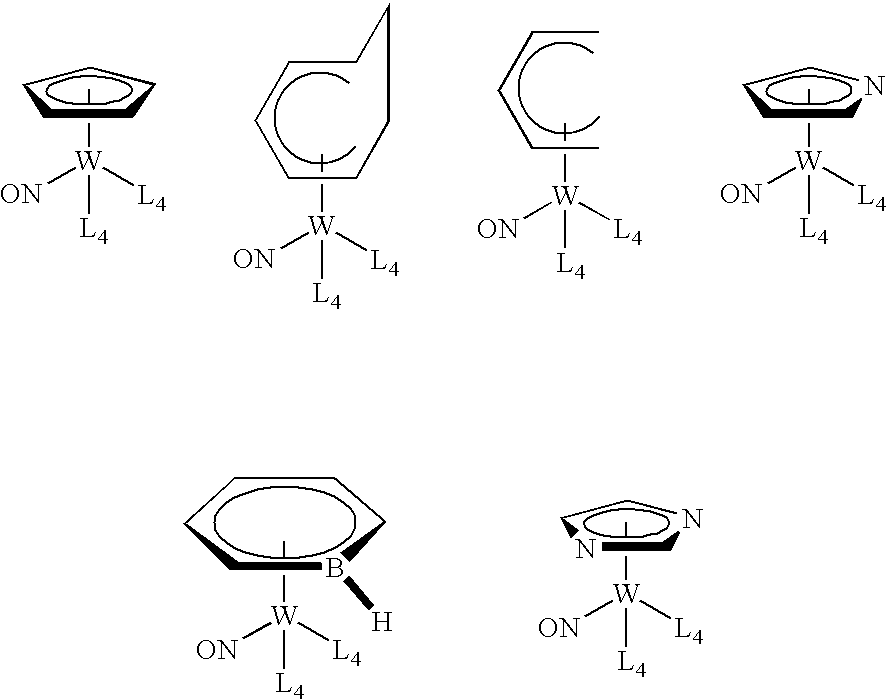Patents
Literature
370 results about "Tungsten nitride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tungsten nitride (W₂N, WN, WN₂) is an inorganic compound, a nitride of tungsten. It is a hard, solid, brown-colored ceramic material that is electrically conductive and decomposes in water. It is used in microelectronics as a contact material, for conductive layers, and barrier layers between silicon and other metals, e.g. tungsten or copper. It is less commonly used than titanium nitride or tungsten films.
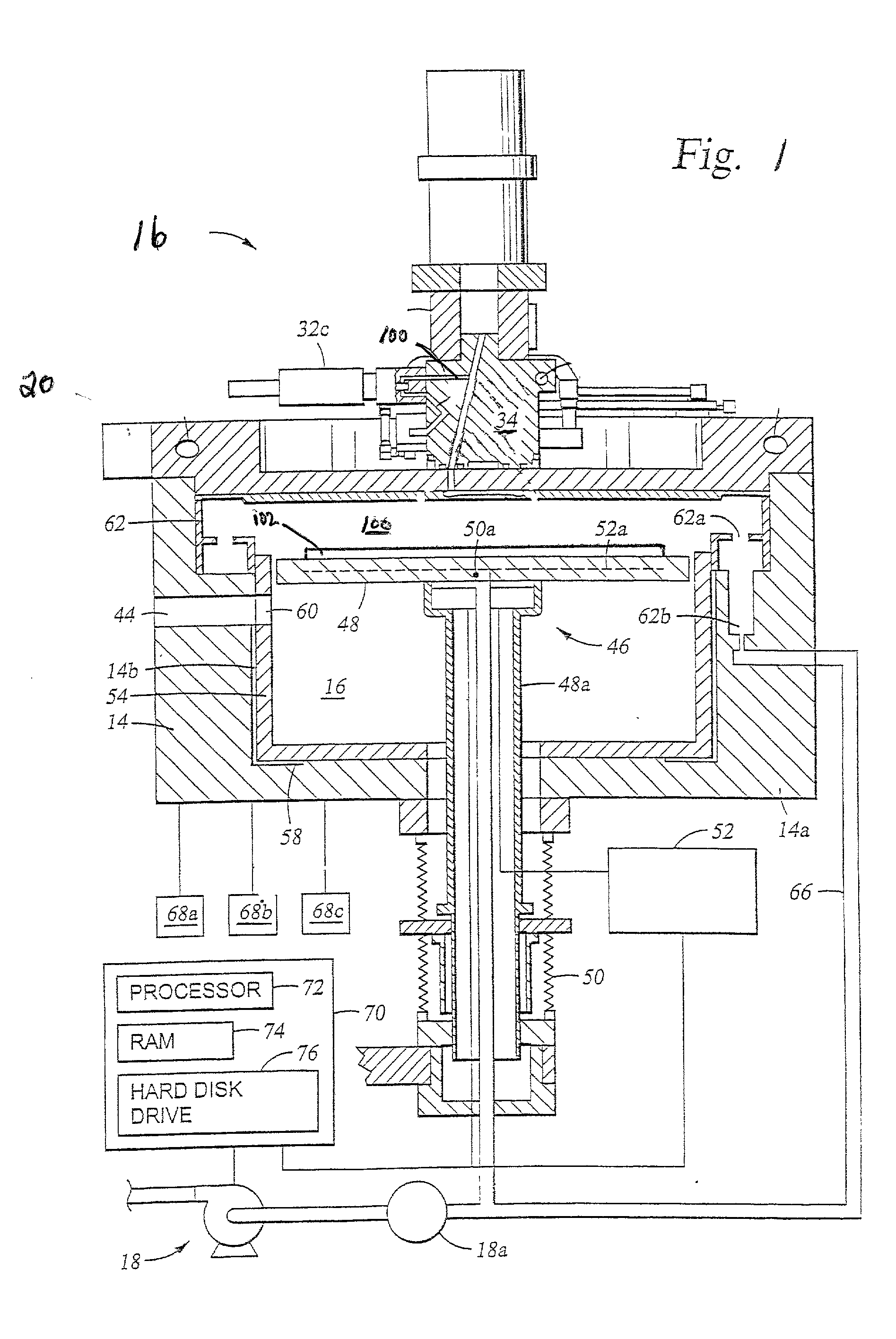
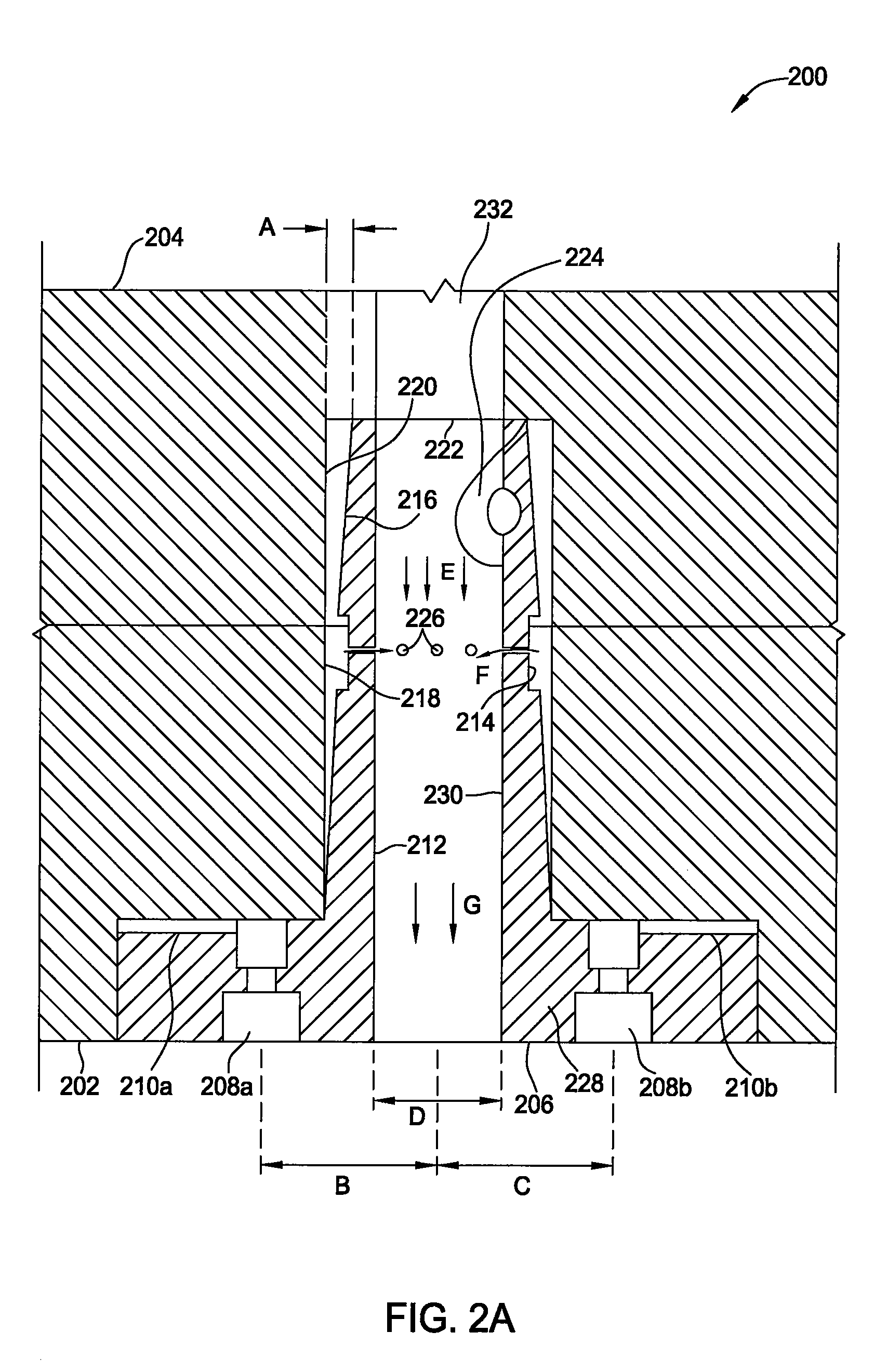
Apparatus and process for plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition
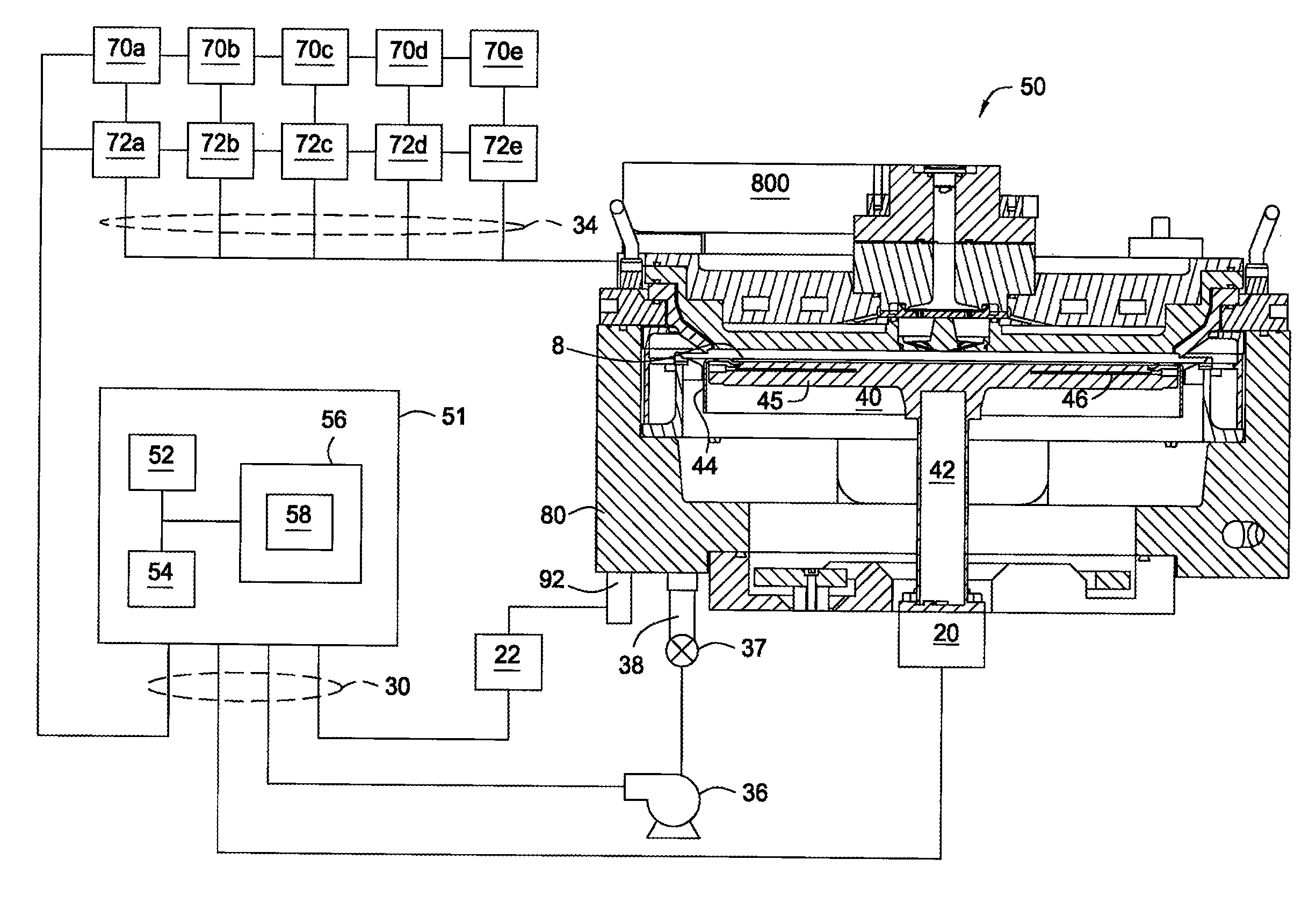
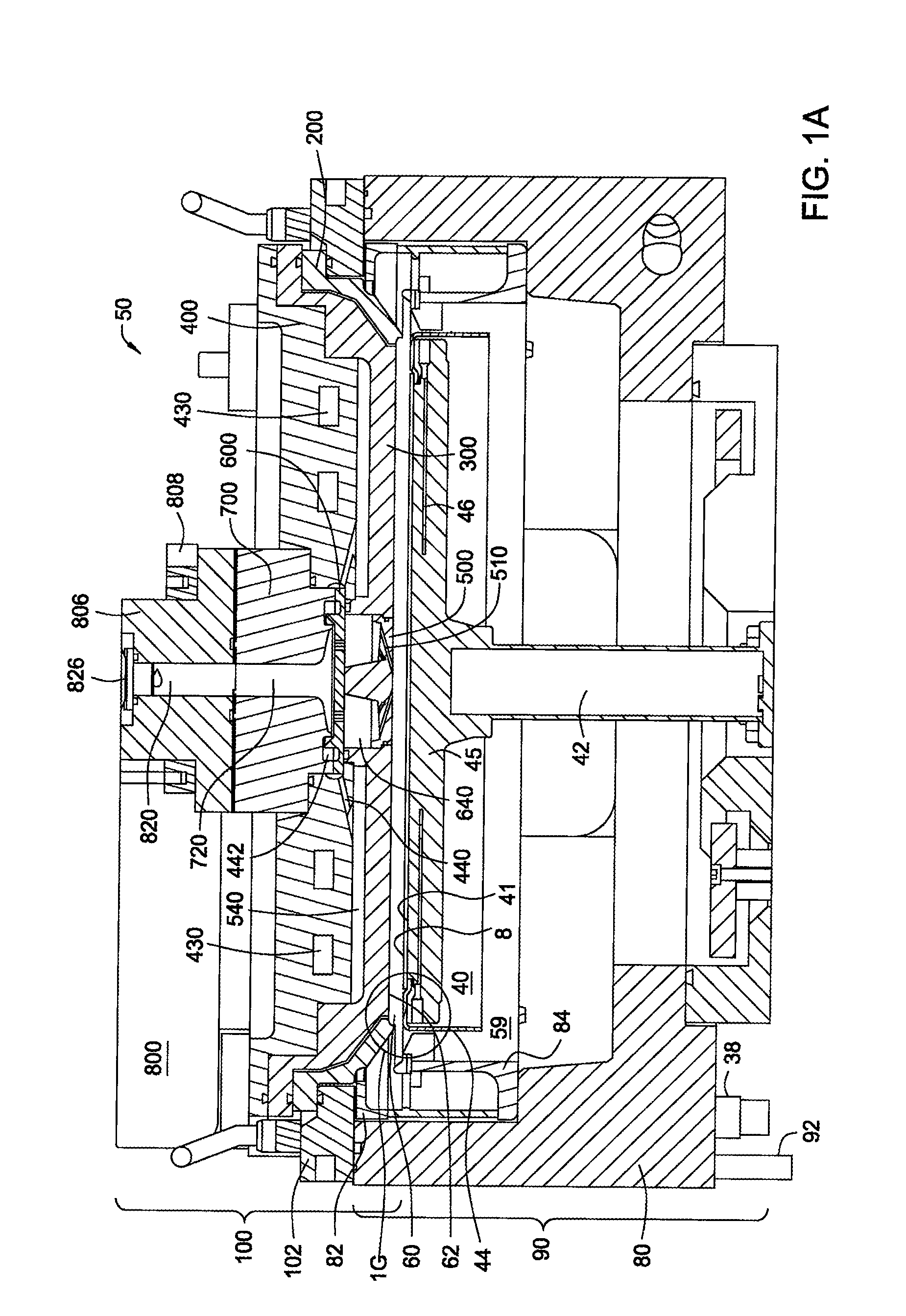
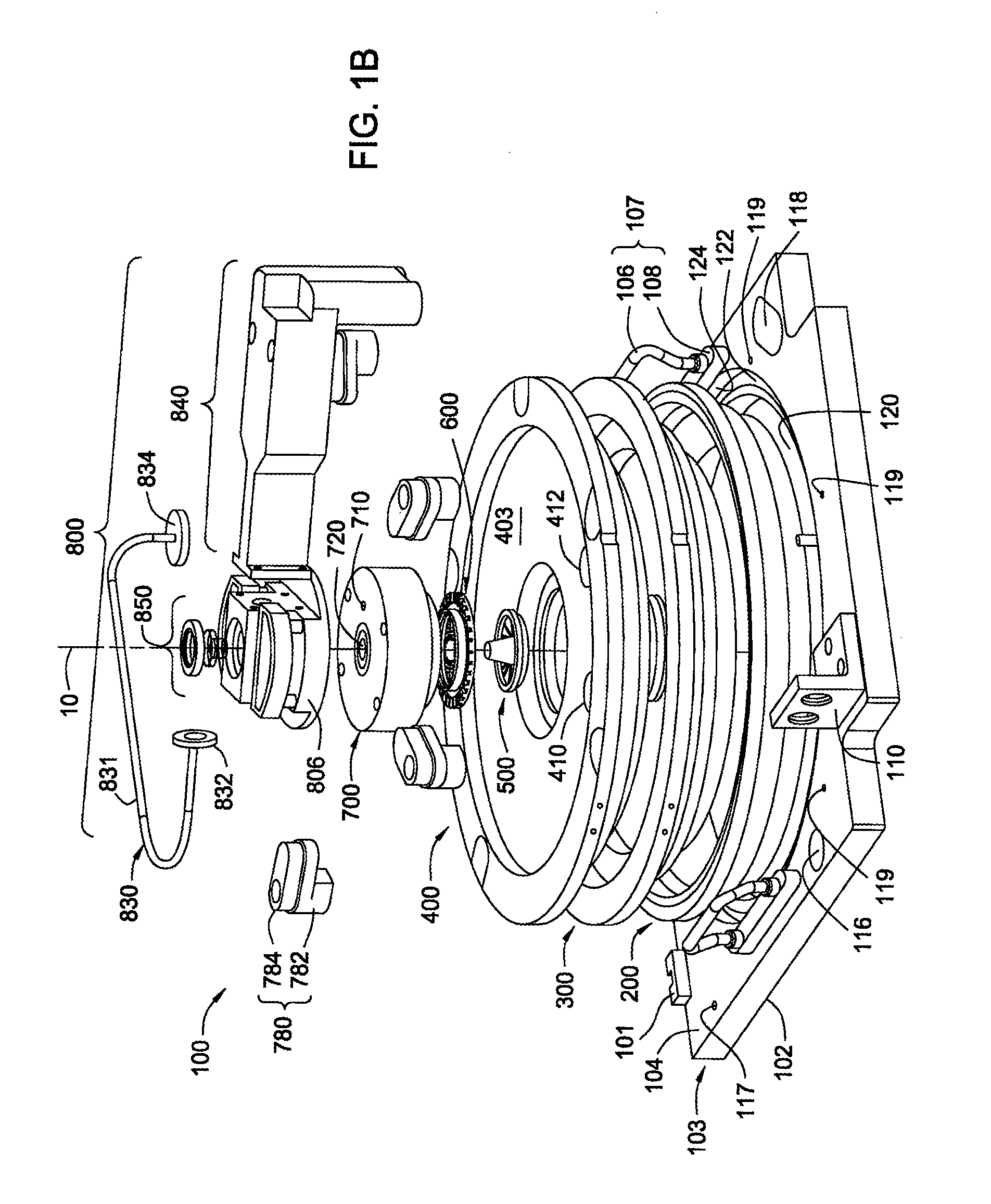
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for forming a material on a substrate during an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process, such as a plasma-enhanced ALD (PE-ALD) process. In one embodiment, a method is provided which includes flowing at least one process gas through at least one conduit to form a circular gas flow pattern, exposing a substrate to the circular gas flow pattern, sequentially pulsing at least one chemical precursor into the process gas and igniting a plasma from the process gas to deposit a material on the substrate. In one example, the circular gas flow pattern has circular geometry of a vortex, a helix, a spiral, or a derivative thereof. Materials that may be deposited by the method include ruthenium, tantalum, tantalum nitride, tungsten or tungsten nitride. Other embodiments of the invention provide an apparatus configured to form the material during the PE-ALD process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
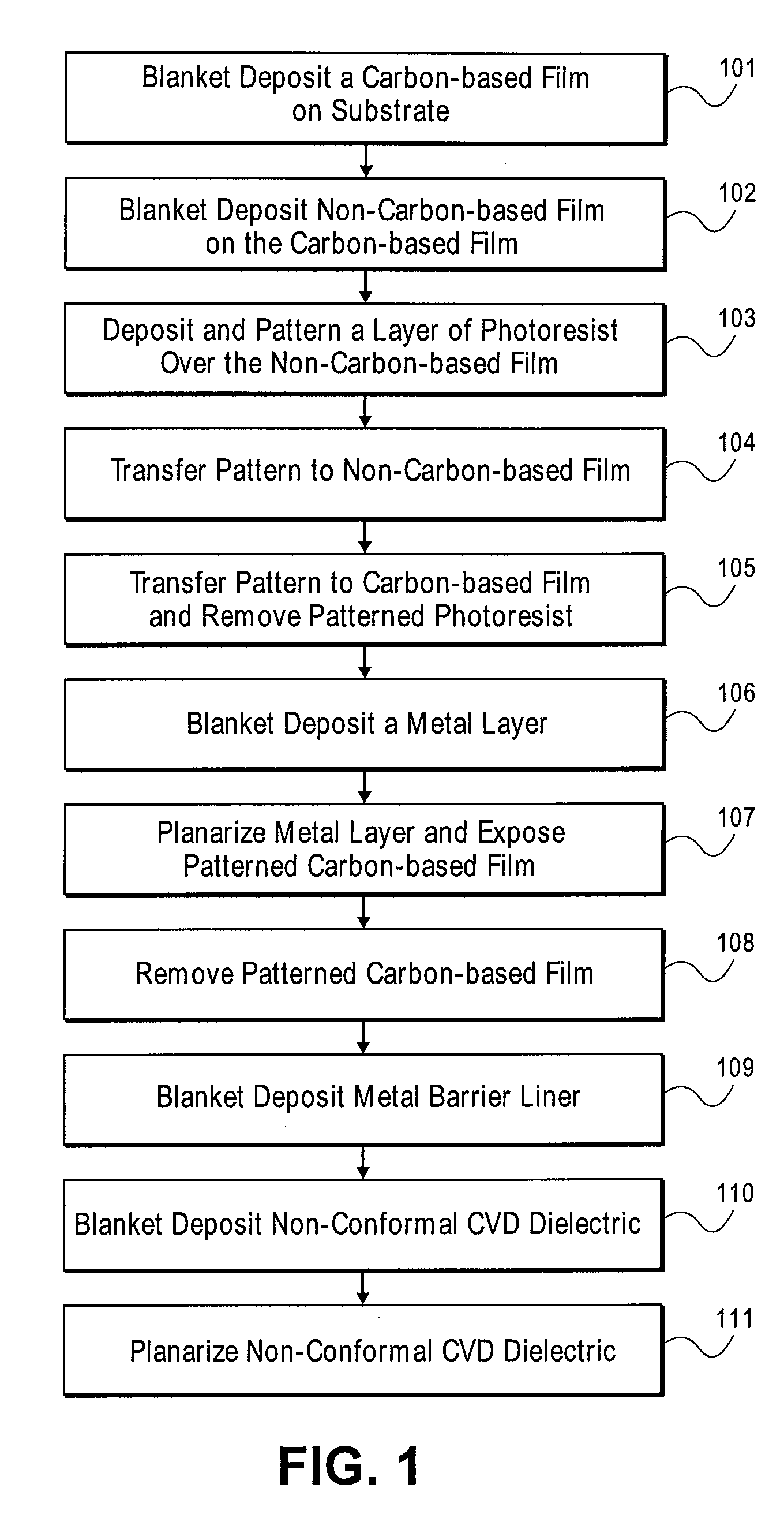
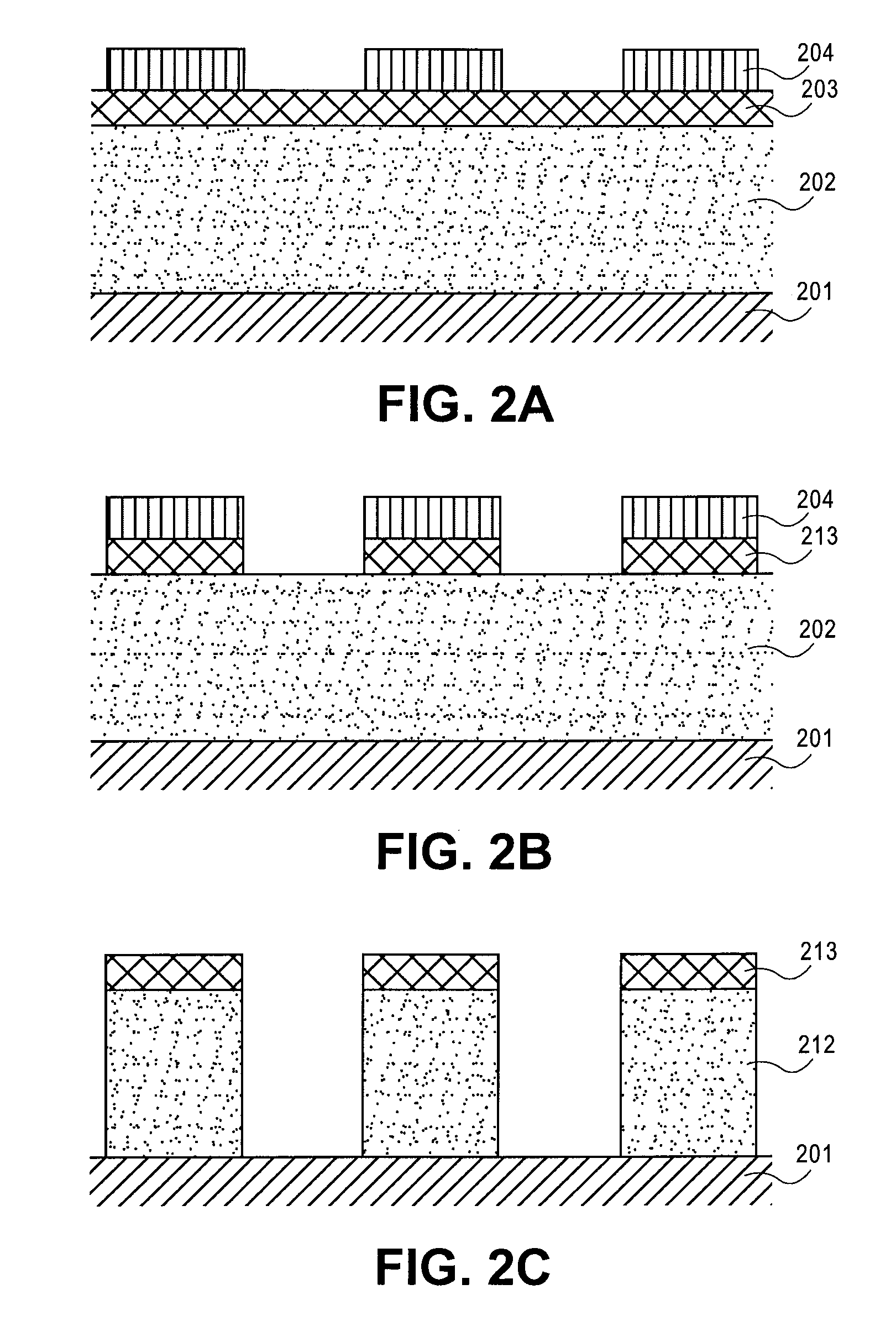
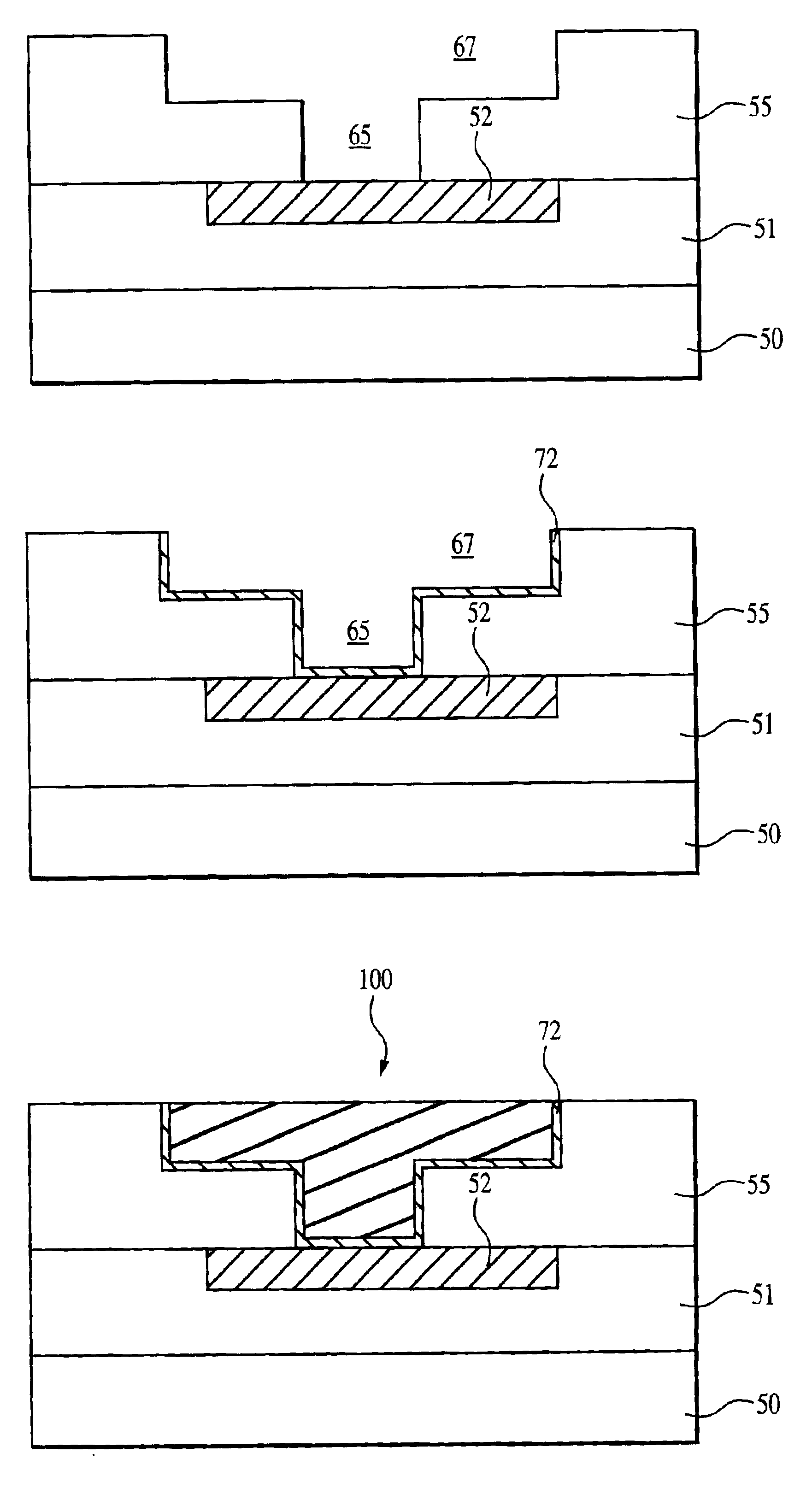
Air gap interconnects using carbon-based films
InactiveUS20100093168A1Improve electrical isolationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal interconnectPorous carbon
A method of forming an interconnect structure comprising: forming a sacrificial inter-metal dielectric (IMD) layer over a substrate, wherein the sacrificial IMD layer comprising a carbon-based film, such as amorphous carbon, advanced patterning films, porous carbon, or any combination thereof; forming a plurality of metal interconnect lines within the sacrificial IMD layer; removing the sacrificial IMD layer, with an oxygen based reactive process; and depositing a non-conformal dielectric layer to form air gaps between the plurality of metal interconnect lines. The metal interconnect lines may comprise copper, aluminum, tantalum, tungsten, titanium, tantalum nitride, titanium nitride, tungsten nitride, or any combination thereof. Carbon-based films and patterned photoresist layers may be simultaneously removed with the same reactive process. Highly reactive hydrogen radicals processes may be used to remove the carbon-based film and simultaneously pre-clean the metal interconnect lines prior to the deposition of a conformal metal barrier liner.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
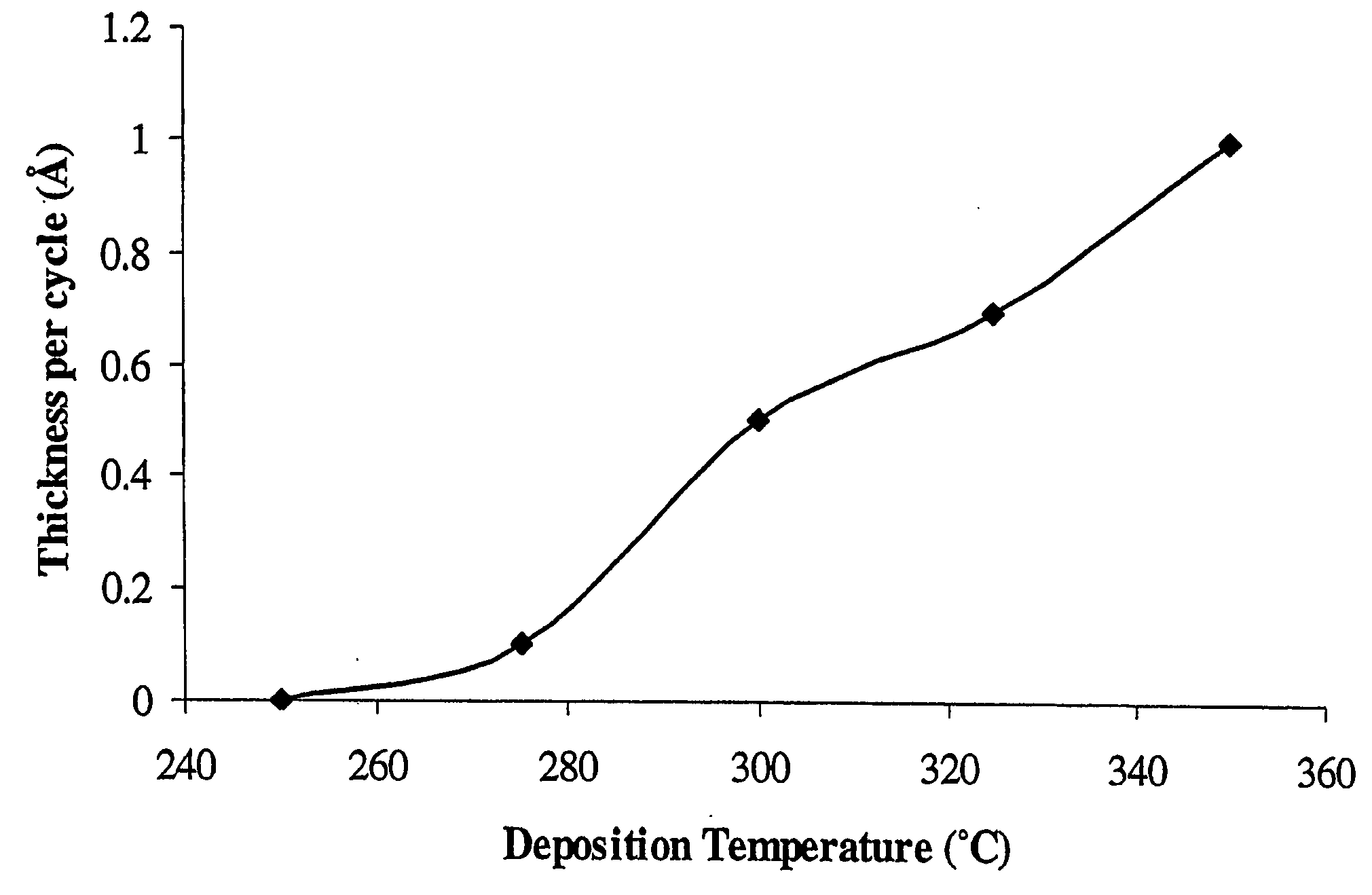
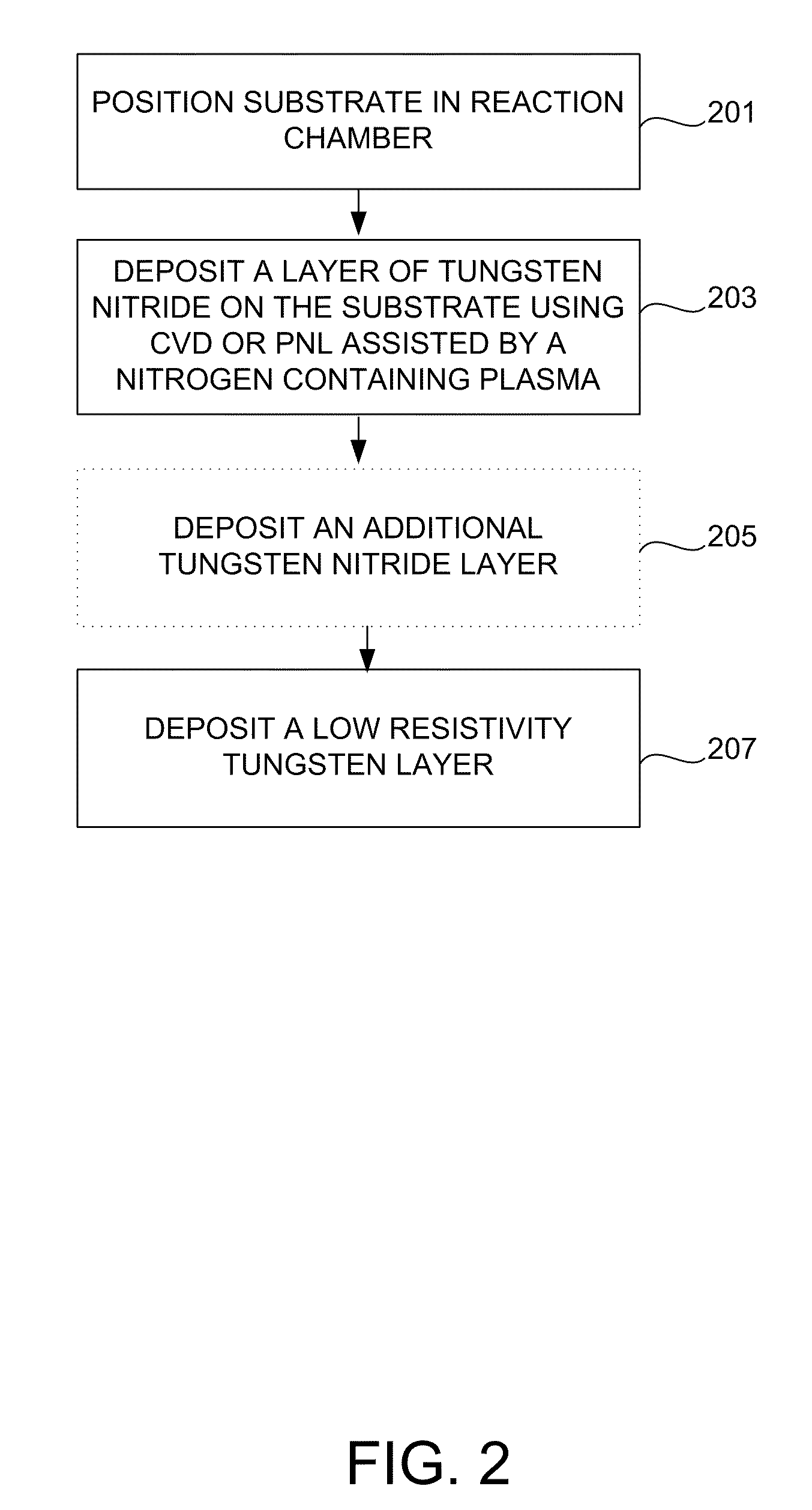
Vapor deposition of tungsten nitride
ActiveUS20060125099A1Uniform thicknessImprove efficiencyMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorGas phase
