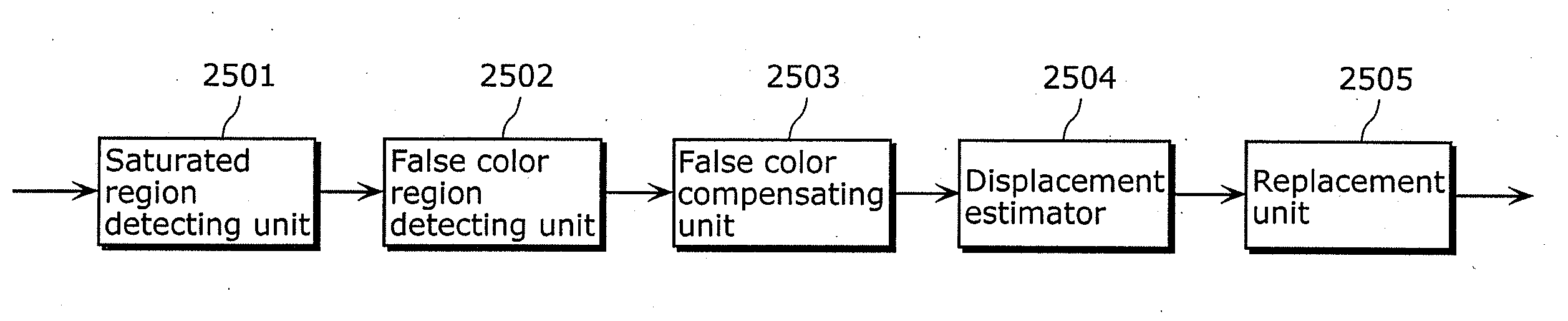
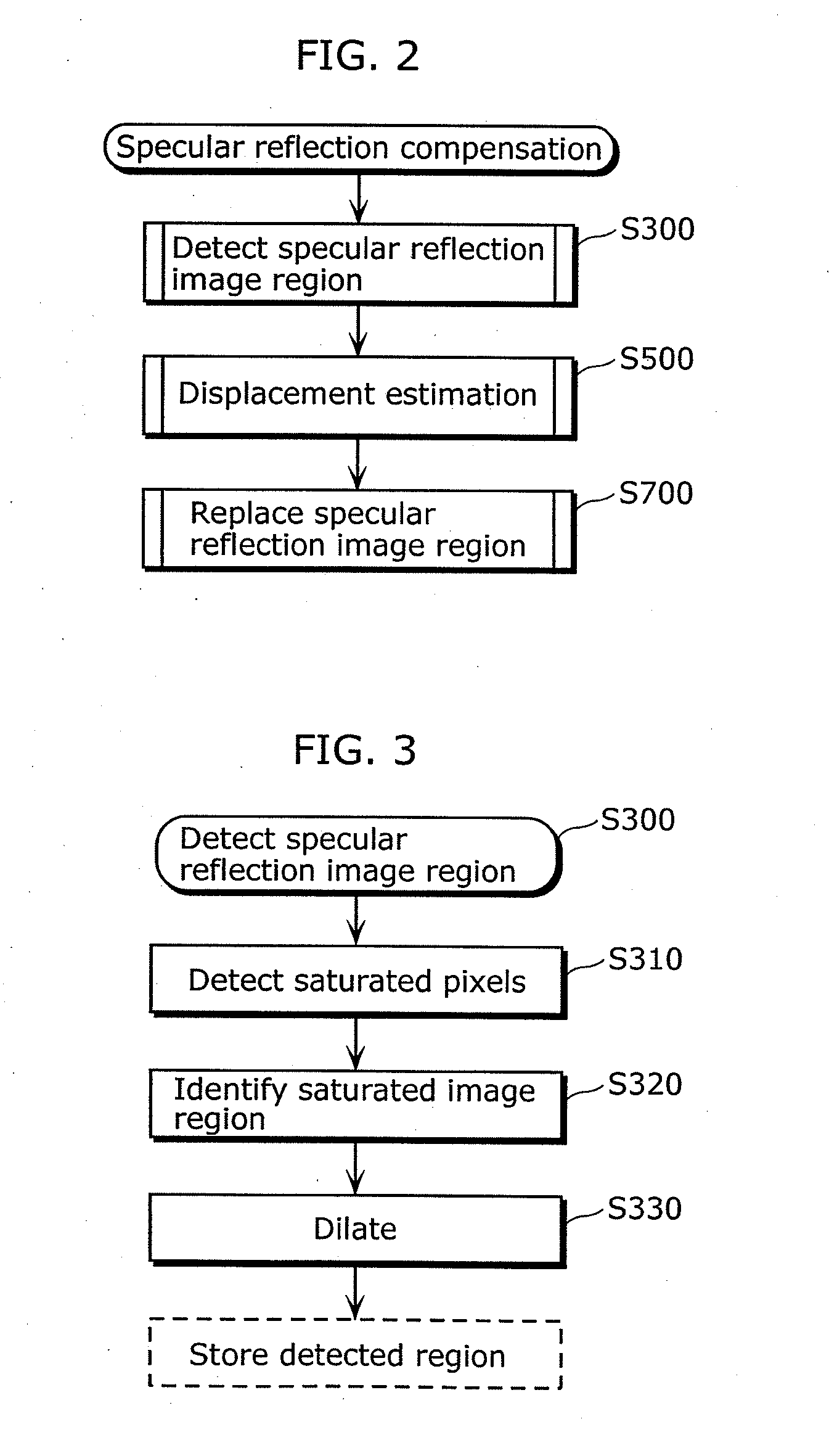
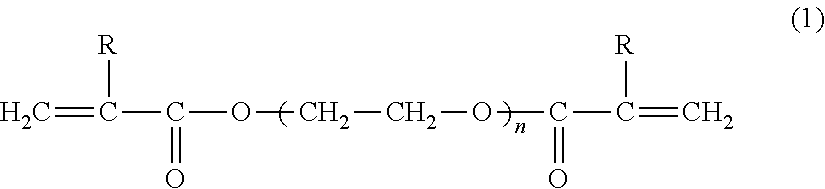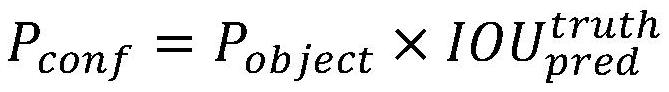Patents
Literature
338 results about "Specularity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
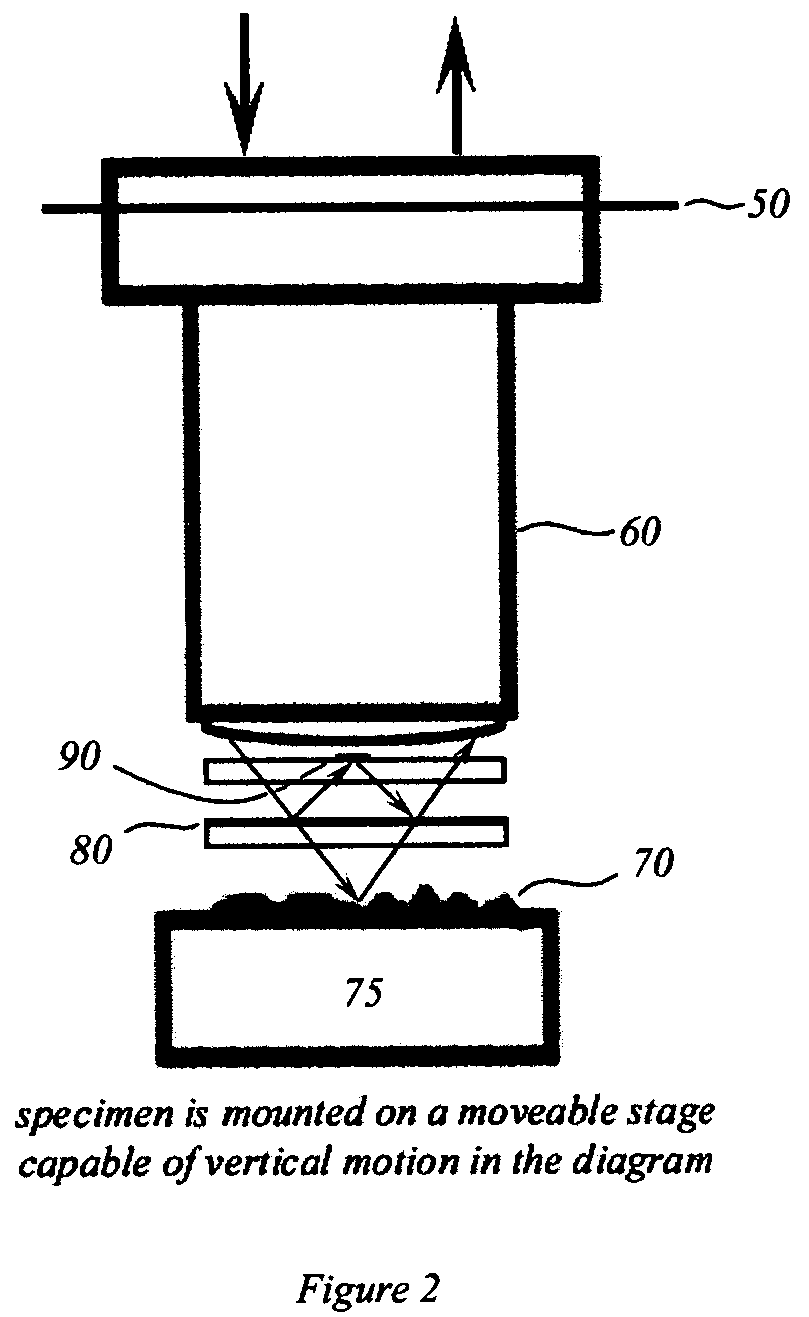
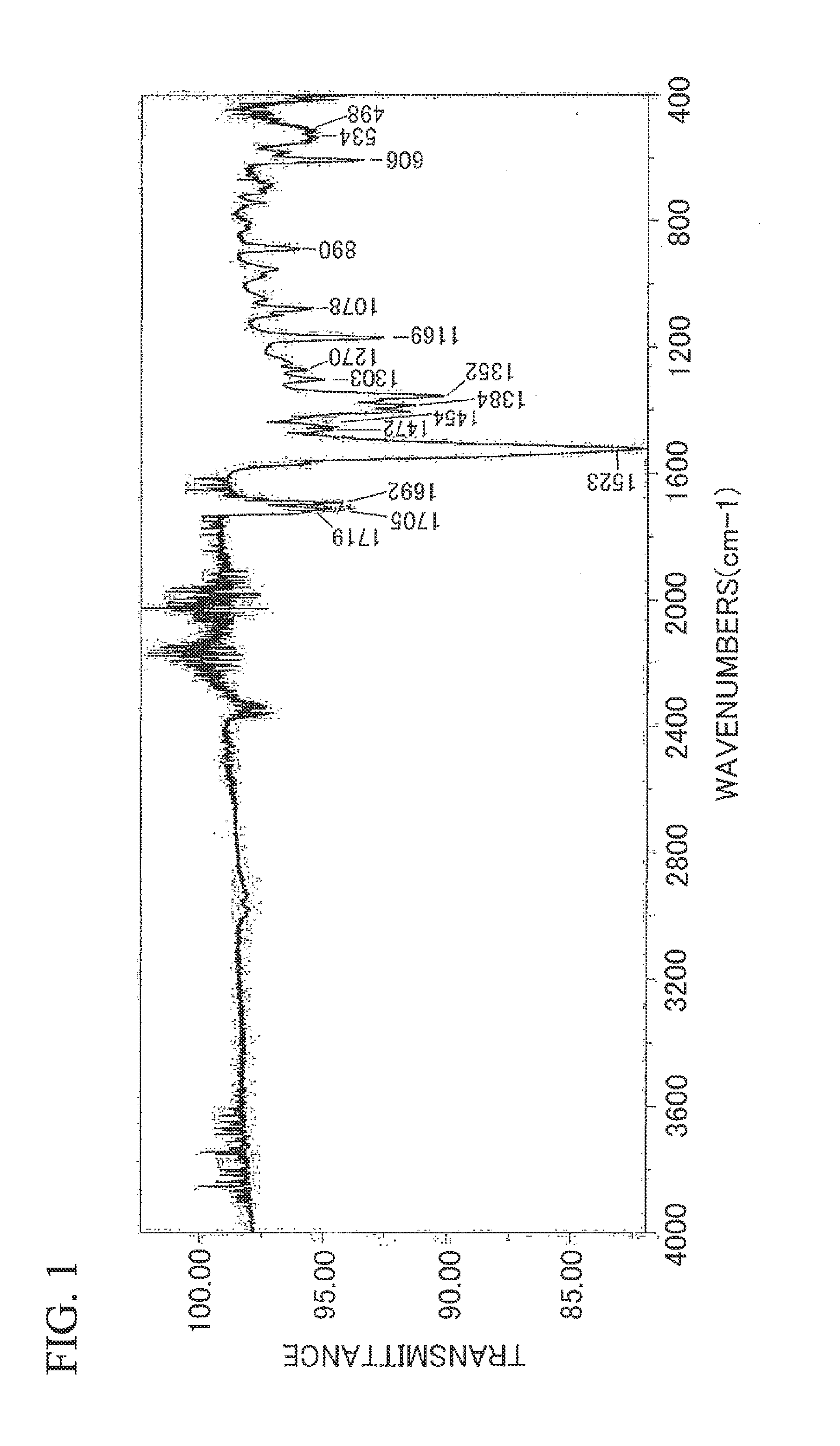
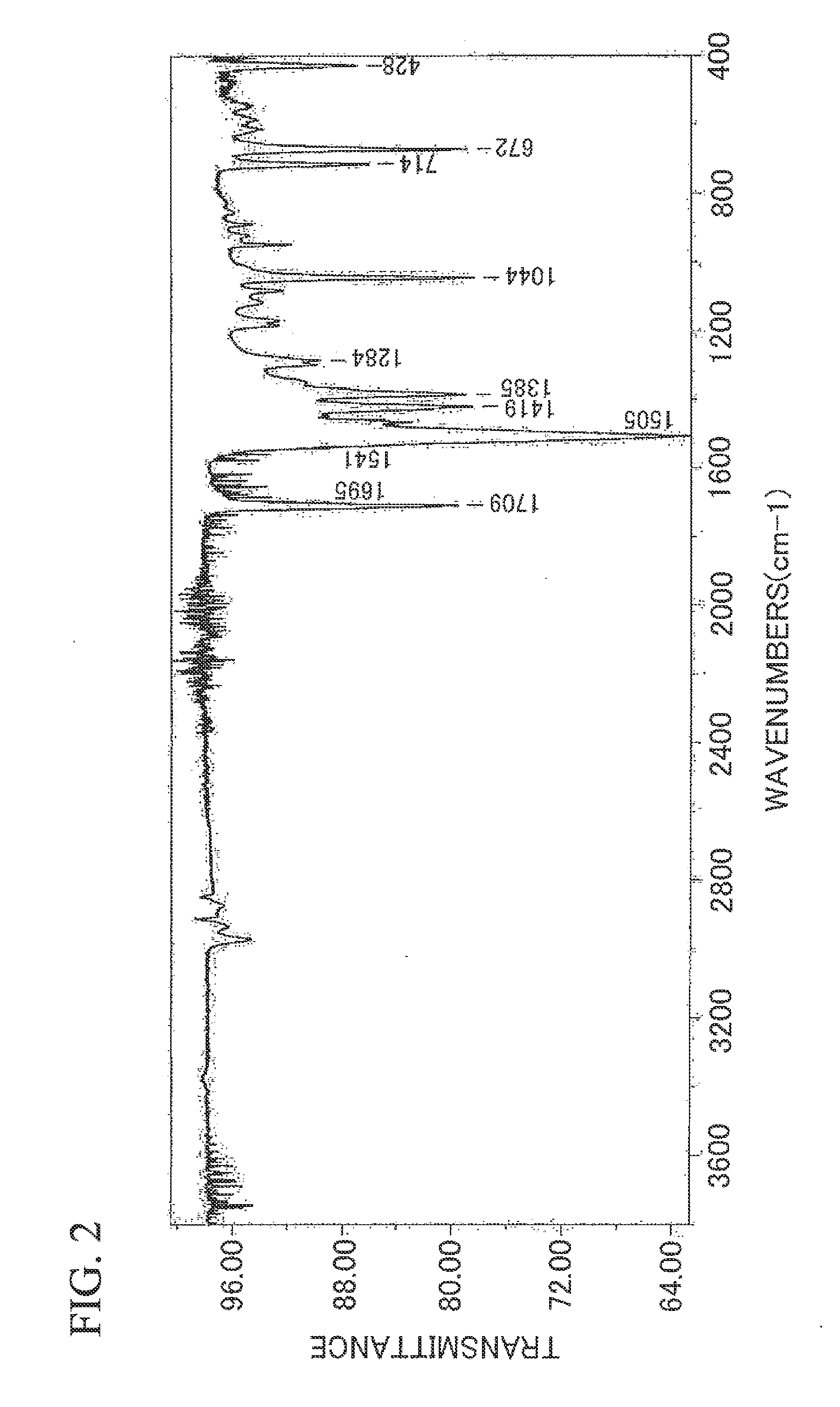
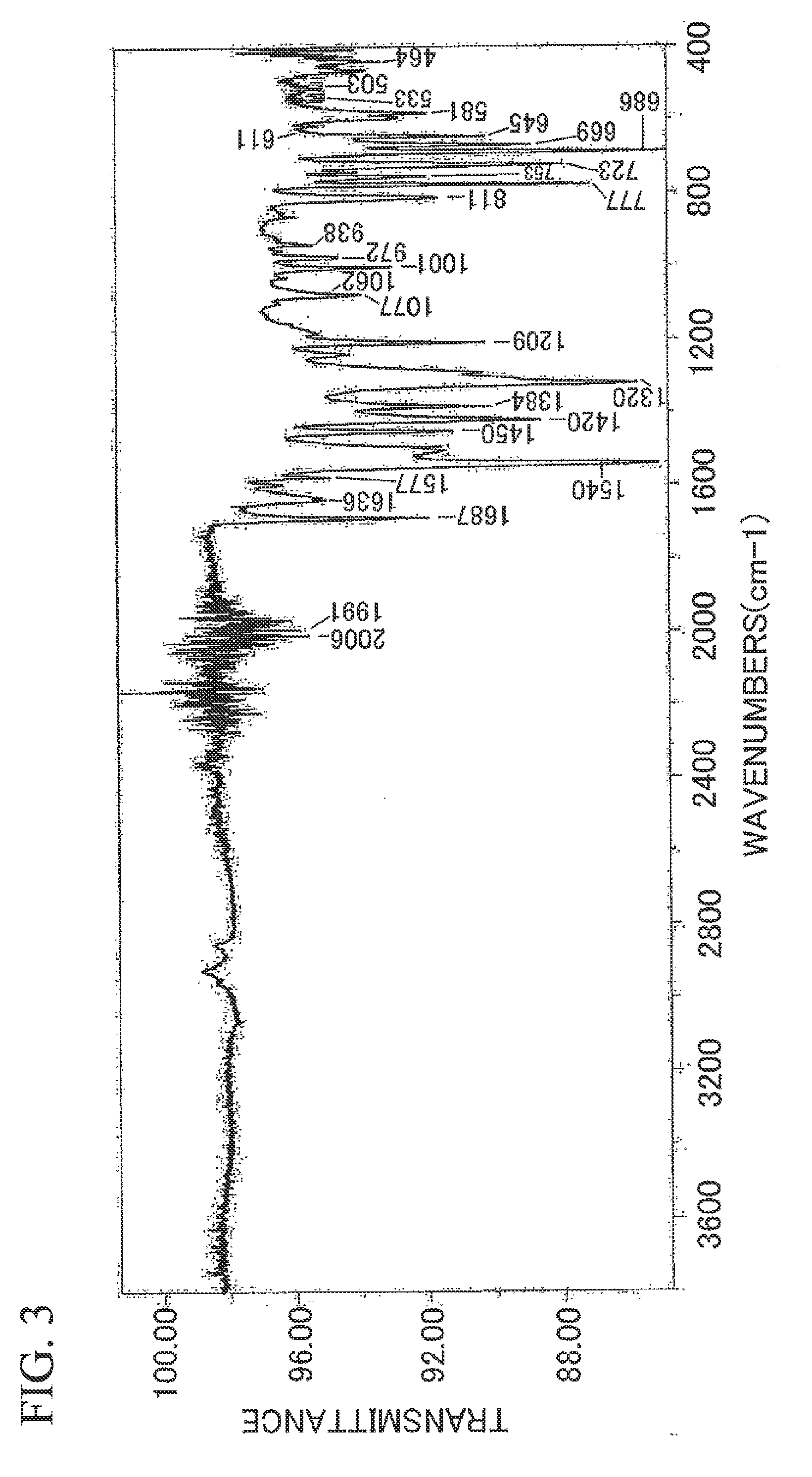
Specularity is the visual appearance of specular reflections.
