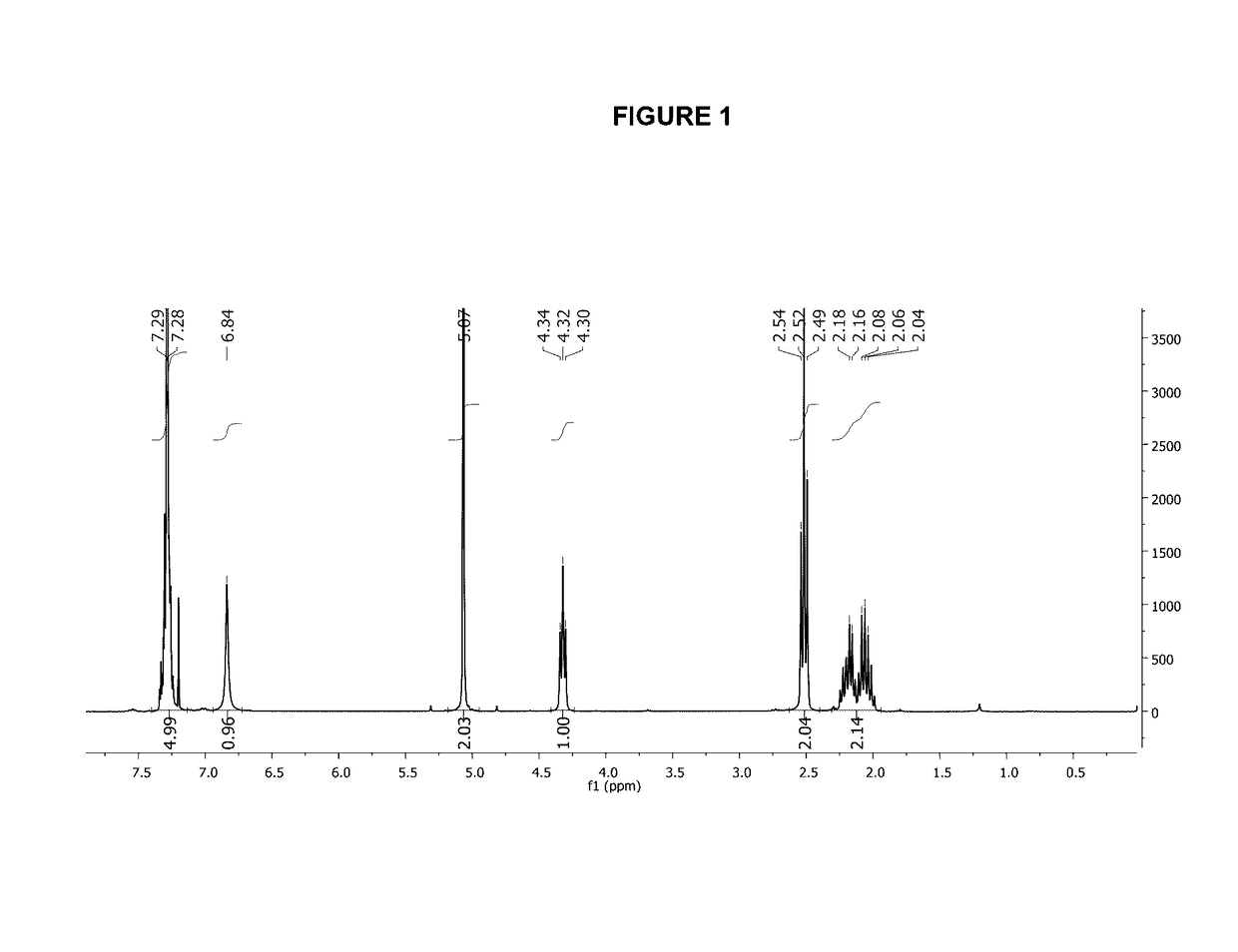
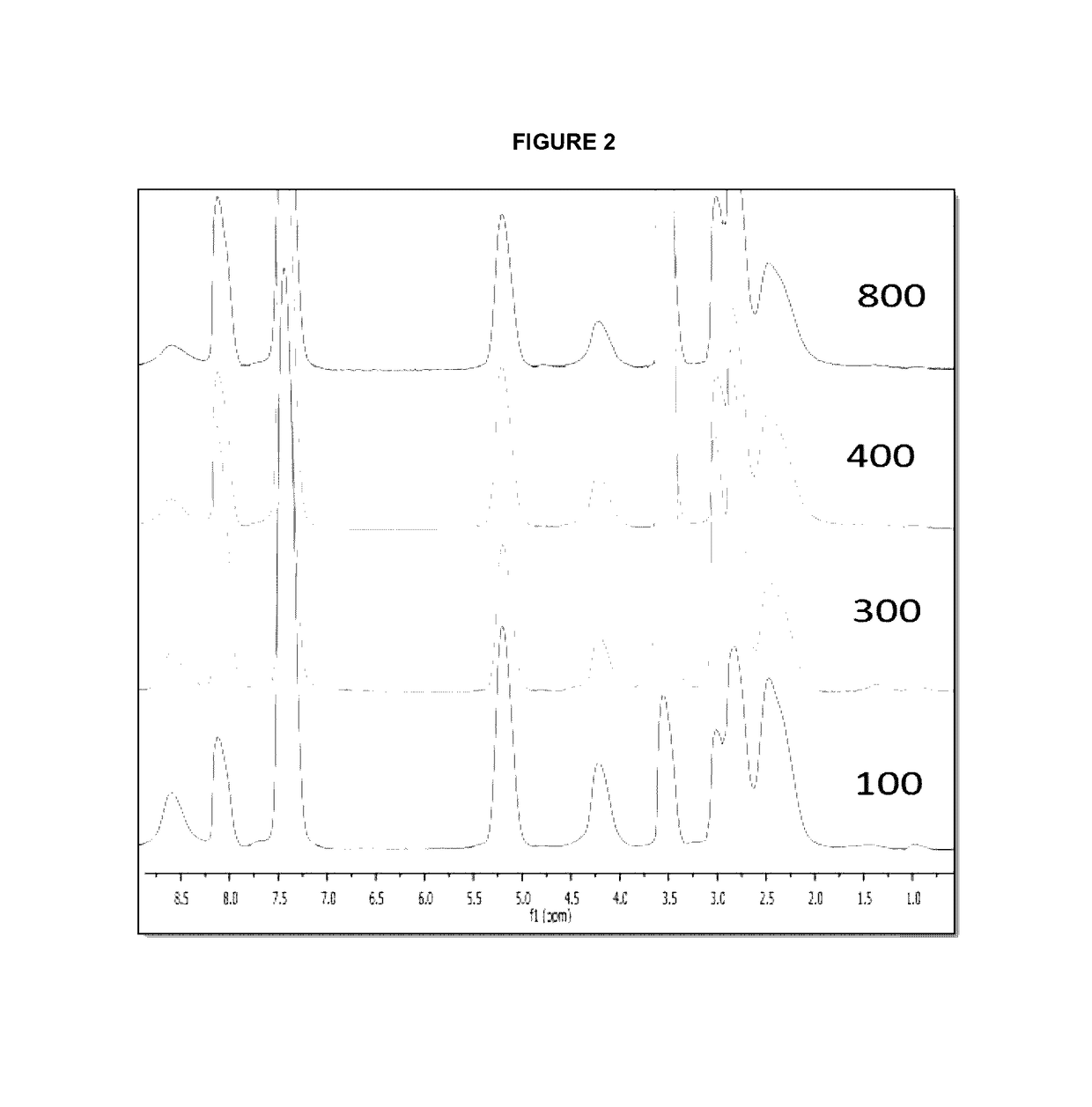
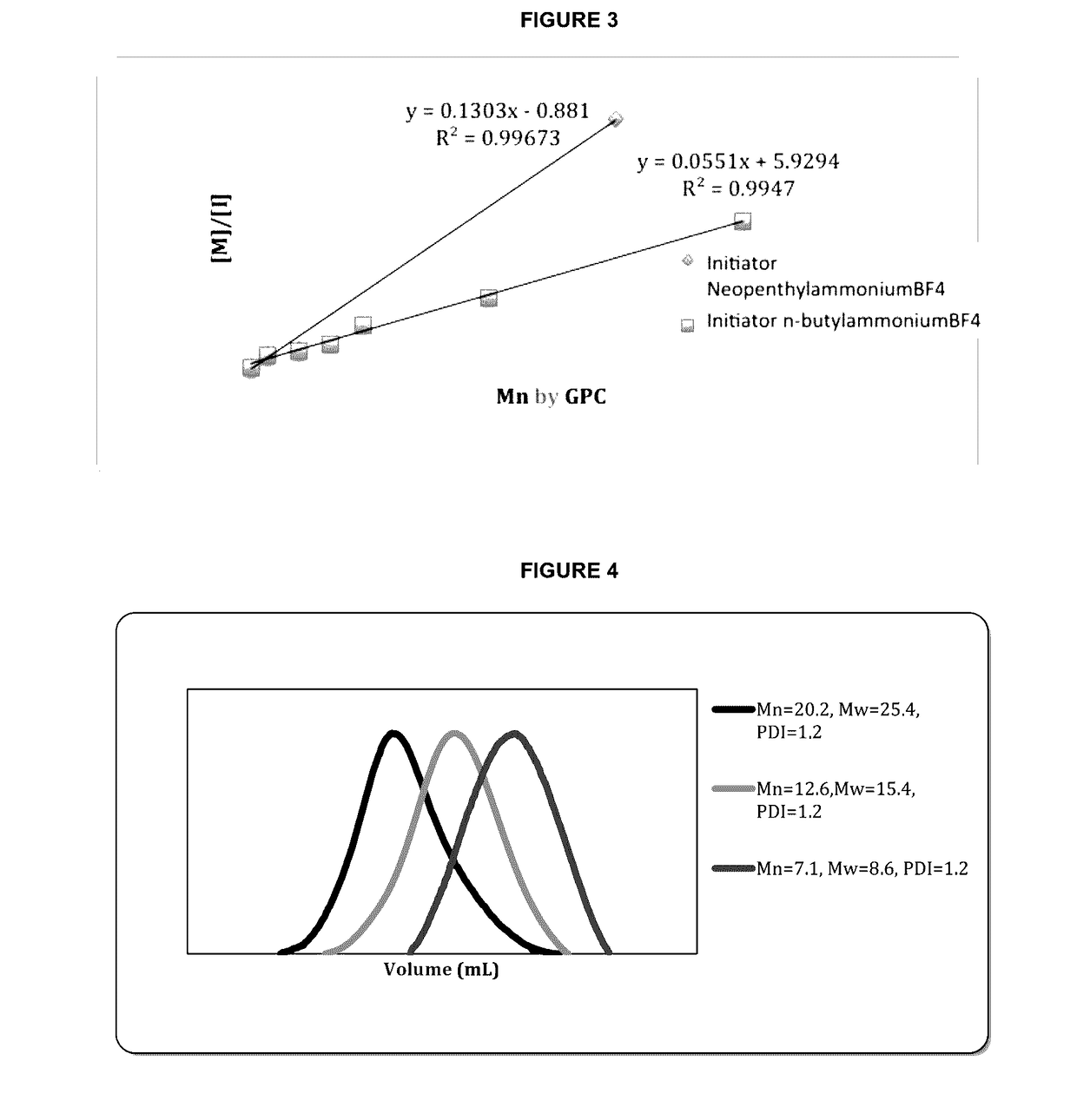
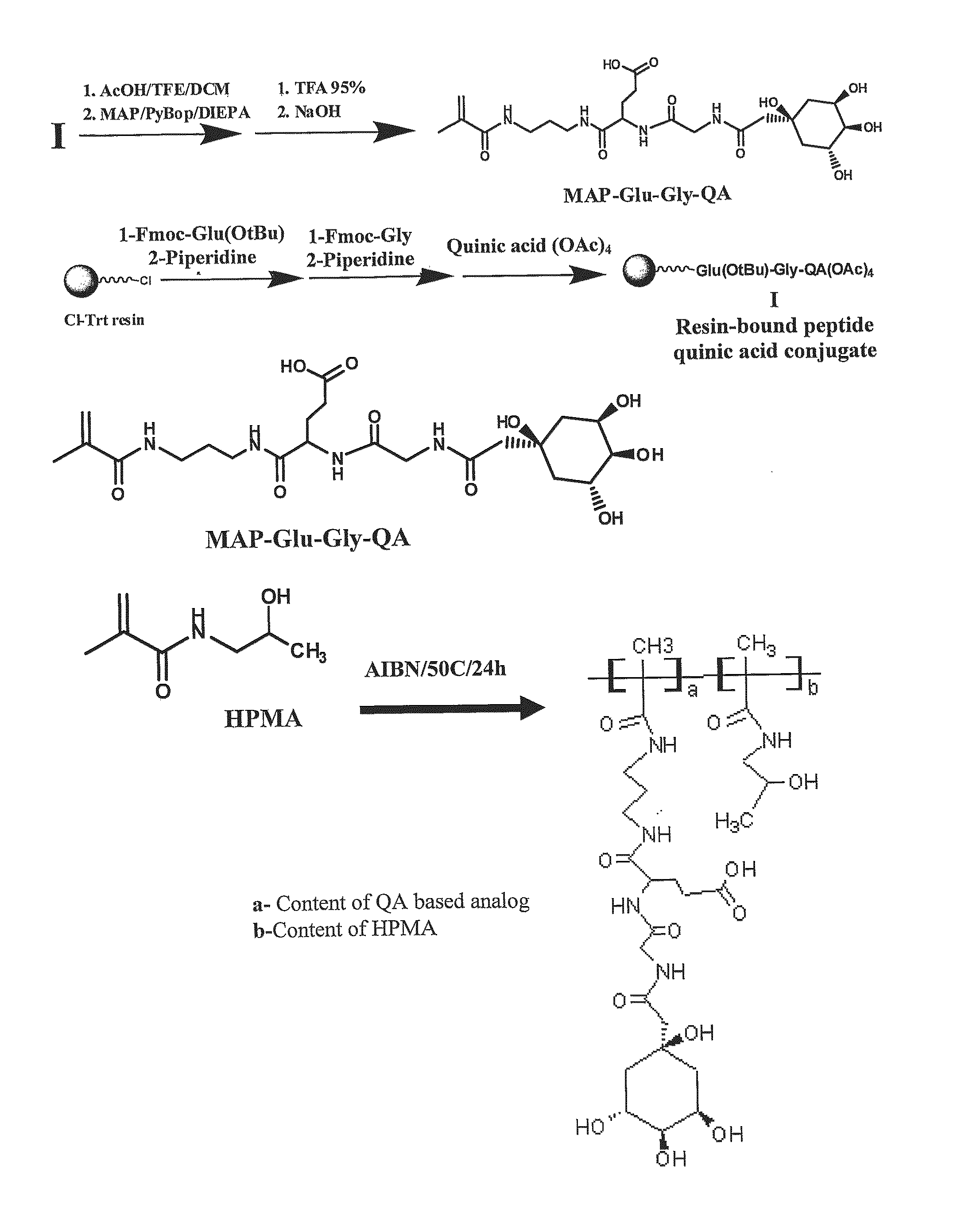
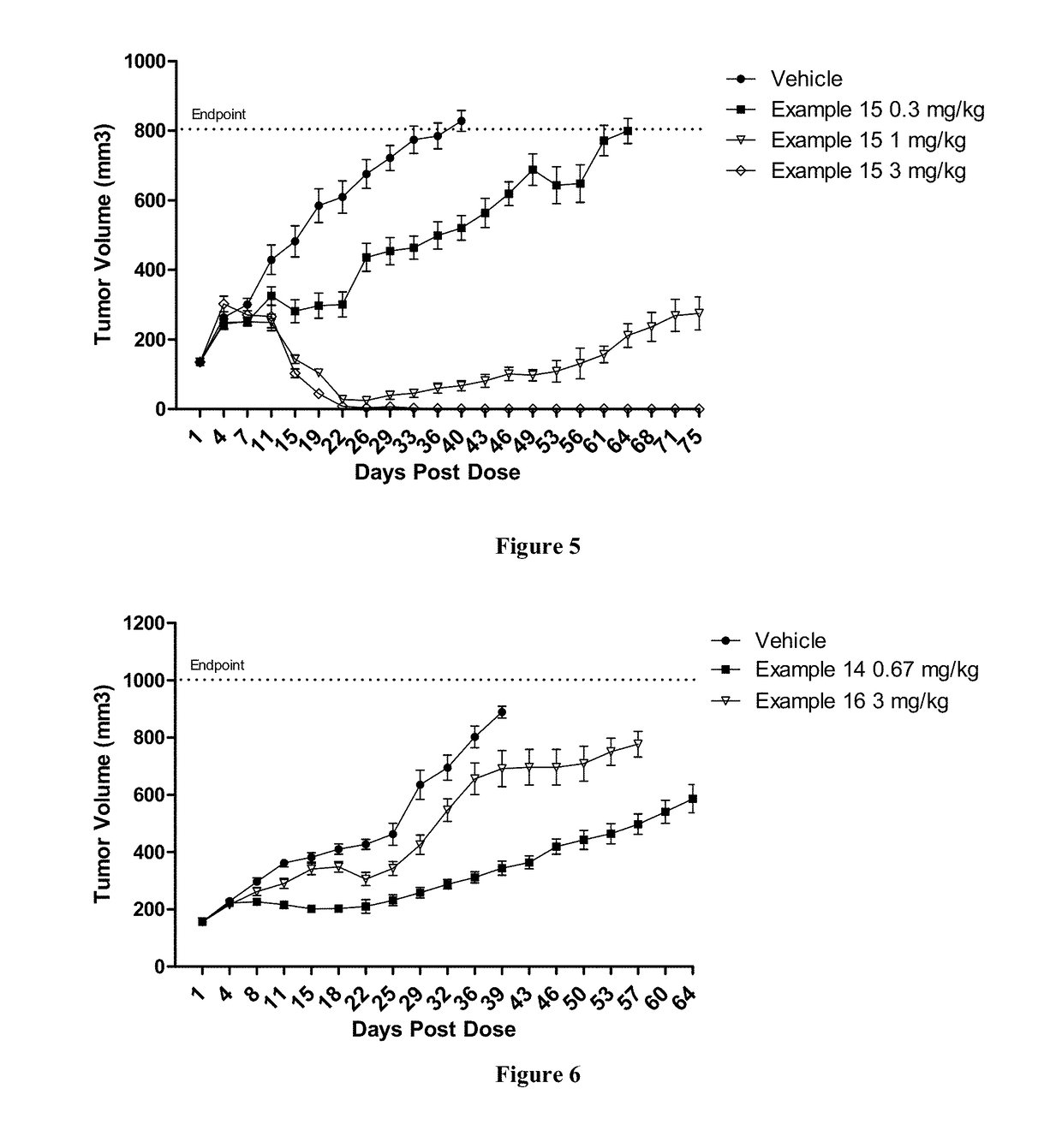
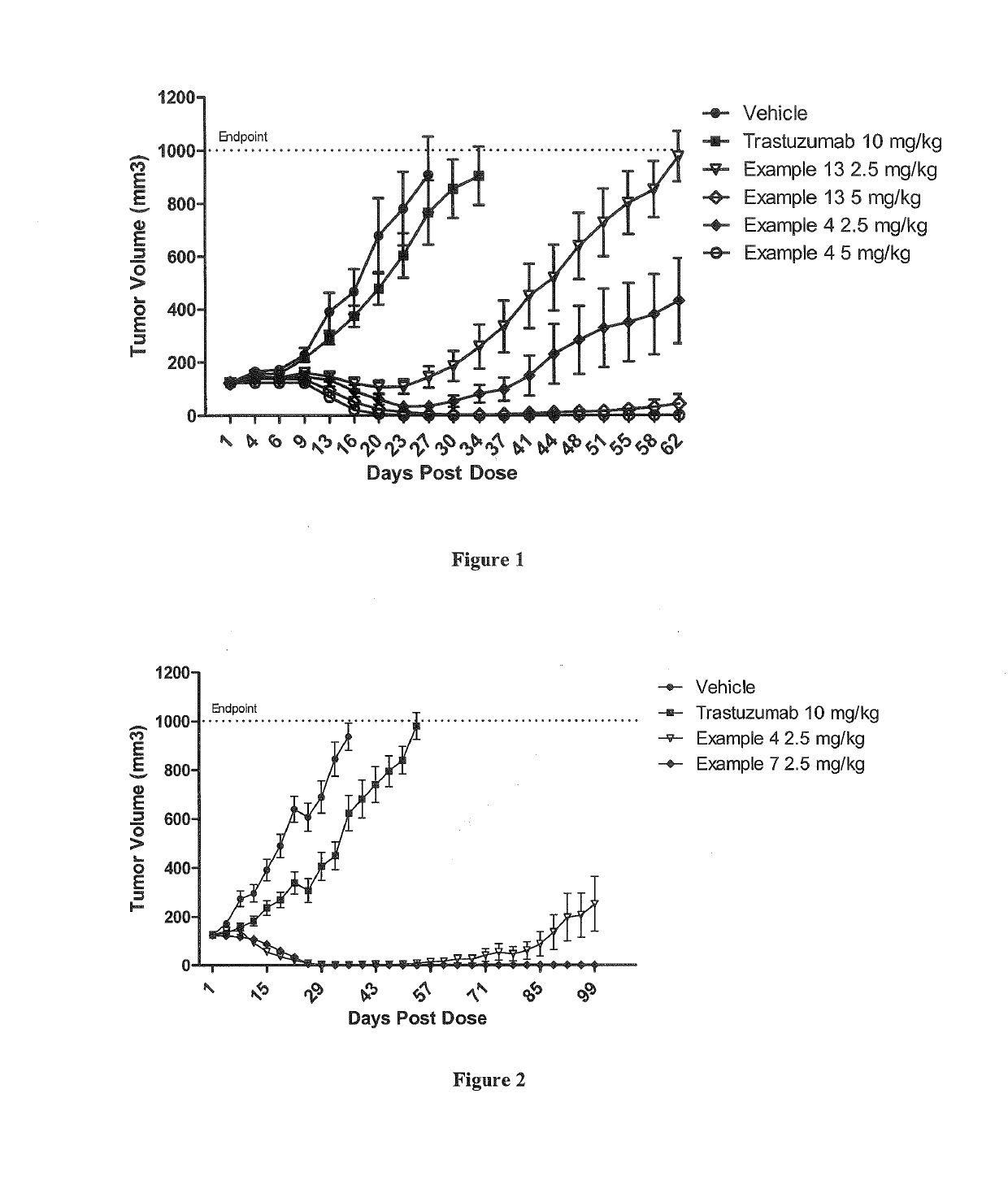
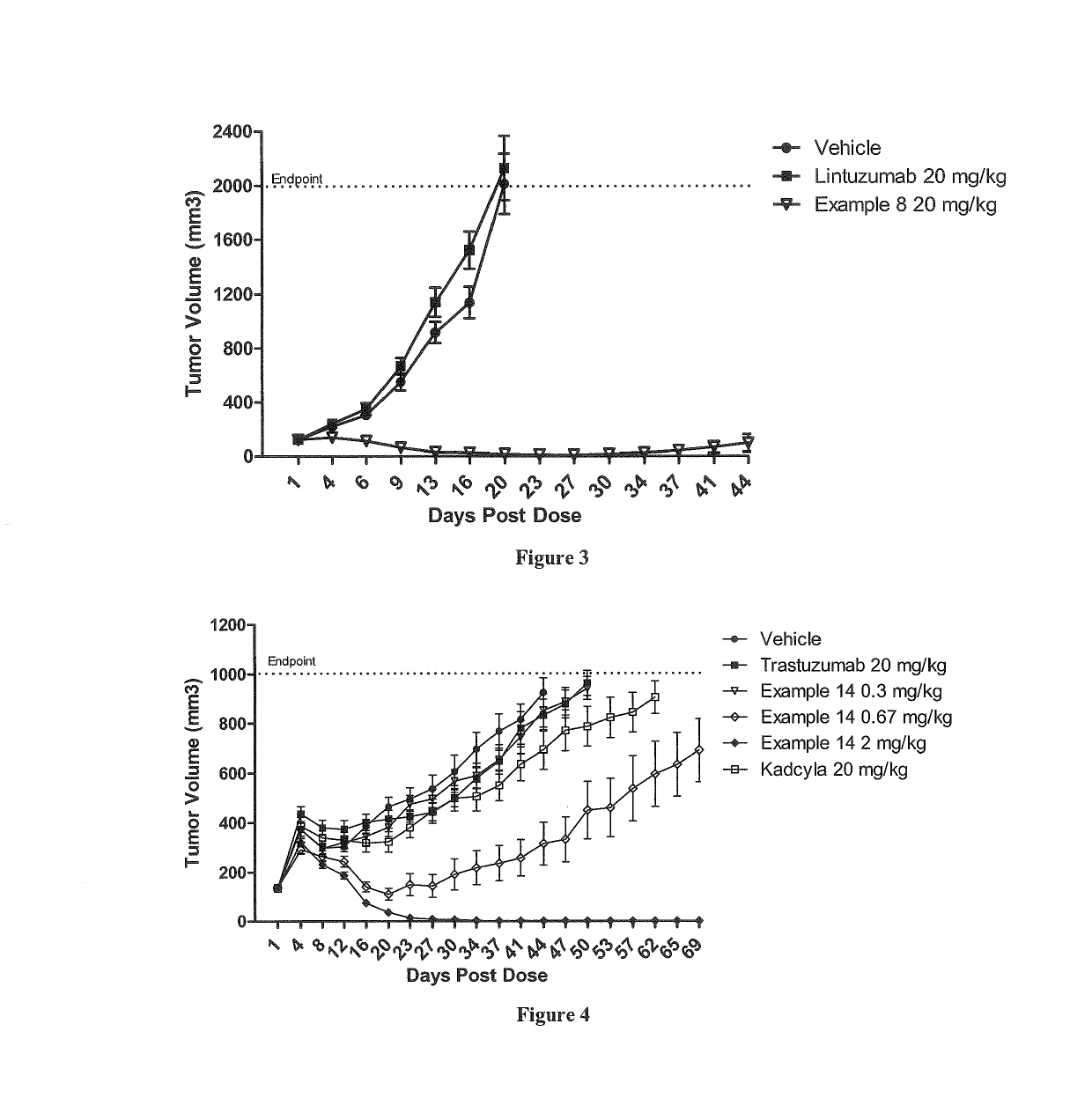
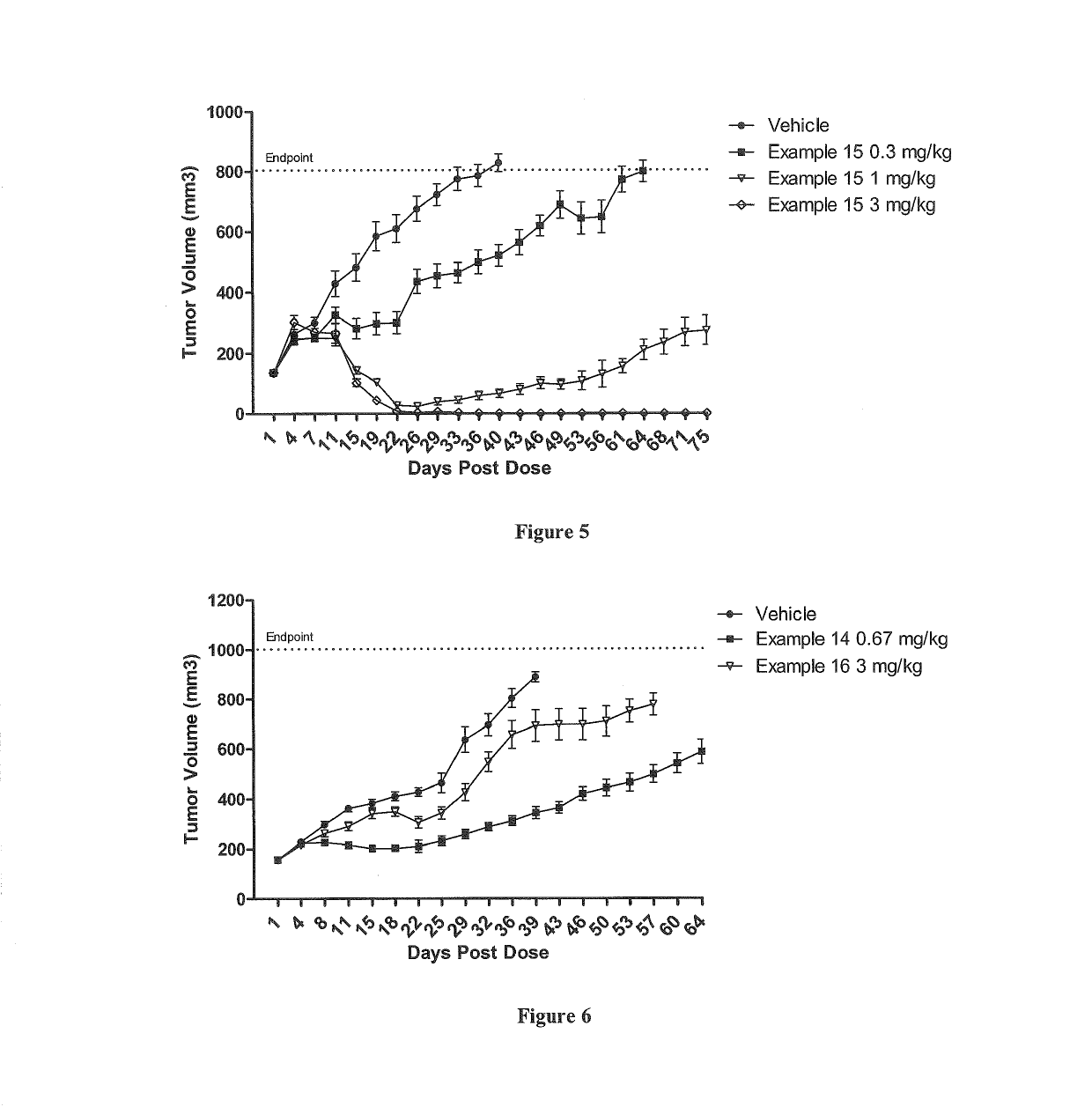
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Polymer-drug conjugates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
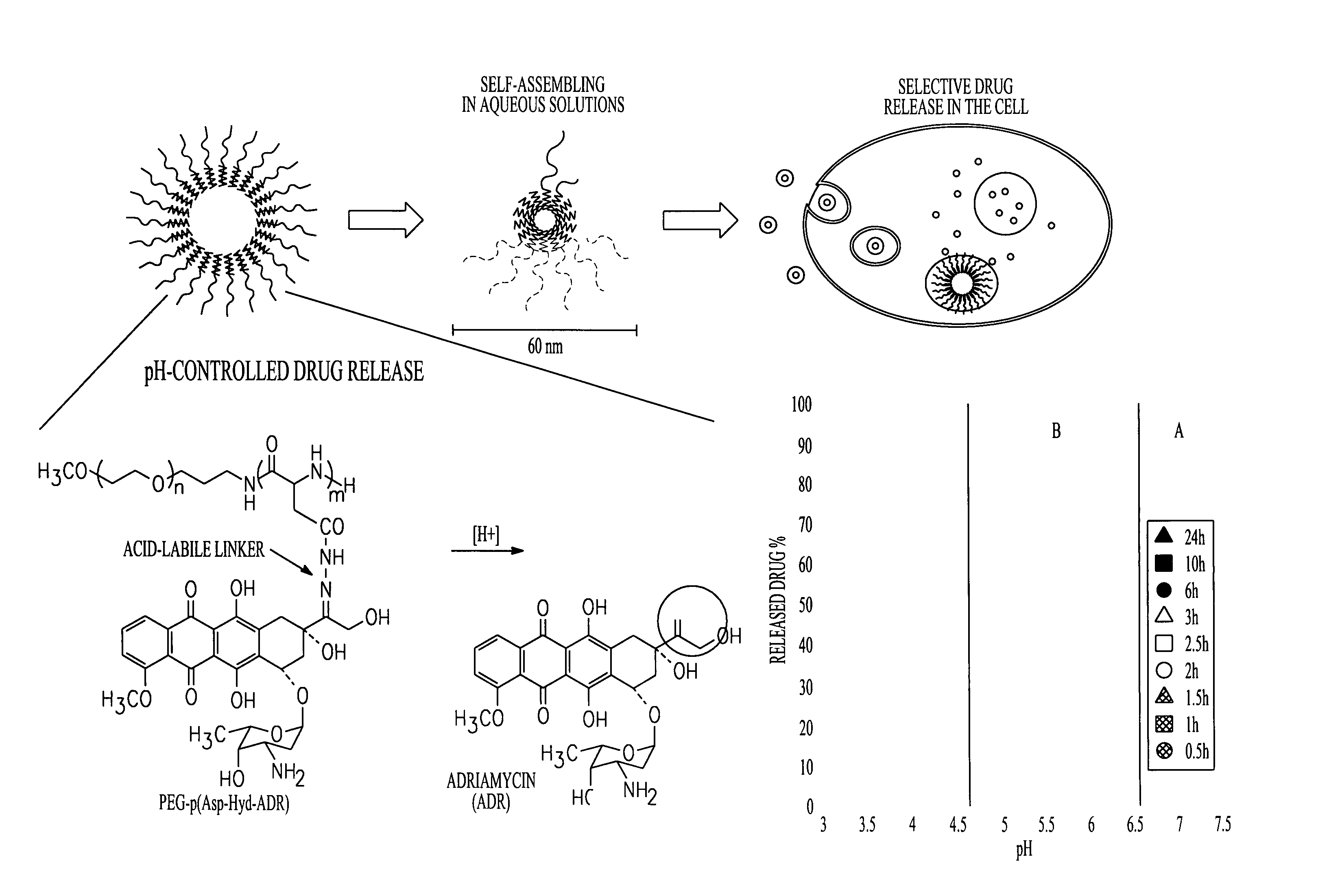
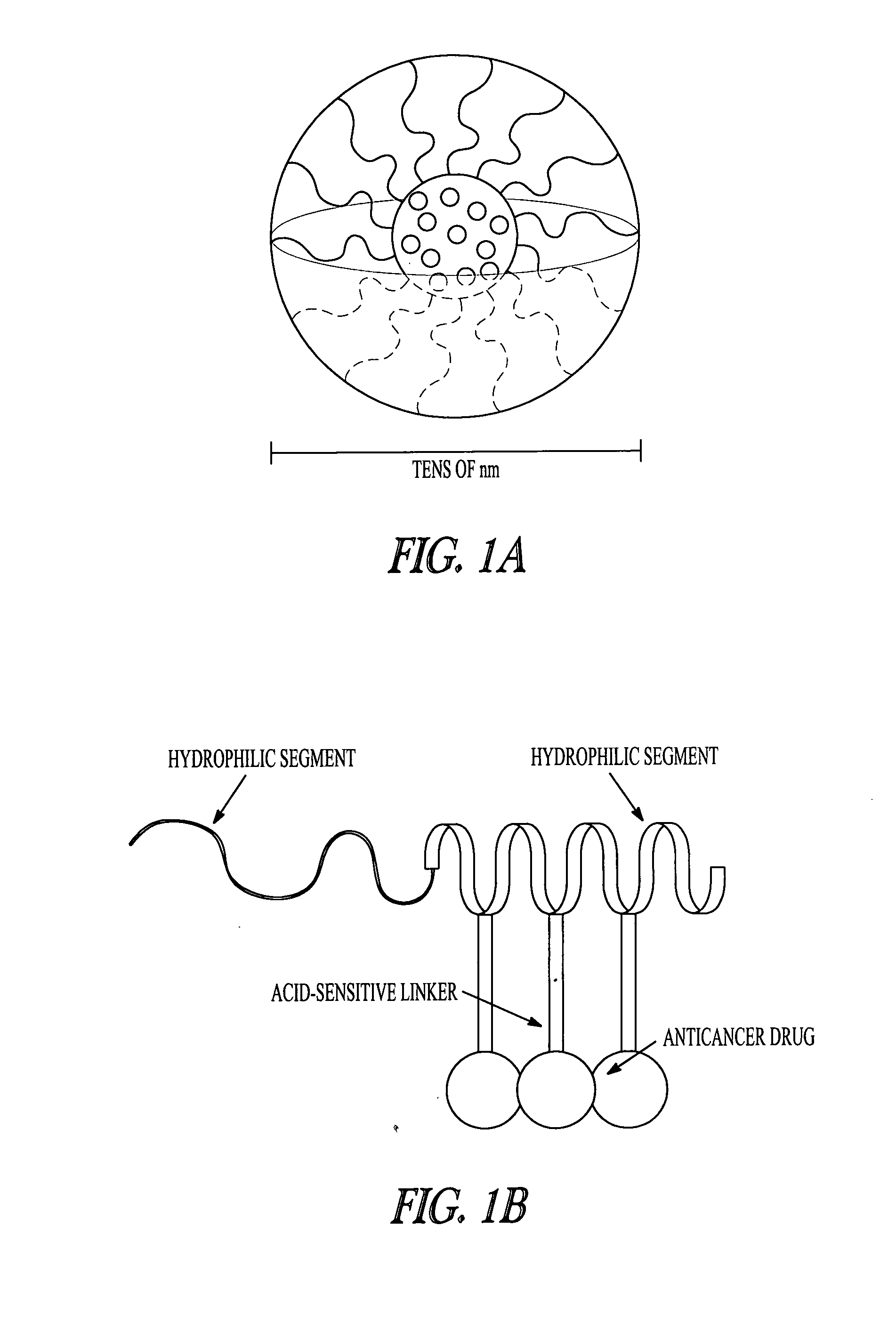
Polymer-drug conjugates are nano-medicine products under development for cancer diagnosis and treatment. There are more than 10 anticancer conjugates in clinical development. Polymer-drug conjugates are drug molecules held in polymer molecules, which act as the delivery system for the drug. Polymer drugs have passed multidrug resistance (MDR) testing and hence may become a viable treatment for endocrine-related cancers. A cocktail of pendant drugs could be delivered by water-soluble polymer platforms. The physical and chemical properties of the polymers used in polymer-drug conjugates are specially synthesized to flow through the kidneys and liver without being filtered out, allowing the drugs to be used more effectively. Traditional polymers used in polymer-drug conjugates can be degraded through enzymatic activity and acidity. Polymers are now being synthesized to be sensitive to specific enzymes that are apparent in diseased tissue. The drugs remain attached to the polymer and are not activated until the enzymes associated with the diseased tissue are present. This process significantly minimizes damage to healthy tissue.
Non-Linear Multiblock Copolymer-Drug Conjugates for the Delivery of Active Agents
ActiveUS20130272994A1Improve propertiesControlled drug and drug release profilePowder deliverySenses disorderUveitisDisease
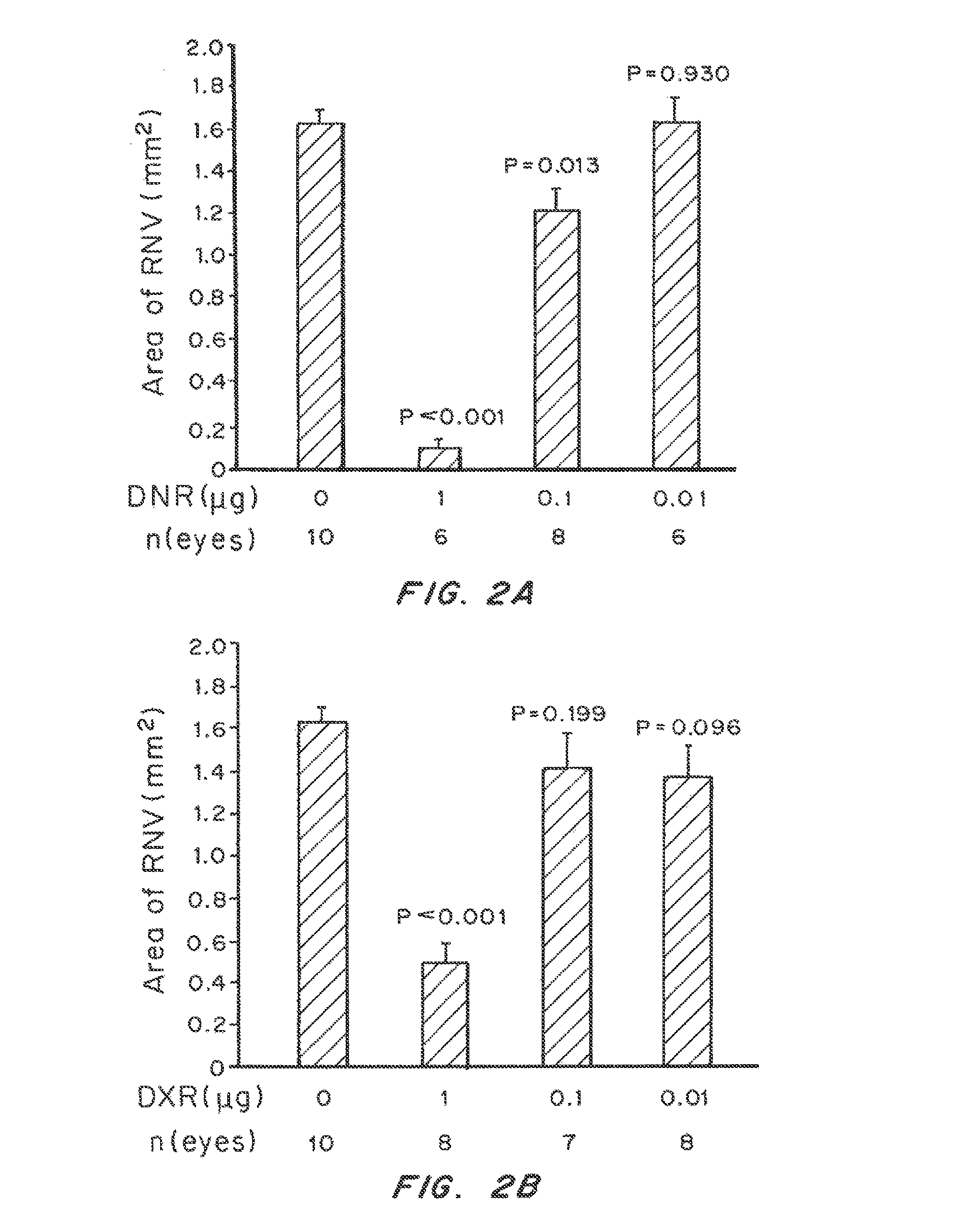
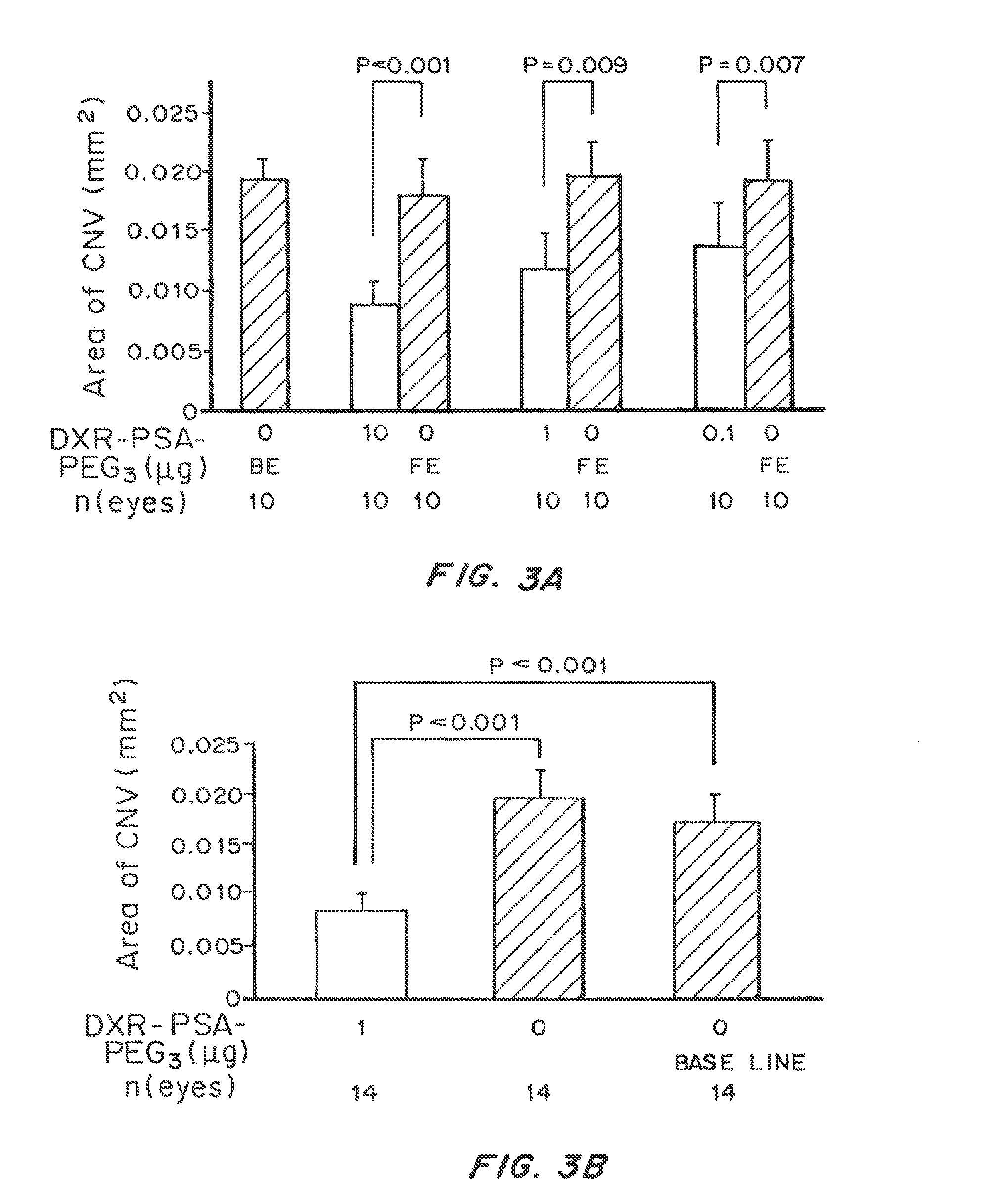
