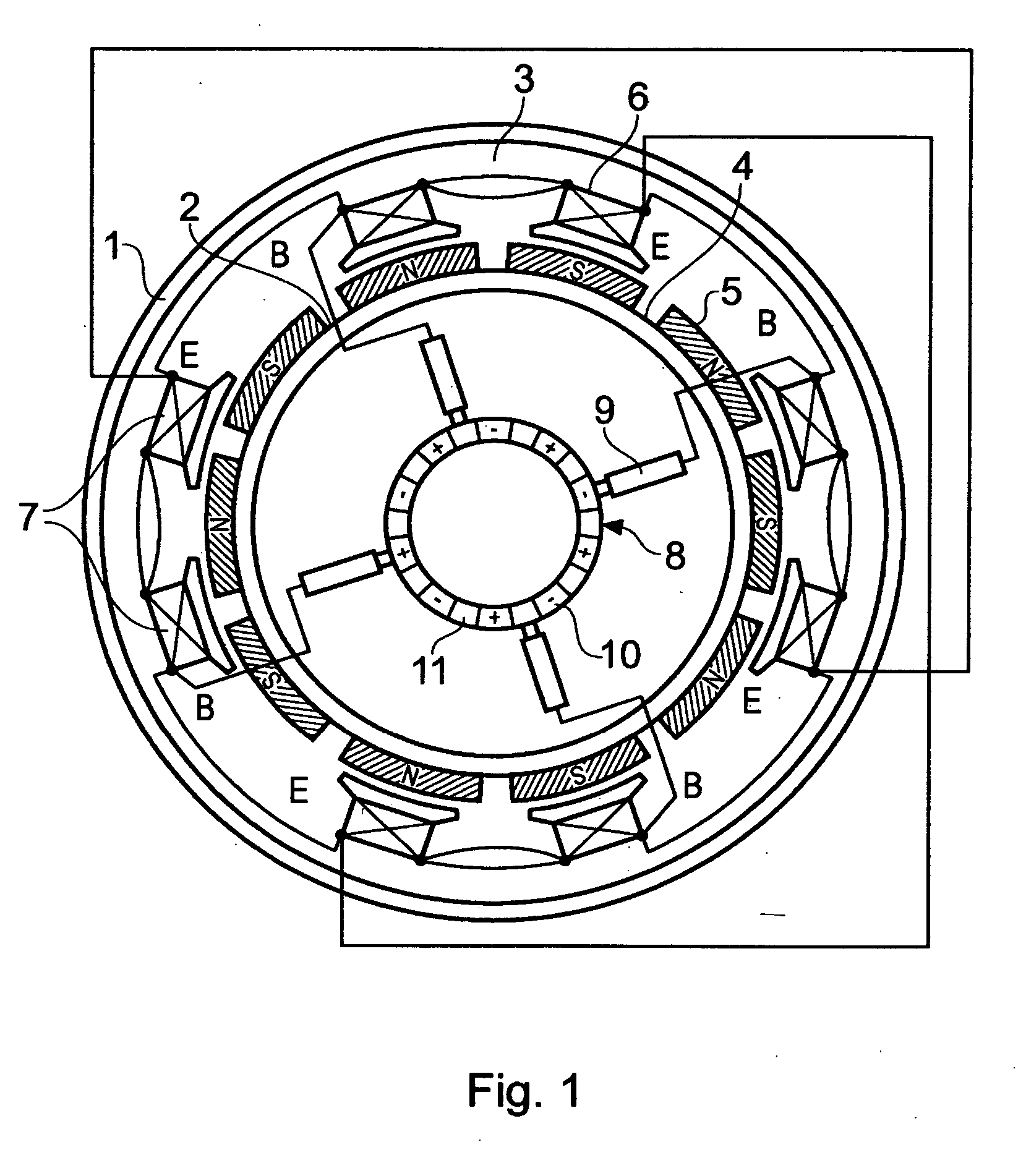
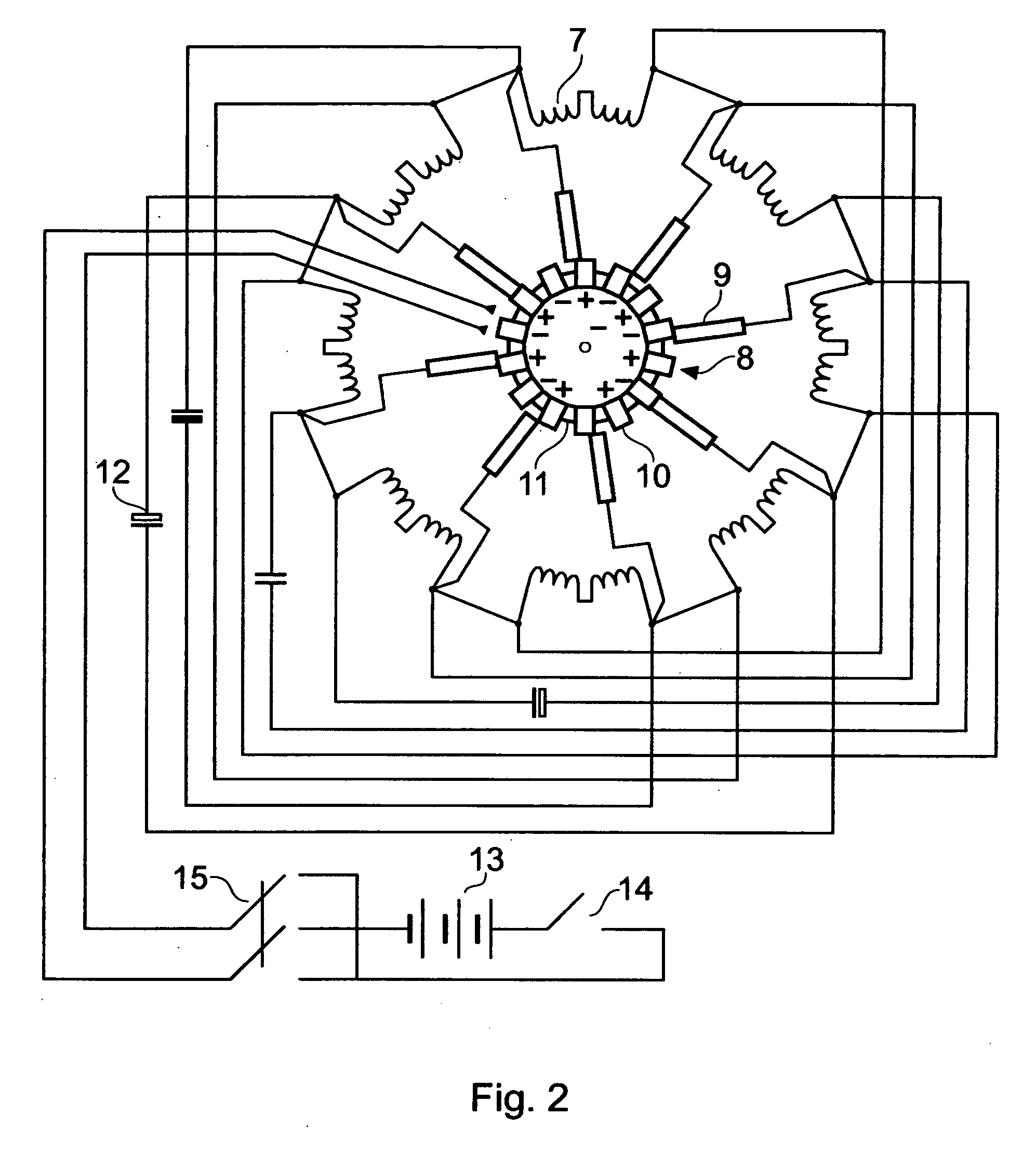
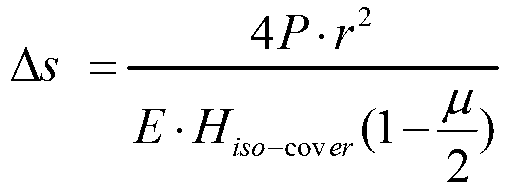Patents
Literature
128results about "AC/AC convertors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
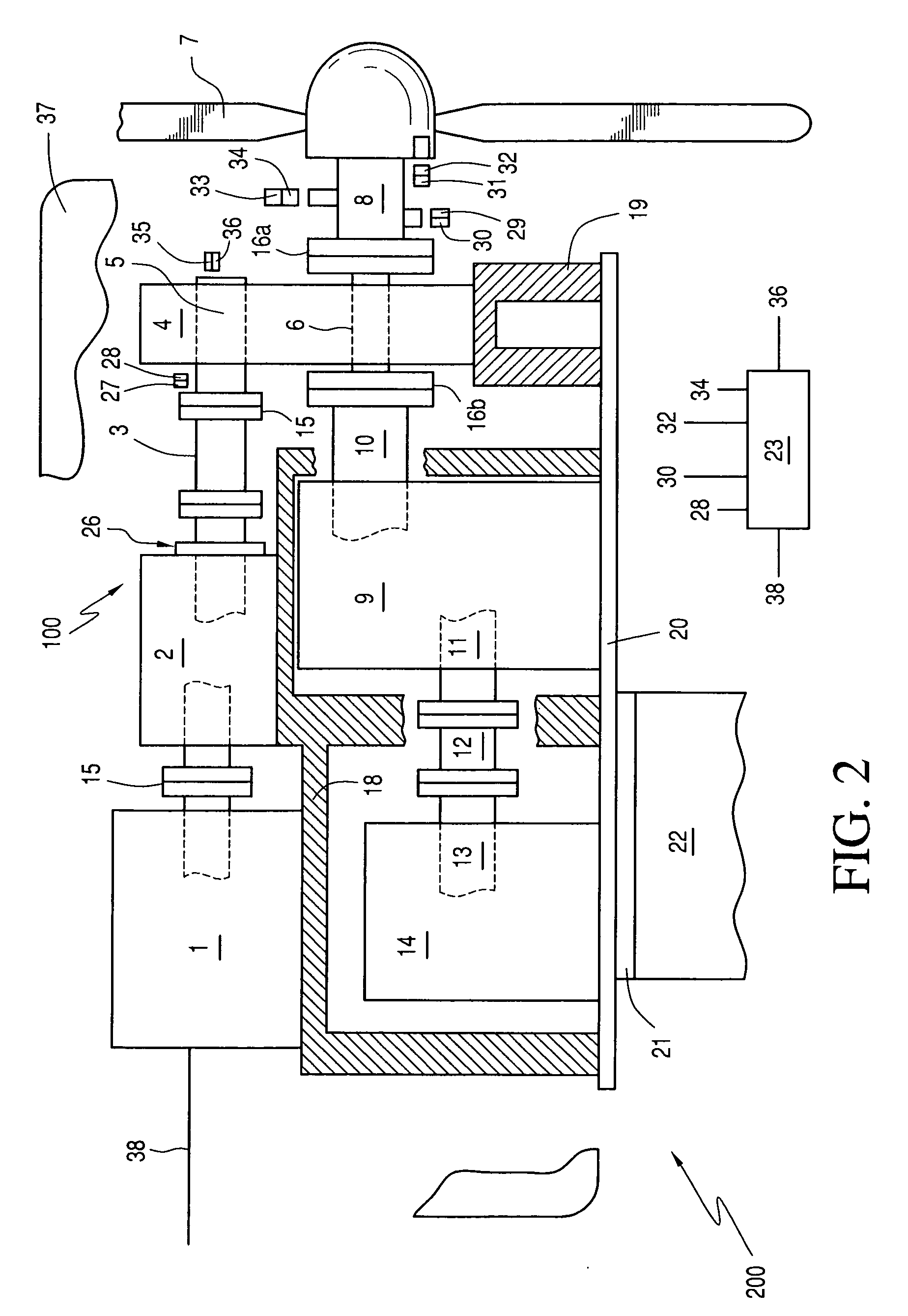
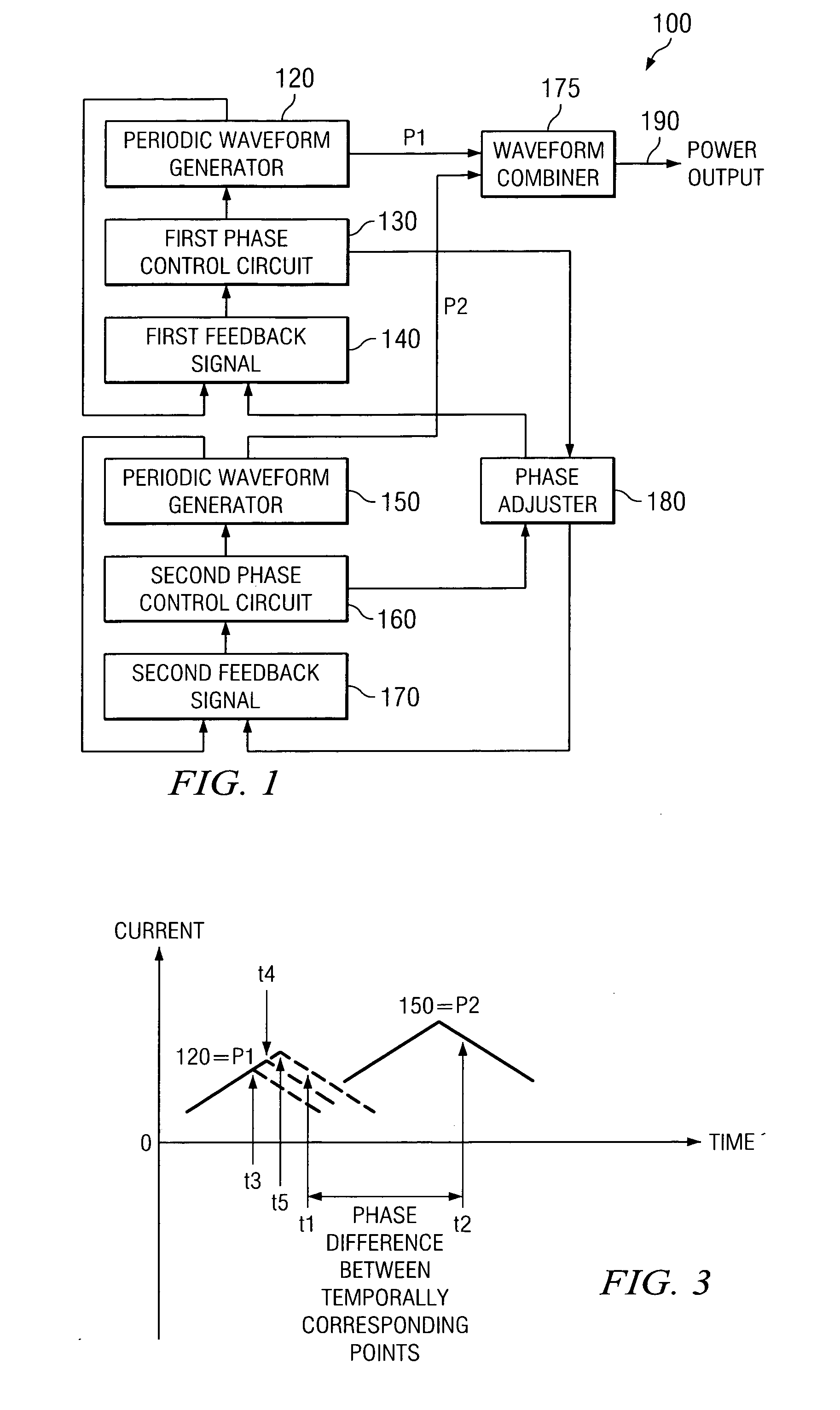
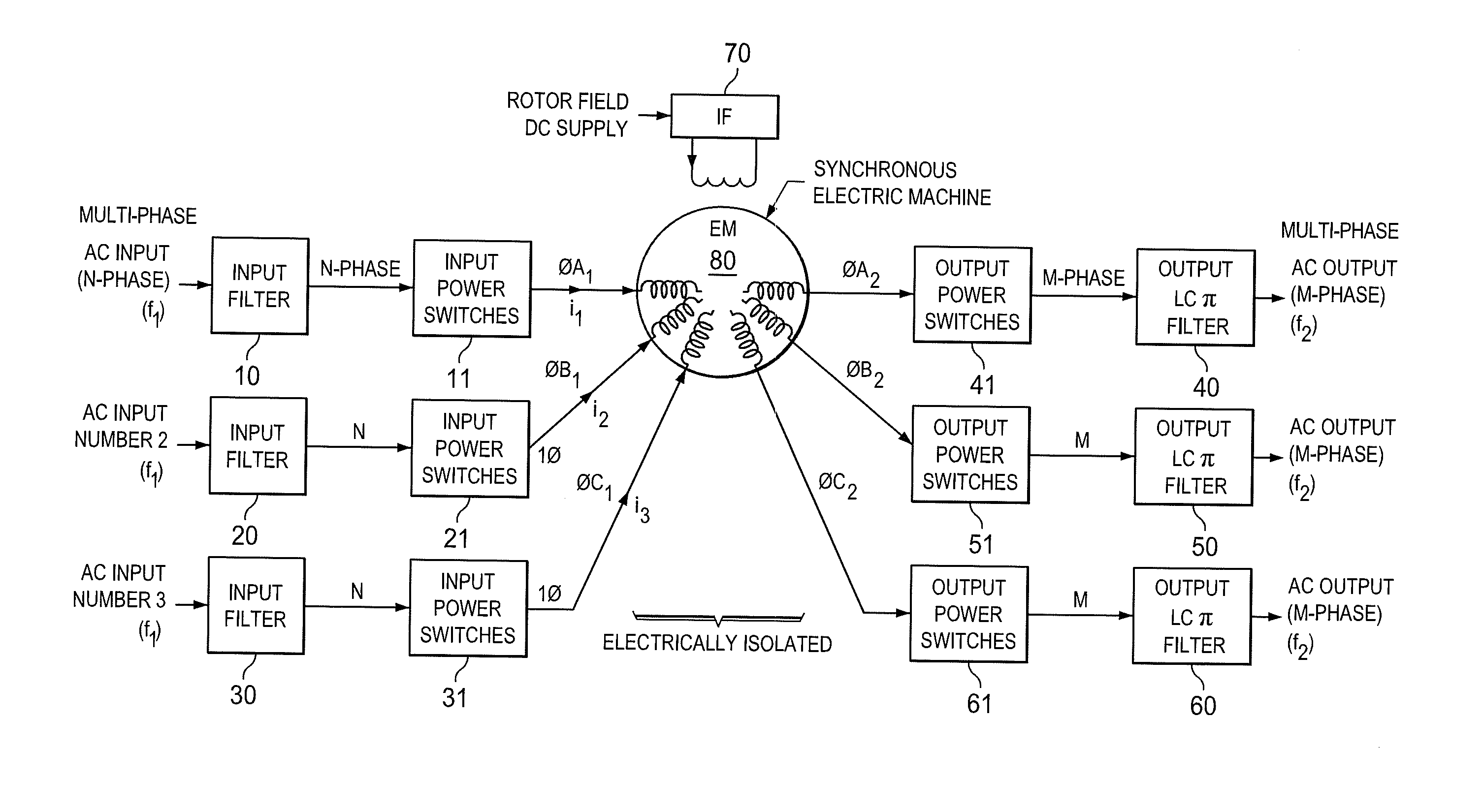
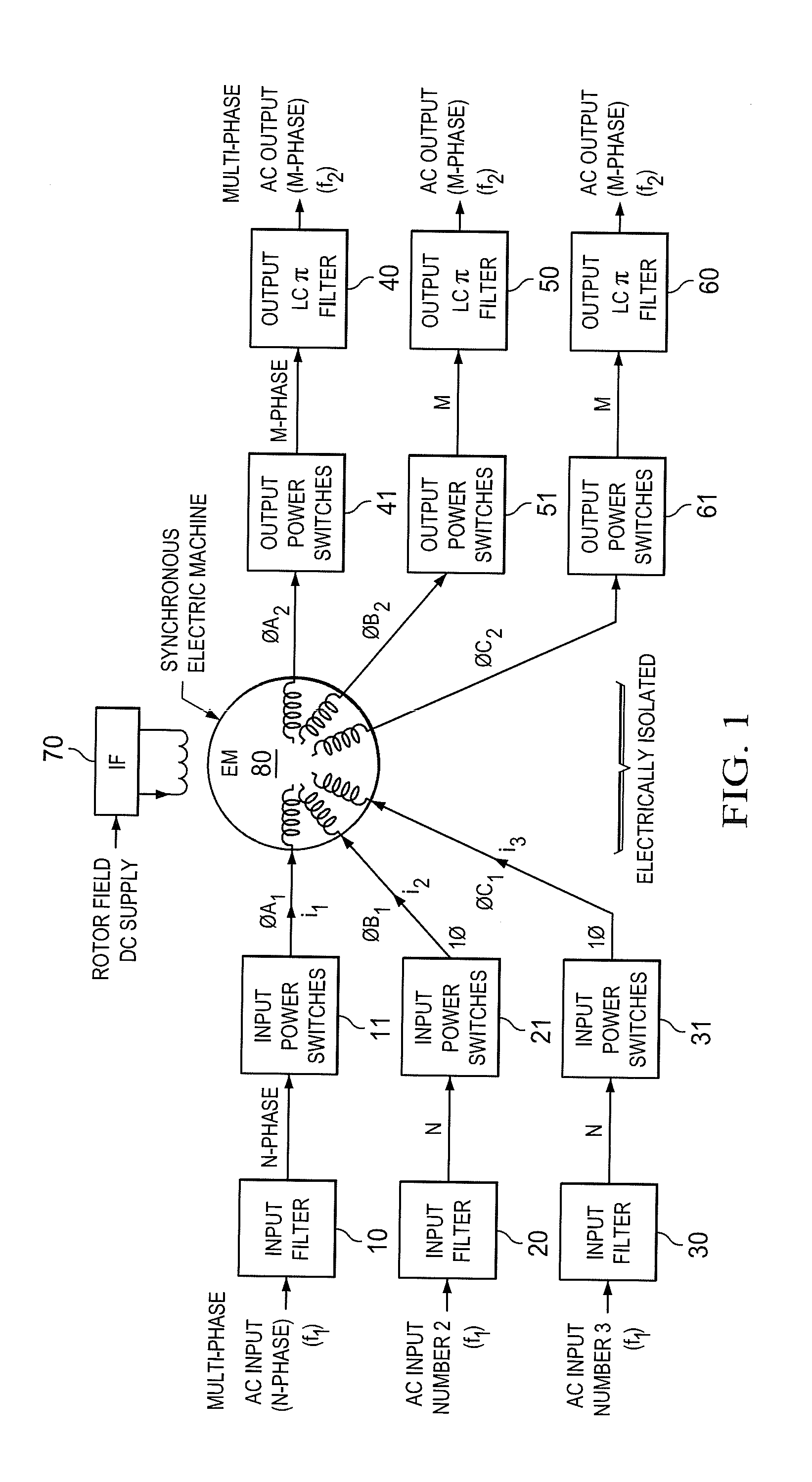
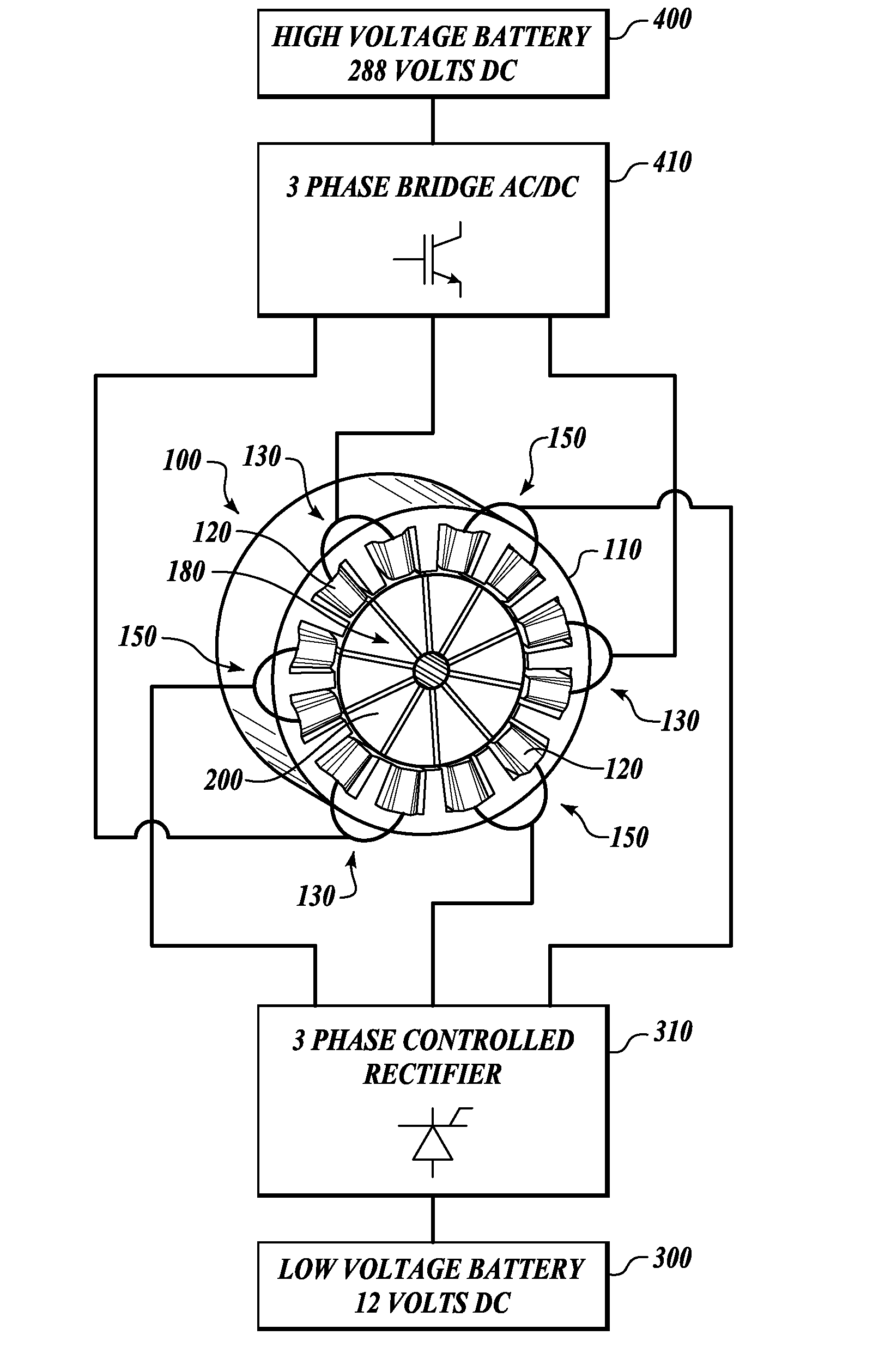
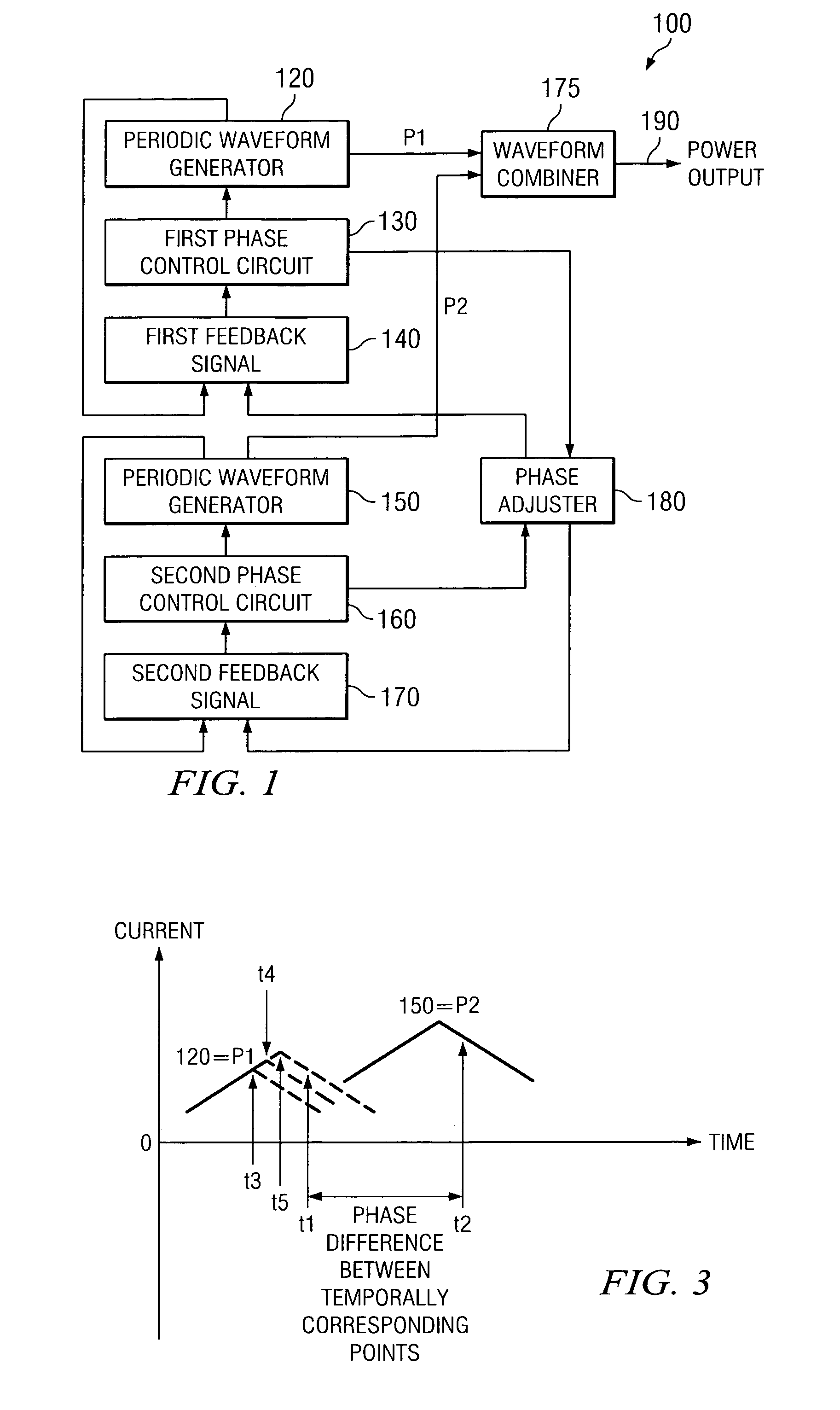
Method and apparatus for multi-phase power conversion
ActiveUS20070253223A1Improve circuit efficiencyReduce and eliminate impactEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringSwitching frequency
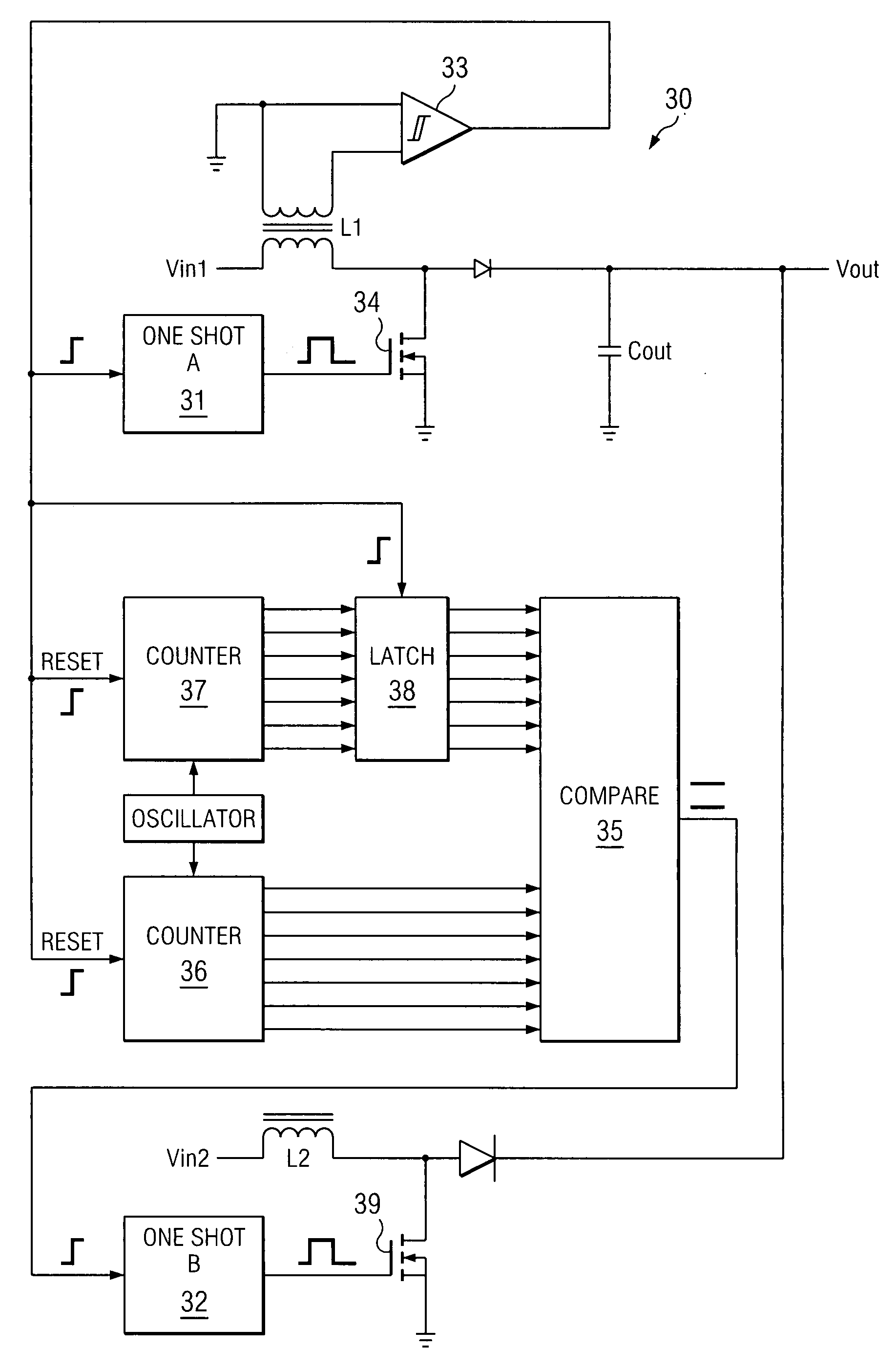
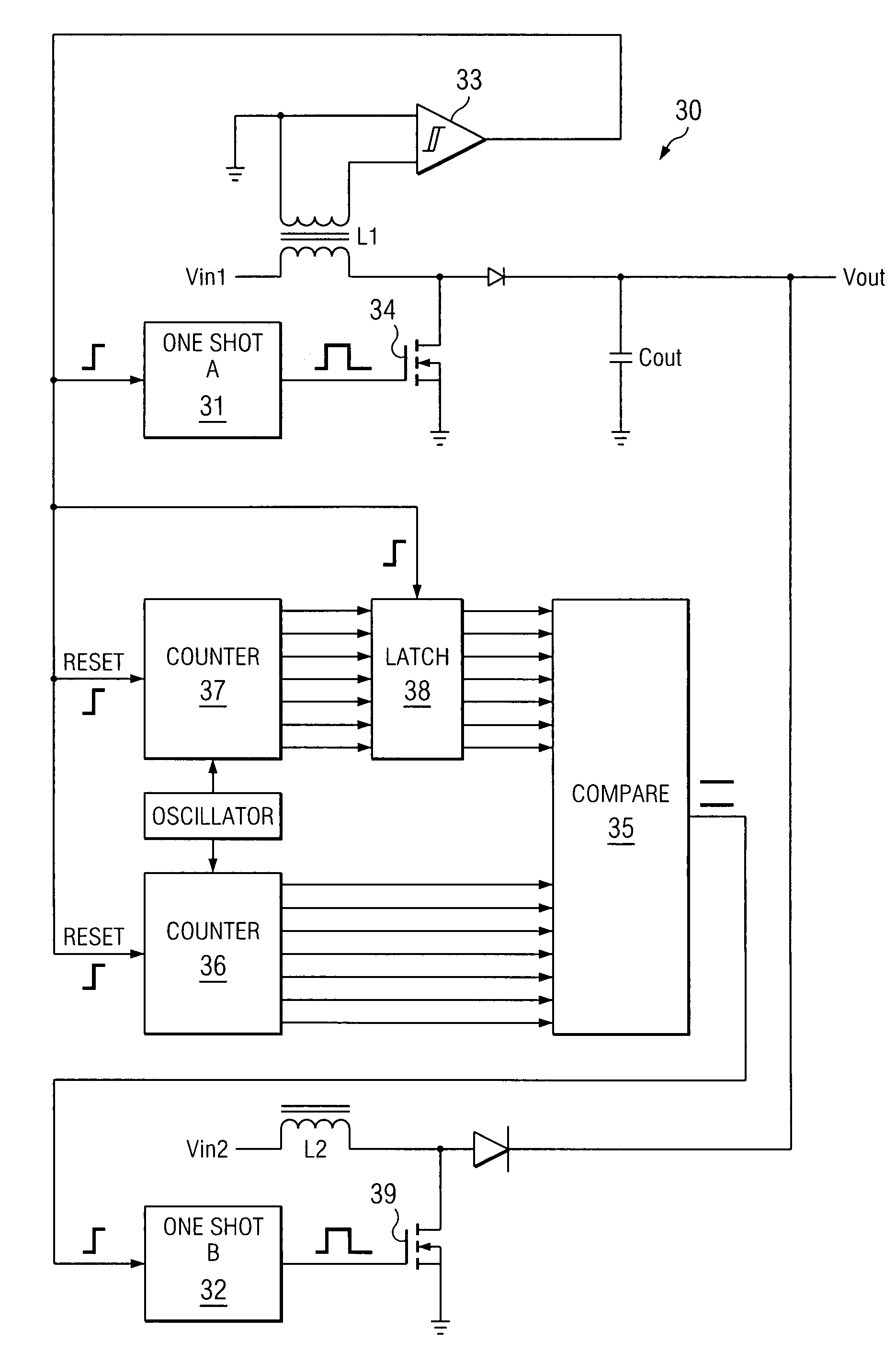
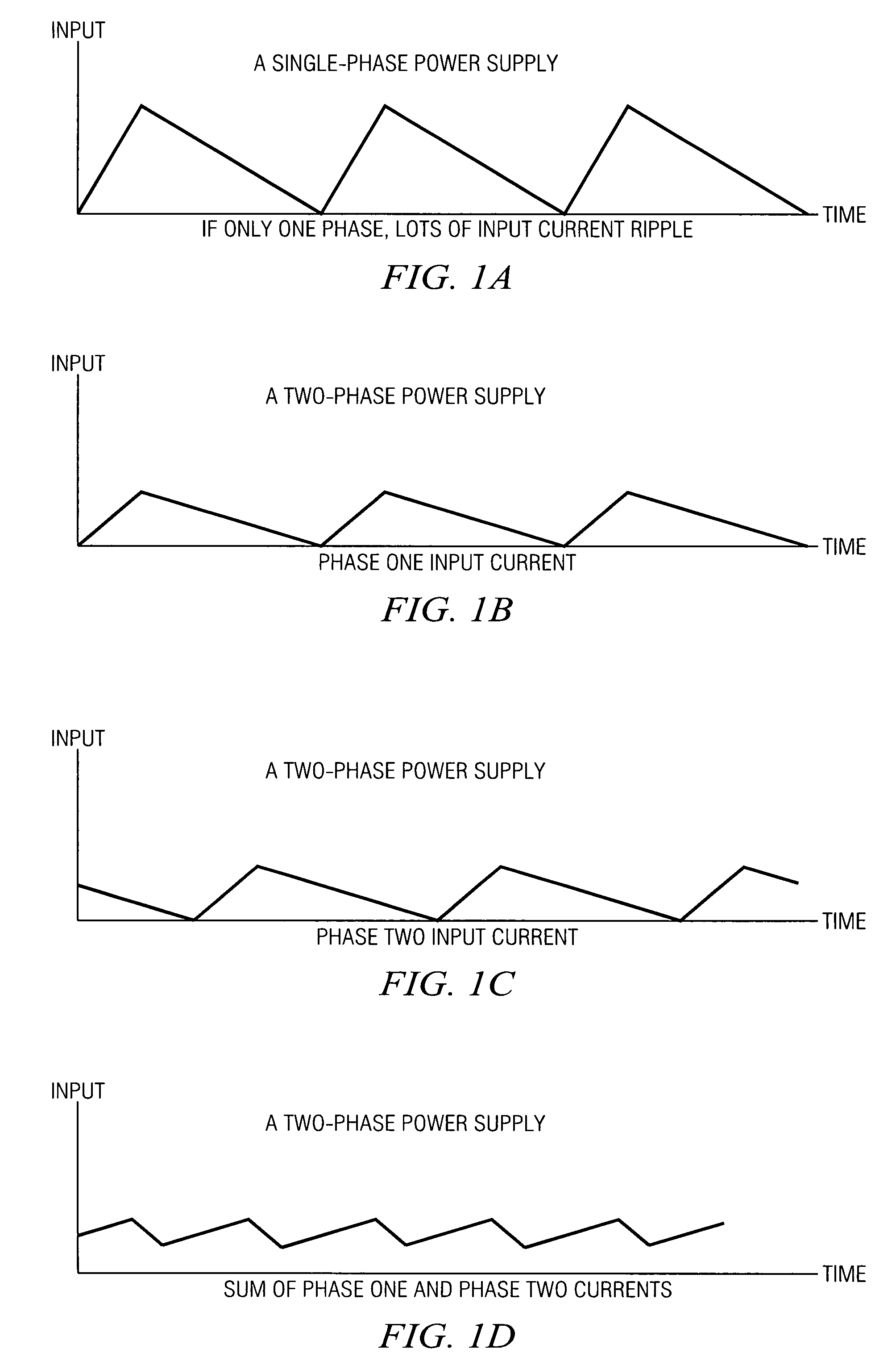
A system and method for power conversion synchronizes multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves variable frequency switching, fixed on-time and provides power factor correction. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves transition mode switching to help reduce switching losses. A phase angle difference detector may be provided for each phase. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that vary with switching frequency, and are synchronized to an average frequency. Current measures can be taken with a single component, such as a resistor. A maximum frequency control limits period width to avoid high frequency switching. An added switch on time improves input voltage crossover distortion. One or more phases can be deactivated in light load conditions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for multi-phase power conversion
ActiveUS7706151B2Reduce switching lossesTempo syncEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSwitching frequencyEngineering
A system and method for power conversion synchronizes multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves variable frequency switching, fixed on-time and provides power factor correction. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves transition mode switching to help reduce switching losses. A phase angle difference detector may be provided for each phase. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that vary with switching frequency, and are synchronized to an average frequency. Current measures can be taken with a single component, such as a resistor. A maximum frequency control limits period width to avoid high frequency switching. An added switch on time improves input voltage crossover distortion. One or more phases can be deactivated in light load conditions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
