Patents
Literature
187results about "Vector cardiography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
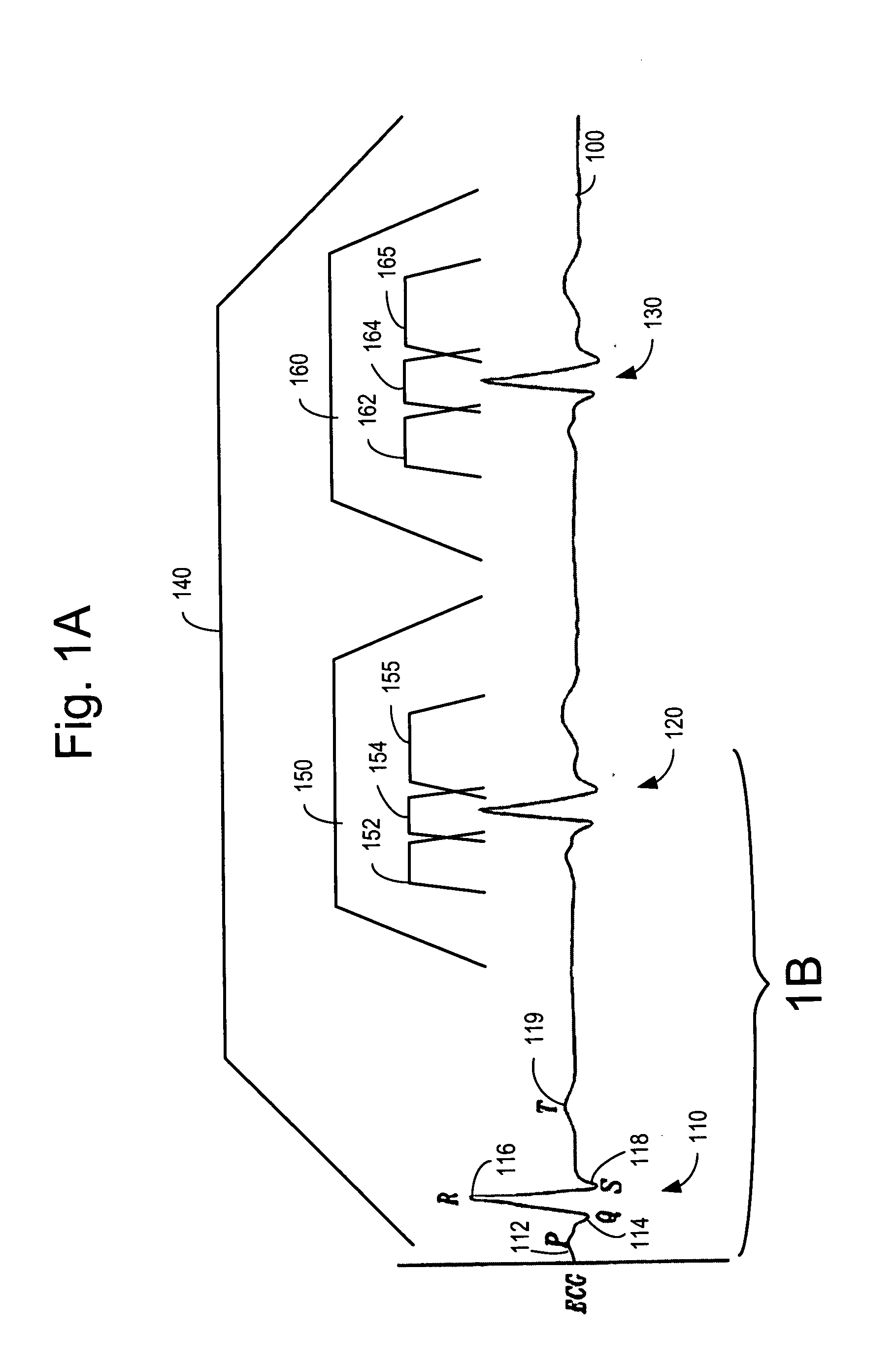
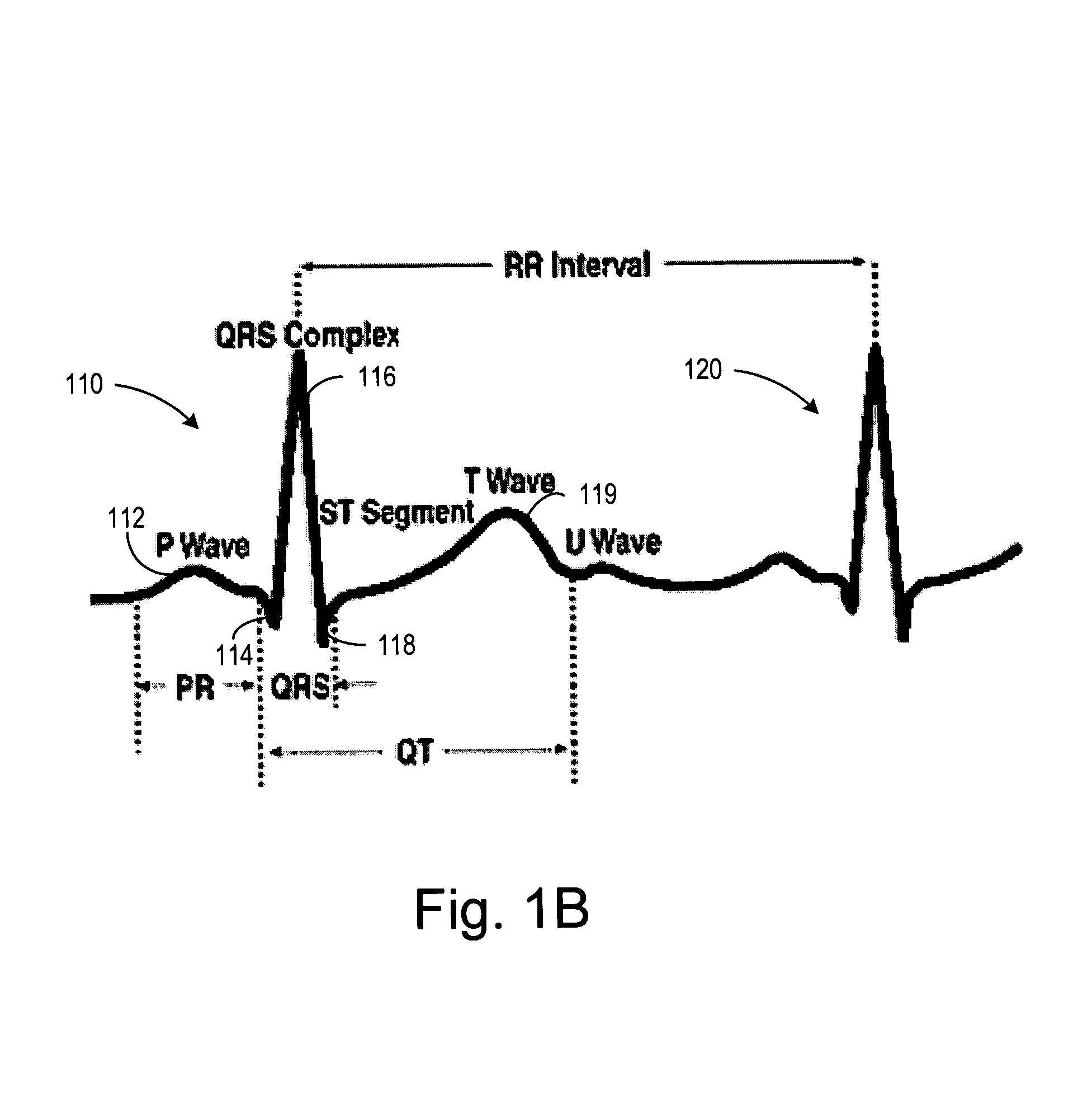
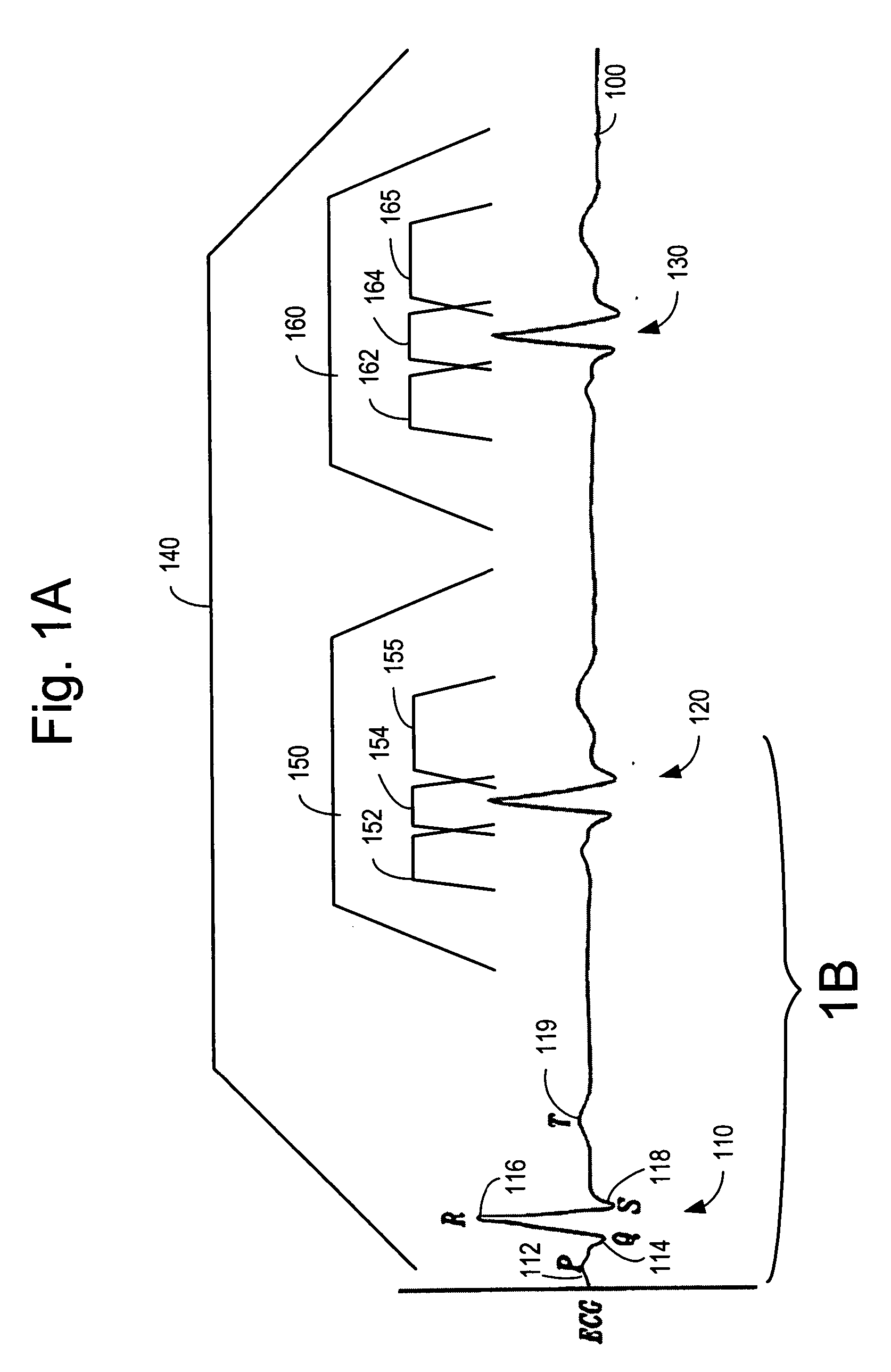
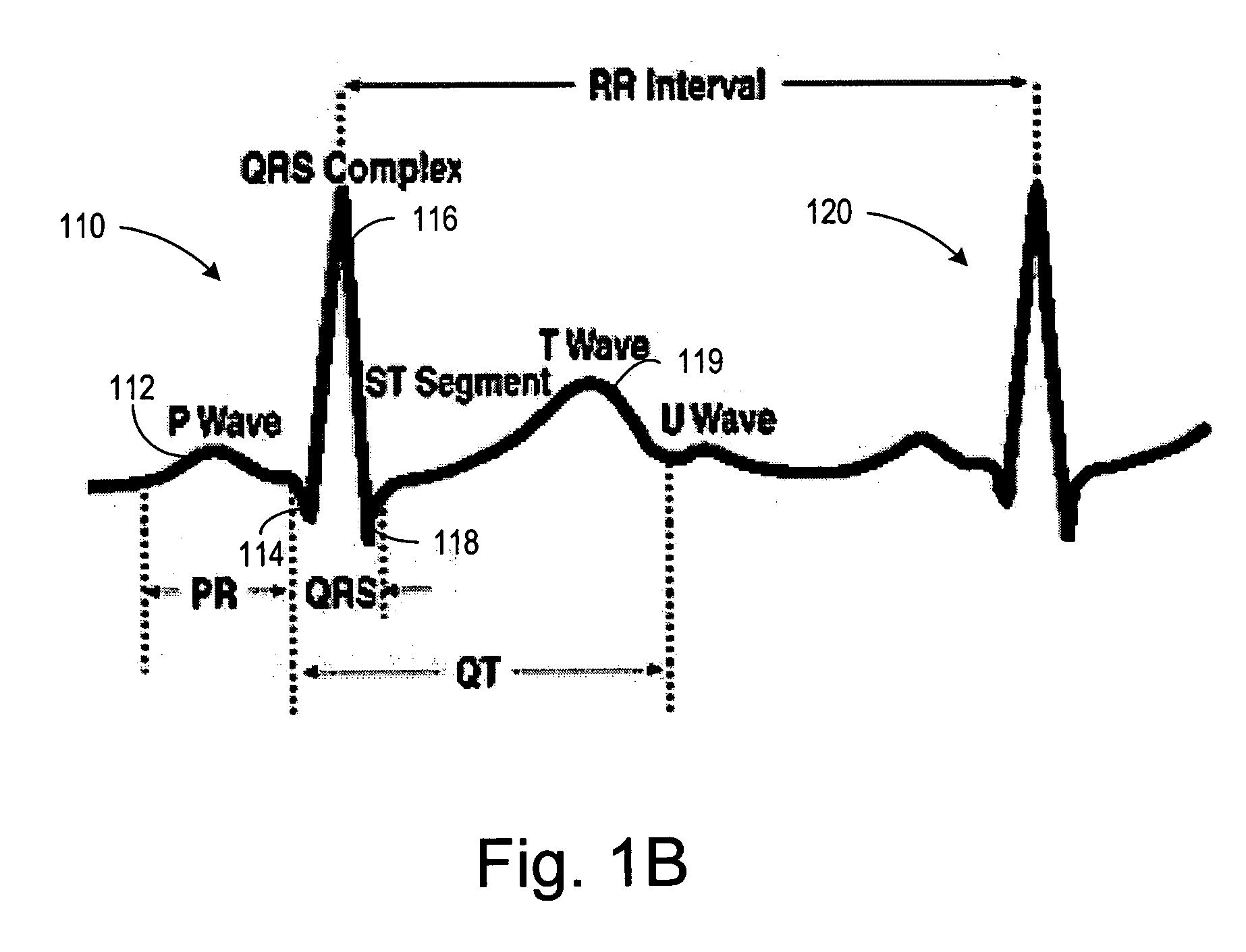
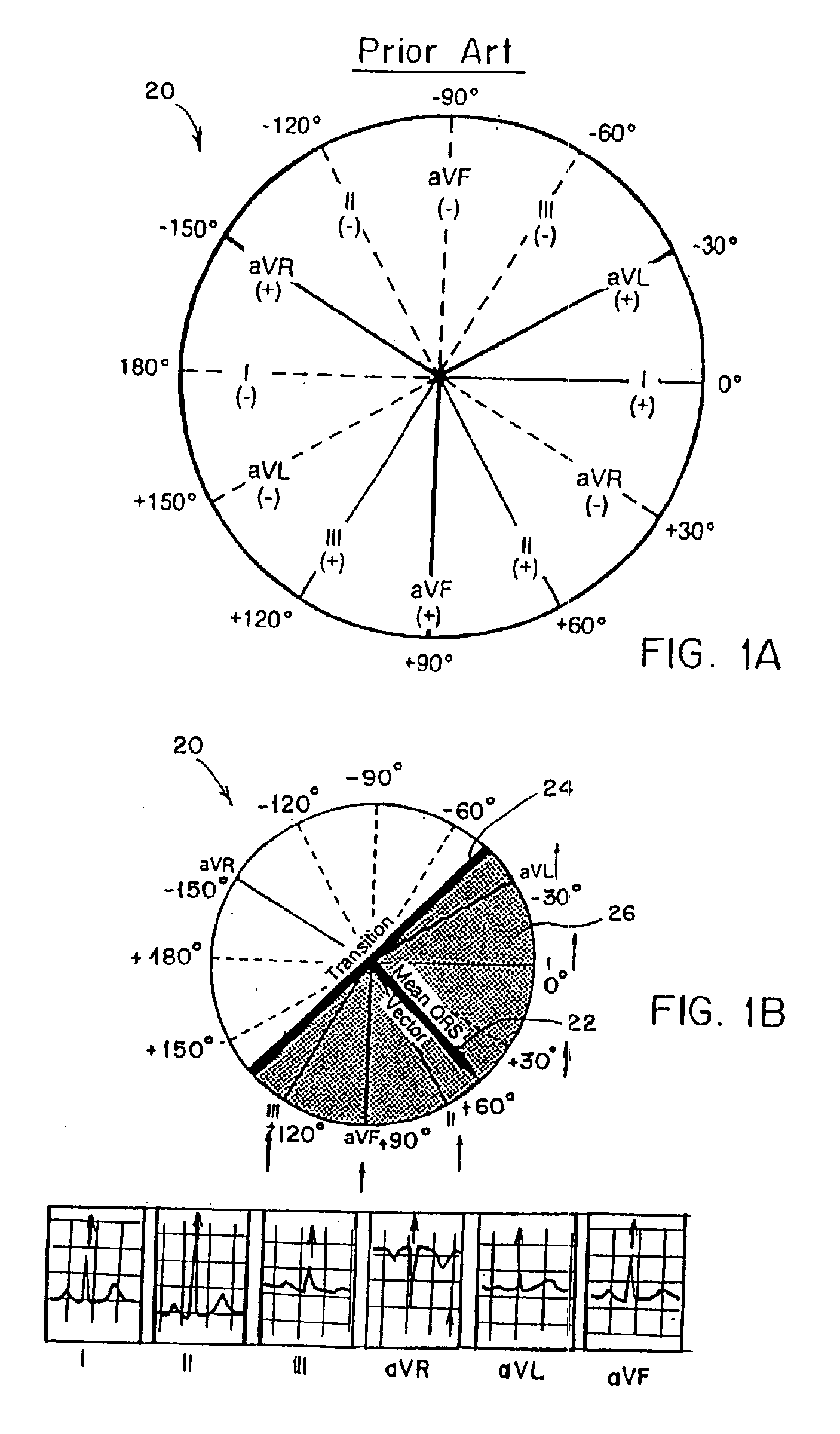
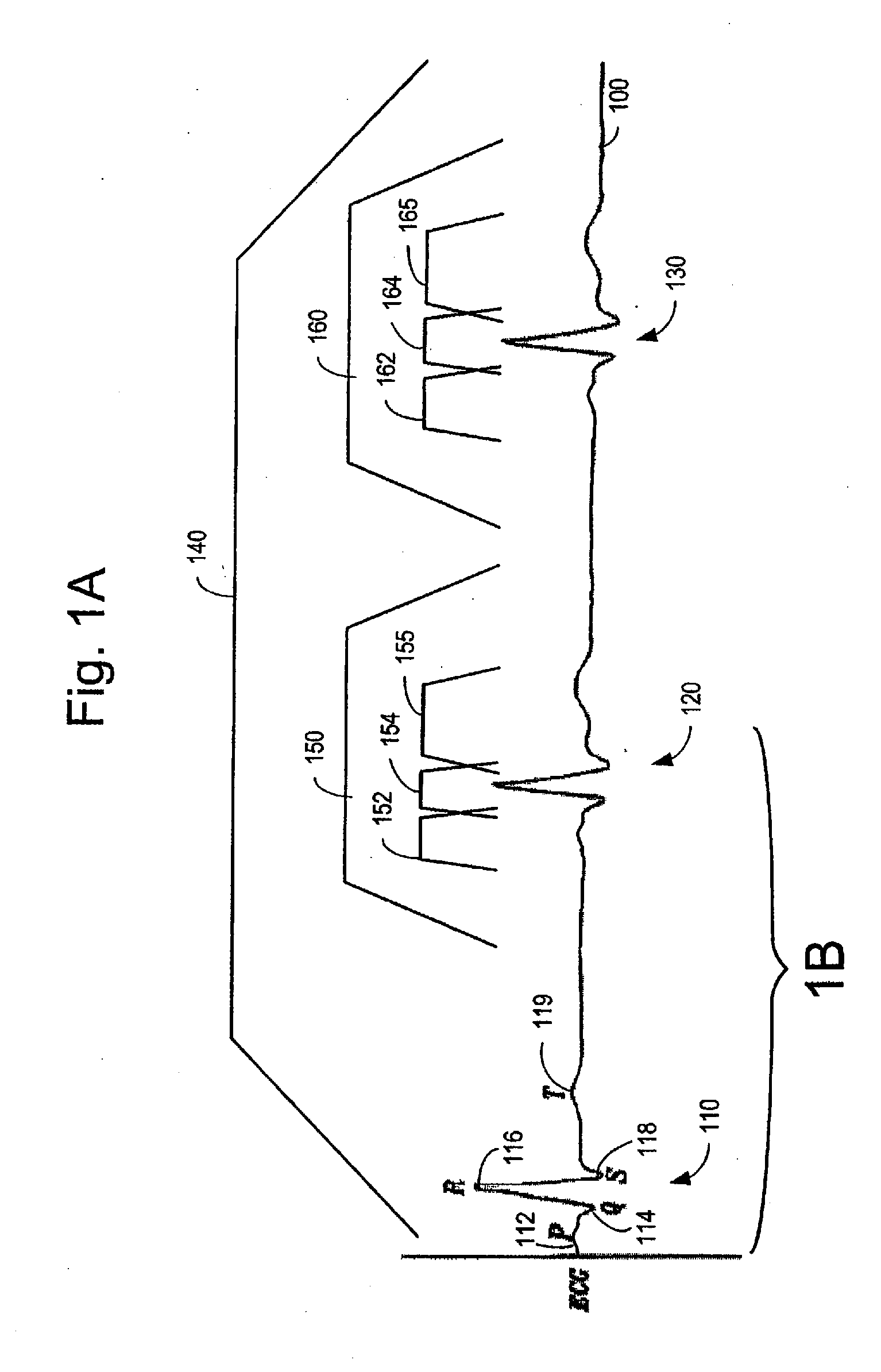
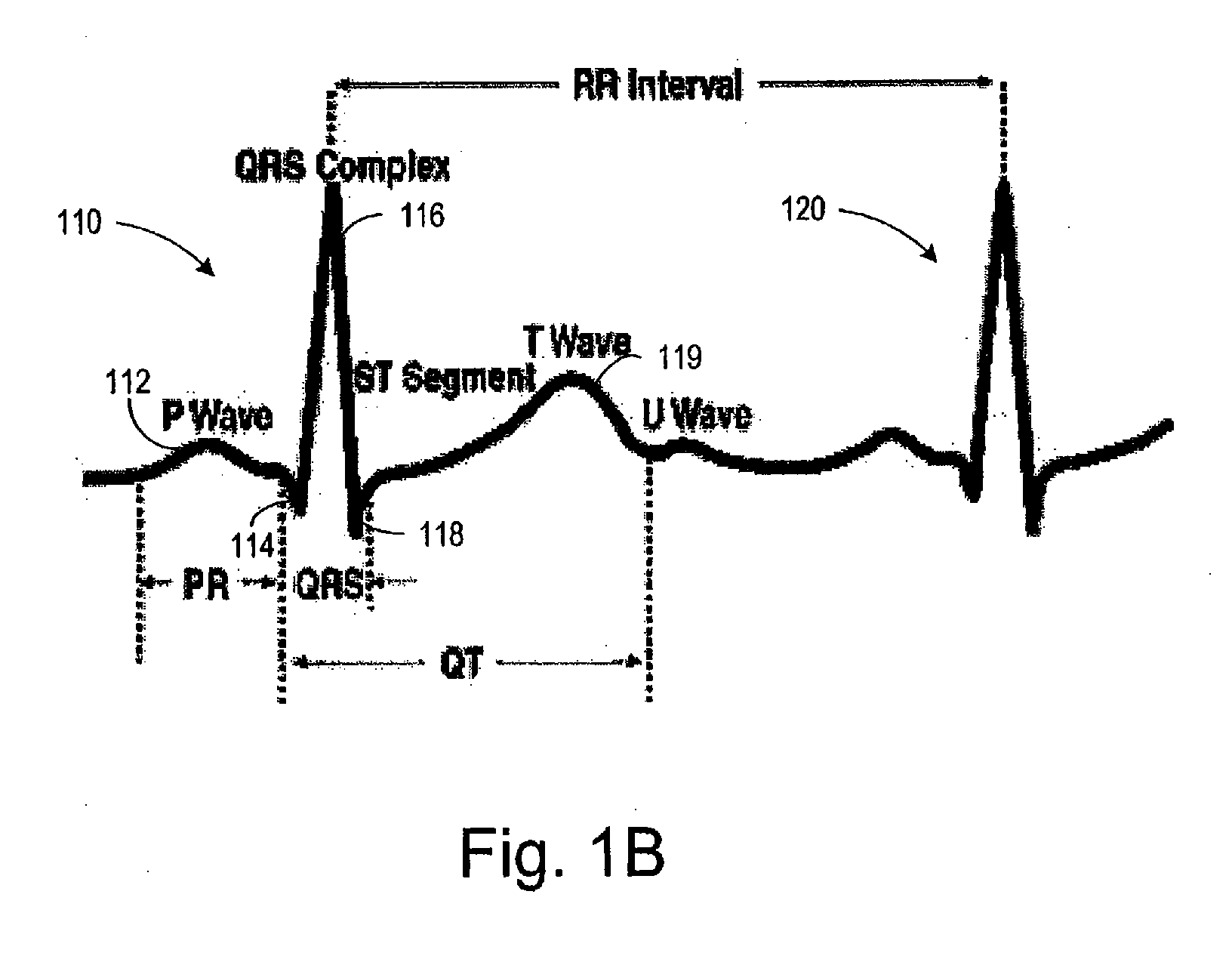
Method of analysis of the electrocardiogram
Owner:TOOLE J GERALD
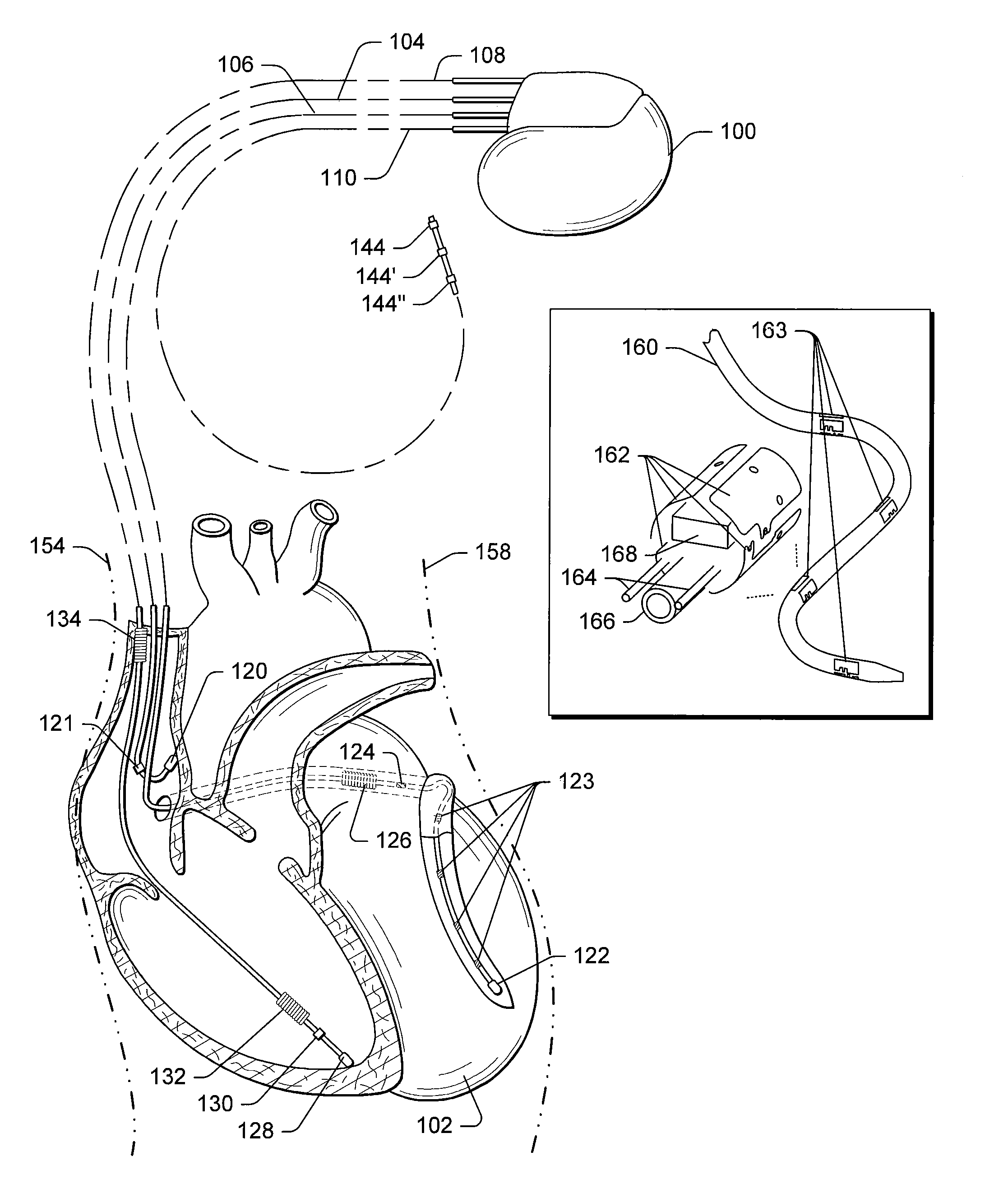
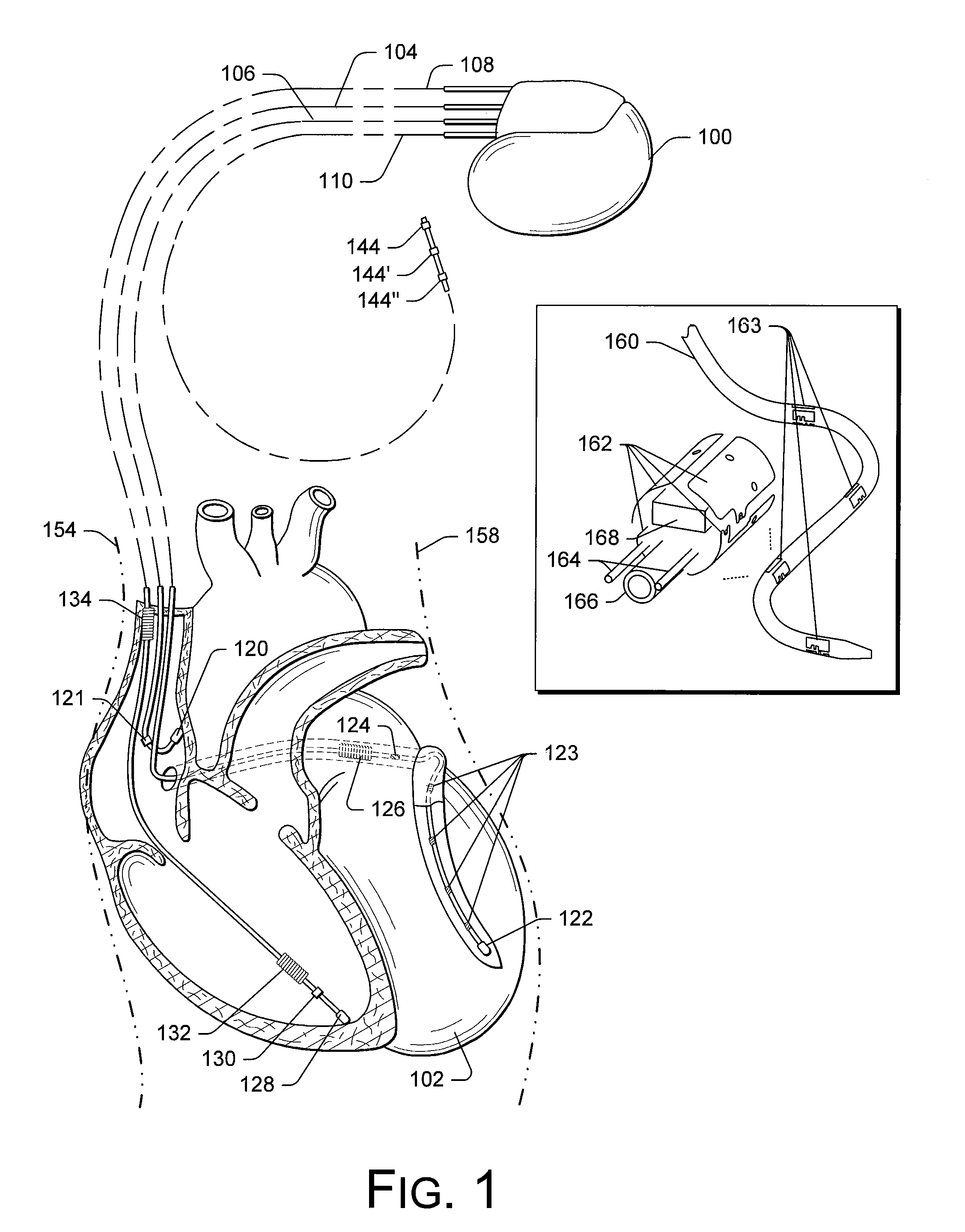
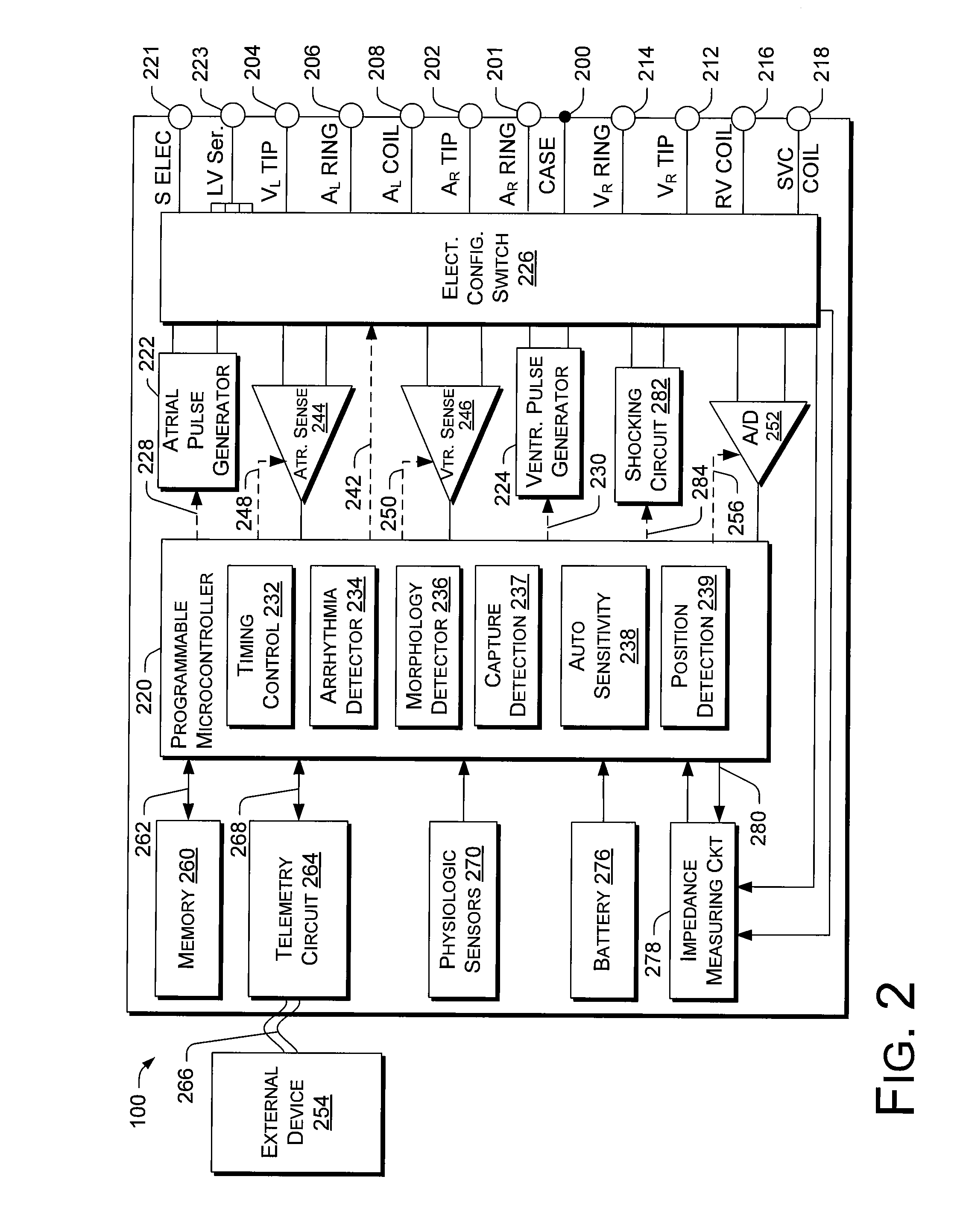
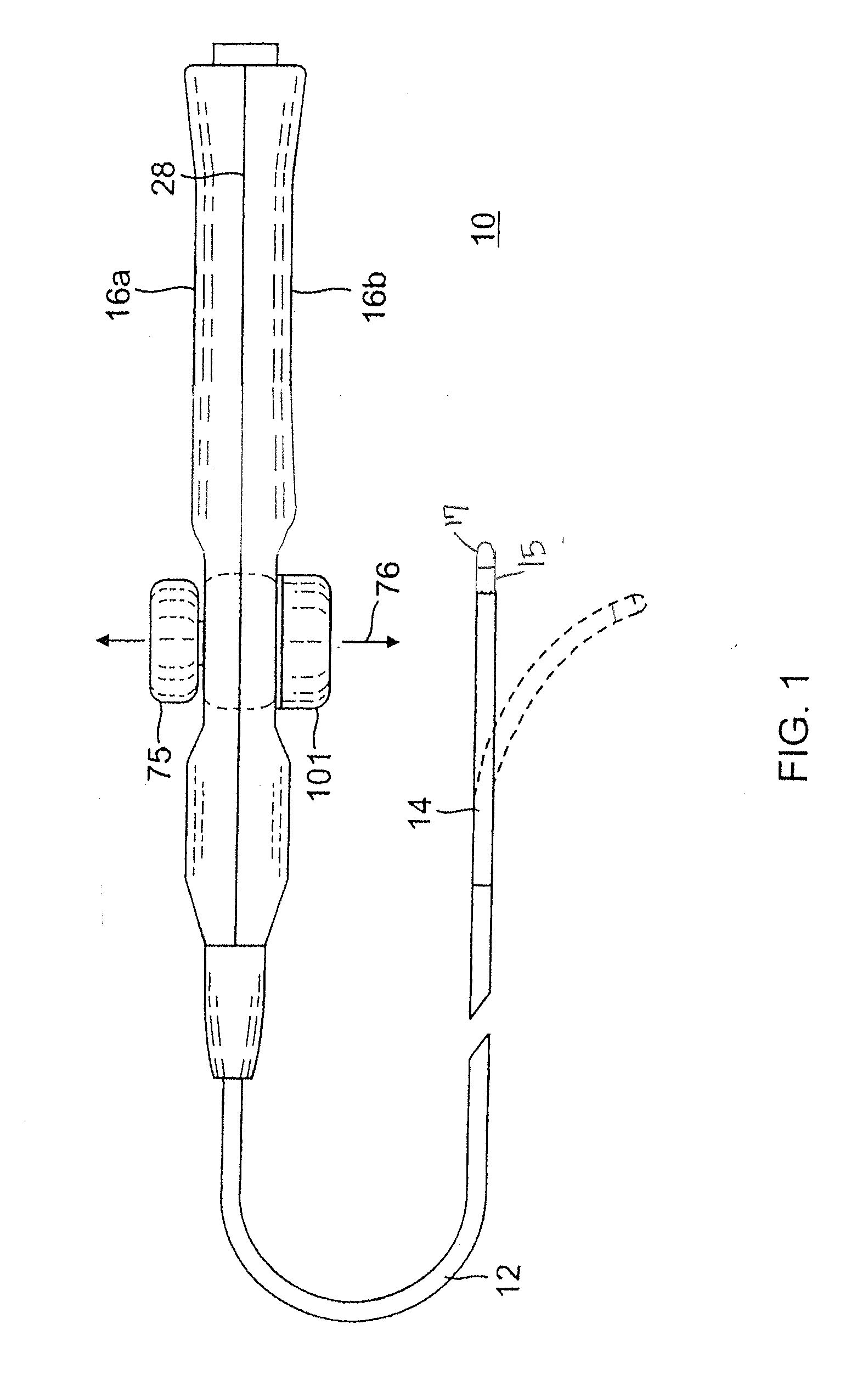
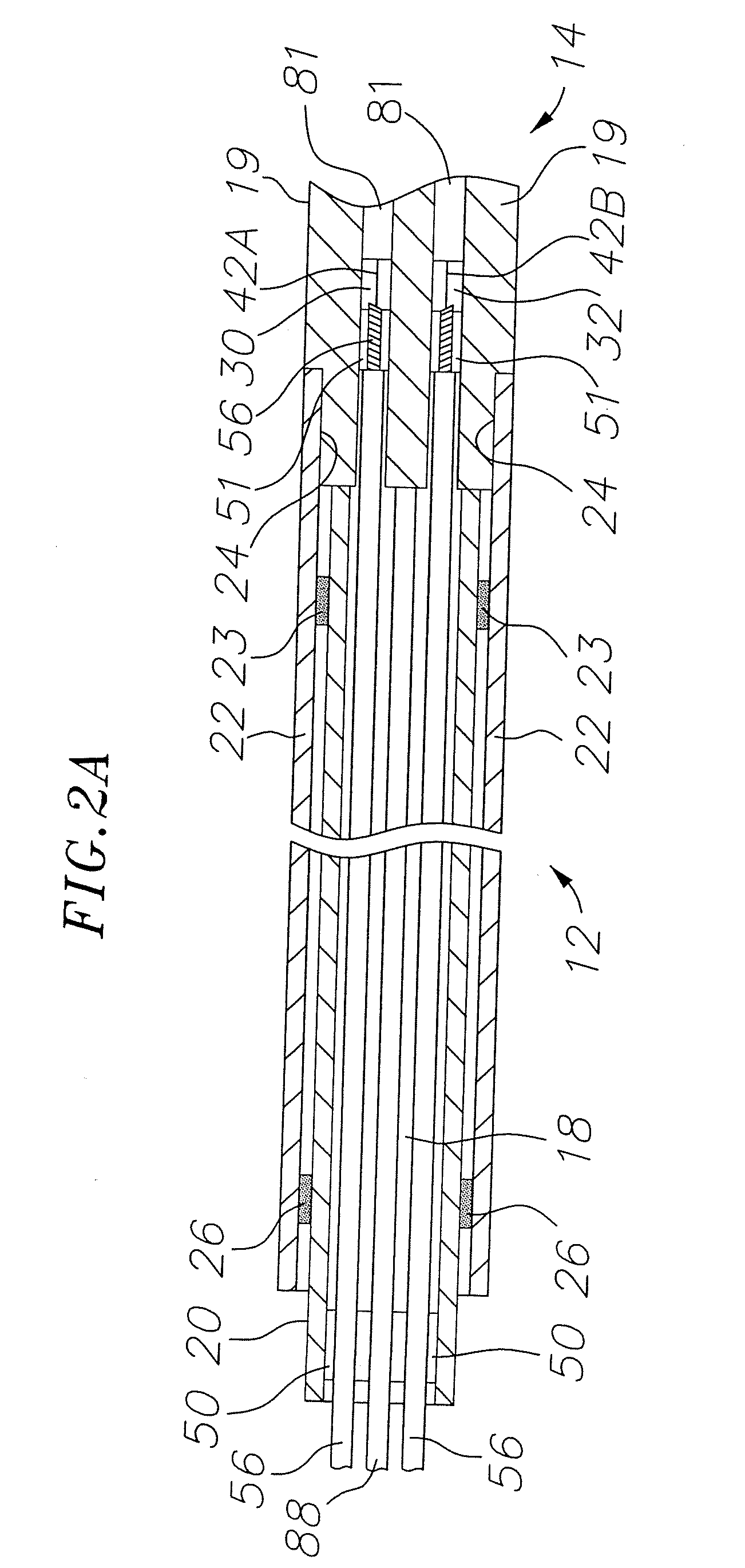
