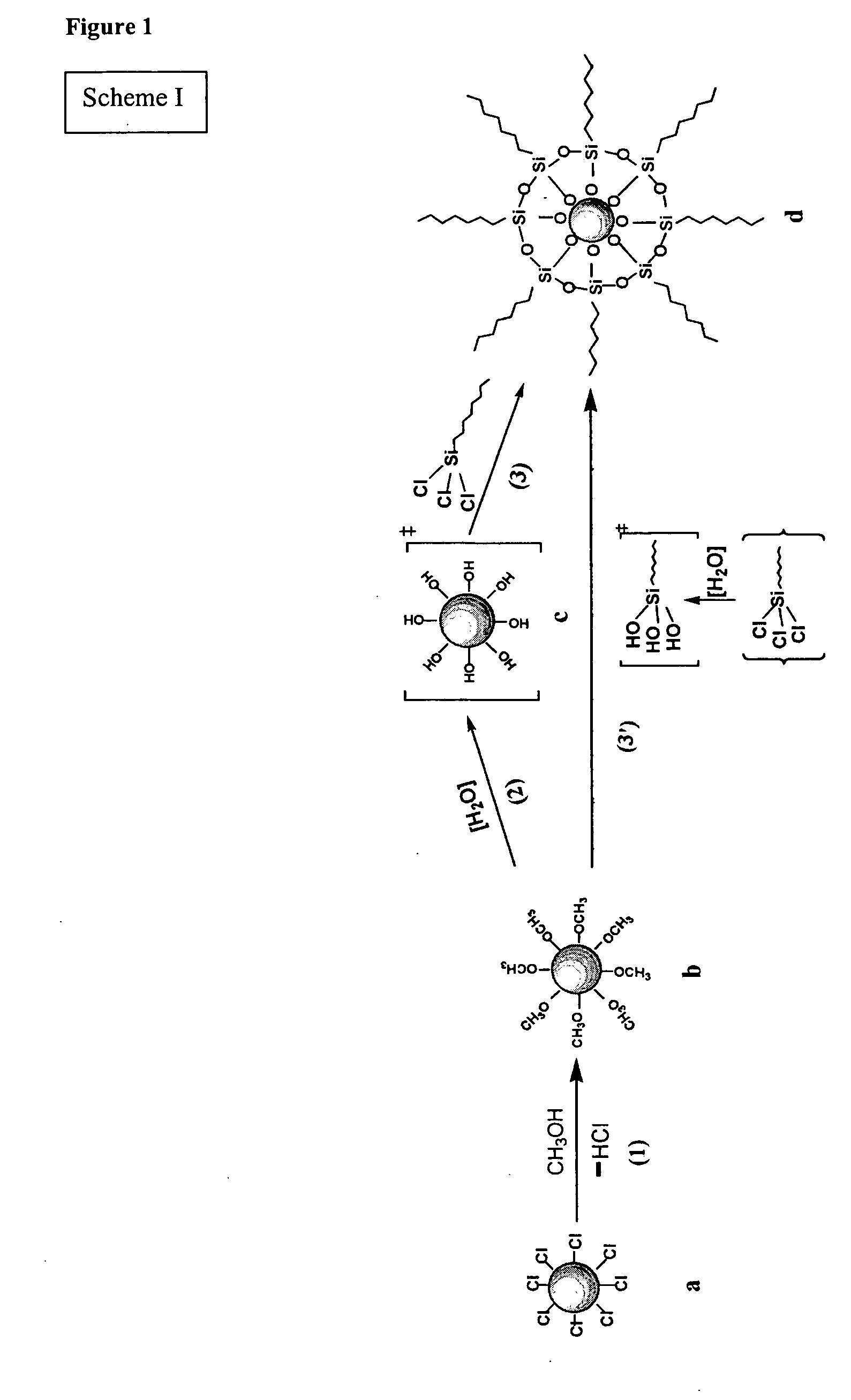
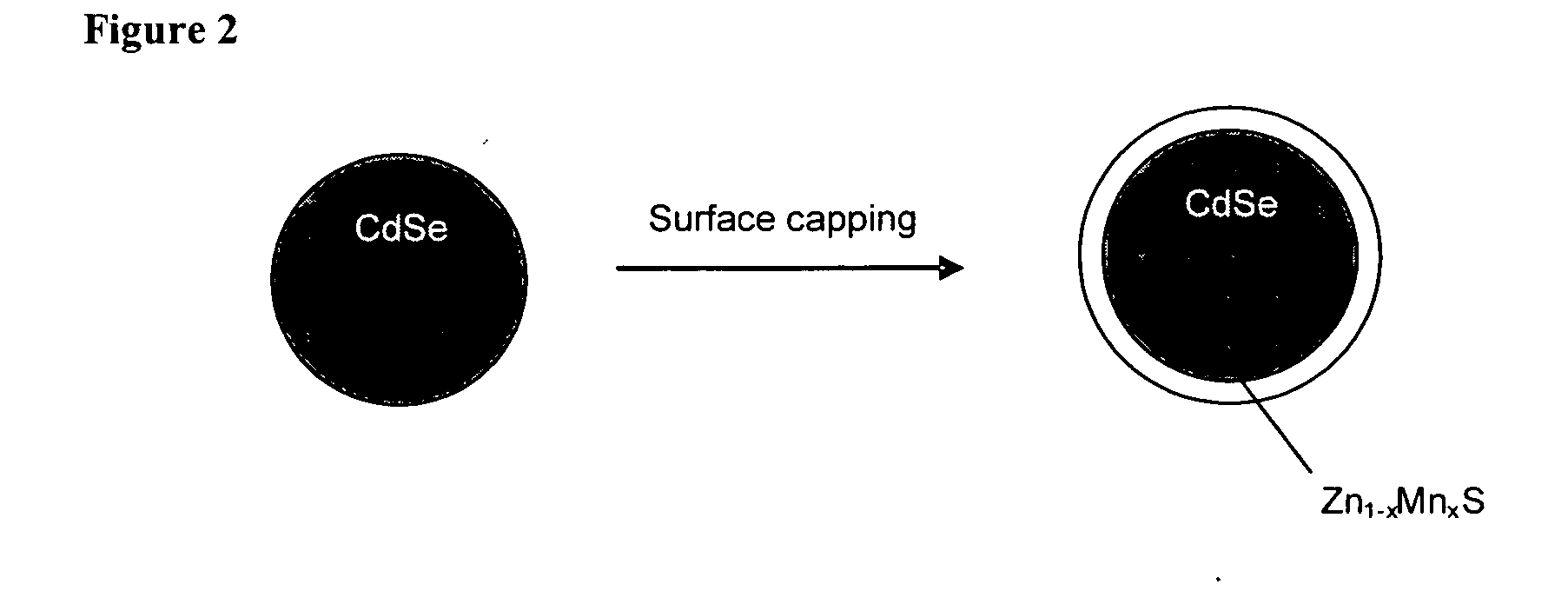
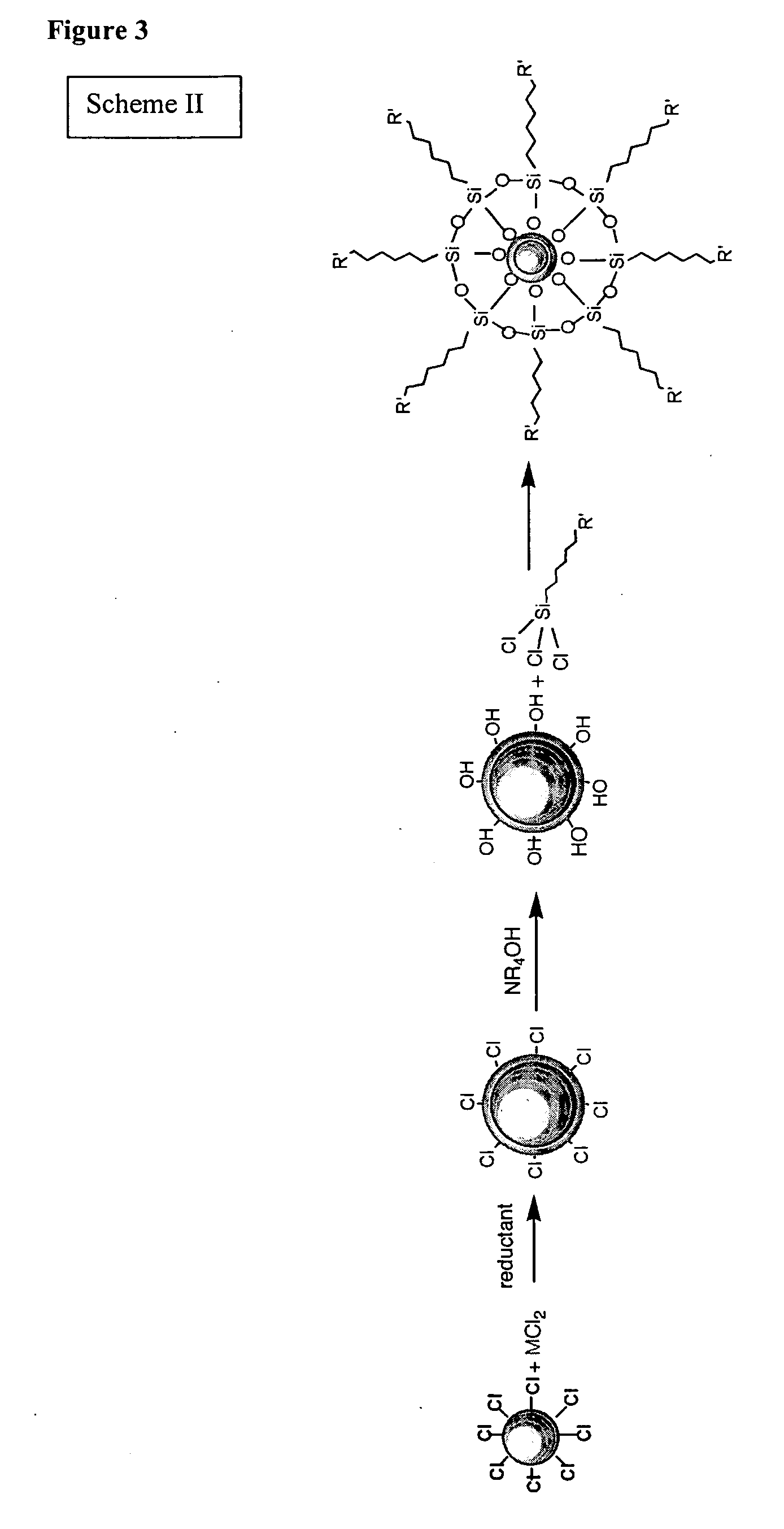
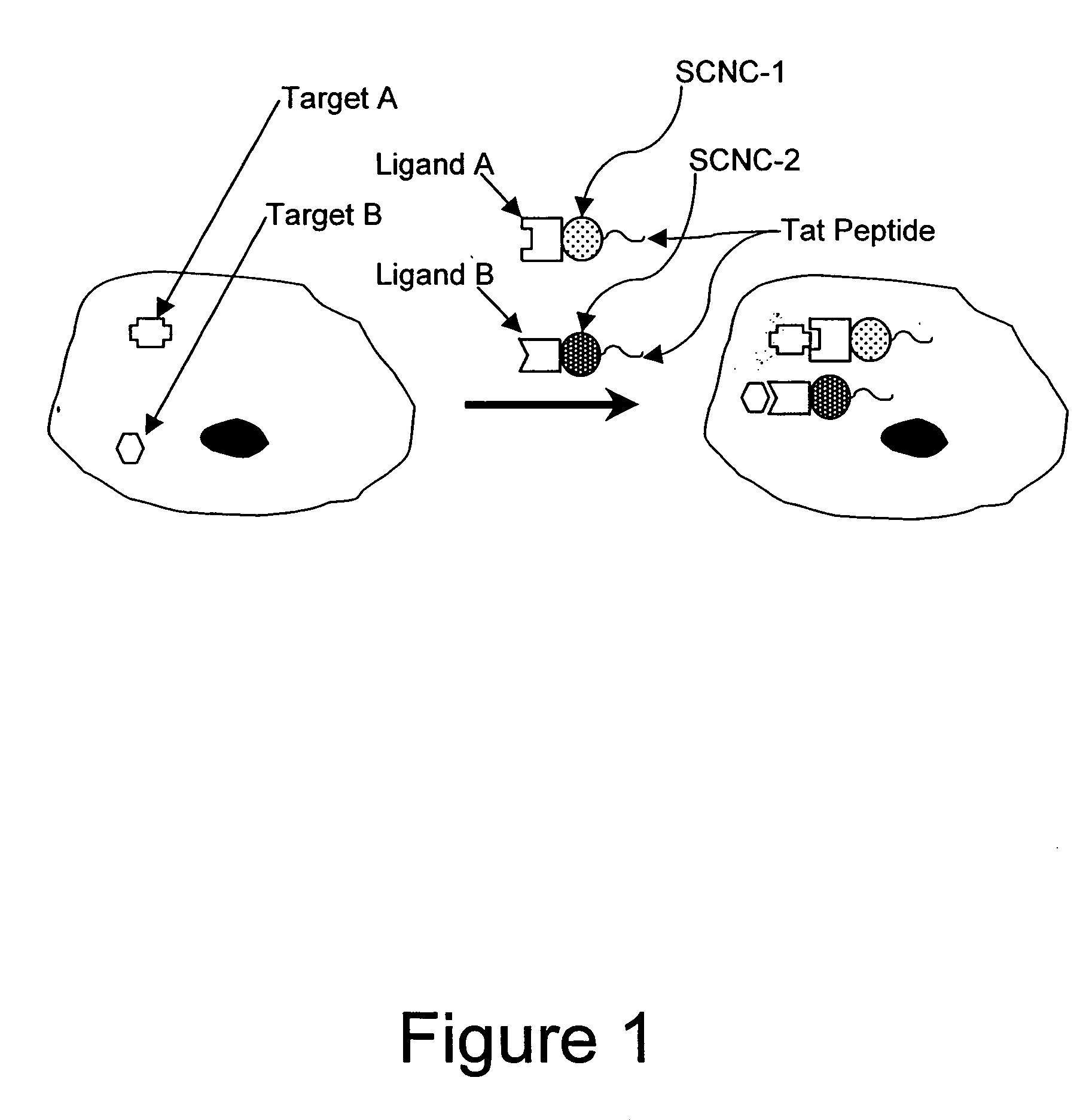
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Semiconductor Nanoparticle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
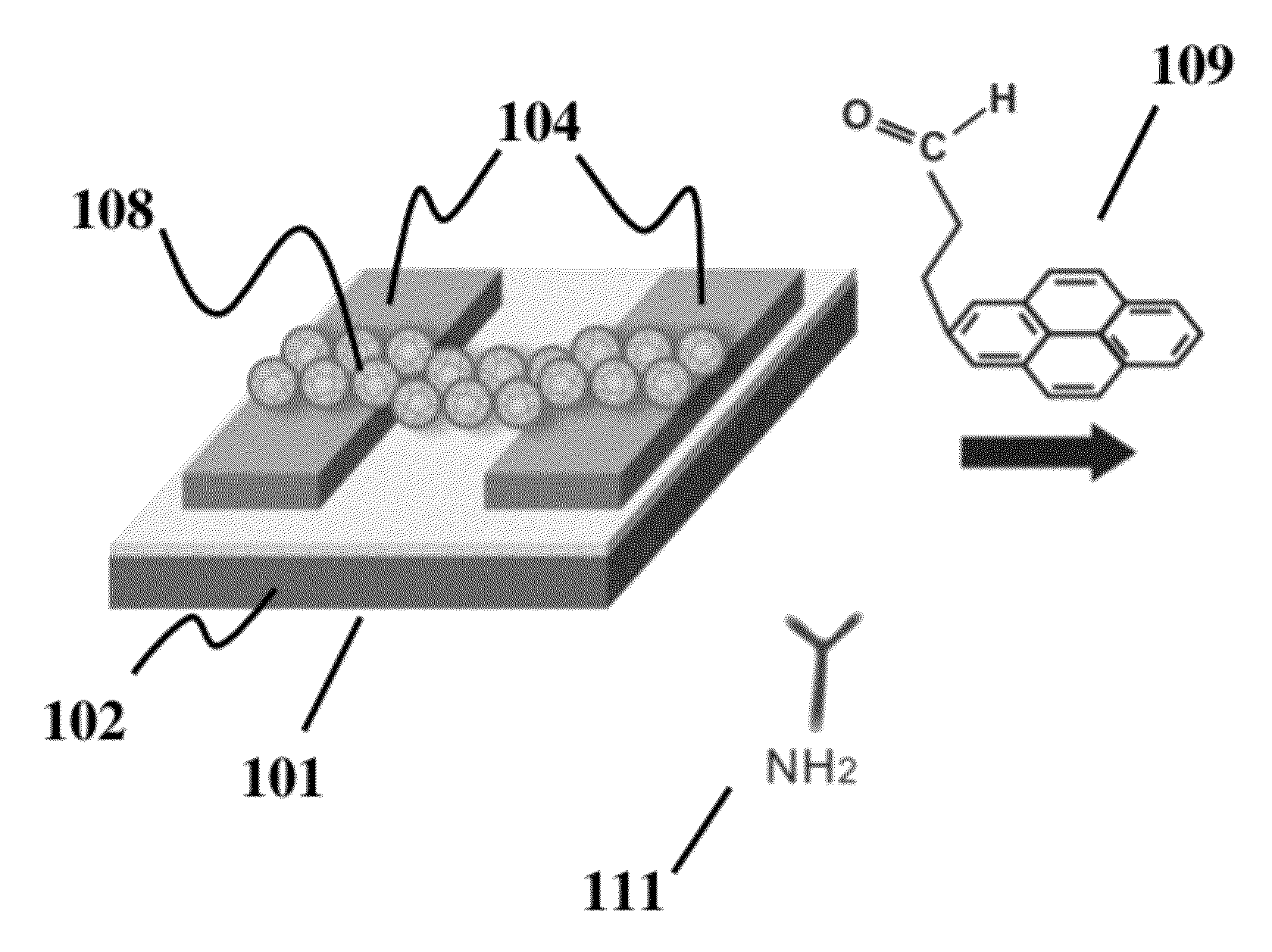
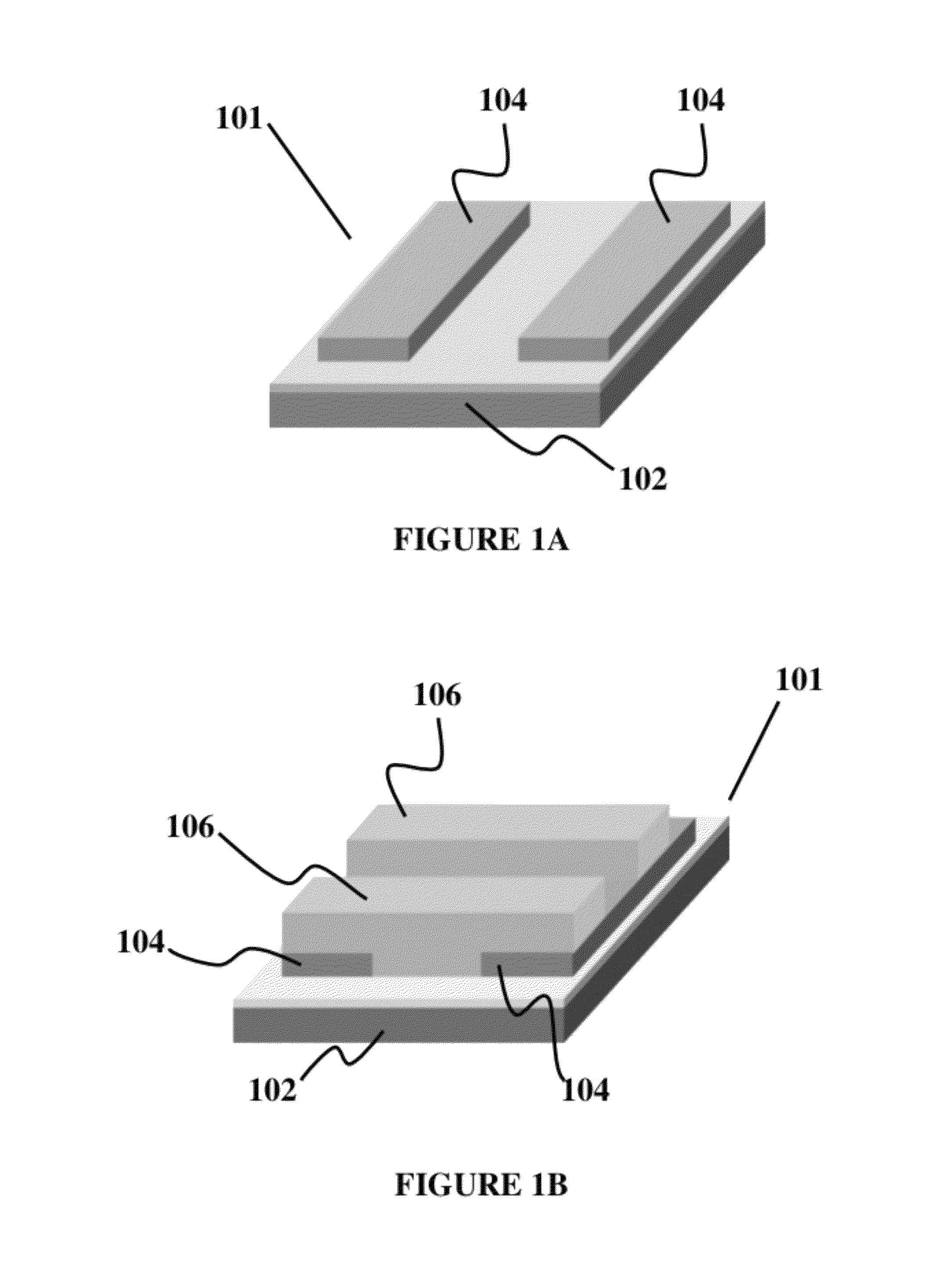
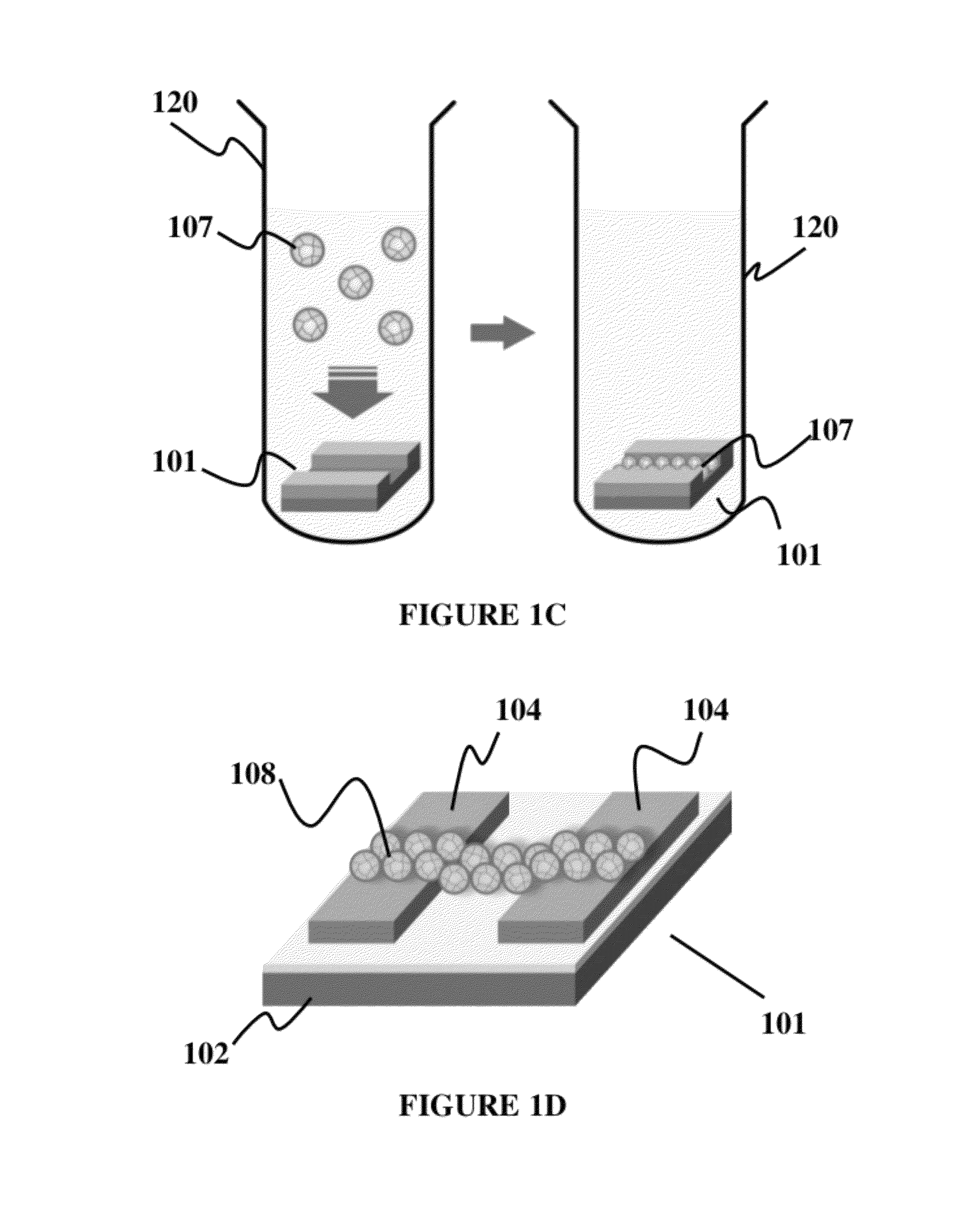
Graphene-encapsulated nanoparticle-based biosensor for the selective detection of biomarkers
ActiveUS20120220053A1Material nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringGraphene
A field effect transistor (FET) with a source electrode and a drain electrode distanced apart from each other on a semi-conductor substrate, and a gate electrode consisting of a uniform layer of reduced graphene oxide encapsulated semiconductor nanoparticles (rGO-NPs), wherein the gate electrode is disposed between and contacts both the source and drain electrodes. Methods of making and assay methods using the FETs are also disclosed, including methods in which the rGO-NPs are functionalized with binding partners for biomarkers.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method and system for systemic delivery of growth arresting, lipid-derived bioactive compounds
ActiveUS20050025820A1Maximizing systemic deliveryCorrection for dispersionOrganic active ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedDendrimerGene Therapy Agent
