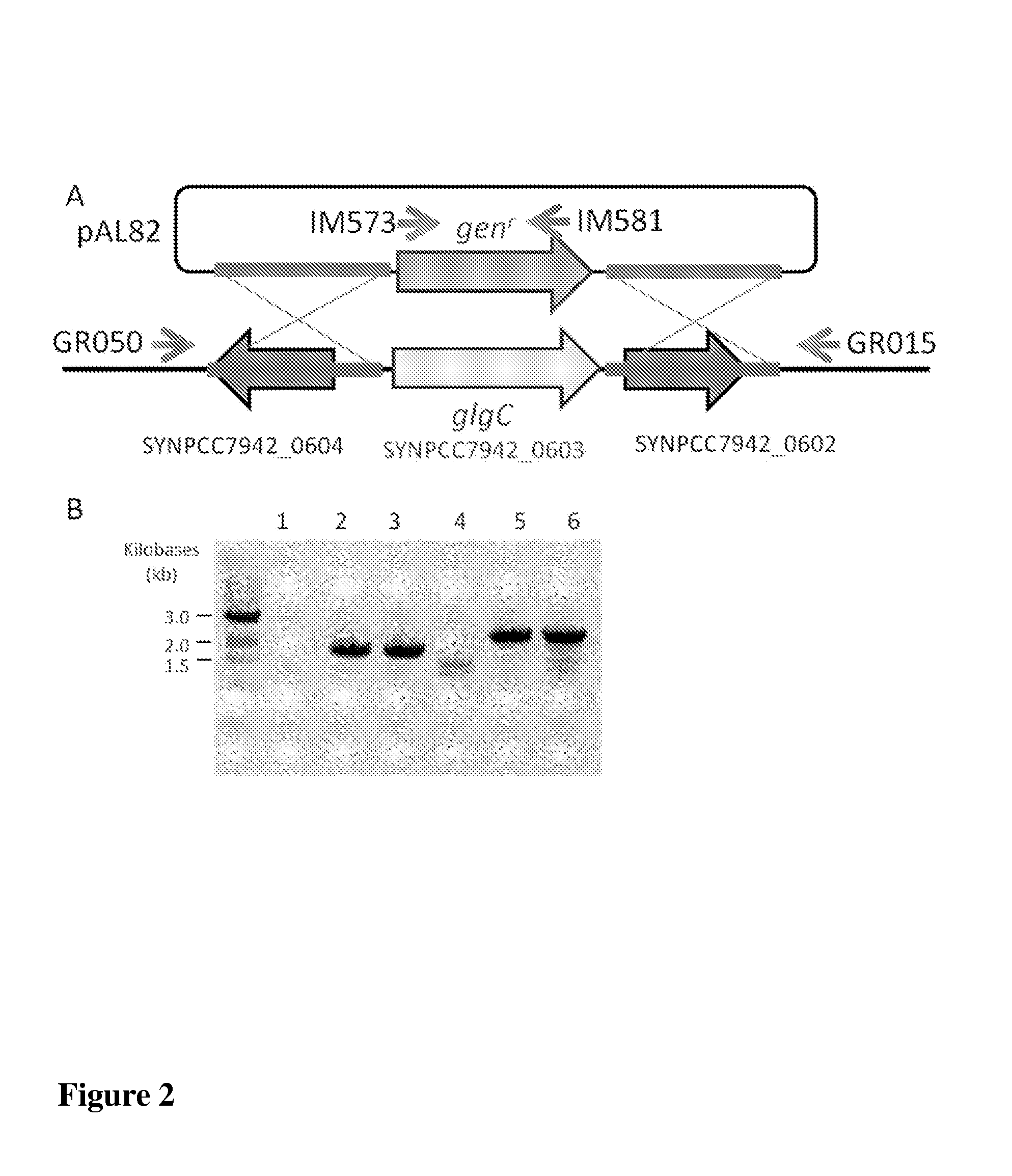
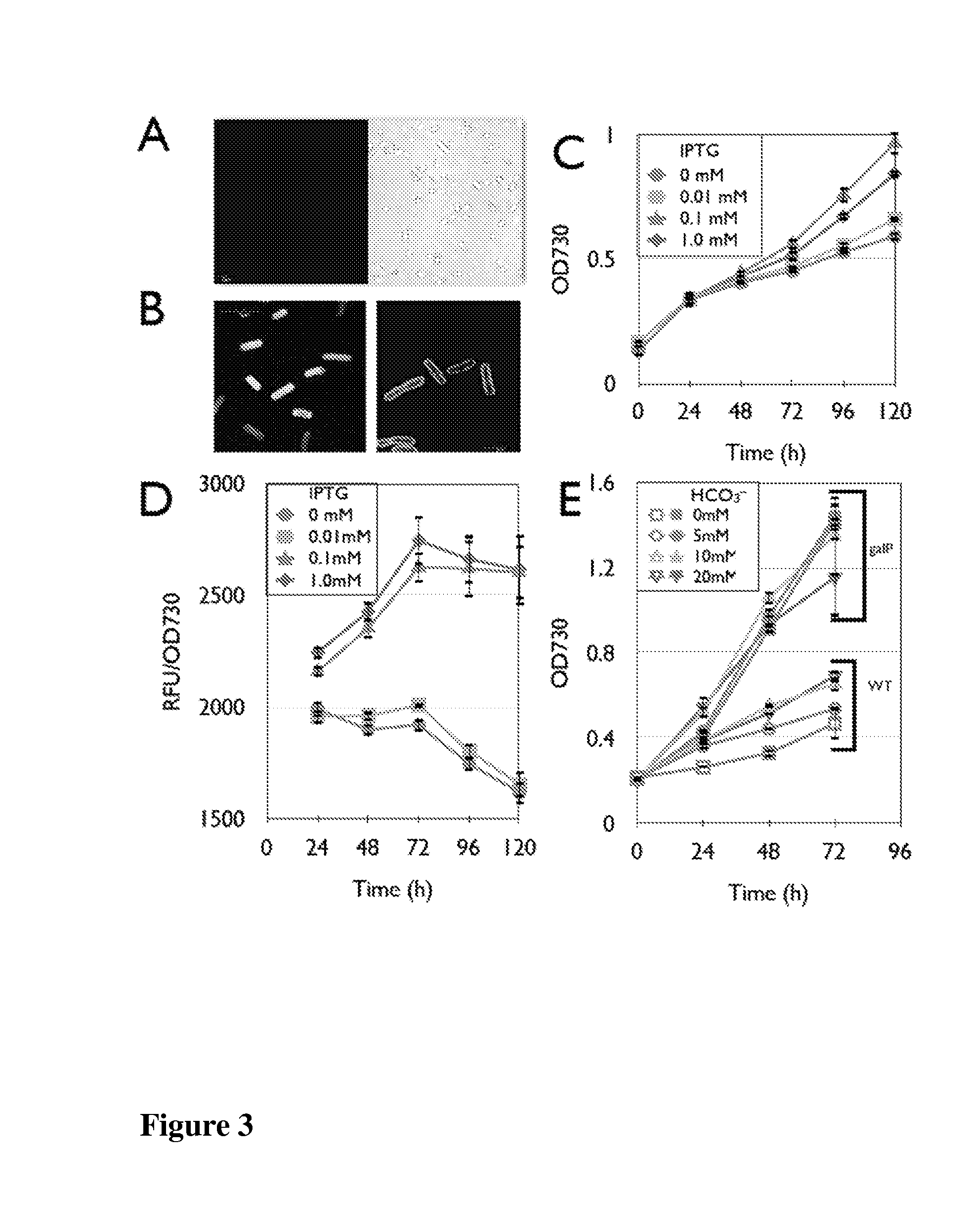
Trophic conversion of photoautotrophic bacteria for improved diurnal properties
The present disclosure relates generally to the growth of recombinant bacterial cells of photoautotrophic species under diurnal conditions. In particular, the present disclosure relates to isolated bacterial cells of photoautotrophic species having increased growth under diurnal conditions by expression of a sugar transporter protein and methods of use thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
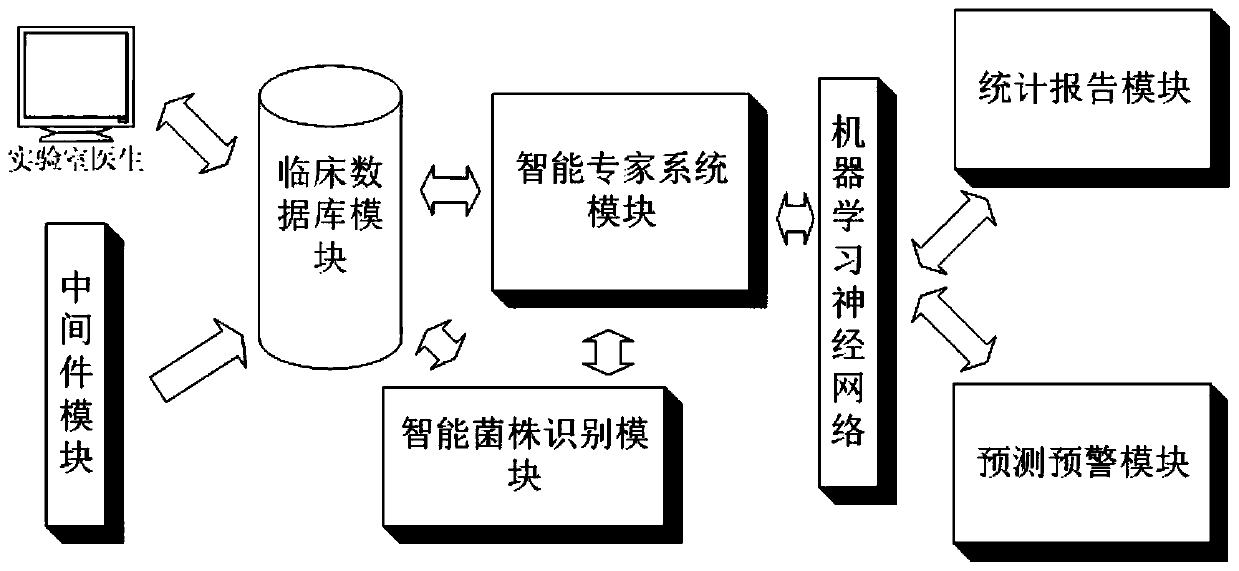
Infection control management system and method based on artificial intelligence
PendingCN110415832AImprove real-time performanceHigh precisionMedical data miningEpidemiological alert systemsKnowledge graphData mining
