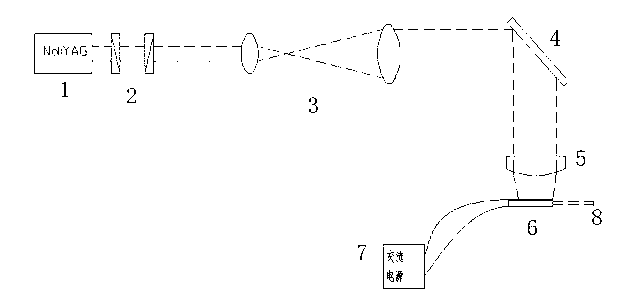
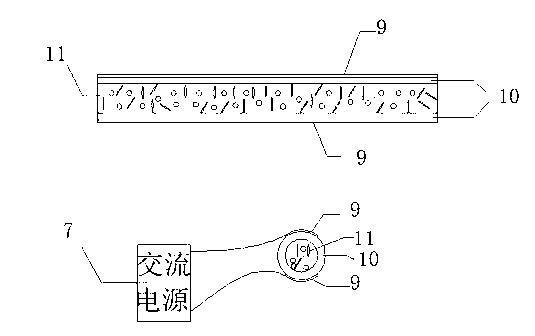
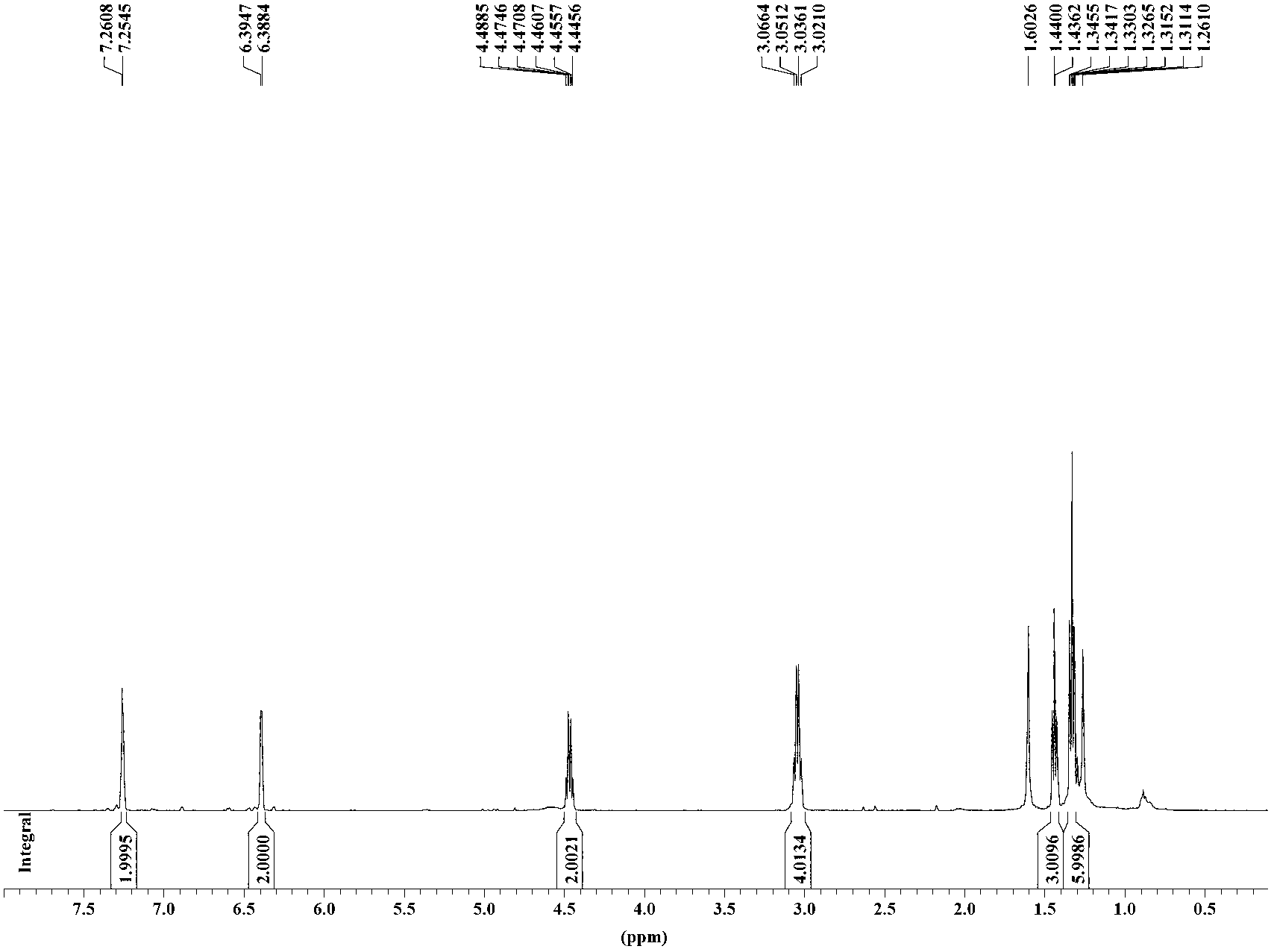
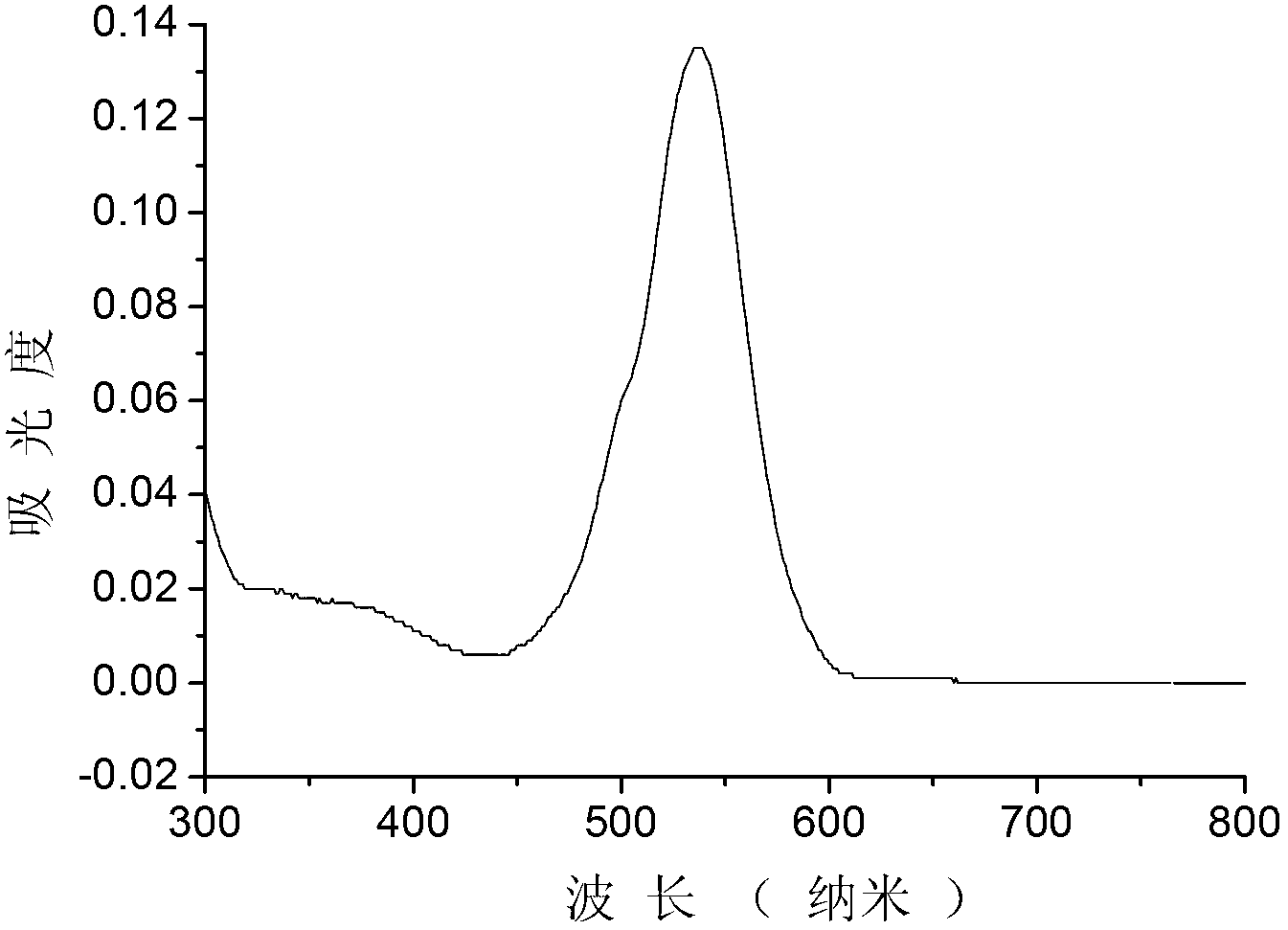
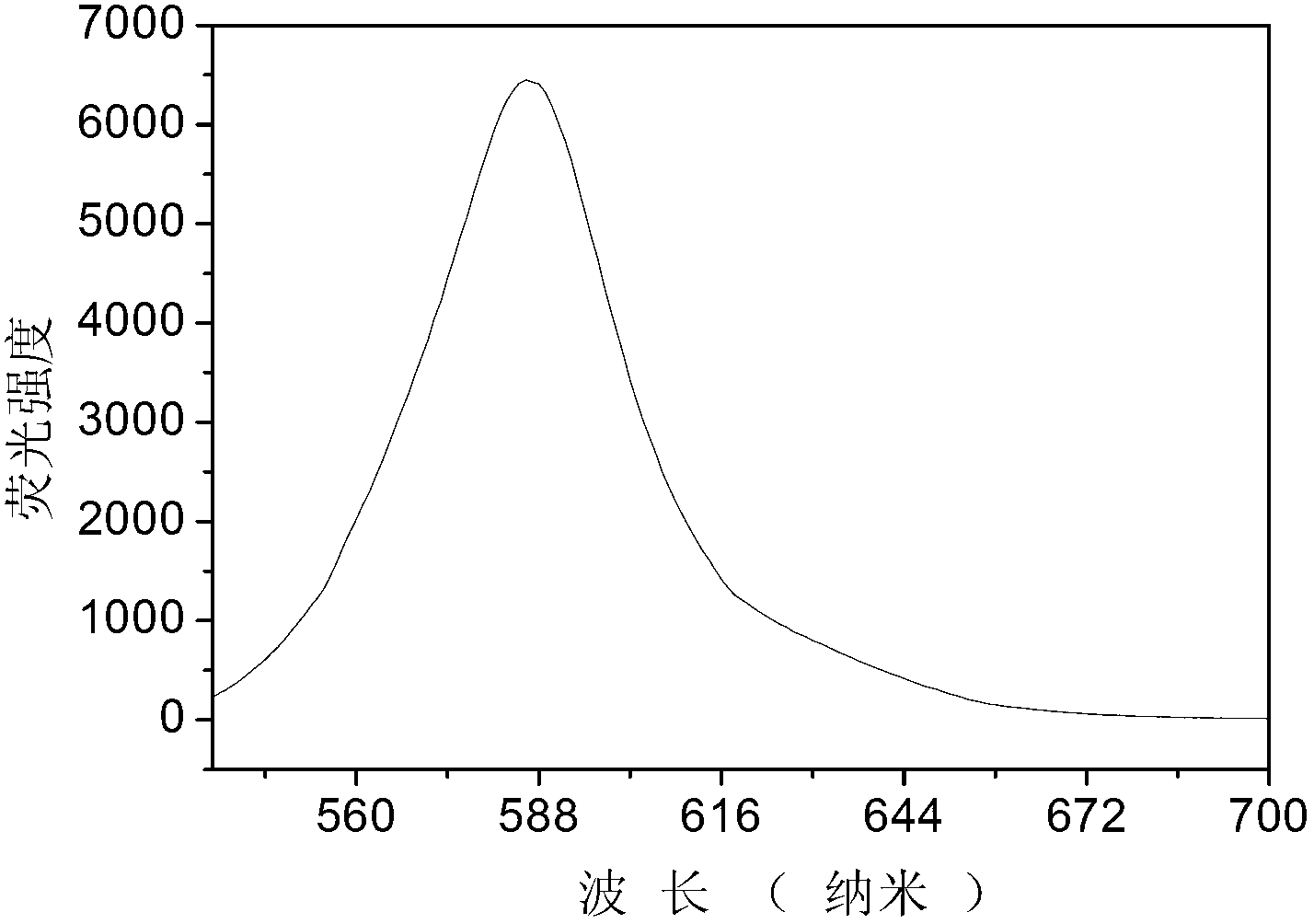
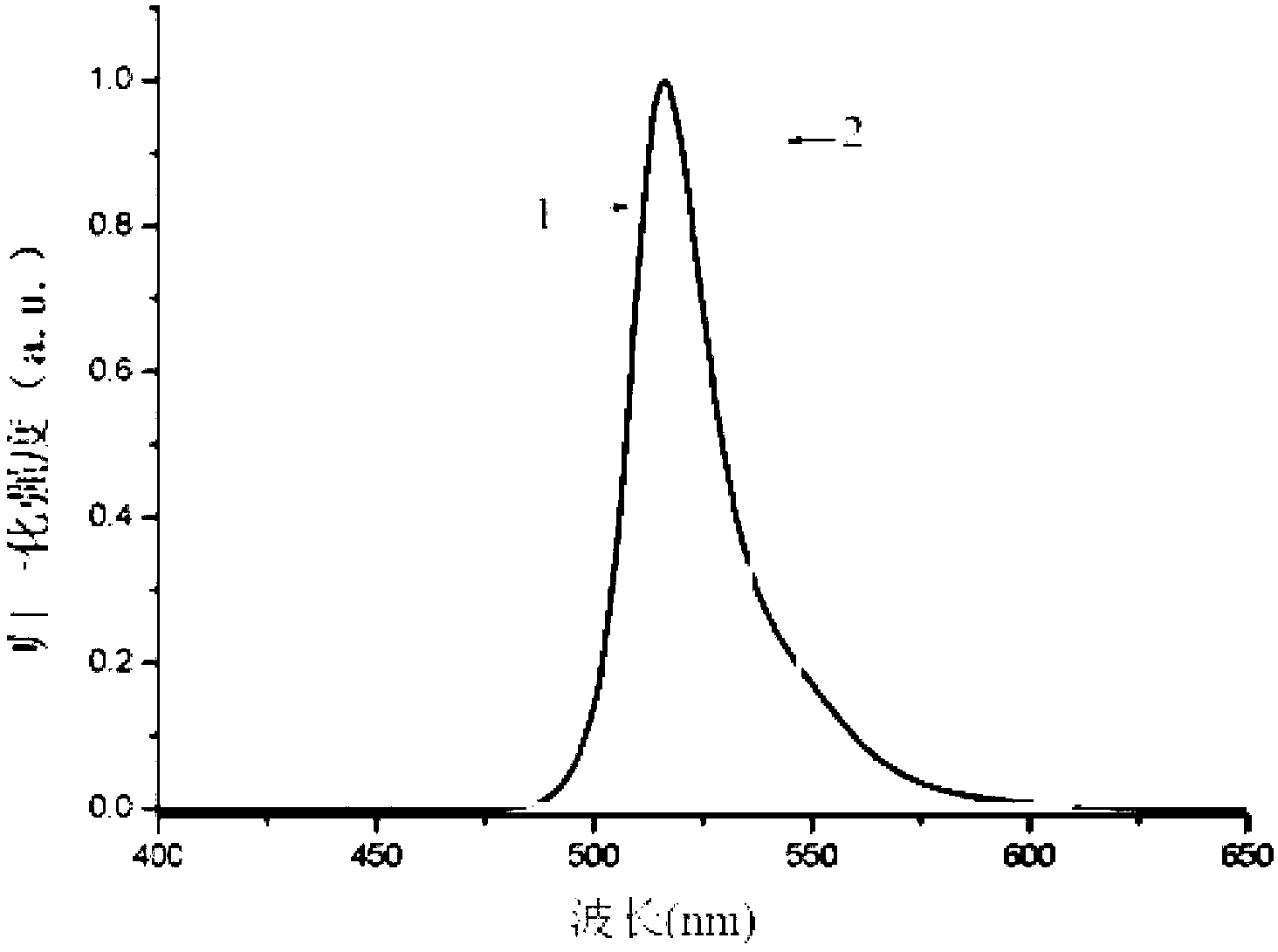
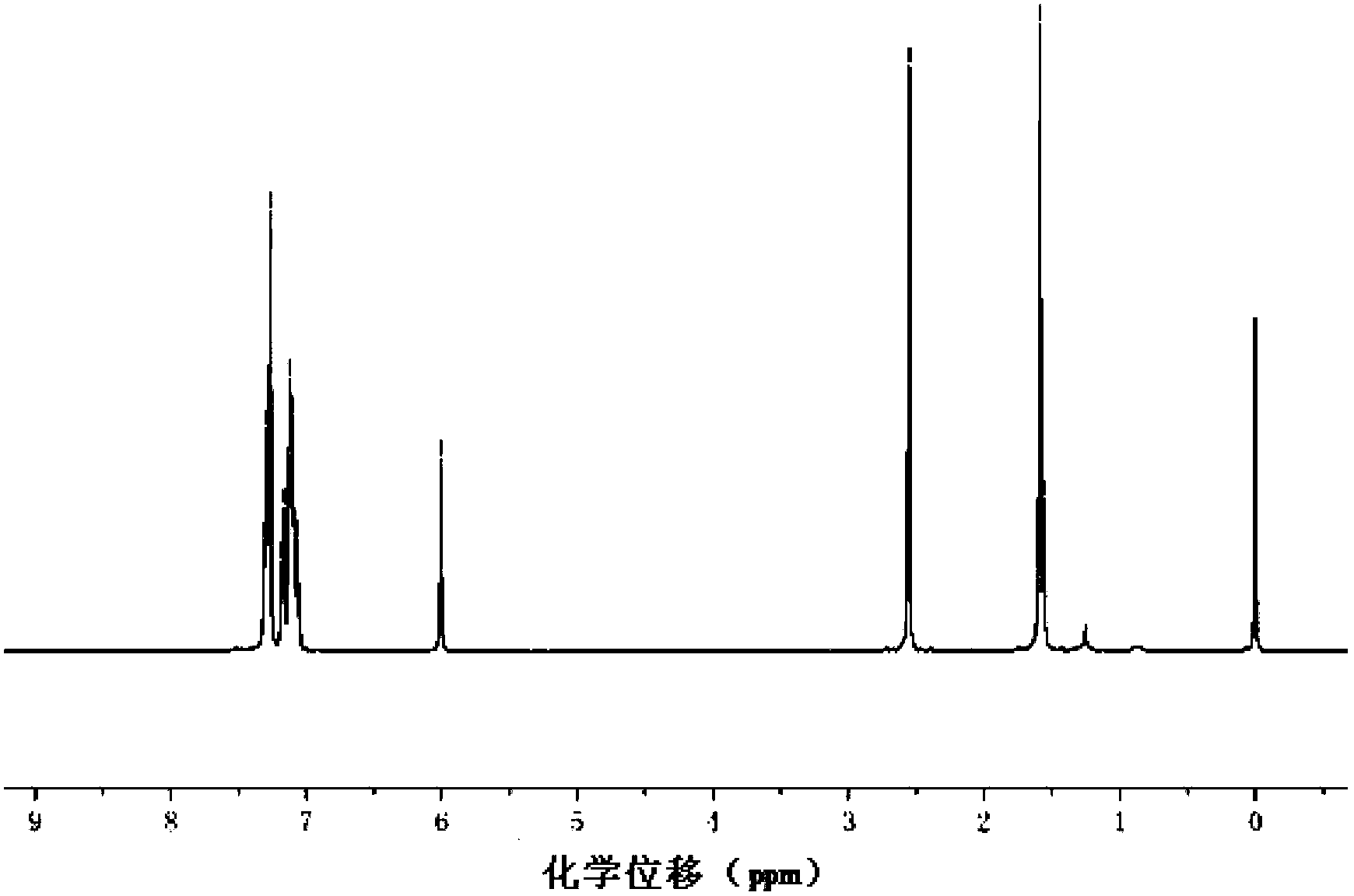
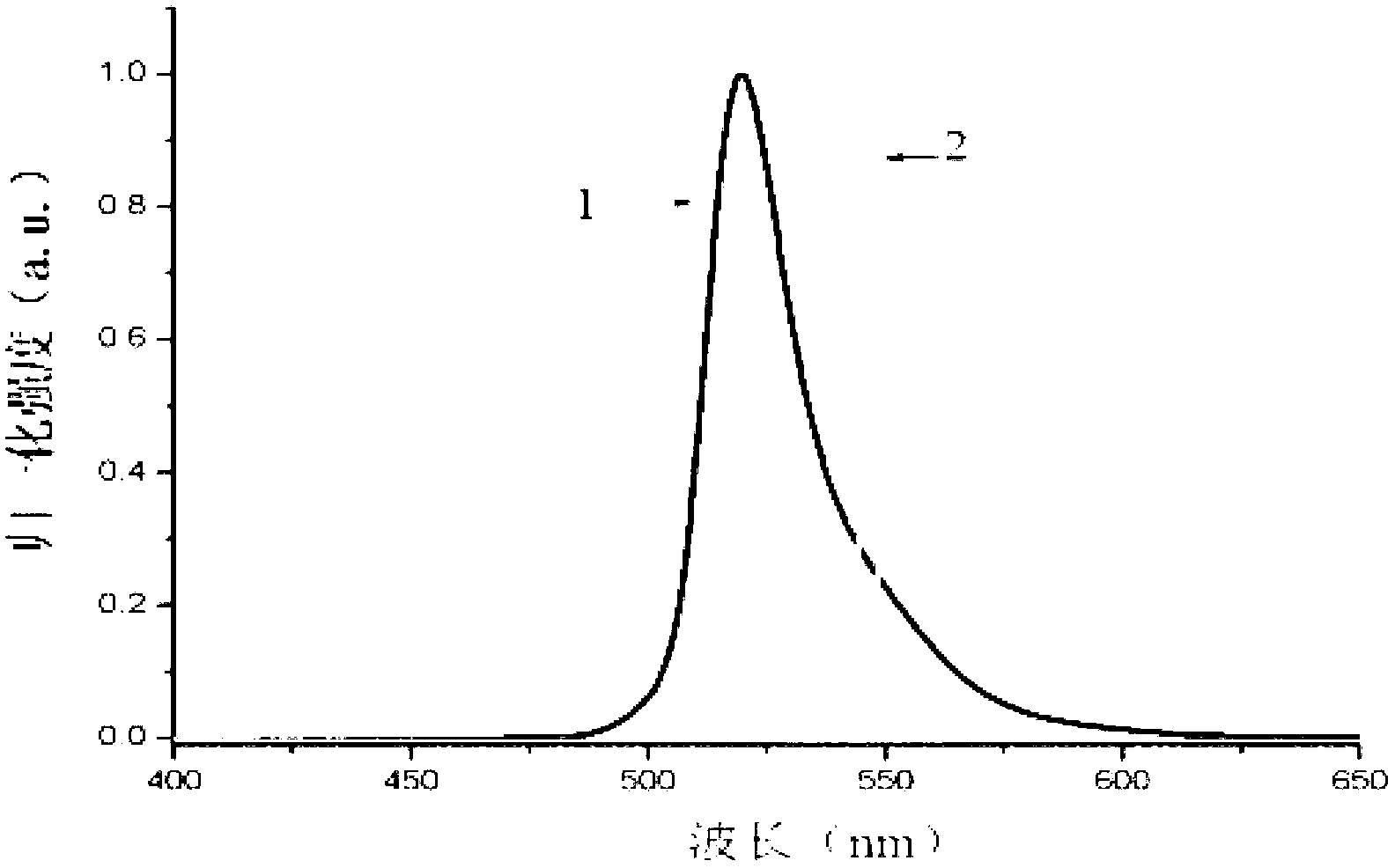
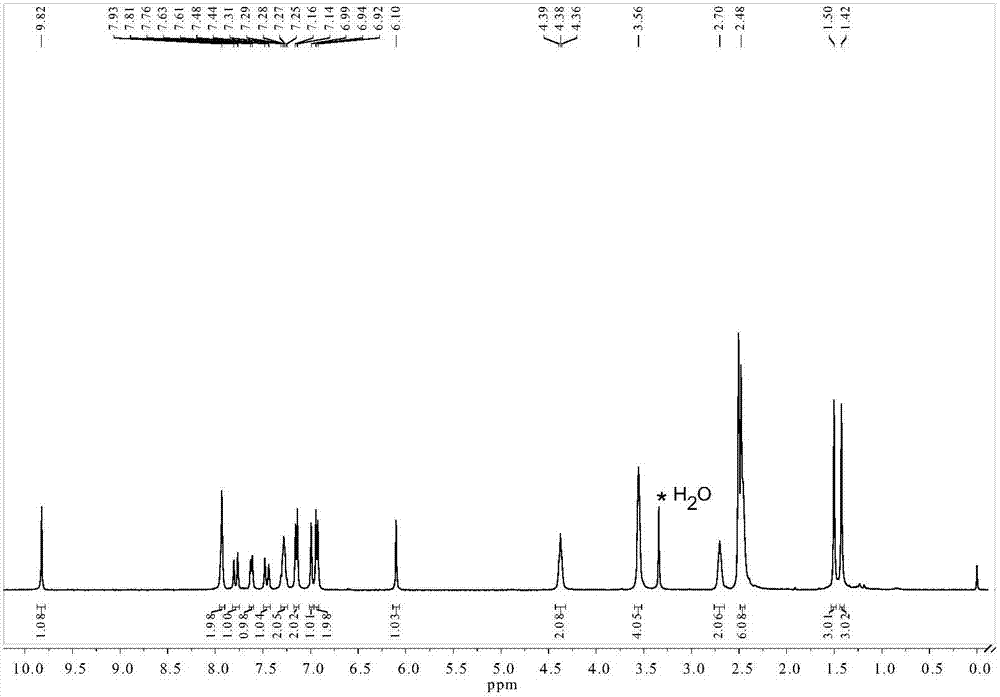
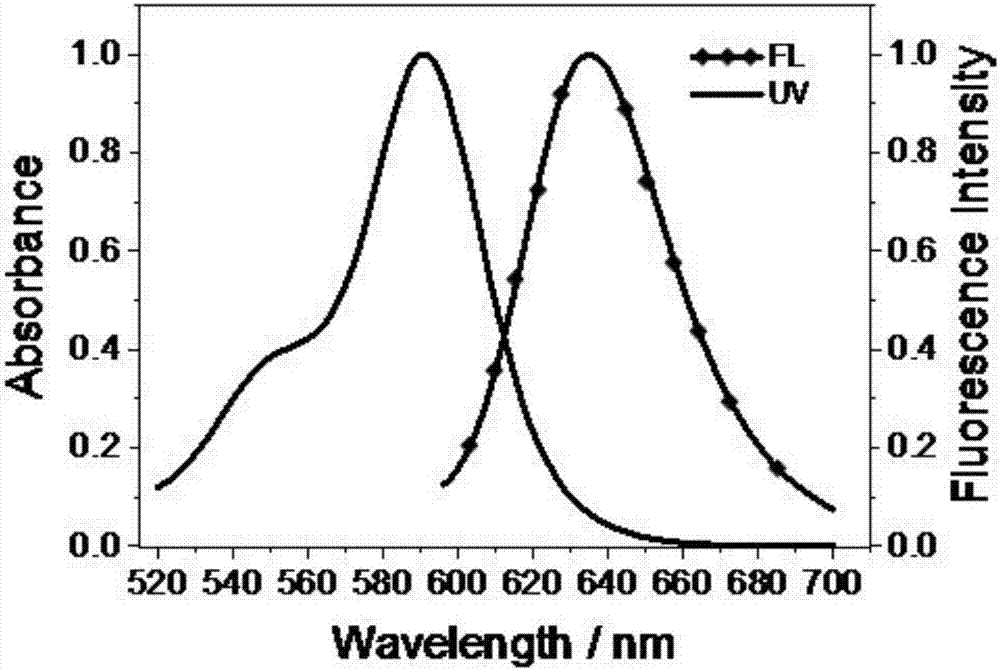
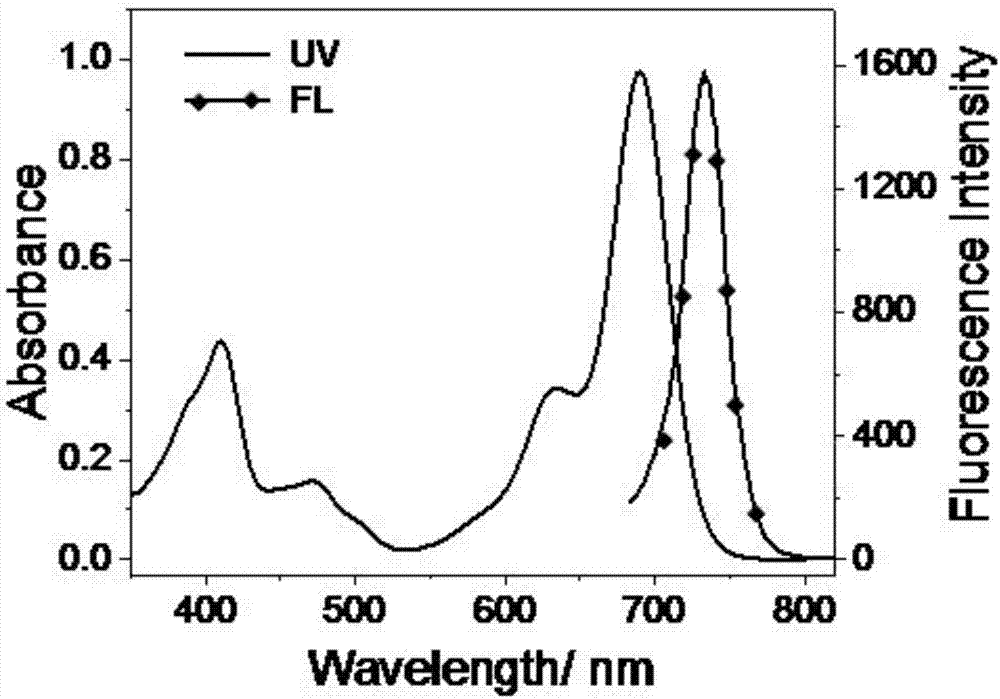
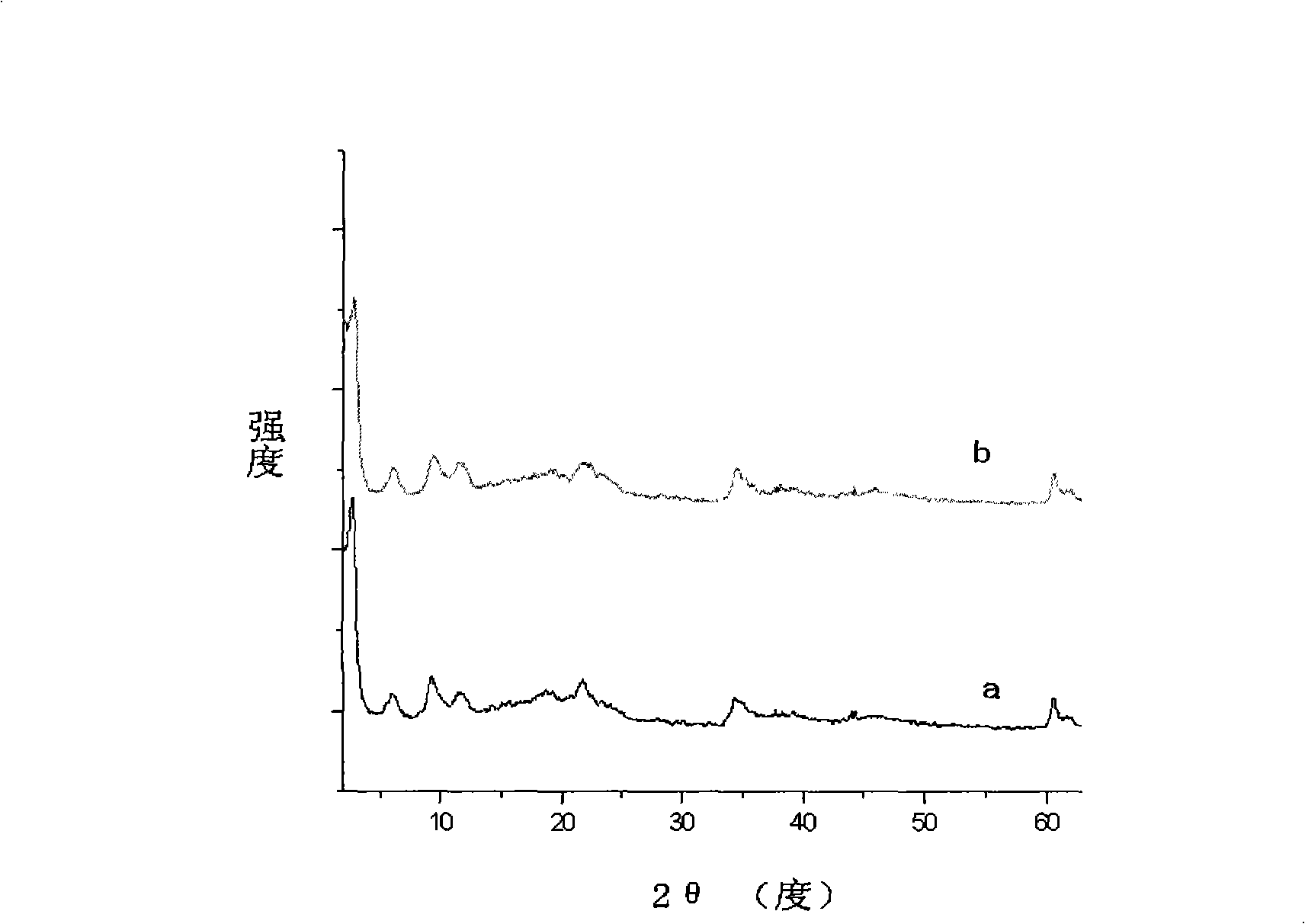
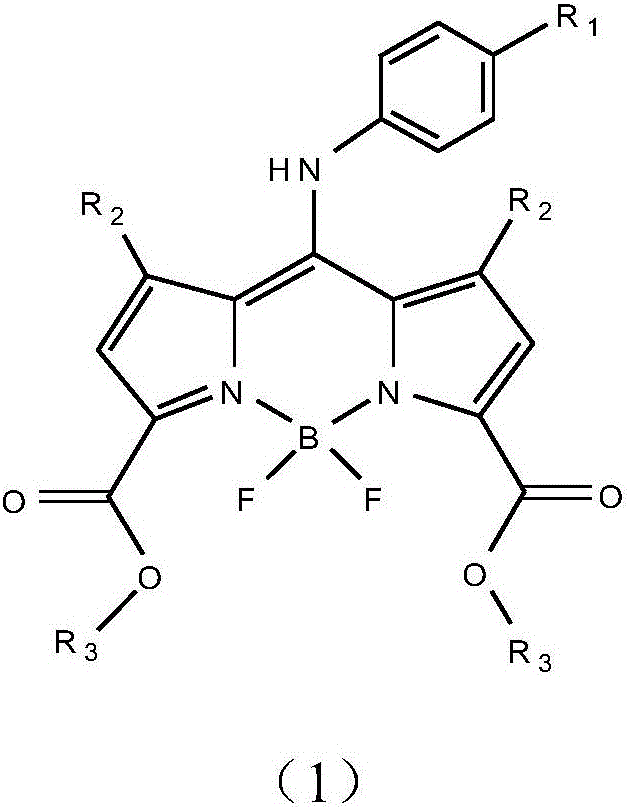
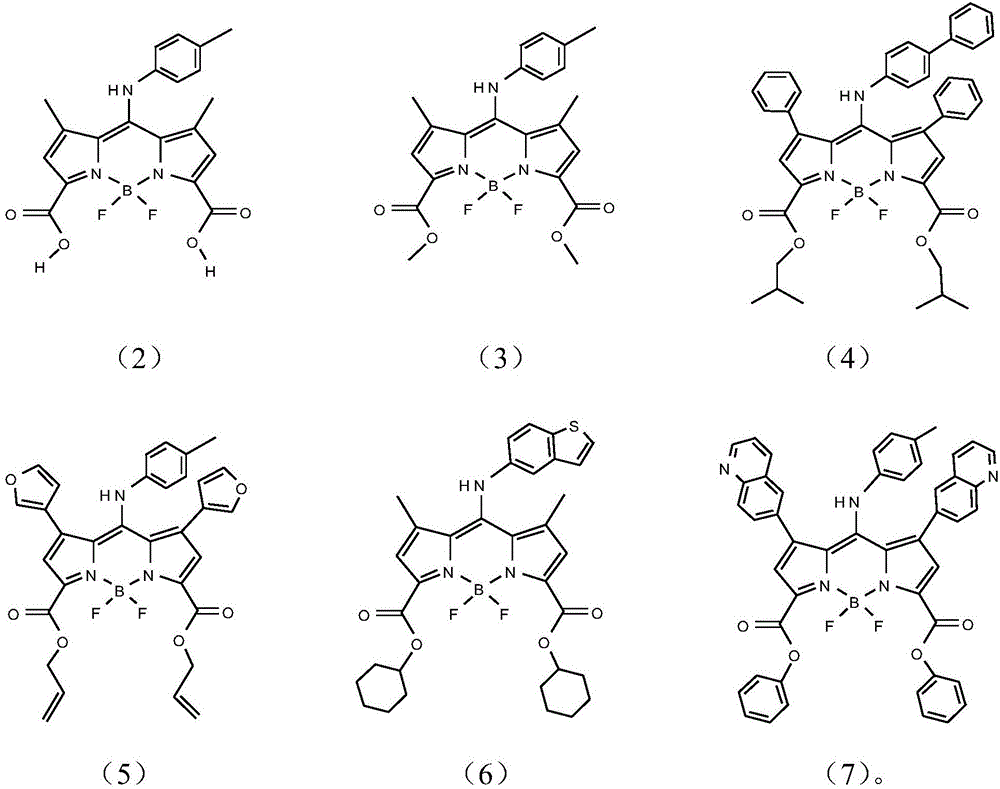
Patents
Literature
136 results about "Laser dye" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
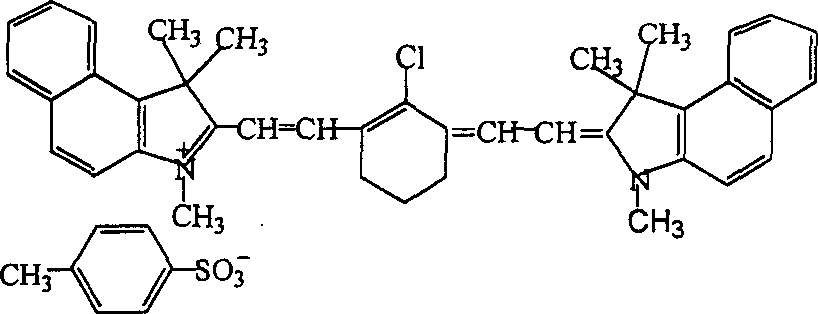
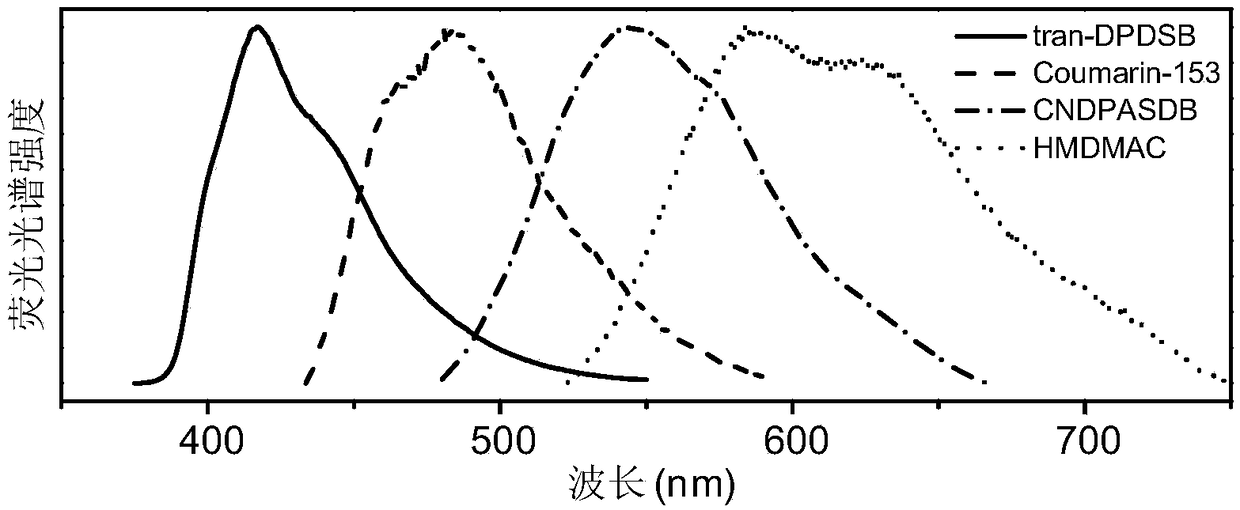
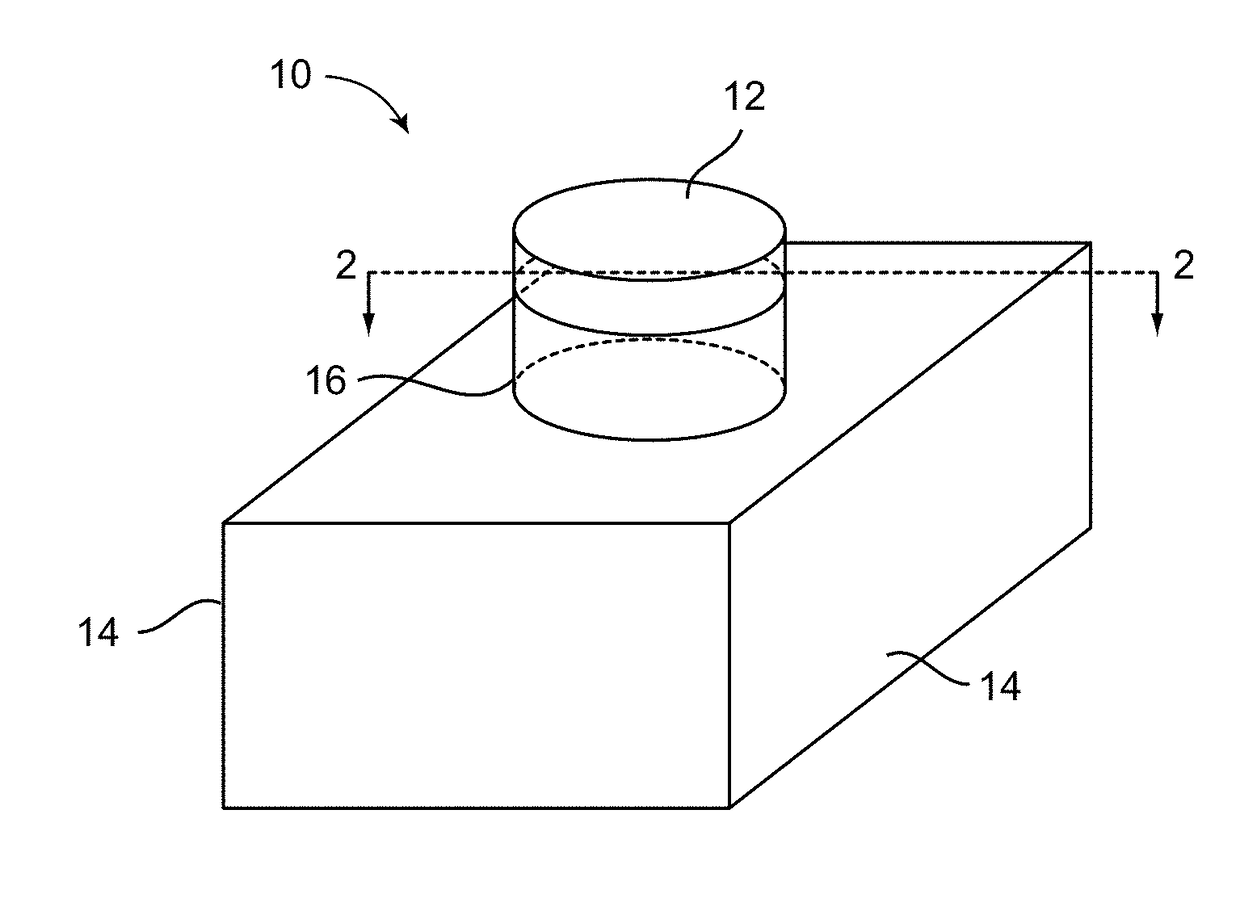
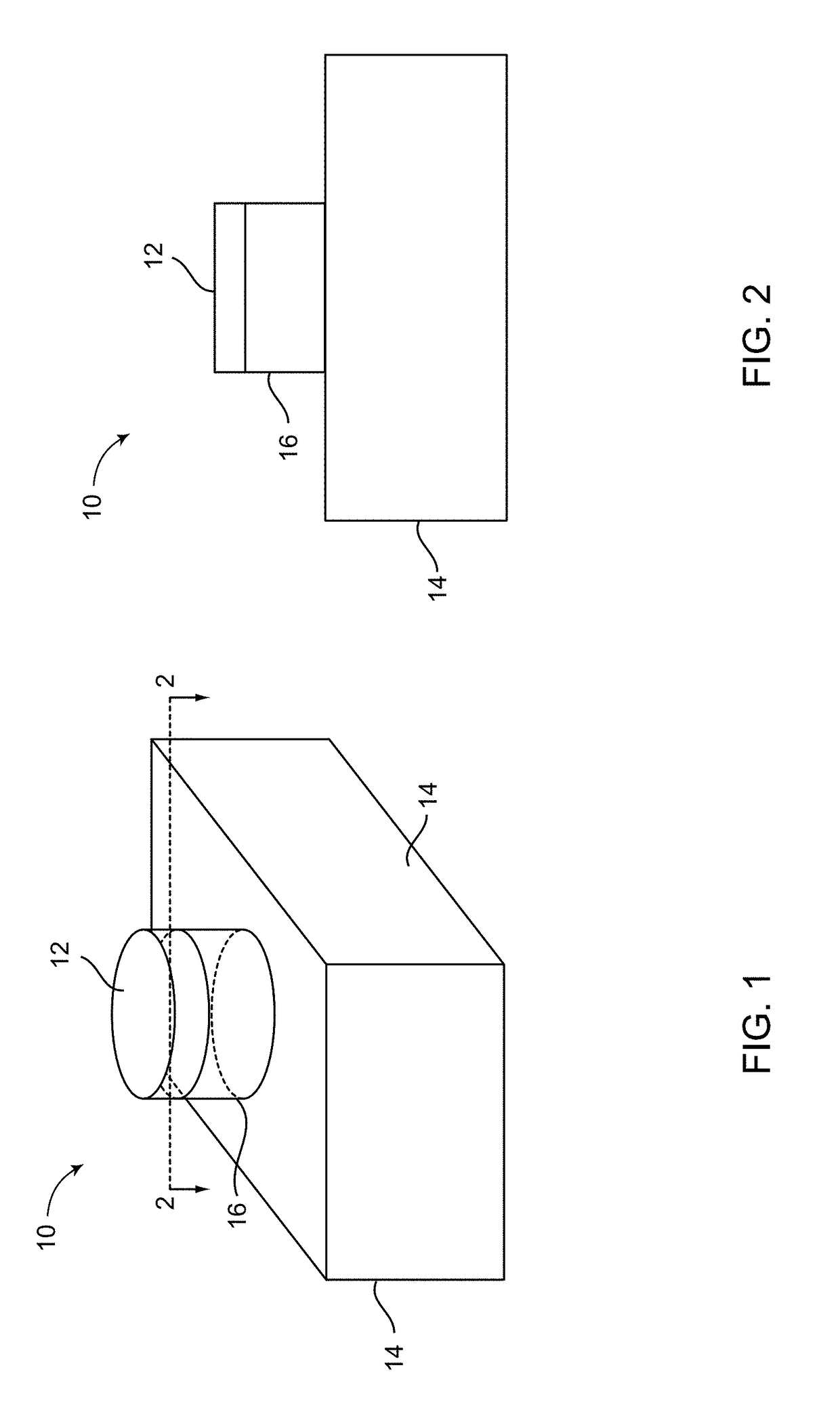
Laser dyes are large organic molecules with molecular weights of a few hundred mᵤ. When one of these organic molecules is dissolved in a suitable liquid solvent (such as ethanol, methanol, or an ethanol-water mixture) it can be used as laser medium in a dye laser. Laser dye solutions absorb at shorter wavelengths and emit at longer wavelengths. Successful laser dyes include the coumarins and the rhodamines. Coumarin dyes emit in the green region of the spectrum while rhodamine dyes are used for emission in the yellow-red. The color emitted by the laser dyes depend upon the surrounding medium i.e.the medium in which they are dissolved. However, there are dozens of laser dyes that can be used to span continuously the emission spectrum from the near ultraviolet to the near infrared.
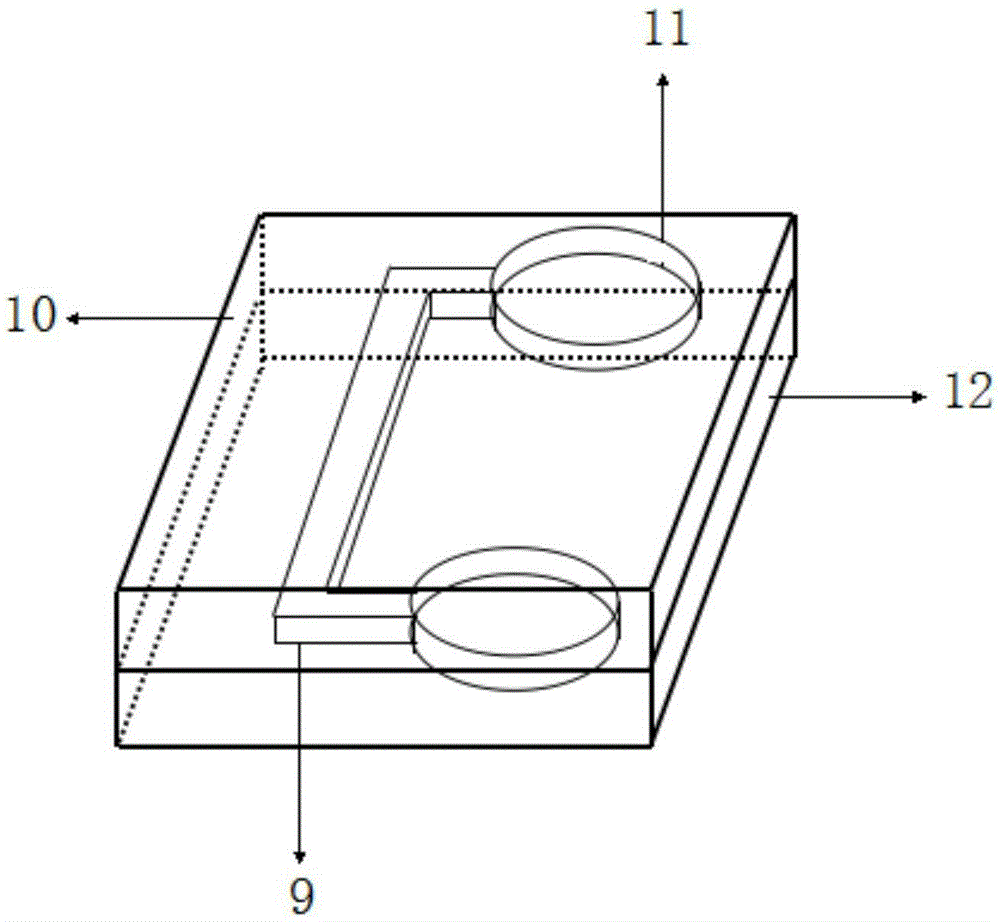
PDLC (polymer dispersed liquid crystal) optical fiber doped with dye and metal nanoparticles and optical fiber random laser
InactiveCN103311784AGuaranteed directional outputStable structureActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionRefractive indexOptical communication
The invention discloses a PDLC (polymer dispersed liquid crystal) optical fiber doped with dye and metal nanoparticles. The optical fiber comprises a hollow optical fiber body and a PDLC polymer solidified in the optical fiber body and doped with the dye and the metal nanoparticles, an indium tin oxide (ITO) conductive layer is axially coated on the outer surface of the optical fiber body, an ITO conductive layer identical with the inner diameter of the optical fiber body in width is formed on the outer layer of the hollow optical fiber body by a vacuum magnetron sputtering method, a homogeneous solution is prepared by PDLCs and an ethanol solution of the laser dye and the metal nanoparticles according to a certain mass ratio, is absorbed into the hollow optical fiber body through the capillary effect and fills up the inner diameter of the hollow optical fiber body through light solidifying to enable the refractive index of the polymer to be larger than that of the optical fiber, and positive and negative voltage is connected through the ITO conductive layer to form an electric field to change axial directions of liquid crystal molecules so as to control outputting of random lasers. The PDLC optical fiber doped with the dye and the metal nanoparticles can be applied to aspects of optical communication, sensing, biomedicine, tunable narrow-band coherent light sources and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Novel red BODIPY fluorescent dye and preparation method and application thereof