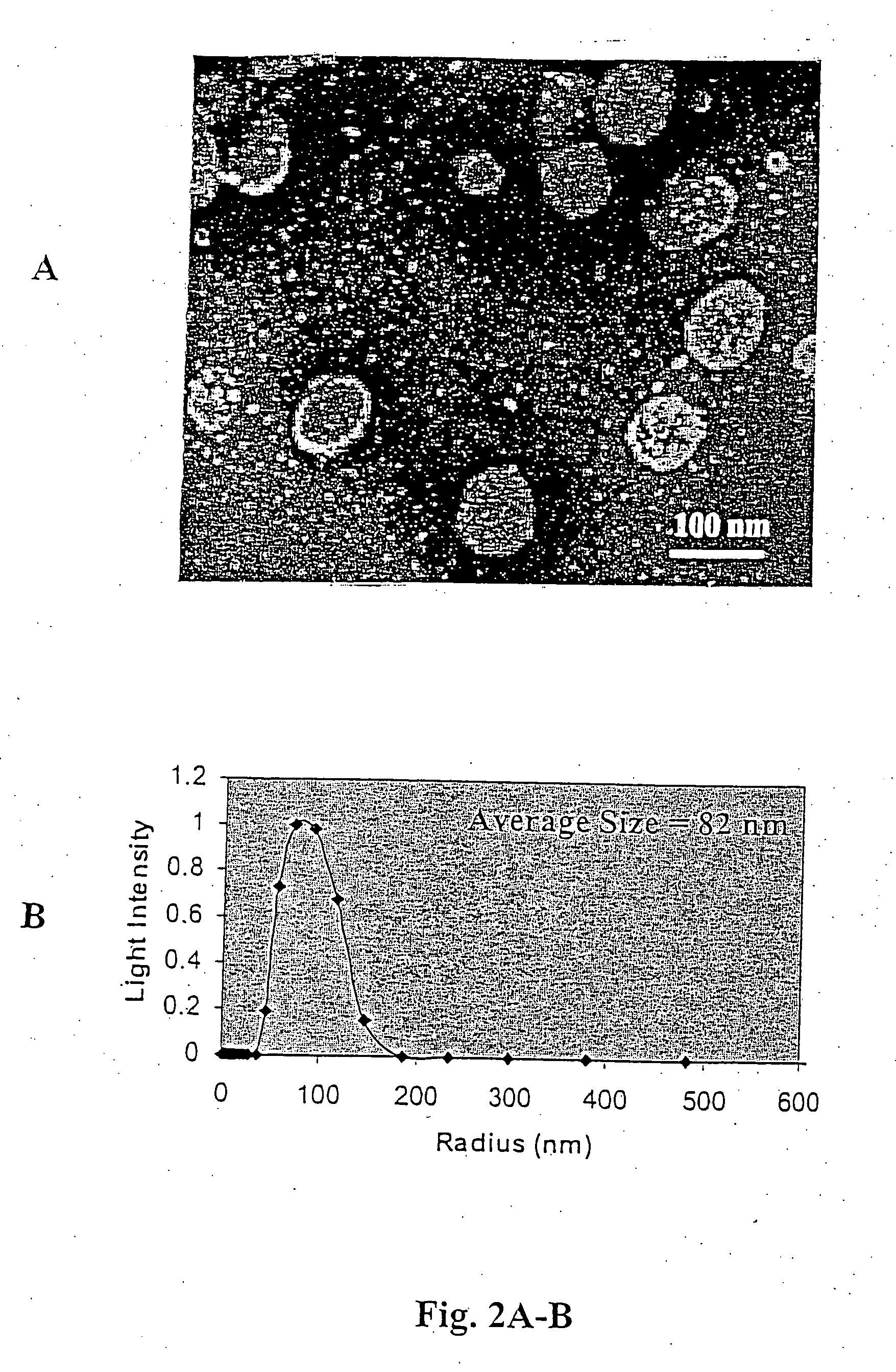
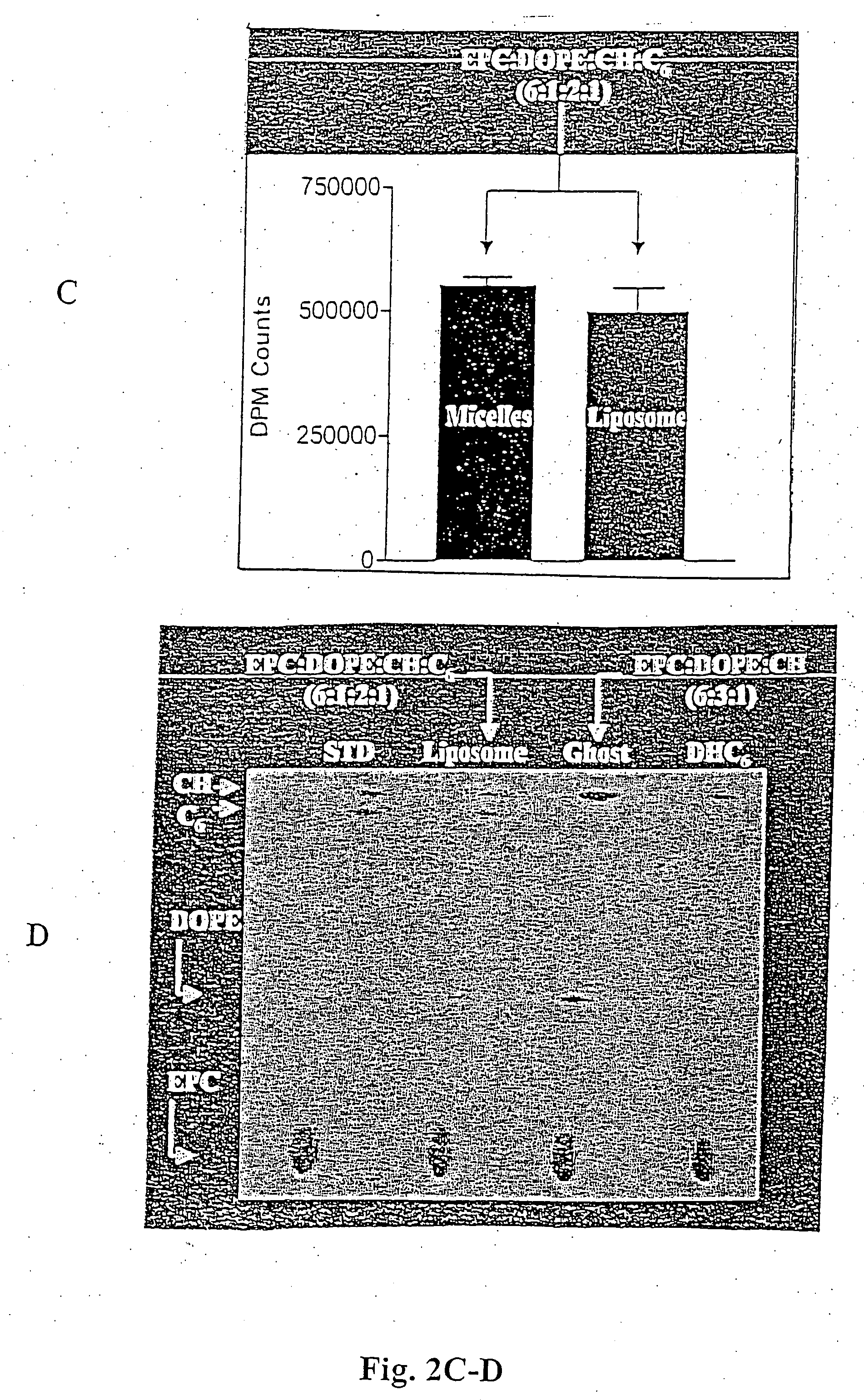
A system and method for optimizing the systemic delivery of growth-arresting lipid-derived bioactive drugs or gene therapy agents to an animal or human in need of such agents utilizing nanoscale assembly systems, such as liposomes, resorbable and non-aggregating nanoparticle dispersions, metal or semiconductor nanoparticles, or polymeric materials such as dendrimers or hydrogels, each of which exhibit improved lipid solubility, cell permeability, an increased circulation half life and pharmacokinetic profile with improved tumor or vascular targeting.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
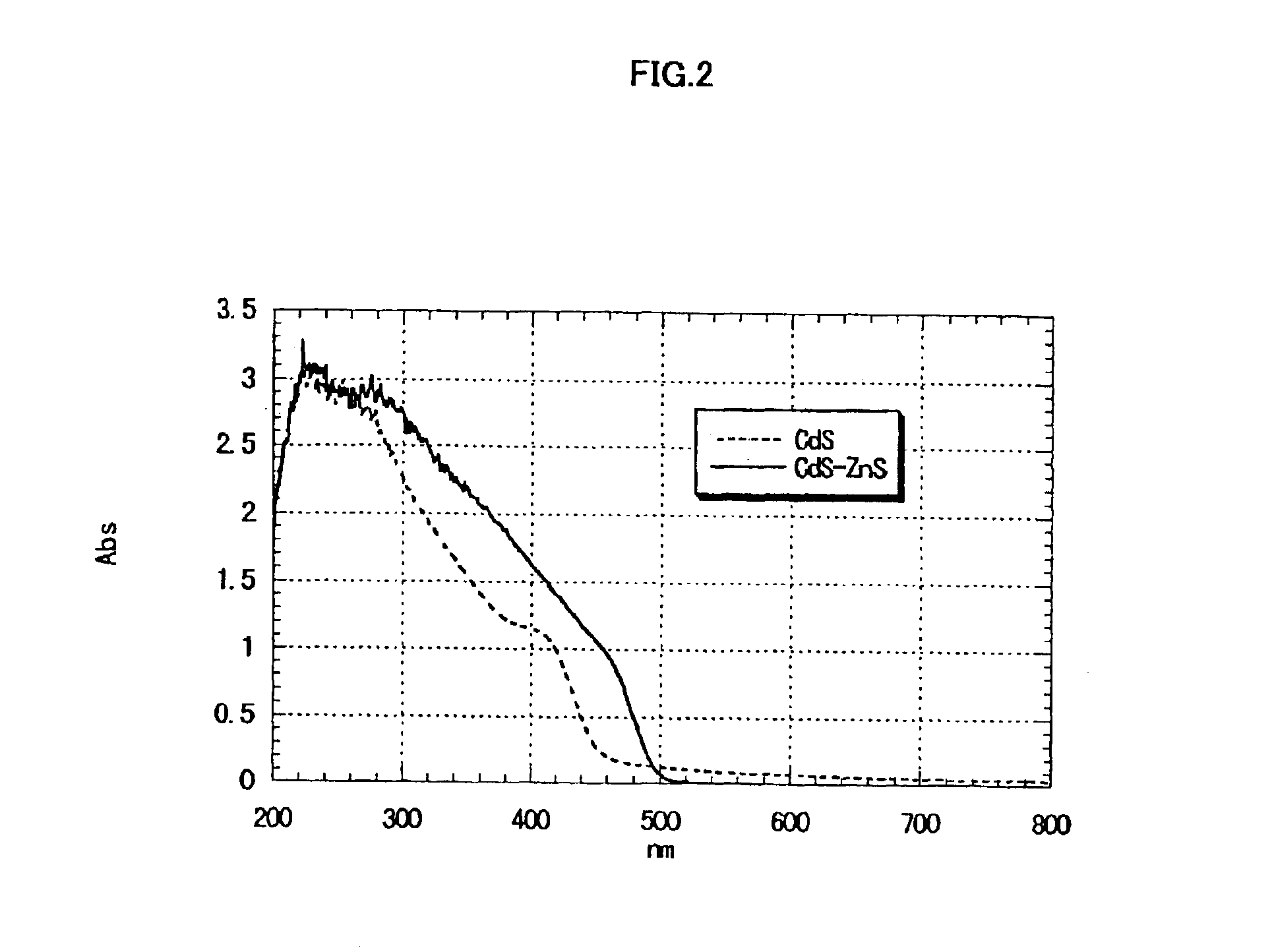
Phosphor materials and illumination devices made therefrom
InactiveUS7279832B2Quality improvementHigh photoluminescence efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescenceColor rendering index
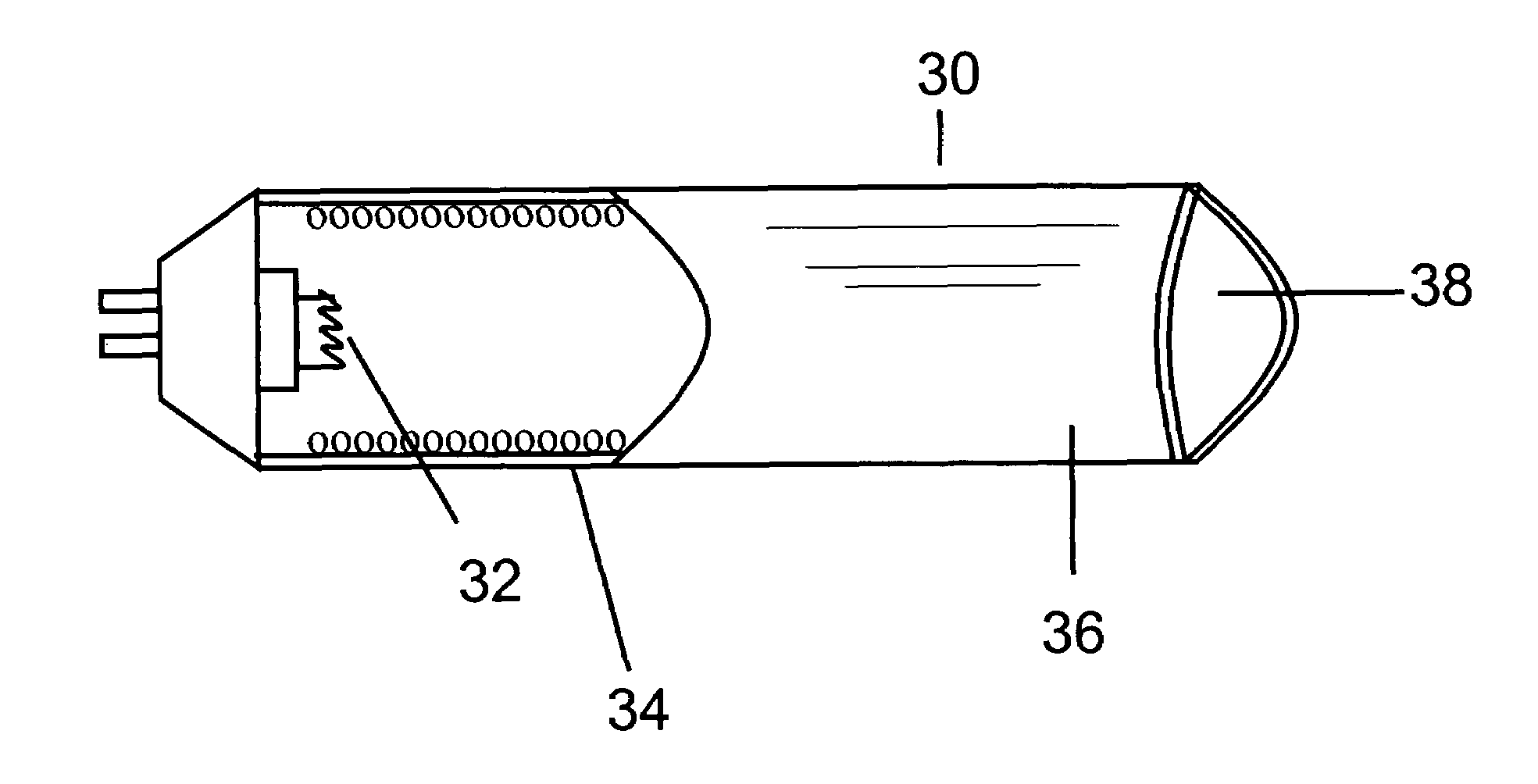
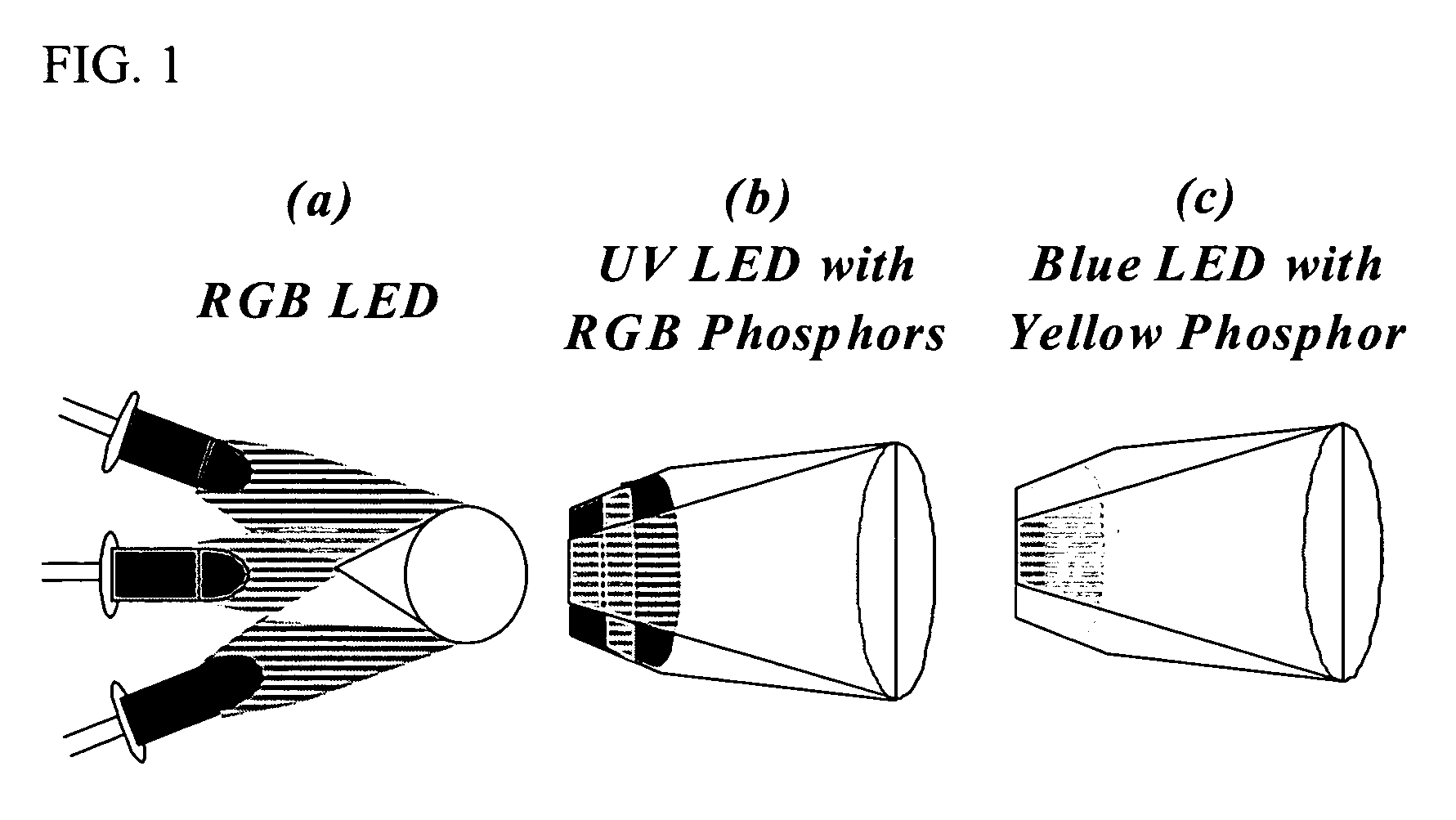
This invention provides a phosphor material capable of absorbing primary light and converting that light into white light having a high color rendering index and illumination devices made from the phosphor material. The white light may have a color rendering index of 100 and may be produced with an efficiency of at least 30 lm / w. In one embodiment, the illumination device includes a secondary light source made from a plurality of Group IV semiconductor nanoparticles.