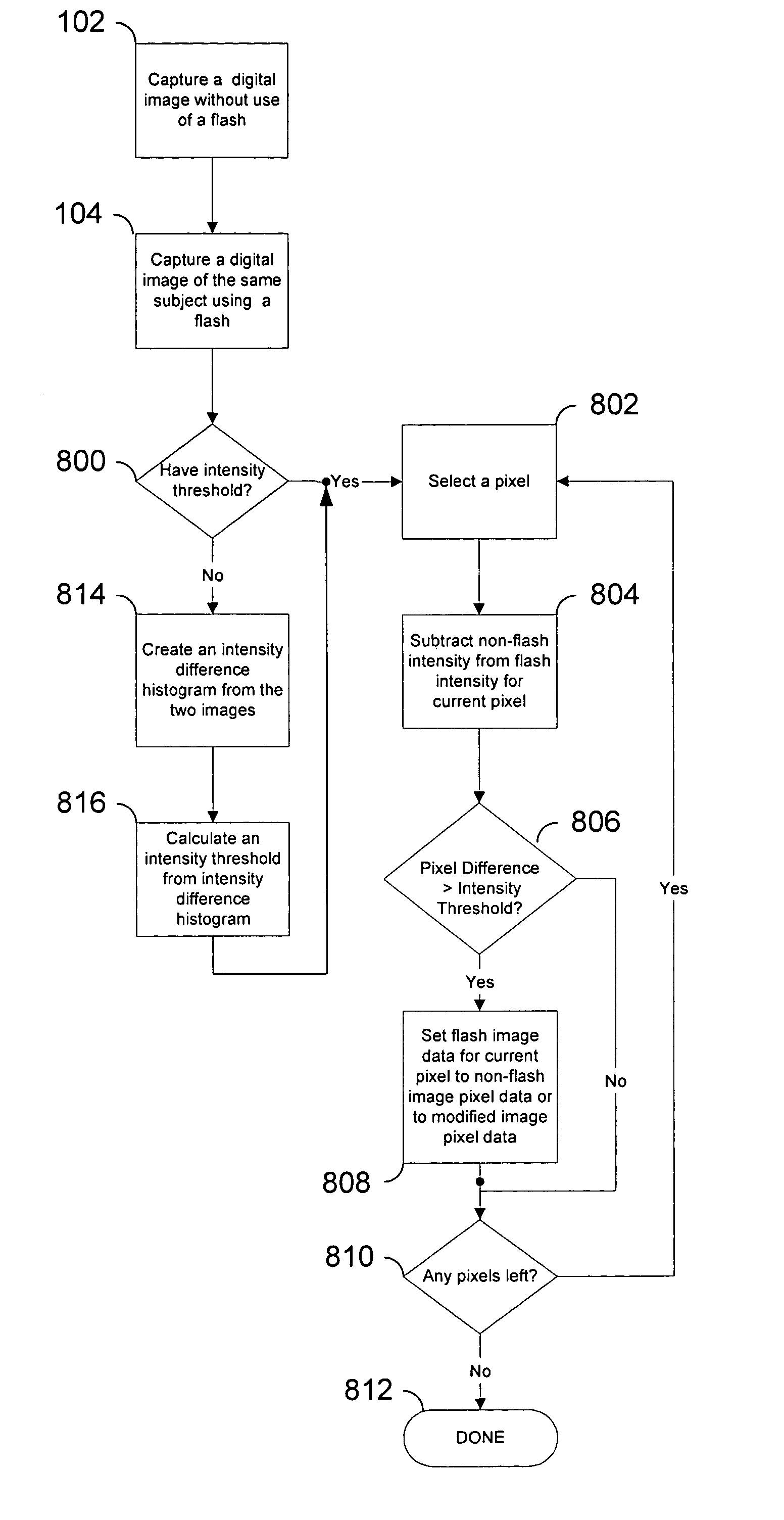
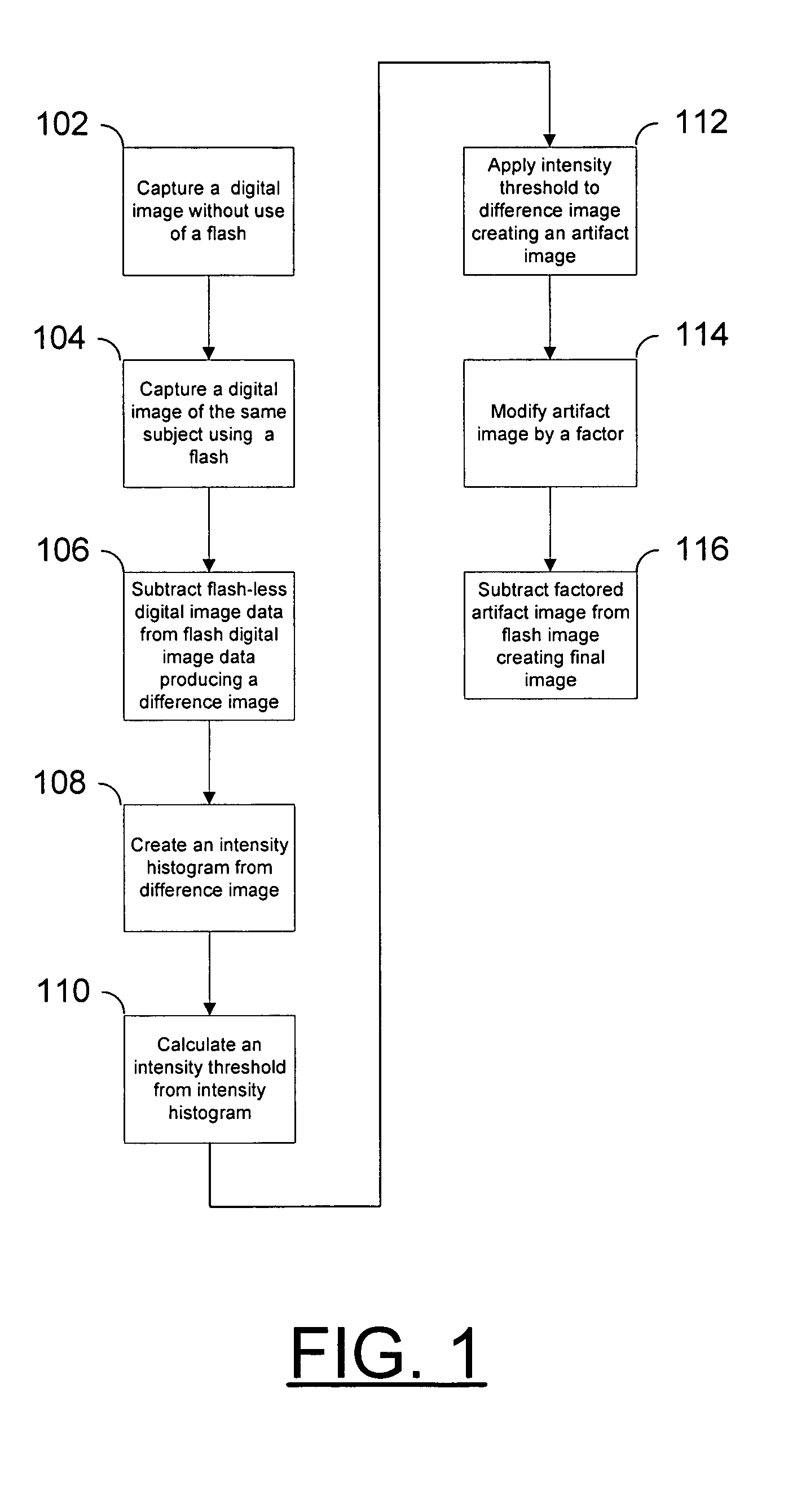
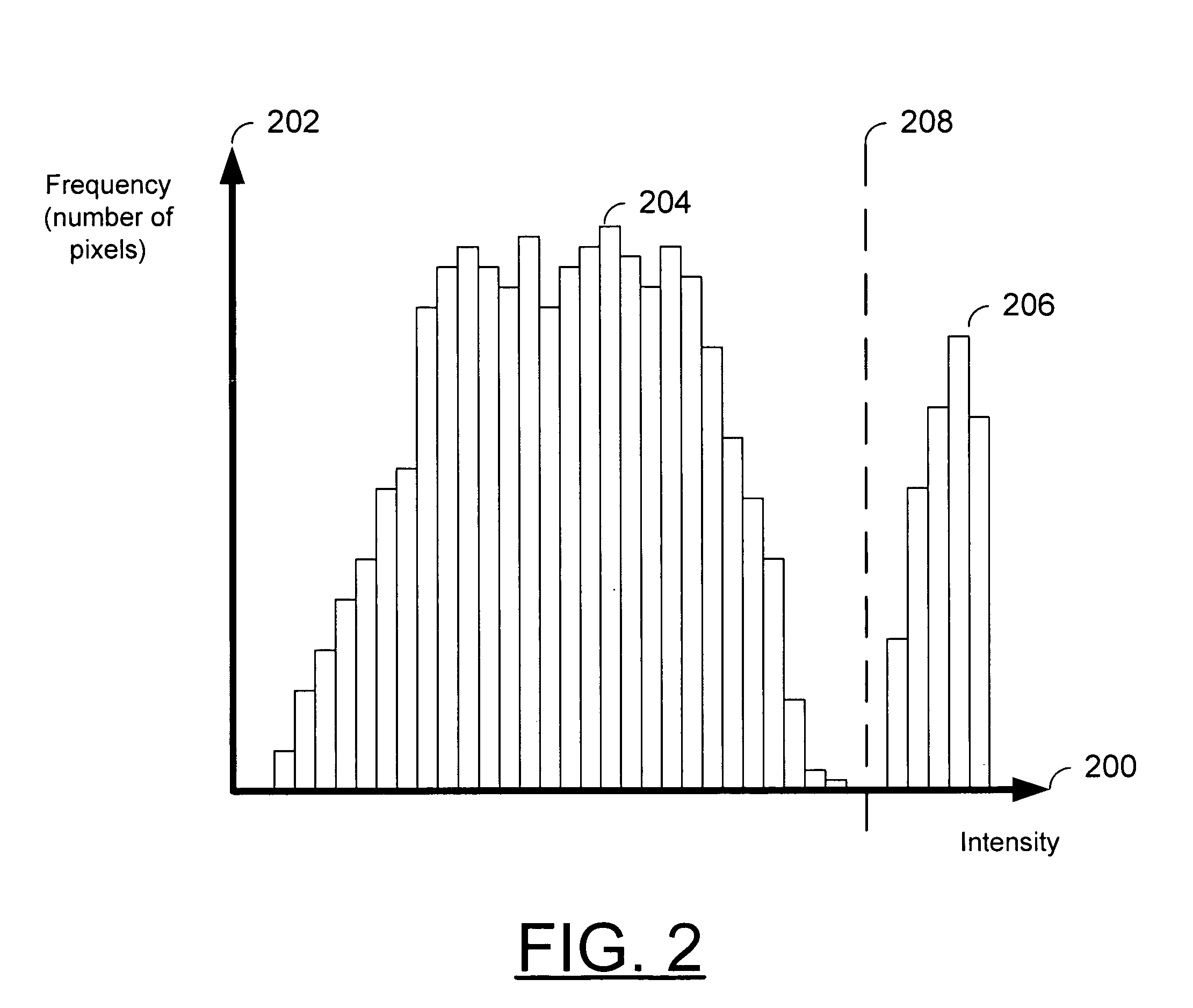
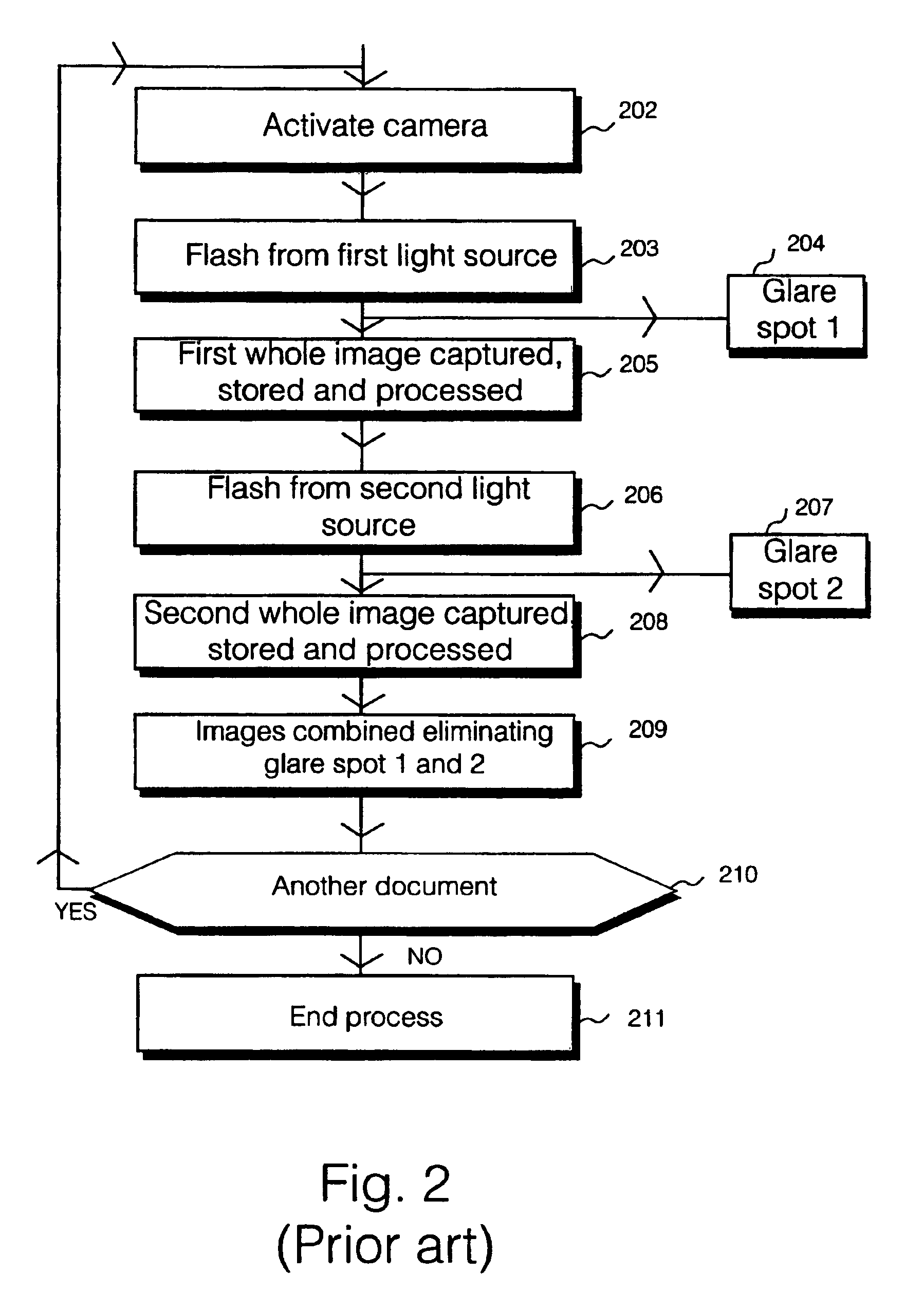
Method and apparatus for the removal of flash artifacts
An image without use of a flash is taken, along with an image using a flash. A difference image is generated by subtracting the flash-less image from the flash image. A threshold is applied to the difference image such that only large differences in intensity remain in the difference image. This artifact image is then subtracted from the flash image, thereby removing flash artifacts such as specular reflections and red-eye. The threshold used may be automatically calculated or may be set by the user. For some applications it may be desirable to set separate thresholds for each dimension of the color space (such as red, green, and blue) used. Once again these separate thresholds may be automatically calculated or may be set by the user.
Owner:APPLE INC
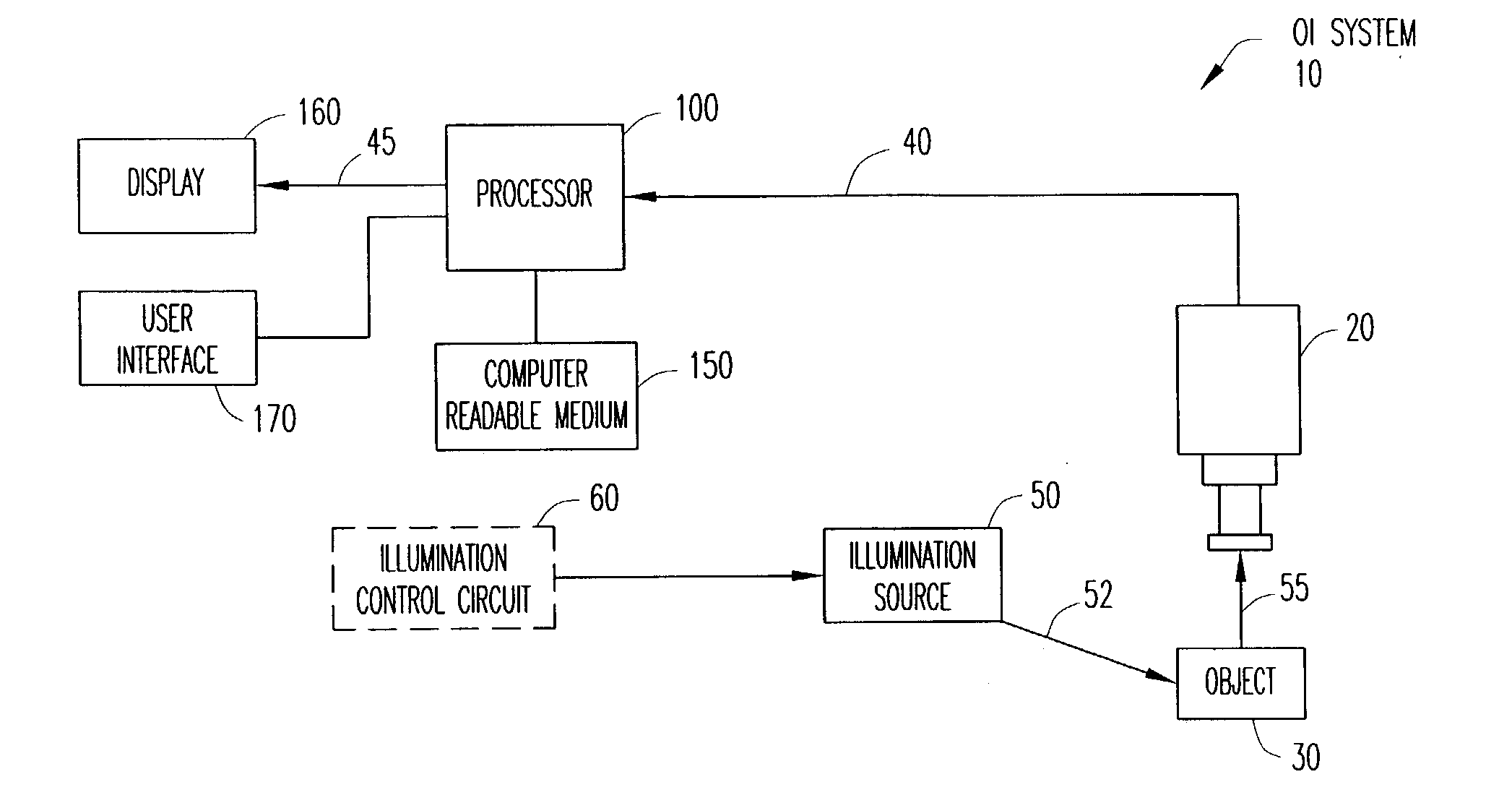
Optical inspection system, apparatus and method for reconstructing three-dimensional images for printed circuit board and electronics manufacturing inspection
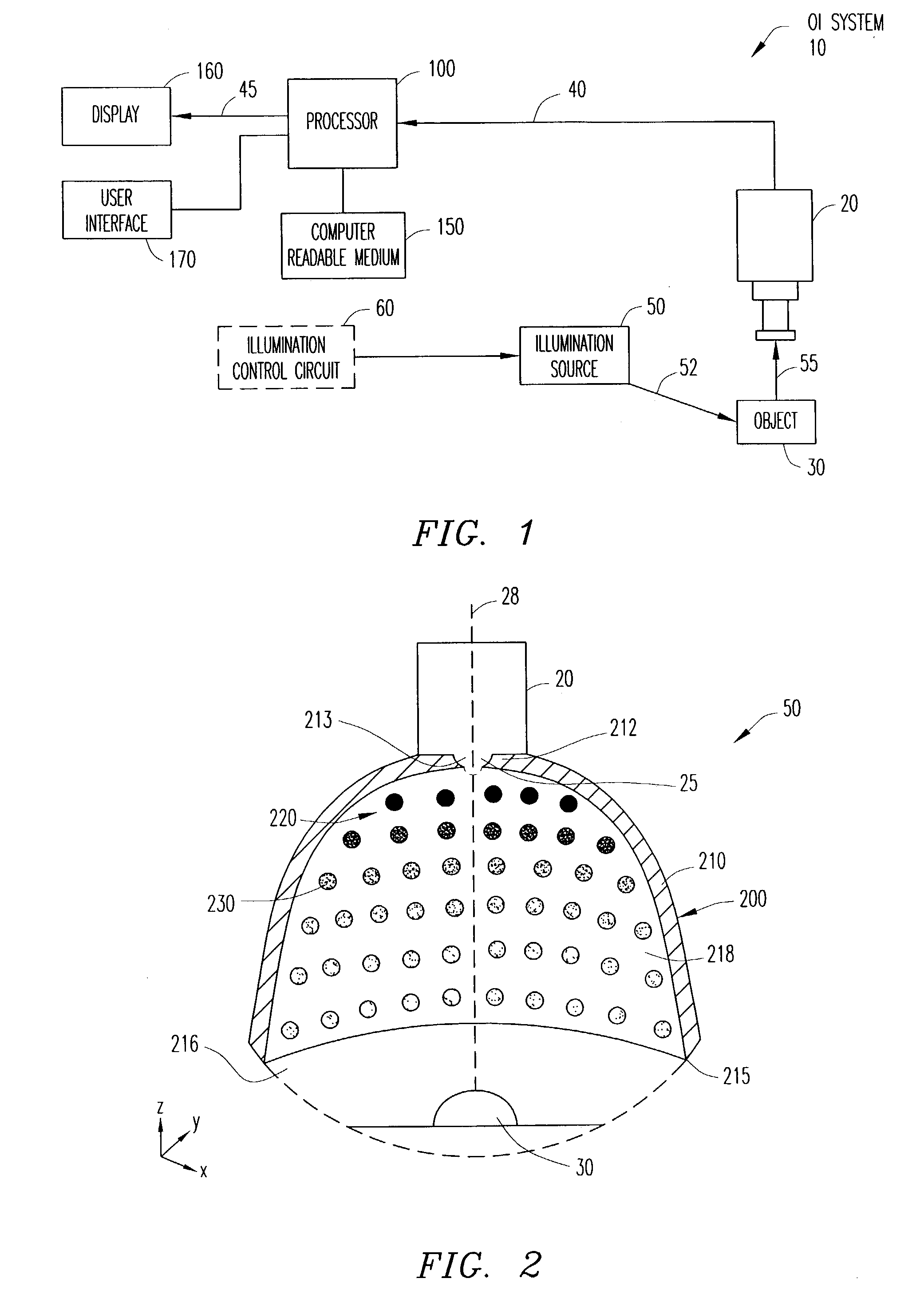
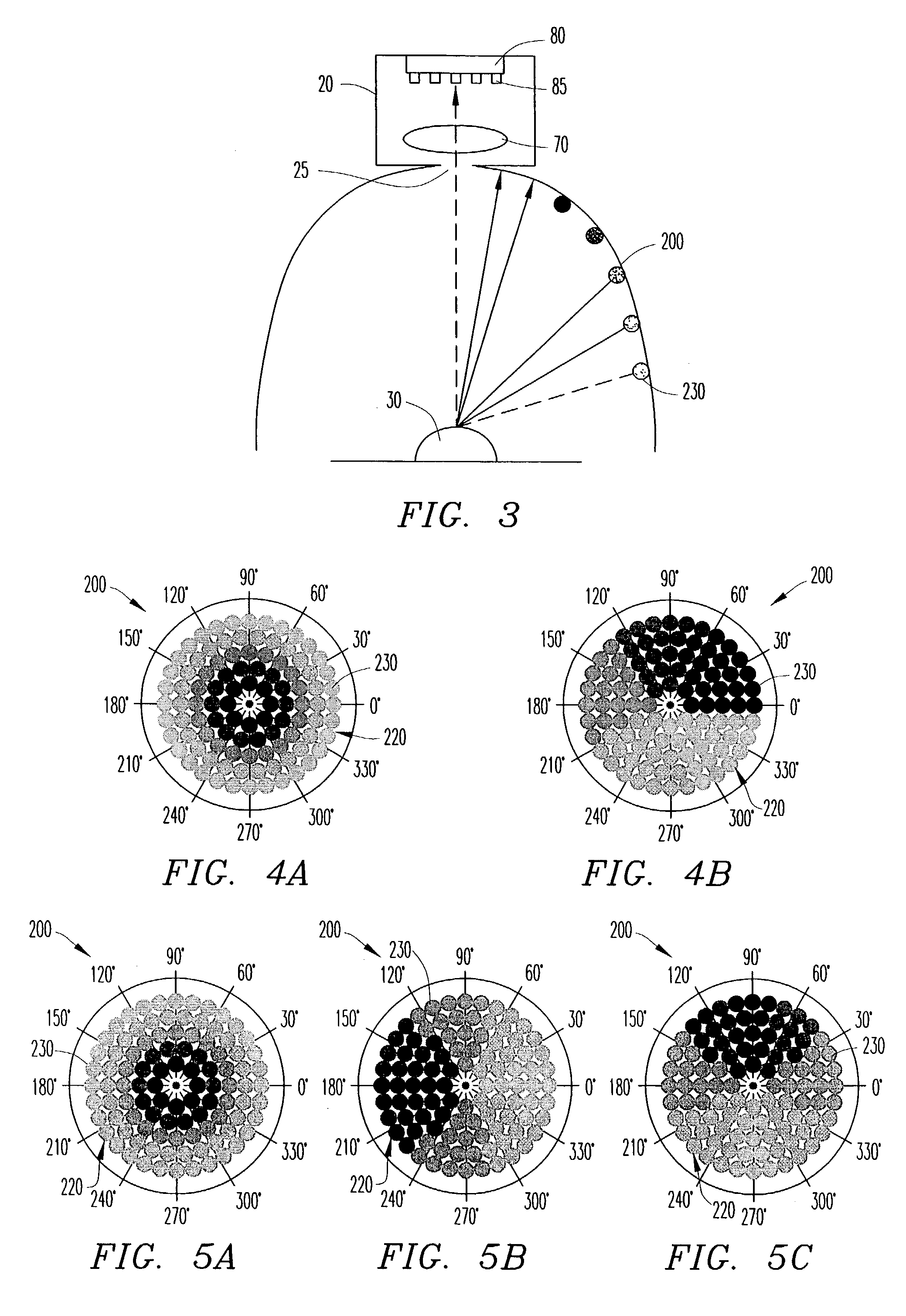
A three-dimensional optical inspection system reconstructs a three-dimensional image of the shape of the surface of an at least partially specular object resident on a printed circuit board by capturing two or more two-dimensional images of the object under different illumination configurations. The diffuse reflection, as well as the specular reflection can be used to reconstruct the three-dimensional image using any reconstruction method, such as photometric stereo. The different illumination configurations can be achieved using an illumination source including light-emitting elements arranged in concentric circular arrays, in which each of the circular arrays is divided into sections. Each section is independently controlled to selectively activate the sections to illuminate the object in a pre-established illumination pattern.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Practical Modeling and Acquisition of Layered Facial Reflectance
ActiveUS20090226049A1Easy to mergeConvenience to workCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsViewpointsDeep level
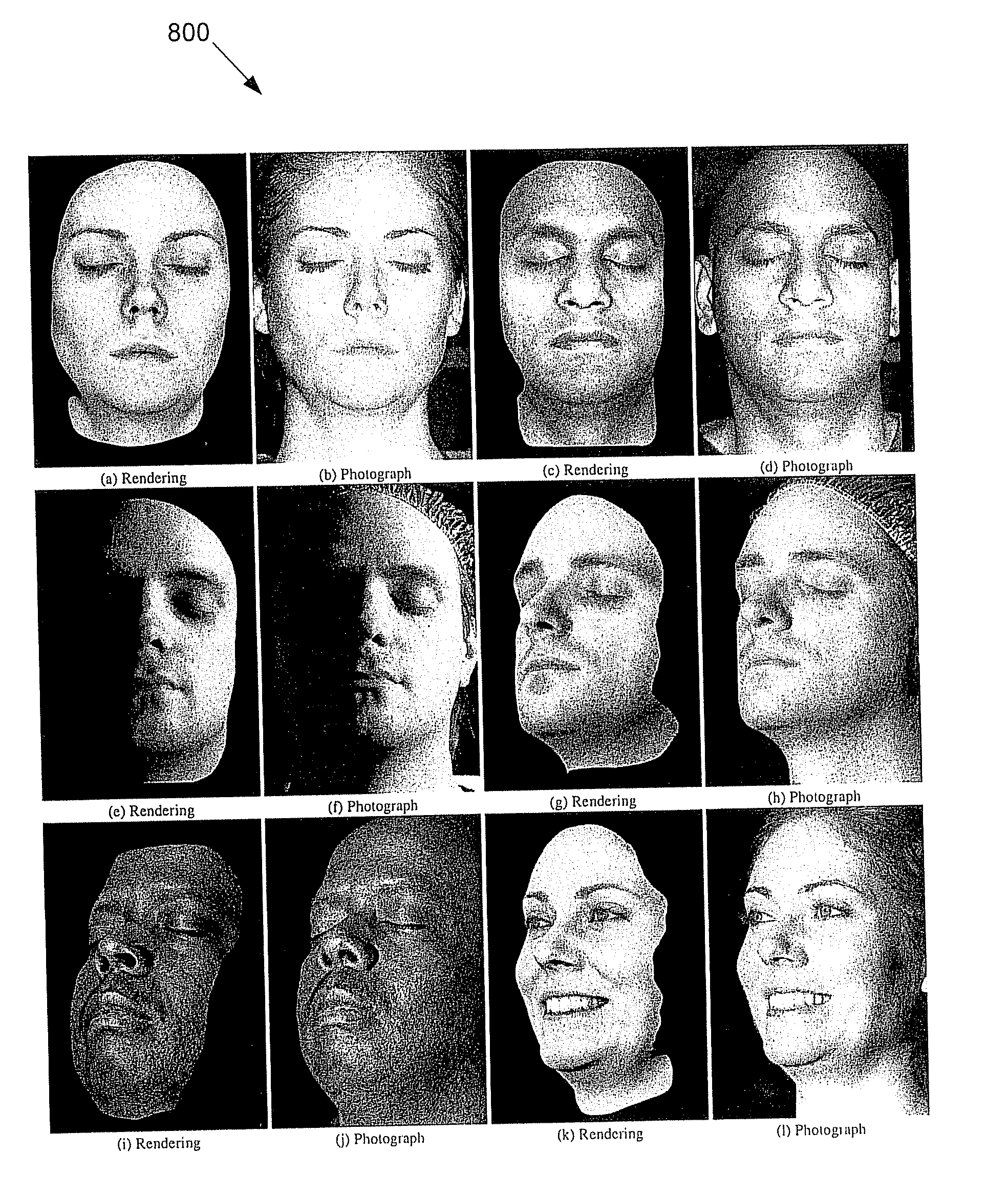
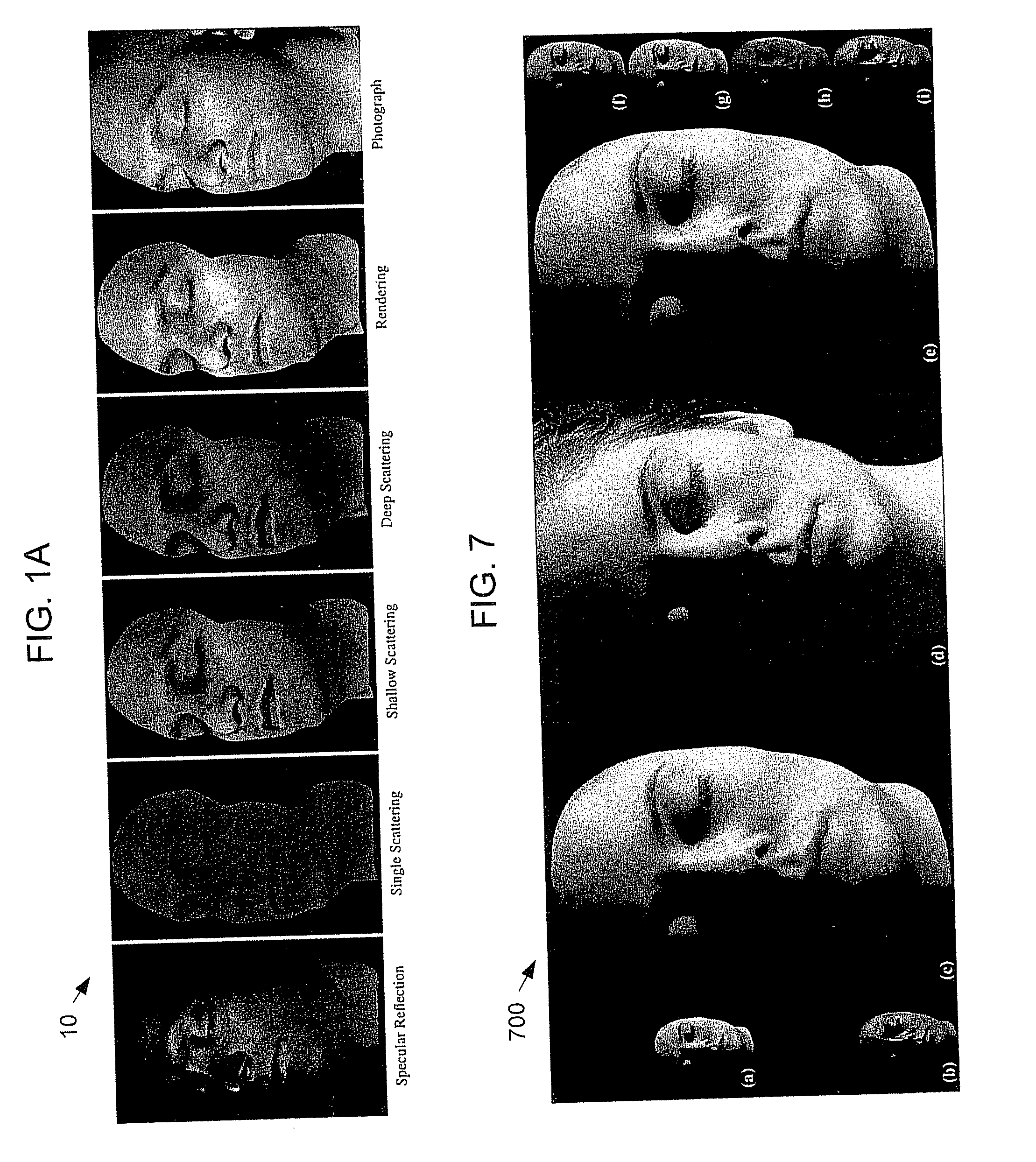
Techniques are described for modeling layered facial reflectance consisting of specular reflectance, single scattering, and shallow and deep subsurface scattering. Parameters of appropriate reflectance models can be estimated for each of these layers, e.g., from just 20 photographs recorded in a few seconds from a single view-point. Spatially-varying specular reflectance and single-scattering parameters can be extracted from polarization-difference images under spherical and point source illumination. Direct-indirect separation can be employed to decompose the remaining multiple scattering observed under cross-polarization into shallow and deep scattering components to model the light transport through multiple layers of skin. Appropriate diffusion models can be matched to the extracted shallow and deep scattering components for different regions on the face. The techniques were validated by comparing renderings of subjects to reference photographs recorded from novel viewpoints and under novel illumination conditions. Related geometry acquisition systems and software products are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Image processing method, and image processing device
InactiveUS20110305388A1Reduce the impactEliminate the effects ofImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingSpecular reflection
The image processing device includes: a specular reflection detector (1110) configured to detect, in a first image, an enlarged region including a saturated region and an adjacent region, the saturated region being a pixel region having a pixel value equal to or larger than a predetermined threshold, and the adjacent region at least partially surrounding the saturated region; and a replacement unit (1130) configured to replace a pixel value of a pixel included at least in the adjacent region, with one of (i) a pixel value of a pixel in a region of a second image that is located at a position corresponding to a position of the enlarged region in the first image and (ii) a pixel value of a pixel adjacent to the pixel in the second image, the adjacent region being included in the enlarged region detected by the specular reflection detector (1110).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Hand-supportable digital imaging-based bar code symbol reading system employing a method of intelligently illuminating an object so as to generate a digital image thereof which is substantially free of noise caused by specular-type reflection of illumination off said object during illumination and imaging operations
