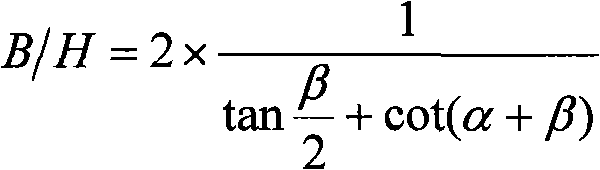Patents
Literature
267results about How to "Reduce shadows" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
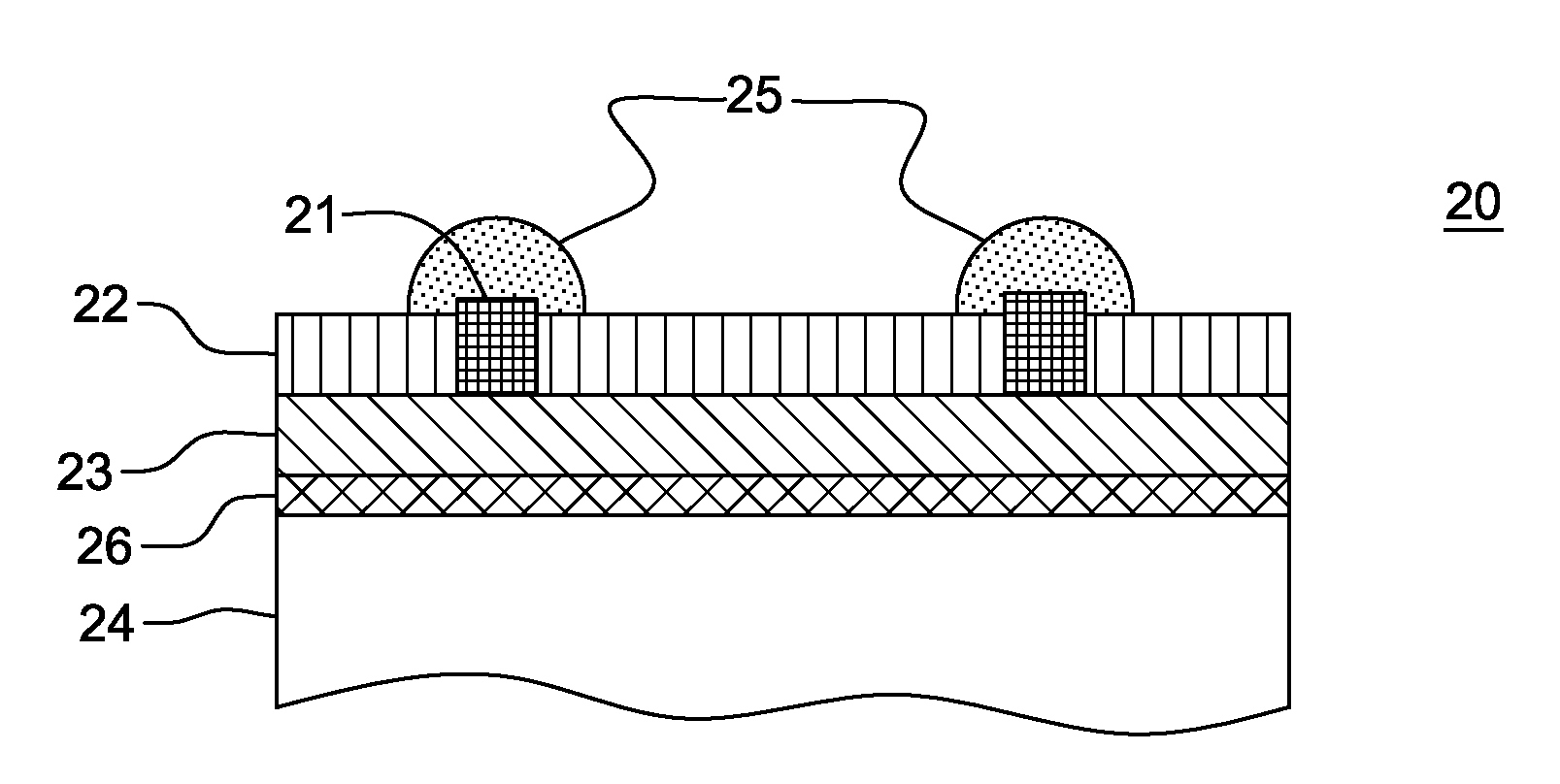
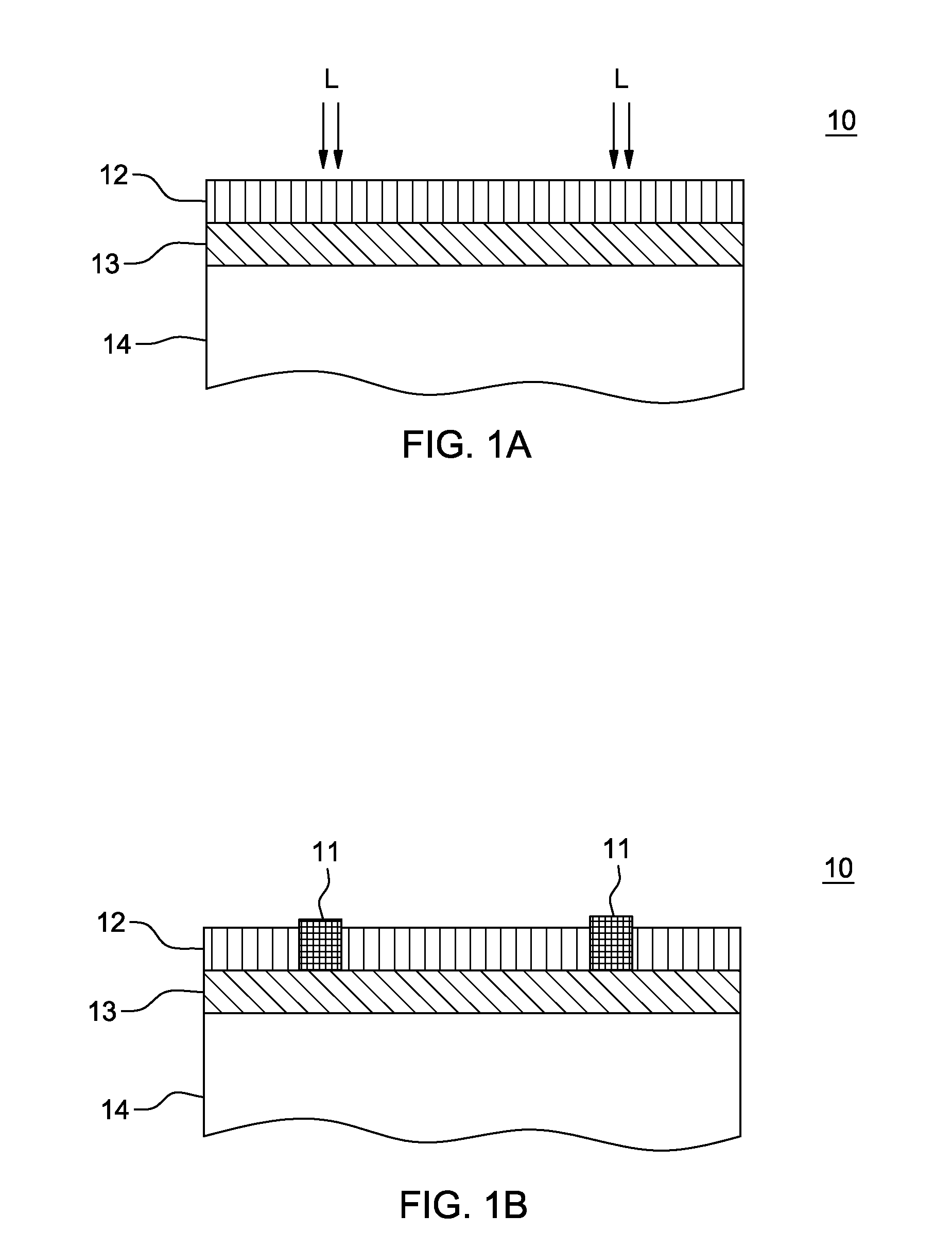
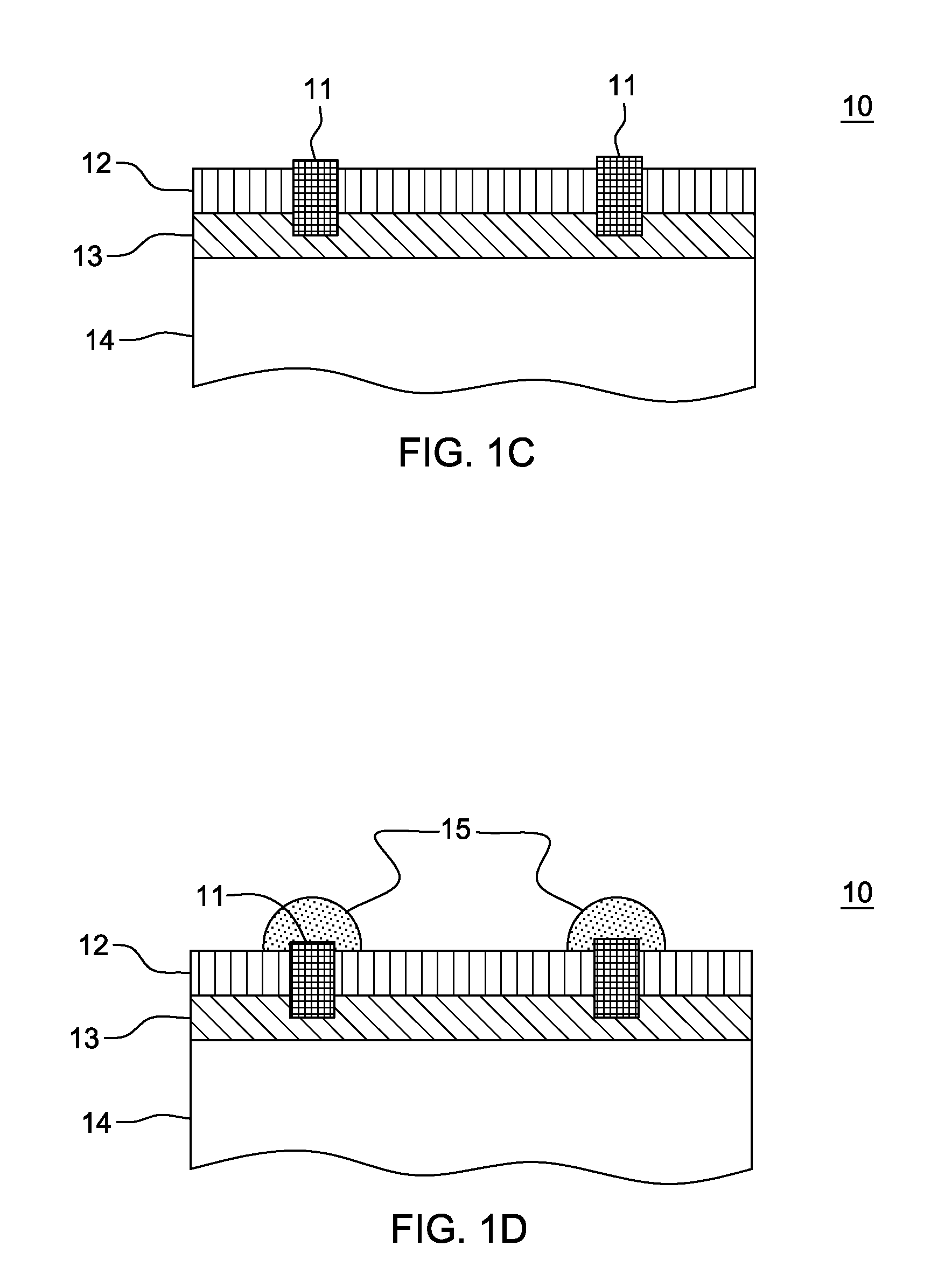
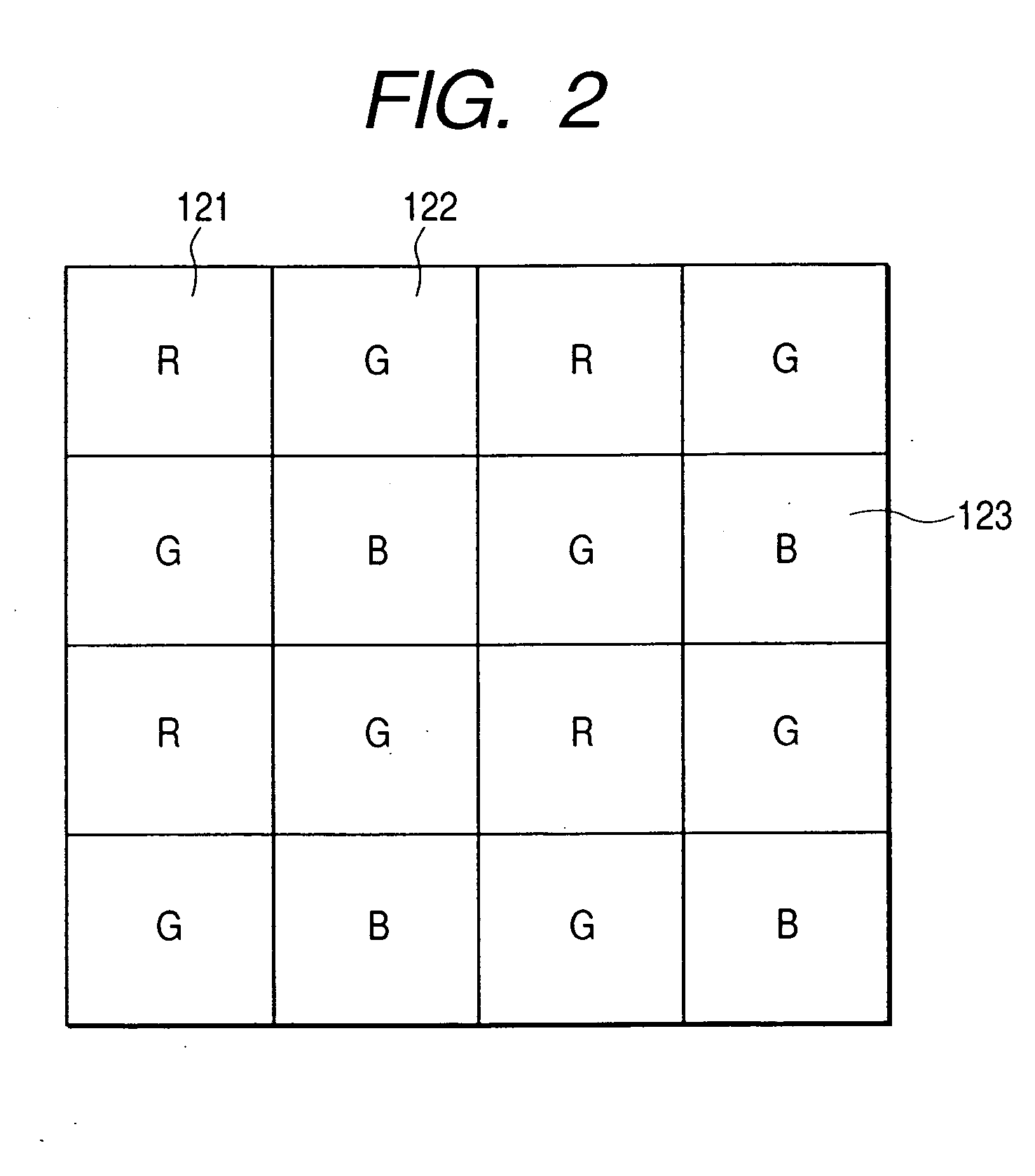
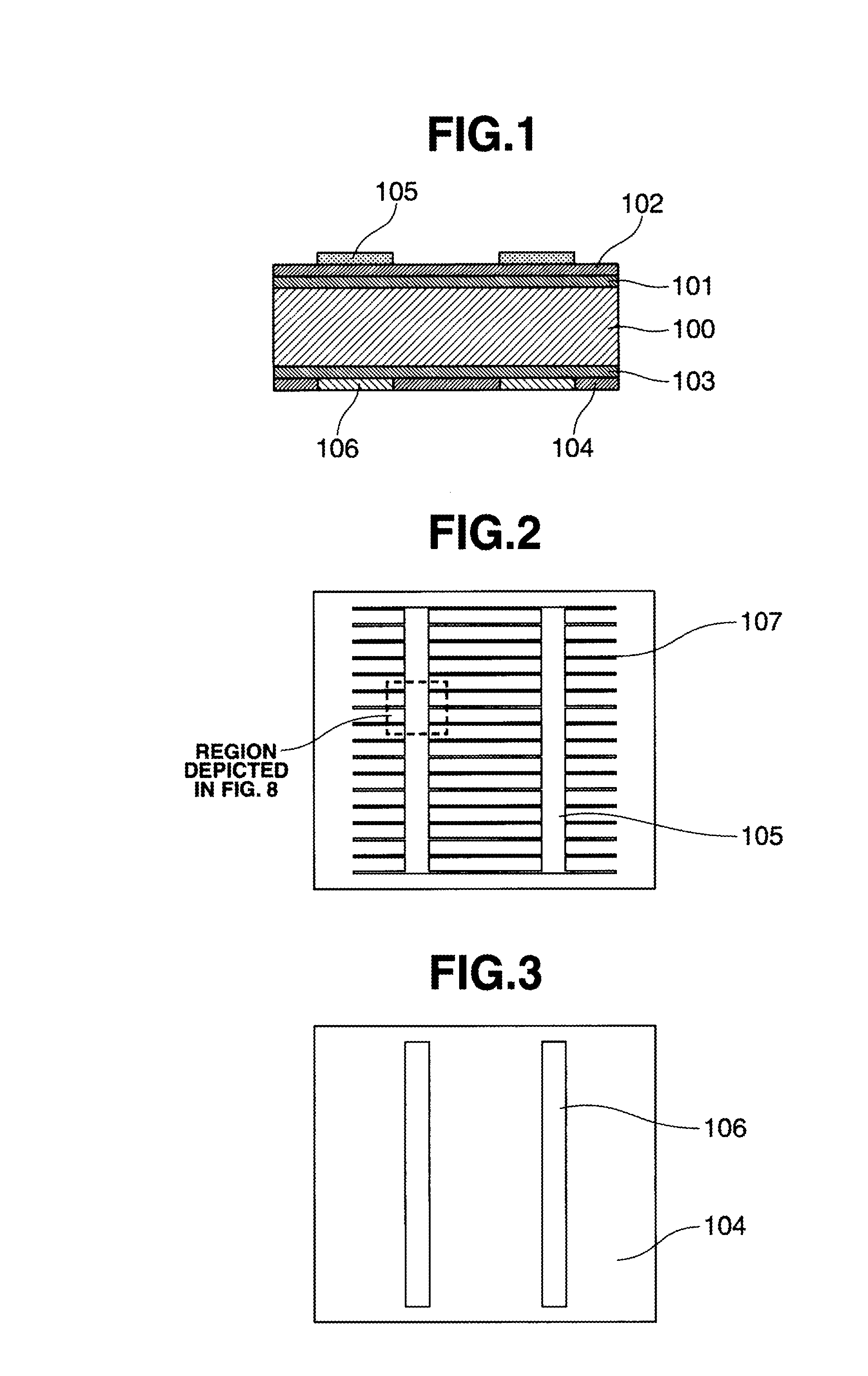
Semiconductor light emitting devices including flexible film having therein an optical element
ActiveUS7355284B2Reduce shadowsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLight emitting deviceSemiconductor
Owner:CREELED INC
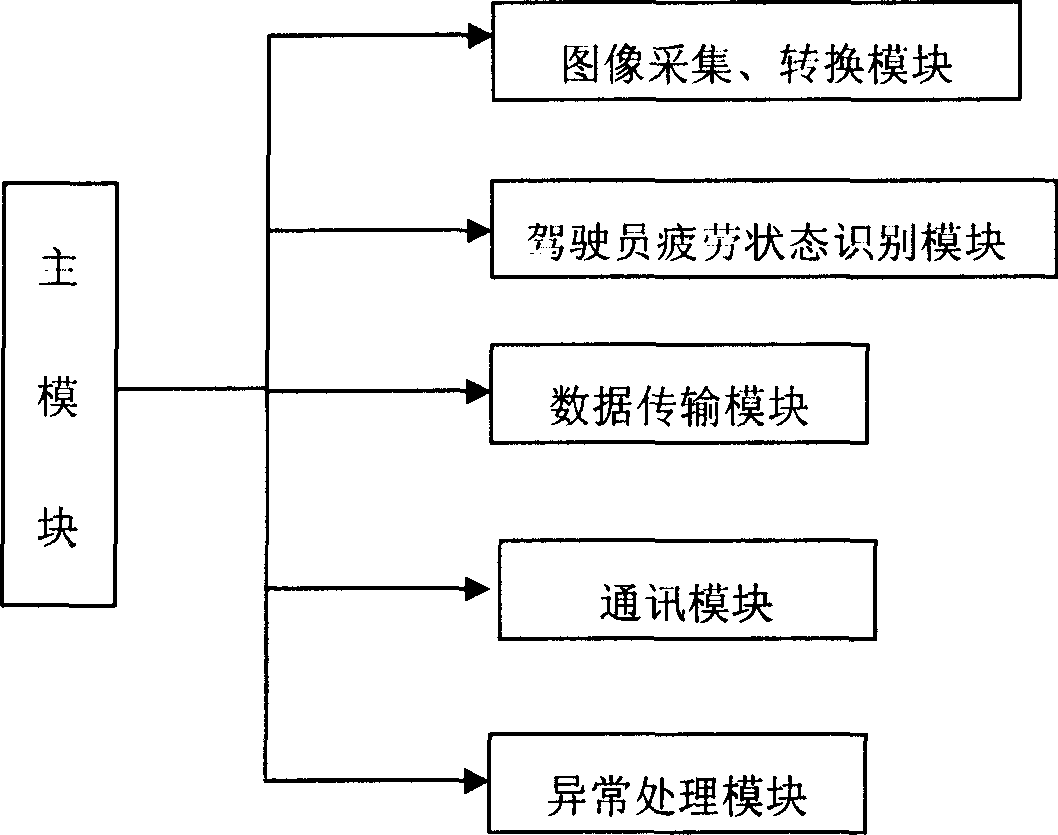
Device for monitoring fatigue driving state and its method
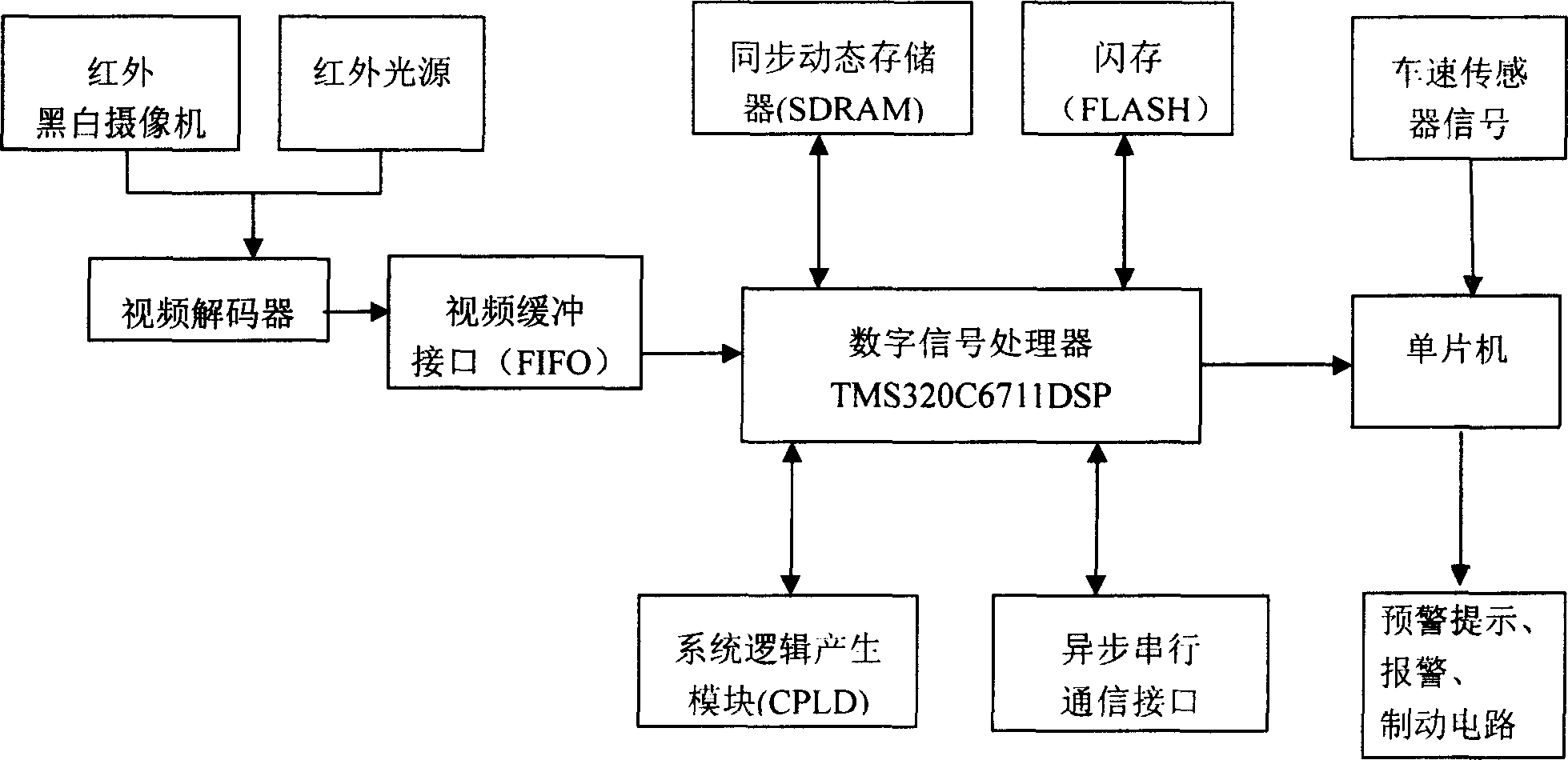
InactiveCN1830389AReduce shadowsImprove imaging effectImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringEye stateTemplate matching
An apparatus for monitoring the fatigue state of the motor-driven vehicle's driver is composed of image acquisition and conversion system, image processing system, fatigue state recognizing system, prompting and alarm system and brake system. Its method includes such steps as acquiring the face images of driver by infrared light and camera, processing the images to obtain eye images, recognizing eye state, calculating the winking duration, frequency and PERCLOS value, and judging the fatigue degree of driver.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
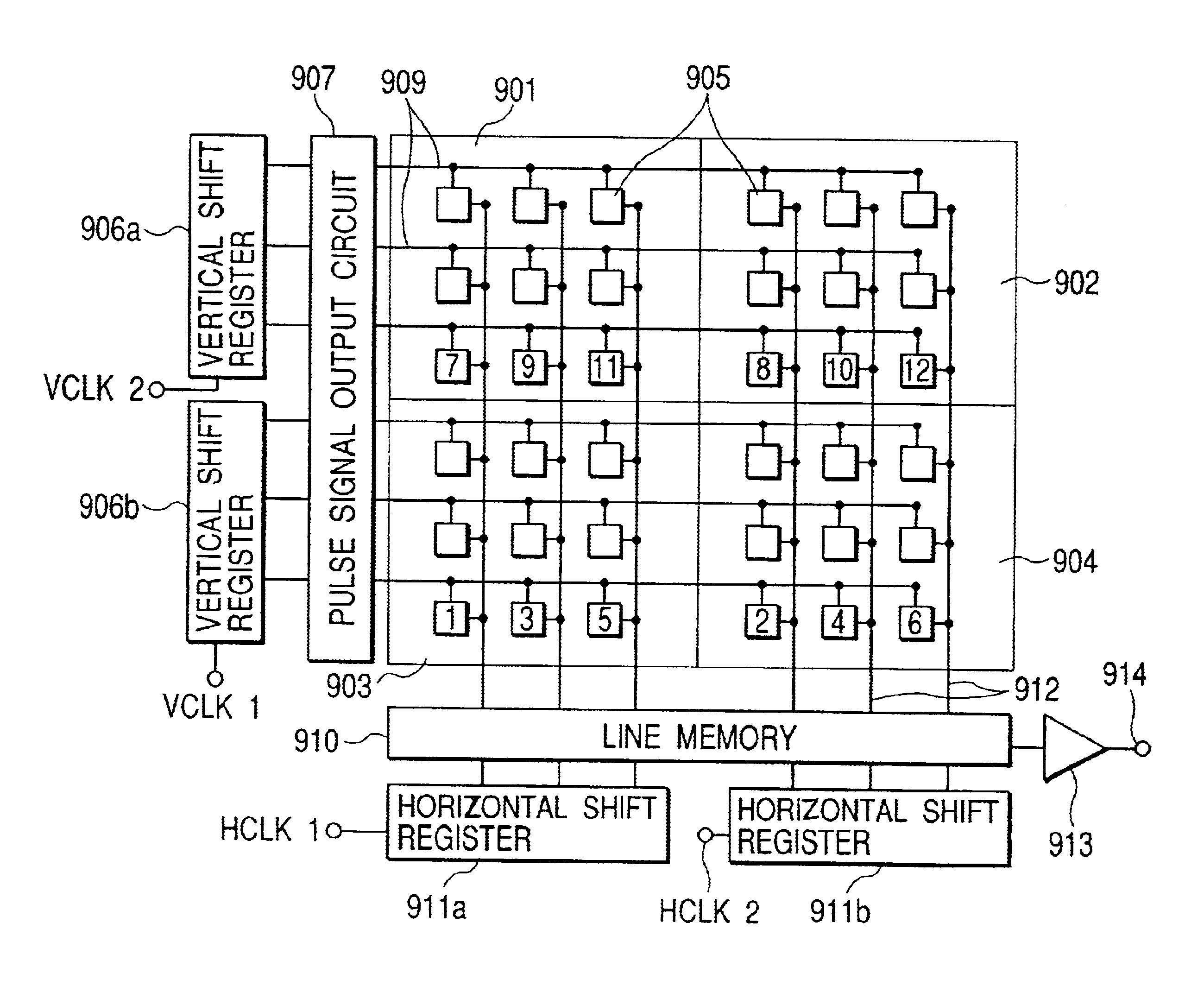
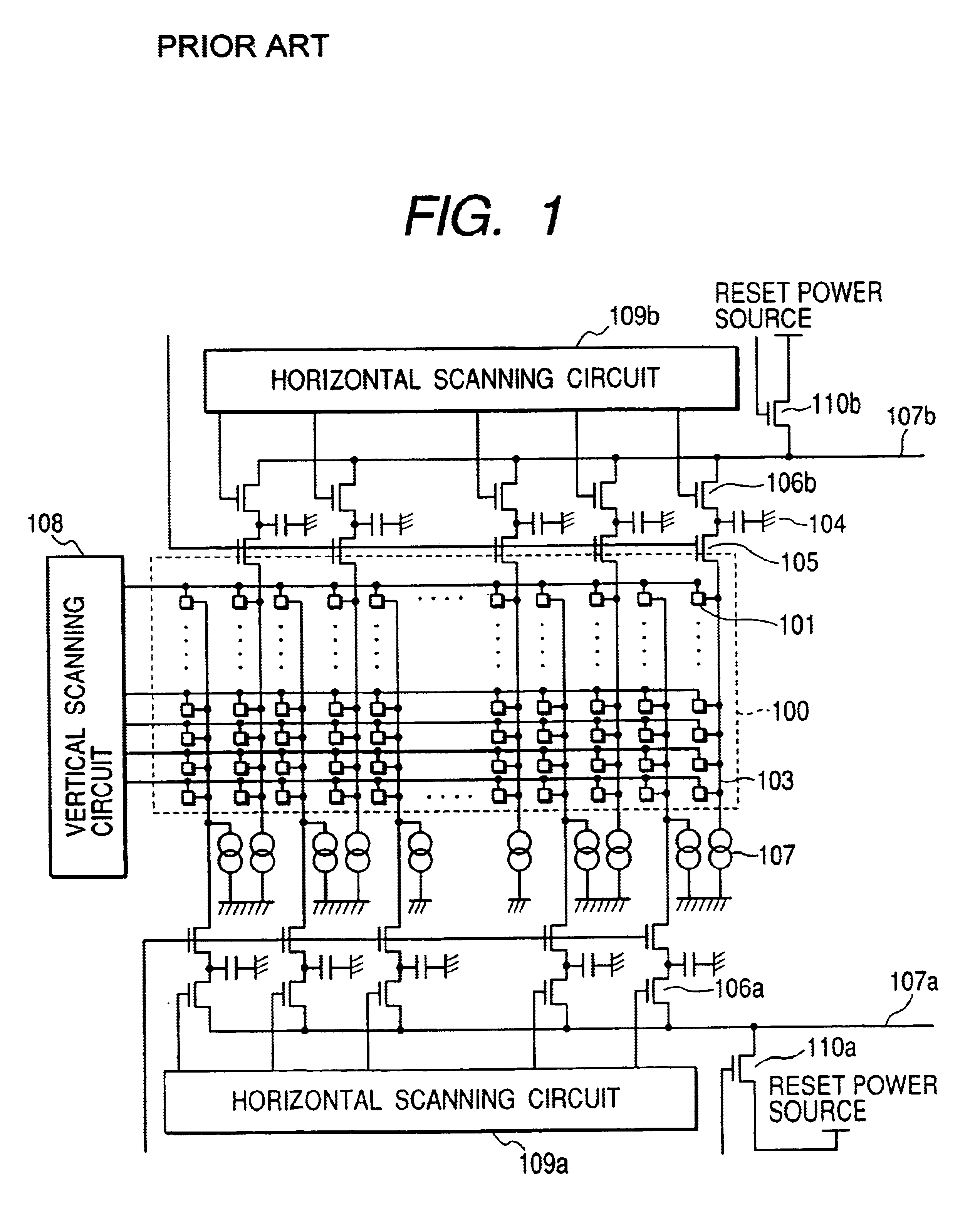
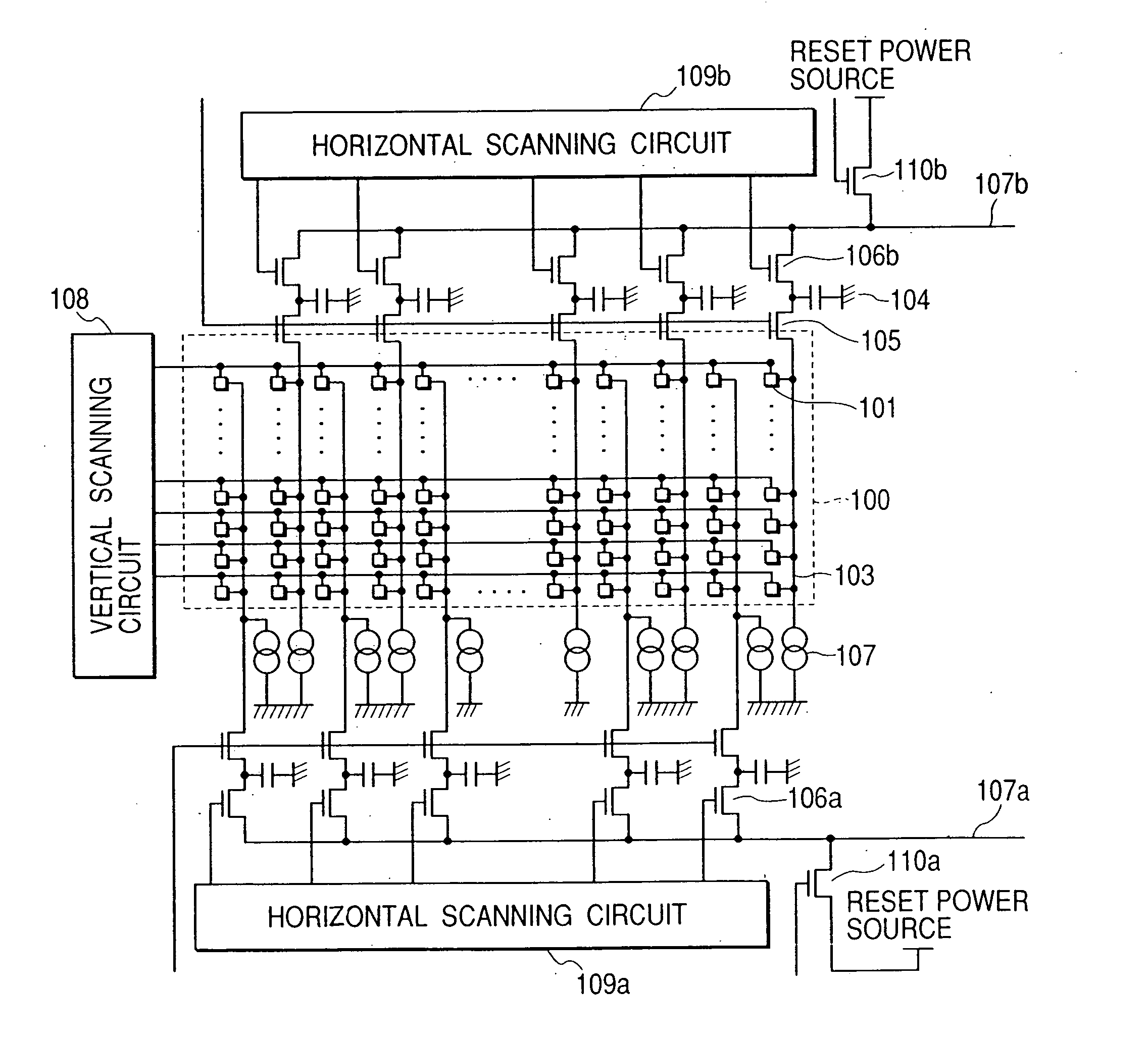
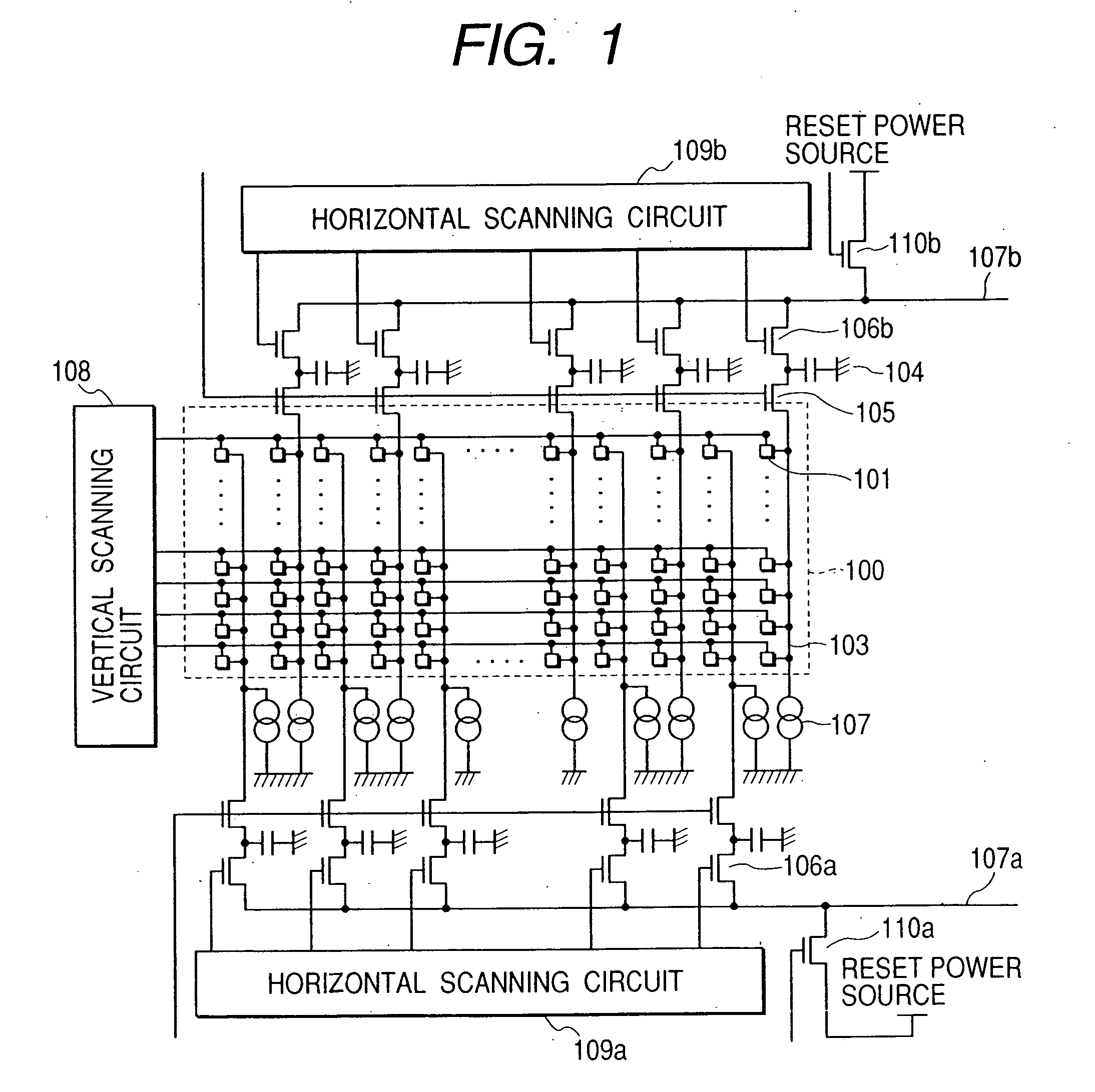
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS6952228B2Reduce lag of timeReduce time lagTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSemiconductor chipComputer science
An image pickup apparatus is provided, which comprises a plurality of image pickup areas formed on a same semiconductor chip and arranged in the horizontal and the vertical directions, each image pickup area having a plurality of pixels arranged in the horizontal and the vertical directions, a plurality of vertical scanning circuits which sequentially scan pixels in the vertical direction to scan a plurality of image pickup areas in the vertical direction independently from each other, a plurality of lenses, at least one of which is provided in each of the plurality of image pickup areas and which focuses light to form an image on the image pickup areas, and a driving circuit which drives the plurality of vertical scanning circuits so that at least a part of a scanning period of each of the plurality of vertical scanning circuits overlaps with each other.
Owner:CANON KK
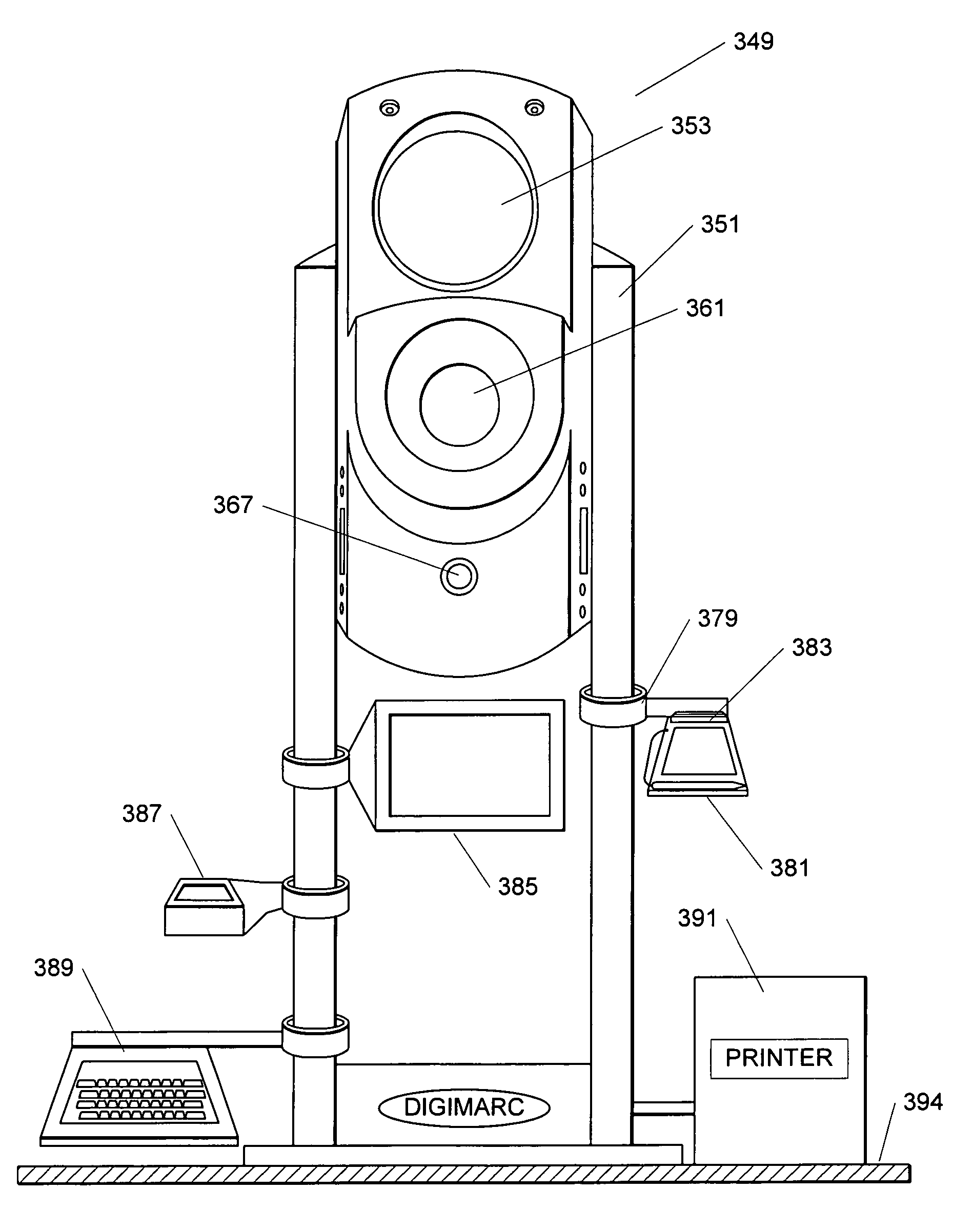
