Patents
Literature
200 results about "Alkyl bromide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synthesis of alkyl bromides. The use of a tetraethylammonium halide in the presences of [Et 2NSF 2]BF 4 (XtalFluor-E) enables efficient chlorination and bromination reactions of a wide range of alcohols. Iodination reactions are also possible albeit in lower yields.
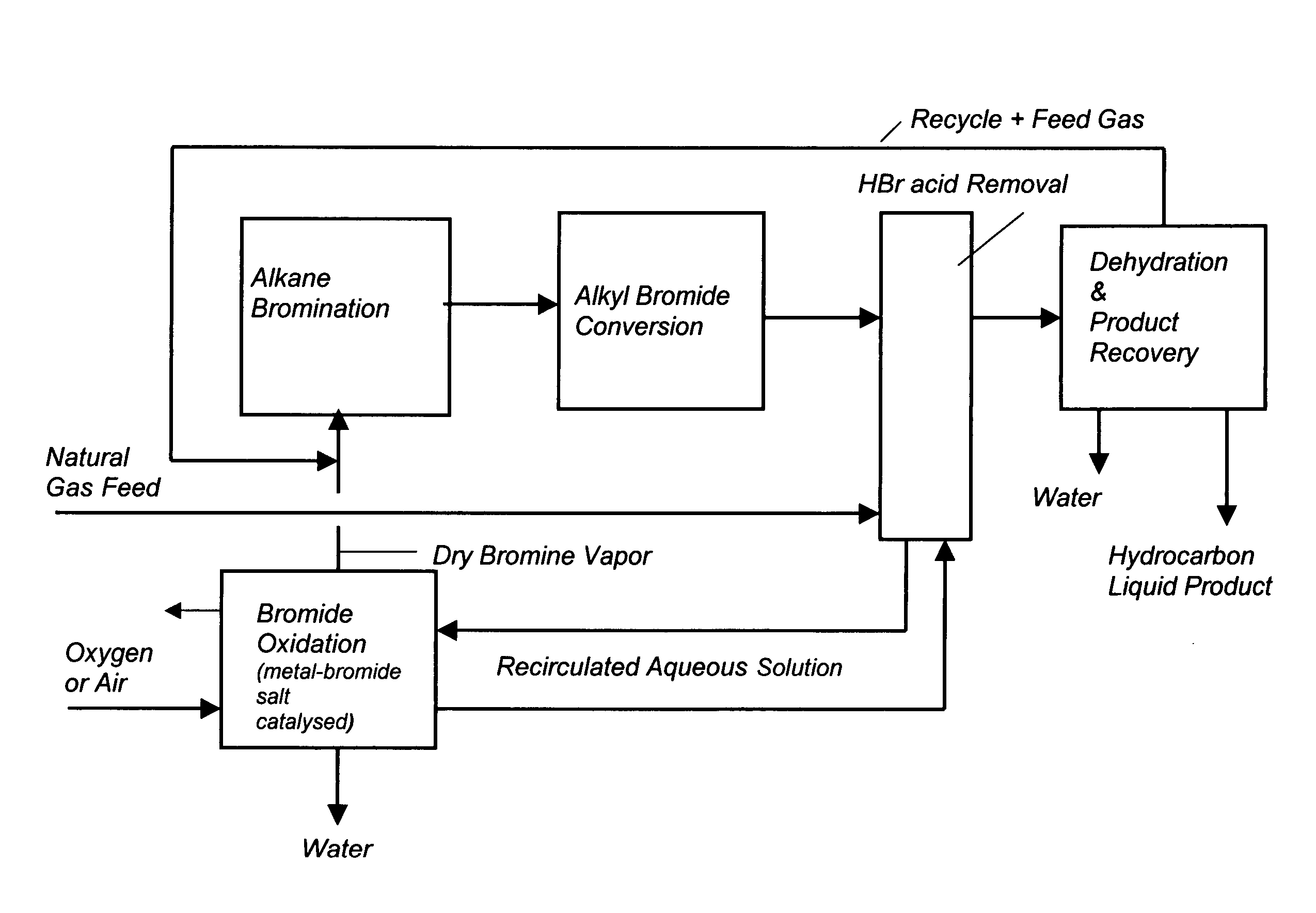
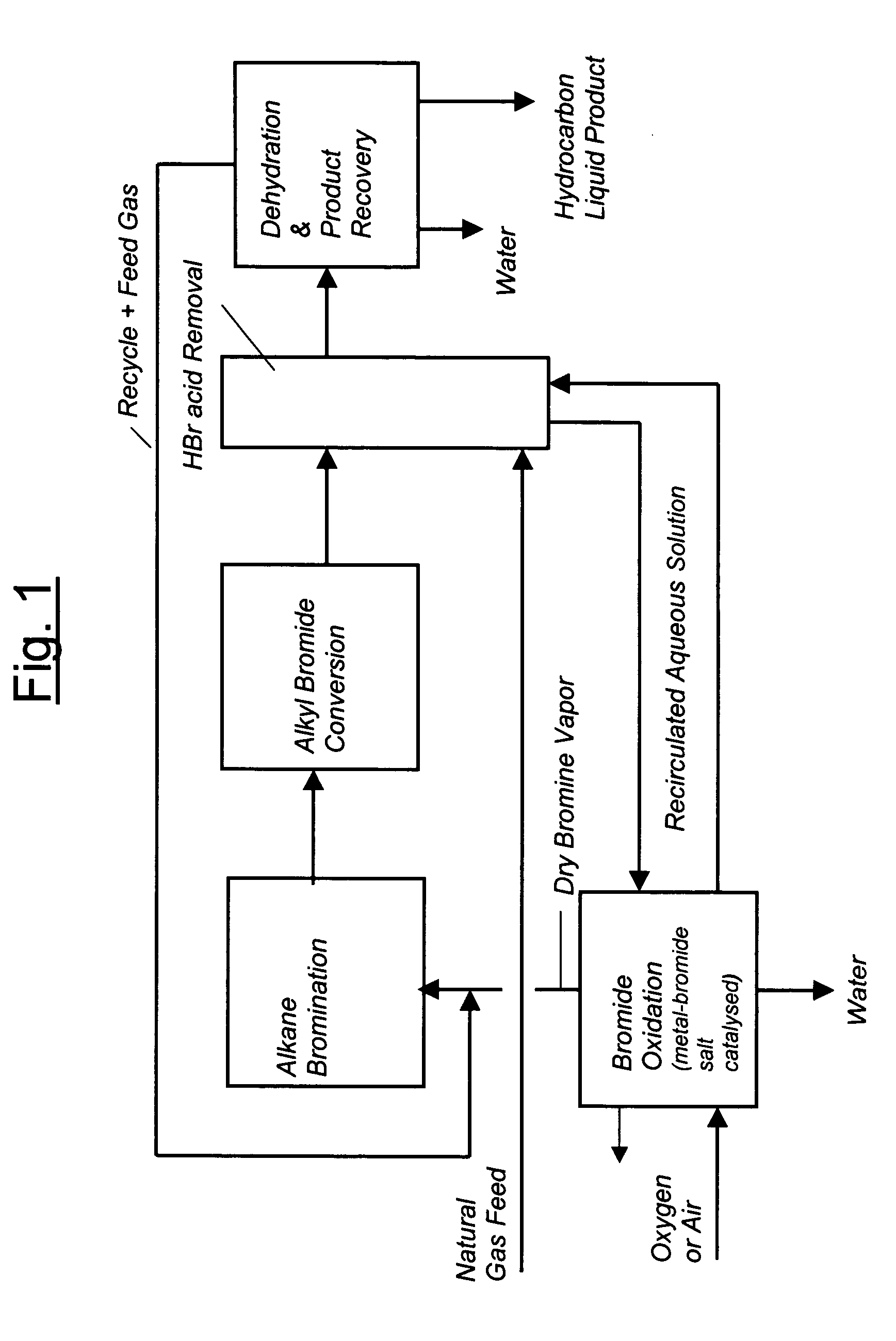
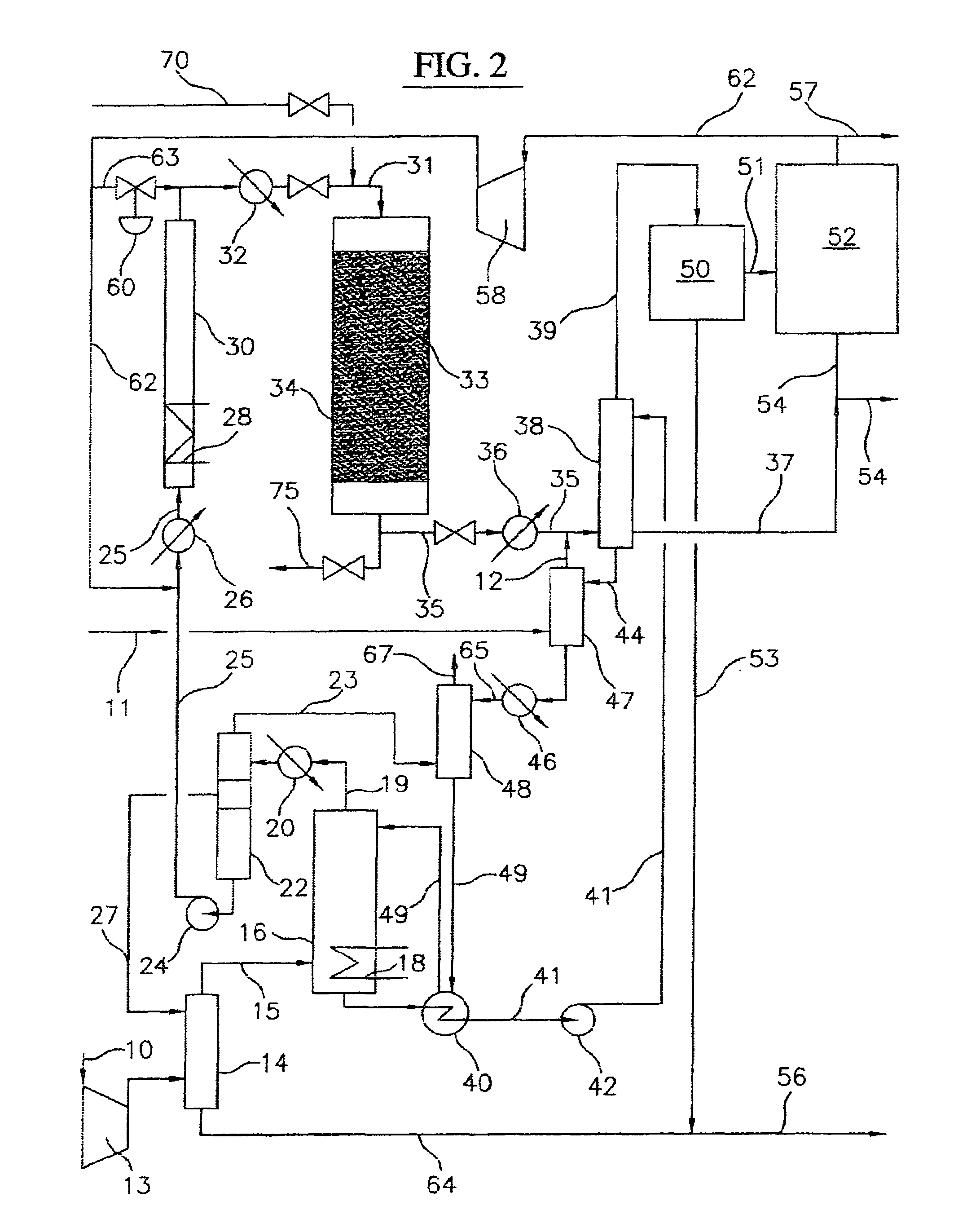
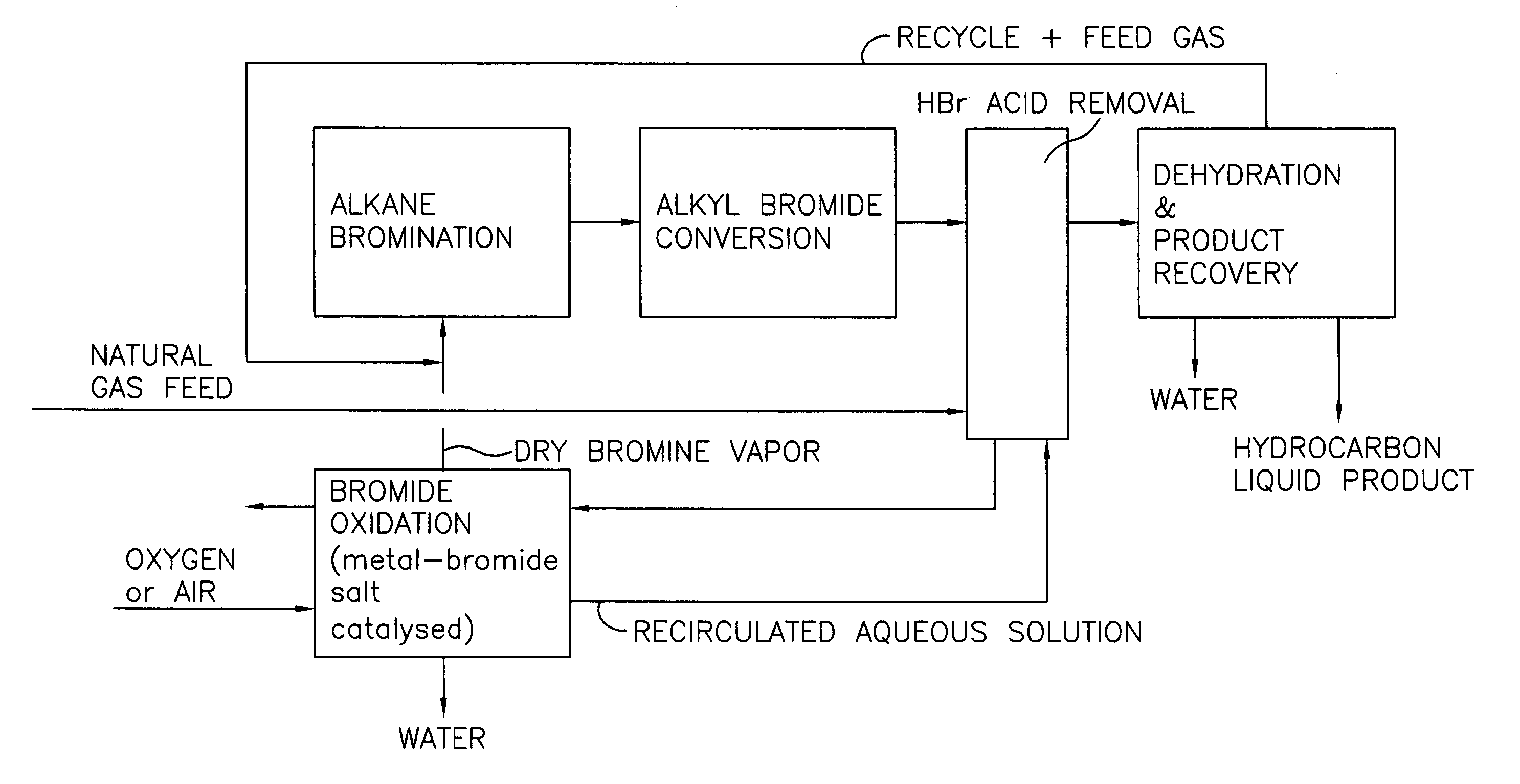
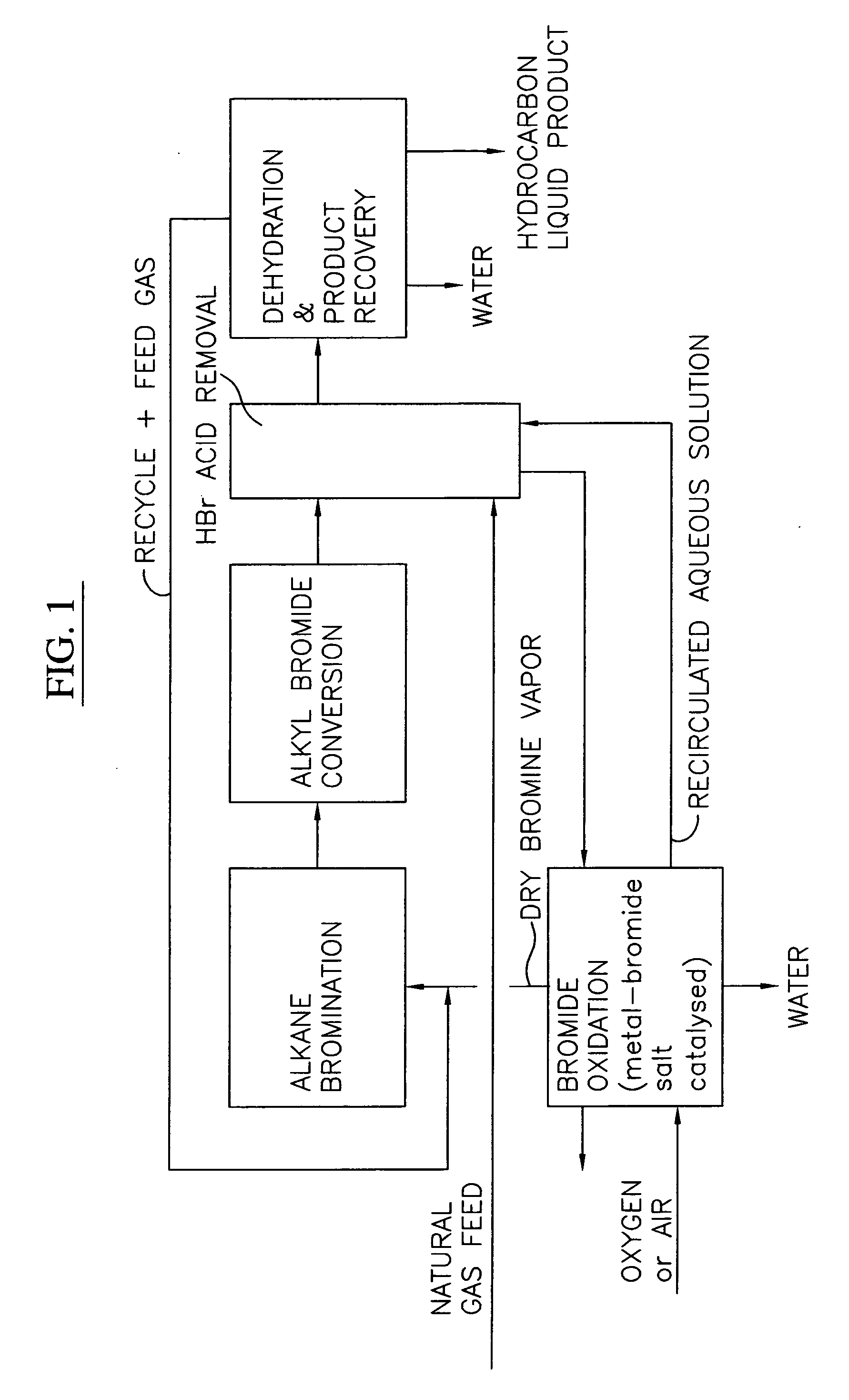
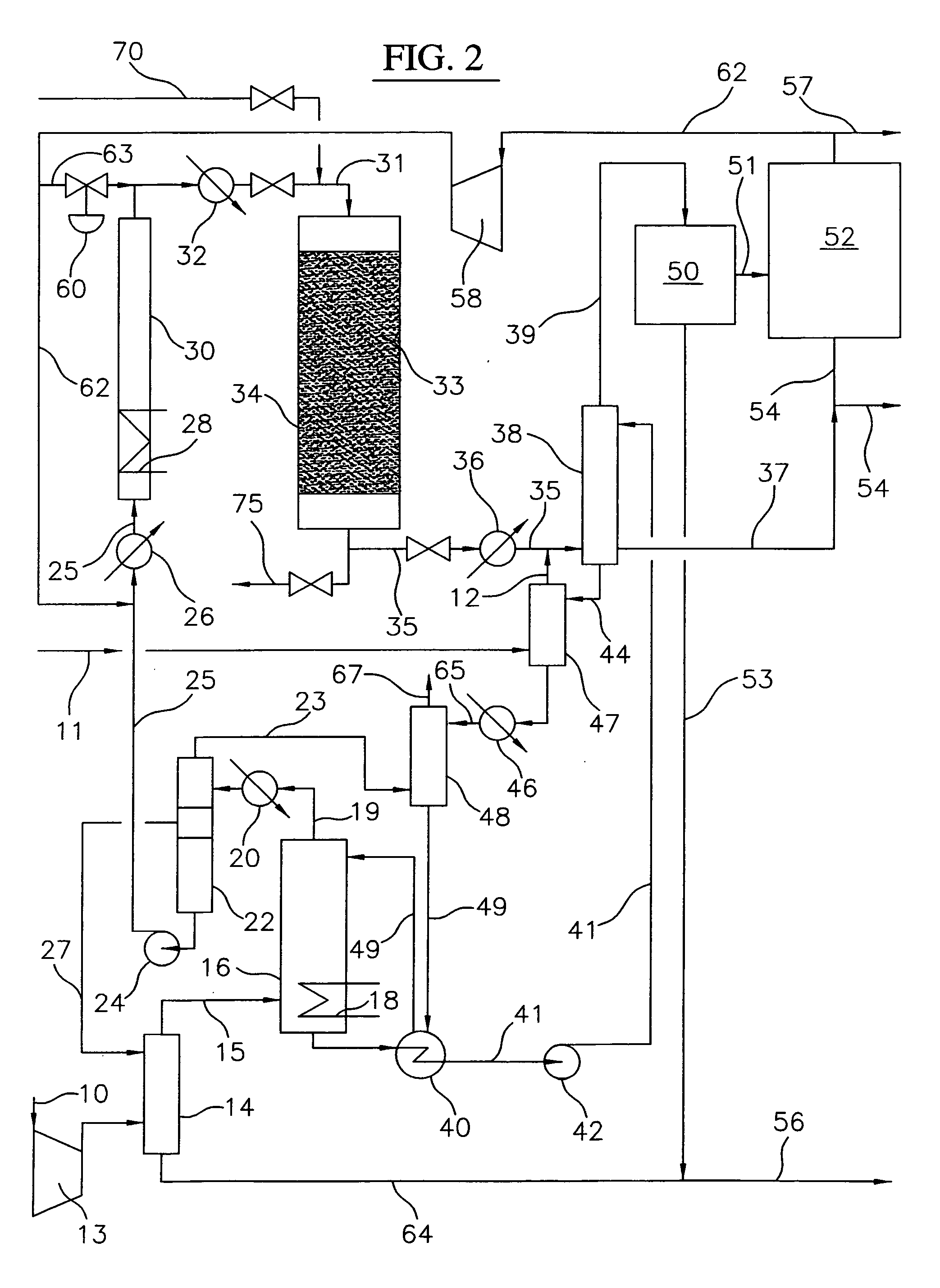
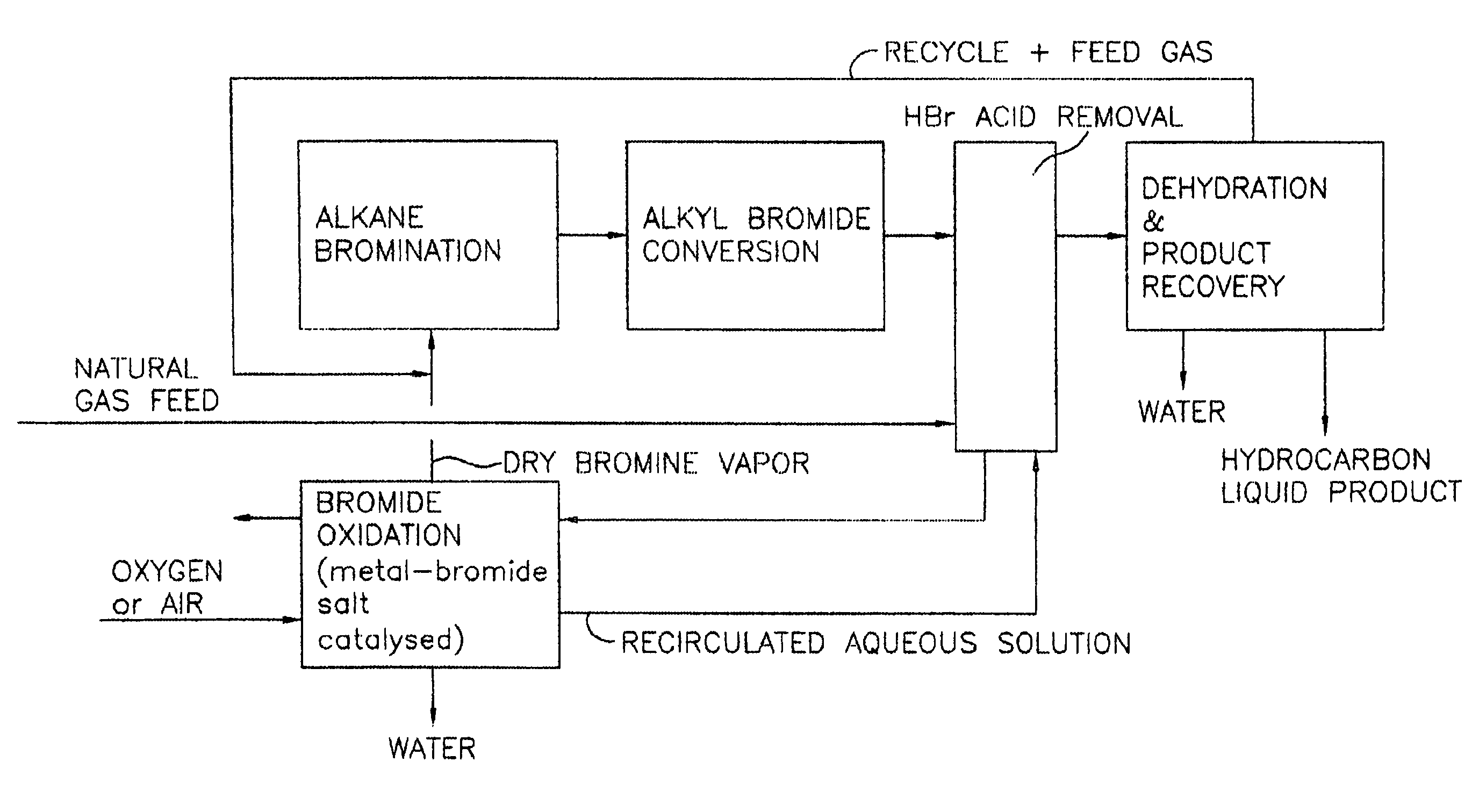
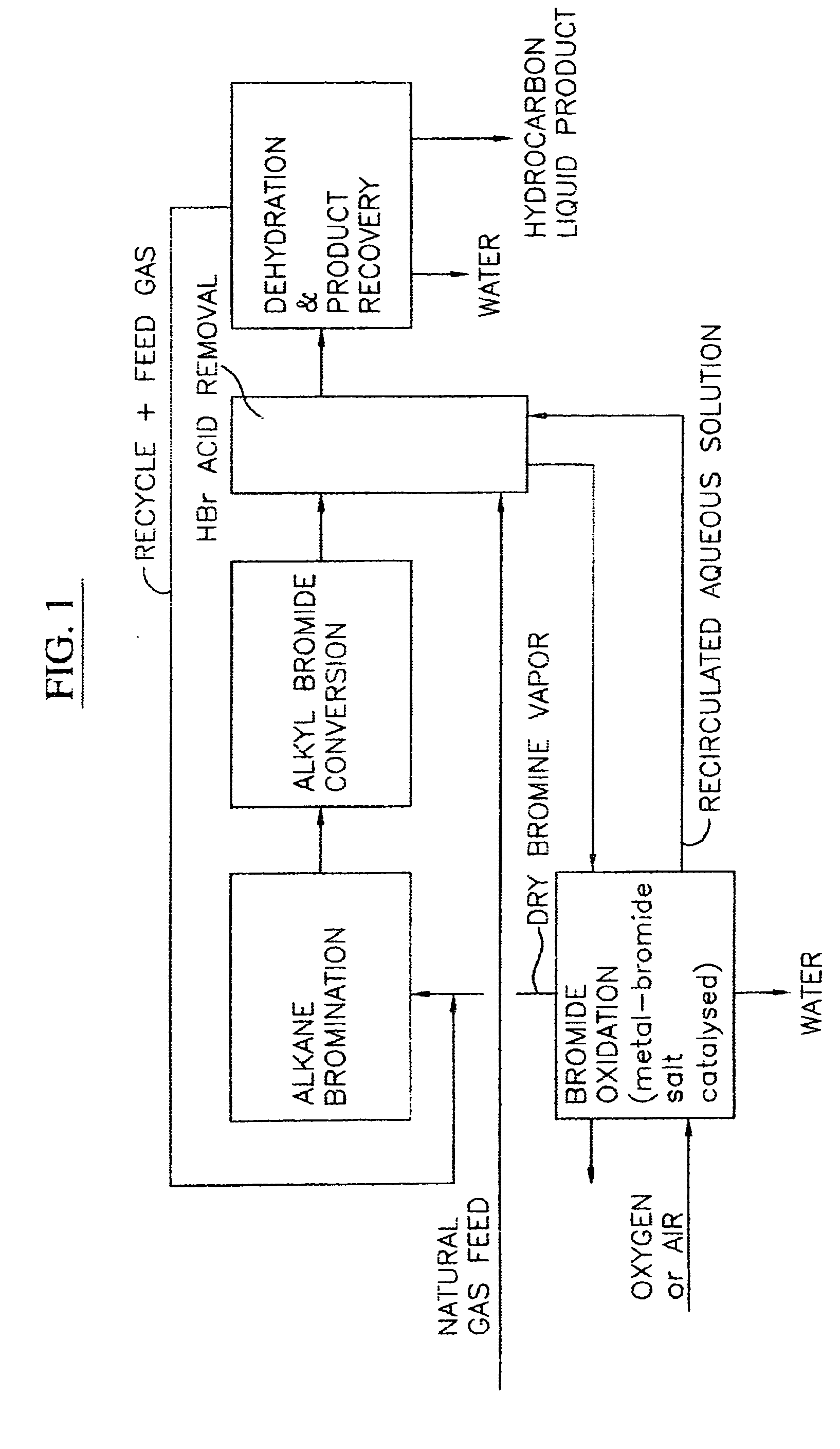
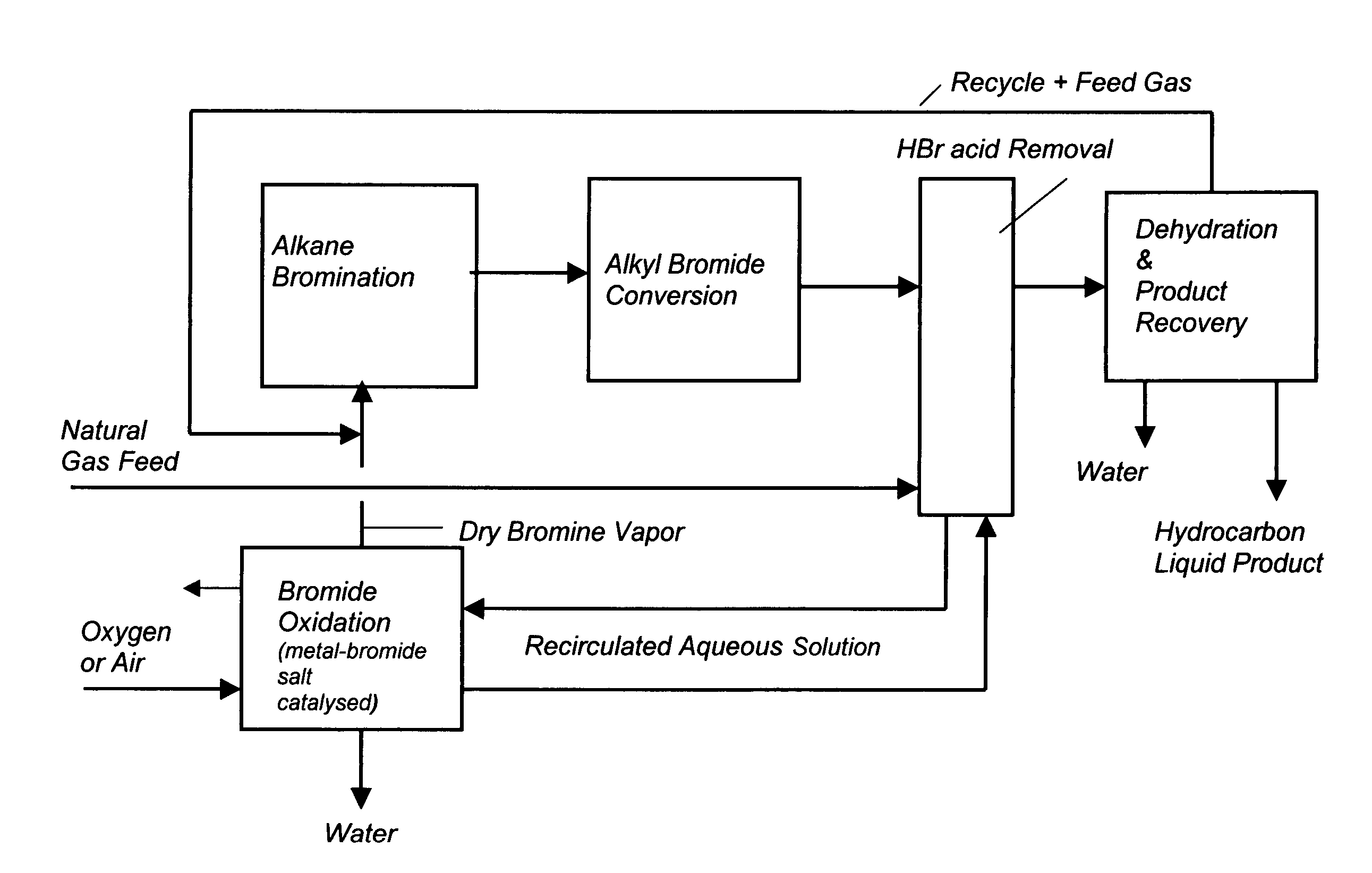
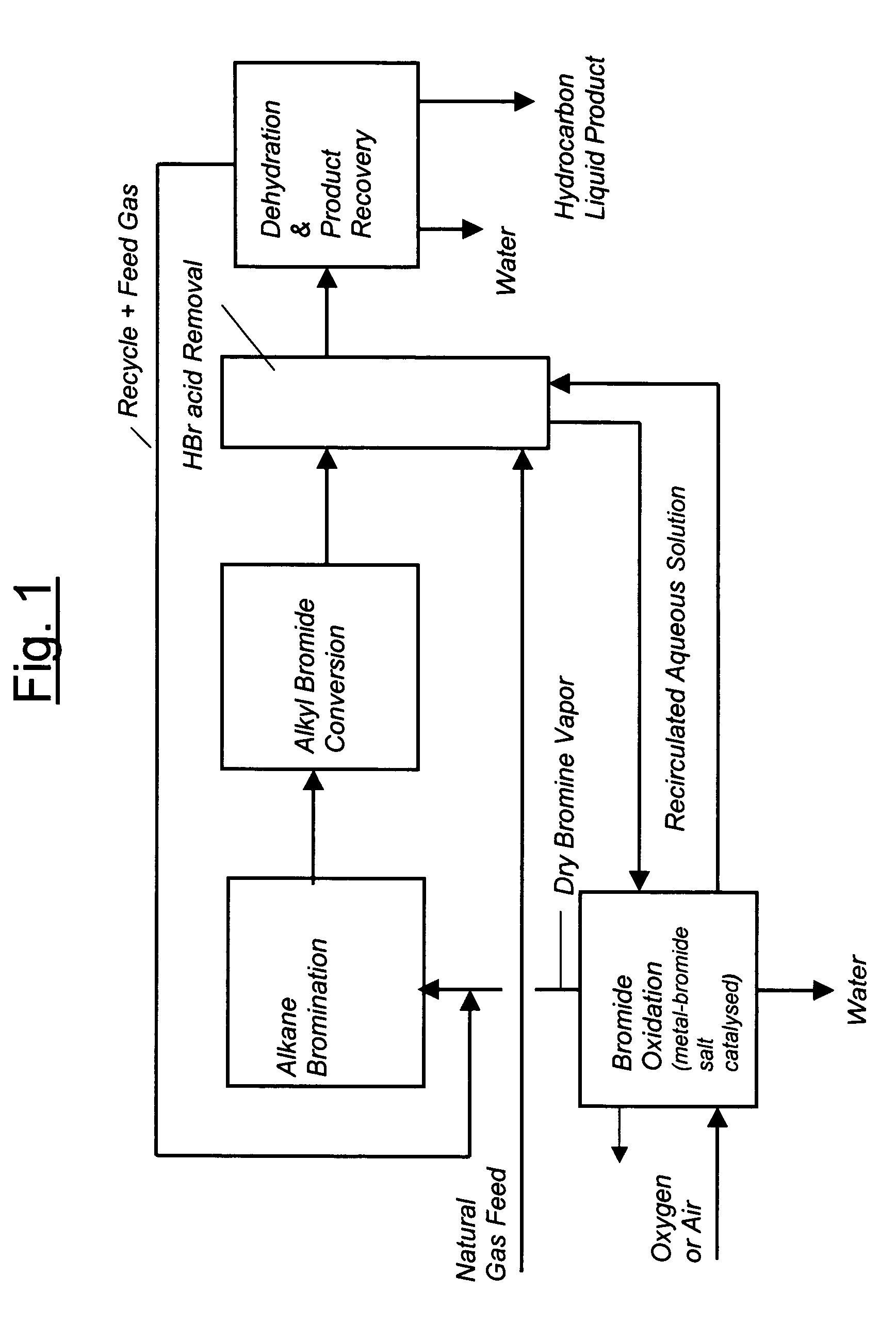
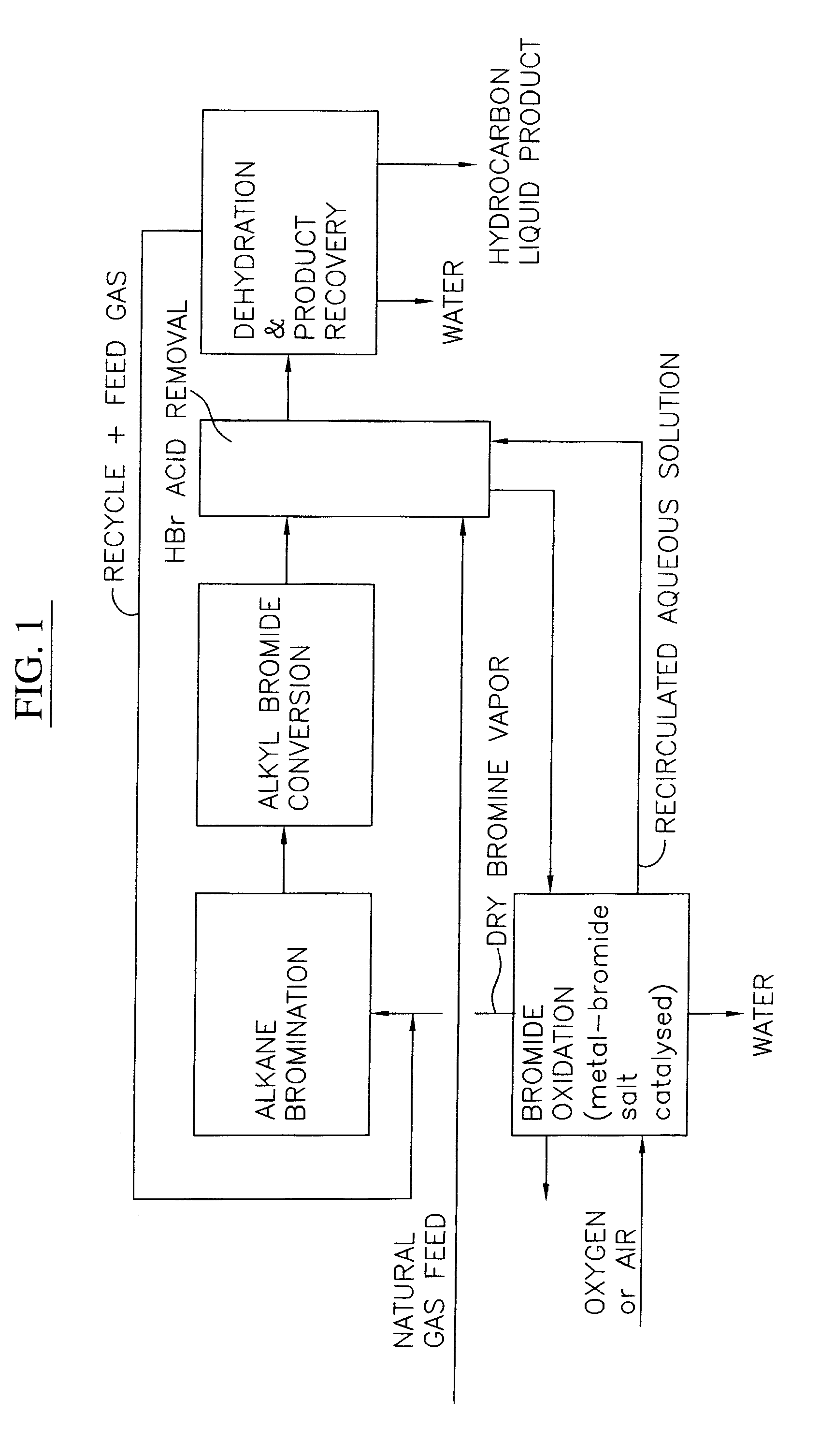
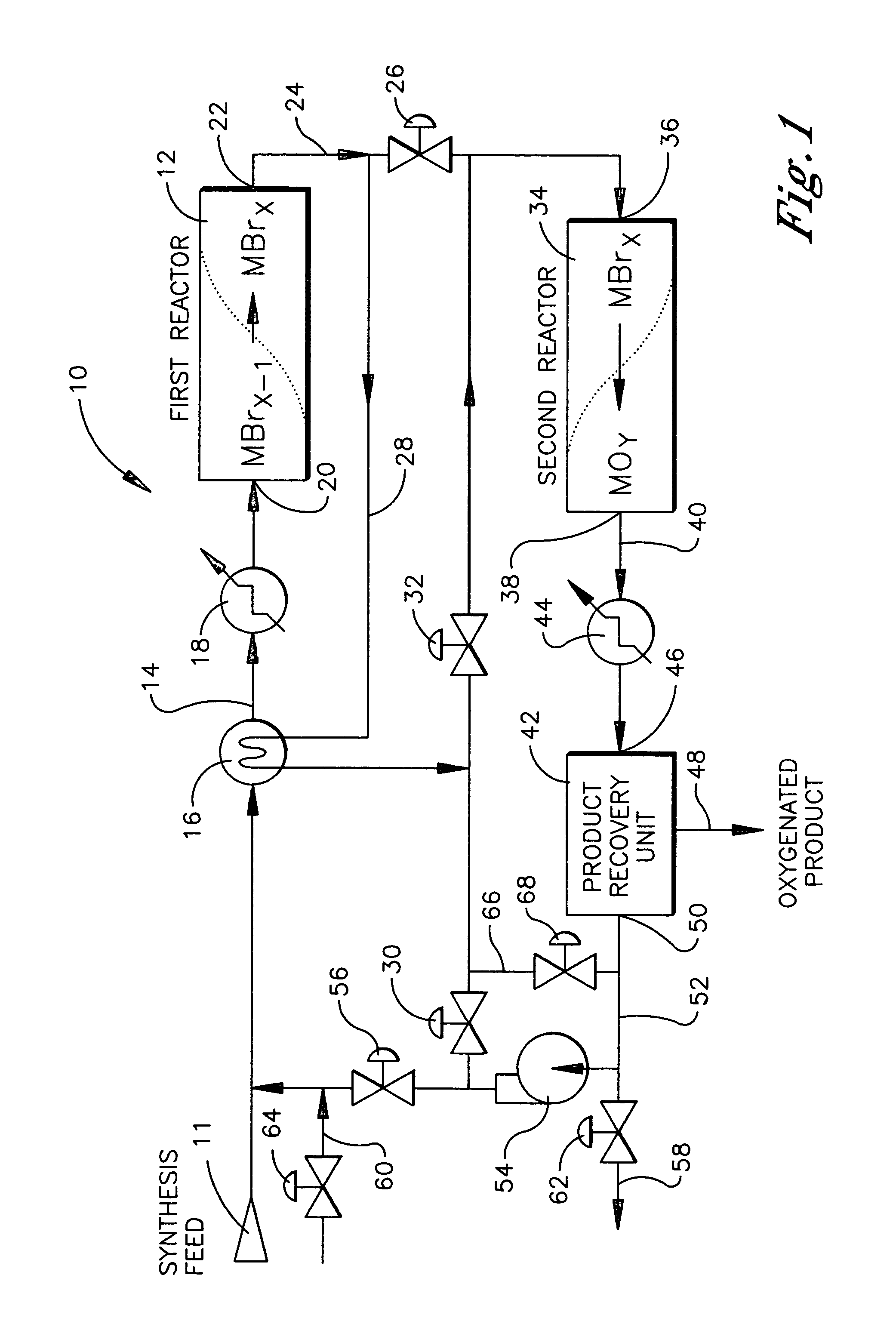
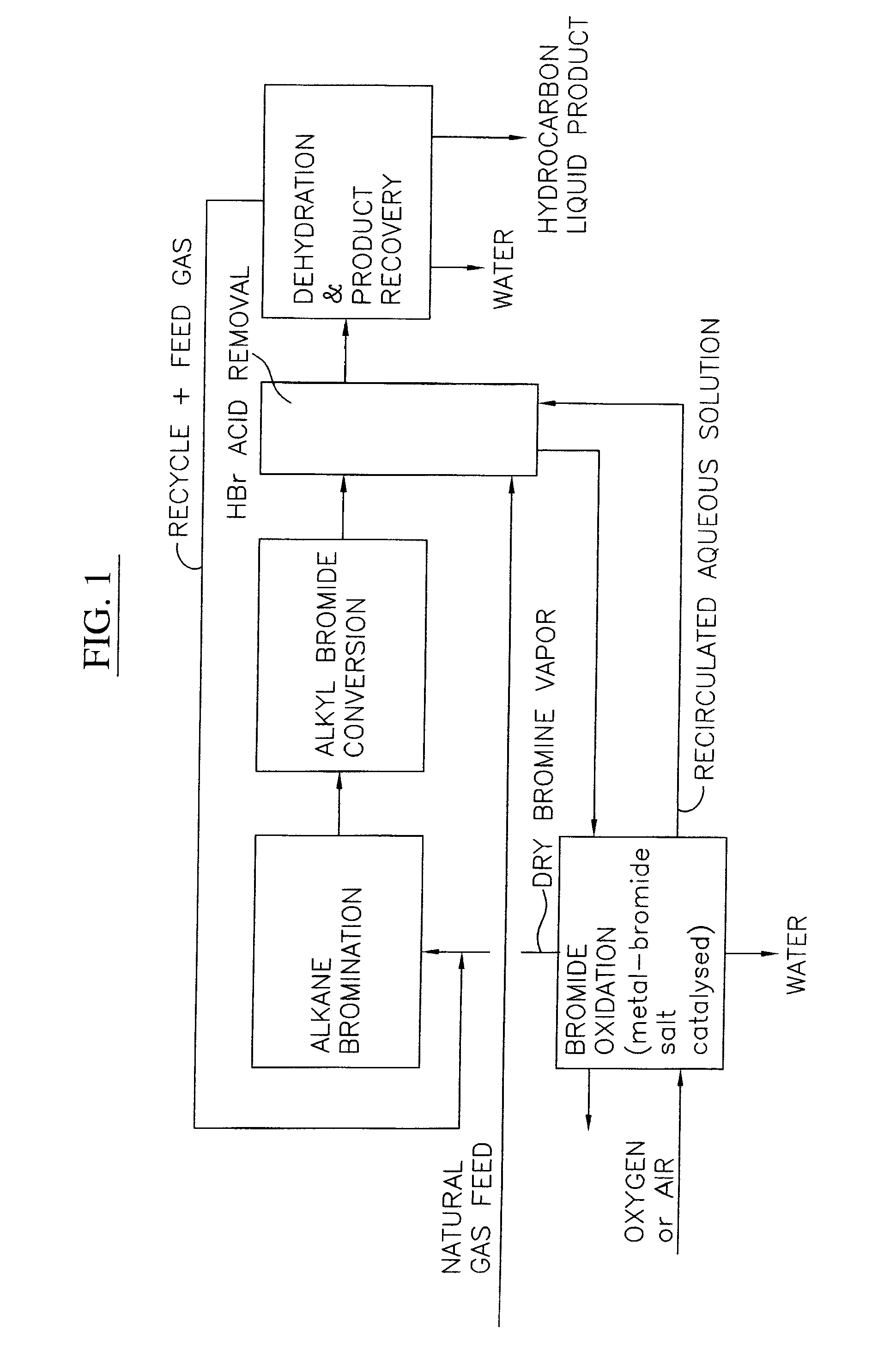
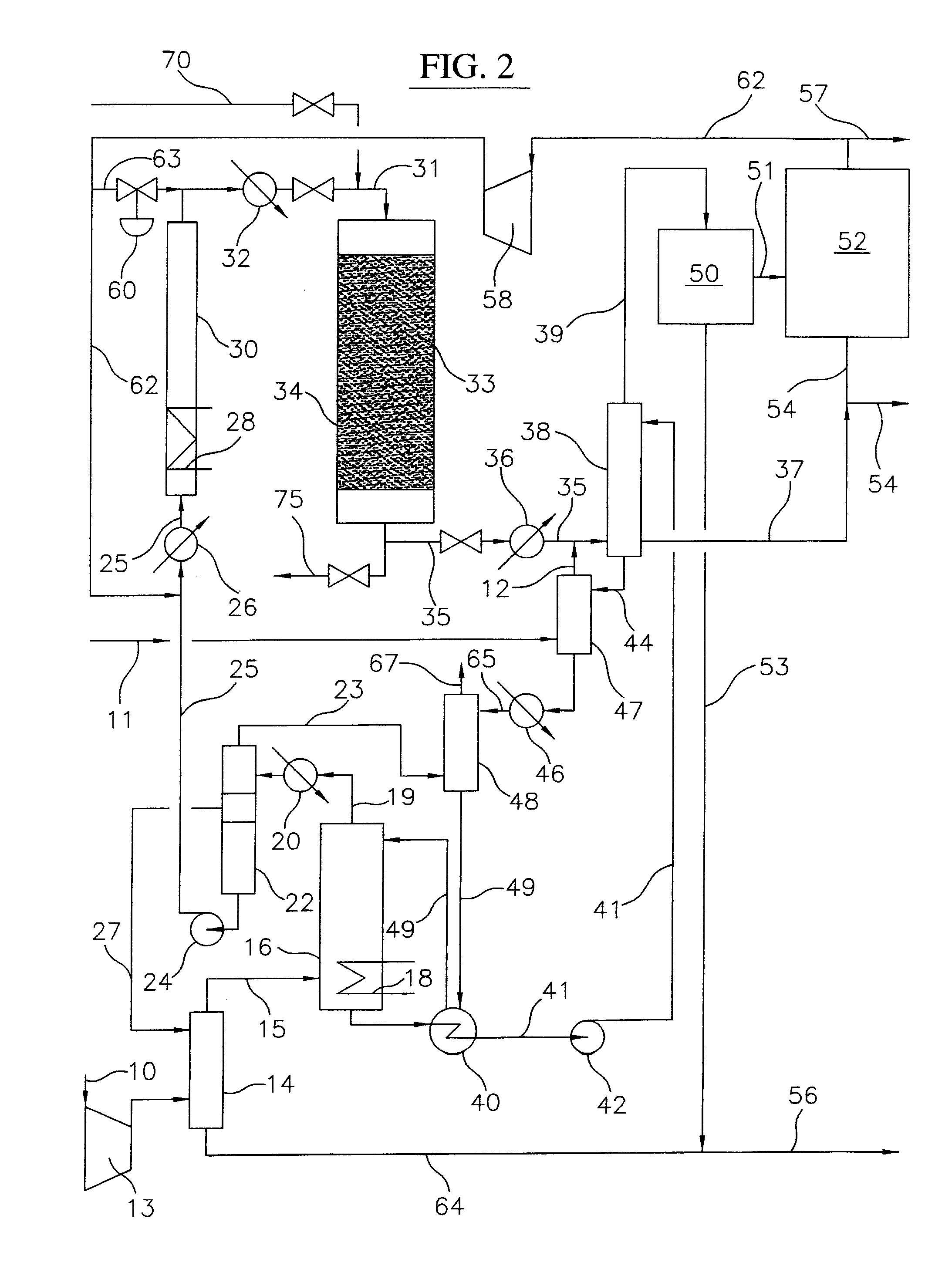
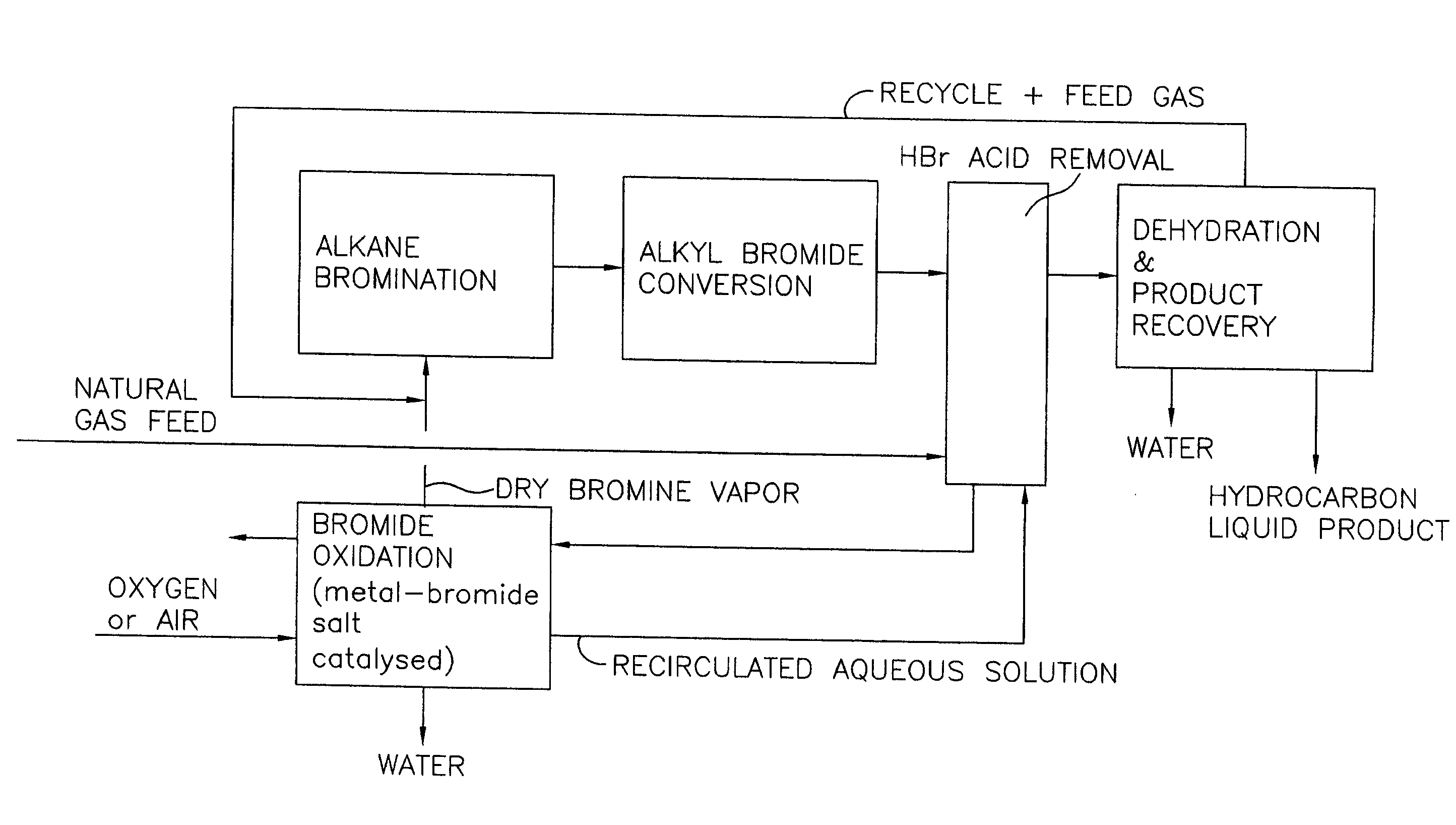
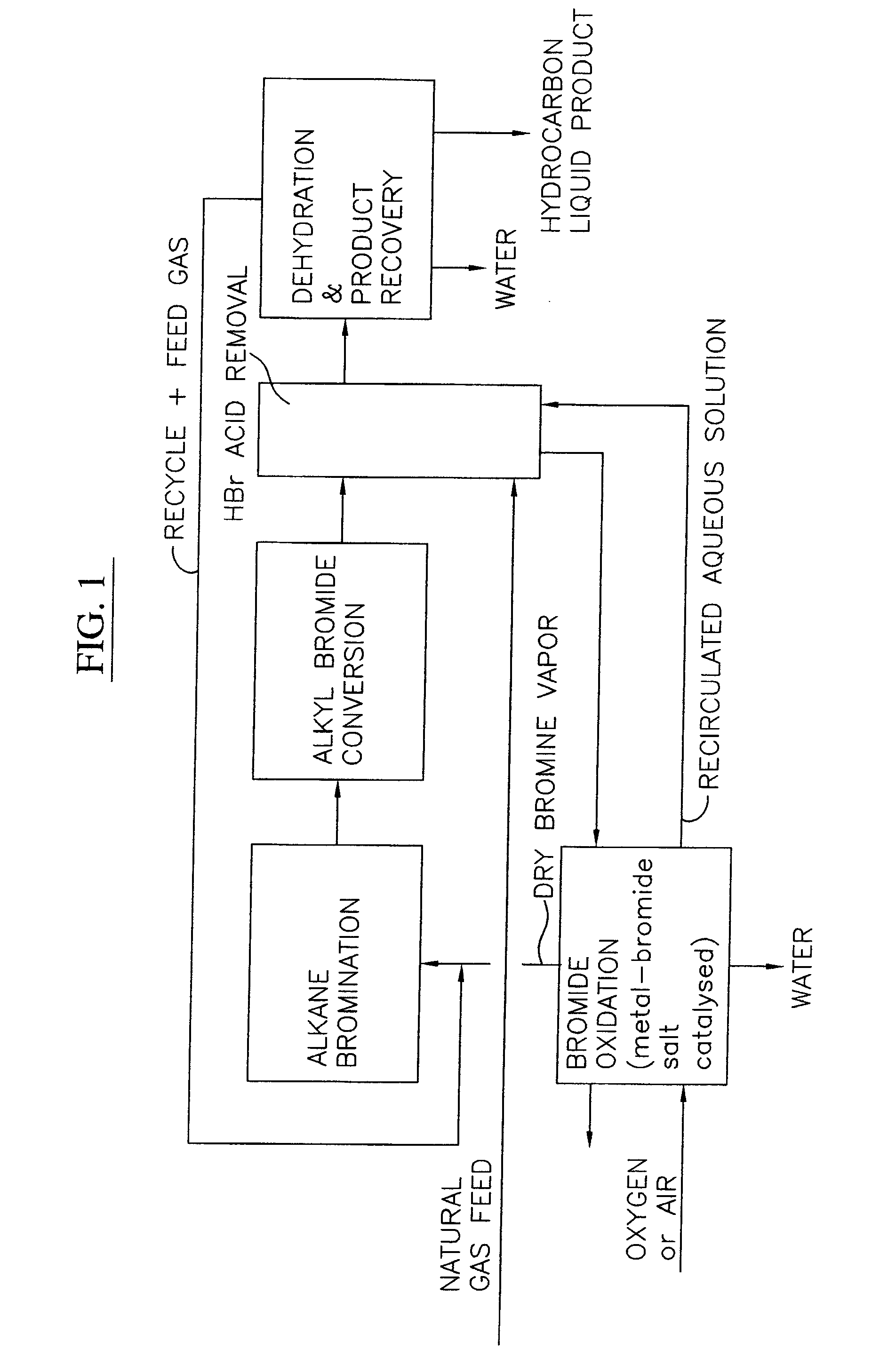
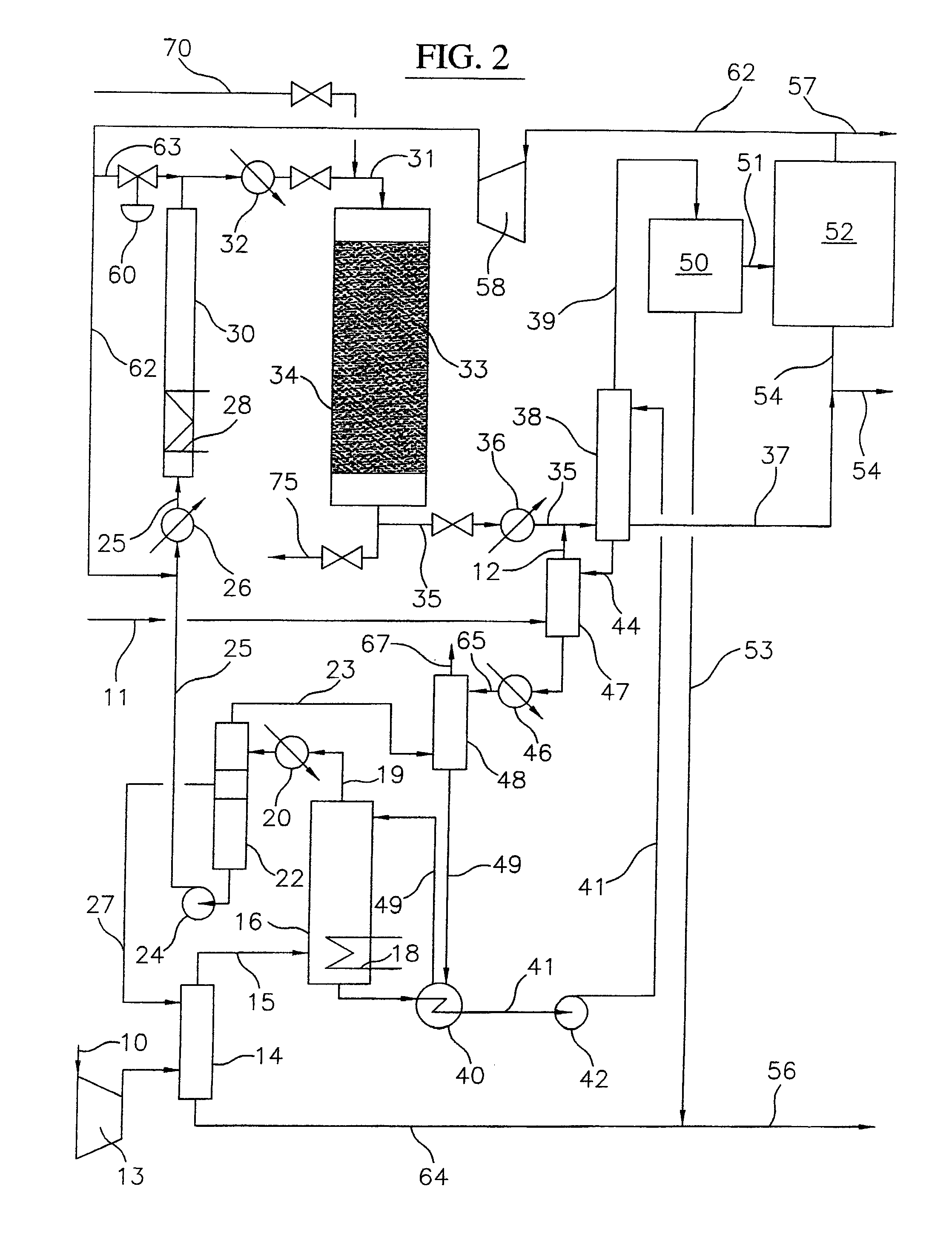
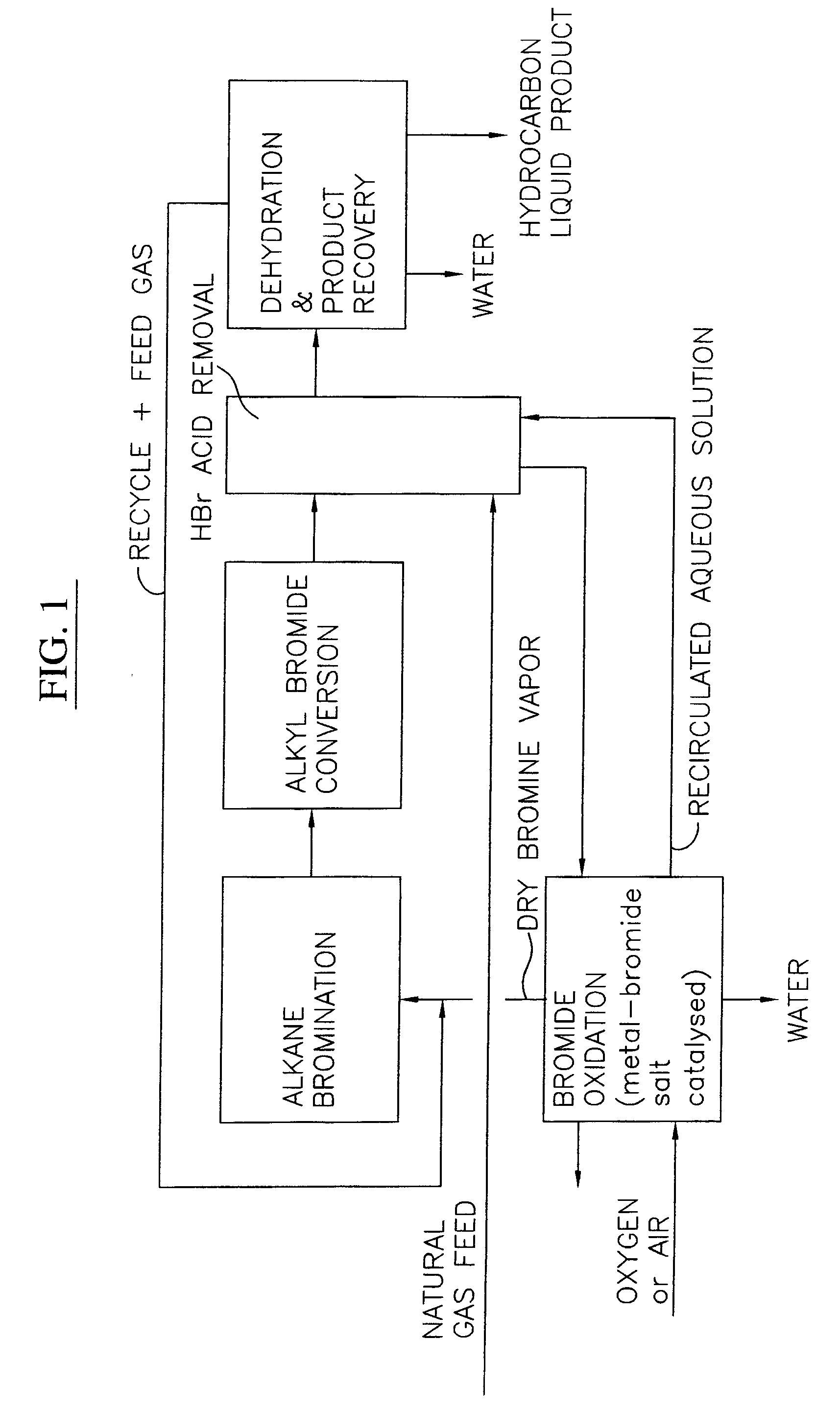
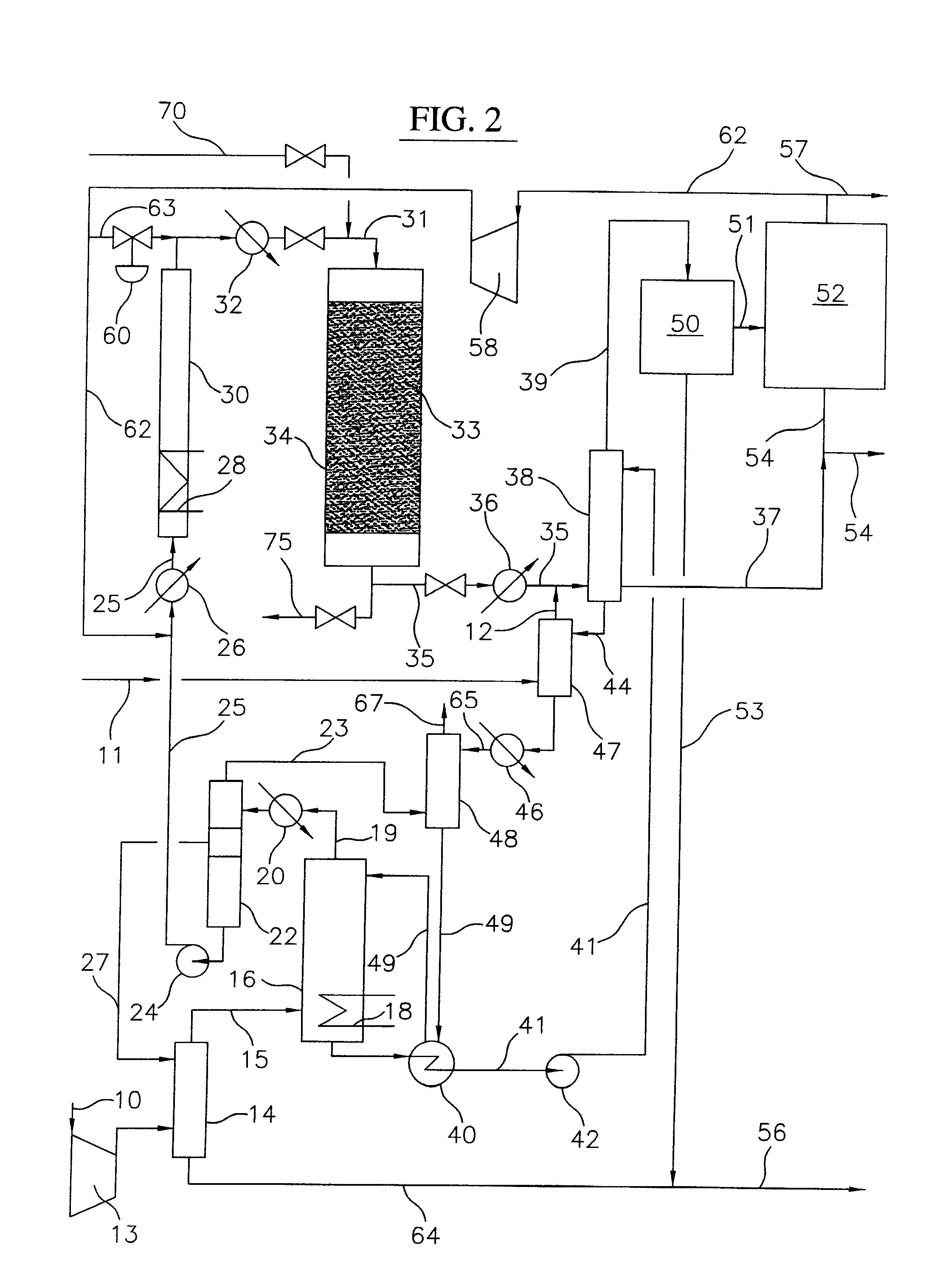
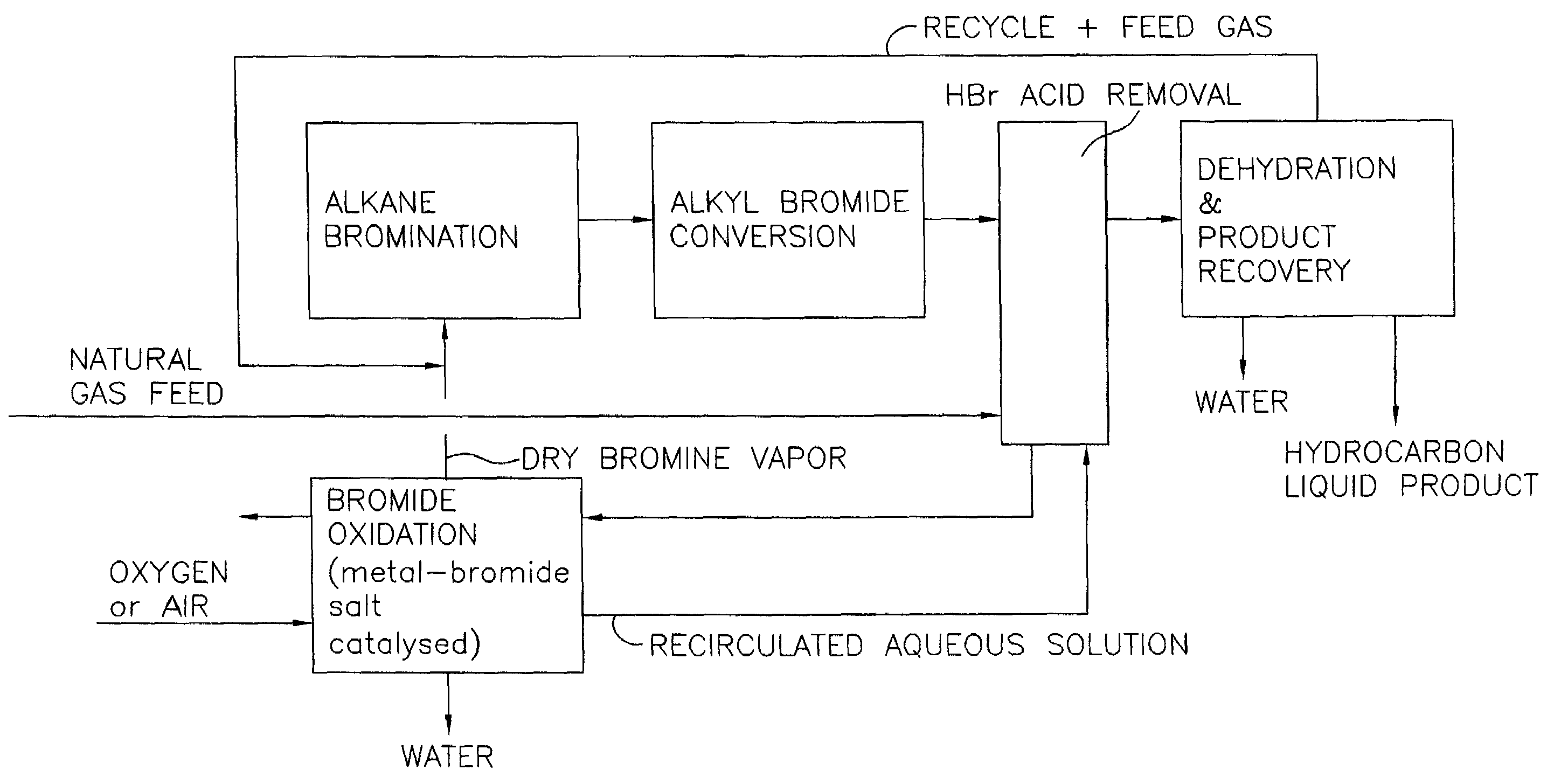
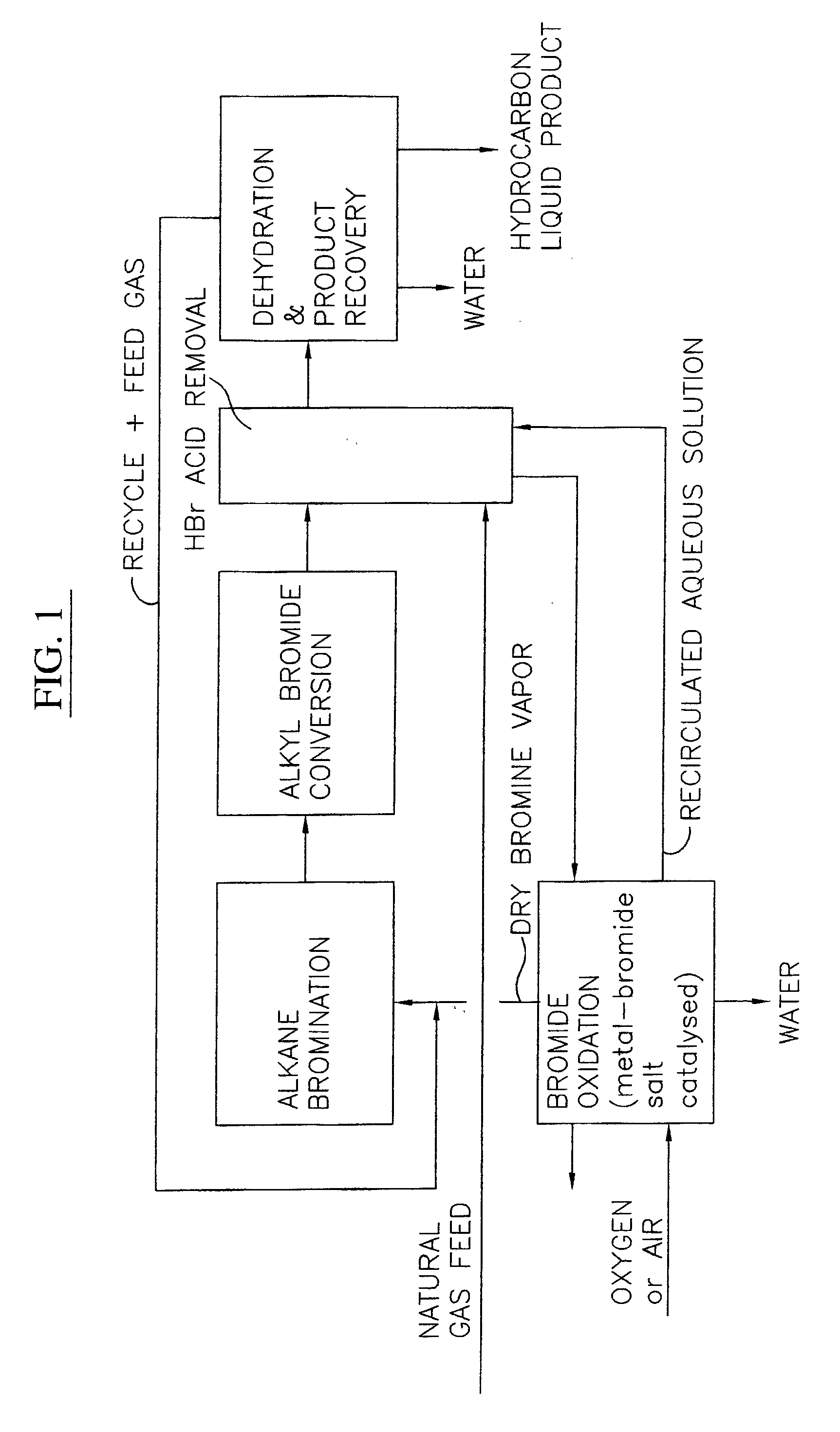
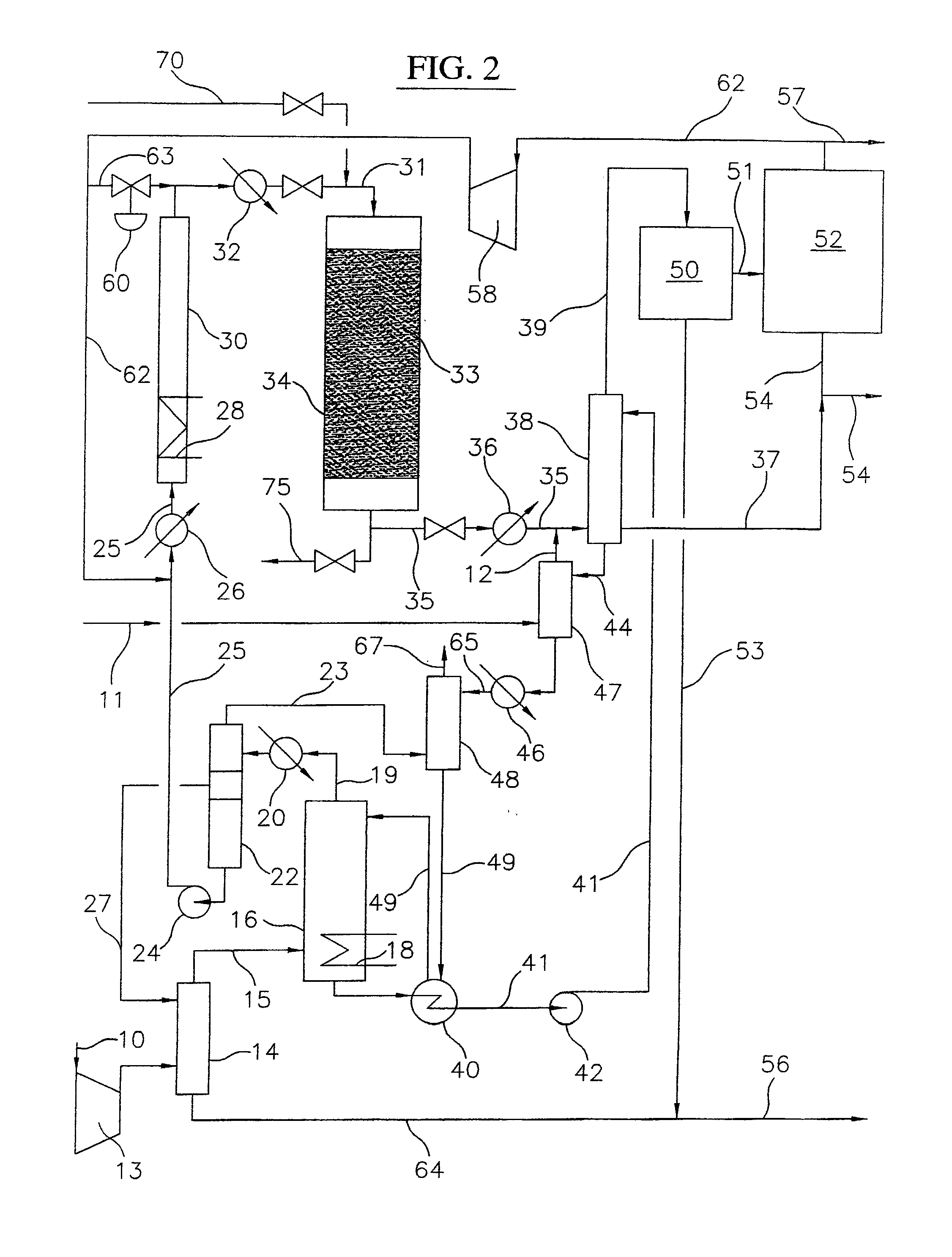
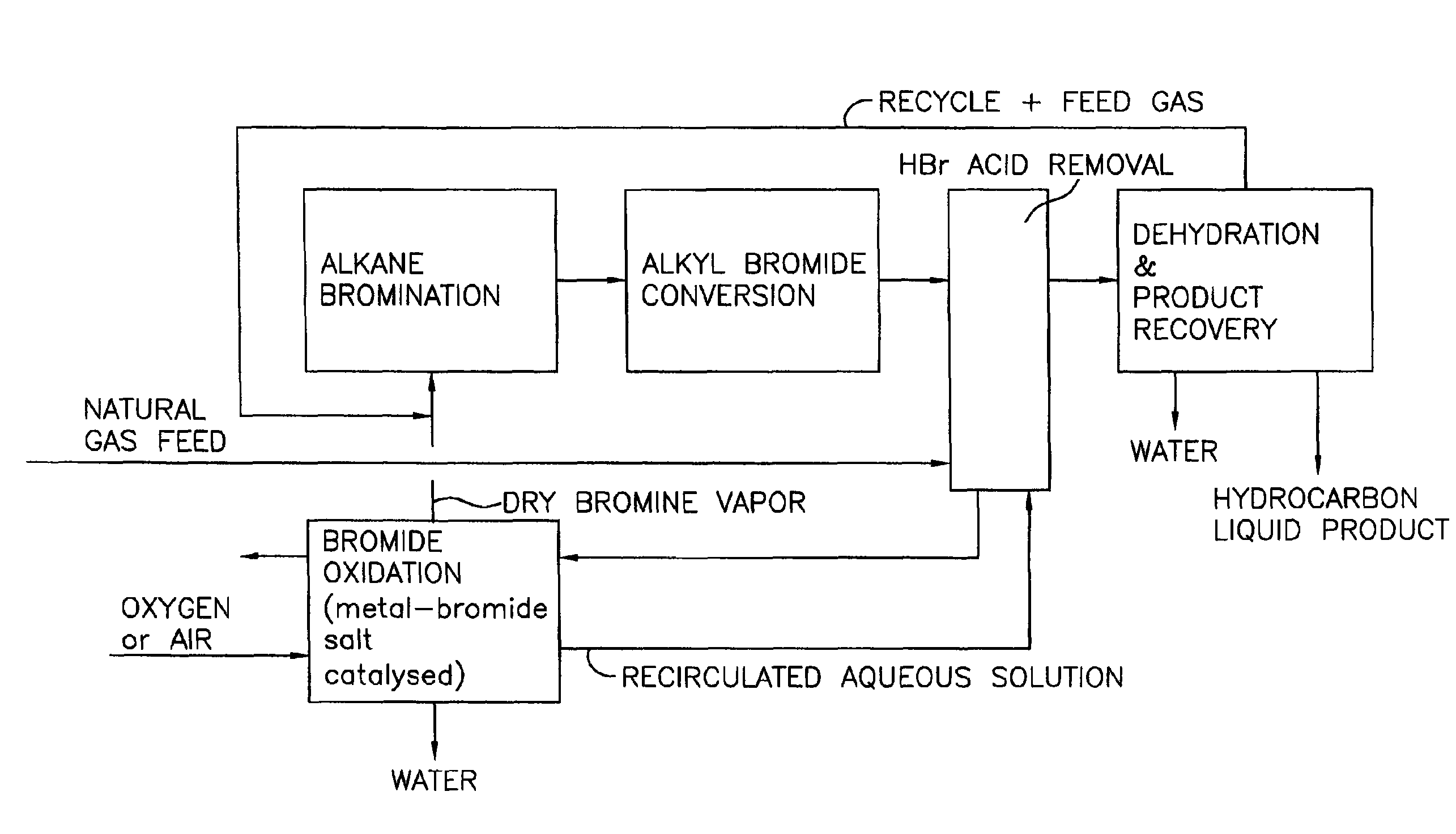
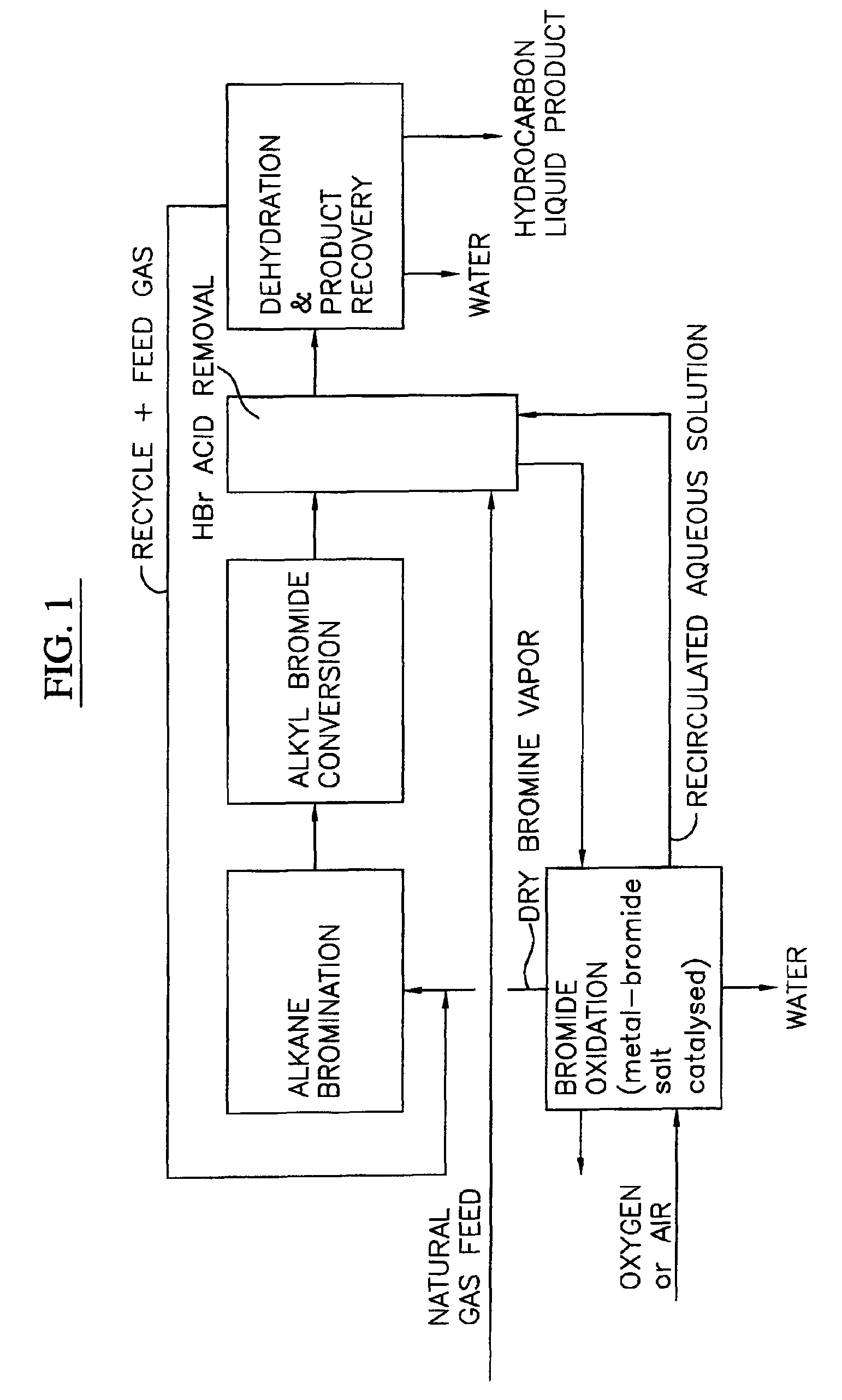
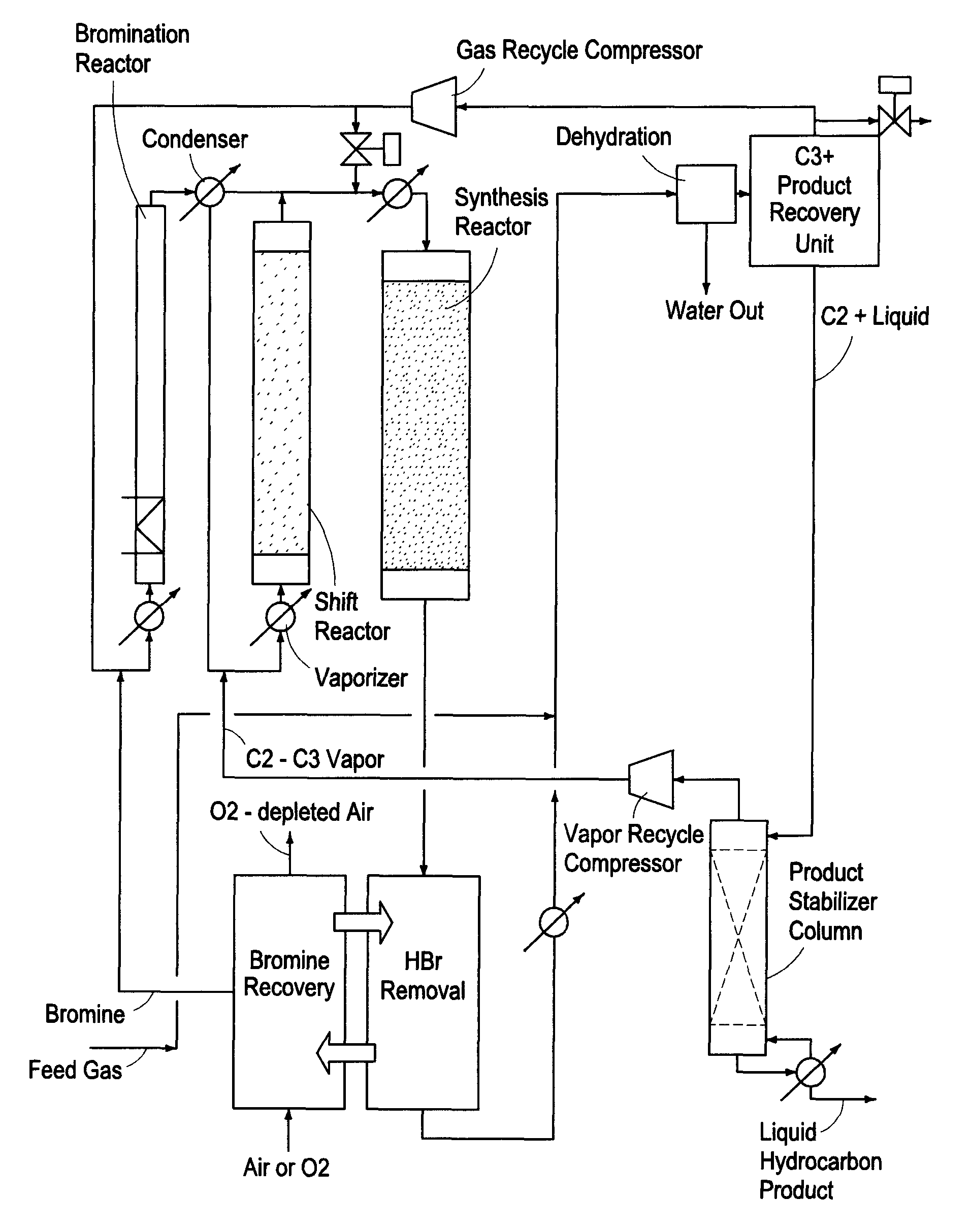
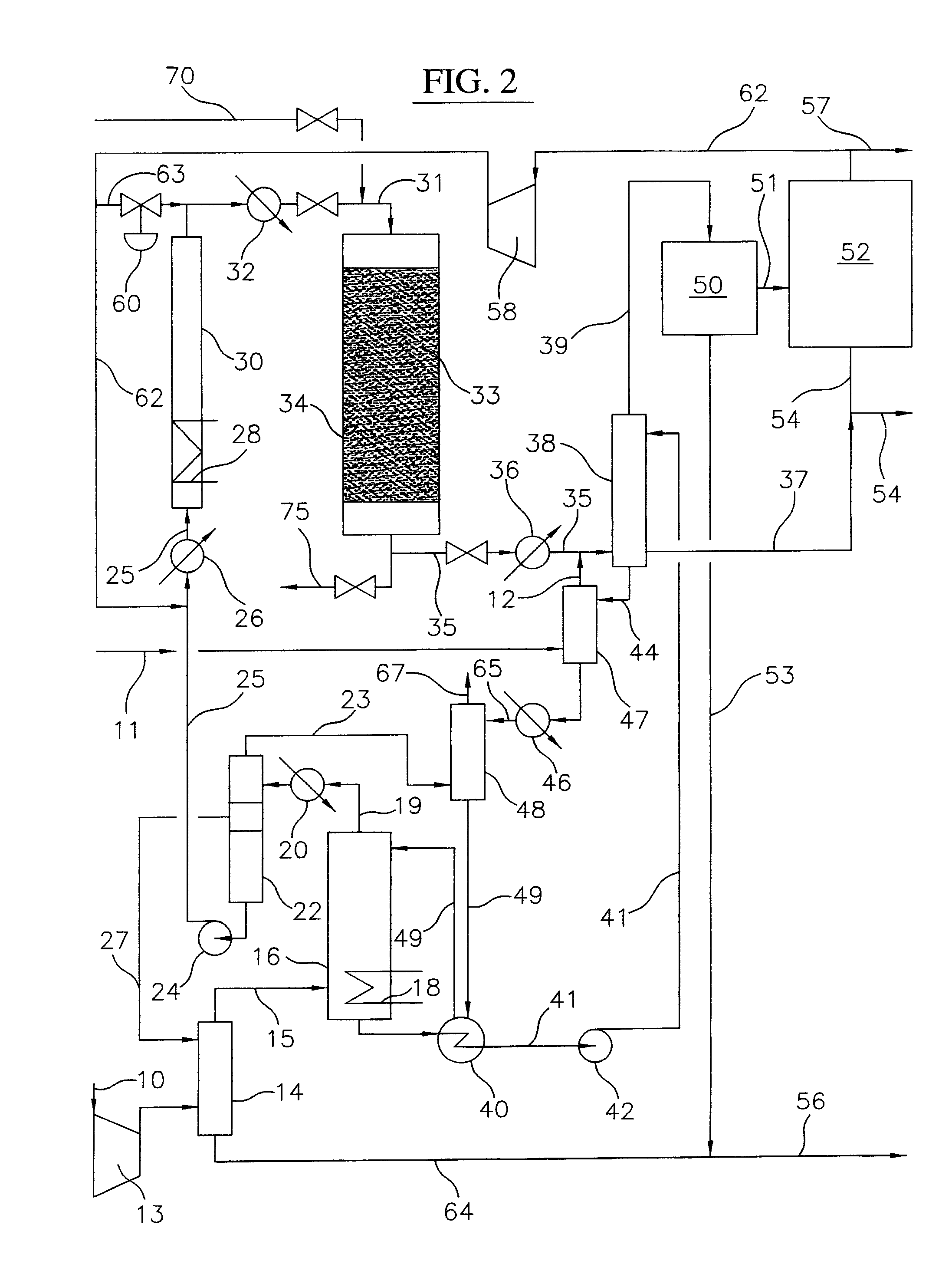
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
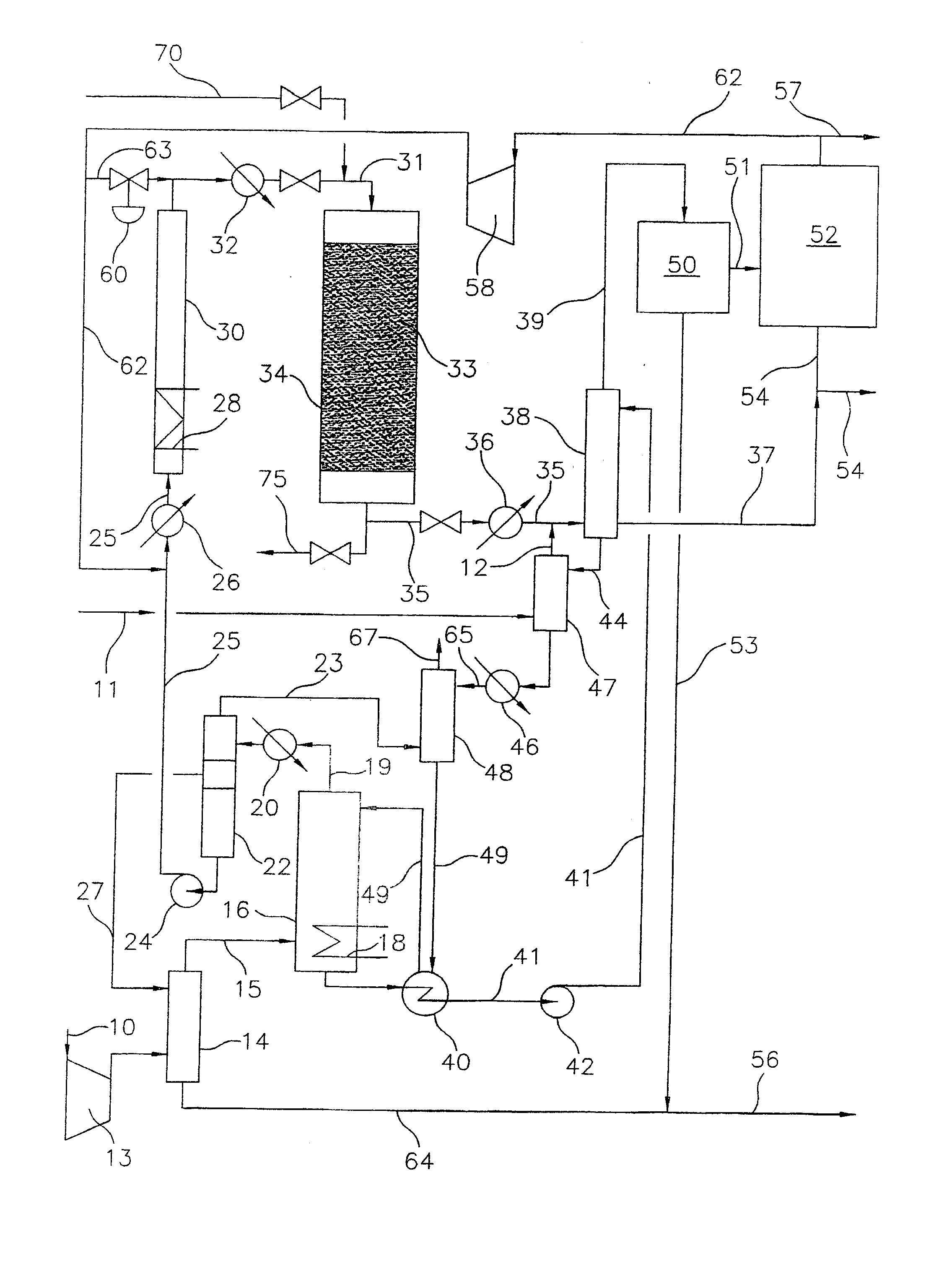
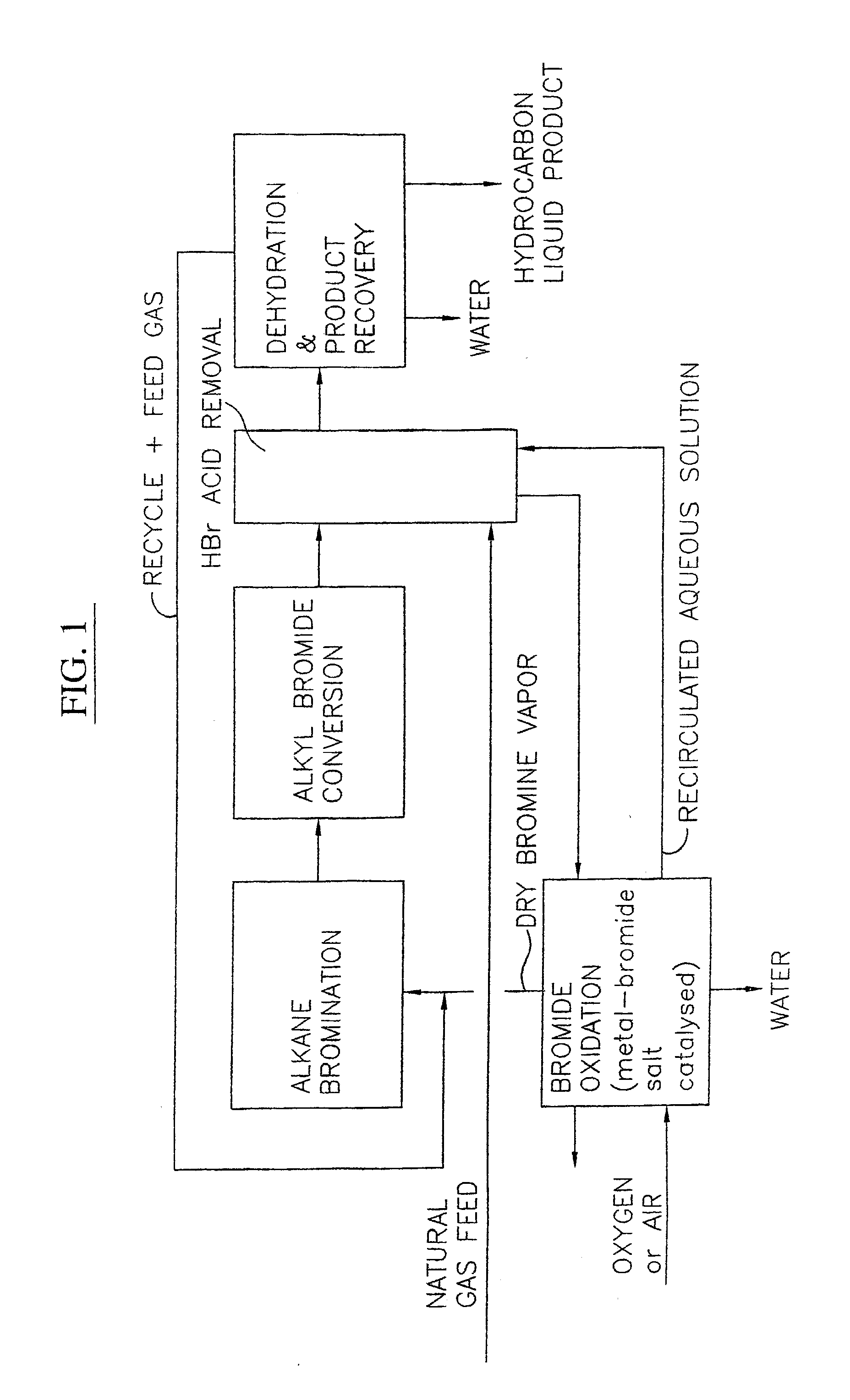
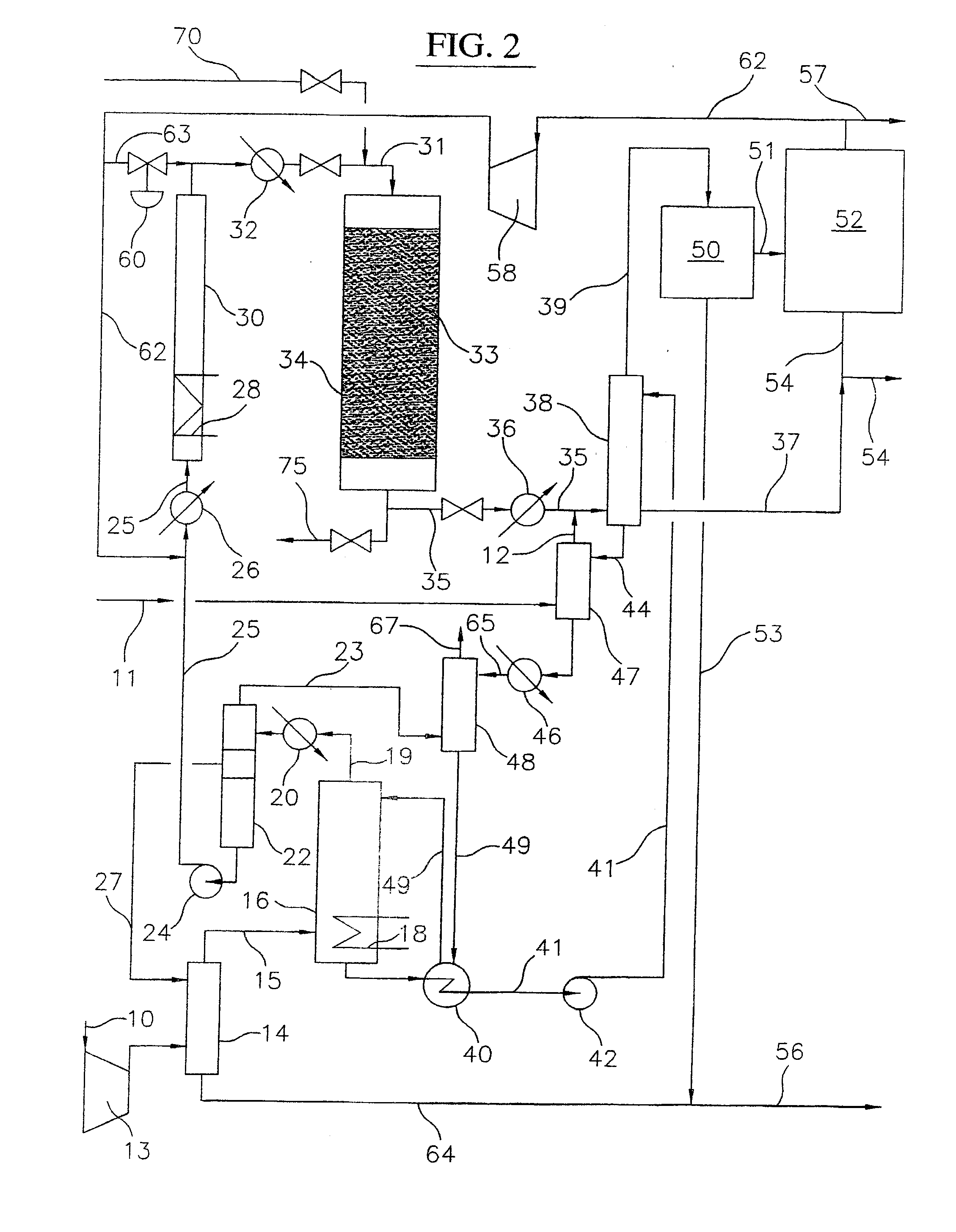
