Method of preparing physiologically active polypeptide conjugate
A technology for physiologically active and conjugated compounds, applied in the field of preparing physiologically active polypeptide conjugates, can solve the problems of reducing peptide activity, reducing preparation yield, inefficiently preparing physiologically active polypeptides, etc., and achieving the effect of increasing in vivo activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
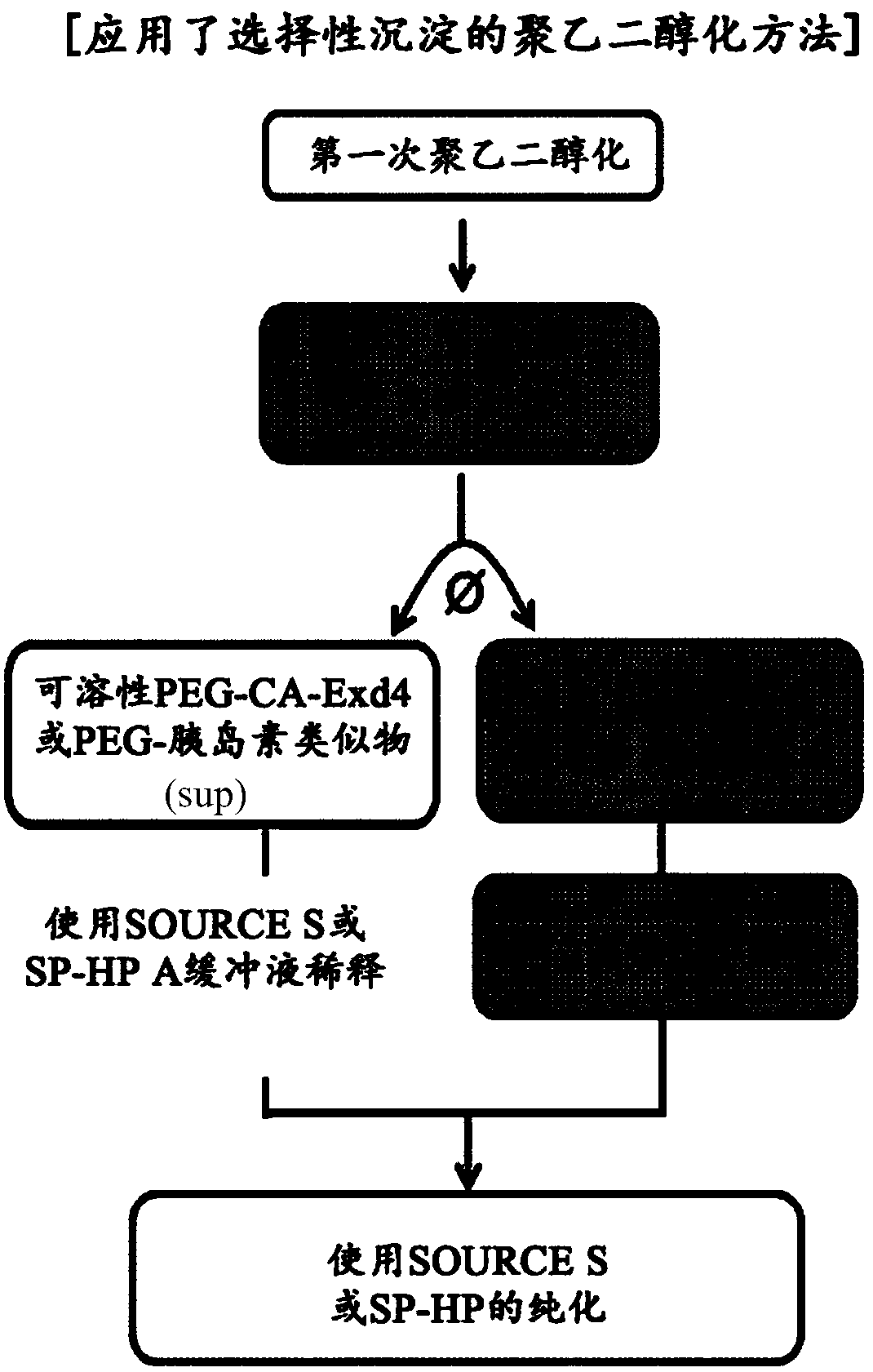
[0111] The preparation method of the present invention may further include isolating the physiologically active polypeptide conjugate after step 2). This procedure can be carried out using various separation methods such as chromatography known in the art. Specifically, ion exchange chromatography, and more specifically, high pressure ion exchange chromatography may be used, but not limited thereto.
[0112] In the present invention, the physiologically active polypeptide conjugate can be separated from the first reaction mixture to prepare an aqueous solution by applying selective precipitation to the first reaction mixture, the second reaction mixture, or a combination thereof.
[0113] In particular, when separating a physiologically active polypeptide conjugate from a mixture of an aqueous solution prepared by applying selective precipitation to the first reaction mixture and a secondary reaction mixture prepared by using the precipitated physiologically active polypeptide...