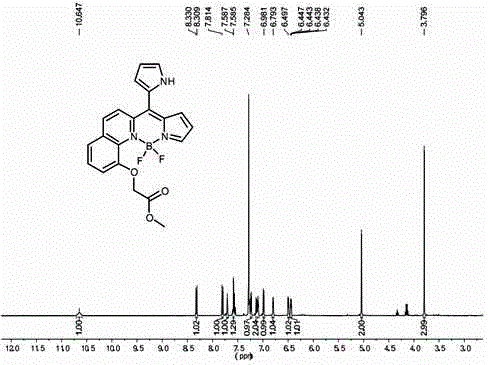
InactiveCN102702768ANarrow absorbencyNarrow fluorescence emission spectrumMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical reaction1,4-Benzoquinone
The invention relates to a novel red BODIPY fluorescent dye with the chemical formula of C10+mH7+nBF2N2+xOy, wherein m, n, x and y are integers from 0 to 100. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving pyrrole with substituent groups R1, R2 and R3 in an organic solution; adding ethyl glyoxylate together with nitrogen to the organic solution for a chemical reaction by using trifluoroacetic acid or toluenesulfonic acid as a catalyst; adding 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone oxidative dehydrogenation; and adding organic amine and a boron trifluoride diethyl ether solution for another reaction. After the reaction solution is concentrated, chromatography is performed with a silicagel column to obtain the fluorescent dye. The fluorescent dye can be used for cell imaging, fluorescent probe or laser dye. The fluorescent dye has the advantages that the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum and the fluorescence emission spectrum of the fluorescent dye are narrow; fluorescent quanta has high efficiency and good light stability; and the fluorescent dye has simple molecular structure and can be synthesized easily, so as to facilitate popularization and application.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Strong fluorescence fluoro-boron dipyrrole compound containing triphenylamine structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103172650AGood symmetryImprove laser efficiencyAzo dyesGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescenceUv vis absorbance
The invention relates to a strong fluorescence fluoro-boron dipyrrole compound containing a triphenylamine structure as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the technical fields of organic chemical industry and fine chemical industry. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: weighing and dissolving formyl substituted triphenylamine and 2,4-dimethyl pyrrolo in a dry dissolvent under the protection of inert atmosphere; adding a catalyst; reacting at a room temperature in a dark place for 6-10 hours; then adding an oxidant; reacting at room temperature for 20-40 minutes; and finally adding organic amine and a boron triflouride complex compound and reacting for 3-8 hours, thus obtaining the strong fluorescence fluoro-boron dipyrrole compound containing a triphenylamine structure. The synthetic method is simple and convenient, and the synthetic compound serves as a laser dye and has relatively high solution pumping laser efficiency, narrowed ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrum and fluorescence emission spectrum, high fluorescence quantum efficiency and good light stability.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lysosome-targeted fluorescent dye capable of realizing red emission and near-infrared emission, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107098923AImprove targetingStable structureAzo dyesGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsLysosomal targetingReaction temperature
