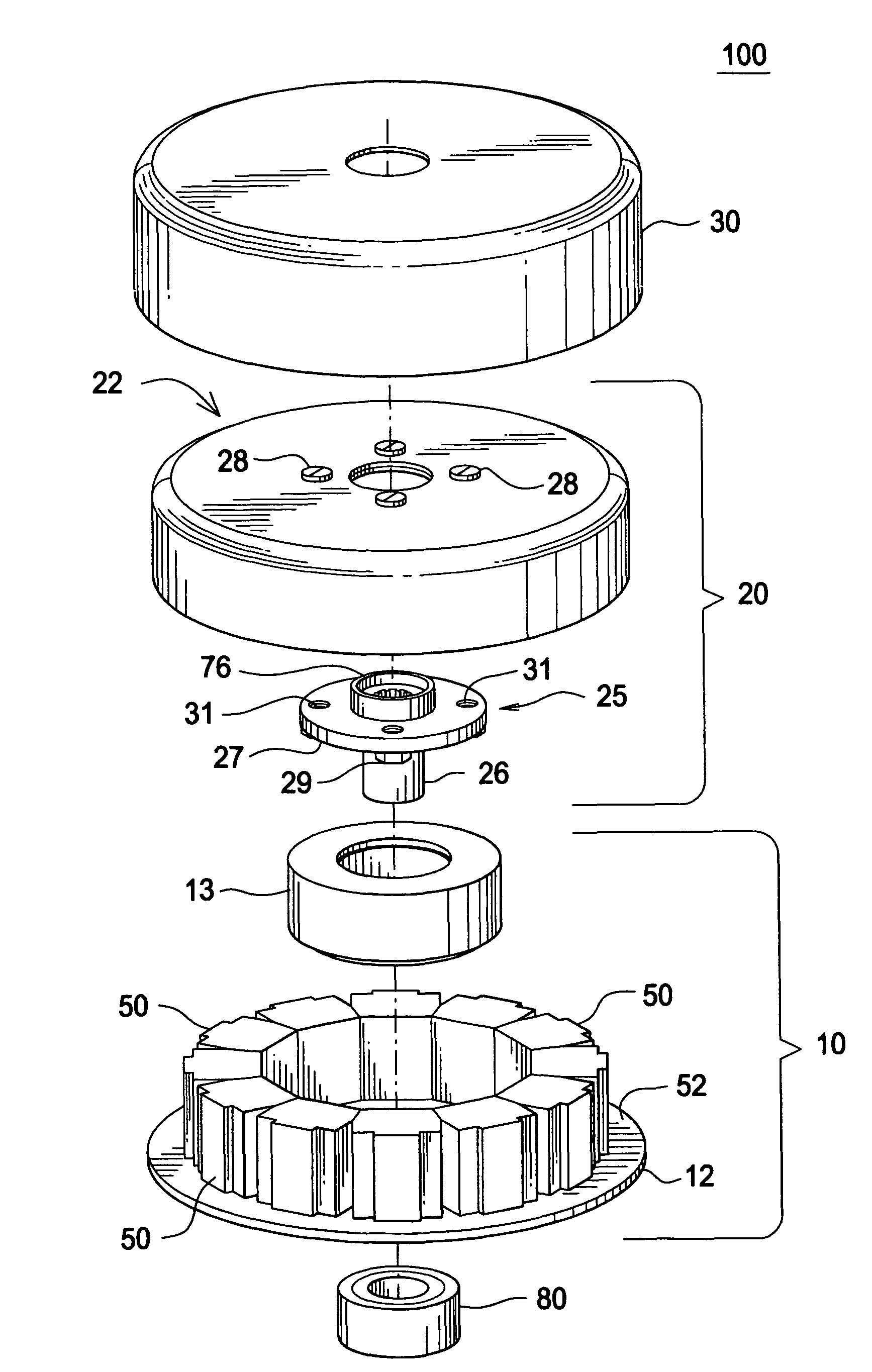
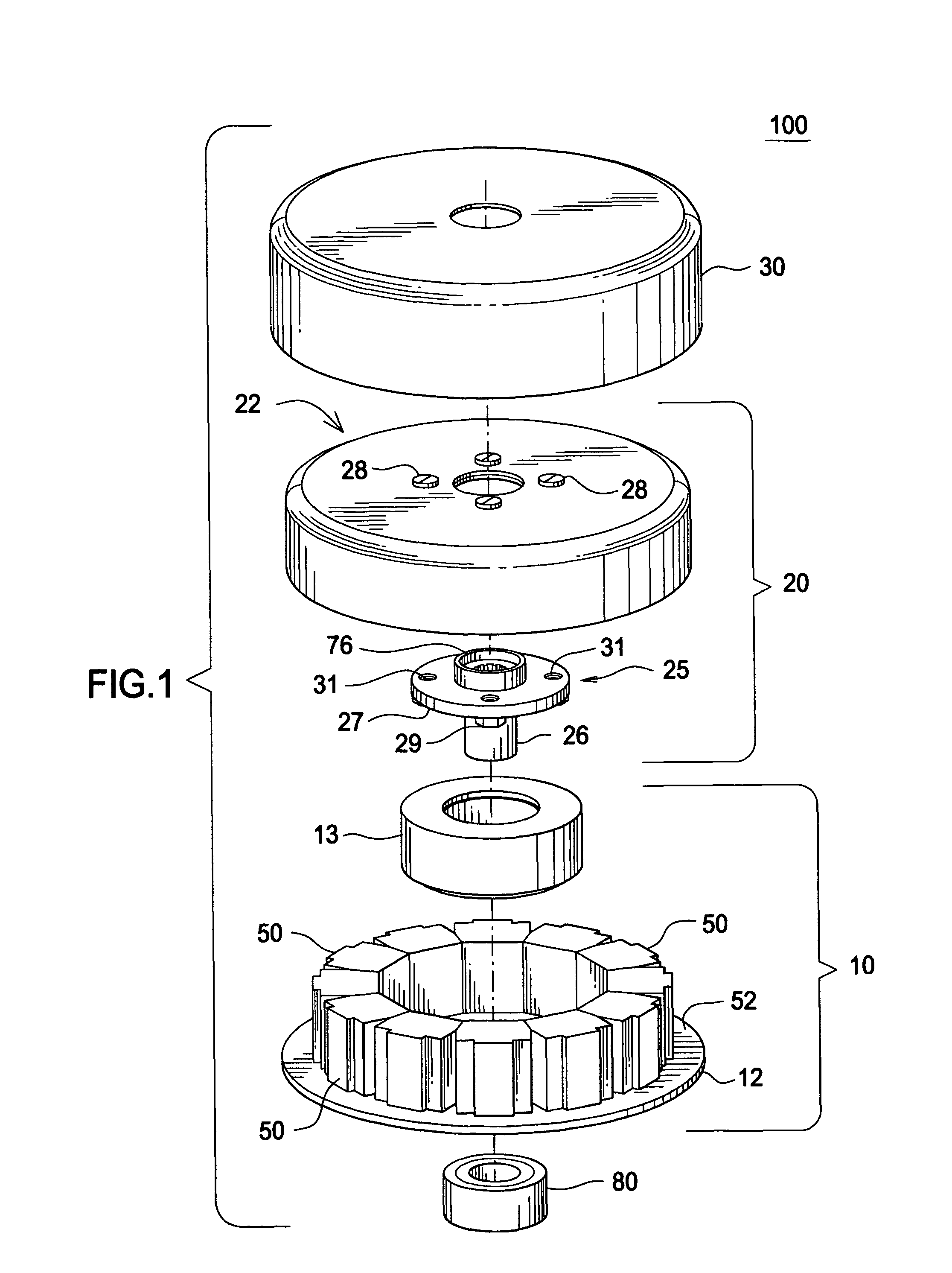
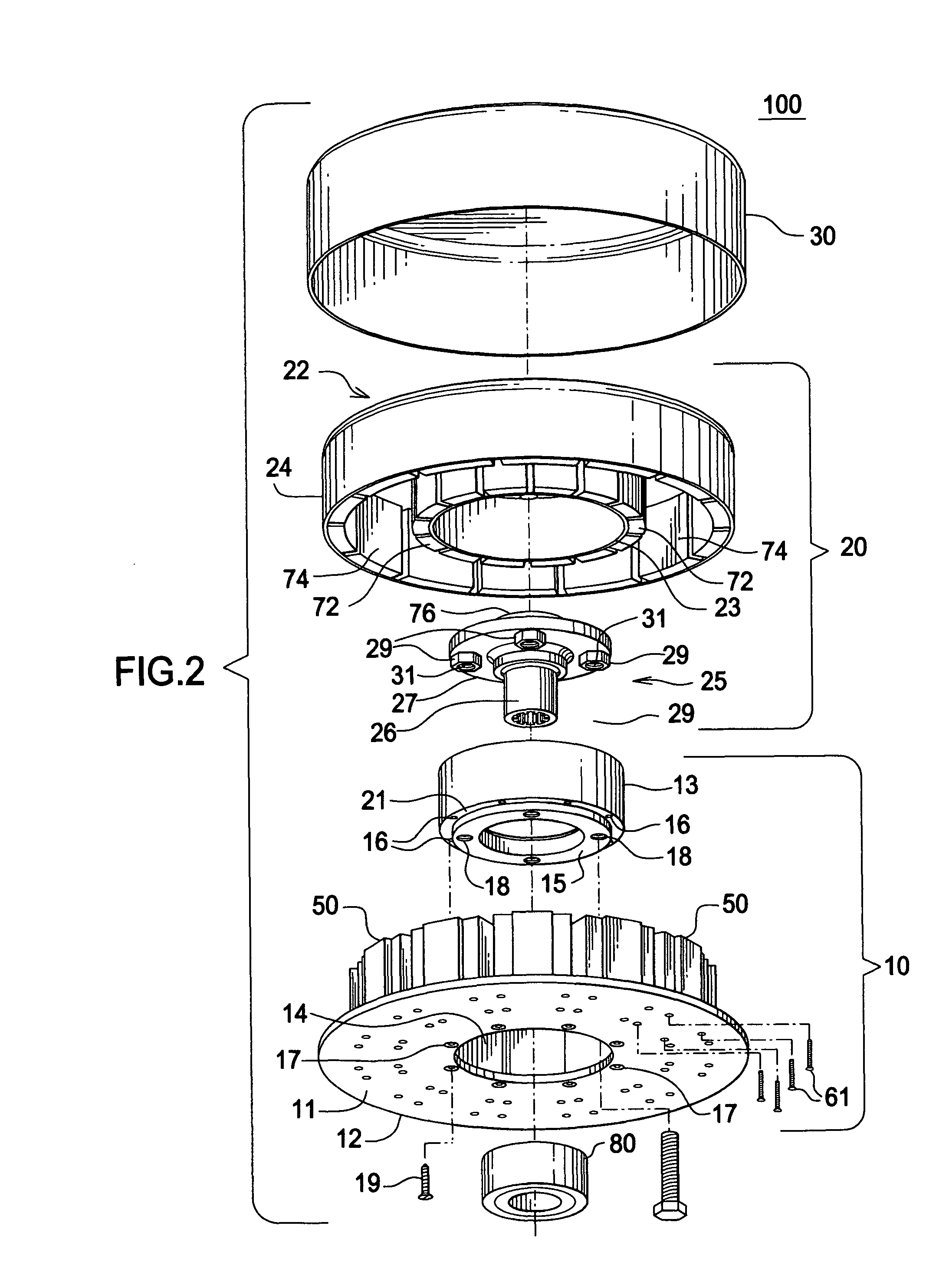
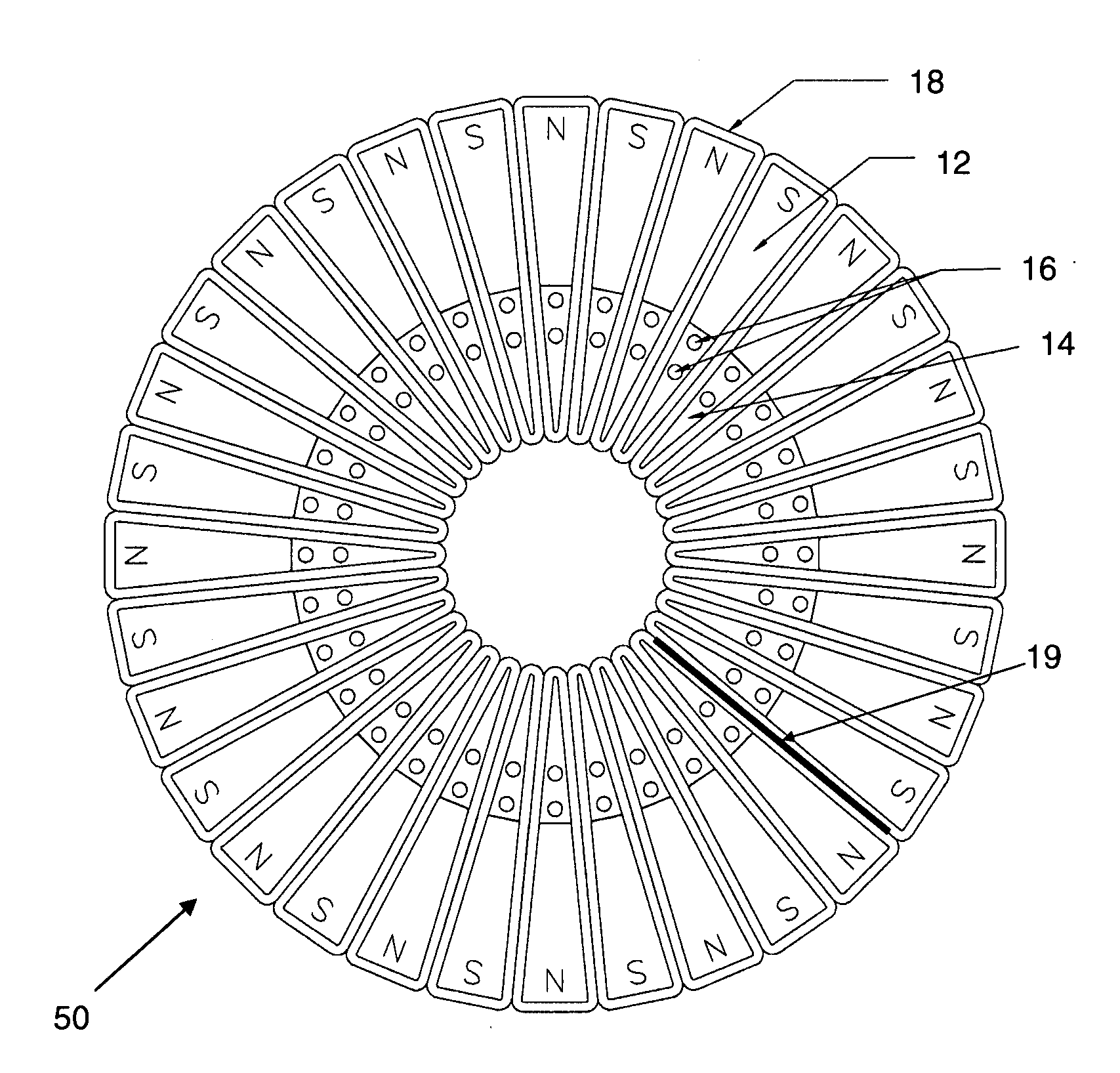
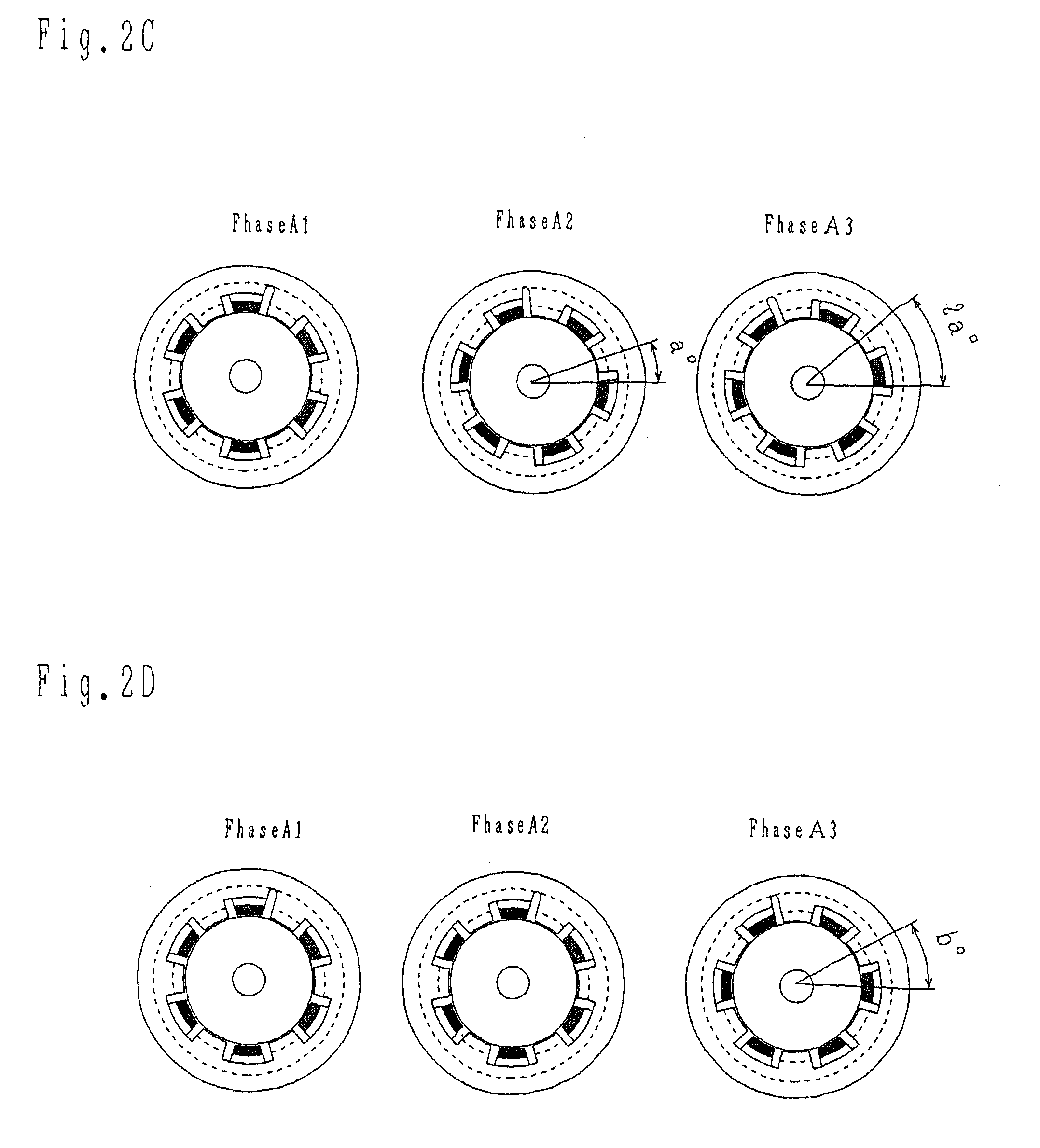
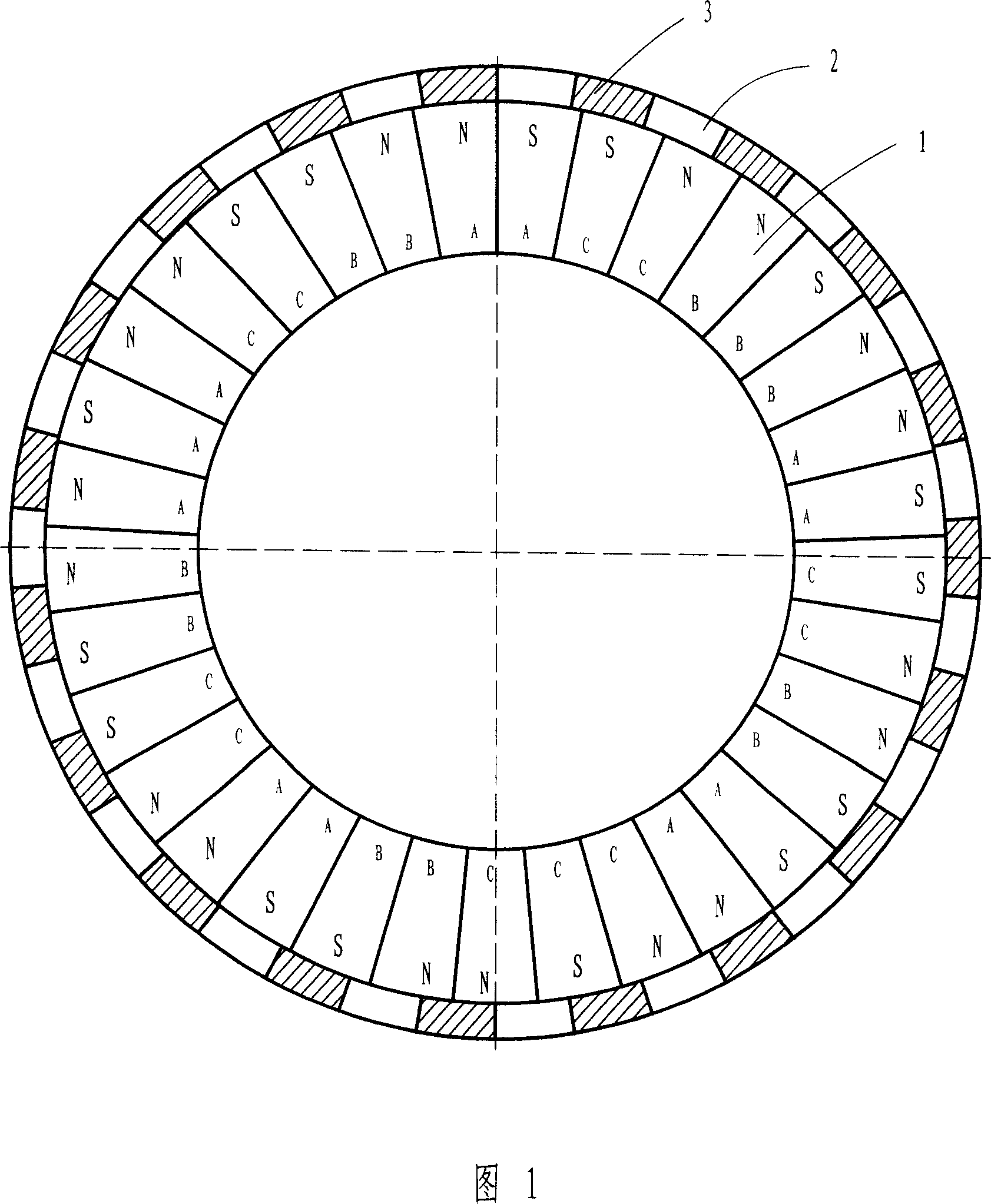
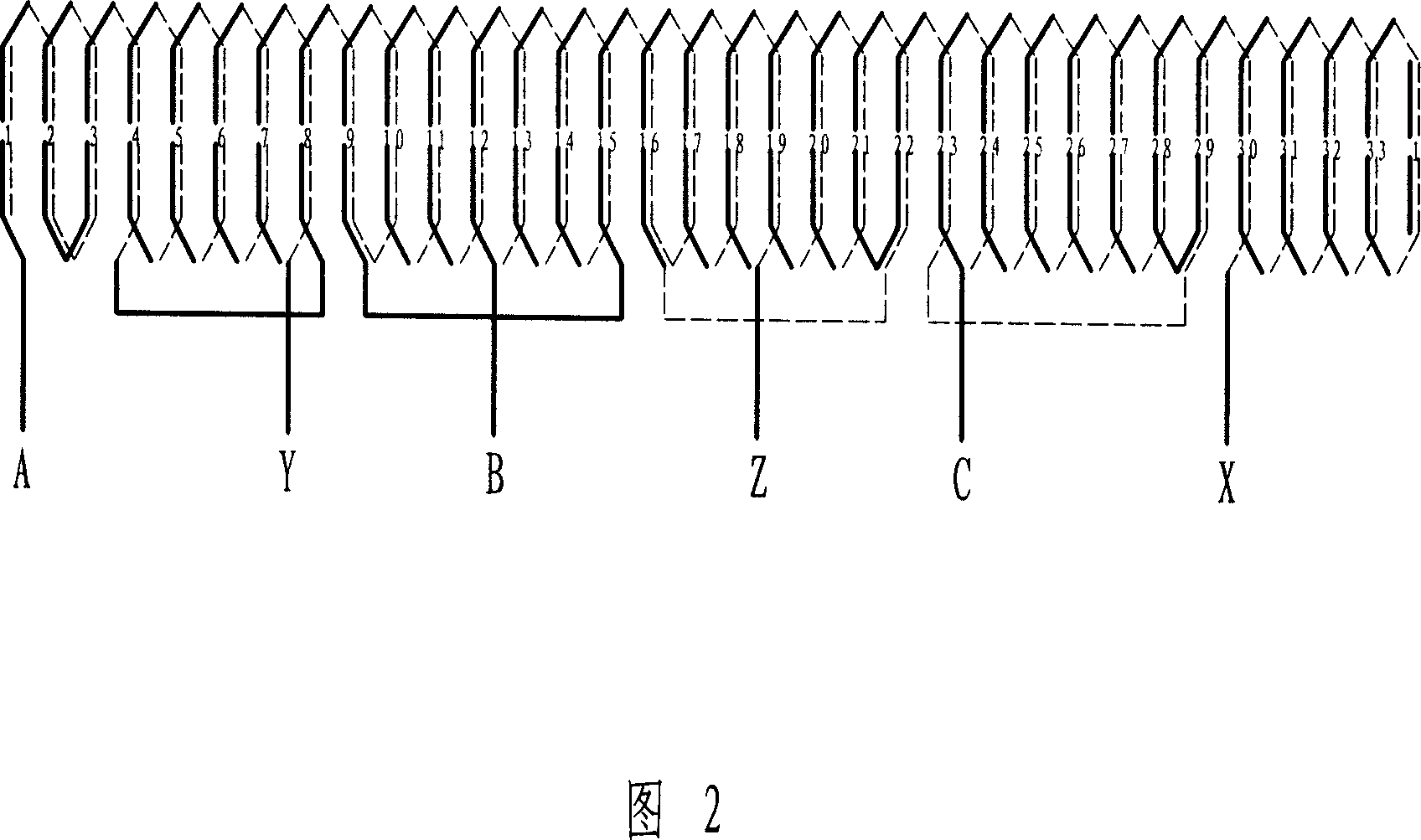
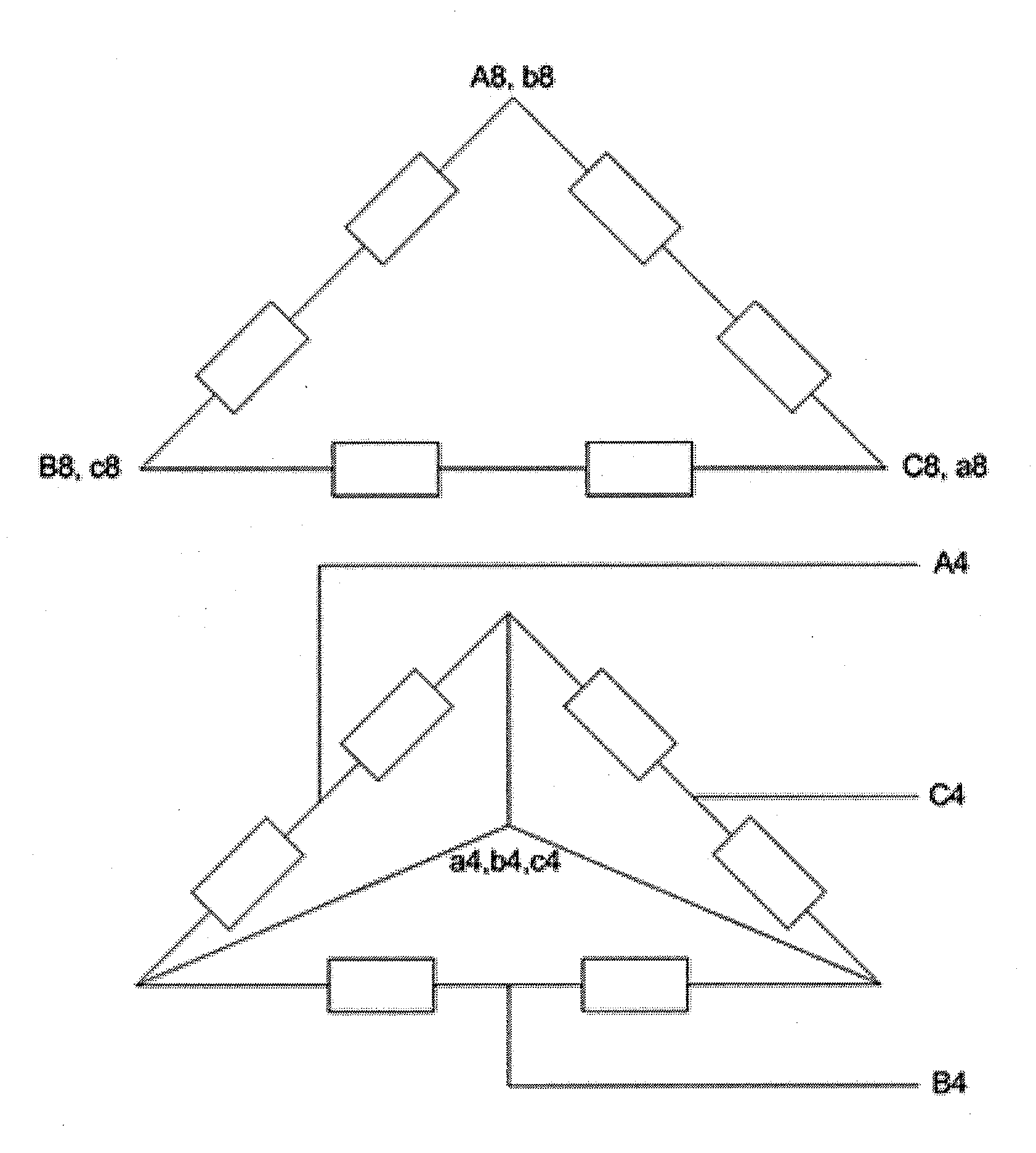
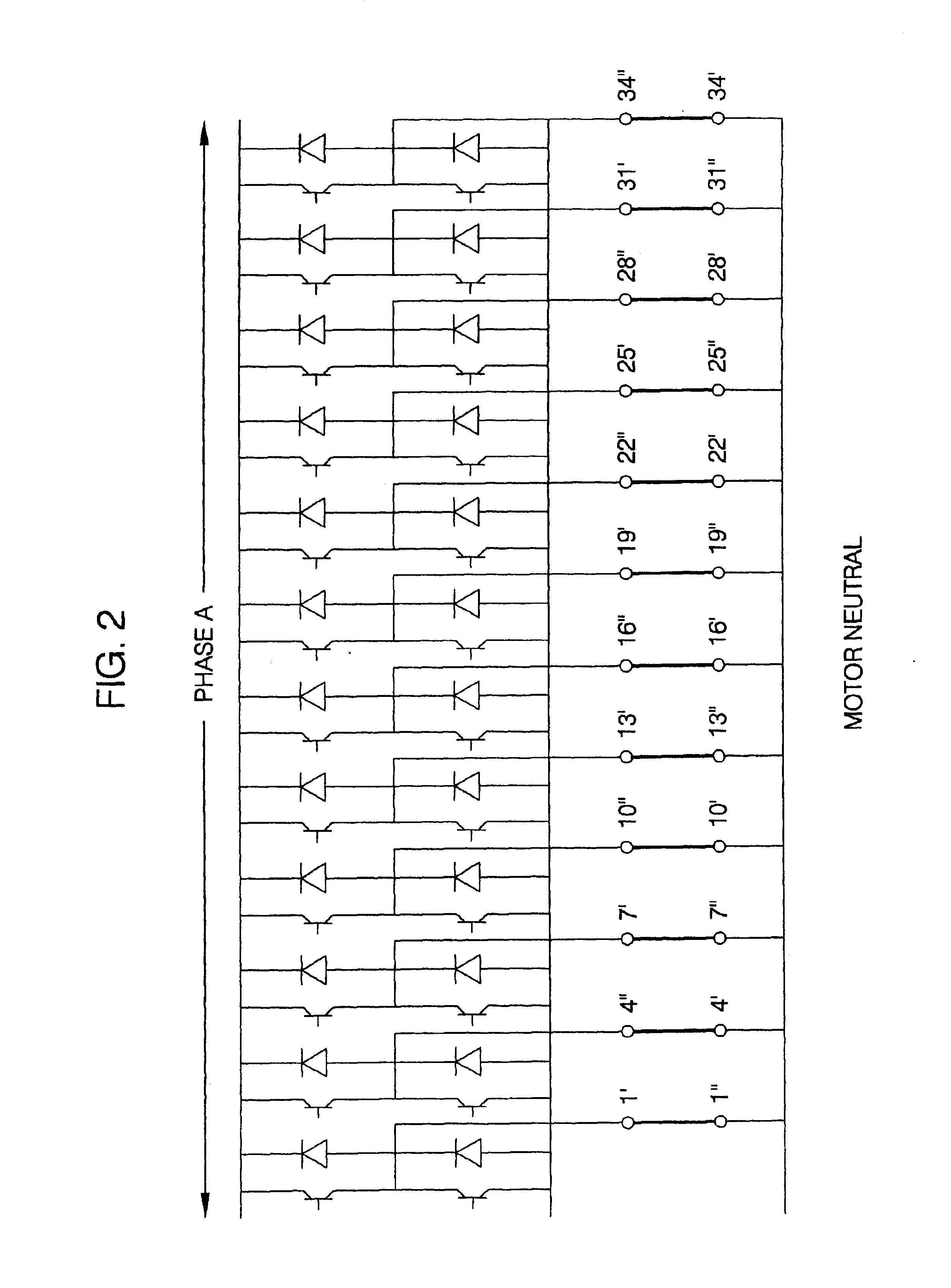
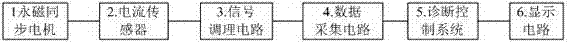Patents
Literature
598 results about "Pole number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
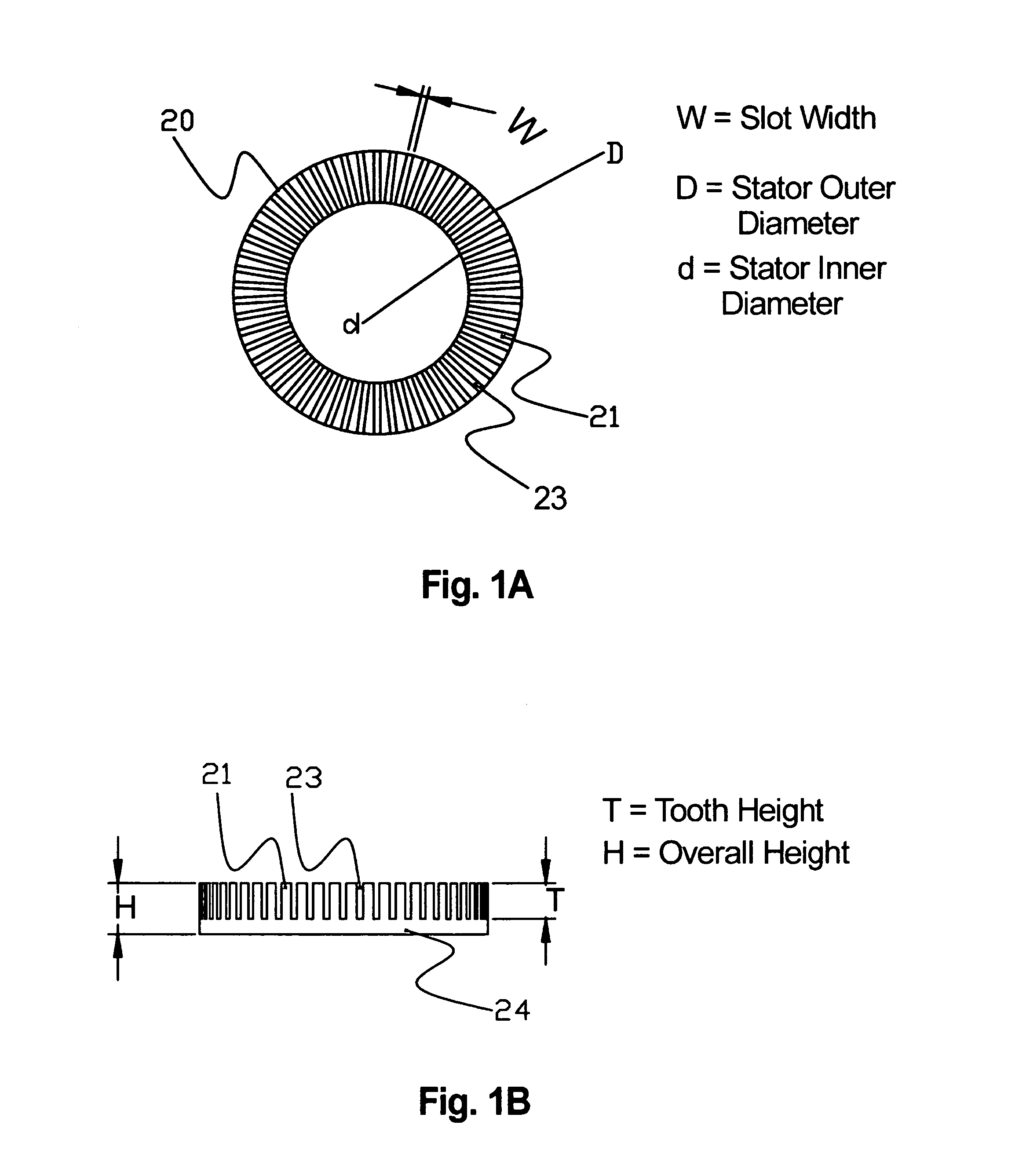
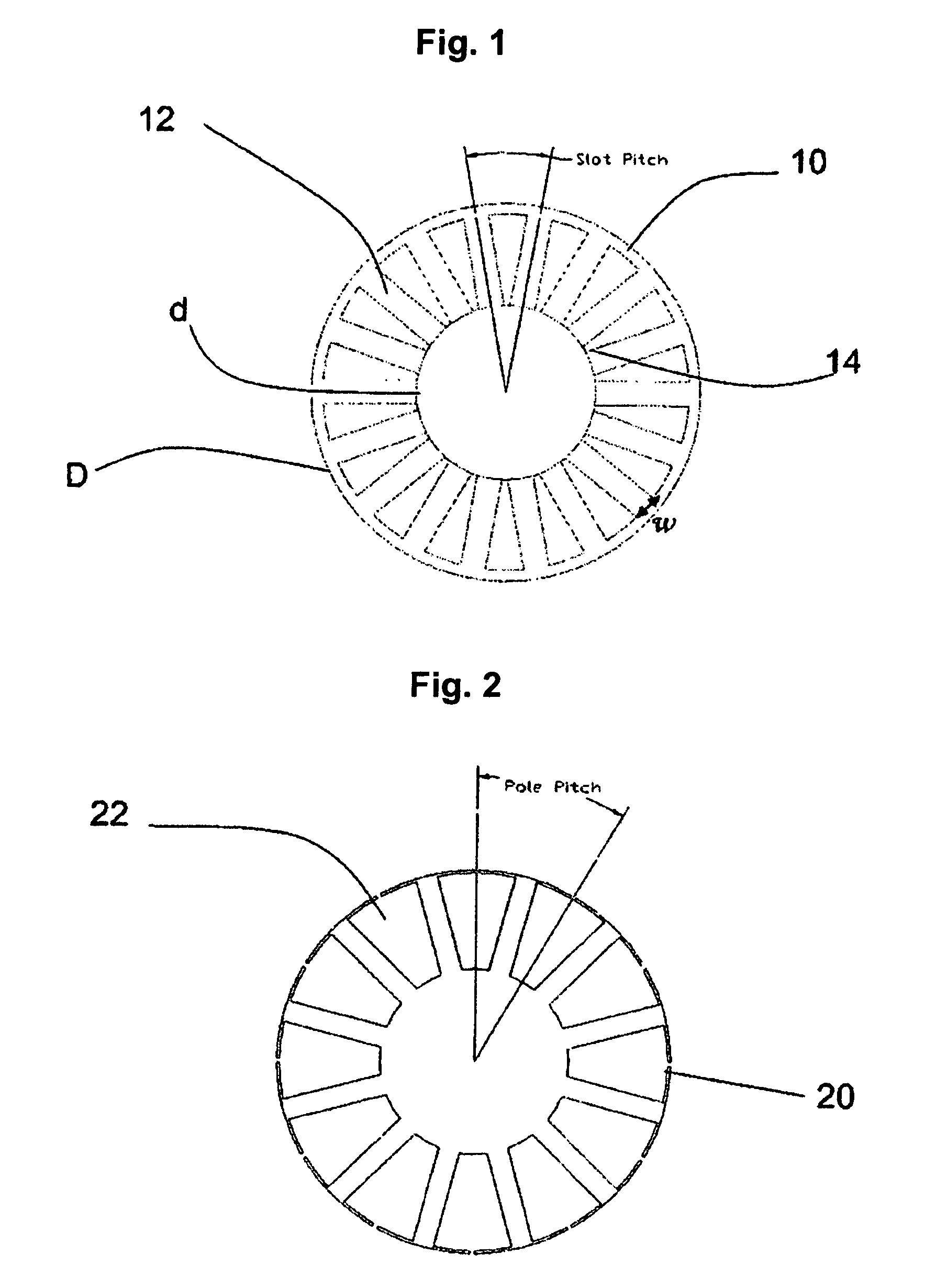
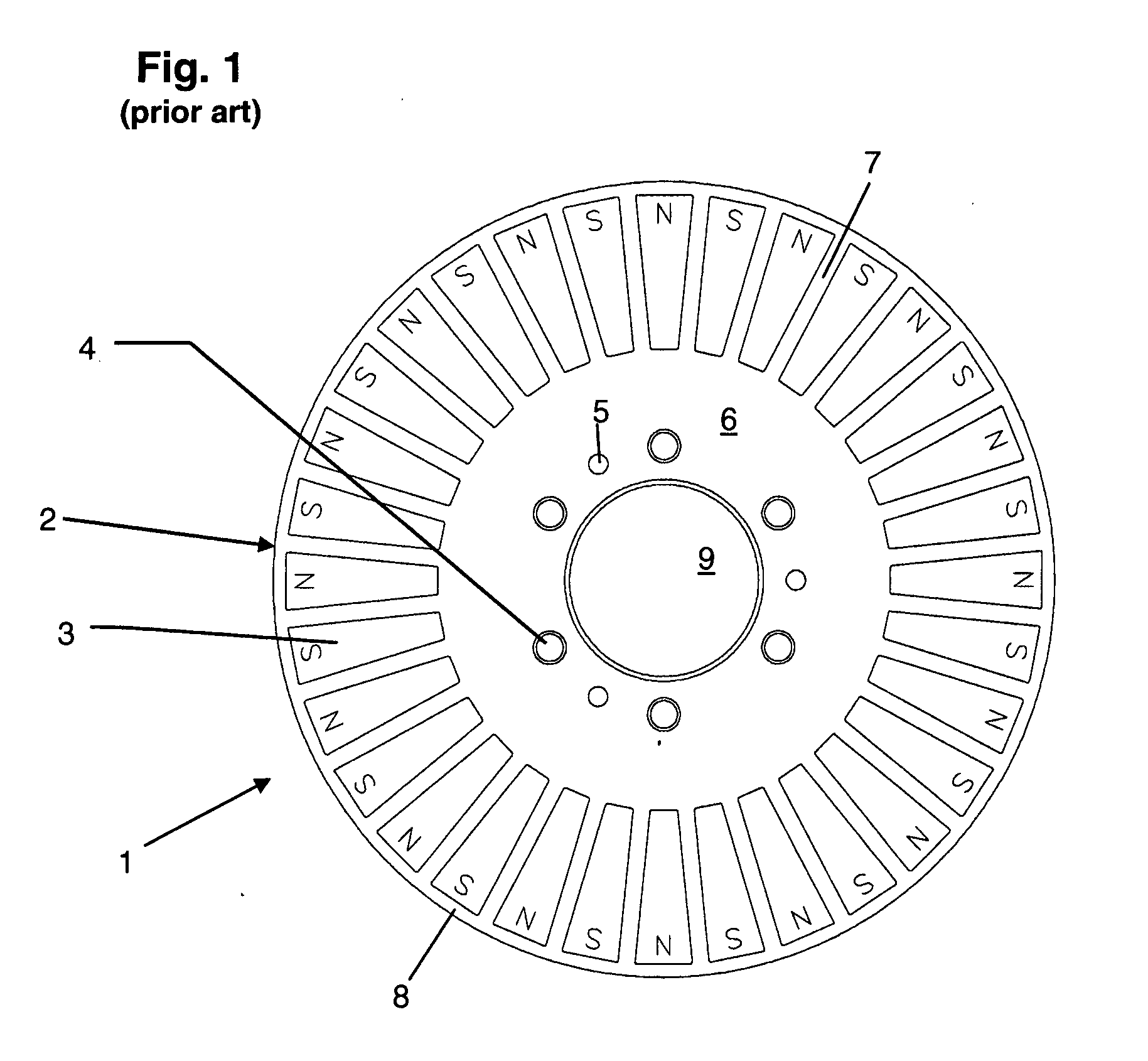
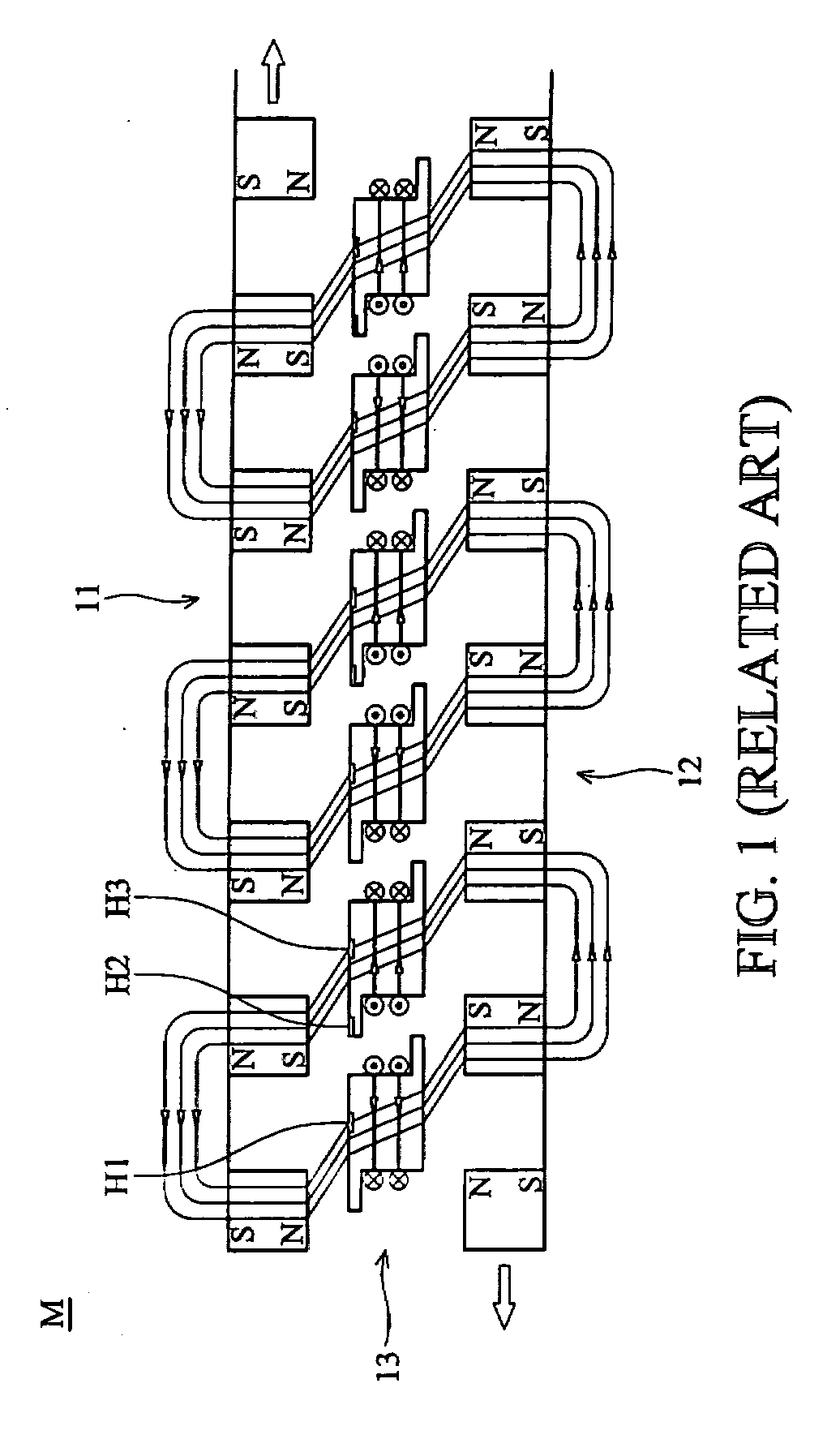
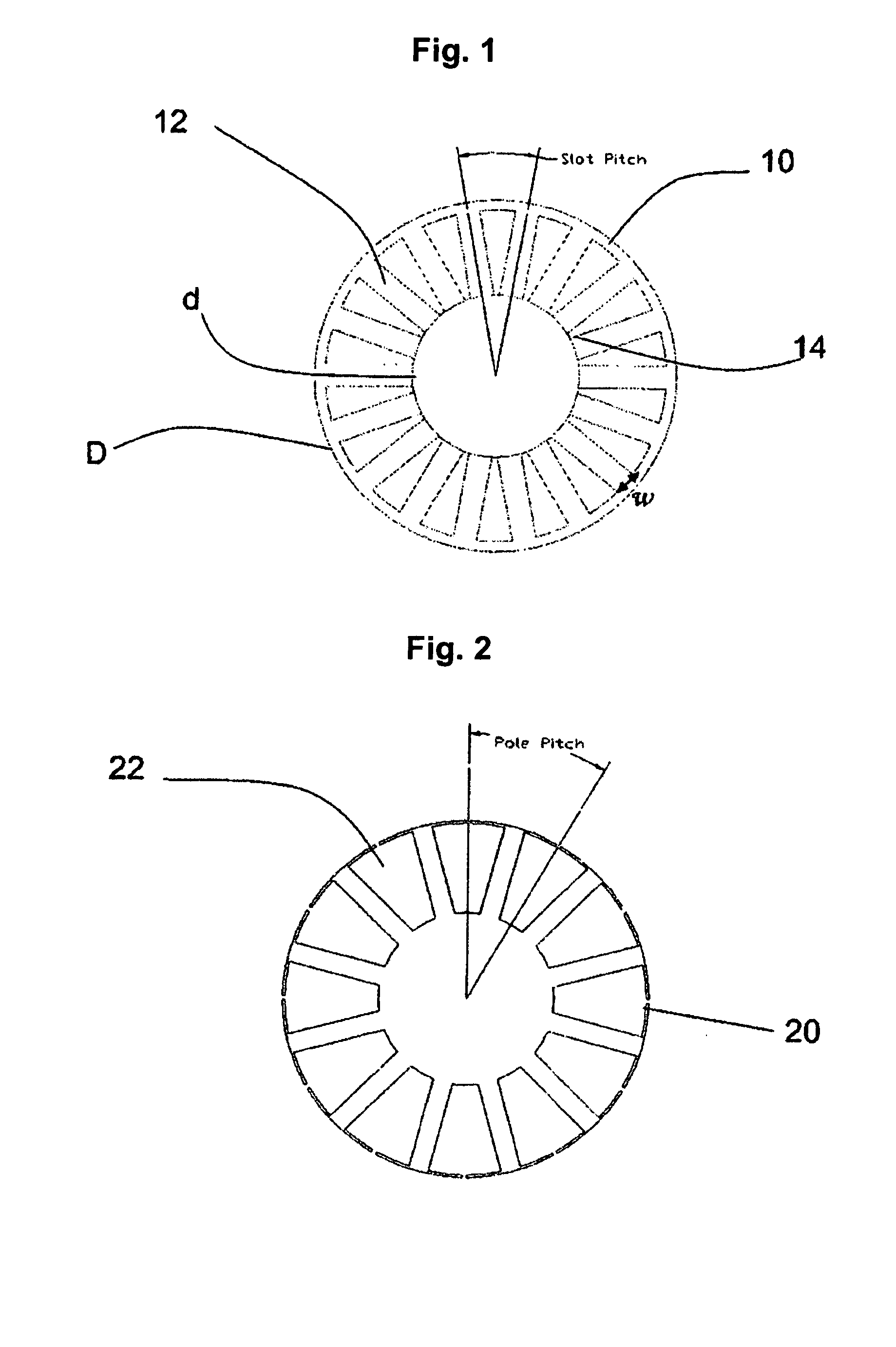
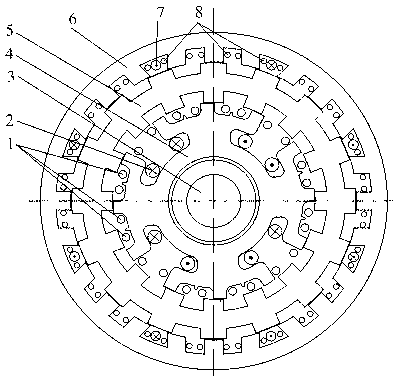
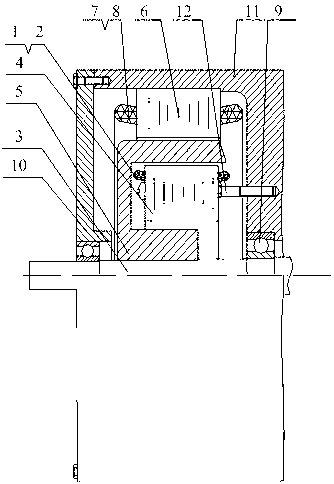
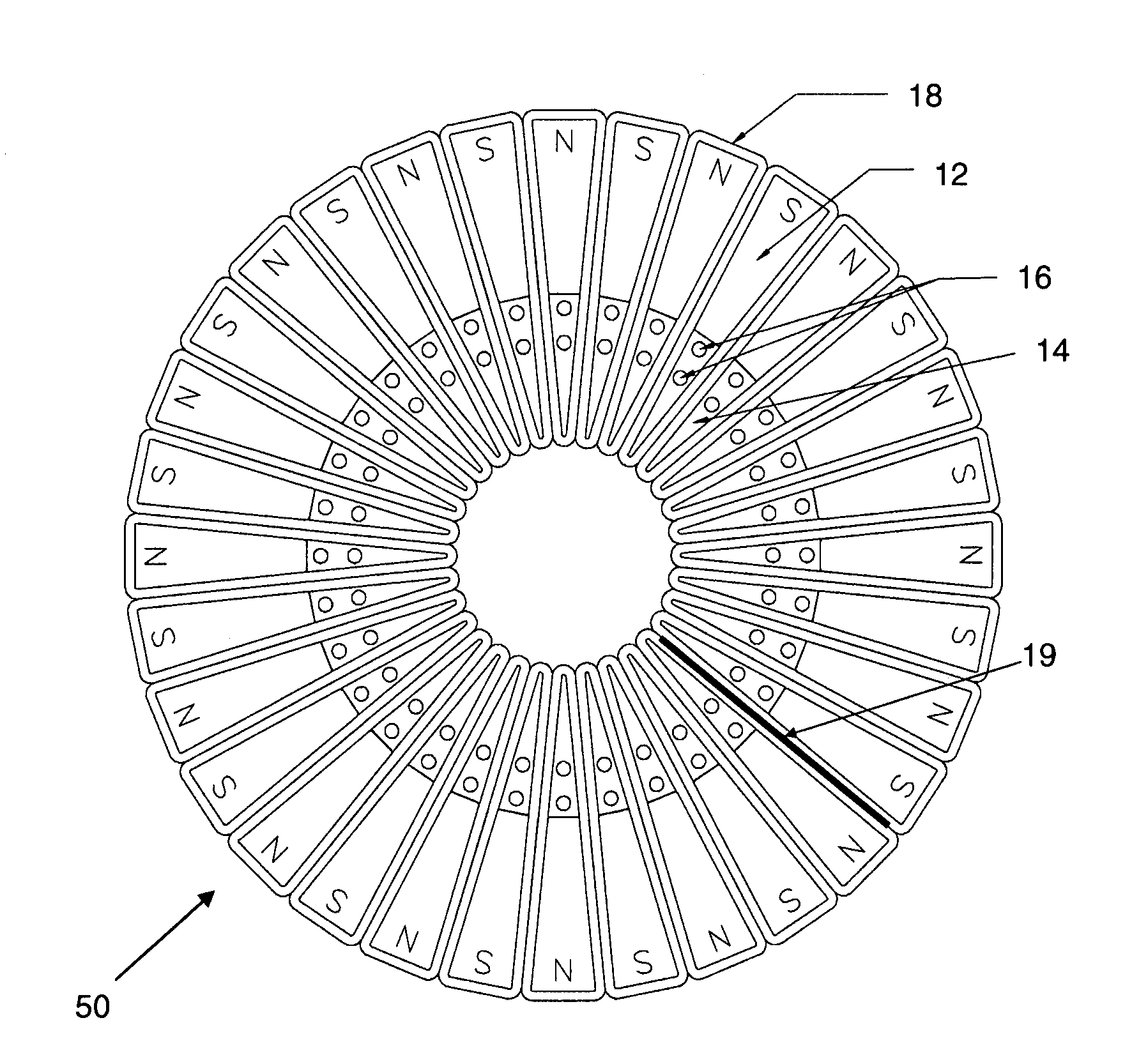
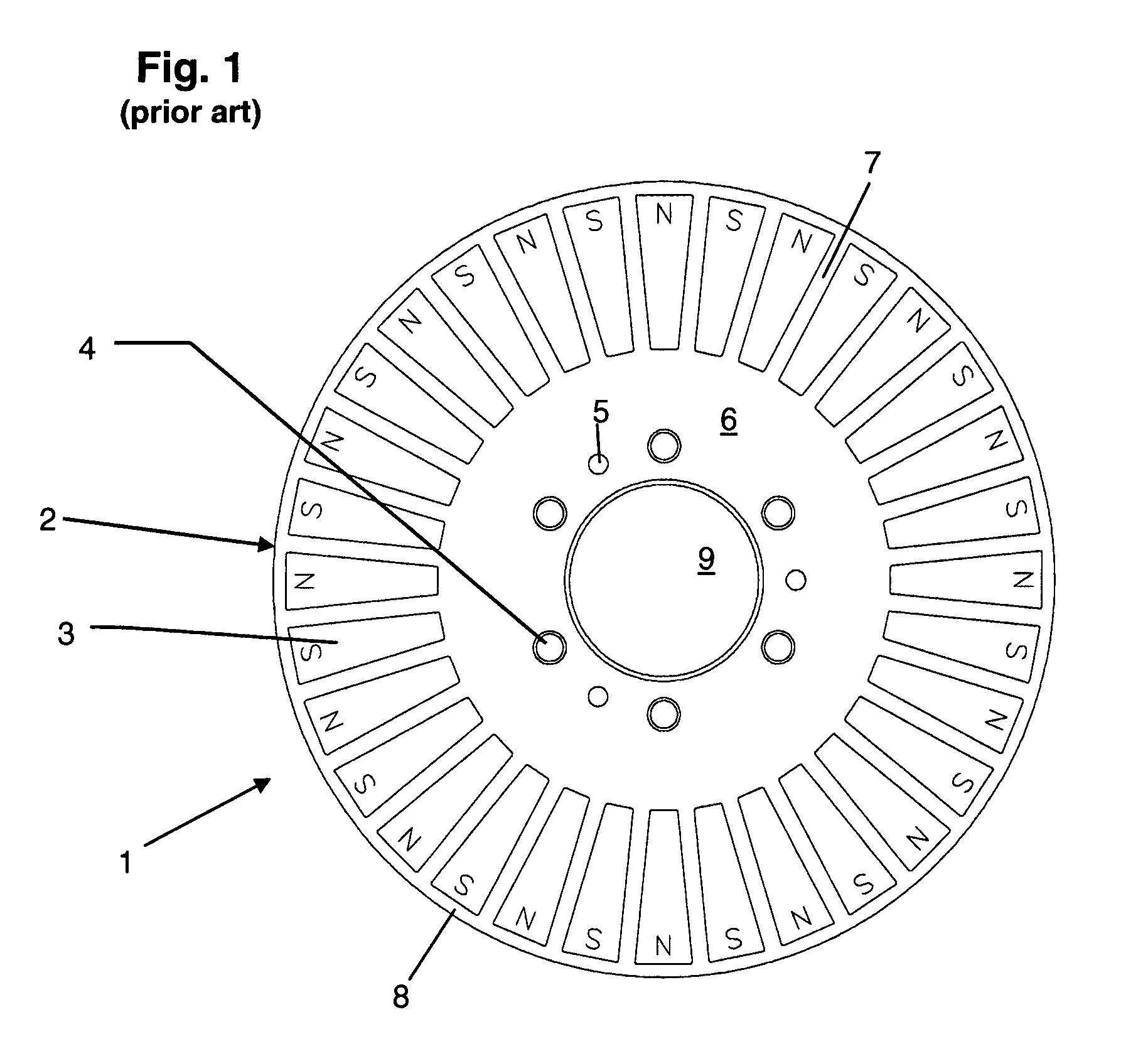
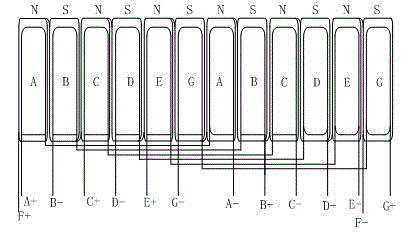
The number of poles or the number of magnetic poles refers to the magnetic poles (NSNSNS……) that appear on the surface created by cutting the motor perpendicularly to the shaft. Basically, the number of poles is an even number (2, 4, 6, 8......). As described on the next page, there are two winding types: distributed winding...