Cardiac activation sequence monitoring and tracking
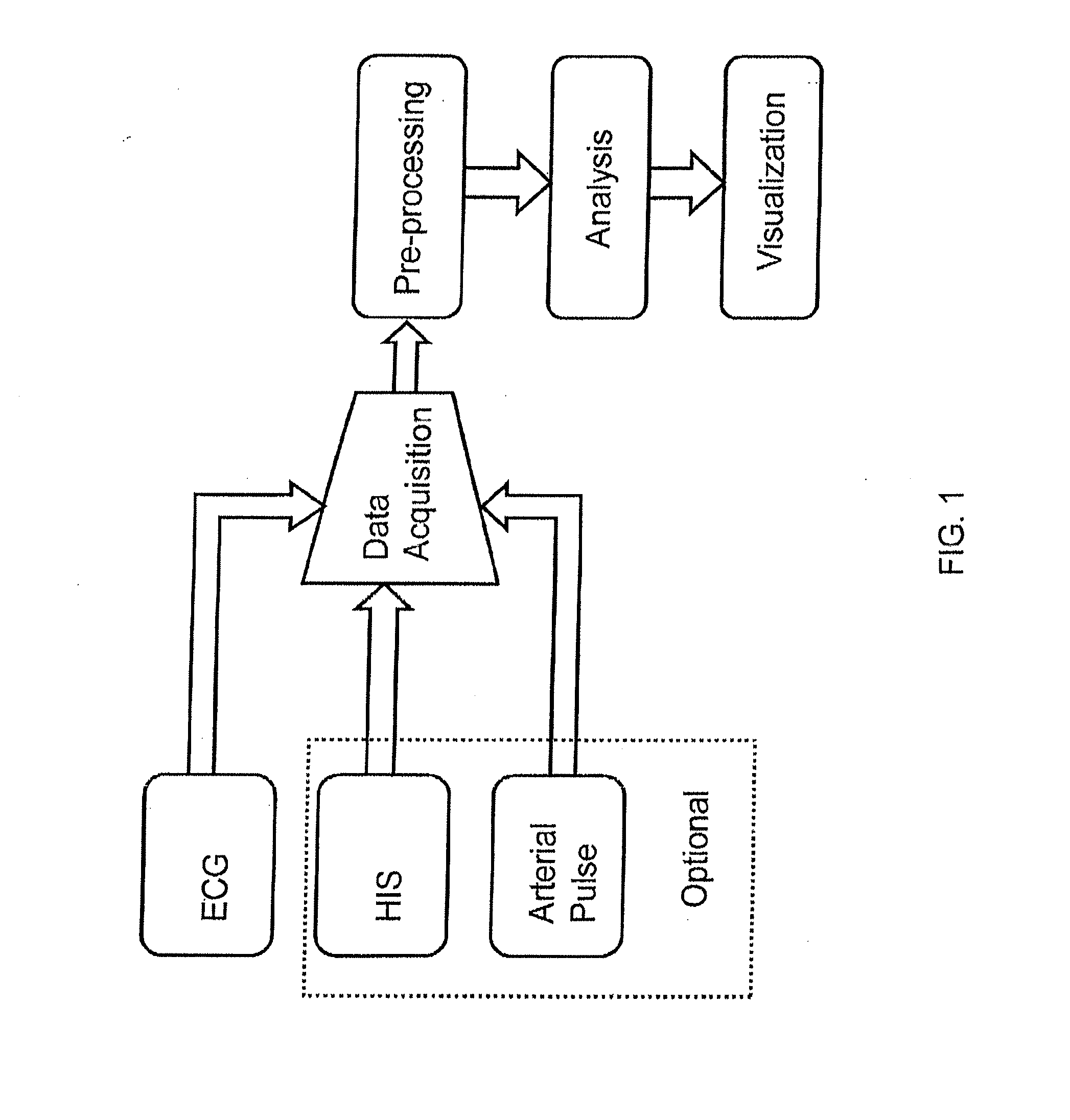
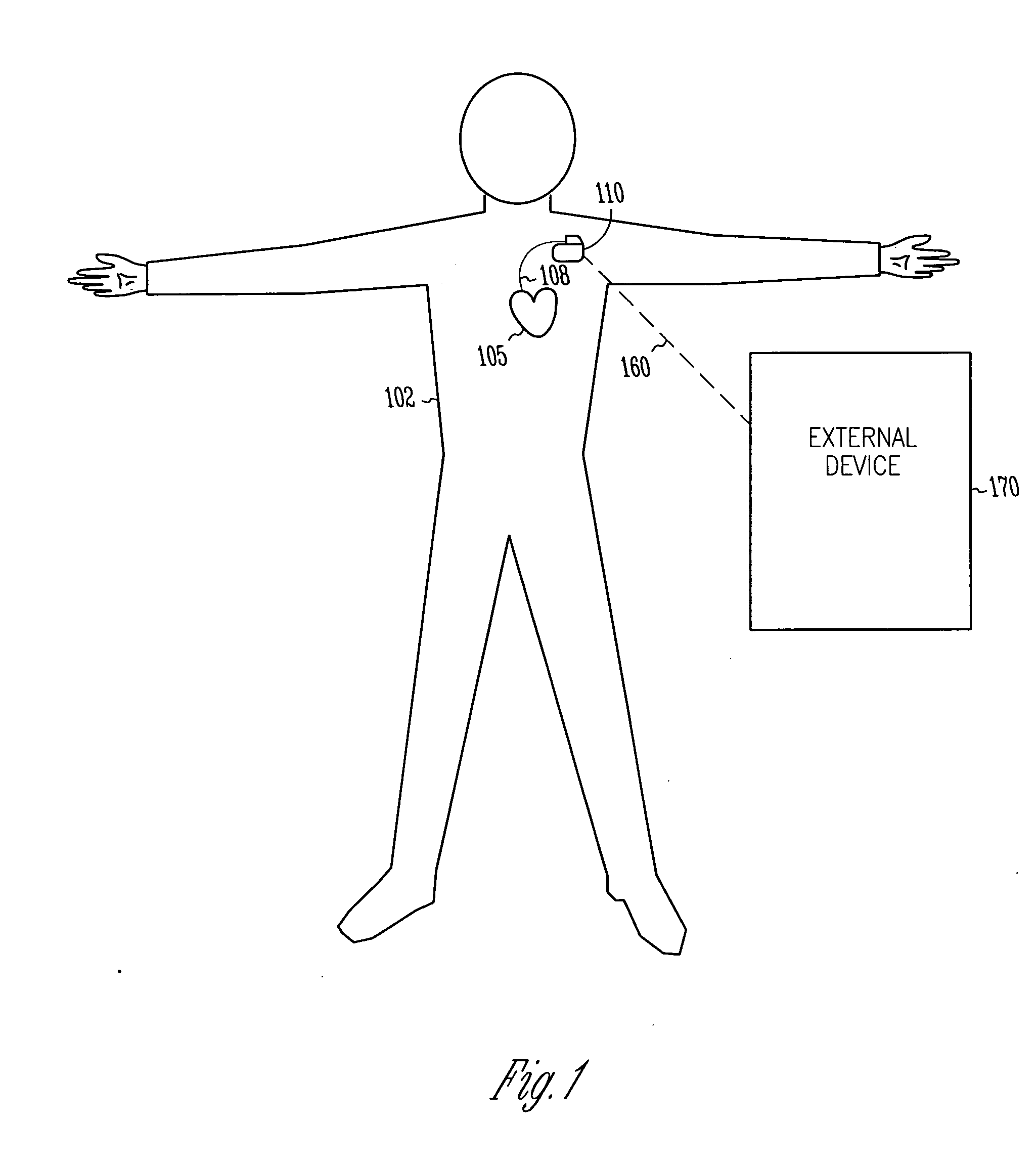
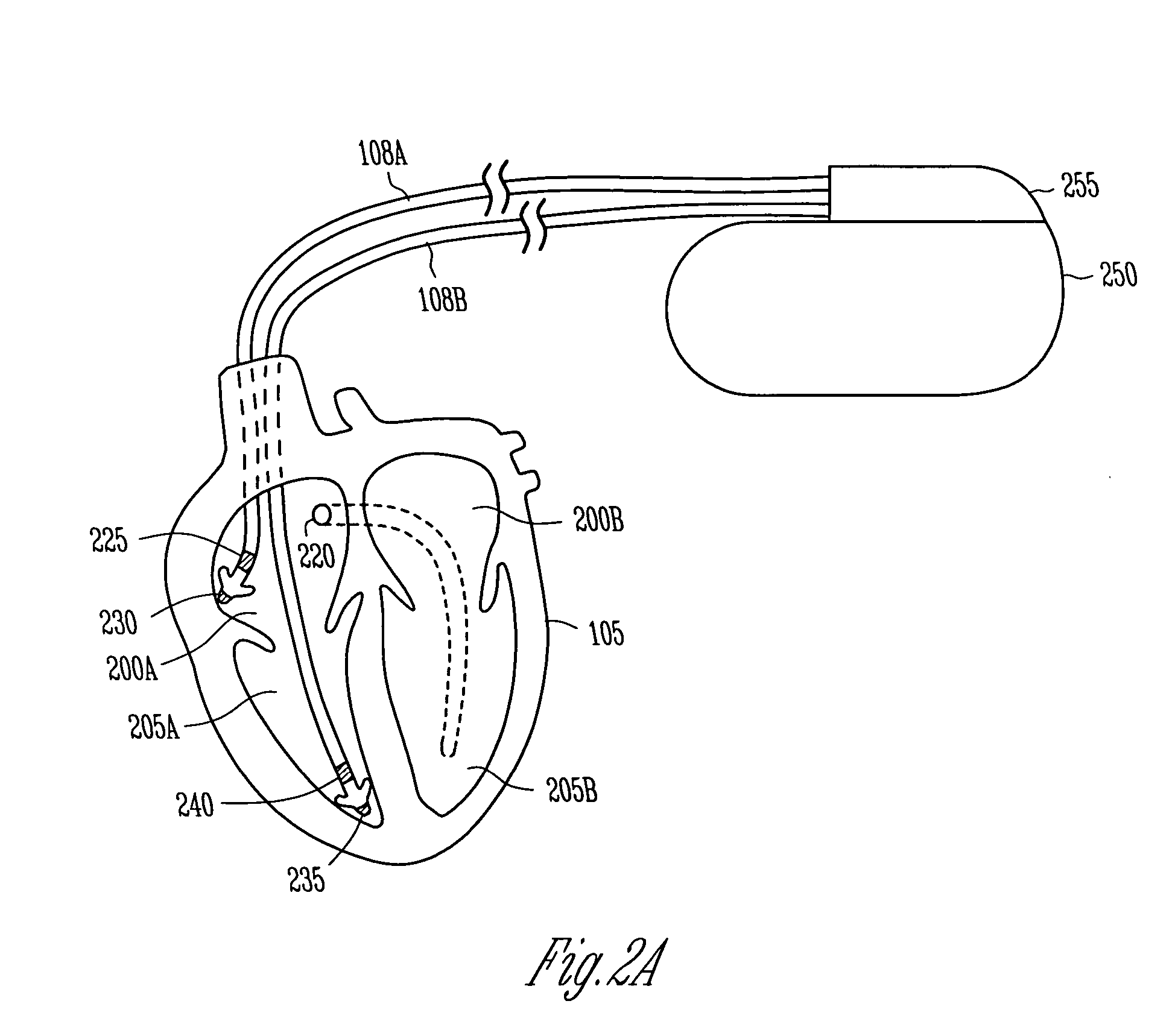
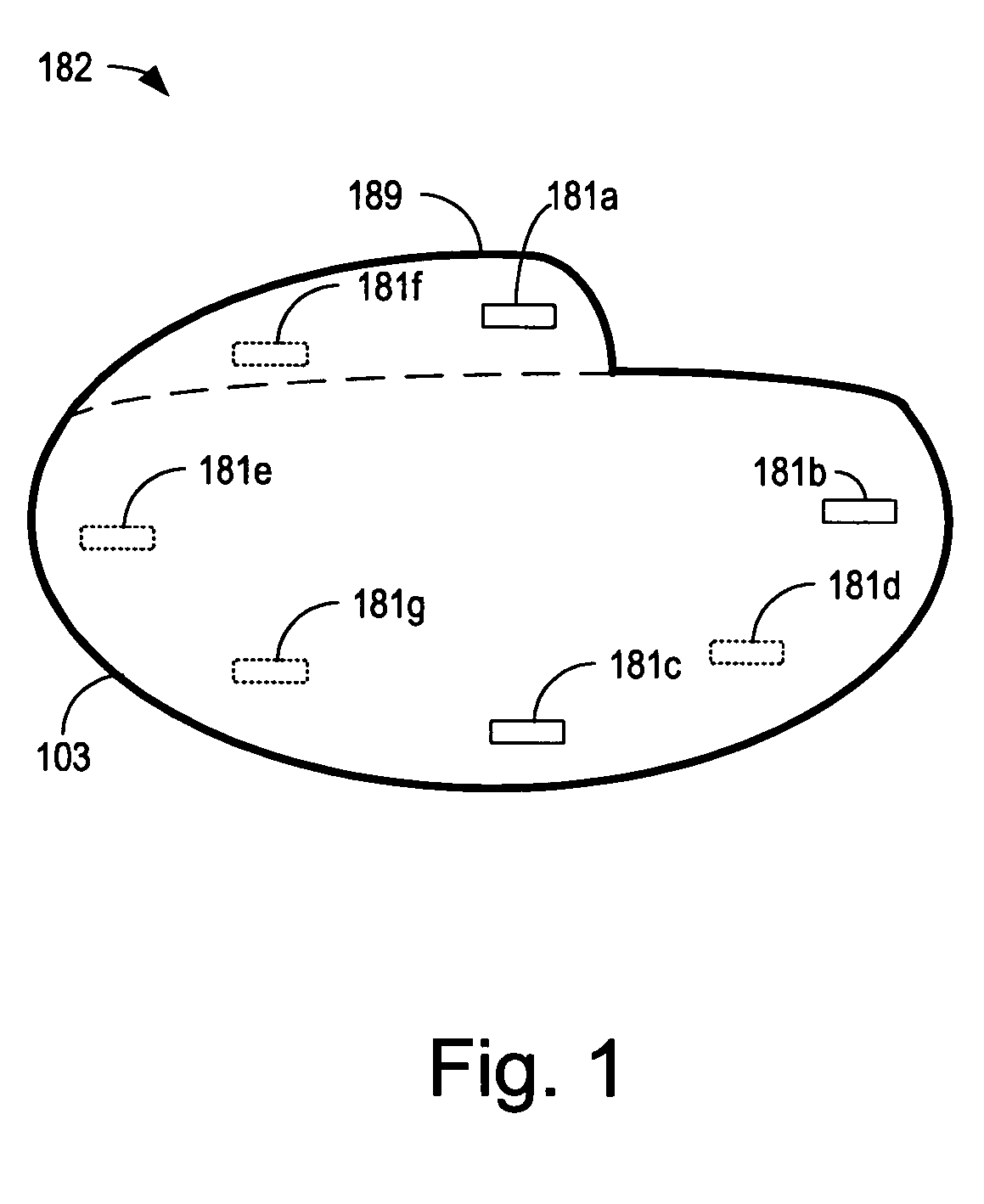
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems provide monitoring, diagnosis, and defibrillation and / or pacing therapies. A signal processor receives a plurality of composite signals associated with a plurality of sources, performs a source separation, and produces one or more cardiac signal vectors associated with all or a portion of one or more cardiac activation sequences based on the source separation. A method of signal separation involves