Patents
Literature
618 results about "Surface reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface reaction. [′sər·fəs rē‚ak·shən] (chemistry) A chemical reaction carried out on a surface as on an adsorbent or solid catalyst.
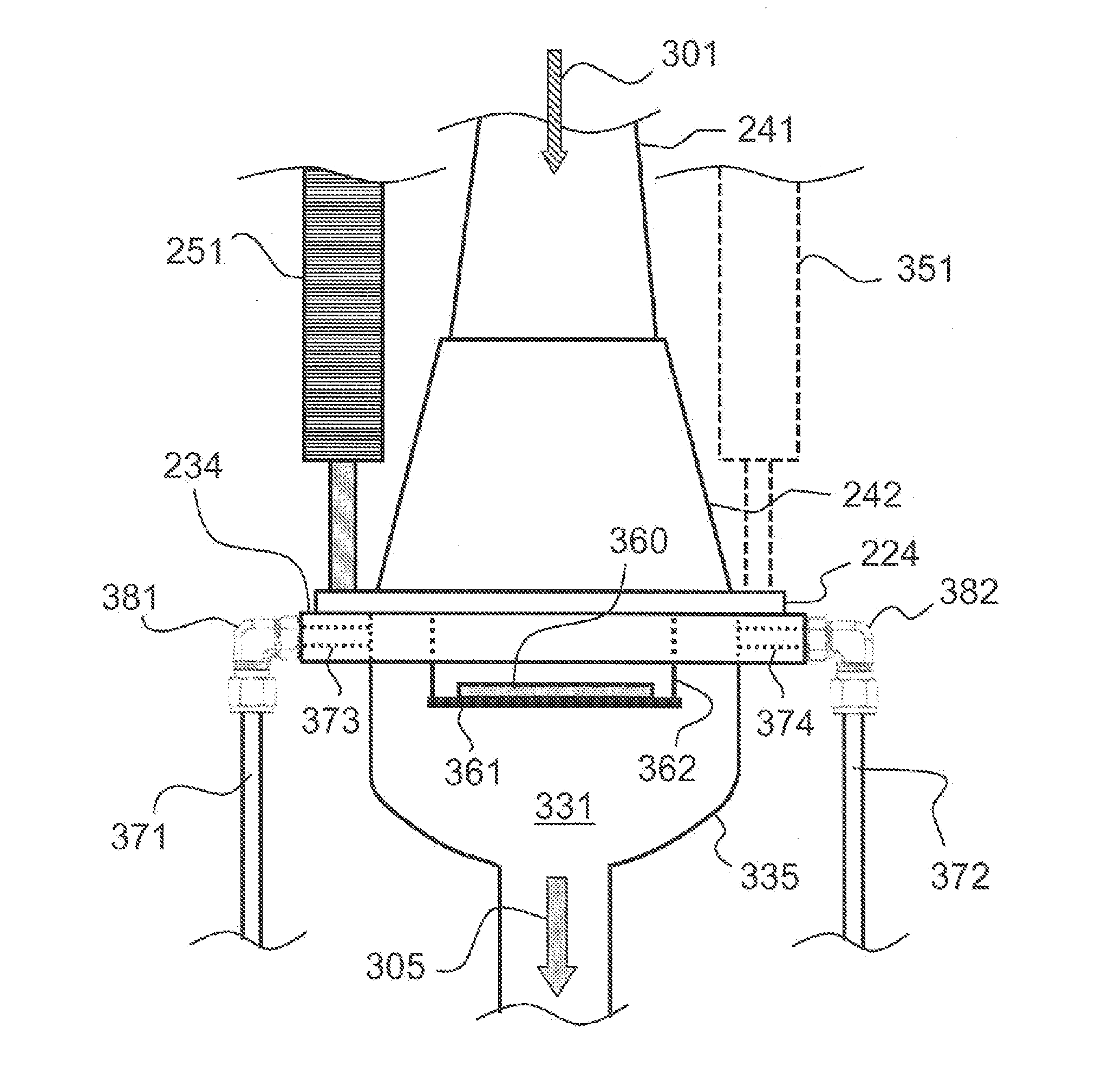
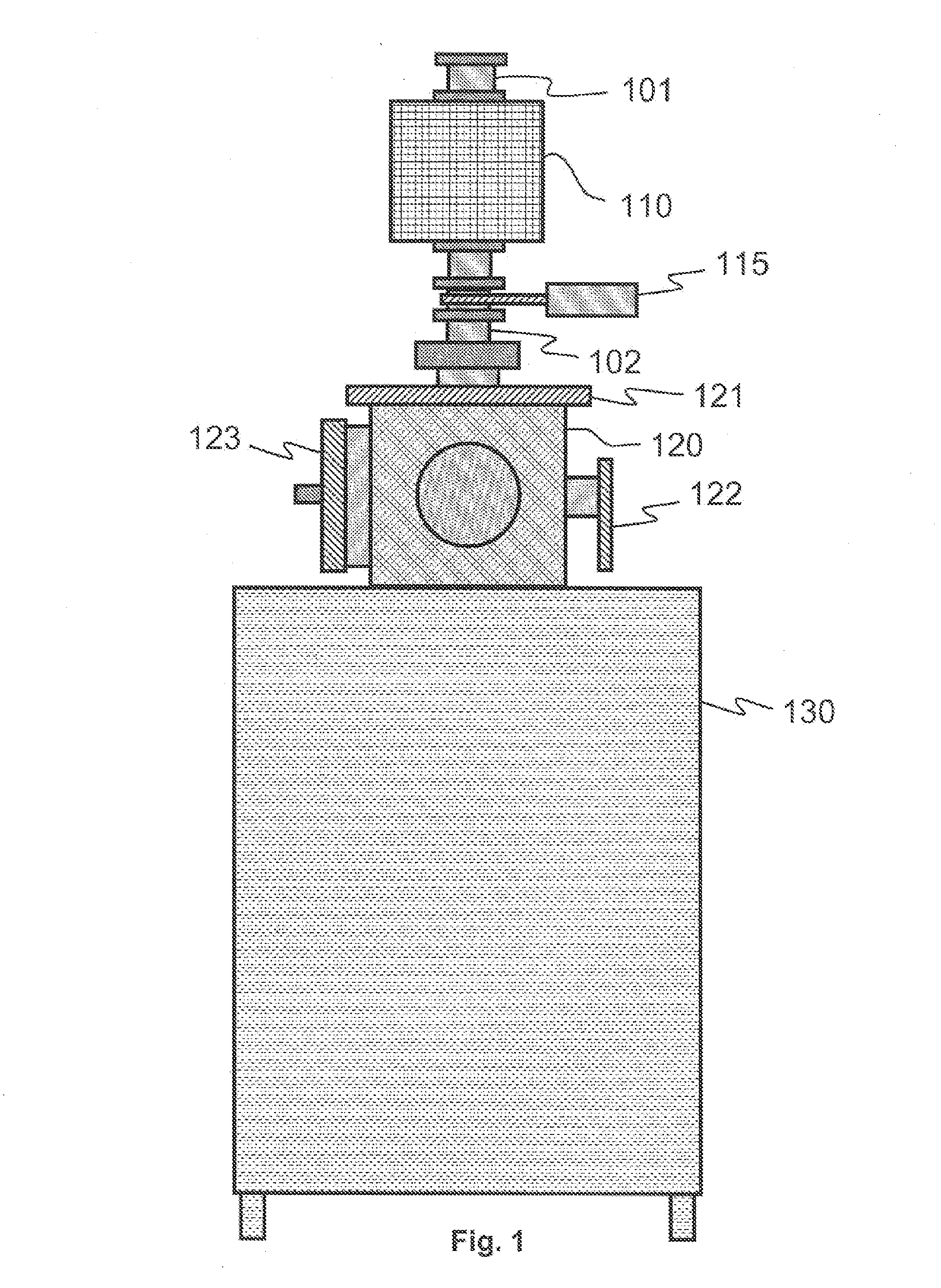
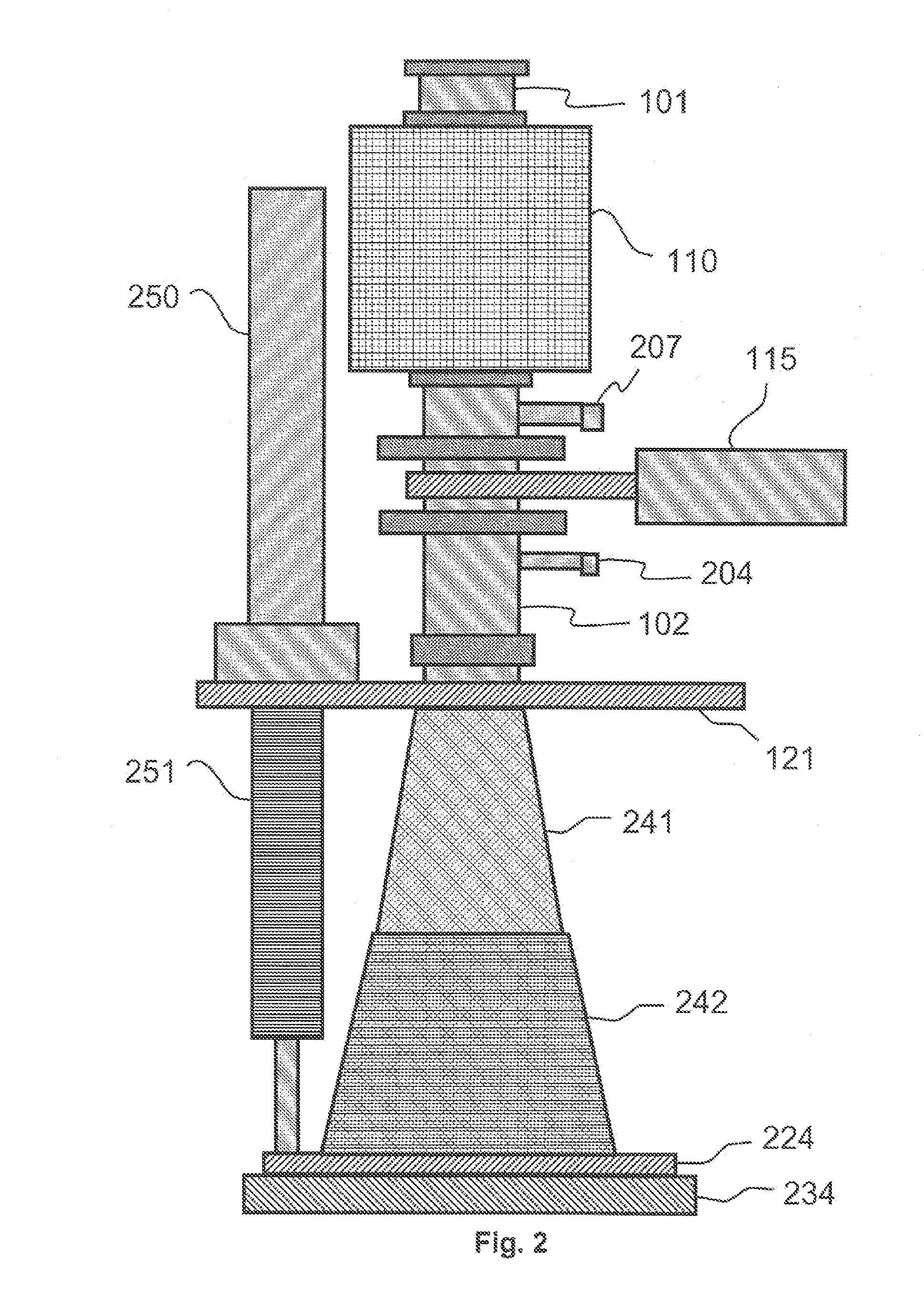
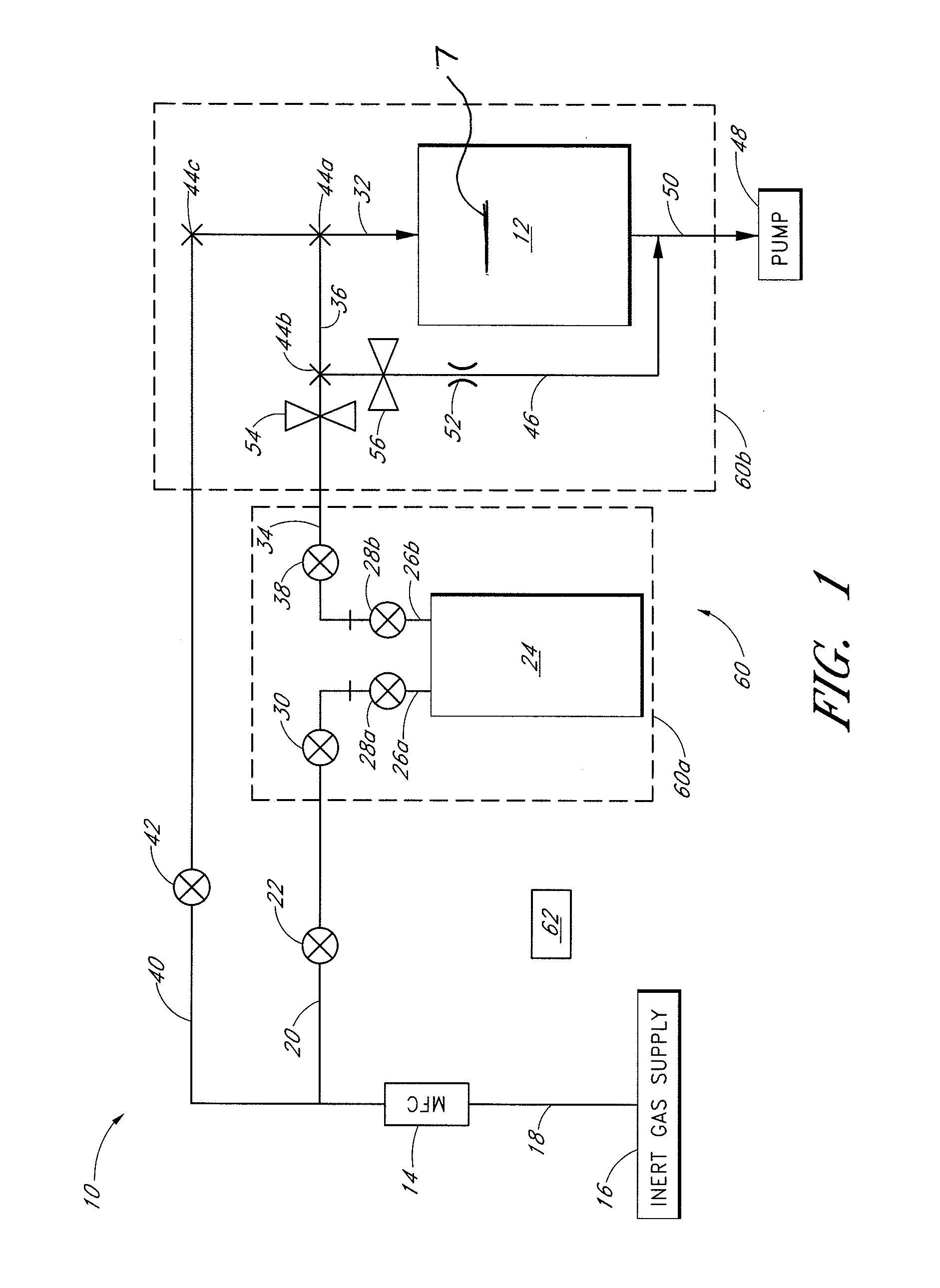
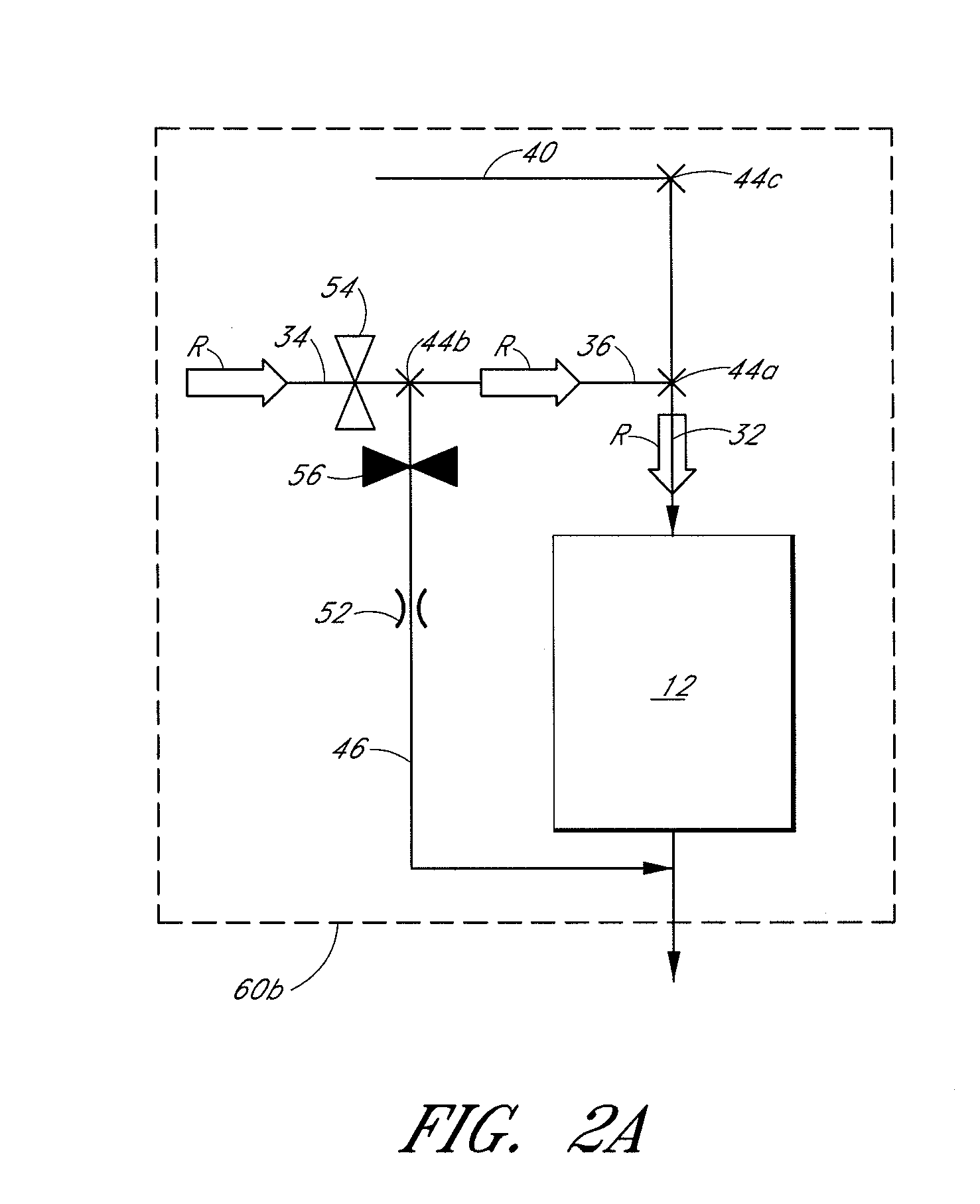
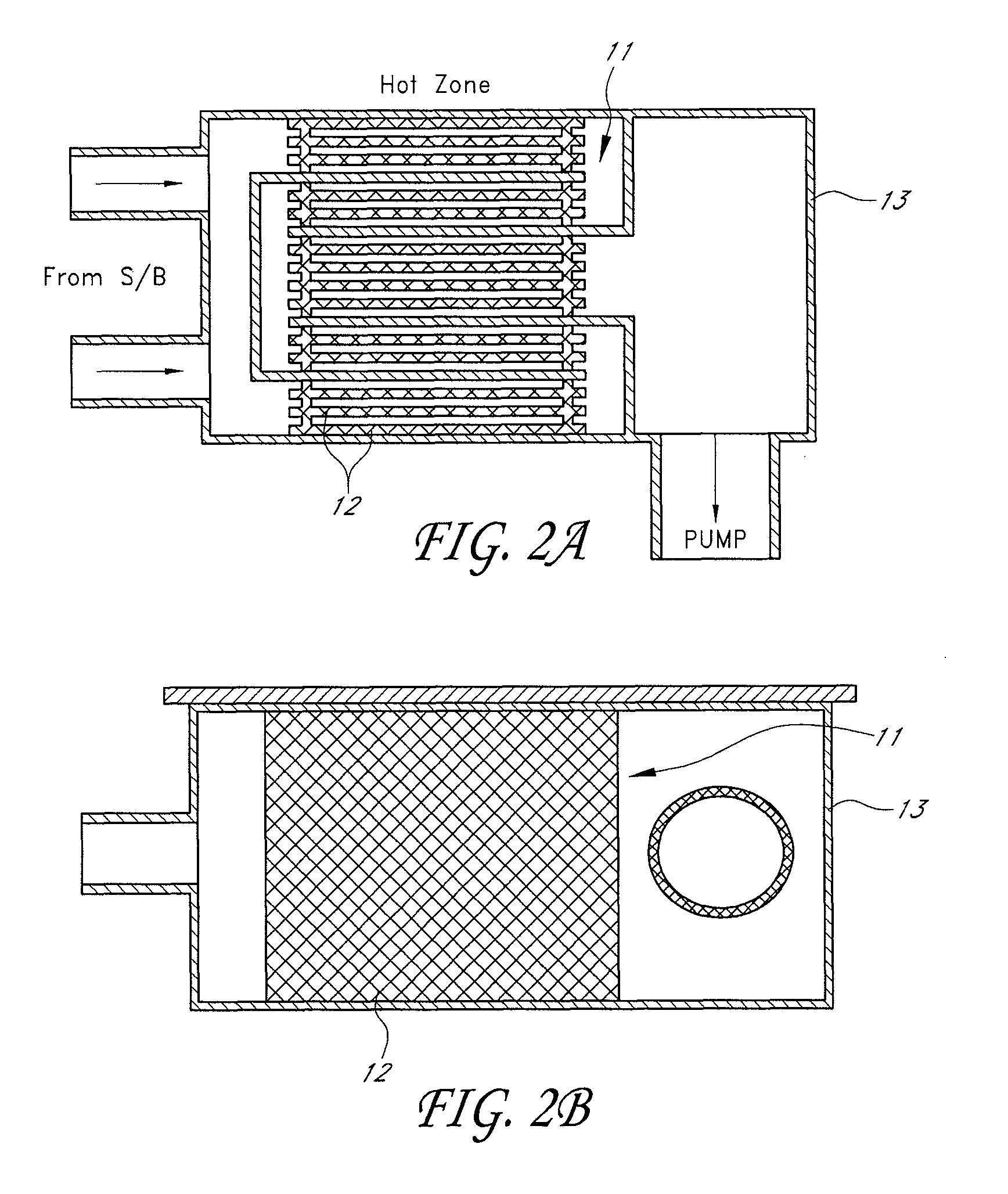
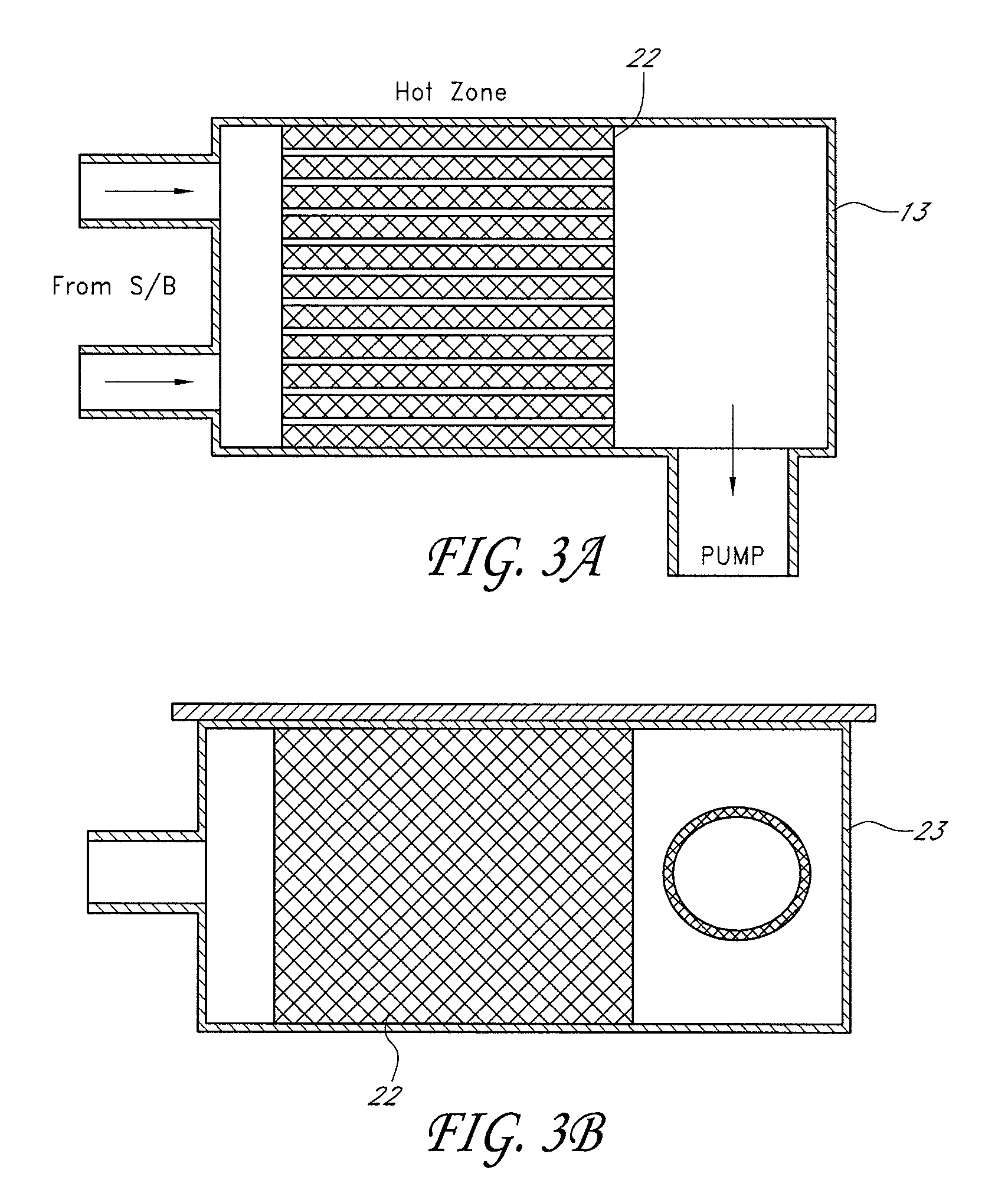
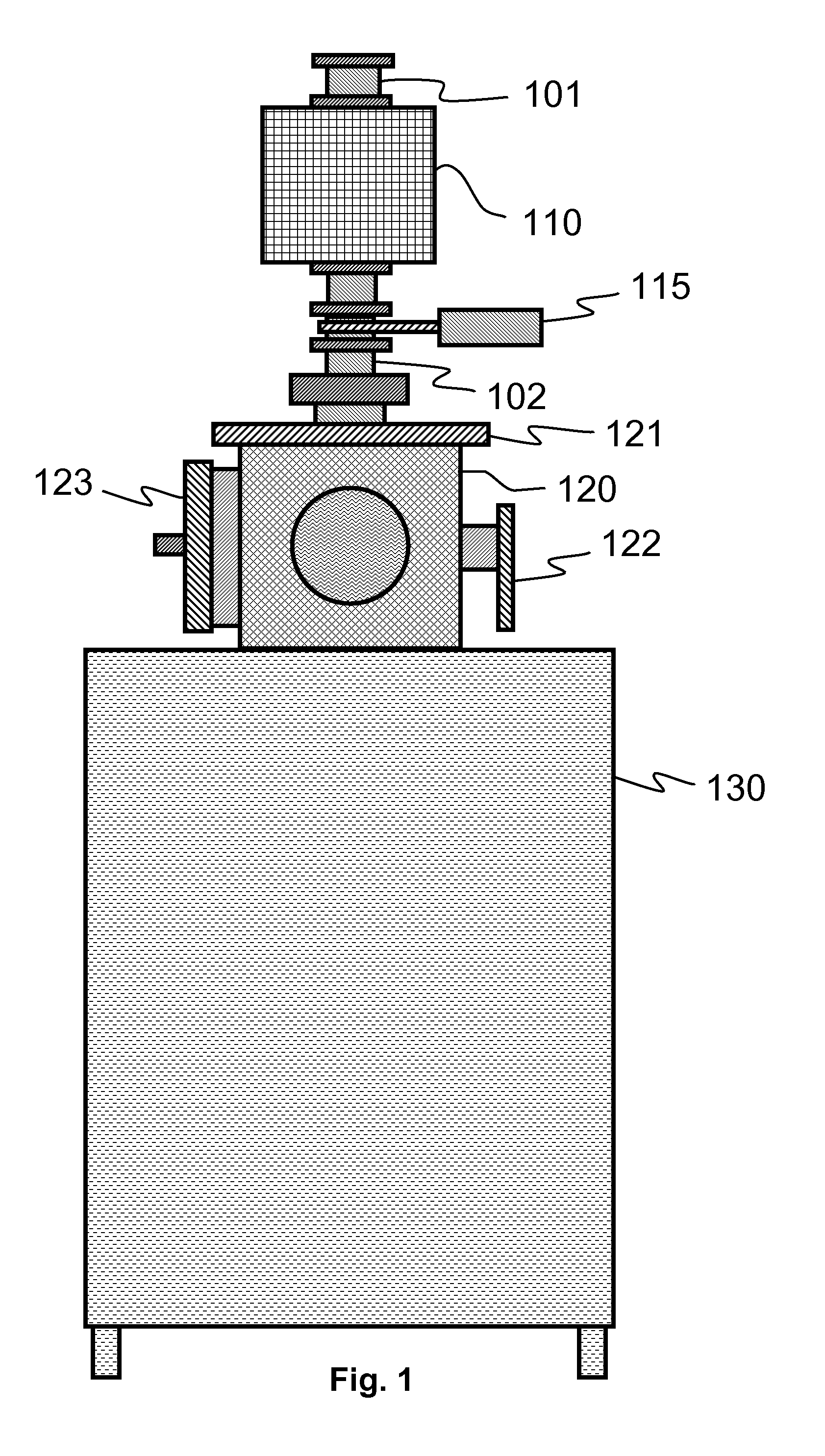
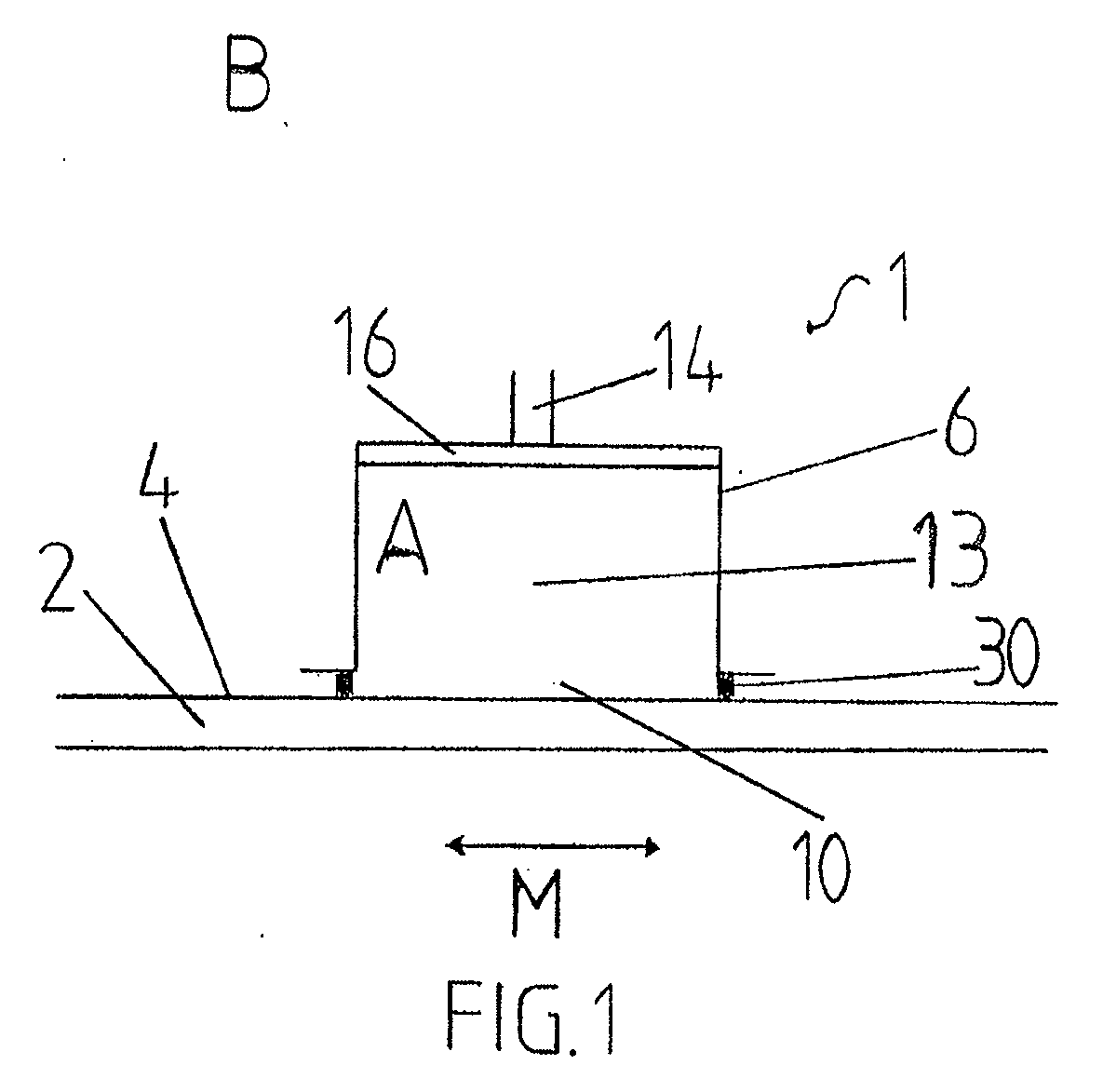
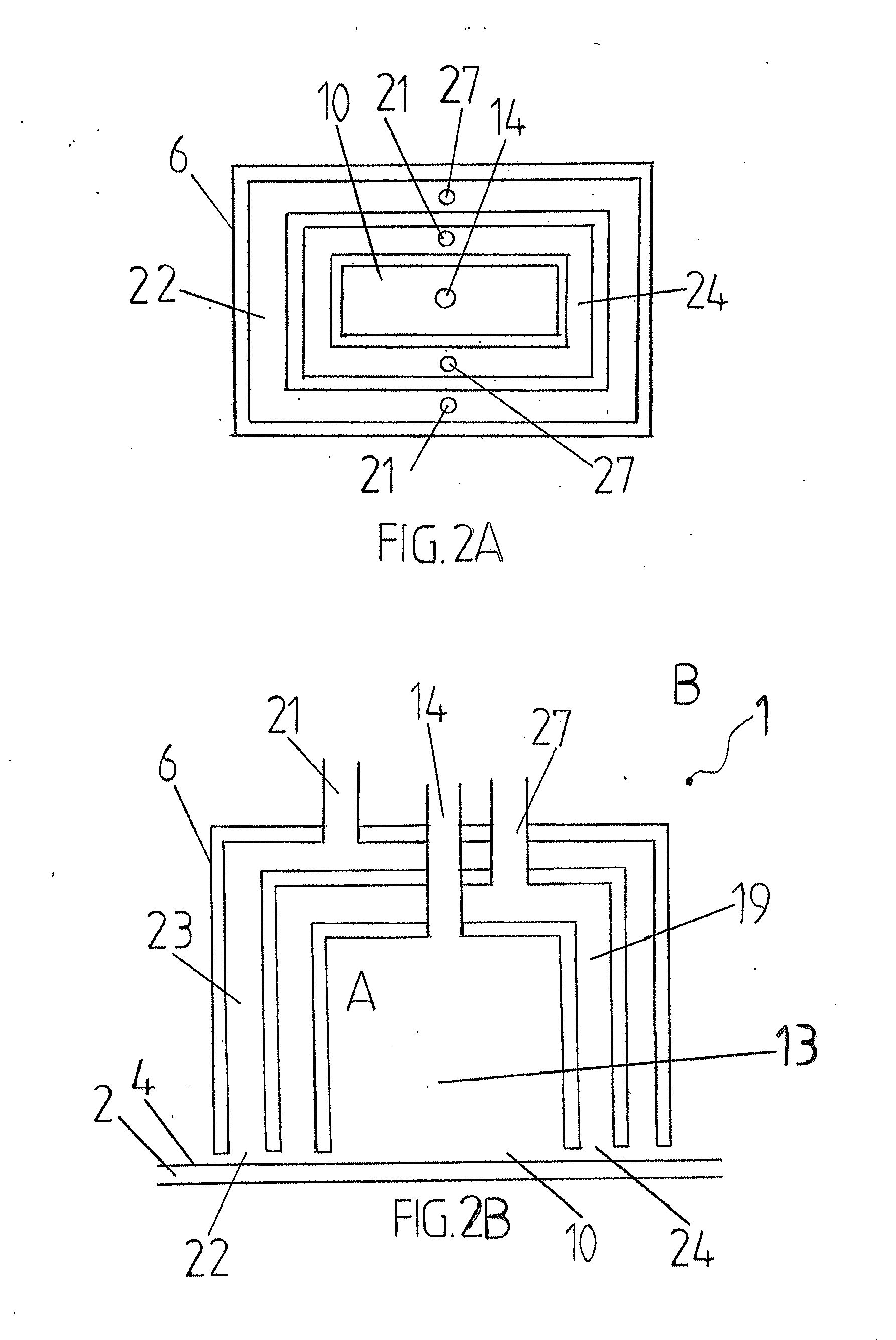
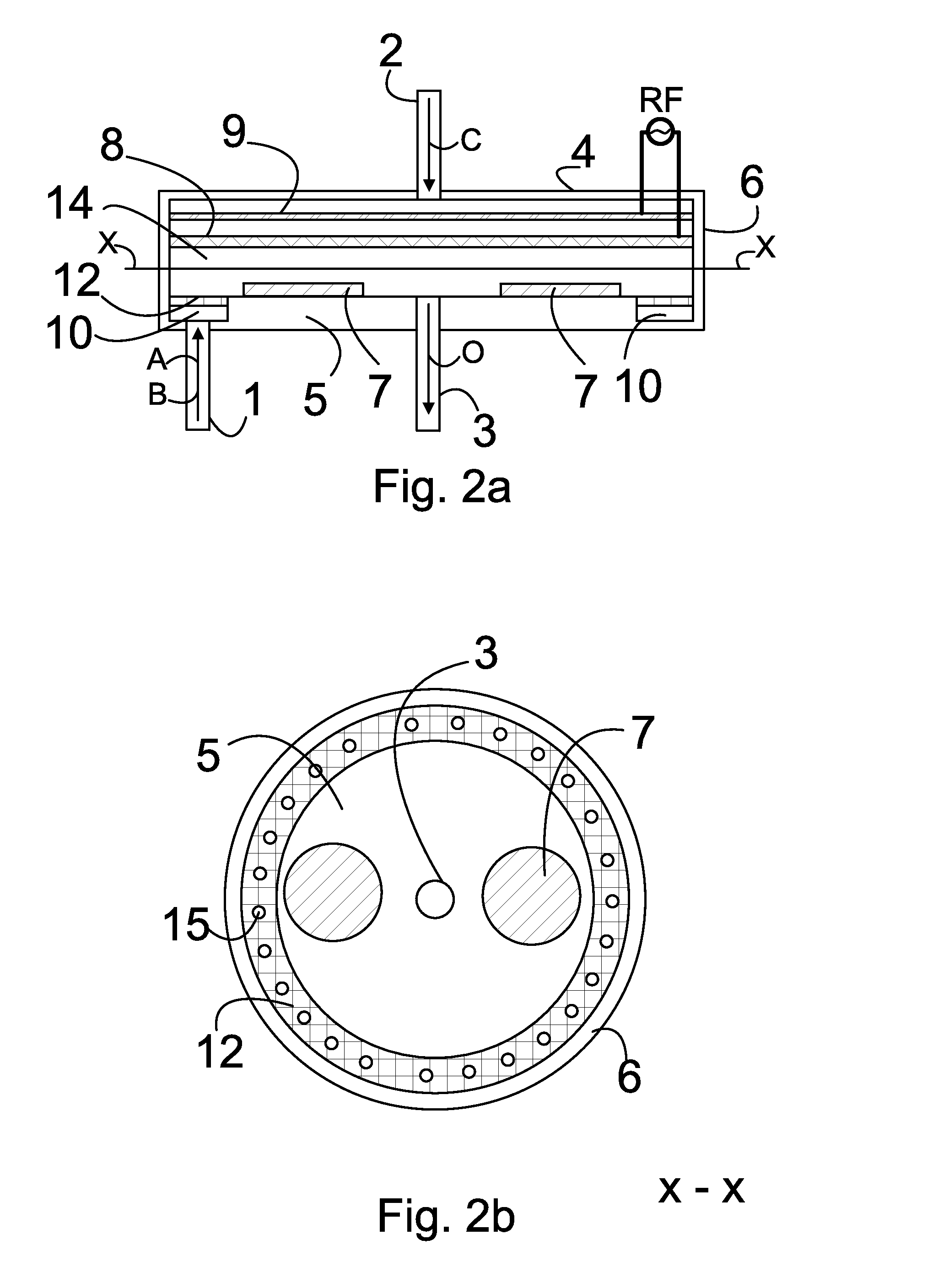
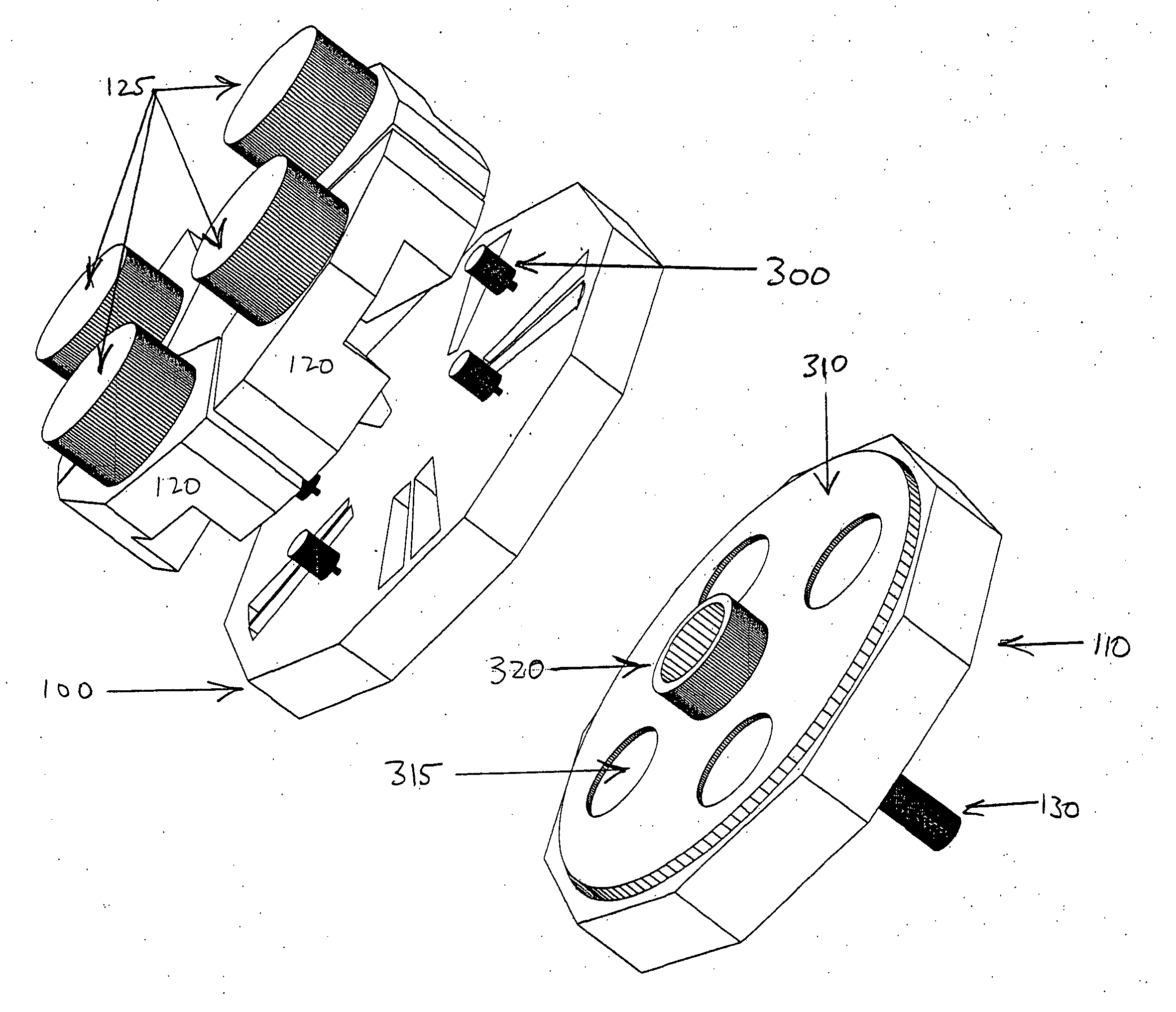
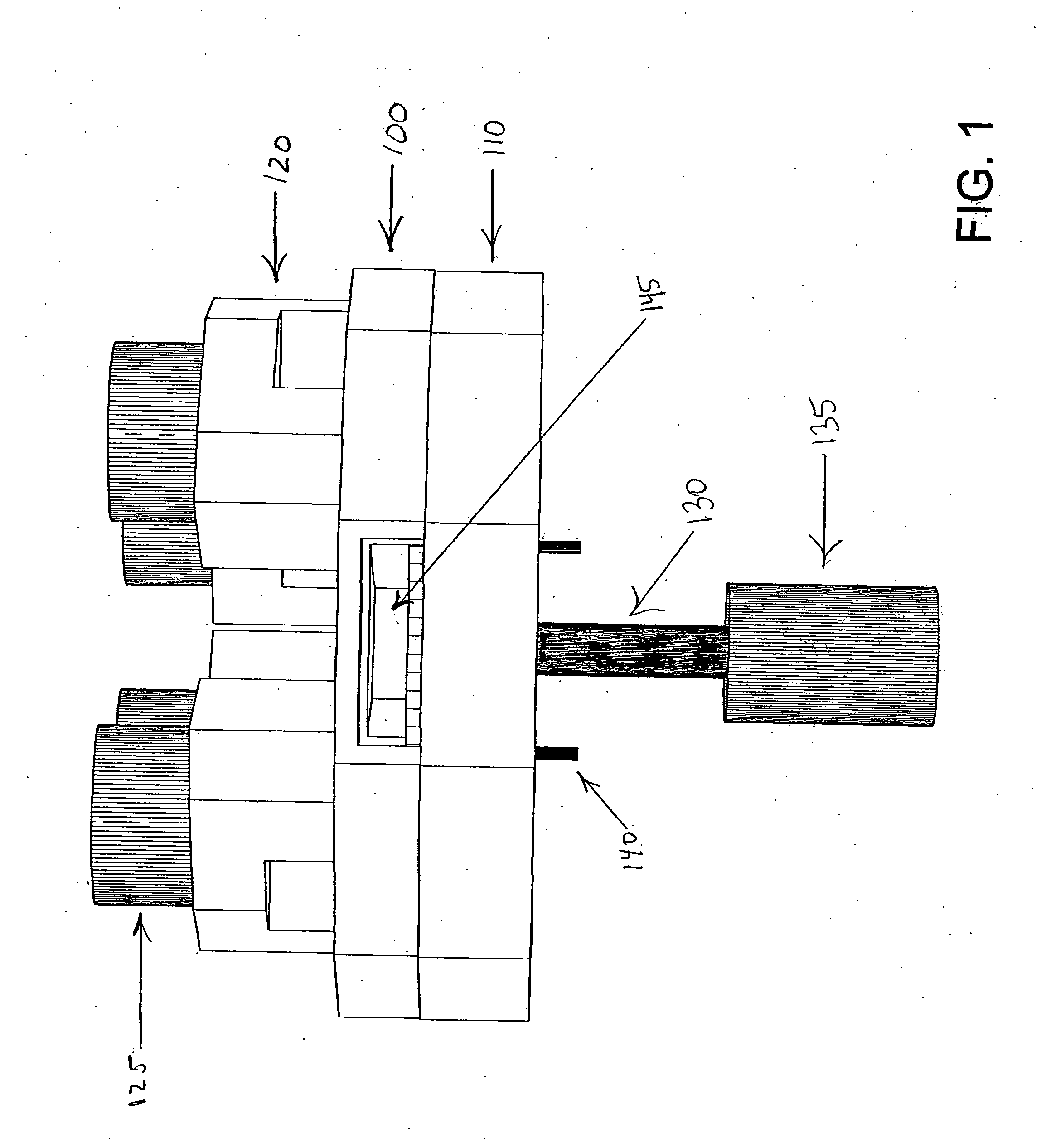
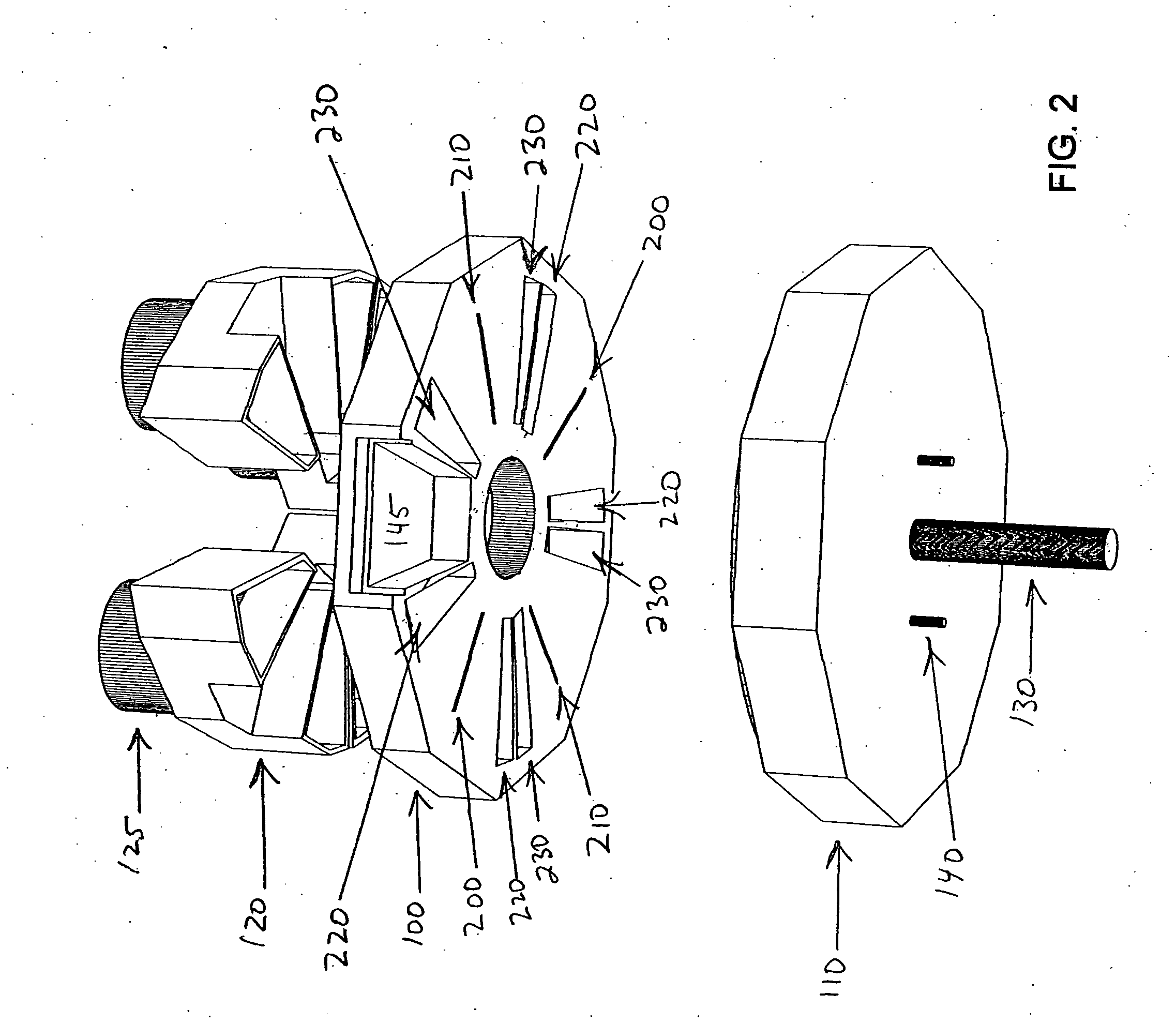
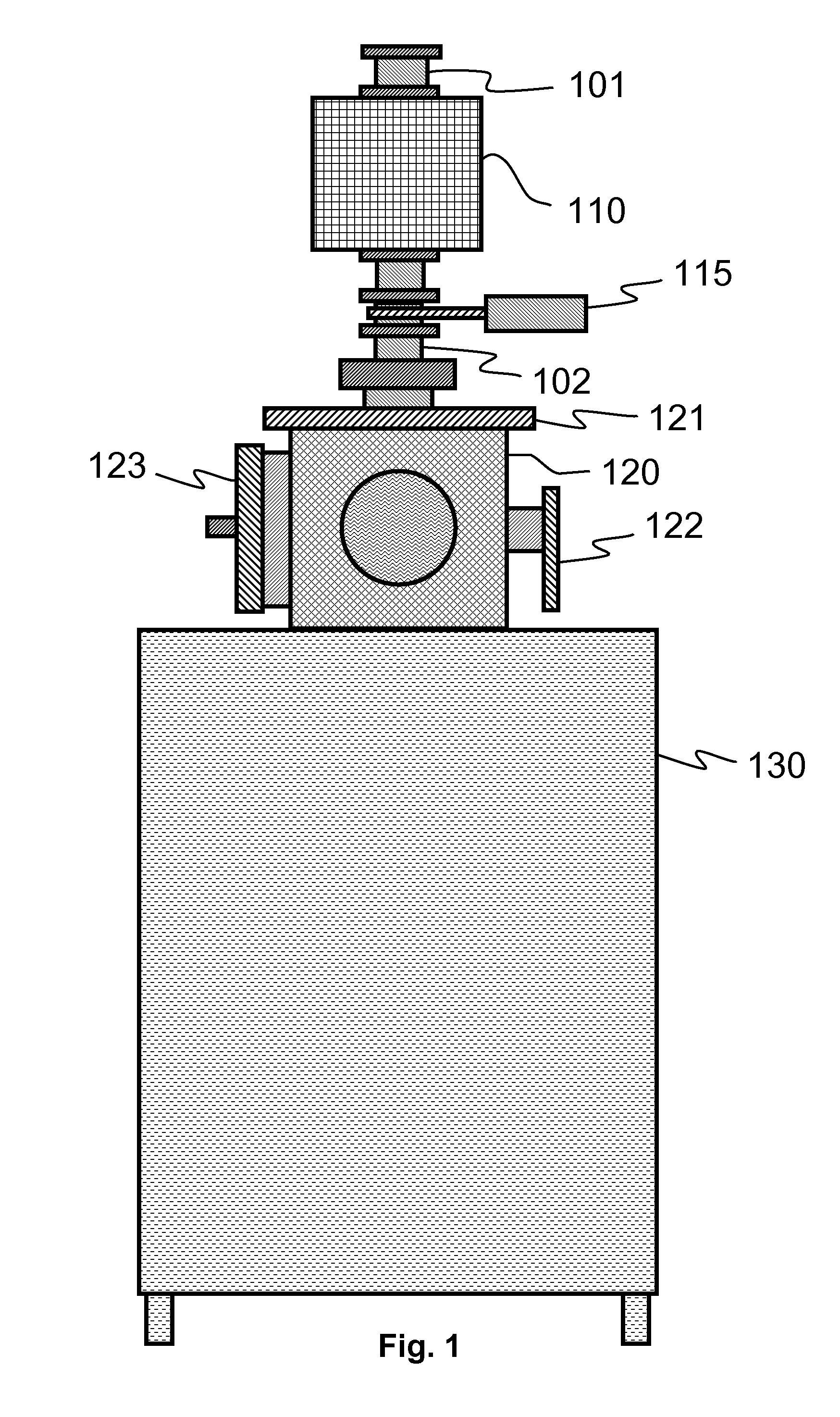
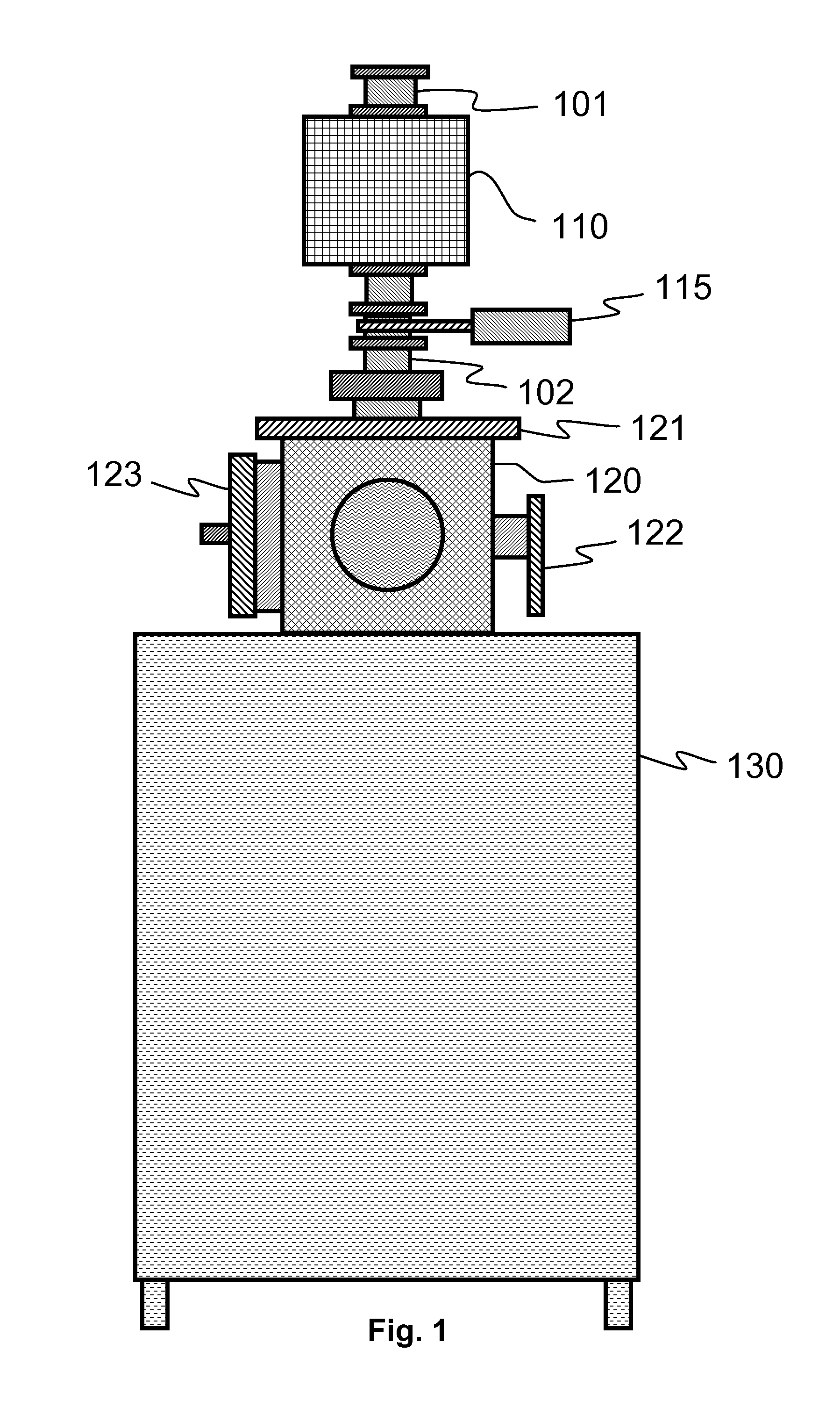
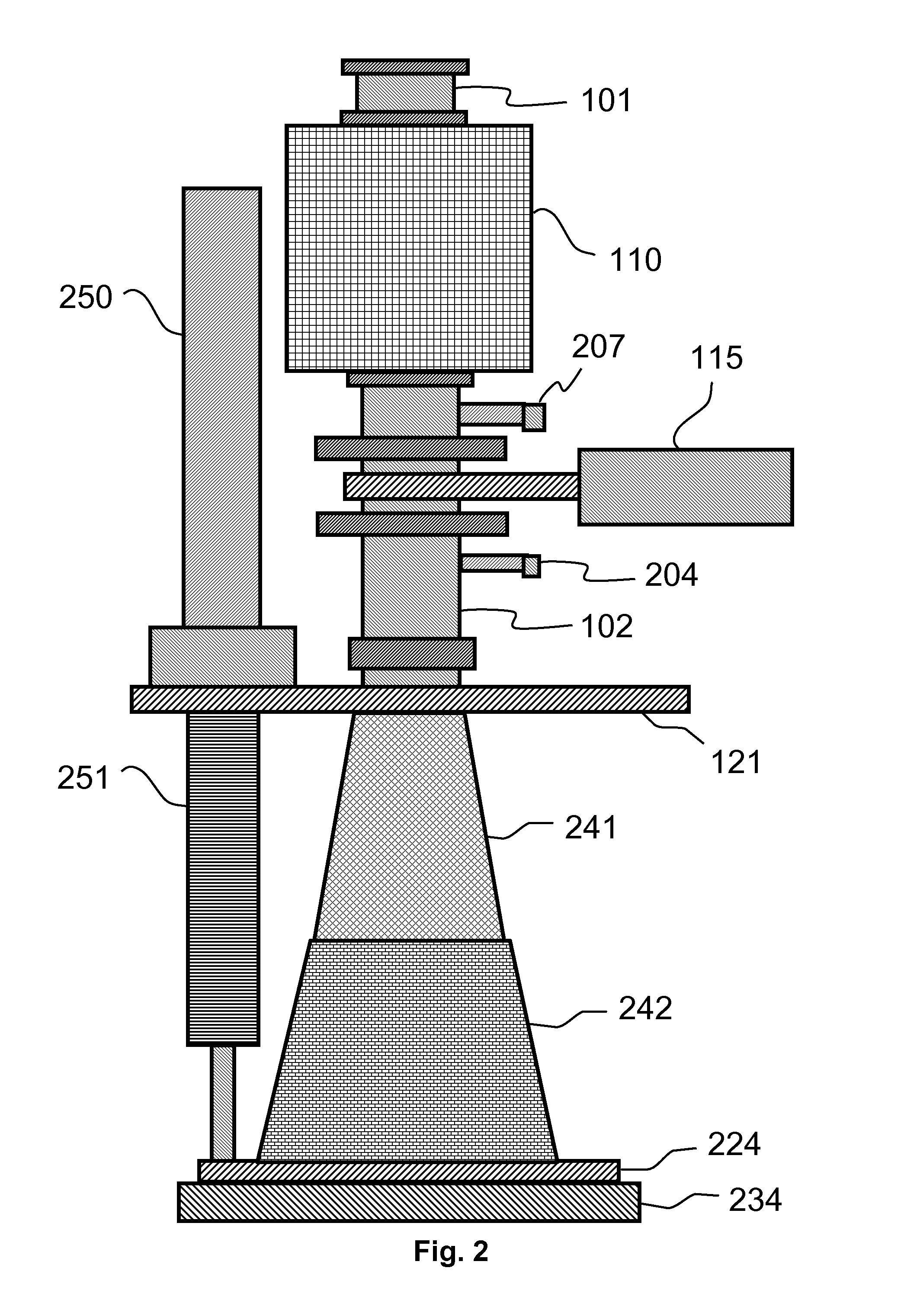
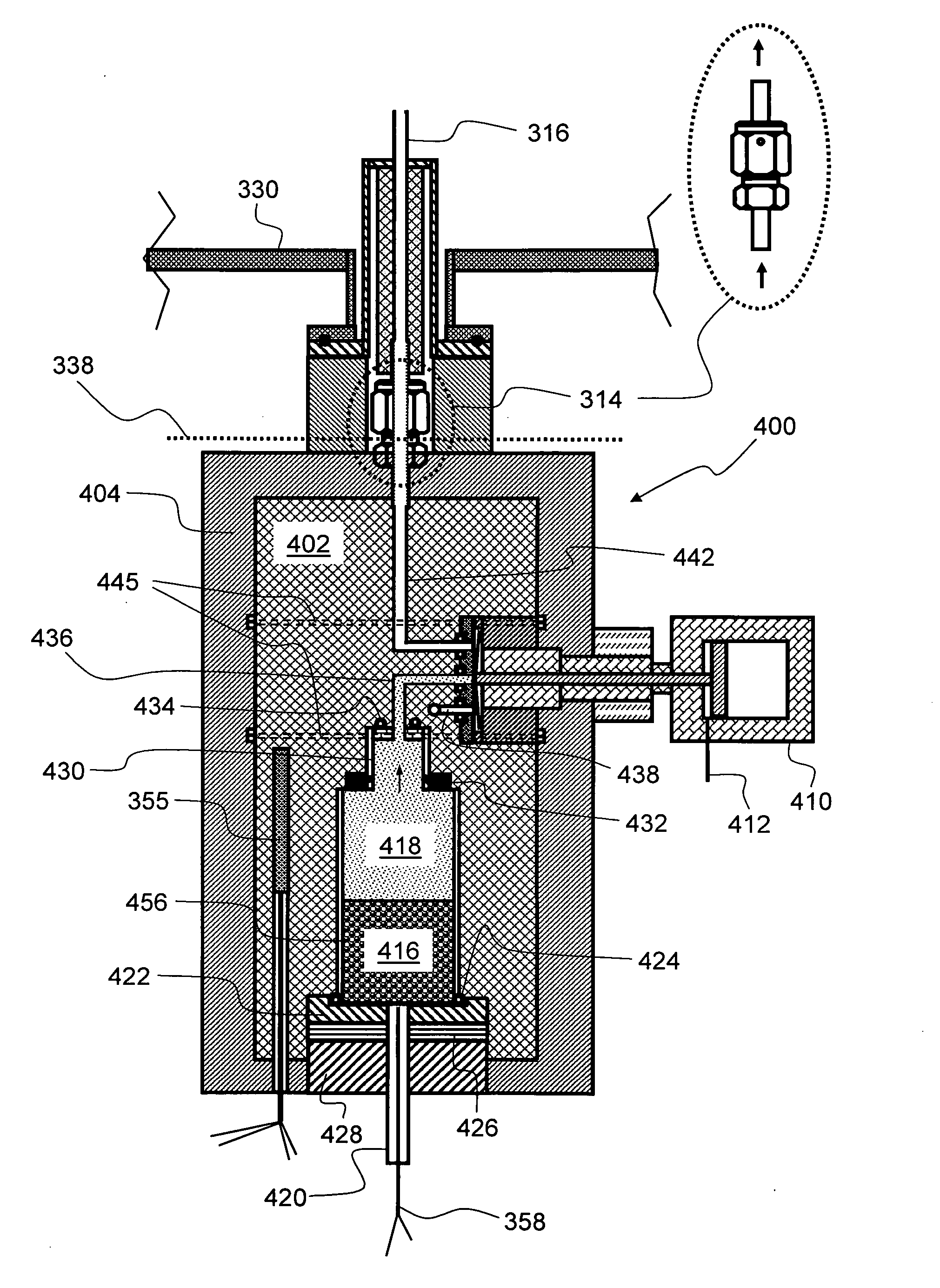
Atomic layer deposition reactor
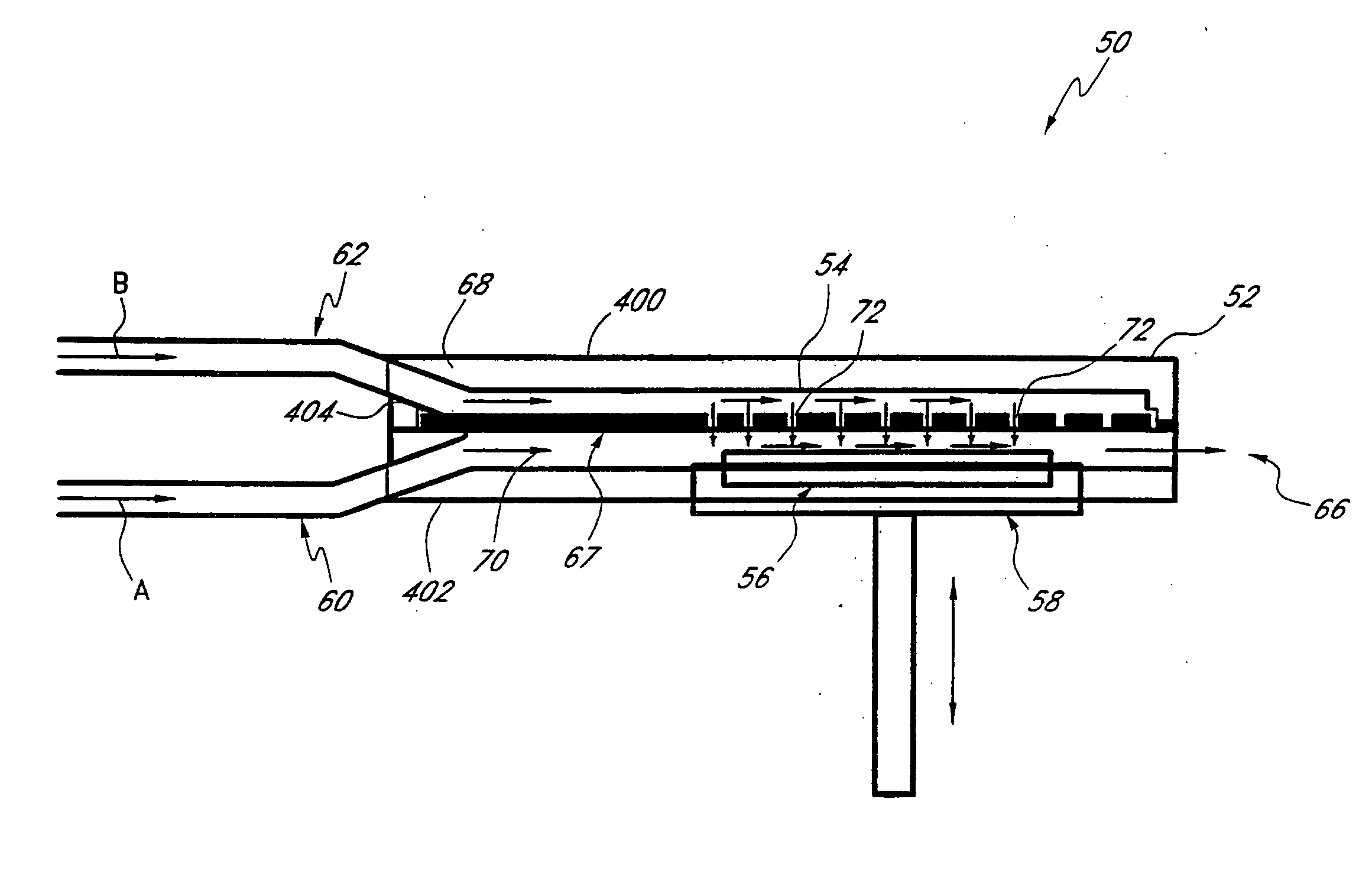
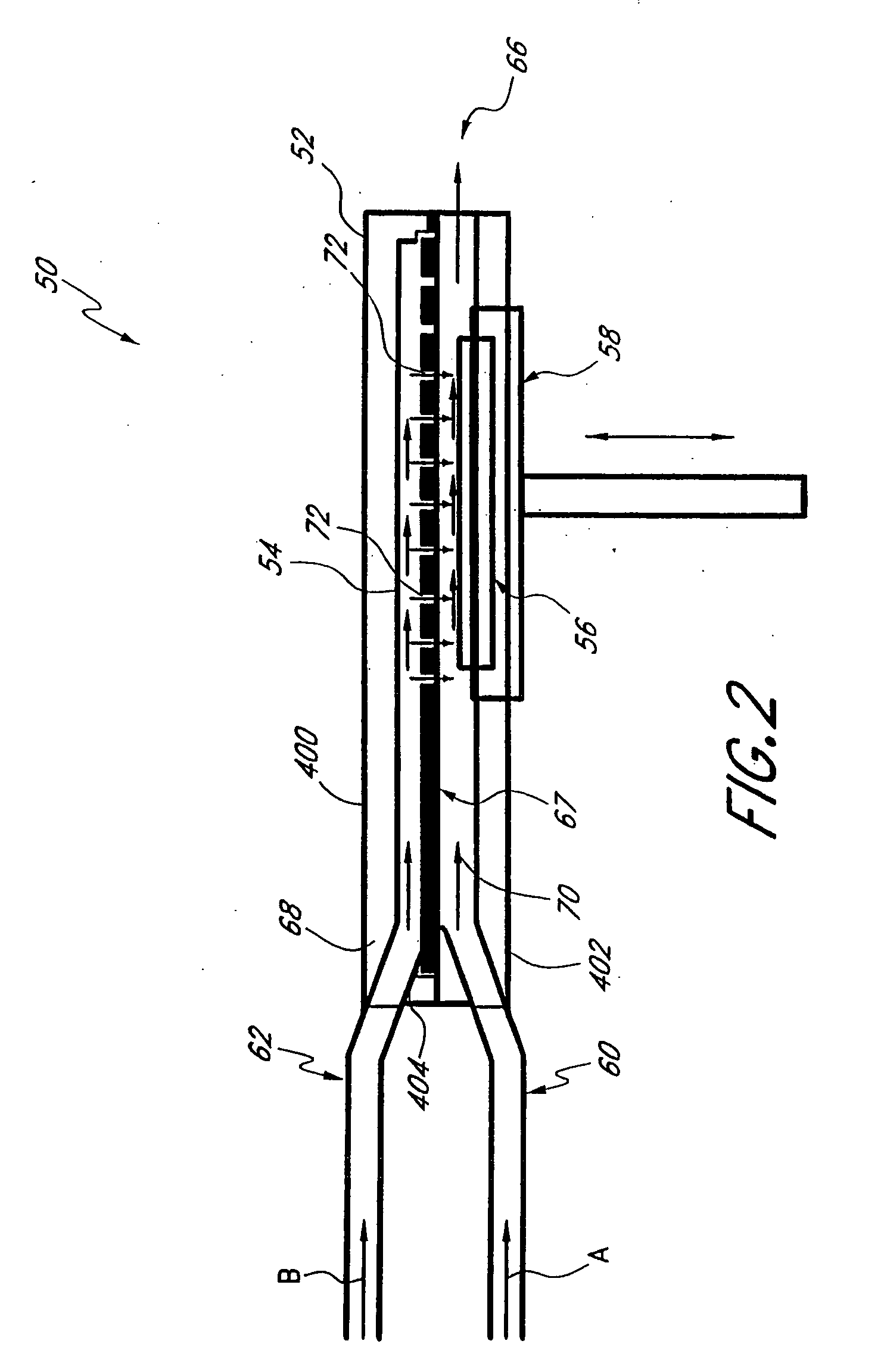
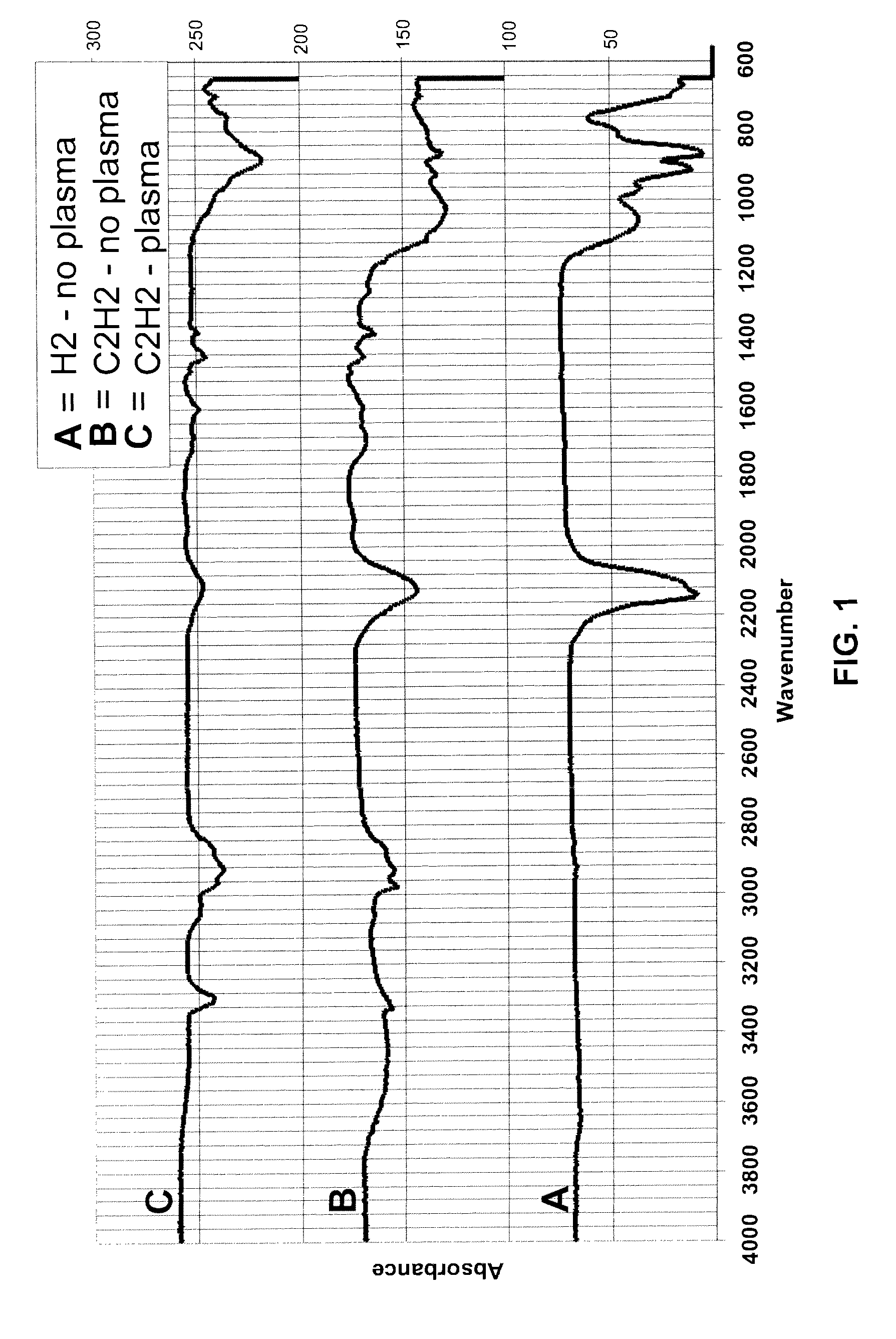
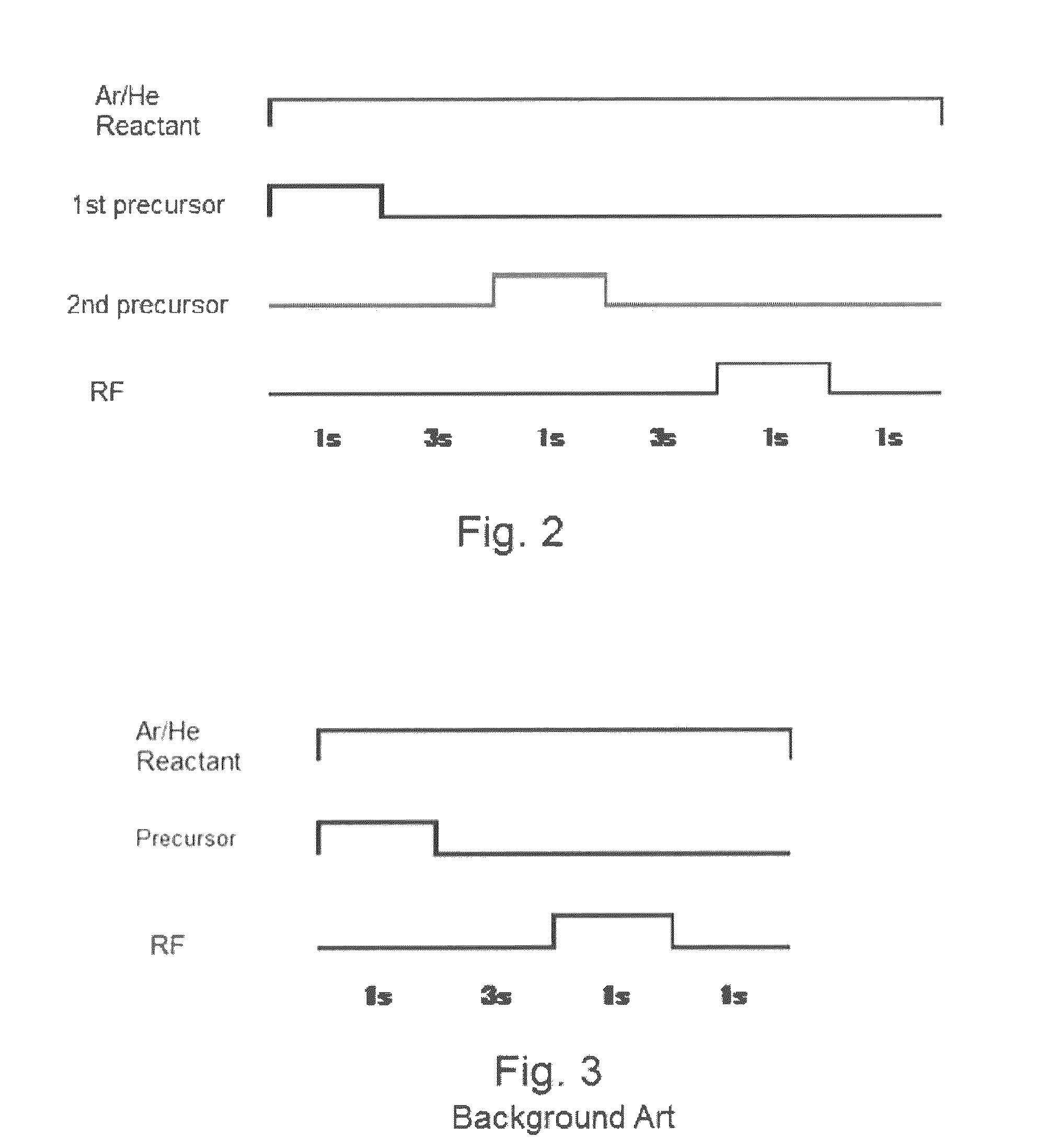
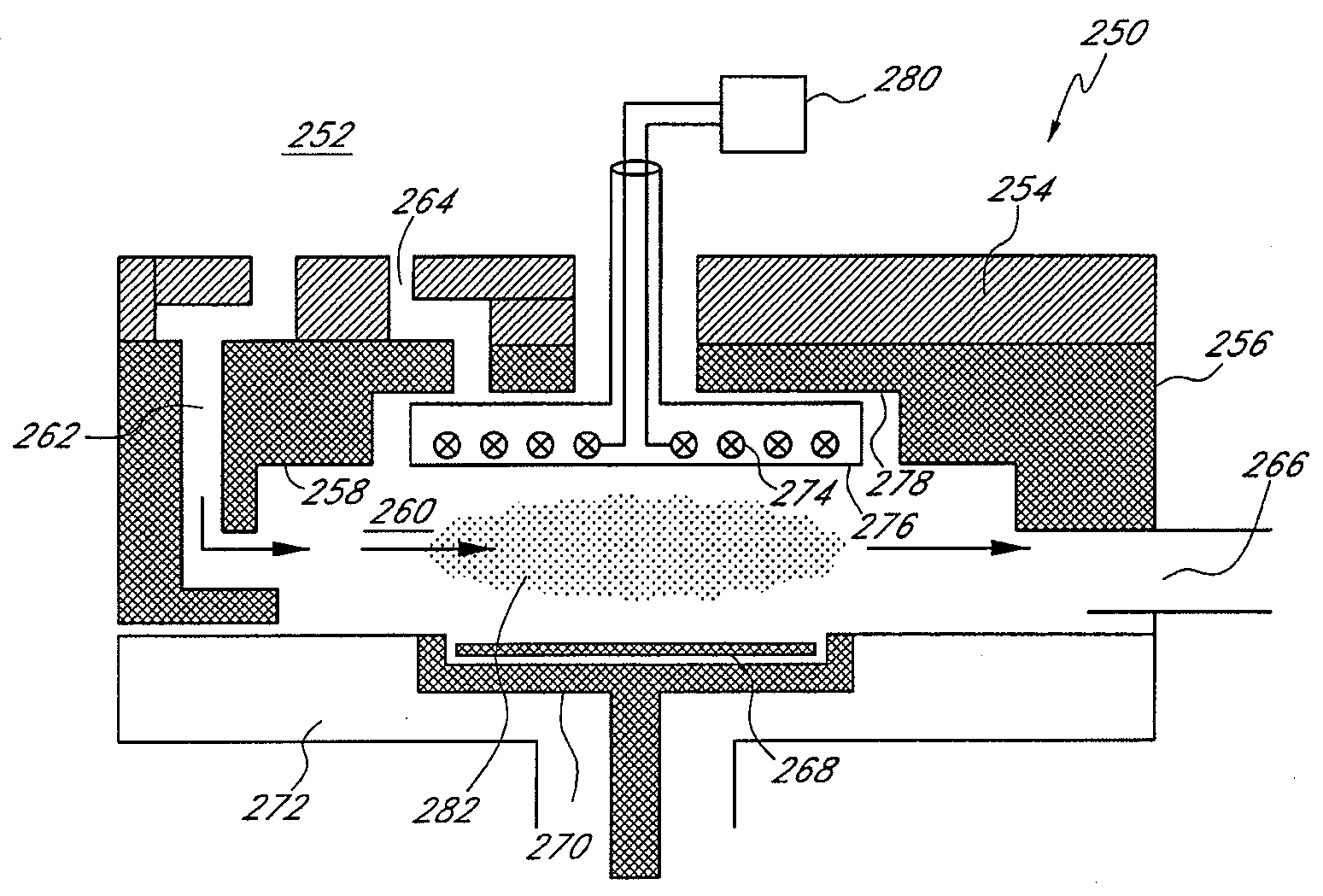
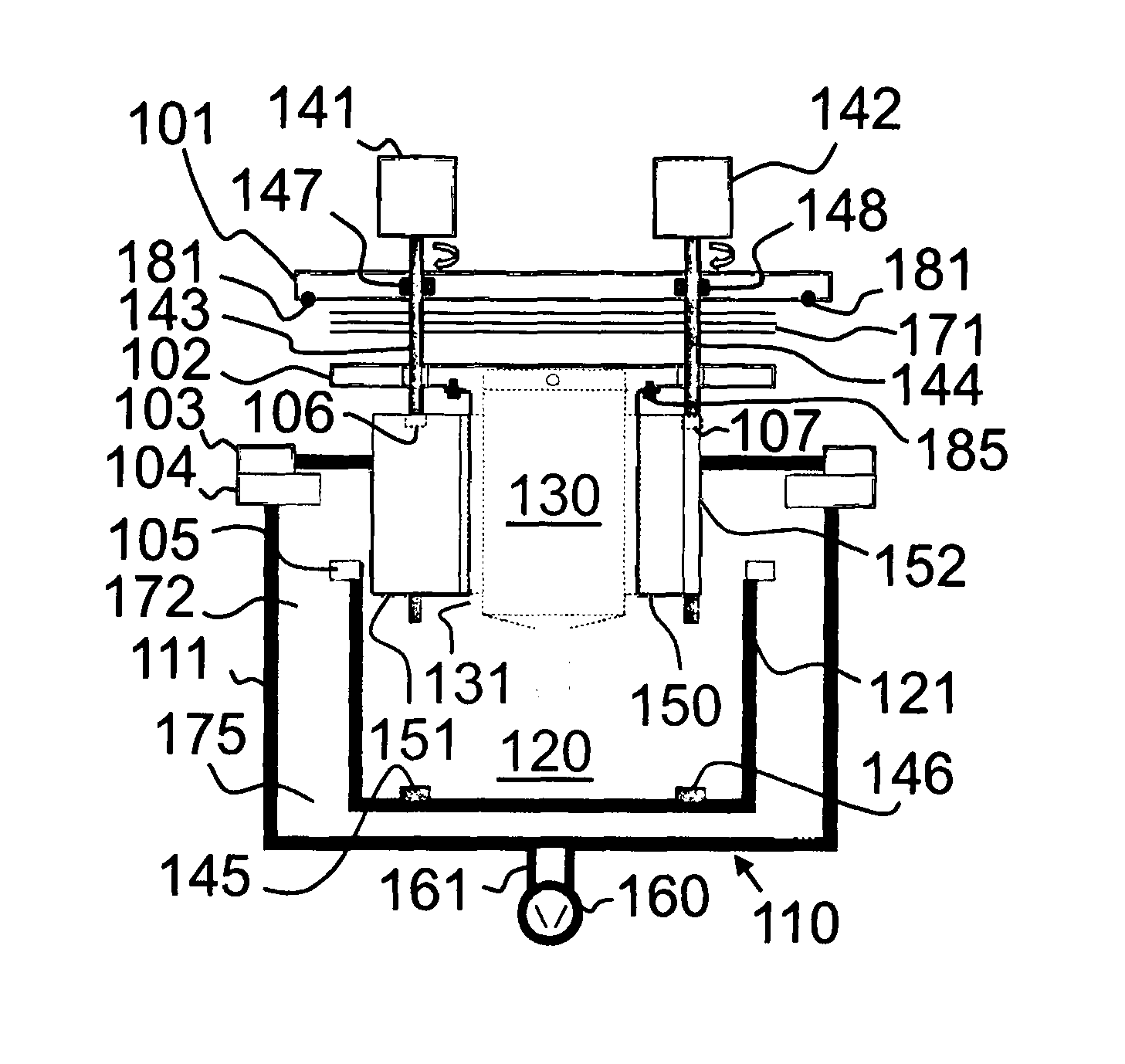
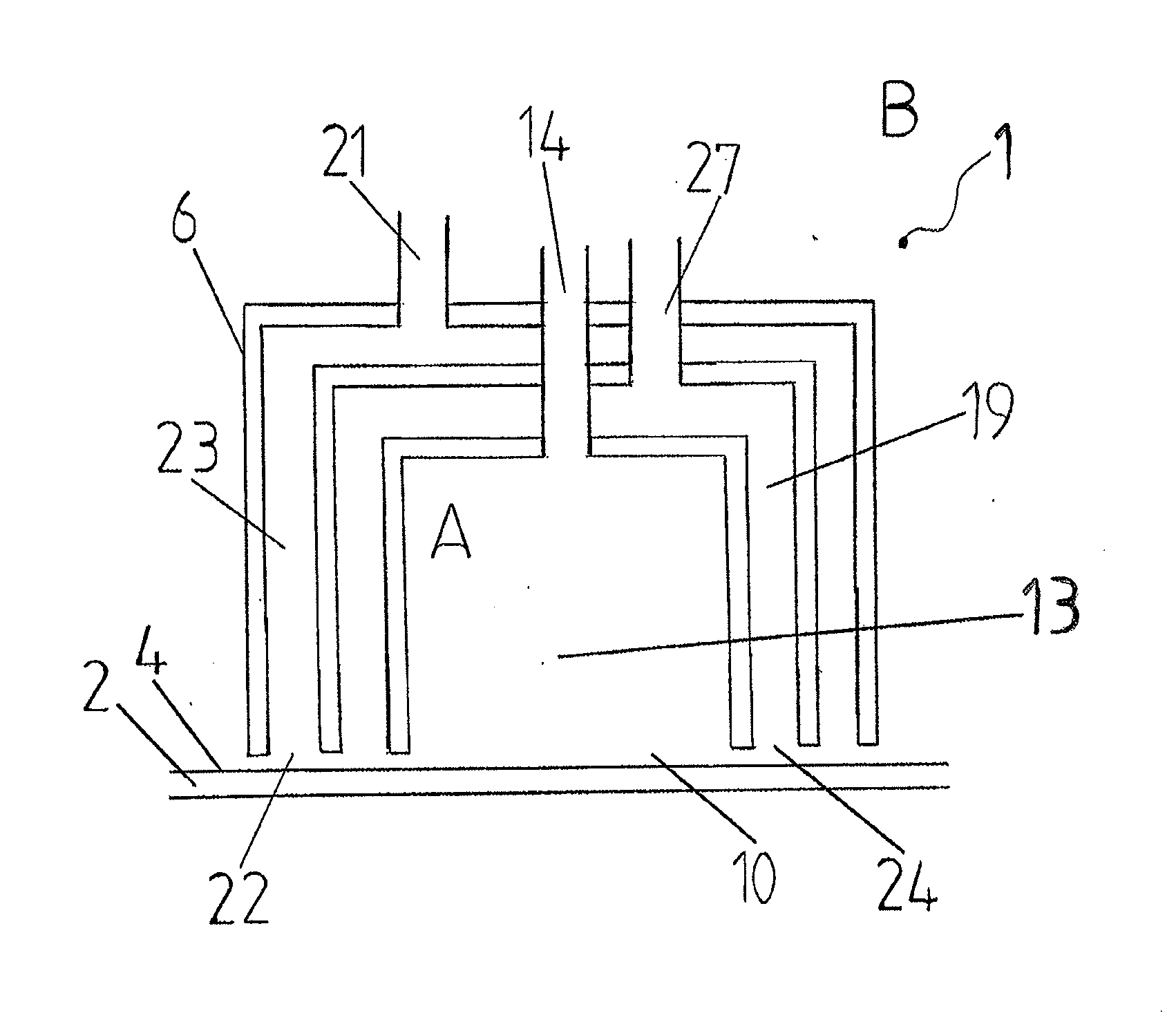
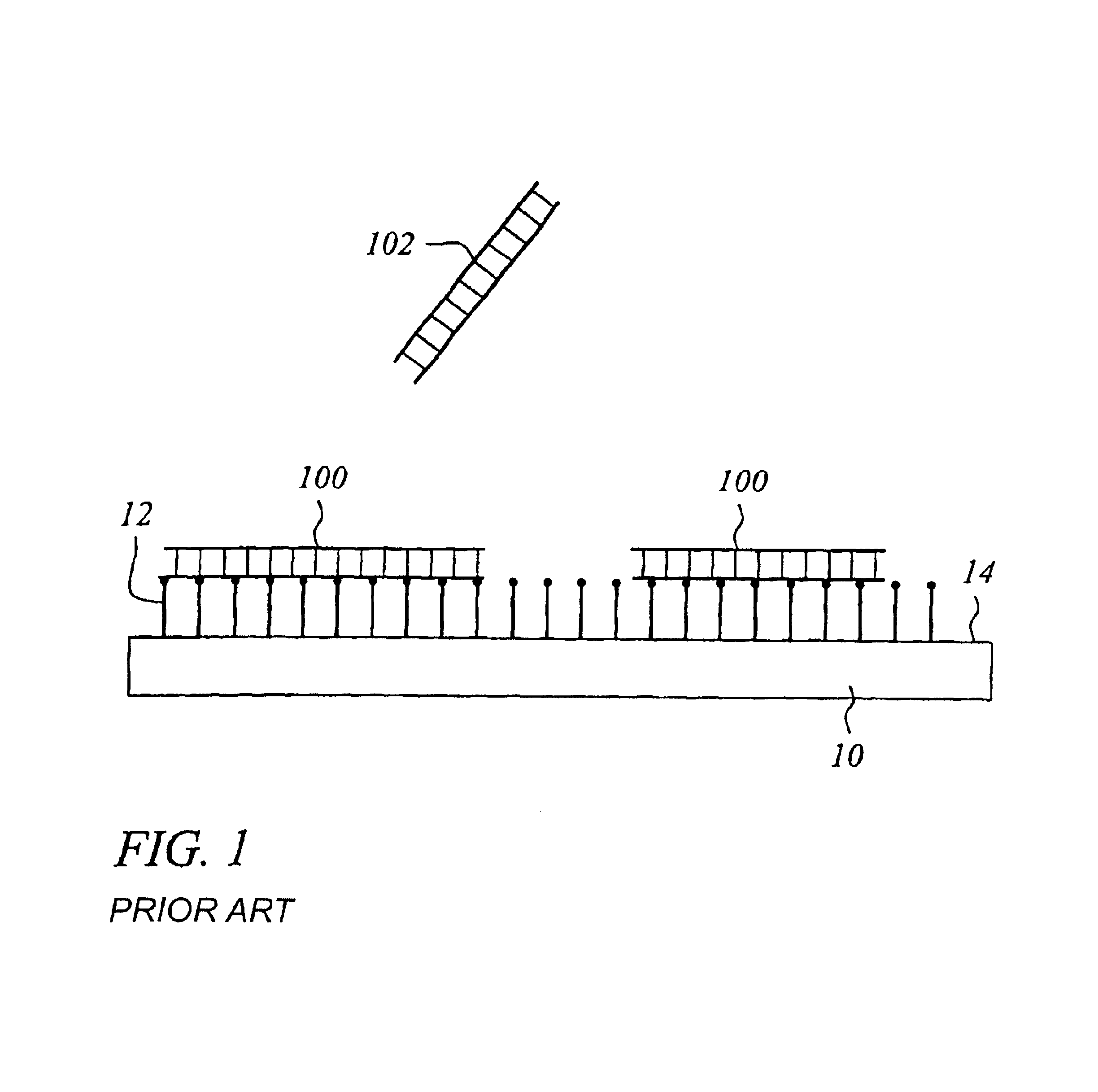
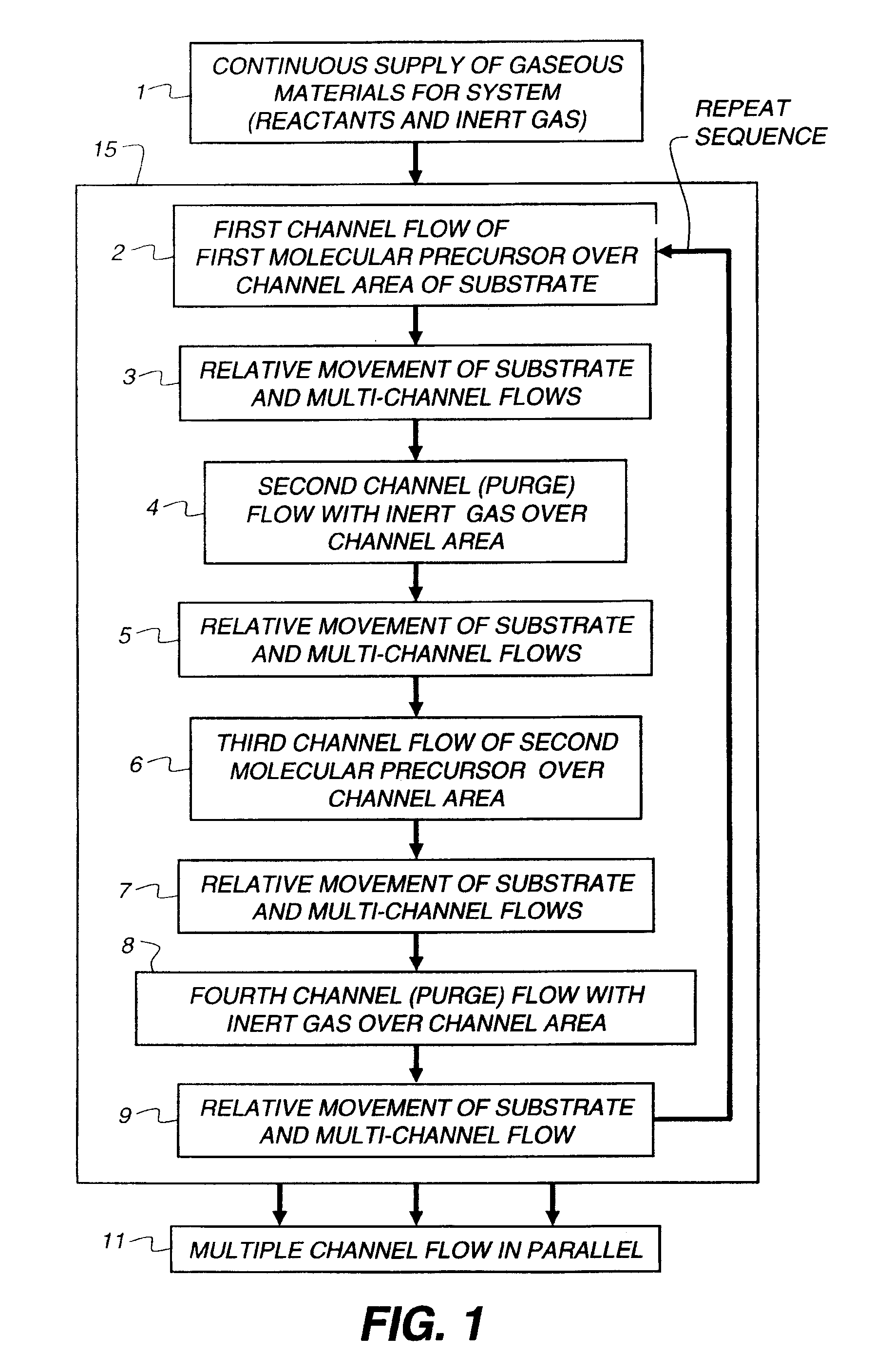
