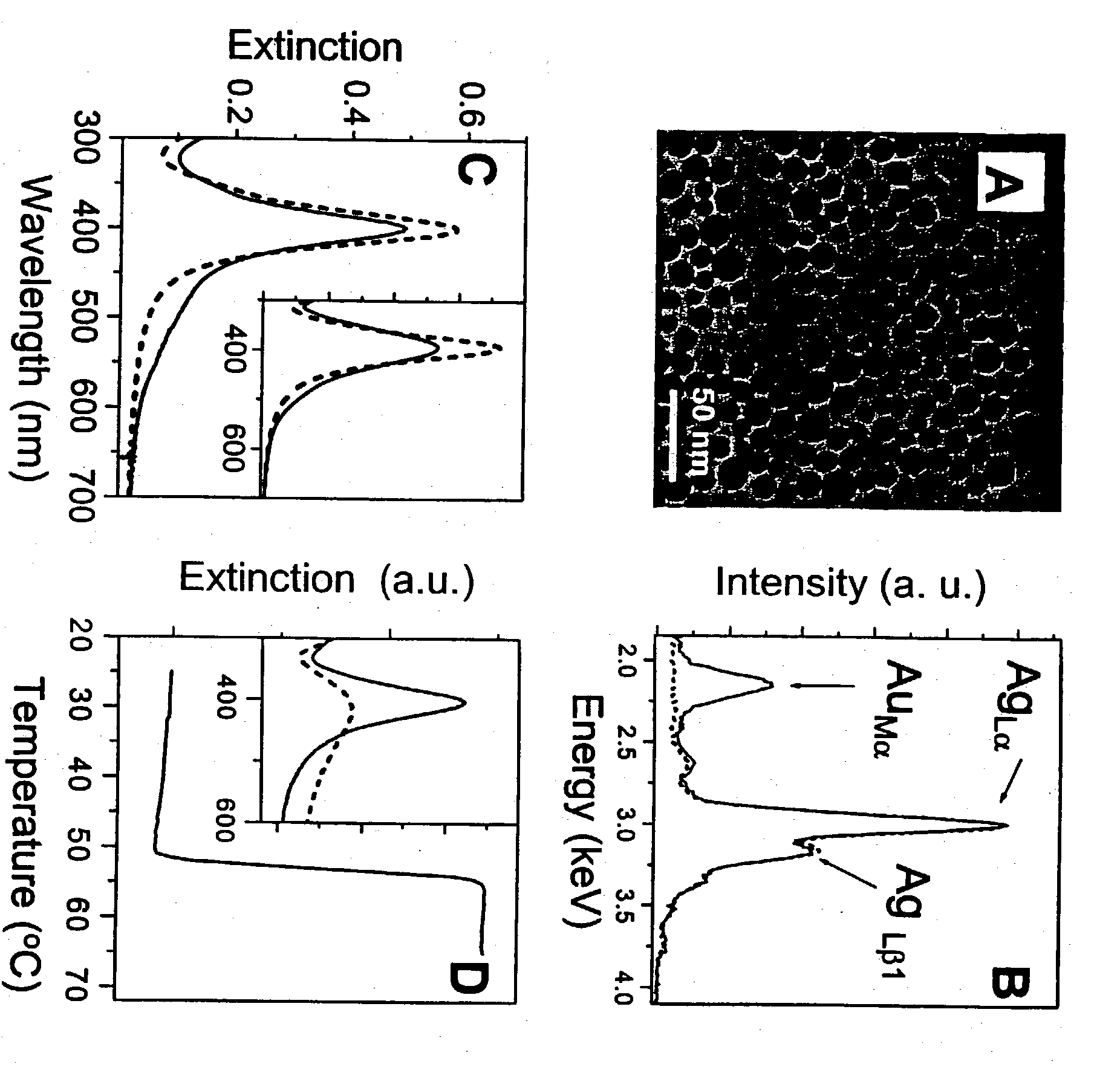
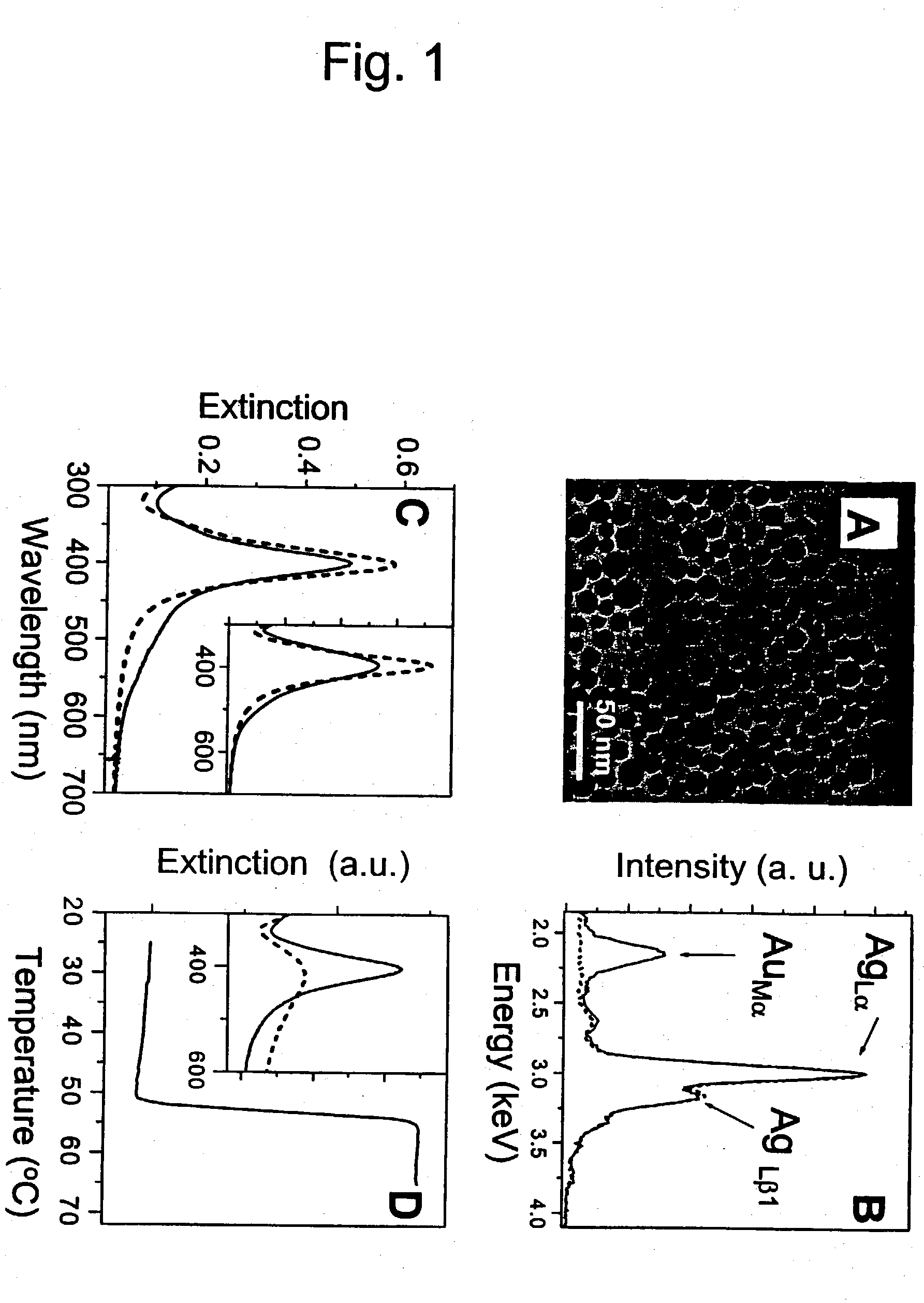
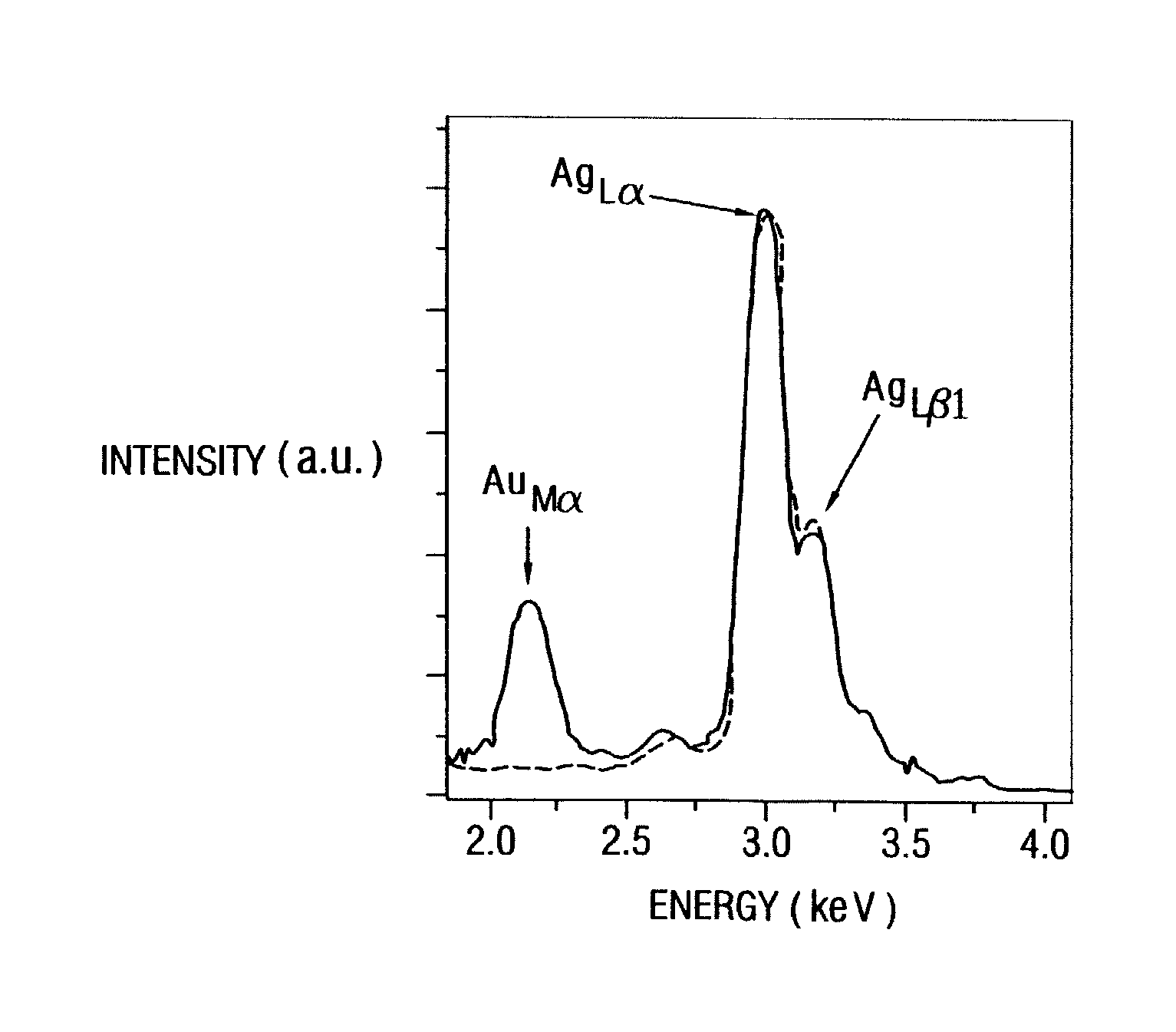
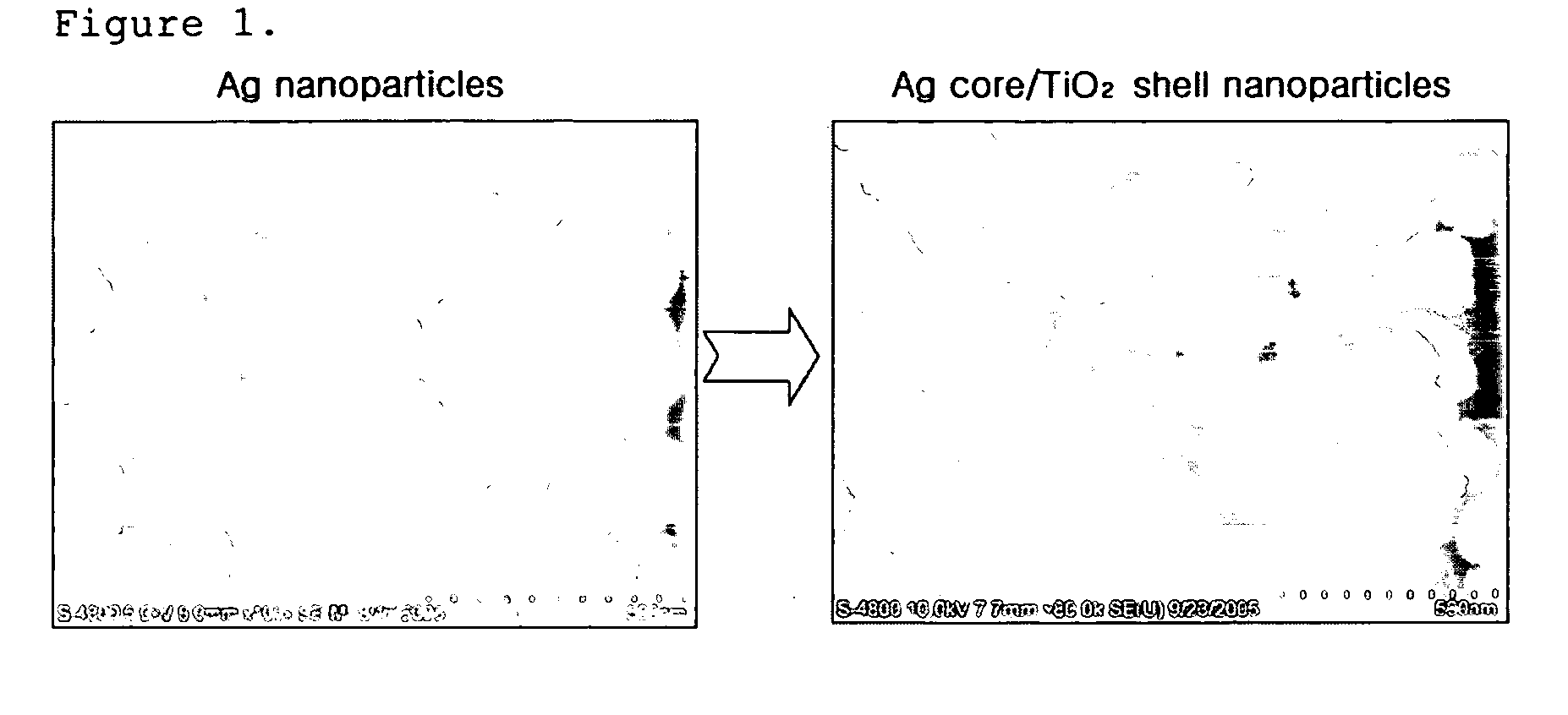
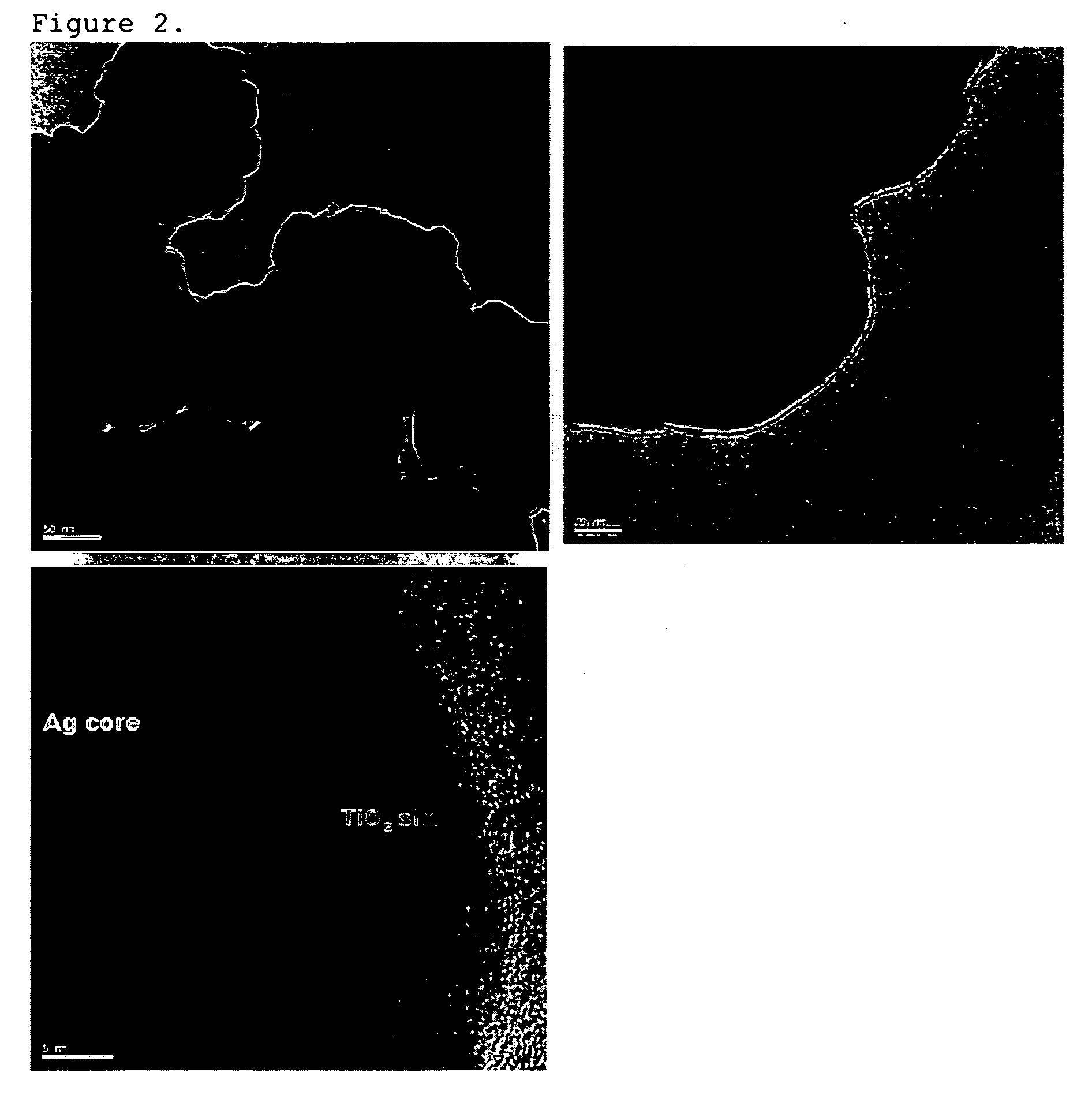
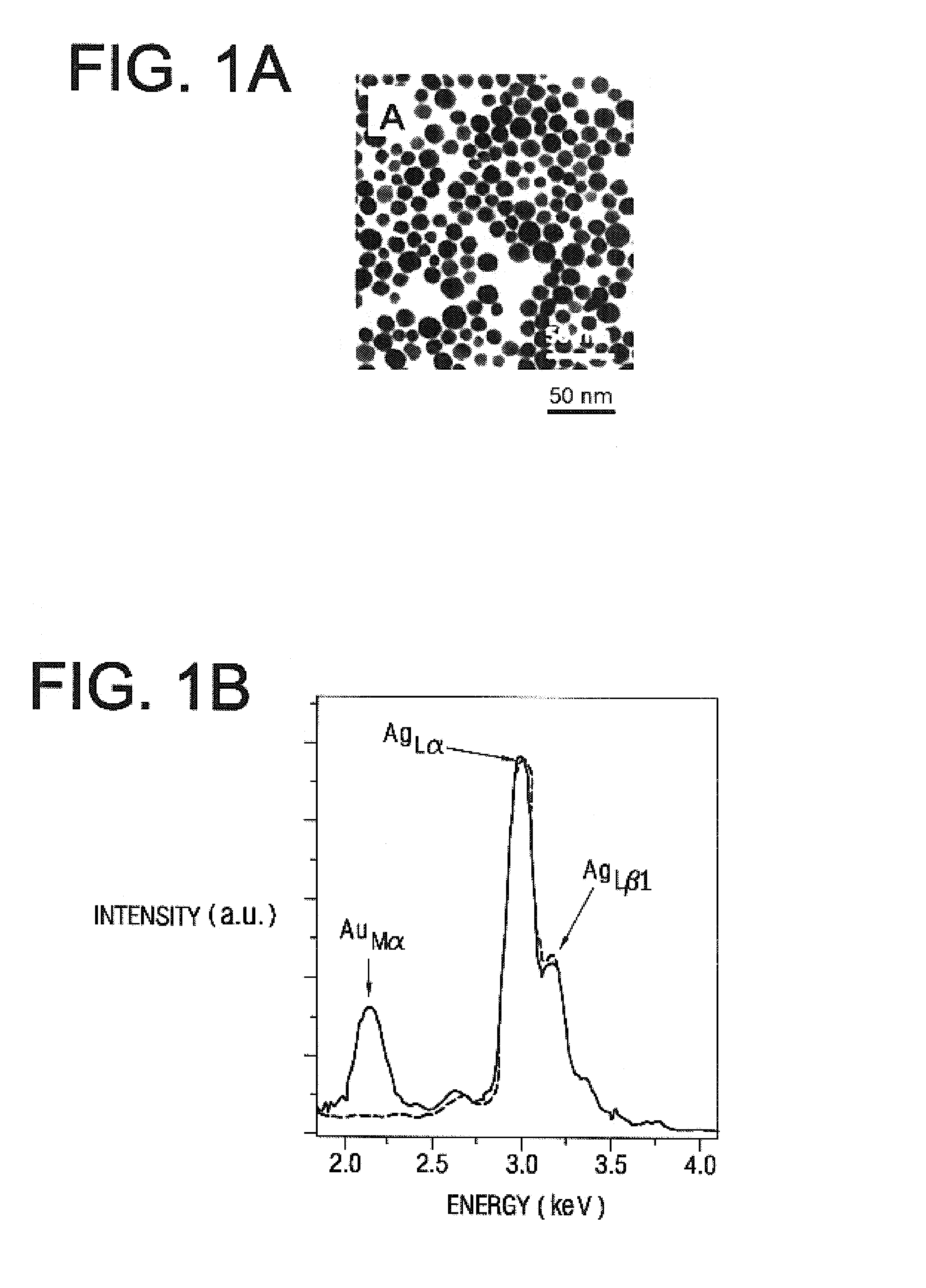
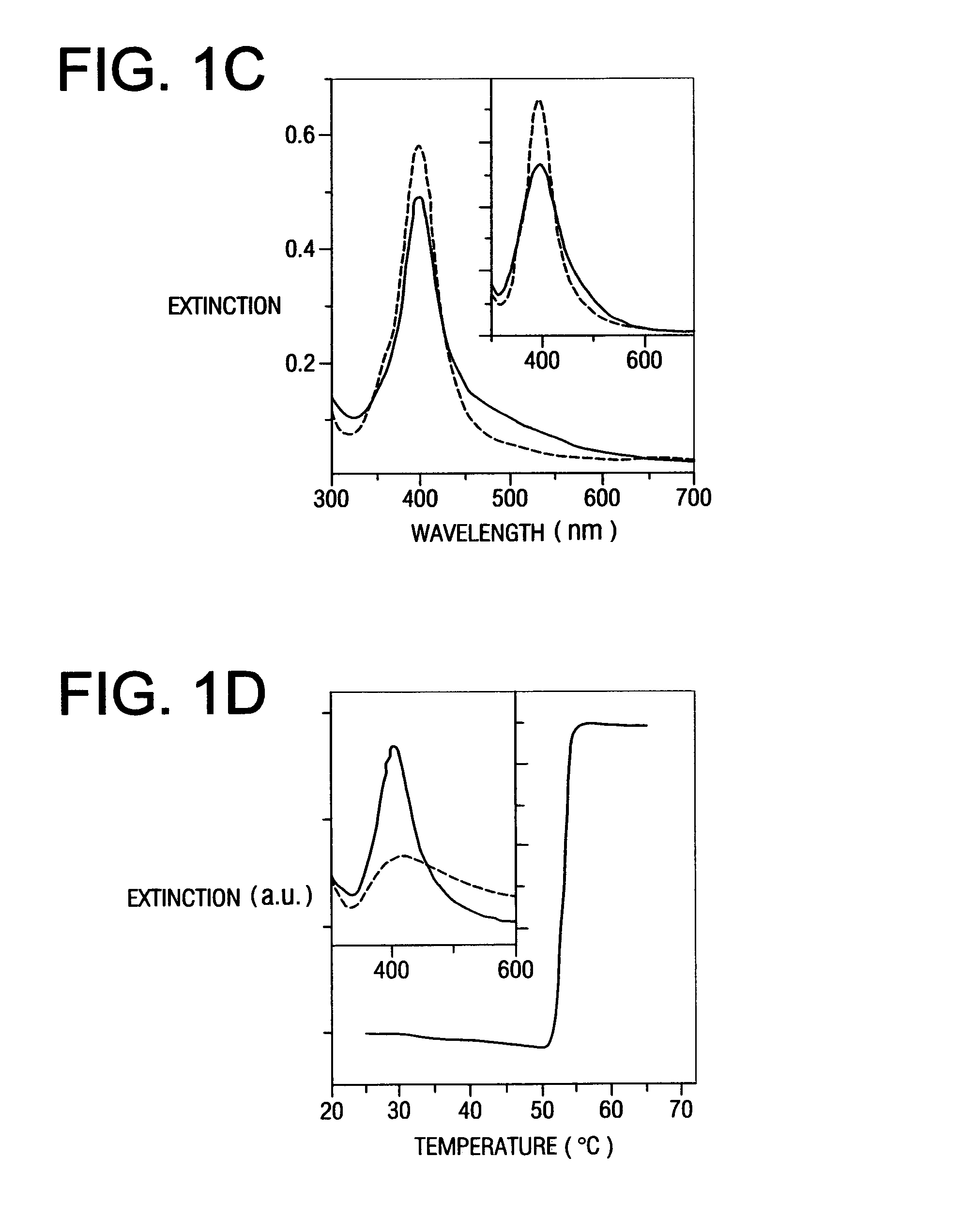
Patents
Literature
307 results about "Core shell nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
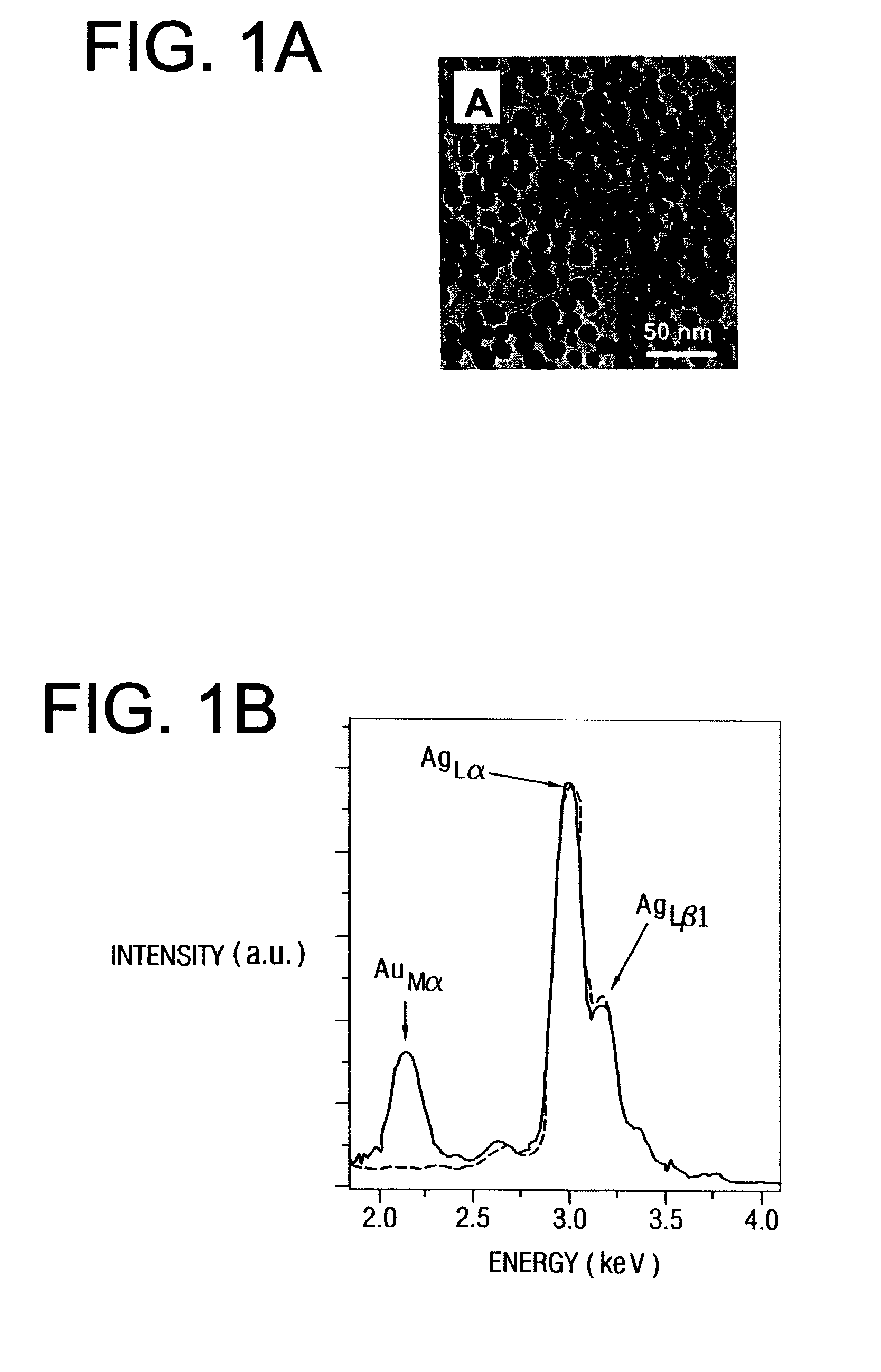
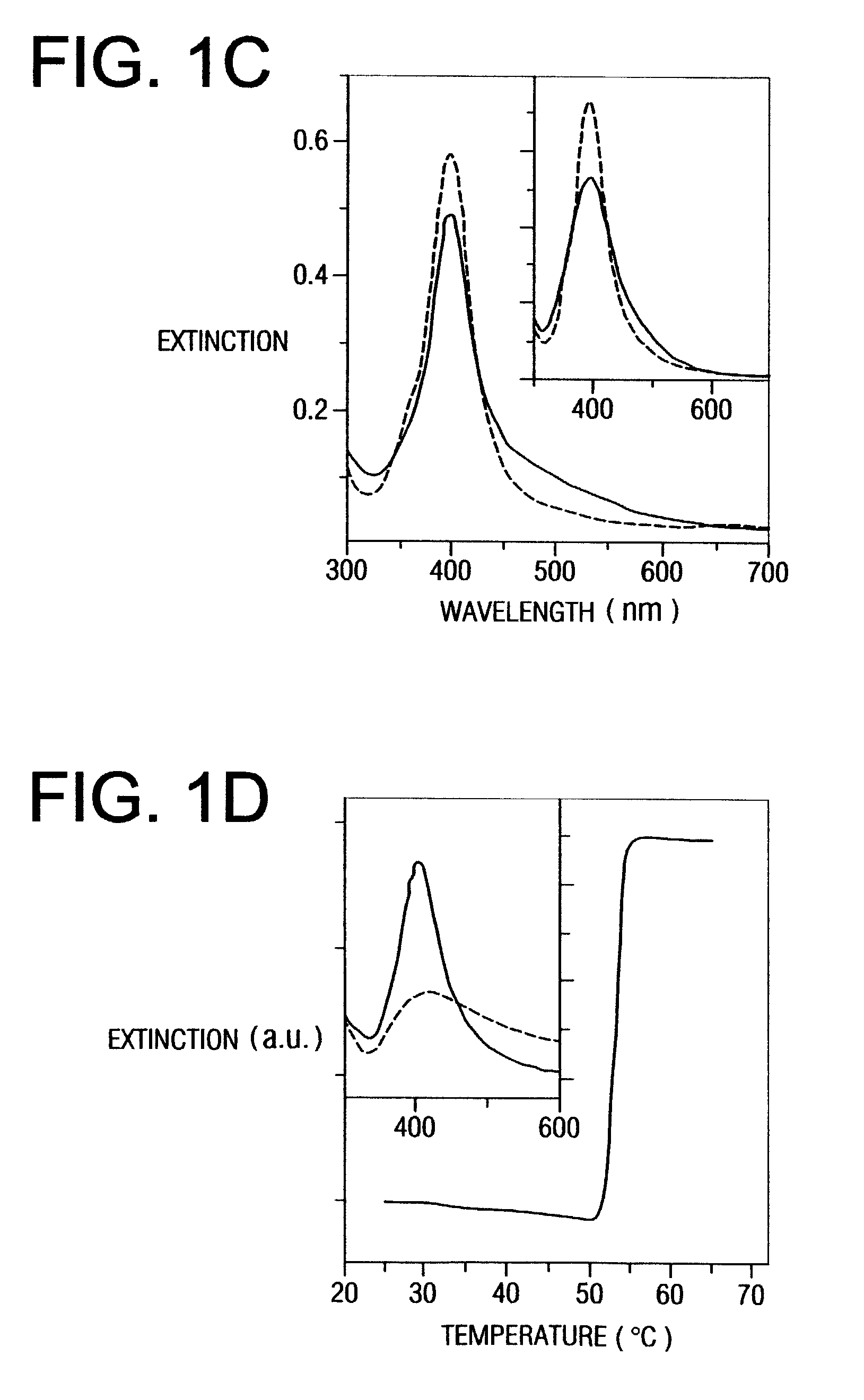
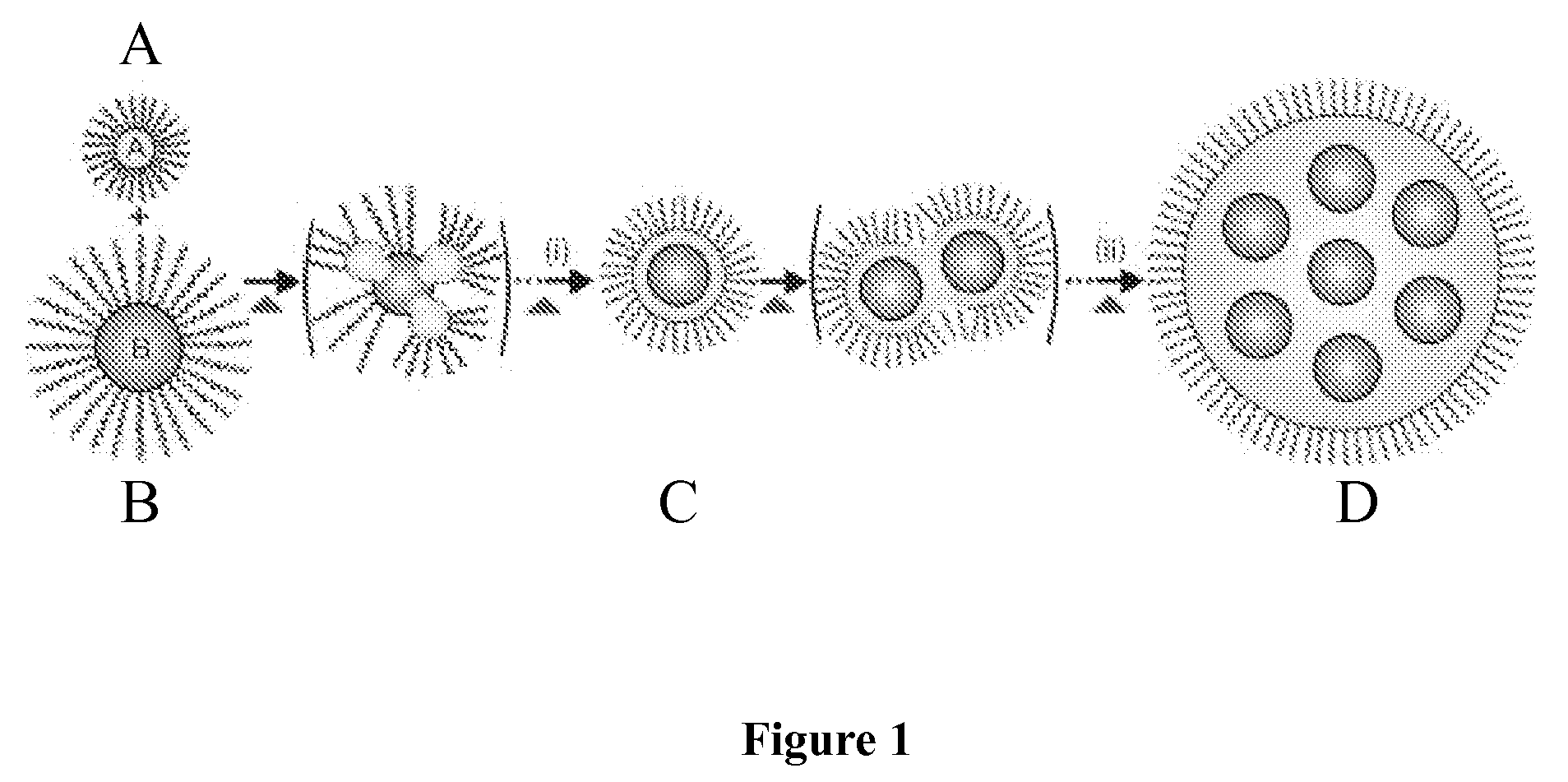
In synthesizing core shell nanoparticles, scientists have studied and found several wet chemical methods, such as chemical precipitation, sol-gel, microemulsion and inverse micelle formation. Those methods have been used to grow core shell chalcogenide nanoparticles with an emphasis on better control of size, shape, and size distribution.
Non-alloying core shell nanoparticles
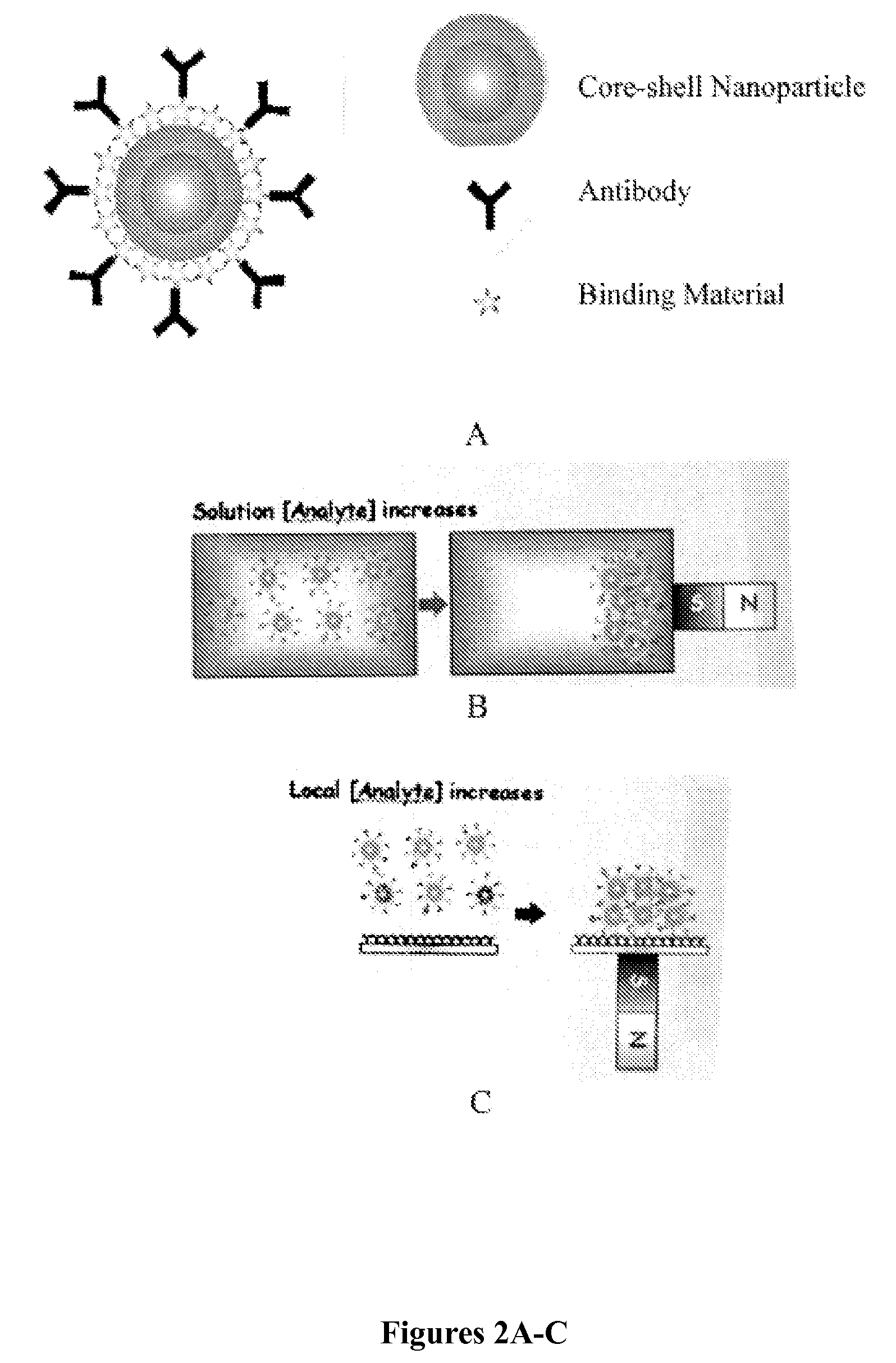
The present invention relates composite core / shell nanoparticles and a two-step method for their preparation. The present invention further relates to biomolecule-core / shell nanoparticle conjugates and methods for their preparation. The invention also relates to methods of detection of biomolecules comprising the biomolecule or specific binding substance-core / shell nanoparticle conjugates.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
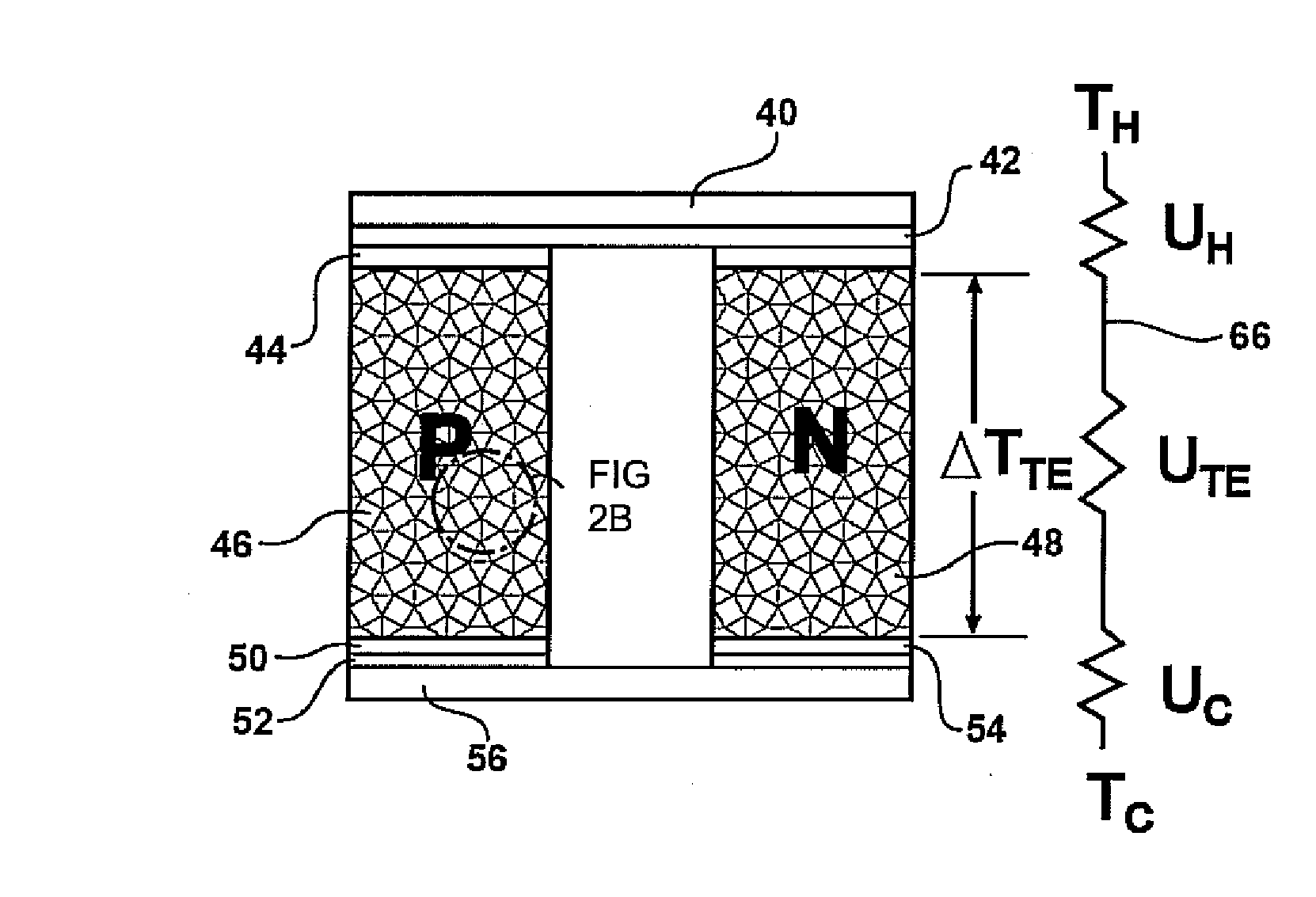
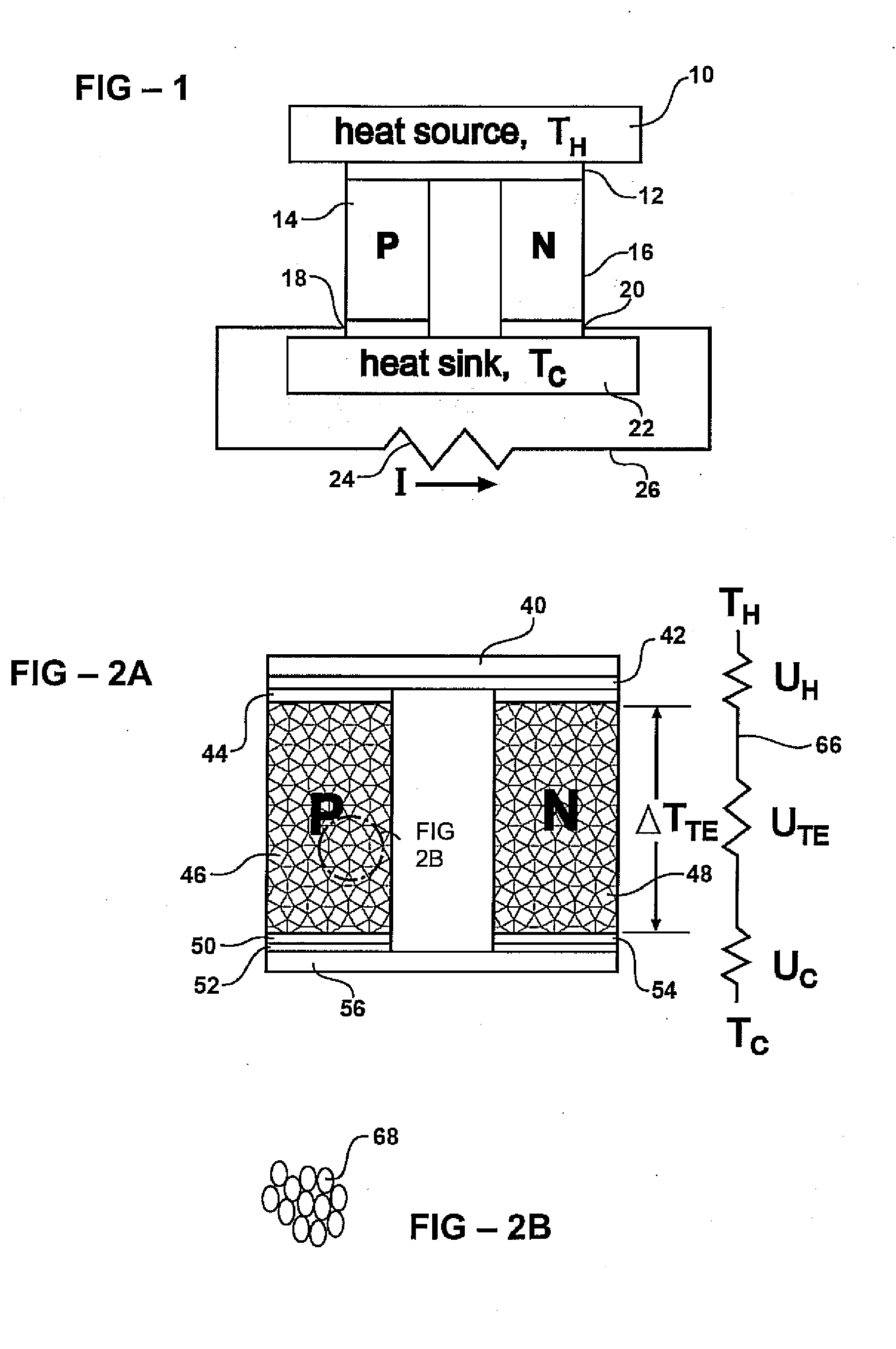
Homogeneous thermoelectric nanocomposite using core-shell nanoparticles
ActiveUS20080087314A1Uniform and improved thermoelectricThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentBismuth tellurideSilicon dioxide
A thermoelectric material comprises core-shell particles having a core formed from a core material and a shell formed from a shell material. In representative examples, the shell material is a material showing an appreciable thermoelectric effect in bulk. The core material preferably has a lower thermal conductivity than the shell material. In representative examples, the core material is an inorganic oxide such as silica or alumina, and the shell material is a chalcogenide semiconductor such as a telluride, for example bismuth telluride. A thermoelectric material including such core-shell particles may have an improved thermoelectric figure of merit compared with a bulk sample of the shell material alone. Embodiments of the invention further include thermoelectric devices using such thermoelectric materials, and preparation techniques. The use of core-shell nanoparticles allows highly uniform nanocomposites to be formed, and embodiments of the invention also includes other materials and devices using core-shell particles.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Chalcogenide solar cells
InactiveUS20070092648A1Overcome disadvantagesMolten spray coatingSolid-state devicesCore shell nanoparticlesSulfur
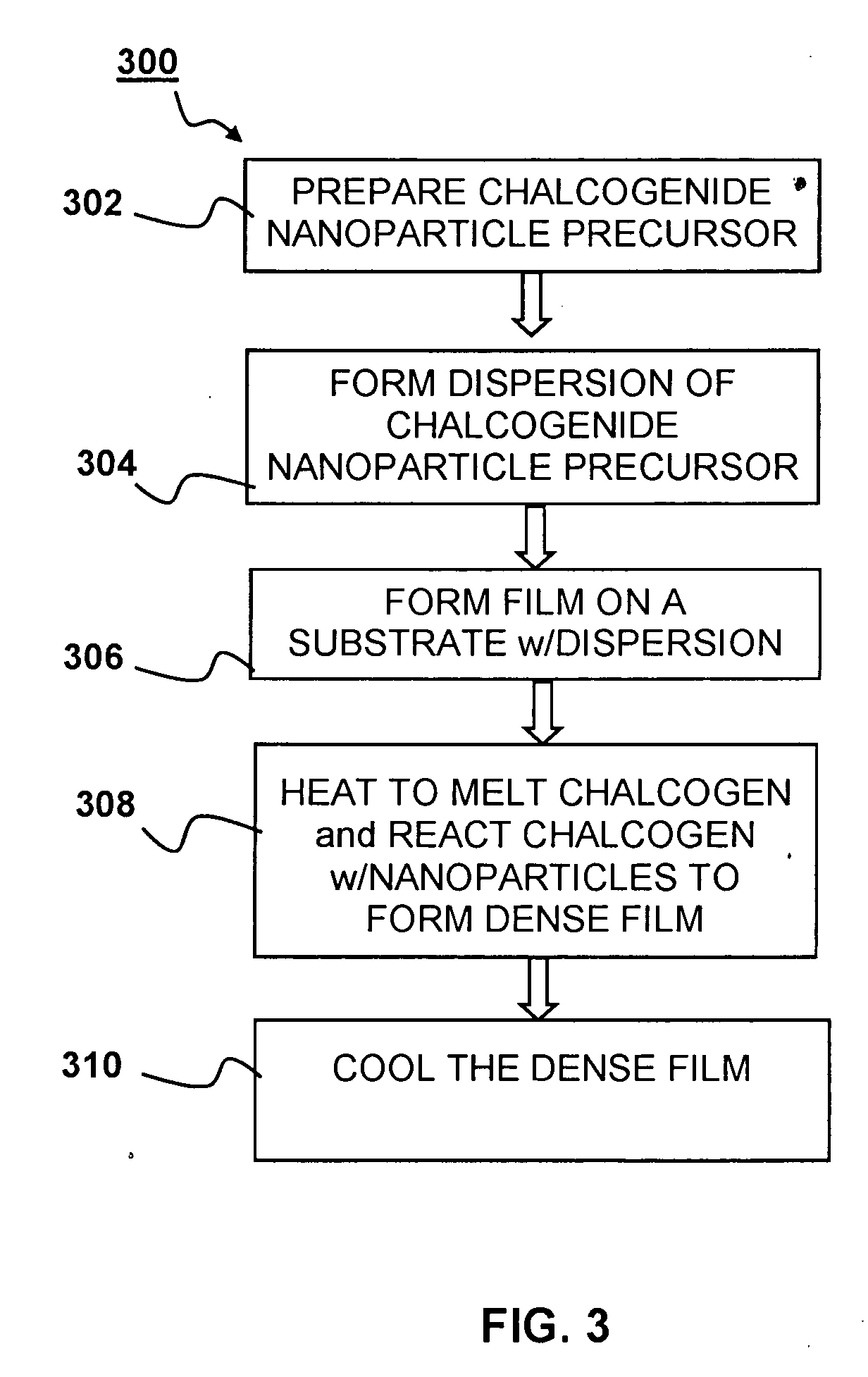
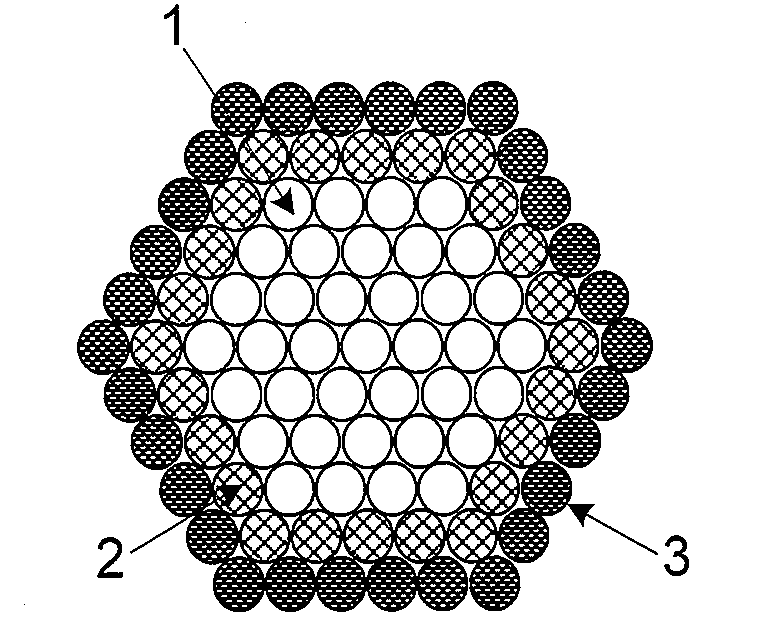
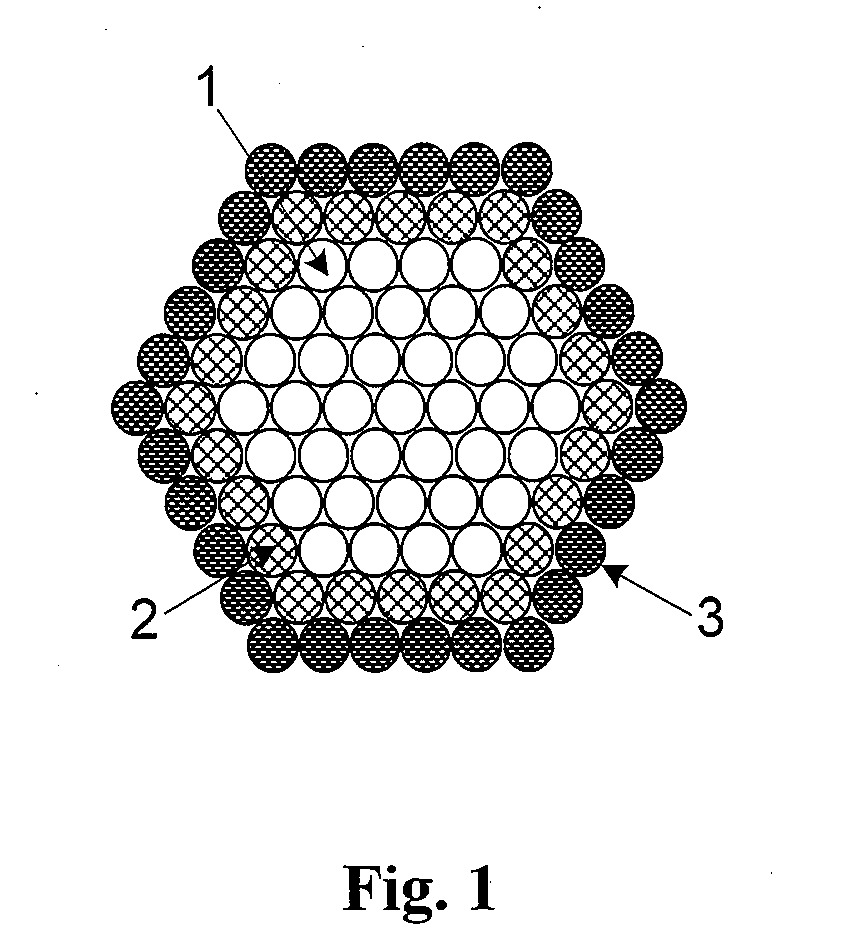
A precursor material for forming a film of a group IB-IIIA-chalcogenide compound and a method of making this film are disclosed. The film contains group IB-chalcogenide nanoparticles and / or group IIIA-chalcogenide nanoparticles and / or nanoglobules and / or nanodroplets and a source of extra chalcogen. Alternatively, the film may contain core-shell nanoparticles having core nanoparticles include group IB and / or IIIA elements, which are coated with a shell of elemental chalcogen material. The method of making a film of group IB-IIIA-chalcogenide compound includes mixing the nanoparticles and / or nanoglobules and / or nanodroplets to form an ink, depositing the ink on a substrate, heating to melt the extra chalcogen and to react the chalcogen with the group IB and group IIIA elements and / or chalcogenides to form a dense film.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
