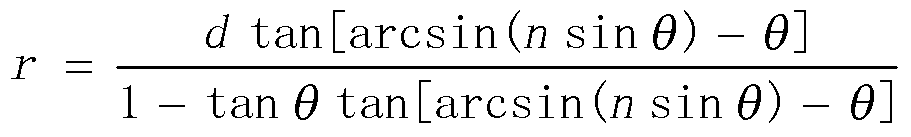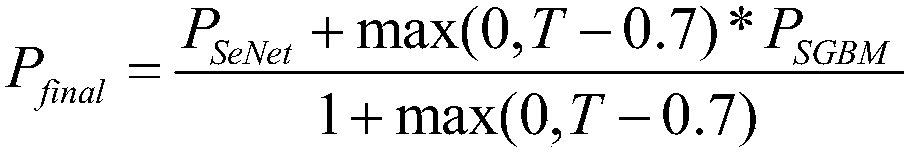Patents
Literature
104 results about "Corneal reflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
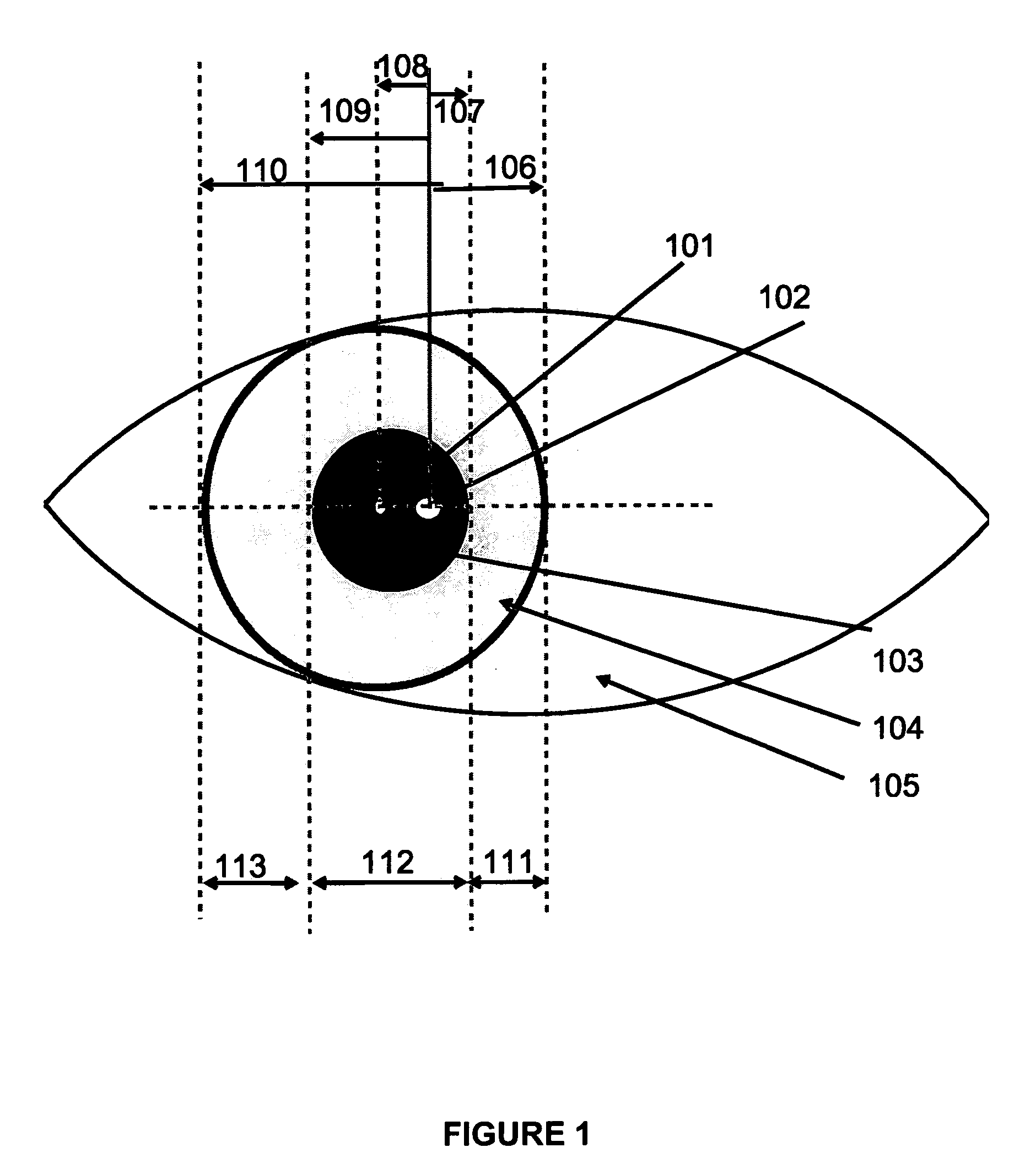
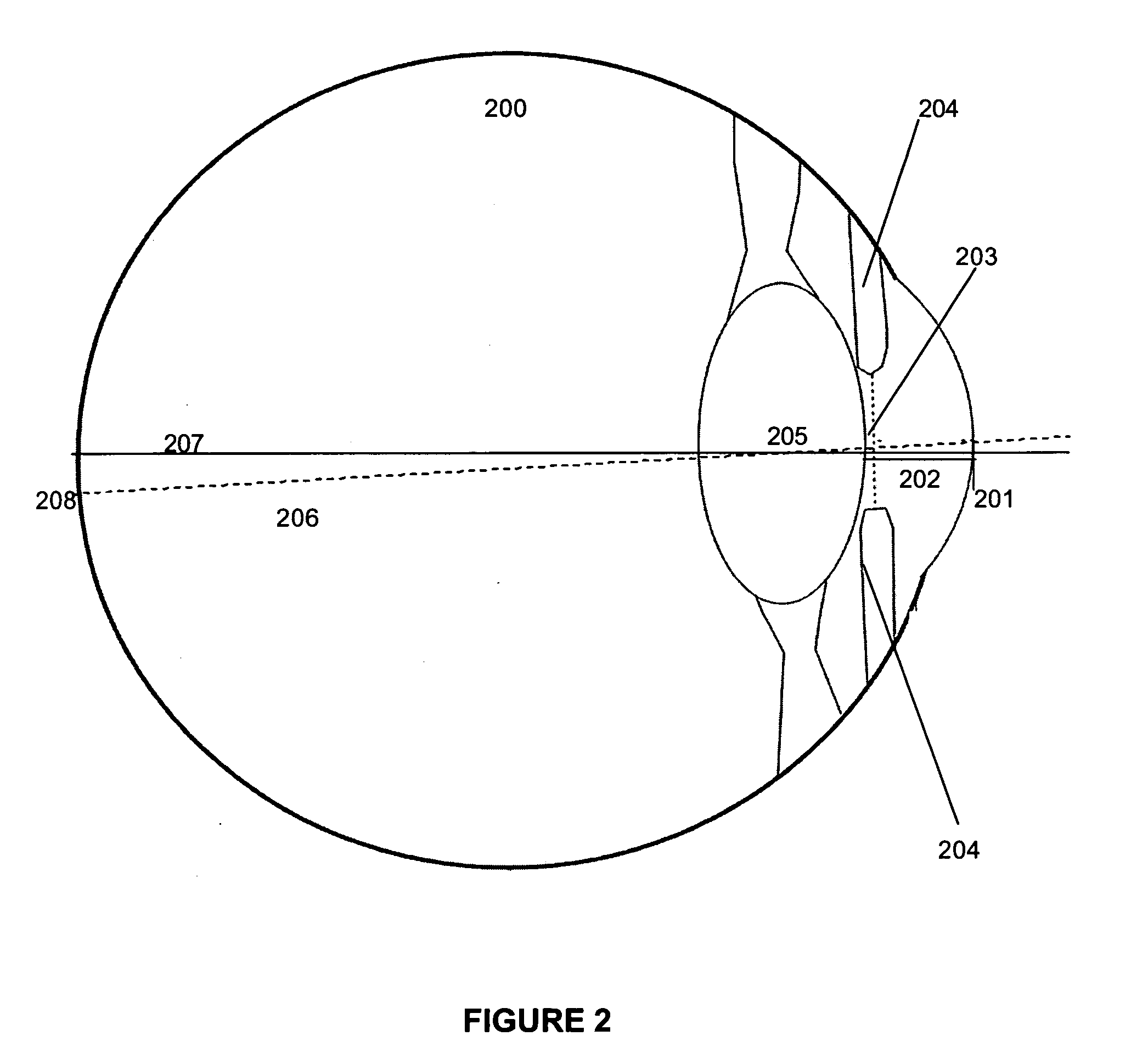
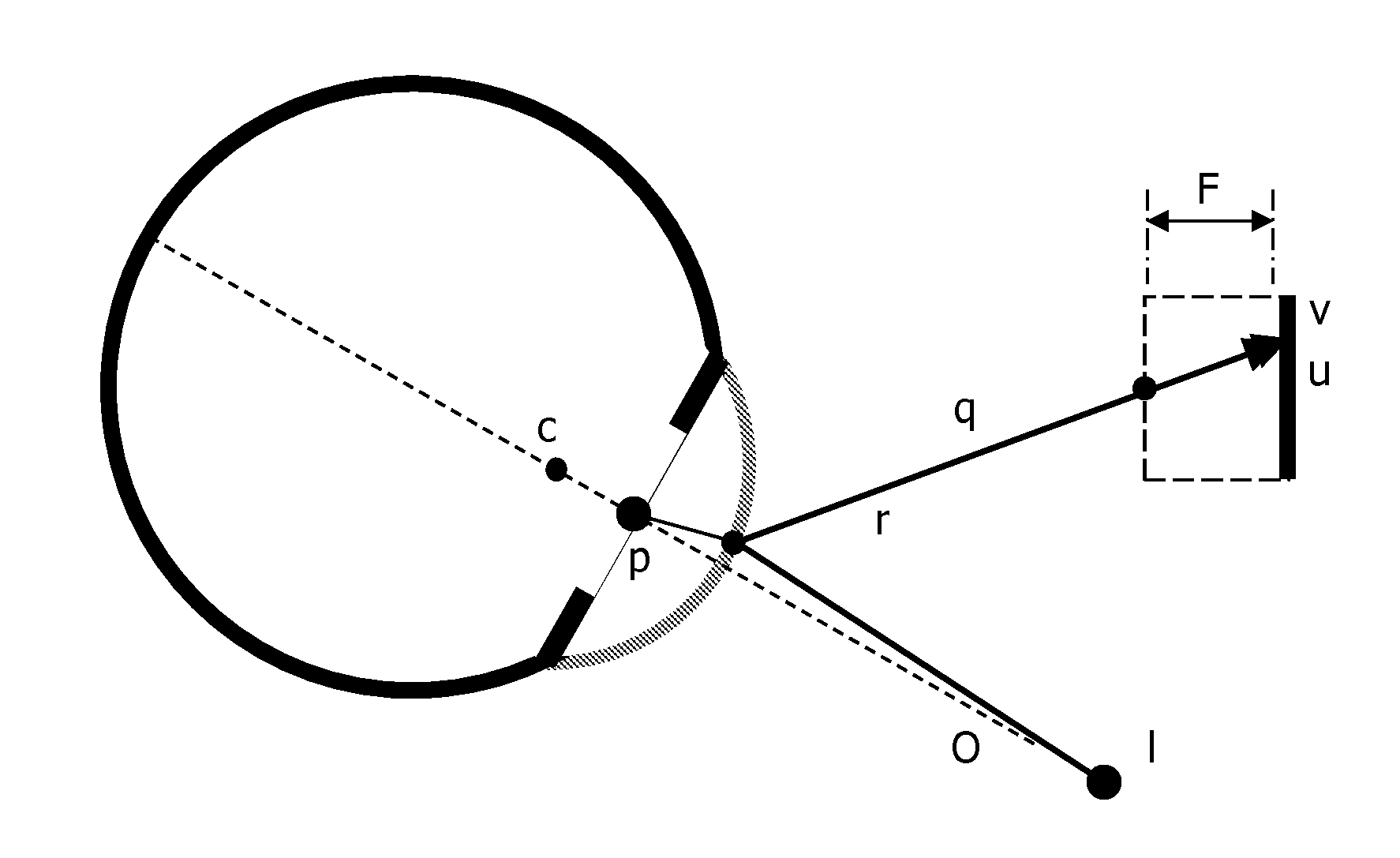
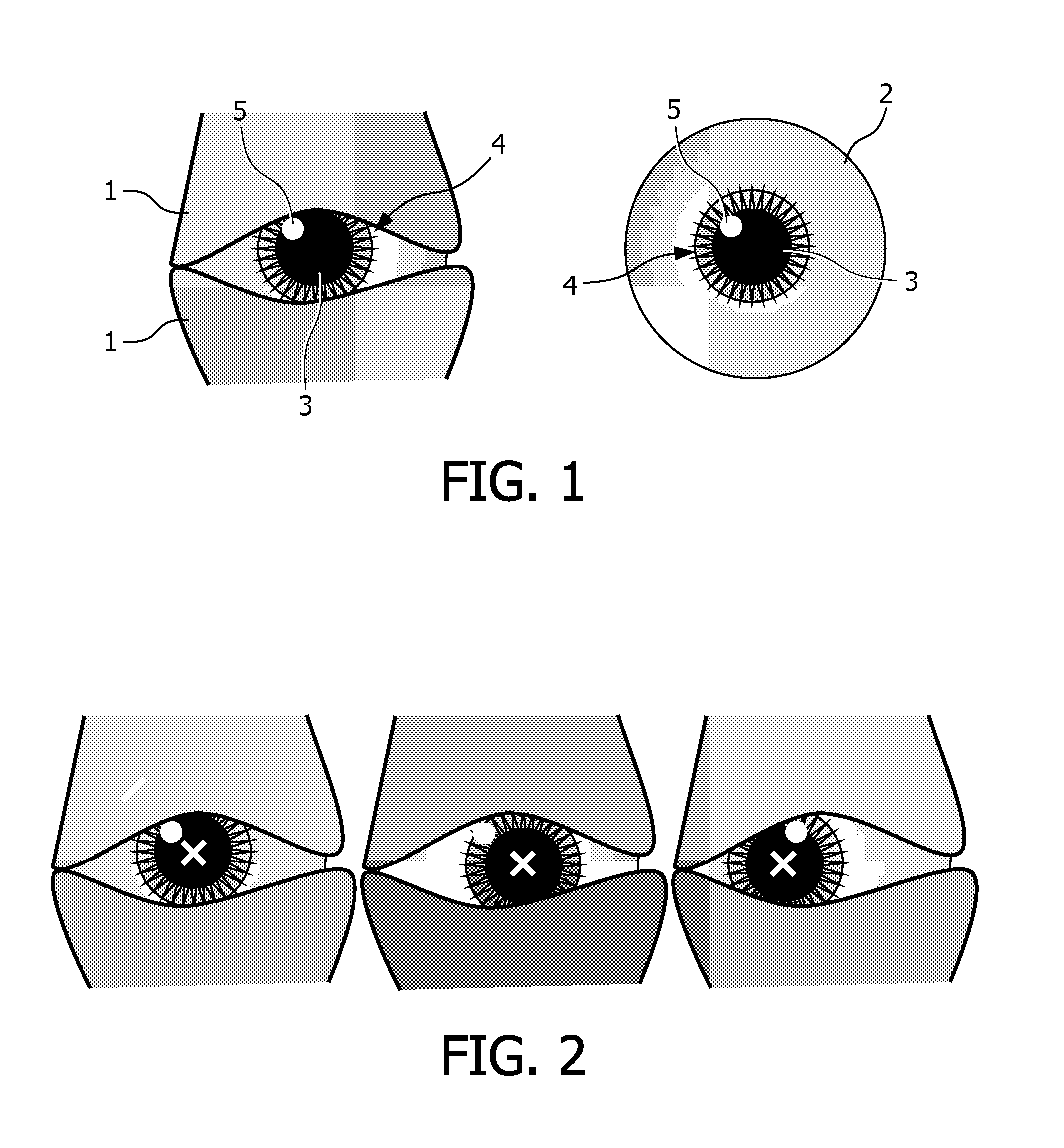
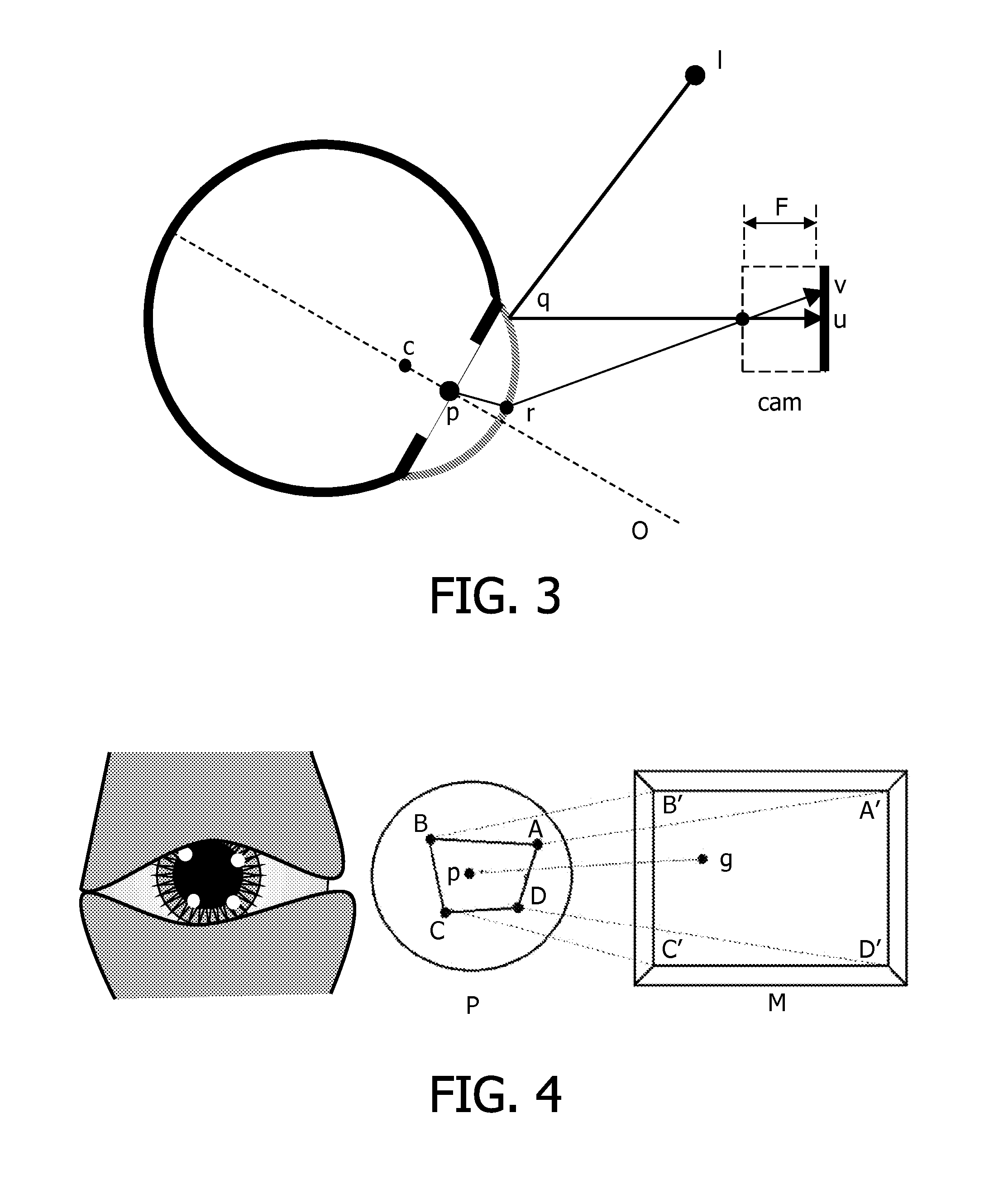
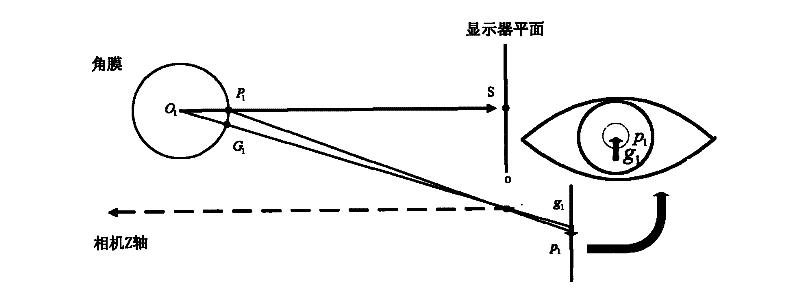
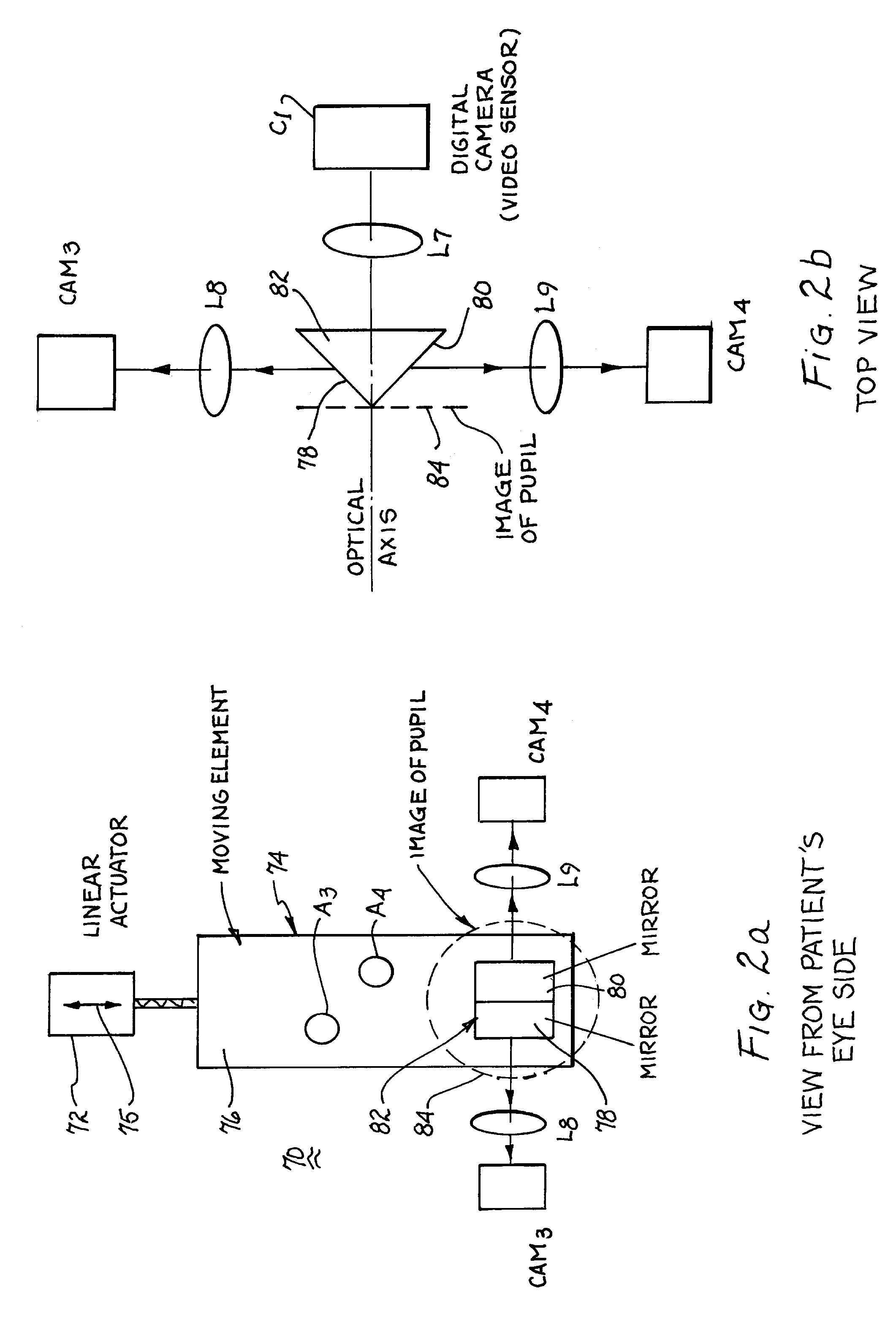
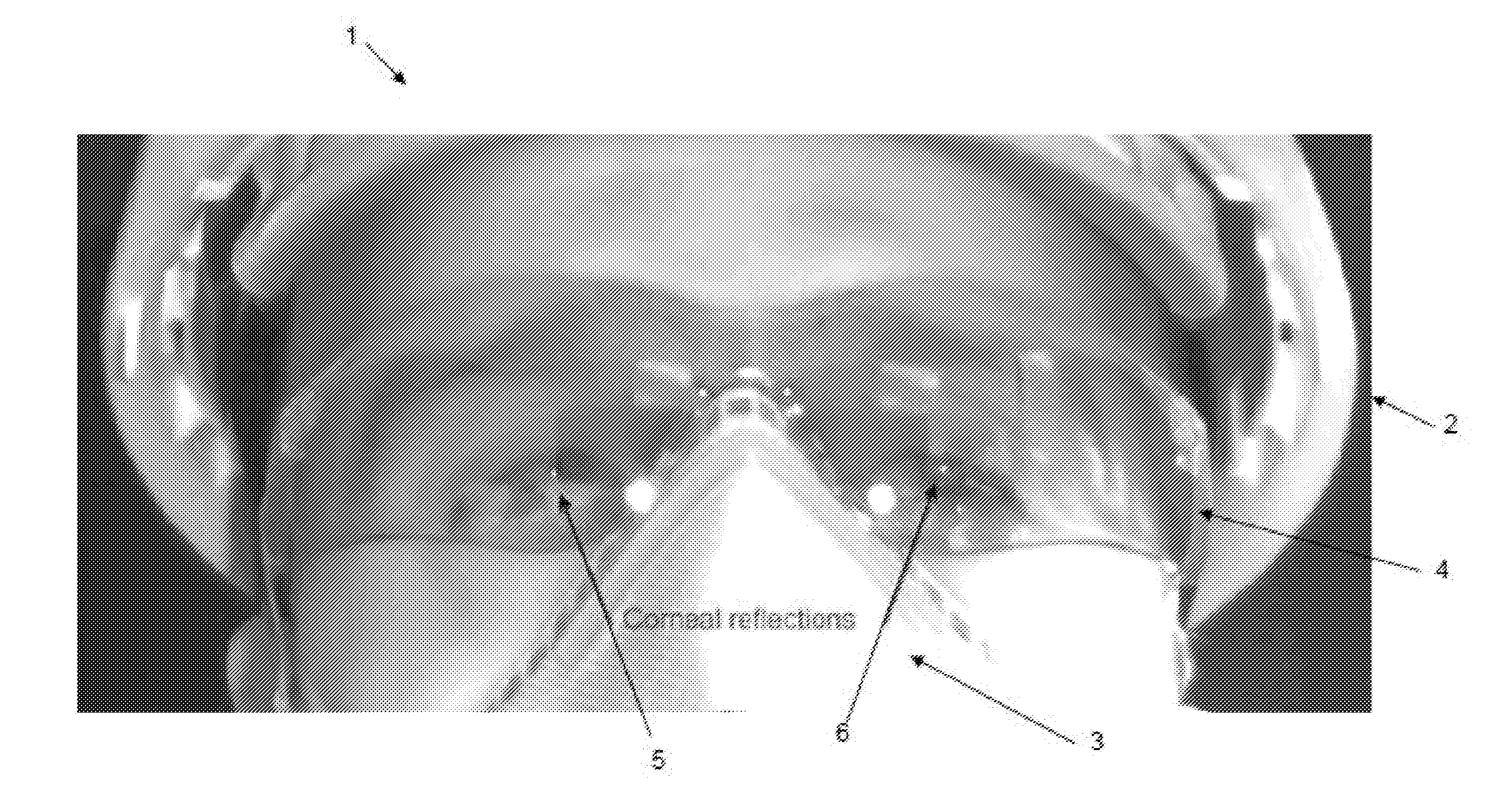
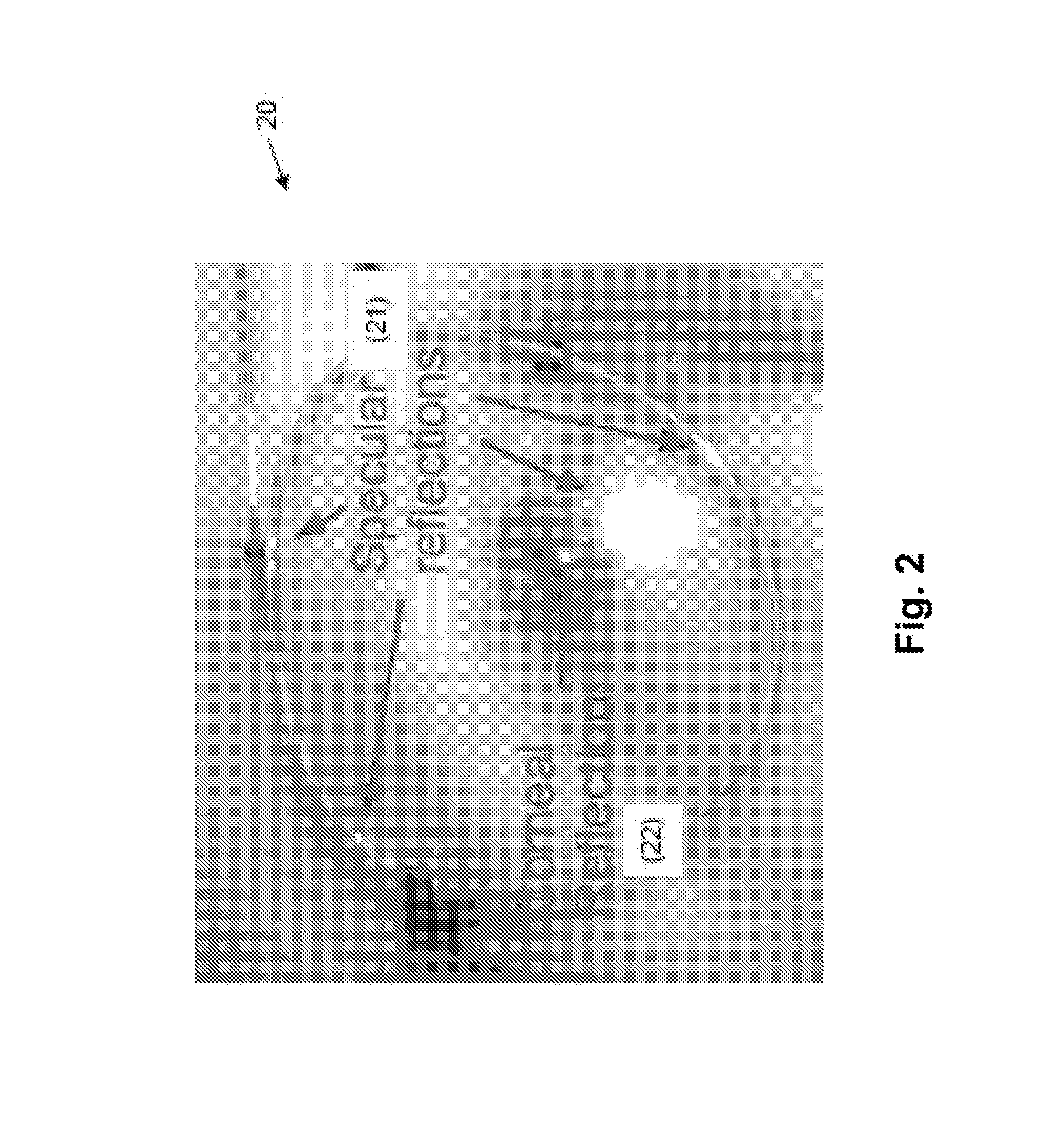
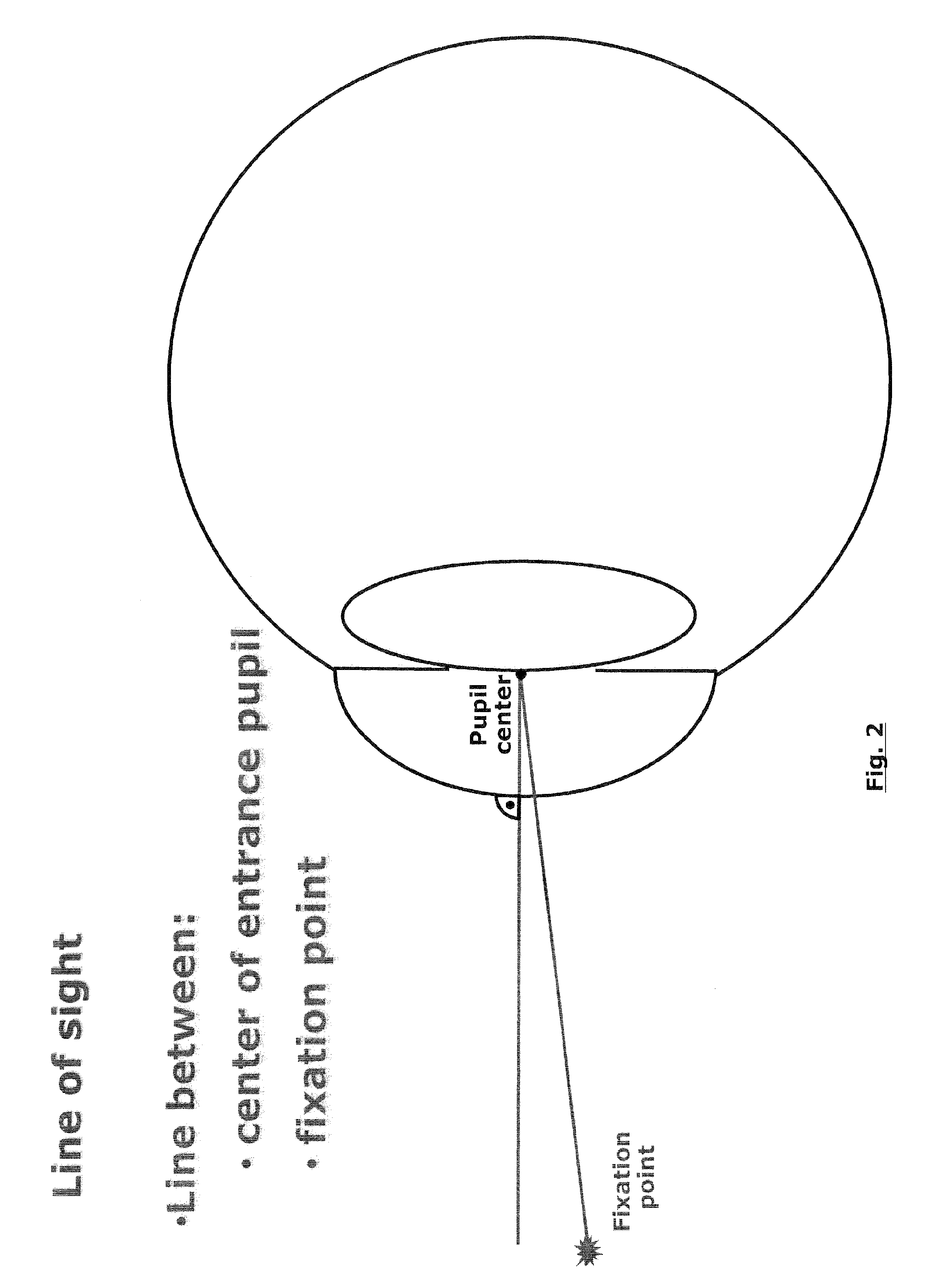
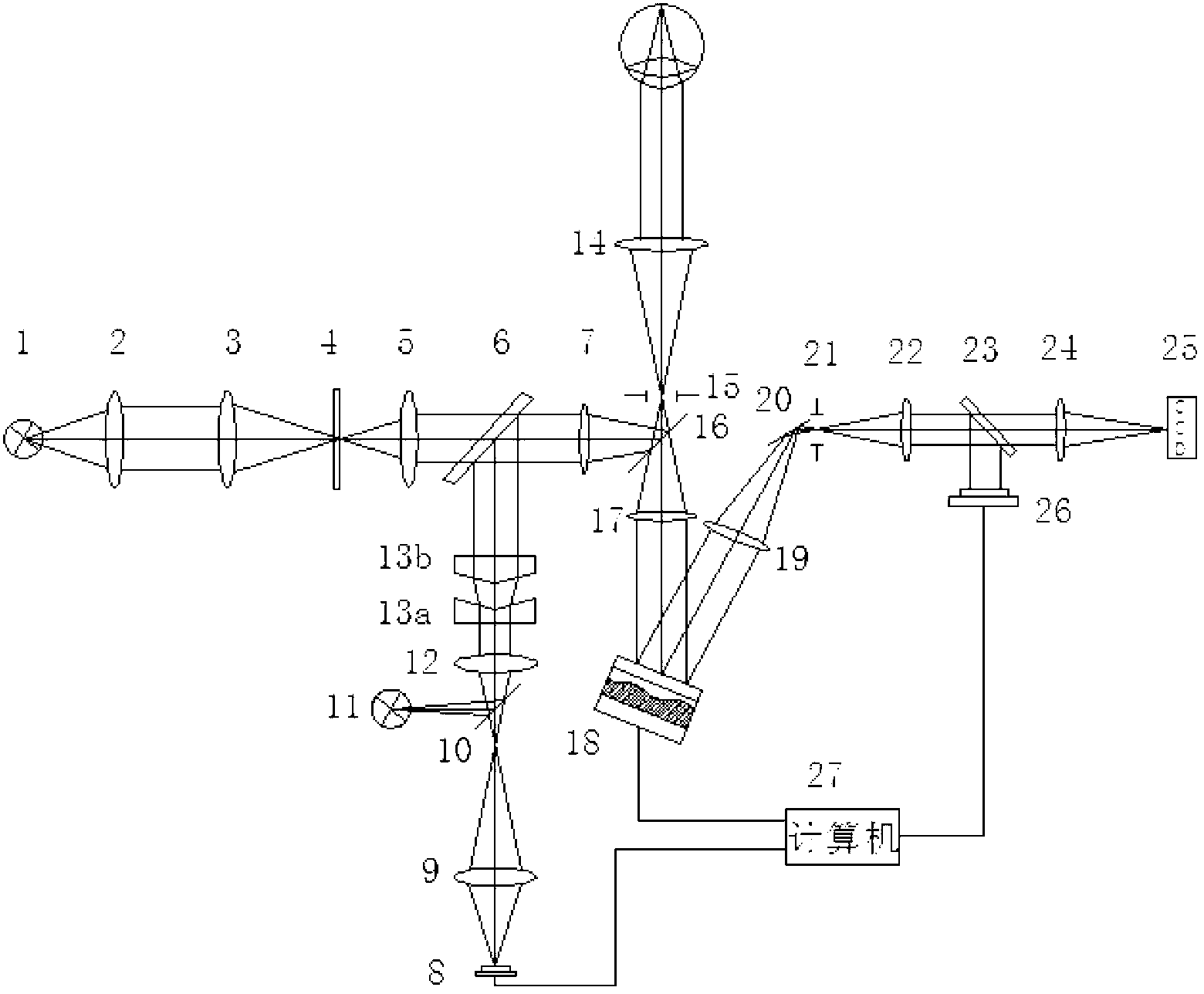
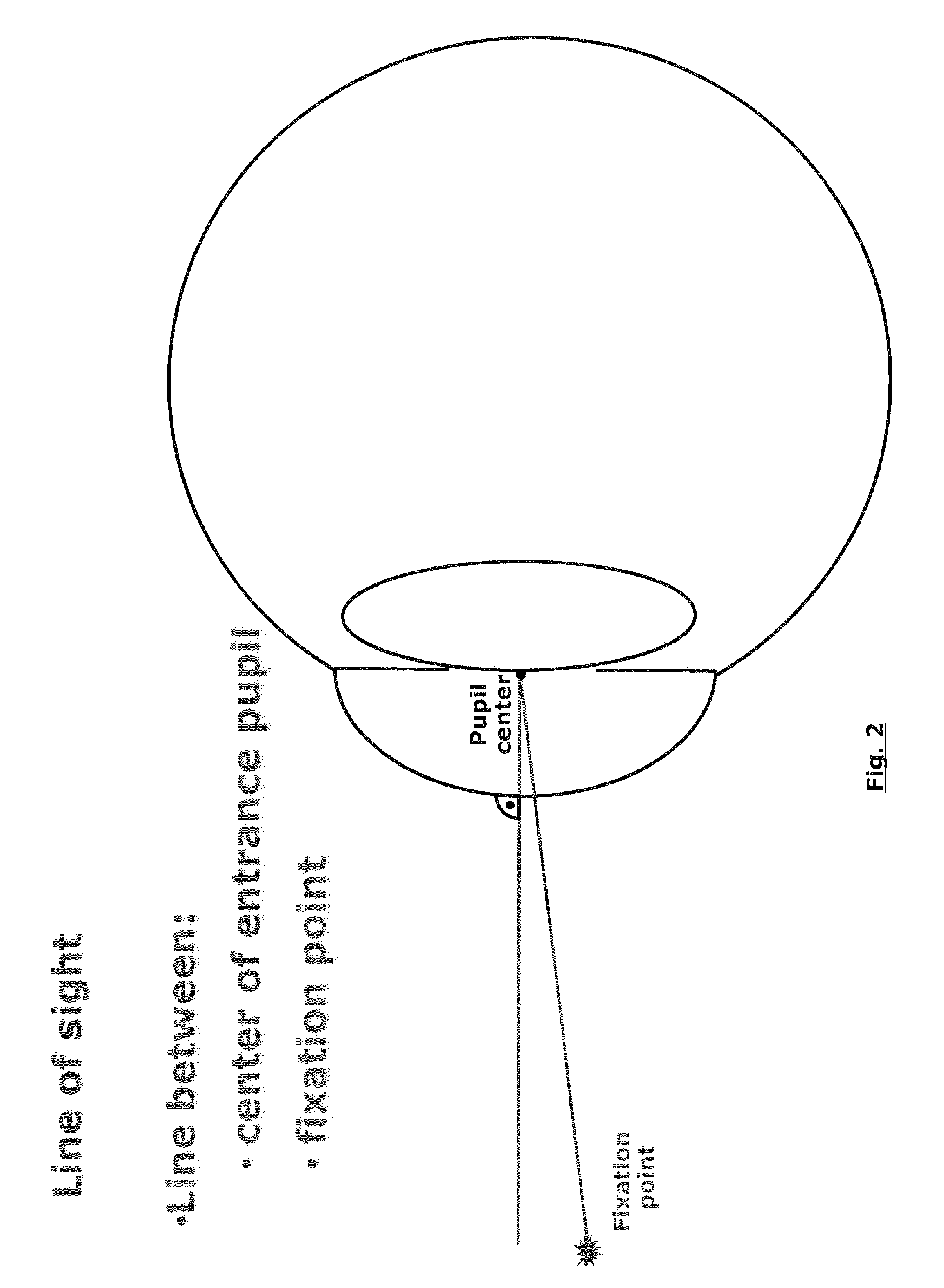
One solution, which every flash photographer has experienced, was to place the light that creates the corneal reflection close to the axis of the lens of the camera. This creates a ‘red reflex’, which is light being reflected back from the surface of the retina and filling the pupil.
