Patents
Literature
602 results about "Micronization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Micronization is the process of reducing the average diameter of a solid material's particles. Traditional techniques for micronization focus on mechanical means, such as milling and grinding. Modern techniques make use of the properties of supercritical fluids and manipulate the principles of solubility.
Tea making method and application thereof in other plant stem-leaf products
InactiveCN101480208AQuality assuranceNo pesticide residuePre-extraction tea treatmentFood preparationPesticide residueEngineering
The invention relates to a tea-making method which scientifically, reasonably and integrally applies prior mature application technologies to a tea-making process, in particular to applications of an ozone sterilization strong oxidation technology, a microwave enzyme and germ deactivation technology, a low-temperature freezing, shredding and crushing technology, a vacuum freezing and drying technology, a colloid milling micronization technology and a spray drying technology to the processing and the production of tea. The invention effectively solves the traditional problems influencing the quality of tea products by agriculture residue, pesticide residue, overproof heavy metal content and overproof total bacterial count, enables the quality of tea products to reach the standard of organic tea, effectively improves the quality of the tea products and the utilization rate of tea raw material and can be applied to other plant stem leaf products.
Owner:刘川汶
Polymeric drug delivery system for hydrophobic drugs
InactiveUS20050249799A1Low oral bioavailabilityStable against aggregationAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryHydrophobic polymerImmediate release
An oral delivery system for Class II drugs that have low oral bioavailability due to their insolubility in water and slow dissolution kinetics and method for making such a drug delivery system are disclosed herein. The formulation may be a controlled release or immediate release formulation. The immediate release formulation contains a Class II drug, together with a hydrophobic polymer, preferably a bioadhesive polymer. In one embodiment, the drug and polymer are co-dissolved in a common solvent. The solution is formed into small solid particles by any convenient method, particularly by spray drying. The resulting particles contain drug dispersed as small particles in a polymeric matrix. The particles are stable against aggregation, and can be put into capsules or tableted for administration. The controlled release formulations contain a BCS Class II drug and a bioadhesive polymer. The controlled release formulations may be in the form of a tablet, capsules, mini-tab, microparticulate, or osmotic pump. Enhancement of oral uptake of the drug from use of bioadhesive polymers occurs through (1) increased dissolution kinetics due to stable micronization of the drug, (2) rapid release of the drug from the polymer in the GI tract; and (3) prolonged GI transit due to bioadhesive properties of the polymers. The combination of these effects allows the preparation of a compact, stable dosage form suitable for oral administration of many class II drugs.
Owner:SPHERICS
Method of forming nanoparticles and microparticles of controllable size using supercritical fluids with enhanced mass transfer
The current invention, Supercritical Antisolvent Precipitation with Enhanced Mass Transfer (SAS-EM) provides a significantly improved method for the production of nano and micro-particles with a narrow size distribution. The processes of the invention utilize the properties of supercritical fluids and also the principles of virbrational atomization to provide an efficient technique for the effective nanonization or micronization of particles. Like the SAS technique, SAS-EM, also uses a supercritical fluid as the antisolvent, but in the present invention the dispersion jet is deflected by a vibrating surface that atomizes the jet into fine droplets. The vibrating surface also generates a vibrational flow field within the supercritical phase that enhances mass transfer through increased mixing. Sizes of the particles obtained by this technique are easily controlled by changing the vibration intensity of the deflecting surface, which in turn is controlled by adjusting the power input to the vibration source. A major advantage of the SAS-EM technique is that it can be successfully used to obtain nanoparticles of materials that usually yield fibers or large crystals in SAS method. Microencapsulation via coprecipitation of two or more materials can also be achieved using the SAS-EM technique.
Owner:UNIV AUBURN
Method of forming nanoparticles and microparticles of controllable size using supercritical fluids and ultrasound
The current invention, Supercritical Antisolvent Precipitation with Enhanced Mass Transfer (SAS-EM) provides a significantly improved method for the production of nano and micro-particles with a narrow size distribution. The processes of the invention utilize the properties of supercritical fluids and also the principles of virbrational atomization to provide an efficient technique for the effective nanonization or micronization of particles. Like the SAS technique, SAS-EM, also uses a supercritical fluid as the antisolvent, but in the present invention the dispersion jet is deflected by a vibrating surface that atomizes the jet into fine droplets. The vibrating surface also generates a vibrational flow field within the supercritical phase that enhances mass transfer through increased mixing. Sizes of the particles obtained by this technique are easily controlled by changing the vibration intensity of the deflecting surface, which in turn is controlled by adjusting the power input to the vibration source. A major advantage of the SAS-EM technique is that it can be successfully used to obtain nanoparticles of materials that usually yield fibers or large crystals in SAS method. Microencapsulation via coprecipitation of two or more materials can also be achieved using the SAS-EM technique.
Owner:UNIV AUBURN
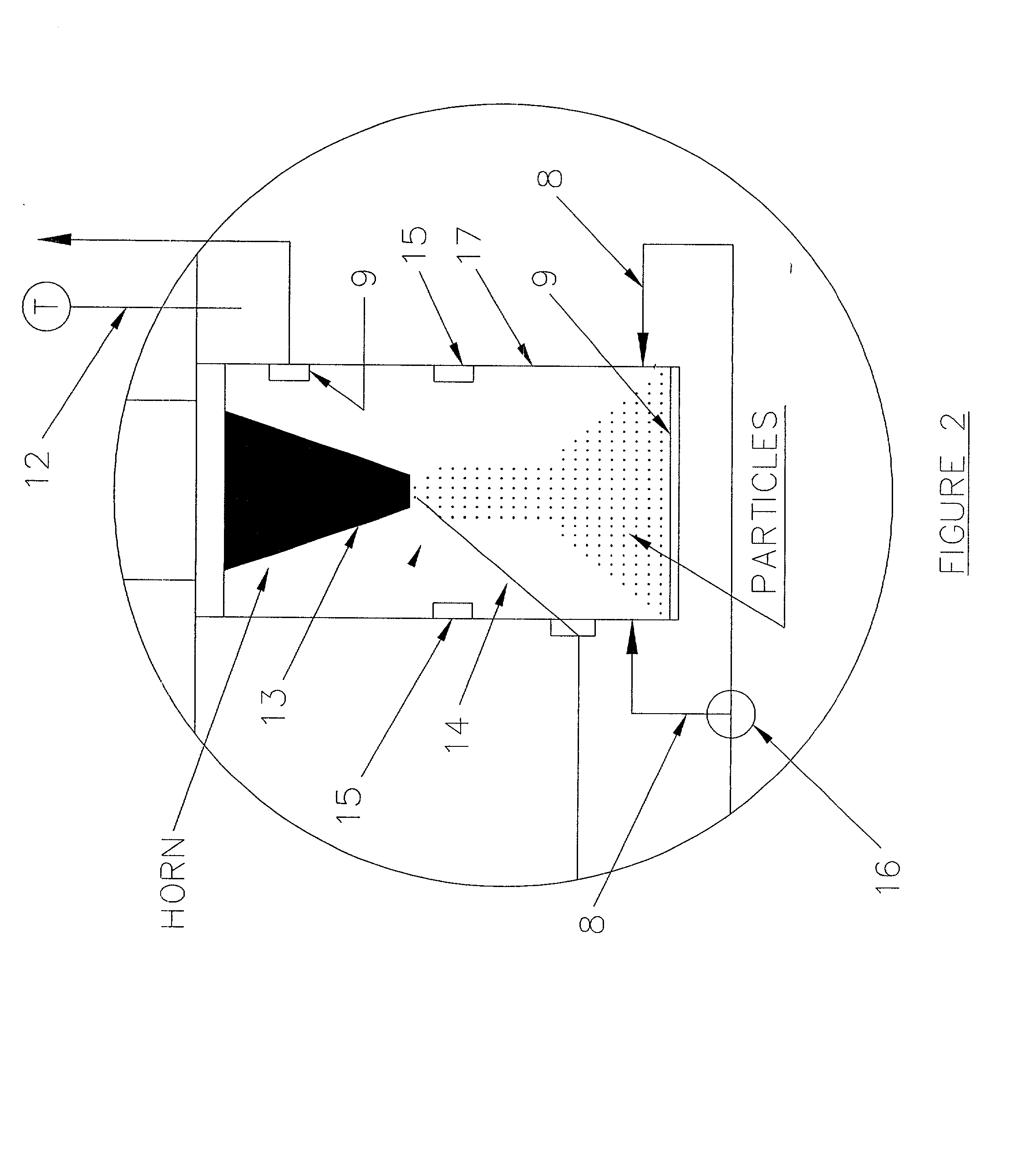
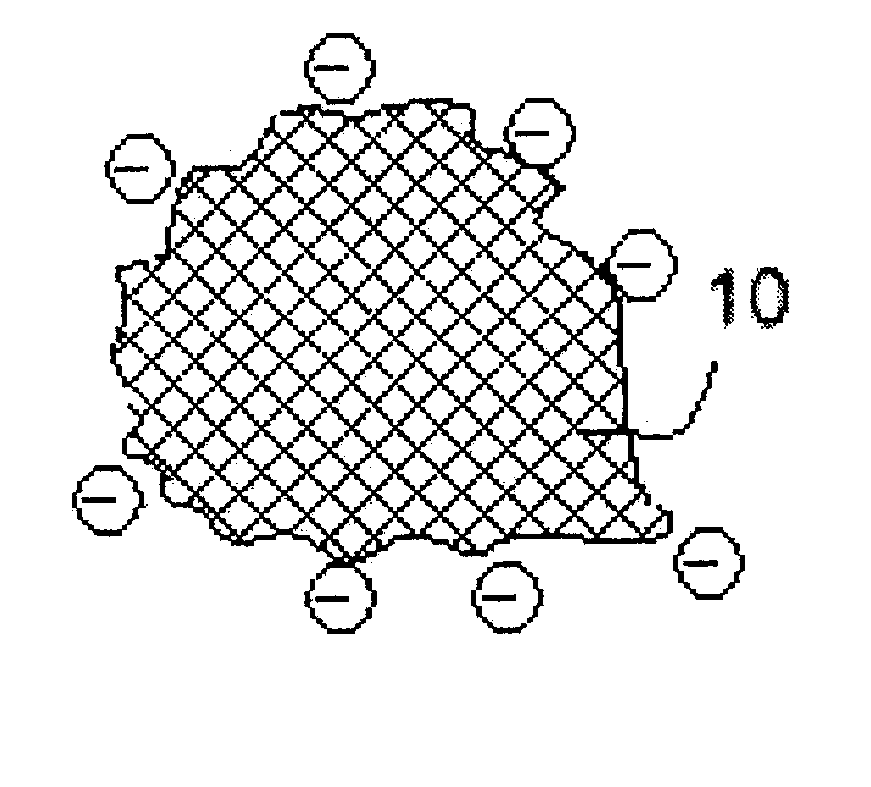
Electro-powder
A method and a process are disclosed for preparation of medical electro-powders. The electro-powder results from preparations of chemical and biological substances to form electro-powders suitable for electrostatic charging and dosing for functionality in a dry powder inhaler device. The electro-powder resulting from the method and process forms an active powder substance or a dry powder medical formulation with a fine particle fraction representing of the order 50% or more of the content having a size ranging between 0.5-5 mum and provides electrostatic properties with an absolute specific charge per mass after charging of the order 0.1x10<-6 >to 25x10<-6 >C / g and presenting a charge decay rate constant Q50>0.1 sec with a tap density of less than 0.8 g / ml and a water activity aw of less than 0.5. In the processing the active substance is a generally pharmaceutical active chemical or biological substance, for instance a polyeptide or any other corresponding substance selected alone or mixed or blended together with one or more excipients being a compound to improve electrostatic properties of the medical dry powder substance or dry powder medical formulation. Further the electro-powder may even be formed as a micro-encapsulation by coating micronized powder with the excipient in such a way that the active substance is capsulated, whereby the powder electrostatic properties mainly comes from the excipient.