Multifunction all in one capture station for creating identification documents
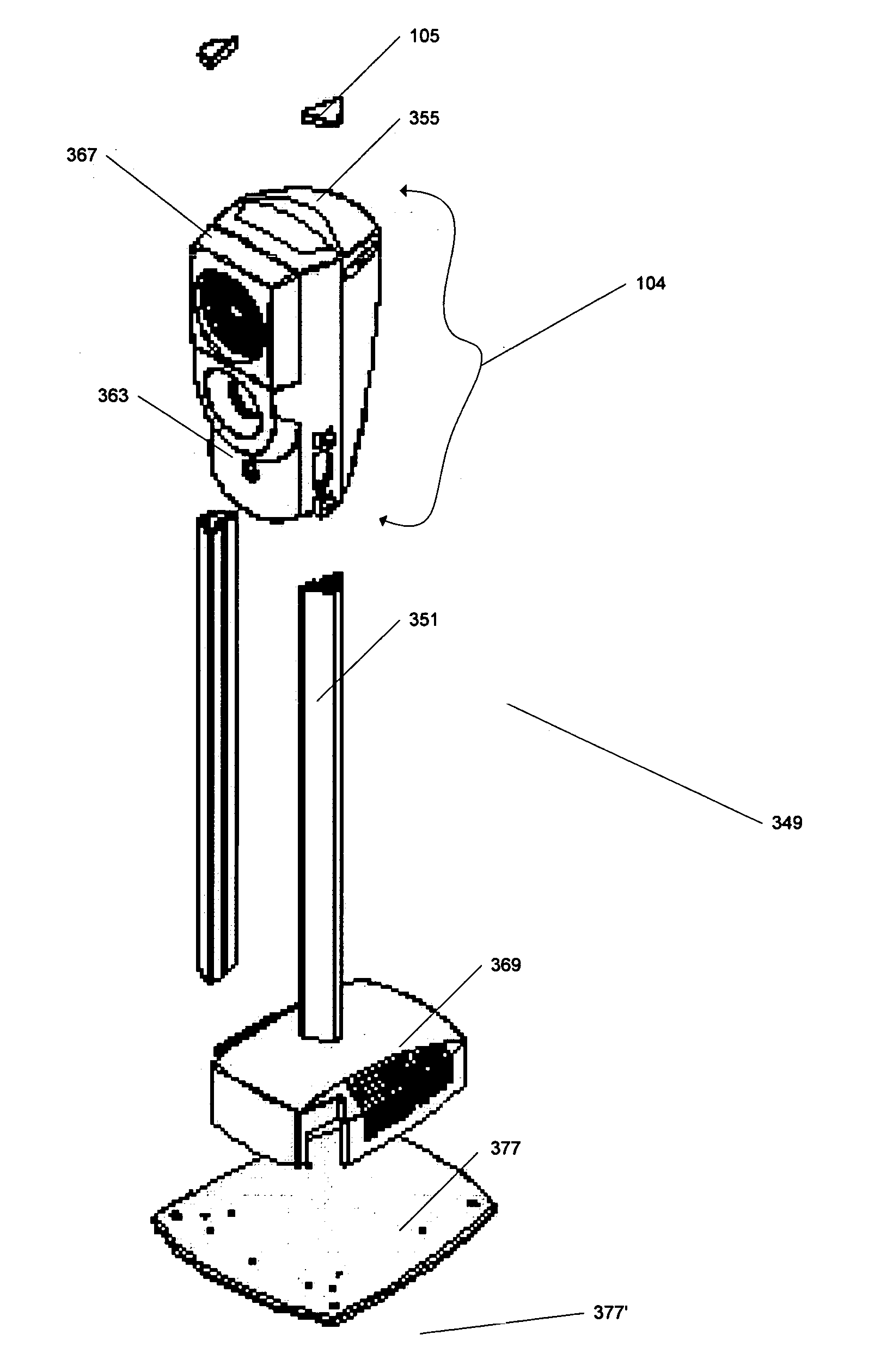
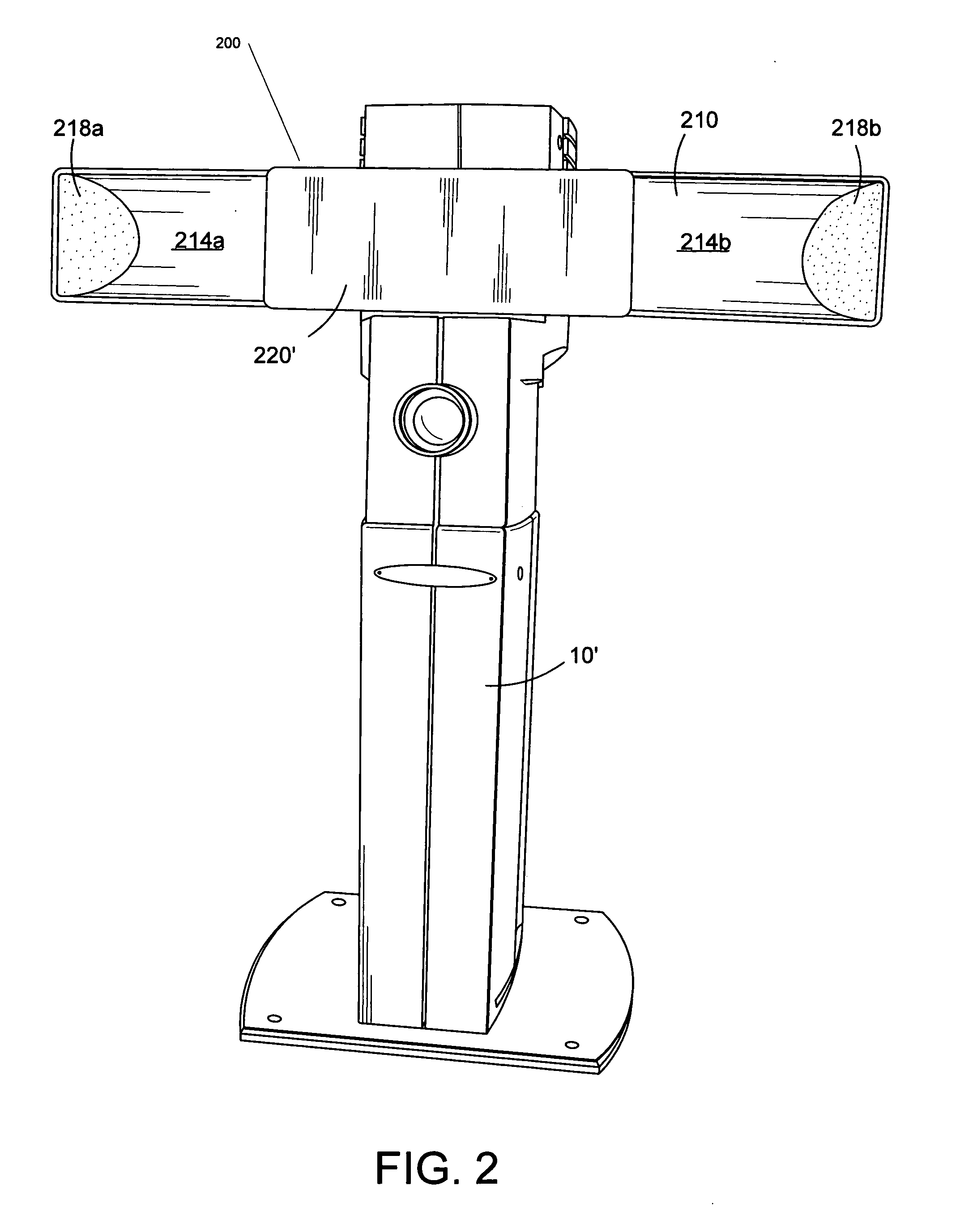
ActiveUS20050243199A1Reduce shadowsEnhanced Shadow Reduction SystemTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionNetwork connectionRemote computer
A capture station for creating identification documents comprises a housing including a camera and lighting device, a base, and at least one leg extending from the base. The housing is mounted to the leg to enable height adjustment of the camera. One configuration of the capture station has two substantially rigid and parallel legs with the housing mounted between the legs. Configurations of the capture station can include a processor, such a CPU or embedded controller, enabling ID document data capture functions to be executed within the capture station, and to be controlled via a remote computer via a network connection. In one embodiment, the processor is housed in the base and communicates with the camera via wiring routed through the leg. Peripherals used in capture functions, such as a fingerprint reader, signature pad, display, etc., may be mounted to the leg via clamps, or a plug in receptacle with power and communication wiring provided in the leg.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
Multifunction all in one capture station for creating identification documents
ActiveUS7646425B2Reduce shadowsEnhanced Shadow Reduction SystemTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionNetwork connectionRemote computer
A capture station for creating identification documents comprises a housing including a camera and lighting device, a base, and at least one leg extending from the base. The housing is mounted to the leg to enable height adjustment of the camera. One configuration of the capture station has two substantially rigid and parallel legs with the housing mounted between the legs. Configurations of the capture station can include a processor, such a CPU or embedded controller, enabling ID document data capture functions to be executed within the capture station, and to be controlled via a remote computer via a network connection. In one embodiment, the processor is housed in the base and communicates with the camera via wiring routed through the leg. Peripherals used in capture functions, such as a fingerprint reader, signature pad, display, etc., may be mounted to the leg via clamps, or a plug in receptacle with power and communication wiring provided in the leg.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
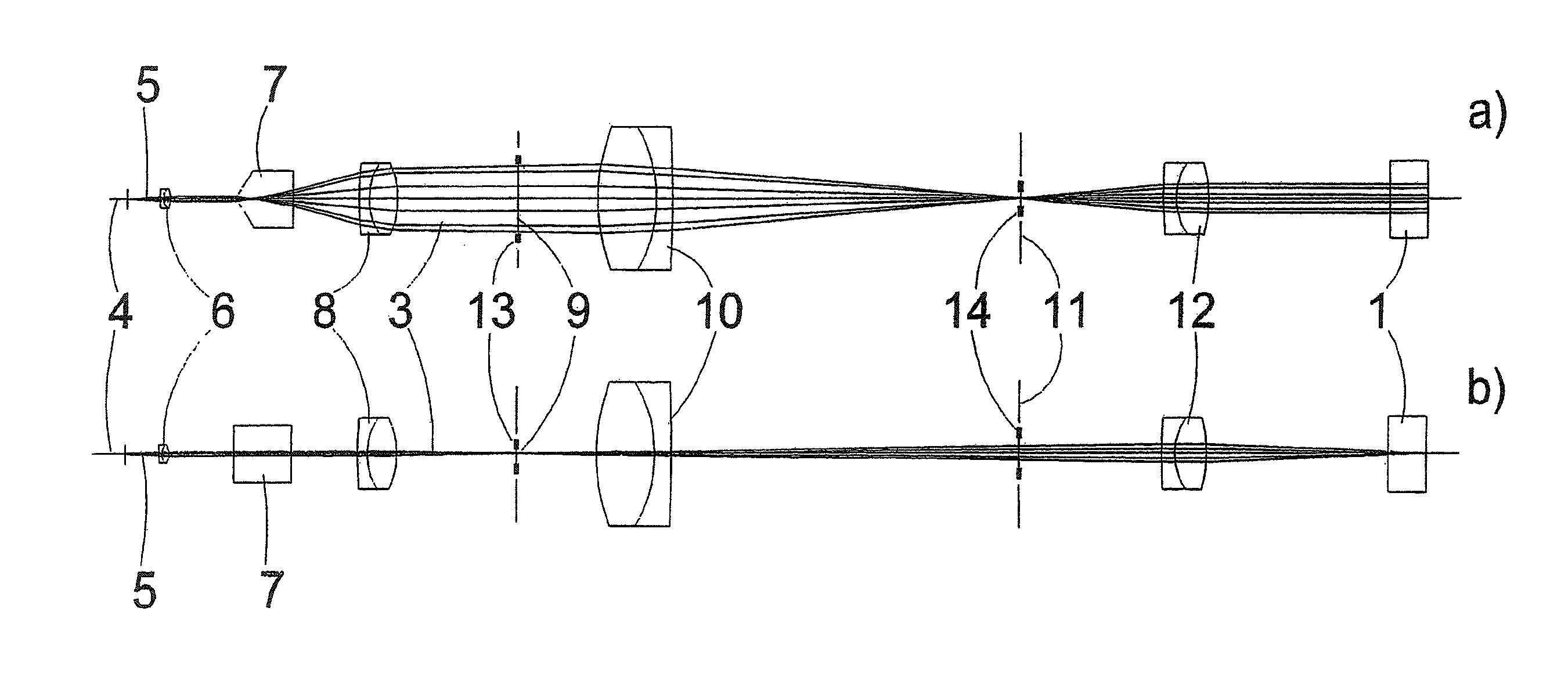
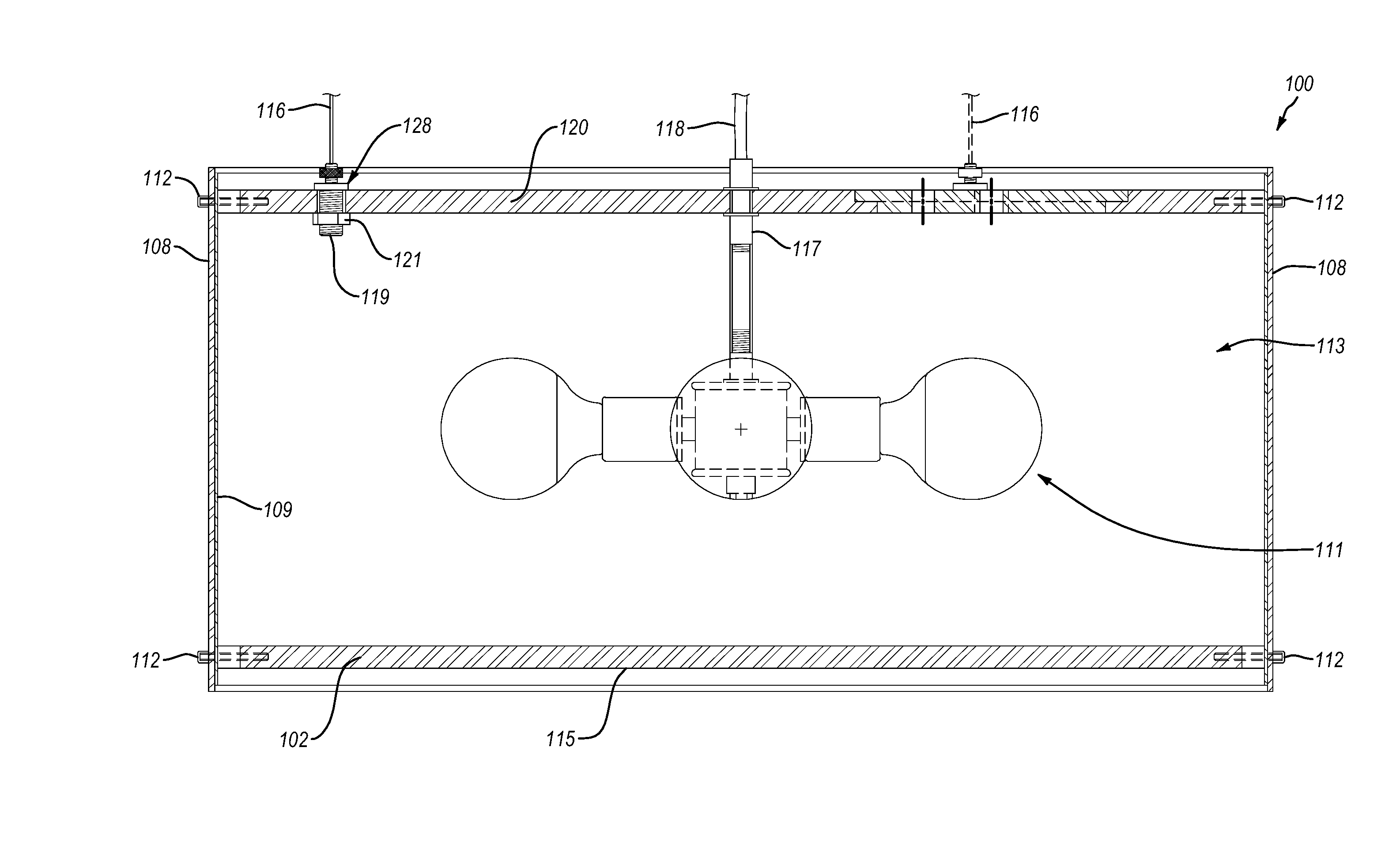