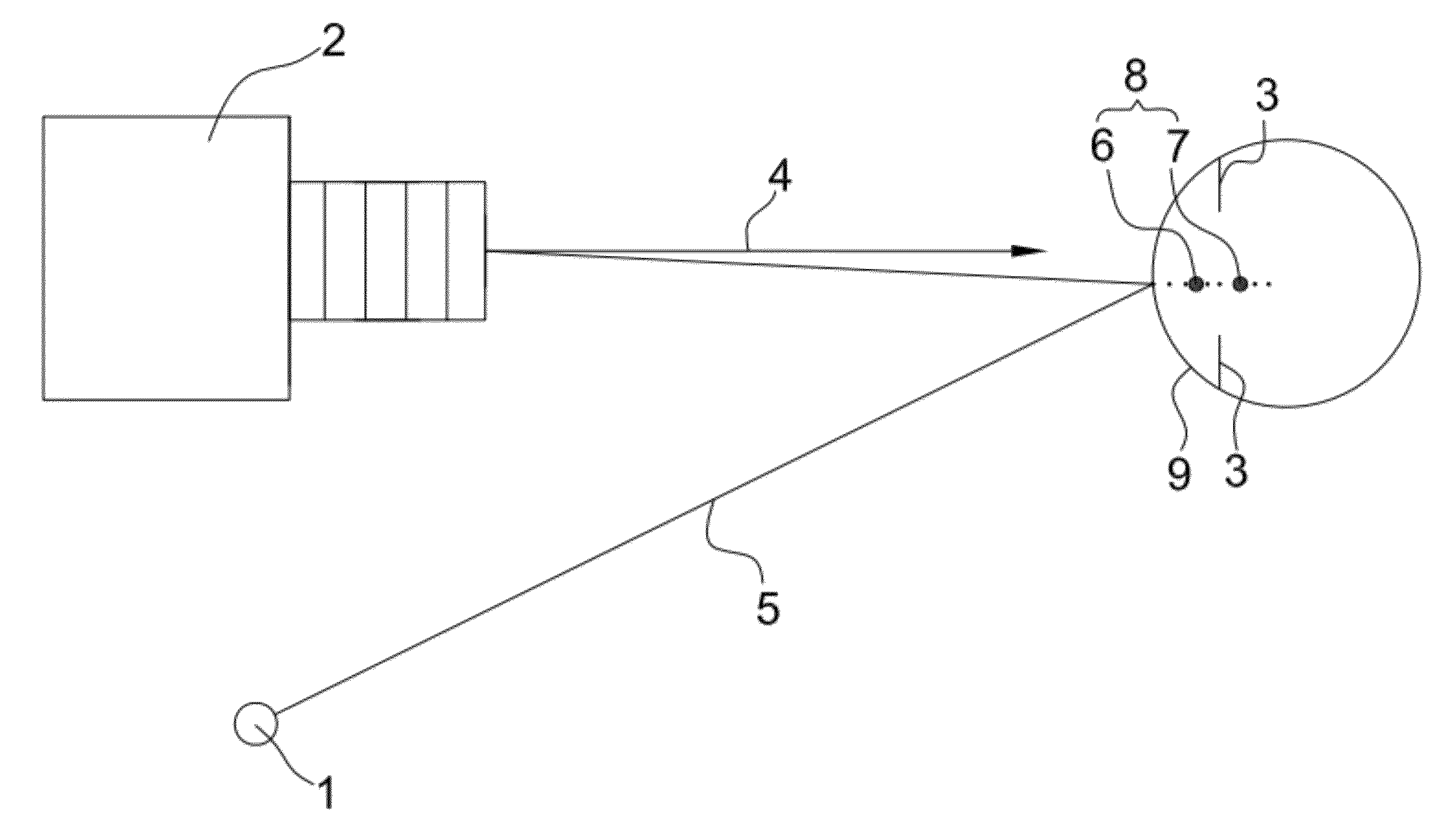
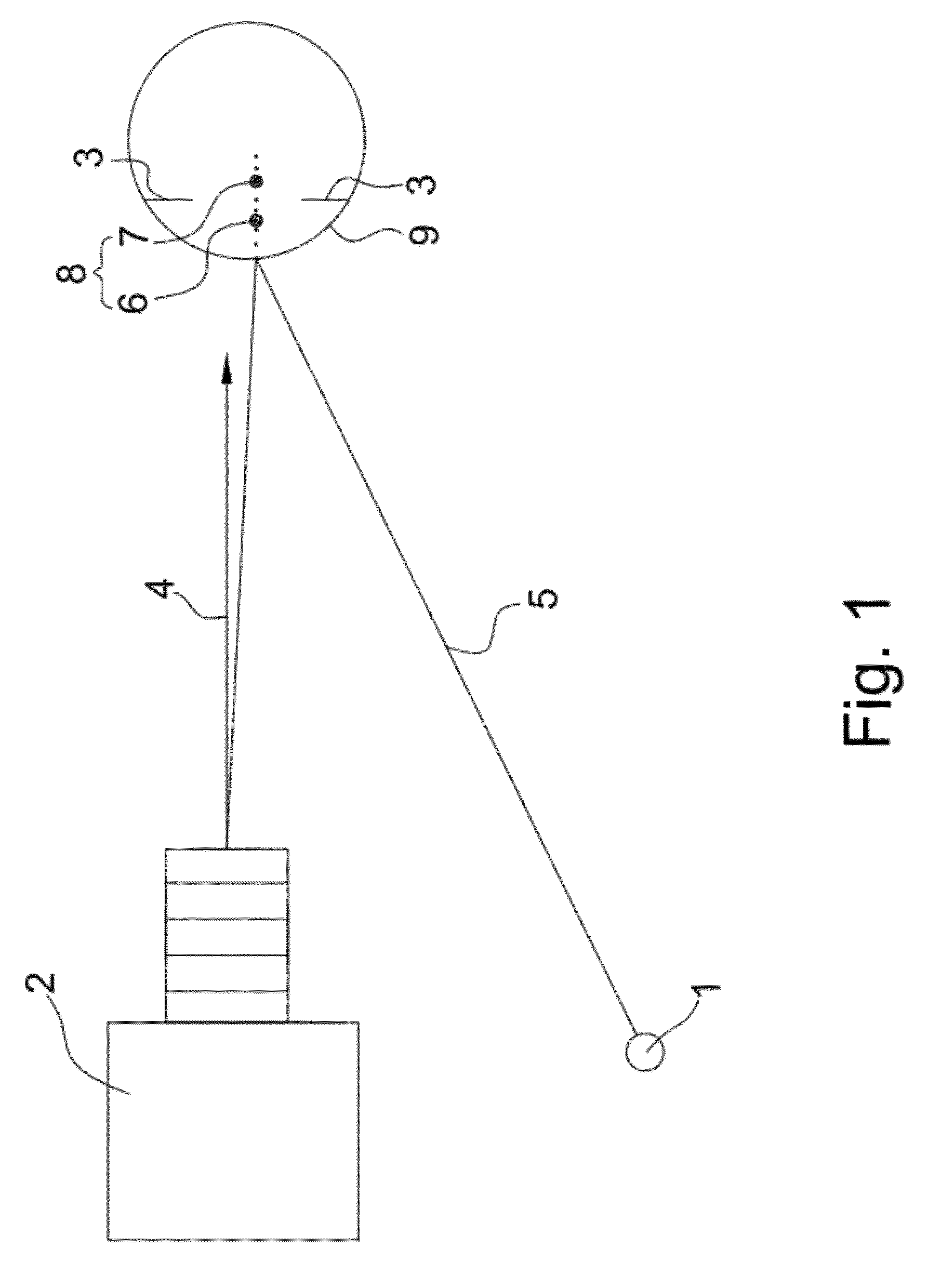
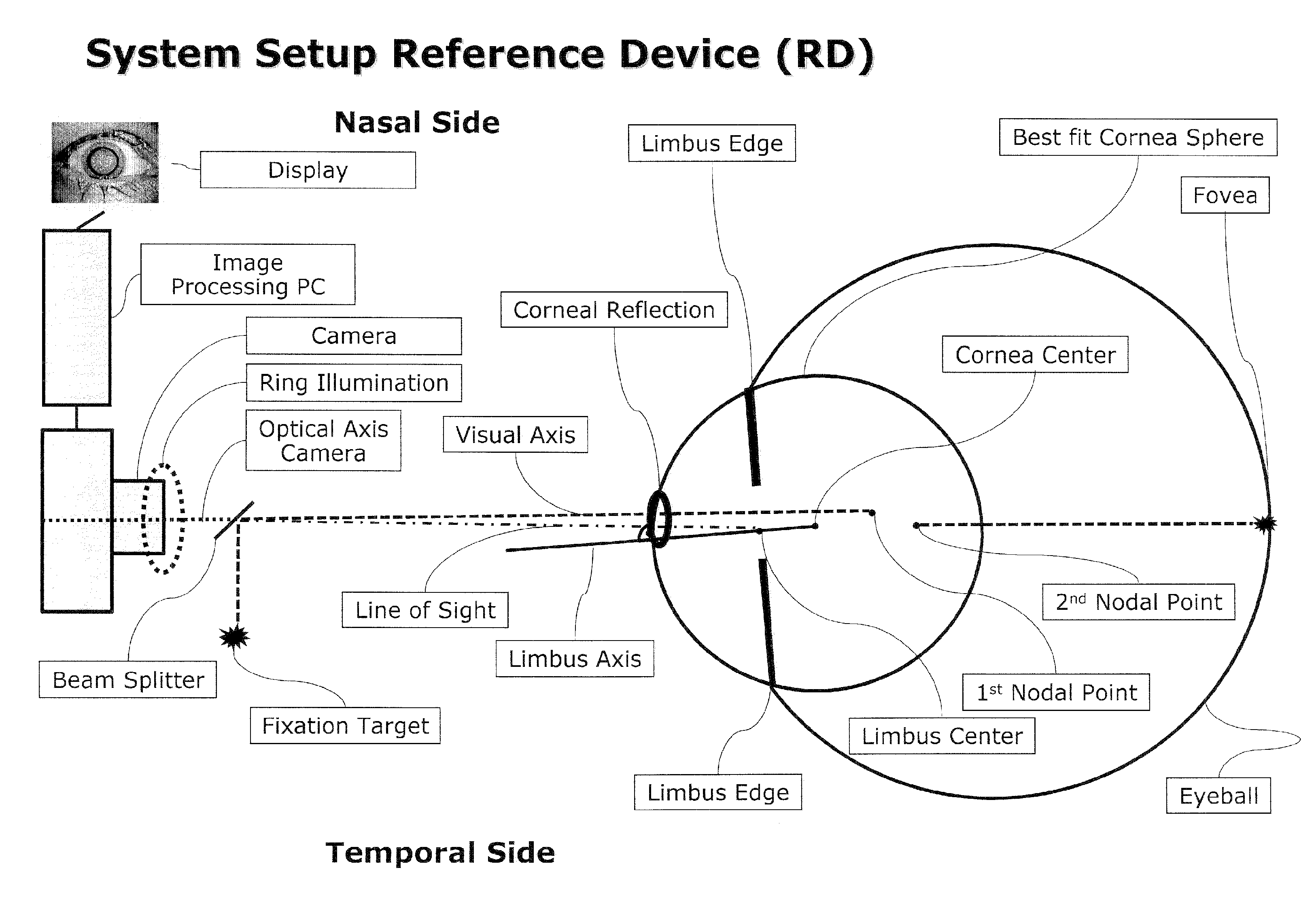
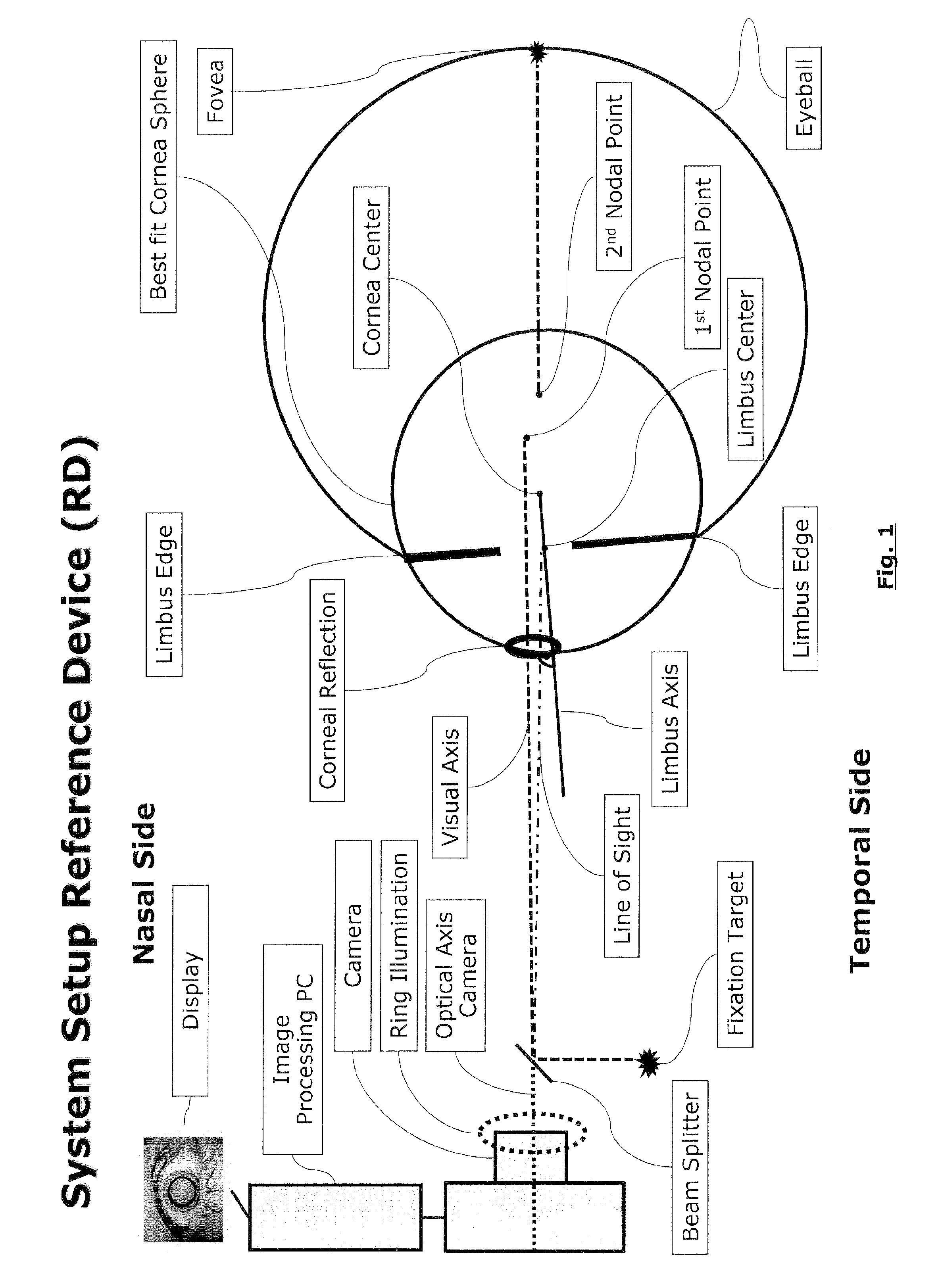
Method and apparatus for calibration-free eye tracking
ActiveUS20060110008A1Extended durationImage enhancementImage analysisCorneal surfaceAngular distance
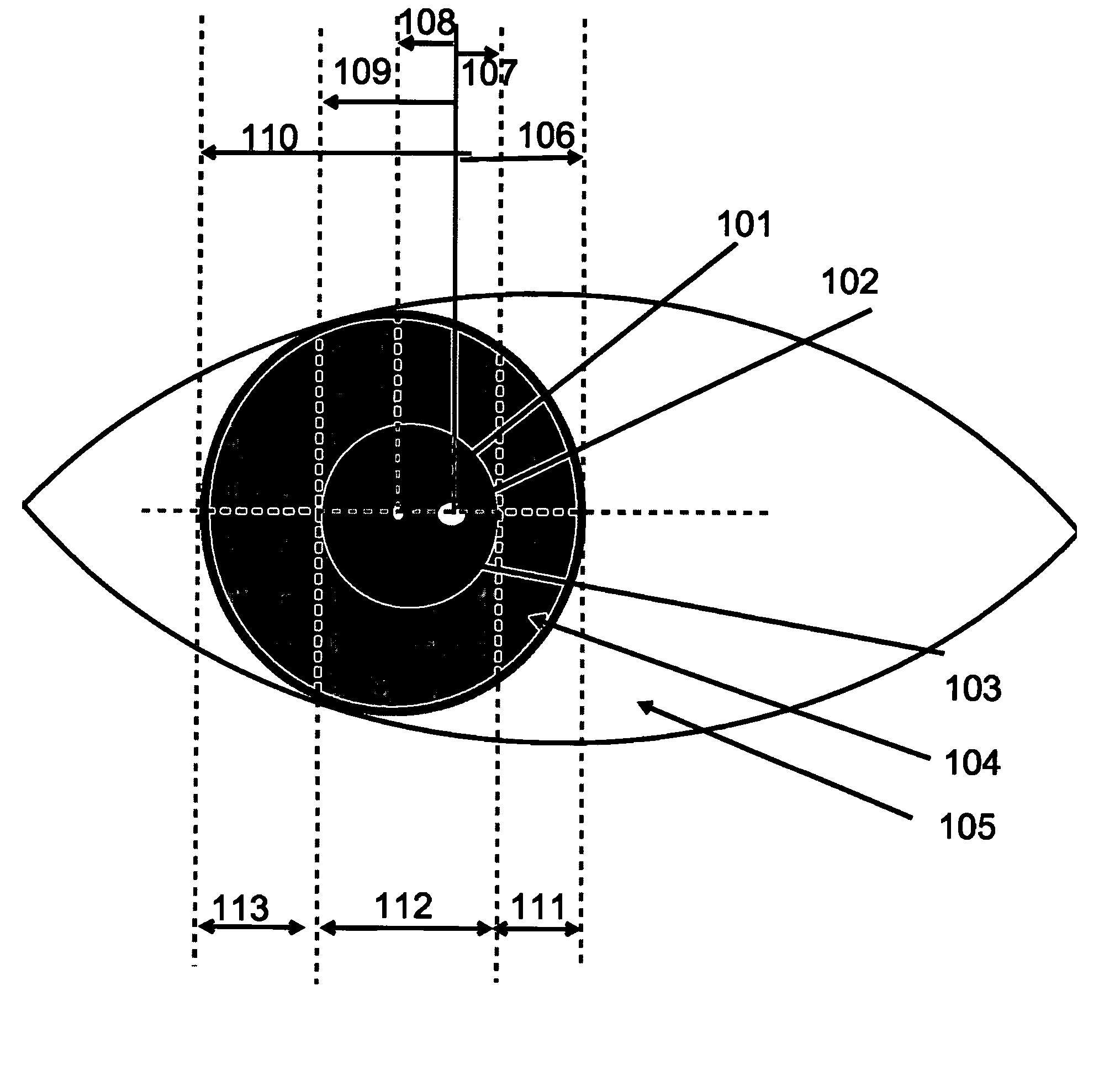
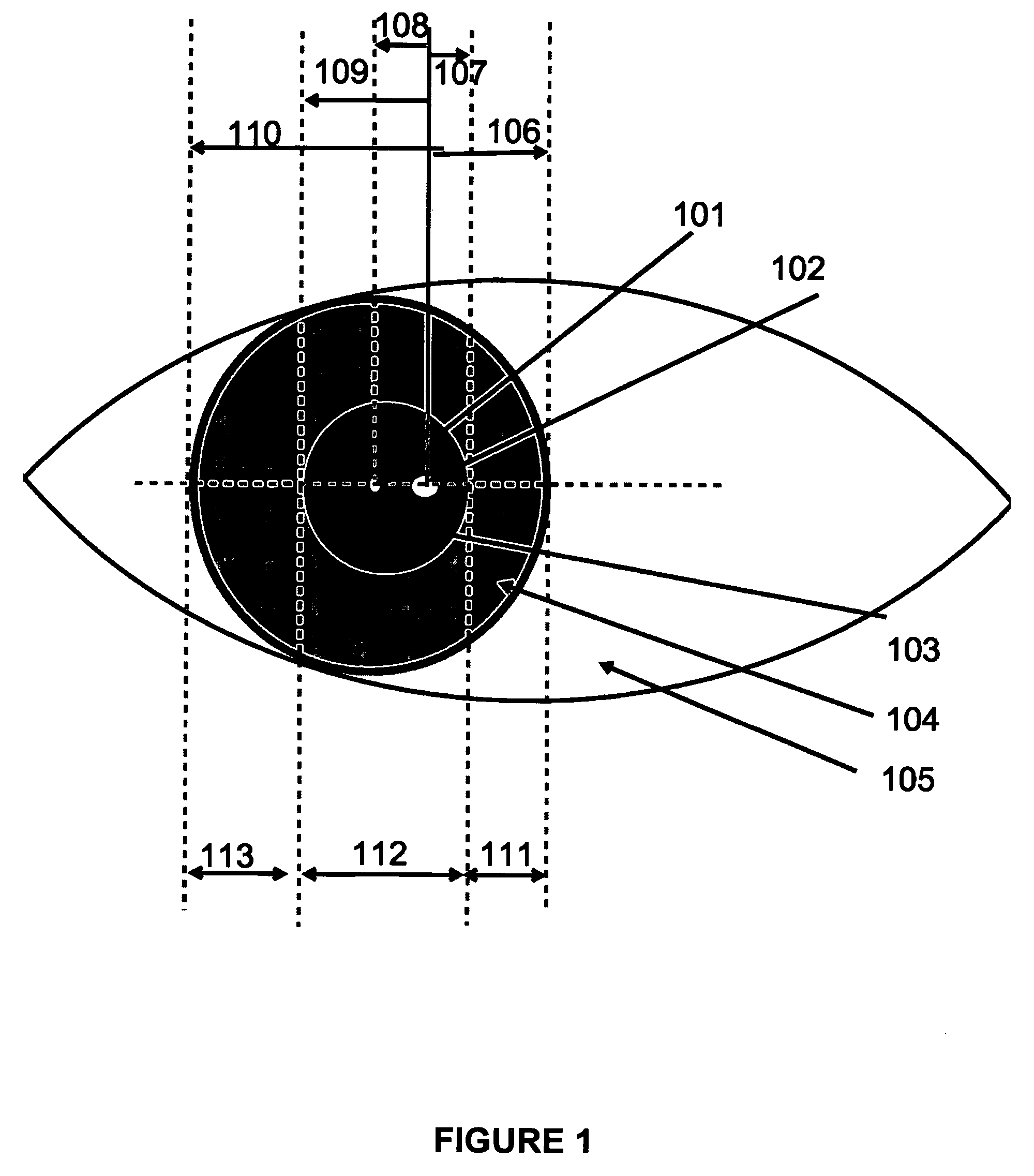
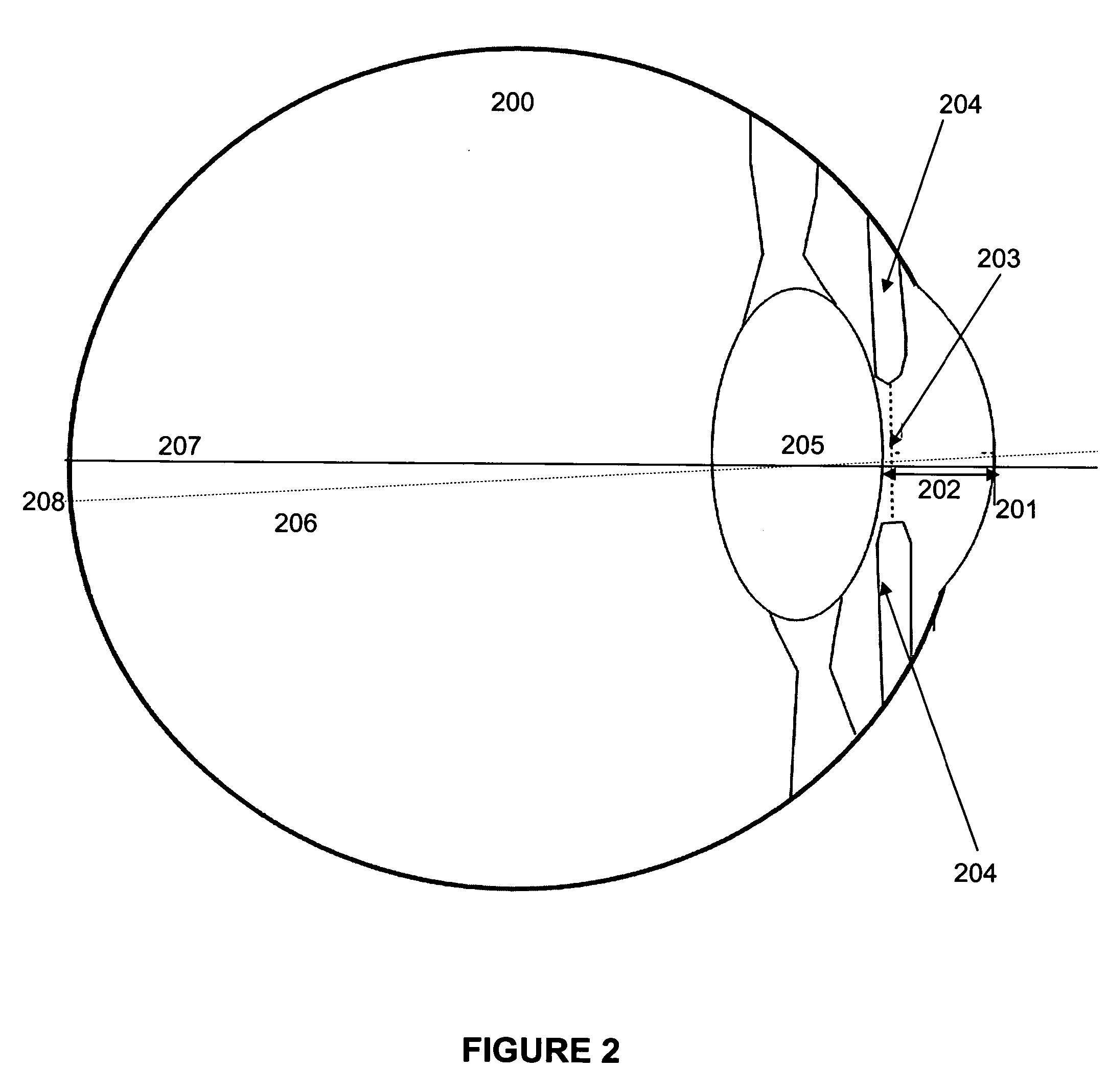
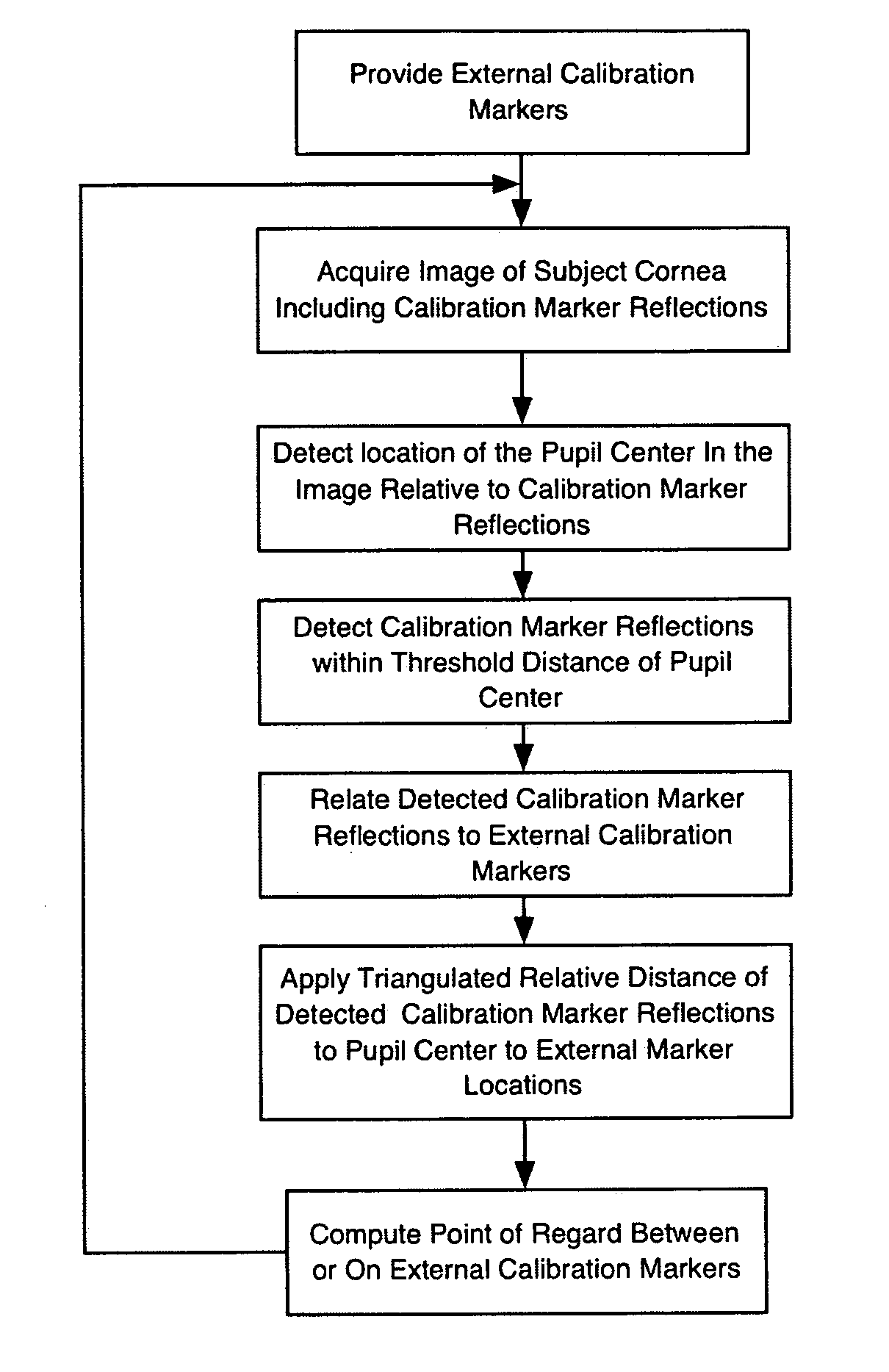
A system and method for eye gaze tracking in human or animal subjects without calibration of cameras, specific measurements of eye geometries or the tracking of a cursor image on a screen by the subject through a known trajectory. The preferred embodiment includes one uncalibrated camera for acquiring video images of the subject's eye(s) and optionally having an on-axis illuminator, and a surface, object, or visual scene with embedded off-axis illuminator markers. The off-axis markers are reflected on the corneal surface of the subject's eyes as glints. The glints indicate the distance between the point of gaze in the surface, object, or visual scene and the corresponding marker on the surface, object, or visual scene. The marker that causes a glint to appear in the center of the subject's pupil is determined to be located on the line of regard of the subject's eye, and to intersect with the point of gaze. Point of gaze on the surface, object, or visual scene is calculated as follows. First, by determining which marker glints, as provided by the corneal reflections of the markers, are closest to the center of the pupil in either or both of the subject's eyes. This subset of glints forms a region of interest (ROI). Second, by determining the gaze vector (relative angular or Cartesian distance to the pupil center) for each of the glints in the ROI. Third, by relating each glint in the ROI to the location or identification (ID) of a corresponding marker on the surface, object, or visual scene observed by the eyes. Fourth, by interpolating the known locations of each these markers on the surface, object, or visual scene, according to the relative angular distance of their corresponding glints to the pupil center.