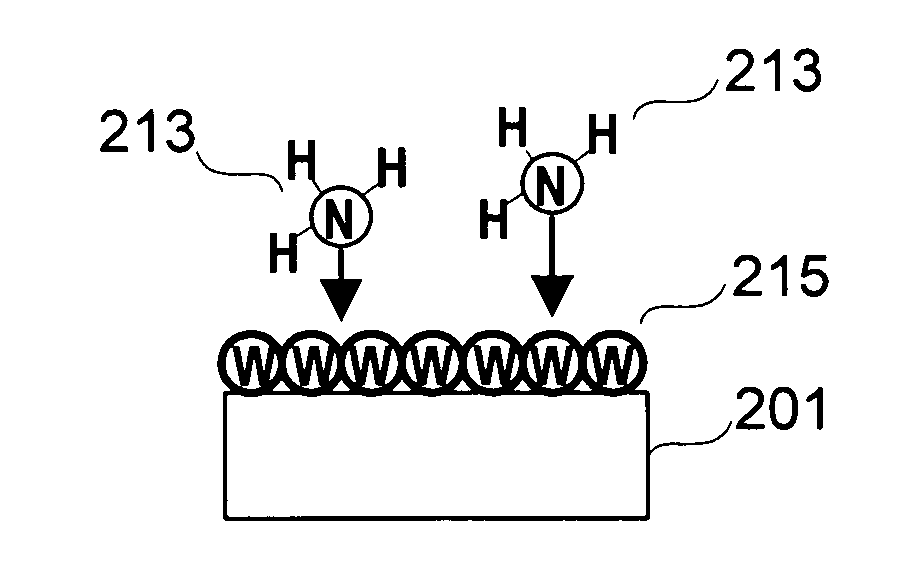
Tungsten nitride films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of vapors of tungsten bis(alkylimide)bis(dialkylamide) and a Lewis base or a hydrogen plasma. For example, vapors of tungsten bis(tert-butylimide)bis(dimethylamide) and ammonia gas supplied in alternate doses to surfaces heated to 300° C. produced coatings of tungsten nitride having very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in holes with aspect ratios up to at least 40:1. The films are metallic and good electrical conductors. Suitable applications in microelectronics include barriers to the diffusion of copper and electrodes for capacitors. Similar processes deposit molybdenum nitride, which is suitable for layers alternating with silicon in X-ray mirrors.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Deposition of tungsten nitride
ActiveUS7005372B2Improve adhesionDeposition thickness is limitedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingArsineTungsten nitride
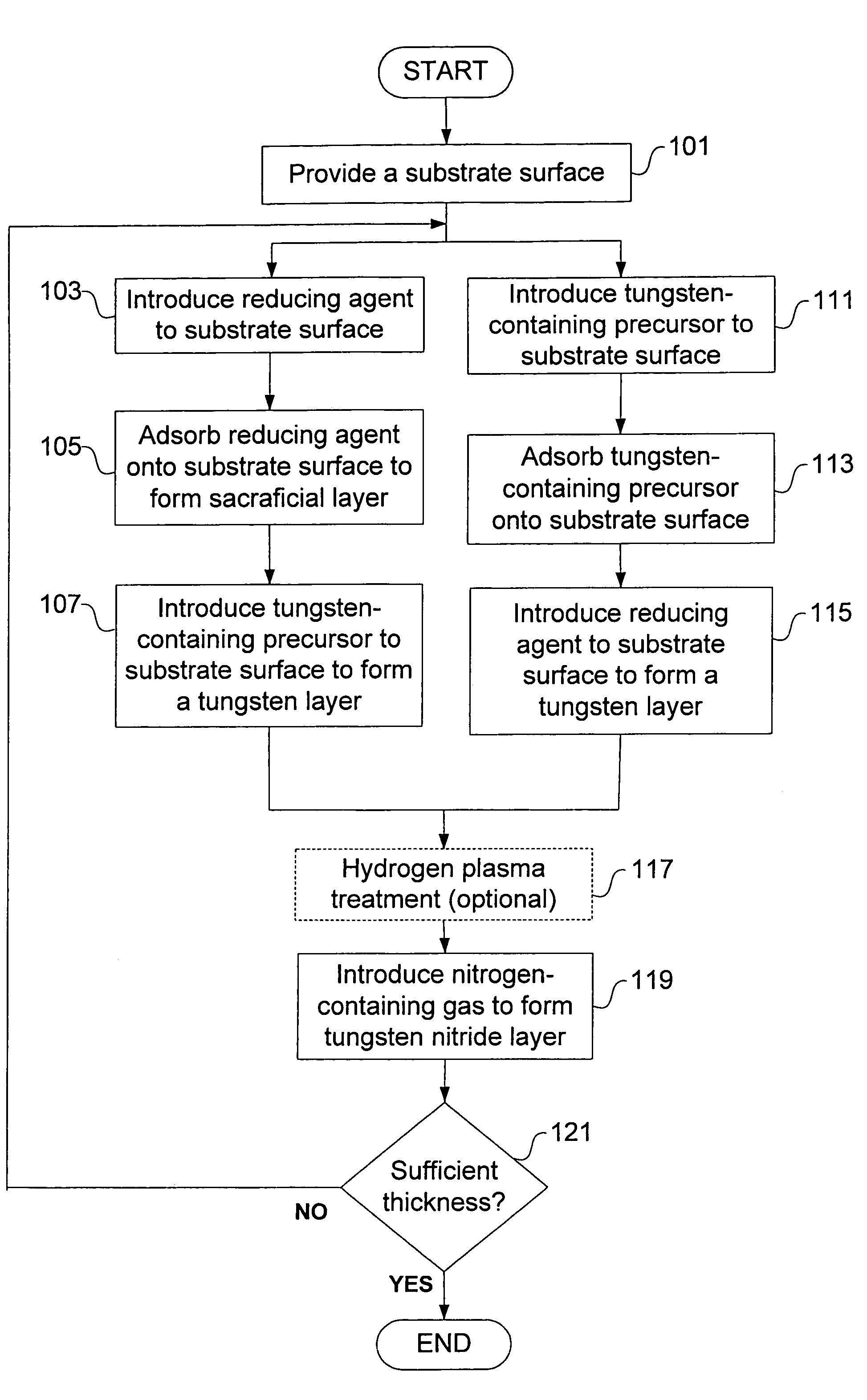
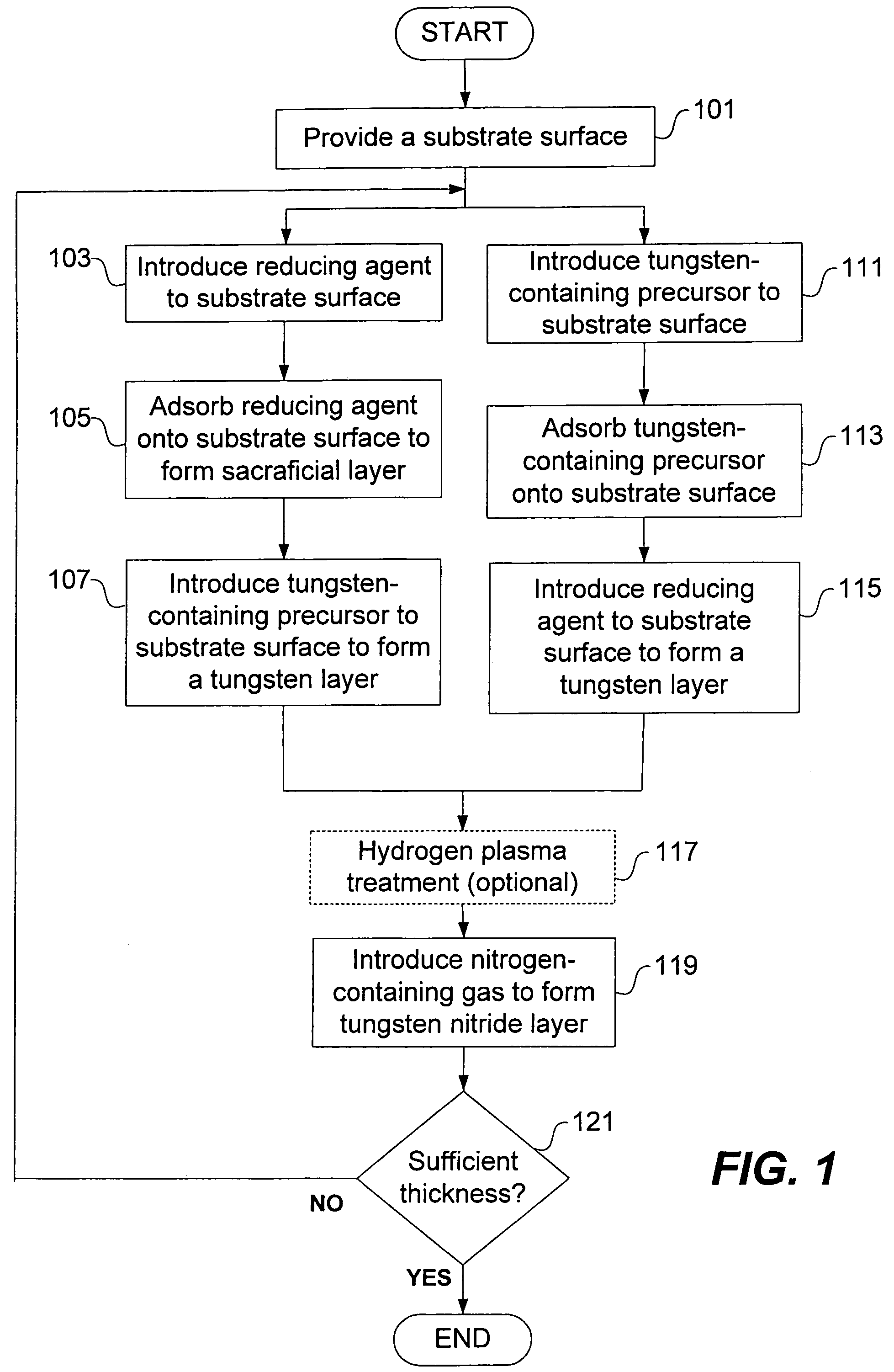
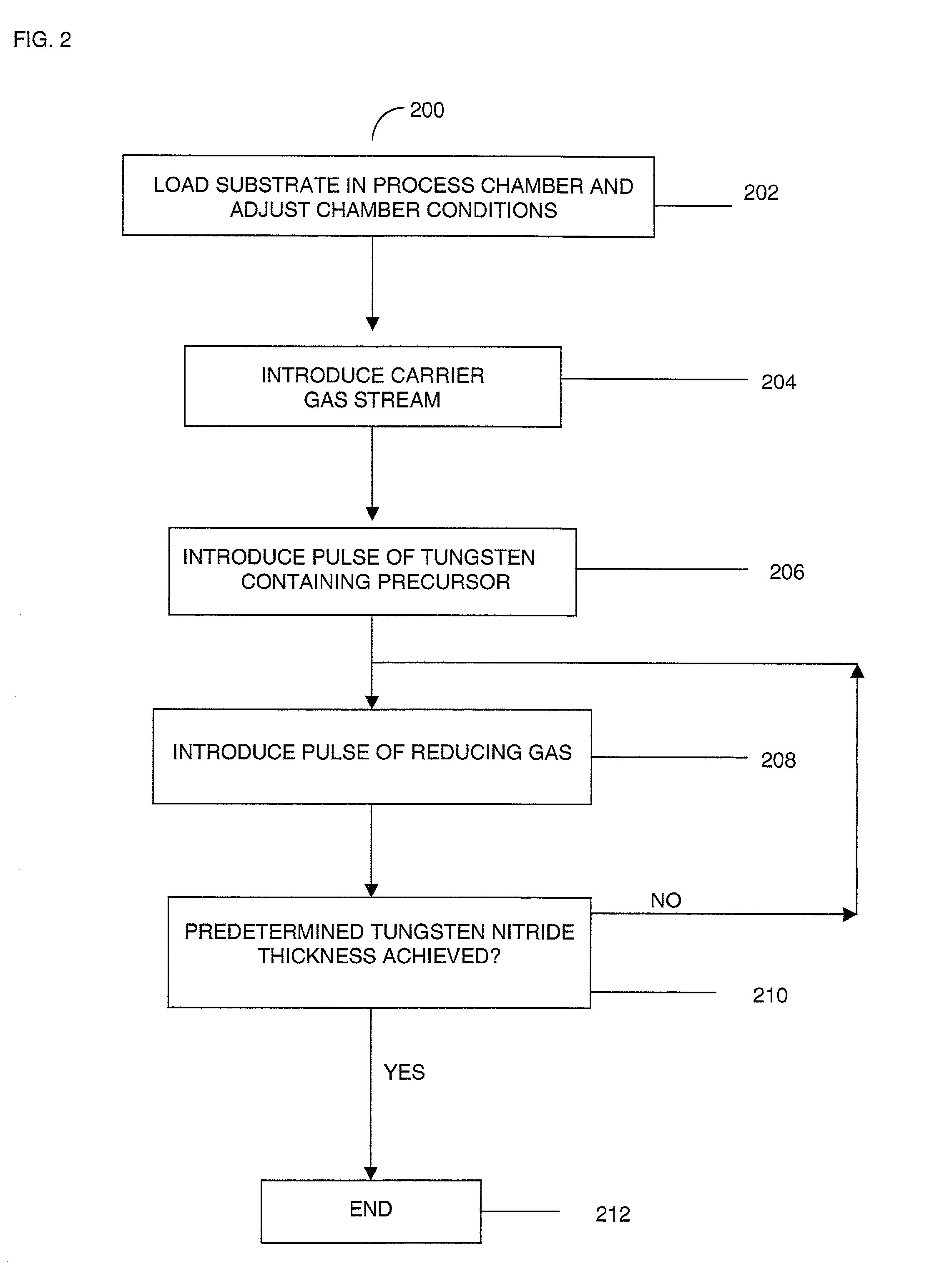
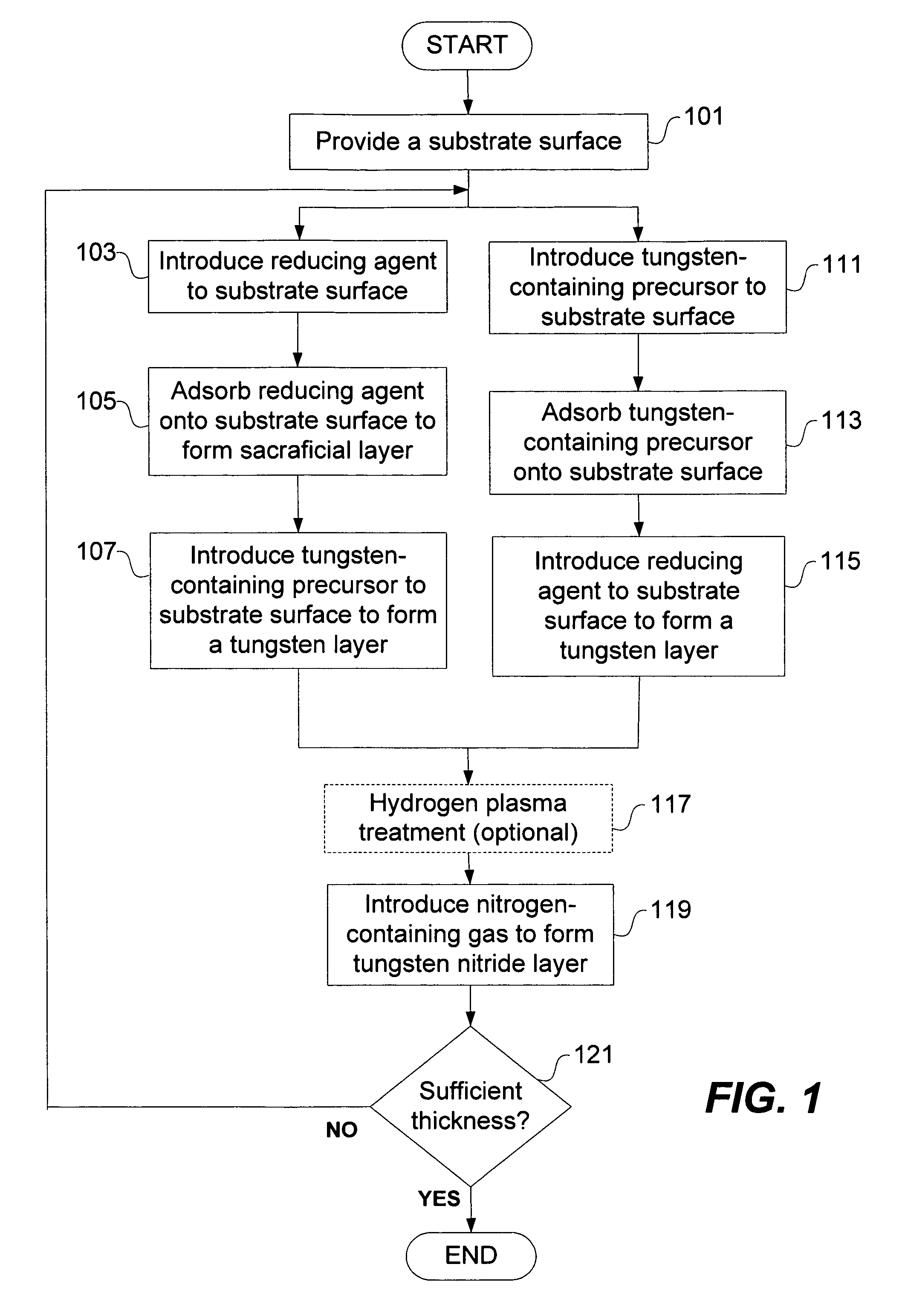
Methods for depositing a tungsten nitride layer are described. The methods form a tungsten nitride layer using a carefully controlled deposition technique such as pulsed nucleation layer (PNL). Initially, a tungsten layer is formed on a substrate surface. The tungsten layer is then exposed to a nitriding agent to form a tungsten nitride layer. Methods of forming relatively thick layers of involve repeated cycles of contact with reducing agent, tungsten precursor and nitriding agent. In some cases, the cycle may also include contact with a dopant precursor such as phosphine or arsine.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Cyclical deposition of tungsten nitride for metal oxide gate electrode
InactiveUS20030161952A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCyclic processTungsten nitride
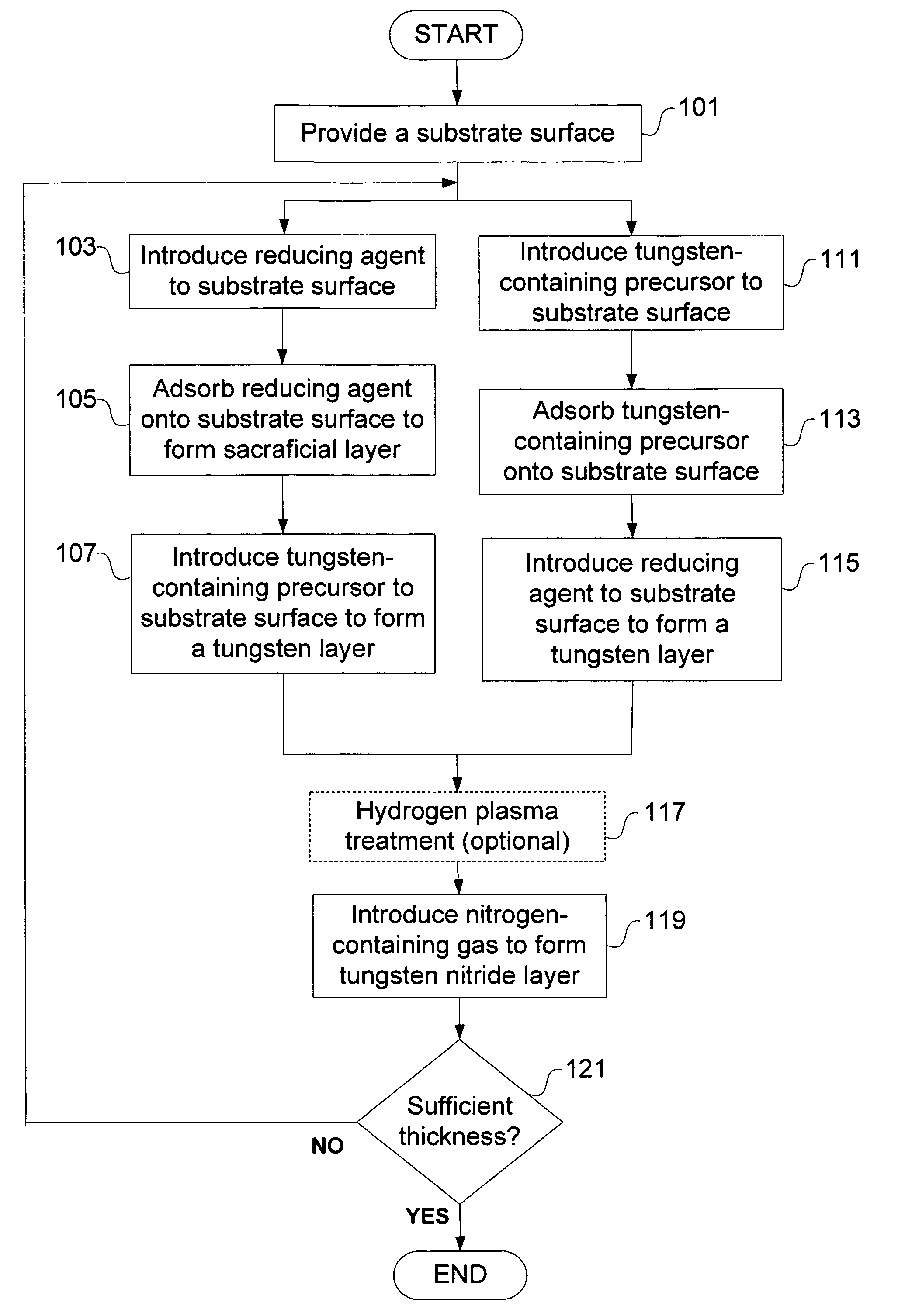
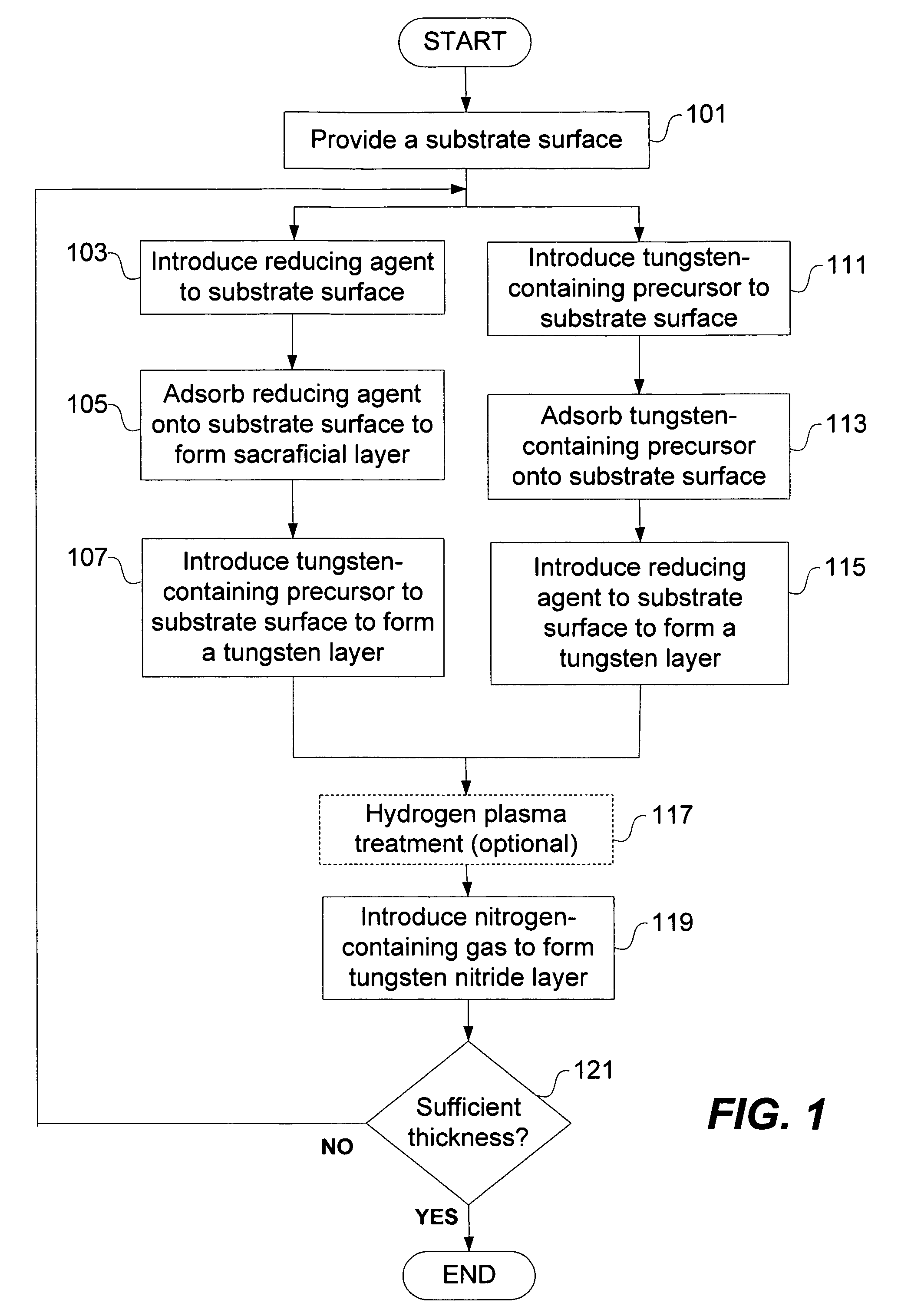
A method for depositing a tungsten nitride layer is provided. The method includes a cyclical process of alternately adsorbing a tungsten-containing compound and a nitrogen-containing compound on a substrate. The barrier layer has a reduced resistivity, lower concentration of fluorine, and can be deposited at any desired thickness, such as less than 100 angstroms, to minimize the amount of barrier layer material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Deposition of tungsten nitride
ActiveUS20060094238A1Improve adhesionControl thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDopantArsine
Methods for depositing a tungsten nitride layer are described. The methods form a tungsten nitride layer using a carefully controlled deposition technique such as pulsed nucleation layer (PNL). Initially, a tungsten layer is formed on a substrate surface. The tungsten layer is then exposed to a nitriding agent to form a tungsten nitride layer. Methods of forming relatively thick layers of involve repeated cycles of contact with reducing agent, tungsten precursor and nitriding agent. In some cases, the cycle may also include contact with a dopant precursor such as phosphine or arsine.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Formation of liner and barrier for tungsten as gate electrode and as contact plug to reduce resistance and enhance device performance
