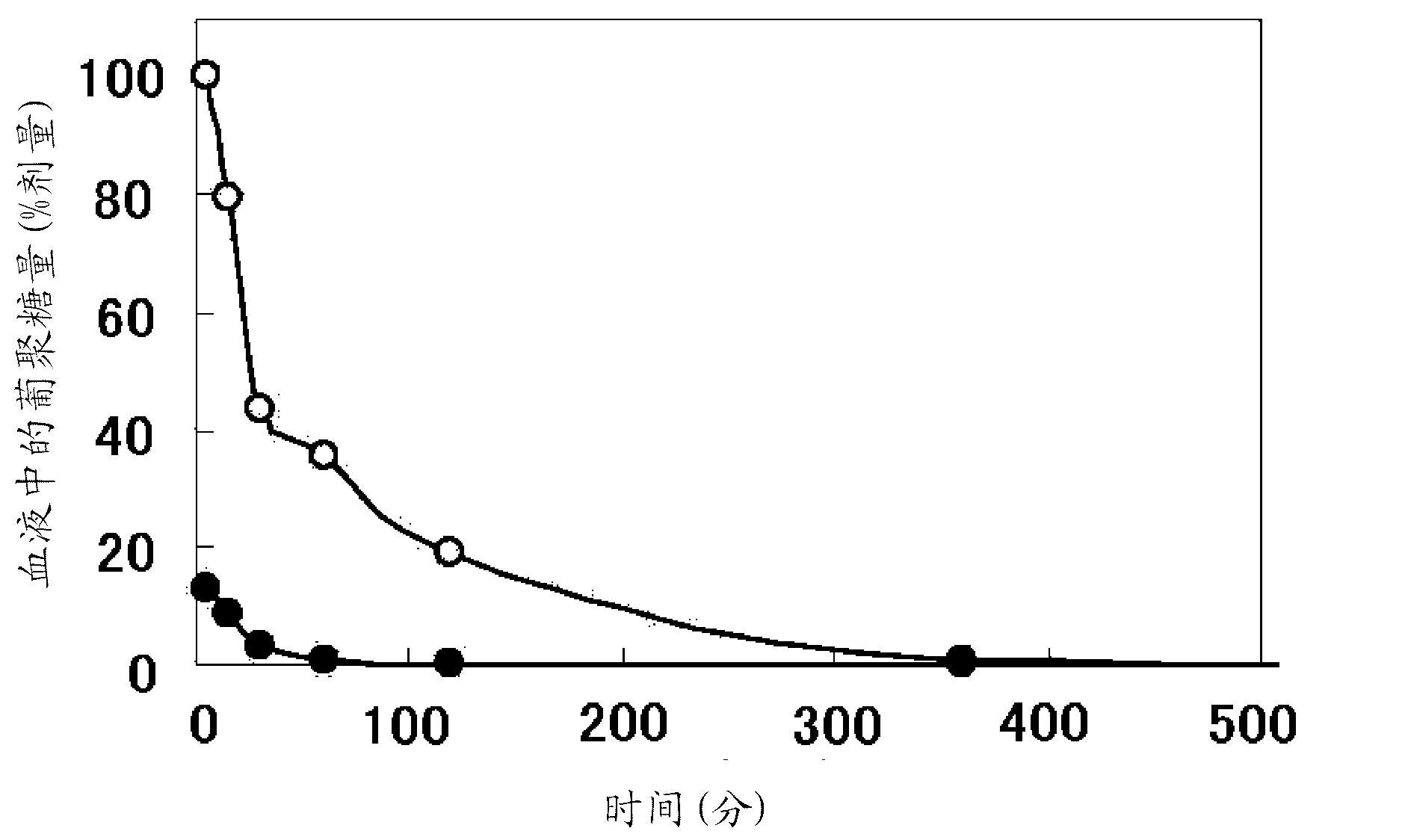
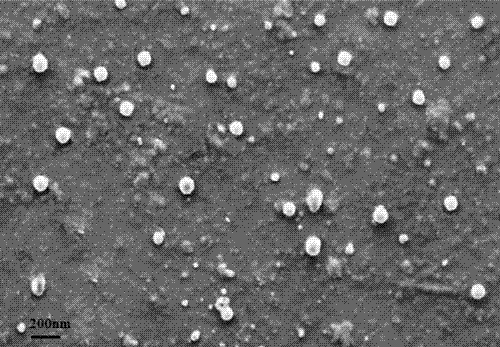
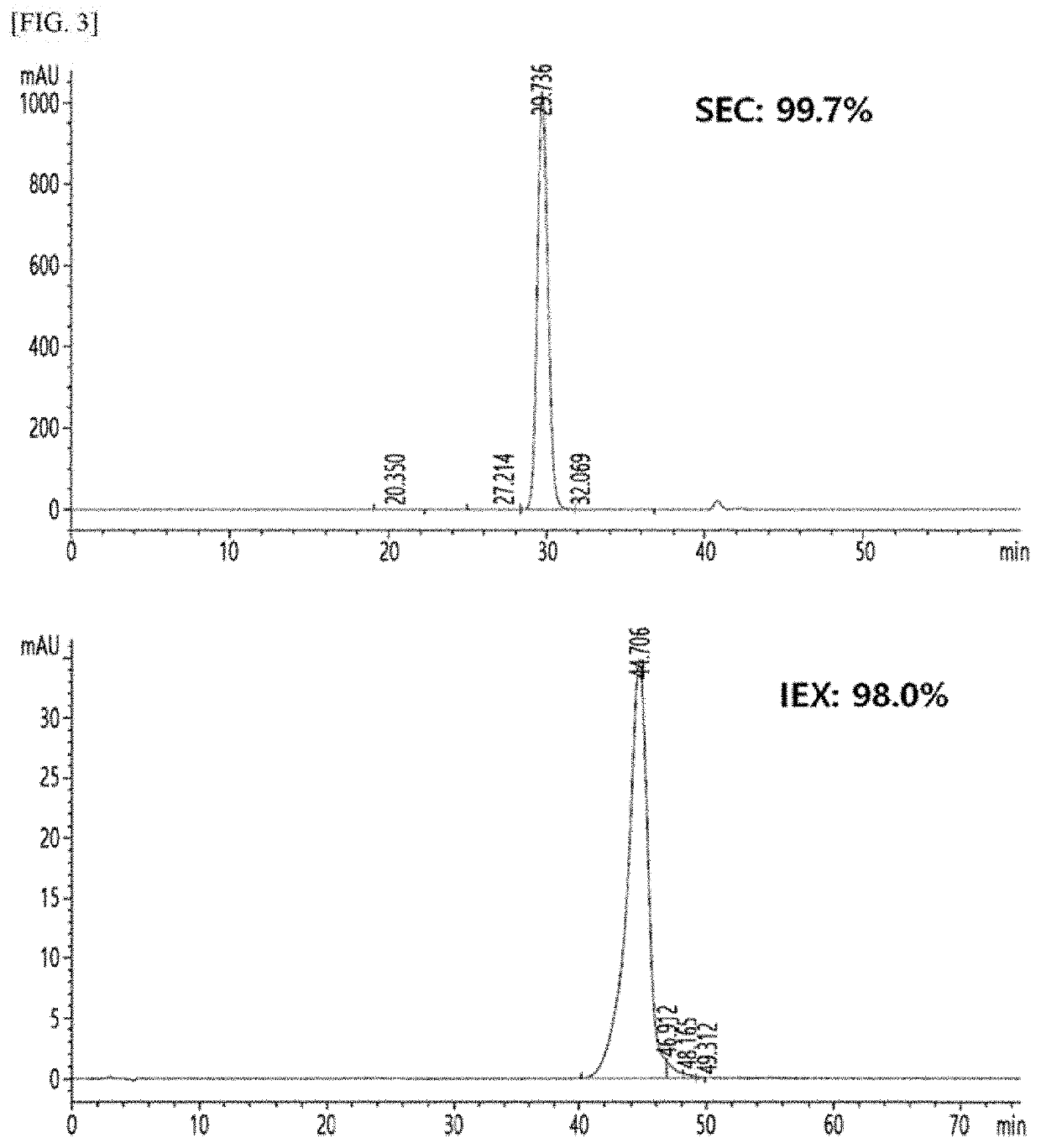
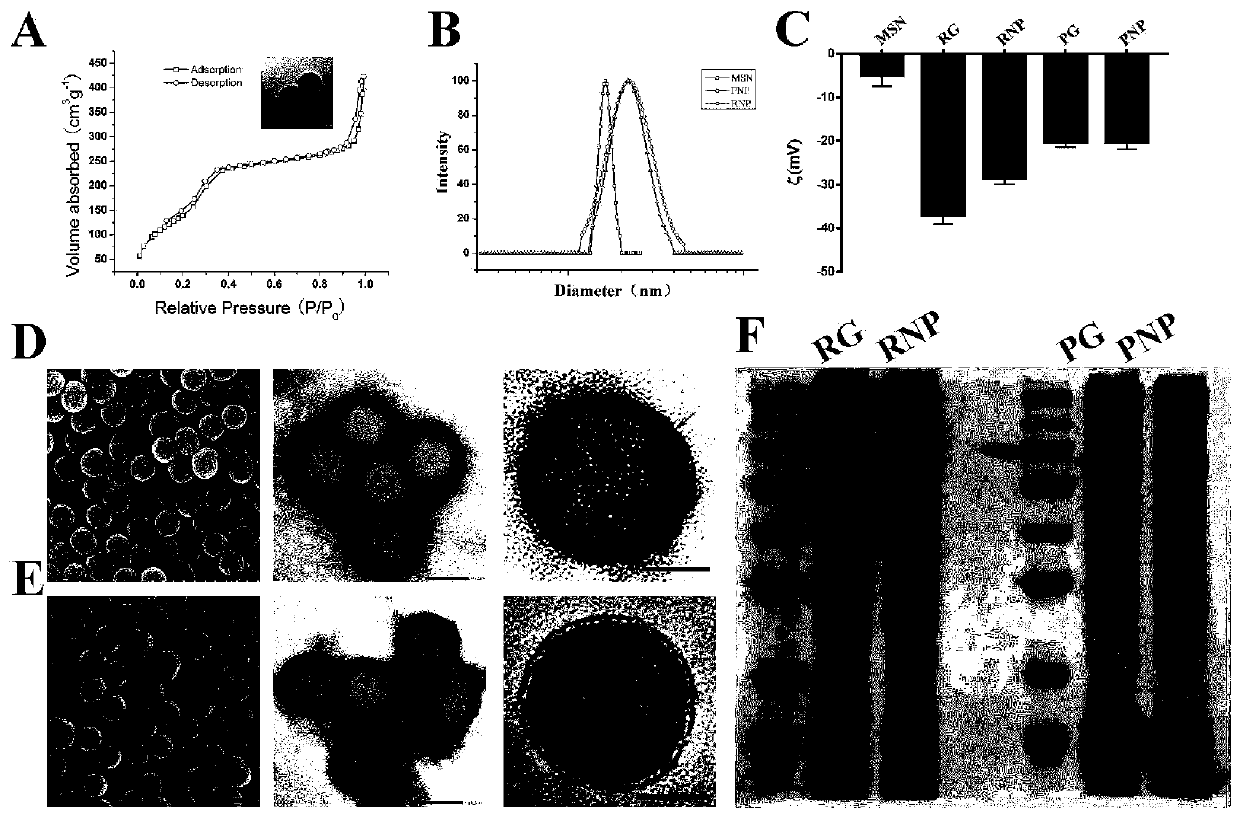
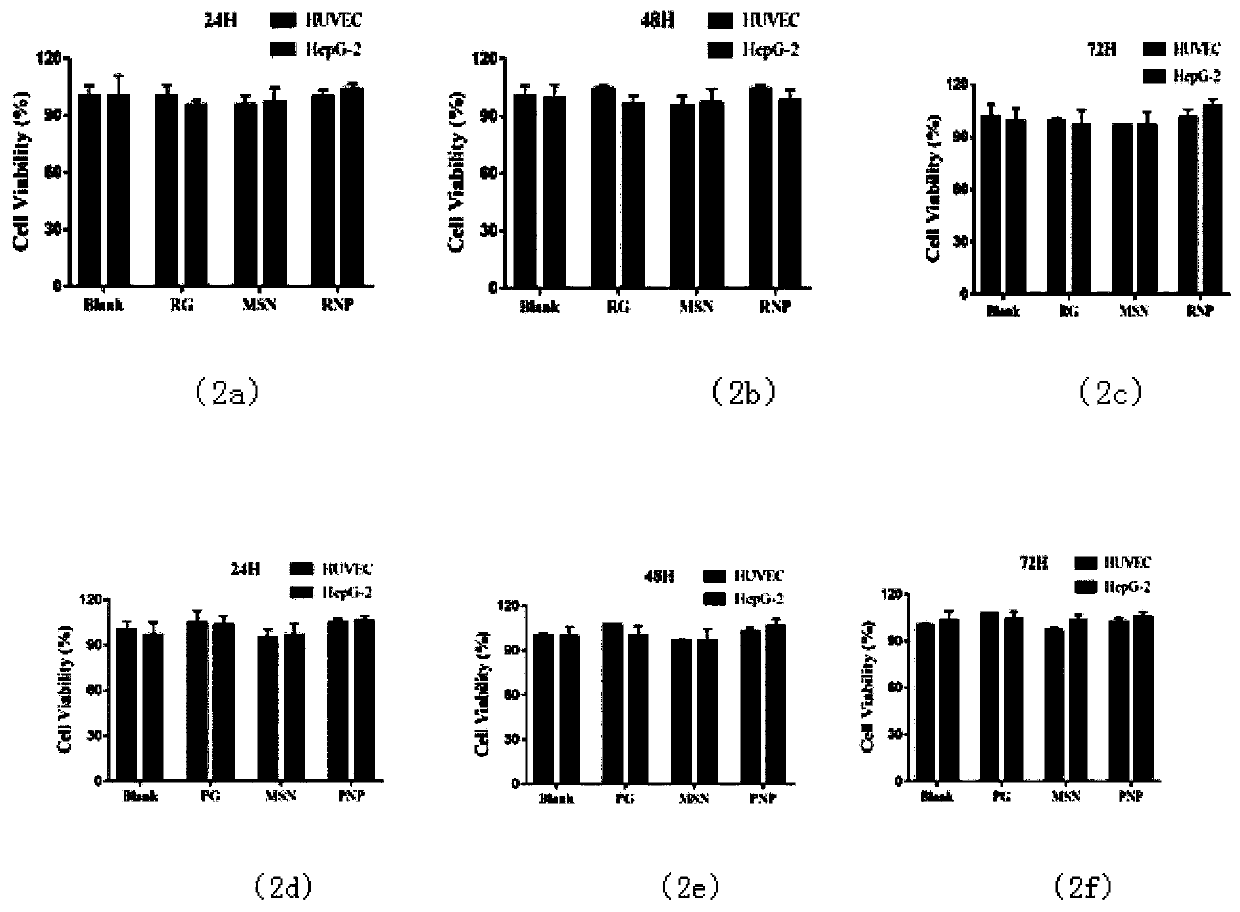
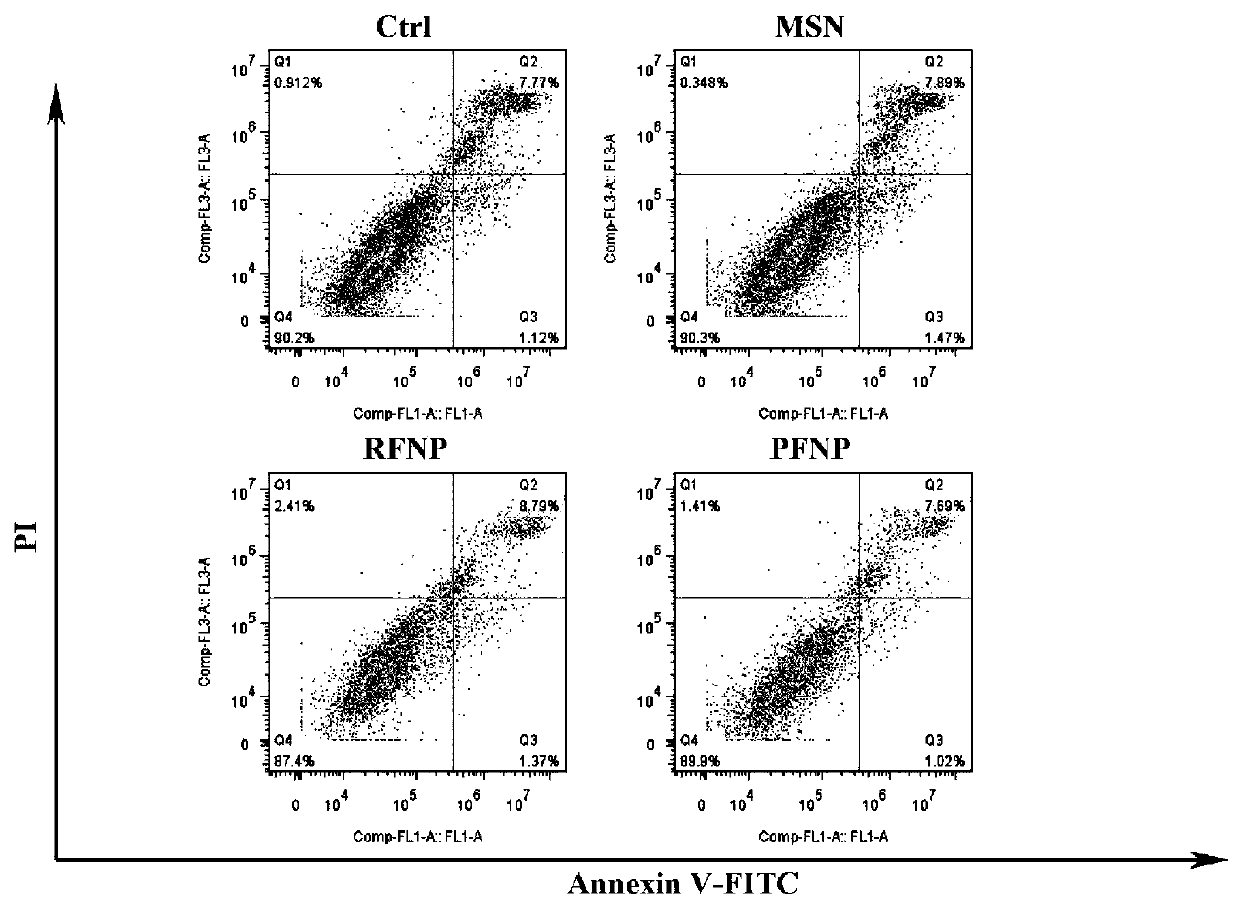
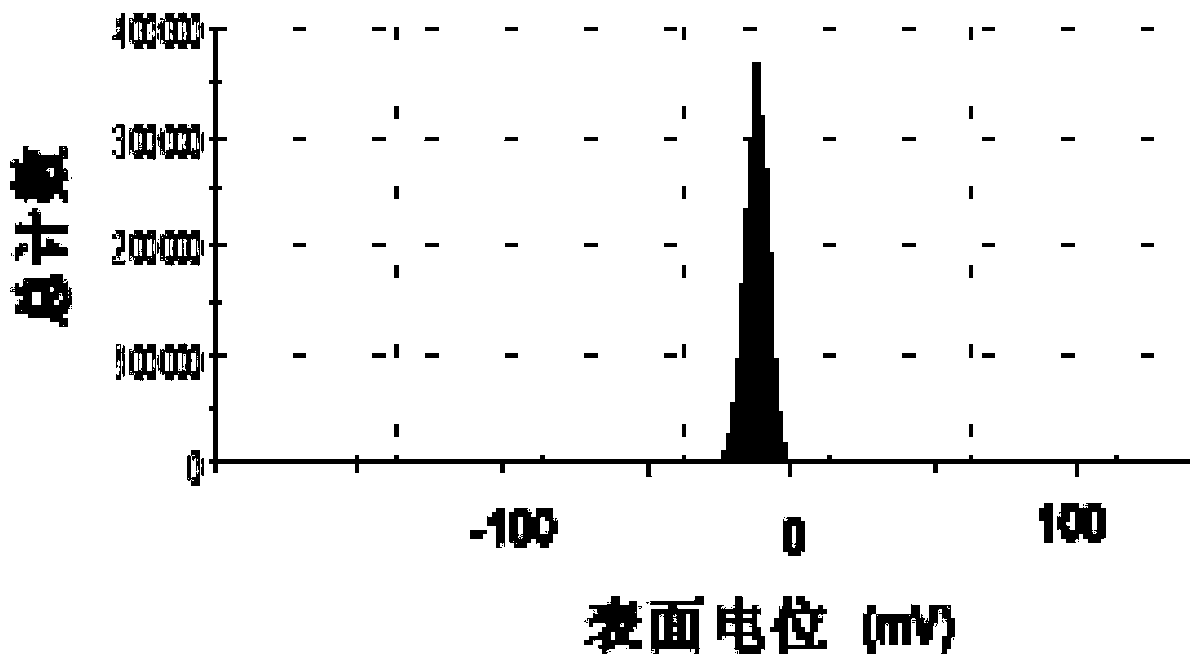
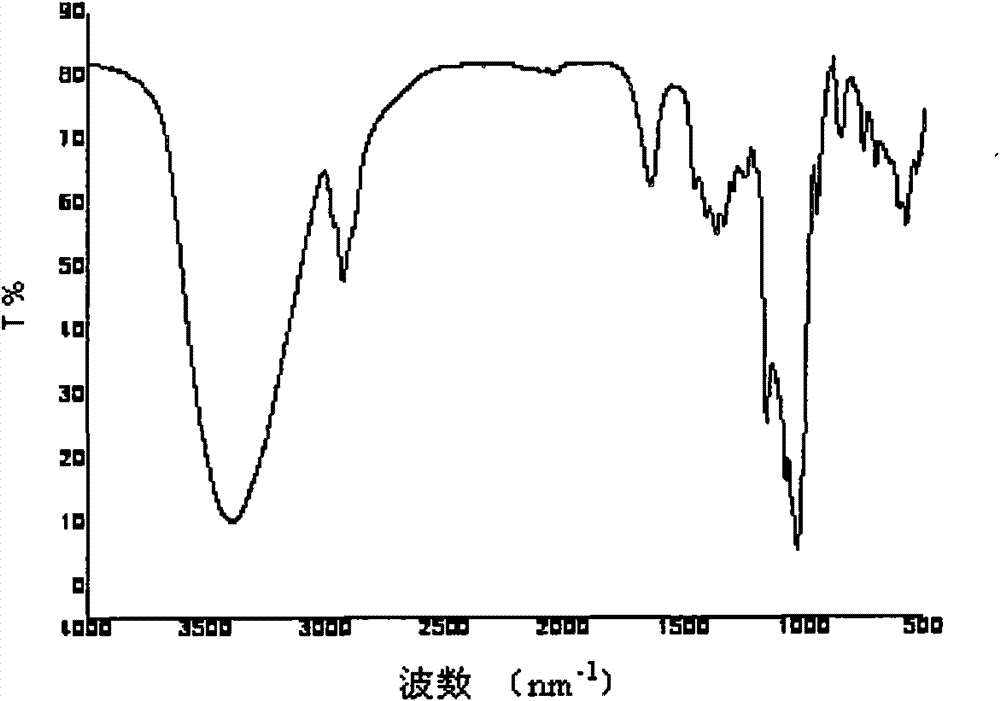
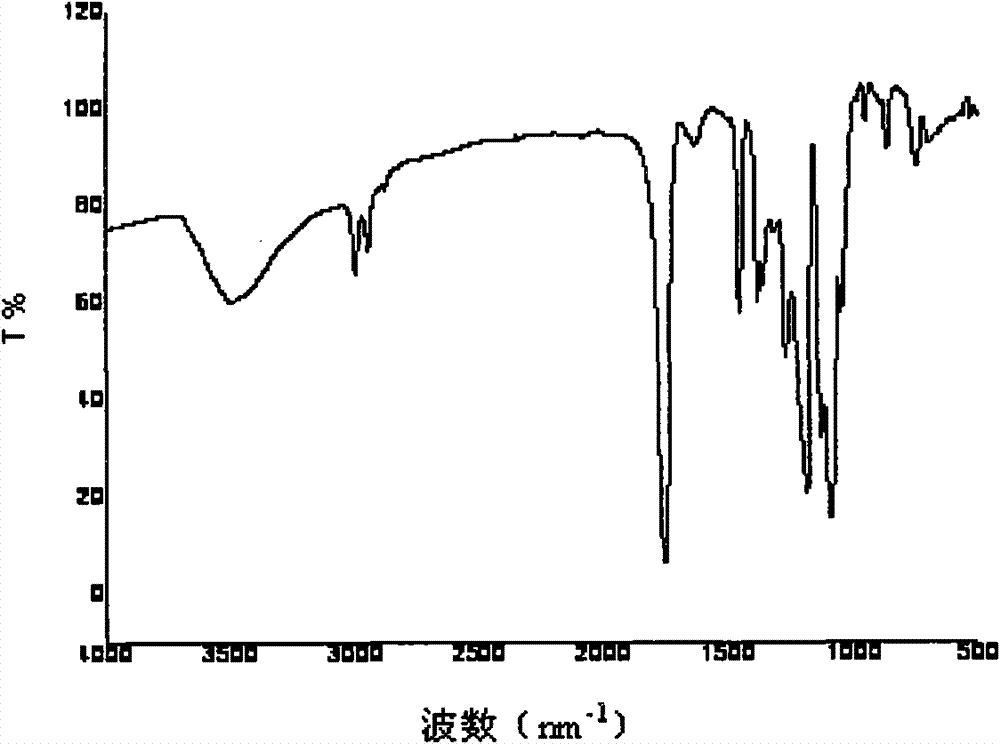
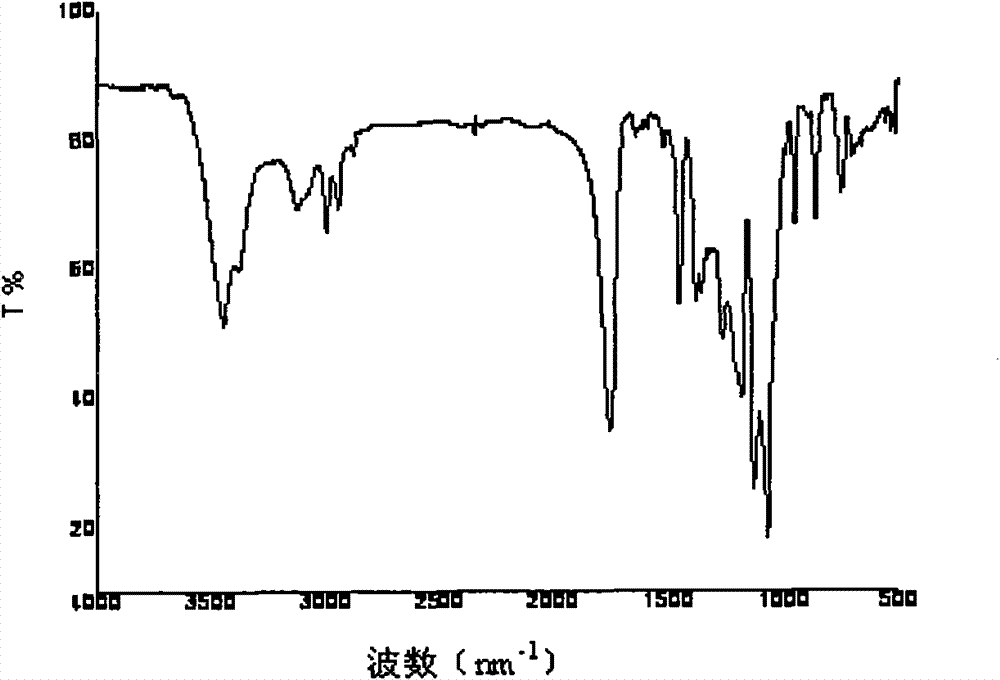
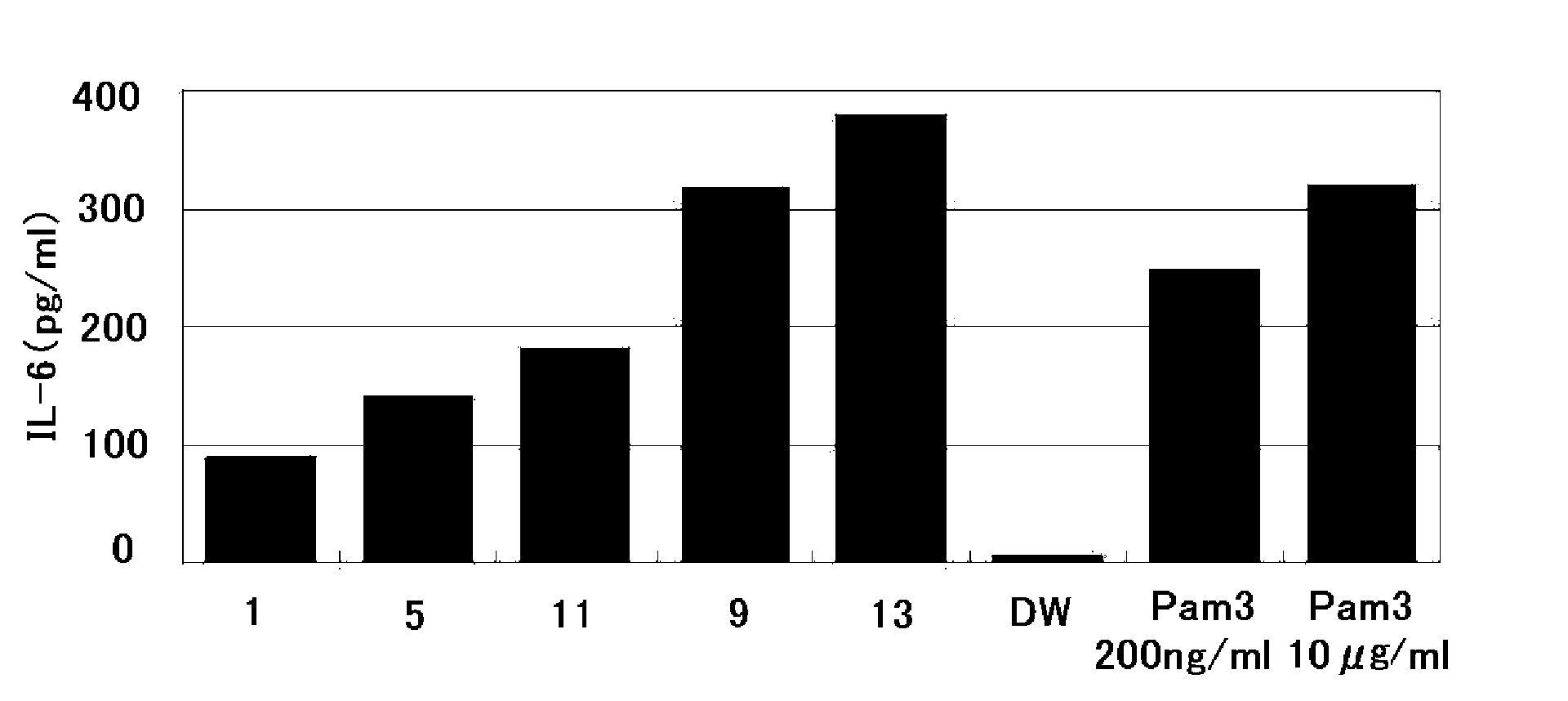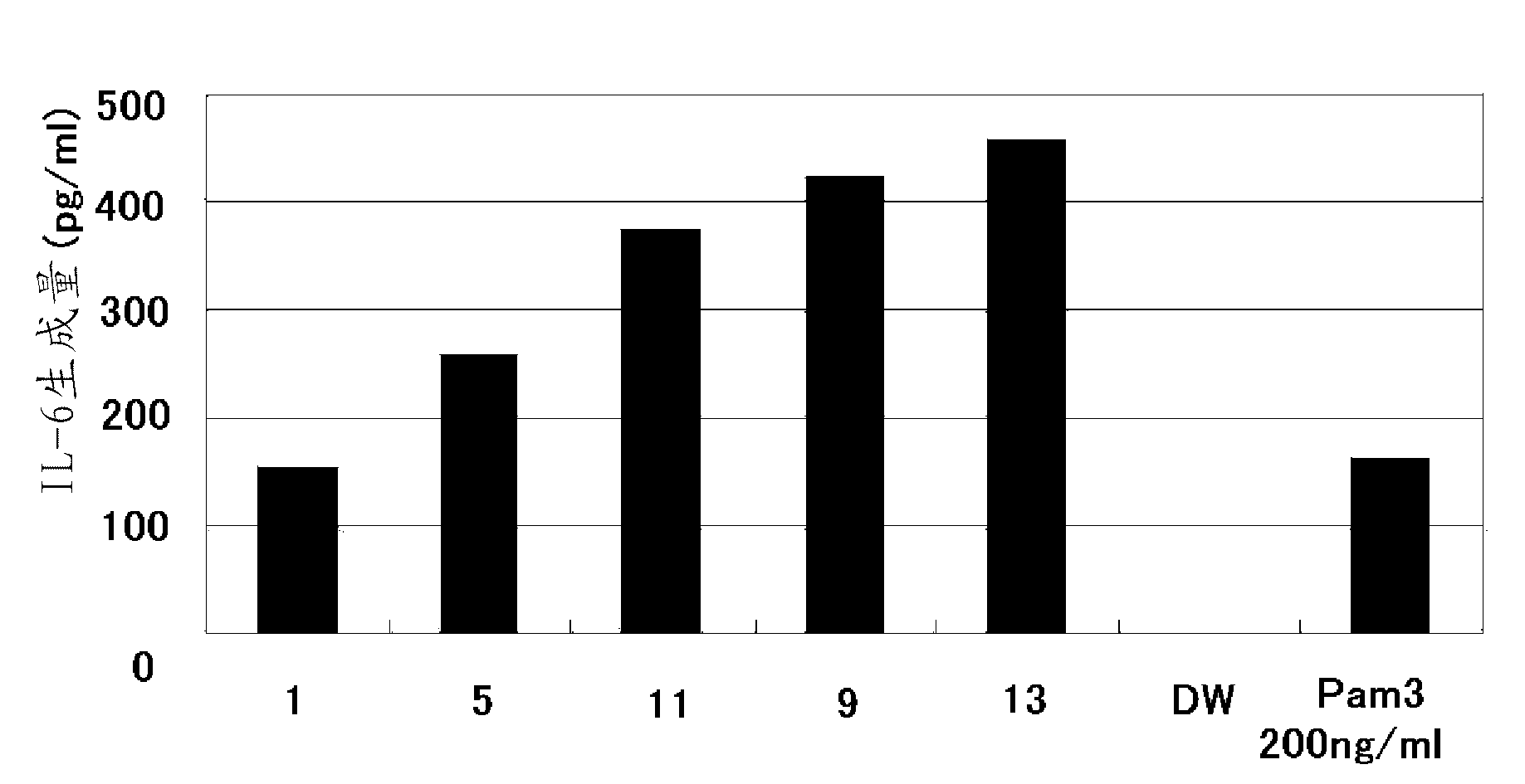Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Prolong blood half-life" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nanoparticle-based imaging agents for x-ray / computed tomography and methods for making same
InactiveUS20070122620A1Prolong blood half-lifeIncrease contrastPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyTomographyCore shell nanoparticles
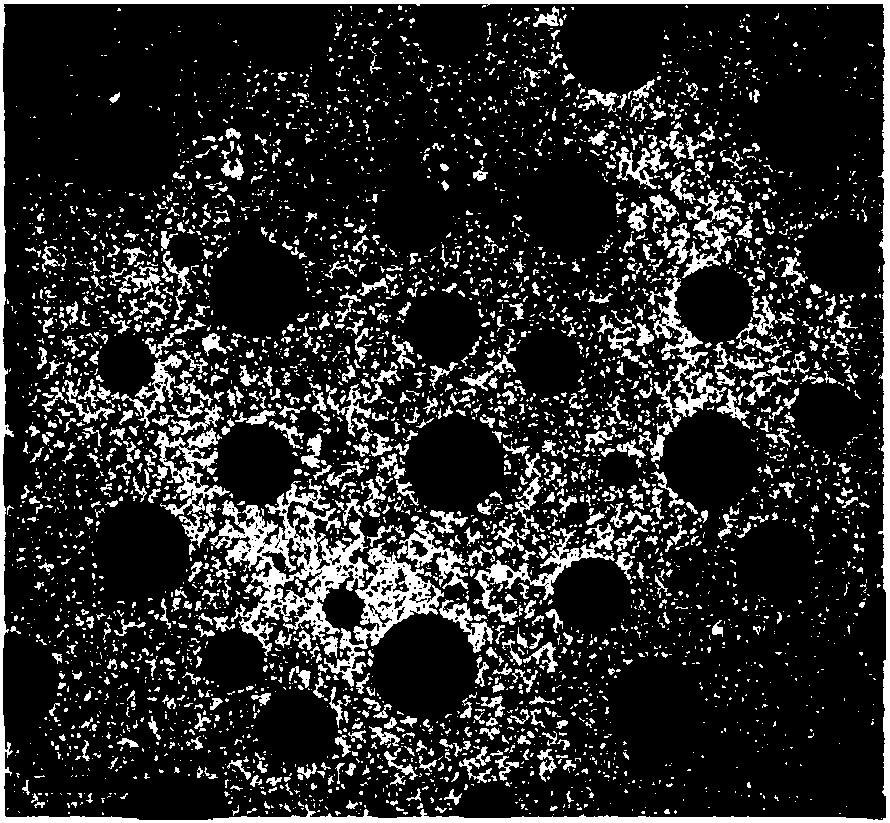
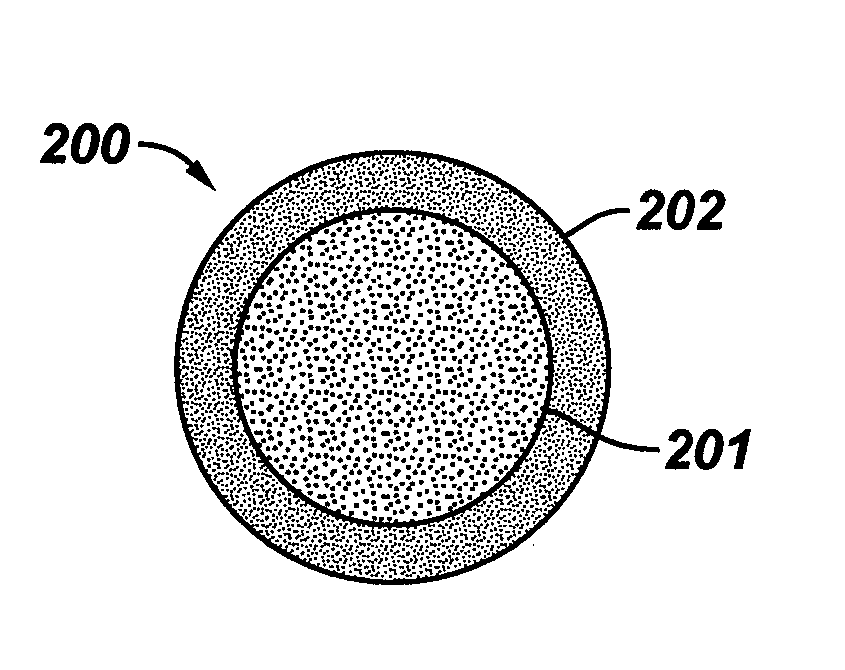
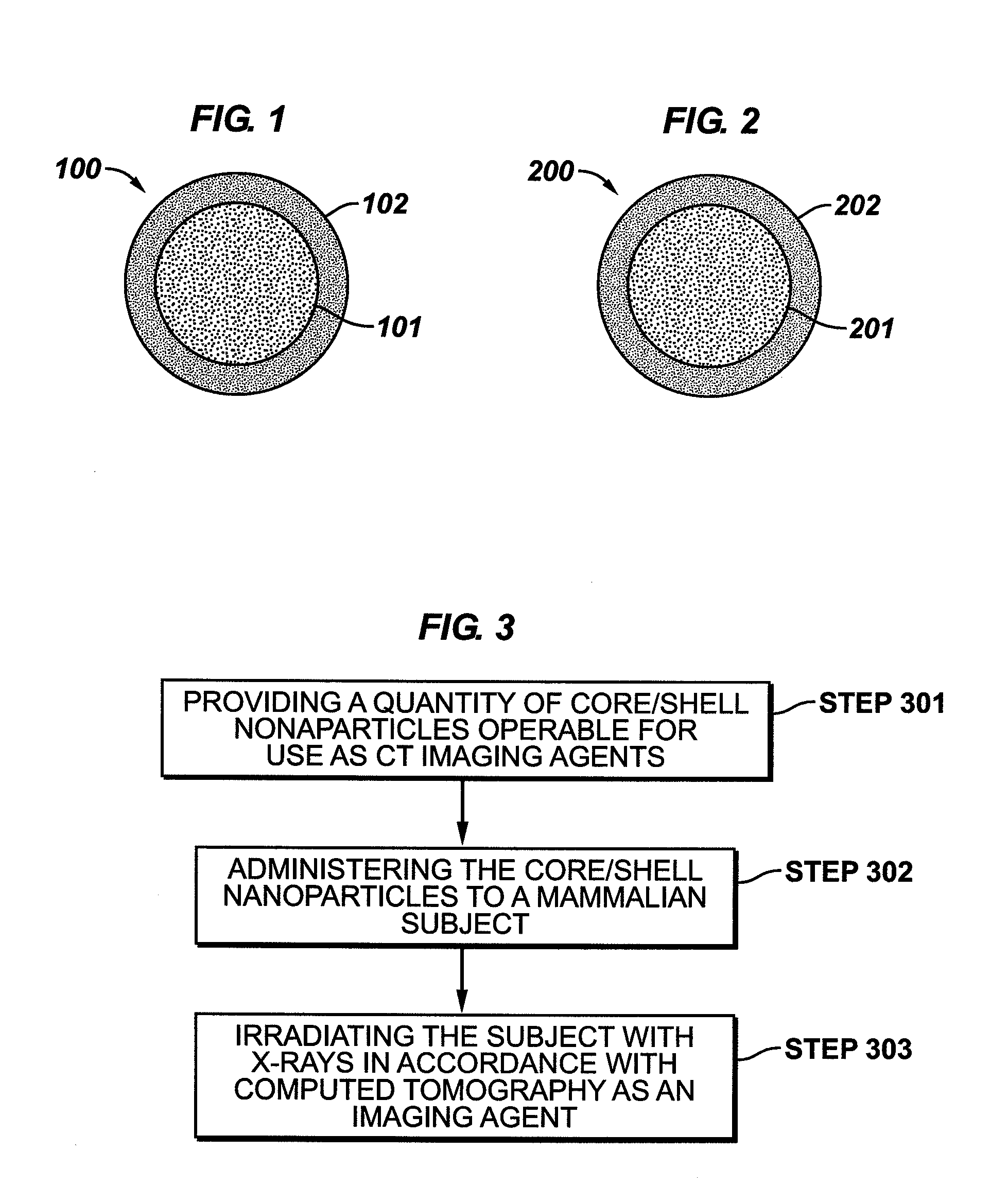
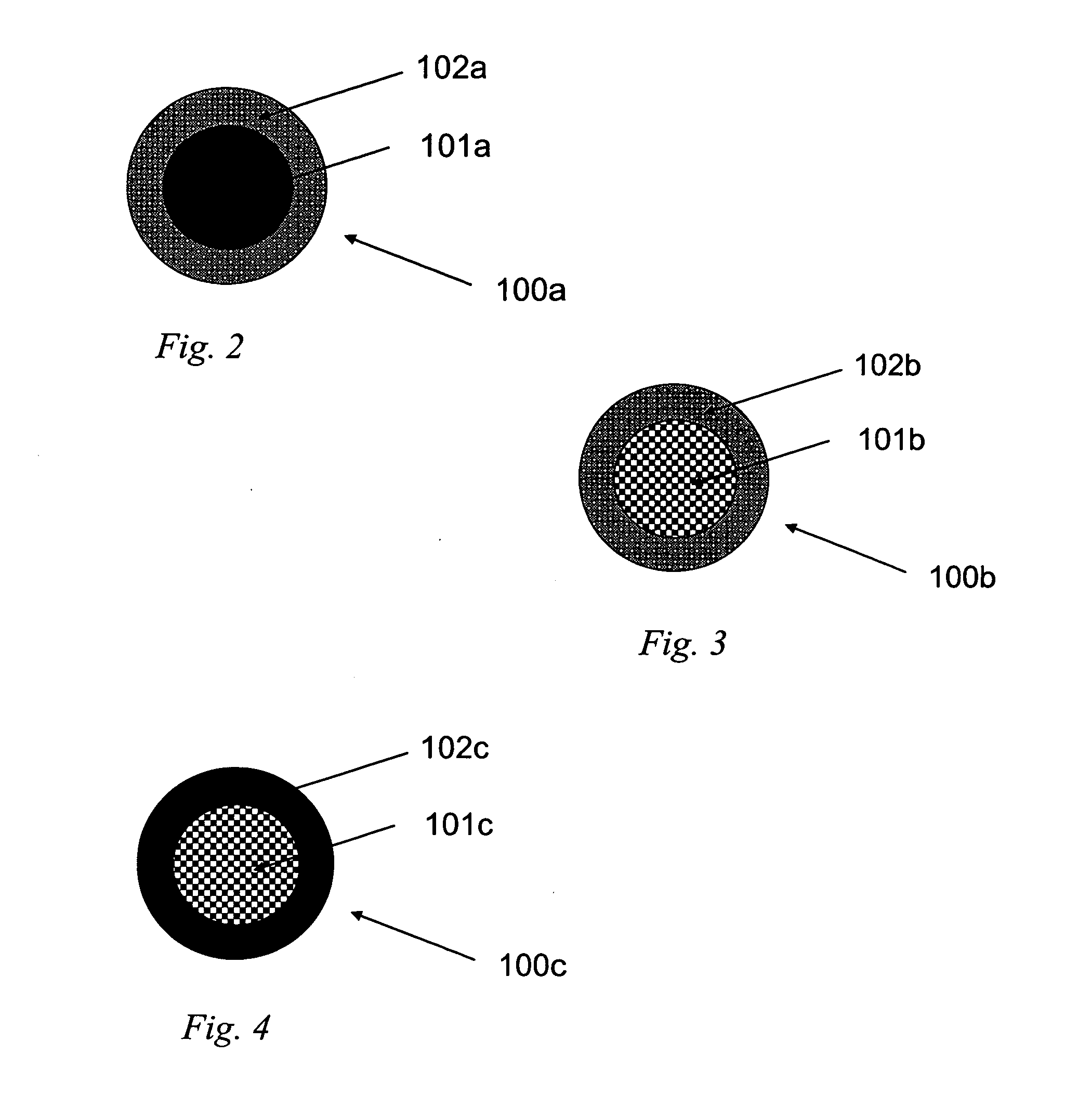
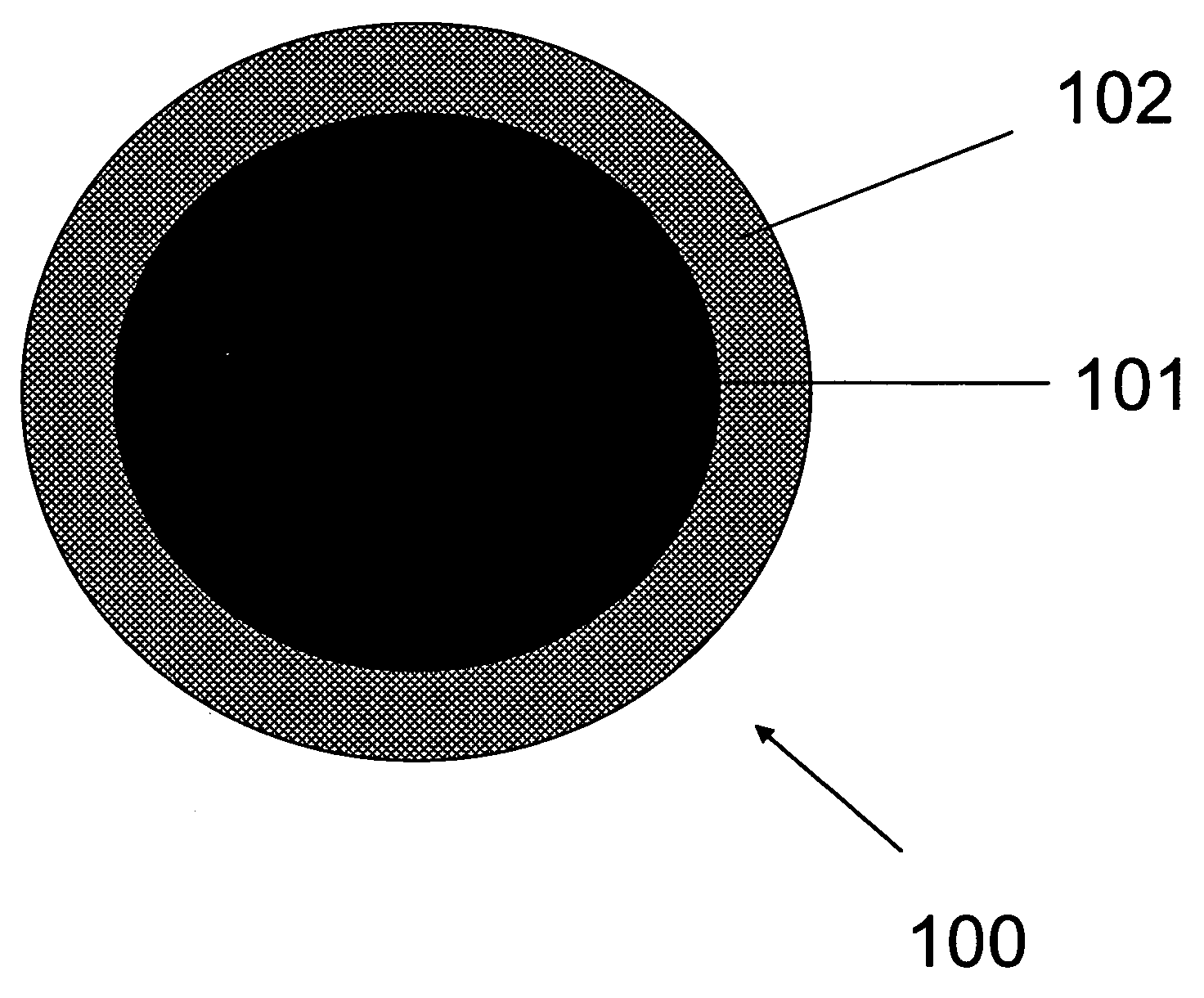
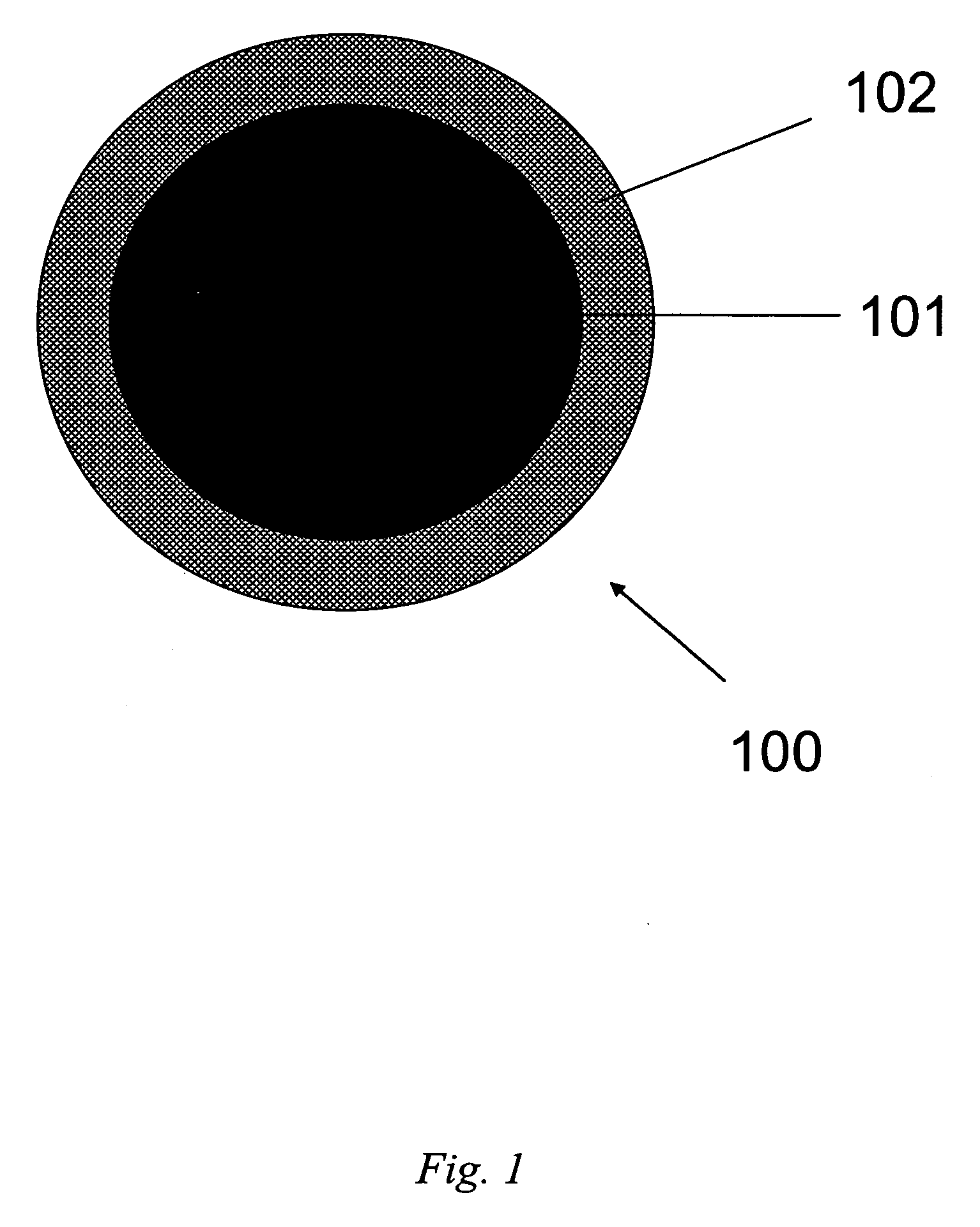
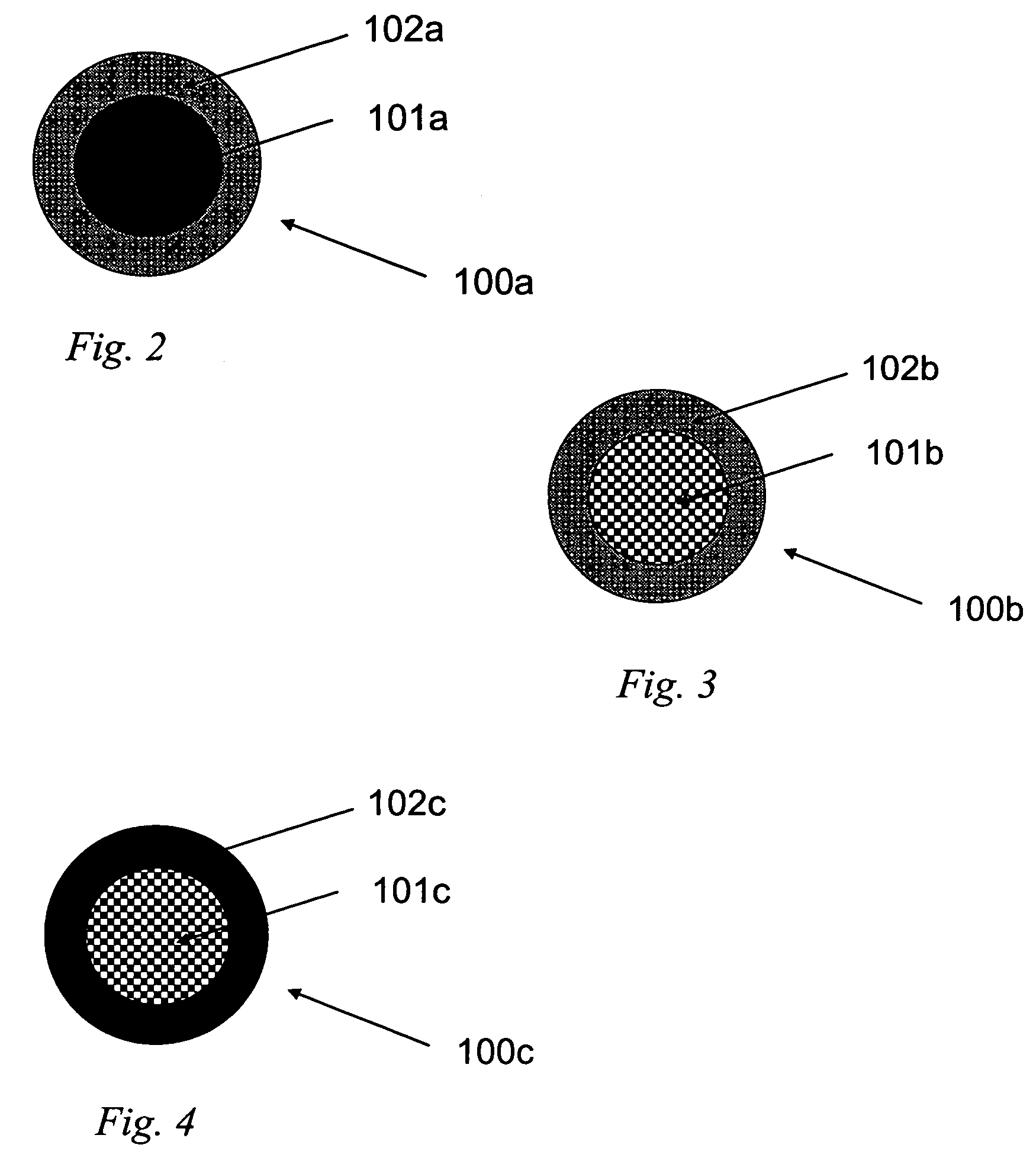
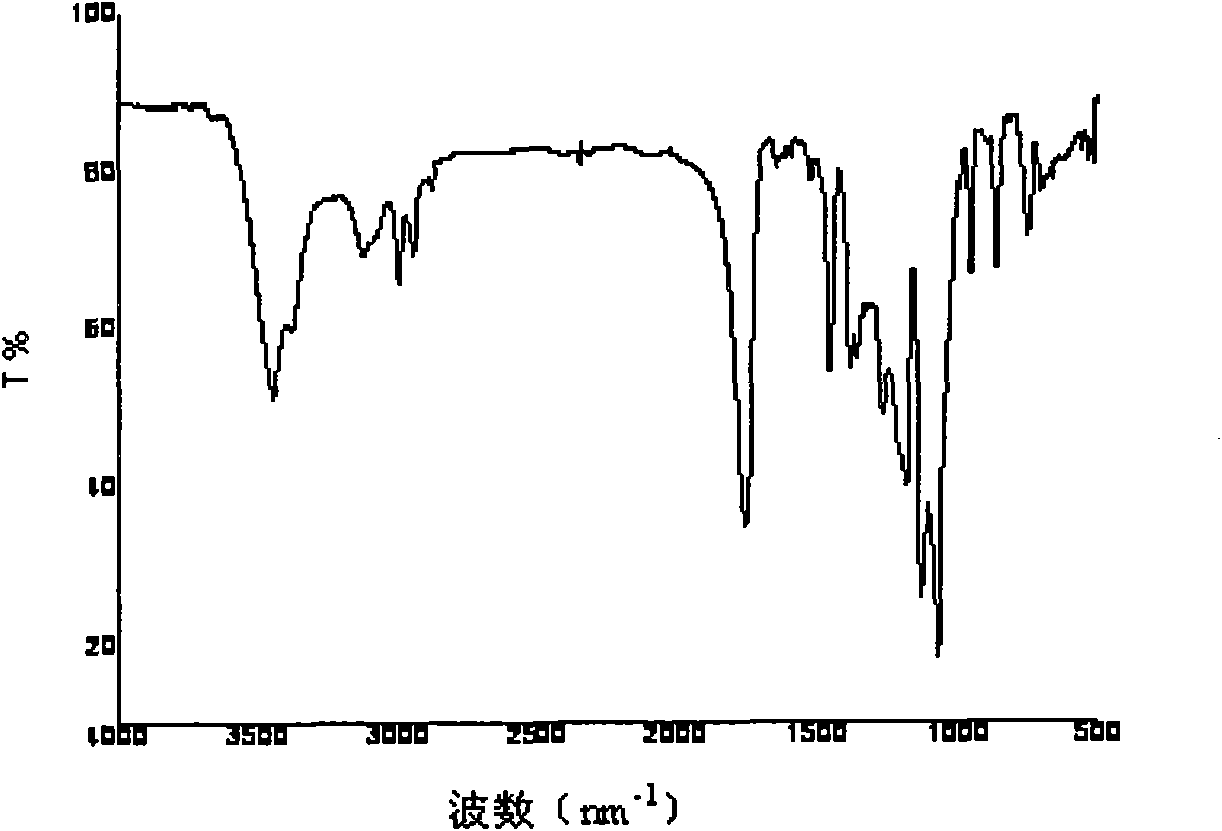
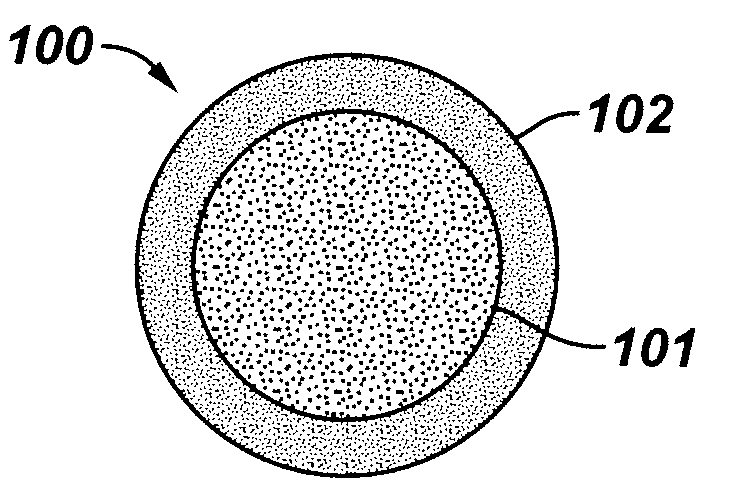
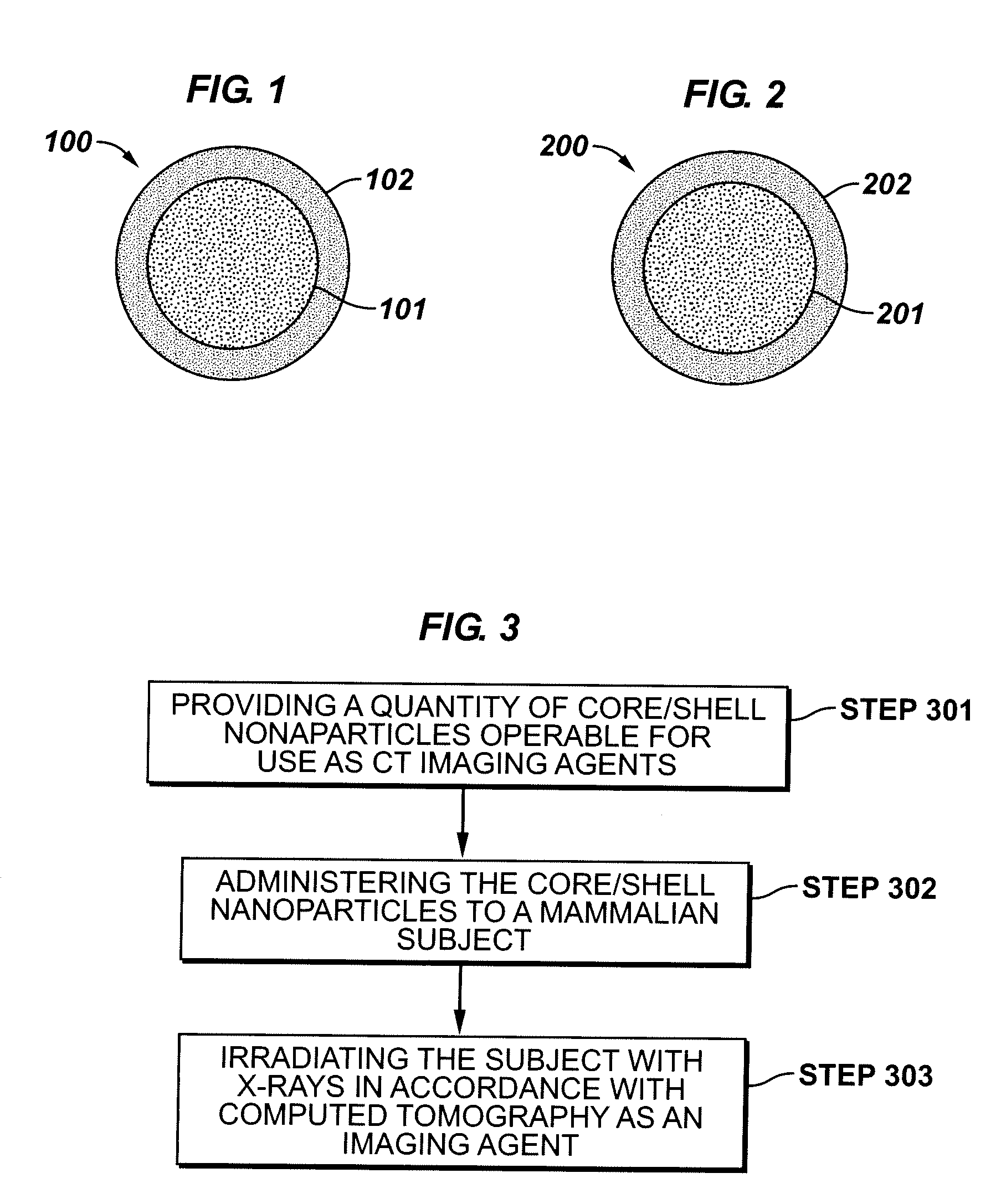
The present invention is generally directed to core / shell nanoparticles, wherein such core / shell nanoparticles comprise a nanoparticle core and a nanoshell disposed about the nanoparticle core such that, in the aggregate, they form a core / shell nanoparticle that is operable for use as an imaging agent in X-ray / computed tomography (CT). Typically, such core / shell nanoparticle-based X-ray CT imaging agents further comprise a targeting species for targeting the imaging agent to diseased sites.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Active targeting type amphipathic polypeptide nano-drug carrier and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN110237035ASmall particle sizeFacilitates endocytosisEmulsion deliveryMacromolecular non-active ingredientsNanocarriersSide chain
The invention provides an active targeting type amphipathic polypeptide nano-drug carrier and preparation and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicines. According to an amphipathic polypeptide, an alkyl chain serves as the hydrophobic end, a polypeptide chain with active targeting functional and side chain modification fluorescent functional molecules serves as the hydrophilic end, and an anti-tumor drug is wrapped in a hydrophobic cavity of a micelle formed by self-assembling the amphipathic polypeptide. The nano-carrier can actively target tumor cells and enter the tumor cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis, the amphipathic polypeptide and phospholipid molecules have strong interaction, and the phagocytosis of a nano-drug by tumor cells is promoted. In the process, tracing can be conducted through fluorescent imaging of fluorescent functional molecules modified on the polypeptide chain, and the tumor imaging aim is realized. Finally, the anti-tumor drug is slowly released to kill tumor cells and restrain the growth of tumors. The amphipathic polypeptide nano-carrier is free of toxin, high in biocompatibility and remarkable in anti-tumor efficiency, and the tumor diagnosis and treatment can be integrated.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nanoparticle-based imaging agents for X-ray/computed tomography
InactiveUS20070098642A1Prolong blood half-lifeIncrease contrastMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryCore shell nanoparticlesX-ray