Owner:CHENG DANIEL +3
Method and apparatus for calibration-free eye tracking using multiple glints or surface reflections
InactiveUS20050175218A1Input/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementCorneal surfaceAngular distance
A system and method for eye gaze tracking in human or animal subjects without calibration of cameras, specific measurements of eye geometries or the tracking of a cursor image on a screen by the subject through a known trajectory. The preferred embodiment includes one uncalibrated camera for acquiring video images of the subject's eye(s) and optionally having an on-axis illuminator, and a surface, object, or visual scene with embedded off-axis illuminator markers. The off-axis markers are reflected on the corneal surface of the subject's eyes as glints. The glints indicate the distance between the point of gaze in the surface, object, or visual scene and the corresponding marker on the surface, object, or visual scene. The marker that causes a glint to appear in the center of the subject's pupil is determined to be located on the line of regard of the subject's eye, and to intersect with the point of gaze. Point of gaze on the surface, object, or visual scene is calculated as follows. First, by determining which marker glints, as provided by the corneal reflections of the markers, are closest to the center of the pupil in either or both of the subject's eyes. This subset of glints forms a region of interest (ROI). Second, by determining the gaze vector (relative angular or cartesian distance to the pupil center) for each of the glints in the ROI. Third, by relating each glint in the ROI to the location or identification (ID) of a corresponding marker on the surface, object, or visual scene observed by the eyes. Fourth, by interpolating the known locations of each these markers on the surface, object, or visual scene, according to the relative angular distance of their corresponding glints to the pupil center.
Owner:CHENG DANIEL +3
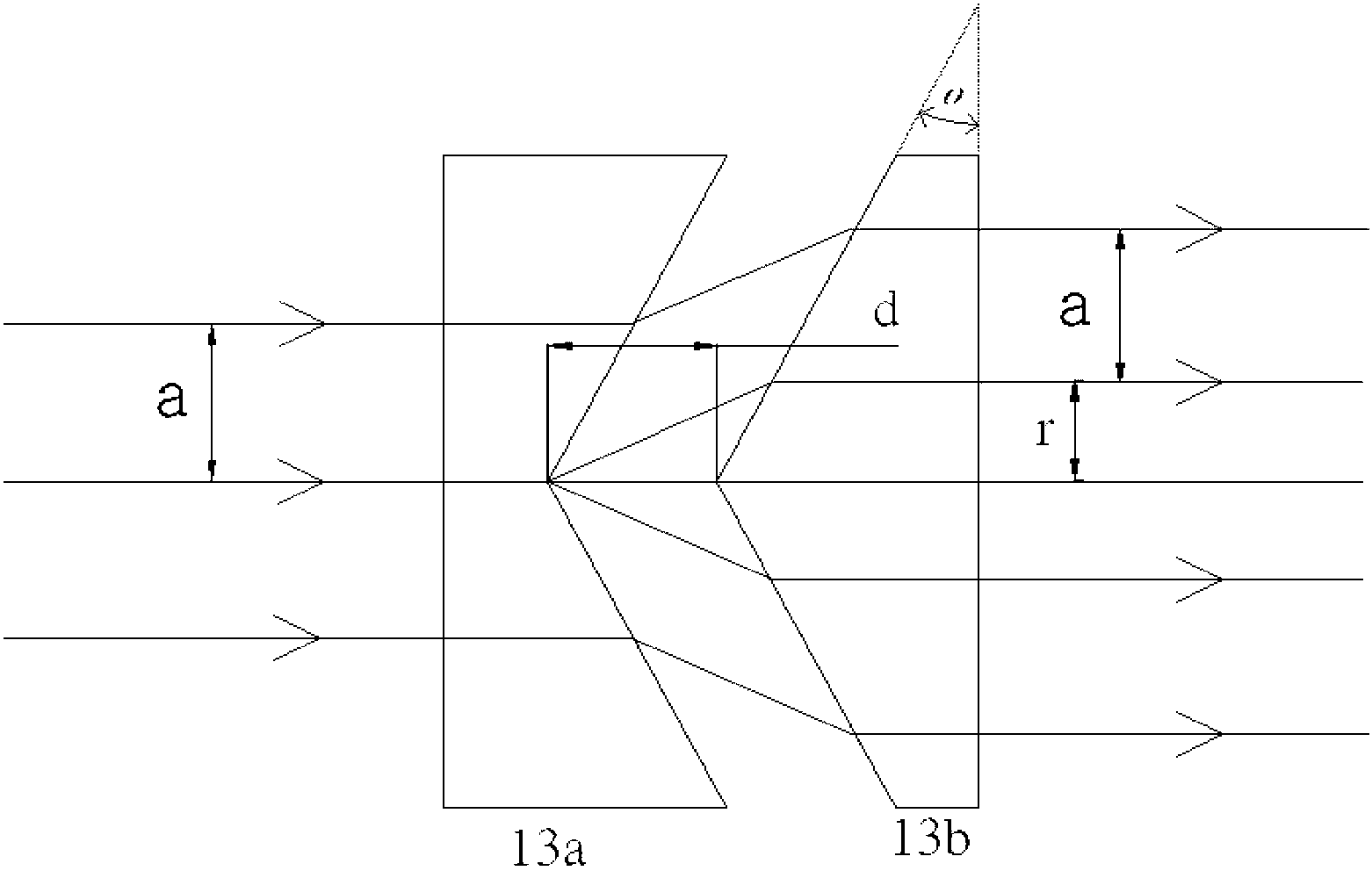
Iris image definition estimation system using the astigmatism of the corneal reflection of a non-coaxial light source
An iris image definition estimation system using the astigmatism of the corneal reflection of a non-coaxial light source to assess both the resolution of the iris patterns and the direction of focus adjustment. The corneal reflection results in two virtual images on the meridional and the sagittal planes. These virtual images are formed behind the cornea and close to the iris. Yet, both are projected onto the same location and result in a composite glint area. In addition, the shape of the glint area of a non-coaxial light source varies with different camera focus settings. Furthermore, due to the high intensity of the glint area, the shape can be easily observed, and the size and the shape of the glint area can be used to determine the resolution of the iris image and the direction of focus adjustment, respectively.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Hand held device and methods for examining a patient's retina
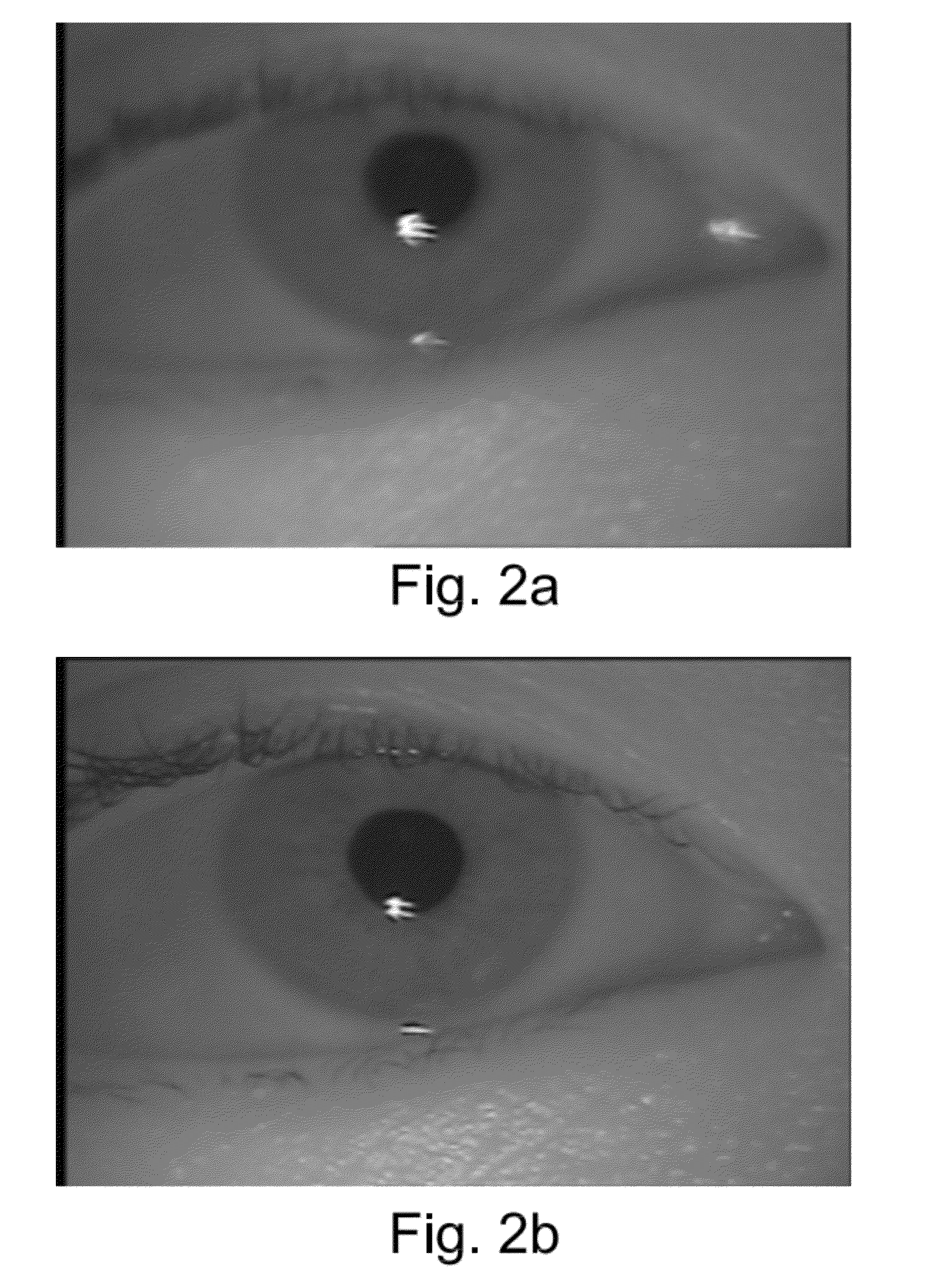
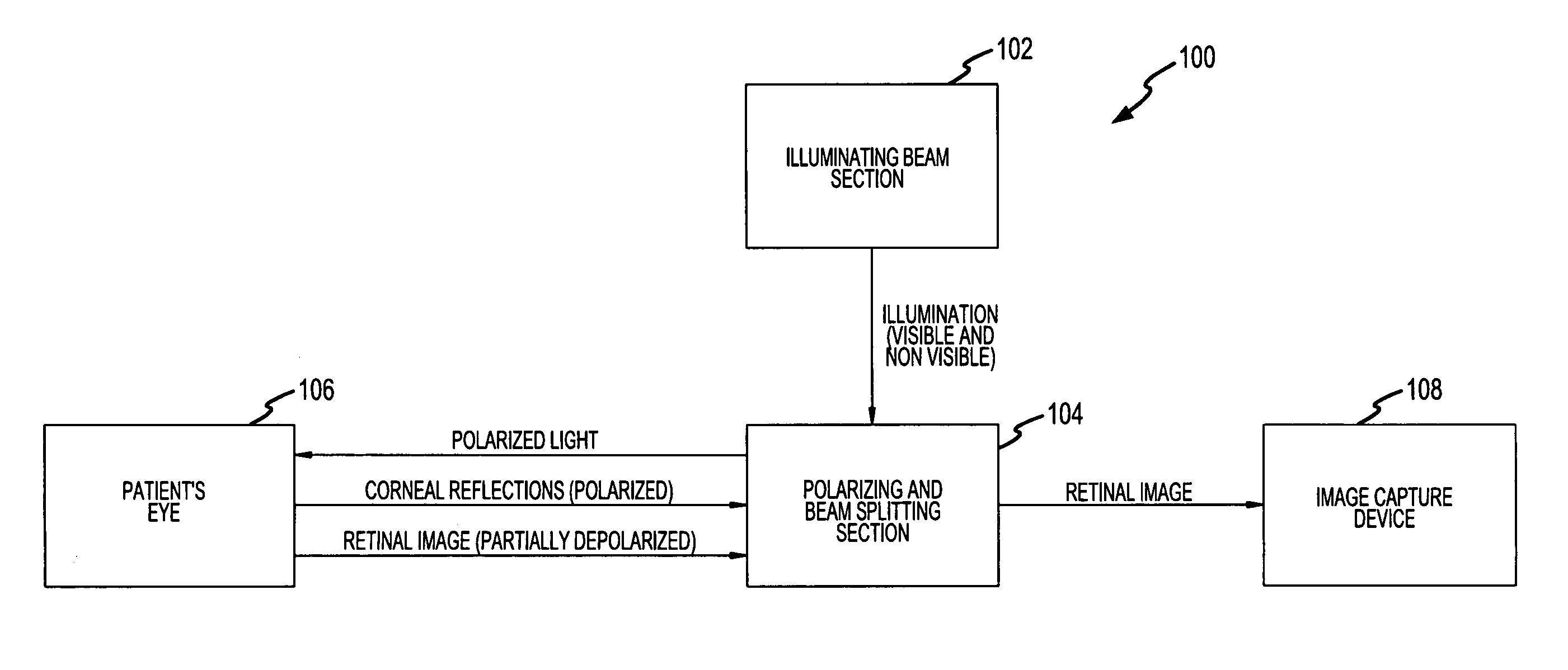
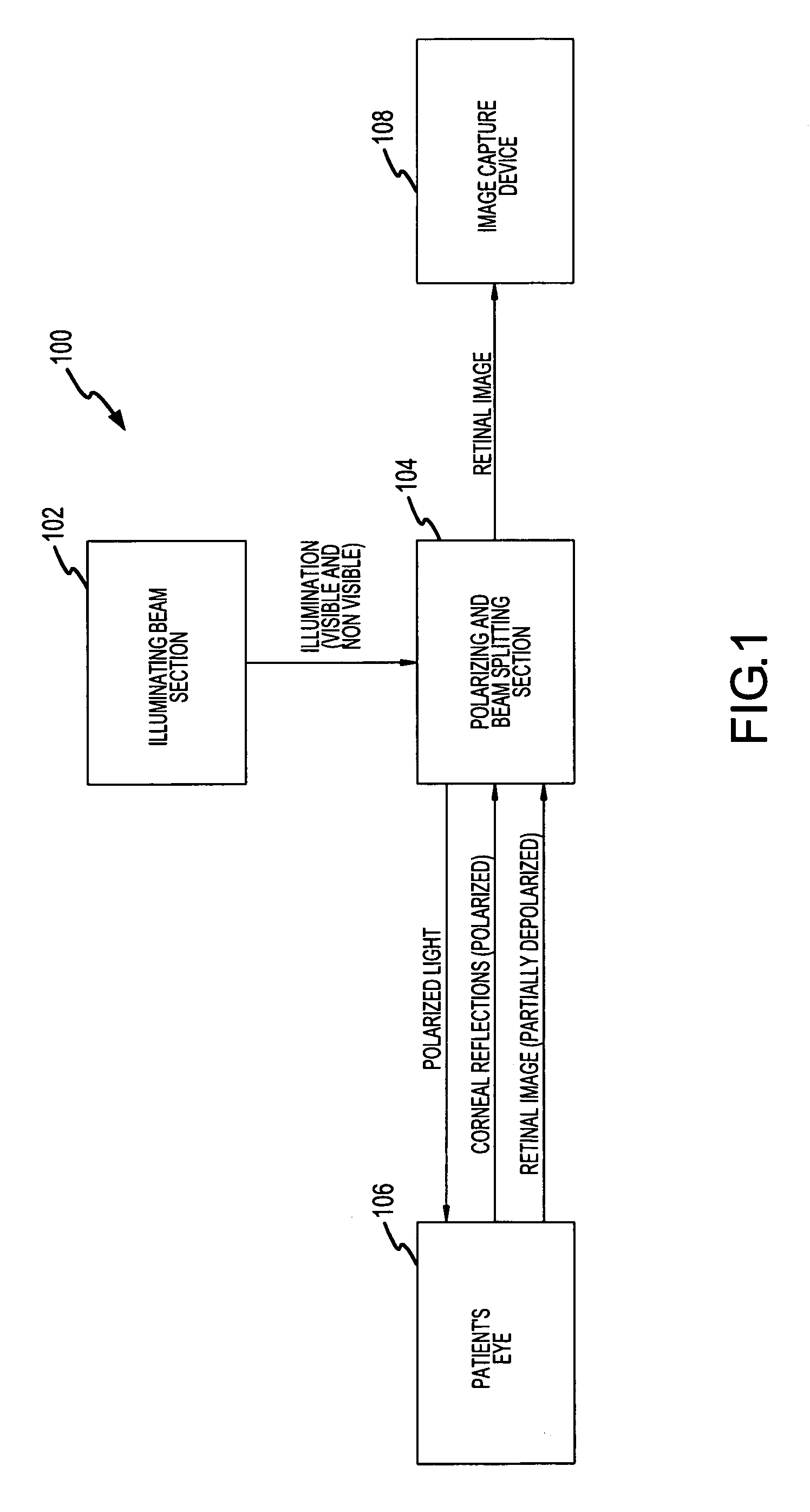
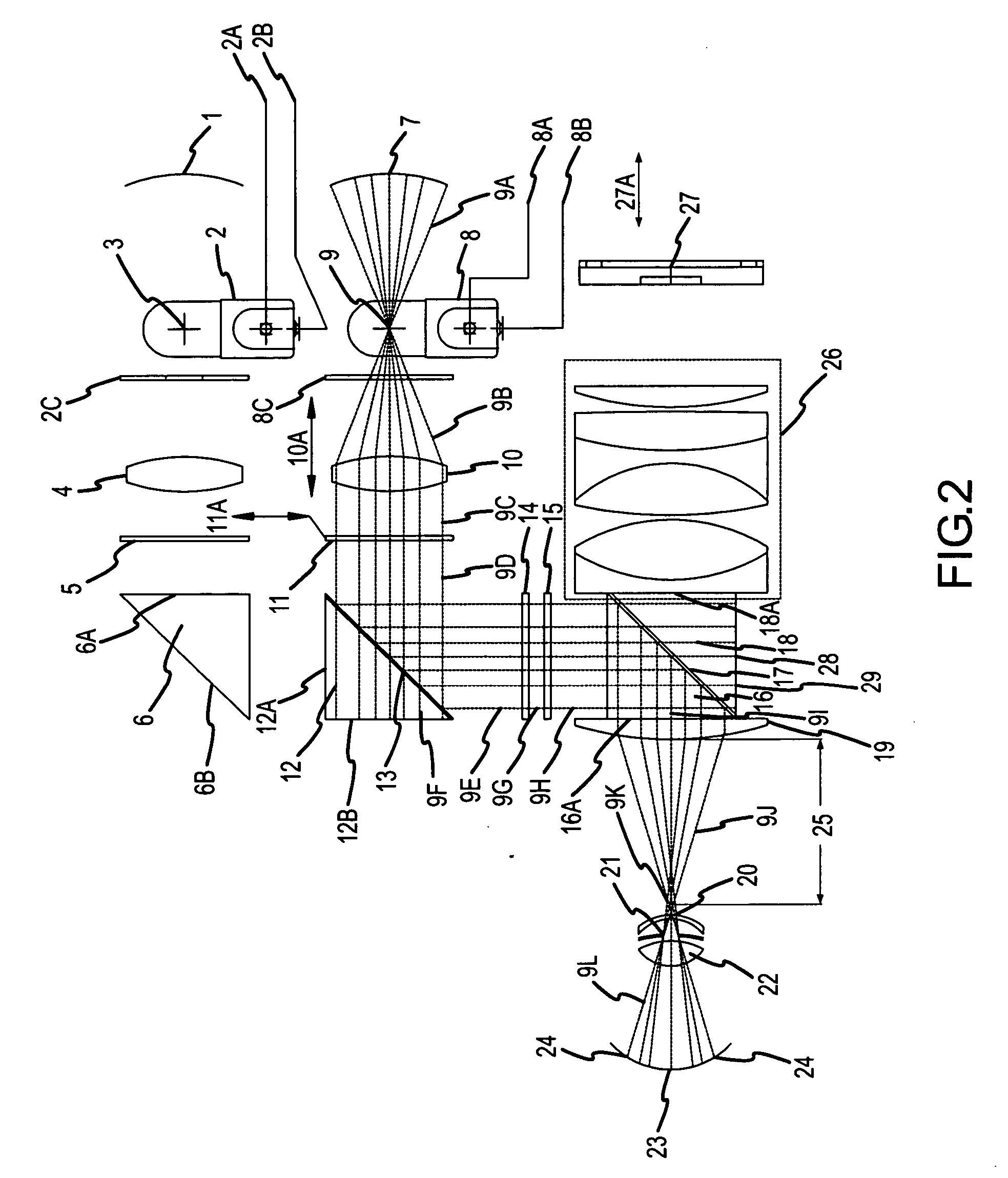
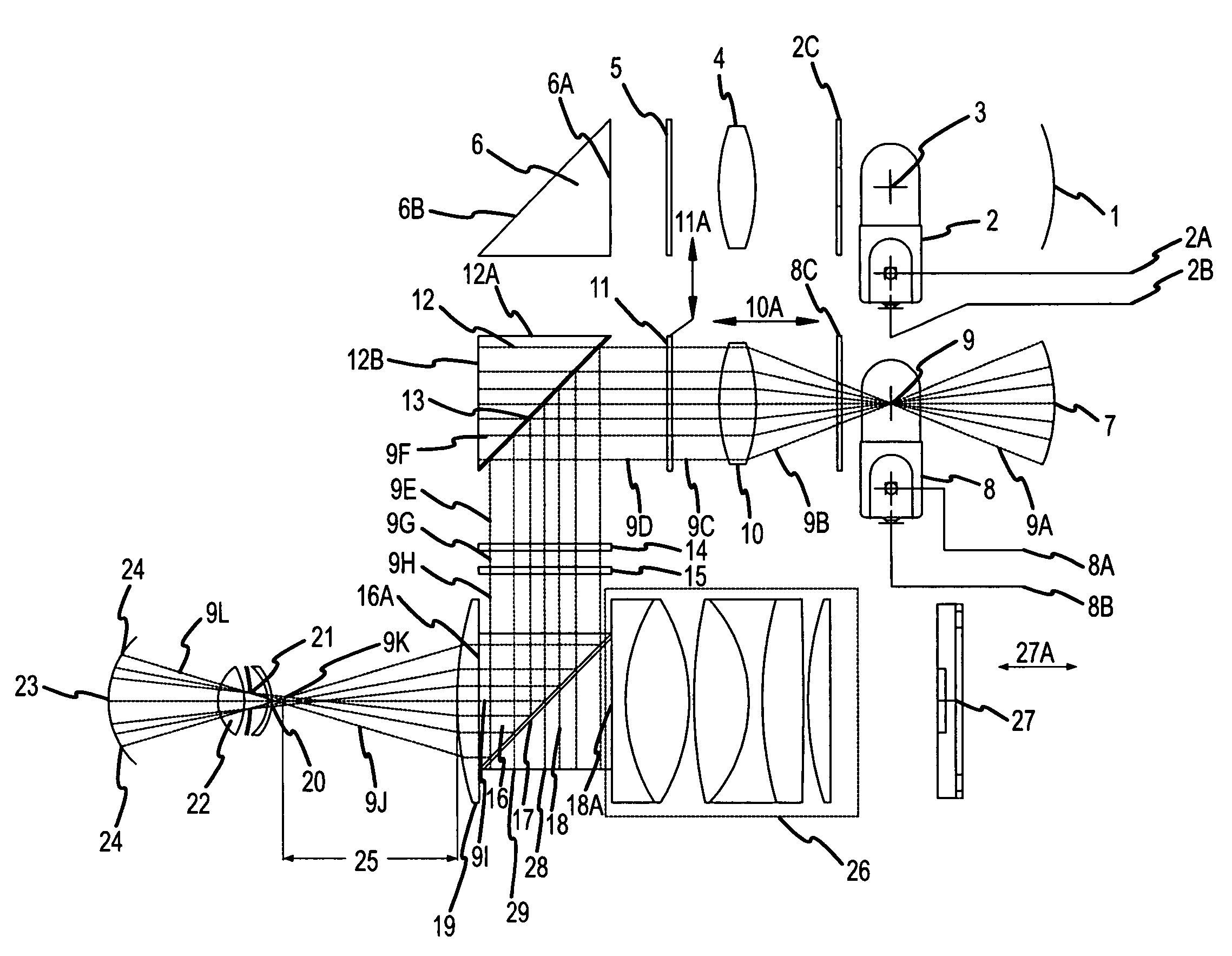
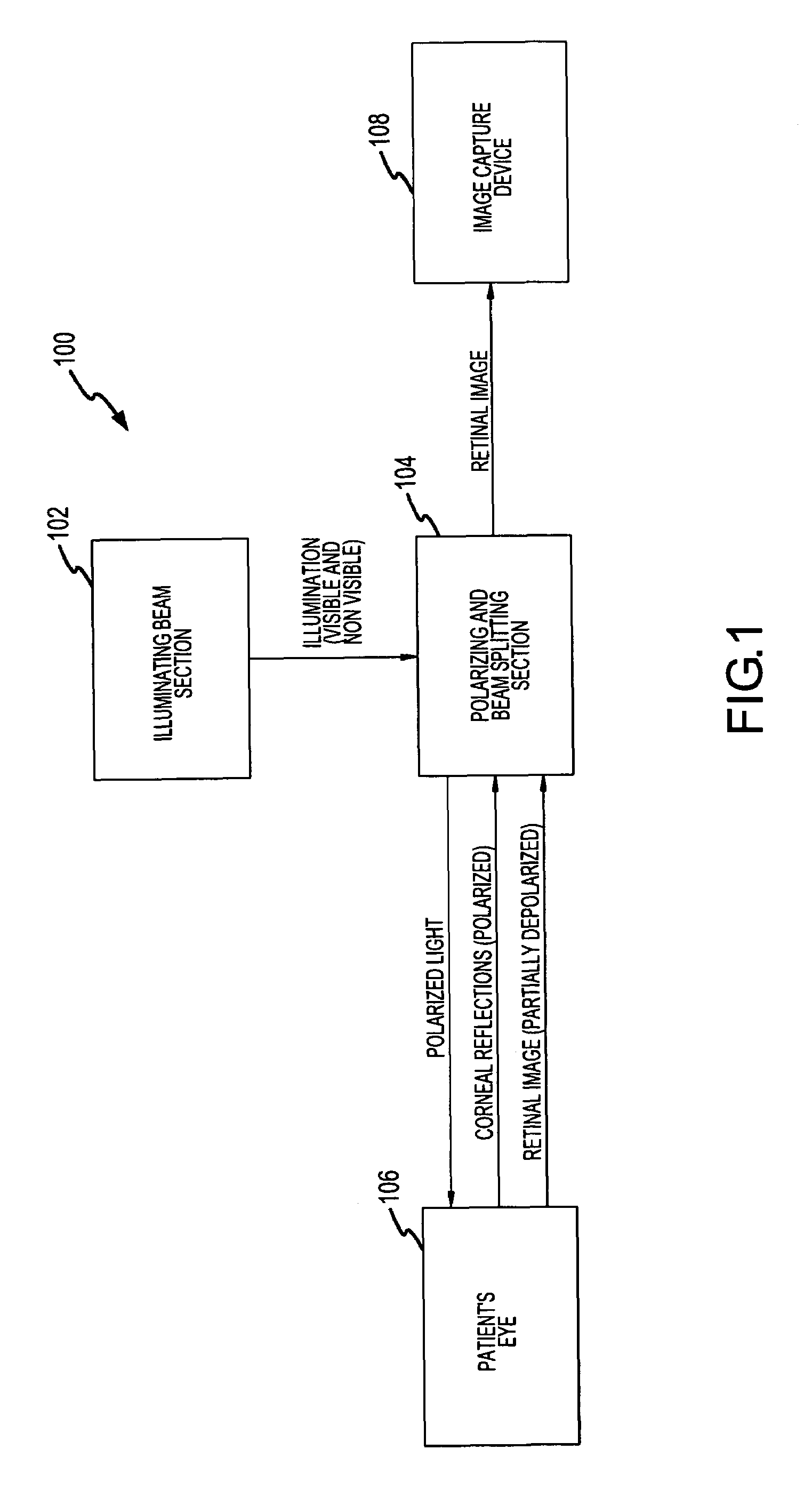
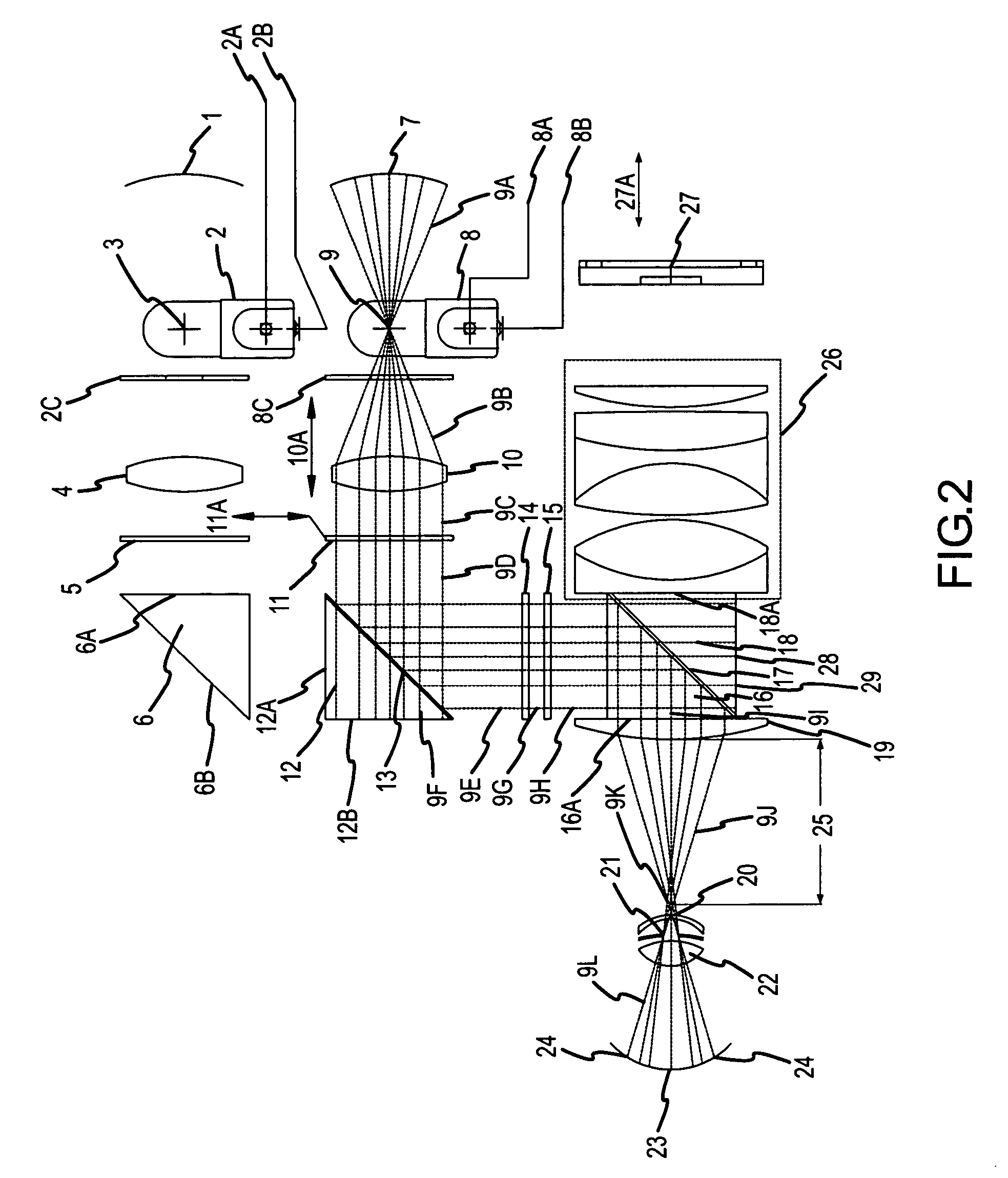
A hand held device for examining a patient's retina. In one example, the device generates visible or non-visible illuminating beams having desired spectral content. The illuminating beams are then polarized to generate polarized light beam(s) that are directed towards the patient's retina. At the patient's eye, a portion of the polarized beam is partially reflected by the cornea and travels back to the device, and another portion of the polarized beam enters the eye through the undilated pupil, illuminates the patient's retina, and generates a reflected retinal image (generally de-polarized) which also travels back to the device. The device receives the retinal image and transmits certain portions of the retinal image on through to an image detector (i.e., CCD or CMOS); and the device deflects the received polarized corneal reflections away from the image capture device. Hence, the image capture device receives retinal images but does not receive the polarized corneal reflected light.