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 400° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Hydrobromic acid vapor is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons. A portion of the propane and butane is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and reacted with the mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid over the synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst to form C5+ hydrocarbons.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20060100469A1High selectivityAvoid disadvantagesBromide preparationRefining with non-metalsAlkaneBromine
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:MARATHON GTF TECH
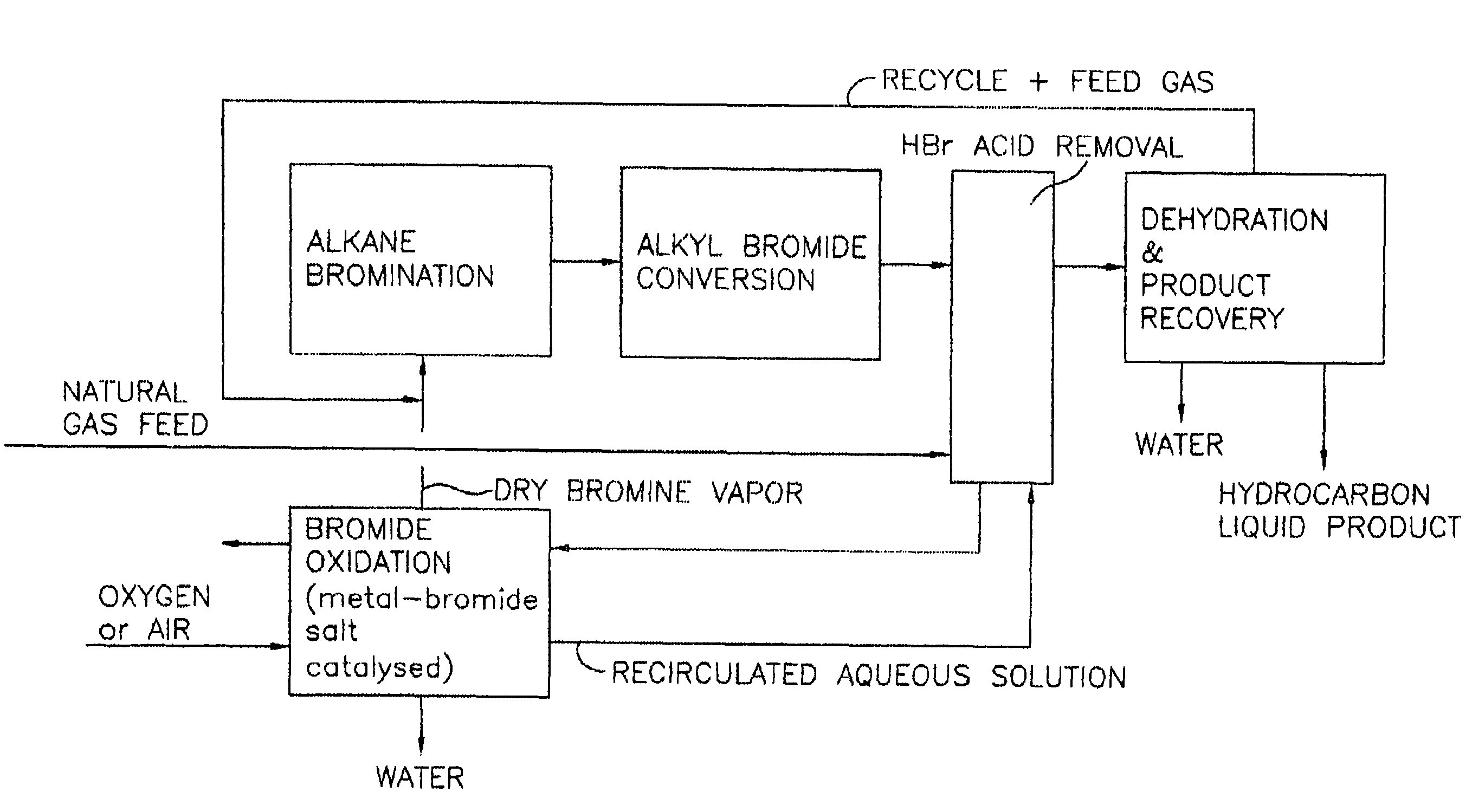
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 450° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Propane and butane which comprise a portion of the products may be recovered or recycled back through the process to form additional C5+ hydrocarbons. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
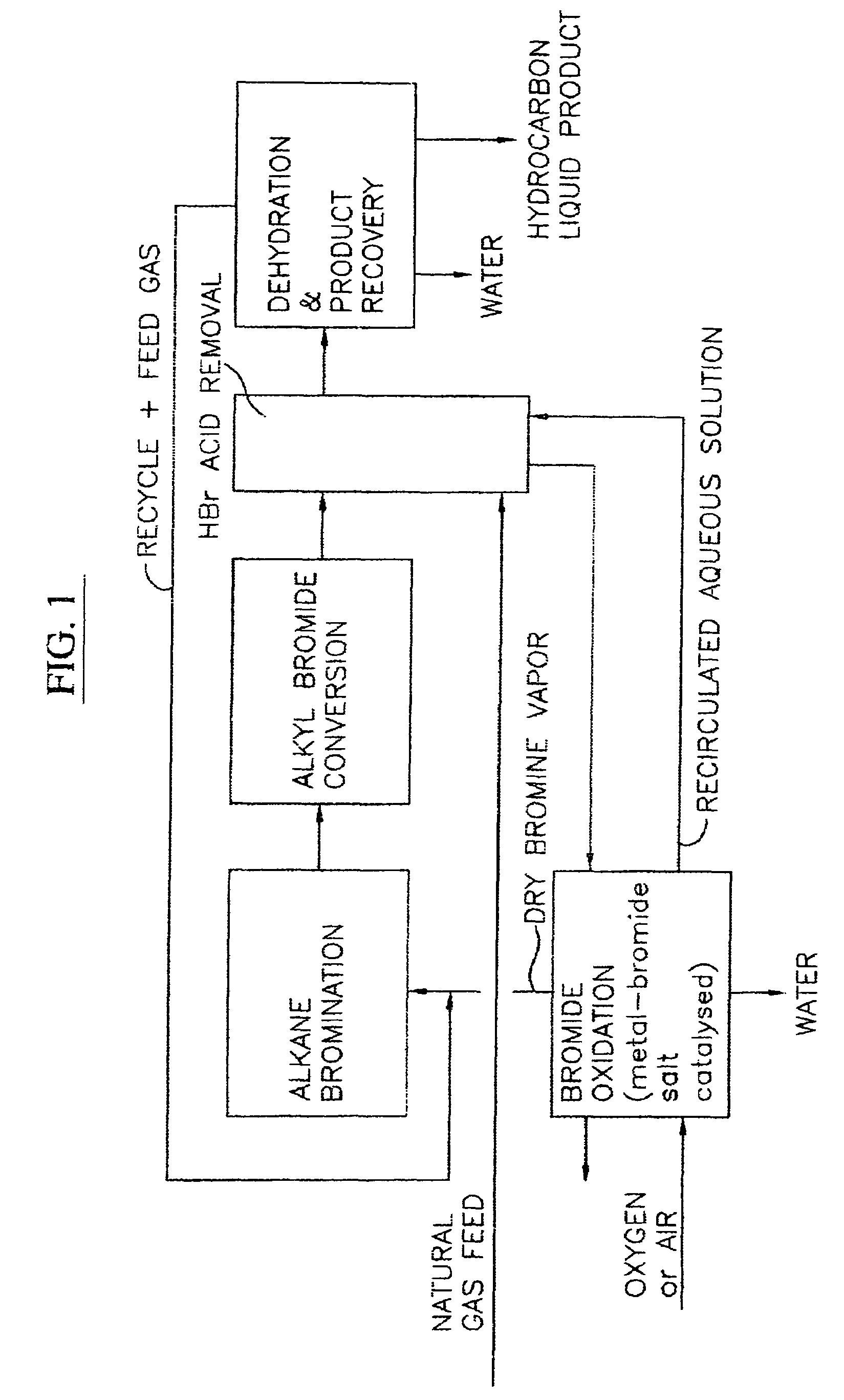
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 400° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Hydrobromic acid vapor is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons. A portion of the propane and butane is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and reacted with the mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid over the synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst to form C5+ hydrocarbons.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is thermally reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide. Poly-brominated alkanes present in the alkyl bromides are further reacted with methane over a suitable catalyst to form mono-brominated species. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrogen bromide. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrogen bromide from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrogen bromide for use in the process, and to selectively form mono-brominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
