Pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
A non-alcoholic, composition technology, used in the prevention or treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, the field of pharmaceutical compositions of long-acting insulin-releasing peptide conjugates, to prevent accumulation, prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Disease, effect of increasing blood half-life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0071] In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a preparation method, which comprises the following steps:
[0072] (1) covalently linking a non-peptidyl polymer having an aldehyde reactive group at its two ends to a lysine residue of exendin-4;
[0073] (2) isolating a conjugate comprising exendin-4 from the reaction mixture of (1), wherein the non-peptidyl polymer is covalently linked to a lysine residue; and
[0074] (3) Covalently linking the immunoglobulin Fc region to the other end of the non-peptidyl polymer of the isolated conjugate, thereby producing a protein conjugate comprising immunoglobulins linked to the respective ends of the non-peptidyl polymer Protein Fc region and exendin-4. More preferably, the non-peptidyl polymer in (1) and the lysine residue of exendin-4 are linked at pH 9.0 or higher.
[0075] The insulinotropic peptide conjugate of the present invention activates major proteins of the insulin signaling pathway via the GLP-1 receptor, and th...
Embodiment 1
[0086] Example 1. Testing the In Vitro Activity of Exendin-4
[0087] Various exendin-4 derivatives used in this experiment were prepared in the same manner as in the present inventor's Korean Patent No. 10-1058315.