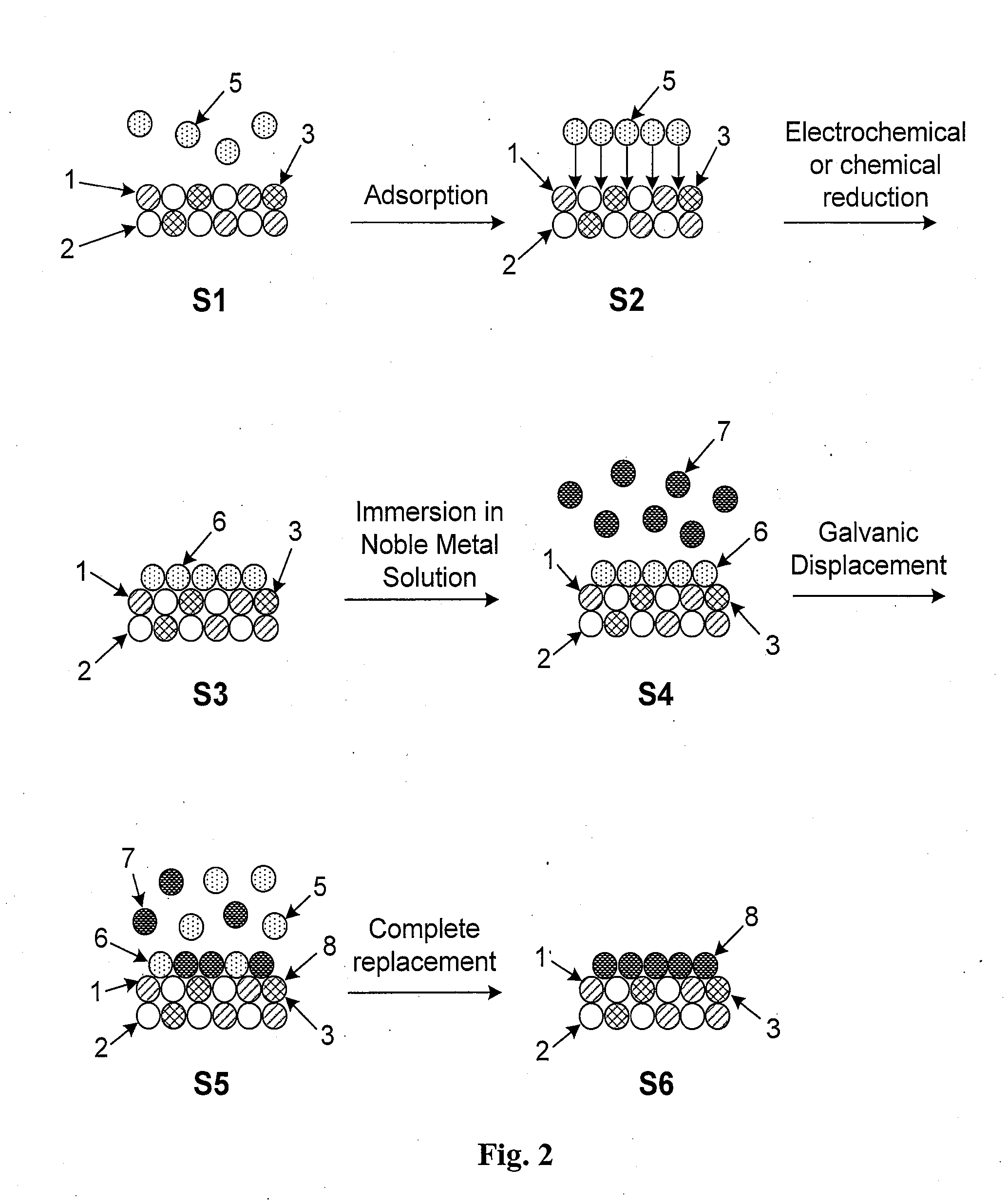
Platinum-Coated Non-Noble Metal-Noble Metal Core-Shell Electrocatalysts
InactiveUS20100197490A1Minimal loadingEfficiently formedMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesAlloyPt element
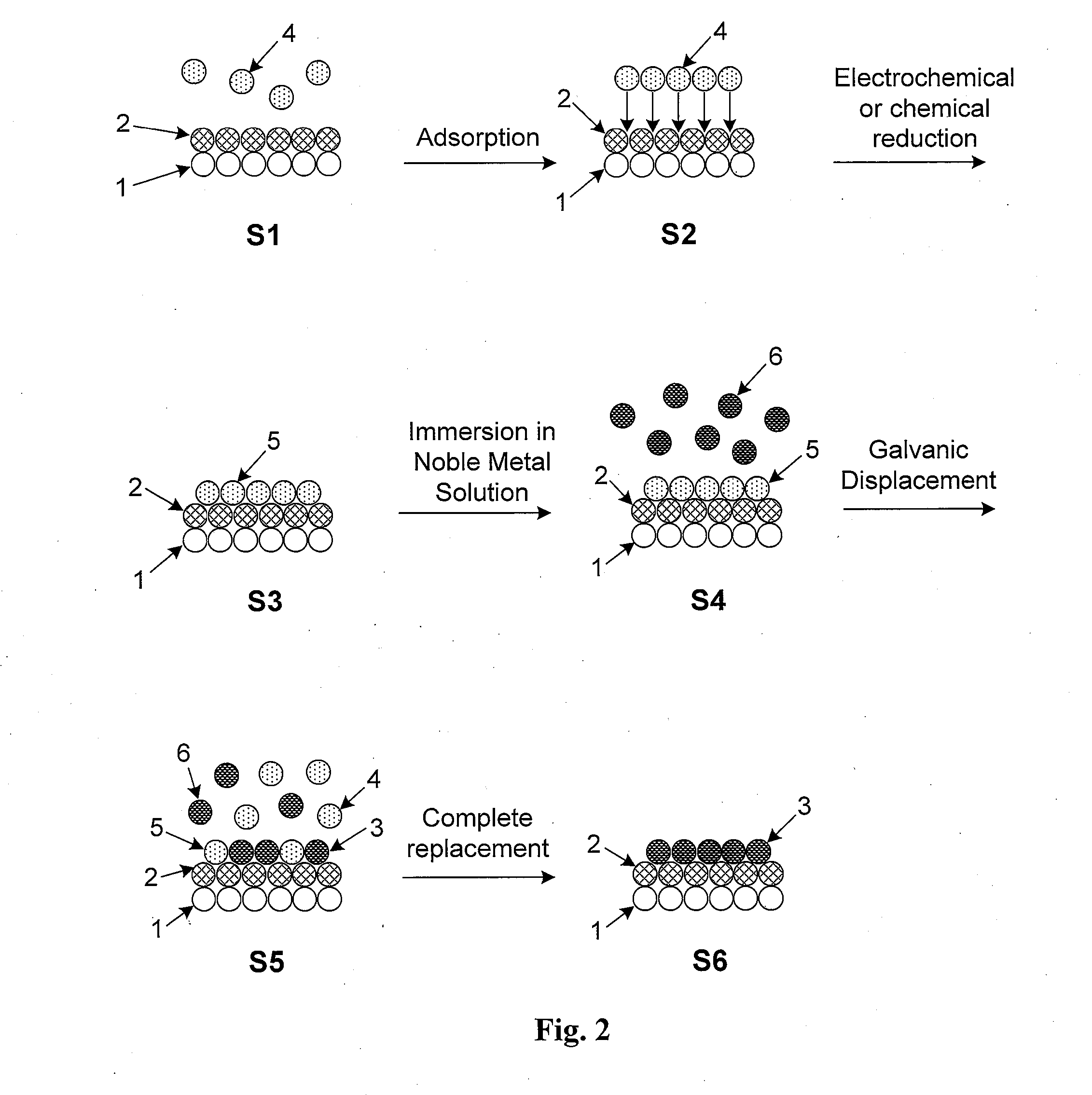
Core-shell particles encapsulated by a thin film of a catalytically active metal are described. The particles are preferably nanoparticles comprising a non-noble core with a noble metal shell which preferably do not include Pt. The non-noble metal-noble metal core-shell nanoparticles are encapsulated by a catalytically active metal which is preferably Pt. The core-shell nanoparticles are preferably formed by prolonged elevated-temperature annealing of nanoparticle alloys in an inert environment. This causes the noble metal component to surface segregate and form an atomically thin shell. The Pt overlayer is formed by a process involving the underpotential deposition of a monolayer of a non-noble metal followed by immersion in a solution comprising a Pt salt. A thin Pt layer forms via the galvanic displacement of non-noble surface atoms by more noble Pt atoms in the salt. The overall process is a robust and cost-efficient method for forming Pt-coated non-noble metal-noble metal core-shell nanoparticles.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Non-alloying core shell nanoparticles
The present invention relates composite core / shell nanoparticles and a two-step method for their preparation. The present invention further relates to biomolecule-core / shell nanoparticle conjugates and methods for their preparation. The invention also relates to methods of detection of biomolecules comprising the biomolecule or specific binding substance-core / shell nanoparticle conjugates.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Non-alloying core shell nanoparticles
The present invention relates composite core / shell nanoparticles and a two-step method for their preparation. The present invention further relates to biomolecule-core / shell nanoparticle conjugates and methods for their preparation. The invention also relates to methods of detection of biomolecules comprising the biomolecule-core / shell nanoparticle conjugates.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
High Stability, Self-Protecting Electrocatalyst Particles
InactiveUS20100216632A1Avoid corrosionCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCore shell nanoparticlesAlloy
High-stability, self-protecting particles encapsulated by a thin film of a catalytically active noble metal are described. The particles are preferably nanoparticles comprising a passivating element having at least one metal selected from the group consisting of columns IVB, VB, VIB, and VIIB of the periodic table. The nanoparticle is preferably encapsulated by a Pt shell and may be either a nanoparticle alloy or a core-shell nanoparticle. The nanoparticle alloys preferably have a core comprised of a passivating component alloyed with at least one other transition metal. The core-shell nanoparticles comprise a core of a non-noble metal surrounded by a shell of a noble metal. The material constituting the core, shell, or both the core and shell may be alloyed with one or more passivating elements. The self-protecting particles are ideal for use in corrosive environments where they exhibit improved stability compared to conventional electrocatalyst particles.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
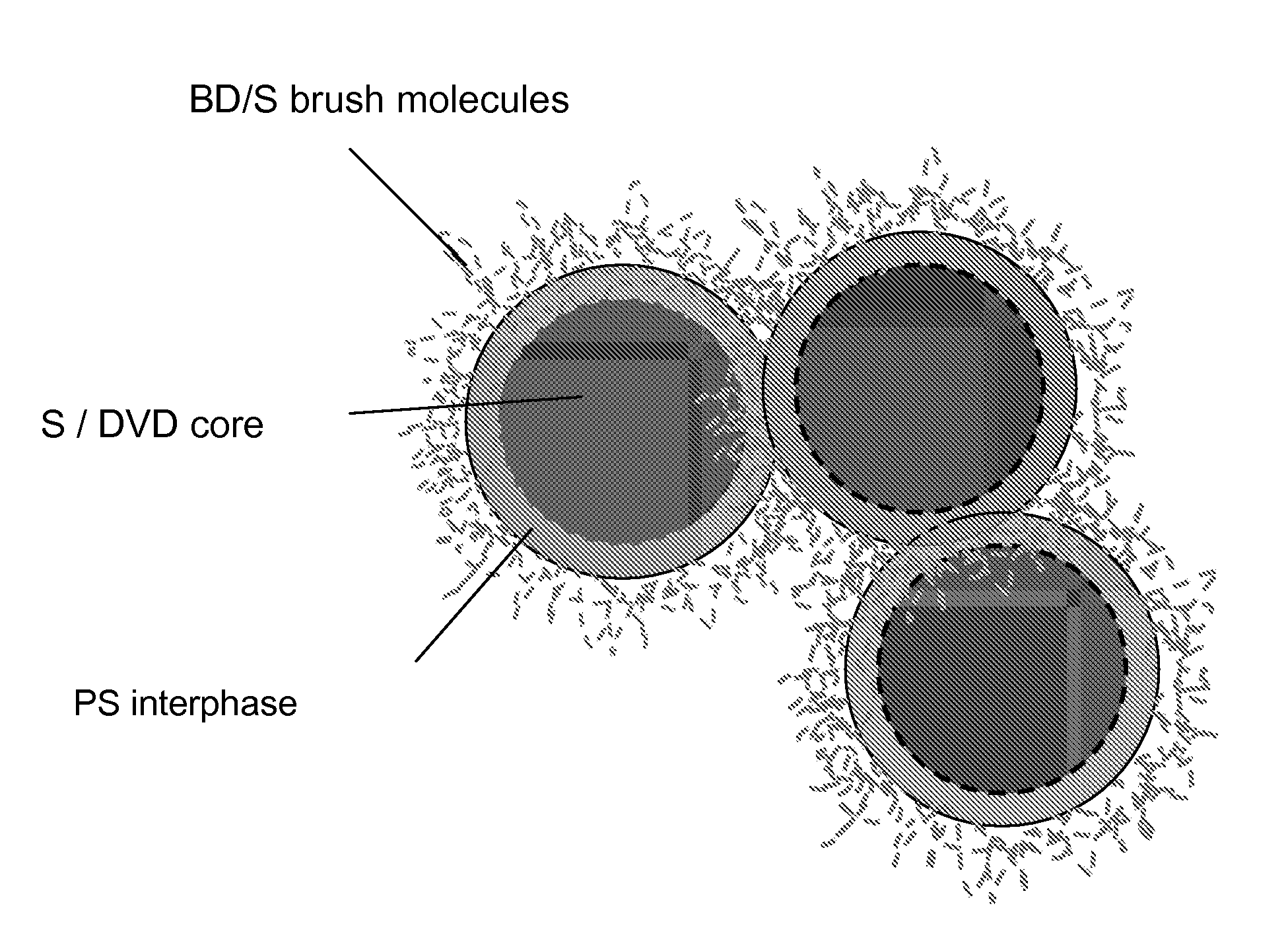
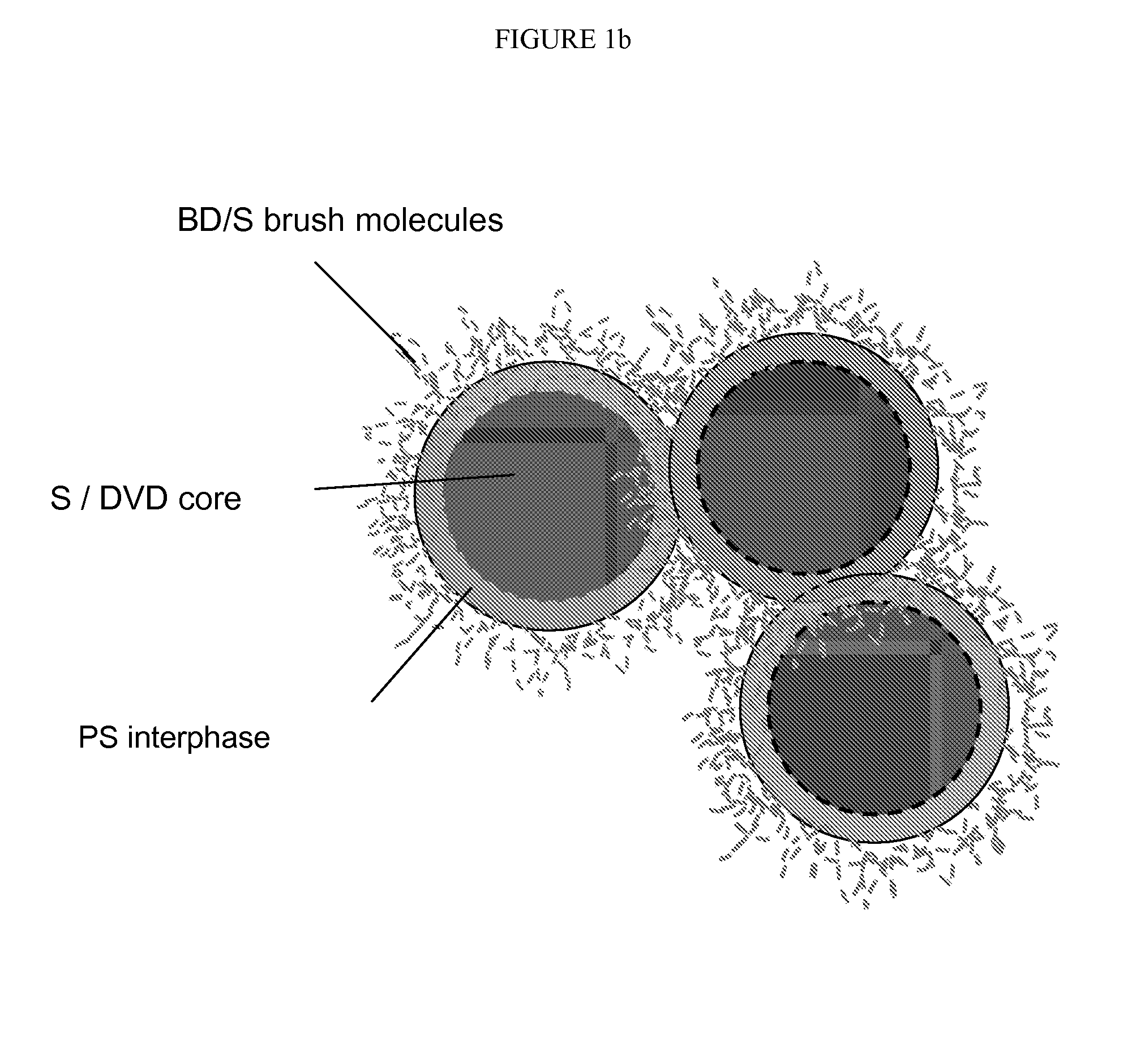
Polymeric core-shell nanoparticles with interphase region
ActiveUS20100004398A1High strengthMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationCore shell nanoparticlesParticle composition
