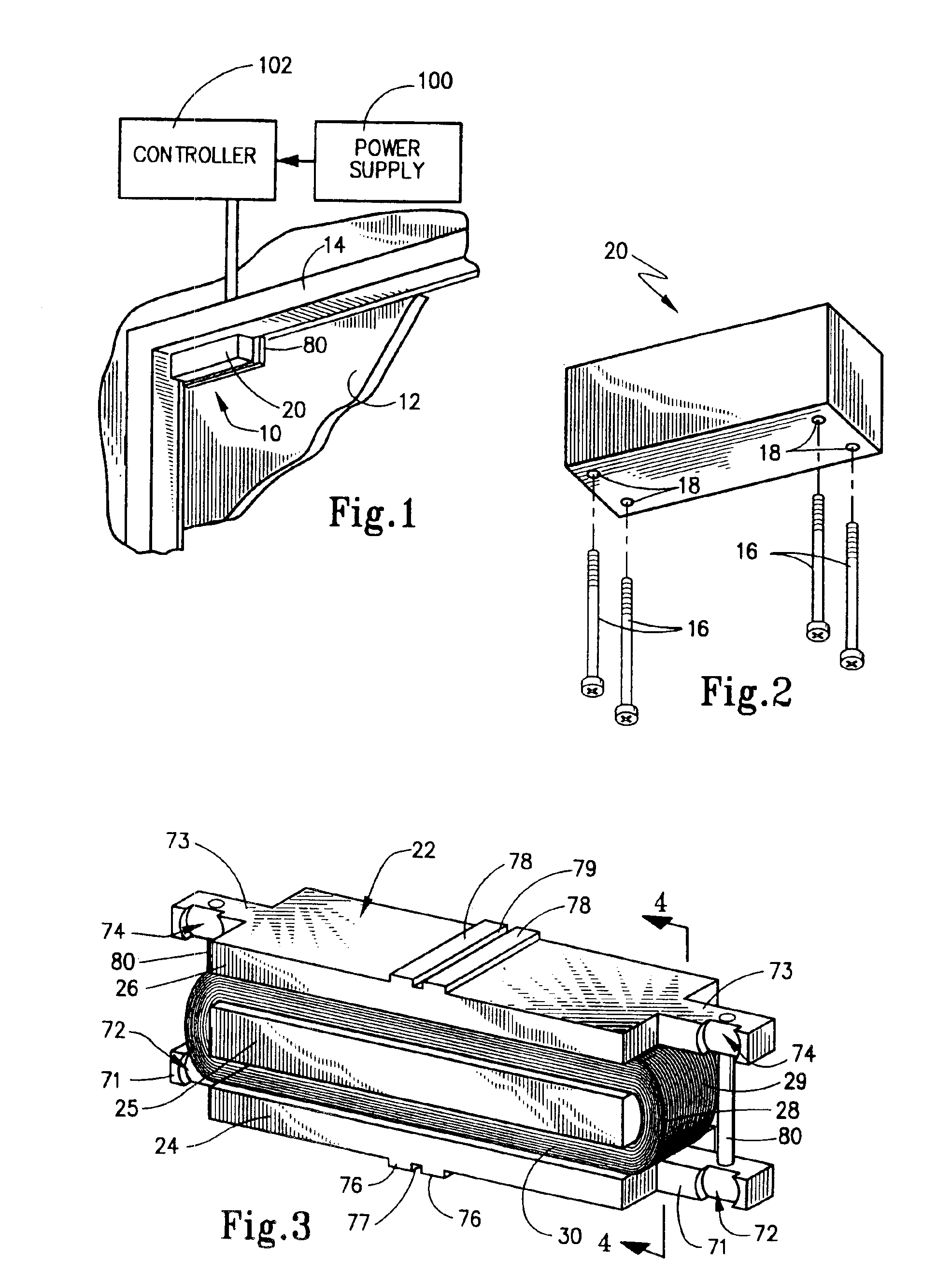
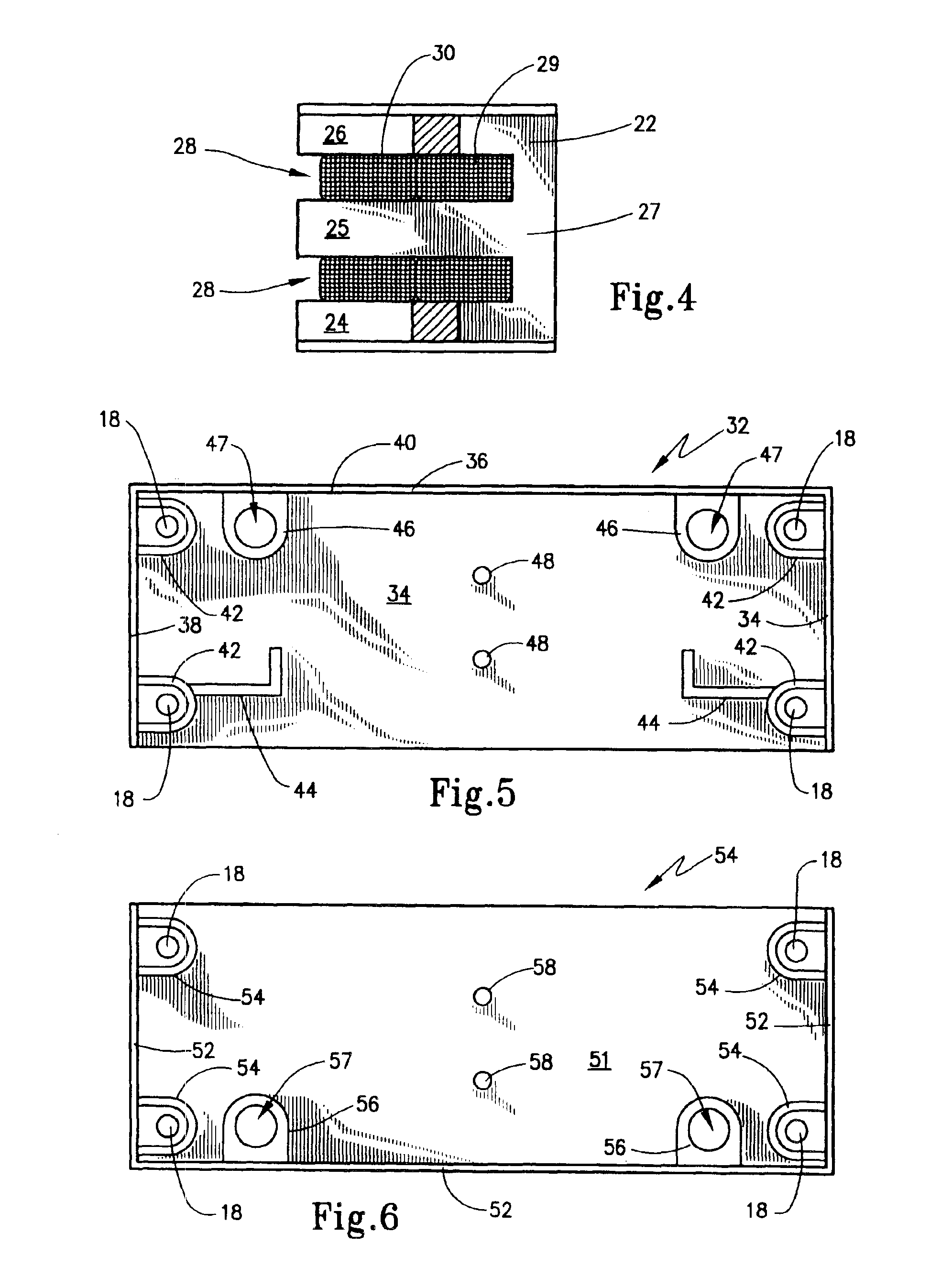
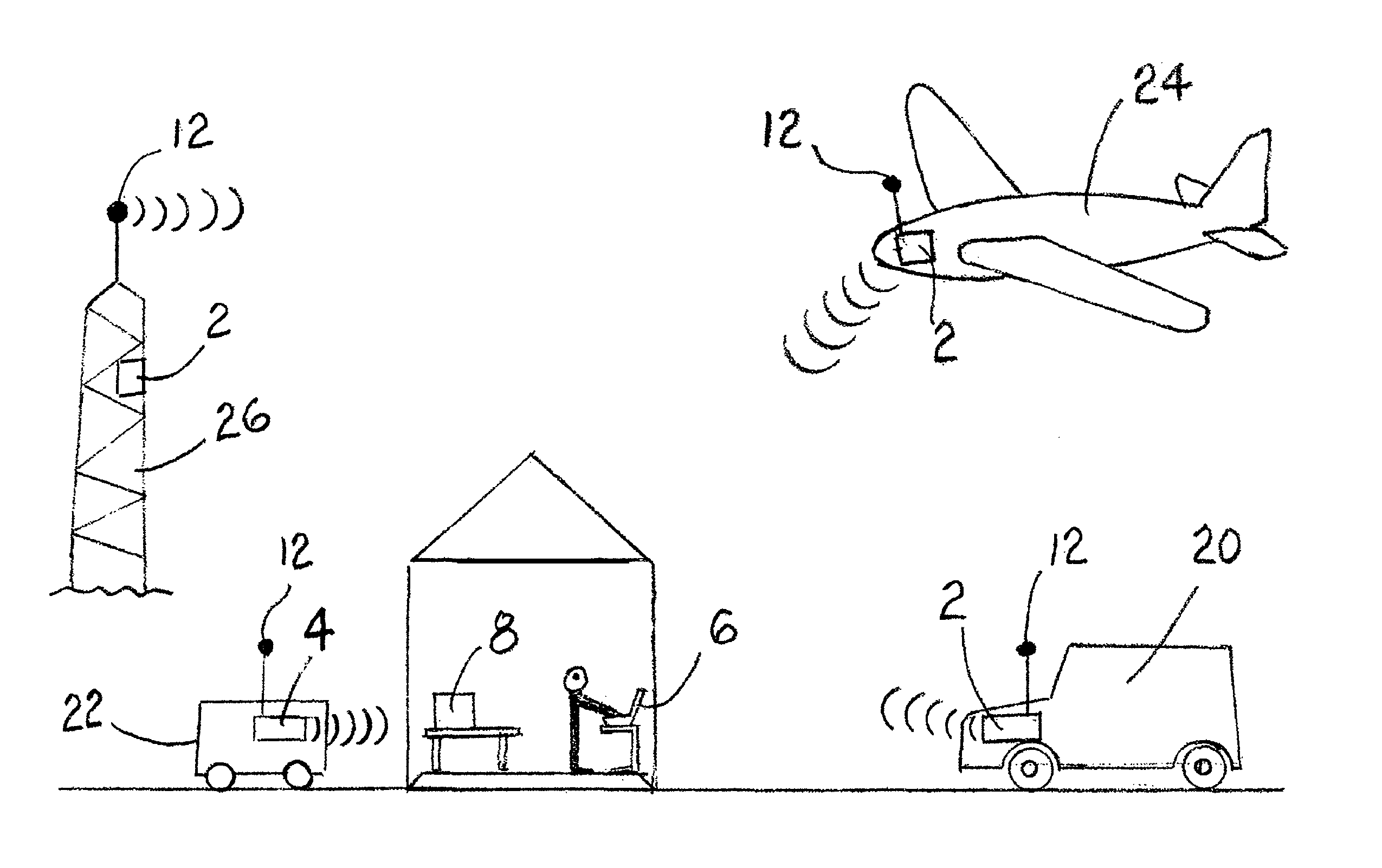
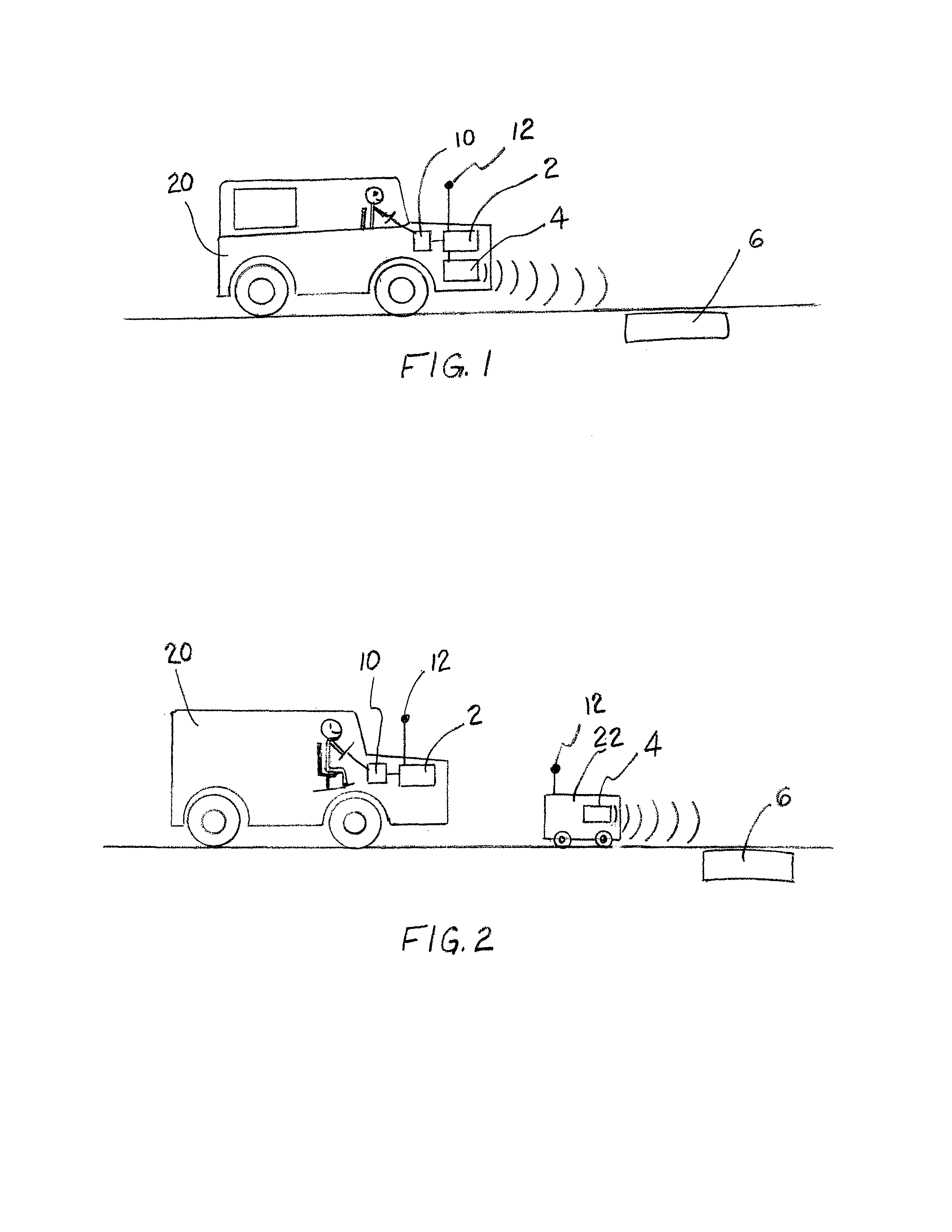
Patents
Literature
1107 results about "Electromagnetic devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Some everyday devices that have electromagnets inside them include: Microphones, speakers, headphones, telephones and loudspeakers ... Household Electromagnetic Devices The solenoid valve inside washing machines that turns water off or on is a type of electromagnet.
Means and method for assessing the geometry of a subterranean fracture during or after a hydraulic fracturing treatment
A method is given of fracturing a subterranean formation including the step of a) pumping at least one device actively transmitting data that provide information on the device position, and further comprising the step of assessing the fracture geometry based on the positions of said at least one device, or b) pumping metallic elements, preferably as proppant agents, and further locating the position of said metallic elements with a tool selected from the group consisting of magnetometers, resistivity tools, electromagnetic devices and ultra-long arrays of electrodes, and further comprising the step of assessing the fracture geometry based on the positions of said metallic elements. The method allows monitoring of the fracture geometry and proppant placement.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
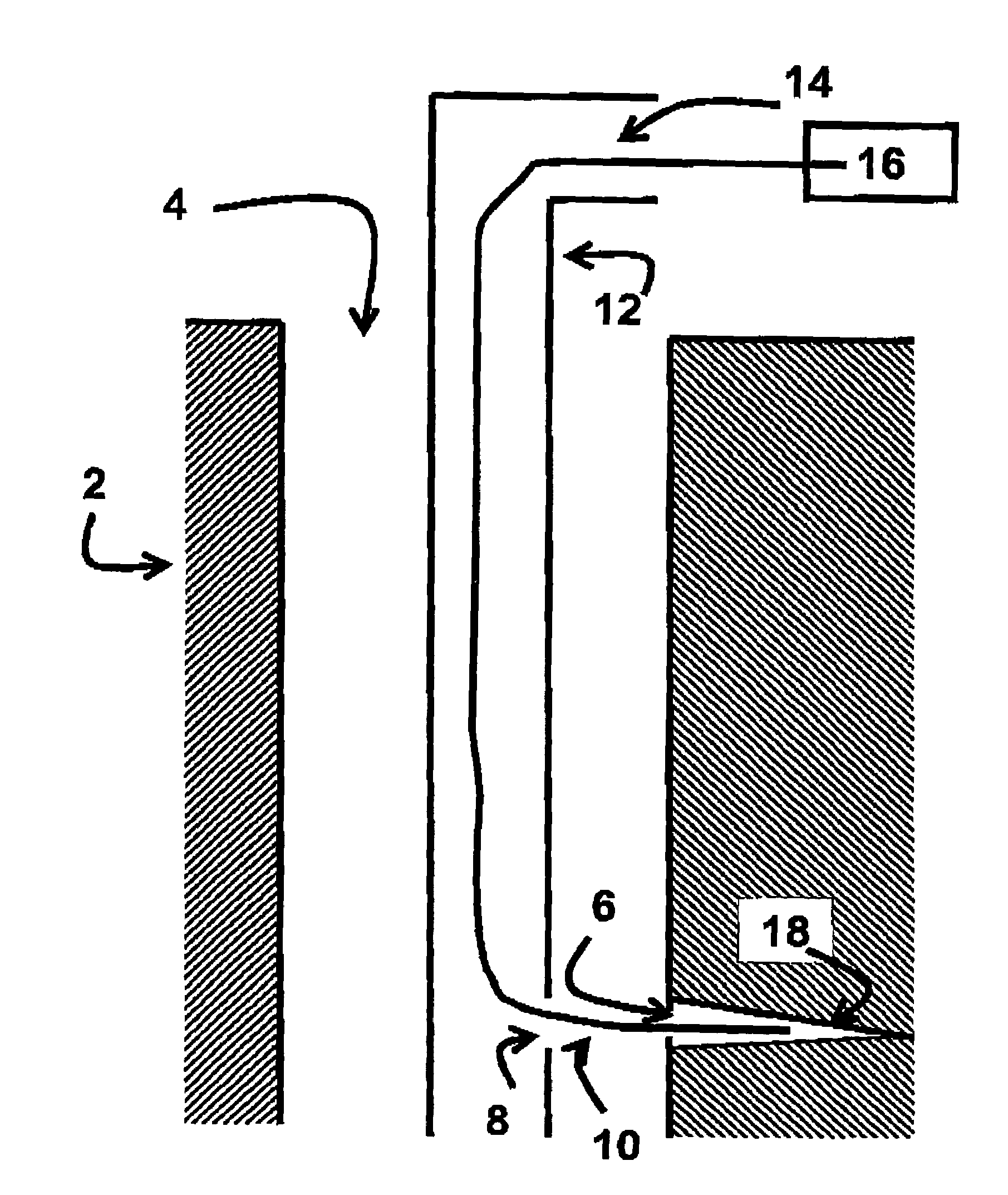
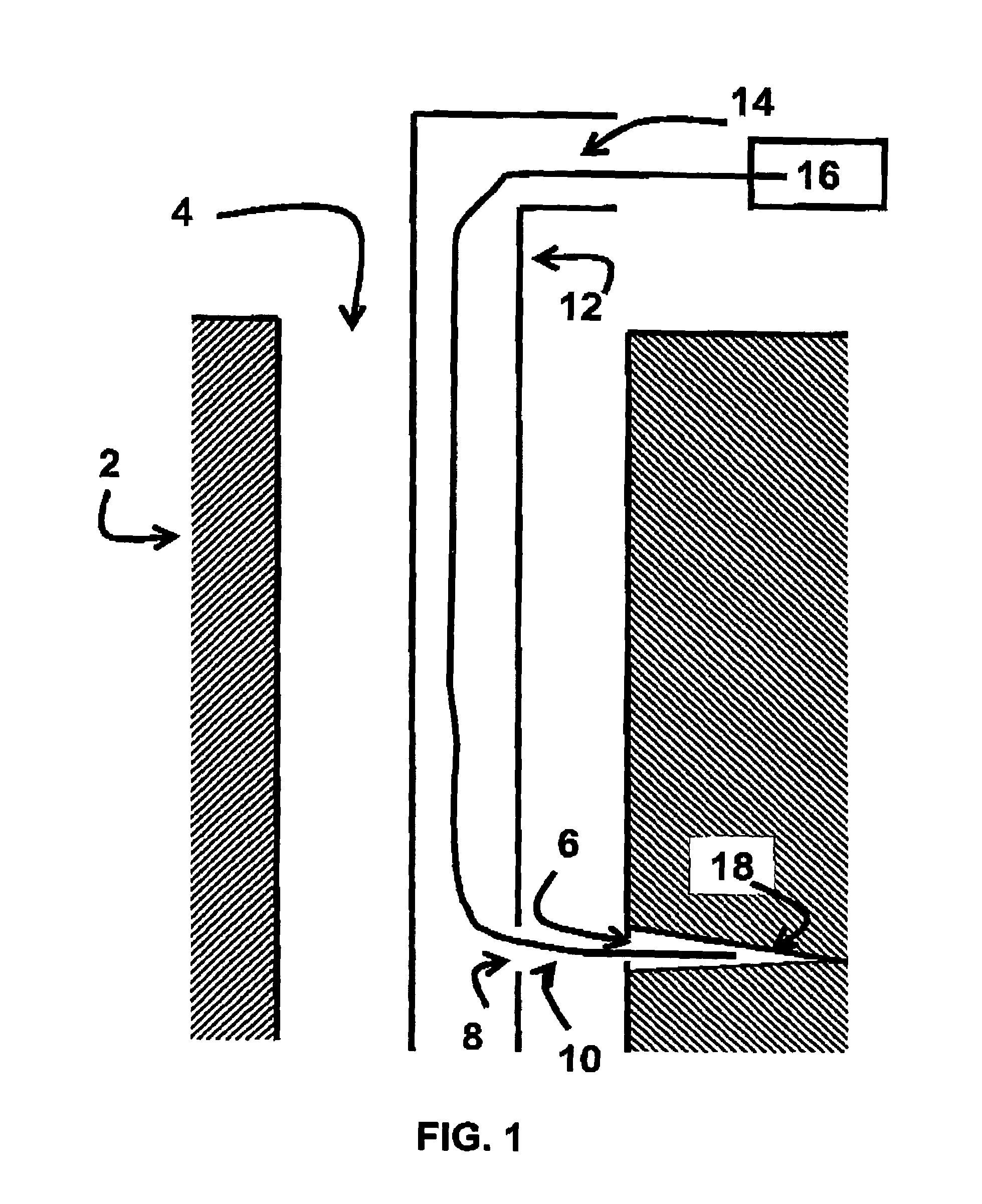
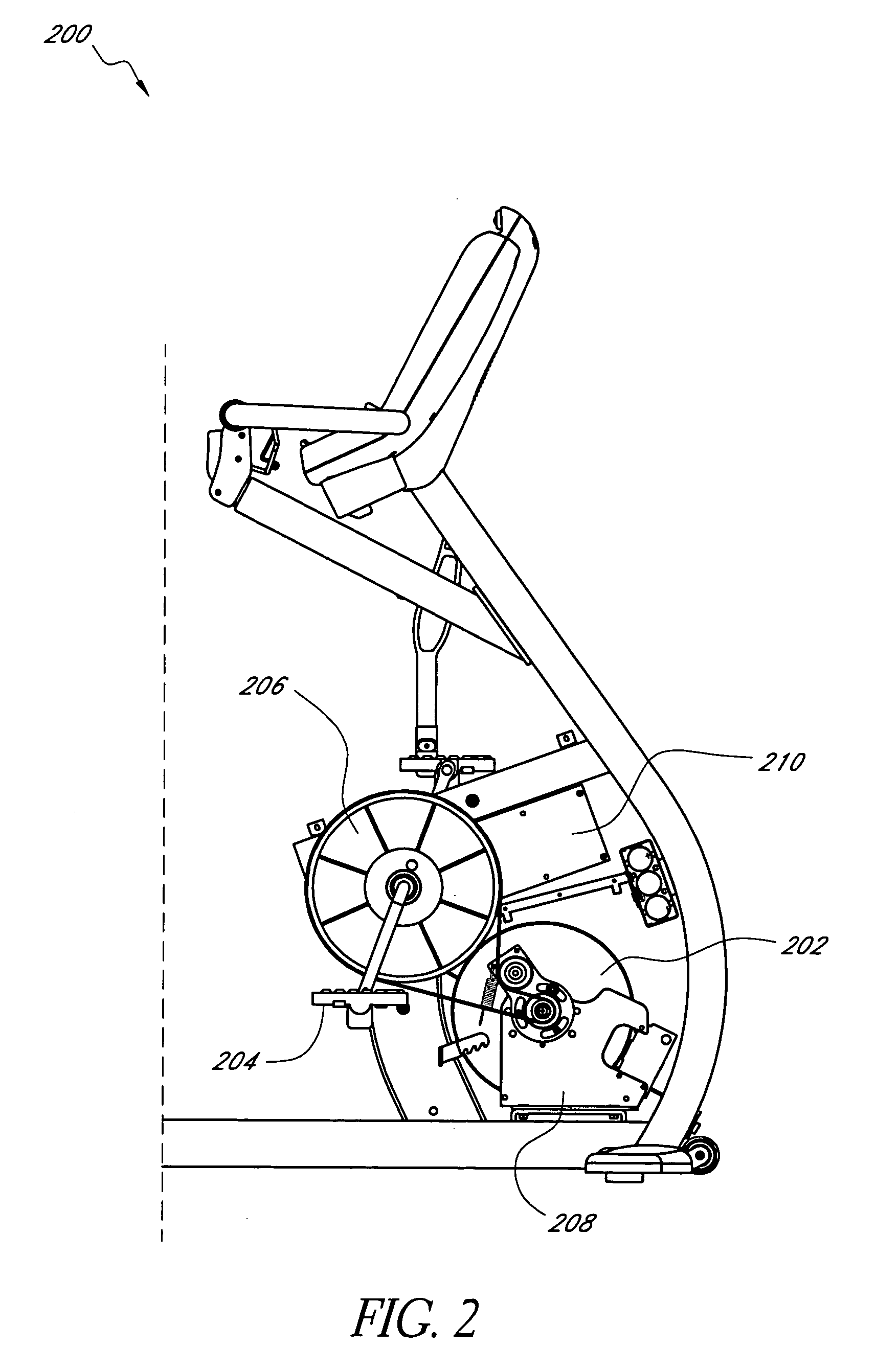
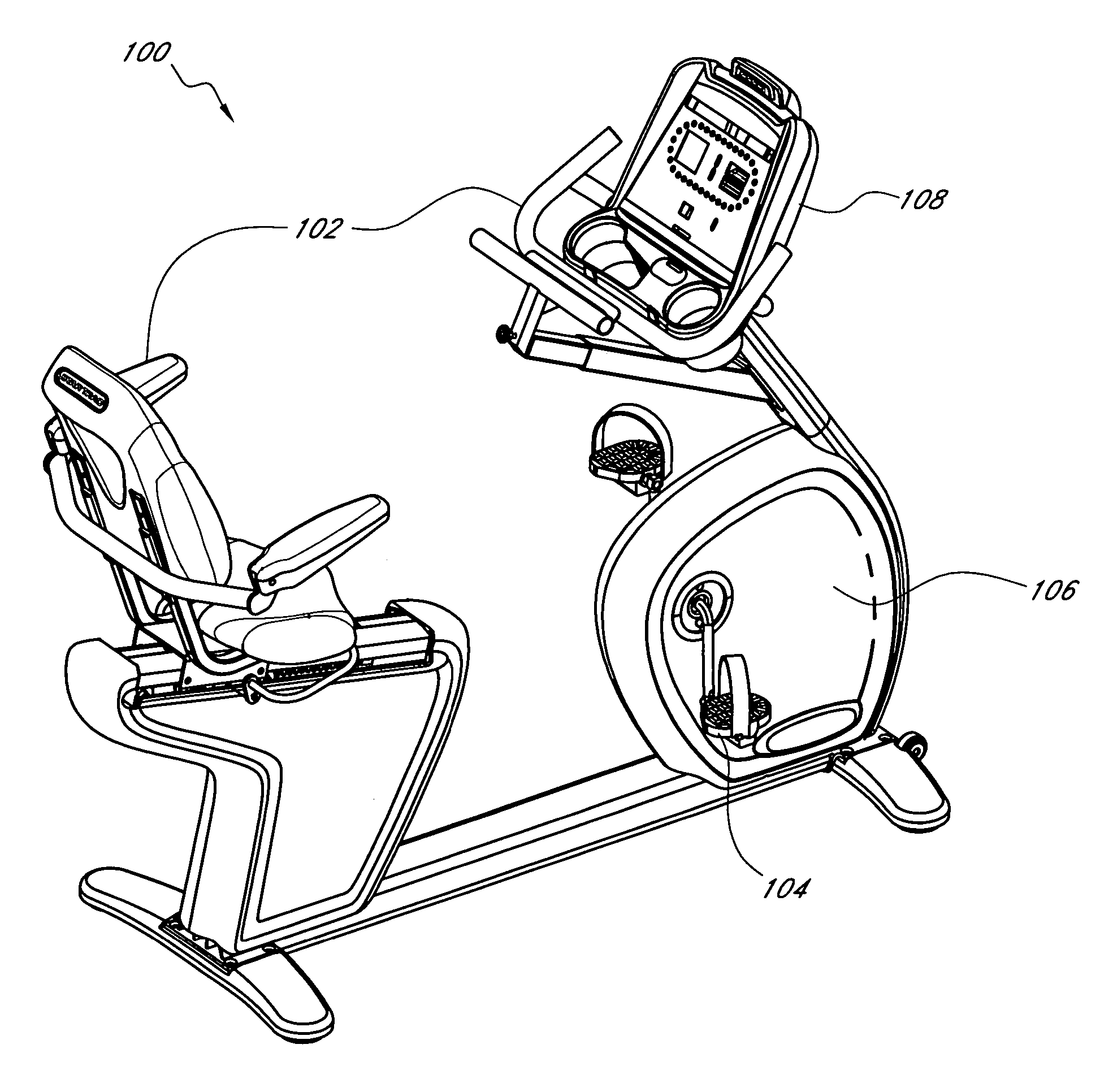
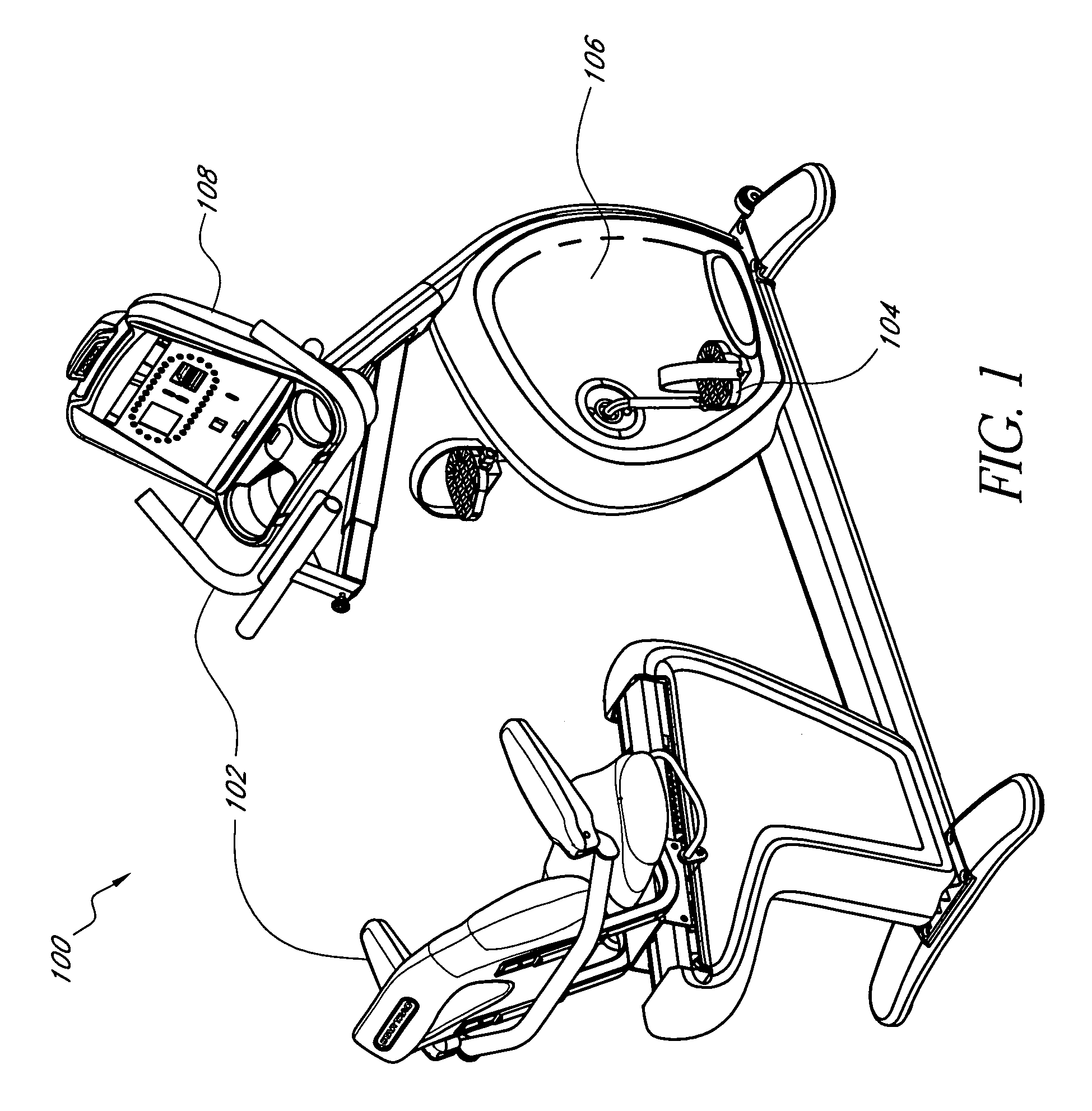
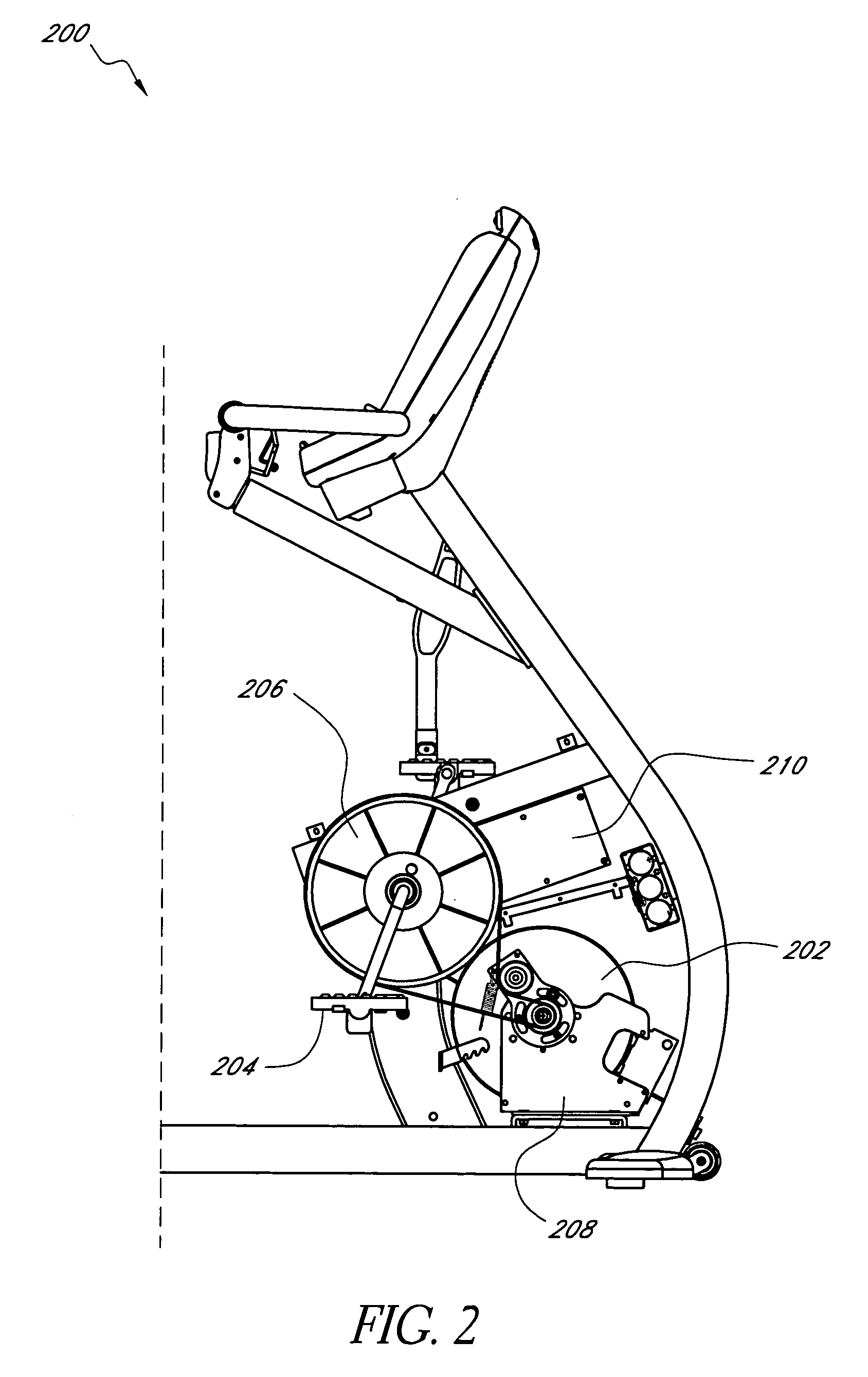
System and method for electronically controlling resistance of an exercise machine
ActiveUS20060003872A1Increases pedal resistanceDecreases pedal resistanceMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceControl system
A stationary exercise machine includes a system for electronically controlling a pedal resistance so as to simulate the riding of a road-going bicycle. The exercise machine includes a control system that monitors pedal velocity and that controls the resistive load generated by an electronically-controlled resistance mechanism. In one example, an electromagnetic device may vary a resistive load placed on a flywheel, which, in turn, varies the pedal resistance experienced by a user. When the user increases the pedal velocity, the resistance mechanism increases the resistive load. When the user decreases the pedal velocity, the resistance mechanism decreases the resistive load. In another example, the resistance mechanism varies the resistive load based on a gear selection by the user. The control system may also take into account other factors, such as the grade of the simulated ride, simulated wind resistance, or other frictional forces when calculating the resistive load.
Owner:CORE HEALTH & FITNESS
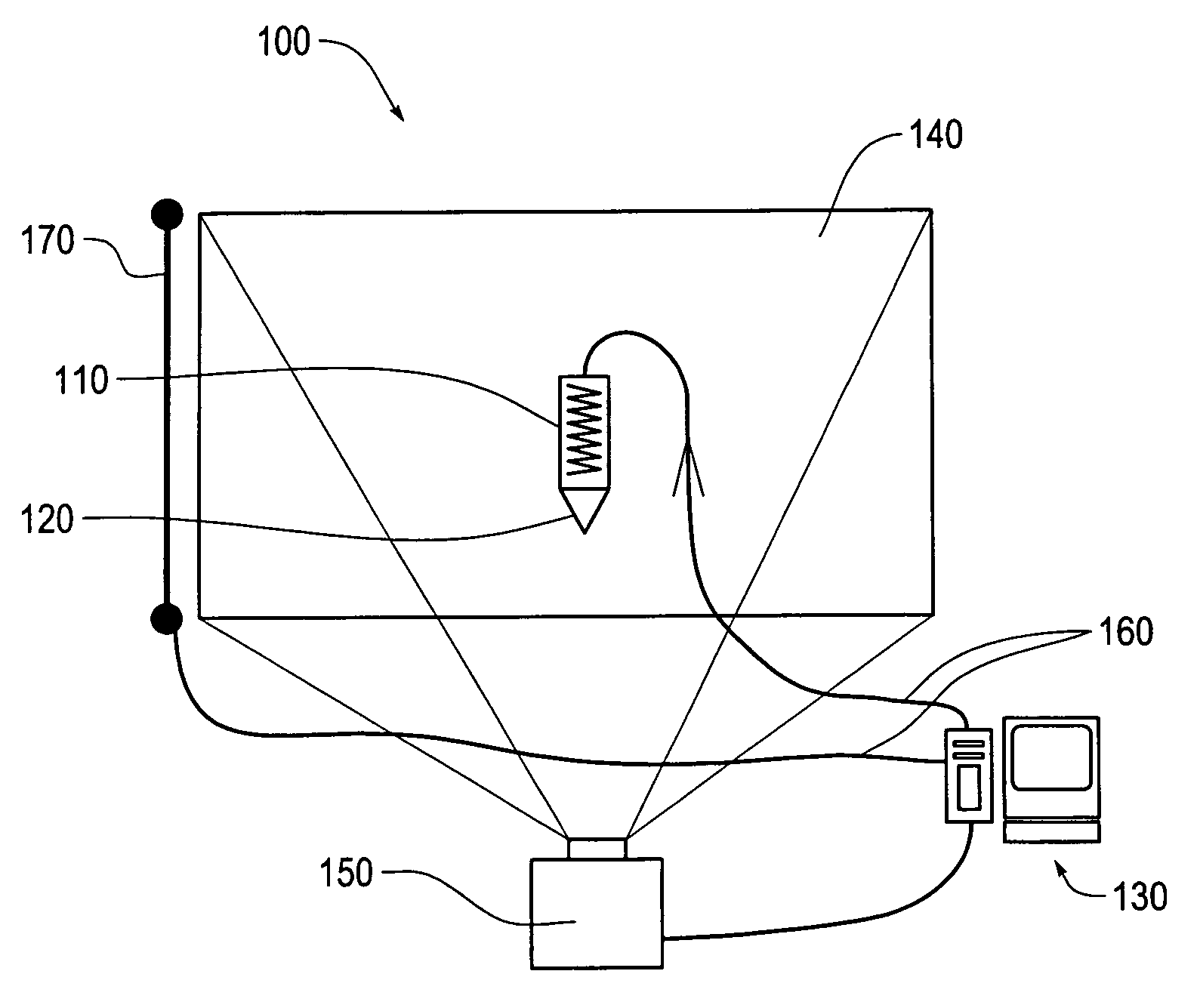
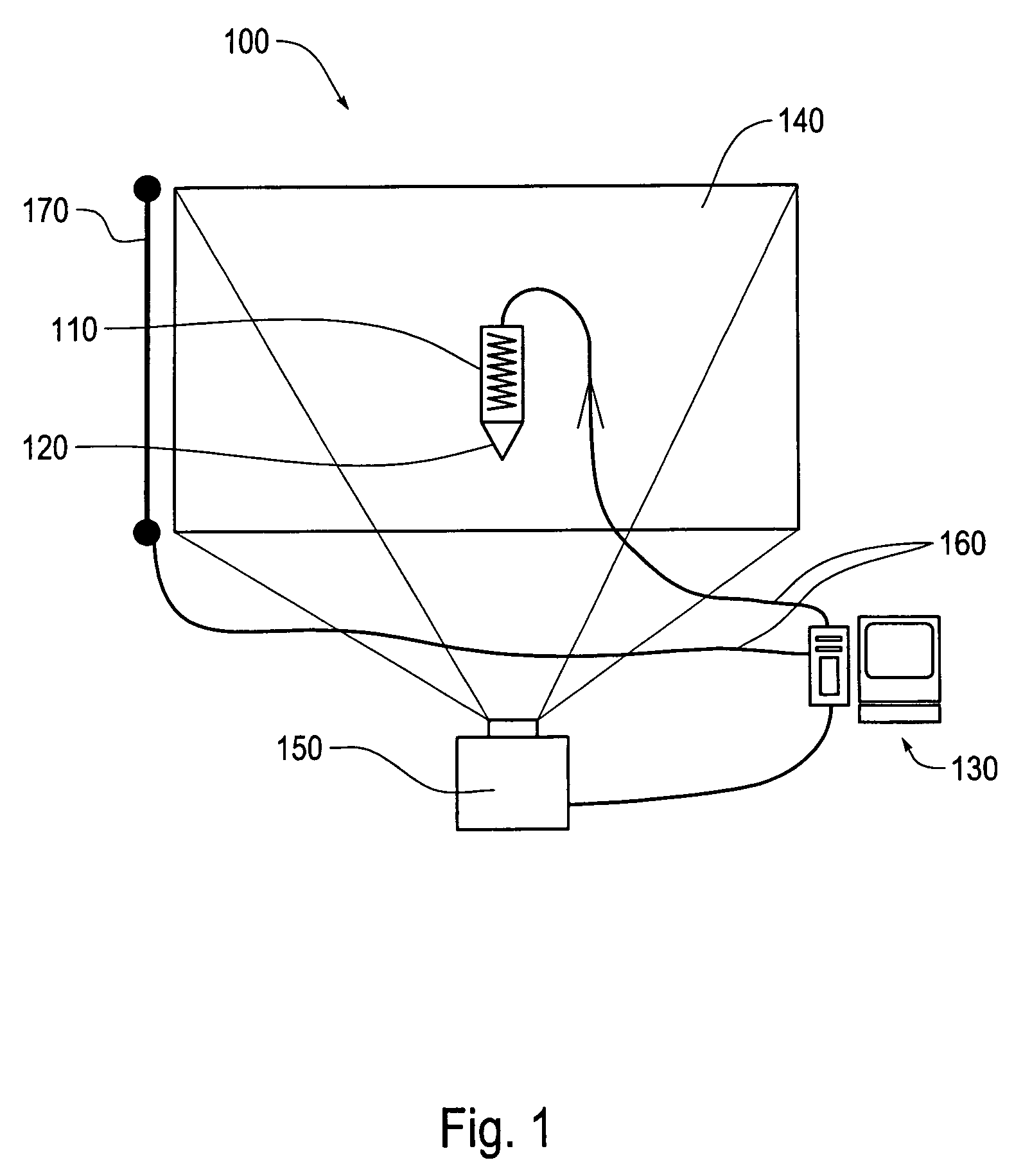
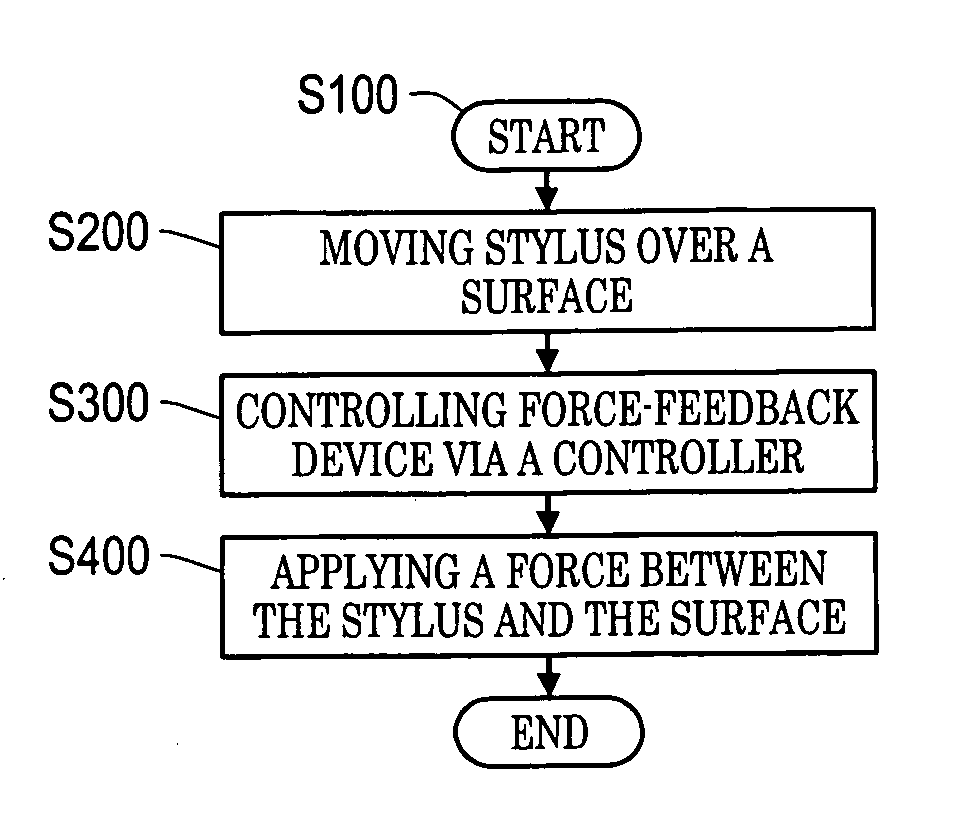
Force-feedback stylus and applications to freeform ink
InactiveUS7508382B2Input/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsFree rotationEngineering