The present invention is generally directed to core / shell nanoparticles, wherein such core / shell nanoparticles comprise a nanoparticle core and a nanoshell disposed about the nanoparticle core such that, in the aggregate, they form a core / shell nanoparticle that is operable for use as an imaging agent in X-ray / computed tomography (CT). Typically, such core / shell nanoparticle-based X-ray CT imaging agents further comprise a targeting species for targeting the imaging agent to diseased sites.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nanoparticle-based imaging agents for X-ray/computed tomography
InactiveUS20070098640A1Prolong blood half-lifeIncrease contrastPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyCore shell nanoparticlesX-ray
The present invention is generally directed to core / shell nanoparticles, wherein such core / shell nanoparticles comprise a nanoparticle core and a nanoshell disposed about the nanoparticle core such that, in the aggregate, they form a core / shell nanoparticle that is operable for use as an imaging agent in X-ray / computed tomography (CT). Typically, such core / shell nanoparticle-based X-ray CT imaging agents further comprise a targeting species for targeting the imaging agent to diseased sites.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand and application thereof
ActiveCN108434468AImprove stabilityIncrease intakeOrganic compound preparationRadioactive preparation carriersStructural formulaRadioactive Label
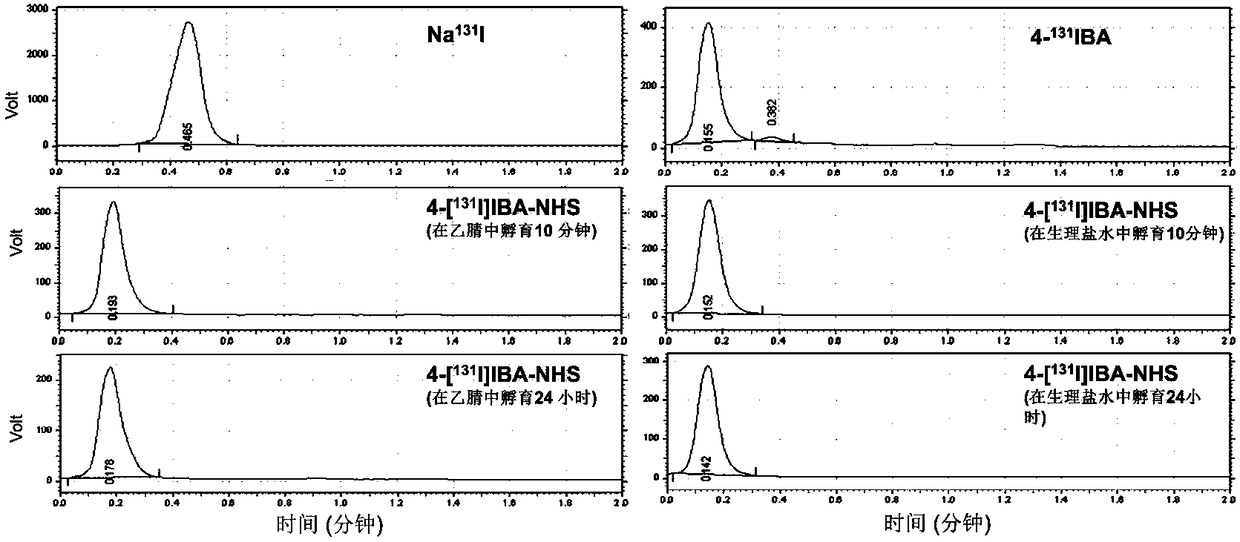
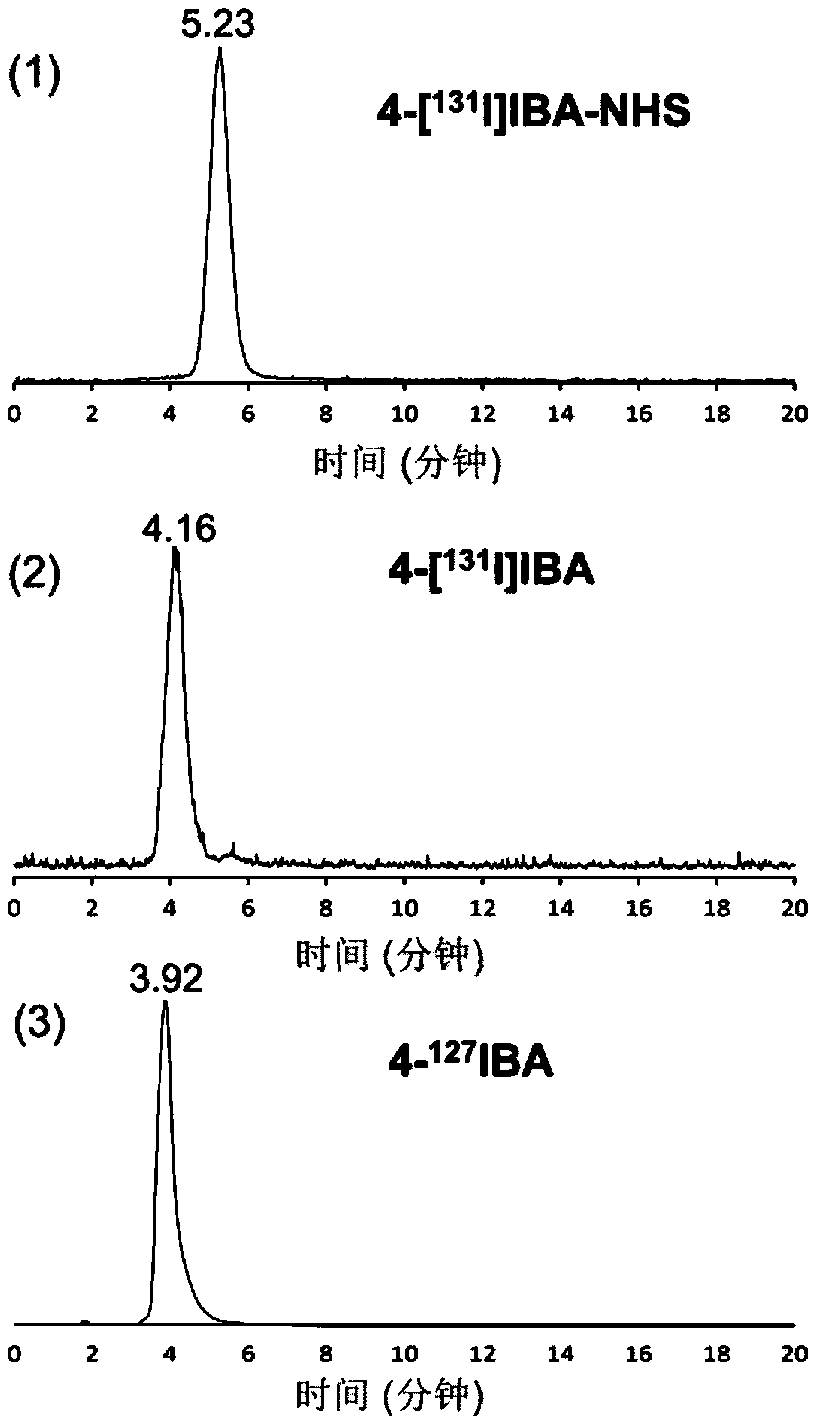
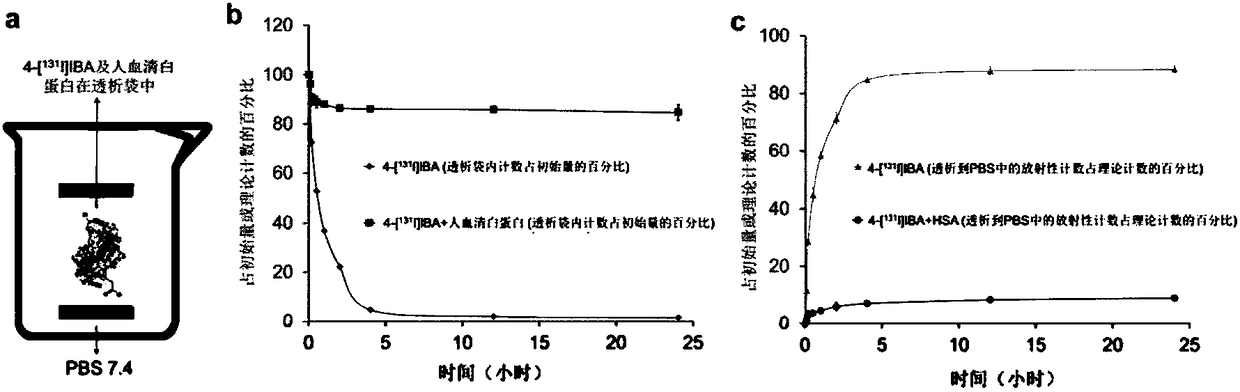
The invention discloses a radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand and application thereof. A structural formula of the radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand is shown in a followingimage, wherein the I is radioactive iodine nuclide, the R is OH or derived from PEG, folic acid, RGD, octreotide, epidermal growth factor, protein, nucleic acid or polysaccharide. The radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple marking method, low cost and good stability. Animal live test results show that the albumin binding ligand hashigher uptake and longer-time retention in blood and further has a higher target / non-target specific value. When the radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand is modified to a target group orother functional groups, pharmacokinetic characters of compound can be obviously improved, a blood half-life period of the compound is prolonged, and the compound is suitable for being utilized as a blood pool, lymph and tumor diagnosing and treating reagent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Nanoparticle-based imaging agents for X-ray/computed tomography
InactiveUS20070098641A1Prolong blood half-lifeIncrease contrastMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryCore shell nanoparticlesX-ray
The present invention is generally directed to core / shell nanoparticles, wherein such core / shell nanoparticles comprise a nanoparticle core and a nanoshell disposed about the nanoparticle core such that, in the aggregate, they form a core / shell nanoparticle that is operable for use as an imaging agent in X-ray / computed tomography (CT). Typically, such core / shell nanoparticle-based X-ray CT imaging agents further comprise a targeting species for targeting the imaging agent to diseased sites.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Preparation method of magnetic resonance contrast agent targeting blood-brain barrier and glioma
InactiveCN109395101AEasy to crossGood dispersionNMR/MRI constrast preparationsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDspe pegPolyethylene glycol
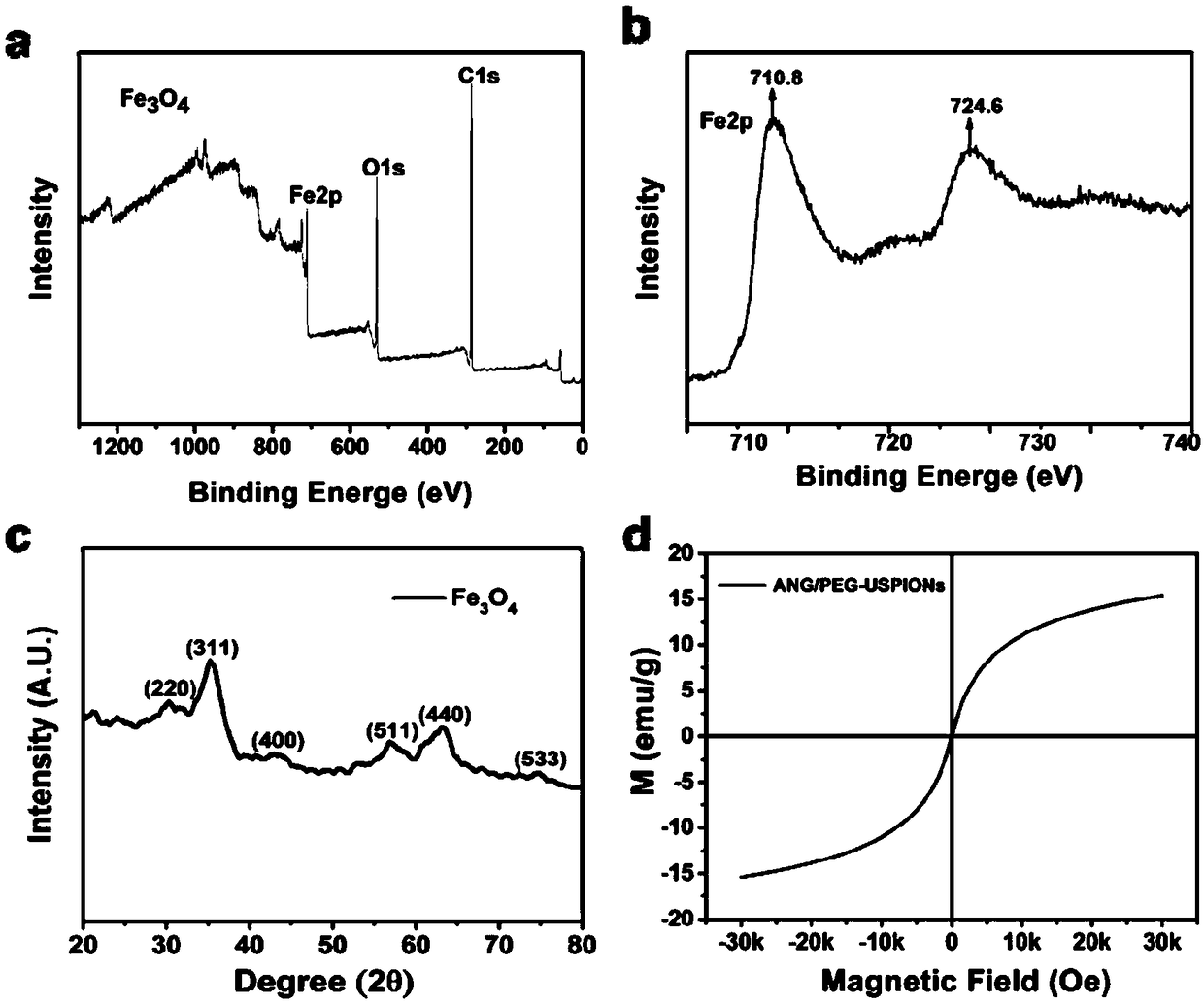
