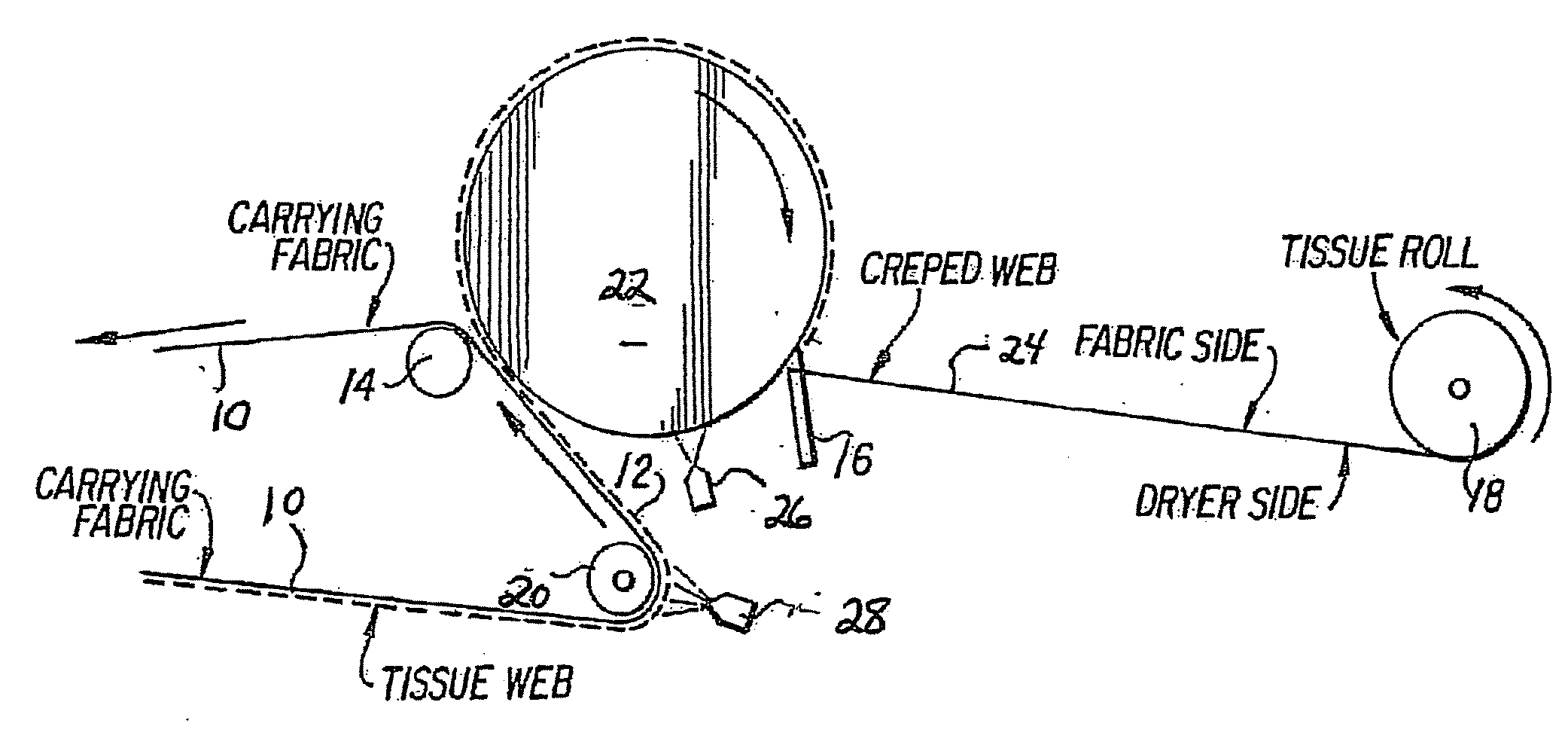
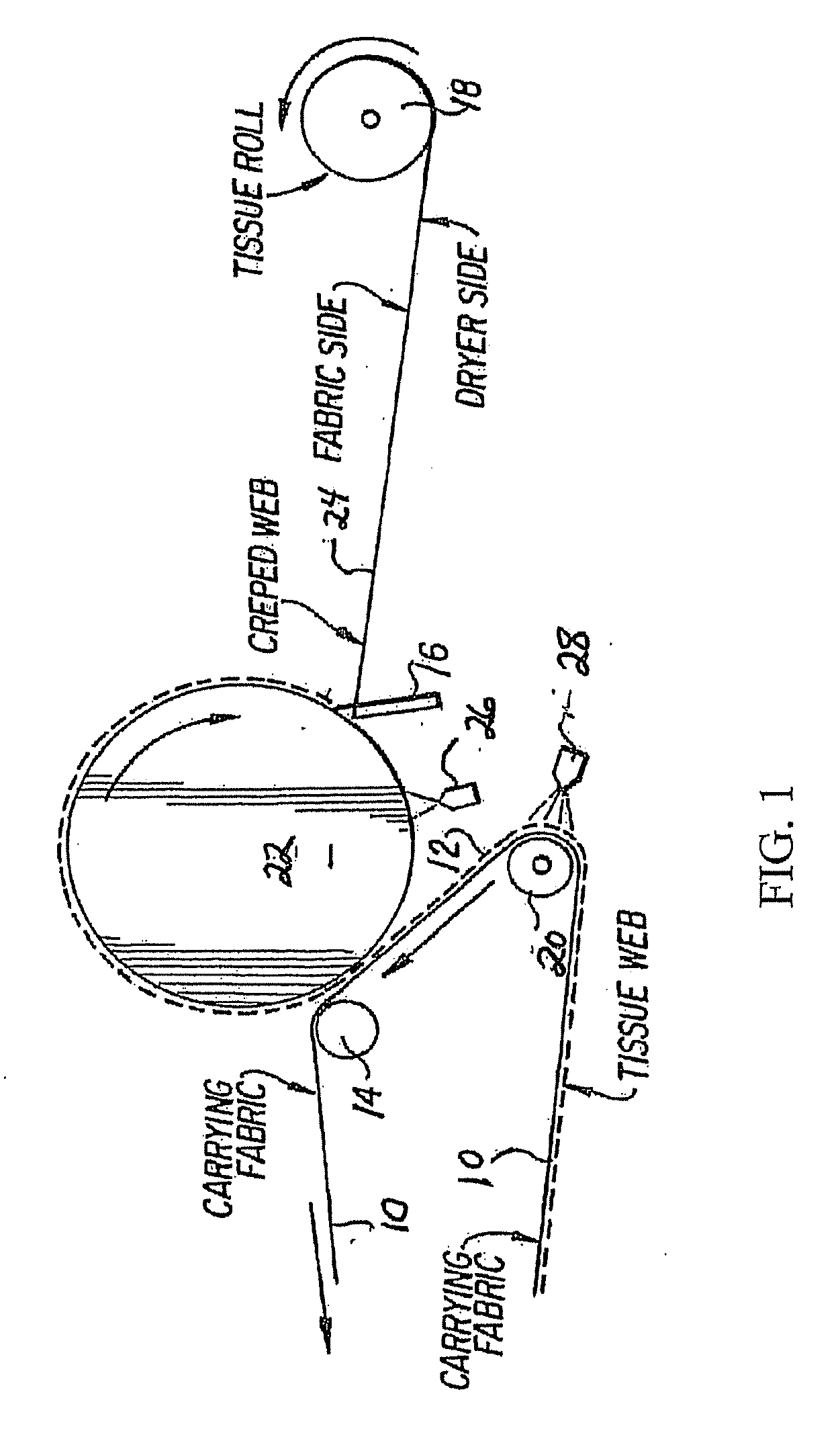
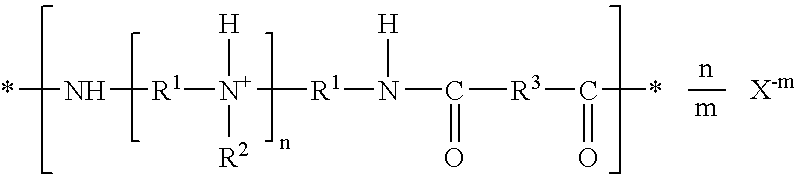
Acidified polyamidoamine adhesives, method of manufacture, and use for creping and ply bond applications
a technology of acidified polyamidoamine and adhesive composition, which is applied in the field of acidified polyamidoamine adhesive composition, can solve the problems of easy dissolution, loss of strength, and high moisture resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Acidic Polyamidoamine, P-1
[0081]Polymer P-1 is produced via condensation polymerization of a 1:1 molar ratio of diethylenetriamine (DETA) and adipic acid. The reaction is conducted neat; no diluents are initially added. The reaction is immediate and exothermic upon addition of the adipic acid to the DETA. Addition of the adipic acid is carried out rapidly enough to ensure that the total charge is finished before the exotherm reaches 100° C. The reaction temperature is raised to 180° C. after the exotherm to drive the polymerization to the desired molecular weight range, the endpoint of which is determined by the collection of condensate water. This material (22.85 g, 70% solids) is diluted with 77.72 g water and acidified by slow addition of 2.17 g concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to a final pH of 4.4, Mw 20,000 Daltons, and a Brookfield LVT viscosity of 308 centipoise.
example 2
Mixtures of P-1 and Epi-Polyamides of Varying Crosslink Density