Various reactors for growing thin films on a substrate by subjecting the substrate to alternately repeated surface reactions of vapor-phase reactants are disclosed. In one embodiment, the reactor comprises a reaction chamber. A showerhead plate divides the reaction chamber into upper and lower parts. A first precursor is directed towards the lower half of the reaction chamber and a second precursor is directed towards the upper half of the reaction chamber. The substrate is disposed within the lower half of the reaction chamber. The showerhead plate includes plurality passages such that the upper half is in communication with the lower half of the reaction chamber. In another arrangement, the upper half of the reaction chamber defines a plasma cavity in which in-situ radicals are formed. In yet another arrangement, the reaction chamber includes a shutter plate, which is configured to selectively open and close the passages in the showerhead plate. In other arrangements, the showerhead plate is arranged to modify the local flow patterns of the gases flowing through the reaction chamber.
Owner:KILPELA OLLI +6
In situ modification of group iv nanoparticles using gas phase nanoparticle reactors
A method for creating an organically capped Group IV semiconductor nanoparticle is disclosed. The method includes flowing a Group IV semiconductor precursor gas into a chamber. The method also includes generating a set of Group IV semiconductor precursor radical species from the Group IV semiconductor precursor gas with a laser pyrolysis apparatus, wherein the set of the Group IV semiconductor precursor radical species nucleate to form the Group IV semiconductor nanoparticle; and flowing an organic capping agent precursor gas into the chamber. The method further includes