The invention discloses an infection control management system and method based on artificial intelligence. The system comprises a middleware module, a clinical database module, a strain identification module, an expert system module, a machine learning neural network and a prediction and early warning module; for newly-separated bacteria and a related antibiotic knowledge graph, the expert systemmodule is used for verifying culture results of antibiotics, selecting a suitable antibiotic list and giving an alarm to the newly-separated bacteria; the machine learning neural network is used forlearning and establishing association rules of the bacteria, the antibiotics and an infection part, establishing a specific knowledge graph according to the relationship of the bacteria, the antibiotics and the infection part, and integrating the specific knowledge graph into the expert system module; the prediction and early warning module establishes a prediction model for predicting infection data and an infection trend within a specific range, and when the predicted value of an infection event is higher than a set threshold value, the prediction and early warning module gives an early warning to medical staff and / or a community. The infection control management system and method based on artificial intelligence can achieve automatic monitoring, analysis and real-time early warning of infection cases and infection conditions in the community.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL +2
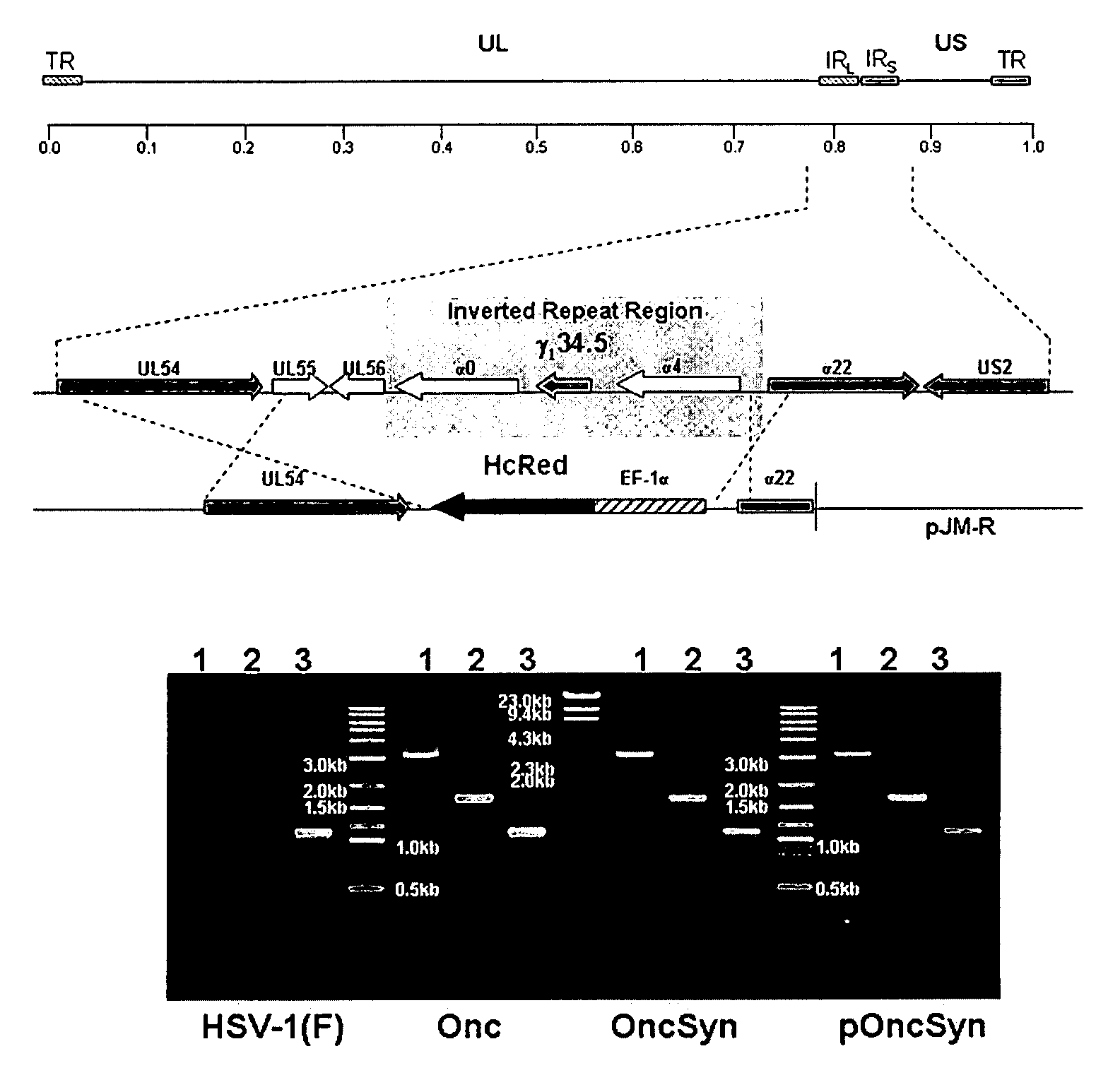
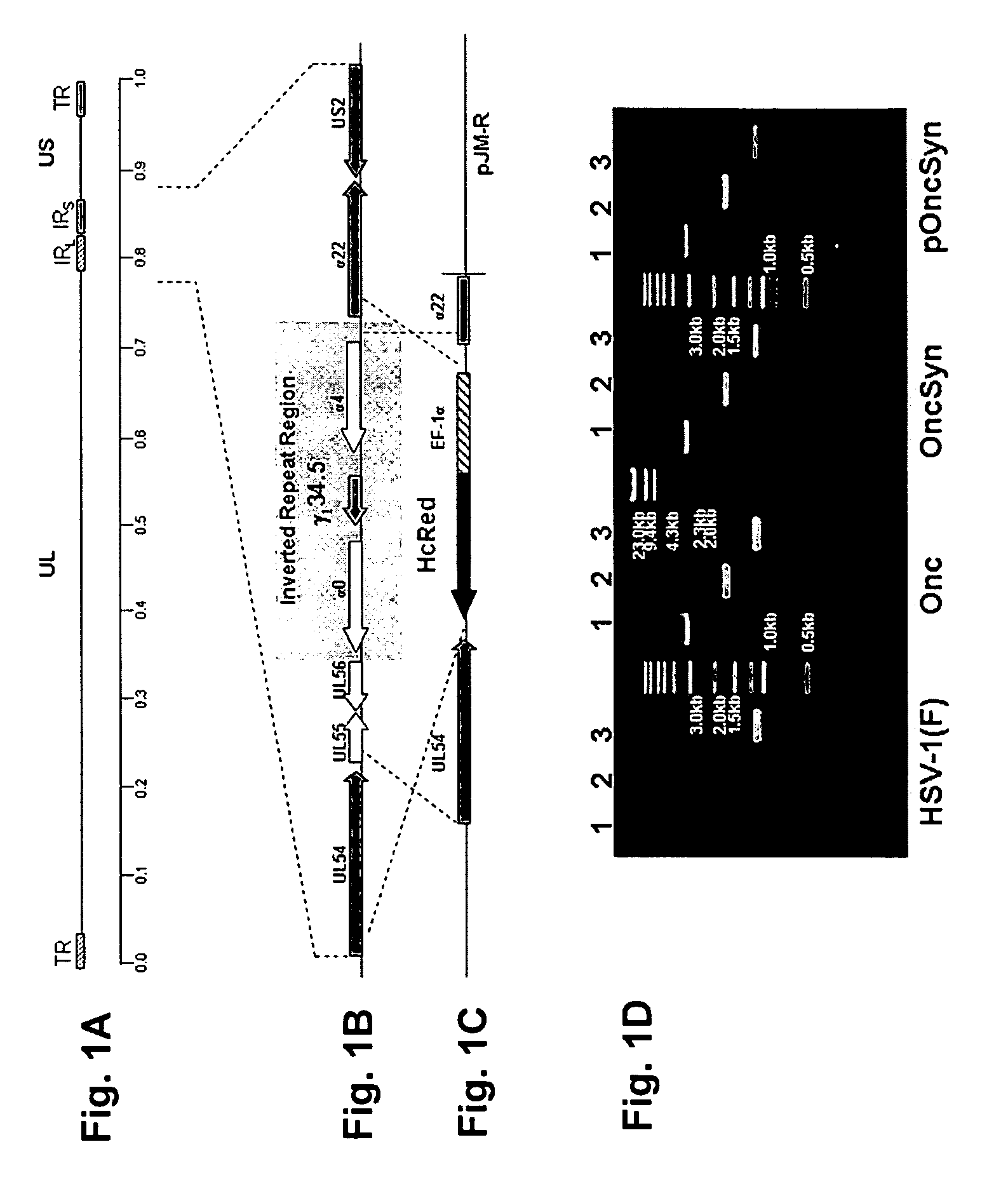
Synthetic Herpes Simplex Viruses Type-1 for Treatment of Cancers
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Process for the preparation of cell beads BOD sensor useful for instant BOD estimation
InactiveUS20030036186A1Least chemical damageLeast physical damageBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesSerratia
Immobilized cell beads incorporating formulated microbial consortium comprising a synergistic mixture of the following bacterial strains namely, Enterobacter sakazaki, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aeromonas sobria selected from the following isolated bacterial strains namely, Yersinia enterocolitica, Aeromonas sobria, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Serratia liquefaciens, Enterobacter sakazaki, Citrobacter amalonaticus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter cloaca, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus are prepared, the formulated microbial consortium is immobilized in an appropriate immobilizing agent resulting in the formation of beads and the beads are used for instant BOD estimation using an electronic device and the formulated cell beads are reusable and are capable of assimilating most of the organic matter present in varied industrial effluents.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
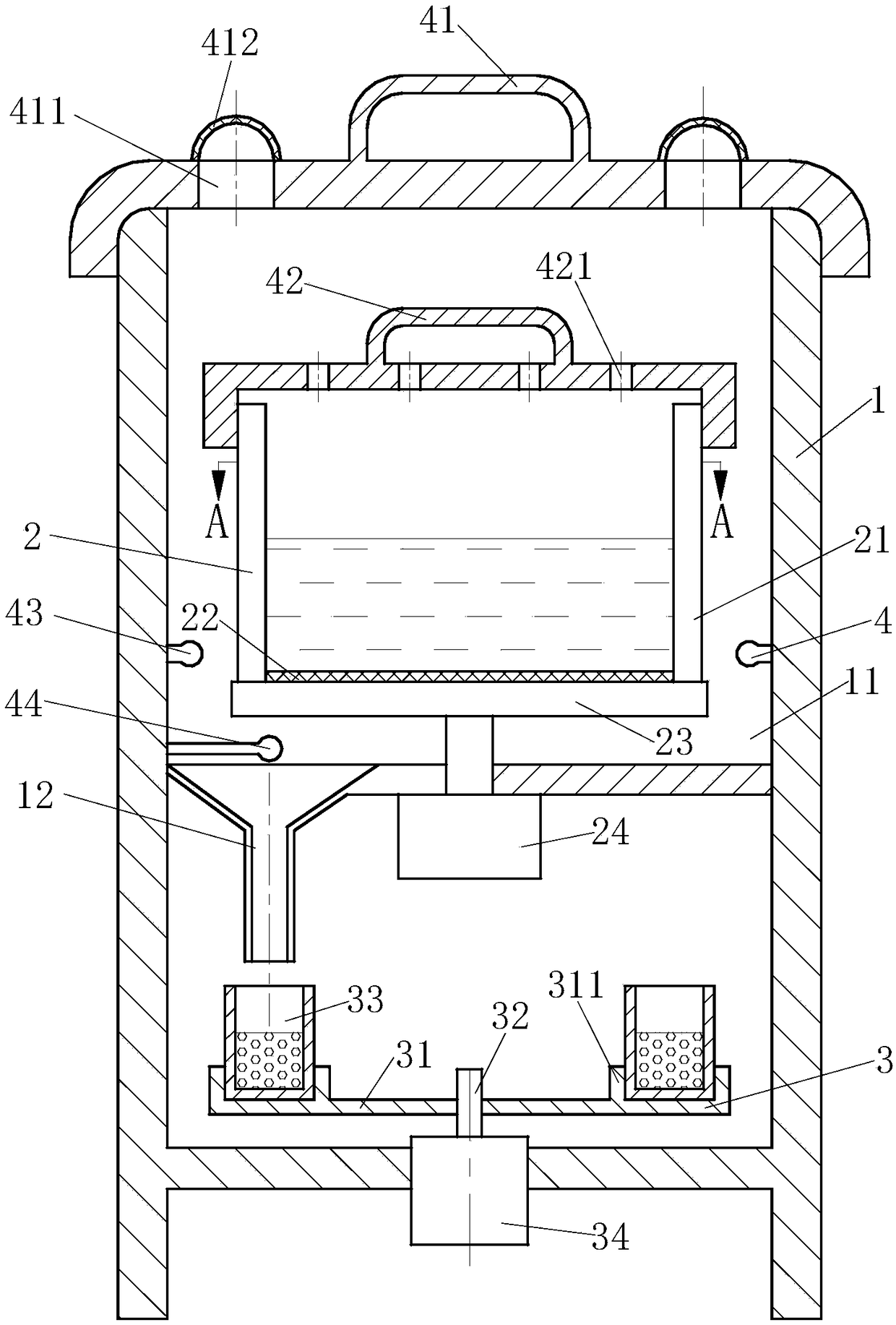
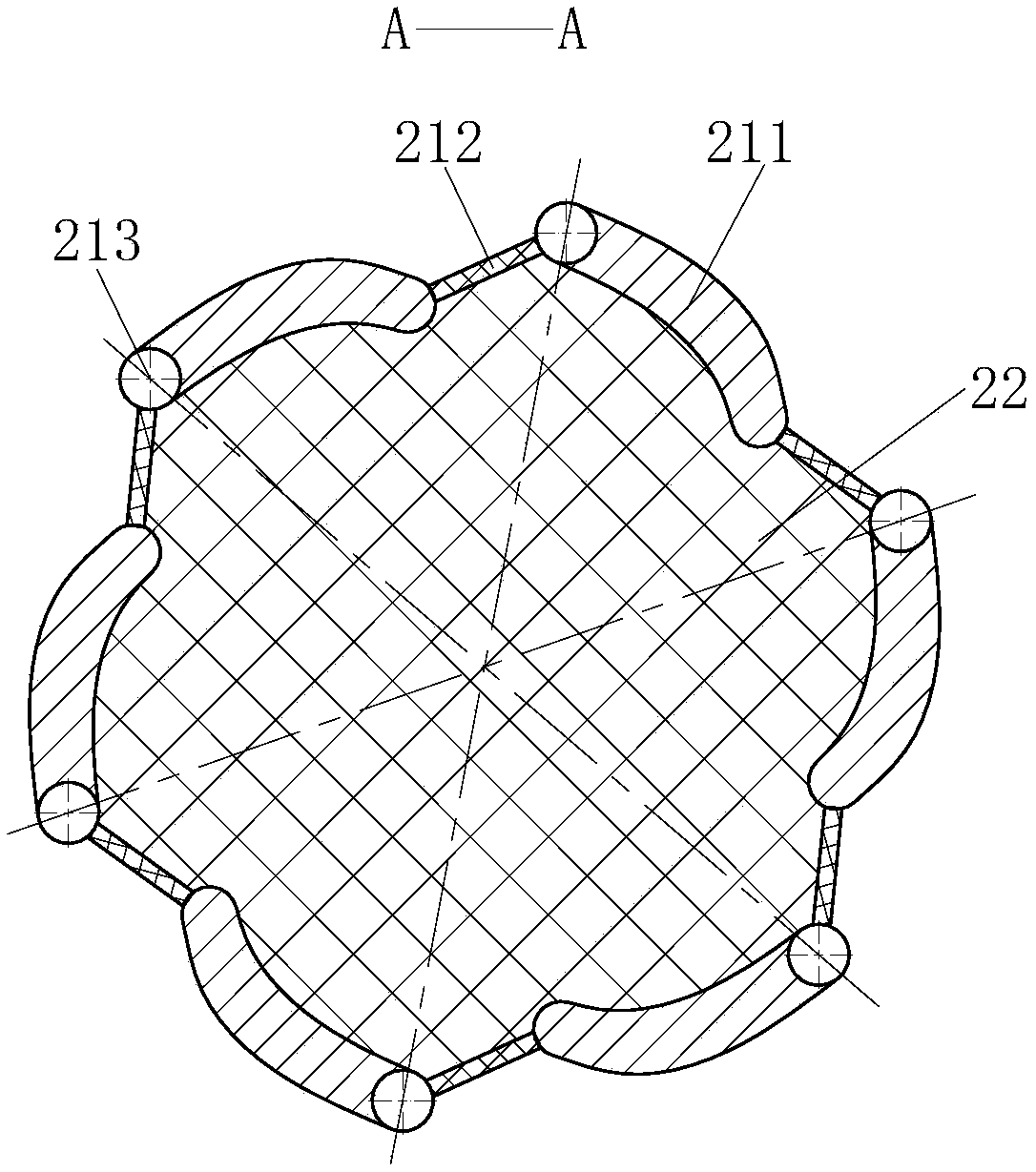
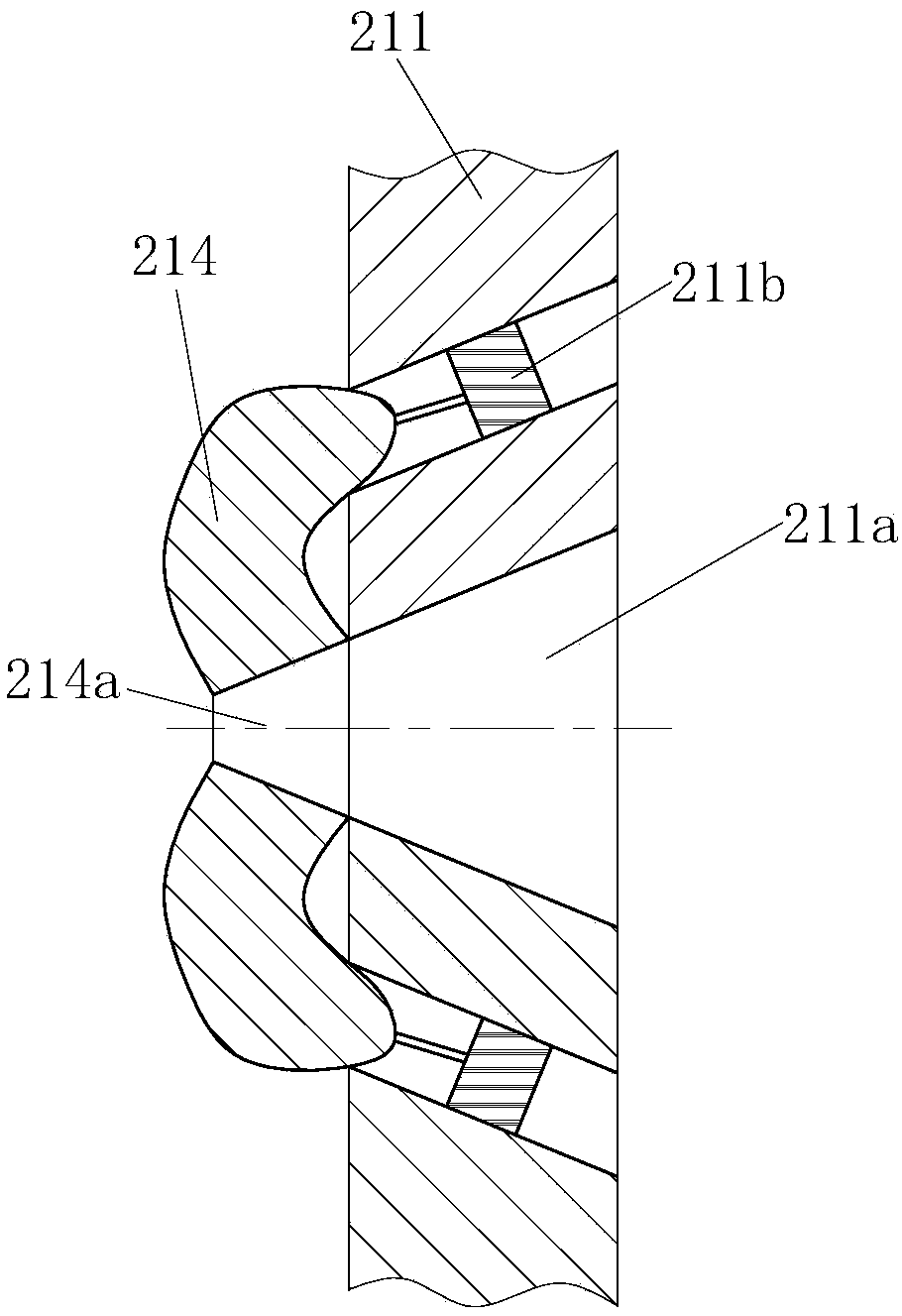
Multistage bacterial liquid bacteria screening equipment
InactiveCN108424836AImprove separation efficiencySave human effortBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBacillus isolates
The invention belongs to the technical field of bacteria separation and particularly relates to multistage bacterial liquid bacteria screening equipment. The multistage bacterial liquid bacteria screening equipment comprises a mounting barrel body, a separation module, an automatic collection module and an anti-pollution module; a temporary storage room is arranged at the upper part of the mounting barrel body and is used for temporary storage of bacteria separated by the separation module; a bacterial liquid release tube is communicated wit the lower end of the temporary storage room and is used for releasing the bacteria in the temporary storage room; the separation module is positioned in the temporary storage room and is used for separating the bacteria of different sizes; the automatic collection module is positioned at the lower end of the bacterial liquid release tube and is used for receiving the bacteria of different sizes released from the bacterial liquid release tube; the anti-pollution module is distributed on the mounting barrel body, the temporary storage room and the separation module and is used for preventing external bacteria or the separated bacteria from polluting bacteria that is being separated. The multistage bacterial liquid bacteria screening equipment provided by the invention can quickly separate in batch and respectively store the various bacteria of different sizes in the bacterial liquid and can improve the bacterial liquid bacteria separation efficiency.