[0082]The product of Example 1 was blended individually with several epi-polyamides commercially available under the tradenames OmniCrepe™ 681-A (designated XP-1), OmniCrepe™-AM (designated XP-2), and OmniCrepe™-AX (designated XP-3), by Kemira North America. These epi-polyamides are derived from the polymerization product of adipic acid and diethylenetriamine, and subsequently treated with epichlorohydrin and sulfuric acid. OmniCrepe™ products are classified as having medium through medium-heavy crosslinked density. OmniCrepe™ 681-A has the lowest crosslink density, the highest adhesion, the lowest insolubility, and the lowest hardness. OmniCrepe™-AM has an intermediate crosslink density level. OmniCrepe™-AX has highest crosslink density, the lowest adhesion, the highest insolubility, and highest hardness.
[0083]Table 1 compares the advantageous properties of acidic polyamidoamine, P-1, to its neutral analog, NP-1. P-1 is...
example 3
[0085]This example demonstrates tunable rewet and % insolubility properties using a metal ion to crosslink acidic polyamidoamine, P-1. To a solution of P-1 was added zirconium acetate at 2, 4, 6, and 12 wt % metal ion relative to total solids. The resulting chelated polymer progressively increased % insolubility and rewet properties with increasing concentration of metal ion, as shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3Metal ion,Rewet(wt %)% Insolubility(wet wt / init. Wt)00026.60.10410.00.16617.00.251239.00.58
[0086]The various embodiments described above provide for a creping and ply bond adhesive compositions having tunable combinations of insolubility, adhesion, rewet and hardness properties.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com