generating a set of organic capping agent radical species from the organic capping agent precursor gas, wherein the set of organic capping agent radical species reacts with a surface of the Group IV semiconductor nanoparticle and forms the organically capped Group IV semiconductor nanoparticle.
Owner:LI XUEGENG +3
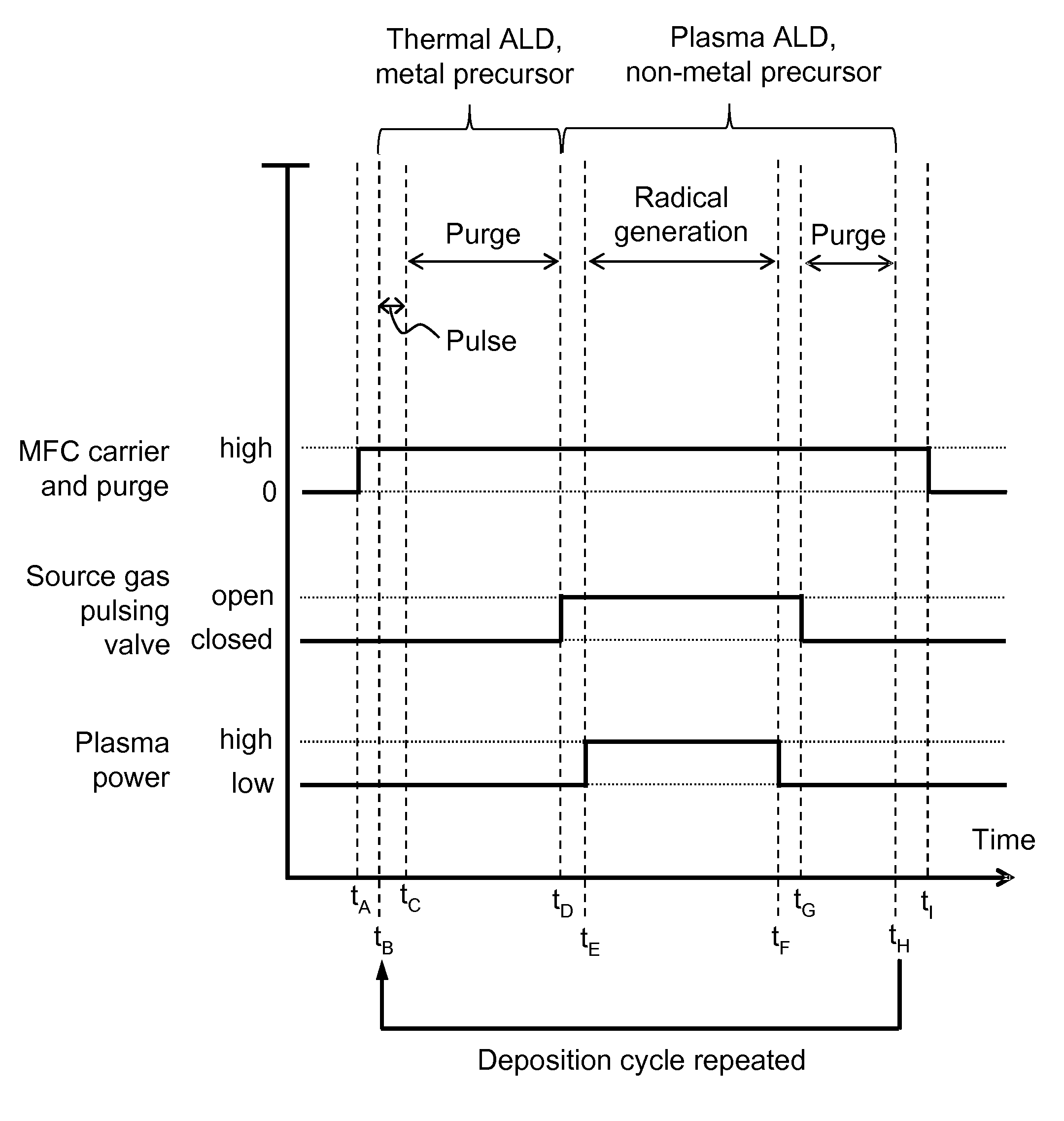
Method for forming Si-containing film using two precursors by ALD
ActiveUS8912101B2Increase probabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface reactionHalogen
A method for forming a silicon-containing dielectric film on a substrate by atomic layer deposition (ALD) includes: providing two precursors, one precursor containing a halogen in its molecule, another precursor containing a silicon but no halogen in its molecule, adsorbing a first precursor, which is one of the two precursors onto a substrate to deposit a monolayer of the first precursor; adsorbing a second precursor, which is the other of the two precursors onto the monolayer of the first precursor to deposit a monolayer of the second precursor; and exposing the monolayer of the second precursor to radicals of a reactant to cause surface reaction with the radicals to form a compound monolayer of a silicon-containing film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
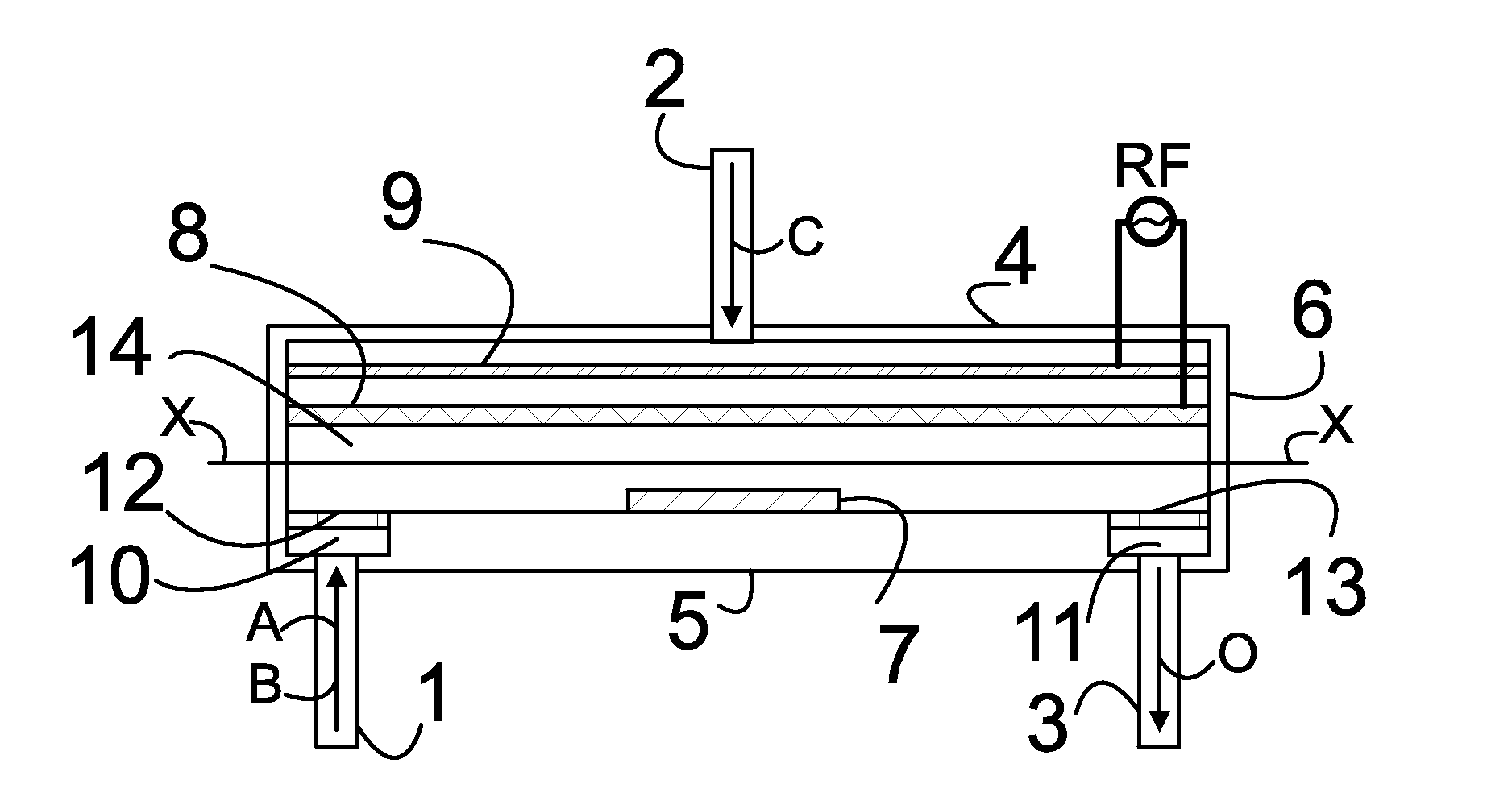
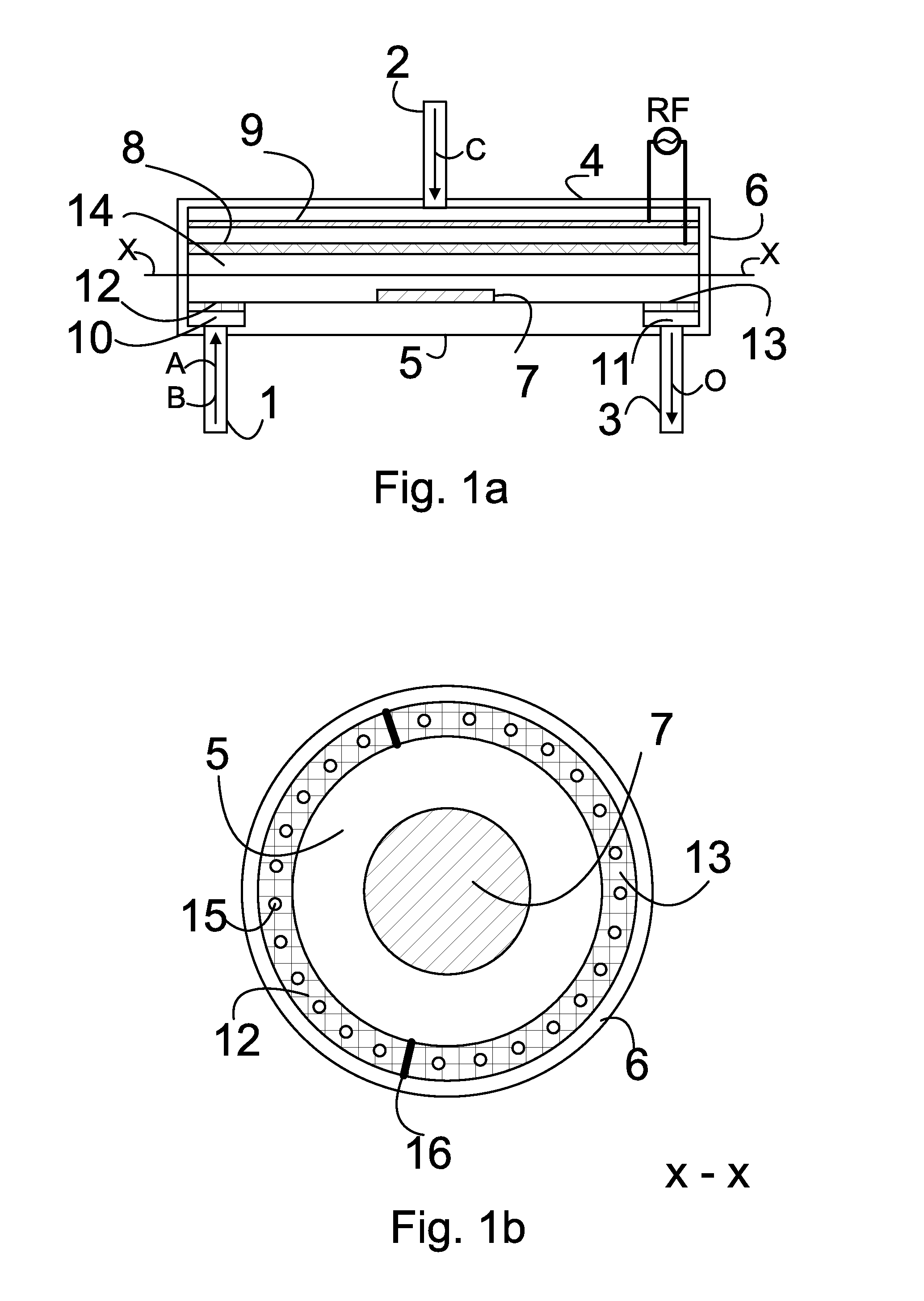
Atomic layer deposition reactor
InactiveUS20080241387A1Electric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface reactionEngineering
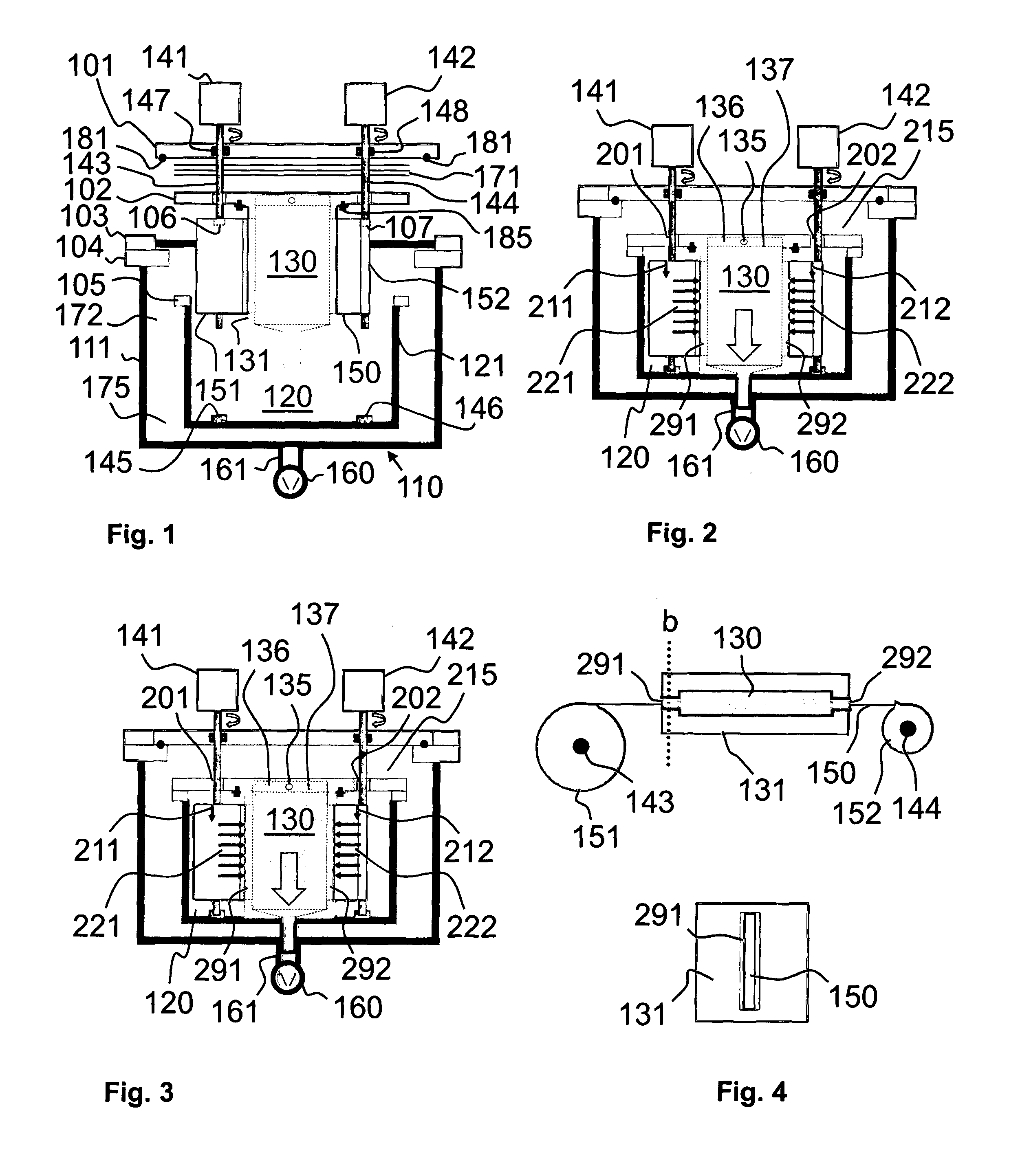