Owner:INNOVALIGHT
Core-shell type nanoparticles and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20070128439A1Increased durabilityHigh strengthMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCore shell nanoparticlesMechanical stability
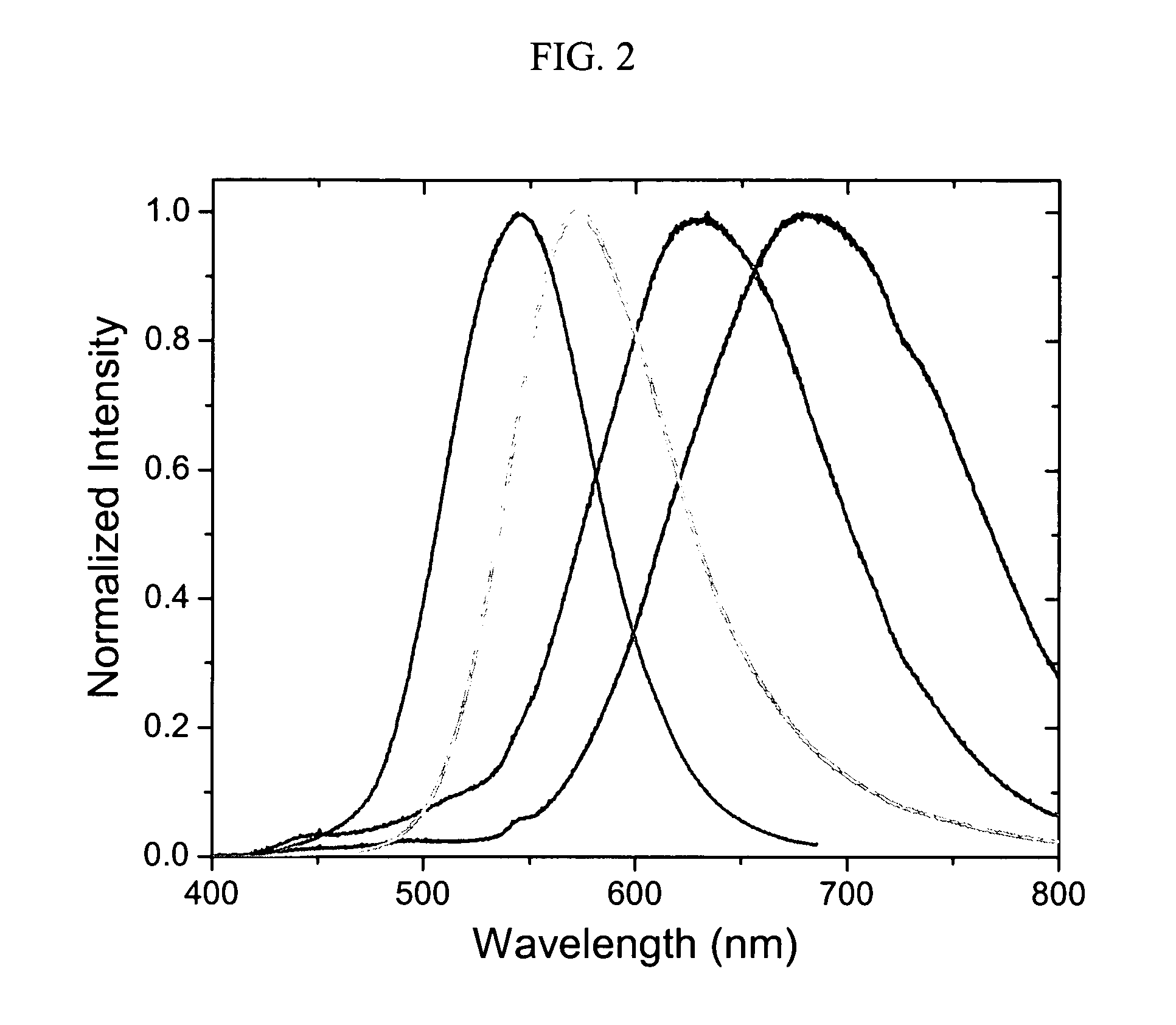
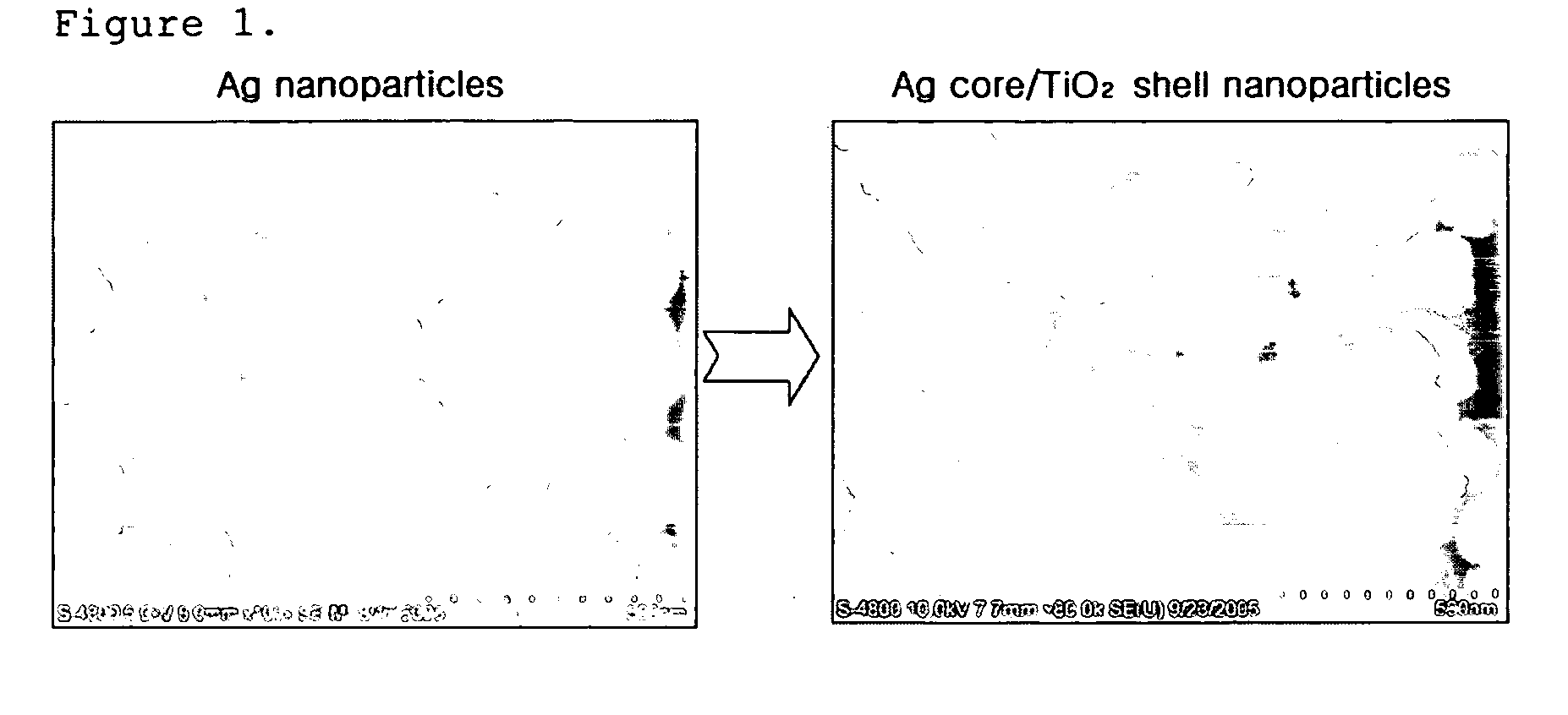
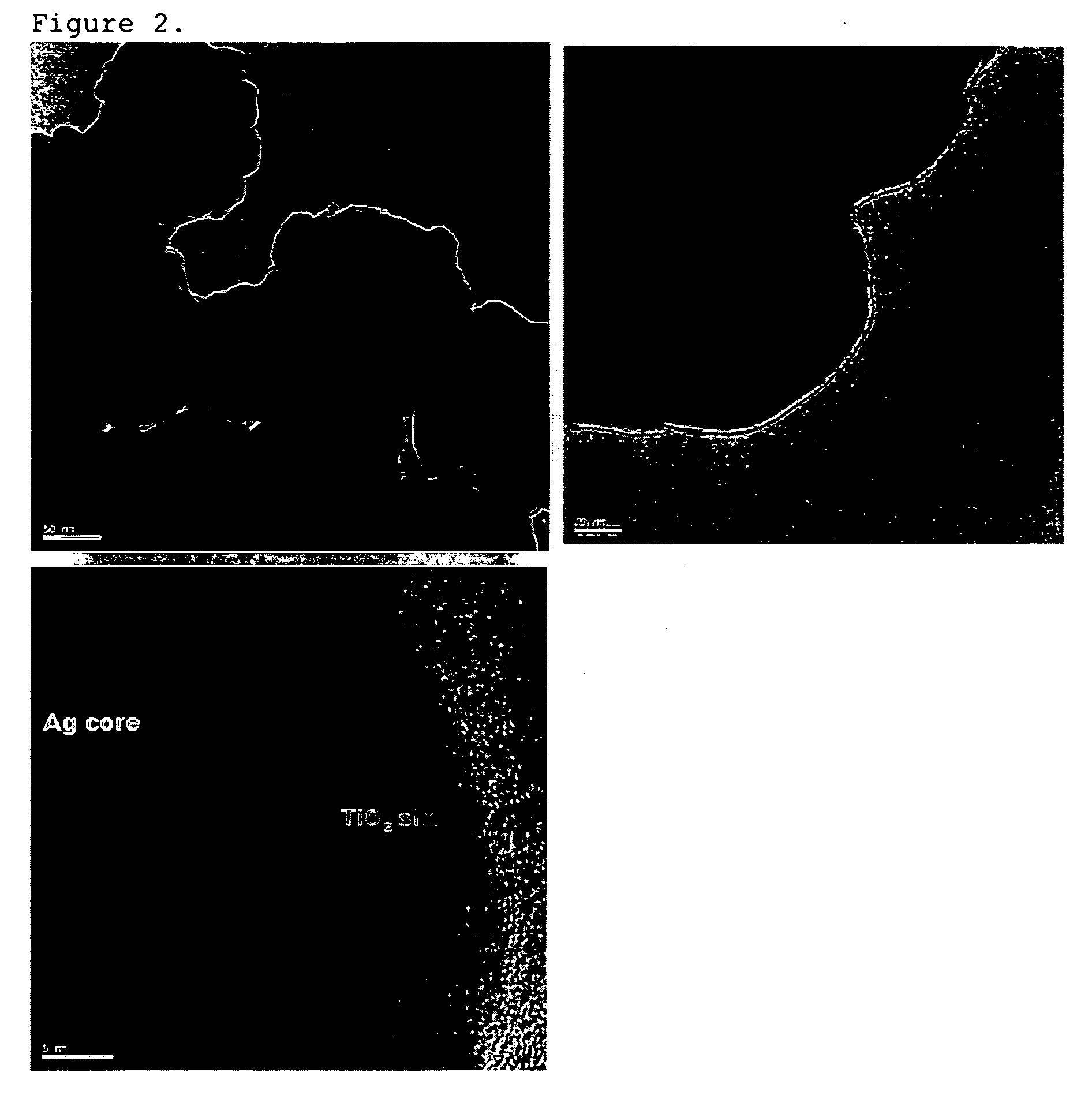
Disclosed herein are core-shell type nanoparticles comprising nanoparticle cores made of a metal or semiconductor, and shells made of crystalline metal oxide formed on the surfaces of the nanoparticle cores, as well as a preparation method thereof. According to the disclosed invention, the core-shell nanoparticles, consisting of metallic or semiconductor cores and crystalline metal oxide shells, can be prepared by epitaxially growing metal oxide on the surfaces of the metallic or semiconductor nanoparticle cores. By virtue of the crystalline metal oxide shells, the core nanoparticle made of metal or semiconductor can ensure excellent chemical and mechanical stability, and the core-shell nanoparticles can show new properties resulting from the interaction between the metal cores and the metal oxide crystal shells.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Agents for use in magnetic resonance and optical imaging
InactiveUS20050220714A1High photoluminescence efficiencyBrighter luminescenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsDual modeSemiconductor Nanoparticles
Semiconductor nanoparticles are doped with paramagnetic ions to serve as dual-mode optical and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. These nanoparticles can be constructed in smaller diameters than typical MRI agents. The dual-modality nature allows the particles to be used for in vivo imaging by MRI, and then followed by histology with optical imaging techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for enhancing transport of semiconductor nanocrystals across biological membranes
InactiveUS20050059031A1Easy to analyzeMany applicationsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsMultiplexingSemiconductor Nanoparticles
Semiconductor nanoparticle complexes comprising semiconductor nanoparticles in association with cationic polymers are described. Also described are methods for enhancing the transport of semiconductor nanoparticles across biological membranes to provide encoded cells. The methods are particularly useful in multiplex settings where a plurality of encoded cells are to be assayed. Kits comprising reagents for performing such methods are also provided.
Owner:INVITROGEN +1
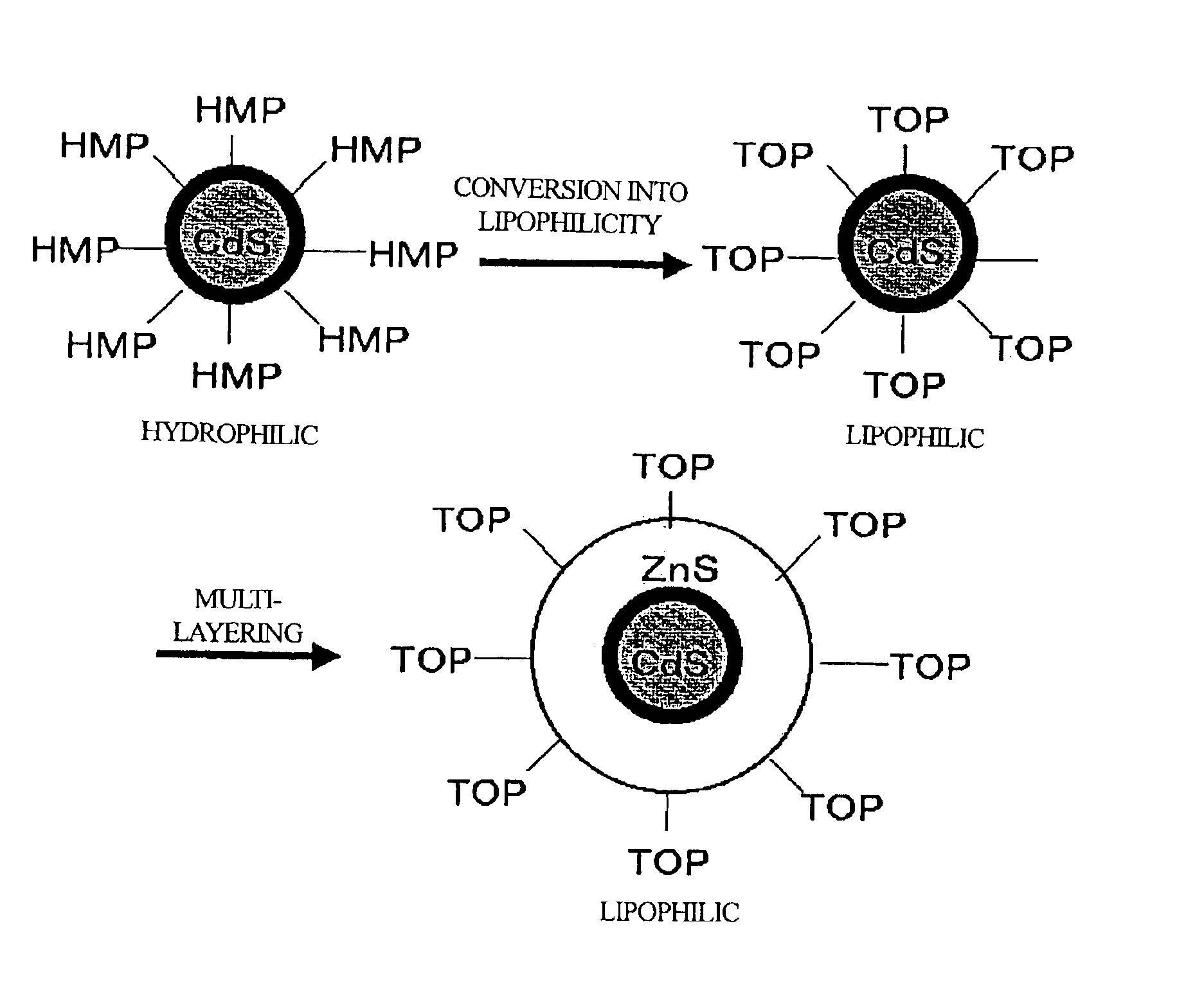
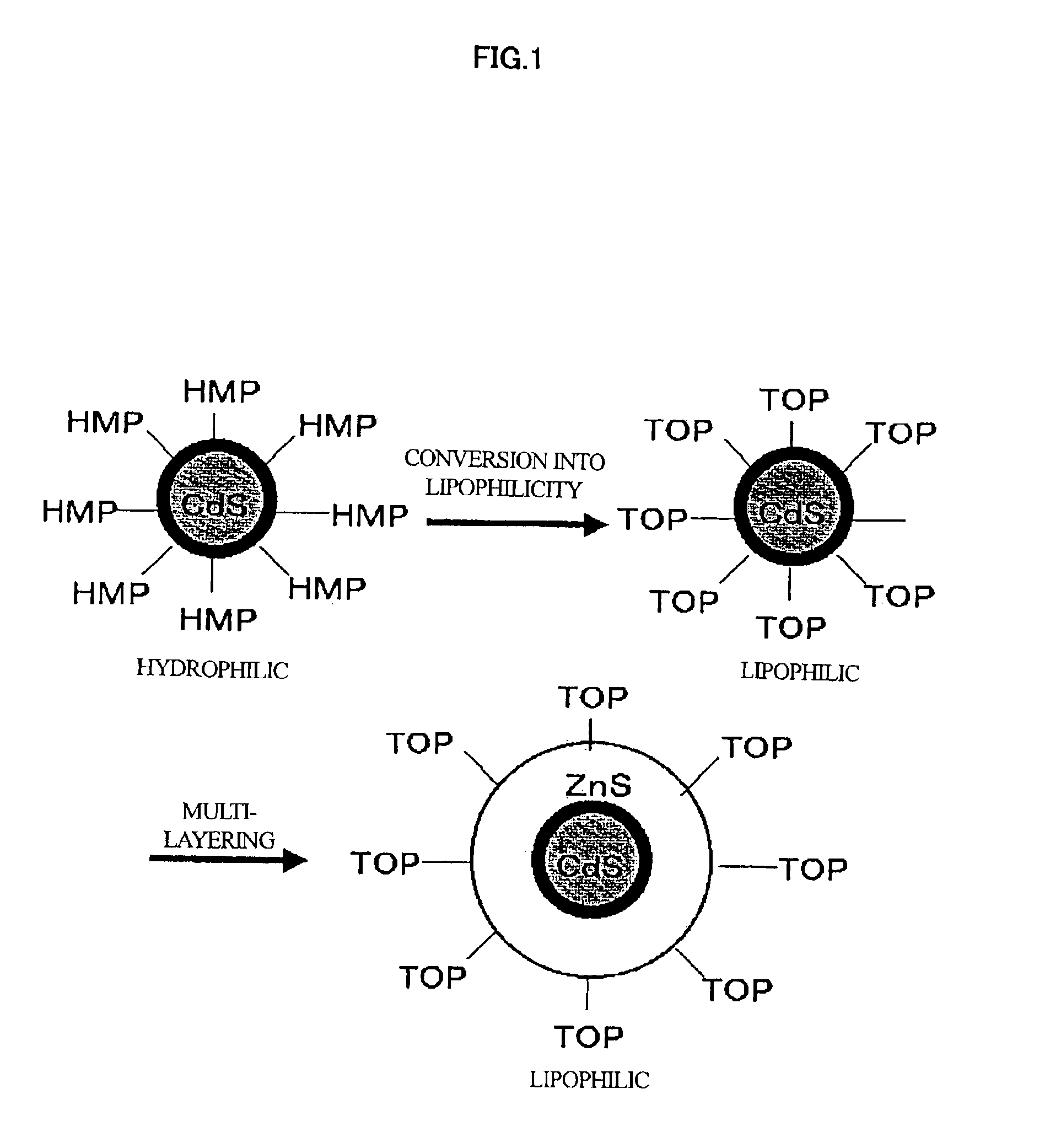
Method of manufacturing a multi-layer semiconductor nanoparticle, and a multi-layer semiconductor nanoparticle manufactured by the method
InactiveUS6911082B2Material nanotechnologyFrom normal temperature solutionsNanometreSemiconductor Nanoparticles
Multi-layered semiconductor nanoparticles having a very narrow grain-size distribution and exhibiting a spectrum having a narrow wavelength-width peak are prepared by a manufacturing method combining a monodisperse semiconductor nanoparticle manufacturing method and a multi-layer semiconductor nanoparticle preparation method. The nature of a solution of monodisperse semiconductor nanoparticles that is stabilized by a surface stabilizer is transformed between hydrophilic and lipophilic by substituting the surface stabilizer. The stabilized semiconductor nanoparticles are then shifted between an aqueous layer and an organic layer. The semiconductor nanoparticles are coated with multiple layers in the organic layer, and the organic layer is drawn off to recover the semiconductor nanoparticles therefrom.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
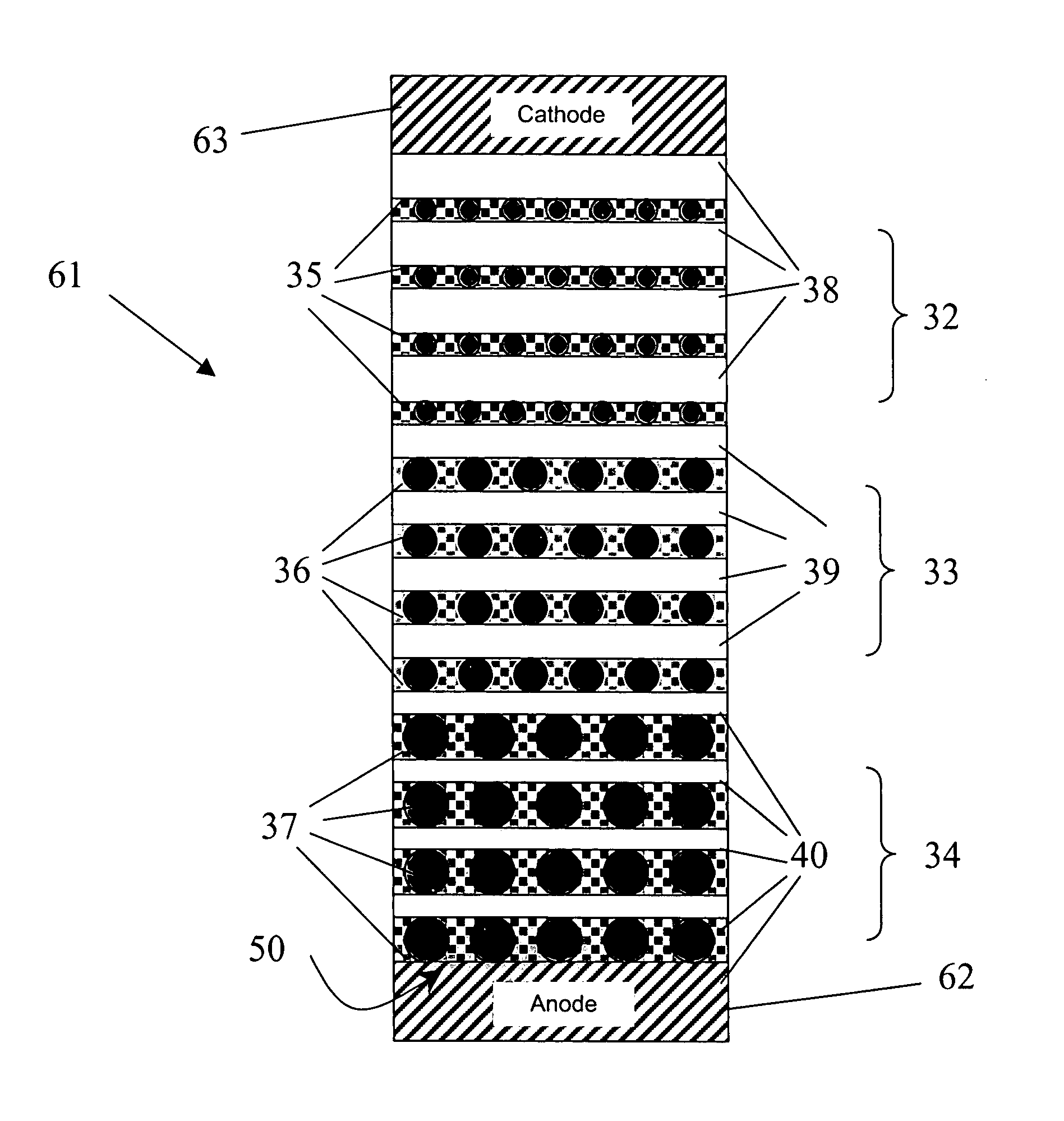
Carbon passivation in solid-state light emitters
A solid state light emitting device comprises one or more active layers comprising semiconductor nano-particles in a host matrix, e.g. silicon nano-particles in silicon dioxide or silicon nitride. The incorporation of carbon in the active layers provides a great improvement in performance through shortened decay time and enhance emission spectra, as well as reliability and lifetime. The emission wavelengths from the nano-particles can be made to correspond to the quantization energy of the semiconductor nano-particles, which allows the entire visible range of the spectrum be covered. Ideally an engineered structure of alternating active and buffer material layers are disposed between AC or DC electrodes, which generate an electric field. The buffer layers are comprised of a wide bandgap semiconductor or dielectric material, and are designed with a thickness, in the direction of an applied electric field, that ensures that electrons passing therethrough picks up enough energy to excite the nano-particles in the adjacent active layer at a sufficient excitation energy to emit light efficiently at a desired wavelength.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV +1
Light-emitting nanocomposite particles
InactiveUS20090001349A1Reliable electrical connectionImprove conductivityElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum dotColloid
A method of making an inorganic light emitting layer includes combining a solvent for semiconductor nanoparticle growth, a solution of core / shell quantum dots, and semiconductor nanoparticle precursor(s); growing semiconductor nanoparticles to form a crude solution of core / shell quantum dots, semiconductor nanoparticles, and semiconductor nanoparticles that are connected to the core / shell quantum dots; forming a single colloidal dispersion of core / shell quantum dots, semiconductor nanoparticles, and semiconductor nanoparticles that are connected to the core / shell quantum dots; depositing the colloidal dispersion to form a film; and annealing the film to form the inorganic light emitting layer.