Permanent magnet synchronous motor and controller therefor
InactiveUS20050248306A1Low costReduce impactTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsLoop control
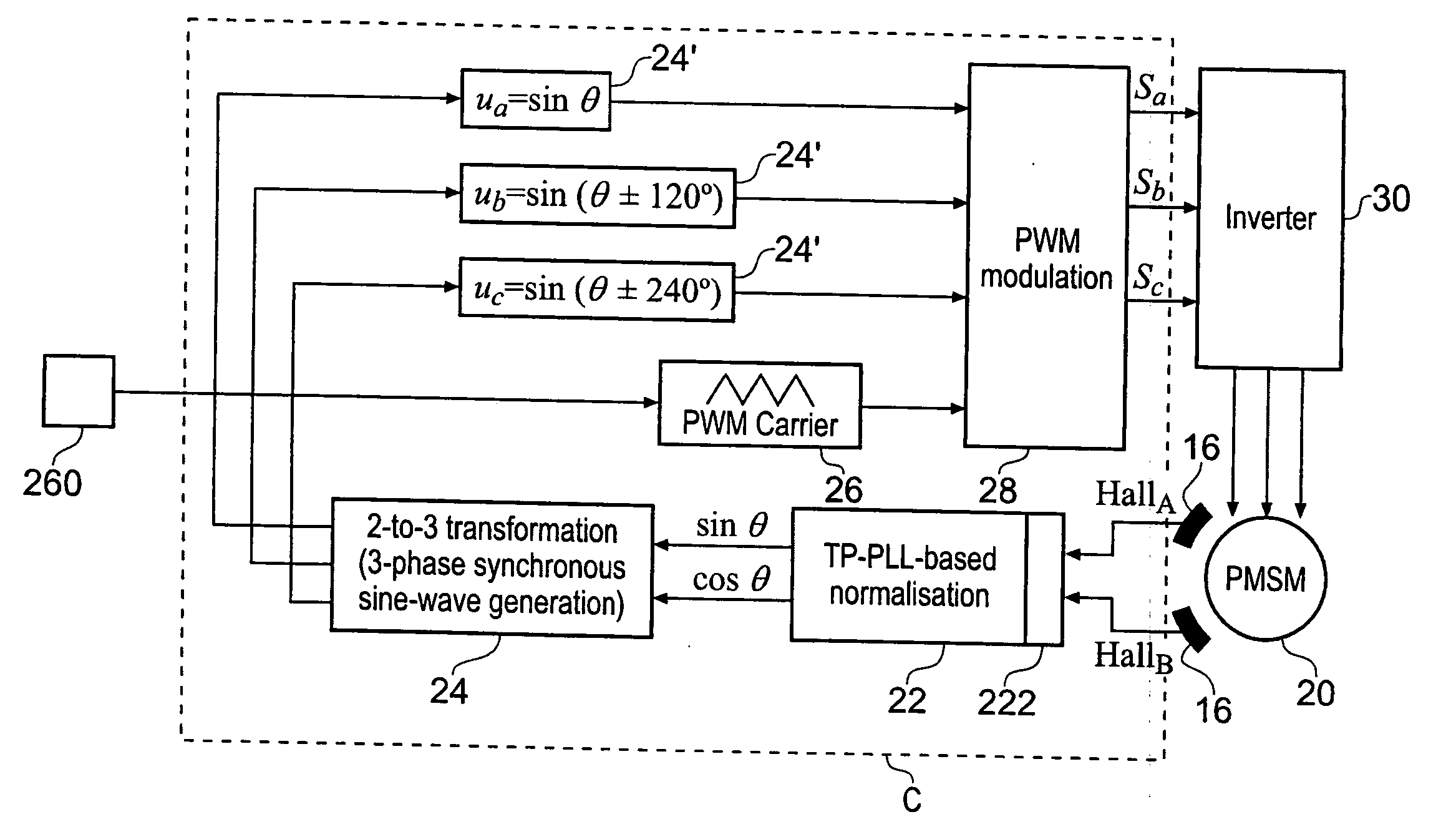
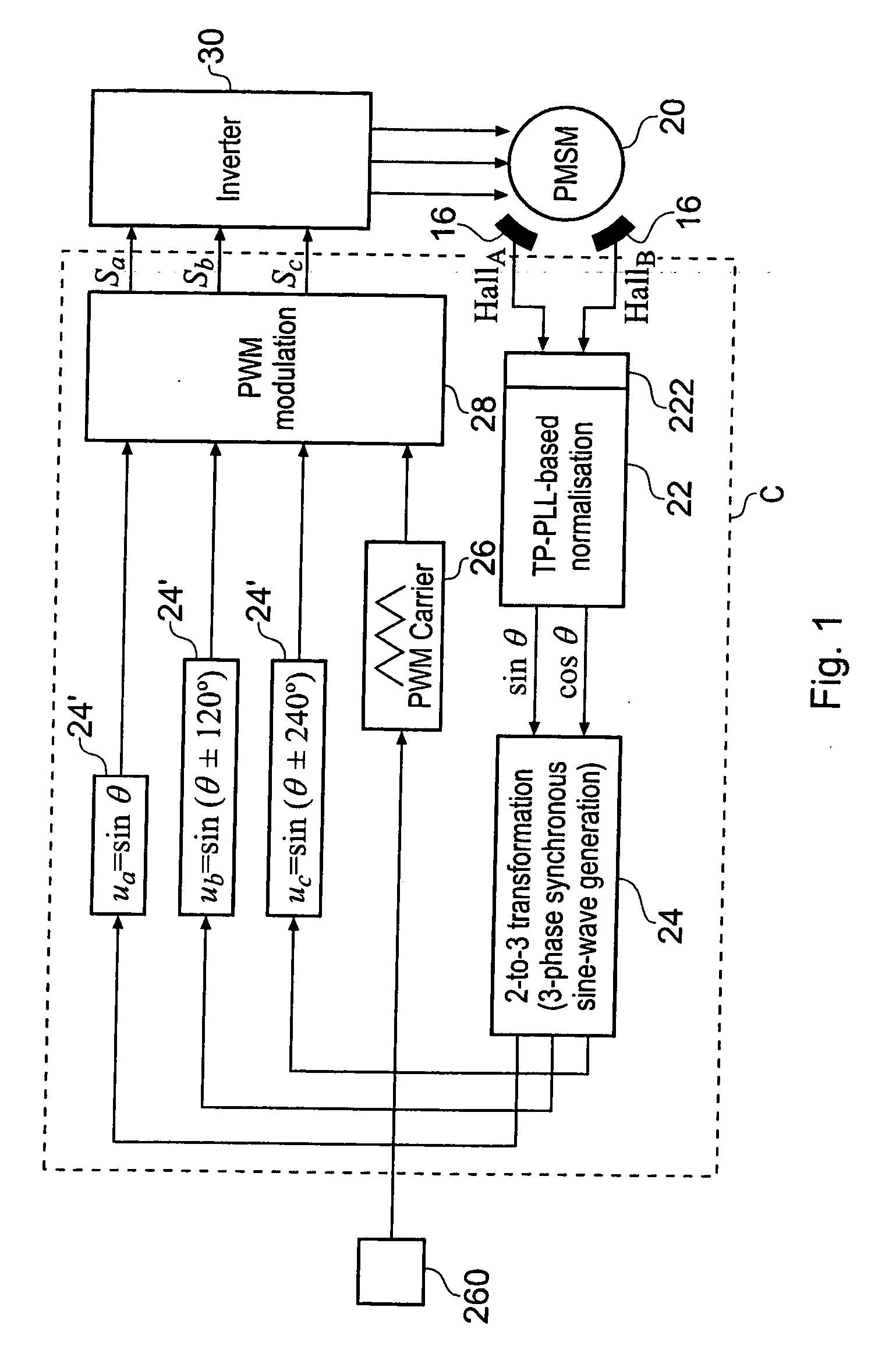
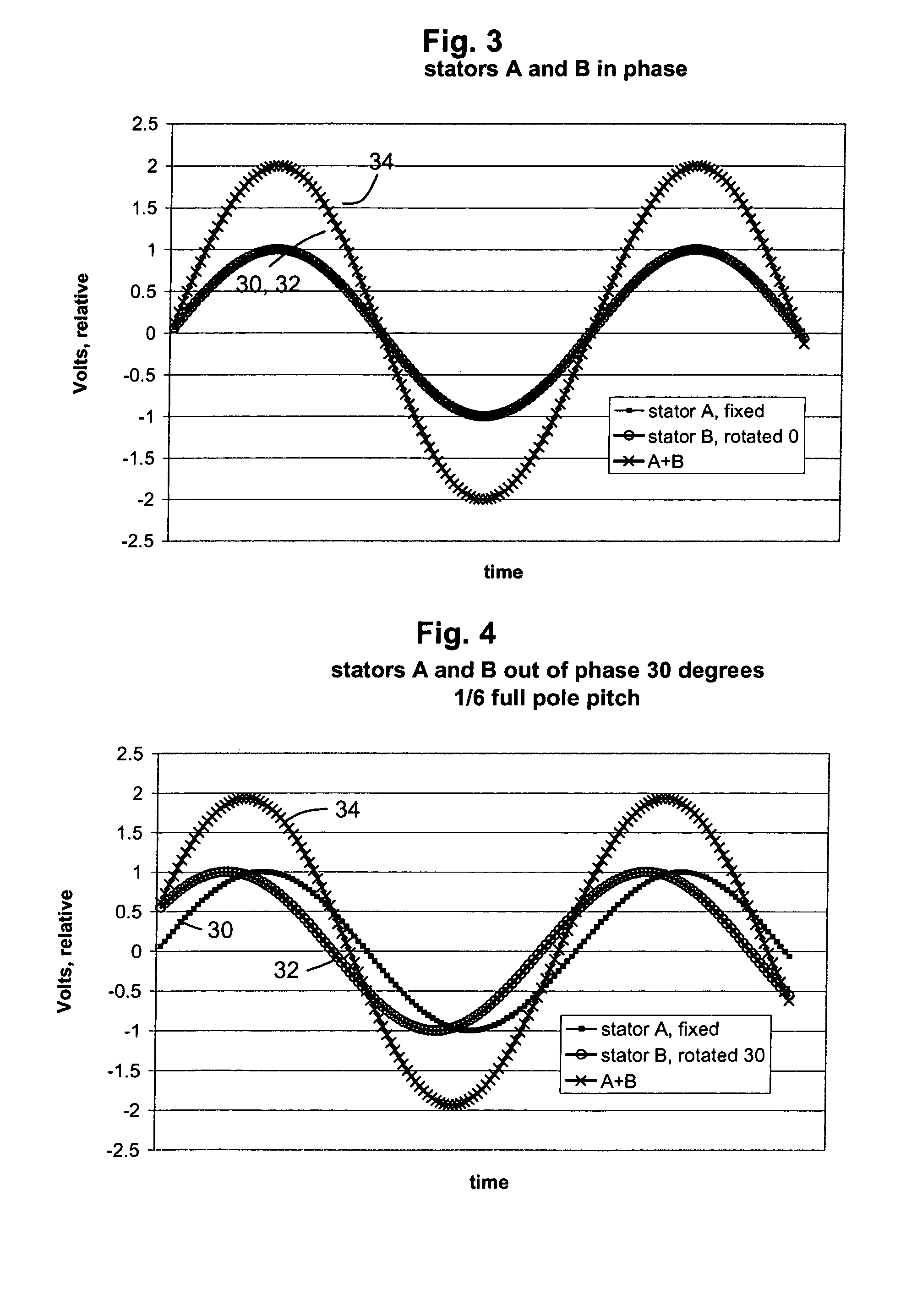
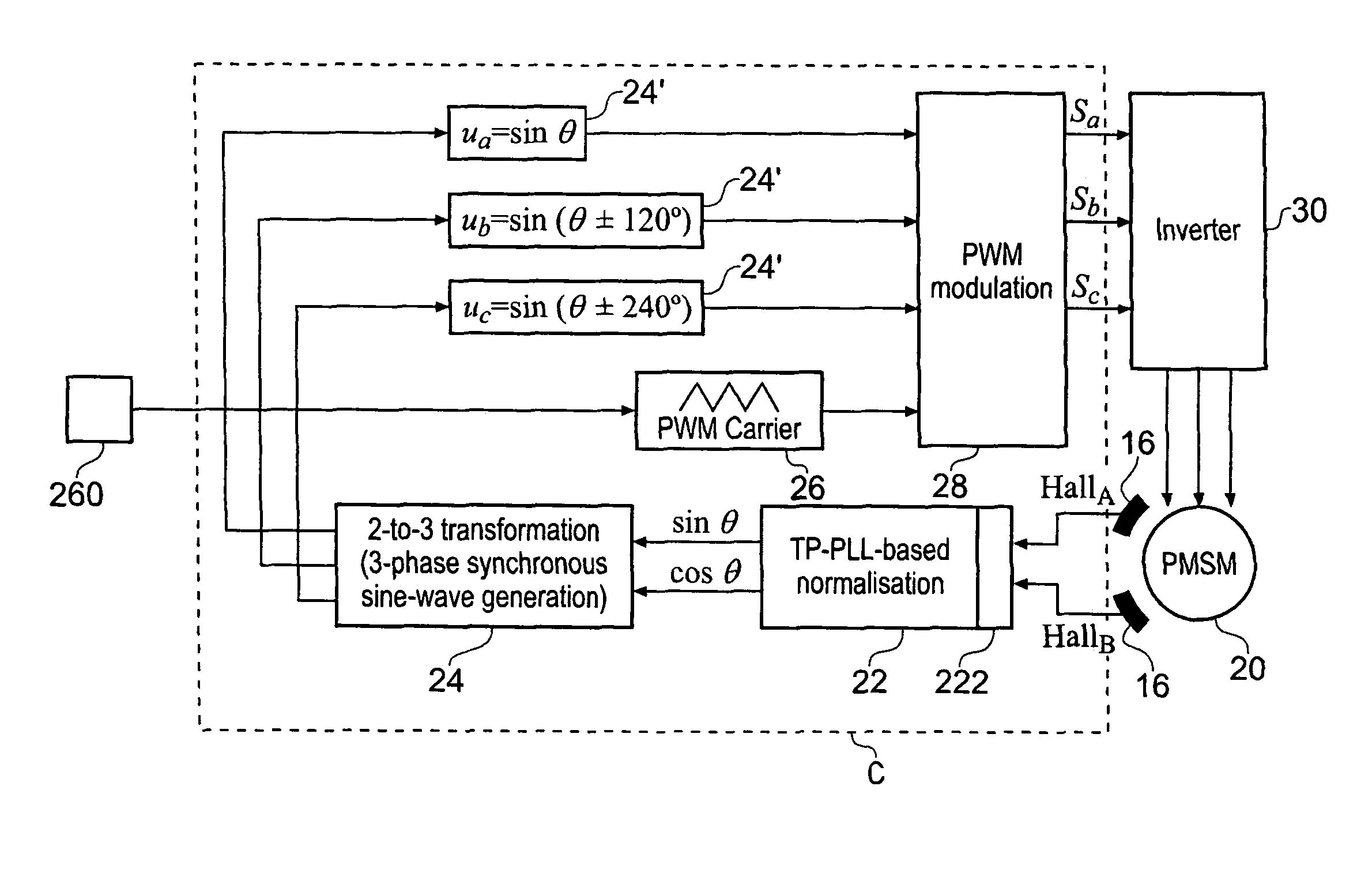
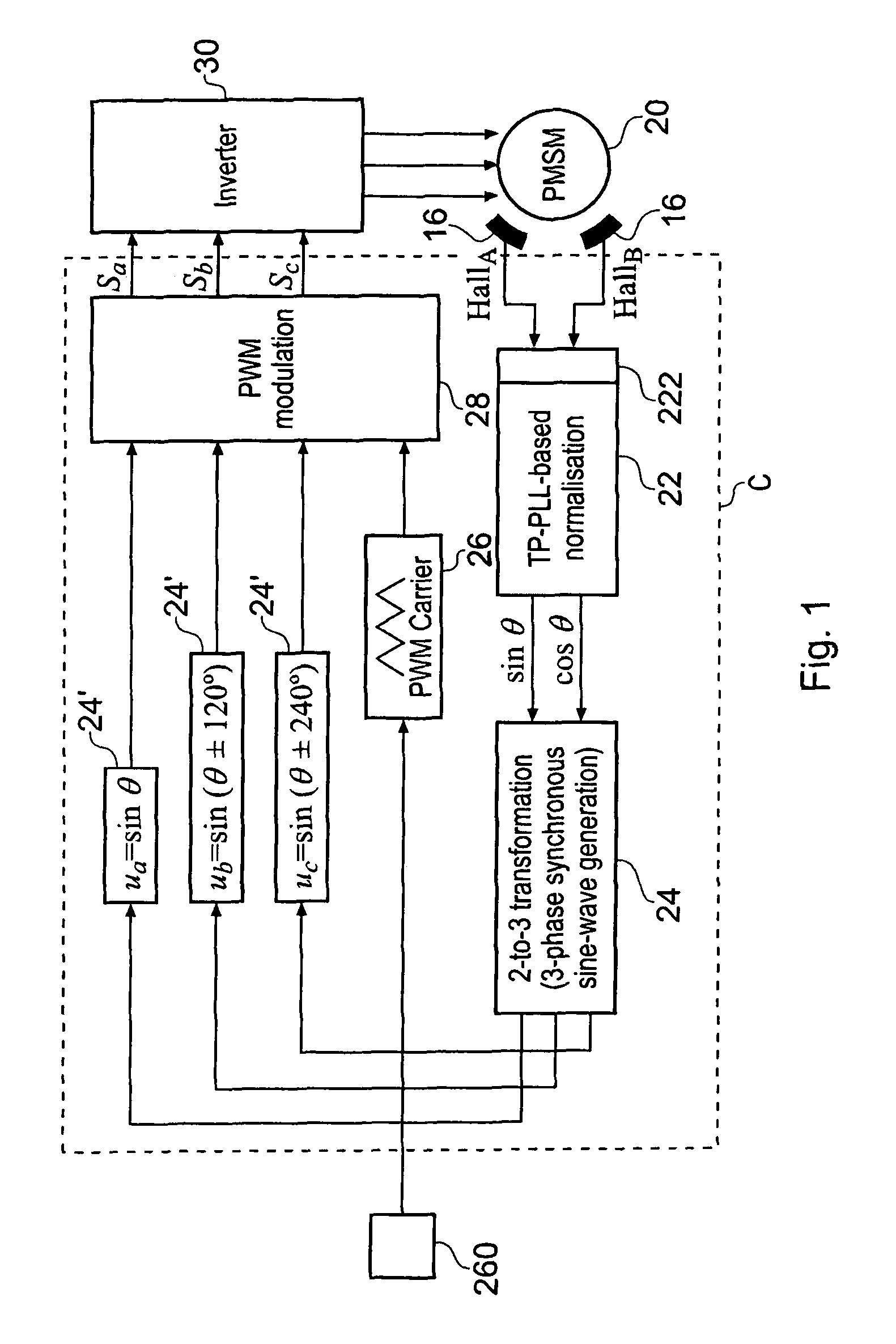
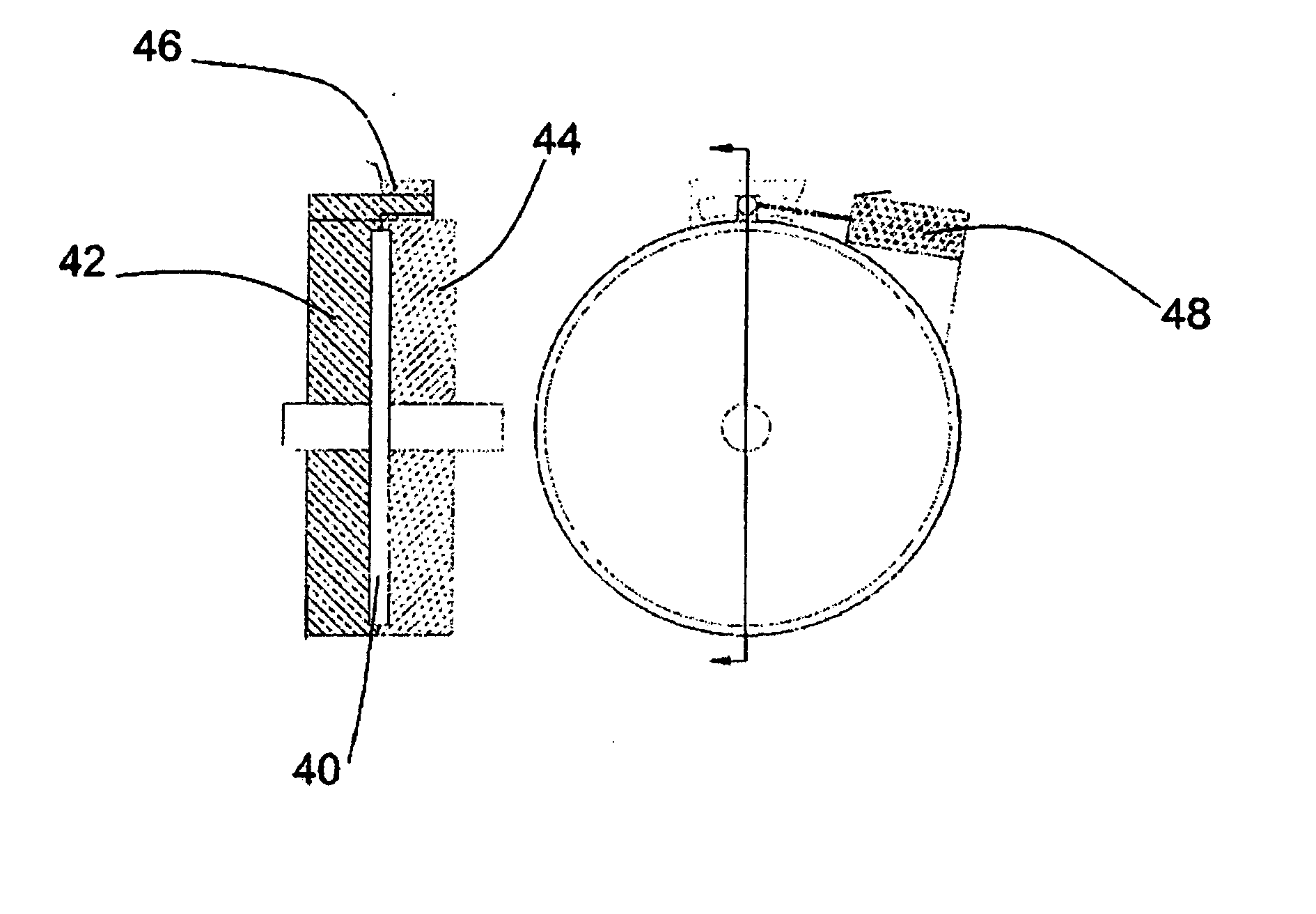
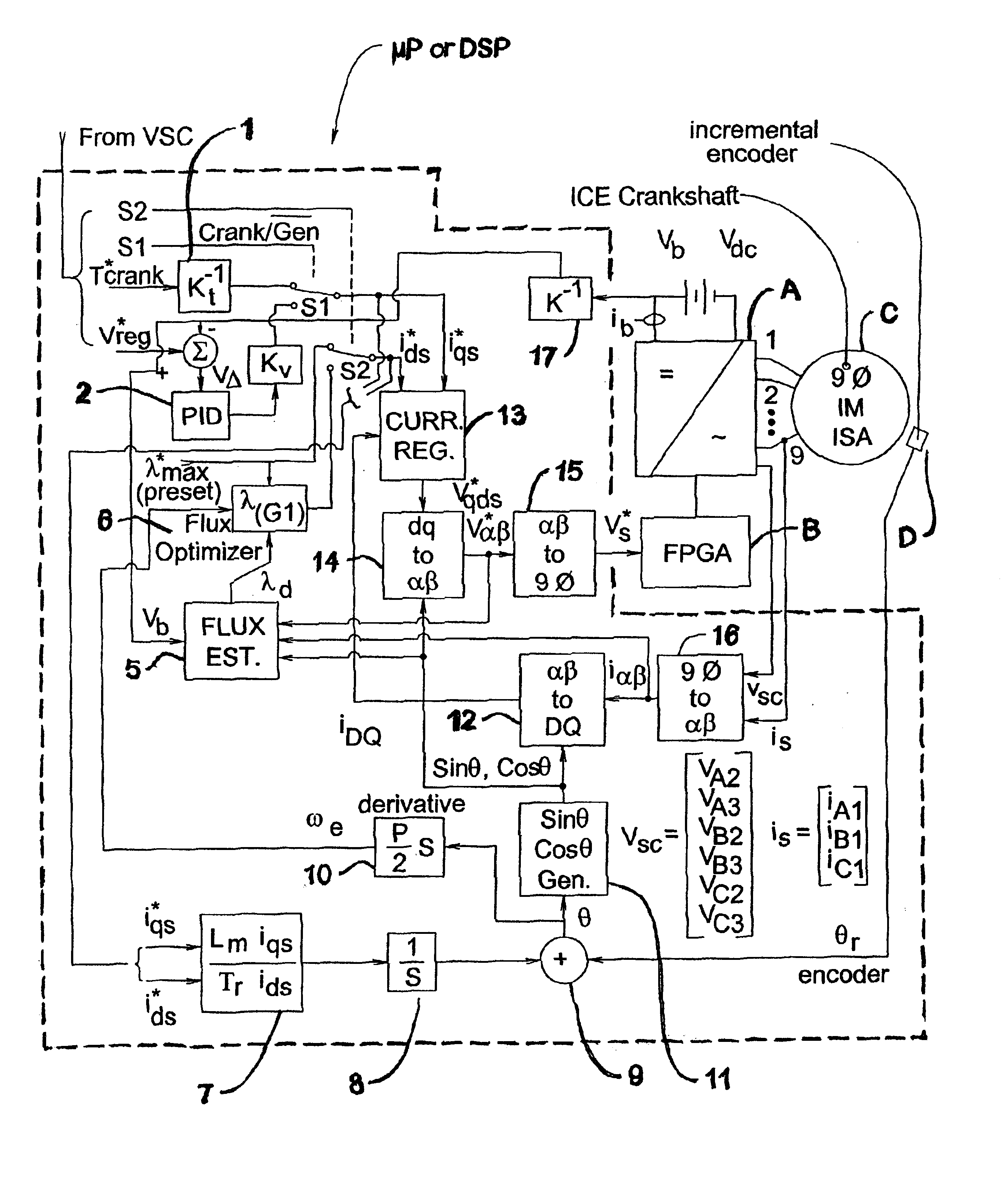
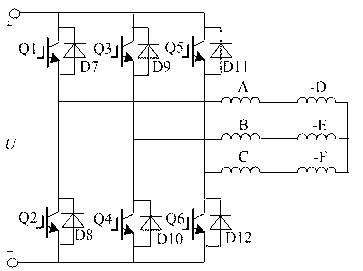
A low-cost sine-wave drive for a 3-phase permanent magnet synchronous AC machines (PMSM) in open-loop control is based on the measurements of two linear Hall sensors. The two Hall sensors are excited by a magnetic ring with the same pole number as the PMSM rotor magnet and sinusoidal flux distributions. The output signals of the Hall sensors are unified through a two-phase-type phase-lock-loop in order to reduce the impact of the sensor mounting non-uniformity during mass production. The peak torque and speed of motor is simply controlled by adjusting the amplitude of pulse-width-modulation carrier. Smooth torque control is achieved due to sinusoidal 3-phase currents. Such a simple sine-wave drive can be achieved with or without the assistance of a