Various reactors for growing thin films on a substrate by subjecting the substrate to alternately repeated surface reactions of vapor-phase reactants are disclosed. The reactor according to the present invention includes a reaction chamber, a substrate holder, a showerhead plate, a first reactant source, a remote radical generator, a second reactant source, and an exhaust outlet. The showerhead plate is configured to define a reaction space between the showerhead plate and the substrate holder. The showerhead plate includes a plurality of passages leading into the reaction space. The substrate is disposed within the reaction space. A first non-radical reactant is supplied through the showerhead plate to the reaction space. The remote radical generator produces the radicals of a second reactant supplied from the second reactant source. The radicals are supplied directly to the reaction space without passing through the showerhead plate.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Atomic Layer Deposition with Plasma Source
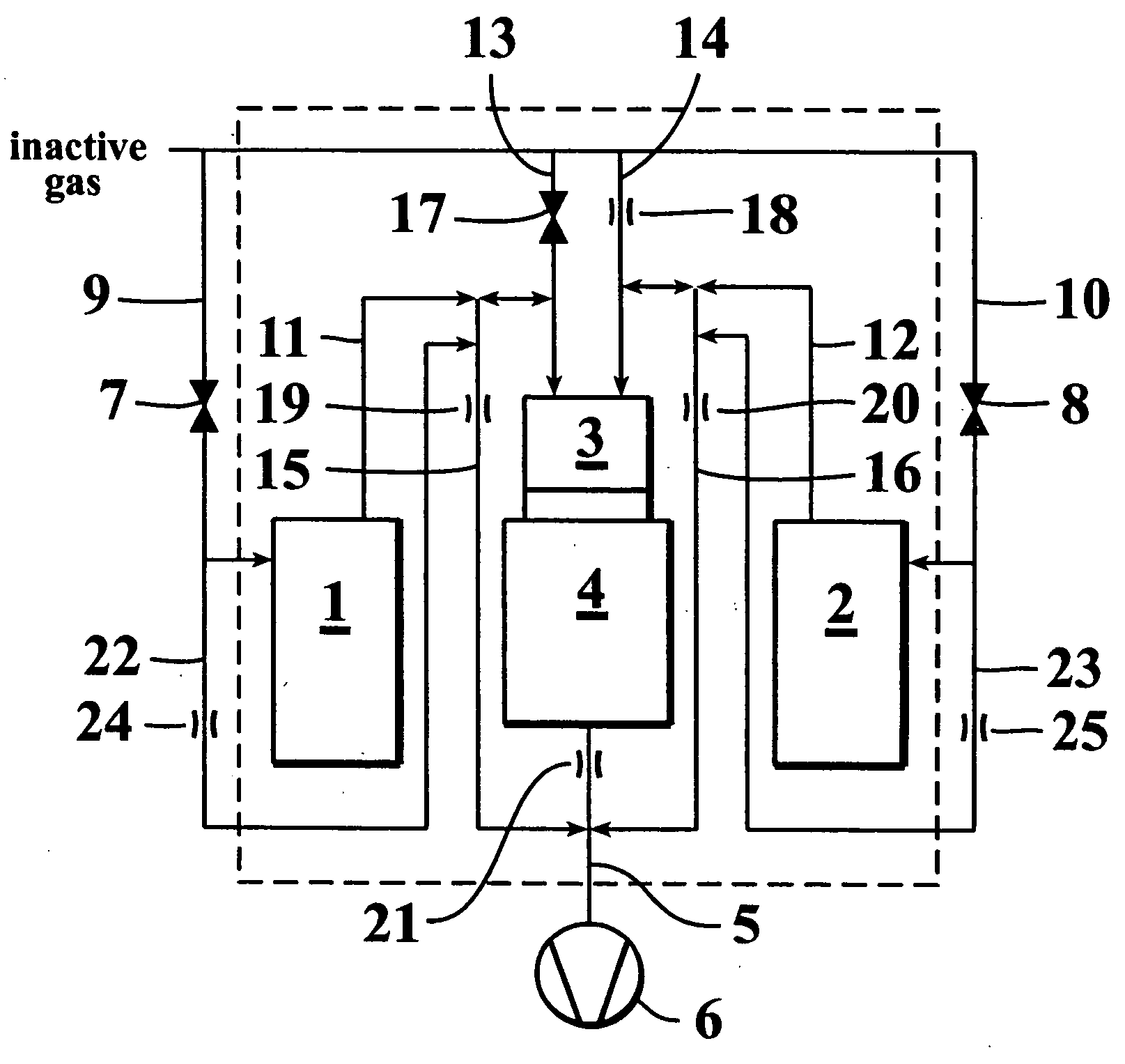
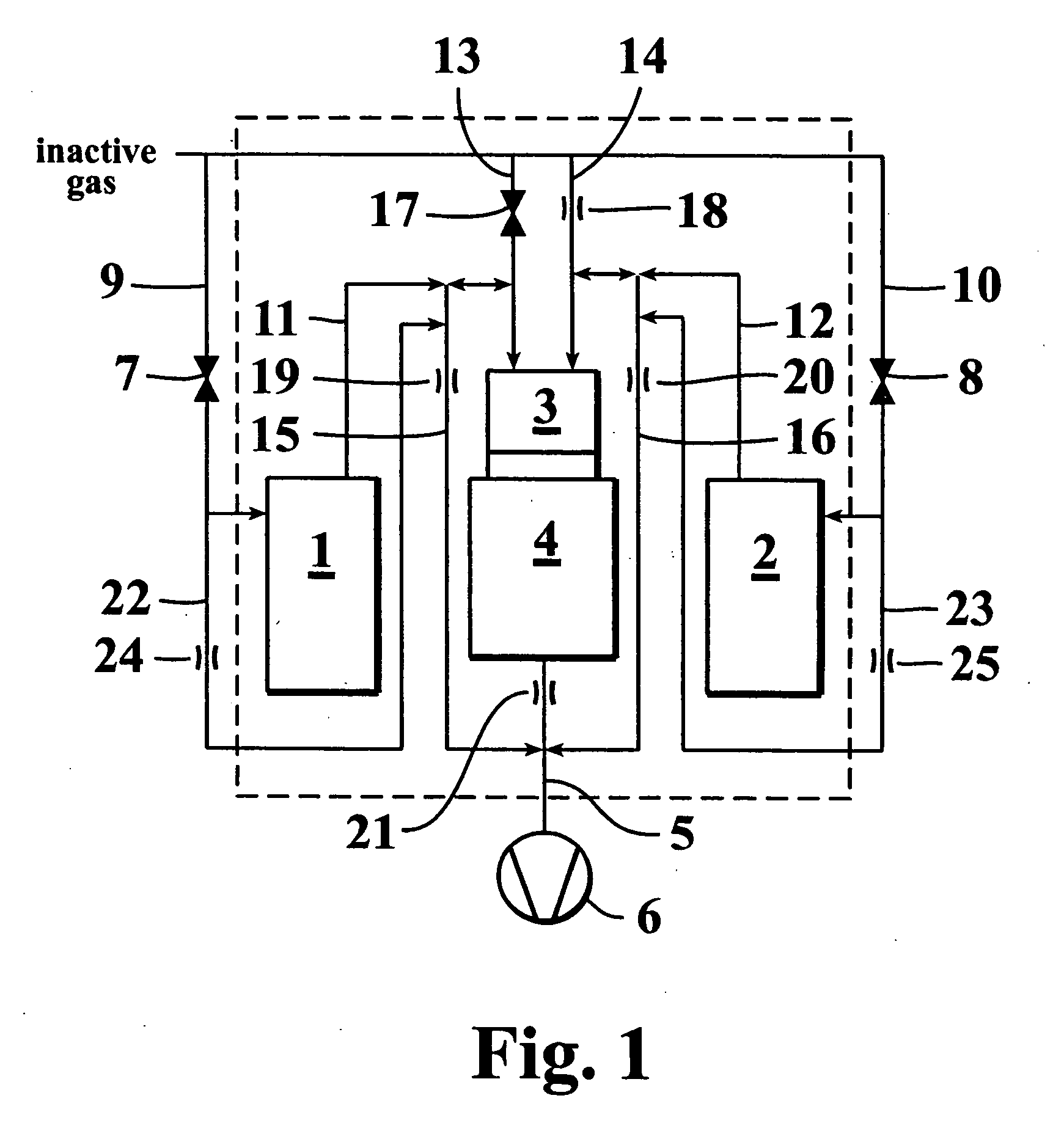
The invention relates to method including operating a plasma atomic layer deposition reactor configured to deposit material in a reaction chamber on at least one substrate by sequential self-saturating surface reactions, and allowing gas from an inactive gas source to flow into a widening radical in-feed part opening towards the reaction chamber substantially during a whole deposition cycle. The invention also relates to a corresponding apparatus.