Non-linear multiblock copolymer-drug conjugates for the treatment and prevention of diseases and disorders of the eye are provided. The polymer-drug conjugates can form nanoparticles, microparticles, and implants that are capable of effectively delivering therapeutic levels of one or more active agents for an extended period of time. Administration to the eye of an active agent in the form of a non-linear multiblock copolymer-drug conjugate produces decreased side effects when compared to administration of the active agent alone. Also provided are methods of treating intraocular neovascular diseases, such as wet age-related macular degeneration as well as diseases and disorders of the eye associated with inflammation, such as uveitis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Controlled release formulations for the delivery of HIF-1 inhibitors
ActiveUS8962577B2Controlled drug and drug release profileReduce solubilityBiocidePowder deliveryDiseaseSide effect
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Polymeric micelles for combination drug delivery
InactiveUS20080248097A1Low water solubilityLower effective doesBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsCancer cellCombination drug therapy
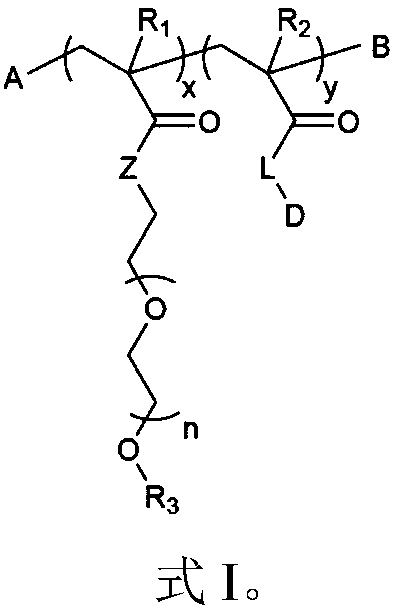
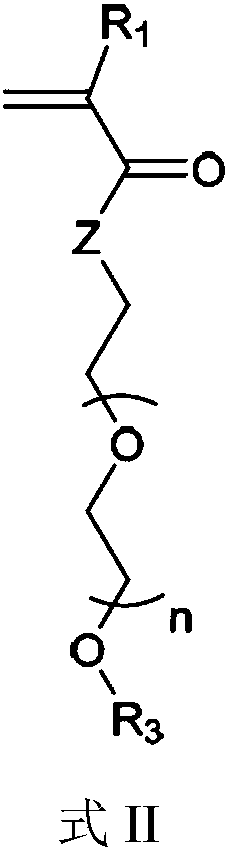
The invention provides block polymers, micelles, and micelle formulations for combination drug therapy. Polyamide block polymers, such as those of formulas I and II are useful, for example, for preparation of mixed drug micelles, including simply mixed micelles, physically mixed micelles, and chemically mixed micelles. The invention further provides methods of treating cancer, and inhibiting and killing cancer cells. Also provided are methods for the preparation of polymer drug conjugates and intermediates for their synthesis.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Controlled Release Formulations for the Delivery of HIF-1 Inhibitors
Controlled release dosage formulations for the delivery of one or more HIF-1 inhibitors are provided. The controlled release formulations contain one or more HIF-1 inhibitors conjugated to or dispersed in a polymeric vehicle. The one or more HIF-1 inhibitors can be dispersed or encapsulated in a polymeric matrix. In some embodiments, the one or more HIF-1 inhibitors are covalently bound to a polymer, forming a polymer-drug conjugate. Polymeric vehicles can be formed into implants, microparticles, nanoparticles, or combinations thereof. Controlled release HIF-1 formulations provide prolonged therapeutic benefit while lowering side effects by releasing low levels of one or more HIF-1 inhibitors and / or HIF-1 inhibitor conjugates over a prolonged period of time. Controlled release dosage formulations can be used to treat or prevent a disease or disorder in a patient associated with vascularization, including cancer, obesity, and ocular diseases such as wet AMD.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