Owner:OCUTRONICS
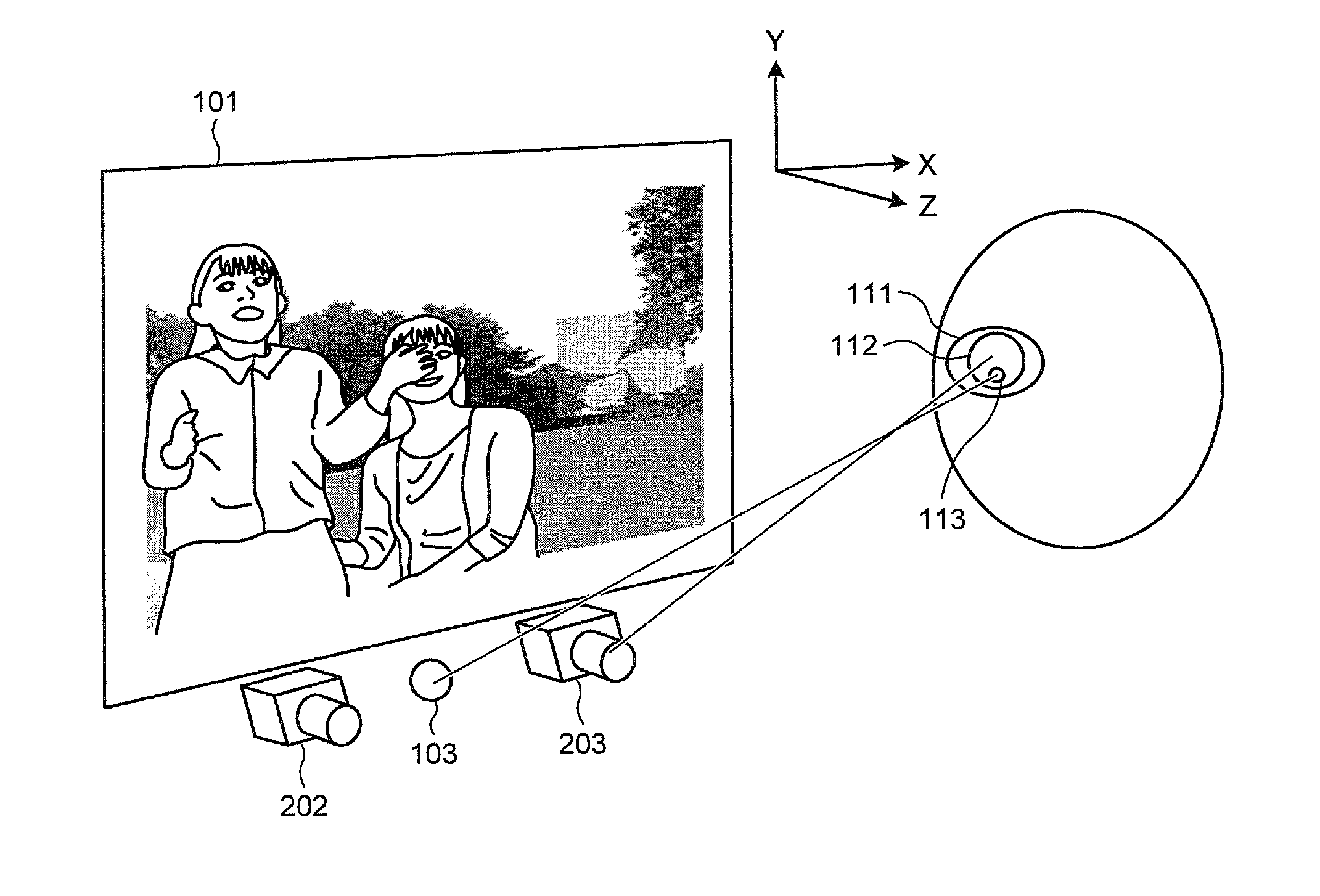
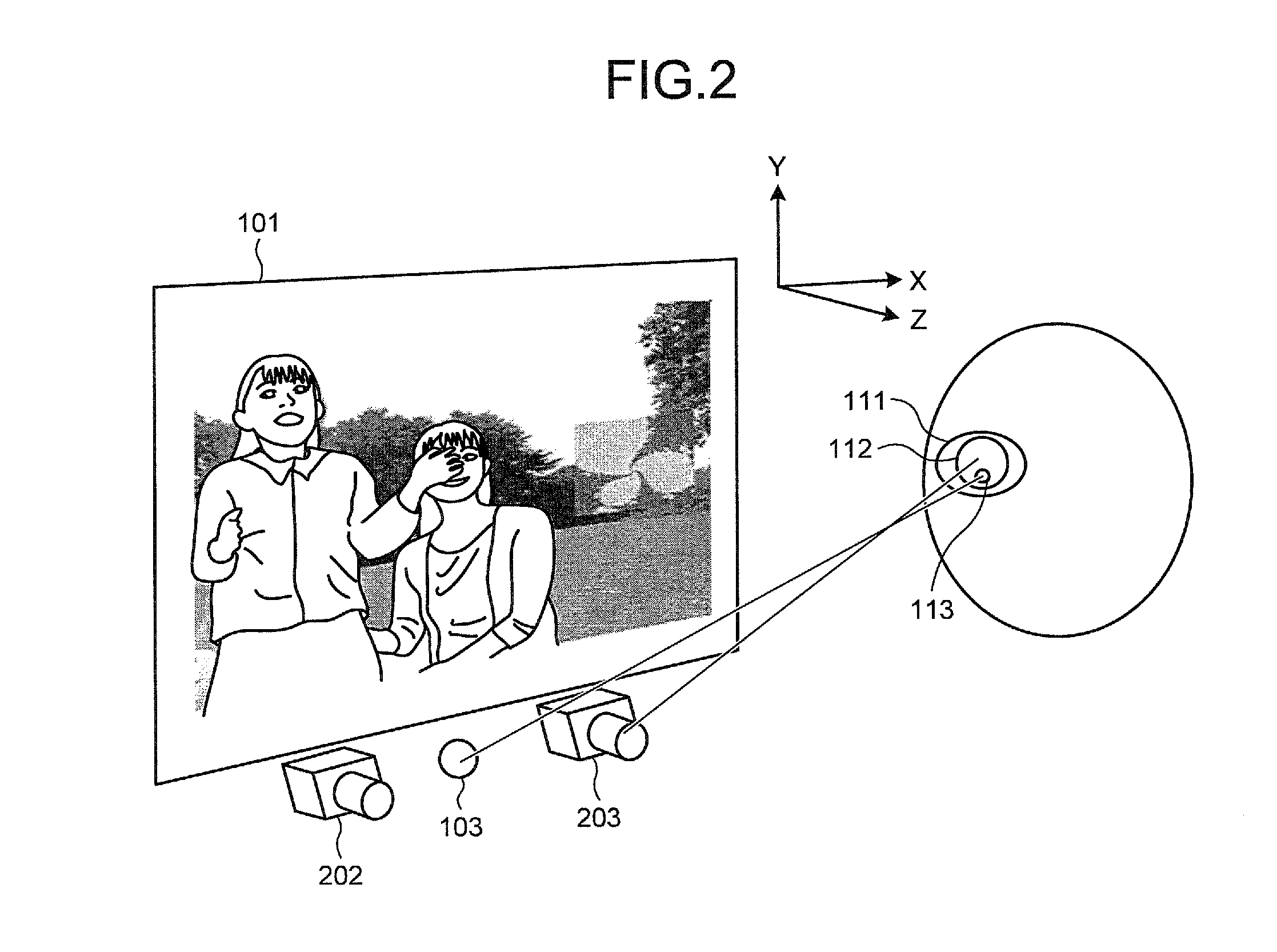
System and method for tracking the point of gaze of an observer
ActiveUS20130002846A1Improve latencyImprove accuracyStatic indicating devicesAcquiring/recognising eyesPoint of gazeComputer science
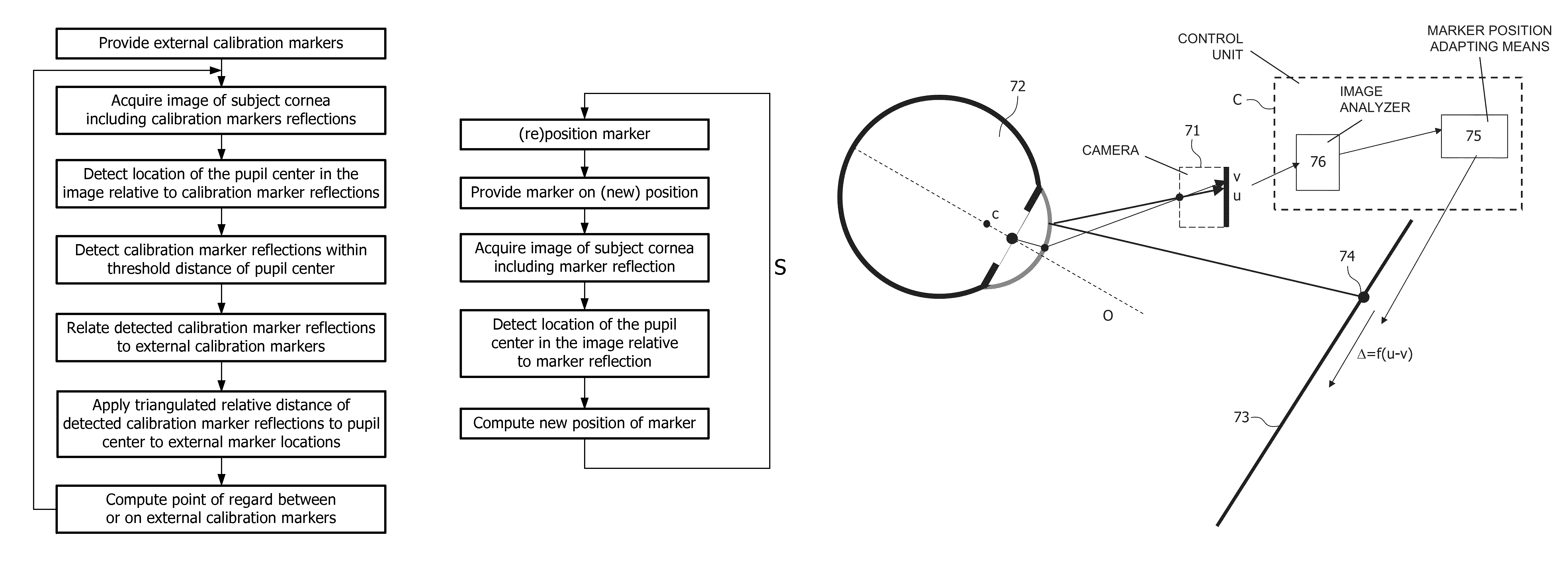
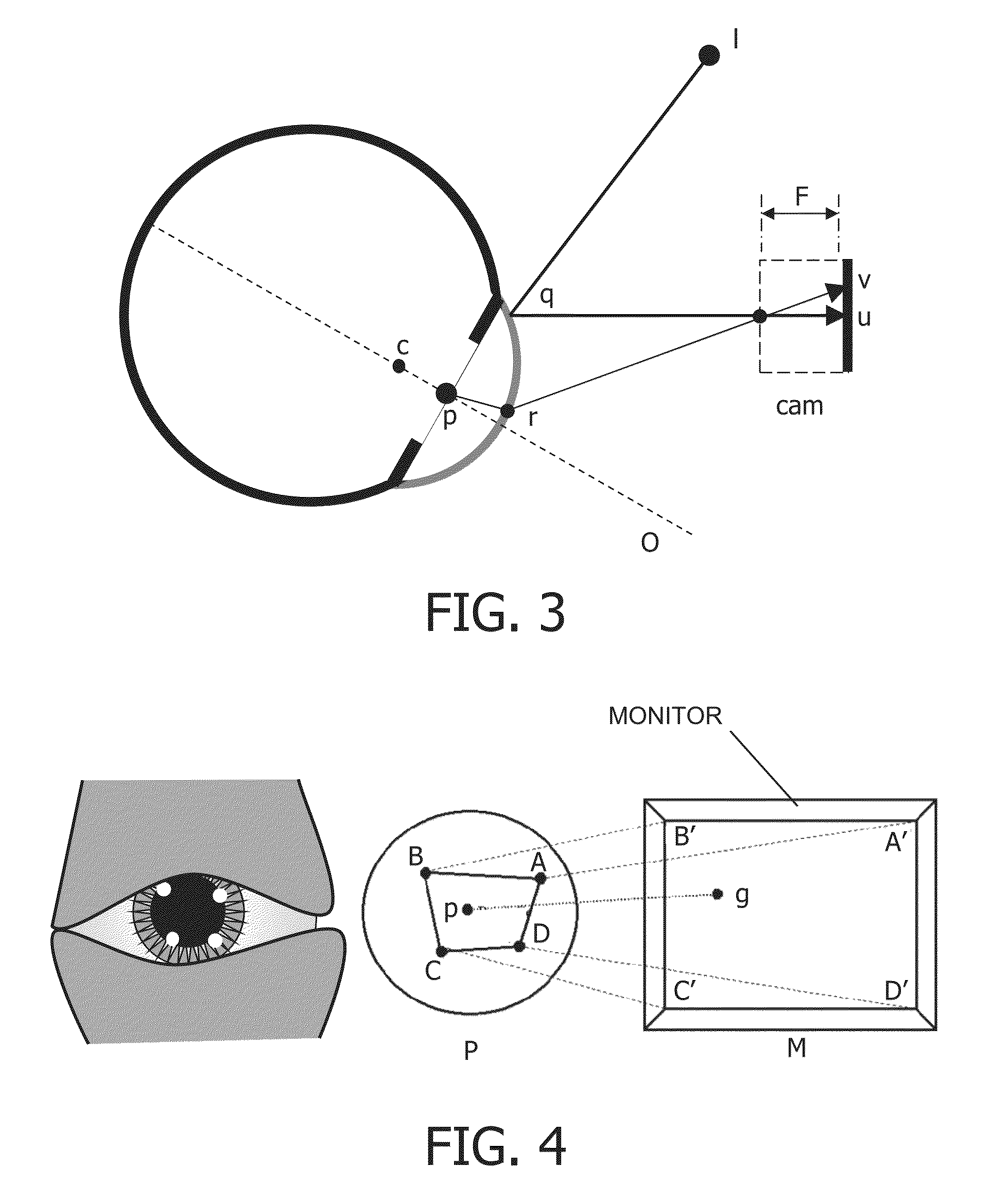
A system for tracking the point of gaze of an observer observing an object comprises a camera for recording an image of an eye of the observer, comprises a means for providing a luminous marker, and means for analyzing the image of the eye to determine the reflection of the marker on the eye and the centre of the pupil. The relative positions of the corneal reflection of the marker and the pupil centre are measured. The marker is repositioned, in dependence on the determined relative positions, to improve correspondence between the corneal reflection of the marker and the pupil centre.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Pupil center-corneal reflection (PCCR) based sight line evaluation method in sight line tracking system
InactiveCN102125422AAchieve estimatesReduced minimum hardware requirementsEye diagnosticsHead movementsEffective solution
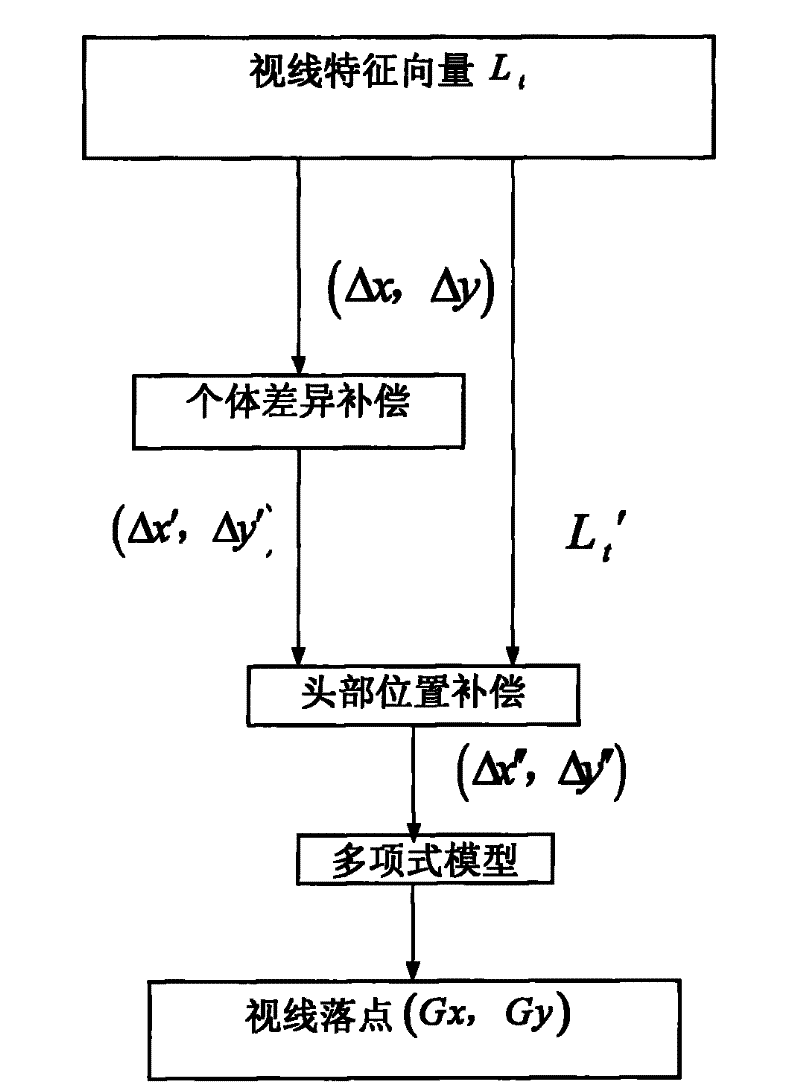
The invention provides a pupil center-corneal reflection (PCCR) based sight line evaluation method in a sight line tracking system, belonging to the field of man-machine interaction. With specific to the main problems on user head motion limits and individual calibration in the traditional PCCR, the invention provides a method for compensating head positions under the conditions of a single camera and a single light source, which realizes the analysis compensation for influences of head positions variation to a pupil center-corneal vector, establishes an individual difference conversion model and further simplifies a calibration process to be a single-point process. Accordingly, a novel sight line evaluation method is developed; and in the method, the requirements of precise sight line evaluation on minimum hardware are decreased to be the single camera (uncalibrated) and the single light source, complex system calibration is unnecessary, natural head-motion sight line evaluation is realized, and user calibration is simplified to be single-point calibration. All links in the method meet the instantaneity requirements, and an effective solution to the sight line tracking system oriented to man-machine interaction is provided.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Eyeshot detection device using distance image sensor
ActiveUS20070014552A1Quick responseAcquiring/recognising eyesUsing optical meansCMOSThree-dimensional space
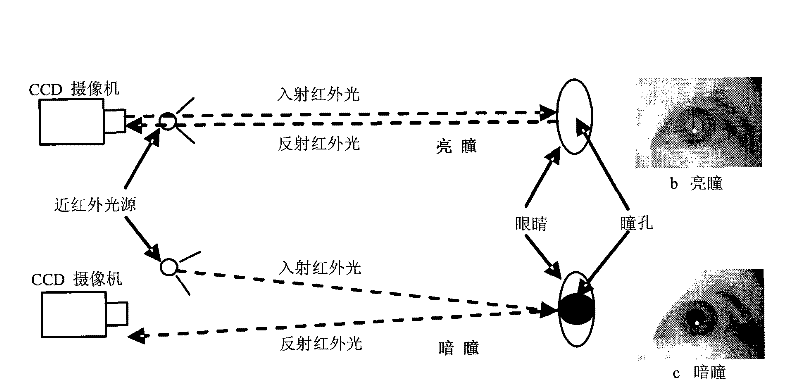
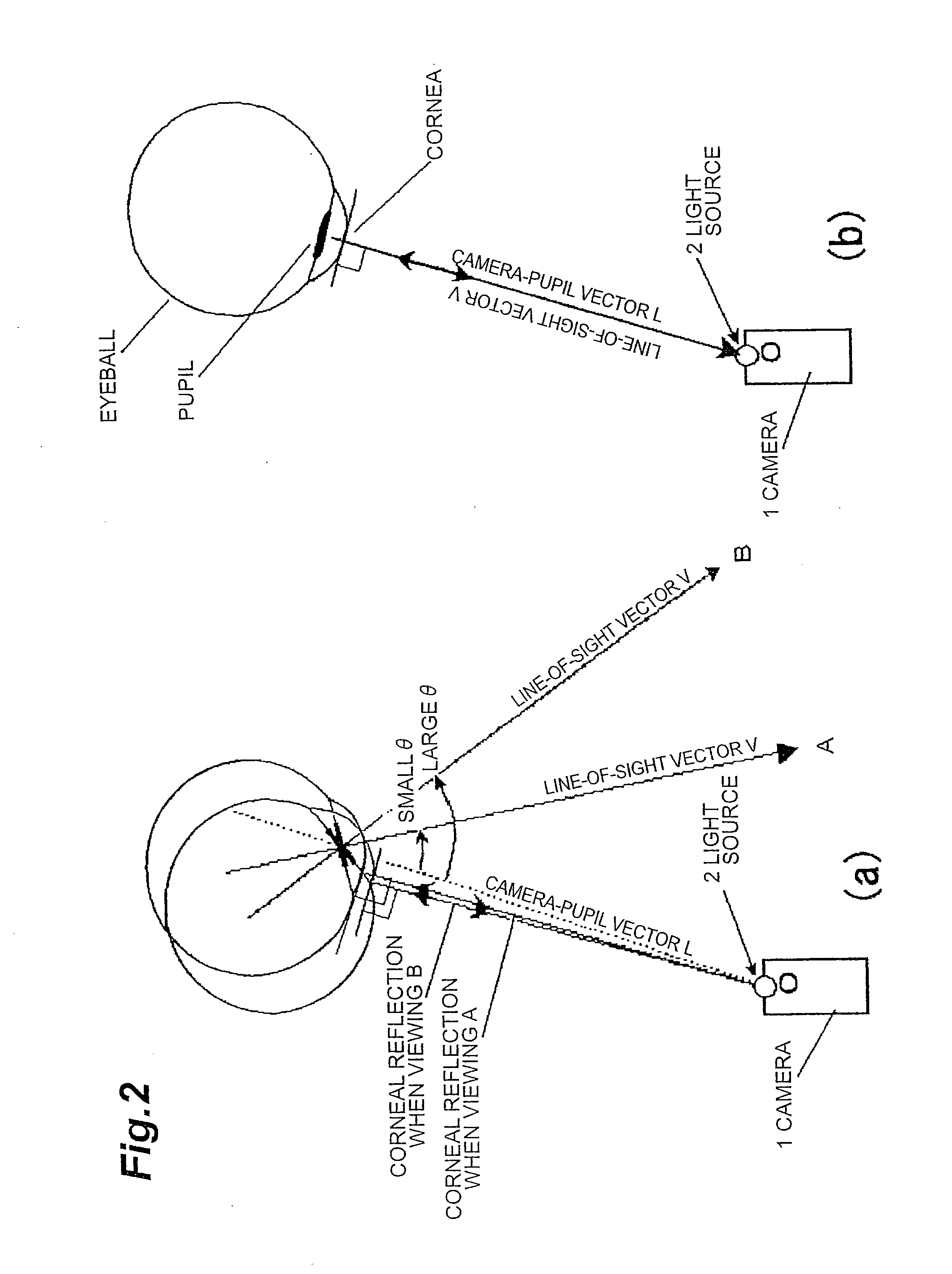
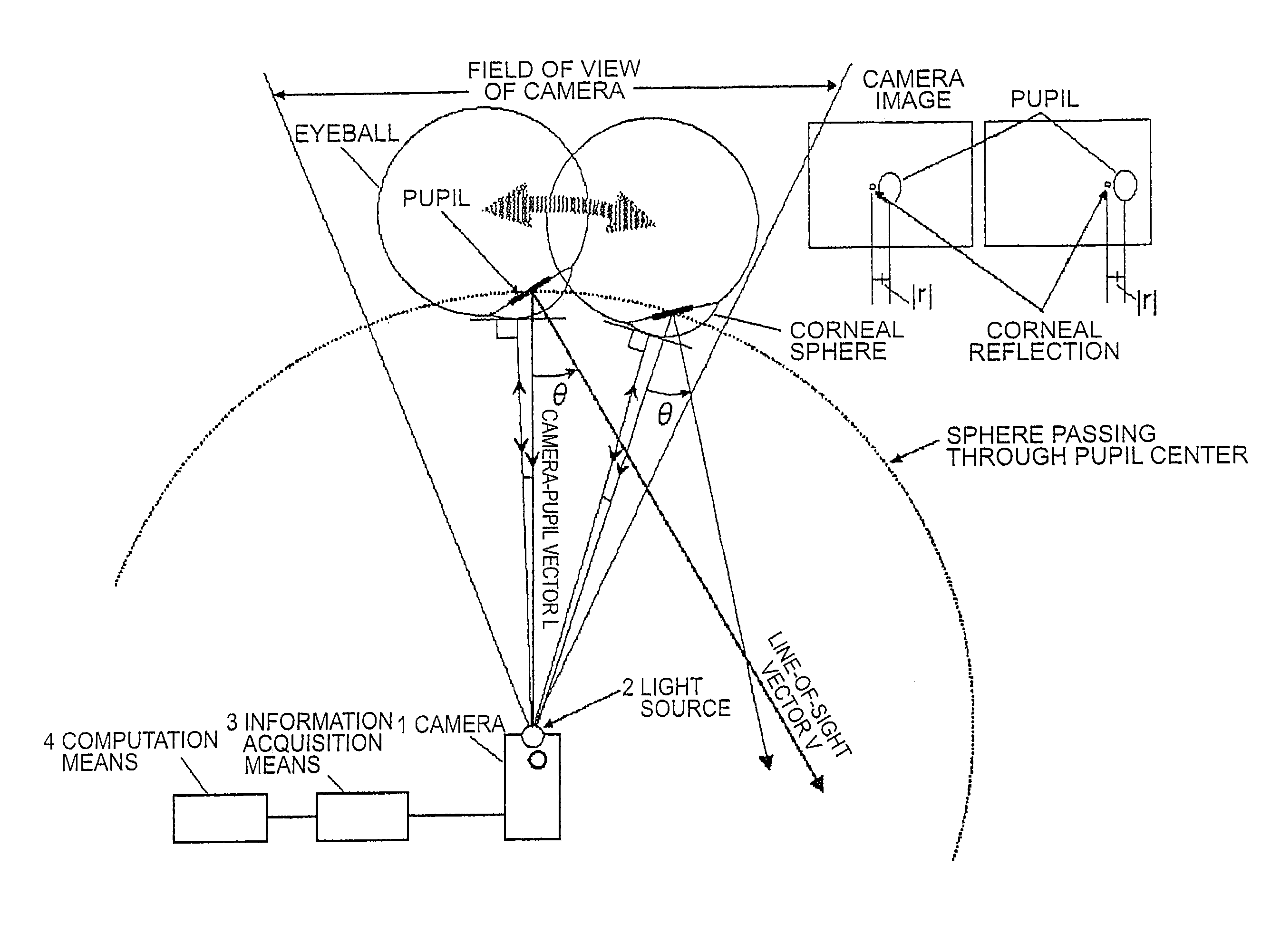
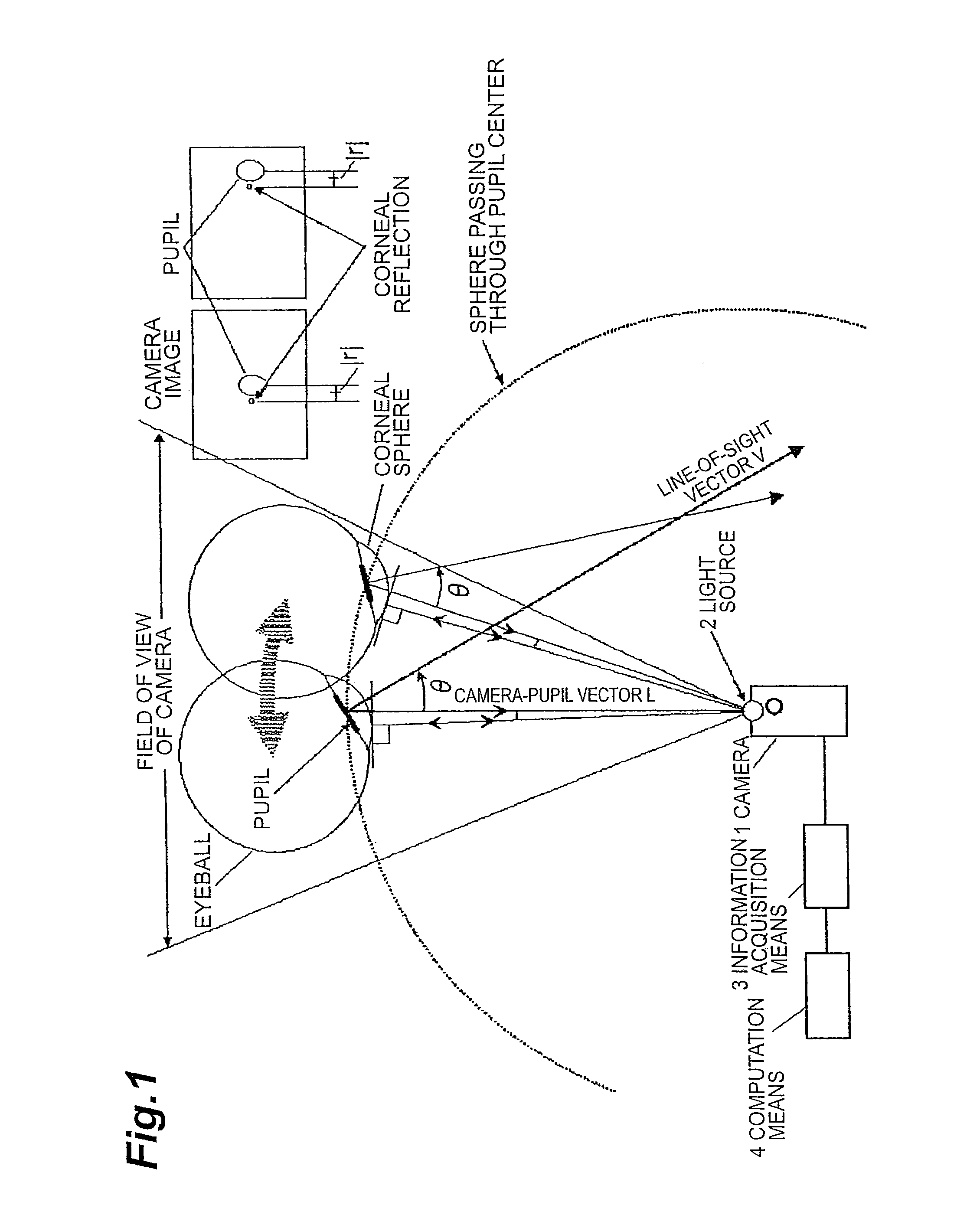
An object of the present invention is, when determining a line-of-sight vector of a subject, to identify a three-dimensional position of a pupil center or corneal reflection center thereof. The line-of-sight vector is determined by measuring a distance from a camera to the pupil center or corneal reflection center of the subject using a two-dimensional CMOS distance image sensor by a light time-of-flight method and obtaining position information of the pupil center and corneal reflection center of the subject using the distance image sensor. If a position and a direction of the camera are identified, a camera-pupil center vector is determined from image information of the pupil center of the subject. Since the camera-pupil center distance has been measured, a pupil center position in a three-dimensional space is determined from the above information. Combining this with two line-of-sight vectors determines a position where line-of-sight vectors intersect, or a view-point.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP SHIZUOKA UNIV
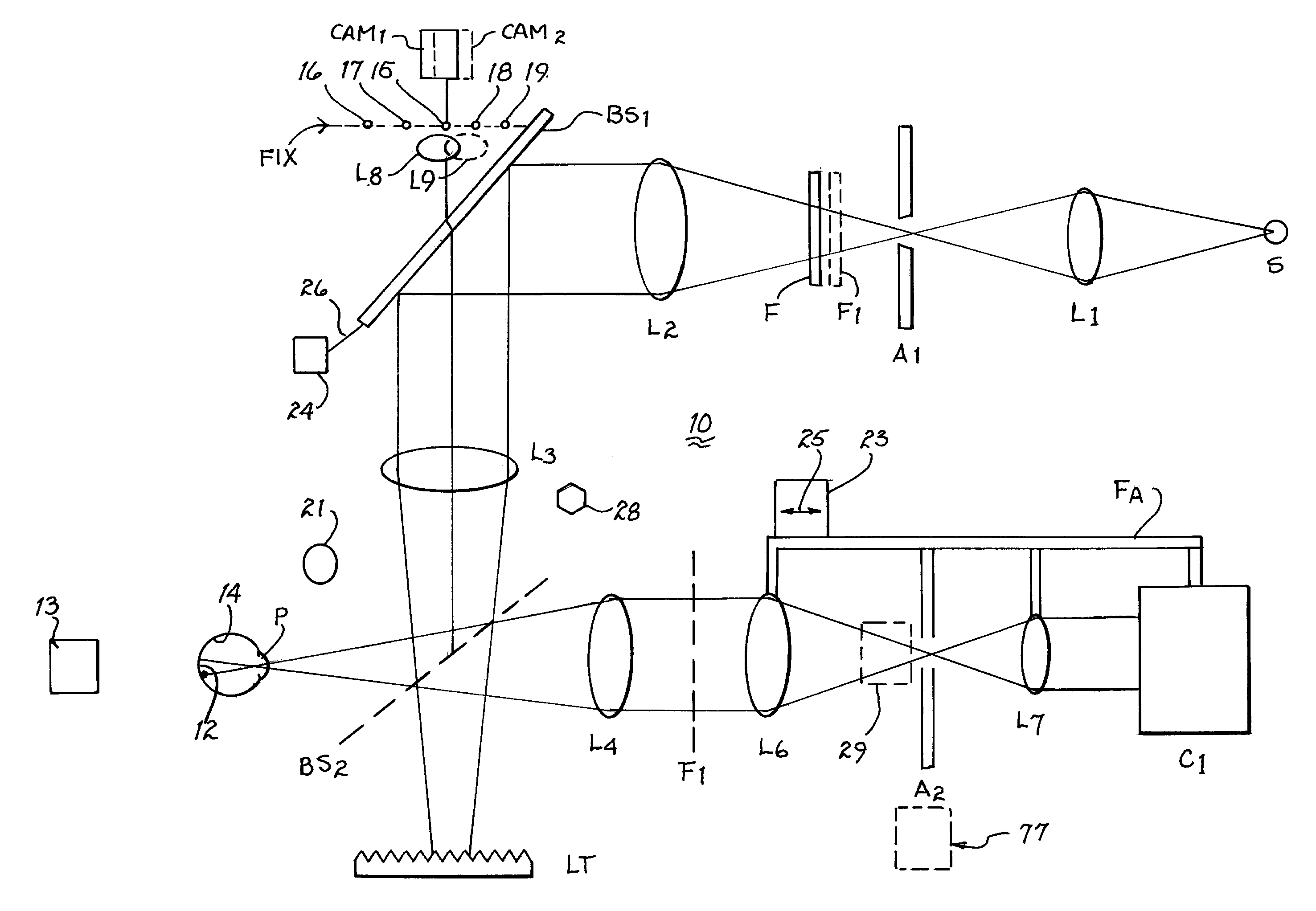
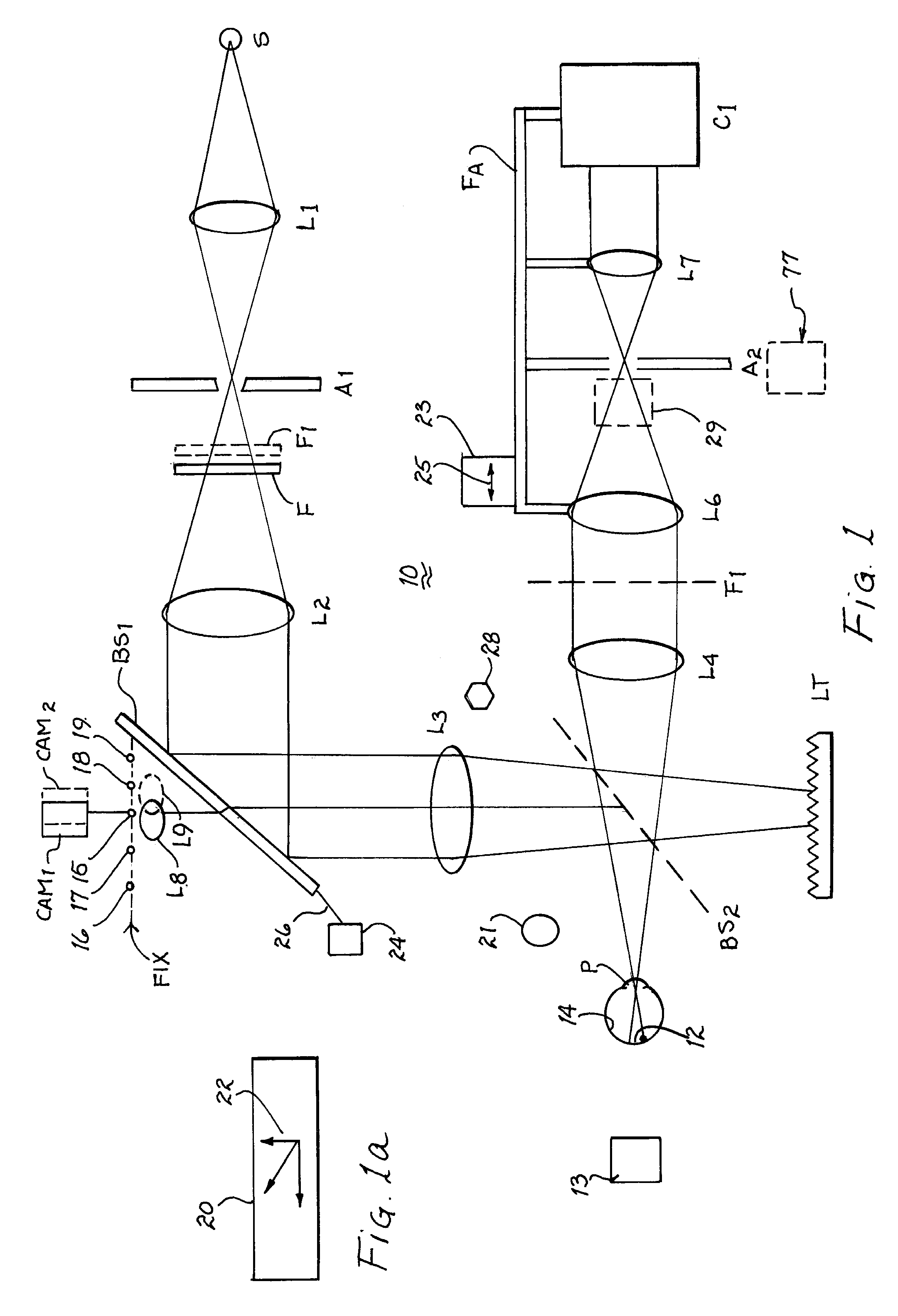
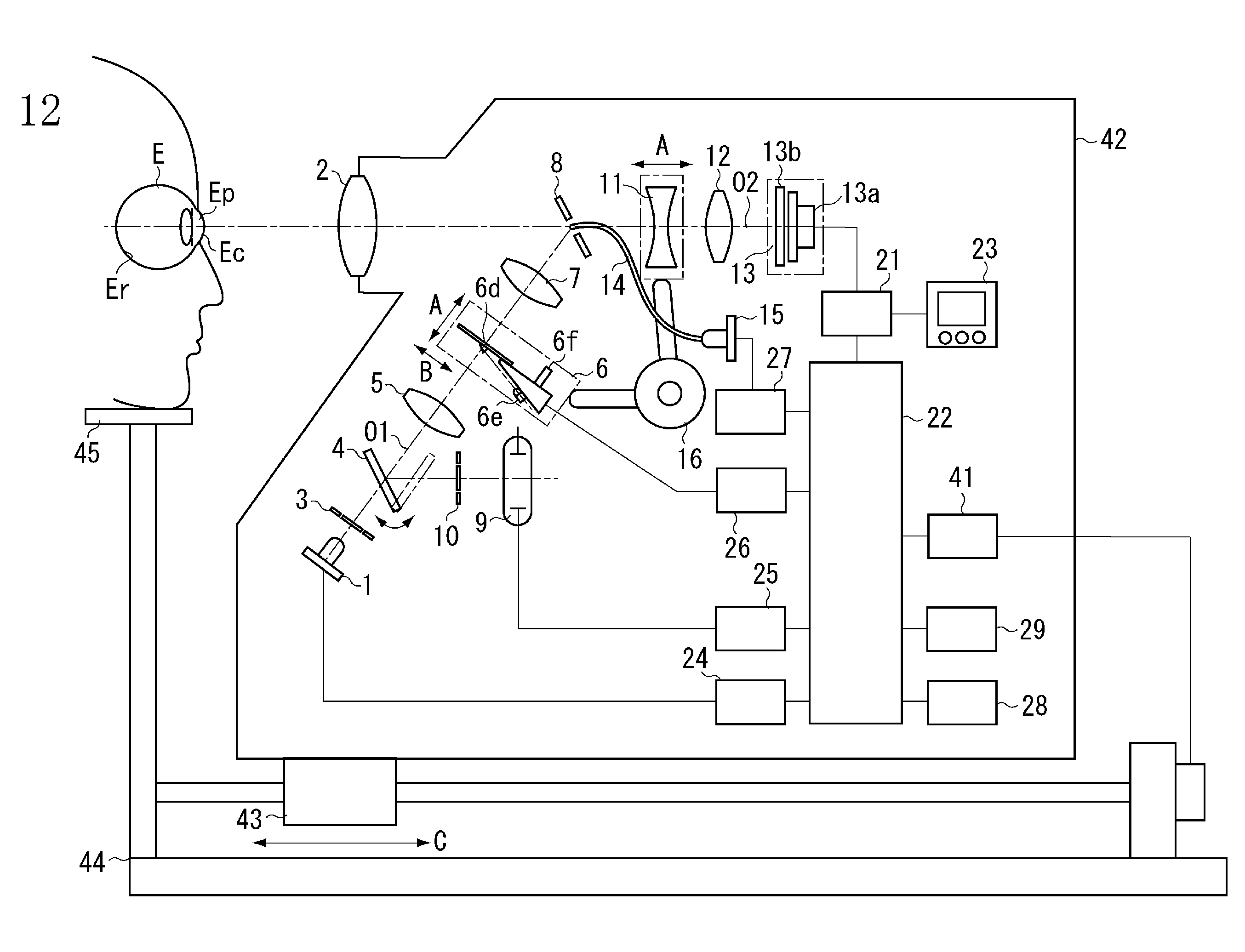
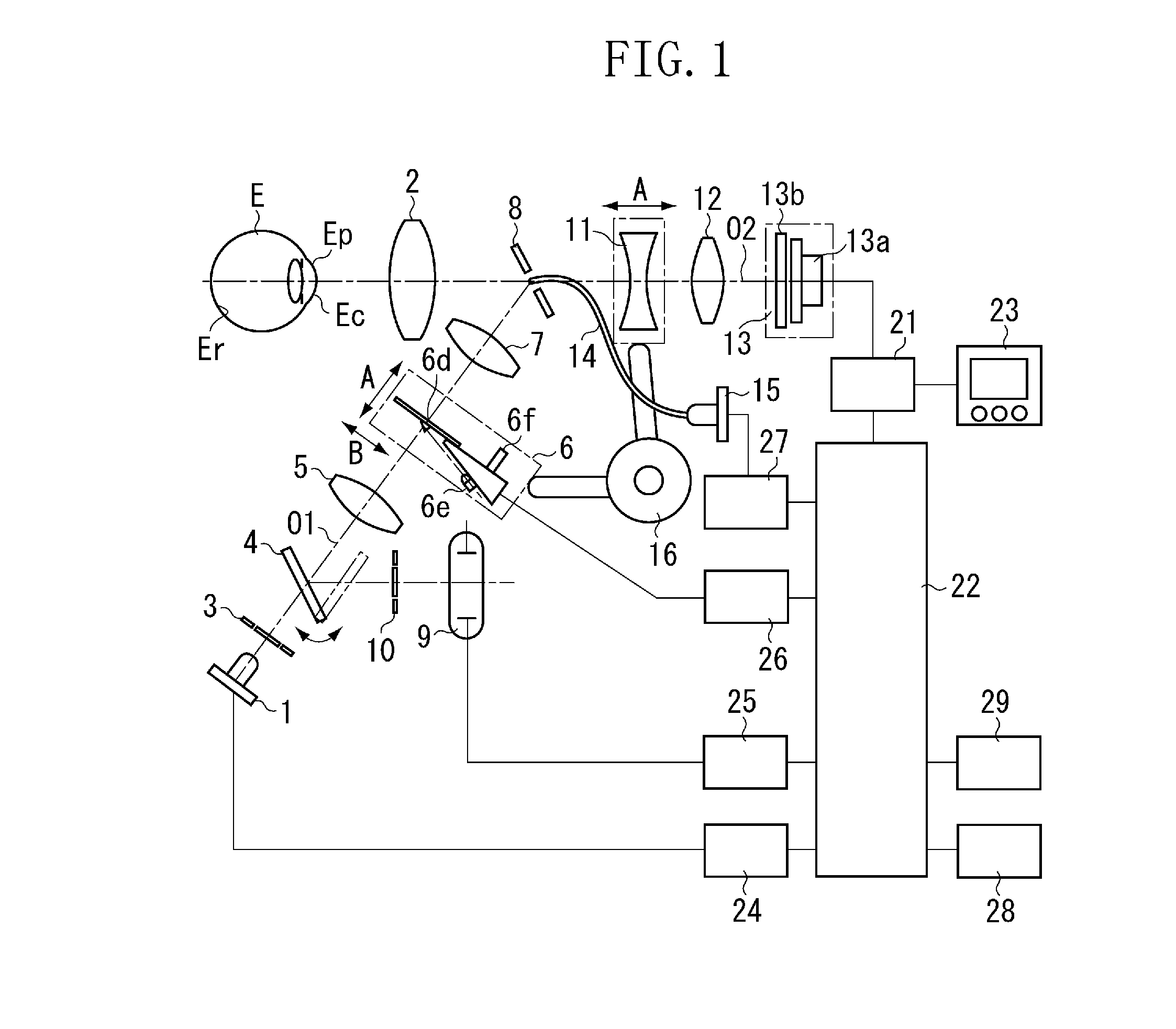
Ocular fundus auto imager
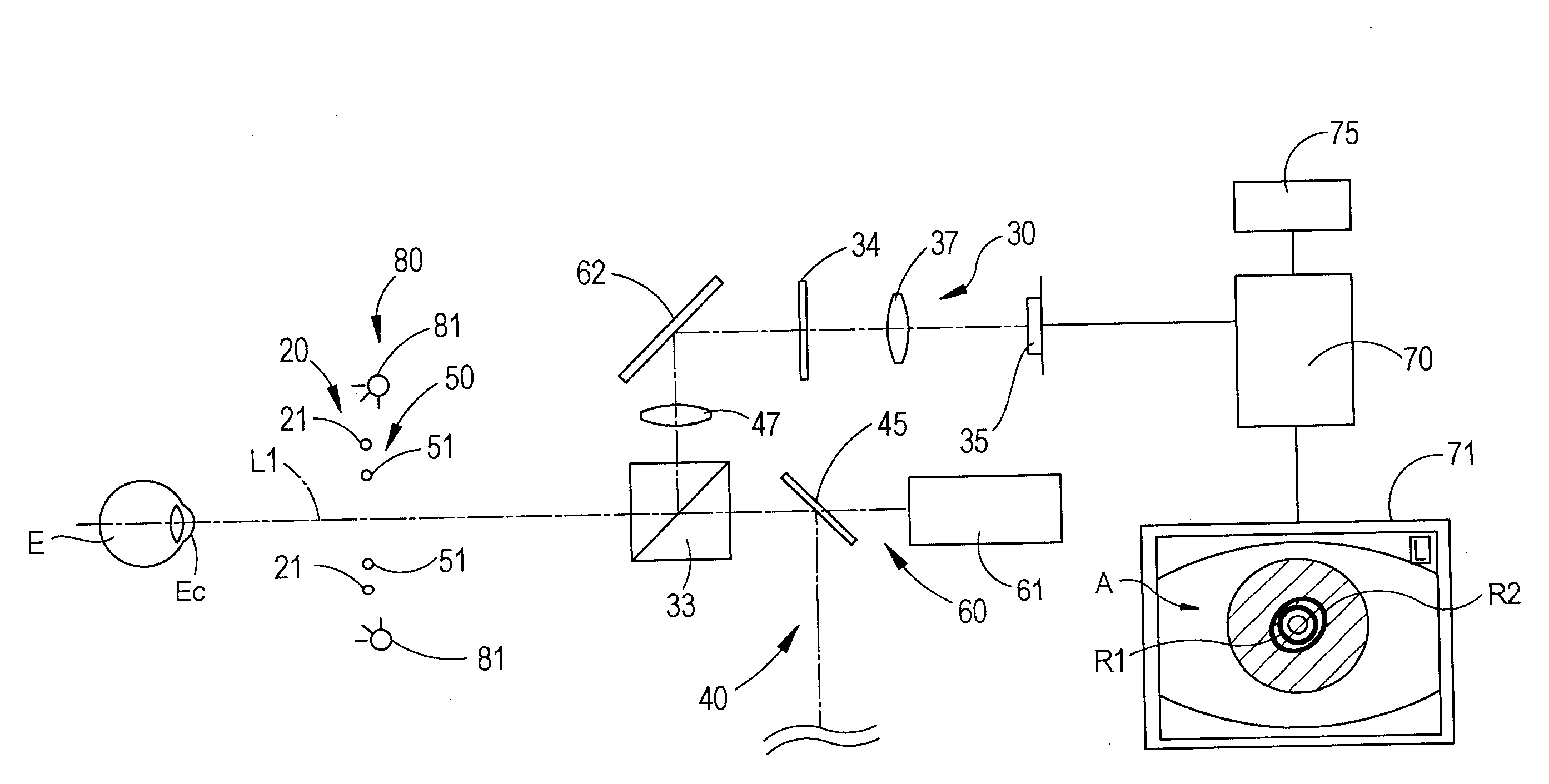
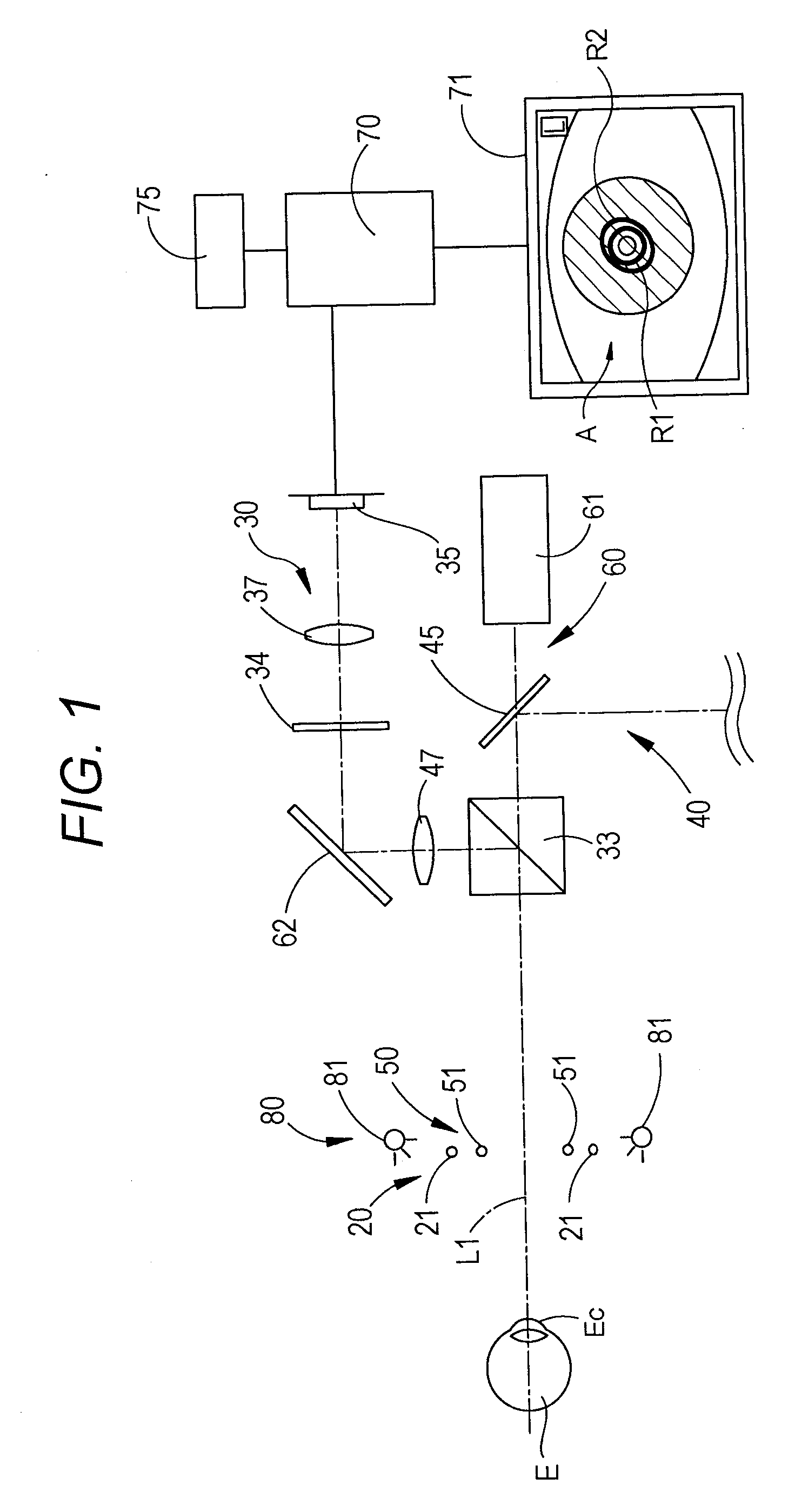
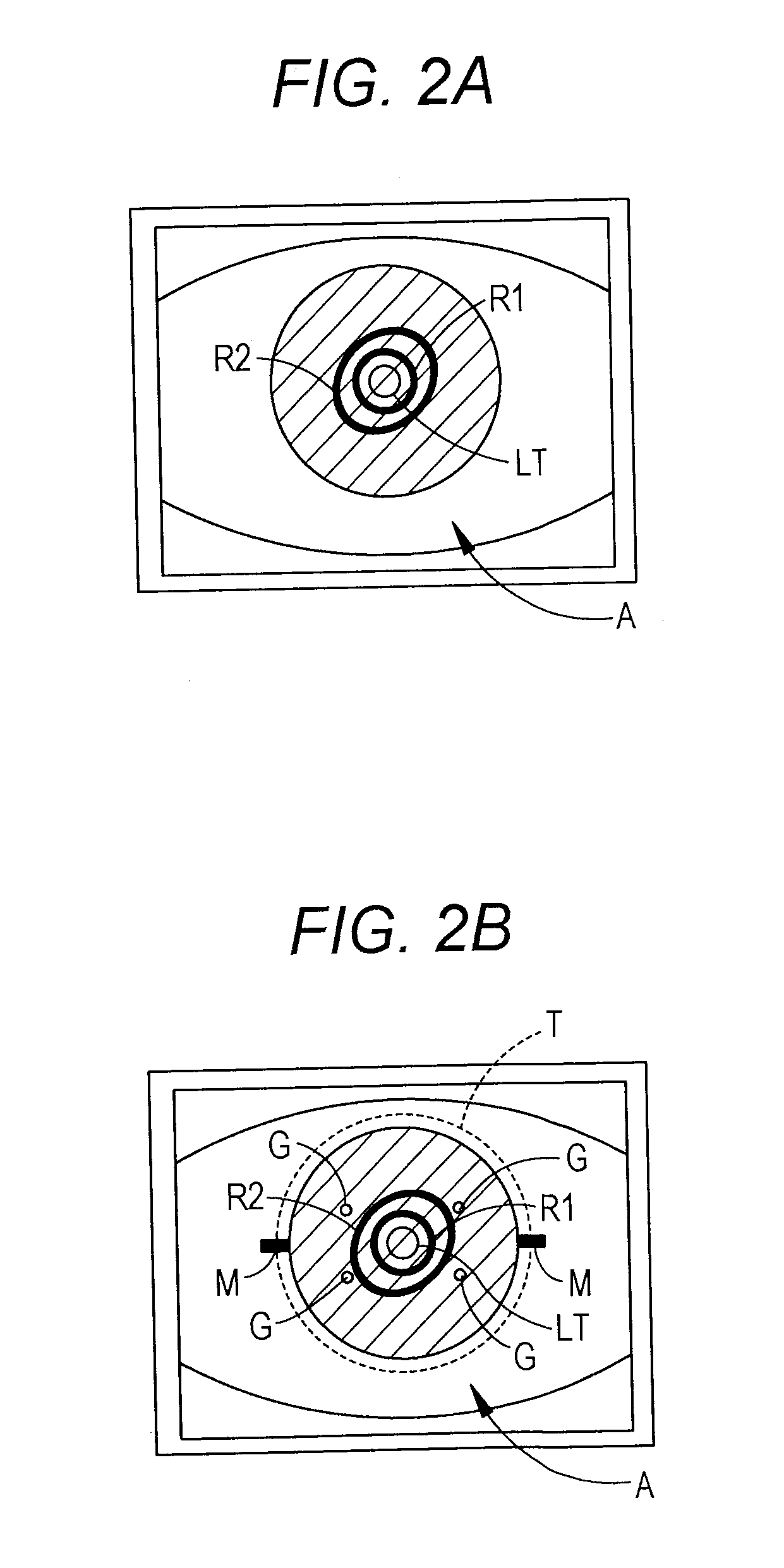
An ocular fundus imager (8) automatically aligns fundus illuminating rays to enter the pupil (P) and to prevent corneal reflections from obscuring the fundus image produced. Focusing the produced fundus image is automatically performed and is based upon the fundus image iself. A head restraint for the patient undergoing examination is in the form of a pair of spectacles which is not only easy to use accurately but significantly reduce the gross alignment between the optical system (8) and the patent's pupil (P).
Owner:VISUAL PATHWAYS
Hand held device and methods for examining a patient's retina