Owner:MEDERIO AG
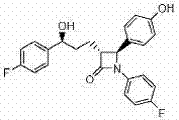
Febuxotat microcrystal and compositions thereof
ActiveCN101085761AHigh dissolution rateOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAcetic acidEthyl ester
The invention discloses a natural non-buta crystallite which is characterized by fine grain size and good dissloving degree and its compound. Said crystallite is prepared through disslovant crystallization, and said disslovatn is non- toxic acetic ester. The invention is characterized in that the product is safe, the preparation method is more environment- friendly, and the micronizing or other extra treatment for process preparing solid medicine and turbid liquor are avoided.
Owner:QIDONG HUATUO PHARMA
Disperse dye composition and disperse dyes
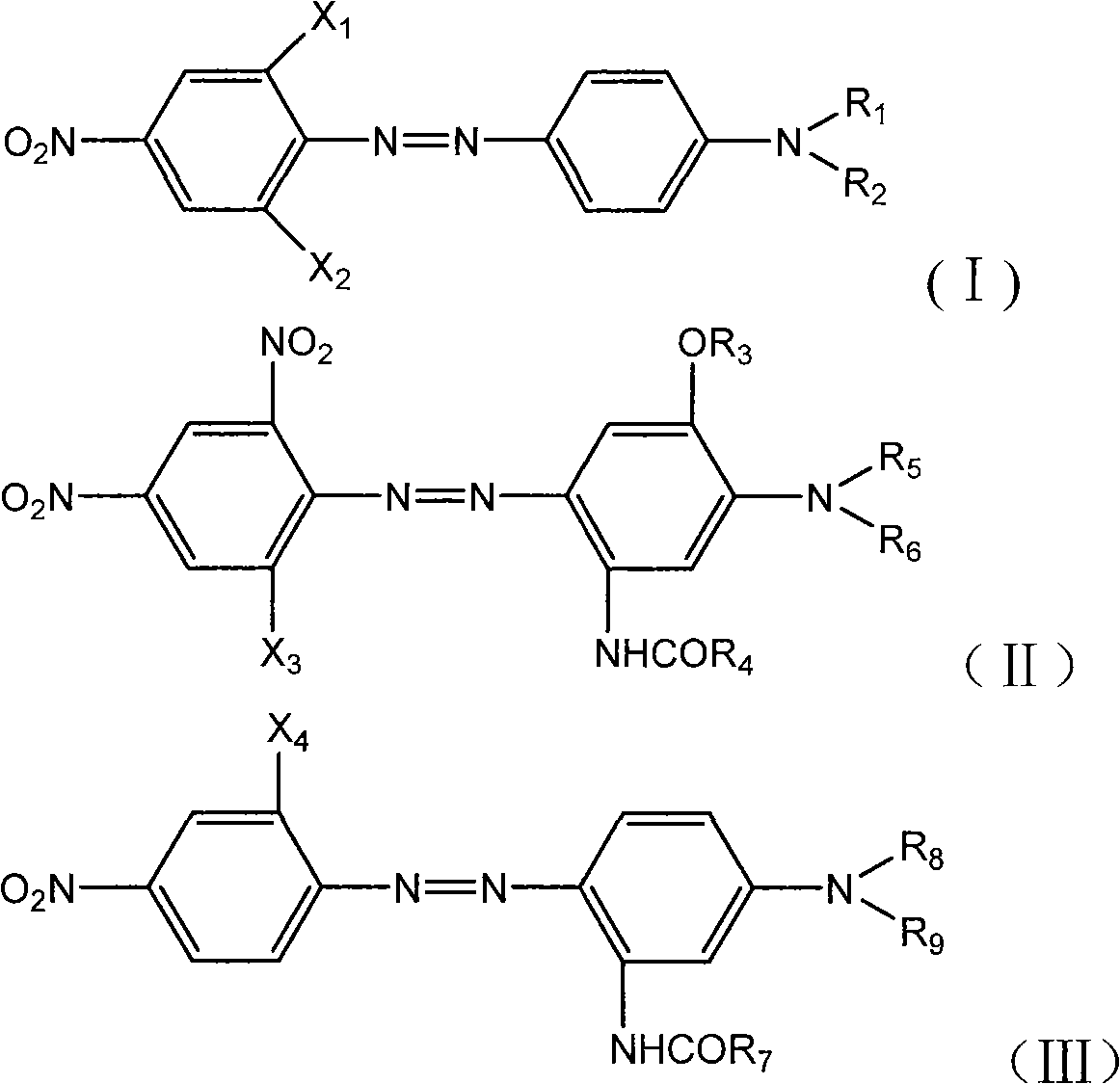
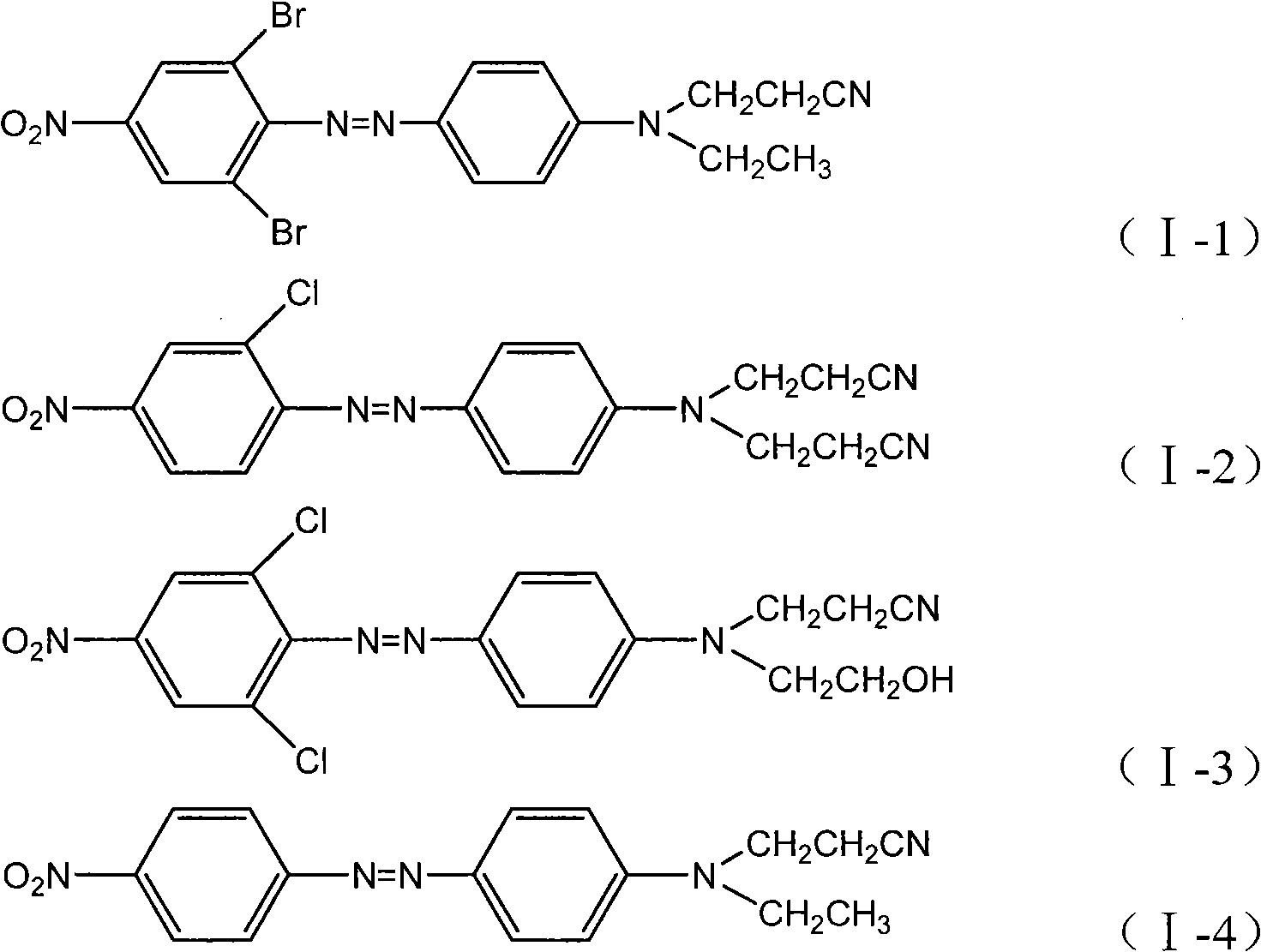
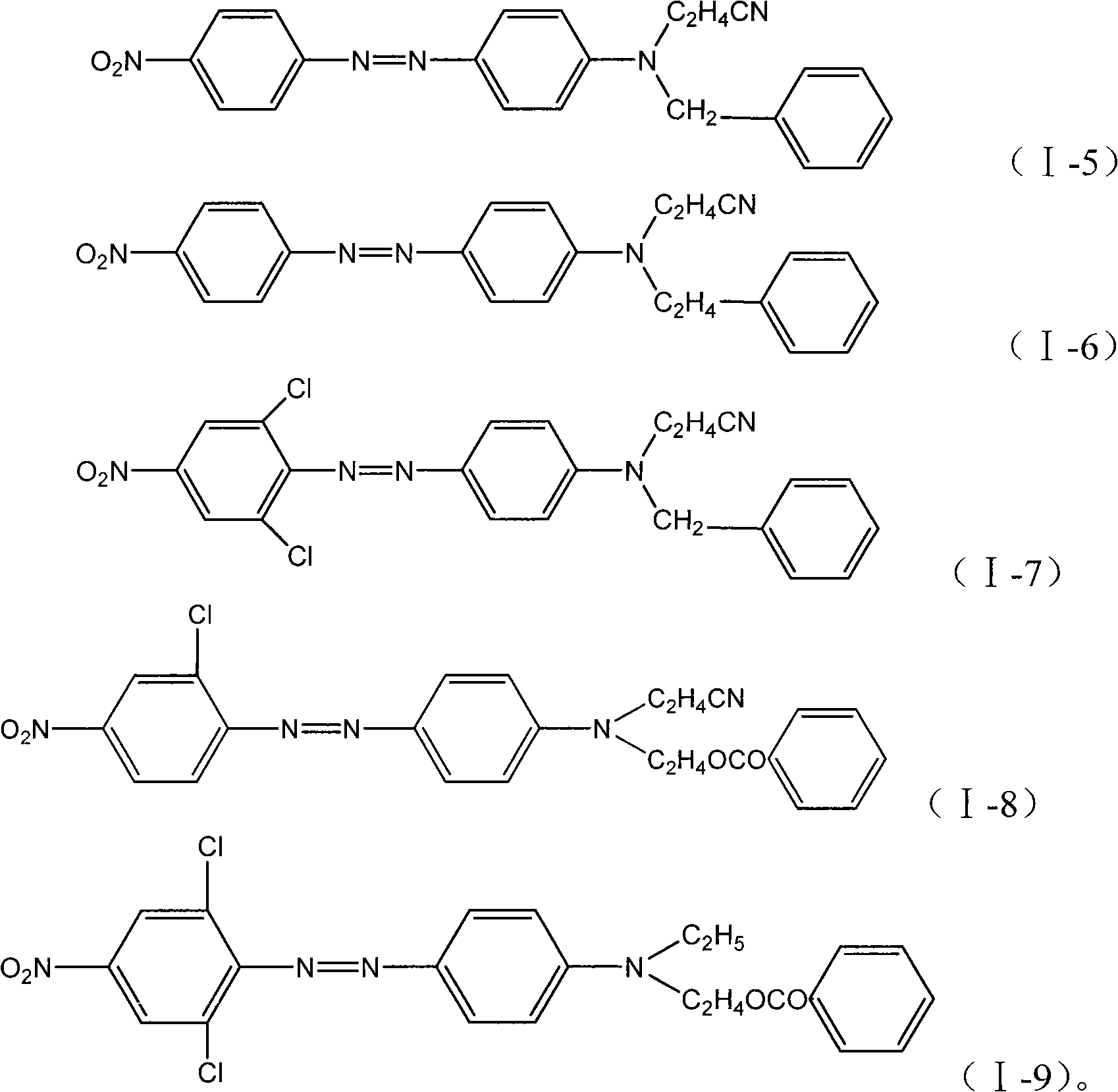
The invention provides a disperse dye composition and a disperse dye. The compositions comprises at least one component A shown as a formula (I), at least one component B shown as a formula (II) and at least one component C shown as a formula (III), wherein based on the component A, the component B and the component C, the mass percentage of the component A is 1 to 49 percent, the mass percentage of the component B is 50 to 98 percent, the mass percentage of the component C is 1 to 49 percent. The disperse dye composition of the invention can used for dyeing in liquid and paste states after micronization or in powdery and granular states after being dried by spray drying. Disperse dyes made by the formula of the disperse dye composition of the invention allow for adjustment of proportion of different dyes in the dyeing of polyester fiber materials to obtain dyed cloth with colors from deep blue to dark and the obtained dyed cloth has the advantages of bright color, good dispersivity, sun fastness, wash resistance, sweat resistance, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LONGSHENG GROUP +1
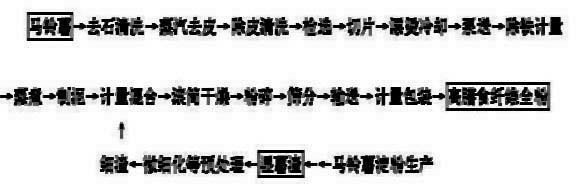
Method for producing potato flake with high dietary fiber content
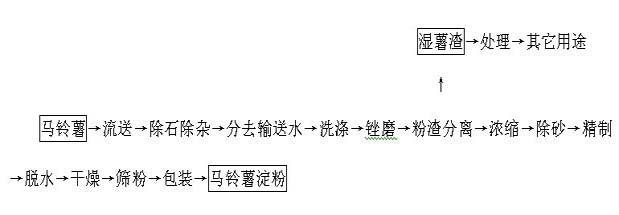
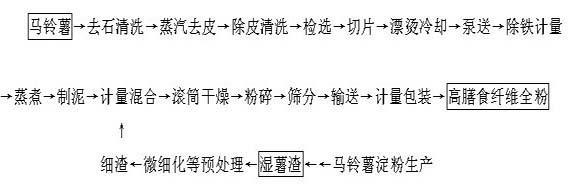
The invention discloses a method for producing potato flake with high dietary fiber content. The method comprises the following steps: after the byproduct of wet potato residue generated through flour-residue separation during potato starch production is subject to acid base interaction, oxidation or enzymolysis and micronization, the micronized dietary fiber of potato is mixed with mashed potatoes obtained through steaming, boiling and smashing in a certain content ratio, the mixture is dried through a roller dryer, the moisture content in the product is smaller than or equal to 10 percent, and the potato flake rich in dietary fiber is produced after crushing and sieving. The method of the invention is suitable for being implemented in whole potato processing production enterprises, the produced potato flake is rich in an excess amount of dietary fiber and can be used as an auxiliary material for processing other foods, therefore, the economic value of the byproduct of starch production, i.e., wet potato residue is greatly increased, and pollution to the environment is reduced.
