Patents
Literature
259 results about "Nozzle throat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
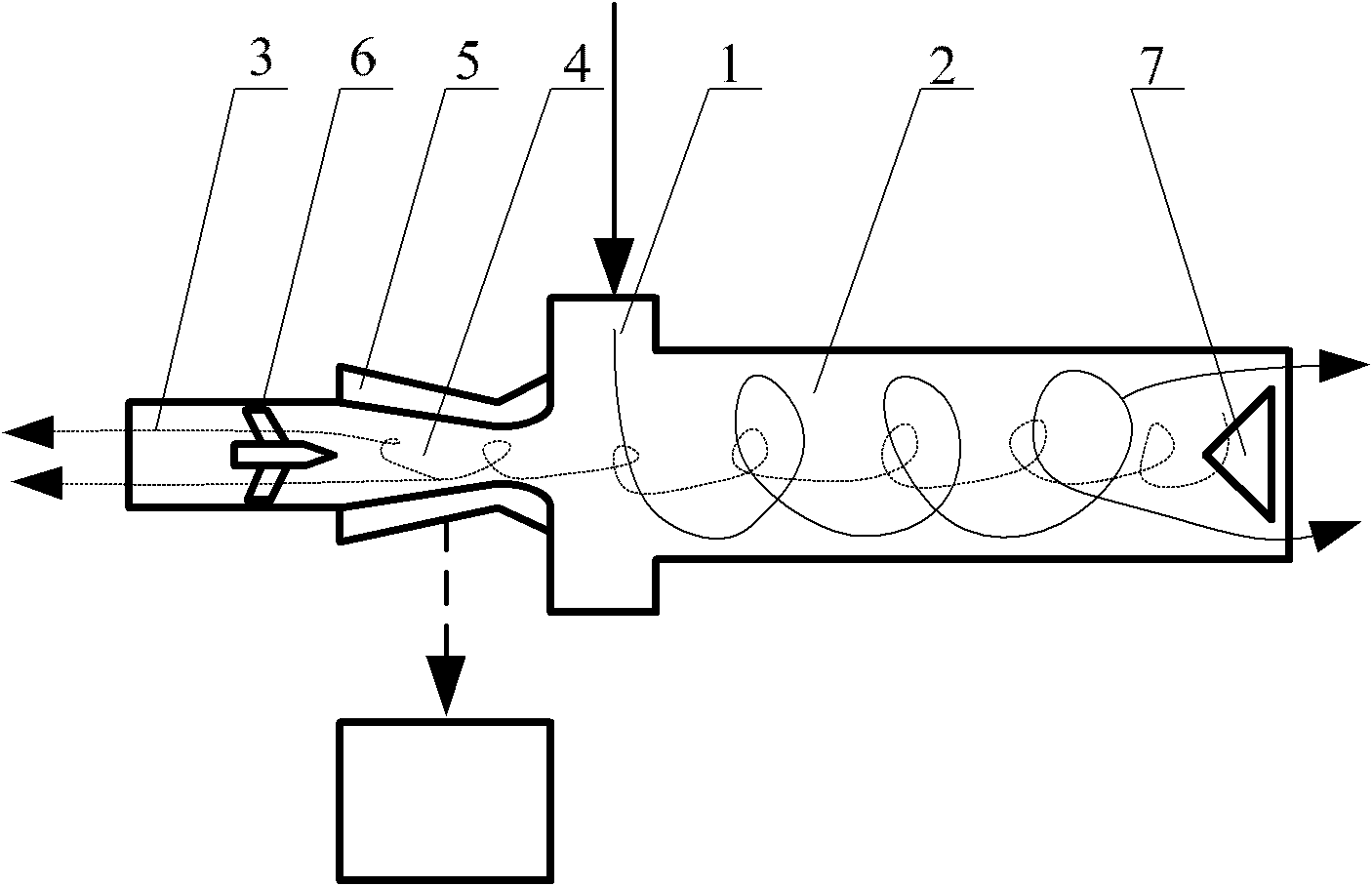
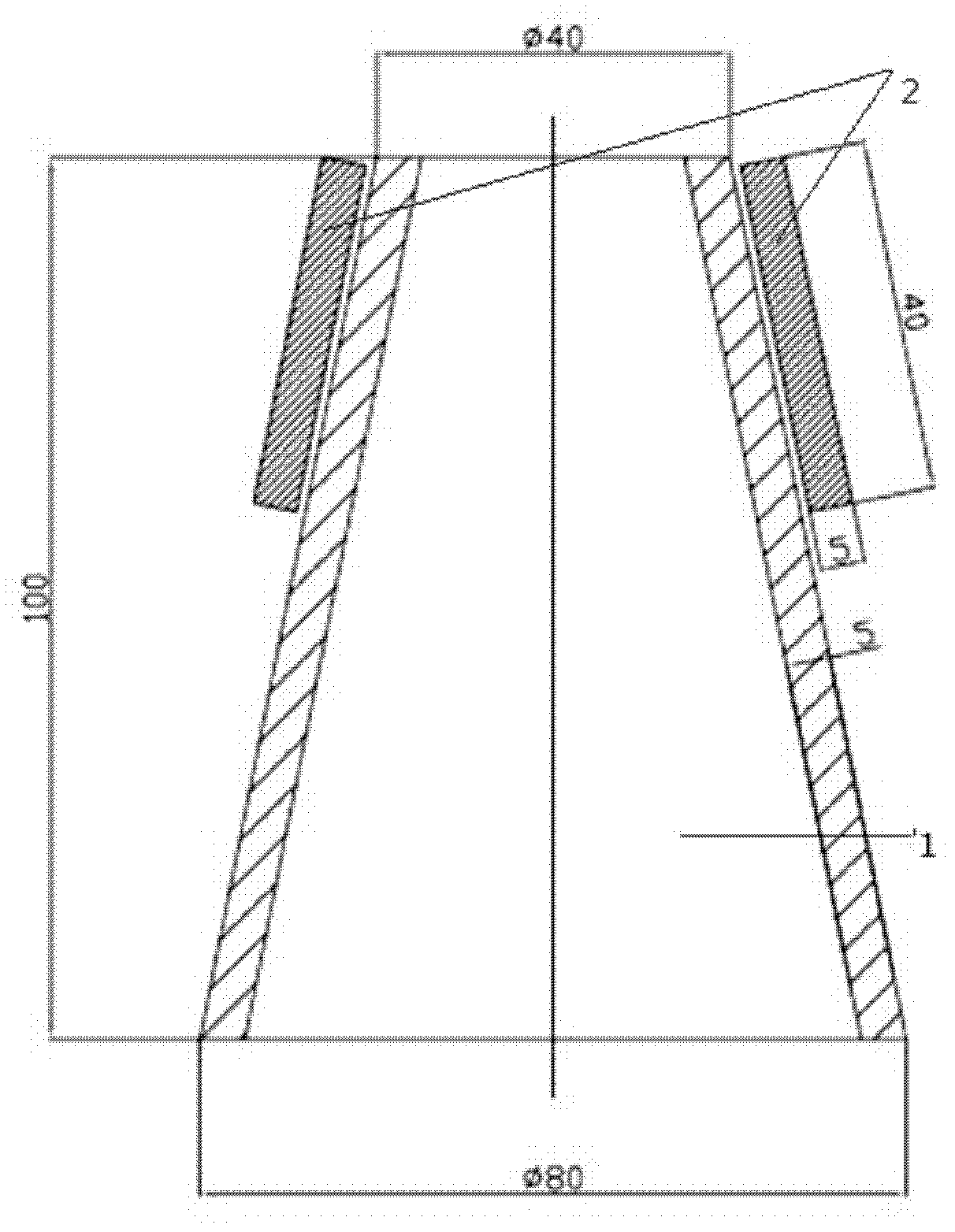
Supersonic swirling separator 2 (Sustor2)
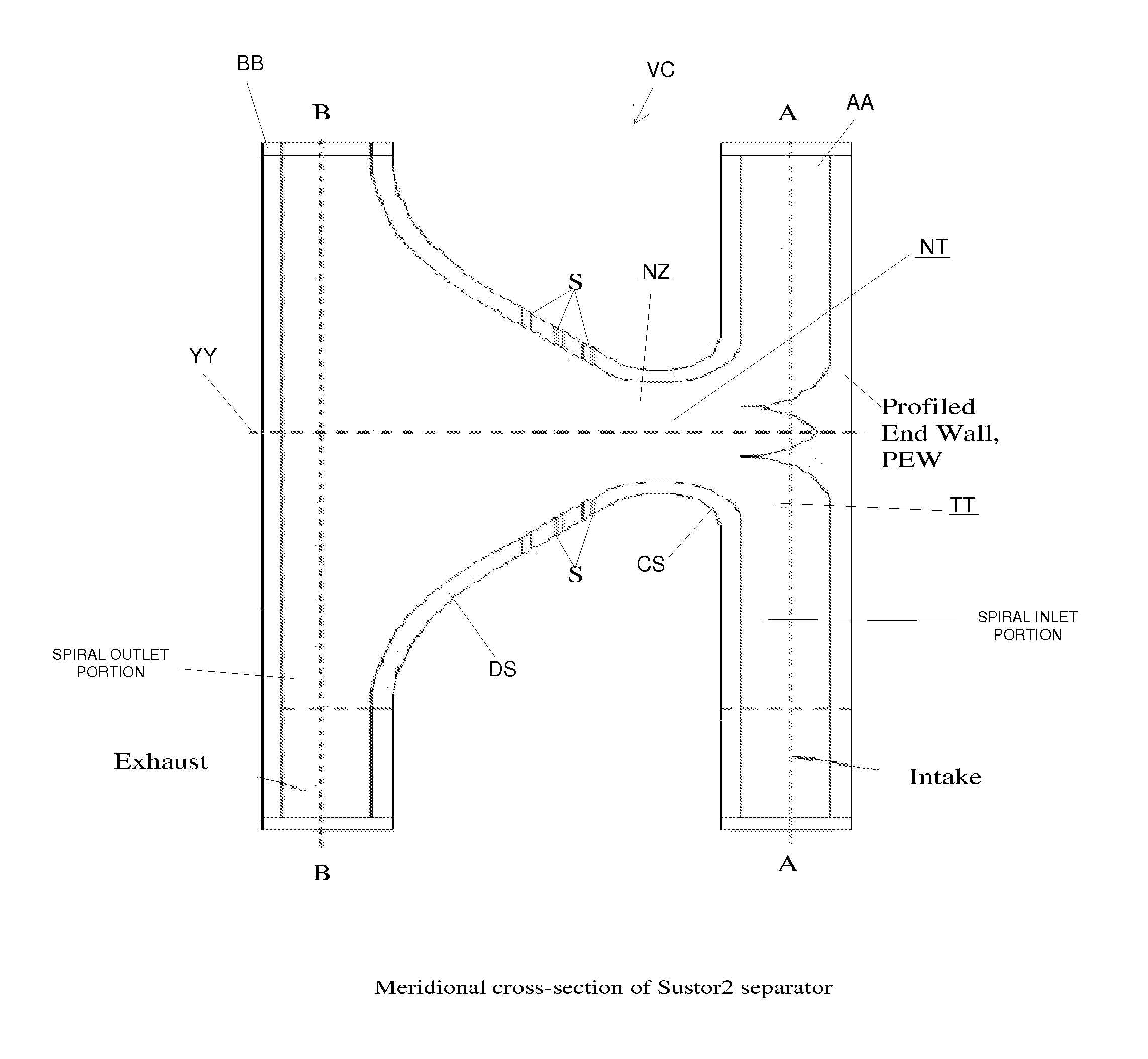
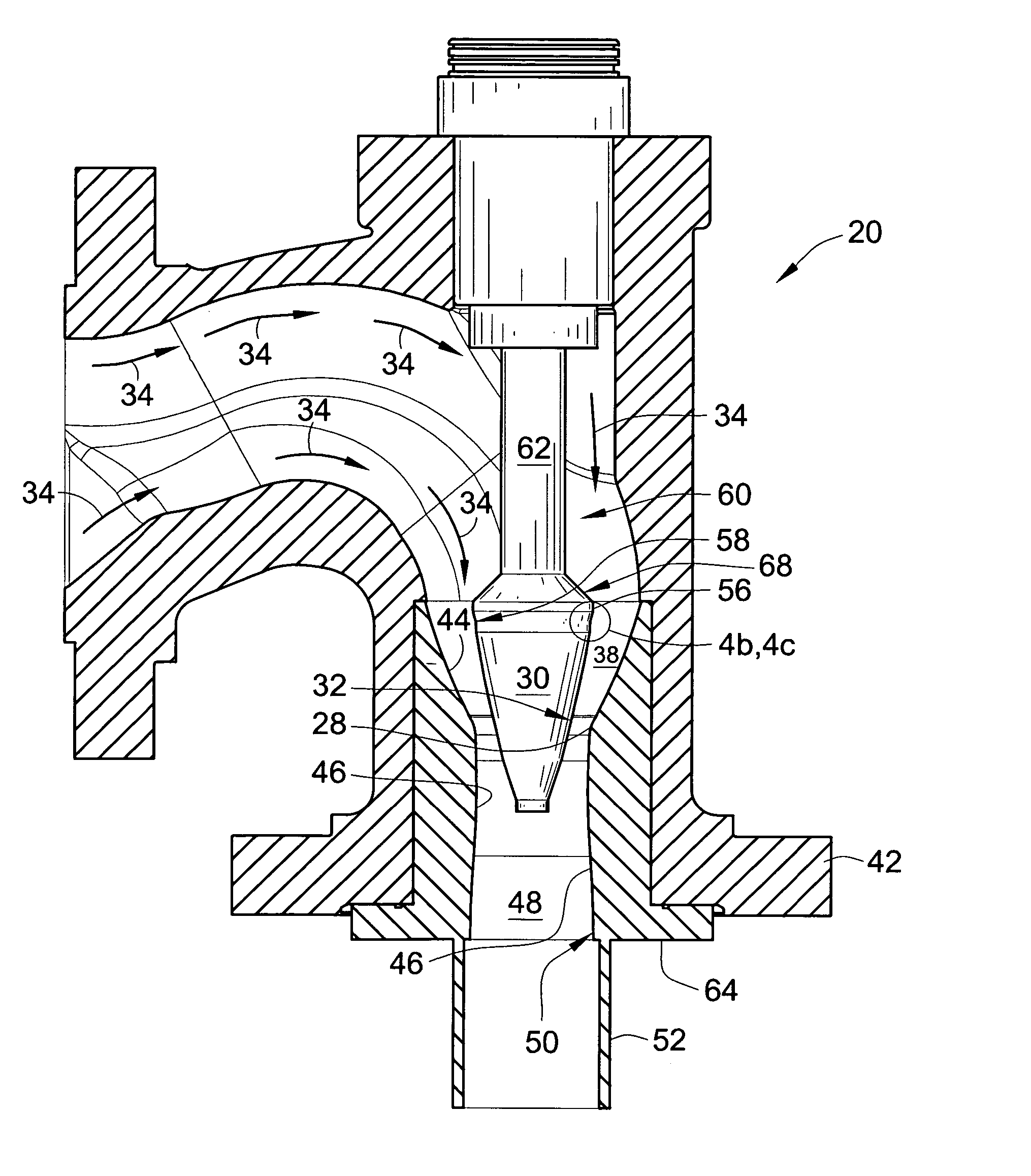
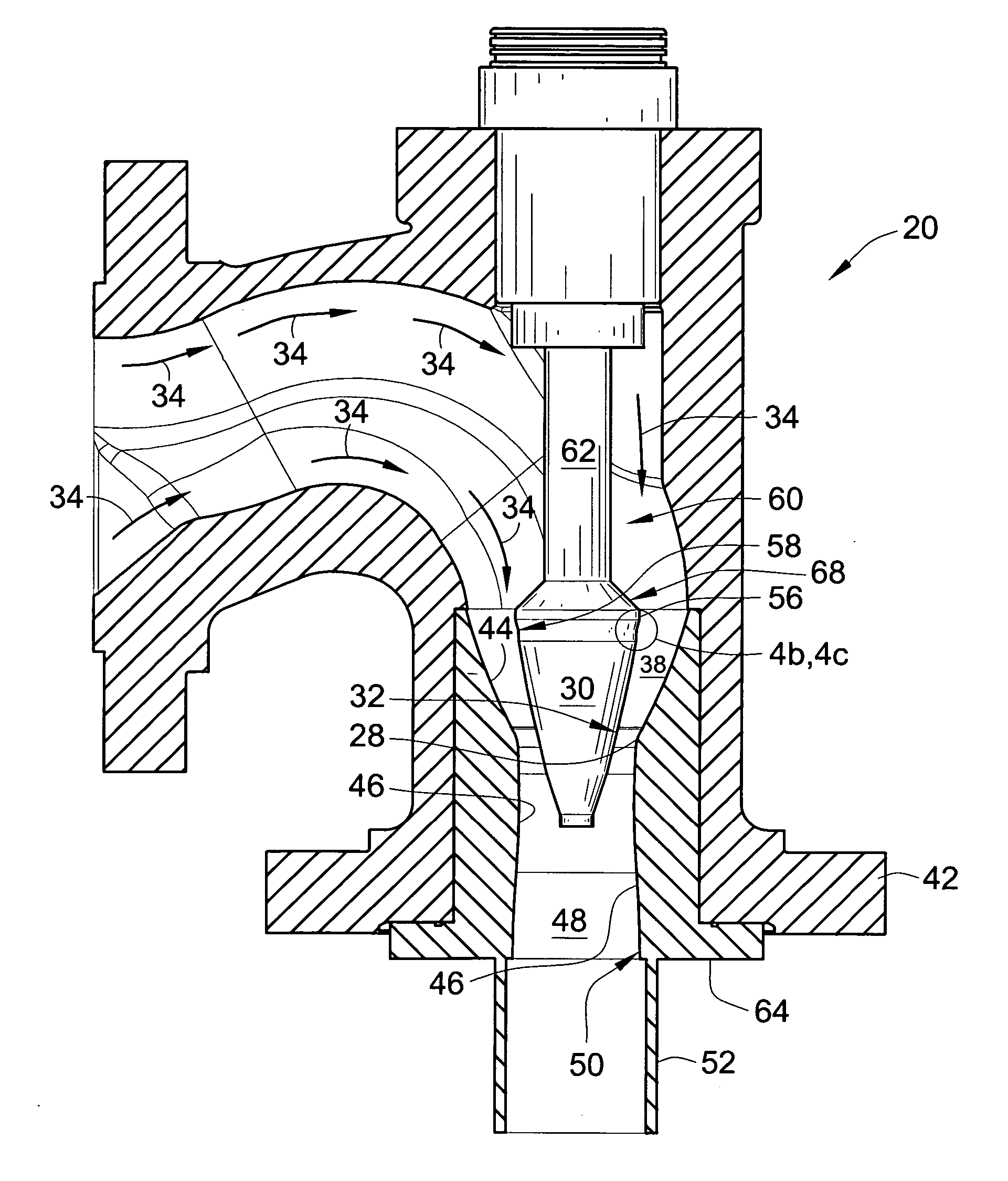
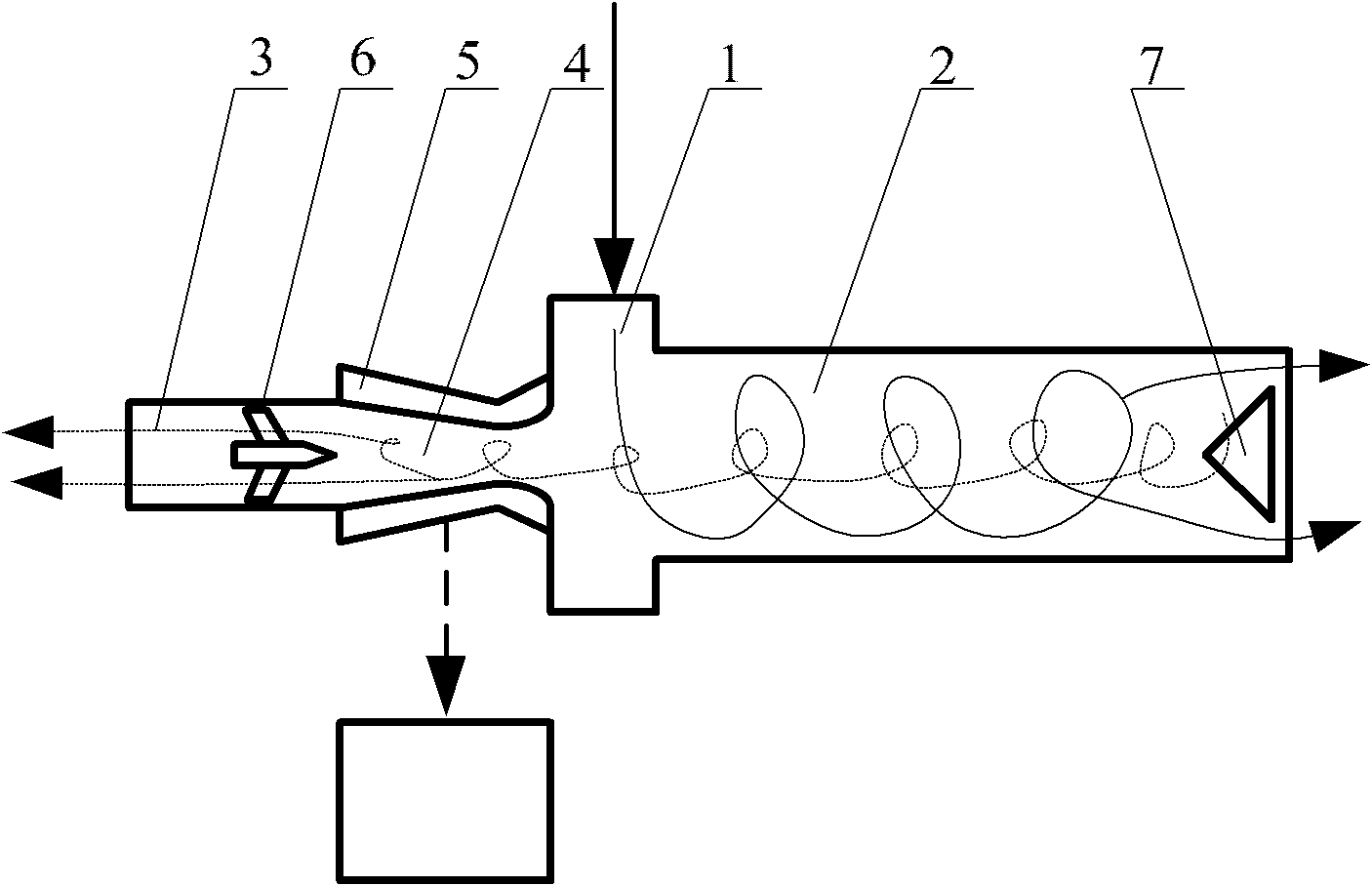
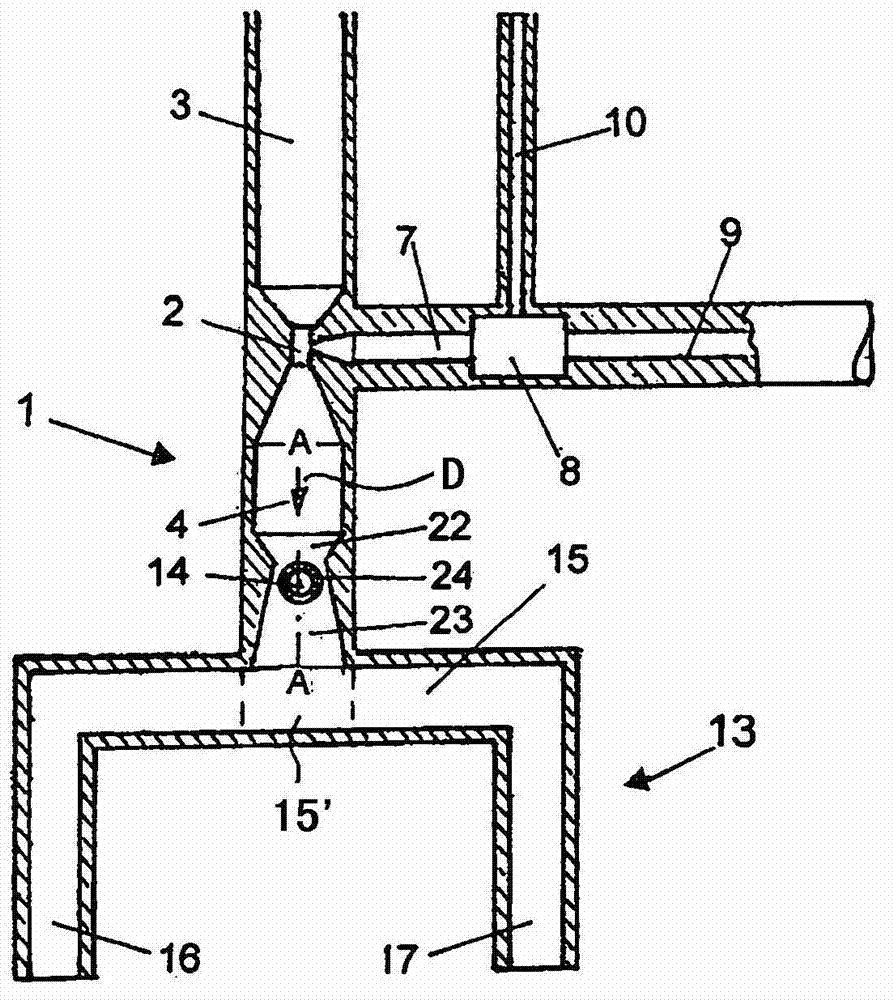
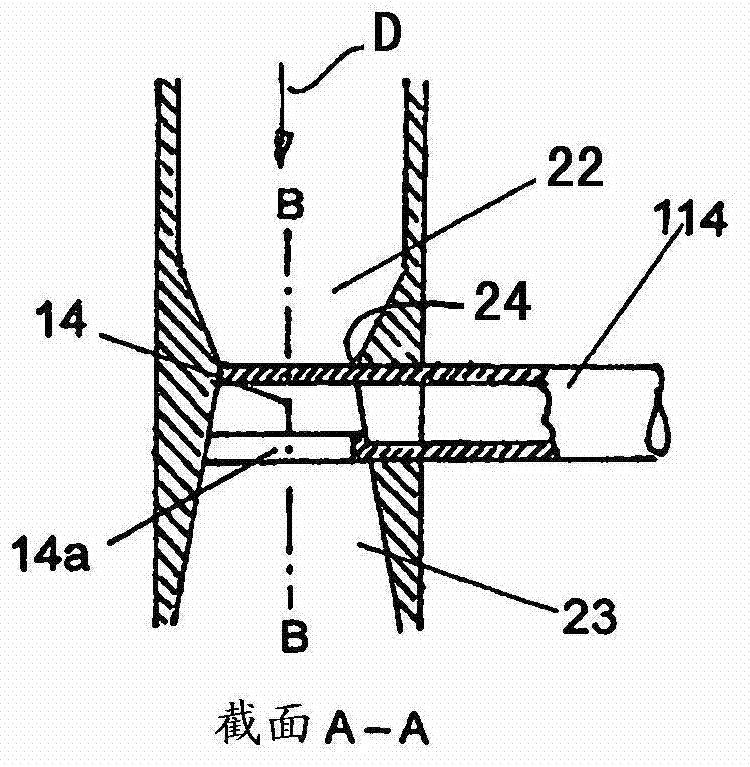
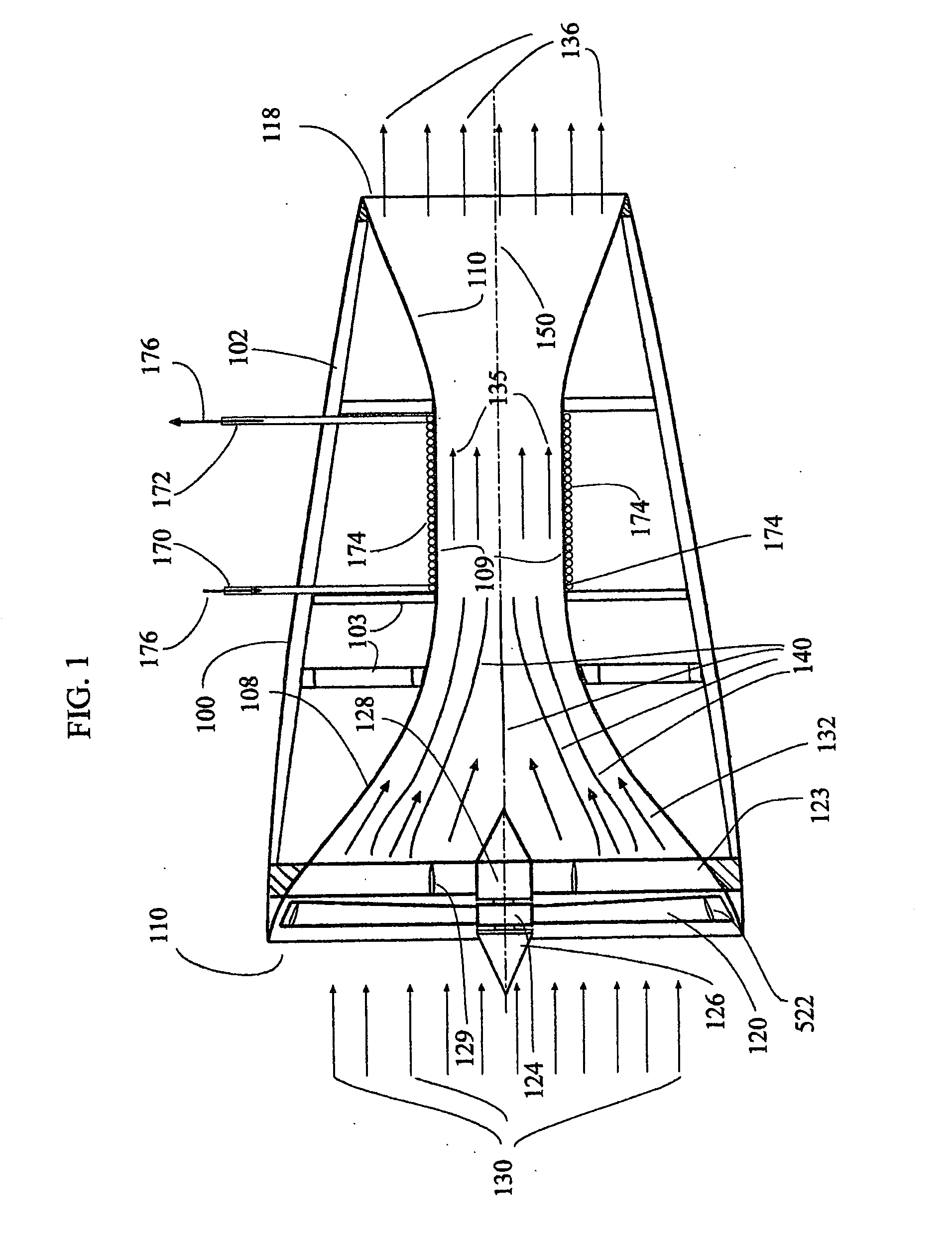
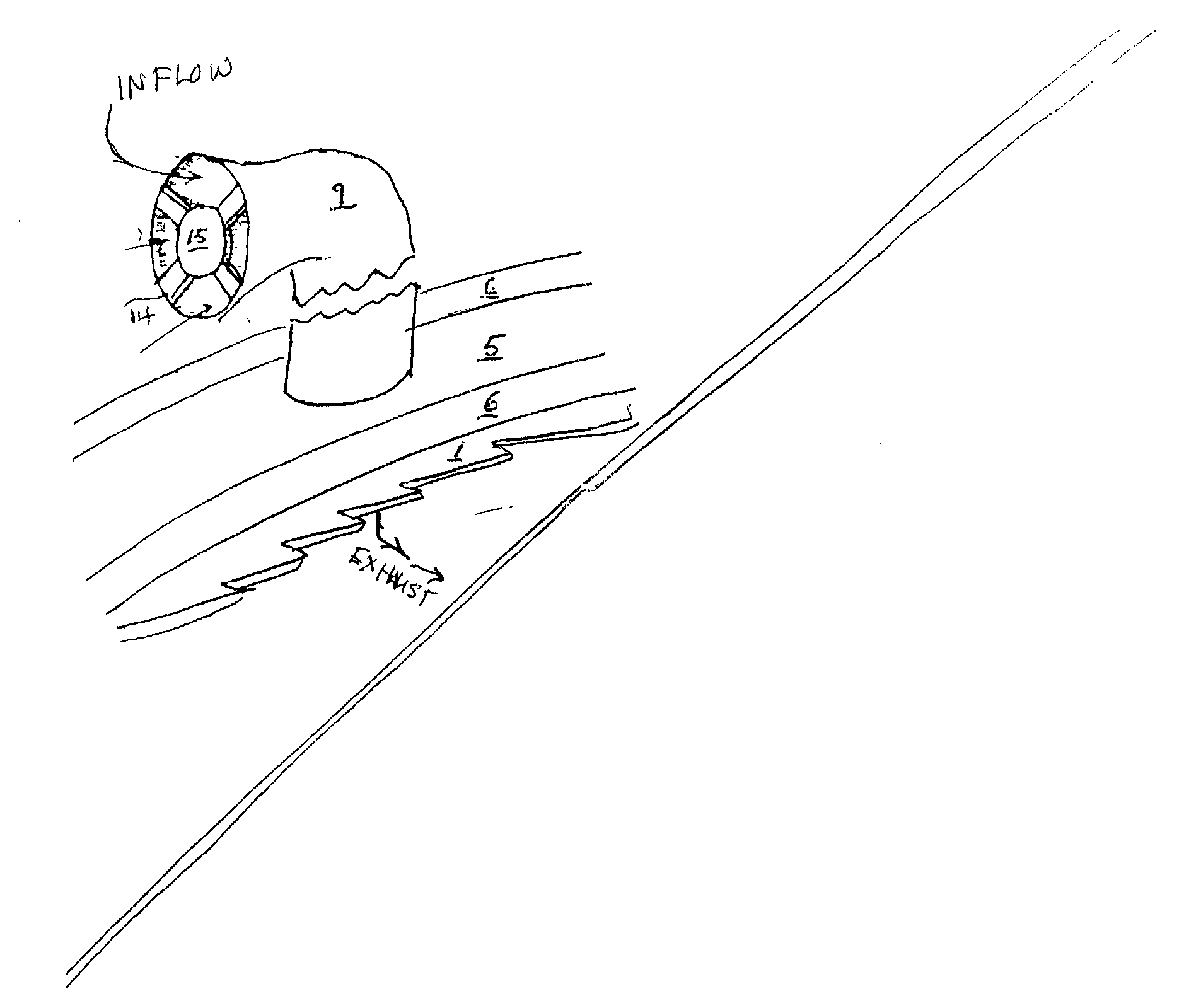
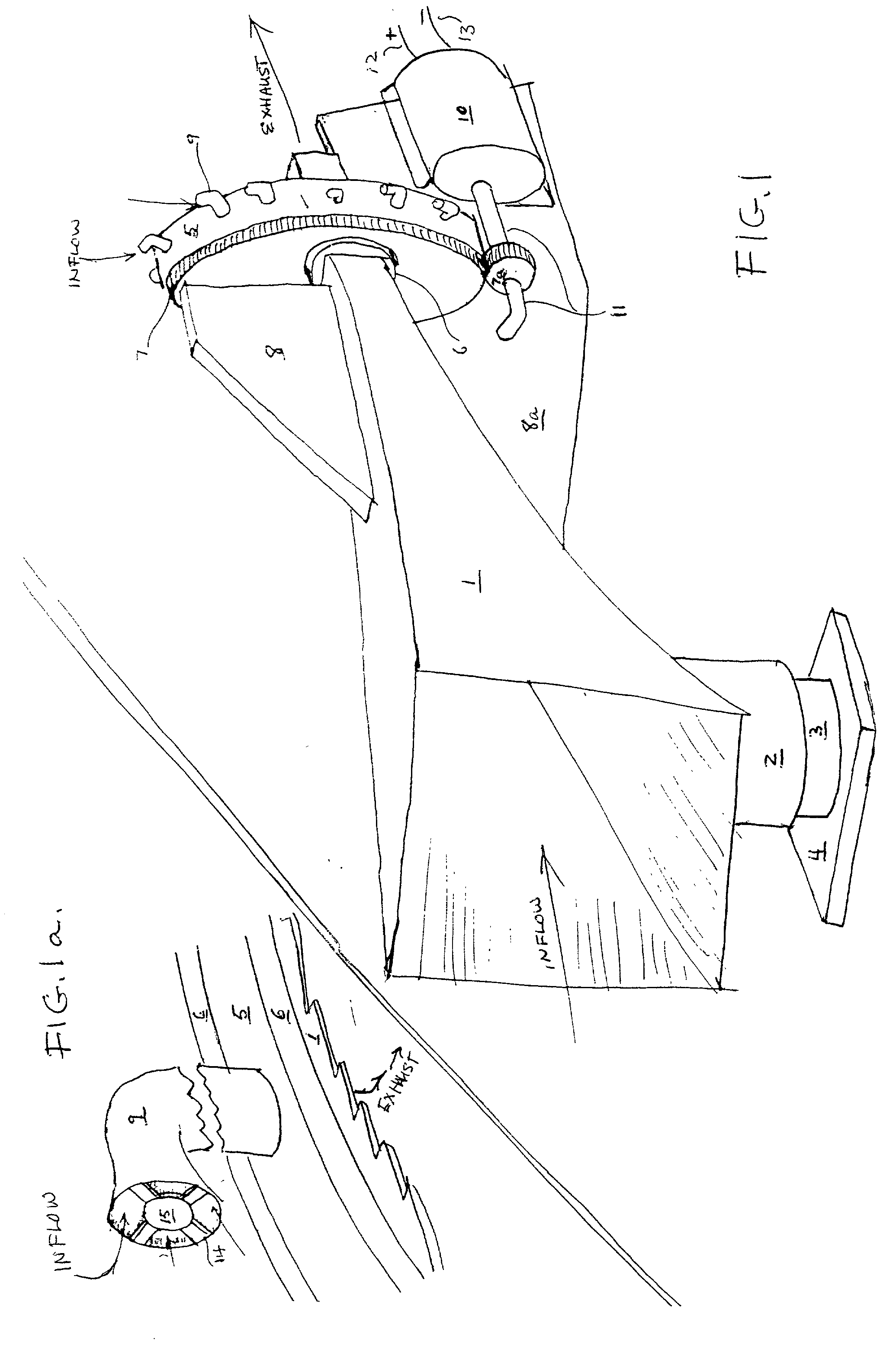
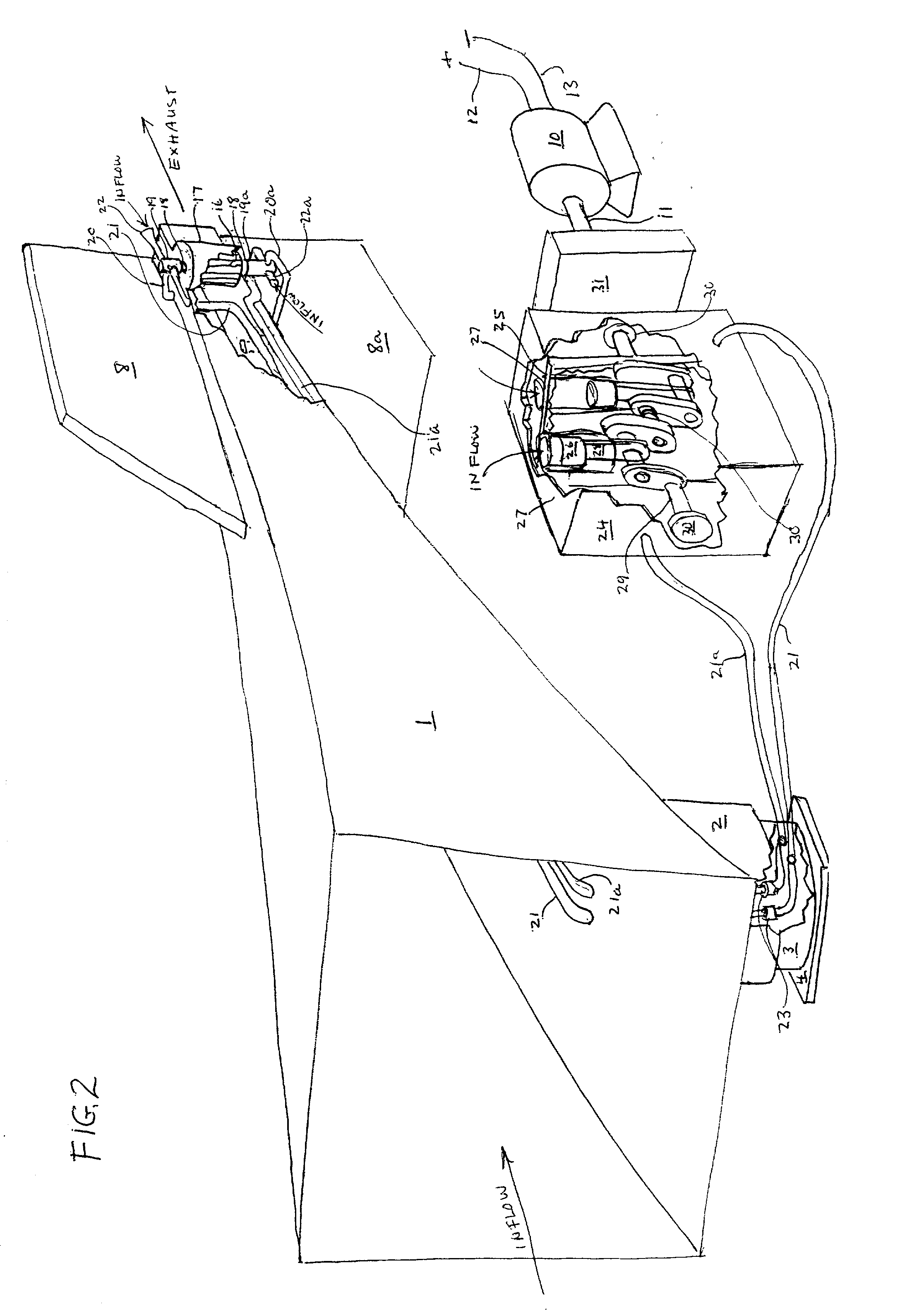
Sustor2 provides deep cooling of a gas flow, practically total condensation of a vapor, and fast and effective removal of the condensed liquid with a significantly reduced pressure losses compared with the prior art. Sustor2 performs the said operations by developing a strong swirling flow starting from its entrance, followed by spiral flow convergence in the inlet disc-like part, and then in a converging-diverging nozzle, by centrifugal removal of droplets, and removal of the liquid film through slits, then by spiral flow divergence and leaving the vortex chamber through tangential outlet.A gas enters from a pipeline (see the arrow in the A-A cross-section shown in FIG. 7) connected to Sustor2 by a flange and the inlet transition pipe ITP in FIG. 7, spirally converged in the disc-like part, marked by A-A in FIG. 6, enters the converging-diverging nozzle (FIG. 6). The flow is high-speed and swirling even at the near-entrance region of the vortex chamber. This swirl results in the centrifugal force that presses the through-flow to the sidewall. The flow accelerates near the nozzle throat up to a supersonic velocity with subsonic axial and supersonic swirl velocity components. This acceleration results in the gas temperature drop down to 200K and even less values. The reduced temperature causes rapid condensation of vapor into droplets. The centrifugal force pushes the droplets to the sidewall where they are removed through slits. Next the dried gas spirally diverges and leaves the vortex chamber through the tangential outlet. This results in the pressure recovery and transformation of the swirl kinetic energy into the longitudinal kinetic energy of the gas. Both the effects decrease pressure losses which is the Sustor2 advantage compared with the prior art.