Owner:郭庆
Trophic conversion of photoautotrophic bacteria for improved diurnal properties
InactiveUS20150240247A1Improve scalabilityLow production costUnicellular algaeBiofuelsMicrobiologyBacillus isolates
The present disclosure relates generally to the growth of recombinant bacterial cells of photoautotrophic species under diurnal conditions. In particular, the present disclosure relates to isolated bacterial cells of photoautotrophic species having increased growth under diurnal conditions by expression of a sugar transporter protein and methods of use thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
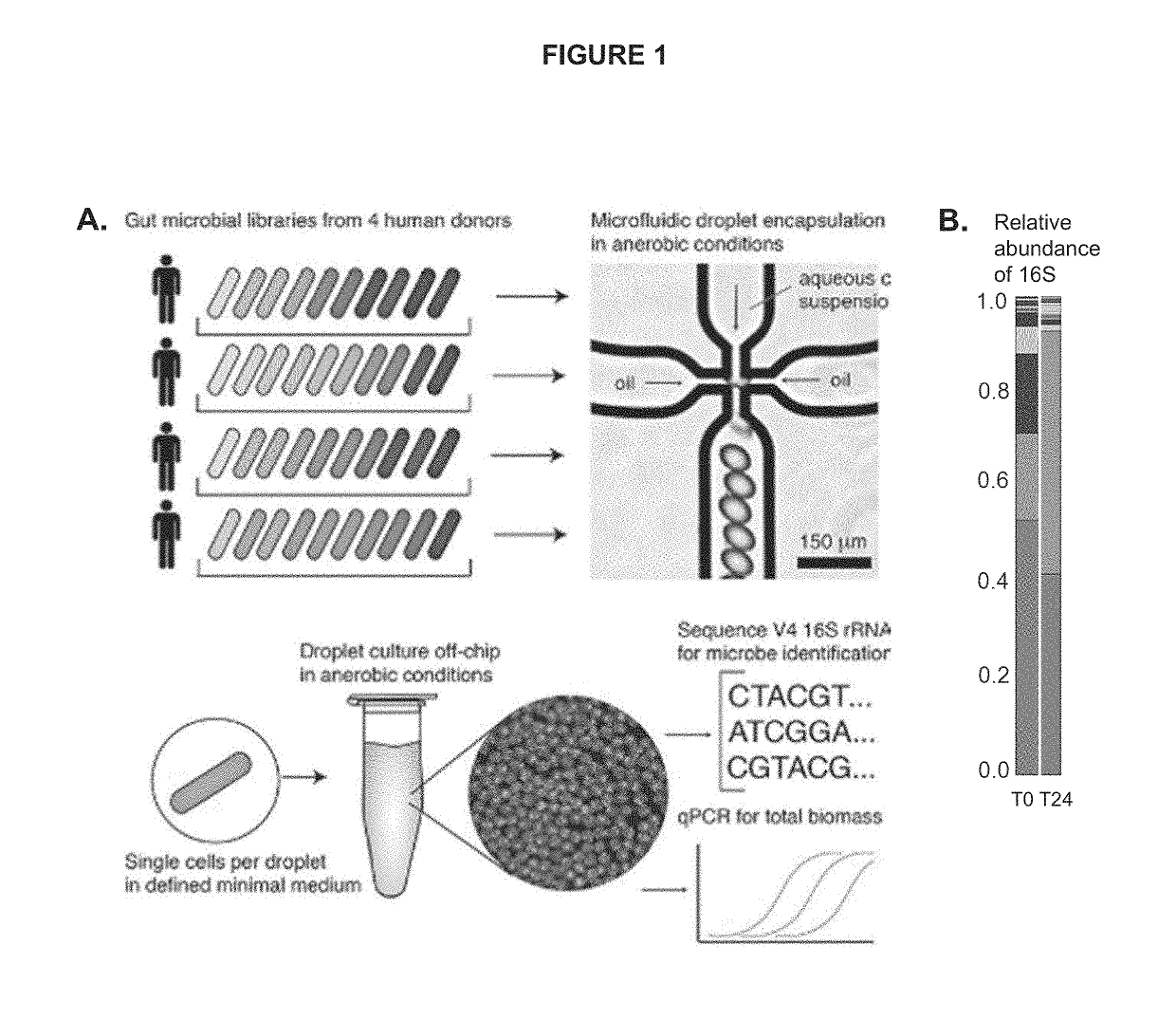