Owner:广州华糖食品有限公司 +1
Solid dispersion and tablets comprising abiraterone acetate, and preparation methods thereof
ActiveCN103070828AAdvantages and Notable ImprovementsGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliverySolubilityMedicine
The invention relates to a solid dispersion and tablets comprising abiraterone acetate, and preparation methods thereof. The solid dispersion is prepared through the steps that: abiraterone acetate and povidone with a weight ratio of 1:0.5-4 are dissolved in chloroform; and reduced-pressure drying is carried out, such that the solid dispersion is obtained. The tablets comprises 1 part of the abiraterone acetate solid dispersion, 2-8 parts of a filling agent, 0.2-0.8 parts of a disintegrating agent, and 0.05-0.1 parts of a lubricant. According to the invention, a micronization technology and a solid dispersion technology are creatively combined, such that abiraterone acetate water solubility is greatly improved. Therefore, abiraterone acetate can be rapidly dissolved in gastrointestinal tract body fluids.
Owner:SHANDONG NEWTIME PHARMA
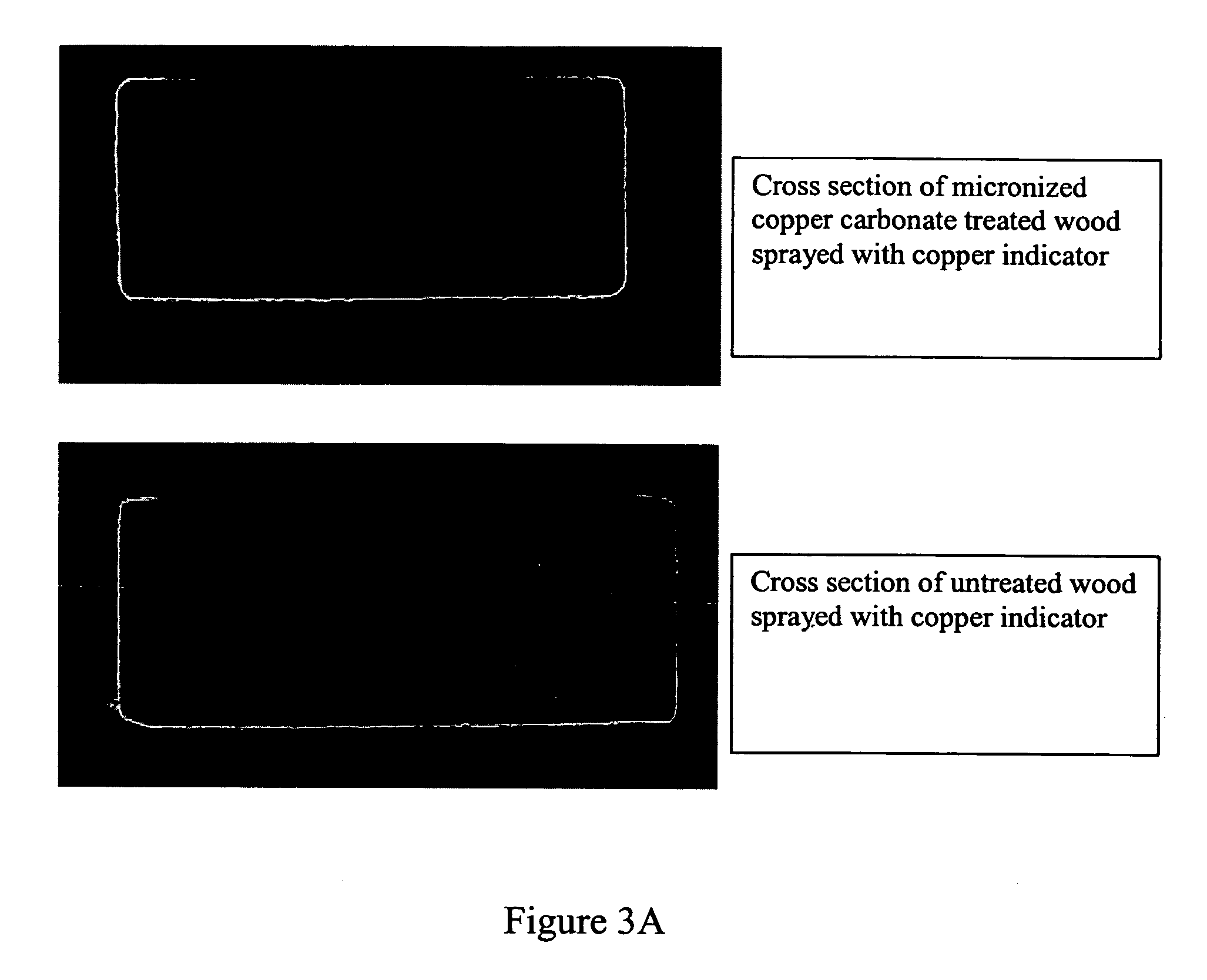
Micronized wood preservative compositions
Owner:OSMOSE
Compound ST-246 containing a crystal water, crystal thereof and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101445478AStable structurePromote crystallizationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryOrganic baseTropane
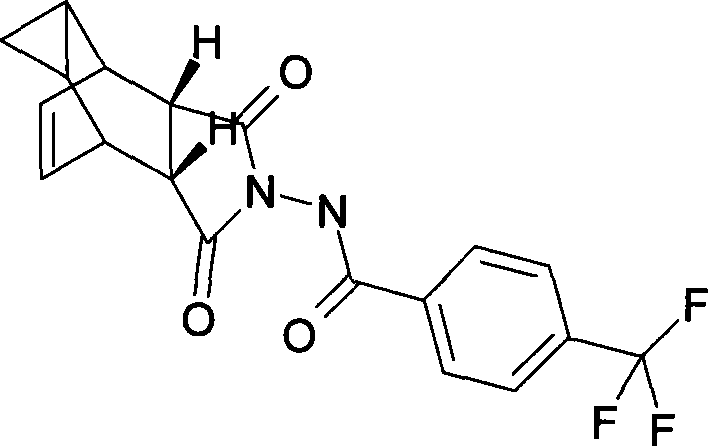
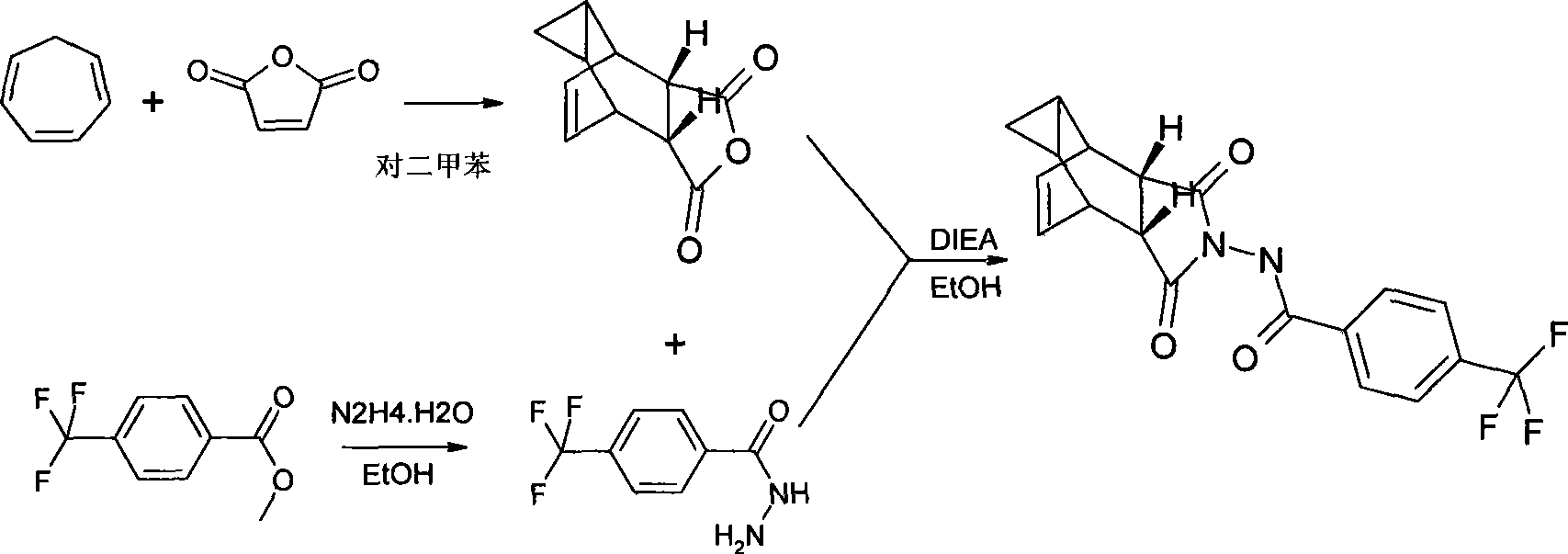
The invention discloses a compound ST-246 containing a crystal water, known as ST-246.H2O. The ST-246.H2O is prepared according to the following method: in the presence of organic base and organic solvent and being under protection of nitrogen, tropane anhydride and p-trifluoromethyl benzoylhydrazine are heated and return flow and reaction solution is cooled and filtered, thereby obtaining the ST-246.H2O. The ST-246.H2O prepared by the method is steady at room temperature, is difficult to lose the crystal water or absorb moisture, is difficult to agglomerate after micronization and is beneficial for improving bioavailability. The compound can be used for preparing anti-poxvirus medicines.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Method for preparing cold water dispersing type carotenoid micro-capsule powder without using organic solvent
ActiveCN103406079ANo residueProcess environmental protectionMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationSuspended particlesVegetable oil
The invention provides a method for preparing cold water dispersing type carotenoid micro-capsule powder without using an organic solvent. The method concretely comprises the following steps: (a) enabling carotenoid crystal to suspend in a water solution containing antioxidant, protective colloid and at least one non-ionic emulsifier; (b) grinding and homogenizing the solution obtained in the step (a) under the nitrogen protection to enable crystal particles to be ground and stably suspend; (c) carrying out micronization on the suspended particles of the obtained solution by a heating device to form an emulsion; (d) dissolving the protective colloid into the emulsion obtained in the step (c), carrying out secondary embedding, dewatering and drying to obtain powder particles. The method can solubilize carotenoid without using the organic solvent or vegetable oil, thus solving the problems of residual solvent, low carrying capacity and the like caused by the existing solvent method and a high temperature melting method. In all the steps of the method, the organic solvent is not used, so that the method is environment-friendly in technology; the process of high-temperature treatment is not needed, so that trans isomer is not produced, and the method is high in carrying capacity and small in loss of active ingredients.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
Starch-base fully biodegradable resin with steady hydrophobic property and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a starch-base fully biodegradable resin with steady hydrophobic property and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of biodegradable materials. The resin comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-50 parts of modified starch, 50-80 parts of fully biodegradable polyester, 0.1-5 parts of a lubricant, and 0.1-0.5 parts of an antioxidant. The starch-base fully biodegradable resin with steady hydrophobic property is rational in design, so that the dispersity of the starch is improved greatly through pre-treatment of the starch; the moisture content is relatively low, so that degradation reaction of the resin in the processing process is also reduced. Through rational micronization function, the performance of the starch-base fully biodegradable resin is improved obviously.