Owner:BORISSOV ANATOLI +2
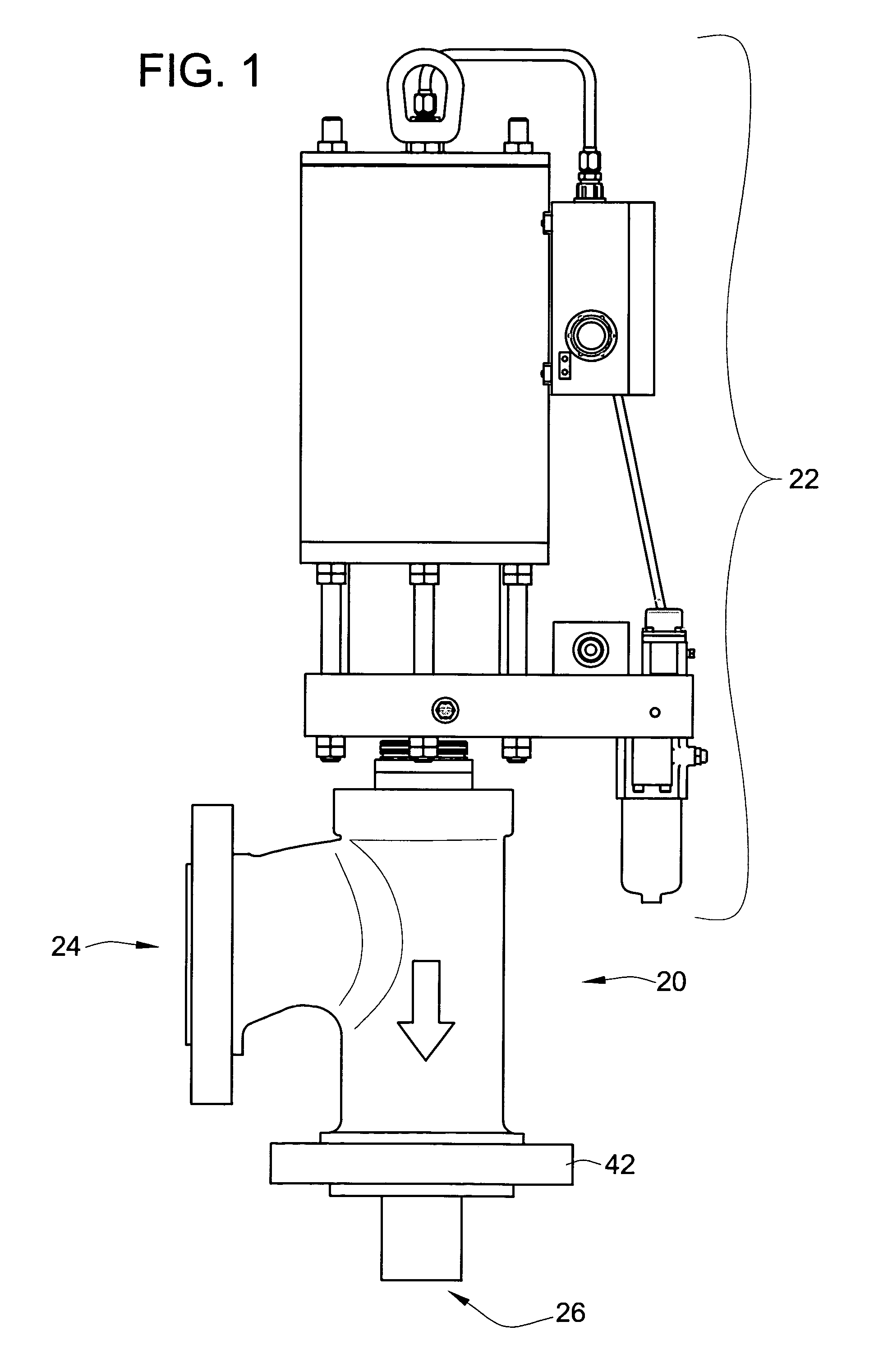
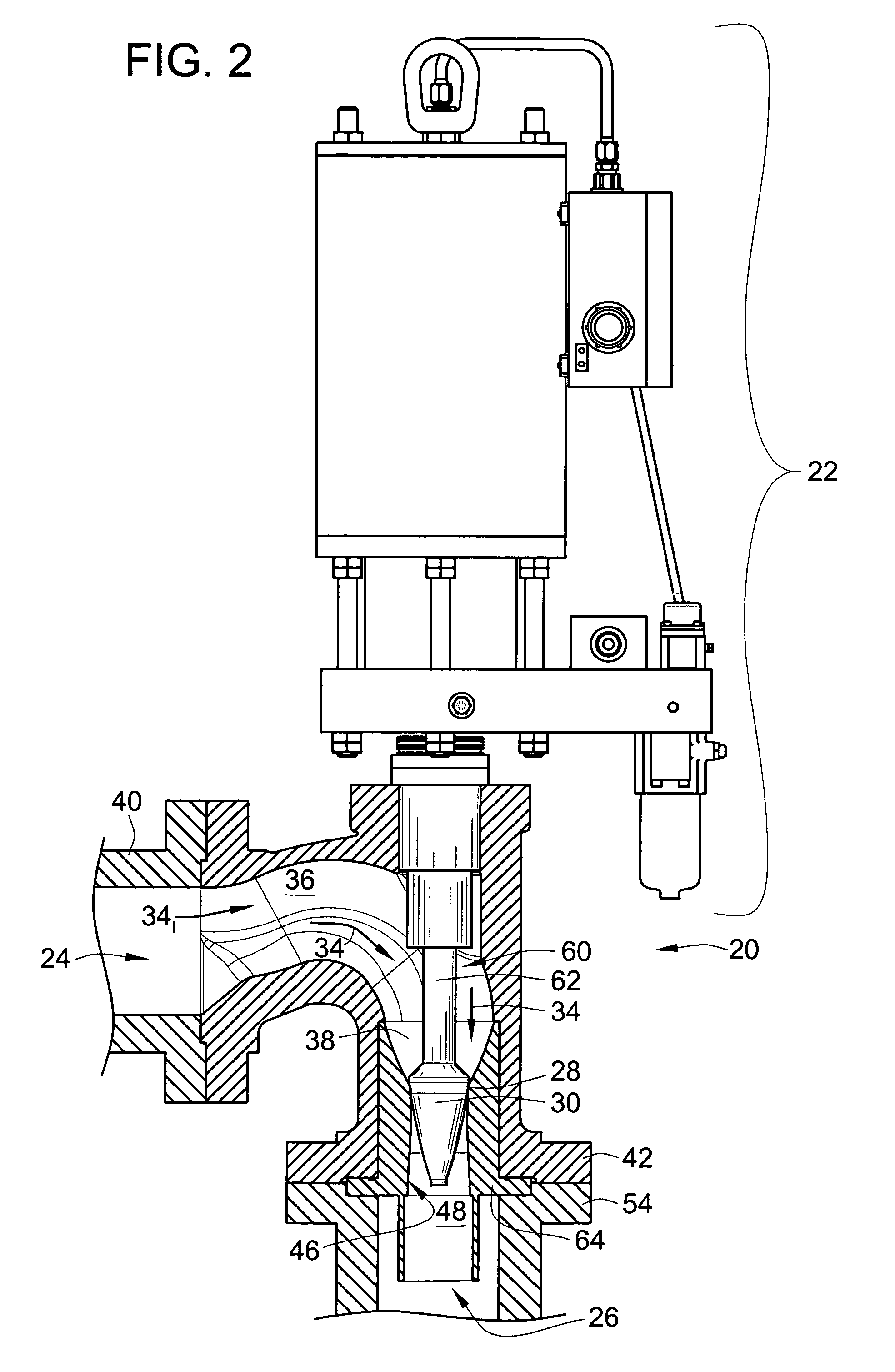
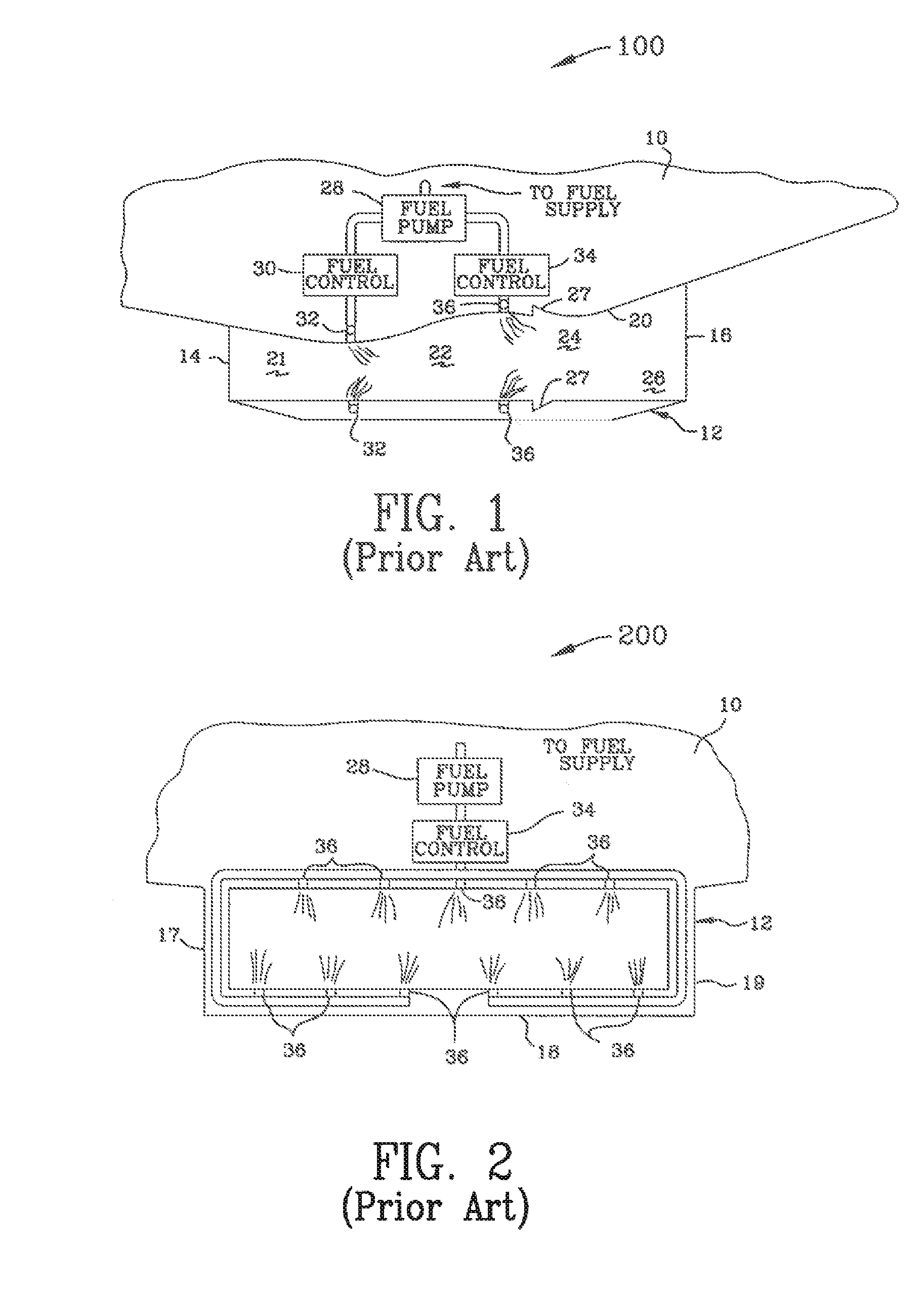
Split shroud exhaust nozzle
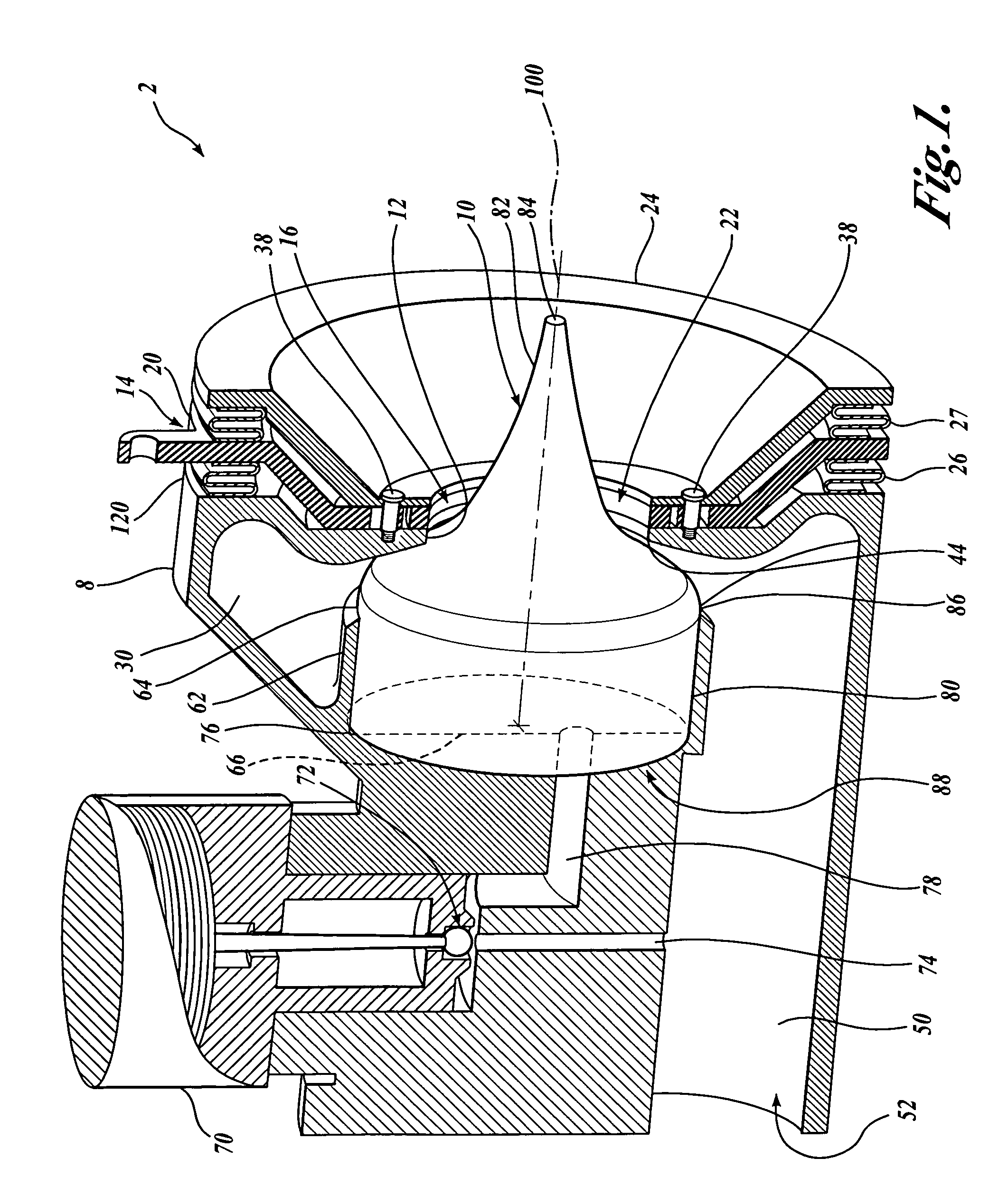
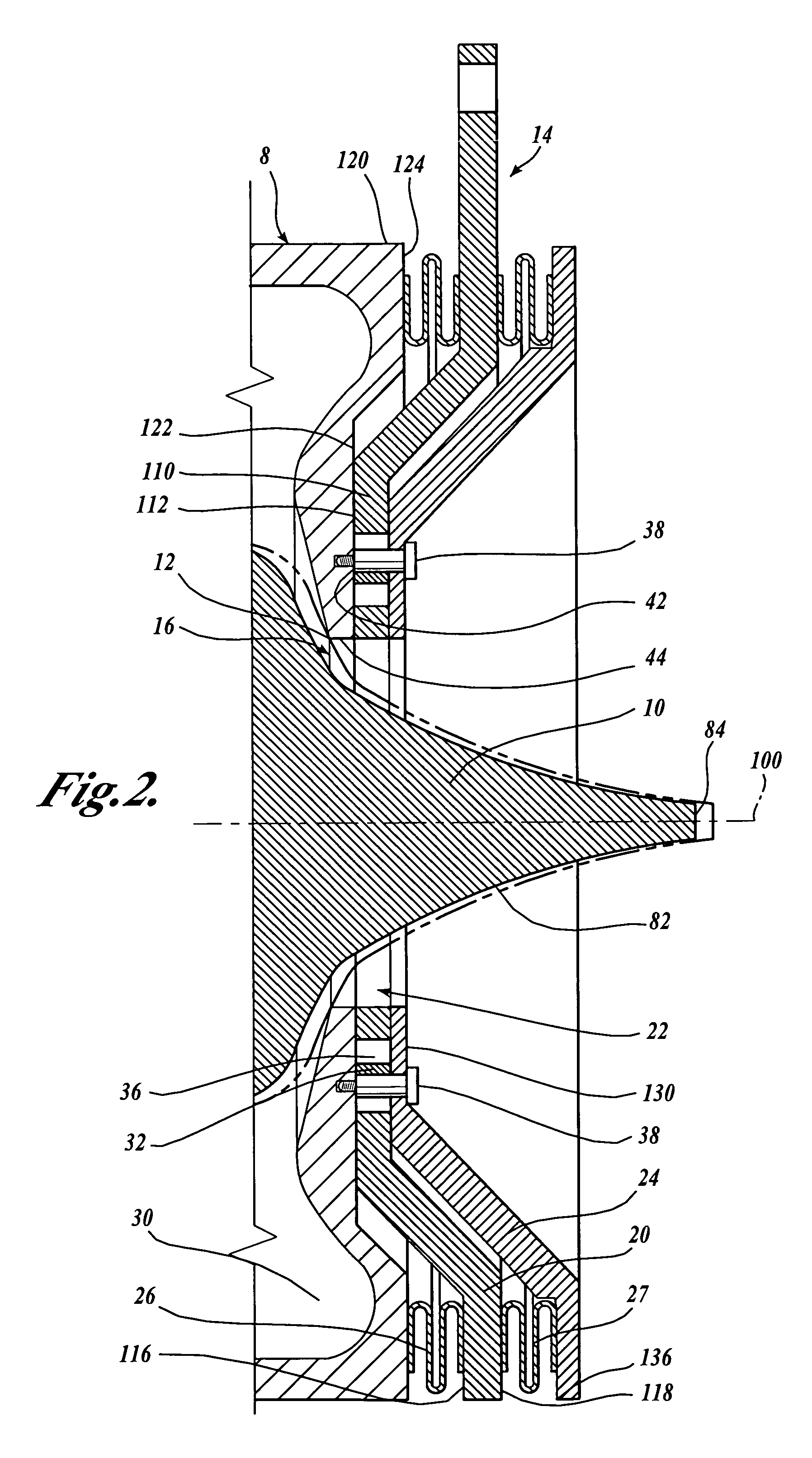
A variable geometry convergent-divergent nozzle for a gas turbine engine includes a centerbody extending rearward along a longitudinal axis of the engine which has a throat section of increased diameter. An inner shroud surrounds the centerbody and cooperates with the centerbody to define the throat of the nozzle. An outer shroud surrounds the inner shroud and cooperates with the centerbody to define the exit area of the nozzle. Both shrouds are independently translatable to provide independent control of the nozzle throat area and the nozzle expansion ratio.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
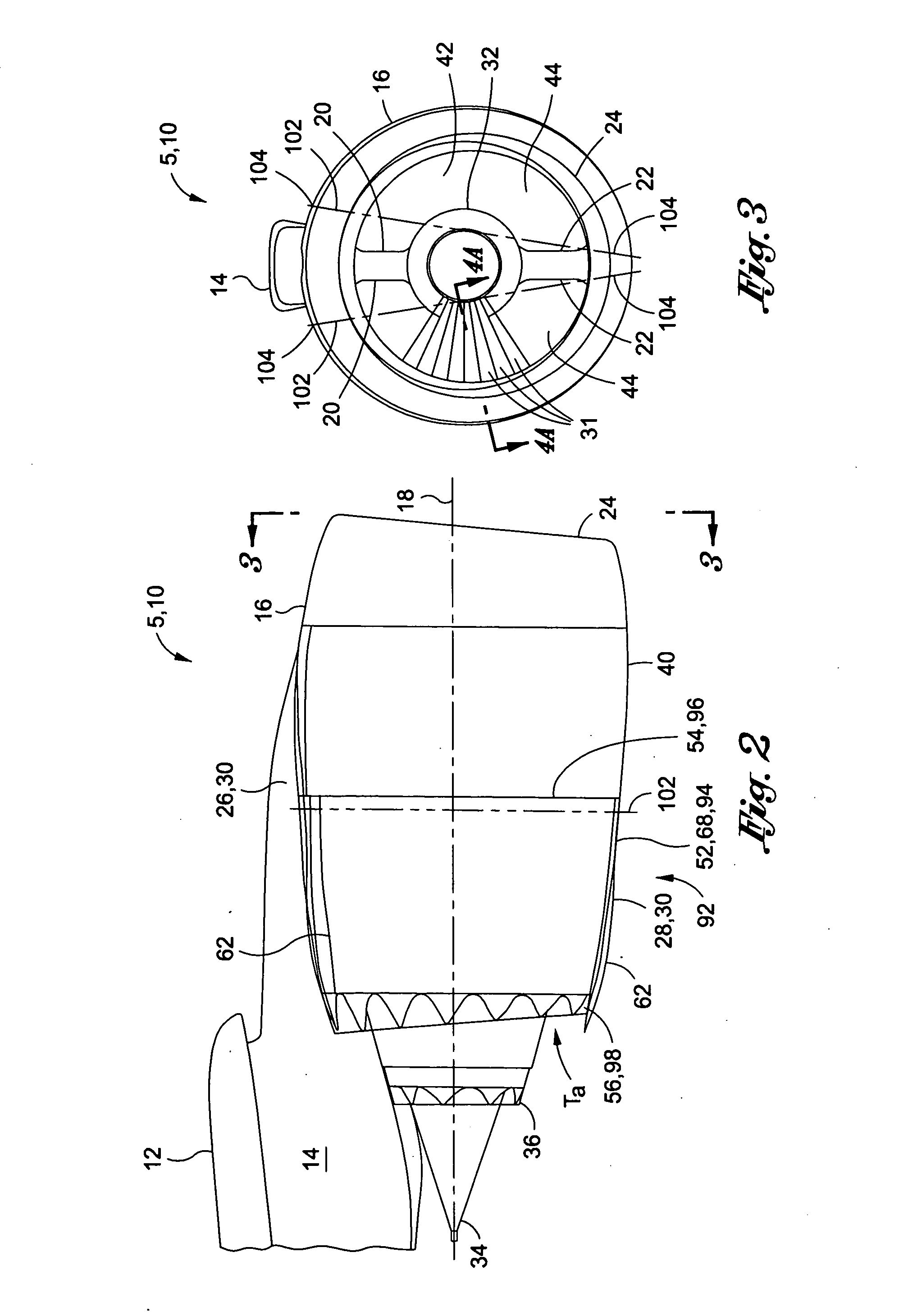
Pivoting fan nozzle nacelle
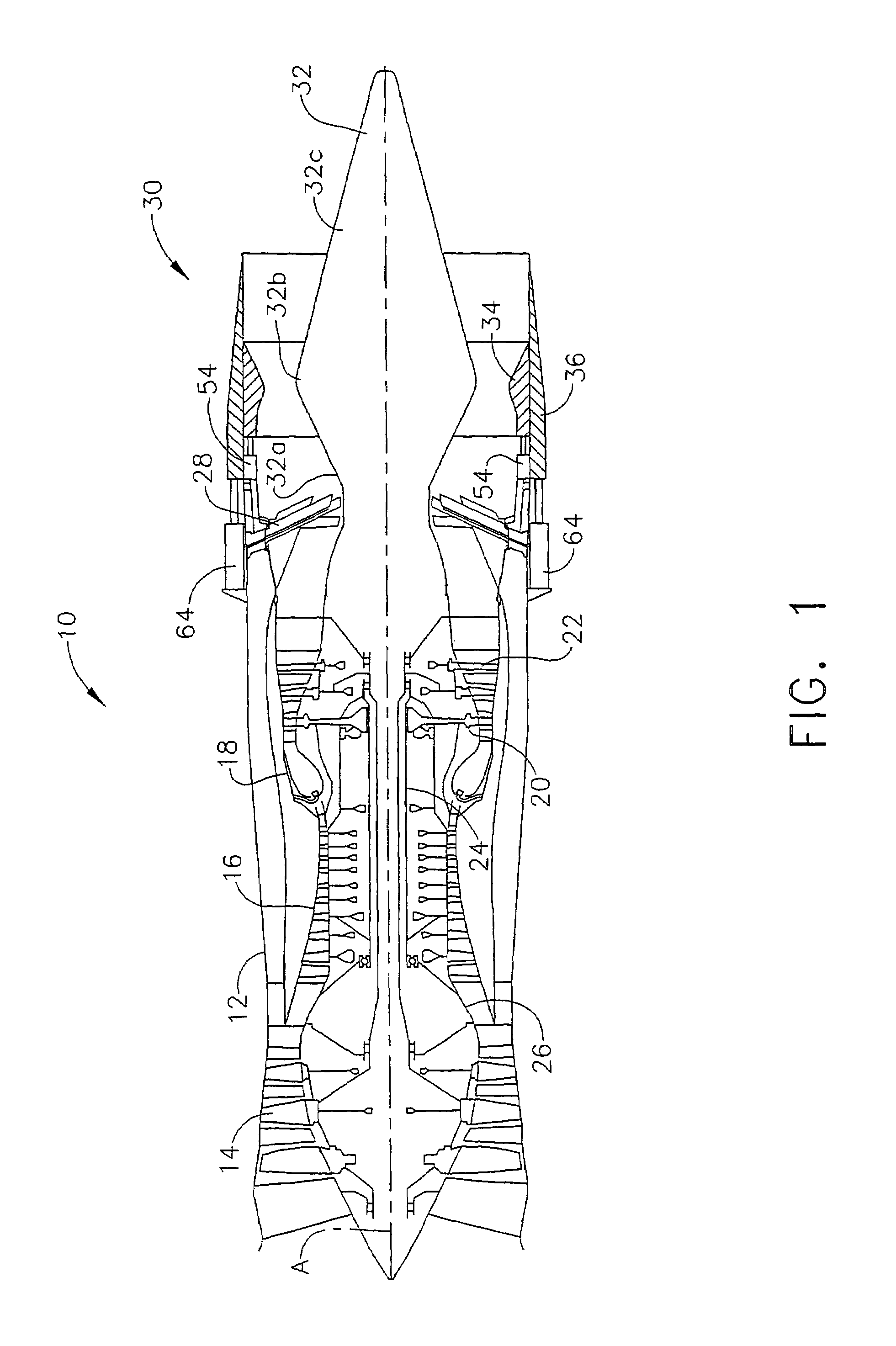
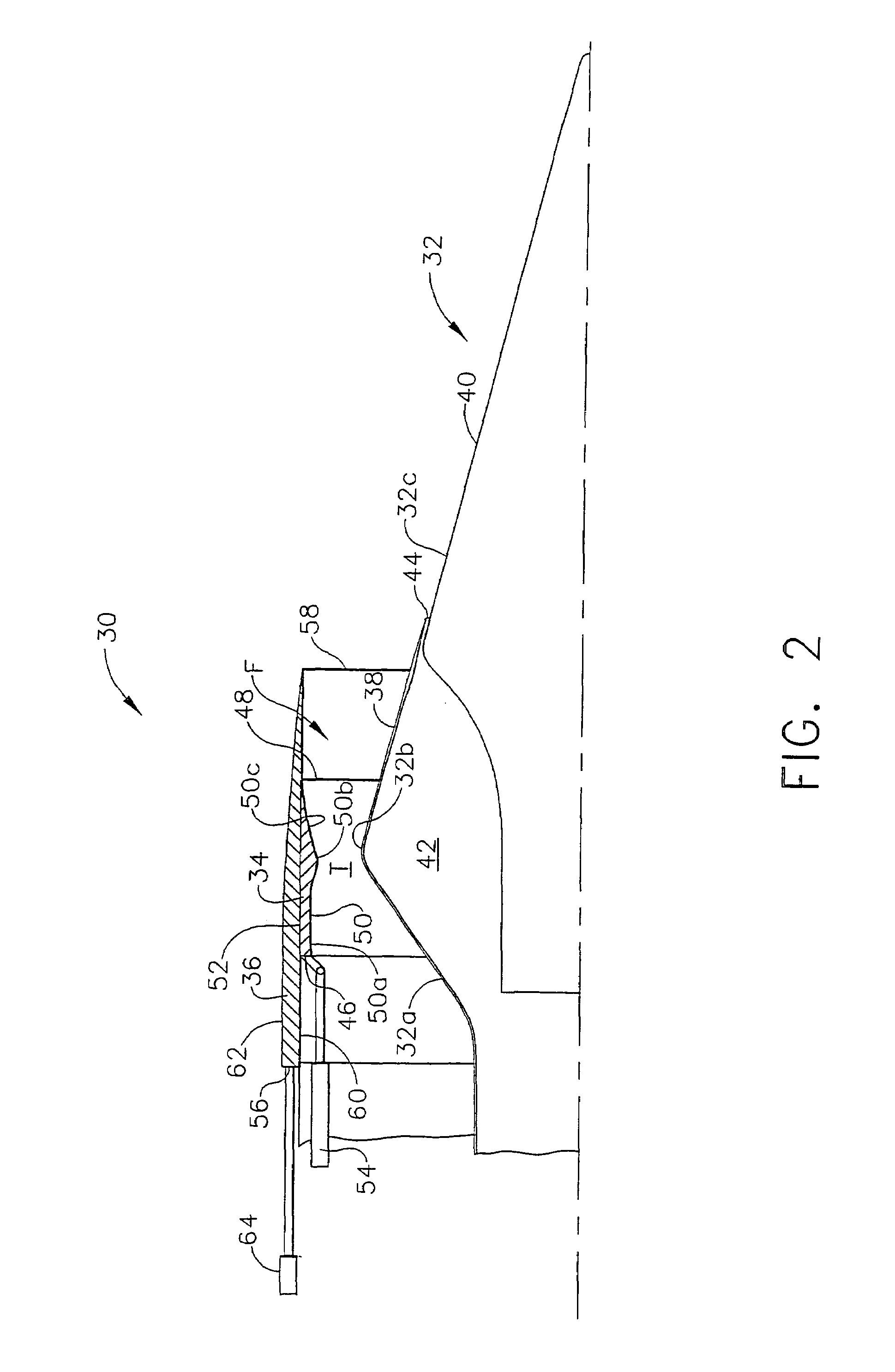
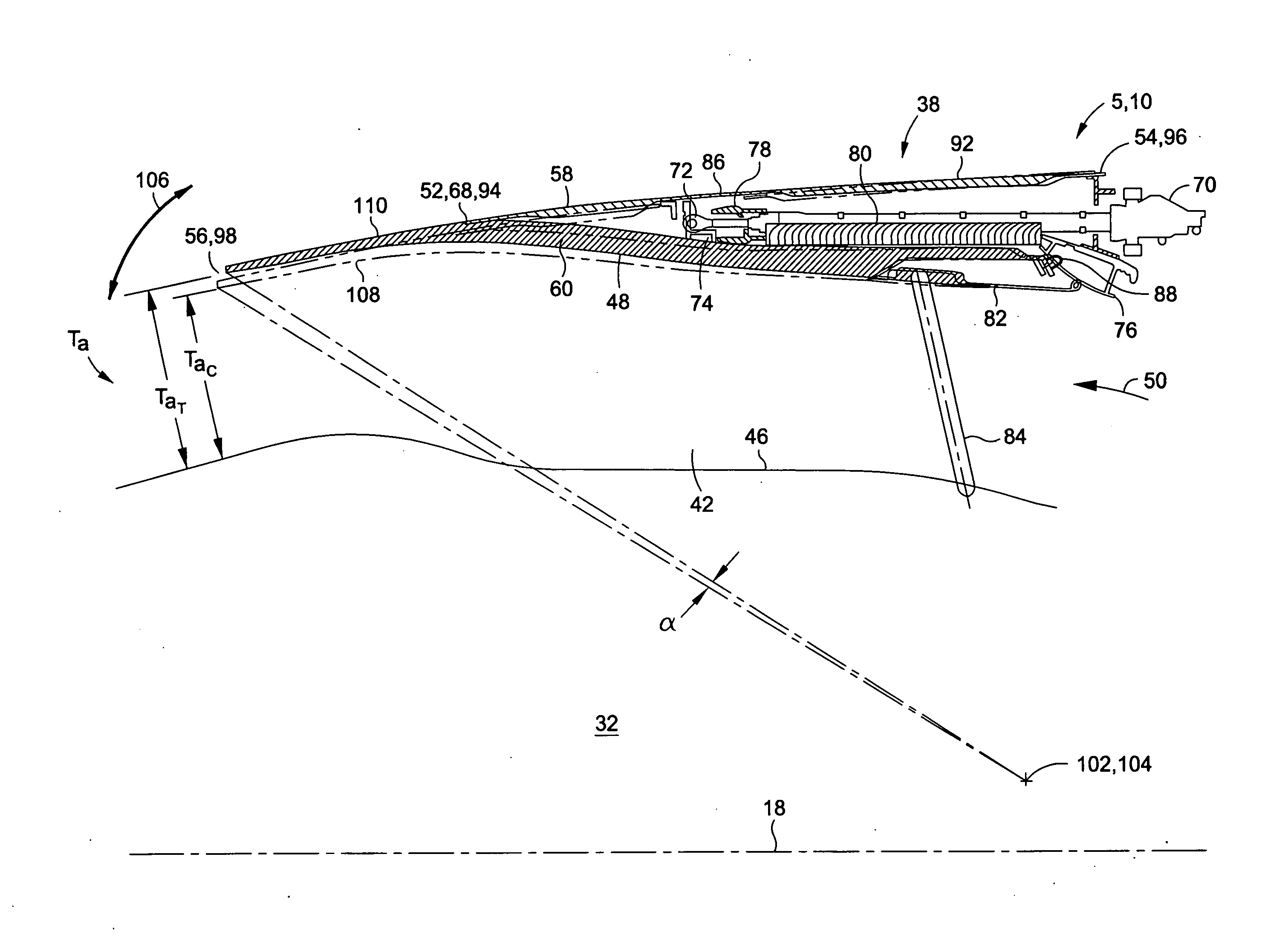
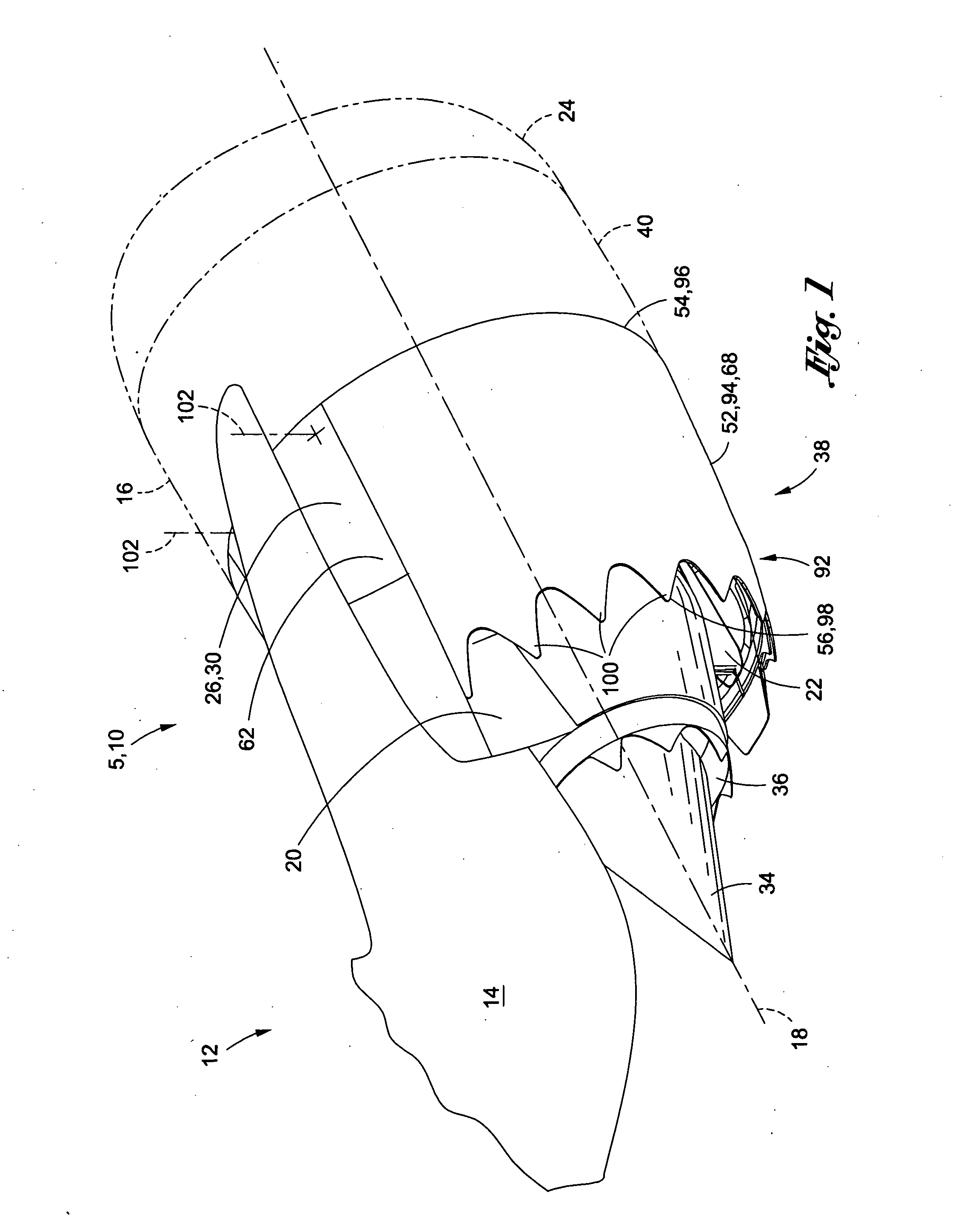
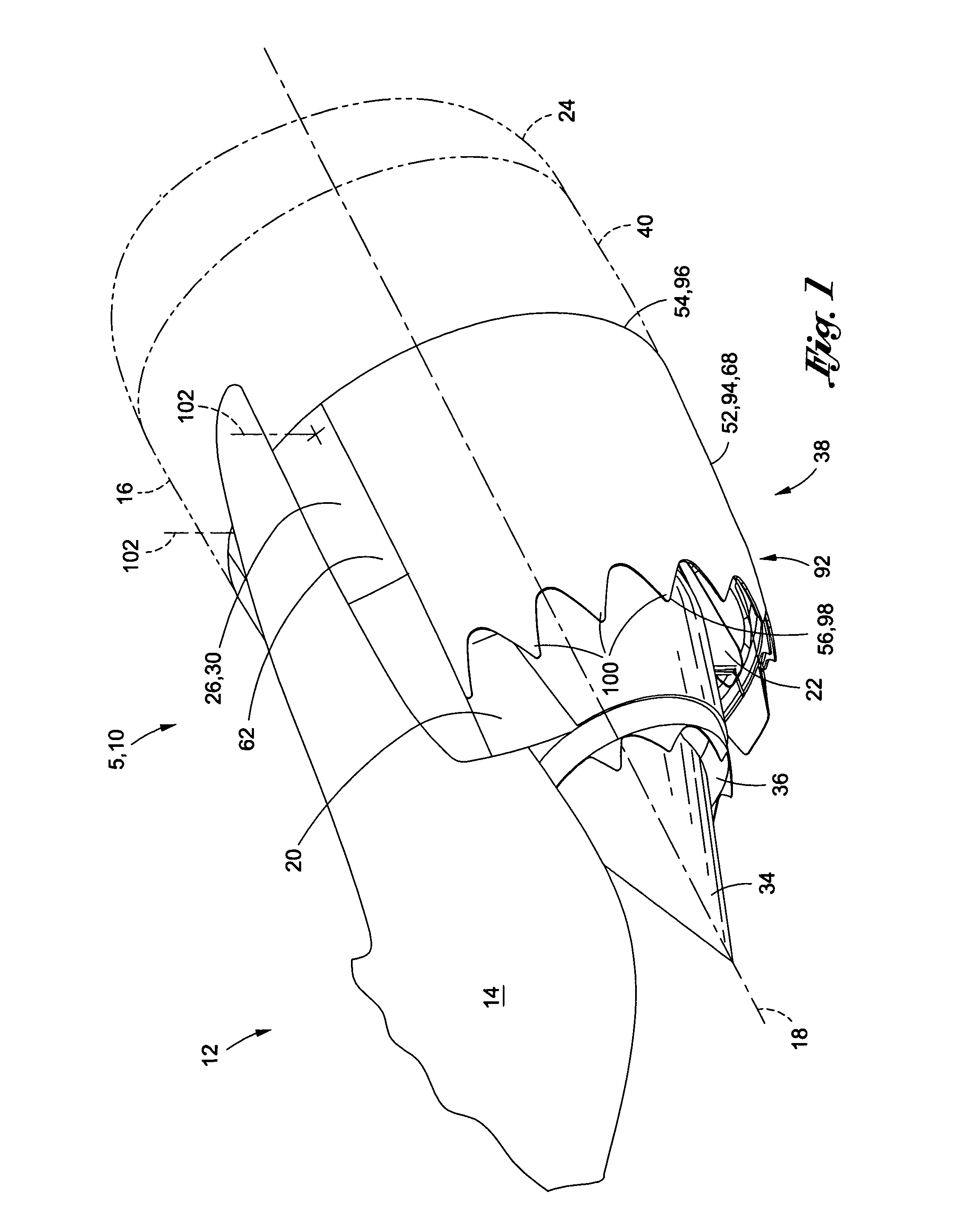
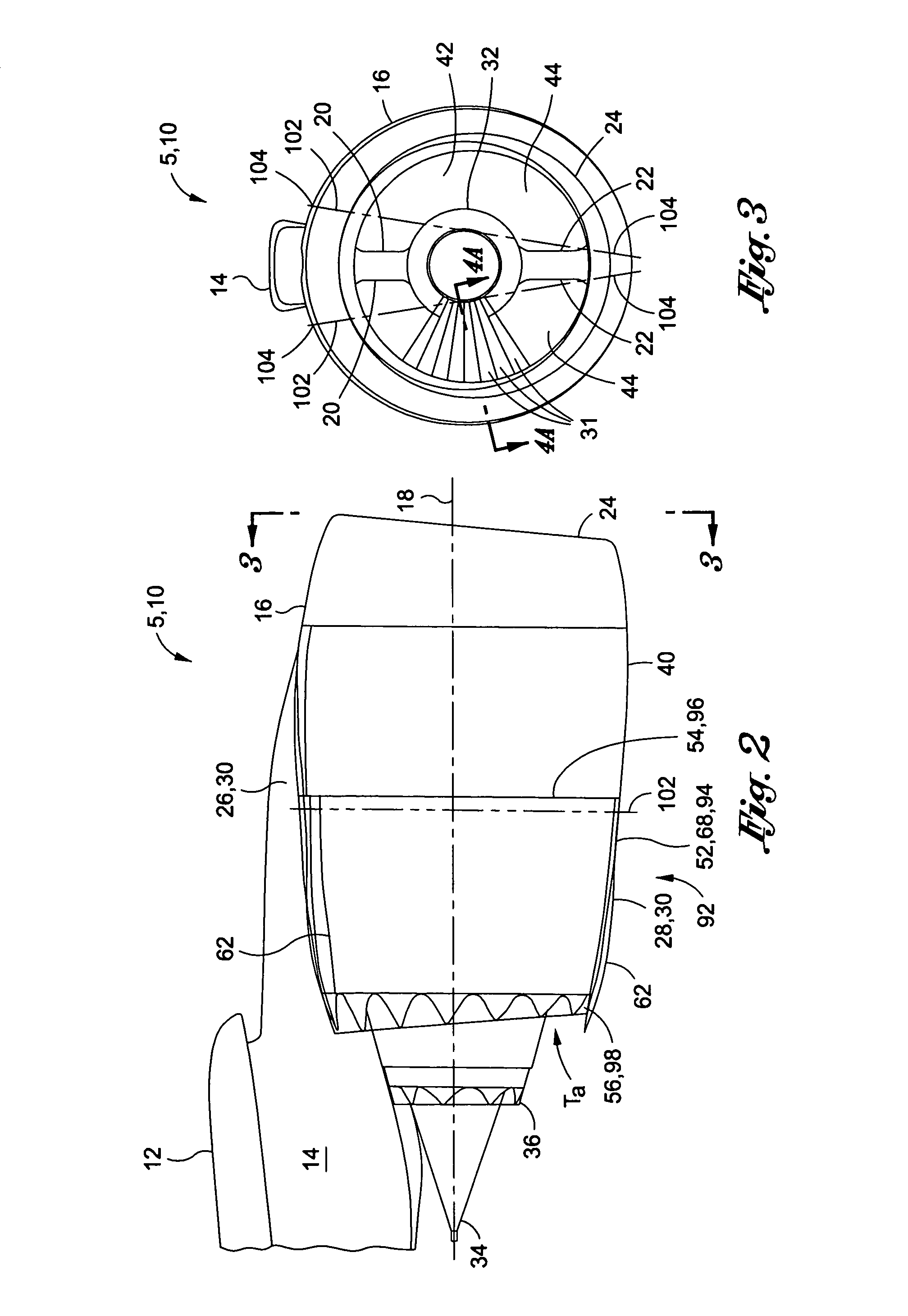
ActiveUS20100126139A1Smooth rotationFacilitate outward pivotingEfficient propulsion technologiesJet propulsion plantsNacelleTrailing edge
A variable area nozzle system for a gas turbine engine includes a fan duct inner wall, a fan duct outer wall disposed in radially spaced relation to the fan duct inner wall, and a fan nozzle. The fan nozzle defines at least a portion of the fan duct outer wall and includes a nozzle aft edge. The fan duct inner wall and the nozzle aft edge collectively define a fan duct nozzle throat area. The fan nozzle is configured to pivot about a pivot axis that may be oriented transversely relative to a longitudinal axis of the gas turbine engine. The fan nozzle may be pivoted from a stowed position to a deployed position in order to vary the fan duct nozzle throat area.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Split shroud exhaust nozzle
ActiveUS20060016171A1Increase the diameterReduce the overall diameterCosmonautic vehiclesEngine manufactureNozzle throatVariable geometry
A variable geometry convergent-divergent nozzle for a gas turbine engine includes a centerbody extending rearward along a longitudinal axis of the engine which has a throat section of increased diameter. An inner shroud surrounds the centerbody and cooperates with the centerbody to define the throat of the nozzle. An outer shroud surrounds the inner shroud and cooperates with the centerbody to define the exit area of the nozzle. Both shrouds are independently translatable to provide independent control of the nozzle throat area and the nozzle expansion ratio.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Thrust vector control
InactiveUS20060150612A1Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusControl vectorControl system
A thrust vector control system for a flight vehicle comprises a fixed nozzle defining a first thrust vector direction and at least one exhaust deflector moveable to a location downstream of said fixed nozzle to provide a second thrust vector direction. Movement of the at least one exhaust deflector may allow for simultaneous control of both thrust vector direction and nozzle throat area. Translational motion of each exhaust deflector may be independently controlled. A flight vehicle incorporating a thrust vector control apparatus, and a method for thrust vector control are also disclosed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