ActiveUS20110233778A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRemote plasmaTungsten nitride
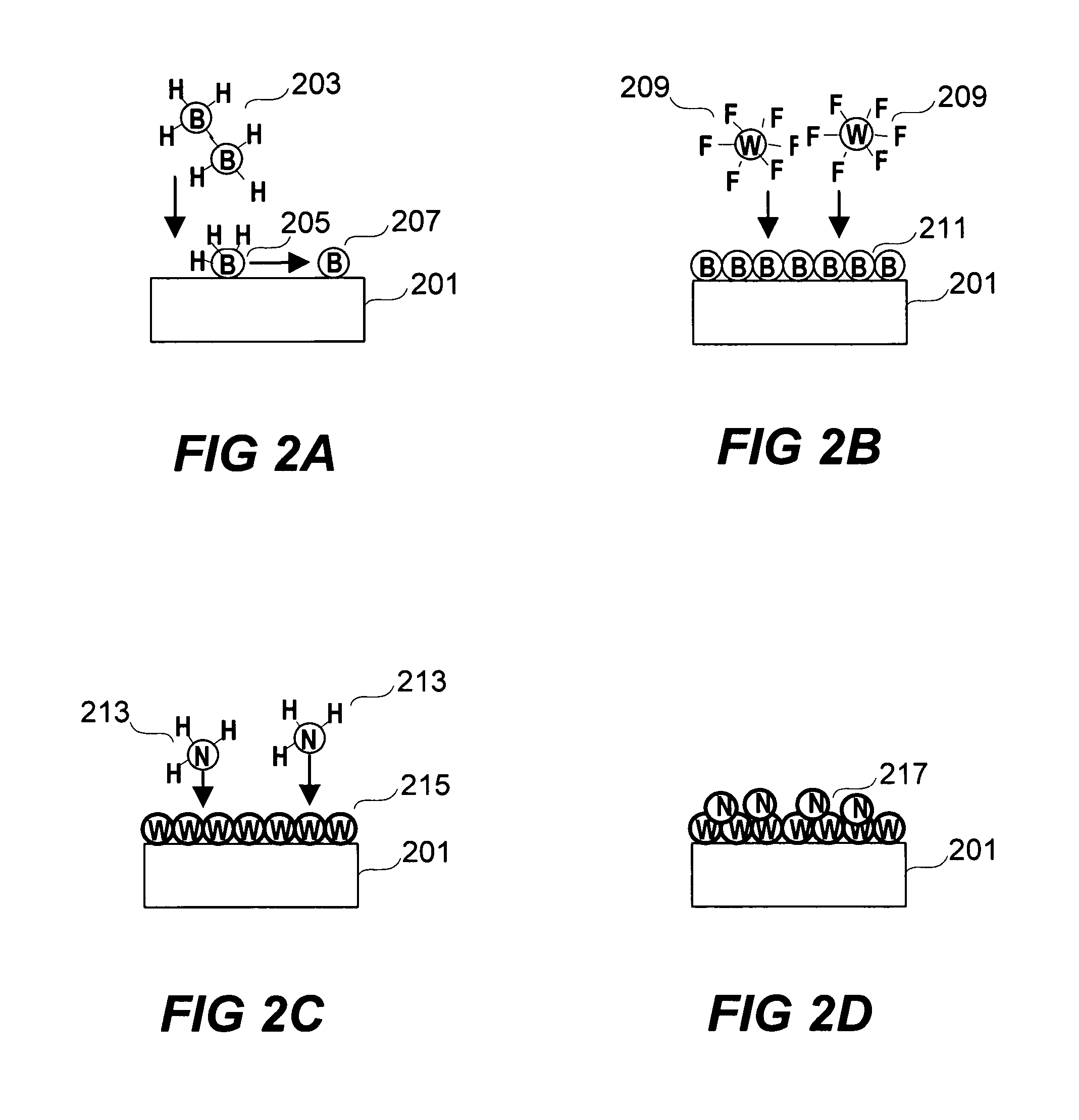
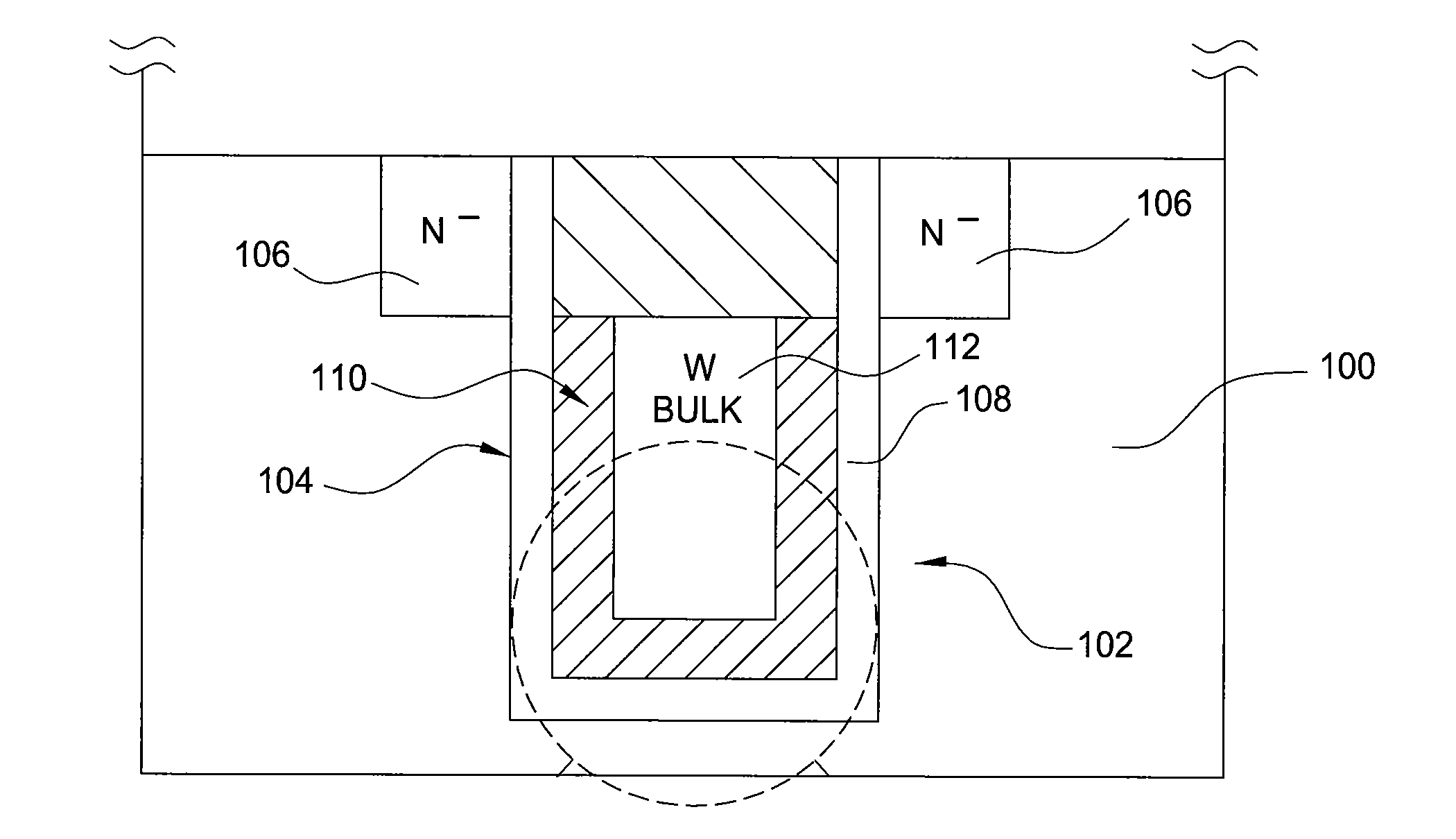
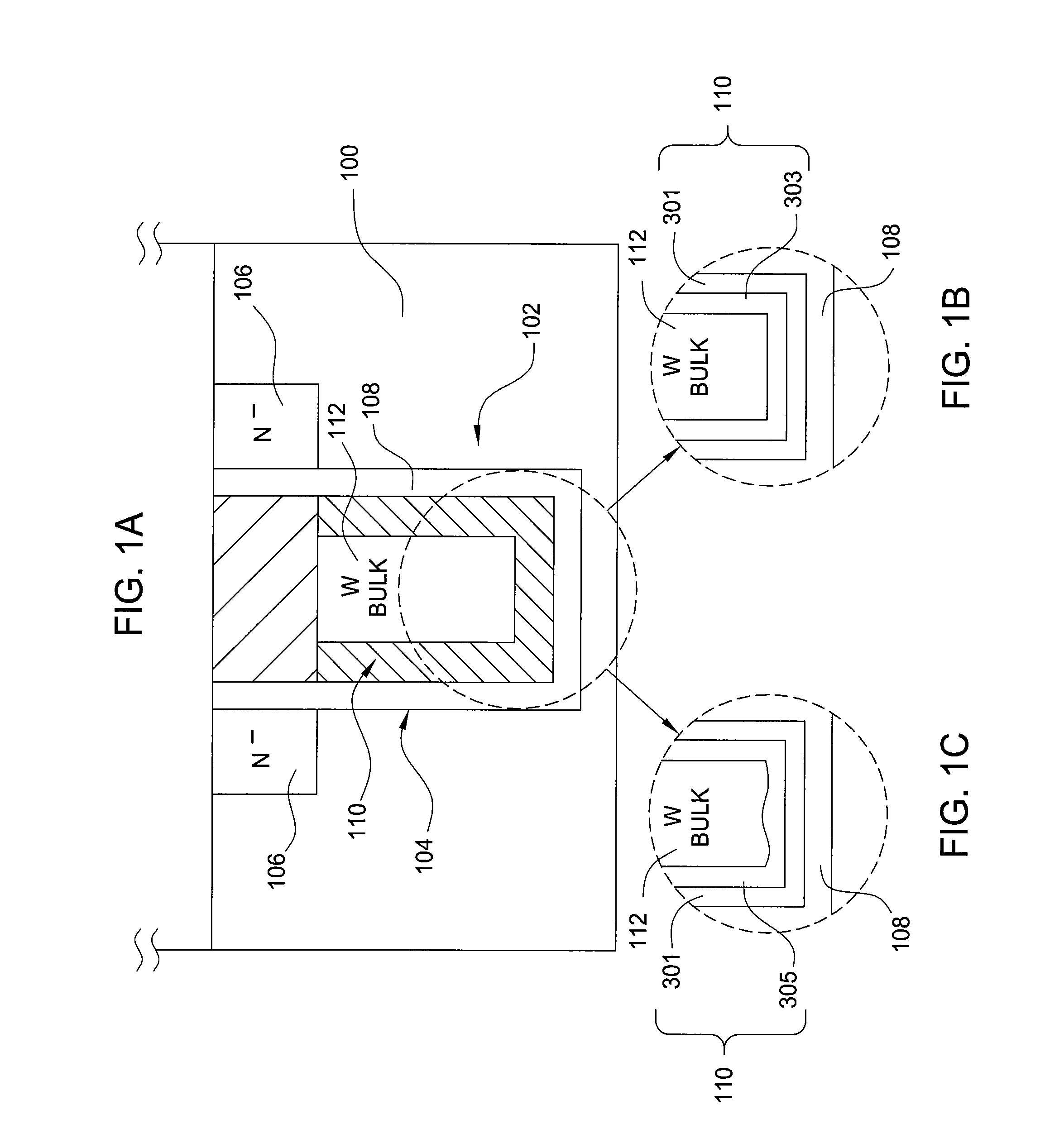
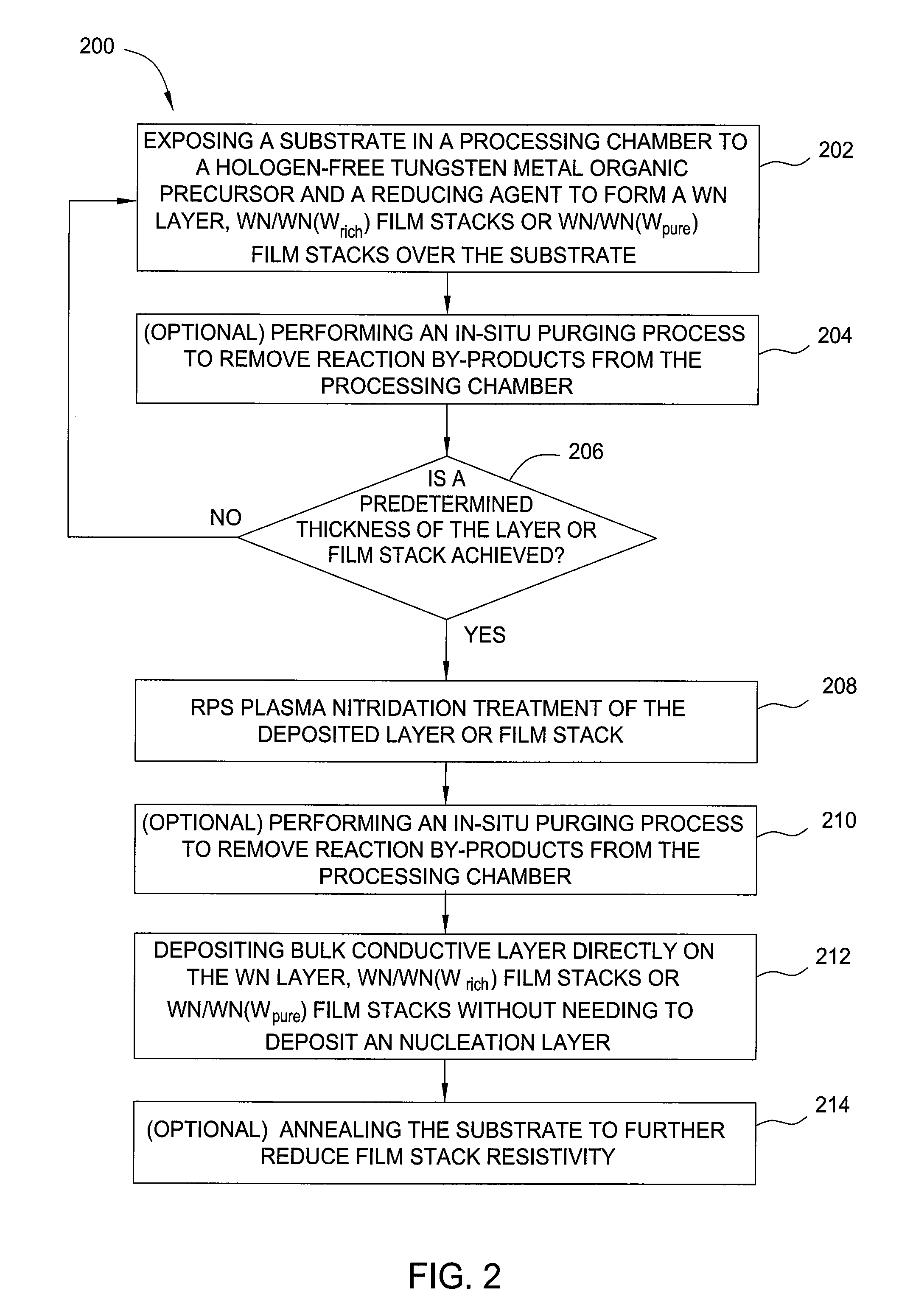
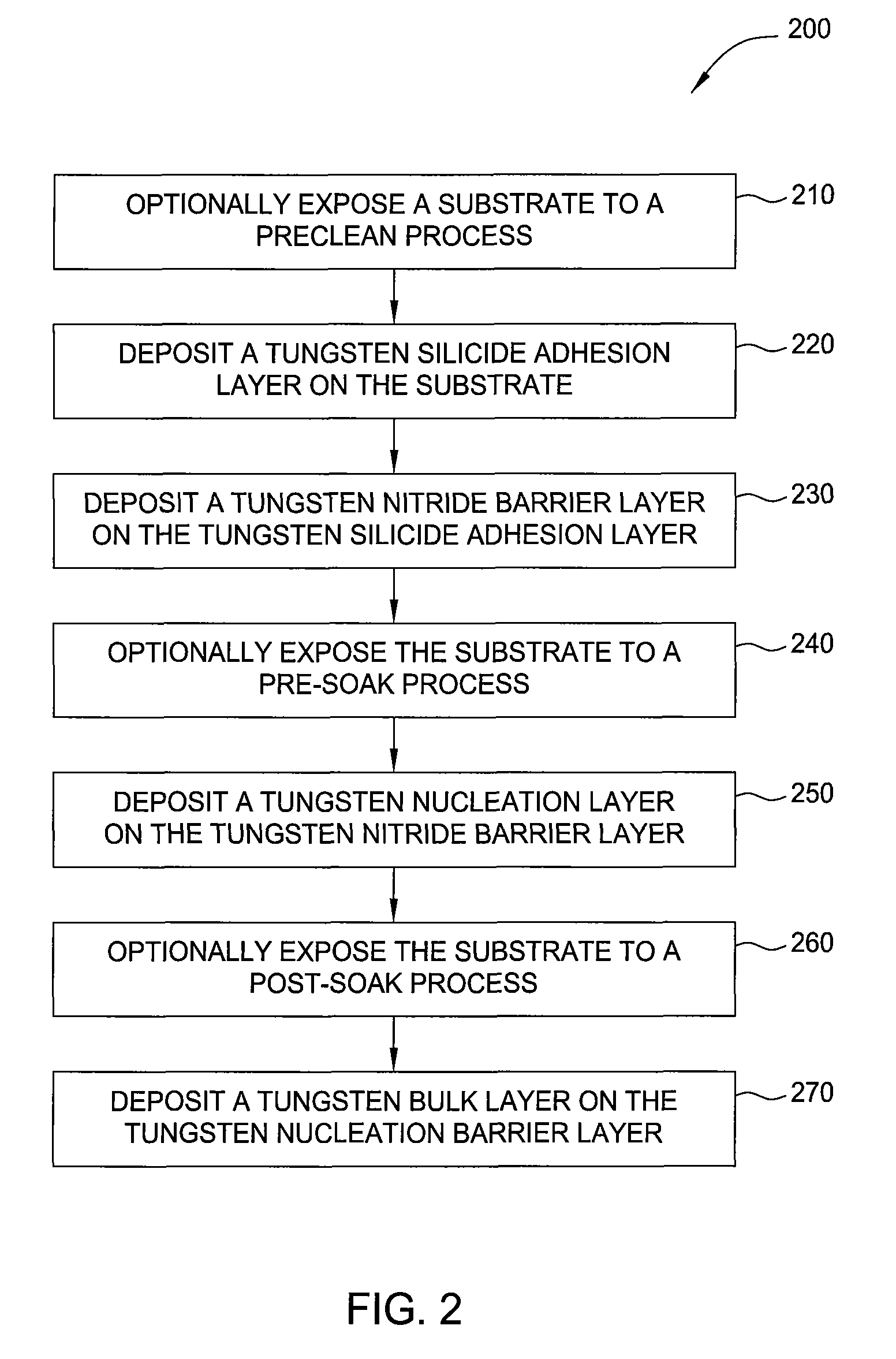
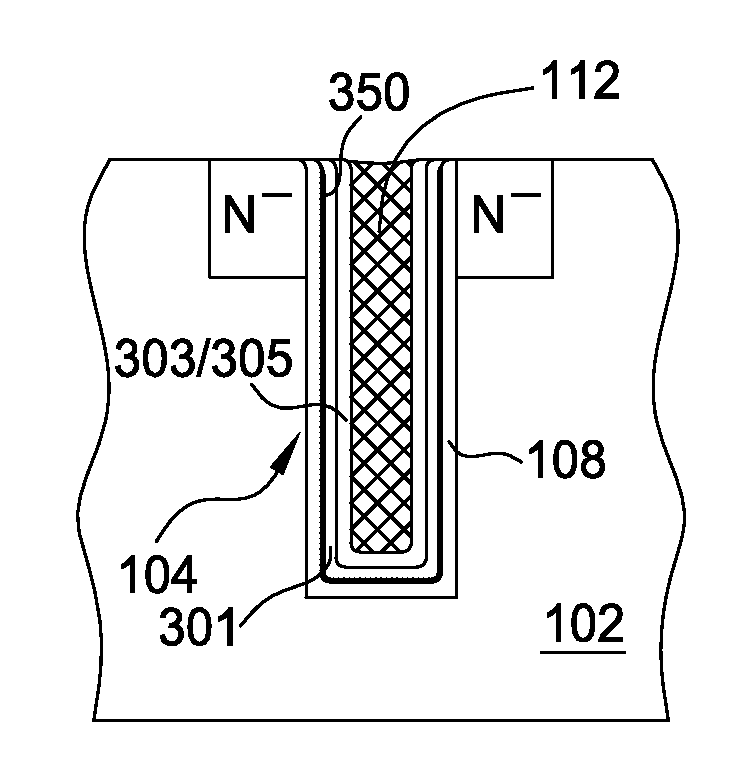
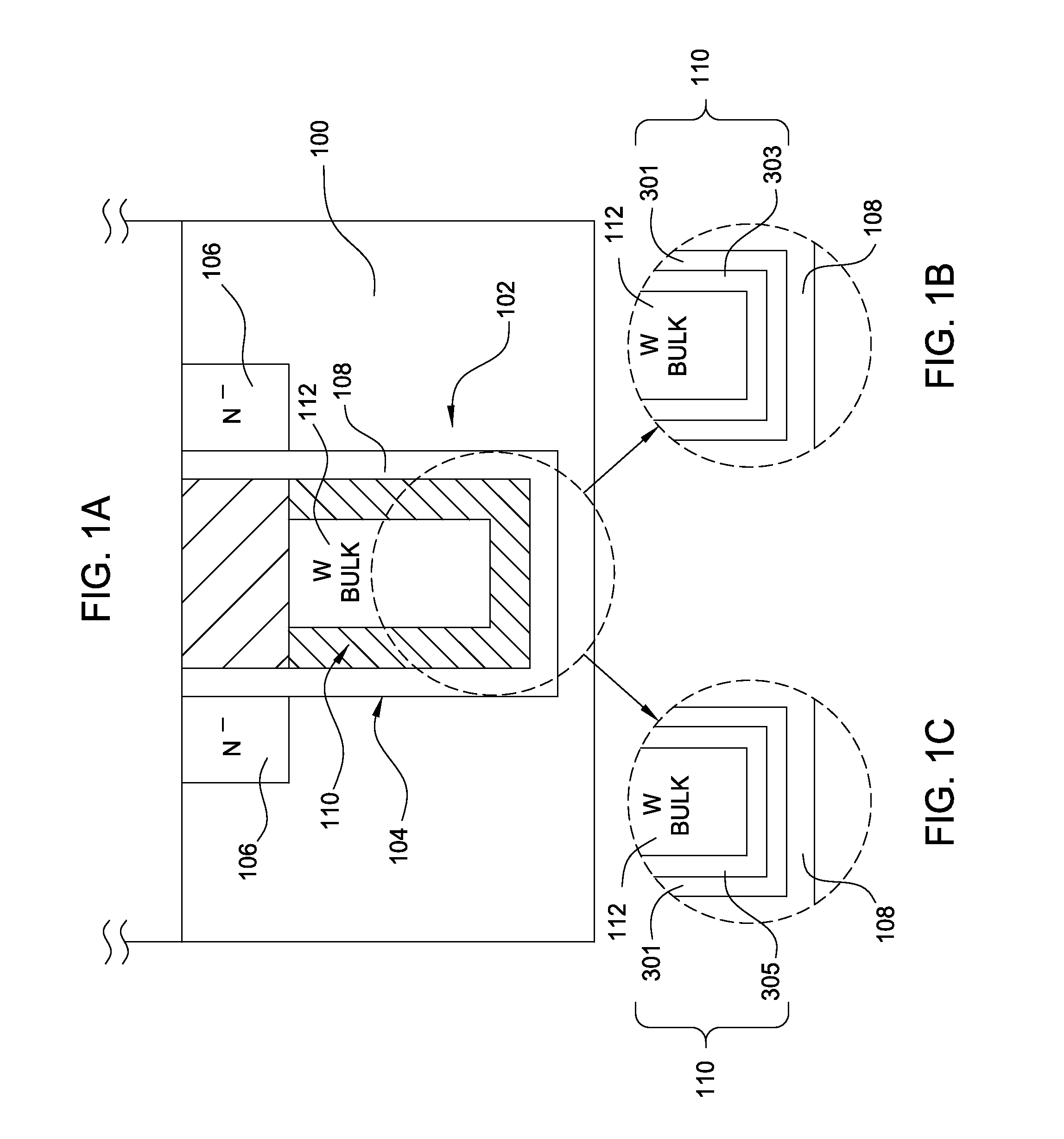
The invention provides a method of forming a film stack on a substrate, comprising depositing a tungsten nitride layer on the substrate, subjecting the substrate to a nitridation treatment using active nitrogen species from a remote plasma, and depositing a conductive bulk layer directly on the tungsten nitride layer without depositing a tungsten nucleation layer on the tungsten nitride layer as a growth site for tungsten.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050059236A1Improve featuresEasy to understandTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorMetal interconnect
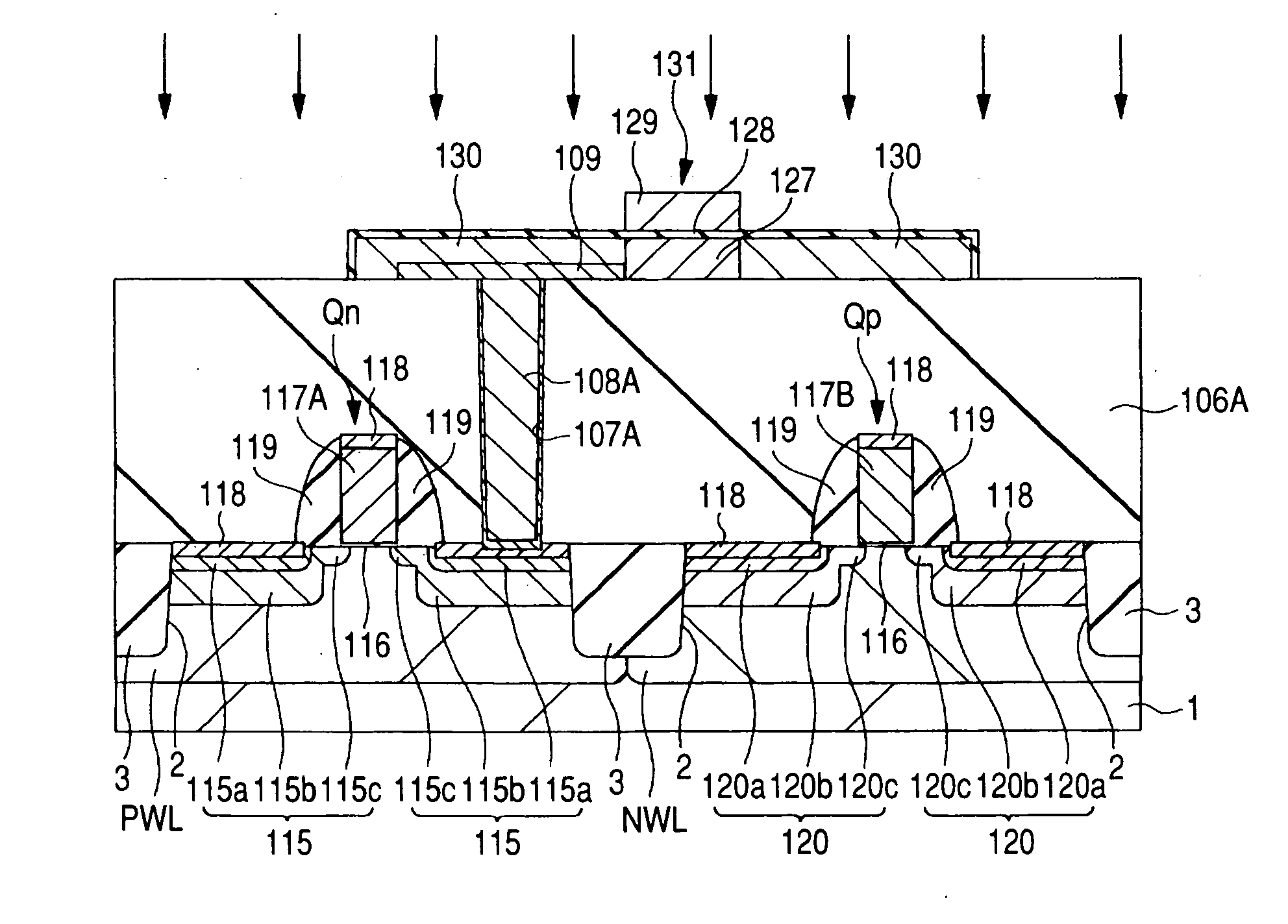
In a semiconductor device, the ohmic contact at the junction between the metal interconnection and the semiconductor layer is lowered by depositing a first conductor layer comprised of, for example, tungsten nitride and a second conductor layer comprised of, for example, tungsten silicide successively from the lower layer so as to cover the upper surface of intermediate conductive layers comprised of a metal, for example, tungsten as a main interconnection material, subsequently introducing an impurity, for example, boron (b) to the second conductor layer, then patterning the first and the second conductor layers thereby forming a conductor layer, and then forming a lower semiconductor layer comprised of, for example, polycrystal silicon for forming a semiconductor region for source and drain of load MISFET of SRAM so as to be in contact with the conductor layer.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Process for low-temperature metal-organic chemical vapor deposition of tungsten nitride and tungsten nitride films
InactiveUS6884466B2Layered productsNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsTungsten nitrideNitrogen
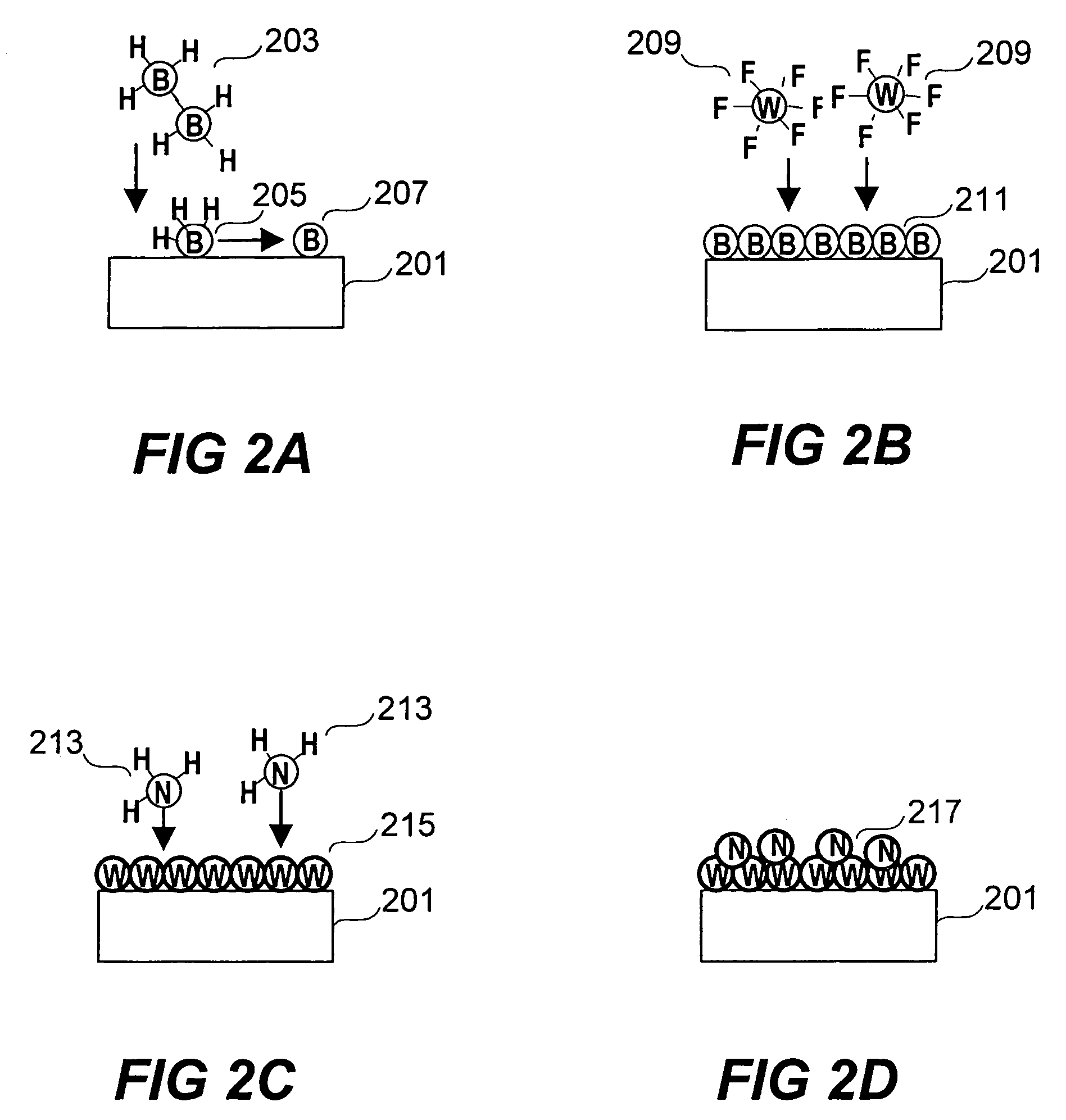
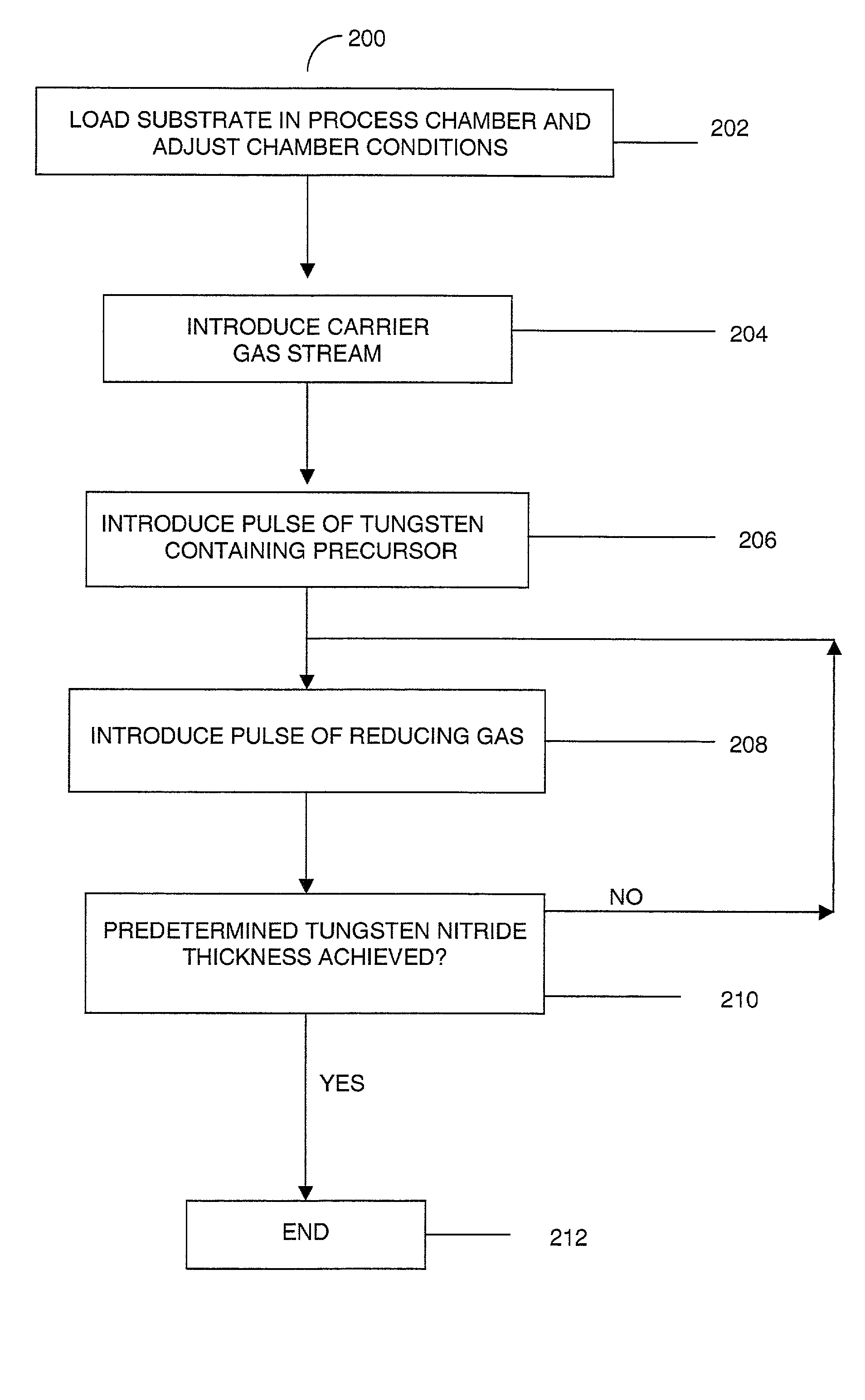
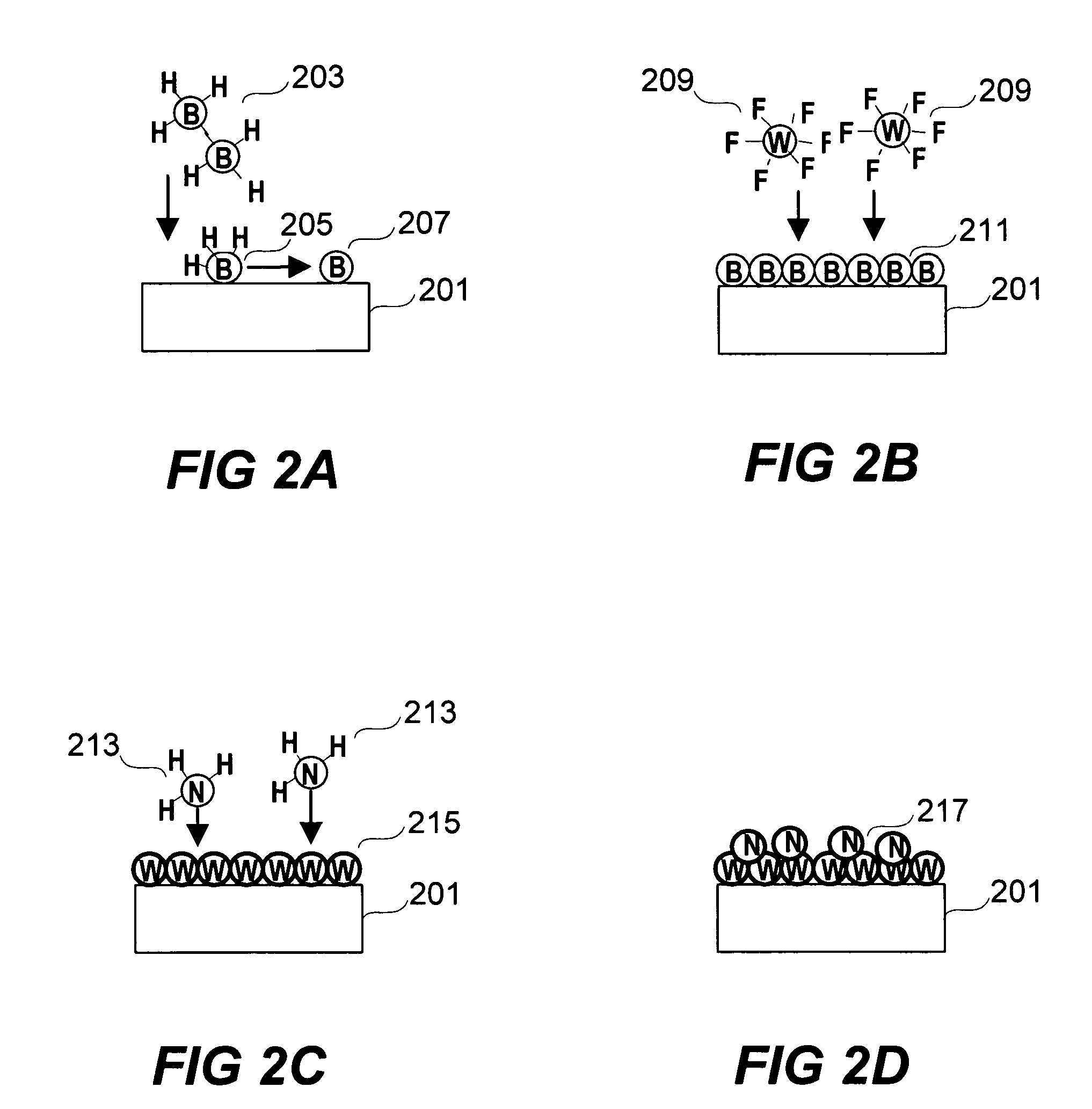
Processes for producing tungsten nitride and tungsten nitride films are provided in which a tungsten carbonyl compound and a nitrogen-containing reactant gas are reacted at a temperature below about 600° C. Tungsten nitride precursors are also included which comprise a tungsten carbonyl compound capable of forming a tungsten nitride film in the presence of a nitrogen-containing reactant gas at a temperature of less than about 600° C. A process for forming a film by atomic layer deposition is also provided which includes introducing a substrate having a surface into a deposition chamber and heating the substrate to a temperature sufficient to allow adsorption of a tungsten source precursor or an intermediate thereof, and thereafter sequentially introducing by pulsing: a tungsten source precursor which is absorbed as a monolayer, a purging inert gas, a nitrogen-containing gas for reacting with the monolayer to form a first tungsten nitride layer on the substrate surface, and an inert purging gas, and repeating the sequence to form a film of desired thickness.