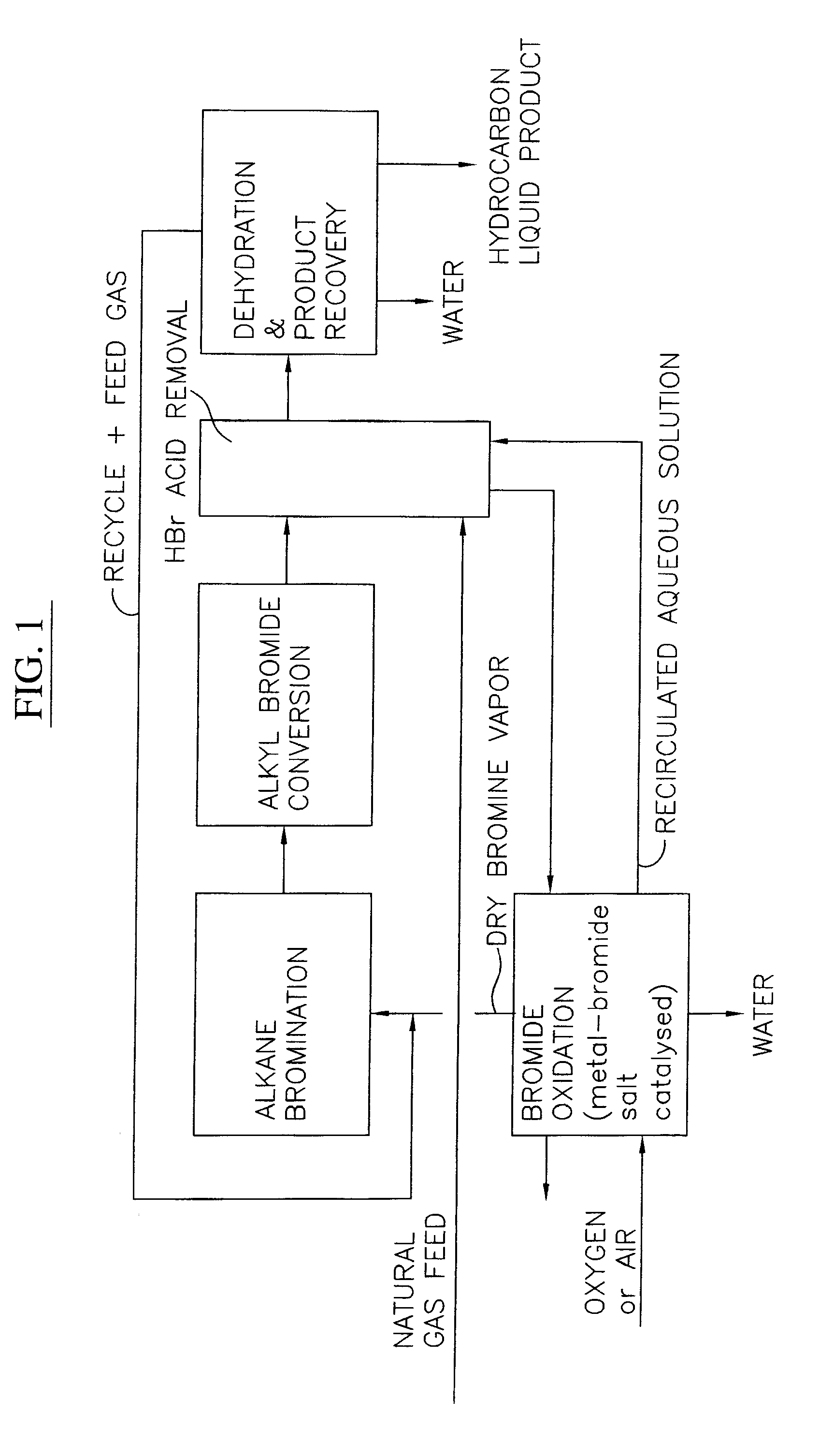
Conversion of alkanes to oxygenates
Owner:MARATHON OIL CO
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process, and to selectively form monobrominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
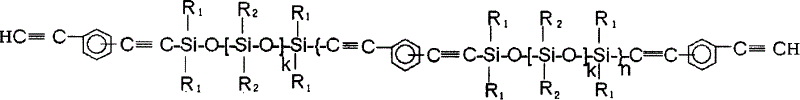
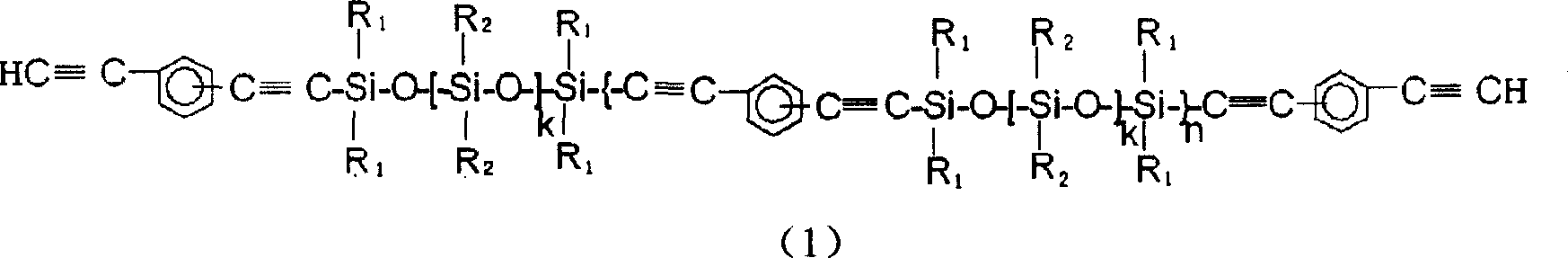
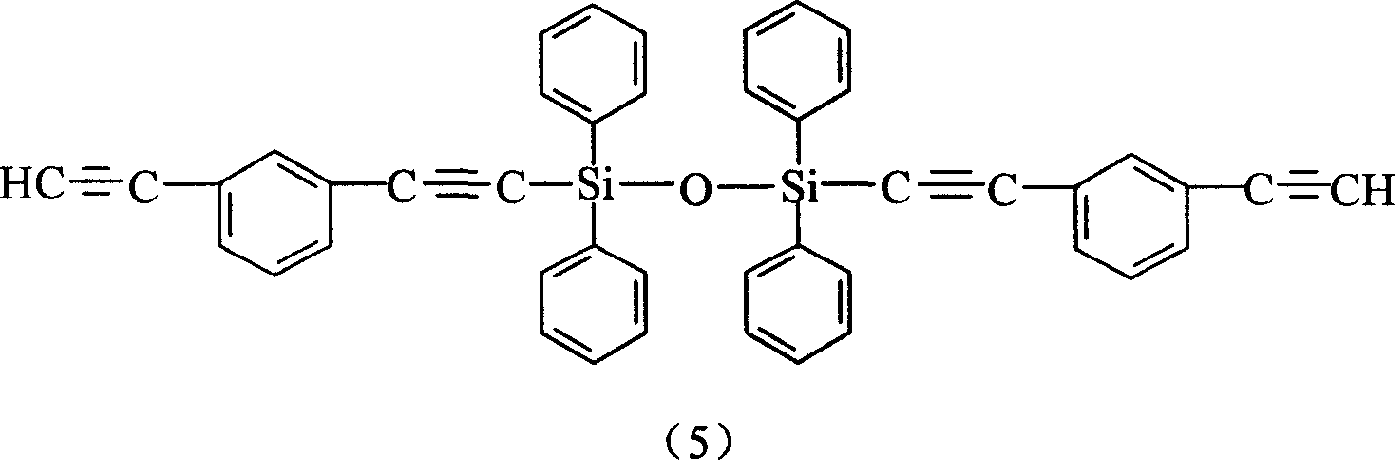
Aryne resin containing silicone
InactiveCN1709928AImprove flexibilityGood high temperature ceramic performanceSilanesGrignard reagent
The invention relates to a kind of arylenealkyne resin containing siloxanes. The said resin makes diethynylene benzene (DEB) and silicon alkyl chloride as raw materials, firstly make use of the reaction of magnesium and alkyl bromide to produce Grignard reagentú¼then react with DEB to produce alkyne Grignard reagent; then react with silicon alkyl chloride, finally hydrolyze and condense in alkaline water liquor, or extend chain with siloxanes chloride, to form a kind of arylenealkyne resin containing siloxanes of new-style structure. The resin designed and synthesized by the invention has good processing property, and can be solidified into crosslinked resin of good thermostability under heat, light or radiative condition. Besides it has good machine capability, electric insulation capability and ceramic performance. So it can be used as the base material of high performance compound material resin, insulation material, the ceramic precursors and so on, and also has wide application prospect in such high technology fields as spaceflight, aviation, navigation and so on.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