A polymeric nanoparticle composition is provided. The nanoparticle may be of a core / shell configuration with an interphase region connecting the core and the shell. The mean average diameter of the polymer nanoparticles may be less than about 250 nm. The size, composition, and / or configuration of the interphase region may be varied to achieve desired physical and / or chemical properties of the resulting polymeric nanoparticles, and of the compositions into which the nanoparticles are compounded.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Nanoparticles from chitosan
InactiveUS20050226938A1Material nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsControlled releaseBiopolymer
Methods are disclosed for preparing crosslinked core and core-shell nanoparticle polymers from chitosan. The final products of the present invention may be used as detergents and as additives for pharmaceutical composition and for drug delivery, and DNA carrier system. The nanoparticles made from biopolymers of the present invention may also be used in controlled release, superabsorbent materials and biomaterials like enzyme immobilization.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DEBRECEN
Core-shell type nanoparticles and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20070128439A1Increased durabilityHigh strengthMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCore shell nanoparticlesMechanical stability
Disclosed herein are core-shell type nanoparticles comprising nanoparticle cores made of a metal or semiconductor, and shells made of crystalline metal oxide formed on the surfaces of the nanoparticle cores, as well as a preparation method thereof. According to the disclosed invention, the core-shell nanoparticles, consisting of metallic or semiconductor cores and crystalline metal oxide shells, can be prepared by epitaxially growing metal oxide on the surfaces of the metallic or semiconductor nanoparticle cores. By virtue of the crystalline metal oxide shells, the core nanoparticle made of metal or semiconductor can ensure excellent chemical and mechanical stability, and the core-shell nanoparticles can show new properties resulting from the interaction between the metal cores and the metal oxide crystal shells.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Non-alloying core shell nanoparticles
InactiveUS7147687B2Useful propertyMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryCore shell nanoparticlesNanometre
The present invention relates composite core / shell nanoparticles and a two-step method for their preparation. The present invention further relates to biomolecule-core / shell nanoparticle conjugates and methods for their preparation. The invention also relates to methods of detection of biomolecules comprising the biomolecule-core / shell nanoparticle conjugates.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Core-shell nanoparticles in electronic battery applications
InactiveUS20130078510A1Shorten cycle lifeCompromise capacitanceMaterial nanotechnologyRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum oxides/hydroxidesCore shell nanoparticlesCore shell
The present invention provides an improved supercapacitor-like electronic battery comprising a conventional electrochemical capacitor structure. A first nanocomposite electrode and a second electrode and an electrolyte are positioned within the conventional electrochemical capacitor structure. The electrolyte separates the nanocomposite electrode and the second electrode. The first nanocomposite electrode has first conductive core-shell nanoparticles in a first electrolyte matrix. A first current collector is in communication with the nanocomposite electrode and a second current collector is in communication with the second electrode. Also provided is an electrostatic capacitor-like electronic battery comprising a high dielectric-strength matrix separating a first electrode from a second electrode and, dispersed in said high-dielectric strength matrix, a plurality of core-shell nanoparticles, each of said core-shell nanoparticles having a conductive core and an insulating shell.