The invention discloses a preparation method of a magnetic resonance contrast agent targeting blood-brain barrier and glioma. The method comprises the following steps of dispersing ferric chloride hexahydrate and sodium oleate in a mixture of ethanol, water and n-hexane to obtain precursor iron oleate; dissolving the precursor in a mixed solution of oleoyl alcohol and diphenyl ether, and stirringthe mixture at about 110 DEG C under nitrogen protection; rising the temperature to about 200 DEG C under nitrogen protection, and carrying out reflux to obtain an oil acid-coated ferroferric oxide nanoparticles; and dispersing the nanoparticles in trichloromethane, adding excess DSPE-PEG-Maleimide for hydrophilic modification, dispersing the modified ferroferric oxide nanoparticles in PBS, and finally grafting specific glioma-targeted molecules Angiopep-2. The magnetic resonance contrast agent can efficiently cross the blood-brain barrier, and can be used as a novel type of magnetic resonanceimaging positive contrast agent for early diagnosis and boundary definition of glioma.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
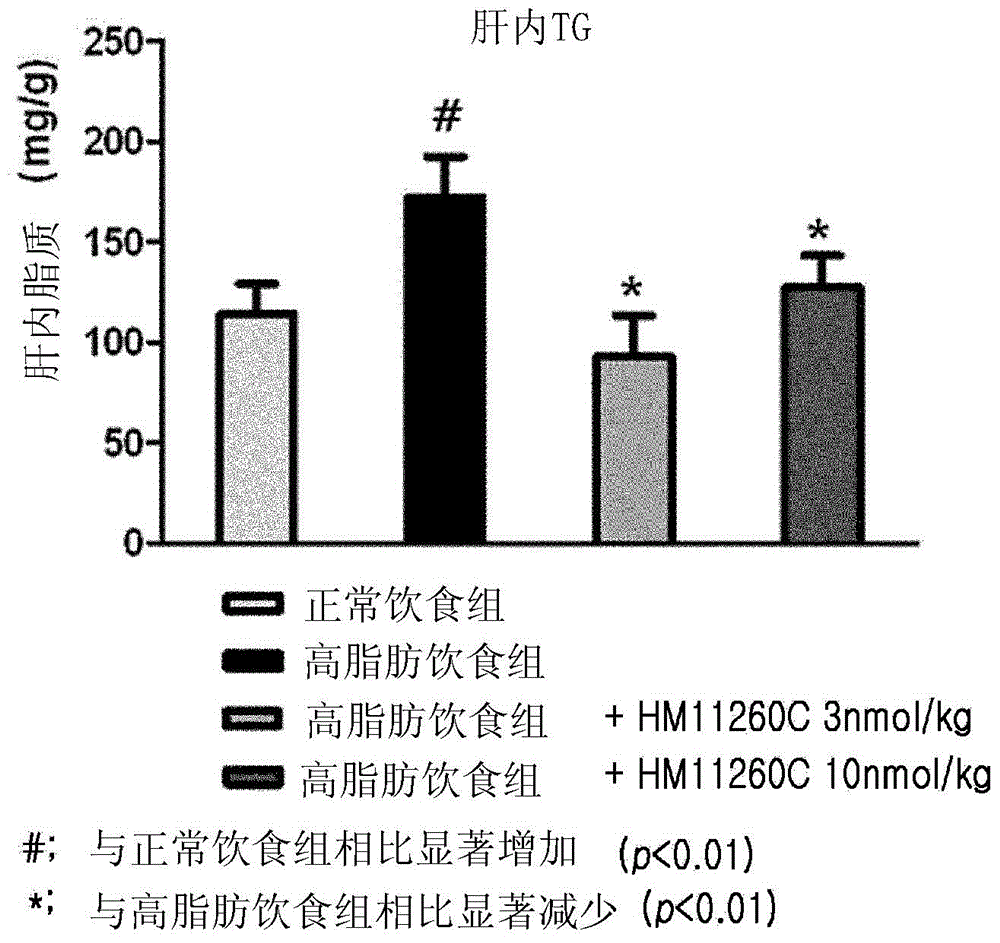
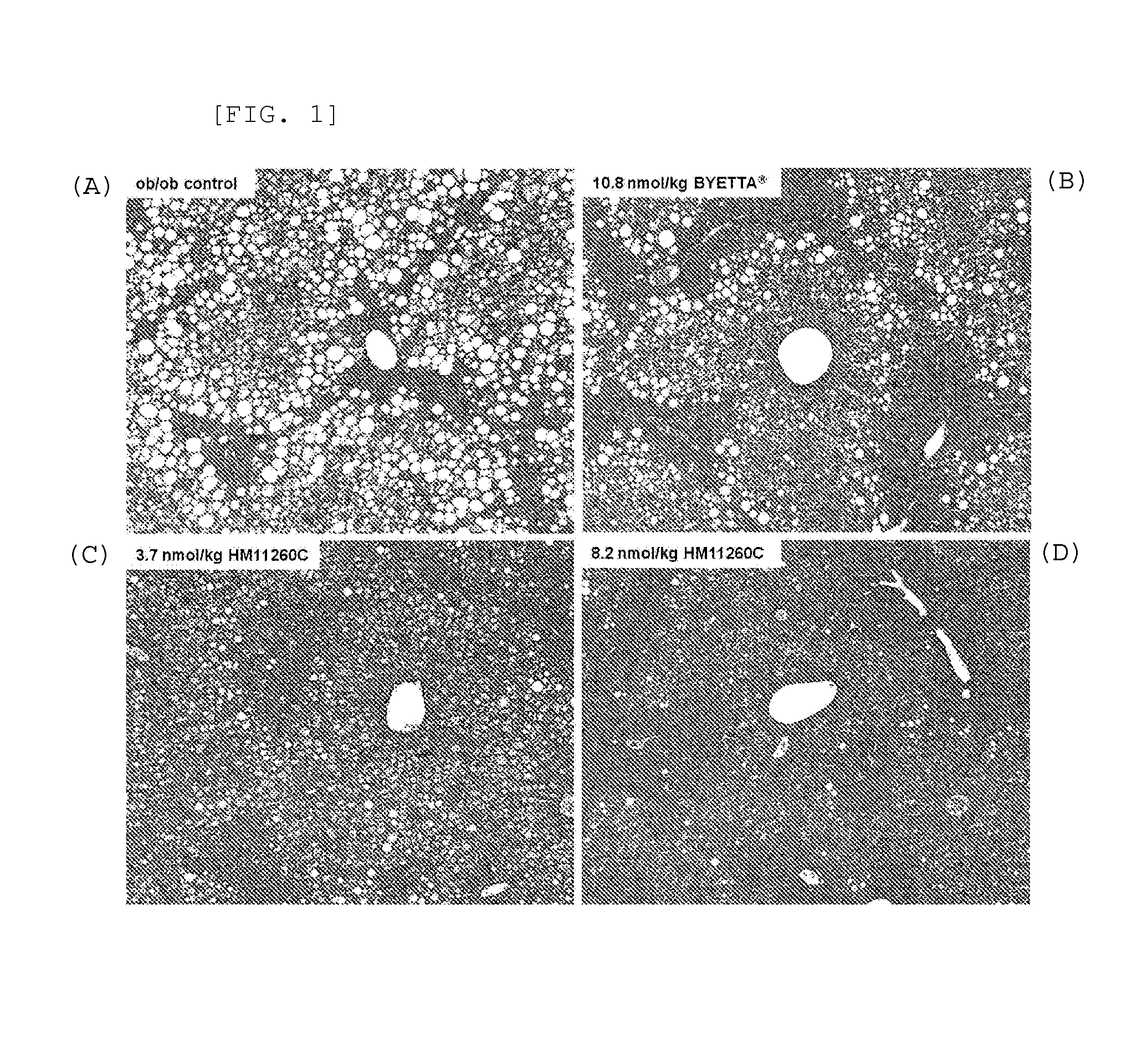
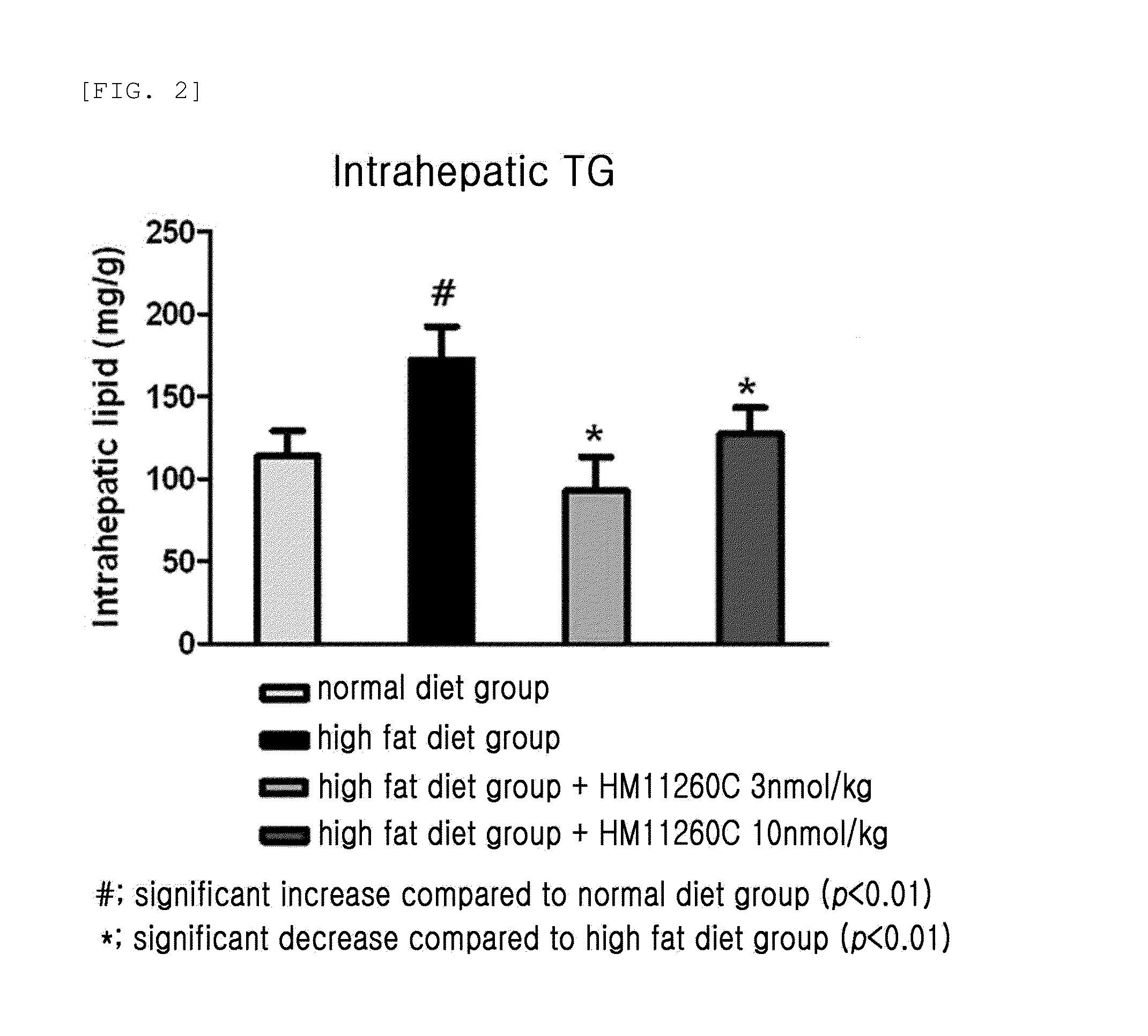
Pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
InactiveCN104159597AAvoid accumulationProlong blood half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHalf-lifeTriglyceride
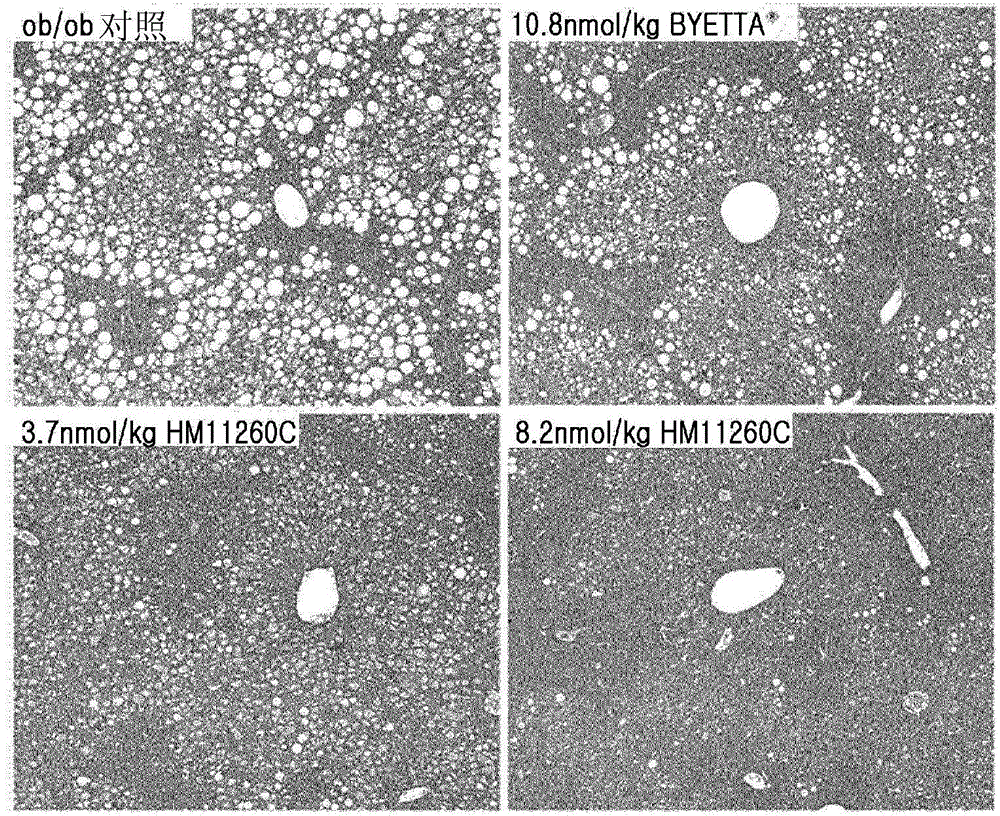
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), including a conjugate prepared by covalently linking an insulinotropic peptide, a non-peptidyl polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc region. The composition of the present invention maintains the in-vivo activity of the peptide at a relatively high level, and remarkably increases the blood half-life, thereby preventing triglyceride accumulation which is a typical feature of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ultimately, it can be desirably employed for the prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Medicinal composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102309763AGood water solubilityImprove utilization efficiencyPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPolyesterActive component
The invention provides a medicinal composition and a preparation method thereof. The medicinal composition comprises a carrier and an active component loaded on the carrier, wherein the carrier is nano particles of cyclodextrin-aliphatic polyester-phosphatidyl ethanolamine graft polymer with the structural formula shown in a formula (1) in the specifications; and in the formula (1), m is an integer from 6 to 8, and G is an oxygen atom or has a formula shown in the specifications.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Nanoparticle-based imaging agents for x-ray/computed tomography and methods for making same
ActiveUS20090087383A1Prolong blood half-lifeIncrease contrastPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyTomographyMaterials science
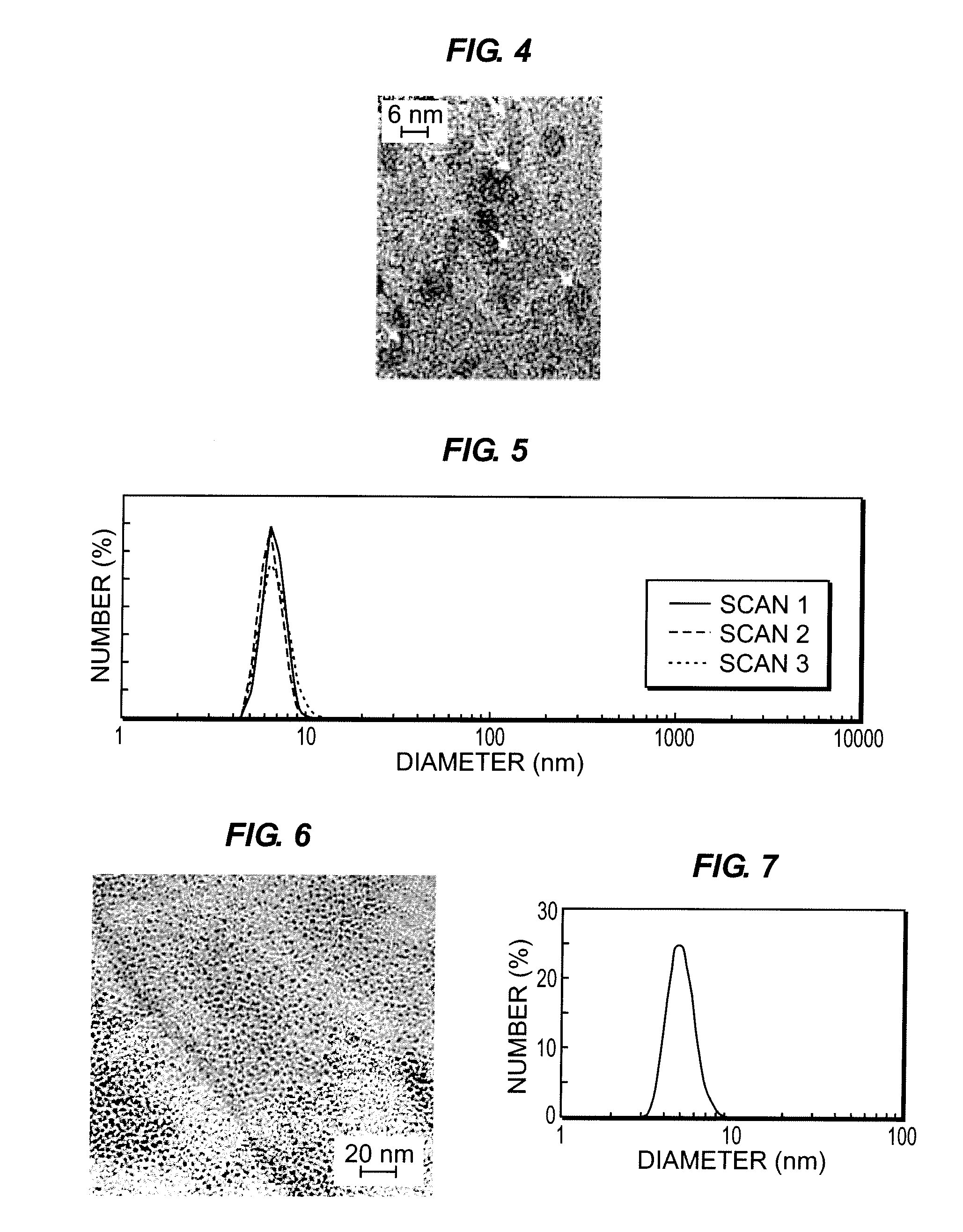
The present invention is generally directed to core / shell nanoparticles, wherein such core / shell nanoparticles comprise a nanoparticle core and a nanoshell disposed about the nanoparticle core such that, in the aggregate, they form a core / shell nanoparticle that is operable for use as an imaging agent in X-ray / computed tomography (CT). Typically, such core / shell nanoparticle-based X-ray CT imaging agents further comprise a targeting species for targeting the imaging agent to diseased sites. Included herein are methods for forming such agents, comprising forming an ensemble of core / shell nanoparticles, wherein the mean diameter of the ensemble of core / shell nanoparticles is selected so as to render the nanoparticles in the ensemble substantially clearable by a mammalian kidney.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Non-reducing end-odified glucan, method for producing same, and use thereof