This invention relates to a force-feedback apparatus which includes a stylus that is equipped with an electromagnetic device or a freely rotating ball. The stylus is functionally coupled to a controller which is capable of exerting a magnetic field to the electromagnetic device or to the rotating ball, which results in a force being created between the stylus and a surface. This invention also relates to a method of using a force-feedback stylus including moving a force-feedback stylus over a surface, controlling a force-feedback device via a controller coupled to the force-feedback stylus and applying a force to the force-feedback stylus via the force-feedback device, the force being determined for at least features on the surface.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Multi-layer printed circuit board transformer winding
InactiveUS20050212640A1High currentImprove efficiencyTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsSurface mountingEngineering
The present invention provides a transformer formed from adjacent conducting layers of a multi-layer PCB and at least one additional conducting layer in contact with the PCB. The inventive transformer includes one or more winding turns of a first winding formed by connecting the multiple layers of the multi-layer PCB with conductive vias and one or more winding turns of a second winding formed by connecting one or more other layers of the multi-layer PCB. The additional conducting layer or layers is connected to respective selected one or more of said conducting layers of said PCB. In one embodiment, an additional conducting layer is soldered to a top conducting layer of the PCB, effectively increasing the cross-sectional area of the top winding layer. In another embodiment, an additional conducting layer is separated from a conducting PCB layer formed on the surface thereof by a layer of insulation, permitting the additional conducting layer to form a separate winding turn. The inventive transformer can be surface mounted to a PCB, and can be used in other electromagnetic devices. The windings thus constructed are capable of accepting larger currents with lower resulting temperature increases than windings formed only from PCBs, and are less expensive to manufacture than PCB-only windings.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
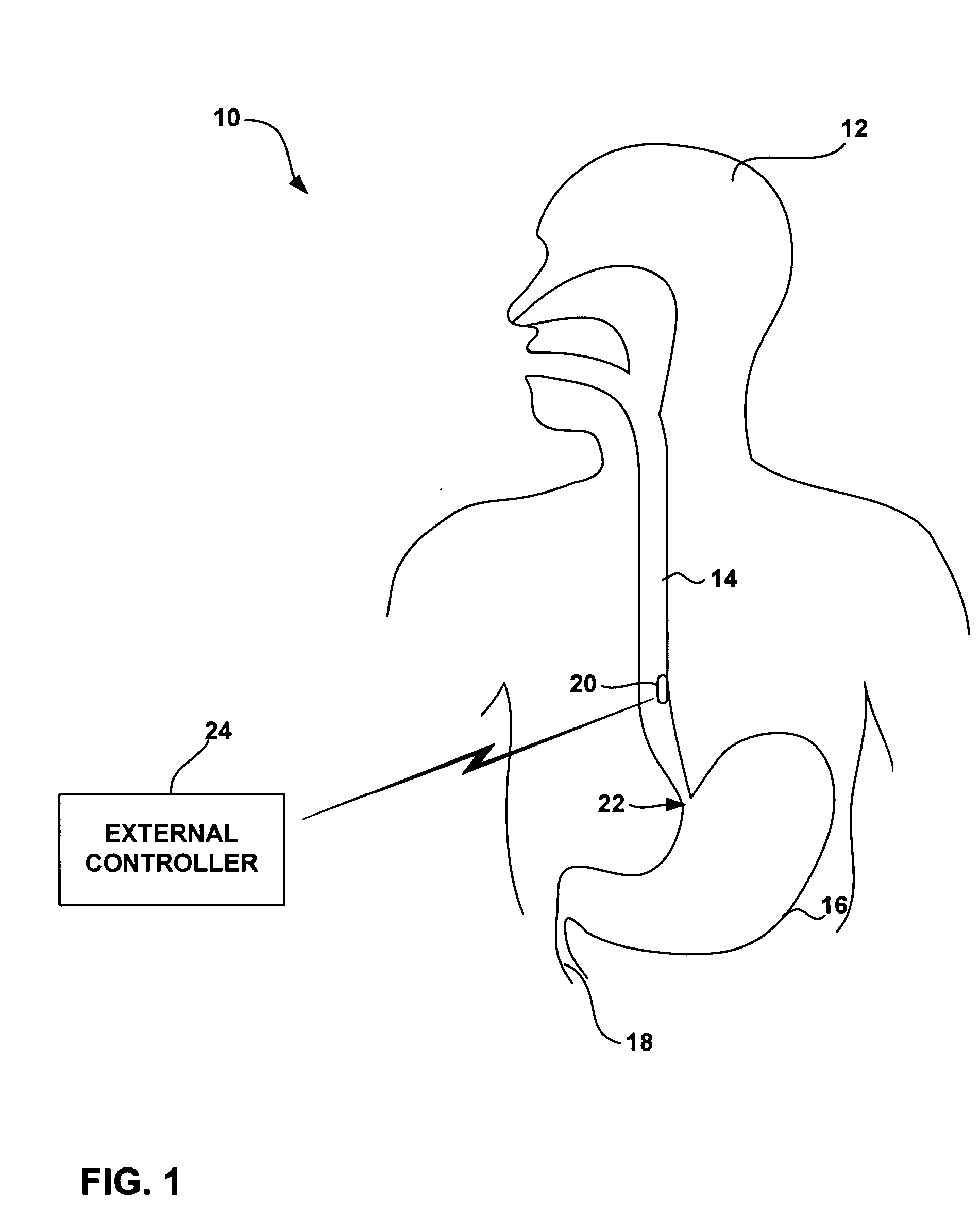
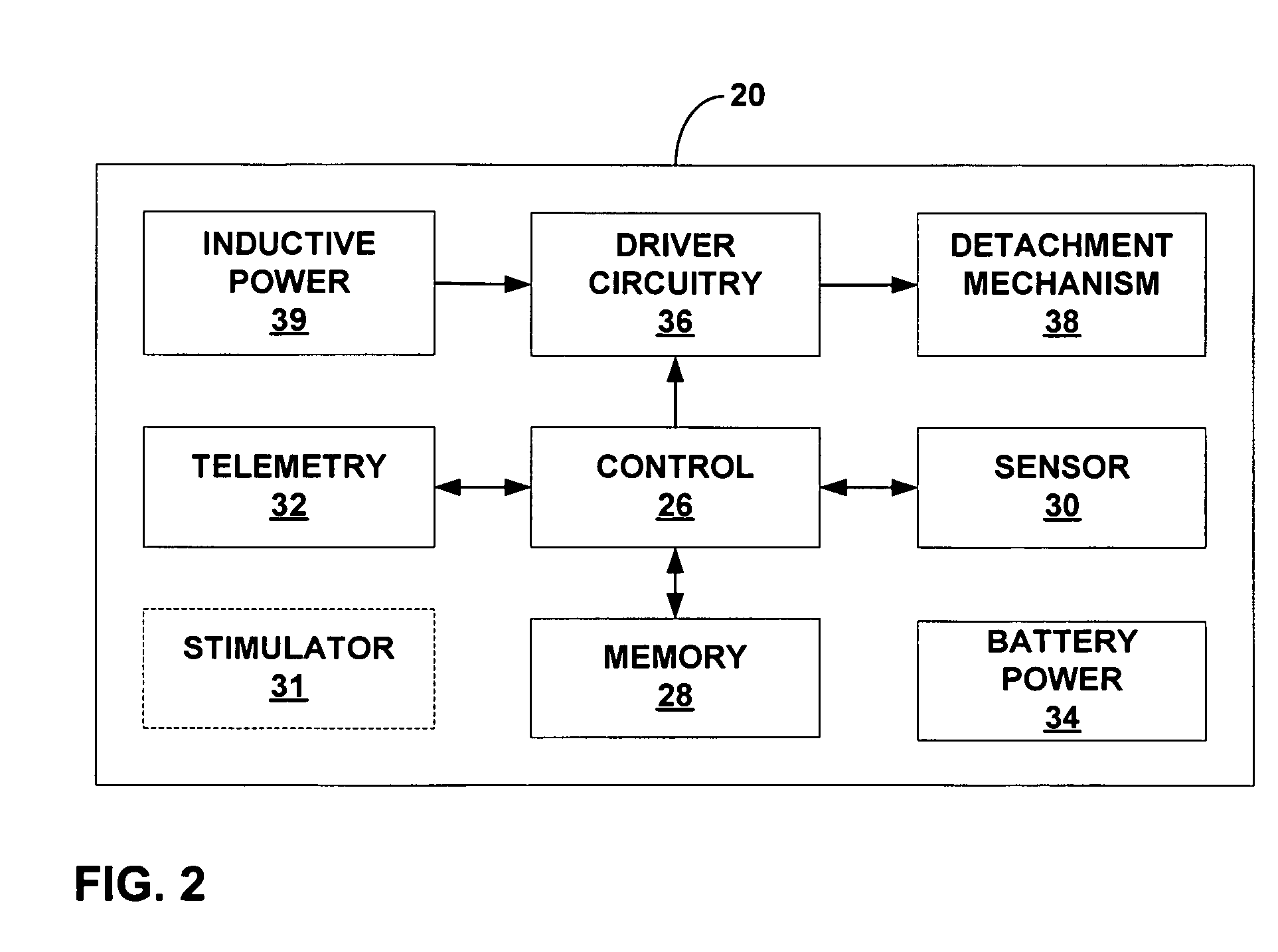
Controlled detachment of intra-luminal medical device
InactiveUS20050222537A1Easy to controlEliminate the problemElectrotherapySurgerySurgical departmentMedical device
An intra-luminal medical device includes a fixation mechanism to attach the medical device to tissue within a body lumen, and a detachment mechanism to permit selective detachment of the medical device from the tissue attachment site without the need for endoscopic or surgical intervention. An electromagnetic device may be provided to mechanically actuate the detachment mechanism. Alternatively, a fuse link may be electrically blown to detach the medical device. As a further alternative, a rapidly degradable bonding agent may be exposed to a degradation agent to detach the medical device from a bonding surface within the body lumen. The medical device may eliminate problems associated with uncertain and inconsistent detachment of intra-luminal medical devices.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
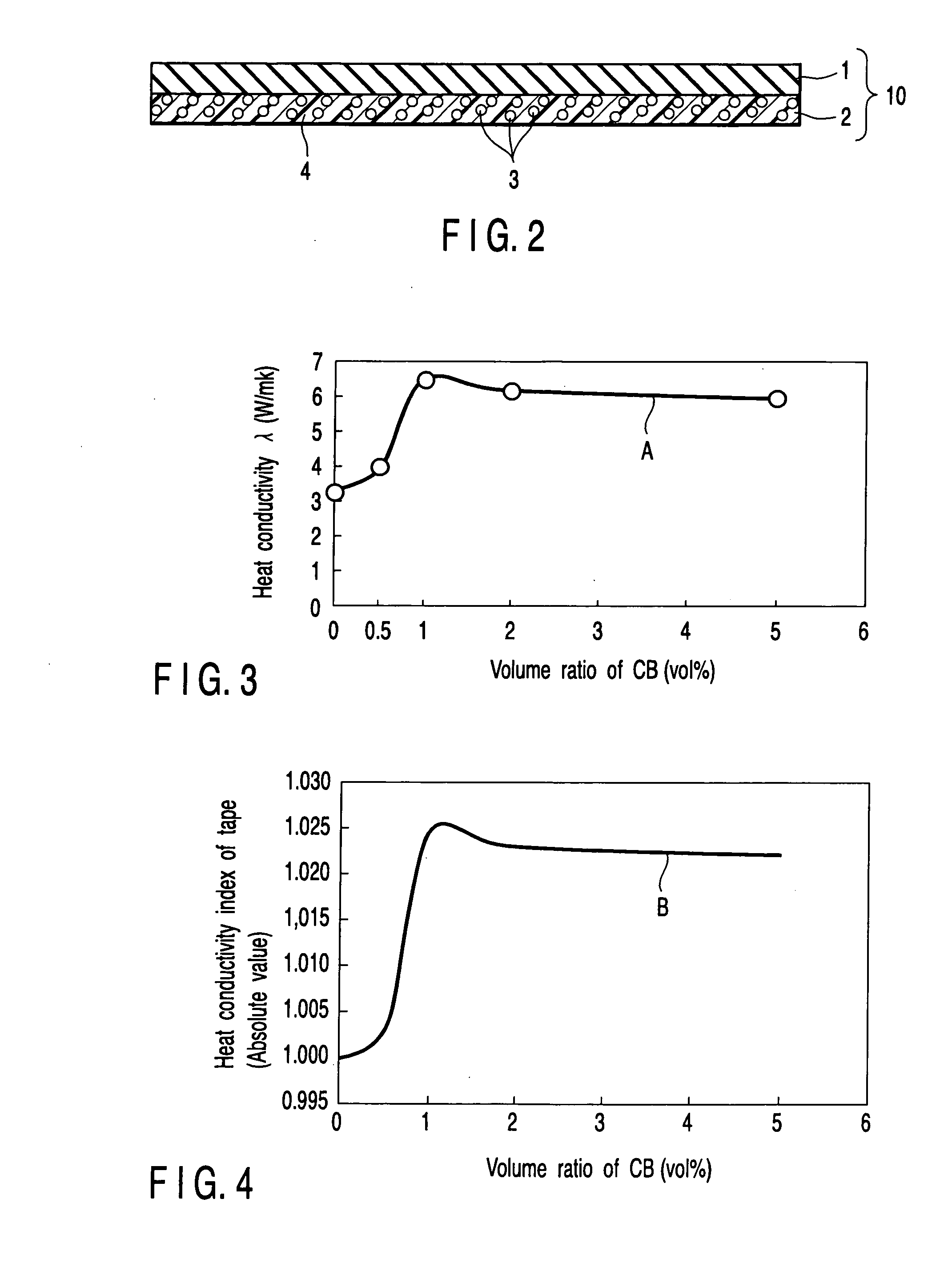
Highly heat conductive insulating member, method of manufacturing the same and electromagnetic device
ActiveUS20050208301A1Easy to manufactureImprove thermal conductivityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsResin matrixMaterials science
The present invention provides a solution to the above-described drawbacks, and more specifically, as the tape-like or sheet-like insulation member, the resin matrix in which the first particles having a heat conductivity of 1 W / mK or higher and 300 W / mK or lower, that are diffused in the resin matrix, and the second particles having a heat conductivity of 0.5 W / mK or higher and 300 W / mK or lower, are diffused, is employed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