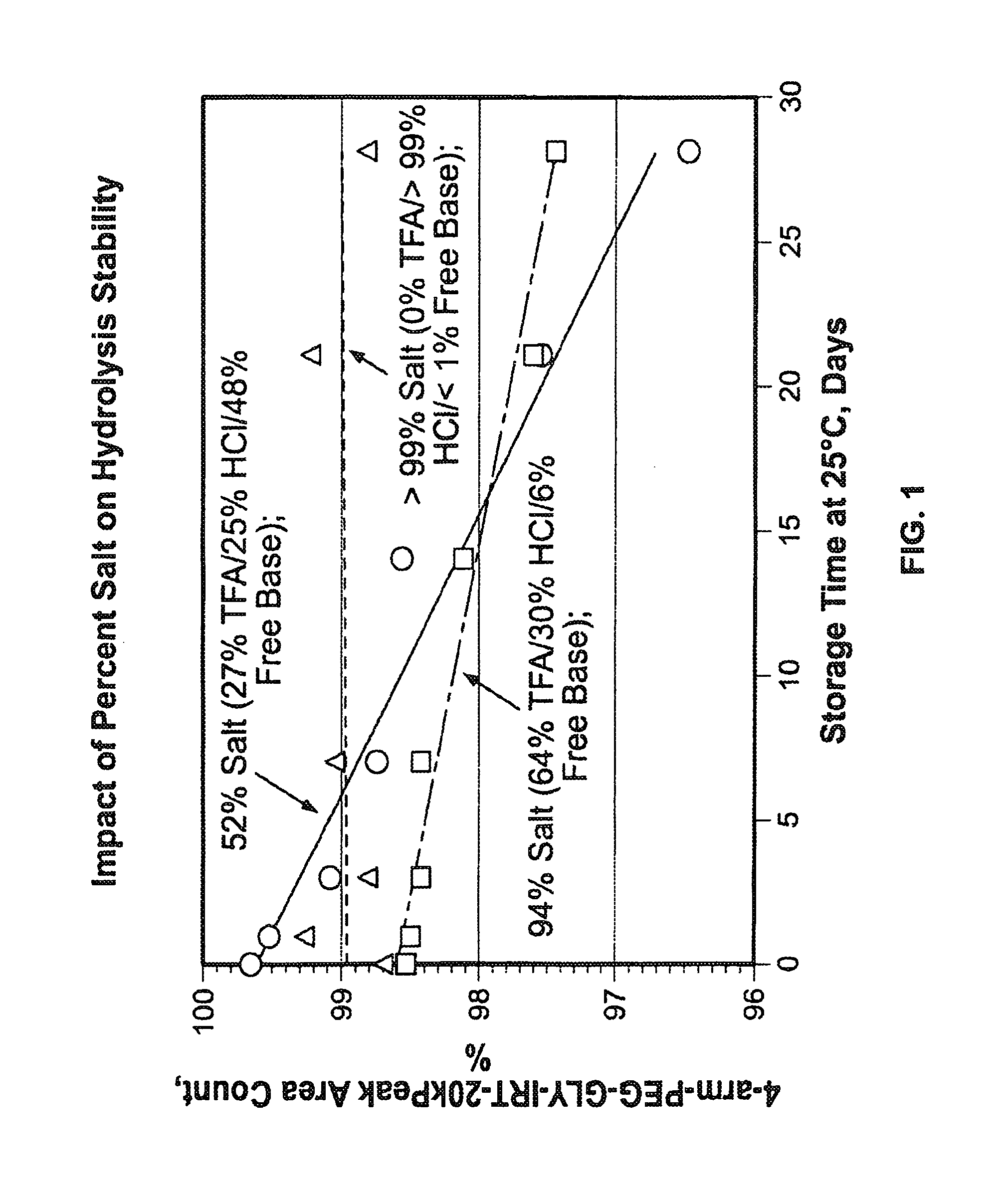
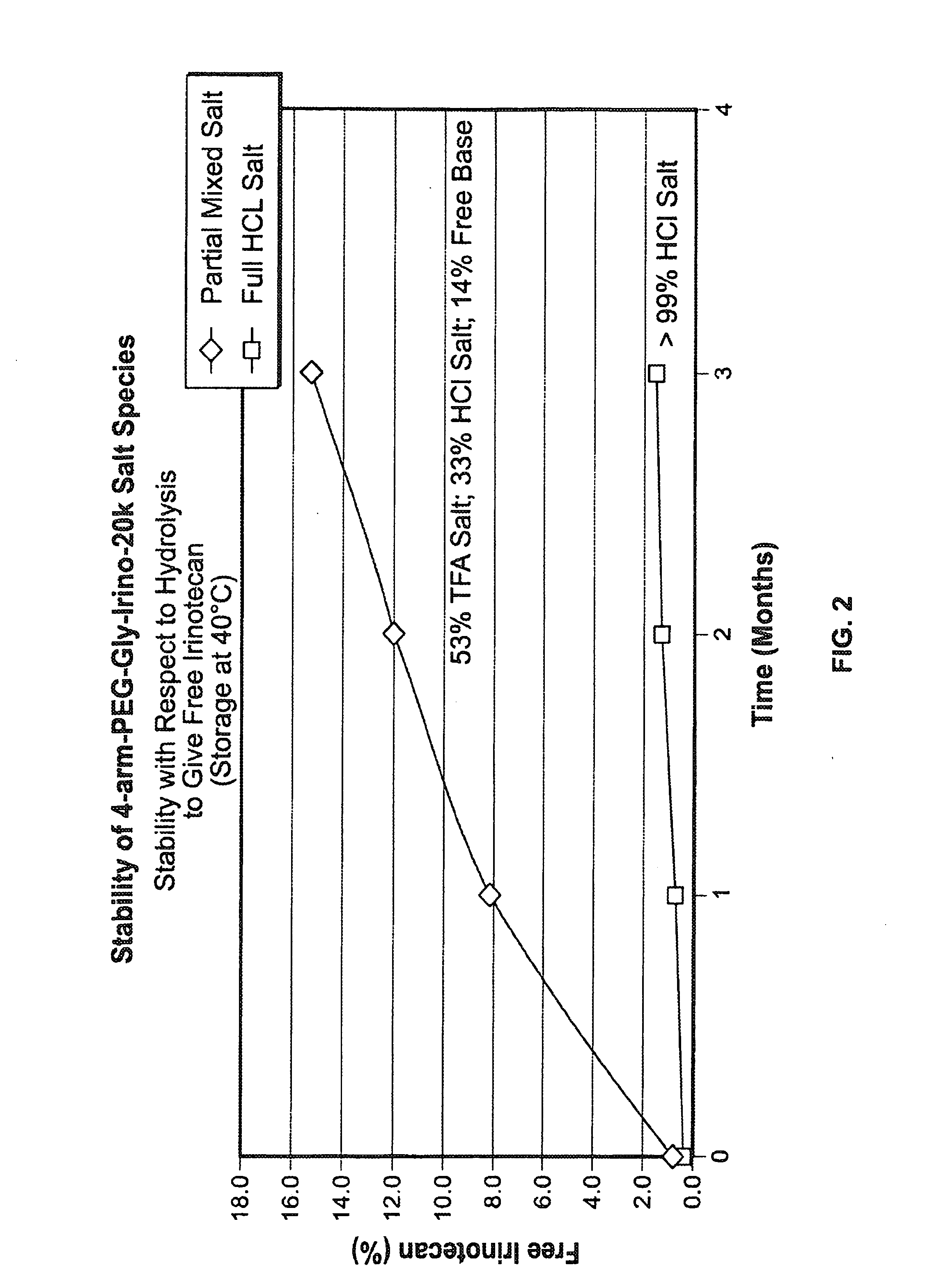
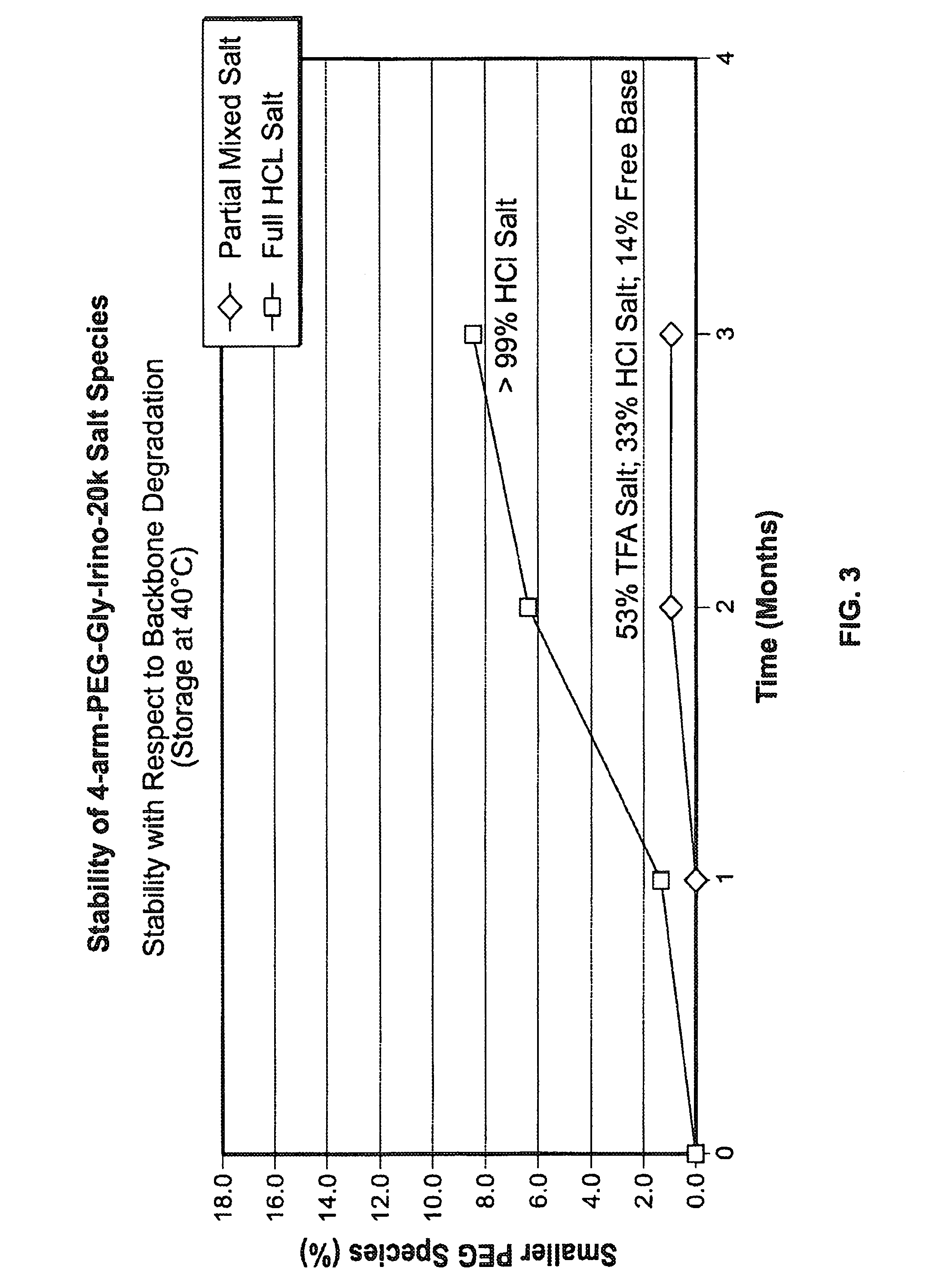
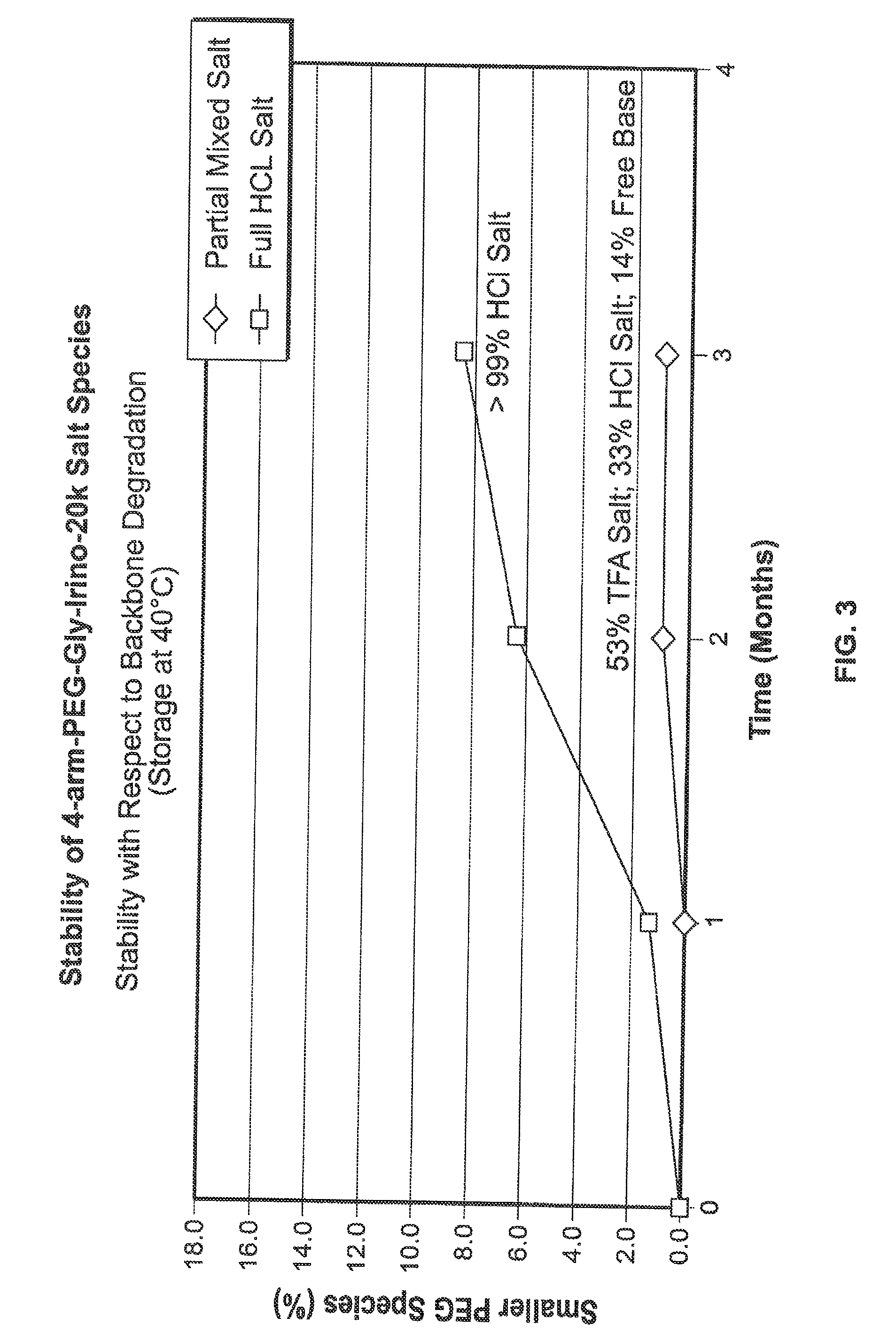
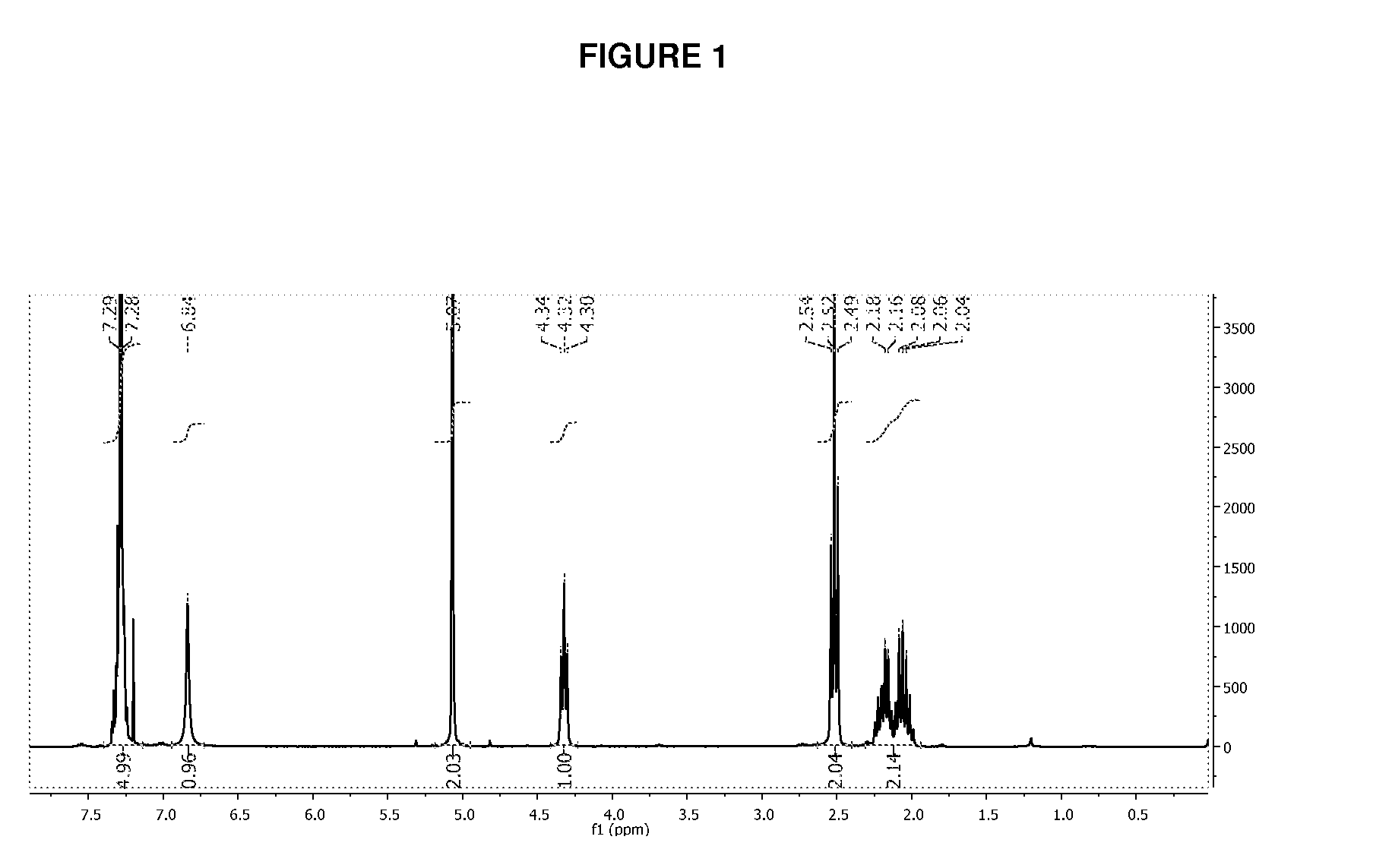
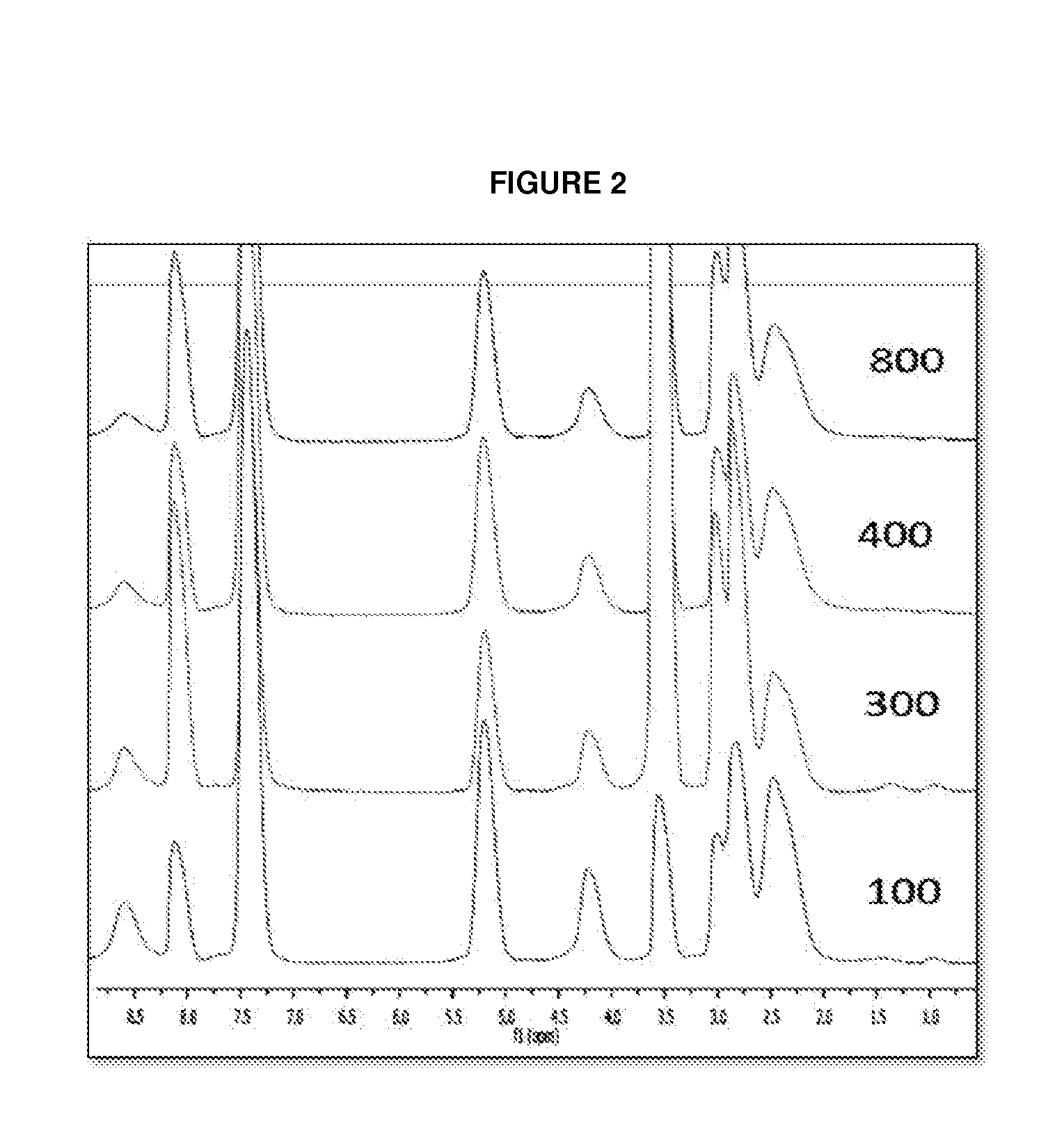
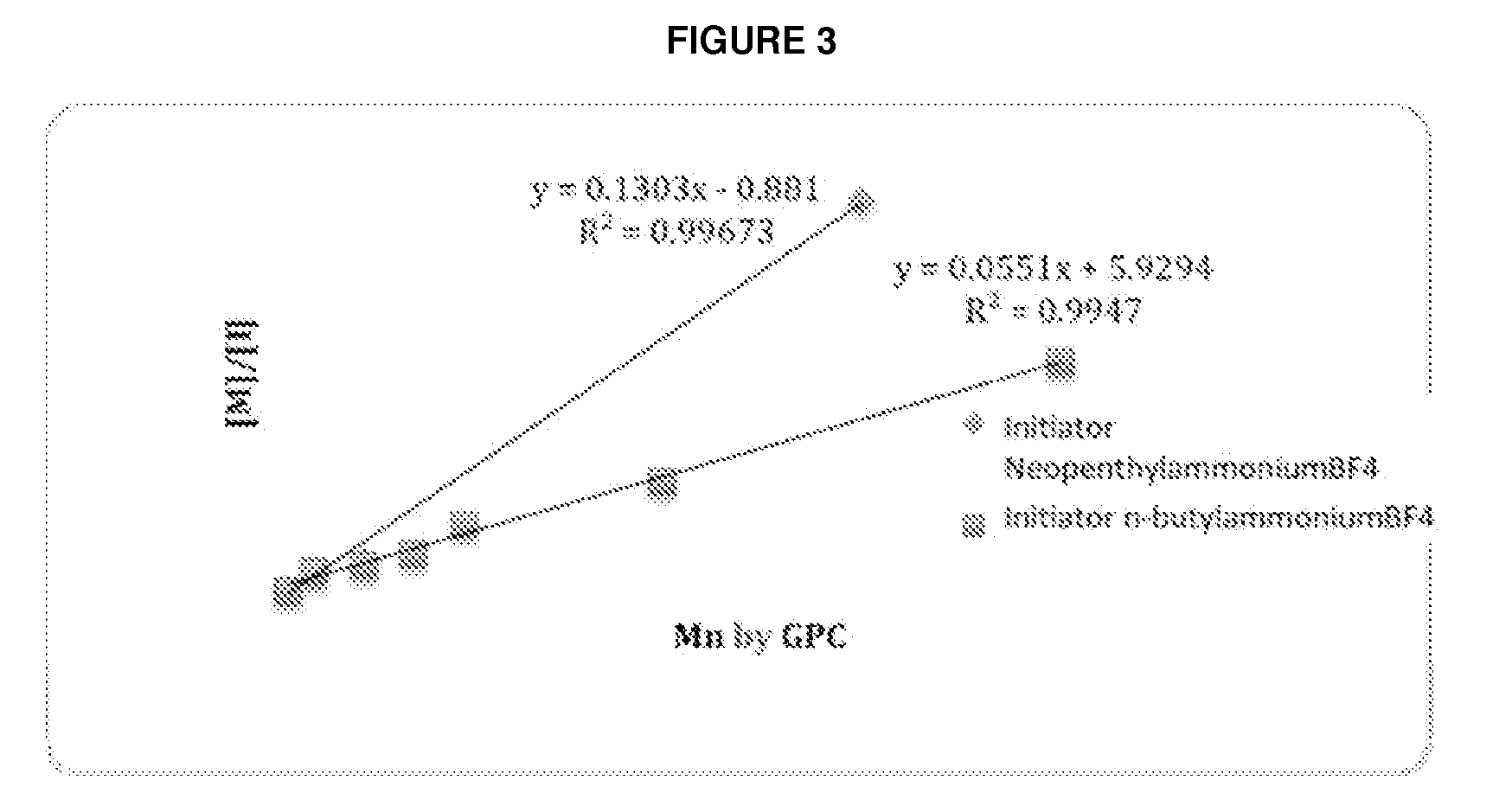
Acid Salt Forms of Polymer-Drug Conjugates and Alkoxylation Methods
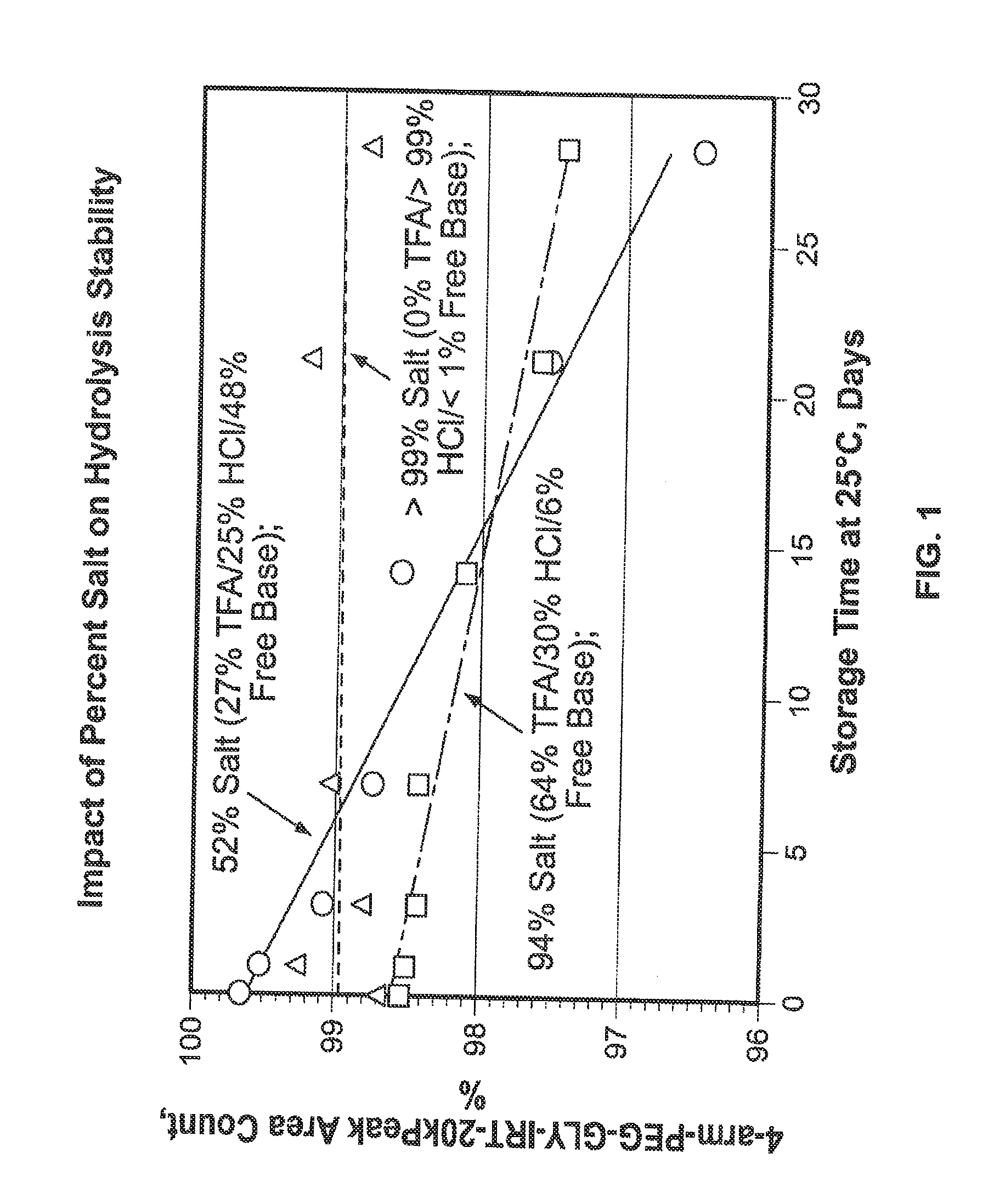
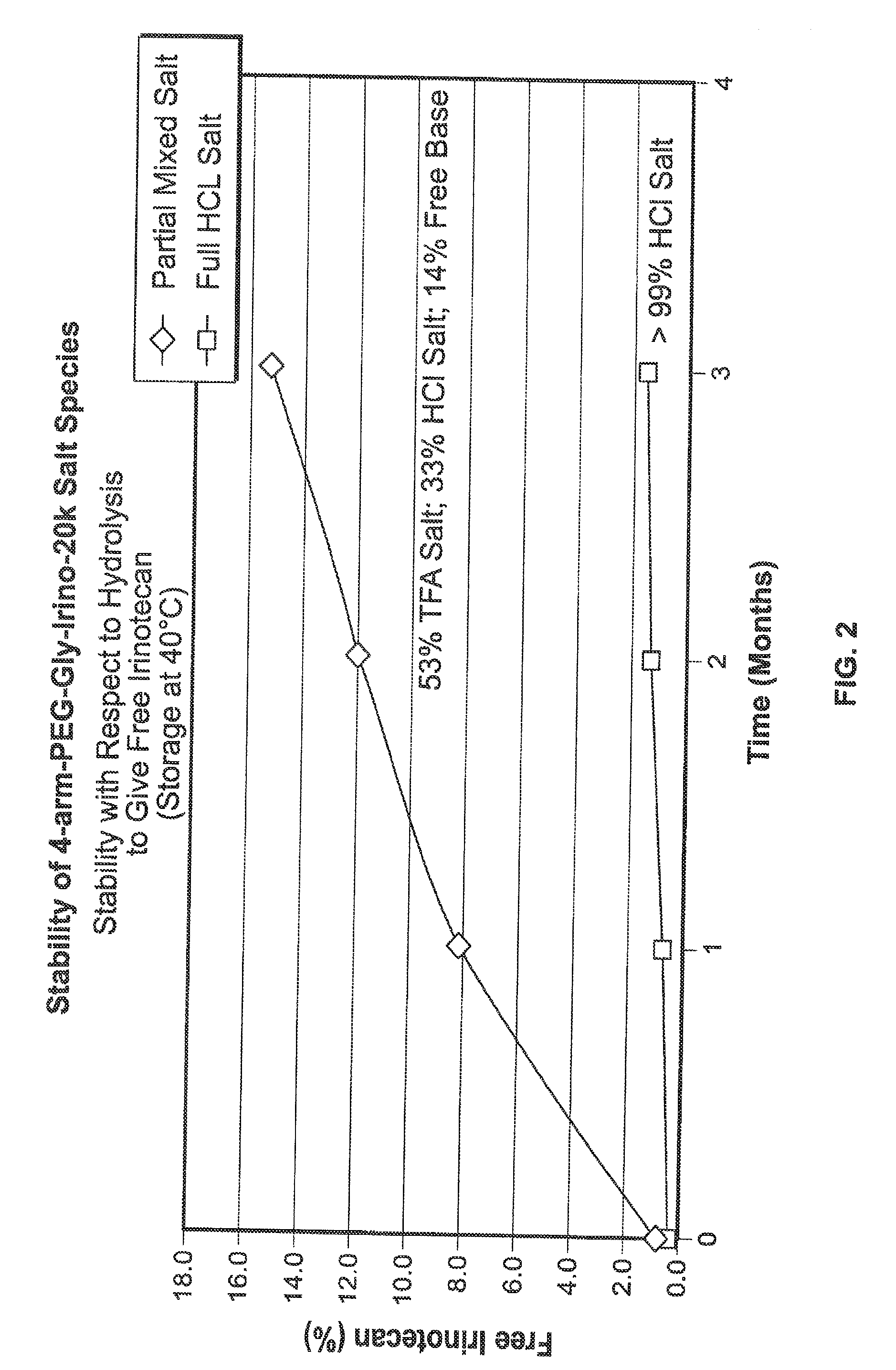
Among other aspects, provided herein is a mixed-acid salt of a water-soluble polymer-drug conjugate, along with related methods of making and using the same. The mixed-salt acid salt is stably formed, and appears to be more resistant to hydrolytic degradation than the corresponding predominantly pure acid salt or free base forms of the polymer-drug conjugate. The mixed acid salt is reproducibly prepared and recovered, and provides surprising advantages over non-mixed acid salt forms of the water-soluble polymer drug conjugate.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Biodegradable, water soluble and ph responsive poly(organo)phosphazenes
InactiveUS20130324490A1Slow drug releaseDelayed therapeutic actionBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsMedicineWater soluble
The present invention relates in general to the field of targeted drug delivery of anti-cancer drugs. More precisely, the present invention concerns polymer drug conjugates, namely, conjugates of poly(organo)phosphazenes and anti-cancer drugs, wherein the conjugates are suitable to selectively release anti-cancer drugs in tumor tissue. In addition, the present invention relates to a method for manufacturing such poly(organo)phosphazene molecule conjugates, to poly(organo)phosphazene molecule conjugates for use in medicine, in particular, to poly(organo)phosphazene molecule conjugates for use in the treatment of cancer, and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such poly(organo)phosphazene molecule conjugates.