Owner:OERLIKON ADVANCED TECH +1
Core-Excited Nanoparticles and Methods of Their Use in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Disease
InactiveUS20130195979A1Cost-effectiveEffective and practicalPowder deliveryNanotechDiseaseExternal energy
Owner:TERSIGNI SAMUEL HARRY
Core-Shell Nanocatalyst For High Temperature Reactions
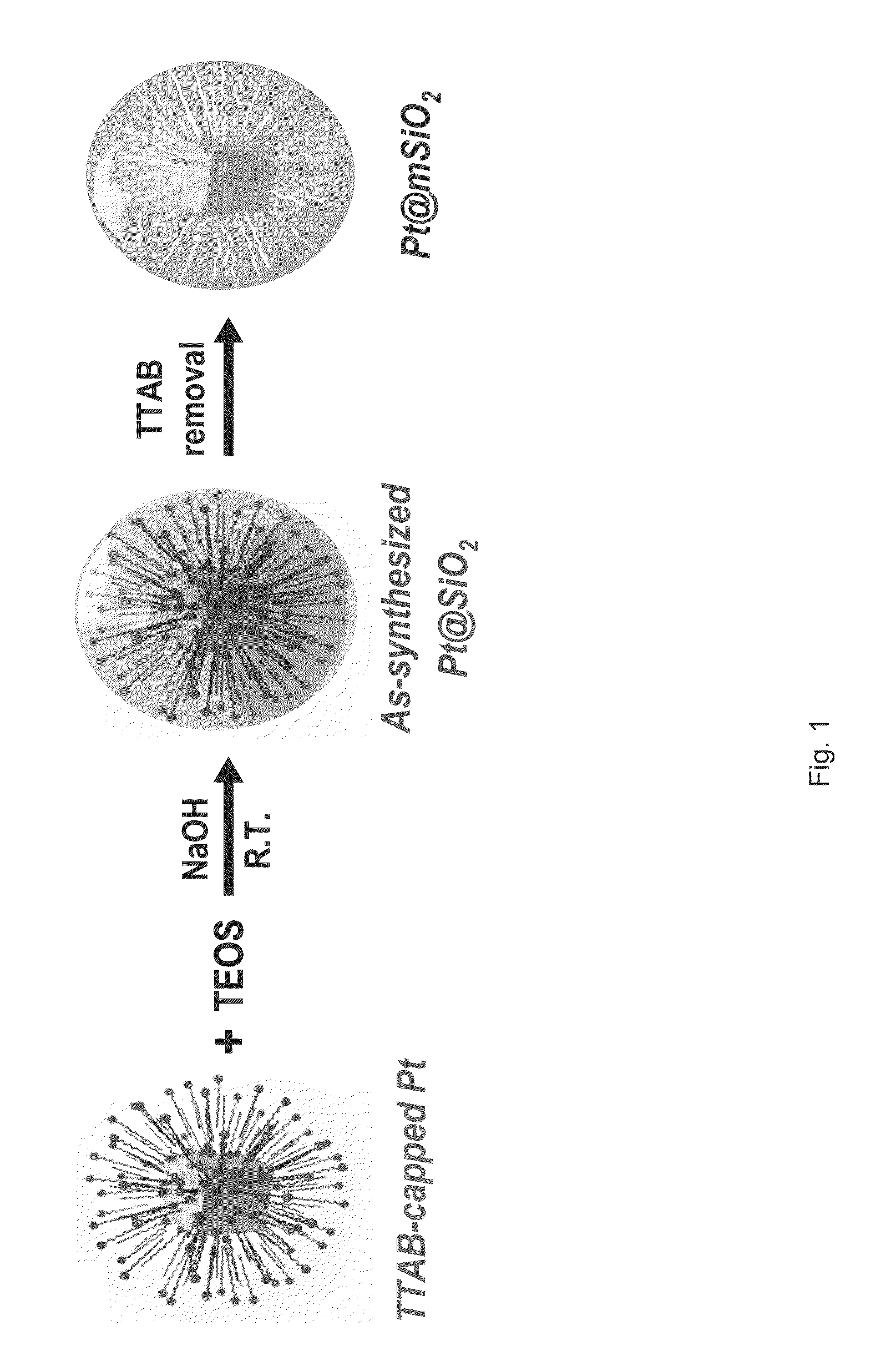
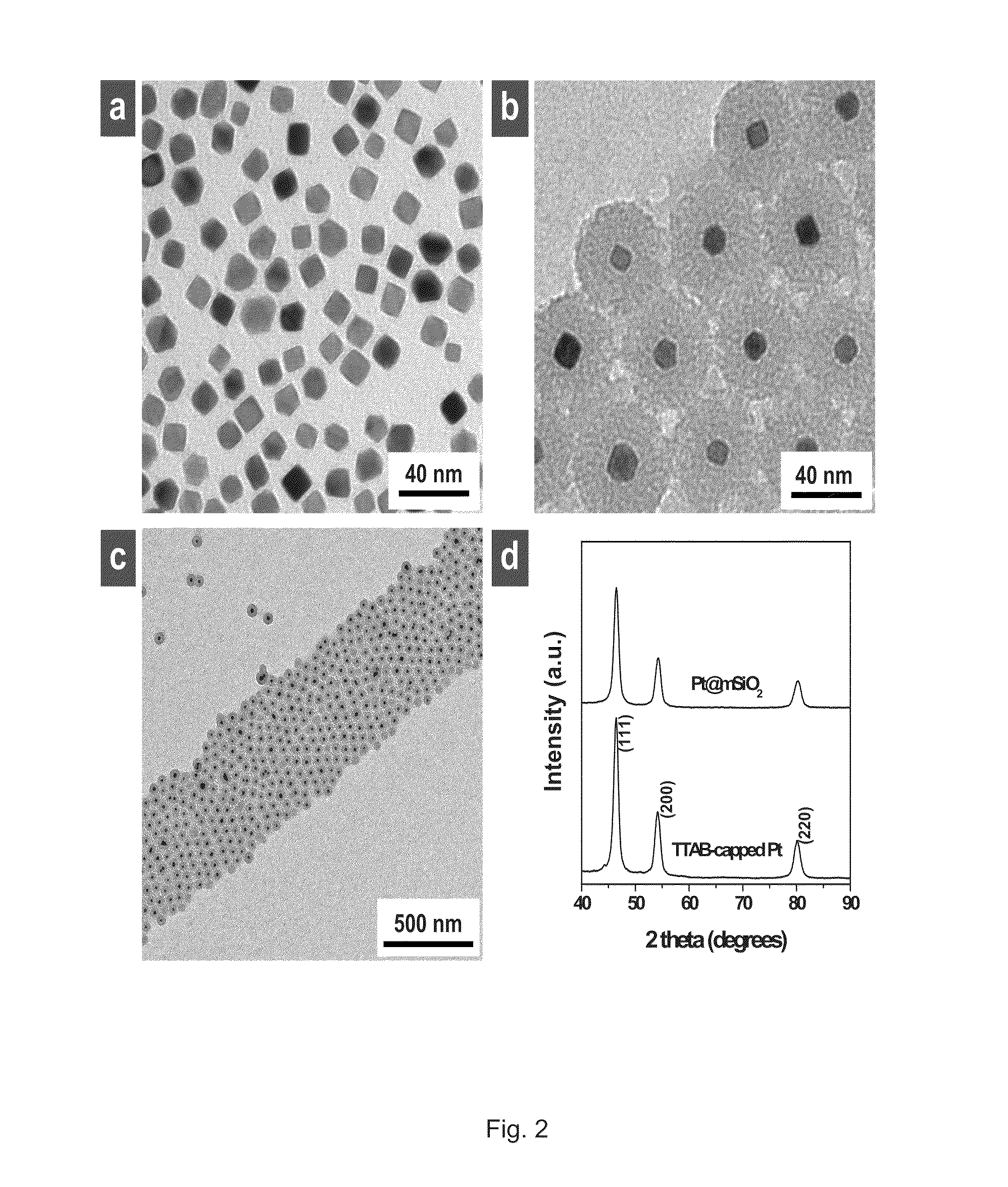
The present invention provides a core-shell nanoparticle that includes a metal-oxide shell and a nanoparticle. Pores extend from an outer surface to an inner surface of the shell. The inner surface of the shell forms a void, which is filled by the nanoparticle. The pores allow gas to transfer from outside the shell to a surface of the nanoparticle. The present invention also provides a method of making a core-shell nanoparticle includes forming a metal-oxide shell on a colloidal nanoparticle, which forms a precursor core-shell nanoparticle. A capping agent is removed from the precursor core-shell nanoparticle, which produces the core-shell nanoparticle. The present invention also provides a method of using a nanocatalyst of the present invention includes providing the nanocatalyst, which is the core-shell nanoparticle. Reactants are introduced in a vicinity of the nanocatalyst, which produces a reaction that is facilitated or enhanced by the nanocatalyst.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
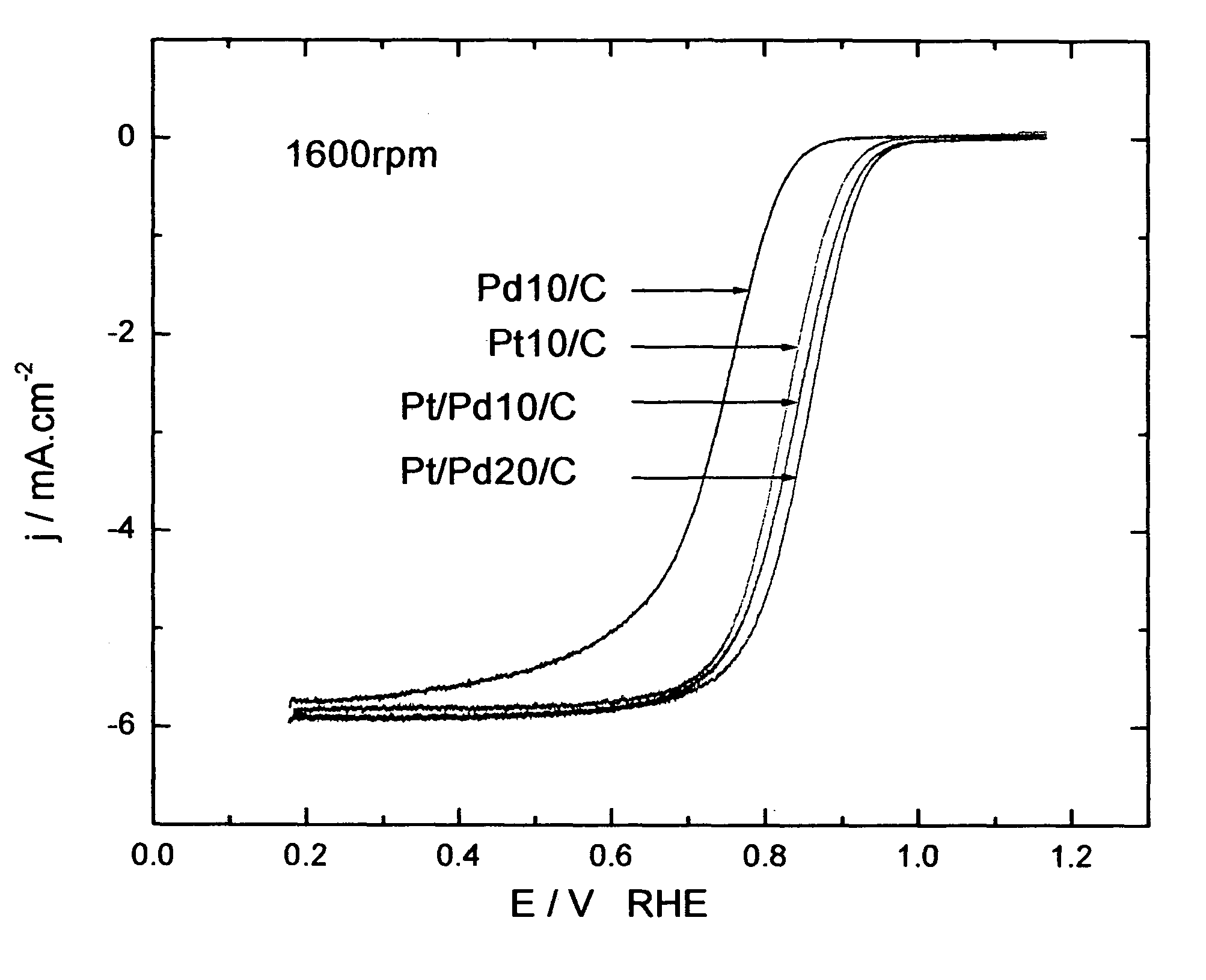
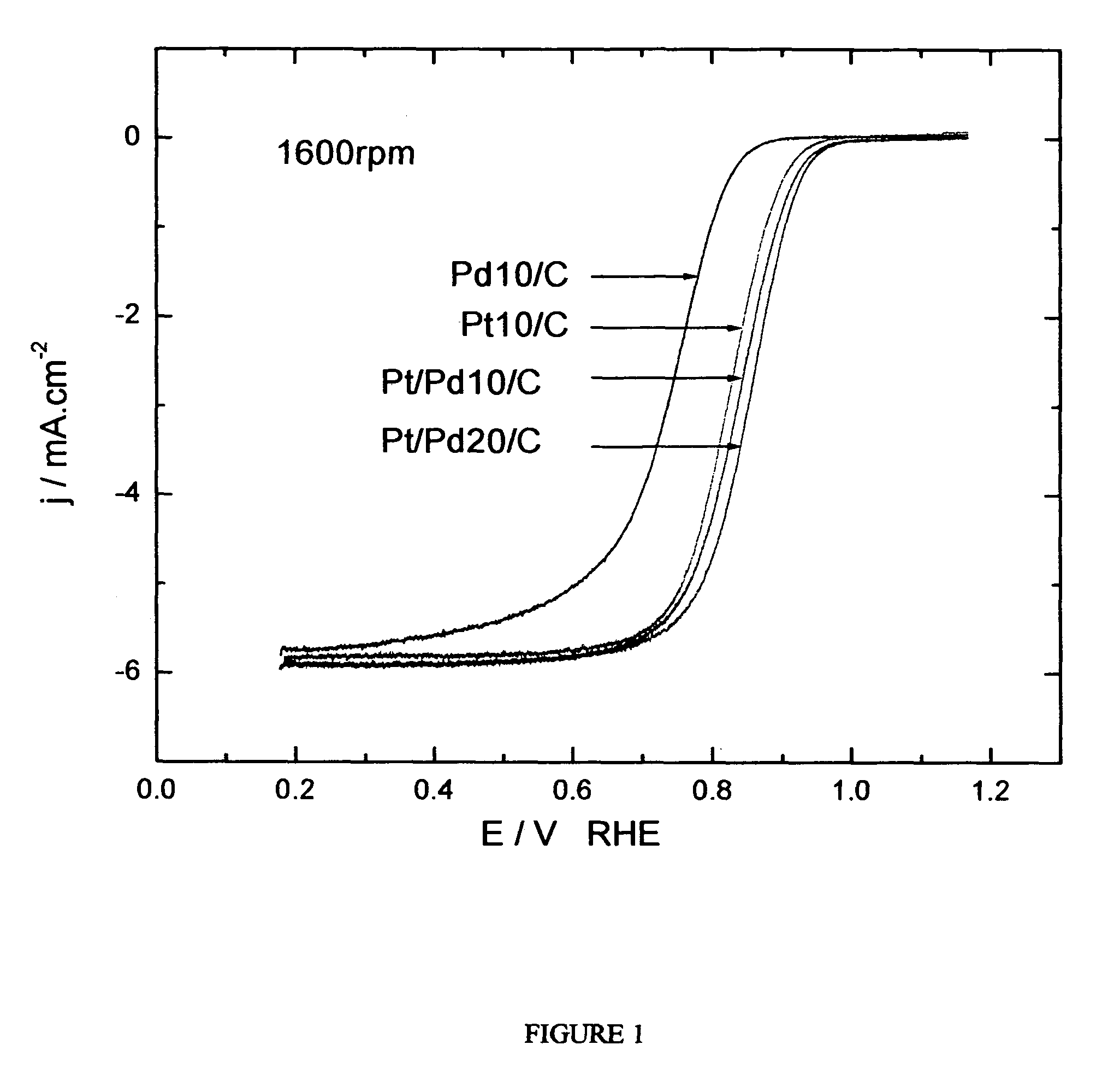
Electrocatalysts having platium monolayers on palladium, palladium alloy, and gold alloy core-shell nanoparticles, and uses thereof
ActiveUS7855021B2High catalytic activityReduce loadCell electrodesMetal-working apparatusRheniumMaterials science
The invention relates to platinum-coated particles useful as fuel cell electrocatalysts. The particles are composed of a noble metal or metal alloy core at least partially encapsulated by an atomically thin surface layer of platinum atoms. The invention particularly relates to such particles having a palladium, palladium alloy, gold alloy, or rhenium alloy core encapsulated by an atomic monolayer of platinum. In other embodiments, the invention relates to fuel cells containing these electrocatalysts and methods for generating electrical energy therefrom.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Synthesis methods of core-shell nanoparticles on a carbon support
ActiveUS20110129763A1Reduce usageNanostructure manufactureLiquid surface applicatorsPlatinumFuel cells
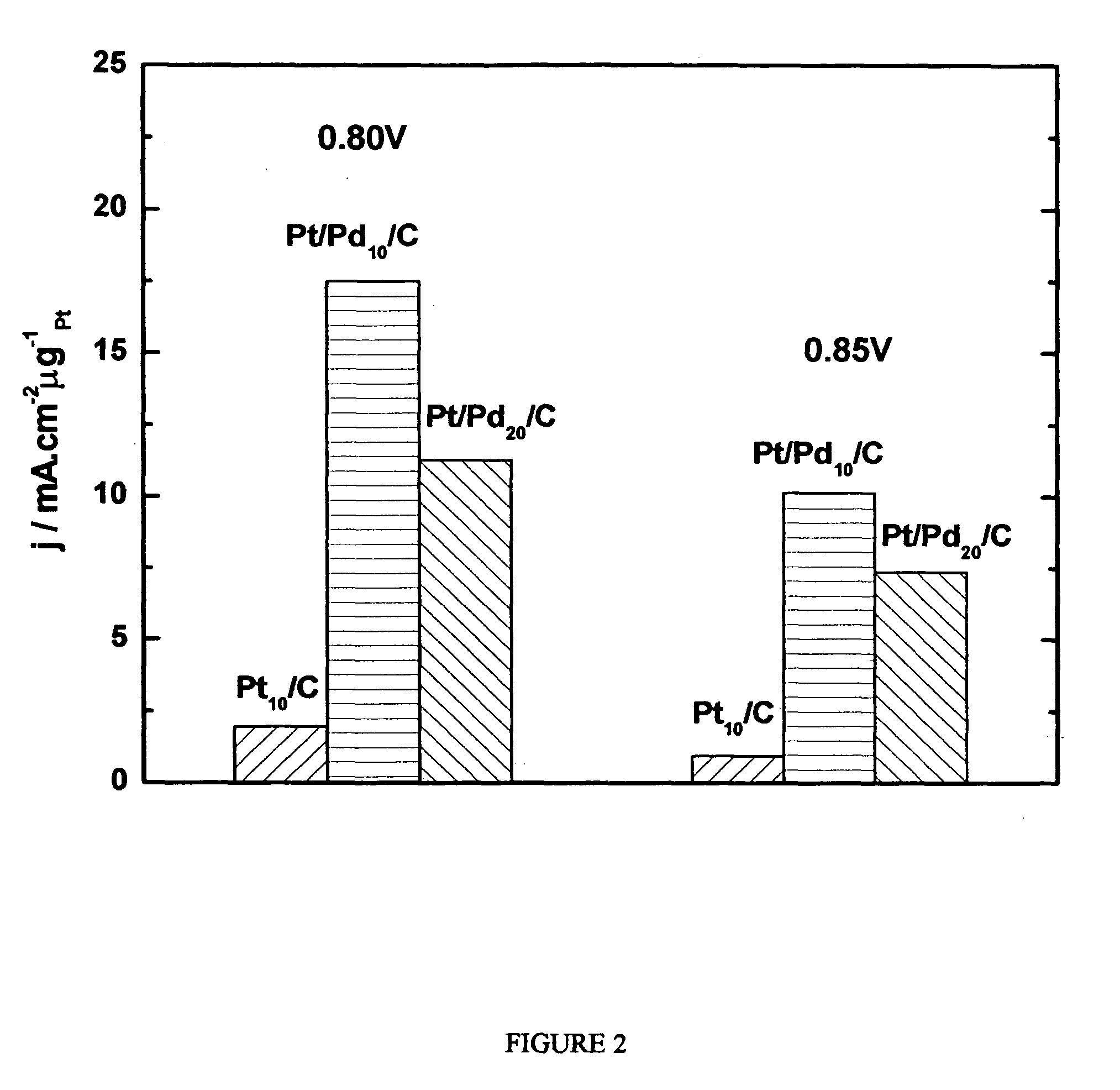
The present invention features a method for preparing core-shell nanoparticles supported on carbon. In particular, the present invention features a method for preparing core-shell nanoparticles supported on carbon, including: dispersing core nanoparticle powder supported on carbon in ethanol; adding a metal precursor which forms a shell and hydroquinone thereto; and mixing and reducing the same. Preferably, the disclosed method for preparing core-shell nanoparticles supported on carbon enables coating of transition metal nanoparticles including platinum on the surface of core metal nanoparticles at a monolayer level. Prepared core-shell nanoparticles of the present invention may be useful as catalysts or electrode materials of fuel cells.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Nanoparticles for delivery of a pharmacologically active agent
InactiveUS20060280798A1Hinder recognitionPowder deliveryMicroencapsulation basedActive agentWater insoluble
Core-shell nanoparticles comprising: (a) a core which comprises a water insoluble polymer or copolymer, and (b) a shell which comprises a hydrophilic polymer or copolymer; said nanoparticles being obtainable by emulsion polymerization of a mixture comprising, in an aqueous solution, at least one water-insoluble styrenic, acrylic or methacrylic monomer and specific hydrophylic monomers or copolymers.