detecting a change in a characteristic of the cardiac signal vector relative to a baseline. One or more vectors and / or activation sequences may be selected, and information associated with the vectors and / or activation sequences may be stored and tracked.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
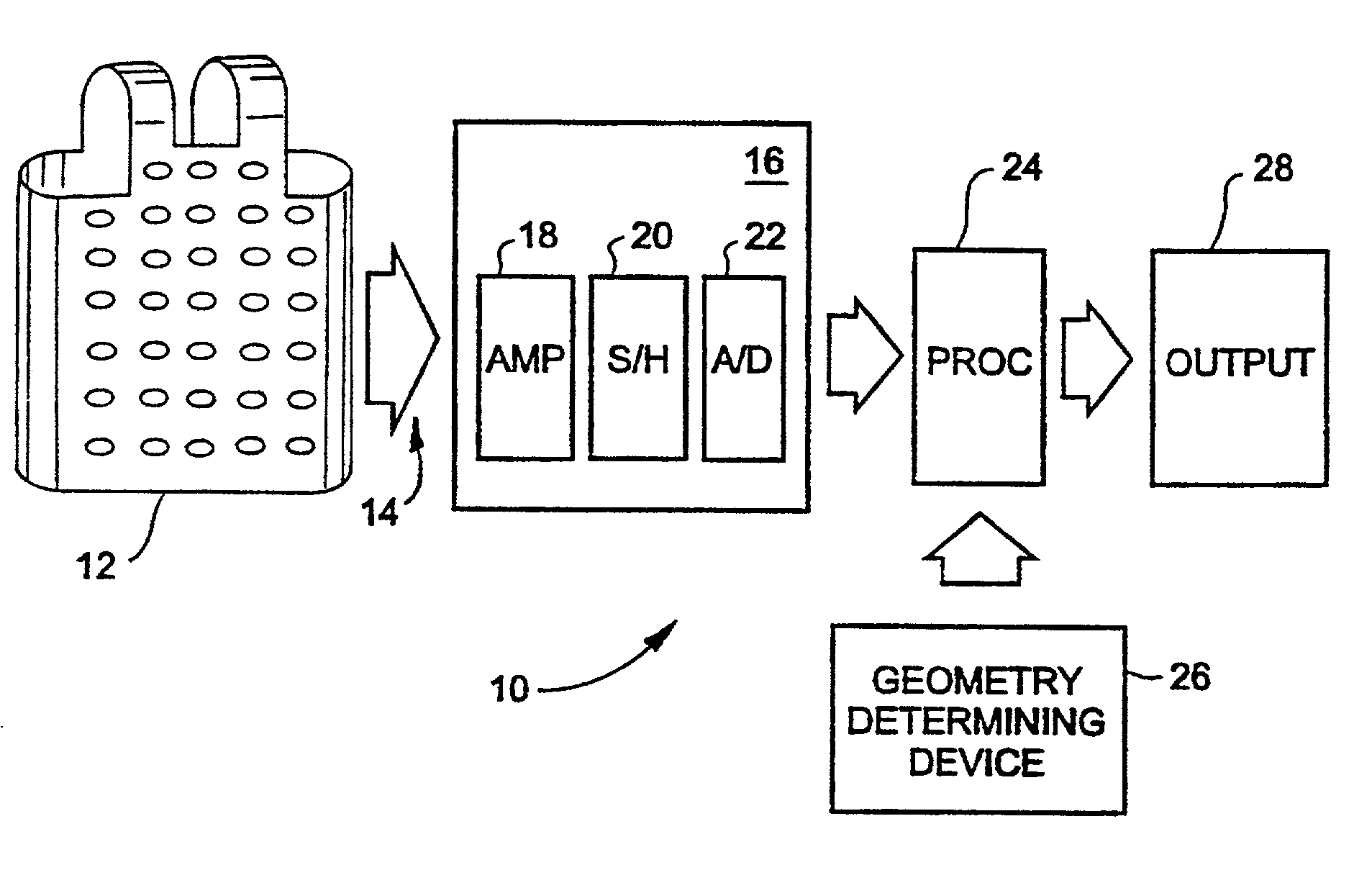
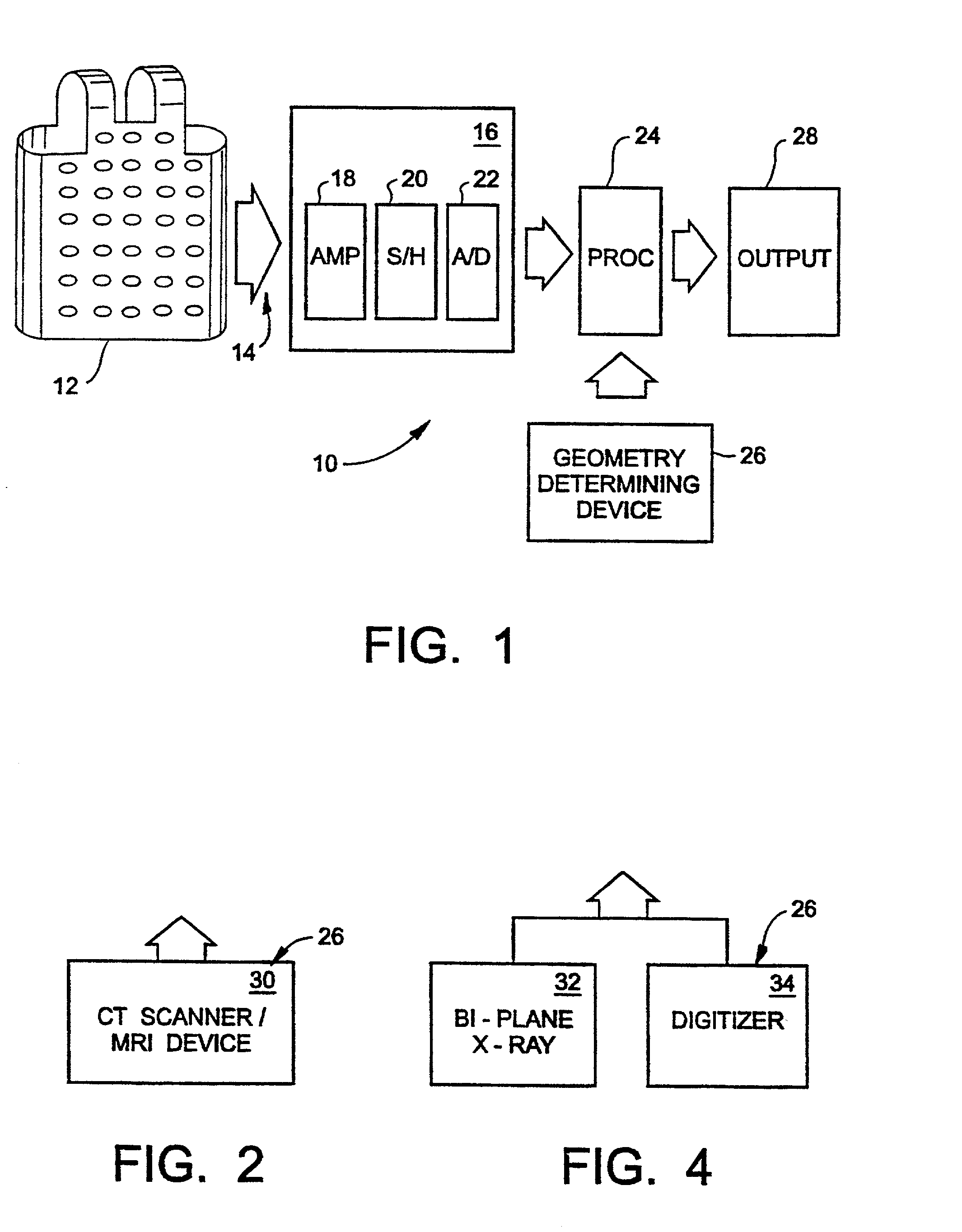
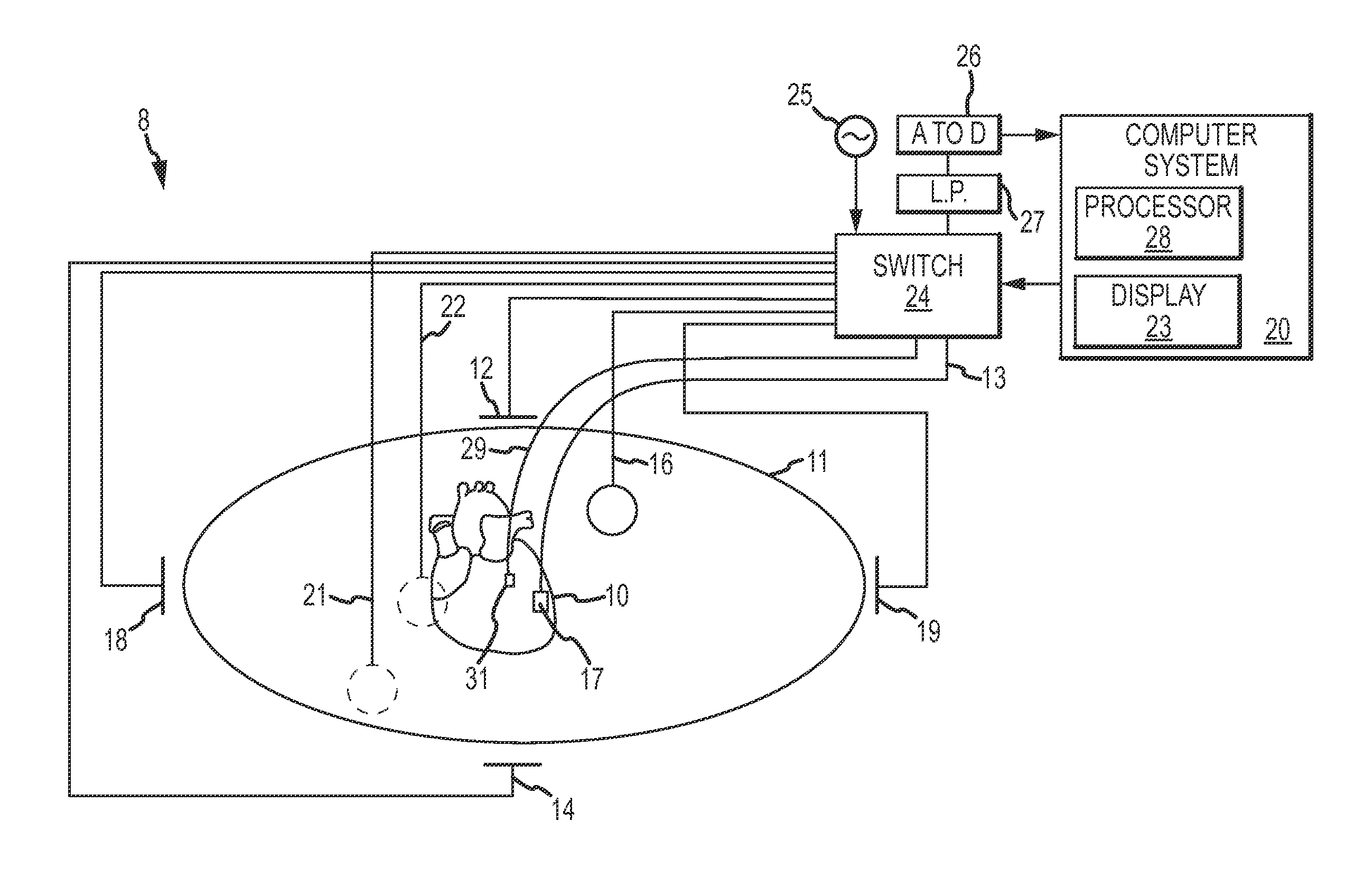
System and method for non-invasive electrocardiographic imaging
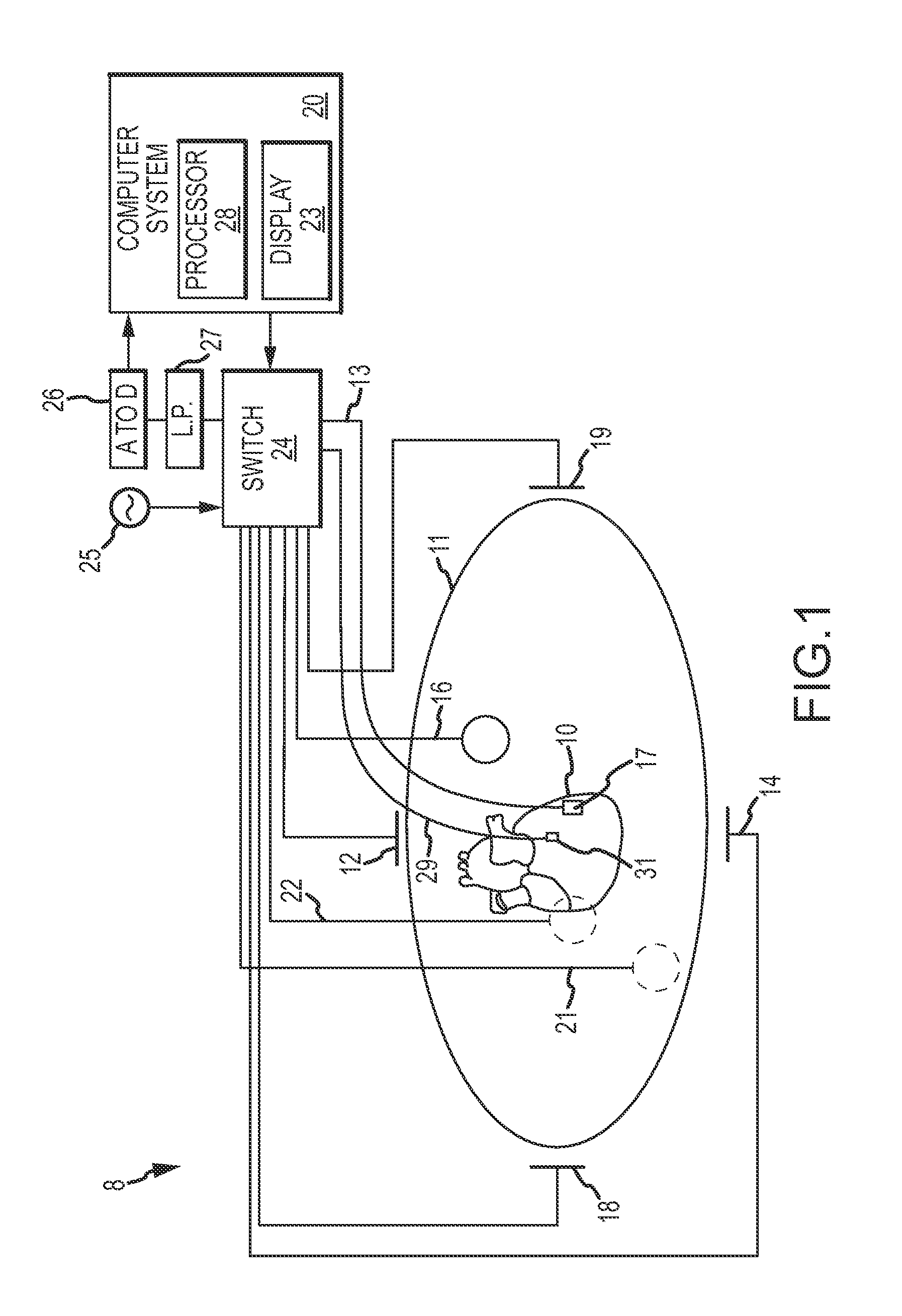
A system and method is provided for non-invasively determining electrical activity of the heart of a human being. Electrical potentials are measured on the body surface via an electrode vest (12), and a body surface potential map is generated. A matrix of transformation based on the geometry of the torso, the heart, locations of electrodes, and position of the heart within the torso is also determined with the aid of a processor (24), and a geometry determining device (26). The electrical potential distribution over the epicardial surface of the heart is then determined based ona regularized matrix of transformation, and the body surface potential map. Using the epicardial potential distributions, epicardial electrogram, isochronal are also reconstructed, and displayed via an output device (28).