The invention discloses a lysosome-targeted fluorescent dye capable of realizing red emission and near-infrared emission, and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of bioluminescence analysis. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a compound with the substituent R in an anhydrous organic solvent and adding morpholinoindolal and a catalyst under the condition of introduction of nitrogen, wherein a mol ratio of morpholinoindolal to the compound with the substituent R is 1-10: 1; and carrying out a reaction at a reaction temperature of 25 to 200 DEG C for 1 to 24 h, concentrating an obtained solution and carrying out silica-gel column chromatography so as to obtain the target fluorescent dye. The fluorescent dye prepared in the invention is applicable to targeted imaging of lysosomes in cells, fluorescent probes or laser dyes. The fluorescent dye has the advantages that the emission wavelength of the fluorescent dye is in a range from red zone to near-infrared zone; the fluorescent dye can prevent interference of biological background fluorescence and has high fluorescence quantum efficiency and good light stability; and the fluorescent dye can be specifically localized in lysosomes, so the fluorescent dye has high application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing rhodamine intercalation hydrotalcite luminescent material
InactiveCN101255334AImmobilizationEvenly dispersedHydrotalciteSilicon compoundsSlurryMembrane reactor
A hydrotalcite composite luminescent material with rhodamine intercalation, which pertains to abio-organic composite luminescent material. The process is preparing solution A with mole ratio of bivalence and tervalence cation M2+ / M3+=2.0-4.0; adding laser dye sulphonated rhodamine and sodium salt of dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid into mixed solution of ethanol and water and fully dissolving to obtain solution of sulphonated rhodamine and dodecyl benzene sulfone acid group containing anion with negative charge B; mixing solution A, B into solution C, preparing NaOH solution; communicating solution C and NaOH solution into full-back-liquid mixing membrane reactor to react, mixing to obtain red slurry, introducing the red slurry into hydrothermal kettle, reacting, absterging by CO2, de-ionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol and centrifugally separating, vacuum drying. Then hydrotalcite system with co-intercalation of suphonated rhodamine and dodecyl sulfone acid group is obtained. Advantages of the invention are that dye molecular is immobilized, and fluorescence quenching caused by dye aggregation is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Laser emitting material, method for making the same and use thereof
InactiveUS20070091967A1Low thresholdActive medium materialOptical light guidesLaser dyeHost material
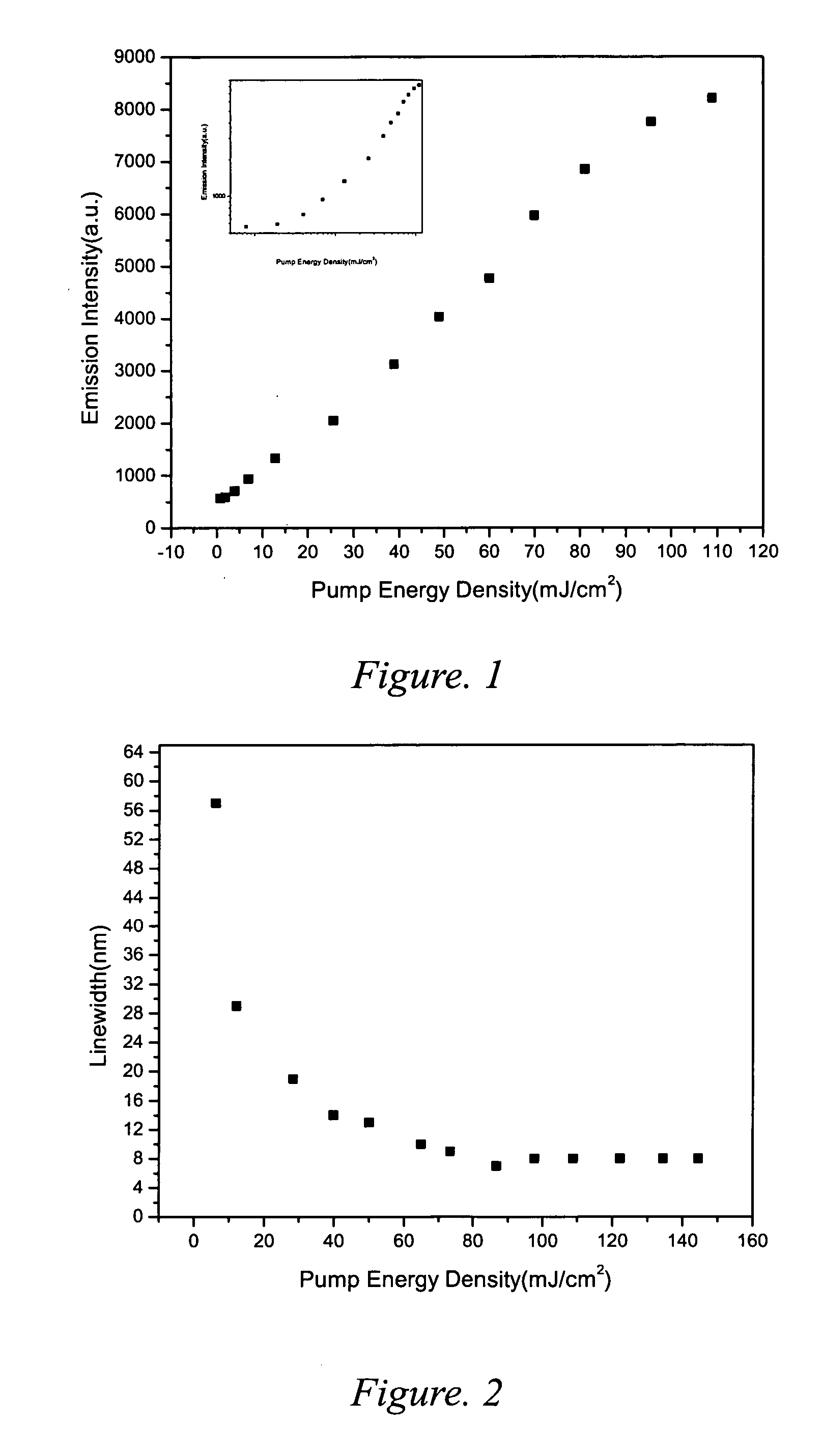
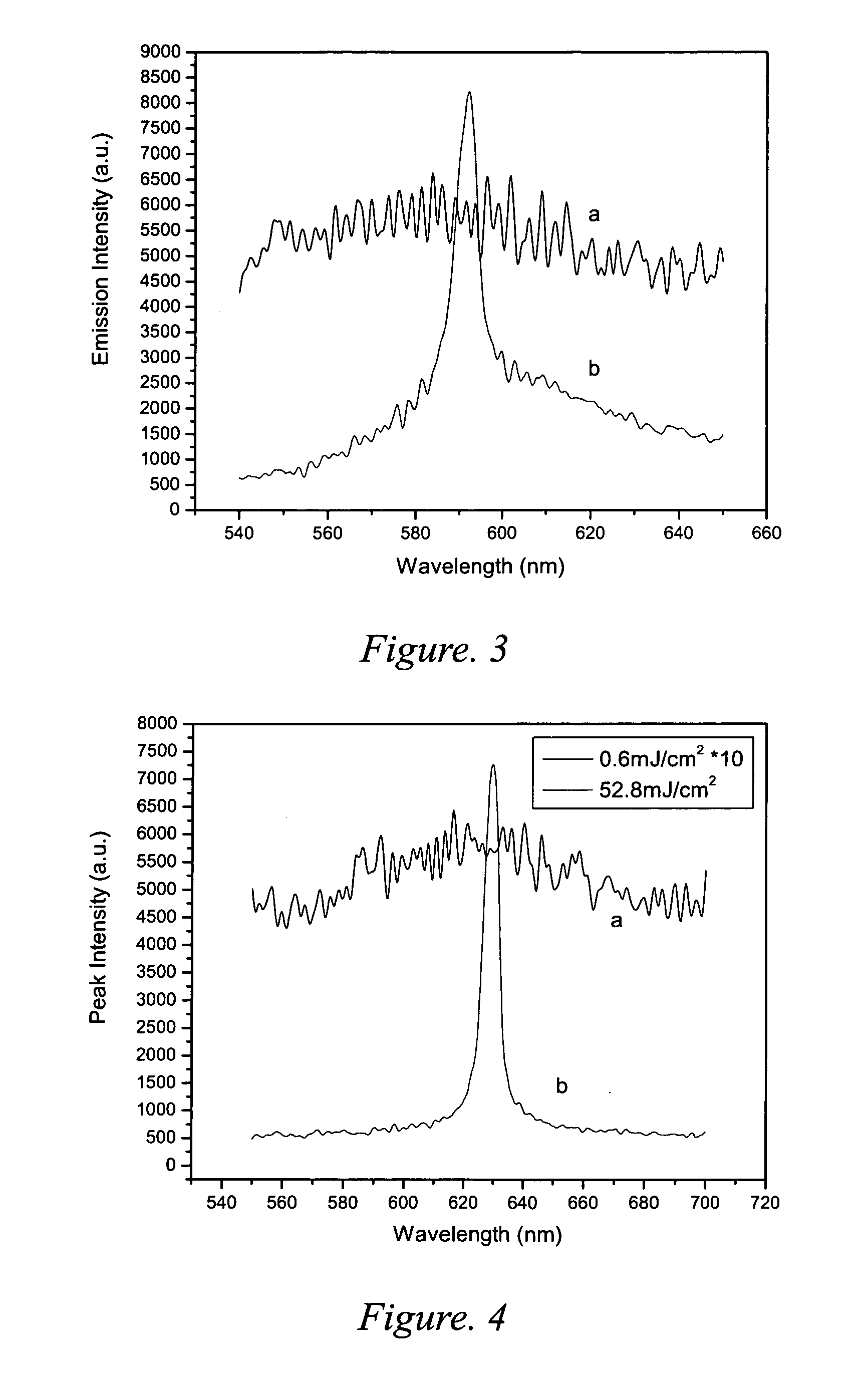
A solid-state laser emitting material for use in conjunction with a light source includes a polymer matrix functioning as host materials, containing laser dye of rhodamine 590 or rhodamine 610 as gain materials and nano-submicron particles as scatters therein. The lowest lasing threshold of the laser emitting material is approximately 5 mJ / cm2 for 585 nm emission and 2 mJ / cm2 for 630 nm emission.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method and apparatus for enhancing plasmon polariton and phonon polariton resonance