micro-controller unit (MCU). No current sensor is required for the motor phase current detection. This motor can be used in industrial applications where there is no strict requirement on torque response and constant speed control of PMSM machines.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Efficient high-speed electric device using low-loss materials
InactiveUS7230361B2Reduce lossHigh frequencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringHigh torque
The invention relates generally to an electric device, such as an electric motor, a generator, or a regenerative motor, having a wound stator core made from advanced low-loss material. In preferred embodiments, the electric device is an axial airgap-type configuration. The invention provides an electric device having a high pole count that operates at high commutating frequencies, with high efficiency and high torque and power densities. Advanced low-loss materials exploited by the present invention include amorphous metals, nanocrystalline metals, and optimized Fe-based alloys.
Owner:BERG & BERG ENTERPRISES
Stator field providing torque and levitation
InactiveUS6879074B2Easy constructionSimple electrical controlShaftsMechanical energy handlingMagnetomotive forceLevitation
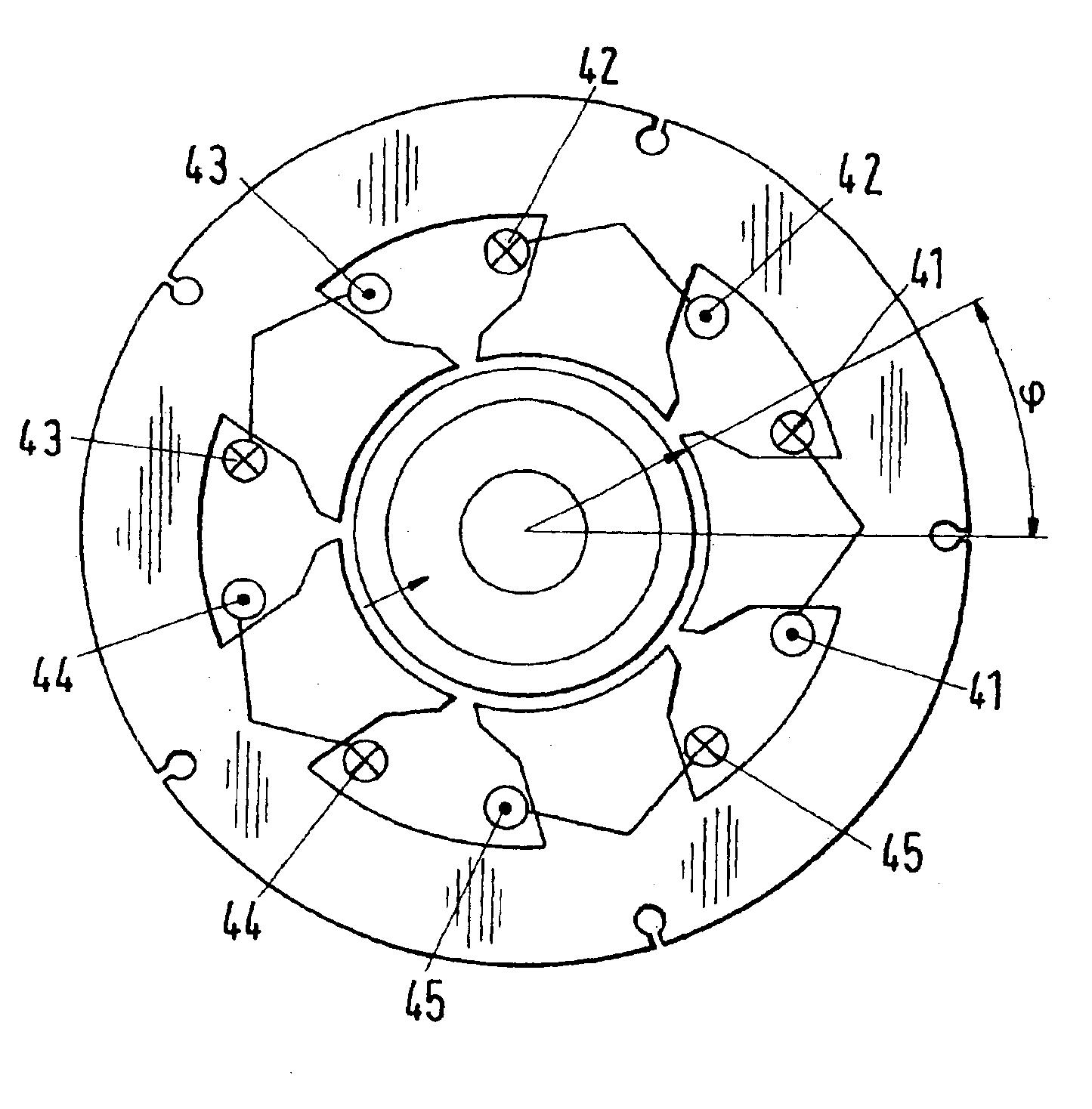
The invention relates to an economical, non-wearing, electrical permanent magnet drive for actively controlling the rotor position in three degree of freedom. The stator windings produce superimposed fields with different pole numbers in the pole pitches by unsymmetrical magnetomotive force distributions.
Owner:LEVITRONIX TECH +1
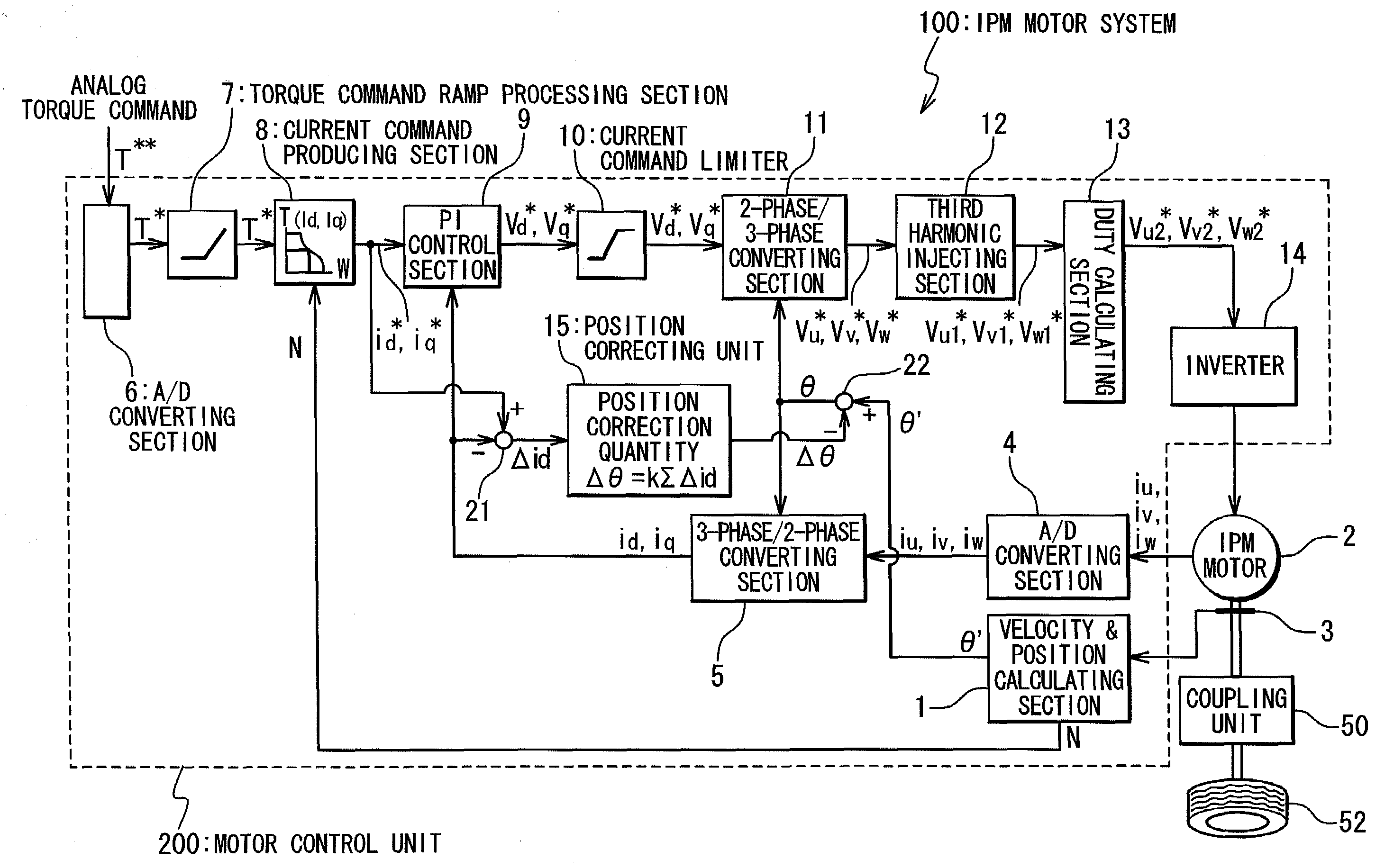
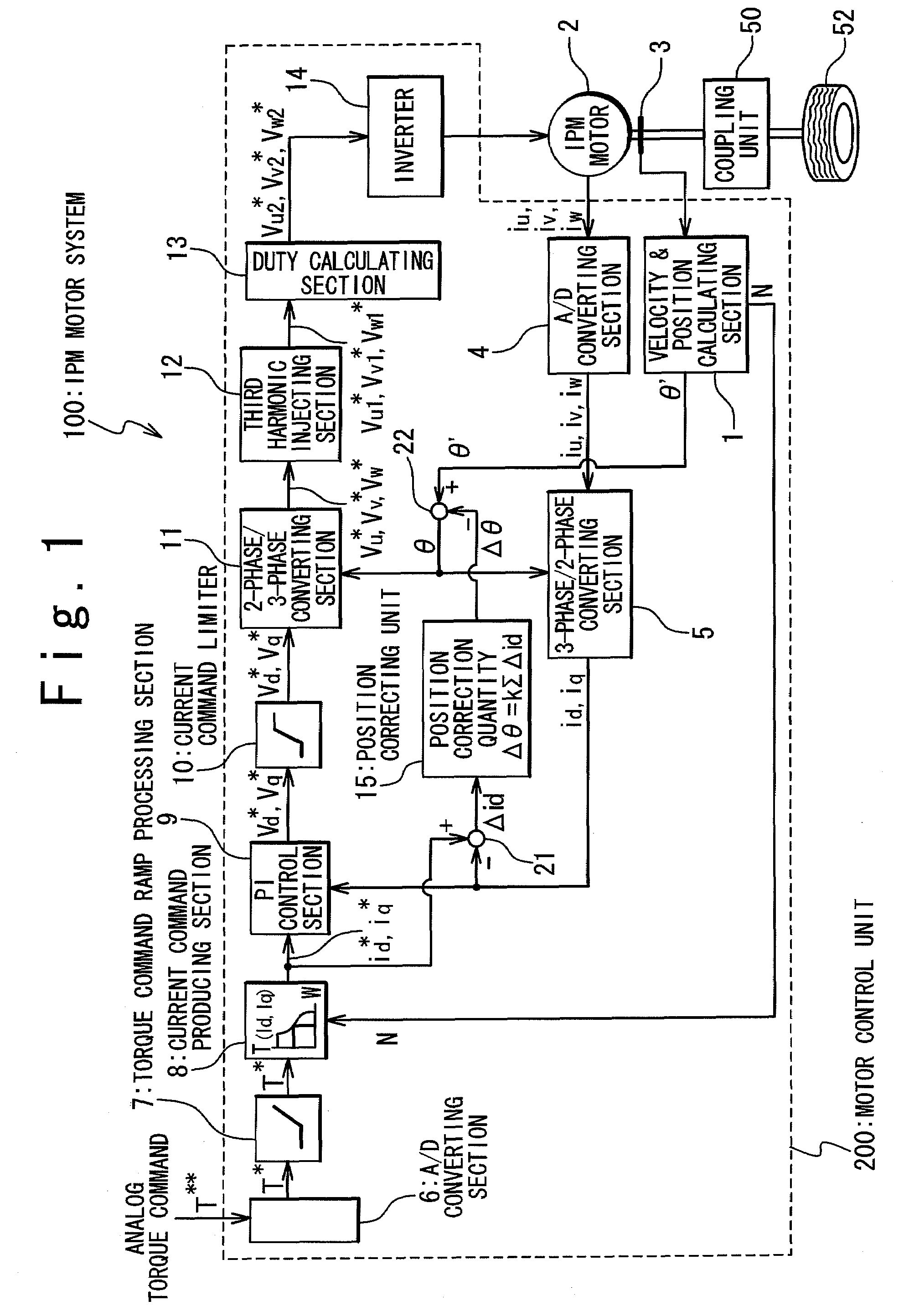
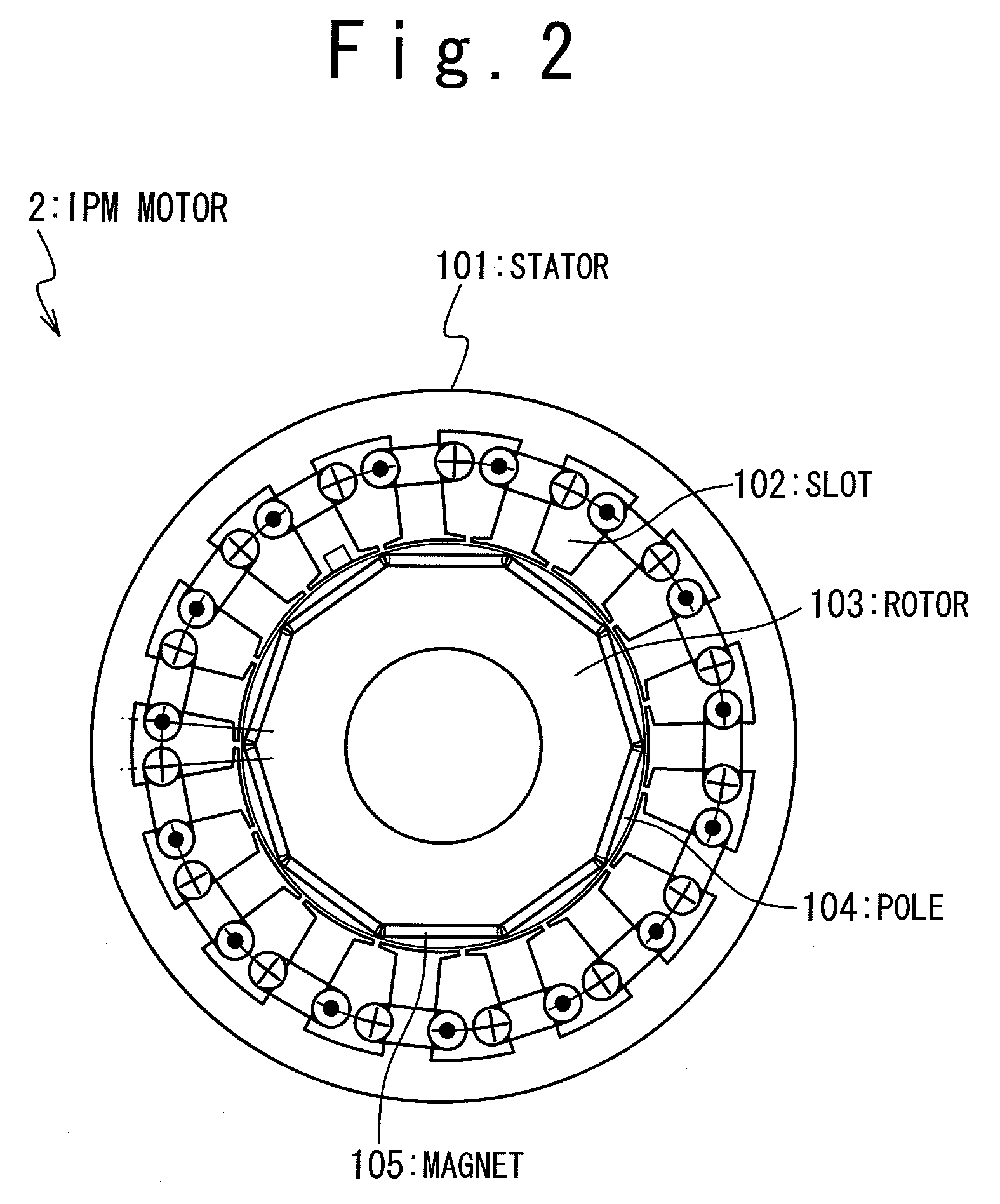
IPM motor system and control method thereof
InactiveUS7733044B2Improve efficiencySynchronous motors startersAC motor controlElectric machineControl theory
An IPM (Interior Permanent Magnet) motor system is provided with an IPM motor provided with a stator having slots and a rotor having poles, and a control unit which controls the rotor to the stator. An estimation precision of an initial angle position of the rotor to the stator is selected such that it is substantially the same as an angle unit precision of stable positions of the rotor to the stator which is based on a combination of the number of poles and the number of slots. In this way, the cheap IPM motor system with a high drive efficiency and a control method of the IPM motor system are provided.