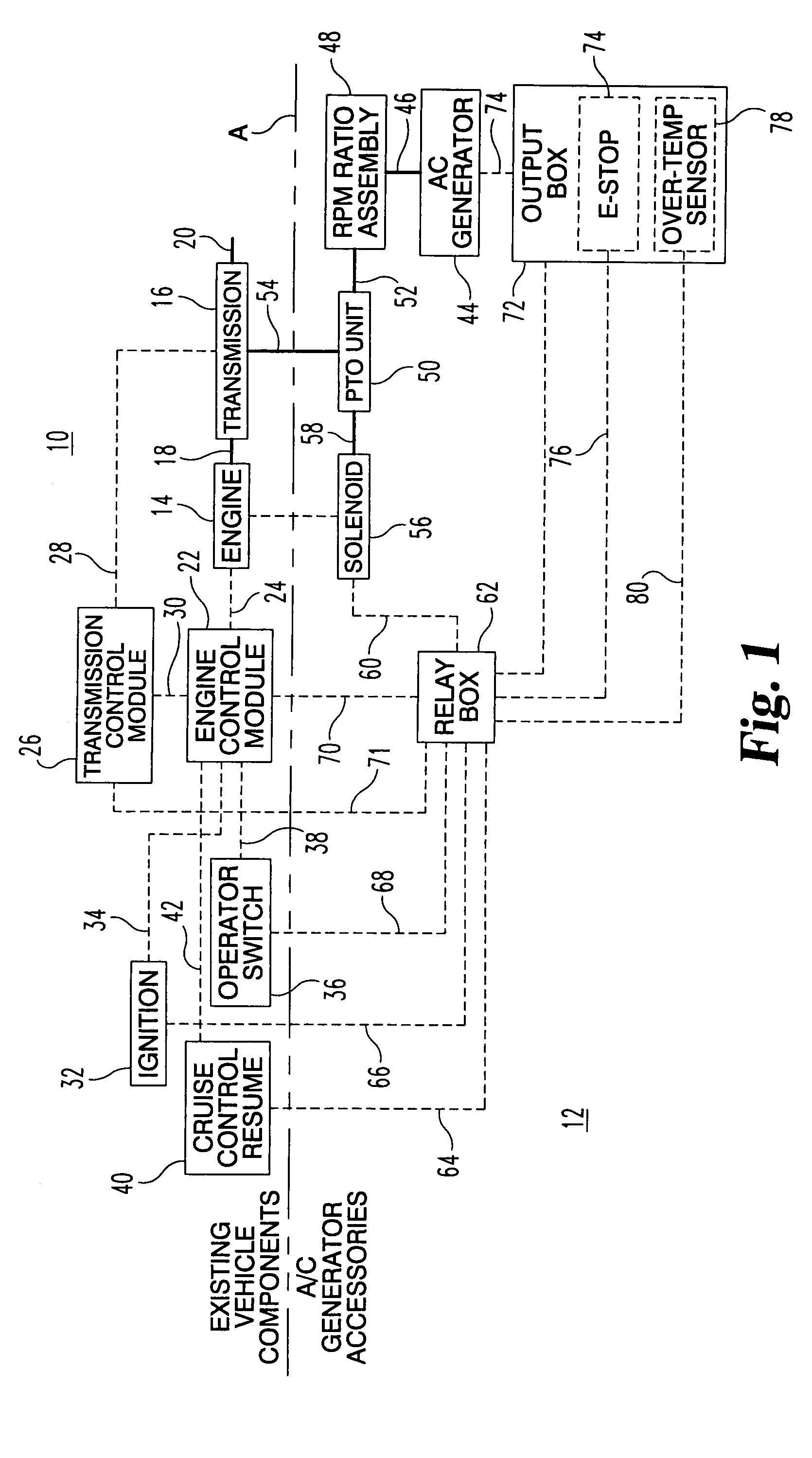
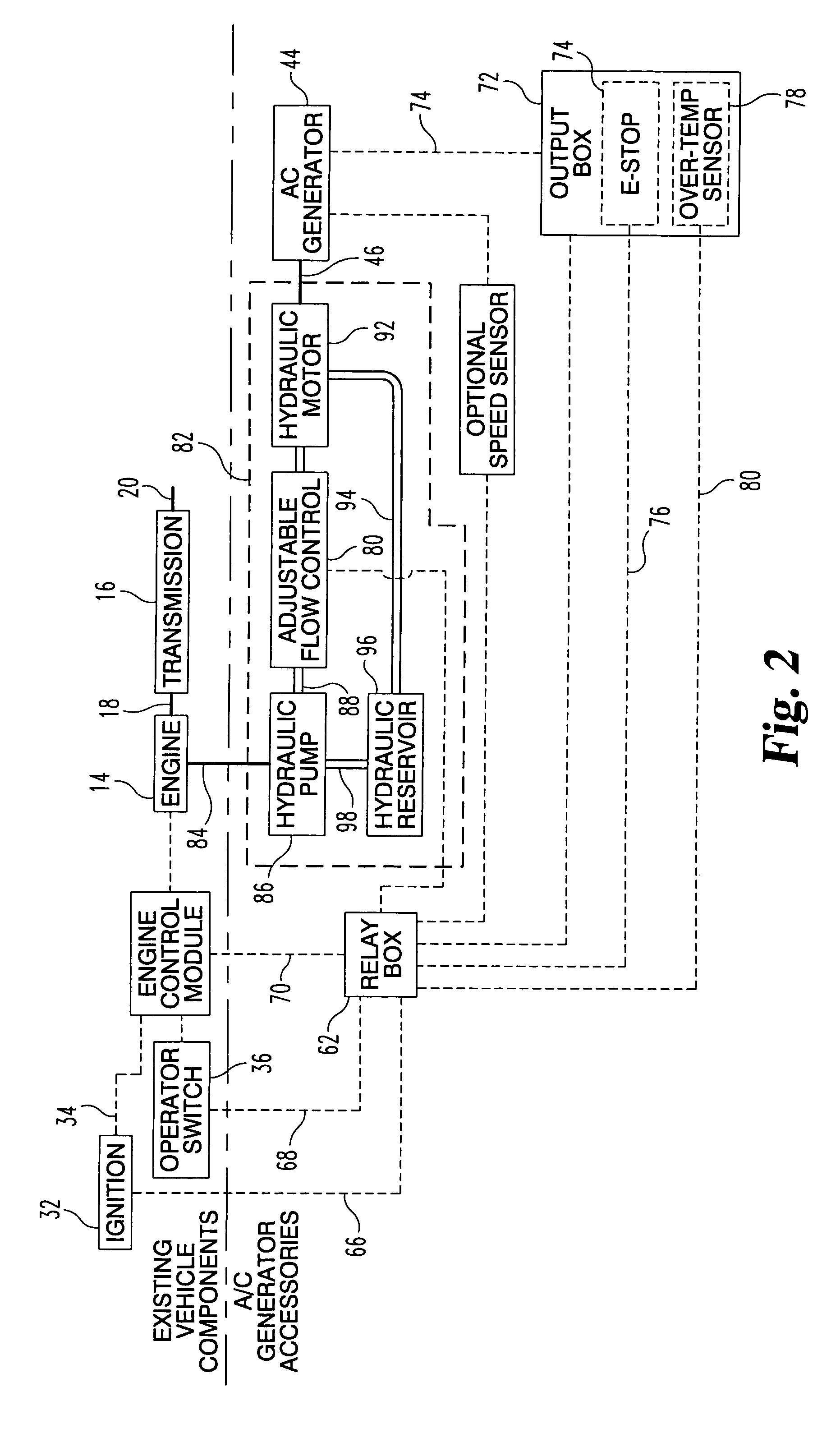
Auxiliary drive/brake system for a wind turbine
An auxiliary drive / brake system for a wind turbine includes an impulse, high torque motor, a gearbox transmission, a drive shaft, and a transfer gearbox that connects to either the wind turbine low-speed shaft or to the wind turbine gearbox. Control of the auxiliary drive / brake system is performed by a programmable computer-based motor drive control system in combination with instrumentation and sensors fitted to the rotating wind turbine components. Torque and horsepower created by the present auxiliary drive / brake system is transferred into the wind turbine low-speed shaft where it combines with the torque and horsepower created by the wind acting on the wind turbine rotor blades, the combined torque and horsepower is transferred from the wind turbine low-speed shaft into the wind turbine gearbox and the wind turbine generator, causing the wind turbine generator to operate and produce electricity which is supplied to the power company.
Owner:CHALLENGER DESIGN
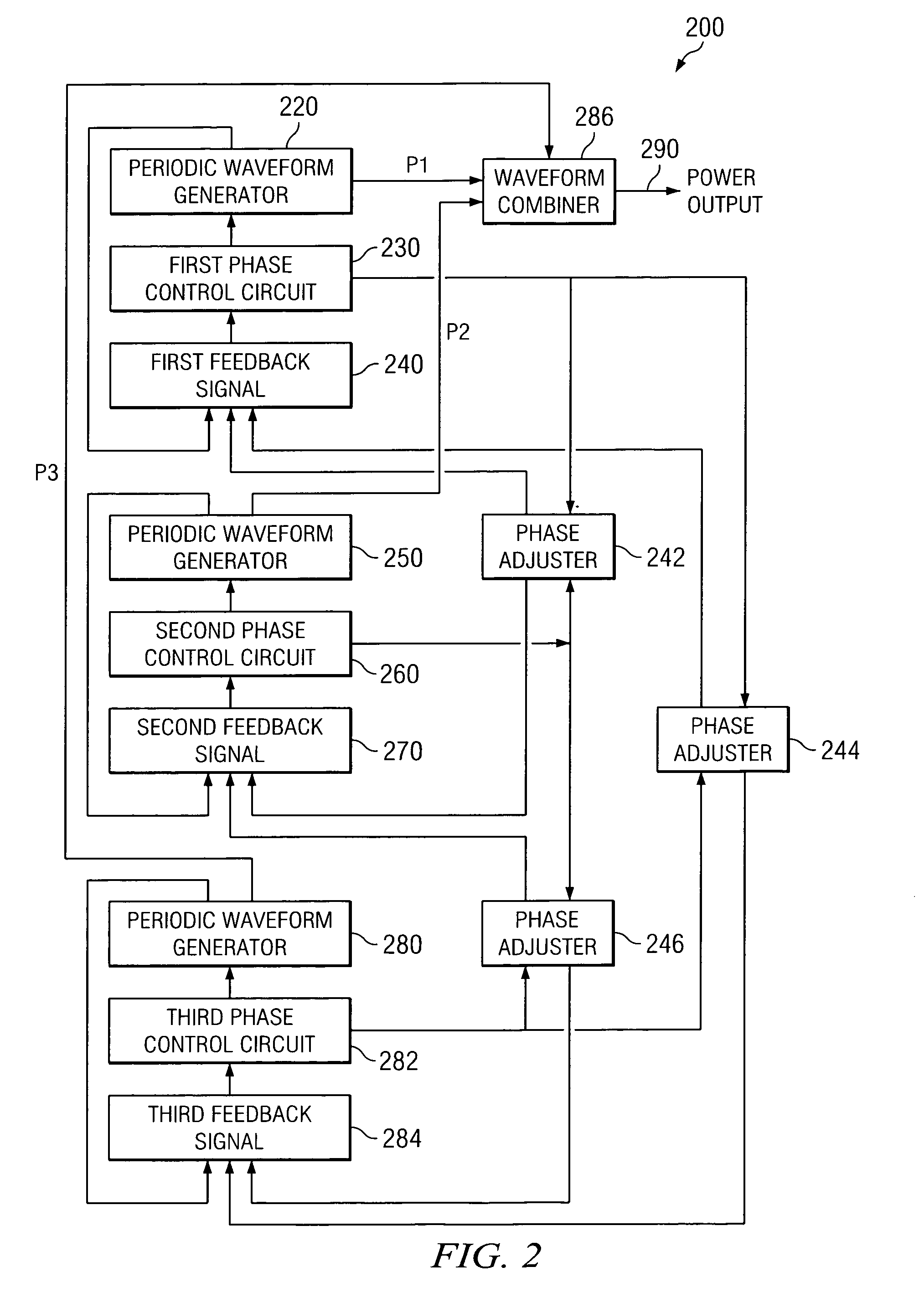
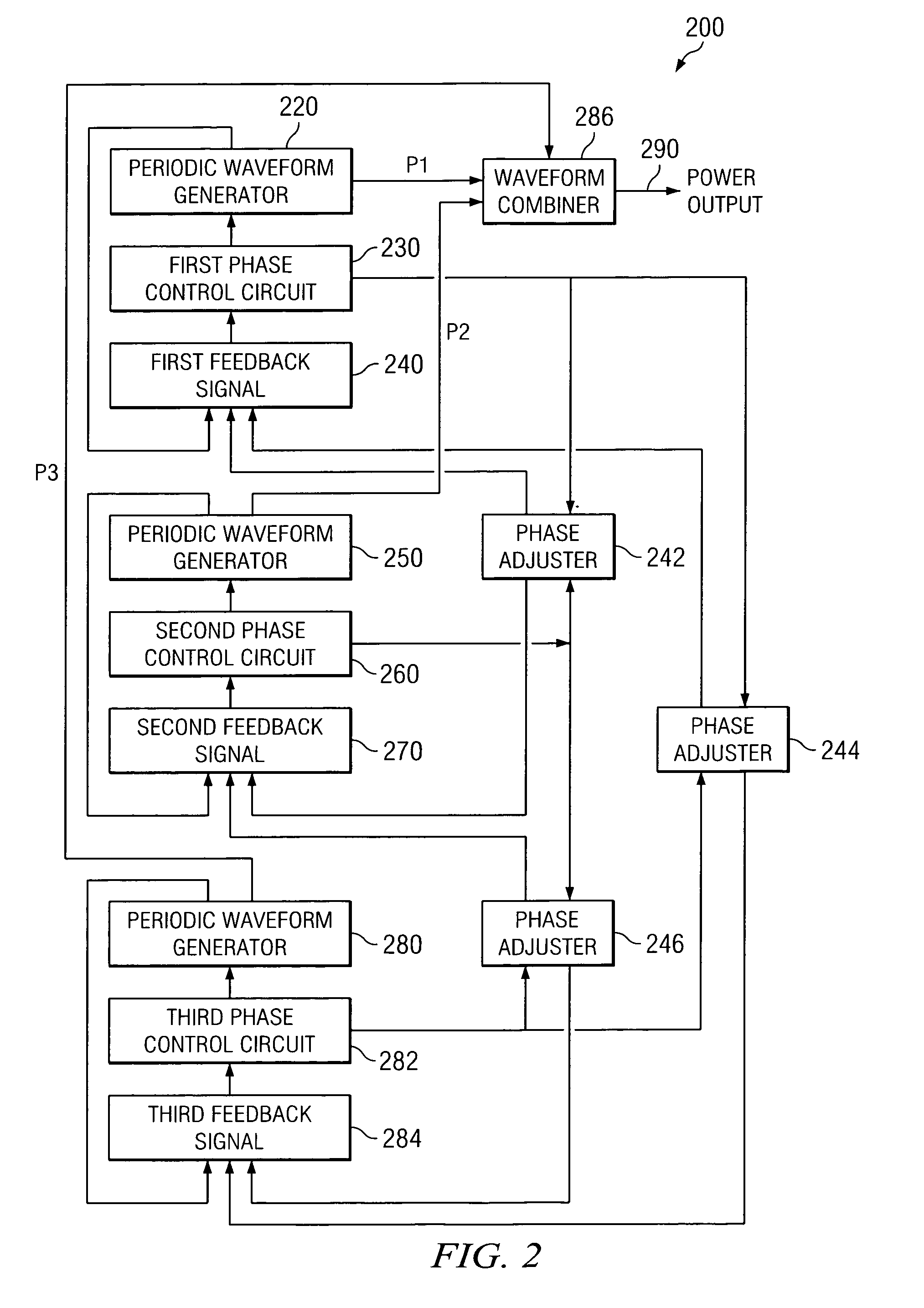
Method and apparatus for power converters having phases spaced at desired phase angles
ActiveUS20070253224A1Reduce switching lossesTempo syncEfficient power electronics conversionAC/AC convertorsPhase angle differencePhase space
A system and method for power conversion synchronizes multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves variable frequency switching, fixed on-time and provides power factor correction. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves transition mode switching to help reduce switching losses. A phase angle difference detector may be provided for each phase. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that vary with switching frequency, and are synchronized to an average frequency.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
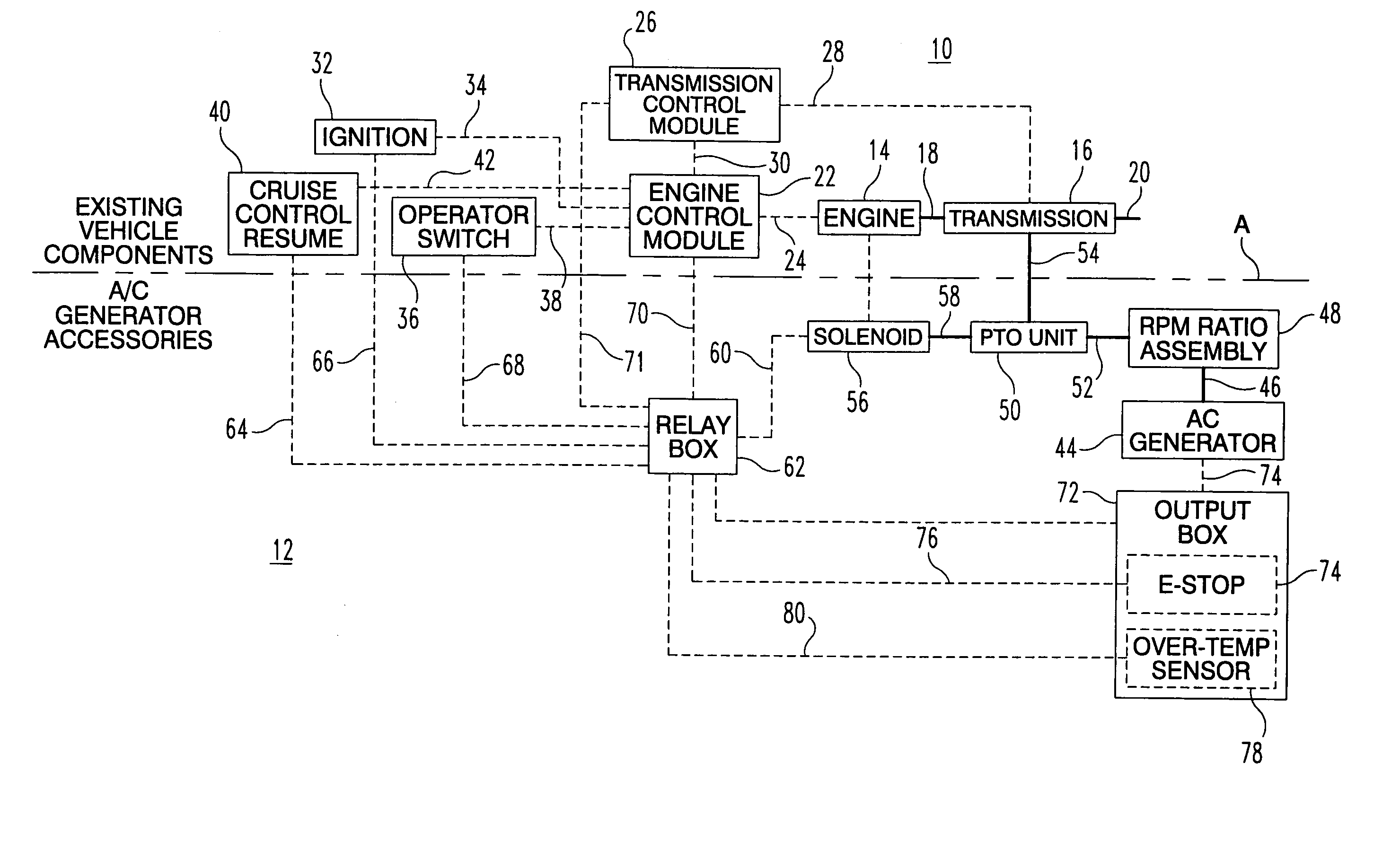
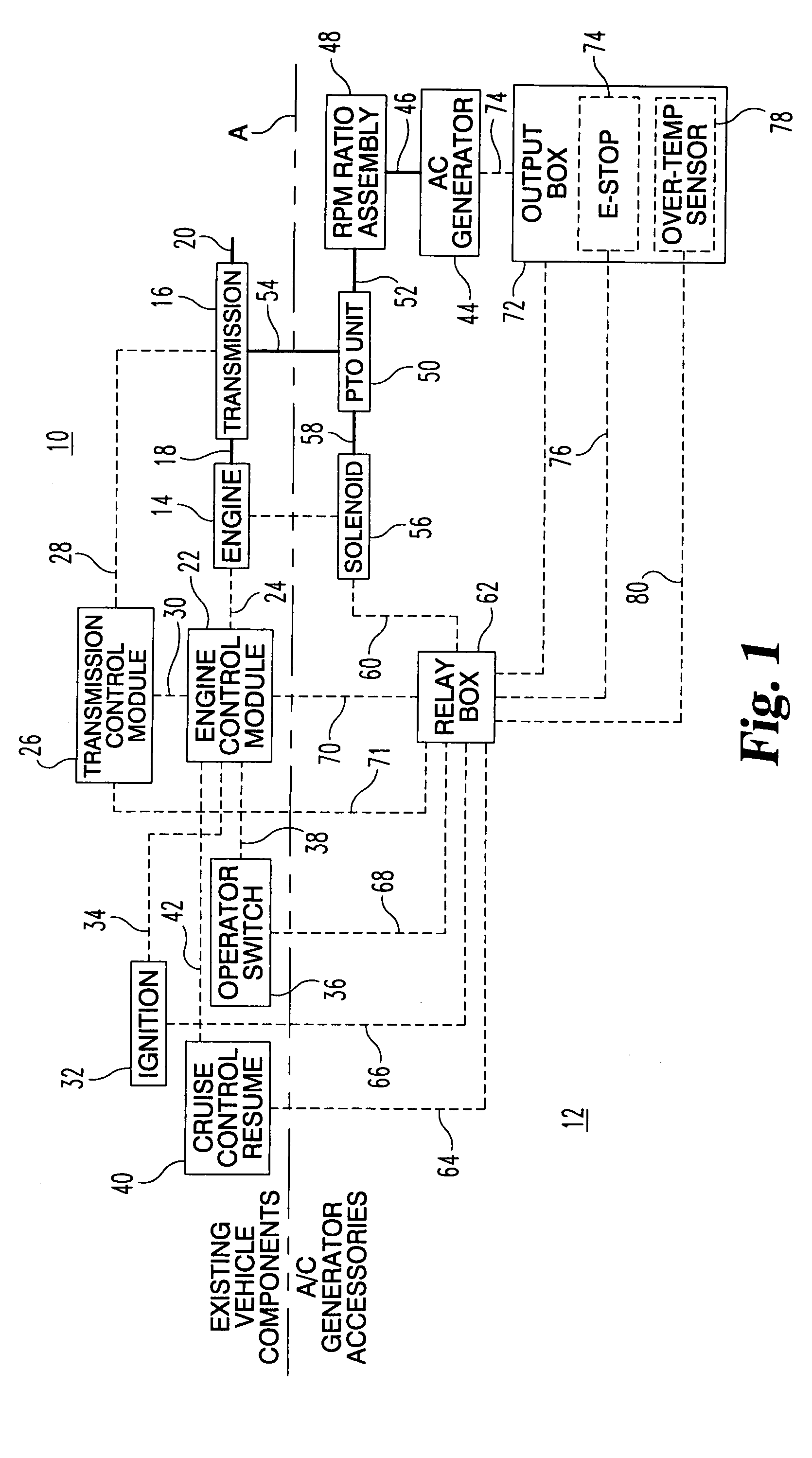
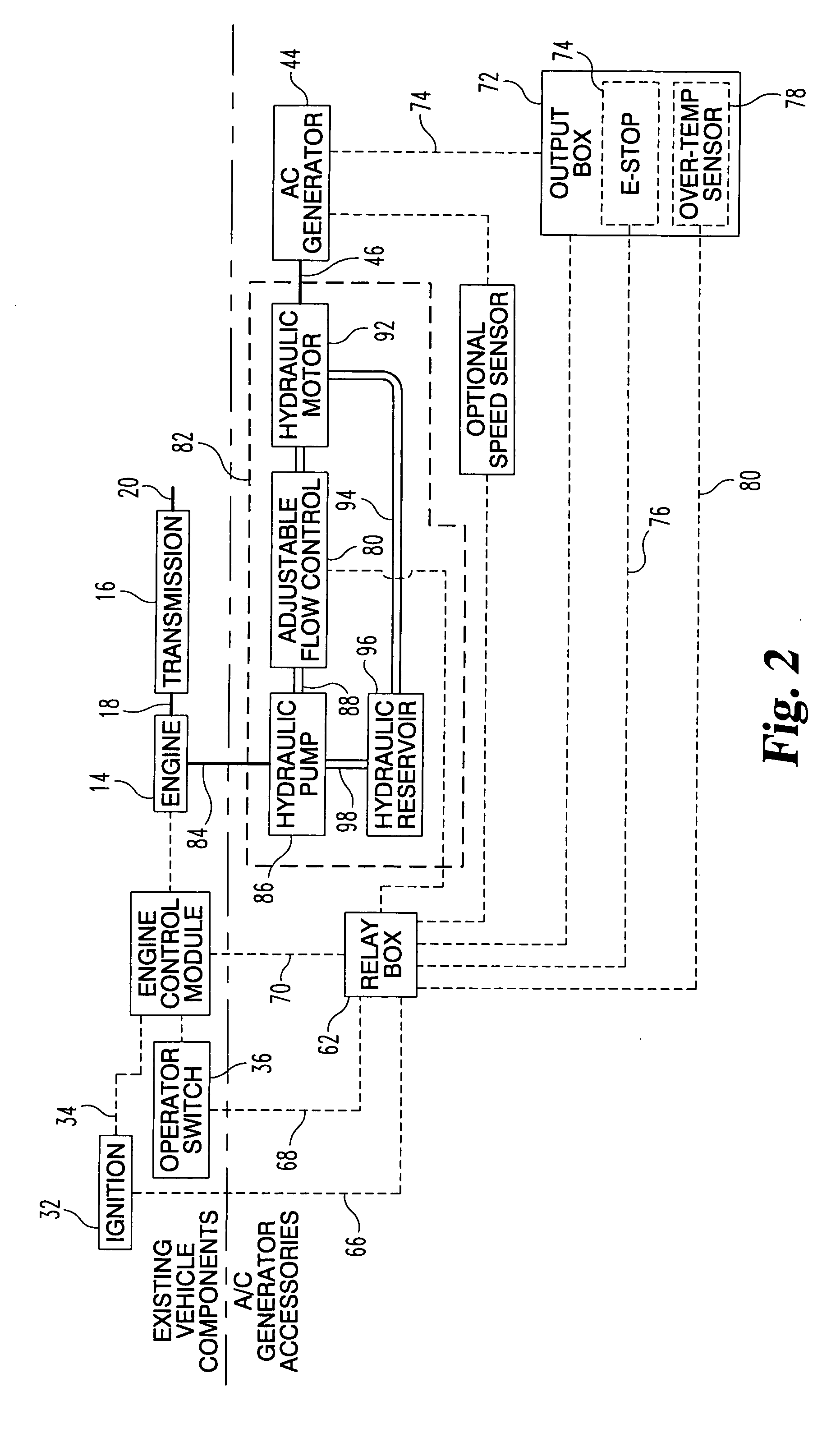
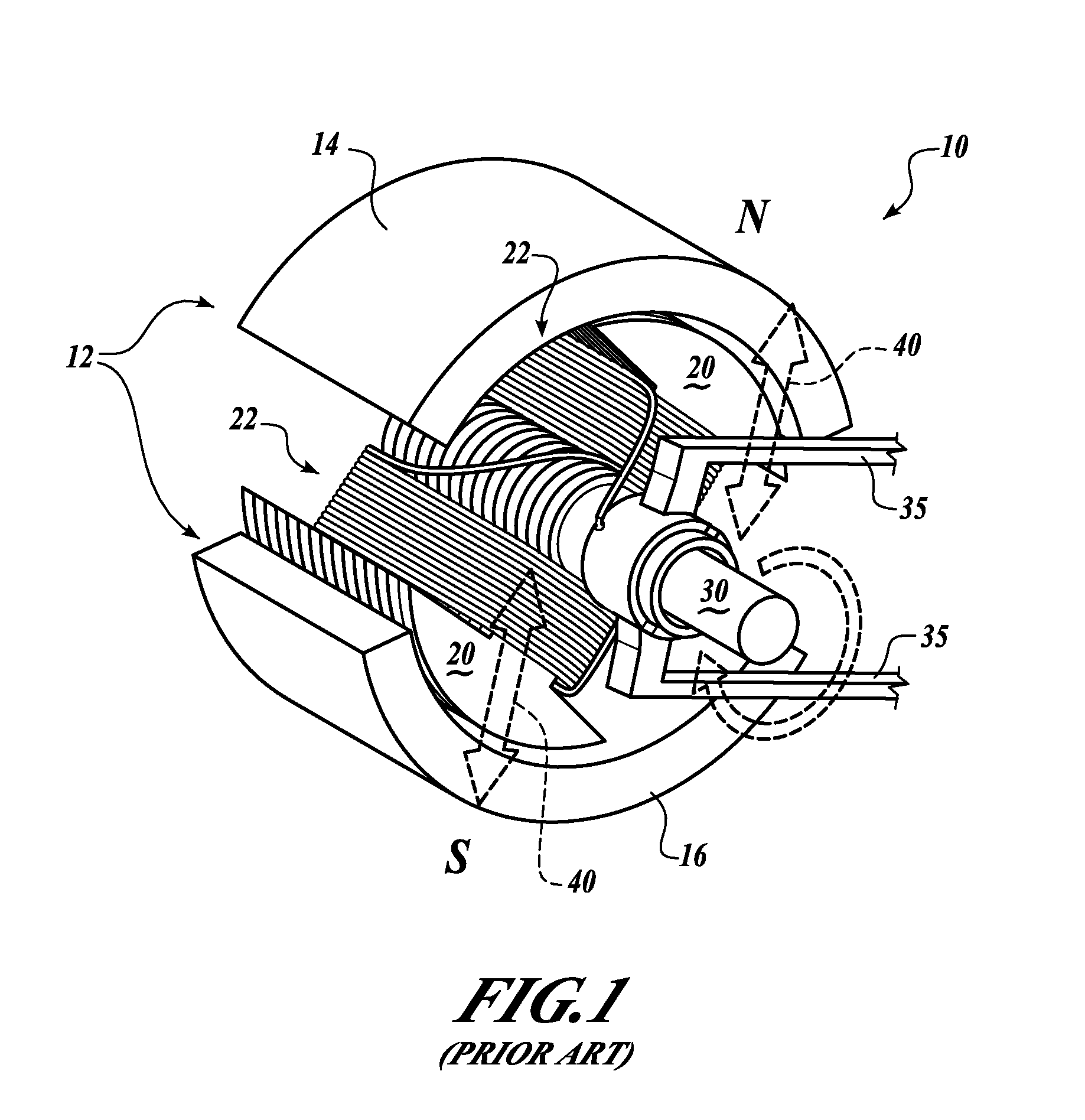
Vehicle mounted electrical generator system
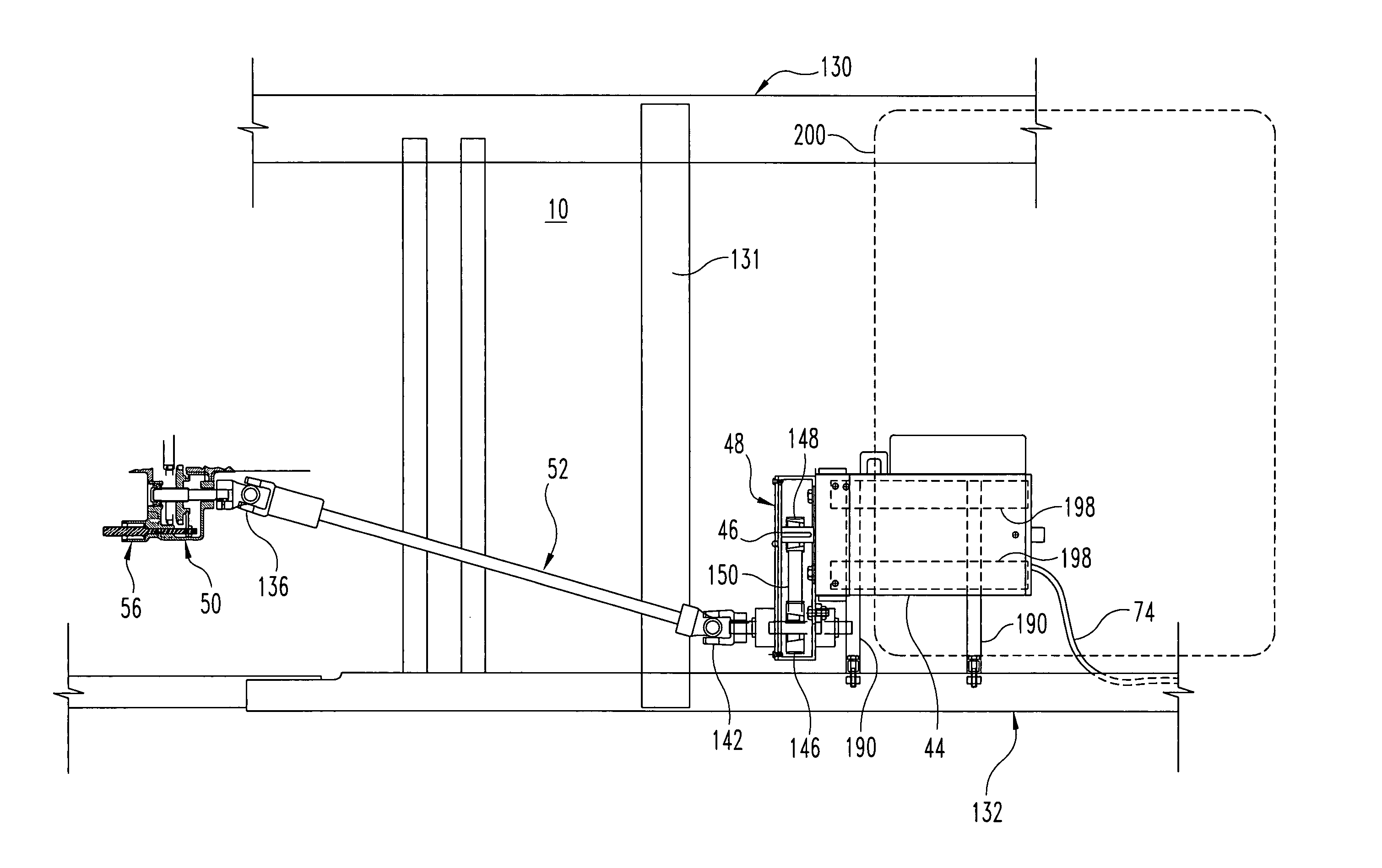
A vehicle mounted AC generator system having an AC generator mounted outside the engine / transmission compartment and connected by drive shaft with universal joints and a belt driven RPM ratio device. The ratio is set to provide accurate AC generator RPM at a preselected engine RPM. The AC generator is mechanically engageable when certain conditions are met and is disconnected when other conditions are present, including an operator emergency stop switch.