Owner:INST SUPERIORE DI SANITA
Method for preparing ferrite/silicon dioxide core-shell nano particles by using ultrasonic treatment
InactiveCN1477082AIncrease the number ofIncrease contentFerrite nanoparticlesCore shell nanoparticles
The present invention relates to a method for using ultrasonic treatment to prepare ferrite-silicone dioxide core-shell nano particle. The method includes the following steps: firstly, using coprecipitation process to prepare ferrte nano particle, then making the ferrite nano particle under the process of ultrasonic treatment, then using inorganic silicone source and organic silicone source to make wrappage to twice so as to obtain the invented ferrite-silicone dioxide core-shell nano particle whose grain size is 50-200 nm. The product can be used in the fields of biological, sealing and magnetic recording material, etc.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
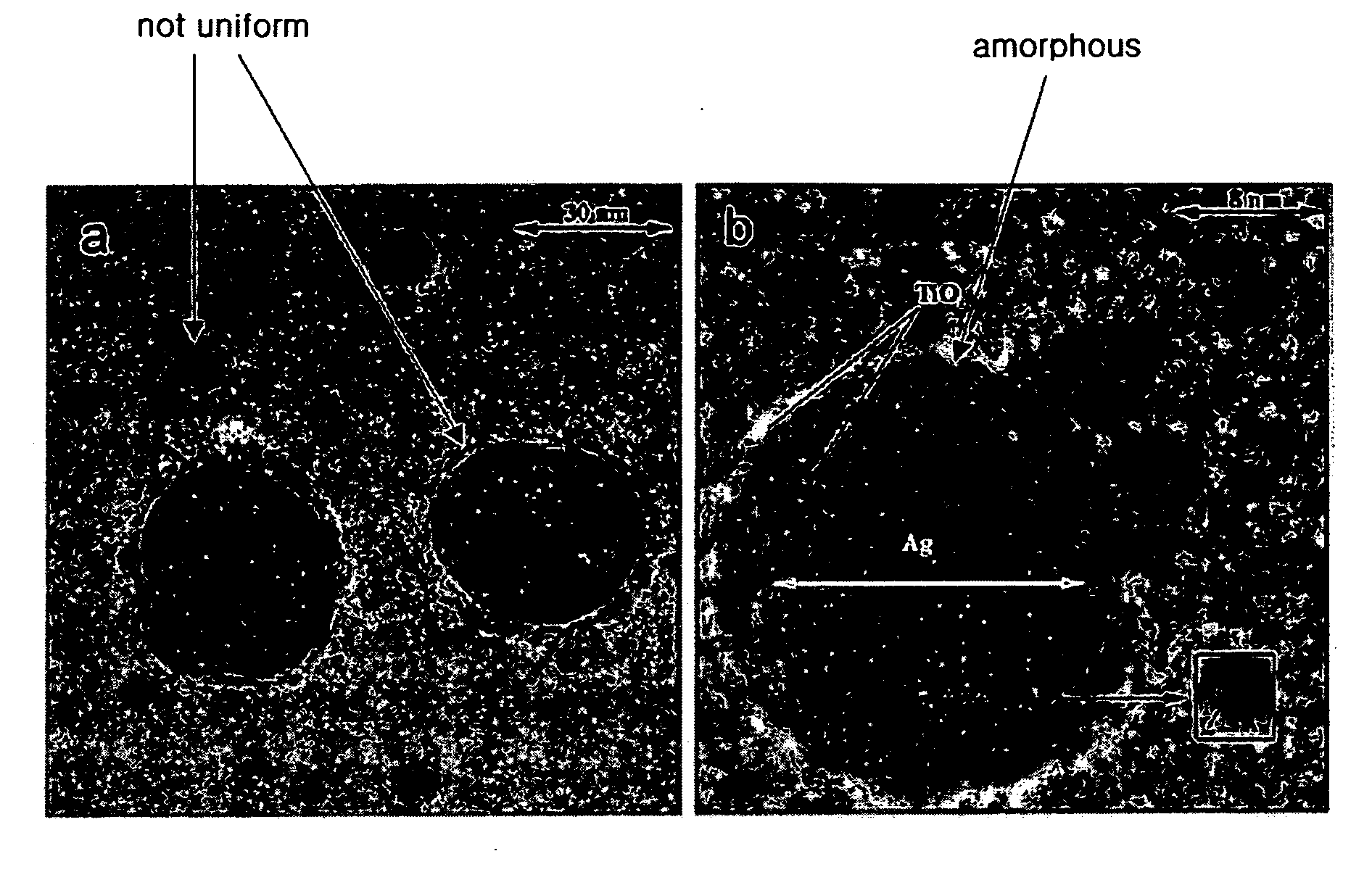
Method for preparing copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles
InactiveCN102335605ASmall particle sizeMorphological components are adjustableElectrolytic capacitorsCell electrodesPolyethylene glycolSolvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles. In the method, cupric ions provided by cuprous chloride are dissolved into ammonia water; an aqueous solution of polyethylene glycol, an aqueous solution of sodium citrate, an aqueous solution of ascorbic acid, a solution of tetrabutyl titanate (absolute ethyl alcohol) and urea are sequentially addedinto the ammonia water; the ammonia water is put into a teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave after the ammonia water is stirred at room temperature; and the nearly-spherical core-shell nanoparticles are prepared through controlling the temperature and the time for the thermal reaction of the mixed solvents. In the method for preparing the copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles, the ascorbic acid serves as a reducing agent and is used for reducing the cuprous ions; and the polyethylene glycol serves as a soft template. The method for preparing the copper-titanium dioxide core-shellnanoparticles has the advantages of simple process, environment-friendliness, low cost and the like; the outer layer of each of the prepared copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles is anatase titanium dioxide, and the inner layer of each of the prepared copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles is cubic-phase copper elementary substance; and the size distribution is even, and the particle size is controllable, thus the copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles can be used as the electrode materials and the photocatalyst materials of dye-sensitized solar cells.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Core-excited nanoparticles and methods of their use in the diagnosis and treatment of disease
InactiveUS8197471B1Minimal side-effectsEffective and practicalPowder deliveryNanotechDiseaseCore shell nanoparticles
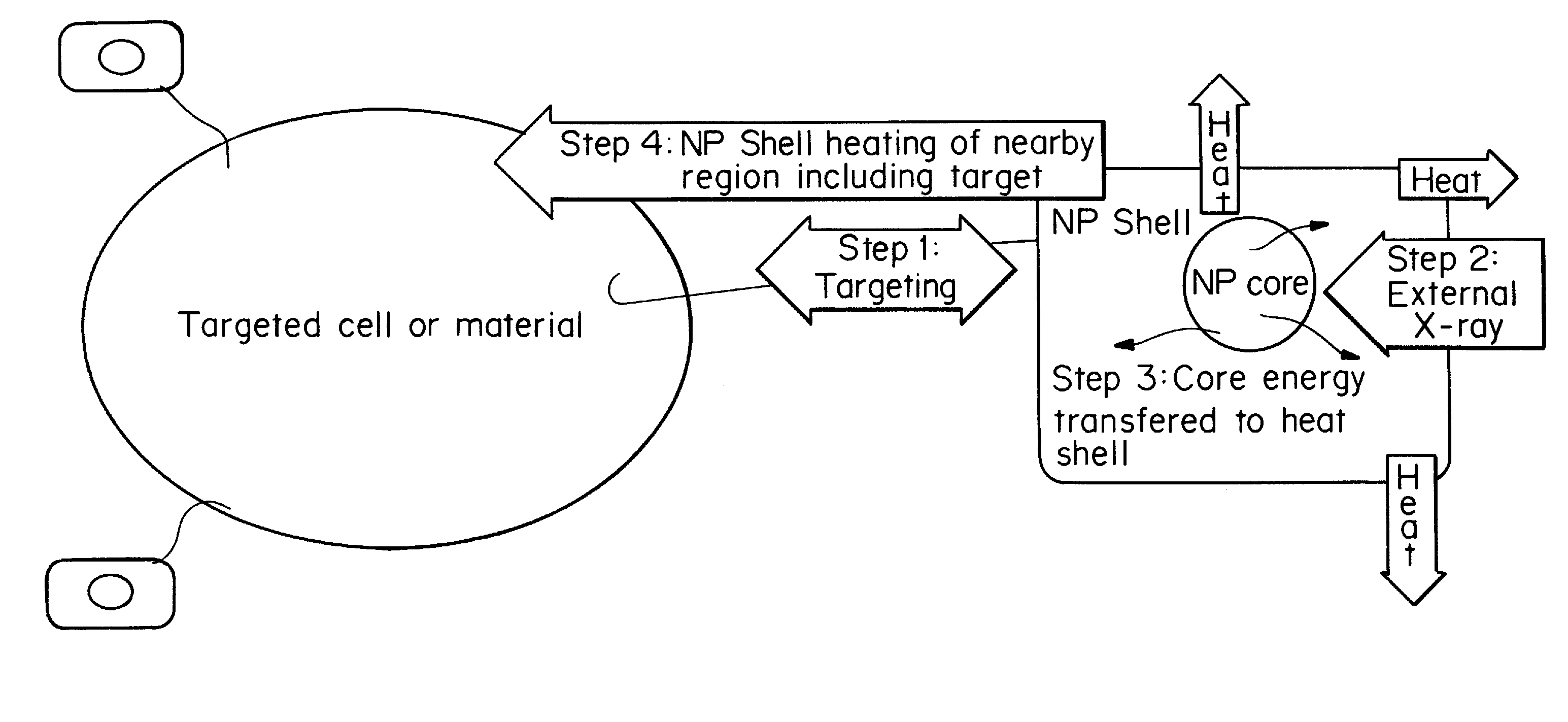
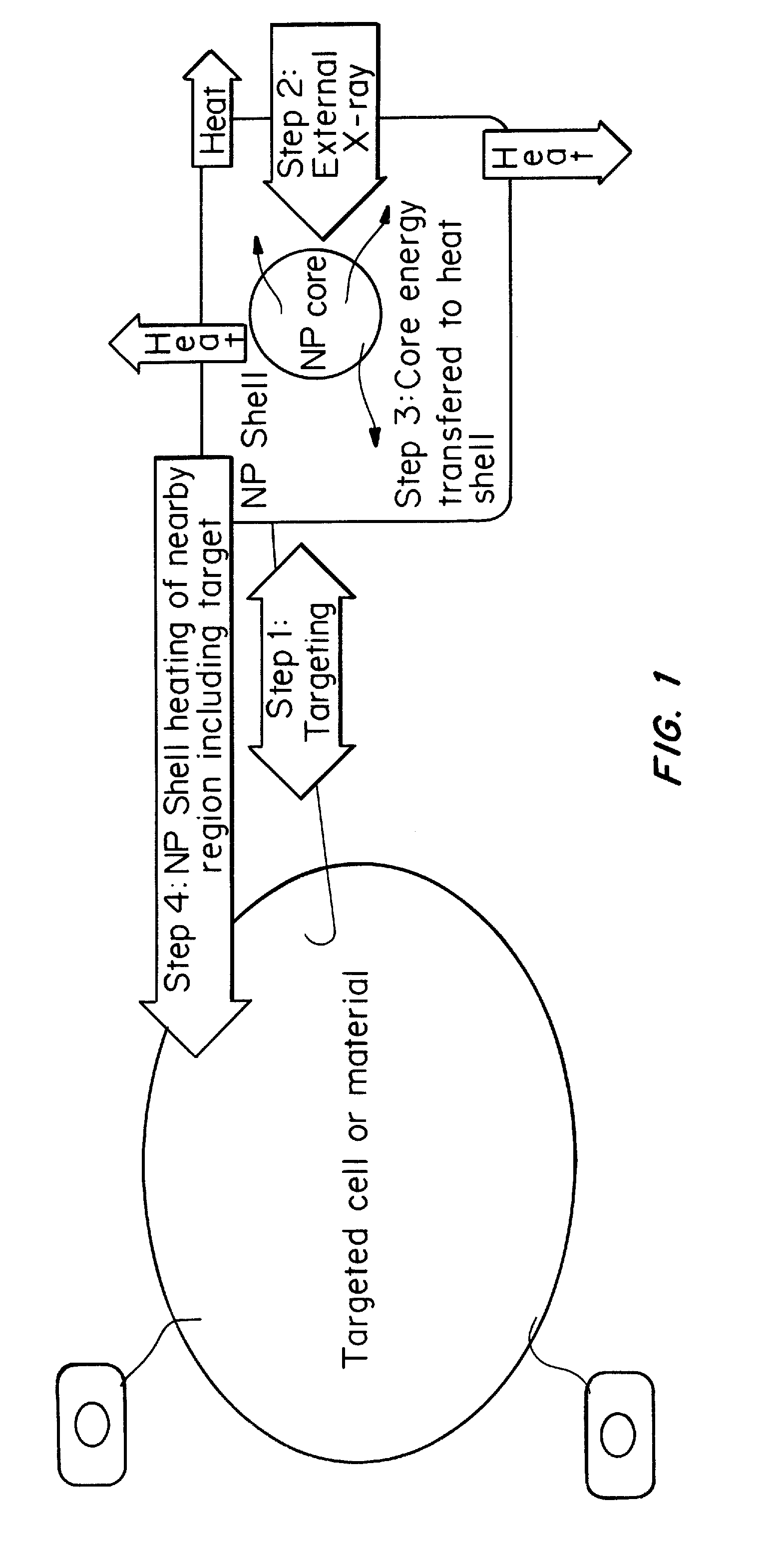
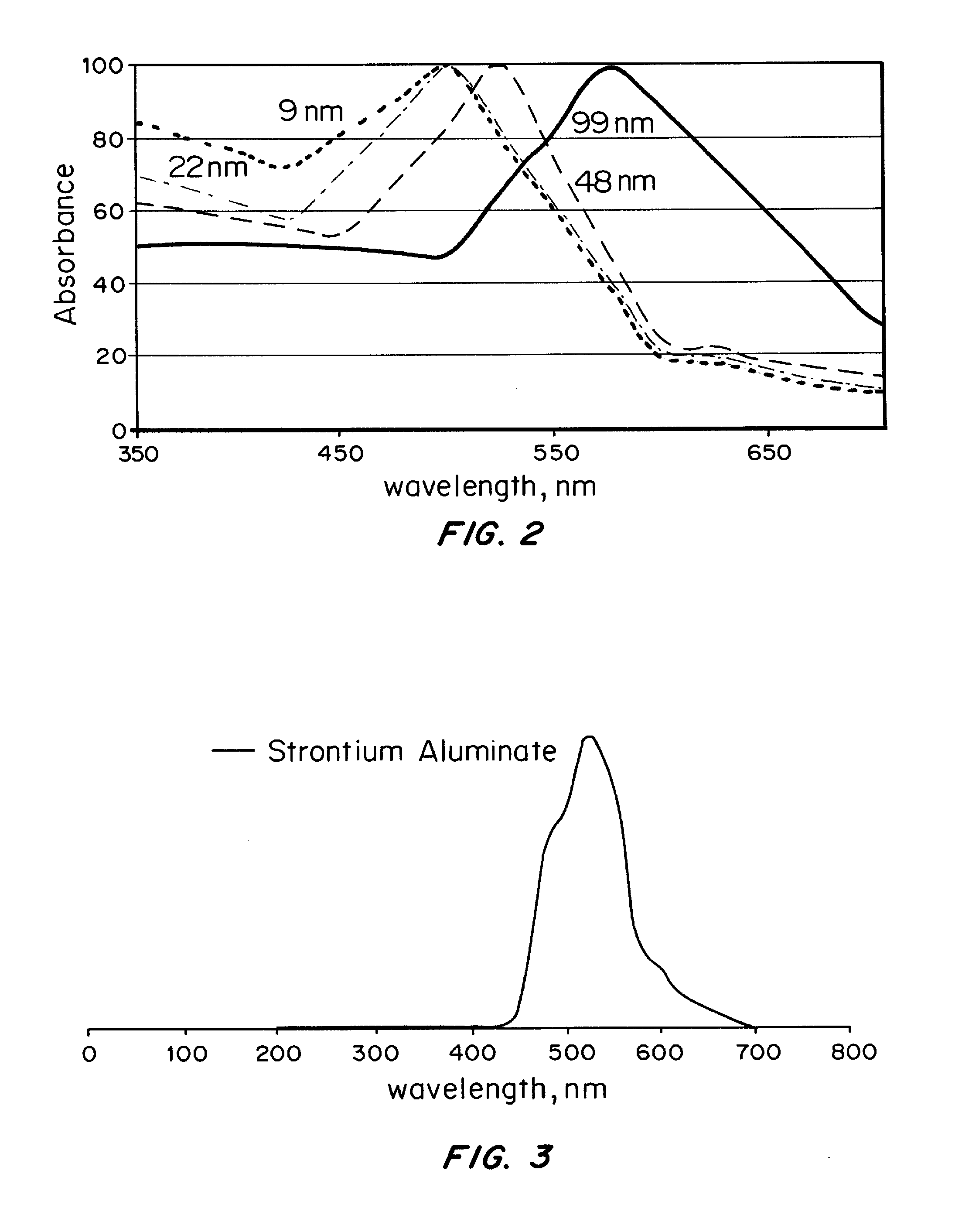
Core-excited nanoparticle thermotherapy (CENT), is an improved material for use in thermotherapy. The CENT method uses both core-exciting energy (including x-rays) and core-shell nanoparticles, specifically designed to absorb radiation in their core structure, then transfer energy from the core to the shell, to heat the outer shell of the nanoparticle. The heated nanoparticle then heats the surrounding region to a temperature sufficient to detect, affect, damage and / or destroy the targeted cell or material. CENT nanoparticles can be bound to targeting agents that deliver them to the region of the diseased cell.