Owner:NIPPON YUSOKI
Automatic field-weakening method for built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN101783536AExtended pole-to-pole flux leakage pathsRealize automatic field weakening speed expansionMagnetic circuit rotating partsLow speedPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention relates to an automatic field-weakening method for a built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor, which solves the problem that field-weakening speed is difficult to widen due to the fixed rotor excitation and small reactance of armature reaction of a direct axis in the conventional permanent magnet synchronous motor in the market. In a rotor magnetic structure of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, a magnetic flux short-circuit block is arranged in a magnetic flux isolating layer in a quadrature axis direction with the help of an automatic adjustment action of a spring; when the rotary speed of the rotor is low, the short-circuit block is positioned at a low-speed position so that interelectrode magnet leakage through the isolating layer is small; when the rotary speed of the rotor is increased, the short-circuit block gradually deviates from the low-speed position to move towards the edge of the rotor under the action of rotating centrifugal force, which expands the interelectrode magnet leakage path; and the leakage magnet flux passing through the isolating layer is increased and the main magnet flux is reduced so that the aim of automatic filed-weakening widening speed is fulfilled in the motor body and a larger speed-adjusting range is reached. The method can be applied to the permanent magnet motors which have uncertain pole numbers and tangential or radial magnet structures.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Selective alignment of stators in axial airgap electric devices comprising low-loss materials
InactiveUS7034427B2Bulky designHigh operating requirementsSynchronous generatorsWindingsLow speedFull wave
An axial gap dynamoelectric machine comprises first and second stators disposed coaxially with an intermediate rotor. The stators are selectively aligned with an axial offset between the positions of their respective teeth and slots. The stators comprise toroidal cores having laminated layers composed of a material selected from the group consisting of amorphous and nanocrystalline metals and optimized Fe-based alloy. Optionally, the machine further comprises misalignment means for adjusting the offset of the stators. Adaptive adjustment permits the machine to be operated to in a mode that reduces the back EMF of the motor, allowing constant voltage to be maintained as speed is increased. Reducing back EMF also allows a wider range of operating speed, especially in combination with use of high pole counts. Alternatively, the machine can be operated, e.g. at lower speed, in a constant torque mode. The machine may exploit the high pole count achievable by use of improved soft magnetic materials. Also provided are techniques for reducing torque ripple during operation, and also for using the stator offset in combination with a dual full wave bridge rectifier arrangement.
Owner:BERG & BERG ENTERPRISES
Permanent magnet synchronous motor and controller therefor
InactiveUS7714529B2Reduce impactStable controlTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsLoop control
A low-cost sine-wave drive for a 3-phase permanent magnet synchronous AC machines (PMSM) in open-loop control is based on the measurements of two linear Hall sensors. The two Hall sensors are excited by a magnetic ring with the same pole number as the PMSM rotor magnet and sinusoidal flux distributions. The output signals of the Hall sensors are unified through a two-phase-type phase-lock-loop in order to reduce the impact of the sensor mounting non-uniformity during mass production. The peak torque and speed of motor is simply controlled by adjusting the amplitude of pulse-width-modulation carrier. Smooth torque control is achieved due to sinusoidal 3-phase currents. Such a simple sine-wave drive can be achieved with or without the assistance of a micro-controller unit (MCU). No current sensor is required for the motor phase current detection. This motor can be used in industrial applications where there is no strict requirement on torque response and constant speed control of PMSM machines.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Stator coil arrangement for an axial airgap electric device including low-loss materials
InactiveUS7190101B2Bulky designHigh operating requirementsSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineStator coil
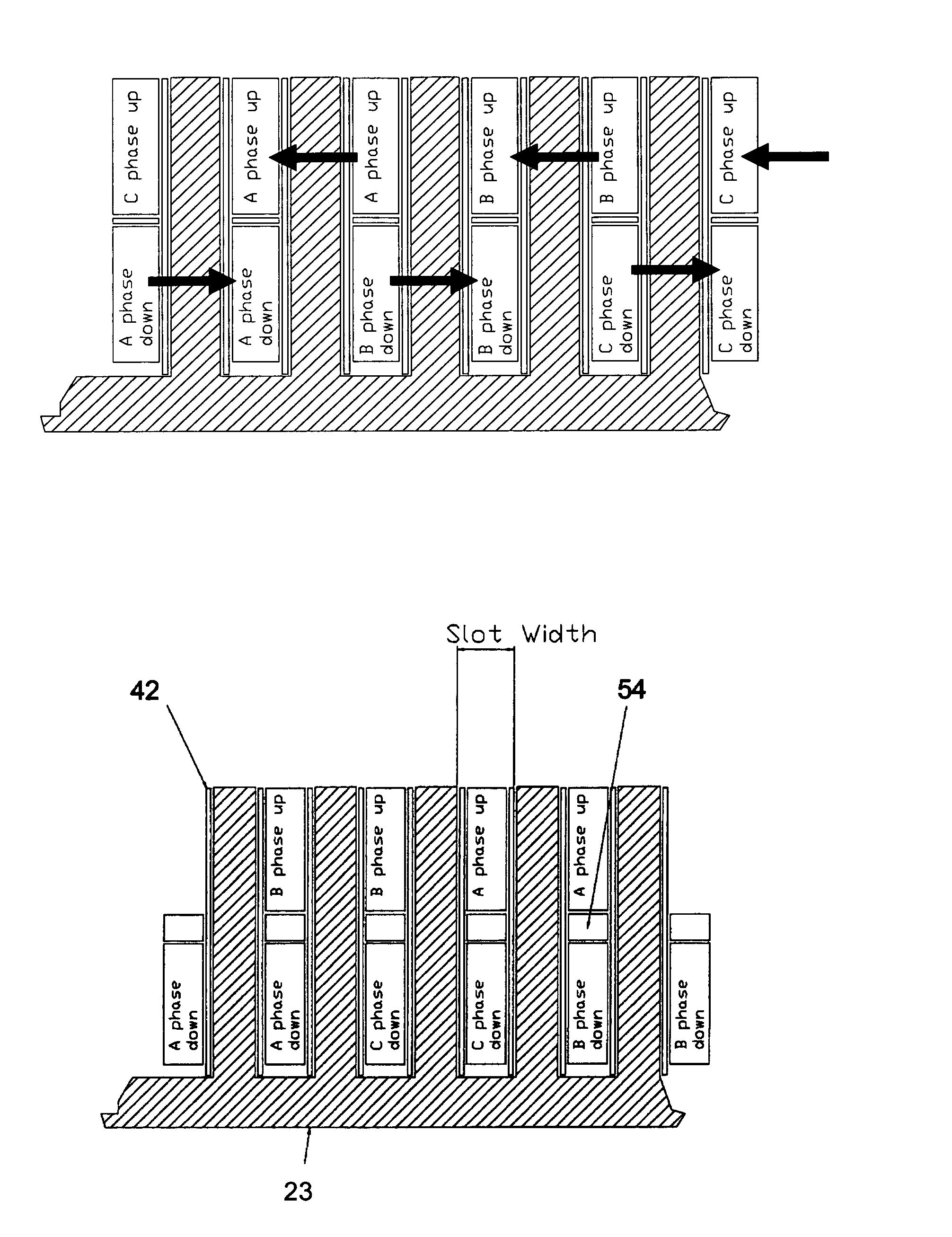
A dynamoelectric, rotating electric machine includes a stator assembly that includes stacked stator coil windings. The machine is preferably a polyphase, axial airgap device. Improved slot filling results from the stacked stator coil configuration. Device performance capability is thereby increased. The stator assembly of the electric device has a magnetic core made from low loss, high frequency material. A high pole count permits the electrical device to operate at high commutating frequencies, with high efficiency, high power density and improved performance characteristics. Low-loss materials incorporated by the device include amorphous metals, nanocrystalline metals, optimized Si—Fe alloys, grain-oriented Fe-based materials or non-grain-oriented Fe-based materials.
Owner:LIGHT ENGINEERING INC
Brushless disk DC motor
InactiveUS7898134B1Increase powerIncrease torqueSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsRing patternMagnetic poles
A brushless disk DC motor that exhibits high power density and light weight and is capable of power regeneration and reverse operation employs a flat circular non-ferrous stator plate having a plurality of electromagnets mounted in a ring pattern on an inner face thereof. Permanent magnets are mounted in equal numbers in inner and outer ring patterns on the outer and inner cylindrical surfaces, respectively, of a pair of steel rotors of different diameter that rotate in concert. The stator plate and the pair of rotors are axially aligned such that the inner and outer rings of permanent magnets rotate adjacent to and inside and outside, respectively, the ring of electromagnets. The electromagnets utilize tape-wound amorphous metal cores to minimize eddy currents and resultant iron losses and to permit the use of heavier gauge copper windings to minimize resistive power losses. A greater number of poles in the form of permanent magnets can be accommodated, the number being limited only by the diameter of the rotor, thus providing increased power and torque over prior art brushless DC motors having a limited number of poles. The present motor exhibits up to 200% more starting torque, thus eliminating the need for a gear box or clutch in electric vehicle applications.
Owner:SHAW BILL S
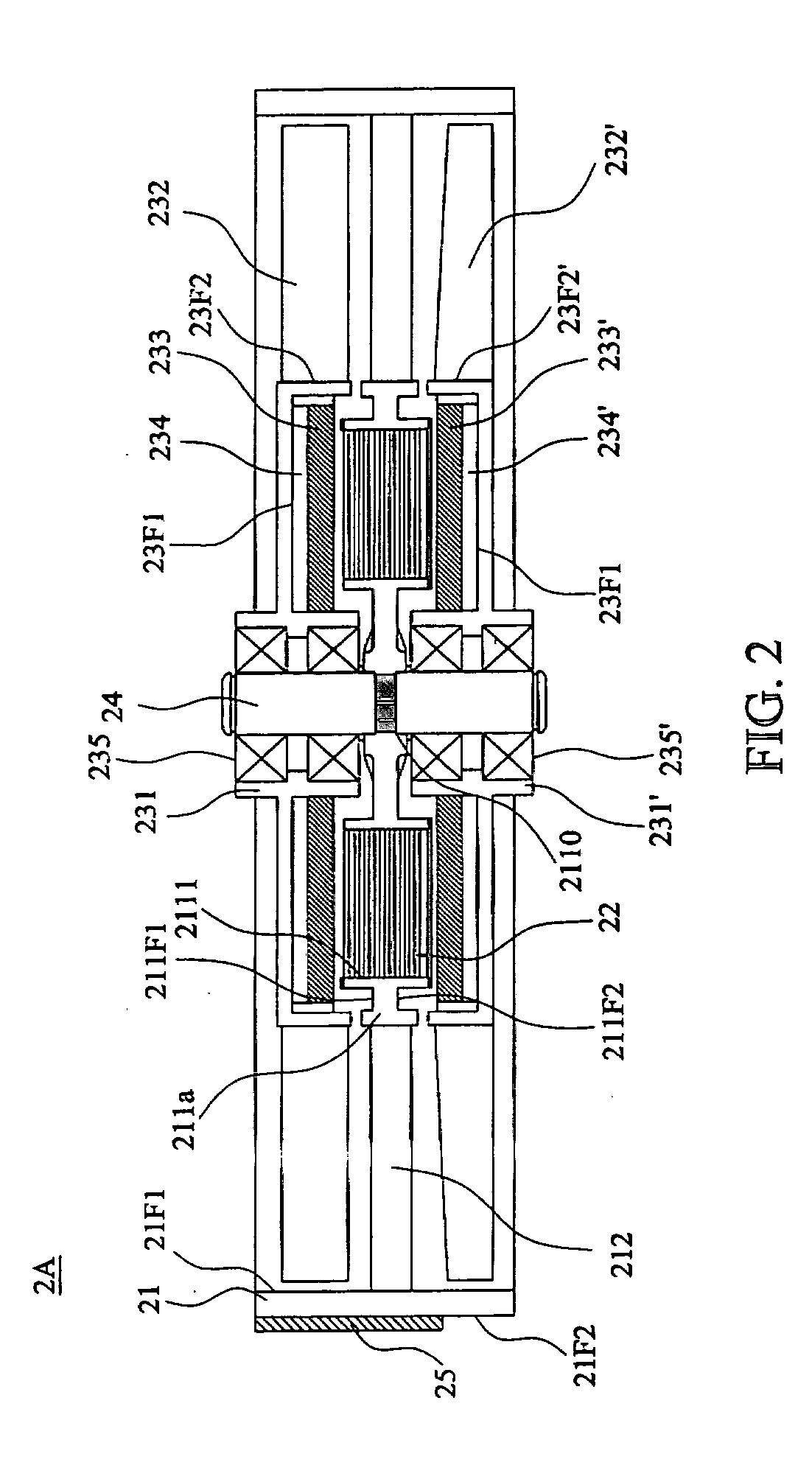
Segmented composite rotor
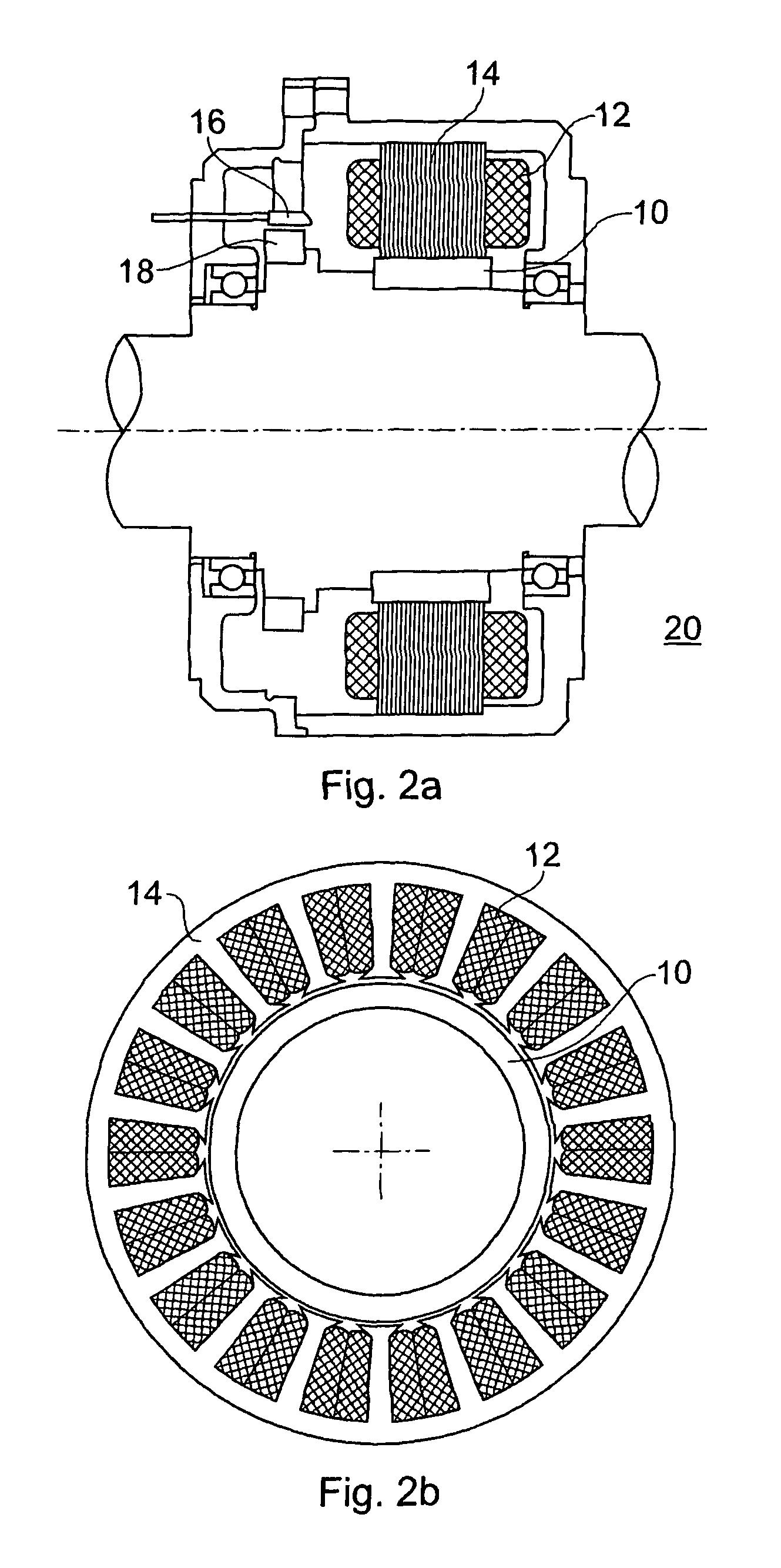
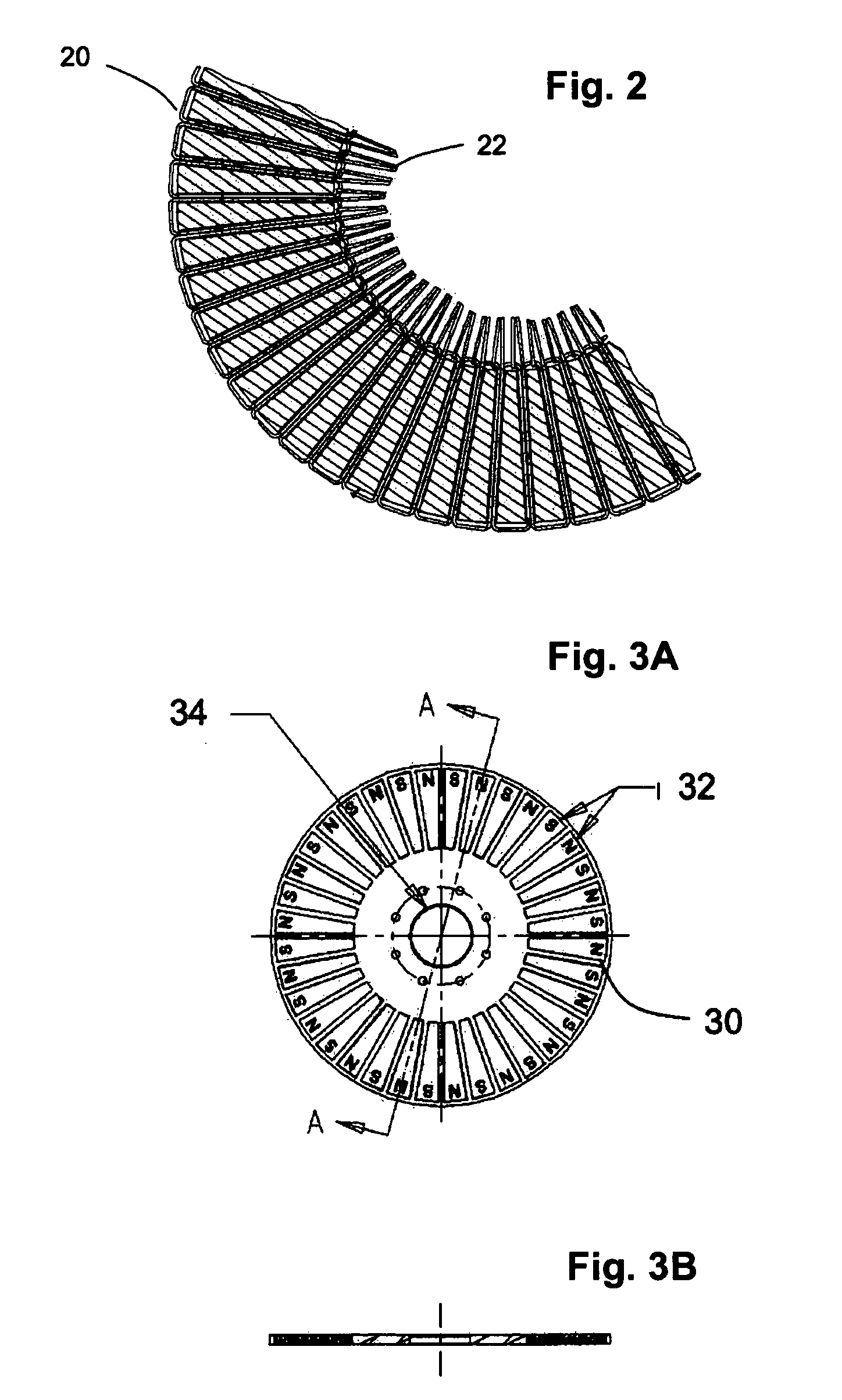
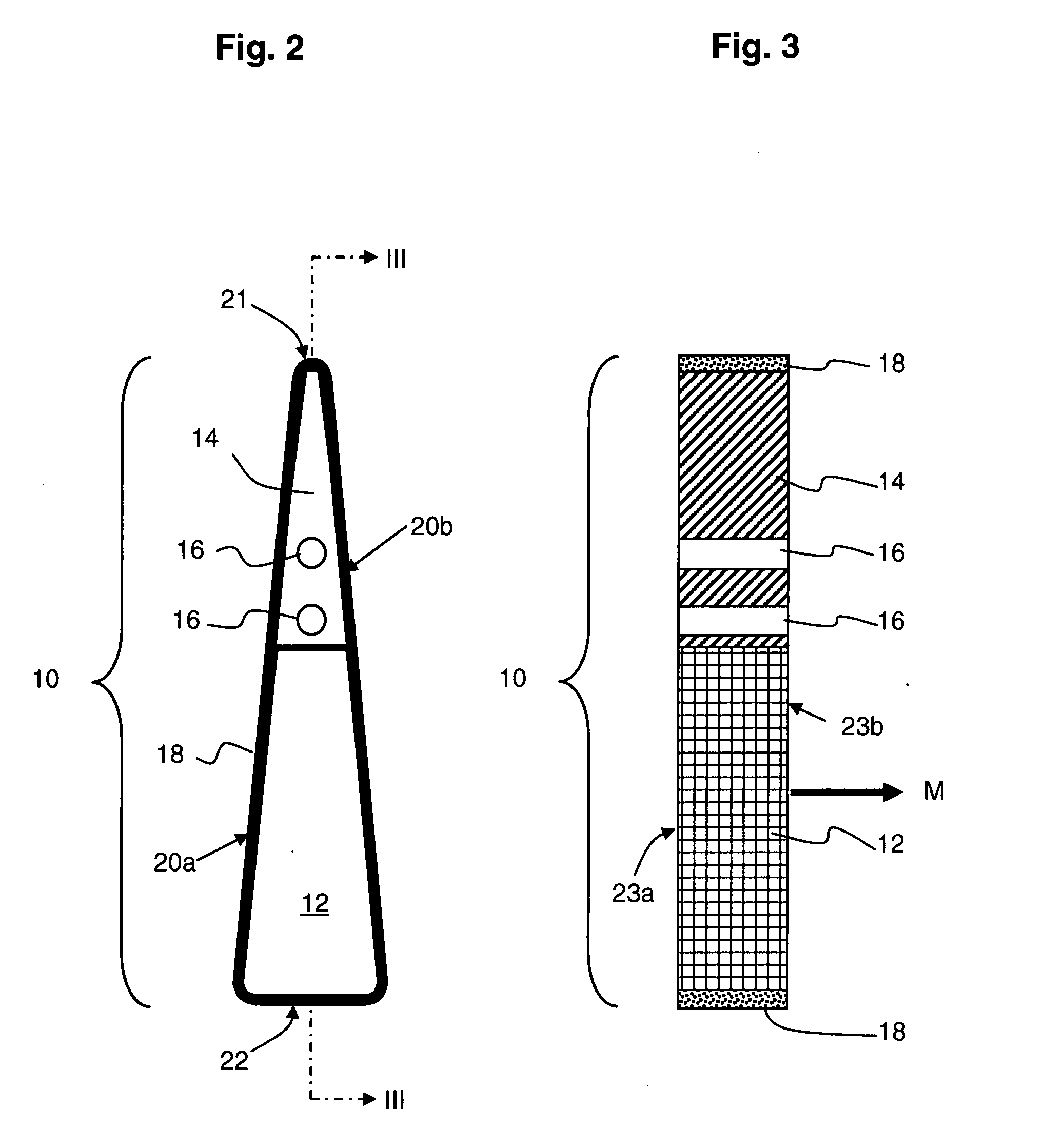
InactiveUS20090072639A1Improve efficiencyIncreased cost-effectivenessMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsPole numberMagnet
A composite rotor for an axial airgap, permanent magnet dynamoelectric machine comprises a plurality of magnet subassemblies adhesively bonded together to form the rotor. Each magnet subassembly comprises a rotor permanent magnet and an optional spacer. A fibrous belt is wrapped around the periphery of each subassembly to provide high tensile strength at least along the radial sides of the subassembly. The belt is preferably infiltrated with an adhesive agent, such as an epoxy resin, that is used to bond the subassemblies. The rotor is thereby provided with high strength and low mass, making it suitable for use in a high-speed, high pole count electric machine.