ActiveCN103282508AProlong blood half-lifeGood quality and stabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsGlucanGalactose
The purpose of the invention is to provide a glucan containing at least one residue selected from an N-acetylglucosamine residue and a galactose residue, and a modified product thereof. A branched glucan according to the invention is a branched glucan in which at least one residue selected from an N-acetylglucosamine residue and a galactose residue is linked via an a-1,4-linkage to each of two or more non-reducing ends among a plurality of non-reducing ends of a branched a-1,4-glucan, and at positions other than the non-reducing ends of the branched a-1,4-glucan, either of an N-acetylglucosamine residue or a galactose residue is not present.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Tanshinone IIAPEG-PLGA-PEG (Tanshinone Polyethylene Glycol-Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid)-Polyethylene Glycol) nanoparticles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107126425ALow toxicityLow costOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to tanshinone IIAPEG-PLGA-PEG (Tanshinone Polyethylene Glycol-Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid)-Polyethylene Glycol) nanoparticles and preparation method thereof. An IIAPEG-PLGA-PEG triblock copolymer is adopted as a carrier material of the nanoparticles, a medicine, namely tanshinone IIA is loaded, the particle sizes of the nanoparticles range from 100nm to 400nm, the loading rate of the tanshinone IIA in the nanoparticles is 10-40%, the encapsulation efficiency is 50-90%, and the tanshinone IIAPEG-PLGA-PEG nanoparticles provided by the invention are simple in preparation process, uniform in size and smooth in surface. In addition, the loading rate and the encapsulation efficiency of medicines can be effectively improved, the hydrophilia, the biocompatibility and the bioavailability of the tanshinone IIA can be improved, medicine release can be effectively controlled, the circulation half-life periods of the medicines in bodies can be prolonged, and very important significances in treating cerebral arterial thrombosis and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases can be achieved.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
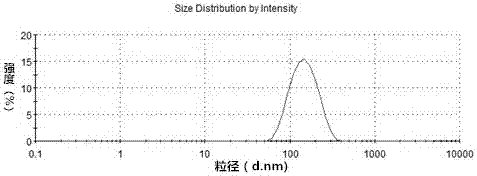
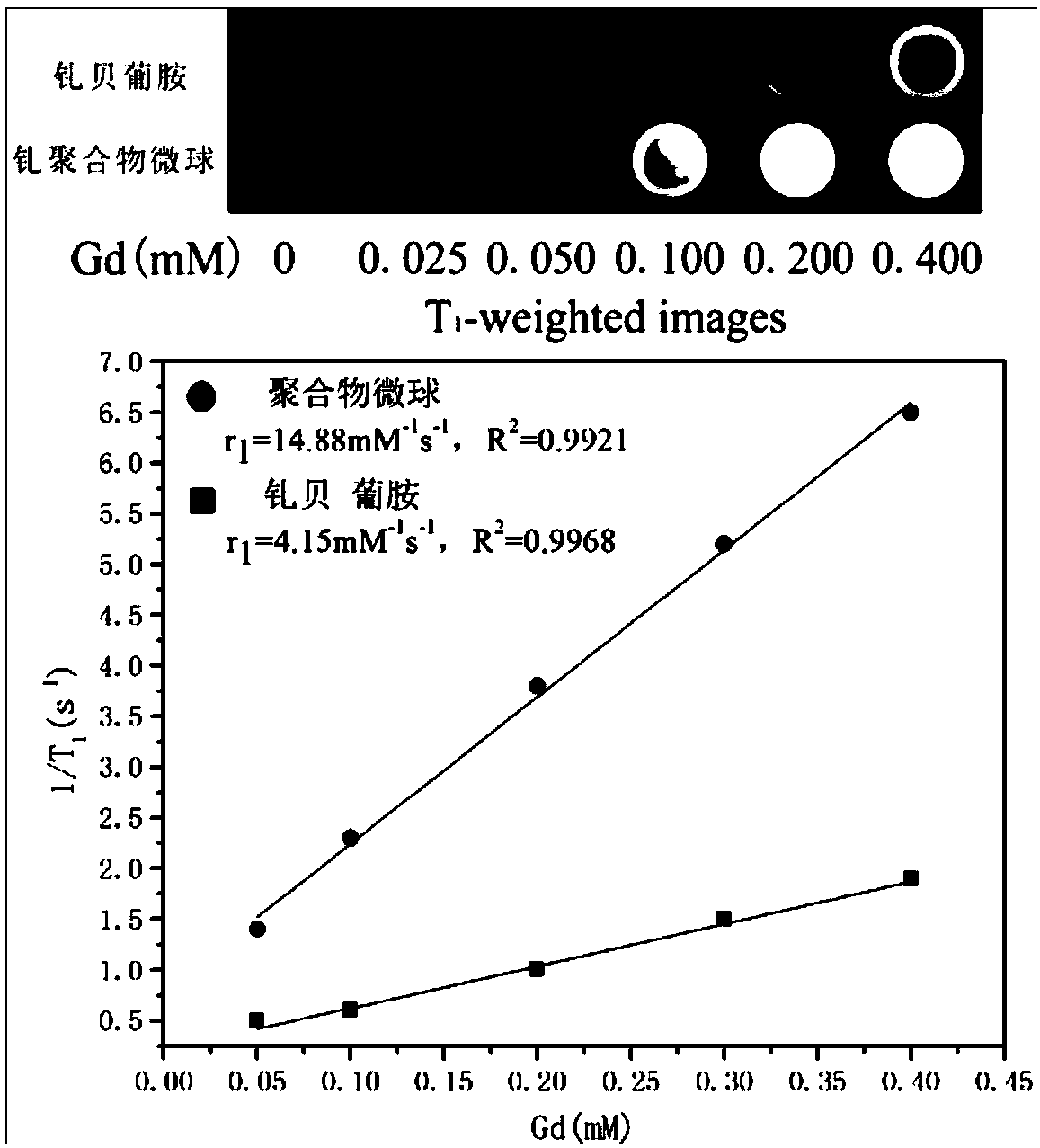
Gadolinium coordination polymer network microsphere and application thereof to magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN108434465AStable structureSynthesis conditions are simpleNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryCross-linkPolymer science
The invention discloses a gadolinium coordination polymer network microsphere and application thereof to magnetic resonance imaging and belongs to the field of material science and biomedical application. The coordination polymer network microsphere is of a net-shaped crosslinking structure; specifically, after an acrylic monomer is coordinated with gadolinium ions, the net-shaped cross-linked gadolinium coordination polymer network microsphere is formed through coordination and free radical polymerization. A preparation method of the polymer microsphere is simple and the cost is low; the polymer microsphere has a stable structure and has a relatively high relaxation rate, a relatively good T1 imaging effect and long blood circulation time; the polymer microsphere has extremely great potential application value in the aspects of diagnosis and treatment of cancers and tumors.