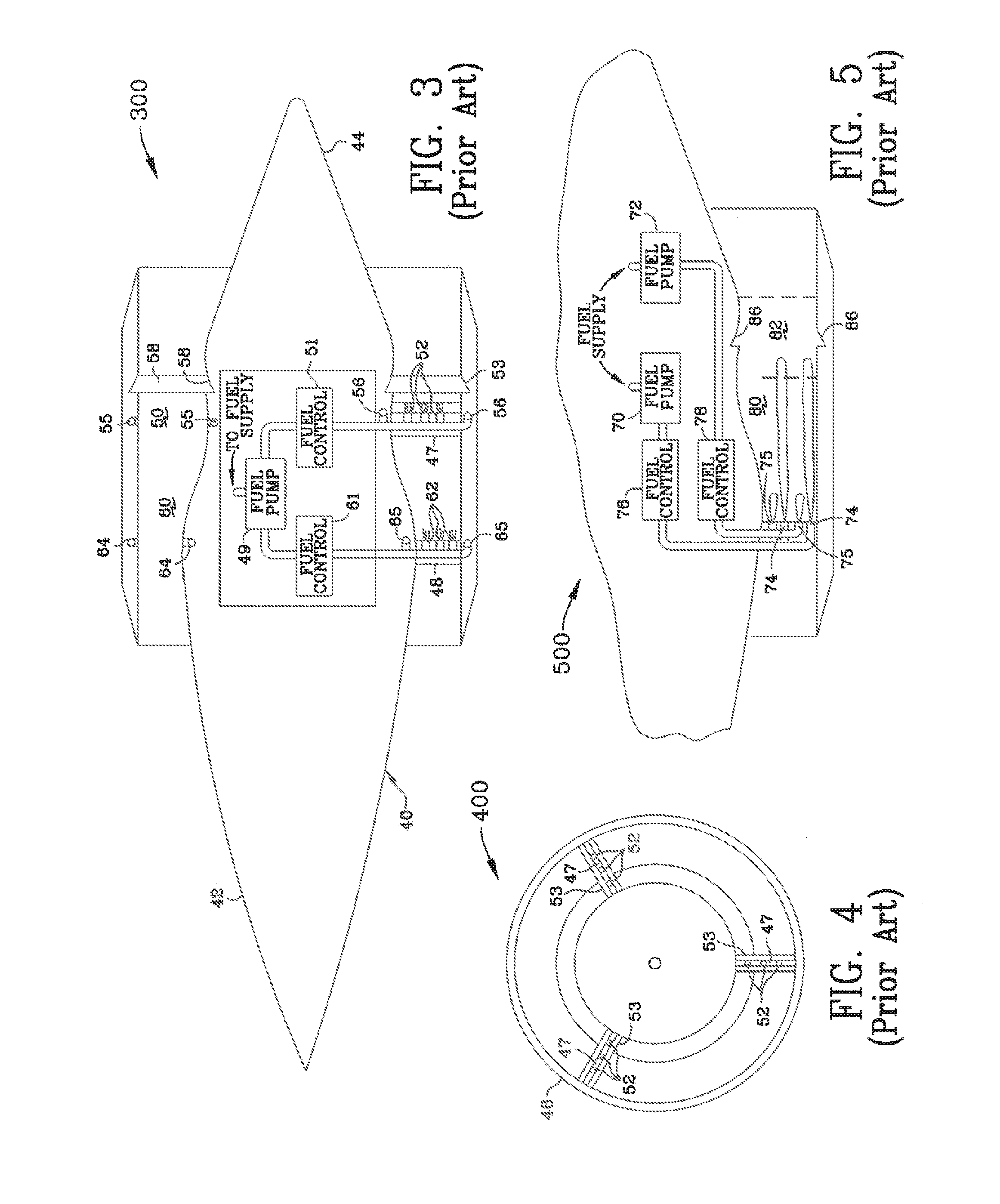
Structure of scroll of variable-throat exhaust turbocharger and method for manufacturing the turbocharger
ActiveUS7351042B2Increased in exhaust turbine capacityEasy constructionWind motor controlPump componentsTurbochargerNozzle throat
A ratio of cross sectional area A of a scroll passage to a scroll radius R (A / R) can be increased without increasing the size of a turbine casing and with very simple construction. An exhaust turbine capacity can thus be increased, so that a variable-throat exhaust turbocharger in which the engine output can be increased results. The turbocharger has a nozzle throat area varying mechanism of which a nozzle assembly unit is composed. A plurality of nozzle vanes are supported rotatably by an annular nozzle mount and an annular nozzle plate is connected to the nozzle mount by a plurality of nozzle supports to sandwich the nozzle vanes. The nozzle plate is located in the scroll chamber by attaching the nozzle assembly unit to the turbine casing to allow the nozzle plate to form part of the inside sidewall face of the scroll chamber and a wall face of the annular flow passage.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENGINE & TURBOCHARGER LTD
Solid rocket ramjet fuel gas flow regulation device driven by linear motor
InactiveCN103423032AExact random adjustmentNo intermediate transmission errorRocket engine plantsRamjetTubular linear motor
The invention discloses a solid rocket ramjet fuel gas flow regulation device driven by a linear motor. The nozzle throat area of a fuel gas generator is changed through the linear motor driving a cone-shaped valve head, and thus the fuel gas flow of the fuel gas generator is regulated; an inner shell structure is formed in the fuel gas generator, a thermal insulation bushing is mounted in an inner shell, the tubular linear motor is arranged in the thermal insulation bushing, a rotor of the linear motor is fixed in the thermal insulation bushing, a stator of the linear motor is fixedly connected with one end of a valve rod, the other end of the valve rod is fixedly connected with the cone-shaped valve head which stretches into a spray pipe of the solid fuel gas generator, one end, close to the cone-shaped valve head, of the valve rod is matched with an inner hole of the thermal insulation bushing, an annular groove is arranged, a movable sealing piece is arranged in the annular groove, and a pressure sensor is mounted at a rear seal head of the fuel gas generator. According to the solid rocket ramjet fuel gas flow regulation device driven by the linear motor, fuel gas flow can be accurately and randomly regulated, the precision is high, the structure is simple and compact, the size is small, the weight is light, and the sealing effect is reliable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High recovery sonic gas valve
ActiveUS7044434B2Turbine/propulsion fuel valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyInlet channelAcoustic wave
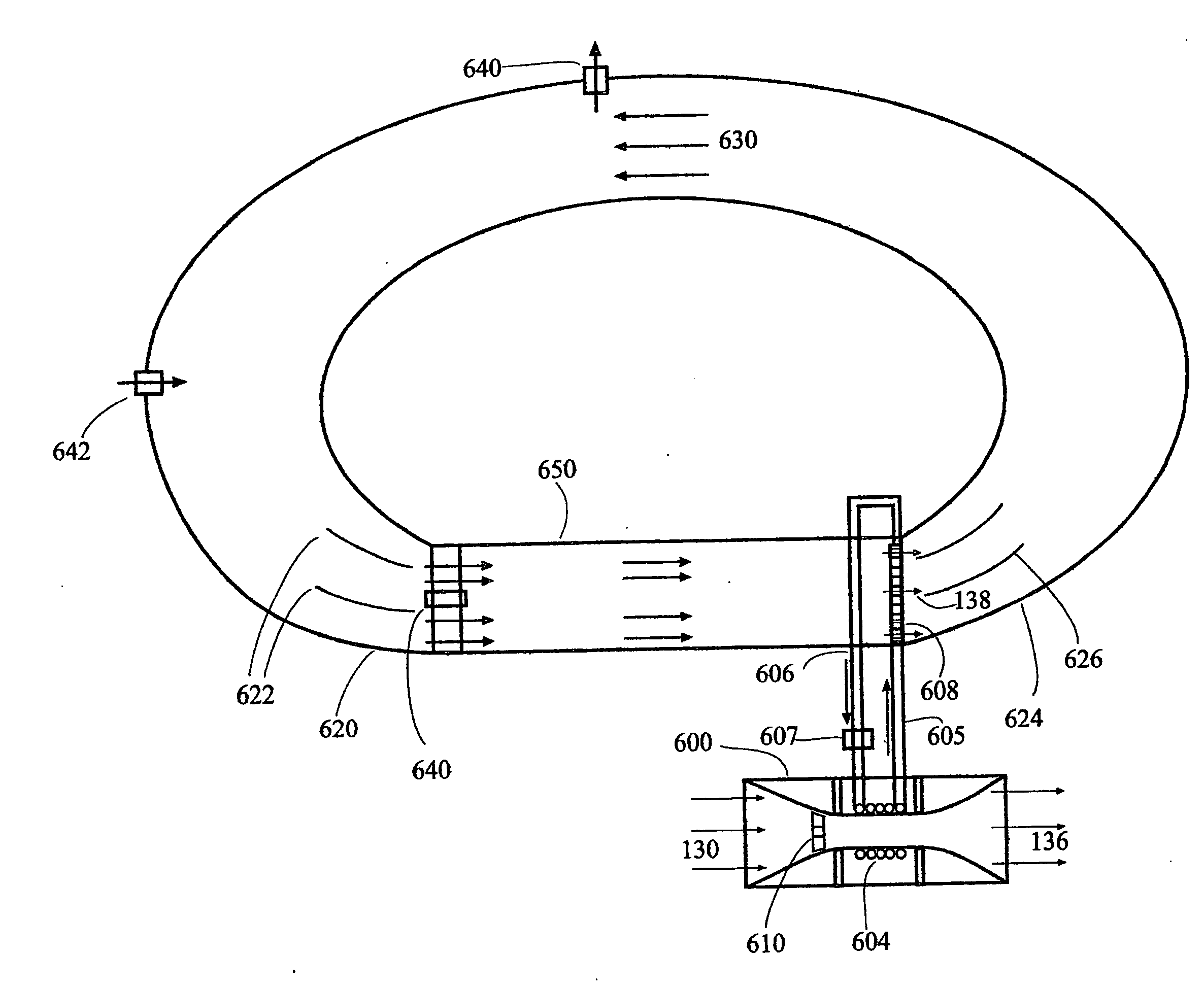