Owner:NANOCO TECH LTD
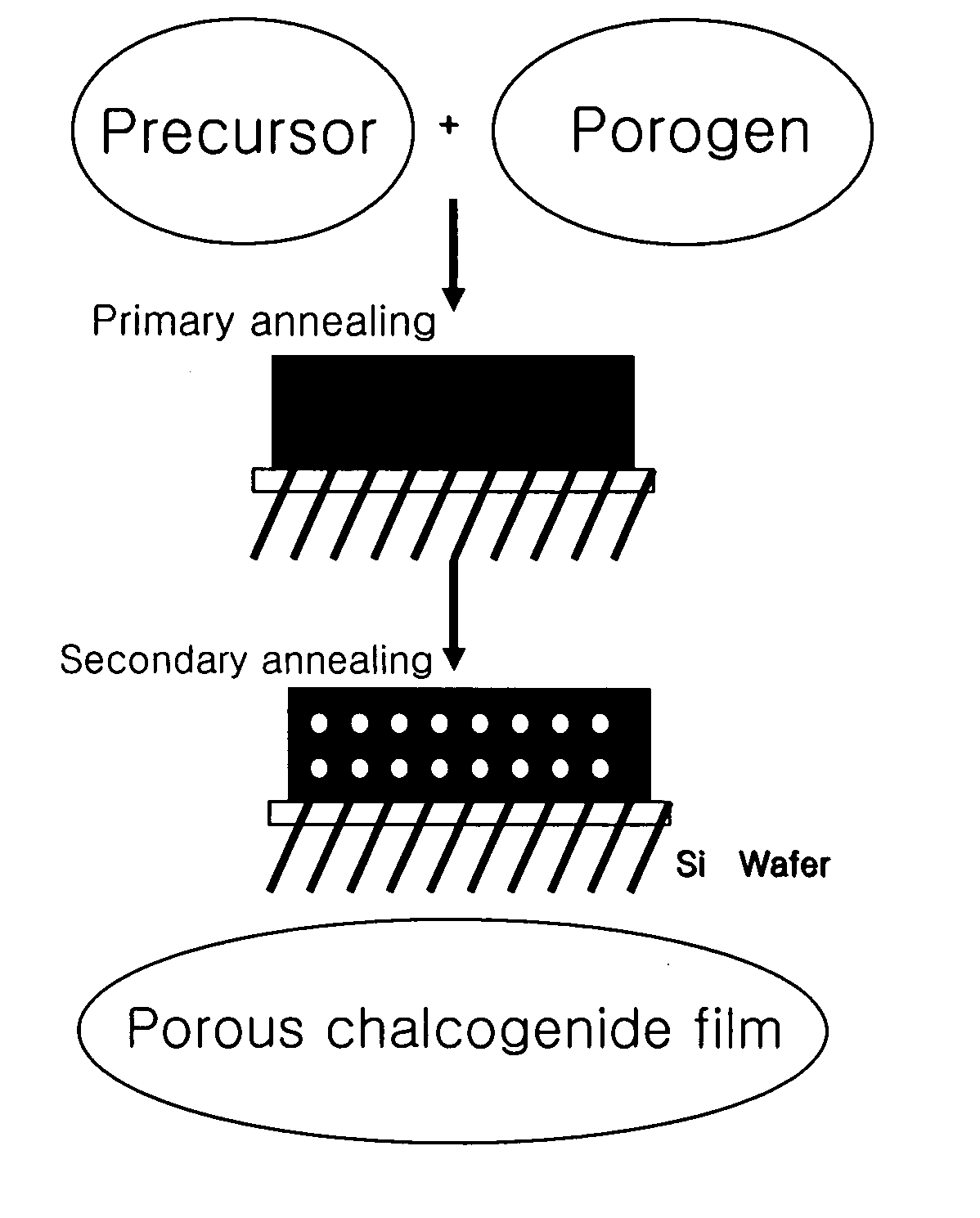
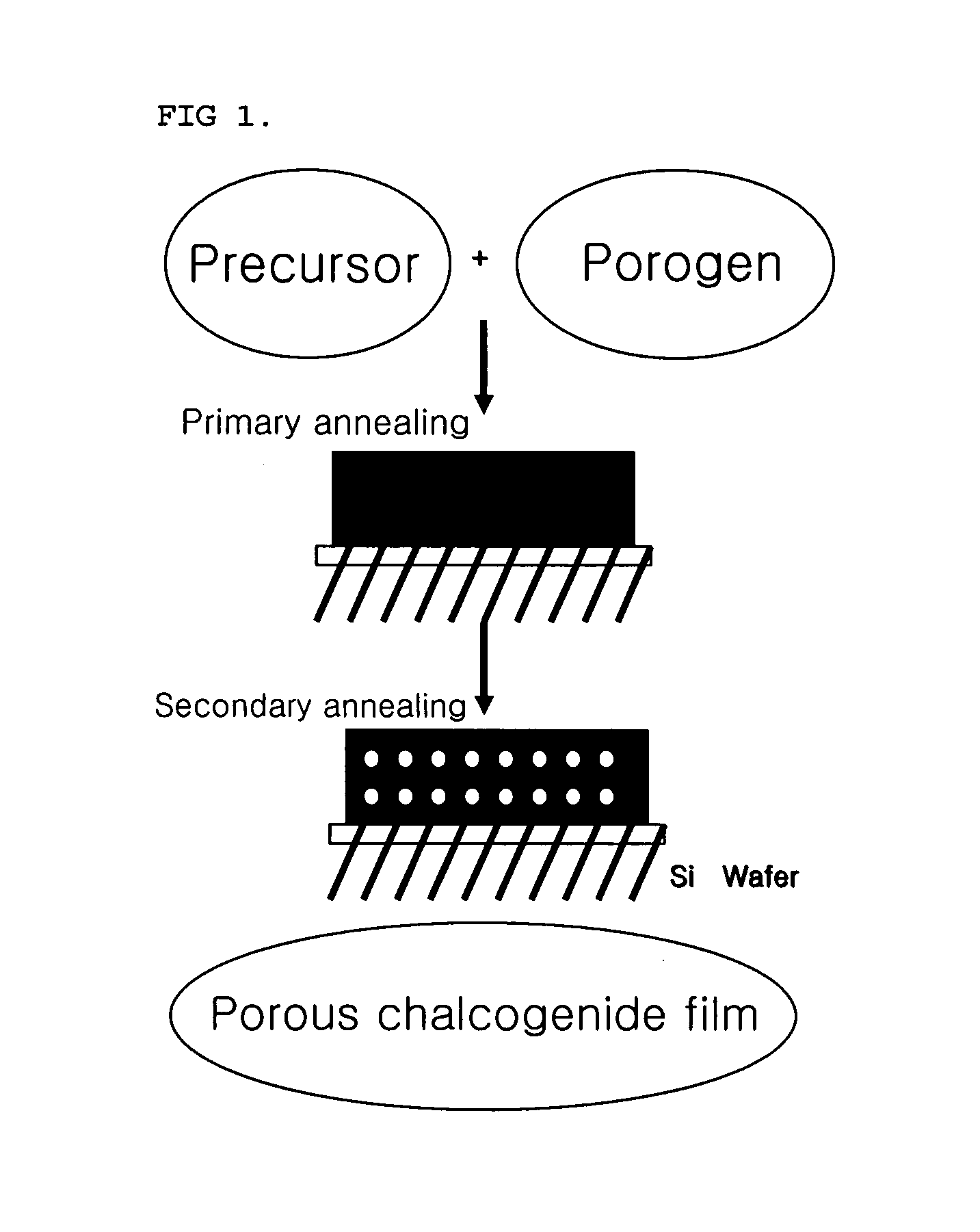
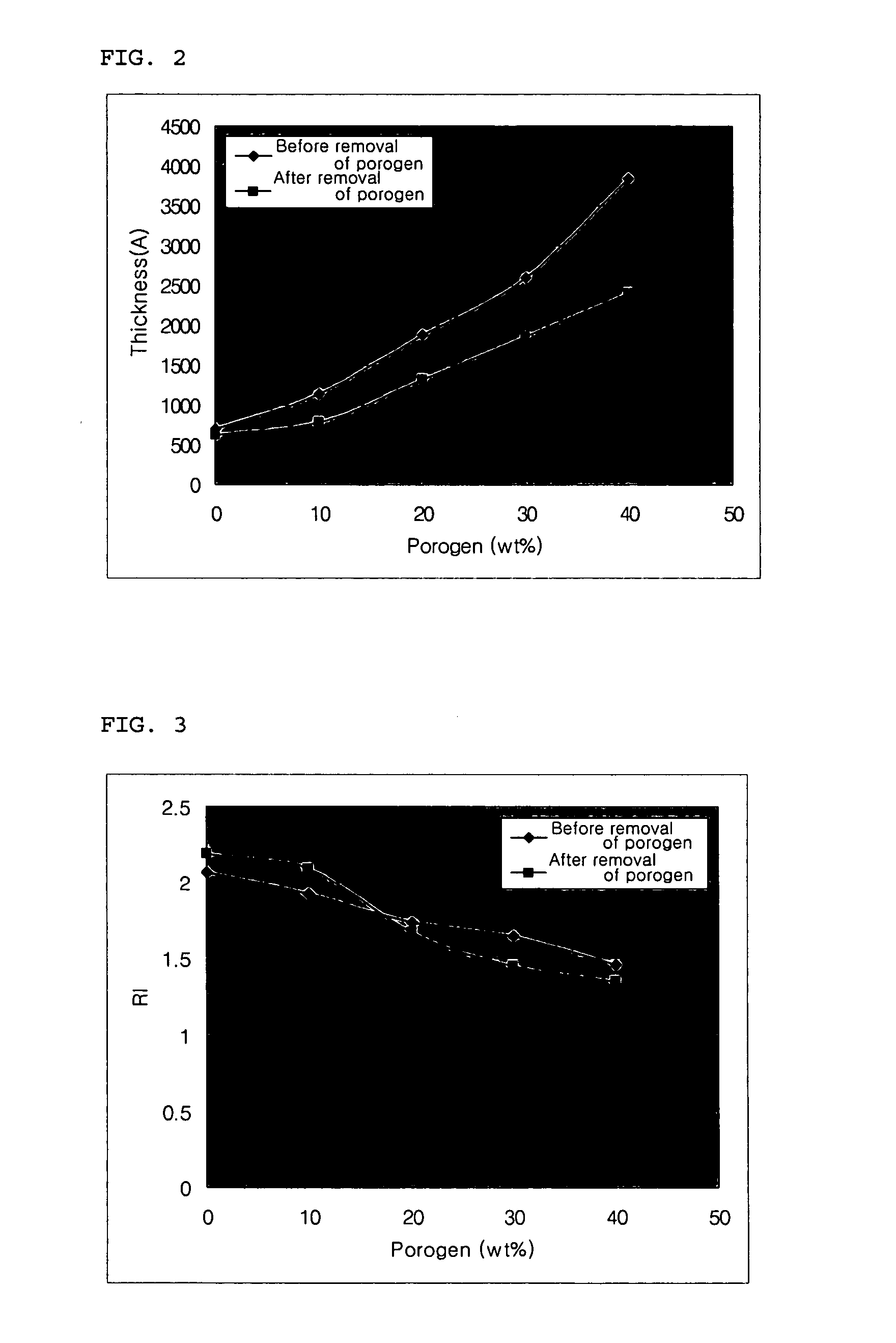
Porous chalcogenide thin film, method for preparing the same and electronic device using the same
InactiveUS20070090346A1High crystallinityImprove electrical performanceGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCadmium sulfidesSulfurCrystallinity
A porous chalcogenide thin film having a microporous structure, a method for preparing the chalcogenide thin film and an electronic device employing the chalcogenide thin film, are provided. The porous chalcogenide thin film has superior crystallinity and can be applied as a semiconductor layer having superior electrical properties to the fabrication of devices by inserting functional metal or semiconductor nanoparticles into nanopores of the thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING CO LTD
Ex-situ doped semiconductor transport layer
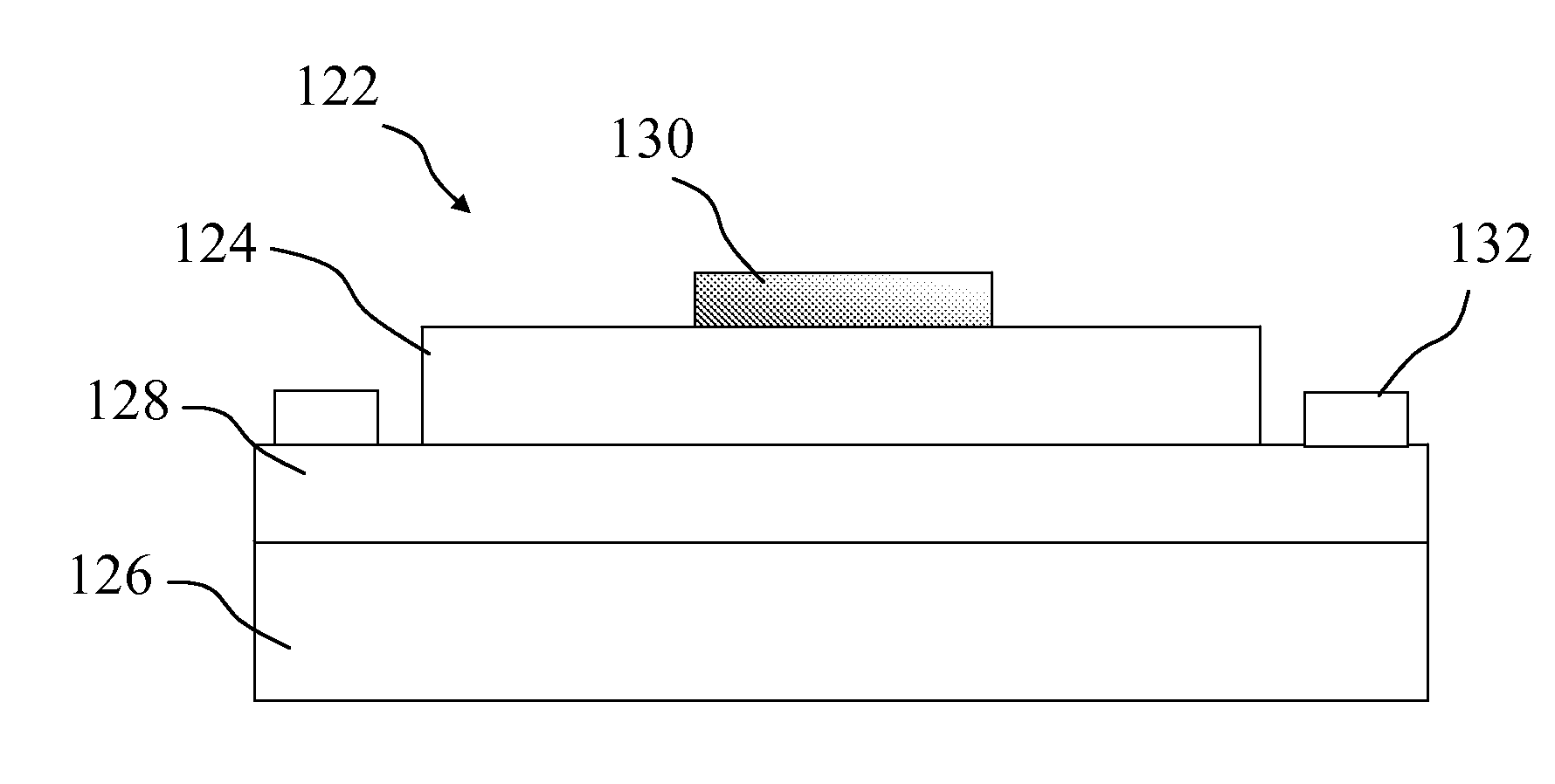
InactiveUS7375011B1Simple methodLimit their usefulnessNanotechLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthDopantTransport layer
A method of making an ex-situ doped semiconductor transport layer for use in an electronic device includes: growing a first set of semiconductor nanoparticles having surface organic ligands in a colloidal solution; growing a second set of dopant material nanoparticles having surface organic ligands in a colloidal solution; depositing a mixture of the first set of semiconductor nanoparticles and the second set of dopant material nanoparticles on a surface, wherein there are more semiconductor nanoparticles than dopant material nanoparticles; performing a first anneal of the deposited mixture of nanoparticles so that the organic ligands boil off the surfaces of the first and second set of nanoparticles; performing a second anneal of the deposited mixture so that the semiconductor nanoparticles fuse to form a continuous semiconductor layer and the dopant material atoms diffuse out from the dopant material nanoparticles and into the continuous semiconductor layer.
Owner:NANOCO TECH LTD
Pixel Structure For A Solid State Light Emitting Device
InactiveUS20080246046A1Minimise currentMaximize flowElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLight emitting deviceHigh field
A light emitting device includes an active layer structure, which has one or more active layers with luminescent centers, e.g. a wide bandgap material with semiconductor nano-particles, deposited on a substrate. For the practical extraction of light from the active layer structure, a transparent electrode is disposed over the active layer structure and a base electrode is placed under the substrate. Transition layers, having a higher conductivity than a top layer of the active layer structure, are formed at contact regions between the upper transparent electrode and the active layer structure, and between the active layer structure and the substrate. Accordingly the high field regions associated with the active layer structure are moved back and away from contact regions, thereby reducing the electric field necessary to generate a desired current to flow between the transparent electrode, the active layer structure and the substrate, and reducing associated deleterious effects of larger electric fields.