Rapid phenotyping and identification of microbes from a complex microbial community
InactiveUS20190241943A1Cost-effectiveHighly efficient high-throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismMicrofluidics
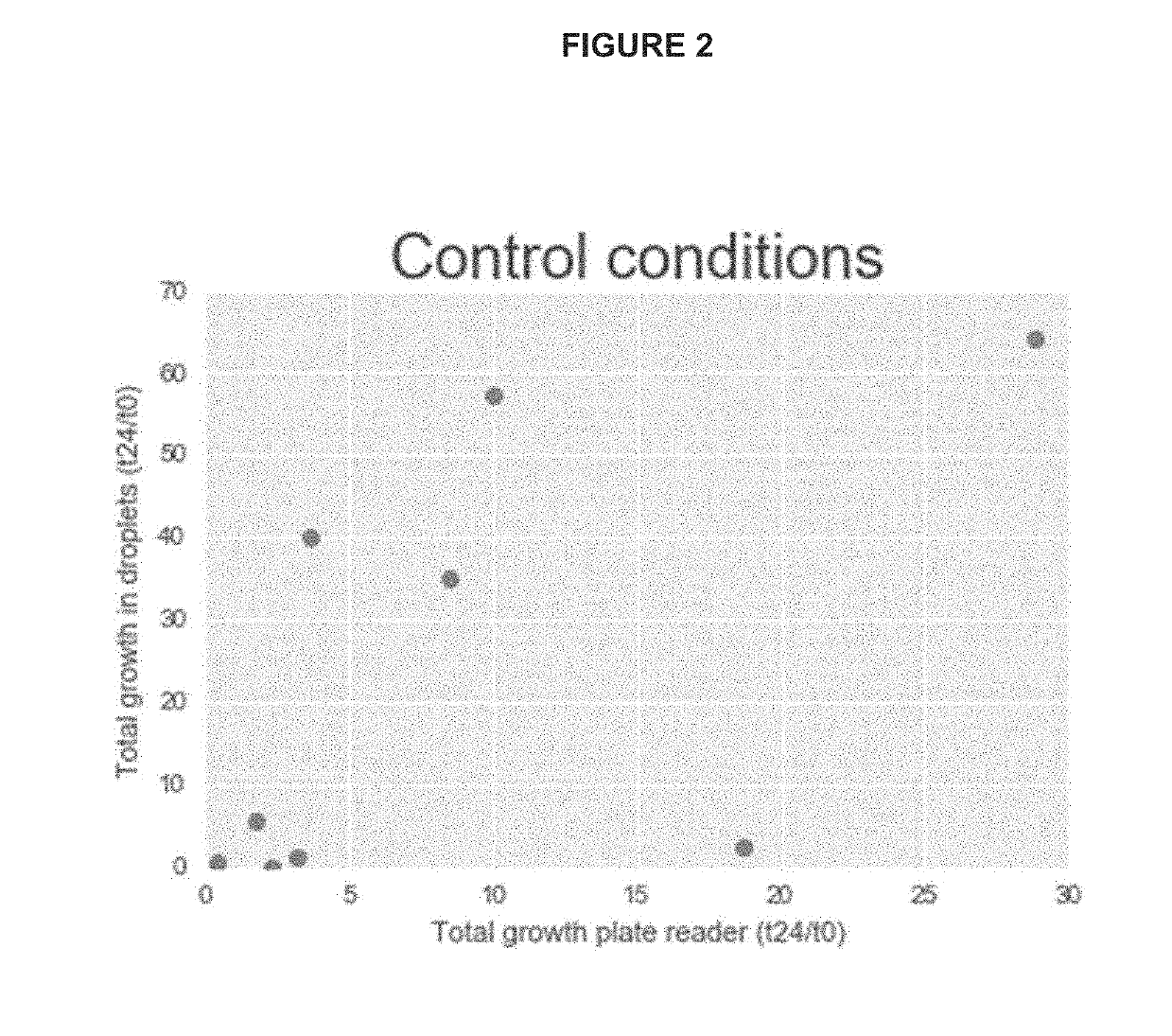
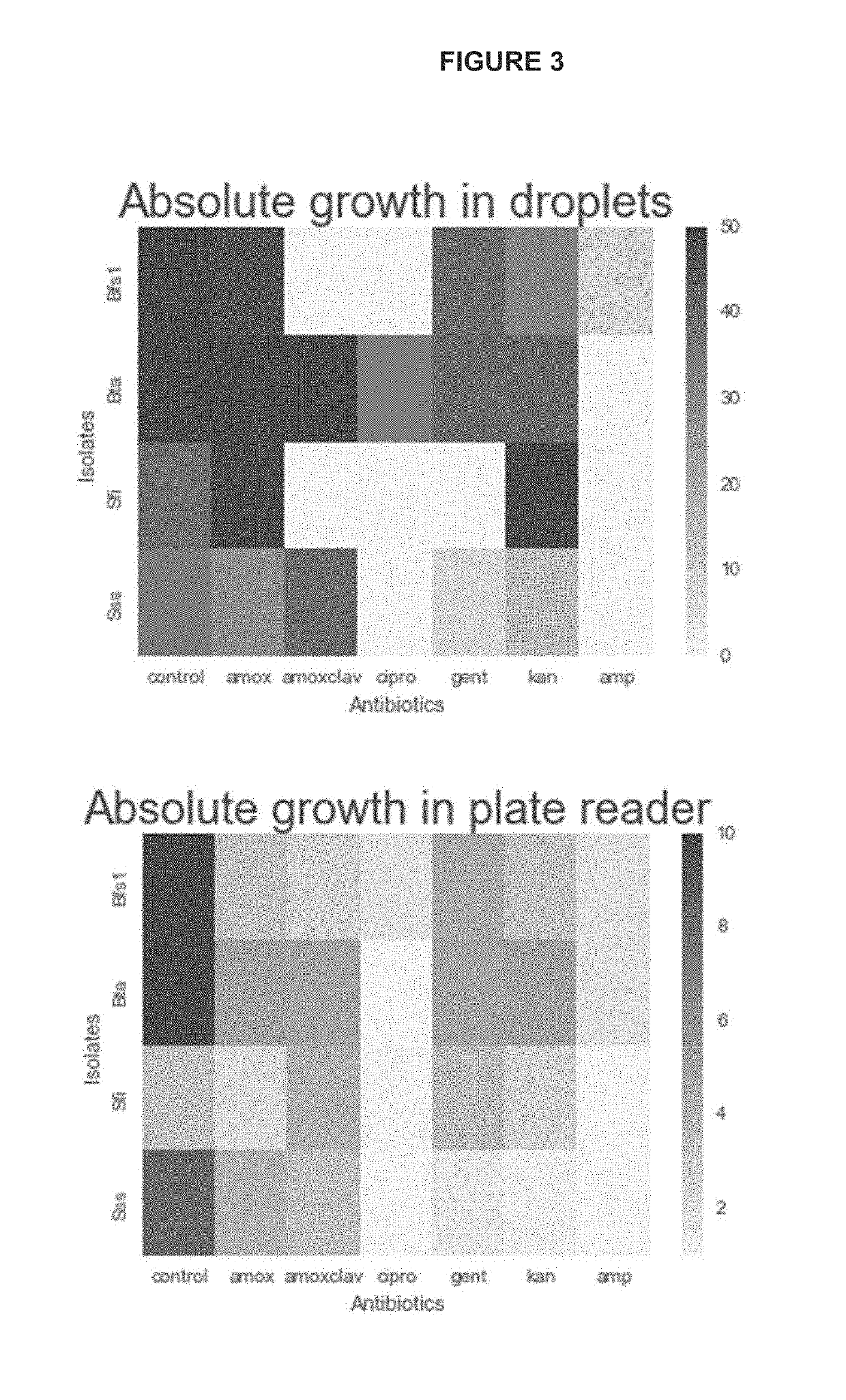
The invention disclosed herein relates generally to the fields of microbiology, ecology and microfluidics. Particularly, the invention disclosed herein provides compositions and methods for isolating, identifying and phenotyping bacteria from complex microbial communities and measuring growth rates of the isolated bacteria in a given environmental condition.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com