A high recovery sonic gas valve design with the inlet flow entering transverse and orthogonal to the outlet flow is presented. The configuration cancels the effects of the inlet flow entering orthogonal to the axis of the nozzle and diffuser. The inlet passage is curved in a manner to let the flow enter along the centerline of the nozzle and diffuser. The nozzle is contoured and provides upstream flow impedance. The diffuser is contoured with the area gradient varying from a low positive value at the nozzle throat then to a maximum value and finally dropping off significantly to near zero prior to the nozzle exit. The diffuser is nearly cylindrical and may extend past the valve outlet flange and protrude into adjacent piping.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
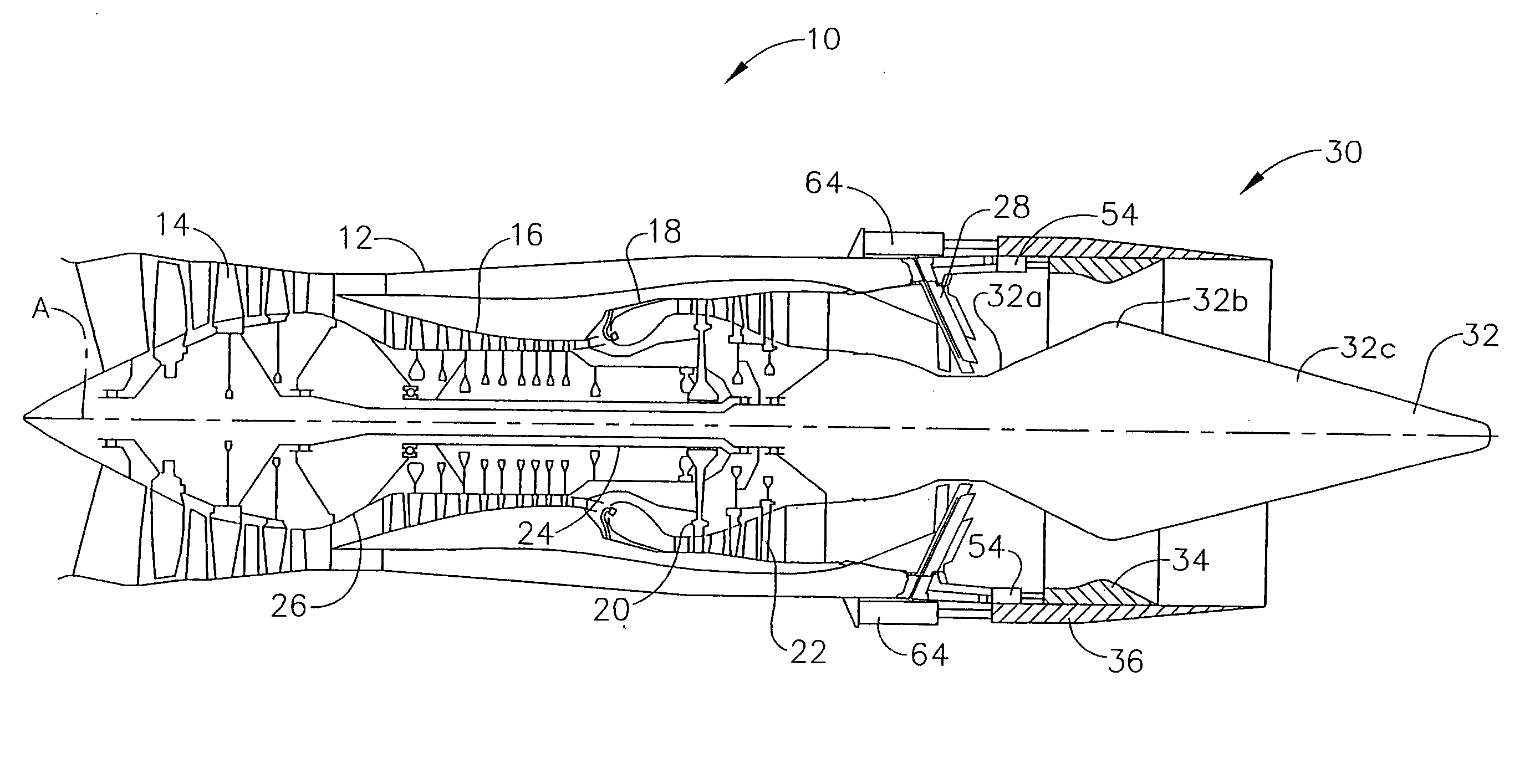
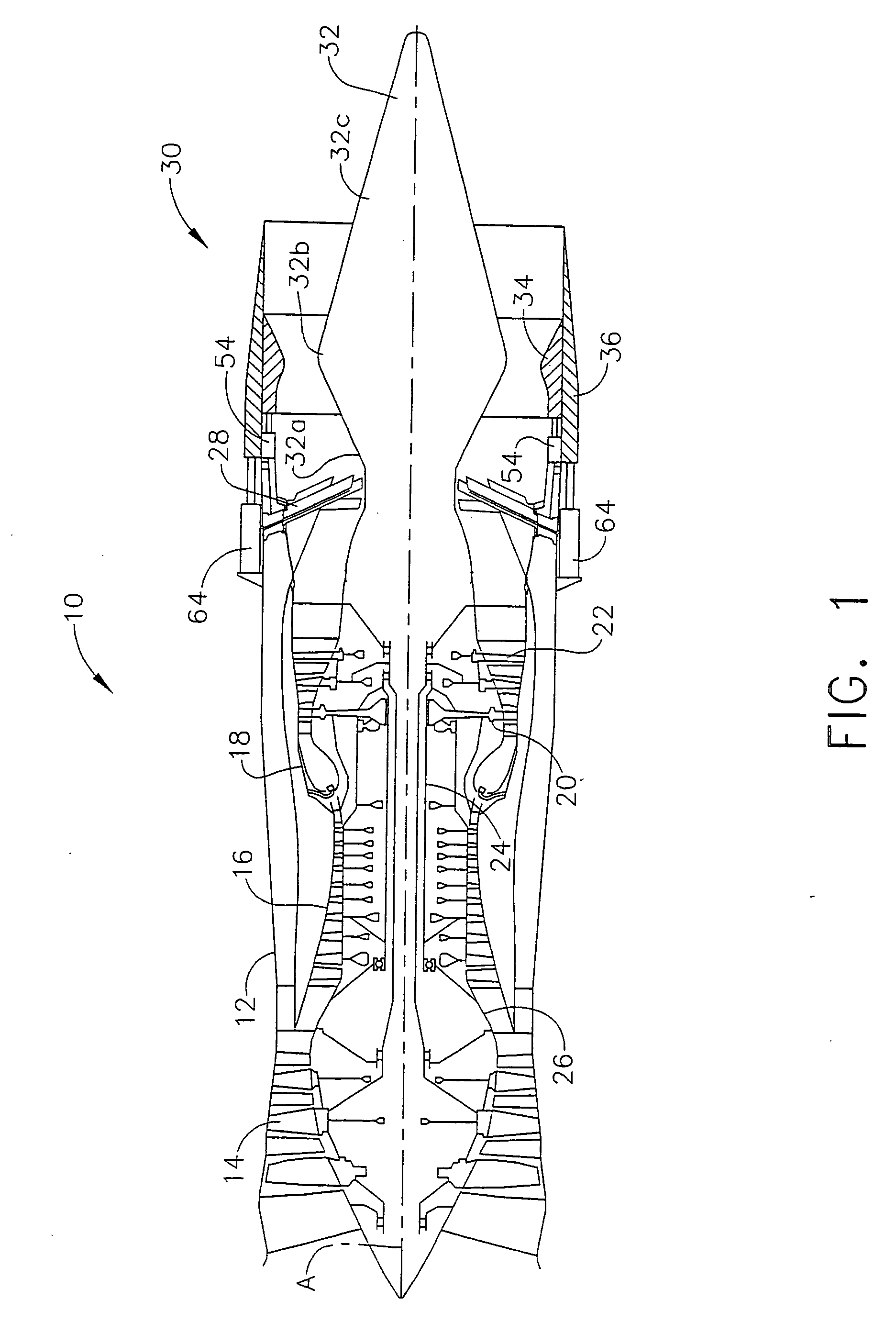
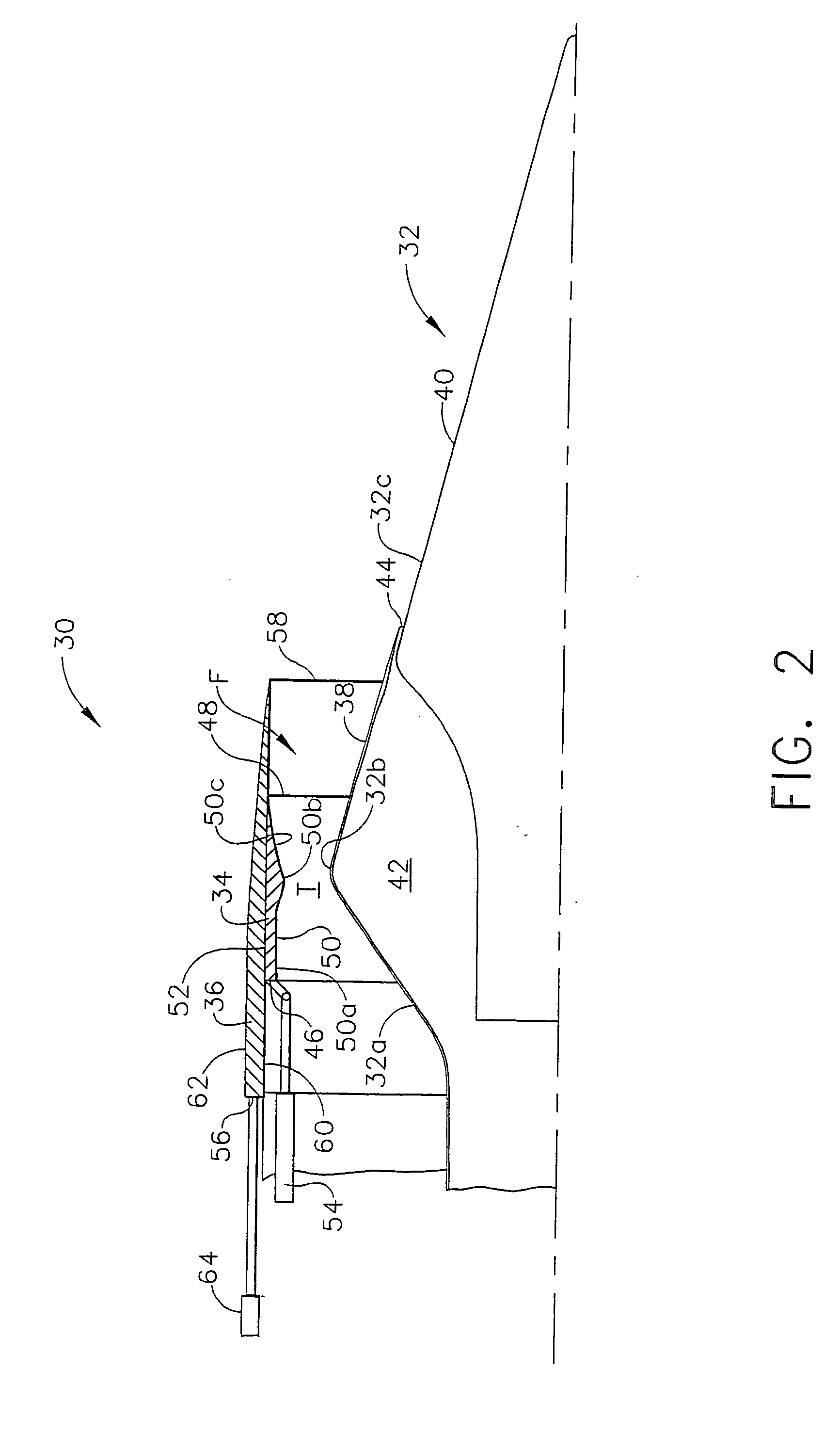
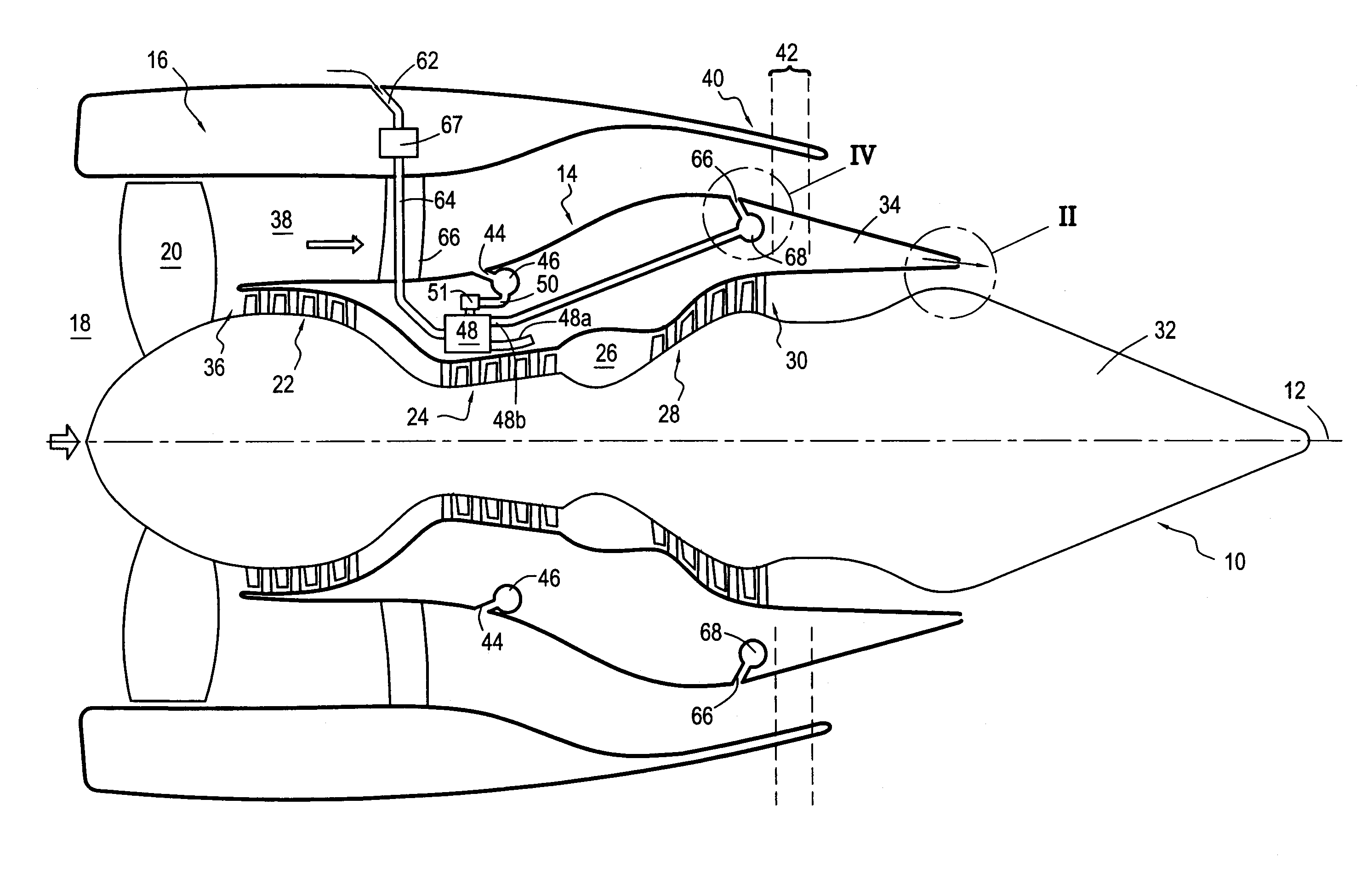
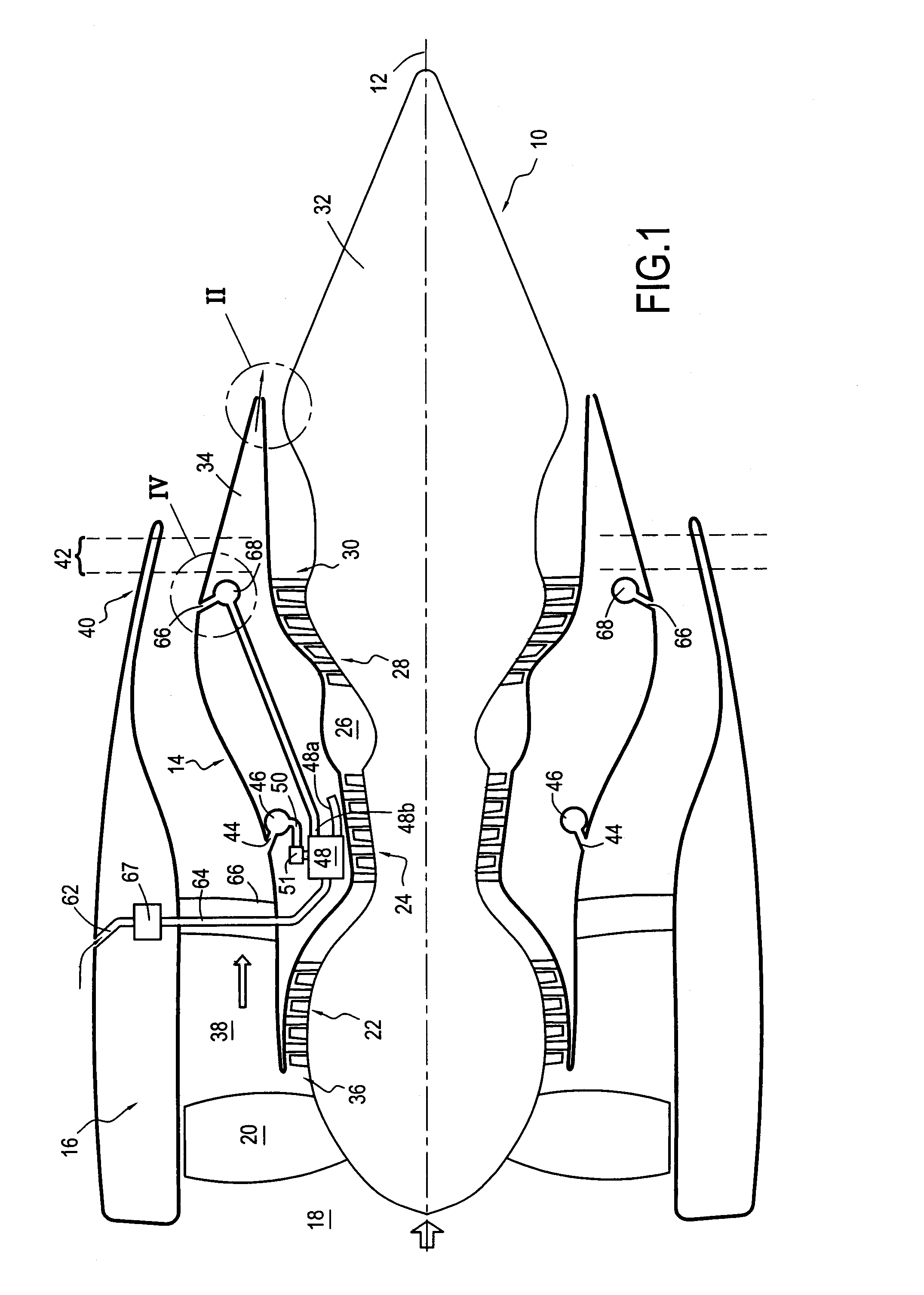
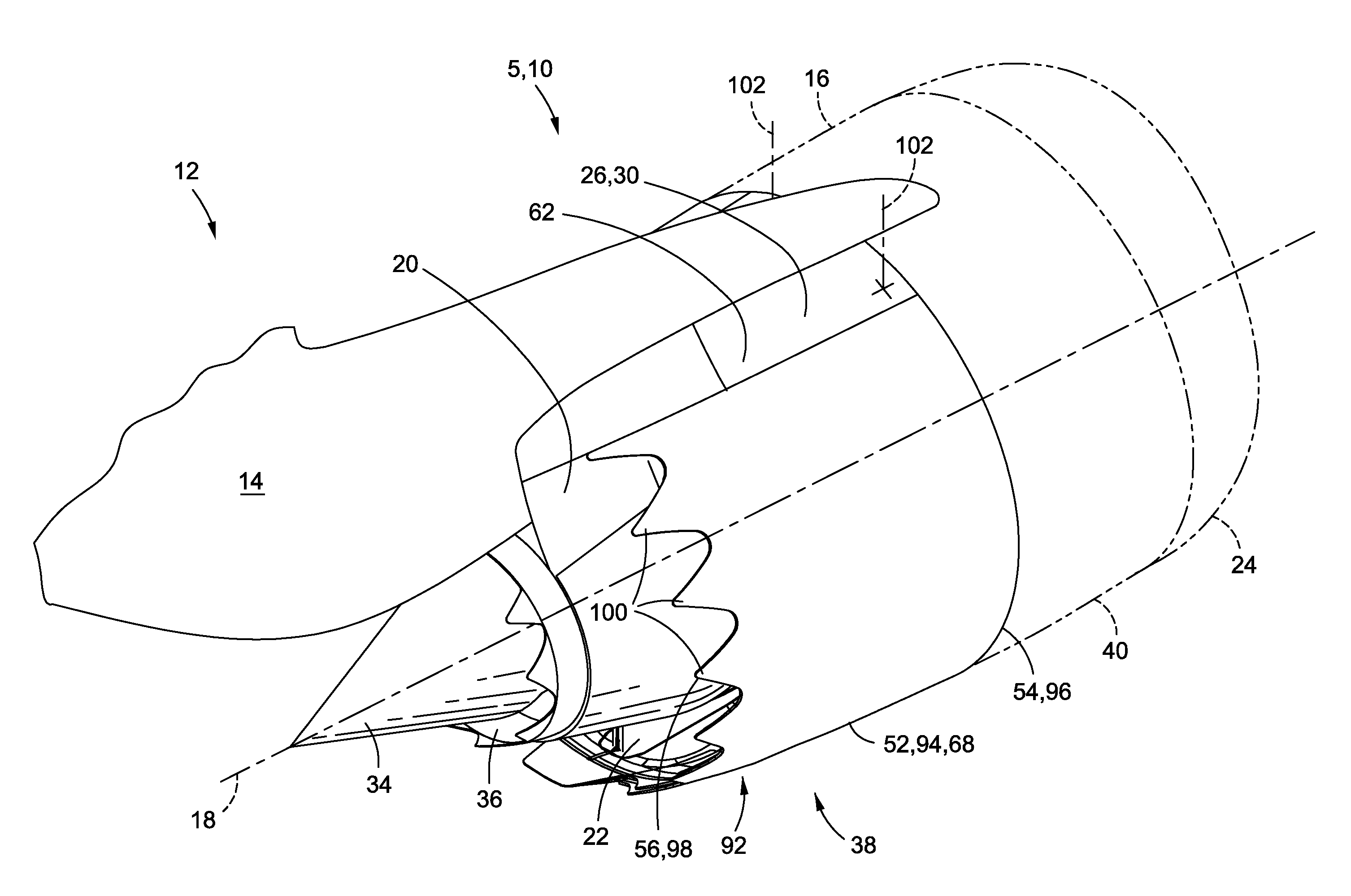
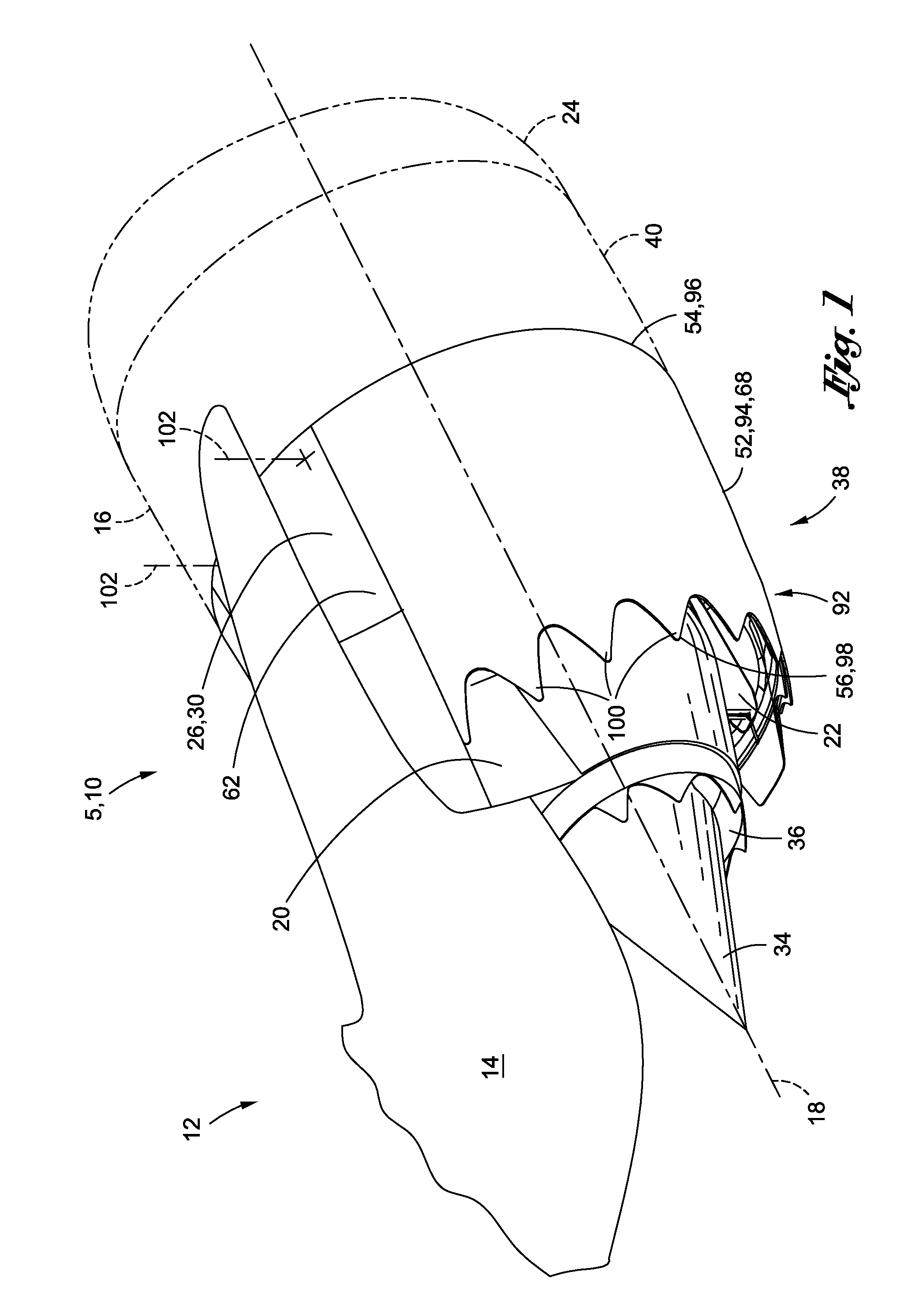
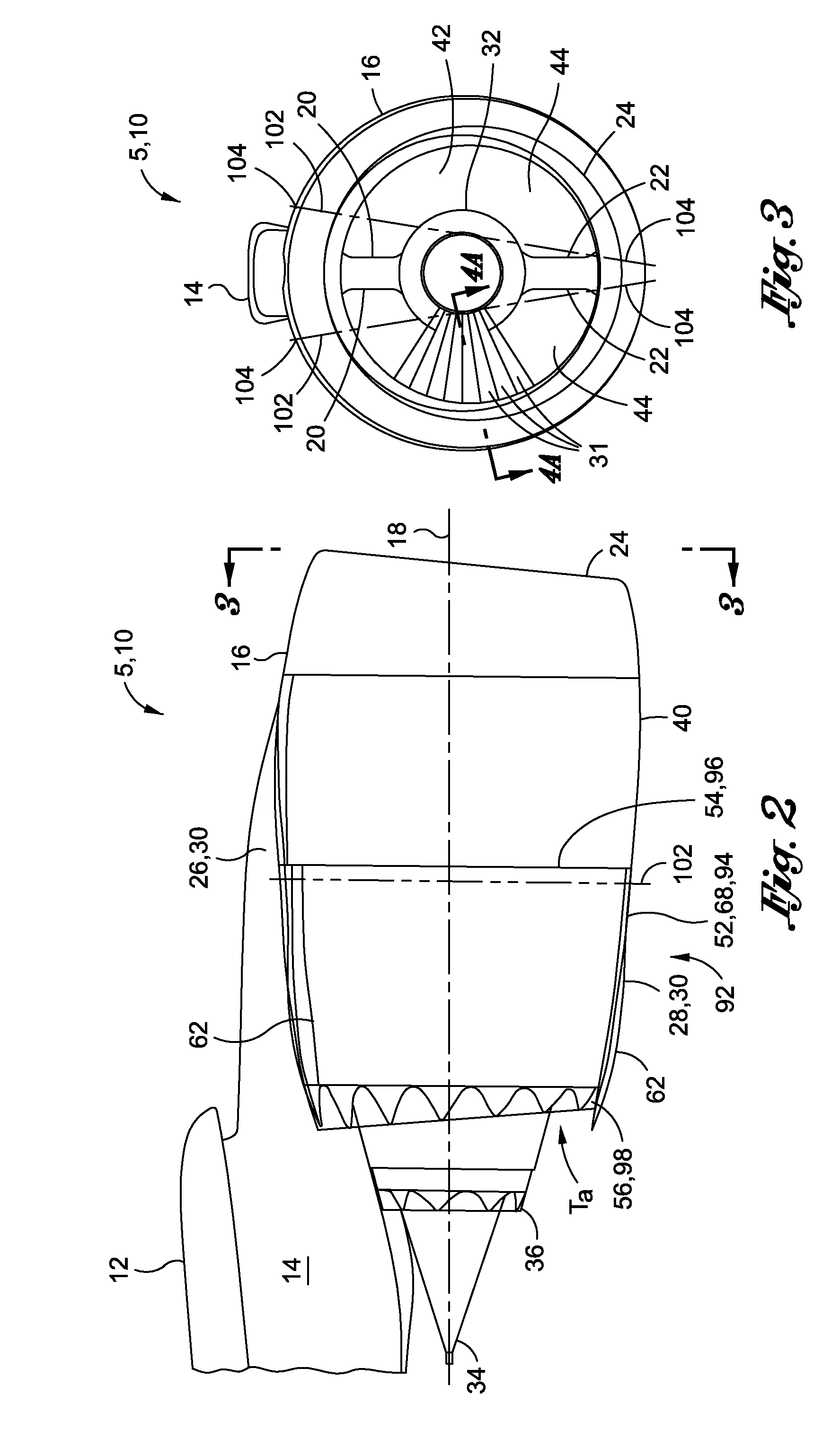
Bypass turbomachine with artificial variation of its throat section
ActiveUS20080141656A1Mitigate such drawbackIncrease ratingsCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusThroatNacelle
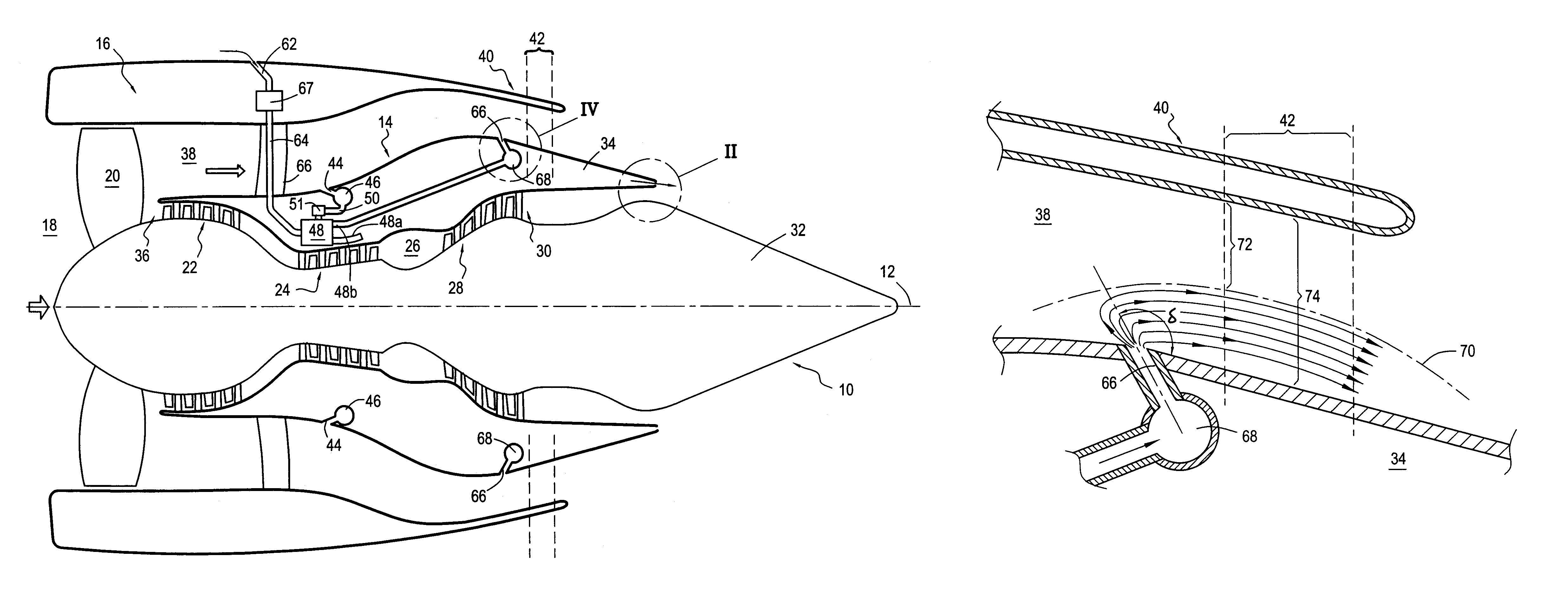
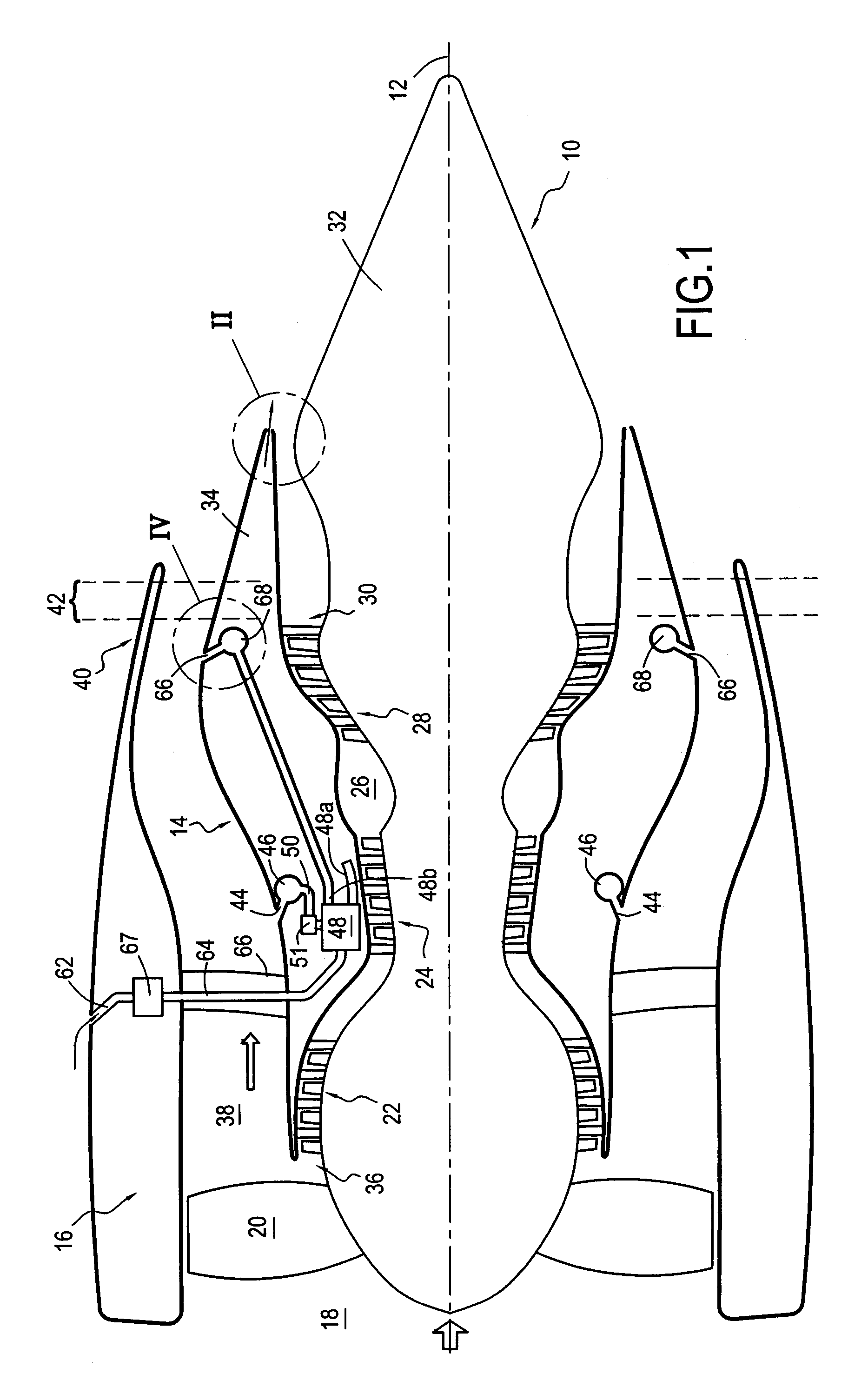
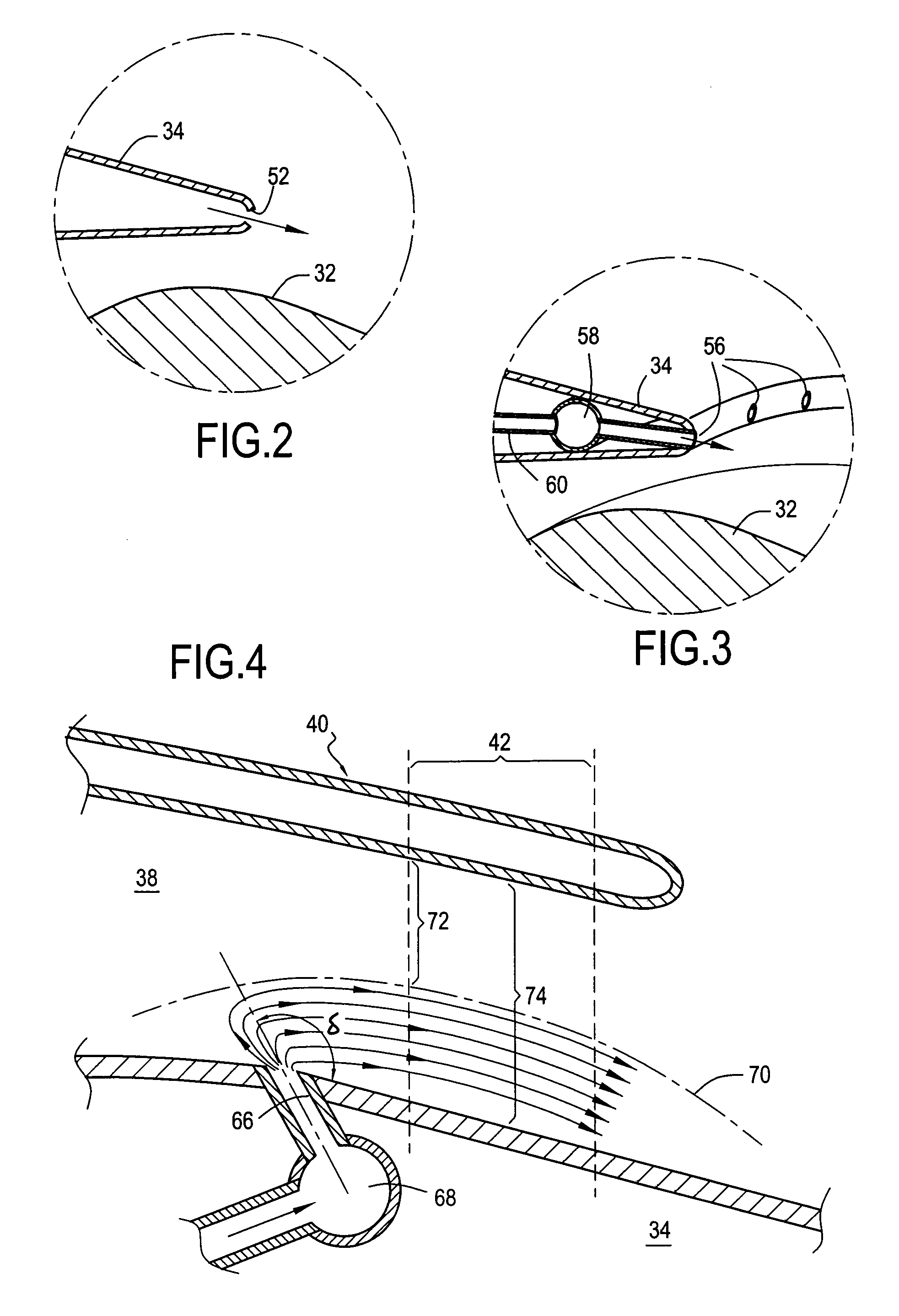
The invention relates to a bypass turbomachine comprising a gas turbine engine provided with a fan disposed on a longitudinal axis of the turbomachine, and an annular nacelle surrounding the engine so as to define a cold stream flow channel, the nacelle having an upstream end surrounding the fan of the engine and a stationary downstream end forming a gas exhaust nozzle, the nozzle having a throat section that corresponds to its smallest cross-section. The turbomachine further comprises means for taking in air from the cold stream flow channel upstream from the nozzle throat section, and means for injecting the taken-in air downstream from the nozzle throat section so as to open the throat section artificially.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Laser-assisted cold spray coating method and nozzle apparatus
ActiveCN103920626AFacilitate depositionAvoid cloggingLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid spraying apparatusTransmittanceSpray coating
The present invention discloses a laser-assisted cold spray coating method and a nozzle apparatus. According to the nozzle apparatus, one side of the nozzle throat portion is a nozzle constriction section, the other side of the nozzle throat portion is a nozzle expansion section, the nozzle side on the nozzle constriction section is provided with a high pressure gas inlet and a light transmittance window for entering of a laser beam, the light transmittance window deviates from the axis line of the nozzle, the nozzle on the nozzle constriction section is provided with a reflecting mirror A, the nozzle side on the nozzle expansion section is provided with a powder inlet, a reflecting mirror B, a reflecting mirror C and a reflecting mirror D, a laser beam entering from the light transmittance window sequentially passes through the reflecting mirror A, the reflecting mirror D, the reflecting mirror B and the reflecting mirror C in the nozzle and then is emitted from the nozzle expansion section, and the powder inlet is positioned between the reflecting mirror D and the reflecting mirror B; and according to the technical scheme, the laser is incident onto the reflecting mirror in the nozzle in a certain angle forming with the nozzle axis line, and the light beam is subjected to multiple reflections through the reflecting mirrors on the inner wall of the nozzle and finally irradiates on the substrate, such that the gas, the powder and the substrate inside the nozzle can be uniformly pre-heated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