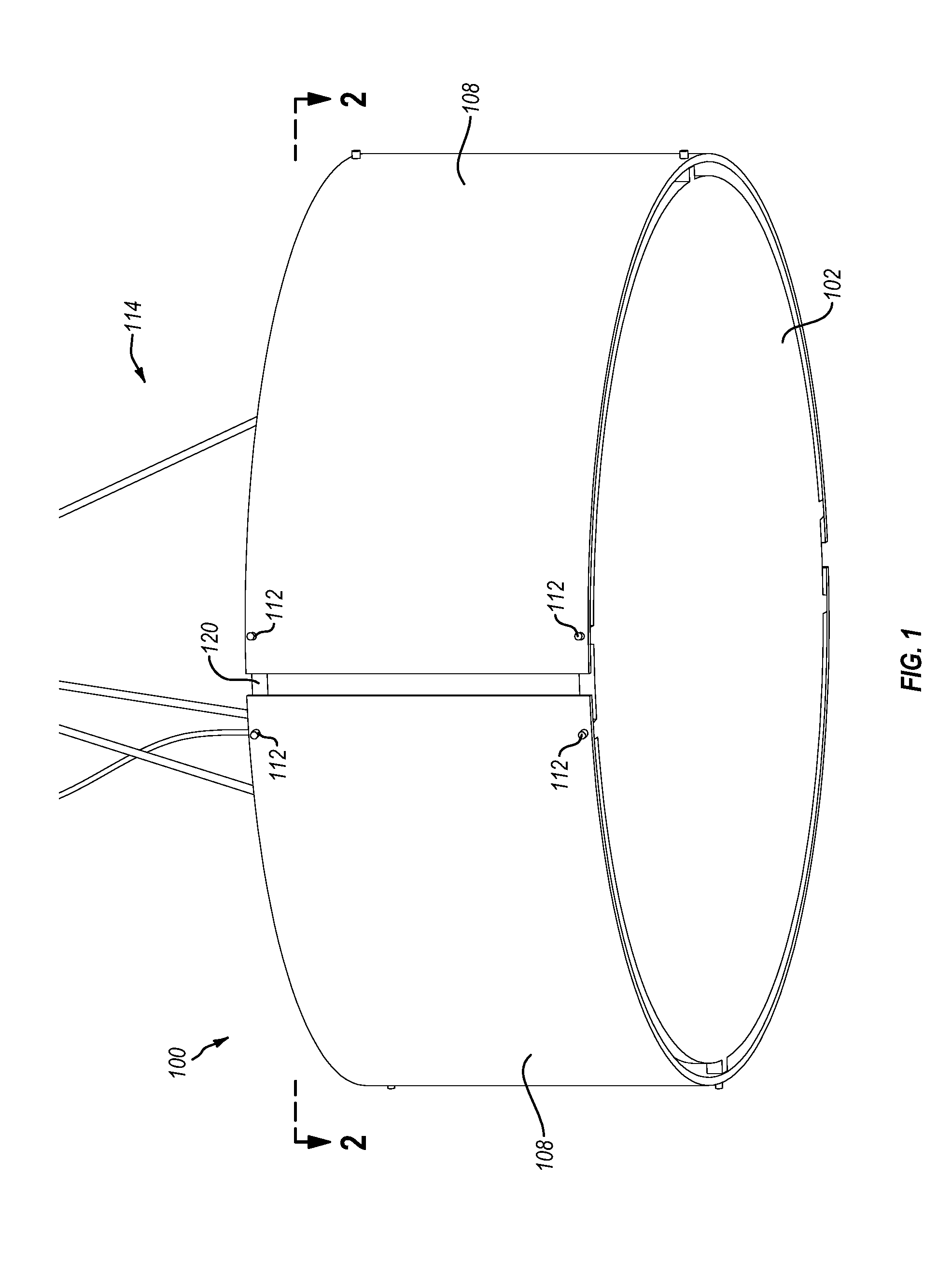
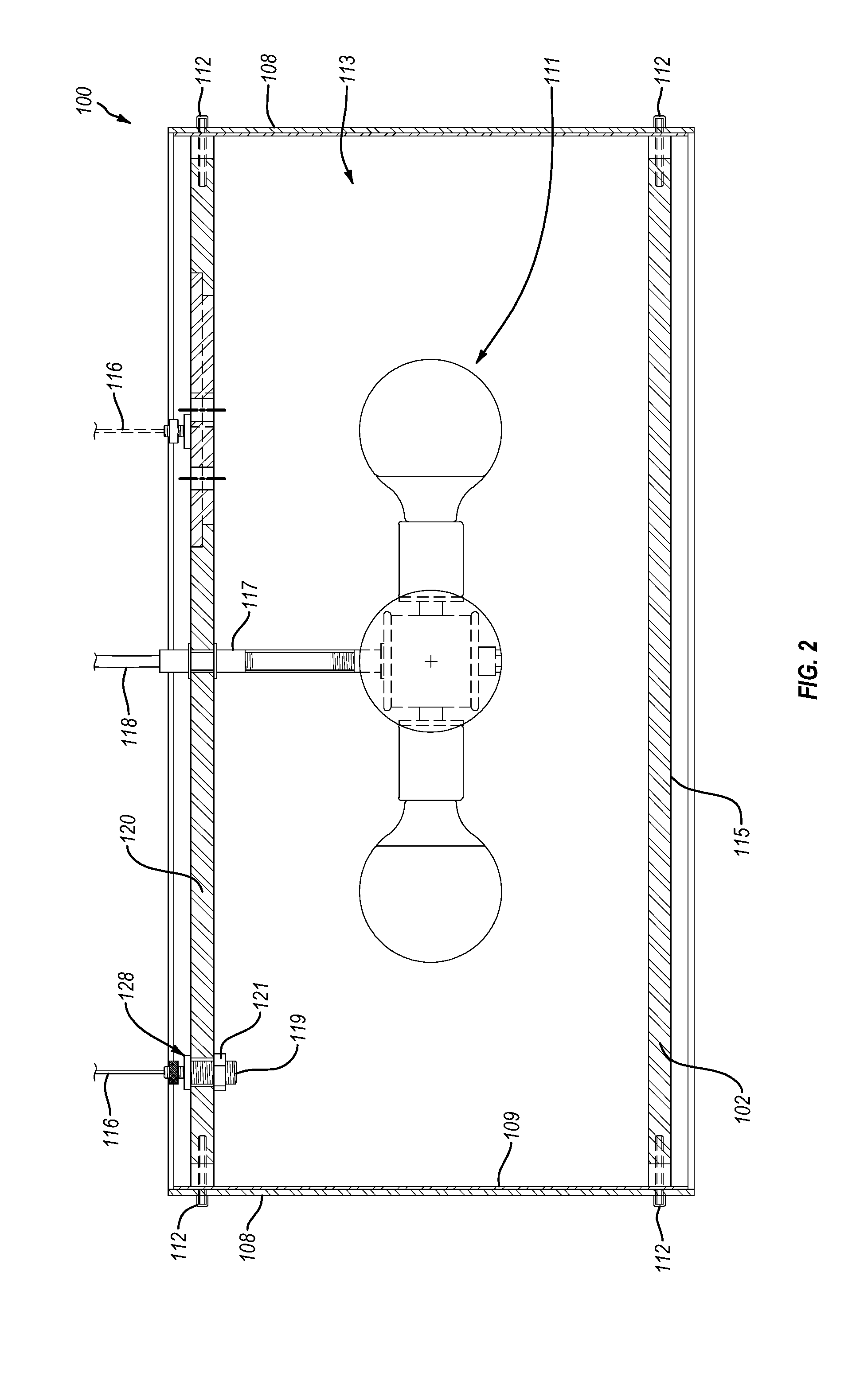
Optical arrangement for the production of a light-sheet
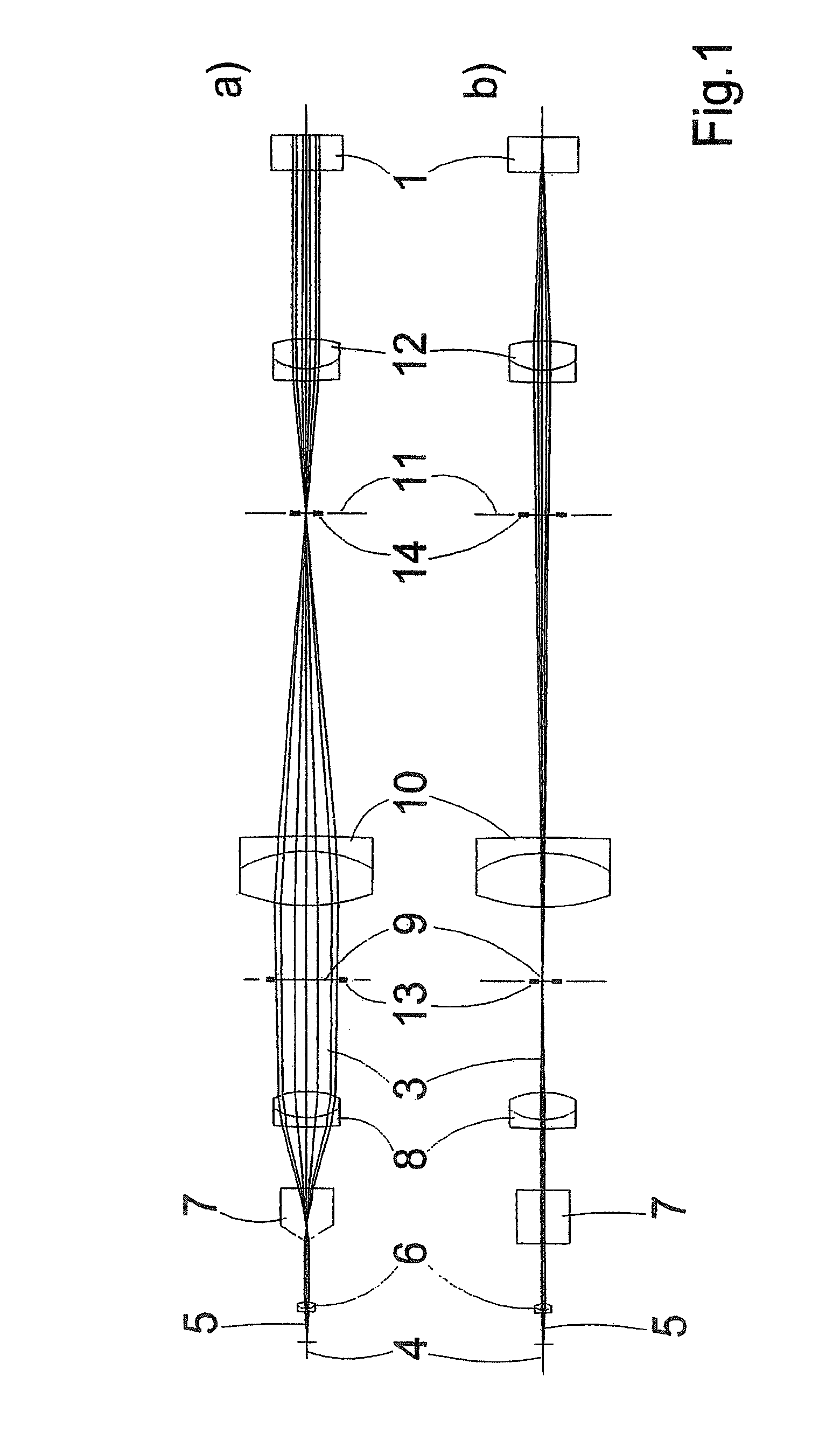
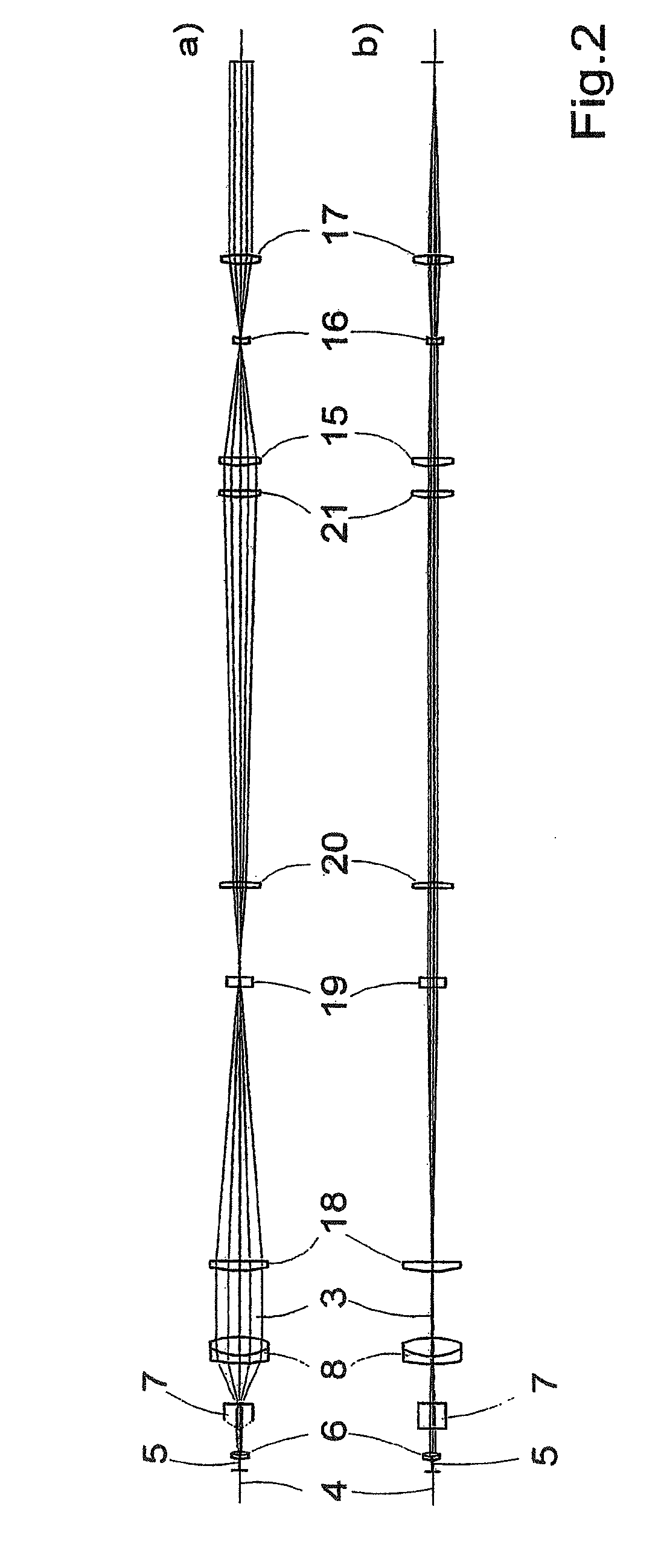
The invention is directed to an optical arrangement with a light source for emitting a light bundle and with optical elements for transforming this light bundle into the shape of a light sheet, particularly suitable for illuminating individual planes of a three-dimensional specimen in selective plane illumination microscopy (SPIM). According to the invention, means are provided for varying the cross section of the light sheet, for varying the length of the light sheet and / or for influencing the direction in which individual beam components extending within the light sheet are directed to the specimen substance. This makes it possible to adapt the geometry of the light sheet to the illumination requirements for observing one and the same specimen plane with a plurality of different objectives and, if required, to reduce shadows occurring within the observed specimen plane as a result of the illumination.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Arrangement and method for the generation of EUV radiation of high average output
InactiveUS20070181834A1Increase rotation speedIncrease productionRadiation pyrometryNanoinformaticsLithographic artistMechanical components
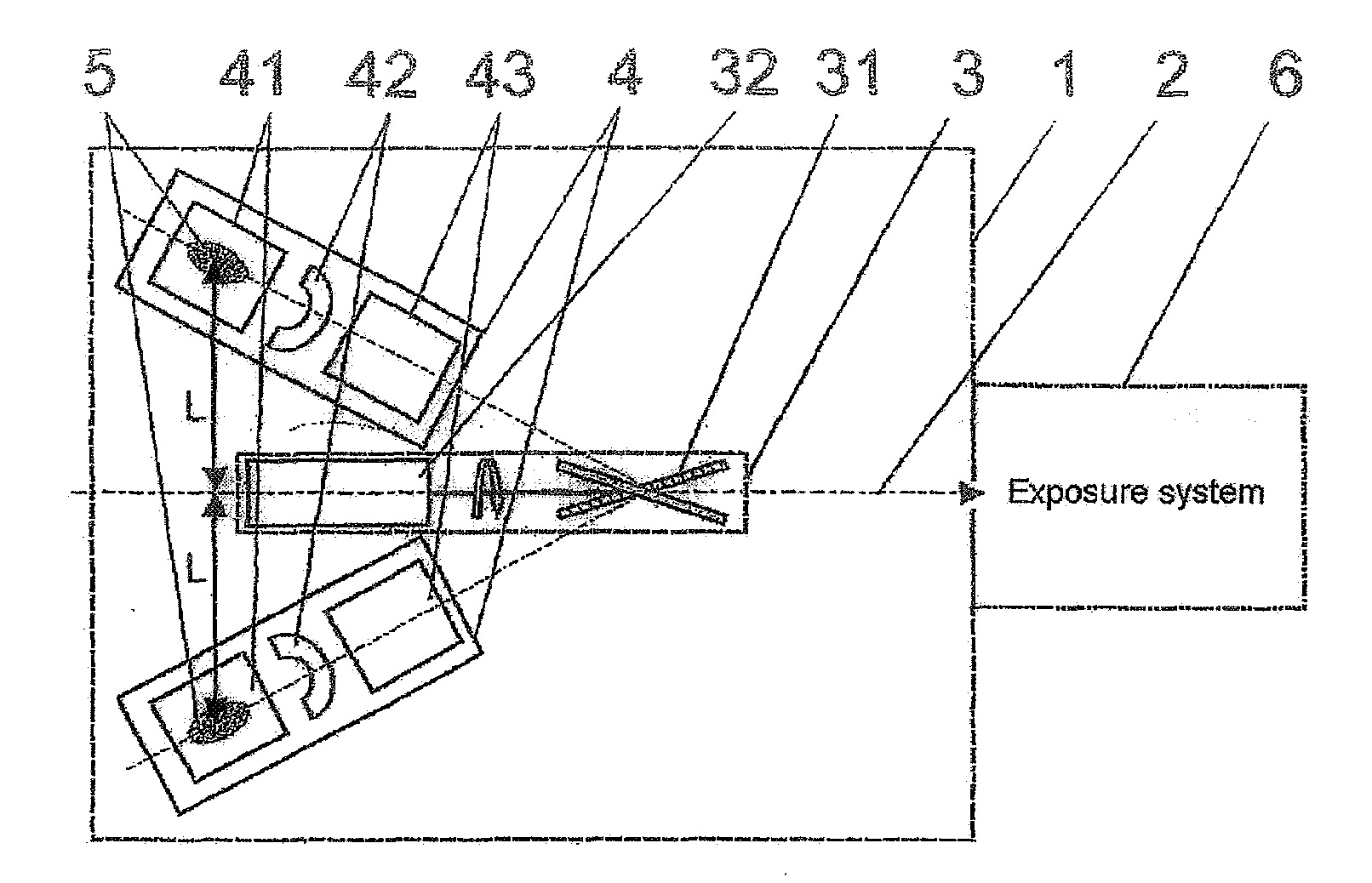
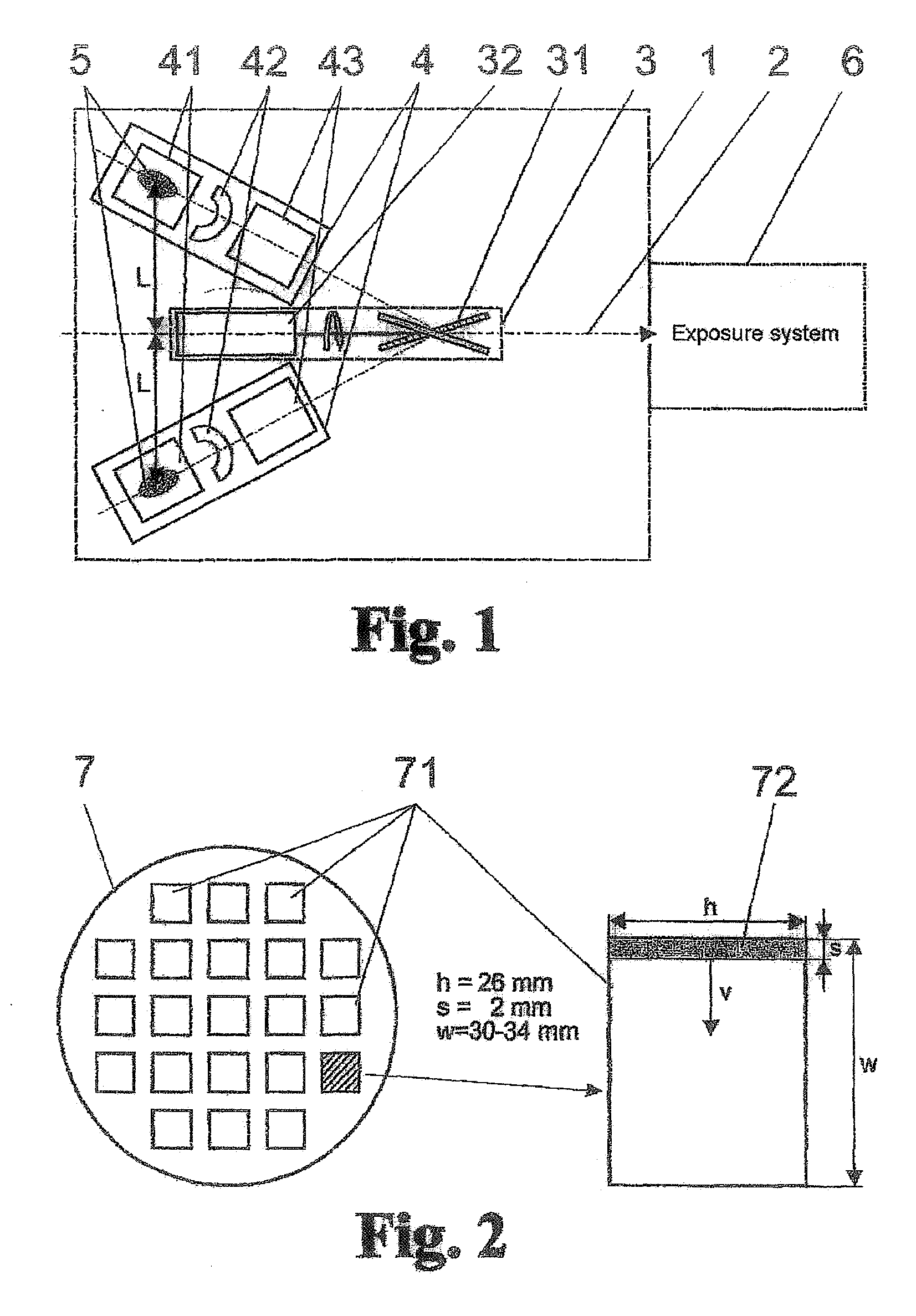
The invention is directed to an arrangement and a method for the generation of EUV radiation of high average output, preferably for the wavelength region of 13.5 nm for use in semiconductor lithography. It is the object of the invention to find a novel possibility for generating EUV radiation of high average output which permits a time-multiplexing of the radiation of a plurality of source modules in a simple manner without overloading the source modules and without requiring extremely high rotational speeds of optical-mechanical components. This object is met, according to the invention, in that a plurality of identically constructed source modules which are arranged so as to be distributed around a common optical axis are directed to a rotatably mounted reflector arrangement which successively couples in the beam bundles of the source modules along the optical axis. The reflector arrangement has a drive unit by which a reflecting optical element is adjustable so as to be stopped temporarily in angular positions that are defined for the source modules and is oriented to the next source module in intervals between two exposure fields of a wafer by means of control signals emitted by an exposure system.