ActiveUS20070273959A1Laser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPicosecond laser pulsePhoton emission
A metallic nano-particle surrounded by an amplifying medium results in a boundary condition that creates a singularity in the particle's dynamic polarizability at the localized surface plasmon resonance and at a critical value of the gain is disclosed. The boundary condition may be time dependent due to excitation by a sub-picosecond laser pulse and couples to the electromagnetic vacuum resulting in photon emission in an analogue of the Unruh Effect. The vacuum emission from 2-D nanostructures embedded in high gain laser dyes predicts energies nearly two orders of magnitude larger than the spontaneous emission background. The vacuum radiation is may have a unique dependence on the excitation.
Owner:SOLARIS NANOSCI
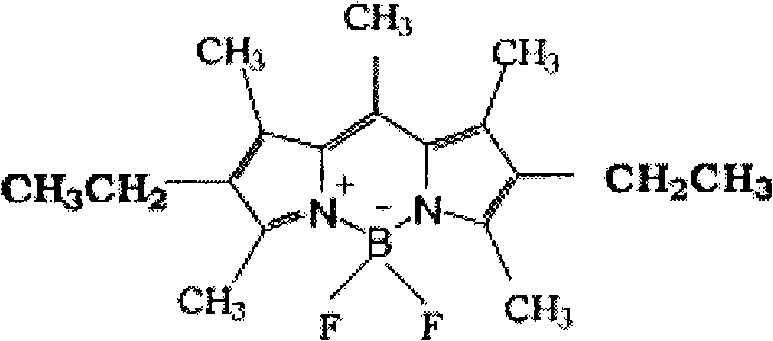
Organic boron difluoride complex
InactiveCN102993224AChemically stableImprove thermal stabilityGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsLuminescent compositionsLaser dyePhotosensitizer
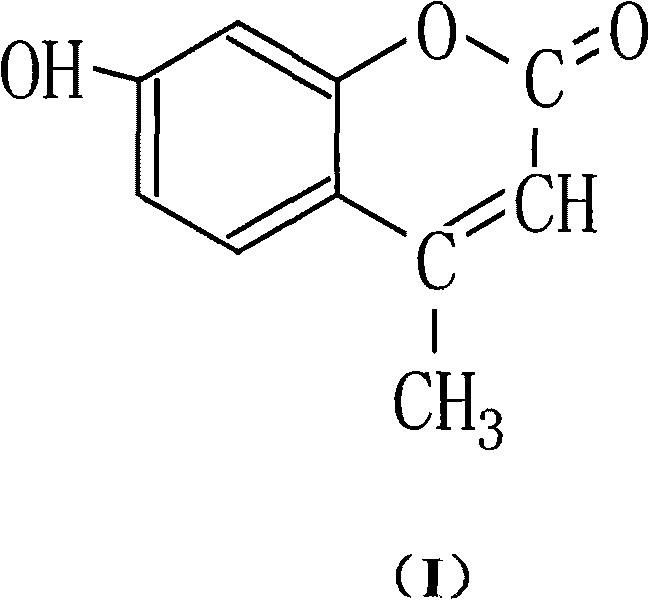
The invention discloses an organic boron difluoride complex. The complex is shown in the structural formula I in the specification, wherein R1 is H or OCH3; and R2 is C6H5, 4-HOC6H4, 4-(CH3)2NC6H4 or 2-C4H4S. The complex can be used for preparing luminescent materials, fluorescent probes, fluorescent tracers, information storage media, laser dyes and photodynamic cancer treatment photosensitizers. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the complex. The complex is prepared through reaction of a corresponding ligand and boron trifluoride diethyl etherate. The complex has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, short reaction time, high product yield, rapidness, simpleness and convenience in separation and purification and high product purity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Infrared BODIPY fluorochrome as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106543213ANarrow absorbencyNarrow fluorescence emission spectrumAzo dyesGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsInfraredUv vis absorbance
The invention relates to the field of optical functional materials, and more specifically relates to an infrared BODIPY fluorochrome. The fluorochrome has a structure shown in a formula (1), wherein R1 and R2 are mutually independent and selected from C1-C10 alkyl, aromatic bases or heterocyclic aromatic bases; R3 is one of H atom, C1-C10 alkyl or aromatic bases. The fluorochrome has the advantages of narrow ultraviolet visible absorption spectroscopy and fluorescence emission spectrum, high molar absorption coefficient, high fluorescence quantum efficiency, good light stability, trace detection, and high sensitivity; and the fluorochrome can be applied to cell imaging, fluorescence probe, laser dye, fluorescence sensor and near infrared dynamics, and different application fields with good practicality.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIYUAN GENT CO LTD
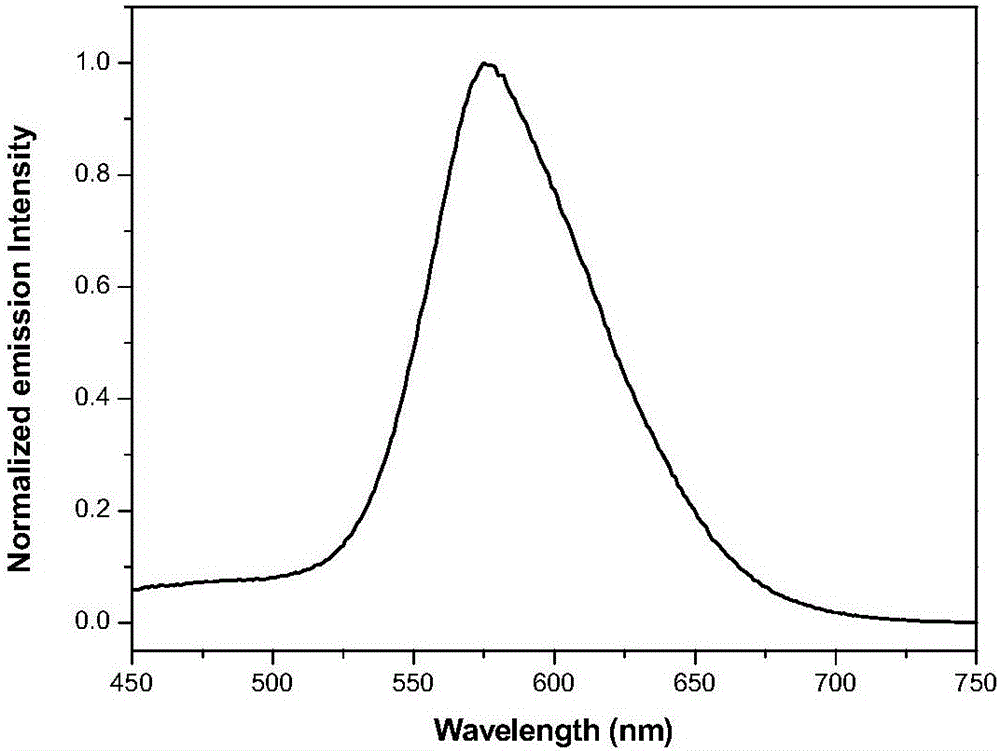
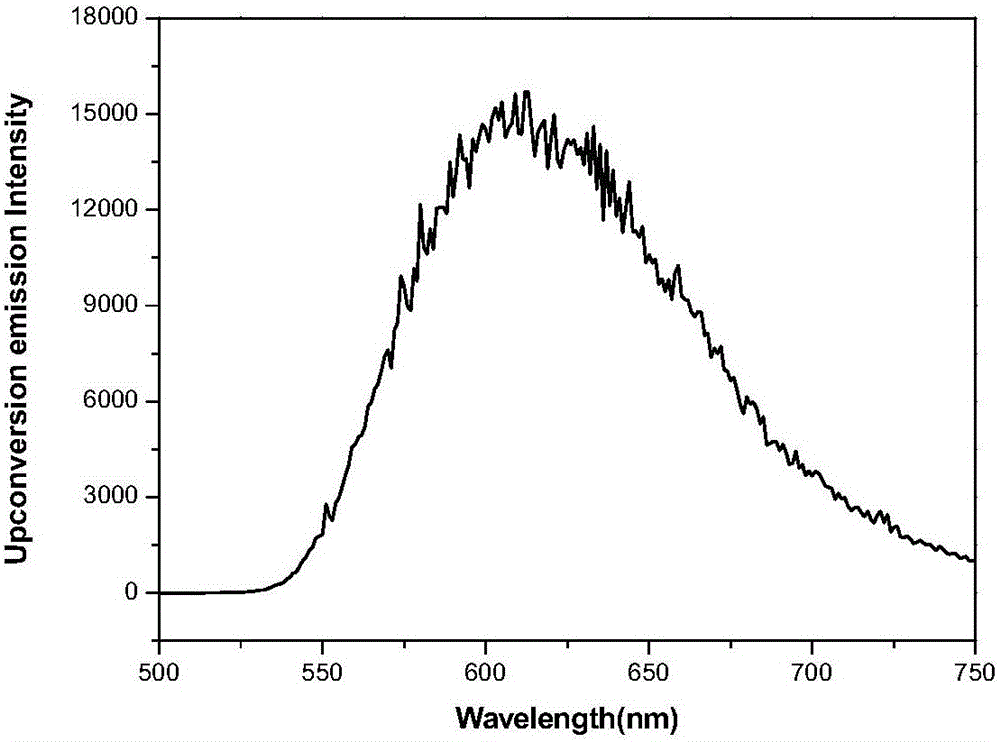
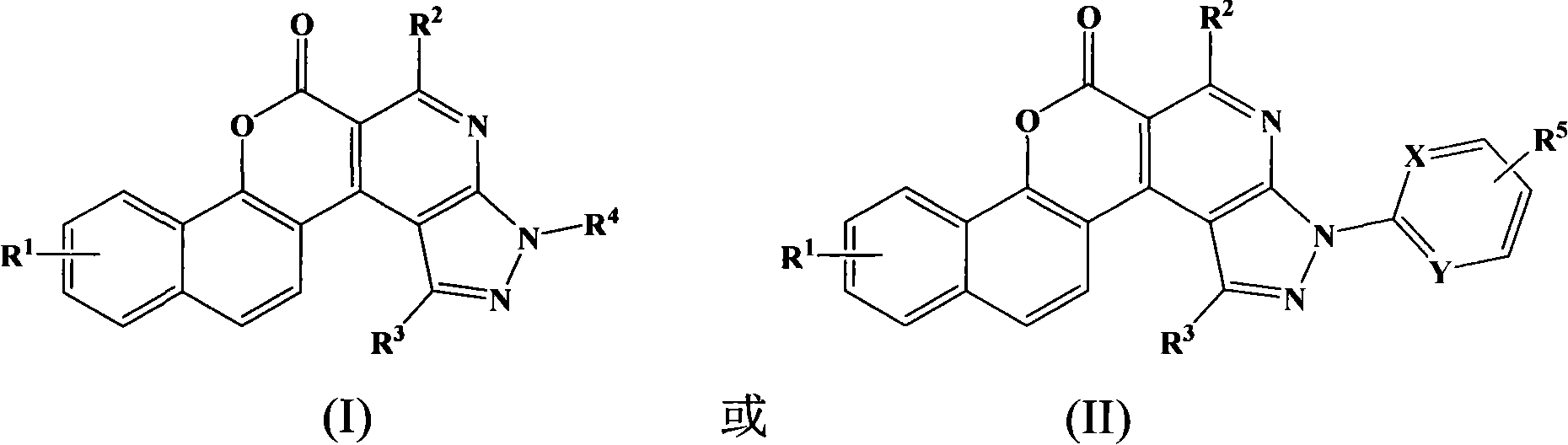