Owner:CONTOUR HARDENING
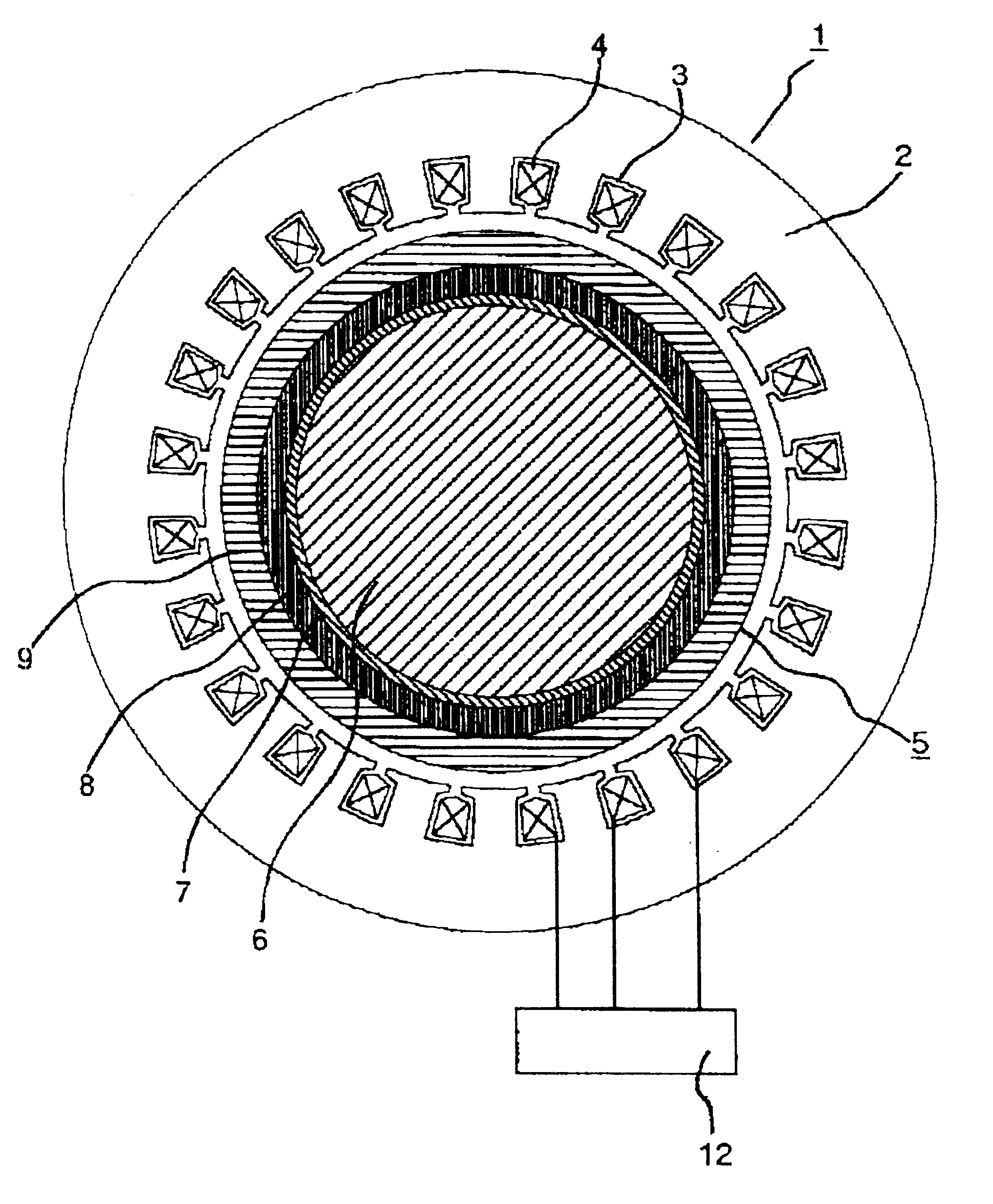
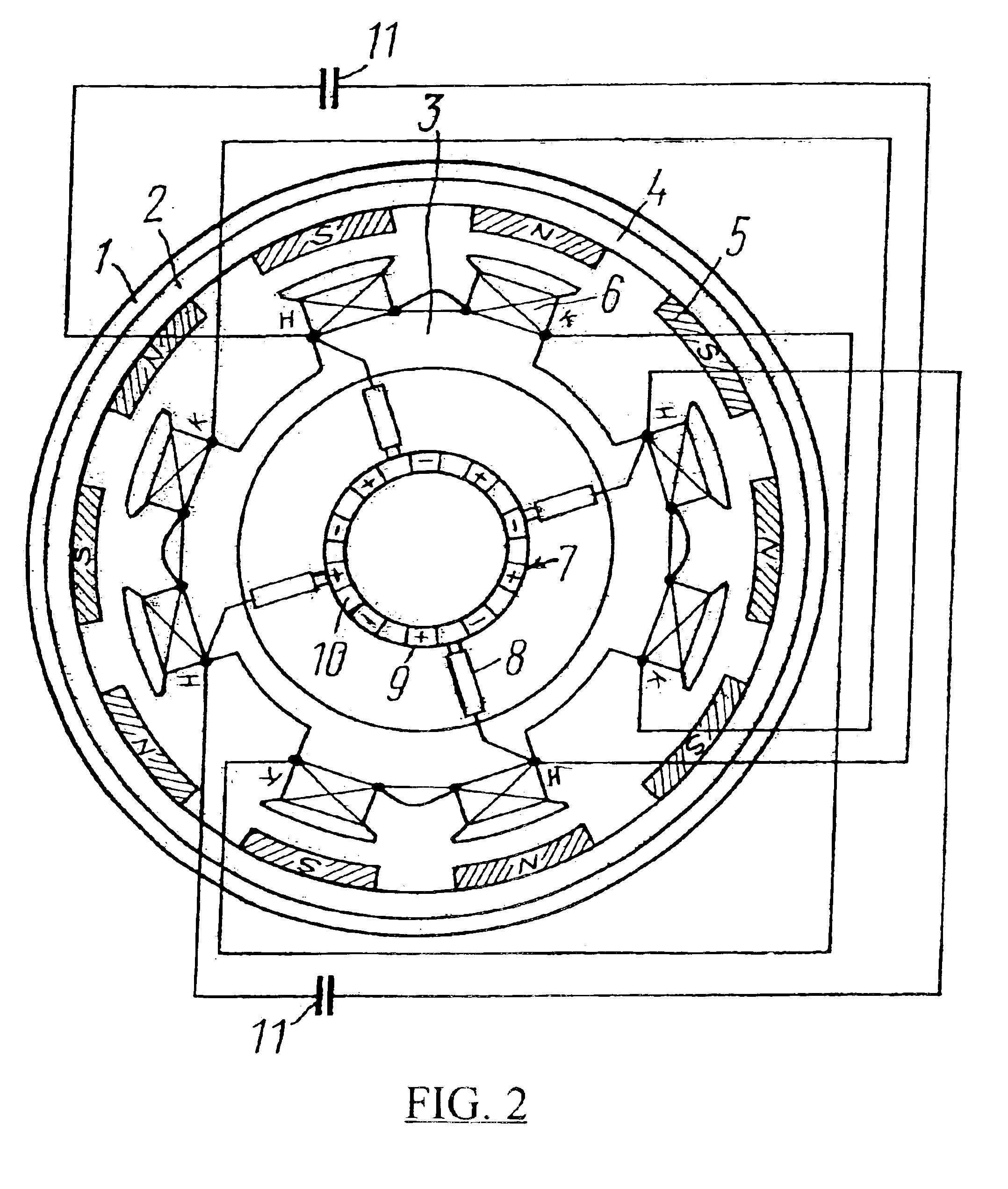
Permanent magnet type synchronous motor and air compressor
InactiveUS6376958B1Magnetic circuit rotating partsPositive displacement pump componentsFiberUltra high speed
Provided are a super-high speed permanent magnet type synchronous motor which causes less loss in a rotor even though it is driven by an inverter adapted to be operated with a fundamental frequency around 1 kHz, and an air compressor. The air compressor having a super-high speed permanent magnet type synchronous motor which is composed of a stator in which armature windings are wound in a plurality of slots formed in a stator core, and a rotor including a shaft made of a conductive magnetic material, a conductive permanent magnet laid around the outer periphery of the shaft, and a reinforcing member made of carbon fibers and laid around the outer periphery of the permanent magnet, wherein a laminated electromagnetic steel sheet is interposed between the shaft and the permanent magnet, and the laminated electromagnetic steel sheet has a high tensile strength higher than 70 kg / mm2.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Power generator and torque amplifier
InactiveUS20050140231A1Simple structureEfficiently obtainedMagnetic circuit rotating partsAC/DC convertorsRotational axisAudio power amplifier
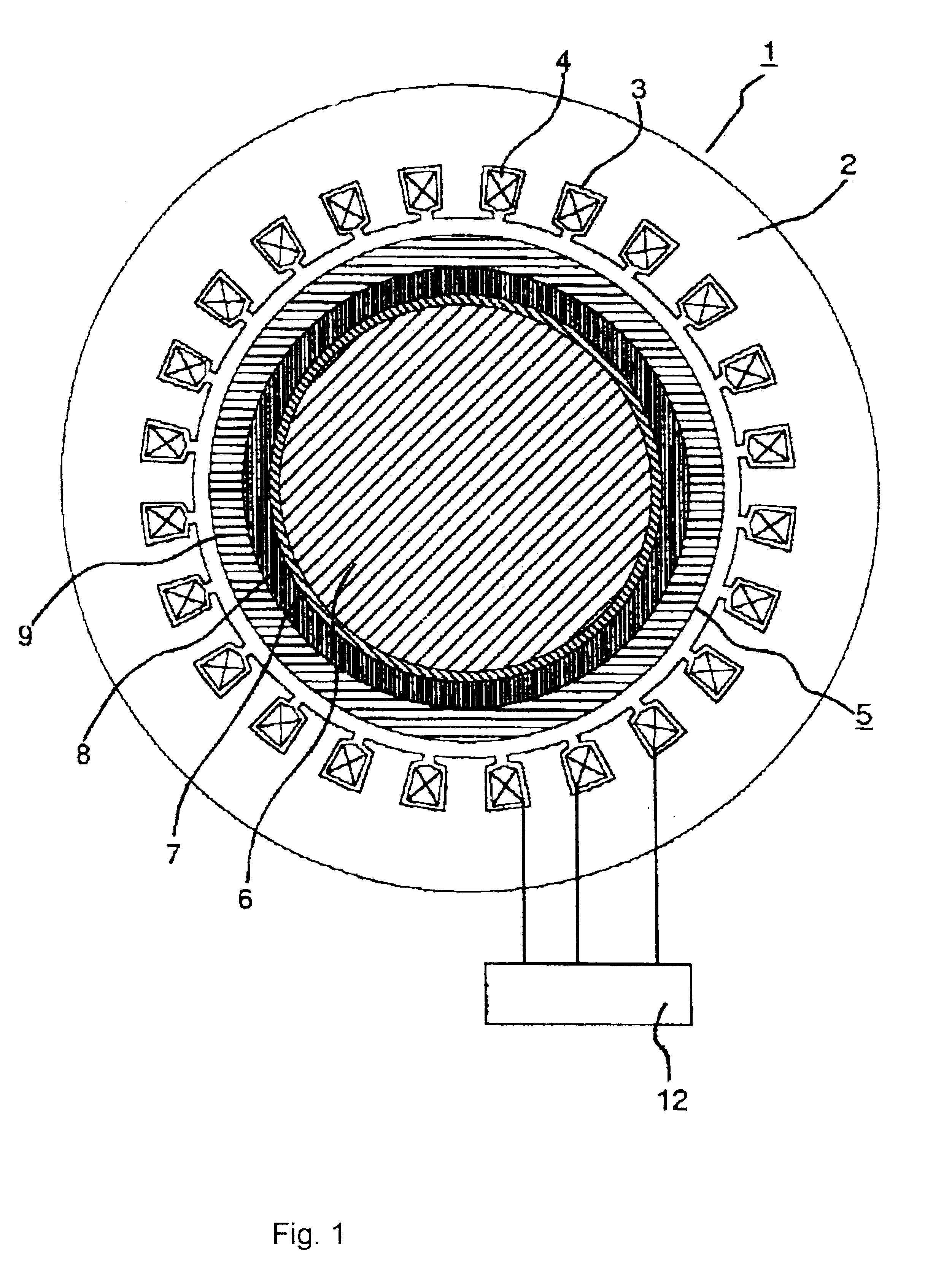
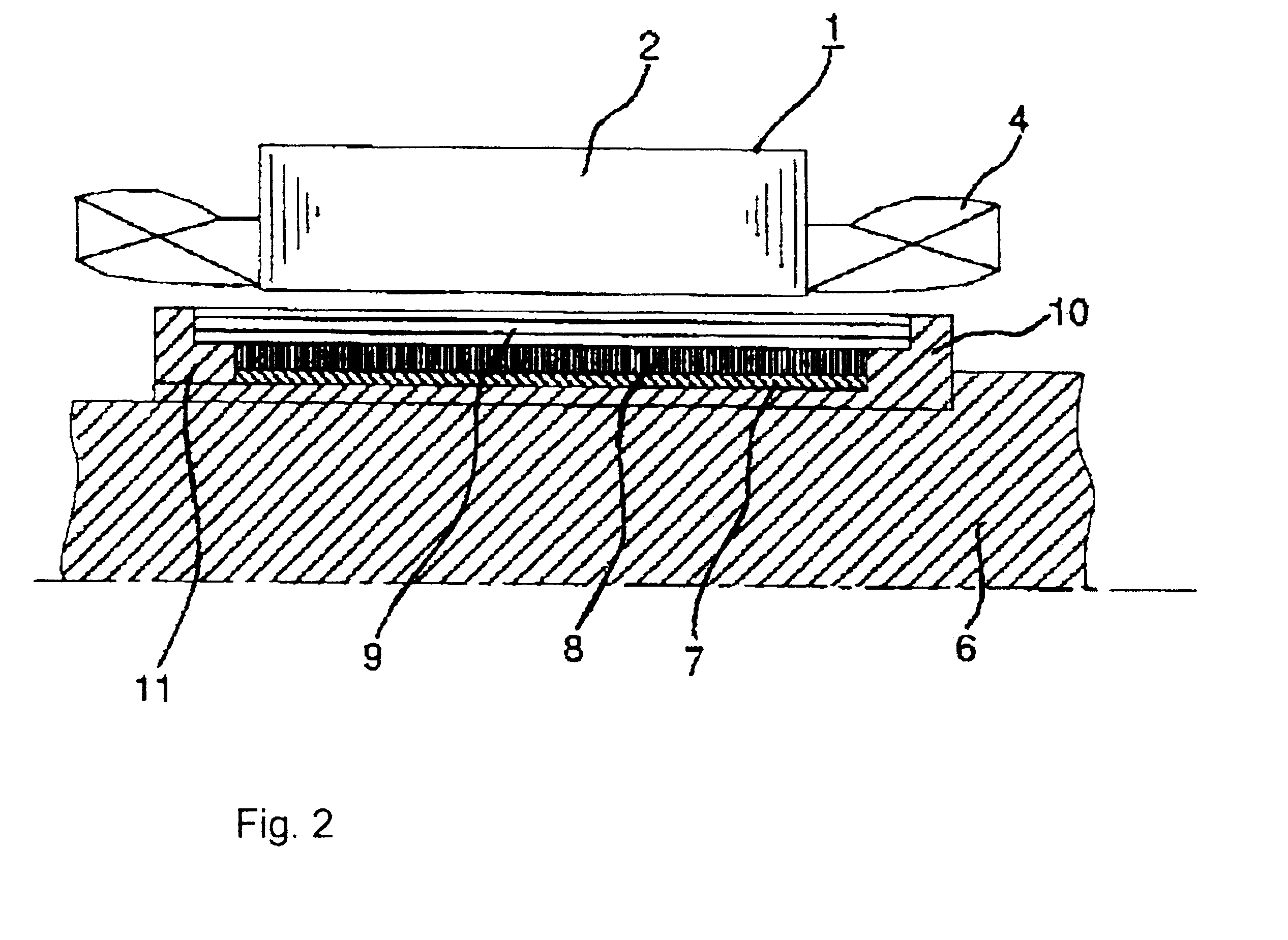
Disclosed is a power generator adapted to provide an electrical power greater than an input power by means of a permanent magnet. The power generator 10 comprises a rotatable rotor 12, a plurality of permanent magnets 16, and a plurality of coreless coils 18. The rotor 12 has a surface including an annular zone 14 formed around the rotational axis 13 thereof. The permanent magnets 16 are disposed along the annular zone 14 at constant intervals in the circumferential direction of the rotor 12 to form an annular array, while uniformly orienting their polarities in a direction orthogonal to the annular zone 14. The coreless coils 18 are supported by a stationary member 11 and disposed along the annular zone to form an annular array, while allowing the respective axes 19 of the coils to intersect with the annular zone 14. The permanent magnets 16 are moved along the coreless coils 18 in conjunction with the rotation of the rotor 12 induced by a rotational force supplied through a center shaft 22 from a torque amplifier 20 disposed below the rotor 12, so as to obtain an output power from the coreless coils 18.