A hand held device for examining a patient's retina. In one example, the device generates visible or non-visible illuminating beams having desired spectral content. The illuminating beams are then polarized to generate polarized light beam(s) that are directed towards the patient's retina. At the patient's eye, a portion of the polarized beam is partially reflected by the cornea and travels back to the device, and another portion of the polarized beam enters the eye through the undilated pupil, illuminates the patient's retina, and generates a reflected retinal image (generally de-polarized) which also travels back to the device. The device receives the retinal image and transmits certain portions of the retinal image on through to an image detector (i.e., CCD or CMOS); and the device deflects the received polarized corneal reflections away from the image capture device. Hence, the image capture device receives retinal images but does not receive the polarized corneal reflected light.
Owner:OCUTRONICS
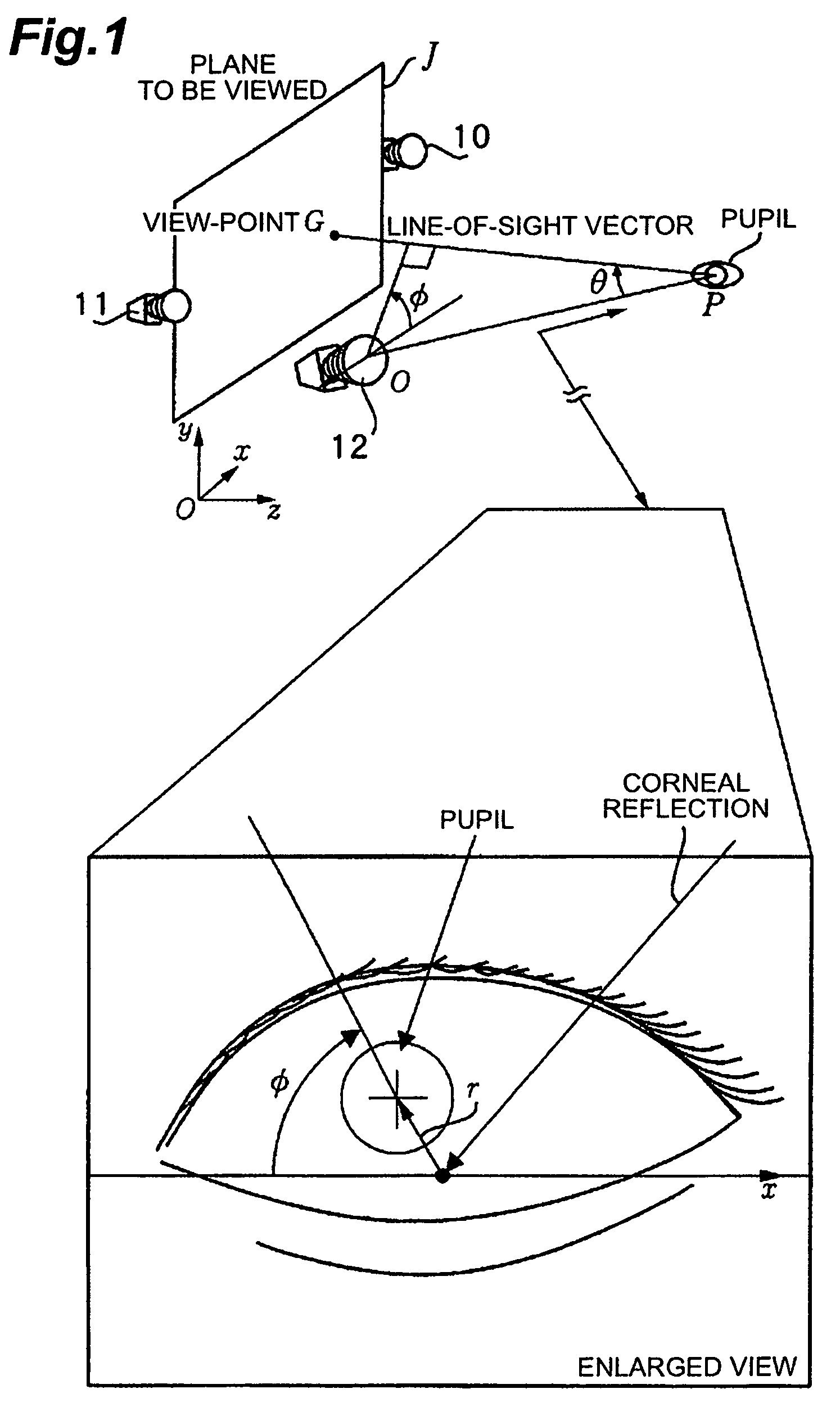
Sight-line detection method and device, and three-dimensional view-point measurement device
ActiveUS7533989B2Minimize limitationAcquiring/recognising eyesEye diagnosticsMeasurement deviceCorneal reflection
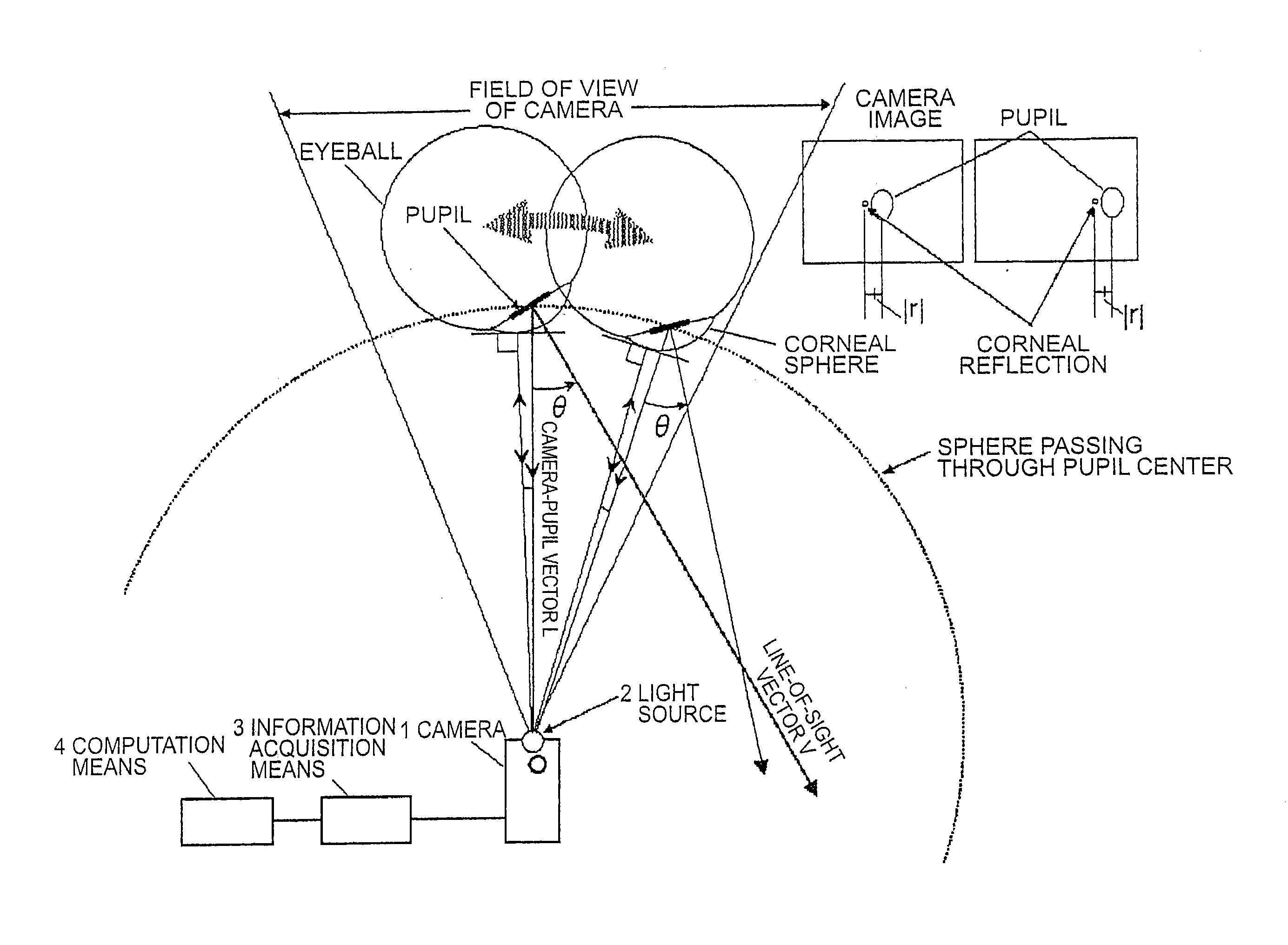
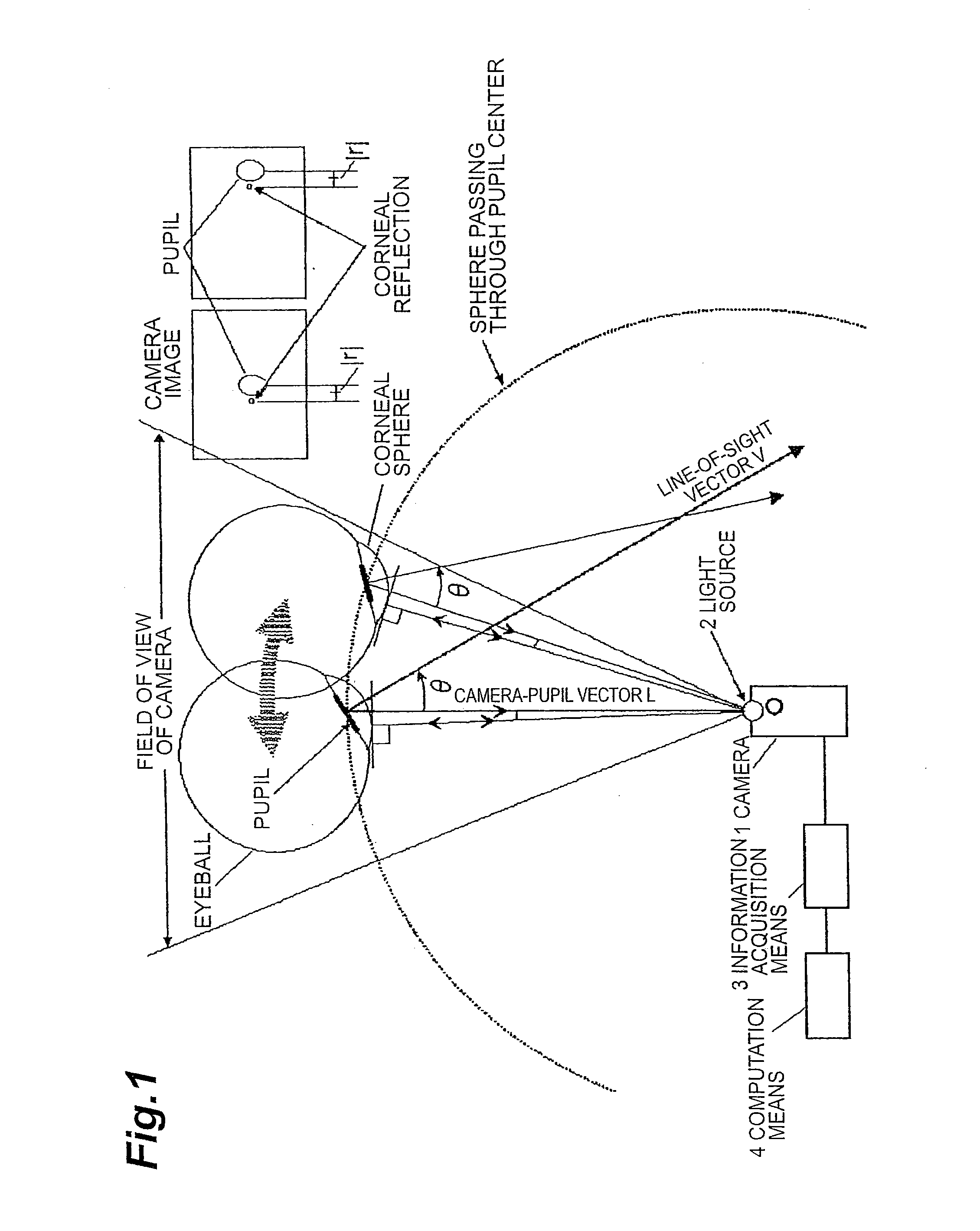
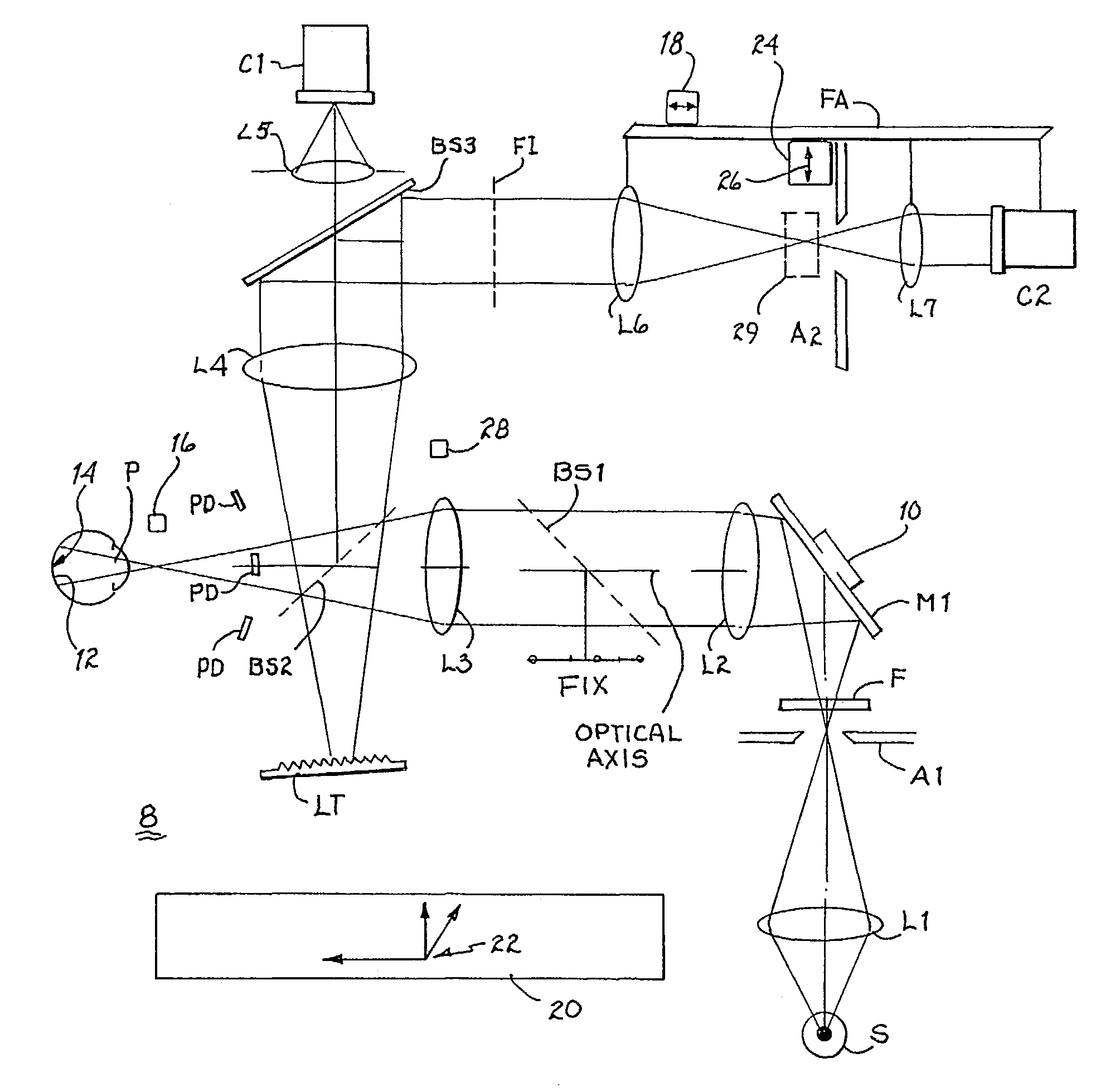
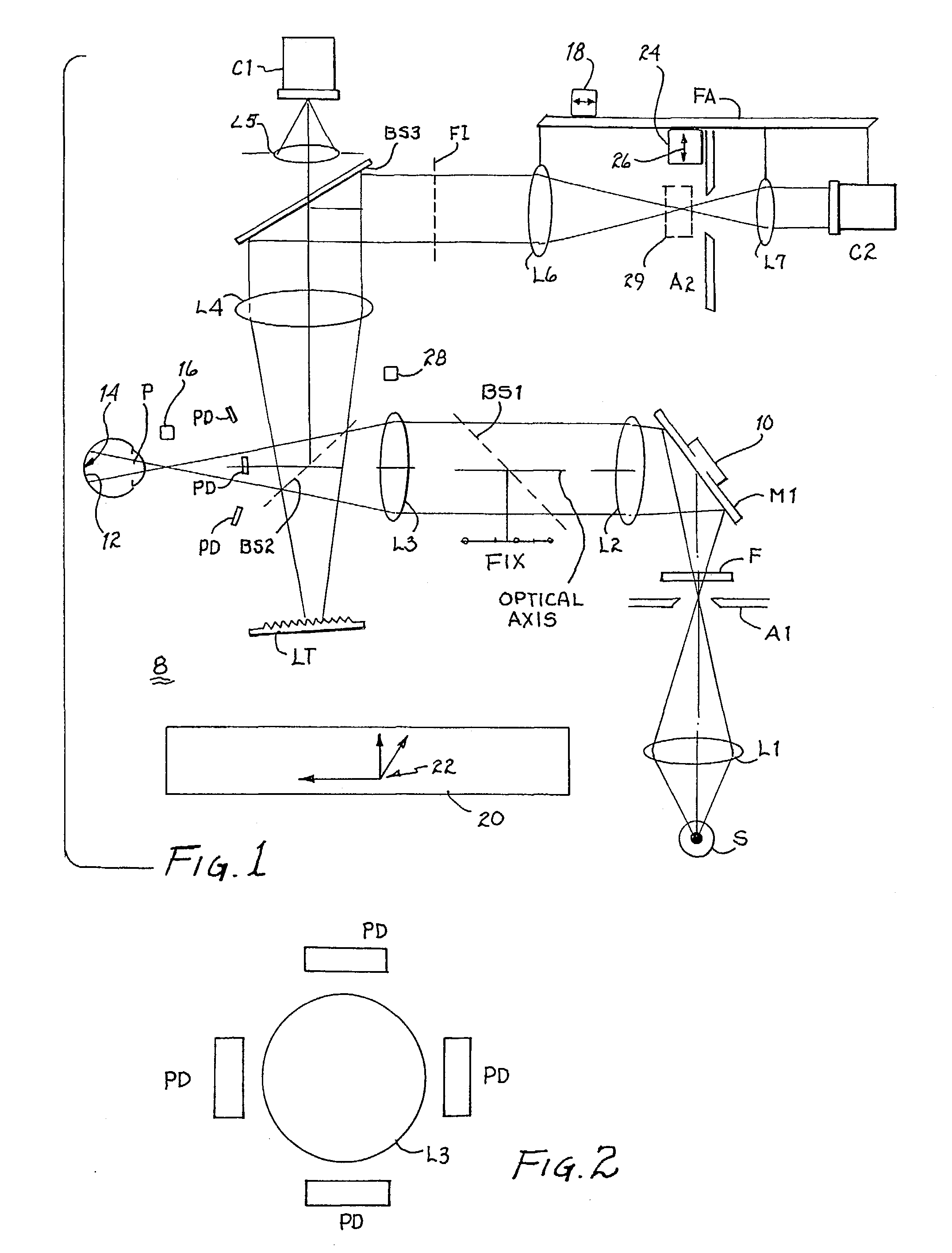
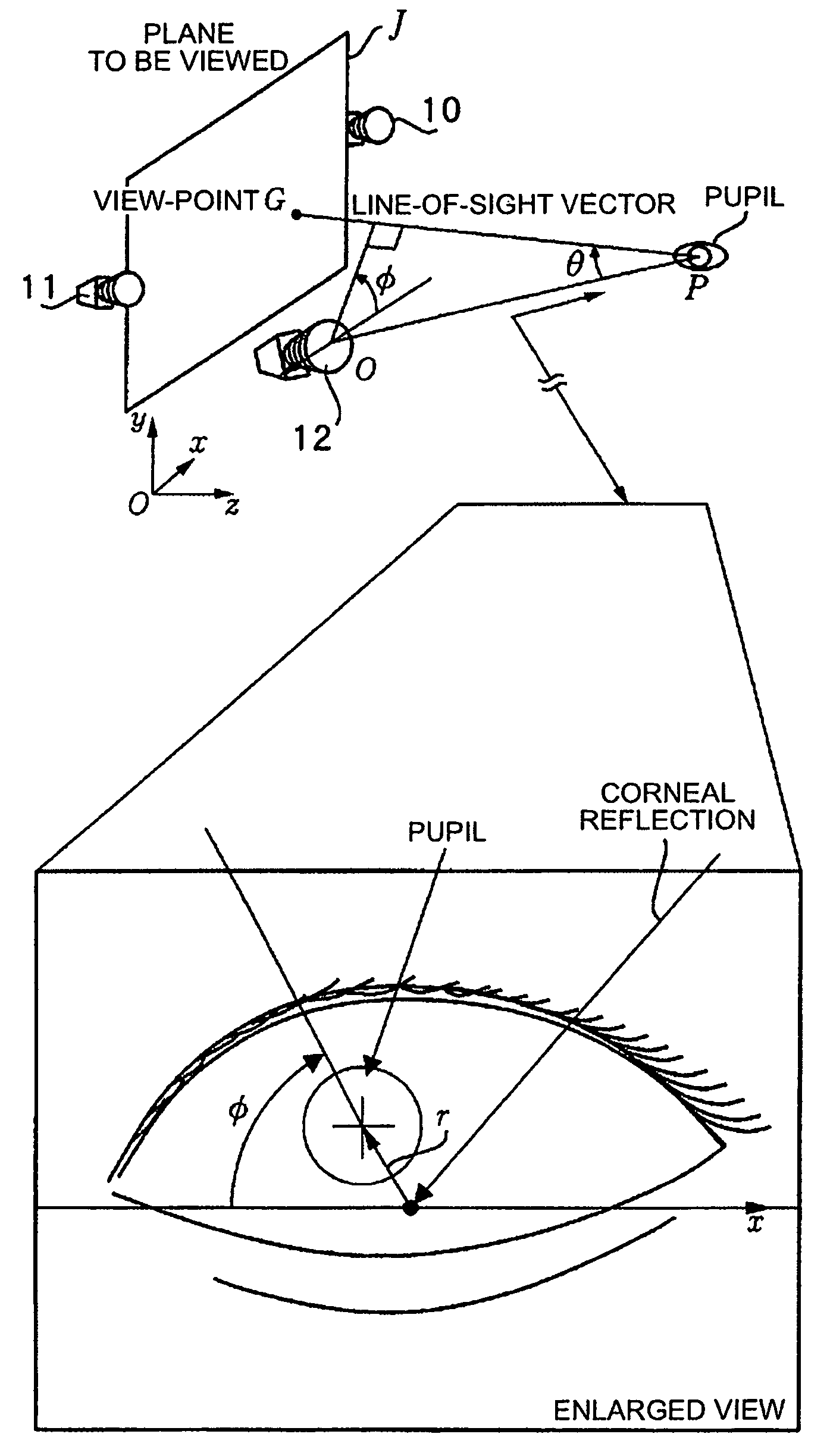
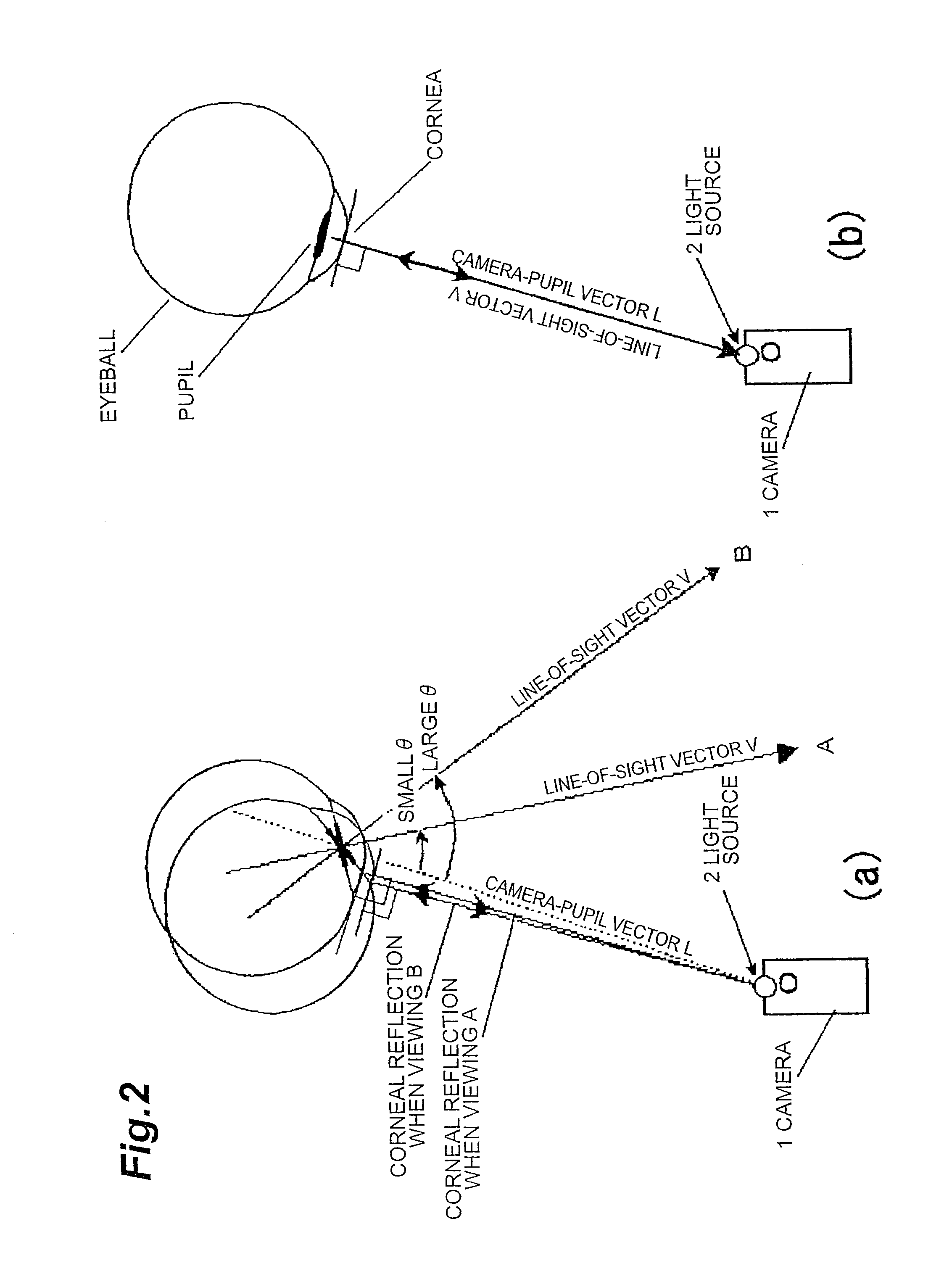
Method and device for detecting a line-of-sight of a subject and a three-dimensional view-point measurement device. The method uses a first camera, that measures the position of a pupil relative to a coordinate system, a second camera having a light source arranged at a known position in the coordinate system, and forming a corneal reflection center to obtain data of a size of vector r from the corneal reflection center to the pupil center and an angle φ of the vector r relative to a coordinate axis of the coordinate system, and a calculation means for calculating a line-of-sight direction based on information from each camera. In determining a relational formula, a subject is made to gaze at a known point to perform measurement and a relational formula is determined. In a line-of-sight determining stage, the subject is measured again using the relational formula. A three-dimensional view-point measurement device can be configured so as to simultaneously measure the lines-of-sights of both eyes with two cameras and two light sources.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP SHIZUOKA UNIV
Simplified ocular fundus auto imager
An ocular fundus imager automatically aligns fundus illuminating rays to enter the pupil and to prevent corneal reflections from obscuring the fundus image produced. Focusing the produced fundus image is automatically performed using a pair of video sensors and is based upon the fundus image itself. A head restraint is used to reduce the gross alignment between the optical system and the patient's pupil.
Owner:VISUAL PATHWAYS
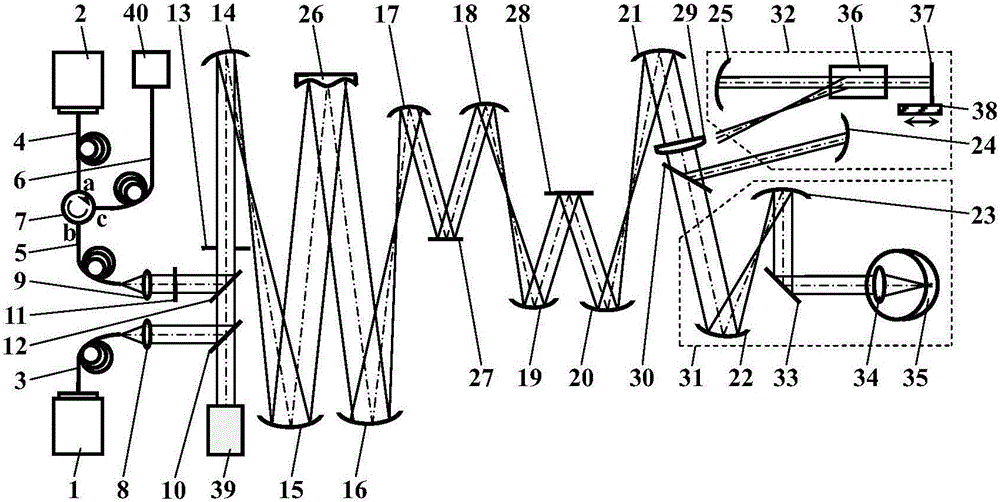
Common-path interference self-adaption optical OCT retinal imaging instrument
ActiveCN105105707AStable imaging resultsQuality improvementOthalmoscopesWavefront sensorHorizontal and vertical
The invention discloses a common-path interference self-adaption optical OCT retinal imaging instrument which comprises a beacon light source, an imaging light source, spherical reflectors, a wavefront correction device, a horizontal scanning galvanometer, a vertical scanning galvanometer, a center reflection edge transmission spectroscope, a wavefront sensor, a detector, an AO control system, an OCT control system, a computer, a wavefront controller and the like. The center reflection edge transmission spectroscope is arranged at the conjugate position of the pupil plane of a human eye. The diameter of the reference light beams formed through center reflection is smaller, the aberration introduced by the wavefront correction device after the reference light beams come and go twice is smaller and can be neglected; the aberration generated when sample light beams formed by edge transmission are illuminated into human eyes can be detected and corrected by the AO system. The interference spectrum formed by the light beams can rebuild high-resolution retinal images. The common-path interference self-adaption optical OCT retinal imaging instrument has the advantages of being resistant to environment interference, free of polarization adjustment, simple in dispersion compensation, capable of inhibiting corneal reflection stray light signals and reducing appearance size and lowering cost, suitable for long-optical-path AO-OCT systems and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for eye detection from glints
ActiveUS20160210497A1Well formedInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisSpecular reflectionEye detection
A method of determining the position of eyeballs within an image, the method including the steps of: (a) capturing a time series of image frames illuminated in a predetermined temporal manner by at least two spaced apart light sources, by at least one imaging sensor; (b) processing the image frames to determine specular reflection locations in the image frames; and (c) utilising the time series evolution of the location of the specular reflections to isolate corneal reflections from the determined specular reflection locations.