Owner:TERSIGNI SAMUEL HARRY
Core-shell nanoparticles with multiple cores and a method for fabricating them
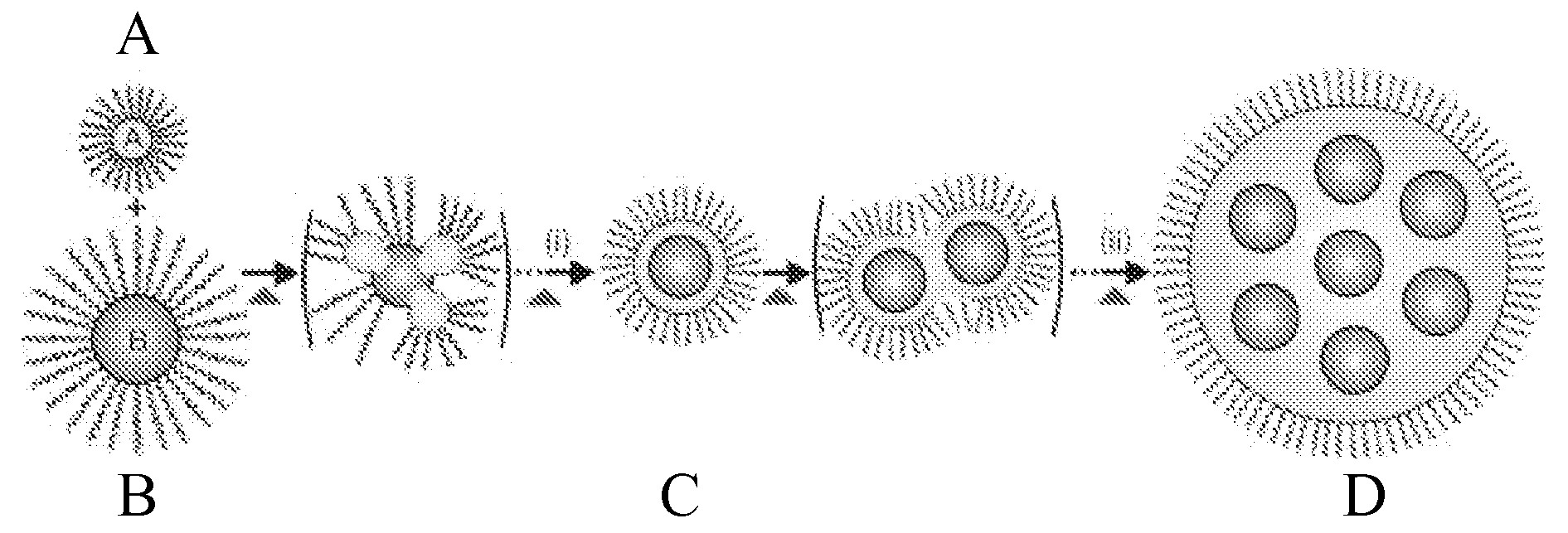
ActiveUS20080226917A1The process is simple and effectiveNanomagnetismNanosensorsCore shell nanoparticlesNanometre
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
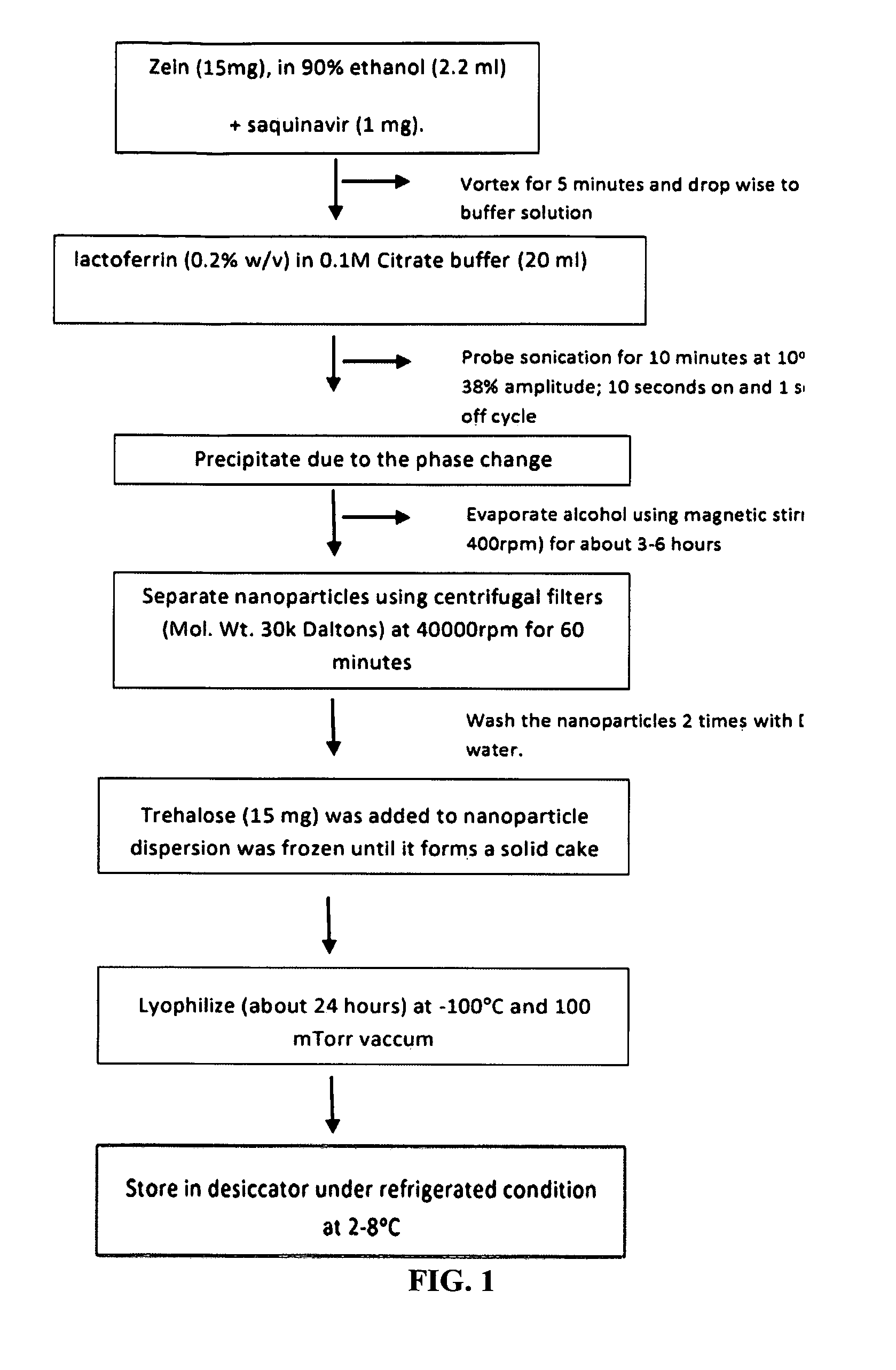
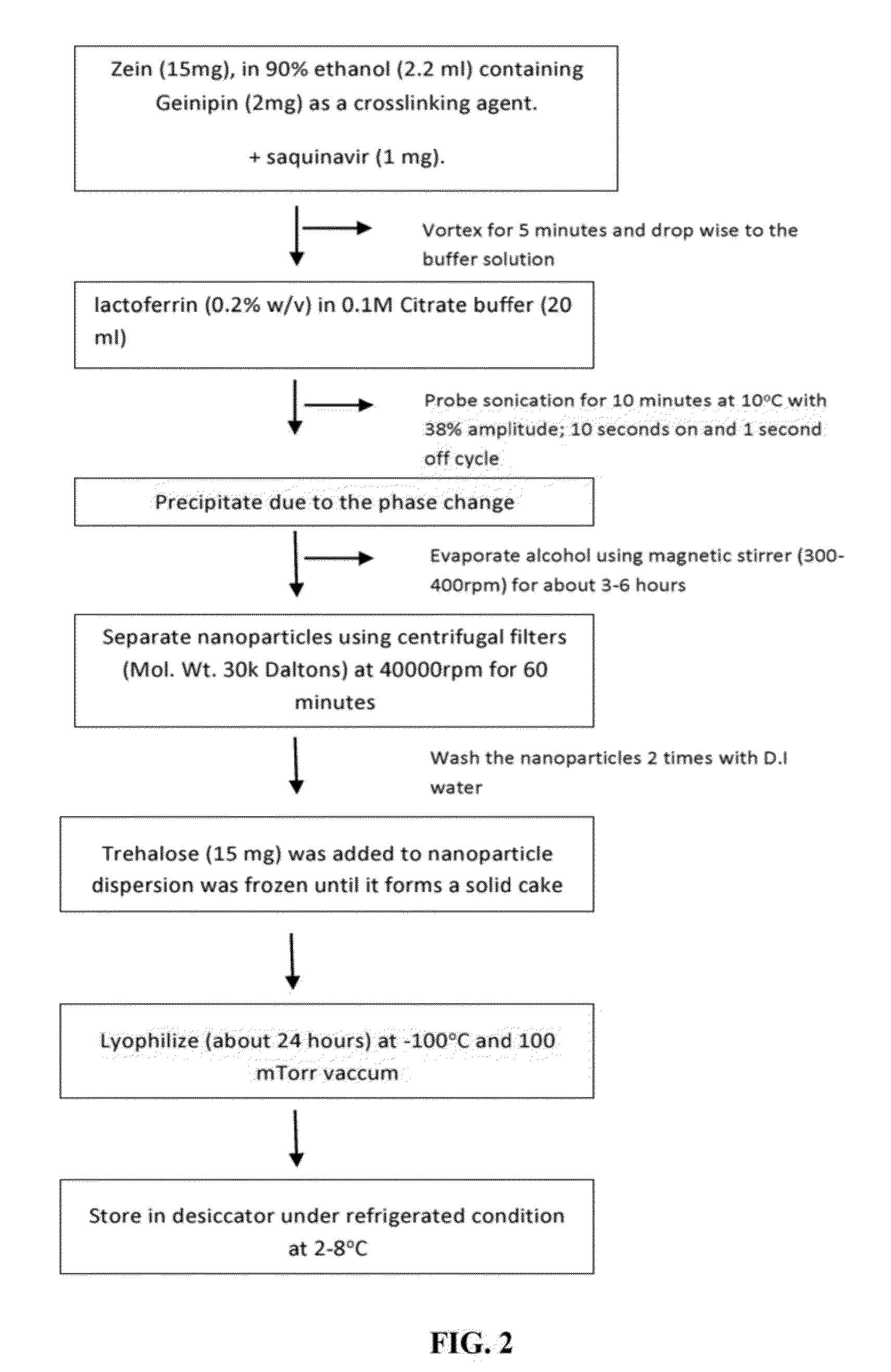
Novel core-shell nanoparticles for oral drug delivery
The invention relates to an oral nanoparticle drug delivery system, including methods for preparing such a system using a hydrophobic water insoluble protein, which nanoparticles may include prolamine to generate said oral drug delivery system.