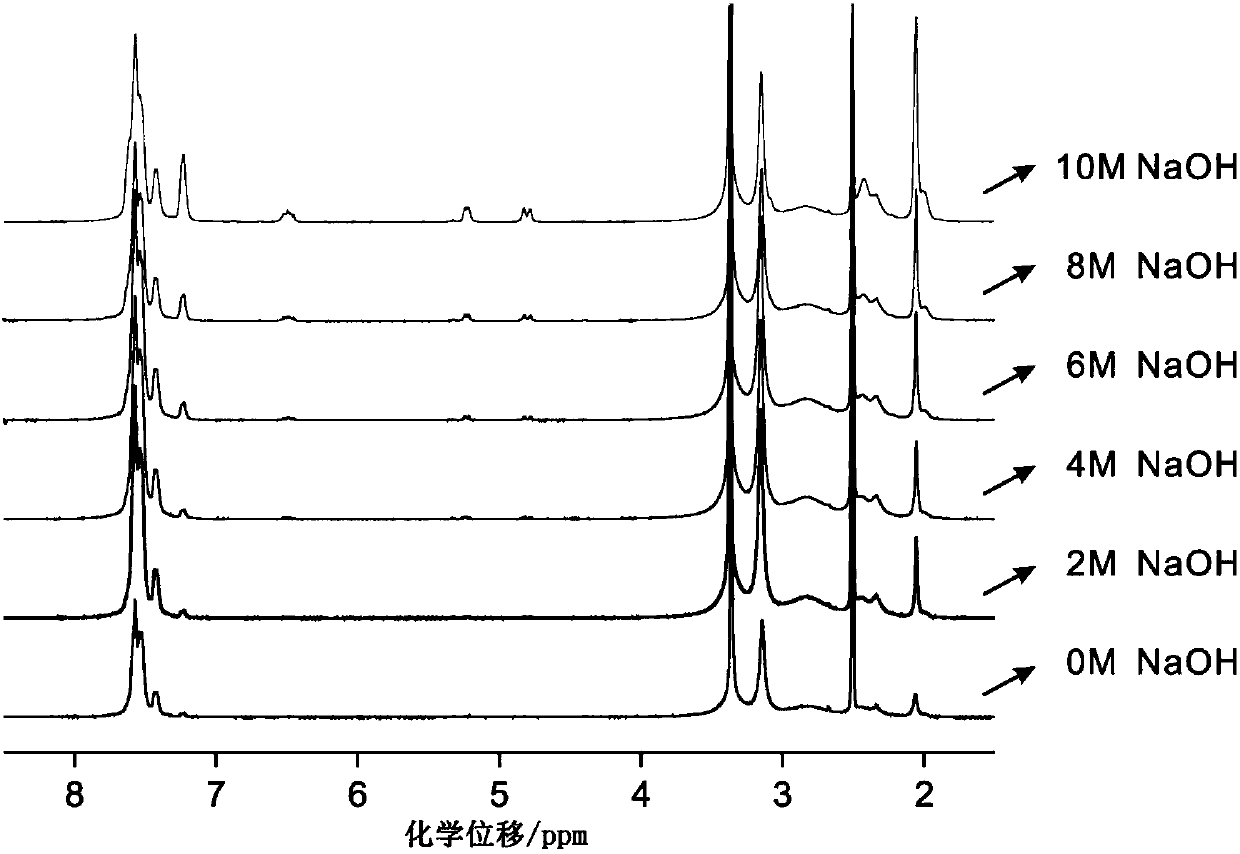
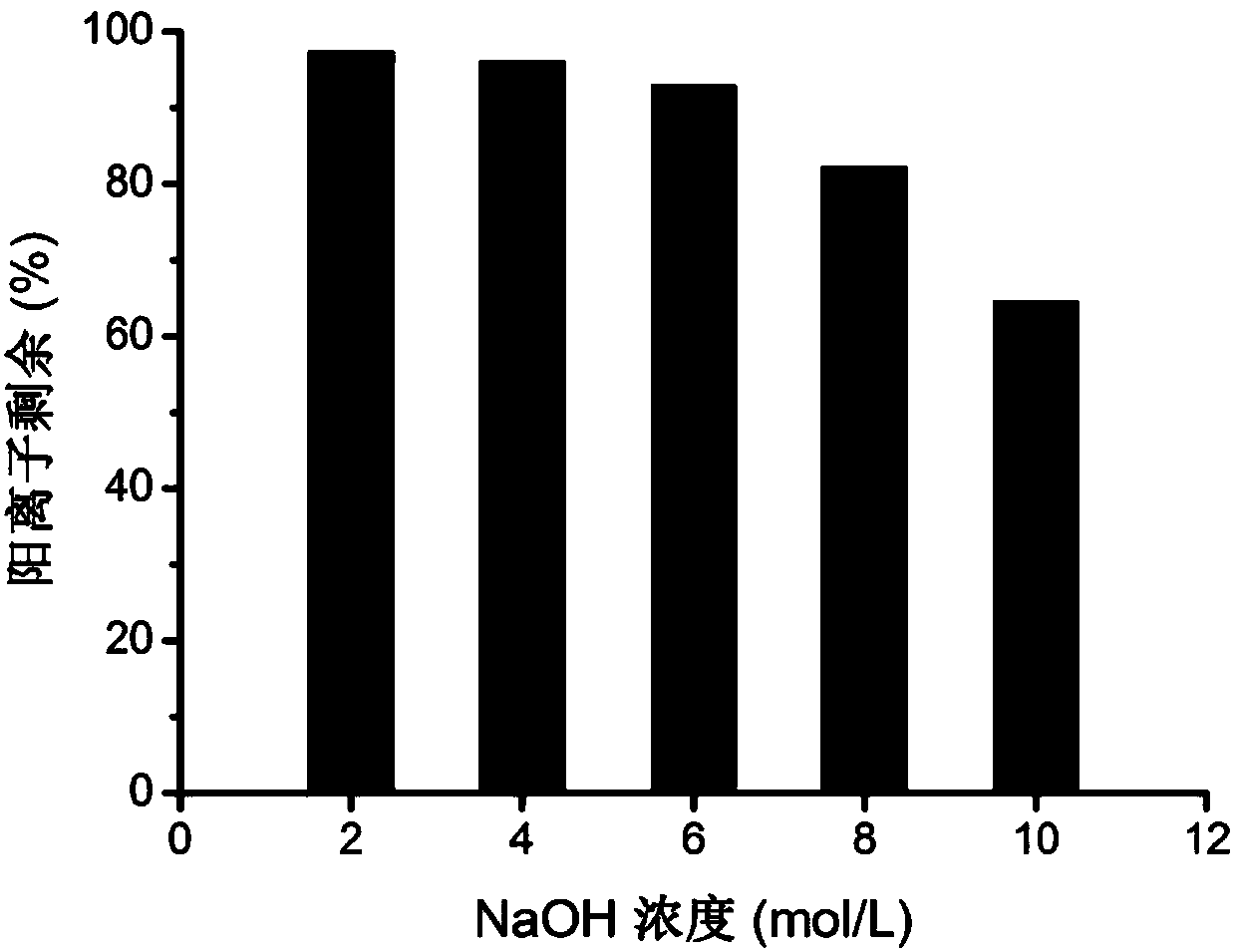
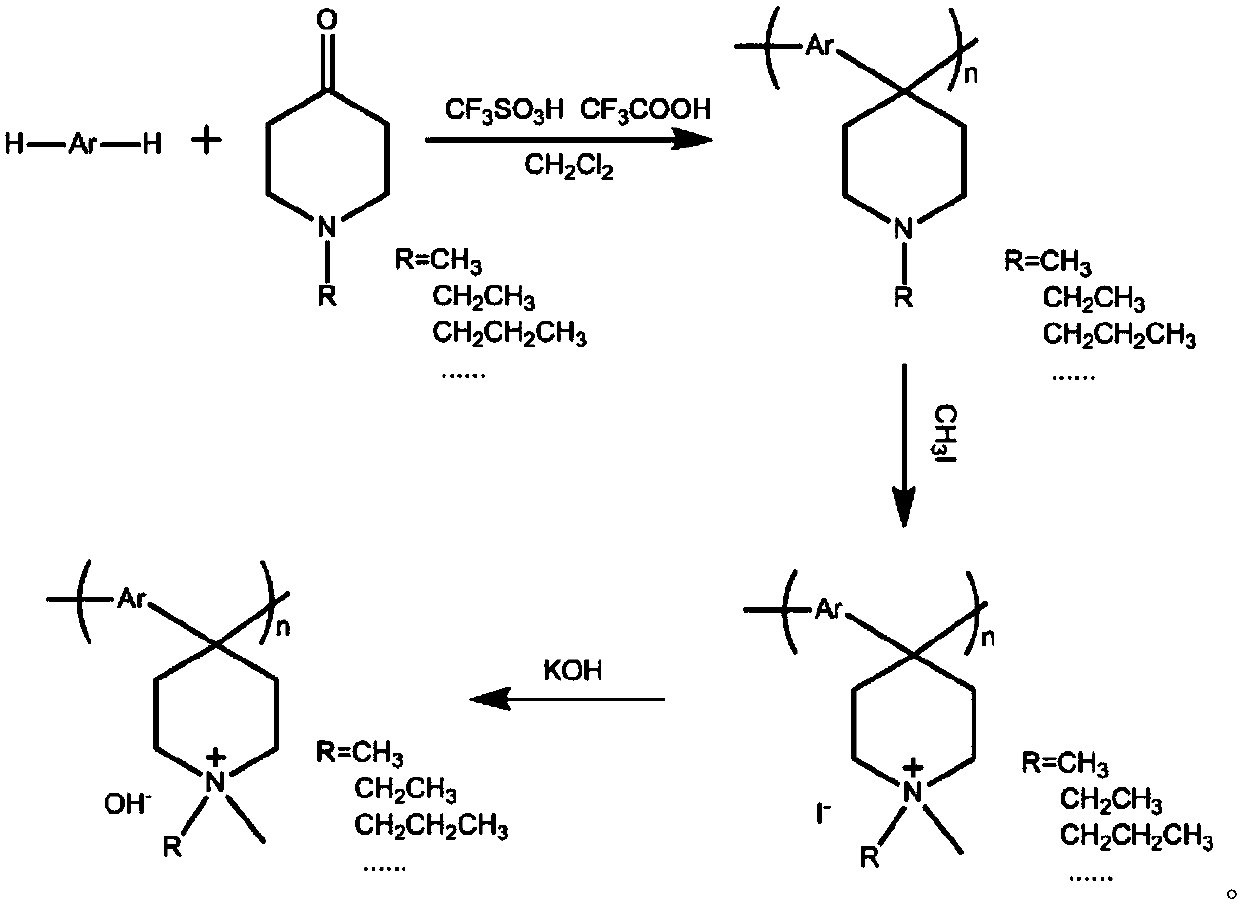
Preparation method of anionic polymer membrane with high chemical stability
The invention discloses a preparation method of an anionic polymer membrane with the high chemical stability, and belongs to the field of ionic polymer membranes. The preparation method comprises thesteps that under catalysis of mixed superacid, an aryl compound and an N-alkyl-4-piperidone compound generate an addition condensation reaction to obtain a linear polymer with high molecular weight and narrow molecular weight distribution; and quaternization modification is conducted on a nitrogen heterocycle on a polymer chain with methyl iodide or alkyl bromide, the obtained quaternized ionic polymer is soaked in a concentrated strong alkaline solution for ion exchange, washing and drying are conducted, and finally the obtained ion polymer is subjected to dissolution casting. According to the preparation method, the experiment process is simple and efficient, and the obtained anionic polymer membrane has the high ionic conductivity and ionic exchange capacity and is very excellent in chemical and heat stability and mechanical strength. The anionic polymer membrane has the very good application prospect and development potential in the alkaline polymer fuel cell field and has the great advantage compared with an anionic polymer membrane applied to a fuel cell at the present stage.