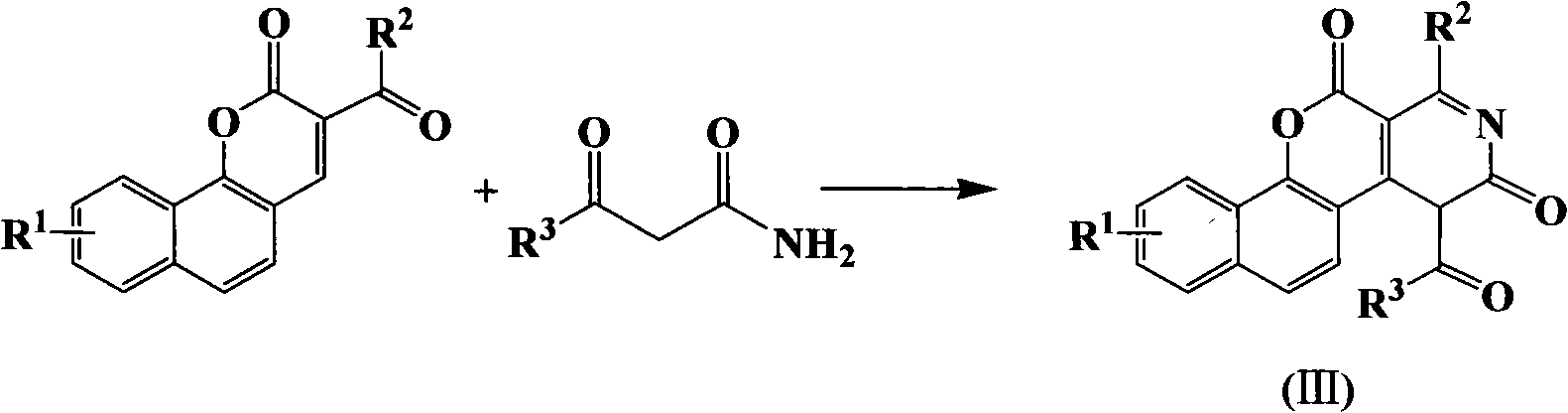
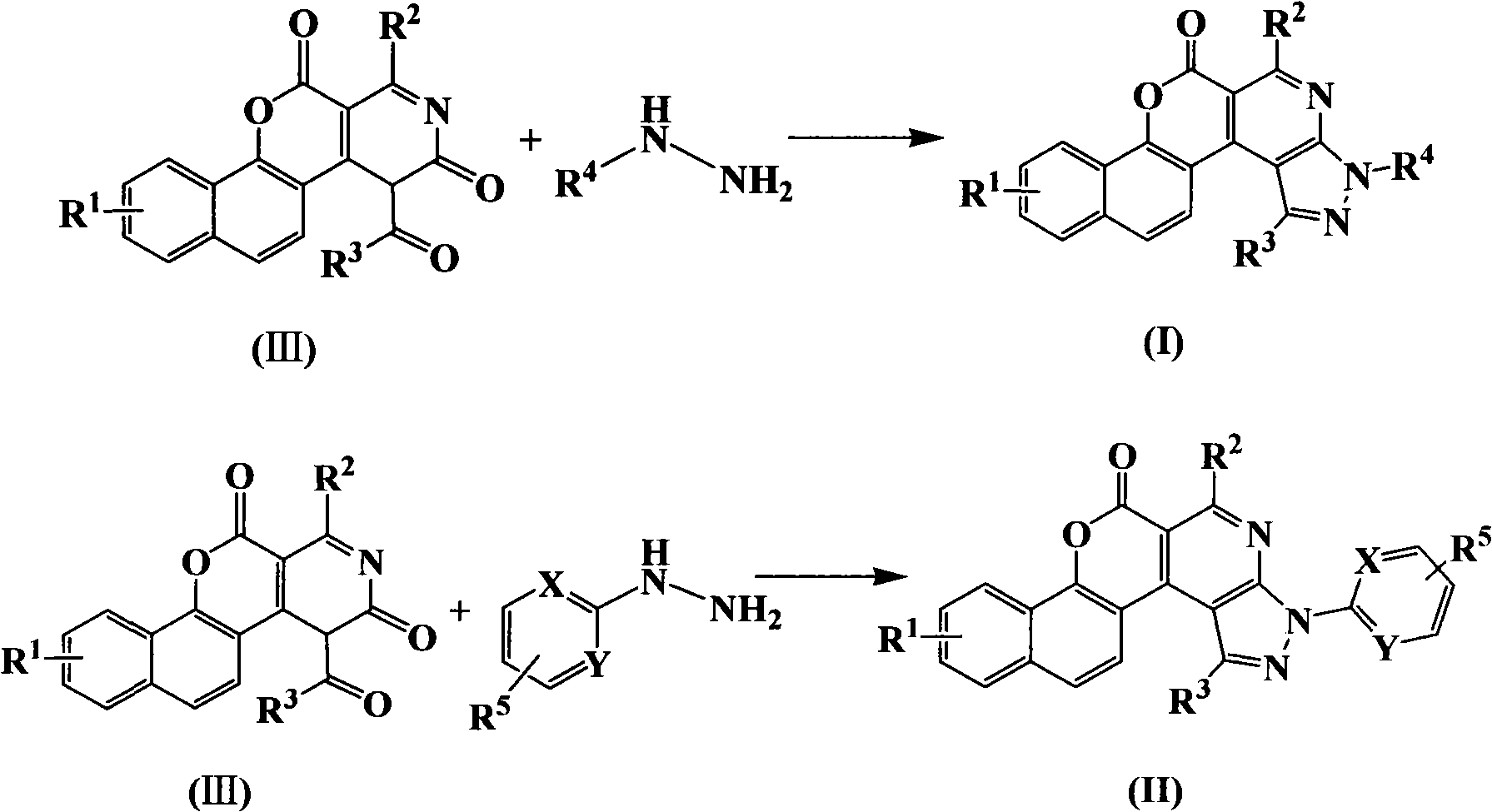
Pyrazoline pyridine-fluorescent coumarin dye derivant, synthesis and uses thereof
ActiveCN101368003AImprove luminous efficiencyCoumarine dyesLuminescent compositionsLaser dyeQuantum yield
The invention belongs to the field of fluorescent dye and laser dye, and relates to coumarin fluorescent dye and laser dye, in particular to pyrazoline naphthyridine coumarin fluorescent dye derivative, and a synthetic method and an application thereof. The pyrazoline naphthyridine coumarin fluorescent dye derivative has very high fluorescent efficiency with the quantum yield of fluorescence of nearly 100 percent; meanwhile, the fluorescent material has excellent heat, light and electricity chemical stability, and can be used as fluorescent dye, laser dye, organic electroluminescent material, fluorescent marking material, fluorescent chemical sensitive material and the other. The pyrazoline naphthyridine coumarin fluorescent dye derivative has structure as seen in formula I or formula II.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
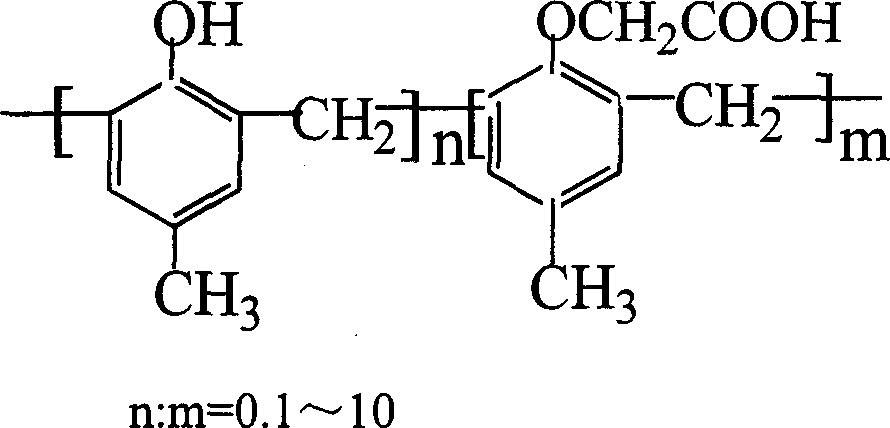
Washed flexible resin plate capable of achieving laser direct imaging
Provided are a washed flexible resin plate capable of achieving laser direct imaging and a preparation method thereof. A photosensitive elastic member of the washed flexible resin plate capable of achieving laser direct imaging is composed of thermoplastic elastic member (A), polybutadiene with end achieving carboxylation (B), polybutadiene with end achieving carboxylation (C), a copolymer (D) of styrene with a side chain containing carbamic acid esterification hydrophilic poly ethoxy-acrylonitrile-poly ethoxy methyl acryloyl oxygen ethyl isocyanate, polymerizable vinyl monomers and a compound of the polymerizable vinyl monomers (E), infrared laser dye (F) and initiating system (G) composed of radical initiators and cation initiators. The system can prepare the environment-friendly washed flexible resin plate which is capable of achieving laser direct imaging and being washed by water and high in sensitivity.
Owner:LUCKY HUAGUANG GRAPHICS
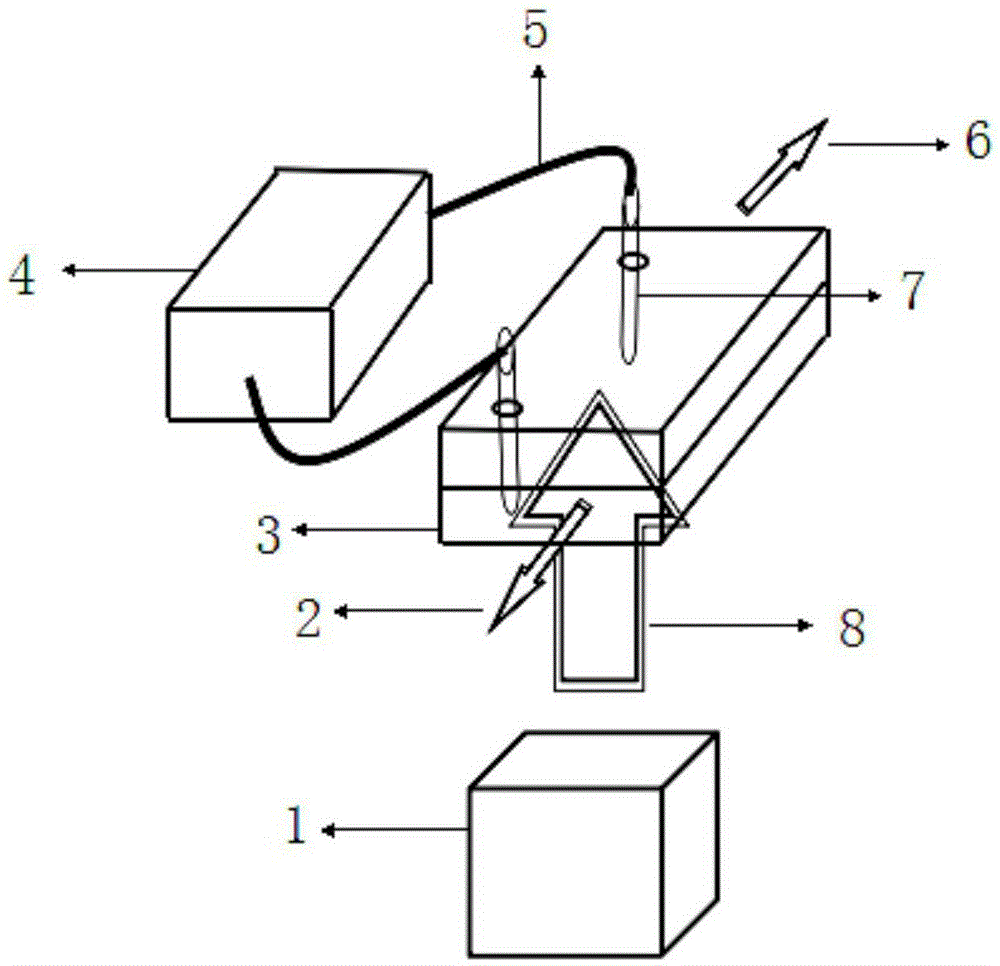
Multi-wavelength liquid drop laser
The invention provides a multi-wavelength liquid drop laser. A first capture light source is connected with a first capture fiber through a first optical isolator, a second capture light source is connected with a second capture fiber through a second optical isolator, and light traps formed by laser beams of the emitting ends of the first capture fiber and the second capture fiber stably capture M liquid drop resonant cavities in matching fluid. M micro nano fibers close to various liquid drop resonant cavities couple pump light into the liquid drop resonant cavities, and the laser dye doped in the liquid drop resonant cavities when stimulated output laser and form an echo wall mode. When the output laser in the liquid drop resonant cavities increases to a certain level, nearby micro nano fibers couple out M wavelength laser. The stable and adjustable multi-wavelength liquid drop laser is realized by combining fiber optical tweezers technology and microballoon resonant cavity theory, and is small in size, high in control force, stable in structure high in Q value and low in output threshold.