Owner:武汉佰强生物医药有限公司
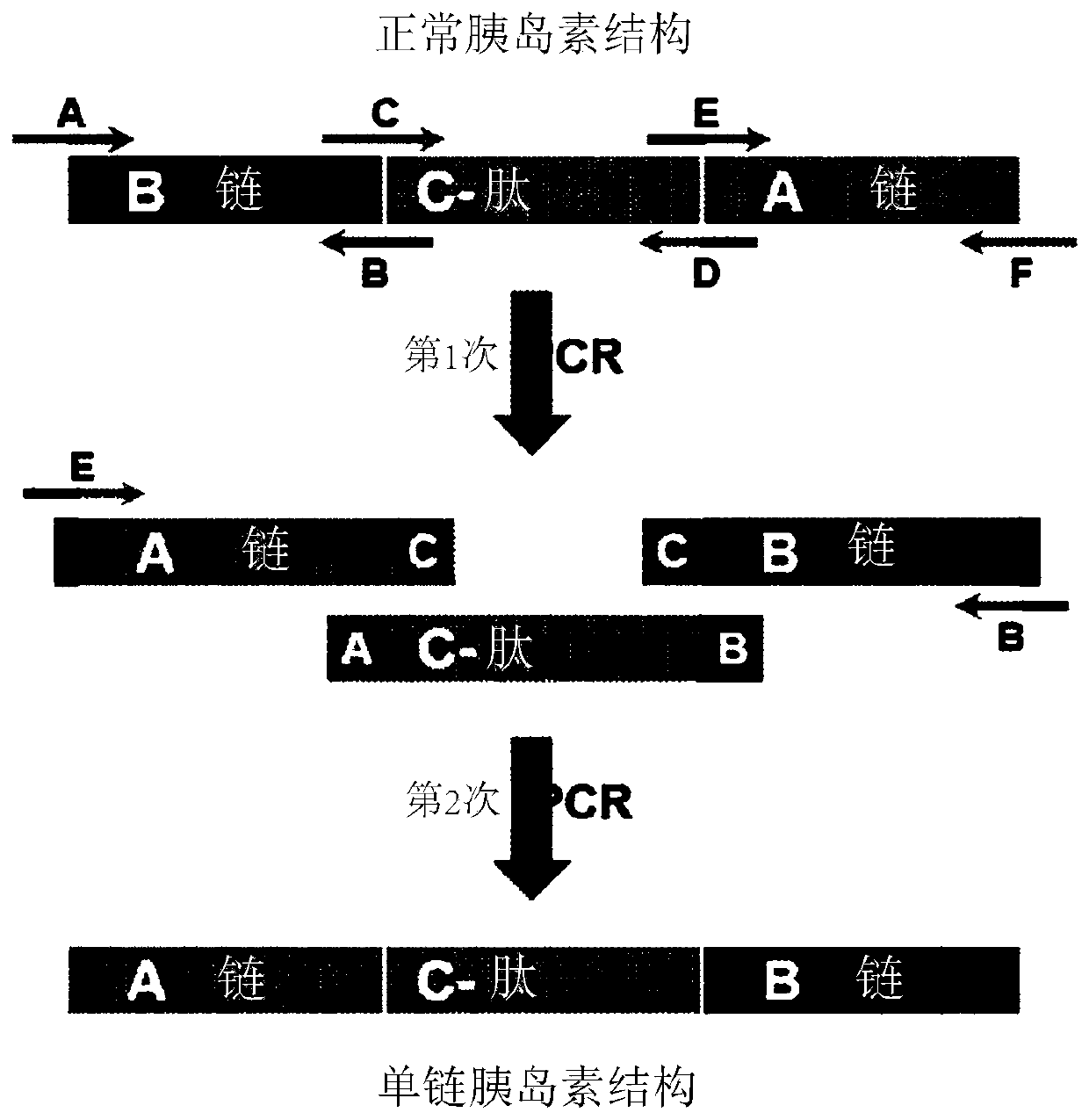
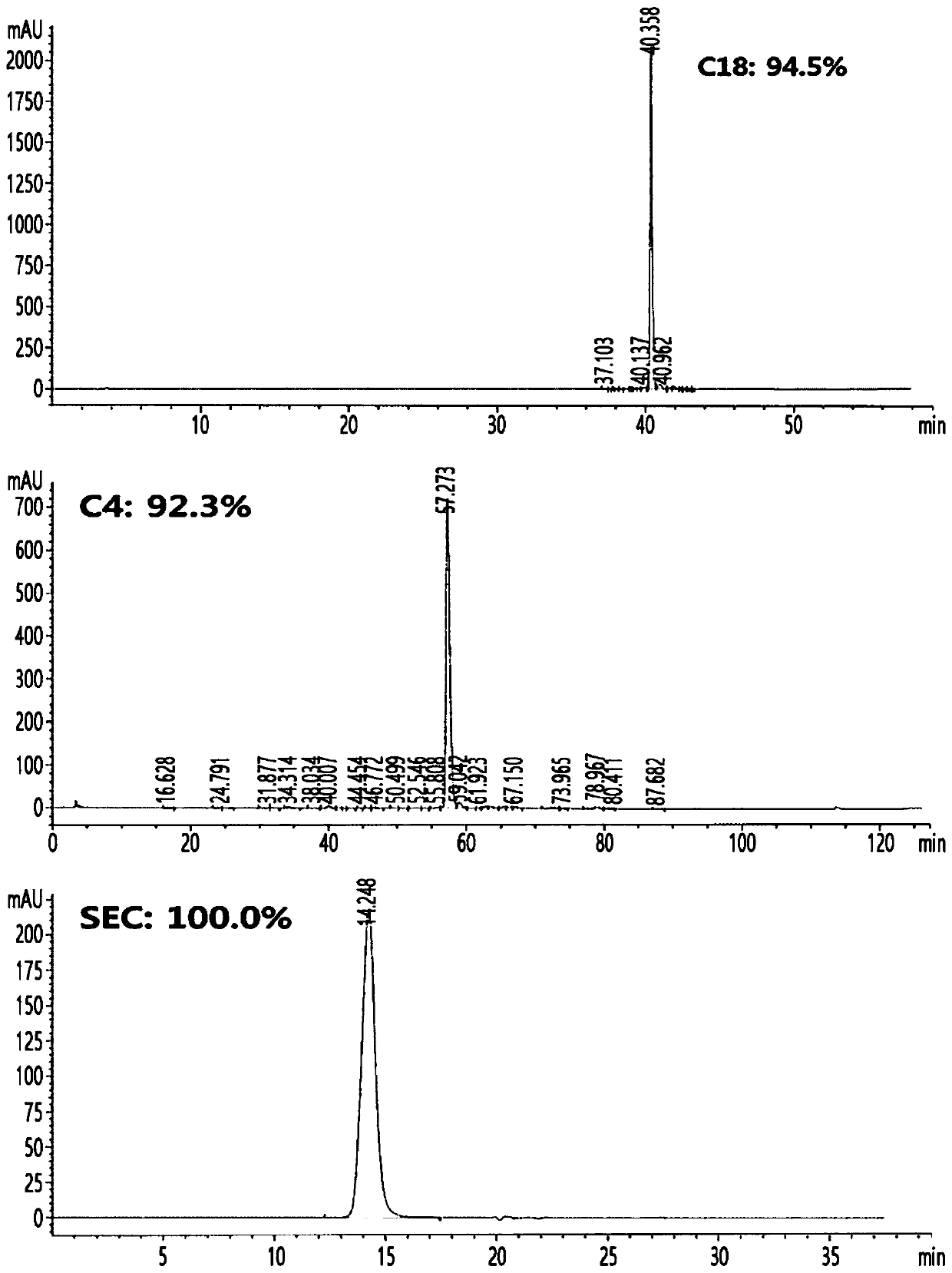
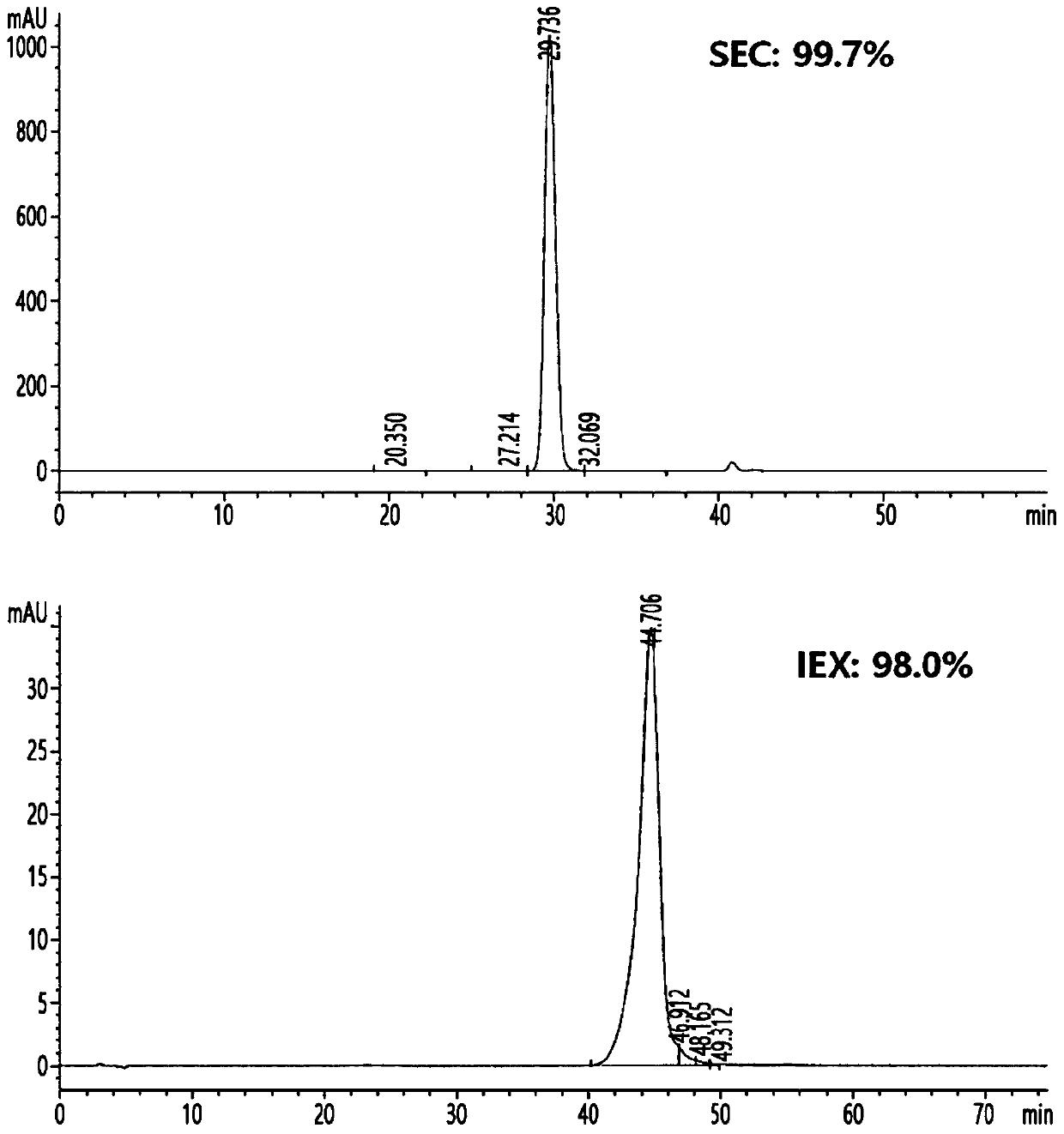
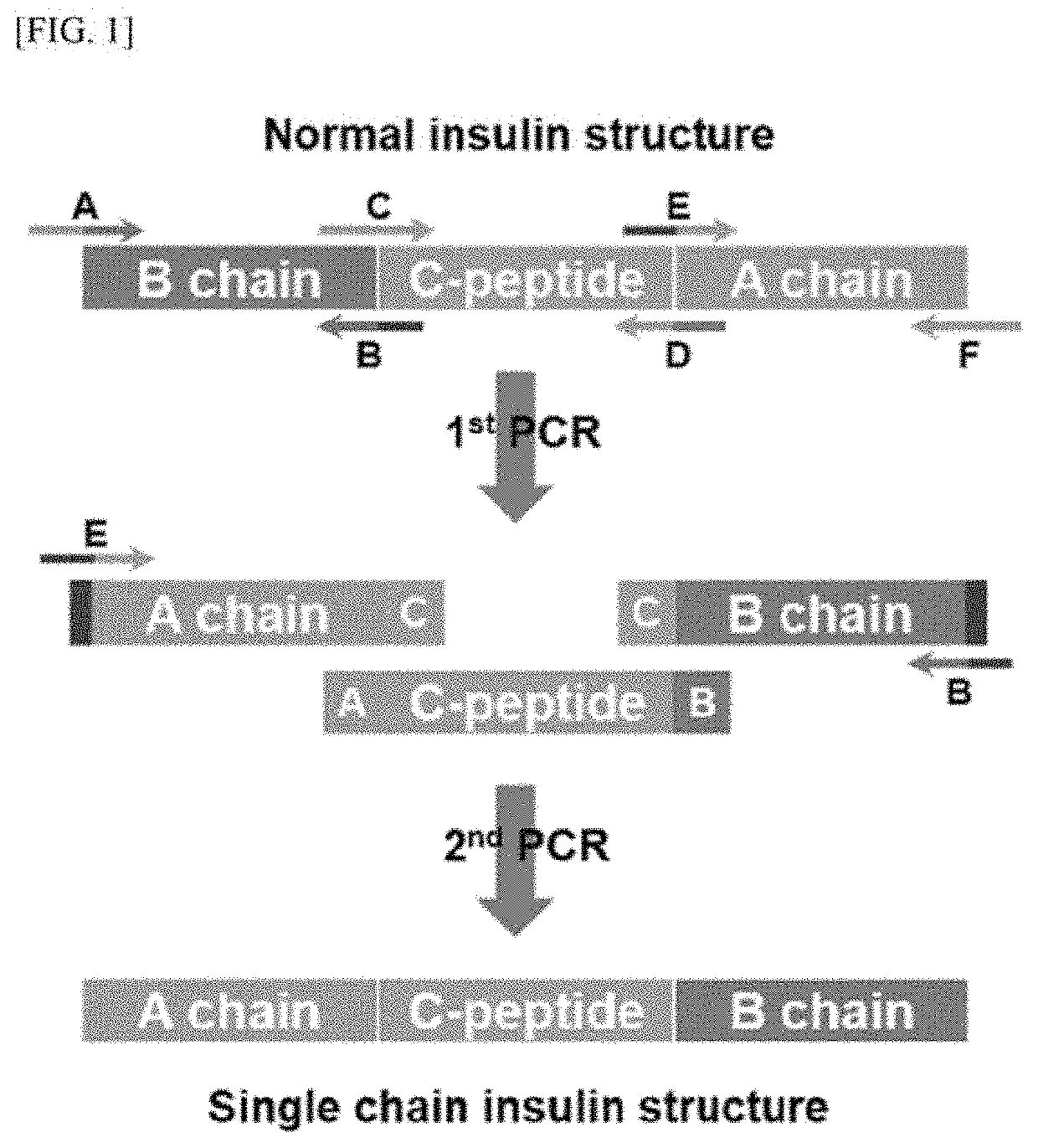
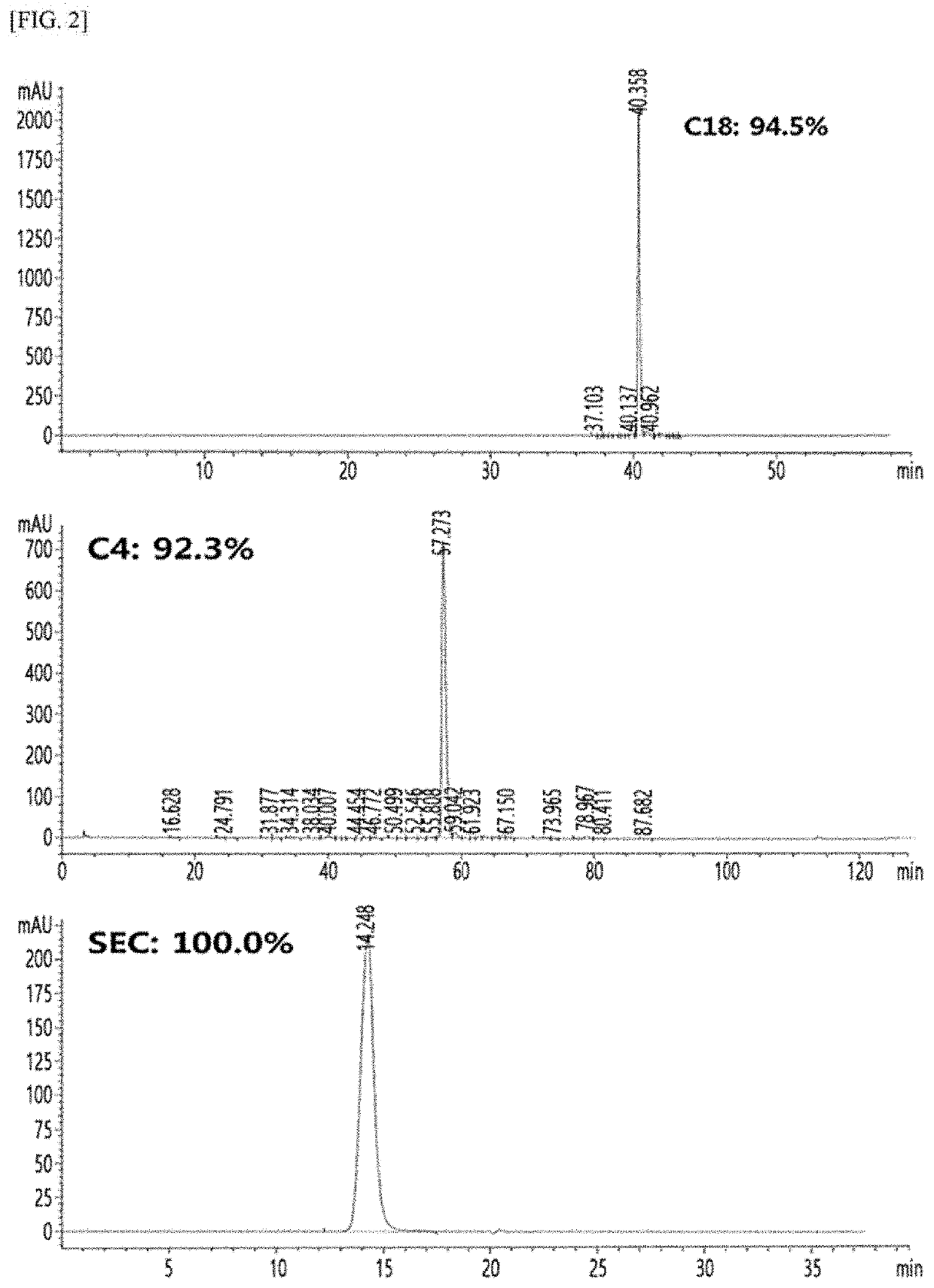
Long-acting single-chain insulin analog and conjugate thereof
PendingCN111386130AStable hypoglycemic effectProlong blood half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsInsulin humulinInternal medicine
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Long-acting single-chain insulin analog and conjugate thereof
InactiveUS20200254108A1Good hypoglycemic effectProlong blood half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiochemistryInsulin humulin
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Application of erythrocyte and activated platelet membranes as carriers in preparation of thrombus treatment drugs
InactiveCN111035766AGood biocompatibilityProlong blood half-lifeInorganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsThrombusCell membrane
The invention discloses an application of erythrocyte and activated platelet membranes as carriers in preparation of thrombus treatment drugs, and relates to the technical field of medical thrombus treatment. The invention firstly provides an application of an erythrocyte membrane and an activated platelet membrane as carriers in preparation of thrombolytic drugs, and secondly, provides a composition for inhibiting and / or dissolving thrombus, comprising a thrombolytic drug, mesoporous silicon, an erythrocyte membrane, an activated platelet membrane and derivative membranes under various physiological and pathological conditions. Experimental research finds that a drug delivery system coated with an erythrocyte membrane and an activated platelet membrane has an obvious thrombolytic effect.The composition for inhibiting and / or dissolving thrombus is obtained by physically adsorbing thrombolytic drugs by utilizing mesoporous silicon, and coating the mesoporous silicon with an erythrocytemembrane and an activated platelet membrane. The thrombolytic drug is carried by the biological membranes, so that the targeting property and the enrichment degree of thrombus can be enhanced, the circulation time is remarkably prolonged, the bleeding risk is reduced, and a good thrombolytic effect is achieved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
PendingUS20150056223A1Improve the level ofProlong blood half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDrugPeptide
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), including a conjugate prepared by covalently linking an insulinotropic peptide, a non-peptidyl polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc region. The composition of the present invention maintains the in-vivo activity of the peptide at a relatively high level, and remarkably increases the blood half-life, thereby preventing triglyceride accumulation which is a typical feature of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ultimately, it can be desirably employed for the prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
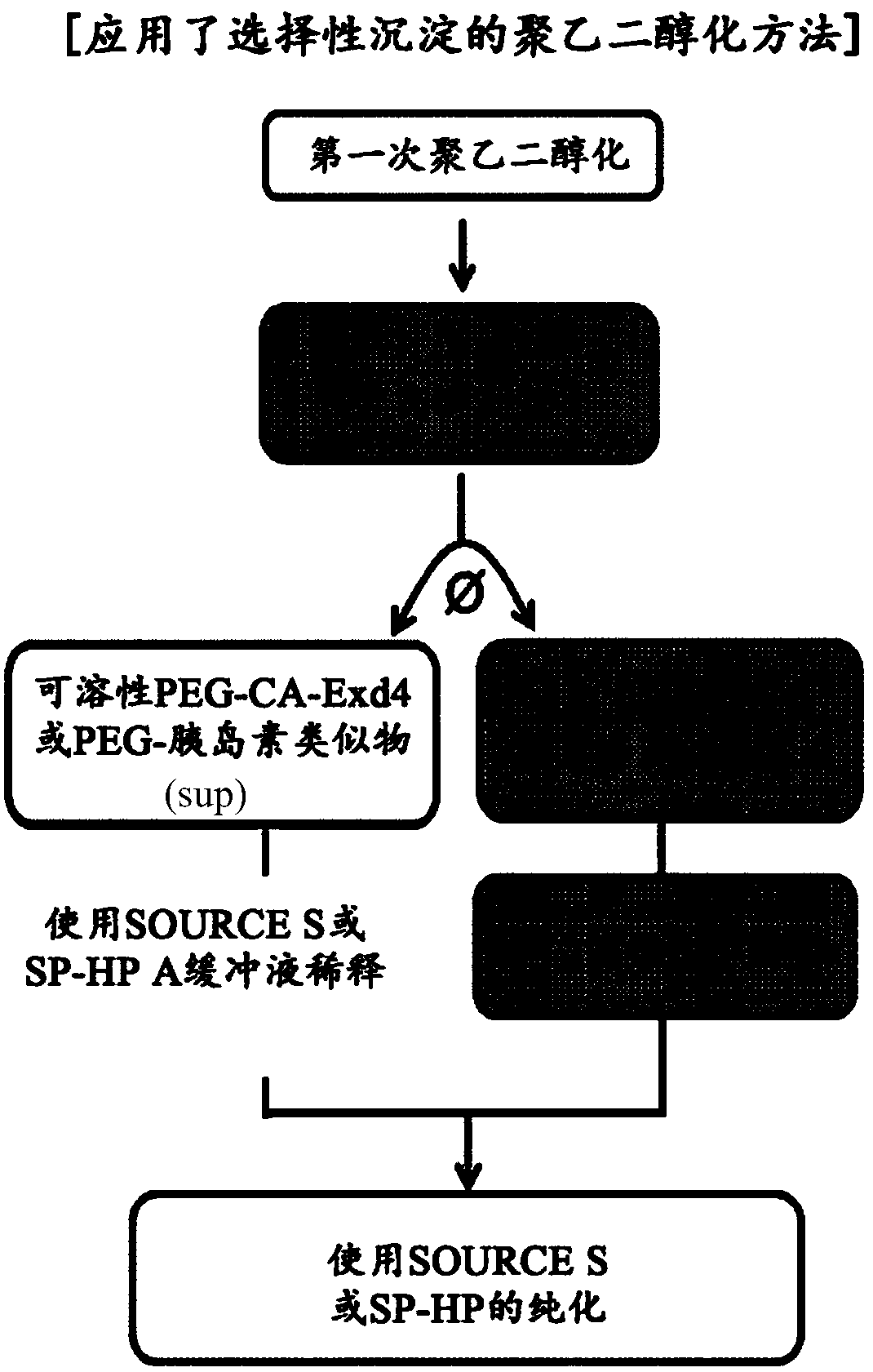
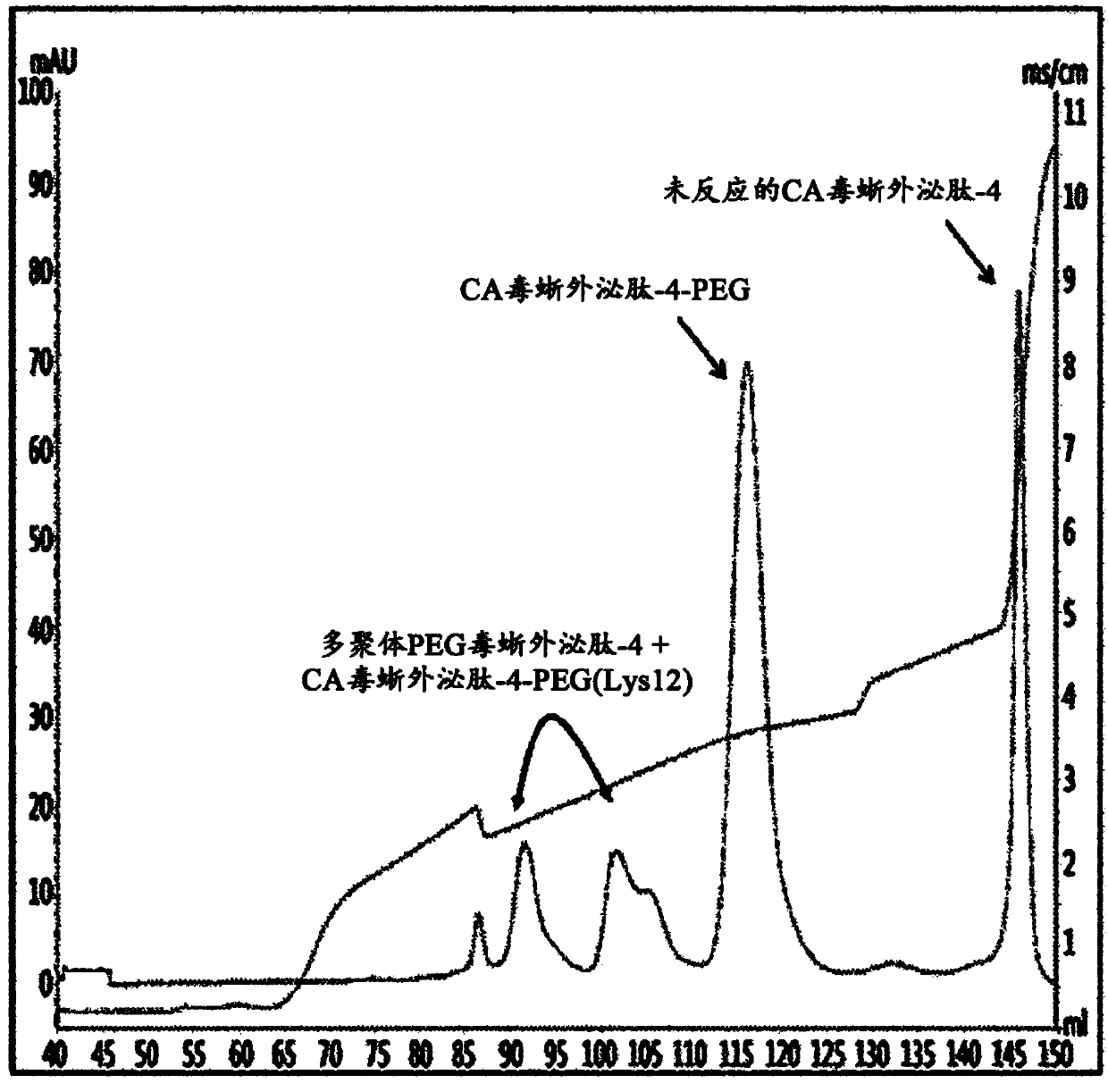
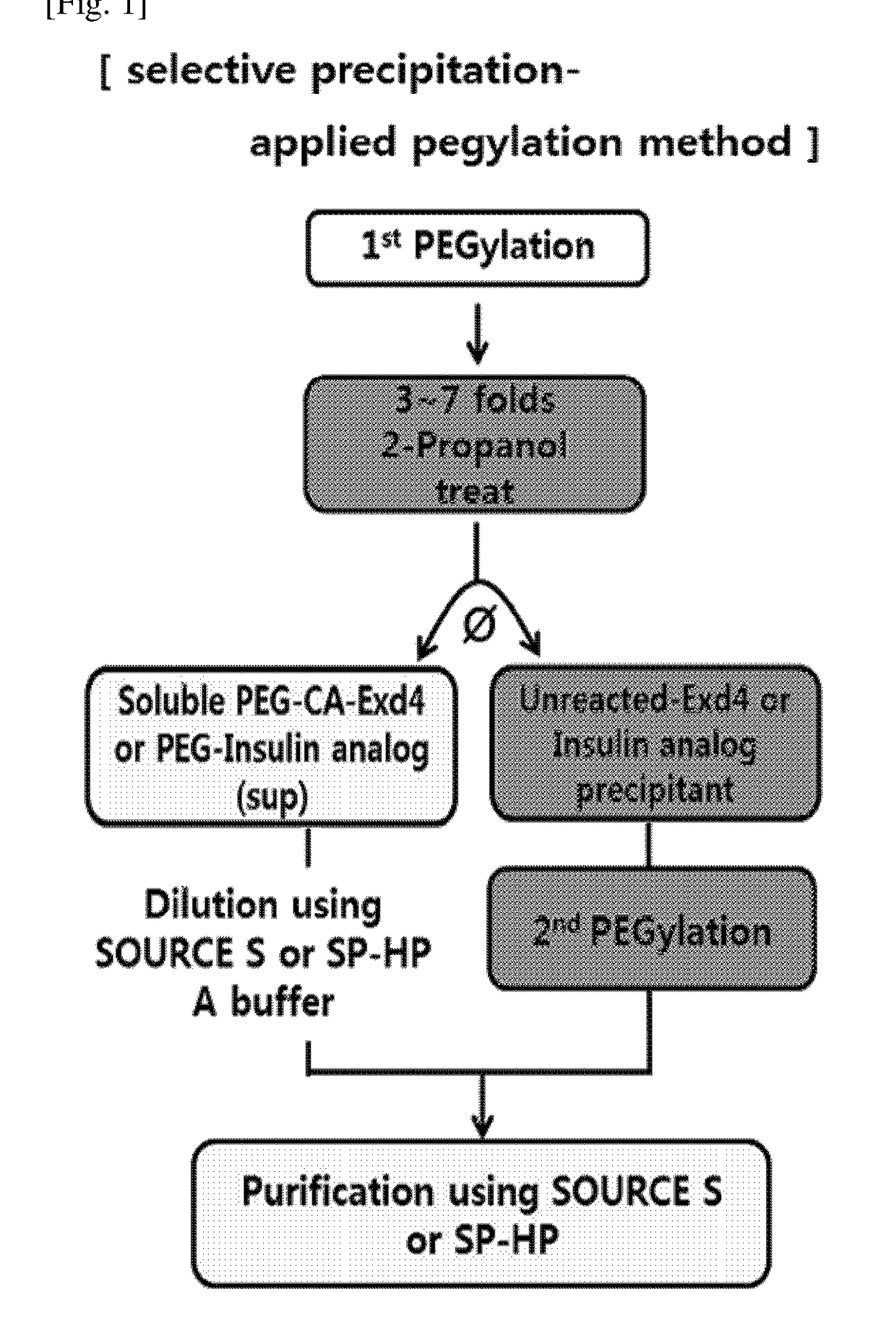
Method of preparing physiologically active polypeptide conjugate
ActiveCN108026143AProlong blood half-lifeAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide preparation methodsPeptide drugHalf-life