[0088]The method for measuring cell viability in vitro was used in order to measure the potency of a depot formulation of exendin-4. In the in vitro activity measurement, RIN-m5F called rat insulinoma cells was used. Because this cell has a GLP-1 receptor, it is often used in methods for measuring the in vitro activity of the GLP-1 family. RIN-m5F was treated with different concentrations of GLP-1, exendin-4 and test materials. EC50 values were determined by measuring the generation of signaling molecule cAMP in cells induced by the test materials, and compared with each other. The results are summarized in Table 1.
[0089] Table 1
[0090] test material
Blood half-life (hr)
[0091] Exendin-4
0.7...
Embodiment 2
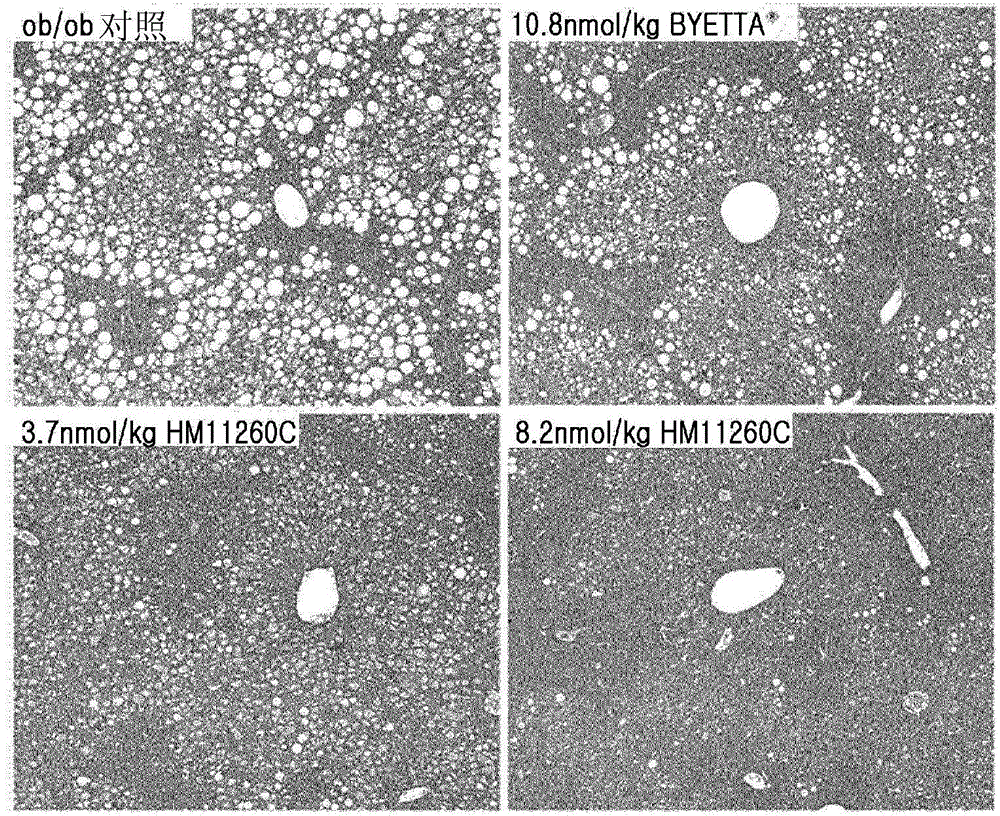
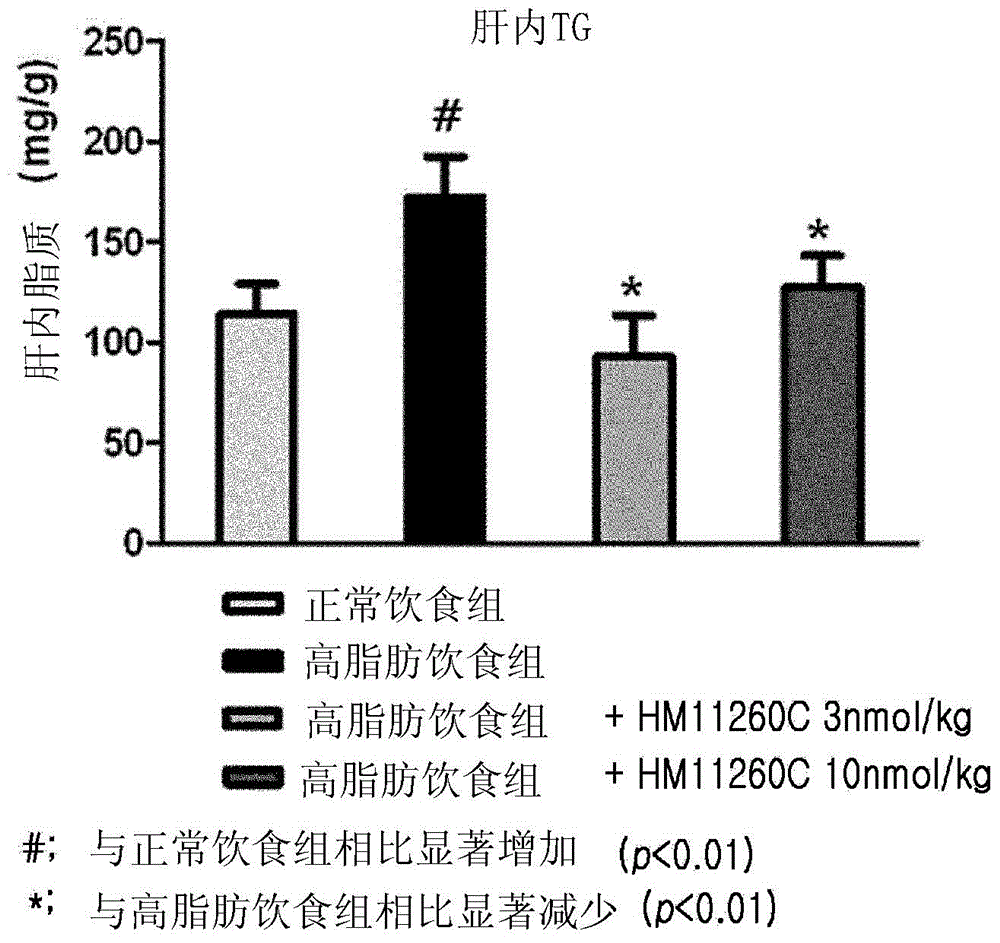
[0095] Example 2. Effect on Fatty Liver Formation in Hypertrophic Animal Model ob / ob Mice
[0096] Grouping of experimental animals
[0097] Female 5-week-old ob / ob mice (C57BL / 6JHamSlc-ob / ob, 24-34 g) were purchased from Slc, Japan. The ob / ob mouse is an animal model commonly used in efficacy testing of anti-obesity and anti-diabetic dosage forms. They had free access to solid feed for experimental animals sterilized by radiation (manufacturer: Picolab Rodent Diet, product name: 5053) and filtered, UV-irradiation-sterilized tap water in drinking water bottles. They were maintained in a GLP compliant crate system requiring a 12 hour dark-light cycle (lights on at 6:00 am and off at 6:00 pm) according to animal care standard guidelines. Thereafter, healthy ob / ob mice were selected and acclimated to laboratory conditions for 1 week. Then, drug administration was performed, and mice were divided into 4 groups and administered as follows.
[0098] Group 1 (negative control)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com