Owner:PICOSUN OY
Method and apparatus for growing a thin film onto a substrate
InactiveUS20100266765A1Increase costIncrease consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface reactionEngineering
An apparatus and method of growing a thin film onto a substrate comprises placing a substrate in a reaction chamber and subjecting the substrate to surface reactions of a plurality of vapor-phase reactants according to the ALD method. Non-fully closing valves are placed into the reactant feed conduit and backsuction conduit of an ALD system. The non-fully closed valves are operated such that one valve is open and the other valve is closed during the purge or pulse cycle of the ALD process.
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
Plasma enhanced ald system
ActiveUS20160281223A1Low vacuum pressureEnhanced atomic layer depositionElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface reactionAtomic layer deposition
An improved Plasma Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition (PEALD) system and related operating methods are disclosed. A vacuum reaction chamber includes a vacuum system that separates a first outflow from the reaction chamber, comprising unreacted first precursor, from a second outflow from the reaction chamber, comprising second precursor and any reaction by products from the reaction of the second precursor with the coating surfaces. A trap, including trap material surfaces, is provided to remove first precursor from the first outflow when the first precursor reacts with the trap material surfaces. When the second precursor includes a plasma generated material, the second precursor is not passed through the trap. An alternate second precursor source injects a suitable second precursor into the trap to complete a material deposition layer onto the trap surfaces thereby preparing the trap material surfaces to react with the first precursor on the next material deposition cycle.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Coating a substrate web by atomic layer deposition
The present invention relates to a method of driving a substrate web (950) into a reaction space of an atomic layer deposition (ALD) reactor and apparatuses therefore. The invention includes driving a substrate web into a reaction space (930) of an atomic layer deposition reactor, and exposing the reaction space to precursor pulses to deposit material on said substrate web by sequential self-saturating surface reactions. One effect of the invention is a simpler structure compared to earlier spatial roll-to-roll ALD reactors. Another effect is that the thickness of deposited material is directly determined by the speed of the web.
Owner:PICOSUN OY
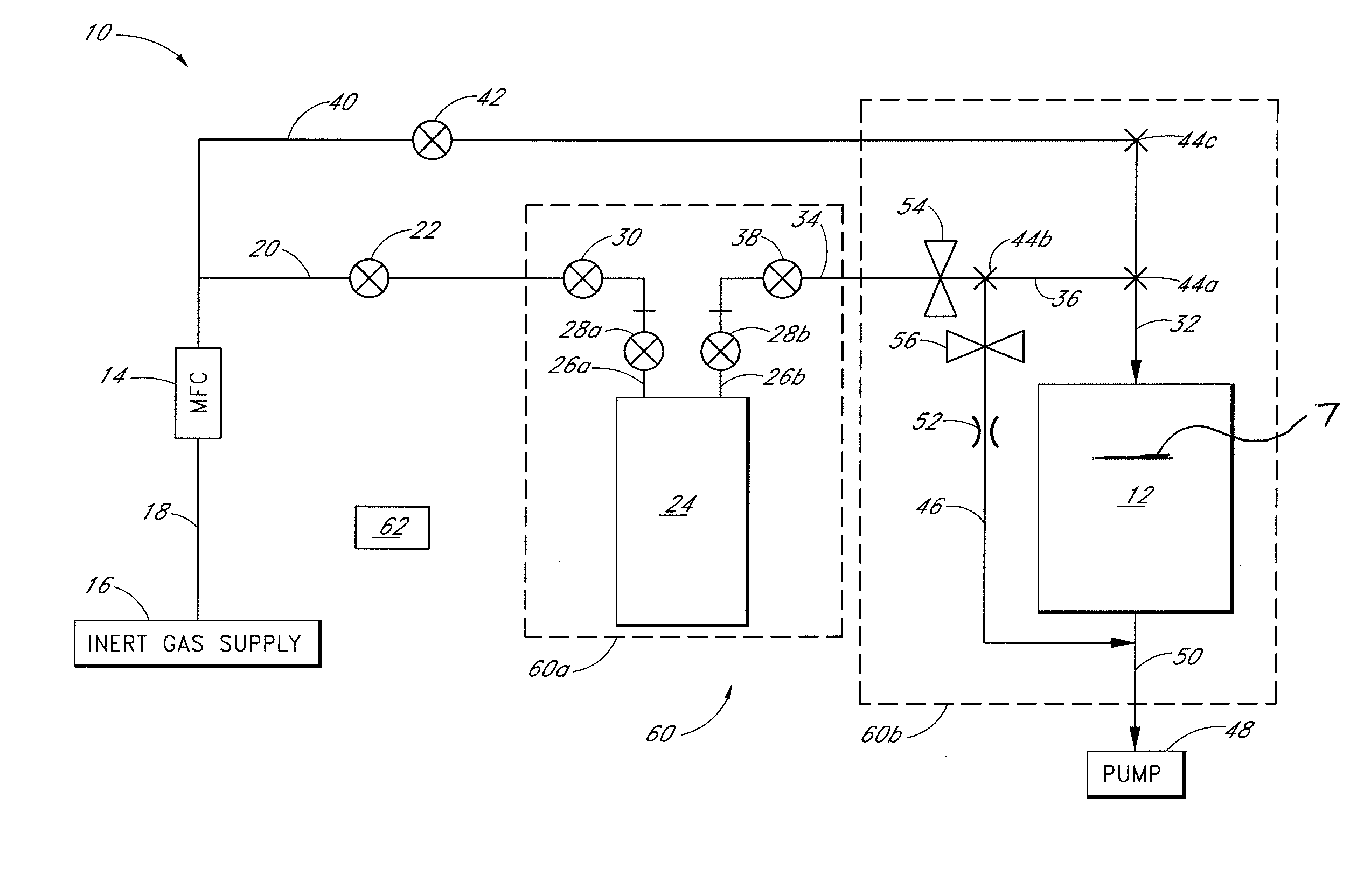
Method and apparatus for removing substances from gases
InactiveUS7799300B2Simple and reliable technicalEliminate the problemAuxillary pretreatmentEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesSurface reactionGas phase
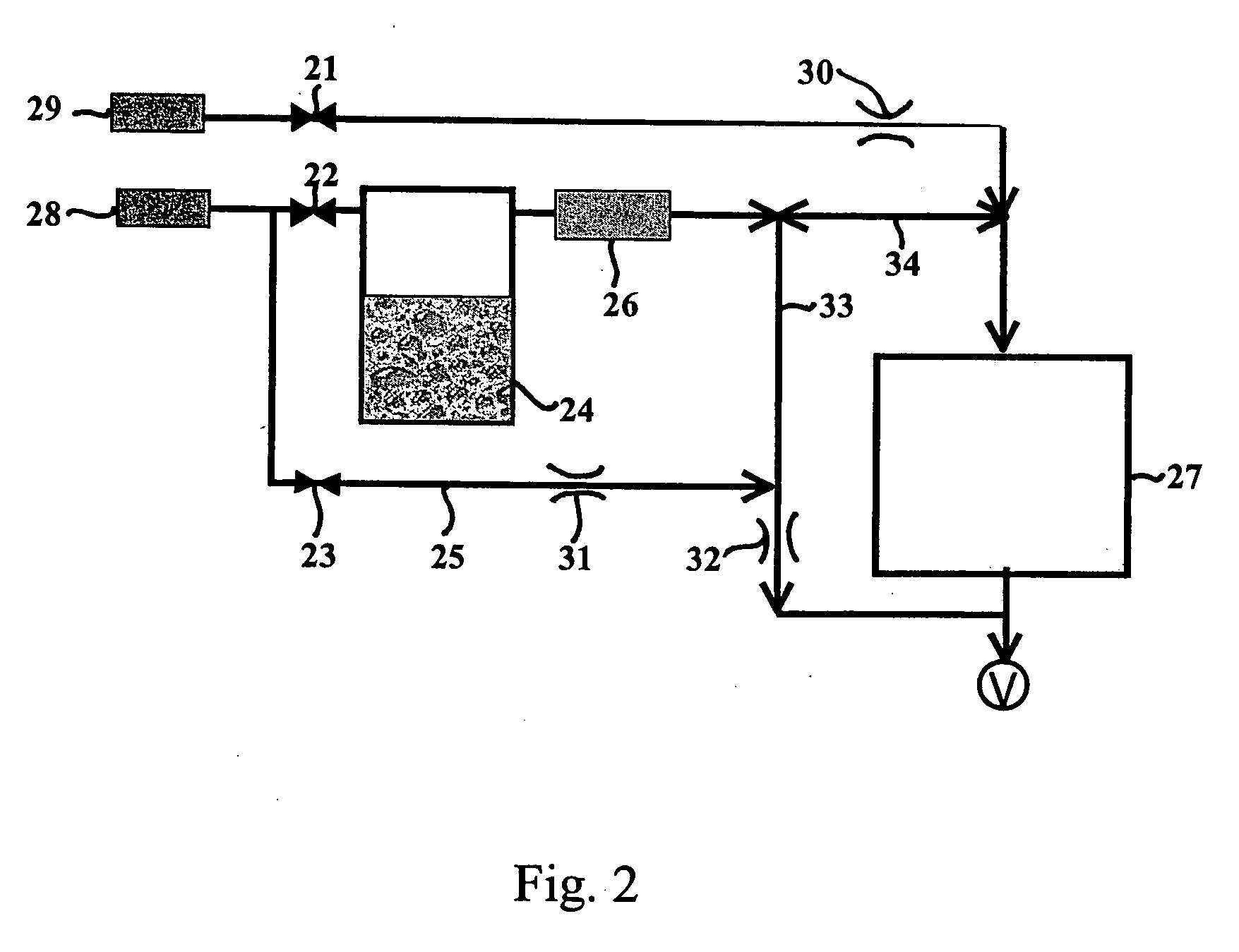
The present invention concerns a method and an apparatus for removing substances from gases discharged from gas phase reactors. In particular, the invention provides a method for removing substances contained in gases discharged from an ALD reaction process, comprising contacting the gases with a “sacrificial” material having a high surface area kept at essentially the same conditions as those prevailing during the gas phase reaction process. The sacrificial material is thus subjected to surface reactions with the substances contained in the gases to form a reaction product on the surface of the sacrificial material and to remove the substances from the gases. The present invention diminishes the amount of waste produced in the gas phase process and reduces wear on the equipment.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Atomic layer deposition with plasma source
ActiveUS9095869B2Liquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesSurface reactionAtomic layer deposition
The invention relates to method including operating a plasma atomic layer deposition reactor configured to deposit material in a reaction chamber on at least one substrate by sequential self-saturating surface reactions, and allowing gas from an inactive gas source to flow into a widening radical in-feed part opening towards the reaction chamber substantially during a whole deposition cycle. The invention also relates to a corresponding apparatus.