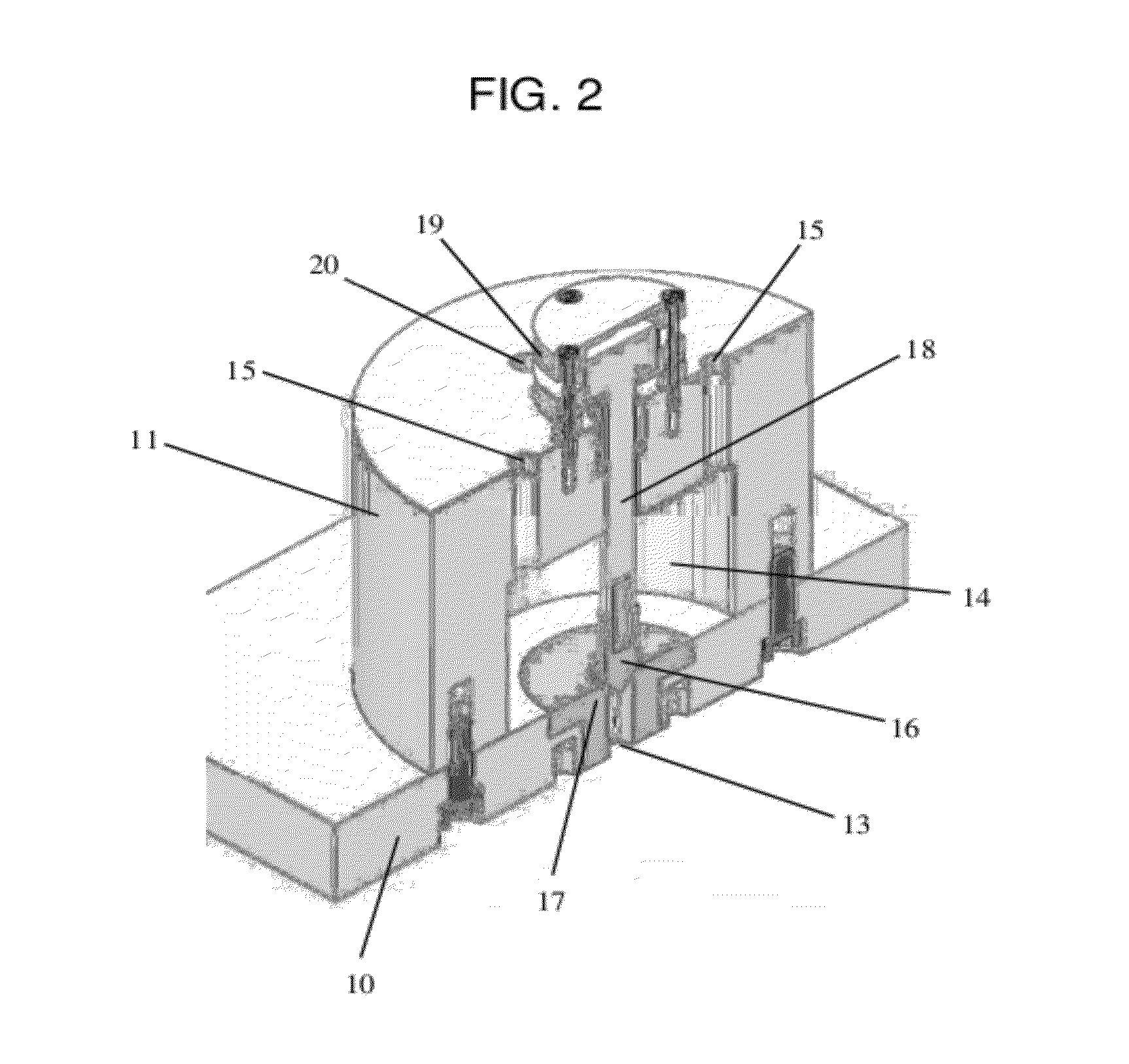
Pivoting fan nozzle nacelle
ActiveUS8127532B2Smooth rotationFacilitate outward pivotingEfficient propulsion technologiesJet propulsion plantsNacelleTrailing edge
A variable area nozzle system for a gas turbine engine includes a fan duct inner wall, a fan duct outer wall disposed in radially spaced relation to the fan duct inner wall, and a fan nozzle. The fan nozzle defines at least a portion of the fan duct outer wall and includes a nozzle aft edge. The fan duct inner wall and the nozzle aft edge collectively define a fan duct nozzle throat area. The fan nozzle is configured to pivot about a pivot axis that may be oriented transversely relative to a longitudinal axis of the gas turbine engine. The fan nozzle may be pivoted from a stowed position to a deployed position in order to vary the fan duct nozzle throat area.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Structure of scroll of variable-throat exhaust turbocharger and method for manufacturing the turbocharger
ActiveUS20060188368A1Improve the exhaust effectIncrease the cross-sectional areaWind motor controlPump componentsTurbochargerEngineering
According to the present invention, the A / R, the ratio of cross sectional area A of scroll passage to scroll radius R can be increased without increasing the size of the turbine casing and with very simple construction and exhaust turbine capacity can be increased, so a variable-throat exhaust turbocharger with which engine output can be increased is provided. The turbocharger is equipped with a nozzle throat area varying mechanism of which the nozzle assembly unit is composed such that a plurality of nozzle vanes are supported rotatably by an annular nozzle mount and an annular nozzle plate is connected to the nozzle mount by means of a plurality of nozzle supports to sandwich the nozzle vanes, the nozzle plate is located in the scroll chamber by attaching the nozzle assembly unit to the turbine casing to allow the nozzle plate to form part of the inside sidewall face of the scroll chamber and a wall face of the annular flow passage.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENGINE & TURBOCHARGER LTD
Differential adjustable unilateral expansion nozzle
The invention provides a differential adjustable unilateral expansion nozzle. In the invention, a nozzle throat area is bilaterally adjustable and differential adjustment can be carried out to ensure that an engine flow variation requirement is satisfied in a whole flight envelope; an nozzle exit area is adjustable to ensure that a gas ideal complete expansion requirement can be satisfied in a certain flight Mach number range; and the upper web of a nozzle is divided into an adjustable upper web and a fixed upper web between which a certain gap exists and the after body of an aircraft can be directly utilized by the fixed upper web so that that the operating force of a movement mechanism can be reduced. A boundary layer discharged from a front fuselage can be injected into the fixed upperweb through the gap under the flight conditions of transonic speed and low supersonic speed; and therefore, the wall static pressure of the fixed upper web is increased, the thrust loss caused by airflow overexpansion is decreased, meanwhile, the pitching moment of the aircraft is reduced and the nozzle is ensured to always achieve a higher thrust coefficient in the broad flight envelope, in addition, the cooling of the fixed upper web can be strengthened and the thermal load and the infrared signal characteristic of the nozzle are reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High recovery sonic gas valve