Owner:GELEST +1
Semiconductor device fabricating method and system for carrying out the same
InactiveUS6399484B1Reduced form requirementsAvoid depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTungsten nitrideNitrogen
A semiconductor device fabricating method includes a preparatory process that brings a first source gas containing tungsten atoms into contact with a workpiece and that does not bring a second source gas containing nitrogen atoms into contact with the workpiece, and a film forming process that forms a tungsten nitride film on the workpiece by using the first and the second source gases so as to fabricate a semiconductor device. The semiconductor device fabricating method is capable of preventing the tungsten nitride film from peeling off from a layer underlying the same when the tungsten nitride film is subjected to heat treatment.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Deposition of tungsten nitride
ActiveUS7691749B2Improve adhesionControl thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingArsineTungsten nitride
Methods for depositing a tungsten nitride layer are described. The methods form a tungsten nitride layer using a carefully controlled deposition technique such as pulsed nucleation layer (PNL). Initially, a tungsten layer is formed on a substrate surface. The tungsten layer is then exposed to a nitriding agent to form a tungsten nitride layer. Methods of forming relatively thick layers of involve repeated cycles of contact with reducing agent, tungsten precursor and nitriding agent. In some cases, the cycle may also include contact with a dopant precursor such as phosphine or arsine.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
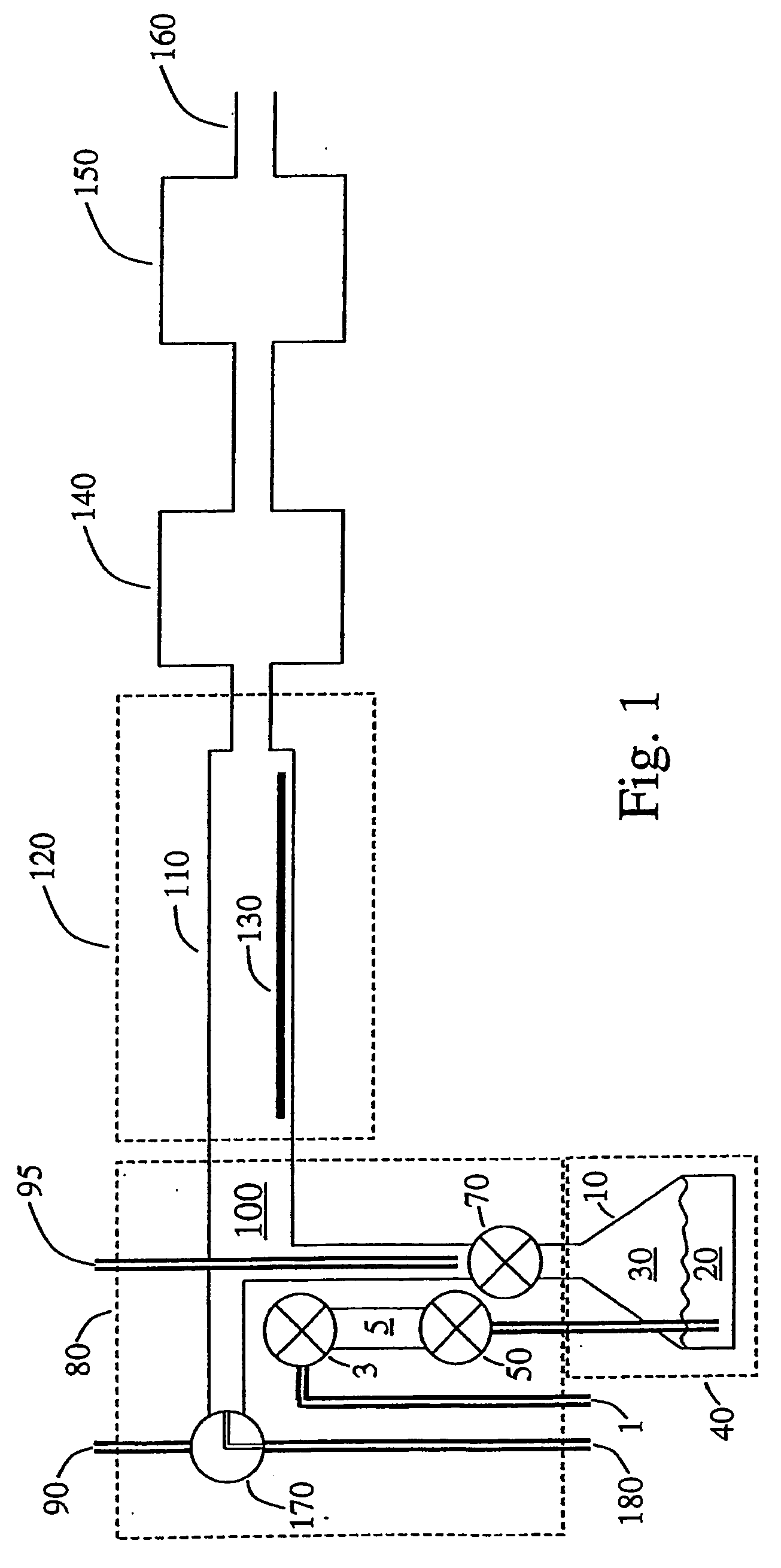
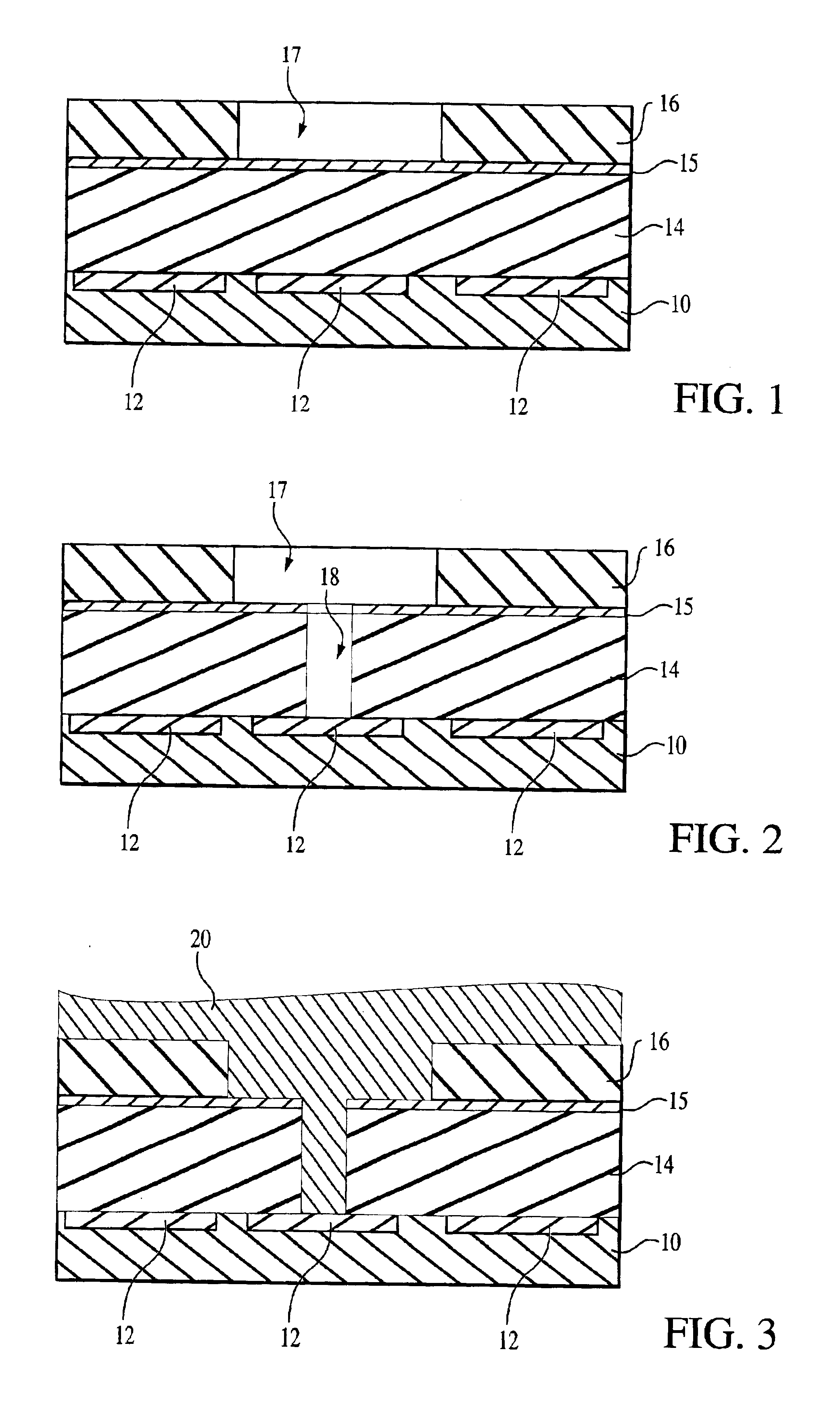
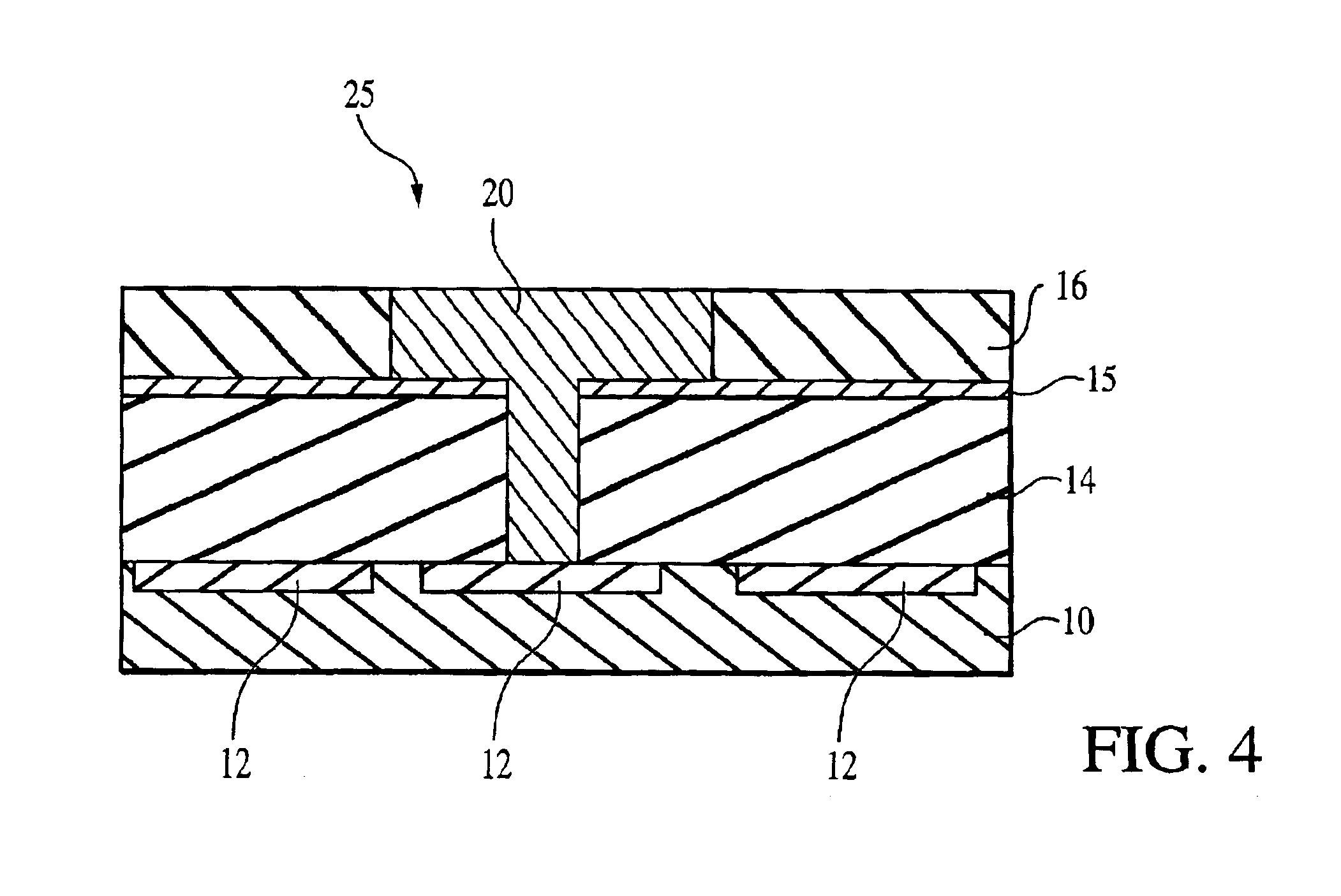
Method for depositing nanolaminate thin films on sensitive surfaces
InactiveUS20050106877A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
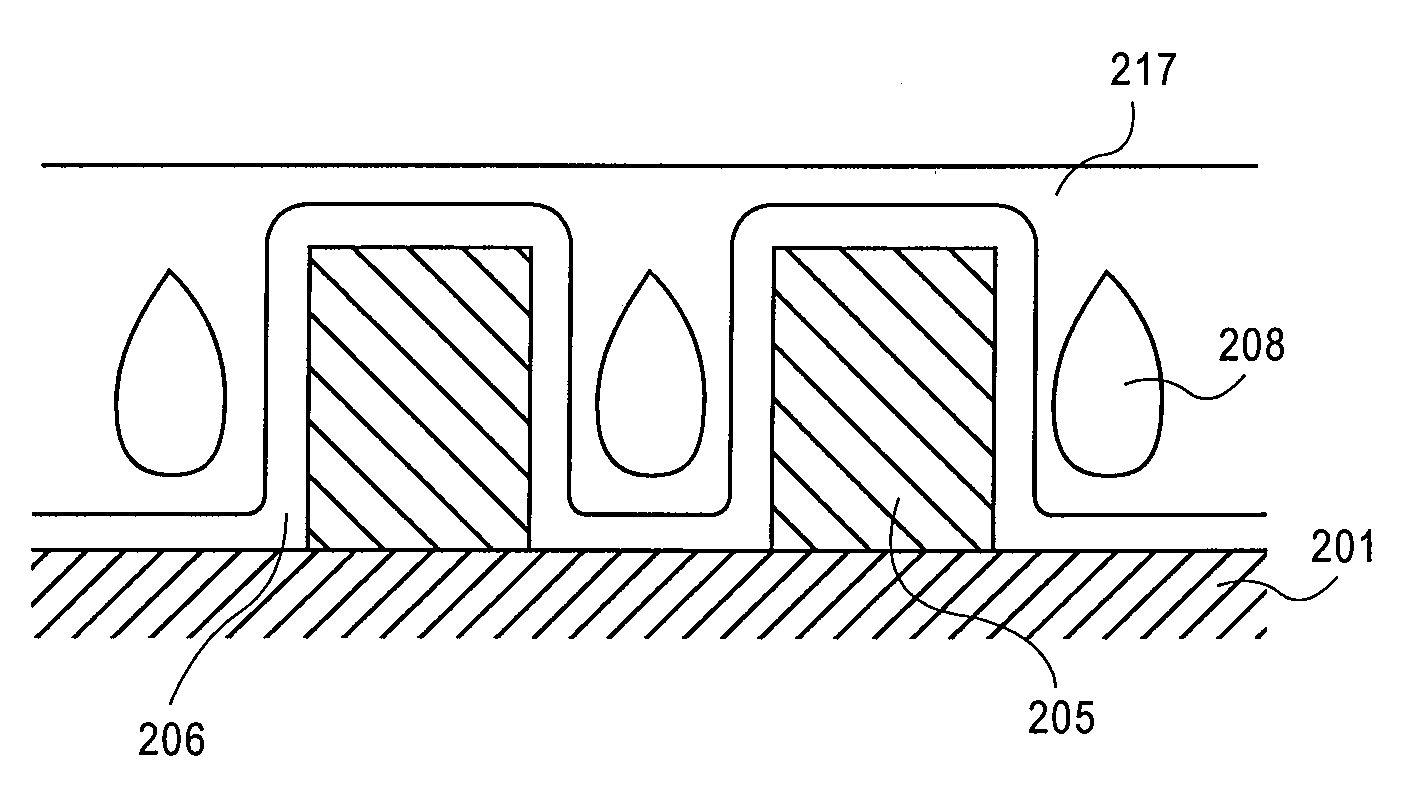
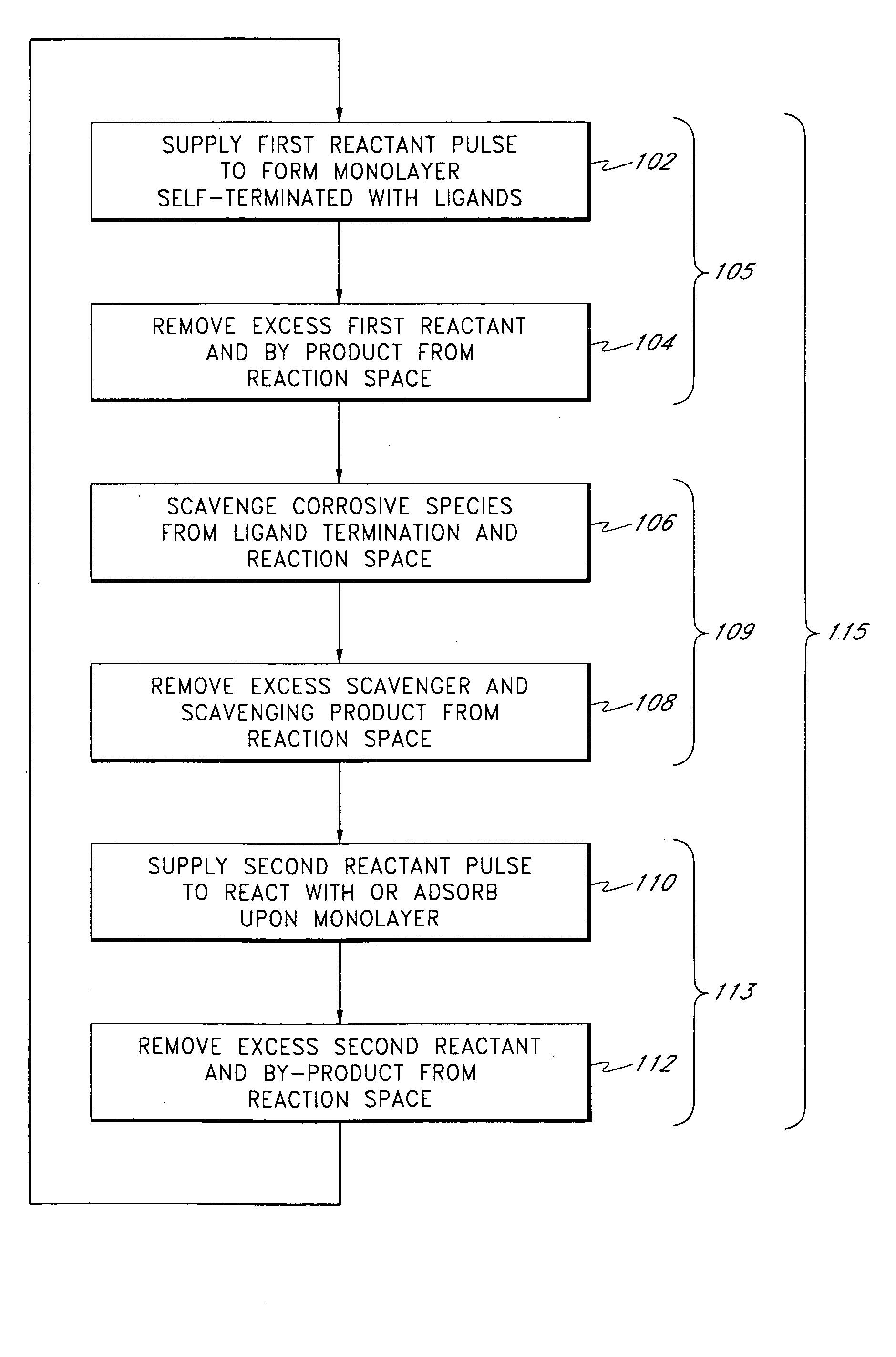
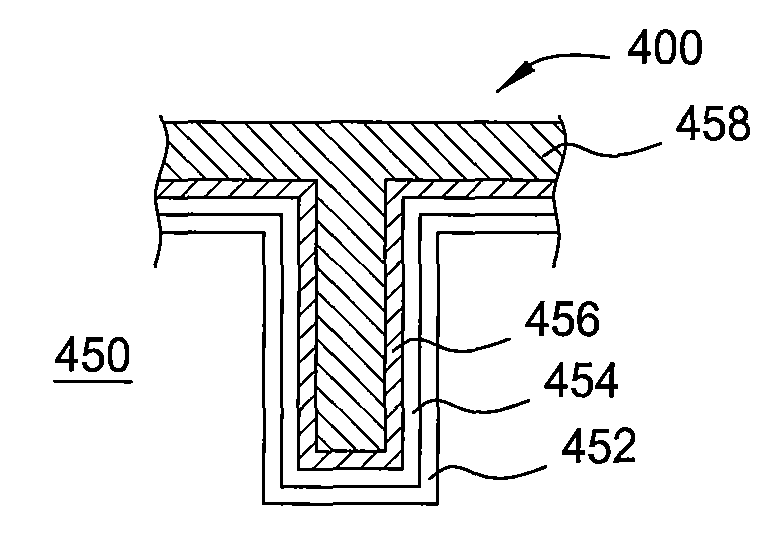
The present method provides tools for growing conformal metal nitride, metal carbide and metal thin films, and nanolaminate structures incorporating these films, from aggressive chemicals. The amount of corrosive chemical compounds, such as hydrogen halides, is reduced during the deposition of transition metal, transition metal carbide and transition metal nitride thin films on various surfaces, such as metals and oxides. Getter compounds protect surfaces sensitive to hydrogen halides and ammonium halides, such as aluminum, copper, silicon oxide and the layers being deposited, against corrosion. Nanolaminate structures (20) incorporating metal nitrides, such as titanium nitride (30) and tungsten nitride (40), and metal carbides, and methods for forming the same, are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Atomic layer deposition of noble metals
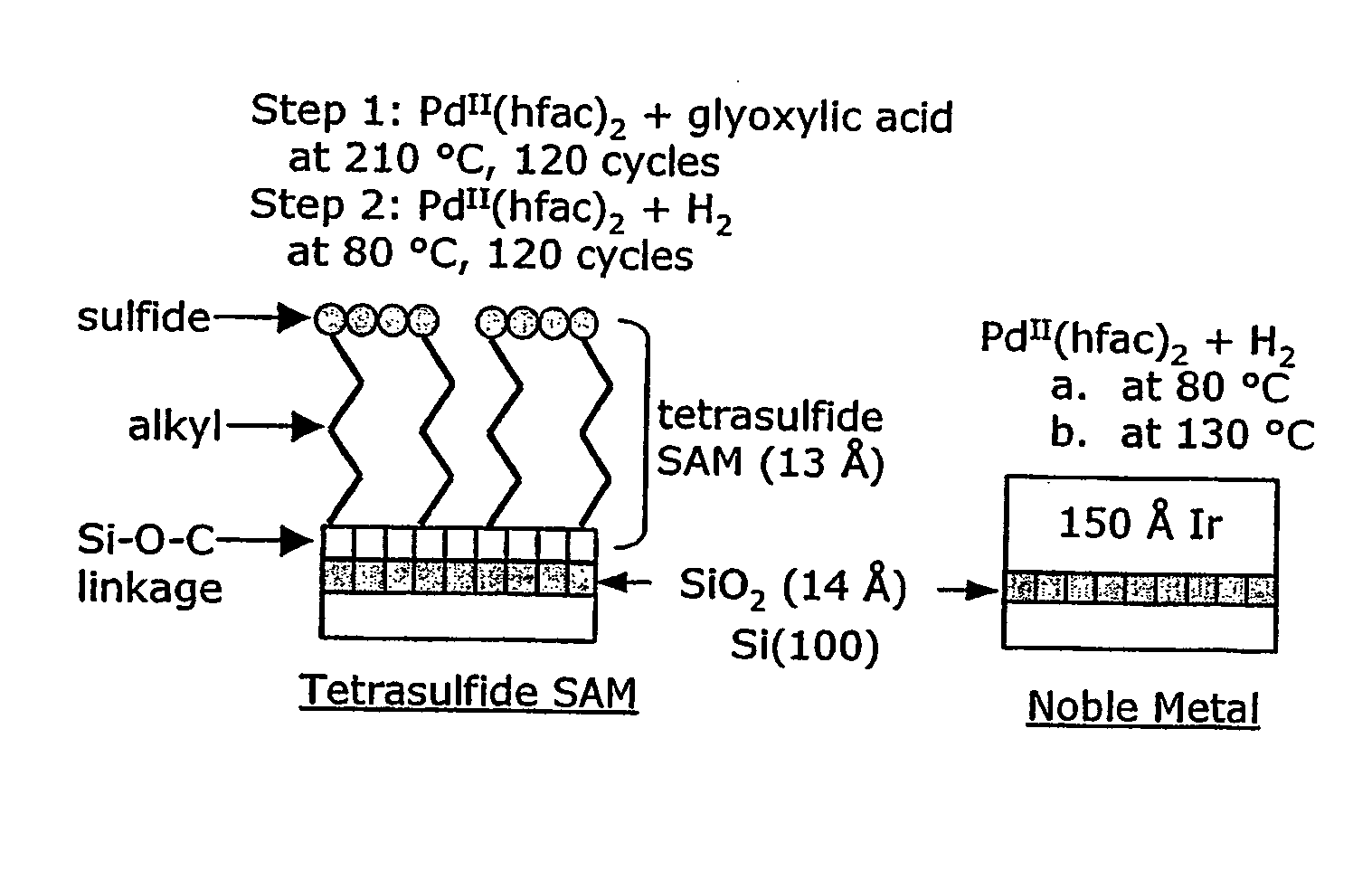
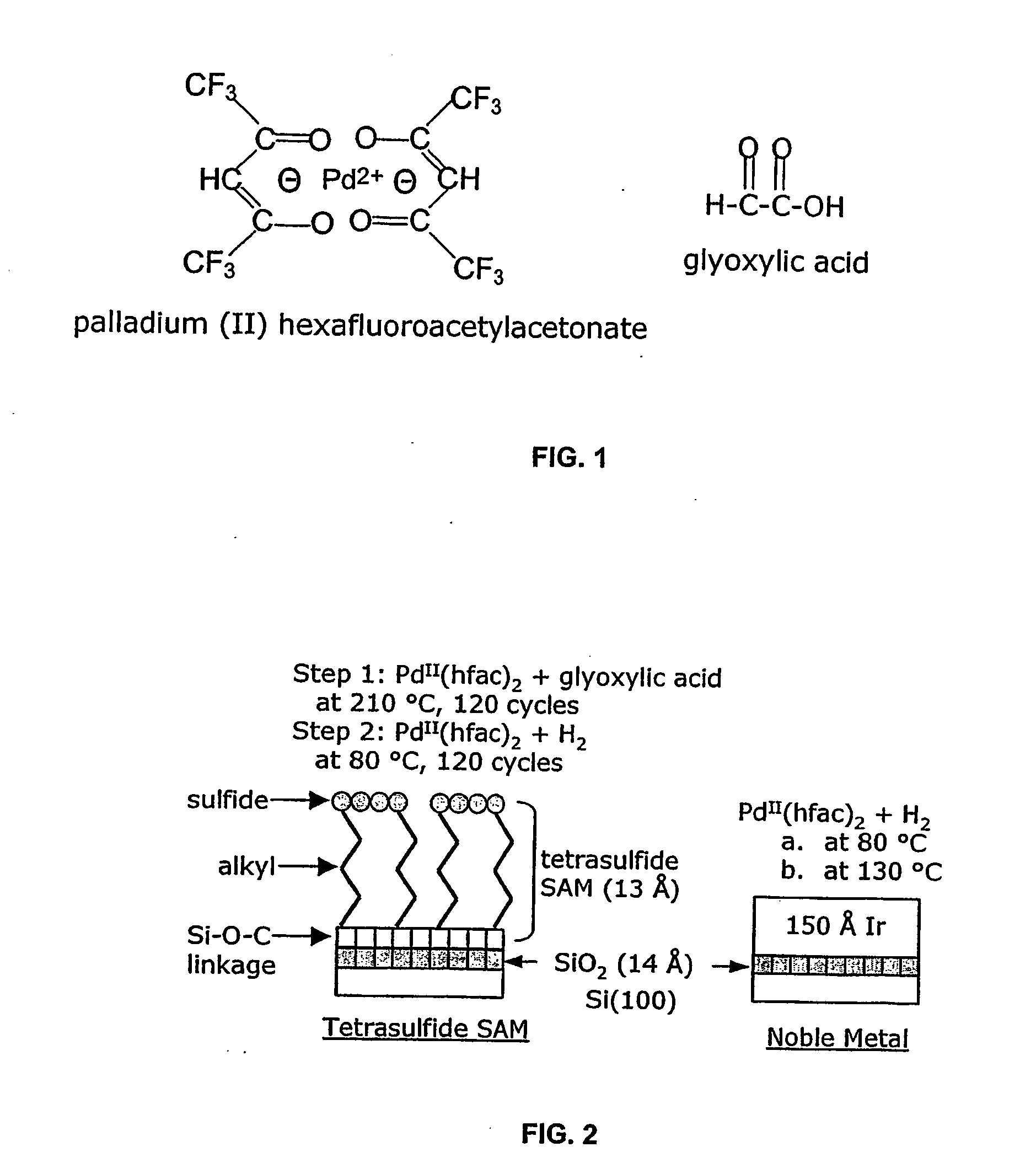
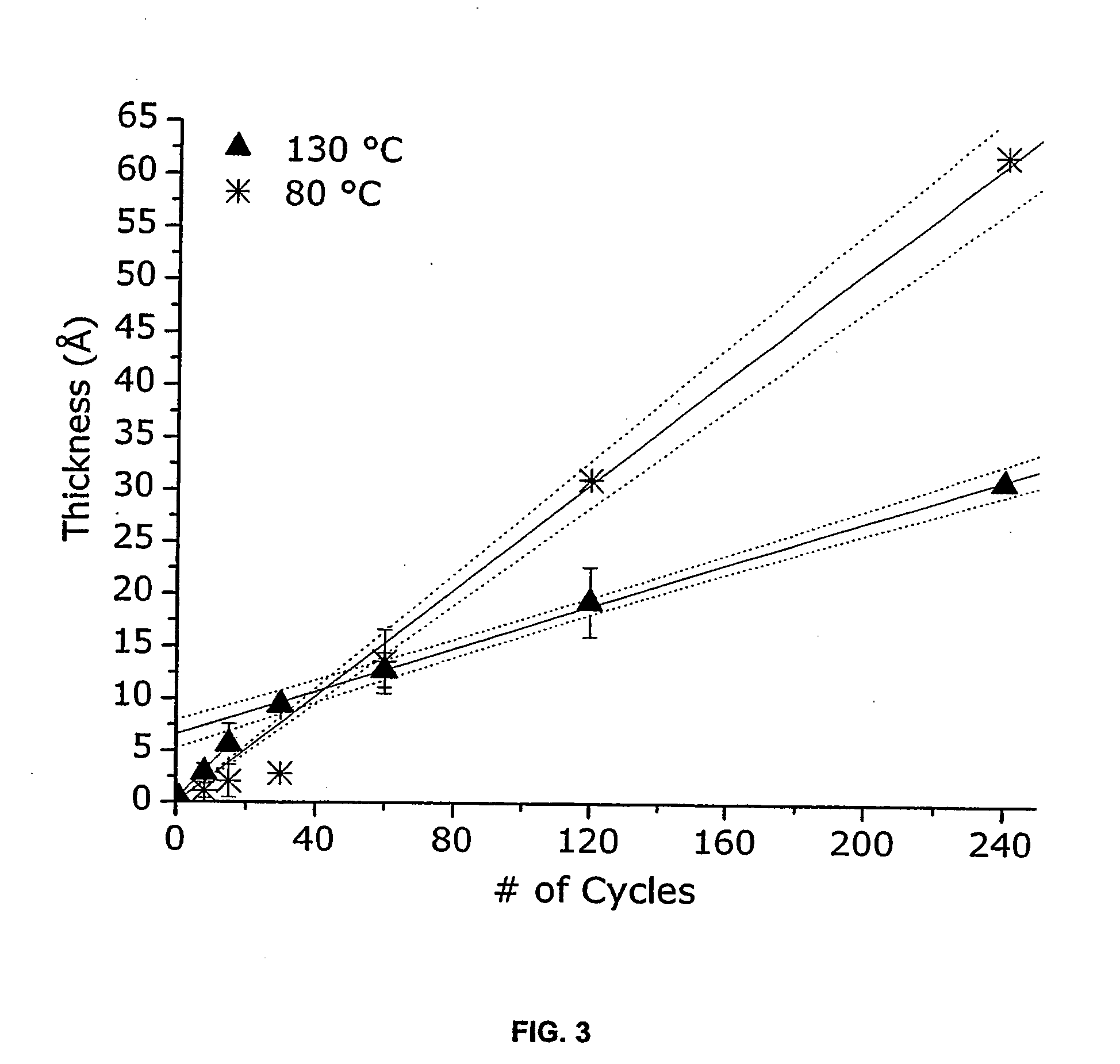
The present invention relates to ALD processes for deposition of a metal selected from Pd, Rh, Ru, Pt and Ir wherein a layer including the metal is formed on a surface composed of a material selected from W, Ta, Cu, Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, Cr, V Nb, tungsten nitride, tantalum nitride, titanium nitride, dielectrics and activated dielectrics at a temperature ranging from >60° C. to <260° C. The layer is formed by sequentially pulsing into a chamber containing the surface a precursor for the metal and a reducing gas selected from hydrogen, glyoxylic acid, oxalic acid, formaldehyde, 2-propanol, imidazole and plasma-activated hydrogen.