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Ischemia detection
InactiveUS6937899B2Reliable detectionReliable treatmentElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerCardiac muscle
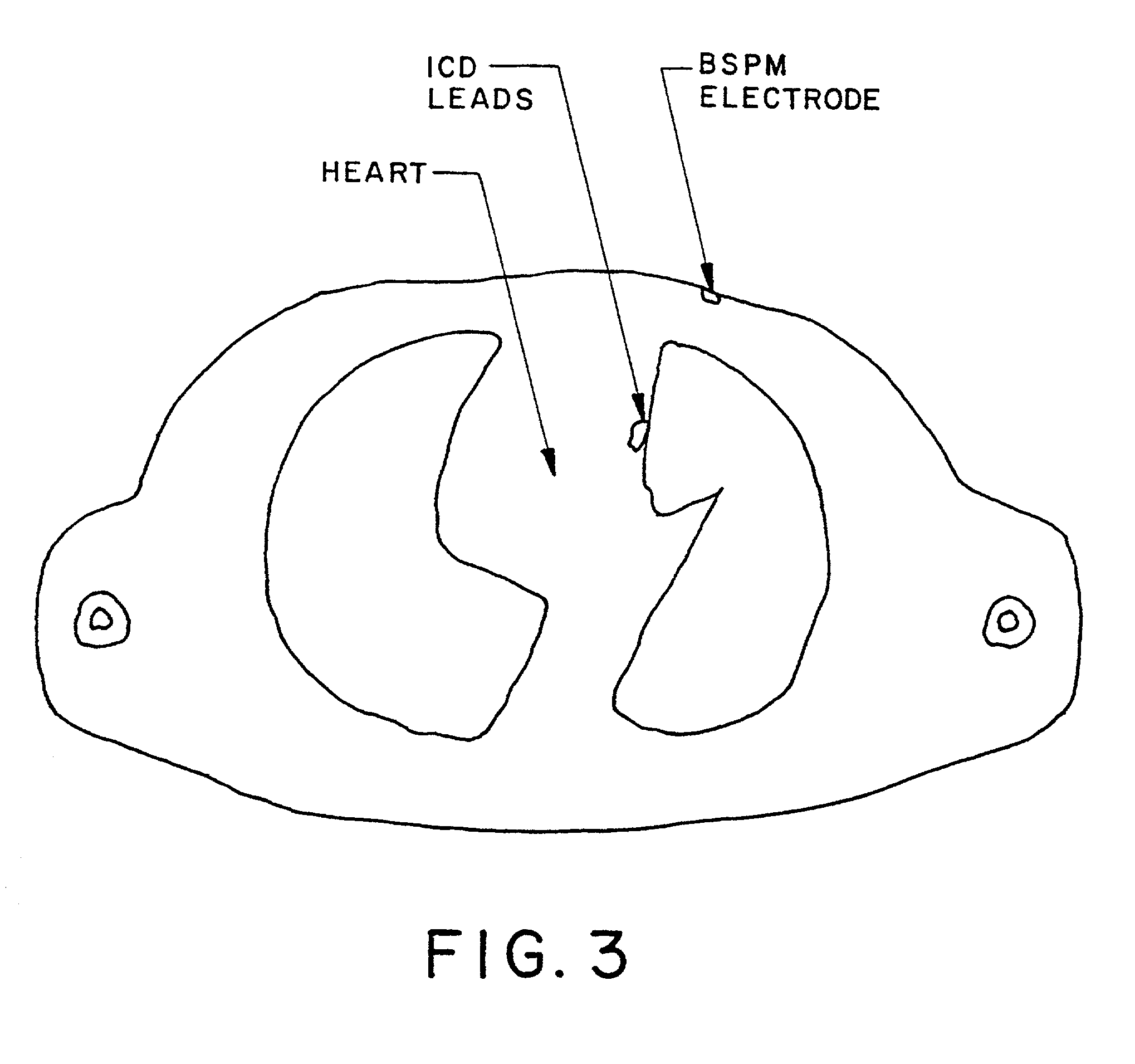
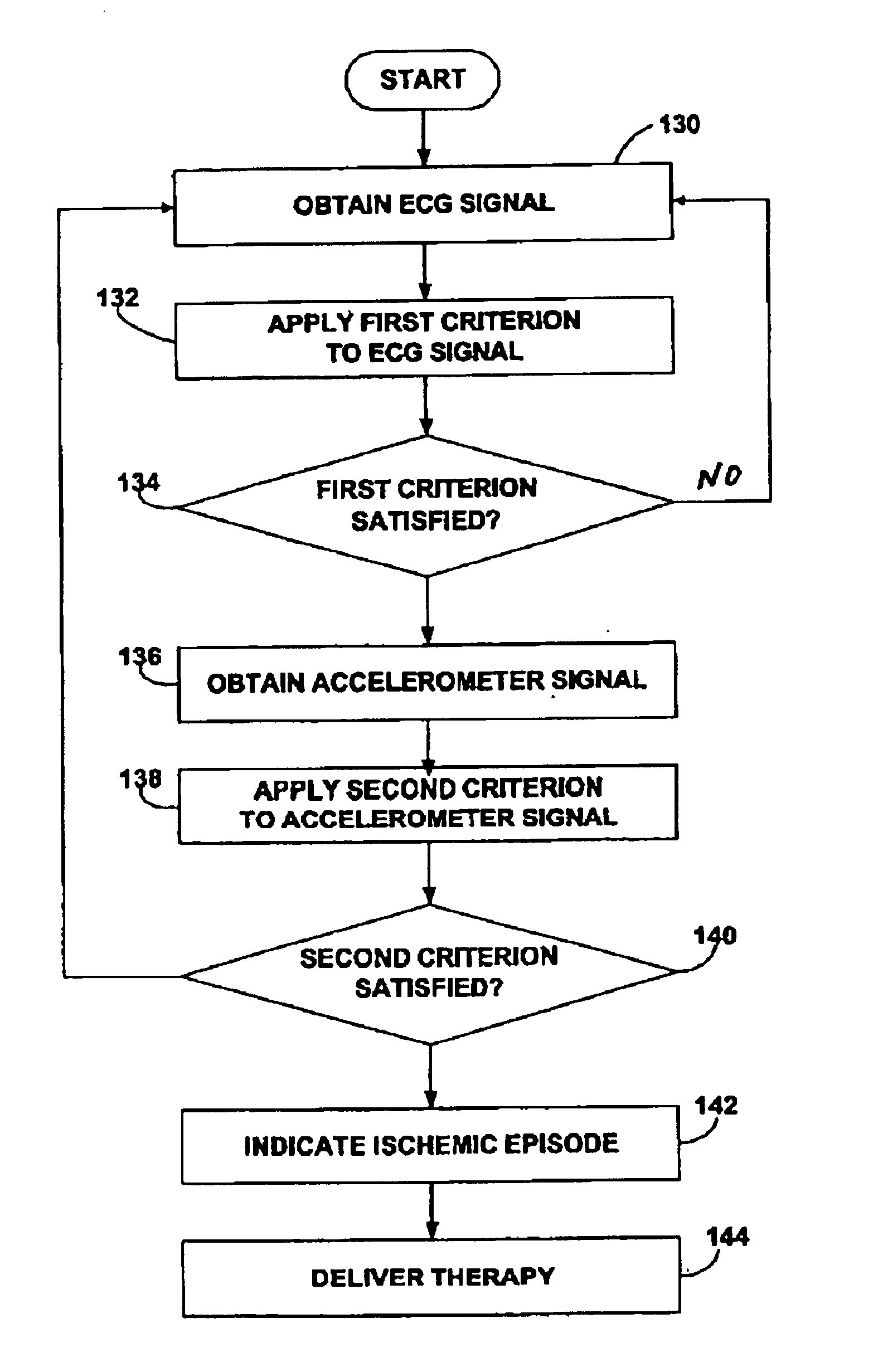
Techniques for detection and treatment of myocardial ischemia are described that monitor both the electrical and dynamic mechanical activity of the heart to detect and verify the occurrence of myocardial ischemia in a more reliable manner. The occurrence of myocardial ischemia can be detected by monitoring changes in an electrical signal such as an ECG or EGM, and changes in dynamic mechanical activity of the heart. Dynamic mechanical activity can be represented, for example, by a heart acceleration signal or pressure signal. The electrical signal can be obtained from a set of implanted or external electrodes. The heart acceleration signal can be obtained from an accelerometer or pressure sensor deployed within or near the heart. The techniques correlate contractility changes detected by an accelerometer or pressure sensor with changes in the ST electrogram segment detected by the electrodes to increase the reliability of ischemia detection.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
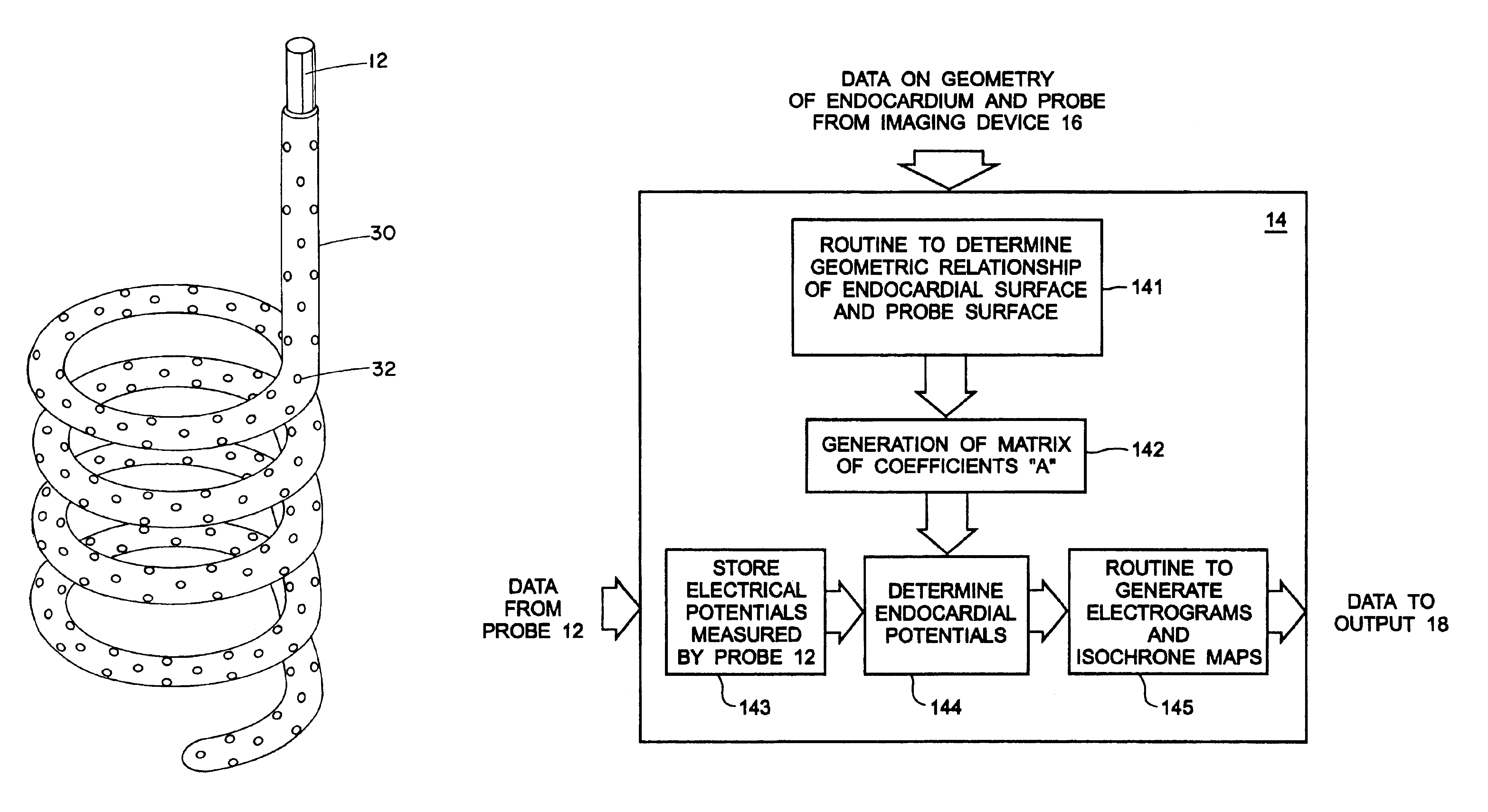
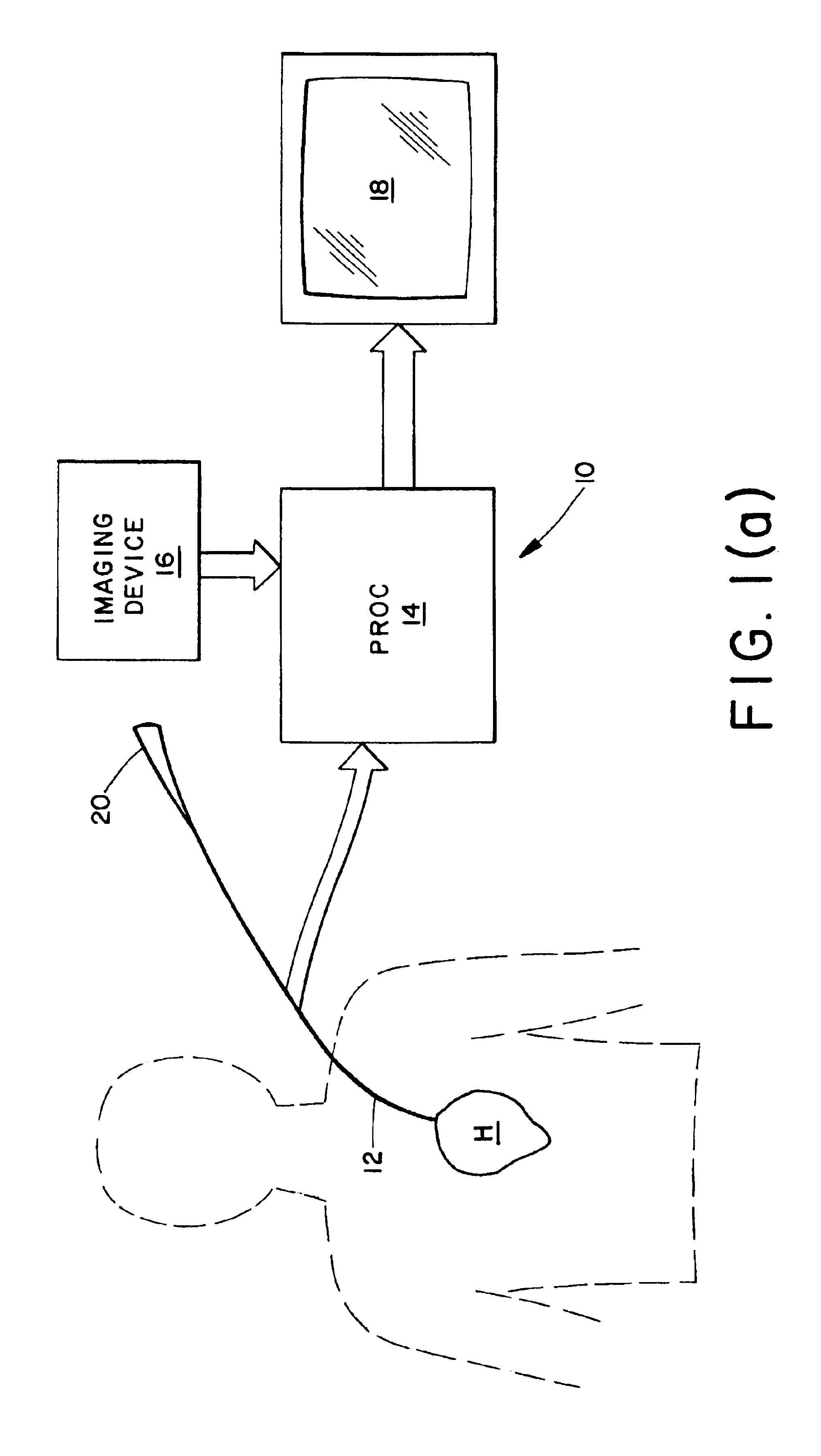
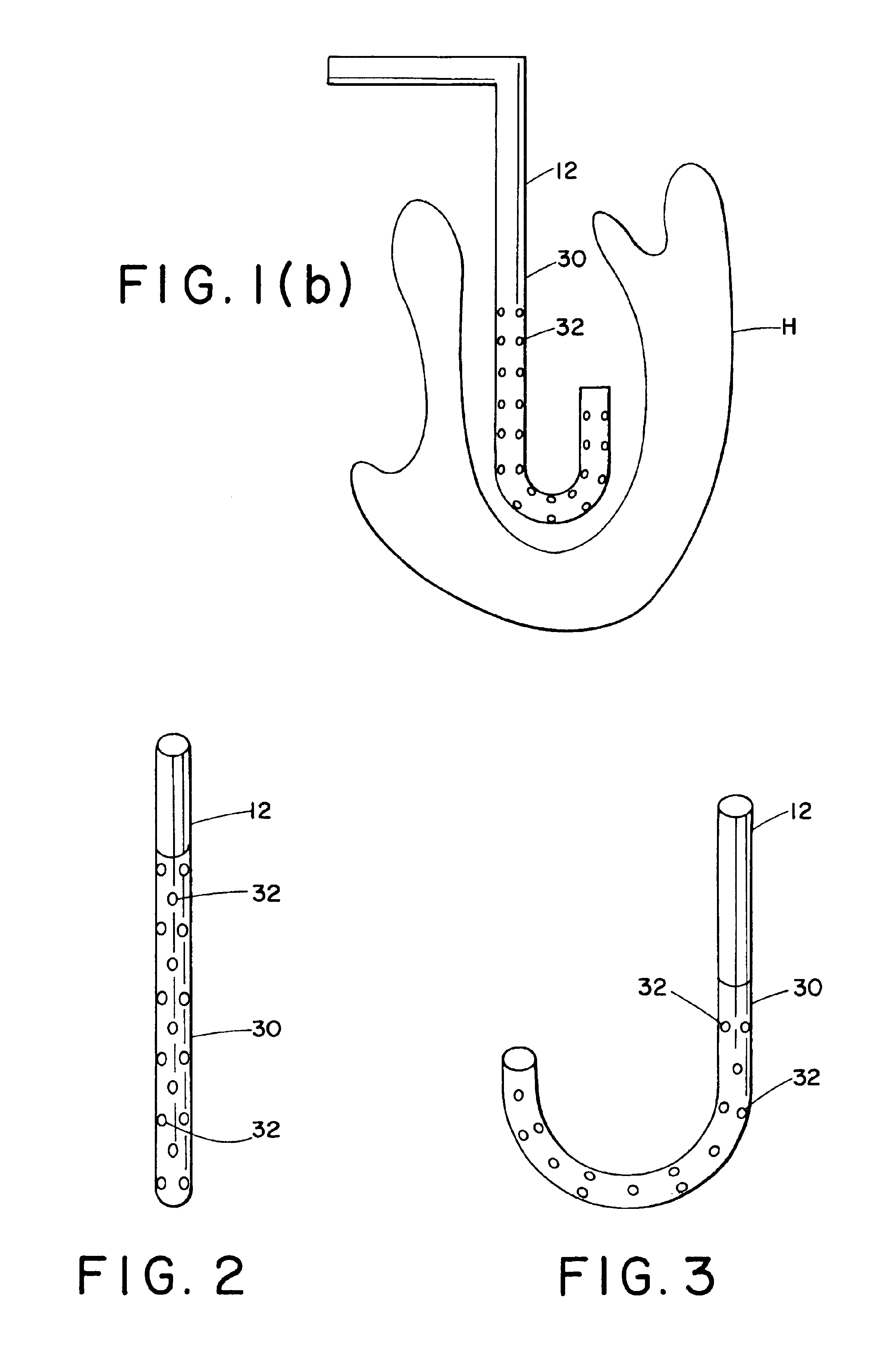
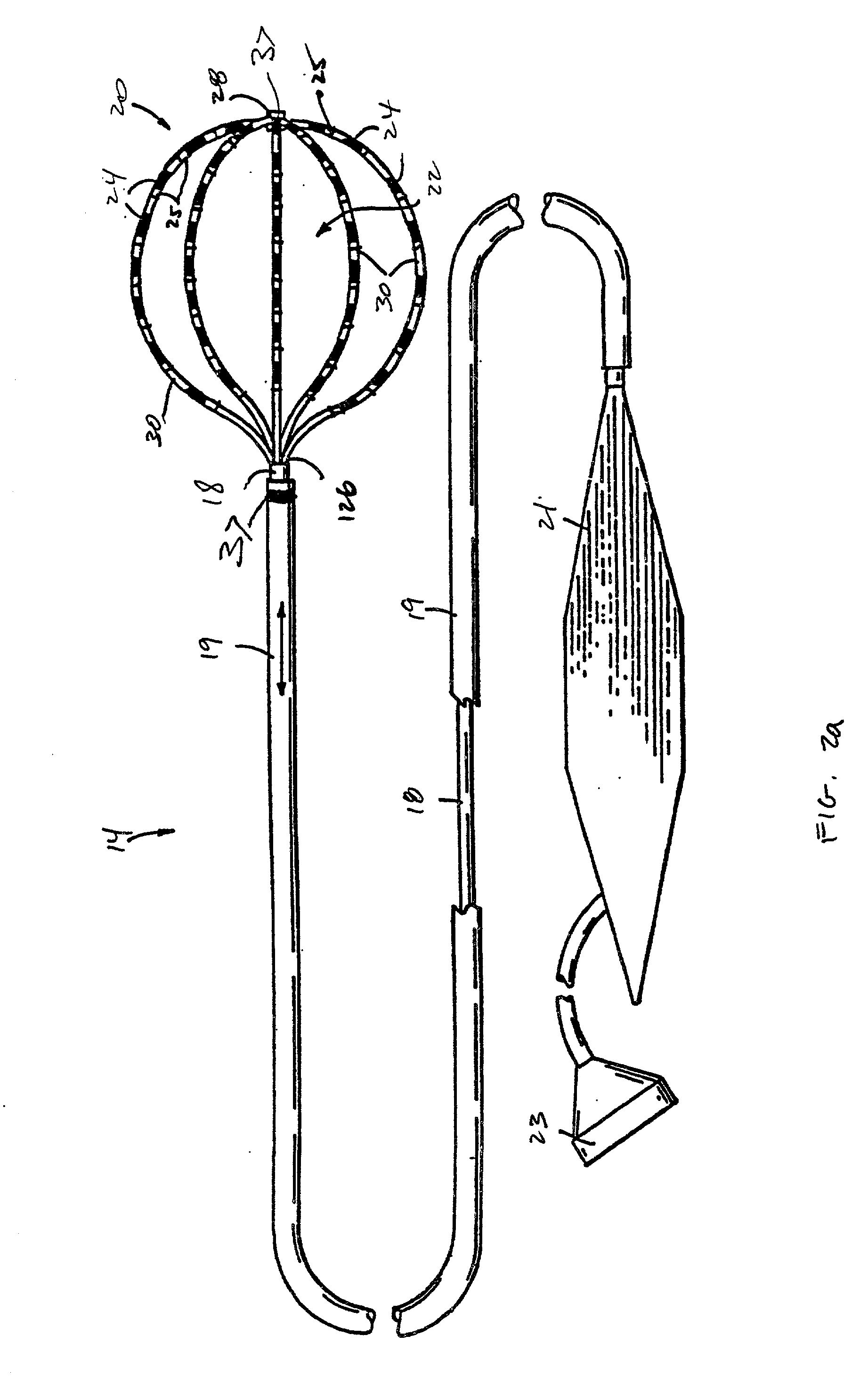
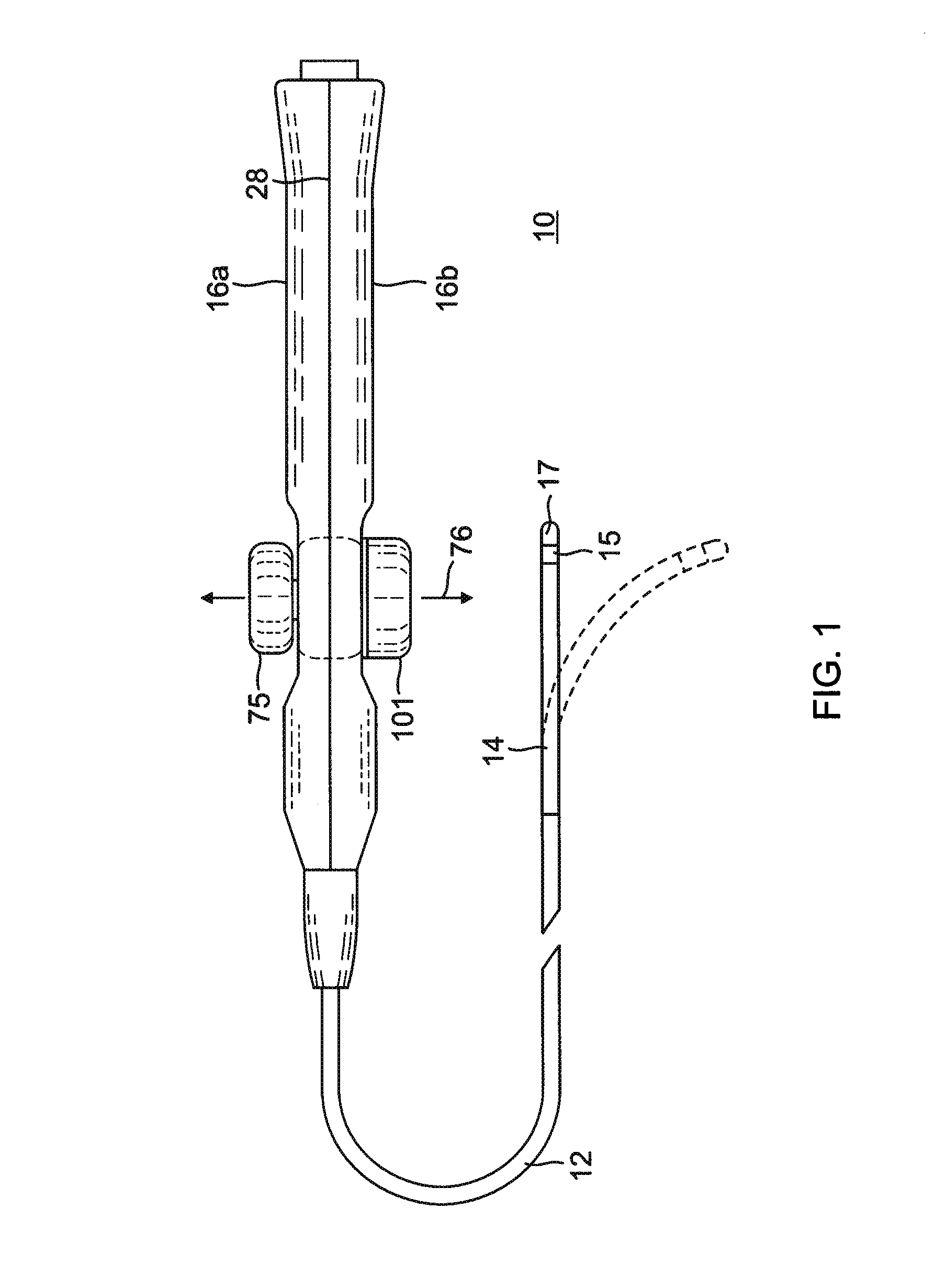
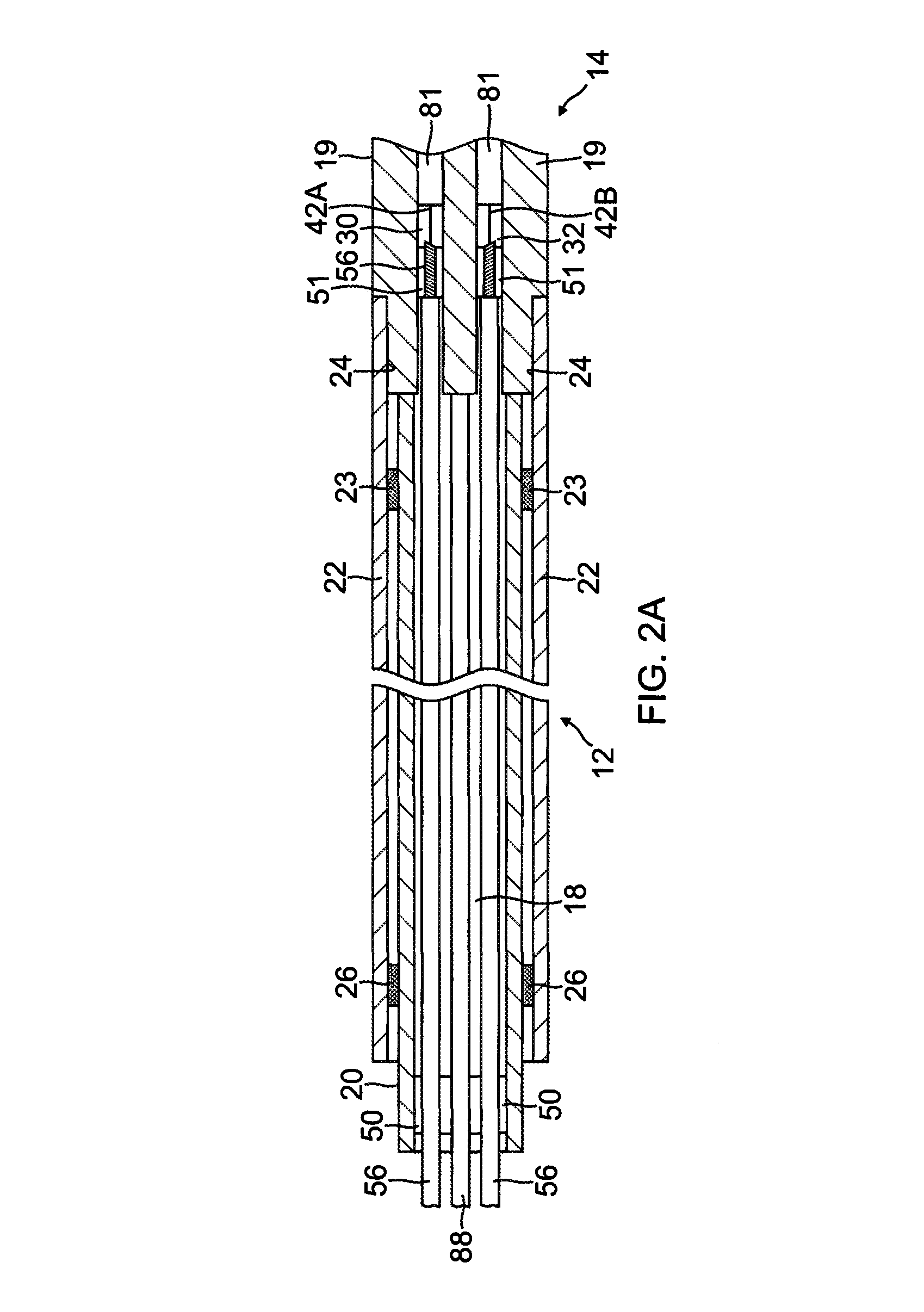
Electrophysiological cardiac mapping system based on a non-contact non-expandable miniature multi-electrode catheter and method therefor
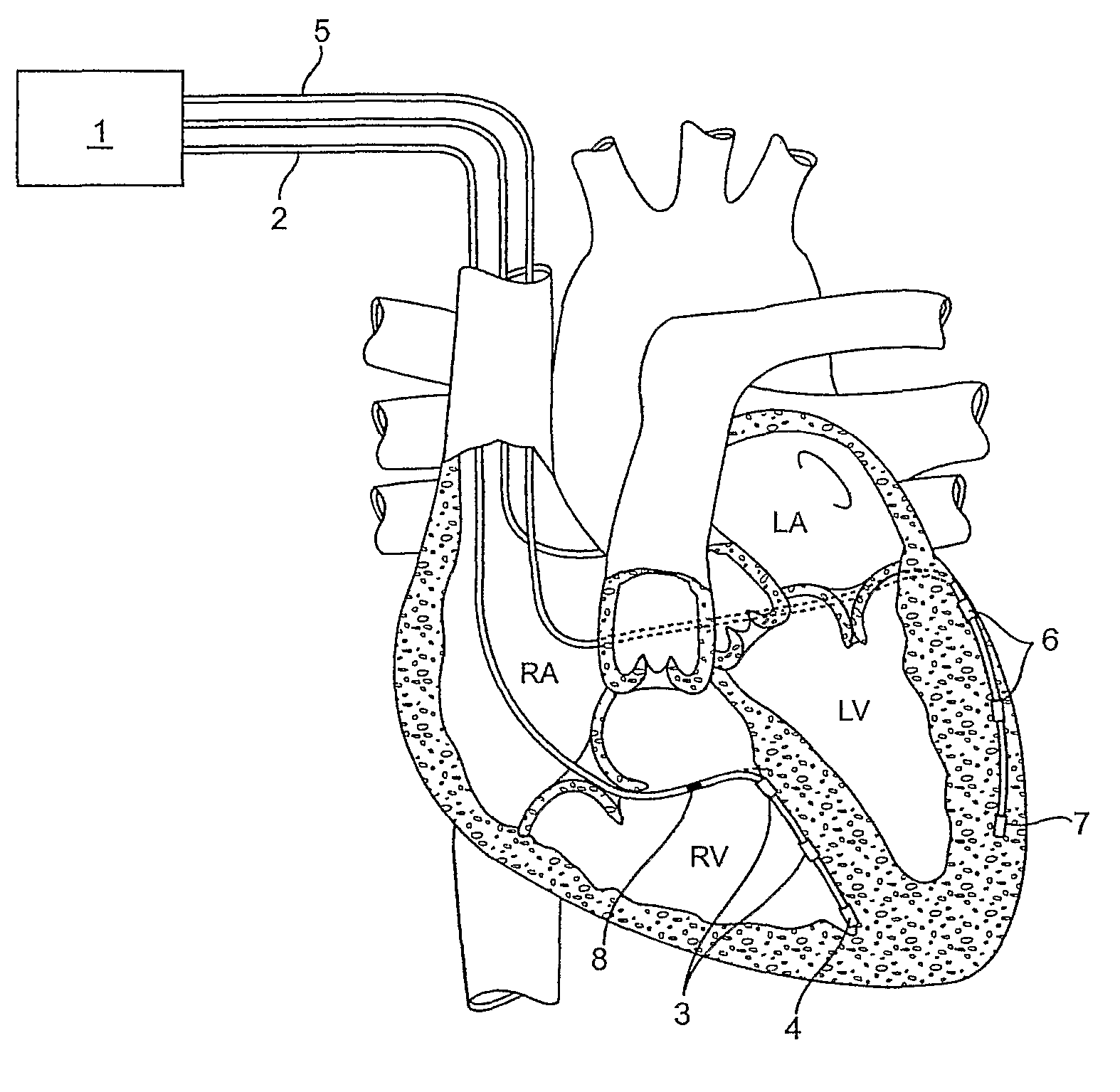
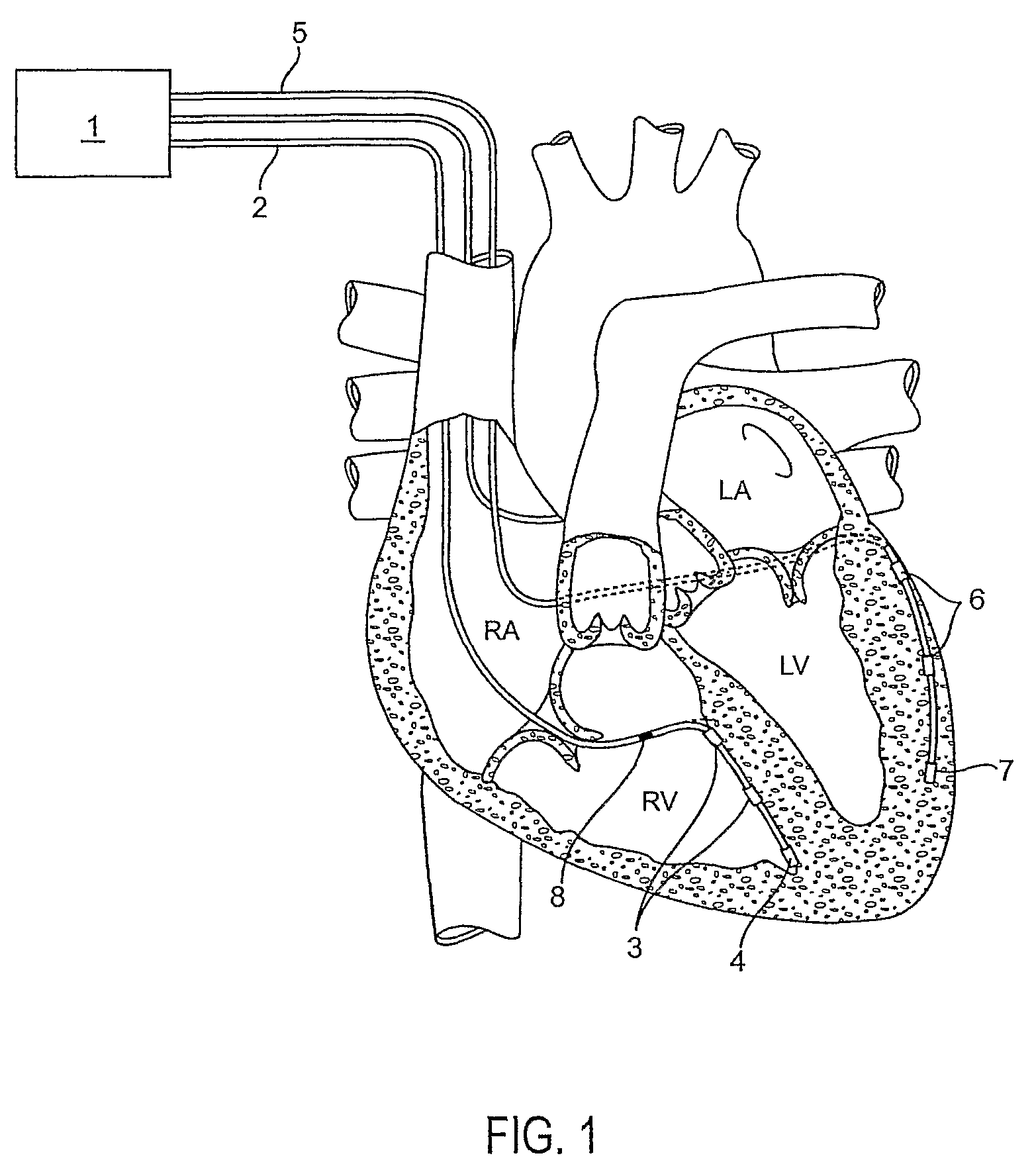
A system (10) for determining electrical potentials on an endocardial surface of a heart is provided. The system includes a non-contact, non-expandable, miniature, multi-electrode catheter probe (12), a plurality of electrodes (32) disposed on an end portion (30) thereof, means for determining endocardial potentials (14) based on electrical potentials measured by the catheter probe, a matrix of coefficients that is generated based on a geometric relationship between the probe surface, and the endocardial surface. A method is also provided.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
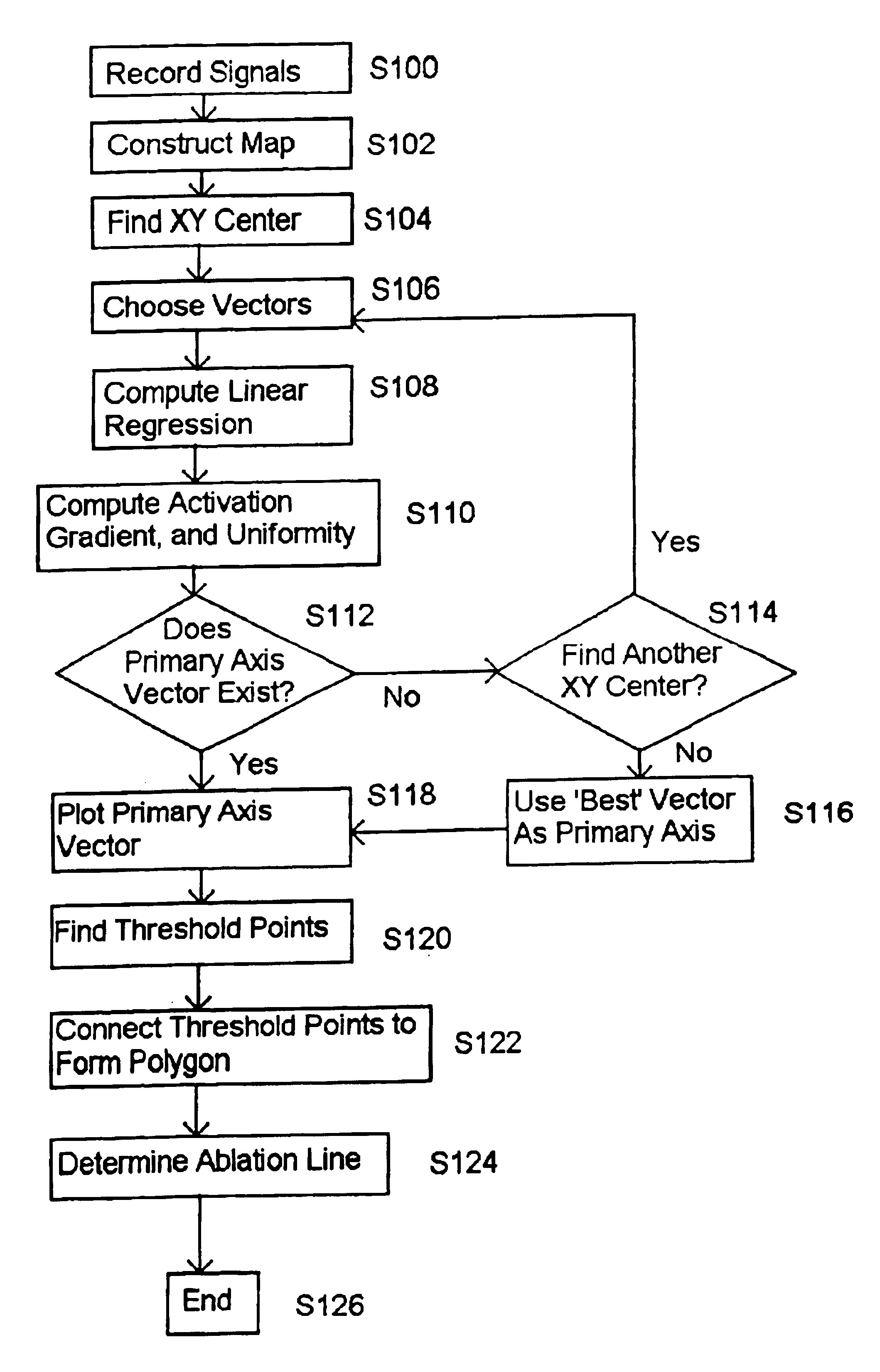
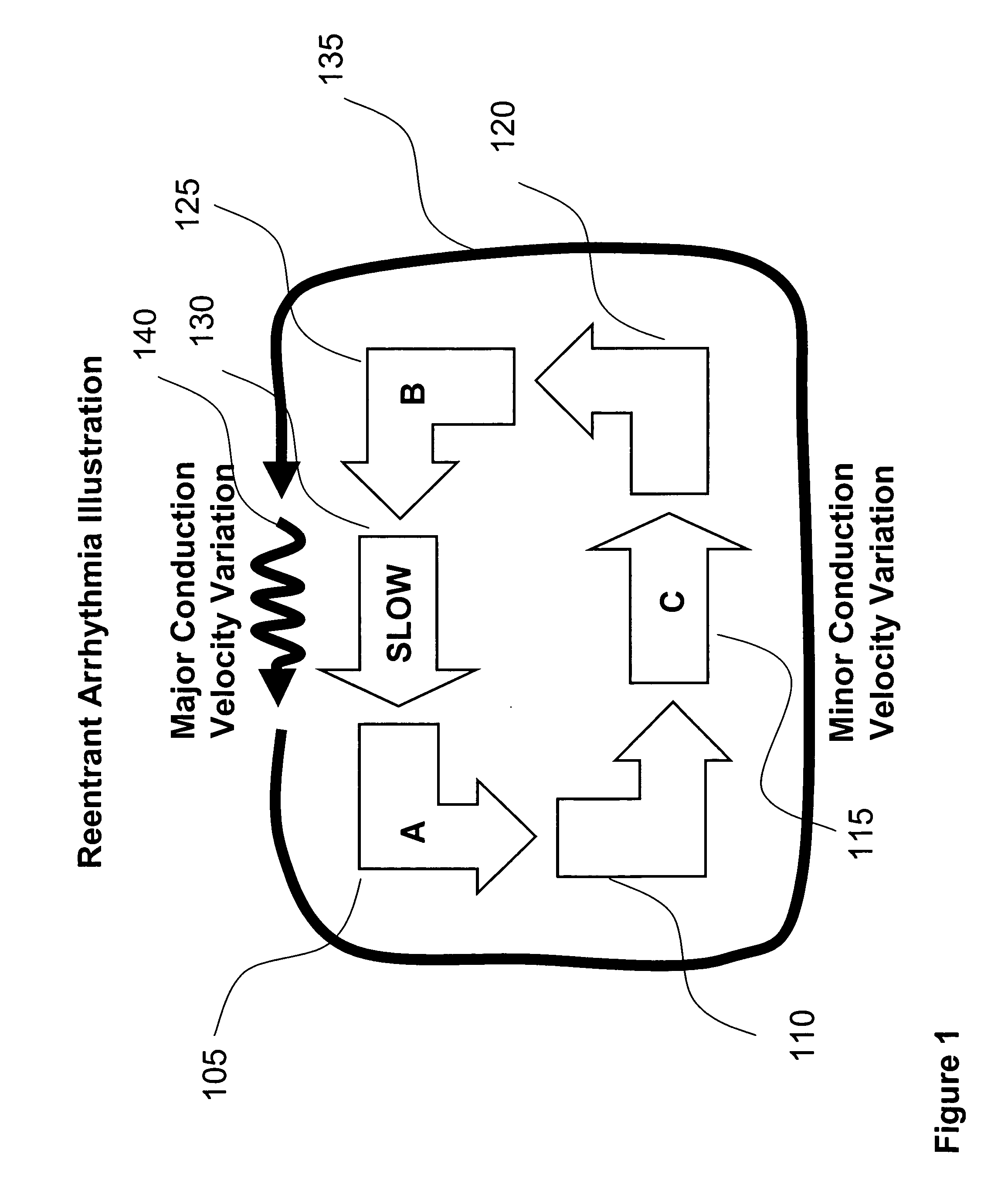
System and method for determining reentrant ventricular tachycardia isthmus location and shape for catheter ablation