Owner:PICOSUN OY
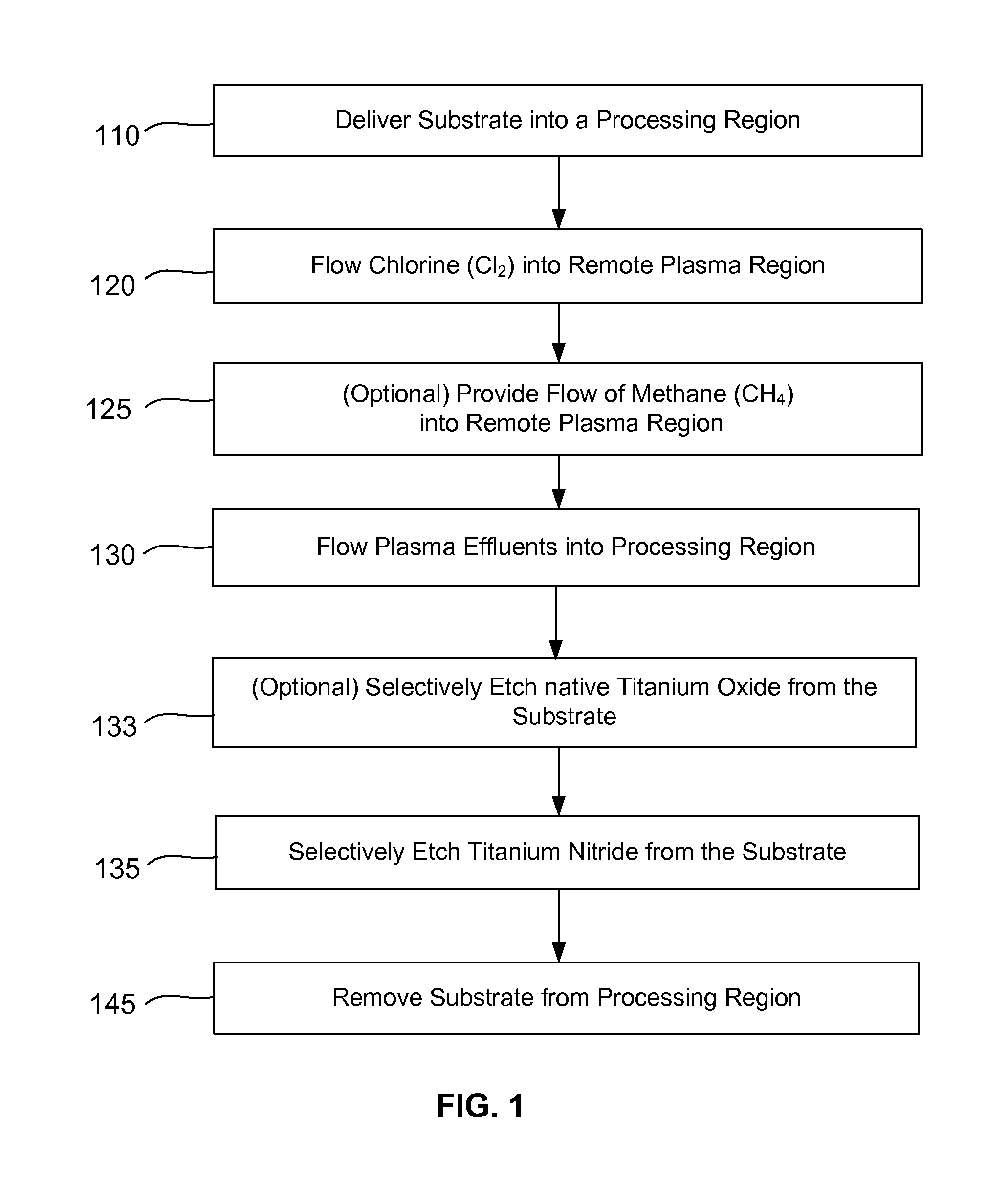
Dry-etch for selective oxidation removal
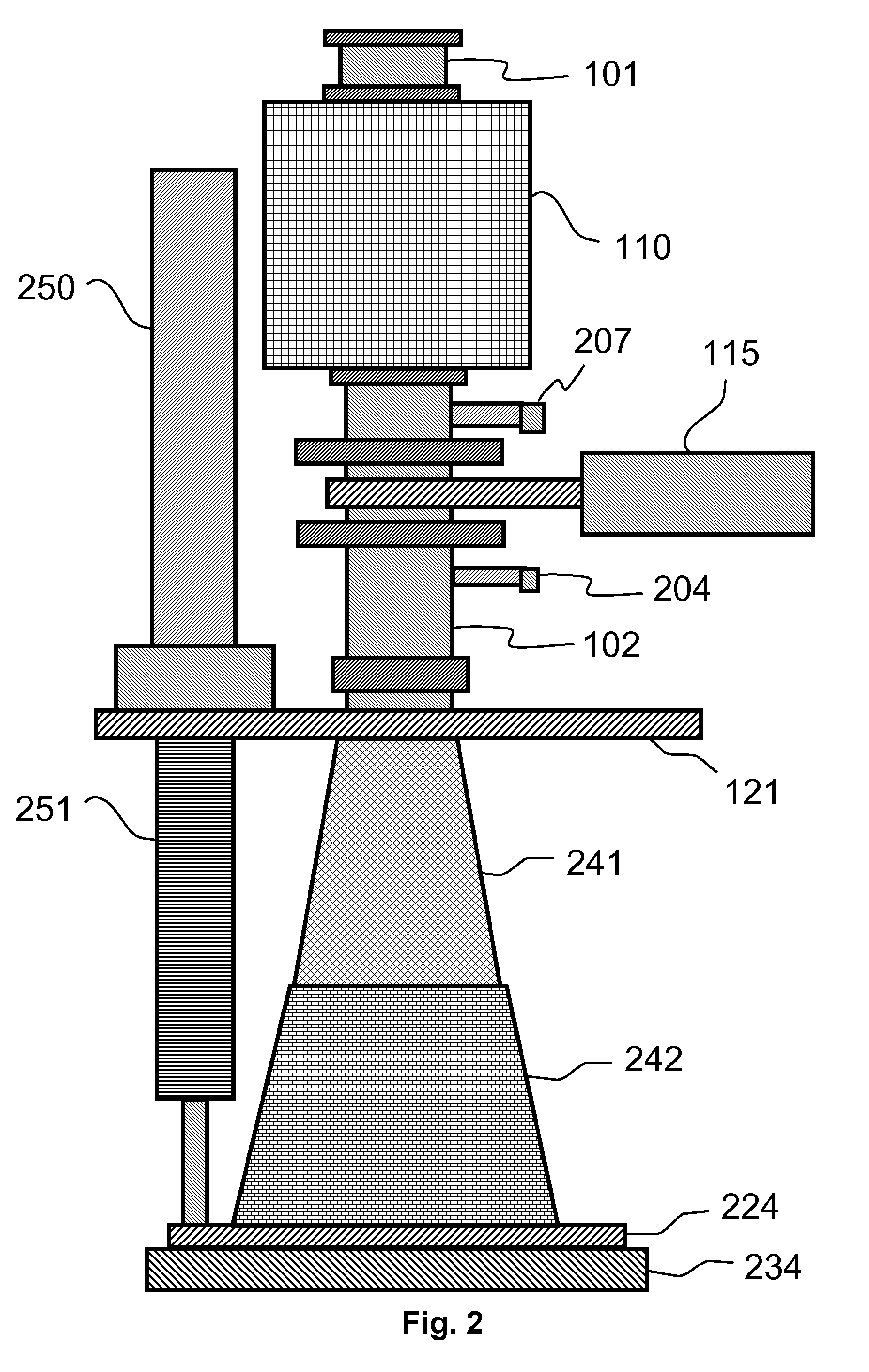
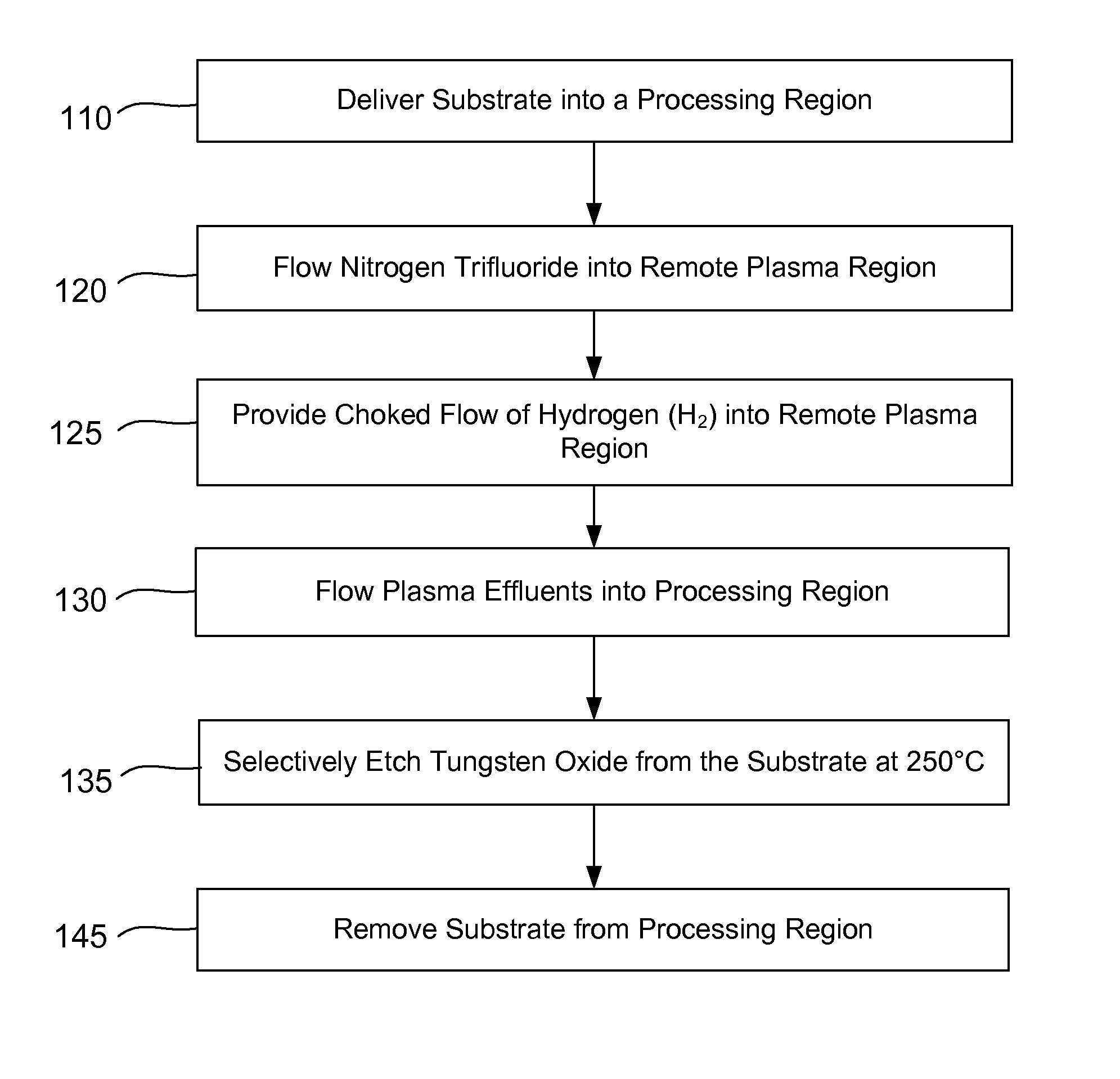
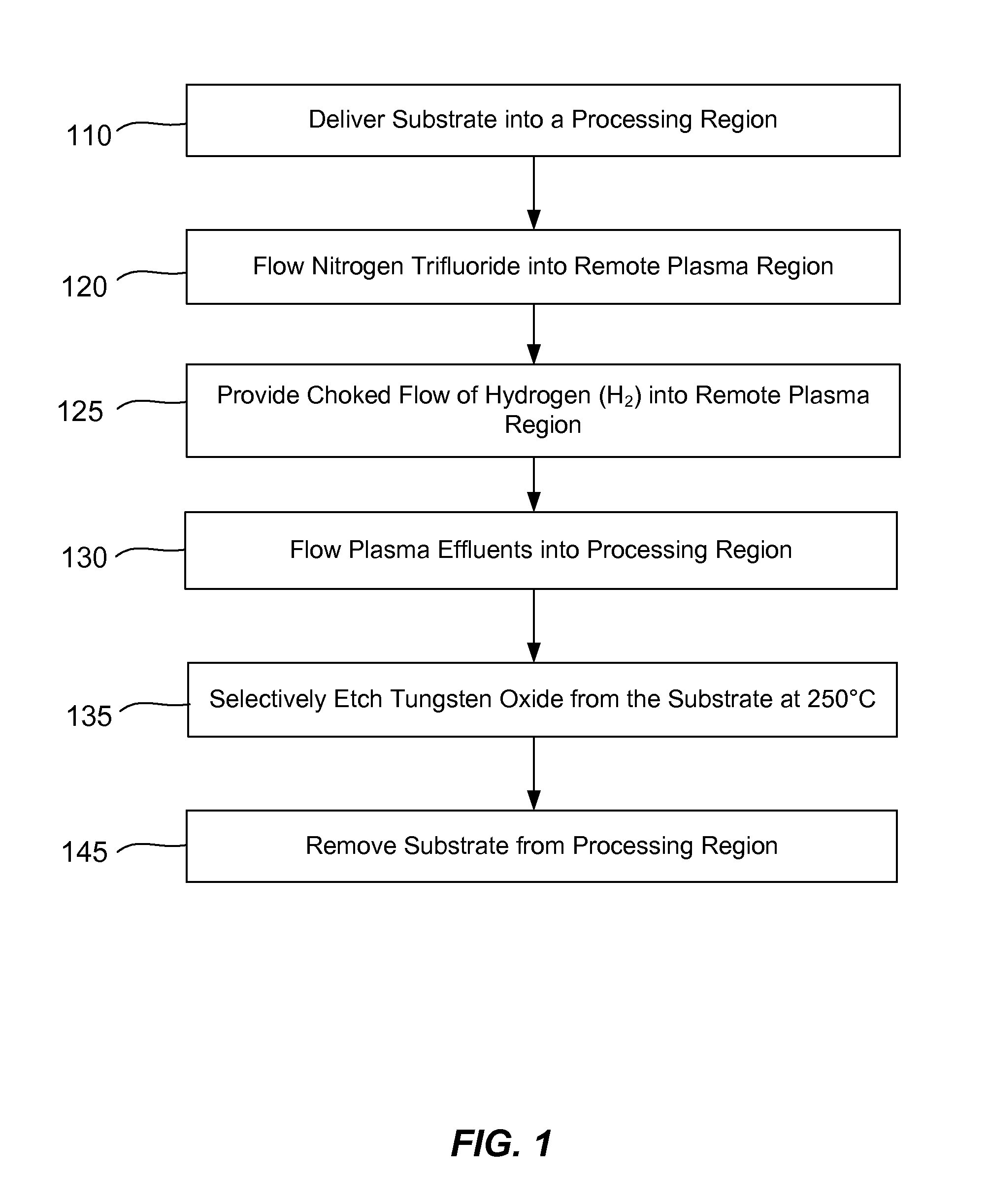
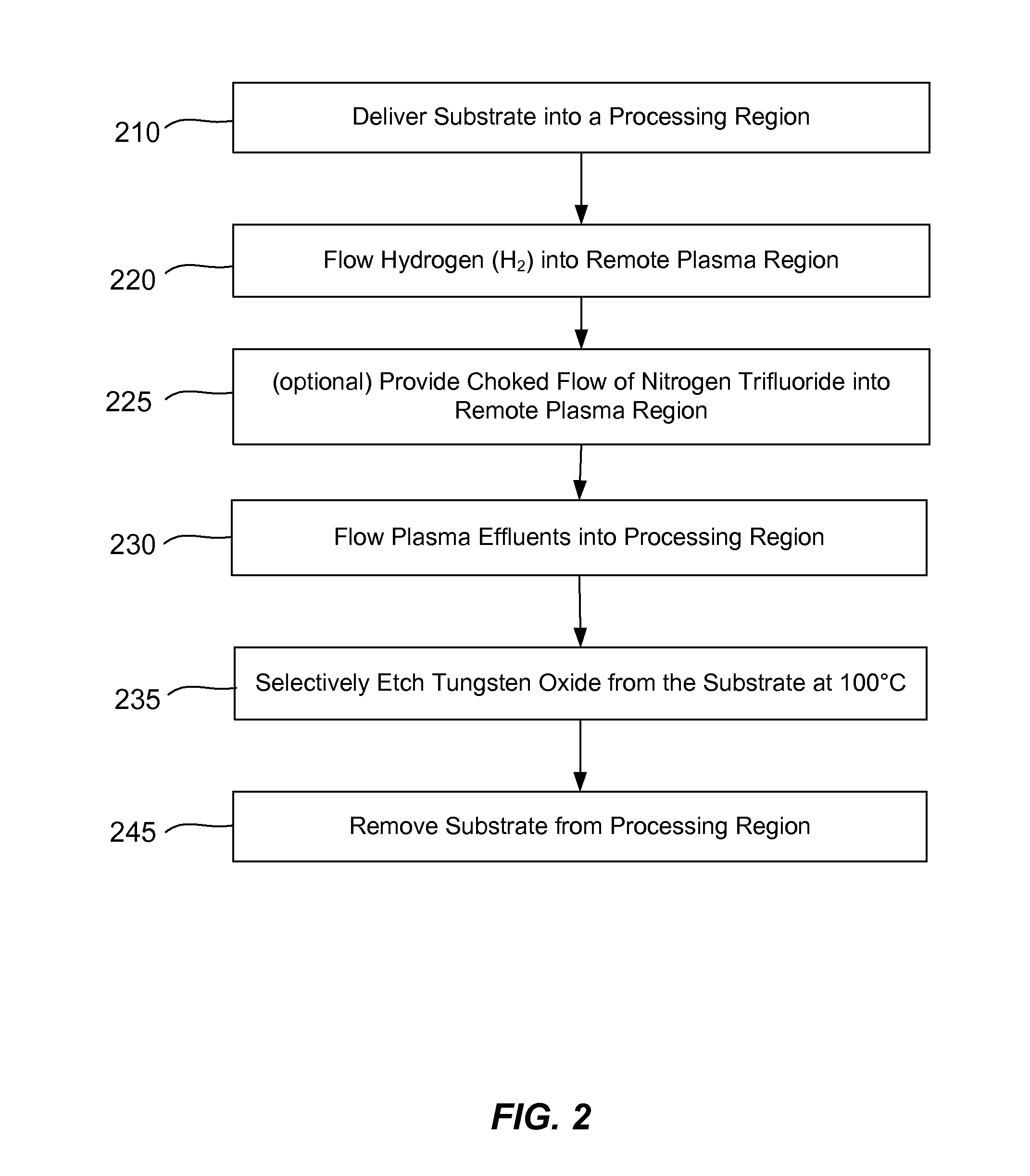
ActiveUS9064816B2Reduces and substantially eliminates numberMaterial removalElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsSurface reactionRemote plasma
Methods of selectively etching tungsten oxide relative to tungsten, silicon oxide, silicon nitride and / or titanium nitride are described. The methods include a remote plasma etch formed from a fluorine-containing precursor and / or hydrogen (H2). Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents react with the tungsten oxide. The plasmas effluents react with exposed surfaces and selectively remove tungsten oxide while very slowly removing other exposed materials. In some embodiments, the tungsten oxide selectivity results partly from the presence of an ion suppression element positioned between the remote plasma and the substrate processing region. The ion suppression element reduces or substantially eliminates the number of ionically-charged species that reach the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
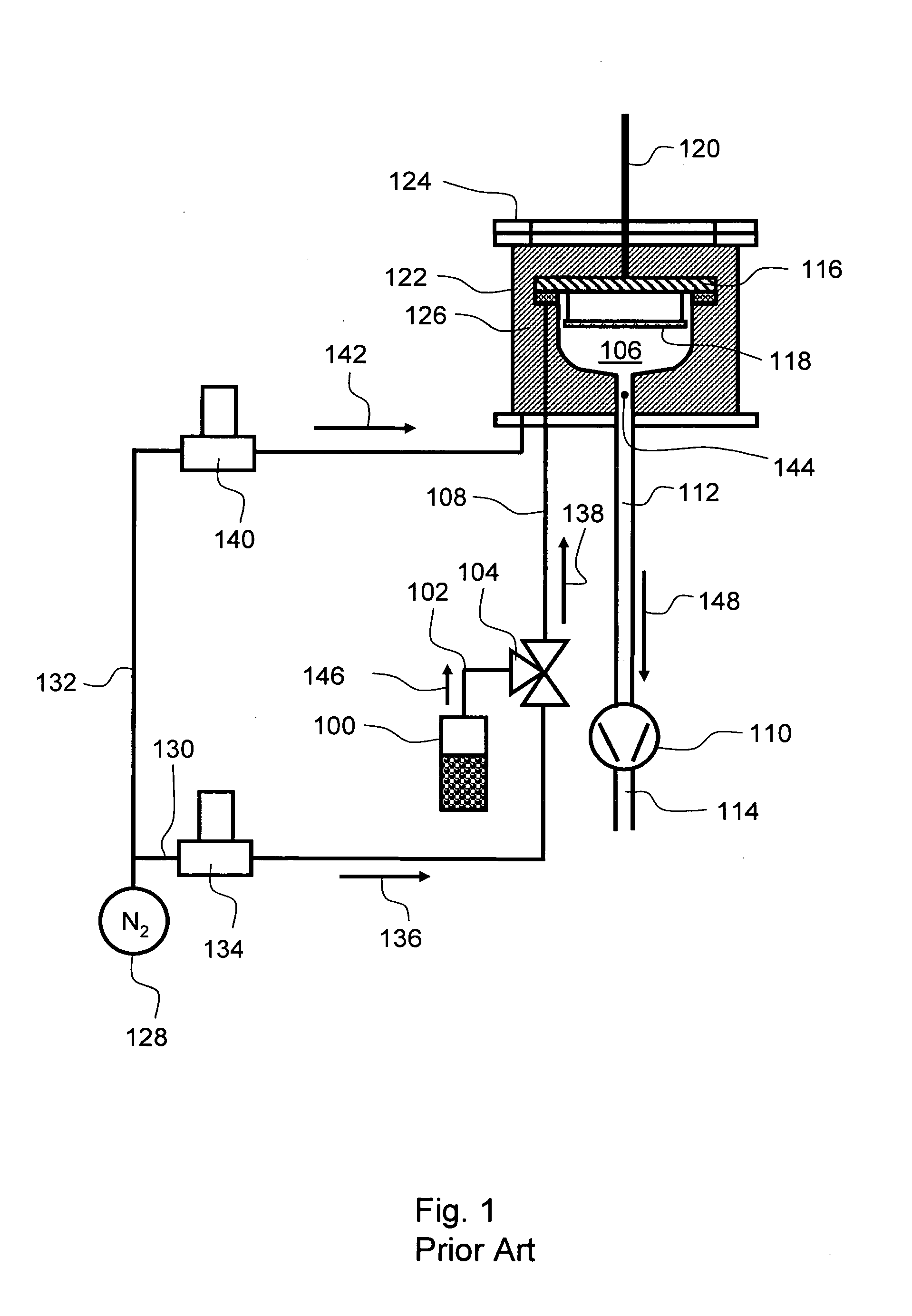
Method of growing a thin film onto a substrate
InactiveUS20040261706A1Uniform smoothnessAvoid it happening againPolycrystalline material growthPressurized chemical processSurface reactionGas phase
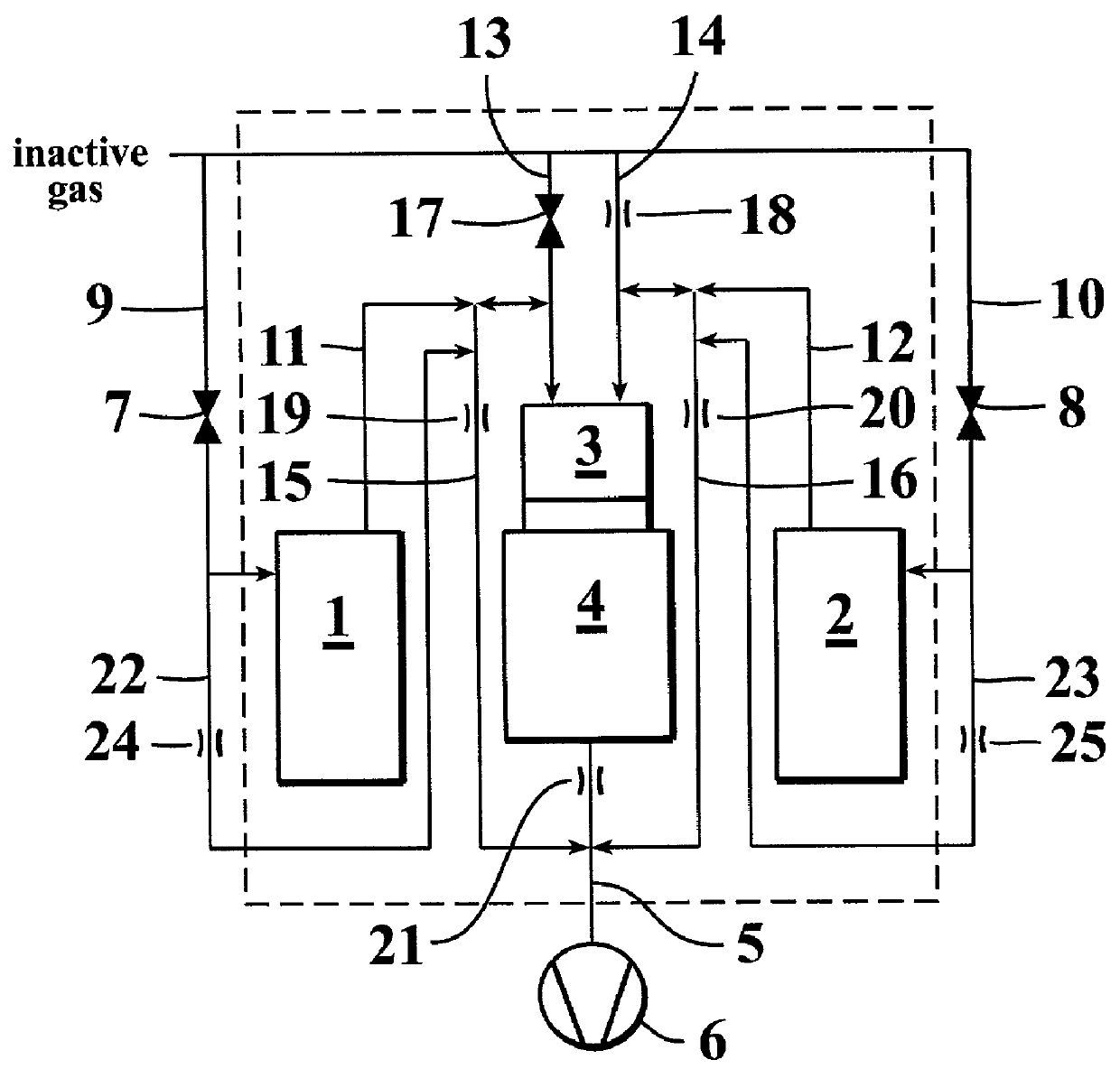
A method of growing a thin film onto a substrate placed in a reaction chamber according to the ALD method by subjecting the substrate to alternate and successive surface reactions. The method includes providing a first reactant source and providing an inactive gas source. A first reactant is fed from the first reactant source in the form of repeated alternating pulses to a reaction chamber via a first conduit. The first reactant is allowed to react with the surface of the substrate in the reaction chamber. Inactive gas is fed from the inactive gas source into the first conduit via a second conduit that is connected to the first conduit at a first connection point so as to create a gas phase barrier between the repeated alternating pulses of the first reactant entering the reaction chamber. The inactive gas is withdrawn from said first conduit via a third conduit connected to the first conduit at a second connection point.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Apparatus and method
ActiveUS20130164458A1Easy to handleEasy to useChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueSurface reactionAtomic layer deposition
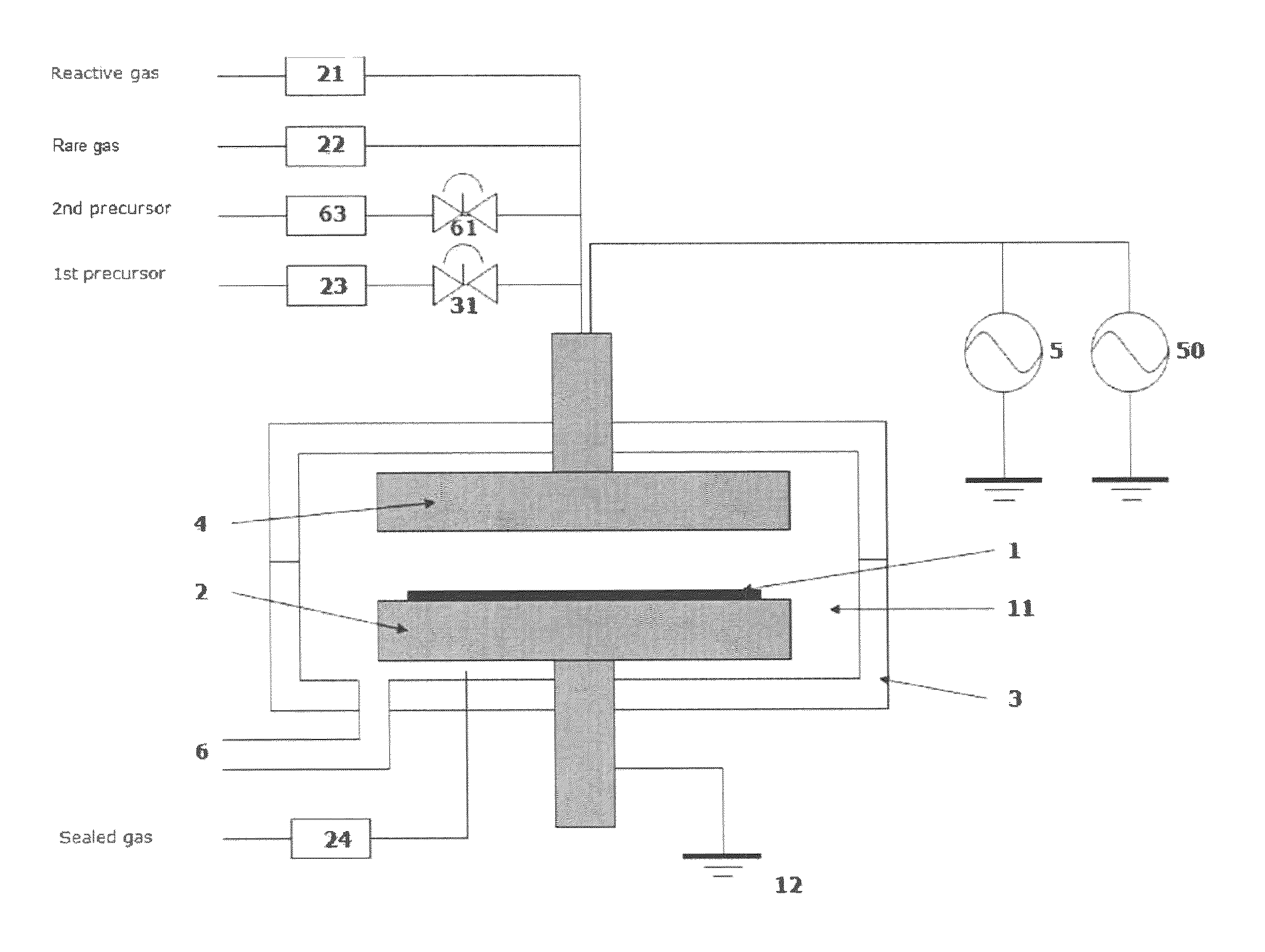
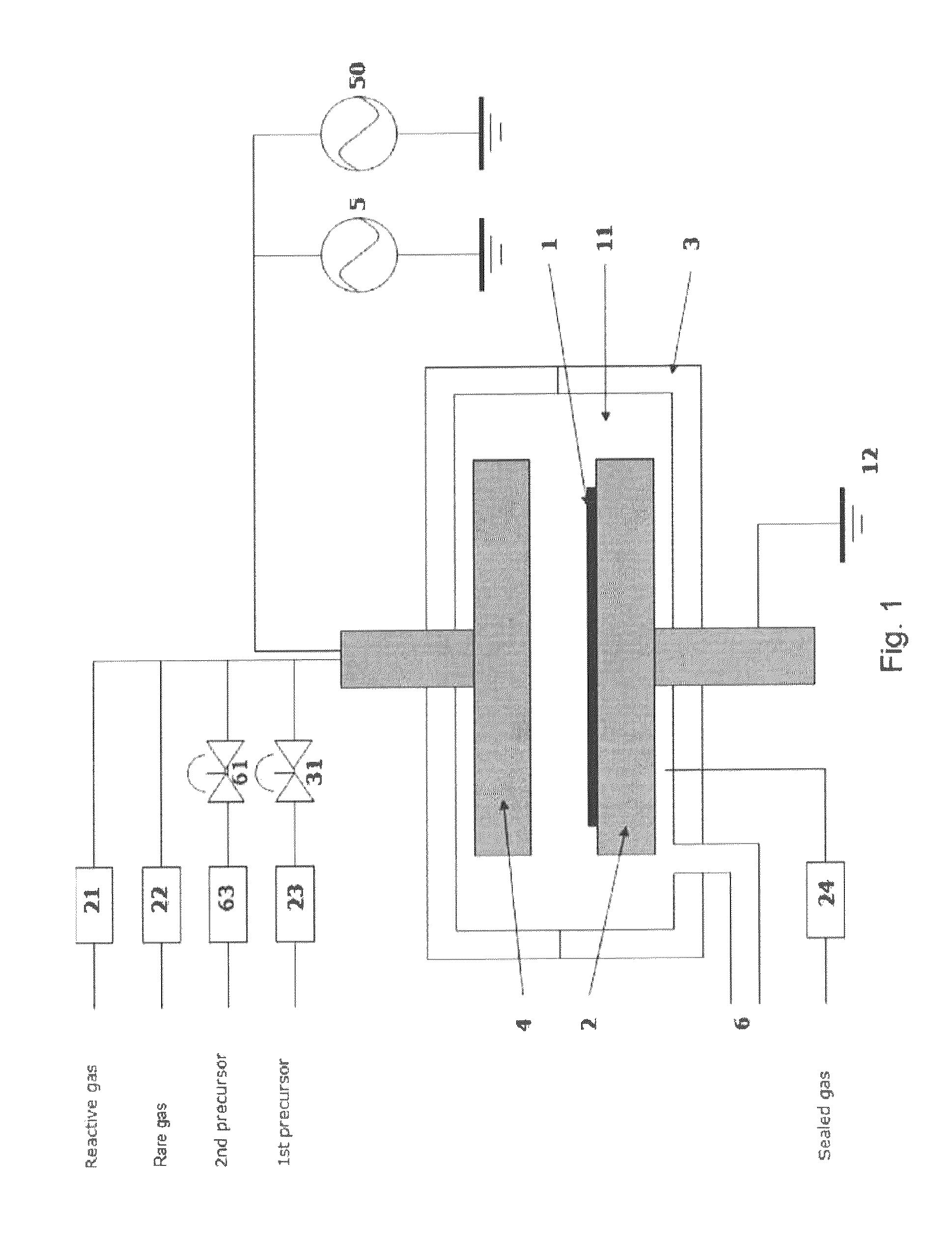
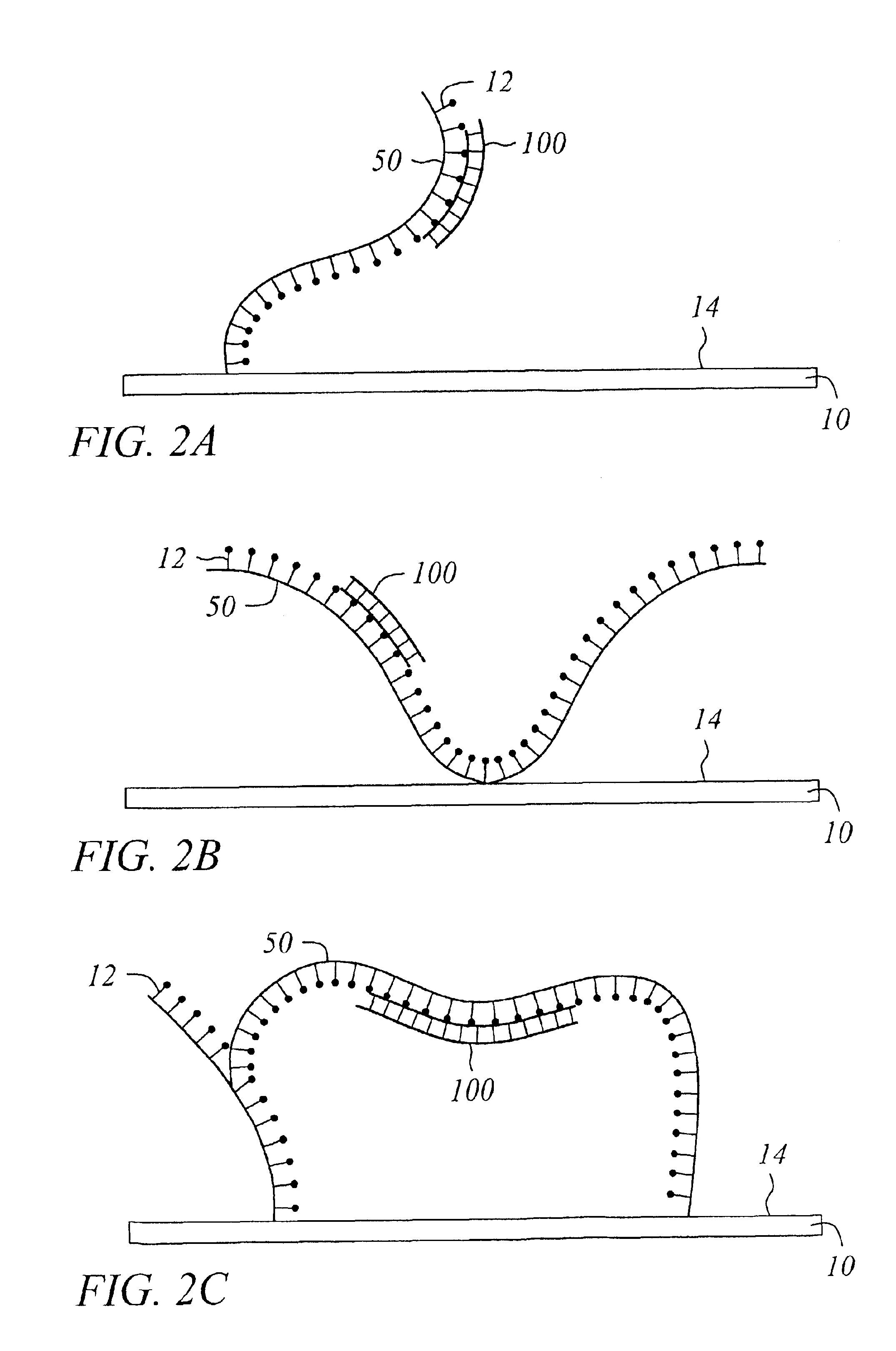
The invention is related to an apparatus and a method for processing a surface of a substrate by exposing the surface of the substrate to alternating surface reactions of at least a first starting material and a second starting material according to the principles of atomic layer deposition method. According to the invention a first starting material is fed on the surface of the substrate locally by means of a source by moving the source in relation to the substrate, and the surface of the substrate processed with the first starting material is exposed to a second starting material present in the atmosphere surrounding the source.
Owner:BENEQ OY
Method and apparatus for generating plasma
InactiveUS20110003087A1Easy to controlImprove uniformityElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface reactionGas phase
A reaction chamber of a reactor for coating or treating a substrate by an atomic layer deposition process (ALD) by exposing the substrate to alternately repeated surface reactions of two or more gas-phase reactants. The reaction chamber is configured to generate capacitively coupled plasma and comprises a reaction space within said reaction chamber, a first inlet to guide gases into the reaction chamber and an outlet to lead gases out of the reaction chamber. The reaction chamber is configured to lead the two or more reactants into the reaction chamber such that the two or more reactants may flow through the reaction space across the substrate in a direction essentially parallel to the inner surface of the lower wall.