Owner:OGOSHI MAKOTO
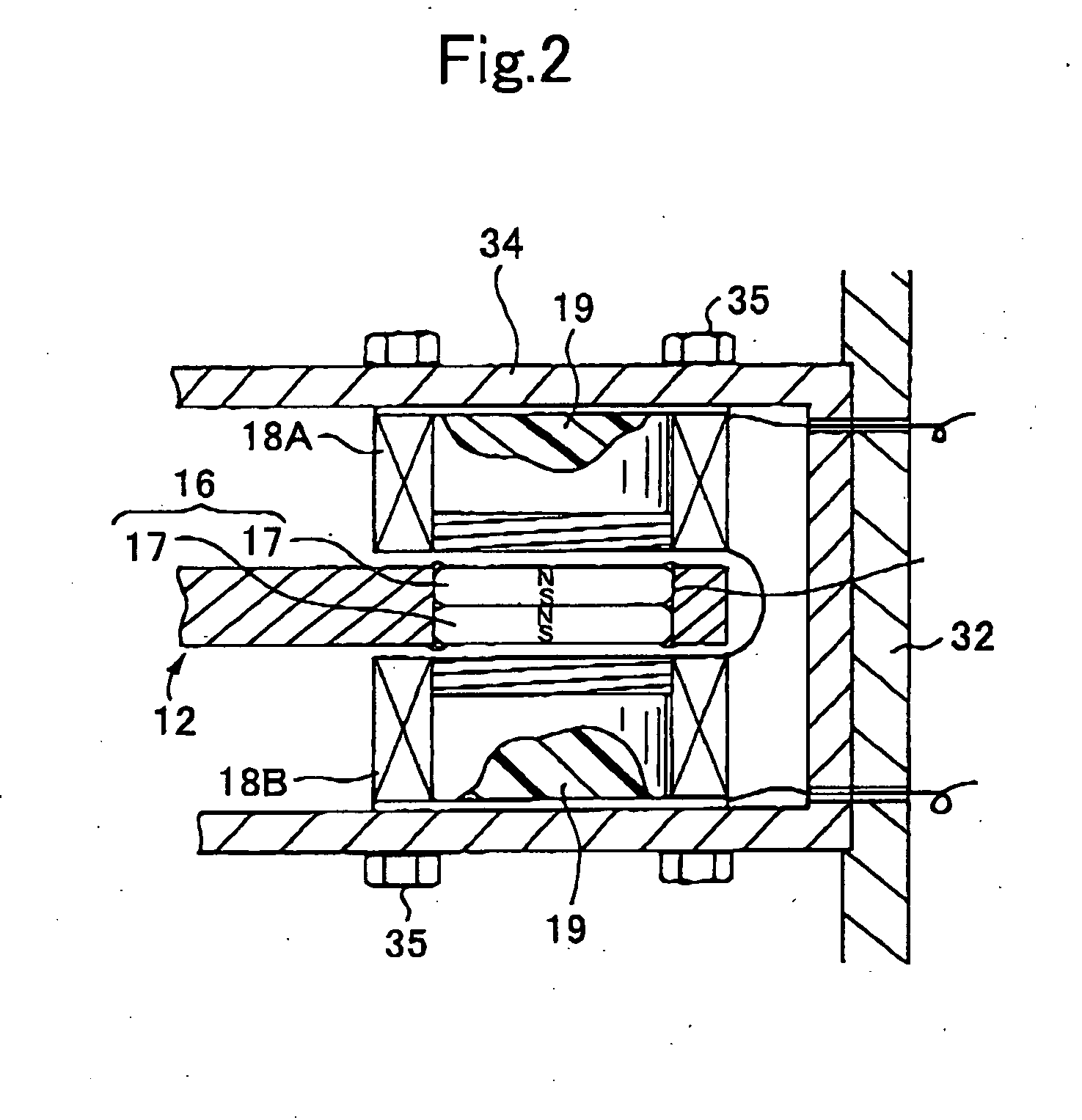
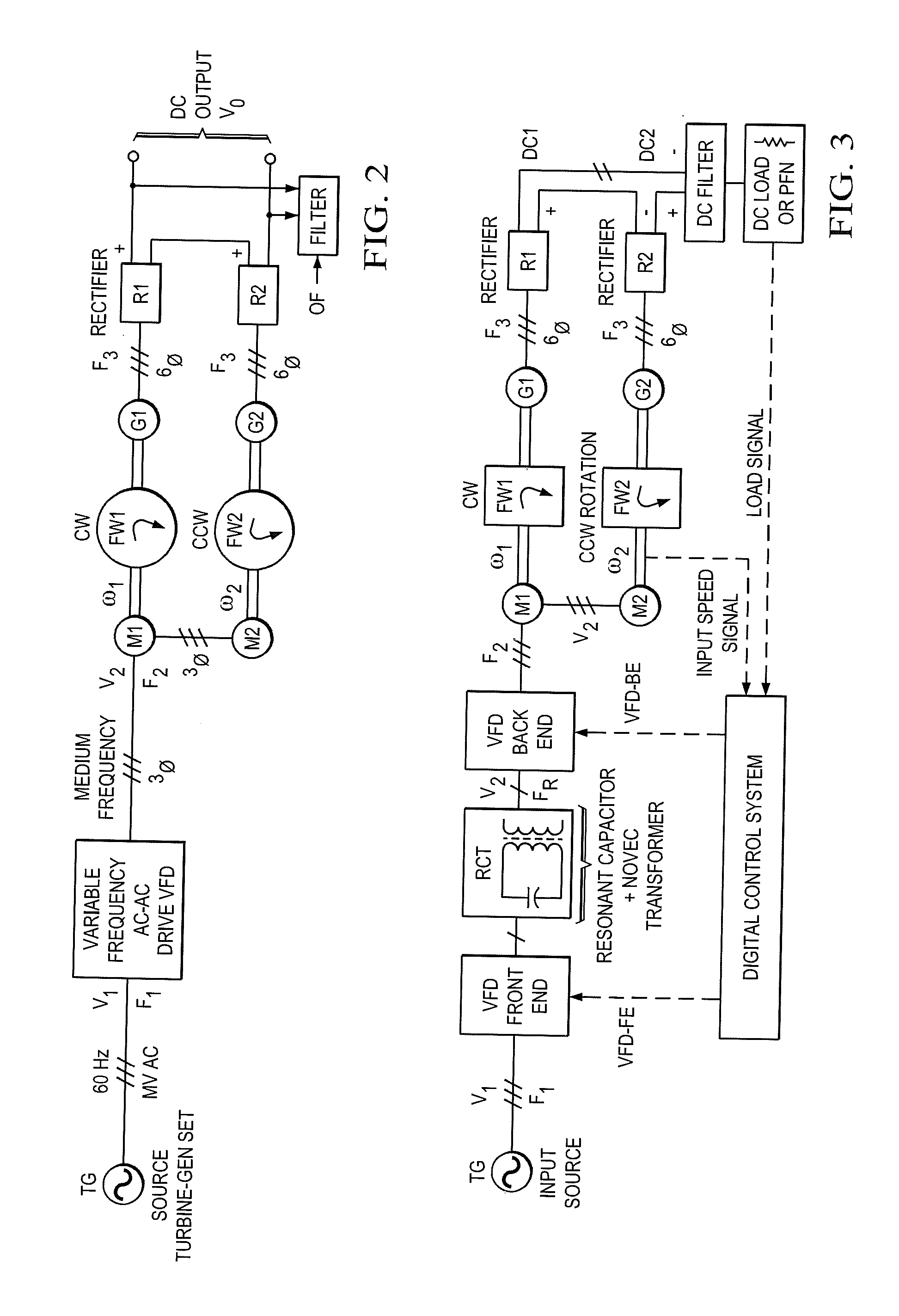
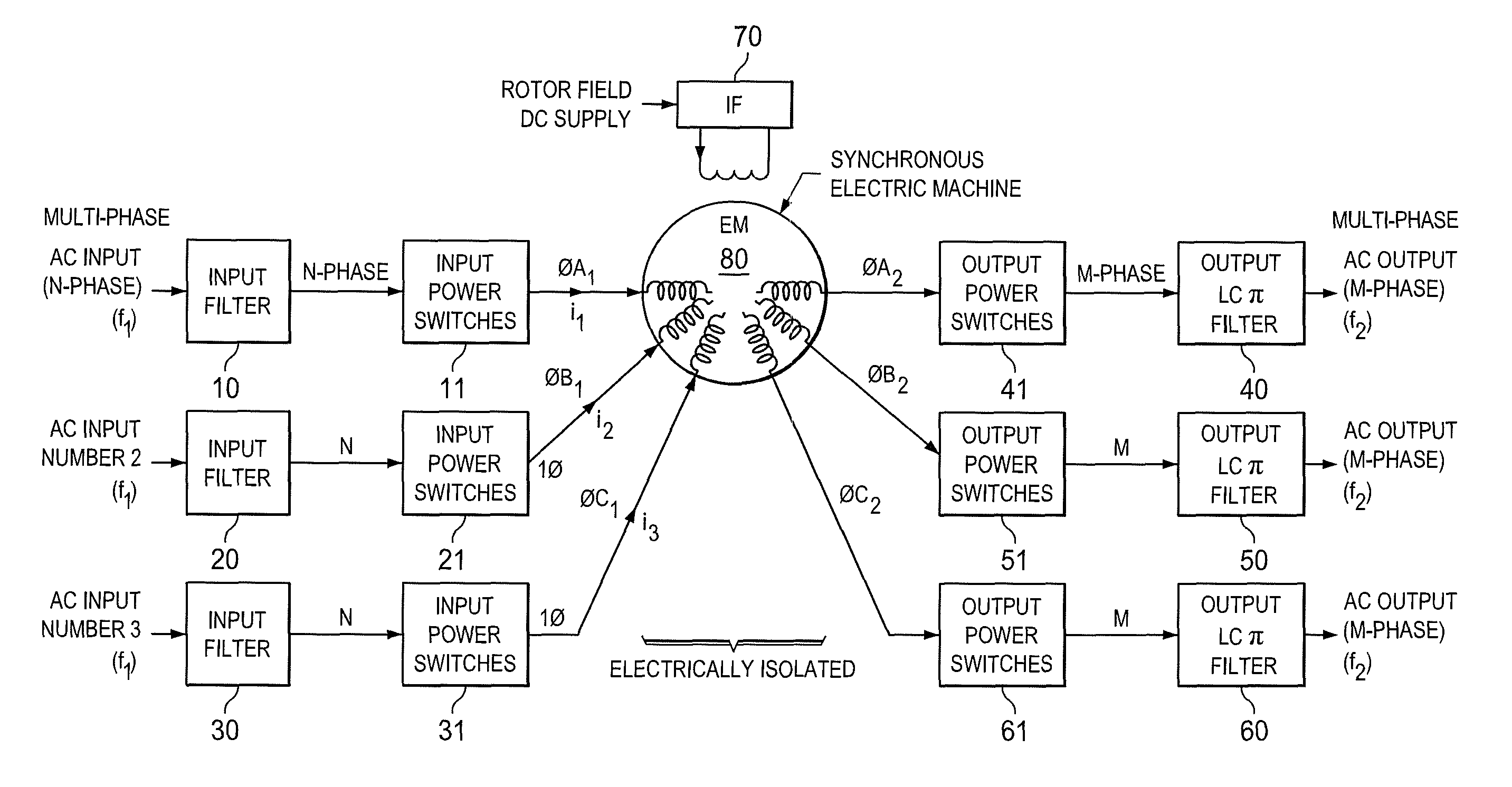
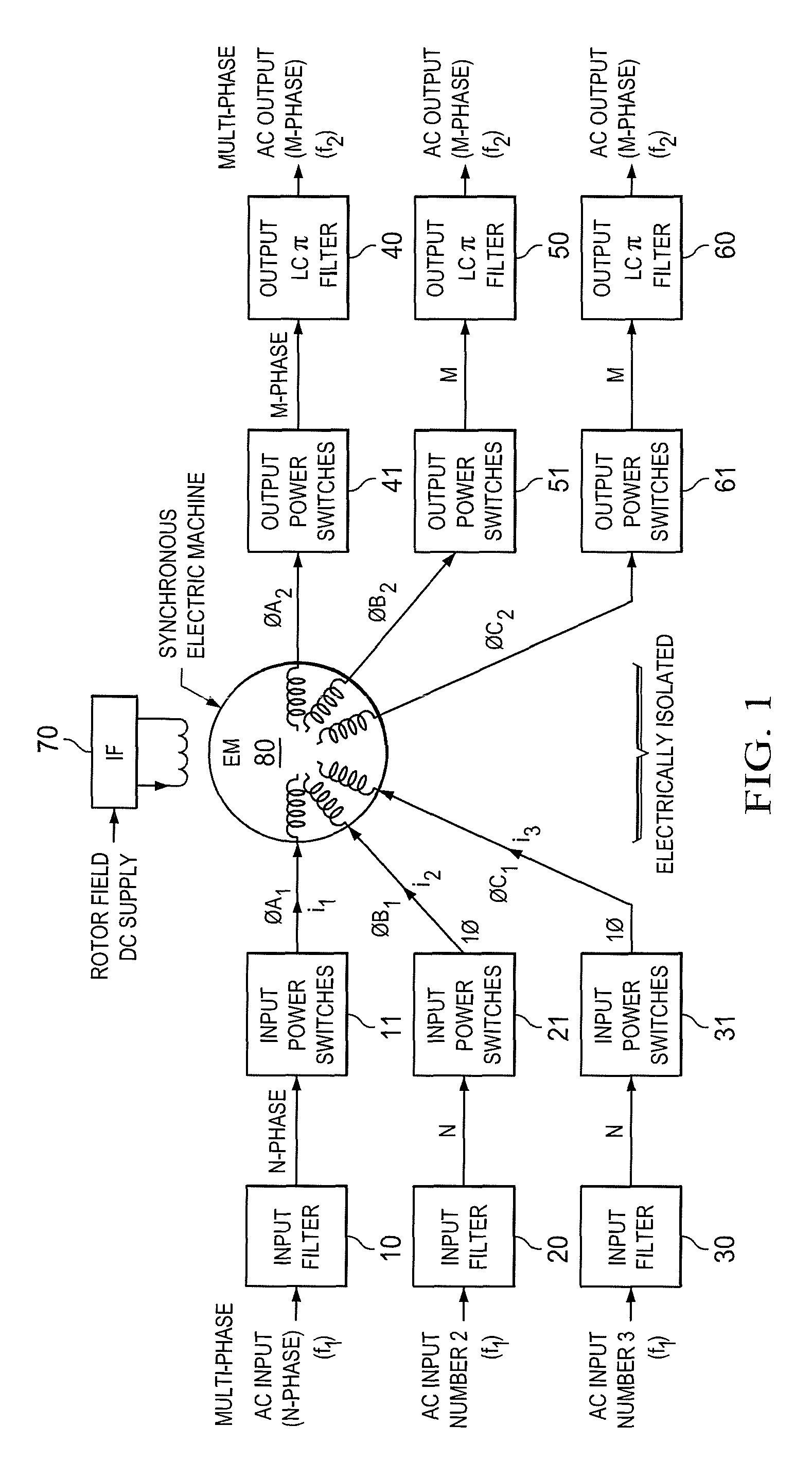
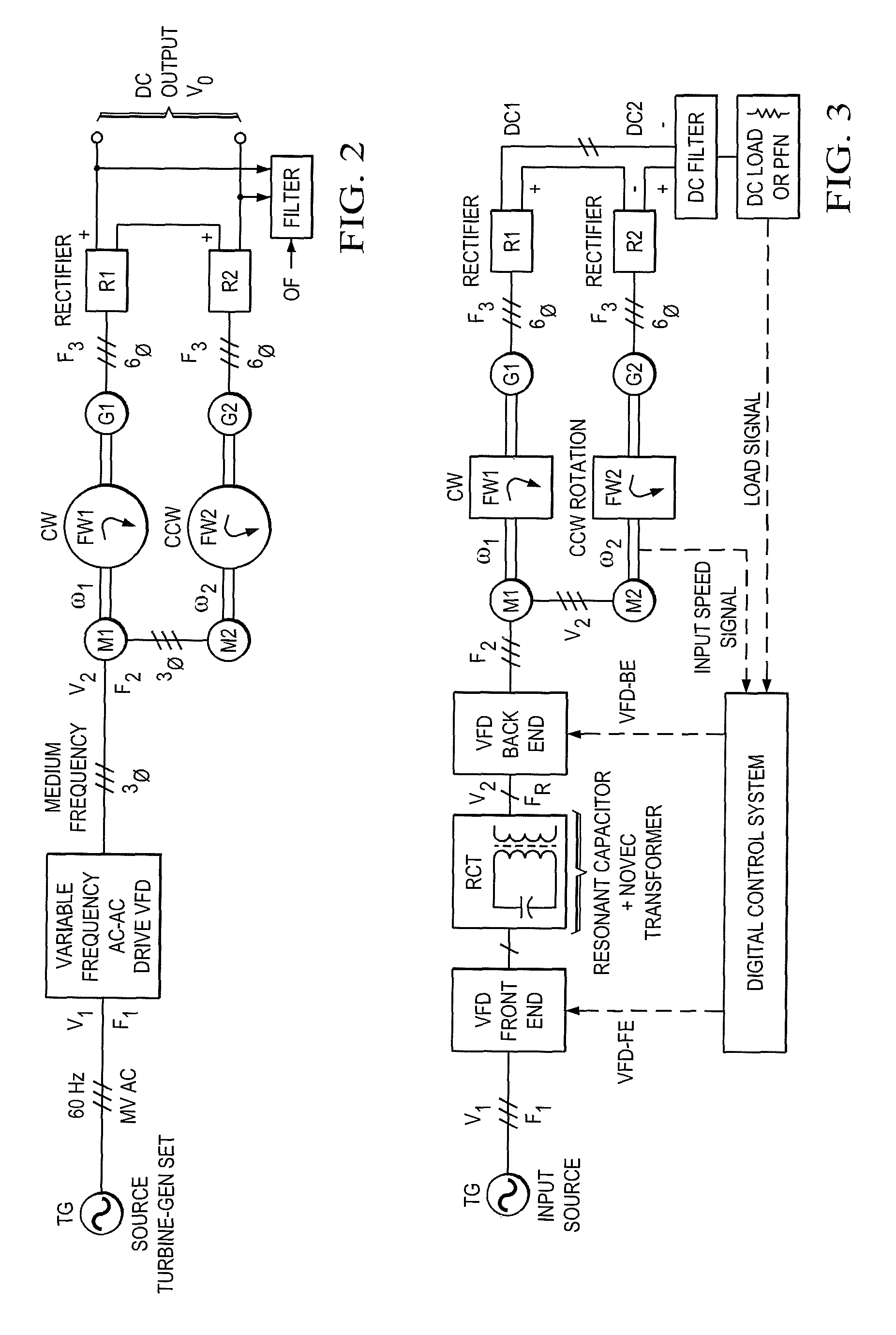
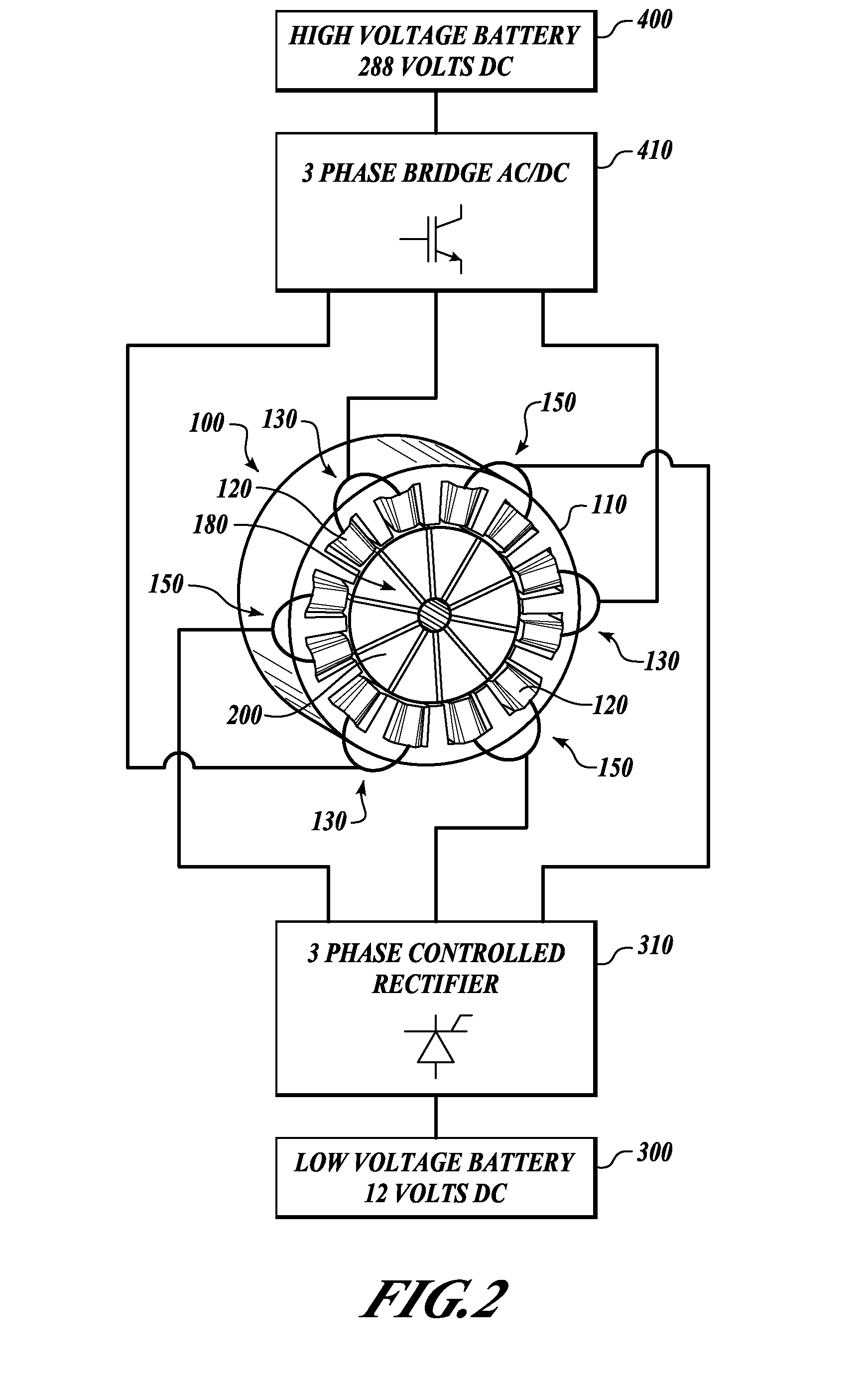
Inertial energy storage system and hydro-fluoro-ether power transformer scheme for radar power systems and large pfn charging
A multi-port storage system includes a dynamo-electric machine with integral rotor inertia forming a primary energy storage system. The dynamo-electric machine has a primary stator winding configured to accept multiple AC input power sources, and has at least two secondary stator windings configured to deliver electric power to multiple loads at different power, frequency and voltage levels. A secondary energy storage system is coupled to the primary energy storage system, and is configured to convert its stored energy to electric power. The dynamo-electric machine is configured to enhance and buffer the secondary energy storage system, and is configured to improve the conversion of the stored energy to electric power. The system may include a step-up transformer responsively coupled to one of the secondary stator windings. The step-up transformer may comprise a single phase or polyphase step-up transformer having internal cooling and electrical insulation between the secondary windings comprising a hydro-fluoro-ether (HFE) vapor and liquid fluid.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Self-contained intelligent cascaded synchronous electric motor-generator tandems of cumulative compound excitation
ActiveUS20100171381A1Easy to operateEfficient energy conversionAC/AC convertorsAutotransformerSynchronous motor
A self-contained intelligent cascaded synchronous electric motor-generator tandem of cumulative compound excitation comprises at least a synchronous electric motor-generator tandem (namely MG tandem), a storage battery cluster and an autotransformer. Each MG tandem comprises at least a pair of motor and generator having a common stator and a common rotor shaft. The storage battery cluster, which provides a DC power to general loads and motor, serves as a DC power reservoir to be recharged by generator. The autotransformer serves to regulate the AC voltage output from generator via multiple output taps thereon for supplying various AC voltages to different external loads. By integrating all components aforesaid with common magnetic flux interacted mutually, upon being energized by DC power from storage battery cluster, the motor will transfer rotational torque to drive the generator in enhanced synergistic manner.