Owner:XTREME TECH
Solar energy module
InactiveUS20100229852A1Load will not be successfulReduce heat lossPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityDouble wall
A low cost mass-produced solar module that extracts both electricity and heat from the sun. One or more reflectors held by a frame reflect the sun's heat into an absorber. Each reflector rotates about its axle to keep its reflected solar energy focused on the absorber. In one embodiment, solar heat is focused to heat fluid that flows to thermodynamic engines that convert the heat to electricity. Engine waste heat is also captured for use as building heat, home hot water or industrial process heat. In another embodiment, solar heat is focused onto photovoltaic devices that directly convert light into electricity. The fluid that cools the photovoltaic devices can be used for building heat, home hot water or industrial process heat. The frame shields the reflectors from ambient wind loads, supports reflector axles accurately and simplifies installation on roofs or walls of buildings. The frame, reflectors, absorber and ancillary components comprise a module that can be shipped, installed and operated by low skill. Most components are fabricated using “double wall” construction formed by two face sheets held apart by a core that reduces their weight and their cost. Reflector surfaces are curved to focus the sun and to provide additional strength. Module design includes methods to install, maintain and verify proper functioning of the modules. In addition, methods show how electrical energy can be derived from the module, both circulating fluids that power thermodynamic engines and by photovoltaic cells that are cooled by the circulating fluid. Sensors contained in the modules detect aberrant behavior and optimize reflector trajectories to extract the most solar heat available. Communication between modules allows optimization of an array of modules.
Owner:BUCKLEY B SHAWN
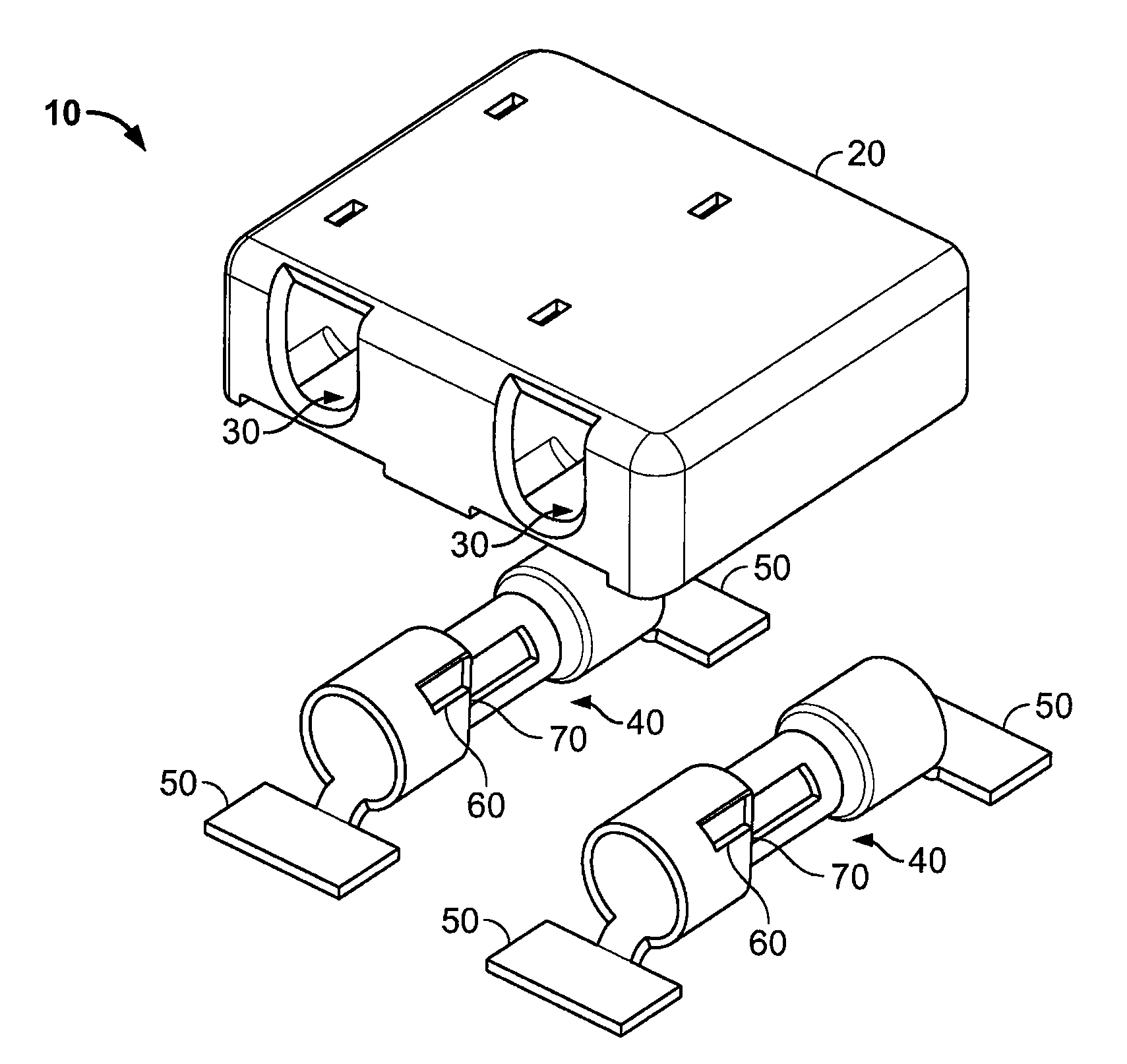
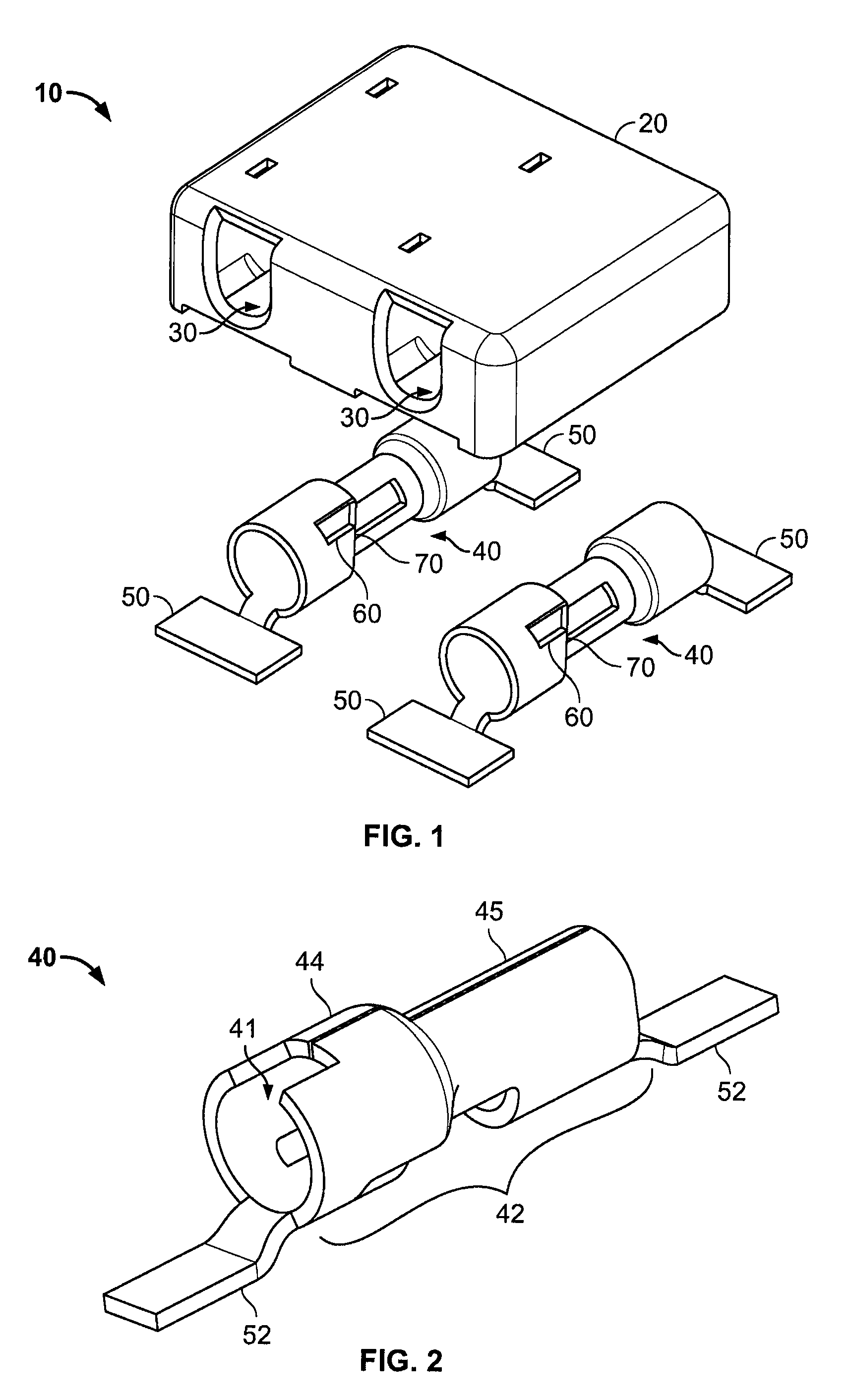
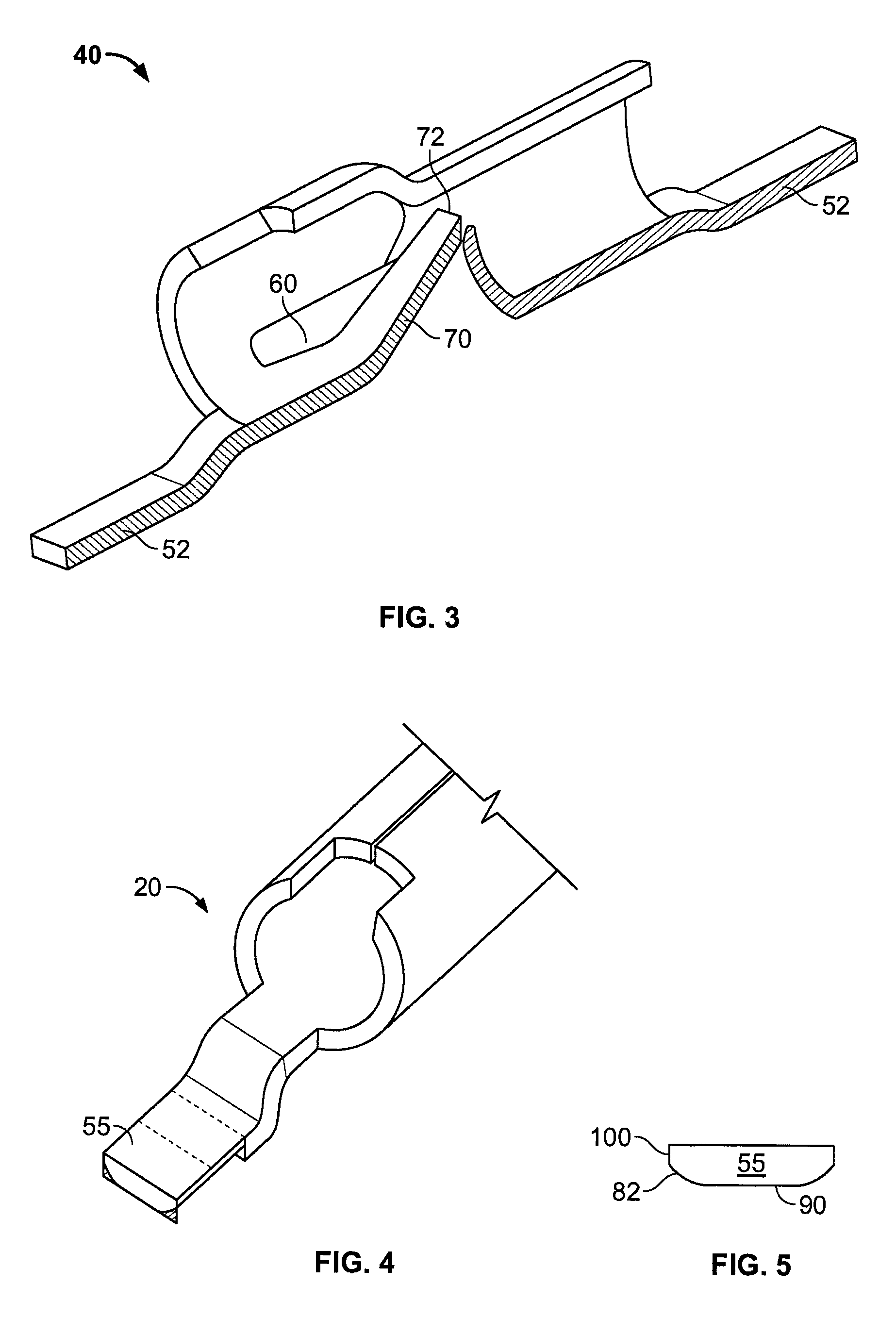
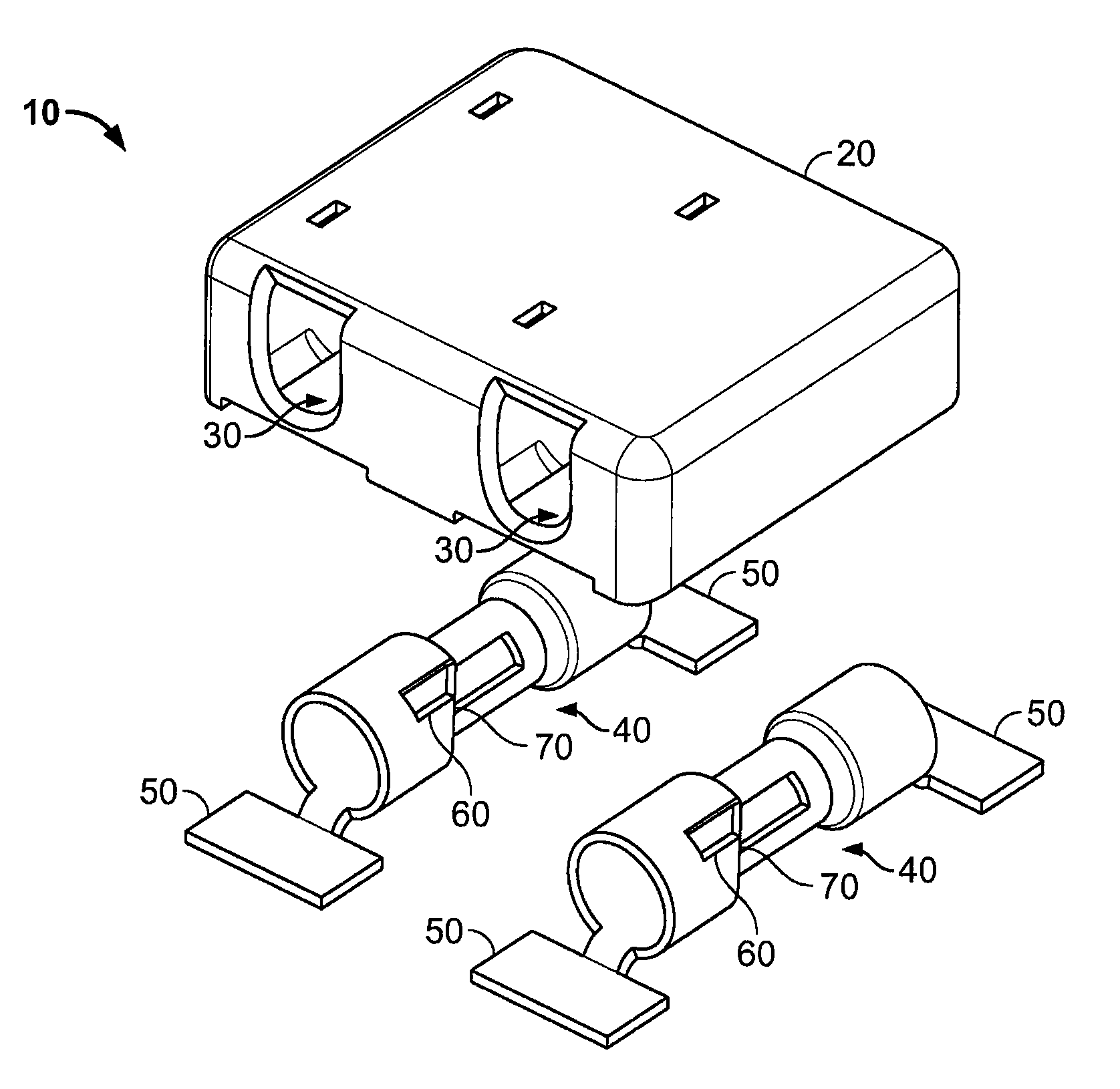
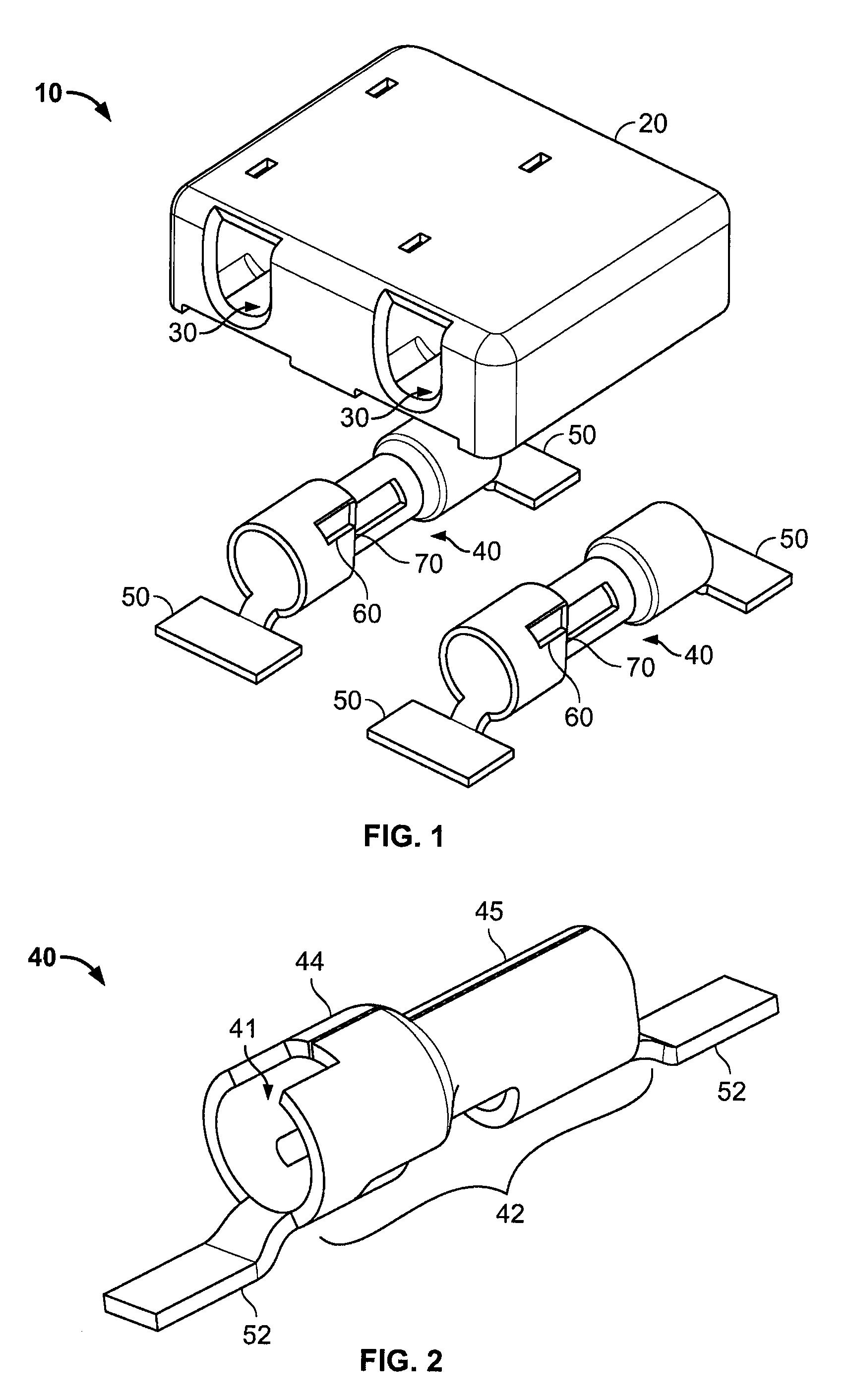
Surface mount poke in connector
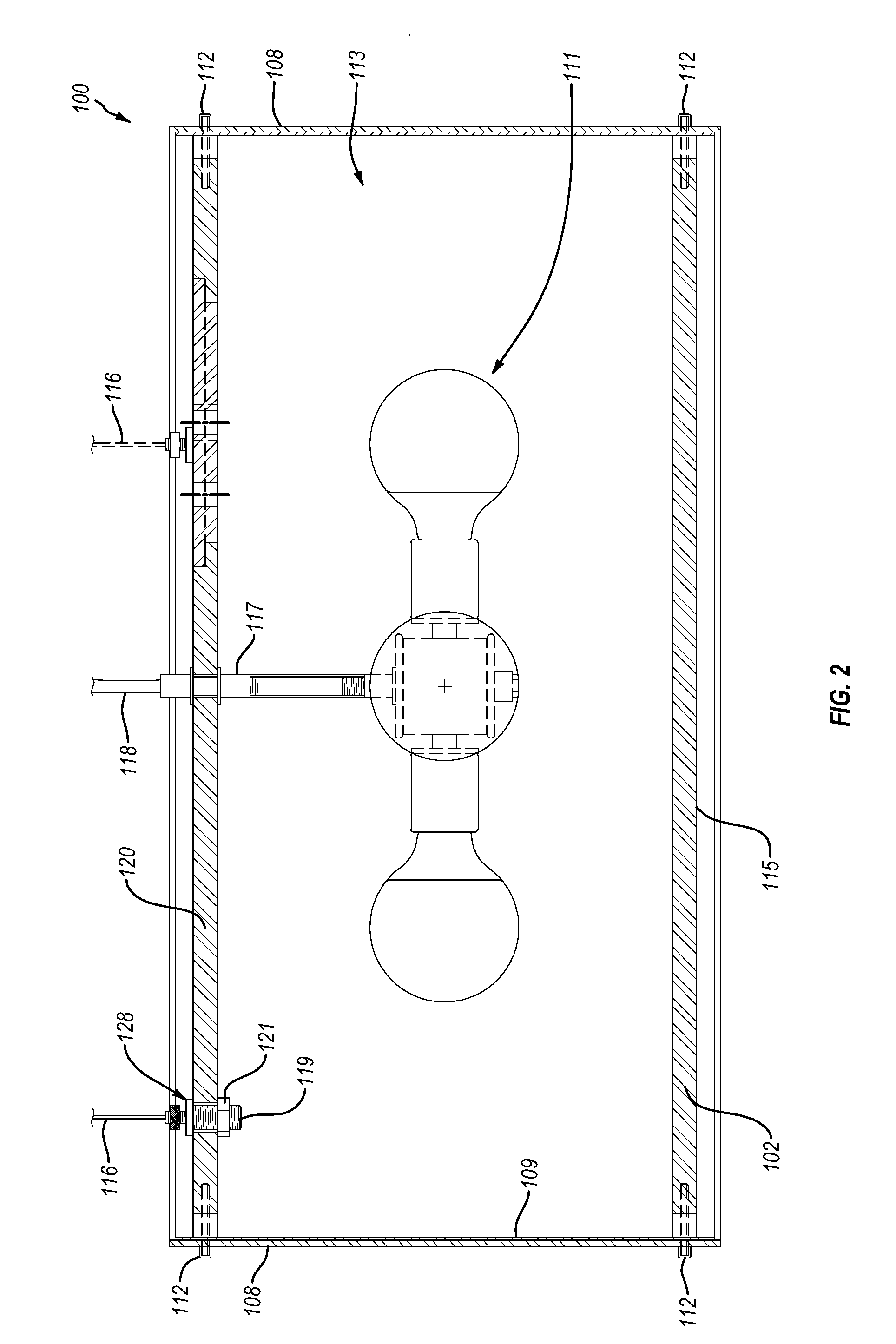
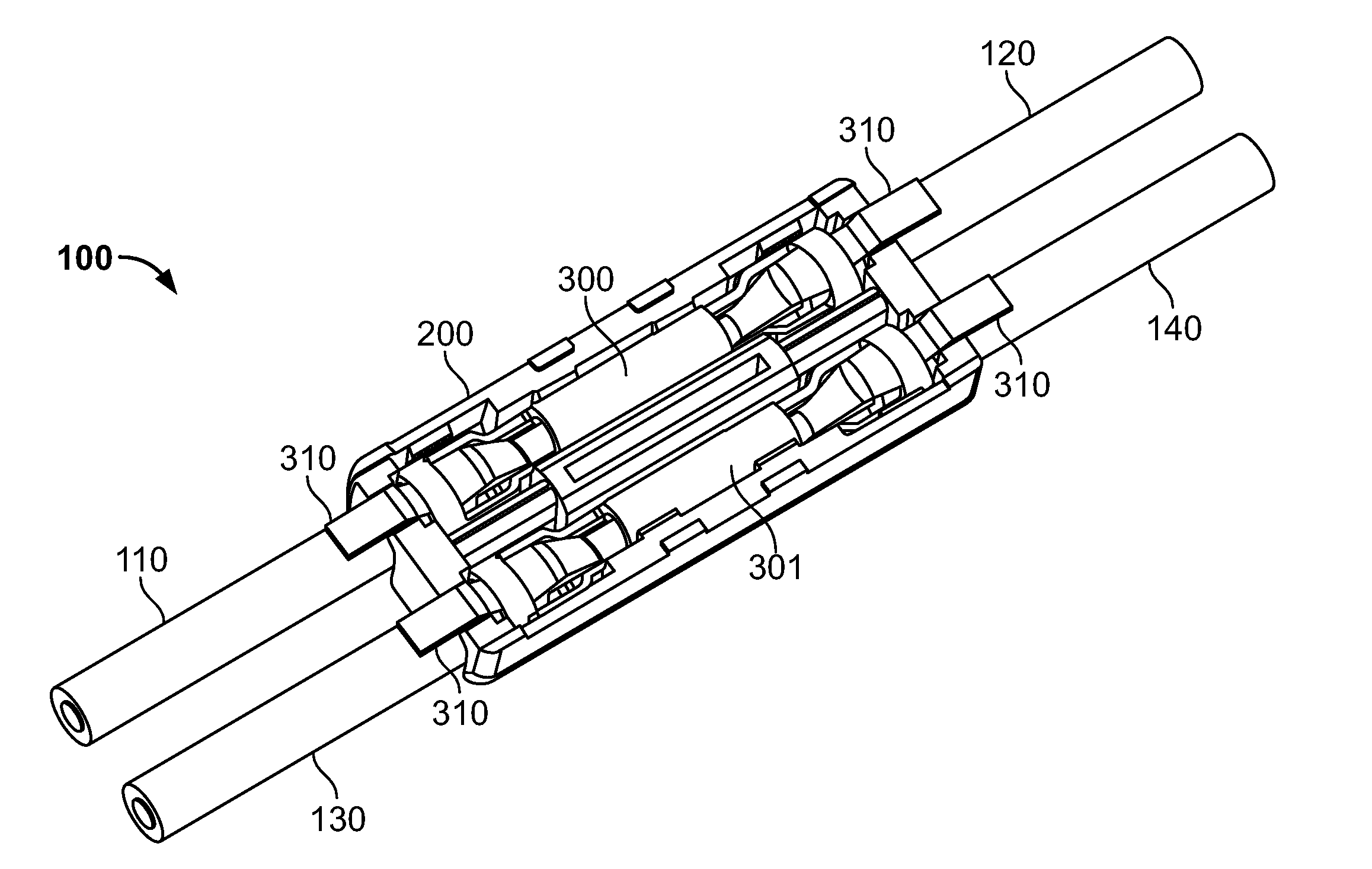
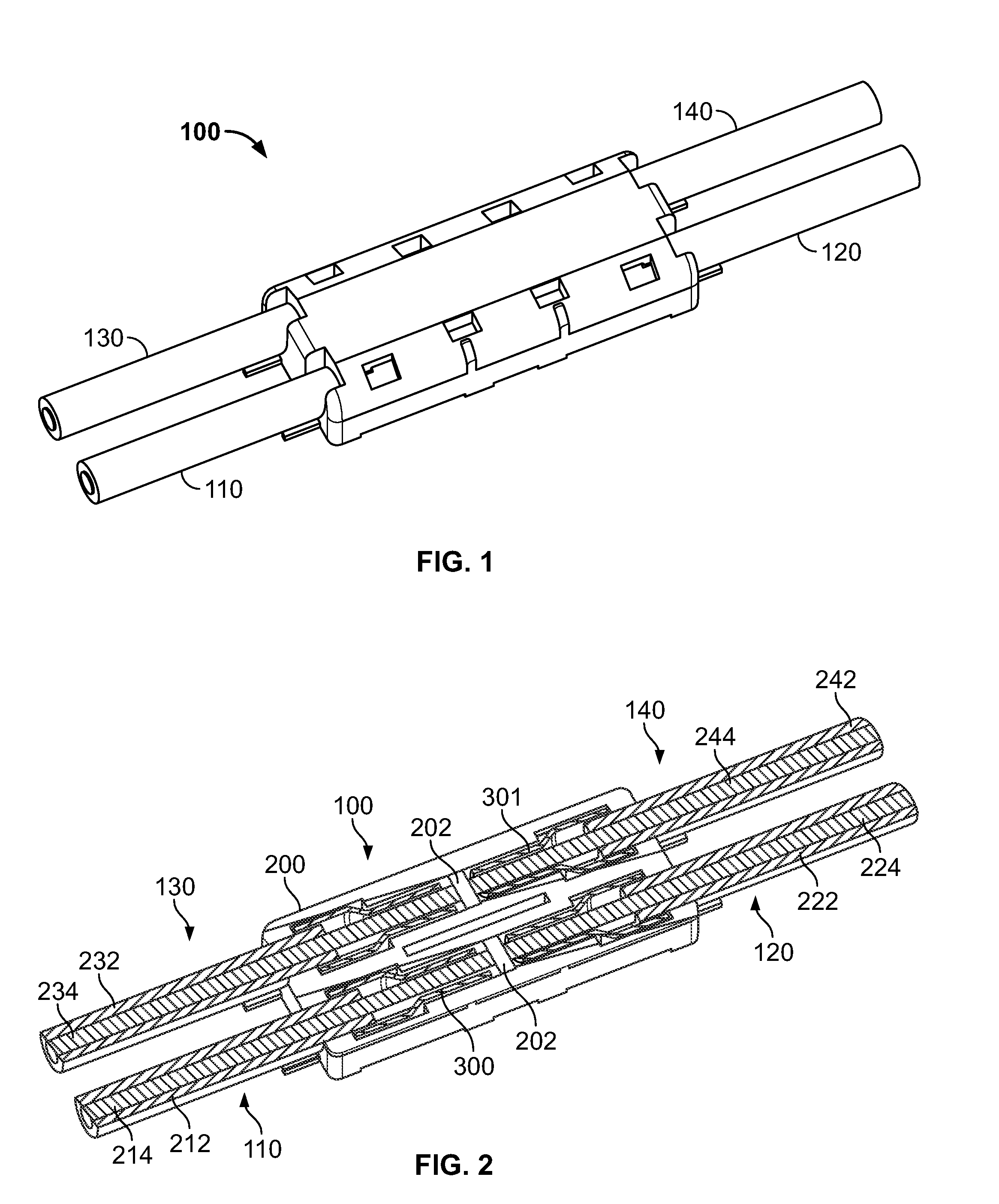
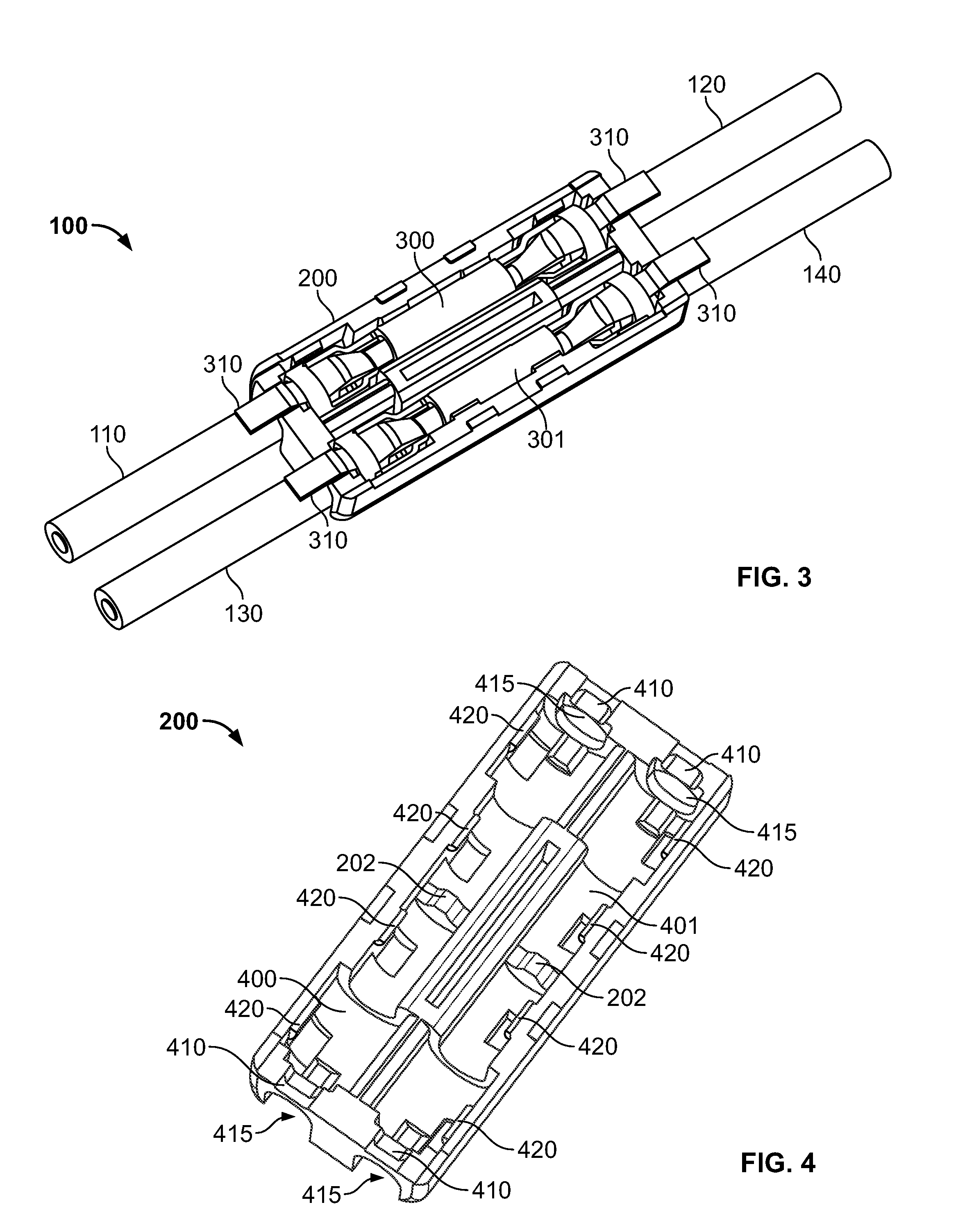