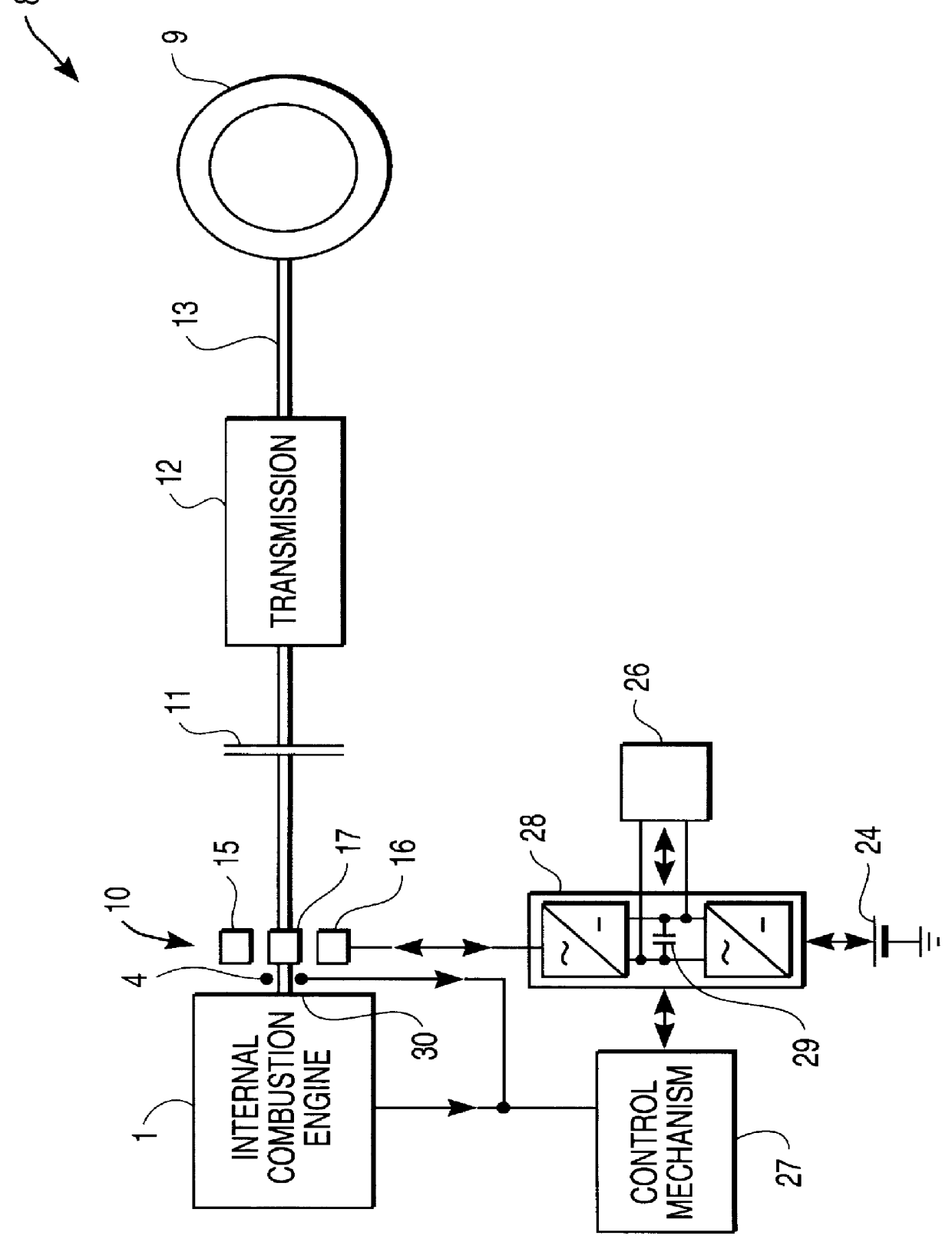
Direct injection of fuels in internal combustion engines
A fuel delivery injector for an internal combustion engine is provided. A fuel injector forms part of a device which provides a combined injection and ignition. The fuel delivery injector comprises first and second portions adapted to be detachably connected together. The first portion incorporates a valve structure having a valve member movable with respect to a valve seat for opening and closing a delivery port, and an actuating member operatively connected to the valve member. An actuator is provided in the second portion. When the first and second portions are connected together, the actuator is operably associated with the actuating member to provide an actuating assembly. Typically, the actuating assembly comprises an electromagnetic device in which the actuating member comprises a solenoid armature and the actuator comprises a solenoid coil, whereby connection of the first and second portions together completes assembly of the electromagnetic device.
Owner:ORBITAL ENGINE CO PTY LTD
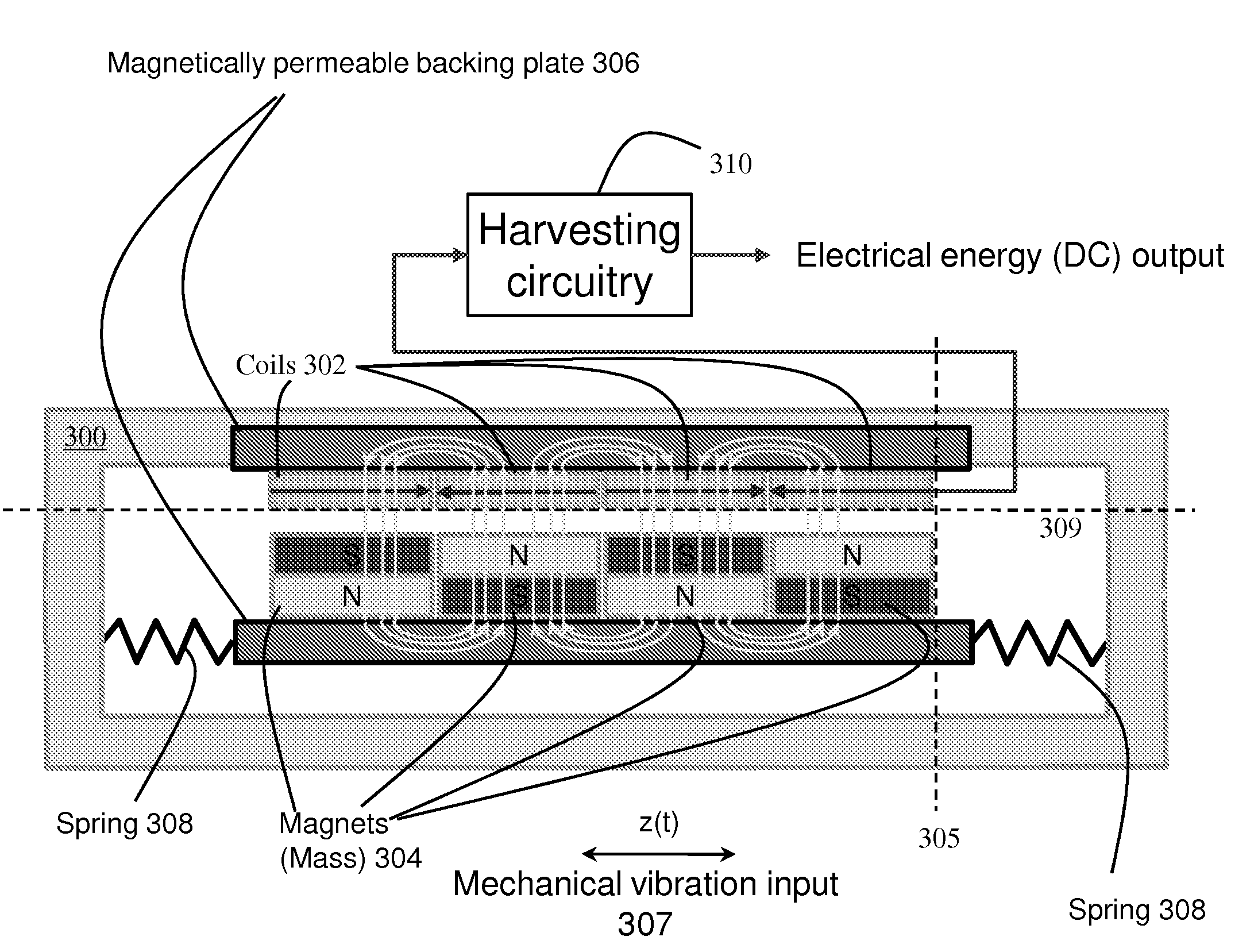
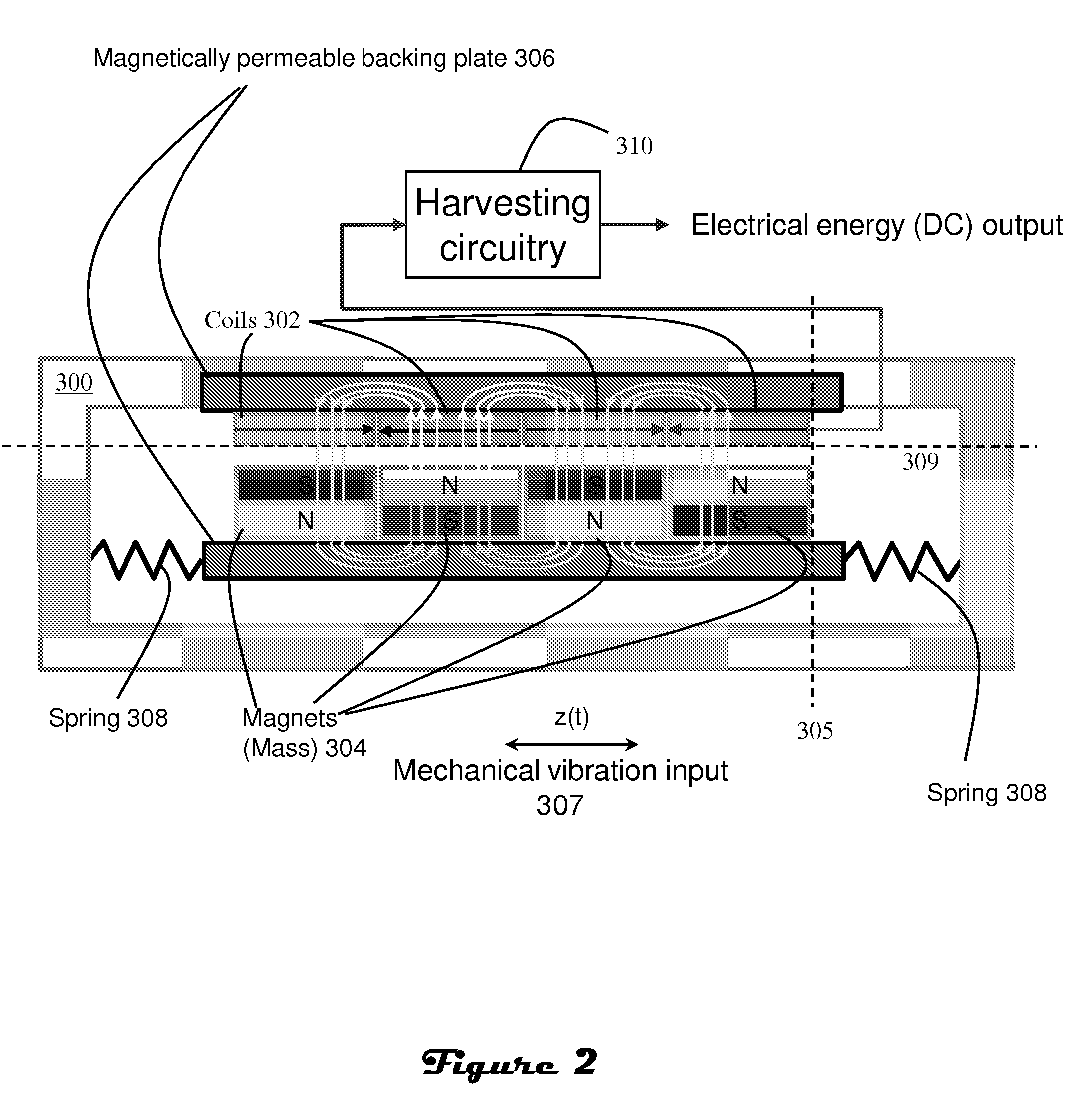
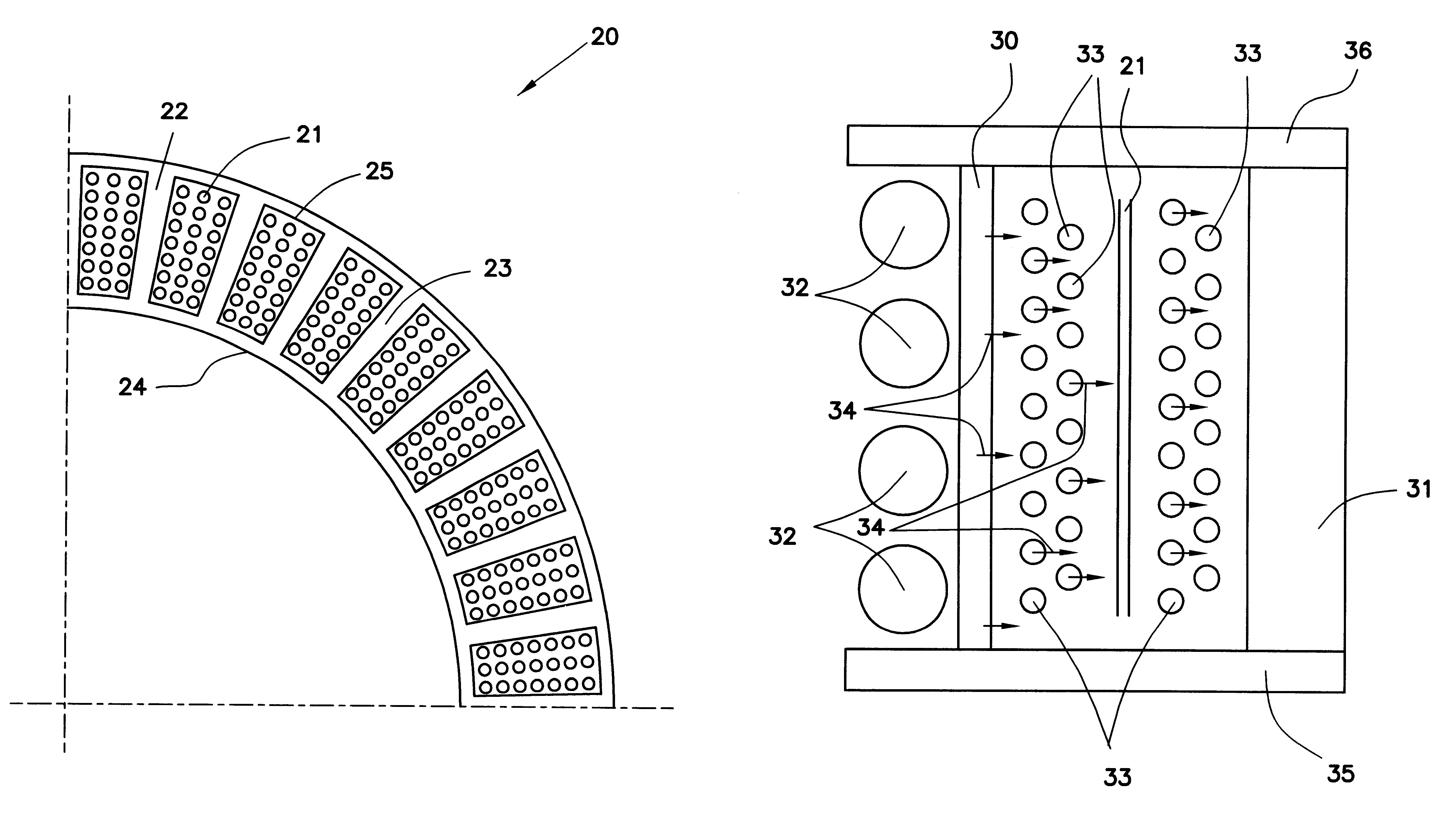
Electromagnetic device having compact flux paths for harvesting energy from vibrations
InactiveUS20100194117A1Improve compactnessEnhanced couplingMachines/enginesMechanical energy handlingDevice formMechanical energy
Electrical energy is produced by harvesting mechanical energy in the form of vibrations which are generally present in tools during the process of drilling oil wells. Electrical energy production is based on the Faraday induction principle whereby changes, i.e., movement, in magnetic flux through a coil induce an electric current through the coil. The changes in magnetic flux are produced by relative motion between at least one set of magnets and at least one coil. In particular, as the flux lines change due to the movement of the magnets, they remain perpendicular to both the direction of motion of the magnets as well as a planar or cylindrical surface defined by the coils. As a result, output for a given size of device is enhanced. Further, flexibility in adapting device form factor to particular shapes is enhanced. For example, a relatively flat device may be implemented using flexural bearing support of the magnets and coils on a printed circuit. The flexural bearings may also function as spring members that define the resonant frequency of the device. Alternative embodiments may be characterized by cylindrical or annular form factors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP +1
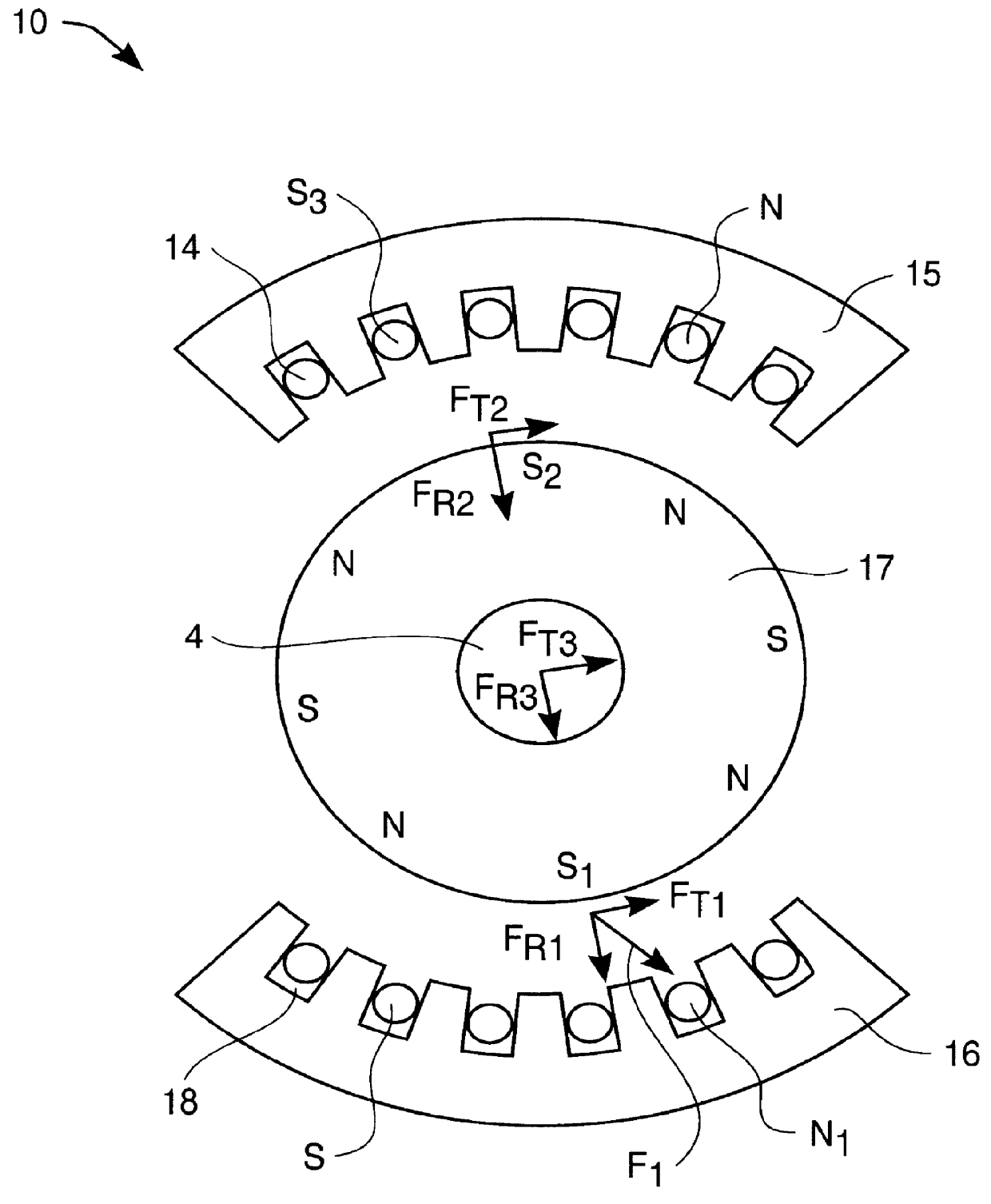
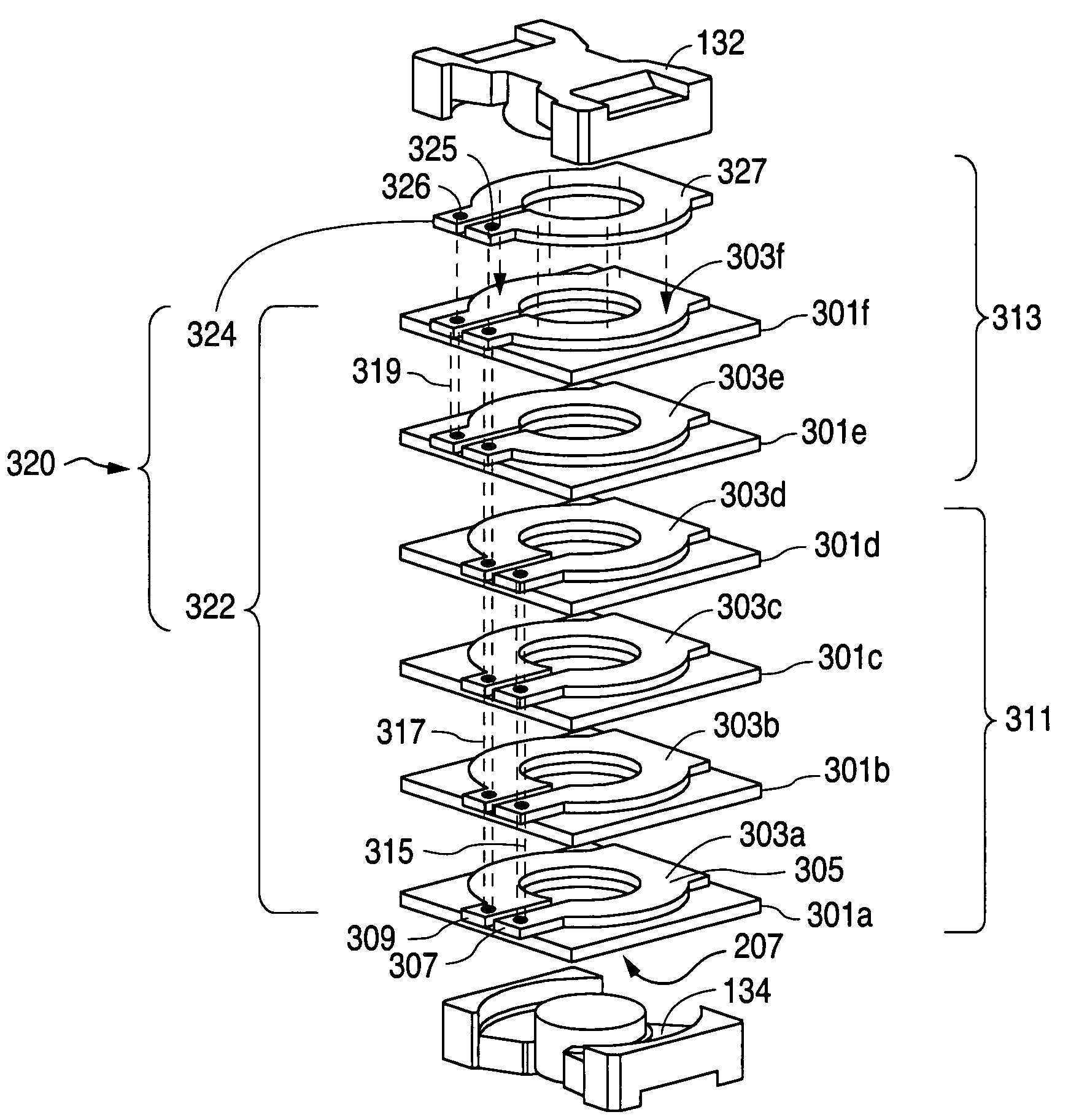
Electromagnetic device with embedded windings and method for its manufacture
InactiveUS6232681B1Maximize electromagnetic couplingGap minimizationSynchronous machinesMagnetic circuit stationary partsReduced sizeConductor Coil
A powdered magnetic material stator core with embedded stator windings and a method for its manufacture. Embedding the windings within a radially compacted powdered magnetic material stator core enables equivalent or better electromagnetic performance in a significantly reduced size. Radial compaction of the powdered magnetic material minimizes the distortion of the stator windings during compaction.