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Oil soluble compound highly effective antirust additive and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an oil soluble built high effective antirust additive and preparing method, which comprises the following steps: allocating 12-30 wt polyhydroxy carboxylic acids, 40-60 wt oleic acid acetal amide boric acid ester, 3-6 wt bromide triethyl cetyl ammonium, 2-6 wt alkyl group bromine generation ammonium salt, 10-30 wt dioctyl regular sebacate, 20-30 wt trolamine, 0. 7-1. 3 wt wool alcohol; getting the product. This product possesses good oil solubility, which can be used as antirust agent for ferrous metal and non-ferrous metals.
Owner:BEIJING TIANBAO TONGHUI MATERIAL PROTECTION TECH
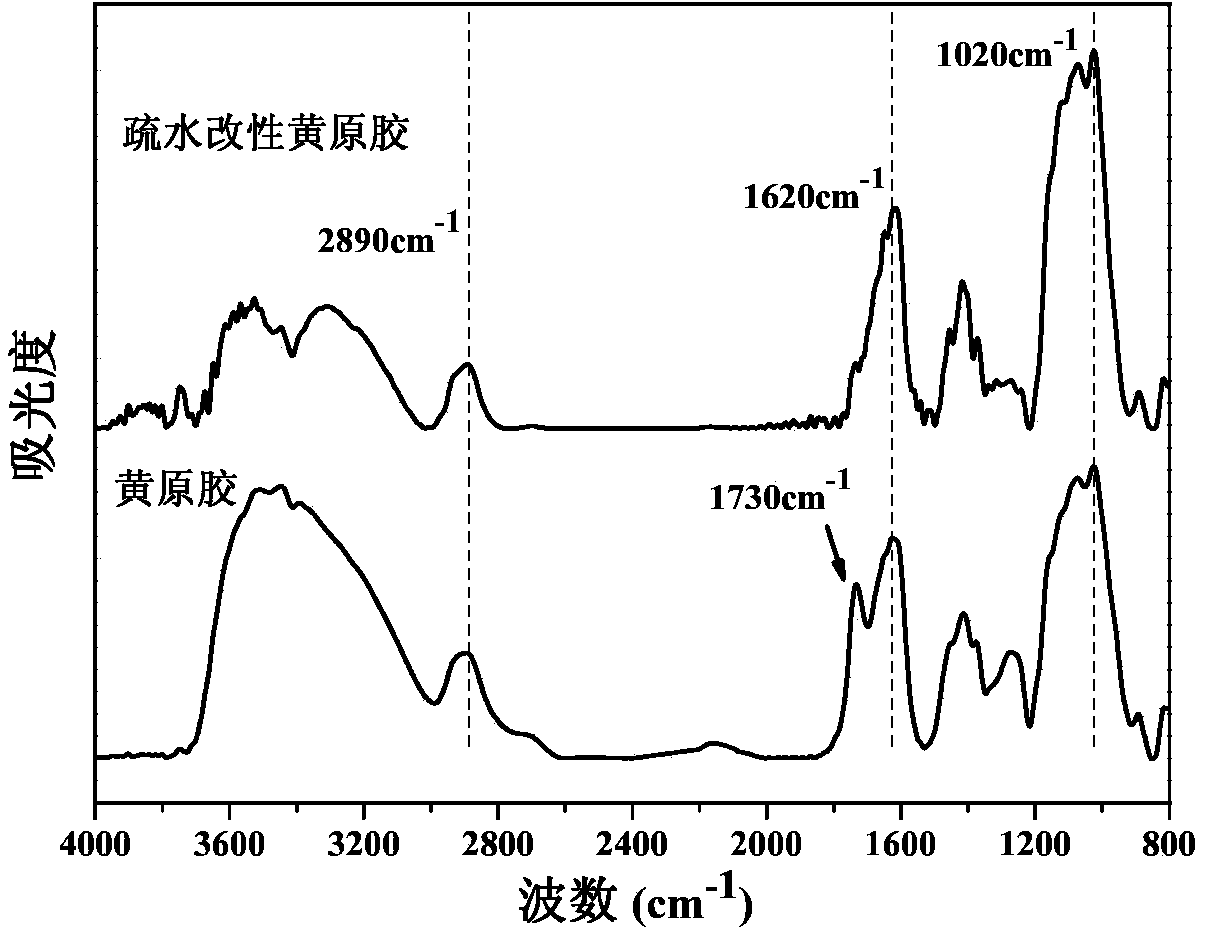
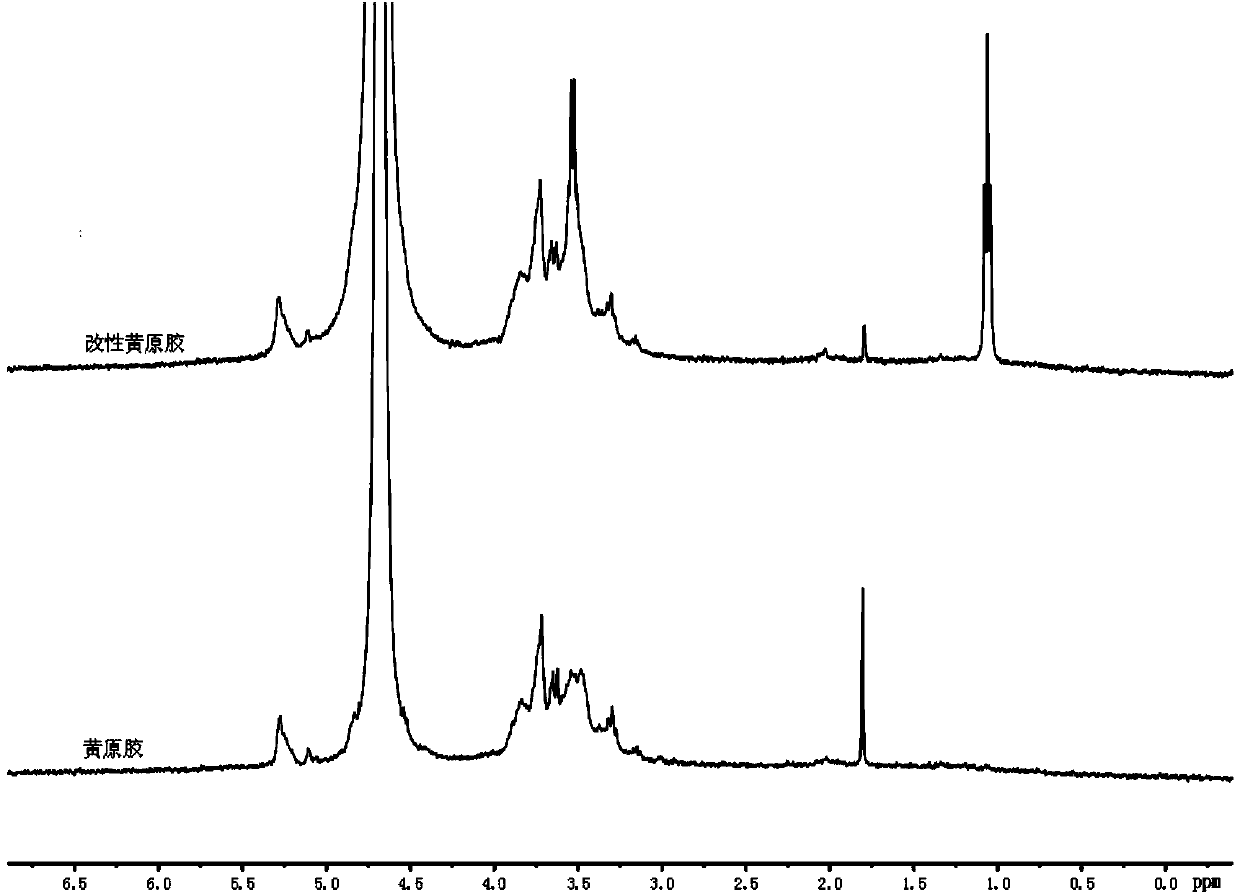
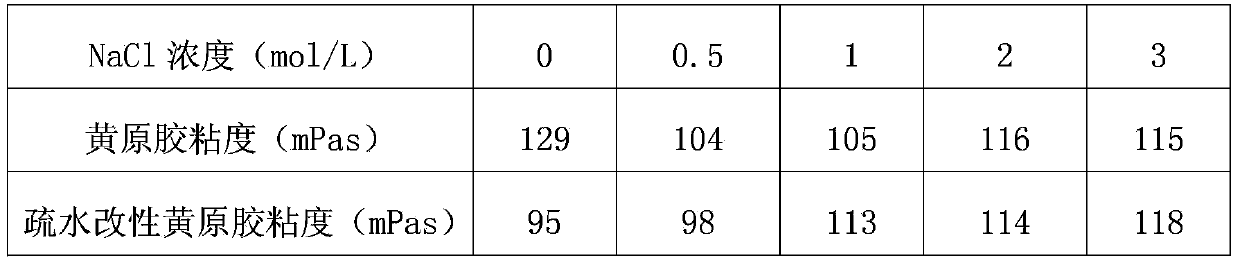
Method for preparing hydrophobically modified xanthan
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydrophobically modified xanthan. The method comprises the following steps: taking water / iso-propyl alcohol mixing liquid as a solvent, taking ammonium lauryl sulfate as an emulsifying agent, taking alkyl bromide as an etherifying agent, and carrying out reaction under the temperature of 30 to 120 DEG C and the pH of 6 to 9 to modify xanthan to obtain the hydrophobically modified xanthan. The conditions of a synthesis reaction are wild, raw materials are easy to obtain, monomer conversion is high, and products are convenient to process. The hydrophobically modified xanthan still has higher viscosity when the xanthan has lower molecular weights, has good salt resistance, has good degradable performance so as to be convenient to perform subsequent sewage treatment, and has good environment affinity. The method is suitable for the oil extraction production of high salinity oil reservoirs.
