Automatic field-weakening method for built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc., can solve the problems of small effective range, increased manufacturing cost, and the inability to adjust the magnetic field of the main magnetic pole of the permanent magnet motor.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
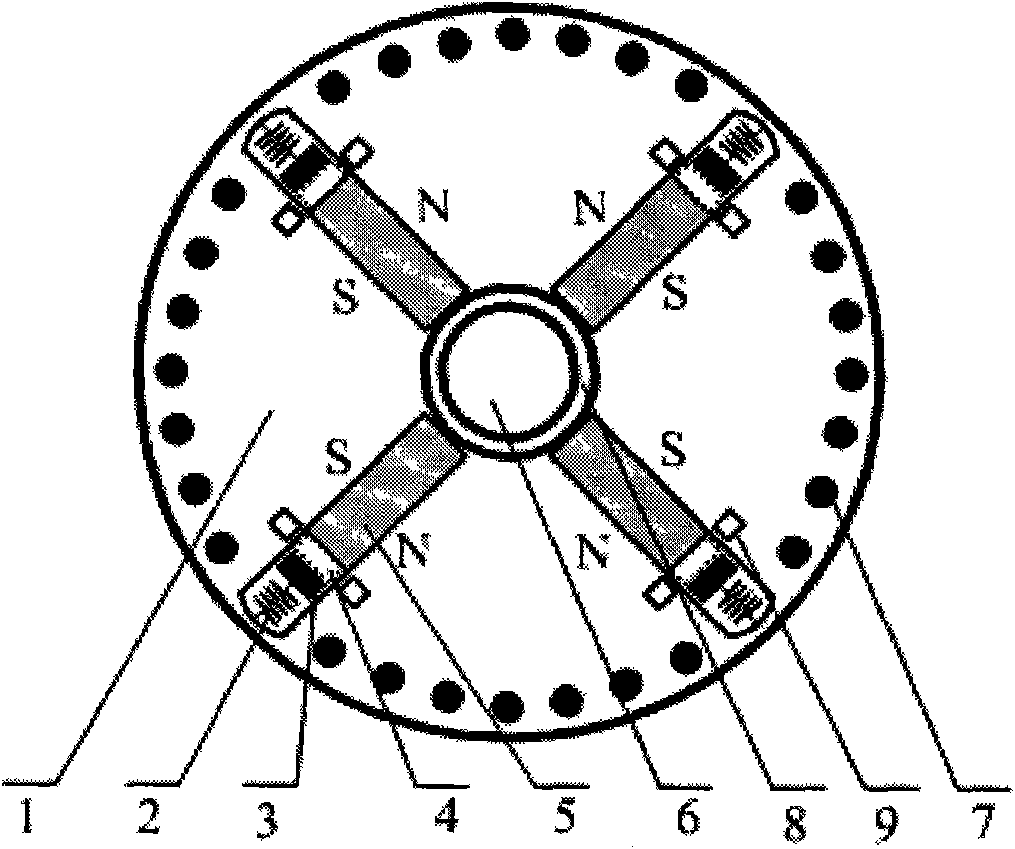
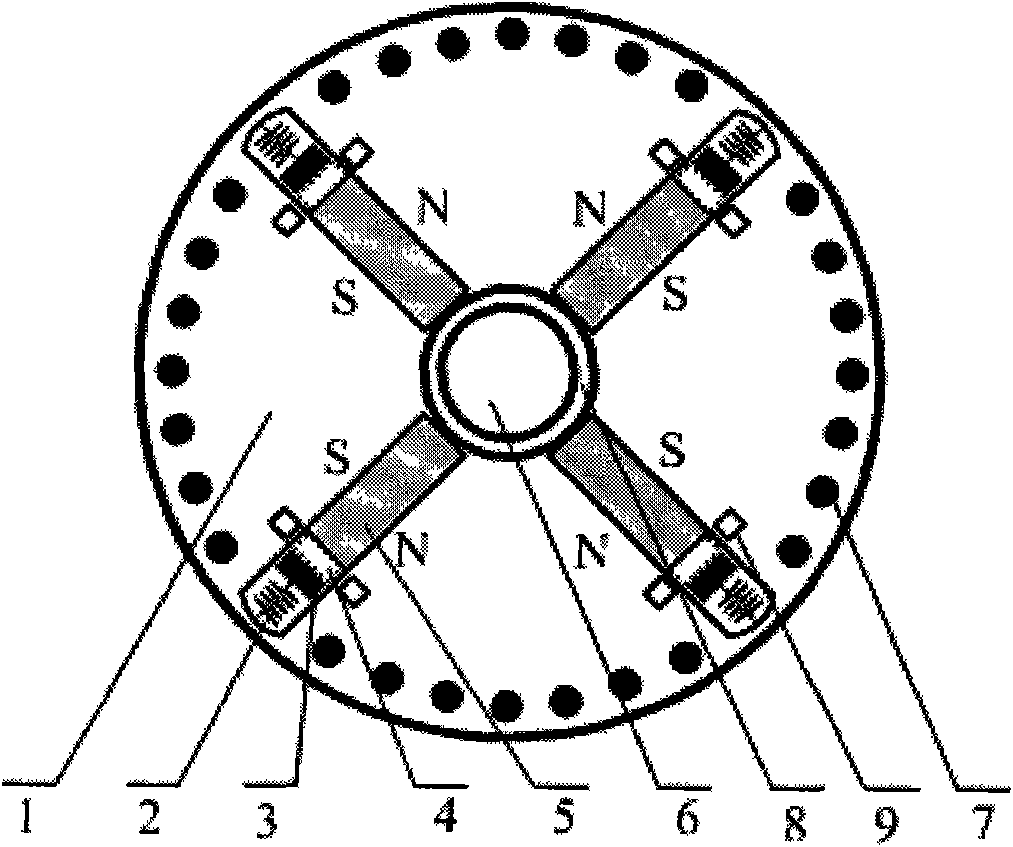
[0014] Specific implementation mode one: for figure 1 In the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor with a four-pole tangential magnetic circuit structure shown, the rotor core 1 is made of laminated silicon steel sheets with a thickness of 0.5 mm, and evenly distributed semi-open or closed slots are punched on the inner side of the outer circumference. Four main pole magnets 5 are symmetrically built into the rotor core 1 , the magnetization direction of the magnets 5 is tangential, and two adjacent magnets together provide magnetic flux for each pole. Several rotor guide bars 7 are arranged on the inside of the outer circumference of the rotor core 1 along the direction of the direct axis. The rotor guide bars 7 are located in the rotor slots and together with the end rings form a cage-type starting winding. On the inside of the outer circumference of the rotor core 1, four chutes 4 are arranged along the direction of the orthogonal axis. Springs 2 and flux short-circuit b...