Owner:KIRSTEEN MGMT GRP
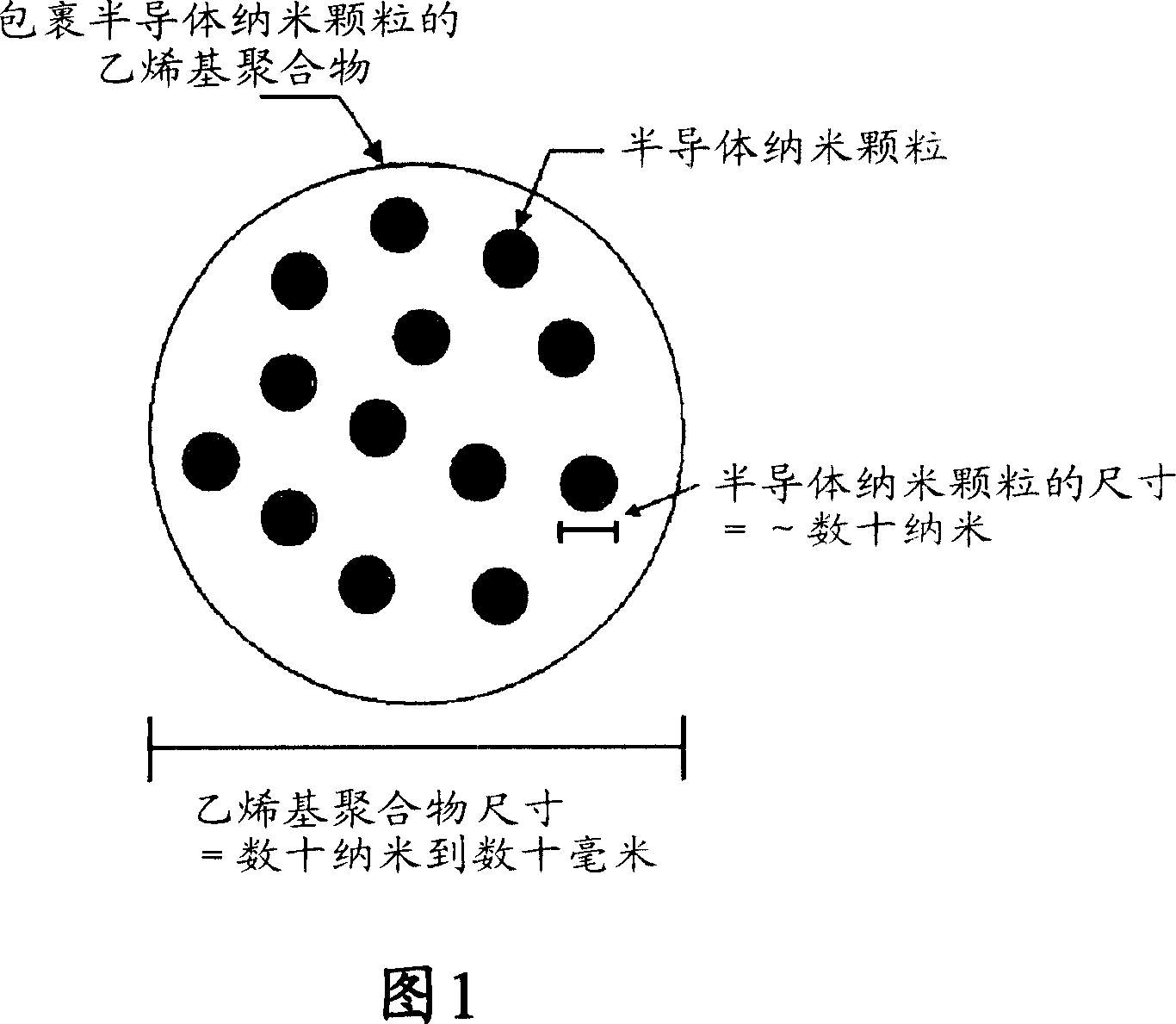
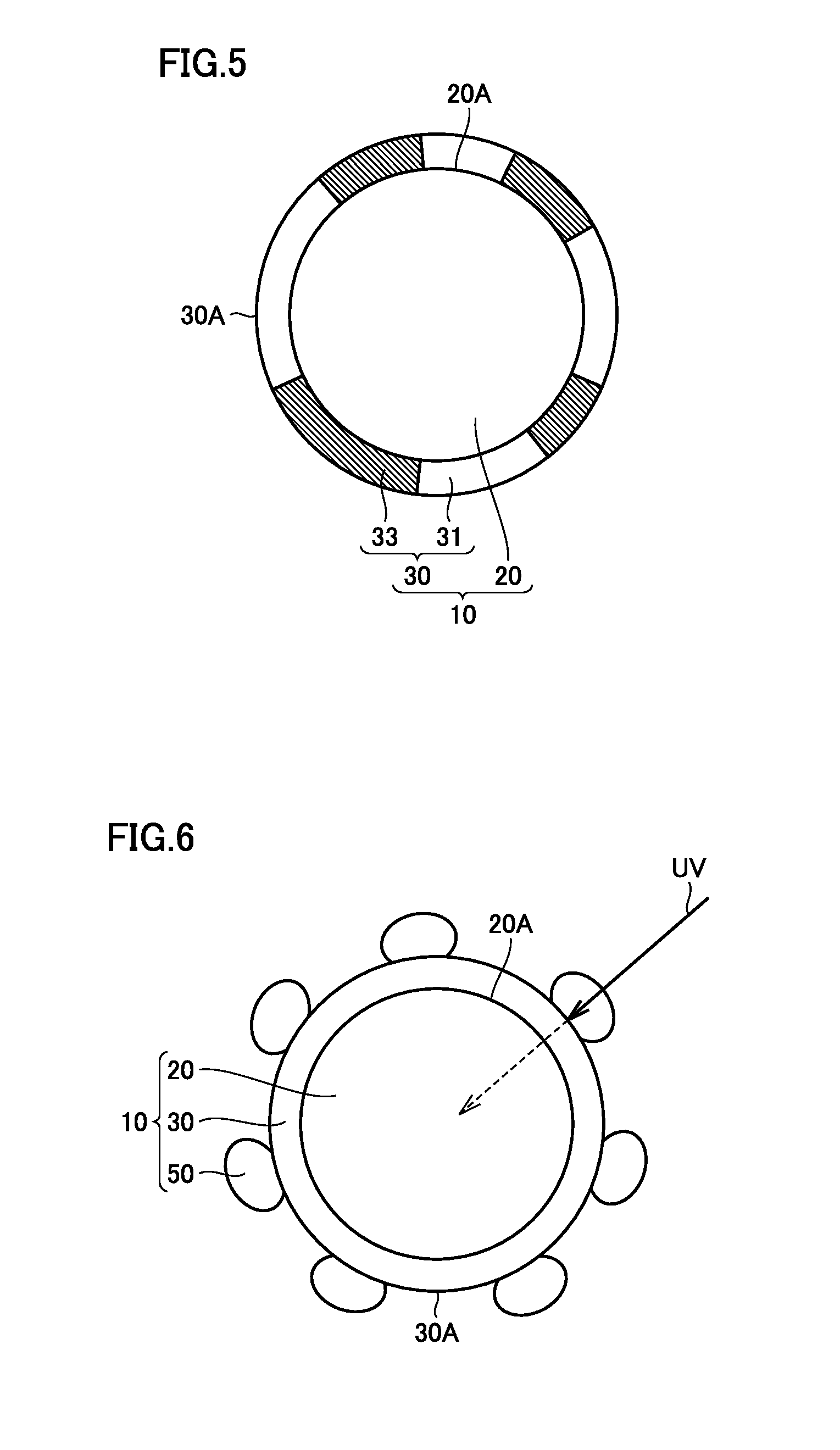
Semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer, vinyl polymer mixture includingthe same, and process of preparing the same
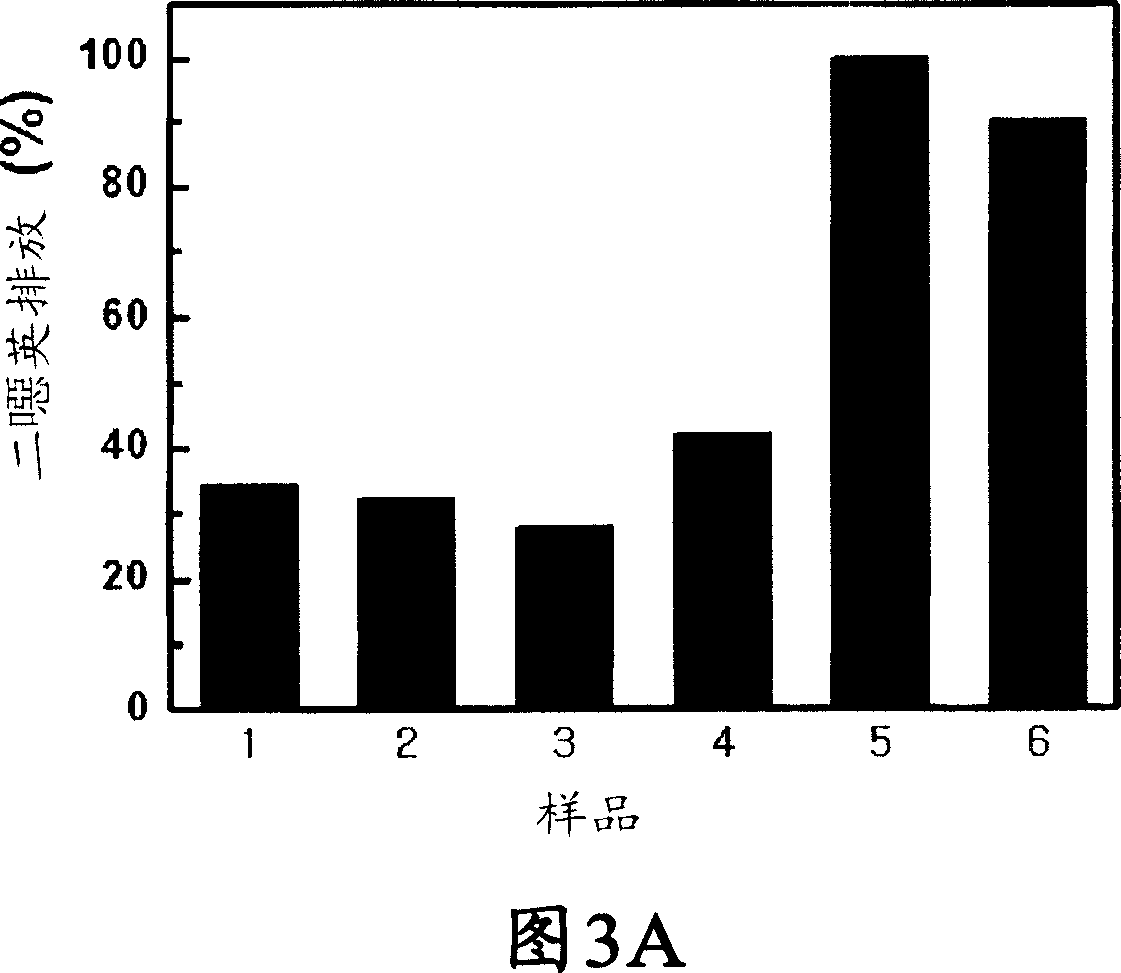
InactiveCN1950430AImprove mechanical propertiesInhibit migrationMaterial nanotechnologyPlasticizerPolyvinyl chloride
Provided is a semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer including vinyl polymer particles; and semi-conductor nanoparticles, uniformly dispersed in the vinyl polymer particles, having an average particle size of 1 to 150 nm, wherein the semiconductor nanoparticles are encapsulated by the vinyl polymer particles. Provided is also a mixture of the semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer with a commercially available vinyl polymer. In the nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer and the mixture, since the semiconductor nanoparticles are encapsulated by the vinyl polymer particles, they are highly dispersed even in vinyl polymer products. Therefore; an aggregation phenomenon of semi-conductor nanoparticles that may be caused by physical mixing of semiconductor nanoparticles and a commercially available vinyl polymer can be prevented, thereby remarkably increasing a reduction in dioxin emission during incineration of the wastes of vinyl polymer products. Furthermore, the semiconductor nanoparticles of the semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer can remarkably increase photodegradation efficiency due to the photocatalytic activity of the nanoparticles. In addition, the semiconductor nanoparticles of the semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer can serve as fillers, thereby enhancing mechanical properties such as tensile strength and modulus of elasticity without lowering impact strength. In particular, in a flexible poly vinylchloride compound manufactured using semiconductor nanoparticles-encapsulating polyvinylchloride and a commercially available phthalate-based low-molecular weight liquid phase plasticizer, a plasticizer migration phenomenon can be prevented by adsorptivity of highly dispersed semiconductor nanoparticles.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
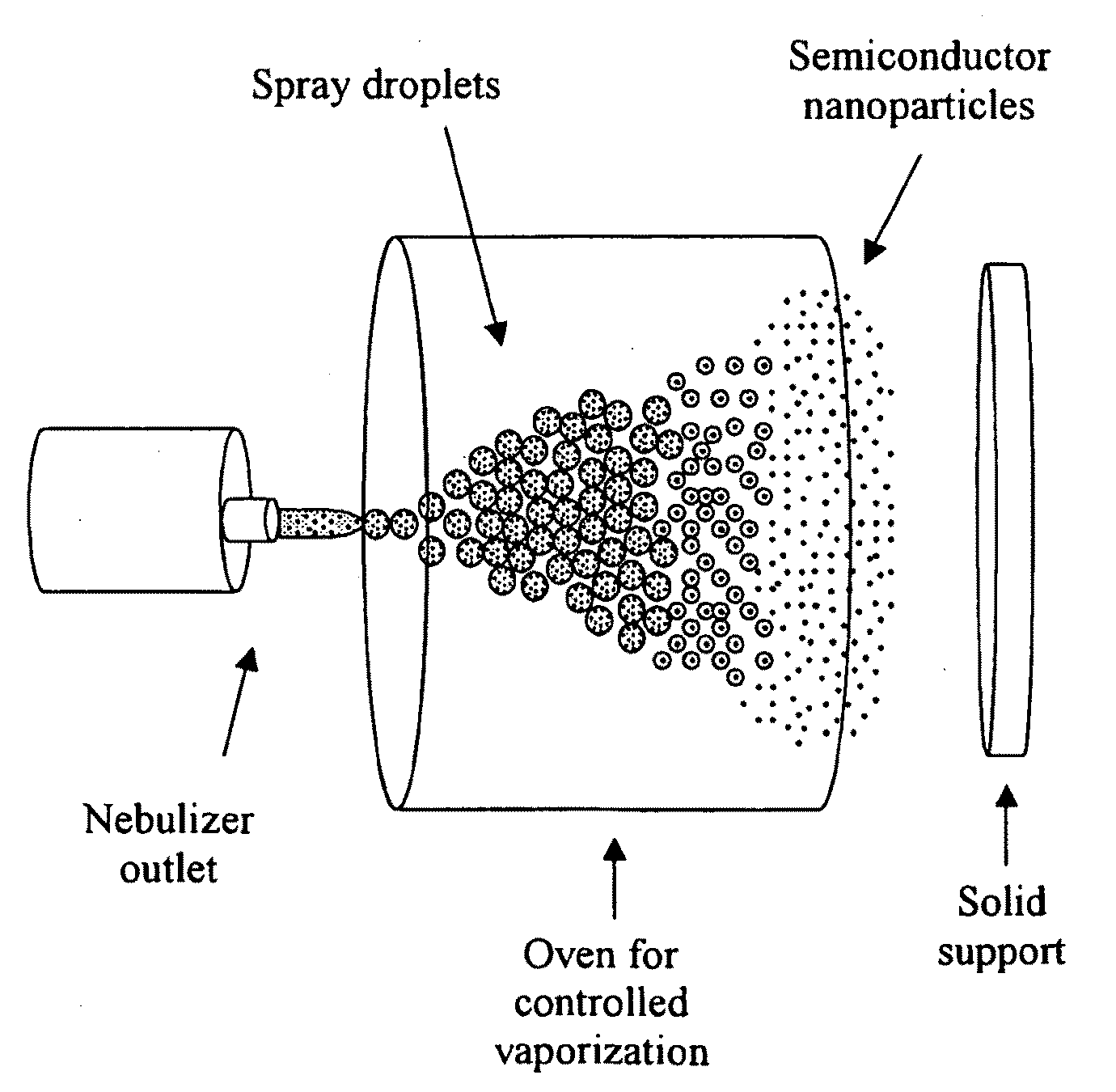
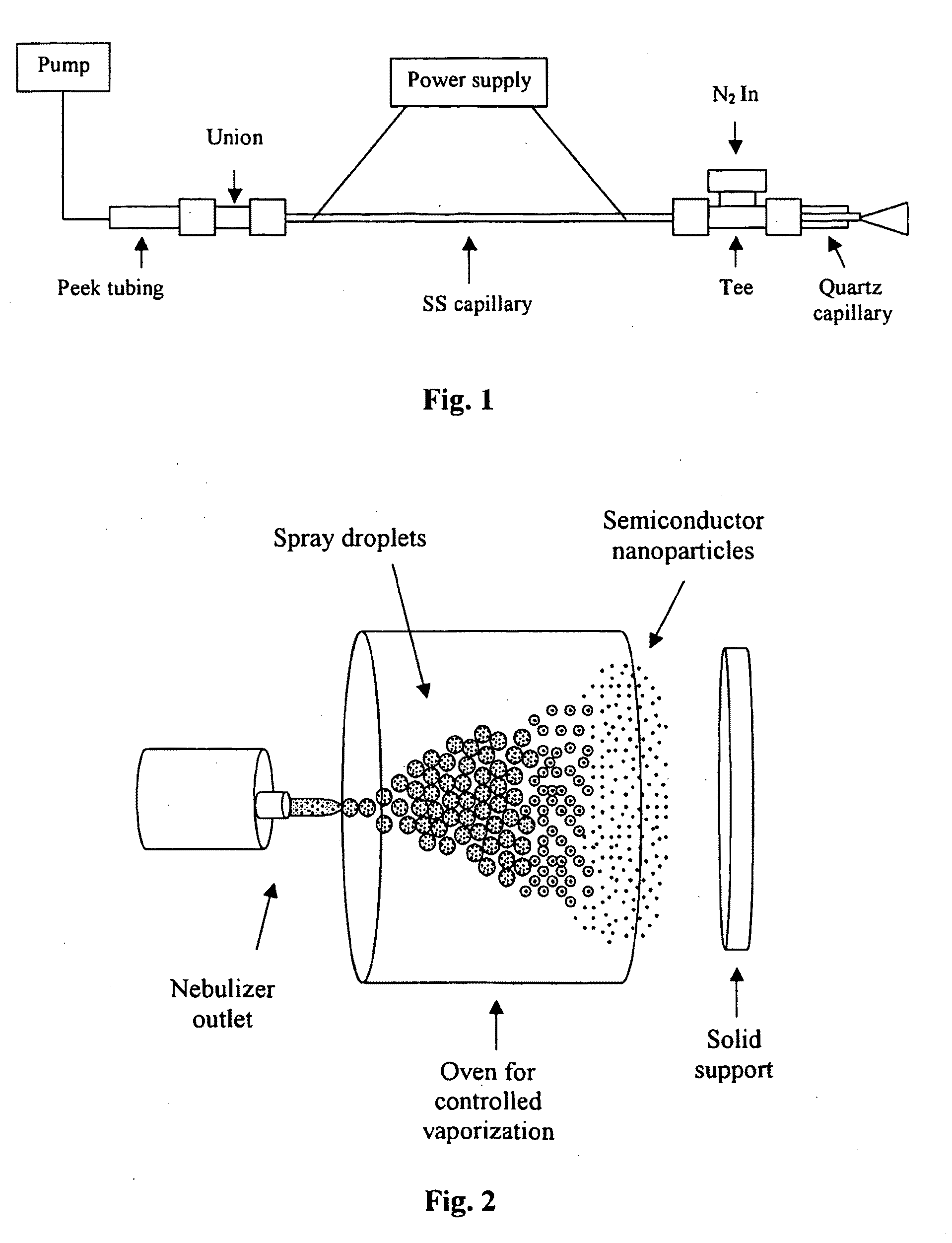
Spray method for producing semiconductor nano-particles
InactiveUS20090263956A1Prevent adverse liquid solvent effectQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyMolten spray coatingSolventChemistry
A method is provided for producing semiconductor nanoparticles comprising: (i) dissolving a semiconductor compound or mixture of semiconductor compounds in a solution; (ii) generating spray droplets of the resulting solution of semiconductor compound(s); (iii) vaporizing the solvent of said spray droplets, consequently producing a stream of unsupported semiconductor nanoparticles; and (iv) collecting said unsupported semiconductor nanoparticles on a support.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Optical catalyst capable of magnetic separated and its preparation method
InactiveCN1954908ASolve the separation problemEfficient separationCatalyst carriersCatalyst activation/preparationPhotocatalytic reactionMicrosphere
A photocatalyst able to be magnetically separated is prepared from ferromagnetic high-molecular microballs as magnetic carrier and the semiconductor nanoparticles with high photocatalytic activity through sol-gel method for carrying said nanoparticles by said microballs.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
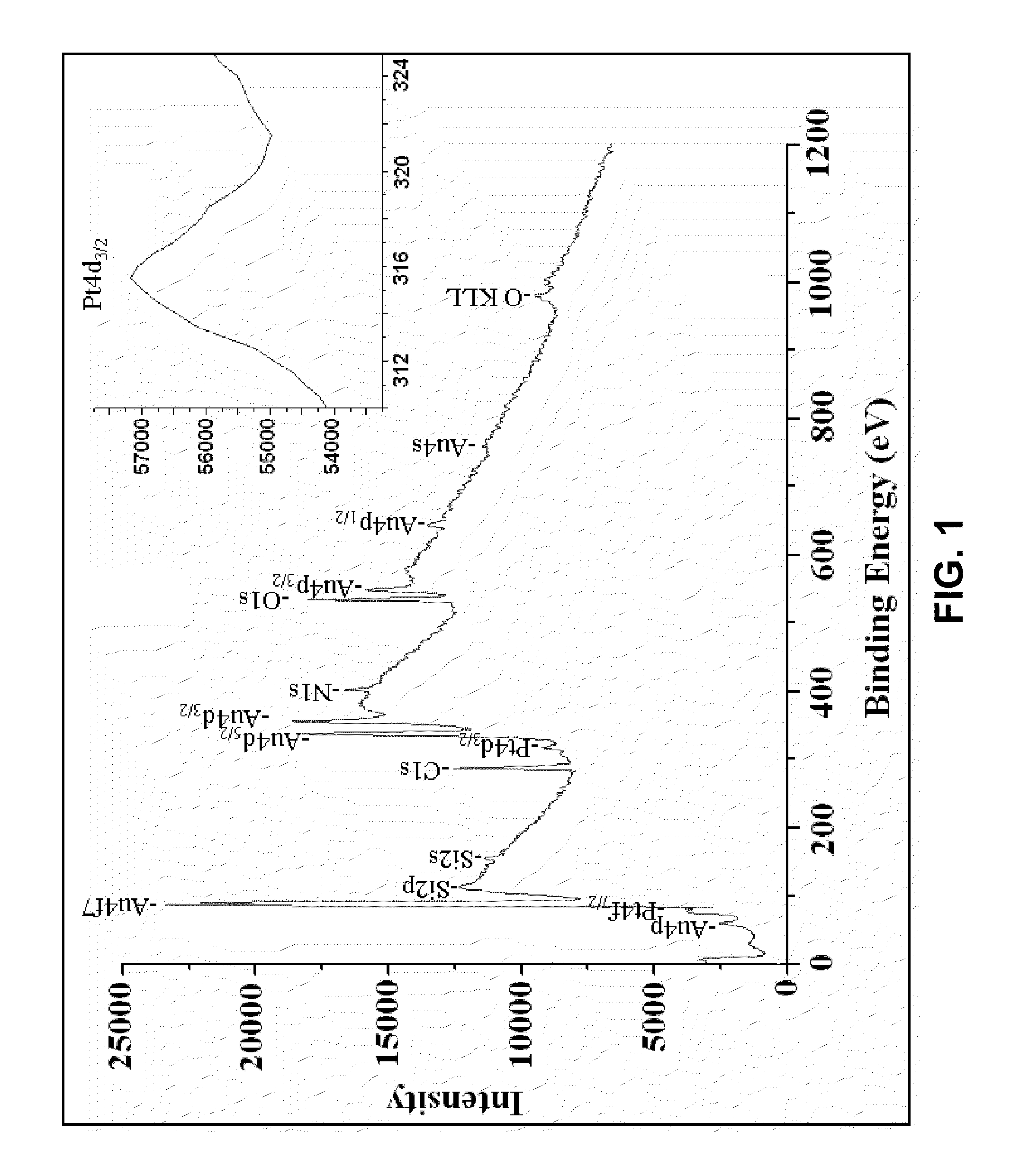
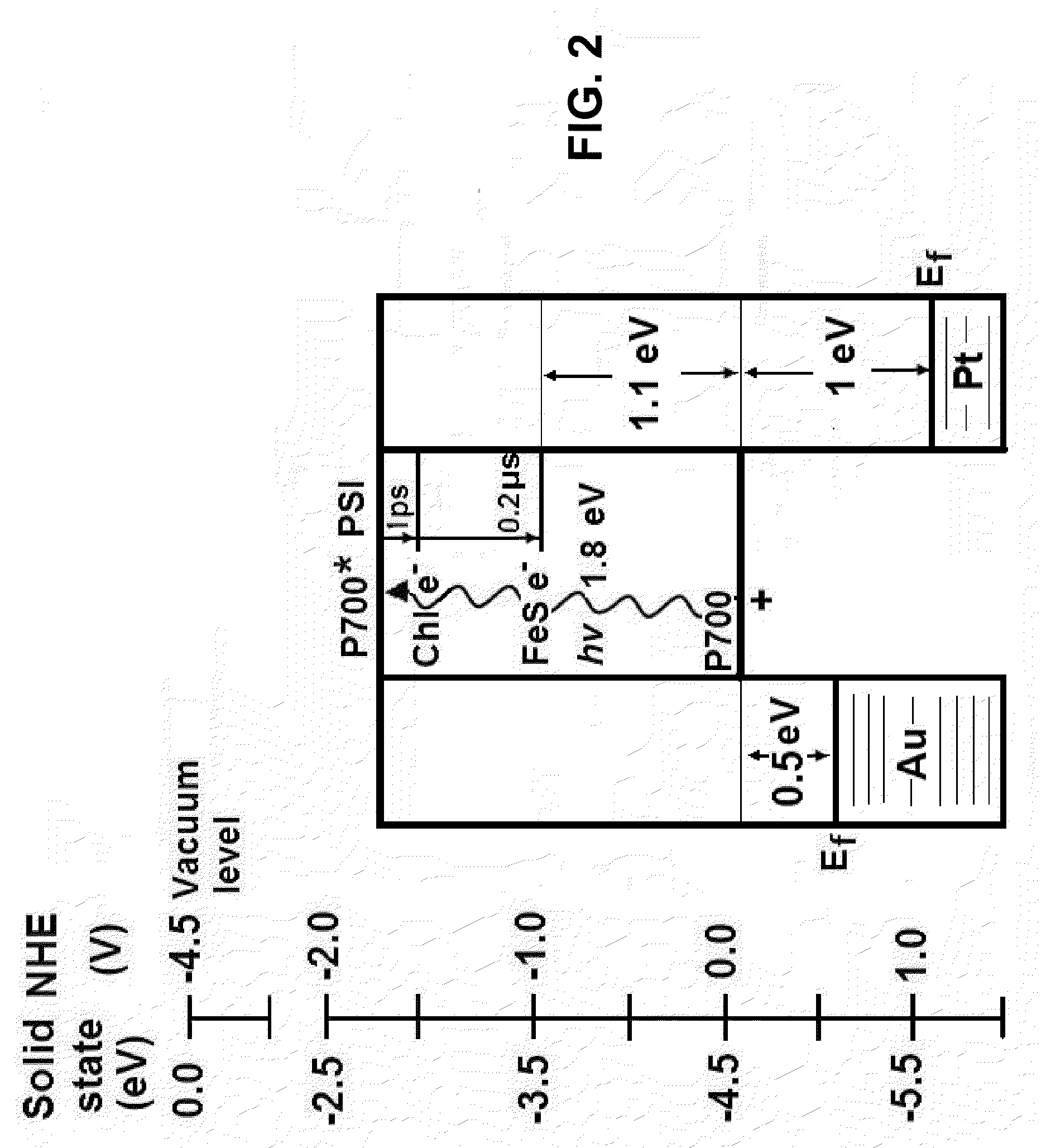
Photoactive nanostructure and method of manufacturing same