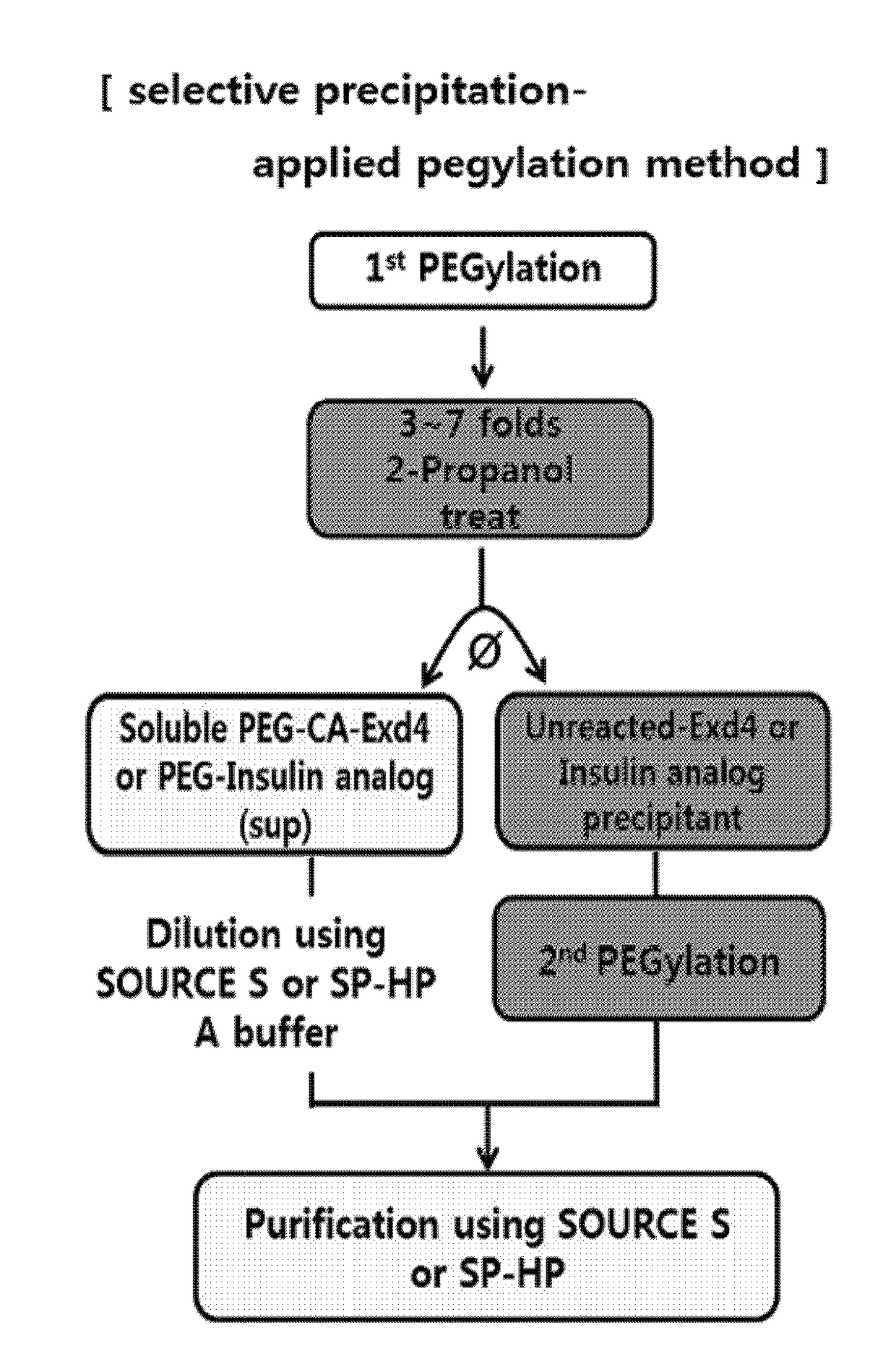
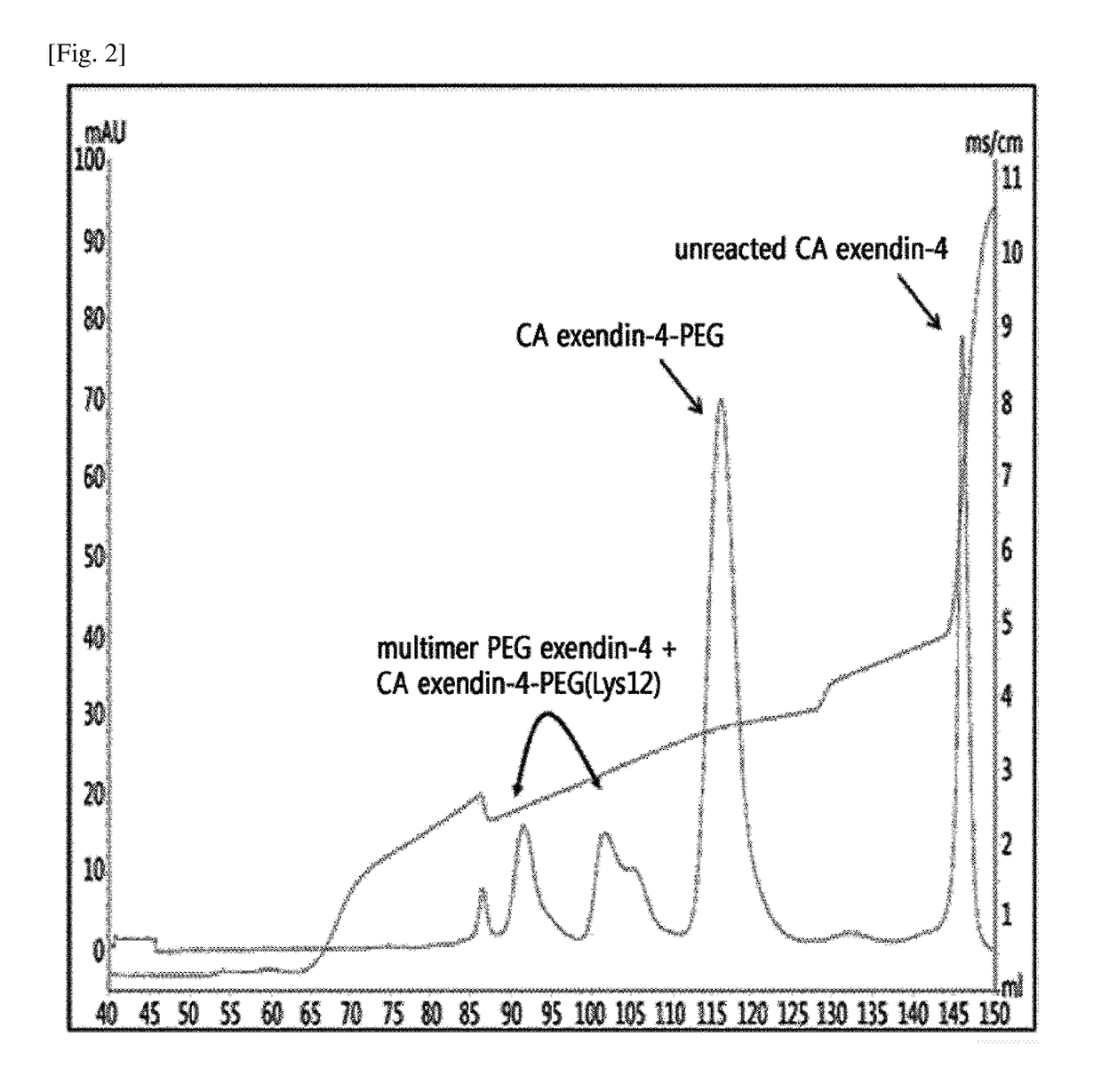
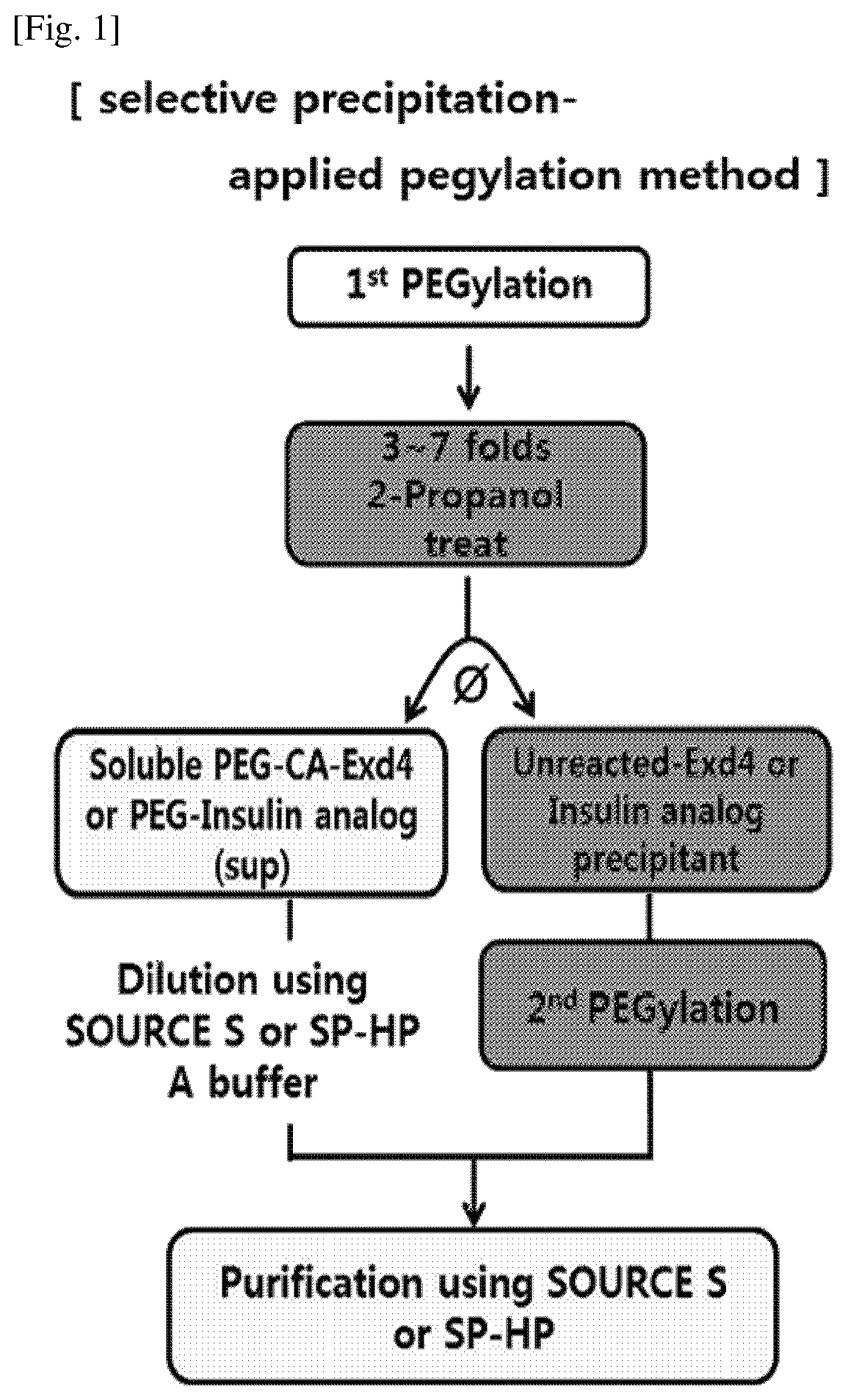
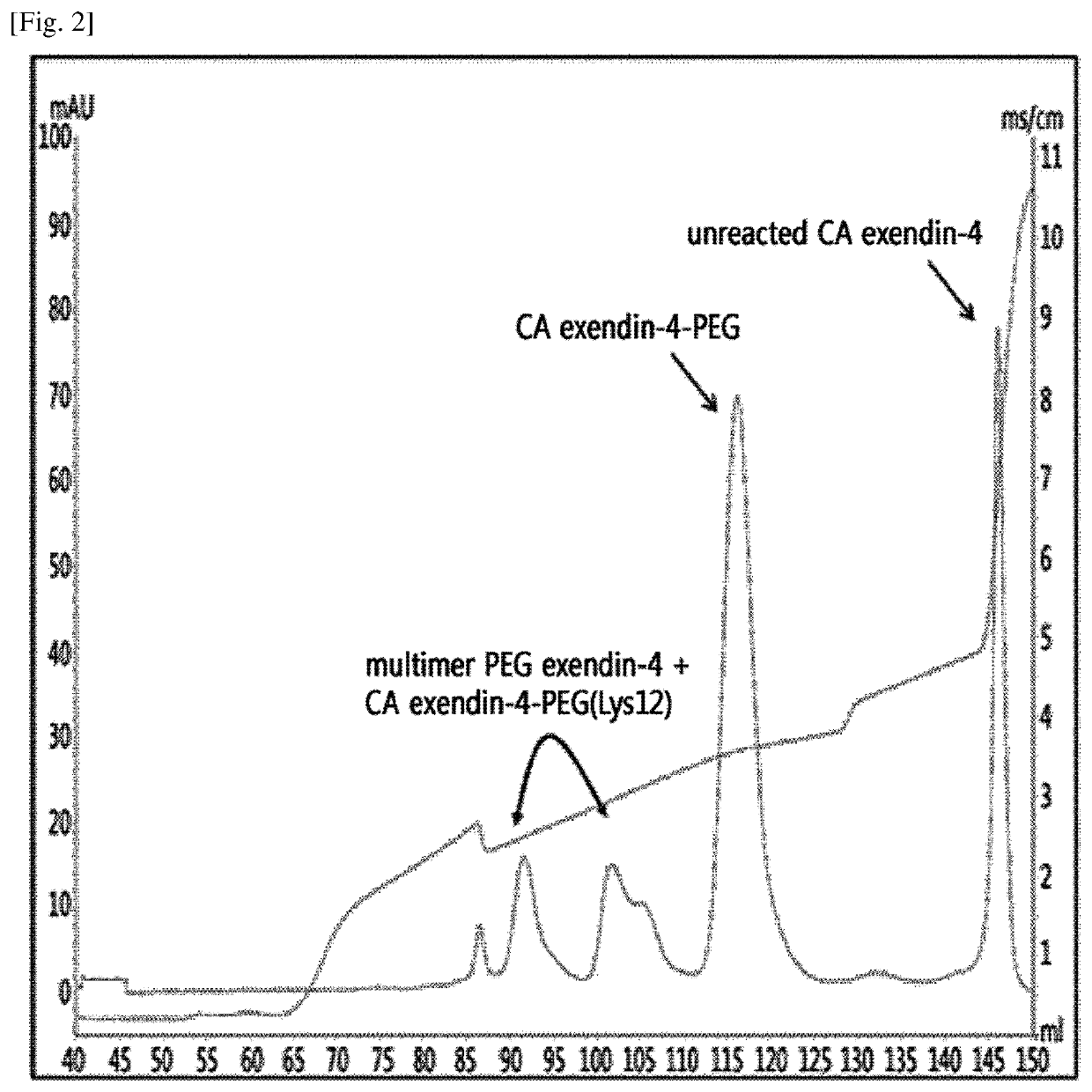
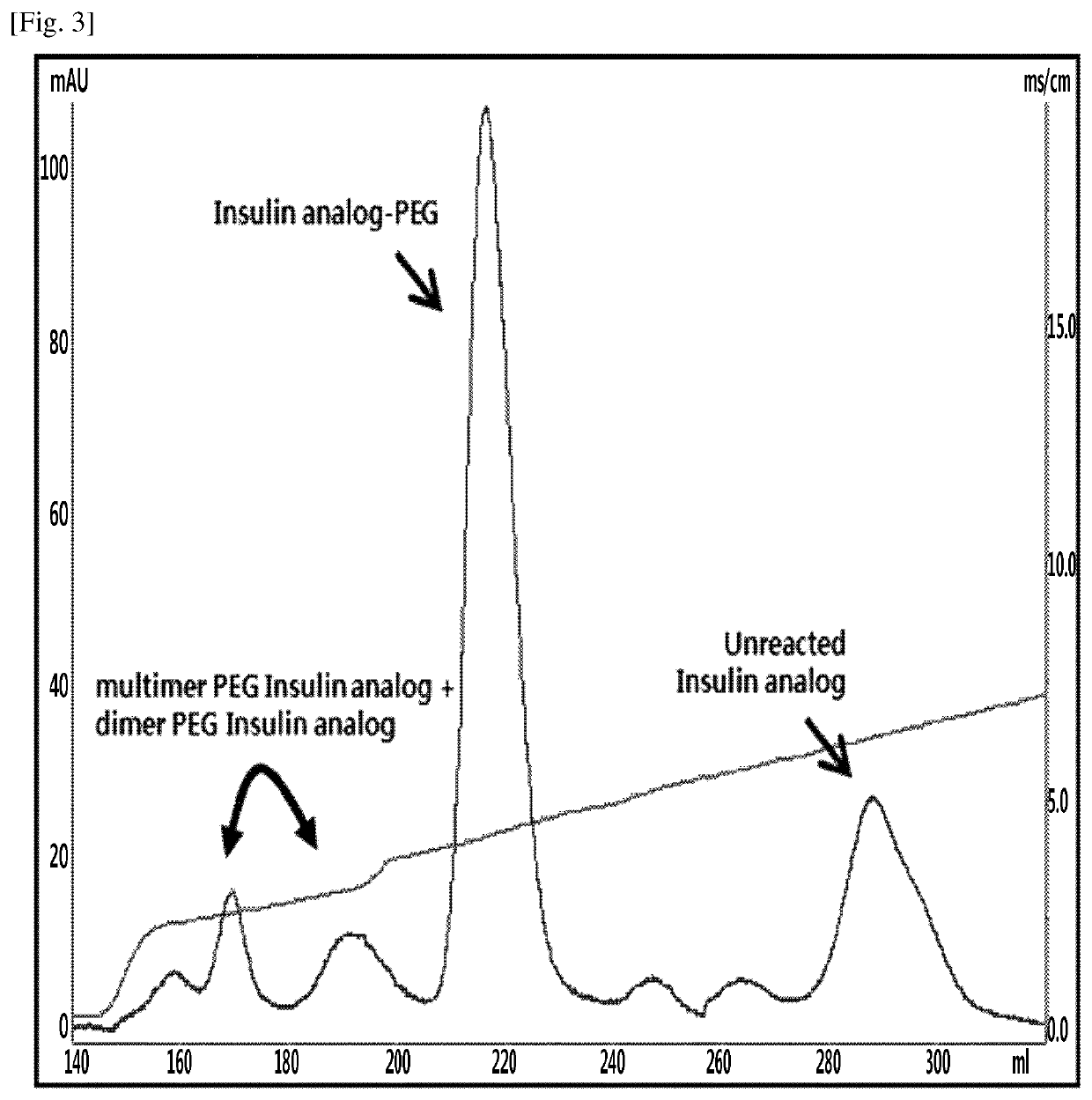
Provided is a method of preparing a physiologically active polypeptide conjugate, in which a physiologically active polypeptide and a non-peptidyl polymer are linked to each other via a covalent bond.The method is to improve an overall yield of the physiologically active polypeptide conjugate by improving a reaction of the non-peptidyl polymer and the physiologically active polypeptide, and particularly, the method is to prepare a physiologically active polypeptide conjugate in a high yield by performing a two-step reaction through selective precipitation. The preparation method of the present invention is used to produce a non-peptidyl polymer-physiologically active polypeptide conjugate and a physiologically active polypeptide-physiologically active carrier conjugate in a high yield, and therefore, the method may be used in the development of long-acting formulations of various peptide drugs which maintain in vivo activity at a relatively high level and have remarkably increased blood half-life.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
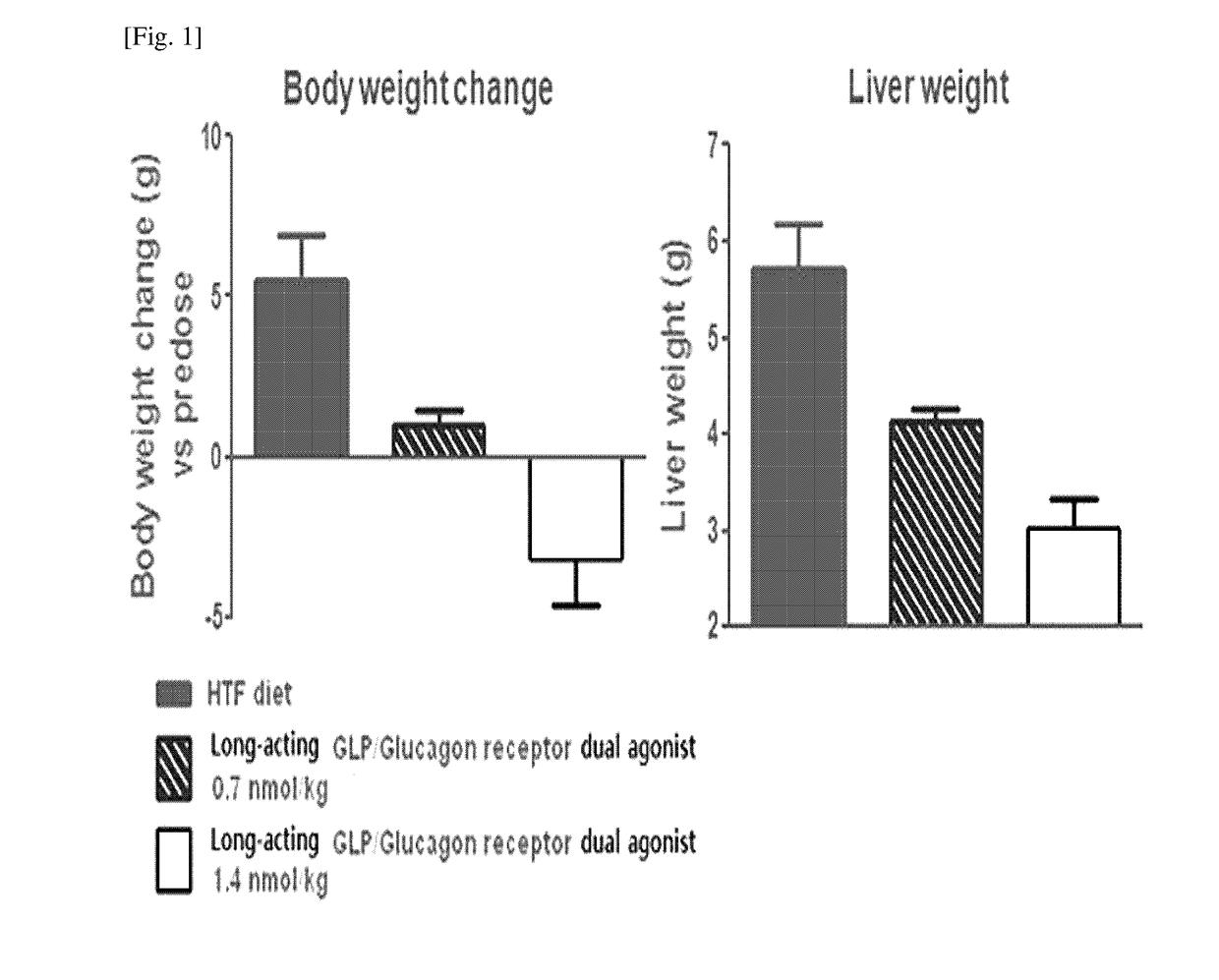
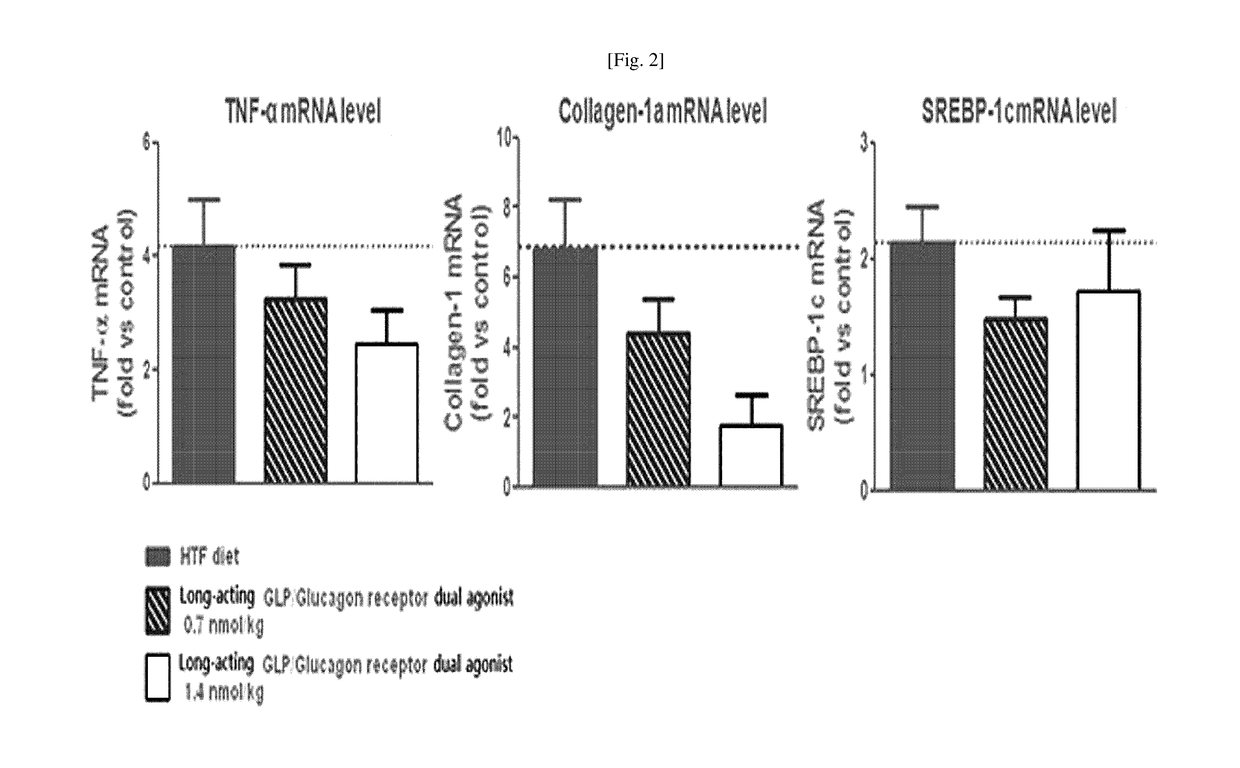
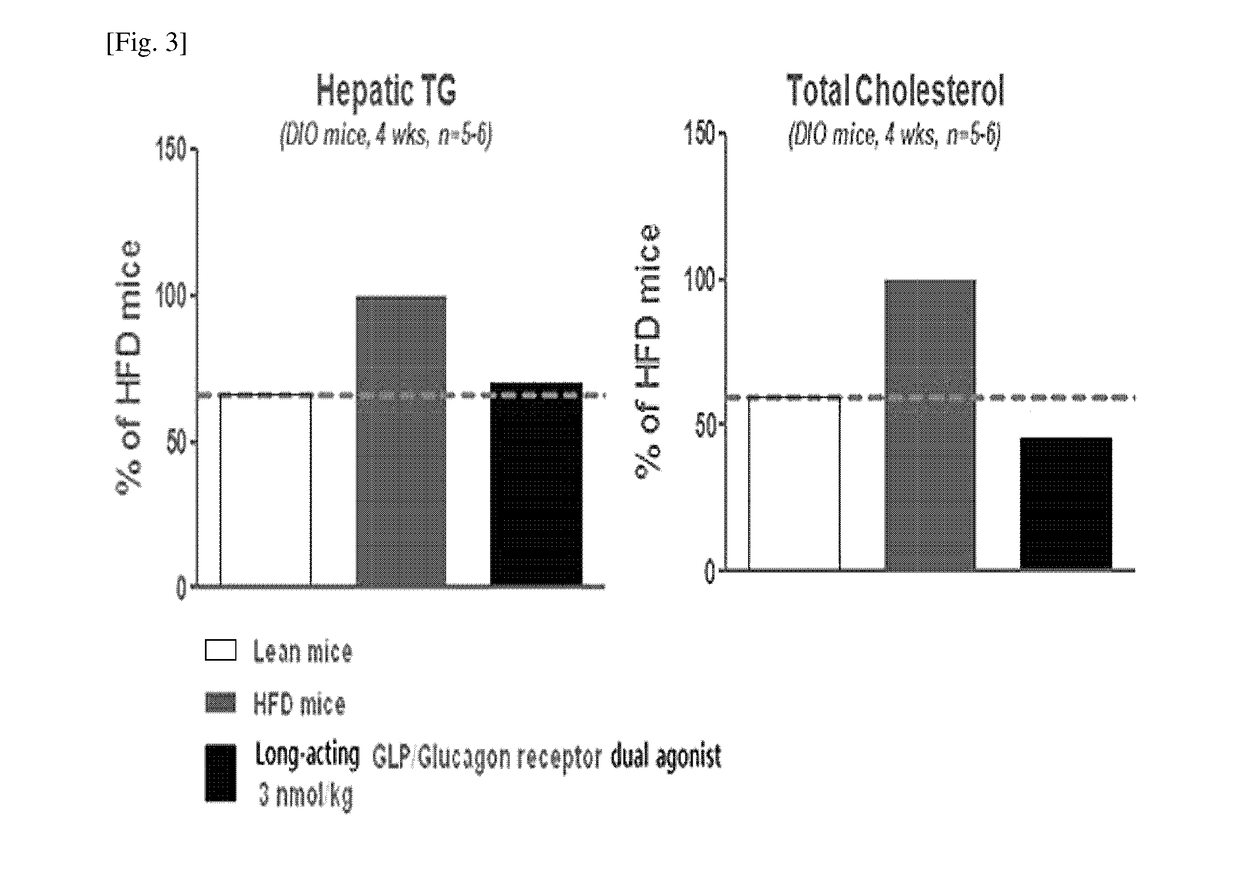
Use of a long acting glp-1/glucagon receptor dual agonist for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
ActiveUS20170298117A1Increase choiceIncrease patient 's convenienceCompounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectGain weight
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease including a long-acting GLP-1 / glucagon receptor dual agonist, and a method for preventing or treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease including administering the composition. The composition of the present invention either has no side effect of weight gain or reduces the side effect of weight gain, which is a side-effect of conventional therapeutic agents for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and reduces the amount of administrations of a long-acting GLP-1 / glucagon receptor dual agonist, thus greatly improving patient's convenience. In addition, the long-acting GLP-1 / glucagon receptor dual agonist of the present invention improves in vivo sustainability and stability.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
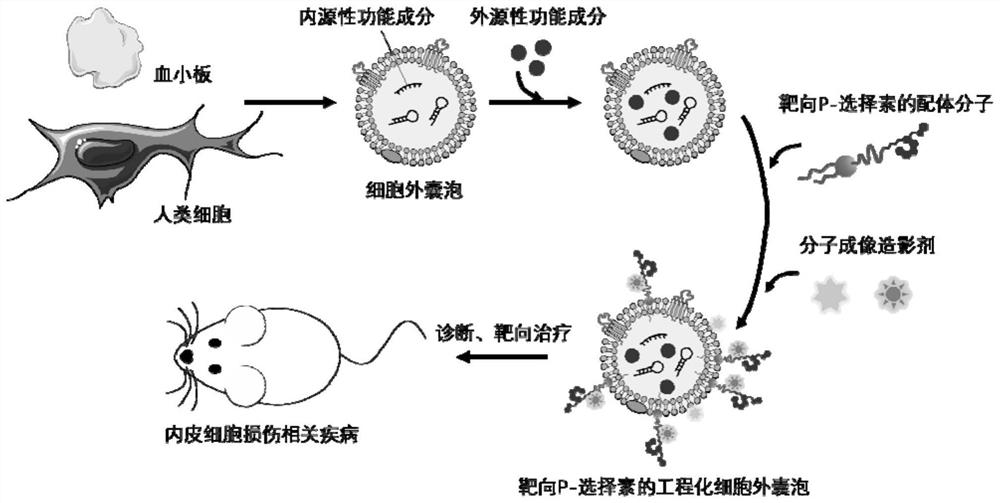
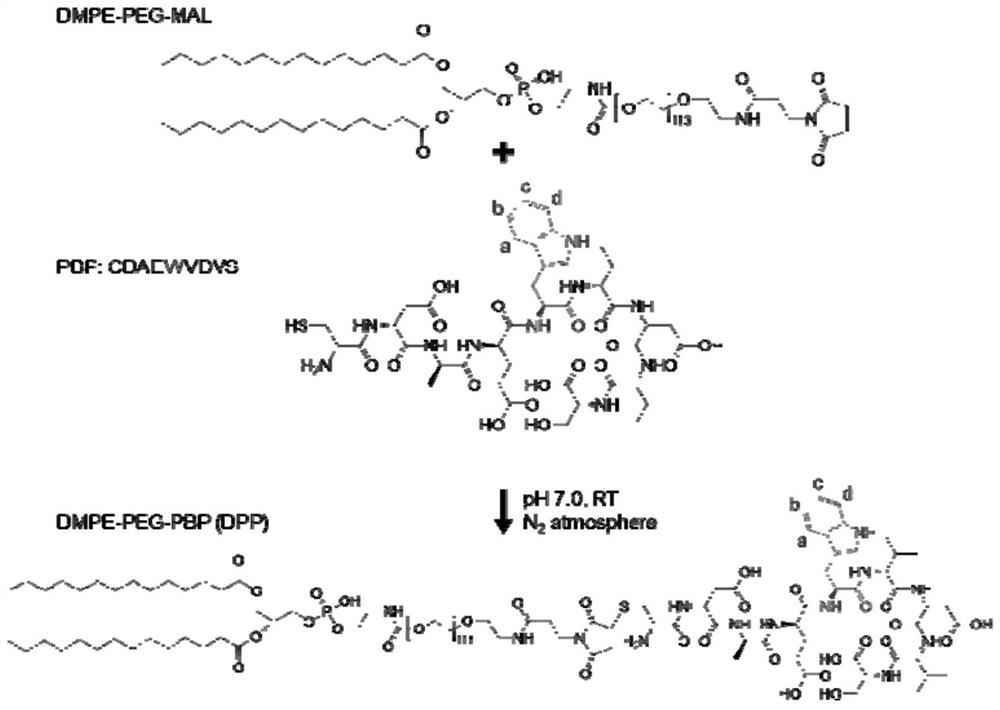
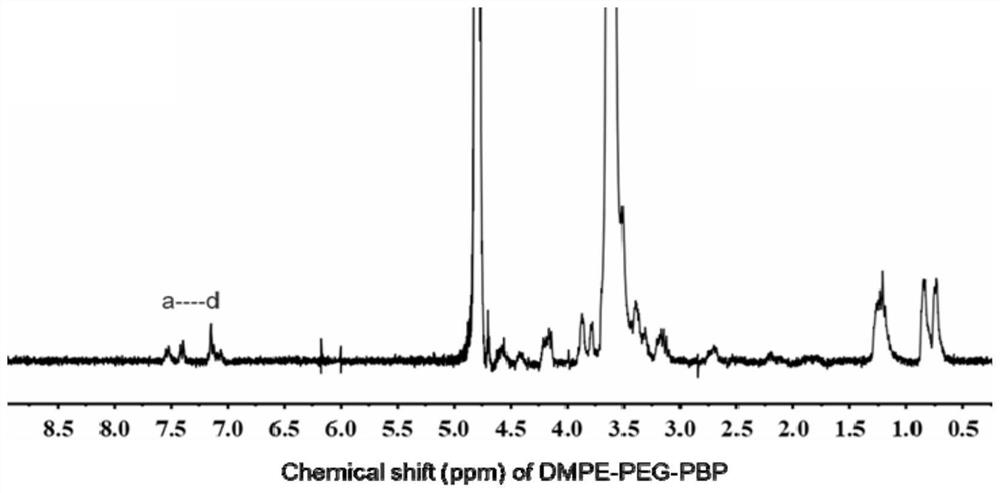
Engineered extracellular vesicle composition targeting P-selectin as well as preparation method and application of engineered extracellular vesicle composition
PendingCN113616810ALow immunogenicityProlong blood half-lifePowder deliveryLuminescence/biological staining preparationDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