Owner:烟台东方神州生物技术有限公司
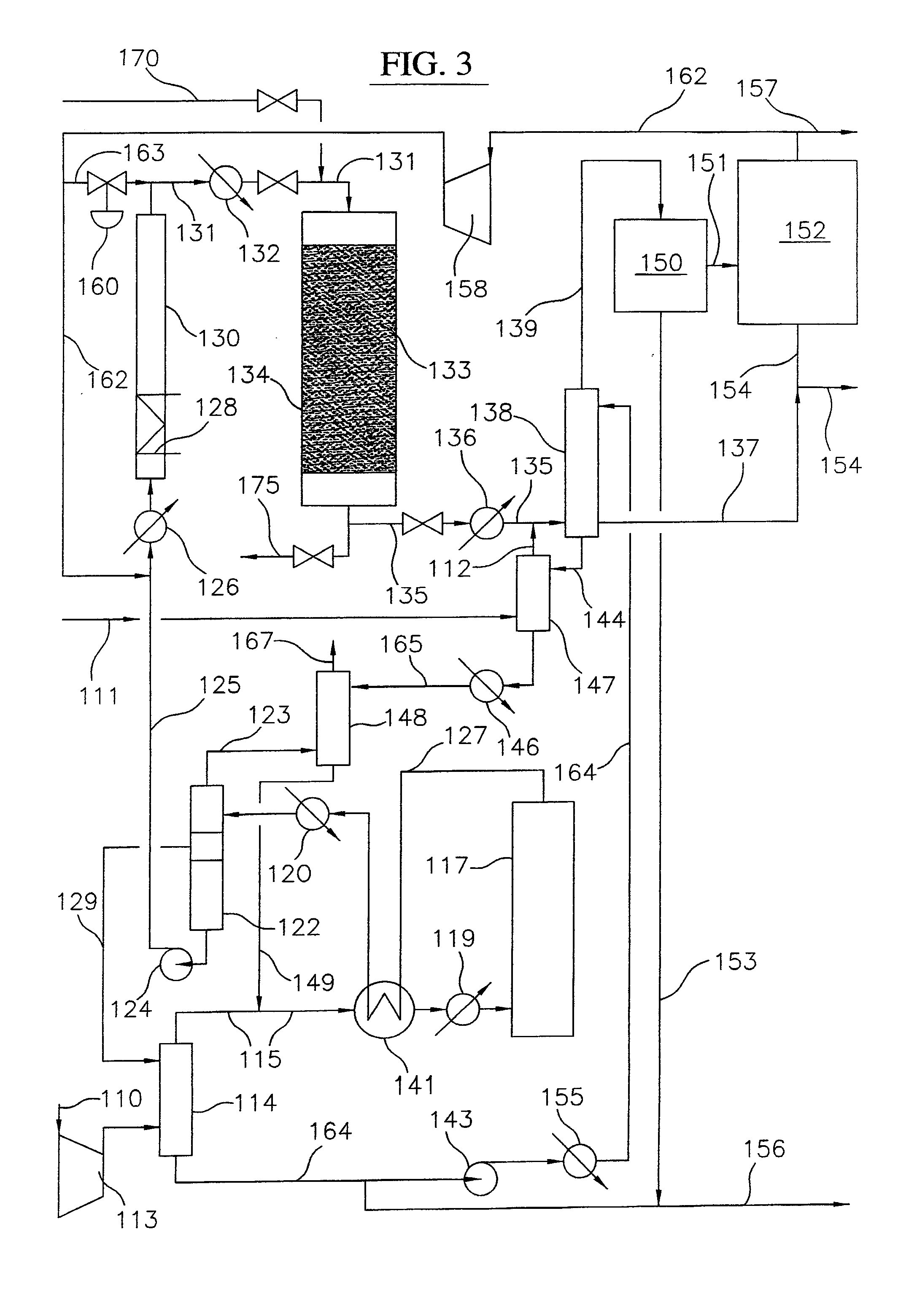
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
Embodiments disclose a process for converting gaseous alkanes to higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereofs wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes may be reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid then may be reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 or an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form hydrobromic acid vapor and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:MARATHON GTF TECH
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080200740A1High selectivityAvoid disadvantagesHydrogen bromideBromide preparationAlkaneBromine
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process, and to selectively form monobrominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
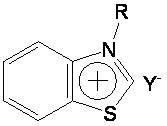
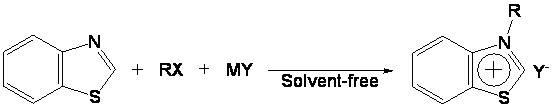
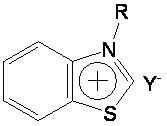
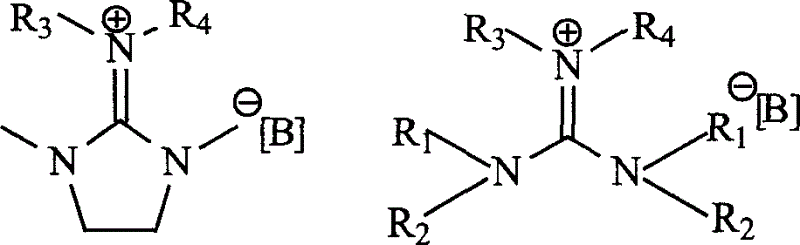
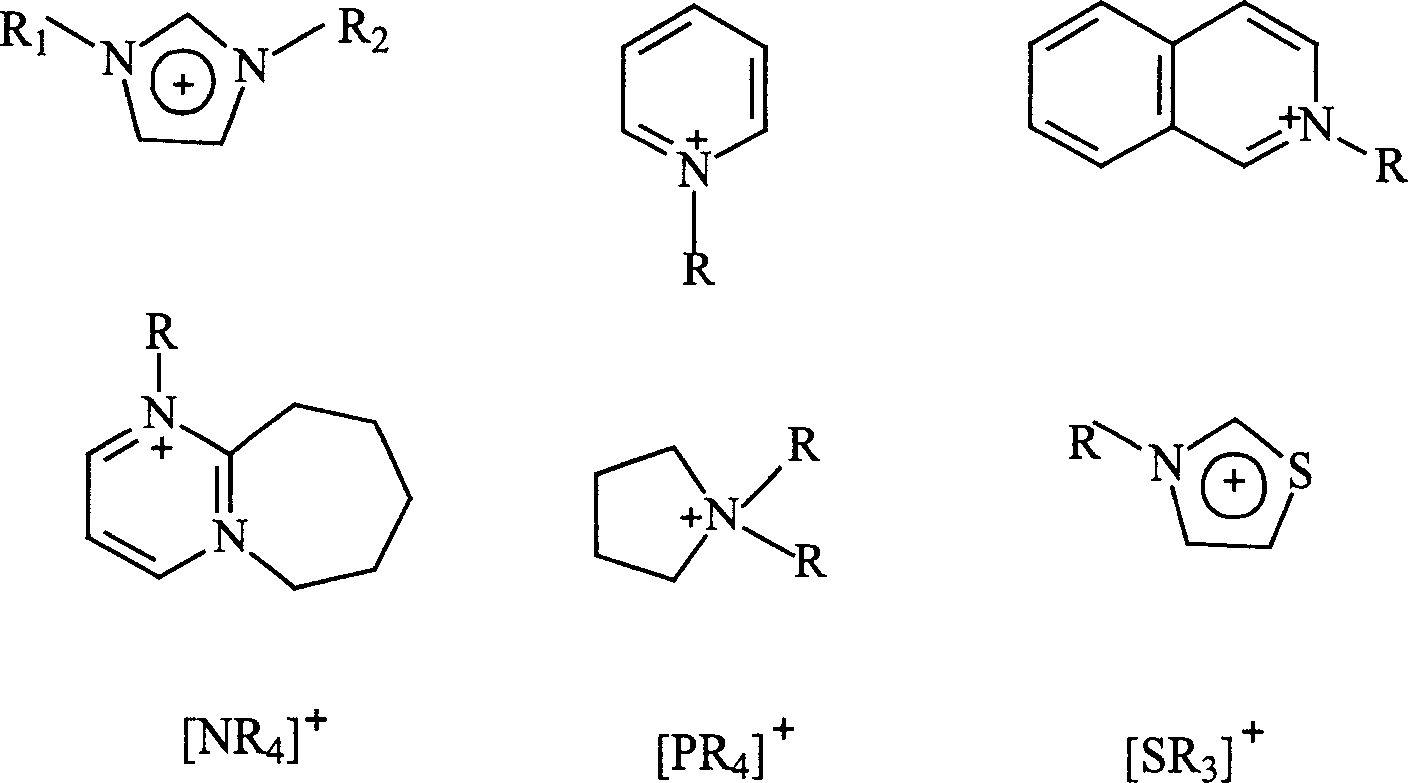
Preparation method and application of novel benzothiazole salt ionic liquid
InactiveCN102153525AScientific research majorGood application prospectOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlkaneSolvent free
The invention discloses a simple preparation method of benzothiazole salt ionic liquid and application thereof to organic catalytic synthesis. In the invention, the benzothiazole salt ionic liquid has a novel structure, benzothiazole N-alkyl quaternary ammonium salt is used as cations (alkyl is one of n-C4H9, n-C5H11 and n- C6H13), BF4<-> or PF6<-> is used as anions. In the preparation method, benzothiazole, chloralkane, alkyl bromide and alkali metal salt or ammonium salt which contains the target anions react in one step under a solvent-free condition. In the invention, the one-step method is used for preparing the benzothiazole salt ionic liquid, therefore, the preparation yield is greatly increased, the use of substrates with high toxicity and high price is avoided, the consumption of organic solvents is reduced, the excessive use of a certain reaction component is avoided, the preparation process is simplified and high product yield is ensured. Therefore, the method has god economy and environmental friendliness and is suitable for mass preparation. The benzothiazole salt ionic liquid can be used as a mild, exclusive and efficient catalyst in benzoin condensation and Biginelli condensation and can be recycled and reused many times.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Hexa alkyl guanidine salt ion liquid and preparing process
The present invention relates to hexa-alkyl guanidine salt ion liquid and its preparation process. The materials 1 ,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolinone and tetra-alkyl urea are produced into intermediate Wilsman salt under the action of phosphorus oxychlooride, oxalyl chloride, thiophosgene, phosgene or dichluoro sulfoxide; the intermediate is then reacted with C10 below aliphatic amine to produce penta-alkyl guanidine; and penta-alkyl guanidine is finally reacted with alkyl bromide or alkyl iodide and methyl or ethyl ester to produce hexa-alkyl guanidine salt ion liquid. The bromine salt and iodine salt may further reacted with various inorganic salt to produce hexa-alkyl guanidine salt ion liquid containing various negative ions. The present invention lays down foundation for the research and development of ionic liquid and provides systemic technology for the industrial production of hexa-alkyl guanidine salt ion liquid..
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
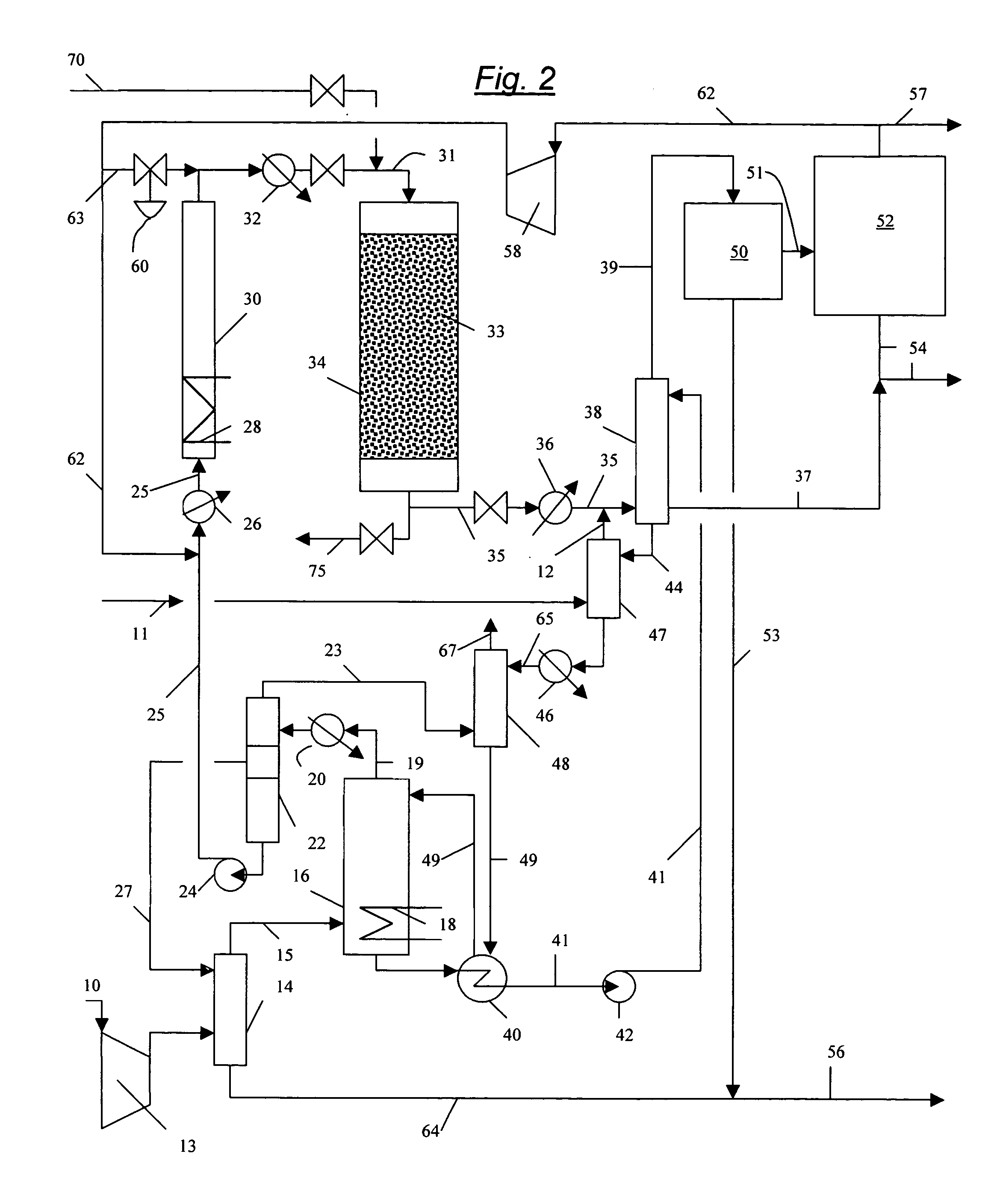
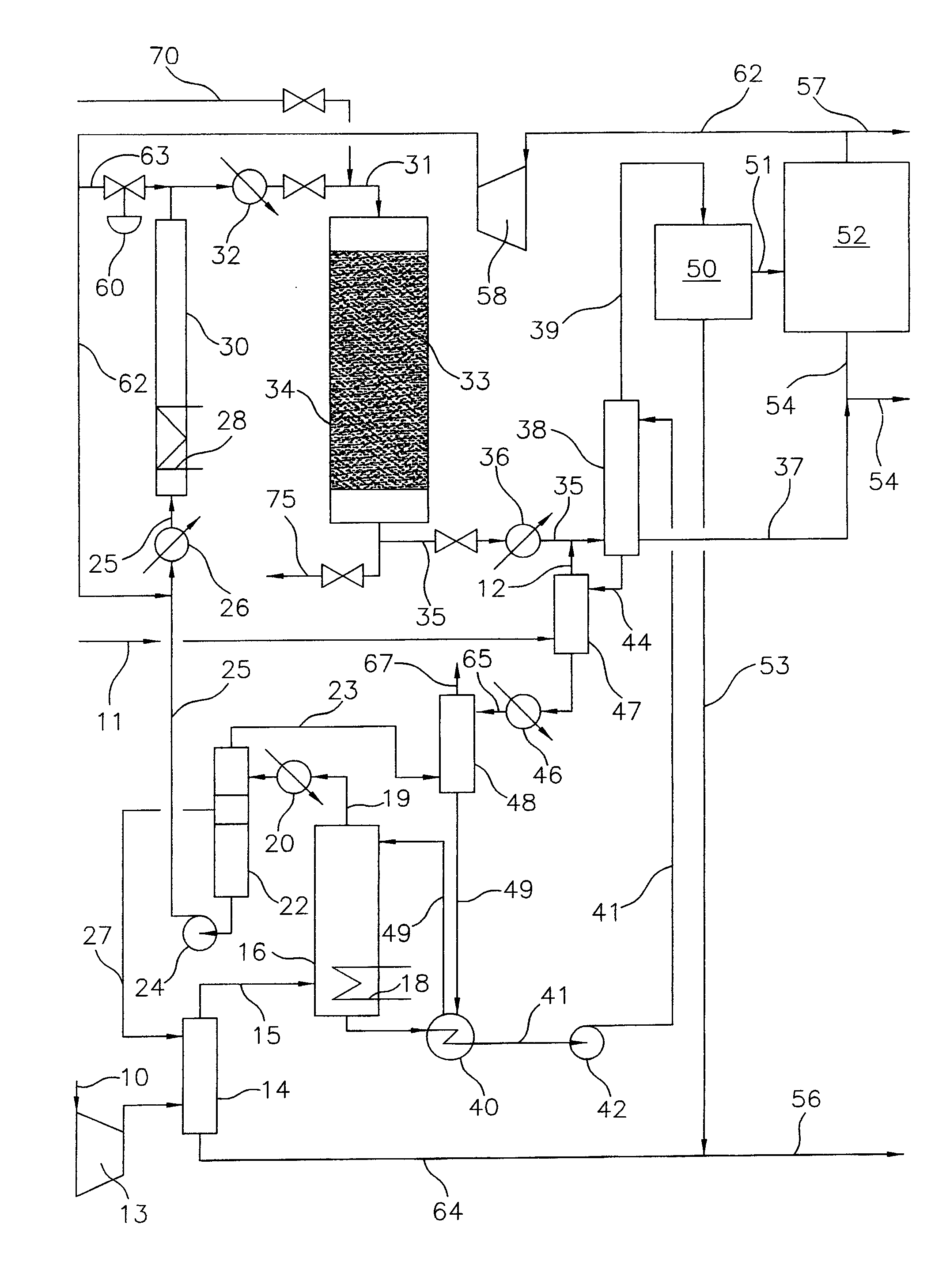
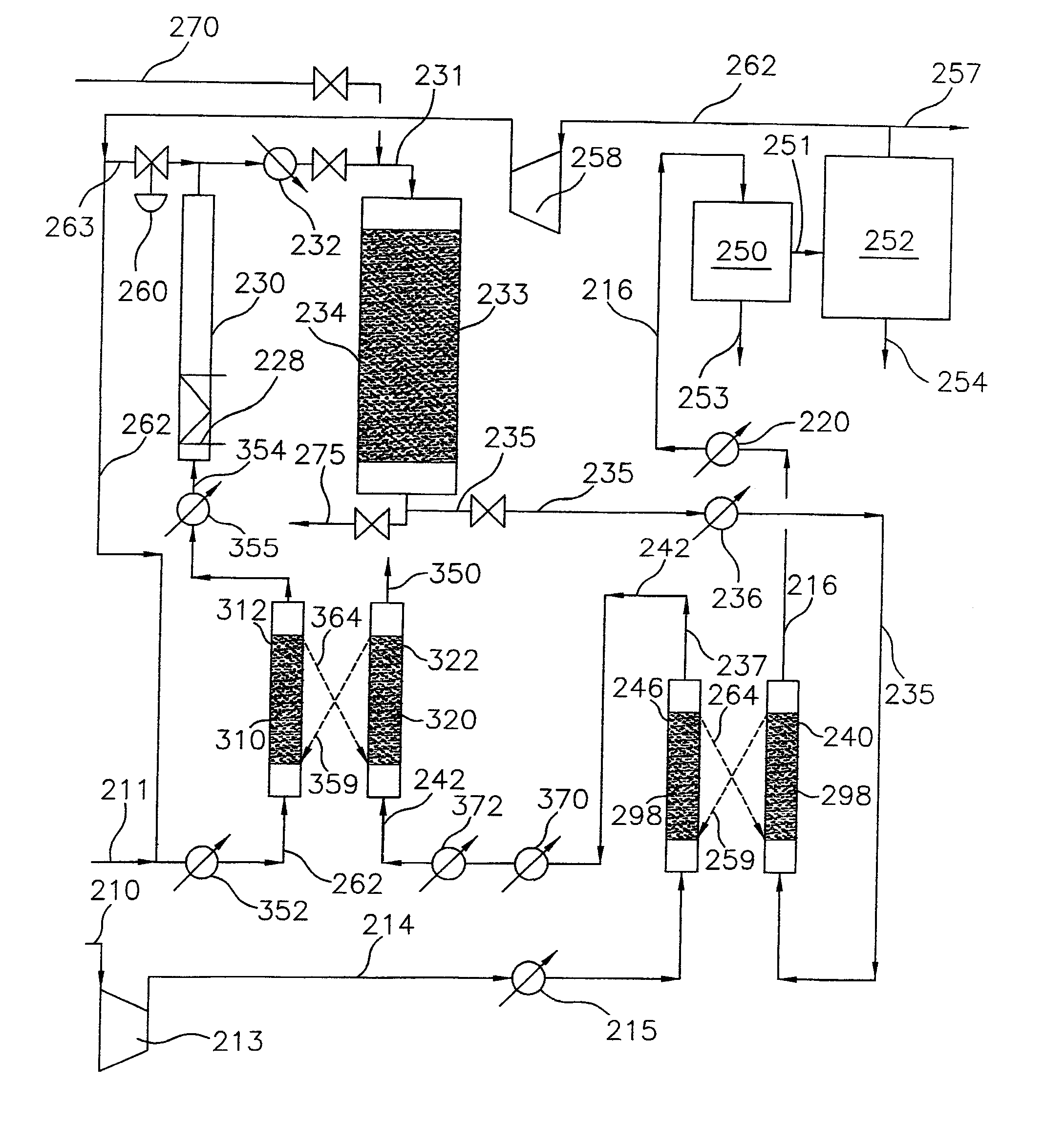
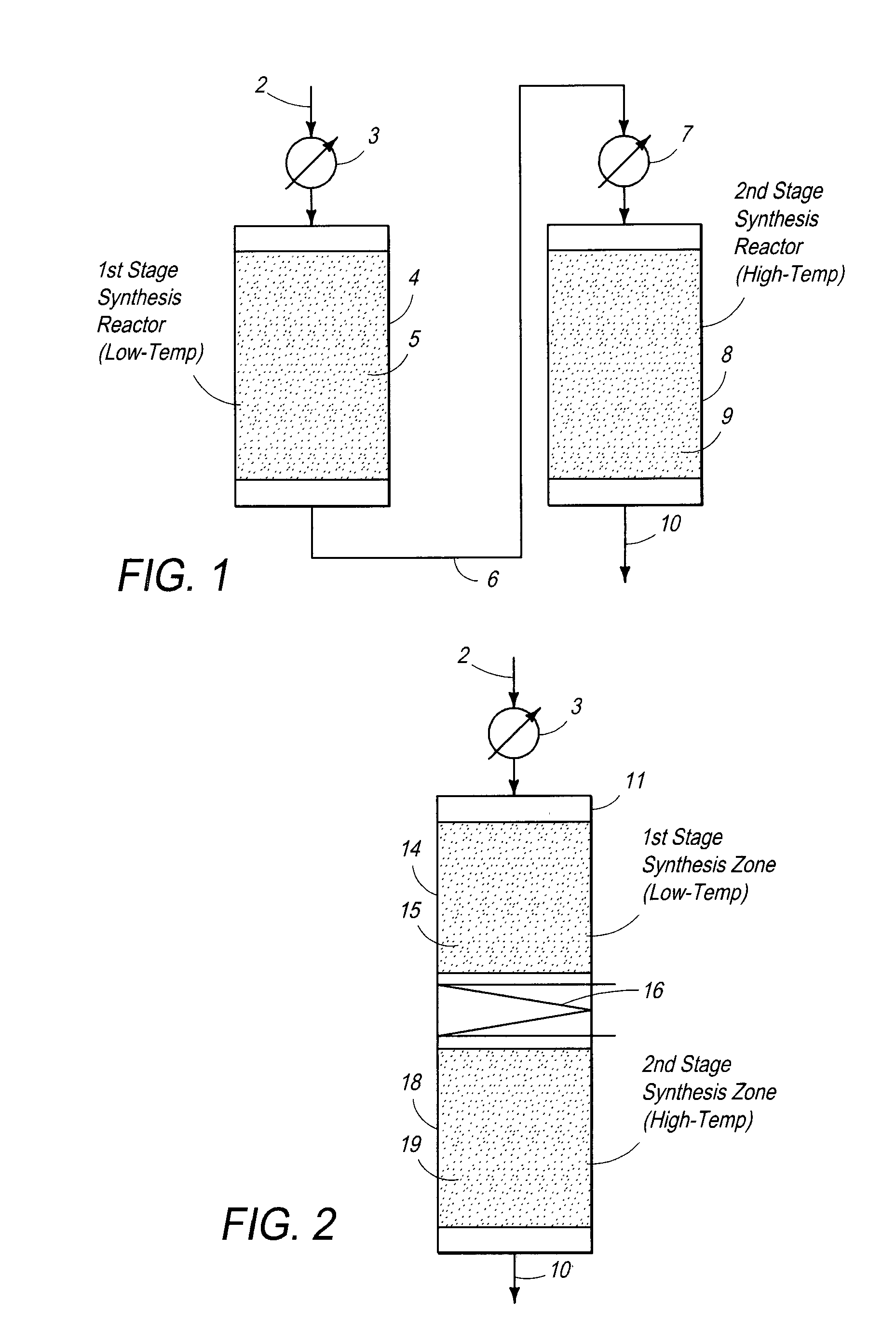
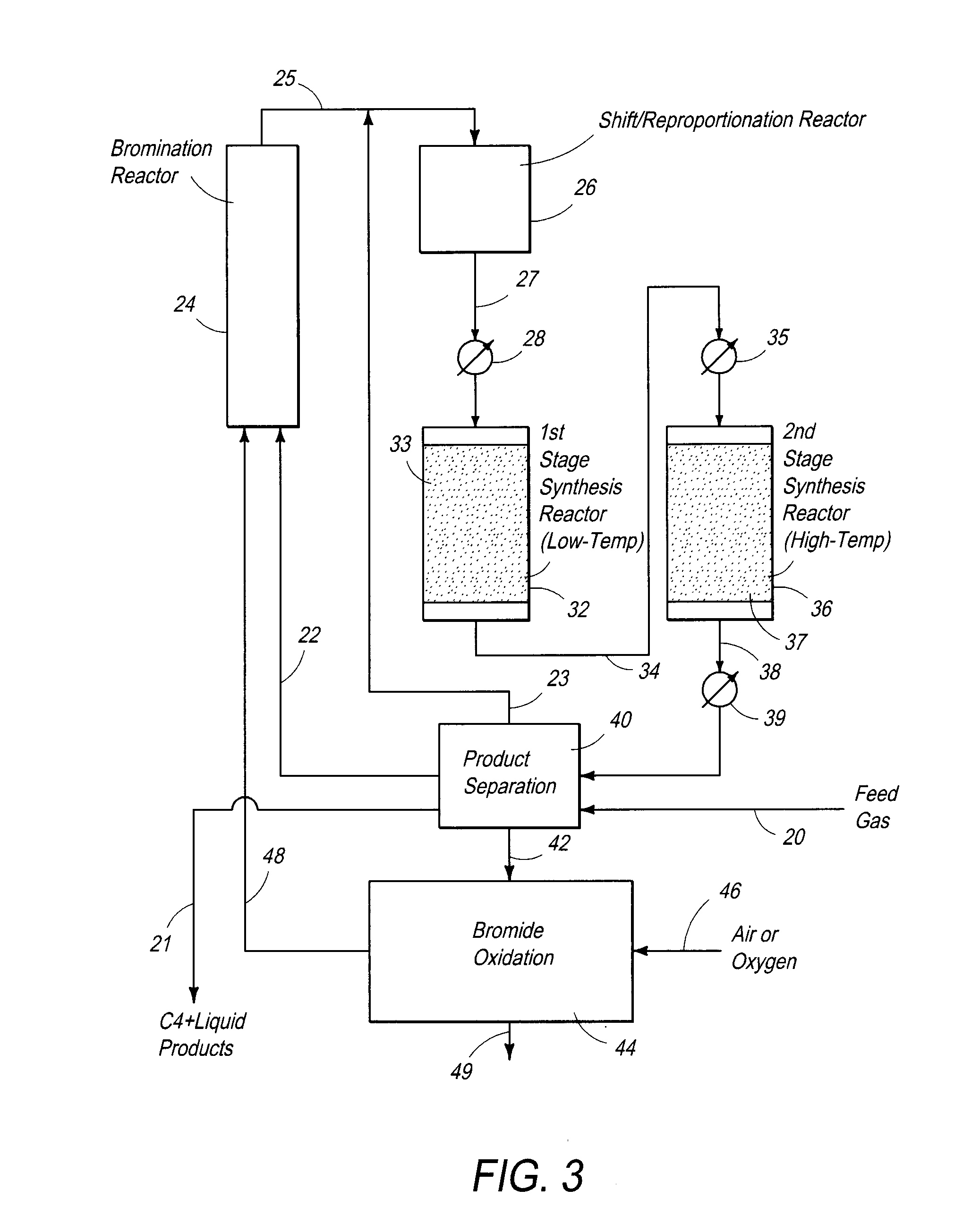
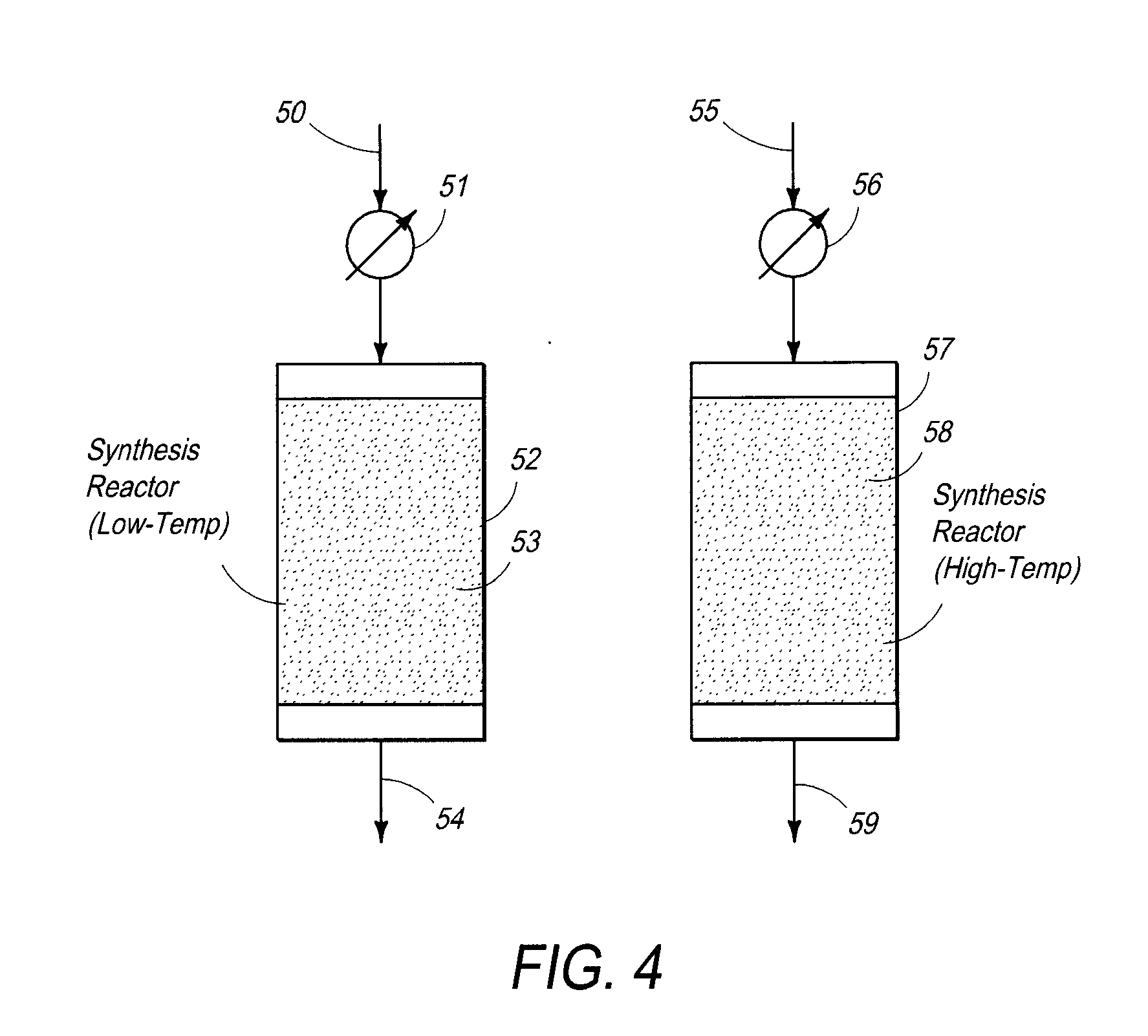
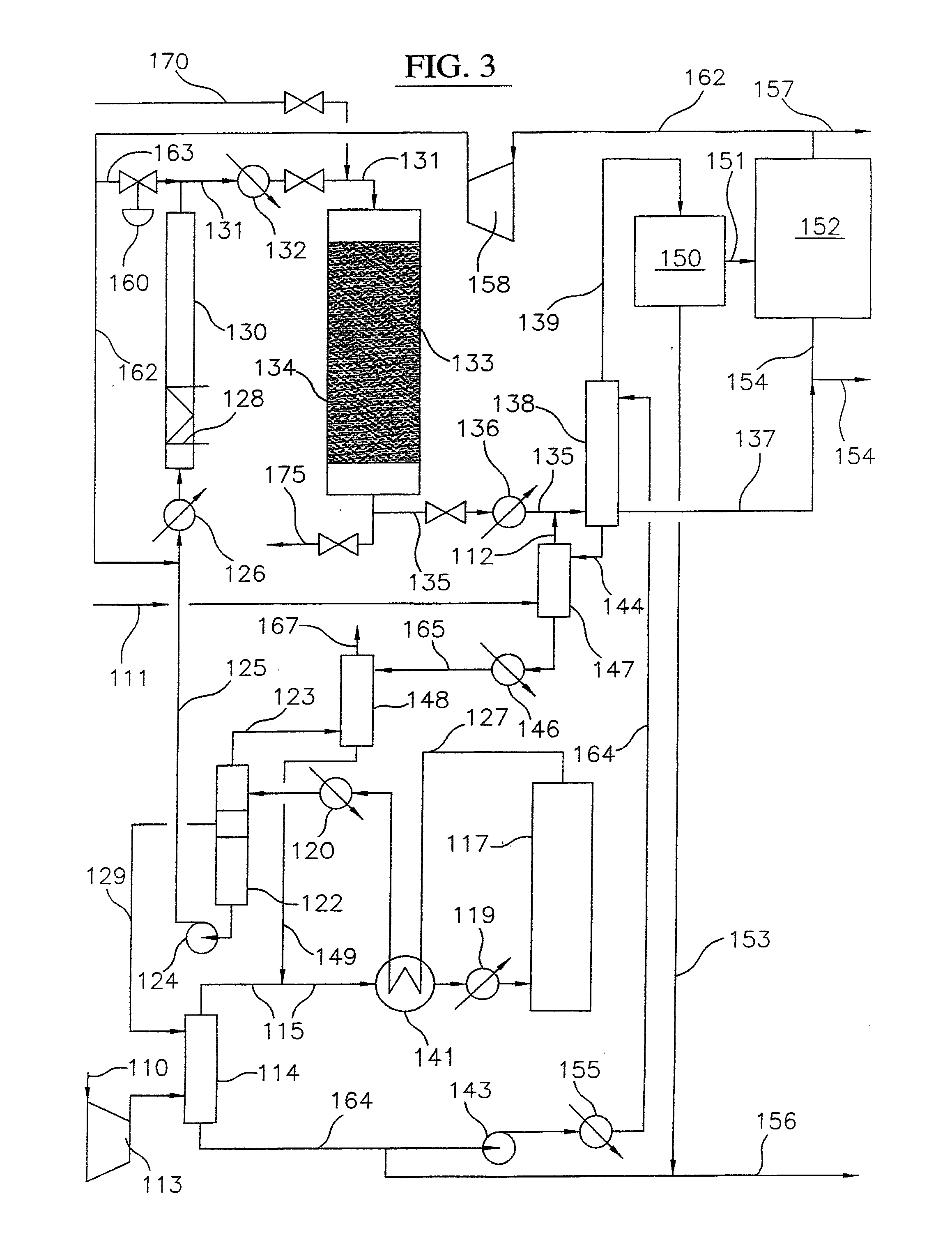
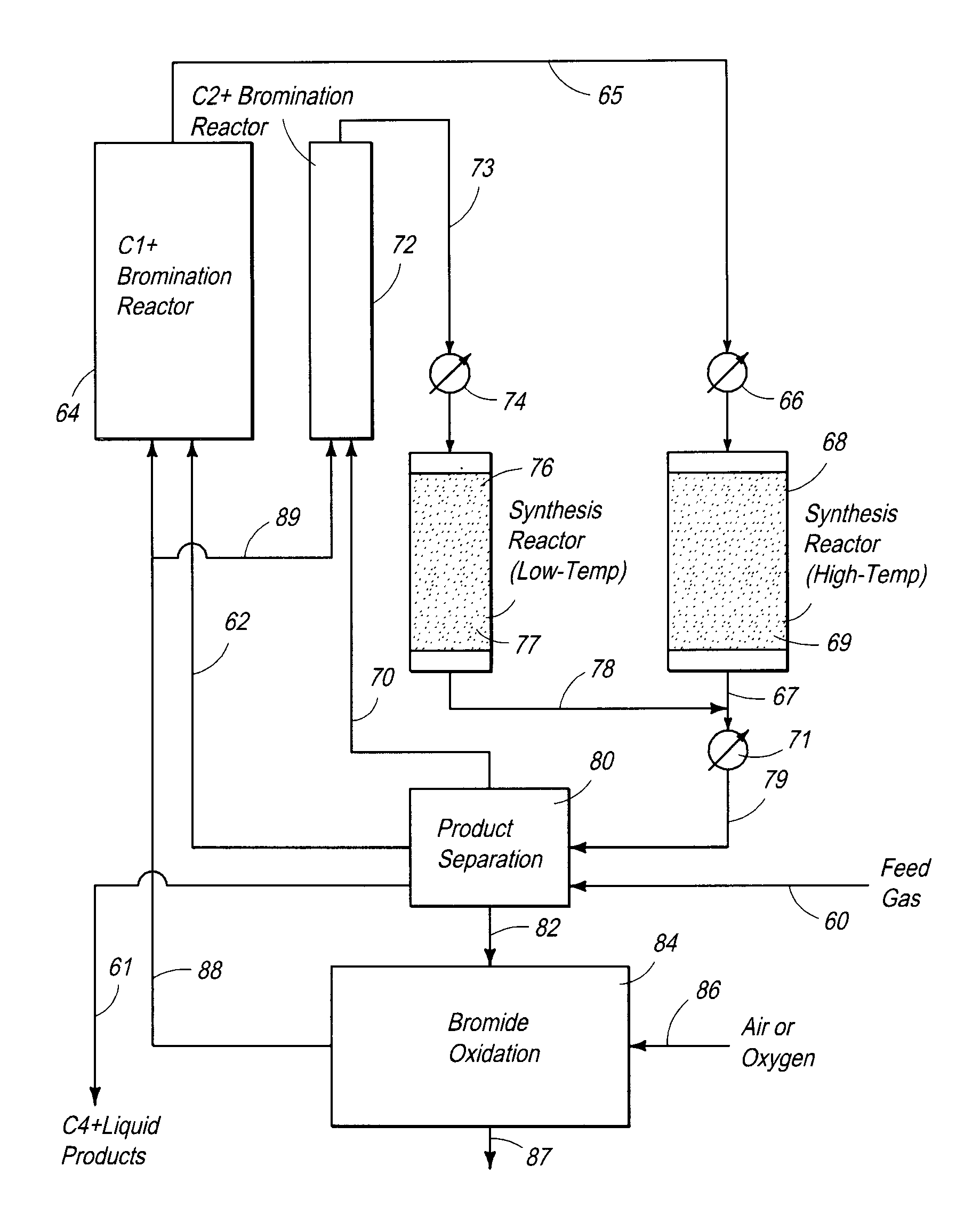
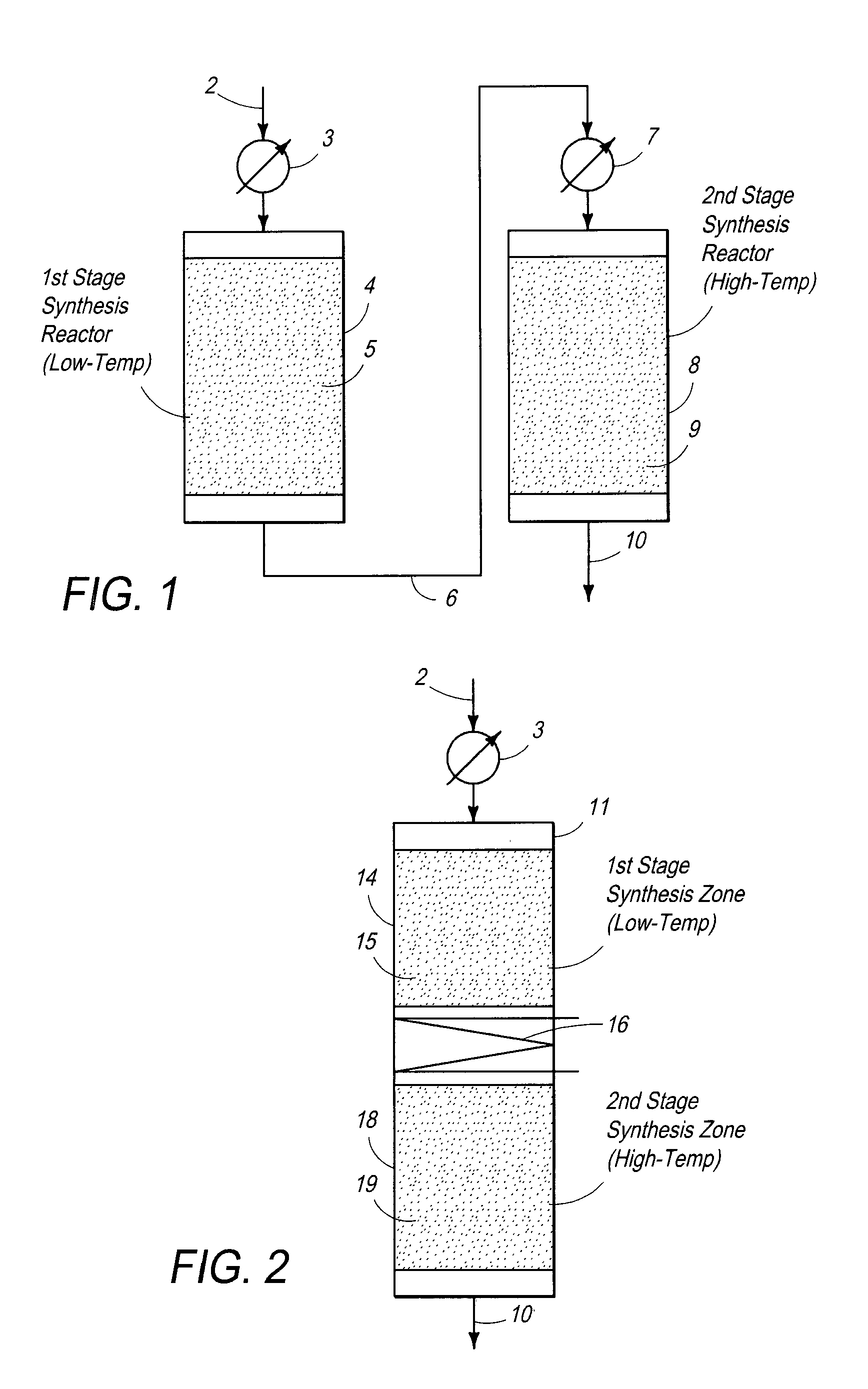
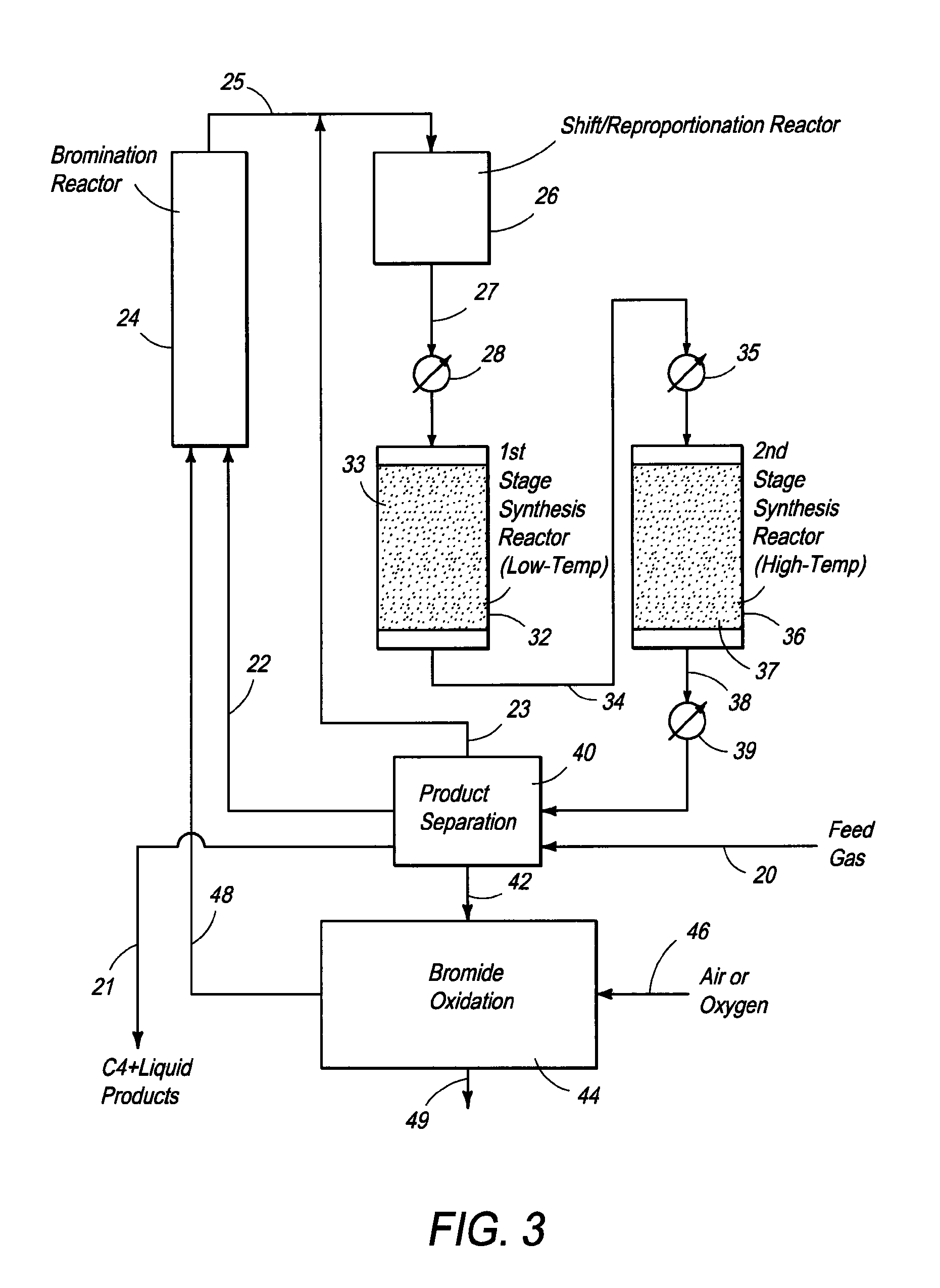
Processes and systems for the staged synthesis of alkyl bromides
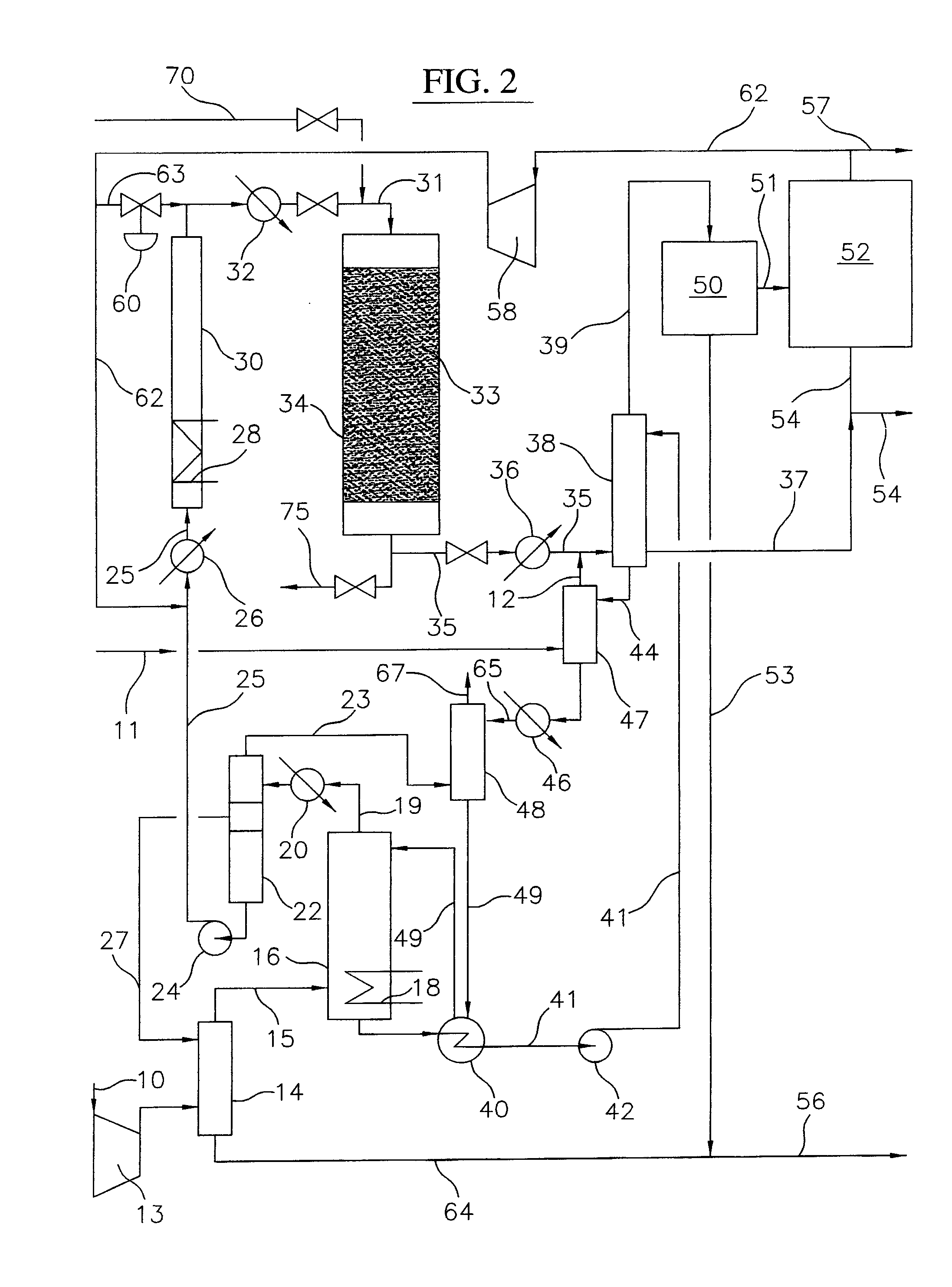
ActiveUS20110218374A1Molecular sieve catalystHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionAlkanePtru catalyst
Processes and systems for synthesizing hydrocarbon products, such as high molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof, from alkyl bromides wherein one or more streams of alkyl bromides may be reacted in sequential or concurrent stages at different temperatures. The catalyst used in the synthesis stages may be the same or different and at least in one instance is chosen to form hydrocarbon products having a significant C6+ paraffin content. The stages may be conducted in one or more reactors and the catalyst may be deployed in fixed beds or fluidized beds.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
Embodiments disclose a process for converting gaseous alkanes to higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereofs wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes may be reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid then may be reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 or an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form hydrobromic acid vapor and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:MARATHON GTF TECH
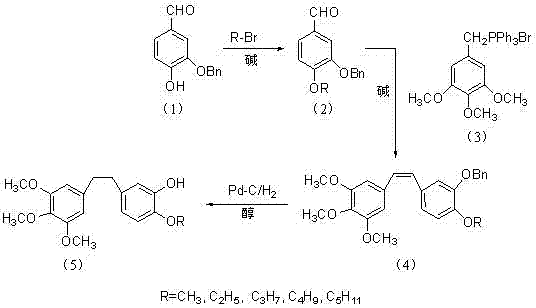
Method for preparing 3,4,5-trimethoxy-3'-hydroxy-4'-alkoxy diphenylethane
InactiveCN103539642AImprove protectionSignificant technological progressOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationPalladium on carbonBenzaldehyde
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons
ActiveUS8008535B2High selectivityAvoid disadvantagesBromide preparationHydrogen bromideAlkaneAlkyl bromide