ActiveUS20050103864A1Reduce manufacturing costUseful applicationCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesIntelligent lightingDigital imaging
A hand-supportable digital imaging-based bar code symbol reader comprises: an automatic object presence detection subsystem; a multi-mode area-type image formation and detection subsystem having narrow-area and wide-area image-capture modes of operation; a multi-mode LED-based illumination subsystem having independently controllable LED illumination arrays; an automatic light exposure measurement and illumination control subsystem; an image capturing and buffering subsystem; an image-processing bar code symbol reading subsystem; an input / output subsystem; and a system control subsystem for controlling the subsystems. The hand-supportable imaging-based bar code reader employs a method of intelligently illuminating objects during image capture, wherein the LED illumination arrays are independently controlled during particular moments of object illumination to generate digital images of objects which, through digital image analysis, are determined to be substantially free of noise (i.e. intense spatial intensity variations) caused by specular-type reflection of illumination off objects during illumination and imaging operations.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Non-contact optical imaging system for biometric identification
InactiveUS20040041998A1Maximize contrastCharacter and pattern recognitionContrast levelOphthalmology
An optical system for imaging the features, ridges, and height variations of an object by exploiting the properties of specular reflection of light to maximize the contrast of the features, ridges, and height variations. The system provides a non-contact method of imaging objects suitable for biometric identification, such as the imaging of fingerprints. The system obtains the strong specular reflection using a properly shaped wave front. Optionally, the system can include a polarizer that filters and thereby enhances the specular reflection from the surface. Optionally, the system can also include pre-processing means for adjusting image brightness, contrast, and magnification.
Owner:HADDAD WALEED S
Method and device for optical navigation
InactiveUS7161682B2Good signalHigh contrast imageInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsRelative motionSpecular reflection
An method and device suitable for navigation on a wide variety of surfaces is introduced. Specular reflection is used to determine relative motion over typical surfaces. A specific application is a computer mouse.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Method and apparatus to produce ultrasonic images using multiple apertures
ActiveUS20080103393A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioNarrow thicknessDiagnostic probe attachmentOrgan movement/changes detectionImaging ProceduresIntercostal space
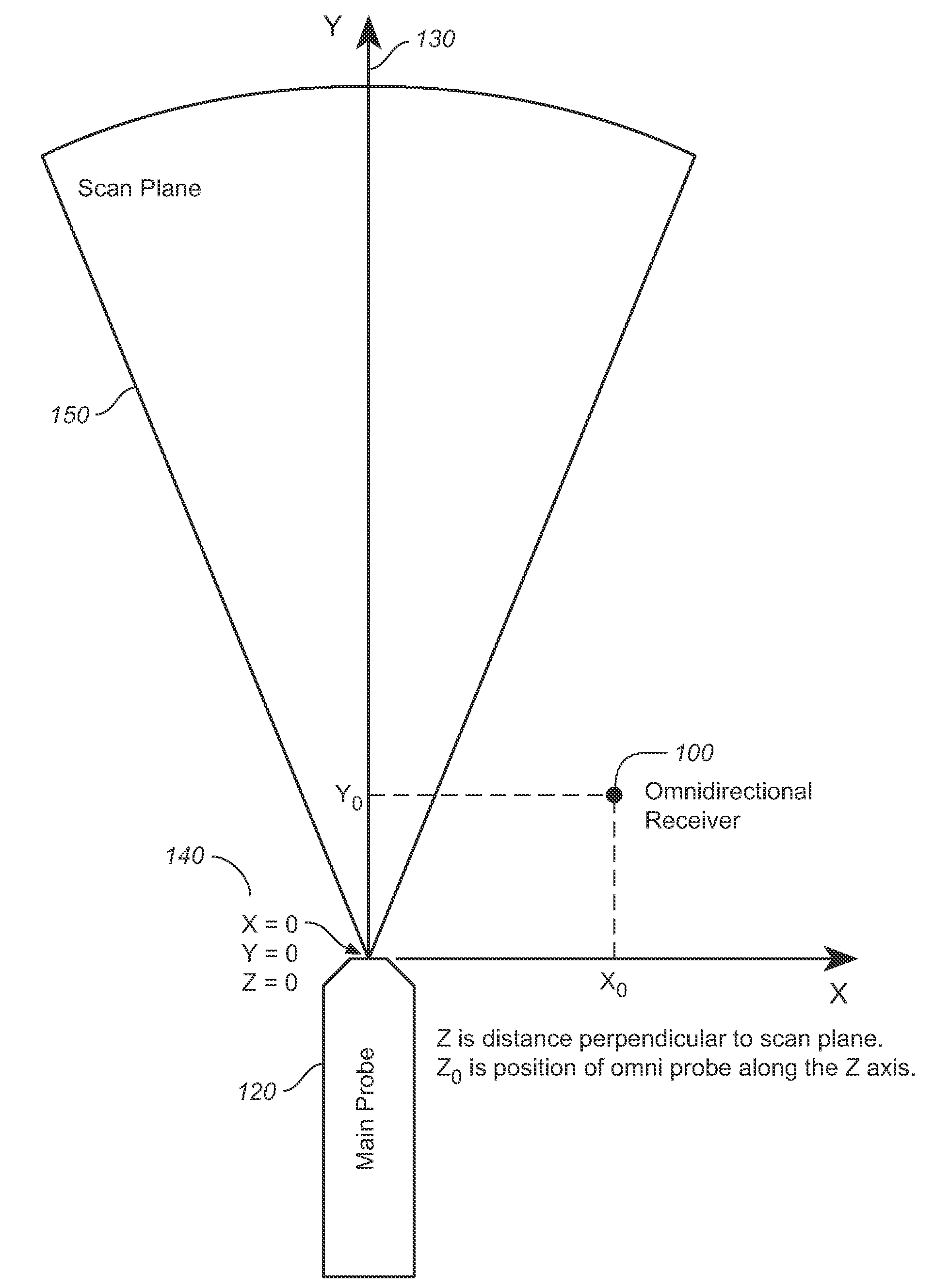
A combination of an ultrasonic scanner and an omnidirectional receive transducer for producing a two-dimensional image from the echoes received by the single omnidirectional transducer is described. Two-dimensional images with different noise components can be constructed from the echoes received by additional transducers. These can be combined to produce images with better signal to noise ratios and lateral resolution. Also disclosed is a method based on information content to compensate for the different delays for different paths through intervening tissue is described. Specular reflections are attenuated by using even a single omnidirectional receiver displaced from the insonifying probe. The disclosed techniques have broad application in medical imaging but are ideally suited to multi-aperture cardiac imaging using two or more intercostal spaces. Since lateral resolution is determined primarily by the aperture defined by the end elements, it is not necessary to fill the entire aperture with equally spaced elements. In fact, gaps can be left to accommodate spanning a patient's ribs, or simply to reduce the cost of the large aperture array. Multiple slices using these methods can be combined to form three-dimensional images.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
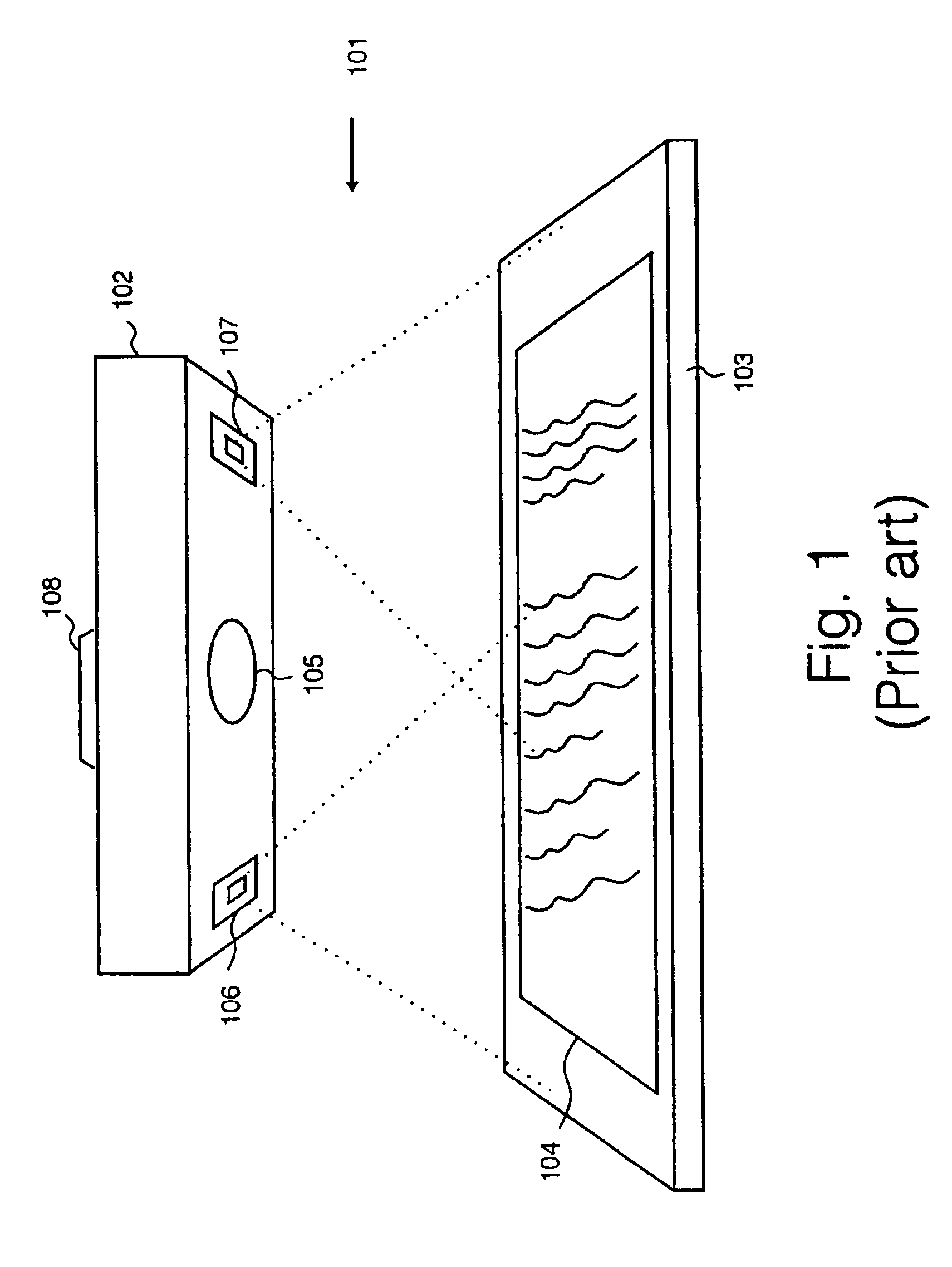
Image detector method and apparatus including plural detector regions and image illuminators
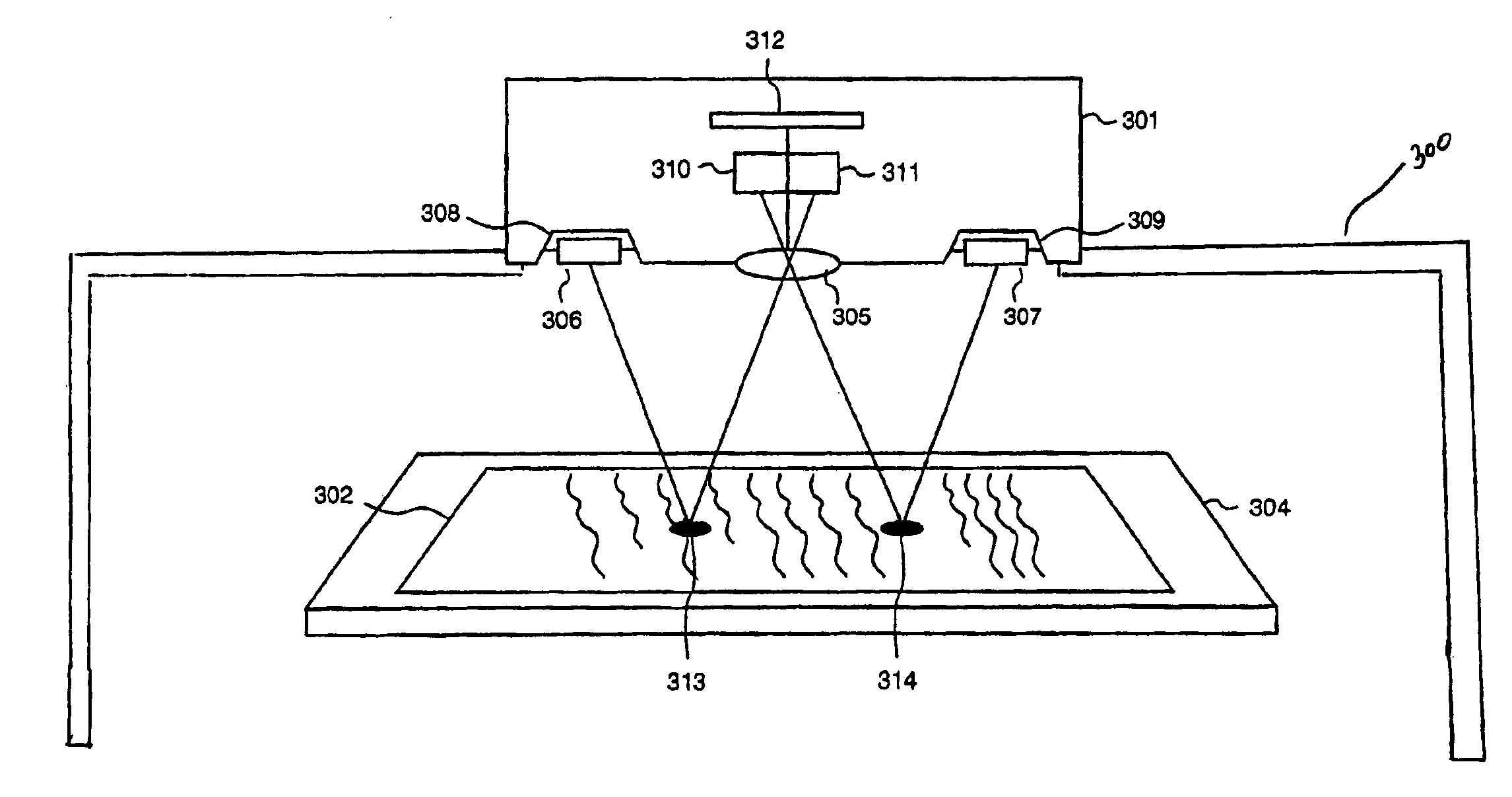
A digital camera has first and second light sources for sequentially illuminating a document from two different directions in response to the camera being activated. The camera has first and second sensor portions. Only the first and second sensor portions respectively respond to images reflected from the document in response to the first and second sources illuminating the document. Images detected by the first and second sensor portions are combined to remove specular reflection from the document image. In a second embodiment, the camera has three sensor portions.