specific Embodiment approach 2
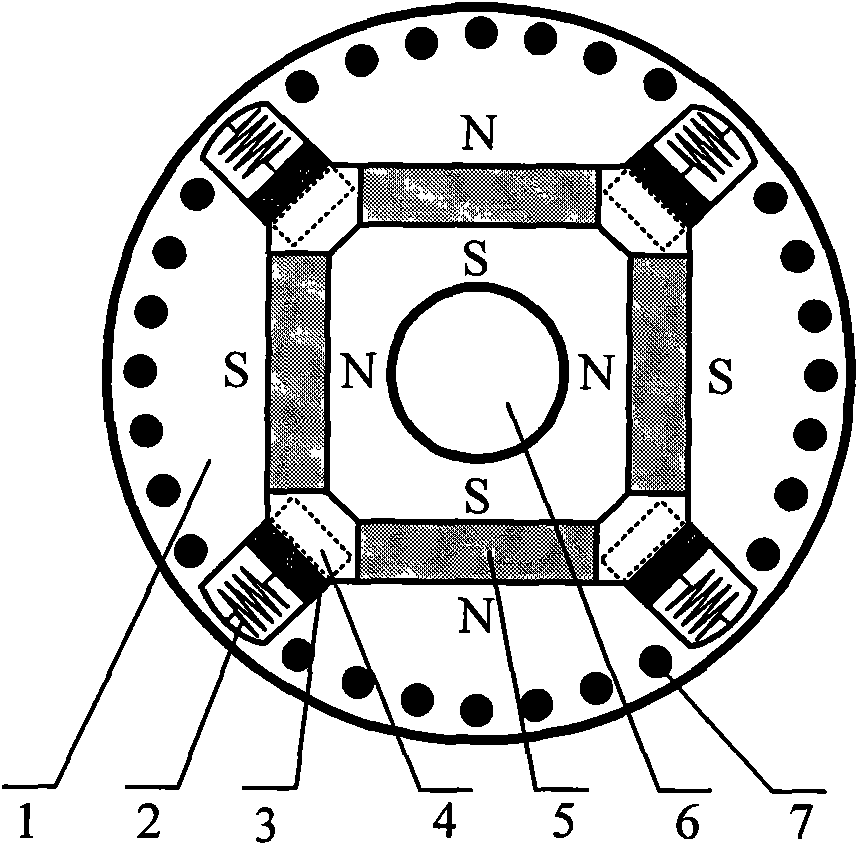
[0015] Specific implementation mode two: for figure 2 In the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor with a four-pole radial magnetic circuit structure shown, the rotor core 1 is made of laminated silicon steel sheets with a thickness of 0.5 mm, and evenly distributed semi-open or closed slots are punched on the inner side of the outer circumference. Four main pole magnets 5 are symmetrically built into the rotor core 1 , the magnetization direction of the magnets 5 is along the radial direction, and each magnet provides magnetic flux for each pole independently. Several rotor guide bars 7 are arranged on the inside of the outer circumference of the rotor core 1 along the direction of the direct axis. The rotor guide bars 7 are located in the rotor slots and together with the end rings form a cage-type starting winding. On the inside of the outer circumference of the rotor core 1, four chutes 4 are arranged along the direction of the orthogonal axis. Springs 2 and flux short...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com