Wavelength tunable laser
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
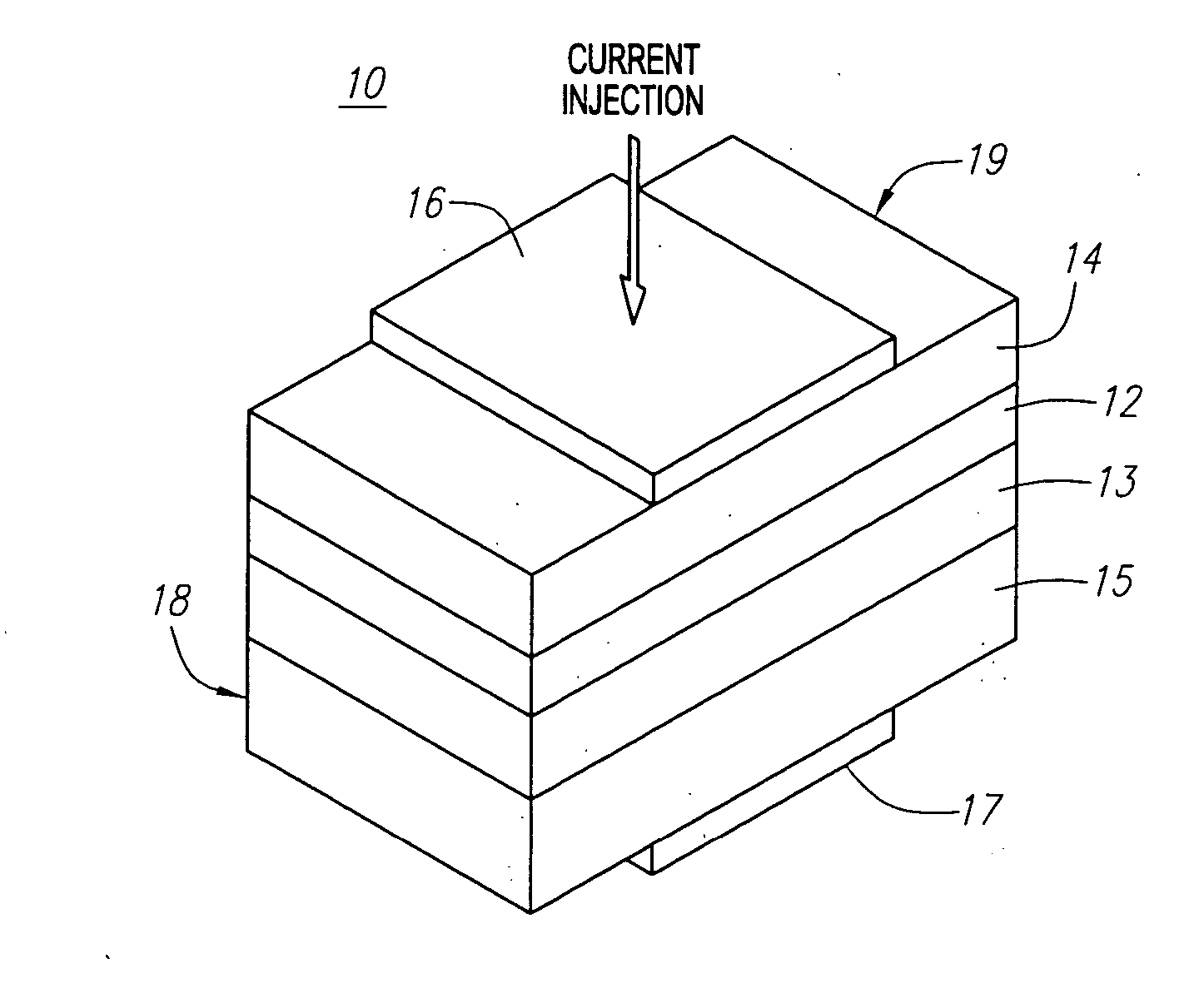
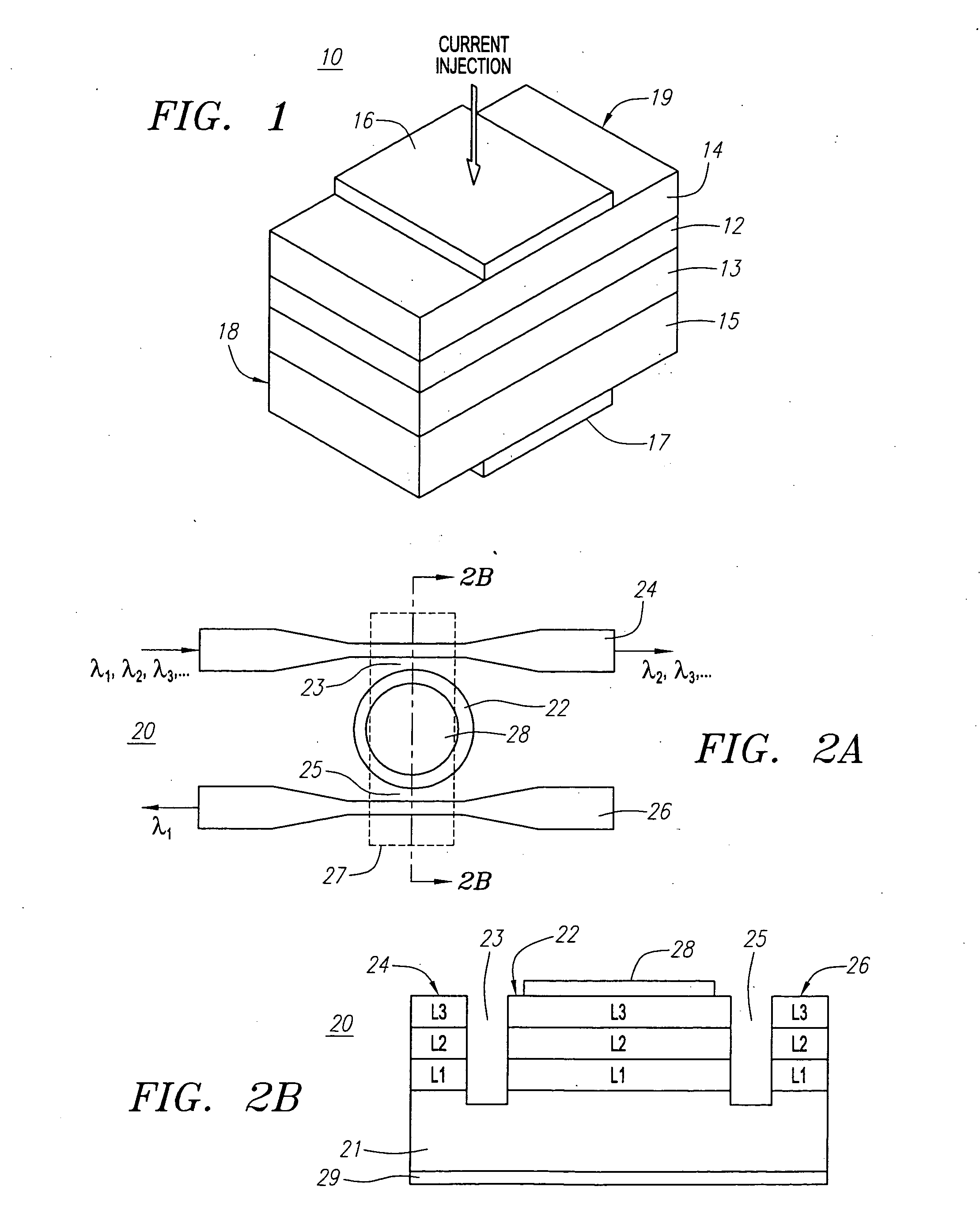
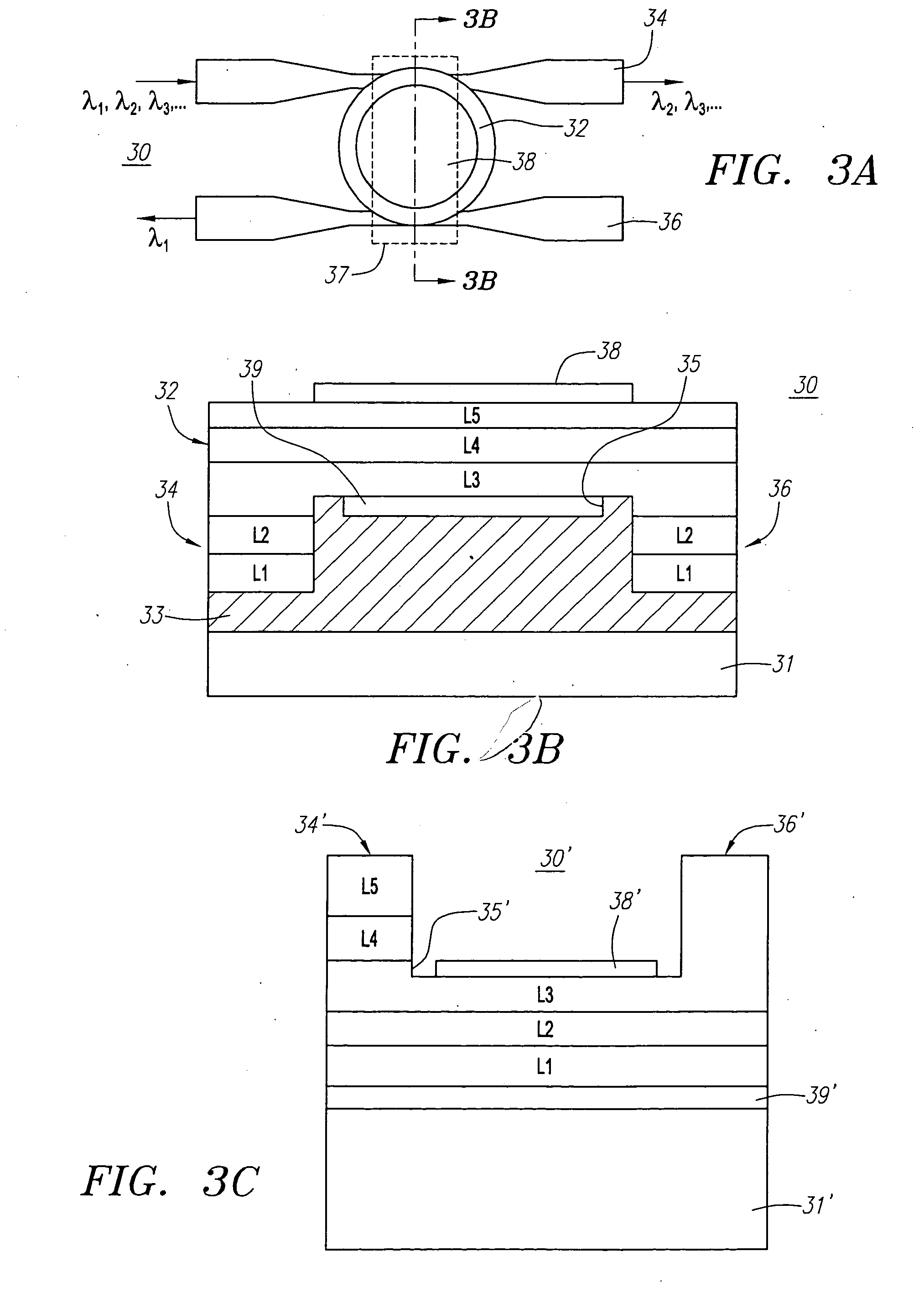
Referring in detail to the figures, a wavelength tunable laser of the present invention, as shown, combines a semiconductor laser diode with a waveguide-coupled optical resonator. The waveguide-coupled optical resonator serves as a wavelength selective, external cavity to realize a tunable laser by applying voltage or injecting current to change the resonance wavelength of the resonator(s).
Turning to FIG. 1, a multi-layer semiconductor wafer structure of a laser diode 10 of the present invention is shown. The laser diode 10 preferably comprises an active or guiding layer 12 sandwiched between two cladding layers 13 and 14 on a substrate 15. The active layer (guiding) 12 is preferably non-doped or insulated and has a higher refractive index (n) and a smaller bandgap than the two cladding layers 13 and 14. The two cladding layers 13 and 14 are preferably highly doped with either n-type or p-type doping in order to reduce contact resistance. The substrate 15 is preferably more highl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com