A method for identifying and localizing a reentrant circuit isthmus in a heart of a subject during sinus rhythm, including: a) receiving electrogram signals from the heart during sinus rhythm via electrodes; b) storing the electrogram signals; c) creating a map based on the electrogram signals; d) finding a center reference activation location on the map; e) defining measurement vectors originating from the center reference activation location; f) selecting from the measurement vectors a primary axis vector indicating a location of the reentrant circuit isthmus in the heart; g) finding threshold points of electrogram signals on the map; h) connecting the threshold points to form a polygon indicating a shape of the reentrant circuit isthmus in the heart.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Systems and processes for refining a registered map of a body cavity
InactiveUS20030078509A1ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionComputer scienceBody cavity
A process of refining a map of a body cavity includes positioning a first probe and a second probe within the body cavity. Mapping elements on the first probe are used to gather local information from a plurality of locations along the body cavity. The absolute locations of the mapping elements are registered in a three-dimensional coordinate system, and are associated with the local information to generate the map. A mapping element on the second probe is then used to gather information local to a location between the plurality of locations along the body cavity. The absolute location of the mapping element is registered in the three-dimensional system and associated with the local information to refine the map.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
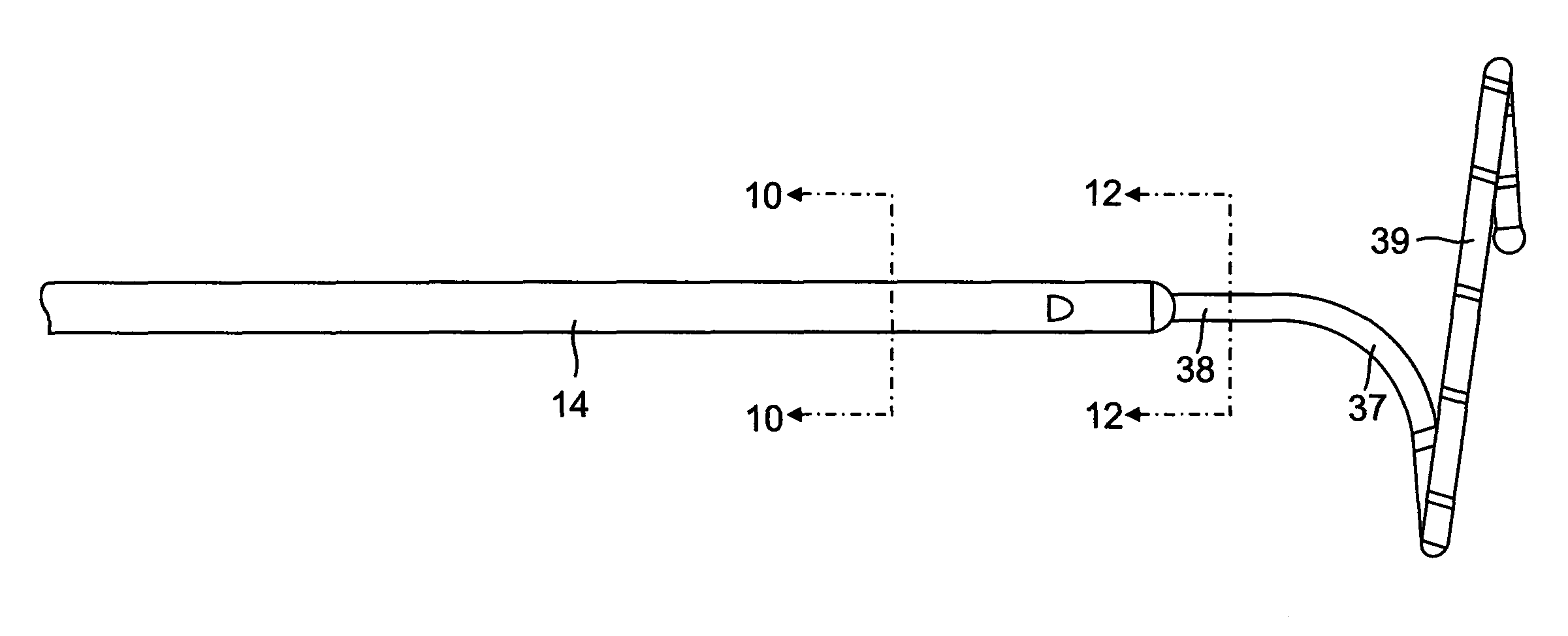
Arrhythmia discrimination using electrocardiograms sensed from multiple implanted electrodes
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems provide for monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation and pacing therapies, or a combination of these capabilities, including cardiac systems incorporating or cooperating with neuro-stimulating devices, drug pumps, or other therapies. Embodiments of the present invention relate generally to implantable medical devices employing automated cardiac activation sequence monitoring and / or tracking for arrhythmia discrimination. Embodiments of the invention are directed to devices and methods involving sensing a plurality of composite cardiac signals using a plurality of implantable electrodes. A source separation is performed using the sensed plurality of composite cardiac signals and the separation produces one or more cardiac signal vectors associated with one or more cardiac activation sequences that is indicative of ischemia. A change of the one or more cardiac signal vectors is detected using the one or more cardiac signal vectors. Cardiac arrhythmias are discriminated using the one or more cardiac signal vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