Owner:LING GANGQIN
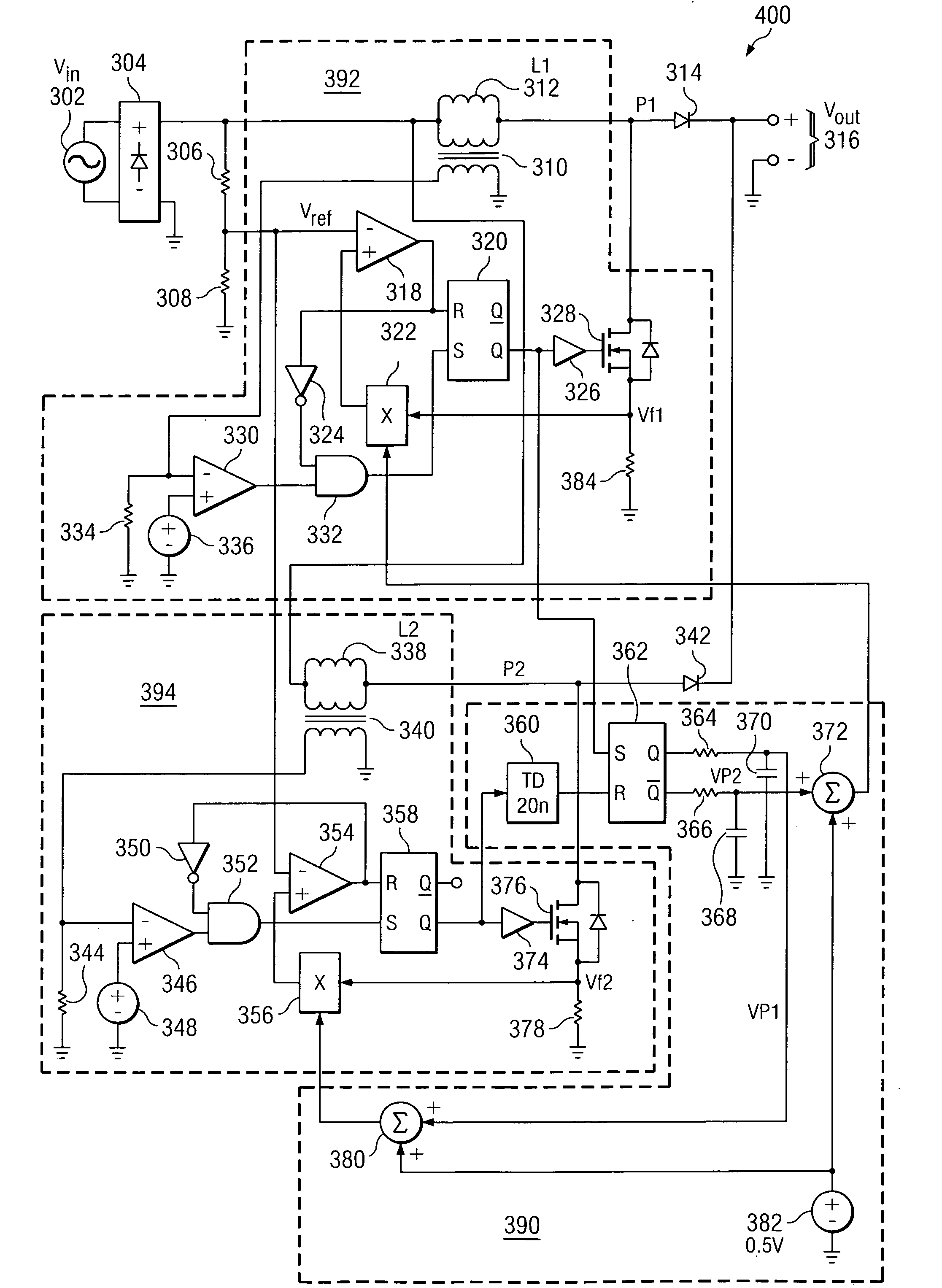
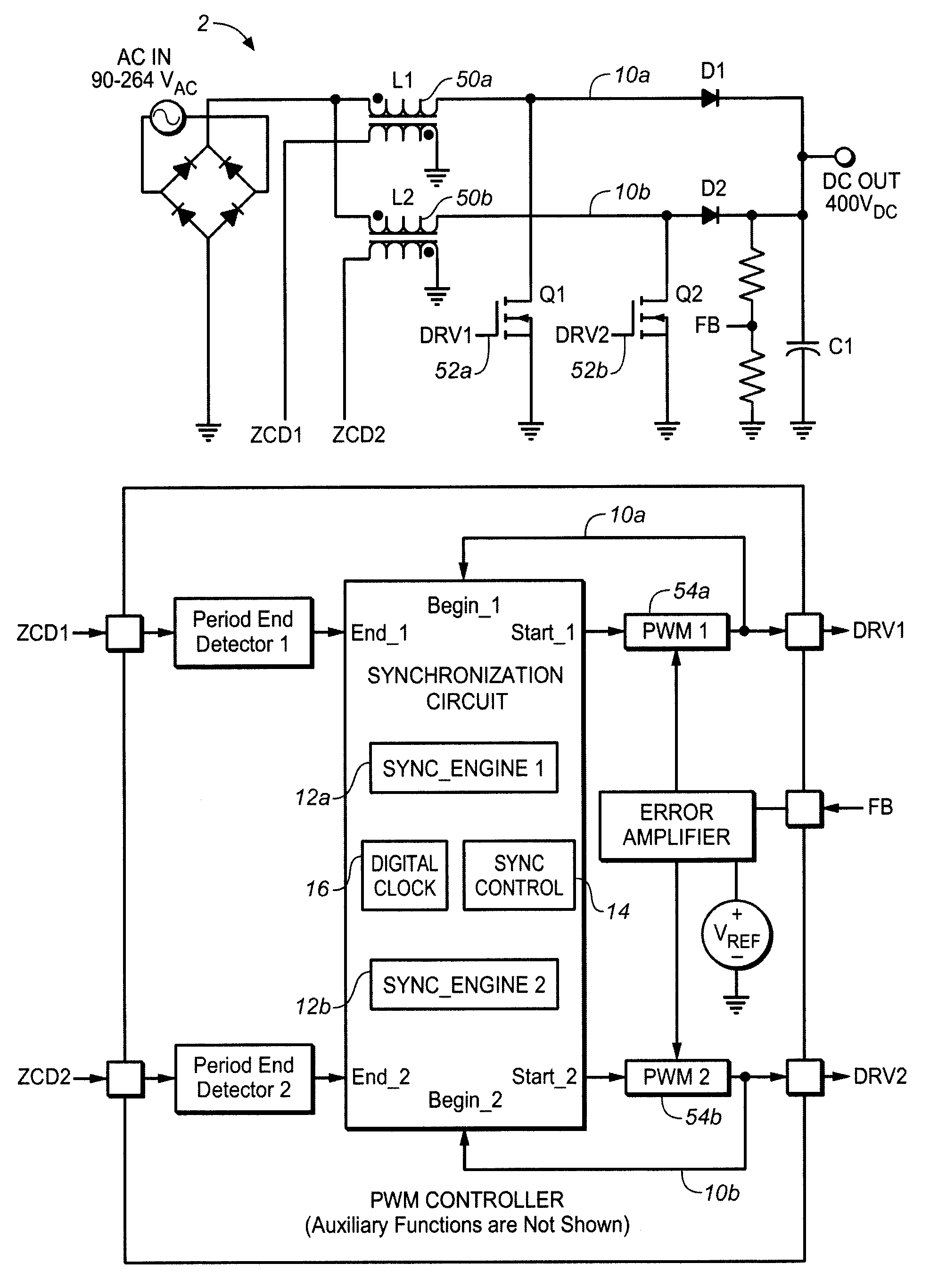
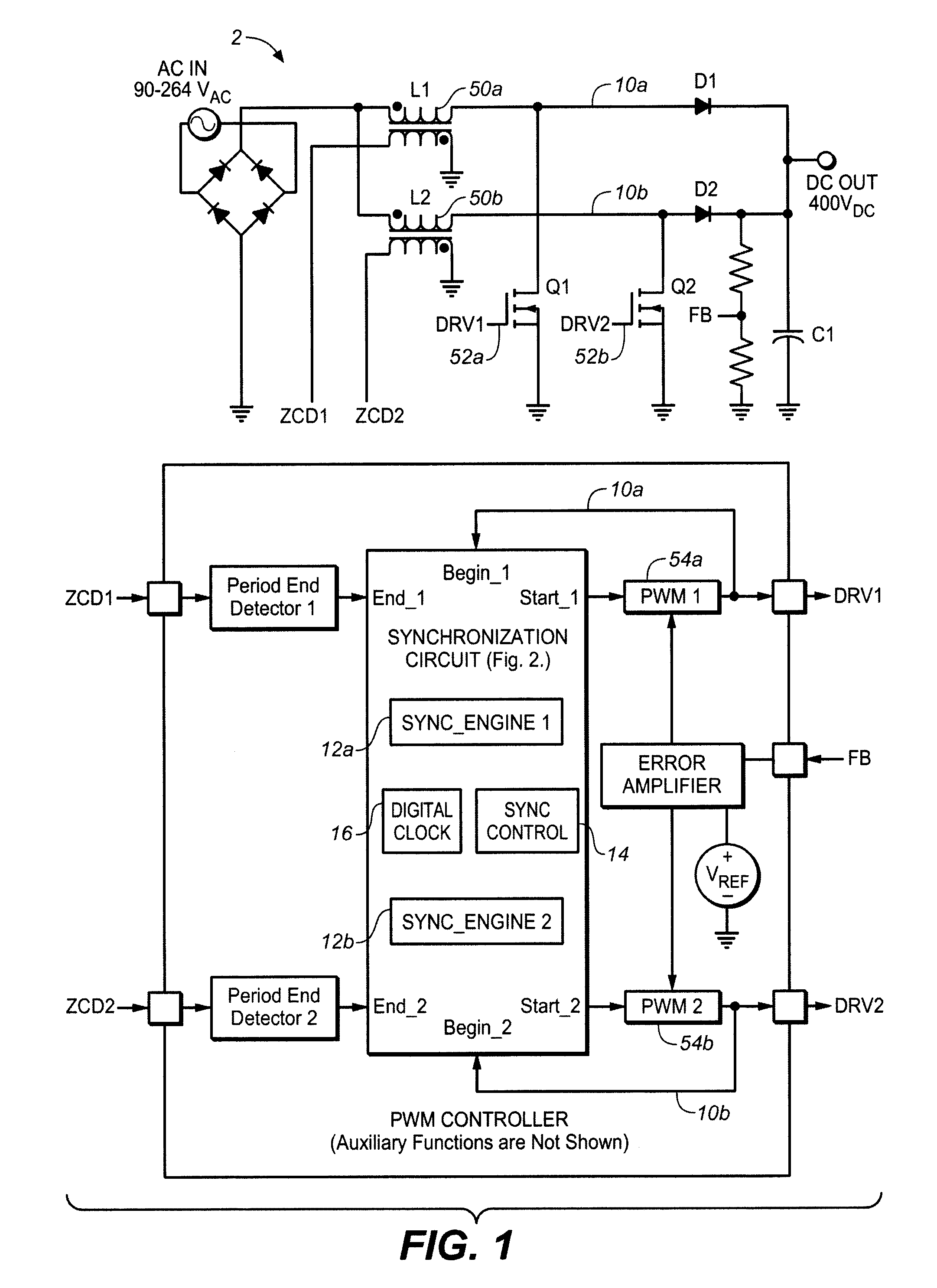
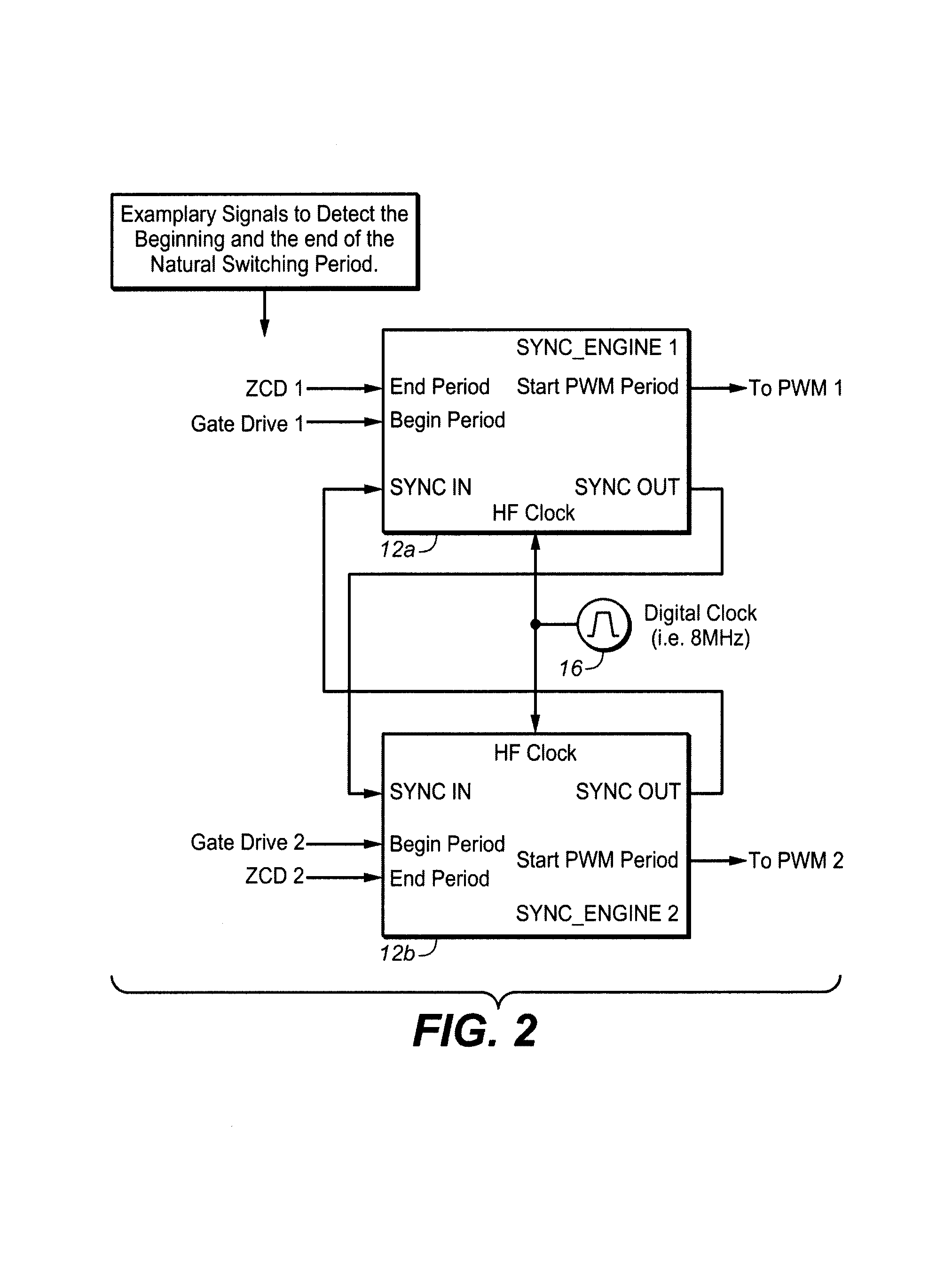
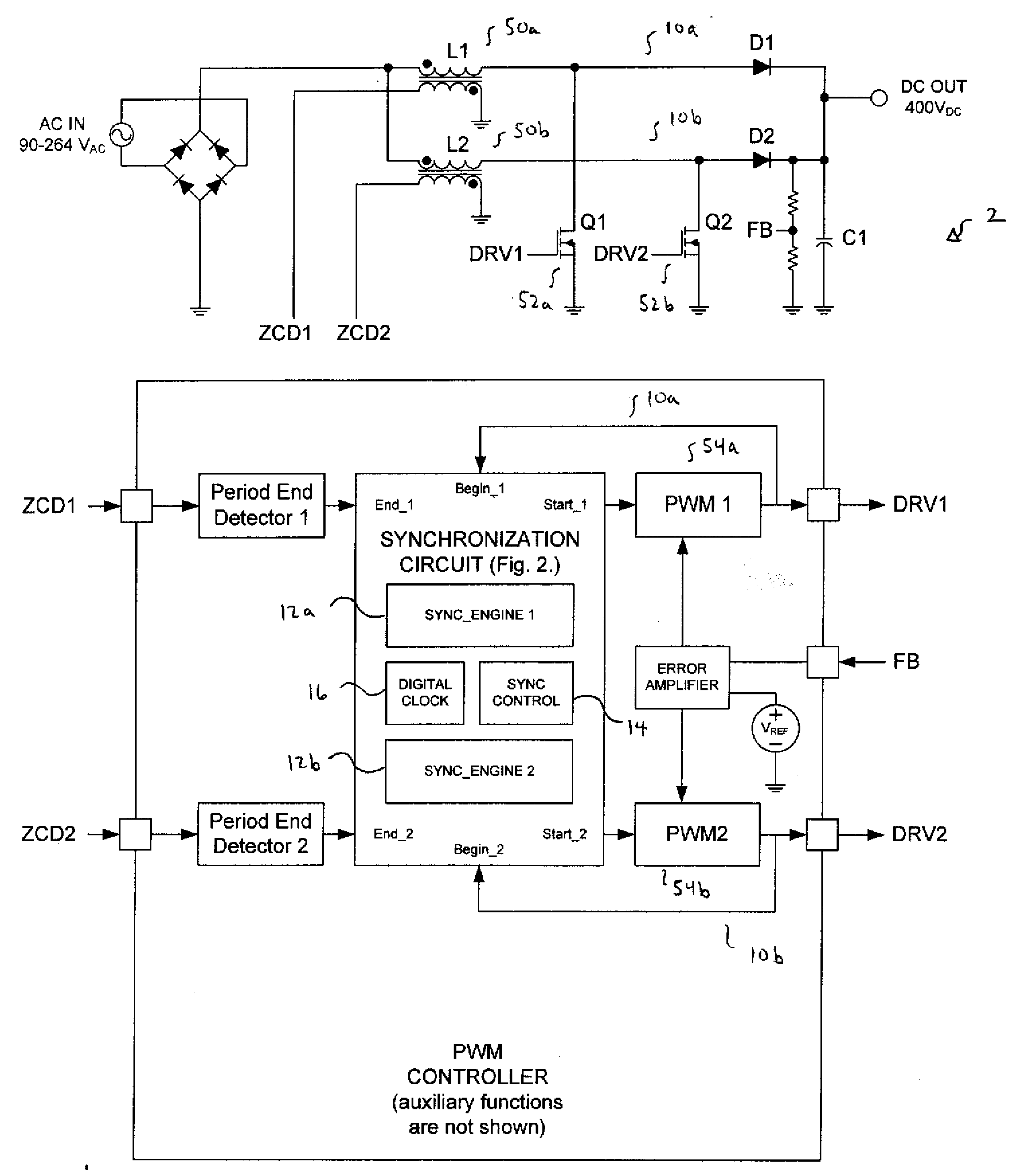
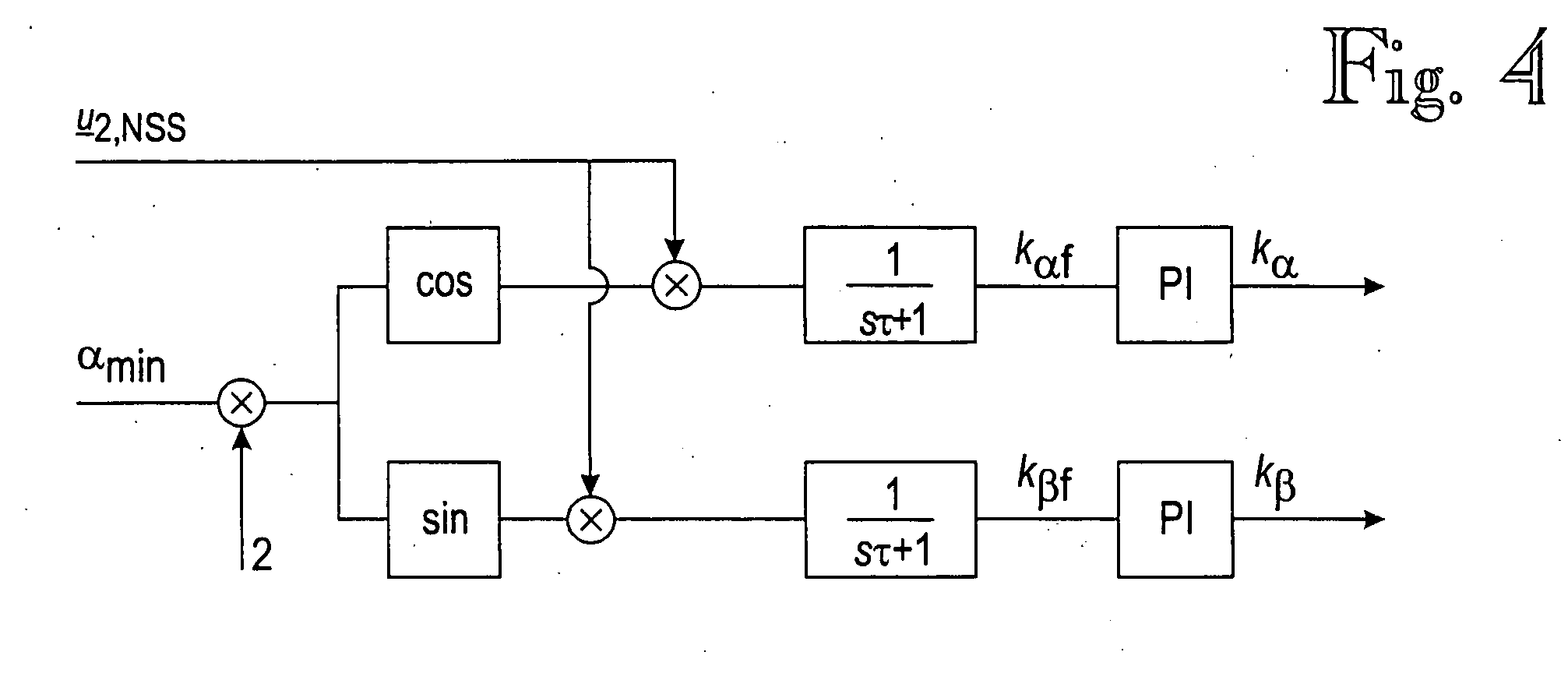
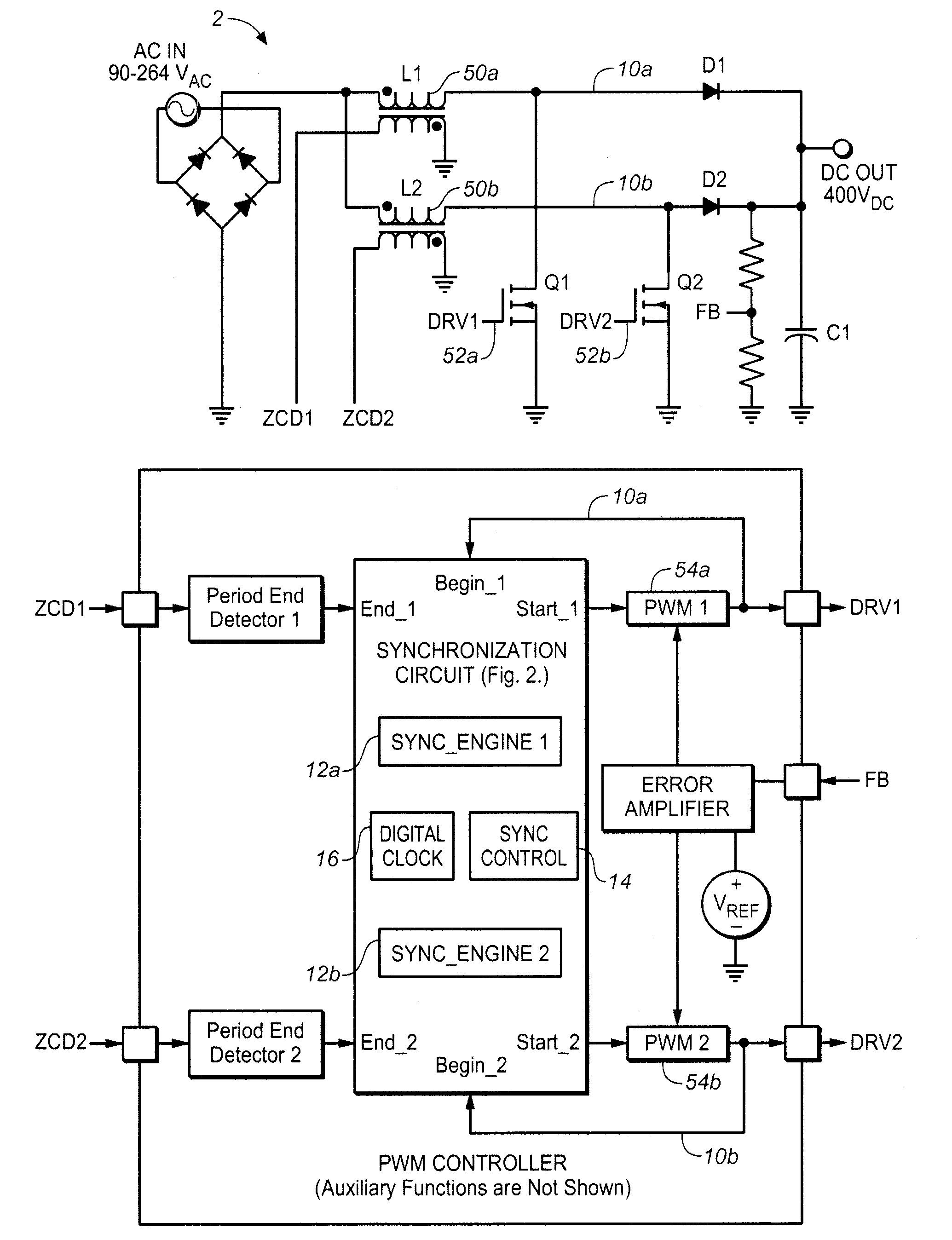
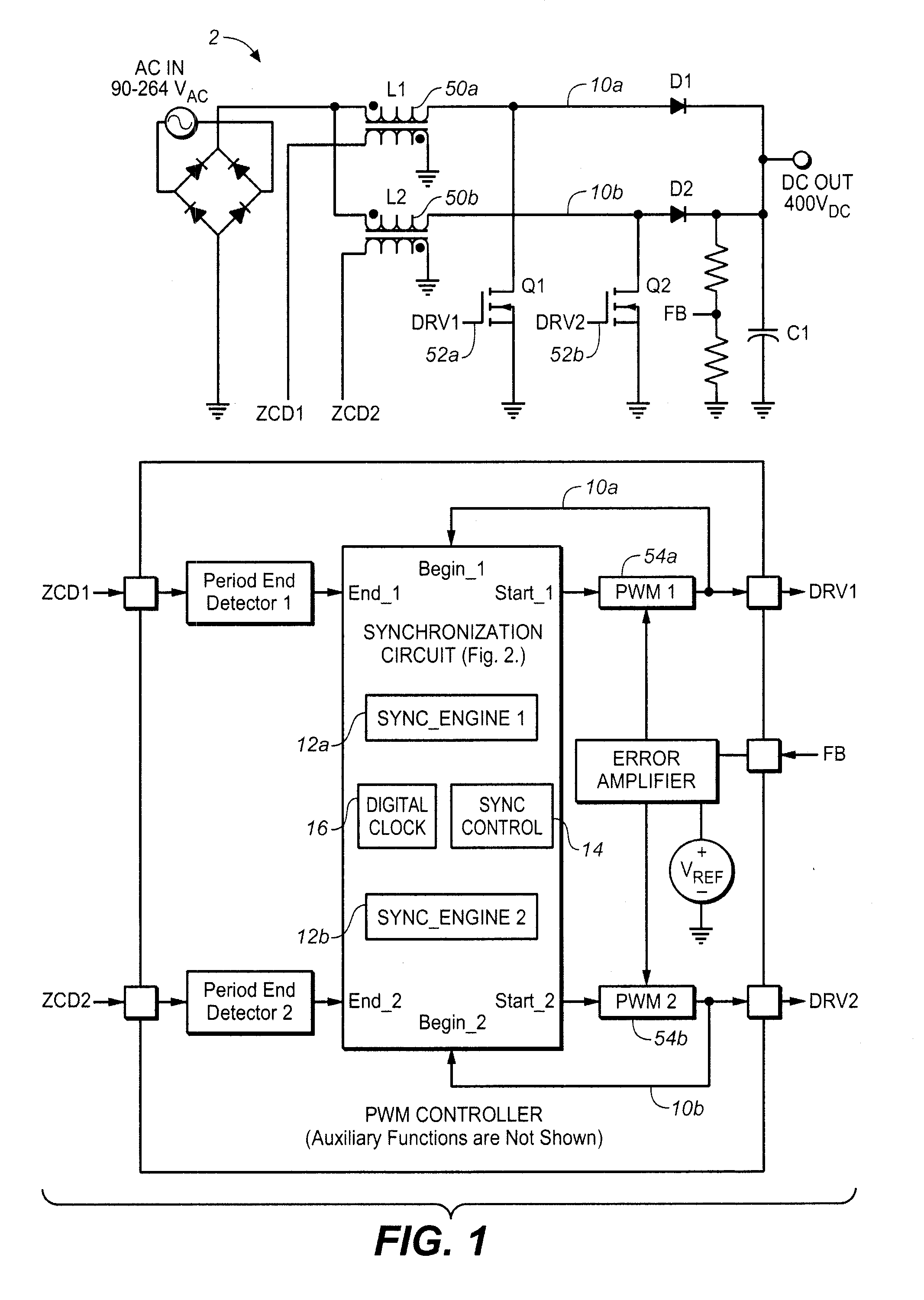
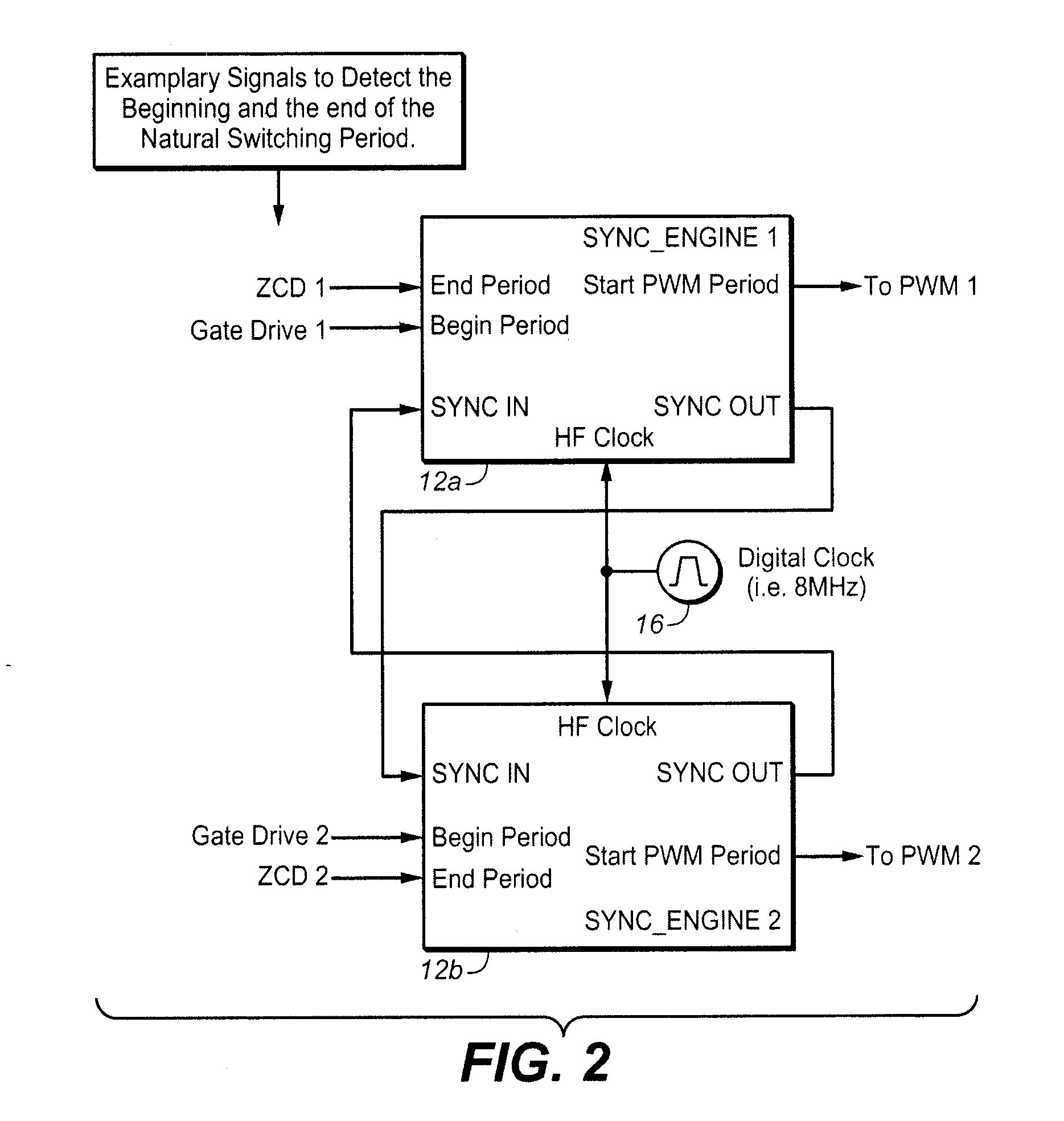
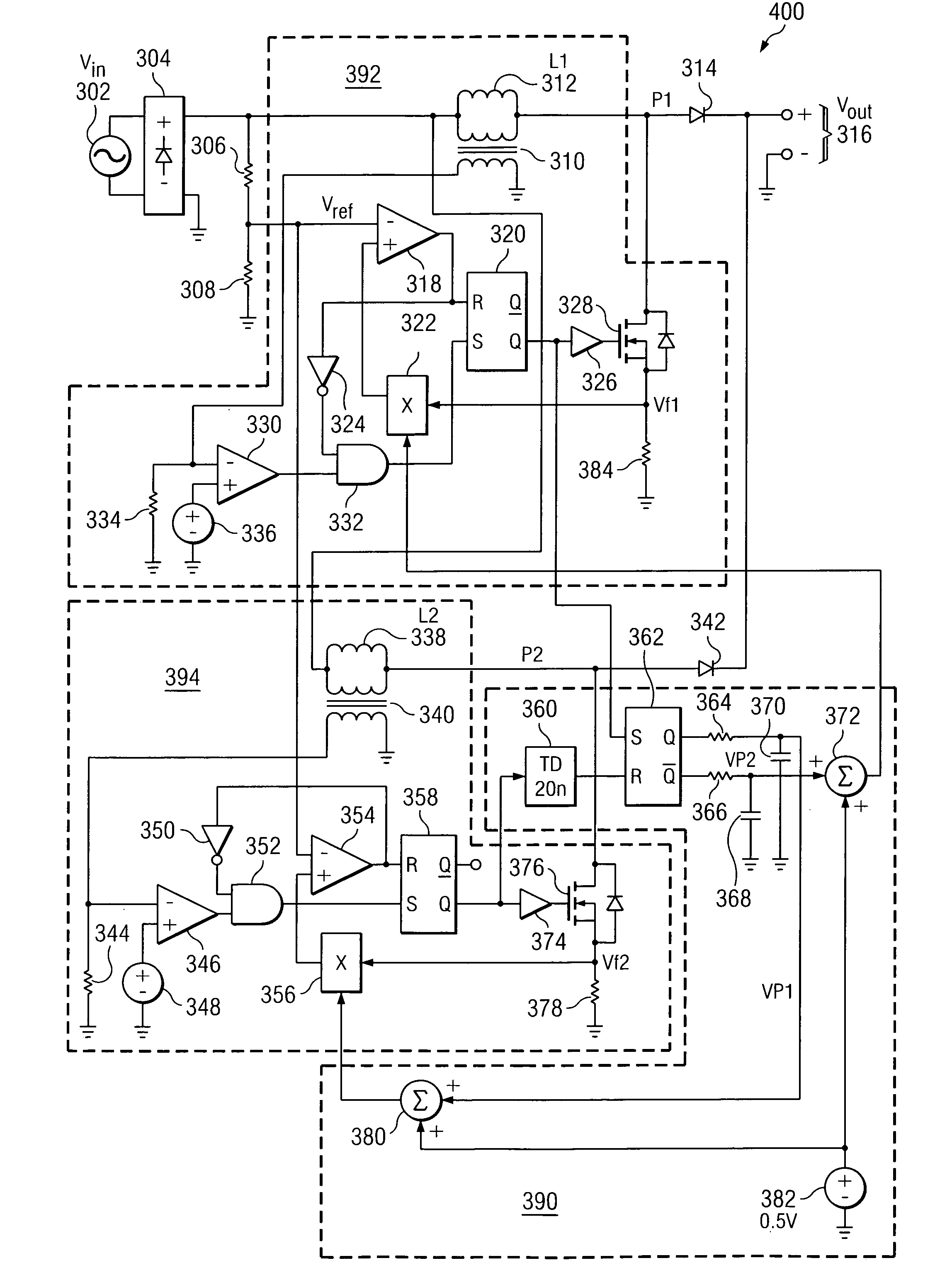
Synchronizing frequency and phase of multiple variable frequency power converters
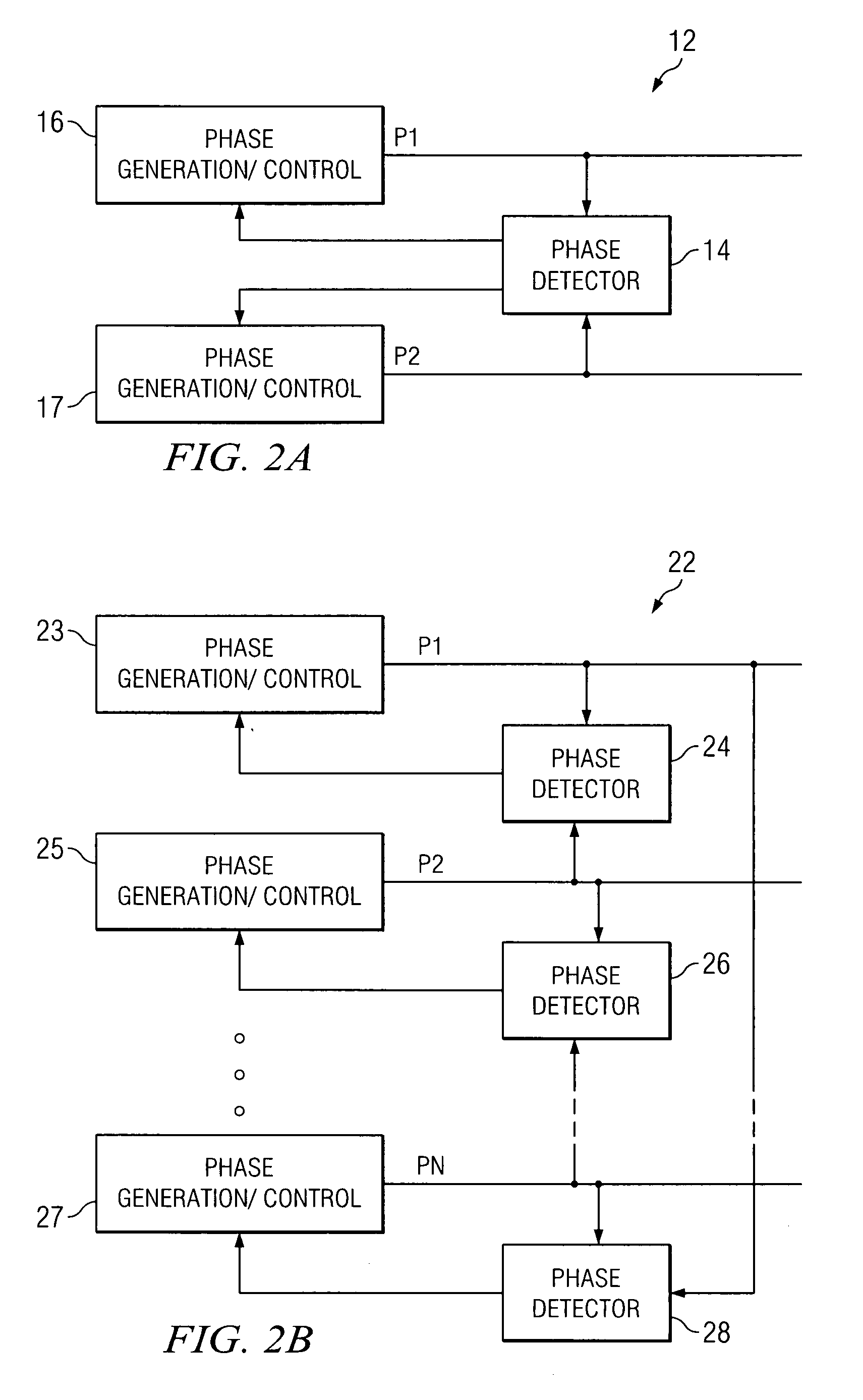
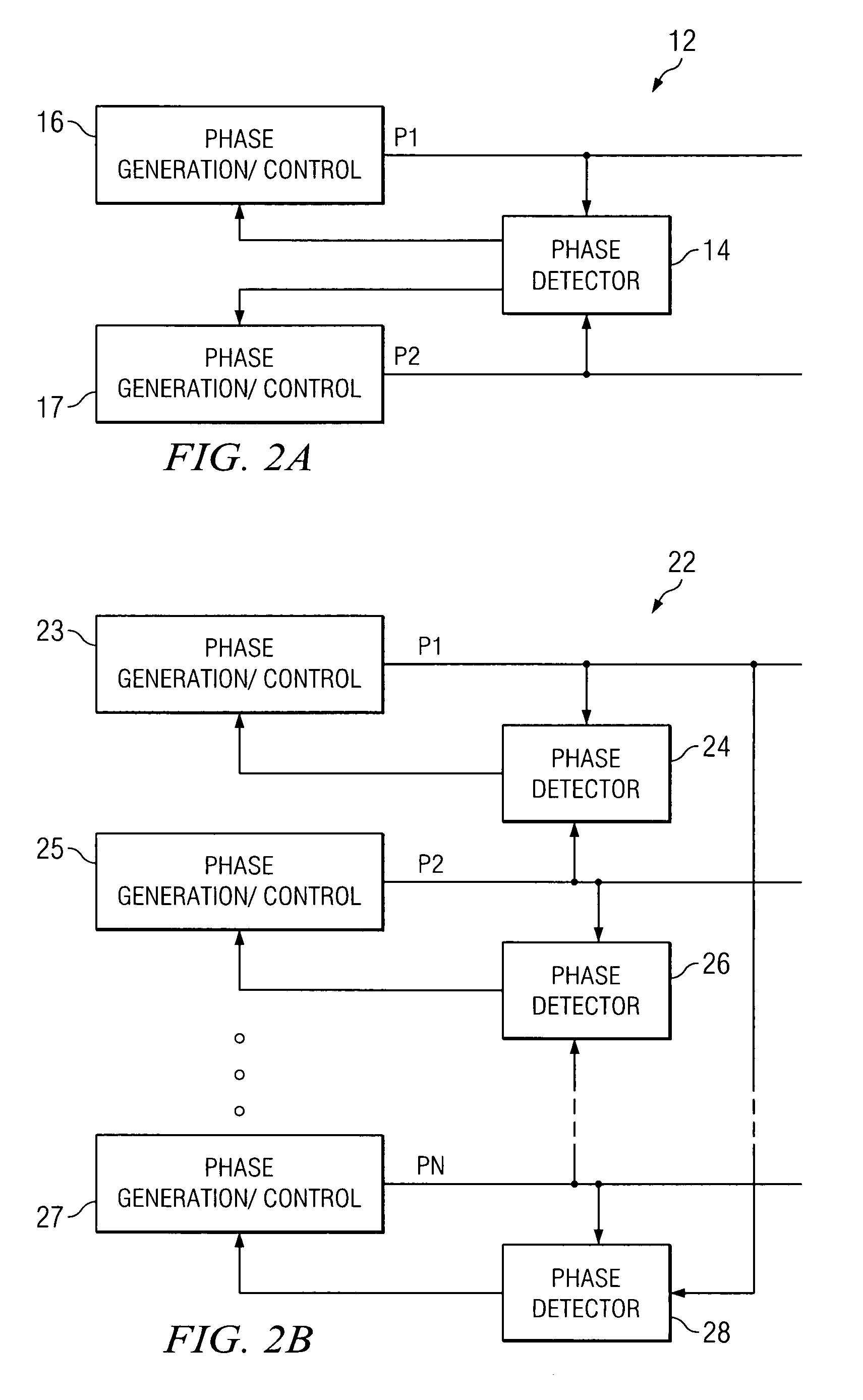
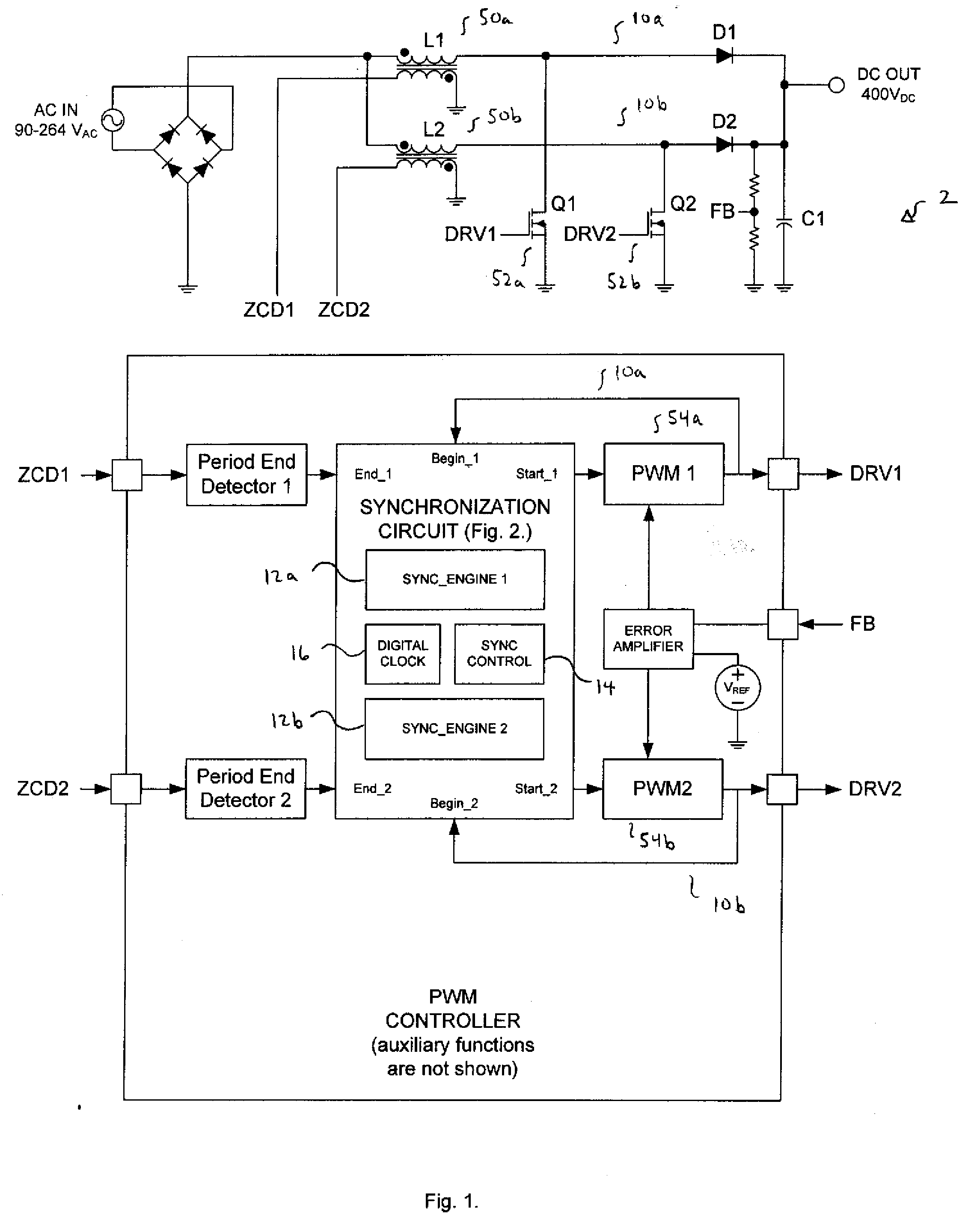
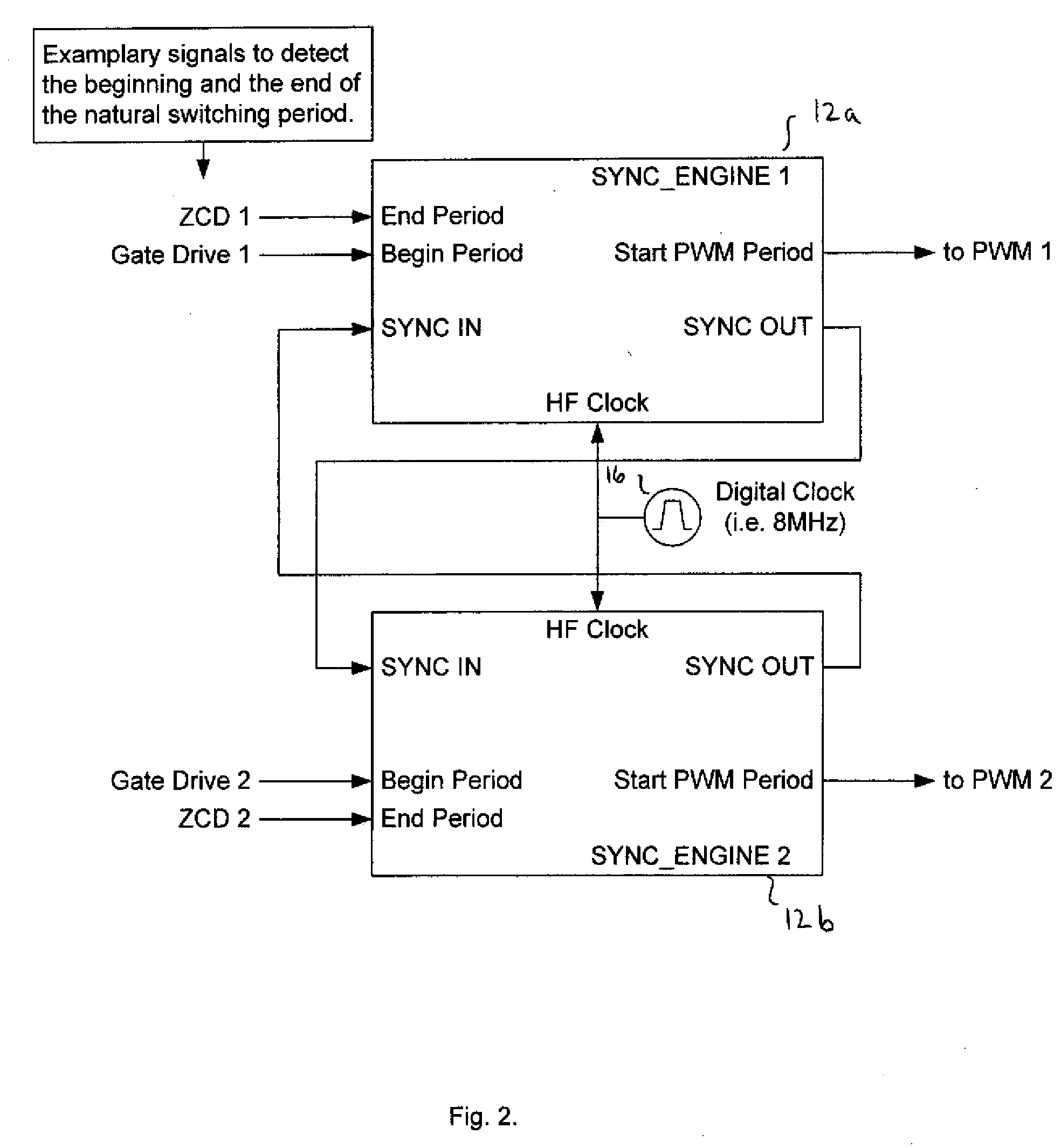
In an embodiment, a power converter system includes a plurality of variable frequency power converters and a plurality of synchronization circuits. Each variable frequency power converter has a switching frequency. Each synchronization circuit is associated with a respective one of the plurality of variable frequency power converters. A control circuit is coupled to and coordinates the plurality of synchronization circuits. The plurality of synchronization circuits and the control circuit are operable to synchronize the switching frequencies of the variable frequency power converters to each other. Each synchronization circuit is operable to: receive a first input signal indicative of the beginning of a switching period for the associated variable frequency power converter; receive a second input signal indicative of the end of the switching period for the associated variable frequency power converter; generate a first output signal for directing a pulse width modulation of the associated variable frequency power converter; and generate a second output signal for coordinating a phase relationship with another variable frequency power converter in the system.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Vehicle mounted electrical generator system
A vehicle mounted AC generator system having an AC generator mounted outside the engine / transmission compartment and connected by drive shaft with universal joints and a belt driven RPM ratio device. The ratio is set to provide accurate AC generator RPM at a preselected engine RPM. The AC generator is mechanically engageable when certain conditions are met and is disconnected when other conditions are present, including an operator emergency stop switch.
Owner:CONTOUR HARDENING
Inertial energy storage system and hydro-fluoro-ether power transformer scheme for radar power systems and large PFN charging
A multi-port storage system includes a dynamo-electric machine with integral rotor inertia forming a primary energy storage system. The dynamo-electric machine has a primary stator winding configured to accept multiple AC input power sources, and has at least two secondary stator windings configured to deliver electric power to multiple loads at different power, frequency and voltage levels. A secondary energy storage system is coupled to the primary energy storage system, and is configured to convert its stored energy to electric power. The dynamo-electric machine is configured to enhance and buffer the secondary energy storage system, and is configured to improve the conversion of the stored energy to electric power. The system may include a step-up transformer responsively coupled to one of the secondary stator windings. The step-up transformer may comprise a single phase or polyphase step-up transformer having internal cooling and electrical insulation between the secondary windings comprising a hydro-fluoro-ether (HFE) vapor and liquid fluid.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
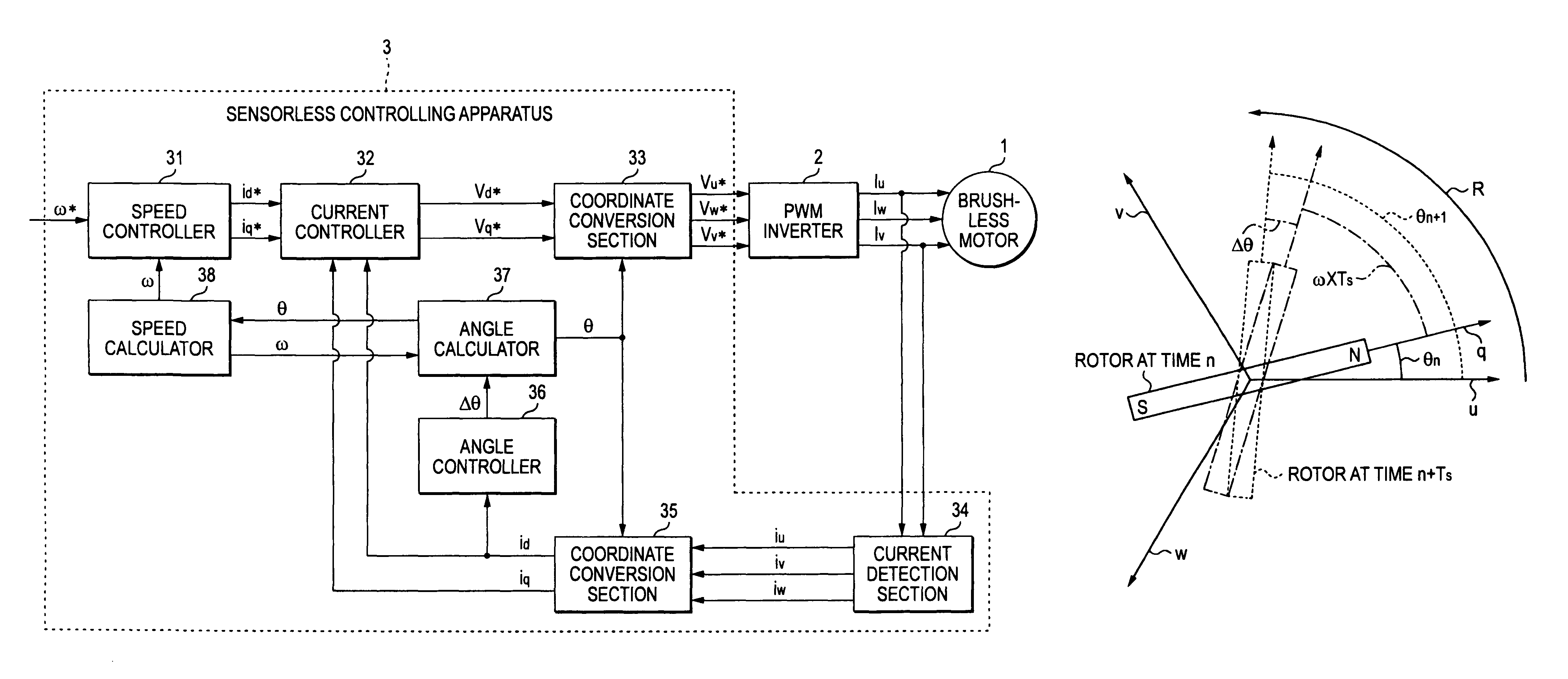
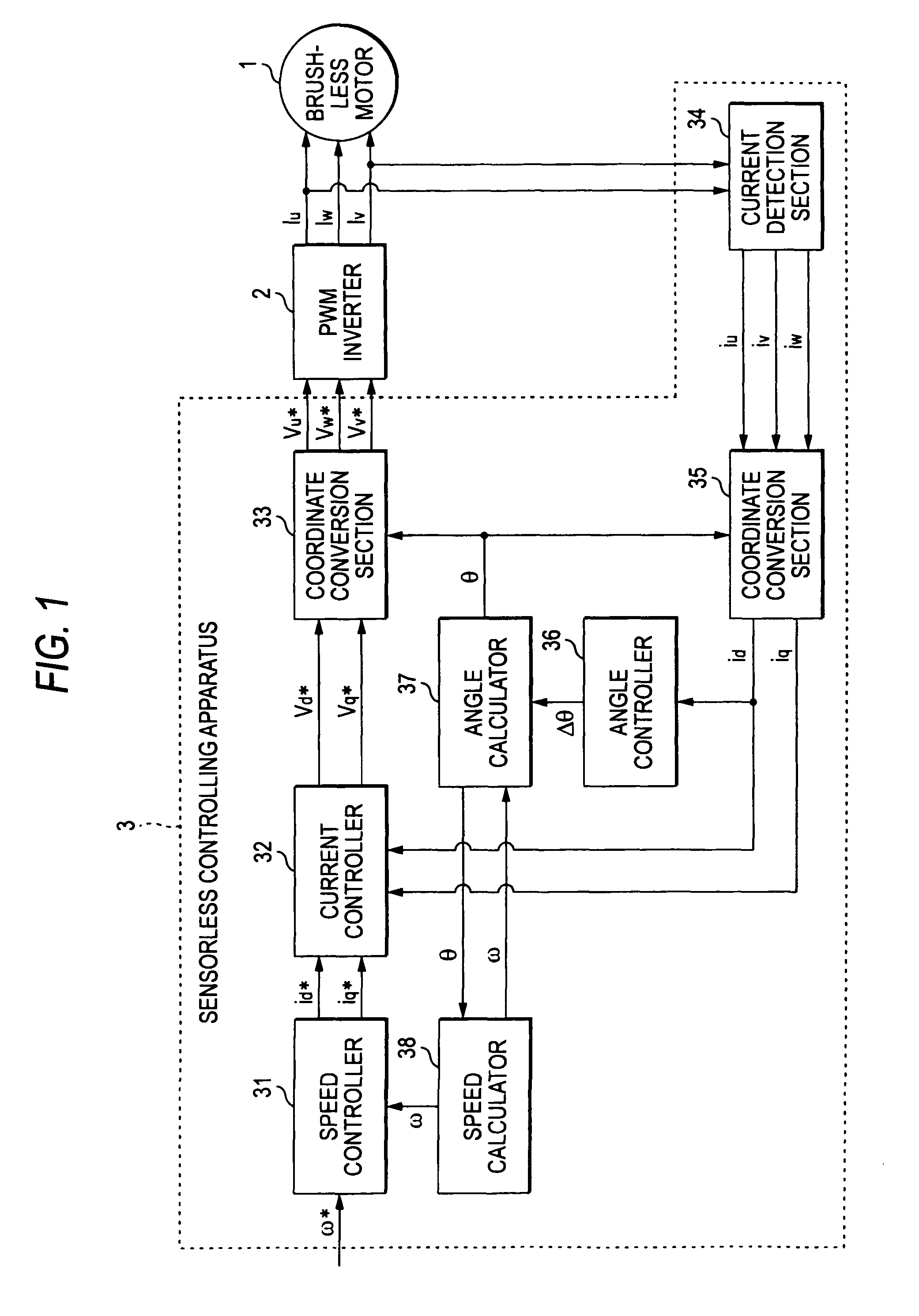
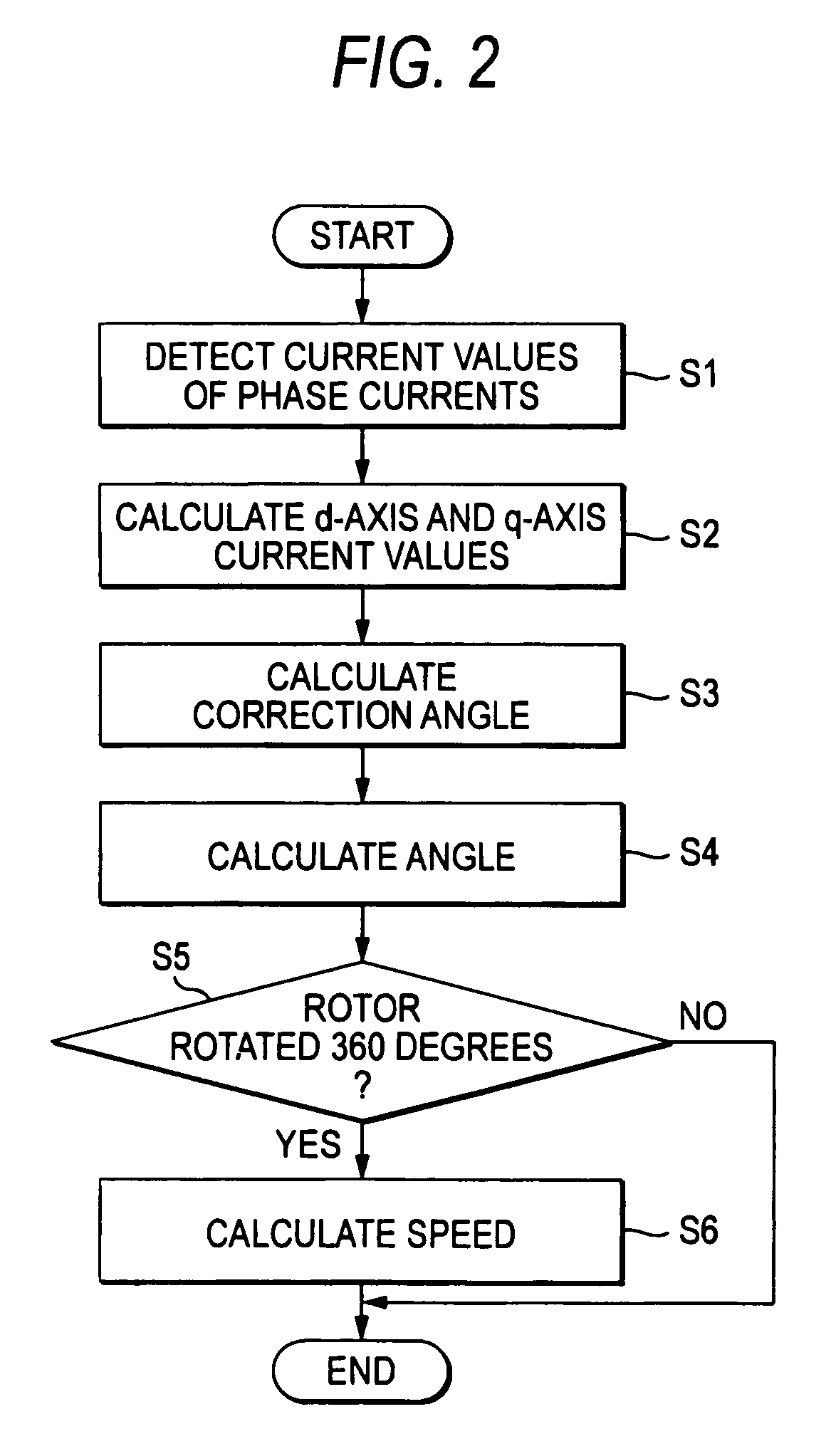
Sensorless controlling apparatus of brushless motor
InactiveUS7944163B2Eliminate needHigh in general versatilitySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsBrushless motorsRotor angle