Owner:JOHANNES KEPLER UNIVERSITY OF LINZ
Targeting carrier material and targeting micelle preparation of liver tumors and preparation methods thereof
ActiveCN108904447AImprove hydrophobicityGood water solubilityKetone active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityDrug release
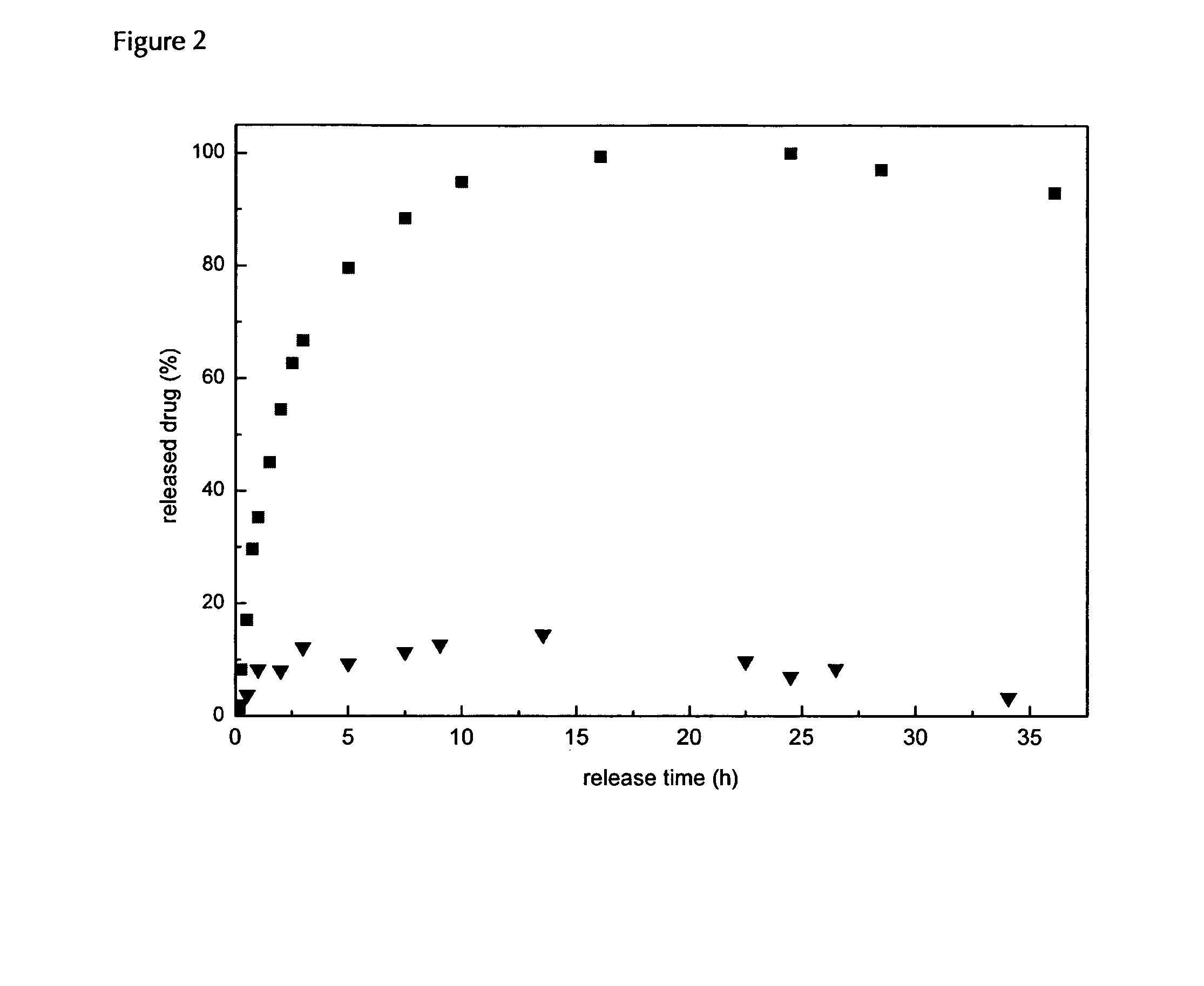
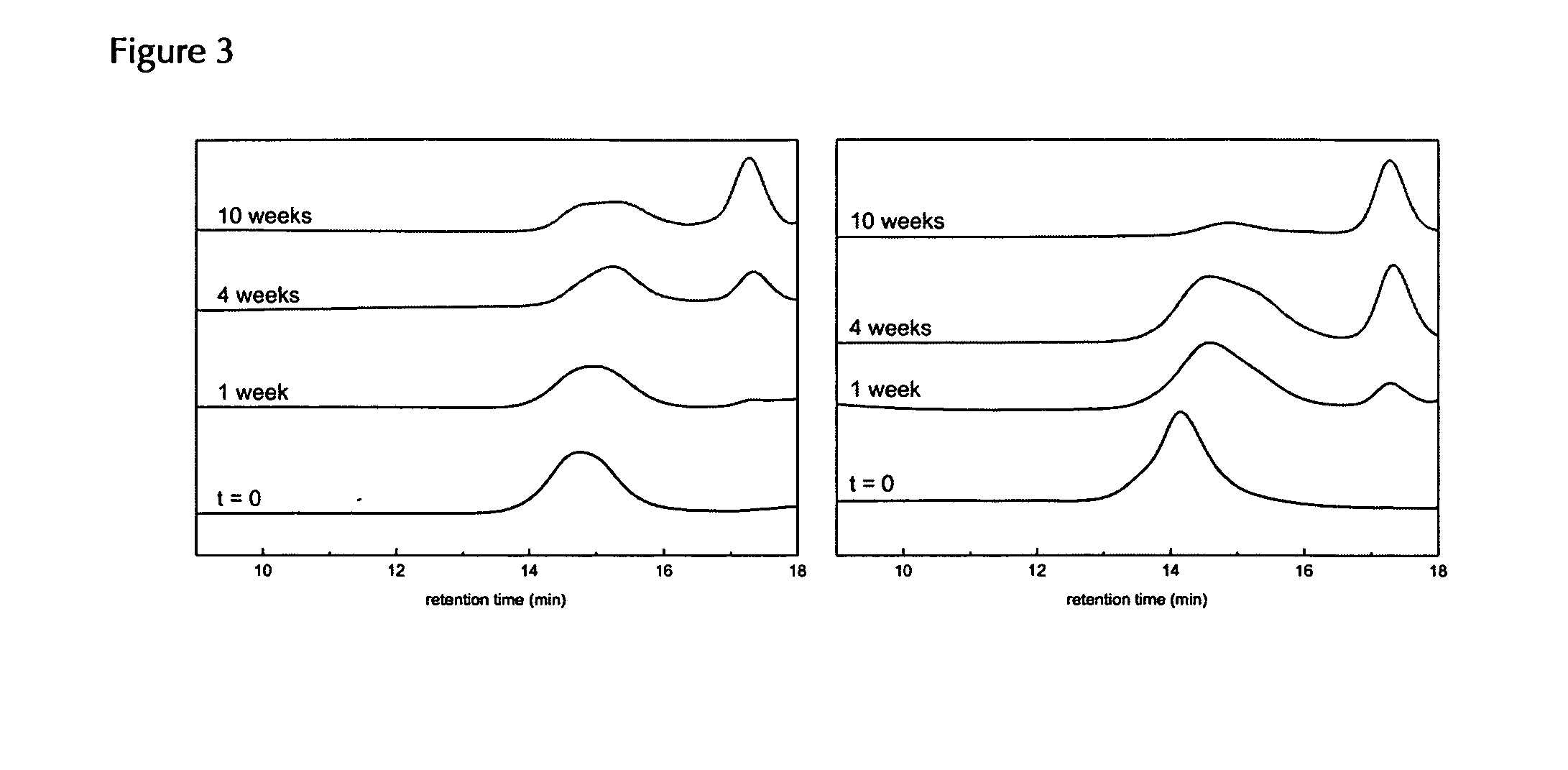
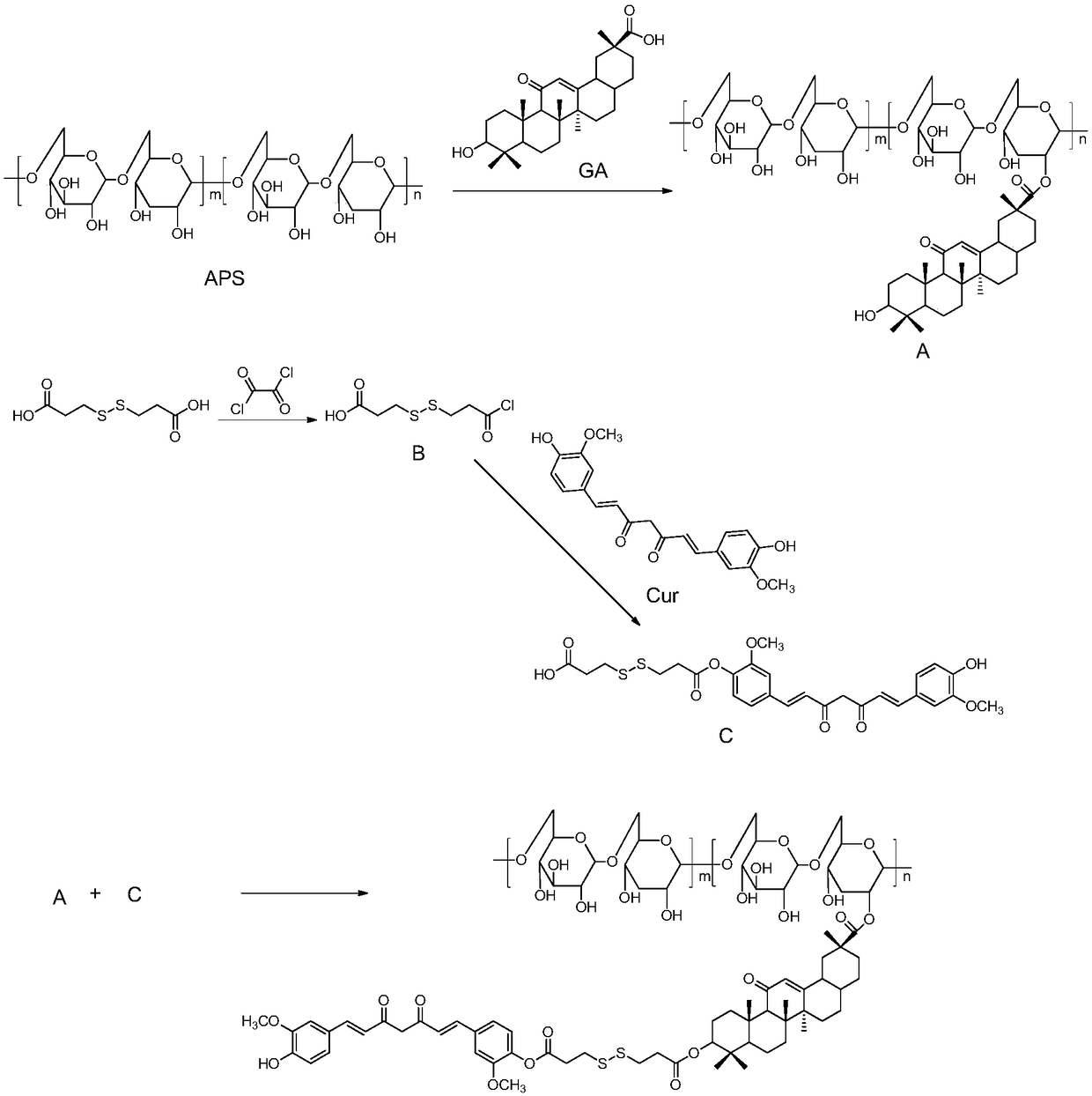
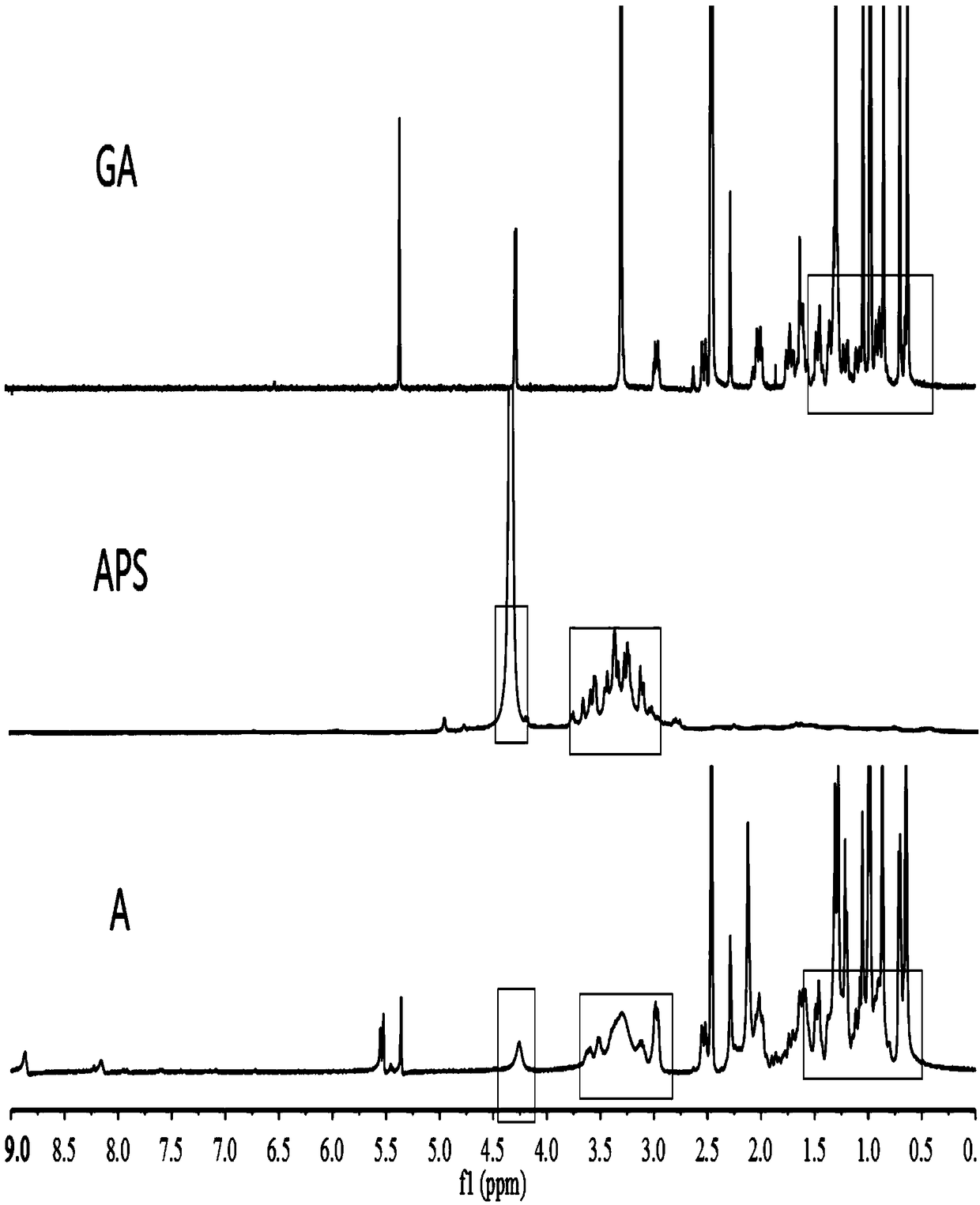
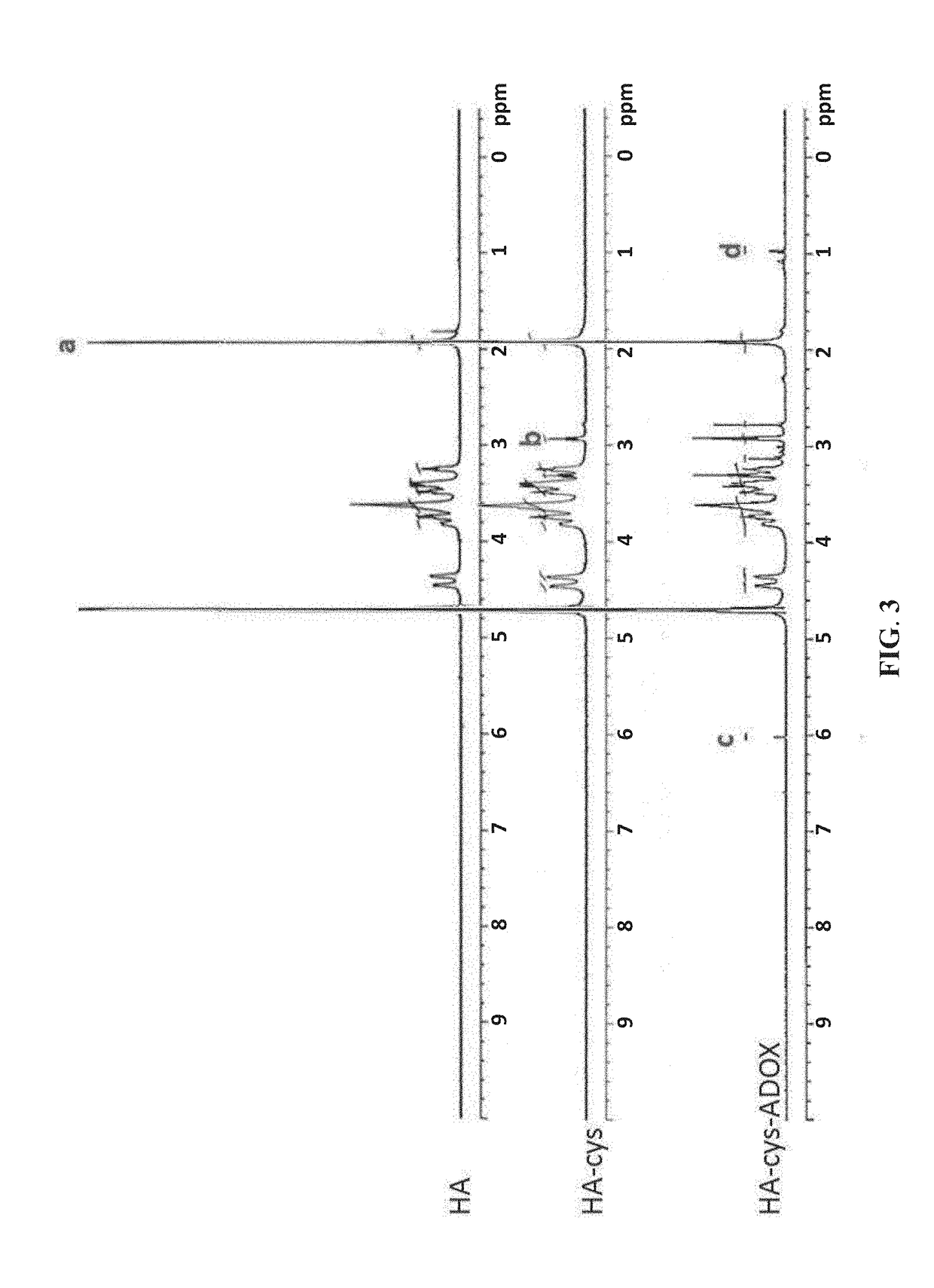
The invention relates to the technical field of targeted drug carriers and preparations, in particular to a targeting carrier material and a targeting micelle preparation of liver tumors and preparation methods thereof. The targeting carrier material of the liver tumors is mainly formed by sequentially and covalently connecting angelica polysaccharide, glycyrrhetinic acid and antitumor drugs for the liver tumors, wherein the glycyrrhetinic acid and the antitumor drugs for the liver tumors are covalently connected through disulfide bonds. The micelle preparation comprises the targeting carriermaterial of the liver tumors and the antitumor drugs for the liver tumors, and the antitumor drugs for the liver tumors are encapsulated in the targeting carrier material of the liver tumors. The carrier material has reduction sensitivity, and can realize targeting selection on a tumor microenvironment with high reducing substances; the micelle preparation is formed by self-assembly of the carriermaterial and the antitumor drugs for the liver tumors; and the solubility and stability of hydrophobic drugs are enhanced by utilizing the characteristics of polymer-drug conjugates of the carrier material, and drug release can be carried out under the reduction environment.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
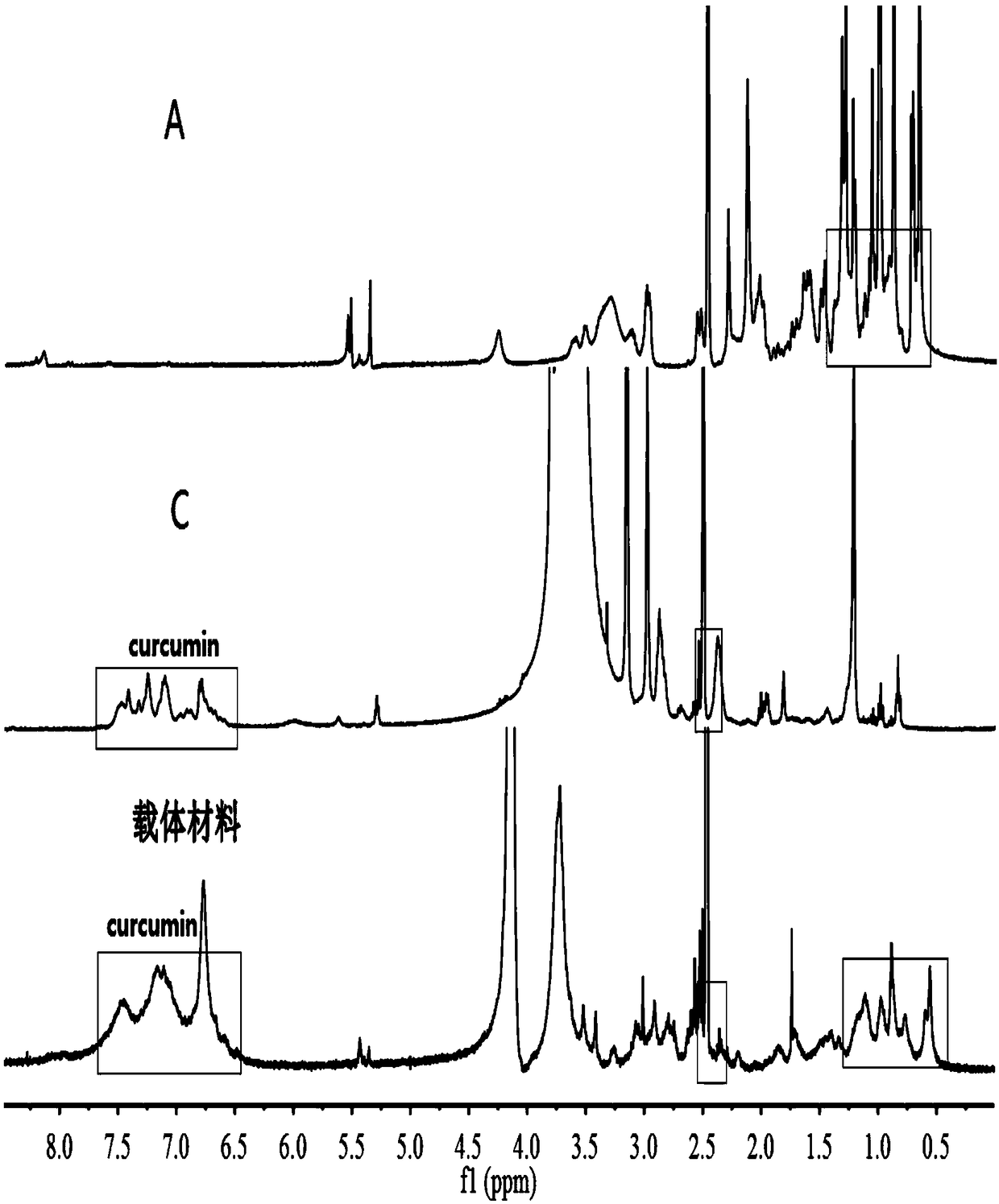
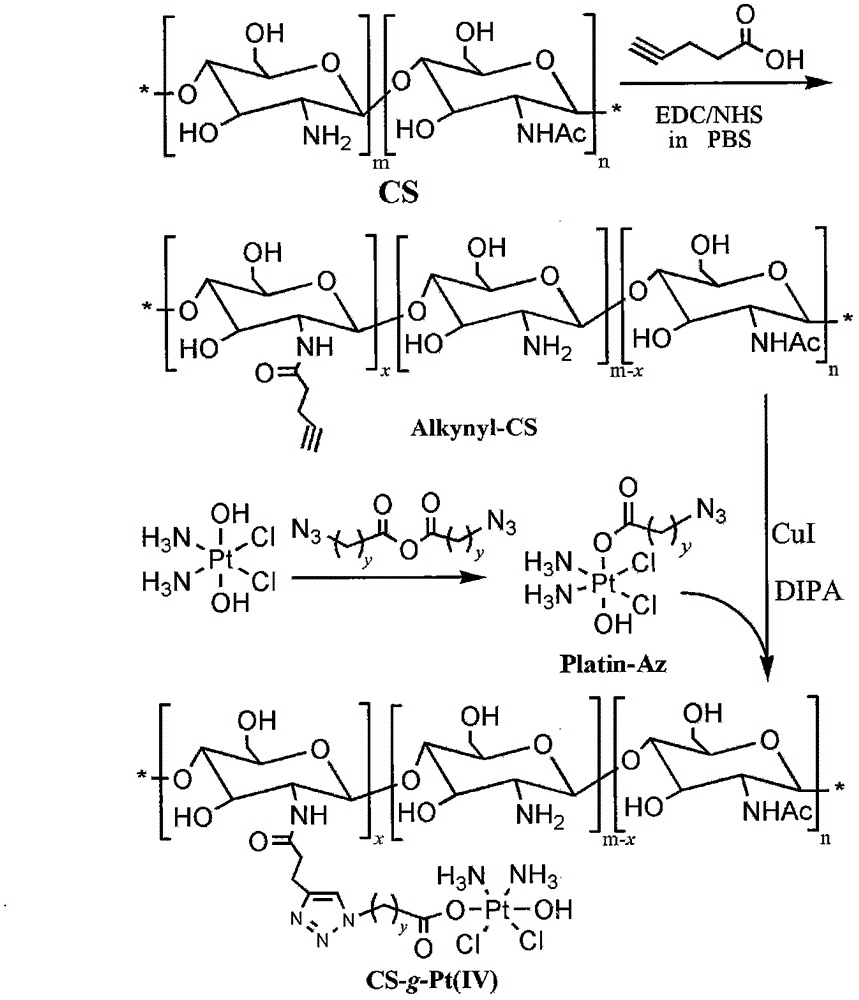
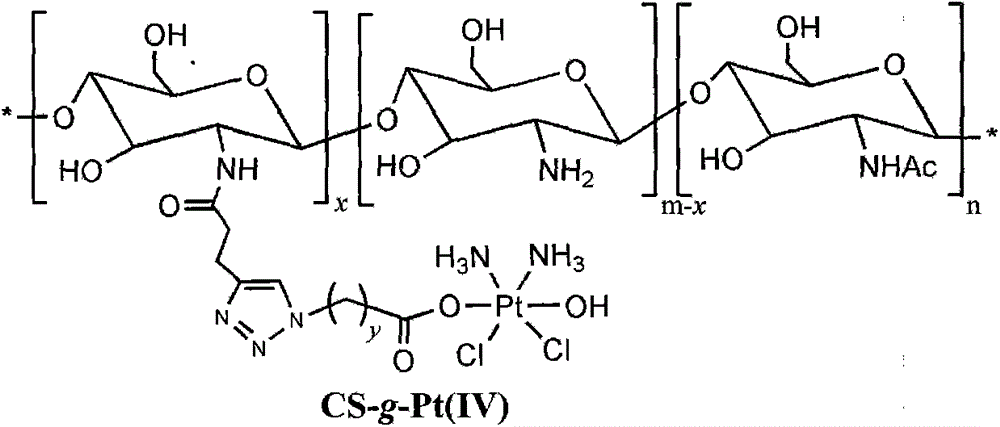
Chitosan-platinum (IV) prodrug conjugate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104587486AProlong blood circulation timeReduce premature releasePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsChemical reactionClick chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer drugs, and particularly relates to a chitosan-platinum (IV) prodrug conjugate and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out amide chemical reaction on chitosan and 4-pentyne acid under the action of a combined catalyst NHS / EDC to obtain alkynyl functionalized chitosan, and then carrying out click chemistry reaction together with a nitrine-modified Pt (IV) coordination compound to obtain the chitosan-platinum (IV) prodrug conjugate. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of mild reaction condition, good selectivity, high efficiency and controllability; the drug leakage caused by incomplete reaction can be reduced; the obtained conjugate enters a tumor cell, and is transformed into a Pt (II) coordination compound under the action of reducing substances in the cell, so as to relatively well act on DNA to kill the tumor cells; and meanwhile, a simple and effective pathway is provided for preparation of targeted controllable light-response polymer drug conjugates.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Biologically active materials
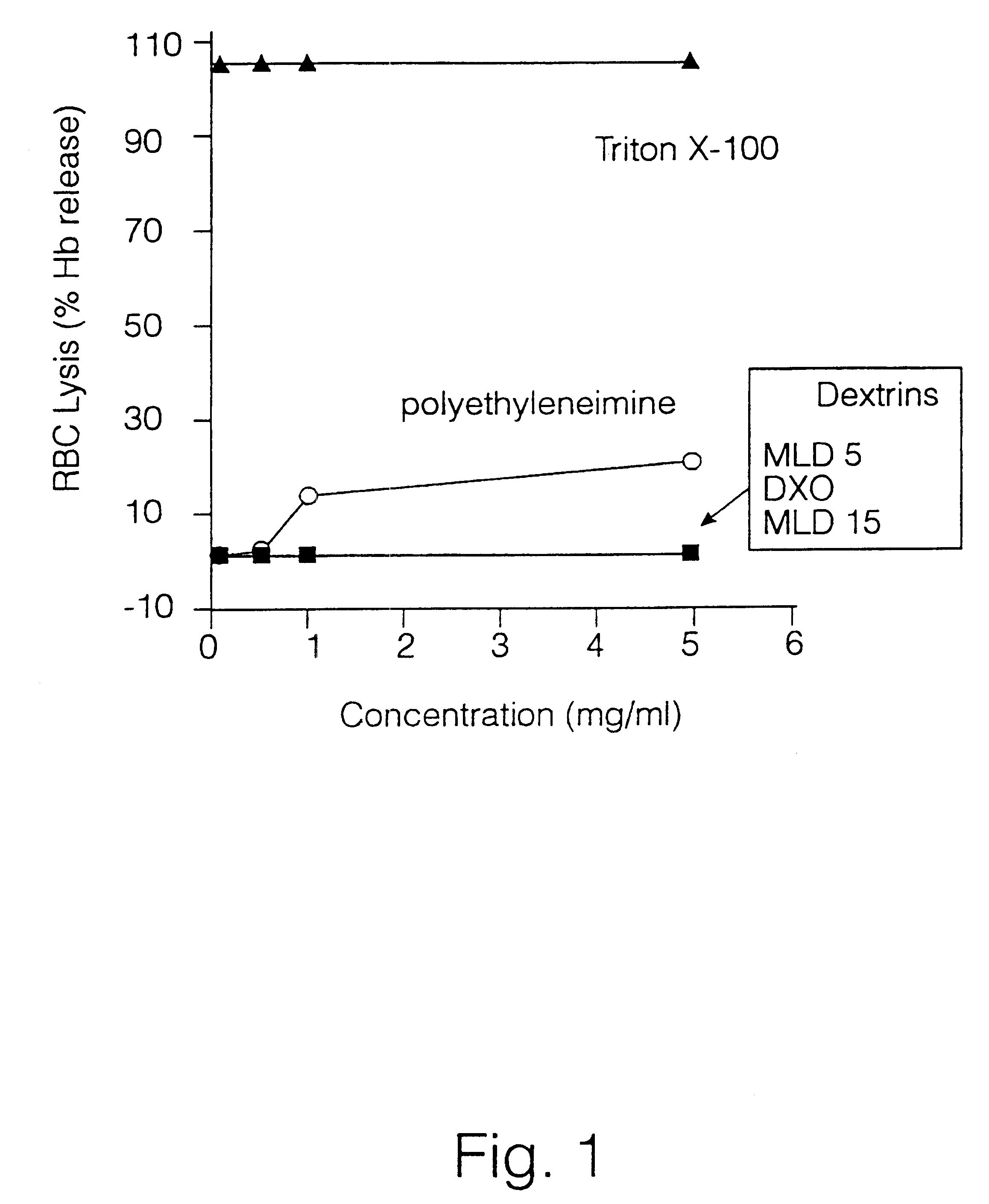
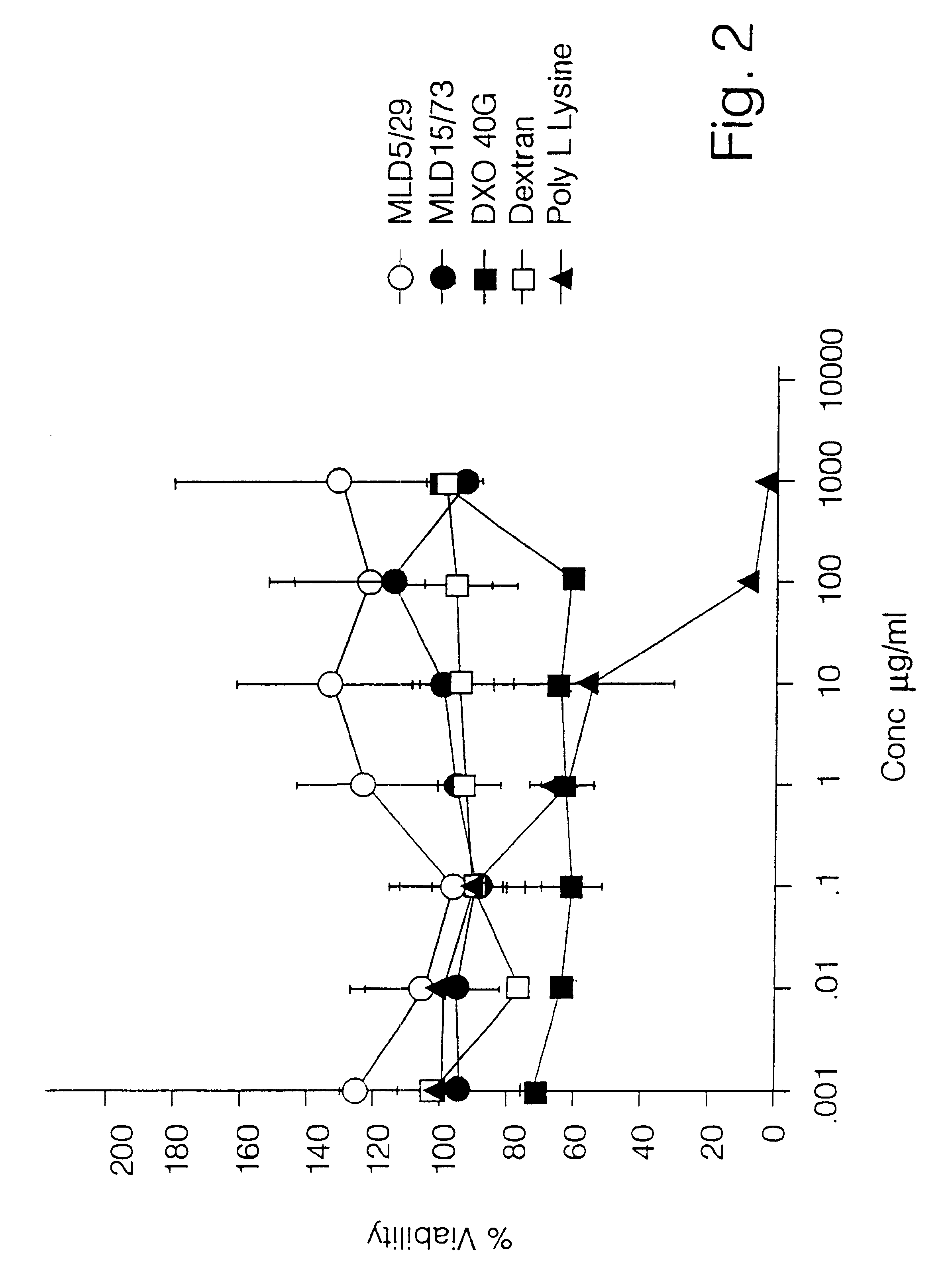
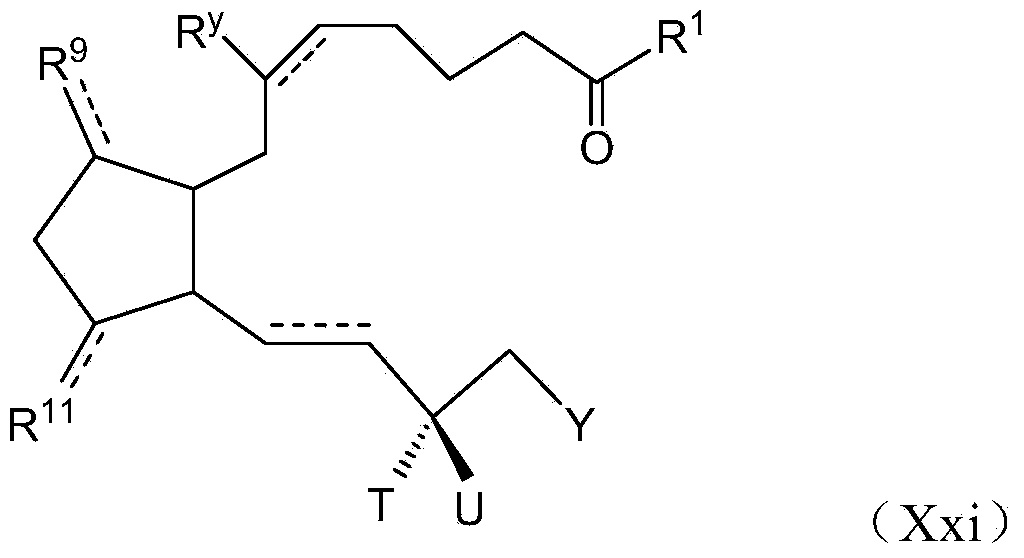
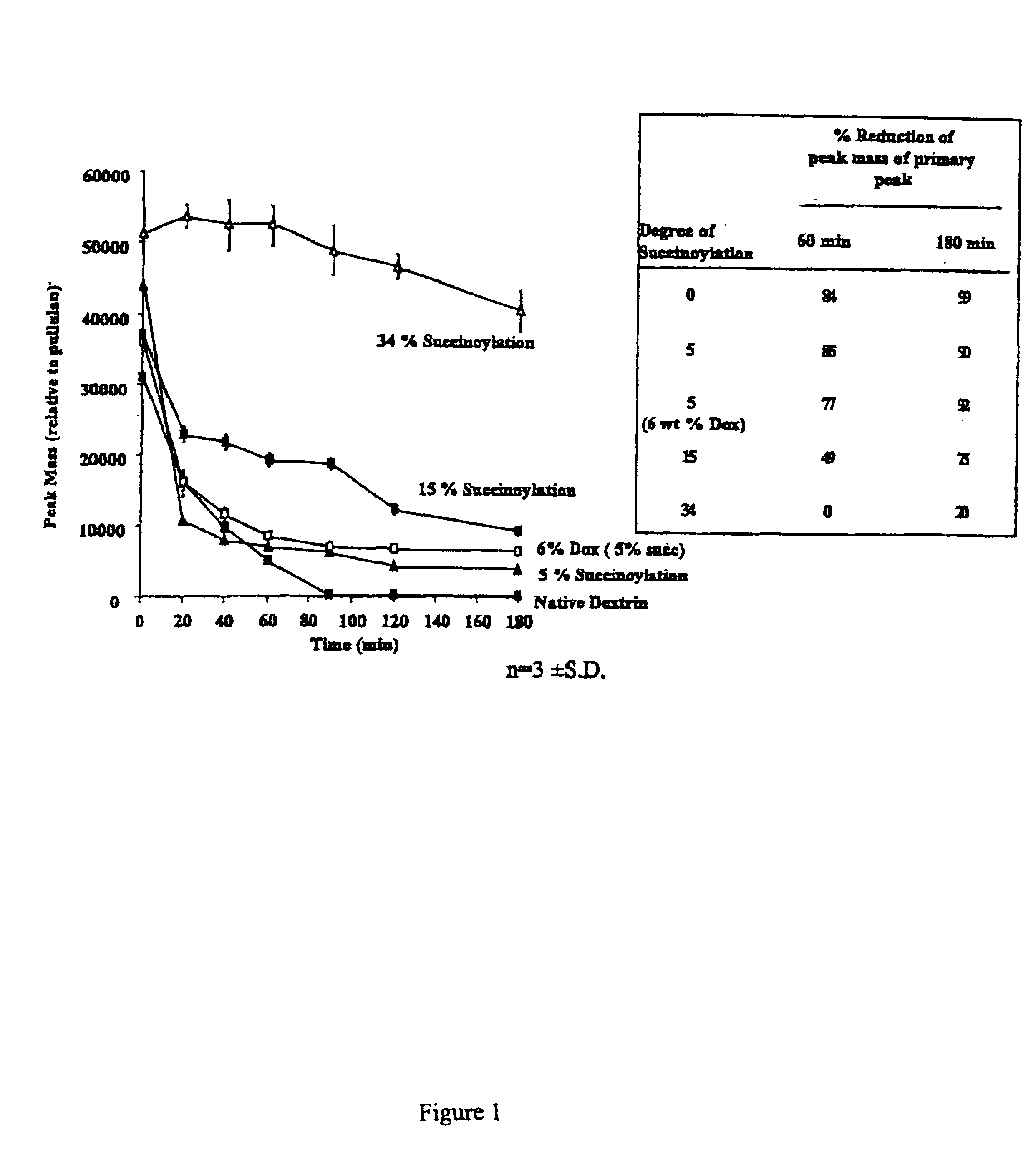
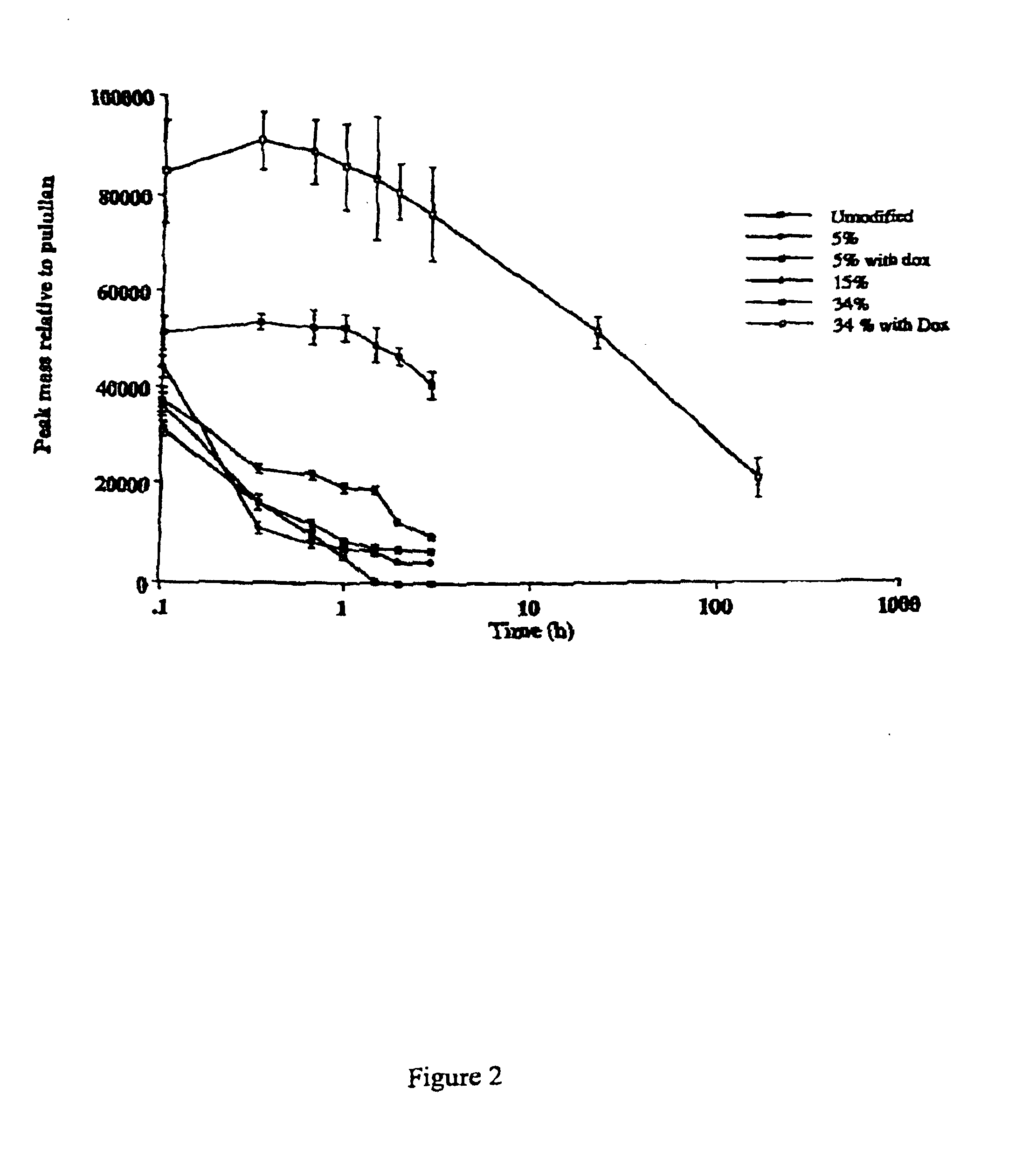
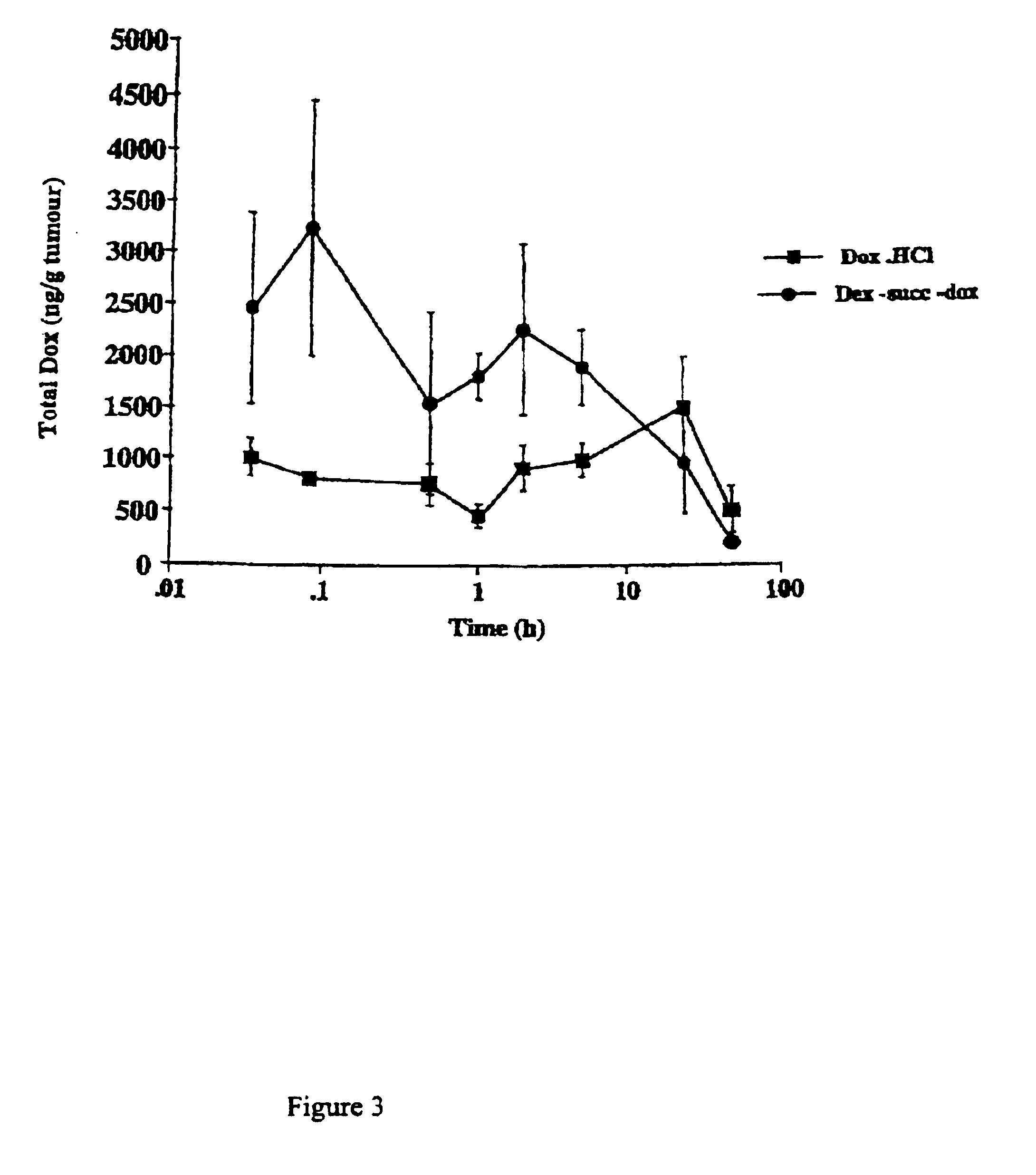
A polymer-drug conjugate, in which the polymer is the polysaccharide dextrin, linked directly or indirectly to the drug, is effective to deliver the drug to a target site and is biodegradable. The conjugate may be prepared by succinoylating dextrin followed by reaction with the drug or a derivative thereof.
Owner:ML LAB PLC
Acid salt forms of polymer-drug conjugates and alkoxylation methods
ActiveUS20150105519A1Organic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationWater solublePolymer-drug conjugates