Owner:REMY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
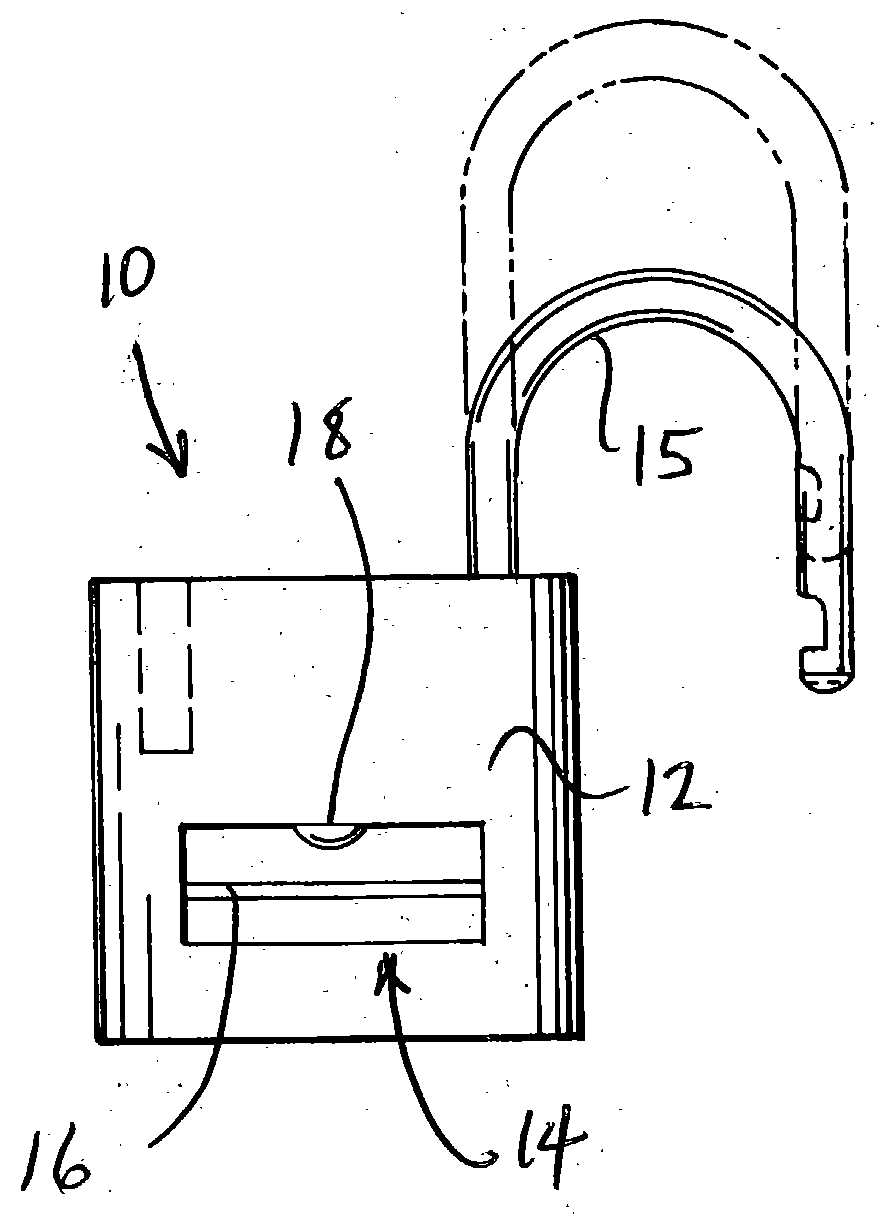
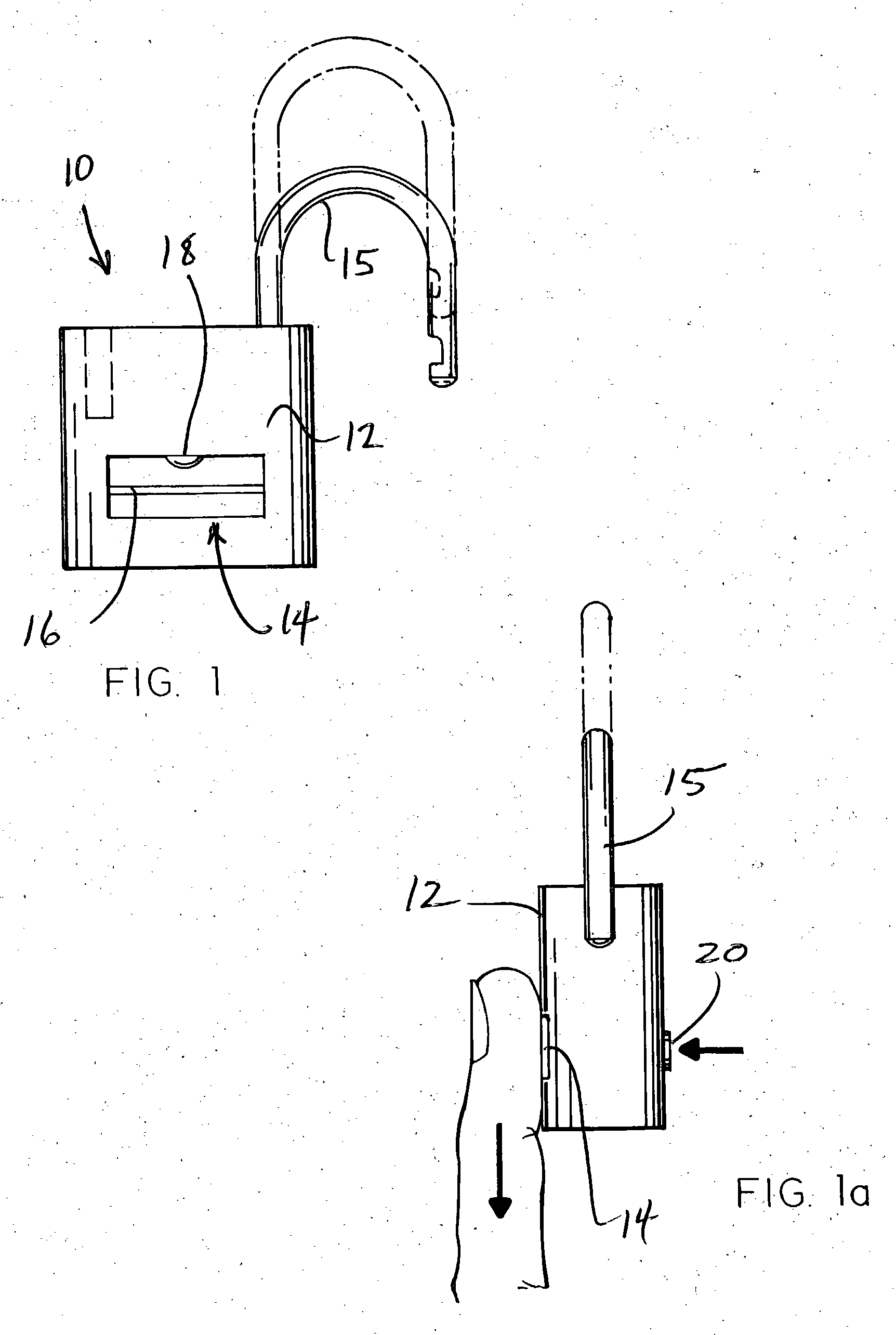
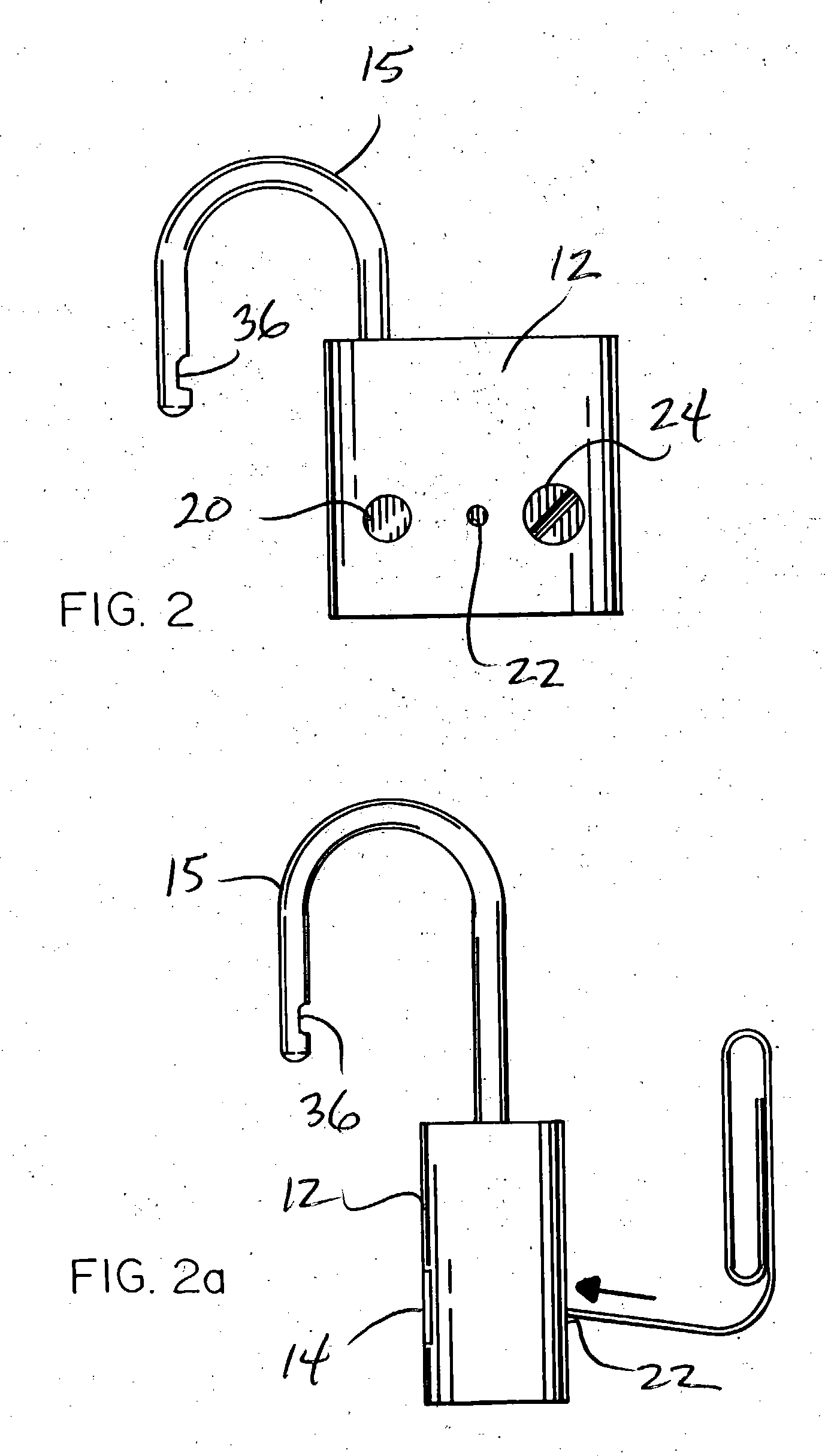
Biometric padlock
A padlock having a body and a shoekle comprises a fingerprint sensor, a fingerprint data memory device and an electromagnetic device activated by a sensed and matched fingerprint to unlock the shackle from the body. Unlock and programming buttons respectively activate the sensor and configure the data memory device to receive new fingerprint data of those authorized to unlock the padlock.
Owner:SUN CONRAD +1
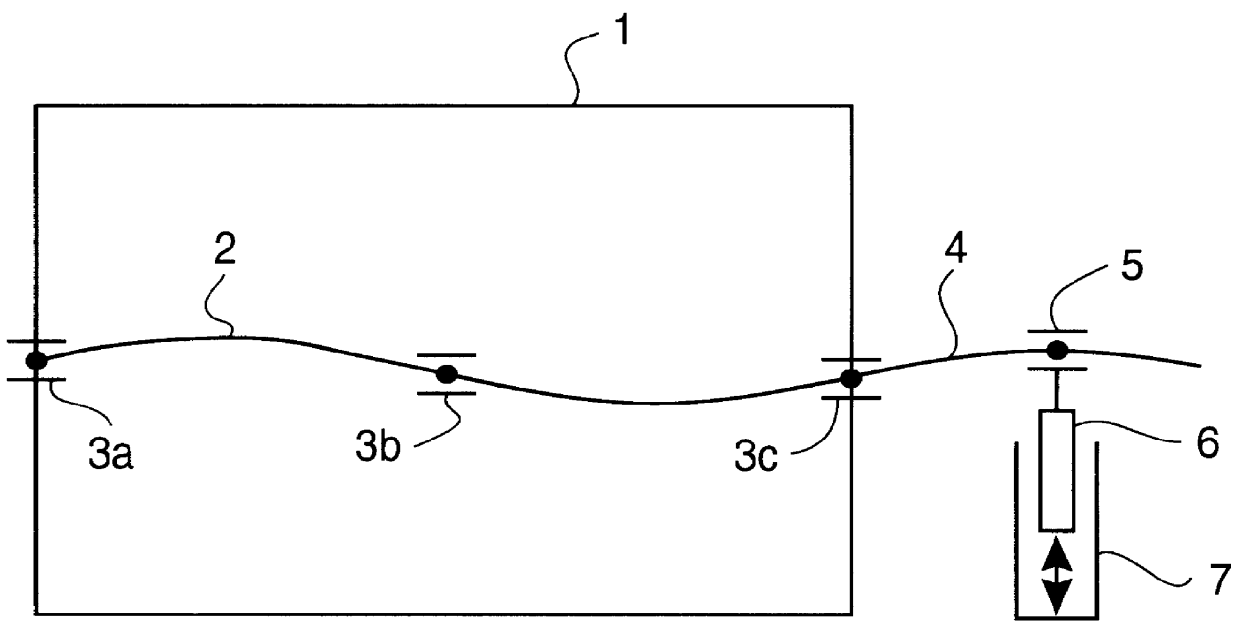
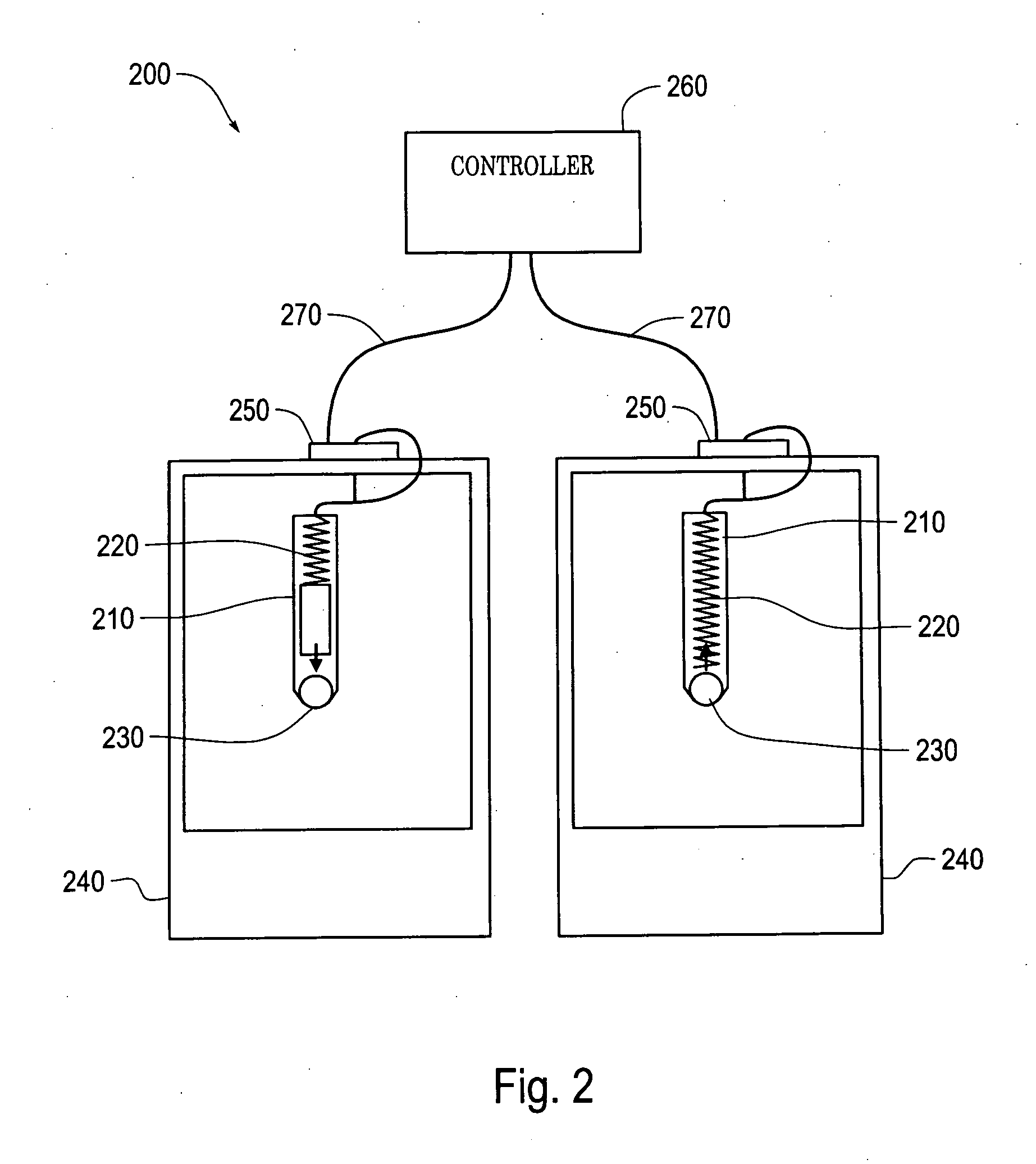
System for actively reducing radial vibrations in a rotating shaft, and method of operating the system to achieve this
InactiveUS6138629AReduce vibrationReduce unevennessRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsDrive shaftEngineering
PCT No. PCT / DE96 / 01665 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 23, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 23, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 31, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 08477 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 6, 1997The invention concerns a system for active reduction of radial vibrations of a rotating shaft (4), especially the drive shaft of an internal combustion engine (1), with at least one active electromagnetic device (7; 10; 15, 16), which is configured and controlled such that it applies radial forces to the shaft (4), which counteract the radial vibrations of the shaft (4).
Owner:CONTINENTAL ISAD ELECTRONICS SYST GMBH & CO KG
Electromagnetic apparatus for respiratory disease and method for using same
A method for altering the electromagnetic environment of respiratory tissues, cells, and molecules comprising establishing baseline thermal fluctuations in voltage and electrical impedance at a respiratory target pathway structure depending on a state of the respiratory tissue, configuring at least one waveform to have sufficient signal to noise ratio to modulate at least one of ion and ligand interactions whereby the at least one of ion and ligand interactions are detectable in the respiratory target pathway structure above the established baseline thermal fluctuations in voltage and electrical impedance, generating an electromagnetic signal from the configured at least one waveform; and coupling the electromagnetic signal to the respiratory target pathway structure using a coupling device.