Owner:SEEING MACHINES
Apparatus for Monitoring One or More Parameters of the Eye
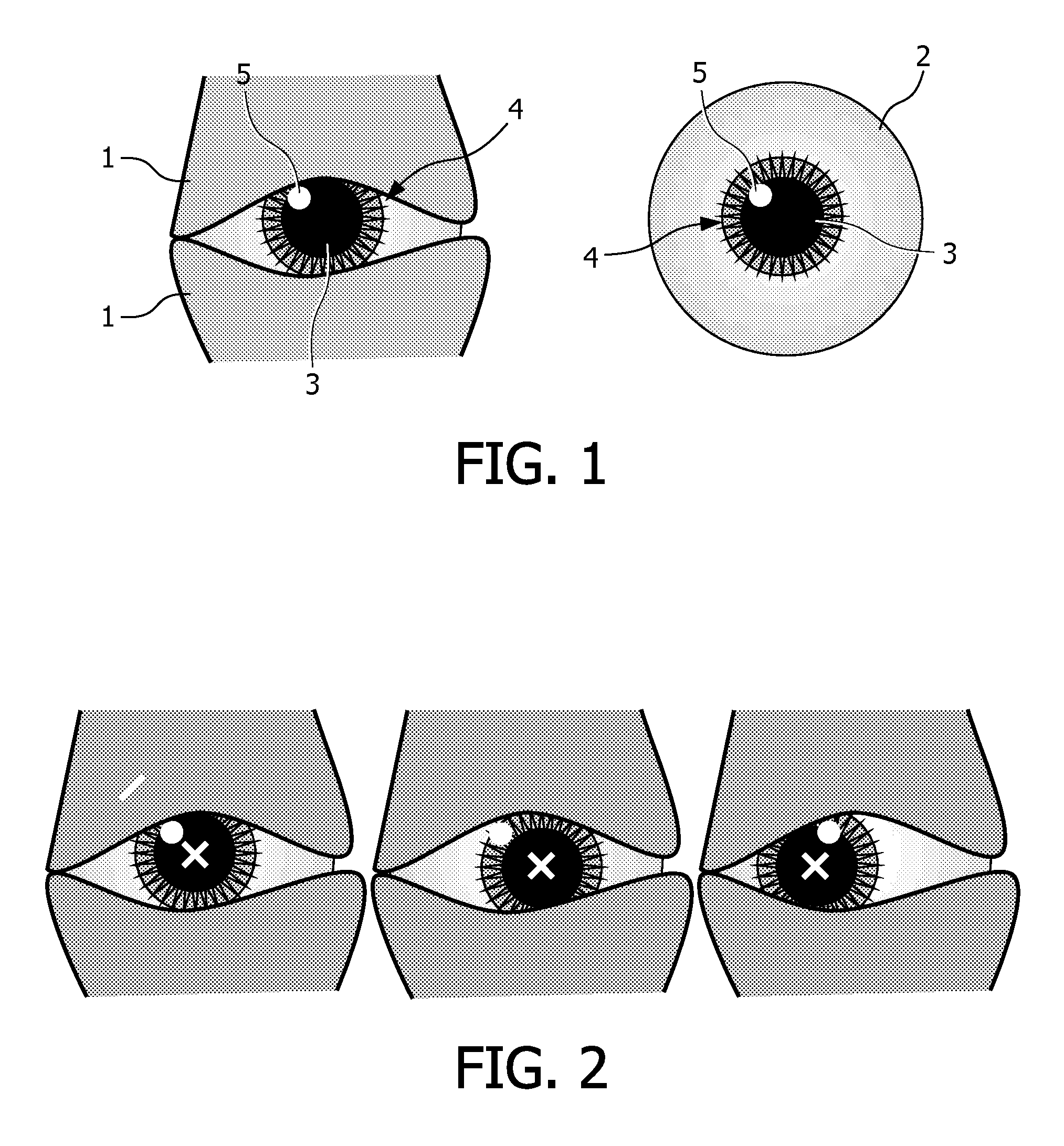
An apparatus for monitoring one or more parameters of the eye of a patient over multiple sessions which are temporally spaced apart and between which the eye of the patient can have moved, said apparatus comprising: a camera for taking one or more images of the eye; an illumination unit for illuminating the eye by a ring-shaped light pattern to generate corneal reflections, said illumination unit being preferably located such that the center of the ring is coaxial with the optical axis of the camera; a module for determining during a first session the location of the corneal reflections in the image of the eye; a module for determining during said first session based on said determined location of the corneal reflections, at least one further parameter of the eye and its coordinates in a first coordinate system based on a geometrical model representing the eye as a spherical eyeball having a spherically shaped cornea mounted thereon; a module for determining during a second session temporally spaced apart from said first session said location of said corneal reflections of the eye and based thereon said further eye parameter and its coordinates in a second coordinate system; a module for determining the eye motion in six degrees of freedom between said first and said second session and for determining a coordinate transformation based thereon; a module for transforming based on said determined eye motion said further eye parameter and its coordinates from said first coordinate system into said second coordinate system; a module for quantifying and / or visualizing the change of said further eye parameter between said first and said second session based on said further parameter and its coordinates measured during said second session and said transformed parameter and its coordinates measured during said first session.
Owner:ALCON INC
System and method for tracking the point of gaze of an observer
ActiveUS9237844B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedInput/output for user-computer interactionStatic indicating devicesPoint of gazeComputer science
A system for tracking the point of gaze of an observer observing an object comprises a camera for recording an image of an eye of the observer, comprises a means for providing a luminous marker, and means for analyzing the image of the eye to determine the reflection of the marker on the eye and the centre of the pupil. The relative positions of the corneal reflection of the marker and the pupil centre are measured. The marker is repositioned, in dependence on the determined relative positions, to improve correspondence between the corneal reflection of the marker and the pupil center.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Eyeshot detection device using distance image sensor
An object of the present invention is, when determining a line-of-sight vector of a subject, to identify a three-dimensional position of a pupil center or corneal reflection center thereof. The line-of-sight vector is determined by measuring a distance from a camera to the pupil center or corneal reflection center of the subject using a two-dimensional CMOS distance image sensor by a light time-of-flight method and obtaining position information of the pupil center and corneal reflection center of the subject using the distance image sensor. If a position and a direction of the camera are identified, a camera-pupil center vector is determined from image information of the pupil center of the subject. Since the camera-pupil center distance has been measured, a pupil center position in a three-dimensional space is determined from the above information. Combining this with two line-of-sight vectors determines a position where line-of-sight vectors intersect, or a view-point.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP SHIZUOKA UNIV
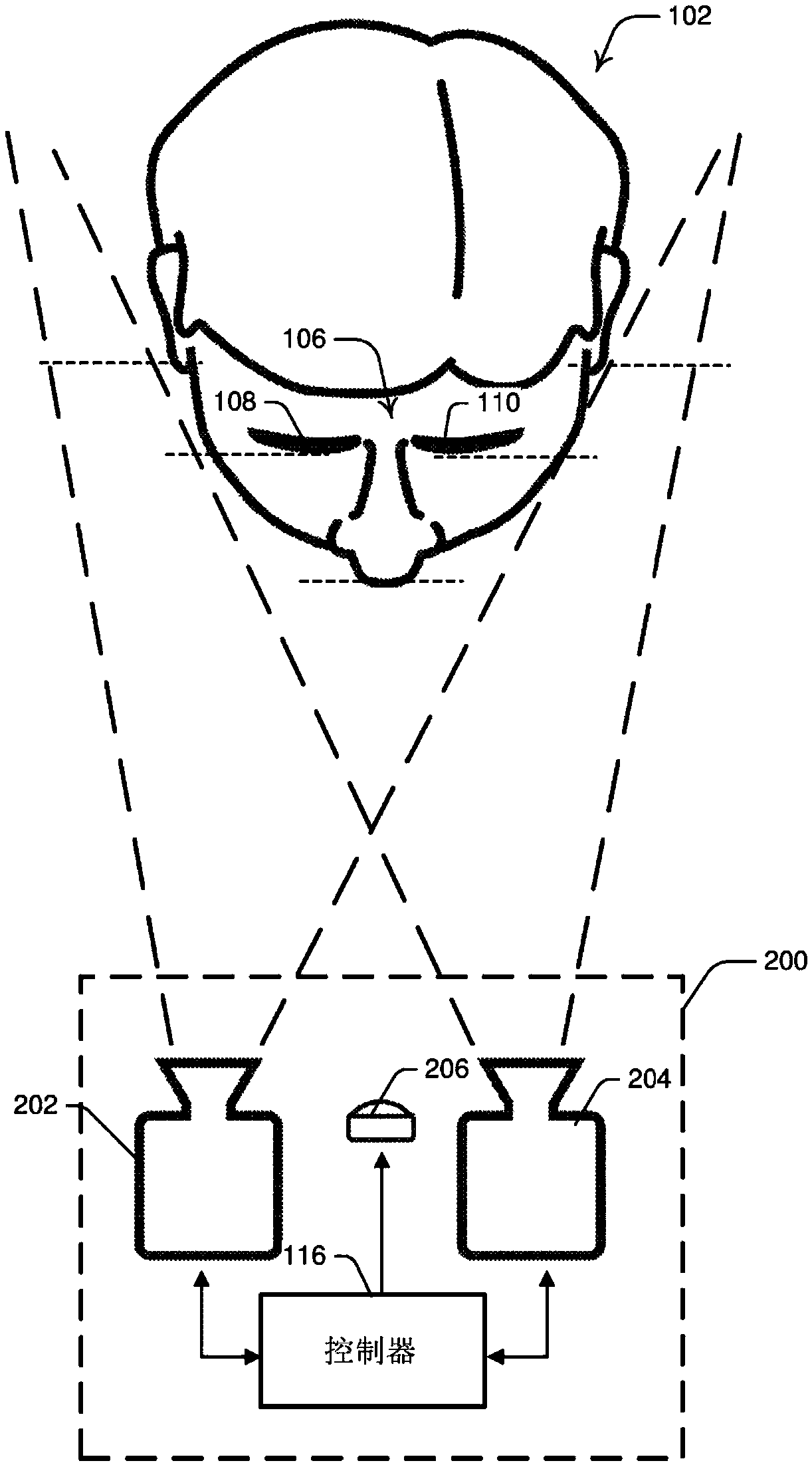
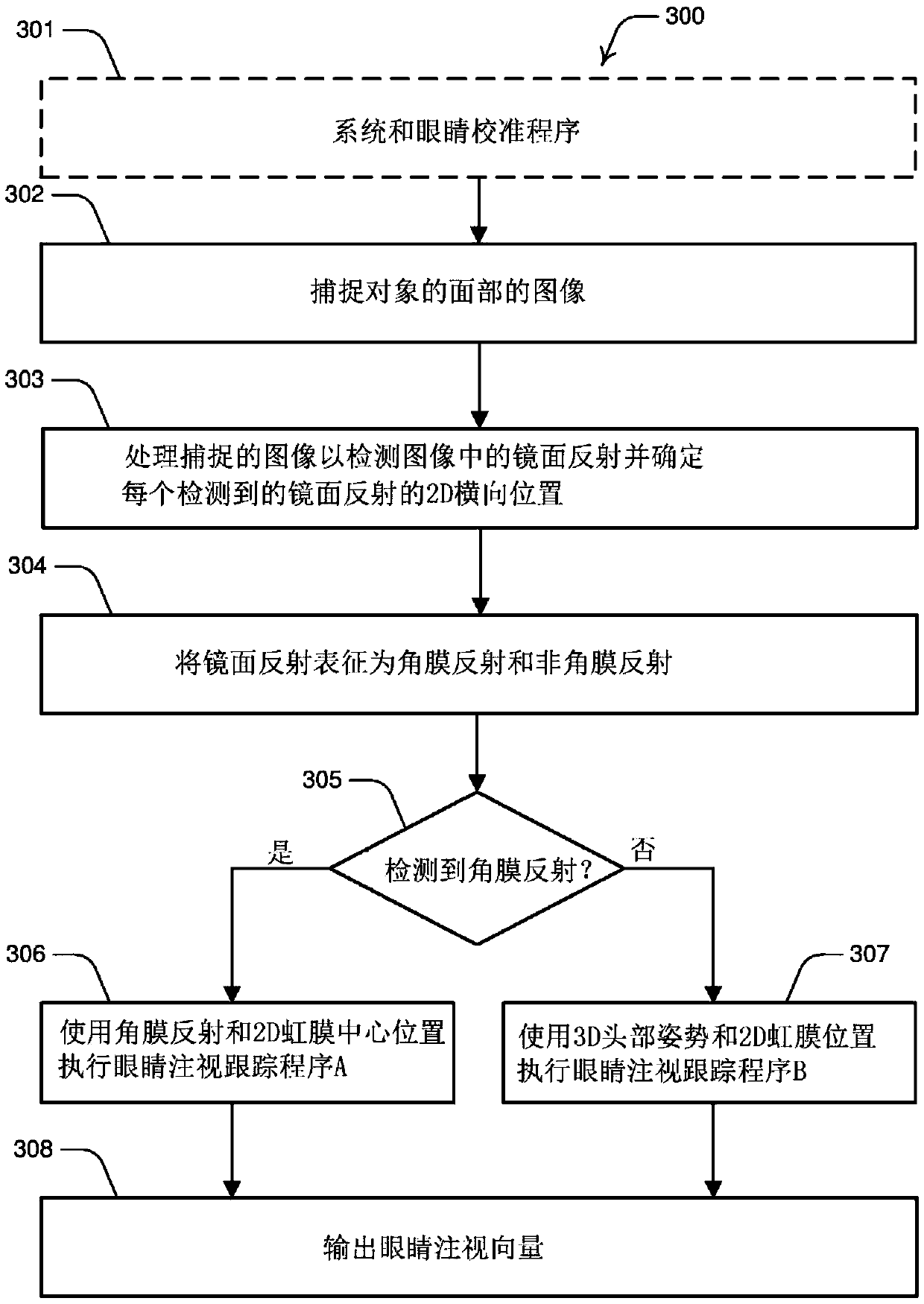
Systems and methods for performing eye gaze tracking
Described herein are systems and methods for performing eye gaze tracking. The method includes capturing, from one or more imaging devices, a sequence of time separated images of the subject's face including one or both of the subject's eyes; processing the images to detect specular reflections present in the images; characterizing the detected specular reflections into corneal reflections and non-corneal reflections; upon detection of at least one corneal reflection, performing a first eye gaze tracking procedure based on the relative positions of the at least one corneal reflection and at least one reference eye feature; upon detection of no corneal reflections, performing a second eye gaze tracking procedure on one or both eyes of the subject based on the estimation of head pose of thesubject and outputting eye gaze vectors of one or both eyes from the first or second eye gaze tracking procedure.