Owner:LIBRE HLDG
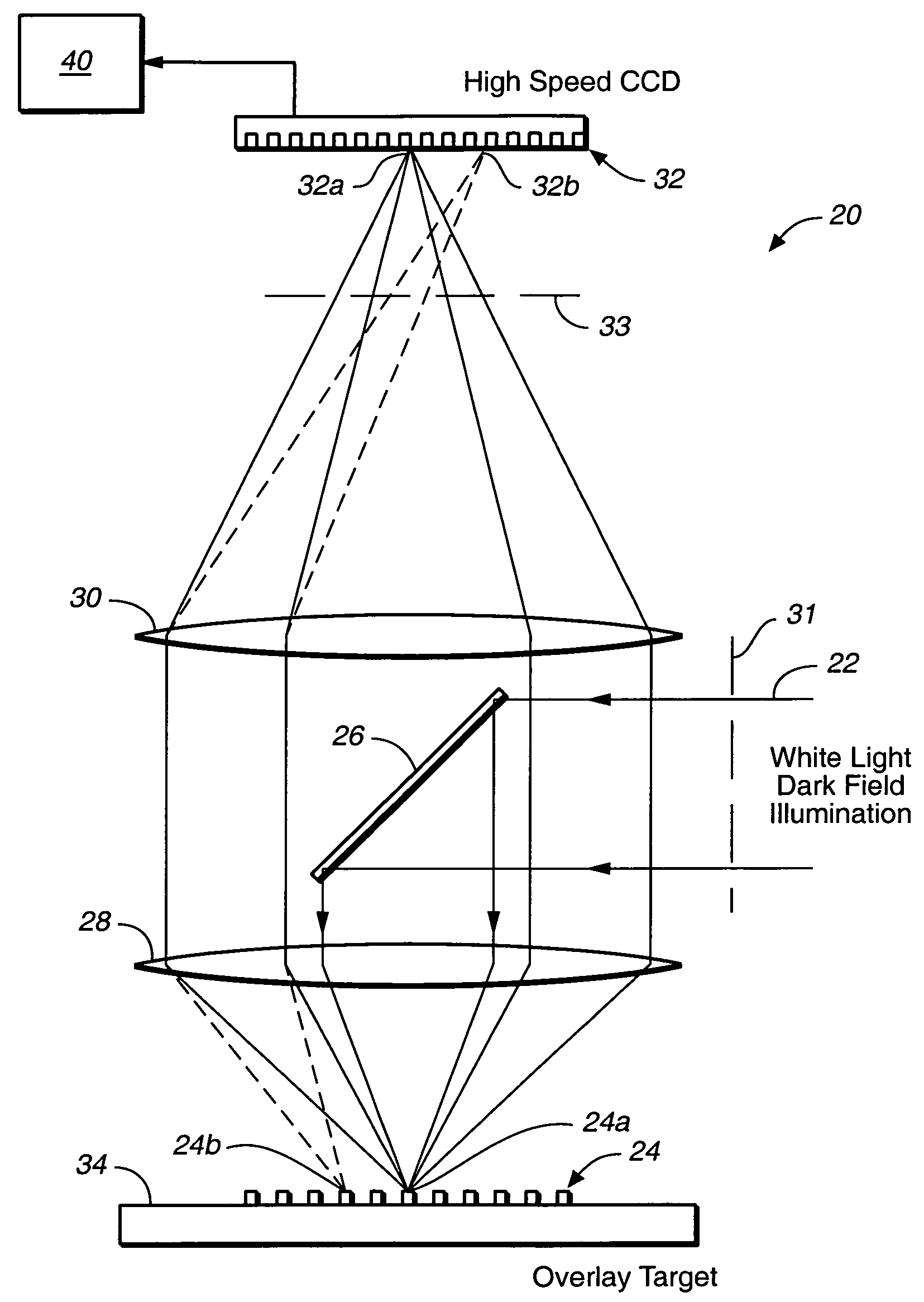
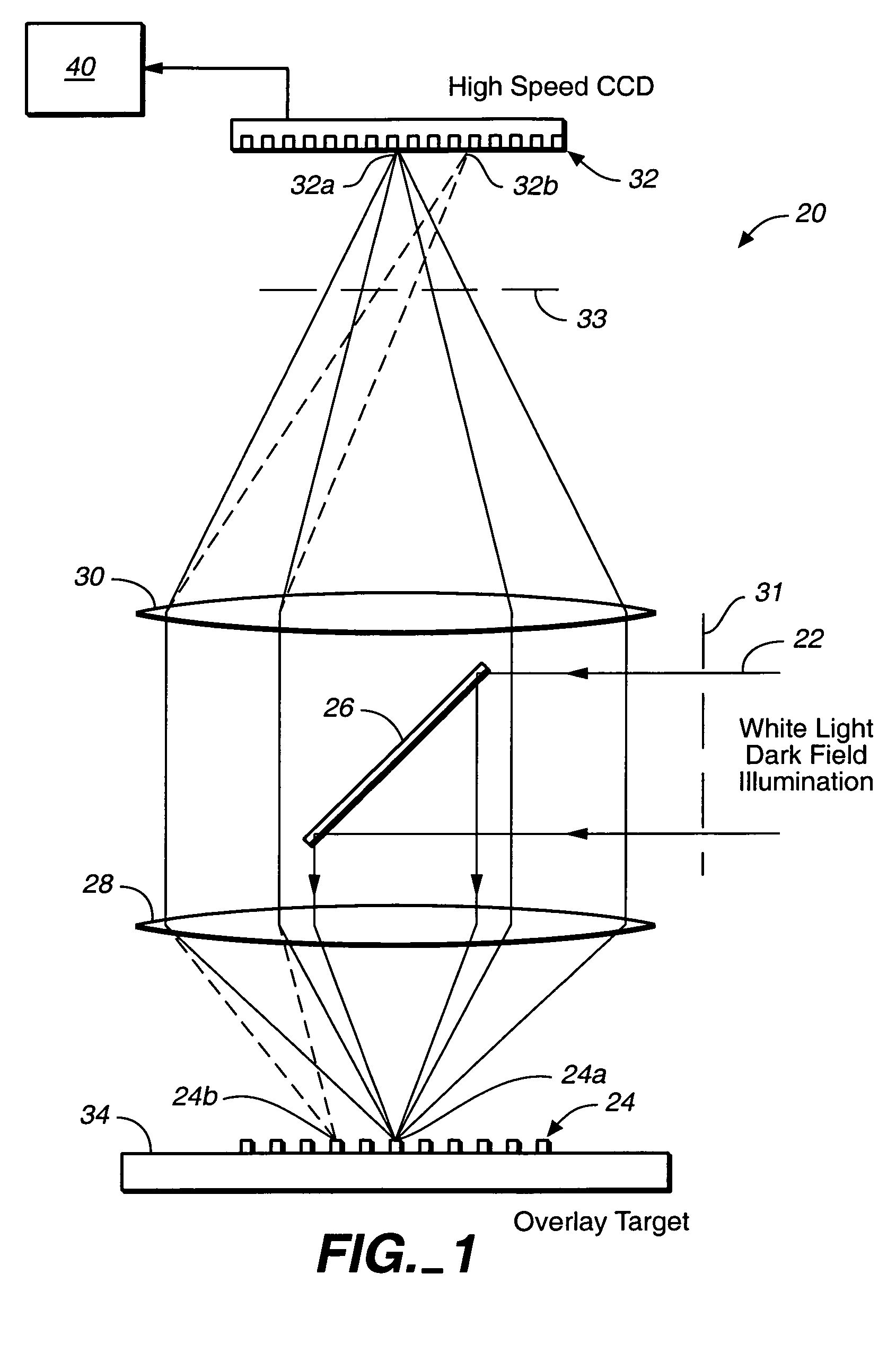
Overlay error detection
InactiveUS7009704B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce contrastPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingData pointSpecular reflection
An overlay target with gratings thereon is illuminated and radiation scattered by the target is imaged onto detectors. A phase difference is then detected between the outputs of the detectors to find the mis-alignment error. In another aspect, an overlay target with gratings or box-in-box structures is illuminated and radiation scattered by the target is imaged onto detectors located away from the specular reflection direction of the illumination in a dark field detection scheme. Medium numerical aperture optics may be employed for collecting the radiation from the overlay target in a bright or dark field configuration so that the system has a larger depth of focus and so that the two structures of the target at different elevations can be measured accurately at the same time. Analytical functions are constructed for the grating type targets. By finding the phase difference between the two gratings at different elevations, misalignment errors can be detected. Analytical functions are constructed as a model for box-in-box type targets where data points away from the edges of the box or bars can be used in the curve fitting. Symmetrical functions are employed to further reduce noise.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Method and Tool for Surface Texture Evaluation
InactiveUS20090116697A1Easy to implementImprove accuracyOptical rangefindersScattering properties measurementsPhysicsSpecularity
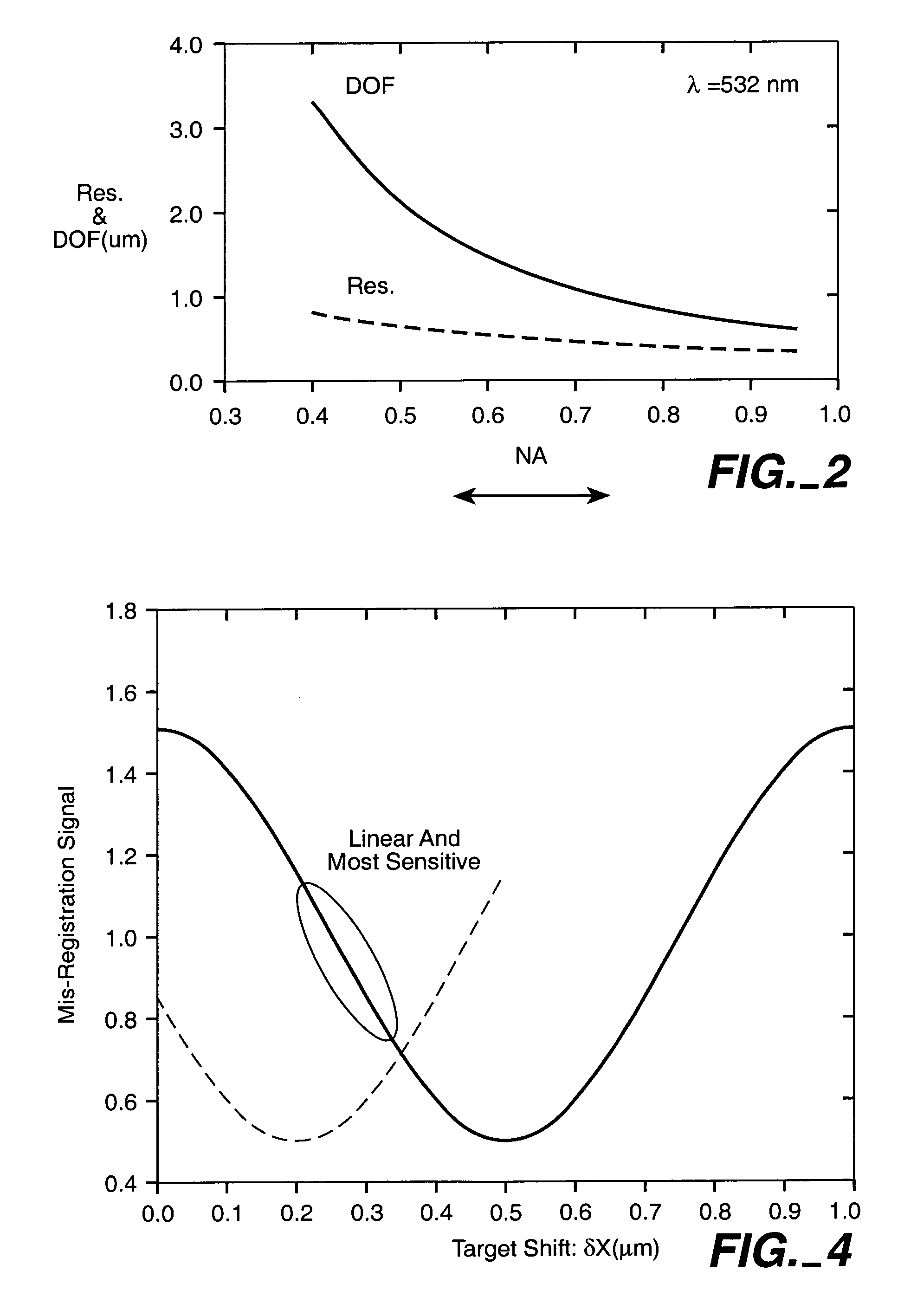
Texture of a surface, for example concrete, is evaluated by capturing images of the surface facing the surface in a direction of an orthogonal axis extending perpendicularly from the surface while sequentially projecting light onto the surface from each of four light source positions spaced circumferentially about the orthogonal axis. A specularity condition is determined to exist in one of the four images by comparing intensities of the images directly with one another. If a specularity condition exists, three images of the four images which are least affected by specularity are used to determining a surface gradient of the surface.
Owner:SHALABY AHMED +1
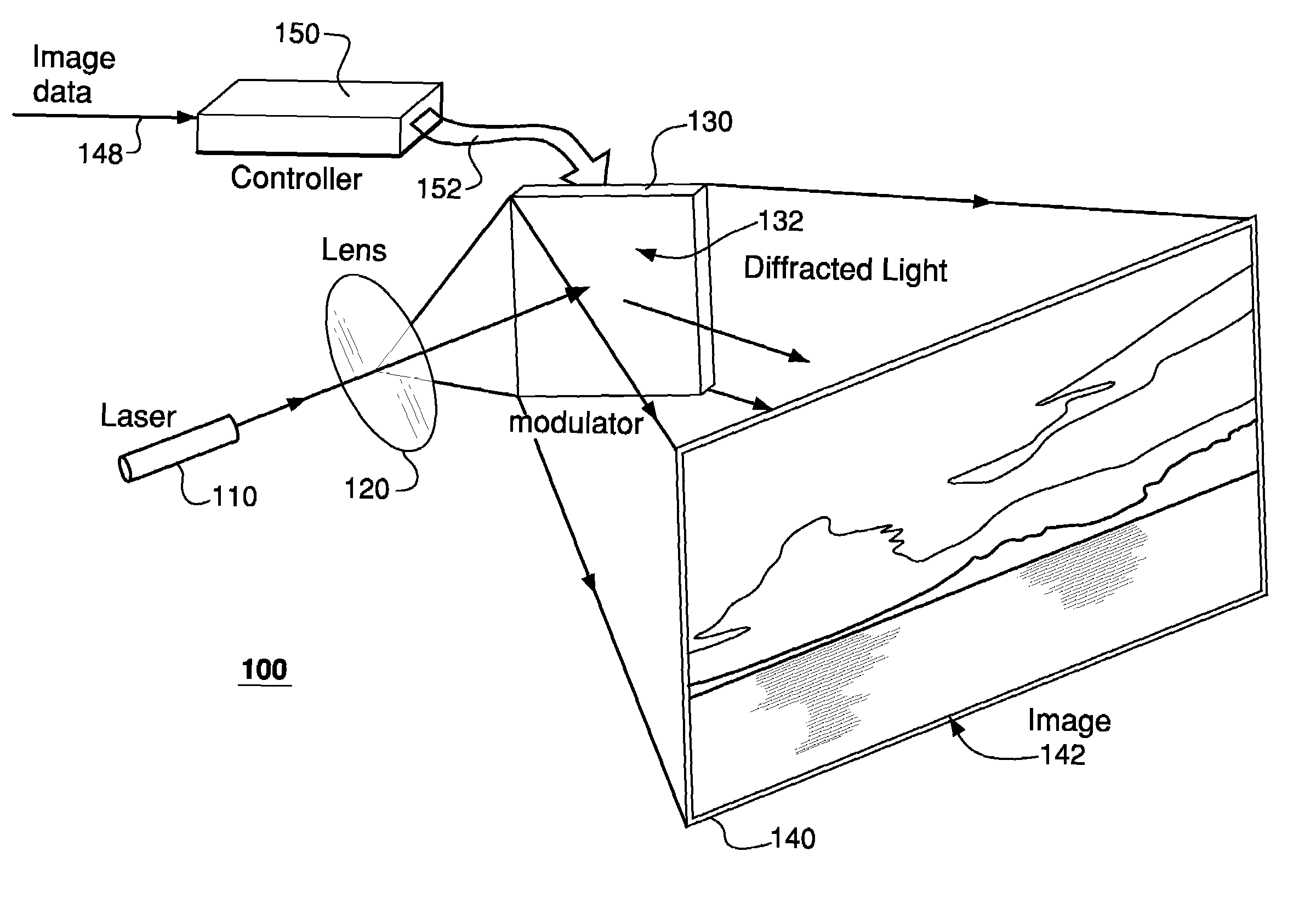
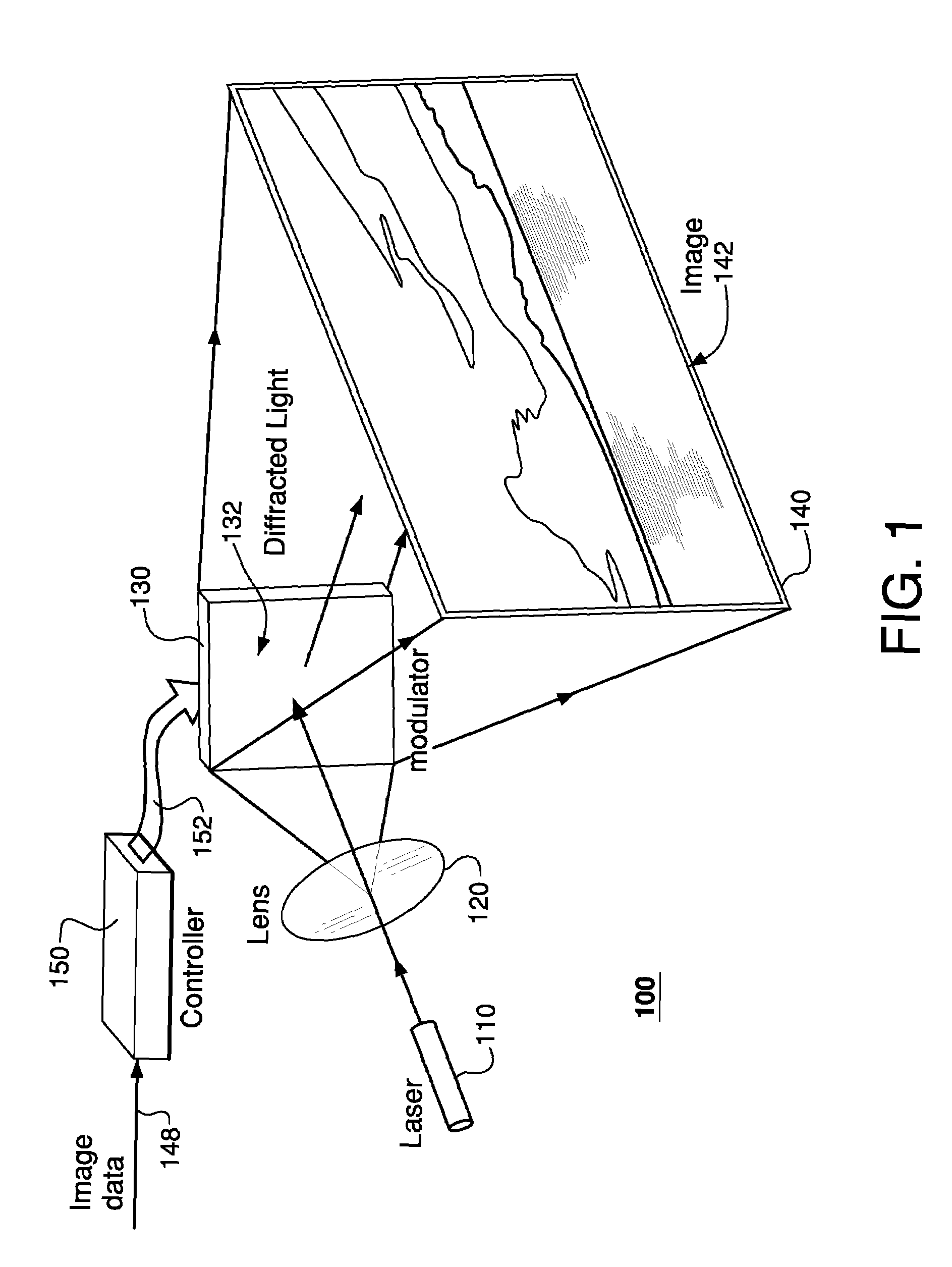
Speckle reduction in laser-projector images
InactiveUS7502160B2Reduce appearance problemsSpeckle reductionProjectorsMountingsSpatial light modulatorProjection image
A laser projector having a configurable spatial light modulator (SLM) adapted to display various spatial modulation patterns and redirect illumination from a laser to form an image on the viewing screen. The laser projector drives the SLM to change spatial modulation patterns at a rate that causes the corresponding sequence of projected images to fuse to mitigate appearance of speckle in the resulting fused image. The SLM can be designed to redirect the illumination using either diffraction or specular reflection of light from the displayed spatial modulation pattern. In one embodiment, the SLM is a MEMS device having an array of individually addressable mirrors supported over a substrate and adapted to move (e.g., translate and / or rotate) with respect to the substrate.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Optical sensor and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20130216245A1Small sizeLow costScattering properties measurementsElectrographic process apparatusPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical sensor is disclosed, including an irradiating system; a first photodetecting system including a first photodetector which is arranged on an optical path of a light which is specularly reflected from a subject; a second photodetecting system including an optical element which is arranged on an optical path of a light which is diffuse reflected from the subject within an incident face in the subject and which separates a linearly polarized component in a second polarizing direction which is orthogonal to a first polarizing direction and a second photodetector which receives a light separated by the optical element; and a restricting member which is arranged on an optical path of an incident light with respect to at least one of the first photodetector and the second photodetector and which restricts a light receiving range in the at least one photodetector.