Owner:YIFAN XINFU PHARMA CO LTD +1
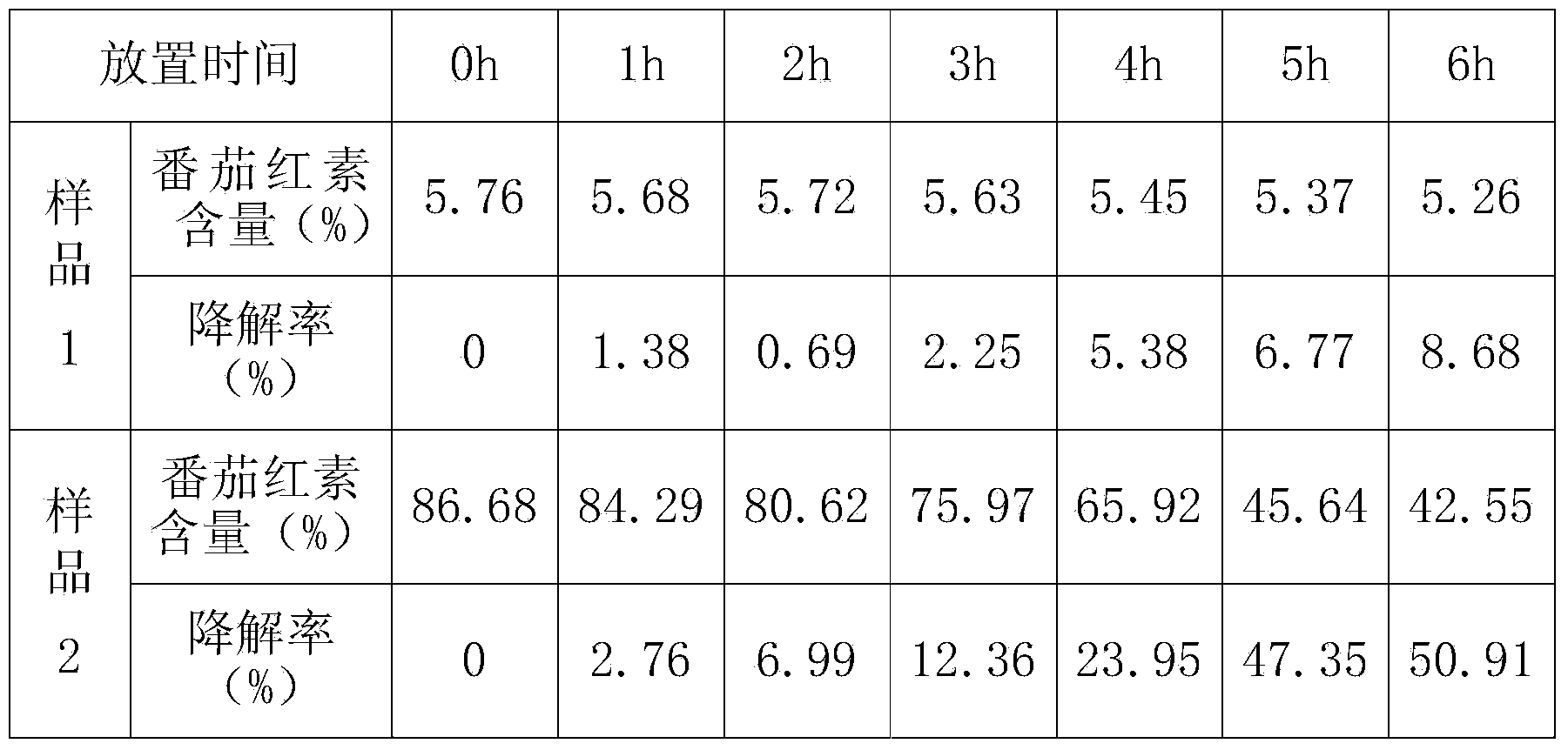
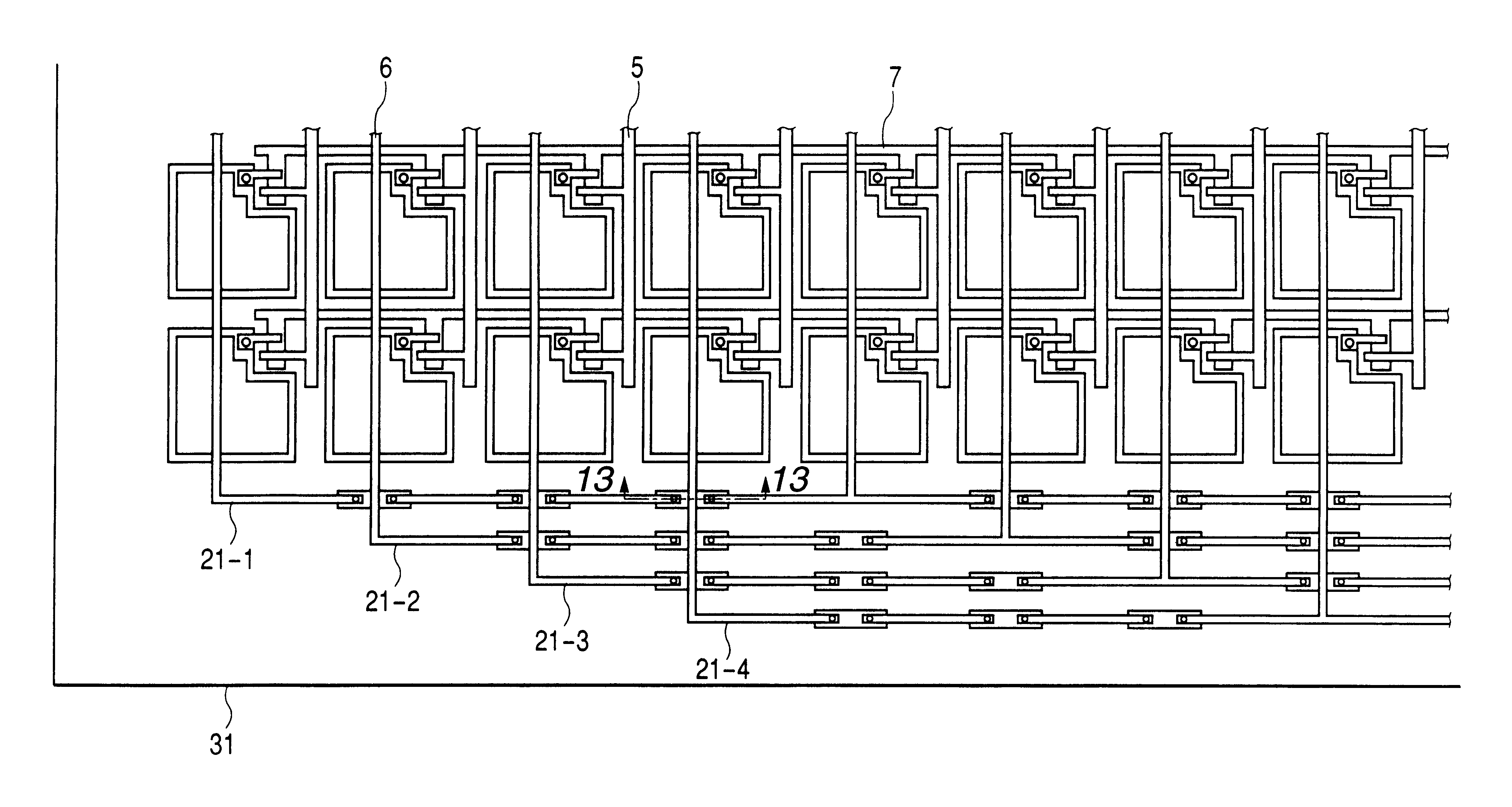
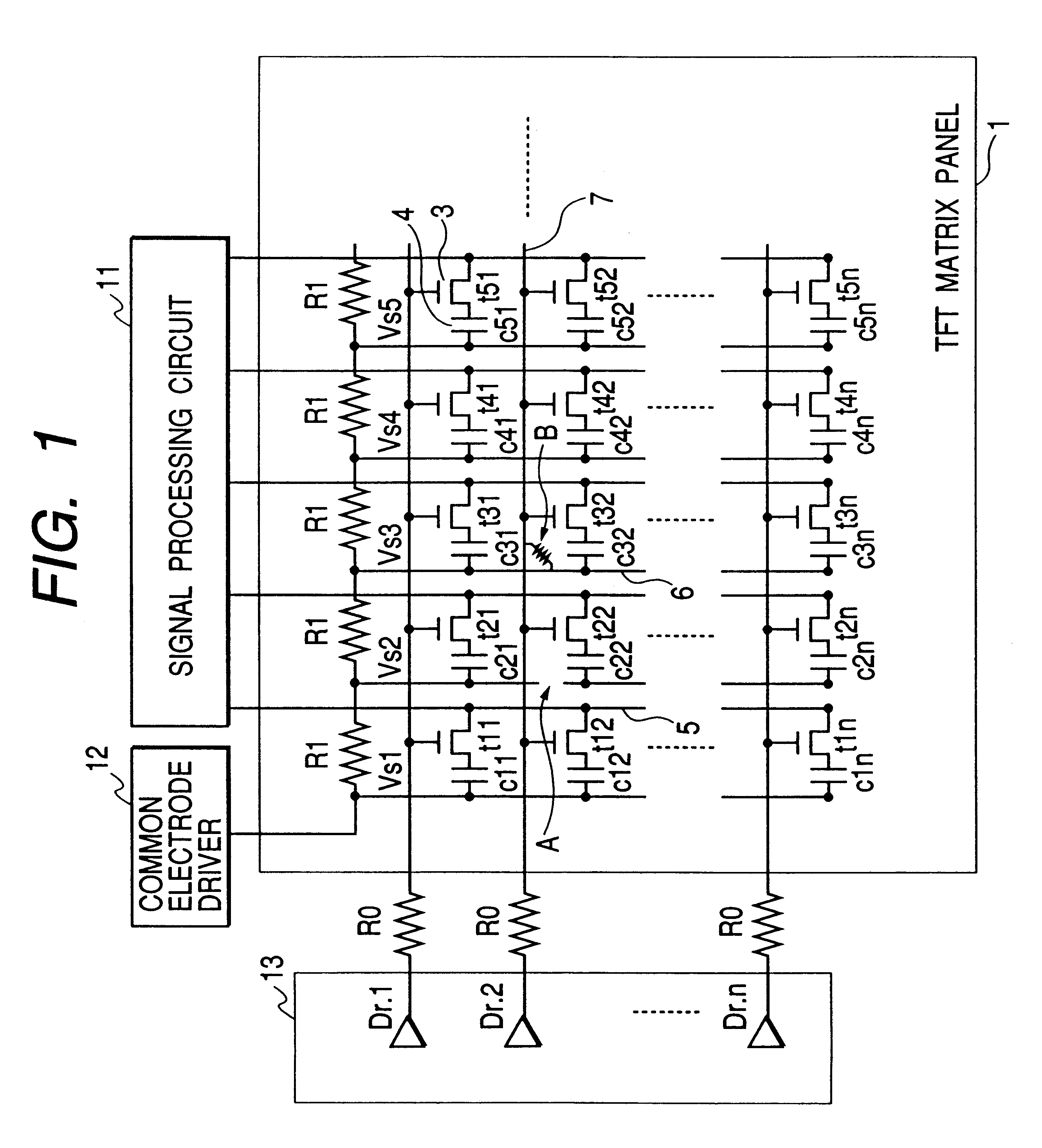
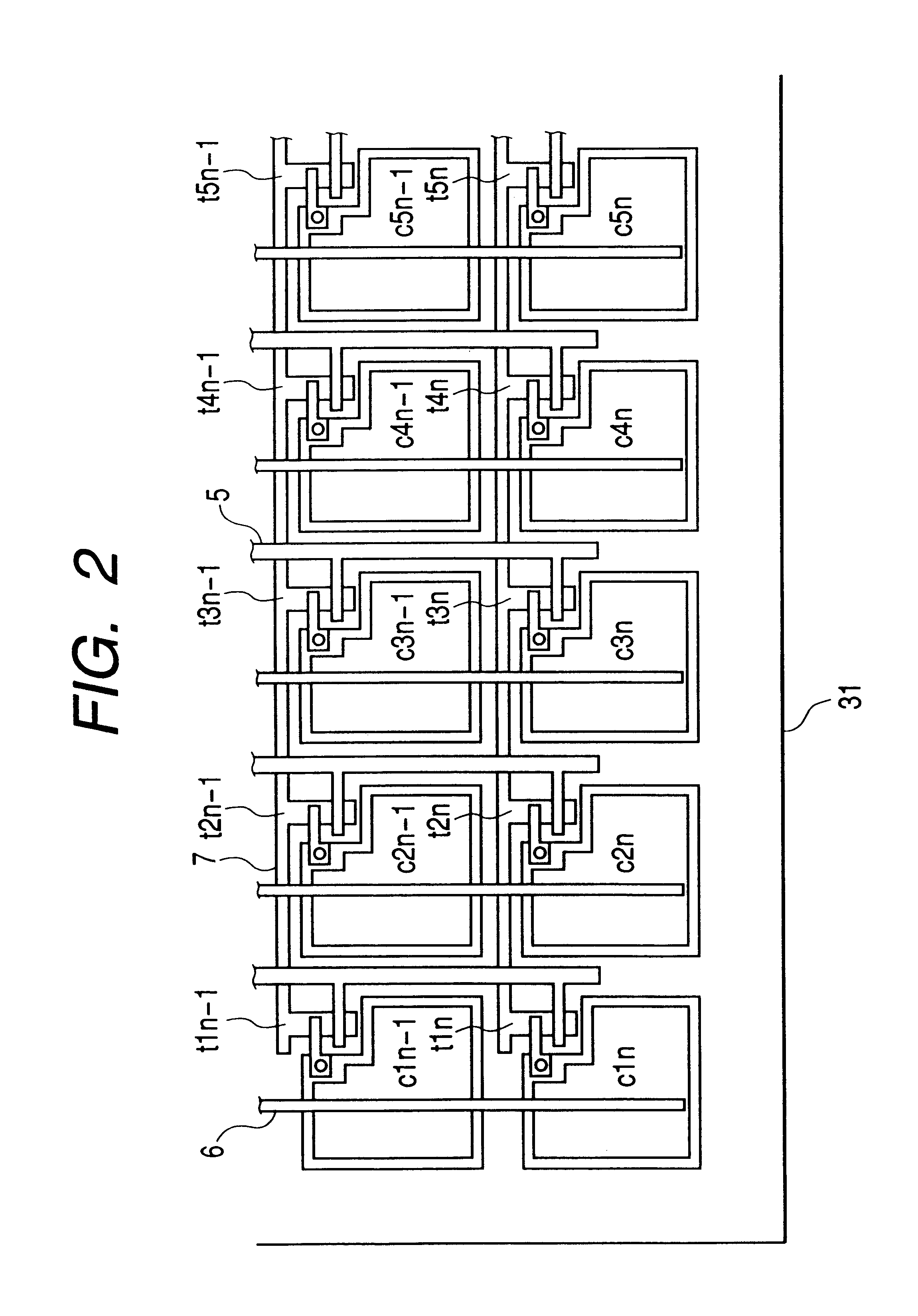
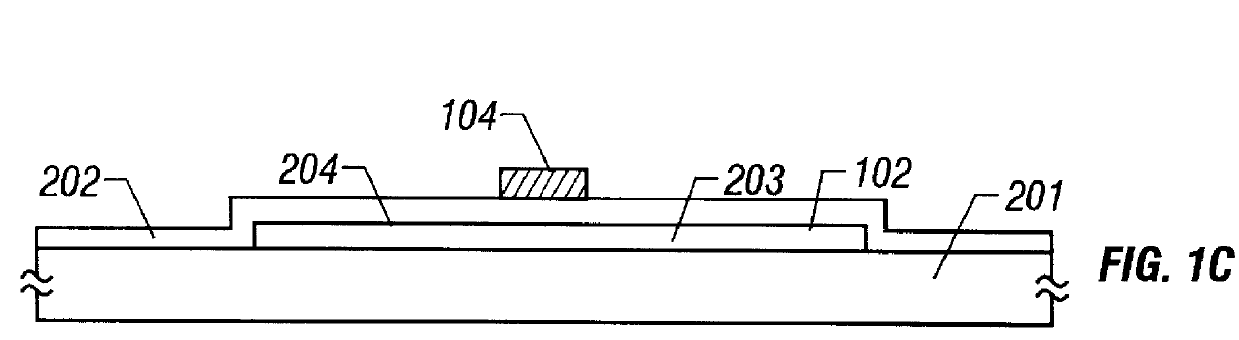
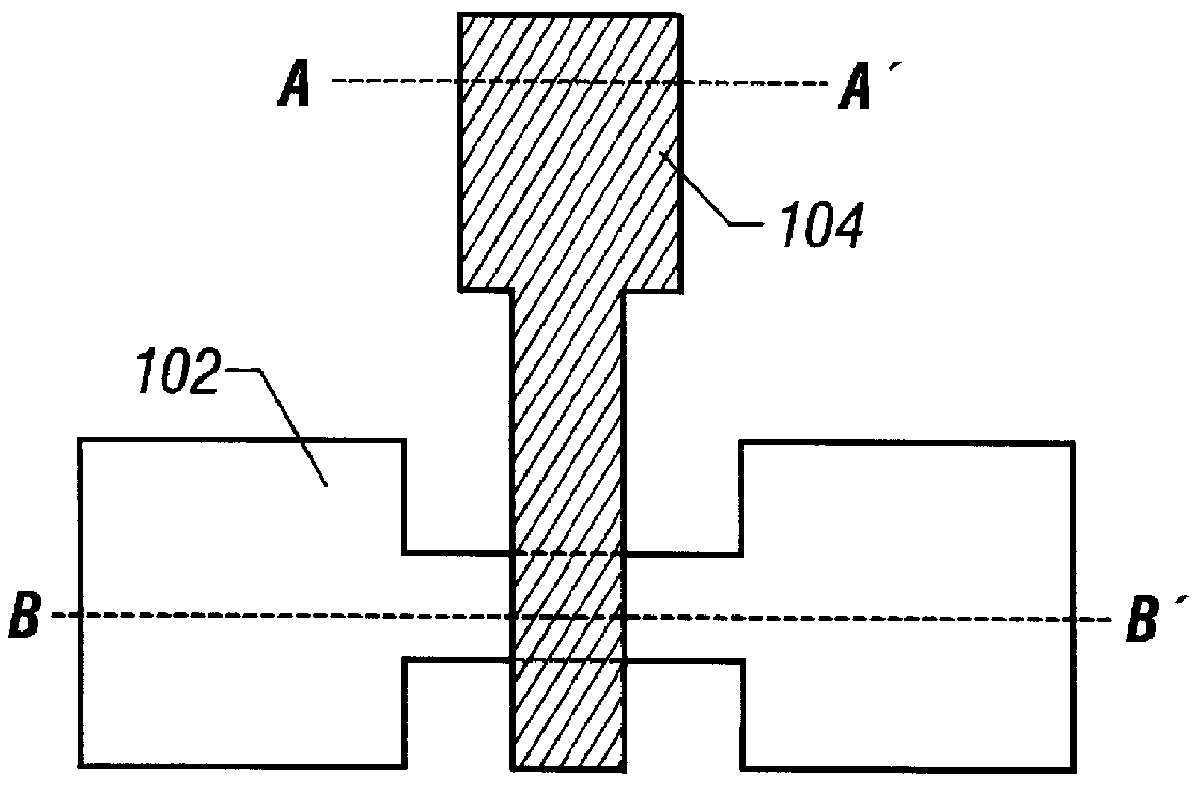
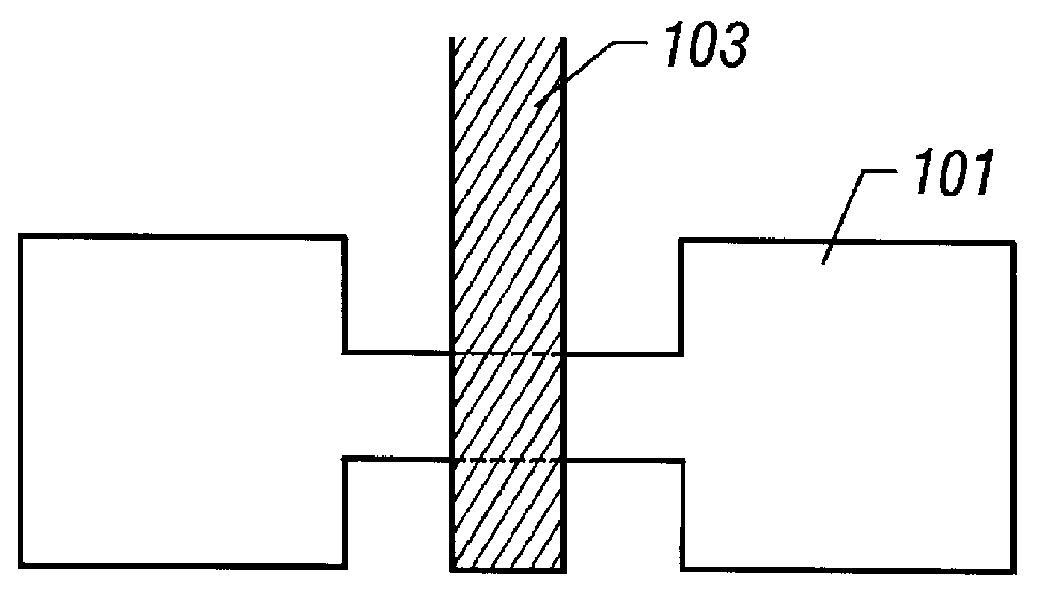
Semiconductor apparatus and method for producing same
In order to prevent a decrease of yield due to a discontinuity of a wire or a short between upper and lower metal wires in production of a TFT matrix panel having pixel capacitors and TFTs and produce the TFT panel in a good yield without decrease of an aperture rate of the pixel capacitor portions even with increase in the size of the panel and with micronization of the pixel pattern, ends of bias lines on the opposite side to connection to a common electrode driver for application of bias are electrically connected to each other by a redundant wire.