Owner:黑龙江省敏动传感科技有限公司
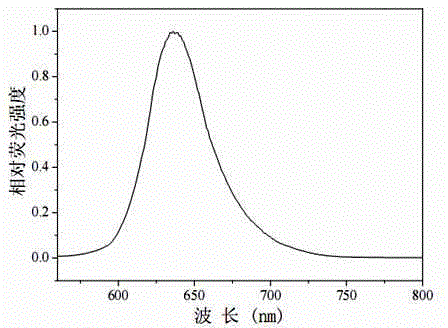
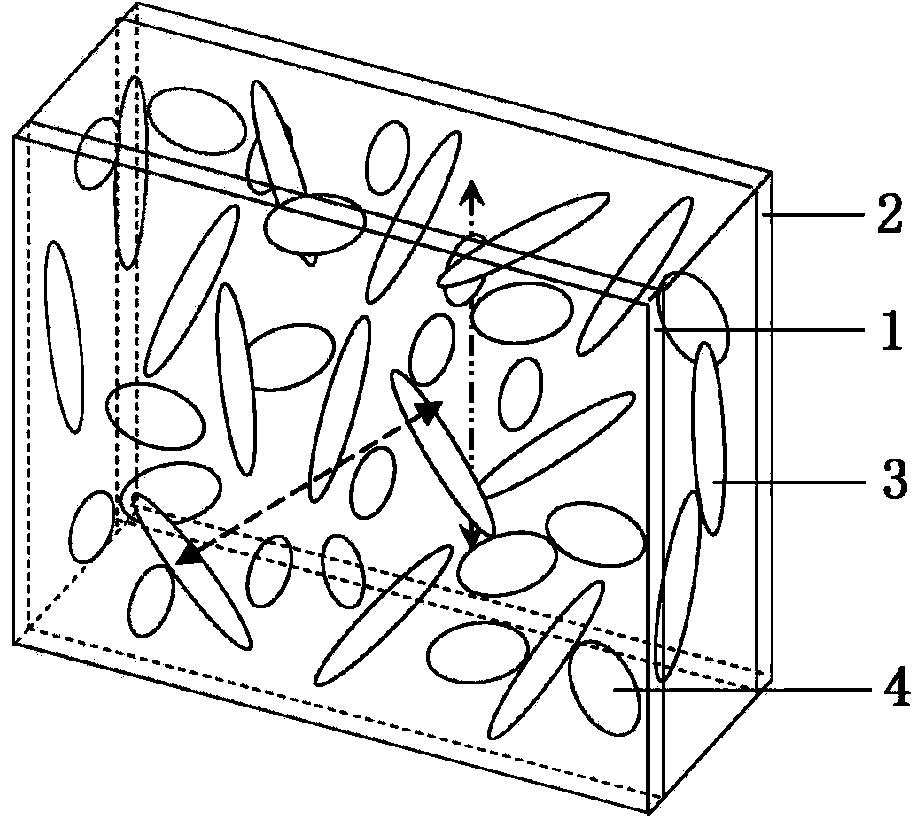
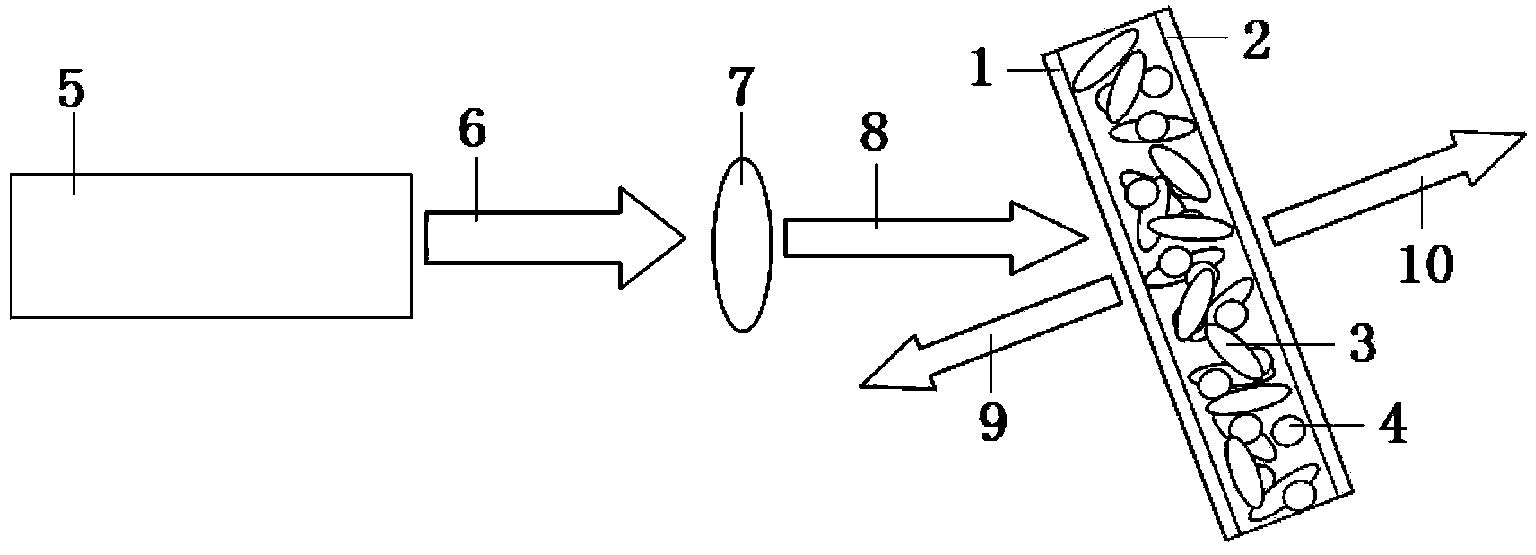
Compensation of influence of environmental temperature on liquid crystal random laser through voltage
The invention discloses a method for compensating the influence of environmental temperature on a liquid crystal random laser through voltage. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, focusing a pump light emitted from a laser by lens, and irradiating focused pump light to a liquid crystal random laser, wherein the liquid crystal random laser is of a box-shaped structure composed of two pieces of glass, the gain medium of the liquid crystal random laser is a mixture solution composed of liquid crystal microdrop and laser dye; then, placing a detector before or behind the liquid crystal random laser so as to detect emitted random laser; and subsequently, applying a basic voltage to the liquid crystal random laser through a glass layer, when the environmental temperature is higher than the optimal working temperature of the liquid crystal random laser, modulating a power supply so as to reduce a loaded voltage value, and when the environmental temperature is lower than the optimal working temperature of the liquid crystal random laser, modulating the power supply so as to boost the loading voltage value. The influence of the environmental temperature on the liquid crystal random laser is modified effectively in a mode of boosting the voltage; and the device is simple in structure, convenient to manufacture and easy to realize.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Application type positive property thermal sensitive computer direct board and process for making same
The invention discloses a kind of coating positive thermal sensitive CTP version and the manufacturing method. The thermal layer of the CTP version is: the coating liquid is created by dissolving filming material with weight of 100, infrared laser dye, heat acid generating agent, cross linker into organic solvent with weight of 300-600, which is coated on the base piece and dried under temperature of 90oC-120 oC for 1-5 minutes and forms a thin film with thickness of 1-2ª–m. The filming material is one or more of carboxy, carboxy methyl or sulfonic group derivant formed by homopolymer and polymer of phenol formaldehyde resin, paramethyl phenol formaldehyde resin, methylol or multi-methylol phenol formaldehyde resin, vinylphenol. The invention will form cross linker structure in the preheated process.
Owner:辽宁正宏豹驰数码科技有限公司
Synthesis of pyrazolinylnaphthalic acid derivatives
InactiveUS20010012905A1Simplify and reduce timeImprove production yieldPerinonesOrganic chemistryChemical industryAryl radical
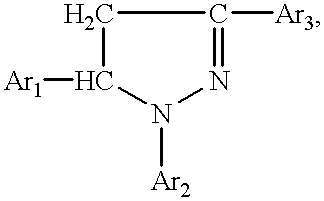
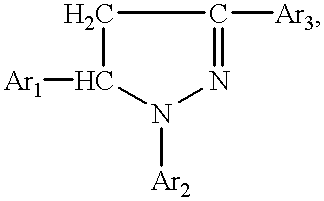
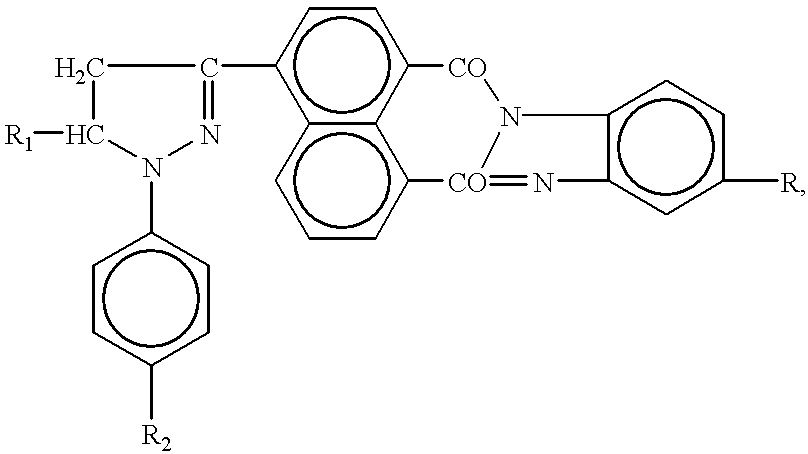
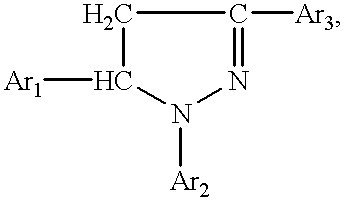
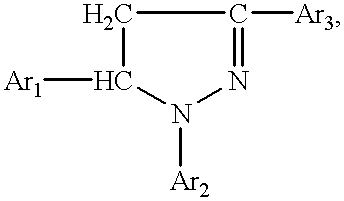
The invention pertains to a method for preparing derivatives of the pyrazolinylnaphthalic acid having the general formula where Ar1 and Ar2 are unsubstituted or substituted phenyl radicals bearing in the para position an alkylated or acylated oxy- or amino group, or a polynuclear aryl radical, and Ar3 is a substituted N-naphthalimid or 1,8-naphthylene-1',2'-benzimidazole. Compounds ofthe above general formula are high-efficient red organic luminophors and are used widely as luminescent components of dyes for plastics and liquid scintillators, in hydrogeology to study water streams, to label the chemical industry wastewaters, as laser dyes, etc.
Owner:EMAGIN CORP
Organic flexible microdisk/metal nanowire heterojunction and preparation method thereof
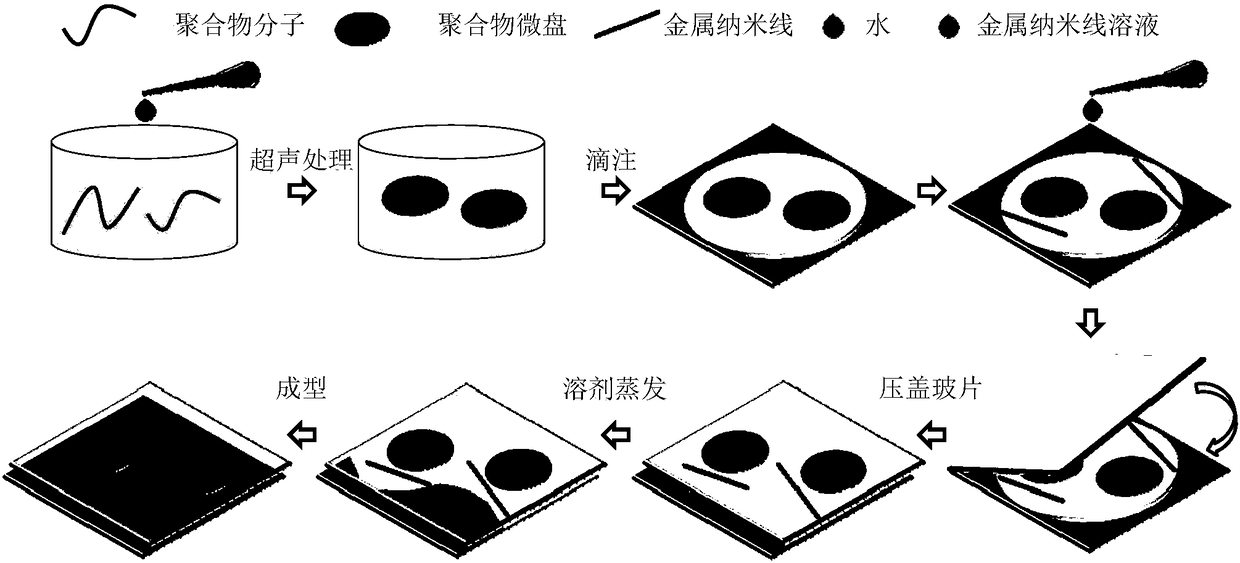
ActiveCN108732662AImprove machinabilityAchieve multicolor laser subwavelength outputOptical elementsHeterojunctionInformation processing
The invention discloses an organic flexible microdisk / metal nanowire heterojunction, a preparation method and application thereof. The organic flexible microdisk / metal nanowire heterojunction comprises organic flexible microdisks adopted as medium light sources, and metal nanowires arranged on mounted on the surface of a medium waveguide. According to the formation of the heterojunction, a composite structure which adopts the organic medium light sources as a main body and the metal nanowires as branches is formed. The flexible organic matrices in the organic flexible microdisk can be doped with a plurality of organic laser dyes, so that the organic flexible microdisks can cover full-visible light spectra. The preparation method is simple and easy to operate. According to the heterojunction prepared by a capillary force-assisted liquid phase self-assembly method, the metal nanowires can be separated from the substrate, and therefore, substrate-induced propagation loss can be eliminated, and the propagation performance of SPPs (surface plasmon polaritons) can be greatly improved. The heterojunction can be used to realize ultra-small-size high-throughput information light sources, the high-throughput information processing of photoelectric information loops, and high-throughput information sensing and can be applied to other fields.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for regulating laser emission of gain medium under all-optical control
InactiveCN102097740ADynamic adjustment of stimulated emission intensitySimple structureLaser detailsLaser dyeRandom laser
The invention discloses a method for regulating the laser emission of a gain medium under all-optical control, which comprises the following steps of: first irradiating a carrier with random mediums by using infrared light beams with the wavelength of lambda2 or green light beams with the wavelength of lambda3; then emitting pump light (1) with the wavelength of lambda1 from a laser, converging the pump light to form stripes by using a cylindrical lens, making the stripes incident onto the carrier, arranging a detector on the bottom edge of the carrier to receive laser emitted from the carrier, and arranging a device for adjusting the energy of the pump light at the front end of the cylindrical lens; and finally prolonging the irradiation time of the red light beams (5) or improving the irradiation intensity of the red light beams (5) to improve the intensity of stimulated emitted light (7), or prolonging the irradiation time of the green light beams (6) or improving the irradiation intensity of the green light beams (6) to improve the intensity of the stimulated emitted light (7), wherein the random mediums are liquid crystal droplets which are dispersed in the azo dye-containing laser dye gain medium. The method provided by the invention ensures fixed environmental temperature, fixed electric field, simple structure and convenience of manufacturing at the same time of ensuring that a random laser can dynamically regulate stimulated emission intensity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation for high-performance solid dye laser medium
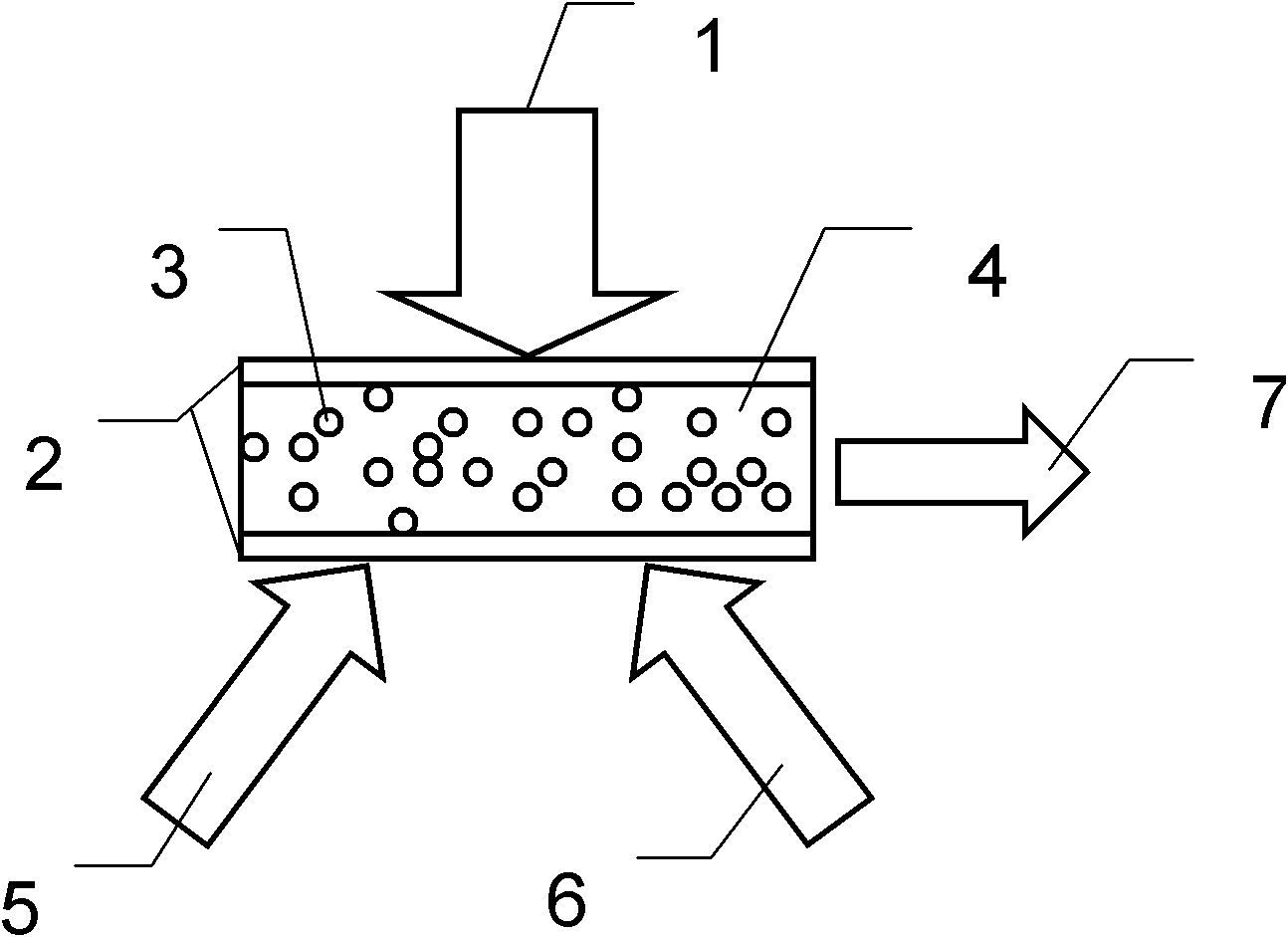
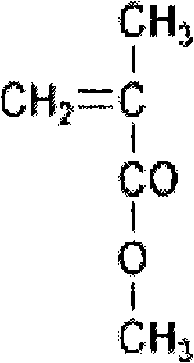
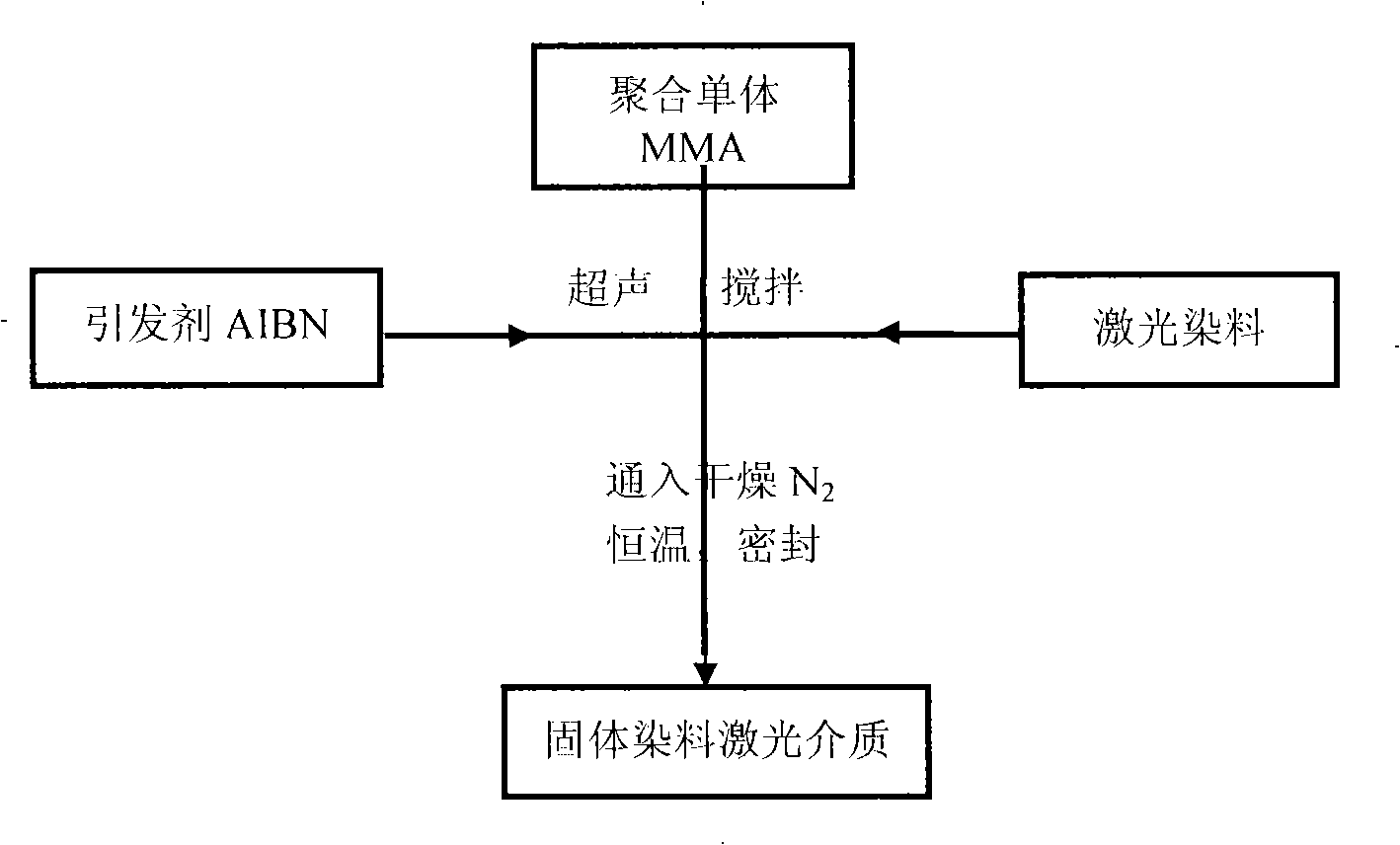
InactiveCN101275040AImprove thermal stabilityExtended service lifeOrganic dyesActive medium materialLaser dyePhoto stability