Owner:SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY
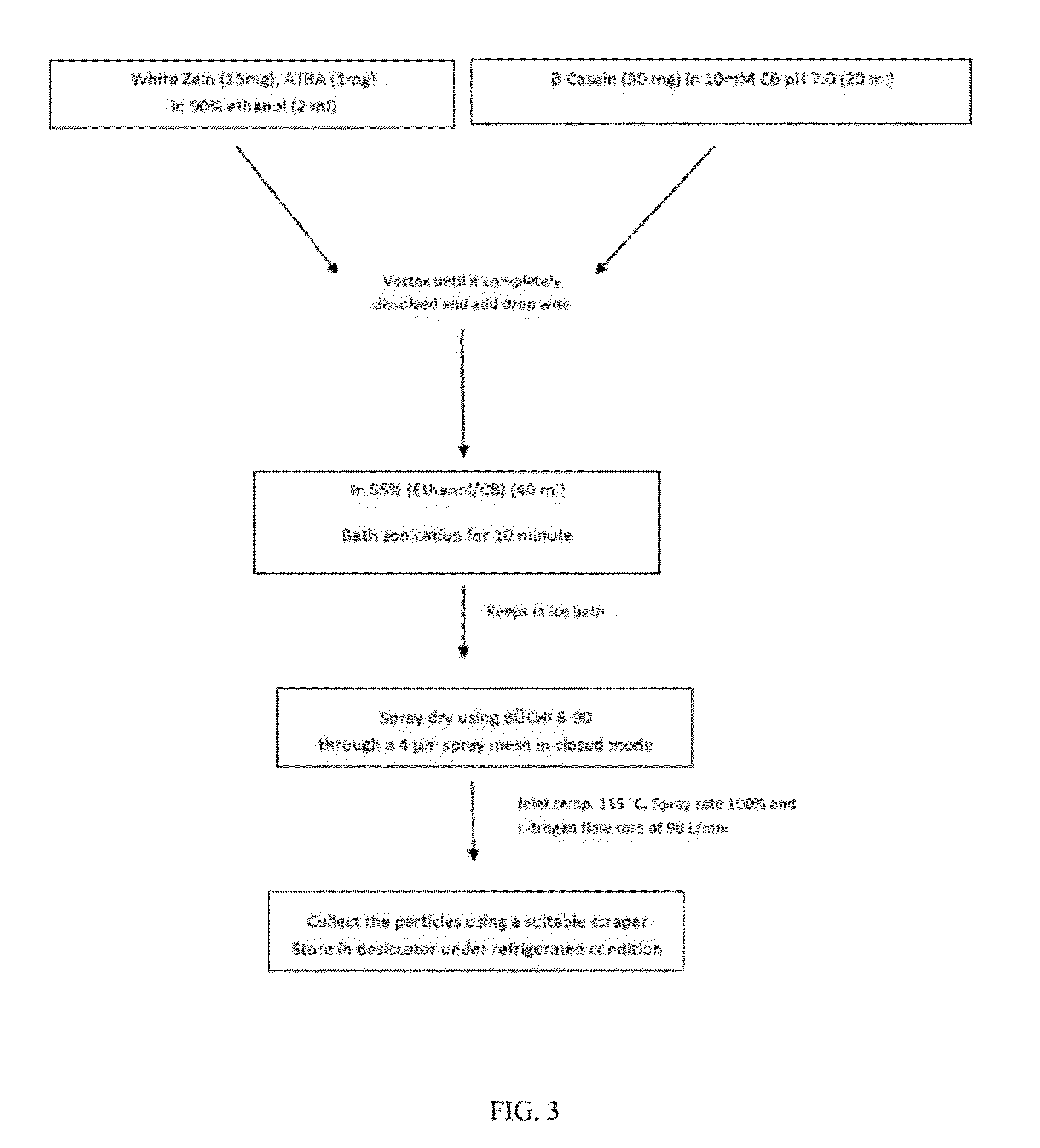
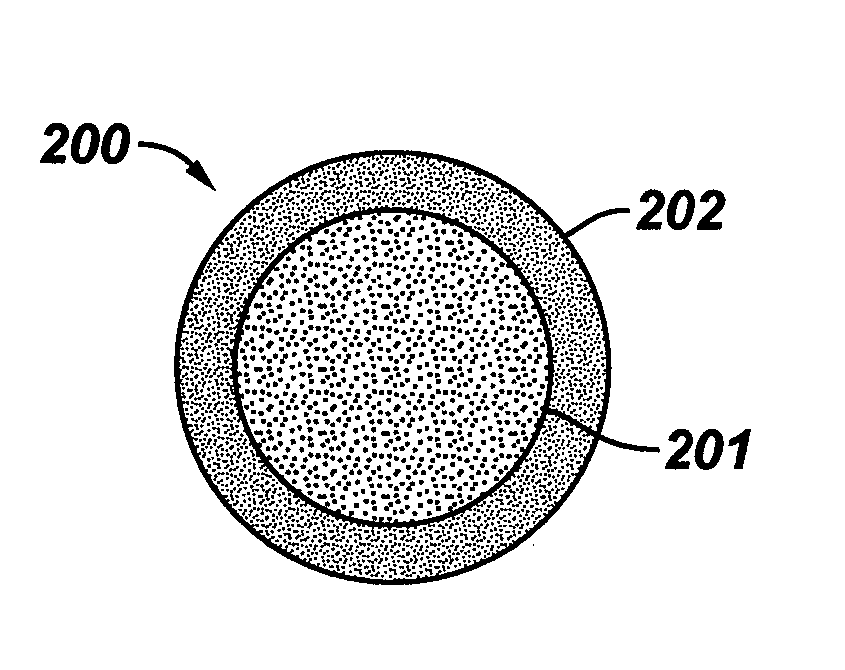
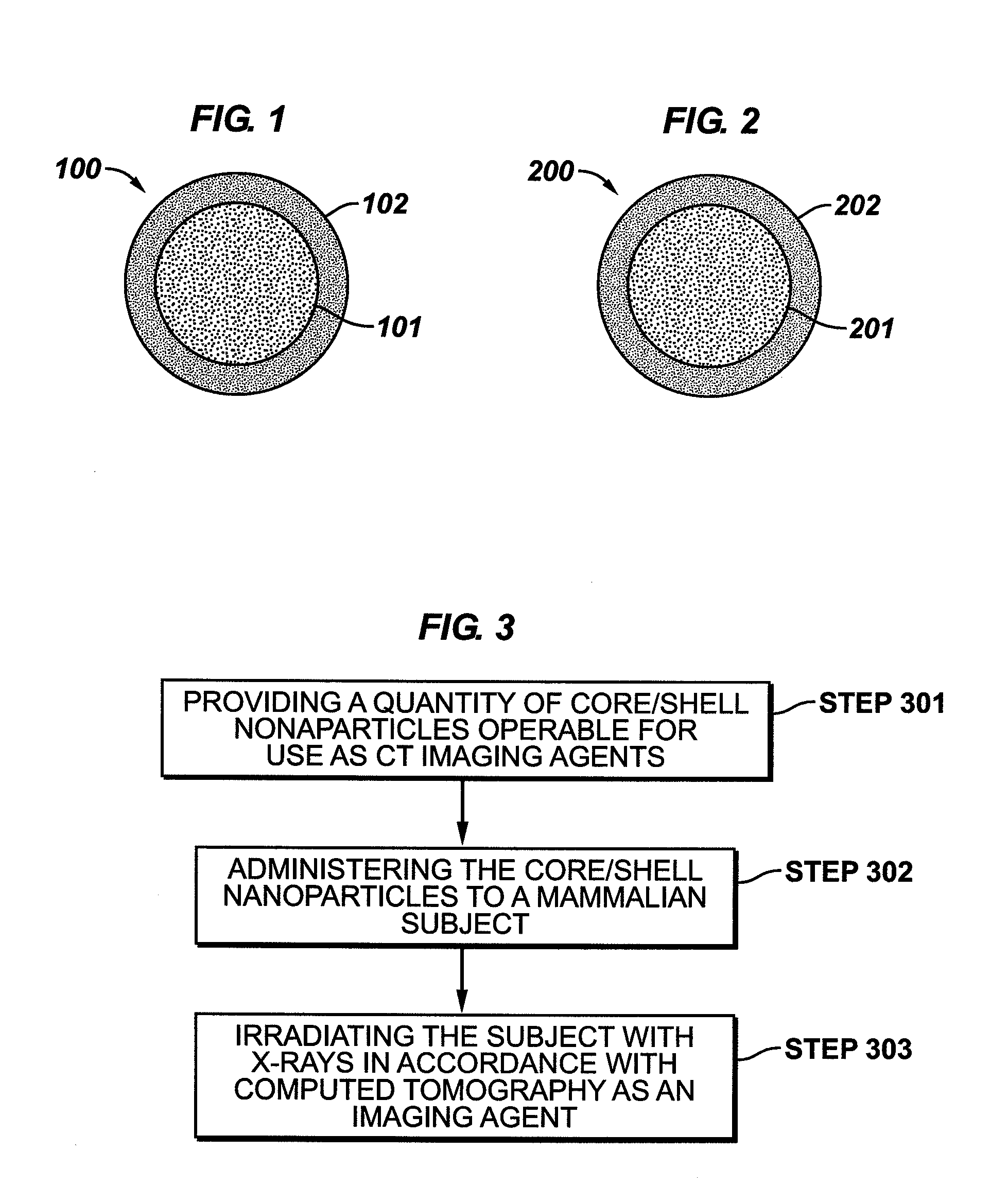
Nanoparticle-based imaging agents for x-ray / computed tomography and methods for making same
InactiveUS20070122620A1Prolong blood half-lifeIncrease contrastPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyTomographyCore shell nanoparticles
The present invention is generally directed to core / shell nanoparticles, wherein such core / shell nanoparticles comprise a nanoparticle core and a nanoshell disposed about the nanoparticle core such that, in the aggregate, they form a core / shell nanoparticle that is operable for use as an imaging agent in X-ray / computed tomography (CT). Typically, such core / shell nanoparticle-based X-ray CT imaging agents further comprise a targeting species for targeting the imaging agent to diseased sites.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Core-First Nanoparticle Formation Process, Nanoparticle, And Composition
InactiveUS20120132346A1Stabilize seedPrevent precipitationMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCross-linkCore shell nanoparticles
A method is provided for synthesizing a core-shell nanoparticle that includes the following steps: providing a polymeric seed (in a solvent) that includes a mono-vinyl monomer cross-linked with a cross-linking agent to form the core of the nanoparticle, the core has an average diameter of from about nanometers to about 10,000 nanometers, and the core has polymer chains with living ends; adding a stabilizer to stabilize the seed and prevent the seed from precipitating out of solution; and grafting a shell species onto the living ends of the core to form the shell of the nanoparticle. A core-first synthesized nanoparticle, along with a rubber composition and tire product are also provided.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
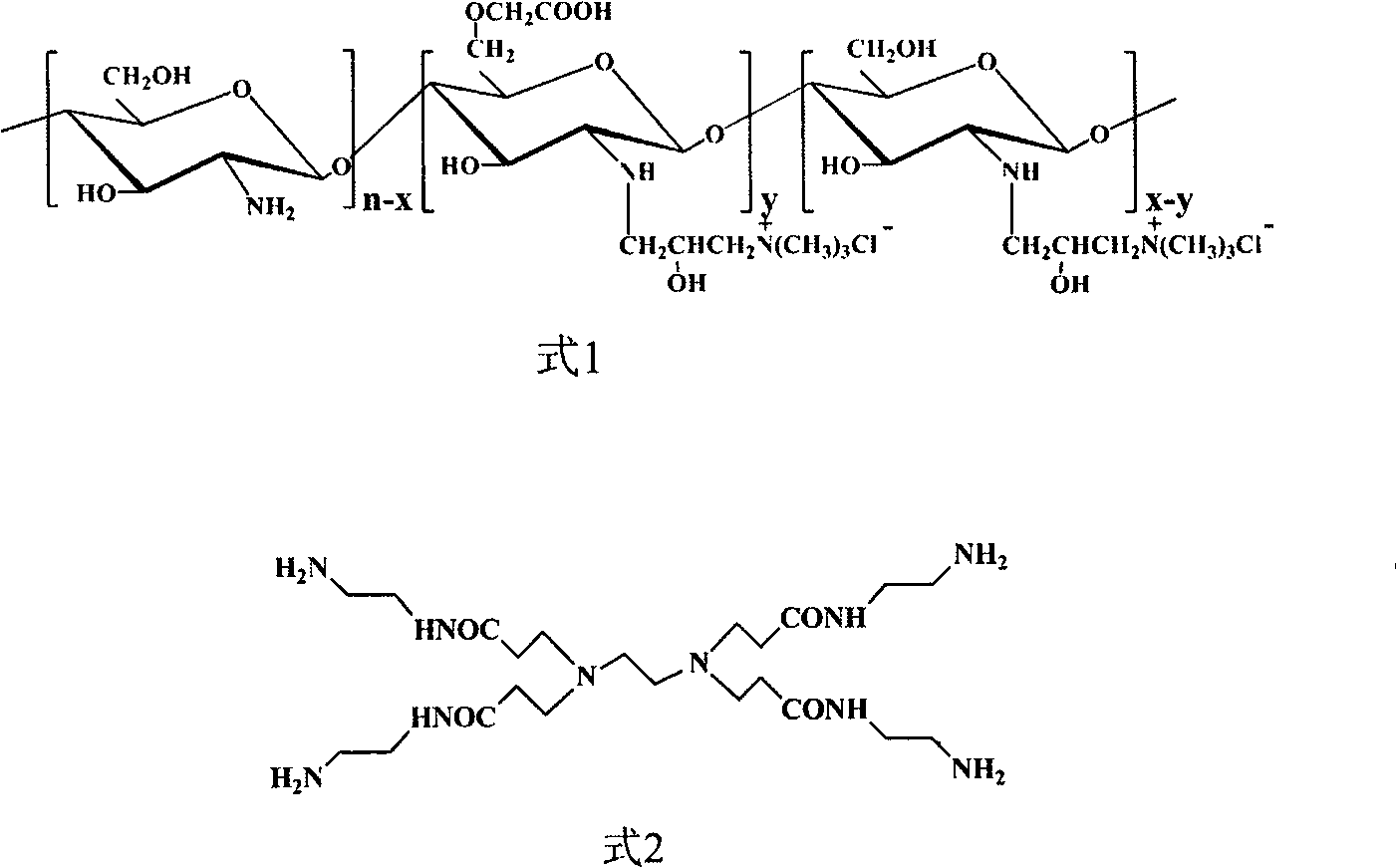
Carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt/PAMAM(Polyamidoamine) core-shell nanoparticles and preparation method
The invention discloses carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt / PAMAM(Polyamidoamine) core-shell nanoparticles and a preparation method. The nanoparticles are chitosan derivatives which are formed in a way that amino-terminated polyamidoamine dendritic macromolecule is grafted with carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt, and the chitosan derivatives are self-aggregated to form core-shell nanoparticles in water solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing quaterisation decoration to amino at a second position of chitosan by CTA (3-Chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride); performing carboxymethyl decoration to hydroxy at a sixth position of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt to synthetize carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt; activating carboxyl of the carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt by using NHS(N-Hydroxysuccinimide) / EDC(carbodiimide) to link the amino-terminated polyamidoamine dendritic macromolecule to synthetize the dendritic chitosan derivatives. The preparation process condition is simple and mild, and the product is easy to purify; and the core-shell nanoparticles of the prepared dendritic chitosan derivatives have the advantages of excellent water-solubility and functionality and has the attractive application prospect in the fields of antibiosis, gene transfer and drug controlled release.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
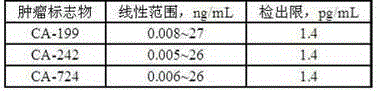
Preparation and application of unmarked electrochemiluminescent tumor marker immunosensor
The invention discloses a preparation method of an unmarked electrochemiluminescent tumor marker immunosensor and application of the immunosensor in detection of tumor markers, and belongs to the field of novel nano functional materials and biosensors. According to the preparation method of the unmarked electrochemiluminescent tumor marker immunosensor, a novel micro-nano material NH4CoPO4 is taken as a substrate so that the luminescence stability of a luminol-hydrogen peroxide luminescent system can be greatly enhanced, and meanwhile, rod-like gold@siver core-shell nanoparticles are taken as a biomimetic catalytic luminescent system, and therefore, an unmarked electrochemiluminescent immunosensor, which is low in cost, high in sensitivity, good in specificity, fast in detection and simple to prepare and is used for detecting tumor makers, can be prepared.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