Owner:SENKEVICH JOHN JOSEPH +1
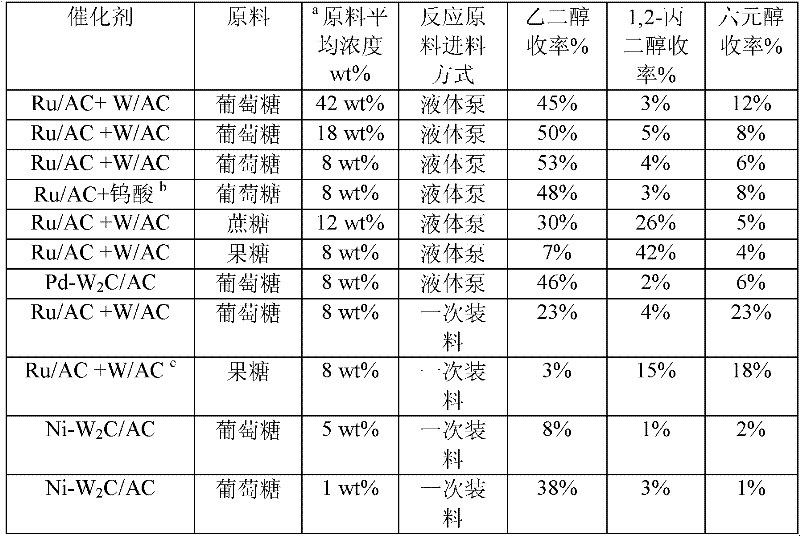
Method for preparing ethylene glycol and 1,2-propylene glycol by using saccharide solution
ActiveCN102675045AIncrease concentrationReduce distillation energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationHydrogen pressurePolyethylene glycol
The invention provides a method for preparing ethylene glycol and 1,2-propylene glycol by using a high-concentration saccharide solution. Reaction raw materials comprise cane sugar, glucose, fructose, fructosan, xylose, soluble lower polyxylose and soluble starch. According to the method, high-concentration saccharide is used as a reaction raw material, and a high-pressure pump feeding mode is used in a reaction process which is performed in a high-pressure reaction kettle; iron, cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, iridium and platinum which serve as transition metal in eighth, ninth and tenth groups are used as hydrogenation active ingredients; the hydrogenation active ingredients form a composite catalyst together with metal tungsten, tungsten carbide, tungsten nitride, tungsten phosphide, tungsten oxide, tungsten sulfide, tungsten chloride, tungsten hydroxide, tungsten bronze, tungstic acid, tungstate, metatungstic acid, metatungstate, paratungstic acid, paratungstate, peroxotungstic acid, peroxotungstate and tungsten-containing heteropolyacid which serve as catalytic active ingredients; and the high-concentration saccharide solution can be efficiently prepared into the ethylene glycol and the propylene glycol at high selectivity and high yield in a one-step catalytic conversion process under the hydrothermal condition that the temperature is 120 to 300 DEG C and the hydrogen pressure is 1 to 13MPa. By the method, the problem of coking of the high-concentration saccharide in the catalytic conversion process can be effectively solved, and high-concentration ethylene glycol and propylene glycol can be prepared by the high-concentration saccharide.
Owner:中科柏易金(郑州)新能源科技有限责任公司
Copper technology for ULSI metallization
InactiveUS6919266B2Reduce diffuseFew process stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTungsten nitrideElectroless deposition
A copper damascene structure formed by direct patterning of a low-dielectric constant material is disclosed. The copper damascene structure includes a tungsten nitride barrier layer formed by atomic layer deposition using sequential deposition reactions. Copper is selectively deposited by a CVD process and / or by an electroless deposition technique.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method for depositing nanolaminate thin films on sensitive surfaces
InactiveUS20060079090A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Organometallic compounds, processes for the preparation thereof and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20080081127A1Improve responseReduce usageGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuit manufacturingElectron donor
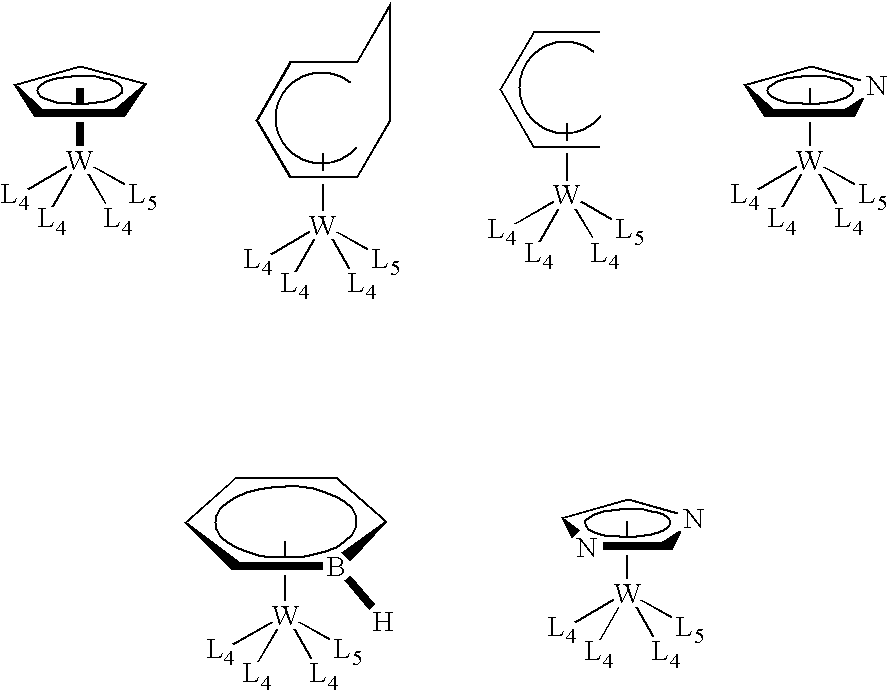
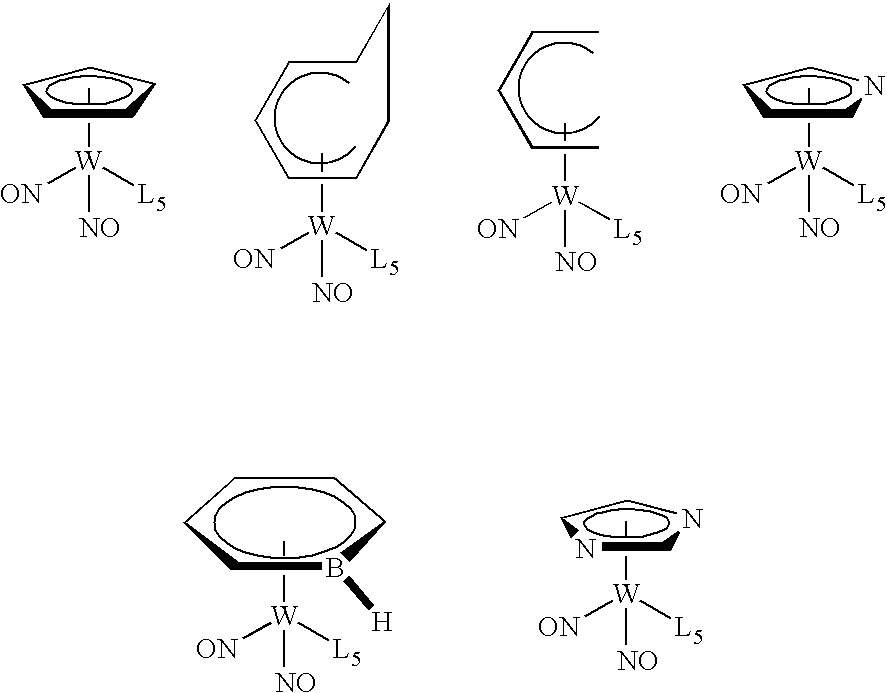
This invention relates to organometallic compounds represented by the formula (L1)yM(L2)z-y wherein M is a Group 5 metal or a Group 6 metal, L1 is a substituted or unsubstituted anionic 6 electron donor ligand, L2 is the same or different and is (i) a substituted or unsubstituted anionic 2 electron donor ligand, (ii) a substituted or unsubstituted cationic 2 electron donor ligand, or (iii) a substituted or unsubstituted neutral 2 electron donor ligand; y is an integer of 1, and z is the valence of M; and wherein the sum of the oxidation number of M and the electric charges of L1 and L2 is equal to 0.; a process for producing the organometallic compounds; and a method for depositing a metal and / or metal carbide / nitride layer, e.g., a tungsten, tungsten nitride, tungsten carbide, or tungsten carbonitride layer, on a substrate by the thermal or plasma enhanced dissociation of the organometallic precursor compounds, e.g., by CVD or ALD techniques. The metal and / or metal carbide layer is useful as a liner or barrier layer for conducting metals and high dielectric constant materials in integrated circuit manufacturing.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Vapor deposition of tungsten materials