Owner:CANON KK
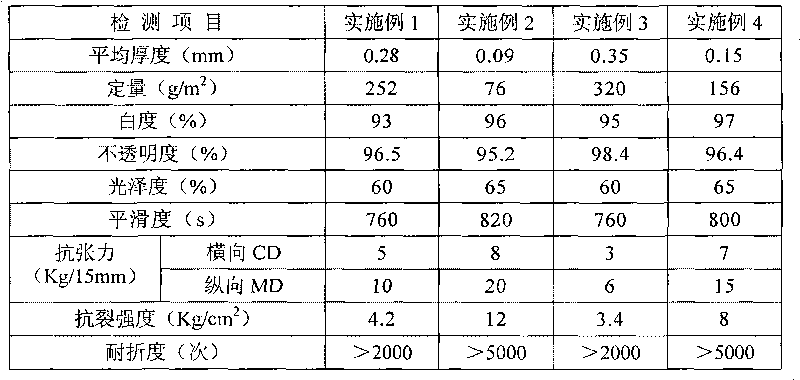
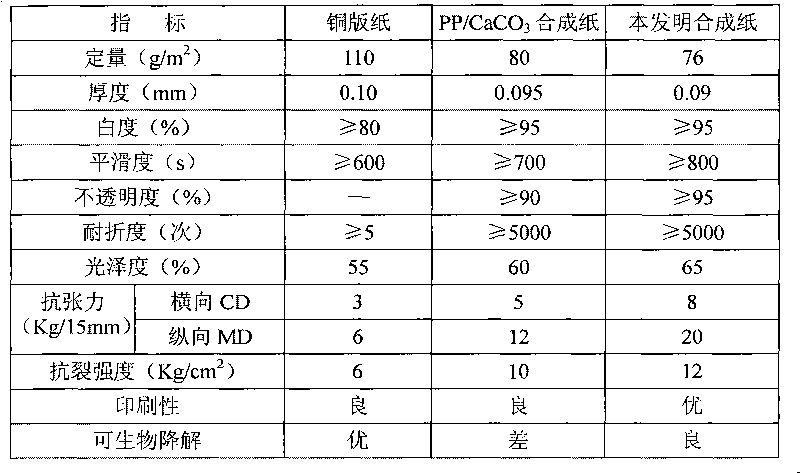
Paper making material, preparation method and paper making method of environment-friendly synthetic paper
ActiveCN101760990AImprove stabilityImprove heat resistanceNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperFiberBlow molding
The invention relates to a paper making material, a preparation method and a paper making method of environment-friendly synthetic paper. The material comprises modified mineral fiber, thermoplastic starch, cellulose derivative, compatilizer, auxiliary components and the like, wherein the average particle diameter of the modified mineral fiber is 5-10 micrometers, the ratio of the length of the modified mineral fiber to the diameter of the modified mineral fiber is 8-15:1, and the modified mineral fiber is treated by fibrosis ultrafine grinding and surface recombination modification; the thermoplastic starch is formed by performing micronization and plasticization modification on norm starch; and the auxiliary components comprise lubricant and colorant. The paper making material is prepared by sequentially mixing the raw material components fully and then extruding and granulating the mixture by a screw extruder at 60-180 DEG C. According to the plastic process mode, the material can be treated by blow molding through a calender or a paper film machine for carrying out two-way stretch to prepare corresponding paper products. The paper making material can overcome the defects of the current synthetic paper and can be widely applied to the fields of commercial printing, publications, office paper, packing and the like, and the processing procedure of making paper by using plastic processing equipment has environmental protection and low cost.
Owner:CHENDU NEW KELI CHEM SCI CO LTD
Method for preparing modified micro granules
InactiveCN102139197AImprove targetingExcellent secondary particle sizeCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentBoiling pointAqueous solution
The invention discloses a method for preparing modified micro granules. Co-precipitation reaction is performed in aqueous solution and between the freezing point and the boiling point of reaction mother solution to generate the micro granules or mixed sediment of micro granule precursor and inorganic sediment. The problems of contradiction between granule micronization and surface modification and difficult separation of the micro granules and the reaction mother solution in the conventional method for preparing the modified micro granules are solved, and the brand-new industrialized production method for modified micro, submicron or nano granules is provided.
Owner:张颖
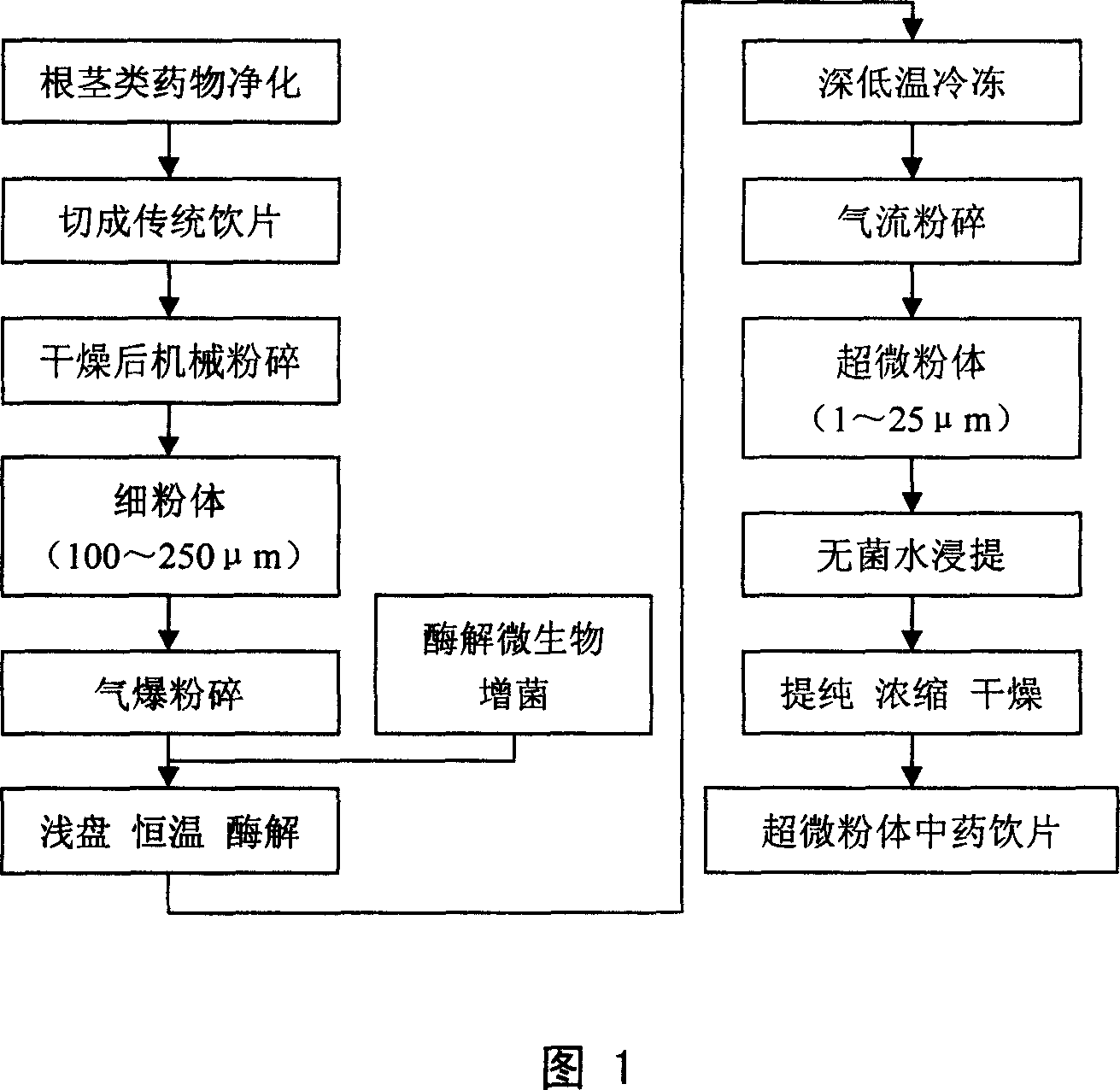
Super micronization method for botanical medicinal, product obtained thereby and use thereof
InactiveCN1994331AAvoid damageIncreased enzymolysis ratePowder deliveryPlant ingredientsEnzymeMicronization
The invention relates to a method for making stem drug containing xylon and cellulose into ultra micro powder, wherein said method comprises that: mechanically breaking; exploding via steam, treating at low temperature, breaking via airflow, enzyme hydrolyzing via microbe enzyme and extracting and separating. The invention also provides relative product and its application for preparing drug, transferring drug element, etc.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Preparation method of ezetimibe medicine composition
InactiveCN103655453AEasy to operateEasy to scale up productionOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineEzetimibe
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ezetimibe medicine composition. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, suspending ezetimibe in a proper solvent to prepare an uniform ezetimibe micron-sized suspension; 2, adding the suspension into a diluent of the medicine composition in a spraying manner and drying to prepare particles and powder of the ezetimibe medicine composition; and 3, preparing the particles and the powder into the ezetimibe medicinal minimum dose unit. Firstly, the medicine is prepared into the micron-sized suspension, granulation is carried out in a one-step granulation manner, the medicine is added into the diluent and finally, the medicinal minimum dose unit is prepared. The preparation method has the benefits that the effect of the preparation method is superior to that of a method in which micronization is carried out after the slightly soluble medicament is separately micronized; and the operation is simple and the large scale production is easy.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES SAIKE PHARMA
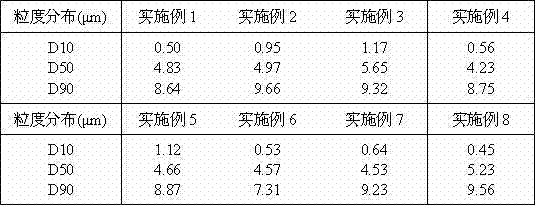
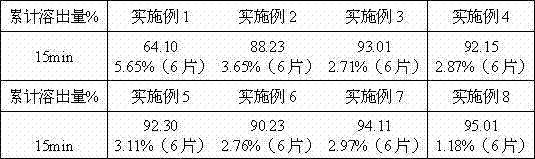
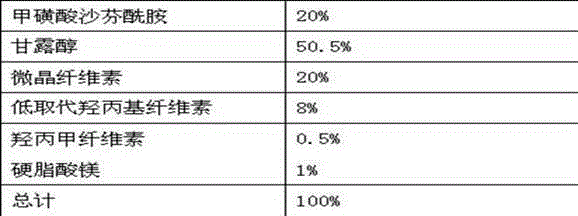
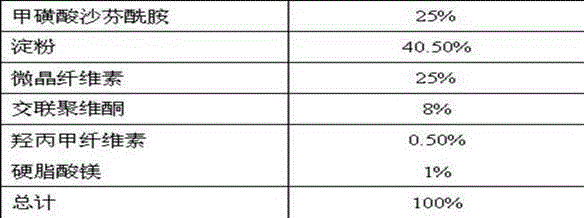
Pharmaceutical composition containing safinamide mesylate and preparation method of pharmaceutical composition
InactiveCN104546747AGuaranteed bioavailabilityEasy to operateOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderWater solubleDissolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and relates to a safinamide mesylate pharmaceutical composition having a good dissolution effect. The pharmaceutical composition contains safinamide mesylate, a water-soluble excipient, a disintegrant, a lubricant and the like, wherein the safinamide mesylate undergoes micronization treatment, and the grain size of 90% of the safinamide mesylate is controlled within 5-50microns, preferably within 10-20microns. The medicine prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is good in dissolution effect, so that the bioavailability of the medicine is effectively improved.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA HAINAN
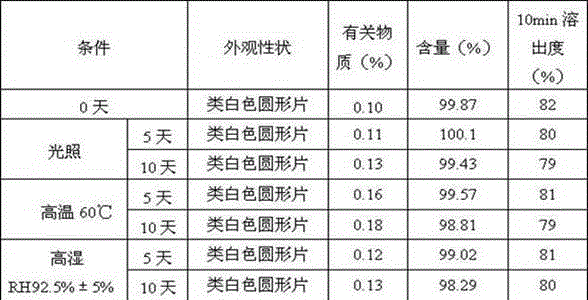
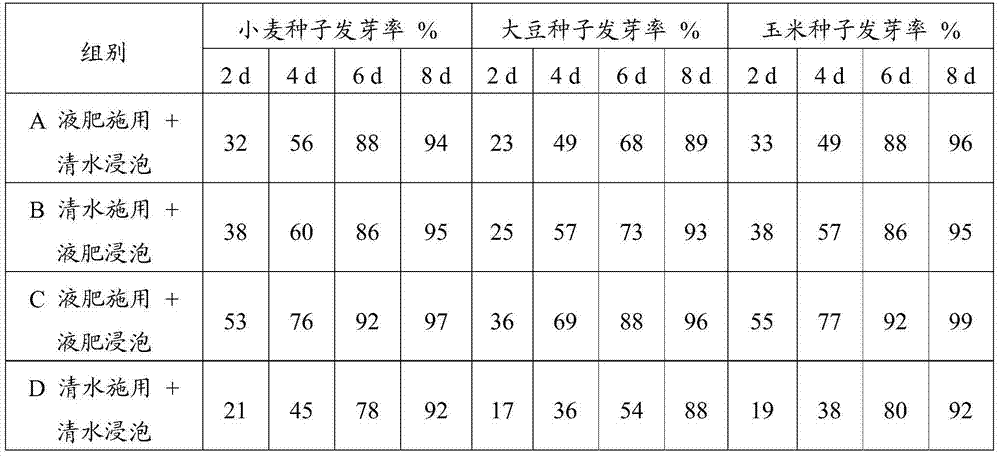
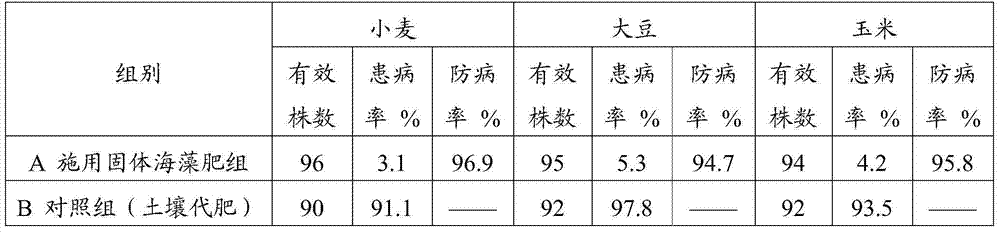
Preparation method of compound microbial seaweed fertilizer
ActiveCN104774094AImprove qualityEfficient use ofBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationMetaboliteSoil properties
The invention discloses a preparation method of a compound microbial seaweed fertilizer. Screened bacillus amylolique faciens WB1 with high alginate lyase activity and bacillus subtilis ABTNL-2 capable of producing various of ablastins are used for fermenting seaweed subjected to enzyme-aid micronization treatment, so as to generate a great deal of micromolecular special-effect metabolites capable of promoting growth of crops, such as alginooligosaccharide, thereby improving the bioactivity of the seaweed fertilizer. Moreover, the advantage that the bacillus amylolique faciens WB1 and the bacillus subtilis ABTNL-2 are capable of inhibiting various pathogenic bacteria of crops can be put into a full play; the compound microbial seaweed fertilizer has a high nutrition added value and has the pesticide-fertilizer integrated functions of improving soil properties and preventing various diseases.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation of chinese herbal composite recipe used in horticulture
InactiveUS20050158403A1Maintain agriculture profitMaintain human healthBiocideDead animal preservationHerbal preparationsNose
A recipe of Chinese herbal composite used in horticulture to kill pests. The practical applications of this recipe include pest killing, germ and virus eradication of vegetables, fruit trees, flowers and economical plants. This recipe is composed of Gleditisia Sinensis, Sophora flavescens, Aloe uere, Stemona tuberose, Brucea jauamica and Dioscorea collettis vice versa. We prepare it with modern principles and scientific methods to emulsion spray. Those so called modern and scientific are the emulsion processes, micronization, permeability and the multiply potency it possessed. Several laboratory and field test proved that this invention had definite effect on the past killing, germ eradiation and virus inhibition. This invention is belongs to non toxic Chinese herbal preparation. The spray does not harm or cause toxic effect as it touch human skin, eyes, nasal mucosa, lip, mouth and tongue. It does not accumulate in human body and pollute environment.