A nanostructure comprising at least one semiconductor nanoparticle bound to a photocatalytic unit of a photosynthetic organism is disclosed. The nanoparticle and a binding between the nanoparticle and the photocatalytic unit are selected such that transfer of electrons from the photocatalytic unit to the nanoparticle is prevented or suppressed relative to transfer of excitons from the nanoparticle to the photocatalytic unit. Uses of same and methods of fabricating devices with same are also disclosed. Nanostructures comprising electrically conductive nanoparticles are also disclosed.
Owner:OHIO UNIV +1
Light emitting diode and light emitting display device including the same
ActiveUS20190115556A1Eliminate the problemStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceInorganic compound
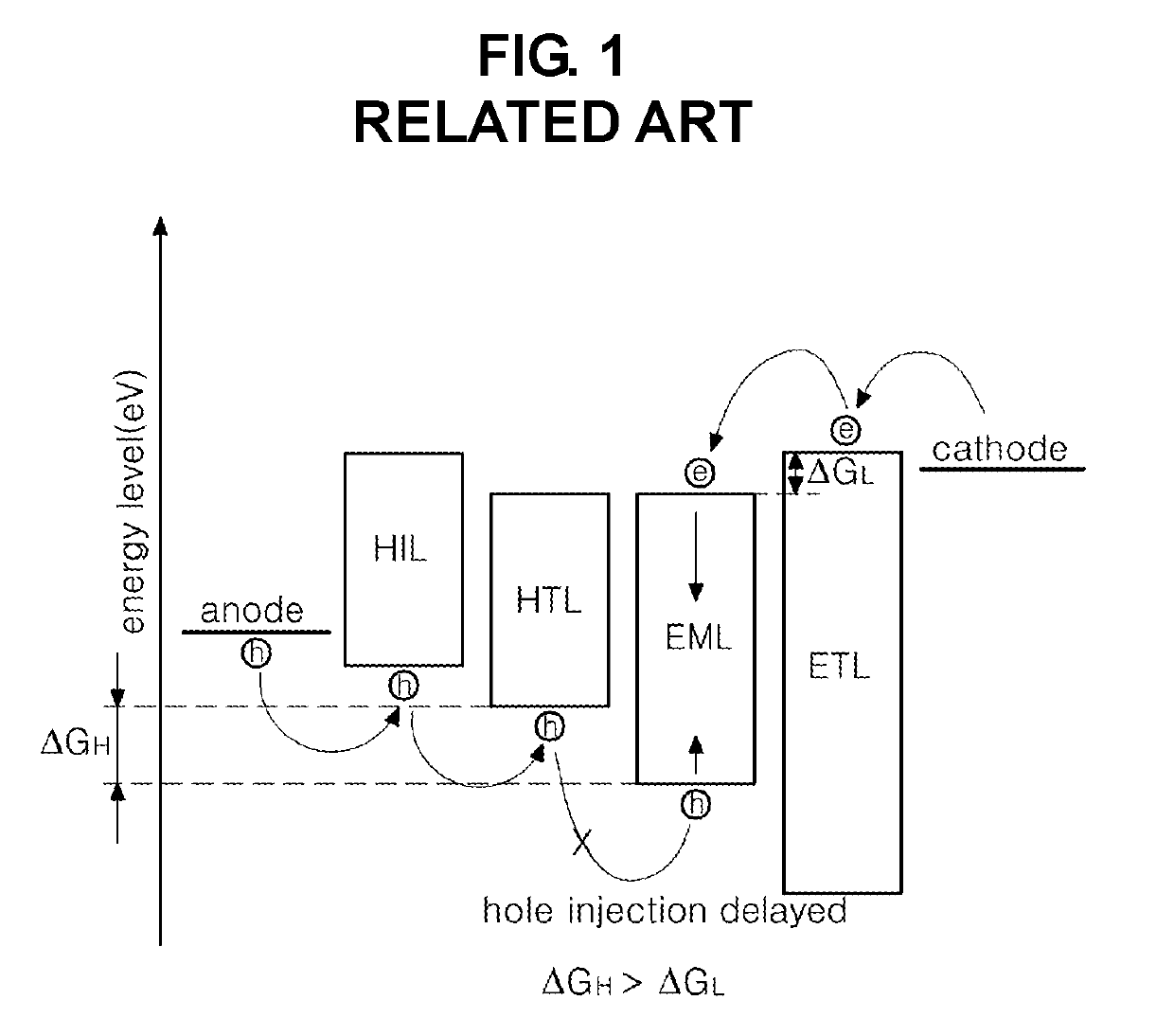
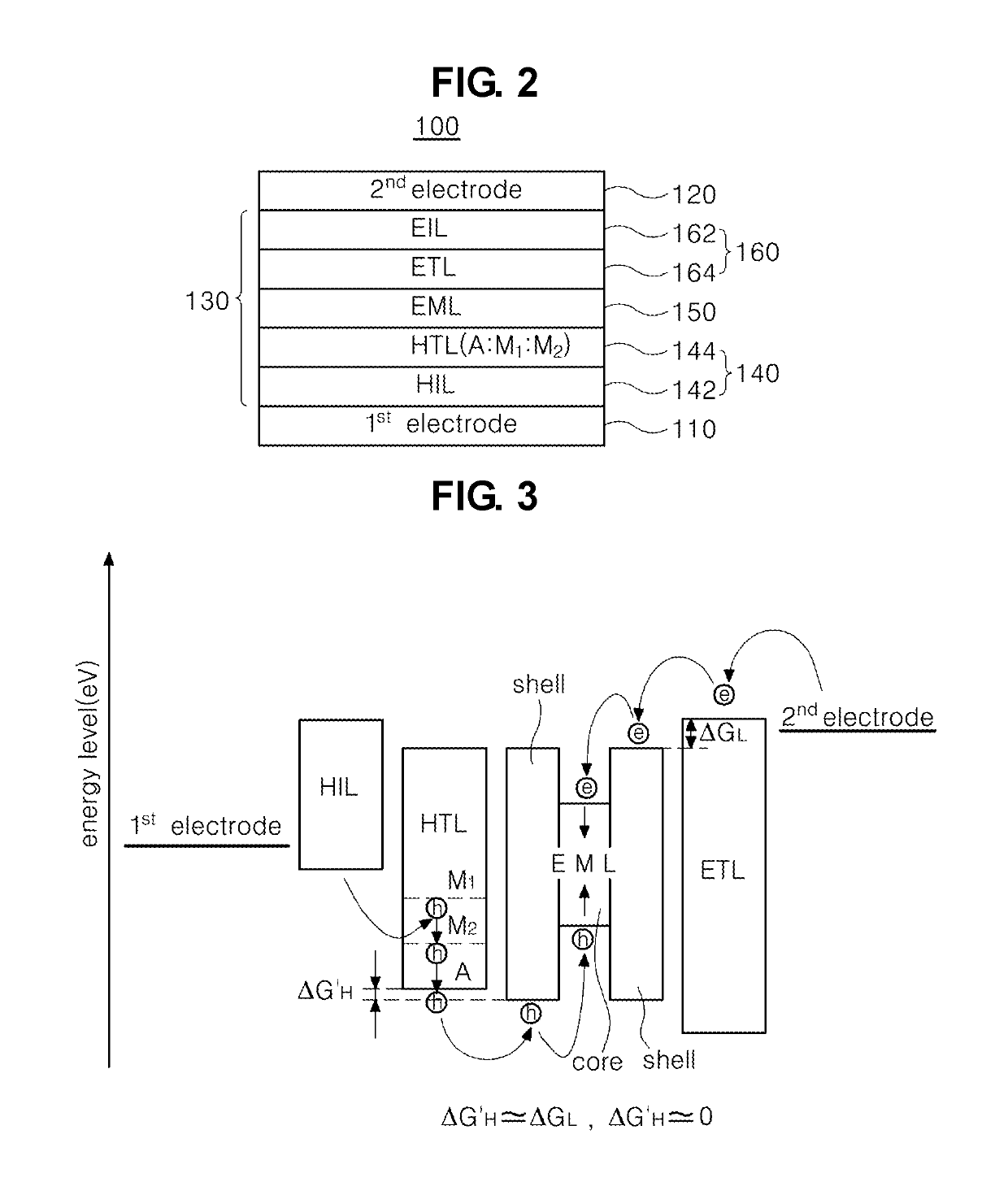
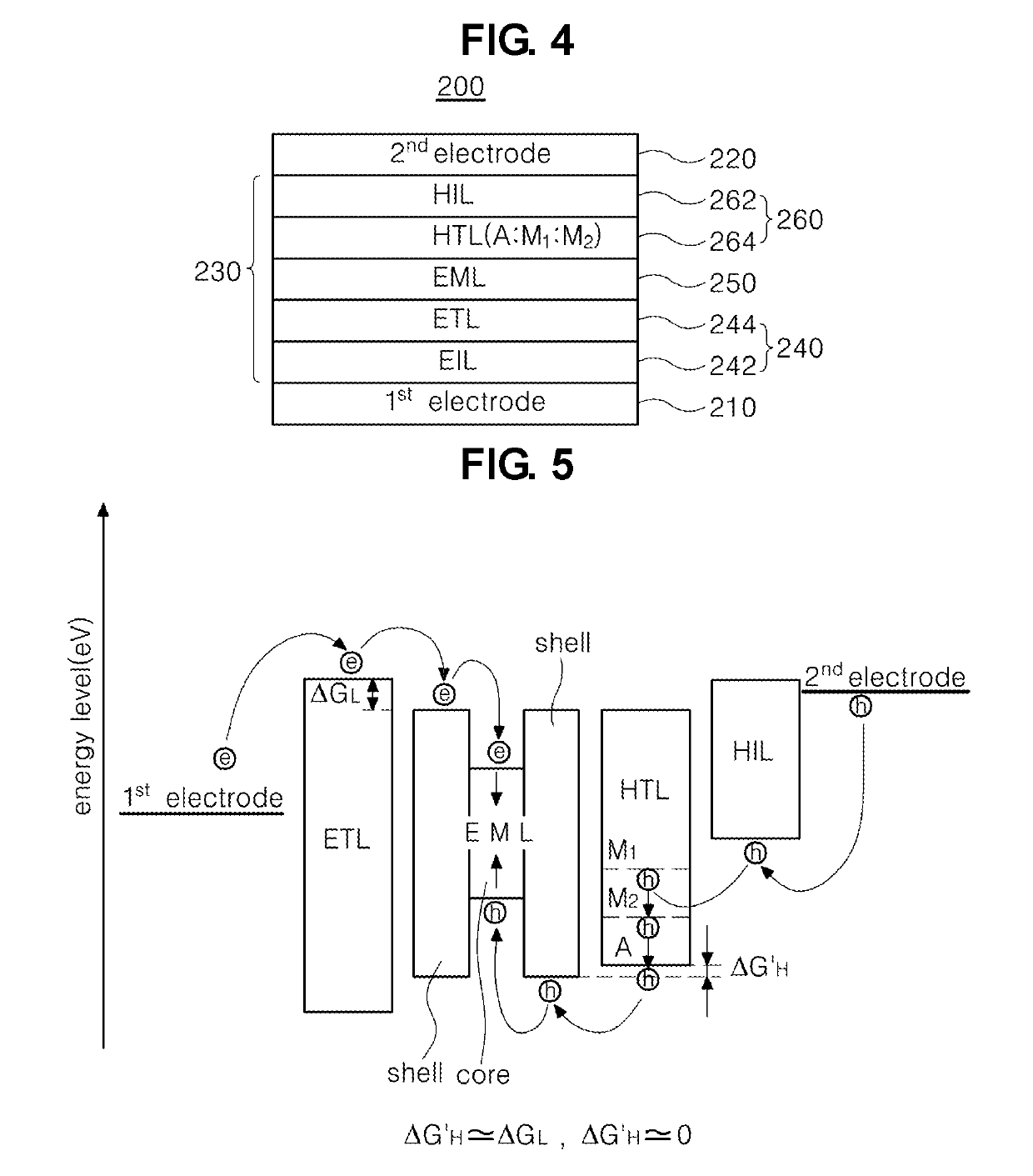
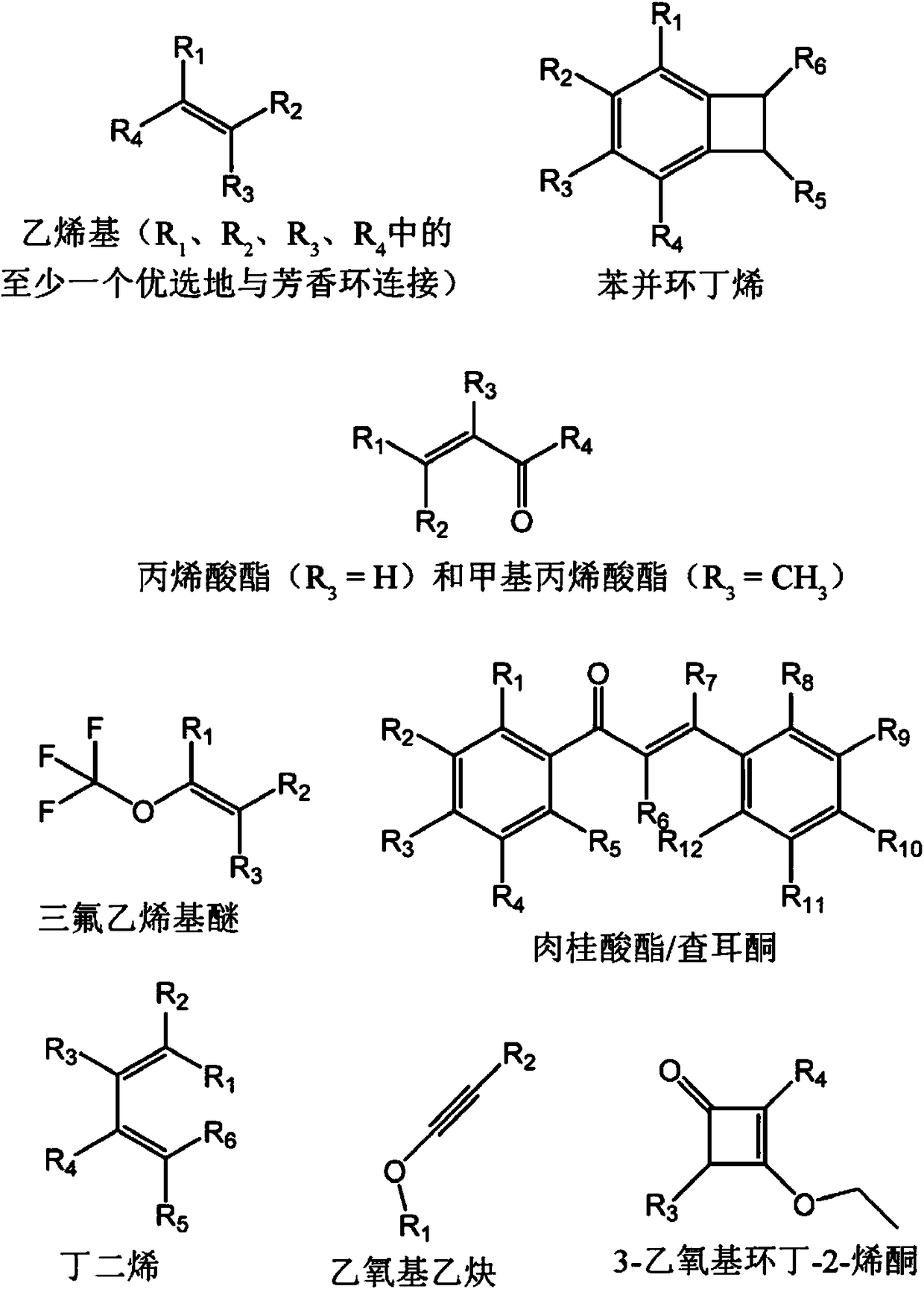
A light emitting diode and a light emitting display device are disclosed. The light emitting diode includes a first electrode and a second electrode facing each other; and a hole transporting layer between the first electrode and the second electrode, wherein the hole transporting layer includes an inorganic compound of a chemical formula 1, A:M1:M2, where the A is a semiconductor nano particle or a nano inorganic particle selected from a metal oxide group, and the M1 and M2 are different from each other and represent metal positive ions which the A is doped with.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Quantum dot light emitting devices
ActiveCN109328402ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsQuantum dot
The present invention provides a quantum dot light emitting diode comprising i) an emitting layer of at least one semiconductor nanoparticle made from semiconductor materials selected from the group consisting of Group II- VI compounds, Group II-V compounds, Group III- VI compounds, Group III-V compounds, Group IV- VI compounds, Group I-III- VI compounds, Group II-IV-VI compounds, Group II-IV-V compounds, or any combination thereof; and ii) a polymer for hole injection or hole transport layer; and the polymer comprises, as polymerized units, at least one or more monomers having a first monomerstructure comprising a) a polymerizable group, b) an electroactive group with formula NAr1Ar2Ar3 wherein Ar1, Ar2 and Ar3 independently are C6-C50 aromatic substituents, and (c) a linker group connecting the polymerizable group and the electroactive group.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
CIGS in-situ doping method
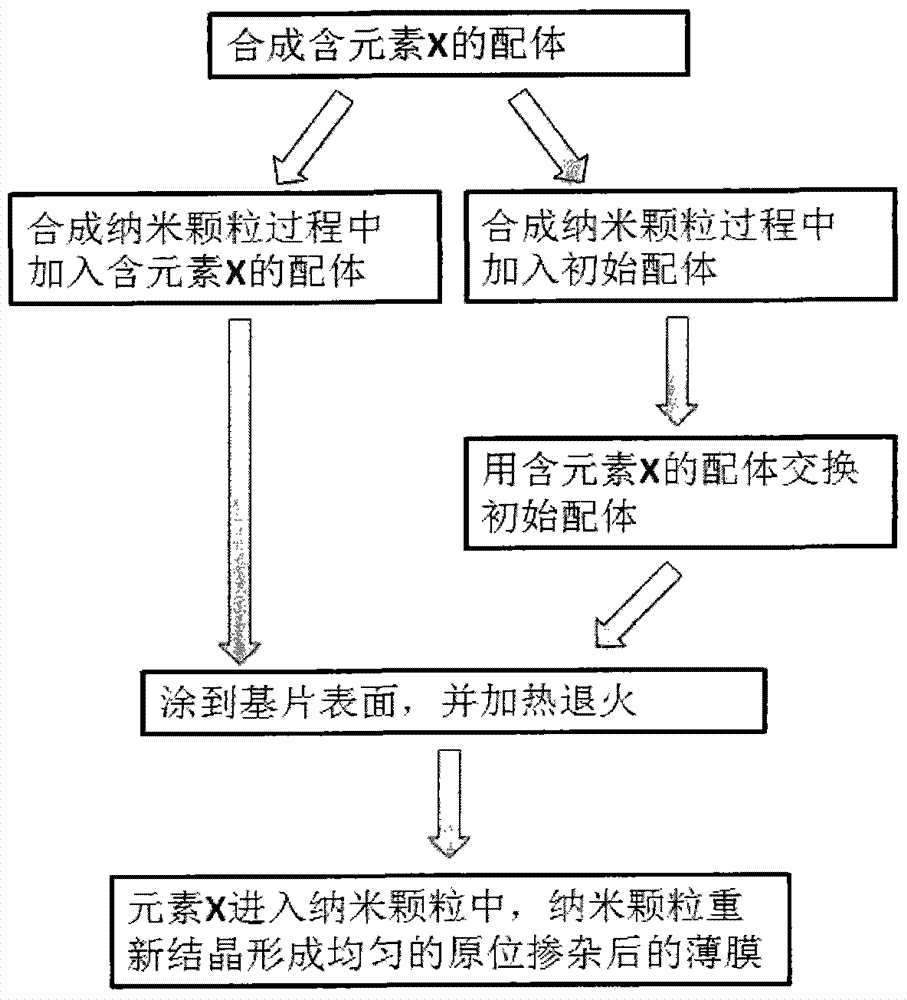
InactiveCN103715281AFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumIn situ doping
The invention discloses a method for in-situ doping of thin film materials. Elements which can be doped comprise selenium (Se), sodium (Na), sulfur (S), tin (Sn), indium (In), antimony (Sb), gallium (Ga), tellurium (Te), molybdenum (Mo), and arsenic (As). According to the invention, ligands containing the elements are connected onto the surfaces of semiconductor nanoparticles and applied onto the surface of a substrate, and then the nanoparticles are recrystallized by annealing to form a thin film. Thus, the in-situ doping of the elements is realized. For CIGS nanoparticles, concrete in-situ doping working procedures are invented, comprising ligand synthesis and exchange; and direct doping and indirect doping are selected on account of different materials. In this way, the in-situ doping of the CIGS nanoparticles in a controllable doping ratio is realized (in the figure, the element X stands for one or more selected from the group consisting of selenium (Se), sodium (Na), sulfur (S), tin (Sn), indium (In), antimony (Sb), gallium (Ga), tellurium (Te), molybdenum (Mo), and arsenic (As)).