Among other aspects, provided herein is a mixed-acid salt of a water-soluble polymer-drug conjugate, along with related methods of making and using the same. The mixed-salt acid salt is stably formed, and appears to be more resistant to hydrolytic degradation than the corresponding predominantly pure acid salt or free base forms of the polymer-drug conjugate. The mixed acid salt is reproducibly prepared and recovered, and provides surprising advantages over non-mixed acid salt forms of the water-soluble polymer drug conjugate.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Controlled Synthesis of Polyglutamates with Low Polydispersity and Versatile Architectures
ActiveUS20150087788A1Lowering indexDegree of improvementRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsDispersityImaging agent
Polyglutamates are well known to be highly biocompatible, biodegradable and multifunctional polymers, which have been already used as building blocks in polymer drug conjugates and polymeric micelles. Those systems have been applied to various medical applications ranging from therapy to molecular imaging. Furthermore a polyglutamic acid (PGA) paclitaxel conjugate has already entered clinical studies (Opaxio™ PGA-PTX conjugate currently in phase III of Clinical trials).In this context, a synthetic pathway to a plethora functional polyglutamates (homopolymers, block-co-polymers, triblocks) with well-defined structure, adjustable molecular weight (Mw) and low dispersity (D=Mw / Mn<1.2) applying the ring opening polymerization (ROP) of N-carboxyanhydrides (NCA) has been developed. Additionally, the acid moieties of the polyglutamates can be activated with 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium (DMTMM) and various functionalities can be easily introduced by “post-polymerization modification” yielding a set orthogonal reactive attachment sides. The reactive moieties, such as azides, maleimides, thiols, alkynes (linear or cyclic) offer the opportunity of specific conjugation of the drugs, targeting moieties or markers. Besides introducing reactive groups the functionalization strategy was also used for PEGylation of PGA reducing charge induced interactions and therefore pharmacological properties, such as blood circulation time may be adjusted.In summary, a tool kit of various polyglutamates has been developed enabling the synthesis of a variety of polymer drug conjugates or polymer based imaging agents. The functional polymeric precursors developed will allow us to functionalize and therefore adjust the polymer properties to a desired application.
Owner:FUNDACION DE LA COMUNIDAD VALENCIANA CENT DE INVESTIGACION PRINCIPE FELIPE
Controlled synthesis of polyglutamates with low polydispersity and versatile architectures
ActiveUS9623125B2Degree of improvementImprove versatilityRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsDispersityImaging agent
Polyglutamates are well known to be highly biocompatible, biodegradable and multifunctional polymers, which have been already used as building blocks in polymer drug conjugates and polymeric micelles. Those systems have been applied to various medical applications ranging from therapy to molecular imaging. Furthermore a polyglutamic acid (PGA) paclitaxel conjugate has already entered clinical studies (Opaxio™ PGA-PTX conjugate currently in phase III of Clinical trials).In this context, a synthetic pathway to a plethora functional polyglutamates (homopolymers, block-co-polymers, tribocks) with well-defined structure, adjustable molecular weight (Mw) and low dispersity (D=Mw / Mn<1.2) applying the ring opening polymerization (ROP) of N-carboxyanhydrides (NCA) has been developed. Additionally, the acid moieties of the polyglutamates can be activated with 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium (DMTMM) and various functionalities can be easily introduced by “post-polymerization modification” yielding a set orthogonal reactive attachment sides. The reactive moieties, such as azides, maleimides, thiols, akynes (linear or cyclic) offer the opportunity of specific conjugation of the drugs, targeting moieties or markers. Besides introducing reactive groups the functionalization strategy was also used for PEGylation of PGA reducing charge induced interactions and therefore pharmacological properties, such as blood circulation time may be adjusted.In summary, a tool kit of various polyglutamates has been developed enabling the synthesis of a variety of polymer drug conjugates or polymer based imaging agents. The functional polymeric precursors developed will allow us to functionalize and therefore adjust the polymer properties to a desired application.