ActiveUS7513793B2Reduce shadowsLow profileLine/current collector detailsFinal product manufactureSurface mountingEngineering
A surface mount poke in connector is disclosed for mounting upon a surface of a printed circuit board, and is particularly applicable for printed circuit boards supporting LEDs. The connector has a securing means for engaging an inserted wire lead without the use of solder.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Localized metal contacts by localized laser assisted conversion of functional films in solar cells
InactiveUS20120060908A1Reduce shadowsImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationElectricityTransparent conducting film
A solar cell, including contact metallization formed using selective laser irradiation. An upper layer is formed in the solar cell including a material which can be selectively modified to electrical contacts upon laser irradiation. Selective laser irradiation is applied to at least one region of the upper layer to form at least one electrical contact in the layer. A remaining region of the upper layer may be a functional layer of the solar cell which need not be removed. The upper layer may be, e.g., a transparent, conductive film, and anti-reflective film, and / or passivation. The electrical contact may provide an electrically conductive path to at least one region below the upper layer of the solar cell.
Owner:TETRASUN
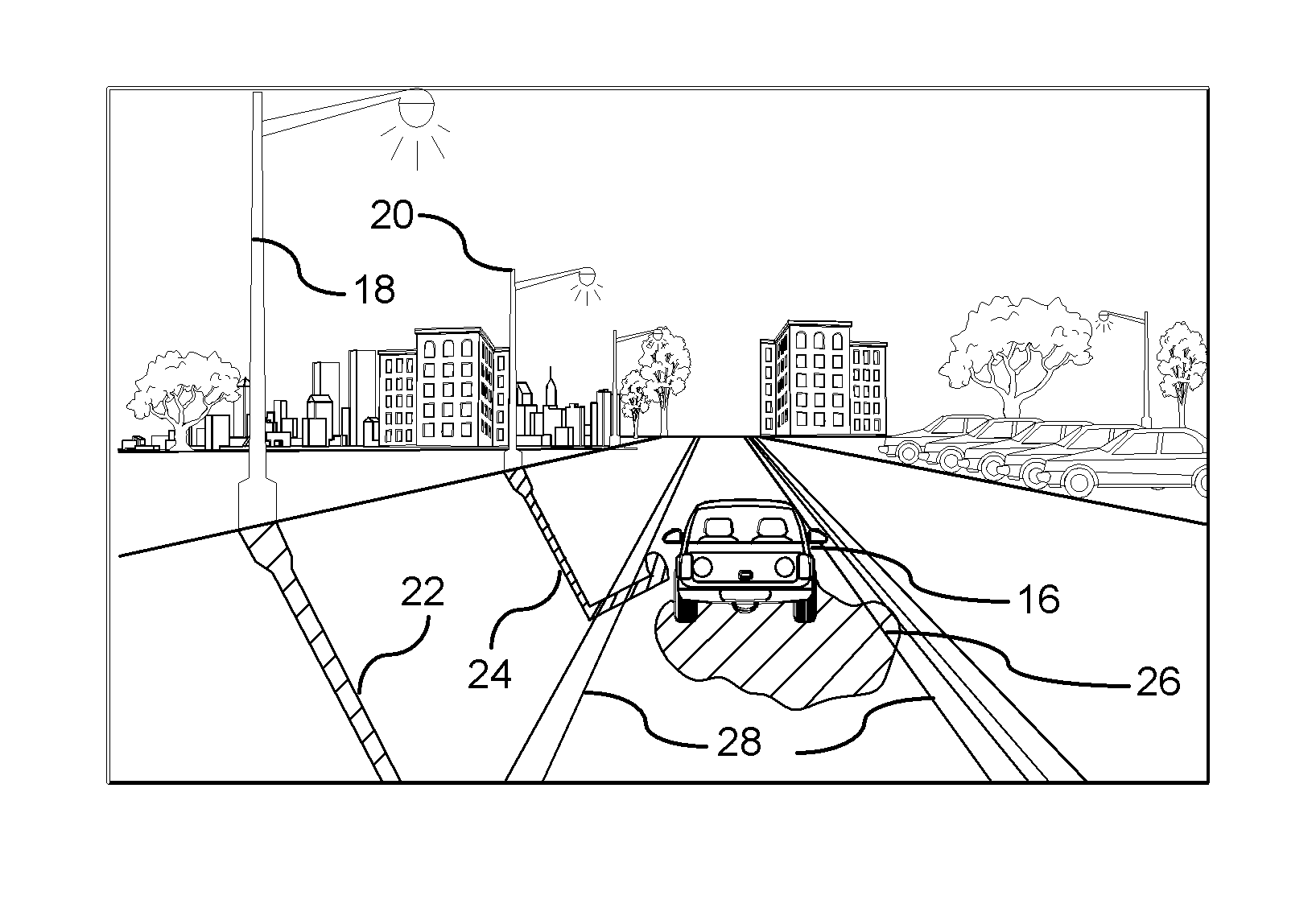
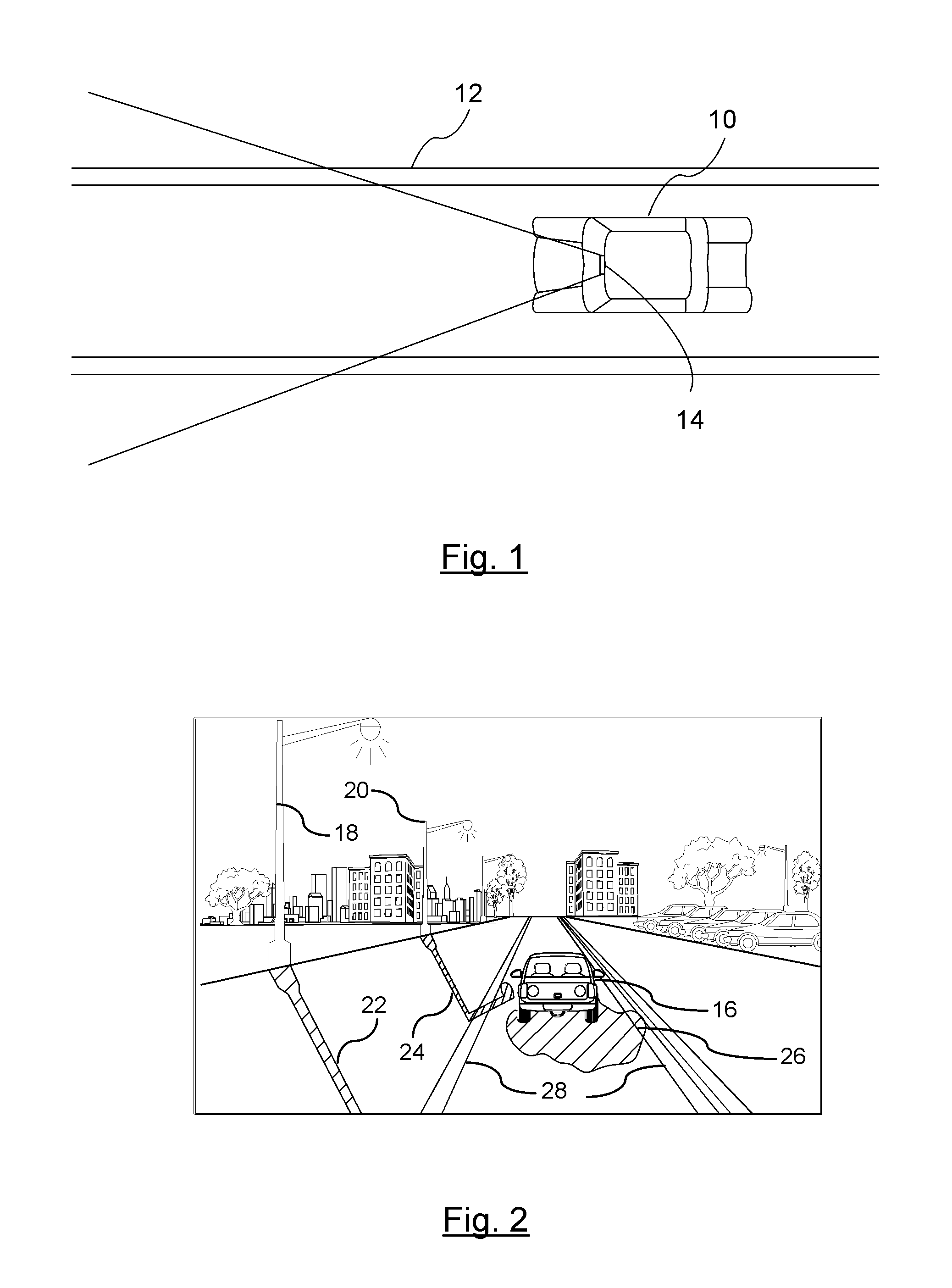
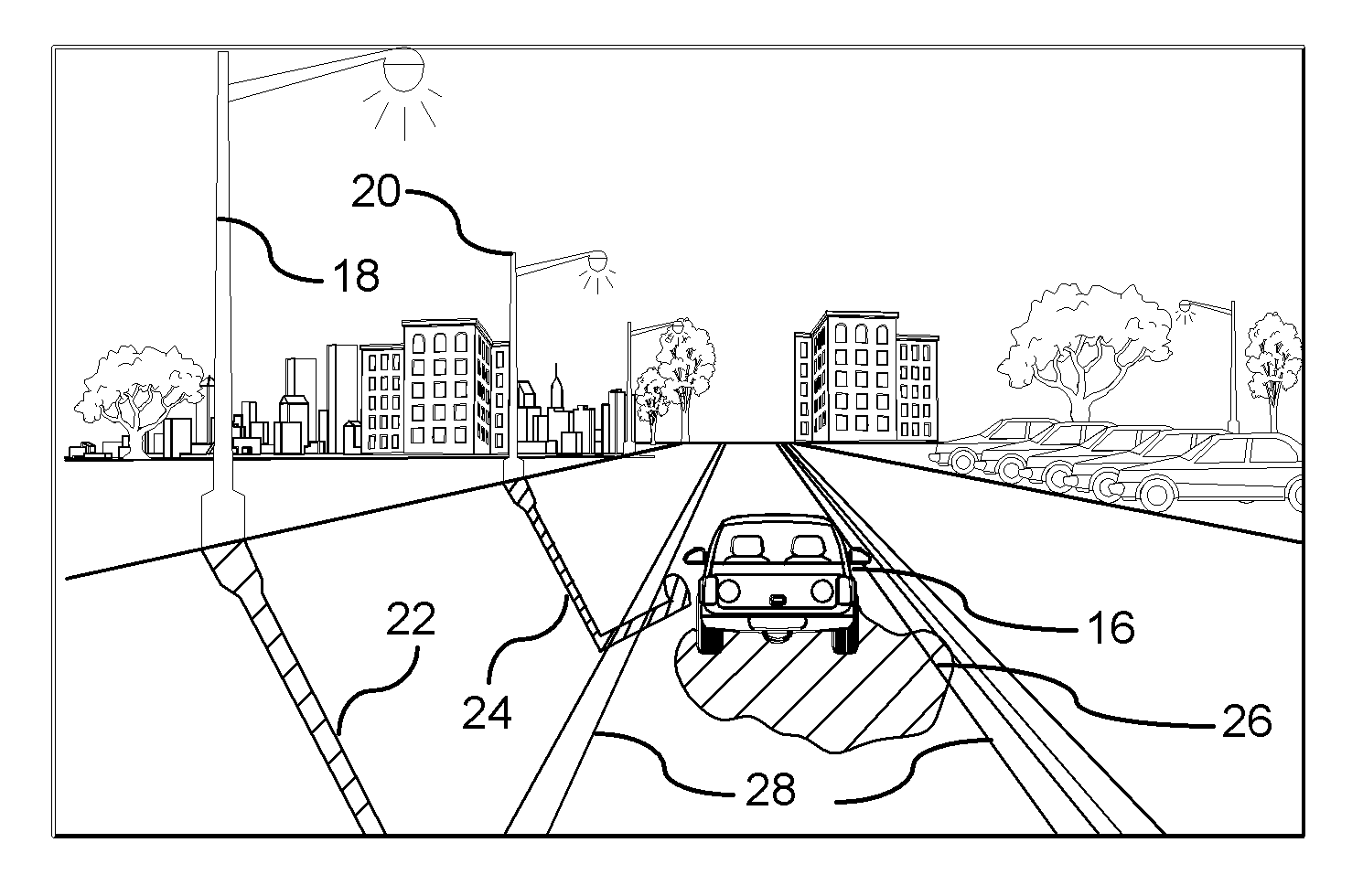
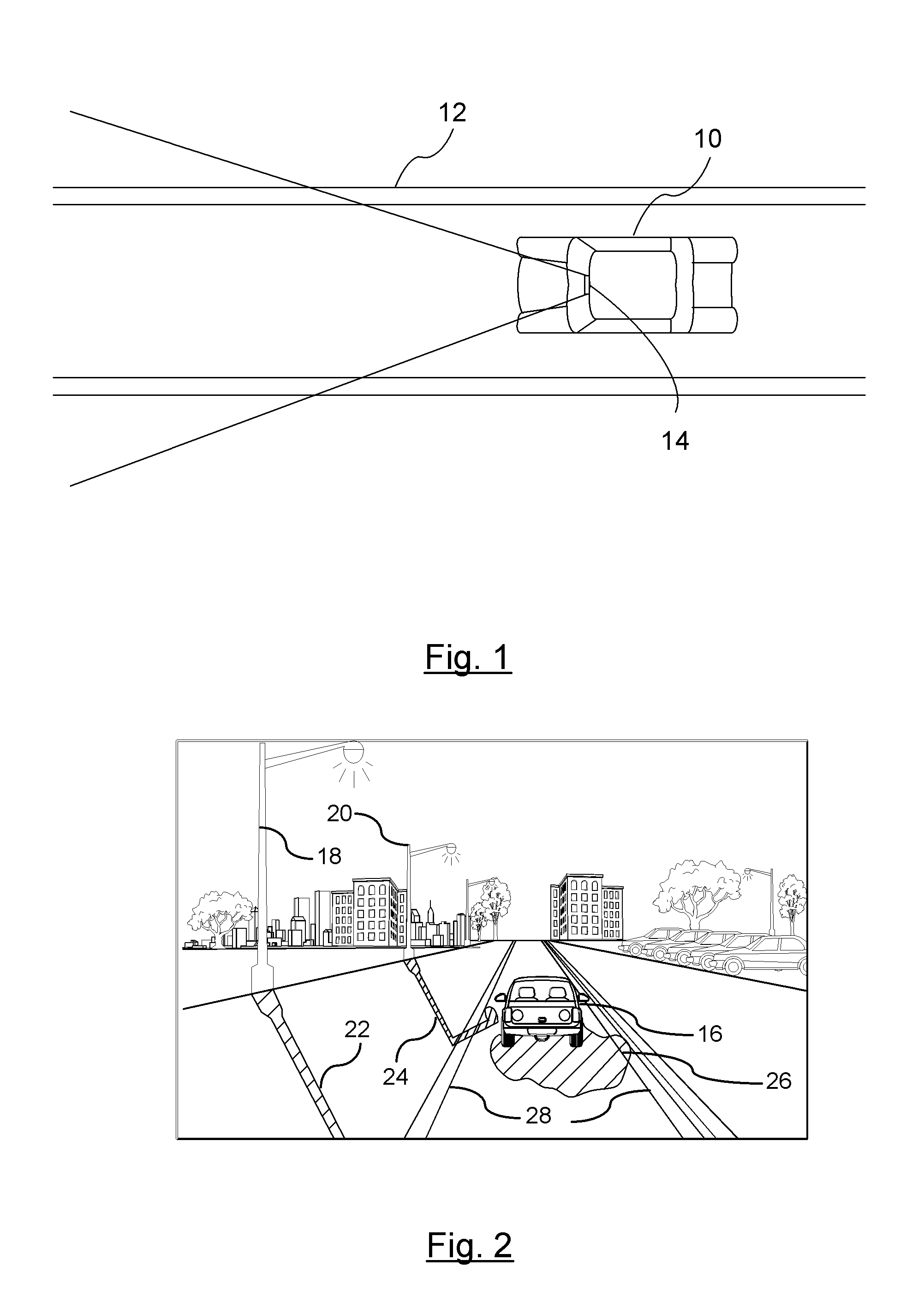
Shadow Removal in an Image Captured by a Vehicle-Based Camera for Clear Path Detection
InactiveUS20120008021A1Reduce shadowsImage enhancementImage analysisVision based systemsVision based
A method for is provided for creating a shadow-reduced image from a captured image for distinguishing a clear path of travel. Each pixel of a captured input image is plotted according to a two dimensional logarithmic graph. A specific color set relating to an associated color value of a clear path. A linear illumination-invariant axis is determined as a function of the specific color set. An illumination direction for the linear illumination-invariant axis is determined. A log-chromaticity value of each plotted pixel of the specific color set is projected on the axis. Edges in the input image and the illumination-invariant