Owner:李远 +2
Nanoparticle phosphor and method for manufacturing the same, semiconductor nanoparticle phosphor and light emitting element containing semiconductor nanoparticle phosphor, wavelength converter and light emitting device
A nanoparticle phosphor includes a nanoparticle composed of a compound semiconductor containing a first metal atom, and an inorganic substance layer provided on at least a part of the surface of the nanoparticle and containing the first metal atom and one or more kinds of hetero atoms. In the inorganic substance layer, the first metal atom is bound to the hetero atom.
Owner:SHARP KK
Semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer, vinyl polymer mixture including same, and process of preparing the same
InactiveUS20090115095A1Improve mechanical propertiesPlasticizer migration is preventedMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialPolyvinyl chlorideSemiconductor Nanoparticles
Provided is a semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer including vinyl polymer particles; and semi-conductor nanoparticles, uniformly dispersed in the vinyl polymer particles, having an average particle size of 1 to 150 nm, wherein the semiconductor nanoparticles are encapsulated by the vinyl polymer particles. Provided is also a mixture of the semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer with a commercially available vinyl polymer. In the nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer and the mixture, since the semiconductor nanoparticles are encapsulated by the vinyl polymer particles, they are highly dispersed even in vinyl polymer products. Therefore; an aggregation phenomenon of semi-conductor nanoparticles that may be caused by physical mixing of semiconductor nanoparticles and a commercially available vinyl polymer can be prevented, thereby remarkably increasing a reduction in dioxin emission during incineration of the wastes of vinyl polymer products. Furthermore, the semiconductor nanoparticles of the semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer can remarkably increase photodegradation efficiency due to the photocatalytic activity of the nanoparticles. In addition, the semiconductor nanoparticles of the semiconductor nanoparticle-encapsulating vinyl polymer can serve as fillers, thereby enhancing mechanical properties such as tensile strength and modulus of elasticity without lowering impact strength. In particular, in a flexible poly vinylchloride compound manufactured using semiconductor nanoparticles-encapsulating polyvinylchloride and a commercially available phthalate-based low-molecular weight liquid phase plasticizer, a plasticizer migration phenomenon can be prevented by adsorptivity of highly dispersed semiconductor nanoparticles.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Light-converting material
ActiveUS20200335670A1Good miscibilityEfficient productionNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor NanoparticlesLuminescent material
Owner:LITEC VERMOGENSVERWALTUNGS GMBH
Semiconductor nanoparticles coated with electroactive polymers
InactiveUS20040197560A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsChemical speciesSelf-assembled monolayer
A method for coating particles and the coated particles obtained thereby are disclosed. The particles are first placed in a solution of a first monomer that forms a self-assembling monolayer on the particles thereby forming coated particles. The coated particles are then suspended in a second solution that includes a chemical species and an initiator for oxidative polymerization. The chemical species has a higher oxidation potential than the monomers. In addition, the chemical species form a homopolymer in the presence of the initiator that is covalently bound to the first monomers. Particles of semiconductors such as Ti02, Si02, Sn02, Al203 can be coated with polymers that alter the bandgap energy of the semiconducting particles and / or provide other useful surface chemistries.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
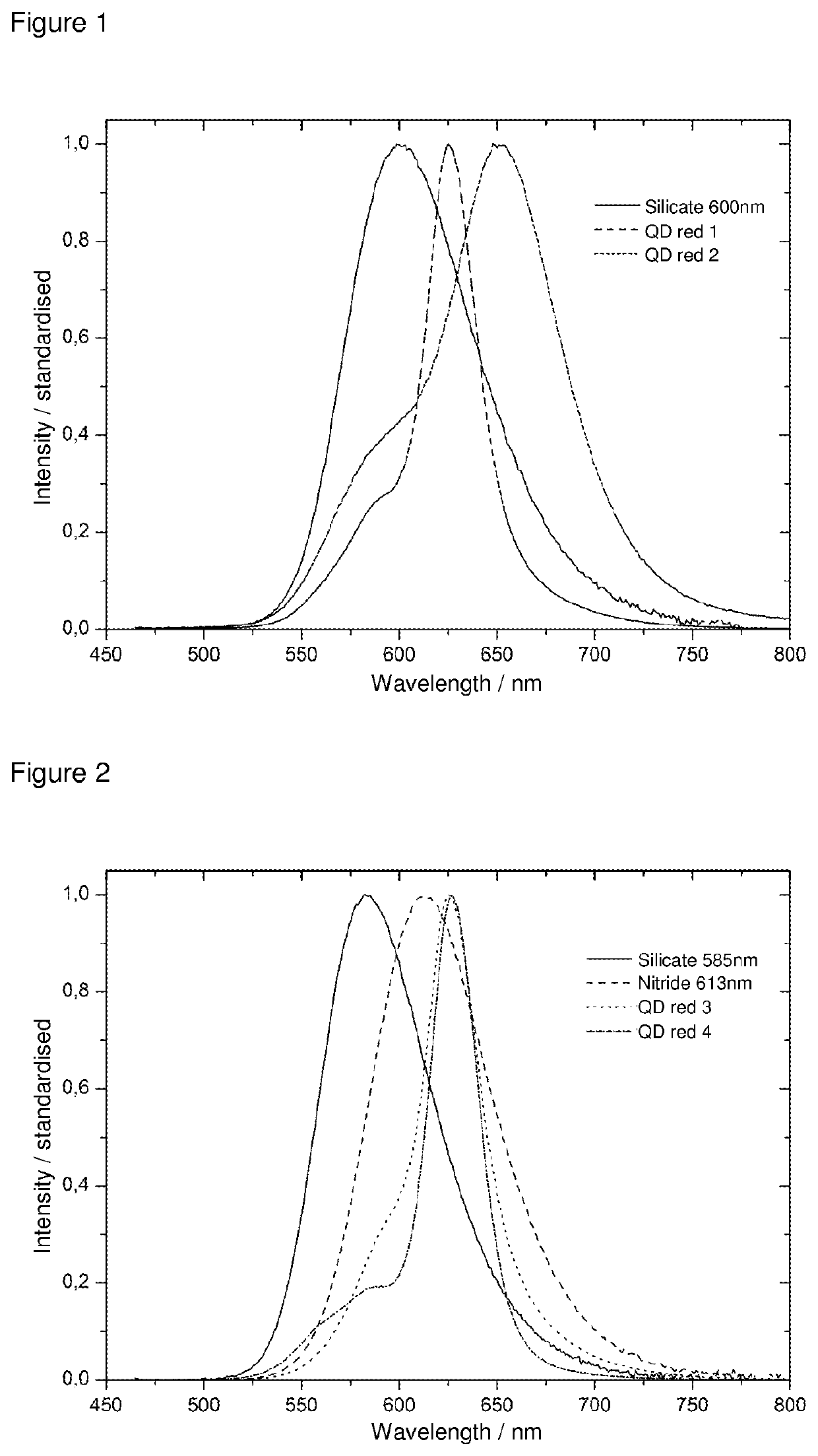
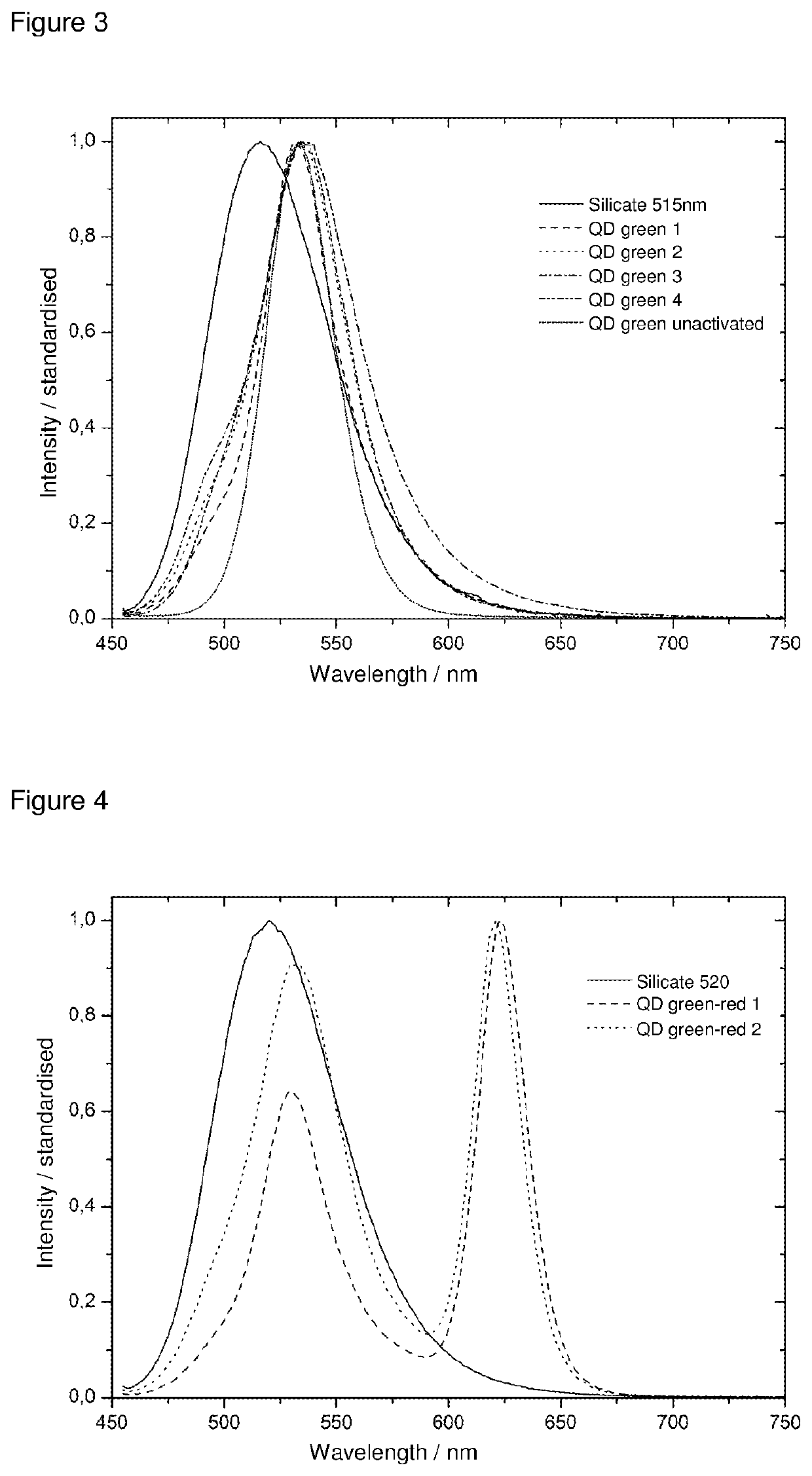
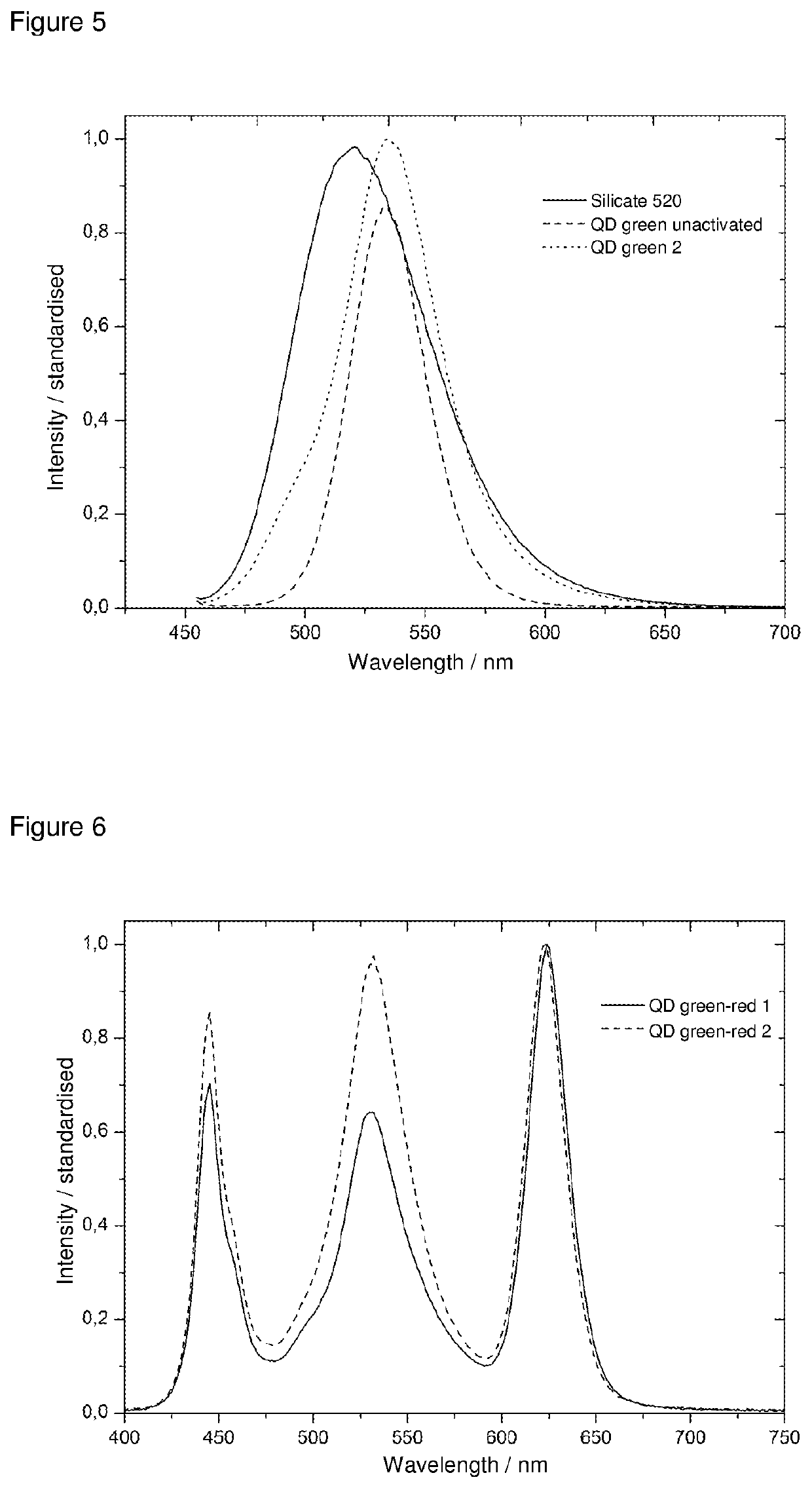
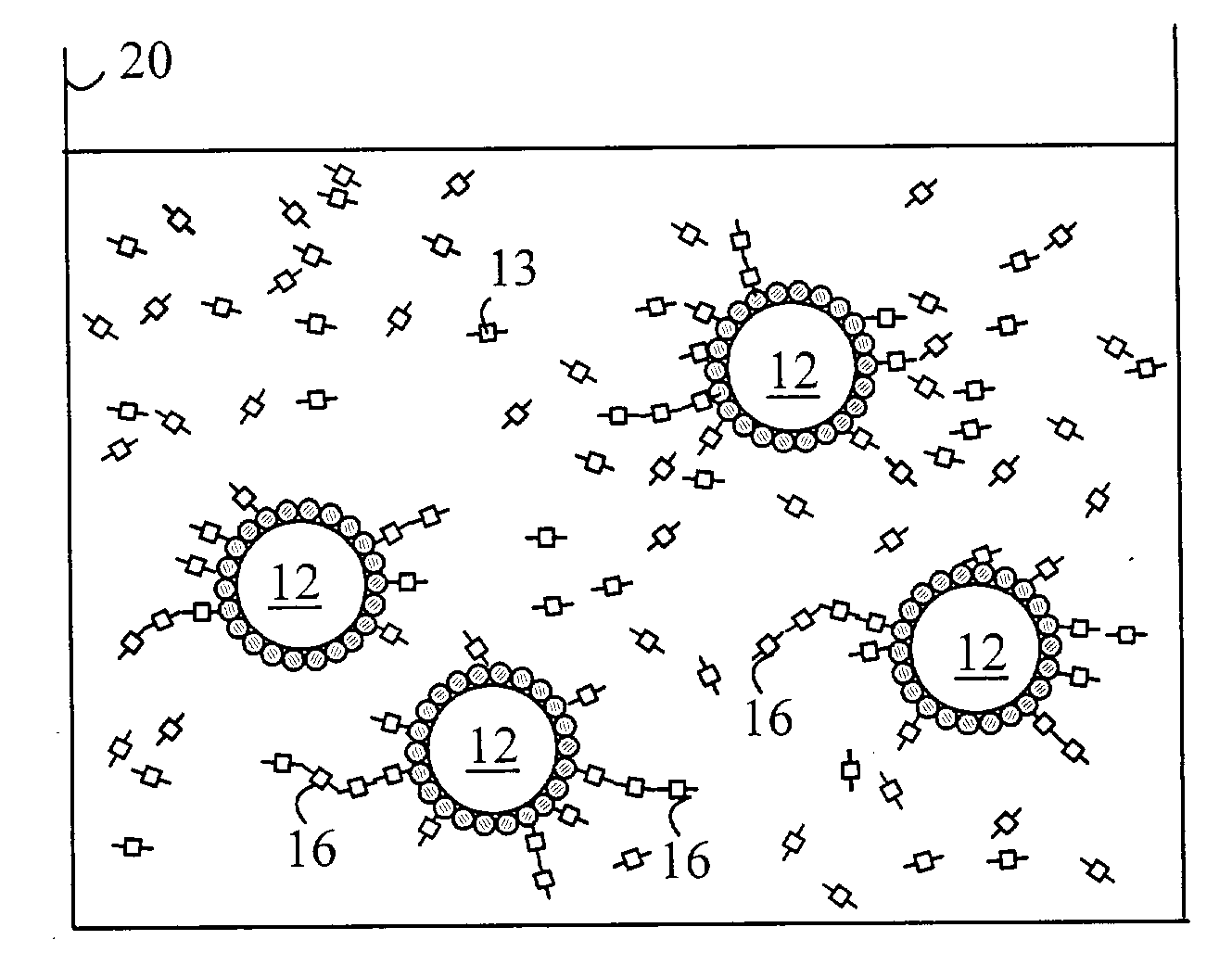
Fluorescent material with semiconductor nanoparticles dispersed in glass matrix at high concentration and method for manufacturing such fluorescent material
InactiveUS7824767B2High fluorescence quantum yieldIncrease concentrationNanotechLiquid surface applicatorsHigh concentrationQuantum yield
The present invention provides a thin-film fluorescent material in which semiconductor nanoparticles in a stable condition maintain a high fluorescence quantum yield and can be held at a high concentration in a glass matrix. The present invention also provides optical devices using the thin-film fluorescent material, such as high-brightness displays and lighting systems. The present invention relates to a fluorescent material, in which semiconductor nanoparticles with a fluorescence quantum yield of 15% or more and a diameter of 2 to 5 nanometers are dispersed in a glass matrix at a concentration of 5×10−4 mol / l or more and a method for manufacturing the same.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Graphene-encapsulated nanoparticle-based biosensor for the selective detection of biomarkers
A field effect transistor (FET) with a source electrode and a drain electrode distanced apart from each other on a semi-conductor substrate, and a gate electrode consisting of a uniform layer of reduced graphene oxide encapsulated semiconductor nanoparticles (rGO-NPs), wherein the gate electrode is disposed between and contacts both the source and drain electrodes. Methods of making and assay methods using the FETs are also disclosed, including methods in which the rGO-NPs are functionalized with binding partners for biomarkers.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Preparation method and application of Co3O4 NP/CD/Co-MOF composite material