InactiveUS7732327B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseTungsten nitride
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
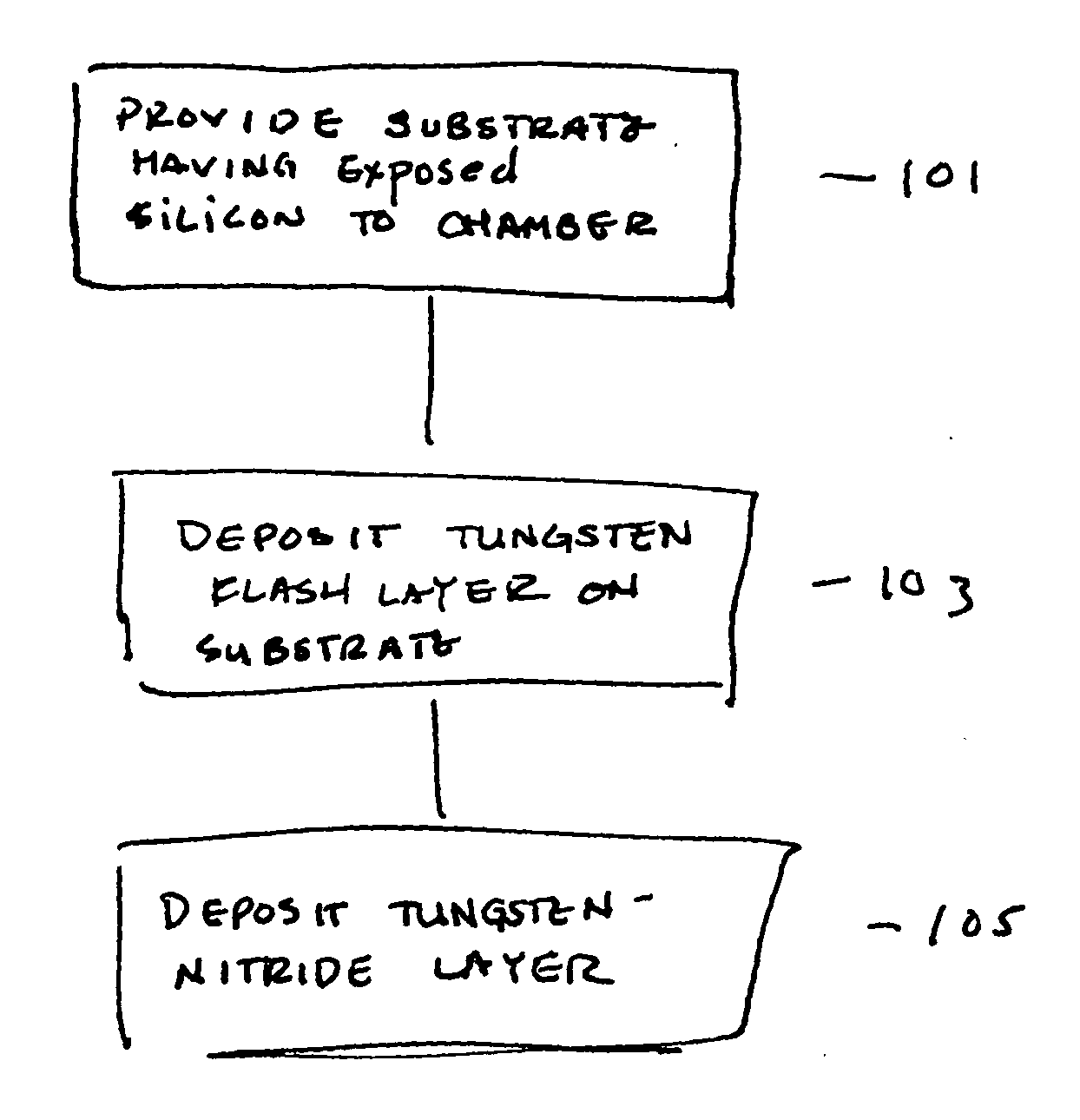
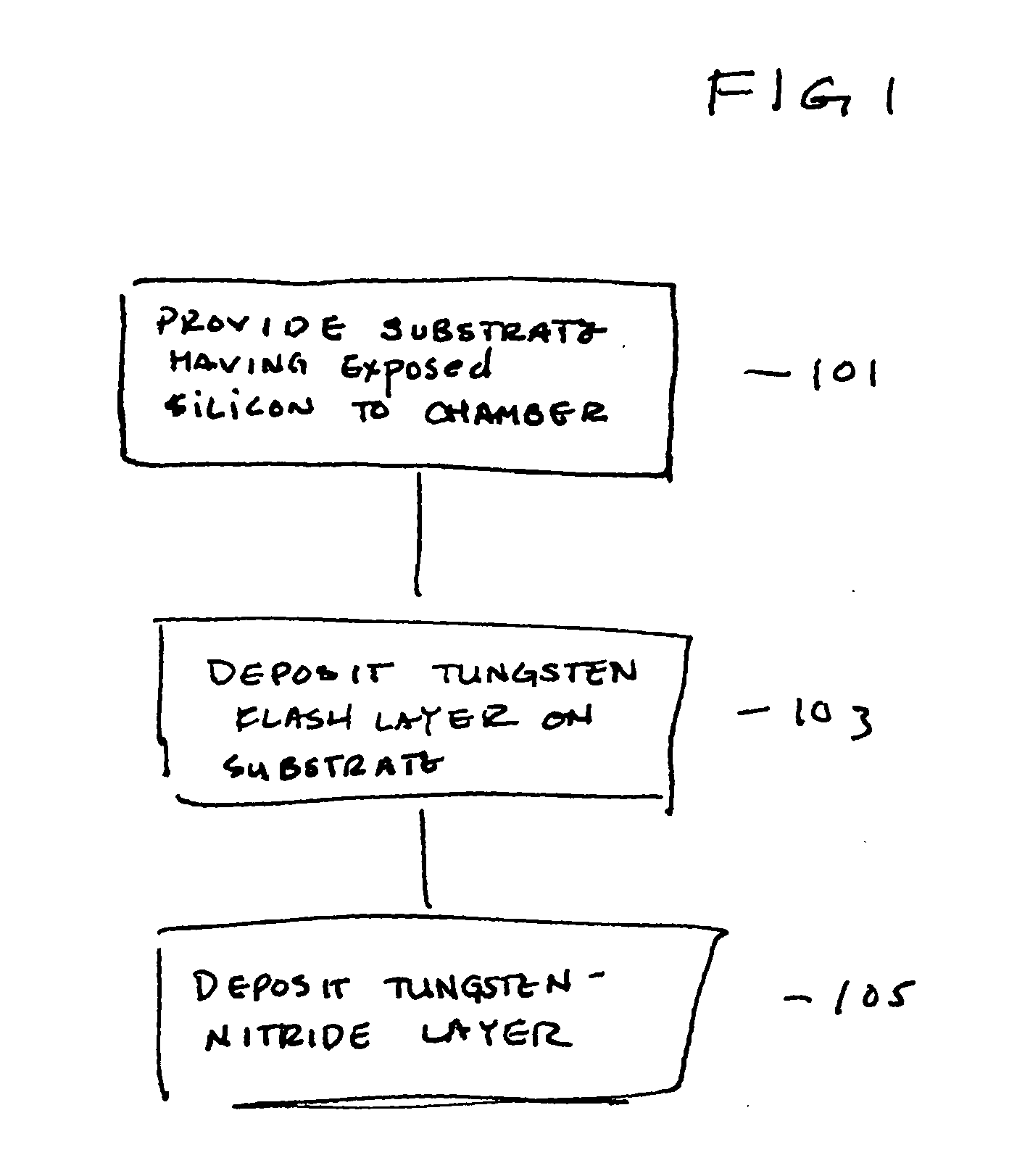
Reducing silicon attack and improving resistivity of tungsten nitride film
ActiveUS7754604B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTungsten nitrideDiffusion barrier
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Ferroelectric integrated circuit having hydrogen barrier layer
InactiveUS6365927B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium nitrideEngineering
A hydrogen diffusion barrier in an integrated circuit is located to inhibit diffusion of hydrogen to a thin film of metal oxide material in an integrated circuit. The hydrogen diffusion barrier comprises at least one of the following nitrides: aluminum titanium nitride (Al2Ti3N6), aluminum silicon nitride (Al2Si3N6), aluminum niobium nitride (AlNb3N6), aluminum tantalum nitride (AlTa3N6), aluminum copper nitride (Al2Cu3N4), tungsten nitride (WN), and copper nitride (Cu3N2). The thin film of metal oxide is ferroelectric or high-dielectric, nonferroelectric material. Preferably, the metal oxide comprises ferroelectric layered superlattice material. Preferably, the hydrogen barrier layer is located directly over the thin film of metal oxide.
Owner:SYMETRIX
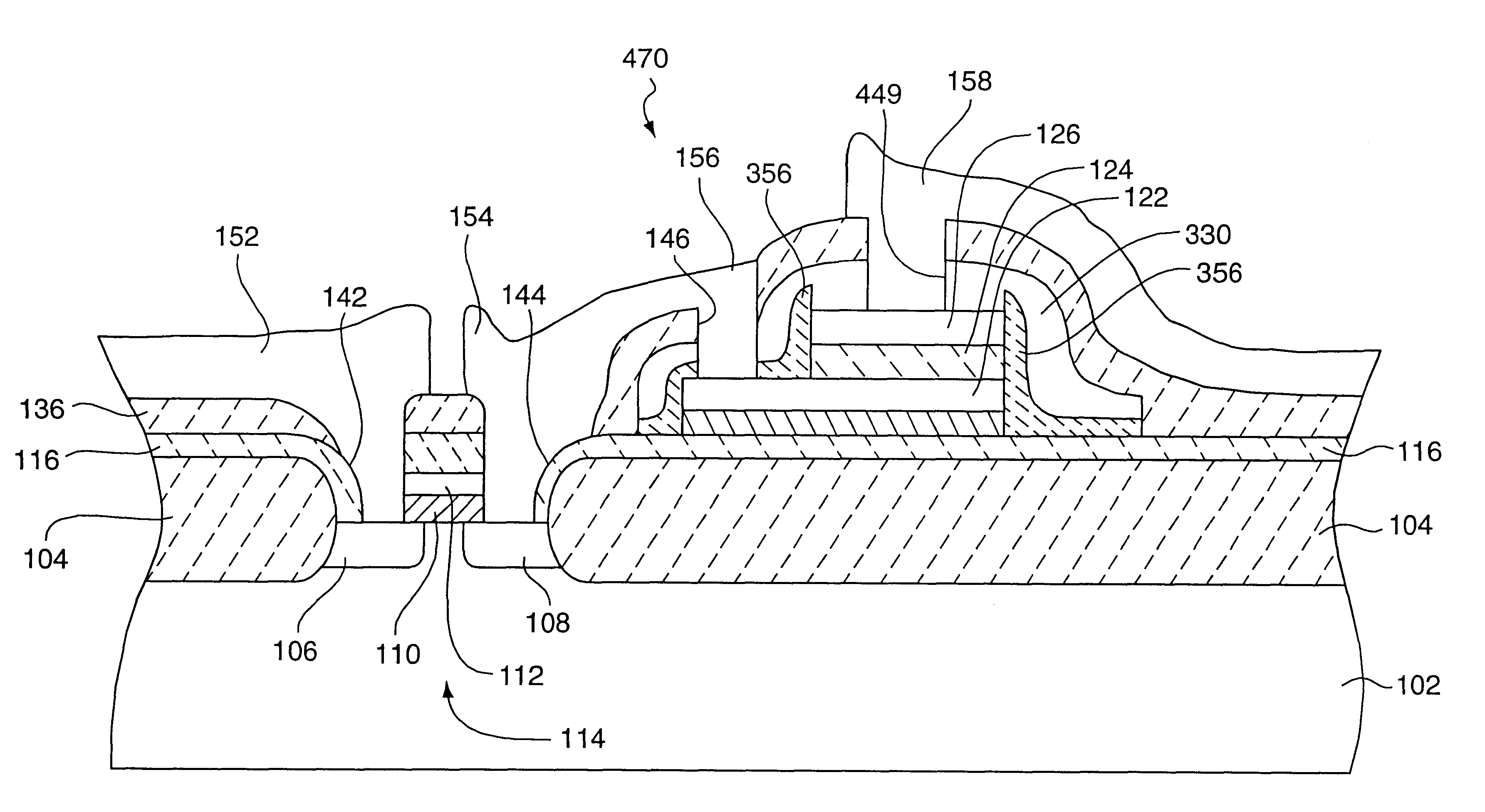
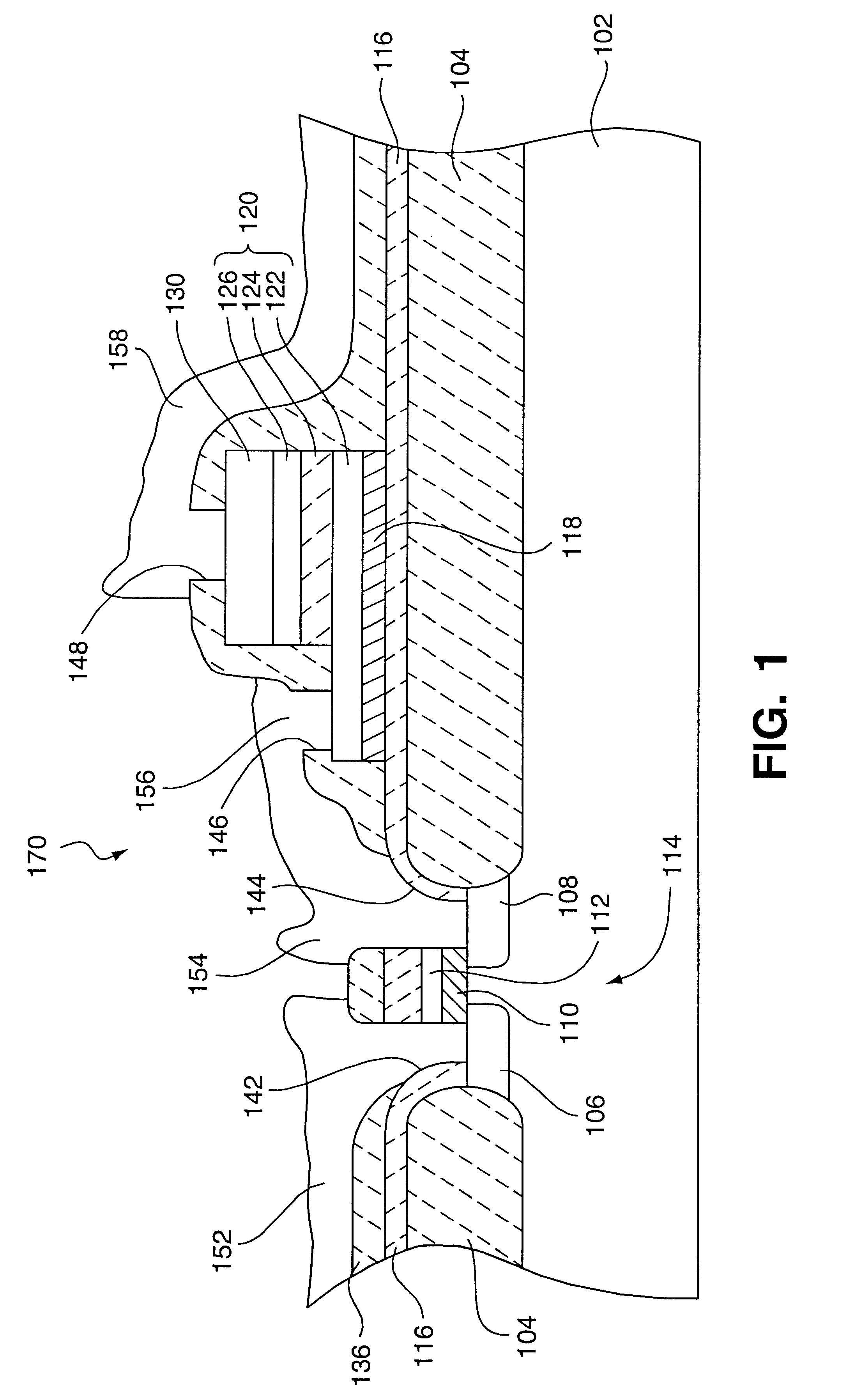
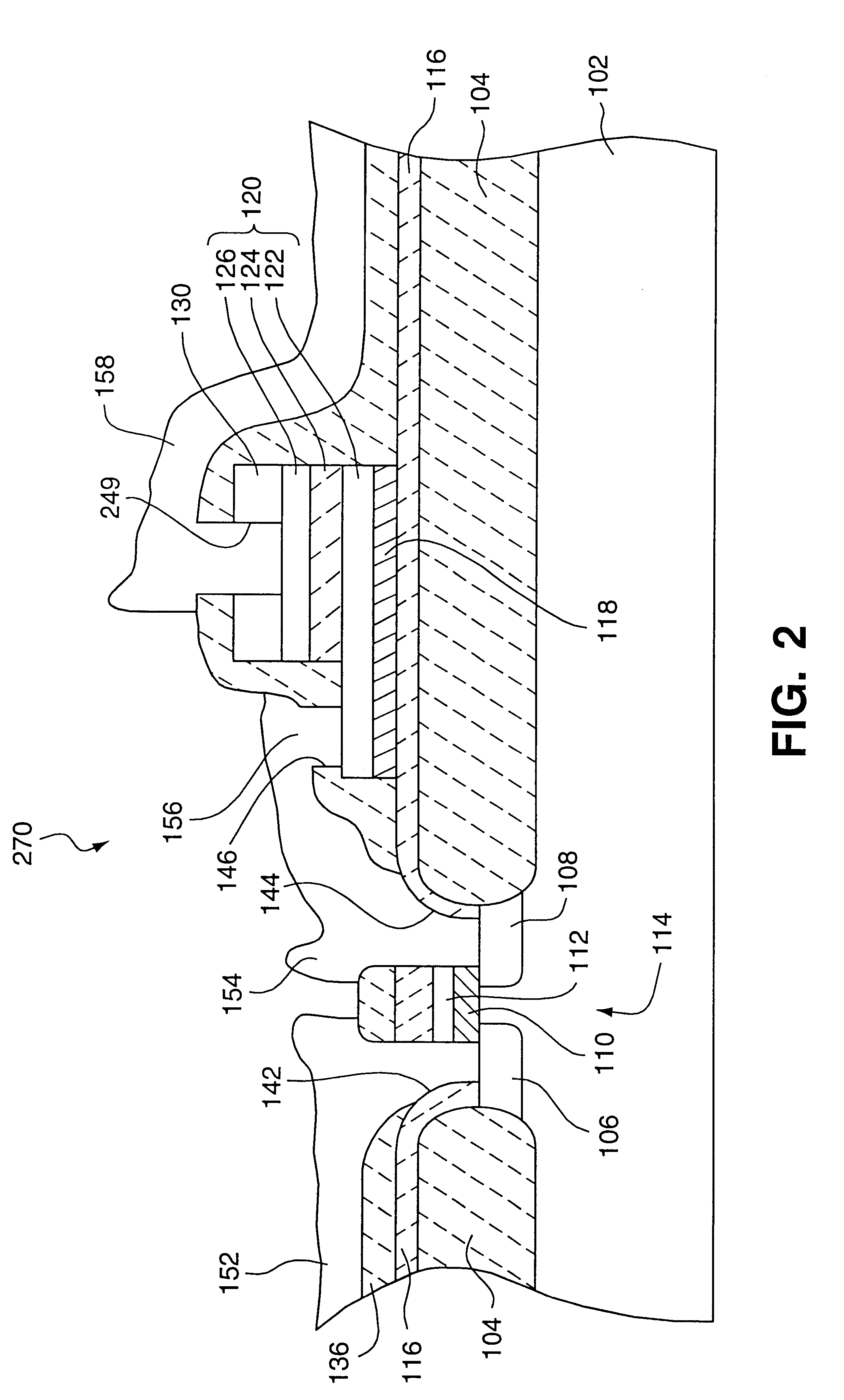
Formation of liner and barrier for tungsten as gate electrode and as contact plug to reduce resistance and enhance device performance
ActiveUS20120231626A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaTungsten nitride
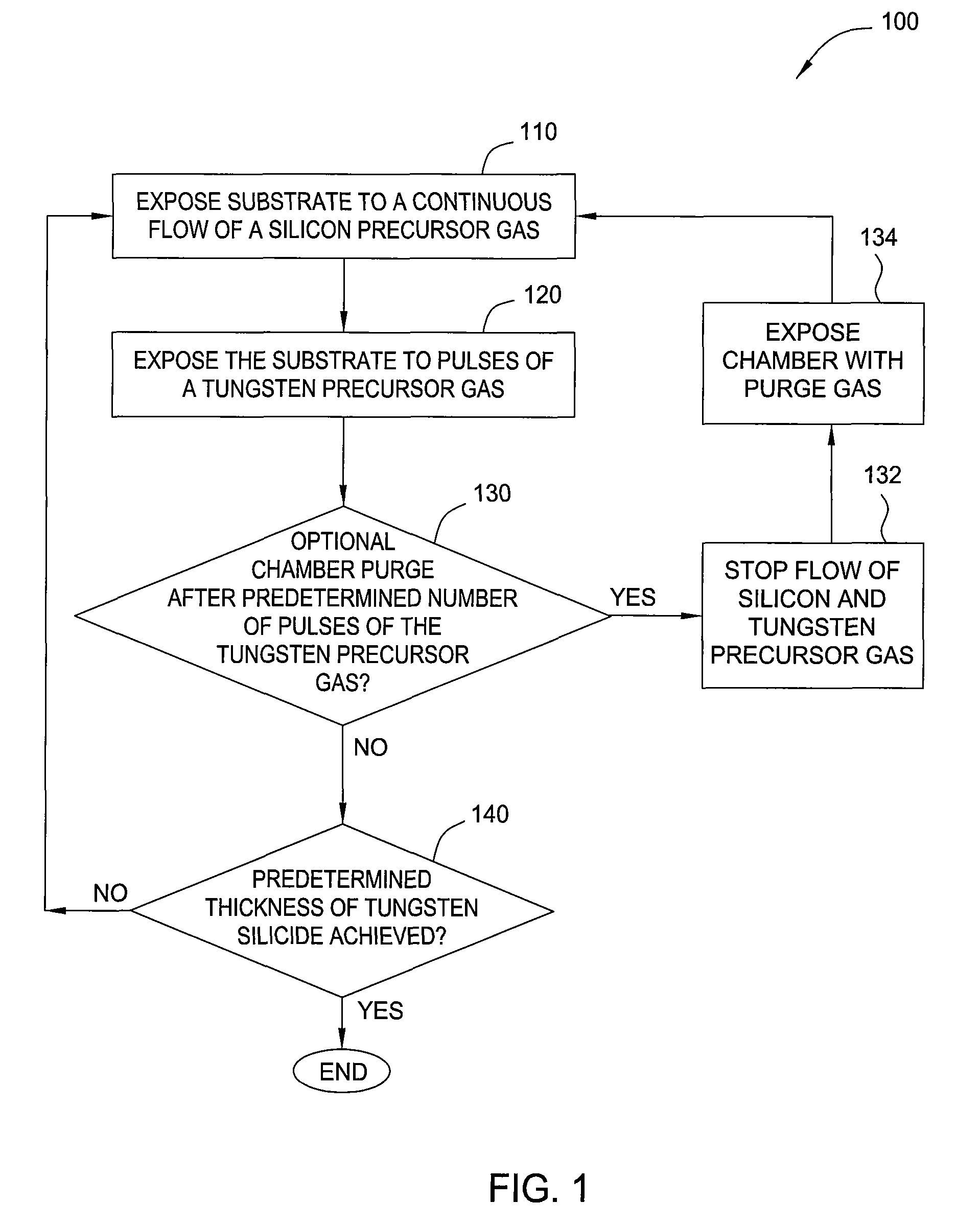
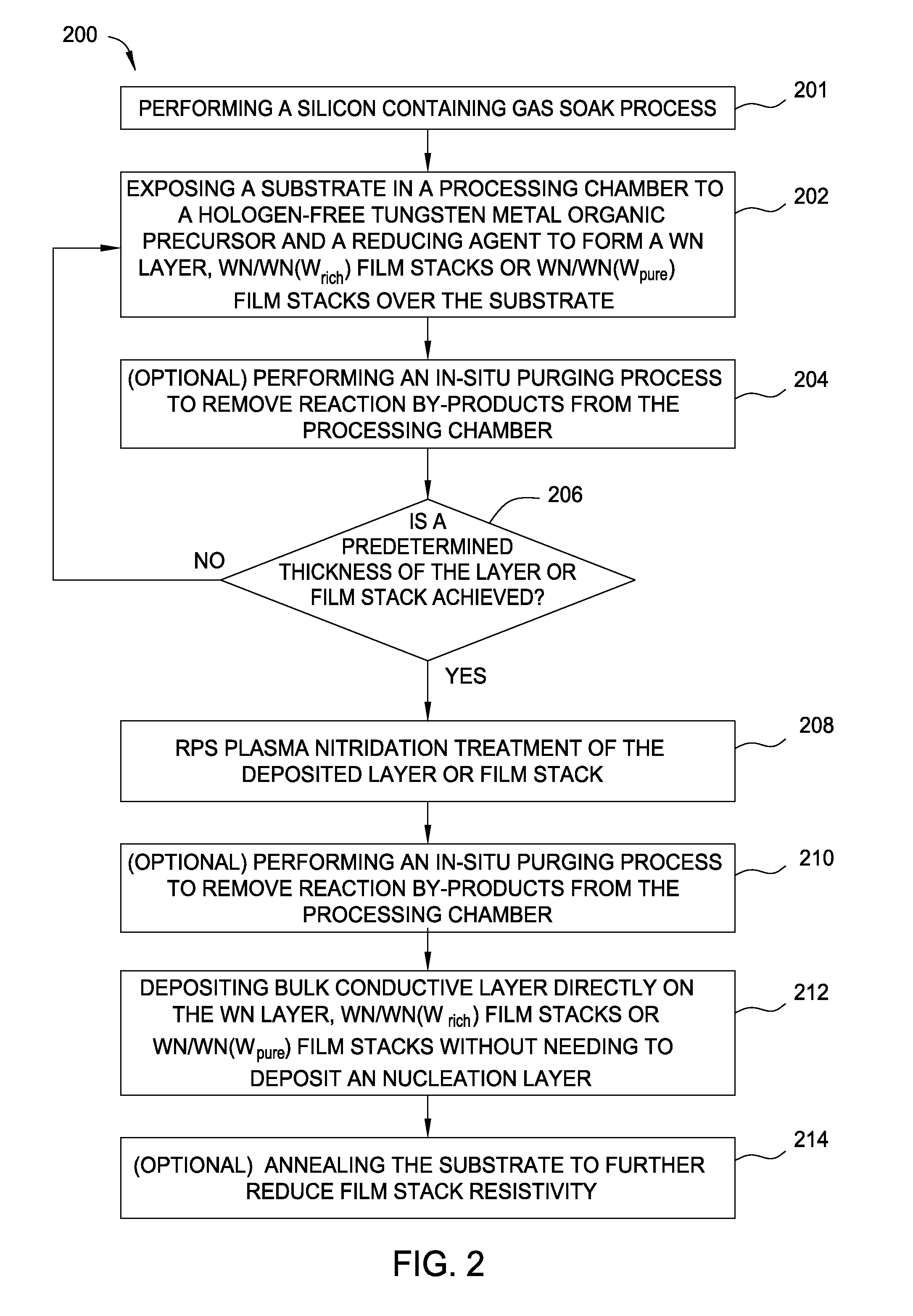
The invention provides a method of forming a film stack on a substrate, comprising performing a silicon containing gas soak process to form a silicon containing layer over the substrate, reacting with the silicon containing layer to form a tungsten silicide layer on the substrate, depositing a tungsten nitride layer on the substrate, subjecting the substrate to a nitridation treatment using active nitrogen species from a remote plasma, and depositing a conductive bulk layer directly on the tungsten nitride layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
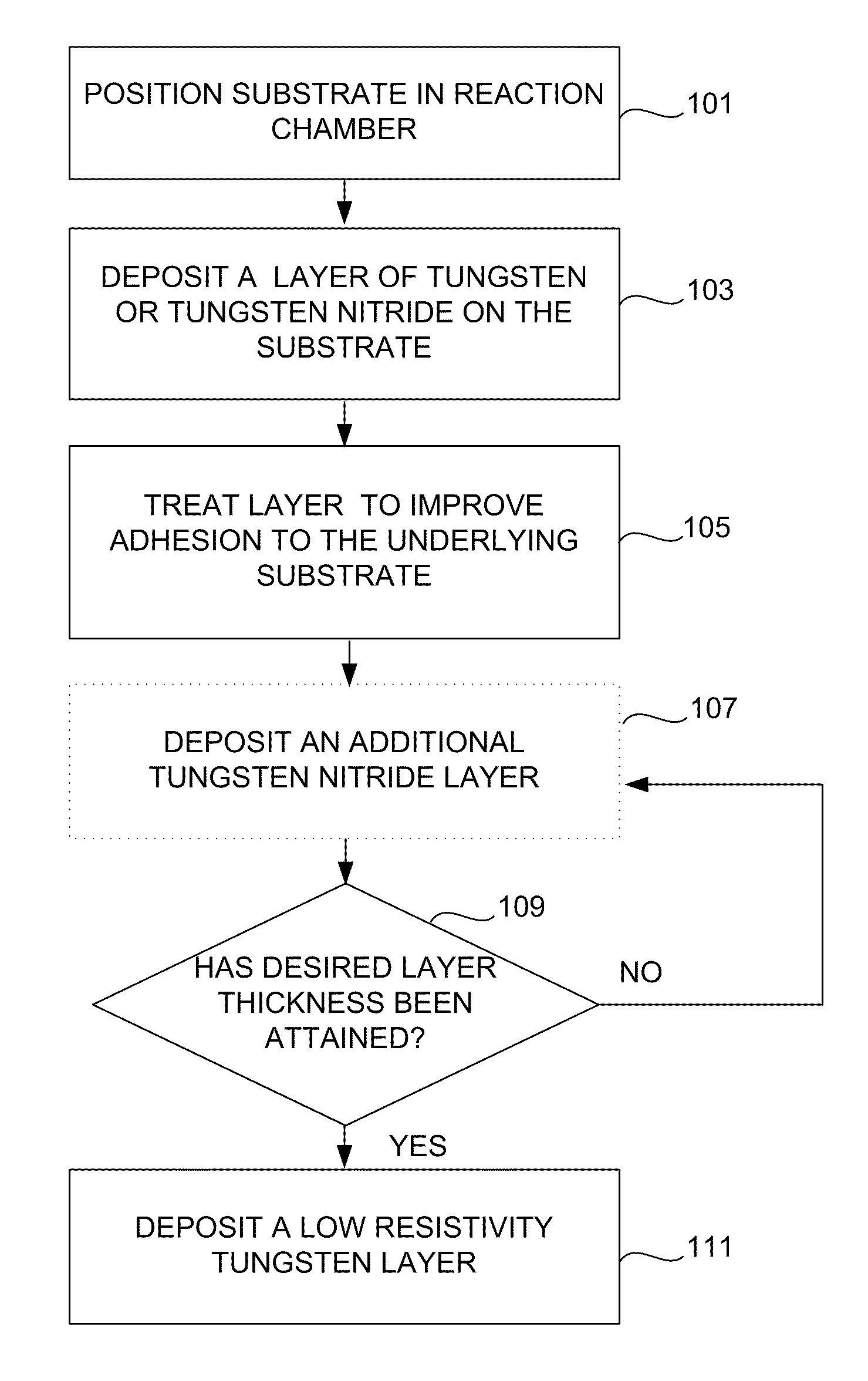
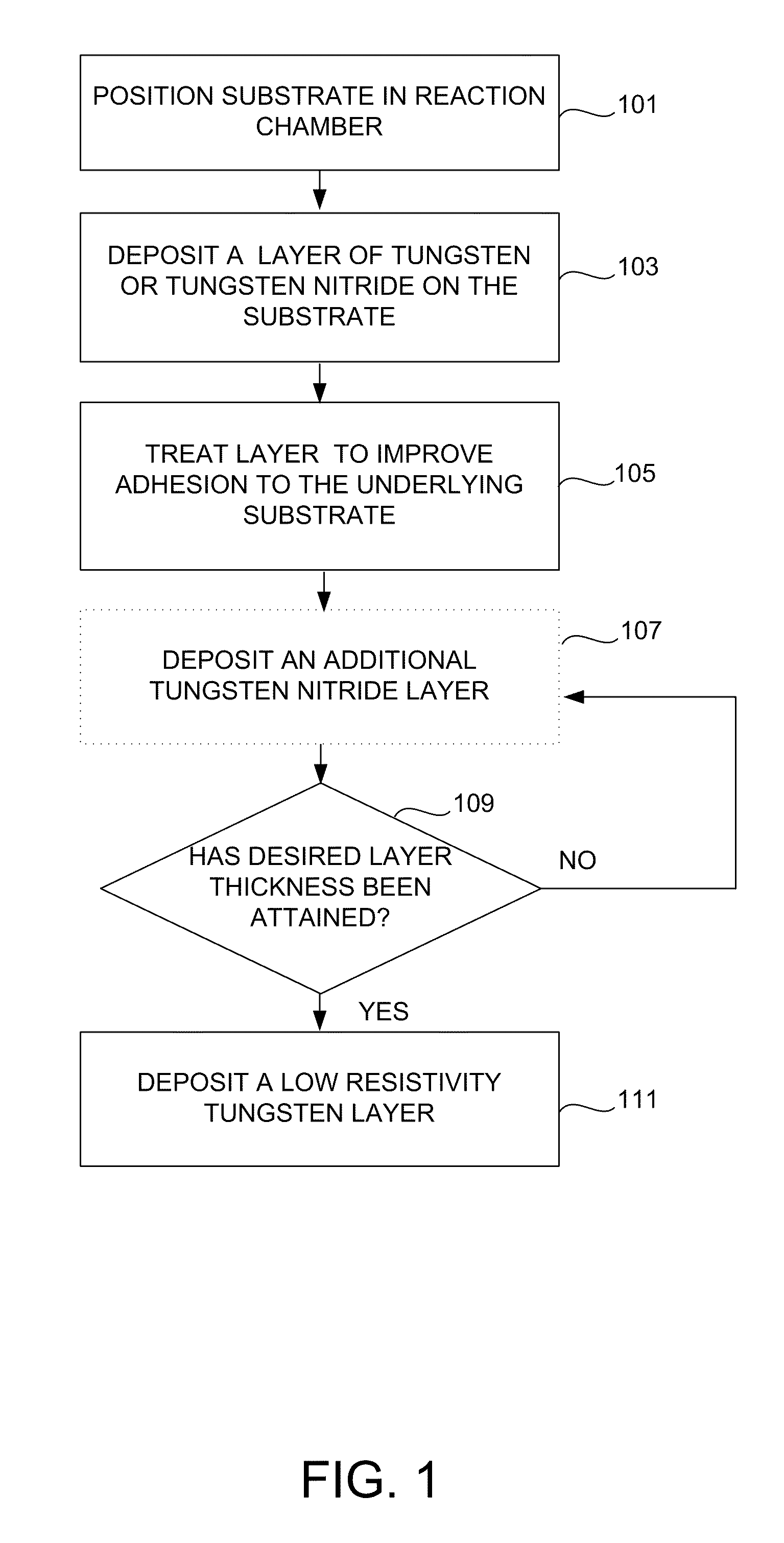
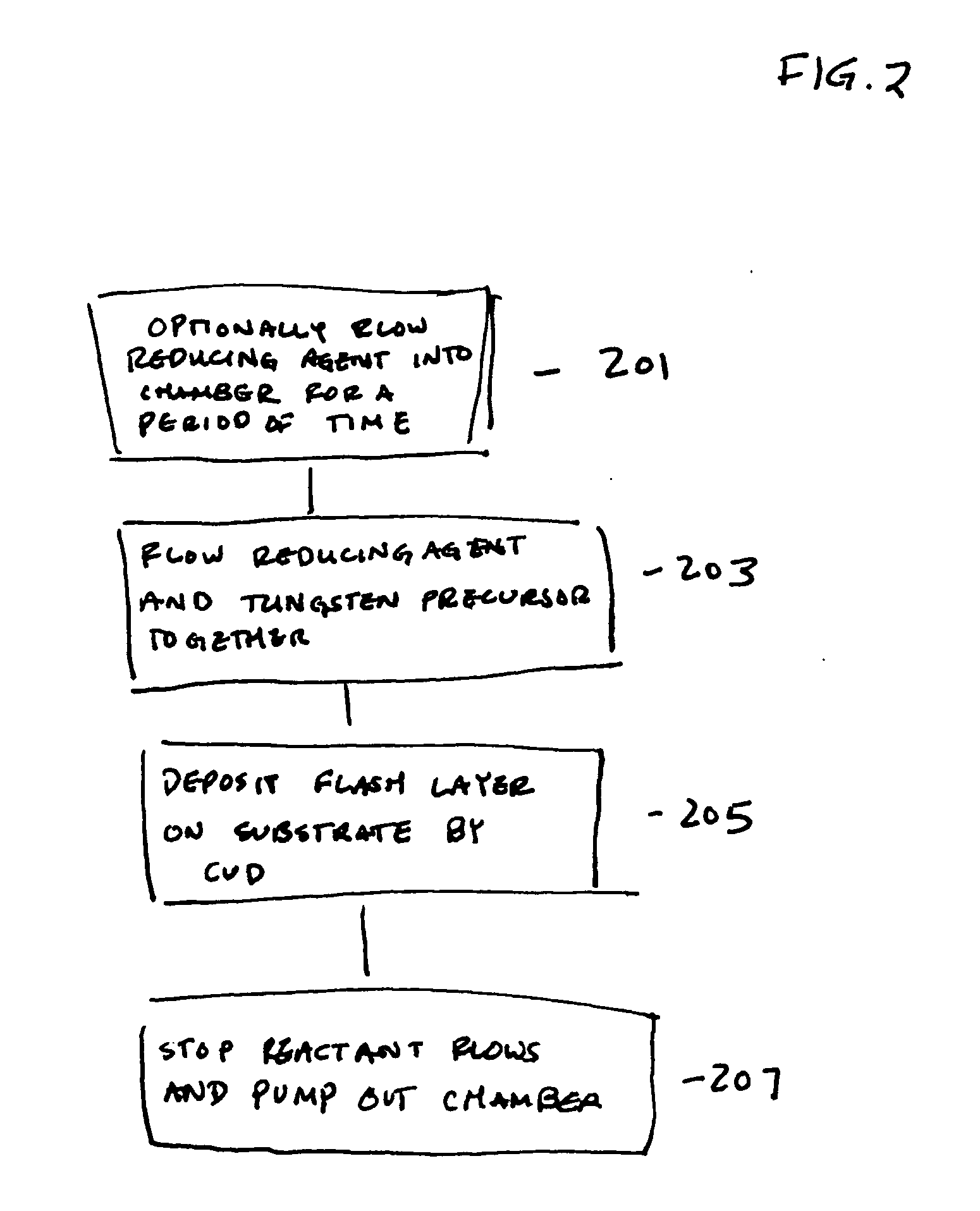
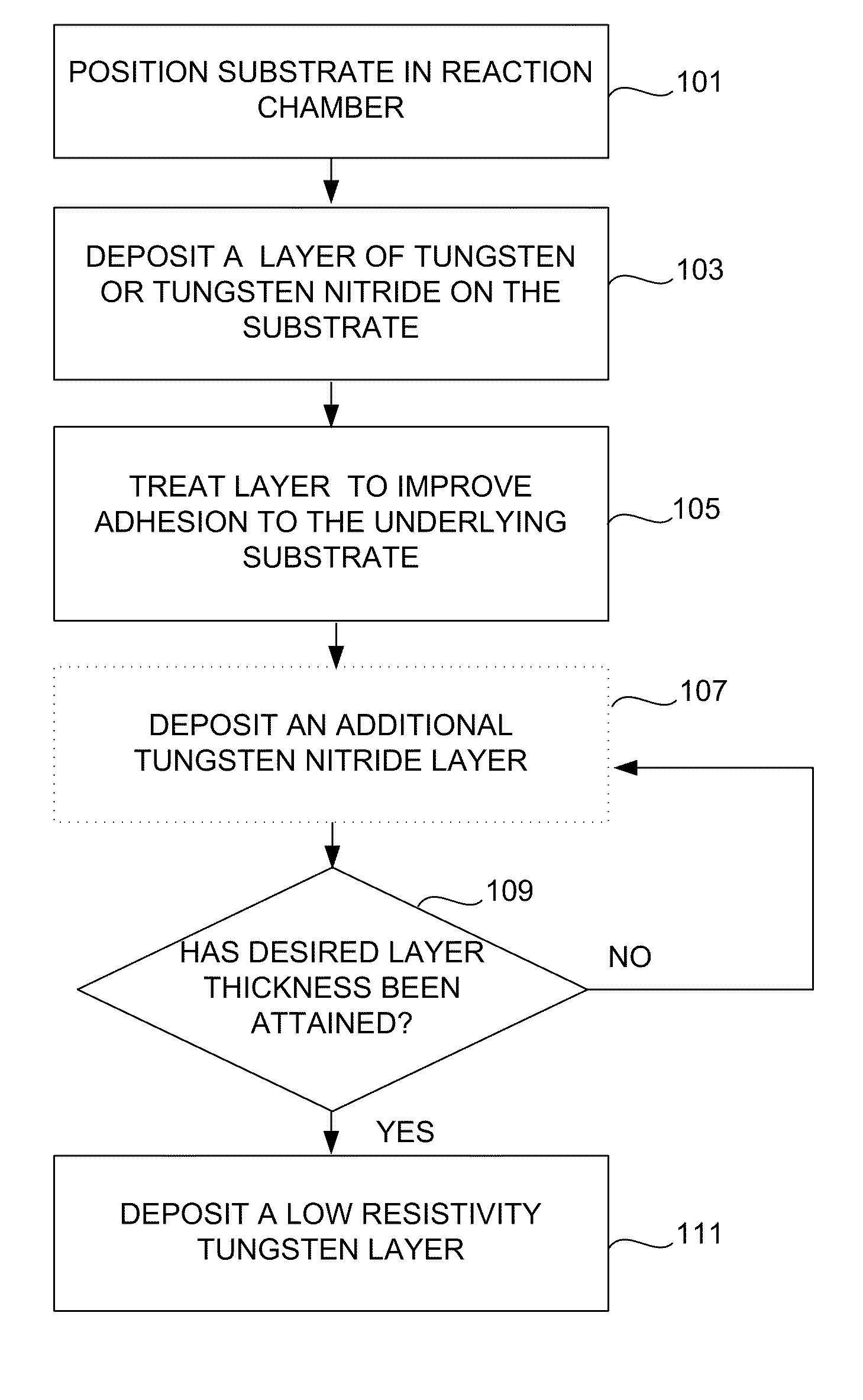
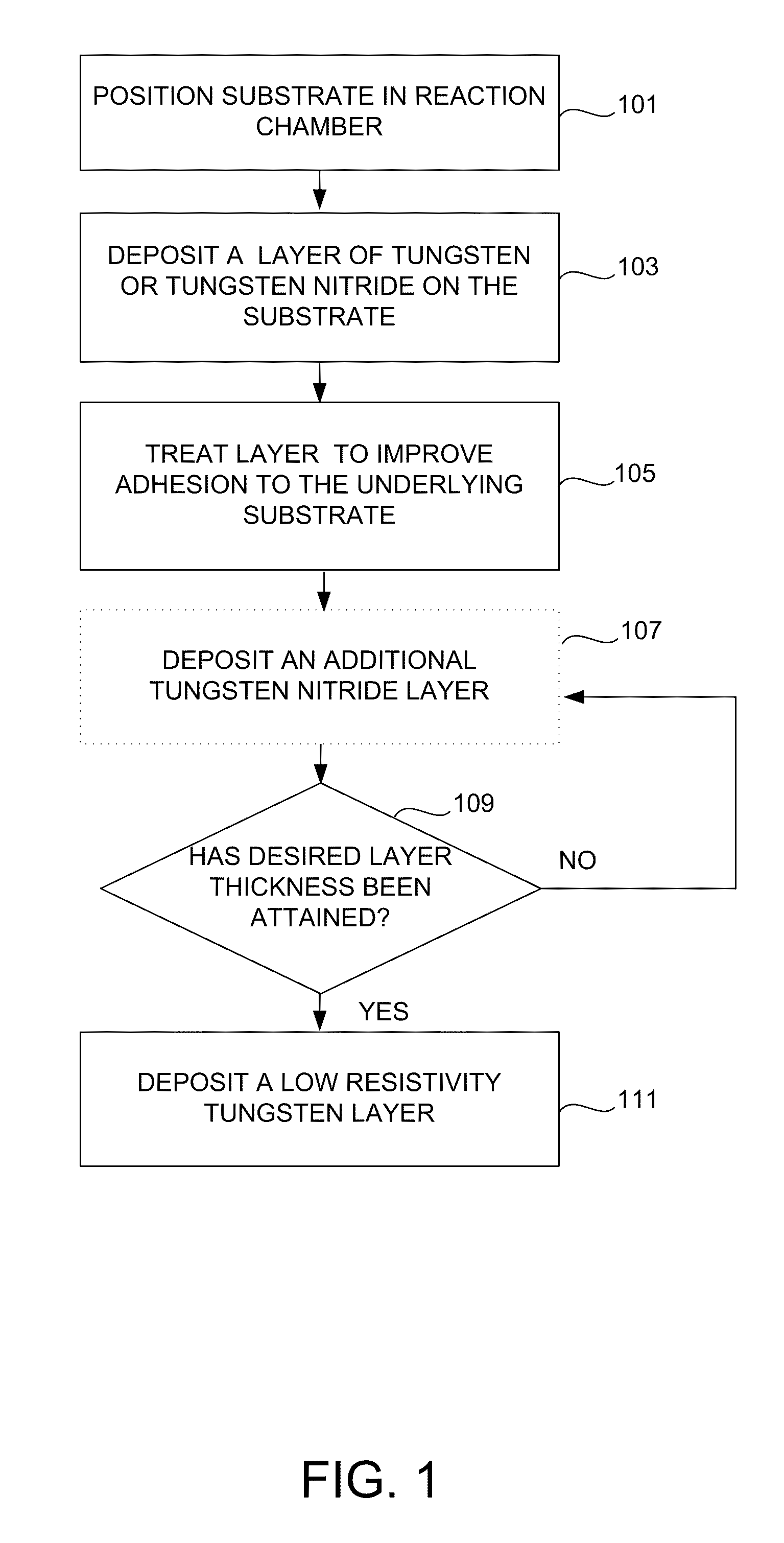
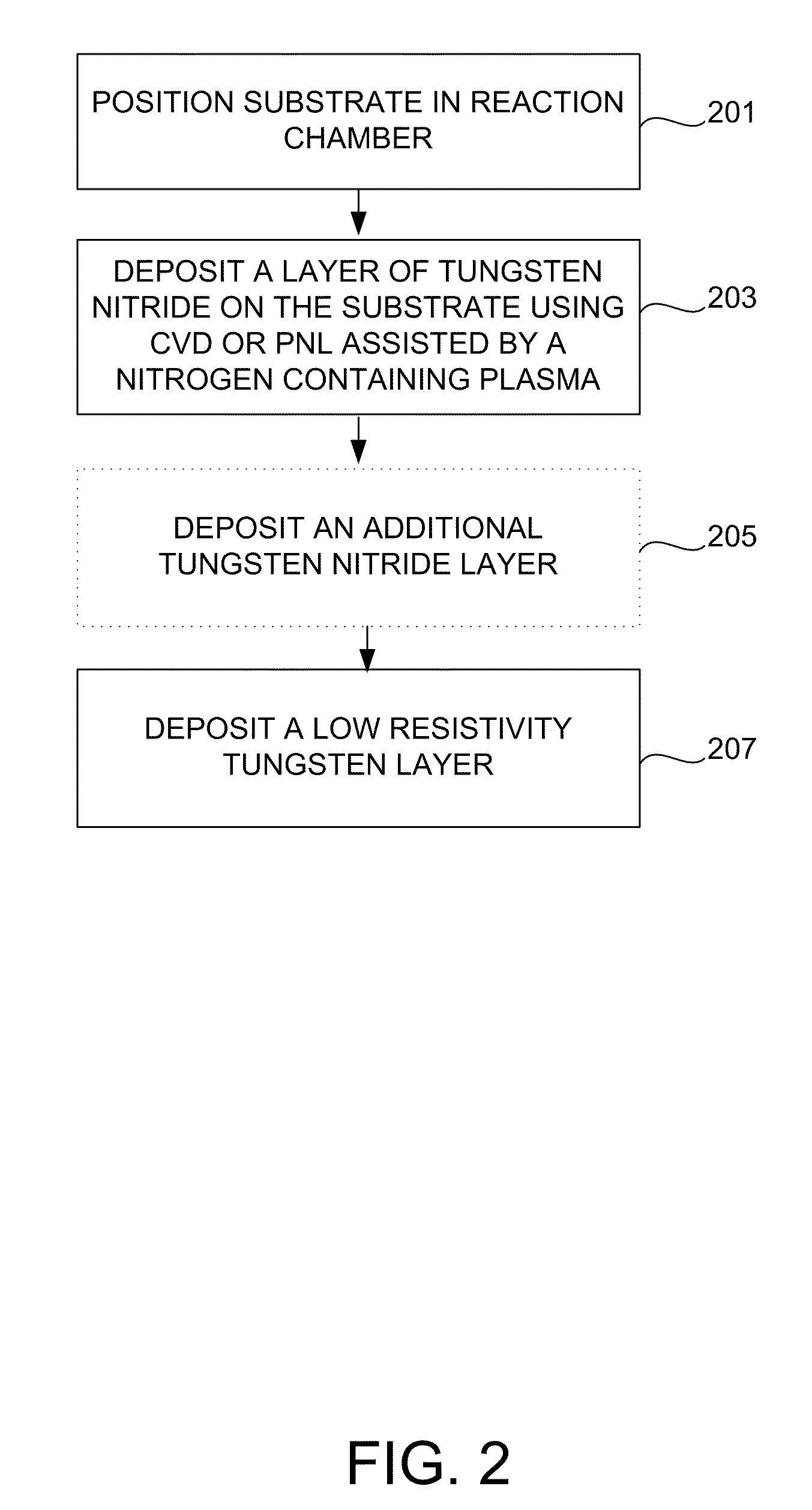
Method for improving adhesion of low resistivity tungsten/tungsten nitride layers
ActiveUS20110059608A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTungsten nitrideGaseous atmosphere
Methods of improving the adhesion of low resistivity tungsten / tungsten nitride layers are provided. Low resistivity tungsten / tungsten nitride layers with good adhesion are formed by treating a tungsten or tungsten nitride layer before depositing low resistivity tungsten. Treatments include a plasma treatment and a temperature treatment. According to various embodiments, the treatment methods involve different gaseous atmospheres and plasma conditions.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Reducing silicon attack and improving resistivity of tungsten nitride film
ActiveUS20080045010A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingTungsten nitride
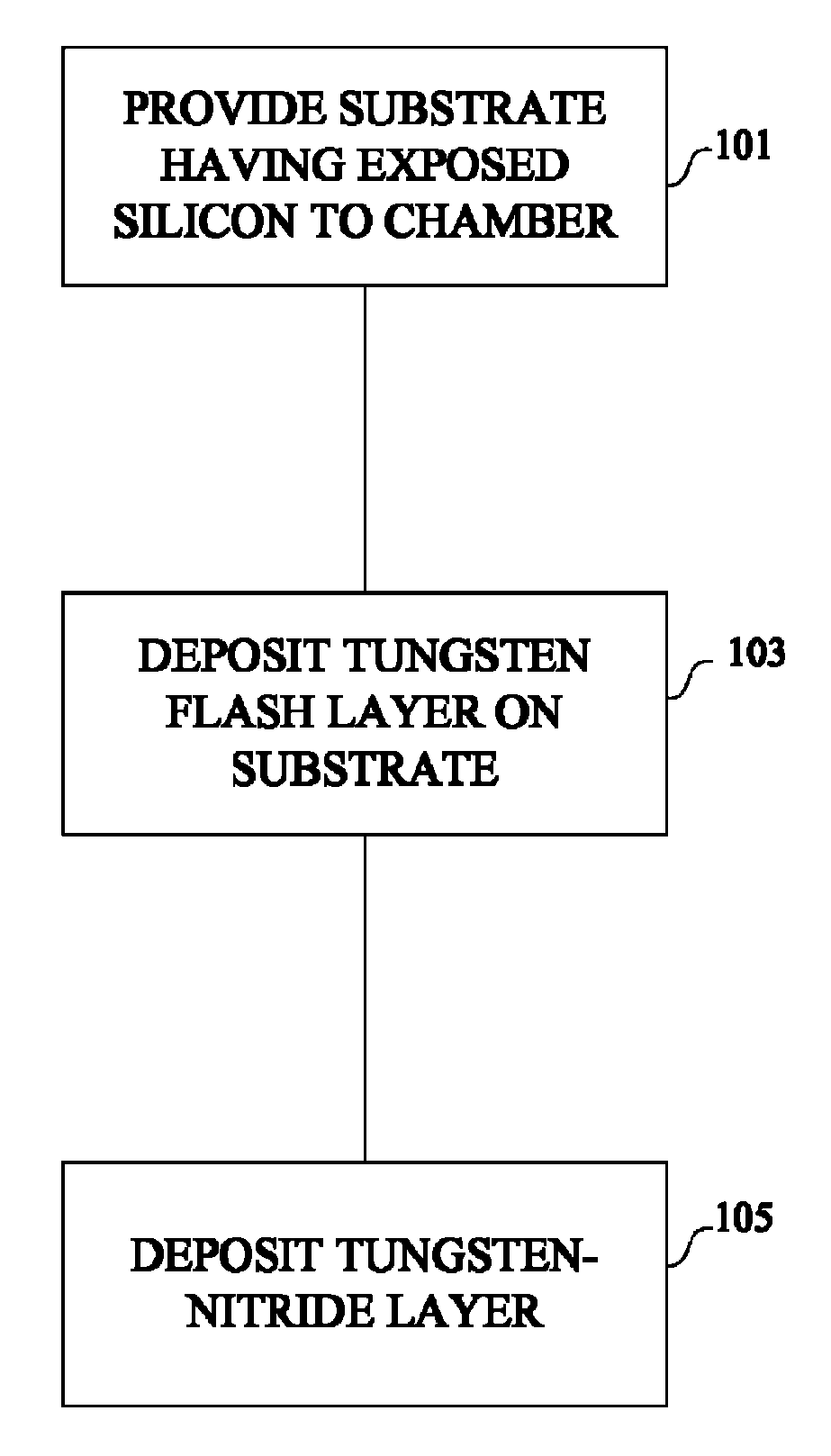
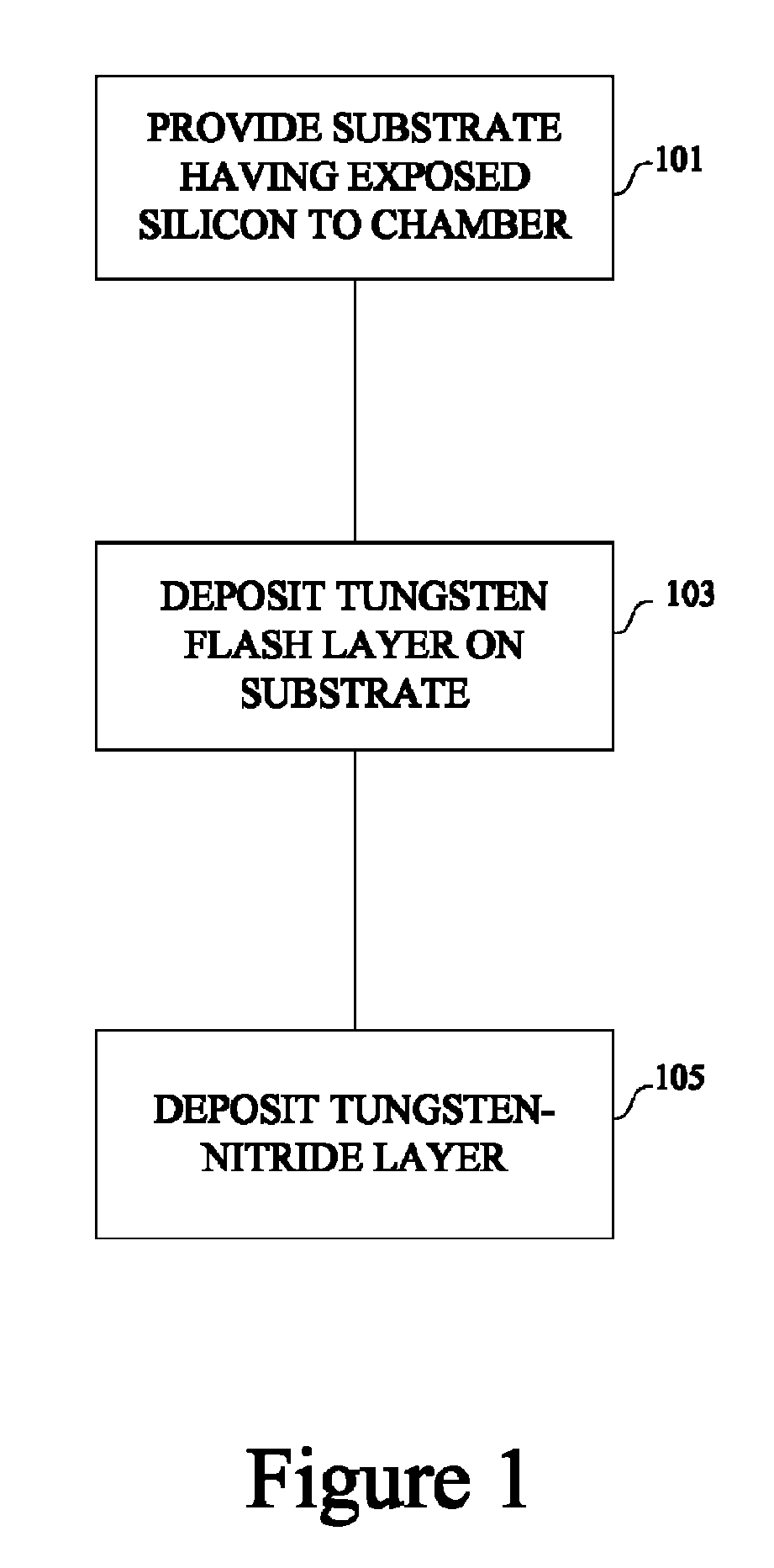
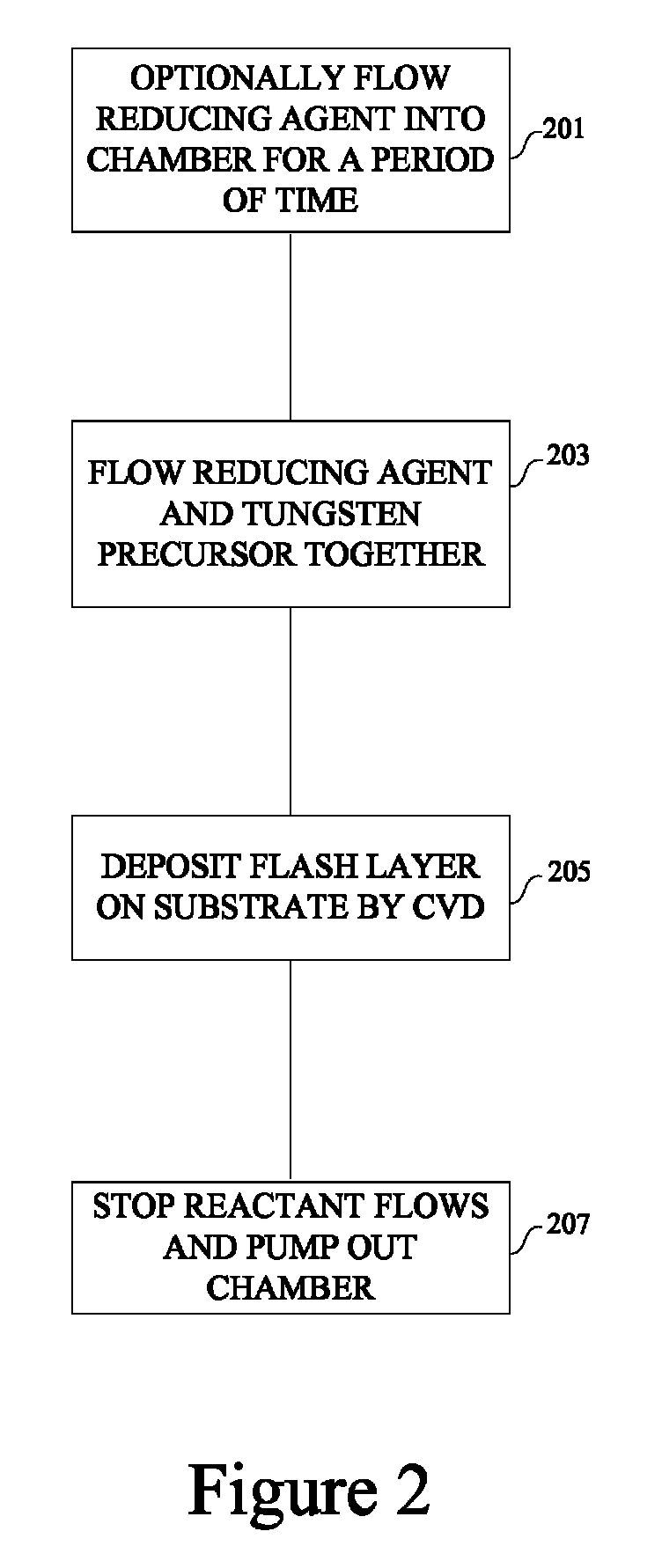
The present invention provides improved methods of depositing tungsten-containing films on substrates, particularly on silicon substrates. The methods involve depositing an interfacial or “flash” layer of tungsten on the silicon prior to deposition of tungsten nitride. The tungsten flash layer is typically deposited by a CVD reaction of a tungsten precursor and a reducing agent. According to various embodiments, the tungsten flash layer may be deposited with a high reducing agent to tungsten-precursor ratio and / or at low temperature to reduce attack by the tungsten precursor. In many cases, the substrate is a semiconductor wafer or a partially fabricated semiconductor wafer. Applications include depositing tungsten nitride as (or as part of) a diffusion barrier and / or adhesion layer for tungsten contacts.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for improving adhesion of low resistivity tungsten/tungsten nitride layers