Owner:RIO GRANDE NEUROSCI
Force-feedback stylus and applications to freeform ink
InactiveUS20050243072A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsFree rotationEngineering
This invention relates to a force-feedback apparatus which includes a stylus that is equipped with an electromagnetic device or a freely rotating ball. The stylus is functionally coupled to a controller which is capable of exerting a magnetic field to the electromagnetic device or to the rotating ball, which results in a force being created between the stylus and a surface. This invention also relates to a method of using a force-feedback stylus including moving a force-feedback stylus over a surface, controlling a force-feedback device via a controller coupled to the force-feedback stylus and applying a force to the force-feedback stylus via the force-feedback device, the force being determined for at least features on the surface.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
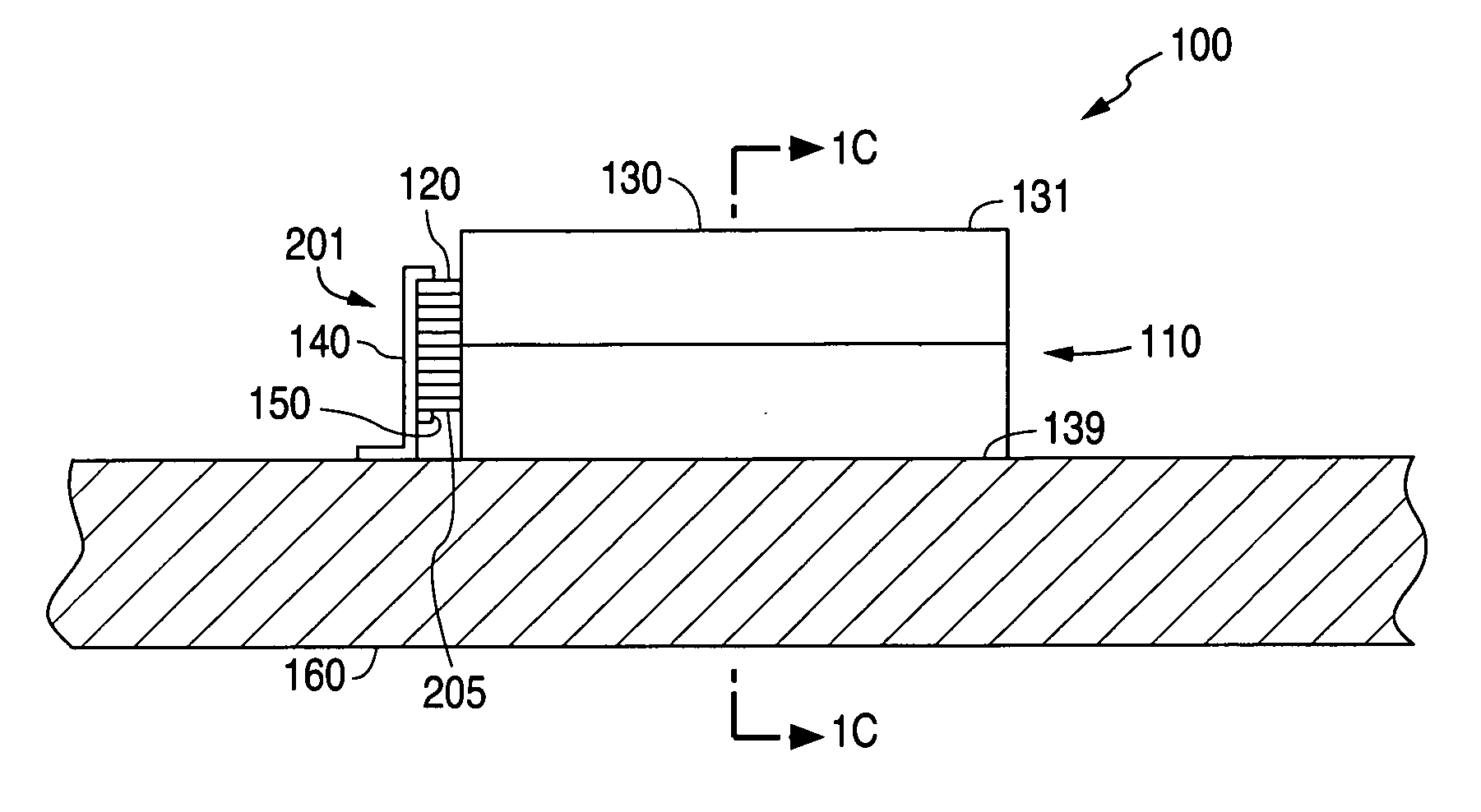
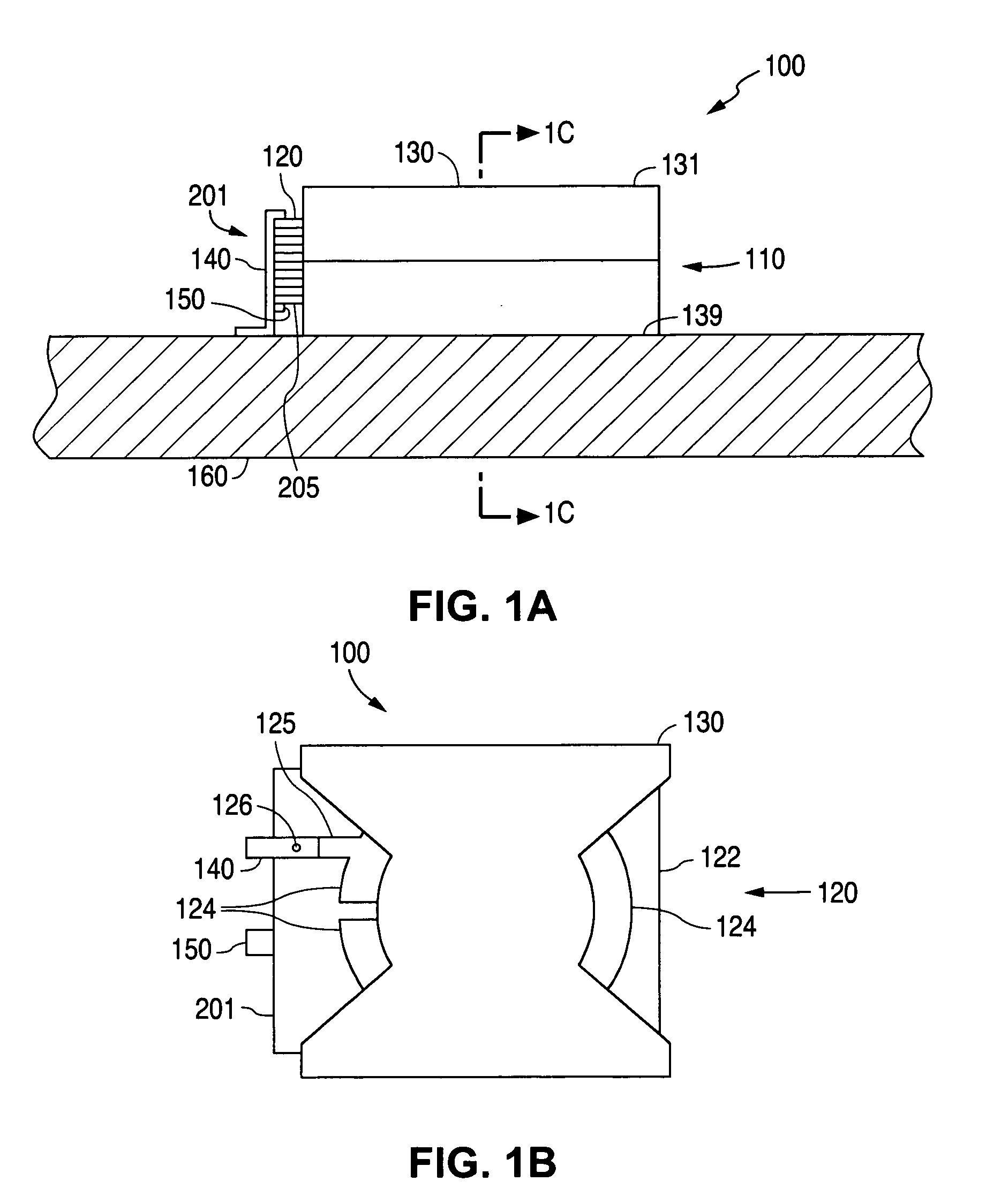
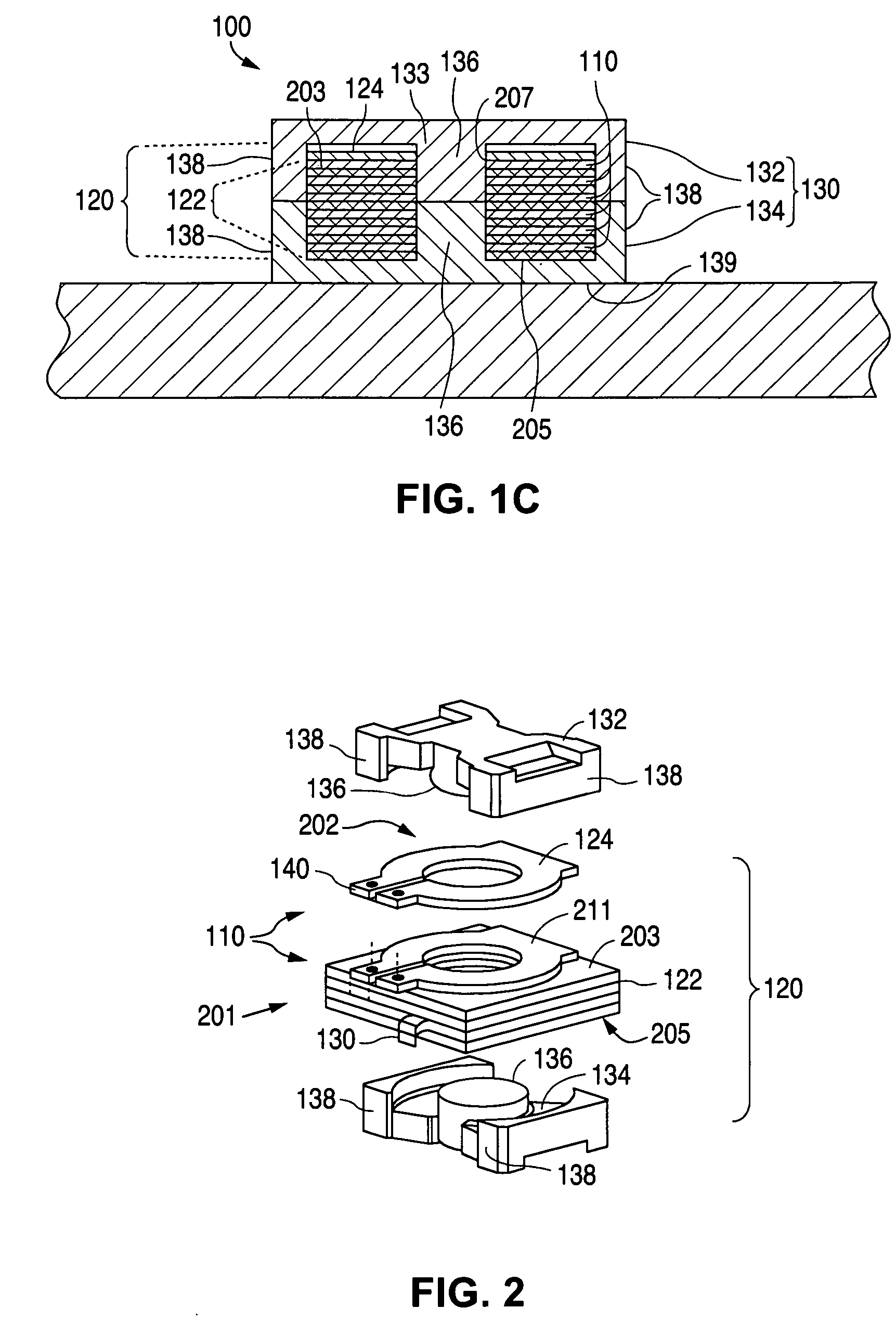
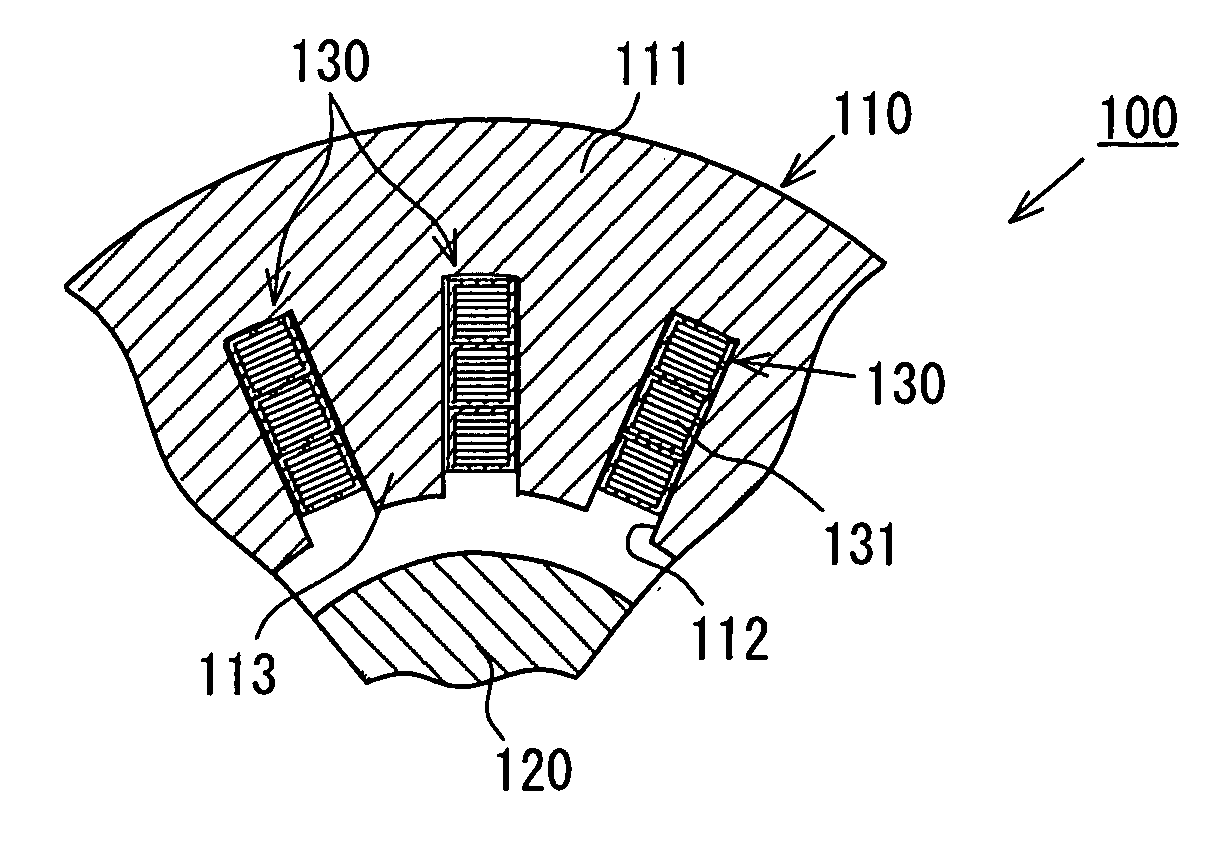
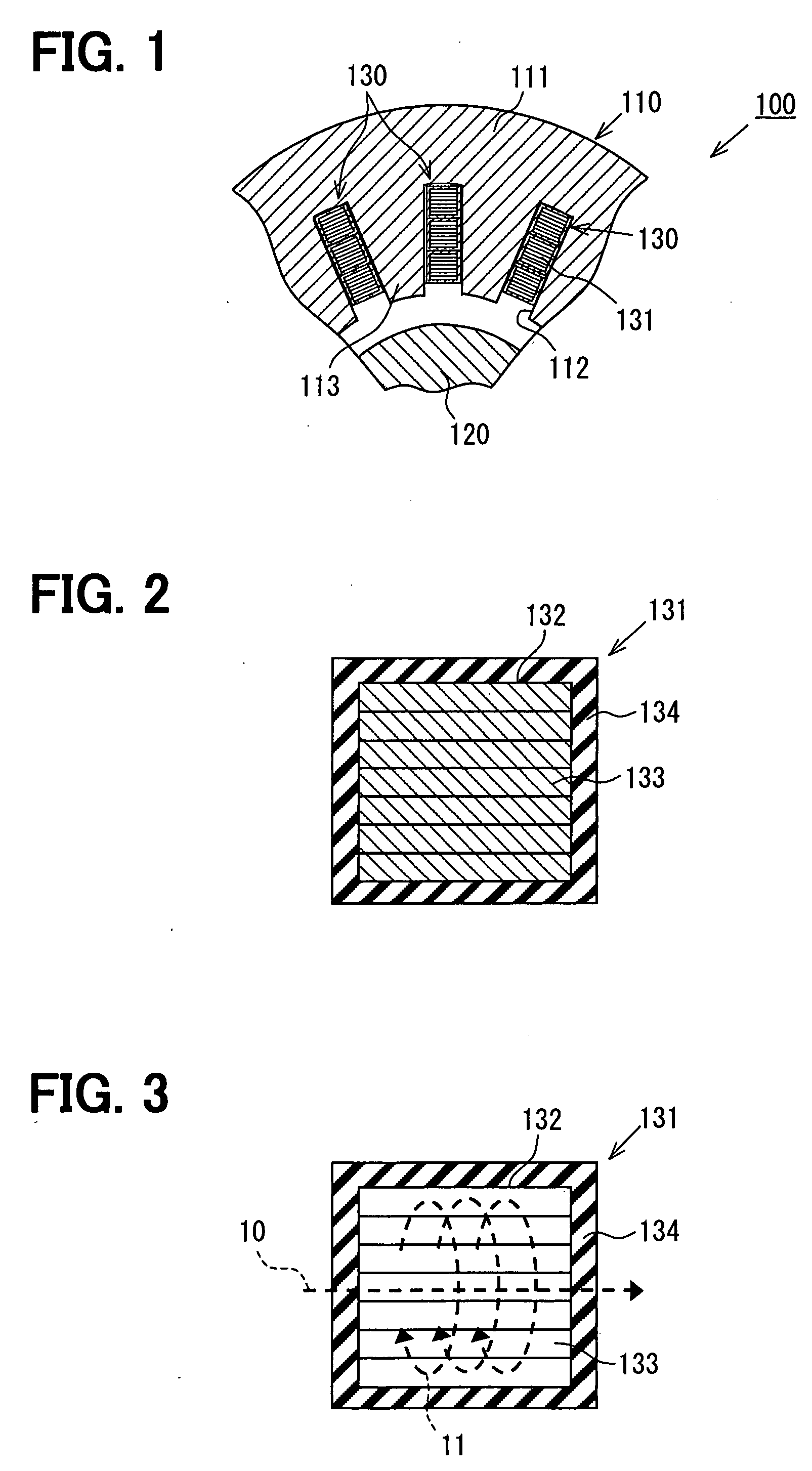
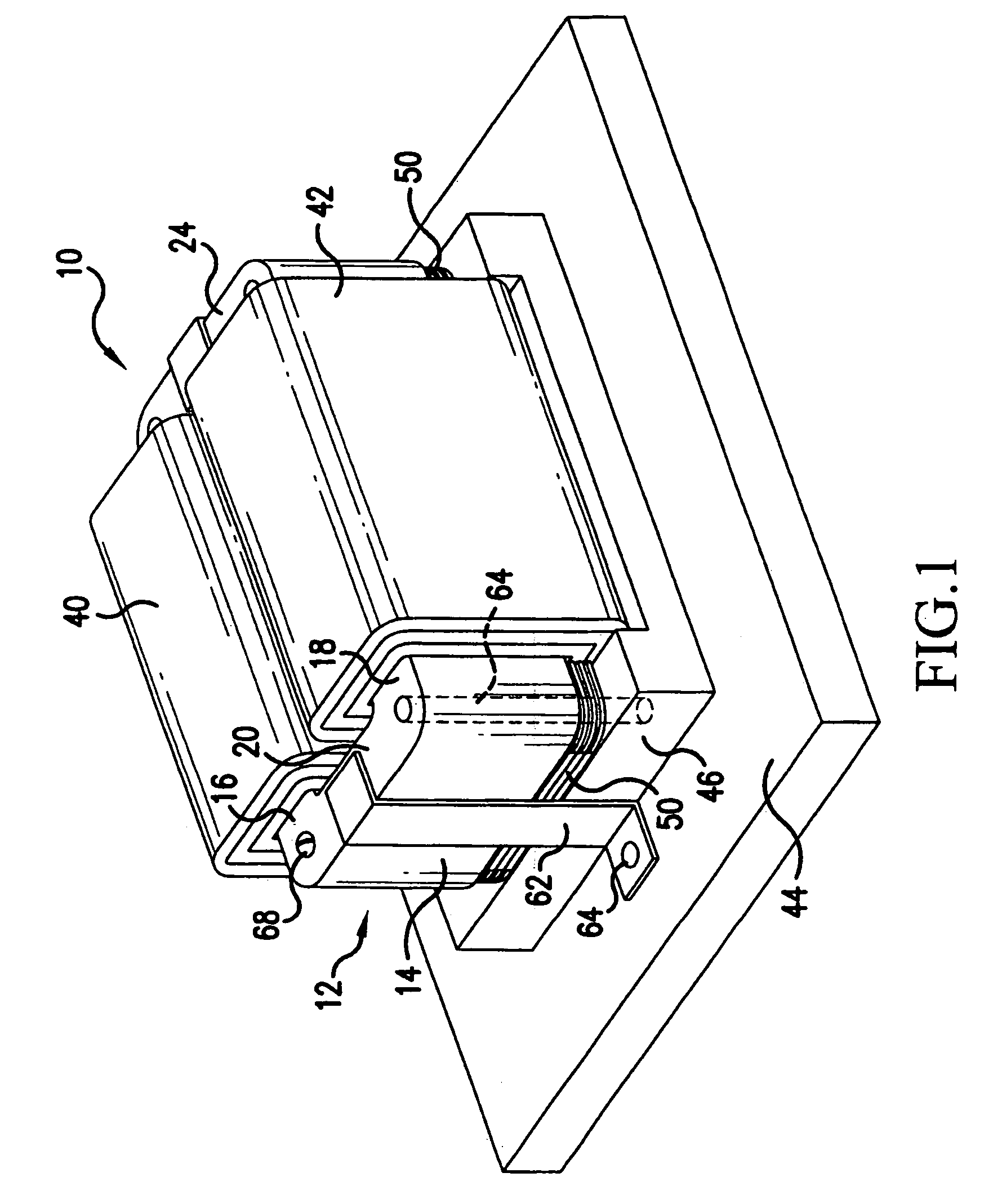
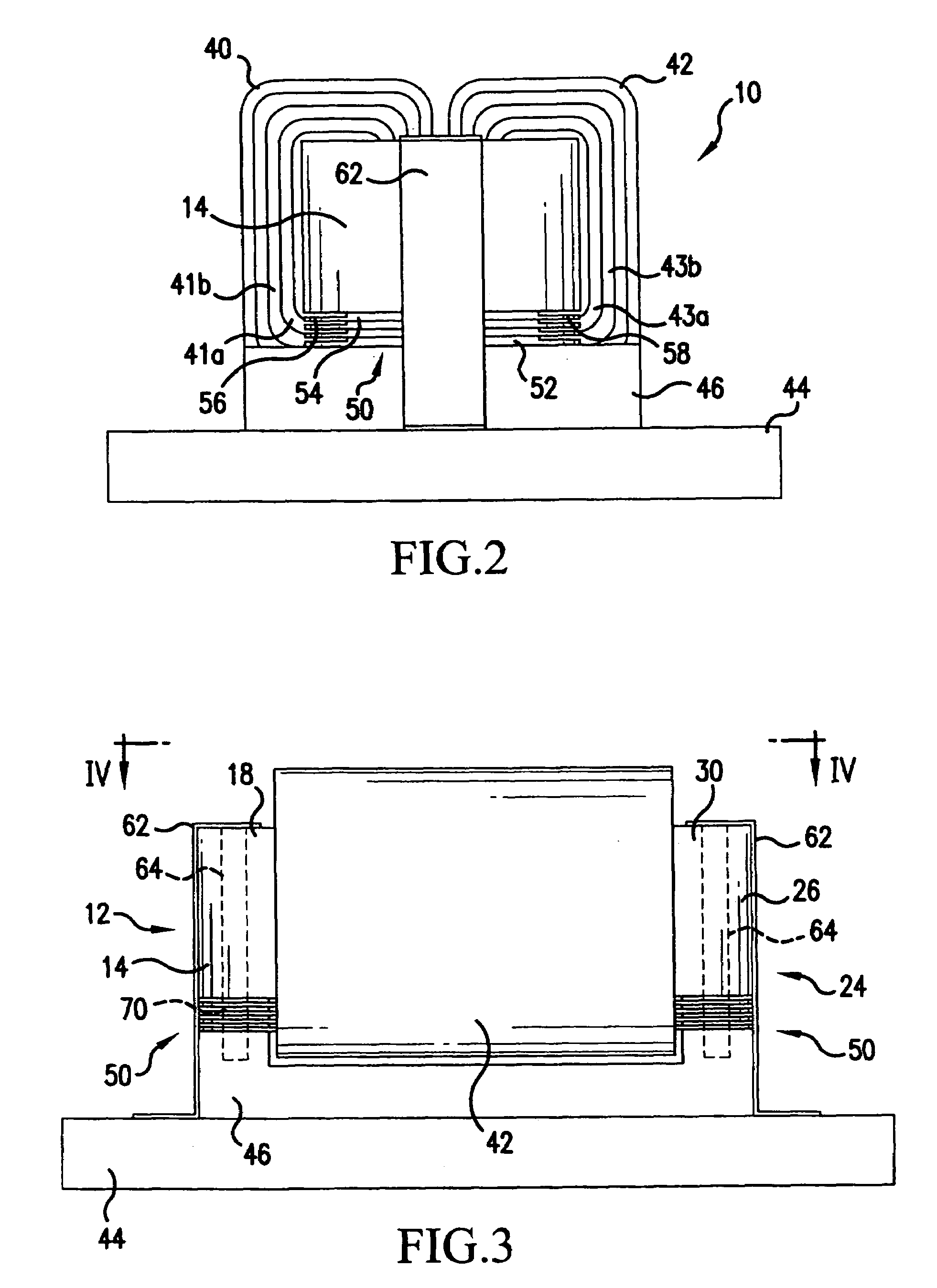
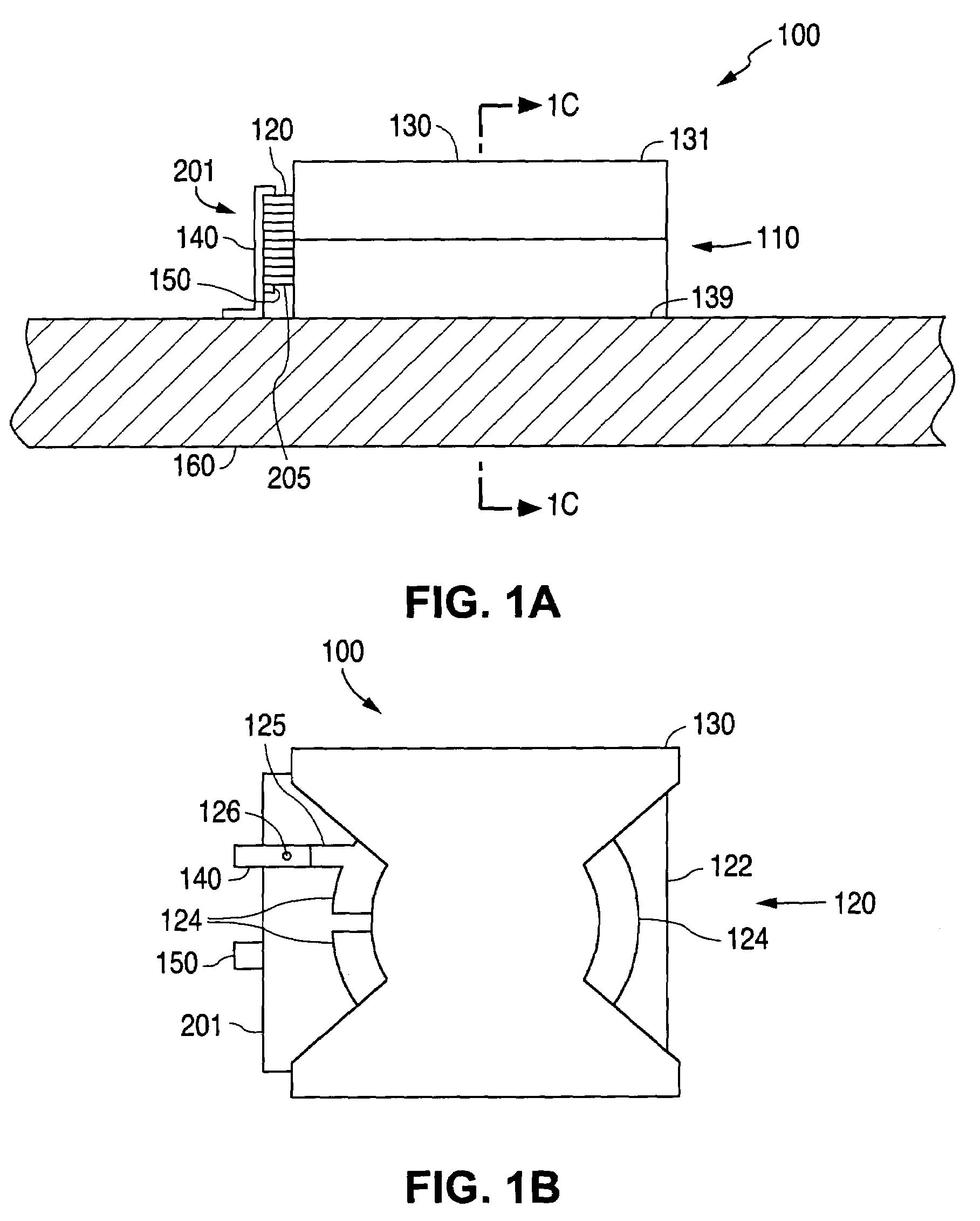
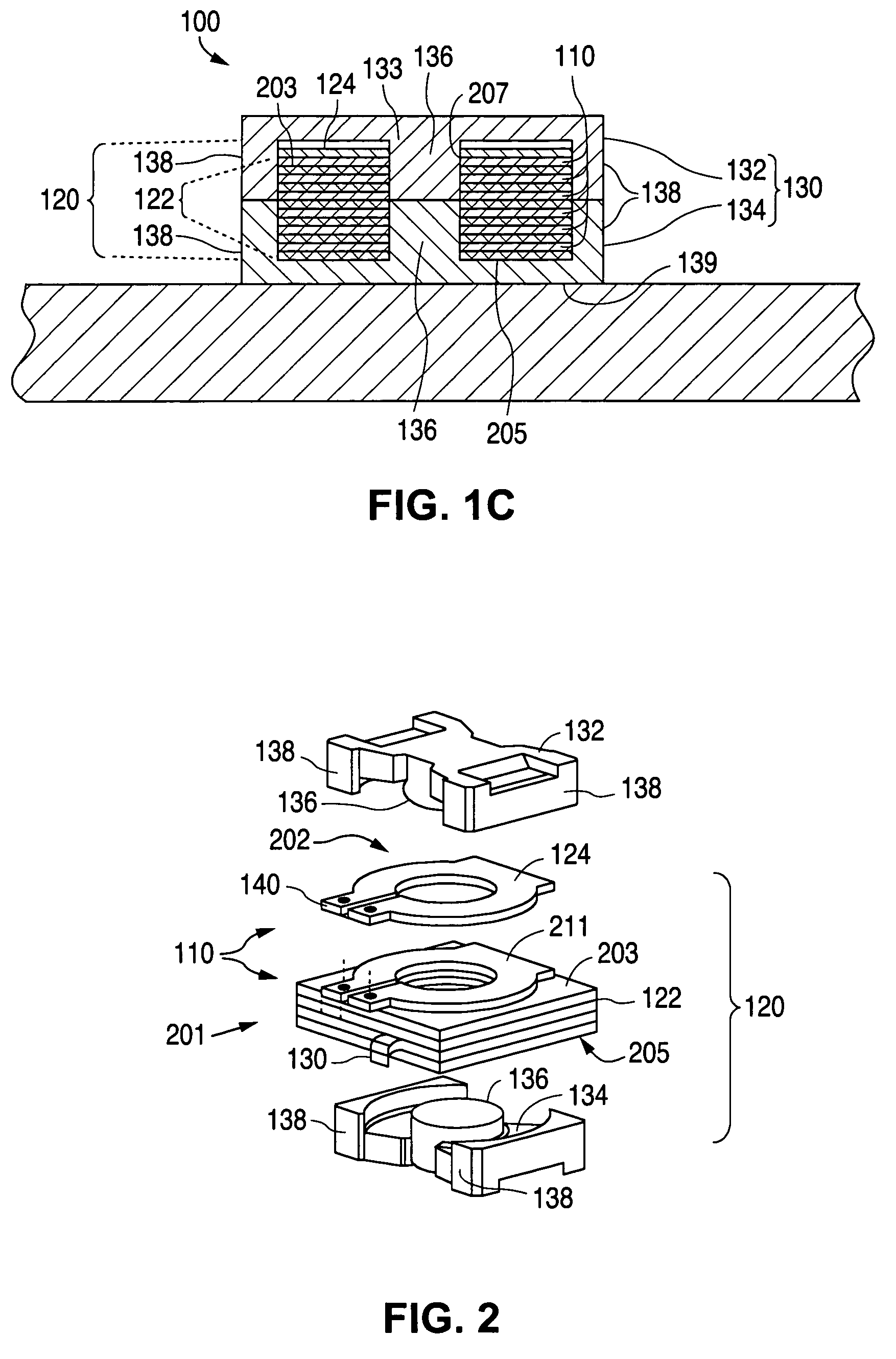
Electromagnetic device
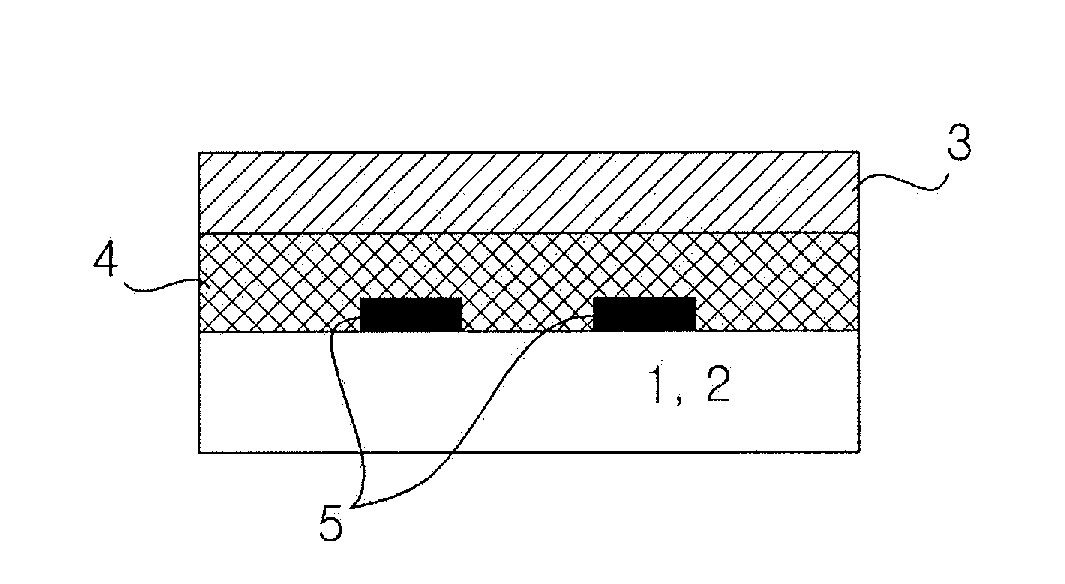
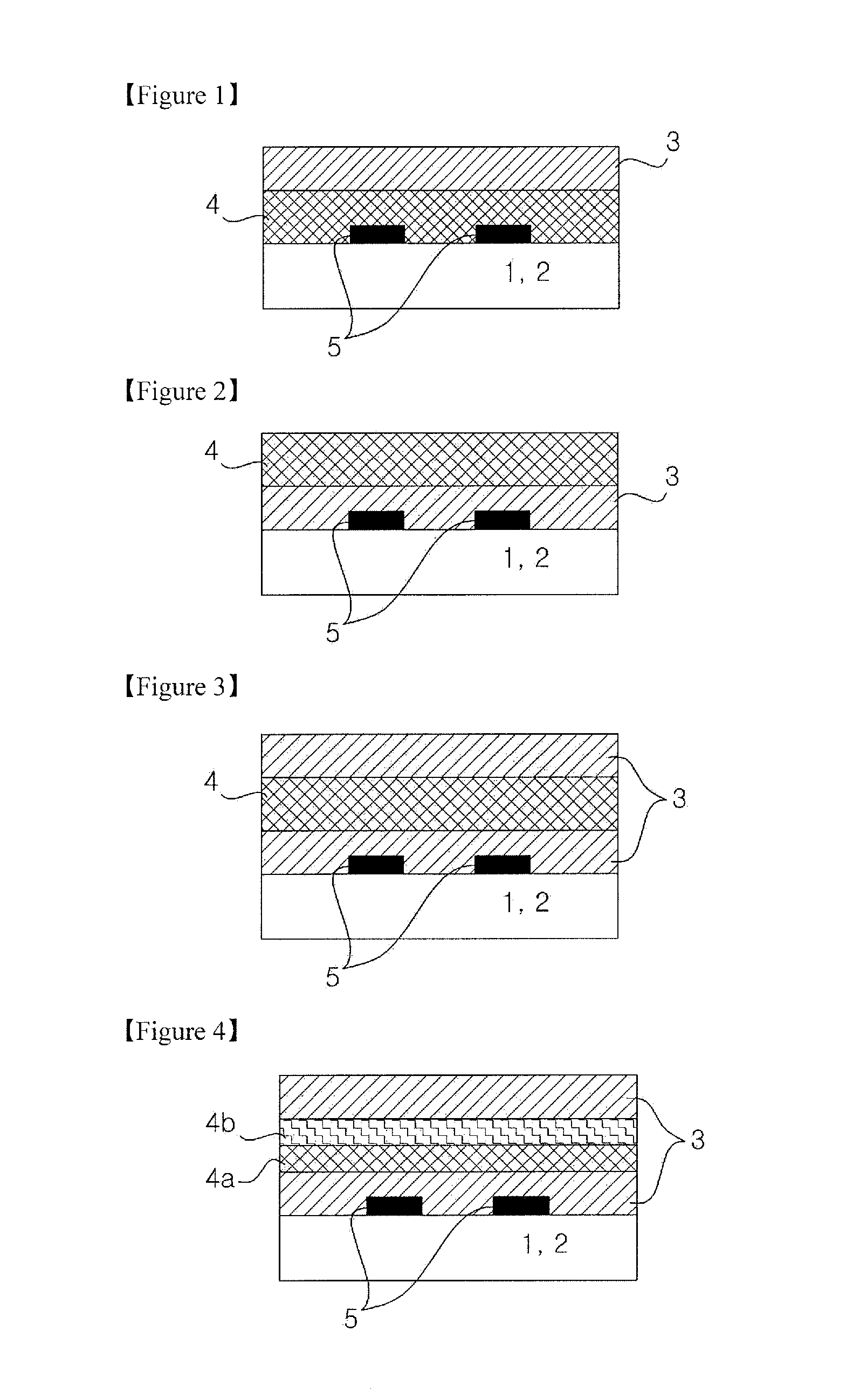
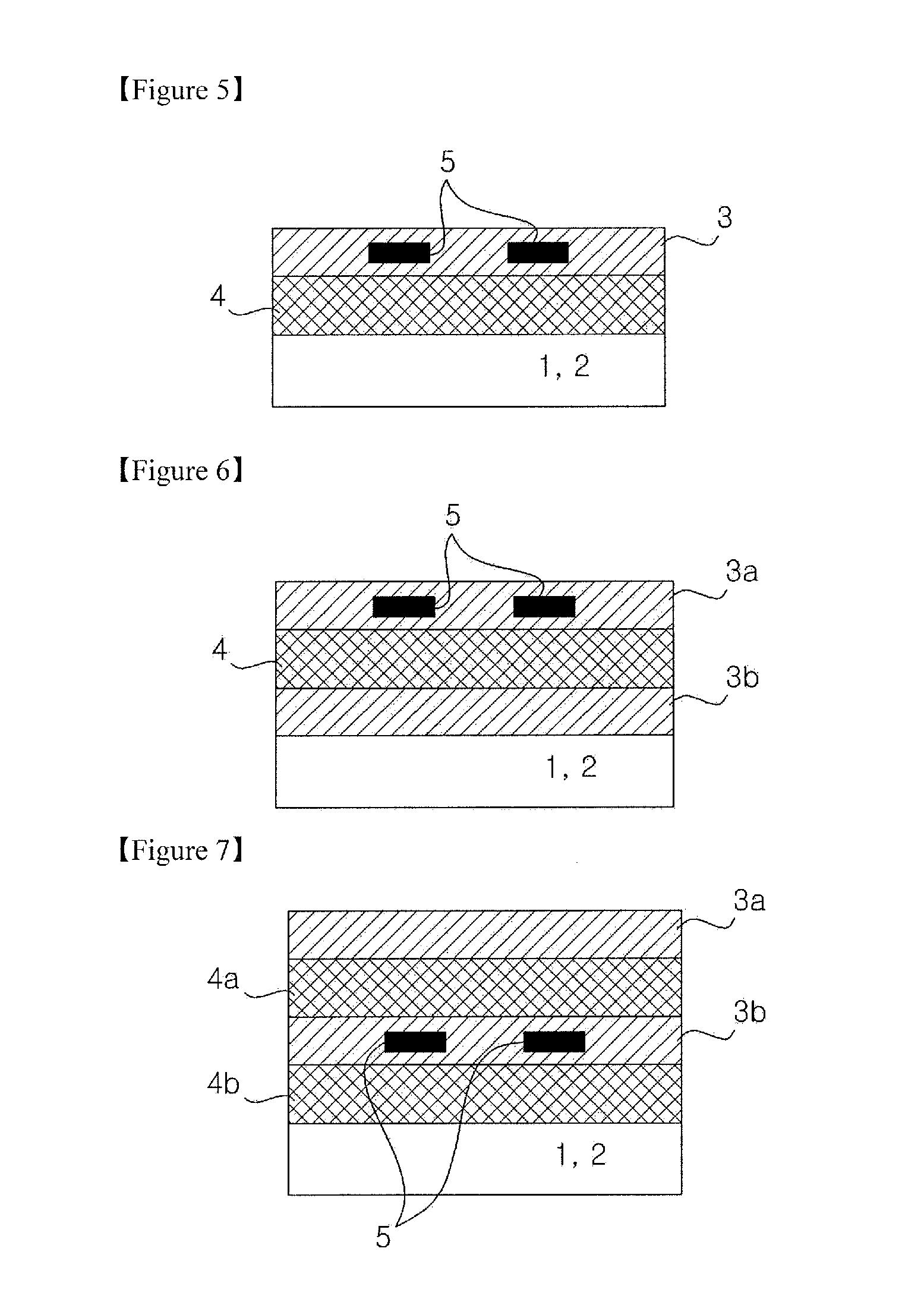
ActiveUS20080007133A1Reduce fillingEddy-current loss is reducedWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuitElectrical conductorEngineering
An electromagnetic device includes a plurality of coils formed by winding conductors. At least some of the conductors are constructed by stacking conductor constructional elements so that an eddy current generated by a leakage flux linked to the conductor is divided. An outer insulating member is disposed on an outer circumferential surface of the conductor stack for electrically insulating the conductor stack from another member. An inner insulating member whose thickness is smaller than a thickness of the outer insulating member is disposed between the conductor constructional elements adjoining to each other in the same conductor stack.
