Bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite membrane for efficient protein adsorption and separation and preparation method of composite membrane
A technology of bacterial cellulose and nanofibers, which is applied in fiber types, fiber treatment, plant fibers, etc., can solve the problems of limited specific surface area of electrospun fibers, difficulty in practical application, and increased protein adsorption. The effect of short time consumption and increased adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A preparation method of bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite membrane for efficient protein adsorption and separation:
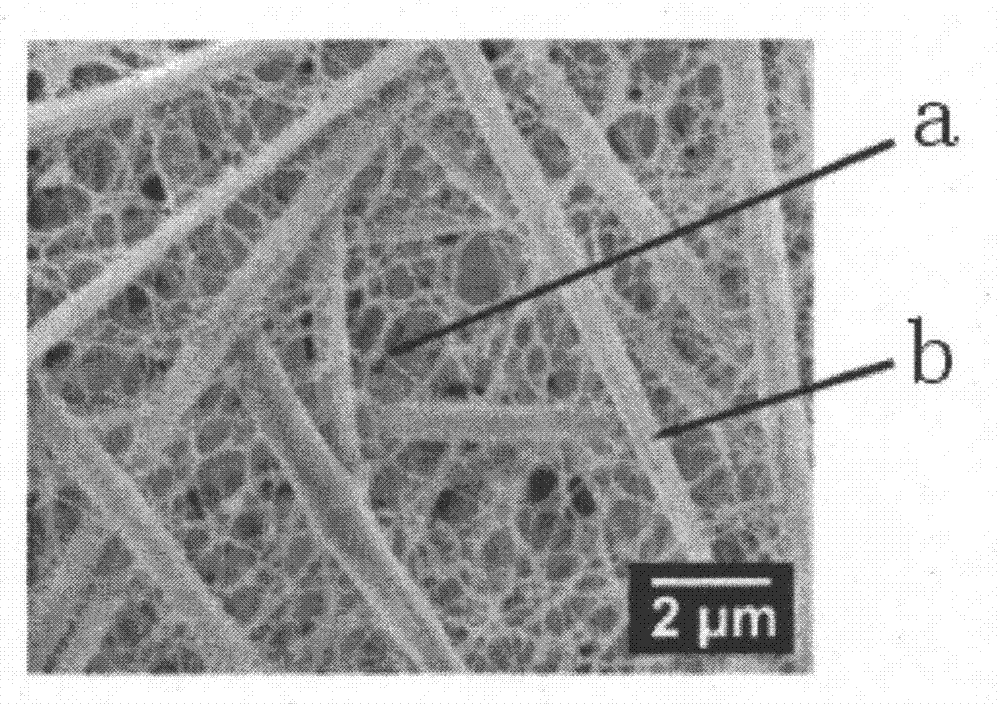
[0030] Step 1: Mechanically dissociate the bacterial cellulose membrane into bacterial cellulose nanofibers with an average length of 300 μm and an average diameter of 100 nm by high-speed stirring and dissociation;
[0031] Step 2: modifying the carboxylic acid group (-COOH) on the surface of the bacterial cellulose nanofiber;
[0032] Step 3: the above-mentioned bacterial cellulose nanofibers are dispersed in water, and a stable bacterial cellulose nanofiber suspension is formed by adding a dispersant alkylphenol polyoxyethylene ether; the mass percentage of bacterial cellulose nanofibers in the suspension is 0.05wt%;
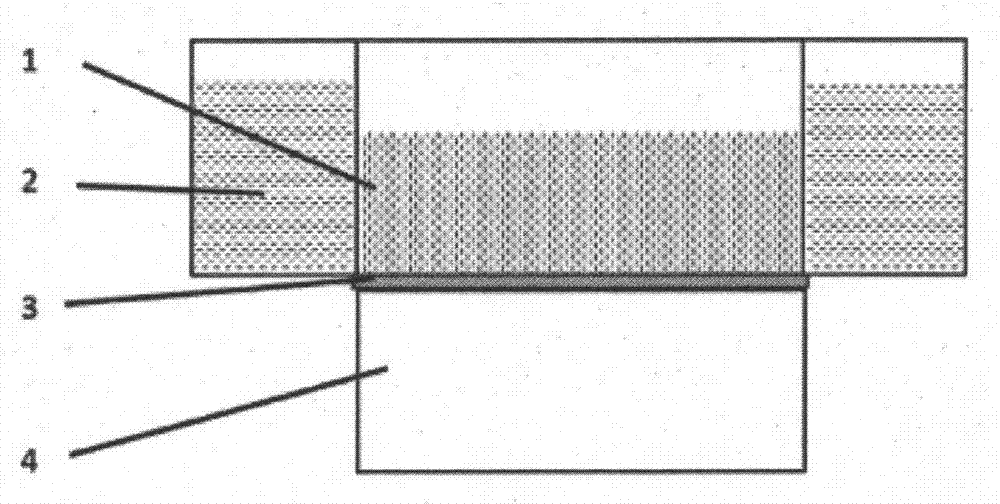
[0033] Step 4: Apply simultaneous ultrasonic filtering (eg figure 1 Shown) method spreads above-mentioned bacterial cellulose nanofiber suspension on the cellulose filter paper surface that pore size is 300 μm to form wet state ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A preparation method of bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite membrane for efficient protein adsorption and separation:
[0037] Step 1: Mechanically dissociate the bacterial cellulose membrane into bacterial cellulose nanofibers with an average length of 180 μm and an average diameter of 80 nm by ultrasonic dissociation;
[0038] Step 2: Modification of sulfonic acid groups (-SO 3 H);
[0039] Step 3: the above-mentioned bacterial cellulose nanofibers are dispersed in methanol, and a stable bacterial cellulose nanofiber suspension is formed by adding a dispersant fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether; the mass percentage of bacterial cellulose nanofibers in the suspension is 0.002wt%;
[0040]Step 4: spread the above-mentioned bacterial cellulose nanofiber suspension on the surface of a polyethylene terephthalate spunbond nonwoven fabric with a pore size of 150 μm to form a wet composite fiber membrane by means of synchronous ultrasonic filtration; the synchronous ul...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A preparation method of bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite membrane for efficient protein adsorption and separation:
[0044] Step 1: Mechanically dissociate the bacterial cellulose membrane into bacterial cellulose nanofibers with an average length of 100 μm and an average diameter of 50 nm by using a high-pressure homogeneous dissociation method;
[0045] Step 2: modifying sulfate groups (-OSO) on the surface of the bacterial cellulose nanofibers 3 H);
[0046] Step 3: the above-mentioned bacterial cellulose nanofibers are dispersed in ethanol, and a stable bacterial cellulose nanofiber suspension is formed by adding the dispersant sodium stearate; the mass percentage of bacterial cellulose nanofibers in the suspension is 0.001wt %;
[0047] Step 4: spread the above-mentioned bacterial cellulose nanofiber suspension on the surface of a polypropylene melt-blown nonwoven fabric with a pore size of 80 μm by synchronous ultrasonic filtration to form a wet composite...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com