ActiveUS20050199840A1Lower pressure ratioTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyEngineeringAcoustic wave
A high recovery sonic gas valve design with the inlet flow entering transverse and orthogonal to the outlet flow is presented. The configuration cancels the effects of the inlet flow entering orthogonal to the axis of the nozzle and diffuser. The inlet passage is curved in a manner to let the flow enter along the centerline of the nozzle and diffuser. The nozzle is contoured and provides upstream flow impedance. The diffuser is contoured with the area gradient varying from a low positive value at the nozzle throat then to a maximum value and finally dropping off significantly to near zero prior to the nozzle exit. The diffuser is nearly cylindrical and may extend past the valve outlet flange and protrude into adjacent piping.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
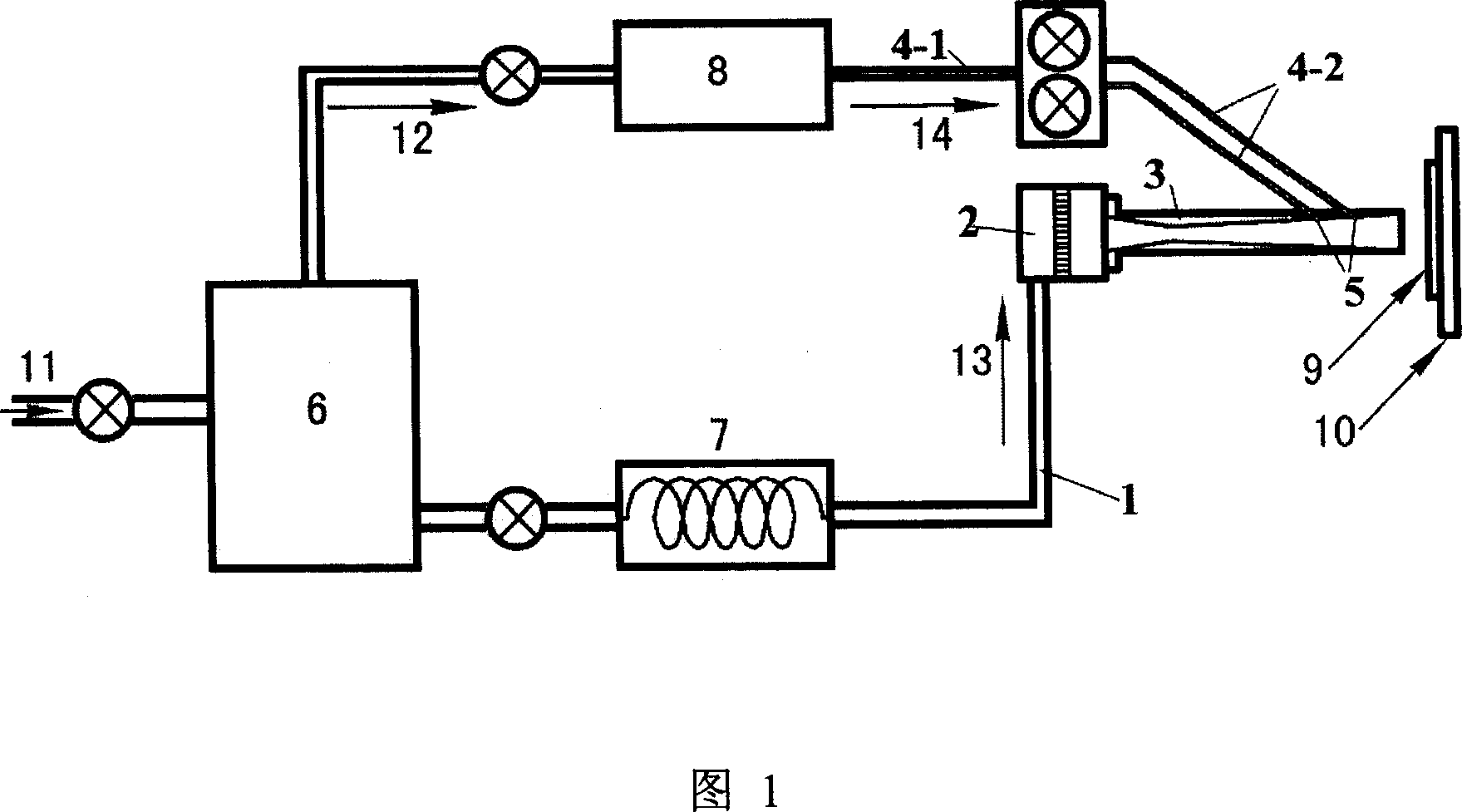
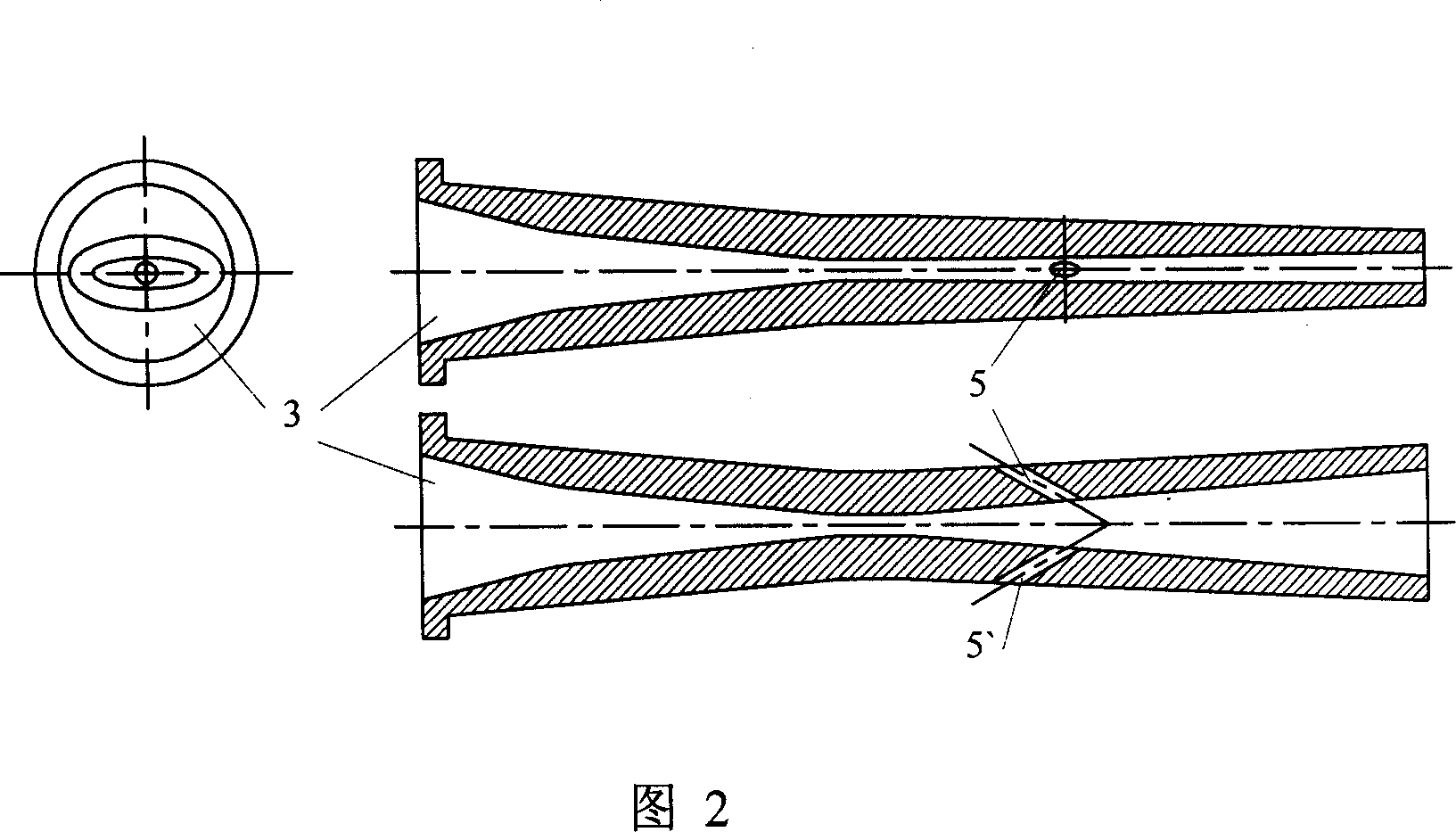
Natural gas separation device
The invention discloses a natural gas separation device. The natural gas separation device comprises a vortex tube, a hot end pipe and a cold end pipe, wherein the gas inlet of the hot end pipe is communicated with the hot gas oulet of the vortex tube; and the natural gas separation device also comprises a Laval nozzle, and the both ends of the Laval nozzle are separately communicated with the cold gas oulet of the vortex tube and the gas inlet of the cold end pipe. When the air flow in the hot end pipe reaches the Laval nozzle, as the nozzle area is reduced, the pressure of the air flow is increased, the flow rate is increased and the air flow can be in a sonic state when reaching the nozzle throat; then with the increasement of the nozzle area, the pressure of the air flow is reduced and gas expands continuously to form sonic air flow, the temperature is reduced rapidly; duing the temperature reduction process of gas, the impurity components such as CO2 and sulfide in the gas are condensated; and the condensated impurity components are thrown to the wall of the nozzle under the centrifugal force of the vortex tube to realize separation. The device of the invention has simple structure, low cost and good separation effect.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Constant volume combustion chamber
InactiveUS9279503B2Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or more disadvantagesImprove business performanceCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCombustion chamberCombustor
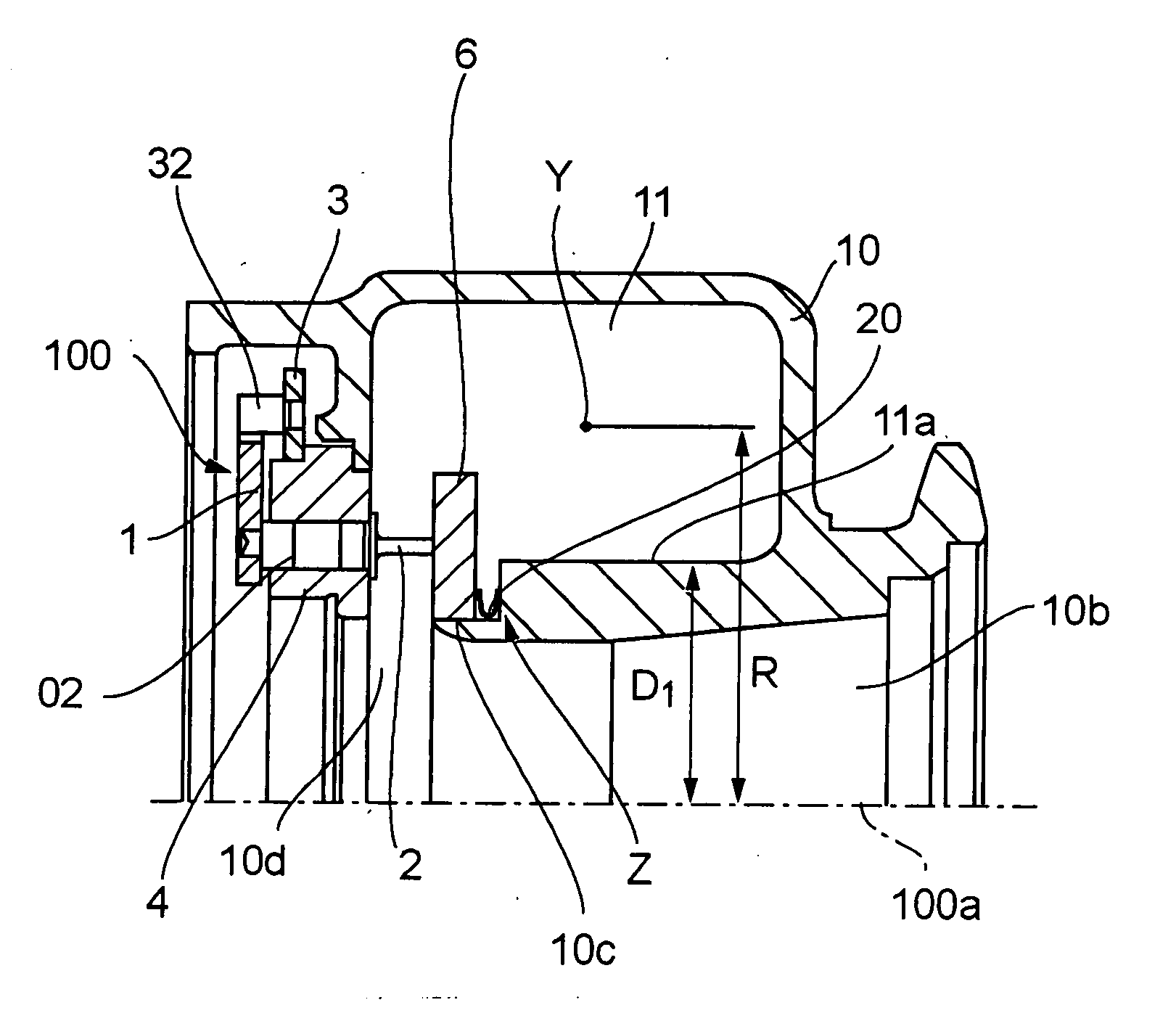
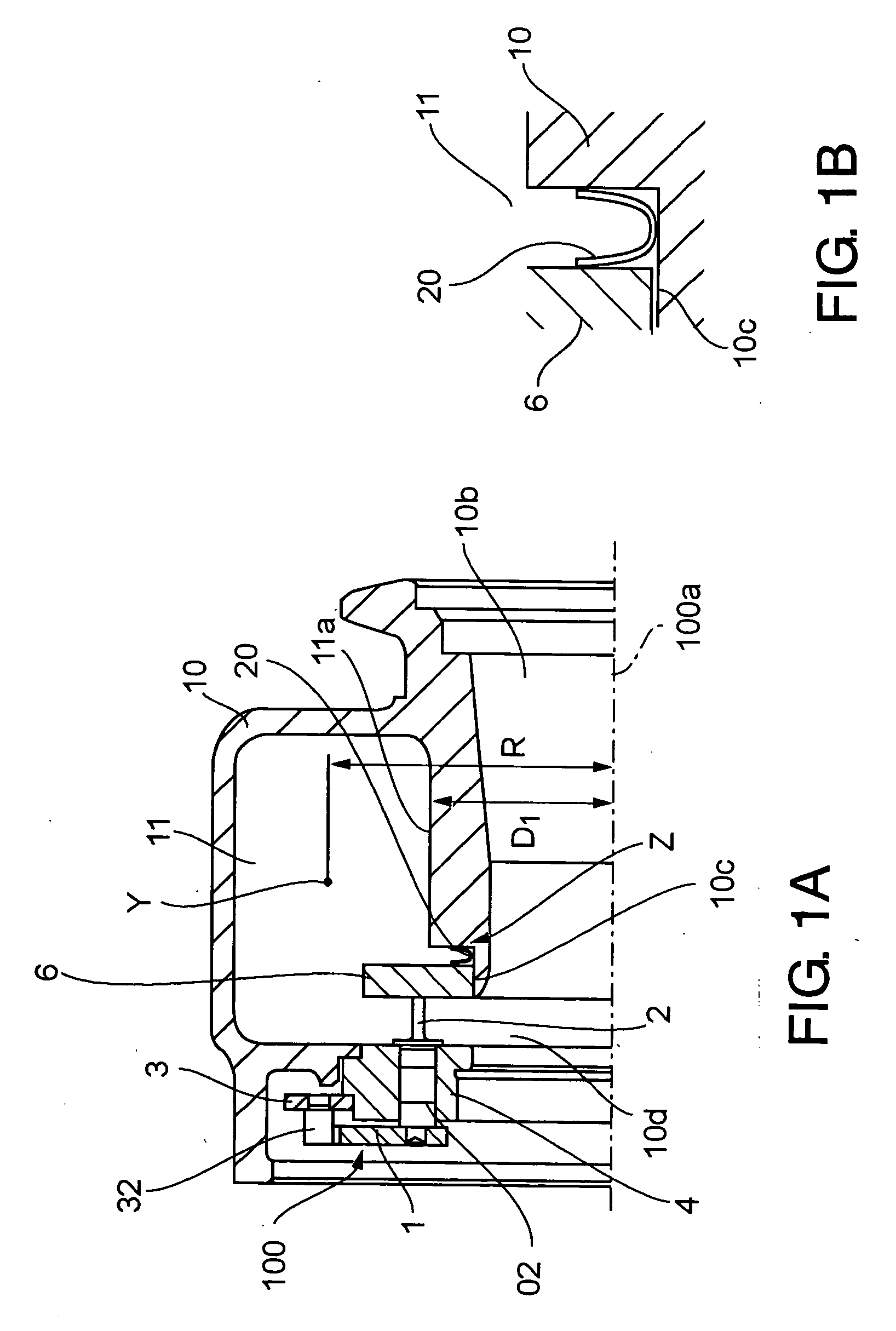
A constant volume combustion chamber, combustor, and method for constant volume combustion involve combusting a fuel in a chamber sealed by a pintle having a conical portion fitted into a conical nozzle throat and pulling the pintle away from the nozzle throat to allow combustion products to exhaust through a nozzle outlet. The shapes and surfaces of the pintle and nozzle throat provide for sealing the chamber at high pressures while resisting surface wear. Operational parameters for the combustor may be computer controlled in response to measured pressures and temperatures in the combustor.