Owner:DENSO CORP
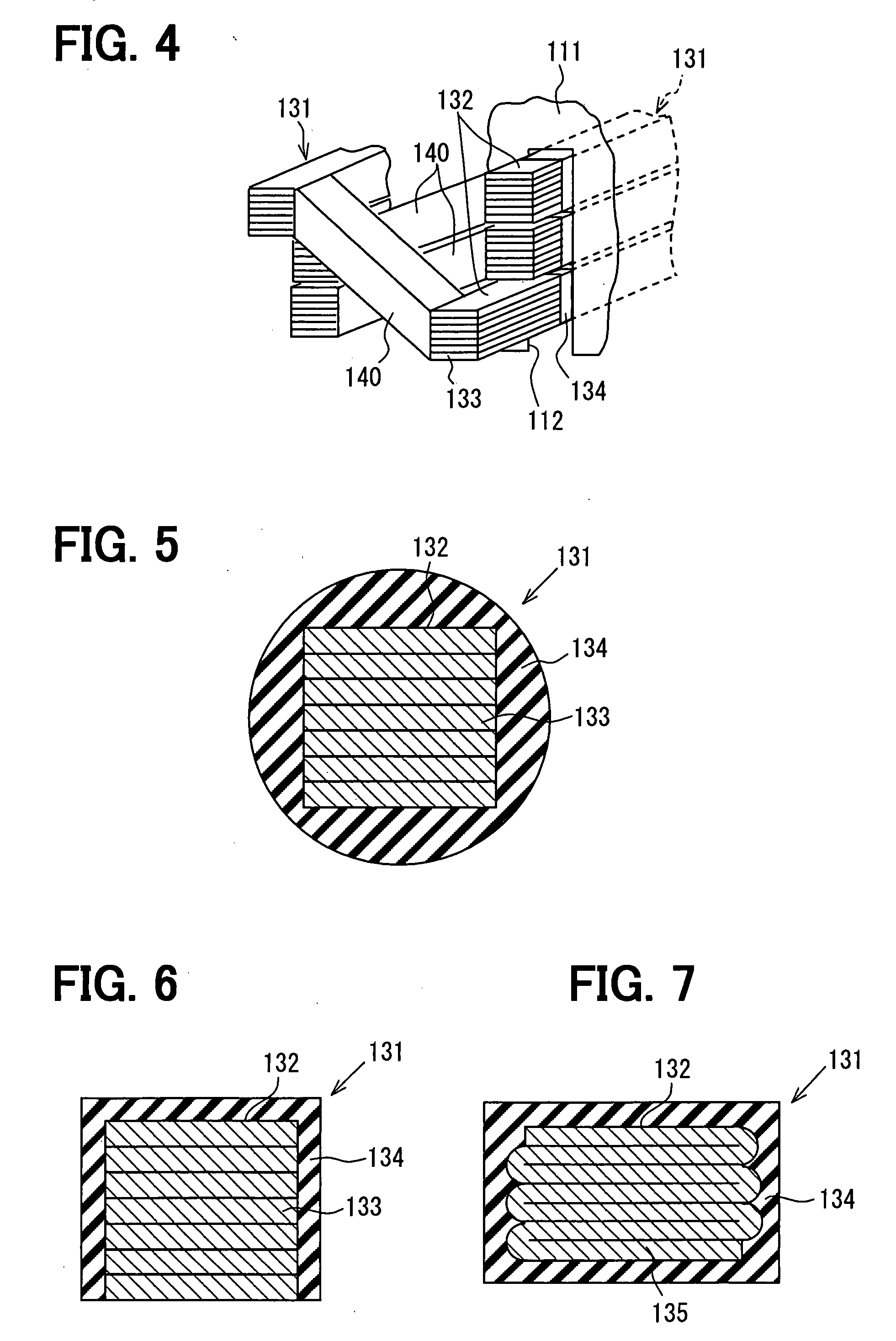
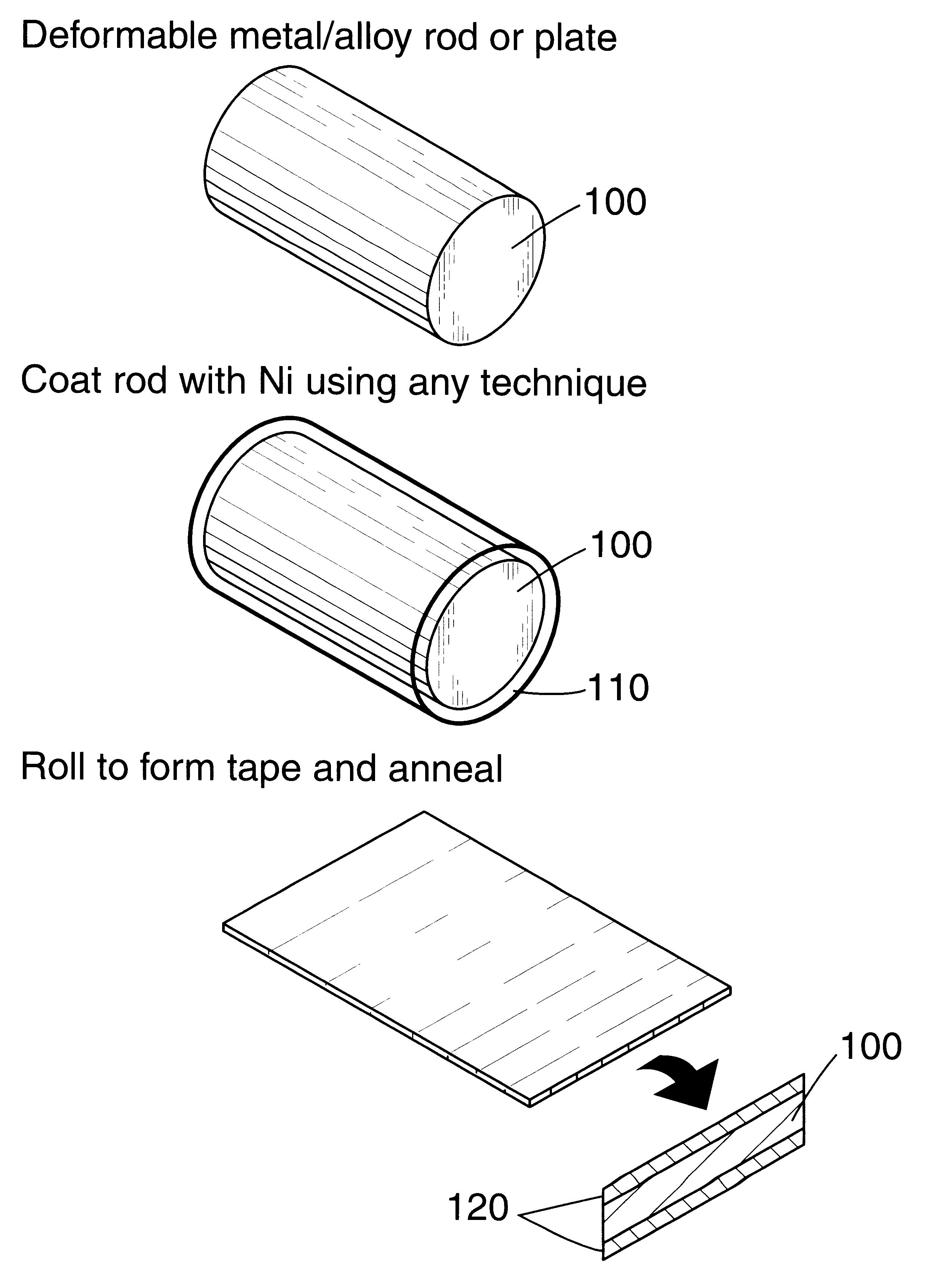
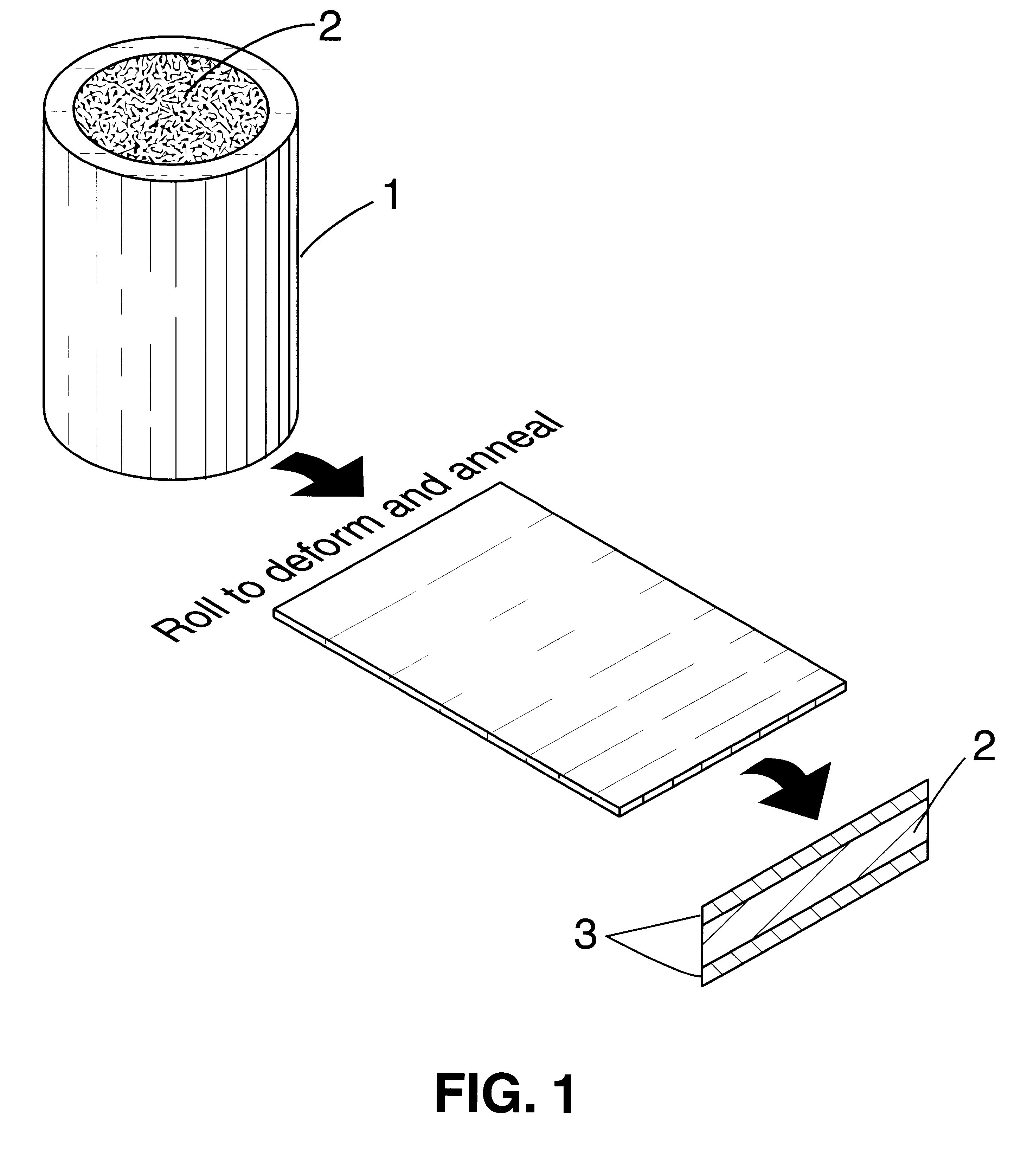
Biaxially textured articles formed by plastic deformation
InactiveUS6180570B1Improve superconductivityPolycrystalline material growthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetalMaterials science
A method of preparing a biaxially textured article comprises the steps of providing a metal preform, coating or laminating the preform with a metal layer, deforming the layer to a sufficient degree, and rapidly recrystallizing the layer to produce a biaxial texture. A superconducting epitaxial layer may then be deposited on the biaxial texture. In some embodiments the article further comprises buffer layers, electromagnetic devices or electro-optical devices.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
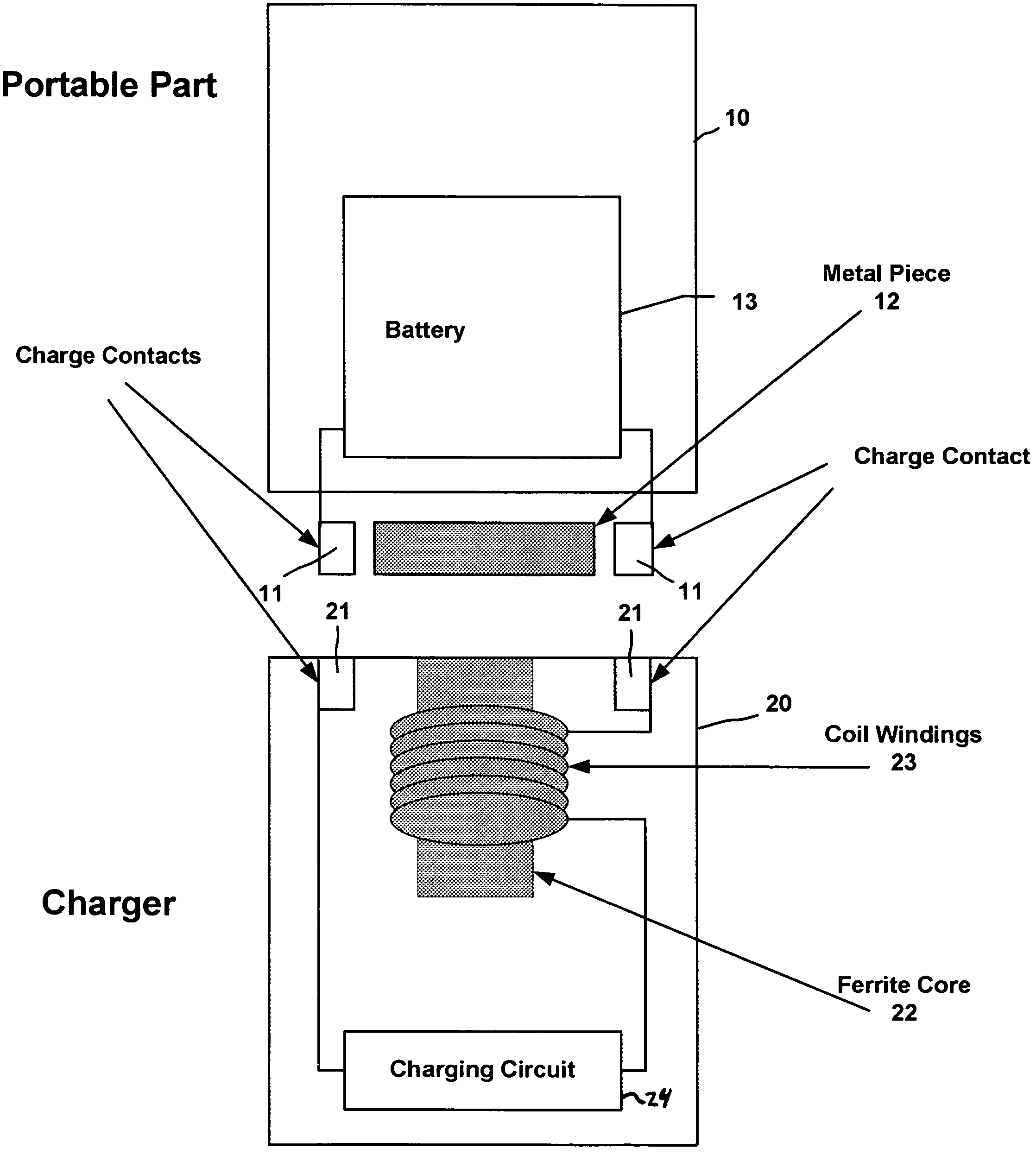
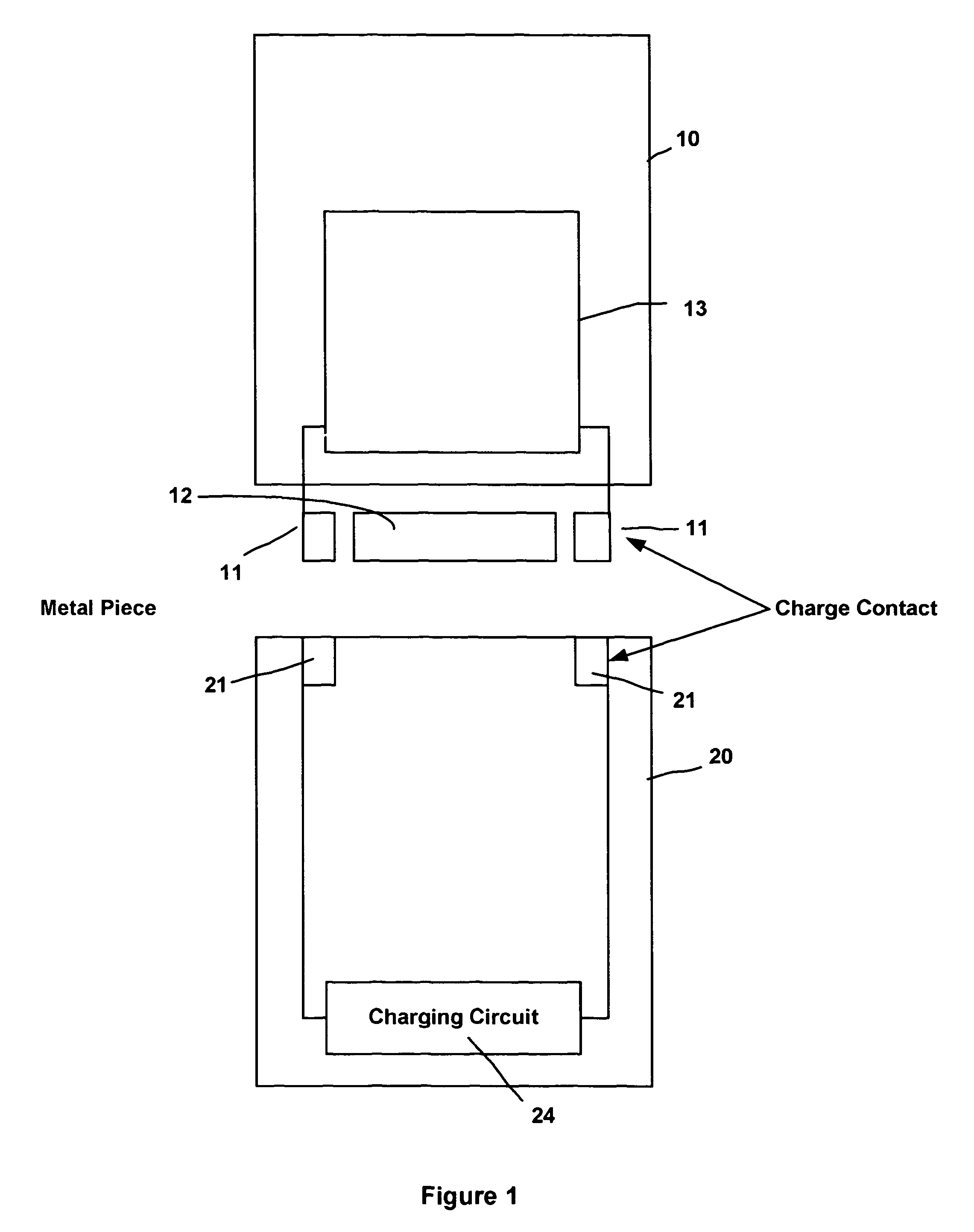
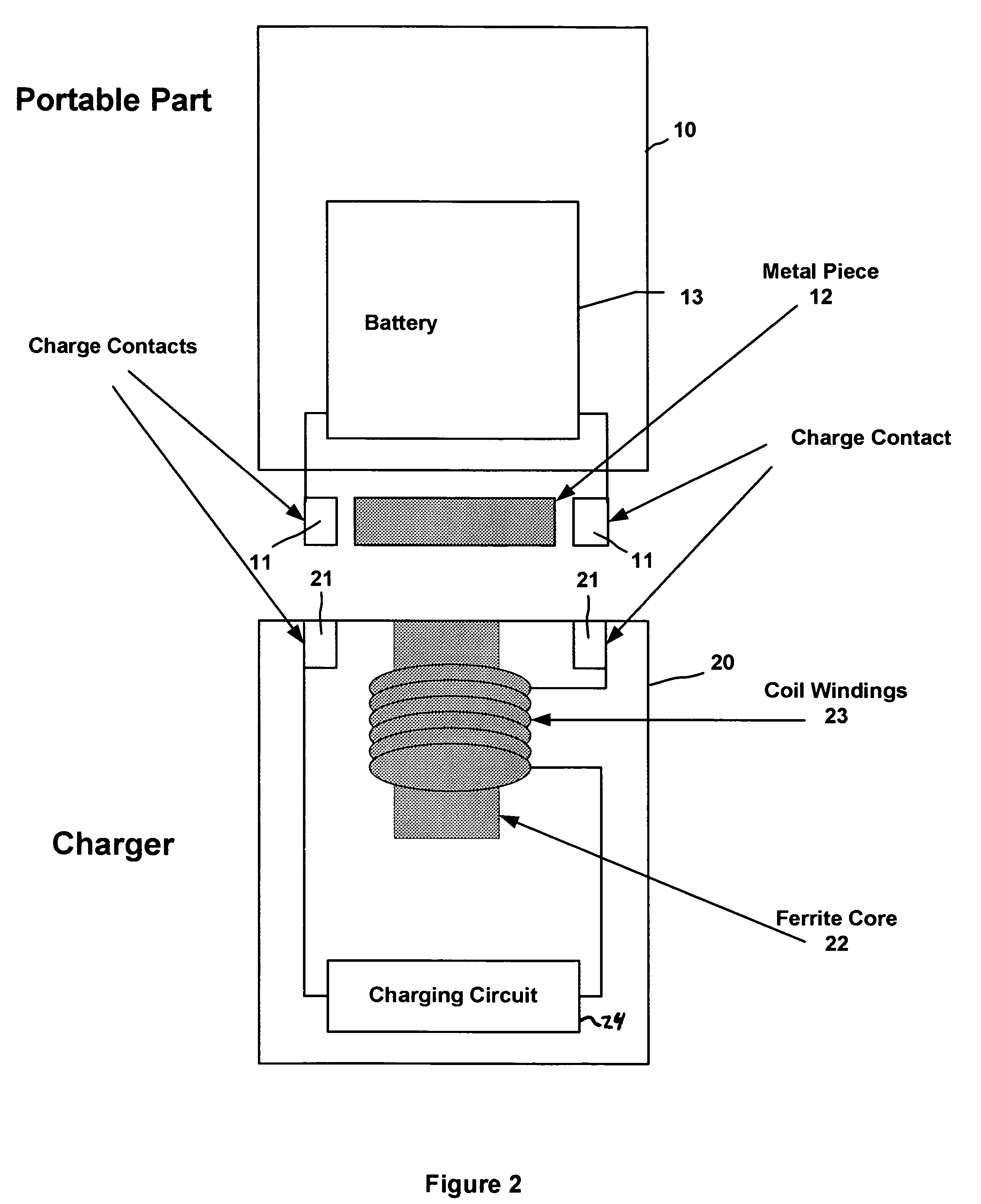
Magnetic holder for rechargeable devices
A charger cradle used for charging a battery of a portable electrical device. An electromagnetic device is disposed within the charger cradle proximate a metal piece of the cordless handset when the cordless handset is placed in a receiving portion of the charger cradle. The electromagnetic device generates a magnetic field when charge contacts of the charger cradle and the cordless handset are in contact and a charging current is conducted from a charging circuit of the charger cradle. The magnetic field attracts the metal piece of the cordless handset and securely holds the cordless handset into the receiving portion while the charging circuit charges the battery of the cordless handset.
Owner:VTECH TELECOMM
Electromechanical locking method and device
InactiveUS6902214B2Reduced size and costHigh locking strengthBuilding locksWing fastenersCatch and releaseMechanical engineering
An electromechanical lock includes a latching assembly secured to a first structure, a catch piece secured to a second structure, and an electromechanical device. The latching assembly includes at least one latch element movable between a capture and release states to mechanically engage and disengage the catch piece, an arming member movable between a first and second positions wherein the latch element is released and captured, and a biasing element to urge the arming member into the first position. When the electromagnetic device is switched “on”, it magnetically engages the arming member with sufficient force to overcome the biasing force whereby movement of the catch piece away from the received state results in the latch element moving into the capture state to prevent separation of the first and second structures; when the electromagnetic device is switched “off”, the first and second structures may be separated.
Owner:SMITH JERRY R
Active improvised explosive device (IED) electronic signature detection
ActiveUS8063813B1Easy to measureFacilitate locating and detectingDefence devicesCommunication jammingElectromagnetic launchMeasurement device
The present invention provides an apparatus and method of detecting, locating, and suppressing electronic devices, specifically IEDs. This RF emission measurement device in some embodiments can also be considered a system for RF emission measurement, location, and suppression. In some embodiments the apparatus comprises a high sensitivity receiver for receiving and analyzing electronic emissions. In other embodiments the apparatus comprises a high sensitivity receiver and an electromagnetic source for illuminating, and / or suppressing an electromagnetic device. The electromagnetic source could be any electromagnetic emitter known in the art, for example a magnetron or an adjustable wideband electromagnetic emitter.