Owner:BERG & BERG ENTERPRISES
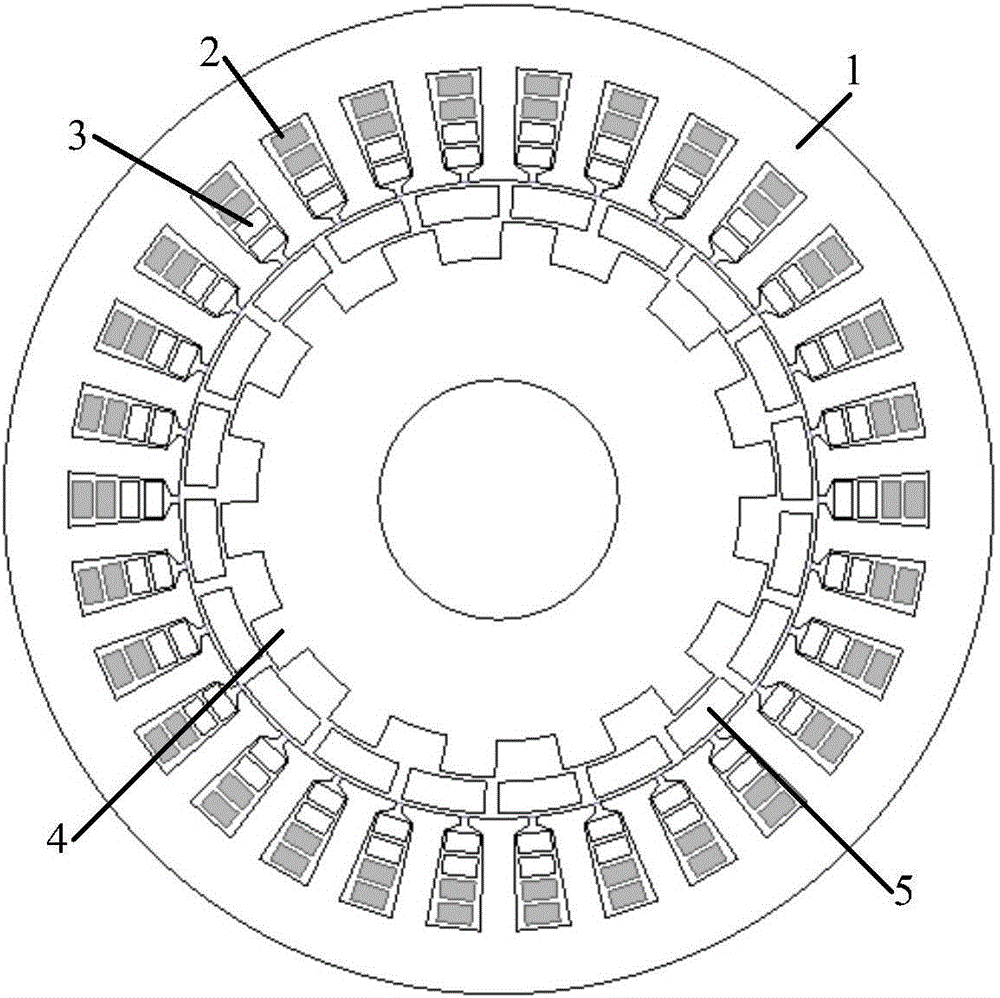
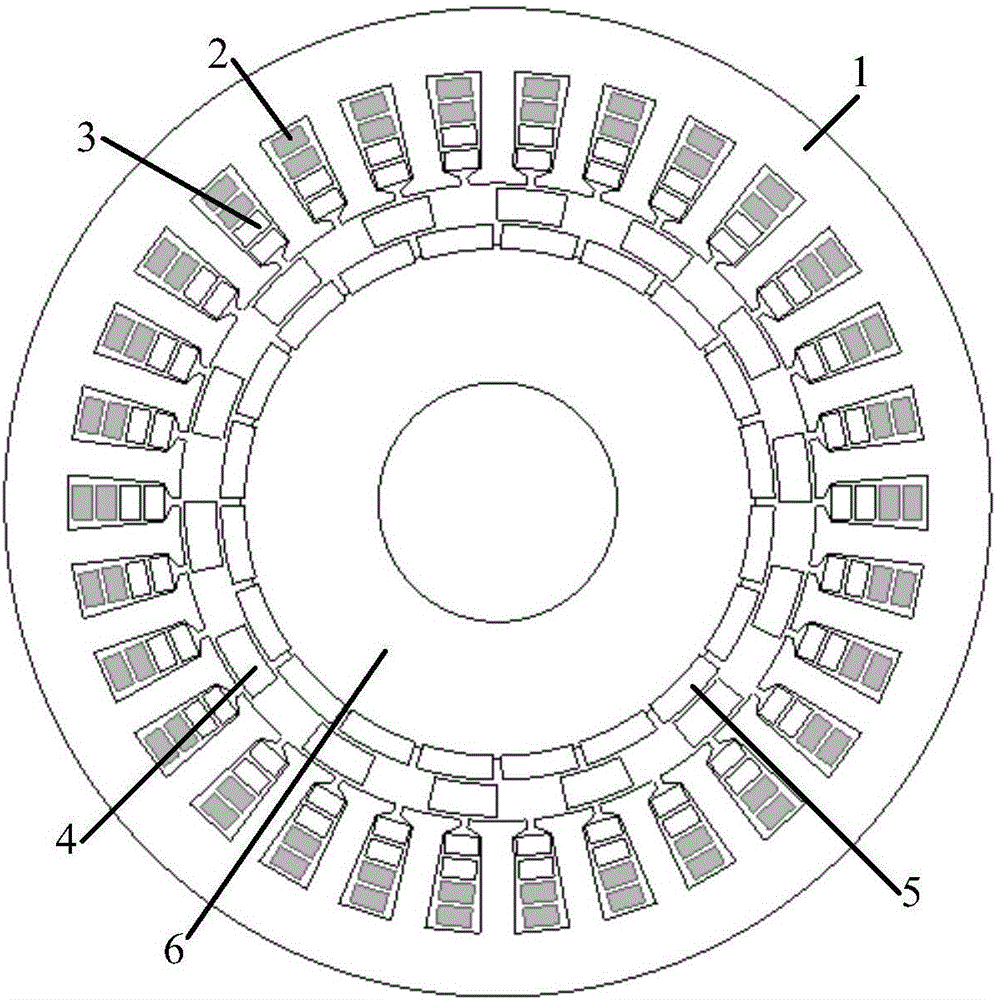
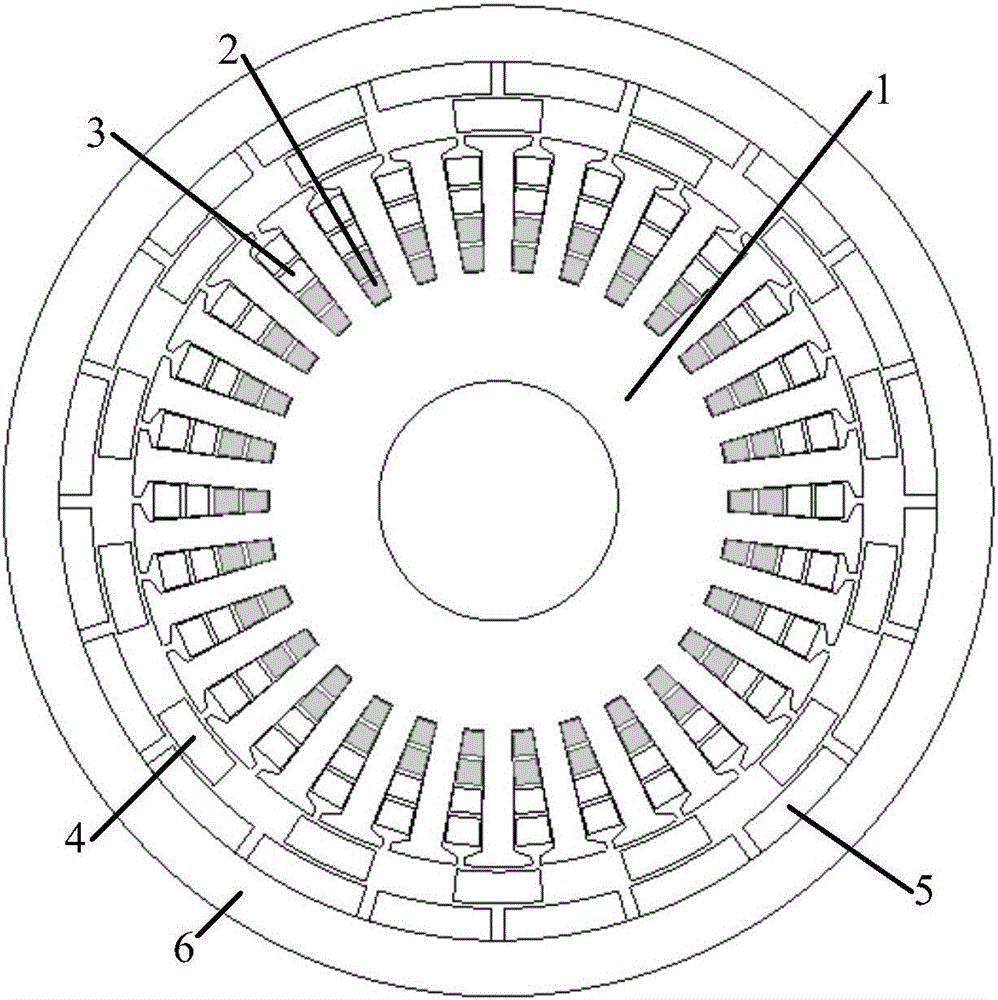
Controllable flux permanent magnetic synchronous motor of multiple pole number built-in mixed rotor magnetic path structure
InactiveCN1617422AChange the magnetizationMemoryMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet rotorSynchronous motor
This invention provides a multiple integral hybrid rotor magnetic circuit structure controlled flux magnet synchronous motor including motor spindle, a stator winding, a stator iron core, AlNiCo magnet, A Nd FeB magent, a rotor iron core, a position sensor, a sensor cable, a motor cable and a converter. The permanent rotor is in an integral hybrid rotor magnetic circuit structure, the magnet in the rotor iron cover is set in U shape, the NdFeB is placed tangentially and the AlNiCo magnet is in radial position characterizing in being called a memory motor since it can apply an amplitude controlled d-axis current vector to change the magnetization intensity of the rotor magnet and remember the changed flux intensity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
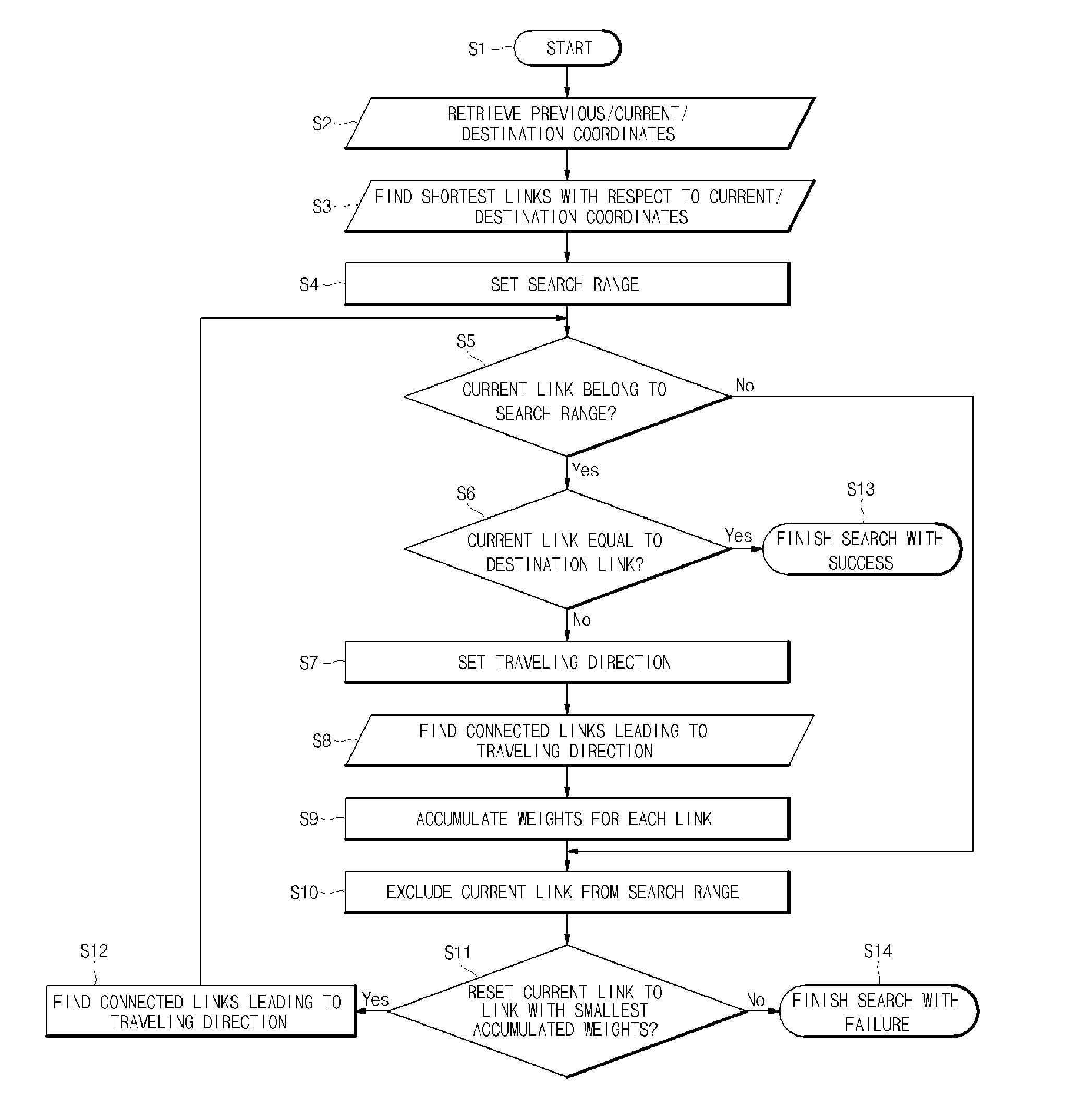
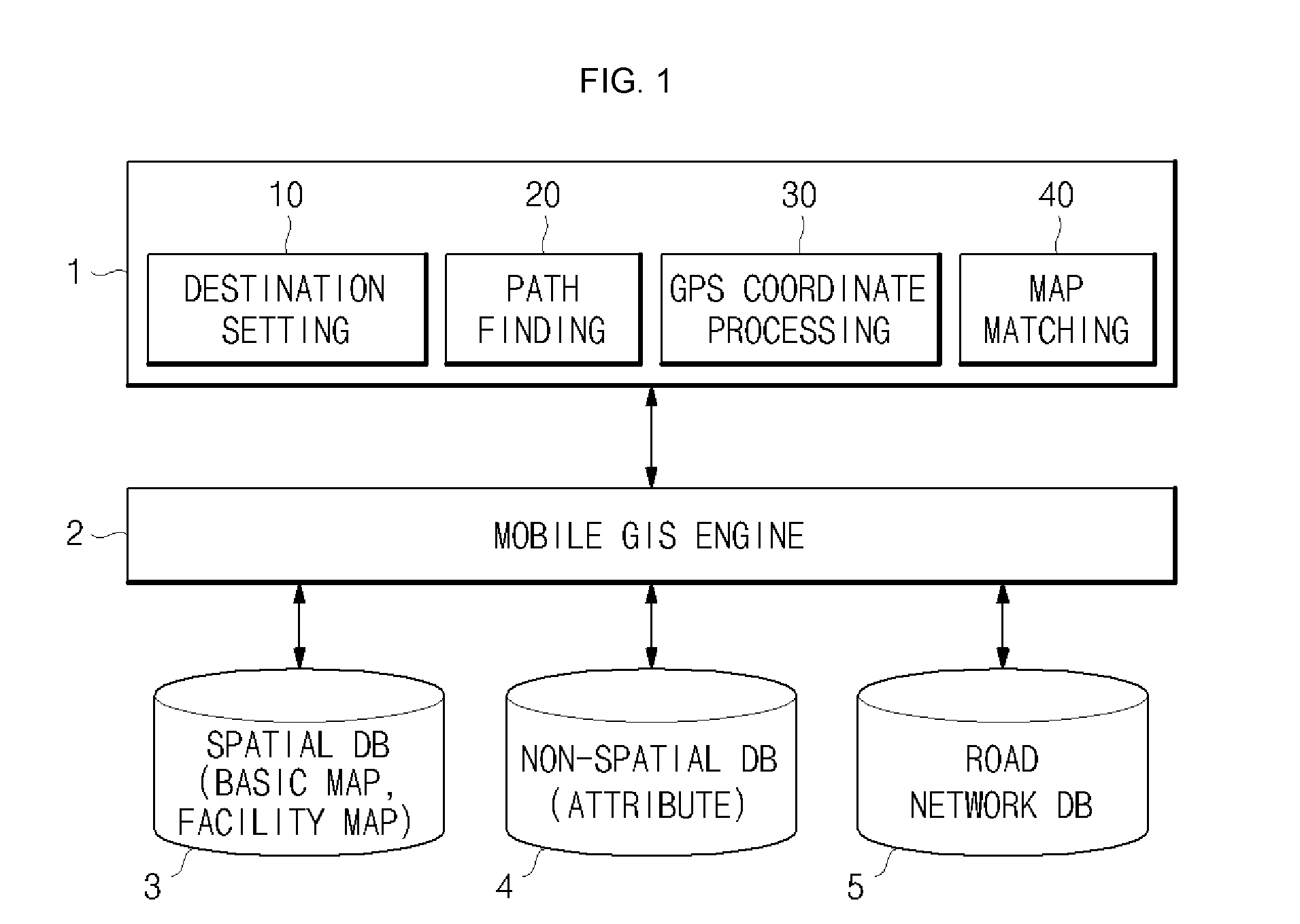
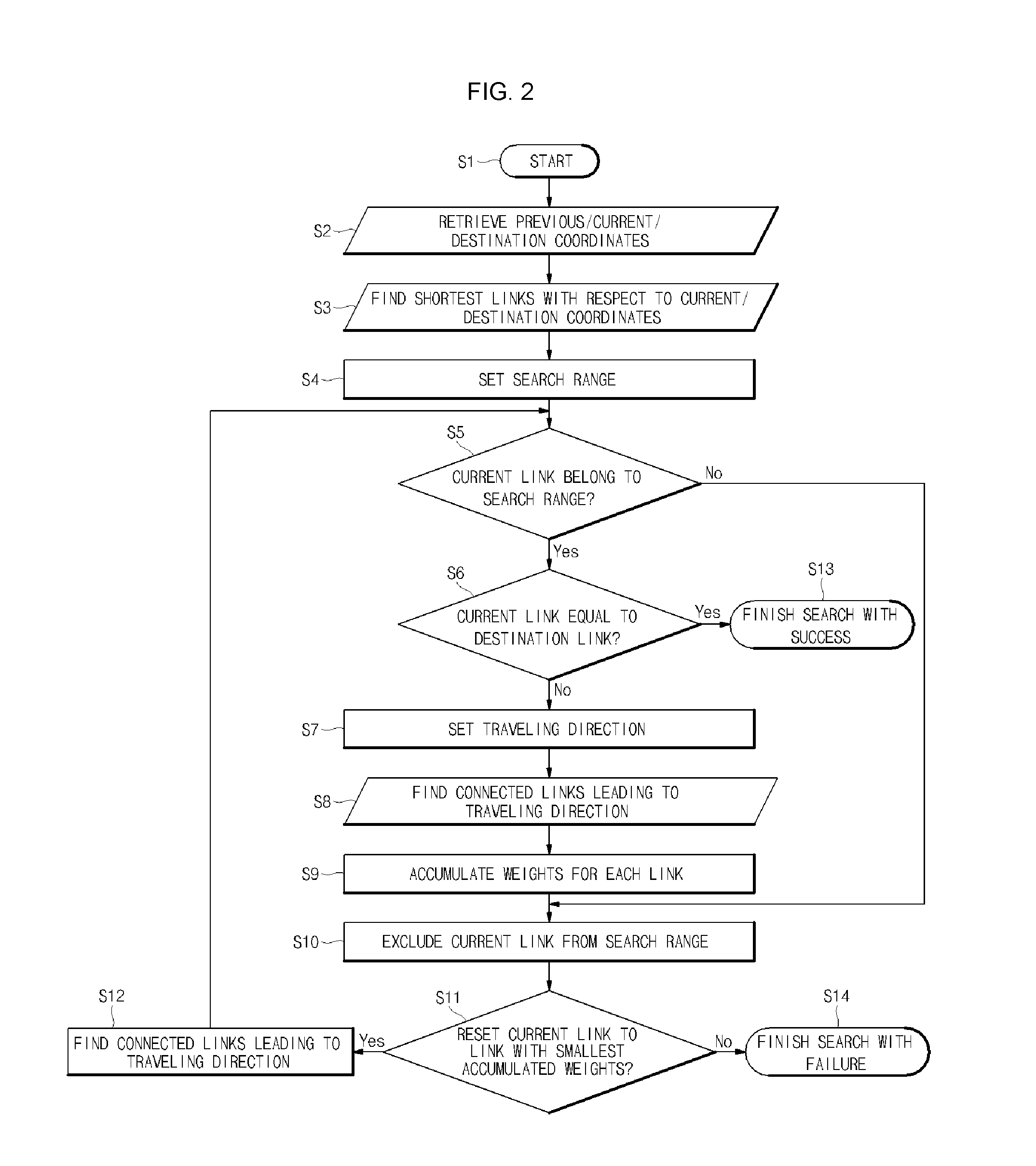
System for power facility navigation
InactiveUS20100114475A1Reduce failure recovery timeGood serviceInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlEngineeringNavigation system
A system for power facility navigation is disclosed. For rapid dispatch in the field service including power failure recovery and maintenance, the destination location can be set using various items such as pole numbers, computerization codes, customer names, trade names, equipment numbers and GIS coordinates. Destination location setting and path finding can be performed in order of priorities assigned to these items and in consideration of characteristics of field service activities. Location coordinates are received through a GPS receiver, coordinate conversion is performed according to a facility GIS coordinate system, and map matching is processed when GPS coordinates do not match facility GIS coordinates. The road network database is composed of linear array structures and the structure of a link is configured to include information regarding all other links connected to the start node and end node in a manner that link information and node attributes are integrated together.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP
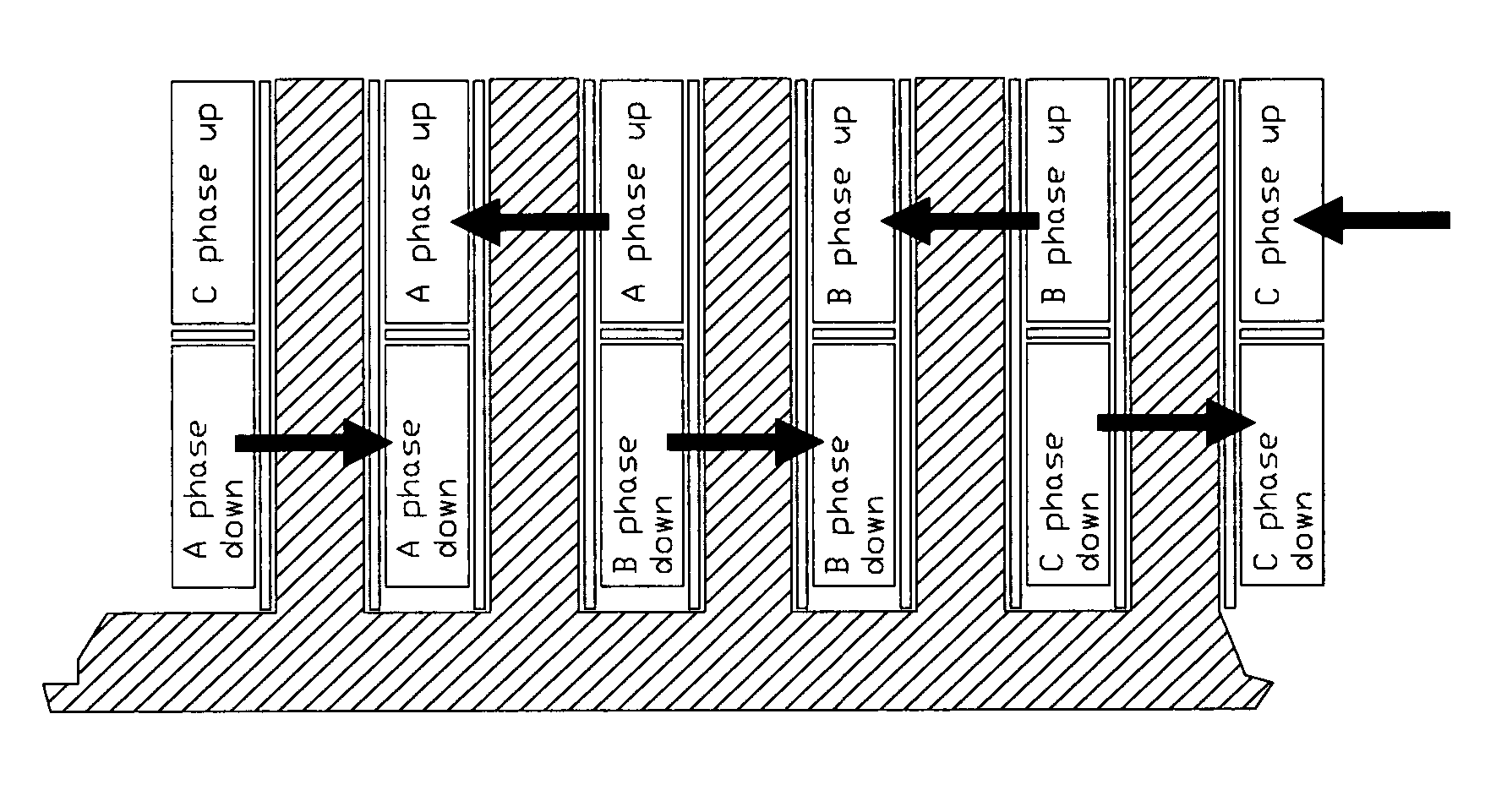
Three-phase opposite rotating motor and fan
ActiveUS20070152536A1Eliminate the effects ofSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsThree-phaseControl theory
A three-phase opposite rotating motor of a fan comprises a stator having a three-phase coil set without a core, a first rotor and a second rotor. The number of the poles of the first rotor is unequal to the number of the poles of the second rotor. The ratio of the number of solenoids of the three-phase coil set and the number of the first poles of the first rotor is 3:4, and the ratio of the number of solenoids of the three-phase coil set and the number of the second poles of the second rotor is 3:2, to ensure the motor works normally in an opposite rotating operation.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
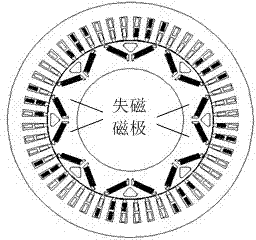
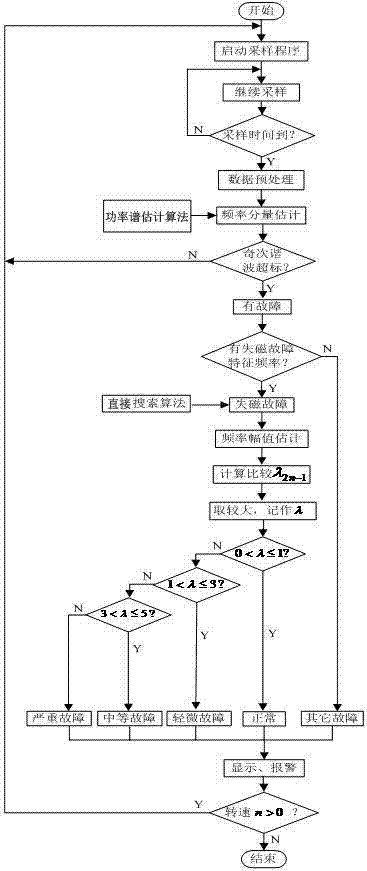
Field failure on-line diagnostic method and system for permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN103926533AEasy to installRunning does not affectDynamo-electric machine testingAnti jammingCurrent range
The invention discloses a field failure on-line diagnostic method and system for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The field failure on-line diagnostic method comprises the steps of (1) sampling a stator three-phase current signal of the motor to be detected, (2) determining a field failure characteristic frequency according to the number of poles of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to be detected, using the field failure characteristic frequency as a field failure characteristic quantity, (3) estimating the frequencies of frequency components in the stator three-phase current signal to be detected, judging whether a field failure happens or not according to whether the field failure characteristic quantity appears or not, and (4) after estimating the amplitudes of the frequency components in the stator three-phase current signal to be detected, calculating the ratios of the amplitudes of the frequency components to the amplitudes of same-frequency components within a same-current range of a motor in the normal state so as to judge the degree of severity of a field failure. The field failure on-line diagnostic system comprises the permanent magnet synchronous motor, a Hall current sensor, a signal conditioning circuit, a data acquisition circuit, a diagnosis control circuit and a display circuit. The field failure on-line diagnostic system is short in sampling time and high in anti-jamming capability, can judge field failures at different rotating speeds and under different load conditions, and is applicable to dynamic on-line monitoring.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Stator coil arrangement for an axial airgap electric device including low-loss materials
InactiveUS20050093393A1Increased stator slot fillImprove efficiencySynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineStator coil
A dynamoelectric, rotating electric machine includes a stator assembly that includes stacked stator coil windings. The machine is preferably a polyphase, axial airgap device. Improved slot filling results from the stacked stator coil configuration. Device performance capability is thereby increased. The stator assembly of the electric device has a magnetic core made from low loss, high frequency material. A high pole count permits the electrical device to operate at high commutating frequencies, with high efficiency, high power density and improved performance characteristics. Low-loss materials incorporated by the device include amorphous metals, nanocrystalline metals, optimized Si—Fe alloys, grain-oriented Fe-based materials or non-grain-oriented Fe-based materials.