Owner:RICOH KK
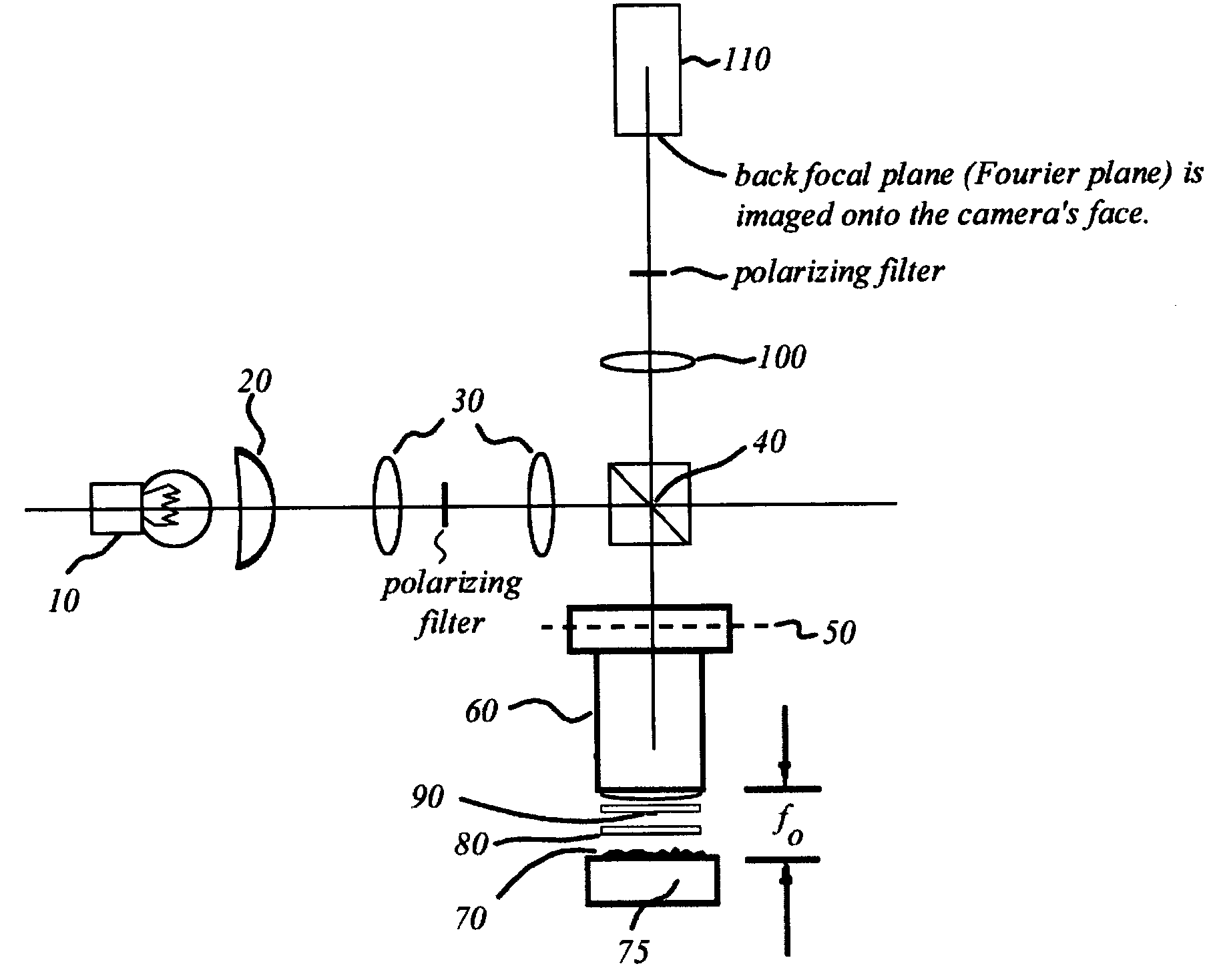
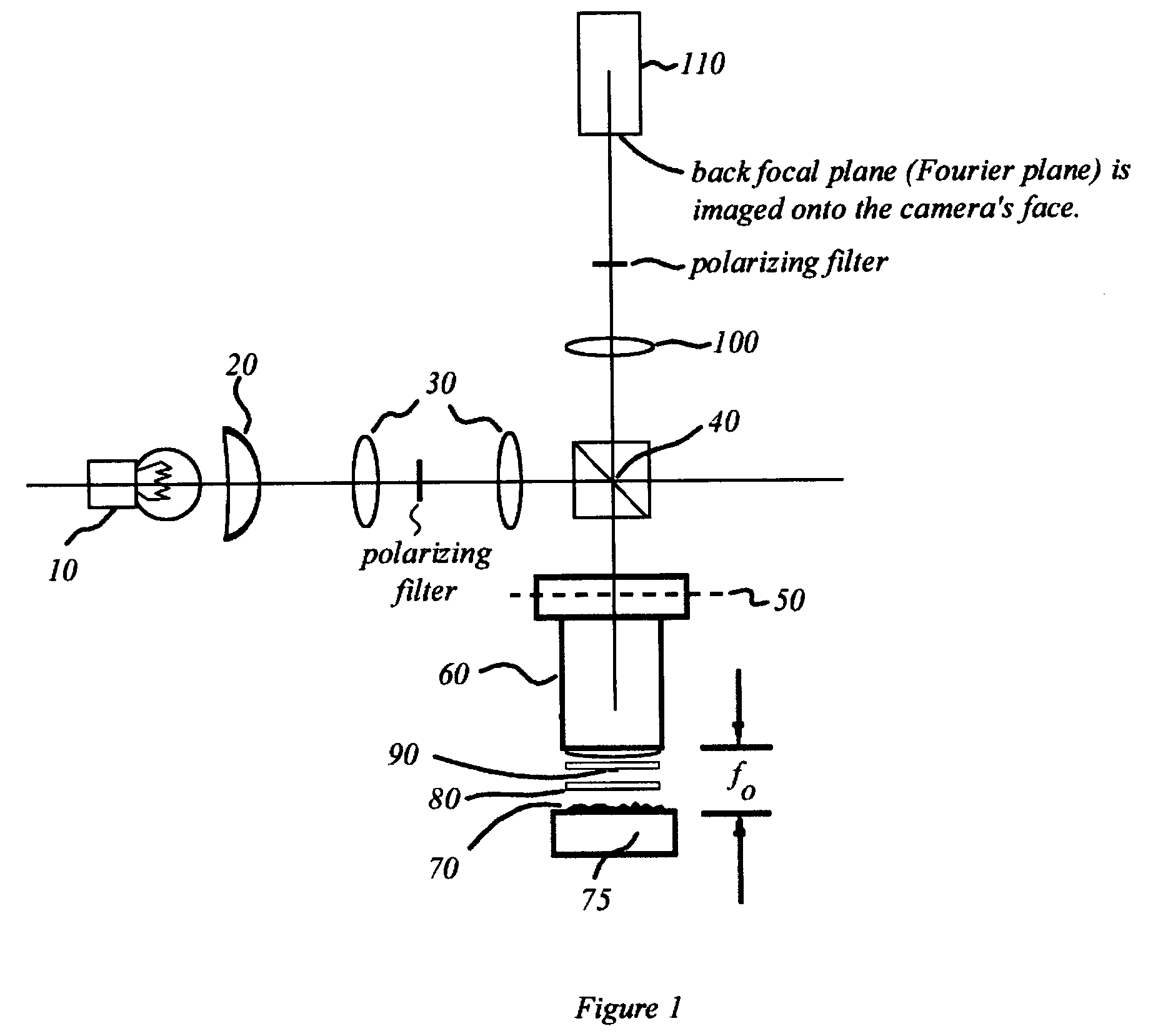
Interference scatterometer
An interference spectroscopy instrument provides simultaneous measurement of specular scattering over multiple wavelengths and angles. The spectroscopy instrument includes an interference microscope illuminated by Koehler illumination and a video camera located to image the back focal plane of the microscope's objective lens while the path-length difference is varied between the reference and object paths. Multichannel Fourier analysis transforms the resultant intensity information into specular reflectivity data as a function of wavelength. This multitude of measured data provides a more sensitive scatterometry tool having superior performance in the measurement of small patterns on semiconductor devices and in measuring overlay on such devices.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
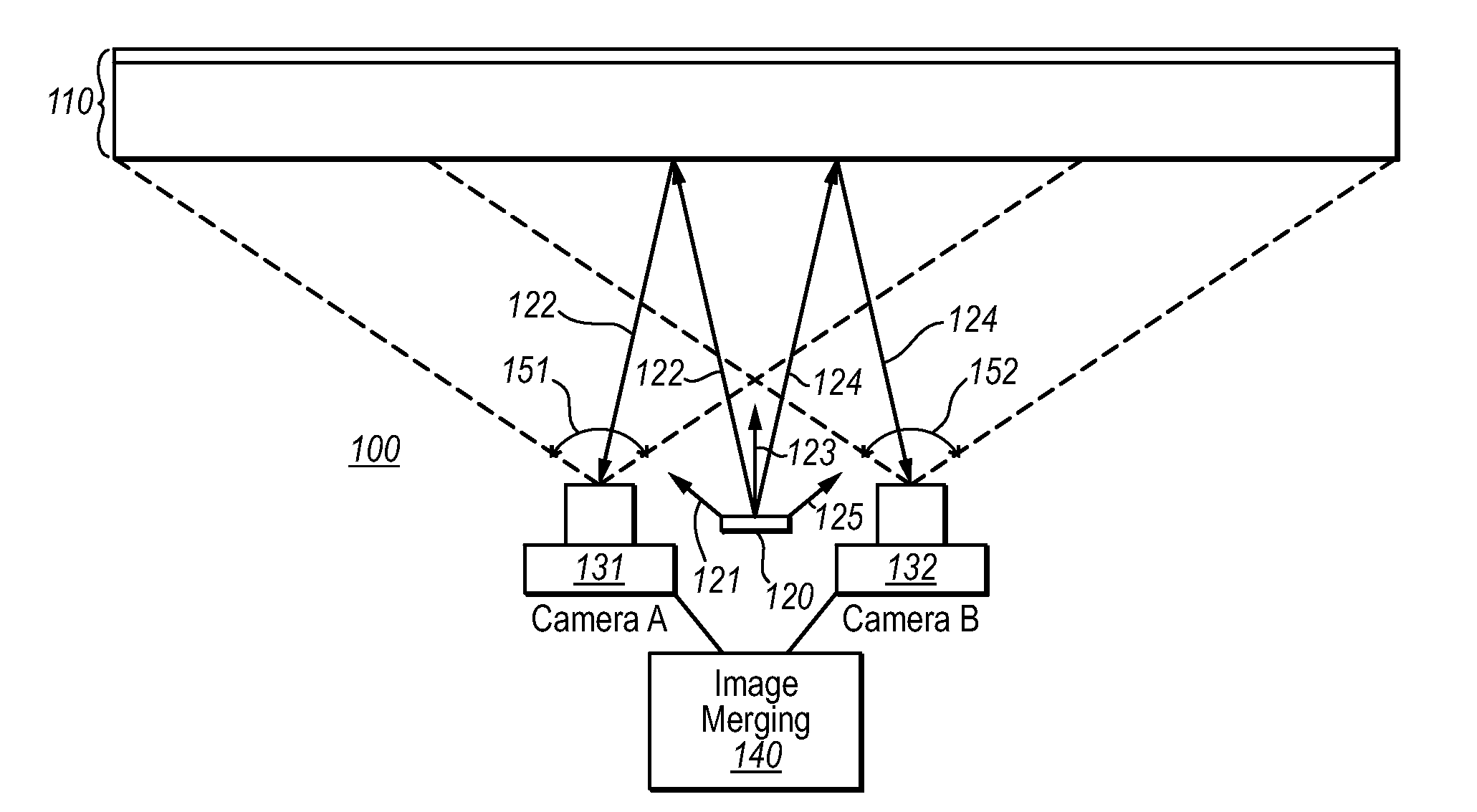
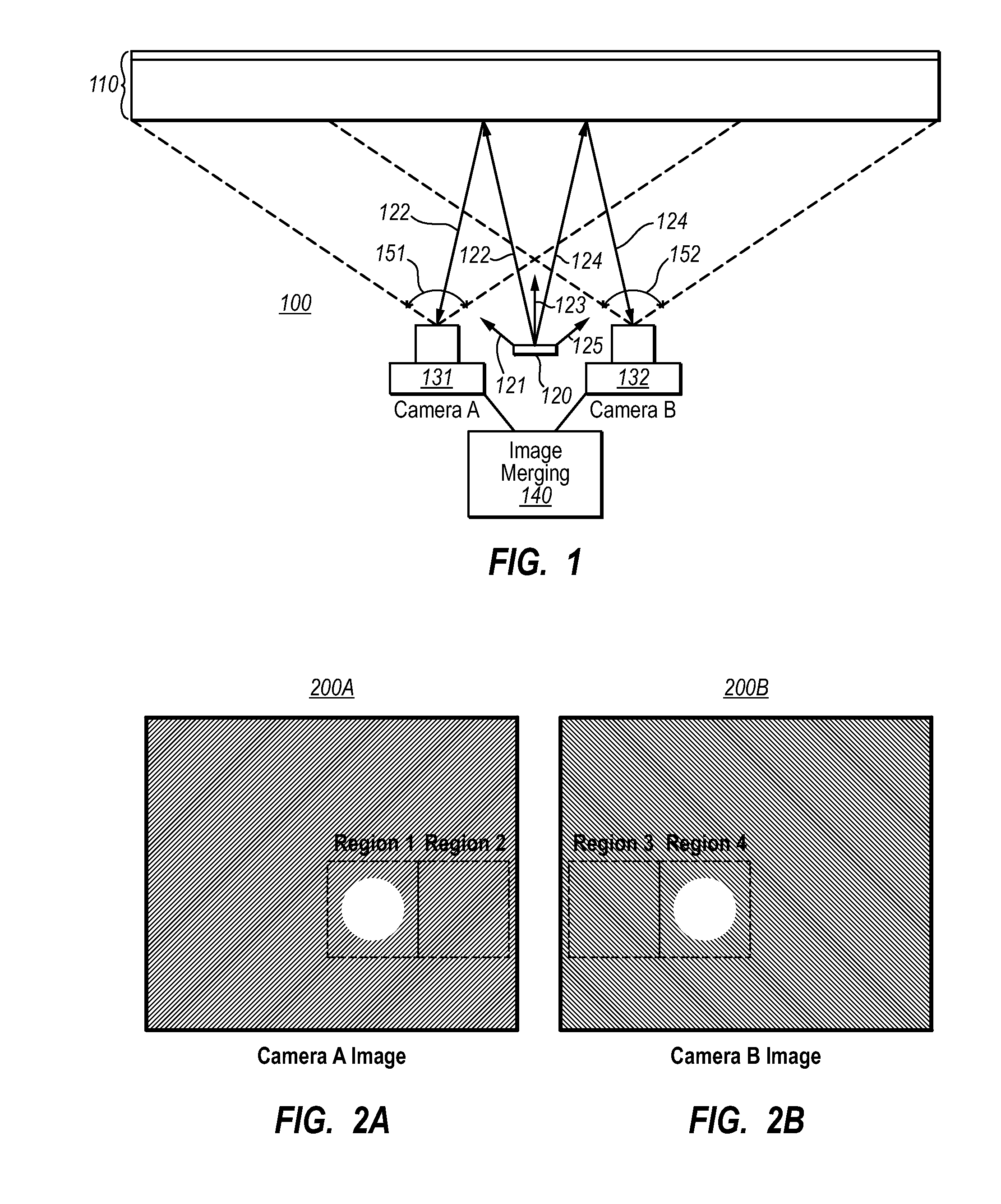
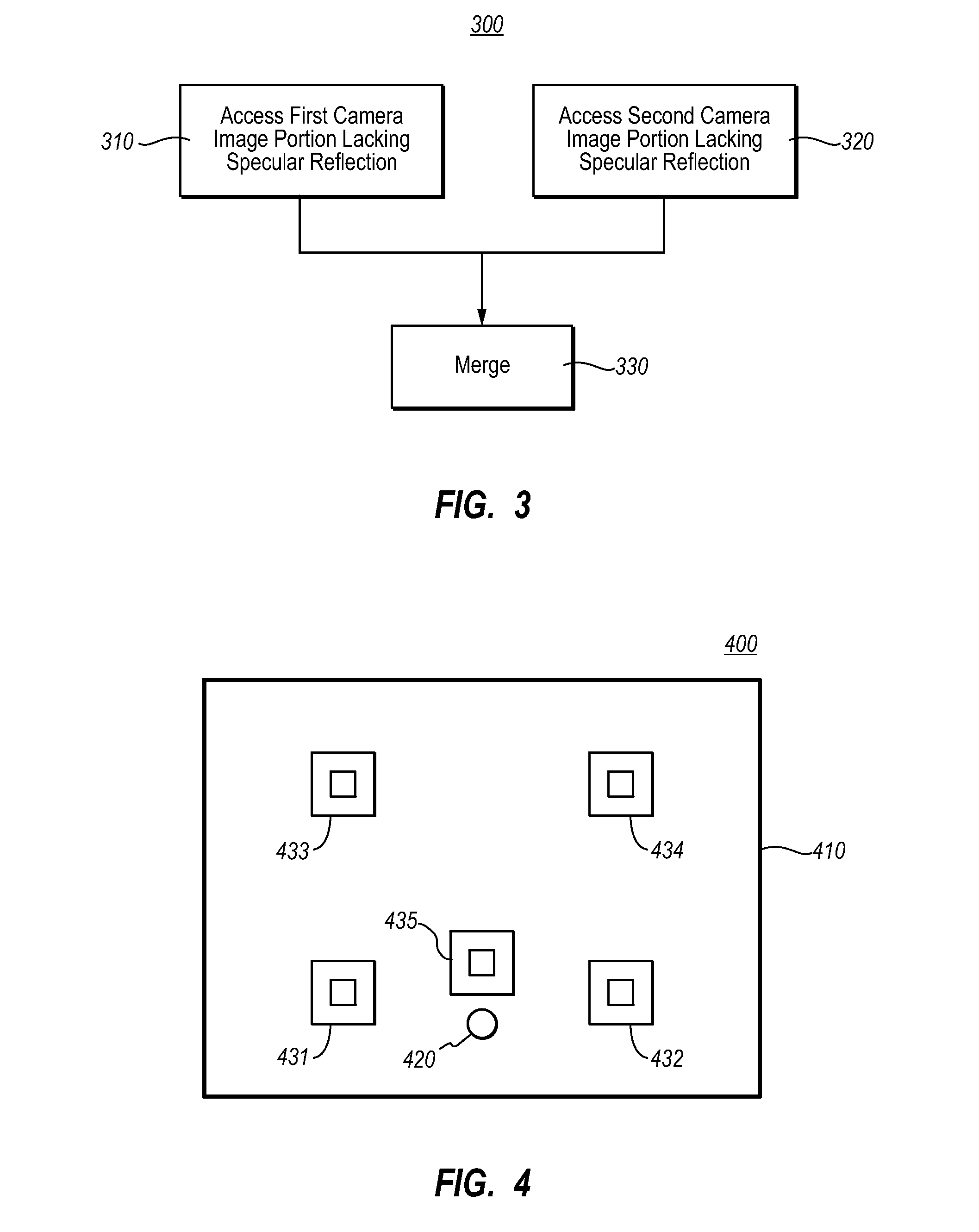
Specular reflection reduction using multiple cameras
InactiveUS20080165266A1Specular reflection is reduced and evenTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionInteractive displaysSpecular reflection
An interactive display system that includes an interactive display screen. An illuminator is positioned to illuminate one of the inner or outer surfaces of the display screen. At least two cameras are placed so as to view the illuminated surface of the display screen. Each of at least one of the cameras are positioned such that specular reflections from the illuminator are received by the camera. The images from the different cameras are merged to form a merged image in which specular reflections are reduced or even cancelled.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Active search sensor and a method of detection using non-specular reflections
ActiveUS20070034776A1Few sweepReliably obtainedAngle measurementPhotometry using reference valueSpecular reflectionReturn time
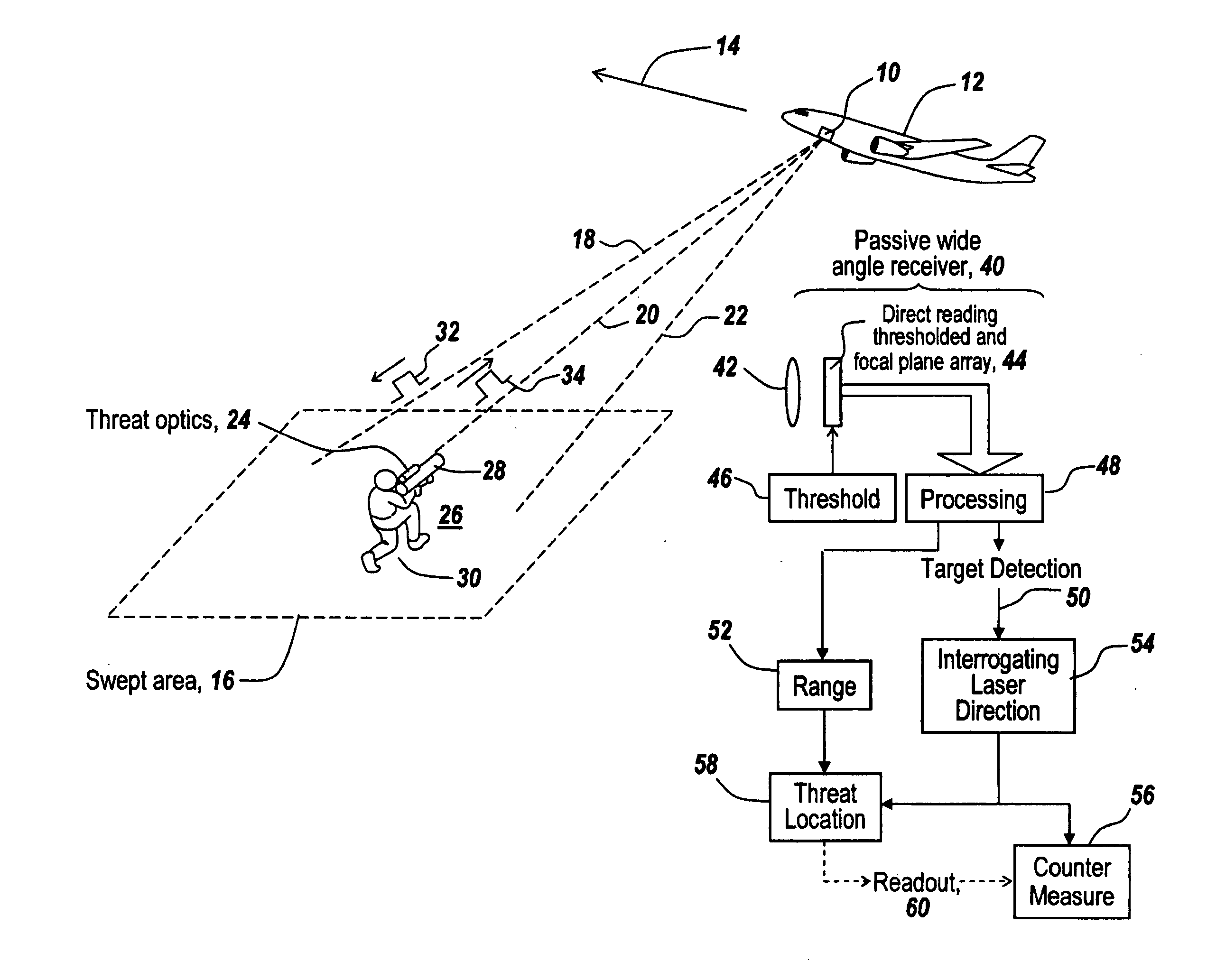
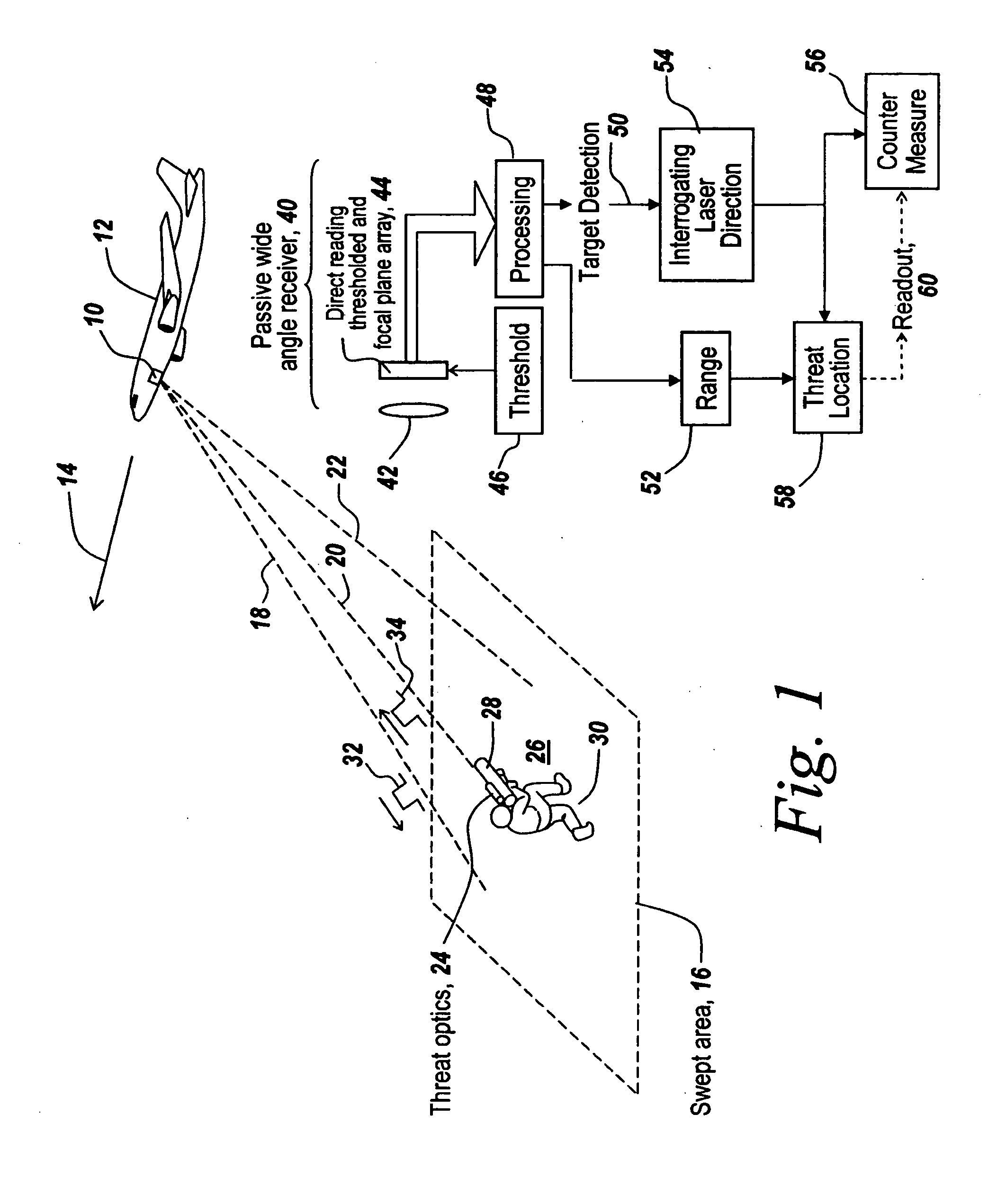
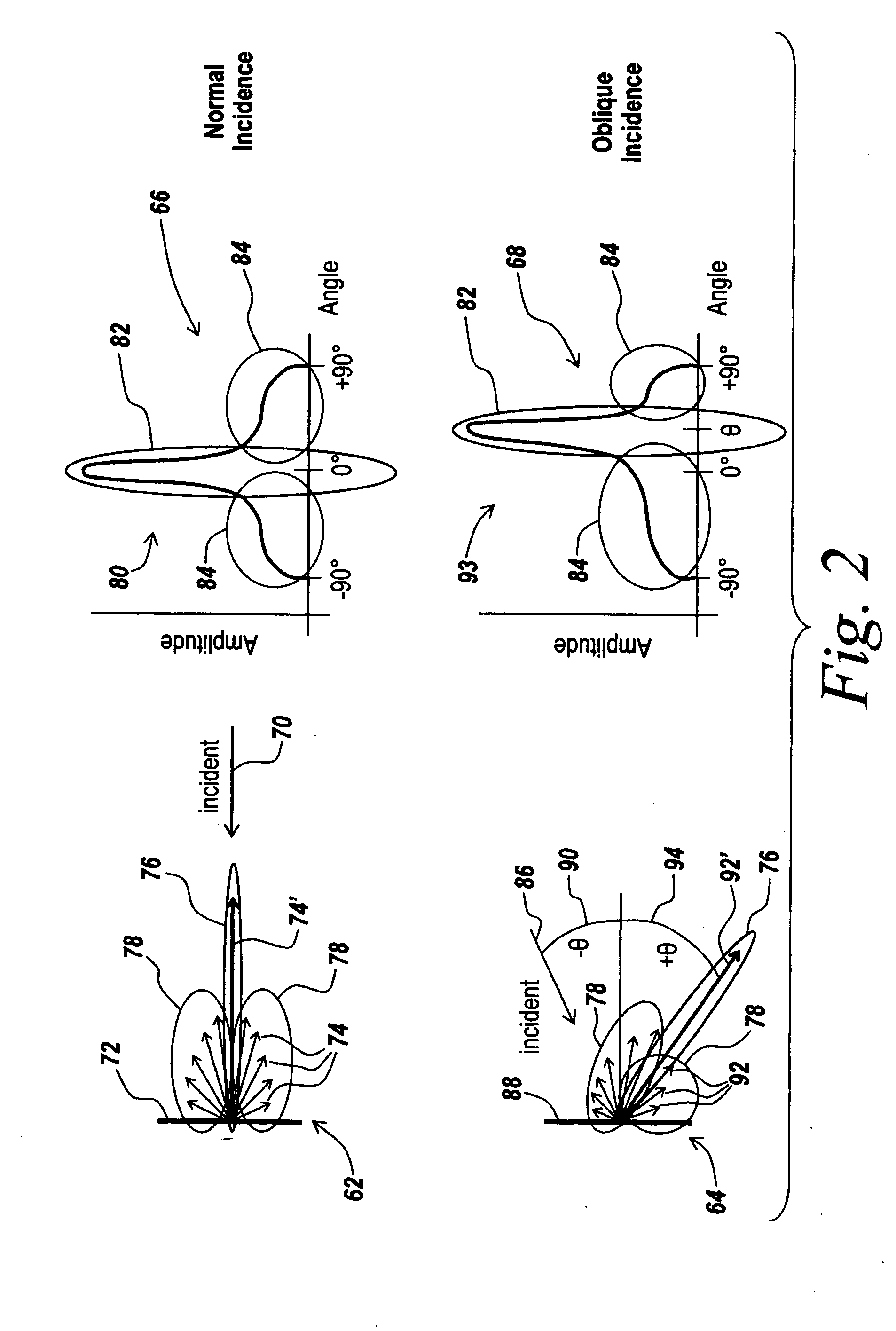
It has been found that target optics produce non-specular, augmented optical returns when interrogated by a laser pulse. This non-specular radiation is detected by an active laser search system employing a direct-reading, thresholded focal plane detector that is able to detect non-cooperating targets with optics that employ a detector or optical element at the focal plane of their receiving optics. The pulses returned from such target optics have a width commensurate with the original transmitted pulse width, whereas passive background noise and the spread out active returns from the ground exhibit temporally long returns. By setting the sensor threshold sufficiently high, the system discriminates against noise and clutter while at the same time reducing the number of sweeps required to detect a target within the search area.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Specular coatings for composite structures
Disclosed herein is a method for bonding dissimilar materials using an elastic adhesive to permit the bond to withstand variations in temperature and pressure. The use of elastic adhesive accommodates previous problems associated with large differences in thermal expansion coefficient between dissimilar materials, and provides a thermally and chemically stable materials combination that withstands large thermal shock loads, such as may be experienced in a space environment. Also disclosed herein is a method for attaching a coating to a structure. In particular applications, the coating may be (1) specular (greater than 98% specularity); or (2) RF reflective for use in applications including but not limited to high frequency satellite communications.