image domain are identified. The identified edges of the input image are compared to identify edges in the illumination-invariant image domain. A determination is made whether a shadow edge is present in response to comparing the edges. A shadow-reduced image is generated for scene analysis by a vehicle vision-based system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
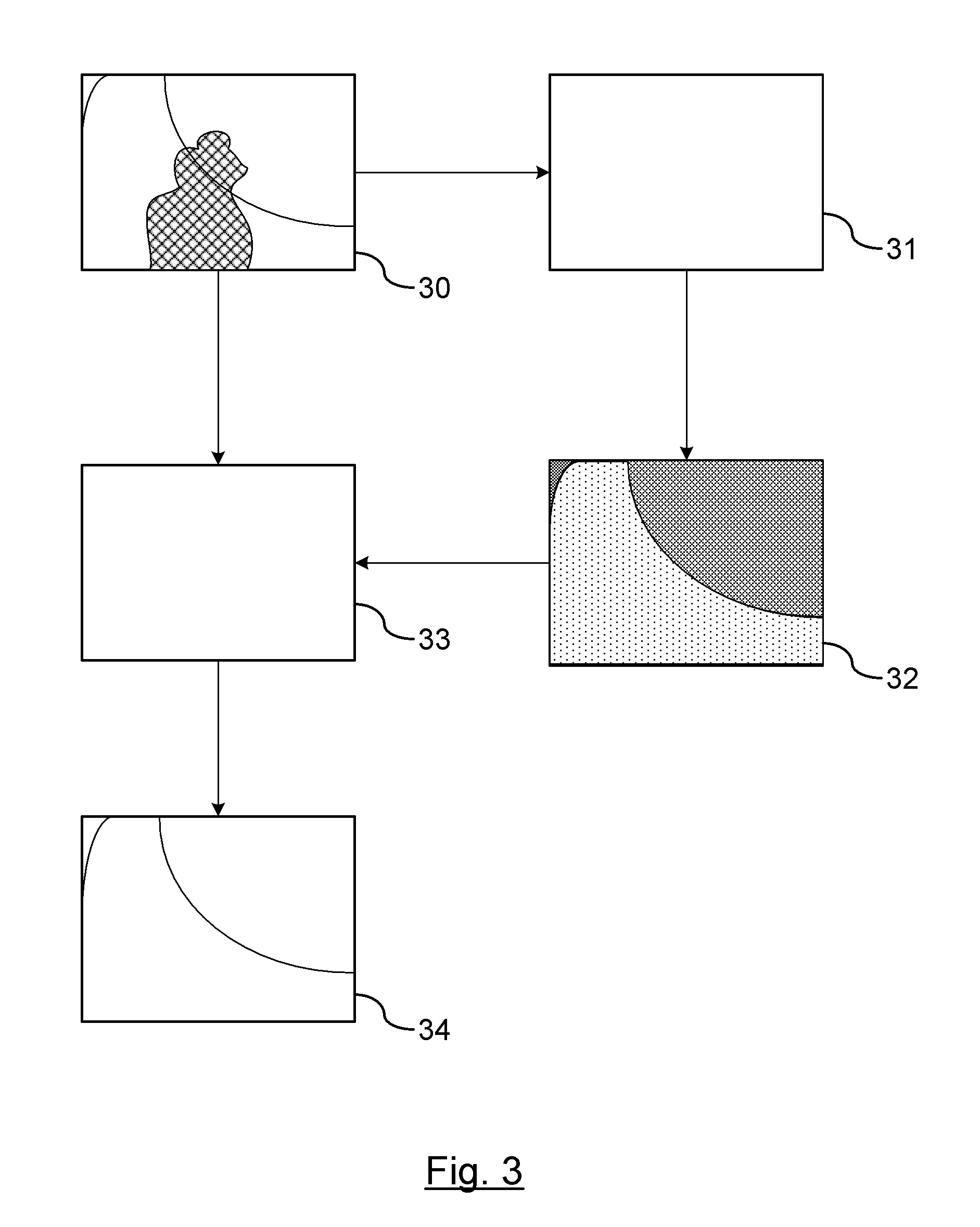
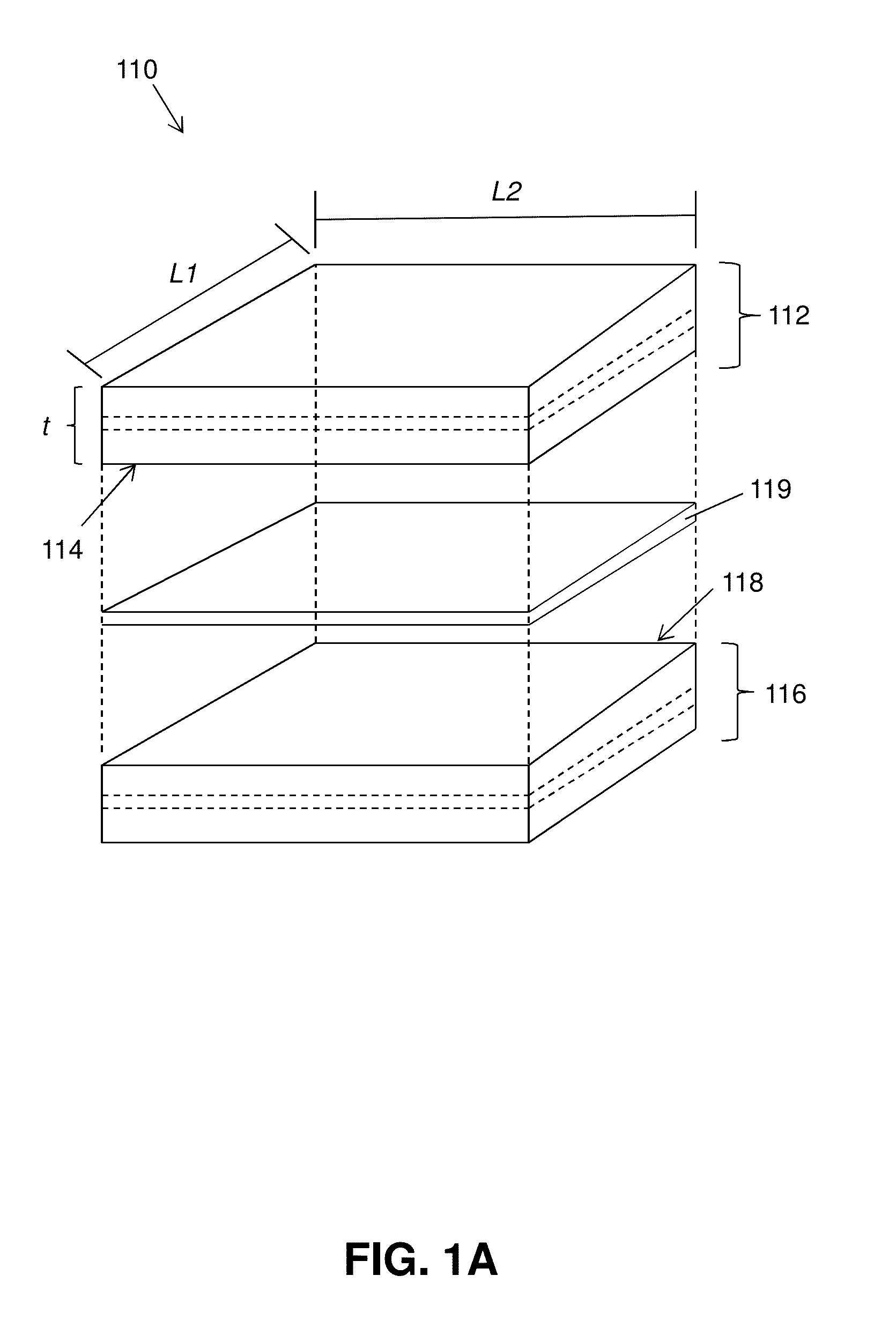
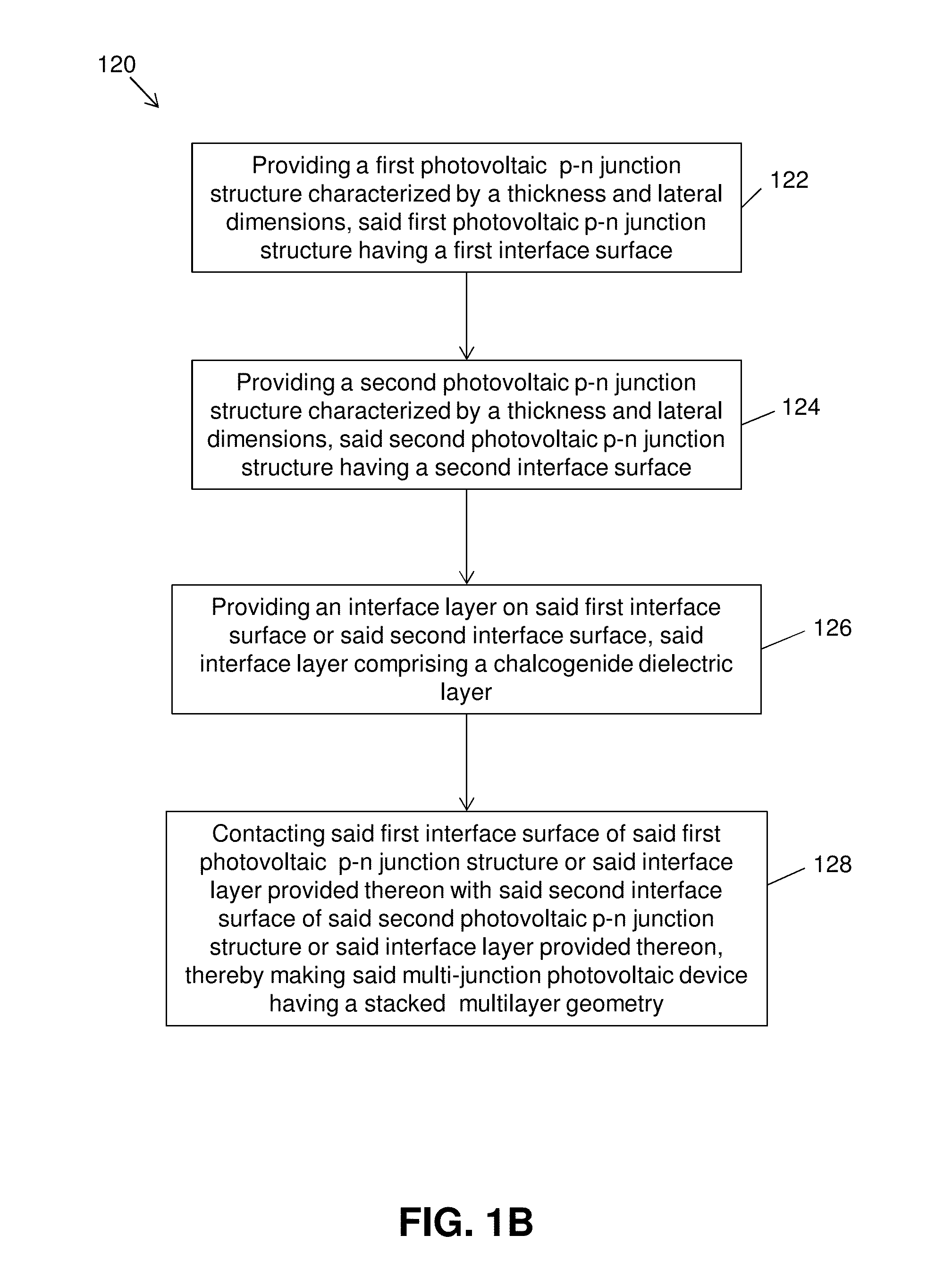
Printing-based assembly of multi-junction, multi-terminal photovoltaic devices and related methods
InactiveUS20150207012A1Improve equipment efficiencyWide wavelength rangeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterface layerEngineering
Multi-junction photovoltaic devices and methods for making multi-junction photovoltaic devices are disclosed. The multi-junction photovoltaic devices comprise a first photovoltaic p-n junction structure having a first interface surface, a second photovoltaic p-n junction structure having a second interface surface, and an optional interface layer provided between the first interface surface and the second interface surface, where the photovoltaic p-n junction structures and optional layers are provided in a stacked multilayer geometry. In an embodiment, the optional interface layer comprises a chalcogenide dielectric layer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
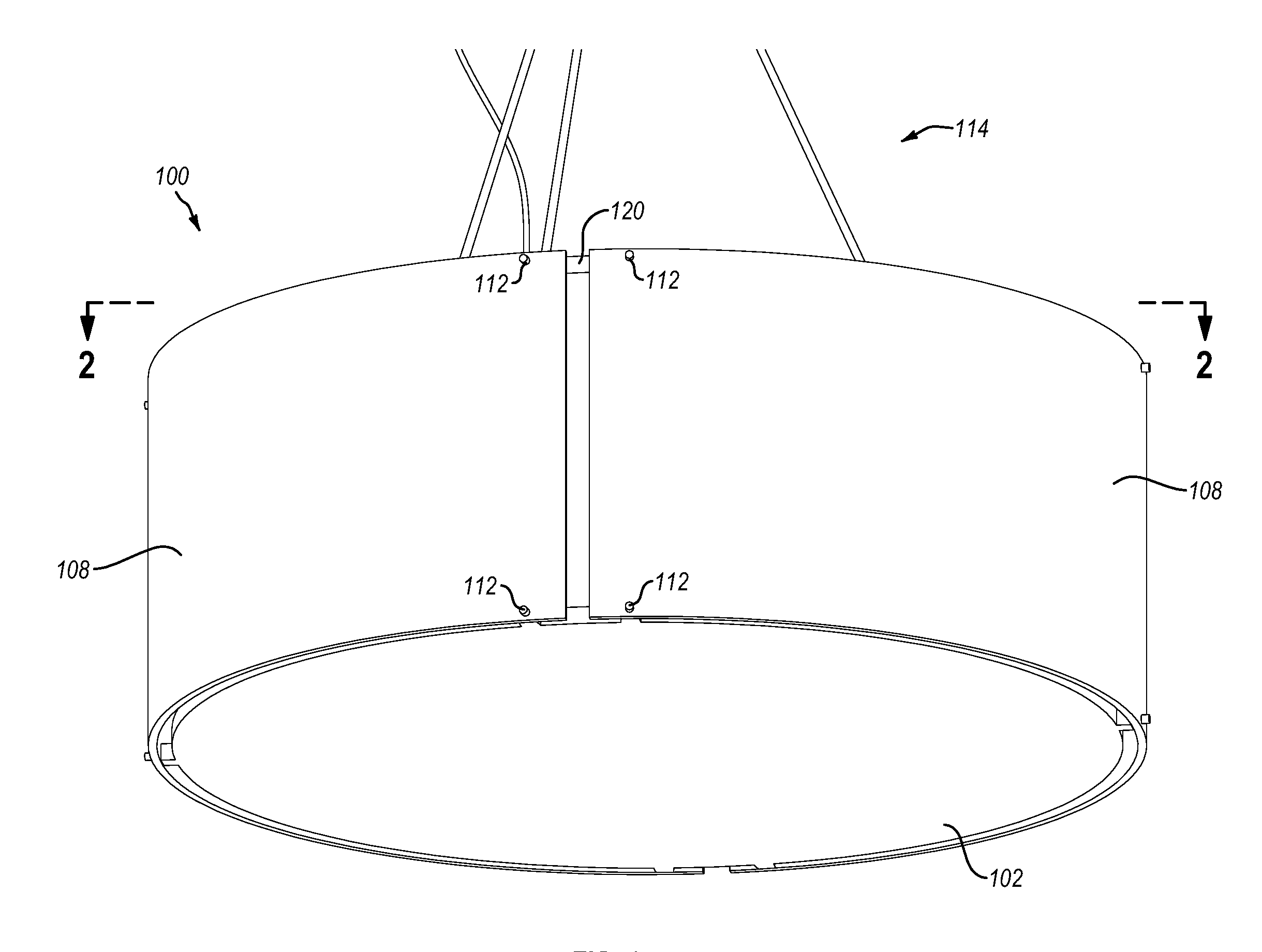
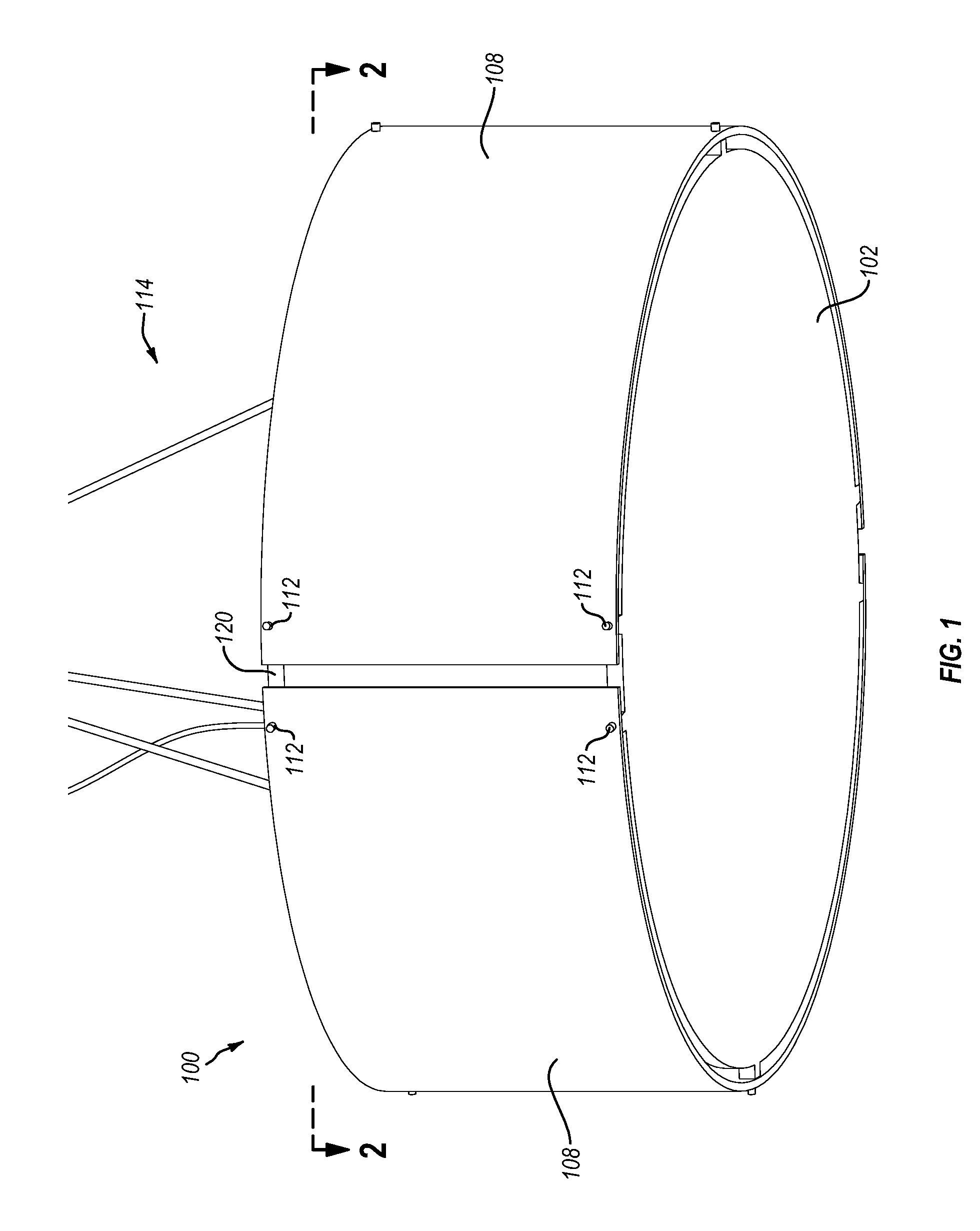
Lighting fixture assembly
InactiveUS20140153257A1Improve aesthetic qualityMinimize visibilityNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceVisibilityInterior space
Implementations of the present invention comprise lighting fixture assemblies that minimize the visibility of hardware and shadows. In particular, the lighting fixture assemblies may include no supporting hardware extending through an internal space defined, in whole or in part, by the lighting fixture assembly. In addition, the lighting fixture assemblies may include a gap between a bottom / top panel and a side panel of the lighting fixture assembly. Accordingly, lighting fixture assemblies of one or more implementations of the present invention can reduce or eliminate the visibility of internal supporting hardware and shadows on the exterior surfaces of the lighting fixture assemblies.