A sensorless controlling apparatus for controlling a brushless motor includes a speed calculator for calculating speed of a rotor ω, an angle calculator for calculating rotor angle θ at a predetermined time interval, and an angle controller for calculating correction angle Δθ based on the current value of a d-axis current (d-axis current value id), thereby controlling the rotor angle θ. The angle calculator uses the correction angle Δθ calculated by the angle controller, the speed ω calculated by the speed calculator, a predetermined time, and the rotor angle θ calculated by the angle calculator at a predetermined time to calculate the rotor angle at the predetermined time interval. Thus, the rotor angle θ calculated by the angle calculator is converged on the true angle of the rotor.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Synchronizing Frequency and Phase of Multiple Variable Frequency Power Converters
ActiveUS20090267658A1Readily apparentPulse automatic controlDc-dc conversionSwitching frequencyControl circuit
In an embodiment, a power converter system includes a plurality of variable frequency power converters and a plurality of synchronization circuits. Each variable frequency power converter has a switching frequency. Each synchronization circuit is associated with a respective one of the plurality of variable frequency power converters. A control circuit is coupled to and coordinates the plurality of synchronization circuits. The plurality of synchronization circuits and the control circuit are operable to synchronize the switching frequencies of the variable frequency power converters to each other. Each synchronization circuit is operable to: receive a first input signal indicative of the beginning of a switching period for the associated variable frequency power converter; receive a second input signal indicative of the end of the switching period for the associated variable frequency power converter; generate a first output signal for directing a pulse width modulation of the associated variable frequency power converter; and generate a second output signal for coordinating a phase relationship with another variable frequency power converter in the system.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Power Plant
InactiveUS20100025128A1Improve transmission efficiencyAvoid draggingHybrid vehiclesGearingPower stationEngineering
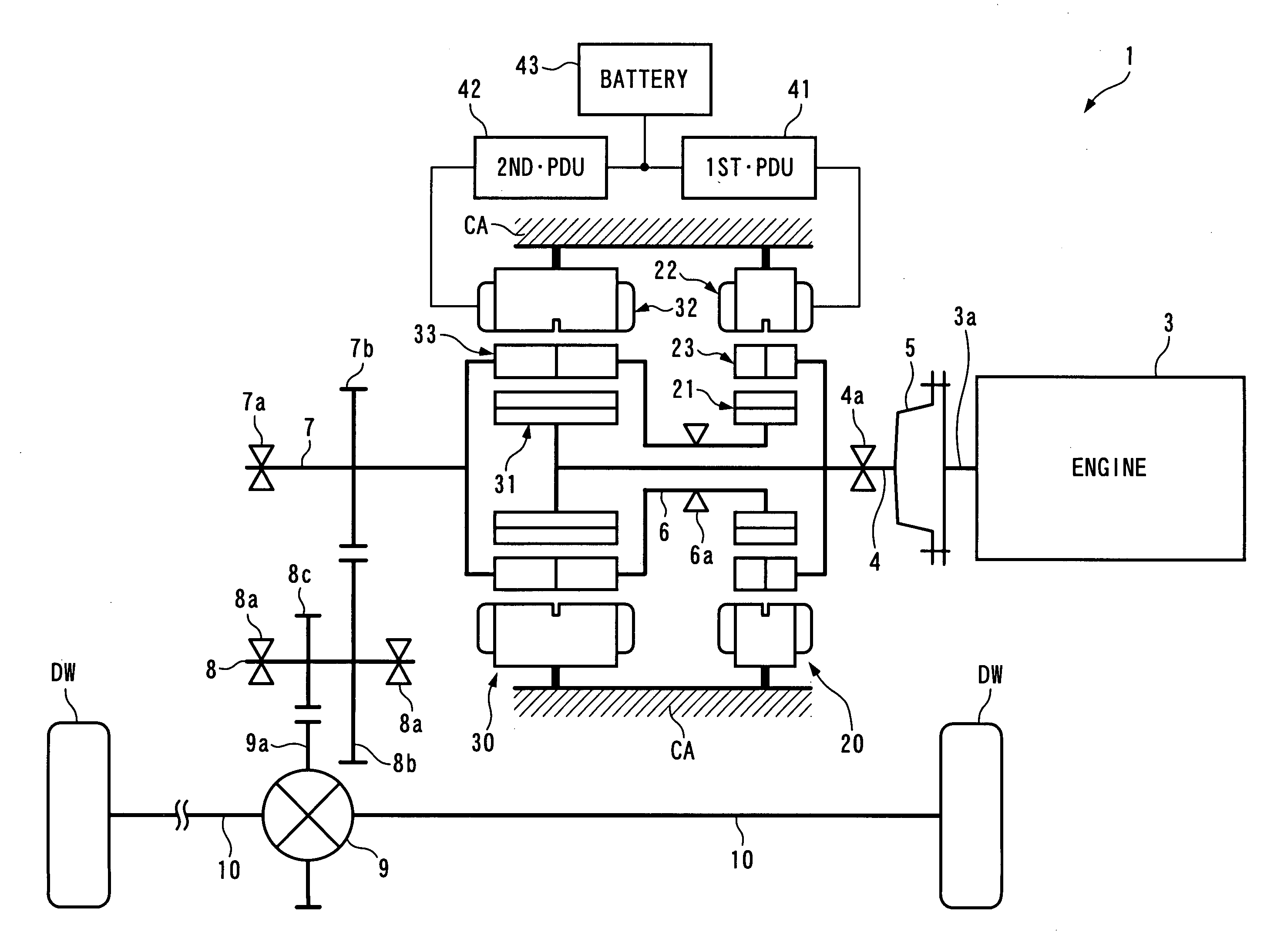
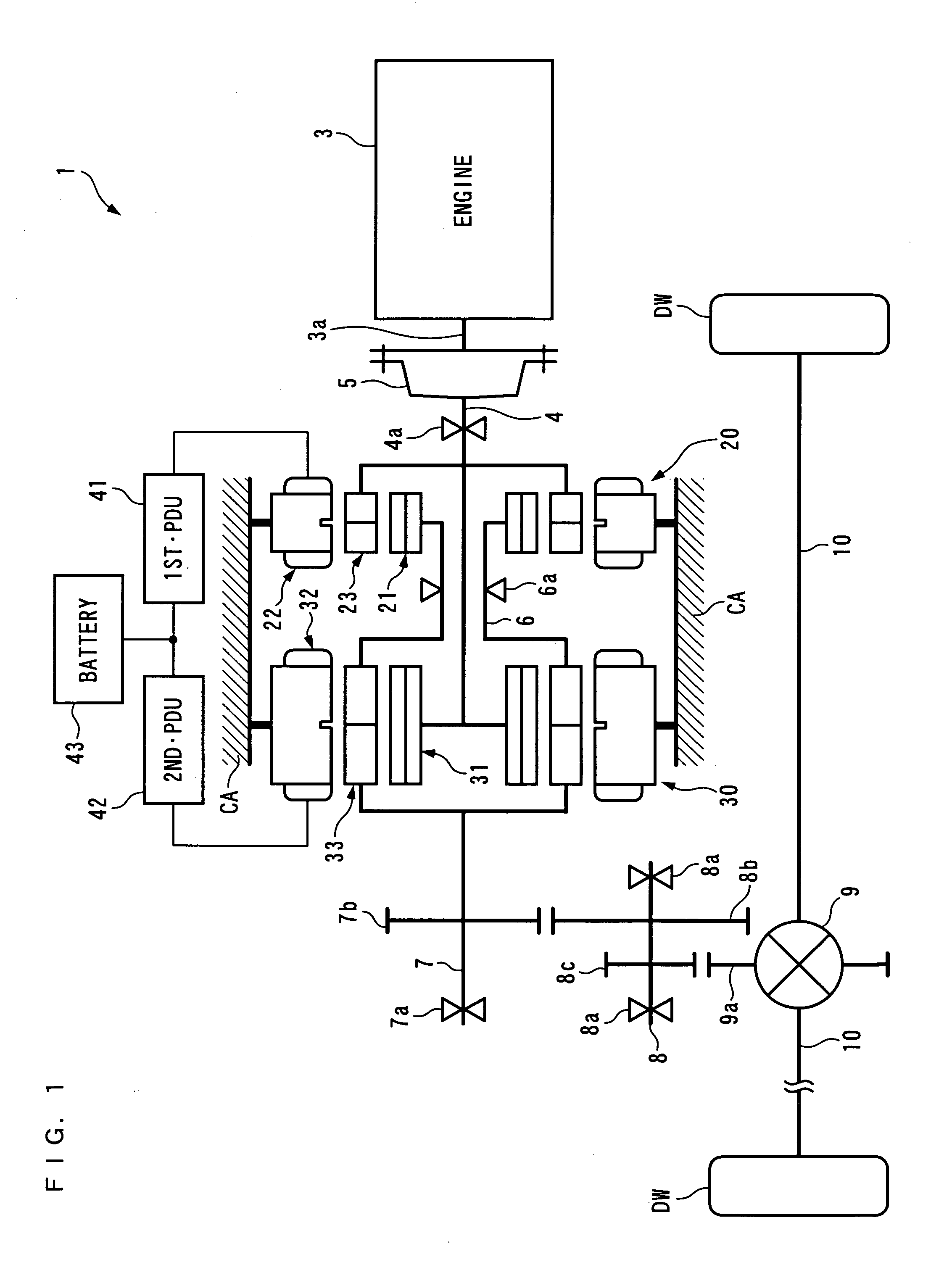
There is provided a power plant which is capable of enhancing driving efficiency with which the power plant drives driven parts. The power plant 1 for driving the driven parts DW and DW includes a prime mover 3, and first and second generator-motors 20, 30. The first generator-motor 20 is comprised of a first stator 22, a first rotor 21 formed by magnets, and a second rotor 23 formed by soft magnetic material elements and disposed between the first stator 22 and the first rotor 21. The second generator-motor 30 is comprised of a second stator 32, a third rotor 31 formed by magnets, and a fourth rotor 33 formed by soft magnetic material elements and disposed between the second stator 32 and the third rotor 31. The first and fourth rotors 21, 33 are mechanically connected to the driven parts DW and DW, and the second and third rotors 23, 31 are mechanically connected to an output shaft 3a of the prime mover 3. The first and second stators 22, 32 are electrically connected to each other via first and second controllers 2, 41, 42.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Pulsed-inertial electric motor
InactiveUS7285889B2Improved performance characteristicsSimple designWindingsMagnetic circuitLow voltageDc current
Owner:ULTRA MOTOR CO LTD
Energy transfer apparatus
A motor and a generator both comprising a rotor and a stator, wherein said rotor and said stator of both said motor and said generator can rotate about a common axis, and wherein both said stators are coupled, and both said rotors are coupled, for one to induce rotation to the other, and wherein the rotation energy may be transferred to a system.