The invention provides a preparation method of a high performance solid dye laser medium. A dye PM567 with the concentration of 5*10<-5>mol / l to 2*10<-3>mol / l, and the concentration ratio between PM567 and C440 is 1:0 to 1:10; the concentration of an initiator is 0.1g / l to 1.5g / 1; the laser dye is mixed with MMA, added with an initiator AIBN, and ultrasonically stirred to lead the dye to be wholly dissolved in MMA; the mixed solution is subpackaged into clean dry test tubes, the test tubes are filled with dry nitrogen to remove oxygen in the test tubes, and finally sealed up and placed into a thermostatic waterbath; when the sample is completely solidified, the prepared solid dye laser medium is taken out from the test tubes. The PM567 polymeric laser medium prepared by the invention has high efficiency, and overcomes the shortcoming that the existing PMMA based solid dye that is only doped with PM567 has poor light stability, and further enhances the performance of polymer based solid dye laser medium.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Organic boron difluoride complex containing N,O-bidentate ligand
InactiveCN102993223AChemically stableImprove thermal stabilityGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsLuminescent compositionsLaser dyePhotosensitizer
The invention discloses an organic boron difluoride complex containing an N,O-bidentate ligand. The complex is shown in the structural formula I in the specification, wherein R is 2,6-dimethoxyphenyl, oxethyl, 2-methoxyphenyl or 2-thienyl. The complex can be used for preparing luminescent materials, fluorescent probes, fluorescent tracers, information storage media, laser dyes and photodynamic cancer treatment photosensitizers. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the complex. The complex is prepared through reaction of a corresponding ligand and boron trifluoride diethyl etherate. The complex has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, short reaction time, high product yield, rapidness, simpleness and convenience in separation and purification and high product purity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Near-infrared fluorine-boron dipyrrole fluorochrome and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103952001AHigh yieldThe synthetic route is simpleMethine/polymethine dyesLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldSolvent
The invention relates to a near-infrared fluorine-boron dipyrrole fluorochrome and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, halogenated isoindole imine and a boric acid reagent Suzuki are coupled, and then the near-infrared fluorine-boron dipyrrole fluorochrome is synthesized through acid catalysis condensation, wherein the emission wavelengths of the fluorochrome in various solvents are greater than 669nm, and the emission spectrum of the fluorochrome and derivatives thereof can reach 748nm. The fluorochrome has relatively high fluorescence quantum yield (0.67-1) and excellent optical physicochemical properties, such as light stability, and has a good application prospect in fields like laser dye and bioanalysis.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Synthesis of pyrazolinylnaphthalic acid derivatives
InactiveUS6288232B2Simplify and reduce timeQuality improvementPerinonesOrganic chemistryChemical industryLaser dye
The invention pertains to a method for preparing derivatives of the pyrazolinylnaphthalic acid having the general formulawhere Ar1 and Ar2 are unsubstituted or substituted phenyl radicals bearing in the para position an alkylated or acylated oxy- or amino group, or a polynuclear aryl radical, and Ar3 is a substituted N-naphthalimid or 1,8-naphthylene-1',2'-benzimidazole. Compounds of the above general formula are high-efficient red organic luminophors and are used widely as luminescent components of dyes for plastics and liquid scintillators, in hydrogeology to study water streams, to label the chemical industry wastewaters, as laser dyes, etc.
Owner:EMAGIN CORP
Fluoro phenylindole compound, application of fluoro phenylindole compound as red organic luminescent material, and preparation method of fluoro phenylindole compound
ActiveCN105001141AStable structurePracticalOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsLaser dyeCyclohexanone
The invention discloses a fluoro phenylindole compound which adopts a structure shown in formula I, application of the fluoro phenylindole compound as a red organic luminescent material, and a preparation method of the fluoro phenylindole compound. The fluoro phenylindole compound is obtained through a reaction between cyclohexanone and 3-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1H-indole-2-yl) acrolein under an alkaline condition. The preparation method is simple to operate, convenient for synthesis and easy for purification; the obtained fluoro phenylindole compound is stable in structure and can be utilized for fluorescence conversion on a strong red color displayed under 800-nm laser excitation, thereby having potential application values in such fields as luminescent equipment, anti-counterfeit technologies, laser dye and fluorescence sensing; the research field of the fluoro phenylindole compound is expanded.
Owner:INST OF ANALYSIS GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI (CHINA NAT ANALYTICAL
Pyrazoline naphthyridine benzocoumarin fluorescent dye derivatives, synthesis method of same, and application of same
InactiveCN101525497ALong emission wavelengthImprove luminous efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLaser dyeQuantum efficiency
The invention belongs to the field of fluorescent dyes and laser dyes, and relates to coumarin fluorescent dyes and laser dyes, in particular to pyrazoline naphthyridine benzocoumarin fluorescent dye derivatives, a synthesis method of the same, and application of the same. The pyrazoline naphthyridine benzocoumarin fluorescent dye derivatives have longer emission wavelength and extremely high luminous efficiency, and the fluorescence quantum efficiency of the derivatives is approximately 100 percent; at the same time, a luminescent material of the derivatives has excellent thermo, photo and electrochemical stability, and can be used as fluorescent dyes, laser dyes, organic electroluminescent materials, fluorescent labeling materials, fluorescent chemosensitive materials and the like. The pyrazoline naphthyridine benzocoumarin fluorescent dye derivatives have a structure shown in a formula (I) or a formula (II).
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
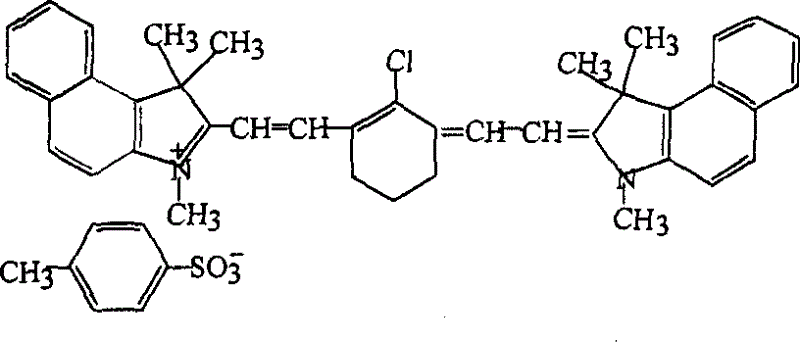
Purifying method of laser dye cumarin-4
The invention belongs to the field of laser dye, particularly to a purifying method of laser dye cumarin-4, which comprises the following steps of: 1. washing a crude product of the laser dye cumarin-4 with a sodium hydroxide aqueous solution; 2. adding dilute sulphuric acid into the alkali laser dye cumarin-4 and processing to obtain light gray laser dye cumarin-4; 3. completely dissolving the product in ethanol, and discoloring with active carbon; 4. crystallizing the ethanol solution, and drying to obtain white laser dye cumarin-4; and 5. recrystallizing the product to finish the purifying process. After conducting alkali washing, repeated recrystallization and active carbon discoloring on the crude product of the laser dye cumarin-4, the impurities contained in the crude product of the laser dye cumarin-4 can be effectively removed, the purity of the laser dye cumarin-4 is effectively improved, the life of the laser dye cumarin-4 in use is prolonged, and the economic performance for preparing the laser dye cumarin-4 is markedly improved.