Embodiment 1
[0128] Example 1. Pegylation of imidazo-acetylexendin-4 and isolation of positional isomers
[0129]Using 3.4K ALD(2) PEG (3.4 kDa PEG with two aldehyde groups) at the Lys of imidazo-acetyl-exendin-4 (CA-exendin-4, Bachem, USA) , NOF, Japan) for PEGylation.
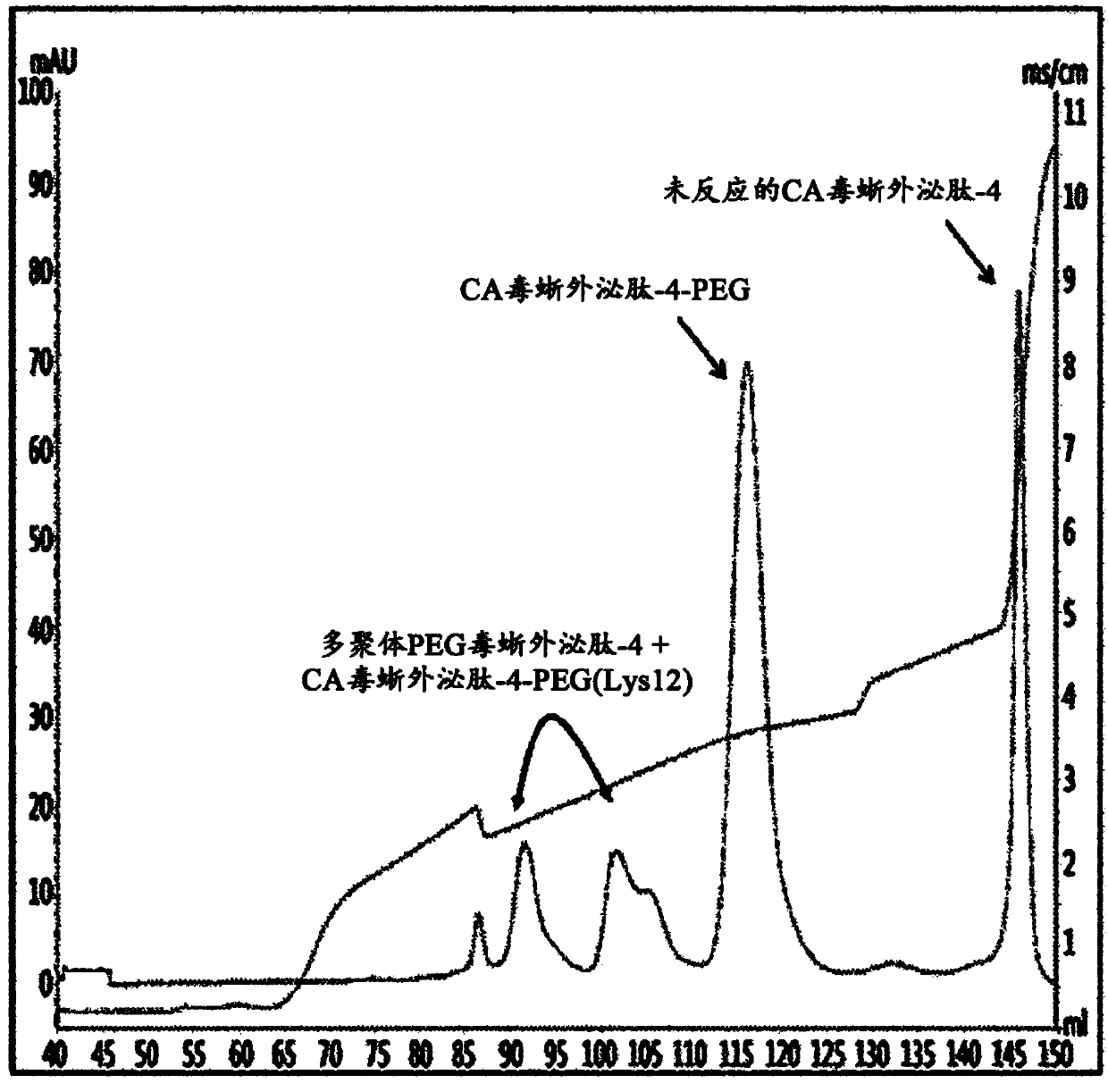
[0130] To pegylate the Lys position of imidazo-acetyl-exendin-4 using 3.4K ALD(2)PEG, the peptide and PEG were separated at about 1: Molar ratios of 3 to 1:30 and peptide concentrations of about 5 mg / mL to 18 mg / mL were reacted for 0.5 hours to 4.0 hours. At this point, the reaction was allowed to react at a pH of 6.5 to 7.5 in 100 mM HEPES buffer (supplemented with reducing agent 20 to 30 mM SCB (NaCNBH 3 ))conduct. Specific reaction conditions and results isolated by the following methods are shown in Tables 1 and 2 below. In detail, they were reacted at a peptide concentration of about 15 mg / mL at 4°C to 8°C for 3 hours, and the results of separation by the following method are shown in figure 2 .