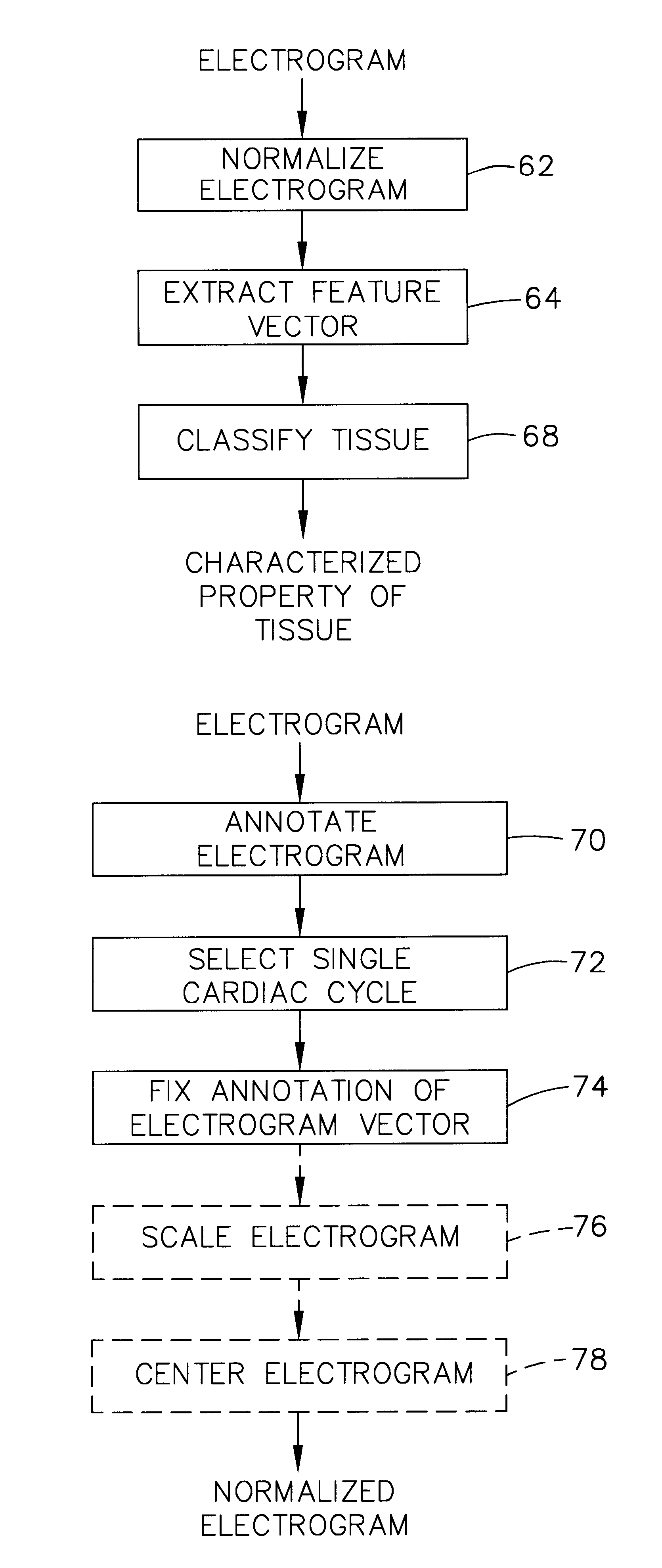
Method and apparatus for characterizing cardiac tissue from local electrograms
The property of cardiac tissue at a local site, a plurality of sites of in a region of a heart may be characterized based on local electrograms measured at the local site, at a plurality of sites or in the region, respectively. The property may be characterized by normalizing the local electrogram, extracting a feature vector from the normalized electrogram, and classifying the tissue property based on the feature vector. The method of may further include computing a map of the tissue property and treating the tissue based on the resultant map. Apparatus to characterize the property includes a catheter and a processor to normalize the local electrogram, extract the feature vector from the electrogram and classify the tissue based on the feature vector.
Owner:SCHWARTZMAN ARMIN +1
Ventricular Pacing In Cardiac-Related Applications
ActiveUS20150257670A1Highly impreciseHighly inaccurateElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationCardiac VentricleVentricular pacing
Owner:NEWSTIM INC
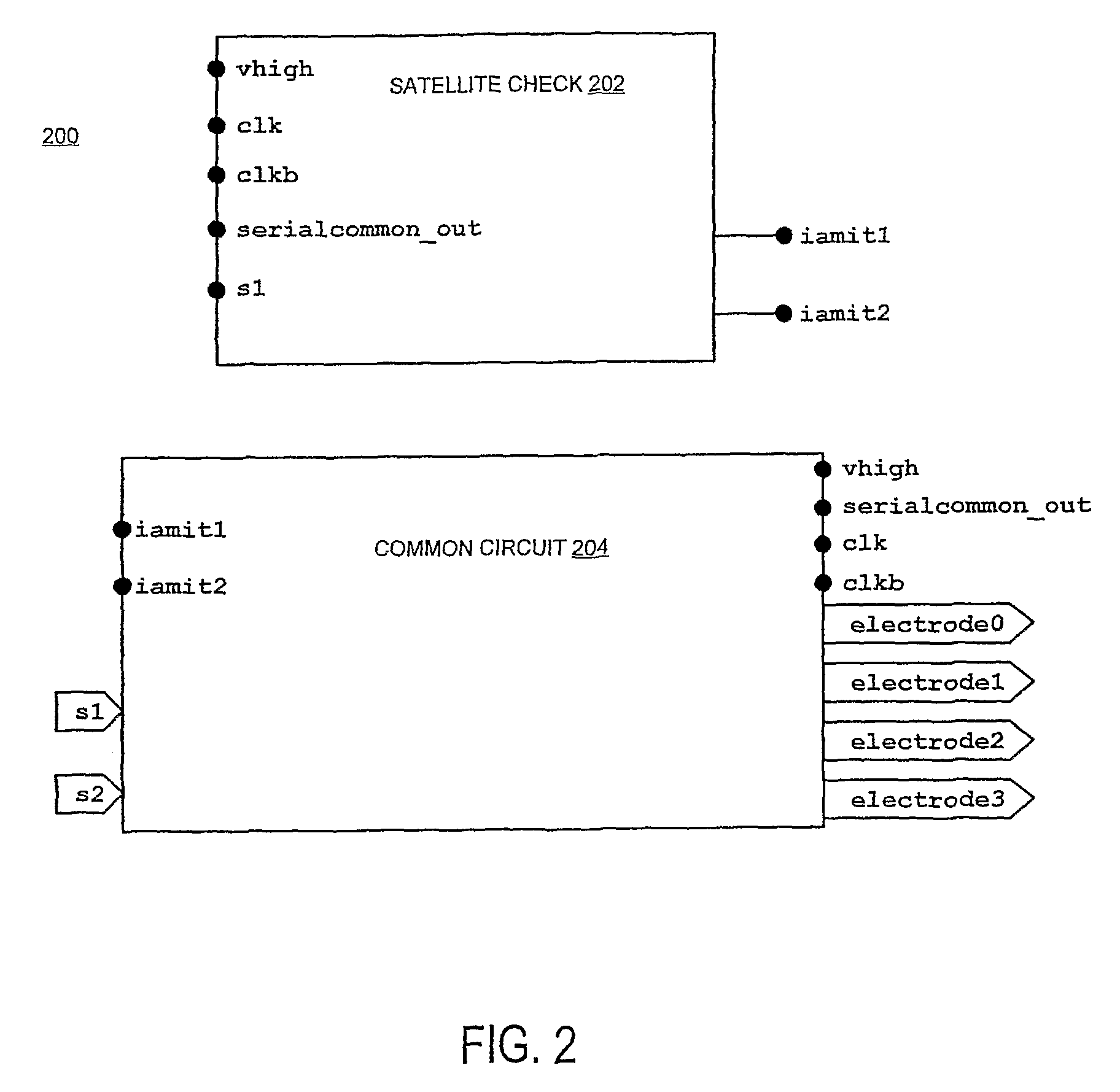
Measuring conduction velocity using one or more satellite devices
InactiveUS7983751B2Readily employedEase of evaluationElectrotherapySensorsClassical mechanicsNerve conduction velocity
A method for measuring the conduction velocity of a depolarization wave in a tissue employs a first satellite located within the tissue and a second that satellite is located within the tissue a distance away from the first satellite, e.g., by using the time of depolarization wave as reported from each satellite and the distance to determine velocity of the wave. Also provided are systems and kits that find use in accordance with the invention.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Optimization Using Vector Measurements Obtained From Realtime Electrode Position Tracking
An exemplary method includes selecting a first pair of electrodes to define a first vector and selecting a second pair of electrodes to define a second vector; acquiring position information during one or more cardiac cycles for the first and second pairs of electrodes wherein the acquiring comprises using each of the electrodes for measuring one or more electrical potentials in an electrical localization field established in the patient; and determining a dyssynchrony index by applying a cross-covariance technique to the position information for the first and the second vectors. Another method includes determining a phase shift based on the acquired position information for the first and the second vectors; and determining an interventricular delay based at least in part on the phase shift.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