Owner:BENEQ OY
Selective titanium nitride removal
ActiveUS20150357205A1Convenient restHigh removal rateElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium nitrideSilicon oxide
Methods are described herein for selectively etching titanium nitride relative to dielectric films, which may include, for example, alternative metals and metal oxides lacking in titanium and / or silicon-containing films (e.g. silicon oxide, silicon carbon nitride and low-K dielectric films). The methods include a remote plasma etch formed from a chlorine-containing precursor. Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents react with the titanium nitride. The plasma effluents react with exposed surfaces and selectively remove titanium nitride while very slowly removing the other exposed materials. The substrate processing region may also contain a plasma to facilitate breaking through any titanium oxide layer present on the titanium nitride. The plasma in the substrate processing region may be gently biased relative to the substrate to enhance removal rate of the titanium oxide layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Multi-zone atomic layer deposition apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060073276A1Quality improvementIncrease deposition rateChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface reactionReactive gas
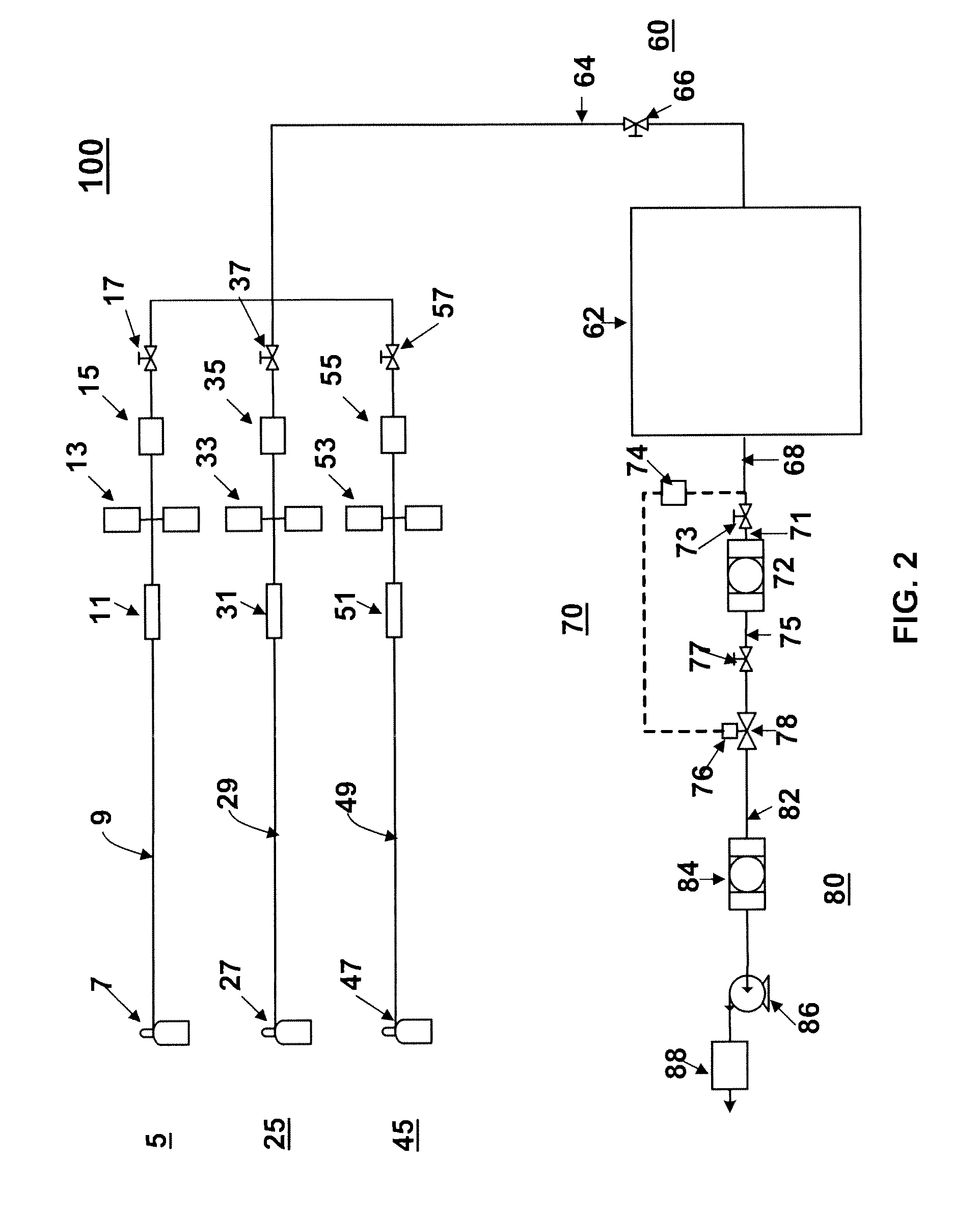
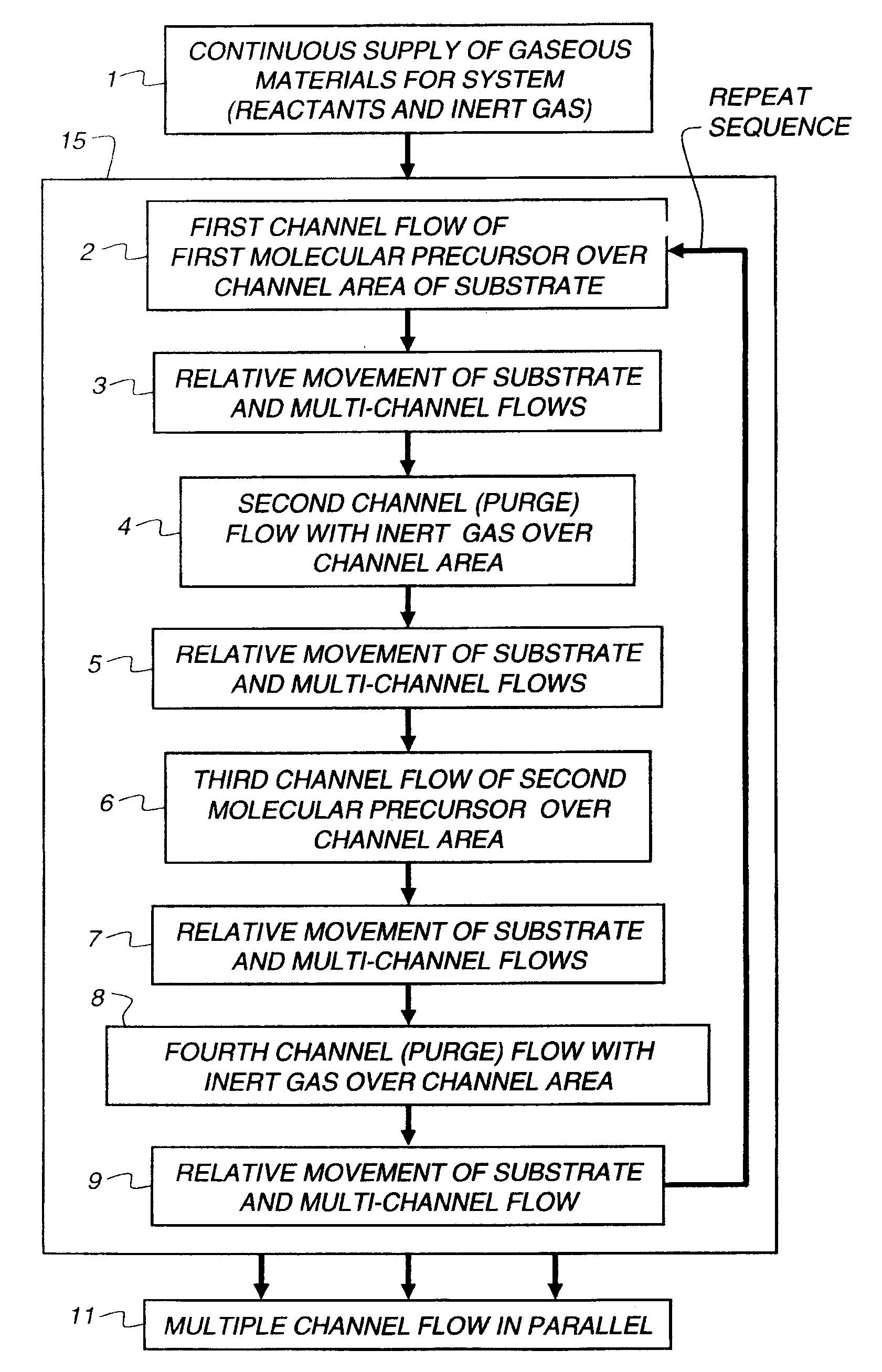
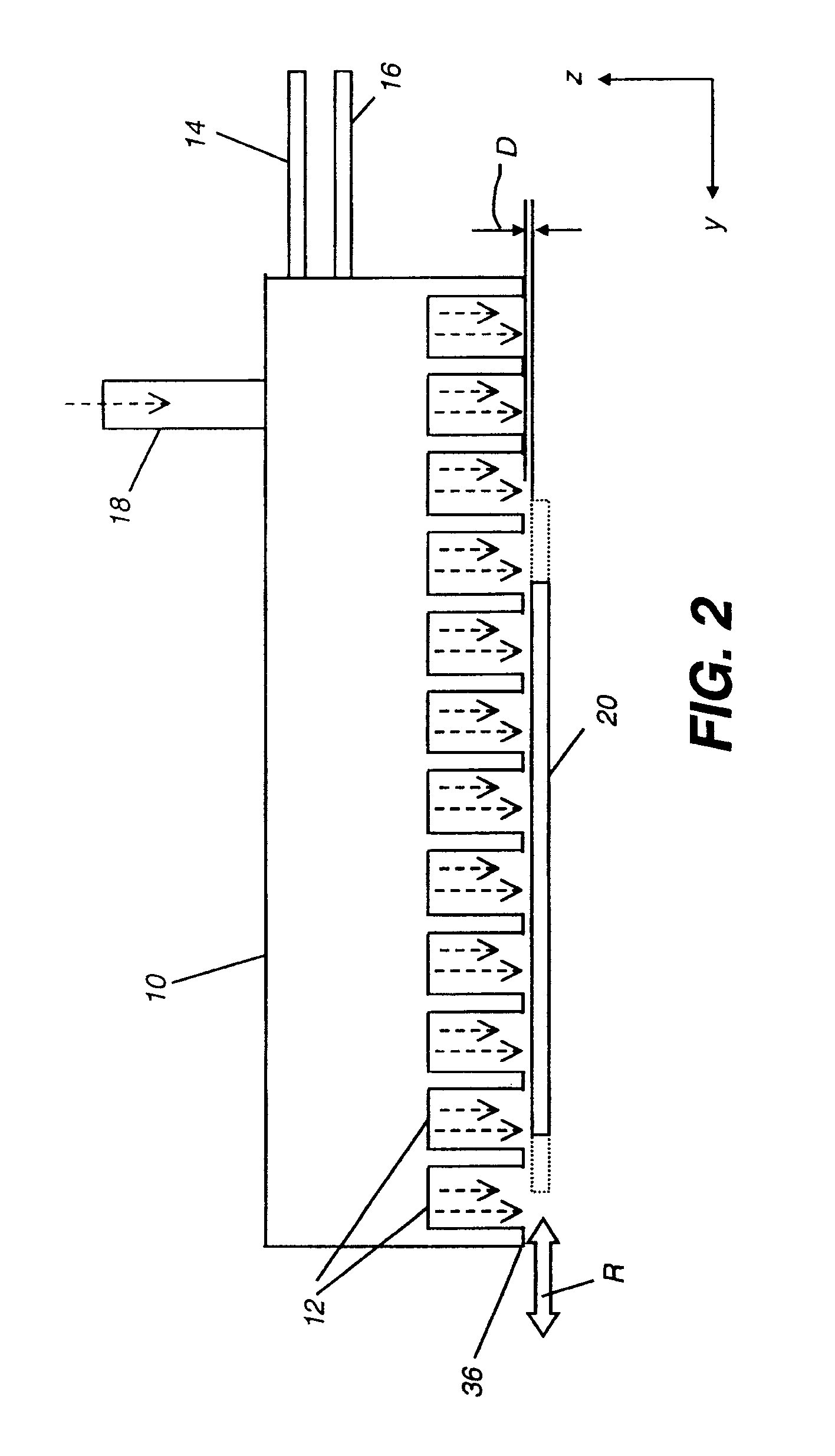
Method and apparatus for producing a thin film on a substrate set in a moving substrate holder is disclosed. Within a deposition chamber, a substrate is moved across a series of dedicated deposition zones and is subjected to repeated surface reactions with at least two different reactants. The reactants are fed into the dedicated deposition zones from a gas supply system that may include high speed valves that are timed to coordinate with the passage of the substrate so as to inject reactive gases repeatedly into the deposition zones. The dedicated deposition zones are separated by dedicated exhaust zones that direct each reactive gas along separate paths so as to minimize or eliminate mixing of different reactive species in the exhaust thus decreasing deposition within the exhaust system.
Owner:ATOMICITY SYST
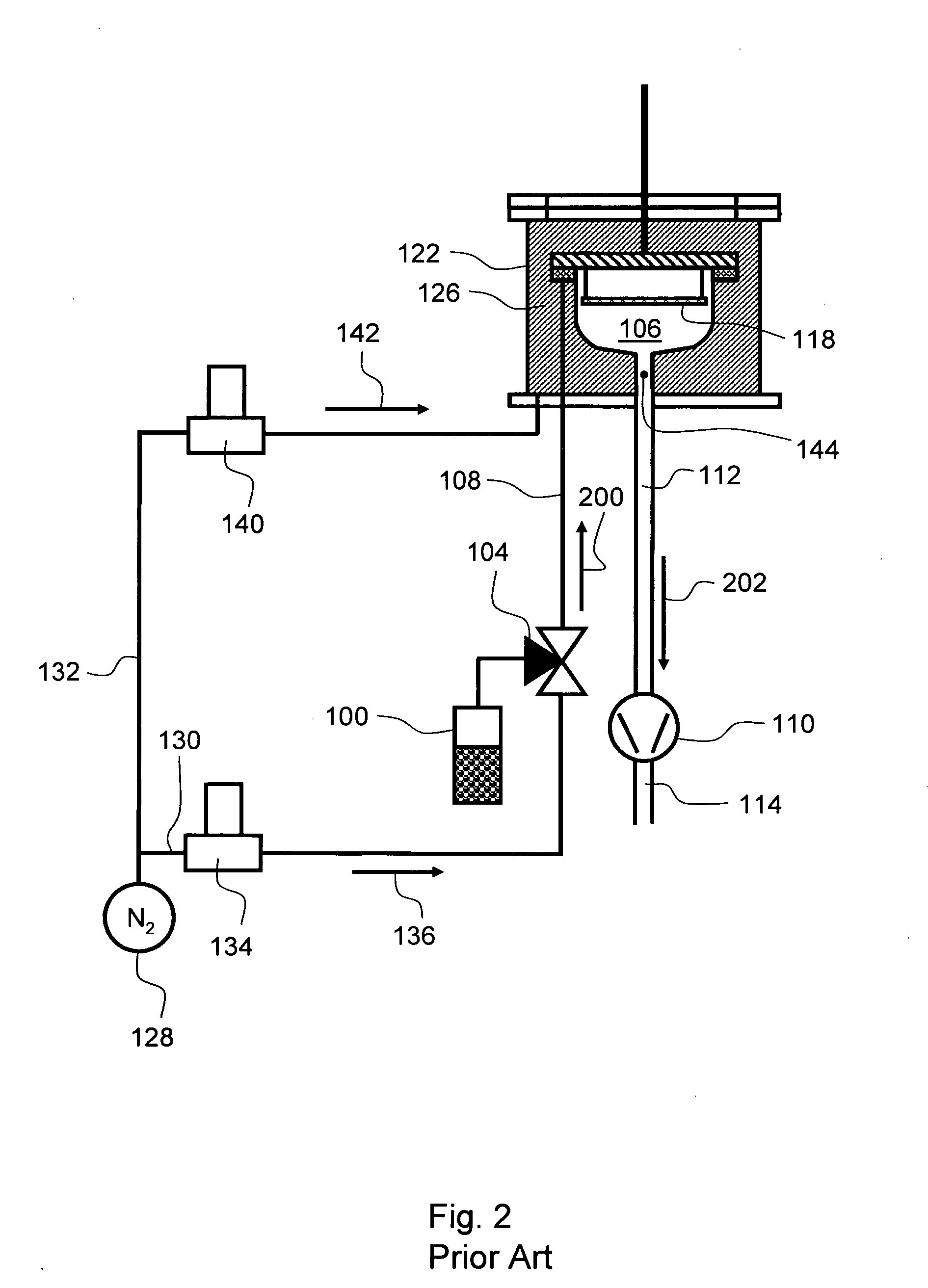
Method of growing a thin film onto a substrate
InactiveUS20010054377A1Reduce wasteGuaranteed uptimePressurized chemical processPolycrystalline material growthSurface reactionGas phase
A method of growing a thin film onto a substrate placed in a reaction chamber according to the ALD method by subjecting the substrate to alternate and successive surface reactions. The method includes providing a first reactant source and providing an inactive gas source. A first reactant is fed from the first reactant source in the form of repeated alternating pulses to a reaction chamber via a first conduit. The first reactant is allowed to react with the surface of the substrate in the reaction chamber. Inactive gas is fed from the inactive gas source into the first conduit via a second conduit that is connected to the first conduit at a first connection point so as to create a gas phase barrier between the repeated alternating pulses of the first reactant entering the reaction chamber. The inactive gas is withdrawn from said first conduit via a third conduit connected to the first conduit at a second connection point.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
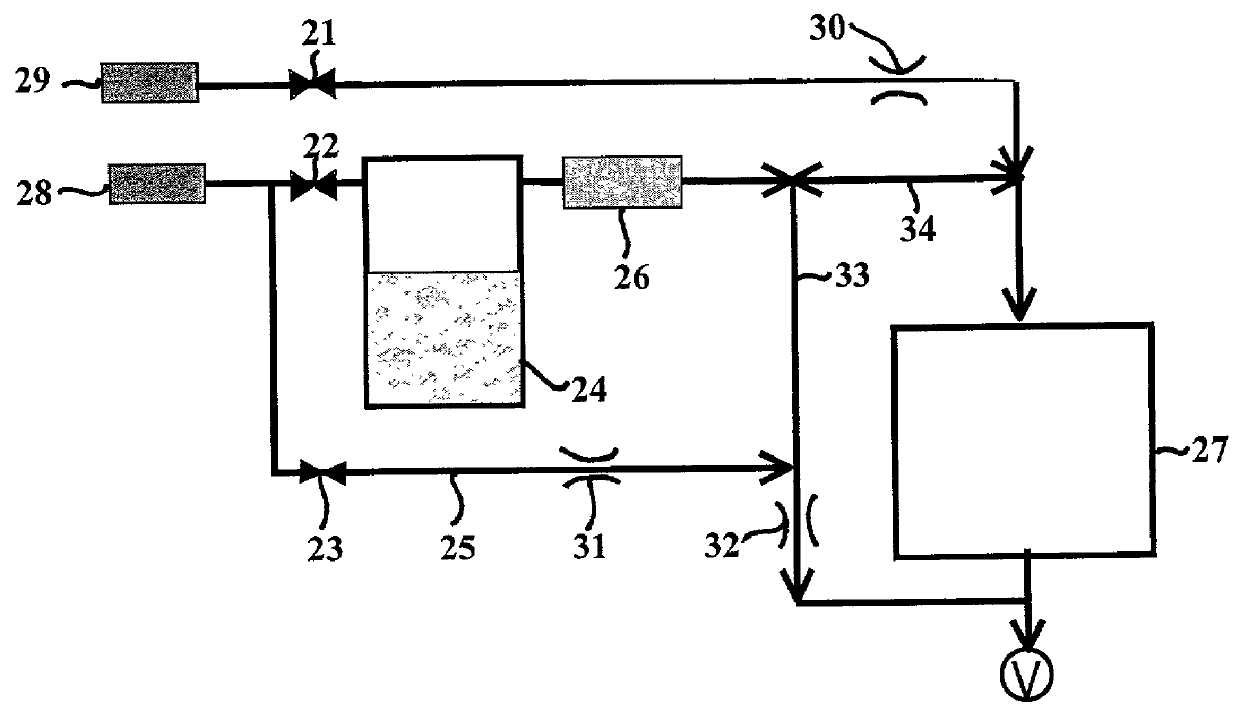
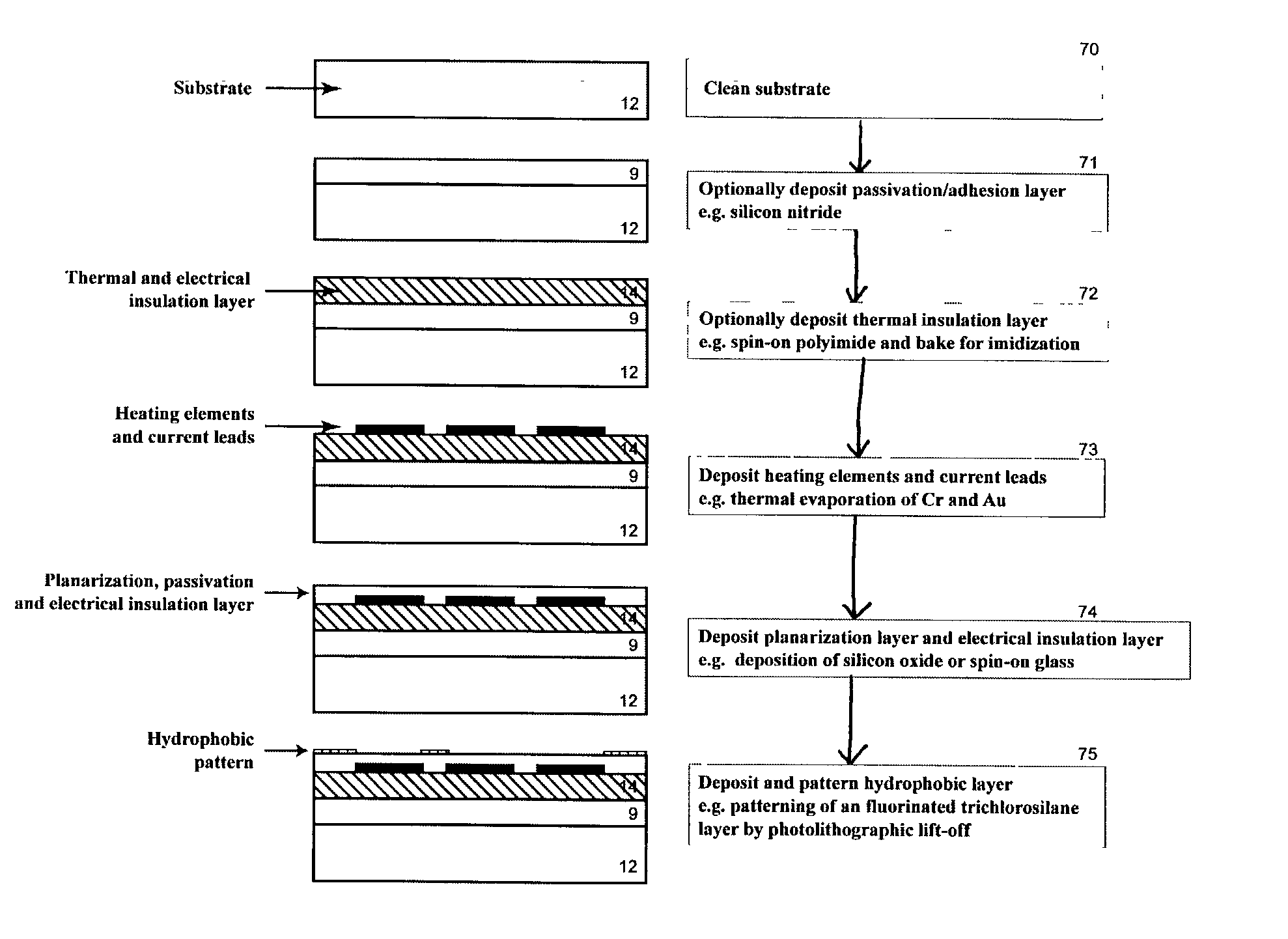
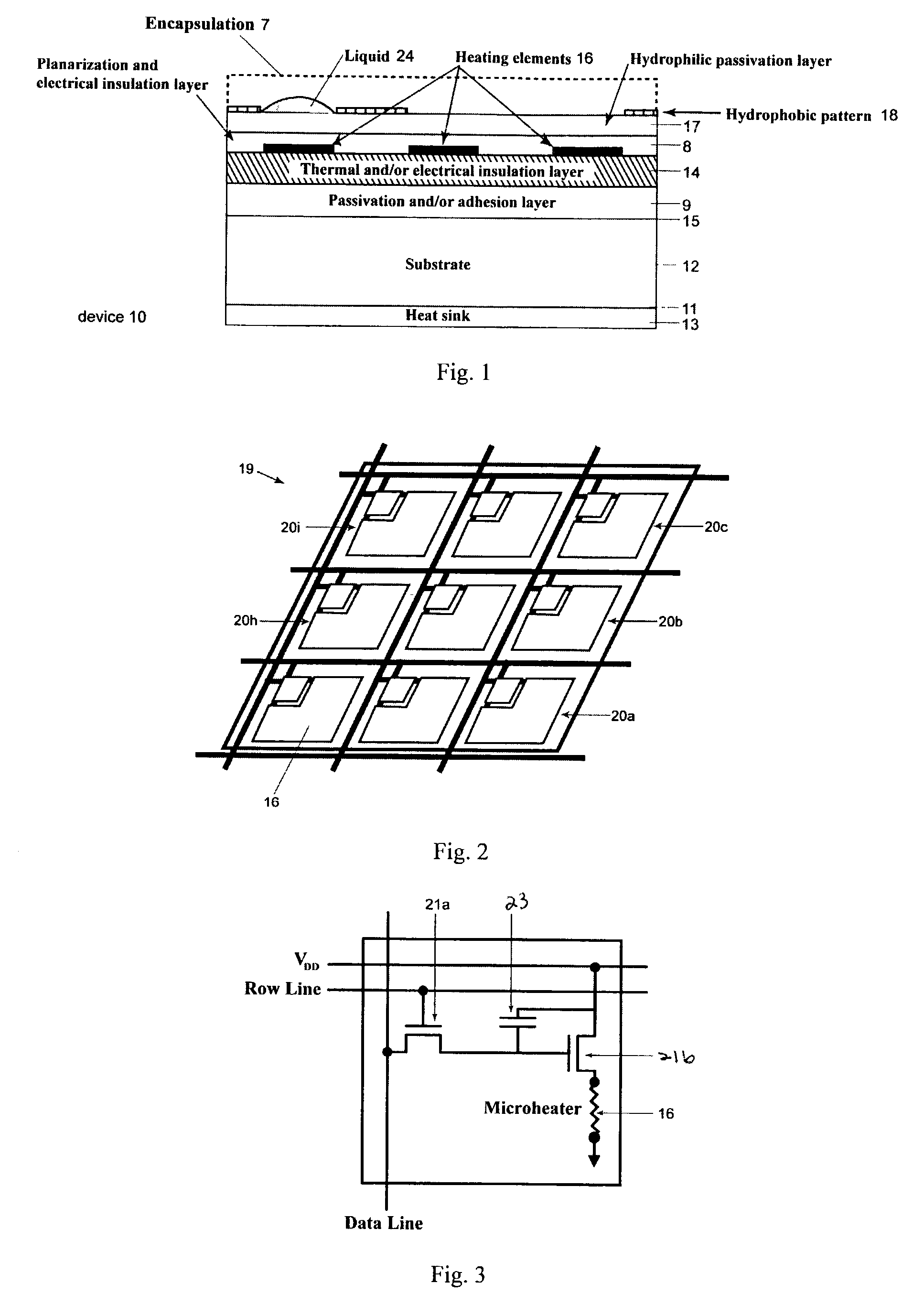
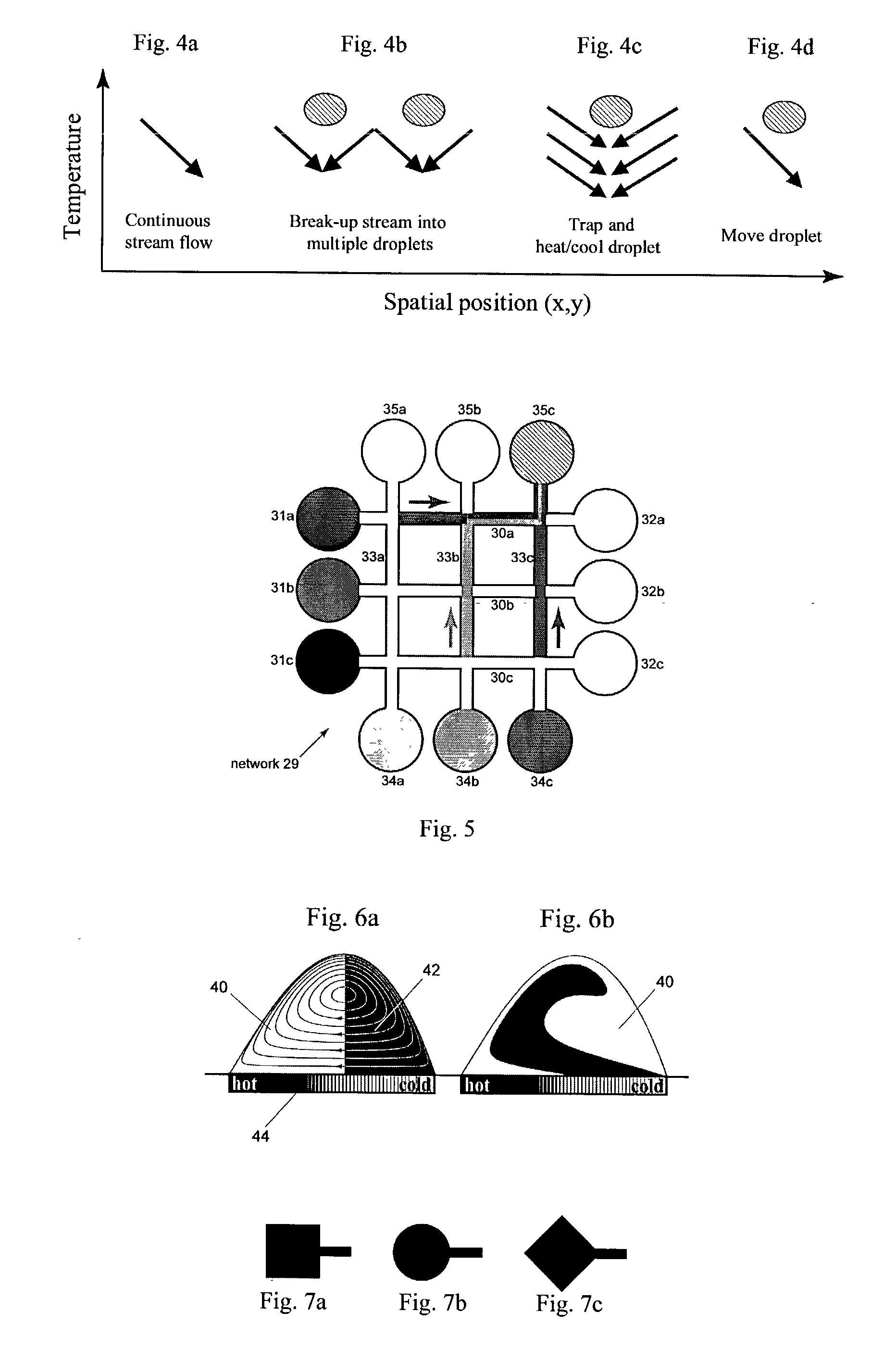
Method and device for controlling liquid flow on the surface of a microfluidic chip
The invention is directed to a method and device for routing, mixing, or reacting droplets or liquid microstreams along the surface of a flat substrate. The flow of liquid microstreams or microdroplets along designated pathways is confined by chemical surface patterning. Individually addressable heating elements, which are embedded in the substrate, can be used to generate flow via thermocapillary effects or to trigger or quench chemical reactions. The open architecture allows the liquid to remain in constant contact with the ambient atmosphere. The device can be used for microfluidic applications or as a surface reactor or biosensor, among other applications.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Atomic Layer Deposition with Plasma Source
The invention relates to method including operating a plasma atomic layer deposition reactor configured to deposit material in a reaction chamber on at least one substrate by sequential self-saturating surface reactions, and allowing gas from an inactive gas source to flow into a widening radical in-feed part opening towards the reaction chamber substantially during a whole deposition cycle. The invention also relates to a corresponding apparatus.