ActiveUS8207062B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTungsten nitrideOptoelectronics
Methods of improving the adhesion of low resistivity tungsten / tungsten nitride layers are provided. Low resistivity tungsten / tungsten nitride layers with good adhesion are formed by treating a tungsten or tungsten nitride layer before depositing low resistivity tungsten. Treatments include a plasma treatment and a temperature treatment. According to various embodiments, the treatment methods involve different gaseous atmospheres and plasma conditions.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
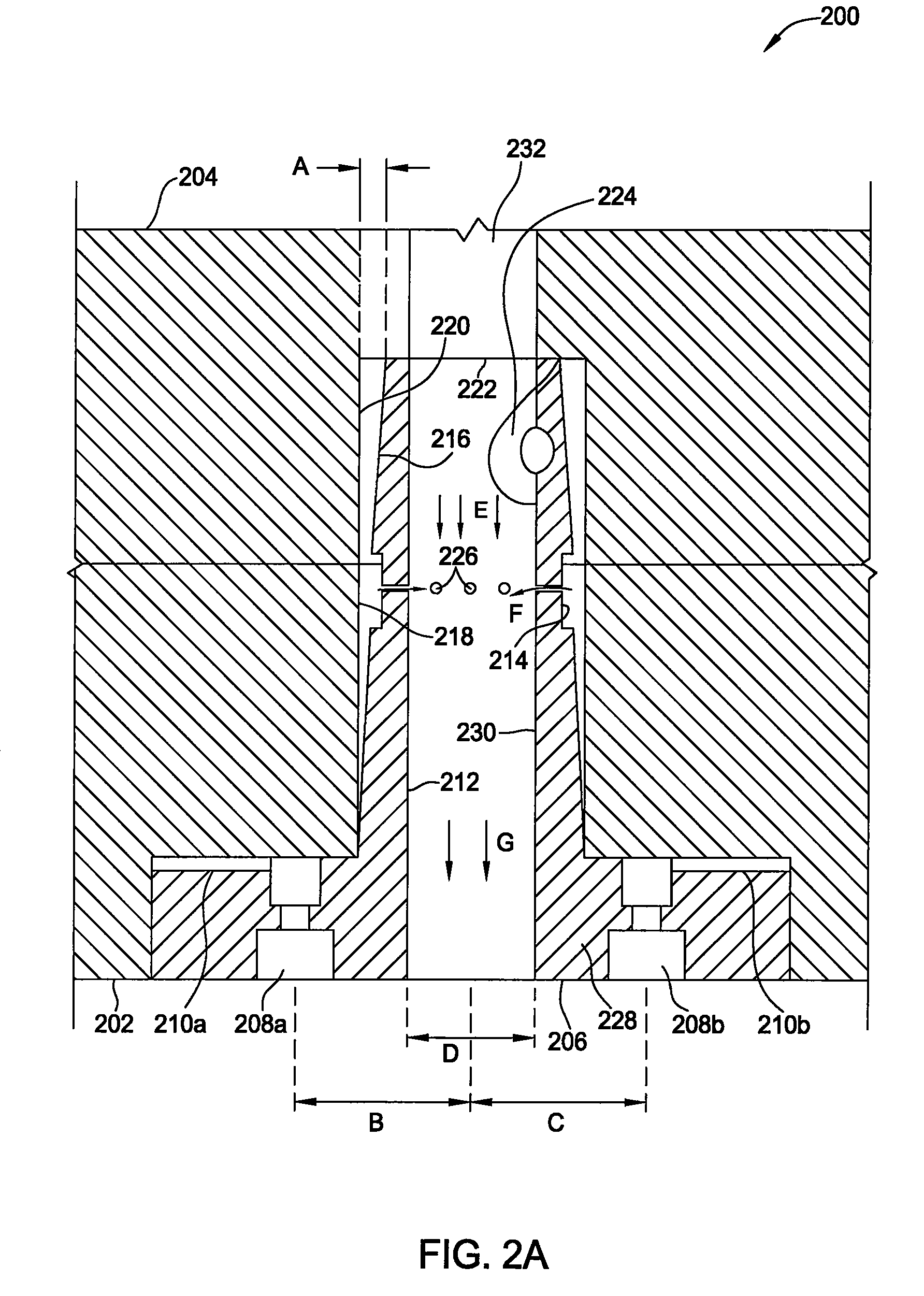
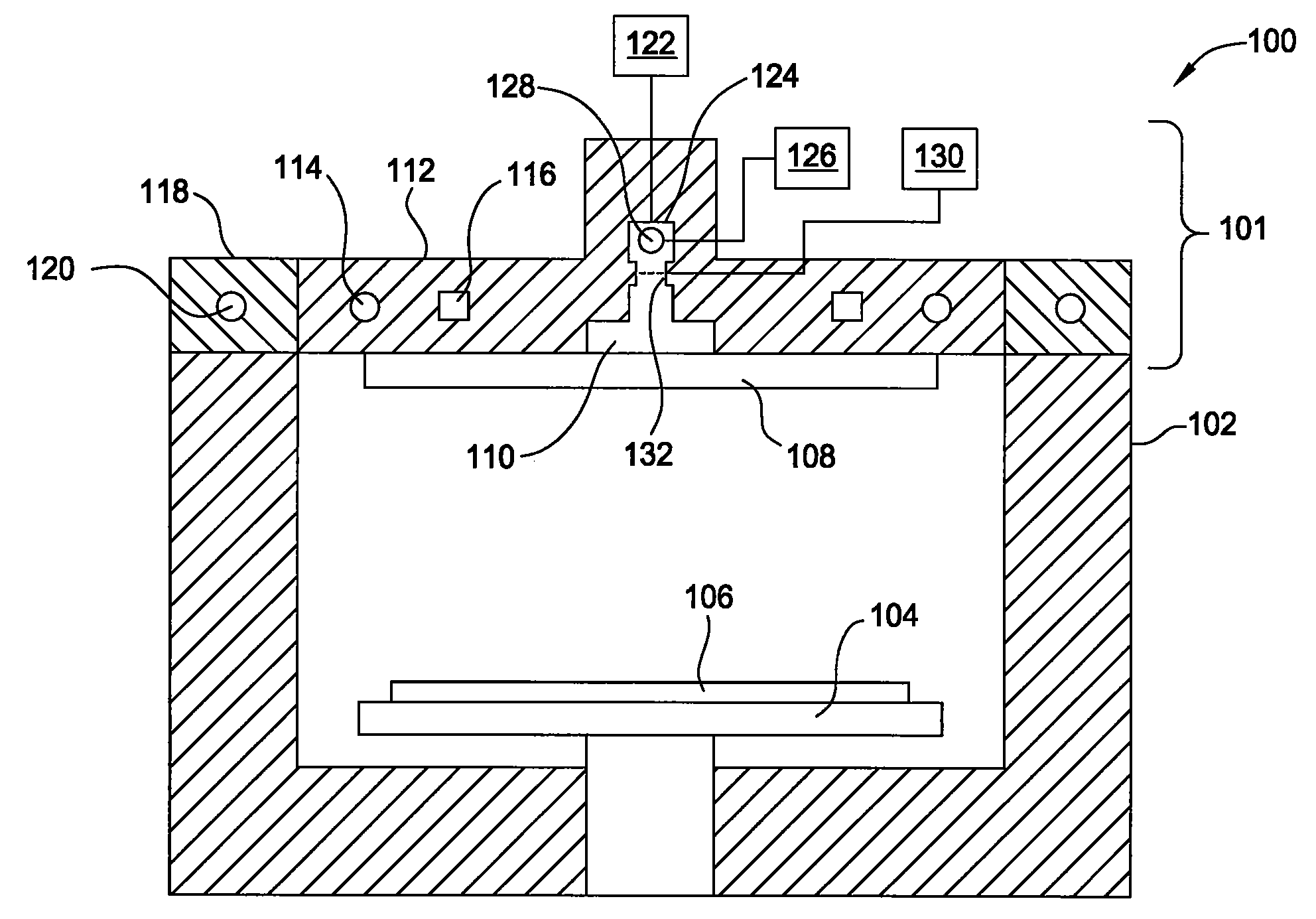
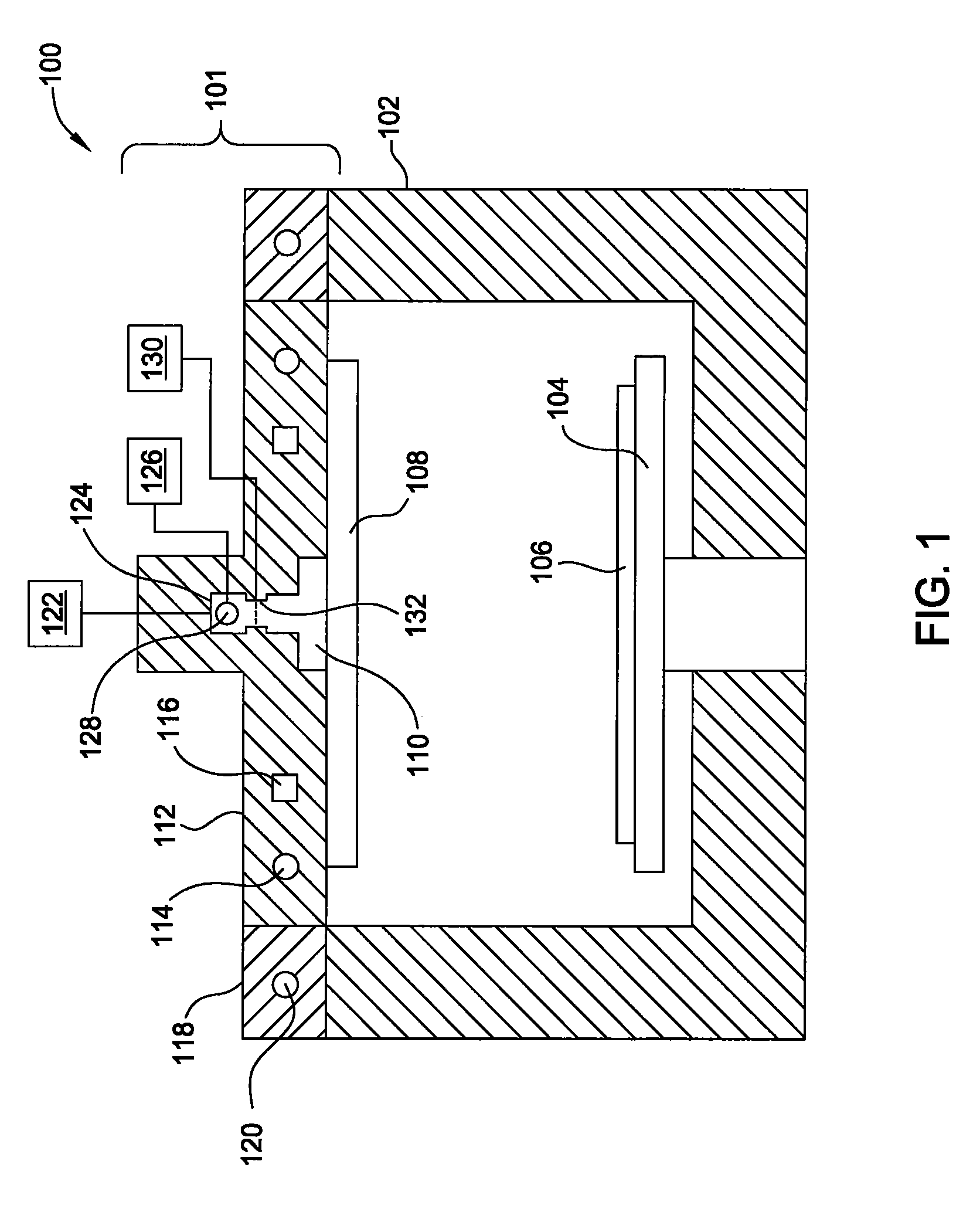
Temperature controlled lid assembly for tungsten nitride deposition
InactiveUS20080202425A1Fast heatingFast coolingChemical vapor deposition coatingTemperature controlElectrical resistance and conductance
Embodiments of the invention provide apparatuses for vapor depositing tungsten-containing materials, such as metallic tungsten and tungsten nitride. In one embodiment, a processing chamber is provided which includes a lid assembly containing a lid plate, a showerhead, a mixing cavity, a distribution cavity, and a resistive heating element contained within the lid plate. In one example, the resistive heating element is configured to provide the lid plate at a temperature within a range from about 120° C. to about 180° C., preferably, from about 140° C. to about 160° C., more preferably, from about 145° C. to about 155° C. The mixing cavity may be in fluid communication with a tungsten precursor source containing tungsten hexafluoride and a nitrogen precursor source containing ammonia. In some embodiments, a single processing chamber may be used to deposit metallic tungsten and tungsten nitride materials by CVD processes.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
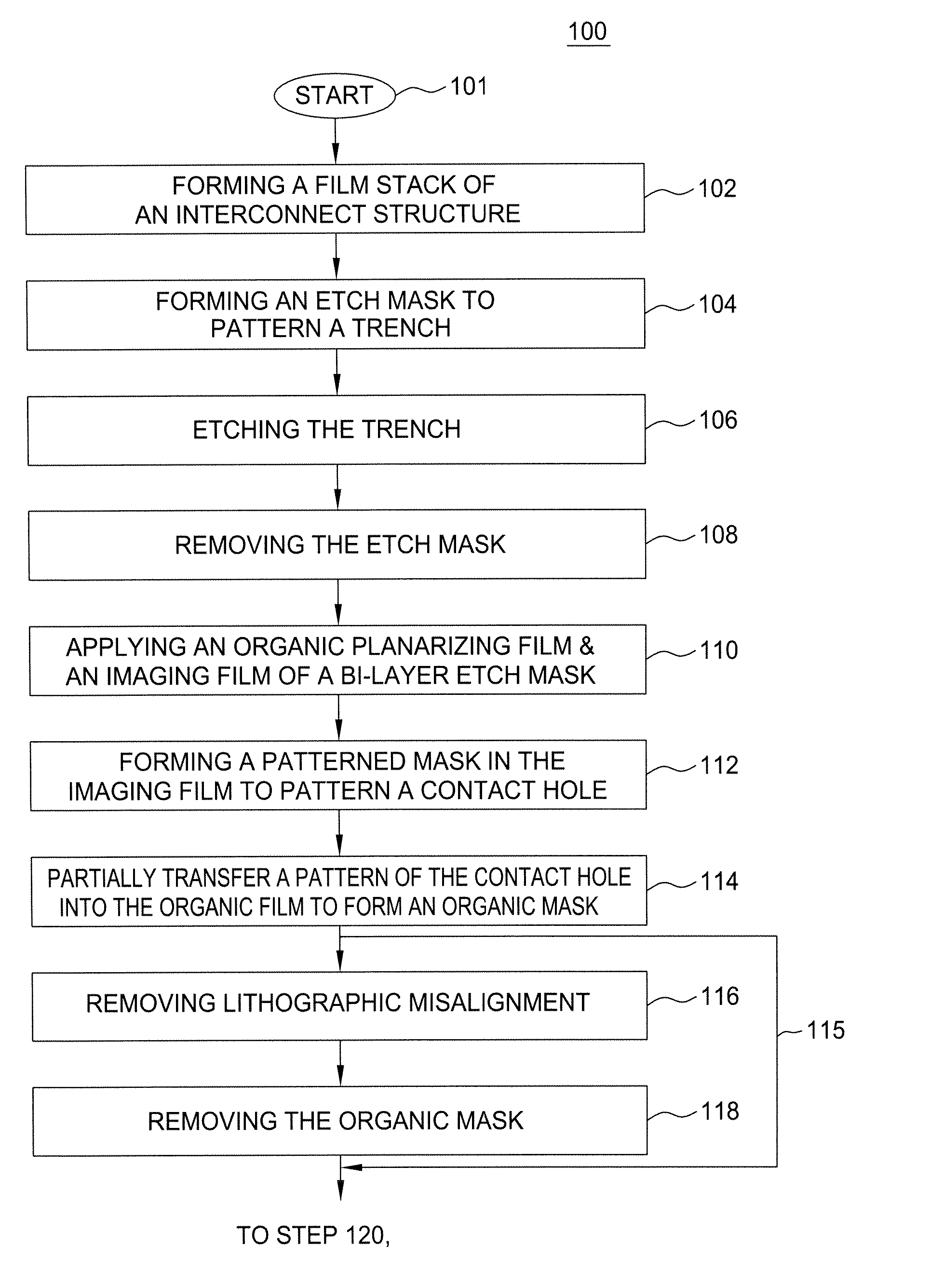
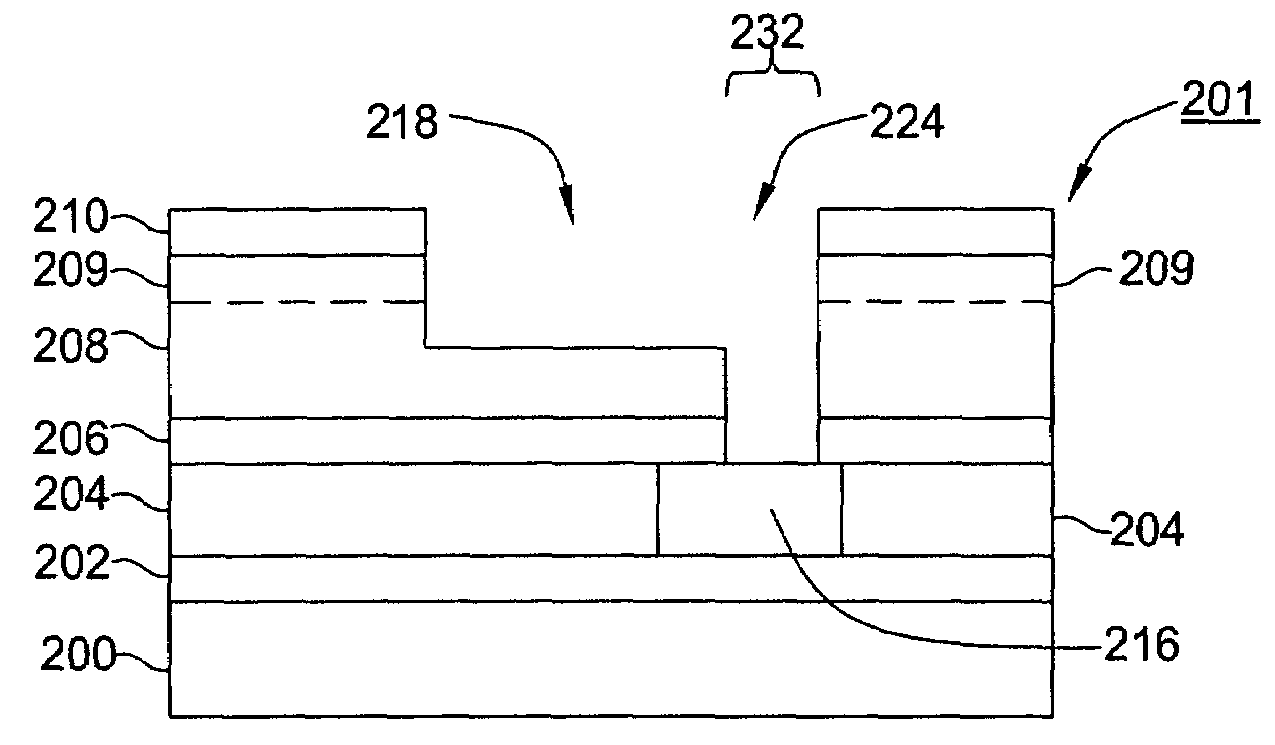
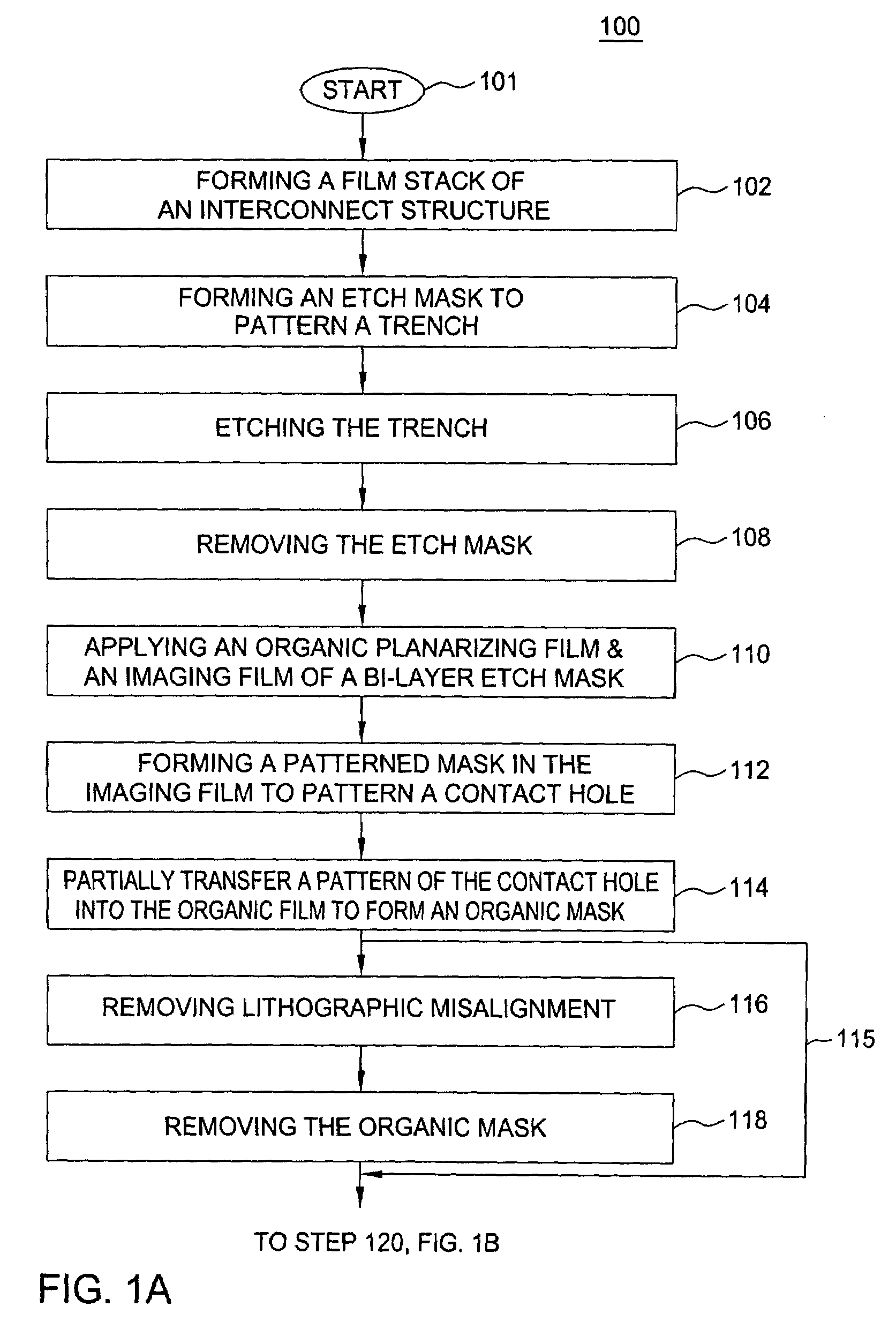
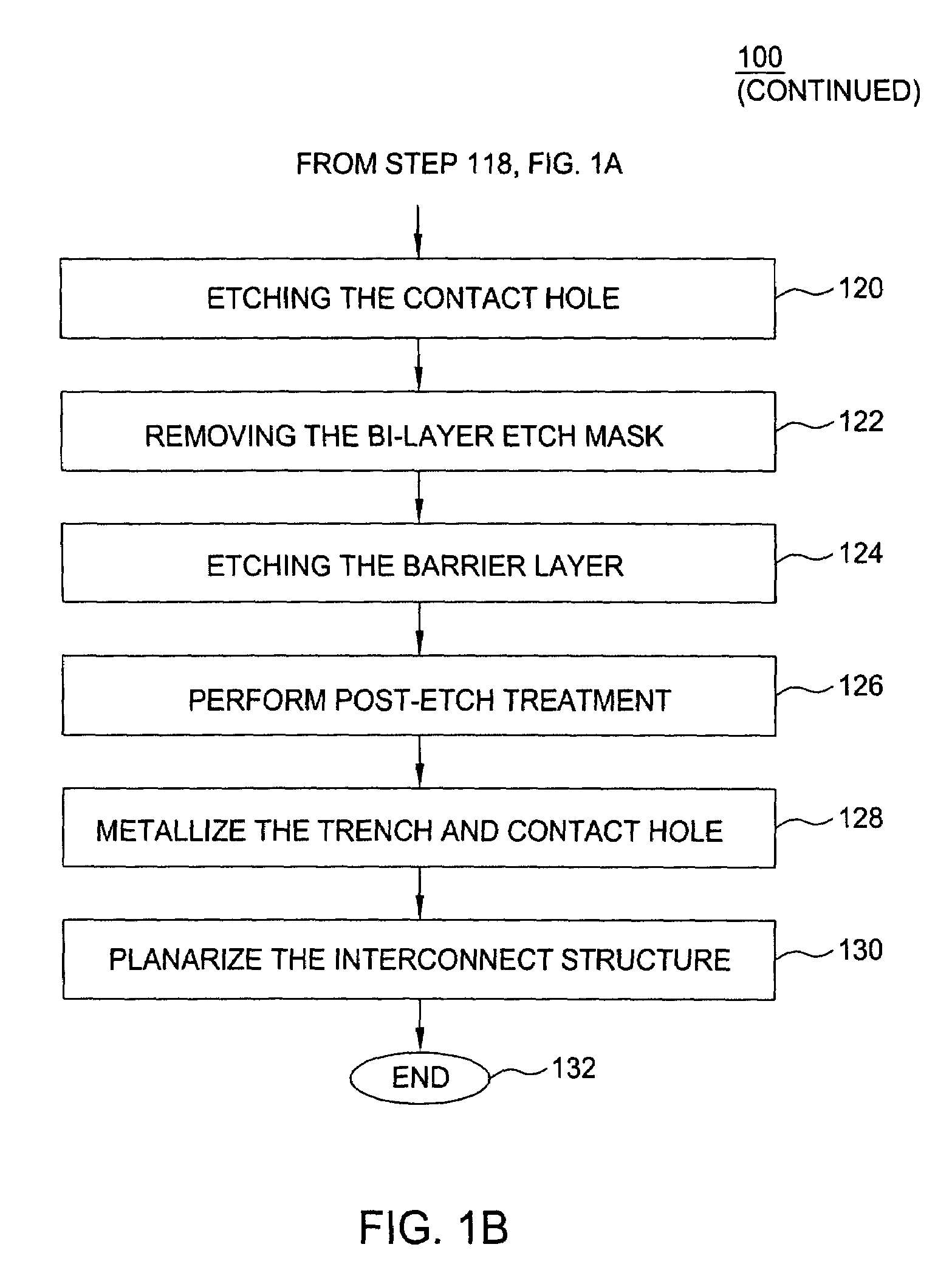
Method of fabricating a dual damascene interconnect structure
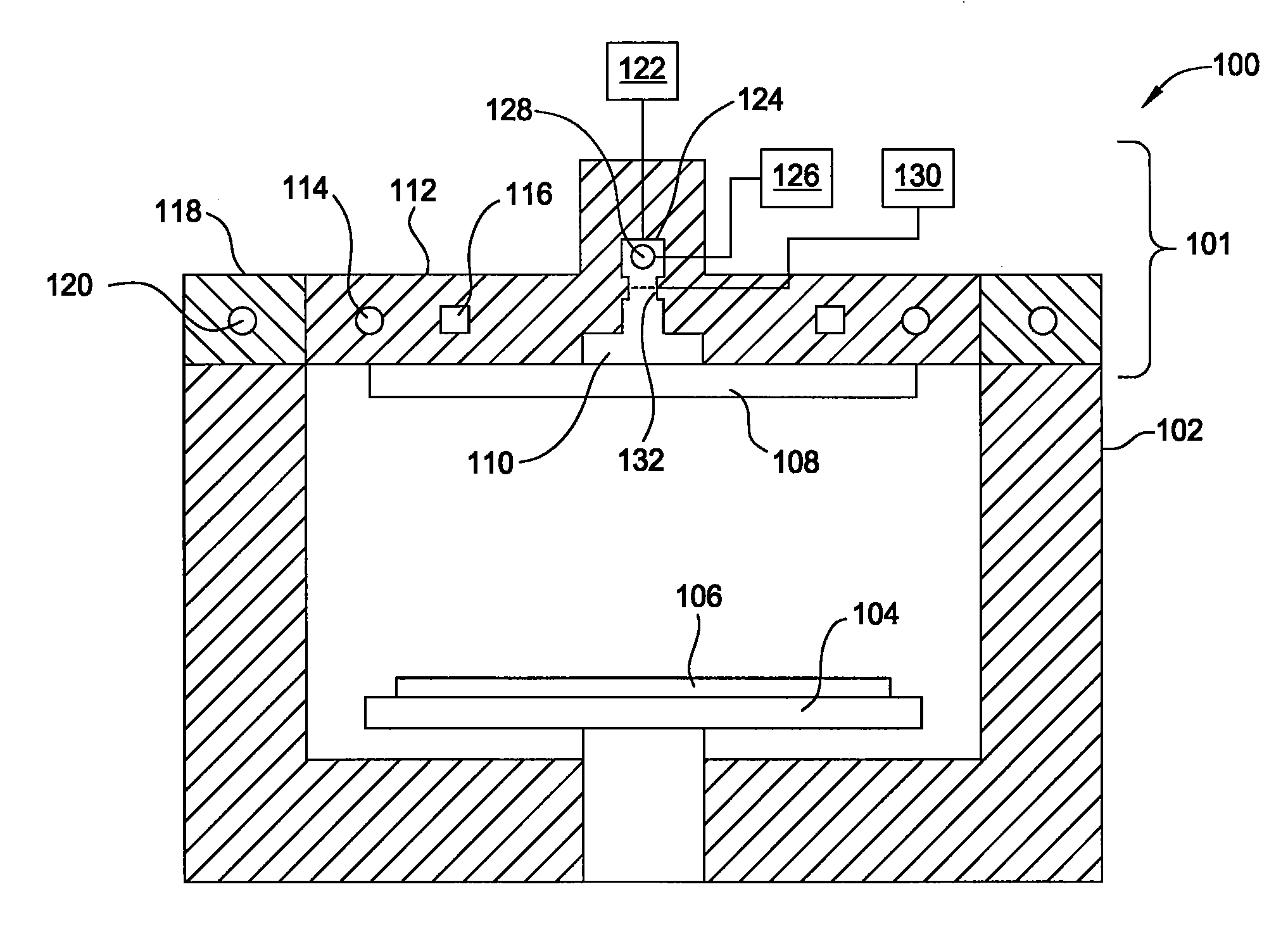
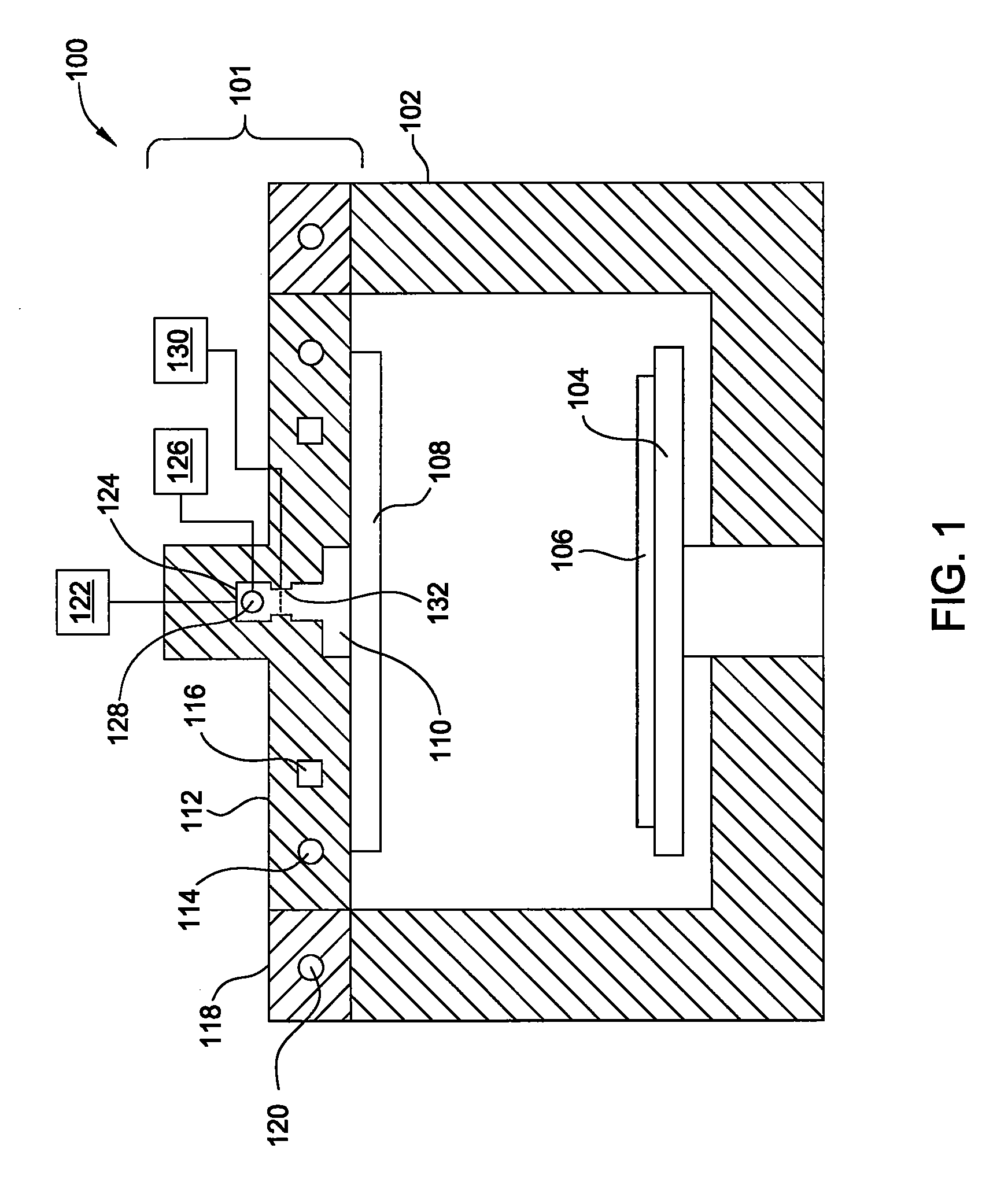
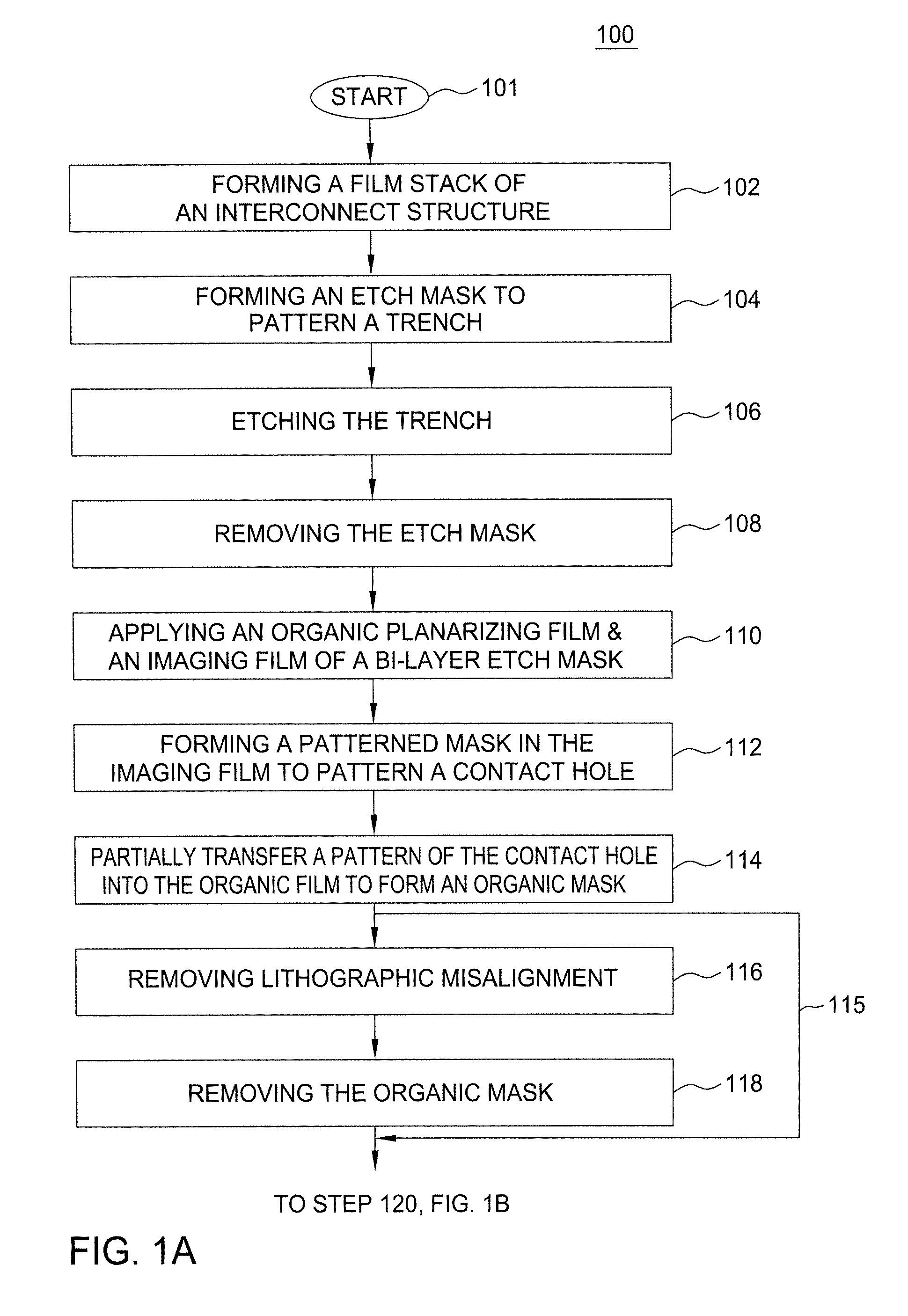
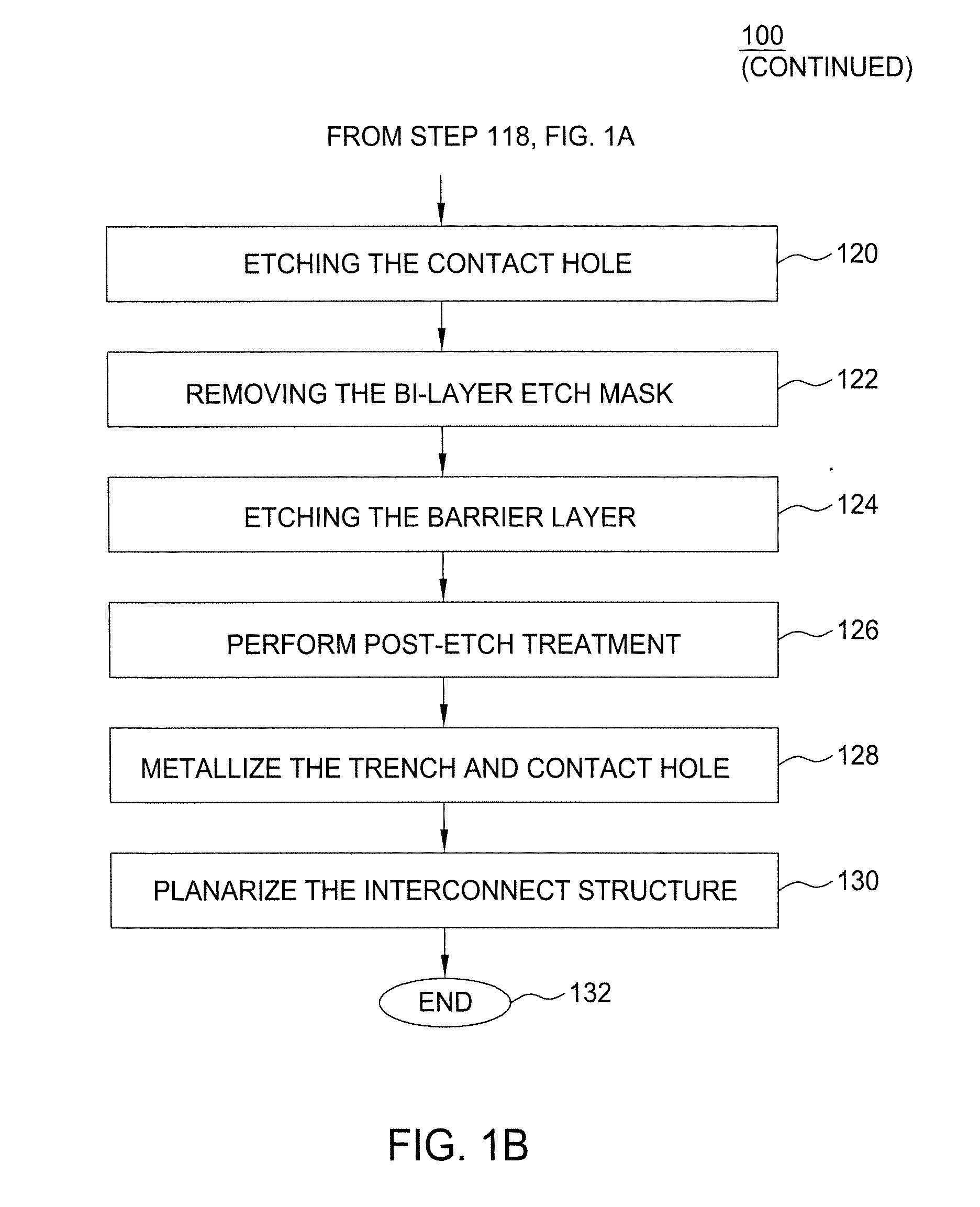
InactiveUS20060216926A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricTitanium nitride
A method of fabricating an interconnect structure (e.g., dual damascene interconnect structure, and the like) of an integrated circuit device is disclosed. The interconnect structure is fabricated using a bi-layer mask comprising an imaging film and an organic planarizing film. The bi-layer mask is used to remove lithographic misalignment between a contact hole, a trench, and an underlying conductive line when the interconnect structure is formed. Additionally, a sacrificial layer may be used to protect an inter-metal dielectric (IMD) layer during subsequent planarization of the interconnect structure. The sacrificial layer may be formed of amorphous silicon (Si), titanium nitride (TiN), tungsten (W), and the like. The interconnect structure may be formed of a metal (e.g., copper (Cu), aluminum (Al), tantalum (Ti), tungsten (W), titanium (Ti), and the like) or a conductive compound (e.g., tantalum nitride (TaN), titanium nitride (TiN), tungsten nitride (WN), and the like).
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Process for tungsten nitride deposition by a temperature controlled lid assembly
InactiveUS20080206987A1Fast heatingFast coolingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTemperature controlGas phase