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the olefins and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Process of preparing alkyl dead-end polyether by polyether with parahydroxyl at molecular chain end
ActiveCN100999580ASolve the problem of low capping rateHigh reactivityPotassium methoxideAlkyl bromide
The process of preparing polyether with end capping alkyl group belongs to the field of polyether synthesis technology. The process includes the reaction of polyether with sec hydroxyl group in the end of molecular chain and strong nucleophilic reagent alkali, the further reaction with alkyl halide, neutralizing with alkali, water washing and filtering to obtain polyether with end capping alkyl group. The strong nucleophilic reagent alkali is alcohol solution of sodium methoxide, alcohol solution of potassium methoxide, solid sodium methoxide, solid potassium methoxide or their mixture; and the alkyl halide is C1-C4 alkyl chloride or alkyl bromide. The present invention has very high reaction activity and effectively raised end capping rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUANGMA TECH
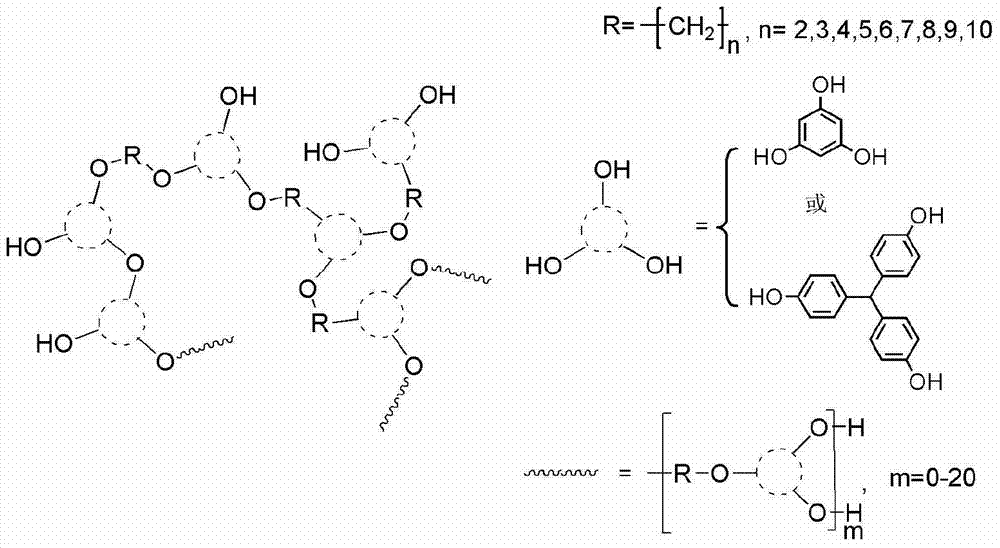
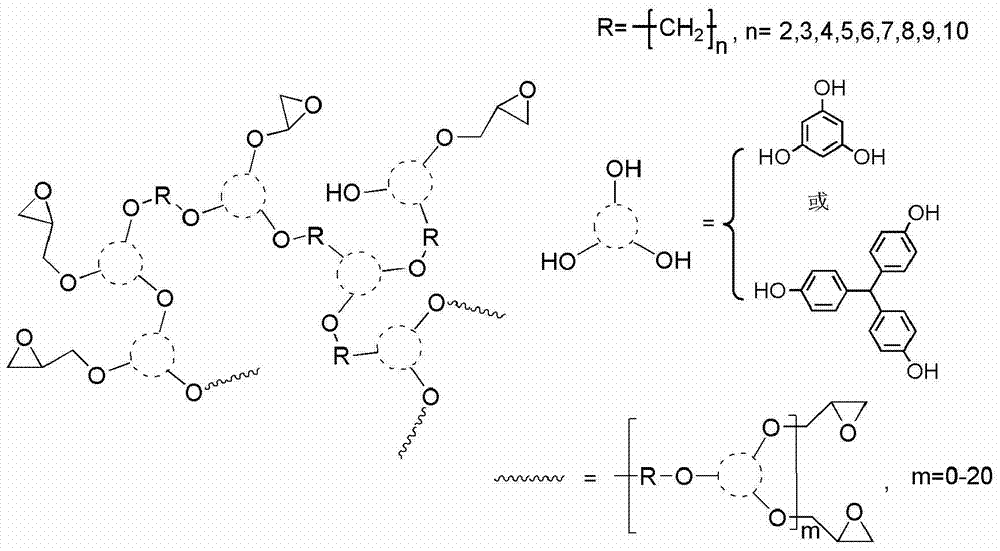
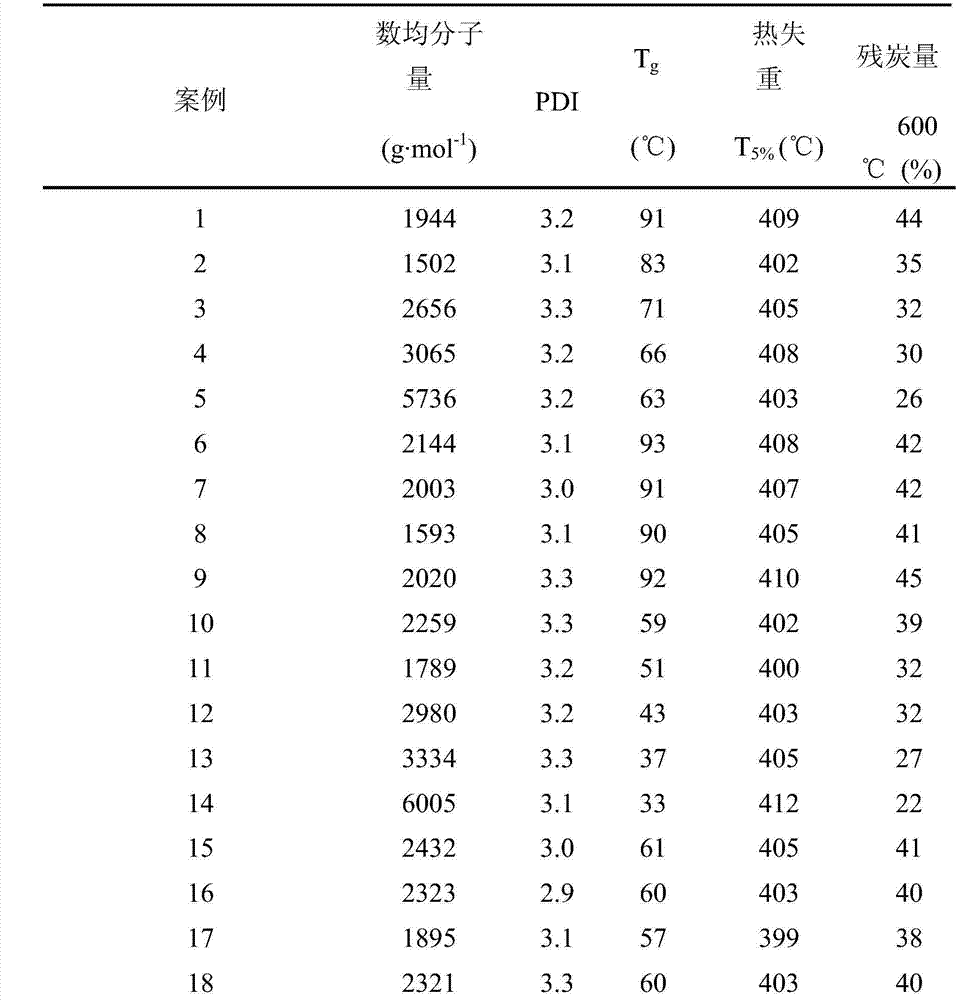
Synthesis method of hyperbranched polymers and modification of epoxy curing product by hyperbranched polymers
The invention relates to a synthesis method of hyperbranched polymers and modification of an epoxy curing product by the hyperbranched polymers. The hyperbranched epoxy polymers are prepared by two reaction steps. In the first step, triatomic phenol and bifunctional alkyl bromides with different carbon chain lengths used as raw materials react to obtain the hyperbranched polymers of which the terminal group is phenolic hydroxyl group. The phenolic hydroxyl group is modified to obtain the polyether-type hyperbranched epoxy polymers of which the terminal group is epoxy group. The modified epoxy material is implemented by introducing different mass percents (3-20%) of hyperbranched polymers into the bisphenol A epoxy resin curing system; and the impact strength and tensile strength of the obtained material are greatly enhanced, and the glass transition temperature is increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is thermally reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide. Poly-brominated alkanes present in the alkyl bromides are further reacted with methane over a suitable catalyst to form mono-brominated species. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrogen bromide. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrogen bromide from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrogen bromide for use in the process, and to selectively form mono-brominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
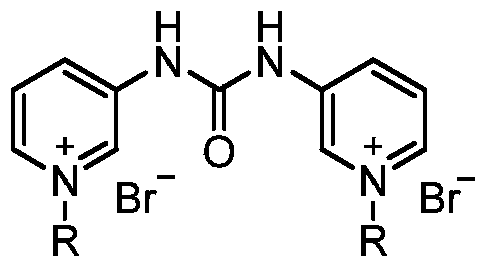
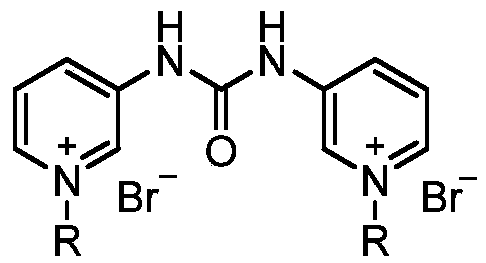
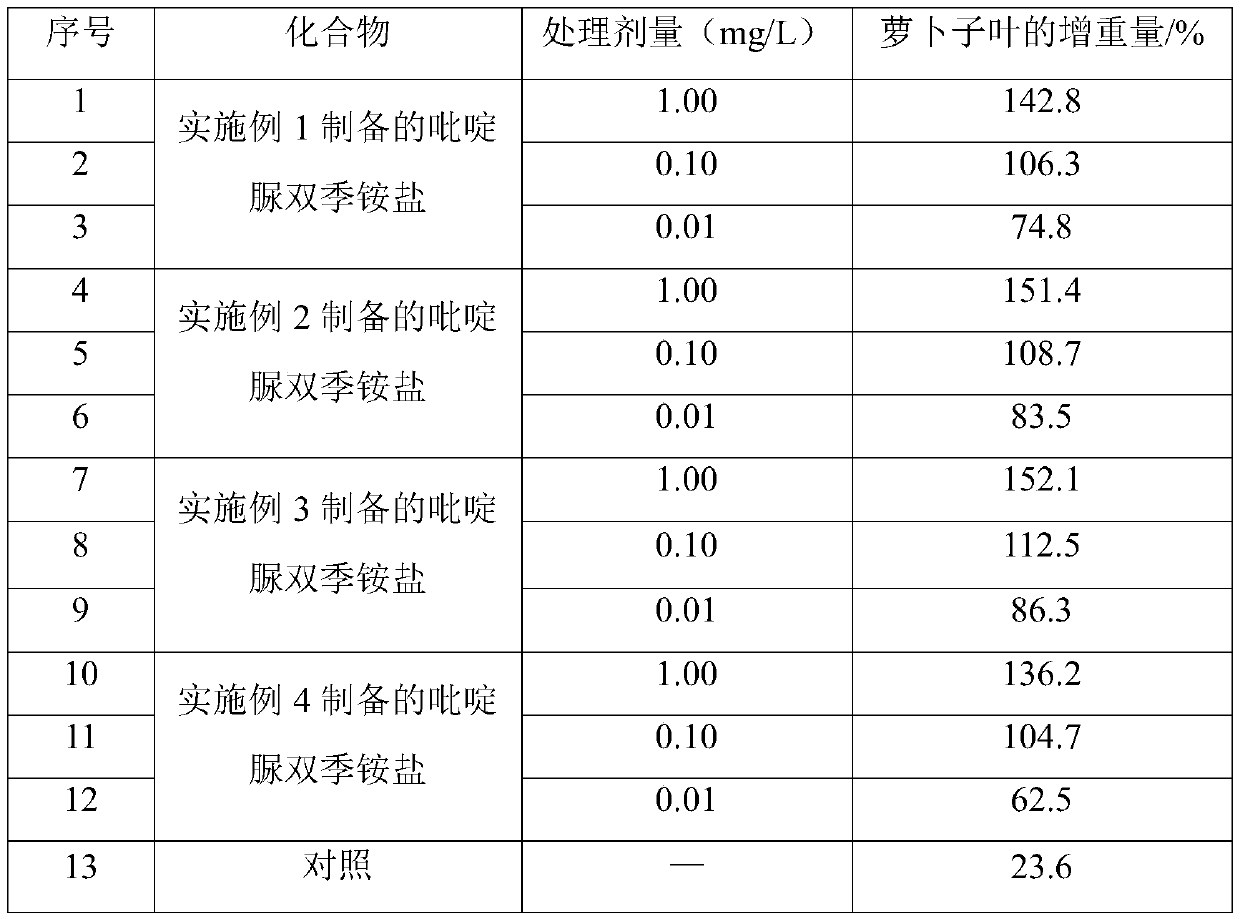
Pyridylurea biquaternary ammonium salt as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105503711APromote divisionGood water solubilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideSolubilitySolvent free
The invention relates to a pyridylurea biquaternary ammonium salt as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the pyridylurea biquaternary ammonium salt comprises the following steps: using 3-aminopyridine as a staring material, conducting reaction on 3-aminopyridine and triphosgene to obtain 1,3-bi(3-pyridyl)urea, and conducting reaction on 1,3-bi(3-pyridyl)urea and alkyl bromide under the solvent-free condition to prepare the pyridylurea biquaternary ammonium salt. According to the method, a solvent-free method is adopted to prepare the pyridylurea biquaternary ammonium salt, so that the environment can be protected, and the yield is relatively high. The provided pyridylurea biquaternary ammonium salt can be used as a plant growth regulator to promote plant cell division, and the problem that the traditional phenylurea plant growth regulator is poor in water solubility is solved.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
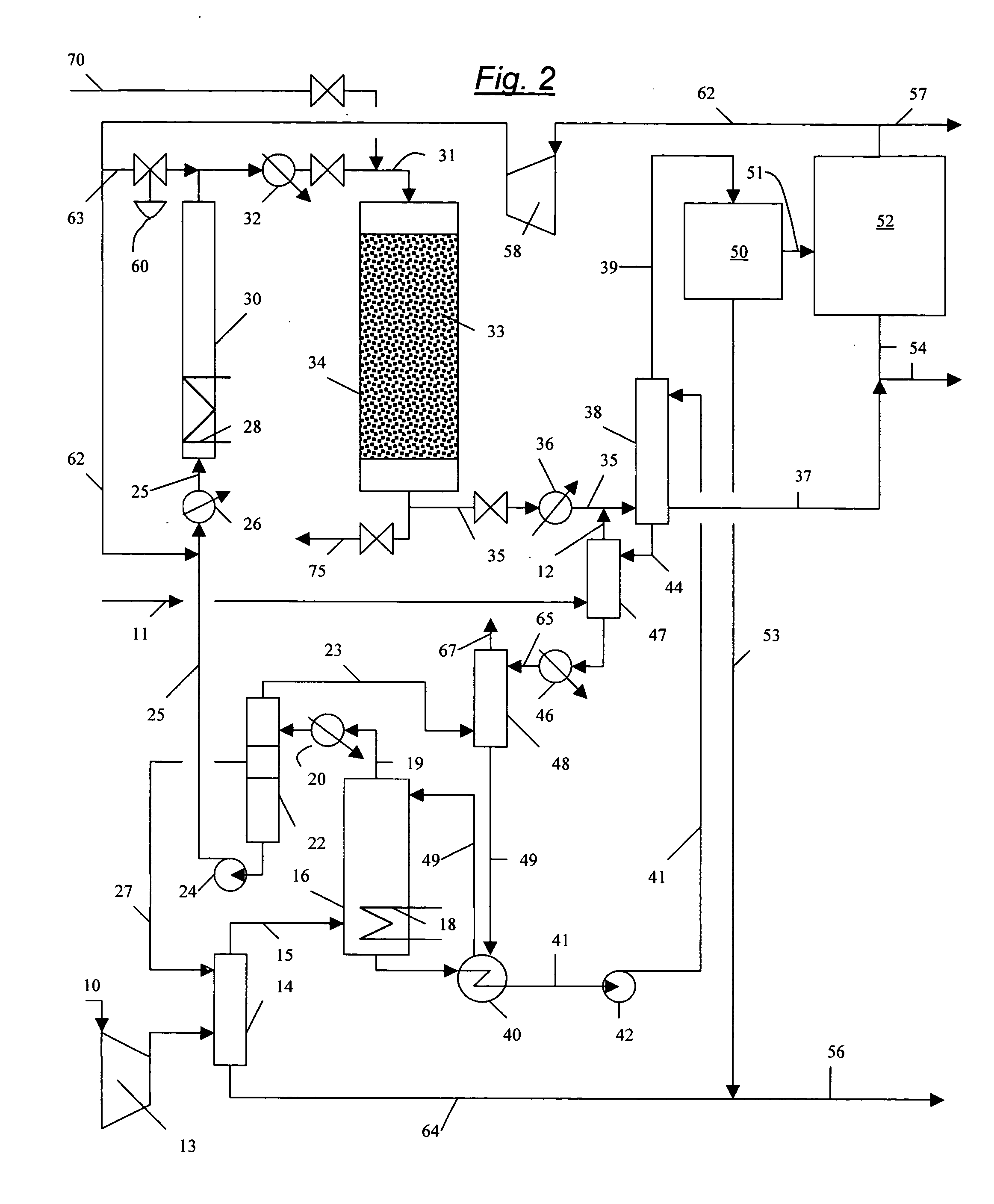
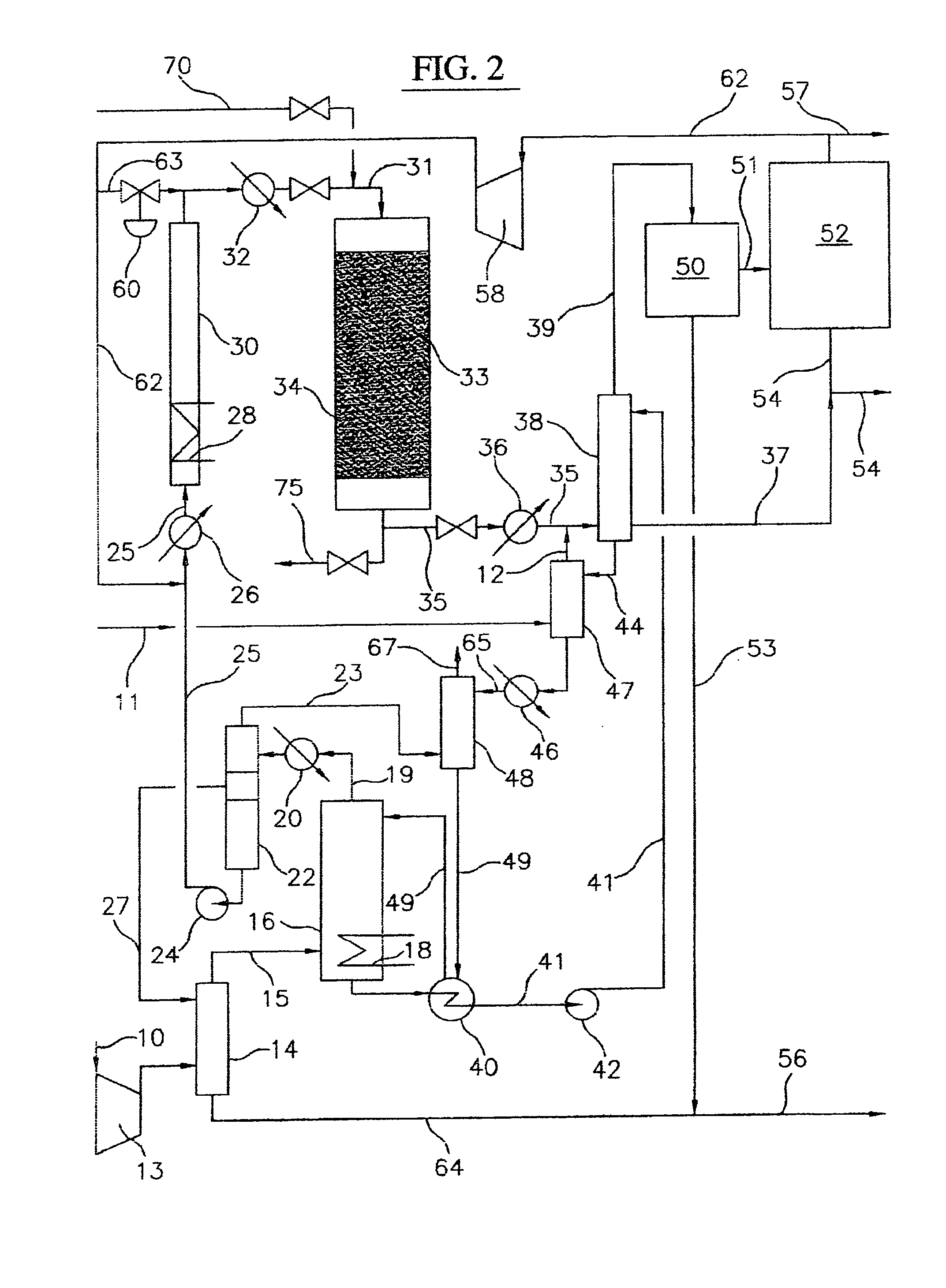
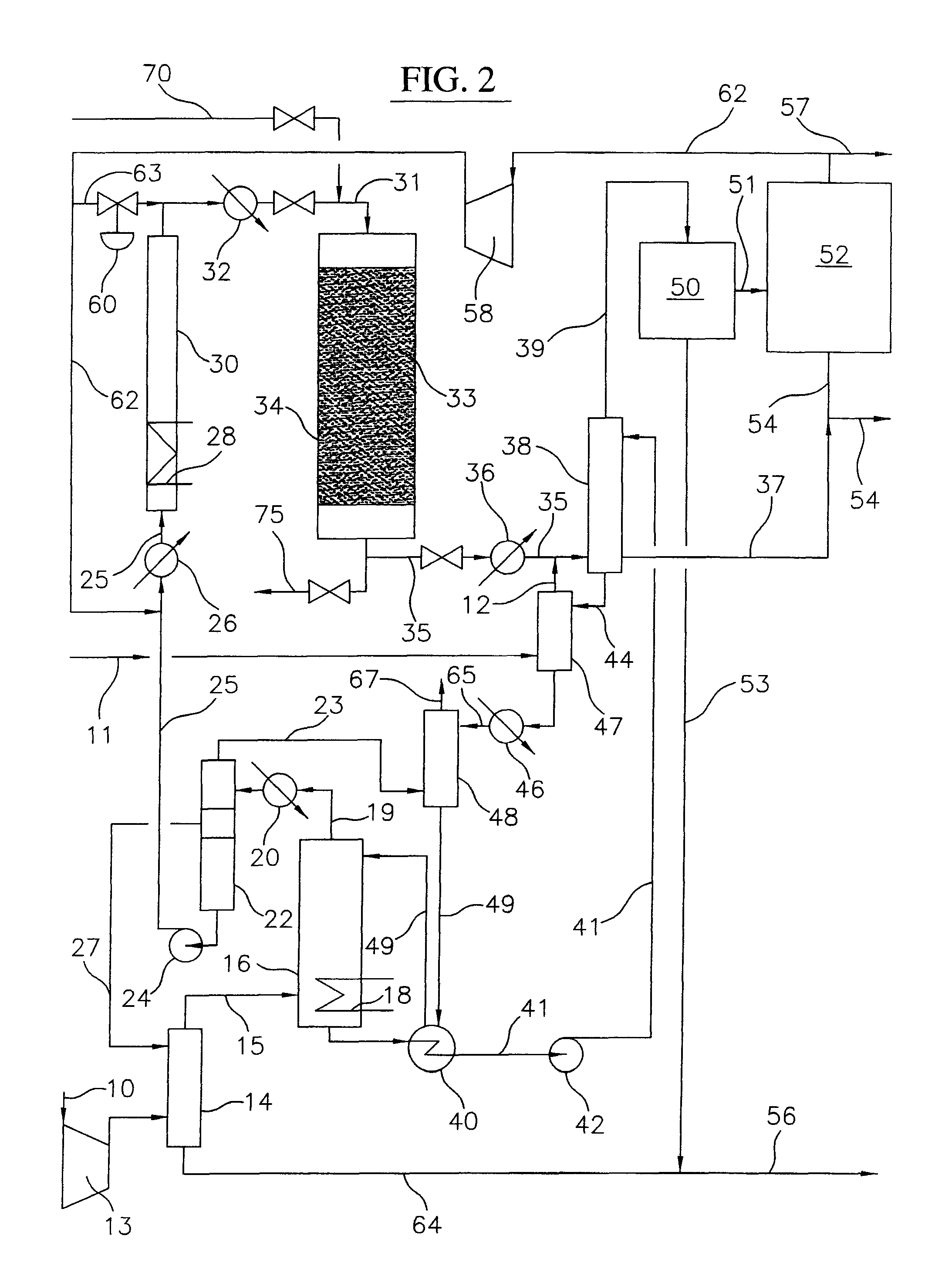
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons using microchannel reactor
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes may be thermally or catalytically reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide. Poly-brominated alkanes present in the alkyl bromides may be further reacted with methane over a suitable catalyst to form mono-brominated species. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide may then be reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrogen bromide. Various methods and reactions are disclosed to remove the hydrogen bromide from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrogen bromide for use in the process, to store and subsequently release bromine for use in the process, and to selectively form mono-brominated alkanes in the bromination step. One or more of the reactions of the processes of the present invention may be conducted in a microchannel reactor.
Owner:GTC TECHNOLOGY US LLC
Preparation of novel polyphosphazene alkaline membrane
InactiveCN102660043AImprove mechanical propertiesGood thermochemical stabilityCell component detailsFuel cell detailsBenzoyl bromidePolyvinyl alcohol