Owner:3FORM
Mask for deposition and method for manufacturing organic light emitting diode display using the same
ActiveUS20130337588A1High resolutionReducing deposition marginLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingDisplay deviceOrganic layer
A deposition mask for forming an organic layer pattern of an organic light emitting diode (OLED) display includes a base member having a first surface facing a substrate of the OLED display, and a second surface facing a side opposite to the first surface, and including a plurality of openings passing through the first surface and the second surface for forming the organic layer pattern. The opening has a pair of first side walls and a pair of second side walls. Each side wall of the openings has an inclination surface inclined with respect to a thickness direction of the base member, and when measuring an inclination angle of the inclination surface with reference to the first surface of the base member, the inclination angle of the first side wall and the inclination angle of the second side wall are different from each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20050270395A1Reduce time lagReduce shadowsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSemiconductor chipHorizontal and vertical
An image pickup apparatus is provided, which comprises a plurality of image pickup areas formed on a same semiconductor chip and arranged in the horizontal and the vertical directions, each image pickup area having a plurality of pixels arranged in the horizontal and the vertical directions, a plurality of vertical scanning circuits which sequentially scan pixels in the vertical direction to scan a plurality of image pickup areas in the vertical direction independently from each other, a plurality of lenses, at least one of which is provided in each of the plurality of image pickup areas and which focuses light to form an image on the image pickup areas, and a driving circuit which drives the plurality of vertical scanning circuits so that at least a part of a scanning period of each of the plurality of vertical scanning circuits overlaps with each other.
Owner:CANON KK
Surface mount poke in connector
ActiveUS20080153344A1Reduce shadowsLow profileLine/current collector detailsFinal product manufactureSurface mountingEngineering
A surface mount poke in connector is disclosed for mounting upon a surface of a printed circuit board, and is particularly applicable for printed circuit boards supporting LEDs. The connector has a securing means for engaging an inserted wire lead without the use of solder.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Shadow Removal in an Image Captured by a Vehicle-Based Camera Using an Optimized Oriented Linear Axis
ActiveUS20120008019A1Reduce shadowsExclude influenceImage enhancementImage analysisVision based systemsVision based
A method is provided for removing an illumination generated shadow in a captured image. Each pixel of the captured input image is plotted on a two dimensional logarithmic graph. A linear axis for the plurality of color sets is determined that is substantially orthogonal to a respective illumination direction of each respective color set. A log-chromaticity value of each plotted pixel is projected on the axis. An orientation of the linear axis is selected to minimize an illumination effect and provide optimum separation between each of the respective color sets on the linear axis. Edges in the input image and illumination invariant image domain are identified. The identified edges of the input image are compared to identify edges in the illumination invariant image domain. A determination is made whether a shadow edge is present in response to the comparison. A shadow-reduced image is generated for scene analysis by a vehicle vision-based system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Laminated diffractive optical element
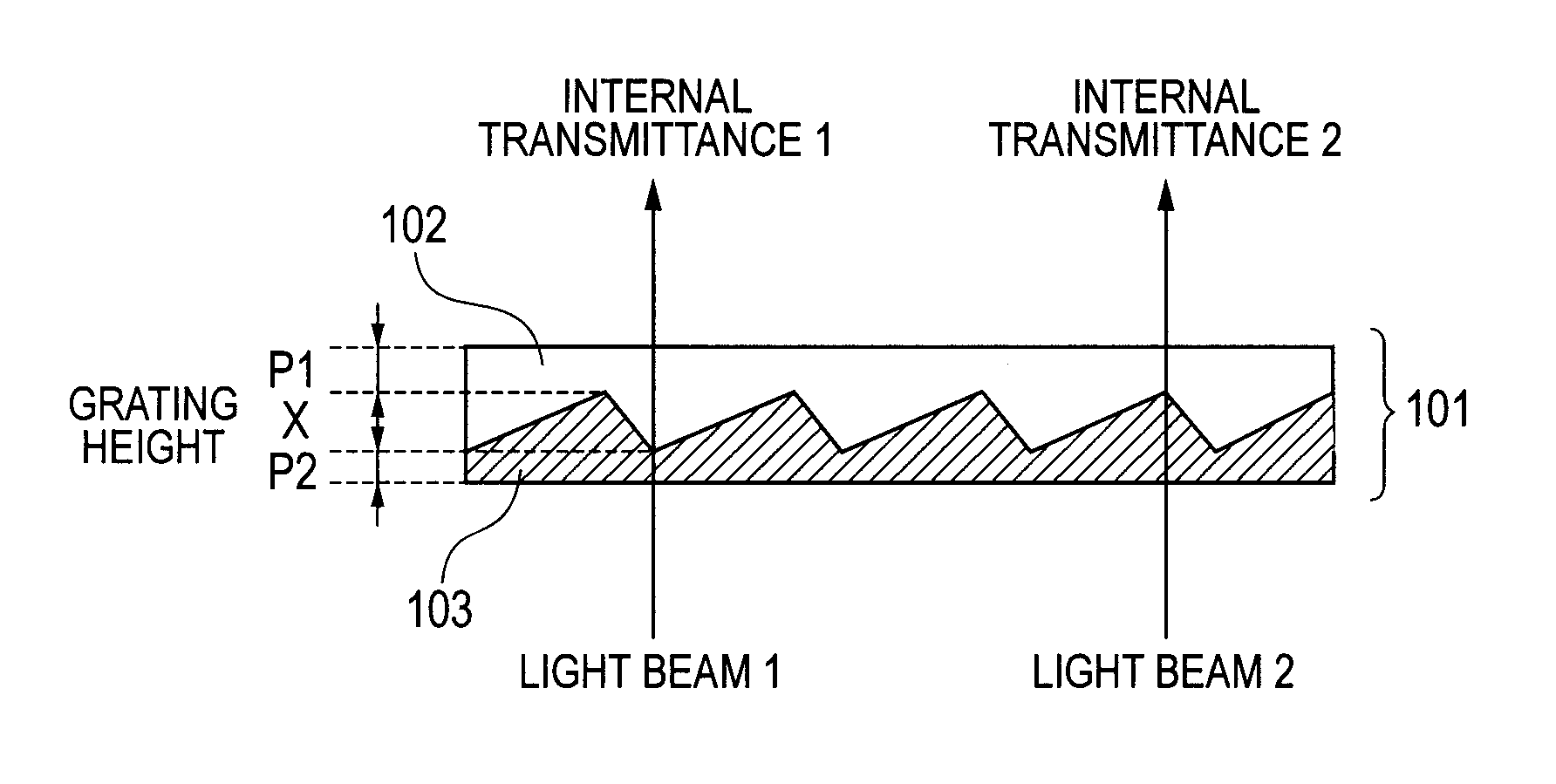
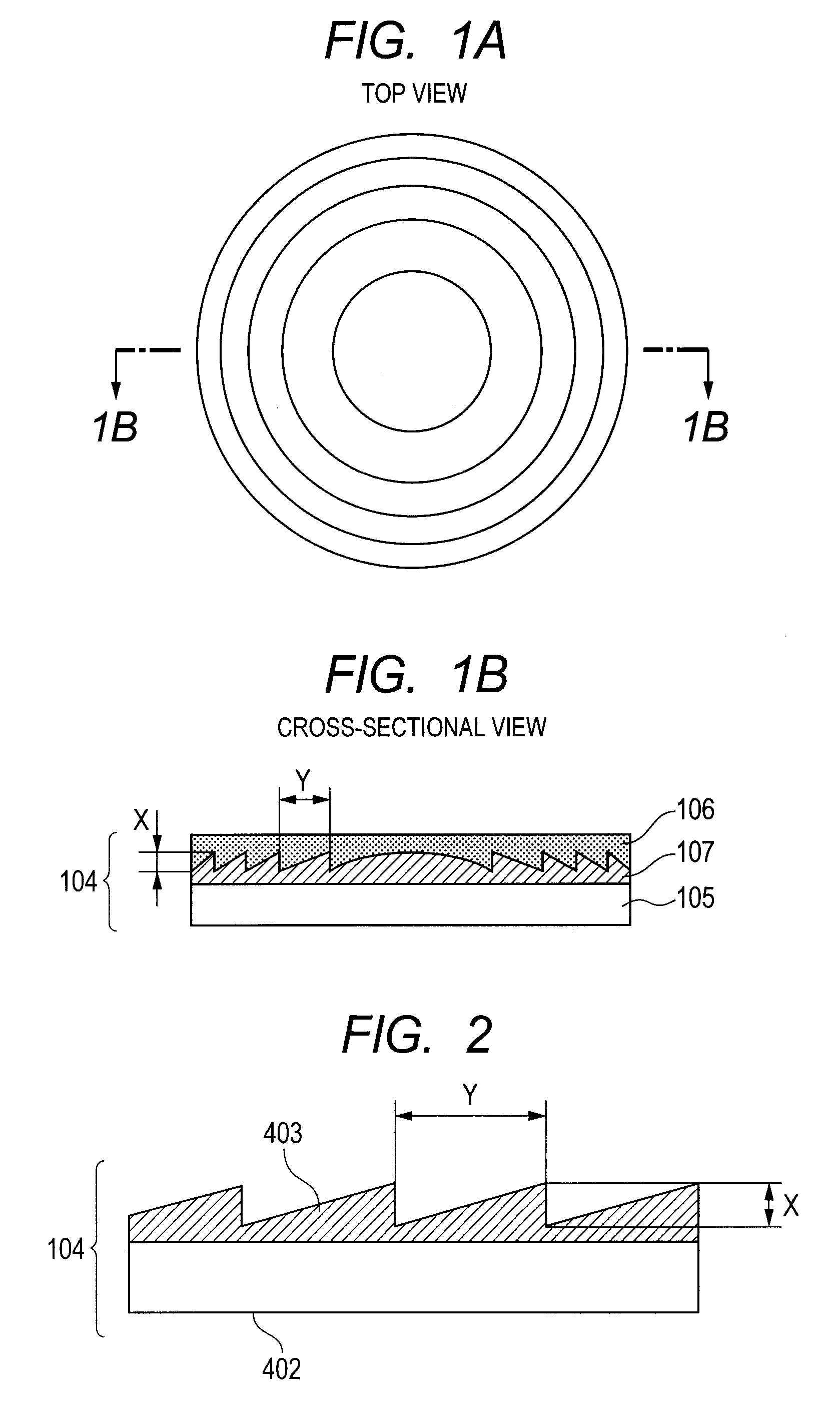
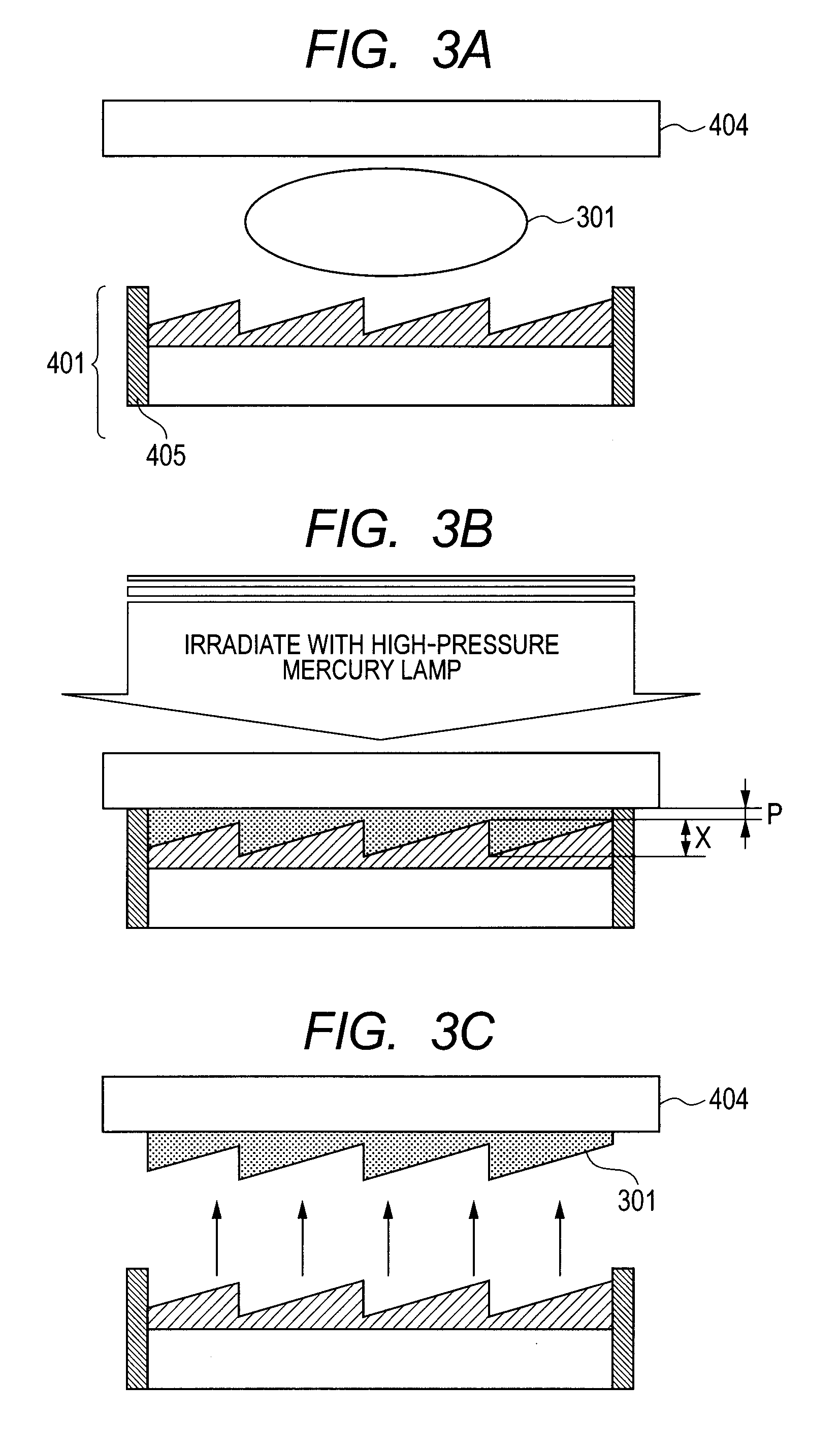
InactiveUS9086537B2Reduced variation in transmittanceReduce shadowsDiffraction gratingsTransmittanceDiffraction optics
A laminated diffractive optical element including a colorant-containing first layer having a diffraction grating surface with a grating height X and a second layer closely stacked on the diffraction grating surface of the first layer, wherein the relation of internal transmittances Tλ, a and Tλ, b of a material (a) for forming the first layer and a material (b) for forming the second layer satisfies the following (Formula 1) and the relation of the maximum and minimum internal transmittances Tλ, MAX and Tλ, MIN of the laminated diffractive optical element satisfies the following Formula (2):2.0%≦|Tλ, a−Tλ, b| (Formula 1)Tλ, MAX−Tλ, MIN≦8.0% (Formula 2)This reduces shading on the image surface resulting from the difference in transmittance of the optical element to provide a laminated diffractive optical element having reduced variation in transmittance.
Owner:CANON KK
Article with curved patterns formed of aligned pigment flakes
In a printed article, pigment flakes are magnetically aligned so as to form curved patterns in a plurality of cross-sections normal a continuous imaginary line, wherein radii of the curved patterns increase along the imaginary line from the first point to the second point. When light is incident upon the aligned pigment flakes from a light source, light reflected from the aligned pattern forms a bright image which appears to gradually change its shape and move from one side of the continuous imaginary line to another side of the continuous imaginary line when the substrate is tilted with respect to the light source.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Flight planning method for airborne synthetic aperture radar
ActiveCN102455185AScientific and reasonable designReduce shadowsInstruments for comonautical navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryLayoverFlight height
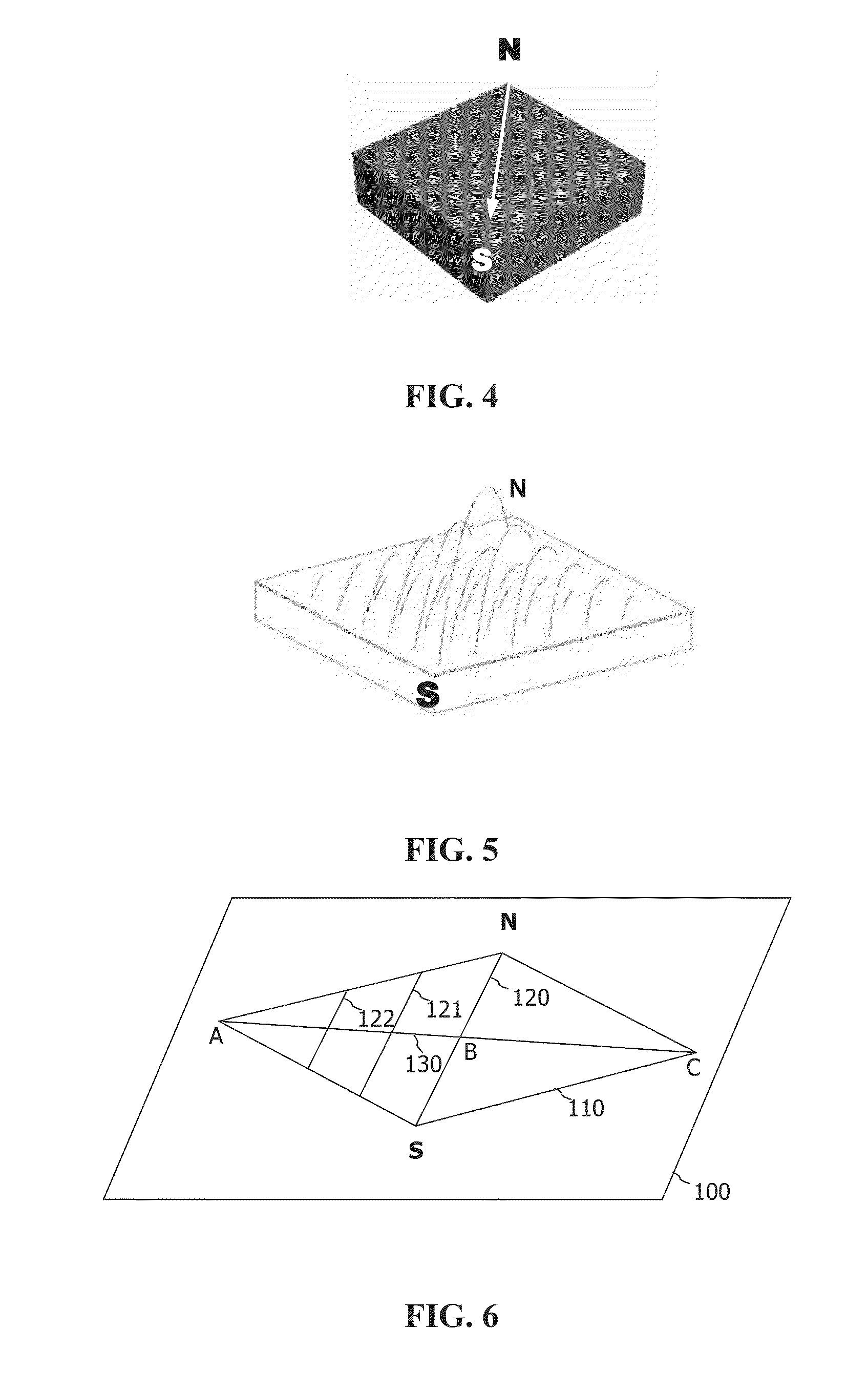
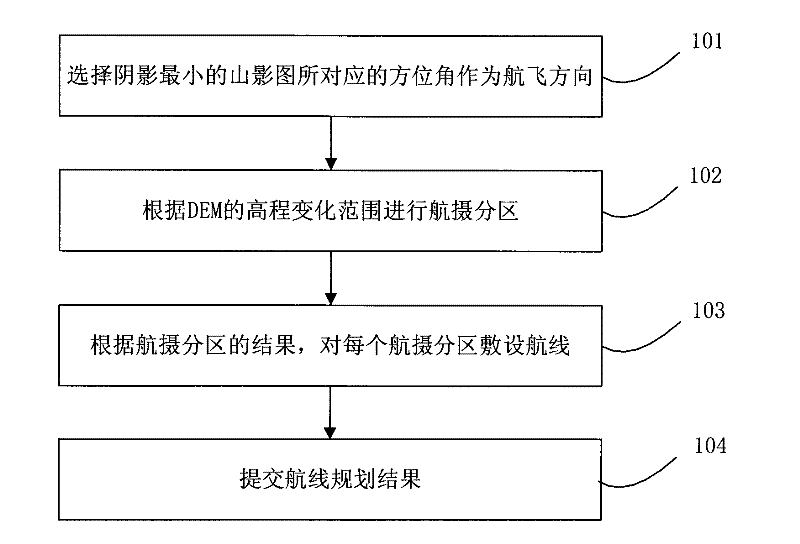
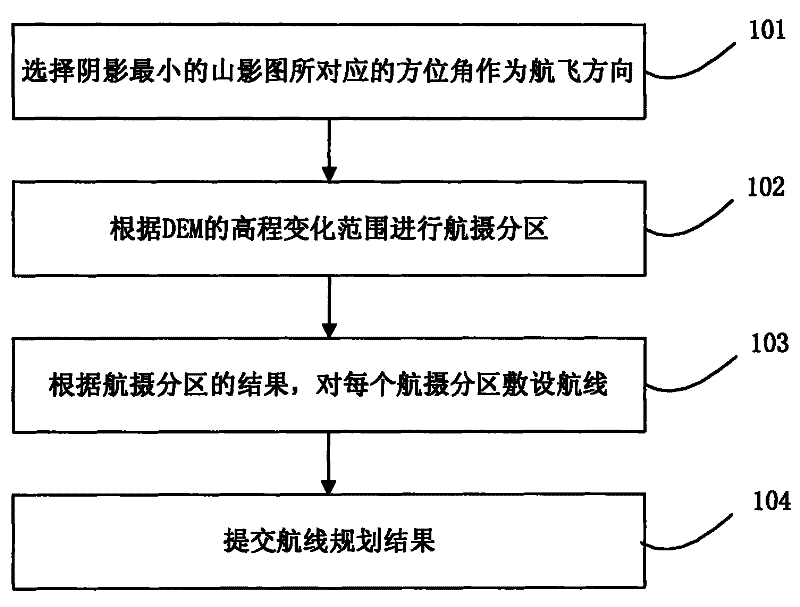
The invention discloses a flight planning method for an airborne synthetic aperture radar. The method comprises the following steps: selecting an azimuth angle corresponding to a mountain shadow image having the smallest shadow as a flight direction; dividing aerial photographic zones according to the range of elevation changes of DEM so as to allow the values of elevation changes of DEM in a same aerial photographic zone to be in a range of 1 / 6 to 1 / 4 of flight height; laying flight routes in each aerial photographic zone according to results of the aerial photographic zones. According to the invention, shadows and the phenomenon of layover on an image of the synthetic aperture radar can be maximally reduced, which enables information content of the image of the synthetic aperture radar to be increased and the image to be easier to interpret; flight planning is scientific and reasonable and can effectively reduce cost for aerial photography and enhance efficiency of aerial photography.
Owner:关鸿亮
Screen printing plate for solar cell and method for printing solar cell electrode
ActiveUS20130291743A1Low costReliable manufacturingLiquid surface applicatorsFinal product manufactureScreen printingShadow loss
The present invention relates to screen printing plate for a solar cell in which an electroconductive paste is used to simultaneously print a bus bar electrode and a finger electrode, the screen printing plate characterized in that the opening width of a finger electrode opening of the screen printing plate is less than 80 μm and a bus bar electrode opening of the screen printing plate has a closed section. The use of this screen printing plate makes it possible to reduce the cost of manufacturing solar cells, prevent the connecting section between the bus bar electrode and the finger electrode from breaking without causing an increase in shadow loss or compromising the aesthetic quality of the solar cells, and manufacture highly reliable solar cells with good productivity.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Acrylic acid emulsion and functional acrylic acid emulsion for unshadowed protective film
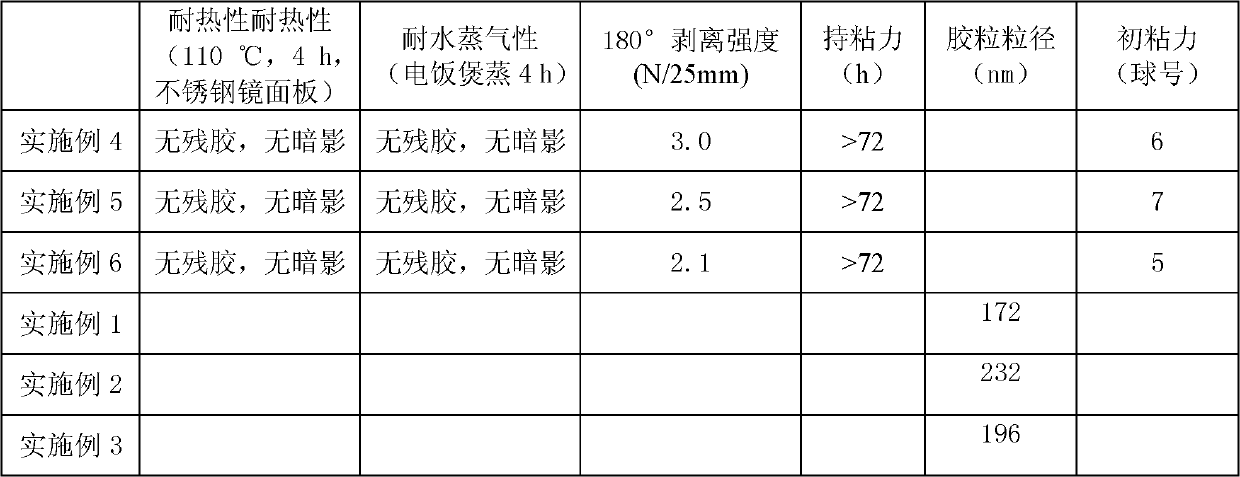
InactiveCN102167773AEvenly distributedReduce shadowsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesPolymer scienceFunctional monomer
The invention relates to acrylic acid emulsion and functional acrylic acid emulsion for an unshadowed protective film comprising the same. The acrylic acid emulsion is compounded with an external cross-linking agent to obtain the functional acrylic acid emulsion for the unshadowed protective film which can be applied to a high-finish stainless steel mirror board to form the unshadowed protective film. A preparation method of the acrylic acid emulsion comprises the following steps of: 1) performing polymerization on a functional monomer and an acrylic ester monomer by pre-emulsification and seeding polymerization processes to prepare an acrylic ester polymer, wherein a comonomer comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 5 to 20 percent of the functional monomer, 5 to 10 percent of hard acrylic ester monomer, 10 to 20 percent of medium soft acrylic ester monomer and 50 to 80 percent of soft acrylic ester monomer; Tg of the hard acrylic ester monomer is more than or equal to 36 DEG C; Tg of the medium soft acrylic ester monomer is between 35 and -25 DEG C; and Tg of the soft acrylic ester monomer is less than or equal to -24 DEG C; and 2) adjusting the pH value of the polymer emulsion prepared in the step 1) to be alkalescent to obtain the acrylic acid emulsion.