Owner:LEE CHIEN YUNG
Mycotoxin binding food and feed additives and processing aids, fungistatic and bacteriostatic plant protecting agents and methods of utilizing the same
InactiveUS20120070516A1Good removal effectGood for healthBiocideFood processingCelluloseProcedure Agents
Method is proposed useful to render harmless mycotoxins that contaminate food, animal feed and assist infection of plant hosts by microbial parasites, comprising binding mycotoxins by a novel adsorbent, consisting partially or in full of plant lignocellulosic biomass or isolated biomass components, e.g., acid hydrolysis lignin, enzymatic hydrolysis lignin, coniferous and deciduous wood, bark and needle particles, rice hulls, used coffee grounds, apricot stone shells, almond, walnut, sunflower hulls, cocoa and peanut shells. The materials may be further improved through genetic modification of plants and physicochemical treatment of lignocellulosic biomass, such as micronization. The resulting adsorbent can bind wide range of mycotoxins, including, mycotoxins difficult to bind (Ochratoxin, T-2, Deoxynivalenol, Nivalenol). Ability of porous materials containing lignin to thermally collapse at melting can be used to irreversibly entrap mycotoxins by adsorbing them in a wet system and then closing lignin pore structure under high-temperature treatment, such as drying.
Owner:CUBENA
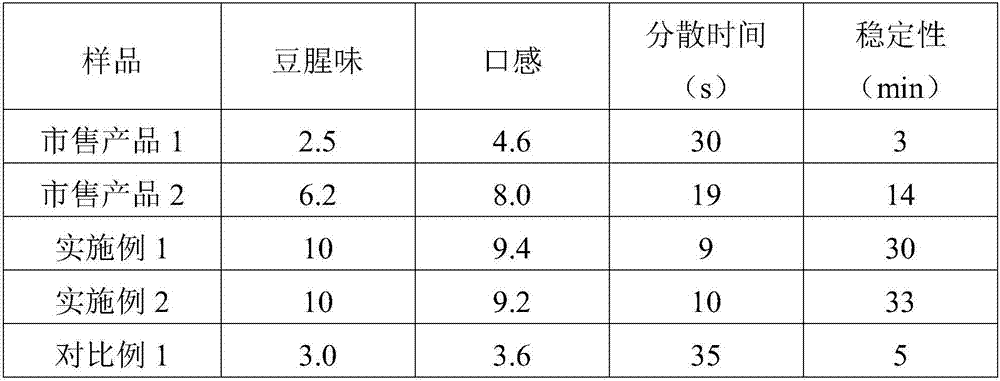
Preparation method of SPI (soybean protein isolate)
ActiveCN107047923AImprove stabilityNo beany smellProtein composition from vegetable seedsVegetable proteins working-upFood industryFlavor
The invention relates to the field of food and food processing, in particular to a preparation method of SPI (soybean protein isolate). The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: extracting defatted soybean meal, separating and carrying out primary sterilization and flash evaporation, acid precipitation, neutralization, enzymatic hydrolysis, secondary sterilization and flash evaporation, drying, ultra-micronization and the like. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, SPI products which are free of beany flavor and salty and bitter taste, good in taste, excellent in dispersion and stable in stability can be produced. SPI prepared with the method is very suitable for being taken as a raw material for processing and producing a soybean protein solid beverage, and the quality of soybean protein solid beverage products can be fundamentally improved. Therefore, the method and product disclosed by the invention are very suitable for technical needs of the current soybean protein production industry, and the popularization and application of the method and product have very important significance on broadening the application of SPI in the food industry.
Owner:SHANDONG YUWANG ECOLOGY FOOD IND
Electronic device and integrated circuit
The present invention provides an integrated circuit structure in which an area necessary for making contact is assured in a multi-layered wiring structure even when a design rule is made rigorous. In a structure in which wires separated above and below by an interlayer insulating film are contacted, the wire at the lower layer is patterned into a pattern of the wire at the upper layer which are made to contact. Thereby, the present invention allows the area necessary for making the contact to be largely assured and to deal with the micronization.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for preparing Poria cocos granules by replacing part of auxiliary materials with ultrafine powder
ActiveCN102526129AHigh in polysaccharidesReduce dosageNervous disorderAntipyreticActive componentColloid
The invention relates to a method for preparing Poria cocos granules by replacing part of auxiliary materials with ultrafine powder. The method comprises the following steps of: (1), taking a Poria cocos decoction tablet, adding water to decoct the Poria cocos decoction tablet once or twice, filtering the decoction, and performing vacuum concentration to obtain a Poria cocos concentrated solutionA, or performing spray drying to obtain a Poria cocos concentrated powder B; (2) taking a Poria cocos decoction tablet, performing micronization, collecting micropowder with the particle diameter of less than 500 meshes, adding water or adding the Poria cocos concentrated solution A obtained in the step (1), adding a proper amount of starch medicinal auxiliary materials, heating and boiling, and milling with a colloid mill once or twice to obtain a Poria cocos micropowder milled solution C, or performing spray drying to obtain a Poria cocos micropowder milled powder D; and (3), uniformly mixing the obtained Poria cocos concentrated solution A and the obtained Poria cocos micropowder milled solution C, and performing spray drying; or uniformly mixing the Poria cocos concentrated powder B and the Poria cocos micropowder milled powder D, and granulating and packaging. By the preparation method, the problem that power floats in the dissolving and orally taking process can be effectively solved, the dissolving dispersibility of the micropowder is improved, the content of an active component Poria cocos polysaccharide is increased, and the using amount of the auxiliary materials is reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG YIFANG PHARMA
Esterification modification method of microcrystalline cellulose
The invention relates to a surface esterification modification method of microcrystalline cellulose and belongs to the technical field of surface modification of solid materials. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps of: carrying out micronization treatment on the microcrystalline cellulose, mixing the micronized microcrystalline cellulose and esterifying agent solution according to a certain mass ratio, heating the system to enable the esterifying agent and hydroxyl on the surface of the microcrystalline cellulose to be subjected to esterification, and finally obtaining the esterified microcrystalline cellulose by centrifugally washing and drying process. Agglomeration phenomenon caused by a hydrogen bonding action between microcrystalline cellulose particles is effectively restrained after the esterification modification treatment; the surface polarity is obviously reduced; the microcrystalline cellulose can be stably dispersed in an organic solvent with the lowest polarity, and a crystal structure of the microcrystalline cellulose is not destroyed by the esterification modification. The esterification modification method of microcrystalline cellulose disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple process, no-added catalyst, low production cost, and green and environment-friendly characteristics. The surface esterified and modified microcrystalline cellulose prepared by the method has good application prospect in the field of polymer composite materials.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
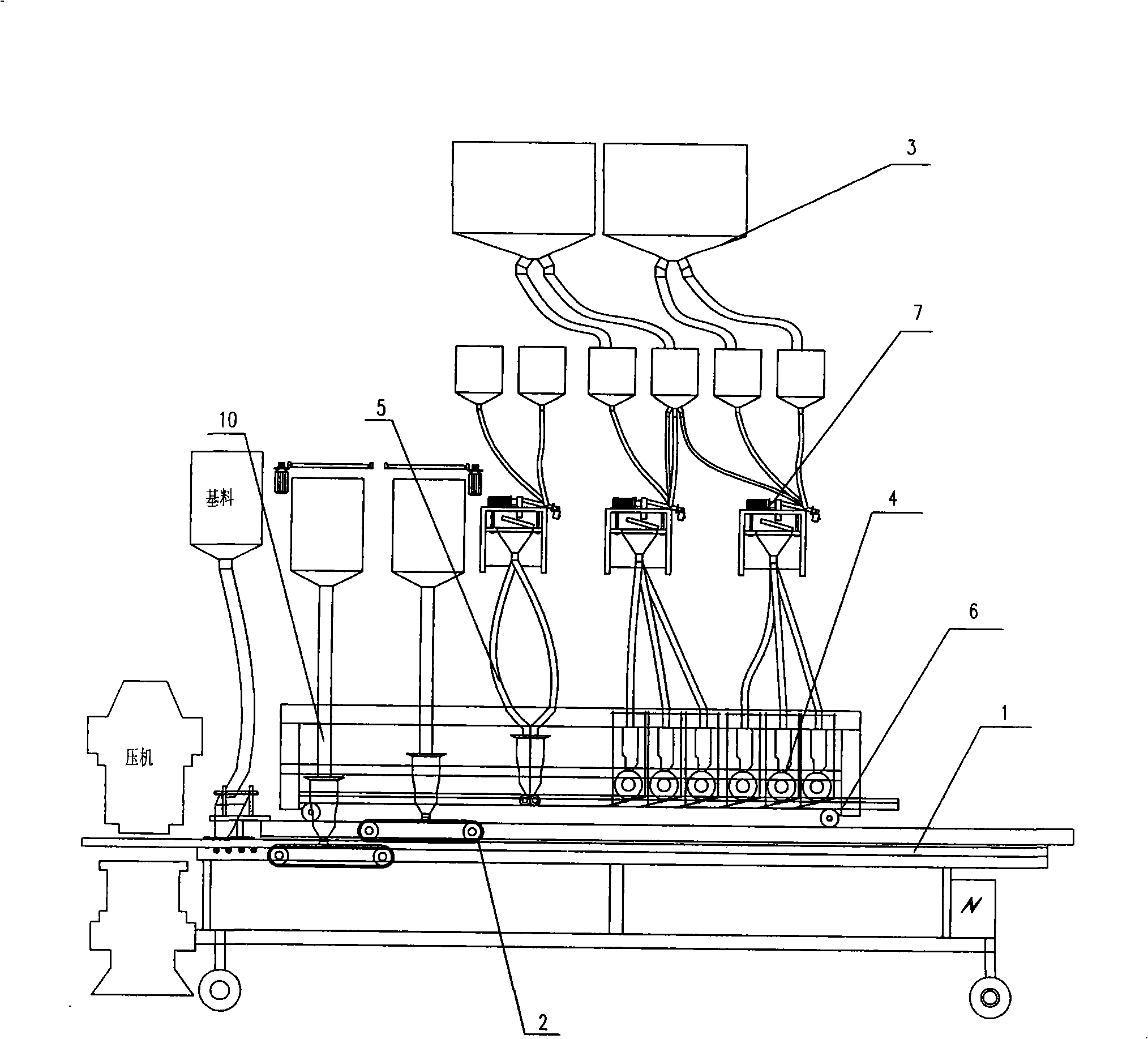
Ceramic tile micro mist cloth technique method and equipment
The invention discloses a process method for laying out the porcelain tile tiny powder and the equipment thereof, which is characterized in that a preparation of a platy grain material and the laying out process are added and the line laying out process is combined based on the prior reverse tiny powder laying out process, the coordinate laying out of the platy grain material, line material, and micronization superficial material is realized, and the porcelain tile product with a strong feeling of three dimensional grain is created. The process method for laying out the porcelain tile tiny powder has the advantages of strong feeling of three dimensional grain, rich texture, natural smooth lines and decoration patterns with three dimensional aesthetic feeling and rich intension compared with the surface decoration texture of the micronization porcelain tile in the prior art.