Owner:PICOSUN OY
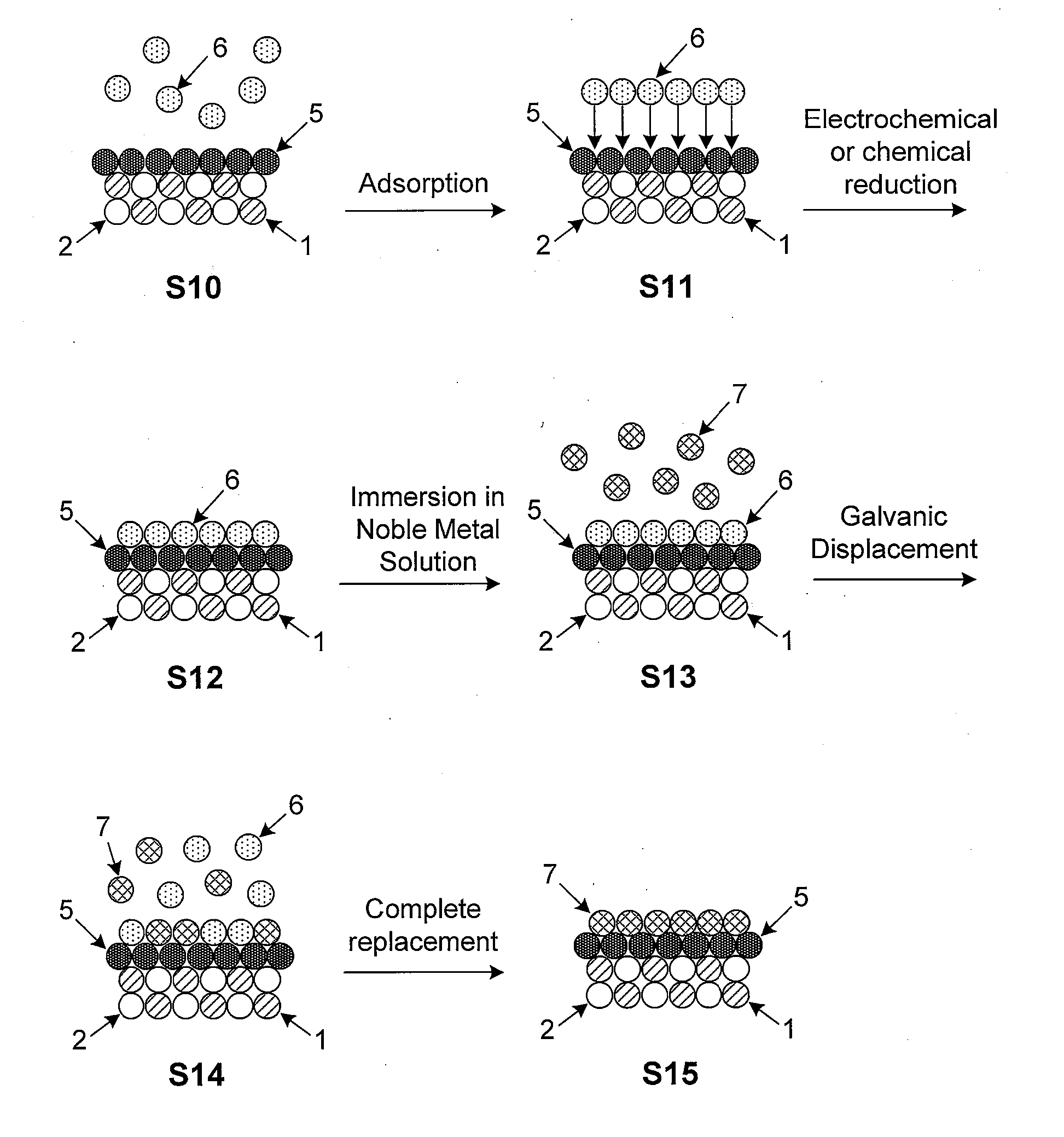
Platinum-Based Electrocatalysts Synthesized by Depositing Contiguous Adlayers on Carbon Nanostructures
InactiveUS20100177462A1High catalytic activityImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsNanostructurePt element
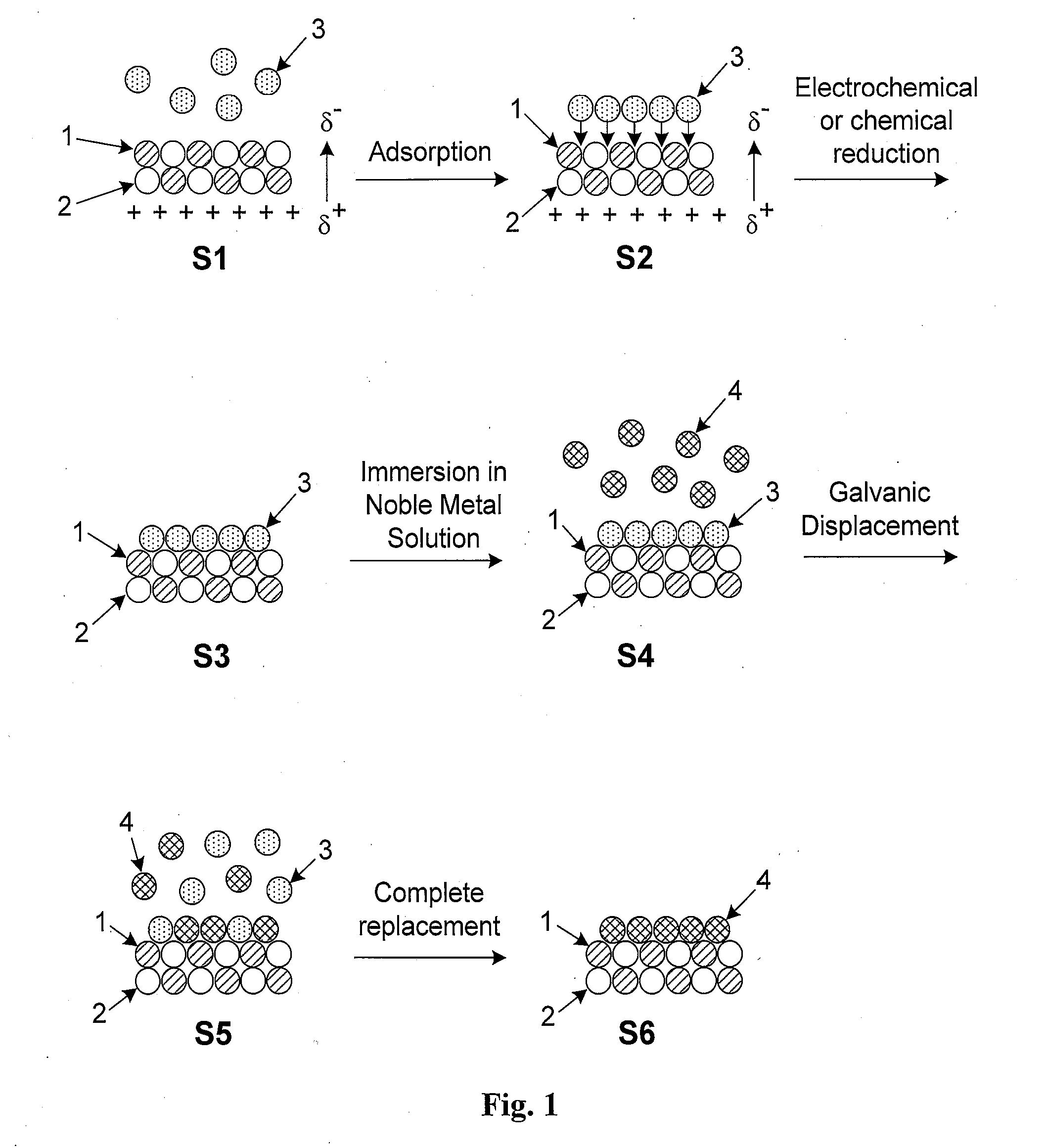
High-surface-area carbon nanostructures coated with a smooth and conformal submonolayer-to-multilayer thin metal films and their method of manufacture are described. The preferred manufacturing process involves the initial oxidation of the carbon nanostructures followed by immersion in a solution with the desired pH to create negative surface dipoles. The nanostructures are subsequently immersed in an alkaline solution containing non-noble metal ions which adsorb at surface reaction sites. The metal ions are then reduced via chemical or electrical means and the nanostructures are exposed to a solution containing a salt of one or more noble metals which replace adsorbed non-noble surface metal atoms by galvanic displacement. Subsequent film growth may be performed via the initial quasi-underpotential deposition of a non-noble metal followed by immersion in a solution comprising a more noble metal. The resulting coated nanostructures may be used, for example, as high-performance electrodes in supercapacitors, batteries, or other electric storage devices.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Reactive silica particles, process for manufacturing the same, use of the same
InactiveUS6160067AGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPigmenting treatmentWeather resistanceOrganic compound
Reactive silica particles capable of producing coatings exhibiting excellent scratch resistance, weather resistance, adhesiveness, and curability, while satisfying a wide spectrum of performances from transparency to semi-transparency and providing a glossy surface as well as a frosty surface. Reactive silica particles comprises silica particles and an organic compound chemically bonded to the silica particles via a silyloxy group, wherein the organic compound has a polymerizable unsaturated group, a group represented by the following formula (1), (wherein X is a group selected from -NH-, -O-, and -S- and Y is a group selected from oxygen and sulfur, provided that when X is -O-, Y is a sulfur atom), and a group represented by the following formula (2), (wherein Z is a group selected from oxygen and sulfur)
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Silicon dioxide aerogel material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a silicon dioxide aerogel material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: by using water glass as silicon source, adding an acid-containing organic solvent free of chlorine ions and fluorine ions to generate a precipitate of sodium ions, potassium ions and other metal salt ions, filtering to remove the precipitate to obtain high-purity silica sol, carrying out a sol-gel process, aging, acidifying, modifying, and drying to obtain the silicon dioxide aerogel material. The acidification before modification enhances the surface reaction activity of the silicon gel, thereby obviously enhancing the modification effect and efficiency. The method has the advantages of low cost and simple and efficient technique, is beneficial to mass high-efficiency production, is free of chlorine ions and fluorine ions in the whole technical process, and enhances the equipment operation safety and reliability; and the product can be used for heat preservation and thermal insulation of nuclear power and liquefied natural gas equipment and pipelines with higher requirement for corrosion resistance, and can also be used for thermal insulation in the field of aerospace, petrochemical engineering, track transportation, ships, automobiles, construction and the like.
Owner:浙江圣润纳米科技有限公司
Method for preparing silicon thin film heterojunction solar cell
InactiveCN1588649AAvoid damageReduce hydrogen contentFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionSilicon thin film
A prepn. method of silicon thin film heterojunction solar cell includes following steps: cleaning substrate, semiconductor cleaning technology is used to do primary cleaing to substrate surface, then do ultrasonic cleaning in deionized water several times; nitrogen blow drying; prepare nitrinsic amorphous silicon layer by heater chemical vapour phase depositing technology, tungsten filament temp. is measured by pyrometer, temp of heater and sample are determined separately by two electric thermo-couples, temp. is controlled by electric temp. controller; to react and grow thin film on substrate surface; to redeposit a transmitting layer on intrinsic amorphous silicon thin film; front and back electrodes forming, sputtering technology is used to form front and back electrodes; finally to proceed vacuum heat annealing process. The thin film produced by the invention has illumination stability, the photoconduction gain can reach to 10 to the power 6 on Am1.5 100mW / cm2 standard illumination.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Conductive adhesive bonding
InactiveUS20060060296A1Reduce resistanceMechanical working/deformationLamination ancillary operationsSurface reactionFuel cells
Electrically conductive workpieces with facing surfaces are bonded with an adhesive that is filled with conductive metal particles that are reactive with the surfaces of the workpieces. In the bonding process the surfaces are coated with the adhesive, pressed together and an electric current passed between them to momentarily melt the conductive particles. The molten droplets agglomerate and wet the facing surfaces. When the molten clusters re-solidify, electrically conductive paths are formed between the workpieces. For example, the practice is useful for bonding ferrous-based or aluminum-based alloy sheets, strips or plates in making products such as bipolar plates for fuel cells.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for depositing titanium nitride films for semiconductor manufacturing
ActiveUS7776733B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface reactionHigh volume manufacturing
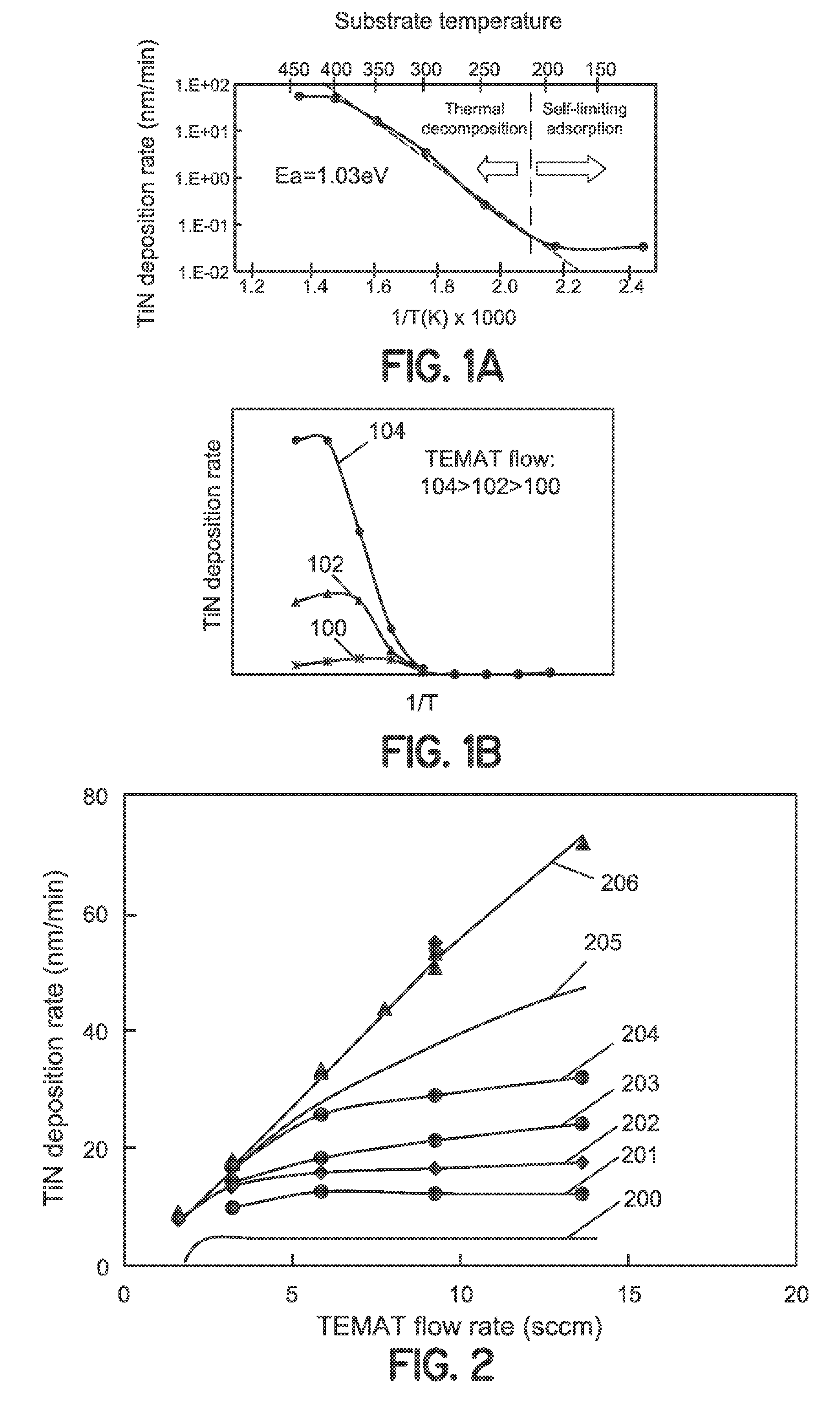
Embodiments of the invention describe TiN deposition methods suitable for high volume manufacturing of semiconductor devices on large patterned substrates (wafers). One embodiment describes a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process using high gas flow rate of a tetrakis(ethylmethylamino) titanium (TEMAT) precursor vapor along with an inert carrier gas at a low process chamber pressure that provides high deposition rate of conformal TiN films with good step coverage in surface reaction limited regime. Other embodiments describe cyclical TiN deposition methods using TEMAT precursor vapor and a nitrogen precursor.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
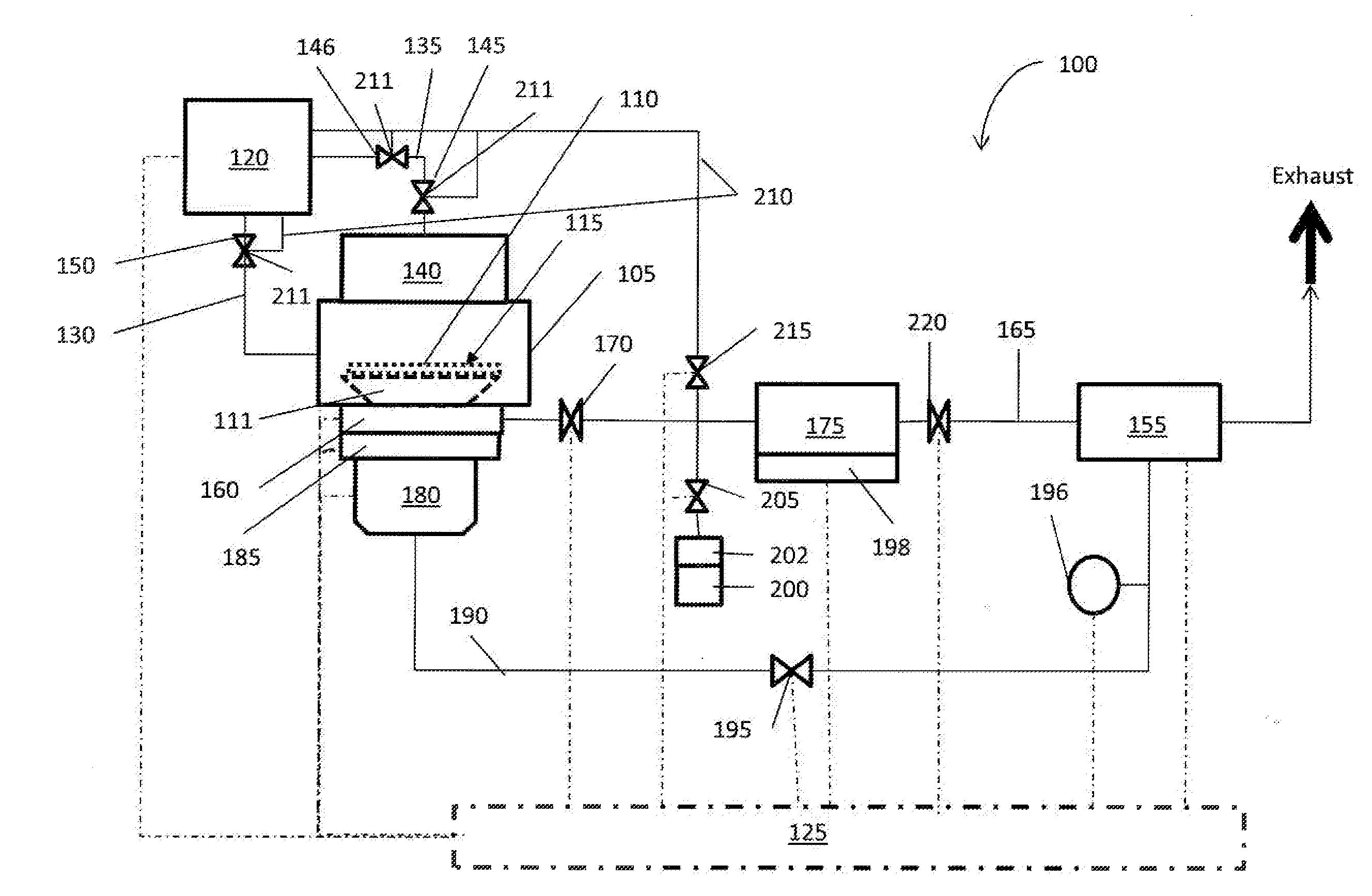
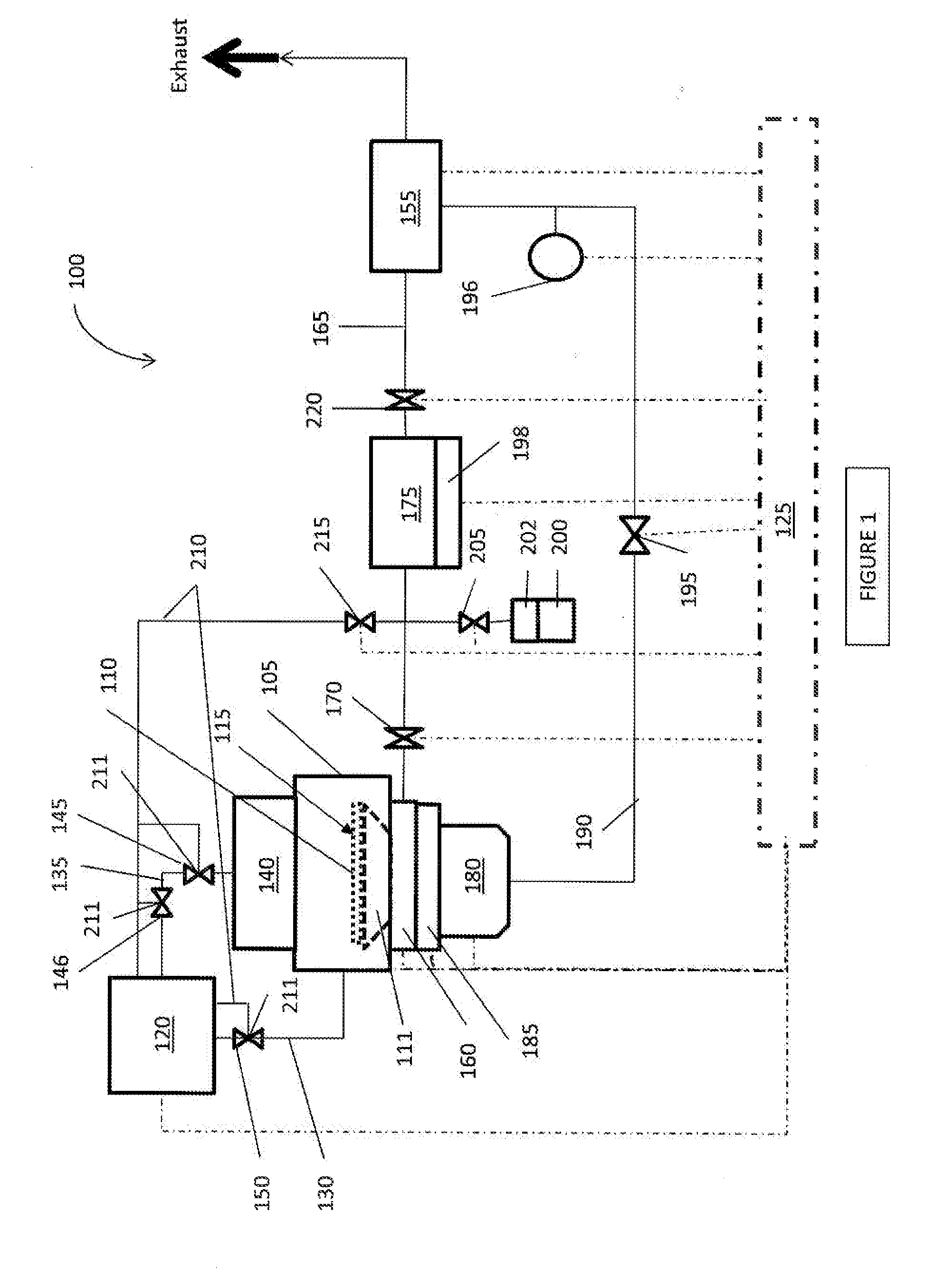
Apparatus and methods for deposition reactors
ActiveUS20090263578A1Avoid condensationPipe heating/coolingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface reactionAtomic layer deposition
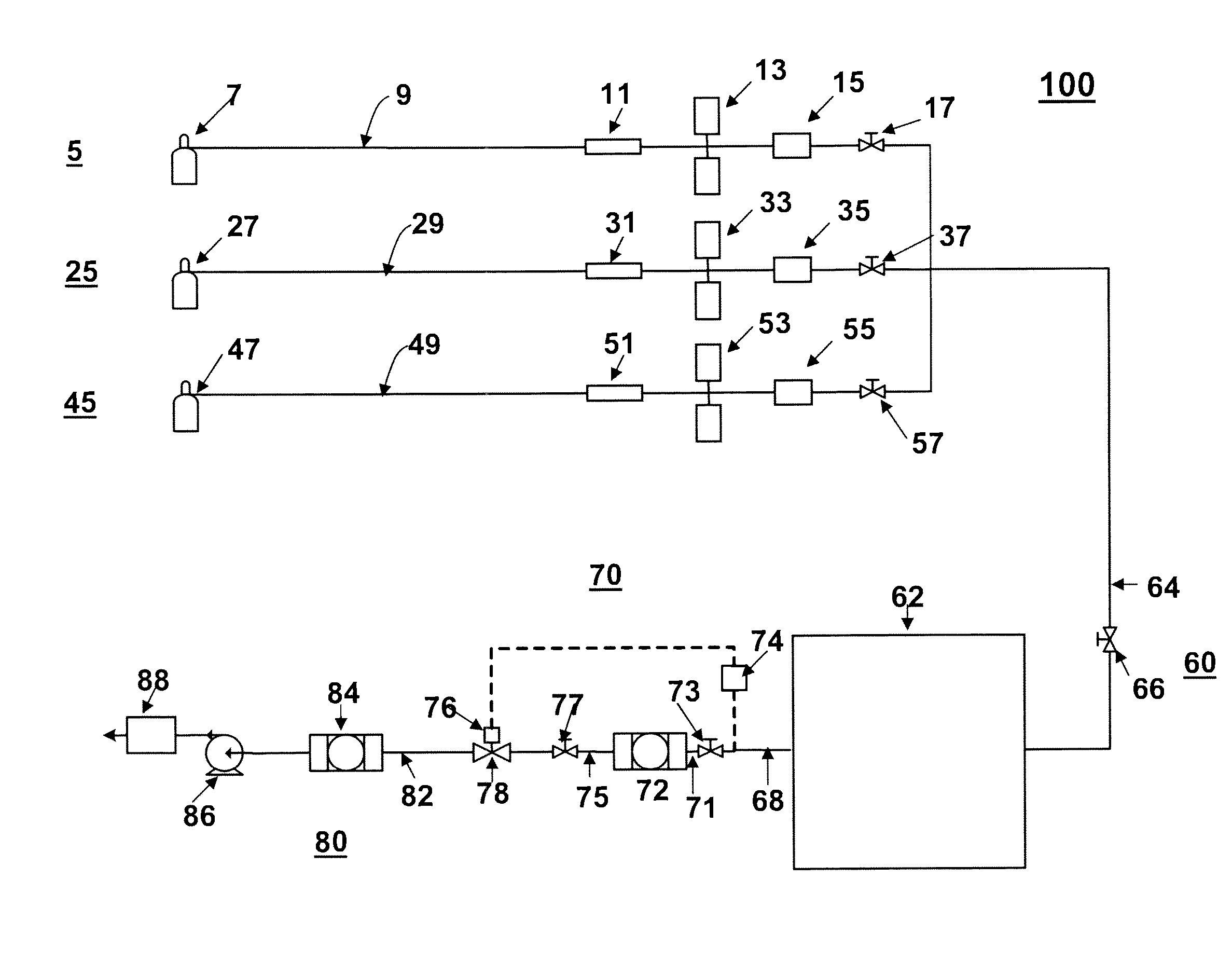
An apparatus, such as an ALD (Atomic Layer Deposition) apparatus, including a precursor source configured for depositing material on a heated substrate in a deposition reactor by sequential self-saturating surface reactions. The apparatus includes an in-feed line for feeding precursor vapor from the precursor source to a reaction chamber and a structure configured for utilizing heat from a reaction chamber heater for preventing condensation of precursor vapor into liquid or solid phase between the precursor source and the reaction chamber. Also various other apparatus and methods are presented.
Owner:PICOSUN OY
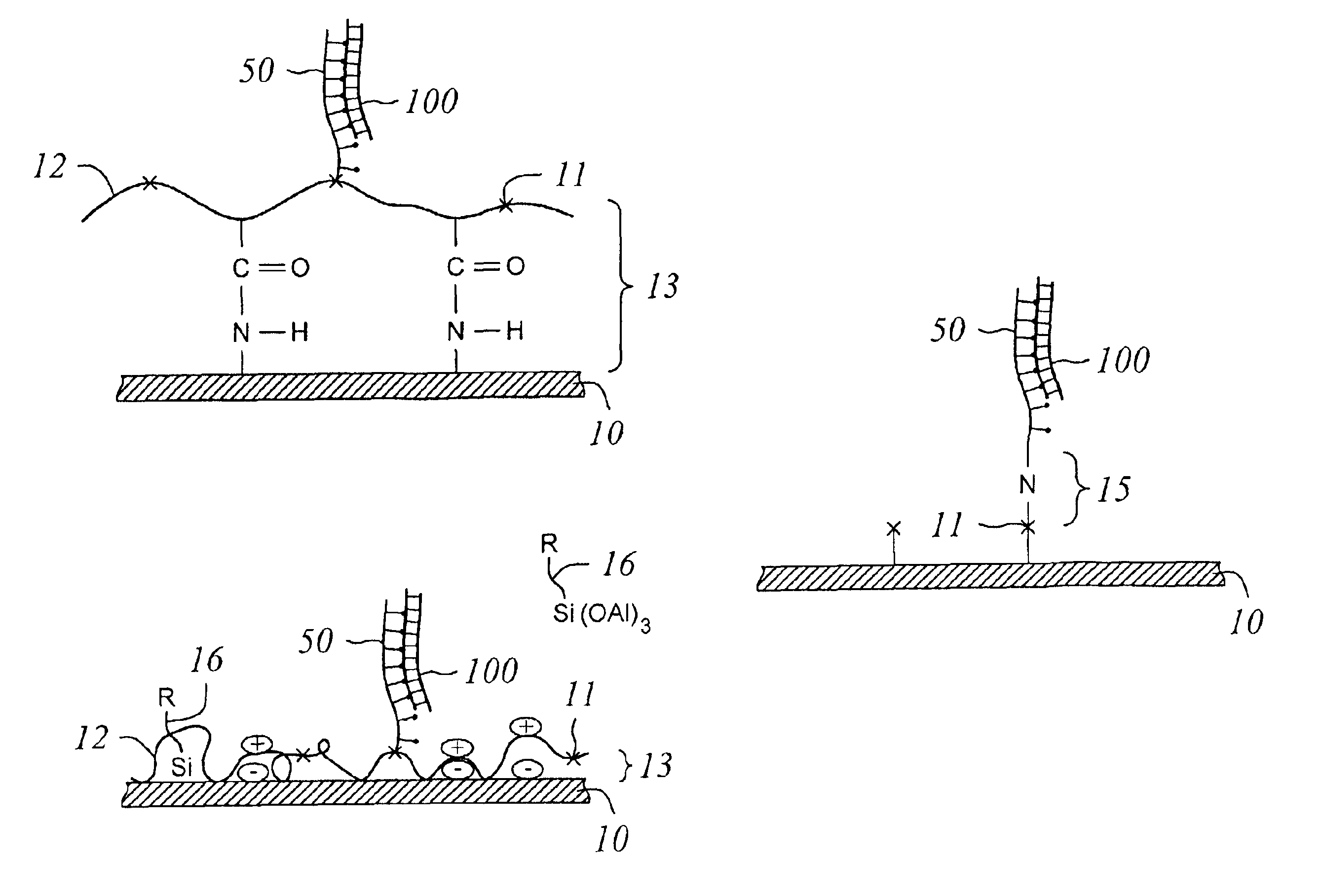
Surface with tethered polymeric species for binding biomolecules
InactiveUS6927029B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSurface reactionReactive site
The invention provides a solid support for adsorbing a biomolecule. The support comprises a surface coating having a non-nucleotidic polymer tethered to a surface reactive site. The polymer comprises a backbone, terminus, and adsorbing moieties covalently attached to the backbone and capable of adsorbing a biomolecule that can assume a plurality of conformations. The polymer is generally tethered to the surface at its terminus and the backbone exhibits sufficient mobility and flexibility such that a biomolecule adsorbed by the adsorbing moieties can assume a desired conformation for hybridization. Also provided is a process for preparing a surface coating having a functionalized surface.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods and compositions for separating or enriching cells
InactiveUS20140008210A1Aid in diagnosis and prognosisImprove efficiencyDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsSurface reactionSputtering
The present invention provides a filtration chamber comprising a microfabricated filter enclosed in a housing, wherein the surface of said filter and / or the inner surface of said housing are modified by vapor deposition, sublimation, vapor-phase surface reaction, or particle sputtering to produce a uniform coating; and a method for separating cells of a fluid sample, comprising: a) dispensing a fluid sample into the filtration chamber disclosed herein; and b) providing fluid flow of the fluid sample through the filtration chamber, wherein components of the fluid sample flow through or are retained by the filter based on the size, shape, or deformability of the components.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Process for forming thin film encapsulation layers
InactiveUS20090081356A1Suitable for processingSolid-state devicesSpecial surfacesSurface reactionReactive gas
A process is disclosed for making a thin film encapsulation package for an OLED device by depositing a thin film material on an OLED device to be encapsulated, comprising simultaneously directing a series of gas flows along substantially parallel elongated output openings, wherein the series of gas flows comprises, in order, at least a first reactive gaseous material, an inert purge gas, and a second reactive gaseous material, optionally repeated a plurality of times, wherein the first reactive gaseous material is capable of reacting with a substrate surface treated with the second reactive gaseous material to form an encapsulating thin film, wherein the first reactive gaseous material is a volatile organo-metal precursor compound. The process is carried out substantially at or above atmospheric pressure, and the temperature of the substrate during deposition is under 250° C.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method for preparing the surface of a dielectric
InactiveUS20010016226A1Maximize capacitanceMinimize dangerPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface reactionElectrical performance
This invention relates to a method for improving the chemical and electrical performance characteristics of a dielectric material especially one with high dielectric constant. The method comprises the steps of first obtaining a high dielectric constant material, the material having a degraded upper surface reduced dielectric constant and then modifying the surface chemistry of said upper surface by reacting said upper surface with a reactant. The reaction enables removal of the degraded layer. In a variant of the method, the gas reactant preferentially reacting with upper surface as compared to the bulk.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com