Owner:LIGHT ENGINEERING INC
Motor
InactiveUS20060244326A1Deterioration of roundnessSuppress synergy superimposition and synergy superimposition resonance of vibrationSpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsDriving currentResonance
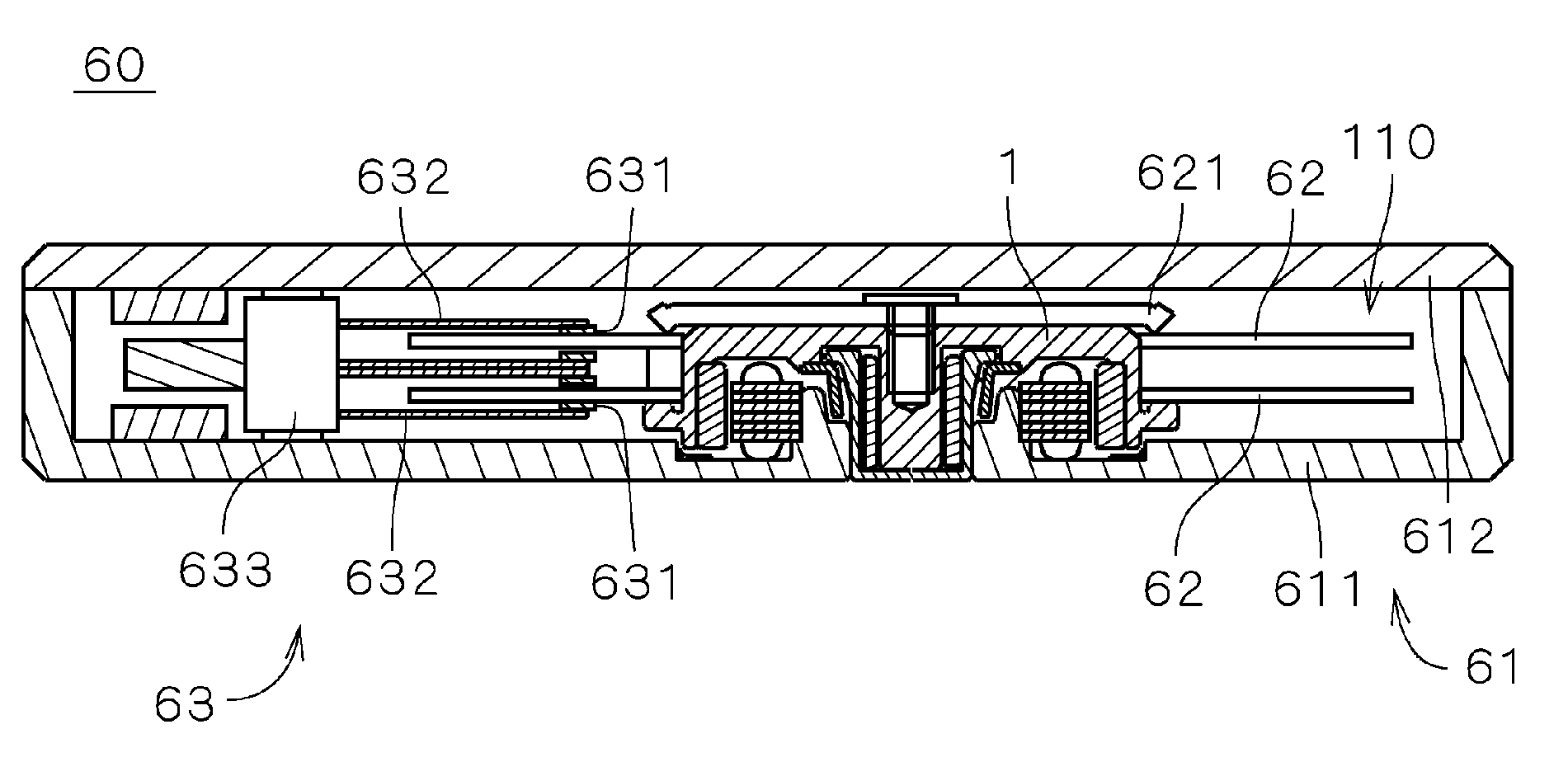
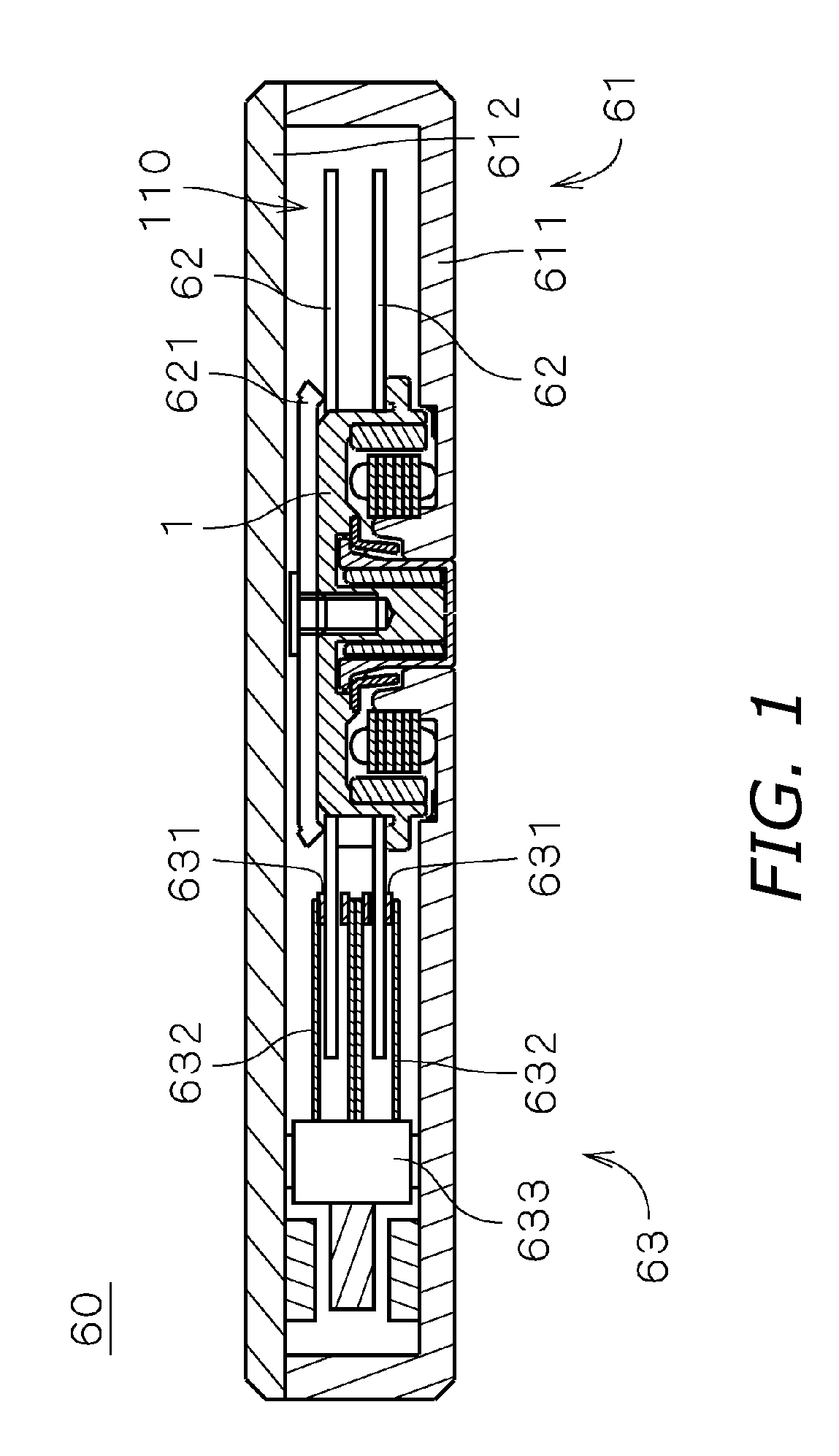
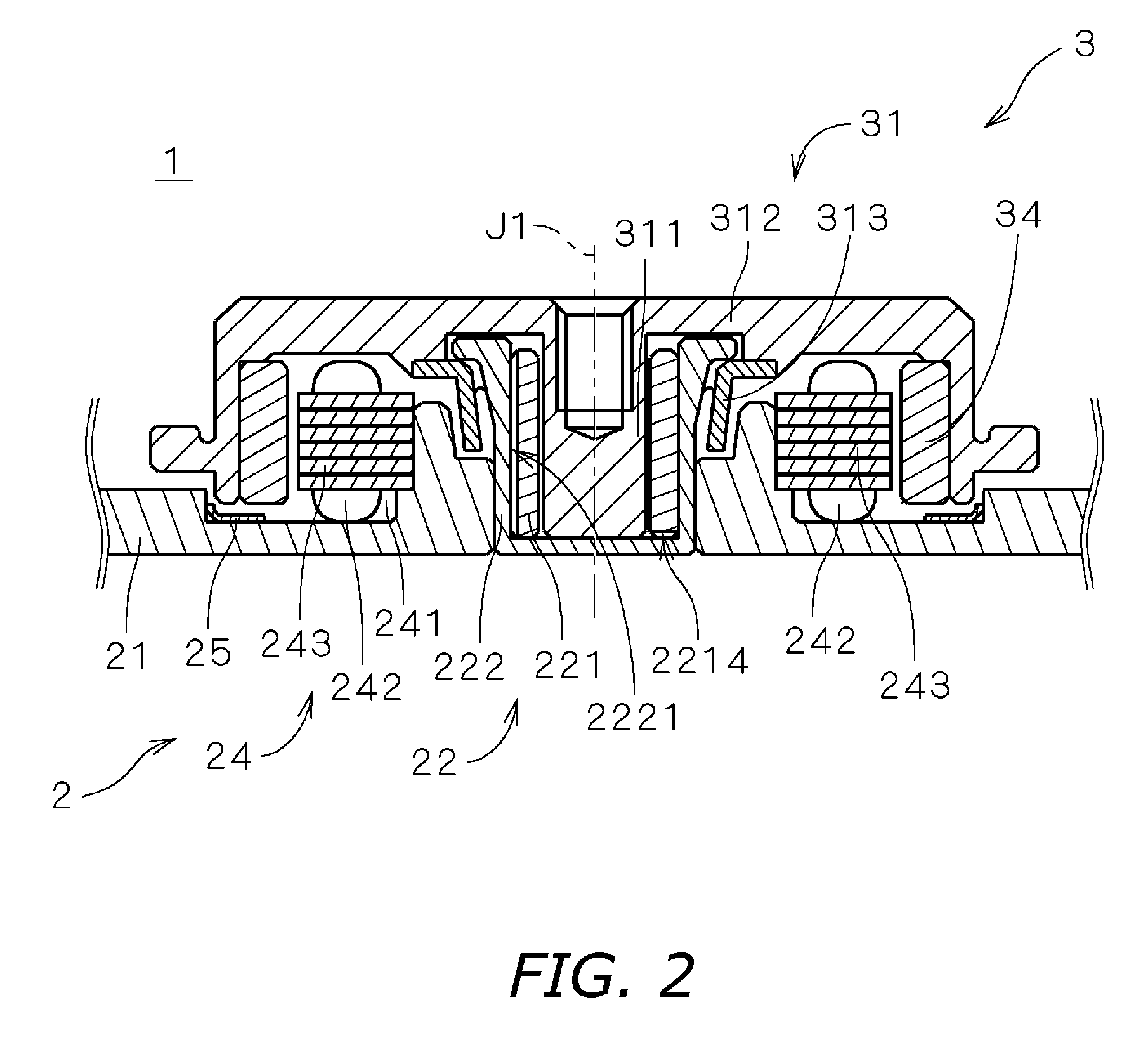
In an electric motor provided with a bearing mechanism utilizing fluid dynamic pressure, it is an object of the invention to restrain synergy superimposition and synergy superimposition resonance of vibration caused by deterioration of roundness of the sleeve and harmonic vibration caused by number of poles or number of phase. In a bearing mechanism which is provided in a motor and which utilizes fluid dynamic pressure of lubricant oil, five straight grooves substantially parallel to the center axis J1 are formed in an outer surface of a sleeve at substantially equal distances from one another in the circumferential direction. The grooves and an inner surface of a sleeve housing form flow paths for circulating the lubricant oil. In the motor, the number of grooves of the sleeve is a relative prime with respect to the number of phase (three phase) of drive current of the motor and the number of poles (eight poles) of the field magnet. With this, it is possible to suppress the synergy superimposition and the synergy superimposition resonance of vibration caused by deterioration of the roundness of sleeve and vibration caused by number of poles of the motor or the number of phase of the drive current.
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Low-power ventilating fan
InactiveCN102330702ASimple structural designReduce startPump installationsNon-positive displacement fluid enginesPermanent magnet rotorAcute angle
The invention provides a low-power ventilating fan which comprises a minisize permanent magnet synchronous motor and an impeller which can be directly driven by the motor and can rotate according to a predetermined rotating direction, wherein the impeller is of an axial-flow type and manufactured in an injection moulding mode, the diameter of the impeller is not more than 150mm; the pole number of a motor stator is 4 or 6 or 8, the winding of the stator is connected to an alternating current power supply according to a specified winding direction; the pole number of a permanent magnet rotor is the same with that of the stator; air gap of each pole can be narrowed along the rotating direction, so that each pole axis of the rotor can deflect an acute angle along the rotating direction in the free state by taking the axis of one pole of the closest stator as a reference; a position sensor can detect the rotor at a set position on the circumference of the rotor, a control circuit can determine the direction of each polar permanent magnet flux and detect the power supply polarity by taking the position as a reference and the output of the sensor so as to determine the axis direction ofeach polar main flux of the stator; when the motor starts, a switch can connect the half wave of the power supply if the main flux axis direction and the permanent magnet flux axis direction are intersected and form the acute angle; or when the motor runs, the switch can connect the half wave of the power supply right now if the main flux axis direction is opposite to the permanent magnet flux axis direction or close to the opposite direction. The ventilating fan has better performance in the starting and running processes, while the cost is relatively low.
Owner:叶露微
Electric rotating machine and electromagnetic machine and apparatus
InactiveUS6933646B2Efficient workSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsBobbinElectric machine
To simplify a winding structure of a stator and a rotor of an alternating current electric machine, in a winding a magnetic field formation of a magnetic pole portion is formed with a bobbin structure. In a structural aspect, an eddy current is lessened in an alternating magnetic field. An iron core is formed with a module work and has a reduced metal die cost and it correspond to an alternation in pole number and an iron core having different capacity.
Owner:KINOSHITA YUKI
Assembled scheme for brushless DC motor slot number and magnetic steel number
InactiveCN101030721AMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionMagnetic polesCopper
The invention is concerned with combination project for slot number of the non-brush direct current machine and the alnico number, the characteristic is: the slot number of the stator iron core is equal to the phase number multiply the prime number K that is smaller that the phase number of the electronic machine; alnico pole number of the rotor is equal to the slot number add the prime number that is not equal to 1 and phase number and smaller than K. the invention is: forms several closing magnetic circuit between the teeth in the electrify magnetic pole, which is not only increase the magnetic circuit conducting area effectively and short the magnetic circuit timely, but also reduce the loss of iron and copper.
Owner:苏州扬名机电有限公司 +1
Alternating current machine with increased torque above and below rated speed for hybrid electric propulsion systems
ActiveUS20100019714A1Less spaceReduce lossesElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersLow speedEngineering
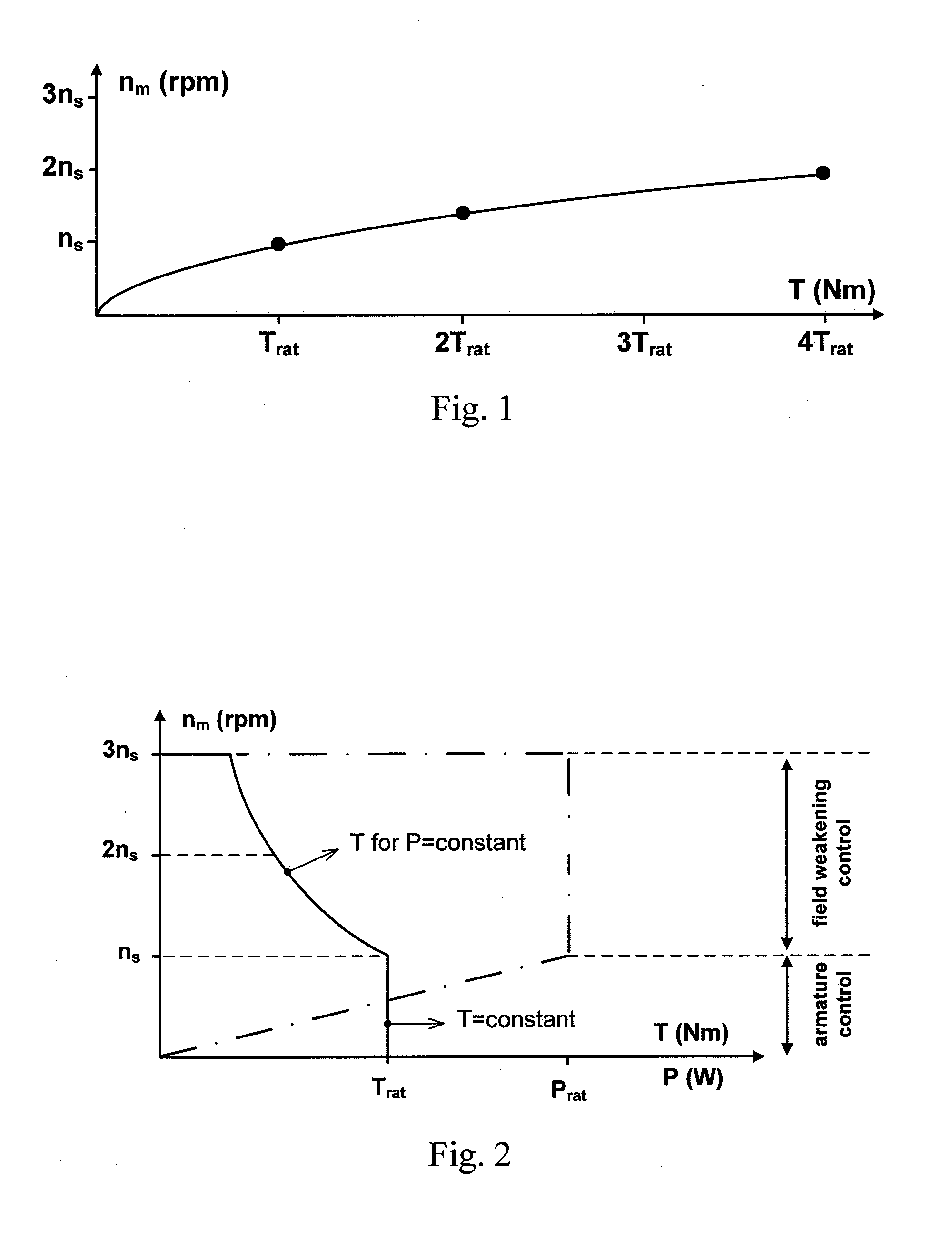
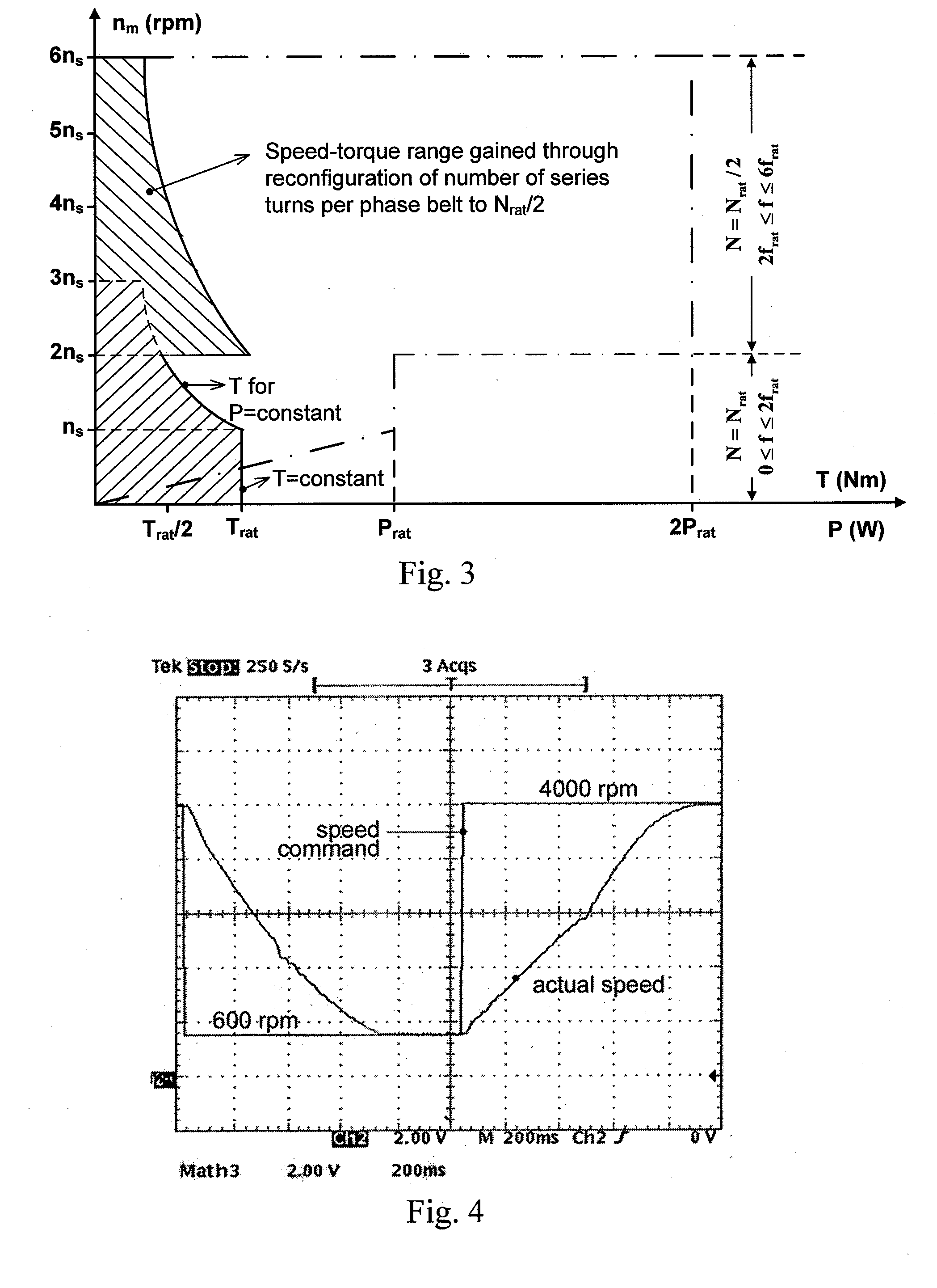
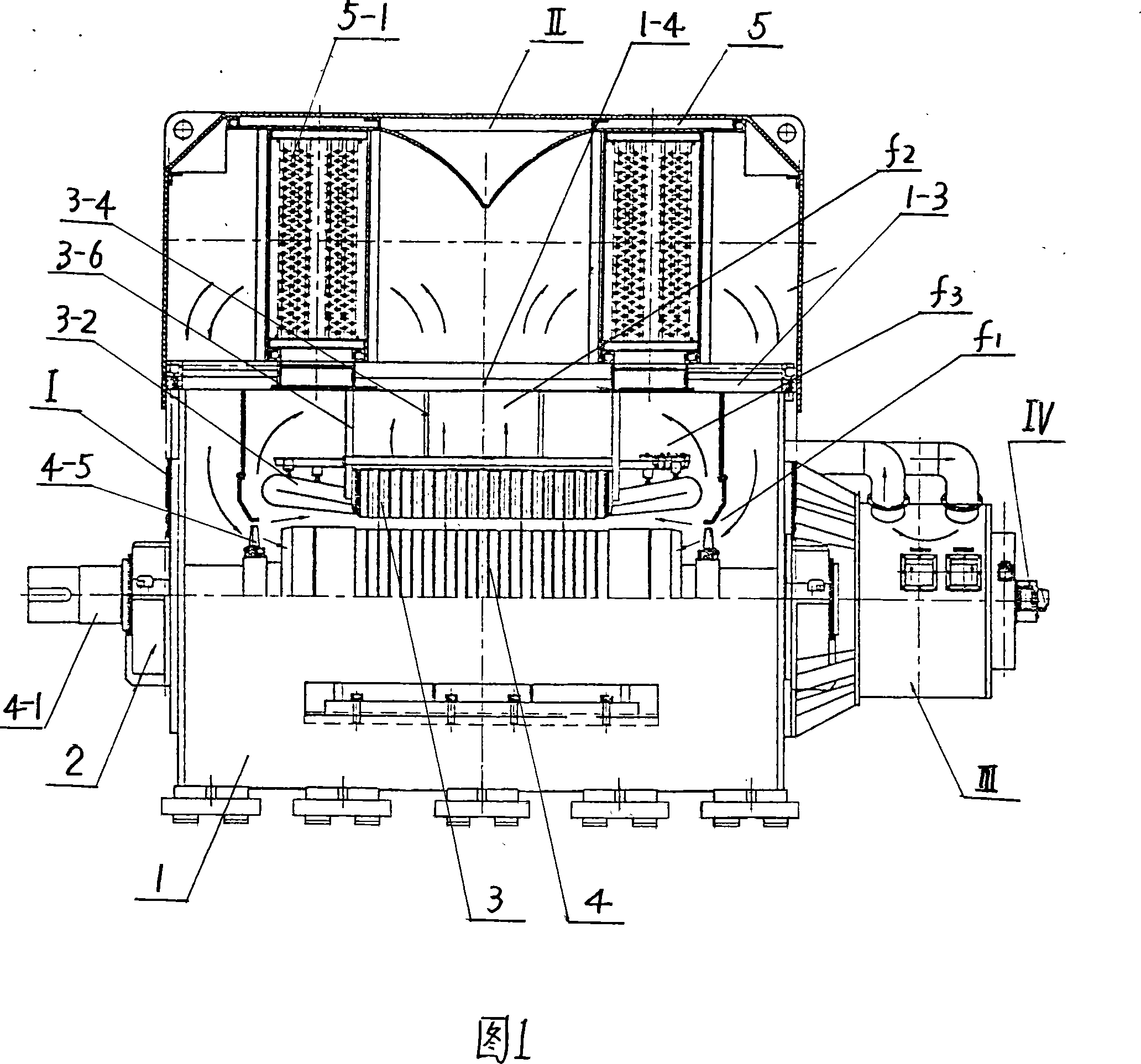
The machine in accordance with the present disclosure is an AC machine whose pole numbers can be switched (from pole p1 to pole p2), and whose number of series turns per phase N can be switched say from N0=Nrated to N1=N0 / 2. Furthermore, it employs an inverter so that the frequency can be changed from a low value (e.g., 5 Hz) to a high value (e.g., 200 Hz). Due to the combination of pole number and number of series turns switching / reconfiguration, a high torque at low speed (e.g., 0 rpm) and a high torque at high speed (e.g., 5,000 rpm) can be achieved, making mechanical gears obsolete. In addition, the output power of the motor can be increased at high speed in direct proportion to the speed increase.