InactiveCN109759143ASimple preparation processEasy to industrializeOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationElectrochemistryCobalt
The invention discloses a preparation method of aCo3O4NP / CD / Co-MOF composite material and application of electrocatalysis based on the composite material, and belongs to the technical fields of nanocatalysis, nanomaterials and the like. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps: reacting cobalt nitrate, glucose, triethylene diamine and terephthalic acid at room temperature to obtain Co-MOF / glucose flaky microcrystals; performing oxidation and pyrolysis on the microcrystals under microwave irradiation to obtain a Co-MOF composite material with semiconductor Co3O4 nanoparticlesand carbon dot CD which are co-doped, namely, the Co3O4 NP / CD / Co-MOF composite material. The composite material has the advantages of low raw material cost for preparation, simple preparation process, low reaction energy consumption and industrial application prospect. The catalyst has high electrochemical activity for the electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation to form ammonia.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
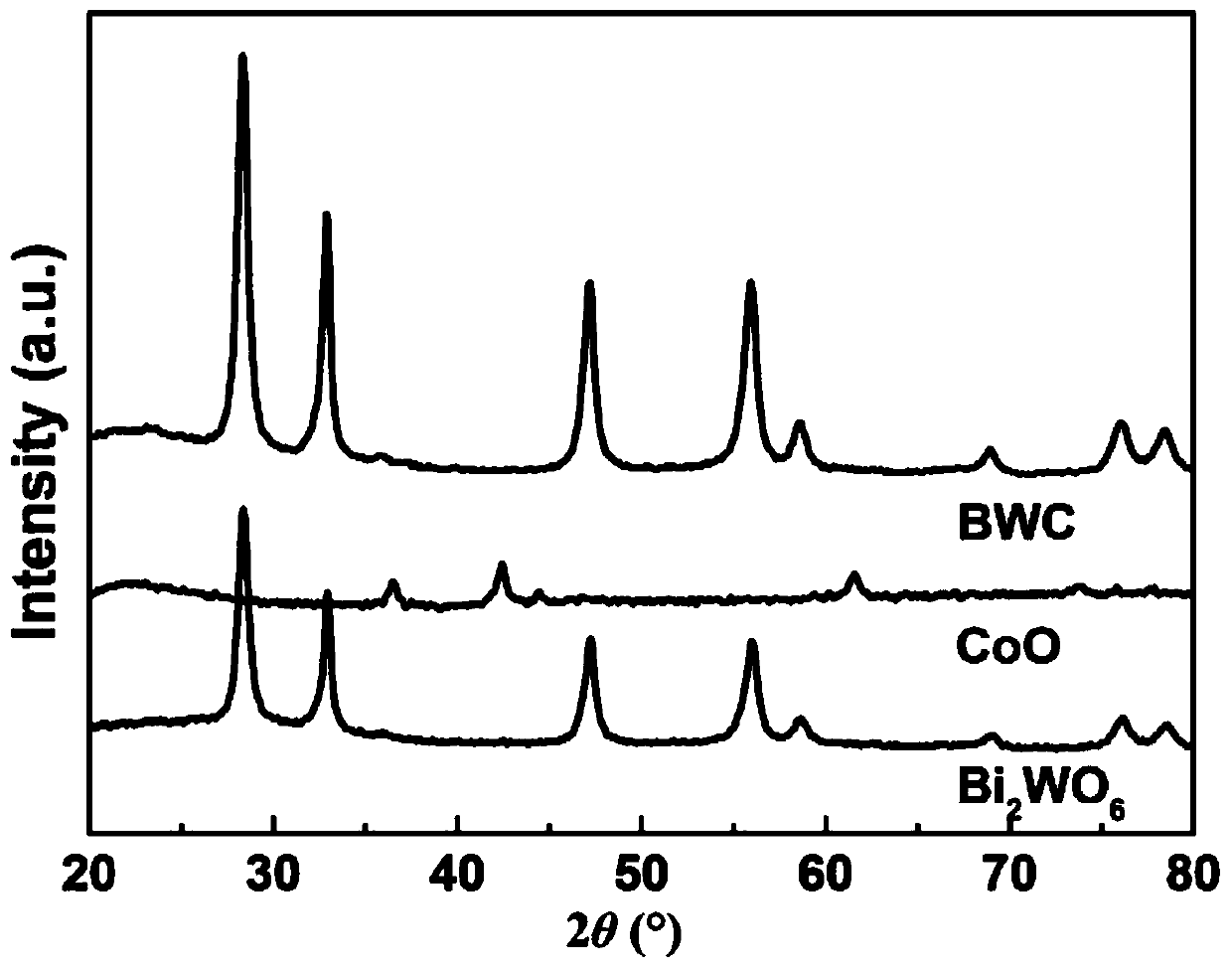
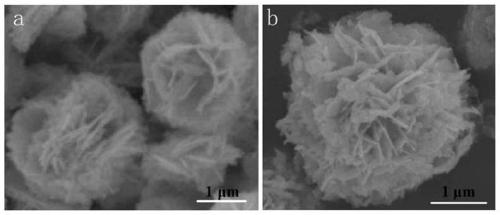
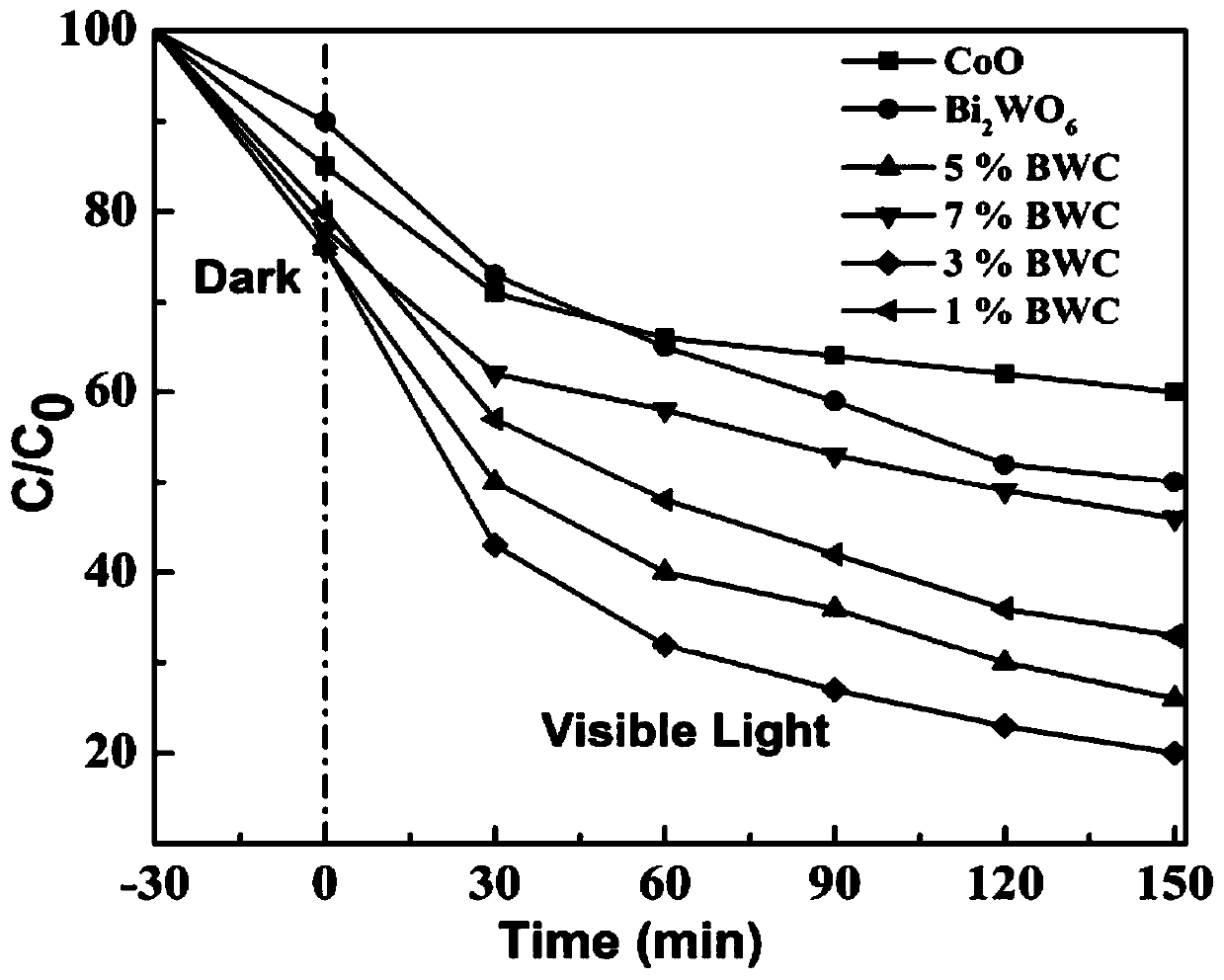
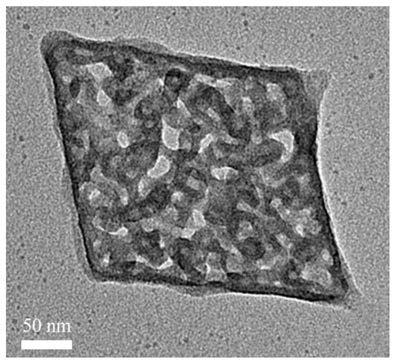
3D flower-like Bi2WO6@CoO heterojunction photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111468134AAppropriate bandgap valueSuitable energy band positionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsHeterojunctionSemiconductor Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a 3D flower-like Bi2WO6@CoO heterojunction photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The 3D flower-like Bi2WO6@CoO heterojunction photocatalyst isprepared by loading semiconductor CoO nanoparticles onto Bi2WO6, and the weight percentage of the CoO nanoparticles is 1-7%. According to the invention, a novel Bi2WO6@CoO (BWC) heterojunction photocatalysis with 3D flower-like grading is constructed; the composite material has a large specific surface area, ultrahigh visible light absorption capacity and enhanced electron-hole pair separation efficiency, and compared with single Bi2WO6 and CoO, the heterojunction material shows enhanced catalytic activity.
Owner:沈阳宏坤电气设备有限公司
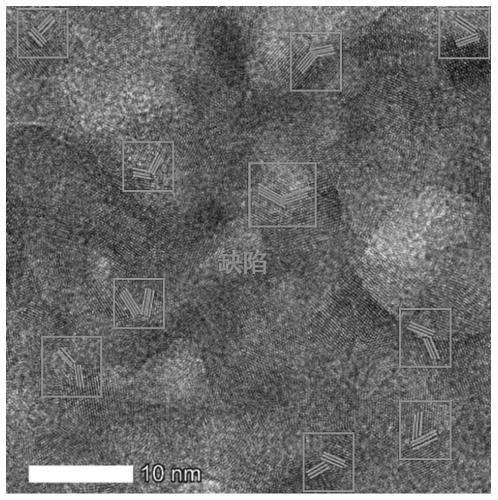
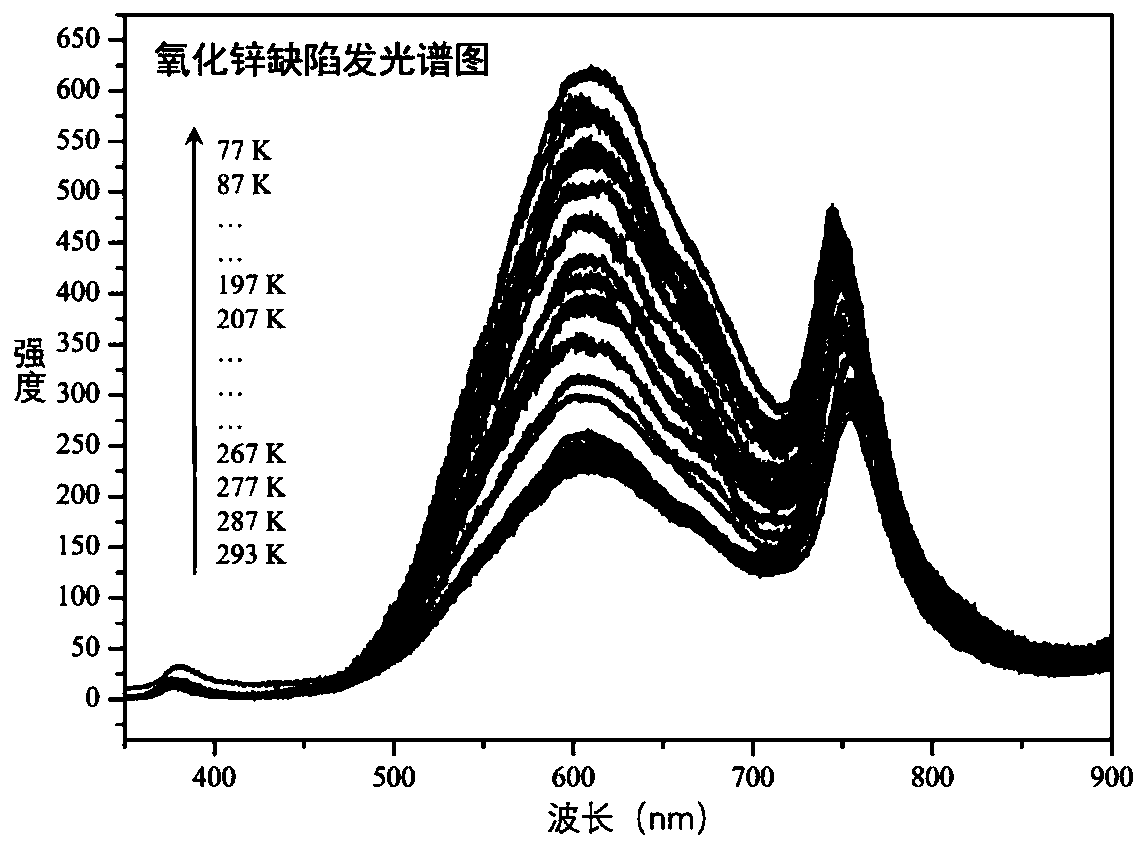
Detection method and application of ultralow-temperature enhanced Raman spectrum signal
ActiveCN111579543AHigh detection sensitivityImprove universalityRaman scatteringMetal oxide nanoparticlesSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention discloses a detection method and application of an ultralow-temperature enhanced Raman spectrum signal. The method comprises the following steps: adsorbing a substance to be detected ona surface enhanced Raman spectrum substrate, and carrying out laser Raman spectrum test on the substance to be detected under the condition of 0.1-287K; wherein the surface enhanced Raman spectrum substrate is semiconductor nanoparticles; the semiconductor nanoparticles including metal oxide nanoparticles, and the metal oxide nanoparticles having surface defects. The method provided by the invention has very good universality and very high SERS detection sensitivity.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
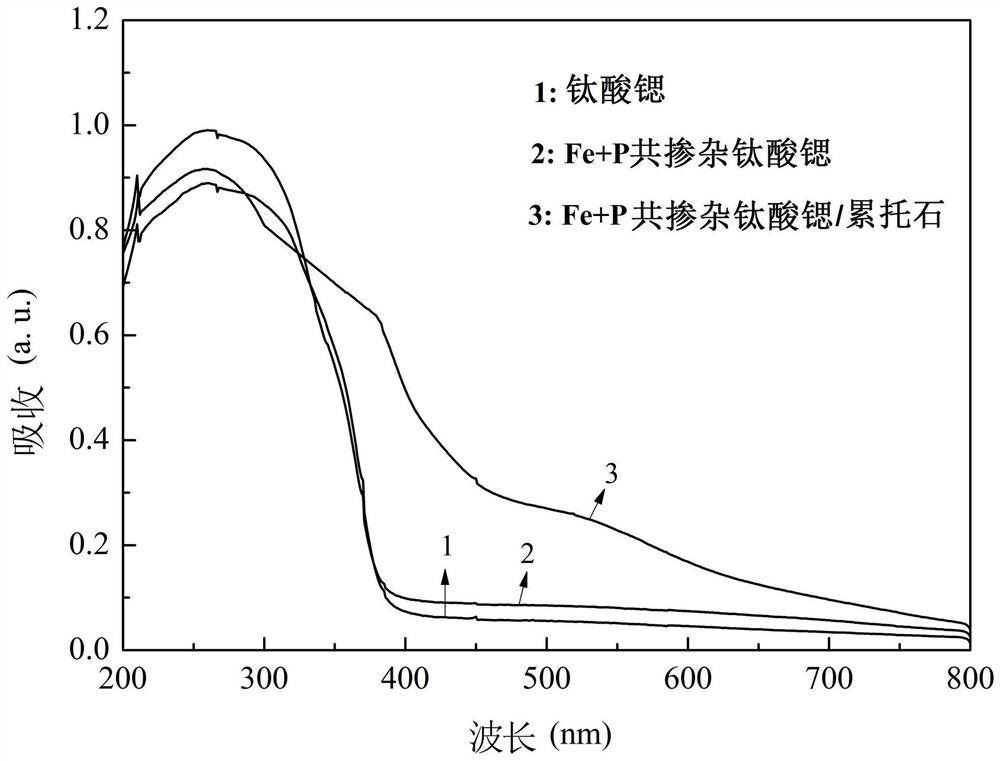
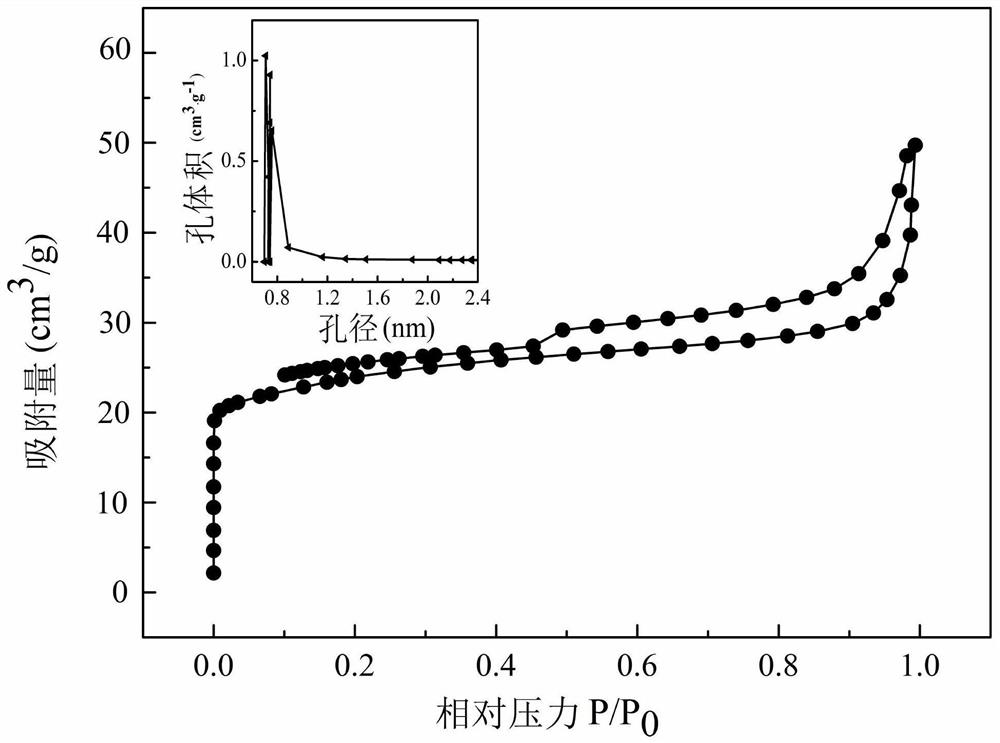
Fe and P co-doped strontium titanate/rectorite composite catalyst and application thereof
InactiveCN112264058AHigh catalytic activityGood cation exchangePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationStrontium titanatePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a Fe and P co-doped strontium titanate / rectorite composite catalyst and application thereof. The composite catalyst is formed by compounding natural clay mineral rectorite serving as a carrier with Fe and P co-doped strontium titanate. In organic pollutant treatment, the composite catalyst can effectively degrade organic pollutants in a visible light range under sunlight radiation, and then the organic pollutants are separated from a reacted solution through a magnetic loading effect and are repeatedly used. According to the composite catalyst, semiconductor nanoparticles with small particle sizes, such as doped and modified nano strontium titanate, are inserted into rectorite to form a pillared composite material so as to expand an interlayer domain, the expanded interlayer domain is high in structural stability, growth of the nanoparticles is inhibited, separation of photo-induced electrons and holes is promoted, and meanwhile, the structure can also improve the specific surface area and pore volume of the composite material, enhance the adsorption performance and effectively remove organic pollutants in industrial wastewater.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Composite fluorescent nano particle used for immunoassay and its preparation method
InactiveCN1459632AStable surface propertiesGood chemical stabilityBiological testingGold layerSemiconductor Nanoparticles
A composite fluorescent nanoparticles for immunodetection is composed of the semiconductor nanoparticle as kernel, such as CdS, CdSe, or ZnS, SiO2 layer coated on the surface of said kernel, and island-shaped gold layer deposited on the SiO2 layer. Its preparing process is also disclosed. Its advantages are high stability and high resolution.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com