The invention discloses an engineered extracellular vesicle composition targeting P-selectin. The engineered extracellular vesicle composition comprises extracellular vesicles, ligand molecules specifically targeting P-selectin, a molecular imaging contrast agent and endogenous or exogenous functional components carried in the extracellular vesicles, wherein the engineered extracellular vesicle is used for specifically recognizing and combining the P-selectin on the surface of an injured endothelial cell, the expression quantity of the P-selectin is indicated through the signal intensity of the molecular imaging contrast agent, and carried endogenous or exogenous functional components are delivered to an injured part. According to the engineered extracellular vesicle composition targeting the P-selectin as well as a preparation method and the application of the engineered extracellular vesicle composition, the engineered extracellular vesicle takes the P-selectin as a target spot to target injured endothelial cell, so that the purpose of targeting diseases related to endothelial cell injury is realized; and the blank that in the prior art, no universal technical means for targeted diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to injured endothelium exists is filled.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method of preparing physiologically active polypeptide conjugate
ActiveUS20180214562A1High yieldProlong blood half-lifeAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDepsipeptidesPeptide drugHalf-life
Provided is a method of preparing a physiologically active polypeptide conjugate, in which a physiologically active polypeptide and a non-peptidyl polymer are linked to each other via a covalent bond. The method is to improve an overall yield of the physiologically active polypeptide conjugate by improving a reaction of the non-peptidyl polymer and the physiologically active polypeptide, and particularly, the method is to prepare a physiologically active polypeptide conjugate in a high yield by performing a two-step reaction through selective precipitation. The preparation method of the present invention is used to produce a non-peptidyl polymer-physiologically active polypeptide conjugate and a physiologically active polypeptide-physiologically active carrier conjugate in a high yield, and therefore, the method may be used in the development of long-acting formulations of various peptide drugs which maintain in vivo activity at a relatively high level and have remarkably increased blood half-life.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Novel prostaglandin derivative
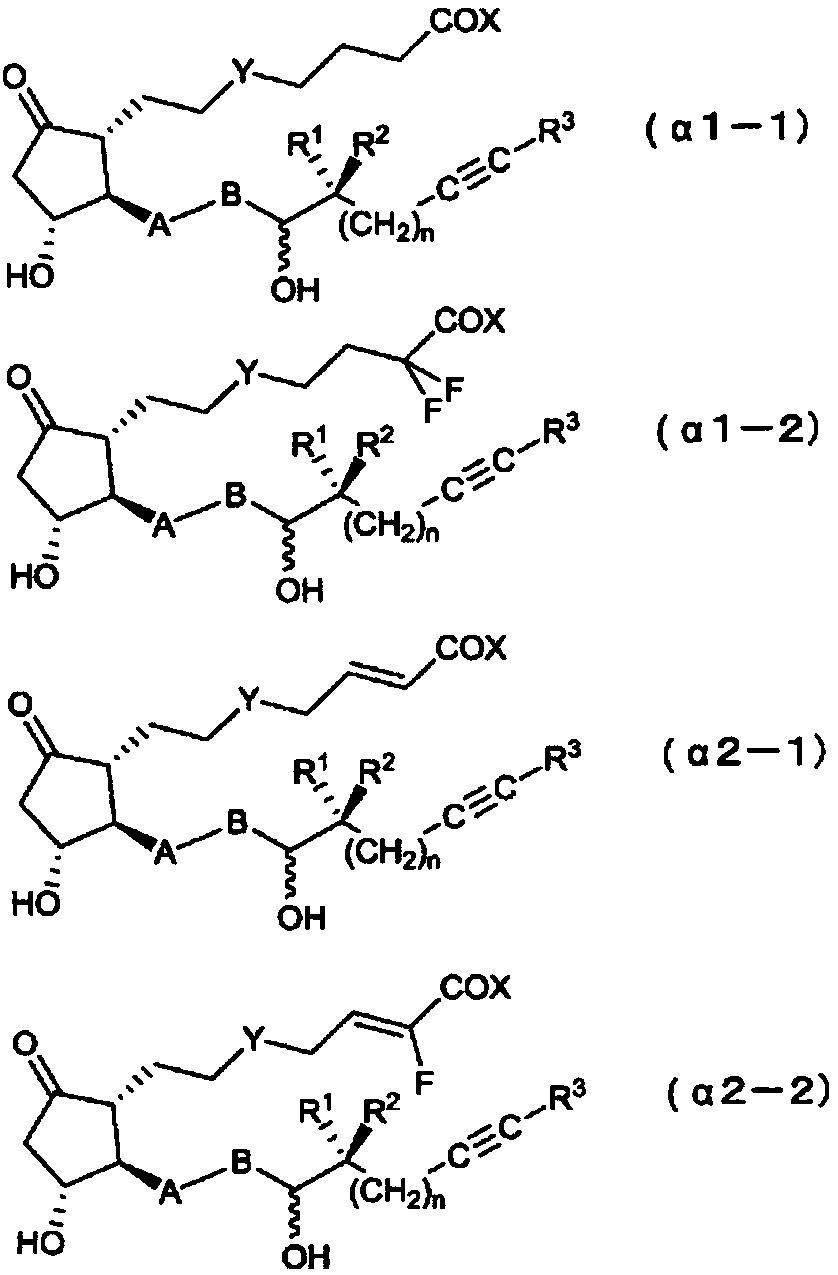
ActiveCN109071427AEnhanced inhibitory effectExcellent blood flow increasing effectOrganic active ingredientsOligosaccharidesArterial Occlusive DiseasesBlood flow
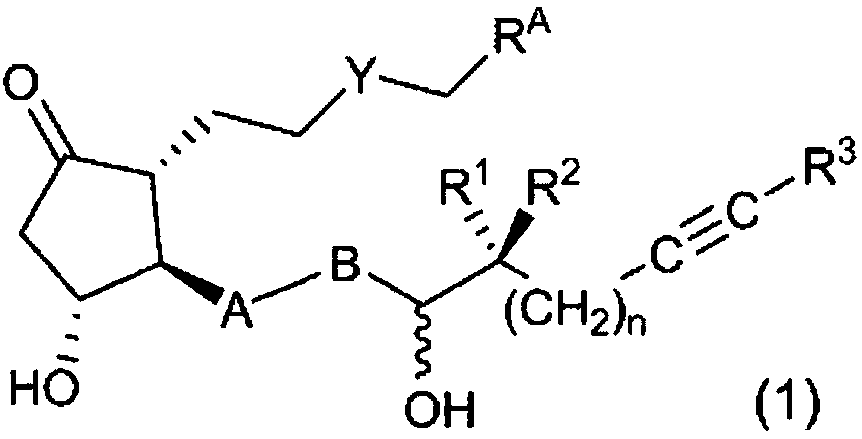
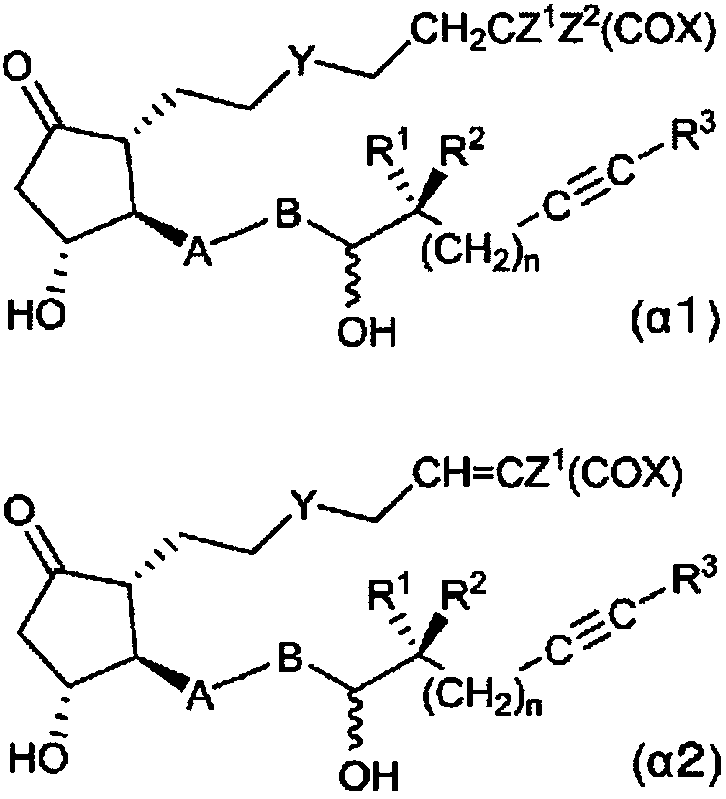
The present invention relates to: a novel prostaglandin derivative having an alkynyl group in a [omega]-chain, particularly a novel prostaglandin derivative having a double bond at position-2 and alsohaving an alkynyl group in a [omega]-chain; and a medicine containing the compound as an active ingredient. According to the present invention, it becomes possible to provide: a compound representedby formula (1) [wherein each symbol is as defined in the description], a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the compound, or a cyclodextrin inclusion complex of the compound or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt; and a medicine which contains the compound as an active ingredient, particularly which can be used for the prevention or treatment of a blood flow disturbance associated with spinal canal stenosis or chronic arterial occlusive disease.