Owner:FUNDACION DE LA COMUNIDAD VALENCIANA CENT DE INVESTIGACION PRINCIPE FELIPE
Vascular delivery systems
ActiveUS20120014904A1Reduce incidenceShorten the progressOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsVascular endotheliumTherapeutic effect
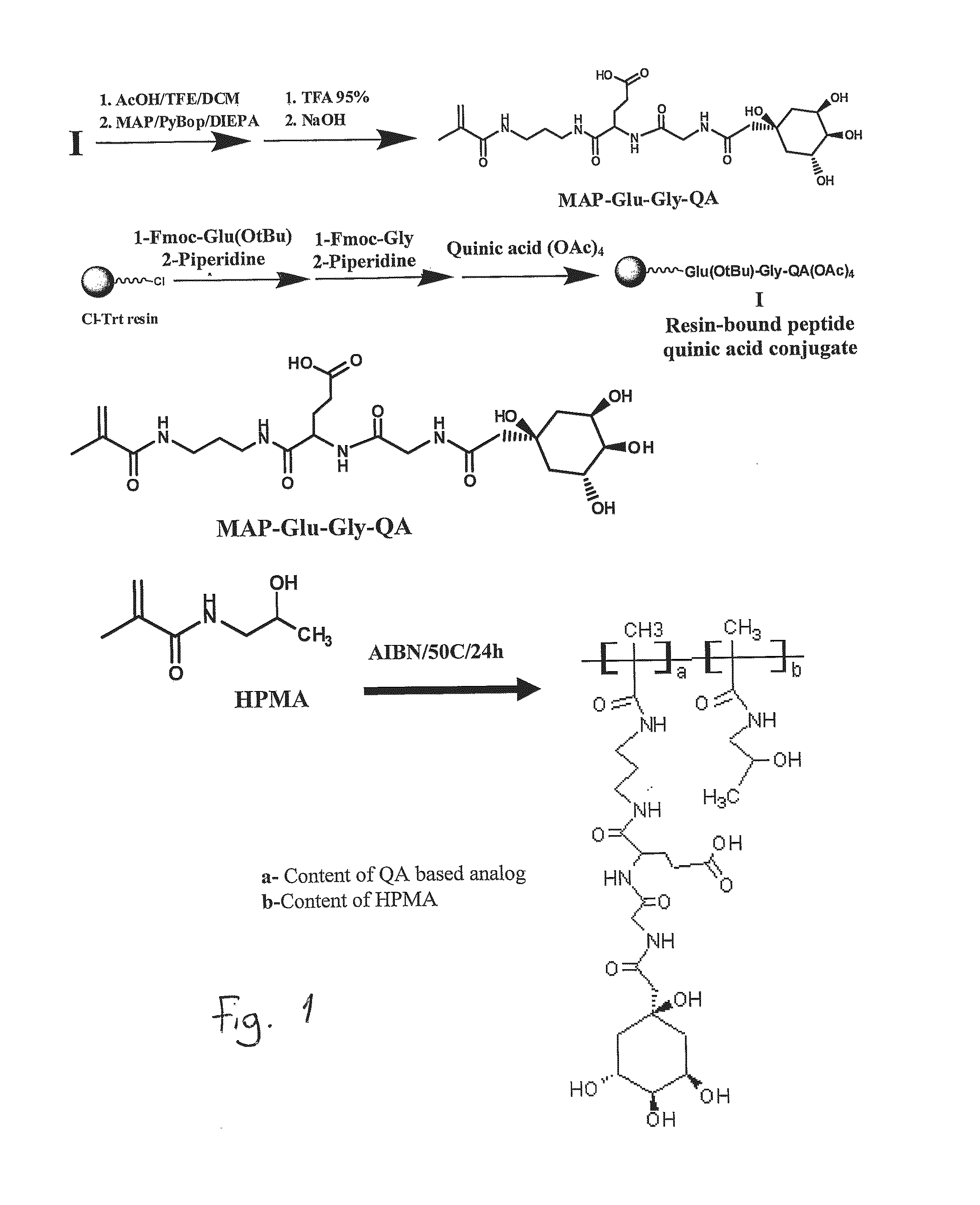
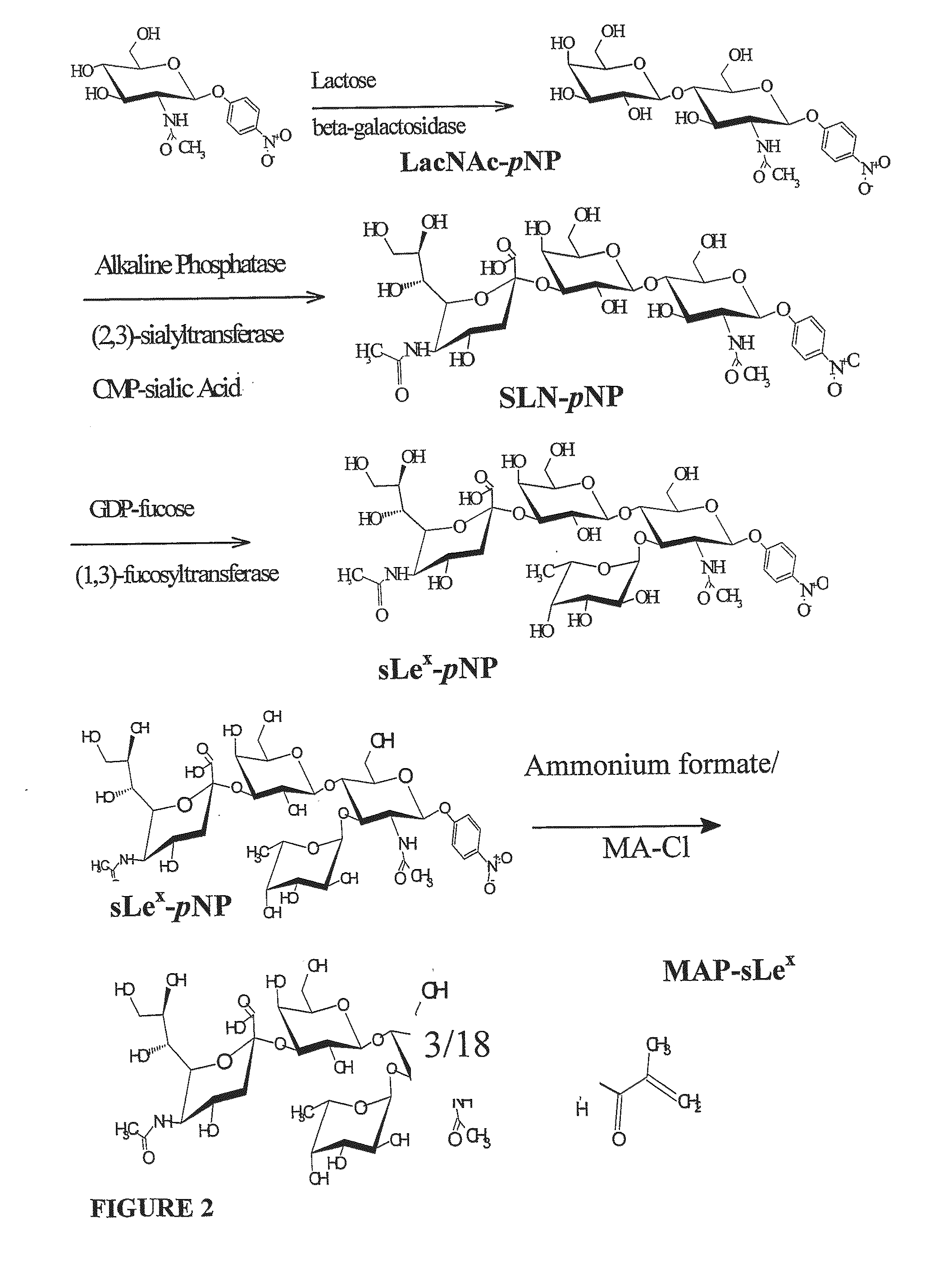
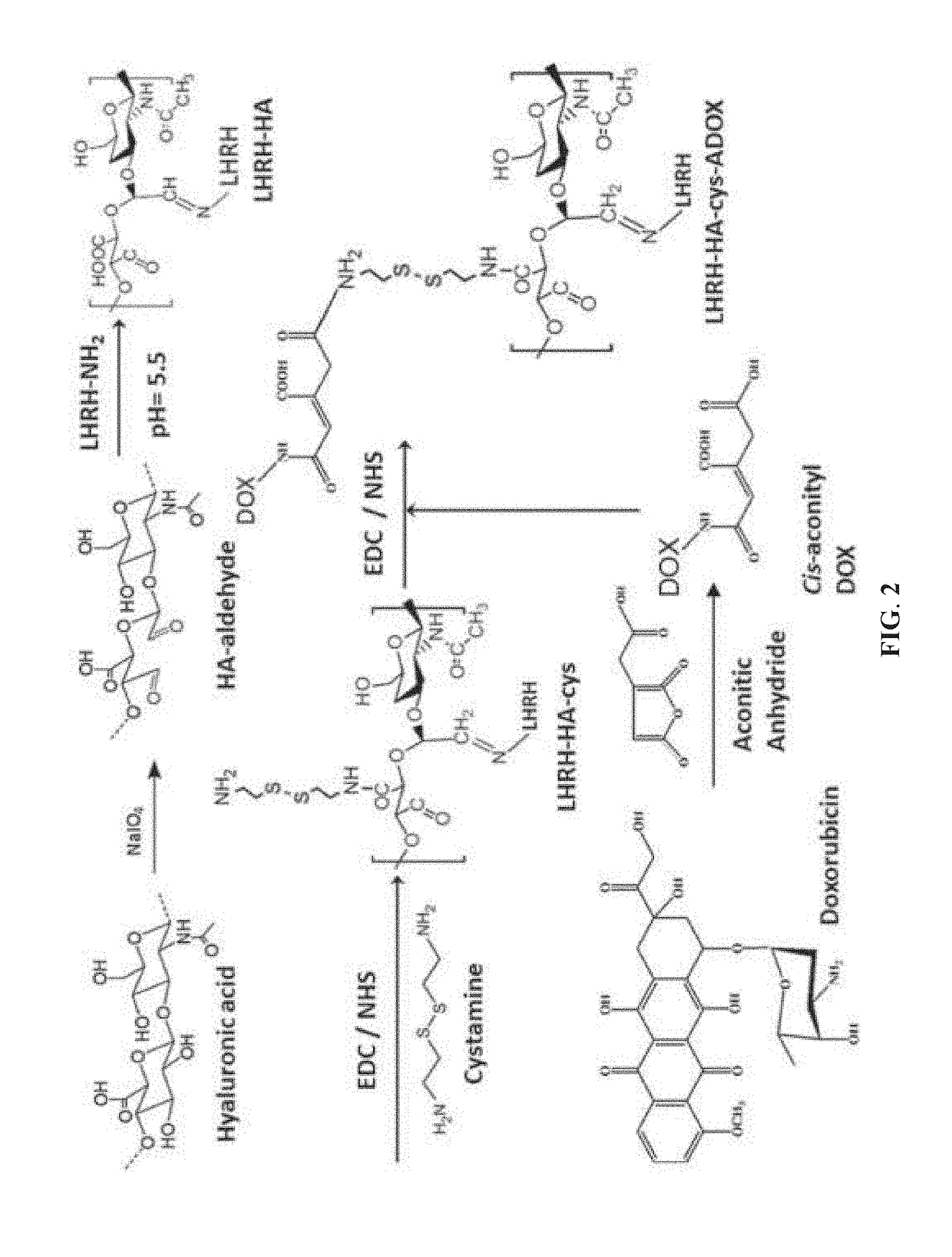
The site-specific expression of selectins on endothelial cells of blood vessels during angiogenesis provides an opportunity to target anti-cancer drugs to the vascular endothelium to extend the range of the therapeutic effect. This invention describes an innovative drug targeting strategy for the selective delivery of the anticancer drugs to endothelial cells by means of polymer-drug conjugates modified with a carbohydrate ligand for the vascular selectins. A model chemotherapeutic drug, doxorubicin, and the E-selectin ligand, sLex, are attached to a biocompatible polymer (HPMA). The selective binding, cellular uptake, intracellular fate, and cell cytotoxicity of the polymer-bound drug are investigated in human endothelial cells.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
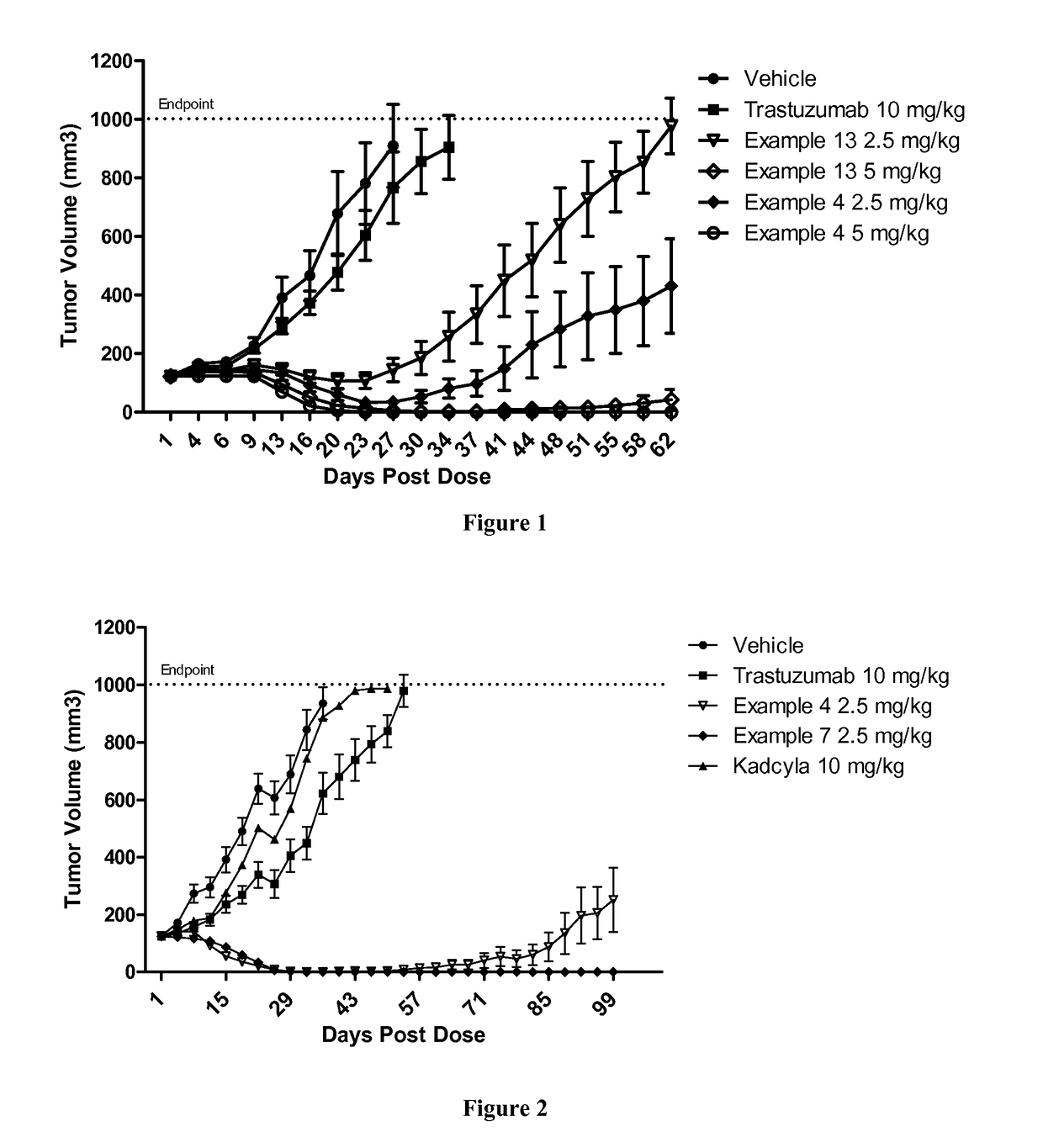
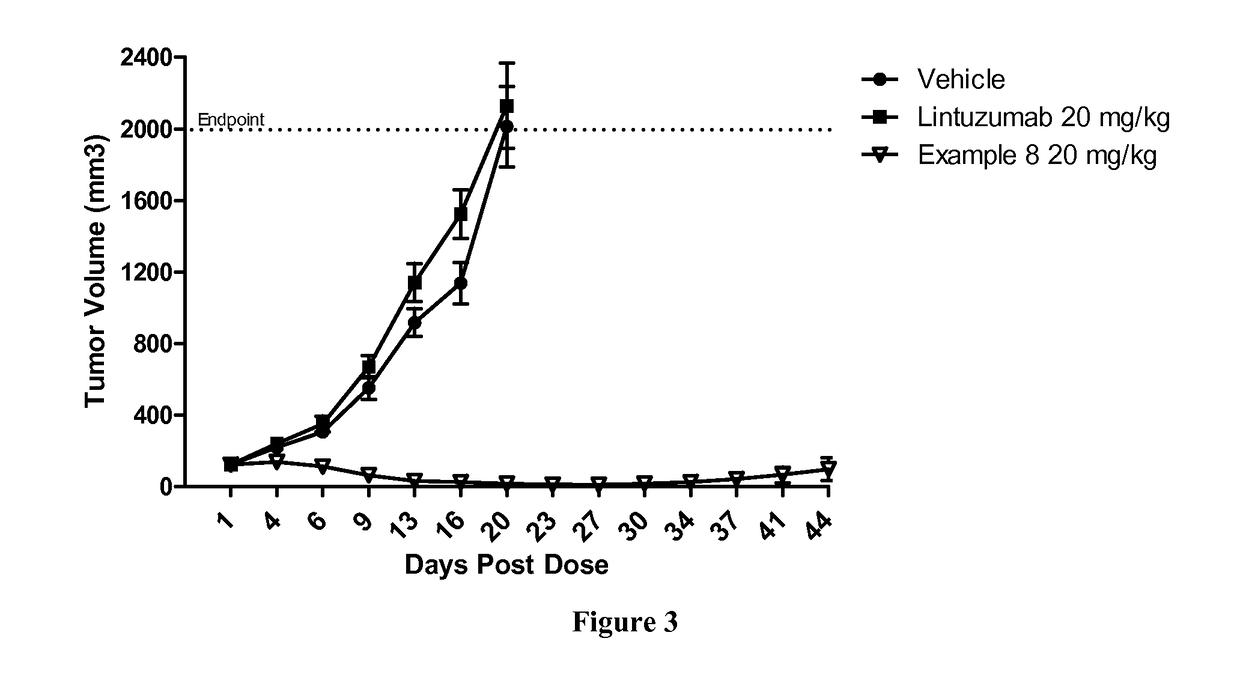
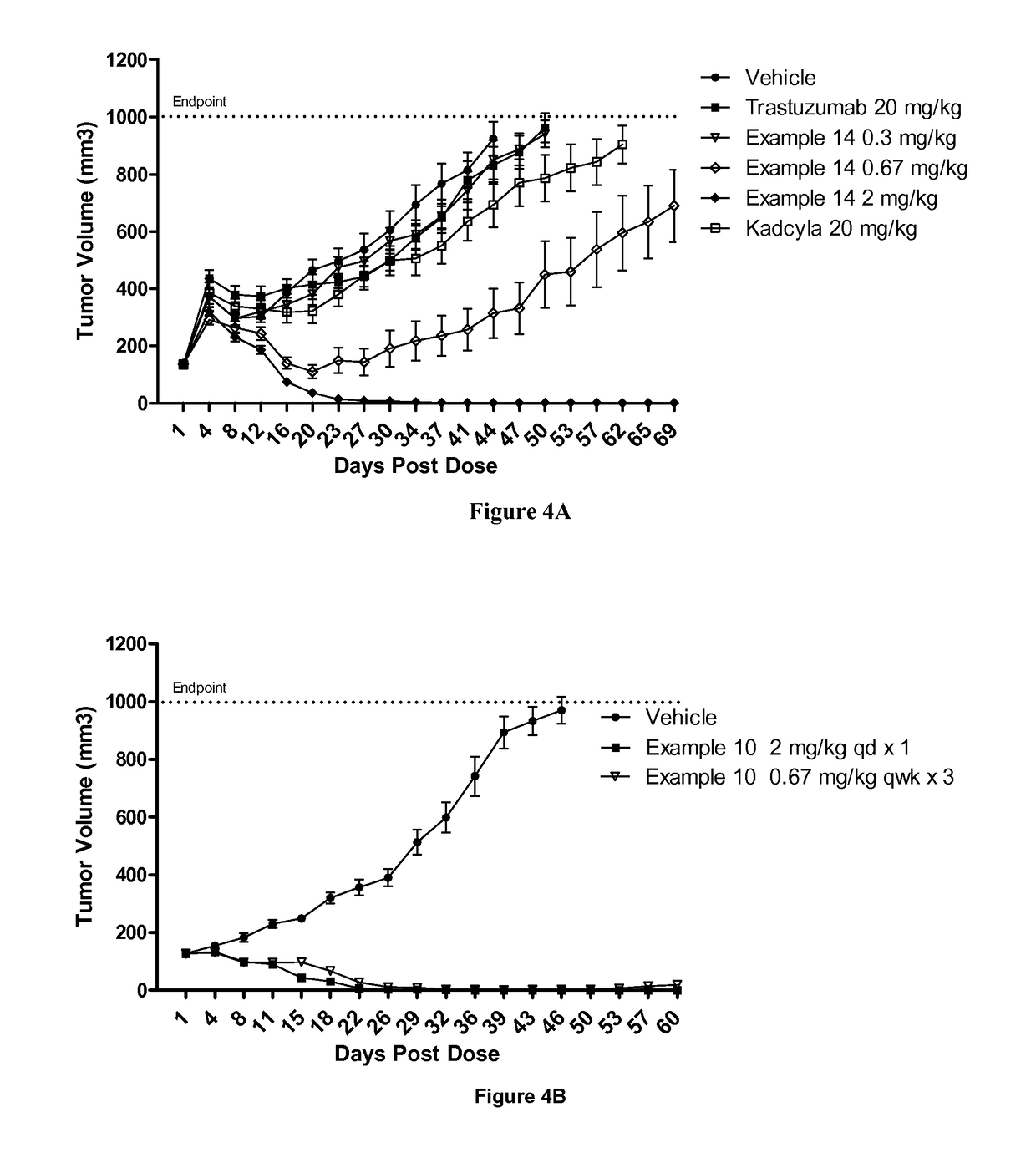
Protein-polymer-drug conjugates
ActiveUS9849191B2Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCombinatorial chemistryPolymer-drug conjugates
A polymeric scaffold useful for conjugating with a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) to form a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate is described herein. The scaffold includes one or more terminal maleimido groups. Also disclosed is a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate prepared from the scaffold. Compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions are also described.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Protein-polymer-drug conjugates
ActiveUS10316080B2Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsPolymer-drug conjugatesStereochemistry
A polymeric scaffold useful for conjugating with a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) to form a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate is described herein. The scaffold includes one or more terminal maleimido groups. Also disclosed is a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate prepared from the scaffold. Compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions are also described.
Owner:ASANA BIOSCI
Self-assembled diblock copolymers composed of pegmema and drug bearing polymeric segments
PendingCN109982719APowder deliveryEther/acetal active ingredientsPharmaceutical SubstancesOrganic chemistry
Owner:RS研究教育咨询医学工业贸易股份有限公司
Methods of preparing stimuli-responsive multifunctional nanoparticles
ActiveUS20180250237A1Low toxicityEasy to usePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMultifunctional nanoparticlesStimuli responsive
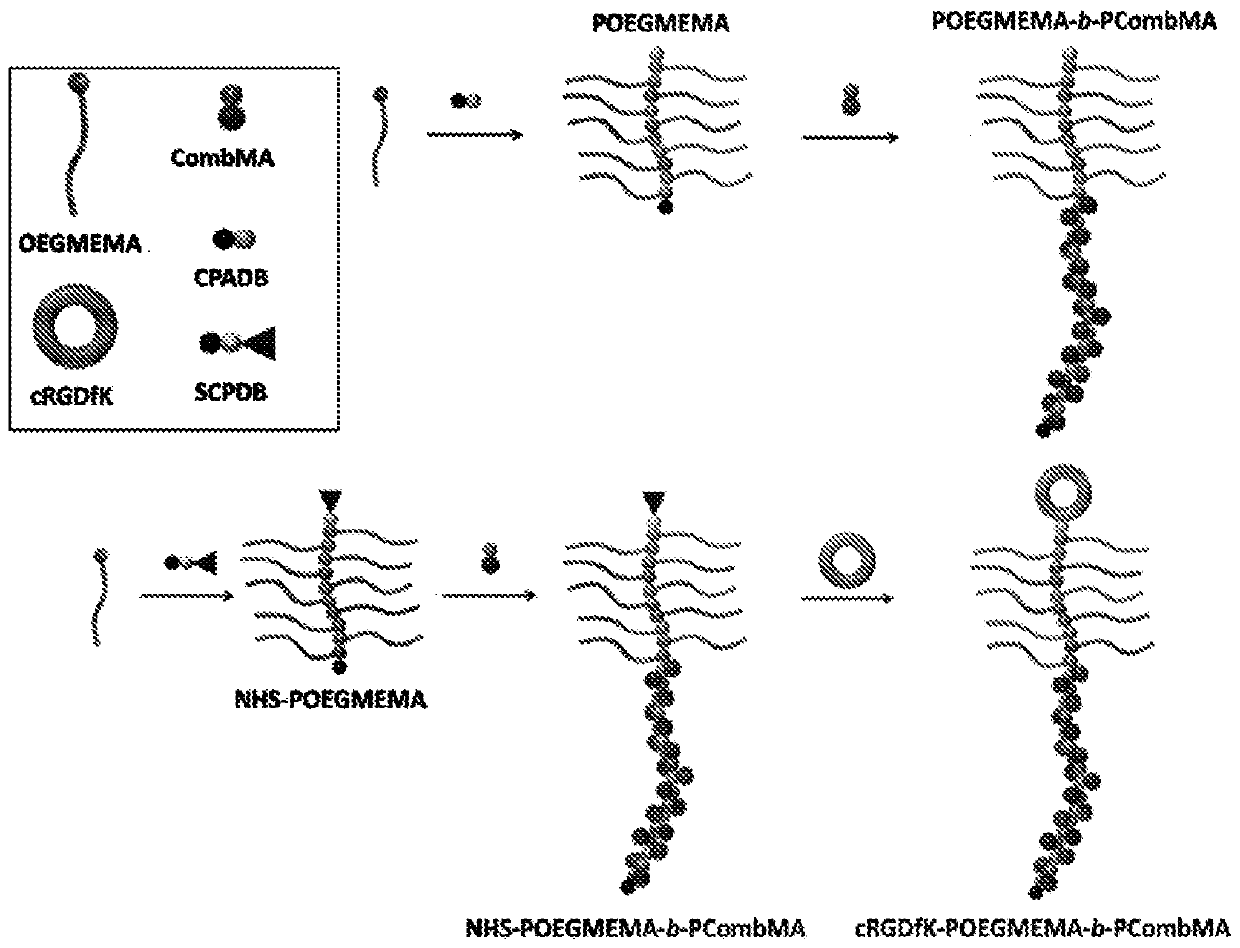
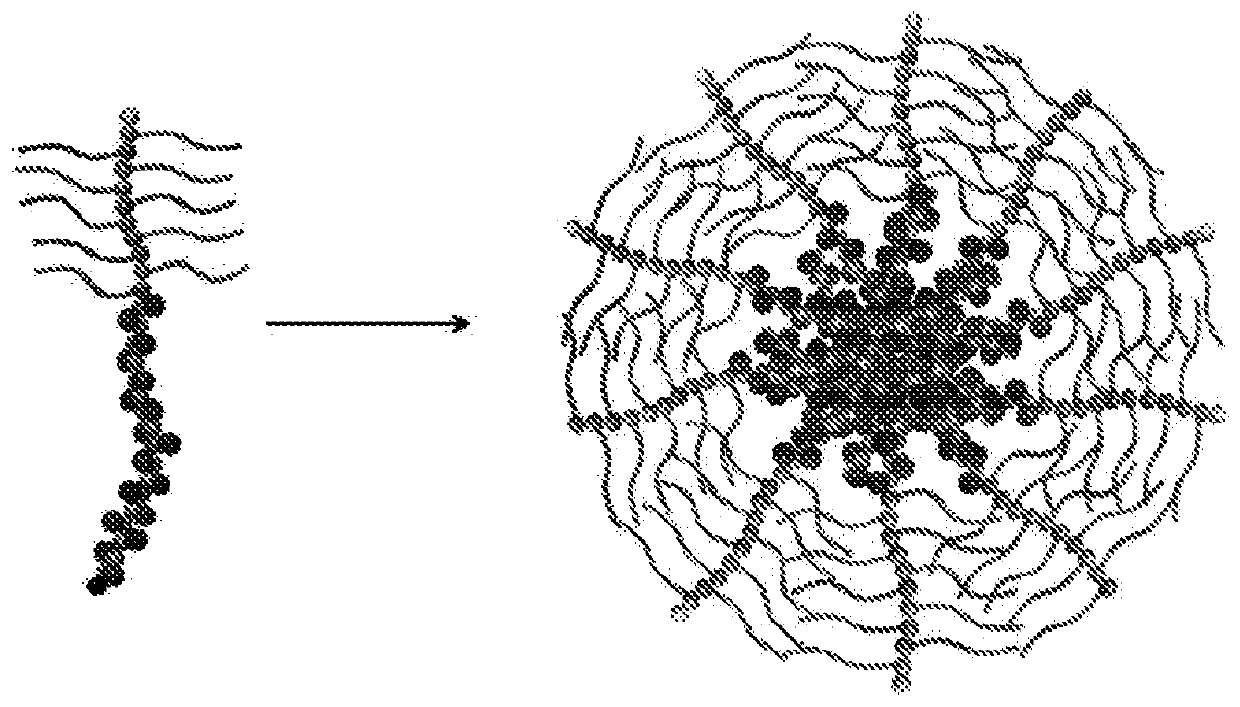
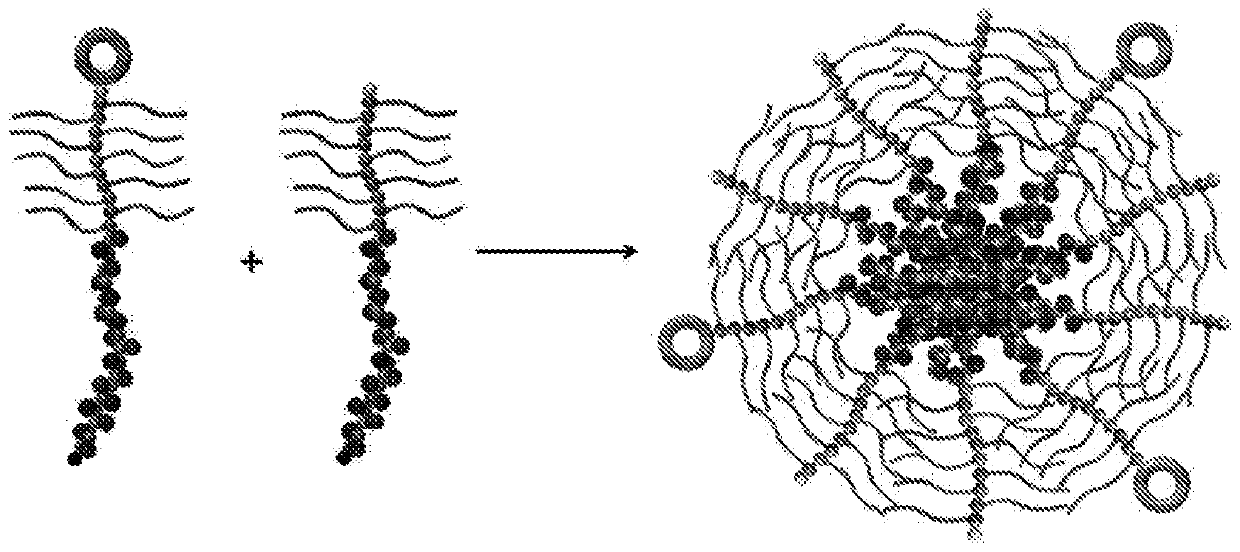
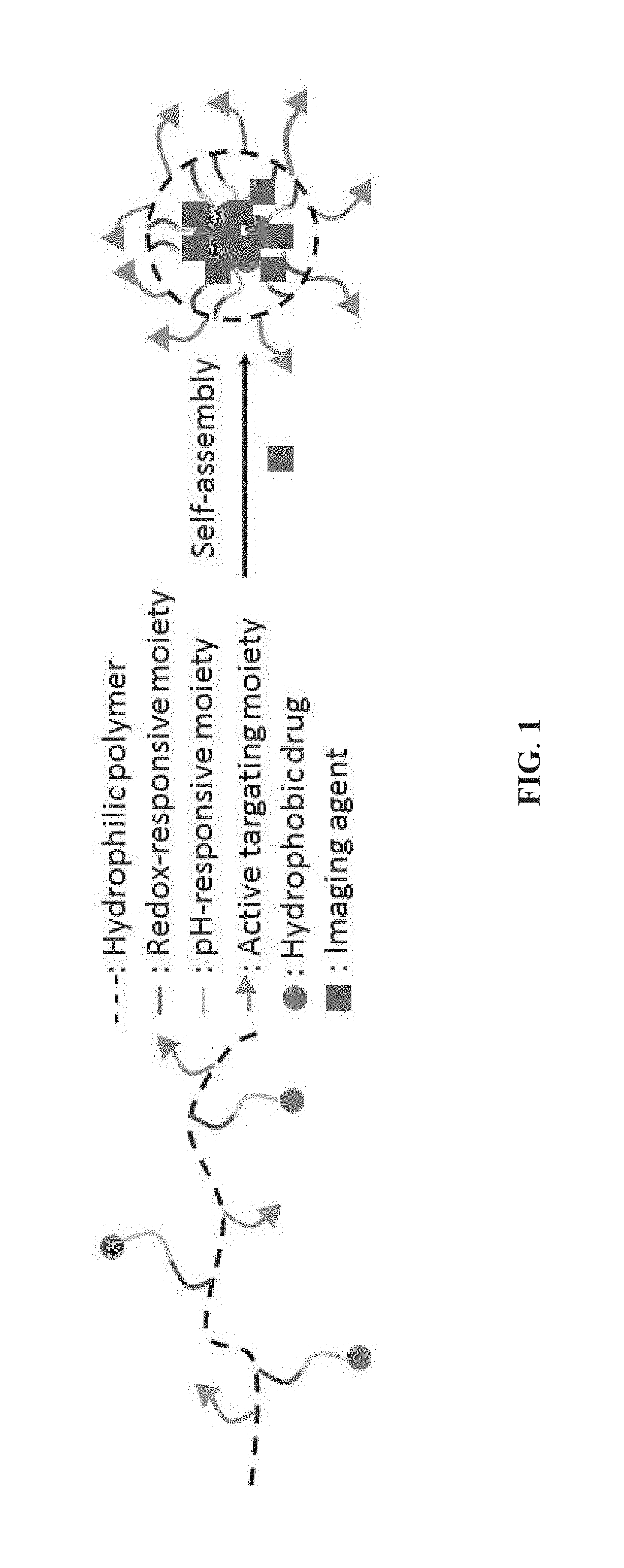
Provided is a method of preparing a stimuli-responsive multifunctional nanoparticle, including in sequence the steps of: (a) conjugating covalently an active targeting moiety to a hydrophilic polymer to form a targeted polymer, (b) conjugating covalently a redox-responsive moiety to the hydrophilic polymer of the targeted polymer to form a targeted redox-responsive polymer, (c) conjugating covalently a pH-responsive moiety of a drug complex to the redox-responsive moiety of the targeted redox-responsive polymer to form a targeted stimuli-responsive polymer-drug conjugate, wherein the drug complex includes a hydrophobic drug covalently linked to the pH-responsive moiety, and (d) adding the targeted stimuli-responsive polymer-drug conjugate and optionally an imaging agent into an aqueous liquid to allow self-assembly into a stimuli-responsive multifunctional nanoparticle, wherein the hydrophobic drug of the stimuli-responsive multifunctional nanoparticle forms a hydrophobic core, and the imaging agent is incorporated within the hydrophobic core.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Polymer-nsaid conjugate
ActiveUS20150150999A1Increase loadEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticMedicineNon steroidal anti inflammatory
The invention relates to polymer-drug conjugate for delivering a substituted alkanoic acid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). The invention also relates to drug delivery systems comprising the polymer-NSAID conjugate. The polymer-NSAID conjugates comprise a substituted alkanoic acid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) conjugated to a biodegradable polymer backbone by an ester linkage.