Owner:CONCEPT FISET
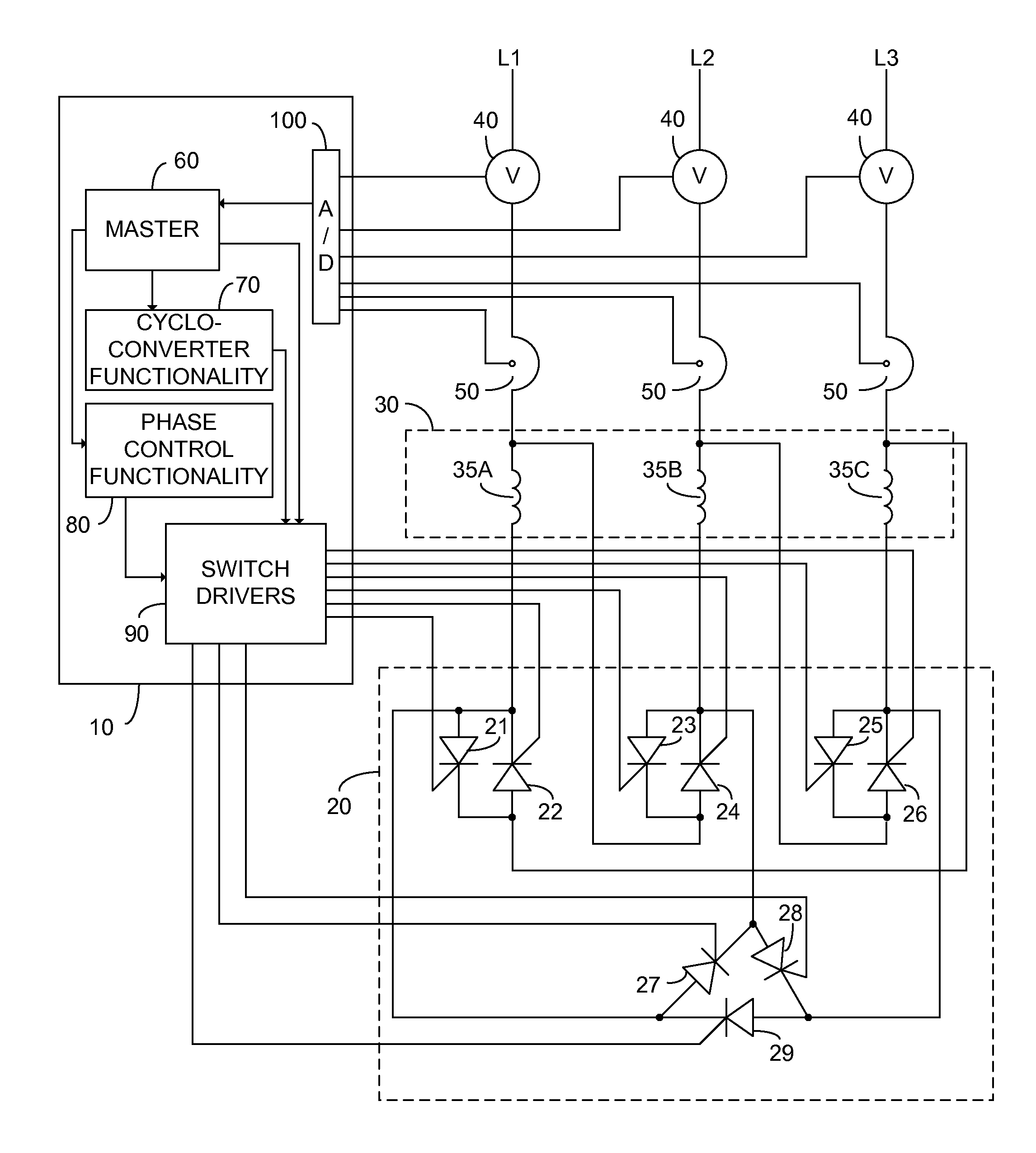
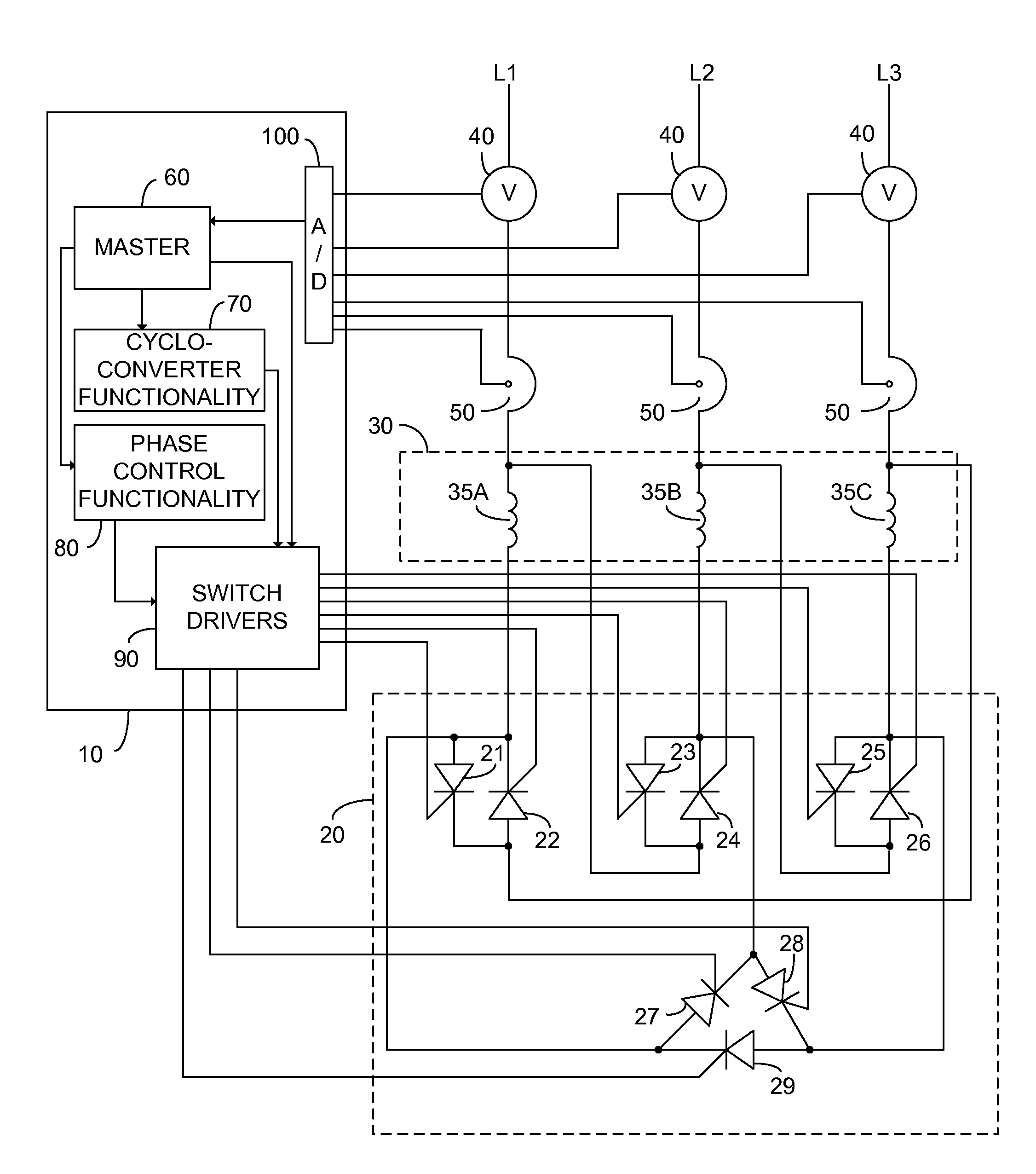
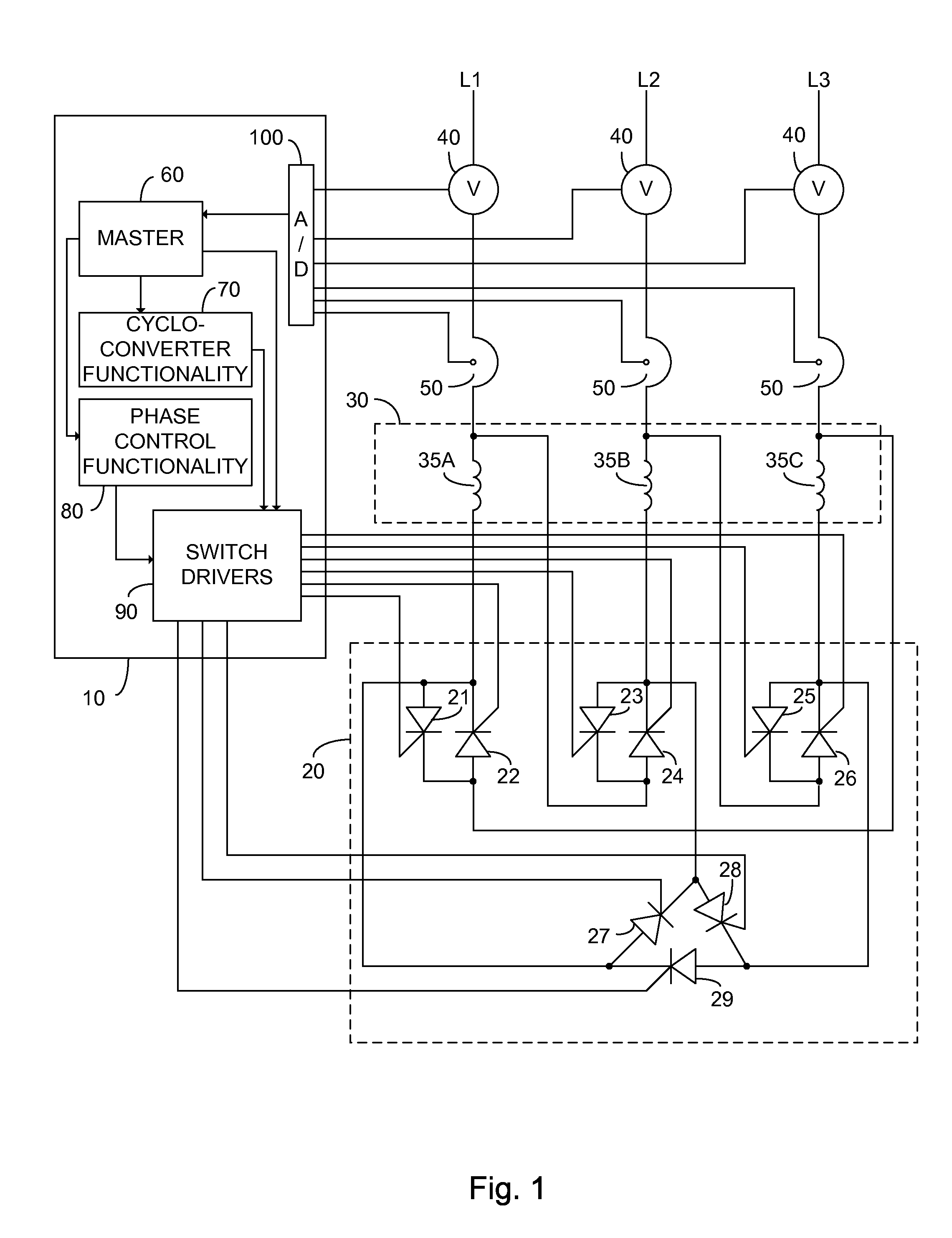
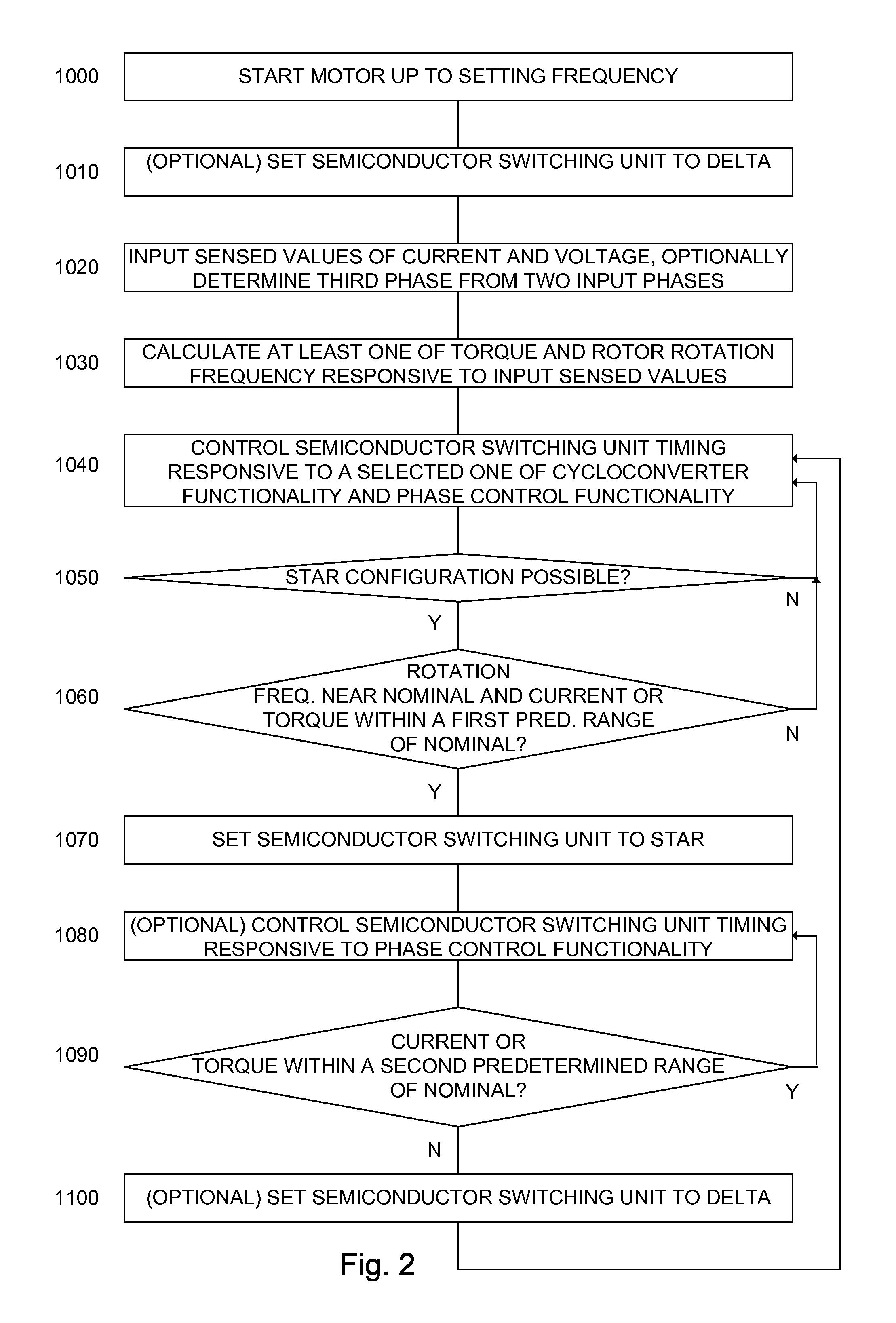
Method and apparatus for AC motor control
ActiveUS8207699B2Reduce power consumptionWeaken energyBatteries circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesMotor controlEngineering
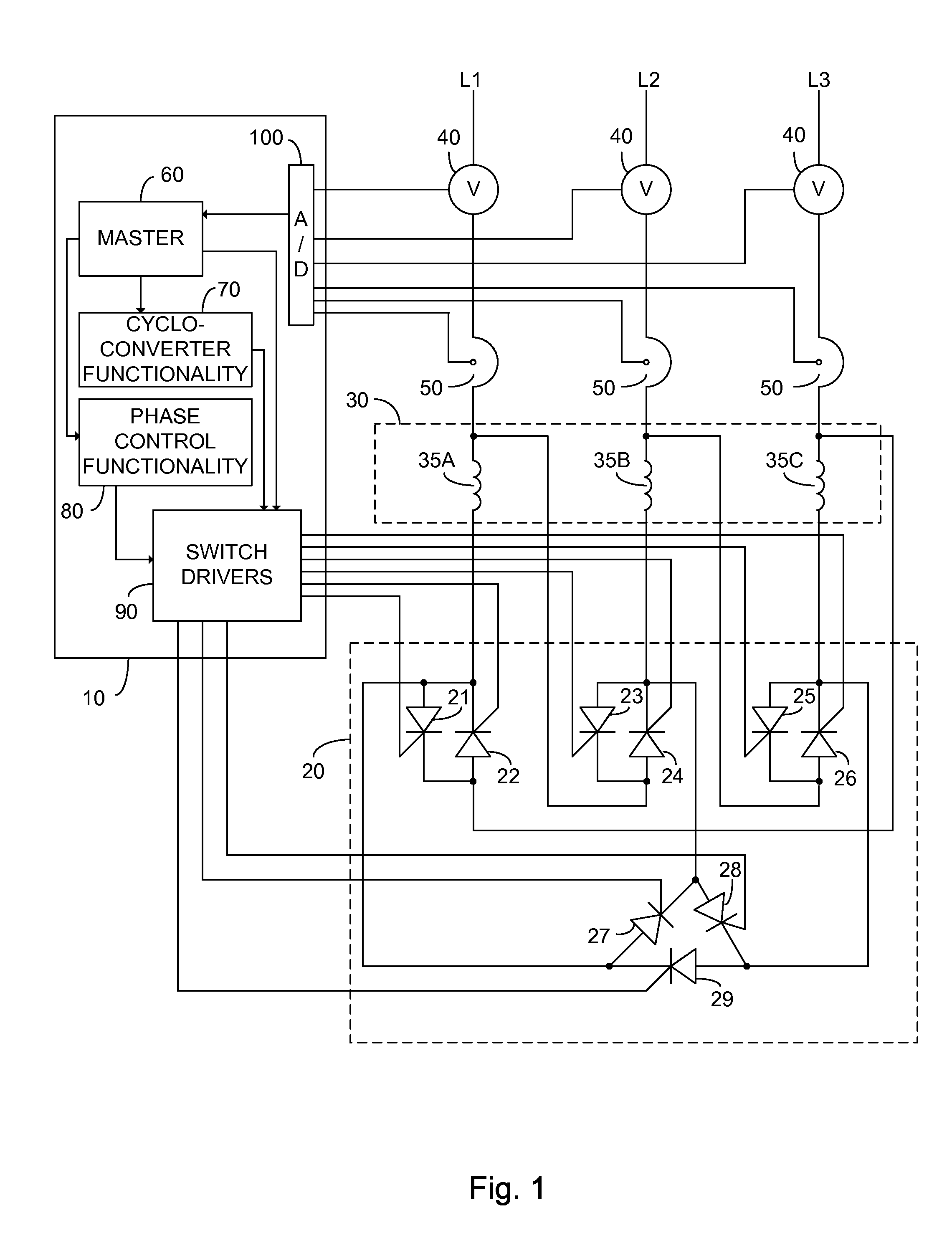
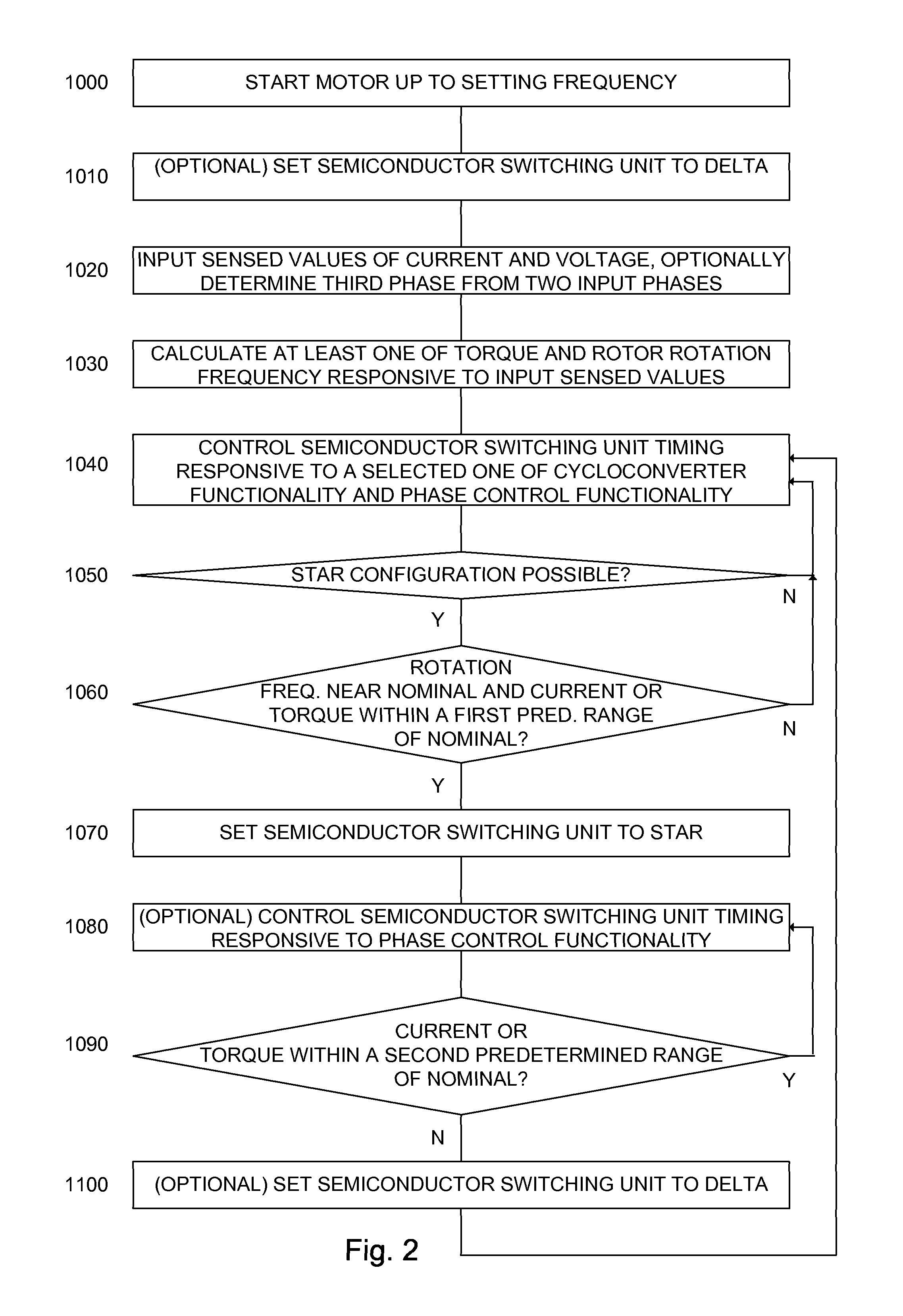
An alternating current motor control system constituted of: a control unit; a cycloconverter functionality; a phase control functionality; and a semiconductor switching unit comprising a plurality of electronically controlled semiconductor switches each associated with a particular winding of a target alternating current motor and each independently responsive to the control unit. In one embodiment the semiconductor switching unit is arranged to connect the windings of the target alternating current motor to a three phase power input in one of a star and a delta configuration responsive to the control unit.