An Organic Solar Cell Using Core-Shell Nanoparticles to Improve Conversion Efficiency
InactiveCN102299261AImprove light absorption efficiencyImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellCore shell nanoparticles
The invention discloses an organic solar cell that uses core-shell nanoparticles to improve conversion efficiency, and aims to provide a new type of organic solar cell that utilizes the surface plasmon enhancement effect of metal-core-shell nano-core-shell particles to improve conversion efficiency and reduce material costs. Battery. It includes a first electrode, a modified layer, an active layer and a second electrode, wherein the core-shell structure nanoparticles with surface plasmon effect are at least contained in the junction of the active layer and the modification layer, inside the active layer and at the junction of the active layer and the second electrode at one or more of these three locations. At the same time, the invention can control and tune the surface plasmon resonance enhancement characteristics of the metal-dielectric core-shell nanoparticles, thereby improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the organic solar cell.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
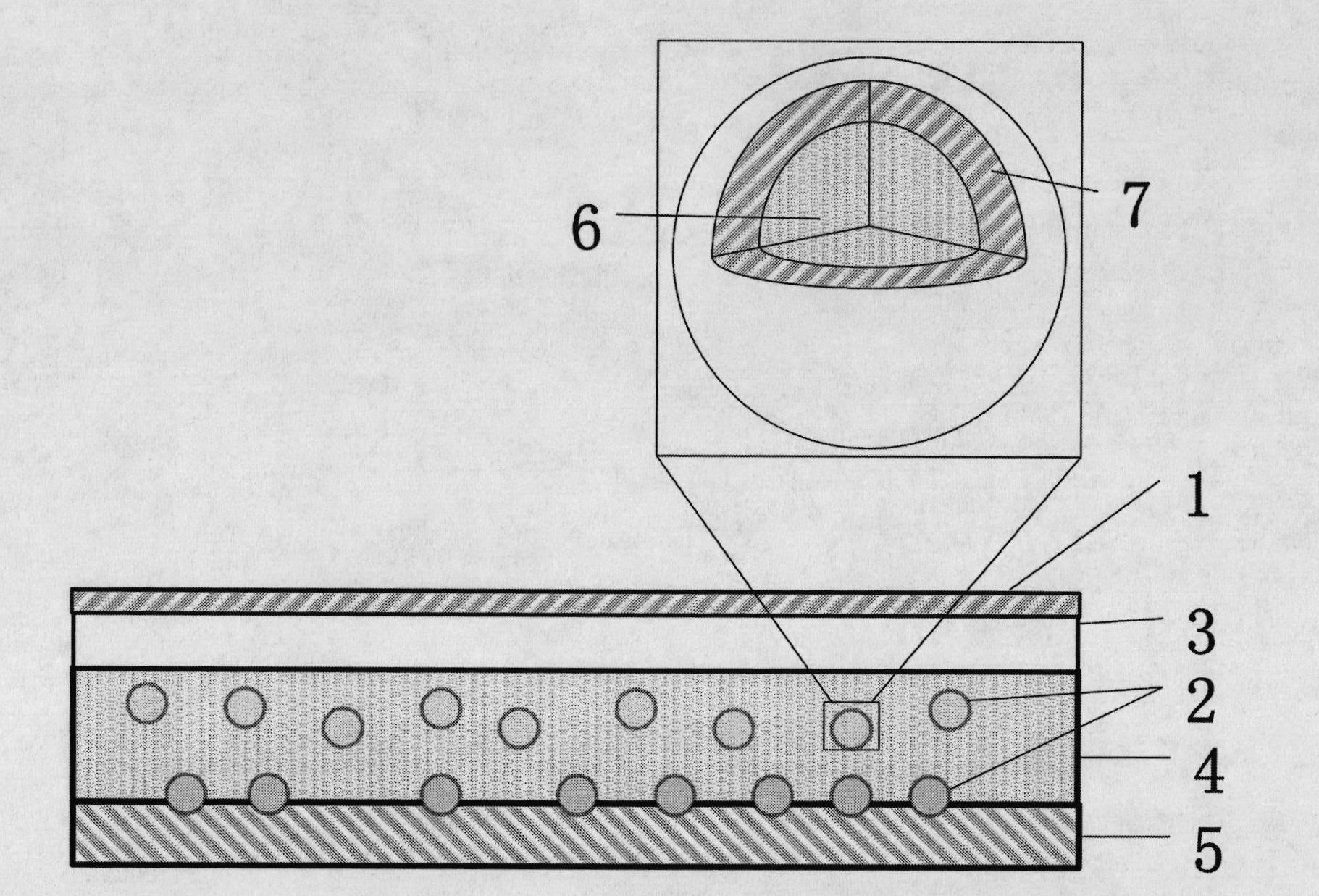
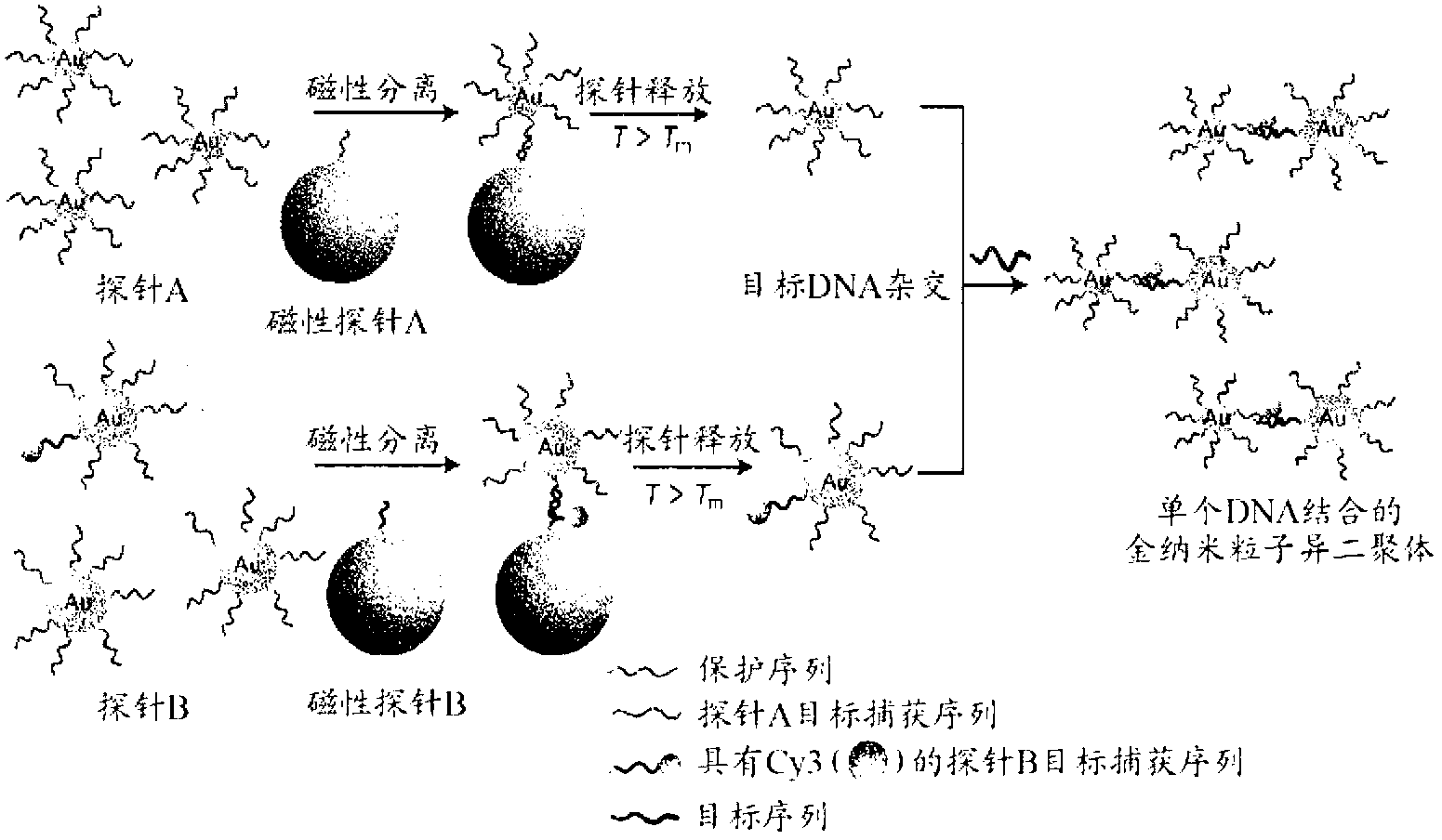
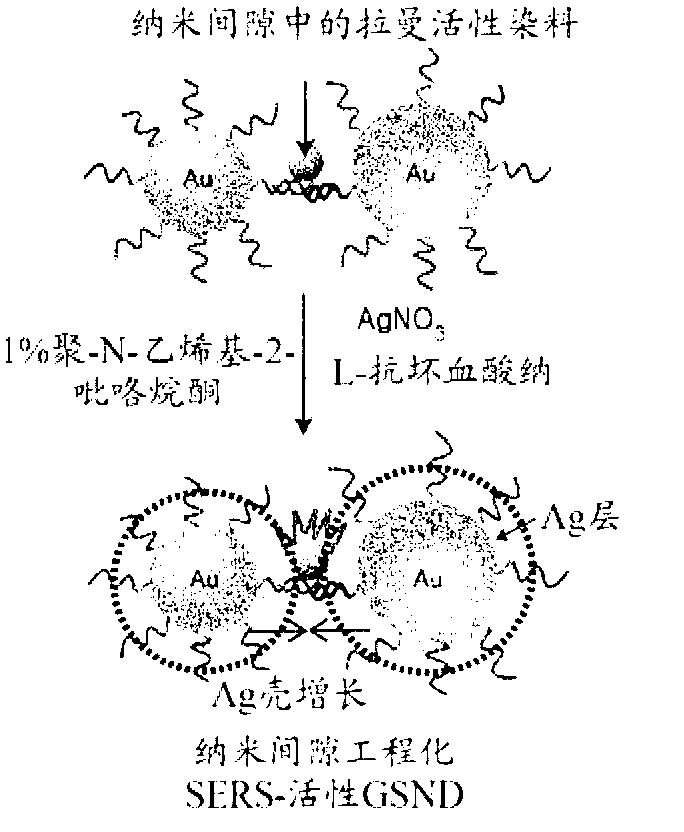
Heterodimer Core-shell Nanoparticle In Which Raman-active Molecules Are Located At A Binding Portion Of A Nanoparticle Heterodimer, Use Thereof, And Method For Preparing Same
ActiveCN102811943AStrong Raman scattering (SERS) signalHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual molecule manipulationCore shell nanoparticlesCore shell
The present invention relates to a nanoparticle heterodimer in which Raman-active molecules are located at a binding portion of the nanoparticle heterodimer, and more particularly, to a core-shell nanoparticle heterodimer comprising: a gold or silver core having a surface to which oligonucleotides are bonded; and a gold or silver shell covering the core. In addition, the present invention relates to the core-shell nanoparticle heterodimer, to a method for preparing same, and to the use thereof.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH +1
Multifunctional stealth nanoparticules for biomedical use
InactiveUS20120082728A1Inhibit aggregationImprove delivery efficiencyPowder deliveryLiquid surface applicatorsCore shell nanoparticlesCoupling
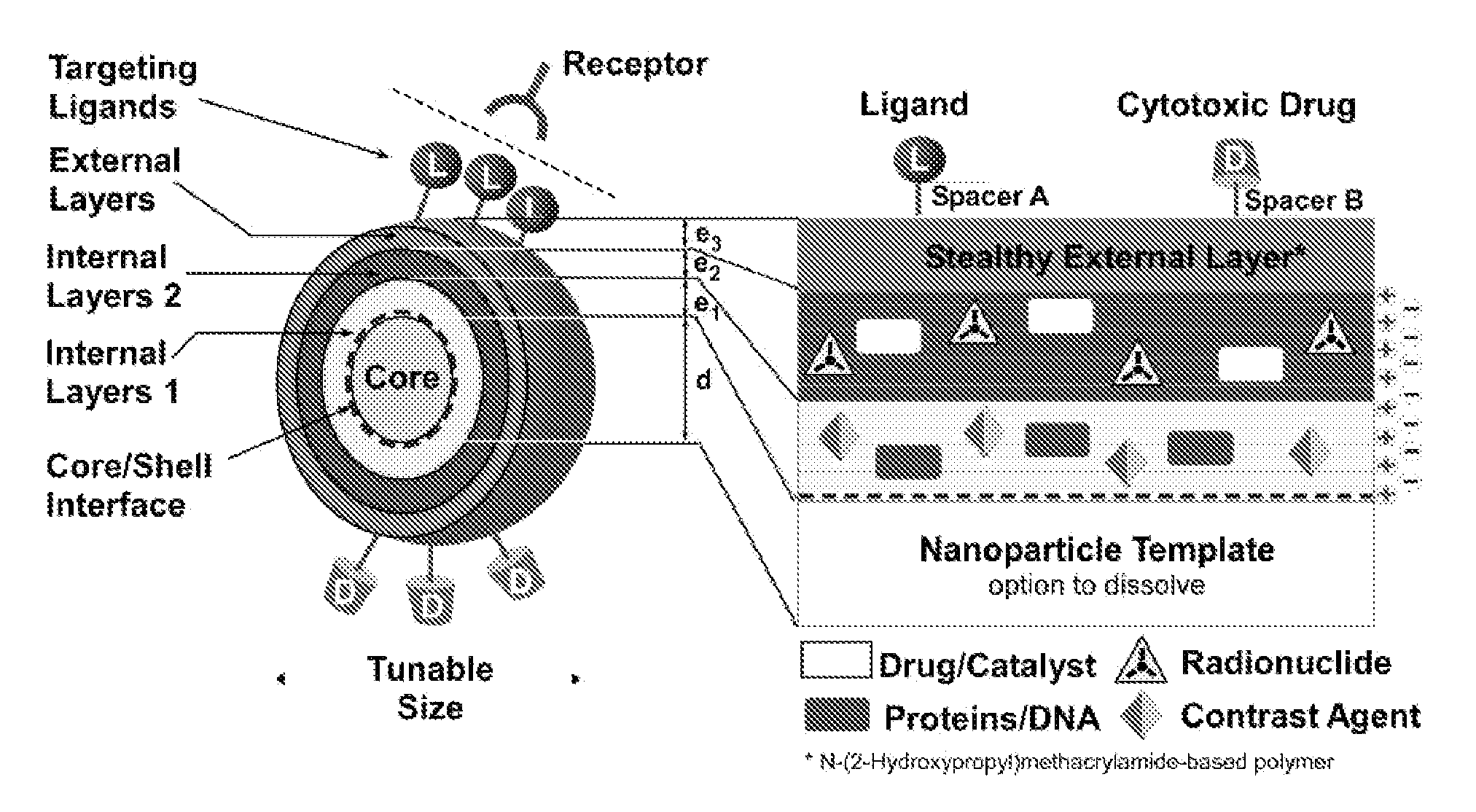
The present invention relates to the field of drug delivery nanosystems. More precisely, the present invention concerns a copolymer with advantageous properties for the outer coating of various nanoparticles. Said copolymer comprises at least three types of monomers with stealthy, coupling and therapeutic properties respectively, as well as an optional fourth type of monomers with targeting properties. The present invention also relates to core-shell or hollow shell nanoparticles coated by an external layer of the copolymer according to the invention. Several types of core-shell nanoparticles are envisaged. The invention also concerns methods for preparing said nanoparticles, as well as pharmaceutical compositions or medicaments comprising them.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
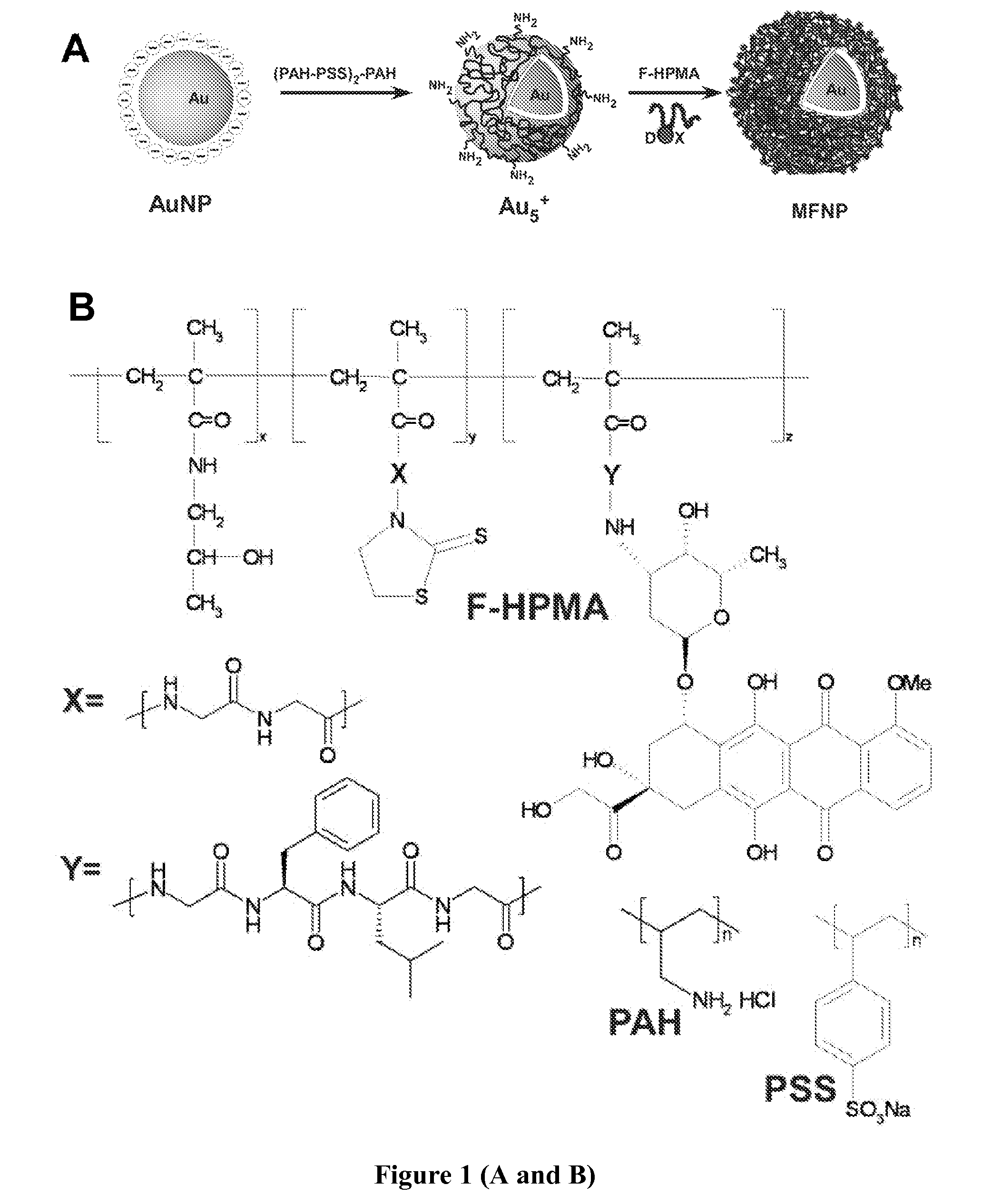
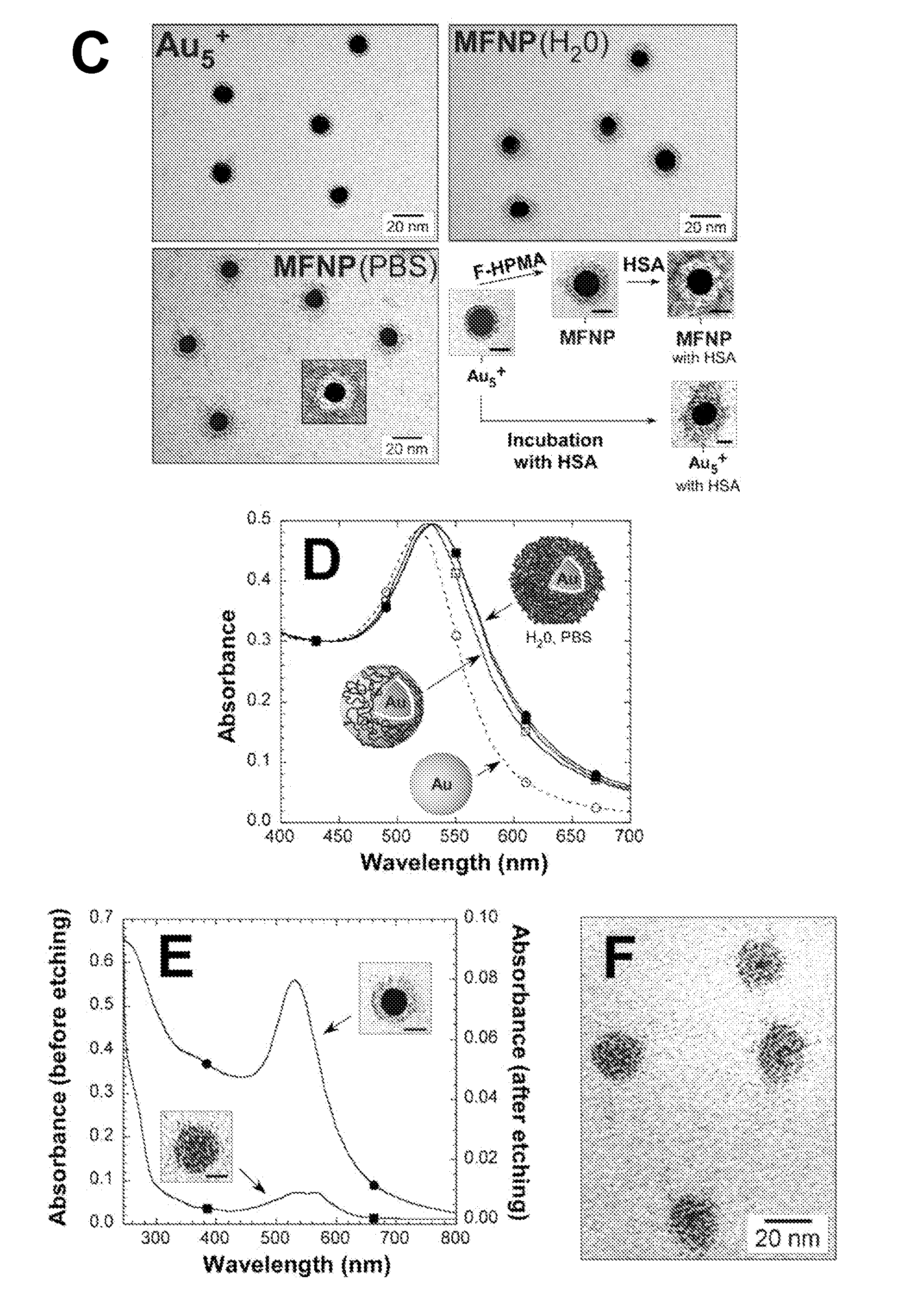
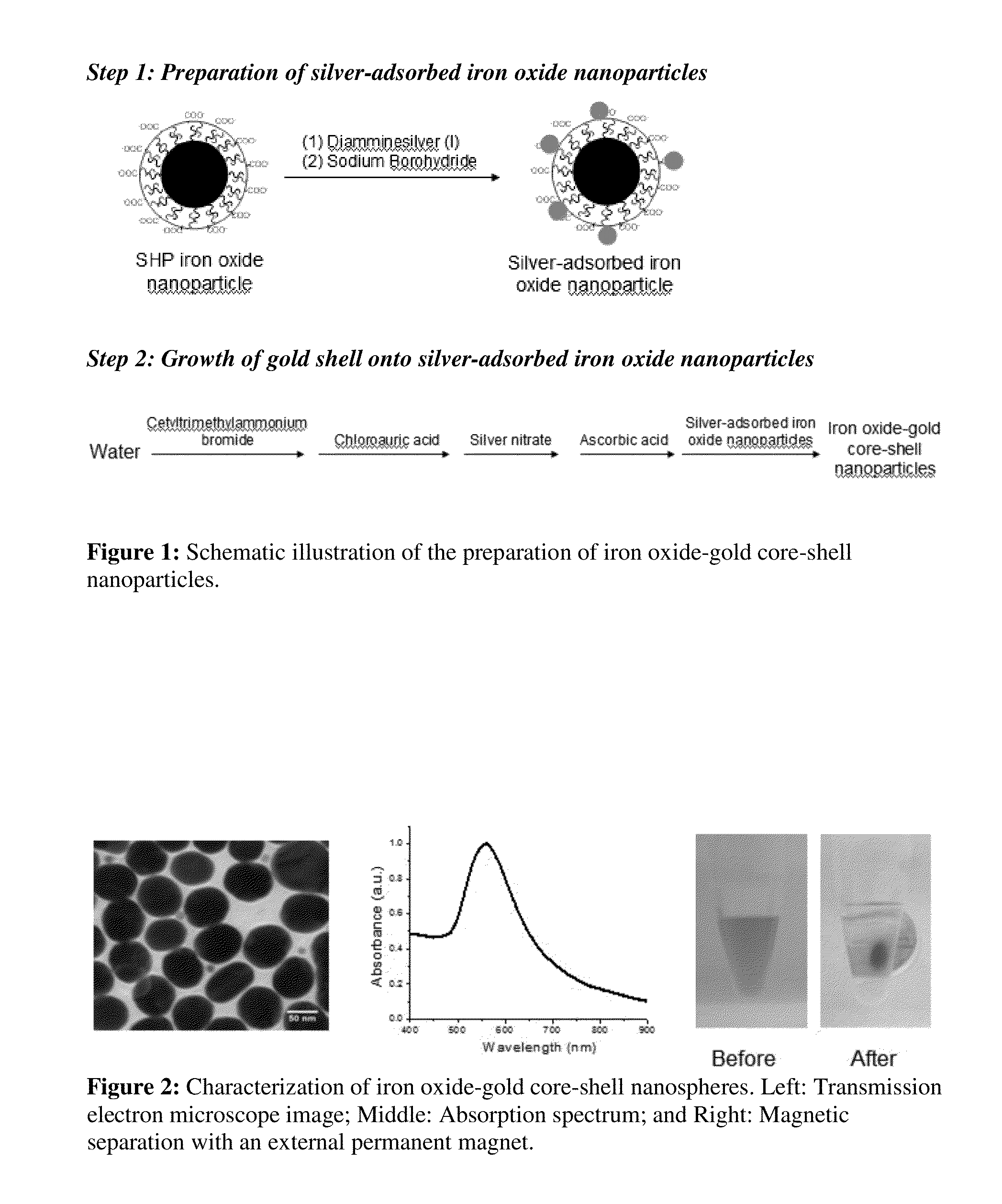
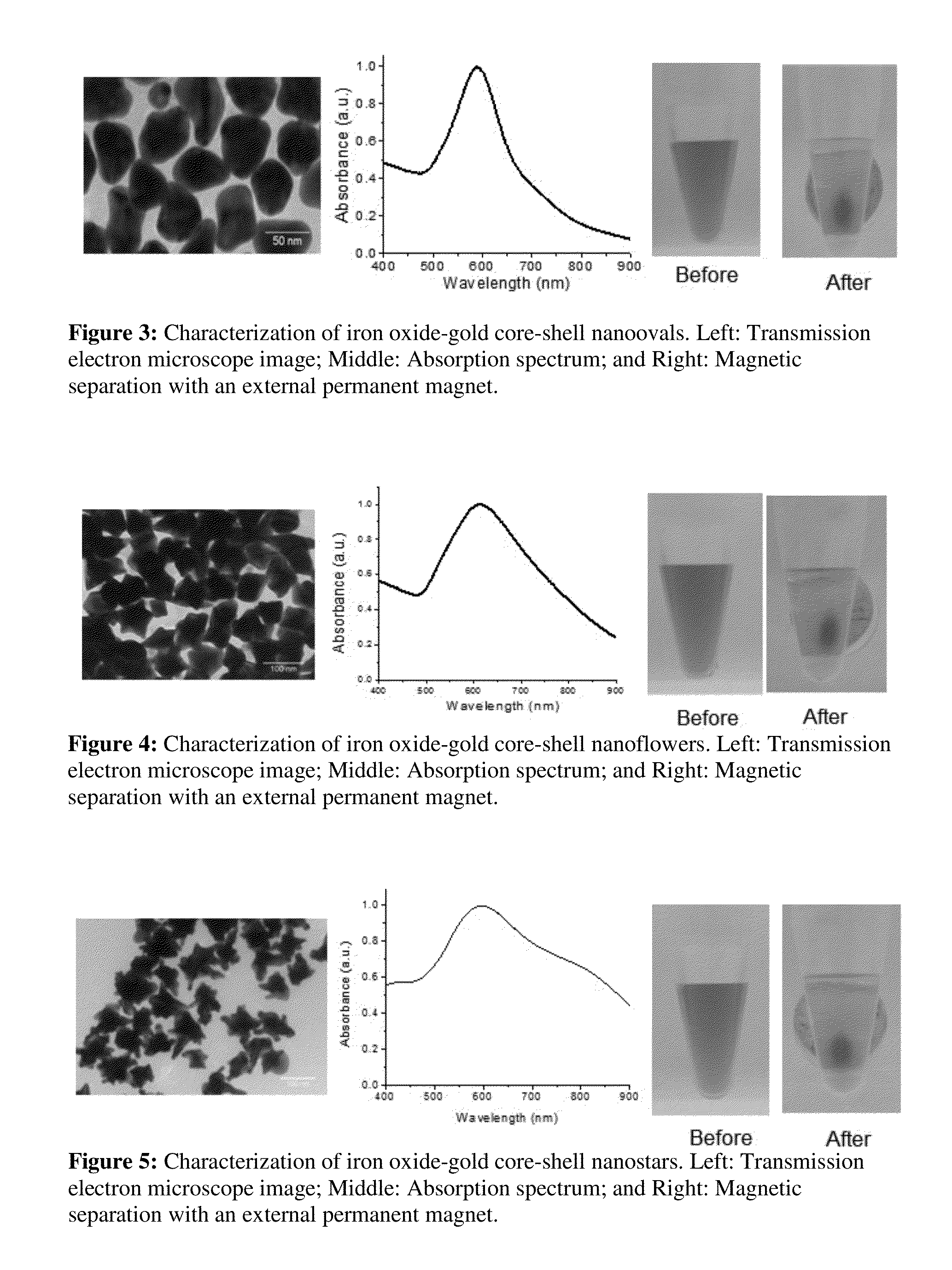
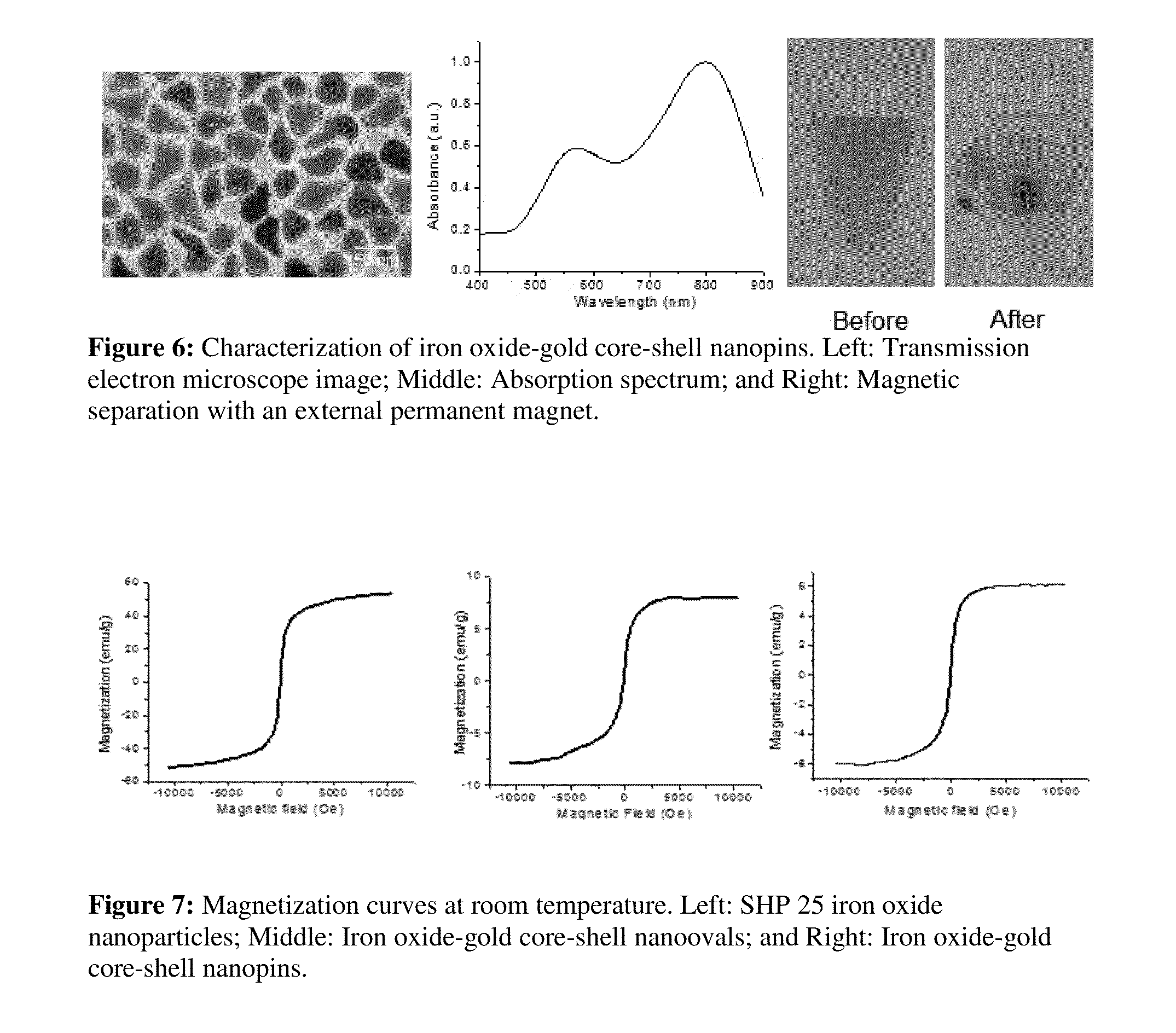
Iron oxide-gold core-shell nanoparticles and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150037818A1Transportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusCore shell nanoparticlesNanometre
Magnetic-optical iron oxide-gold core-shell nanoparticles are disclosed. Methods for making and using the nanoparticles are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MEMPHIS RESEARCH FOUNDATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com