Owner:POLYACTIVA
Biodegradable, water soluble and pH responsive poly(organo)phosphazenes
Owner:JOHANNES KEPLER UNIVERSITY OF LINZ
Non-linear multiblock copolymer-drug conjugates for the delivery of active agents
ActiveUS10159743B2Improve propertiesControlled drug and drug release profilePowder deliverySenses disorderUveitisDisease
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Cleavable polymer drug conjugates
PendingCN109475637AReduce accumulationLow toxicityEther/acetal active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMethacrylatePolymer science
Owner:RS研究教育咨询医学工业贸易股份有限公司
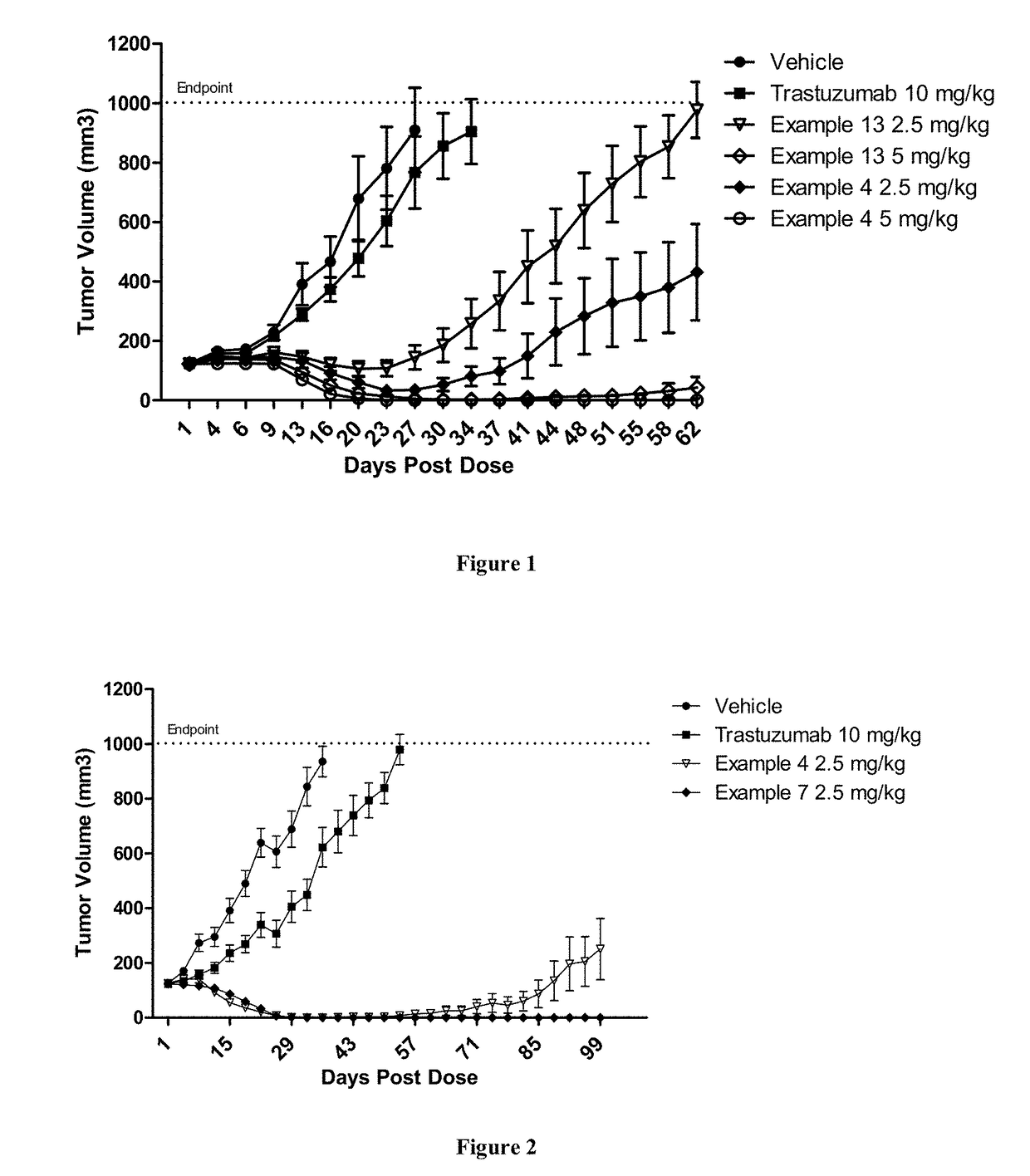
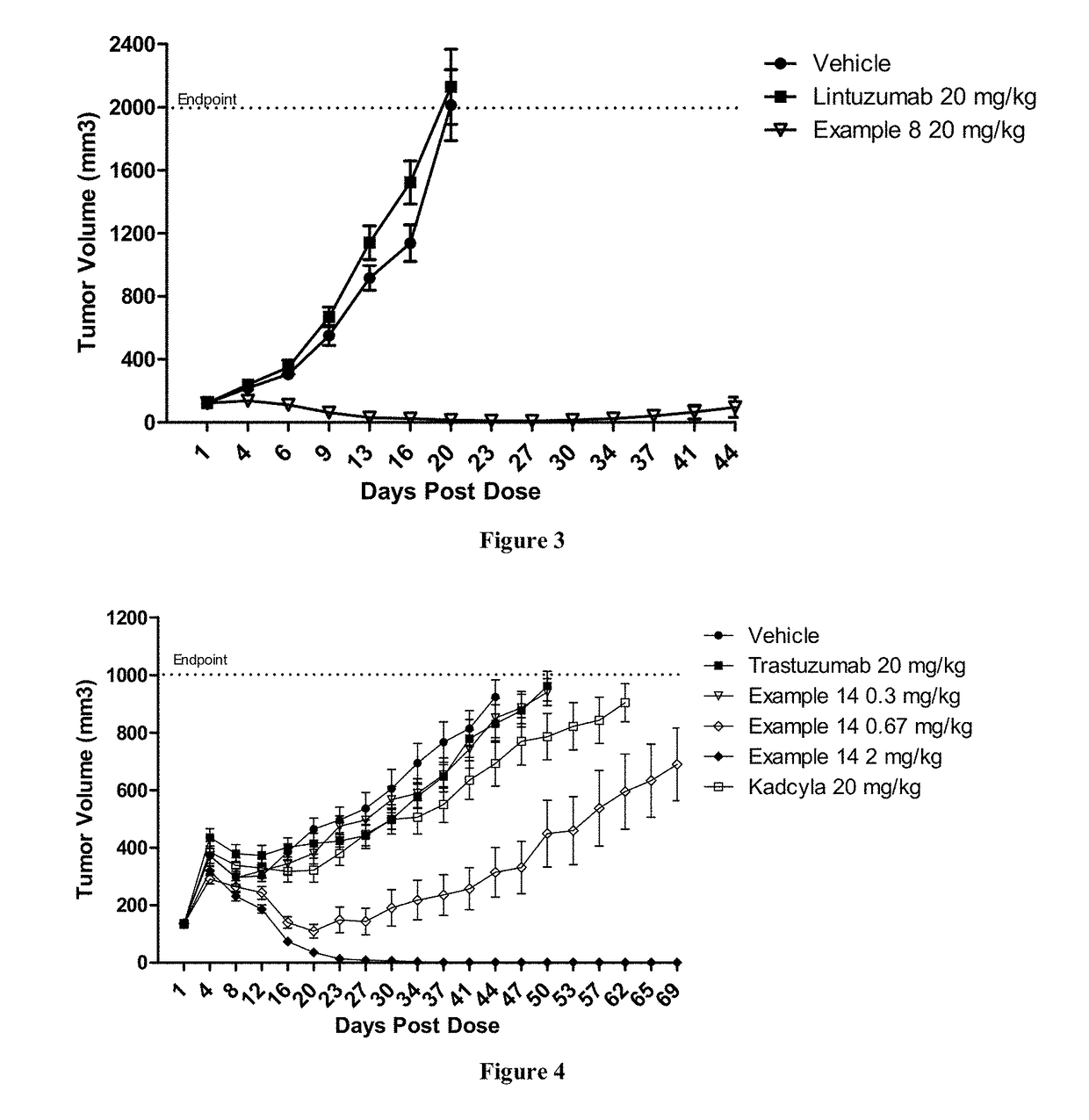
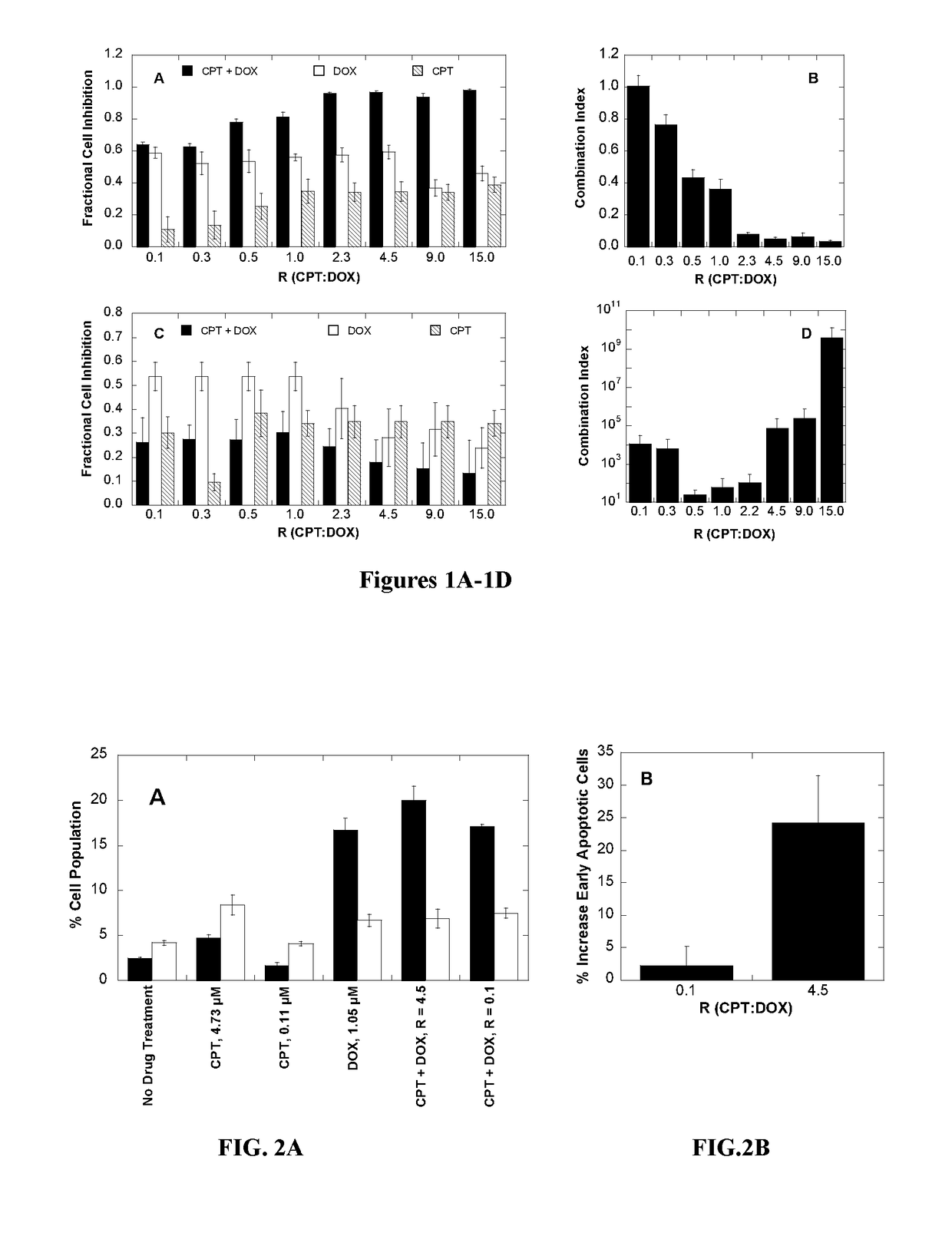
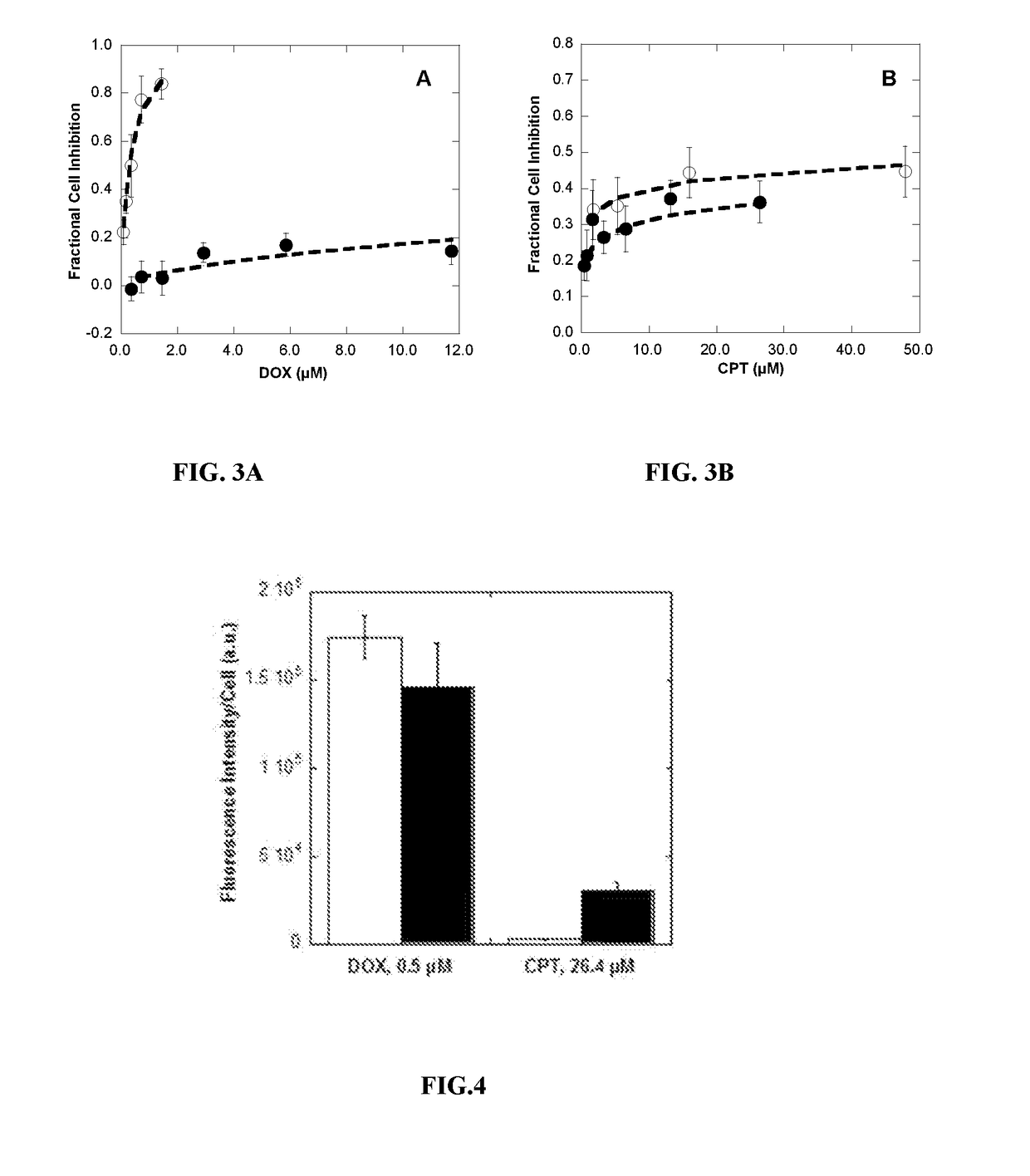
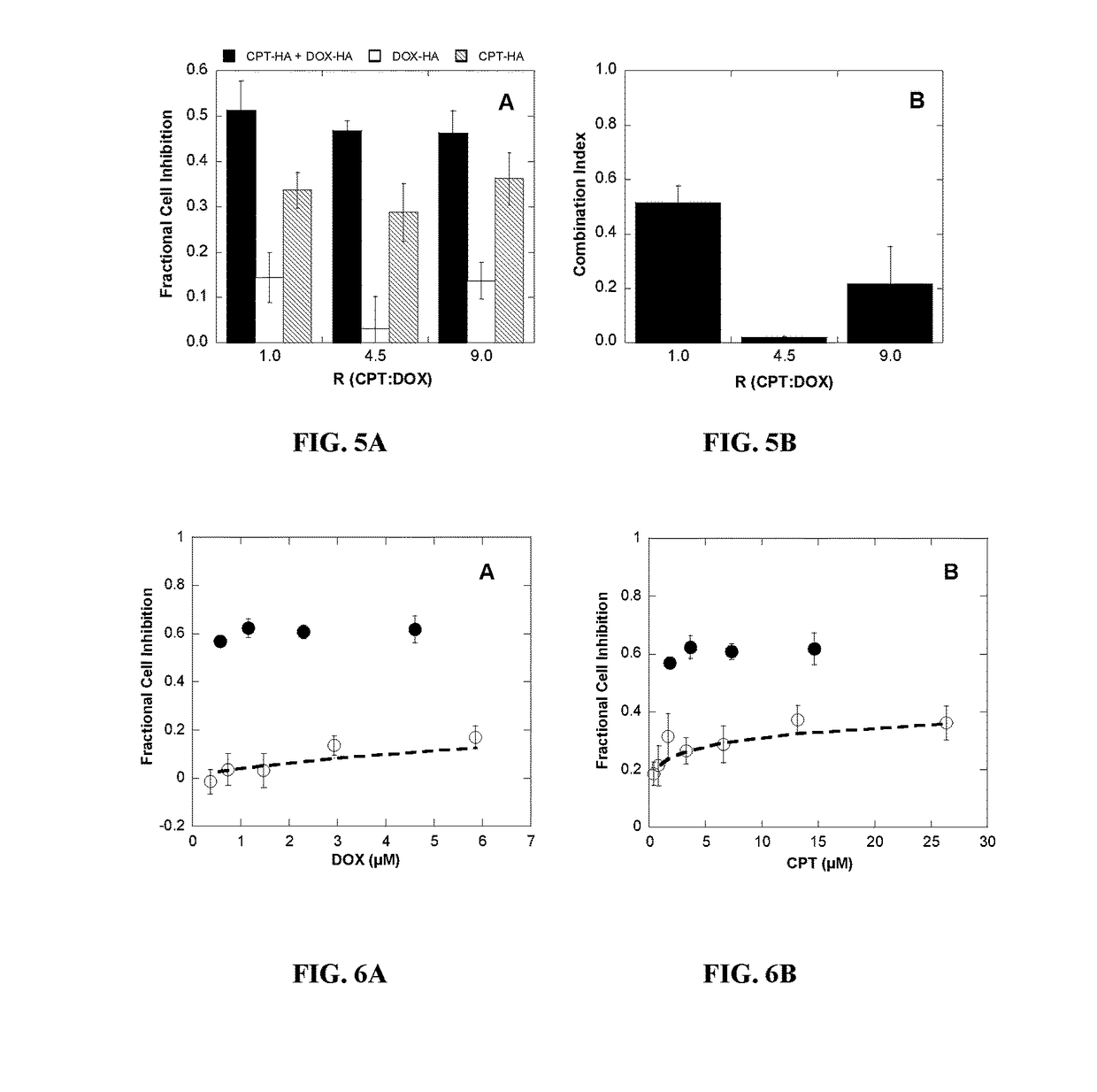
Polymer-drug conjugates for combination anticancer therapy
ActiveUS20180036419A1Reduce and prevent tumor growthEliminate side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAnticarcinogen
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising two or more therapeutically active agents, such as two or more anticancer agents, conjugated to one or more biocompatible polymers, wherein the molar ratio of the agents and / or schedules of delivery provide a synergistic therapeutic effect, are described. Methods of making and using the pharmaceutical compositions are further described. In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical compositions contain topoisomerase I and topoisomerase II inhibitors conjugated to the same or different biocompatible polymers. The two or more anticancer agents are covalently coupled to the polymer(s), and thereby can be delivered to a tumor at a molar ratio which provides a synergistic effect. Optionally, the agents are coupled indirectly to the polymer(s) via a linker.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Protein-polymer-drug conjugates and methods of using same
InactiveUS9808528B2Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsHer2 expressionOrganic chemistry
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
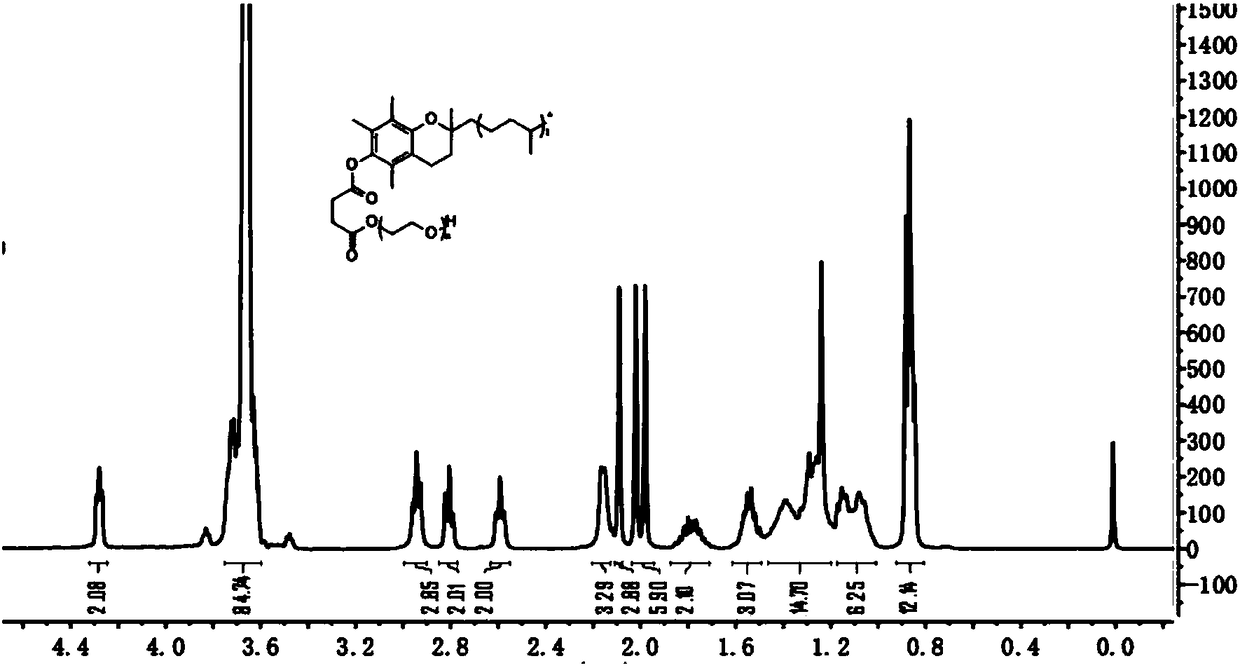
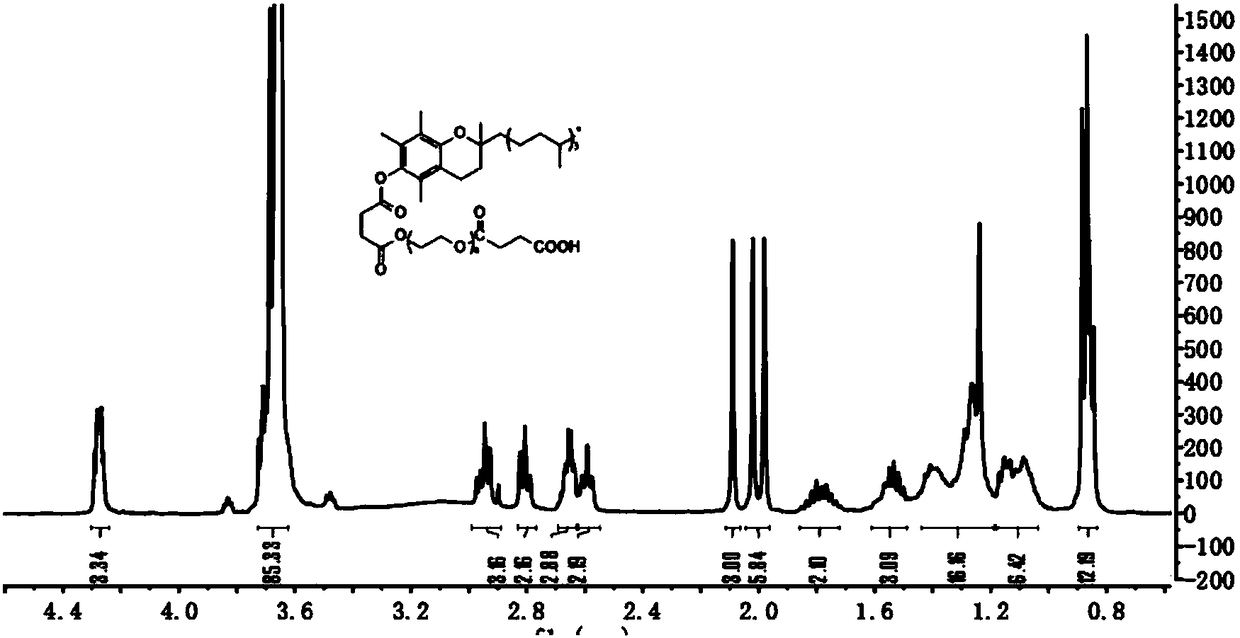
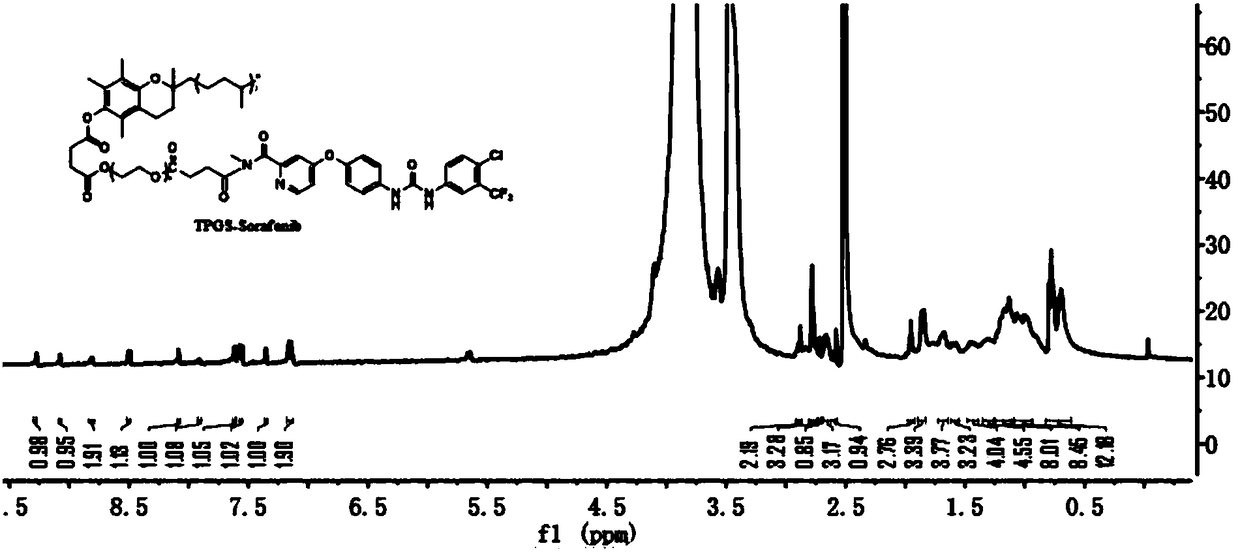
Polymer-drug conjugate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108578712AImprove solubilityImprove anti-tumor effectPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliverySynthesis methodsCoupling reaction
The invention provides a TPGS-sorafenib conjugate and a synthesis method thereof. The conjugate drug can be self-assembled into a micelle in water, which takes sorafenib as a hydrophobic kernel and takes TPGS as a hydrophilic shell, so that the dissolvability and an anti-tumor effect of the sorafenib can be improved, and the drug resistance of the sorafenib is reduced. The TPGS-sorafenib conjugatedrug is prepared by the following steps: activating TPGS and succinic anhydride (SA) through ring-opening reaction to obtain carboxyl-modified intermediate TPGS-SA, then connecting TPGS-SA to the sorafenib through typical carbodiimide coupling reaction, and finally obtaining the TPGS-sorafenib.