Owner:NASA
Broadened-specular reflection and linear subspaces for object recognition
InactiveUS7058217B2High precisionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionReflectance functionMachine vision
The present invention is a method of deriving a reflectance function that analytically approximates the light reflected from an object model in terms of the spherical harmonic components of light. The reflectance function depends upon the intensity of light incident at each point on the model, the intensity of light diffusely reflected, and the intensity of light broadened-specularly reflected in the direction of an observer. This reflectance function is used in the process of machine vision, by allowing a machine to optimize the reflectance function and arrive at an optimal rendered image of the object model, relative to an input image. Therefore, the recognition of an image produced under variable lighting conditions is more robust. The reflectance function of the present invention also has applicability in other fields, such as computer graphics.
Owner:NEC CORP
Silver Ink Composition and Substrate
ActiveUS20130121872A1Superior glossinessSuperior specularityConductive materialInksAcetic acidSilver ink
There is provided with a silver ink composition which is formed by blending one or more kinds of silver β-ketocarboxylates selected from the group consisting of silver isobutyrylacetate, silver benzoylacetate, silver propionylacetate, silver acetoacetate, silver α-methylacetoacetate, and silver α-ethylacetoacetate, and an aliphatic primary or secondary amine having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, and a substrate with a surface on which a metallic silver layer which is formed by heating the silver ink composition is provided. According to the invention, it is possible to obtain a silver ink composition suitable for forming a metallic silver layer which has superior glossiness and specularity, and a substrate with a surface on which a metallic silver layer is formed using the silver ink composition.
Owner:TOPPAN EDGE INC
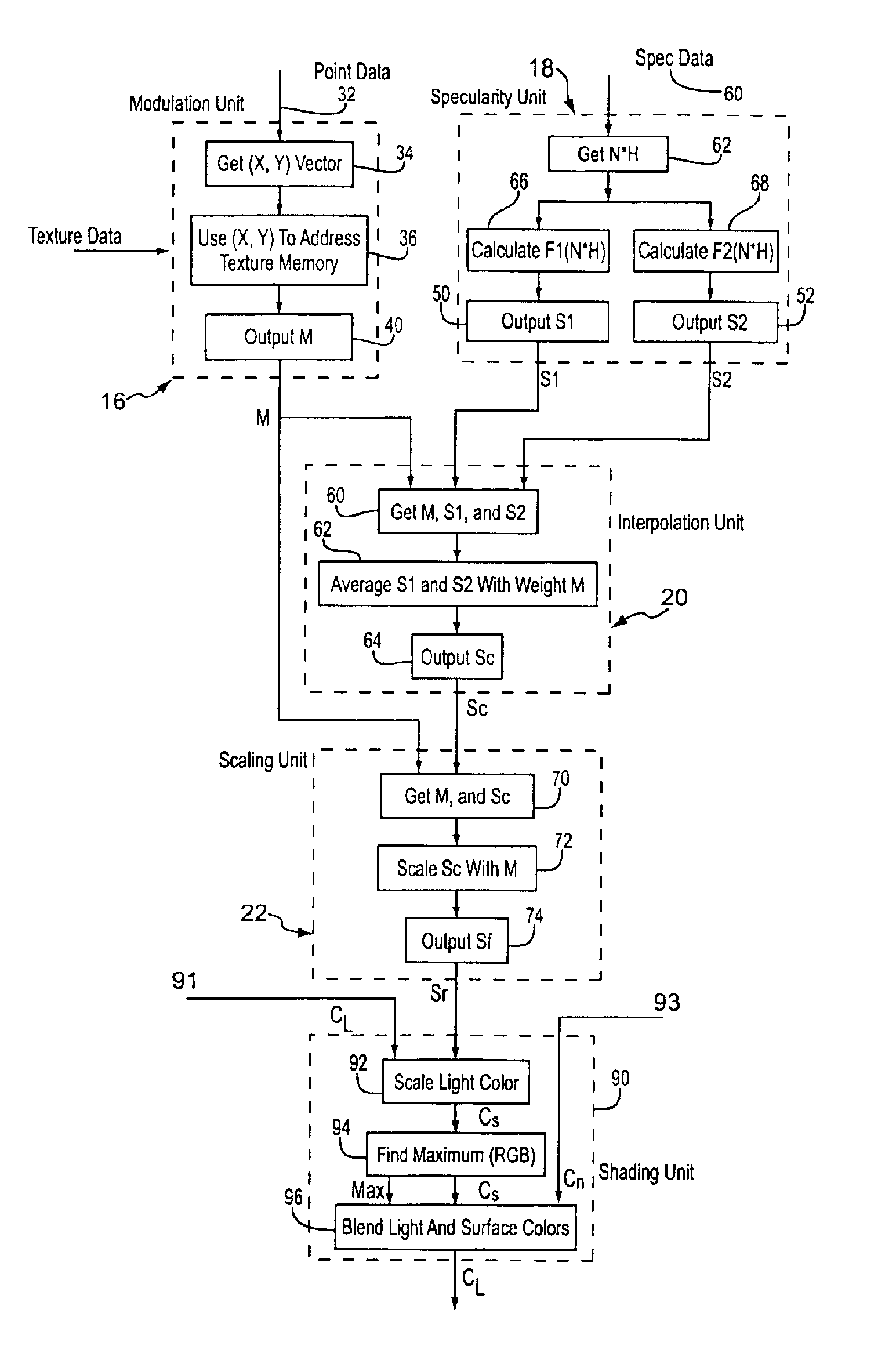
Dirt map method and apparatus for graphic display system
InactiveUS7071937B1Improve realismCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingRough surfaceGraphics
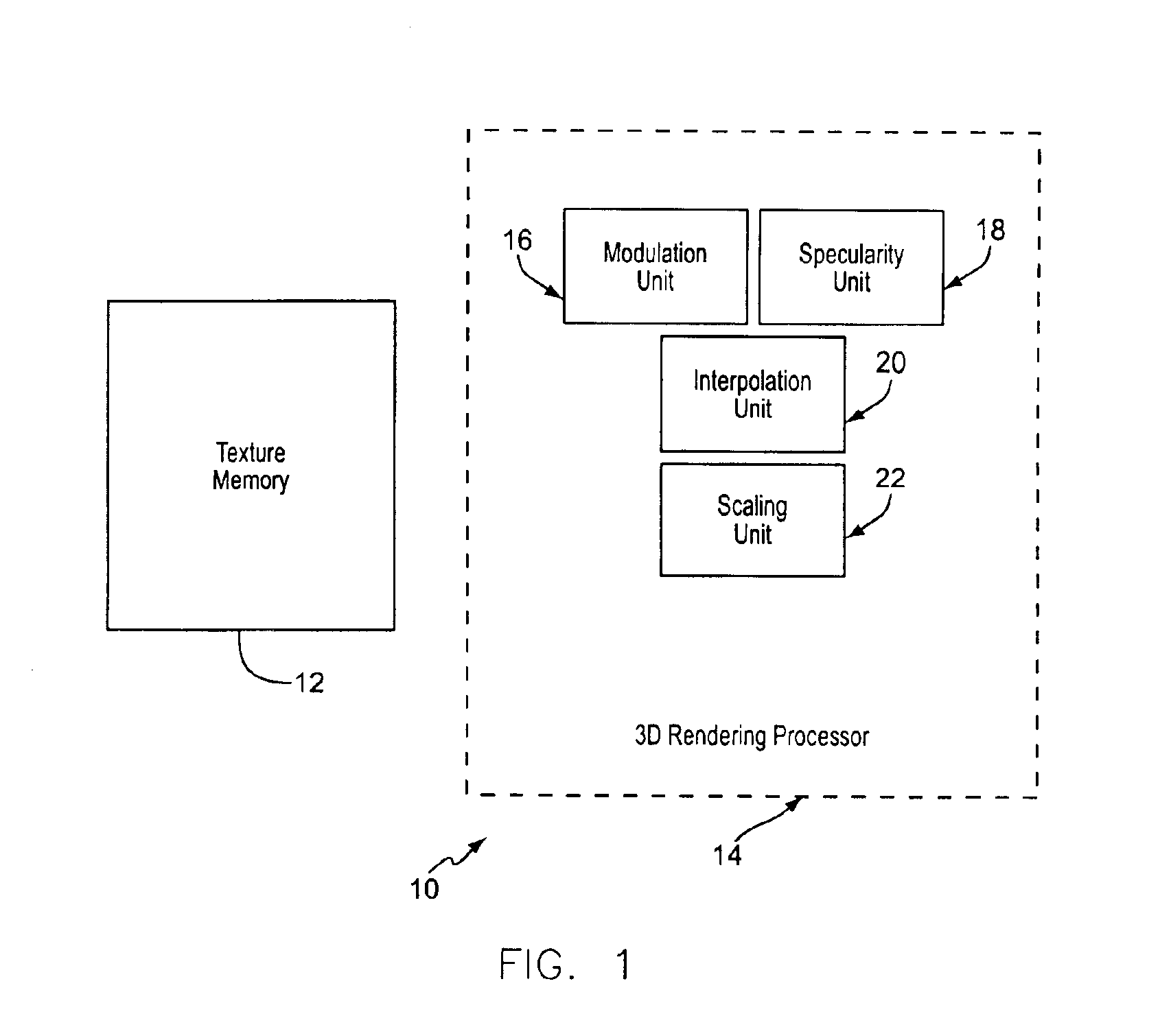
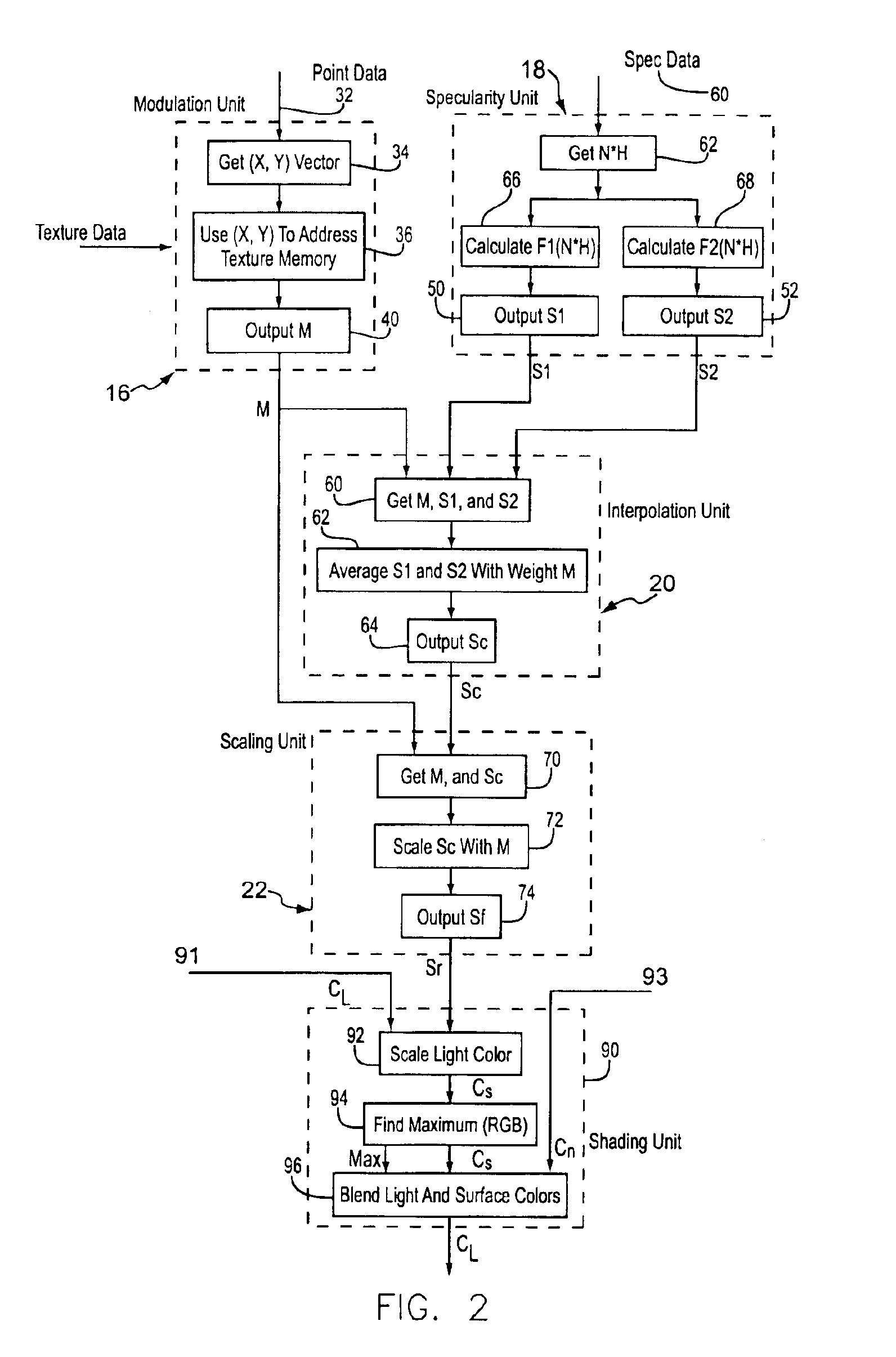
A method and system for map based per-pixel specularity modulation of a surface in a real time 3D graphics renderer through the use of interpolated specularity function or environmental map values. One or more functional modules calculate a pair of specular light intensity values or color values. Each specularity value is representative of the specular light reflected by the given pixel at an extreme surface reflectance characteristic, i.e. one may represent reflection from a very smooth surface while the other represents reflection from a very rough surface. A specularity modulation, or dirt map, value is arrived at by either a procedural calculation based on surface offset coordinates or by retrieval from a two-dimensional map contained in a texture memory. The specularity modulation value is then used as a weight to interpolate the pair of specularity values. The resulting interpolated specularity value is then optionally scaled by the modulation value (or a derivative thereof) to produce a final specularity value. This final specularity intensity or color value is then passed to a lighting unit that modulates pixel color appropriately to include the given specular light.