Embodiments of the invention provide processes for vapor depositing tungsten-containing materials, such as metallic tungsten and tungsten nitride. In one embodiment, a method for forming a tungsten-containing material is provided which includes positioning a substrate within a processing chamber containing a lid plate, heating the lid plate to a temperature within a range from about 120° C. to about 180° C., exposing the substrate to a reducing gas during a pre-nucleation soak process, and depositing a first tungsten nucleation layer on the substrate during a first atomic layer deposition process within the processing chamber. The method further provides depositing a tungsten nitride layer on the first tungsten nucleation layer during a vapor deposition process, depositing a second tungsten nucleation layer on the tungsten nitride layer during a second atomic layer deposition process within the processing chamber, and exposing the substrate to another reducing gas during a post-nucleation soak process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for depositing nanolaminate thin films on sensitive surfaces
InactiveUS7329590B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCorrosive chemicalHydrogen halide
The present method provides tools for growing conformal metal nitride, metal carbide and metal thin films, and nanolaminate structures incorporating these films, from aggressive chemicals. The amount of corrosive chemical compounds, such as hydrogen halides, is reduced during the deposition of transition metal, transition metal carbide and transition metal nitride thin films on various surfaces, such as metals and oxides. Getter compounds protect surfaces sensitive to hydrogen halides and ammonium halides, such as aluminum, copper, silicon oxide and the layers being deposited, against corrosion. Nanolaminate structures (20) incorporating metal nitrides, such as titanium nitride (30) and tungsten nitride (40), and metal carbides, and methods for forming the same, are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL NV
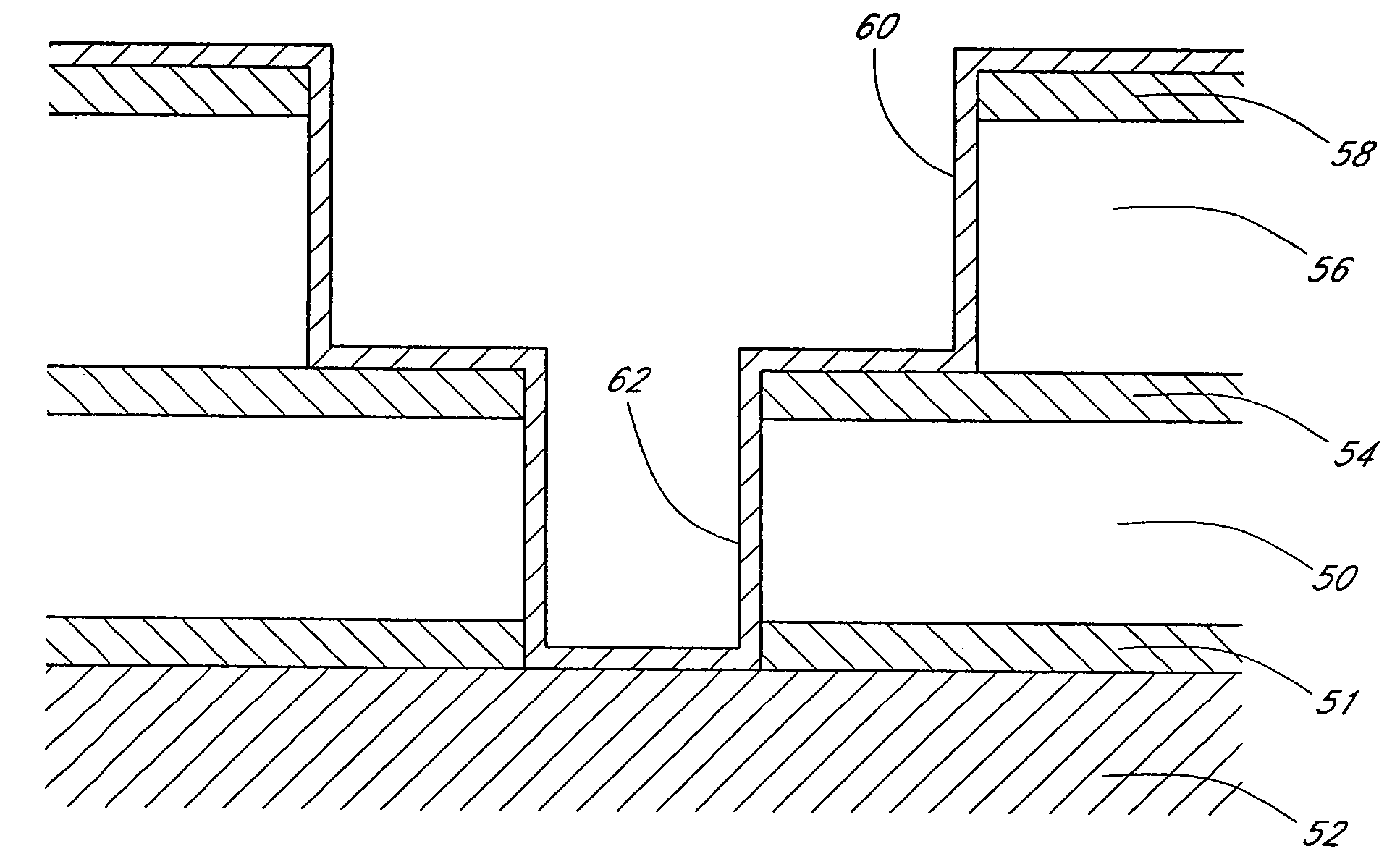
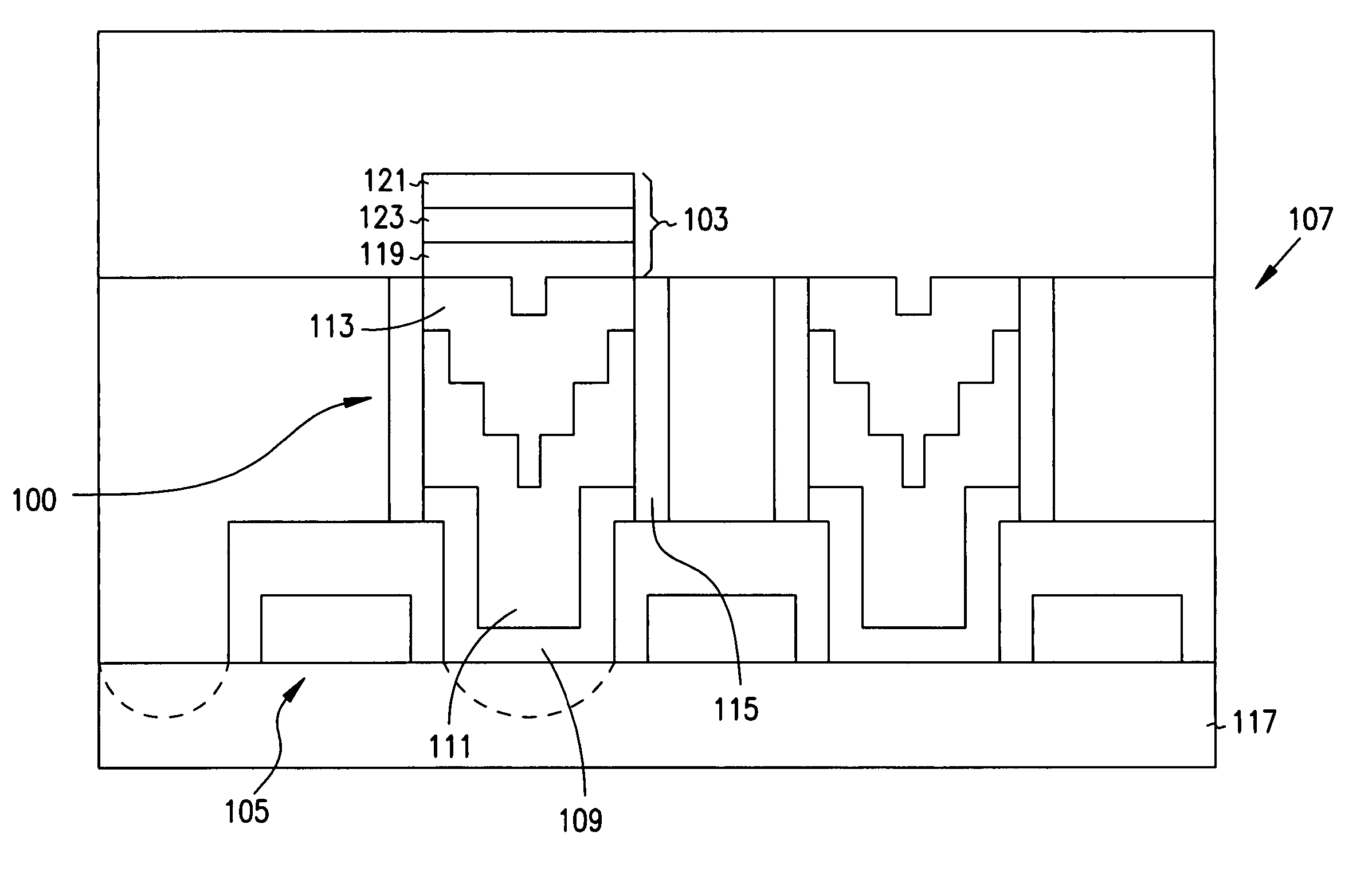
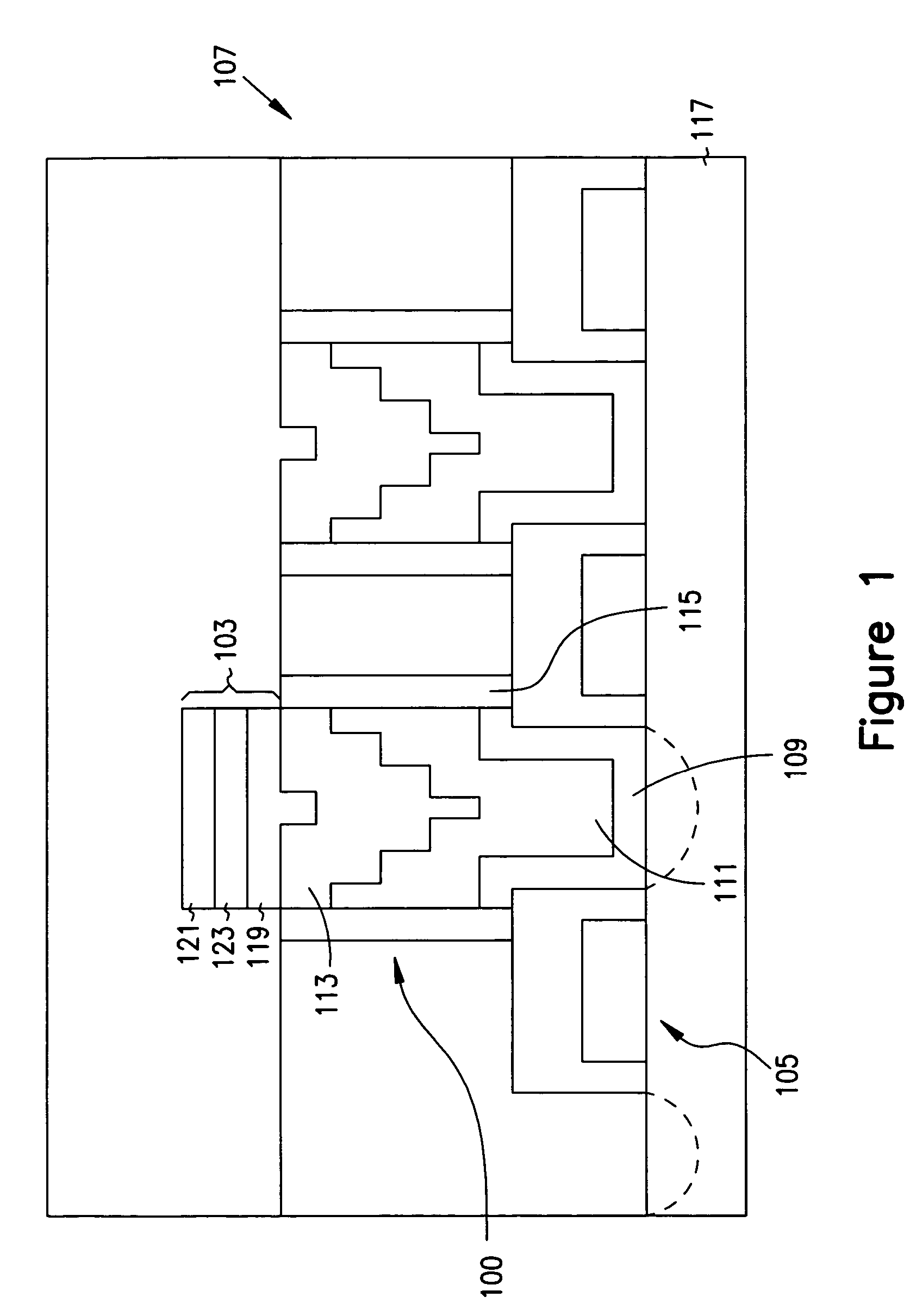
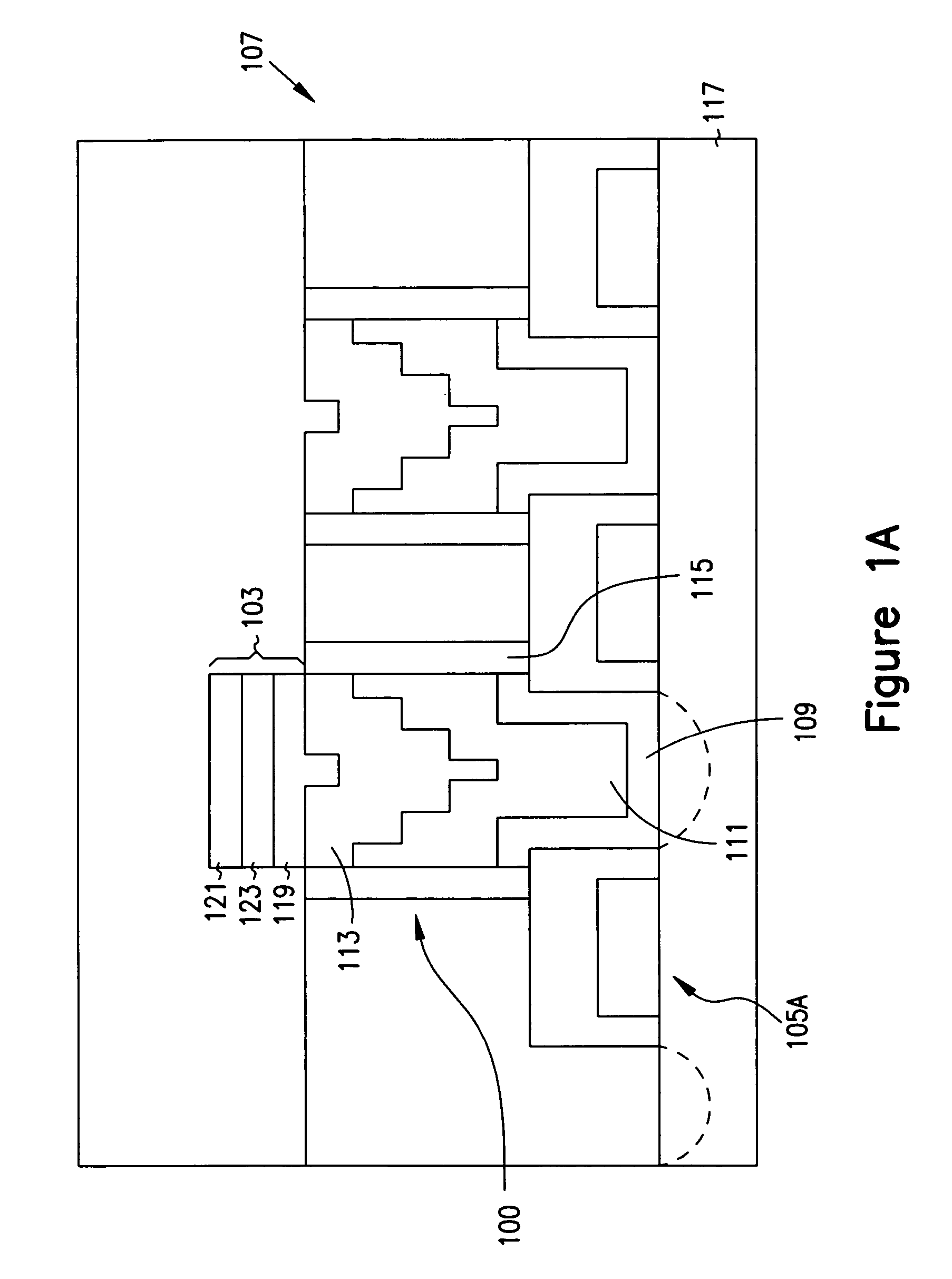
Method of forming a contact structure including a vertical barrier structure and two barrier layers
InactiveUS7071055B2Improve circuit reliabilityAvoid electrical propertiesTransistorThyristorTungsten nitrideIntegrated circuit
This invention relates to contact structures for use in integrated circuits and methods of fabricating contact structures. In one embodiment, a contact structure includes a conductive layer, one or more barrier layers formed above the conductive layer, and a barrier structure encircling the polysilicon layer and the one or more barrier layers. In an alternate embodiment, a contact structure is fabricated by forming a polysilicon layer on a substrate, forming a tungsten nitride layer above the polysilicon layer, and etching the polysilicon layer and the tungsten nitride layer to a level below the surface of a substrate structure. A silicon nitride layer is formed above the tungsten nitride layer, and a ruthenium silicide layer is formed above the silicon nitride layer. The ruthenium silicide layer is then polished.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method of fabricating a dual damascene interconnect structure
InactiveUS7115517B2Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricTitanium nitride
A method of fabricating an interconnect structure (e.g., dual damascene interconnect structure, and the like) of an integrated circuit device is disclosed. The interconnect structure is fabricated using a bi-layer mask comprising an imaging film and an organic planarizing film. The bi-layer mask is used to remove lithographic misalignment between a contact hole, a trench, and an underlying conductive line when the interconnect structure is formed. Additionally, a sacrificial layer may be used to protect an inter-metal dielectric (IMD) layer during subsequent planarization of the interconnect structure. The sacrificial layer may be formed of amorphous silicon (Si), titanium nitride (TiN), tungsten (W), and the like. The interconnect structure may be formed of a metal (e.g., copper (Cu), aluminum (Al), tantalum (Ti), tungsten (W), titanium (Ti), and the like) or a conductive compound (e.g., tantalum nitride (TaN), titanium nitride (TiN), tungsten nitride (WN), and the like).
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com