Owner:TIANJIN CHEM REAGENT RES INST
Asymmetric near-infrared BODIPY fluorescent dye as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104650610AGood light stabilityImprove applicabilityAzo dyesFluorescence/phosphorescenceInfraredDehydrogenation
The invention discloses an asymmetric near-infrared BODIPY fluorescent dye. The chemical formula of the dye is C(18+m)H(13+n)BF2N(2+x)Oy, wherein m, n, x and y are all integer within 1 to 100. The preparation method of the dye comprises the following steps: dissolving a substituent group-containing pyrrole solution in an organic solvent; adding a quinolinaldehyde derivative at presence of nitrogen to perform catalytic reaction; adding 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone for oxidative dehydrogenation; finally adding organic amine and a boron trifluoride diethyl ether solution; reacting again; concentrating a reaction solution; performing chromatography by utilizing a silica gel column to obtain the asymmetric near-infrared BODIPY fluorescent dye. The asymmetric near-infrared BODIPY fluorescent dye disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being narrow in ultraviolet visible absorption spectrum and fluorescence emission spectrum and good in optical stability, can be applied to cell imaging, fluorescence probes or laser dyes, and is good in practical application; the method is simple and easy to implement, can be used for obtaining near-infrared BODIPY without multi-step reaction, can save raw materials and is easy to popularize and apply practically.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Device and method for emitting double-faced random lasers with different polarization directions
InactiveCN103825163ASimple structureEasy to implementActive medium shape and constructionLaser dyeRandom laser
The invention discloses a device and a method for emitting double-faced random lasers with different polarization directions. The device comprise a box-packed structure prepared from two glass substrates, as well as liquid crystal and a laser dye filled in the box-packed structure, wherein a liquid crystal orientation agent is coated on the inner surfaces of the two glass substrates to form an orientation film, and the orientation film is orientated to enable the orientations on the two glass substrates to be different; when a pump light is irradiated on one surface of the box at a certain angle, random lasers capable of carrying out linear polarization on the both surfaces of the box are emitted vertically to the surfaces of the box, and the polarization directions and the orientations of the emission surfaces are the same. The device and method disclosed by the invention have the advantages of being simple and convenient, easy to realize, and low in energy loss.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical fluid three-color composite random laser
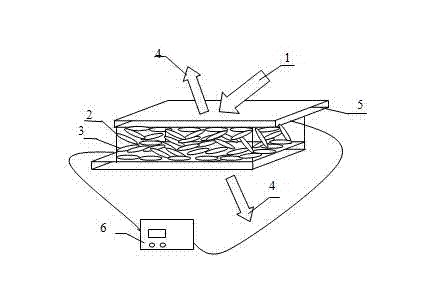
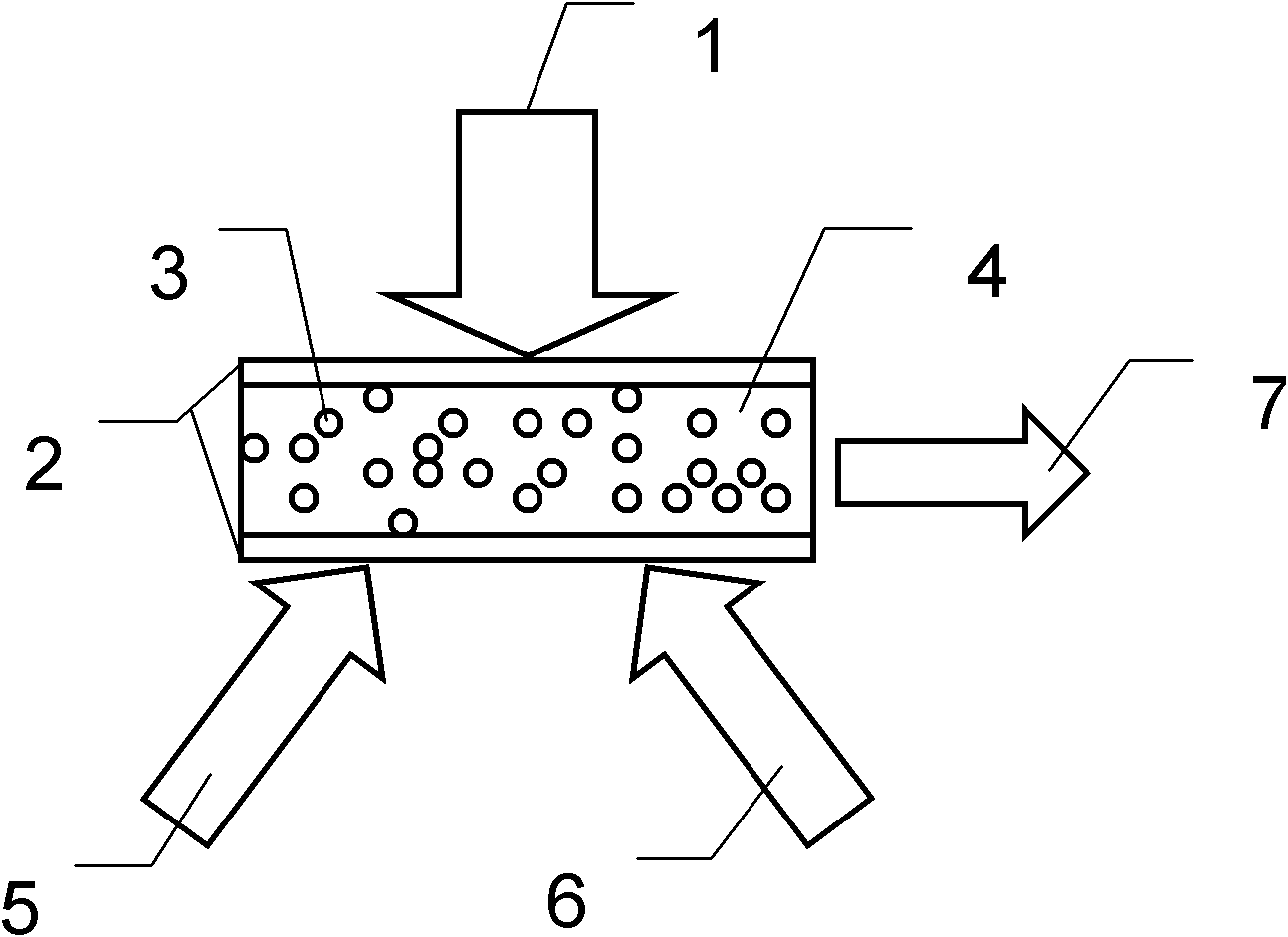
InactiveCN105305219AImprove reconfigurabilityStochastic laser pattern stabilizationActive medium materialPeristaltic pumpReconfigurability
The invention discloses an optical fluid three-color composite random laser which comprises the components of an external pumping optical circuit, a micro-fluidic chip and a precise peristaltic pump. The micro-fluidic chip is obtained through combining a substrate and a cover plate through bonding. A micro-fluidic channel is constructed in the substrate. Cylindrical recessed troughs are constructed at two ports of the micro-fluidic channel. The recessed troughs are communicated with the external surface of the cover plate and are respectively used as a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet. The precise peristaltic pump is connected with the micro-fluidic channel, thereby forming a fluidic loop for circulation of a laser dye. Pumping light which is emitted from the external pumping optical circuit is irradiated into the micro-fluidic channel of the micro-fluidic chip. The light which is emitted from the micro-fluidic chip is random laser which is obtained through combining three colors (red, green and blue). The optical fluid three-color composite random laser has advantages of unidirectional light outlet, high reconfigurability, stable random laser mode and long-time operation. Furthermore because dye solution flow dynamically, dye regeneration is promoted and a no-easy bleaching advantage is realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
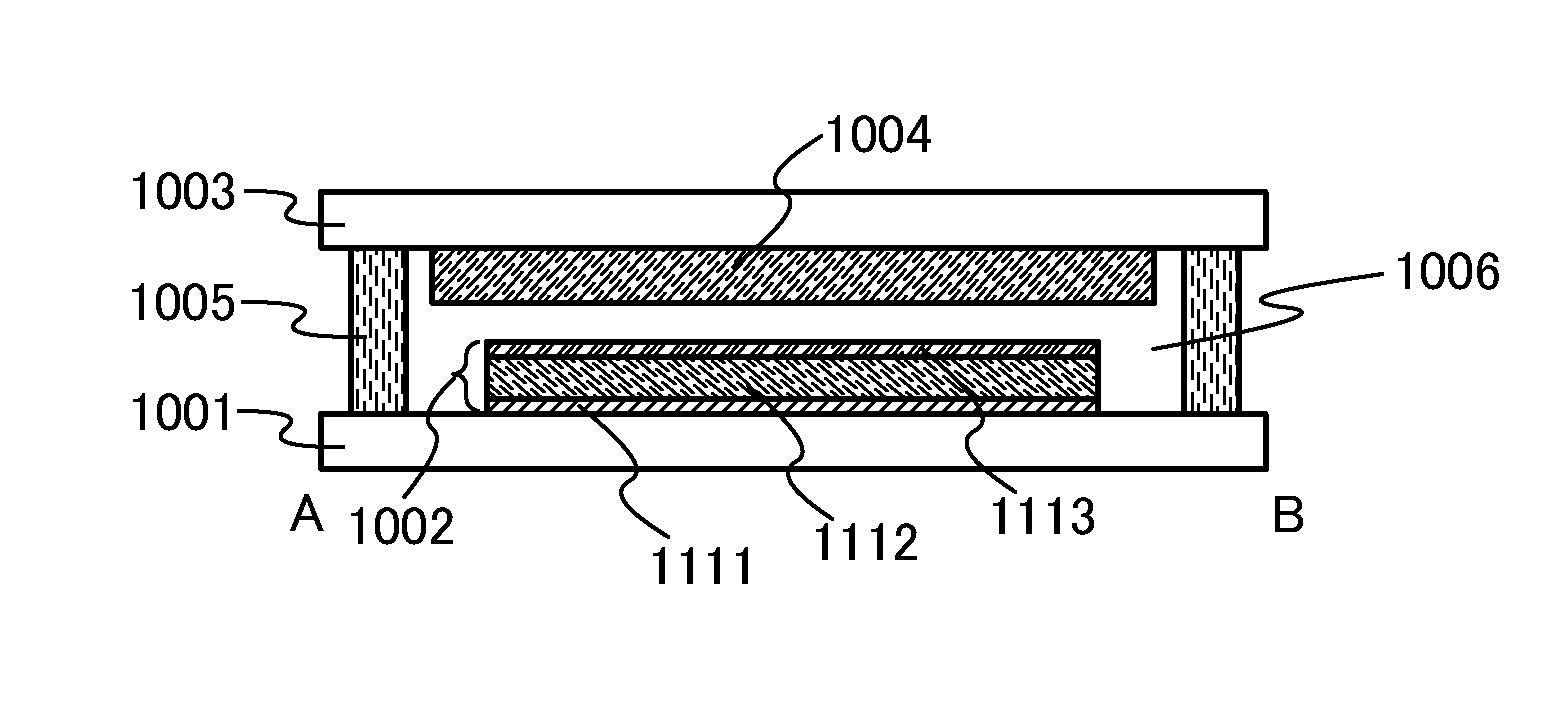
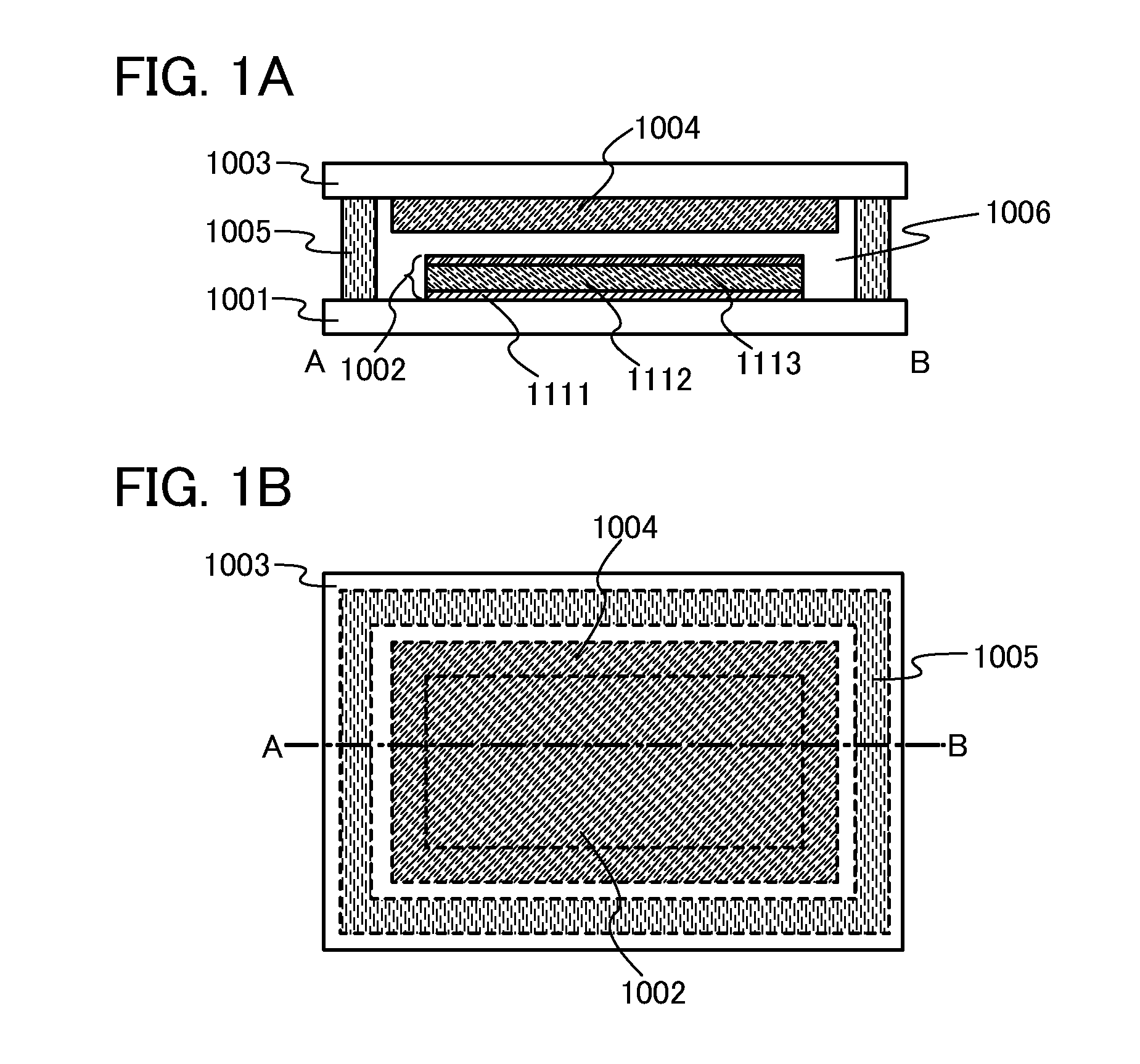
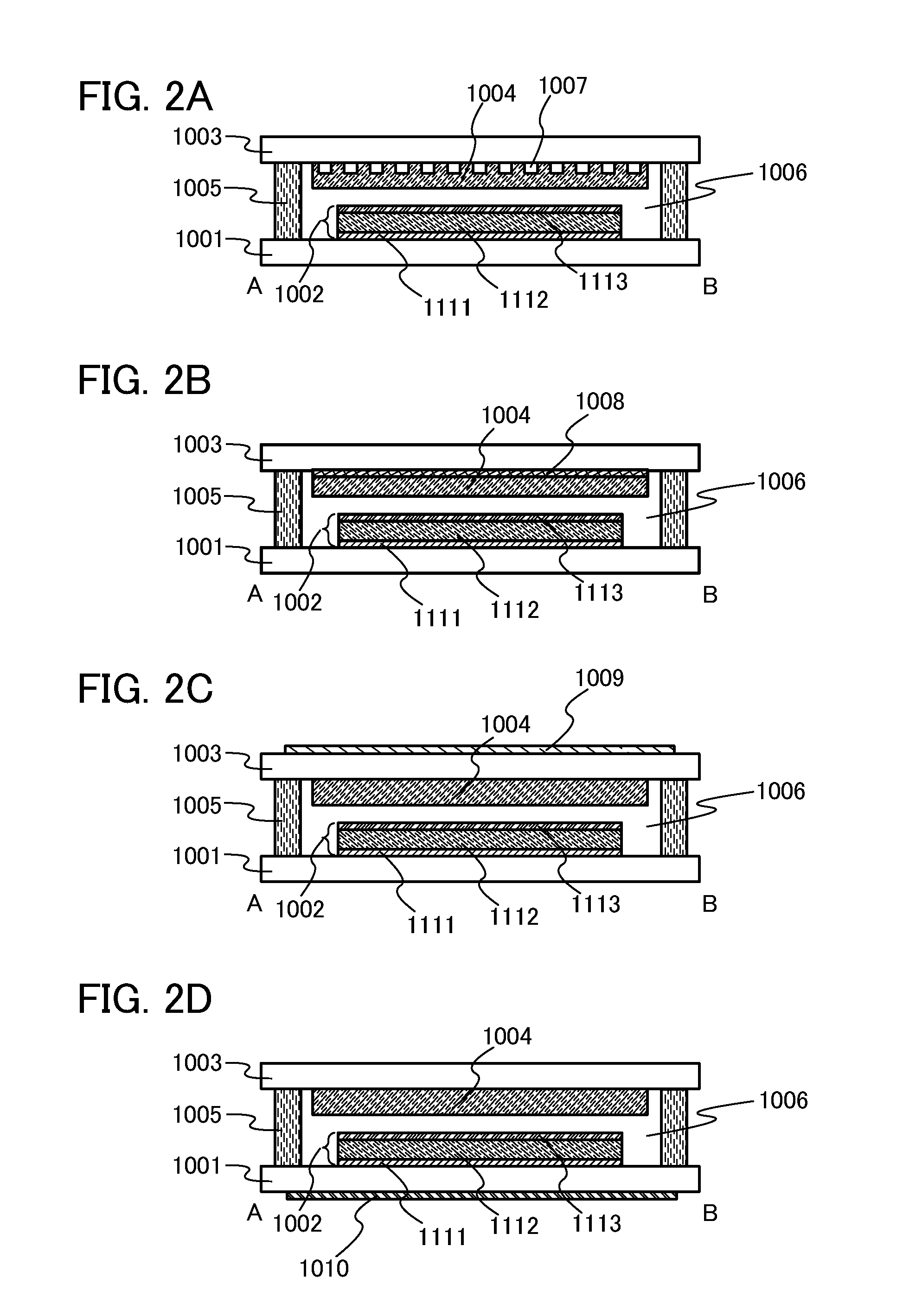
Organic laser device
ActiveUS8494021B2Quality improvementImprove featuresLaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusLaser dyeOrganic laser
To provide a small and lightweight organic laser device which can be manufactured in a reproductive manner and from which laser light with a desired wavelength can be obtained. A first substrate provided with a light-emitting element having a light-emitting layer between a pair of electrodes and a second substrate provided with a laser medium including a laser dye face each other and one of the pair of electrodes, which is placed between the light-emitting layer and the laser medium, has a light transmitting property. With such a structure, a laser device with which a laser medium and a light source are integrated can be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Sensing System Based on a Fluorophore Array
A sensing system for explosives is provided. The sensor is based on a layered structure of approximately a monolayer of a fluorophore deposited onto a few nm of a transparent polymer, supported by a substrate. The fluorophores can be xanthene laser dyes, which have high quantum yields, and the polymers can be commodity materials polymethylmethacrylate and polyvinylidene difluoride. The different fluorophore / polymer combinations give different emission responses to analytes, including both signal quenching and enhancement. The pattern of responses can be used to identify the analyte. The common explosives TNT, PETN, RDX, HMX, and TATP as gas phase species can all be uniquely identified at room temperature using only the natural vapor pressure of the explosive to deliver sample to the sensor.
Owner:BOARD OF GOVERNORS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION STATE OF RHODE ISLAND & PROVIDENCE PLANTATIONS
Method for reducing full light switch pump power, full light switch and its preparing method
InactiveCN101051166AReduce excitation powerReduced all-optical switchNon-linear opticsLaser dyeLength wave
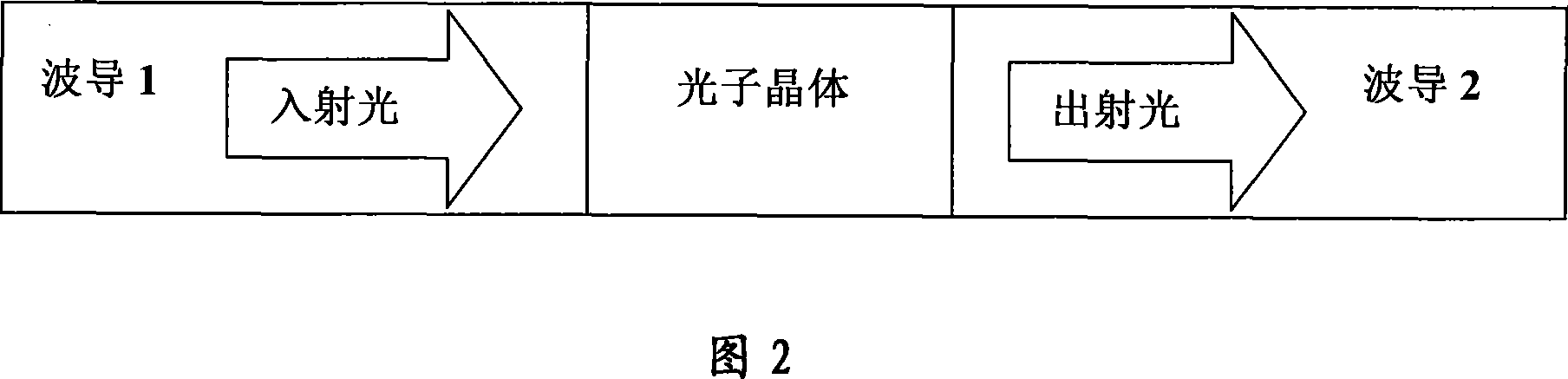
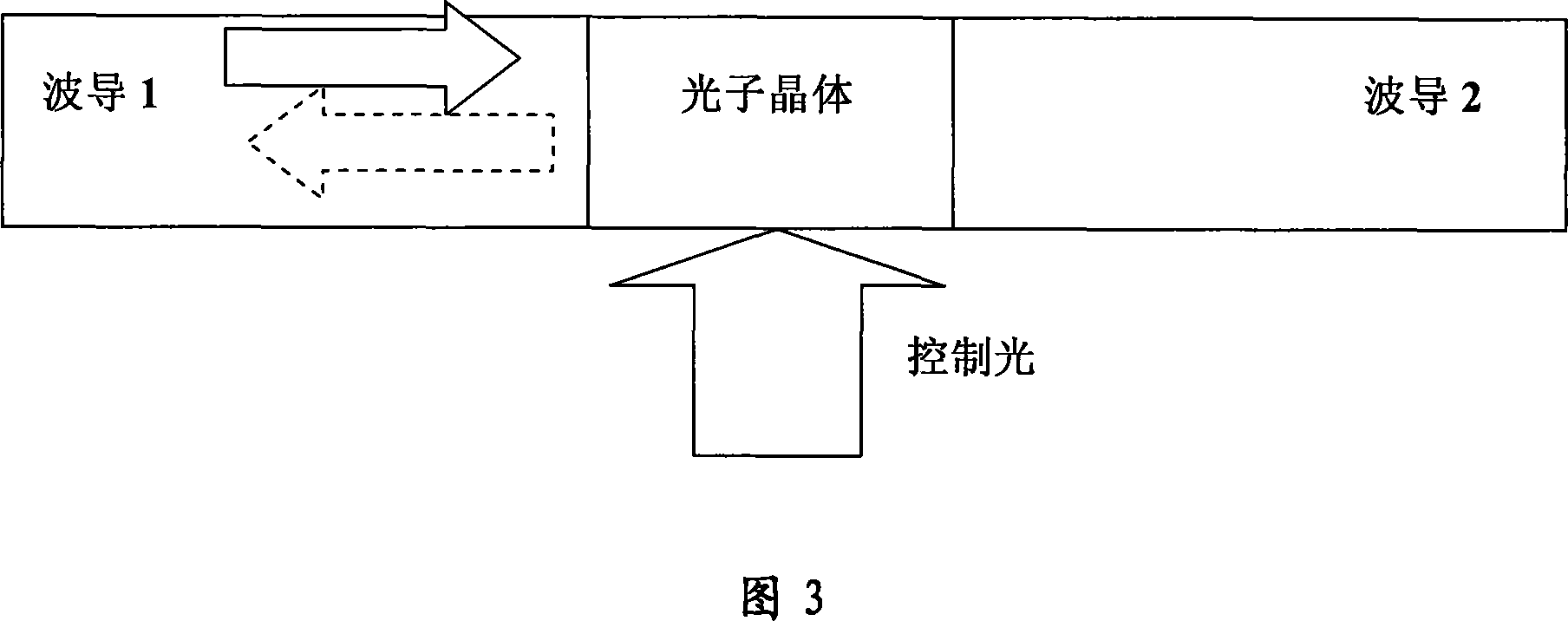
A method for decreasing the pumping power of all optical switch includes using composite material prepared by conjugated polymer and laser dyestuff to form 2-D photon crystal, coupling detection laser into 2-D photon crystal, locating wavelength of detection laser at edge of photon belt gap on 2-D photon crystal, using a pumping laser to excite said 2-D photon crystal for realizing all optical switch and making wavelength of pumping laser be at linear absorption belt of optical dyestuff on said 2-D photon crystal.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com