Owner:AGC INC +1
Liposome composition of compound with STING agonistic activity, preparation method and application of liposome composition
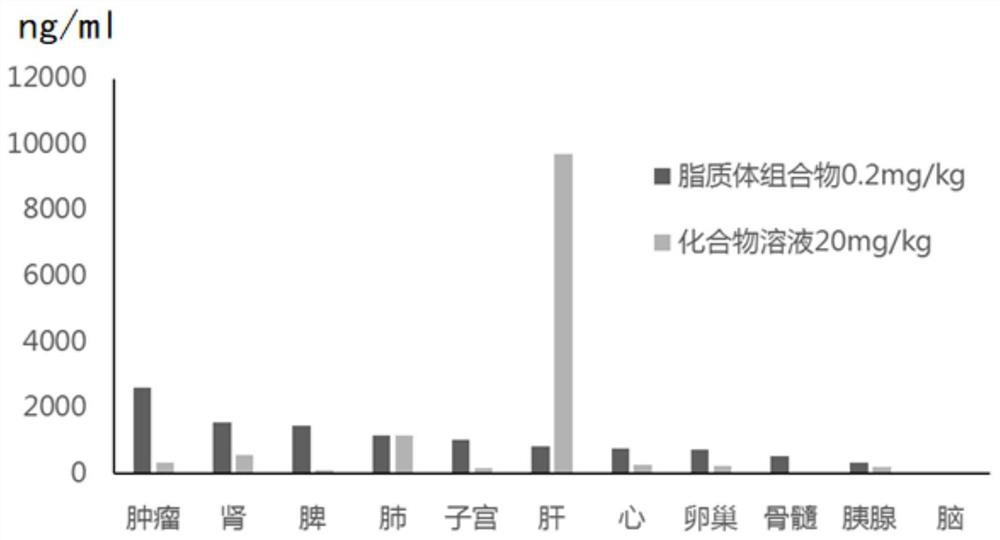
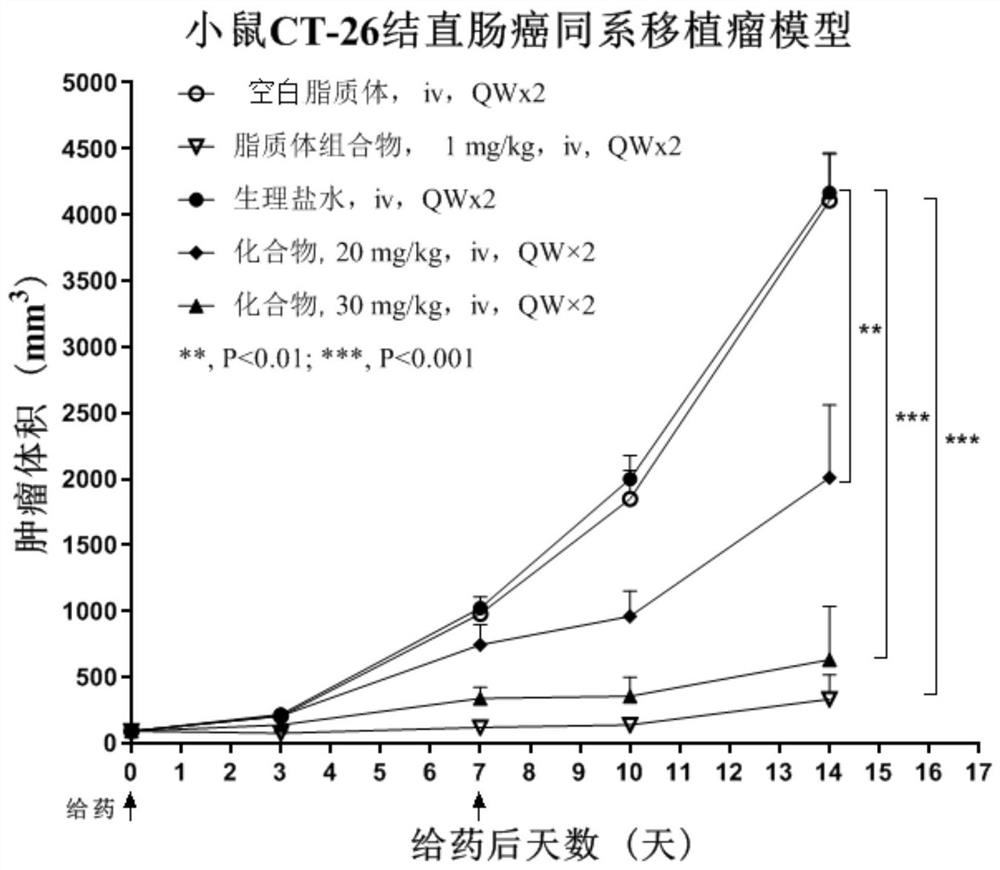
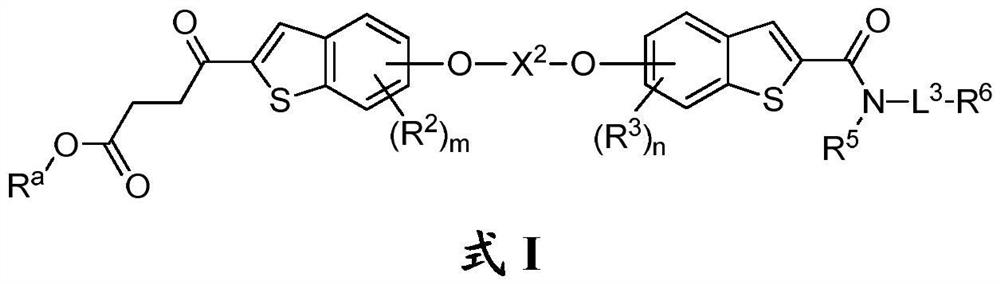
PendingCN114053431AProlong blood half-lifeImprove anti-tumor effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLiposome membraneMedication risk
The invention relates to a liposome composition of a compound with STING agonistic activity, a preparation method and application of the liposome composition. Specifically, the invention relates to a liposome of a compound as shown in a formula I. The liposome contains a liposome membrane and an inner water phase encapsulated in the liposome membrane, wherein the inner water phase contains a compound formed by metal ions and the ionized compound as shown in the formula I. The liposome can improve the tissue targeting property of the compound shown in the formula I, enhance the anti-tumor curative effect, prolong the blood circulation time, enhance the compliance of a patient and / or reduce the clinical medication risk;.
Owner:SICHUAN KELUN PHARMA RES INST CO LTD
A dual-functional imaging-guided photothermal diagnosis and treatment integrated nanoparticle and its preparation method
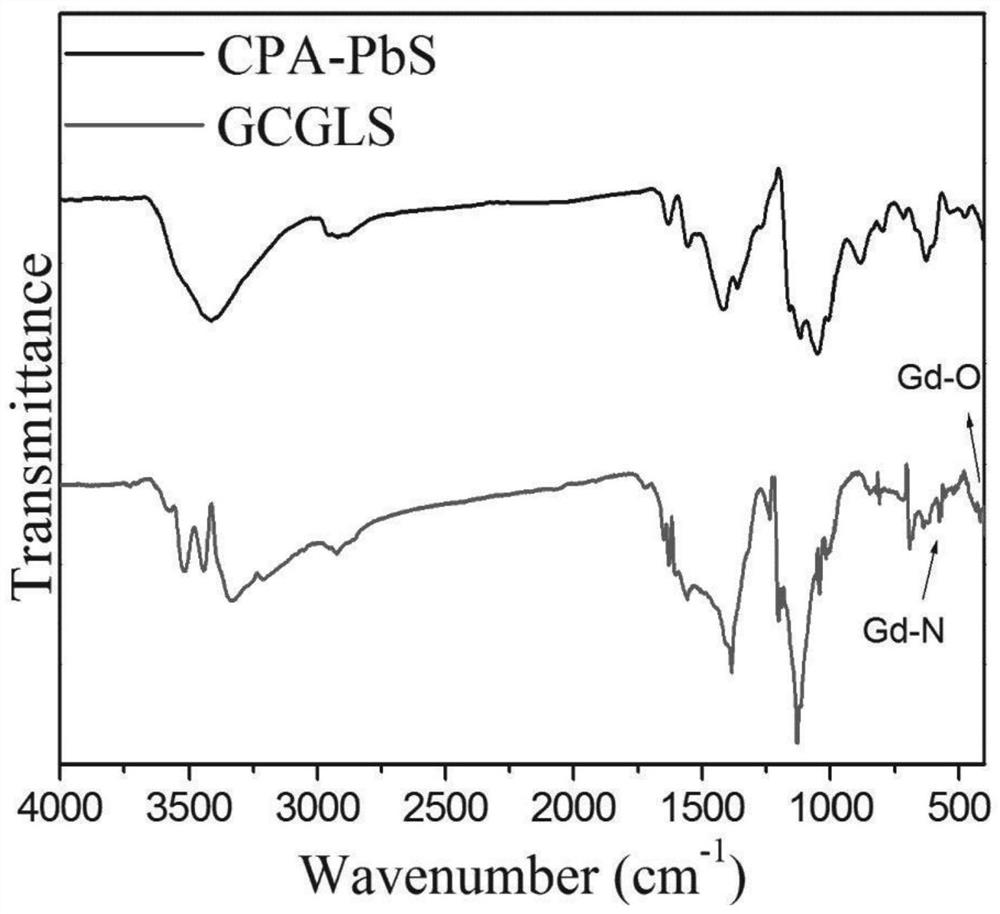
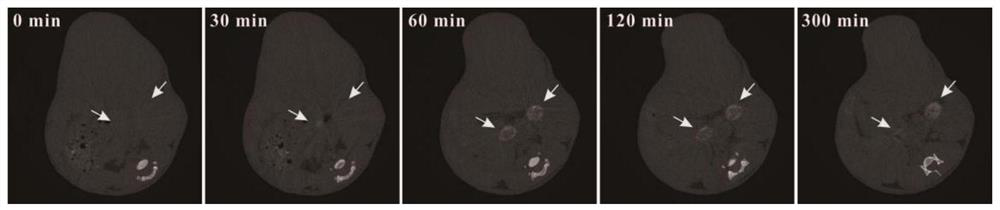
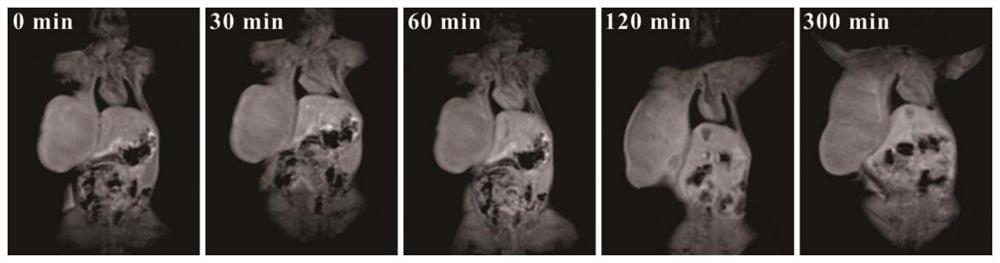
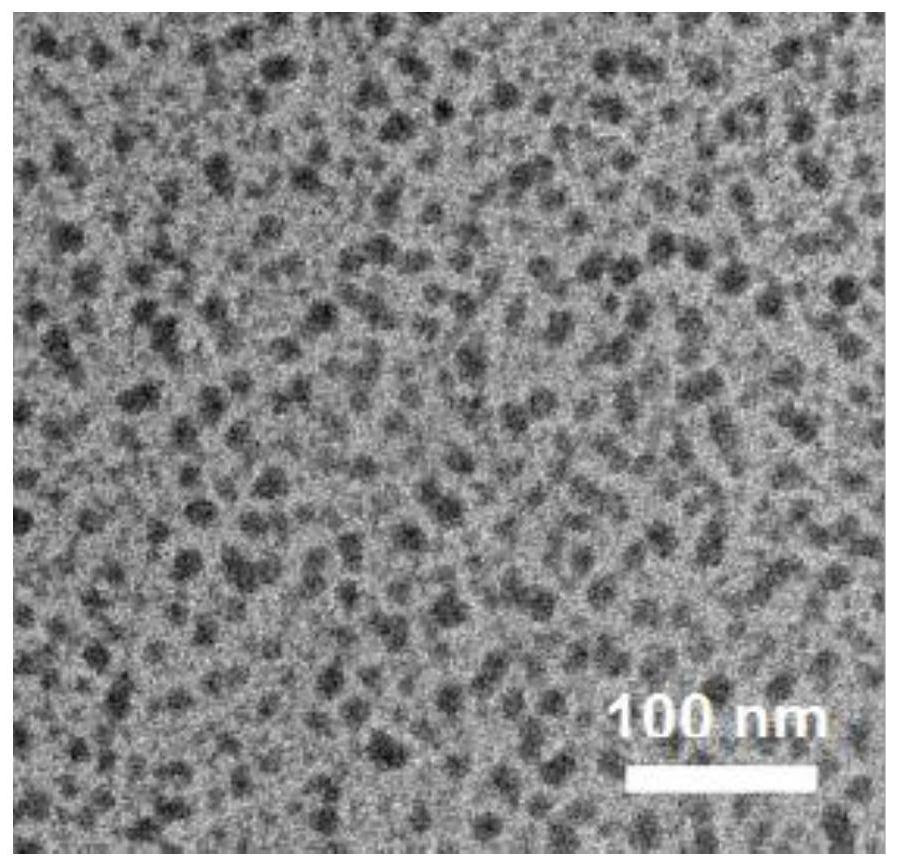
ActiveCN107998390BFunctionalExcellent photothermal performancePowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsMethacrylatePtru catalyst
The invention relates to bifunctional imaging guided photo-thermal diagnosis and treatment integral nanoparticles and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, lead sulfide nanoparticles are prepared by taking lead acetate, sodium sulfide, mercaptoethanol and 3-chloropropionic acid as raw materials, and water as a solvent; S2, a gadolinium-containing complex is prepared by taking acrylic acid, phenanthroline hexahydrate gadolinium chloride as monomers, and ethanol as a solvent; S3, the lead sulfide nanoparticles and the gadolinium-containing complex are put into polyethyleneglycol methacrylate, further a catalyst and an activating agent are added, and the components are enabled to react, so as to obtain gadolinium complex and polyethyleneglycolmethacrylate grafted nanoparticles. The nanoparticles have the beneficial effects that a gadolinium complex is grafted with the surfaces of the lead sulfide nanoparticles for a first time, the obtained nanoparticles have CT (Computed Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) imaging guide functions and meanwhile are good in photo-thermal effect; the nanoparticles are relatively long in blood half-life period and low in biotoxicity, thereby having relatively high potential application values in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
An active targeting amphiphilic polypeptide nano drug carrier and its preparation and application
ActiveCN110237035BHigh physiological stabilityHigh cell phagocytosis efficiencyEmulsion deliveryMacromolecular non-active ingredientsSide chainPhospholipid
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A low-molecular-weight heparin sustained-release preparation and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN104906045BWith sustained release effectAvoid "peak and valley fluctuations"Organic active ingredientsPowder deliveryChemical LinkageSide effect
The present invention provides a low-molecular-weight heparin sustained-release preparation, a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the low-molecular-weight heparin sustained-release preparation comprises nanoparticles formed by polypeptides and low molecular weight heparin, and the polypeptides are cross-linked through chemical bonds. The present invention adopts any one or a combination of at least two of self-assembly technology, freeze-drying technology, homogenization technology, emulsification technology, embedding technology or spray-drying technology to prepare low molecular weight heparin sustained-release preparation. The low-molecular-weight heparin sustained-release preparation of the invention has a release rate of only about 20% within 500 hours under in vitro conditions, has a sustained-release effect, can effectively prolong its blood half-life, avoid the "peak-to-valley fluctuation" of the drug, and reduce the dosage of the low-molecular-weight heparin solution. The risk of hemorrhage when the dose is used, the toxic and side effects of the drug are reduced, the compliance of patients is improved, and the treatment efficiency of the disease is improved, and can be used for the prevention and treatment of thrombosis diseases. The preparation method of the invention is simple and has broad application prospects.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Medicinal composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102309763BGood water solubilityImprove utilization efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPolyesterActive component
The invention provides a medicinal composition and a preparation method thereof. The medicinal composition comprises a carrier and an active component loaded on the carrier, wherein the carrier is nano particles of cyclodextrin-aliphatic polyester-phosphatidyl ethanolamine graft polymer with the structural formula shown in a formula (1) in the specifications; and in the formula (1), m is an integer from 6 to 8, and G is an oxygen atom or has a formula shown in the specifications.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Method of preparing physiologically active polypeptide conjugate
ActiveUS11123436B2High yieldProlong blood half-lifeAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDepsipeptidesPeptide drugHalf-life
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
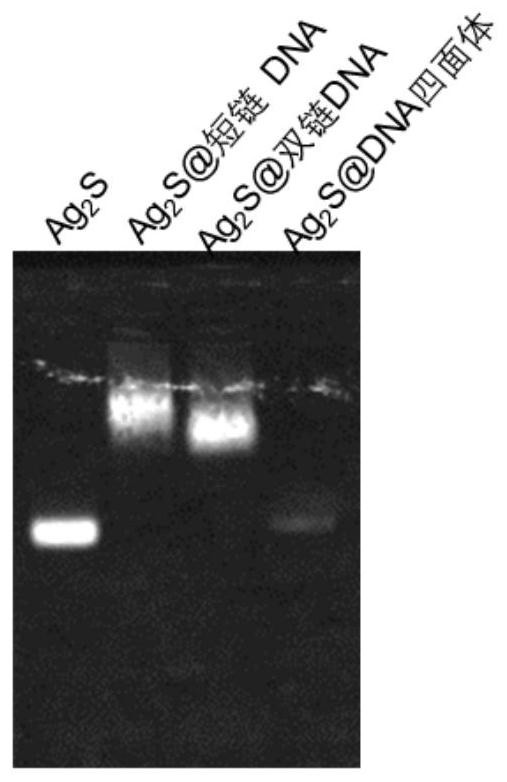
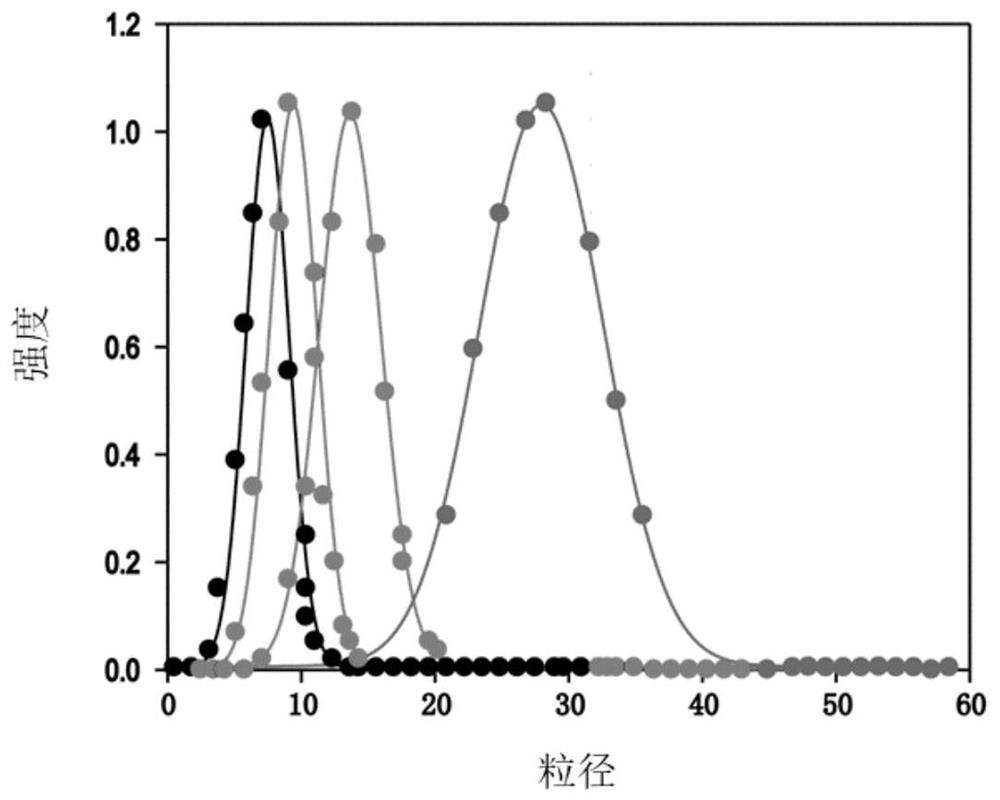
A DNA-wrapped near-infrared zone two nanoparticle complex and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111643682BProlong blood half-lifeGood biocompatibilityIn-vivo testing preparationsA-DNABiocompatibility
The present invention provides a DNA-wrapped near-infrared zone II nanoparticle complex and its preparation method and application. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1: combining a solution containing functionalized DNA with a surface functional group Mixing the near-infrared region II nanoparticles, so that the functionalized DNA is covalently coupled to the functional groups on the surface of the near-infrared region II nanoparticles, to obtain a DNA-wrapped near-infrared region II nanoparticle complex; and S2: Inject the DNA-wrapped nanoparticle complex in the second near-infrared region into the experimental animal body through the tail vein, and observe the metabolism of the compound in the living body in the second-infrared near-infrared imaging system. The nanoparticle complex in the second near-infrared region prepared according to the present invention has the advantages of fast liver metabolism, long blood half-life, no obvious toxicity in cells and animals, high biocompatibility, etc., and has advantages in in vivo imaging and drug distribution. Significant advantage.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A radioactive iodine-labeled protein-binding ligand and its application
ActiveCN108434468BImprove stabilityIncrease intakeOrganic compound preparationRadioactive preparation carriersStructural formulaRadioactive Label
The invention discloses a radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand and application thereof. A structural formula of the radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand is shown in a followingimage, wherein the I is radioactive iodine nuclide, the R is OH or derived from PEG, folic acid, RGD, octreotide, epidermal growth factor, protein, nucleic acid or polysaccharide. The radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple marking method, low cost and good stability. Animal live test results show that the albumin binding ligand hashigher uptake and longer-time retention in blood and further has a higher target / non-target specific value. When the radioactive iodine marked protein binding ligand is modified to a target group orother functional groups, pharmacokinetic characters of compound can be obviously improved, a blood half-life period of the compound is prolonged, and the compound is suitable for being utilized as a blood pool, lymph and tumor diagnosing and treating reagent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com