Owner:NOKOMIS
Linear/rotary electromagnetic device
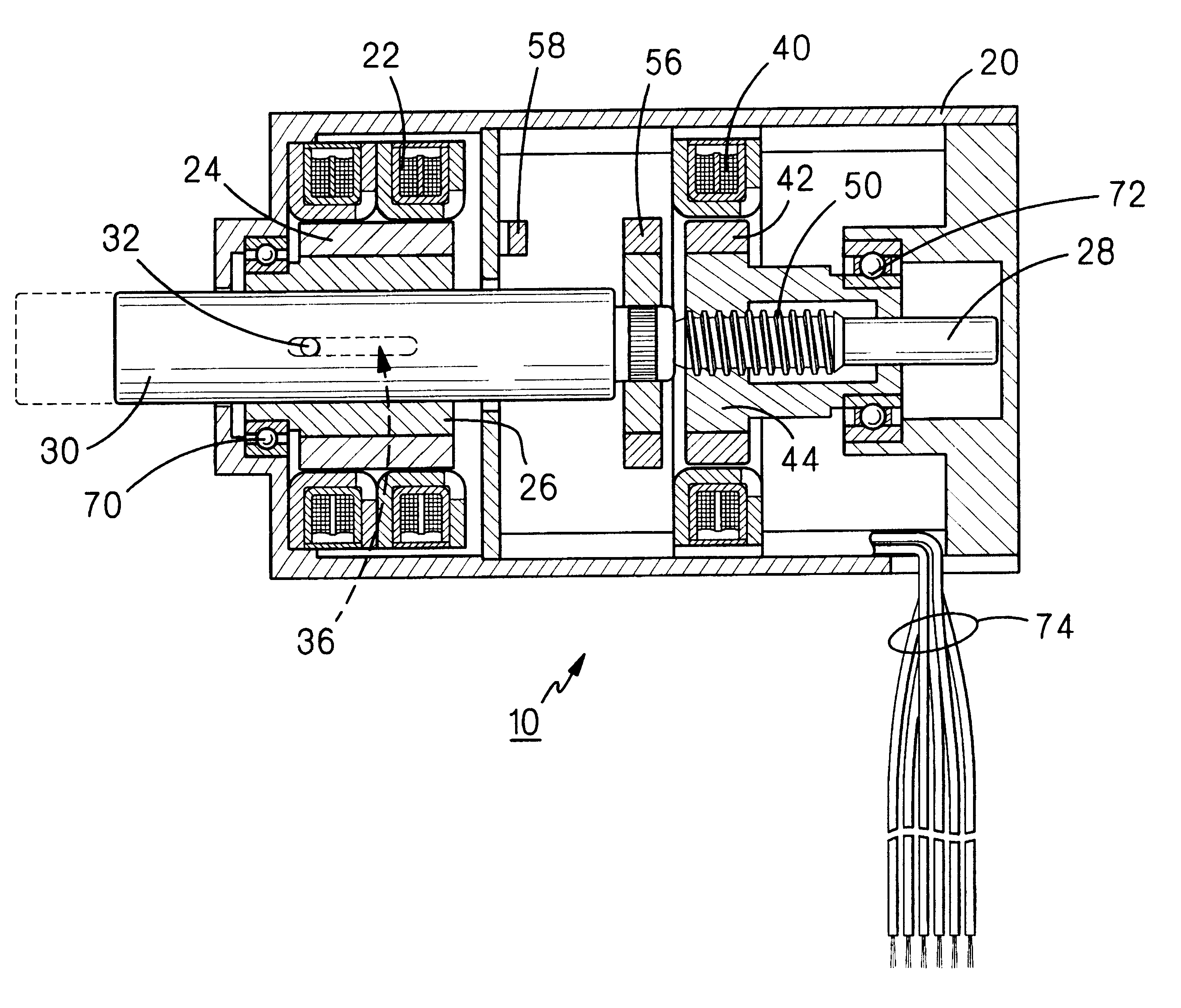
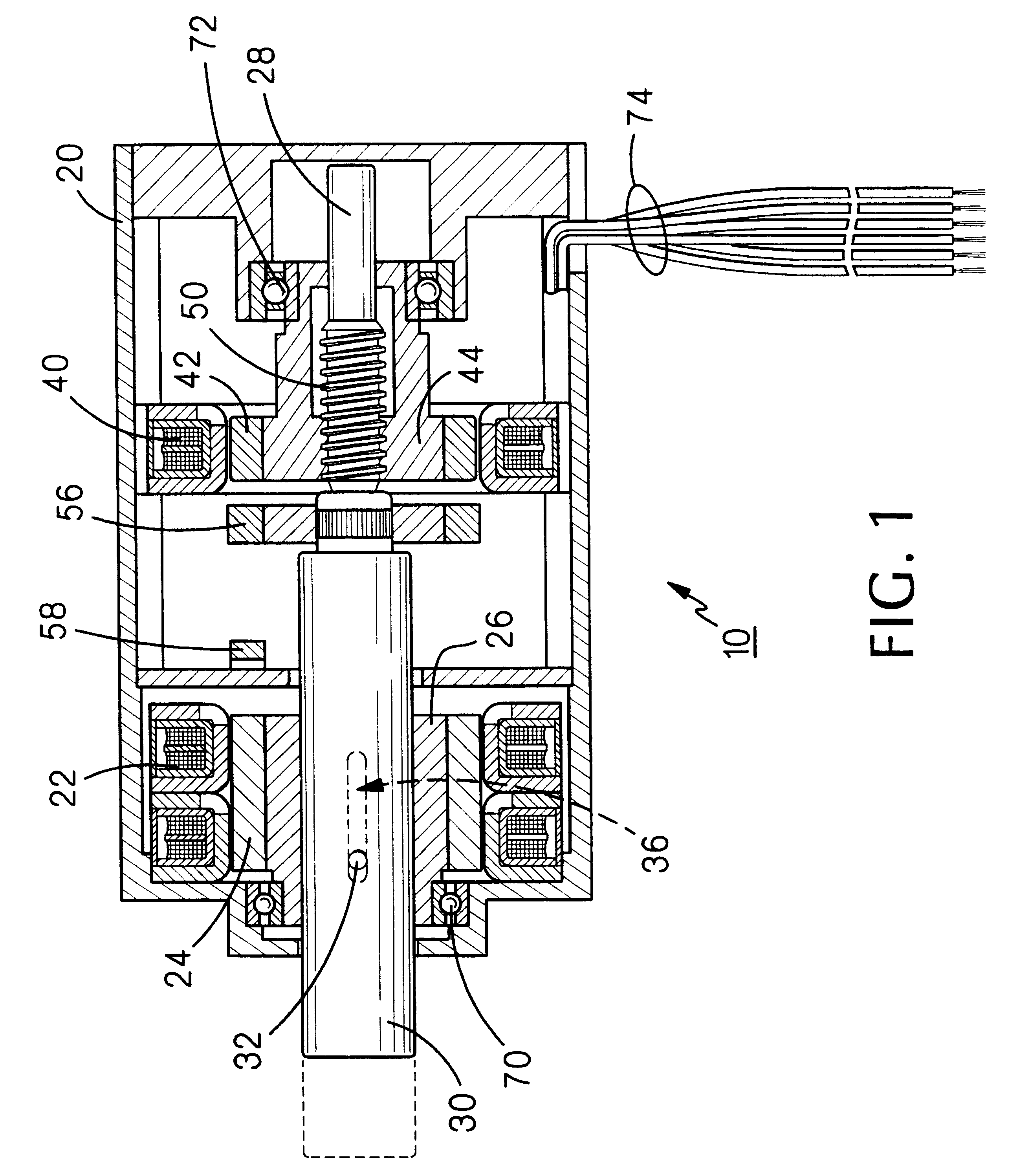
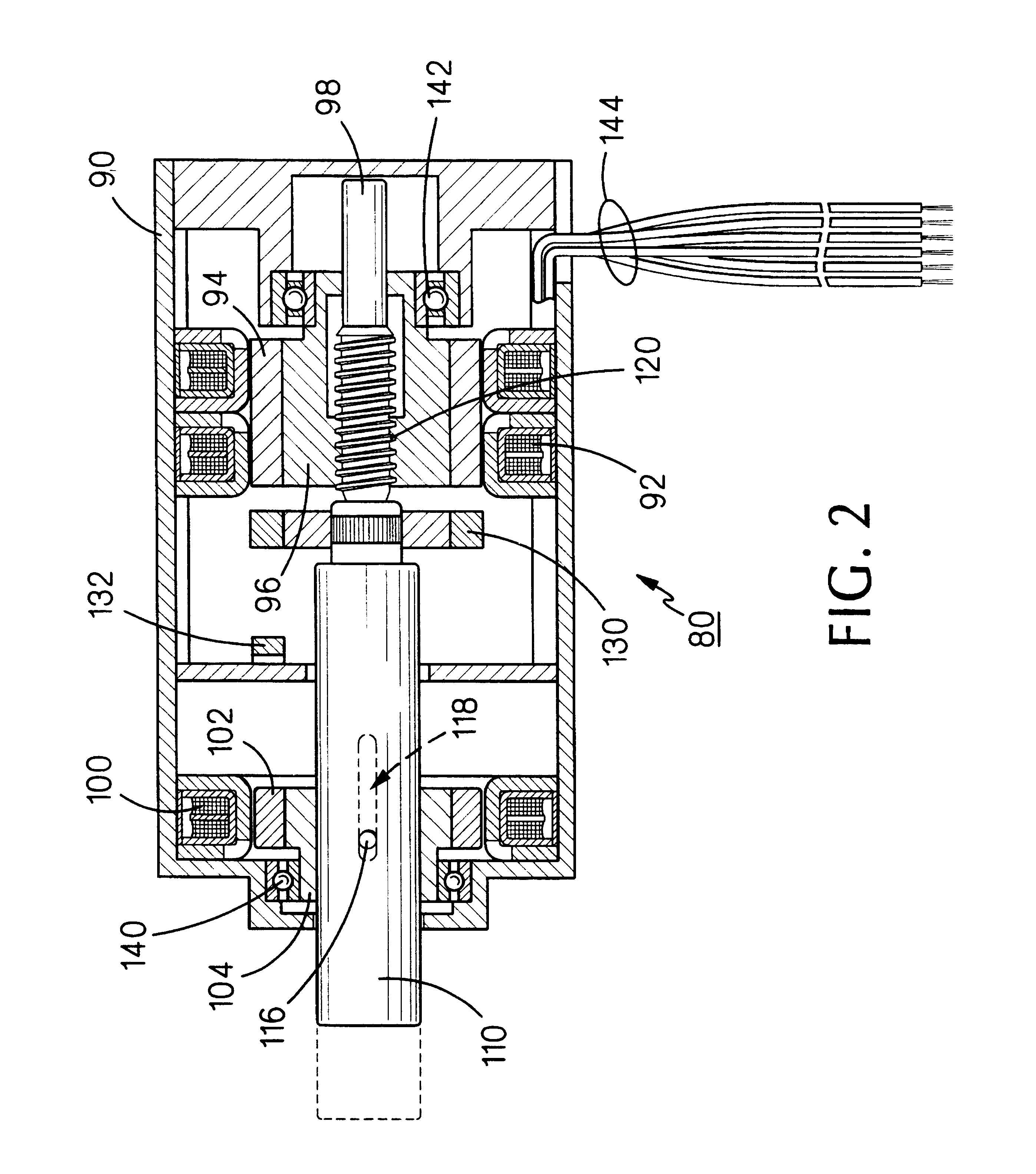
InactiveUS6211591B1Programme-controlled manipulatorMultiple dynamo-motor startersElectric machineEngineering
In a preferred embodiment, a linear / rotary electromagnetic device, including: a housing (20); first and second stators (22 and 40) disposed in the housing, first and second rotors (24 / 26 and 42 / 44) disposed in the housing and magnetically interacting, respectively, with the first and second stators; the first stator and the first rotor comprising a rotary motor; the second stator and the second rotor comprising an electromagnetic brake; a shaft (28) extending through a portion of the housing and axially through the first and second rotors, the shaft having a threaded portion (50) extending through a complementary threaded portion (44) of one of the first and second rotors; whereby; when the electromagnetic brake is locked and the rotary motor is rotated in a first direction, the shaft will move axially in a first direction; when the electromagnetic brake is locked and the rotary motor is rotated in the second direction, the shaft will move axially in a second direction; and when the electromagnetic brake is released and the rotary motor is rotated, the shaft will rotate with the rotary motor.
Owner:TRITEX
Passive layer for attenuation of near-field electromagnetic waves and heatdissipation including graphene, and electromagnetic device including the same
ActiveUS20140218867A1Reduce distractionsReduce noiseMagnetic/electric field screeningDecorative surface effectsUltrasound attenuationGraphene
The present invention relates to a passive layer including graphene for the attenuation of near-field electromagnetic waves and heat dissipation. The passive layer blocks electromagnetic waves radiated from an external electronic device or prevents electromagnetic waves generated in an electronic device from emitting to the outside. The passive layer is designed to reduce interference between transmission circuits of a device in the near-field region or influence such as malfunction caused by external electromagnetic waves. The present invention also relates to an electromagnetic device and a circuit board, each including the passive layer.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Modular heatsink, electromagnetic device incorporating a modular heatsink and method of cooling an electromagnetic device using a modular heatsink
InactiveUS7164584B2Transformers/inductances coolingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionModular designHeat spreader
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Slot-type induction charger
ActiveUS20130093386A1Less installation spacePractical to useBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectricityElectrical connector
A slot-type induction charger having light, thin, short and small characteristics is disclosed to include a power base holding therein a control module and a power-supplying coil module in a base member thereof for inducing an electric current, and an induction charging receiver set in the base member for receiving the induced electric current by electromagnetic induction from the power base for charging an electromagnetic device being connected to an electrical connector thereof. The power-supplying coil module and the power-receiving coil module each includes a magnetic conductor and a series of coils being alternatively and reversely wound around the magnetic conductor.
Owner:FU TONG TECH
Anti-terrorism communications systems and devices
InactiveUS20050273330A1Simplify the communication processFast transferSubstation equipmentSpeech recognitionEngineeringElectric power
An array of electromagnetic implements which, singly or in combination, enable audio, analog or digital communications over short or long distances using low power and a narrow (audio) bandwidth of 3 KHz or less, preferably 1 KHz or less. These electromagnetic implements maintain or restore emergency communications during terrorist and related disasters when commercial power is unavailable and traditional communications infrastructures and systems have failed. Conveyance of data is accomplished by computer generated voice transmission or by variously engineered tone transmissions, with or without quadrature amplitude modulation, forward error correction, and / or vocabulary encoding, among other features. Receipt of the data may be controlled by automated prioritization and transcription as well as manual or automated display on a computer screen.
Owner:JOHNSON RICHARD G
Multi-layer printed circuit board inductor winding with added metal foil layers
ActiveUS7248138B2High currentImprove efficiencyTransformers/inductances casingsPrinted electric component incorporationInductor windingsSurface mounting
The present invention provides an electromagnetic component formed from adjacent conducting layers of a multi-layer PCB and two additional conducting layers in contact with the PCB. The inventive component includes one or more winding turns formed by connecting the multiple layers of the multi-layer PCB with conductive vias and by connecting the additional conducting layers to respective top and bottom surfaces of the PCB. In one embodiment, one of the conducting layers is soldered to a top conducting layer of the PCB and the other of the conductive layers is soldered to a bottom conducting layer of the PCB, effectively increasing the cross-sectional area of the top and bottom winding layers. In another embodiment, the additional conducting layers are separated from the adjacent conducting PCB layers by a layer of insulation, permitting the additional conducting layers to form separate winding turns. The inventive winding stack can be surface mounted to a PCB, and can be used as an inductor, or in other electromagnetic devices. The winding thus constructed is capable of accepting larger currents with lower resulting temperature increases than windings formed only from PCBs, and are less expensive to manufacture than PCB-only windings.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
System and method for electronically controlling resistance of an exercise machine
ActiveUS7648446B2Increases pedal resistanceDecreases pedal resistanceMuscle exercising devicesMovement coordination devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceControl system
A stationary exercise machine includes a system for electronically controlling a pedal resistance so as to simulate the riding of a road-going bicycle. The exercise machine includes a control system that monitors pedal velocity and that controls the resistive load generated by an electronically-controlled resistance mechanism. In one example, an electromagnetic device may vary a resistive load placed on a flywheel, which, in turn, varies the pedal resistance experienced by a user. When the user increases the pedal velocity, the resistance mechanism increases the resistive load. When the user decreases the pedal velocity, the resistance mechanism decreases the resistive load. In another example, the resistance mechanism varies the resistive load based on a gear selection by the user. The control system may also take into account other factors, such as the grade of the simulated ride, simulated wind resistance, or other frictional forces when calculating the resistive load.
Owner:CORE HEALTH & FITNESS
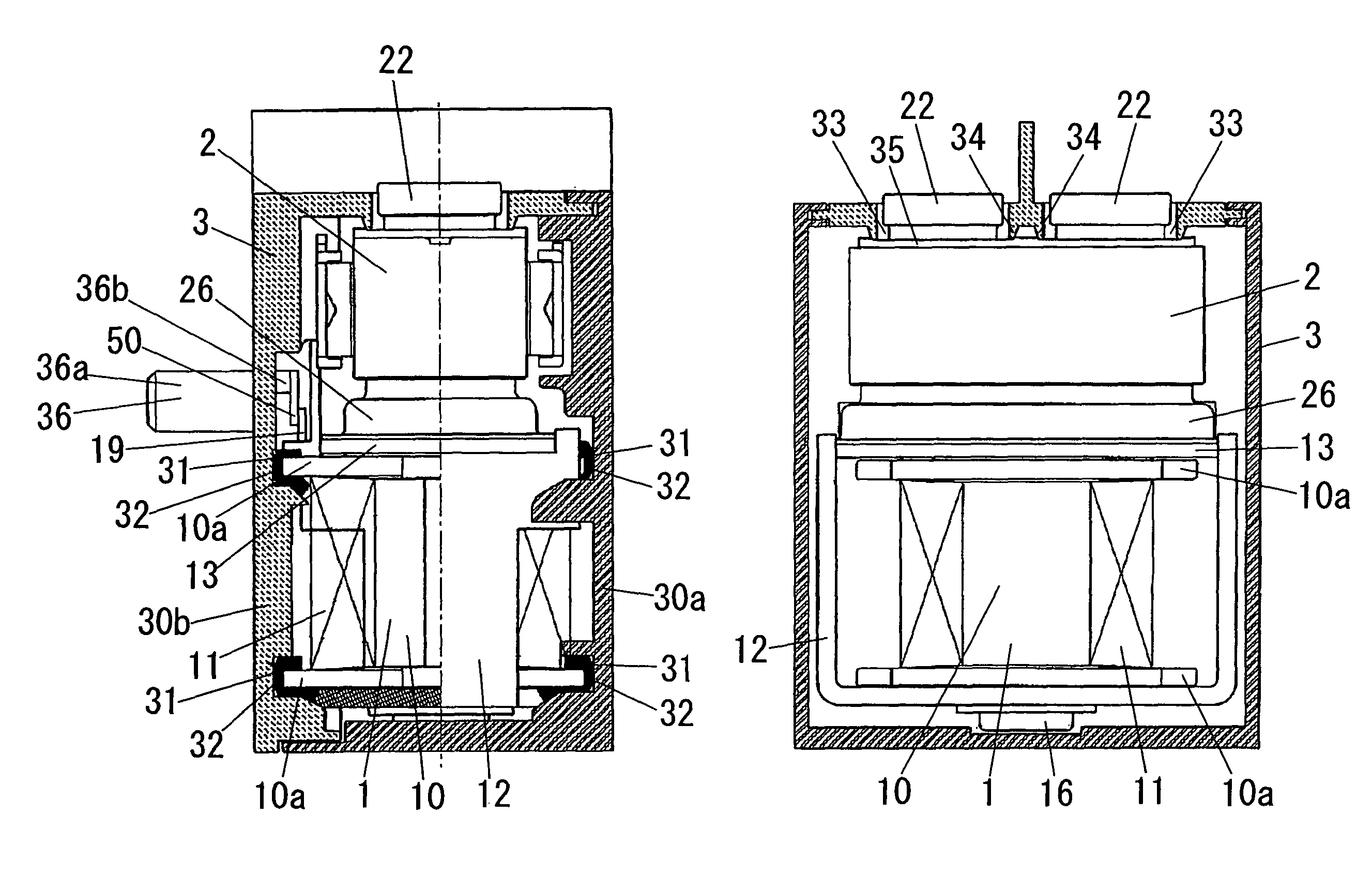
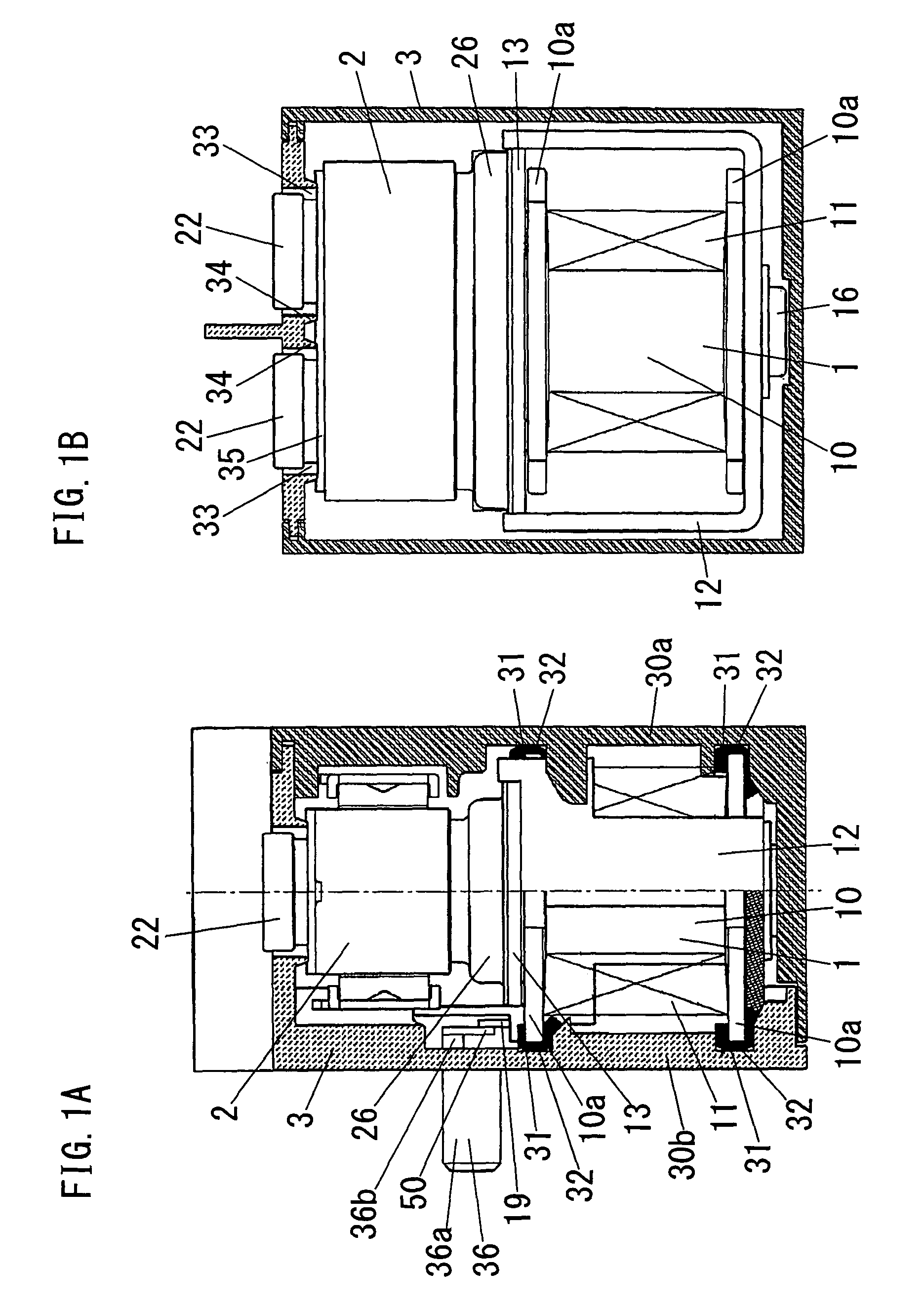
Electromagnetic switching device
ActiveUS7876183B2Reduce vibrationReduce impactContact vibration/shock dampingElectromagnetic relay detailsBobbinEngineering
This electromagnetic switching device comprises an electromagnetic device 1 in which a movable core 15 comes into contact with or separates from a fixed core 14 in response to energization of an excitation coil 11 wound around a coil bobbin 10 a contact device 2 with a fixed contact 21 and a movable contact which comes into contact with or separates from the fixed contact in conjunction with a movement of the movable core 15 of the electromagnetic device, and a boxy case 3 configured to house the electromagnetic device and the contact device. The coil bobbin 10 has a flange 10a at its end in an axis direction of the coil bobbin, and the case 3 has, on its inner surface, a recess 31 into which a periphery of the flange 10a of the coil bobbin is fitted, and a cushioning member 32 for absorbing an impact which is transmitted from the electromagnetic device to the case is disposed in the recess, and the flange of the coil bobbin is supported by the recess through the cushioning member whereby the electromagnetic device is supported in the case.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Slot-type induction charger
ActiveUS8729854B2Increasing the thicknessLight and thin and short and small characteristicBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectricityEngineering
A slot-type induction charger having light, thin, short and small characteristics is disclosed to include a power base holding therein a control module and a power-supplying coil module in a base member thereof for inducing an electric current, and an induction charging receiver set in the base member for receiving the induced electric current by electromagnetic induction from the power base for charging an electromagnetic device being connected to an electrical connector thereof. The power-supplying coil module and the power-receiving coil module each includes a magnetic conductor and a series of coils being alternatively and reversely wound around the magnetic conductor.
Owner:FU TONG TECH
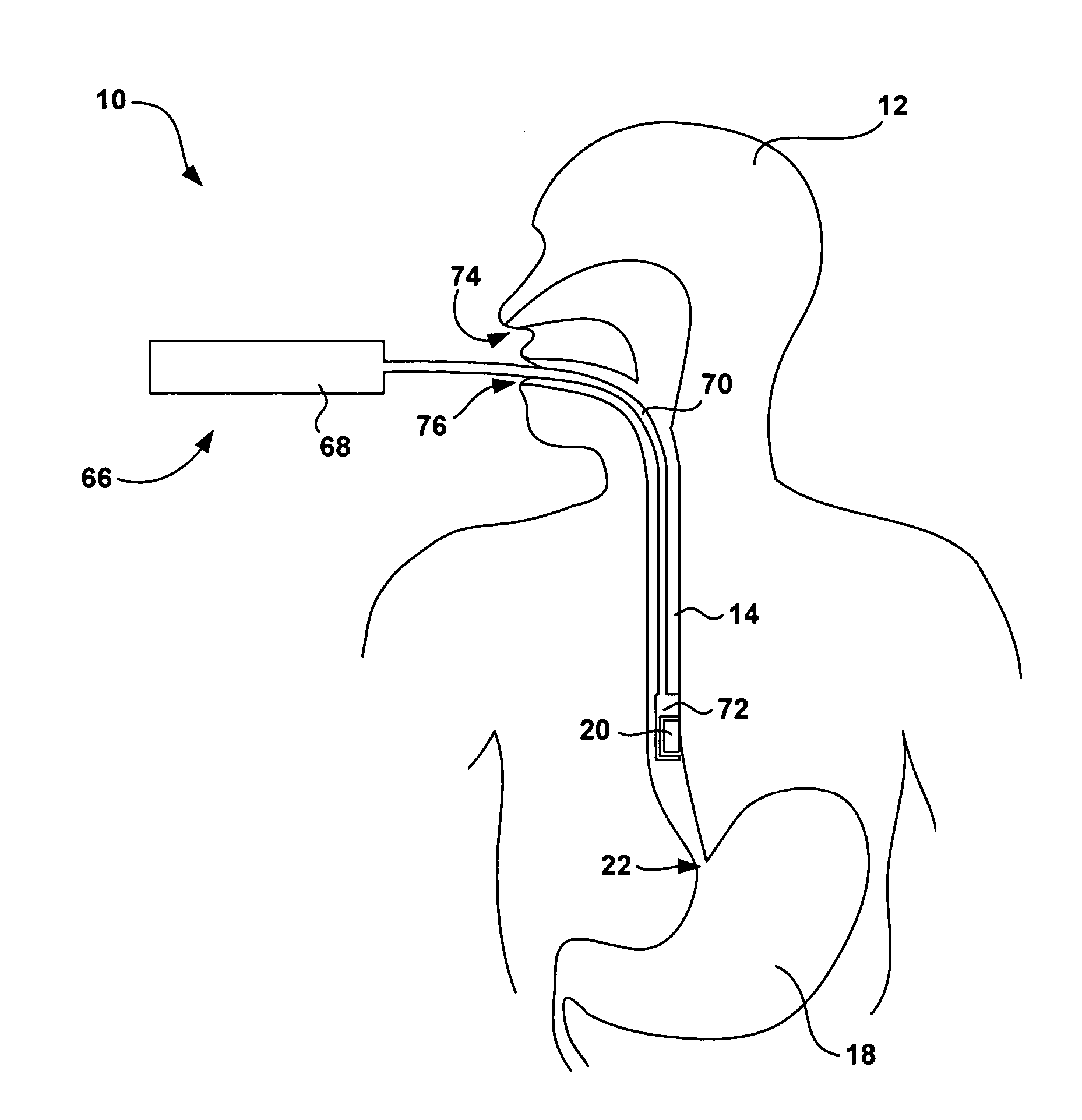
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and method of using same
ActiveUS20080207985A1Avoid problemsElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationPulsed DC
The present disclosure relates to an apparatus and associated methods to produce analgesia in a mammal by providing an electrical nerve stimulus utilizing a pulsed input of low level electrical current, wherein the level of current is measurable with the measurements utilized to at least adjust the strength of the current according to selected parameters. Additionally, the use of magnets to produce a magnetic field to further control chronic and acute pain. In exemplary implementations, the apparatus maintains continuous monitoring of the electrical characteristics of TENS at the site of input and output, and the electrical input can be modified during treatment to obtain desired electrical input. More particularly the disclosure relates to an electromagnetic apparatus incorporating pulsed direct current, two or more electrodes, and at least two dipole antennas wherein the dipole antenna circuits receive and analyze signal from the dipole antennas, using the information from signal analysis within the methods for producing analgesia in mammals. The strength of the current that the patient is receiving at the targeted site as the actual field is measured by the dipole antennas and adjustment is not dependent on subjective measurements to ascertain whether the proper amplitude, frequency and pulse duration are being applied.