Owner:FUCHS EWALD FRANZ
High-capacity non-salient pole nest plate type synchronous generator
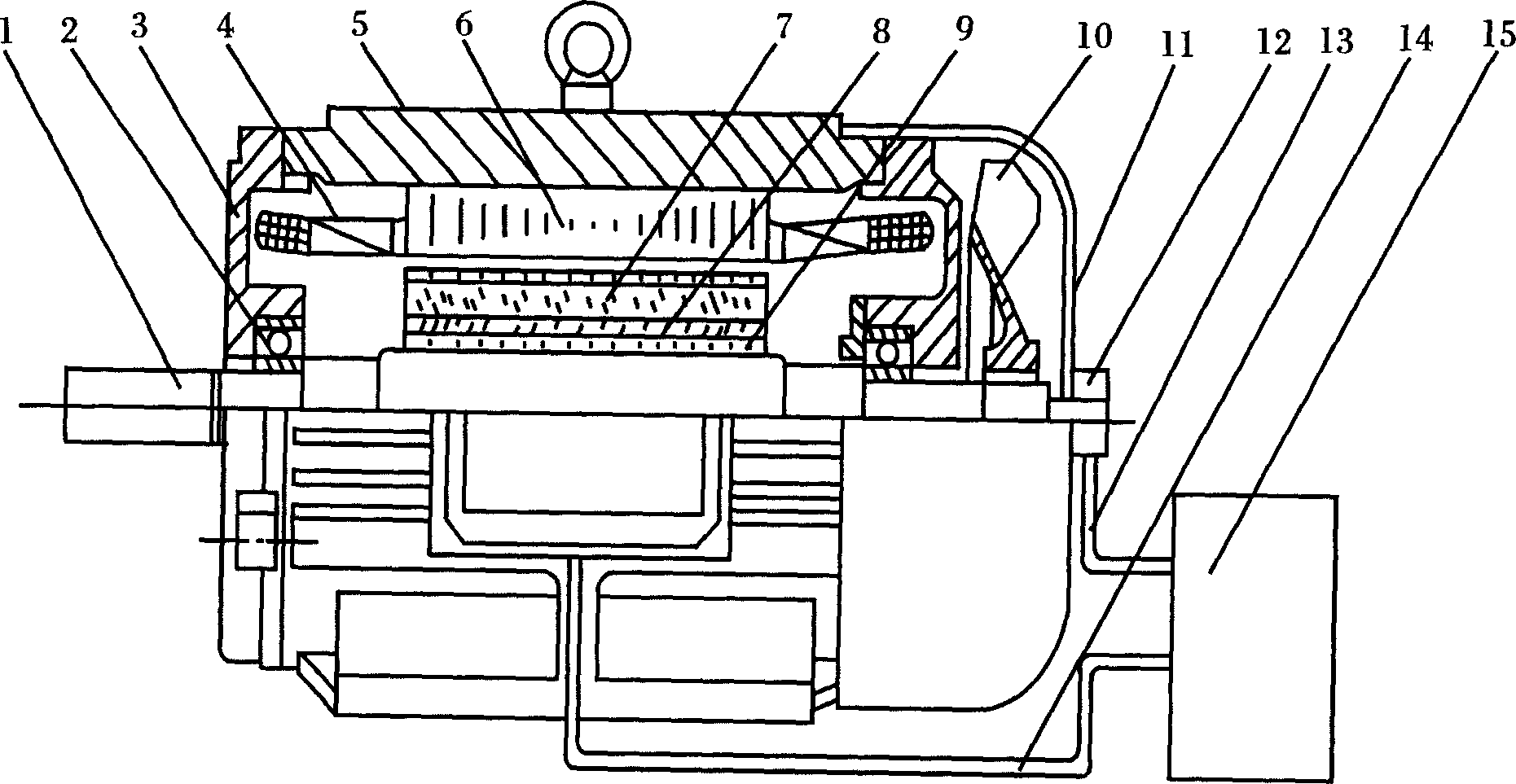
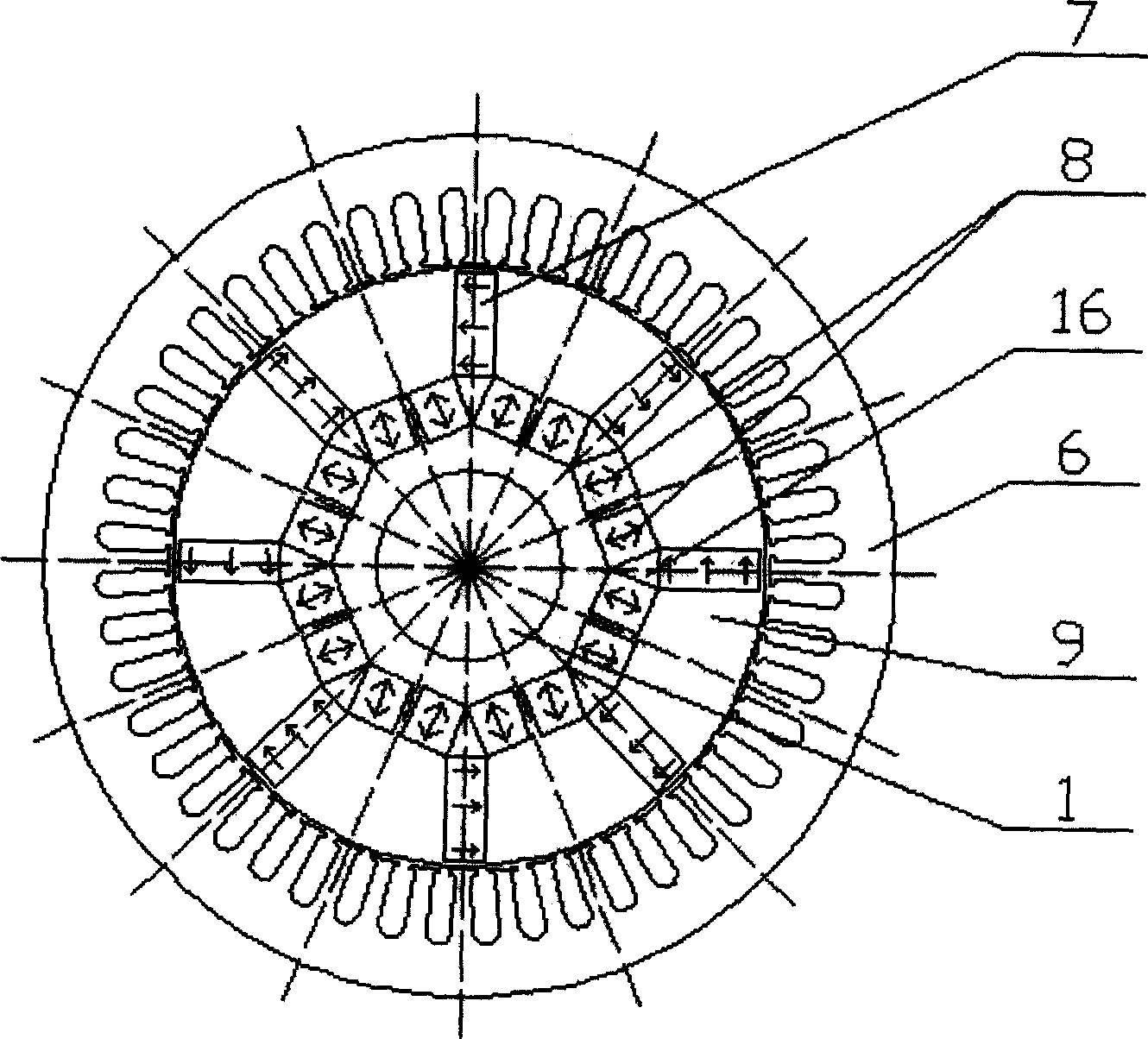
ActiveCN101227129AEasy offlineGuaranteed accuracySynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsEngineeringDynamo
The invention relates to a large capacity non-salient pole plate fine type synchronous generator, which is characterized in that a main generator is provides with a stator which is sleeved with a motor base split unit and a rotor which is connected with a motor base through an end cover bearing, an exciting end of a rotor rotating shaft is provided with a brushless excitation system with a high pole number, the tail end of the system is provided with a grounding detecting device, and a cooling system comprises a cooling device which is positioned on the main generator, four ducted cooling paths which circulates in multiply return circuits and is formed by a stator ventilating circuit, a rotor ventilating circuit, an air gas ventilating circuit and an exciting dynamo ventilating circuit of the main generator. The generator has the advantages of reasonable design of the whole system, compact structure, complete function of each portion, convenient installation and maintenance, reliable operating property, high quality of voltage and electric current which are produced and the like, which saves manufacturing cost.
Owner:WOLONG ELECTRIC NANYANG EXPLOSION PROTECTION GRP CO LTD
Brushless DC motor with stepped skewed rotor
InactiveUS6906443B2Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsSkew angleElectric machine
A brushless DC permanent magnet motor having a step skewed rotor including a rotor shaft having a portion having a substantially uniform cross sectional configuration defined by N planar sides of substantially equal length and width wherein N is equal to the number of poles of the motor, first and second annular sets of N number of substantially identically shaped bread loaf magnets one of which is attached to each of the N planar sides of the rotor shaft wherein the magnets of the first set have their orientation reversed with respect to the magnets of the second set and the magnets of the first set are offset or skewed by a predetermined skew angle from the magnets of the second set of magnets to form a stepped skewed rotor.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Selective alignment of stators in axial airgap electric devices comprising low-loss materials
InactiveUS20050040728A1Bulky designHigh operating requirementsSynchronous generatorsWindingsLow speedFull wave
An axial gap dynamoelectric machine comprises first and second stators disposed coaxially with an intermediate rotor. The stators are selectively aligned with an axial offset between the positions of their respective teeth and slots. The stators comprise toroidal cores having laminated layers composed of a material selected from the group consisting of amorphous and nanocrystalline metals and optimized Fe-based alloy. Optionally, the machine further comprises misalignment means for adjusting the offset of the stators. Adaptive adjustment permits the machine to be operated to in a mode that reduces the back EMF of the motor, allowing constant voltage to be maintained as speed is increased. Reducing back EMF also allows a wider range of operating speed, especially in combination with use of high pole counts. Alternatively, the machine can be operated, e.g. at lower speed, in a constant torque mode. The machine may exploit the high pole count achievable by use of improved soft magnetic materials. Also provided are techniques for reducing torque ripple during operation, and also for using the stator offset in combination with a dual full wave bridge rectifier arrangement.
Owner:BERG & BERG ENTERPRISES
Halbach array external rotor of composite-structure permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN101707405ALess internal fluxReduce core iron lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsCouplingMagnetic poles
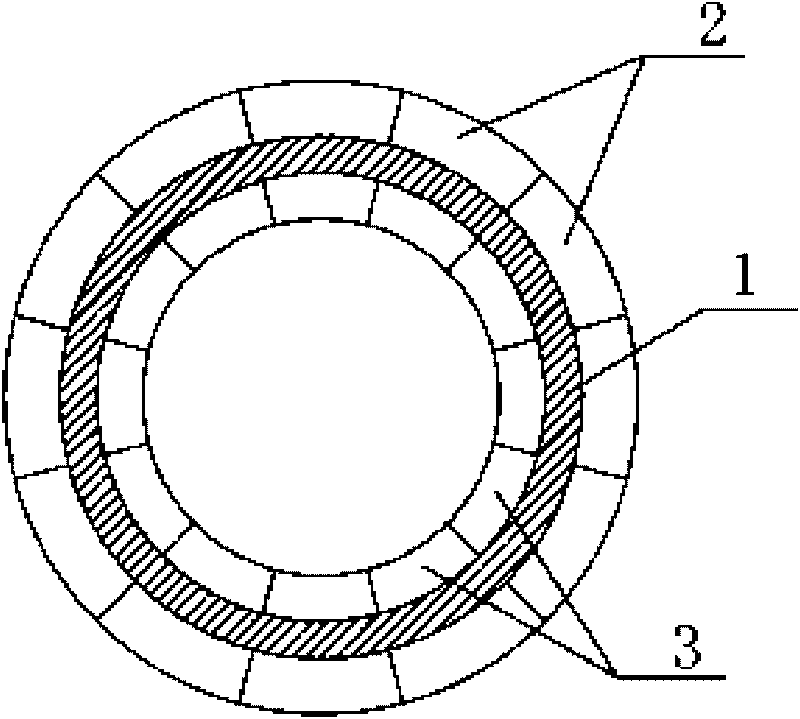
The invention discloses a Halbach array external rotor of a composite-structure permanent magnet motor, relating to an external rotor of a composite-structure permanent magnet synchronous motor and solving the problems of magnetic coupling and flexible selection of pole numbers of a composite-structure motor. A rotor core of the external rotor is of a cylindrical iron core, all permanent magnets in the outer layer and the inner layer of Halbach permanent magnet array are tile-shape permanent magnets which are evenly distributed inside and outside the rotor core in the circumferential direction, and the inner surfaces of one sides of the tile-shaped permanent magnets with weakened magnetic field in the outer layer Halbach permanent magnet array and the outer surfaces of one sides of the tile-shaped permanent magnets with weakened magnetic field in the inner layer Halbach permanent magnet array are respectively and fixedly connected with the outer surface and the inner surface of the rotor core. Magnetic flux in the rotor core is extremely less whether pole numbers are equal or not, so that independent control can be realized, a whole hybrid power system is in coordinated operation, and motors combined together can flexibly select magnetic pole numbers as required by actual power grade and base speed.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Toroidally wound induction motor-generator with selectable number of poles and vector control
InactiveUS6876176B2Increase torqueReduce speedElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersEngineeringMotor–generator
A system including an induction machine with a toroidally wound stator and a squirrel cage rotor is presented. The toroidally wound stator has a plurality of phase windings. A position sensor may be operatively connected to the induction machine for providing a position indication that is indicative of a relative position of the rotor and the stator. The system also includes an inverter having a plurality of solid-state switches and a control system. The inverter has the same number of phases as the toroidal induction machine. The inverter is connected to selectively energize the phase windings. A programmable microprocessor, such as a digital signal processor, is operatively connected to the induction machine and includes a program to implement vector control of the induction machine. The microprocessor can also control the inverter so that the induction machine operates with a predetermined number of poles using pole phase modulation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Underwater hollow hub-free propeller
InactiveCN101546939AWork lessIncrease the number of polesRotary propellersMechanical energy handlingUnderwaterPropeller
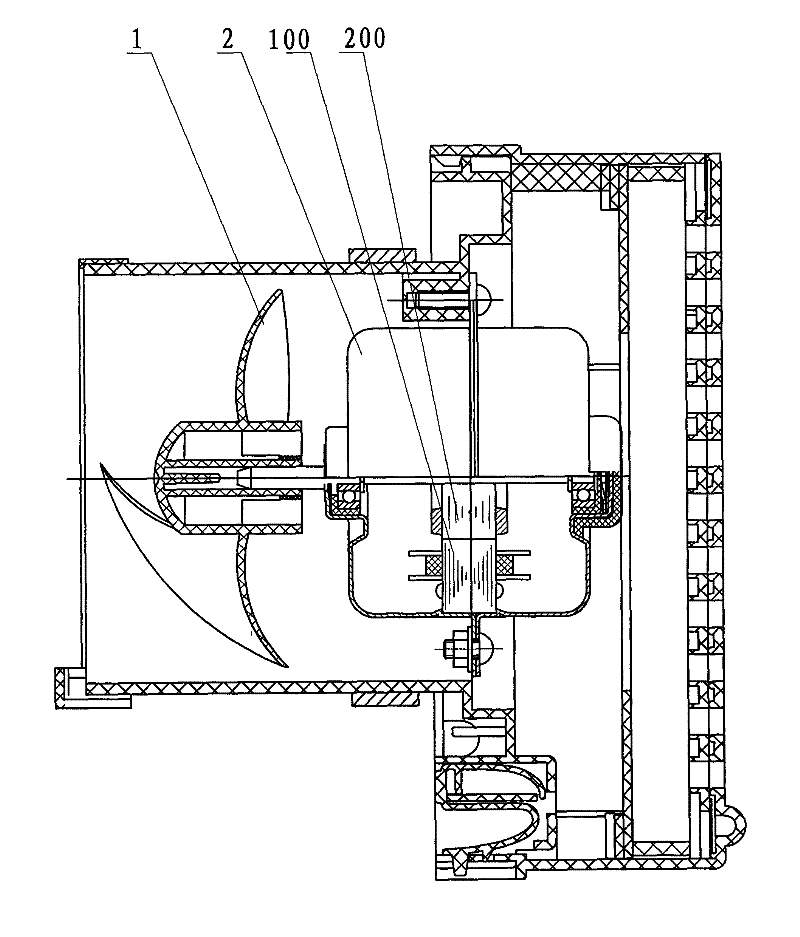
The invention provides an underwater hollow hub-free propeller, which comprises a motor shell, a stator coil, a stator silicon-steel sheet, a rotor permanent magnet, a rotor, a screw propeller and a ceramic bearing. The stator coil is wound on the stator silicon-steel sheet, the stator coil wound on the stator silicon-steel sheet is arranged at the center of the motor shell, the rotor has a hollow annular structure, split poles of the rotor permanent magnet are fixed on the rotor to form a hollow structural rotor, the screw propeller is fixed inside the hollow rotor, and the screw propeller, the rotor and the rotor permanent magnet form a whole; and the rotor is fixed in the motor shell through the ceramic bearing. When blades rotate, induced resistance and cavity bubble phenomenon are not generated so as to greatly improve the efficiency of the screw propeller. Moreover, because the diameter of a motor is enlarged, the pole number of the motor is increased and the torque of the motor is improved, the underwater hollow hub-free propeller is particularly suitable for working in an environment with large water depth and large density; and because the motor and the screw propeller of the underwater propeller have an integral hollow structure, the underwater hollow hub-free propeller can be easily arranged on a ship hull.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Internal-external double-stator electro-magnetic double-salient starter generator
ActiveCN103001423ACrack ratioImprove space utilizationDynamo-electric machinesStarter generatorCombustion
The invention provides a double-stator electro-magnetic double-salient starter generator capable of effectively utilizing internal and external space of a rotor. A unit motor of the generator is of a 12 / 8 / 6 pole structure, namely external stator pole number of the motor is 12N, rotor pole number is 8N, internal stator pole number is 6N, and N is a natural number. The external stator and the rotor of the motor is matched with a traditional 6 / 4 pole unit motor in pole number. External stator pole arc coefficient is 0.5. The internal stator and the rotor of the motor is matched with a 6 / 8 pole unit motor in pole number, and the internal stator pole arc coefficient is 0.25. Phase difference of an internal armature winding and an external armature winding of the motor is 60-degree electrical angle and is capable of achieving small phase-shifting torque pulsation. The starter generator completely utilizes internal space of the starter generator of a flat structure and is suitable for being applied to automobiles and small combustion engines.
Owner:TANGSHAN JINSHI SUPER ABRASIVE
Segmented composite rotor
InactiveUS7714479B2High strengthReduce weightMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
A composite rotor for an axial airgap, permanent magnet dynamoelectric machine comprises a plurality of magnet subassemblies adhesively bonded together to form the rotor. Each magnet subassembly comprises a rotor permanent magnet and an optional spacer. A fibrous belt is wrapped around the periphery of each subassembly to provide high tensile strength at least along the radial sides of the subassembly. The belt is preferably infiltrated with an adhesive agent, such as an epoxy resin, that is used to bond the subassemblies. The rotor is thereby provided with high strength and low mass, making it suitable for use in a high-speed, high pole count electric machine.
Owner:BERG & BERG ENTERPRISES
Motor for directly driving electric drum
ActiveCN104600881ASimple structureWork reliablyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machinePhase angle difference
The invention provides a motor for directly driving an electric drum. The motor for directly driving the electric drum comprises a stator iron core, a rotor iron core, a drum wall, an exciting winding, an armature winding, a shaft and the like. The motor for directly driving the electric drum is of an outer rotor structure. The outer side of the rotor iron core and the drum wall are fixed together. When the stator pole number of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 6N and the rotor pole number of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 7N, a pole arc coefficient of a stator of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 0.333, and a pole arc coefficient of a rotor of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 0.5. When the stator pole number of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 6N and the rotor pole number of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 5N, the pole arc coefficient of the stator of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 0.4, and the pole arc coefficient of the rotor of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 0.5. The motor for directly driving the electric drum is provided with a six phase winding, and phase angle difference of the six phase winding is 60 electrical degrees. The six phase winding is divided into two channels which are isolated from each other, and when one phase or one channel of the six phase winding breaks down, the other channel can run in fault tolerant mode, and accordingly reliability of a system is improved, and the motor for directly driving the electric drum can be used to directly drive the drum.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Brushless dual-mechanical-port permanent magnet motor based on magnetic field modulation principle
ActiveCN106374704AReduce structural complexityReduce manufacturing difficultyMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
The invention discloses a brushless dual-mechanical-port permanent magnet motor based on a magnetic field modulation principle. The brushless dual-mechanical-port permanent magnet motor comprises a single stator (1), modulation rotors (4) and permanent magnet rotors (5), wherein a closing slot is formed in the surface of the stator (1); two sets of windings with different numbers of pole pairs are placed in the slot; one set of the winding is a modulation winding while the other set of the winding is a permanent magnet winding; the pole pair number PAI of the permanent magnet winding is equal to the pole pair number Pm of the permanent magnet rotors, so that the stator and the permanent magnet rotors can form a permanent magnet motor structure; and meanwhile, the pole pair number PA of the modulation winding is equal to an absolute value of a sum value or a difference value of a salient pole number Pf of the modulation rotors and the pole pair number Pm of the permanent magnet rotors, so that the stator, the modulation rotors and the permanent magnet rotors can form a magnetic field modulation motor structure. The brushless dual-mechanical-port permanent magnet motor is complex in structure, and the manufacturing difficulty is greatly lowered; and in addition, a single-stator and double-air-gap structure of the motor is more compact, so that relatively high torque density can be realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com