Owner:CCVG
Antireflection film, manufacturing method of antireflection film, kit including antireflection film and cleaning cloth
InactiveUS20160091635A1Improve antifouling performanceReduce reflectivityBoard cleaning devicesCarpet cleanersEngineeringSpecular reflection
There is provided an antireflection film including an unevenness structure having an average cycle shorter than a visible light wavelength on a transparent substrate film, wherein in the unevenness structure, an average aspect ratio of an average height of convex portions or an average depth of concave portions to an average cycle is from 1.0 to 3.0, a water contact angle to an unevenness structure surface is 100° or more, and a specular reflectance is 2.0% or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Advanced media determination system for ink jet printing
The present invention provides a system for classifying the type of input media entering an inkjet or other printing machine without requiring any special manufacturer markings to identify the media. The leading edge of the input media (170) is optically scanned with a violet light (520) to obtain diffuse reflectance (200) and specular reflectance (200') values. These reflectance values are Fourier transformed to produce a spatial frequency signal for the input medium. Compare this spatial frequency with known values for different media types, in terms of major categories such as transparencies, glossy photo media, fine paper, plain paper, and within these categories such as matte photo premium media and very glossy photo media and other specific media types to classify input media. Select the optimal print mode for a given media type, producing outstanding images without user intervention. A printing machine for implementing the method is also provided.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO
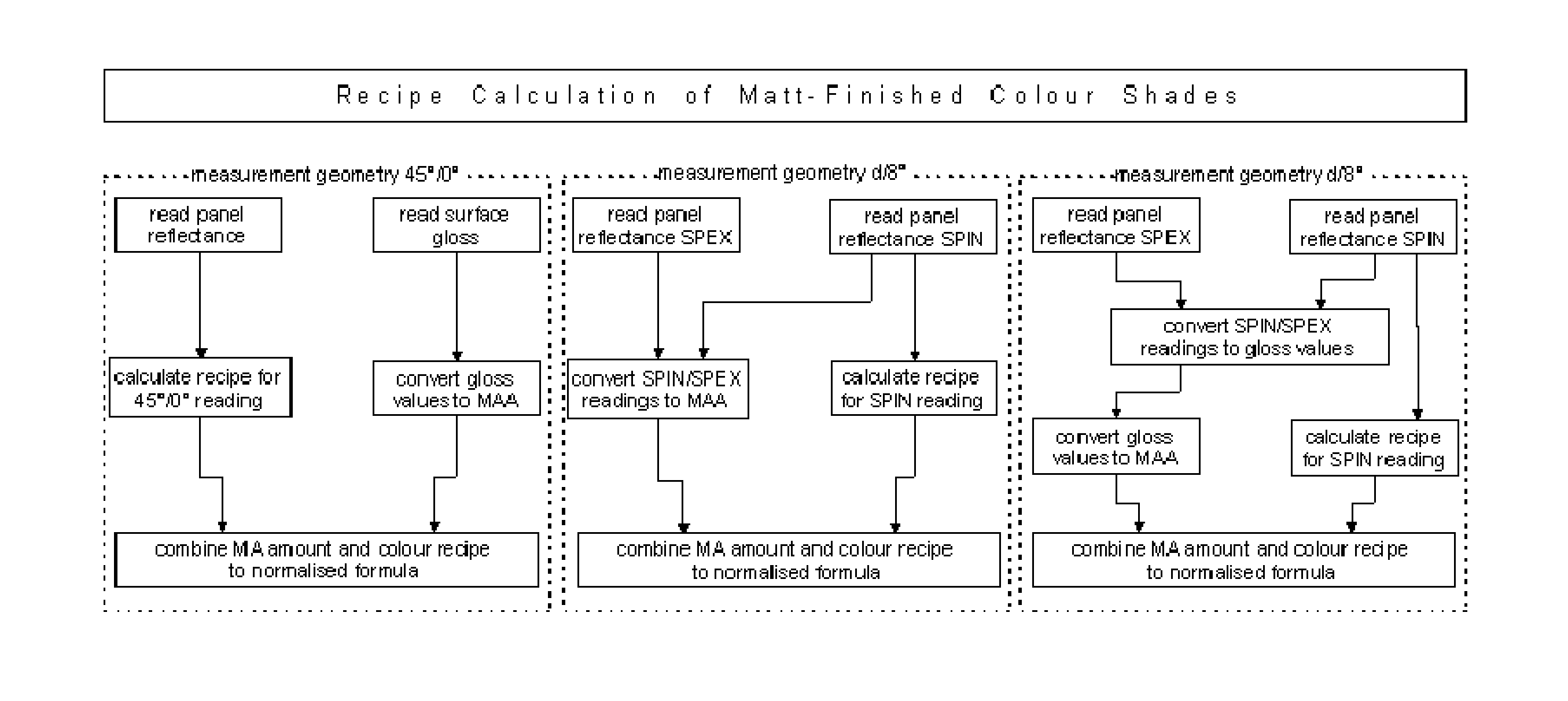
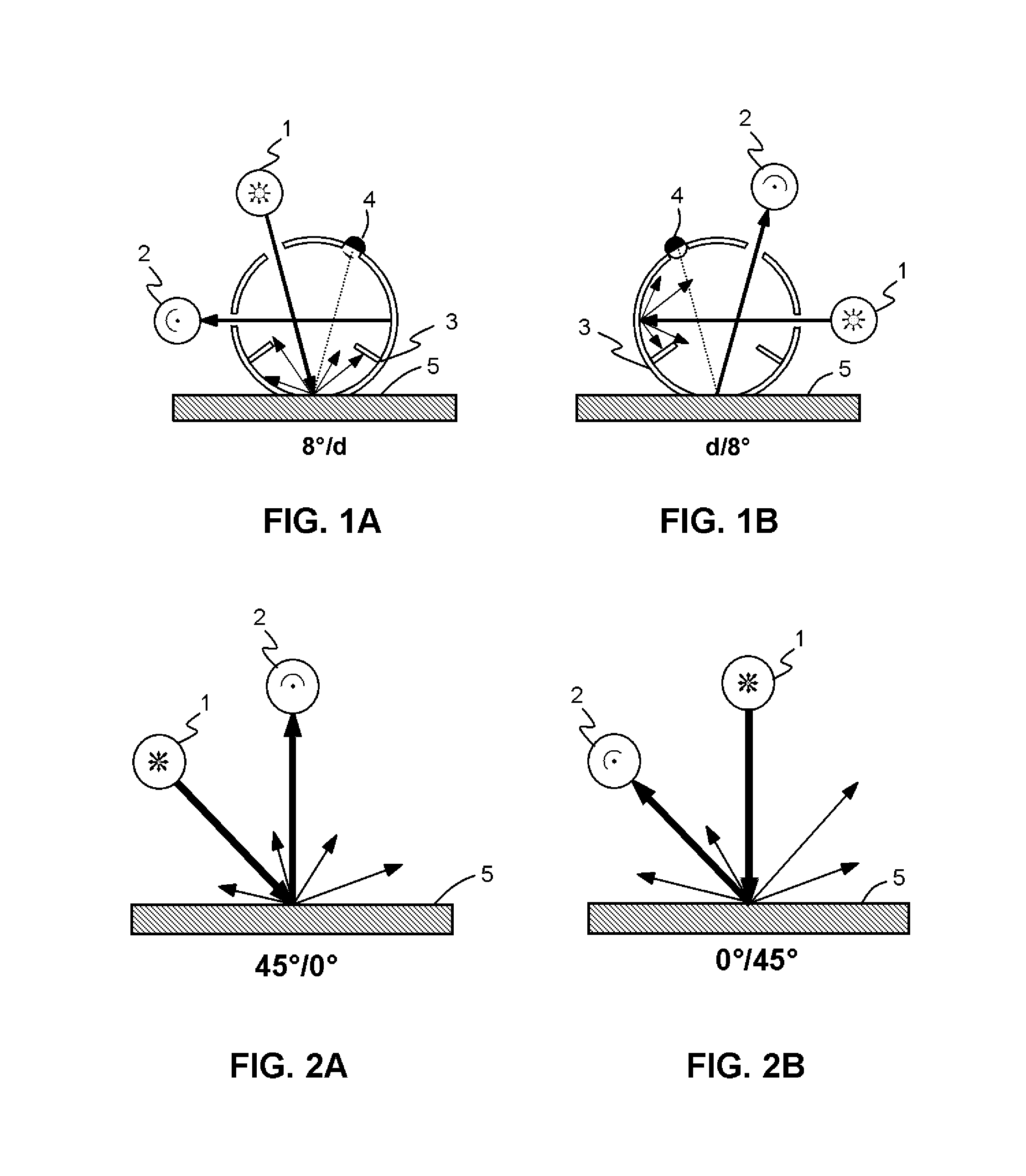
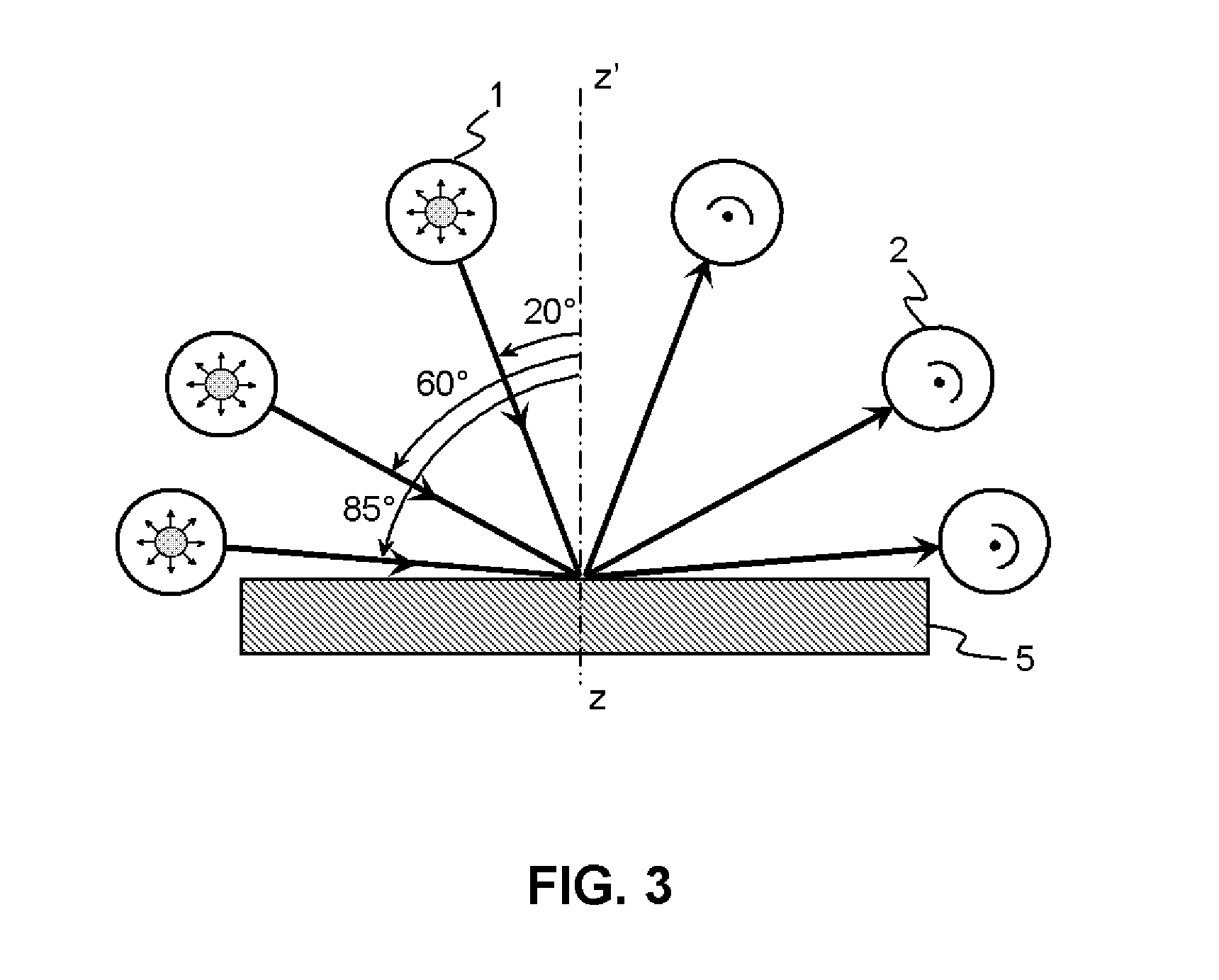
Colour recipe calculating method for matt colour standards
ActiveUS20140350895A1Reduce processing timeAttractive priceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceScattering properties measurementsMeasuring instrumentSpins
The invention relates to a method for colour recipe calculation for matt colour standards with the steps: A) experimentally determining reflection spectra R(exp) of the colour standard, comprising a first reflection spectrum (SPIN) and a second reflection spectrum (SPEX), with an integrating sphere colour measurement instrument, wherein said first reflection spectrum (SPIN) is obtained at (A1) d / 8°—geometry with the specular component included, and said second reflection spectrum (SPEX) is obtained at (A2) d / 8°—geometry with the specular component excluded; B1) calculating a recipe for the matt colour standard based on the experimentally determined reflection spectrum R(exp) with the specular component included, which has been corrected for the specular component, or B2) comparing the experimentally determined reflection spectrum R(exp) with the specular component included, en which has been corrected for the specular component, with reflection spectra associated to colour recipes of a colour recipe database for glossy colour shades and identifying from said colour recipe database a stored reflection spectrum which comes closest to the experimentally determined reflection spectrum R(exp) of the matt colour standard, as well as the associated colour recipe; C) converting reflection spectra data of the experimentally determined reflection spectra (SPIN, SPEX) of the matt colour standard to gloss values, and D) converting the gloss values obtained to the amount of matting agent (MAA) with the assistance of previously prepared calibration curves for the available colorant system.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Face recognition method and system for personal identification and authentication
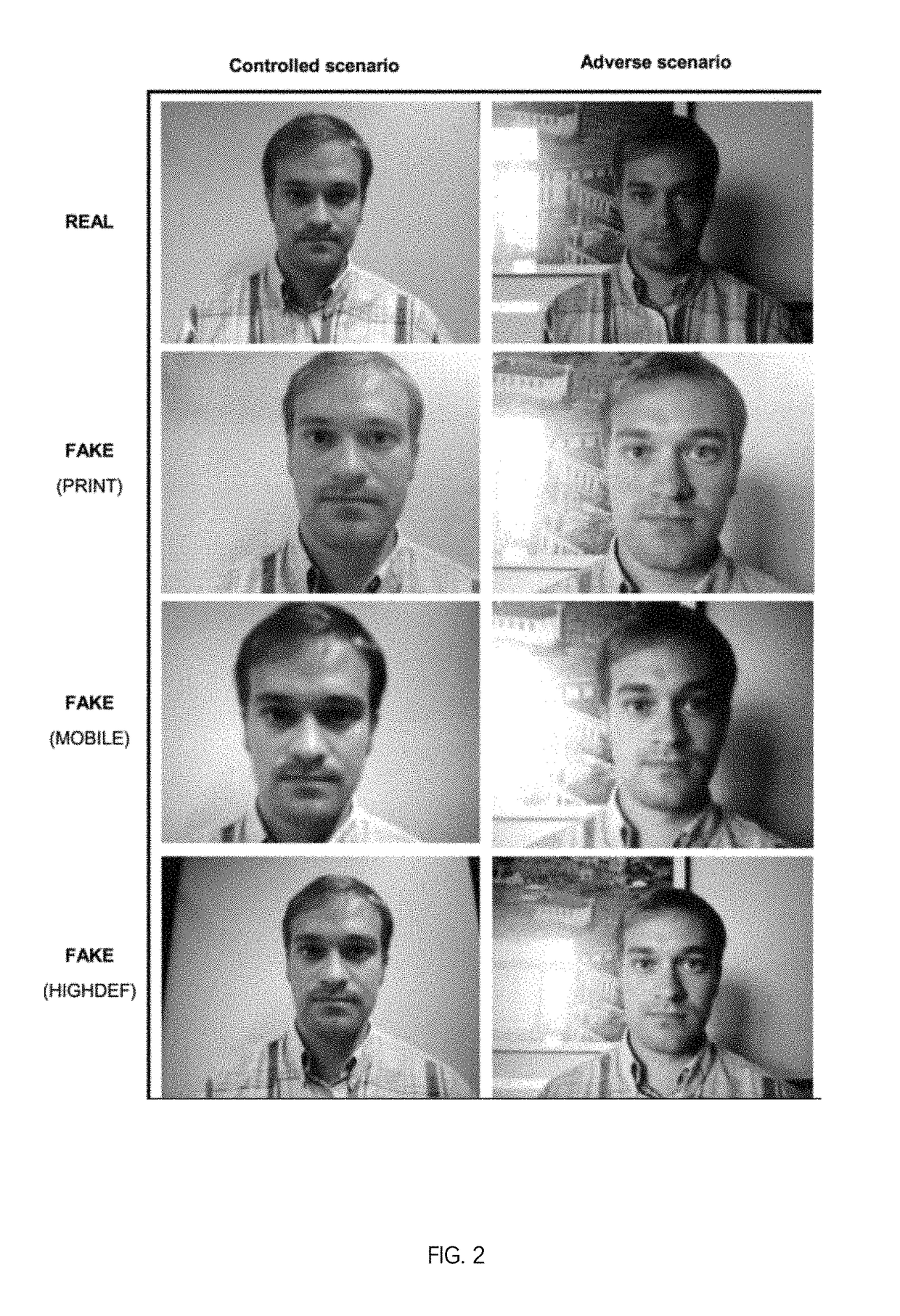
ActiveUS10061996B1Efficient detectionFalse rejectionDigital data authenticationSpoof detectionPattern recognitionScan line
The present invention comprises capturing an image of a subject to be authenticated; a step of face verification; followed by the process steps of a scan line detection test, a specular reflection detection test, and a chromatic moment and color diversity feature analysis test in no particular order. The method requires a subject to present her face before a camera, which can be the built-in or peripheral camera of e.g. a mobile communication device or a mobile computing device. The method also requires displaying to the subject certain instructions and the real-time video feedback of the subject face on a display screen, which can be the built-in or peripheral display screen of the mobile communication device or mobile computing device.
Owner:HAMPEN TECH CORP LTD
Optical cavity and laser
InactiveUS20050163184A1Less thermal gradientExpand selectionOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialFinesseOptical cavity
A novel laser cavity structure is disclosed which pertains to laser resonator geometries possessing circular symmetry, such as in the case of disk or spherical lasers. The disclosed invention utilizes a very-high finesse Bragg reflector (VHF-BR) thin film reflectors of many layer pairs of very small refractive index difference, the VHF-BR deposited on a surface of revolution, thereby forming an optical cavity. These dielectric reflectors are disposed in such a way as to allow selection of preferred low order modes and suppression of parasitic modes while allowing a high cavity Q factor for preferred modes. The invention disclosed, in its preferred embodiments, is seen as particularly useful in applications requiring high efficiency in the production and coupling of coherent radiation. This is accomplished in a cavity design that is relatively compact and economical. Of particular novelty is the combination of the disclosed cavity design with polymer multilayers. The ability to deposit an unusually large number of polymer thin films without loss of specularity, while maintaining very low extinction, renders the disclosed polymer-based cavity particularly well-suited for higher mode discrimination, more rugged and light-weight cavities, as well as economical fabrication.
Owner:HILLIARD DONALD BENNETT
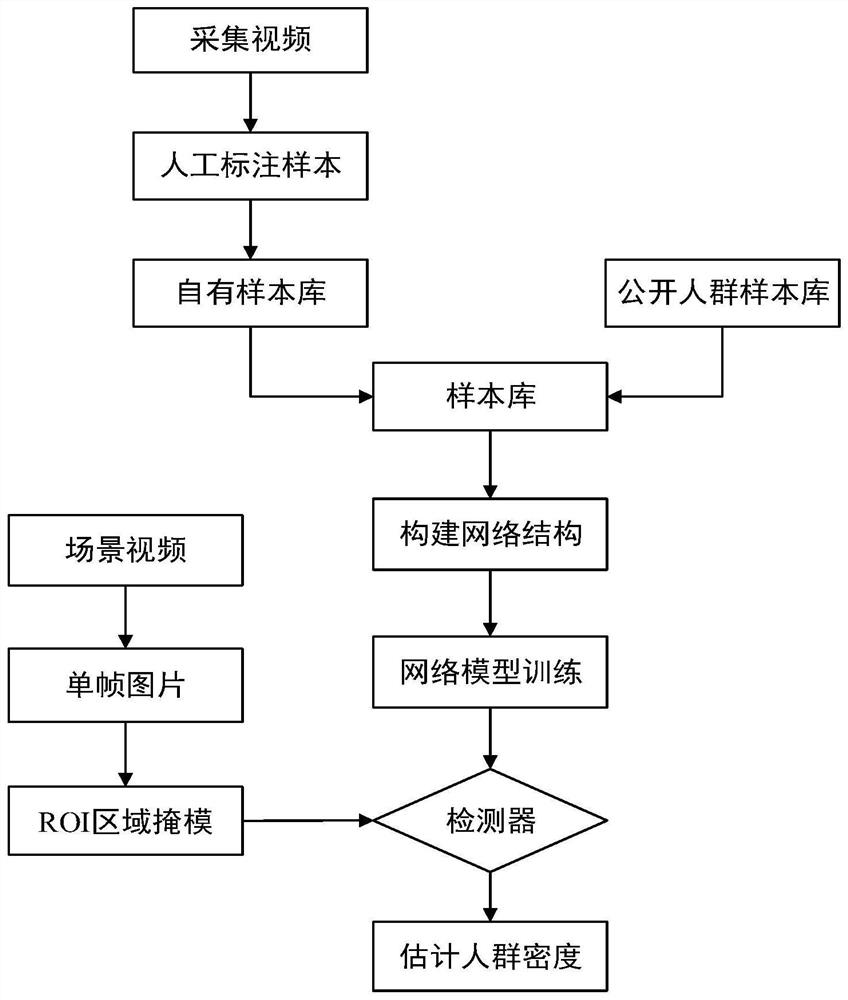
Subway crowd density estimation method and system based on target detection
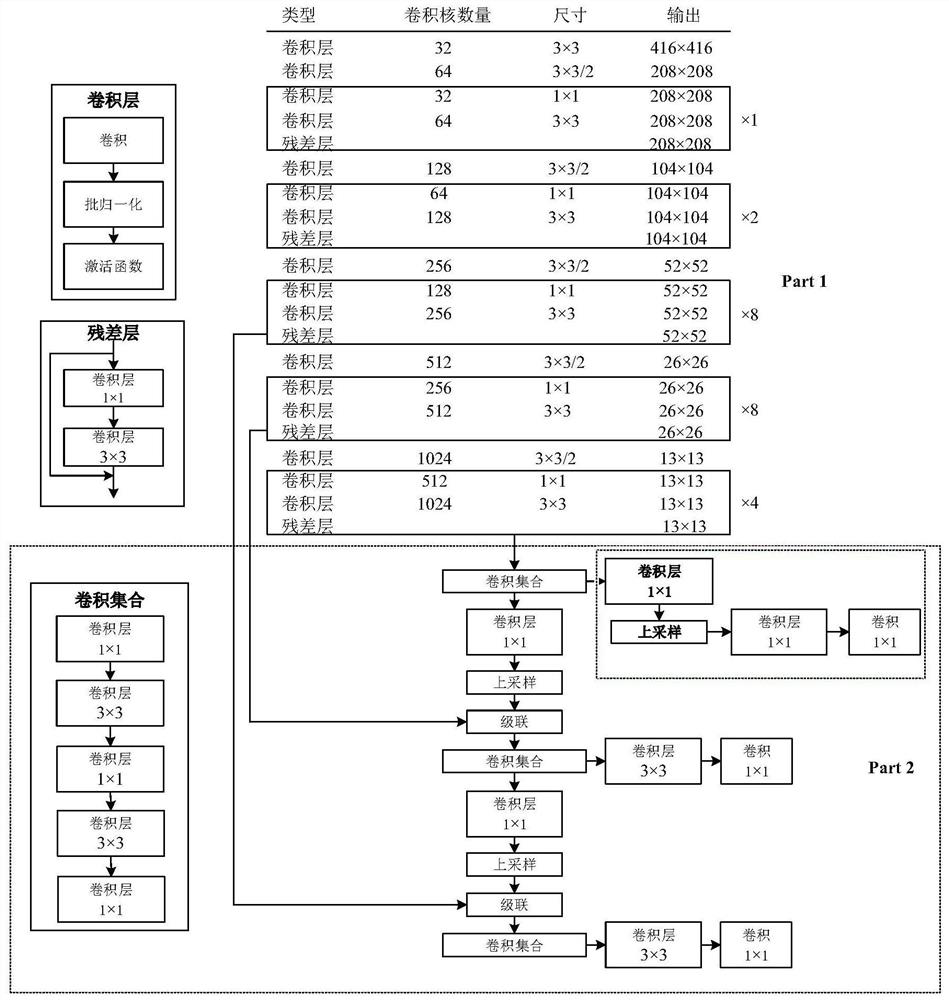
PendingCN111832489AOvercome the mutual occlusion problemAvoid occlusionBiometric pattern recognitionNeural architecturesHuman bodyAlgorithm
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Optical black surface
InactiveUS20140029103A1Easy to optimizeFine surfaceCoatingsOptical elementsEngineeringSpecular reflection
The present invention relates to optical black material which absorbs light. The device has a plurality or matrix of cells, each cell by a specular and diffuse absorbing material generating mostly specular reflection which is captured.