Owner:STREAMLINE AUTOMATION LLC
Coffee/espresso machine with a milk froth generating device for the preparation of cappuccino
Owner:EUGSTER FRISMAG
Thrust vector control system for a plug nozzle rocket engine
A thrust vector control system for a plug nozzle rocket engine for propelling and maneuvering a vehicle is disclosed. The plug nozzle rocket engine includes a housing having a nozzle throat, a plug disposed within the housing and positioned within the nozzle throat to define a space between the plug and the nozzle throat, and a thrust diverter moveably disposed relative to the housing to define an asymmetric pressure distribution along the plug for thrust-vectoring. In one embodiment, the thrust diverter is normally biased to a non-thrust-vectoring position, but is moveable in a plane substantially perpendicular to an axis extending longitudinally through the plug.
Owner:AEROJET ROCKETDYNE INC
A method for cooling air and devices
ActiveUS20100162685A1Avoid accumulationLower flow temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCompression machinesElectricityCold air
A method of constructing self-powered air-conditioner comprises a convergent divergent nozzle where powered fan pushes air into said nozzle. While the pushed air accelerates toward the nozzle throat it becomes colder as air internal energy transformed into kinetic energy. An axial turbine installed within the nozzle throat extracts energy from the air in the nozzle and drives an electrical generator that provides electricity to the fan electric motor. Alternatively the turbine and fan are installed on common shaft, which could be the electric generator shaft. The cold air within the nozzle throat cools the nozzle throat skin, which serves as air-conditioner core. The cold nozzle skin is wrapped with coiled pipes in which liquid flows, becomes colder and this cold liquid flows away to heat exchanger where air is flowing through it and becomes colder. This cold air is then flows into spaces needed to be air-conditioned.
Owner:HIRSHBERG ISRAEL
Dual-mode combustor
InactiveUS8484980B1Reduce the Mach numberContinuous combustion chamberPower plant arrangements/mountingRamjetCombustion chamber
A new dual-mode ramjet combustor used for operation over a wide flight Mach number range is described. Subsonic combustion mode is usable to lower flight Mach numbers than current dual-mode scramjets. High speed mode is characterized by supersonic combustion in a free-jet that traverses the subsonic combustion chamber to a variable nozzle throat. Although a variable combustor exit aperture is required, the need for fuel staging to accommodate the combustion process is eliminated. Local heating from shock-boundary-layer interactions on combustor walls is also eliminated.
Owner:NASA
Magnetic nozzle of variable specific impulse magnetic plasma rocket
InactiveCN102434414AChange the strength of the magnetic fieldWide range of workMachines/enginesUsing plasmaSprayerAlloy
The invention relates to a magnetic nozzle of a variable specific impulse magnetic plasma rocket, aiming at solving the problem of speed waste during acceleration of a plasma body in an electric propulsion system and relating to the design technology of the magnetic nozzle of the variable specific impulse magnetic plasma rocket. The magnetic nozzle of the variable specific impulse magnetic plasma rocket is used for changing a circumferential speed of the plasma body to an axial speed and belongs to the magnetic fluid technology field. The magnetic nozzle which is used as the last stage of the variable specific impulse magnetic plasma rocket is arranged at the tail end of a rocket engine and consists of a sprayer nozzle and a superconducting coil, wherein, the sprayer nozzle is arranged at the tail end of a shell body of the rocket engine and is an expanding nozzle, the nozzle expansion ratio which is the ratio between a nozzle exit area and a nozzle throat area is 40:1, the nozzle is made of a heat-resisting and ablation-resisting alloy material to reduce ablation and thrust eccentricity.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Flow quantity self-adjusting jetting stream vacuum generator
InactiveCN101113744AReduce the effective cross-sectional areaReduce consumptionJet pumpsMachines/enginesVacuum levelEngineering
The invention discloses a flow auto-adjustment jet flow vacuum generating device, comprising a section of flow auto-adjustment and a vacuum generating section. A needle valve used for adjustment is positioned at the front of a jet nozzle throat of the vacuum generating section. Meanwhile the needle valve can feed back the vacuum pressure to a right cavity of an active cylinder of the vacuum generating device to make a pressure difference between the right cavity and a left cavity of the active cylinder which is communicated with the atmosphere to drive the active valve and to drive the passive valve through magnetic driving, finally to drive the needle valve which is fixedly connected with the passive valve to move. The invention not only realizes the dual purposes of fast response in vacuum and saving energy sources, but also realizes the auto adjustment to the flow of air supply for the position of the needle valve can be adjusted according to vacuum level. Meanwhile, if the vacuum level changes, the needle valve can look for a new balance point automatically. Thus the vacuum generating device has the function of automatic adjustment of the air supply flow and is suitable for various working conditions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Constant Volume Combustion Chamber
InactiveUS20120317956A1Simplified ignition systemAbsence of extremely high pressureCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCombustorCombustion chamber
A constant volume combustion chamber, combustor, and method for constant volume combustion involve combusting a fuel in a chamber sealed by a pintle having a conical portion fitted into a conical nozzle throat and pulling the pintle away from the nozzle throat to allow combustion products to exhaust through a nozzle outlet. The shapes and surfaces of the pintle and nozzle throat provide for sealing the chamber at high pressures while resisting surface wear. Operational parameters for the combustor may be computer controlled in response to measured pressures and temperatures in the combustor.
Owner:STREAMLINE AUTOMATION LLC
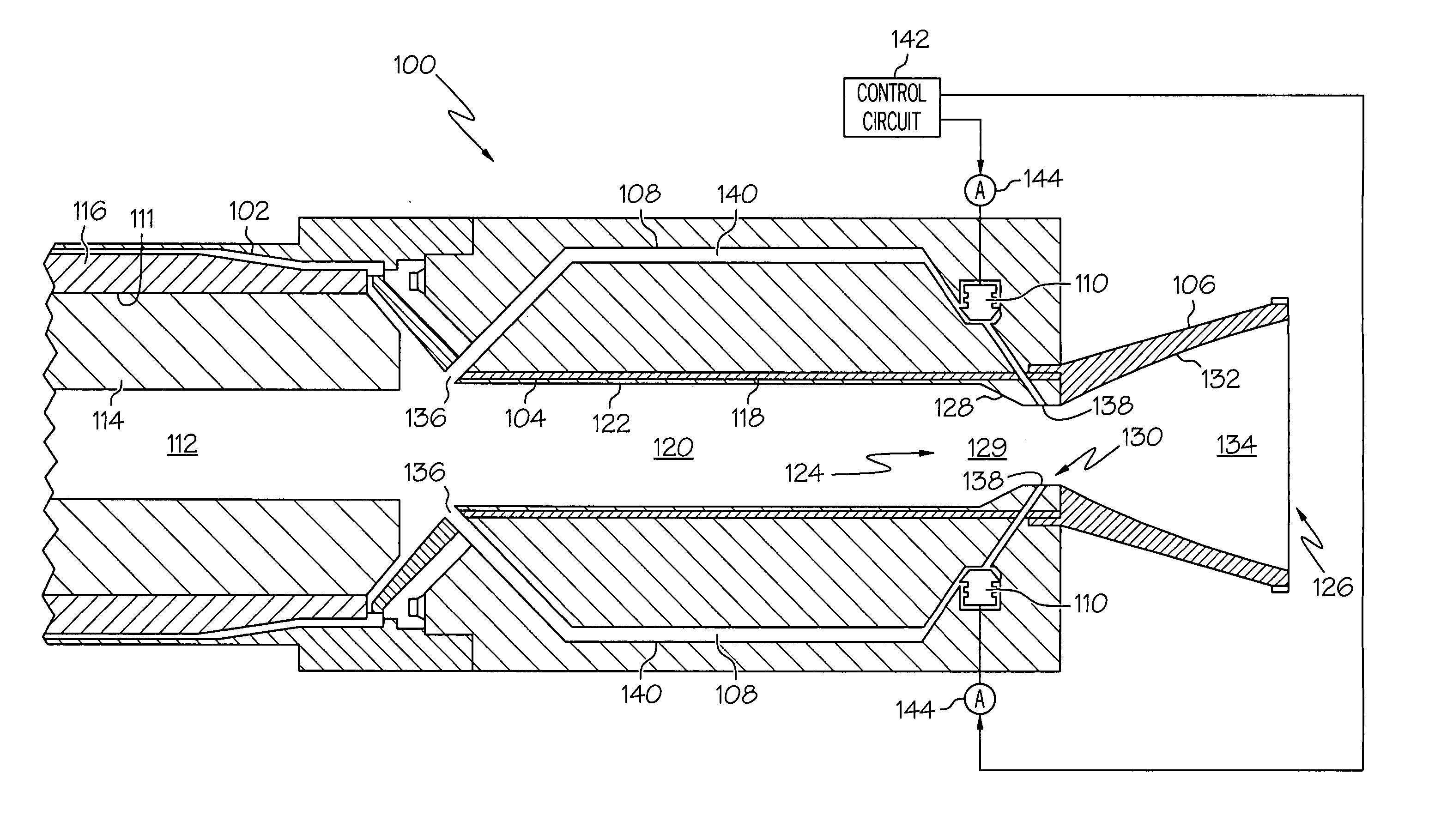
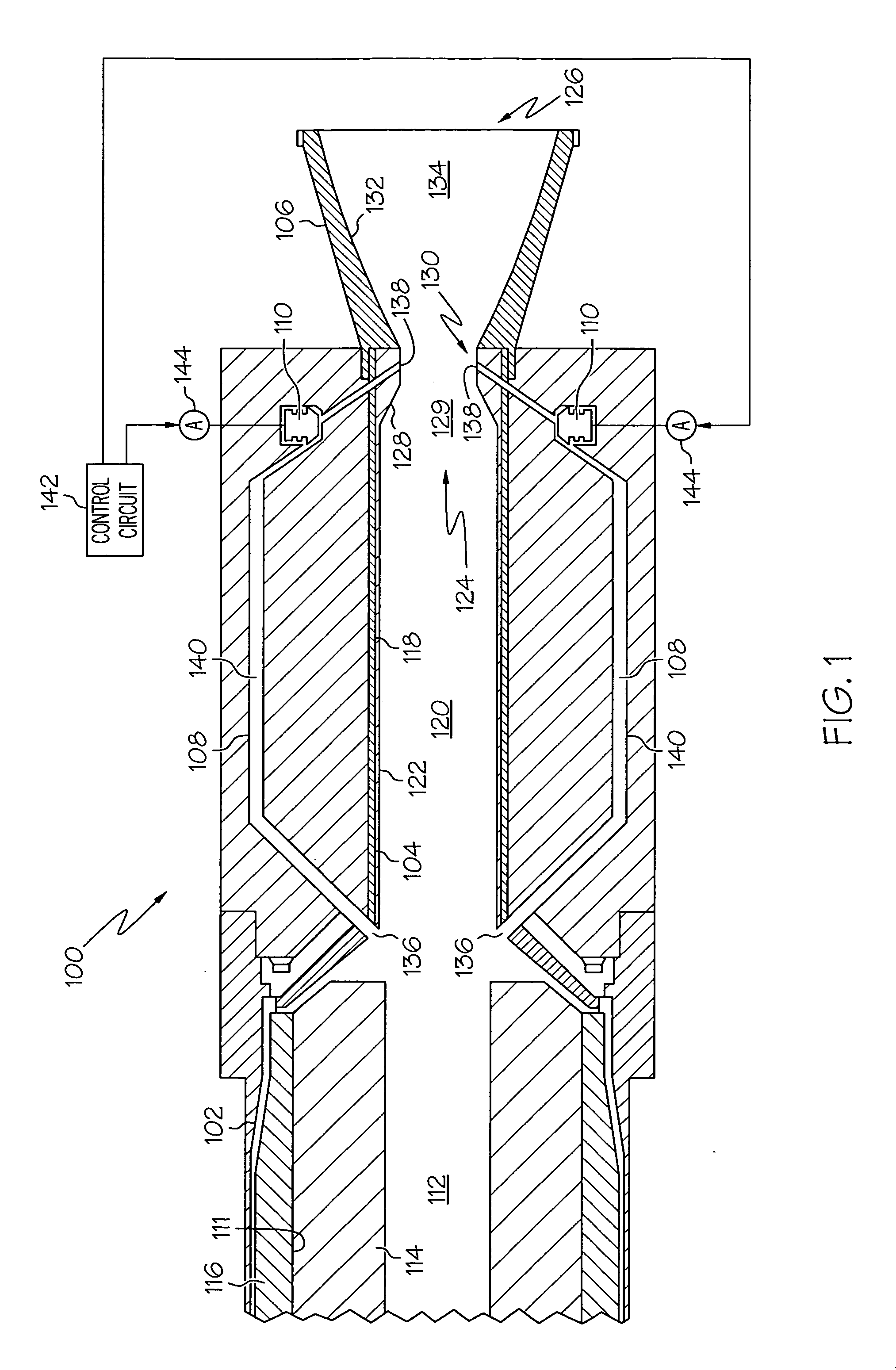
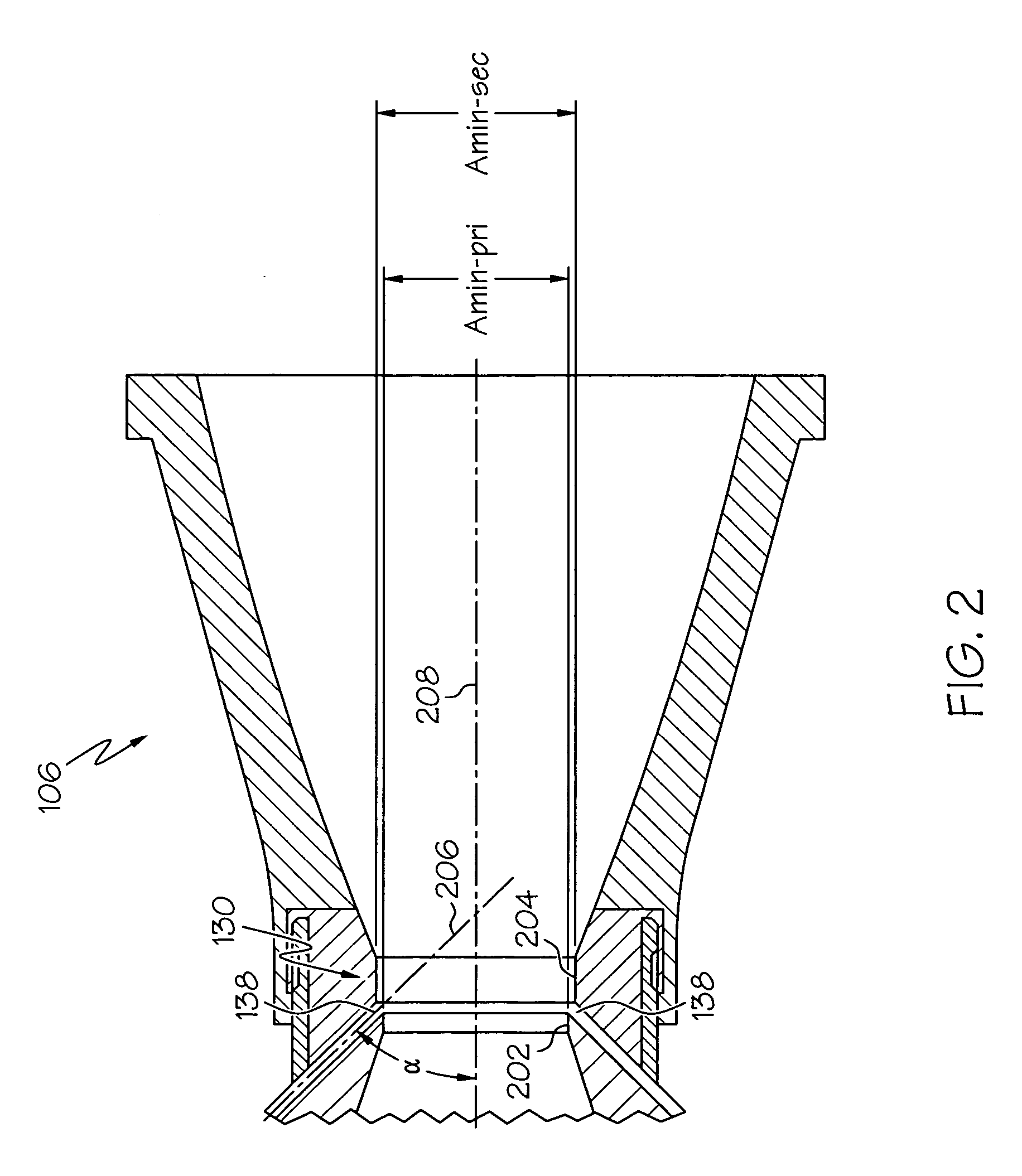
Method of varying a fan duct nozzle throat area of a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20120124963A1Smooth rotationFacilitate outward pivotingCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusNozzle throatTurbine
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Bypass turbomachine with artificial variation of its throat section
ActiveUS7950218B2Mitigate such drawbackIncrease ratingsCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusNacelleStream flow
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Dual-Mode Combustor
InactiveUS20150013305A1Reduce the Mach numberContinuous combustion chamberPower plant arrangements/mountingRamjetCombustion chamber
A new dual-mode ramjet combustor used for operation over a wide flight Mach number range is described. Subsonic combustion mode is usable to lower flight Mach numbers than current dual-mode scramjets. High speed mode is characterized by supersonic combustion in a free-jet that traverses the subsonic combustion chamber to a variable nozzle throat. Although a variable combustor exit aperture is required, the need for fuel staging to accommodate the combustion process is eliminated. Local heating from shock-boundary-layer interactions on combustor walls is also eliminated.
Owner:US GOVT ADMINISTATOR OF NASA
Cold air dynamical spray-painting method and apparatus of delivering powder through down stream
InactiveCN1958171AMelting point does not causeTemperature controlLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid spraying apparatusCold airMetallurgy
A cold-pneumatic spray coating method and apparatus by feeding powder at downstream is disclosed. Said method includes such steps as heating the working gas, delivering it to upstream of the flow channel in Laval nozzle, using the carrying gas to deliver the metallic powder to be sprayed to the downstream divergent segment via powder delivering tube, accelerating it by working gas, and spraying it. The cross-section the flow channel in divergent segment is elliptical or the combination of ellipse and rectangle. Its advantage is no pollution and blocking of nozzle throat.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Wind machines
Wind machines are disclosed in which the pressure energy of the wind is converted into electrical energy. A nozzle unobstructed by any turbine or propeller bearing a significant load is made to face the wind. The nozzle converts the pressure energy of the wind into kinetic energy. In one embodiment a turbine is disposed around the throat of the nozzle and air sucked through the turbine and exhausted through the throat of the nozzle. An obstruction at the turbine inlets is placed in such a way as to cause a pressure variation on either side of the obstruction, causing the turbine to rotate. In a second embodiment a small turbine within the throat of the nozzle is made to revolve several three way ball valves. These valves open and close passage-ways so as to admit or evacuate air from one side of pistons in cylinders of an atmospheric engine. The low pressure in the volume of the nozzle throat serves as an energy sink. The other side of the pistons are open to the atmosphere.
Owner:NEWMAN EDWIN
Method for preparing copper-base tungsten coating through compounded process of laser and thermal spraying
ActiveCN101717910AImprove heat resistanceImprove thermal shock resistanceMolten spray coatingThermal sprayingCoating system
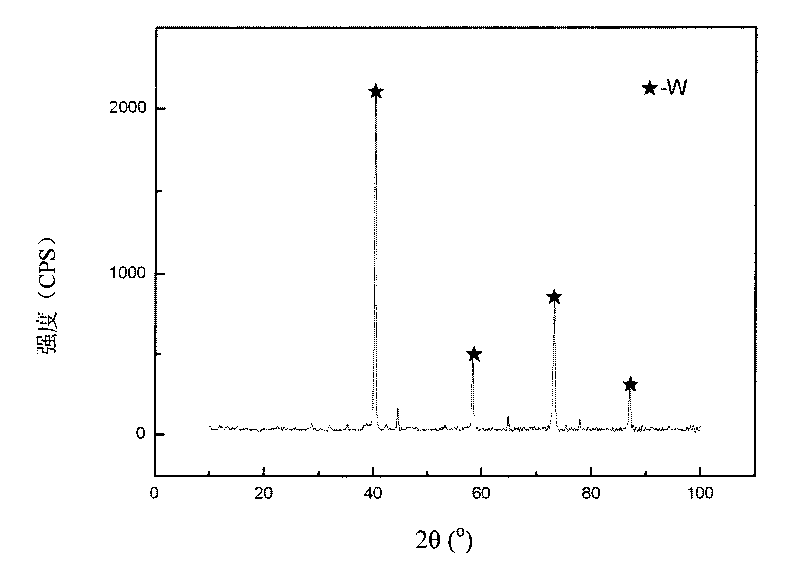
The invention relates to a method for preparing a copper-base tungsten coating through a compounded process of laser and thermal spraying. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a nickel base alloy transition bottom layer on the surface of a copper matrix by using a low pressure plasma coating system, and remelting the transition bottom layer with laser beams; and then preparing an intermediate transmission layer and the tungsten coating of a Ni-W alloy by using the low pressure plasma coating system, and then remelting with the laser beams to obtain the tungsten coating. By using a gradient coating structure, the method effectively solves the problem of thermal stress caused by mismatching of the coefficient of thermal expansion of the copper and the tungsten, and improves the cohesion strength of the tungsten coating and the matrix, the tungsten coating and the tungsten coating. The coating and the matrix can achieve metallurgical bonding by using the laser beam remelting, bonding property is also improved and the tungsten coating with compact surface is obtained. The tungsten coating prepared by the method has excellent anti-heat radiation and anti-thermal shock properties and is suitable to be used as heated end component materials in equipment, such as first wall material in a ray target, a rocket nozzle, an airplane nozzle throat and a nuclear fusion device.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF NEW MATERIALS
Rocket motor nozzle throat area control system and method
InactiveUS20050284128A1Not significantly affect overall motor efficiencyAircraft navigation controlCosmonautic vehiclesCombustion chamberControl system
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com