Owner:WILSON SPENCE L
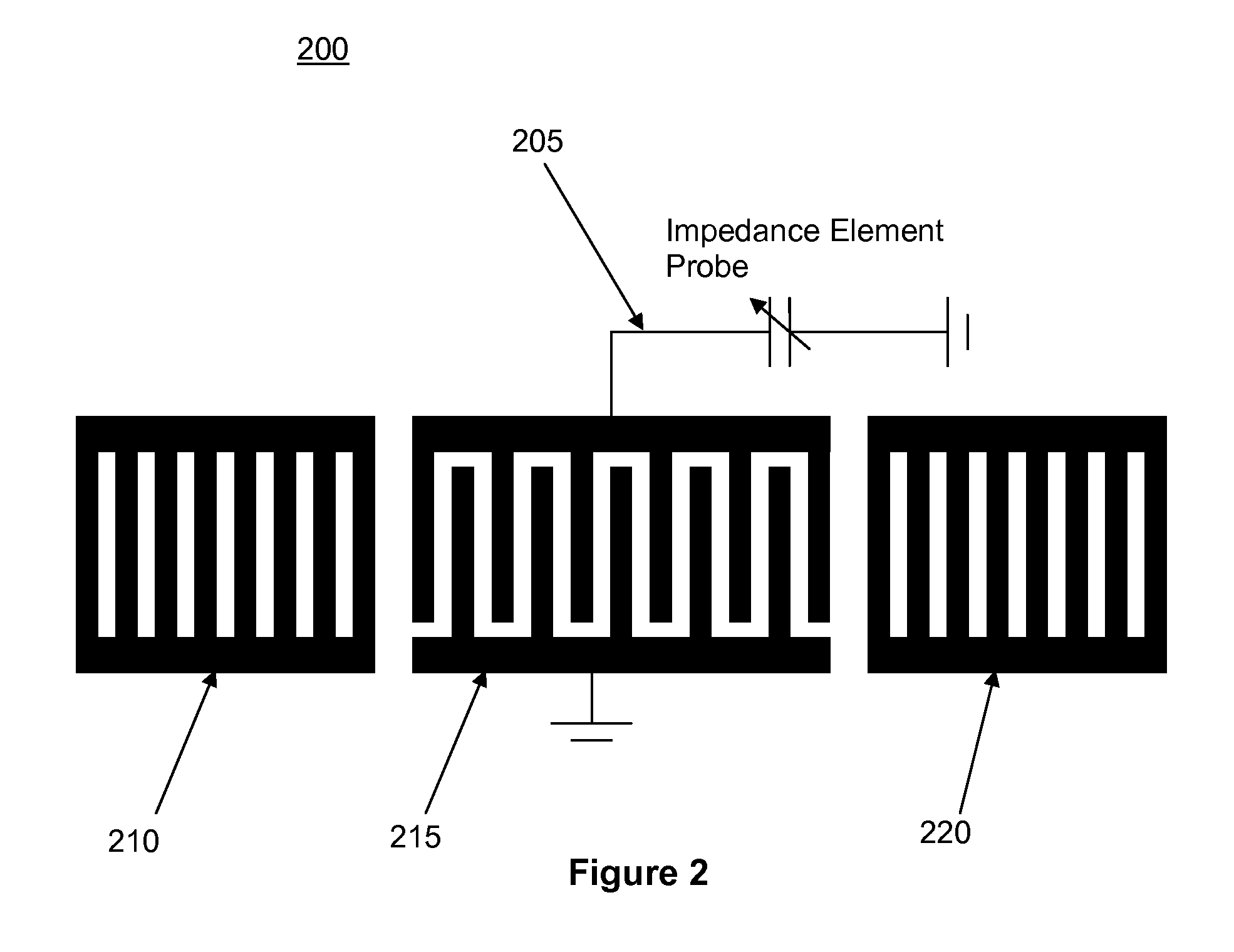
Acoustic wave device physical parameter sensor
InactiveUS20090206844A1Small sizeLow priceAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic measurementsSurface acoustic wave sensorMicroelectromechanical systems
An acoustic wave sensor employs an electromagnetic device (EMD) to transduce and amplify the response of an impedance element to a physical measurand. One embodiment uses a magnetic field sensor employing a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) capacitor to affect a change in the response of a SAW filter.
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP HIGH PERFORMANCE TIMING
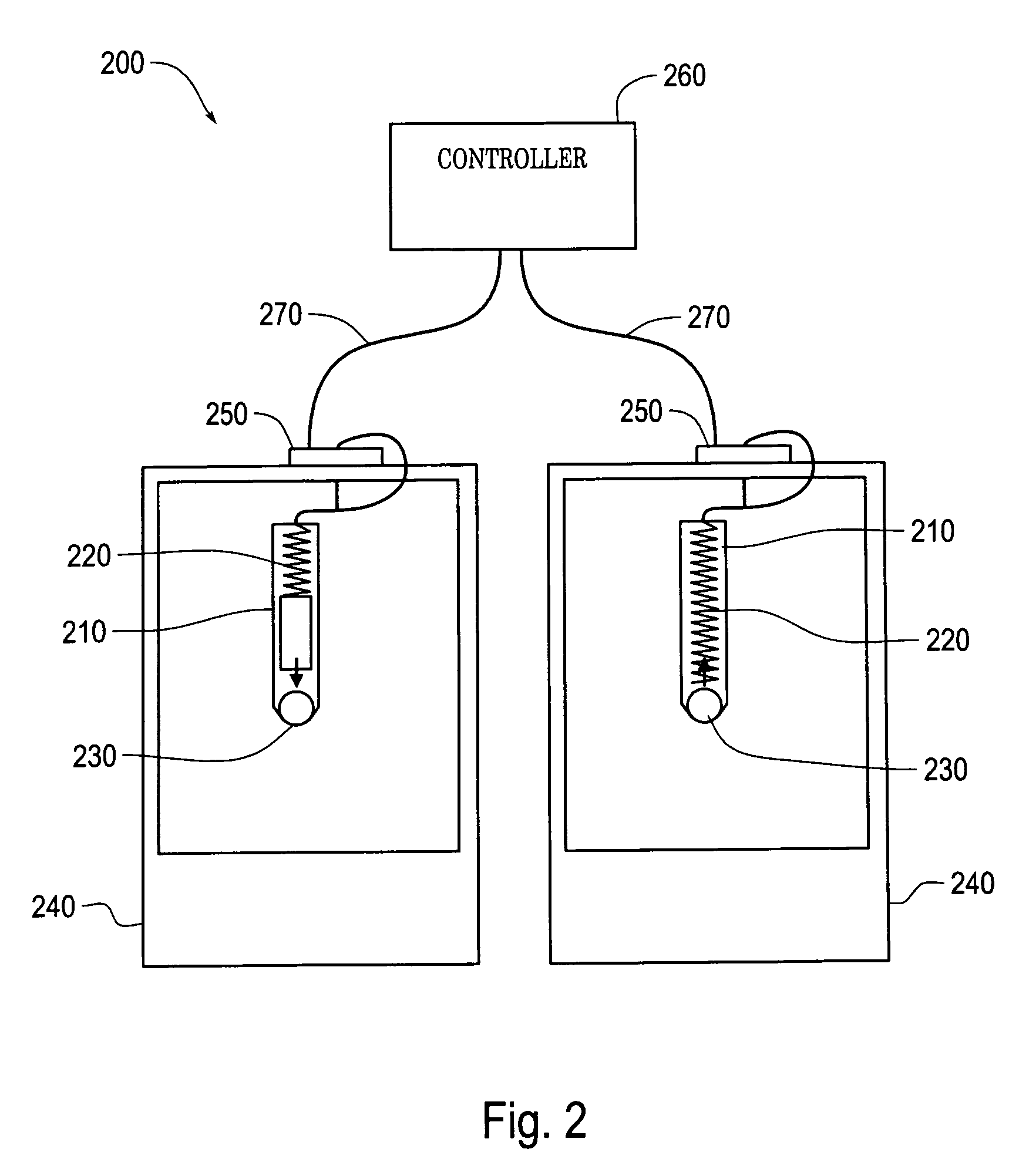
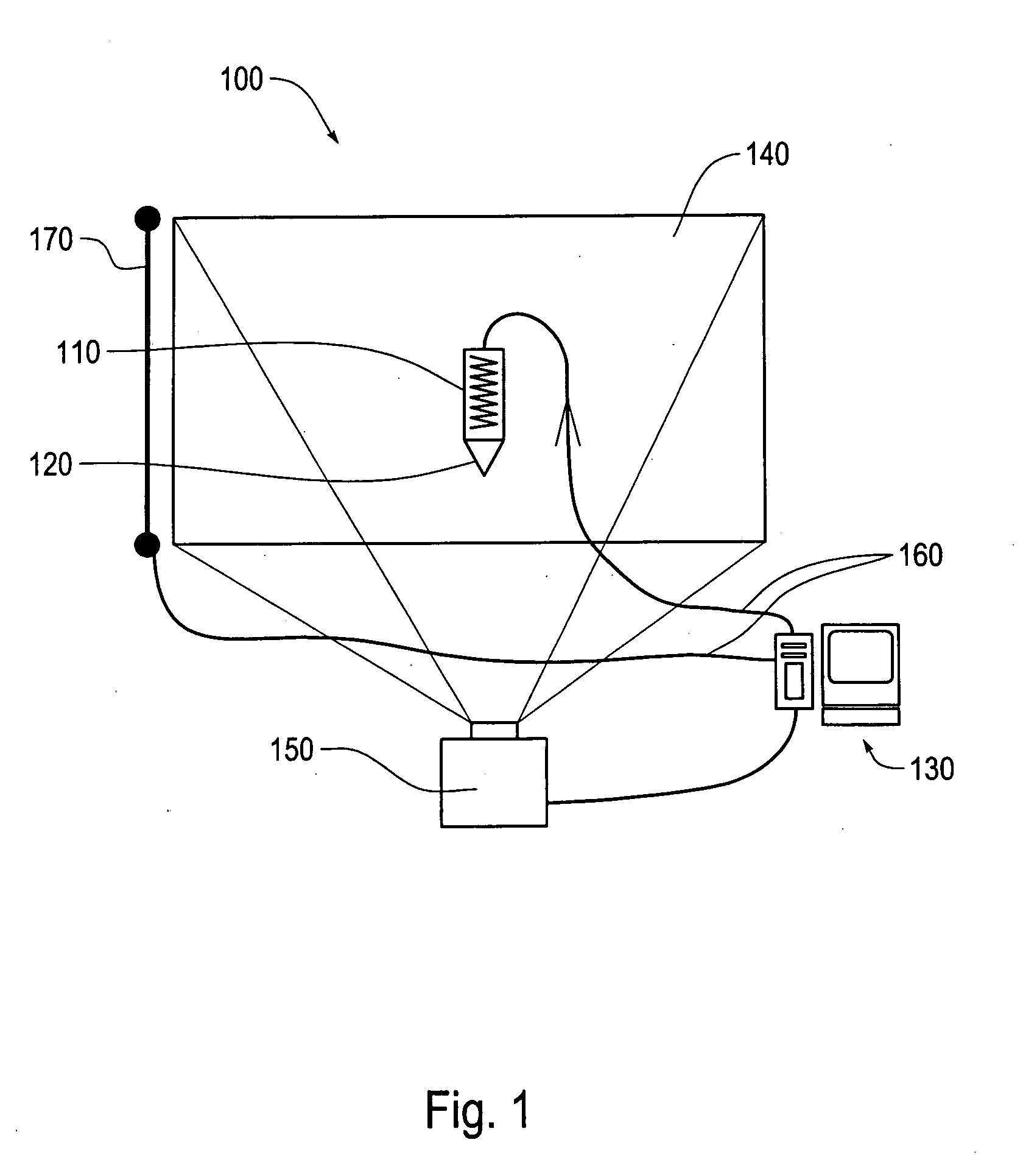
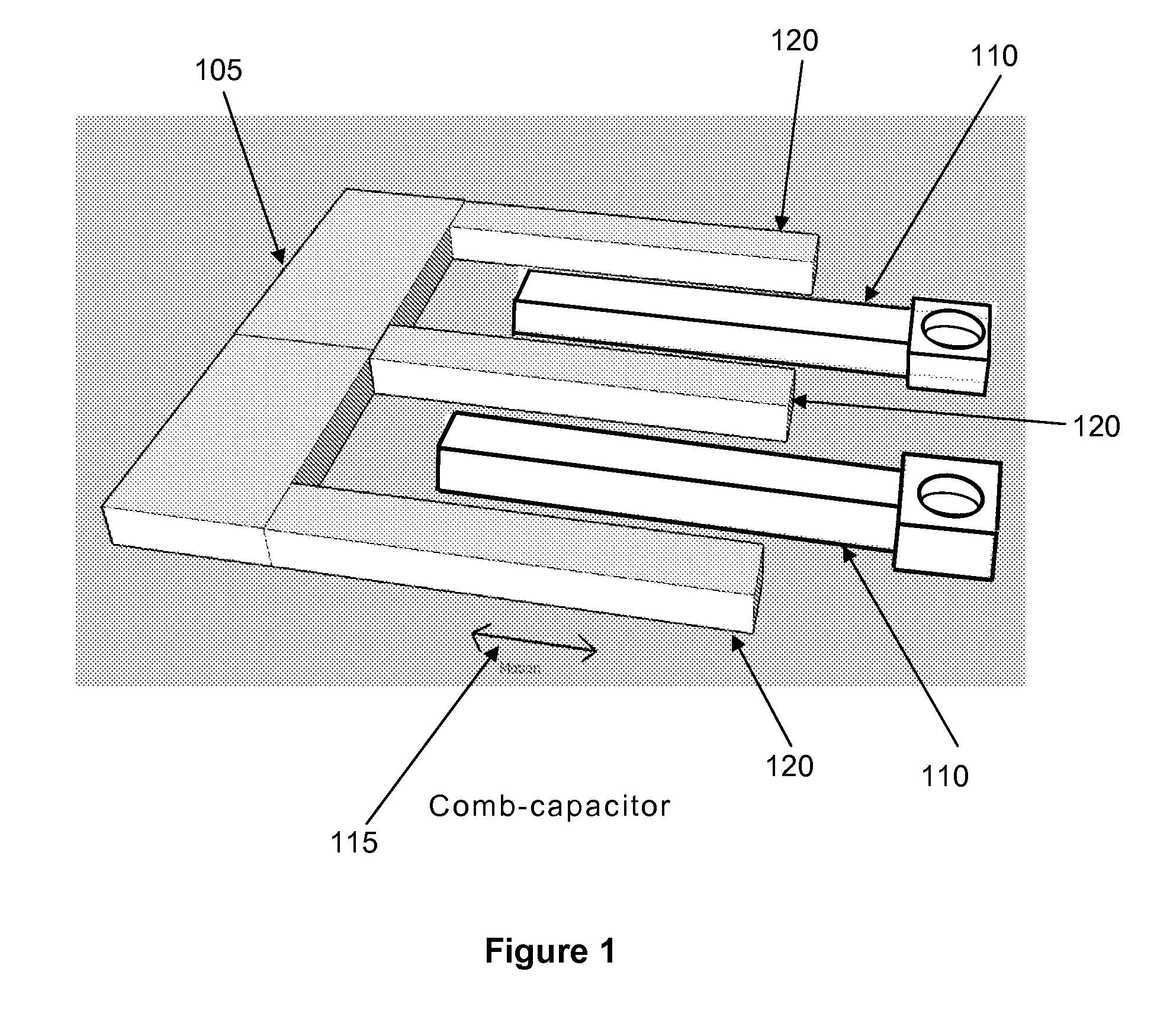
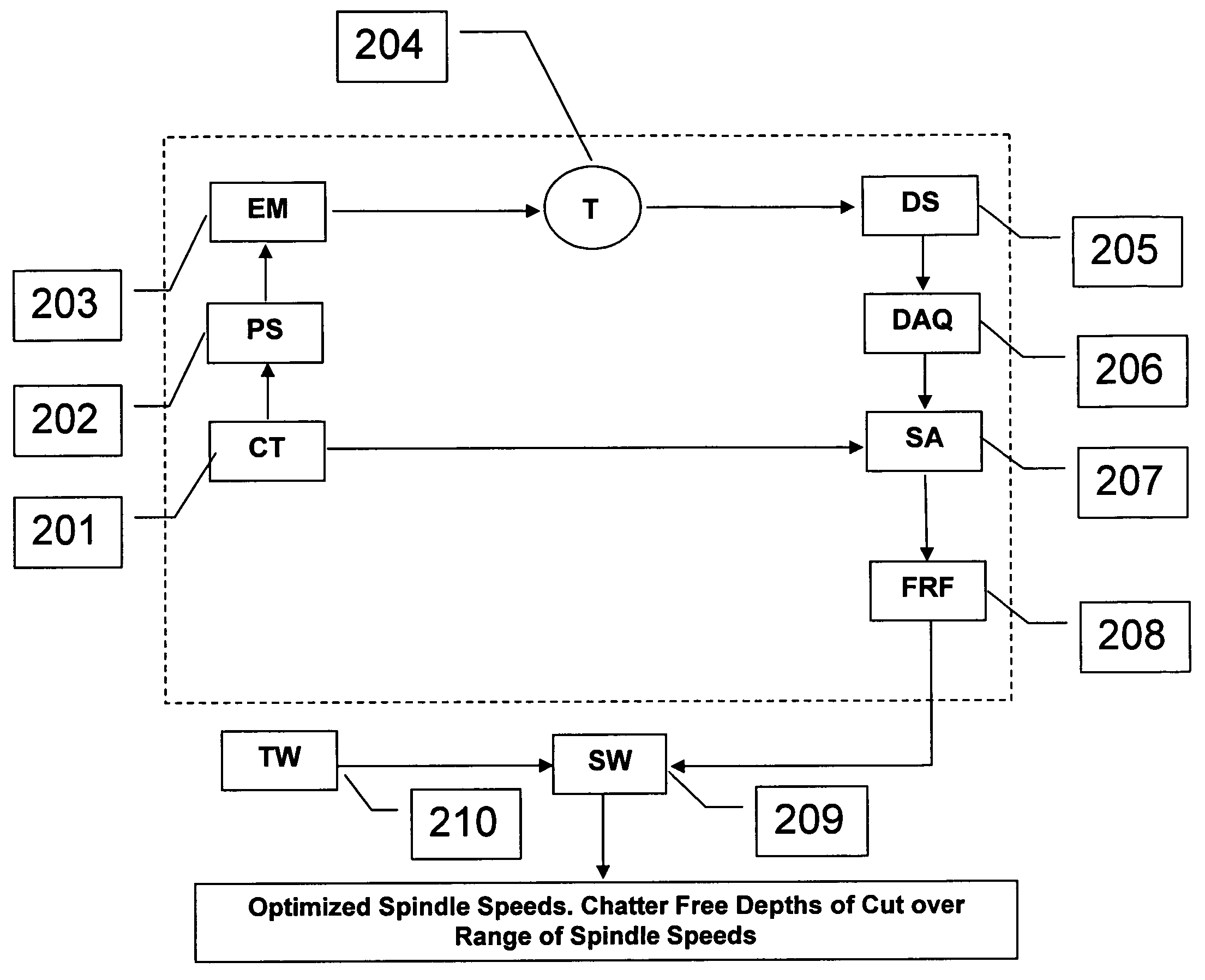
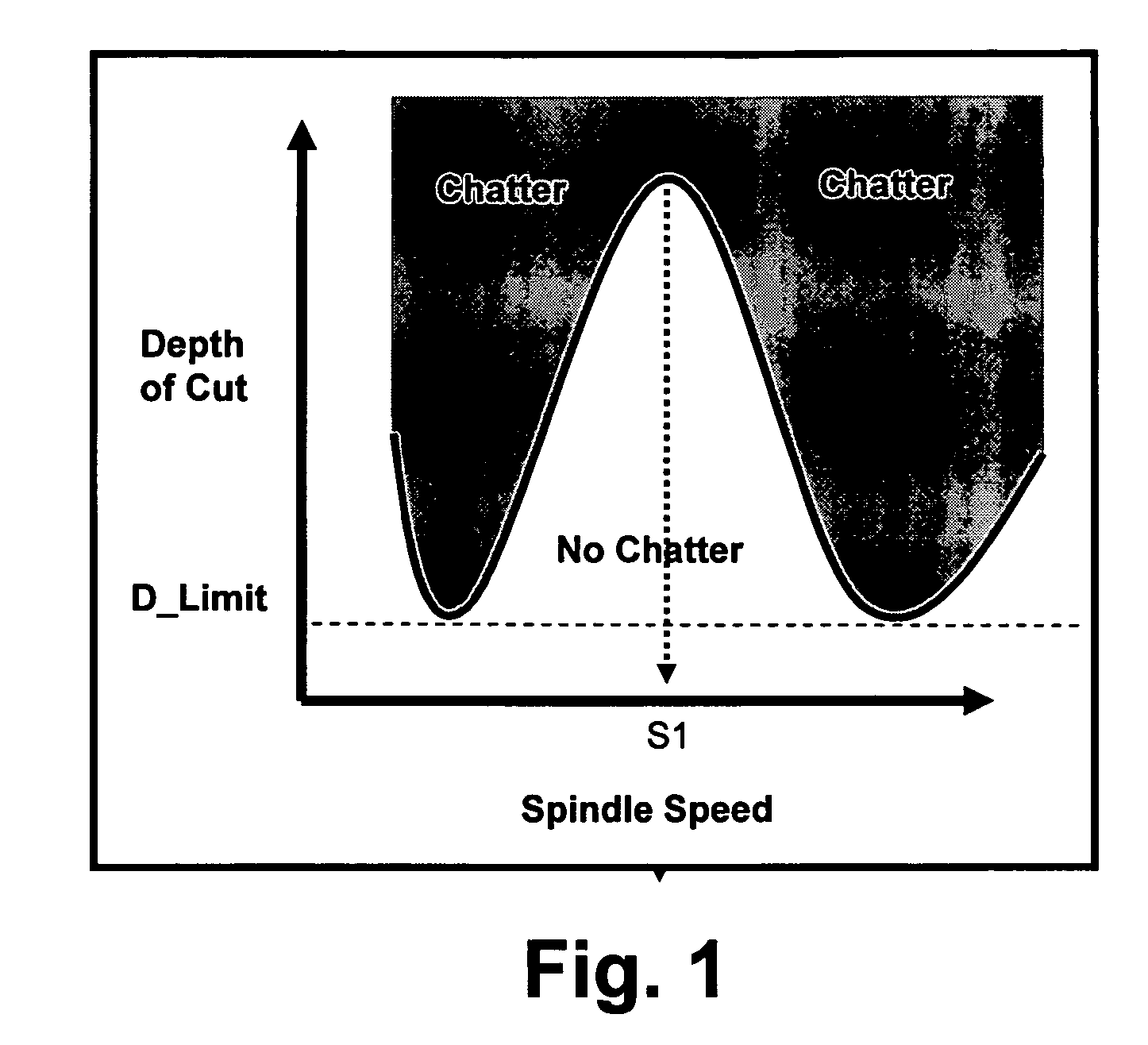
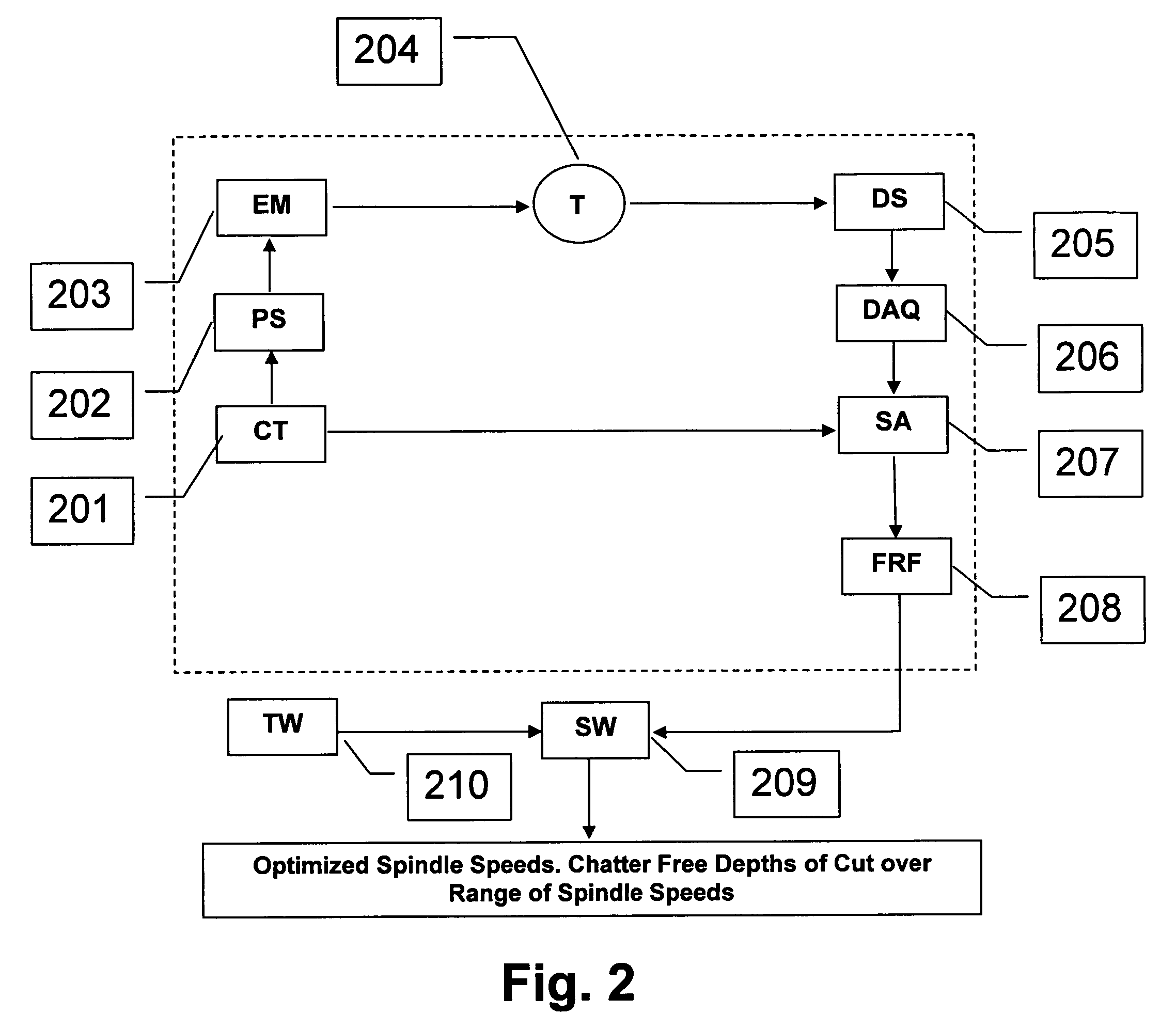
Active electromagnetic device for measuring the dynamic response of a tool in a CNC machine
InactiveUS6993410B2Minimal expertiseVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingAccelerometerAutomatic control
The present invention provides a device for determining the dynamics of a tool sited in a CNC machine, as encapsulated by the Frequency Response Function. The device uses an actively controlled electromagnet to excite forces on the tool. The force is excited in a non-contact manner, allowing the force to be applied to both a stationary and a rotating tool. The displacement is measured by standard means, such as accelerometers, optical displacement or capacitance sensors. The ratio of the force and the displacement in the frequency domain is the Frequency Response Function. The force may be applied as a pure sine wave, providing the Frequency Response Function at the frequency of the sine wave. Varying the frequency of the sine wave provides the Frequency Response Function over the range of frequencies of interest. The control of the force profile is handled entirely by the automated controls and requires no special skills, training or manual interaction by the user. No separate force sensor is required, since the electromagnetic force on the tool may be accurately determined from the design of the electromagnet and the tool position, geometry and material.
Owner:ESTERLING DONALD M
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com