Owner:SEEING MACHINES
Head-mounted visual aiming control system
InactiveCN108732746AAccurately determineControl movementOptical elementsLocation trackingControl system
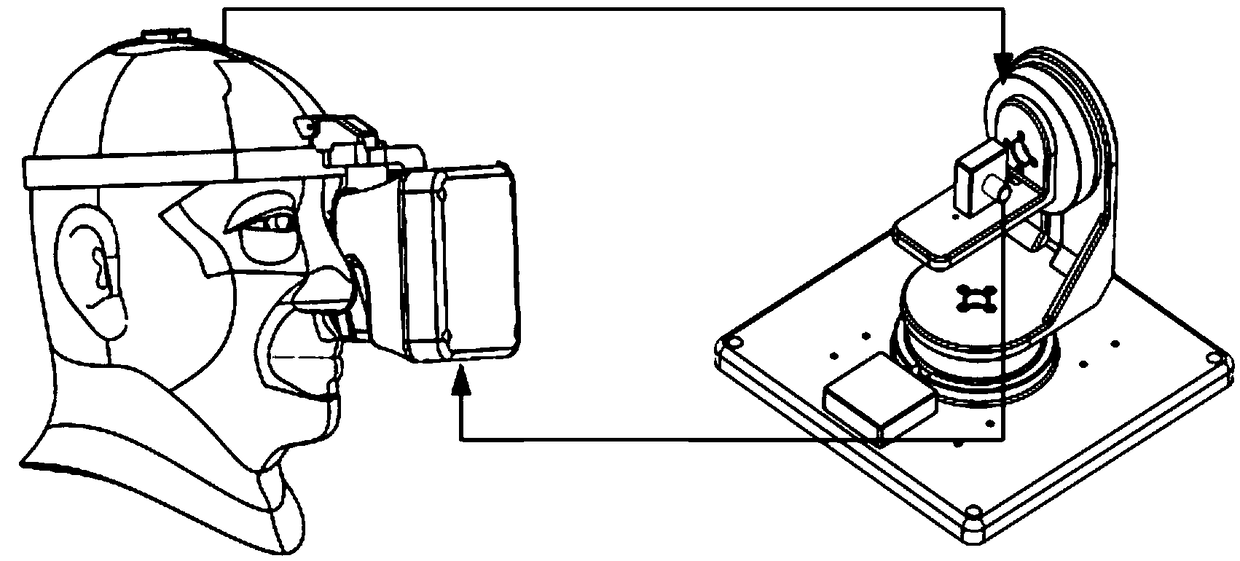
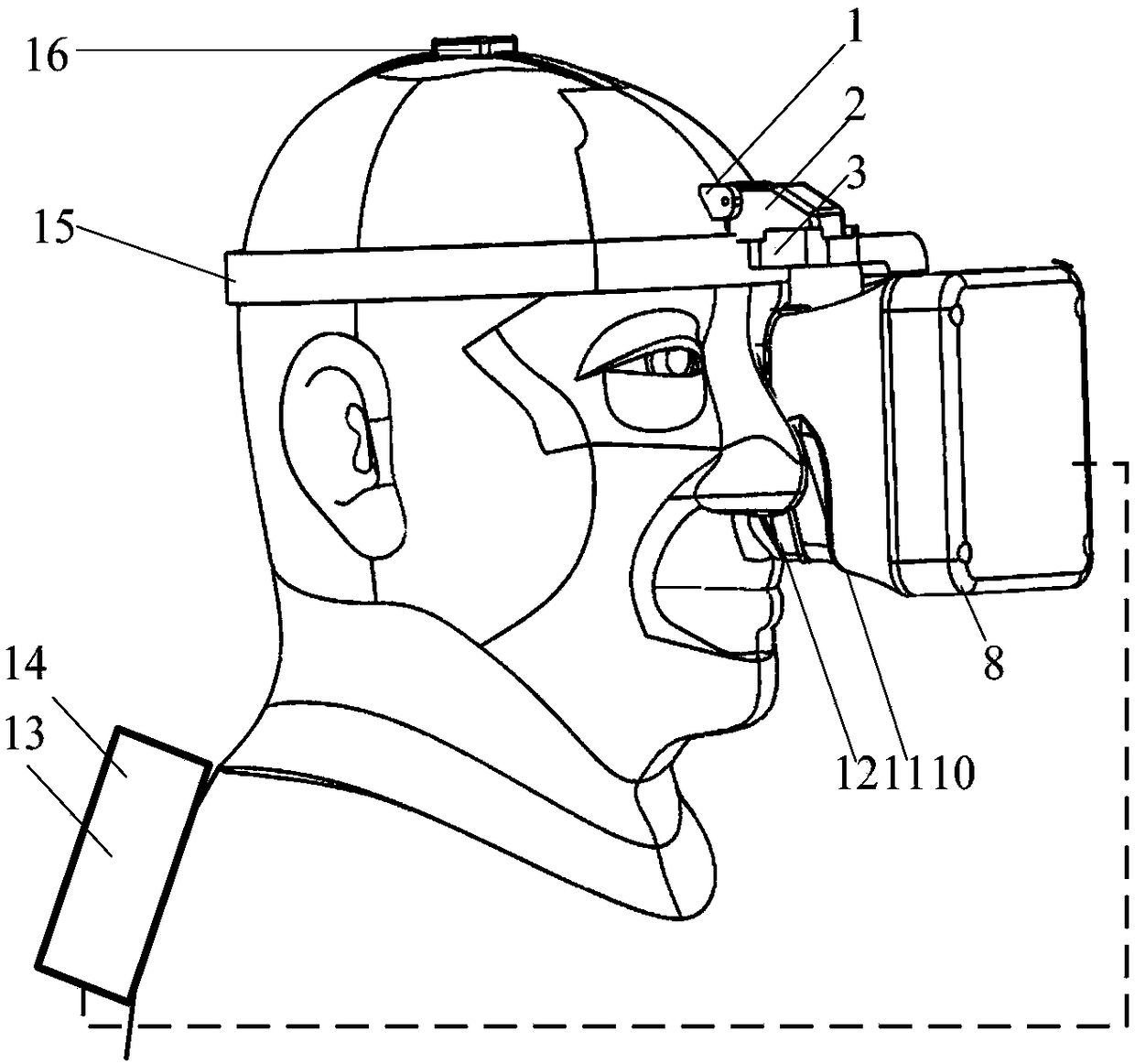
The invention relates to the wearable intelligent device technology field and particularly relates to a head-mounted visual aiming control system. The head-mounted visual aiming control system is characterized in that a visual detection tracking device is worn on a head of a user, the head-mounted visual aiming control system comprises a position tracker, an eye camera, a corneal reflection infrared light source, an eye movement processing module, a head-mounted display and an optical system, wherein a servo holder is provided with a camera and is under the control of a control board to move,the scene image information acquired by the camera is received by a data processing and communication module, the scene image information is sent to a display screen driving board, the ocular fixationpoint information and the head pose information are fused by the data processing and communication module, corresponding detection tracking of the fused information and the scene image information acquired by the camera is carried out, the detection tracking result is sent to the control board, and simultaneous movement of visual movement is carried out by the servo holder. The head-mounted visual aiming control system is advantaged in that the servo holder can be controlled more accurately for movement according to the intention of eye movement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
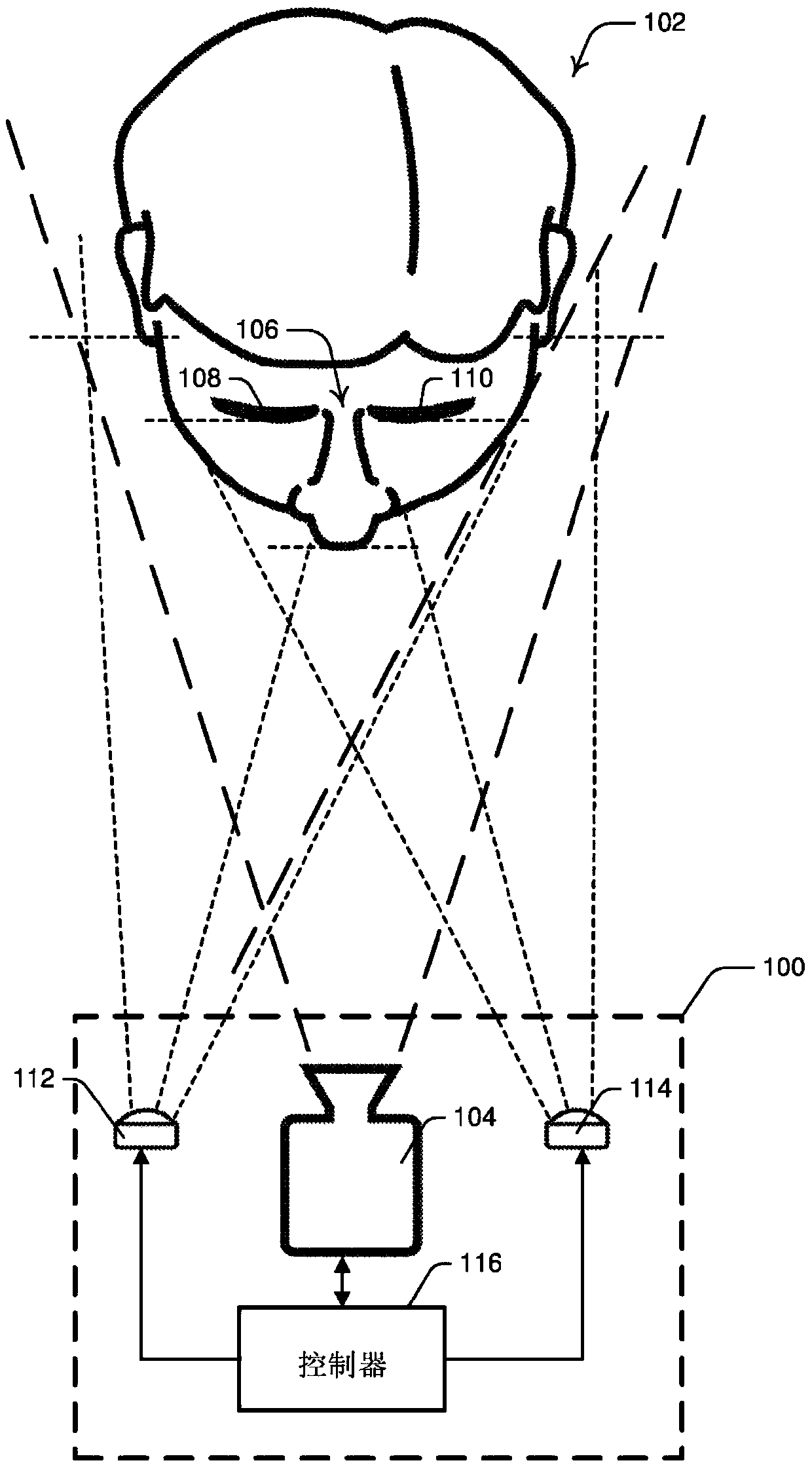
Eye gaze detection supporting device and eye gaze detection supporting method
An eye gaze detection supporting device includes an illuminator including a light source that performs irradiation with light, a plurality of imaging units, position detectors that detect a first position indicating a center of a pupil and a second position indicating a center of corneal reflection, from an image of an eye ball of a subject irradiated with light by the illuminator, and captured by the imaging units, and a calculator that calculates a fourth position indicating a curvature center of a cornea, based on a position of the light source, a third position on a display, the first position, and the second position.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
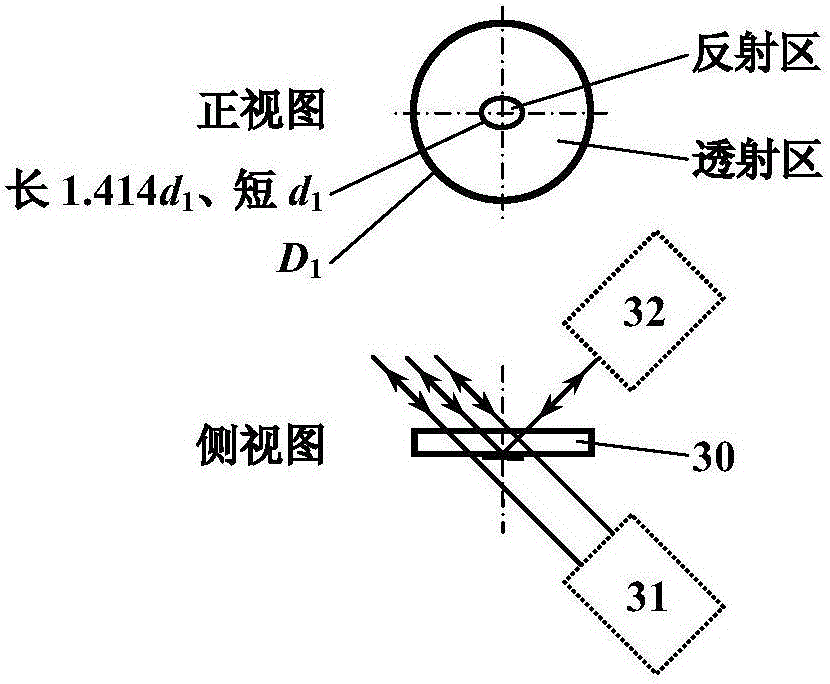
Annular lighting device for eye ground camera
An annular lighting device for an eye ground camera relates to the field of medical optics, and solves the problems that the utilization rate of lighting system energy is low, retina lighting is not uniform, and annular diaphragm with high cost is used in the conventional eye ground camera. A lighting source sent out by a light source generates uniform annular faculae after passing through a lighting optical system; the uniform annular faculae light cornea edge areas of people, and can keep away from cornea central areas capable of strongly reflecting light, so that the uniformity of eye ground lighting is improved; further, the width of annular light beams can be changed through adjusting the distance between a positive axial conical mirror and a negative axial conical mirror in a lighting light path to be adapted to different eyes of people; and real images are formed in the middle of the system for two times, the influence of stray light such as cornea reflected light on the imaging quality is greatly reduced through adding confocal filtering apertures and adopting a reflecting mirror foldable light path.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
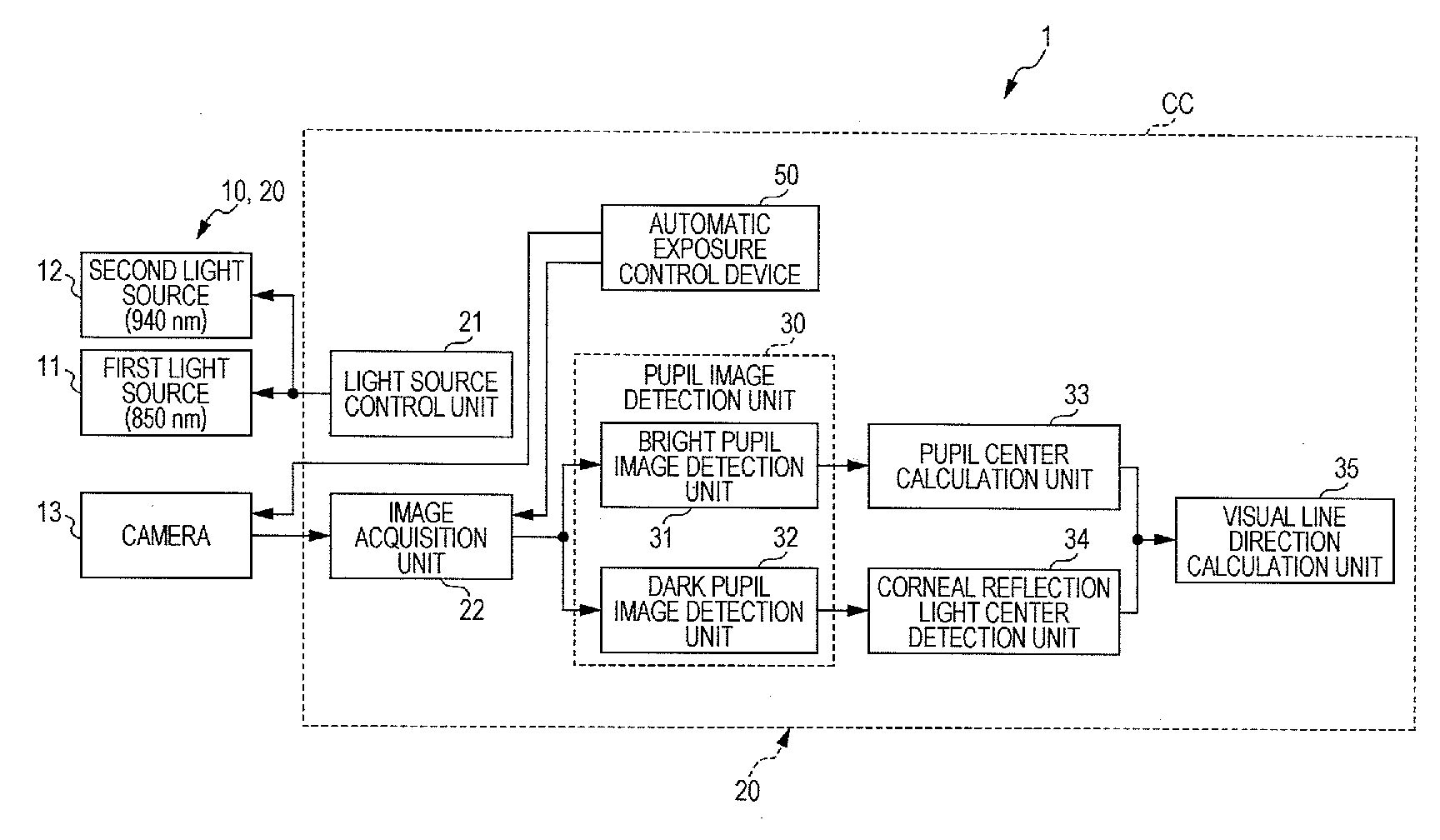
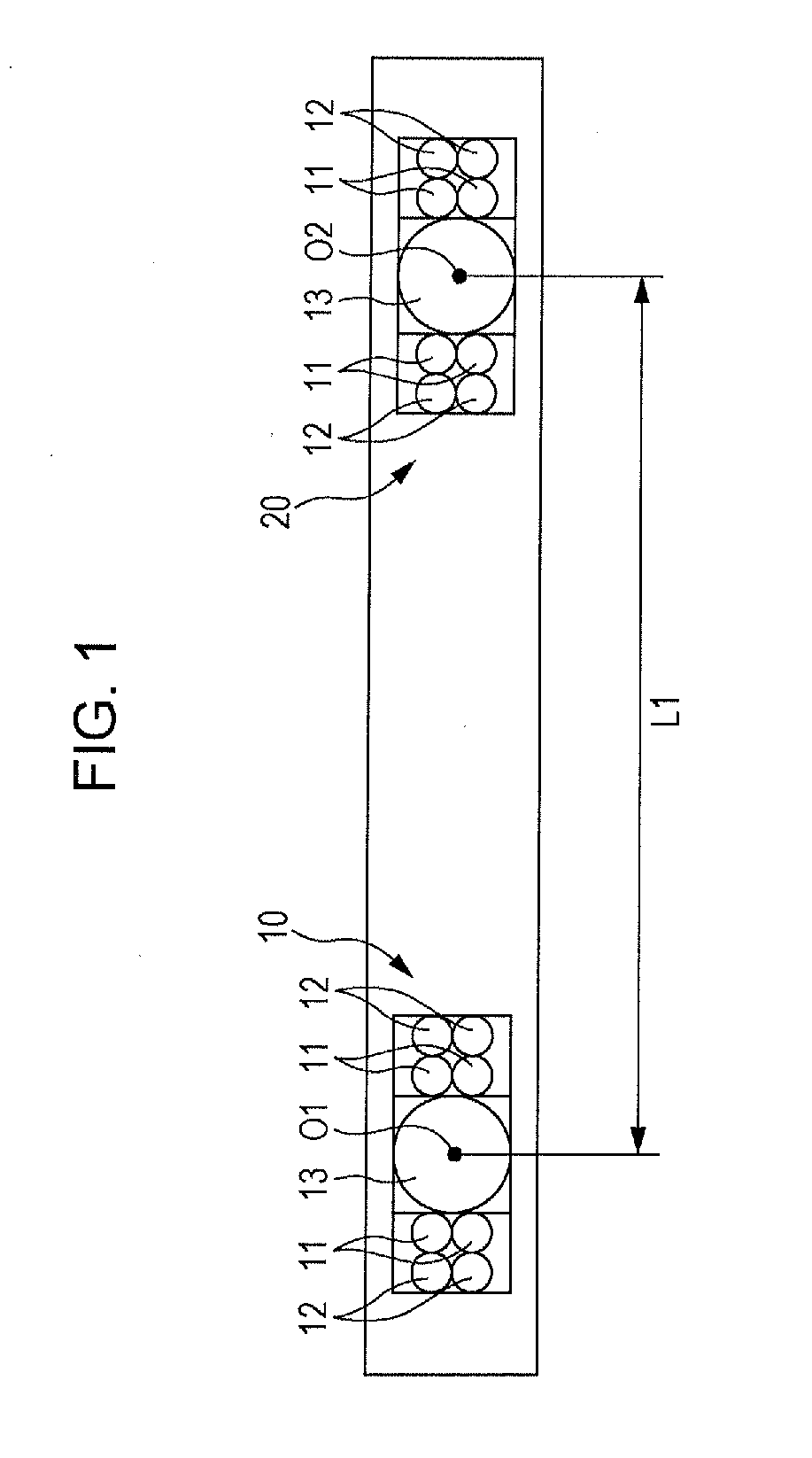
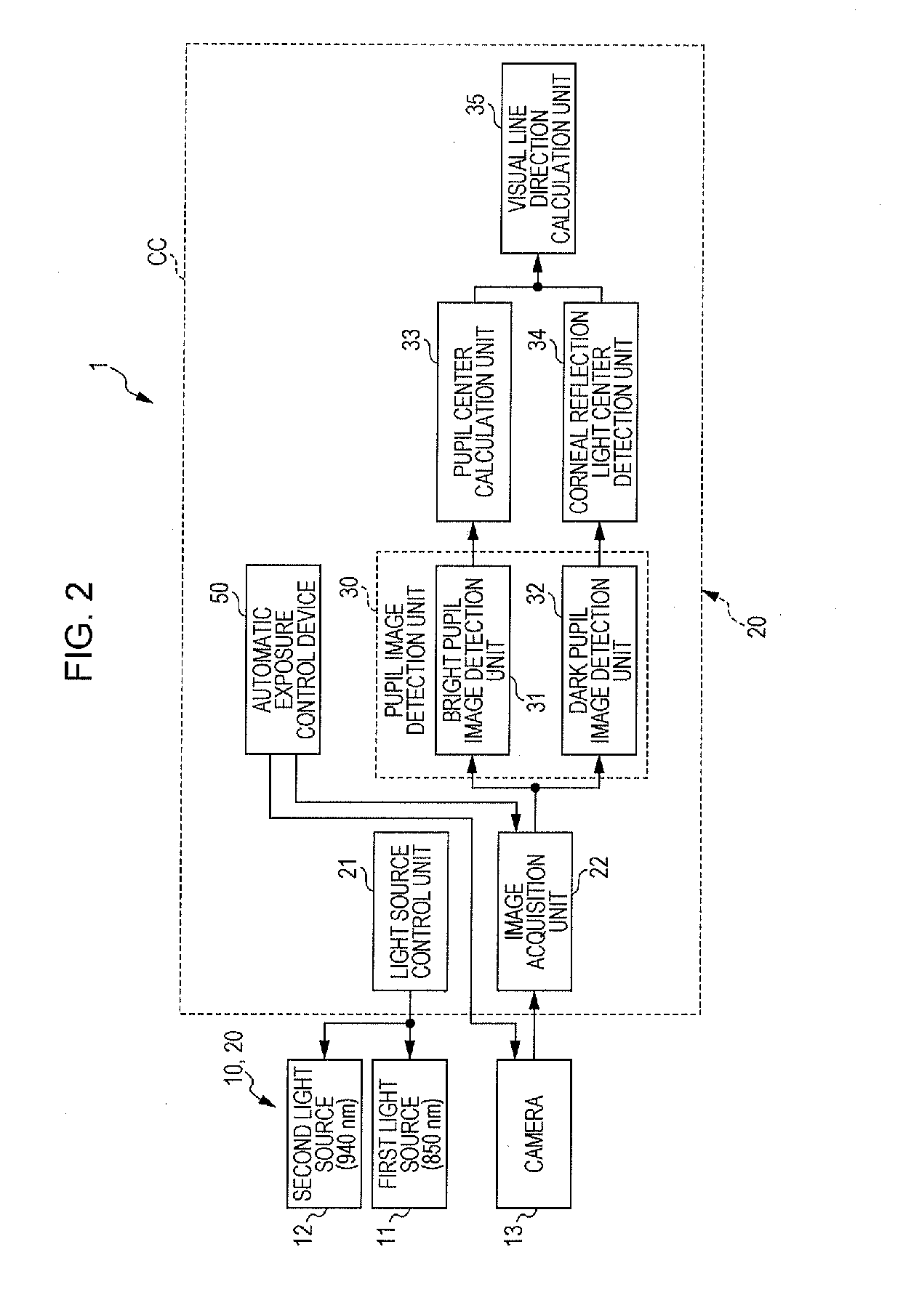
In-vehicle imaging device
InactiveUS20160063334A1Automatic controlImage enhancementTelevision system detailsIn vehicleLightness
The face image of a passenger is acquired by a camera set in a vehicle cabin, the positions of a pupil and corneal reflection light of the face image are detected, and a visual line direction is calculated from the pupil and the corneal reflection light. A condition for automatic exposure control is predetermined, and the exposure time (shutter time) of the camera is controlled in accordance with the exposure condition. In a driving interval in the sunny daytime, the reference time of image luminance for the automatic exposure control is shortened, thereby enabling to follow the fluctuation of luminance inside a vehicle. In a driving interval in a cloudy condition and a driving interval in the night-time, the reference time of image luminance for the automatic exposure control is lengthened, thereby keeping automatic exposure from responding to the light of headlights of an oncoming vehicle.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Apparatus for monitoring one or more parameters of the eye
Owner:ALCON INC
Automatic pupillometer with visual verification
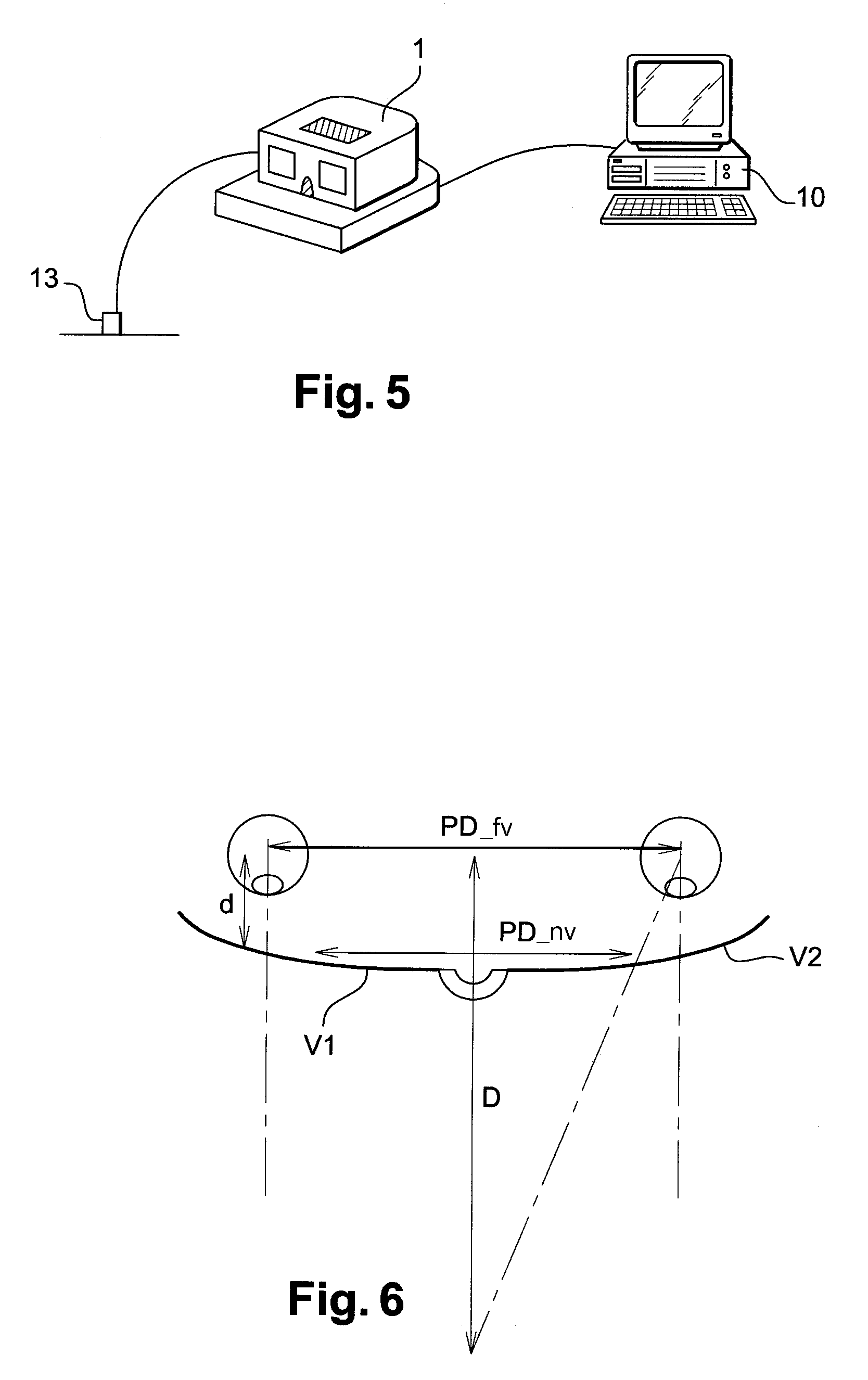
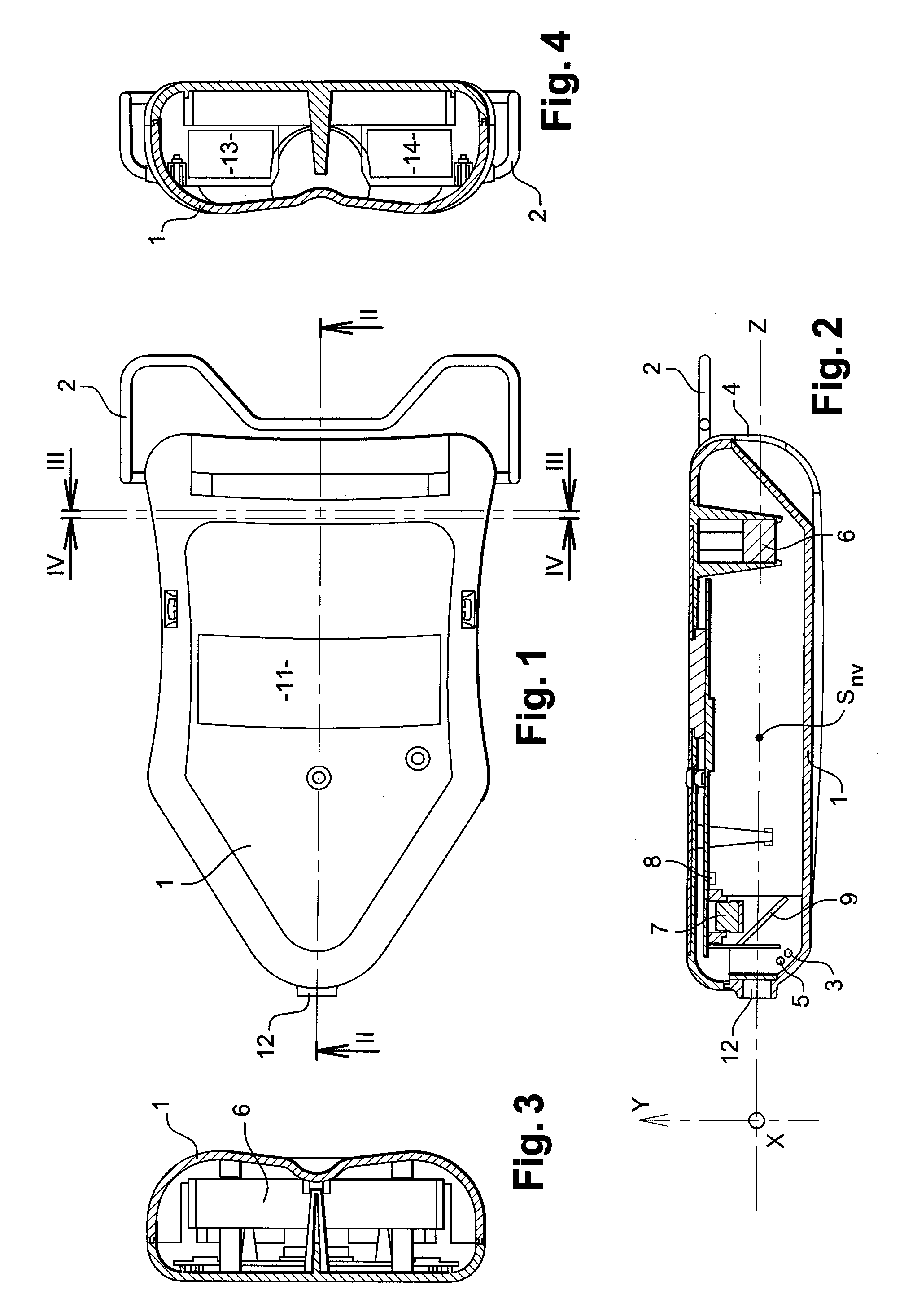
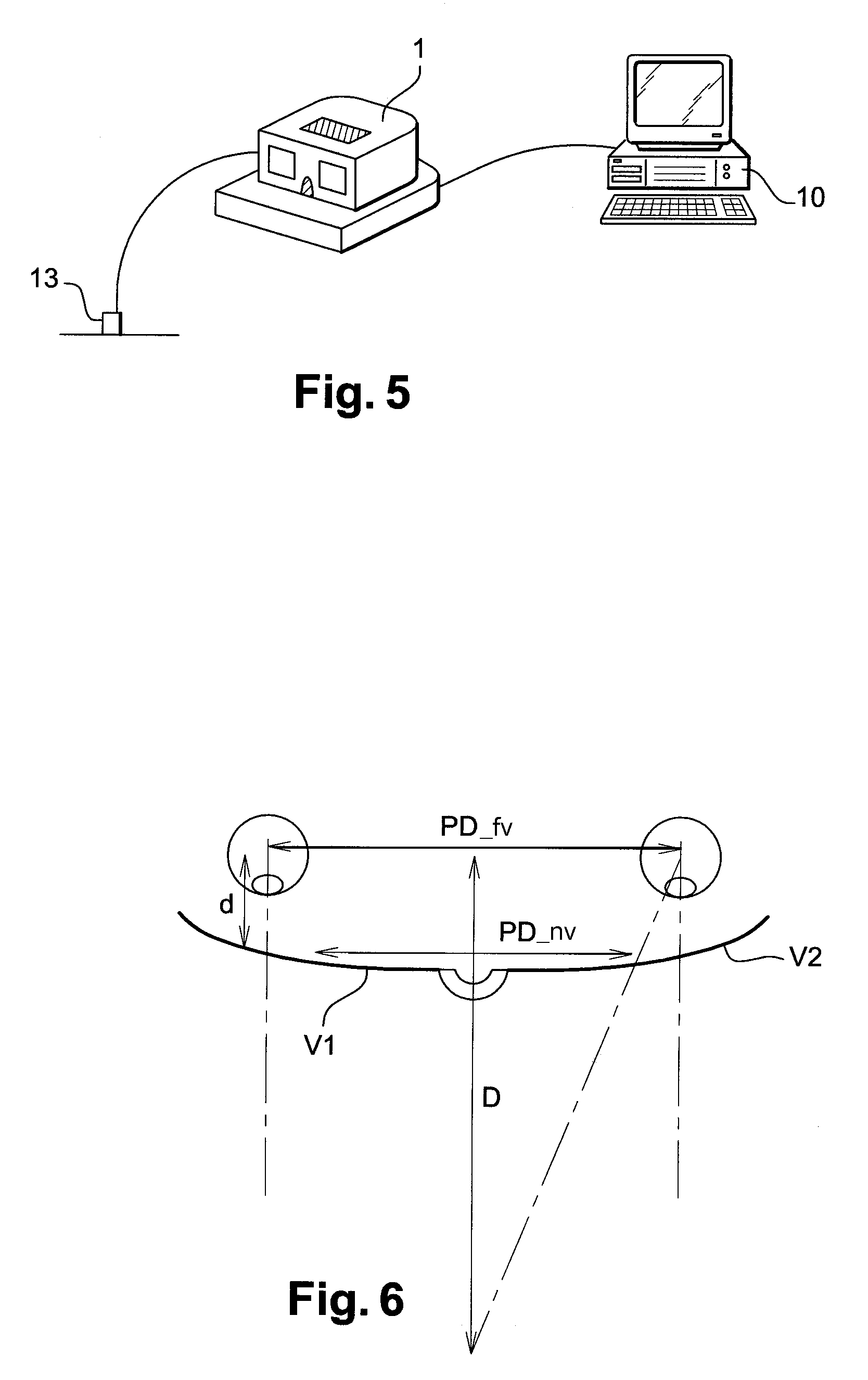
The invention relates to an automatic pupillometer comprising a light source suitable for generating a corneal reflection on at least one of the eyes of an individual facing first and second windows, a collimator lens serving at least to position the light source to correspond to far vision of the individual, a detection receiver for automatically locating said reflection, and a calculator for calculating the pupillary distance of said individual. According to the invention, the pupillometer also comprises a third window where the eye of an observer responsible for the measurement is designed to be placed in the vicinity of the focus of said lens so as to view and verify measurement conditions.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
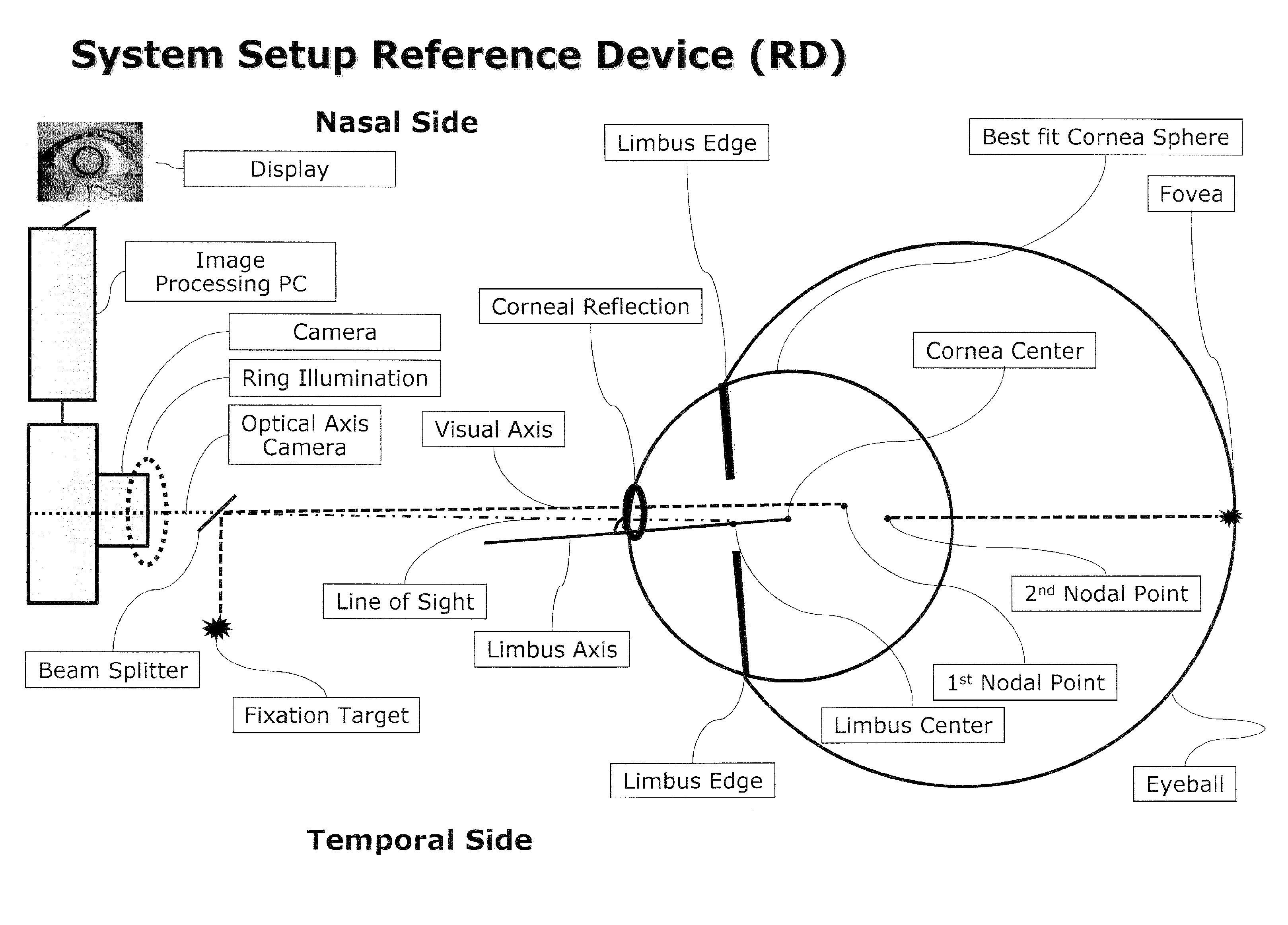
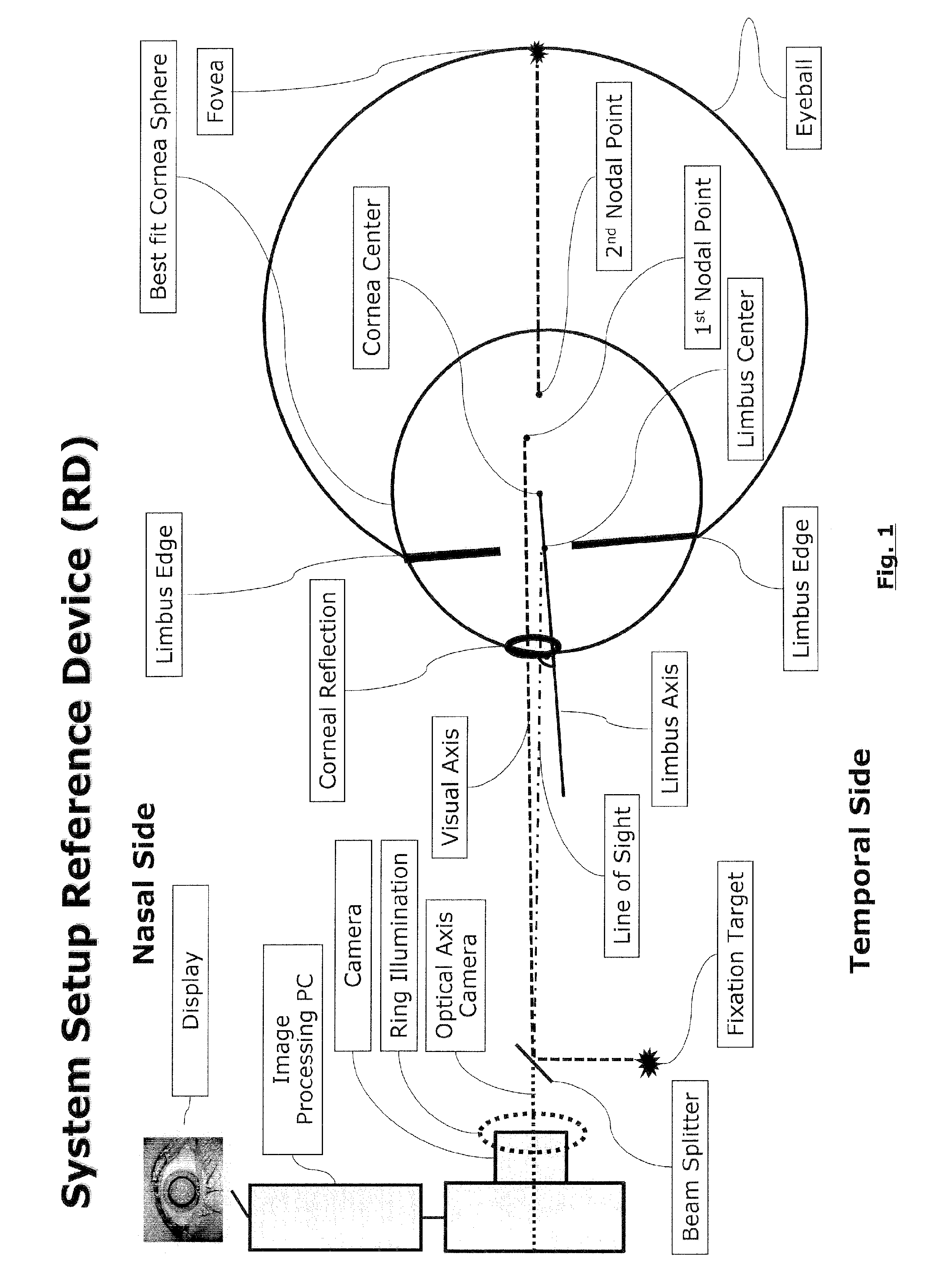
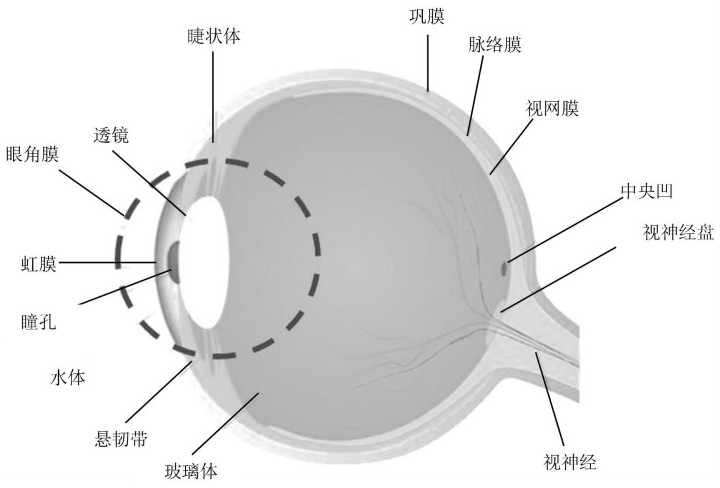
Cornea shape measurement apparatus
A cornea shape measurement apparatus outputs data useful for prescription as well as injection and installation of a TORIC-IOL. This apparatus includes: a projecting optical system projecting an index for measurement onto a cornea; an illuminating optical system illuminating an anterior segment on which a reference mark is placed; an imaging optical system capturing an anterior segment image containing the reference mark and an image of the index reflected from the cornea; an image processor overlaying an astigmatic axis mark indicating a direction of an astigmatic axis of the cornea, which is calculated based on the index image, on the anterior segment image; and a controller displaying the anterior segment image, which contains the astigmatic axis mark, on a display.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
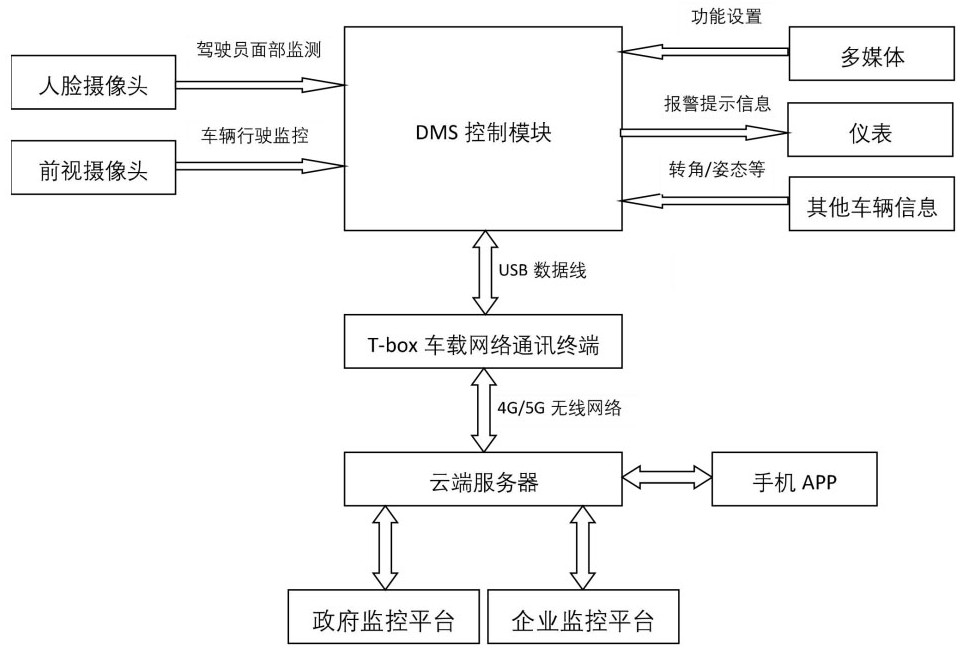
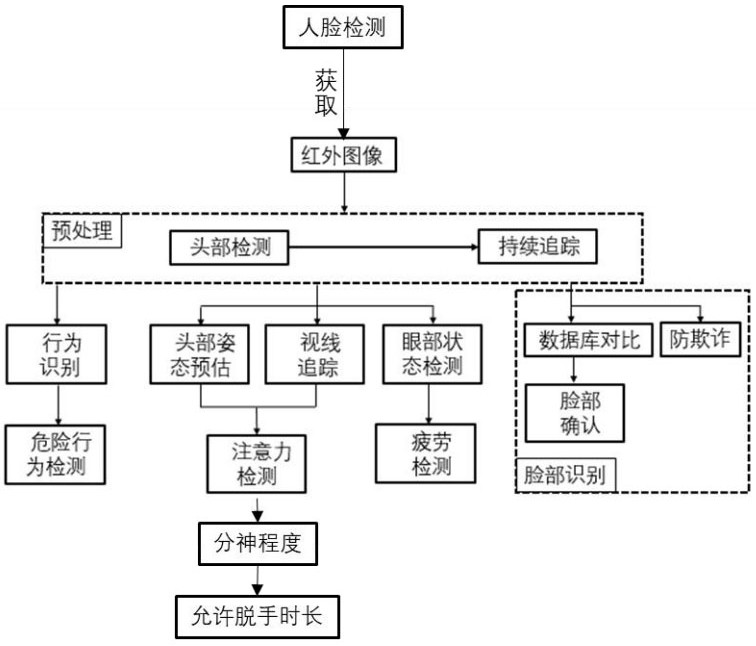
Fatigue driving and improper driving behavior monitoring method and active safe driving monitoring system
ActiveCN112289003ARelieve fatigueAvoid missed alarmsAcquiring/recognising eyesAlarmsFace detectionEye state