[0131] In a ...
Embodiment 2
[0138] Example 2. Pegylated insulin analogs and separation of positional isomers
[0139] PEGylation was performed at the N-terminus of the β-chain of the insulin analog using 3.4K ALD(2)PEG (WO2014-133324, Hanmi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Korea).
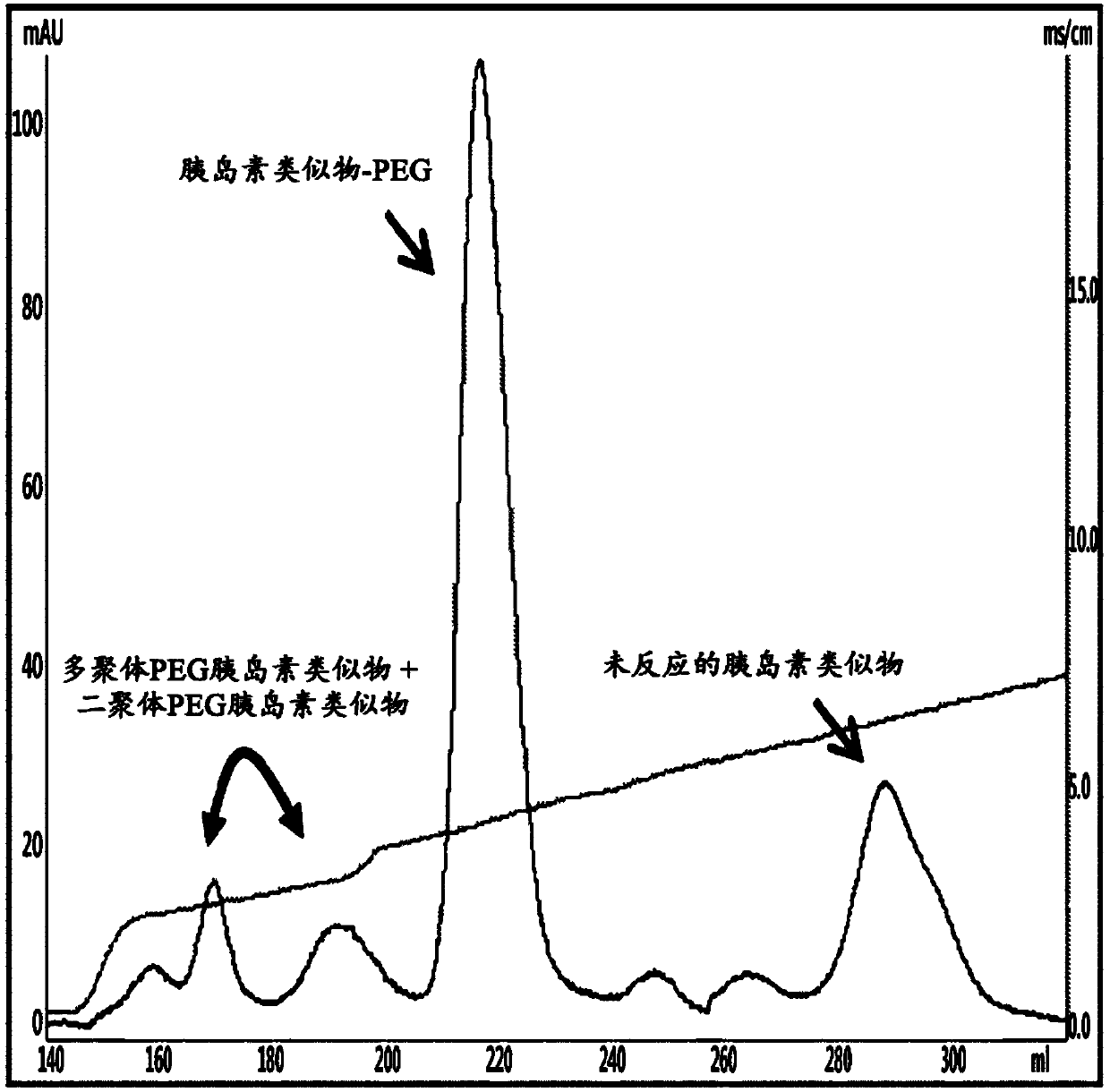
[0140] To pegylate the N-terminal position of an insulin analogue using 3.4K ALD(2)PEG, peptide and PEG were prepared at a molar ratio of about 1:4 and about 5 mg / mL to A peptide concentration of 18 mg / mL was reacted for 0.5 hours to 4.0 hours. At this point, the reaction was allowed to proceed in 50 mM sodium citrate buffer solution at a pH of 4.0 to 6.0, and the reducing agent 3-5 mM SCB (NaCNBH 3 ). In detail, they were reacted at a peptide concentration of about 5 mg / mL at 4°C to 8°C for 2 hours, and the results of separation by the following method are shown in image 3 .
[0141] Insulin analogue-PEG was separated from each reaction solution using a SP-HP column with a linear concentration gradient of KCl in a citrate buffe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com