Owner:ELSA CJSC
Compensation method for a voltage unbalance
InactiveUS20050201130A1Condition may changeAC/AC convertorsDynamo-electric converter controlElectricityReference vector
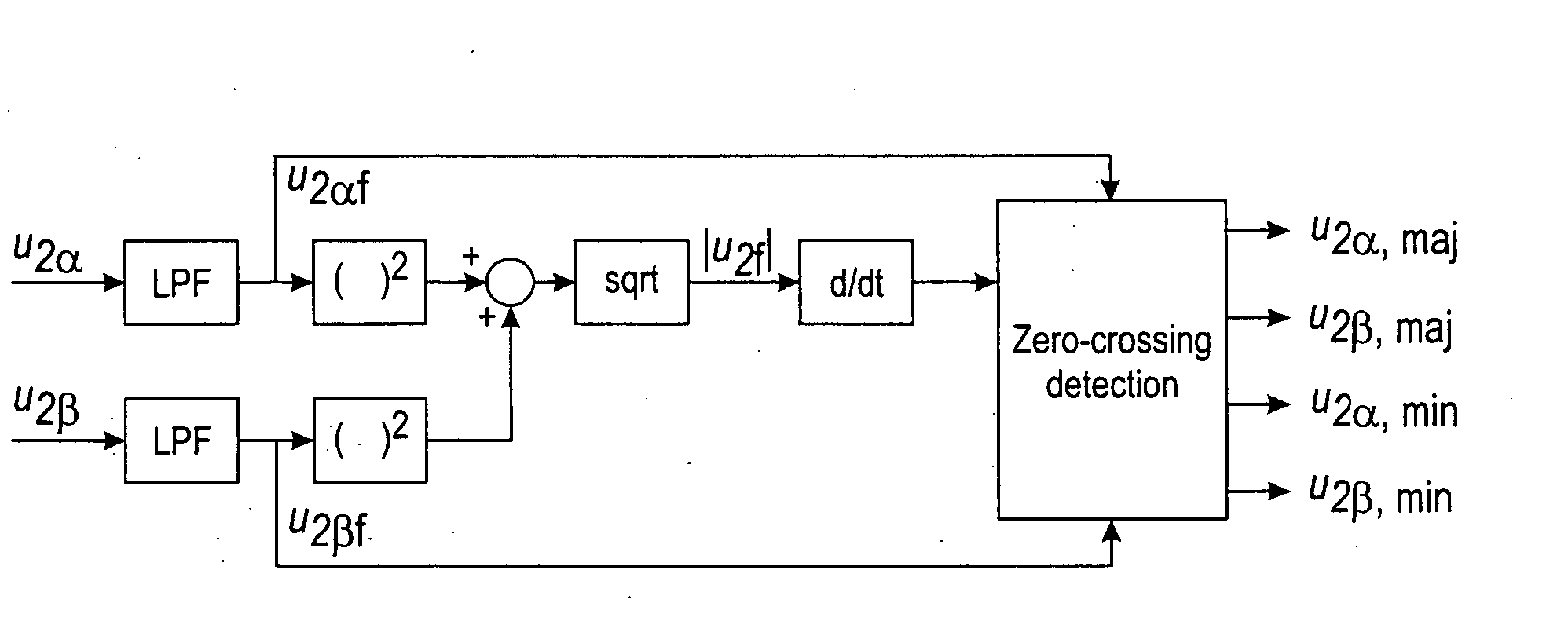
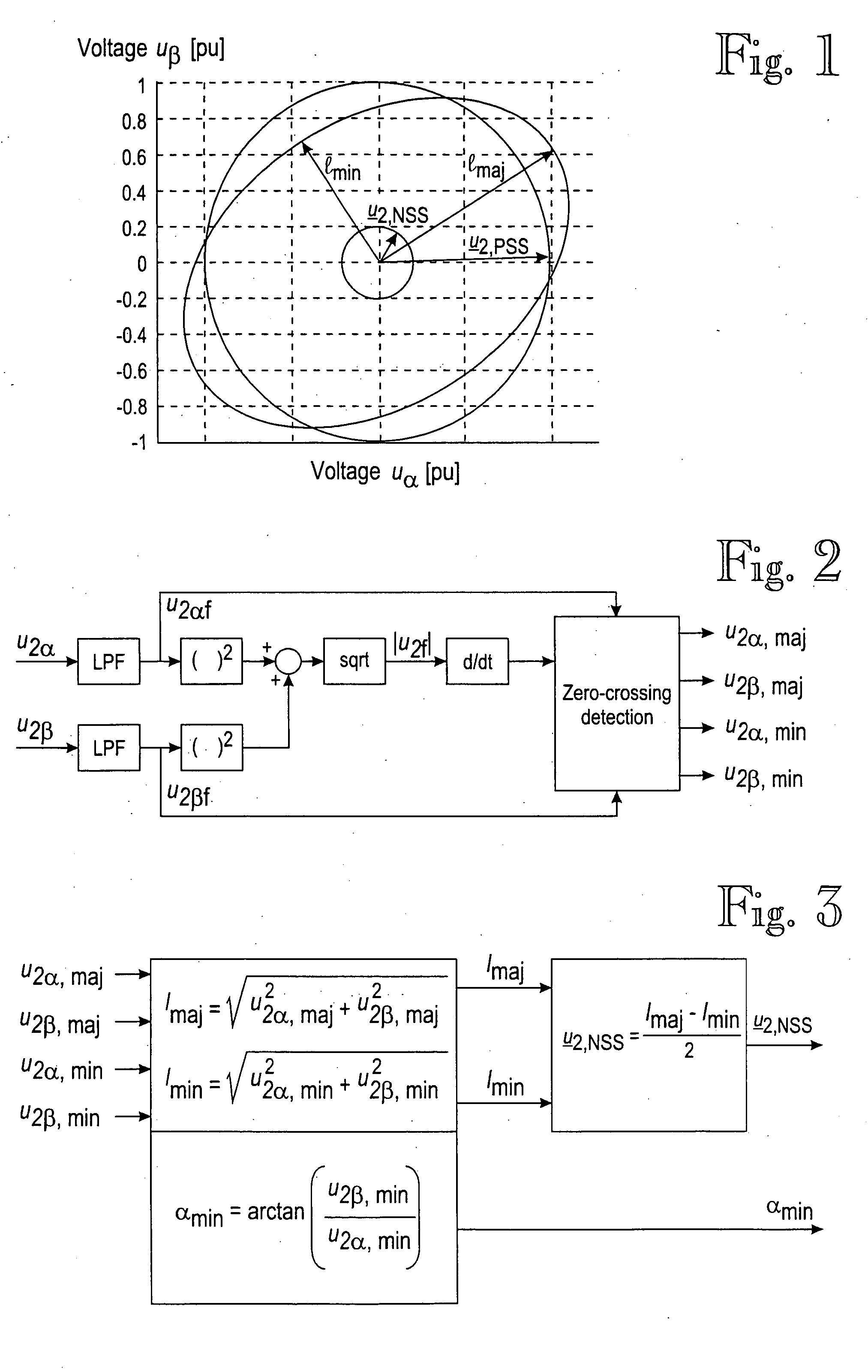
The invention relates to a method for compensating for a voltage unbalance in an electrical network, which is fed by using an apparatus based on controlling a flux linkage vector or a voltage vector. Concerning the apparatus based on controlling the flux linkage vector, the method comprises the steps of determining a flux linkage reference vector comprising a positive sequence component and a negative sequence component, and controlling the feeding apparatus of the network in such a manner that the flux linkage vector thereof follows the reference vector with predetermined precision. The negative sequence component of the flux linkage reference vector is arranged to compensate for the amplitude and phase unbalance of the voltage in the electrical network to be fed.
Owner:ABB OY
Synchronizing Frequency and Phase of Multiple Variable Frequency Power Converters
In an embodiment, a power converter system includes a plurality of variable frequency power converters and a plurality of synchronization circuits. Each variable frequency power converter has a switching frequency. Each synchronization circuit is associated with a respective one of the plurality of variable frequency power converters. A control circuit is coupled to and coordinates the plurality of synchronization circuits. The plurality of synchronization circuits and the control circuit are operable to synchronize the switching frequencies of the variable frequency power converters to each other. Each synchronization circuit is operable to: receive a first input signal indicative of the beginning of a switching period for the associated variable frequency power converter; receive a second input signal indicative of the end of the switching period for the associated variable frequency power converter; generate a first output signal for directing a pulse width modulation of the associated variable frequency power converter; and generate a second output signal for coordinating a phase relationship with another variable frequency power converter in the system.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Axis static state vacuum partition method of integrated rotary transformer
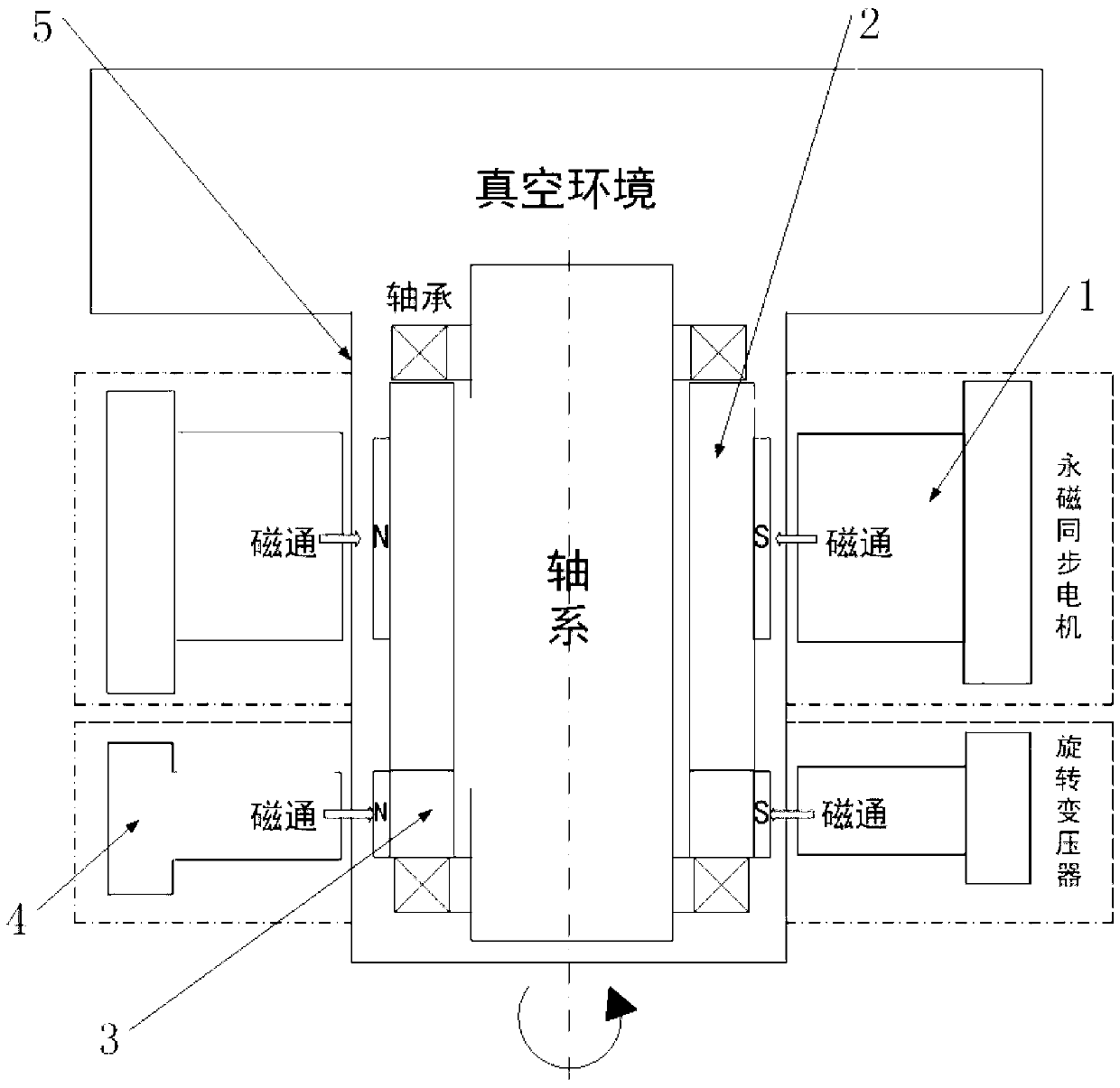
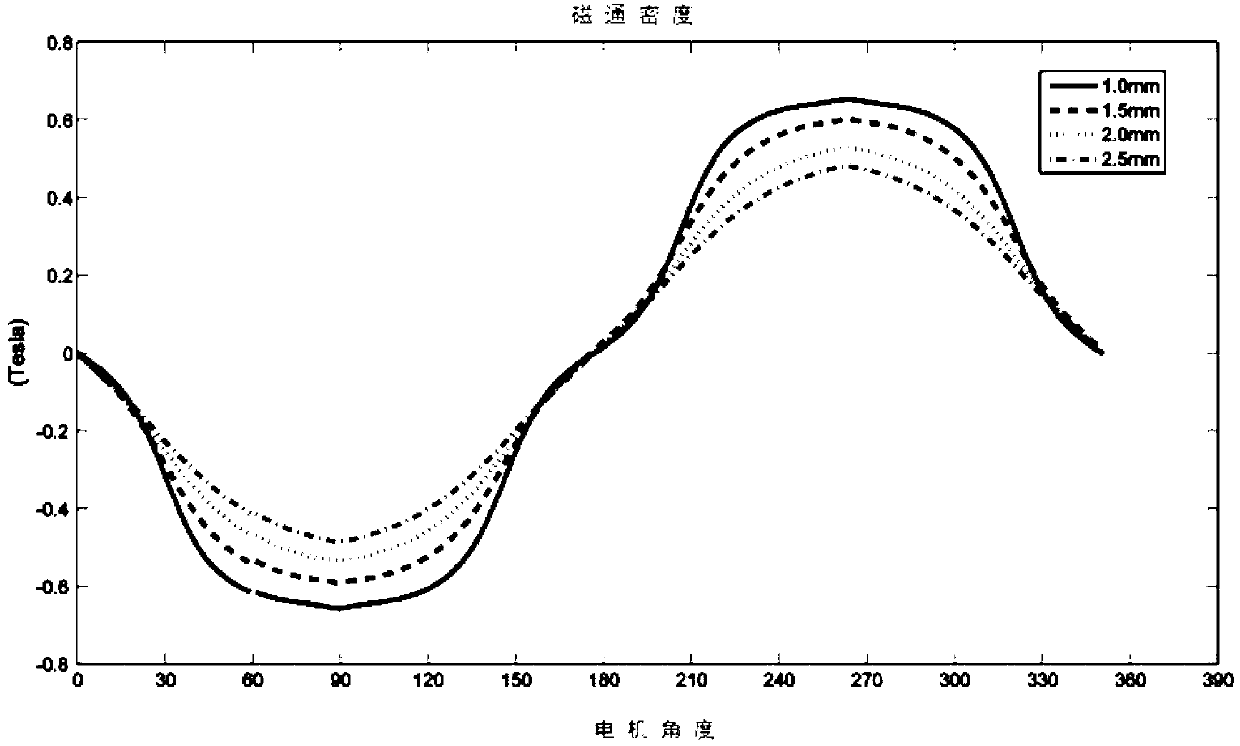
ActiveCN103219856AImprove dynamic response performanceSmall inertiaAC/AC convertorsLocation detectionContact free
The invention provides an axis static state vacuum partition method of an integrated rotary transformer. The axis static state vacuum partition method comprises the following steps of first, using a permanent magnet synchronous motor with a magnetic directly-driving function to serve as an axis driving and transmission component; second, using a sine and cosine magnetic-resistive type rotary transformer to serve as a position detection part of a motor; third, conducting lengthening on the end portion of an inner magnetic rotor of the motor, removing an inner magnetic rotor of the rotary transformer, forming integrated inner magnetism, and enabling the motor and the rotary transformer to share one integrated inner magnetic rotor through the rotor; and fourth, sealing the integrated inner magnetic rotor of the motor and the rotary transformer in a partition sealing sleeve, and using the partition sealing sleeve to limit radial and axial movement of a magnetic body. The integrated rotary transformer achieves a zero-transmission mode, is stable in operation and small in noise, and achieves contact-free zero-leakage sealing transmission.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Multiple winding electric machine
An exemplary embodiment provides an electrical machine apparatus that includes a rotor coupled to an armature and a stator surrounding the rotor. The stator has a series of coils; the series of coils configured into a first group of coils and a second group of coils, the first group of coils electrically and magnetically isolated from the second group of coils. The electric machine is capable of simultaneously acting as an electric motor and generating electricity as an alternator.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for ac motor control
ActiveUS20110006709A1Improve motor efficiencyReduce power consumptionDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesBatteries circuit arrangementsControl systemEngineering
An alternating current motor control system constituted of: a control unit; a cycloconverter functionality; a phase control functionality; and a semiconductor switching unit comprising a plurality of electronically controlled semiconductor switches each associated with a particular winding of a target alternating current motor and each independently responsive to the control unit. In one embodiment the semiconductor switching unit is arranged to connect the windings of the target alternating current motor to a three phase power input in one of a star and a delta configuration responsive to the control unit.
Owner:ELSA CJSC
Two speed electric motor with link wound dual-commutator and dual-armature winding
InactiveUS20050225198A1Rotary current collectorMagnetic circuit rotating partsLow speedElectric machine
A permanent magnet D.C. electric motor includes a stator housing, permanent magnet structure, and an armature assembly. The armature assembly includes a shaft rotatably mounted in the stator housing, lamination structure, first and second coil windings associated with the lamination structure, a first commutator electrically connected with the first coil windings, and second commutator electrically connected with the second coil windings, each of the first and second commutators being generally cylindrical and having a plurality of commutator segments. Certain segments of the first commutator and certain segments of the second commutator are electrically connected. The motor also includes a brush card assembly including a high speed side having first brush structure associated with the first commutator, and a low speed side having a second brush structure associated with the second commutator, and switches for selectively connecting a D.C. voltage in such a way as to cause the armature assembly to rotate at a first speed and a second speed.
Owner:BROSE FAHRZEUGTEILE GMBH & CO KG HALLSTADT (DE)
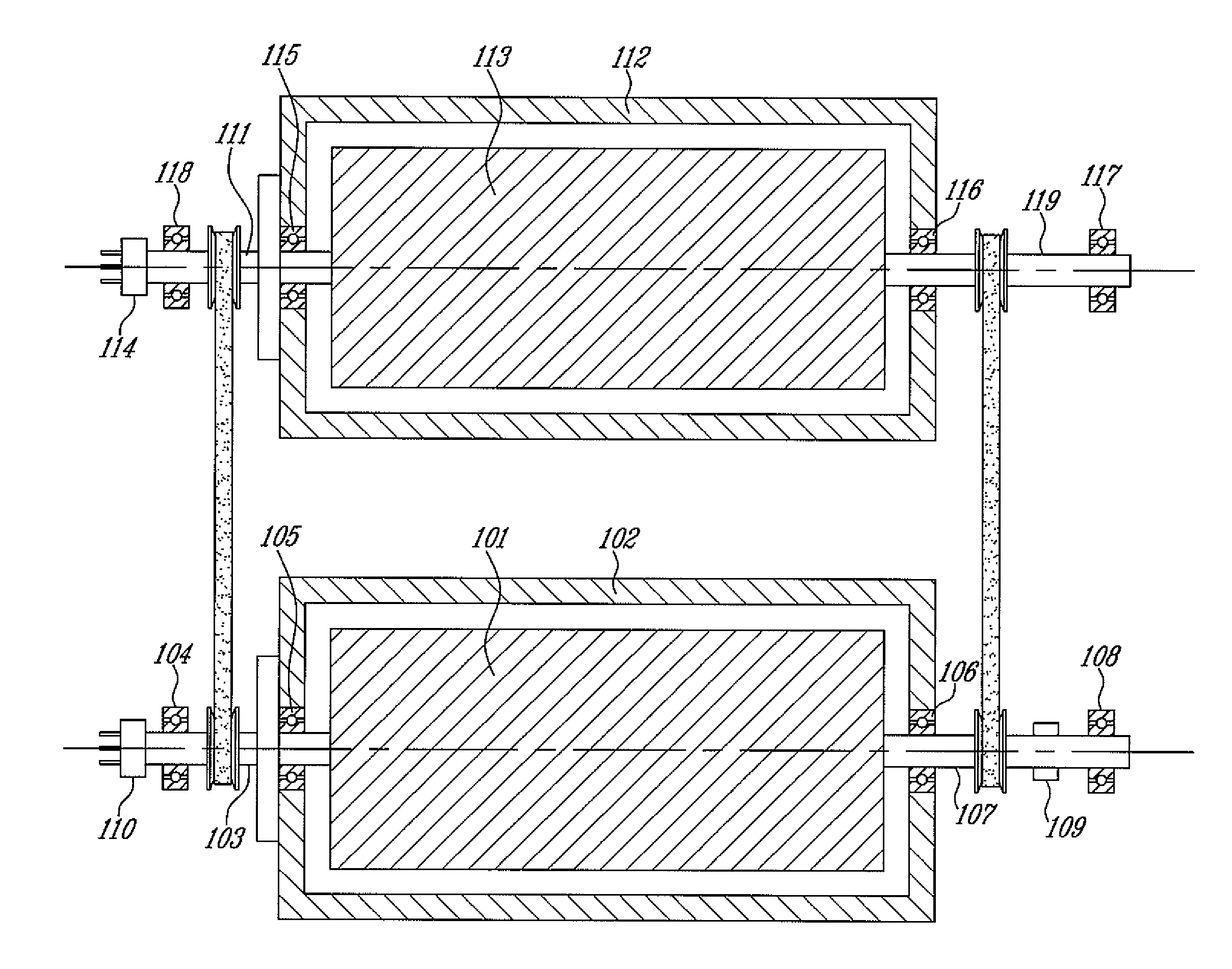
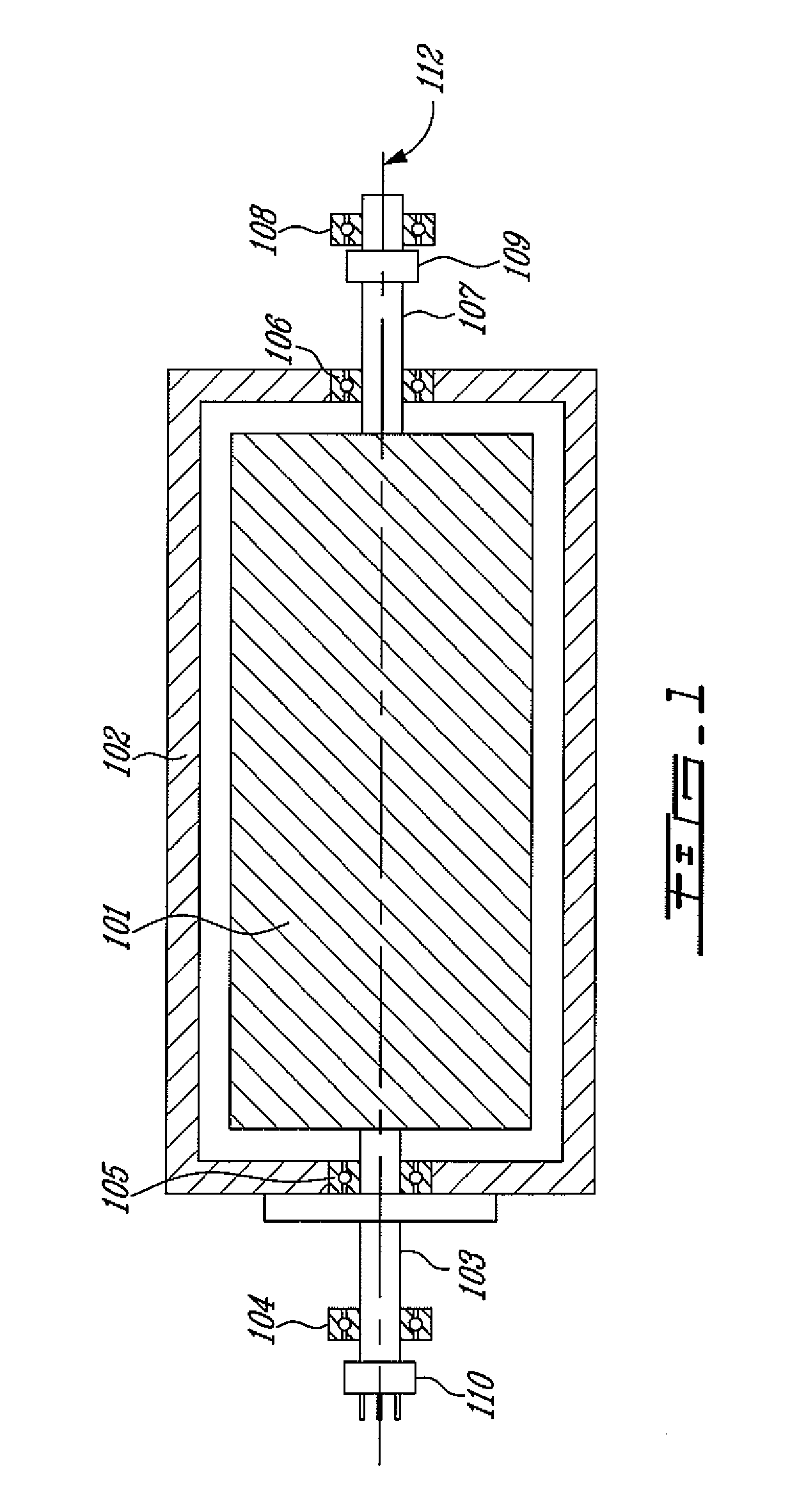
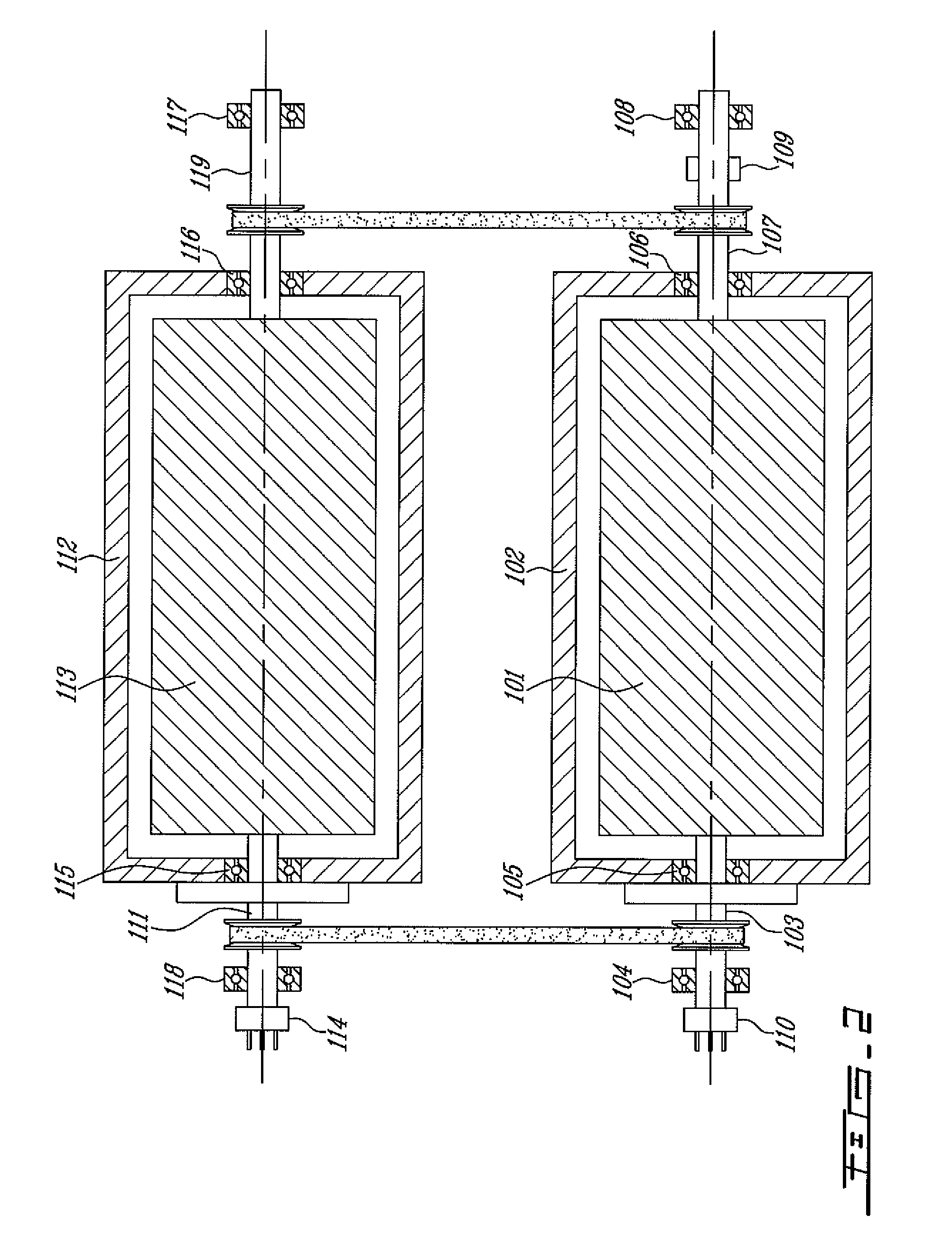
High frequency rotary transformer for synchronous electrical machines
ActiveUS20120218069A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric machineConductor Coil
A high frequency rotary transformer for an electrical machine includes a primary transformer component having a primary transformer winding, and a secondary transformer component having a secondary transformer winding. The primary transformer winding is configured to be coupled to a DC power source via a DC to AC converter. The secondary transformer winding is configured to be coupled to a winding of the rotor. Each of the primary and secondary transformer components are mechanically coupled to either the stator or the rotor. The secondary transformer component is configured to rotate with respect to the primary transformer component to produce a magnetic flux via the primary transformer winding and the secondary transformer winding.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Electrical energy generating brushless DC motor
ActiveUS20160049854A1Maximize efficiencyLimiting amount of back-EMF generatedMechanical apparatusBatteries circuit arrangementsConductor CoilPowertrain
Owner:NY THOU M
Electric motor
InactiveUS6975054B2Improve featuresIncrease torqueSynchronous generatorsRotary current collectorHigh torqueControl theory
An electric motor includes a stator which carries permanent magnets, and a rotor which carries electromagnets. A particular arrangement of connecting up the windings of the electromagnets to the distributing collector and the selection of the ratio of stator magnets to rotor electromagnets enable higher torque to be achieved. The main field of application is in motor-wheels of vehicles.
Owner:ULTRA MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for power converters having phases spaced at desired phase angles
ActiveUS7701730B2Reduce switching lossesTempo syncEfficient power electronics conversionAC/AC convertorsPhase spacePhase angle difference
A system and method for power conversion synchronizes multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves variable frequency switching, fixed on-time and provides power factor correction. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves transition mode switching to help reduce switching losses. A phase angle difference detector may be provided for each phase. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that vary with switching frequency, and are synchronized to an average frequency.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Concentric motor power generation and drive system
An apparatus is provided and includes a hub, including first and second opposing faces, a first sidewall fixed at opposite ends thereof to the first and second opposing faces to define a first interior between the first and second opposing faces and a second sidewall fixed to one of the first and second opposing faces to define a second interior within the first interior, a first assembly, disposed within the second interior, to generate current from input mechanical energy and a second assembly, electrically coupled to the first assembly and disposed within the first interior, to generate mechanical energy from current associated with the current generated by the first assembly.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Pulsed-inertial electric motor
InactiveUS20060232154A1Improved performance characteristicsSimple designWindingsMagnetic circuitLow voltageDc current
The invention relates to electric motors, particularly to low-voltage gearless commutator motors, and can be used as motor-wheels in transportation vehicles and in other technologies. The aim of the present invention is to provide an electric motor with increased performance characteristics, relatively simple design, and high reliability. A pulsed inertial electric motor according to the invention comprises: (i) a stator with circular magnetic conductor on which an even number of permanent magnets are uniformly arranged with a certain pitch; (ii) a rotor separated from the stator by air gap and bearing an even number of electromagnets, each electromagnet consisting of two coils with opposite winding directions connected in series, which are arranged over the circle in pairs one opposite to another; (iii) a collector distributor mounted on the stator body, containing circularly arranged current-conducting plates separated by insulating spacers and connected with alternating polarity to a dc current source, and (iv) current collectors-brushes mounted on the rotor and capable of contacting with plates of the collector distributor, whereby all brushes are connected to identical (beginning or end) terminals of the windings of said electromagnets and interconnected so that the coils in the opposite electromagnets are connected to each other via one identical terminal and to the opposite brushes via another identical terminal, with the number n of permanent magnets in the stator and the number m of electromagnets in the rotor selected so as to obey the relations n=10+4k, m=4+2l, where k is an arbitrary integer (k=0, 1, 2, . . . ) and l is any integer such that 0≦l≦k.
Owner:ULTRA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com