Owner:宁波市杭州湾医院
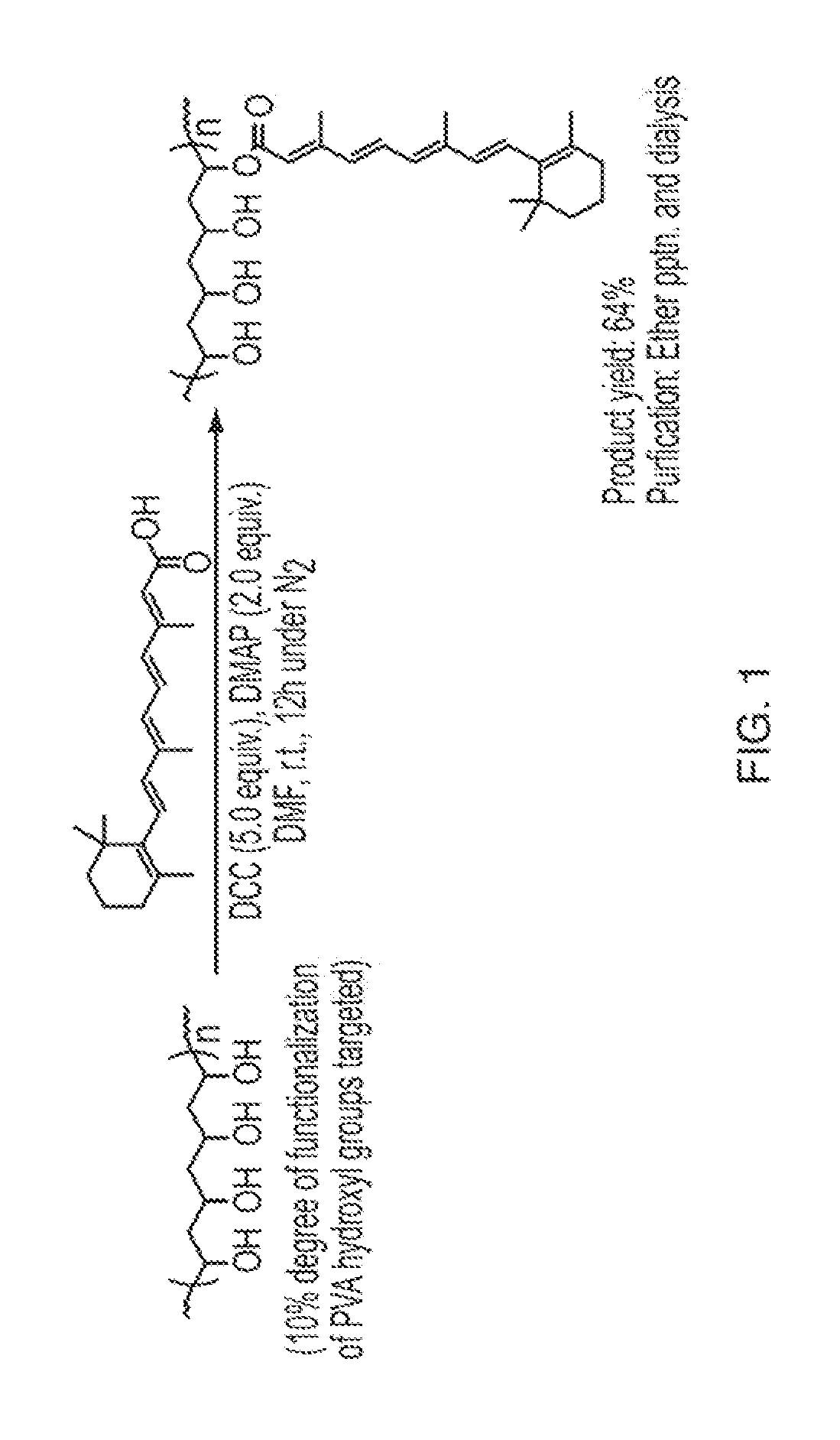
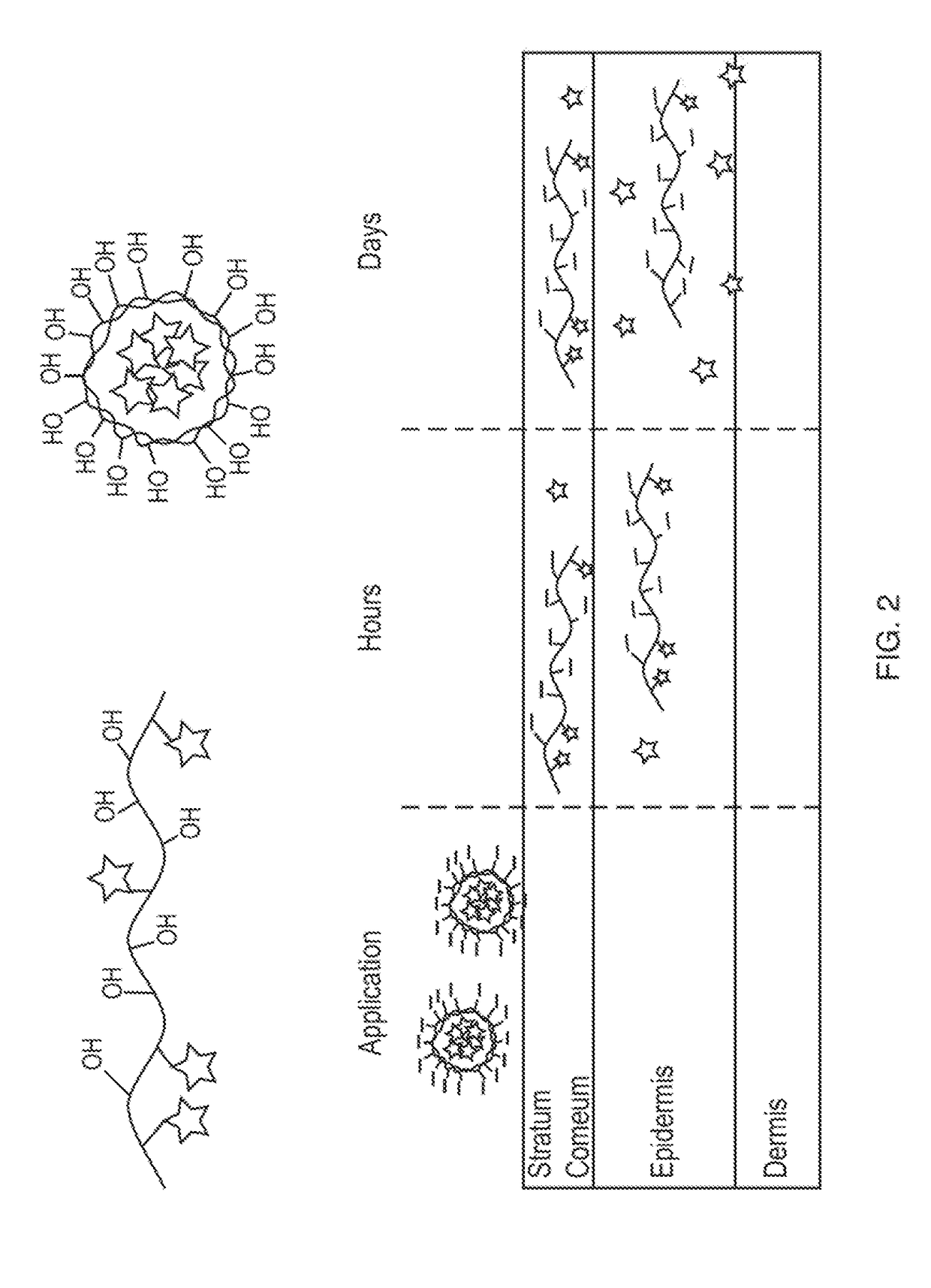
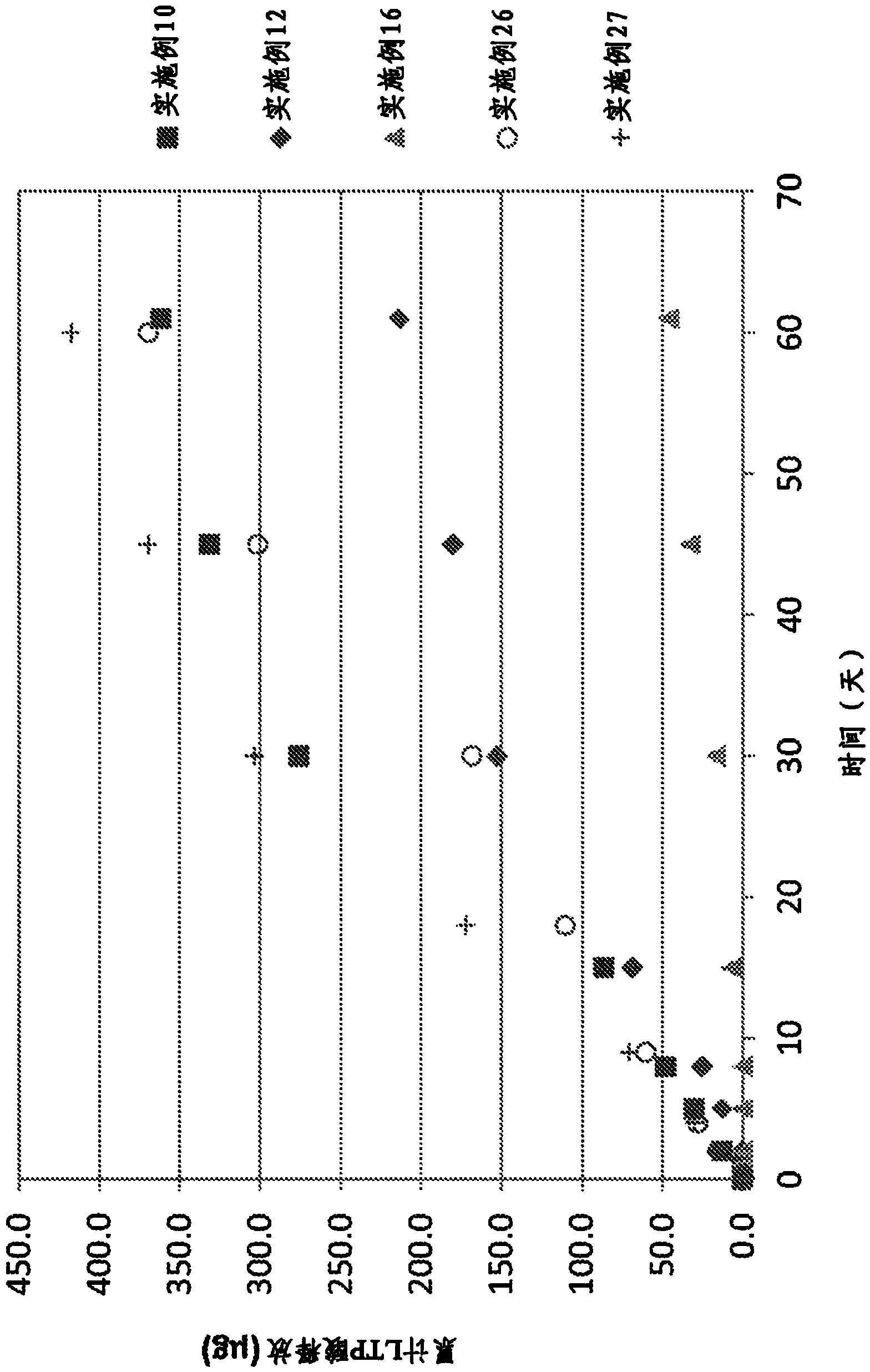
Nano-fibular nanoparticle polymer-drug conjugate for sustained dermal delivery of retinoids
ActiveUS20180185513A1Enhancing dermal accumulationReduces application site inflammationPowder deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsRetinoidNanoparticle
Disclosed herein are conjugated polymers comprising a polymer and an all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) prodrug covalently bound to the polymer by a hydrolysable linker L or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and methods of using same to treat certain disorders. In an embodiment, the conjugated polymer comprises poly (vinyl alcohol) covalently bound to ATRA through an ester linkage.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
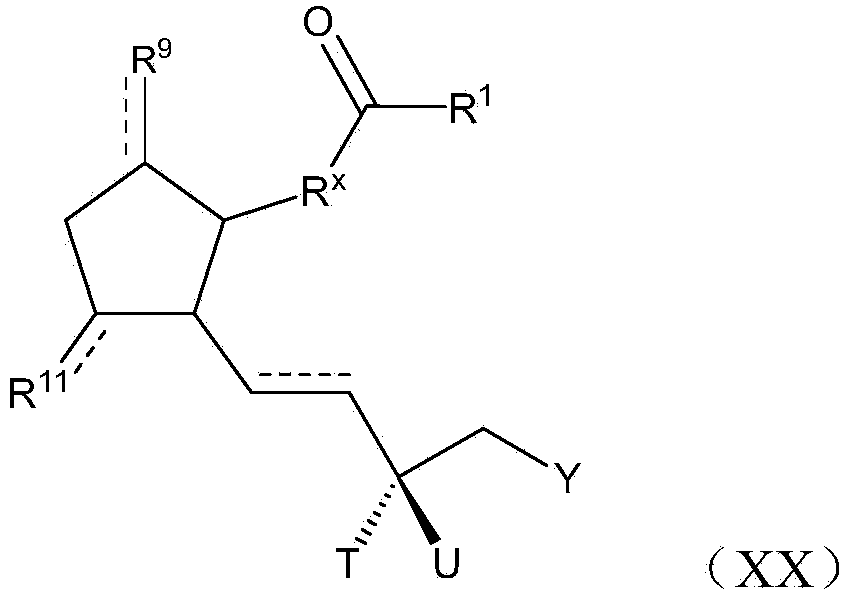
Polymer conjugated prostaglandin analogues
Owner:POLYACTIVA
Biologically active materials
InactiveUS6818630B1Reduce probabilityImprove stabilityBiocideSugar derivativesDiagnostic agentCytotoxic drug
The present disclosure concerns biologically active materials, particularly materials that comprise a biodegradeable polymer linked to a biologically active agent. The disclosure further concerns materials known as polymer-drug conjugates that typically contain a therapeutic agent, for instance a bioactive cytotoxic drug linked to a polymer backbone. The linkage typically is a convalent linkage. However, in some embodiments the disclosure concerns other polymer conjugates including those where the biologically active agent is an imaging agent, such as a tyrosinamide, a diagnostic agent, or a targeting agent, such as biotin.
Owner:ML LAB PLC
PH/cathepsin B step-by-step response polymer-drug conjugate and micelle, as well as preparation method and application of pH/cathepsin B step-by-step response polymer-drug conjugate and micelle
PendingCN113698555APrecise deliveryOvercoming double hurdlesOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseasePolymer science
The invention provides a series of polymer-drug conjugates and micelles with pH / cathepsin B step-by-step response characteristics, as well as a preparation method and application of the polymer-drug conjugates and micelles. The polymer-drug conjugate is composed of a hydrophilic chain segment and a hydrophobic chain segment, the hydrophilic chain segment is mainly composed of a highly hydrophilic polymer such as polyethylene glycol, and the hydrophobic chain segment is composed of a polyalkyl amino acrylate unit with a tertiary amino structure as shown in a structural formula 1 described in the specifications and a drug precursor unit with a Gly-Phe-Leu-Gly polypeptide connecting arm, wherein each symbol is defined in the specifications. In addition, the invention also provides application of the polymer-drug conjugate and the micelle in chemotherapy of tumor and inflammatory diseases and combined application of immunotherapy and photodynamic therapy.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Polymer-drug conjugate based on a polyisoolefin-based copolymer
InactiveCN107249640AReduce releaseSlower and more controlled releaseStentsSurgeryActive agentInsertion stent
A polymer-drug conjugate, which can be used in medical applications such as stents, has at least one active agent conjugated through a carboxylic acid moiety to a copolymer derived from at least one isoolefin monomer and at least one copolymerizable monomer, where the copolymerizable monomer is at least one multiolefin monomer, a [beta]-pinene monomer or a mixture thereof. Such conjugates show improved adhesion to stainless steel and a substantial decrease in burst release of paclitaxel form a drug eluting stent (DES).
Owner:ARLANXEO SINGAPORE PTE LTD +1
Multifunctional polymer nanoparticle, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107050467AImprove solubilityImprove securityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic active ingredientsSuperparamagnetismGlioma
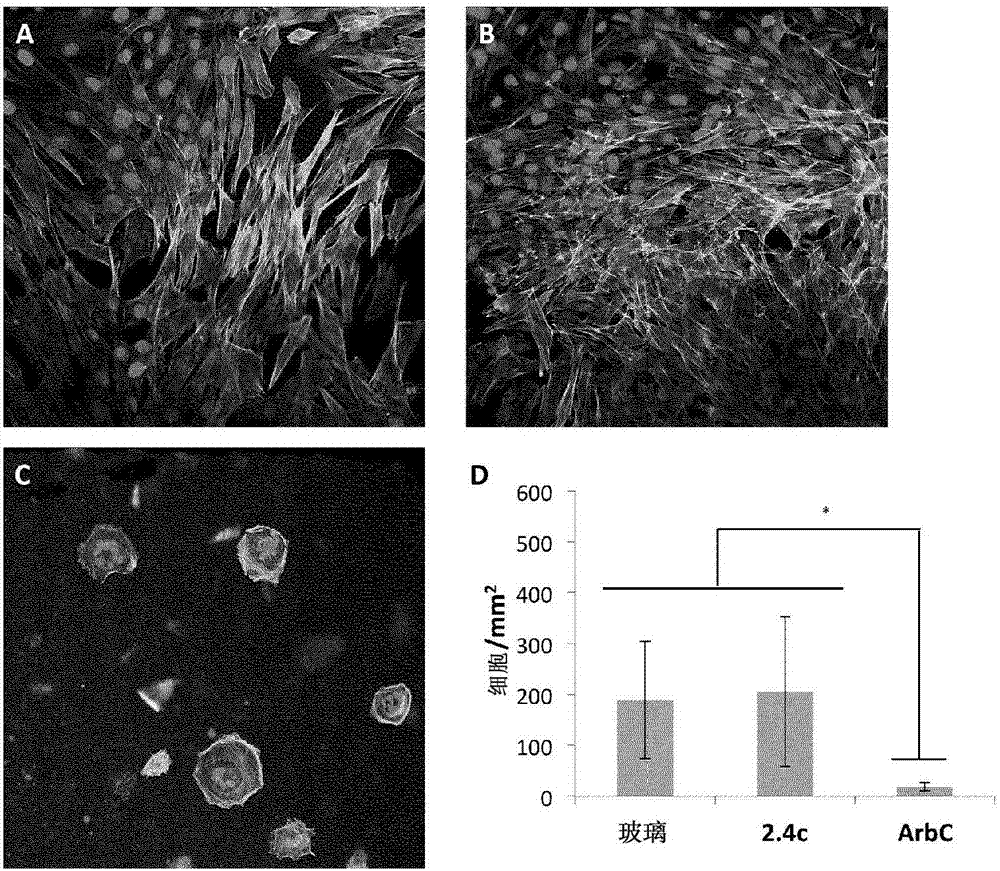
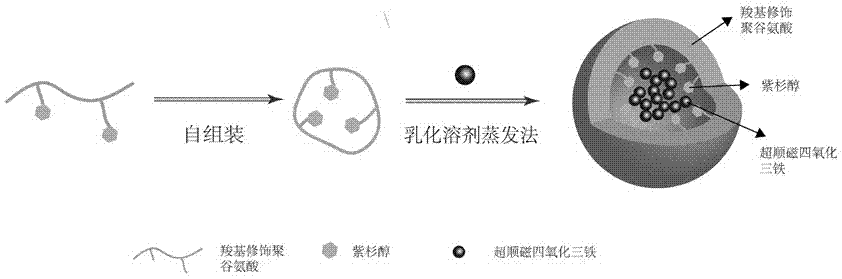
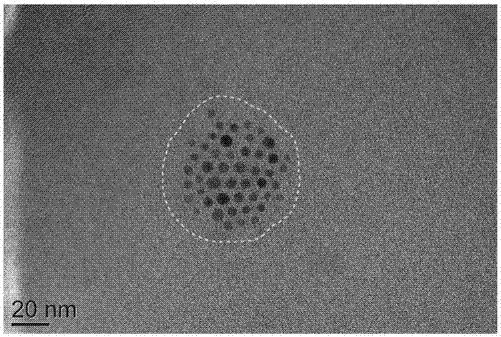
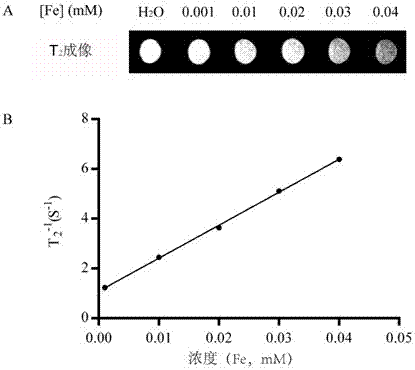
The invention discloses a multifunctional polymer nanoparticle, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The nanoparticle is formed by a center core and a capsule shell coating the core, wherein the center core is superparamagnetic ferroferric oxide SPION contrast agent, and the outer capsule shell is polyglutamic acid modified polymer-drug conjugate pGG-PTX of polymer conjugated taxol containing two carboxyl groups; and an emulsion-solvent evaporation method is adopted for preparing the nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is applied to preparation of medicines for treating and diagnosing glioma, and has an image function to feed back development of a medicine in real time, so that the time for diagnosis and treatment can be shortened for clinical doctors in the future, and a powerful support is provided to accurate judgment of illness conditions and reasonable individual administration.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com