Owner:FOSHAN DONGPENG CERAMIC +1
Hydrochloric acid cefetamet pivoxil dispersible tablet and method for preparing the same
ActiveCN101219124AThe content of the main drug is uniformGood content uniformityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDissolutionBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a cefetamet pivoxil hydrochloride tablet and a preparation method thereof. On the premise of specific active ingredients of the cefetamet pivoxil hydrochloride, the invention takes into account the varieties and dosages of disintegrating agents and joint usage thereof, suitable components and ratios of bonding agents and other filling agents, and the micronization treatment of the raw and auxiliary materials and selection of corresponding optimized process conditions. Experiment results indicate that compared with the prior art, the product of the invention has quick disintegration and dissolution and stable quality.
Owner:SHANDONG LUOXIN PARMACEUTICAL GROUP STOCK CO LTD +1
Preparation method of Chinese wolfberry powder
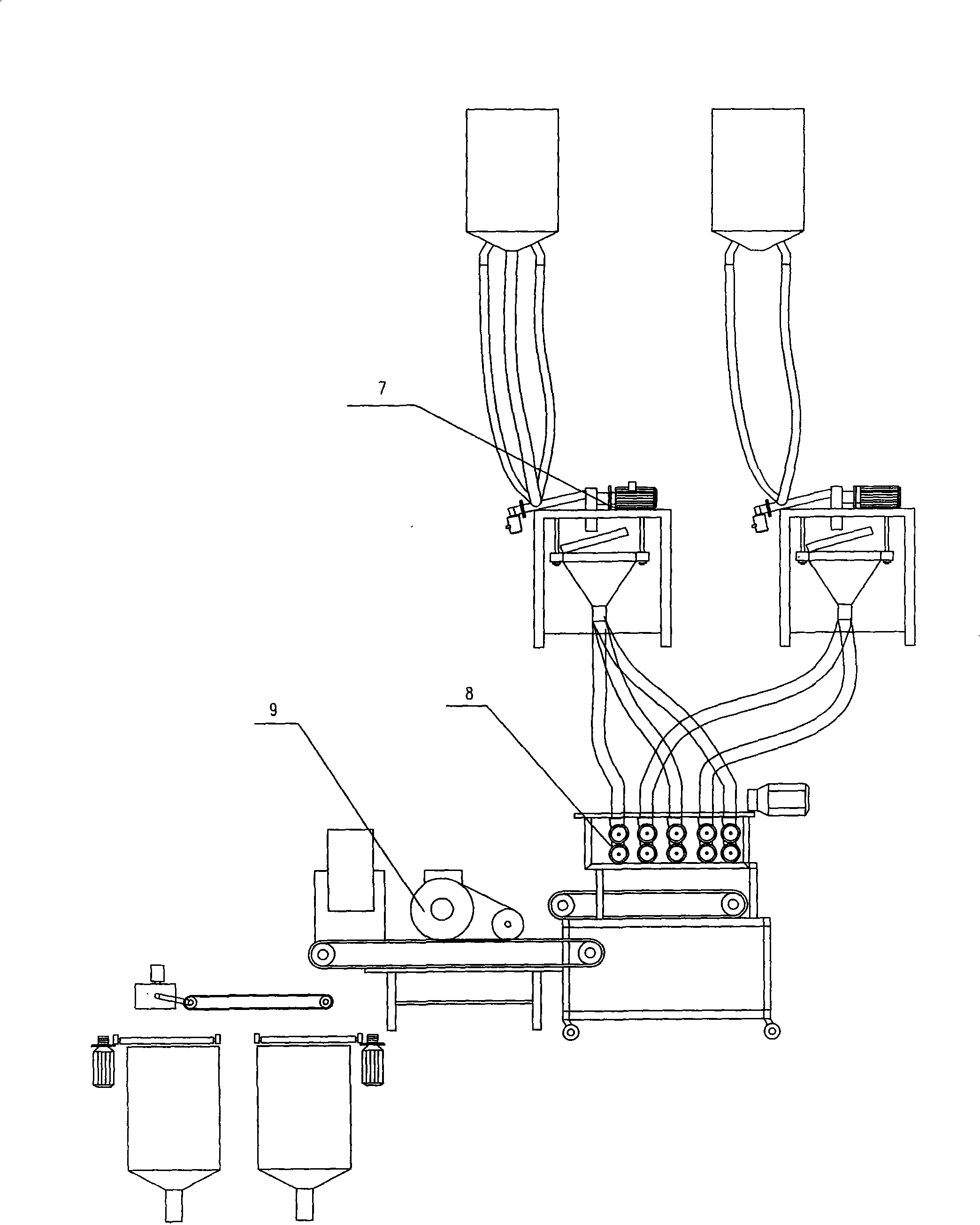
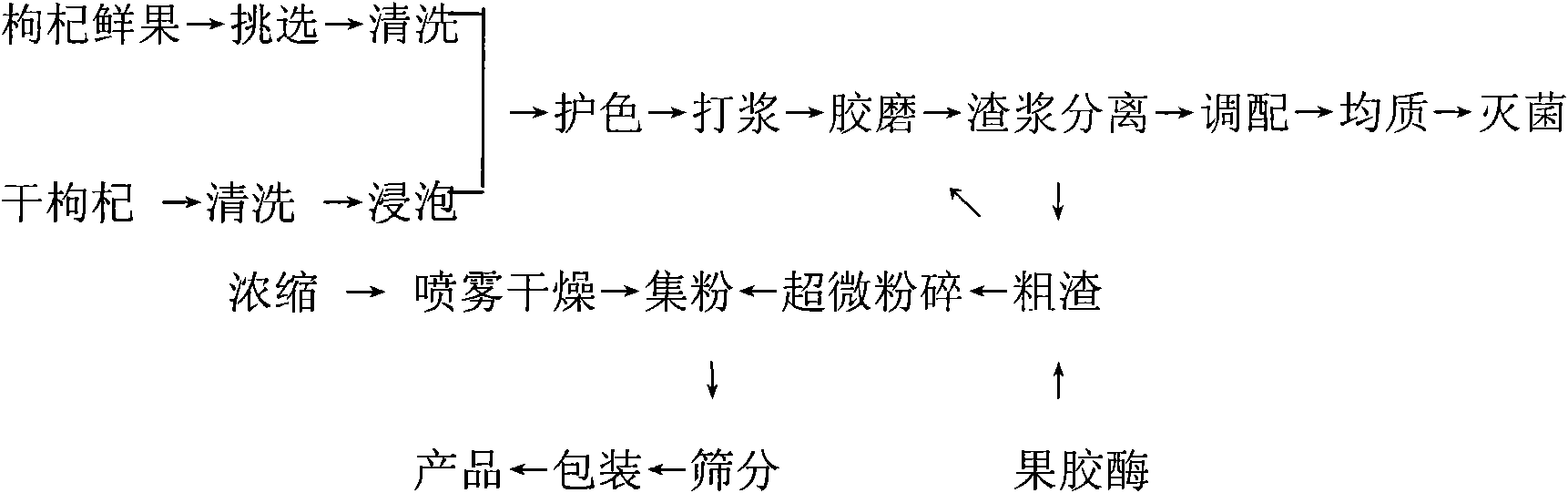
InactiveCN101606667AKeep natural colorPure tasteFruit and vegetables preservationFood shapingPectinaseSide effect
The invention discloses a preparation method of Chinese wolfberry powder, comprising the steps: using fresh or dry wolfberries as main raw materials; obtaining a wolfberry powder product by processing the fresh or dry wolfberries through the procedures of picking, cleaning or soaking, protecting color, pulping, grinding rubber, secondary processing, blending, homogenizing, sterilizing, concentrating, dry spraying, drying fog, collecting powder, sieving, packing and storing products, wherein the secondary processing procedure comprises the steps: reprocessing filtered coarse residues; decomposing the filtered coarse residues by adding pectinase; reprocessing the filtered coarse residues after being returned into a colloid mill; processing non-enzymatic coarse residues by adopting micronization to obtain fine powder; recovering the fine powder into a powder collecting bin; and then, obtaining a wolfberry powder product by processing the fine powder through the procedures of sieving, packing and storing products. The Chinese wolfberry powder has good color, high solubility, good mouth feel, no side effect, short production period and high profit. The preparation method of Chinese wolfberry powder provides high-quality powdered food for increasing the physical quality of humans and can be widely applied to the industries of food, health products, and the like.
Owner:WUXI VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Preparation process for ultrafine glibenclamide particles
InactiveCN102397257ASimple processEasy to operateMetabolism disorderSulfonylurea active ingredientsSlurryGlibenclamide
The invention discloses a preparation process for ultrafine glibenclamide particles, which belongs to the field of micronization of drugs. The process comprises the following steps: preparing an organic solution of glibenclamide; dissolving pharmaceutic adjuvants in water to form an aqueous solution and controlling the temperature of the aqueous solution to be 2 to 50 DEG C; mixing the above mentioned two solutions to prepare medicinal slurry, carrying out spray drying on the medicinal slurry, and controlling inlet temperature to be 100 to 170 DEG C, outlet temperature to be 60 to 95 DEG C, a feeding speed to be 5 to 40 ml / min and compressed air pressure to be 0.4 to 0.8 MPa so as to obtain ultrafine glibenclamide powder. The ultrafine powder provided in the invention has good stability, and more than 85% of the powder can be dissolved within 2.5 minutes; the process is simple and is easy to operate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com