The invention relates to an active or auxiliary protection method and system for safe driving of a vehicle. A driver fatigue driving and improper driving behavior monitoring method based on a sight tracking technology employs a stable sight algorithm and a precise sight tracking algorithm fusion scheme, and comprises the steps of: collecting face data, and positioning face information in an image;continuously detecting the head posture of the driver, comparing the face data with face data in a database, and confirming a real face; positioning the feature points in the image by adopting the stable sight algorithm, adaptively establishing a head 3D model, and determining the driver behavior, head direction, sight direction and eye state; adopting a corneal reflection method combining brightpupil and dark pupil to obtain the precise sight of the driver in the precise sight tracking algorithm; and determining the distraction degree of the driver according to the head posture and the sight direction, and further determining the duration allowing the driver to release hands. An active safe driving monitoring system comprises a driver face detection module, a forward-looking monocular camera, a DMS control module, a man-machine interaction system and a T-box vehicle-mounted network communication terminal.
Owner:JIANGLING MOTORS
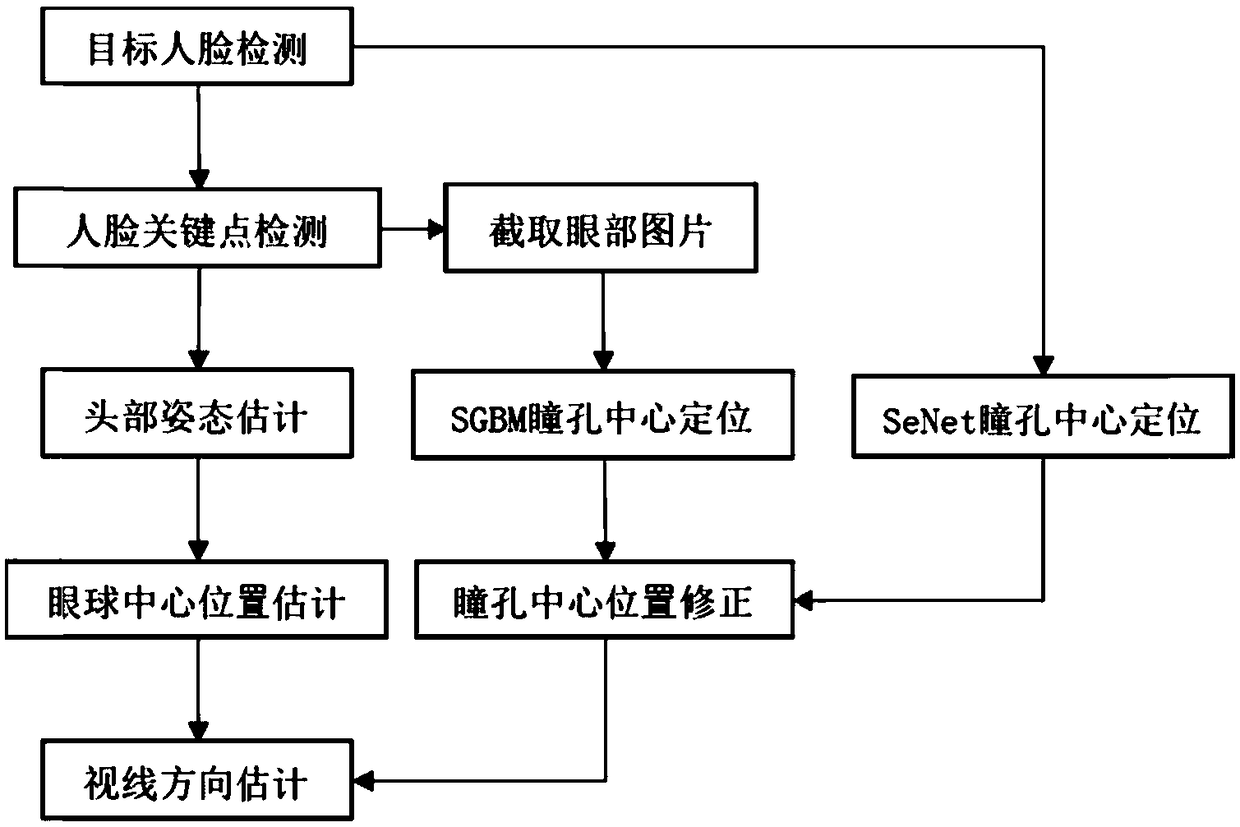
A line-of-sight estimation method based on key point matching
ActiveCN109344714AHigh precisionImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionTemplate matchingCrucial point
The invention discloses a line-of-sight estimation method based on key point matching, belonging to the field of computer vision. After the pupil key points are initially located by the depth network,the invention adopts the SGBM template matching method to further modify the pupil center position. Compared with the existing line-of-sight estimation methods, it can locate pupil center more accurately, especially for the case of large head or eyeball bias. The implementation of the invention can effectively improve the accuracy of the line-of-sight estimation. Compared with the pupil-corneal reflection method, only a single network camera is adopted, thereby greatly reducing the equipment cost. Compared with the existing methods based on single image processing, the proposed algorithm doesnot need to restrict the pose of the head, and the robustness of the algorithm is greatly improved. By matching the 3D face model, the limitation that the existing database can not represent all poseis avoided, which increases the practicability of the method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ophthalmic apparatus
When the fundus camera is positioned on the same side as the subject's eye relative to an appropriate position (front-focus state), the positioning index light source turned on in blue produces most-focused positioning index images. The positioning index light sources become more blurred in order of green and red. When the camera is positioned on the opposite side of the subject's eye relative to the appropriate position (rear-focus state), the positioning index light source turned on in red produces most-focused images. The positioning index light sources become more blurred in order of green and blue. Based on a degree of the blur of the individual positioning index images in red, green, and blue reflected by the cornea of the subject's eye, the calculation unit calculates whether to move the camera body closer to or farther away from the subject's eye and allows the display unit to display the information.
Owner:CANON KK
Automatic pupillometer with visual verification
The invention relates to an automatic pupillometer comprising a light source suitable for generating a corneal reflection on at least one of the eyes of an individual facing first and second windows, a collimator lens serving at least to position the light source to correspond to far vision of the individual, a detection receiver for automatically locating said reflection, and a calculator for calculating the pupillary distance of said individual. According to the invention, the pupillometer also comprises a third window where the eye of an observer responsible for the measurement is designed to be placed in the vicinity of the focus of said lens so as to view and verify measurement conditions.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
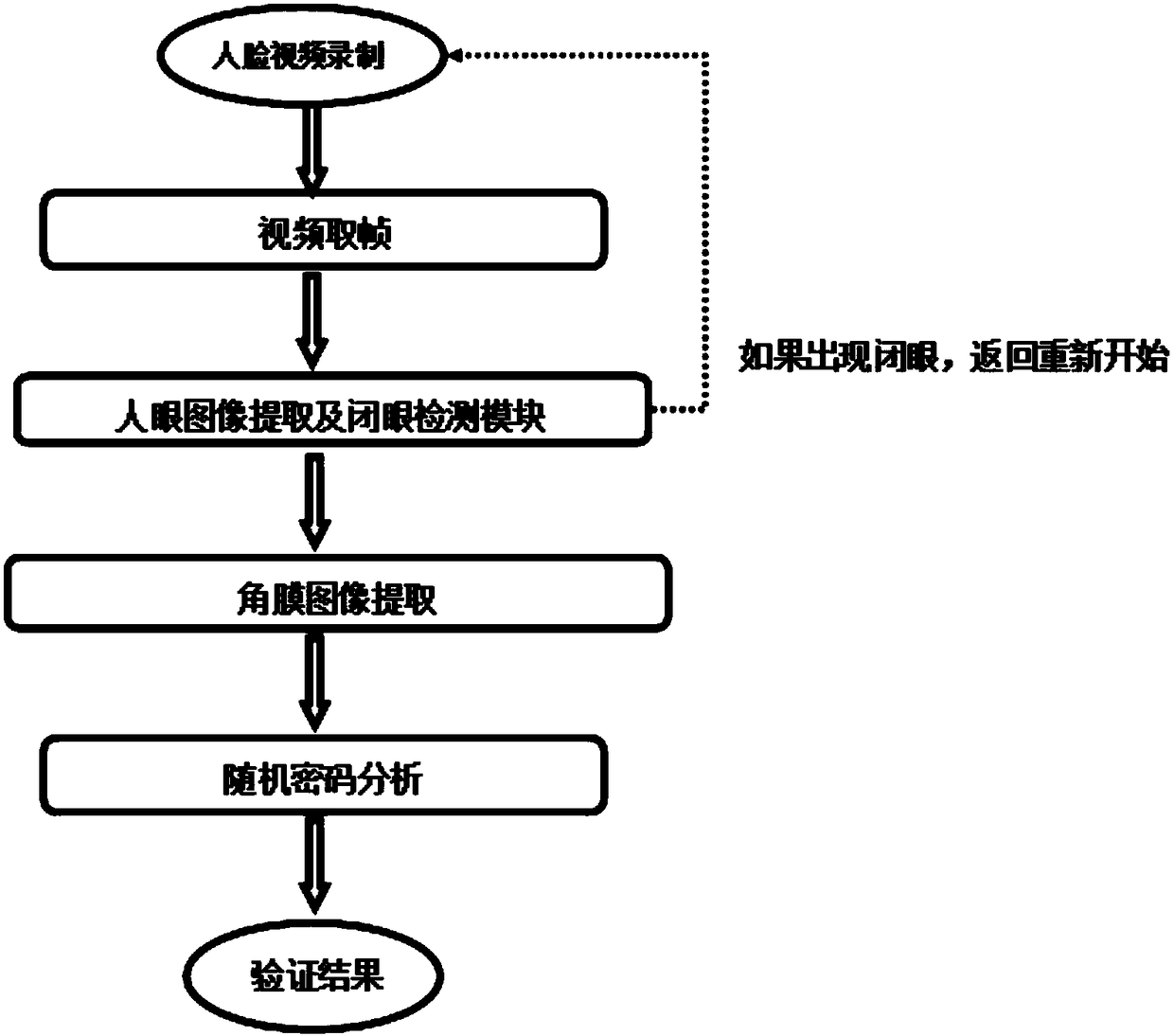
Corneal reflection and optical coding-based human face living body detecting method and system
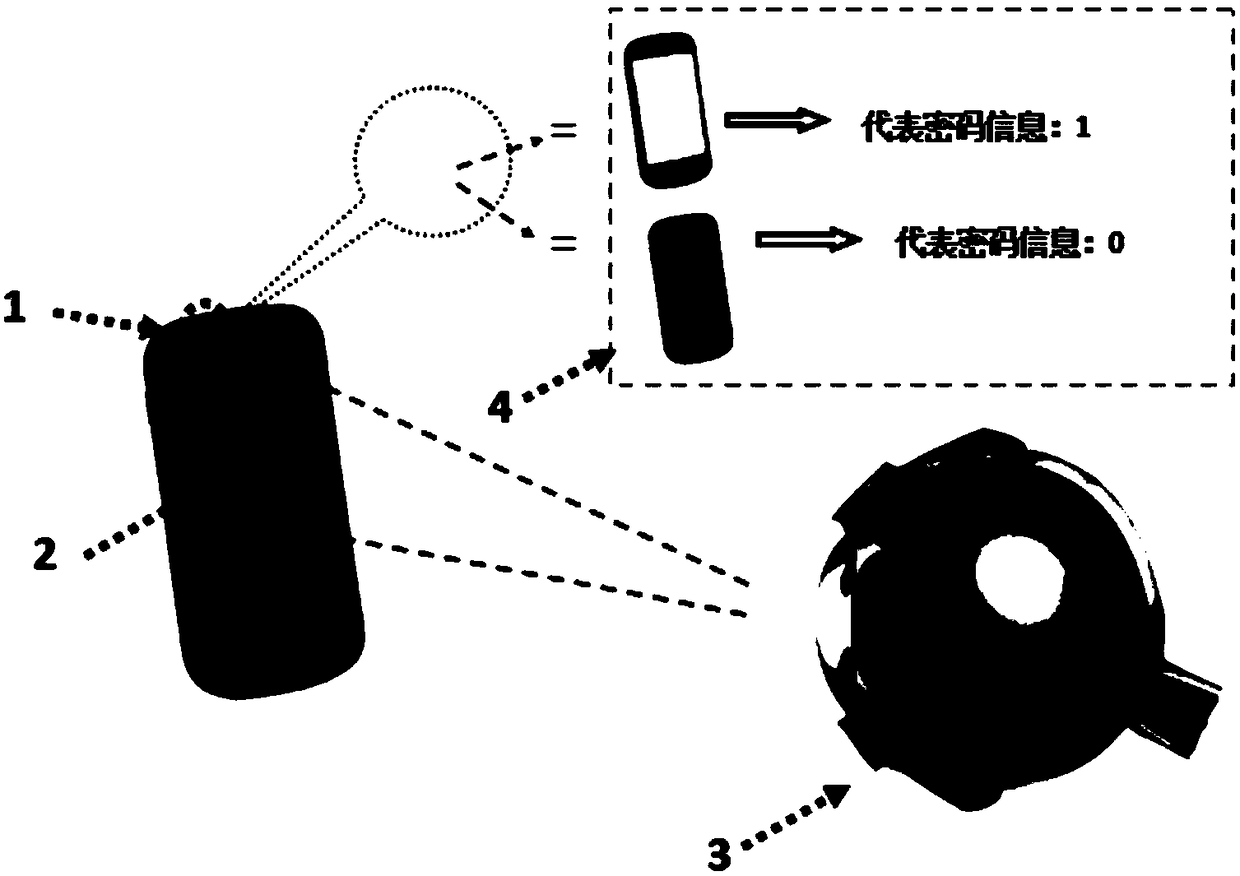
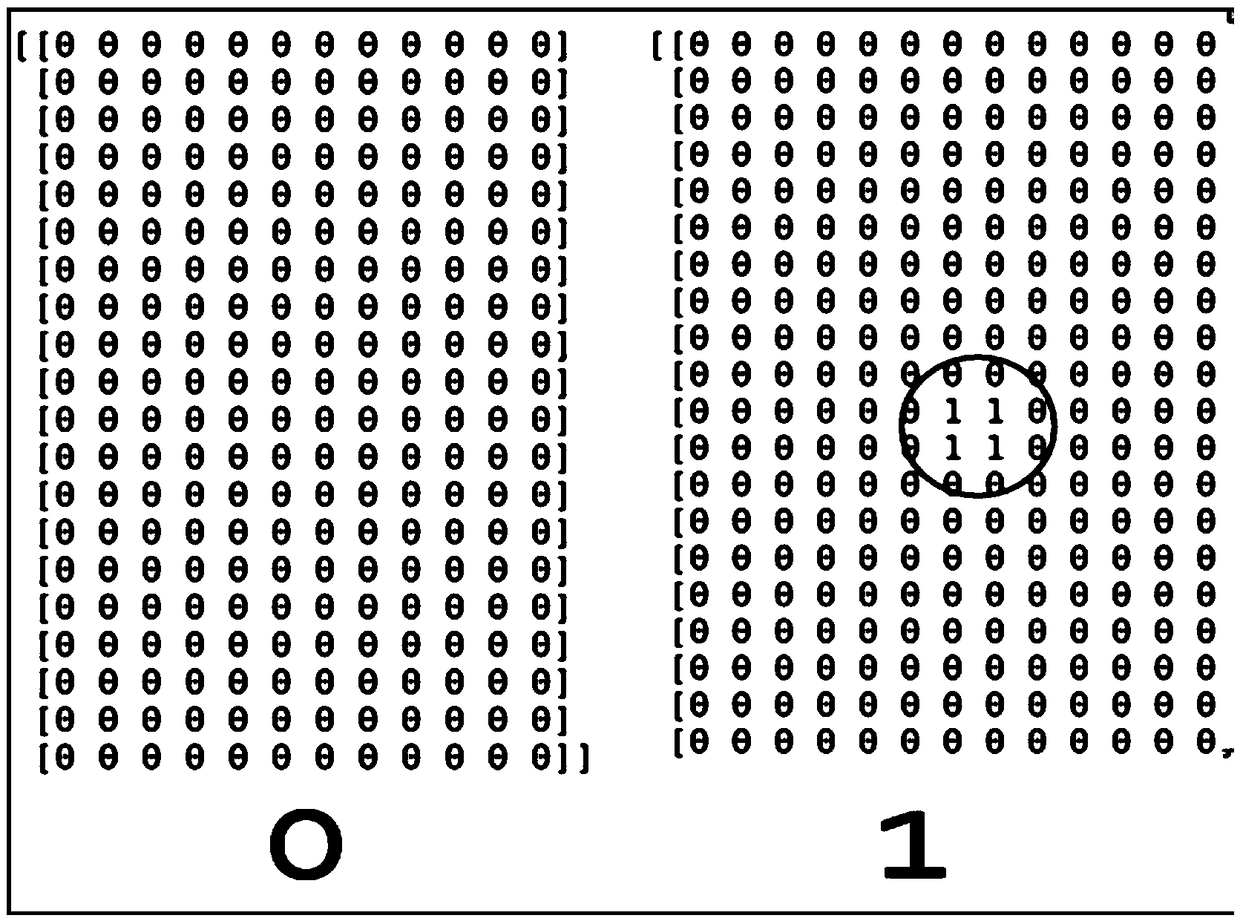
ActiveCN108647650ASolve difficult to extractEasy extractionAcquiring/recognising eyesSpoof detectionImaging processingPassword
The invention discloses a corneal reflection and optical coding-based human face living body detecting method and system, belongs to the security technical field of resisting human face recognition attacks and particularly relates to the processing and the analysis of corneal images. The method comprises the steps of representing each piece of binary password information by using brightness or darkness of light through an optical coding mode and reflecting the brightness and darkness change by a cornea; and obtaining corneal reflection information by extracting the brightness and darkness information of a corneal image and realizing the human face living body detection through information comparison. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that only the brightness and darkness information of the corneal image needs to be extracted and the problem that the corneal reflection information is difficult to extract can be solved; the method has very low requirements on camera pixels and later image processing and analysis, so that the method is easy to realize, economical and effective; and the method has very high security and common attacks of face recognition can be resisted.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
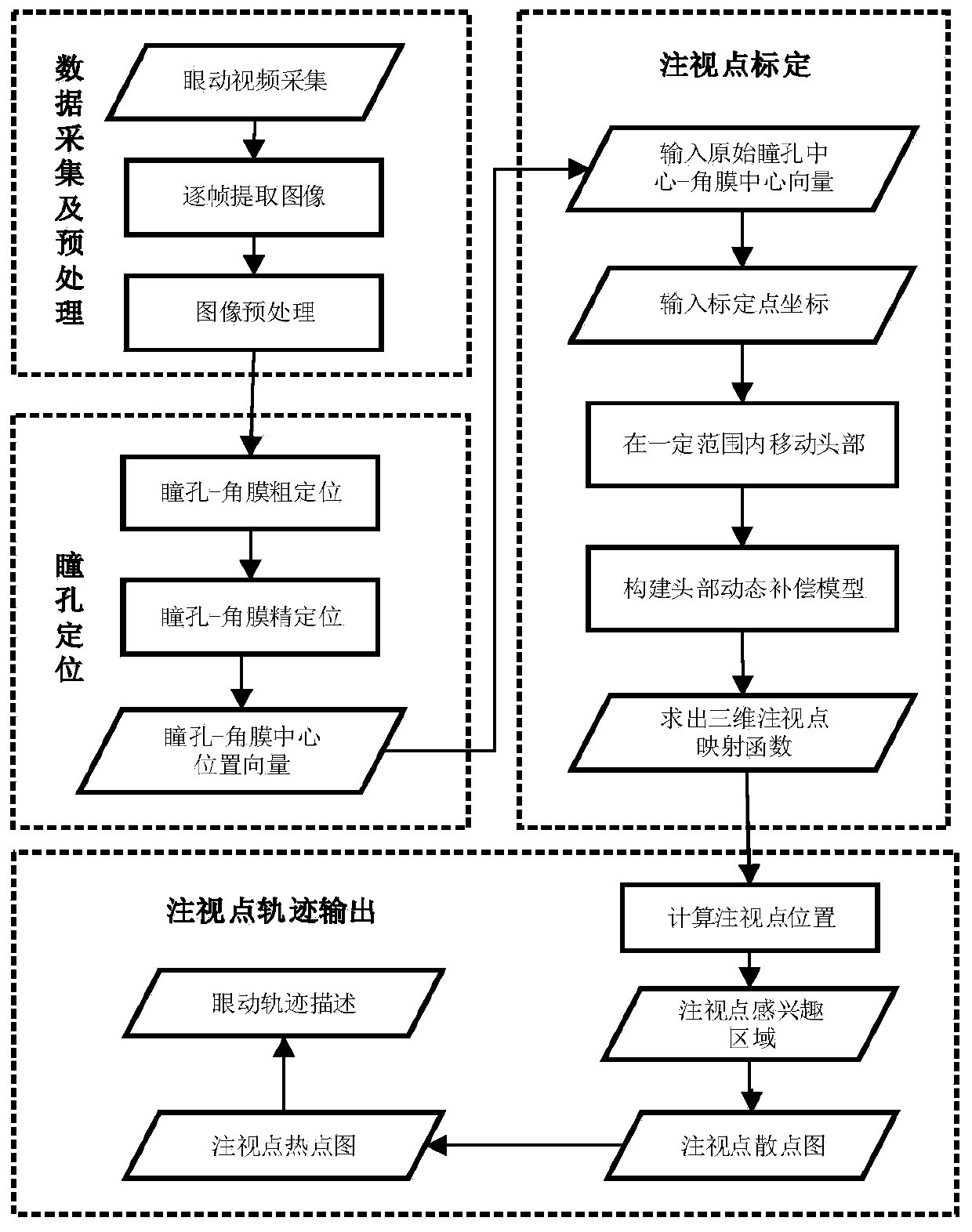
Fixation point track description method and system based on video analysis
ActiveCN111443804AEasy to operateImprove description accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingFixation pointThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a fixation point trajectory description system based on video analysis. The fixation point trajectory description system comprises a data acquisition and preprocessing module,a pupil positioning module, a fixation point calibration module and a fixation point trajectory description module. The invention further discloses a fixation point track description method based on video analysis. A video eye movement image is collected; pretreatment operation is carried out, the coordinates of the pupil center and the corneal reflection facula center in an eye pattern are solvedthrough a pupil coarse positioning method and a pupil fine positioning method, the three-dimensional space mapping relation between a vector formed by the pupil center and the corneal reflection facula center and a fixation point is solved in combination with a dynamic head compensation model, and fixation point track description is conducted through the mapping function. According to the invention, the fixation point track of the user is obtained on the basis of establishing the fixation point three-dimensional space mapping relation, the pre-judgment capability of people on the region of interest of the user is improved, the optimization of advertisement webpage layout can be effectively supported, and the method has the advantages of being simple to use, high in method precision, largein application potential and the like.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com