Owner:南京夜视丽精细化工有限责任公司
Shadow Removal in an Image Captured by a Vehicle Based Camera Using a Non-Linear Illumination-Invariant Kernel
ActiveUS20120008020A1Reduce shadowsExclude influenceImage enhancementImage analysisVision based systemsVision based
A method is provided for removing an illumination generated shadow in a captured image. An image is captured by an image capture device. Each pixel of the captured image is represented by a respective color value in a logarithmic graph. A non-linear illumination-invariant kernel is determined. An illumination direction for each respective color set is determined in the logarithmic graph that is orthogonal to the non-linear illumination-invariant kernel. A log-chromaticity value of each plotted pixel is projected on the non-linear illumination-invariant kernel. Edges are identified in the input image. Edges are identified in the illumination-invariant image domain. The identified edges are compared. A determination is made whether a shadow is present in response to an edge identified in the input image and an absence of a correlating edge in the illumination-invariant image domain. A shadow-reduced image is generated for scene analysis by a vehicle vision-based system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Lighting fixture assembly
InactiveUS9028114B2Improve aesthetic qualityMinimize visibilityNon-electric lightingLighting support devicesVisibilityInterior space
Implementations of the present invention comprise lighting fixture assemblies that minimize the visibility of hardware and shadows. In particular, the lighting fixture assemblies may include no supporting hardware extending through an internal space defined, in whole or in part, by the lighting fixture assembly. In addition, the lighting fixture assemblies may include a gap between a bottom / top panel and a side panel of the lighting fixture assembly. Accordingly, lighting fixture assemblies of one or more implementations of the present invention can reduce or eliminate the visibility of internal supporting hardware and shadows on the exterior surfaces of the lighting fixture assemblies.
Owner:3FORM
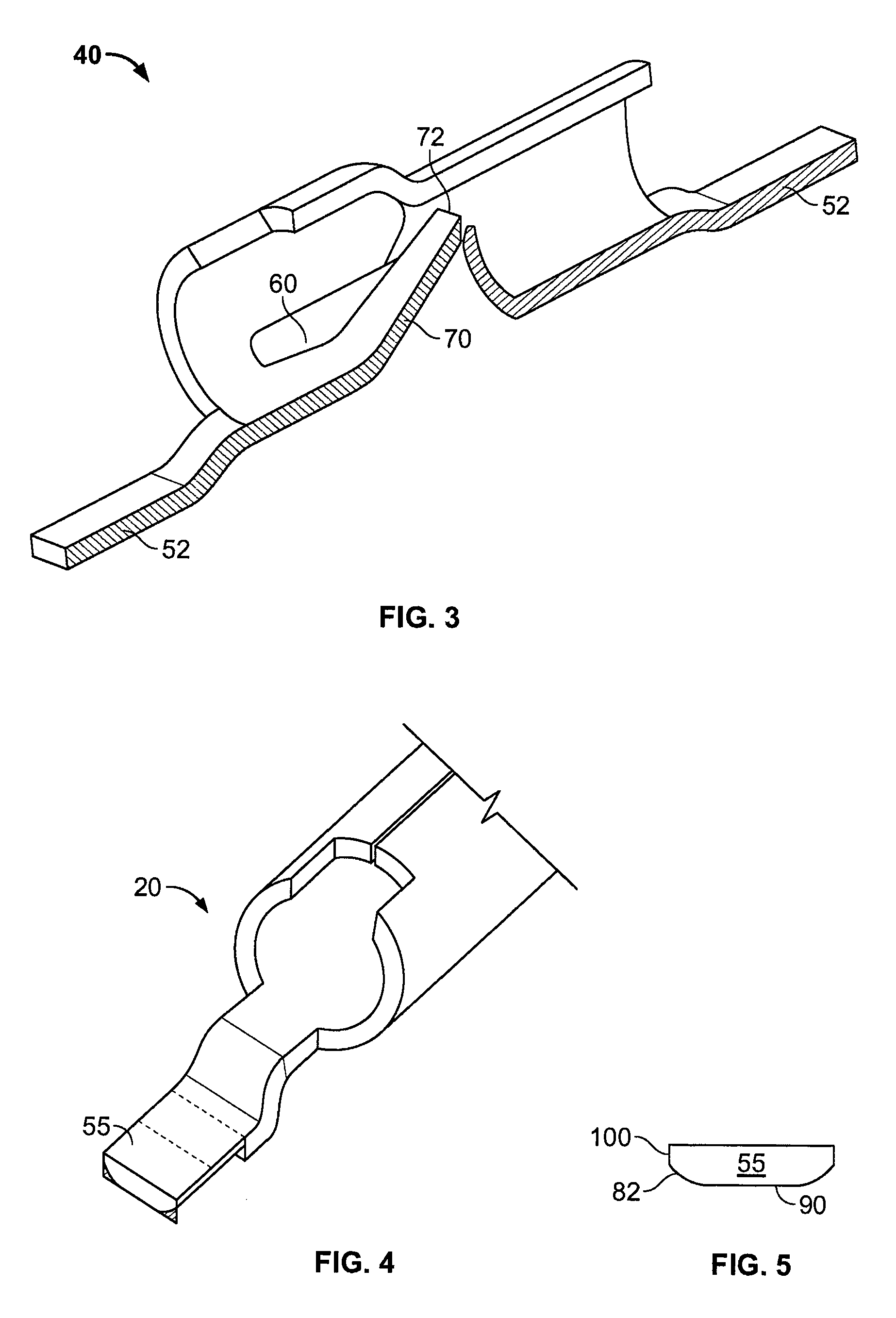
Surface mount poke-in connector
ActiveUS7448901B2Reduce shadowsLow profileLine/current collector detailsSoldered/welded conductive connectionsSurface mountingEngineering
A surface mount poke in connector is disclosed for mounting upon a surface of an electrical device such as printed circuit board, and is particularly applicable for printed circuit boards supporting LEDs. The connector includes a contact having an engaging mechanism for securing a first and second wire leads to the contact. The contact further has attachment points for connecting the connector to an electrical device surface by soldering.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
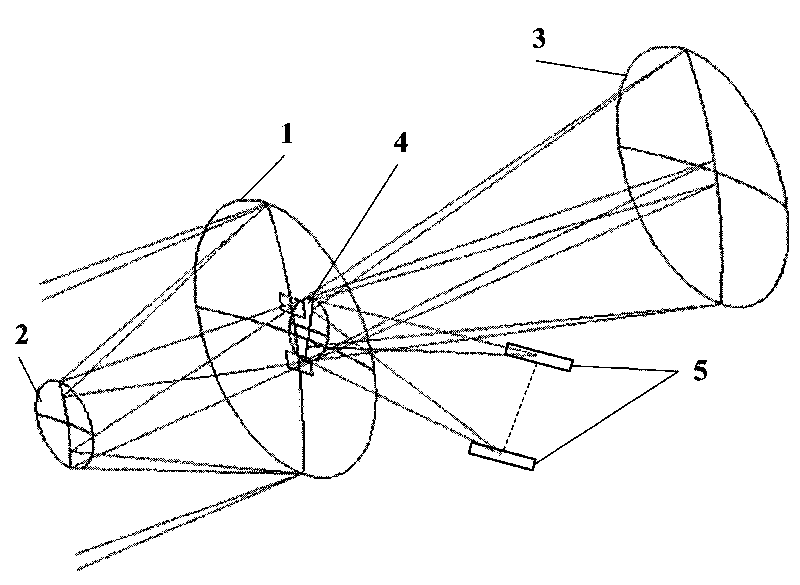
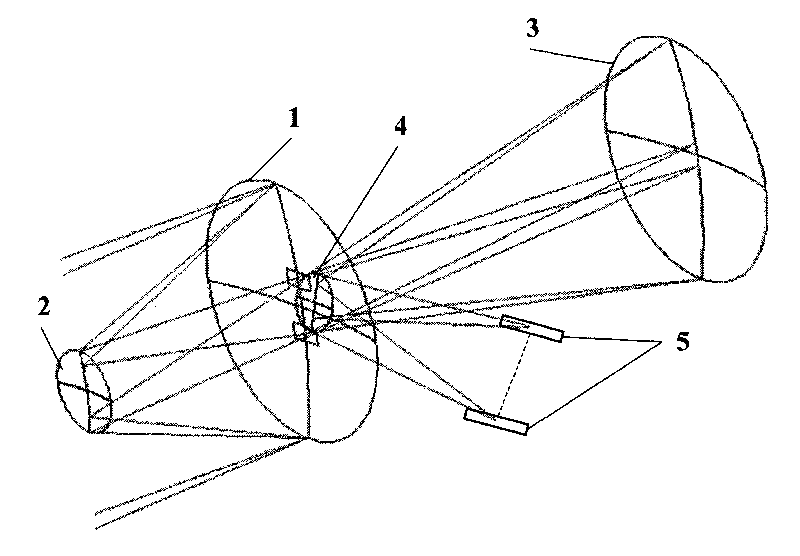
Optical system for stereo mapping with low base-height ratio
ActiveCN101718550AImprove stabilityImprove mapping accuracyPicture taking arrangementsPlane mirrorOptoelectronics
The invention provides an optical system for stereo mapping with a low base-height ratio, which is used in a bias-field, adopts a coaxial tri-mirror system in which a primary mirror, a secondary mirror, a tertiary mirror and a reflecting plane mirror are completely shared, and is formed by combining two independent optical imaging paths. Two groups of incident light rays each of which has an included angle of 1 to 6 degrees sequentially reach the primary mirror, the secondary mirror and the tertiary mirror; and finally, the incident light rays are respectively reflected to two independent receiving image planes for imaging by the reflecting plane mirror. By using the bifocal surface as well as the primary mirror, the secondary mirror, the tertiary mirror and the reflecting plane mirror which are simultaneously shared, the invention is capable of simultaneously imaging in front and rear fields of view, therefore, the stereoscopic mapping with a low base-height ratio and high precision can be achieved by the reflection-type optical system capable of imaging on a single-camera and double-channel basis. The optical system has the advantages of high optical-mechanical structural integrity, small size, light weight, convenient real-time on-orbit detection and high stability of inner orientation elements. Therefore, the optical system is particularly applicable to single-track push-broom stereo imaging and mapping by a satellite camera in surveying and mapping with a low base-height ratio.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
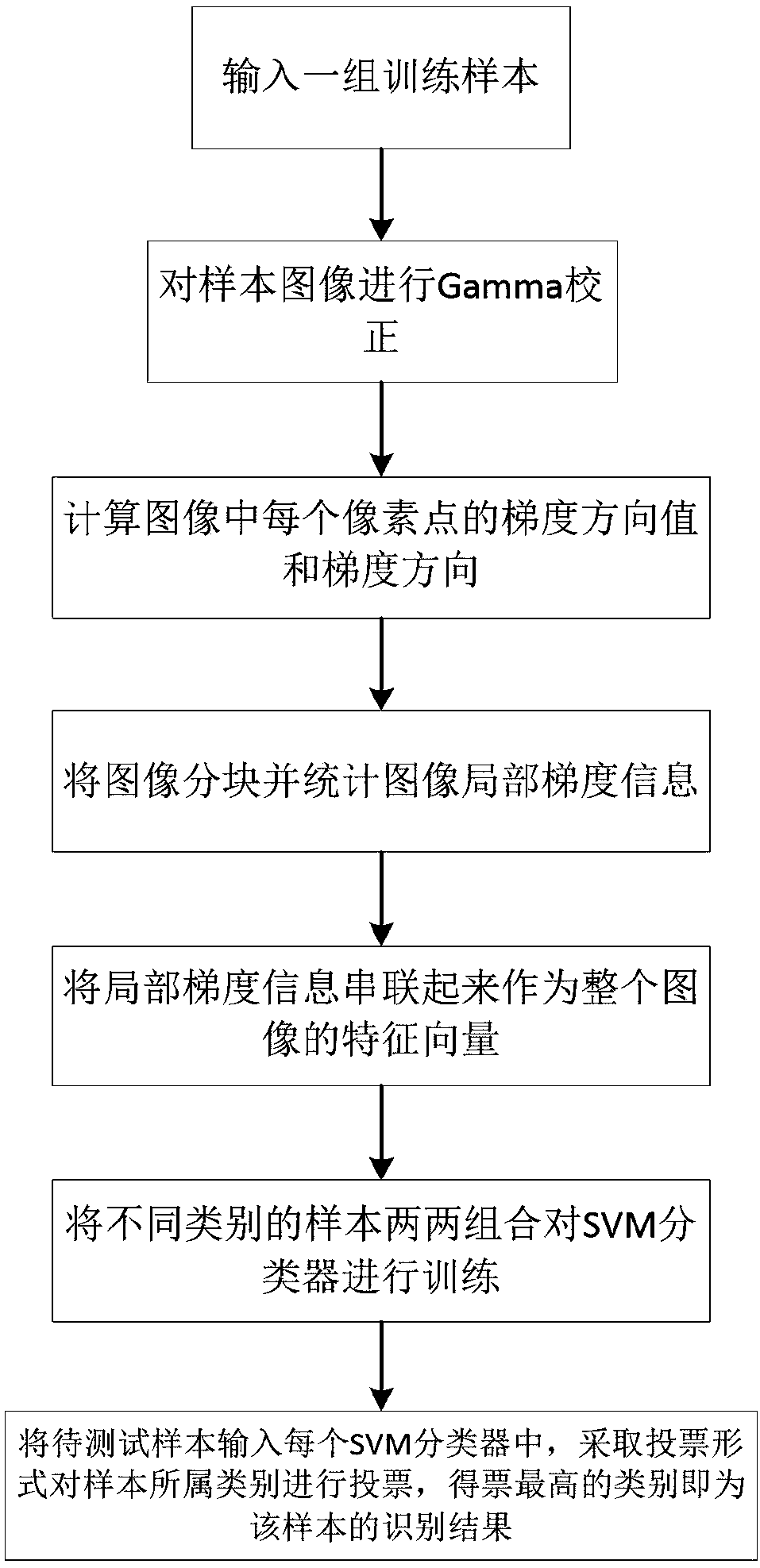
Face recognition method based on HOG feature and SVM multi-classifier
InactiveCN107066958AReduce shadowsImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionTime complexitySample image
The invention discloses a face recognition method based on a HOG feature and a SVM multi-classifier. The method comprises training the SVM multi-classifier by calculating and counting the feature formed by a HOG of the local area of a face image, and recognizing a sample image in a way of voting in pairs. A type with the most votes is the recognition result of the sample. The method achieves a high recognition rate while guaranteeing low time complexity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Shell body joint structure and jointing method thereof
ActiveCN1547427AReduce shadowsSlow flowCouplings bases/casesElectrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawersBody jointsEngineering
The invention relates to a kind of shell joint structure and its joint method. The joint structure consists at least two parts: upper shell, which bears a joint including(from its outside to its inside orderly) first concave, first convex, first flute and second convex; and lower shell, which also bears a joint including(from its outside to its inside orderly) first concave, first convex and second concave. In addition, the first concave and the first convex of the upper shell are relative to the first convex of the lower shell, and the first flute and the first convex of the upper shell are relative to the first convex and the second concave of the lower shell respectively, thus jointing the upper shell and the lower one together. Through the use of this type of shell joint structure and its joint method, shell shadow and line flows can be reduced and the increase of the electricity climbing distance of the electric clearance after the combination of the shells will enhance the appearance of the shells of electric devices and their components as well as their electric characteristic.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC +1
Systems and methods for simultaneous near-infrared light and visible light imaging
PendingUS20210015350A1Reduce disruption and disruptionImprove usabilityEndoscopesMicroscopesFluorescenceMaterials science
Disclosed herein are imaging systems and methods for simultaneous near-infrared light and visible light imaging of a sample comprising: a detector to form a fluorescence image of the sample and a visible image of the sample; a light source configured to emit infrared light to induce fluorescence from the sample; and a plurality of optics arranged to direct the infrared light toward the sample and form the fluorescence image of the sample and the visible light image of the sample on the detector, wherein the infrared light is directed to the sample substantially coaxially with fluorescence light received from the sample in order to decrease shadows.
Owner:BLAZE BIOSCI
Modular furniture system
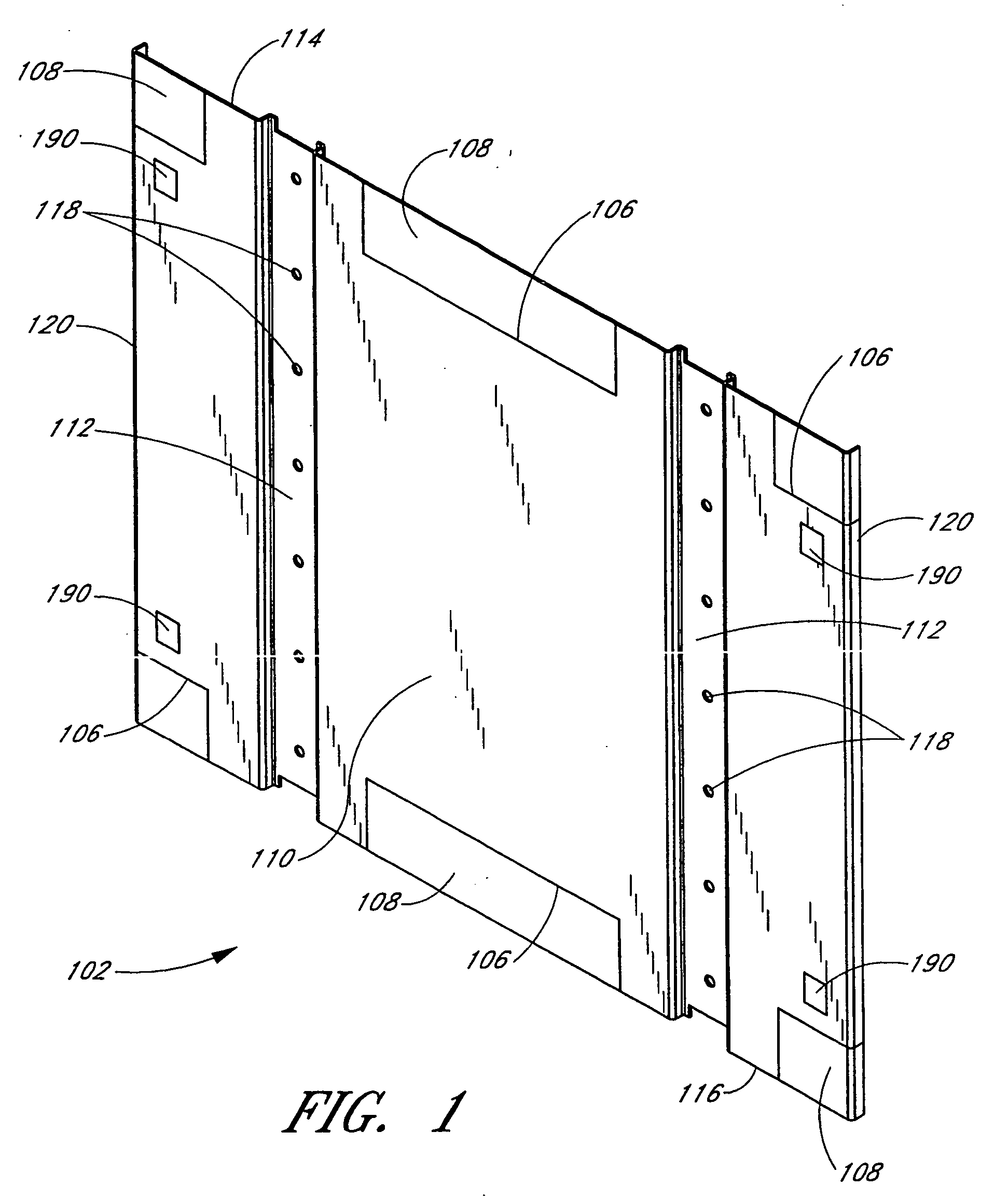
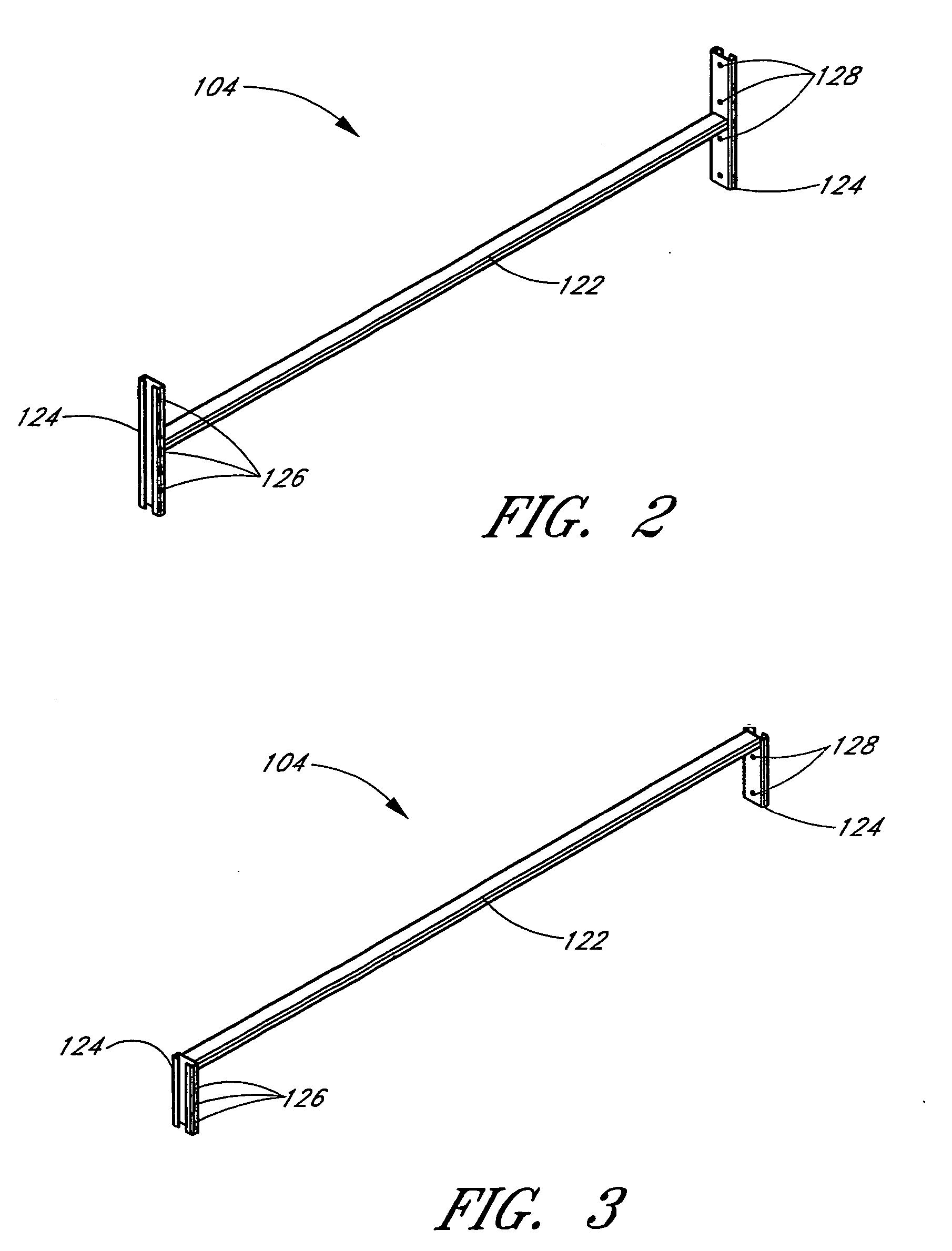
InactiveUS20050162051A1Save raw materialsReduce shadowsSectional furnitureDismountable cabinetsModularitySurface plate
A modular furniture system based on a fundamental building block is provided. The building block, or cell, includes first and second end plates and at least one horizontal support beam. A plurality of stacked and / or side-by-side cells provide a framework that can be arranged in an almost limitless number of ways. The cells serve as both storage space and division between neighboring work spaces, thus conserving raw materials and recovering floor space. The cells further provide raceways for concealing electrical wires and data cables, and are adapted for supporting work surfaces and connecting to vertical panels. The cells are adapted to receive various storage components, such as drawers, which may be inserted from both a front side and a back side of each cell. The cells are also adapted to receive tiles, which may cover open sides of each cell and / or cover the end plates of each cell. The tiles may provide any of a multitude of different aesthetic and functional surfaces. A single cell or stack of cells may include a foundation for increased rigidity and sturdiness.
Owner:HNI TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com