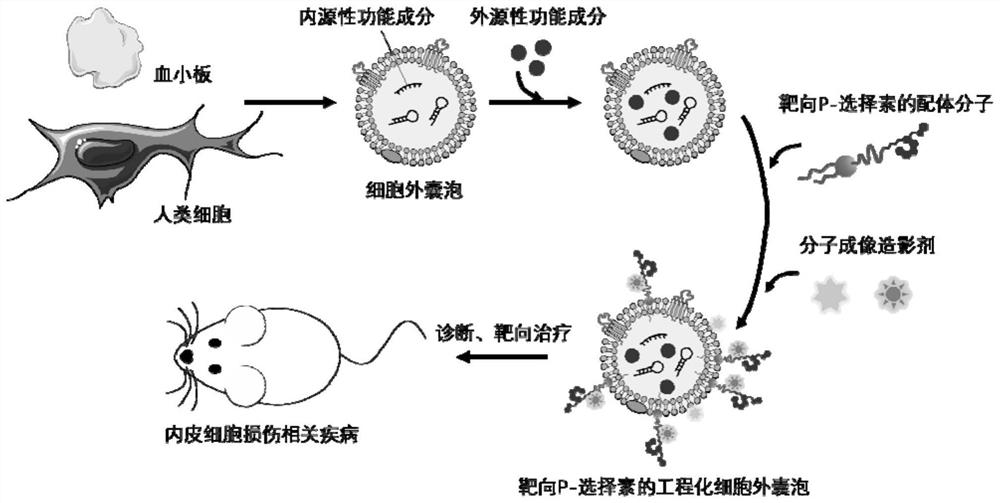
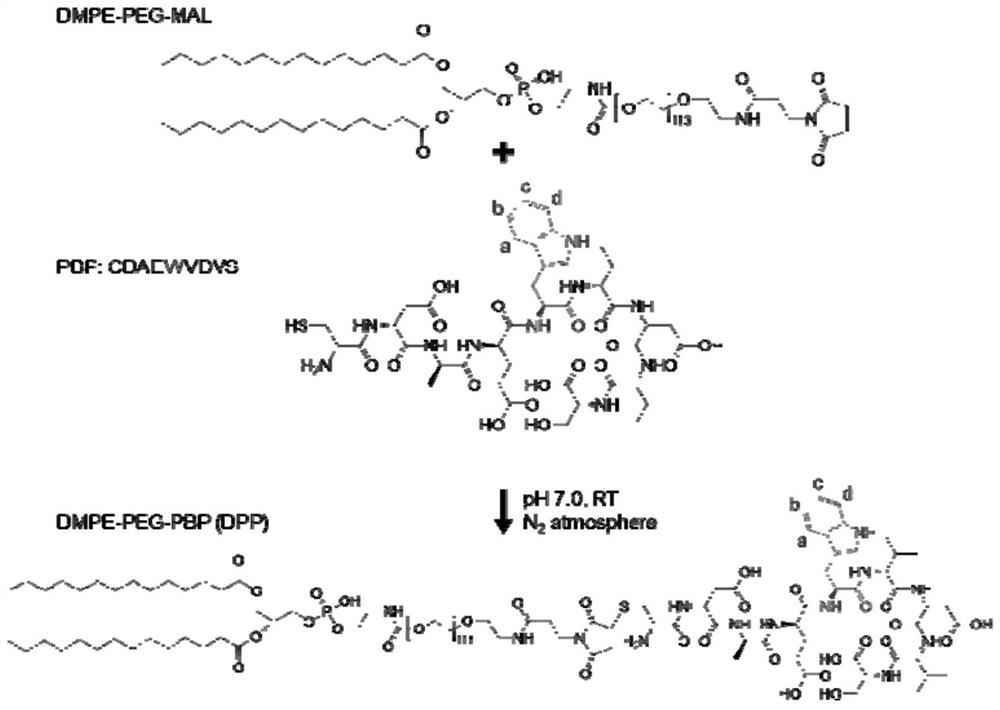
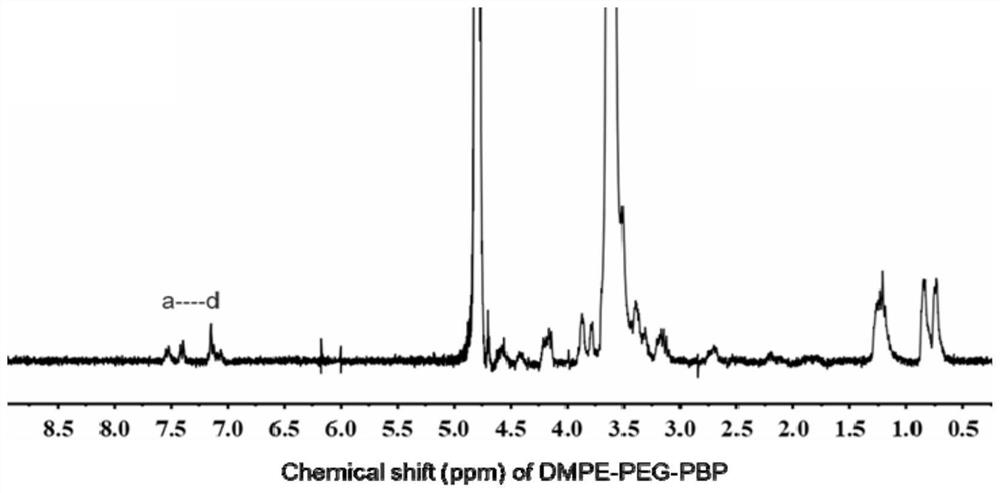
Engineered extracellular vesicle composition targeting P-selectin as well as preparation method and application of engineered extracellular vesicle composition
A selectin, engineered technology used in the field of biomedicine to achieve the effects of high biosafety, low immunogenicity and long blood half-life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] A method for extracting extracellular vesicles secreted by human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells is as follows:
[0055] 1) Before the experiment, normal fetal bovine serum (FBS) was centrifuged at 120,000g for 18 hours at 4°C to remove extracellular vesicles (EVs) in fetal bovine serum, and filtered through a needle filter of 0.22 μm to remove Fetal bovine serum (EV-freeFBS) of EVs; and use the above-mentioned EV-free FBS to configure the complete medium without EV (comprising 10% EV-free FBS, 1% double antibody, 1% glutamine, 1% non-essential amino acids, 87% DMEM / F12 medium), used to cultivate human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hP-MSCs);
[0056] 2) When normally cultured at 75cm 2 When the confluence of hP-MSCs in the cell culture flask reaches 80%, discard the old medium, add 10 mL of EV-free complete medium, continue to culture for 24 hours, and then collect the conditioned medium for gradient centrifugation to separate EVs;
[0057] 3) Centr...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The method of using nitric oxide hydrogel to culture human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and loading endogenous functional components in their extracellular vesicles is as follows:
[0063] 1) Coat the nitric oxide hydrogel with a concentration of 2 μg / μL on a surface of 75 cm 2 The bottom of the cell culture flask should be placed in a cell culture incubator at 37°C for more than 2 hours;
[0064] 2) hP-MSCs were cultured in cell culture flasks coated with nitric oxide hydrogel, and the EVs secreted by hP-MSCs cultured on the nitric oxide hydrogel were isolated and extracted according to the extraction method in Example 1;
[0065] 3) The endogenous functional components loaded in the isolated EVs were detected and confirmed by ELISA and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR technology.
Embodiment 3
[0067] The method of loading exogenous functional component doxorubicin in extracellular vesicles by co-incubation is as follows:
[0068] 1) Collect the conditioned medium of the MDA-MB-231 cells, and separate and extract the EVs secreted by the MDA-MB-231 cells according to the extraction method in Example 1;
[0069] 2) Add 1 mmol / L doxorubicin (Dox) to the isolated and extracted EVs, mix well and place in a cell culture incubator at 37°C for 30 min;
[0070] 3) Transfer the EVs / Dox mixture after co-incubation into an ultracentrifuge tube, add 40 mL of sterile PBS to wash once, centrifuge at 100,000 g for 120 min, and the final pellet is the Dox-loaded MDA-MB-231 cell-derived EVs;
[0071] 4) To confirm the loading efficiency of Dox in EVs by detecting the fluorescence signal of Dox at 590nm wavelength.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com