Owner:BUDLESKI WILLIAM FRANK
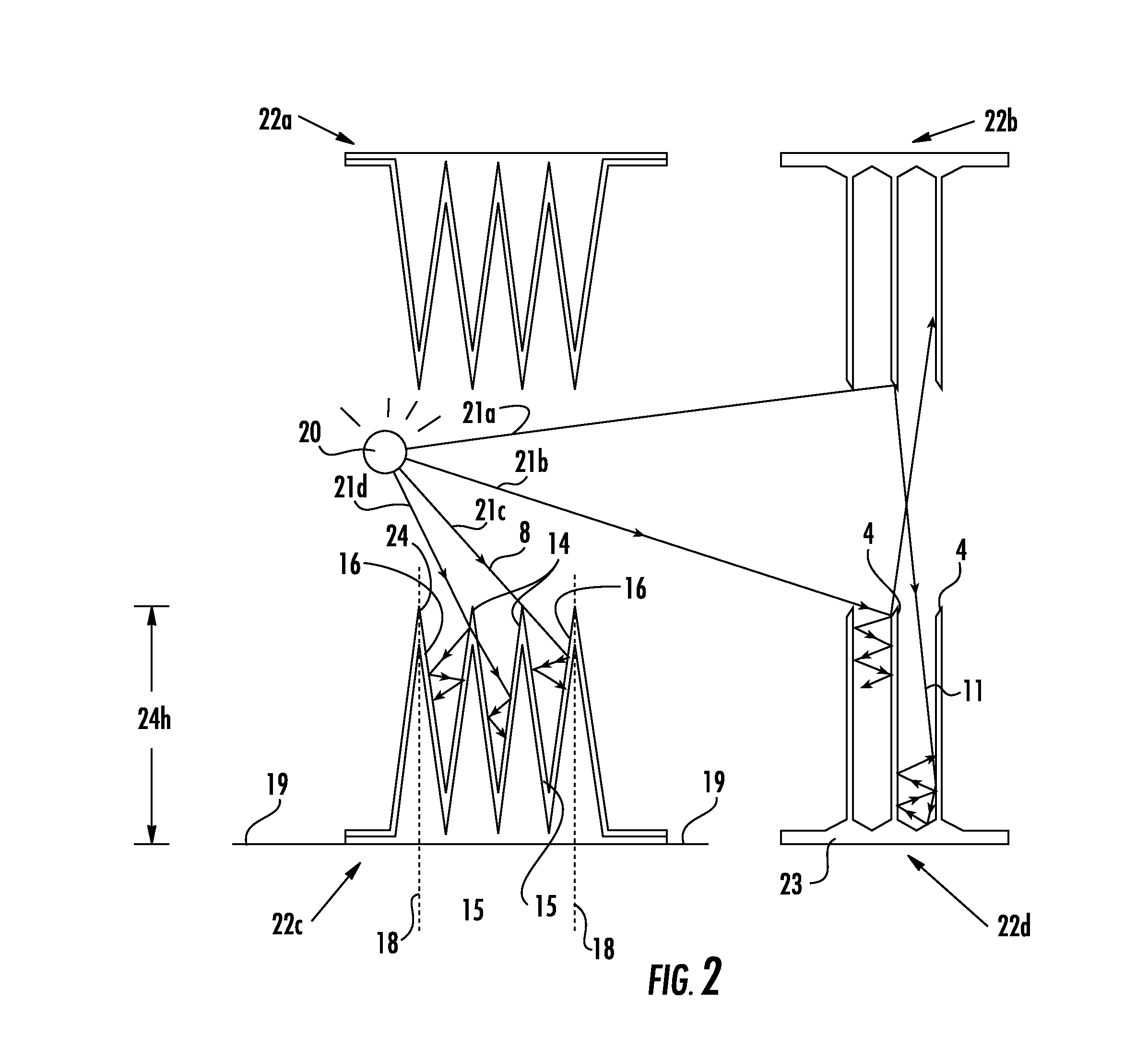
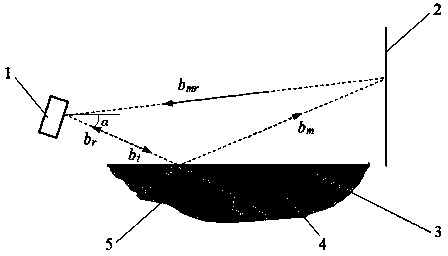
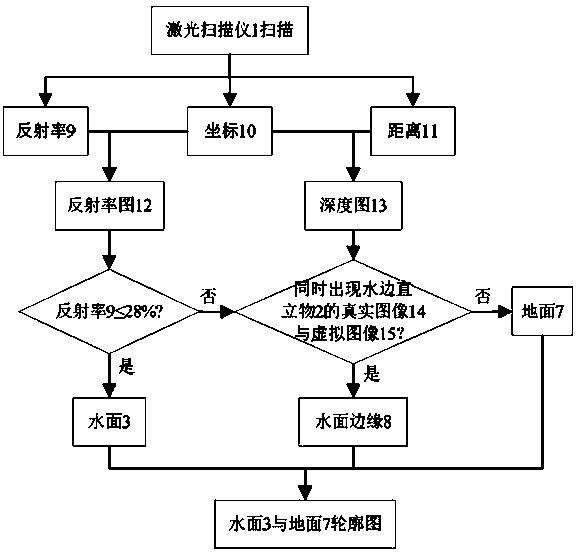
Laser scanning based water surface detection method
InactiveCN103512636ASolving the key challenge of detecting interferenceMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsDiffuse reflectionMirror image
The invention discloses a laser scanning based water surface detection method and relates to the field of robots. A laser scanner conducts 3D laser scanning on the front at a relatively small level inclination angle alpha, the reflectivity of the water surface is lower than 28%, the reflectivity of the ground is remarkably greater than 28% and no specular reflection phenomenon exists within the detection range of the laser scanner. Meanwhile, if a water-side upright object exists within the detection range of the laser scanner, then a laser beam is reflected because of the specular reflection of the water surface, irradiates the surface of the water-side upright object and generates diffuse reflection on the surface of the water-side upright object to allow partial energy to be received by the laser scanner, then the 3D laser scanner can obtain a real image of the water-side upright object, and a virtual image of the water-side upright object subjected to the specular reflection of the water surface, wherein the real image of the water-side upright object and the virtual image of the water-side upright object are identical in shapes and different in distances. Therefore, the water-side upright object can be judged so as to judge the edge of the water surface. The laser scanning based water surface detection method is simple and fast, and can be used to accurately distinguish the water surface and the surrounding environment under any light conditions outdoors to achieve detection of the water surface.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
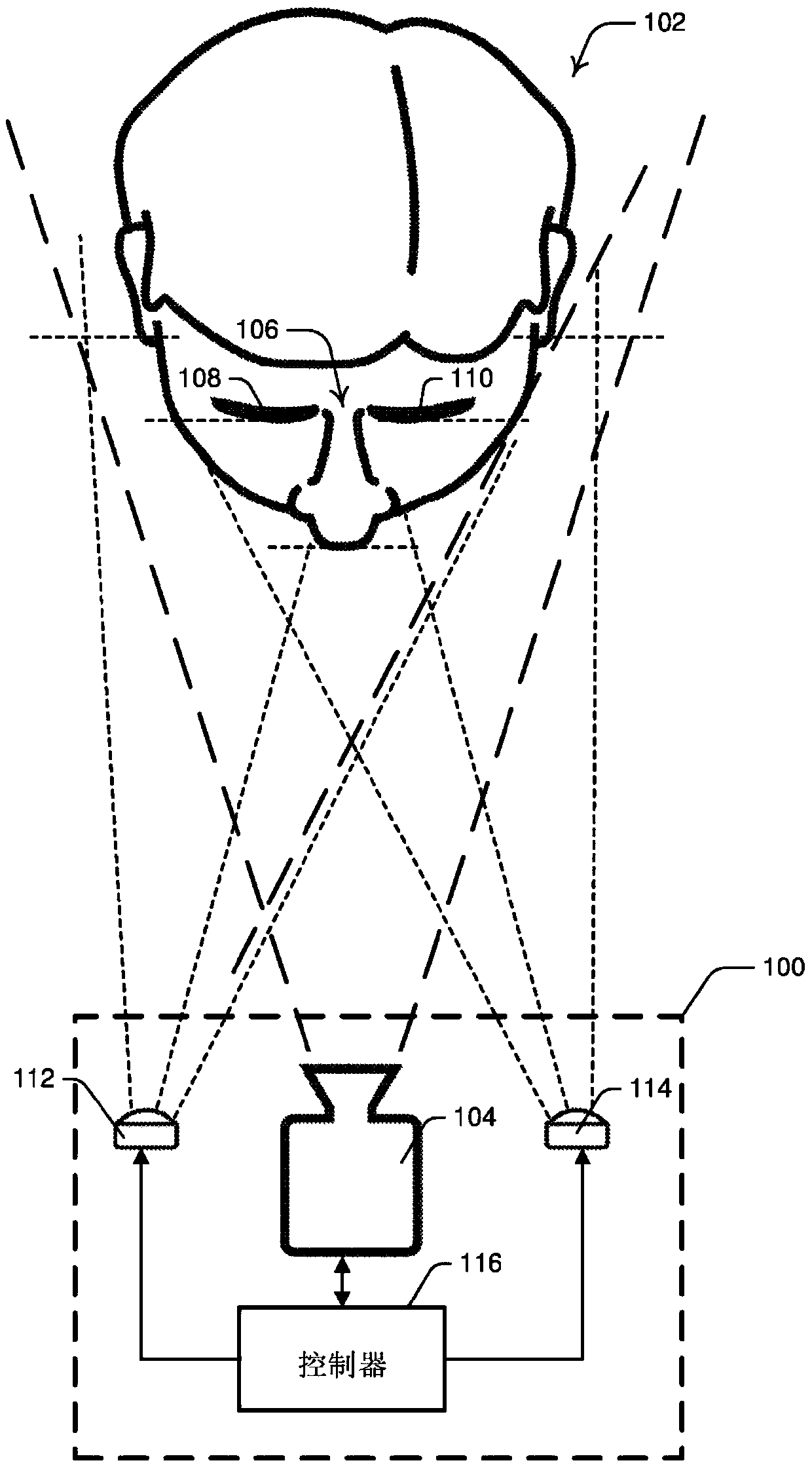
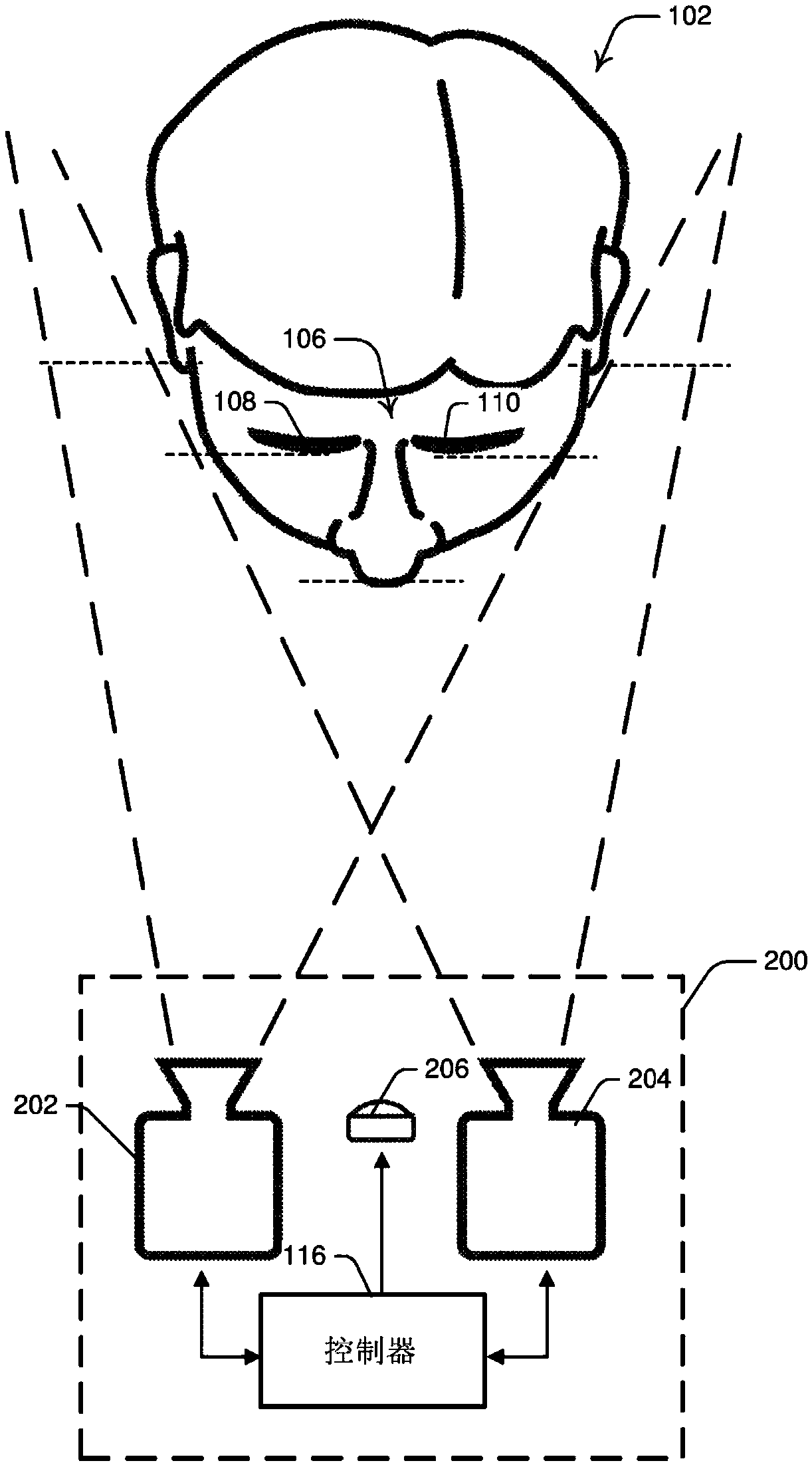
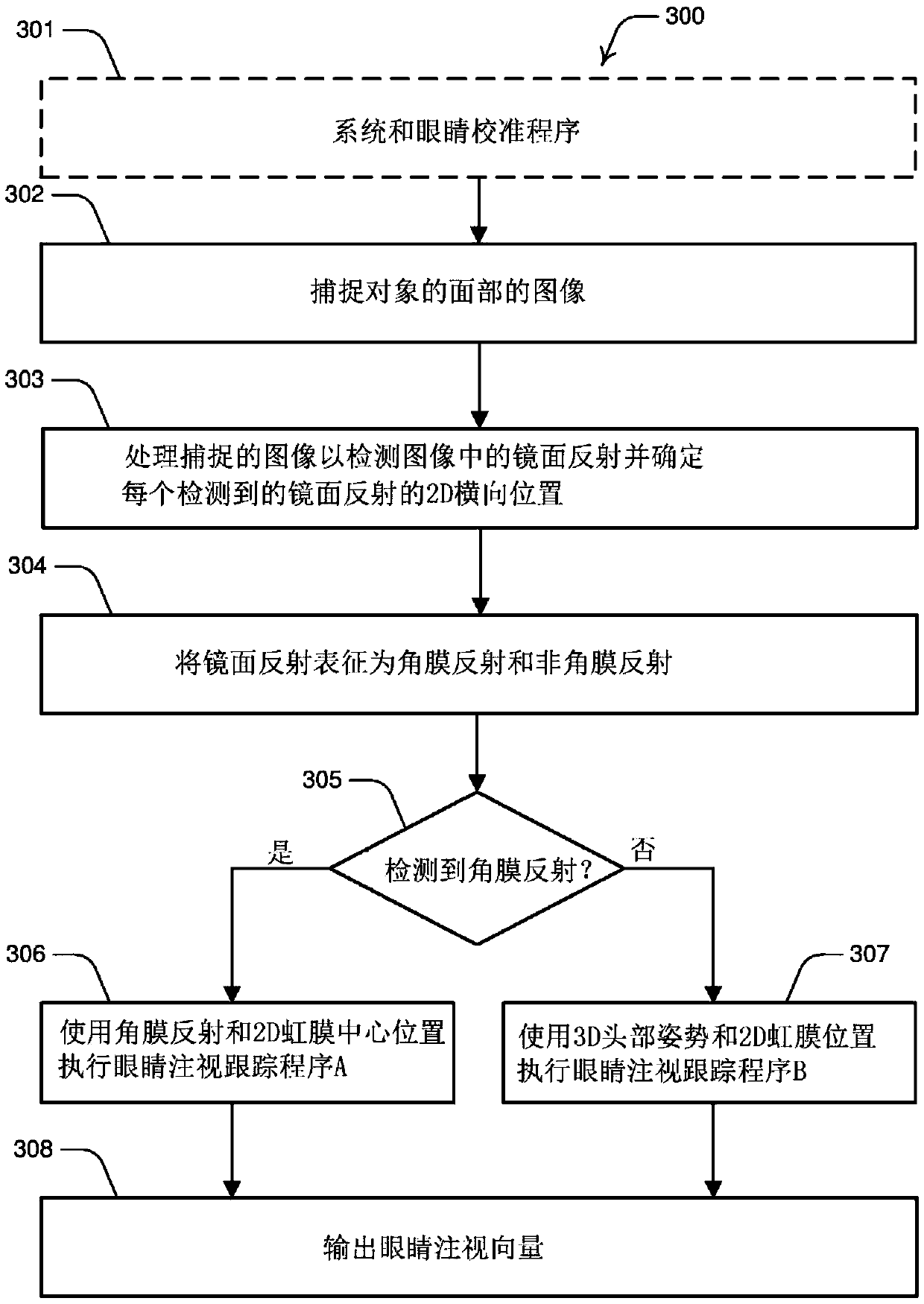
Systems and methods for performing eye gaze tracking
Described herein are systems and methods for performing eye gaze tracking. The method includes capturing, from one or more imaging devices, a sequence of time separated images of the subject's face including one or both of the subject's eyes; processing the images to detect specular reflections present in the images; characterizing the detected specular reflections into corneal reflections and non-corneal reflections; upon detection of at least one corneal reflection, performing a first eye gaze tracking procedure based on the relative positions of the at least one corneal reflection and at least one reference eye feature; upon detection of no corneal reflections, performing a second eye gaze tracking procedure on one or both eyes of the subject based on the estimation of head pose of thesubject and outputting eye gaze vectors of one or both eyes from the first or second eye gaze tracking procedure.
Owner:SEEING MACHINES
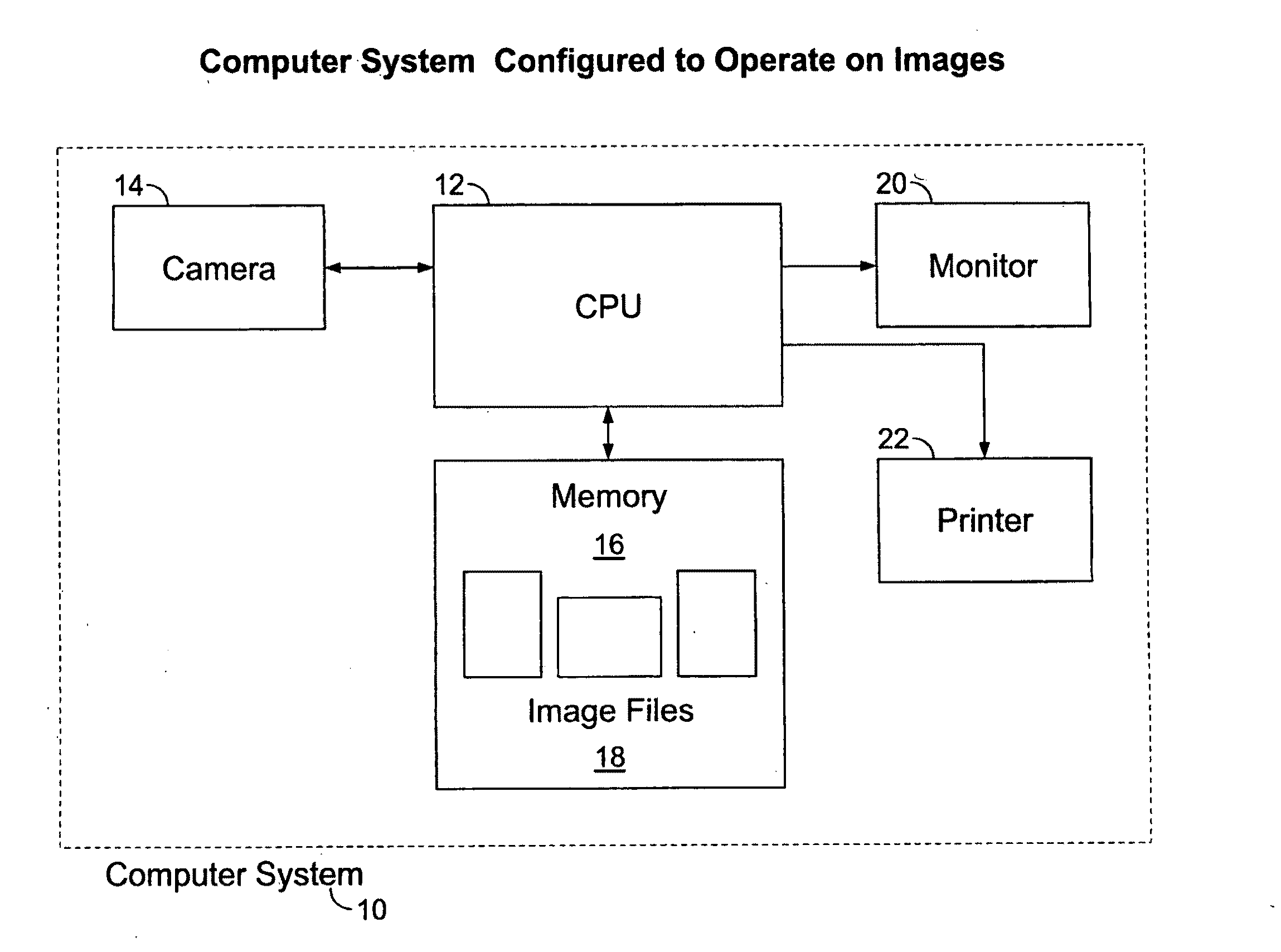
System and method for detection of specularity in an image
In a first exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an automated, computerized method is provided for processing an image. According to a feature of the present invention, the method comprises the steps of providing an image file depicting an image, in a computer memory, assembling a feature vector for the image file, the feature vector containing information regarding a likelihood that a selected region of the image file is specular, providing a classifier derived from a computer learning technique, computing a classification score for the selected region of the image file, as a function of the feature vector and the classifier and classifying the region as being specular, as a function of the classification score.
Owner:INNOVATION ASSET COLLECTIVE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com