The invention provides a preparation method of a novel polyphosphazene alkaline membrane for a fuel cell. The preparation method of the polyphosphazene alkaline membrane comprises the following steps of: performing a quaternary phosphatization reaction on polyphosphazene loaded with benzyl bromide or alkyl bromide at the tail end of a branch chain and a quaternary phosphatization reagent to obtain quaternary phosphatization polyphosphazene; dissolving into an organic solvent, and performing curtain coating and membrane forming; and soaking with an alkaline liquor, wherein triaryl phosphine or trialkyl phosphine can be taken as the quaternary phosphatization reagent. A preparation method of a polyphosphazene crosslinked alkaline membrane comprises the following steps of: doping a crosslinking agent into the quaternary phosphatization reagent; reacting with polyphosphazene loaded with benzyl bromide or alkyl bromide at the tail end of a branch chain to obtain crosslinked quaternary phosphatization polyphosphazene; dissolving into an organic solvent, and performing curtain coating and membrane forming; and soaking with an alkaline liquor, wherein the crosslinking agent can be a polyethylene glycol sodium salt or diamine. A preparation method of a polyphosphazene coblended alkaline membrane comprises the following steps of: doping a polyalcohol into quaternary phosphatization polyphosphazene; performing curtain coating and membrane forming; and soaking with an alkaline liquor, wherein the polyalcohol can be polyethylene glycol or polyvinyl alcohol.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
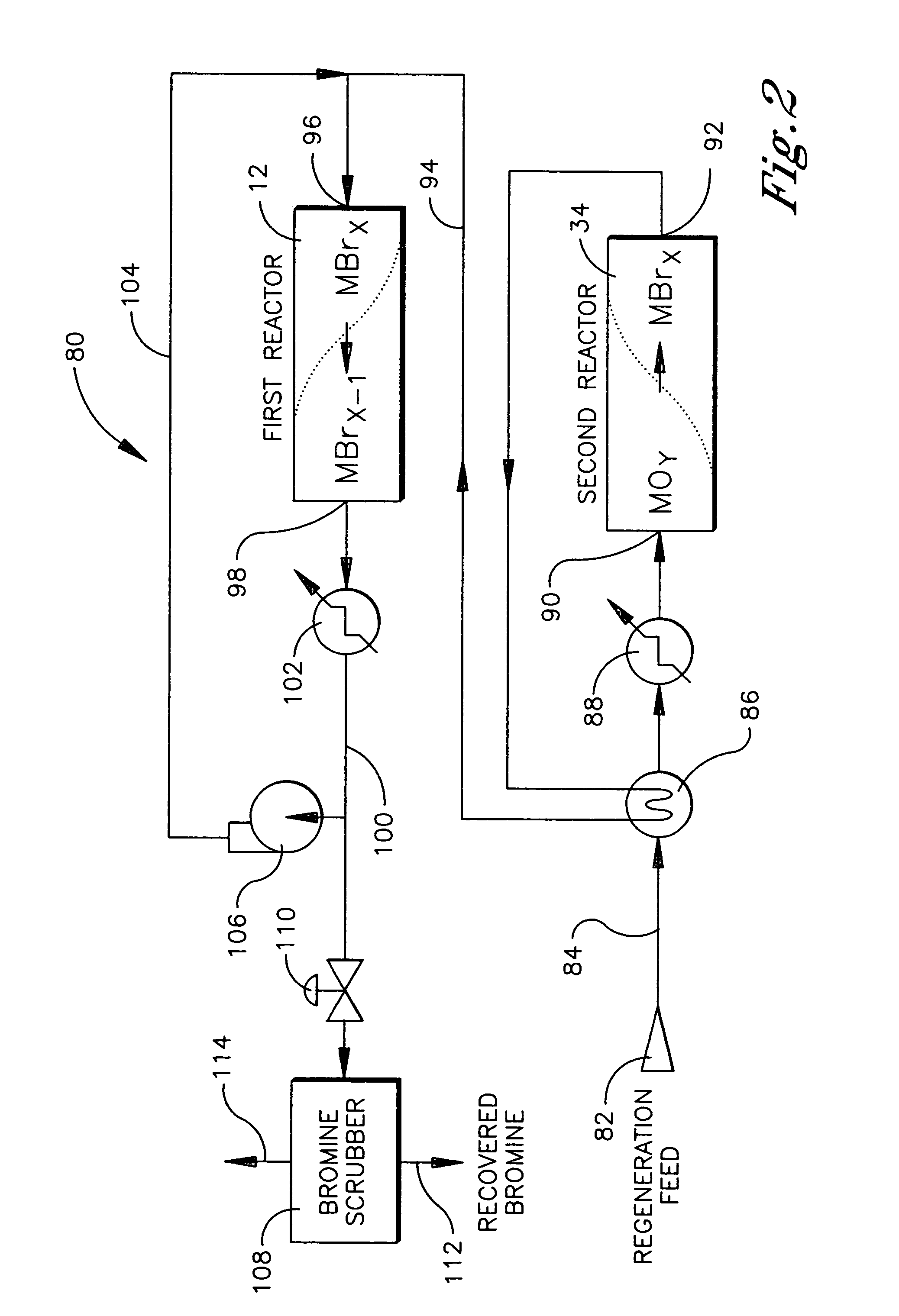
Processes and systems for the staged synthesis of alkyl bromides
ActiveUS8367884B2Molecular sieve catalystHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionFluidized bedAlkyl bromide
Processes and systems for synthesizing hydrocarbon products, such as high molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof, from alkyl bromides wherein one or more streams of alkyl bromides may be reacted in sequential or concurrent stages at different temperatures. The catalyst used in the synthesis stages may be the same or different and at least in one instance is chosen to form hydrocarbon products having a significant C6+ paraffin content. The stages may be conducted in one or more reactors and the catalyst may be deployed in fixed beds or fluidized beds.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
N, N-dimethyl-N [3-(carbohydrate amide group)] propyl group-N-alkyl ammonium bromide and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN102875410ABoth bactericidalGood compatibilitySugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystAlkyl bromide
The invention relates to N, N-dimethyl-N [3-(carbohydrate amide group)] propyl group-N-alkyl ammonium bromide of which the general formula of structure is as follows: wherein the R is a long chain alkyl of the C8-C14; and the glycosyl is a single-glycosyl or a dual-glycosyl. The synthetic method provided by the invention has the advantages that the synthetic process is simple, the requirement to equipment is low, the method is suitable for industrialization, the required reaction temperature is low, pressure and catalyst are not required, the reaction positions on the glycosyl are certain, the reaction is balanced, the amount of generated substitution products is not large, and the productivity is high.
Owner:CHINA RES INST OF DAILY CHEM IND
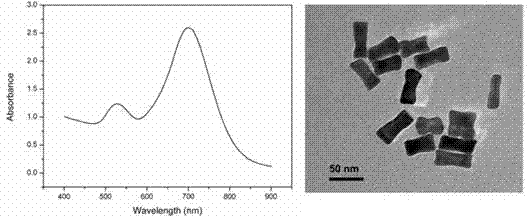
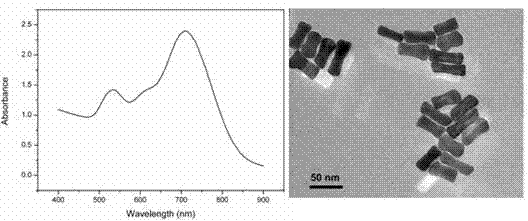
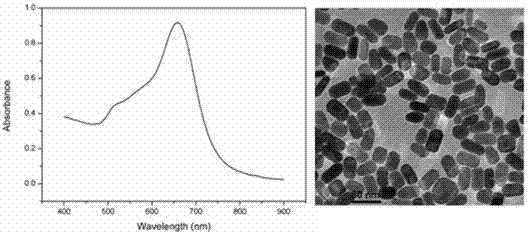
Dog-bone-shaped gold nanocrystal preparing method
ActiveCN104841950ARaw materials are easy to getEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyAlkyl bromideAmmonium bromide
The invention discloses a dog-bone-shaped gold nanocrystal preparing method. The dog-bone-shaped gold nanocrystal preparing method includes the steps of adding an aqueous cetyl ammonium bromide solution in an aqueous chloroauric acid solution, adding a silver nitrate solution, mixing fully, adding ascorbic acid, and mixing with stirring to obtain a growth solution; mixing the aqueous cetyl ammonium bromide solution with the aqueous chloroauric acid solution, adding a sodium borohydride solution, and stirring until the mixed solution turns into claybank so as to obtain a seed solution; adding the seed solution in the growth solution, mixing with stirring, and standing for growing to obtain dog-bone-shaped gold nanocrystals. The dog-bone-shaped gold nanocrystal preparing method has the advantages of easily-available raw materials, simplicity in operation, good repeatability, low cost, high controllability and capabilities of obtaining stable and efficient dog-bone-shaped gold nanocrystal and obtaining different sizes of dog-bone-shaped gold nanocrystals by means of reacting condition adjustment, has important application value for synthesis of large-scale dog-bone-shaped gold nanocrystals and is of important guiding significance to gold nanocrystal preparing method research.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
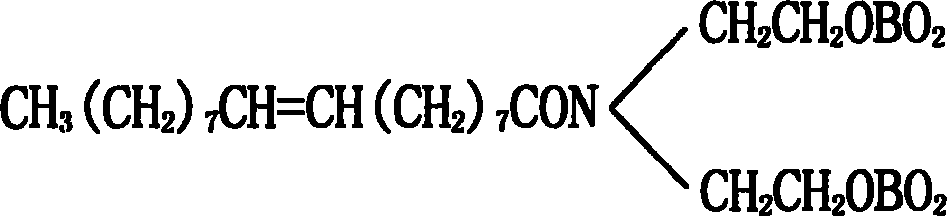
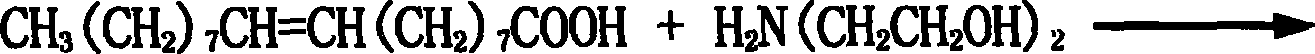
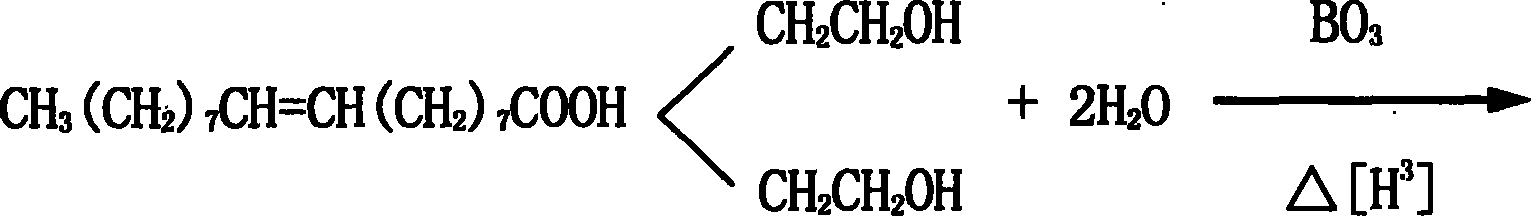

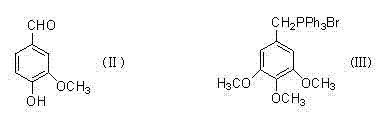

![N, N-dimethyl-N [3-(carbohydrate amide group)] propyl group-N-alkyl ammonium bromide and synthetic method thereof N, N-dimethyl-N [3-(carbohydrate amide group)] propyl group-N-alkyl ammonium bromide and synthetic method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bda4f7e9-9344-40f9-b331-f04d709a3f63/1209171021271.PNG)
![N, N-dimethyl-N [3-(carbohydrate amide group)] propyl group-N-alkyl ammonium bromide and synthetic method thereof N, N-dimethyl-N [3-(carbohydrate amide group)] propyl group-N-alkyl ammonium bromide and synthetic method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bda4f7e9-9344-40f9-b331-f04d709a3f63/1209171021272.PNG)
![N, N-dimethyl-N [3-(carbohydrate amide group)] propyl group-N-alkyl ammonium bromide and synthetic method thereof N, N-dimethyl-N [3-(carbohydrate amide group)] propyl group-N-alkyl ammonium bromide and synthetic method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bda4f7e9-9344-40f9-b331-f04d709a3f63/1209171021273.PNG)