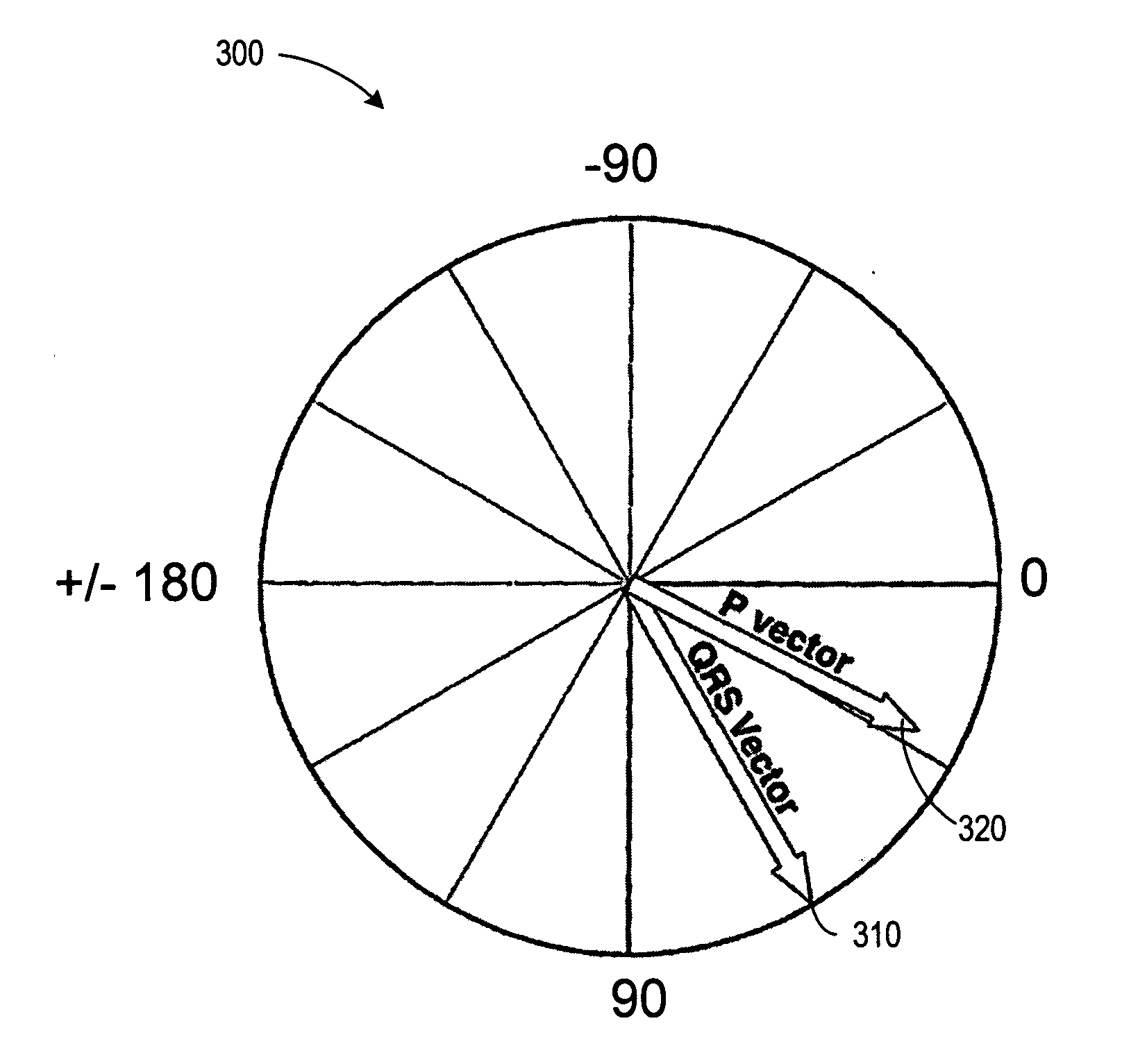
Diagnostic method utilizing standard lead ECG signals
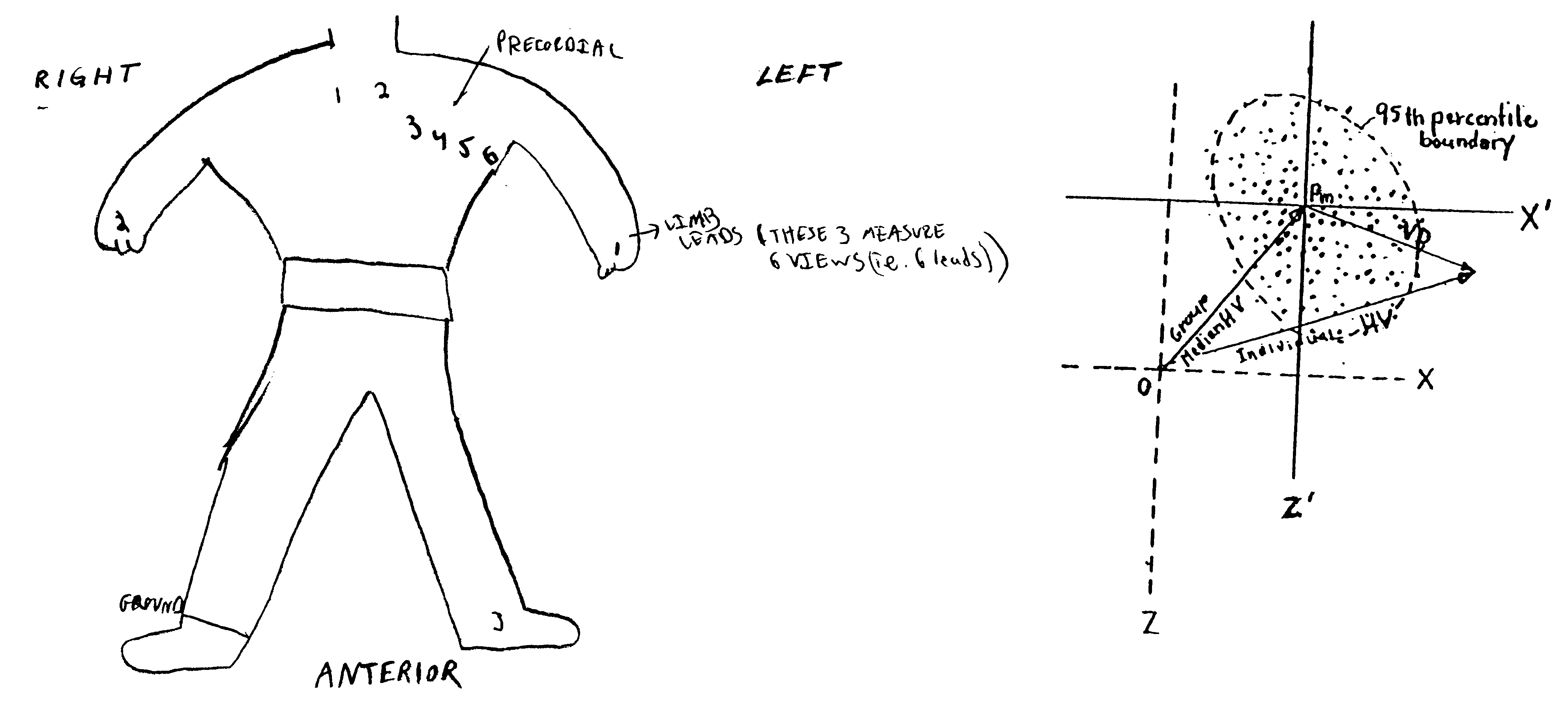
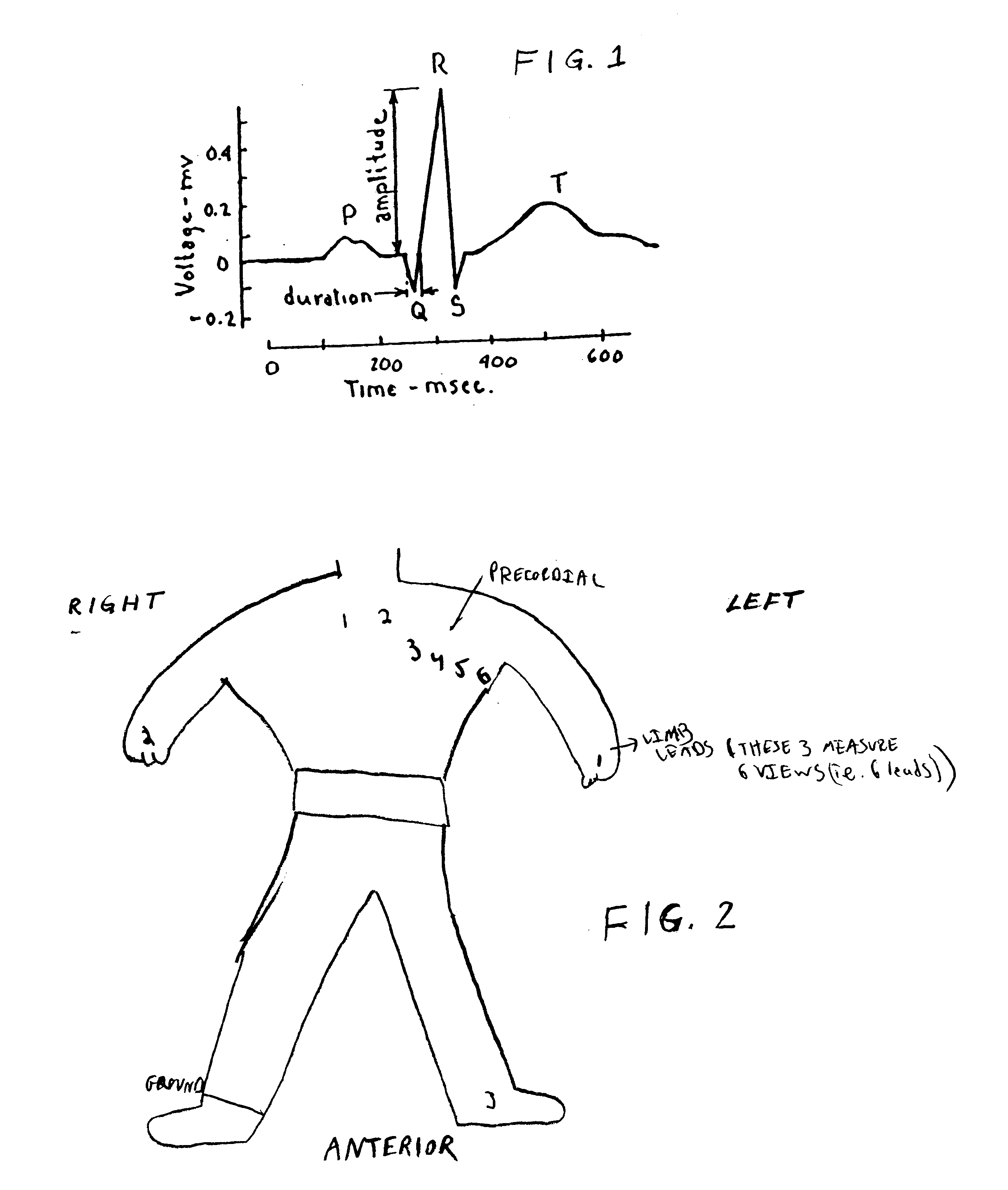
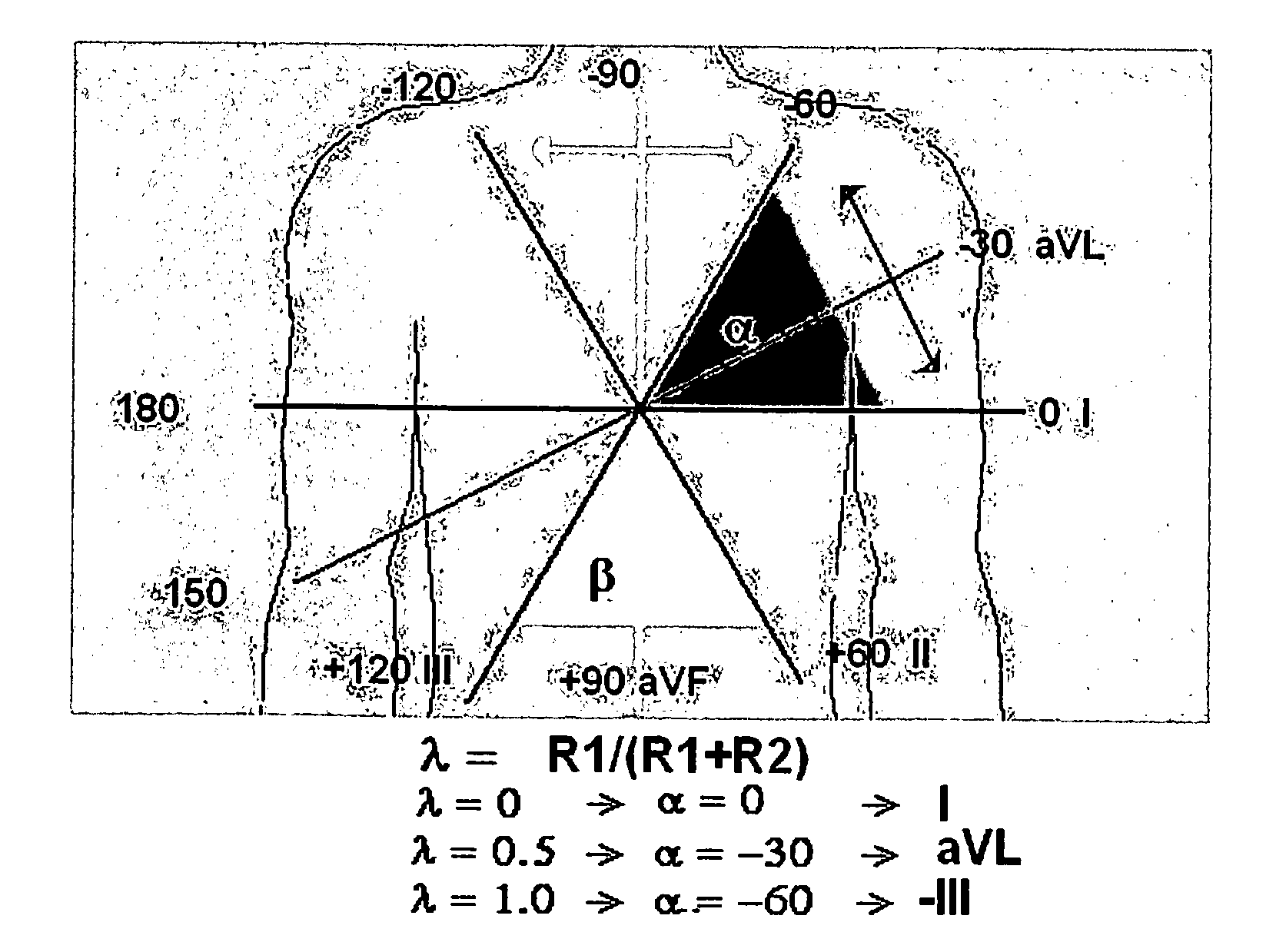
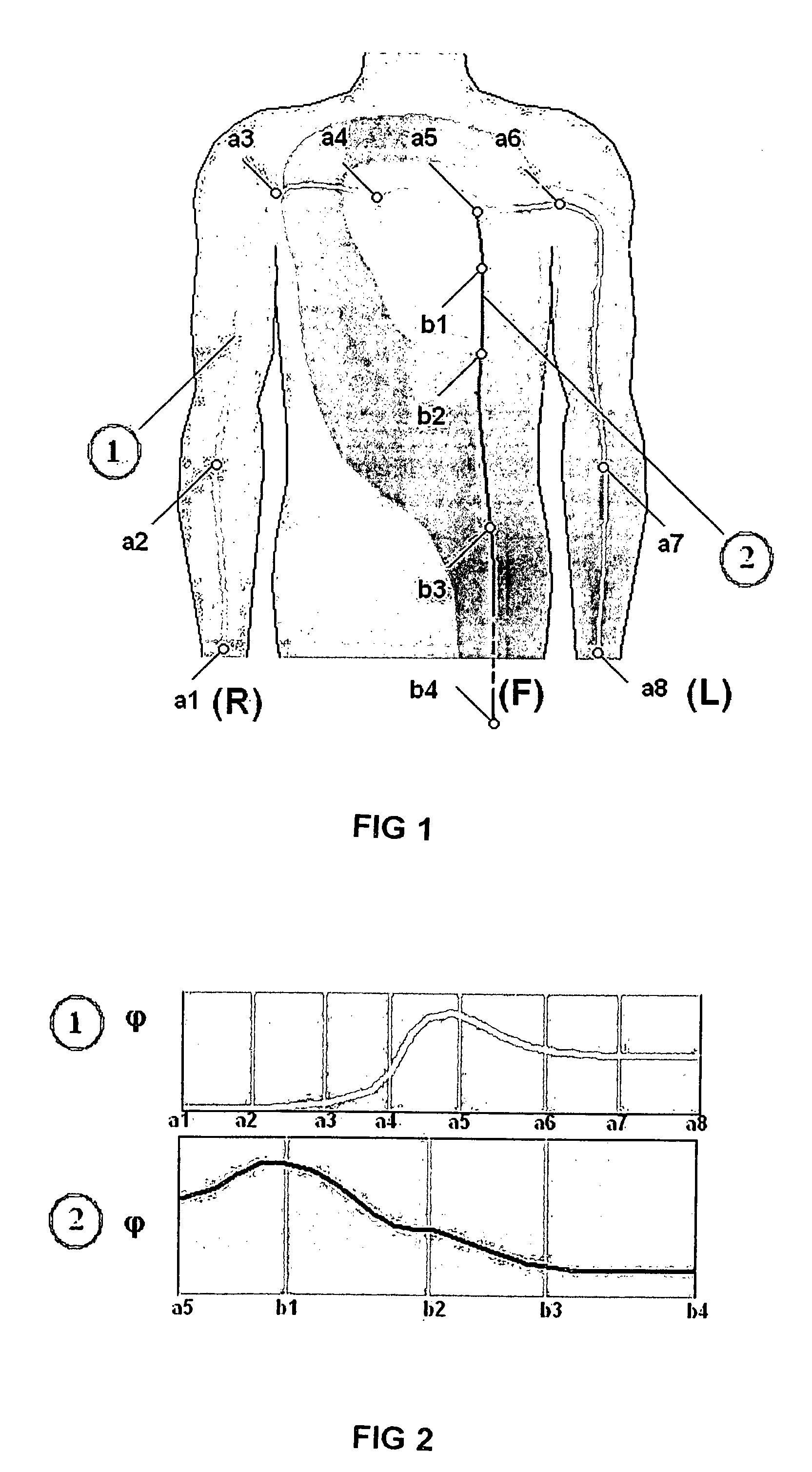
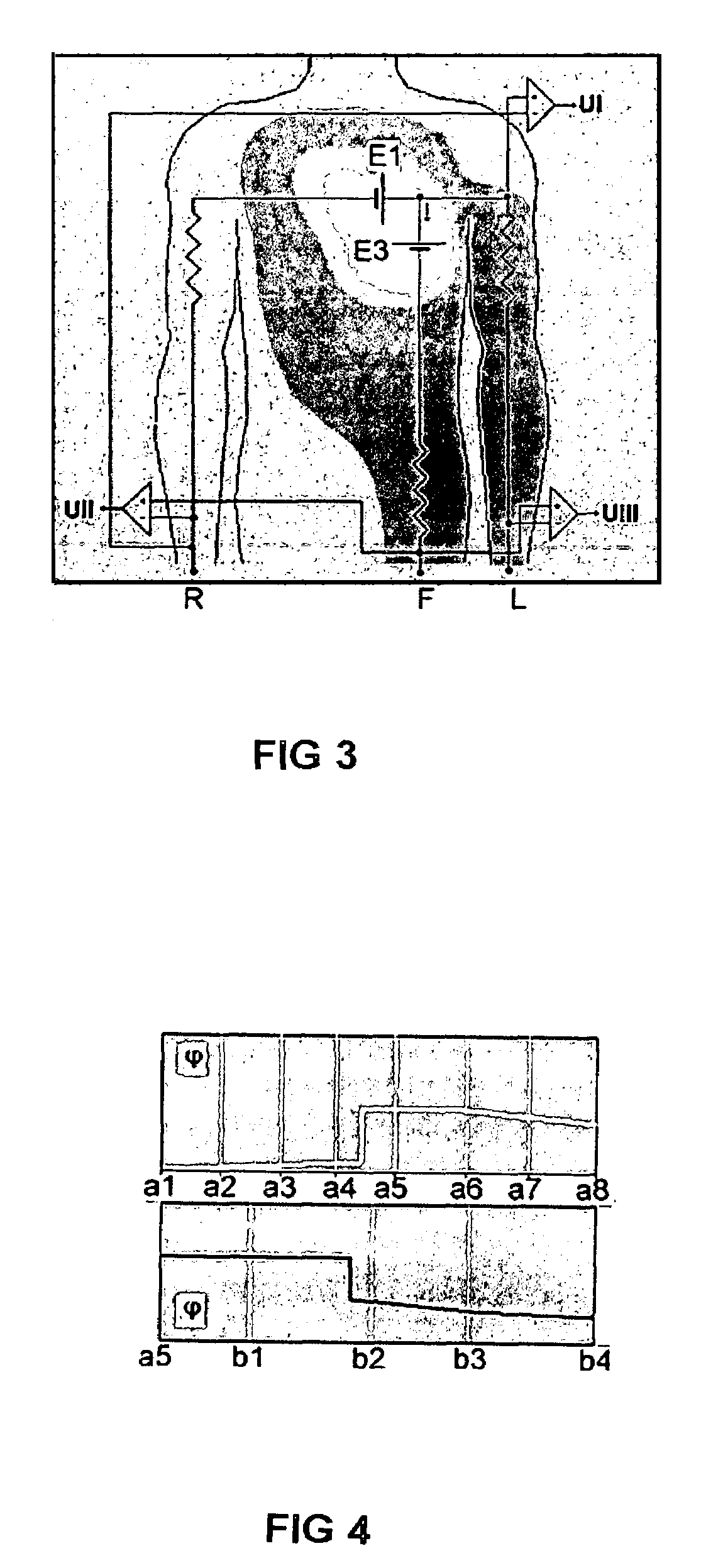
A new and superior strategy for analyzing electrocardiograms (ECG) is disclosed. The strategy utilizes standard leads obtained from only limb electrodes from a conventional electrocardiography system. The strategy determines new additional leads which are utilized in a new calculation of values which upon appropriate analysis, provide new information as to electrical fluctuations in the heart. Also disclosed are processes for mapping and transposing the values in digital form and optionally upon a three-dimensional heart model. And, related systems and computer-readable media are disclosed for performing these processes.
Owner:INCUMED 1 INC
Catheter with single axial sensors
ActiveUS20120172703A1Easy to anchorElectrocardiographySurgical navigation systemsLocalization systemMedicine
A catheter is provided with improved position and / or location sensing with the use of single axis sensors that are mounted directly along a length or portion of the catheter whose position / location is of interest. The magnetic based, single axis sensors are provided on a single axis sensor (SAS) assembly, which can be linear or nonlinear as needed. A catheter of the present invention thus includes a catheter body and a distal member of a particular 2D or 3D configuration that is provided by a support member on which at least one, if not at least three single axis sensors, are mounted serially along a length of the support member. In one embodiment, the magnetic-based sensor assembly including at least one coil member that is wrapped on the support member, wherein the coil member is connected via a joint region to a respective cable member adapted to transmit a signal providing location information from the coil member to a mapping and localization system. The joint region advantageously provides strain relief adaptations to the at least one coil member and the respective cable member from detaching.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
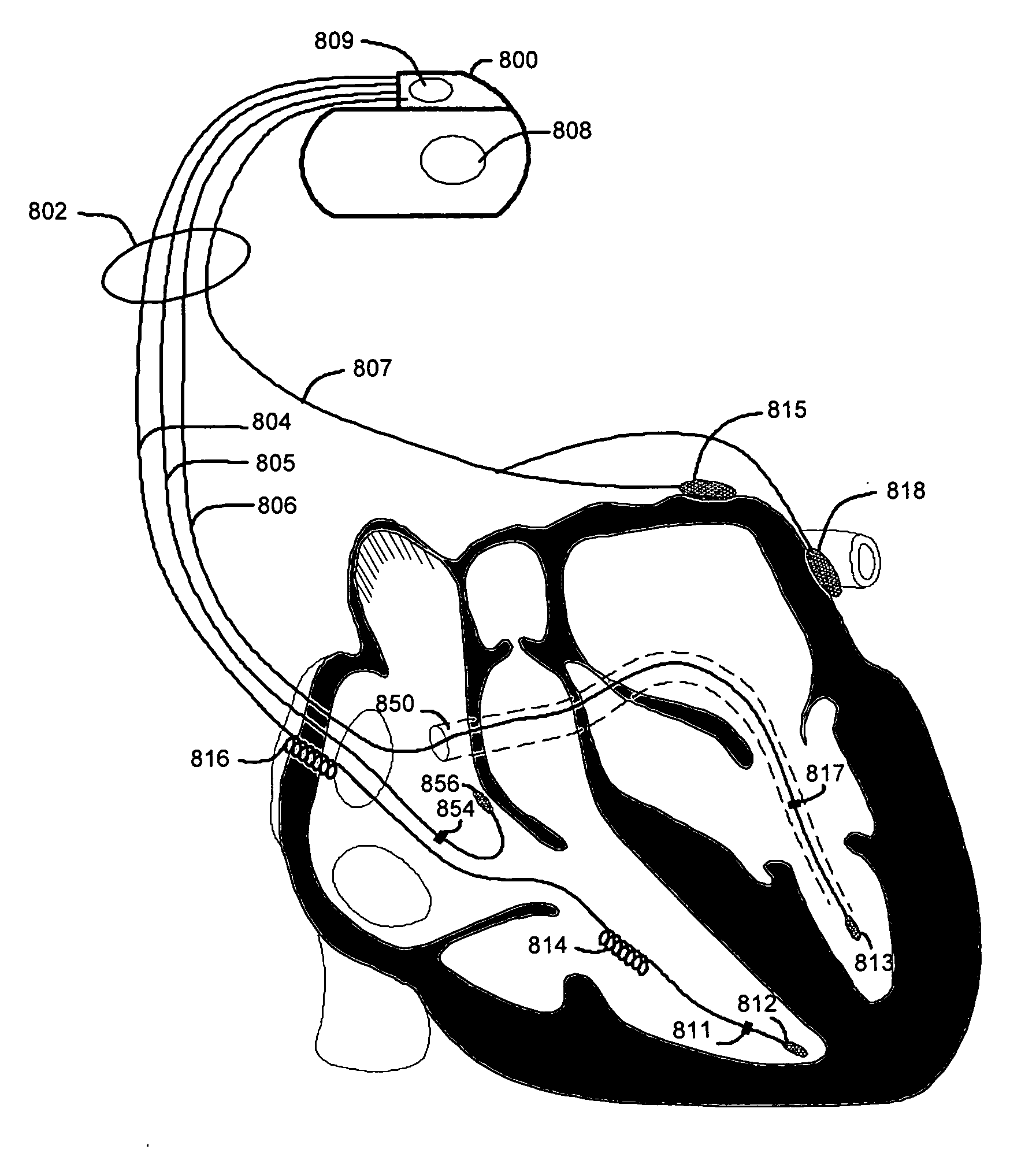
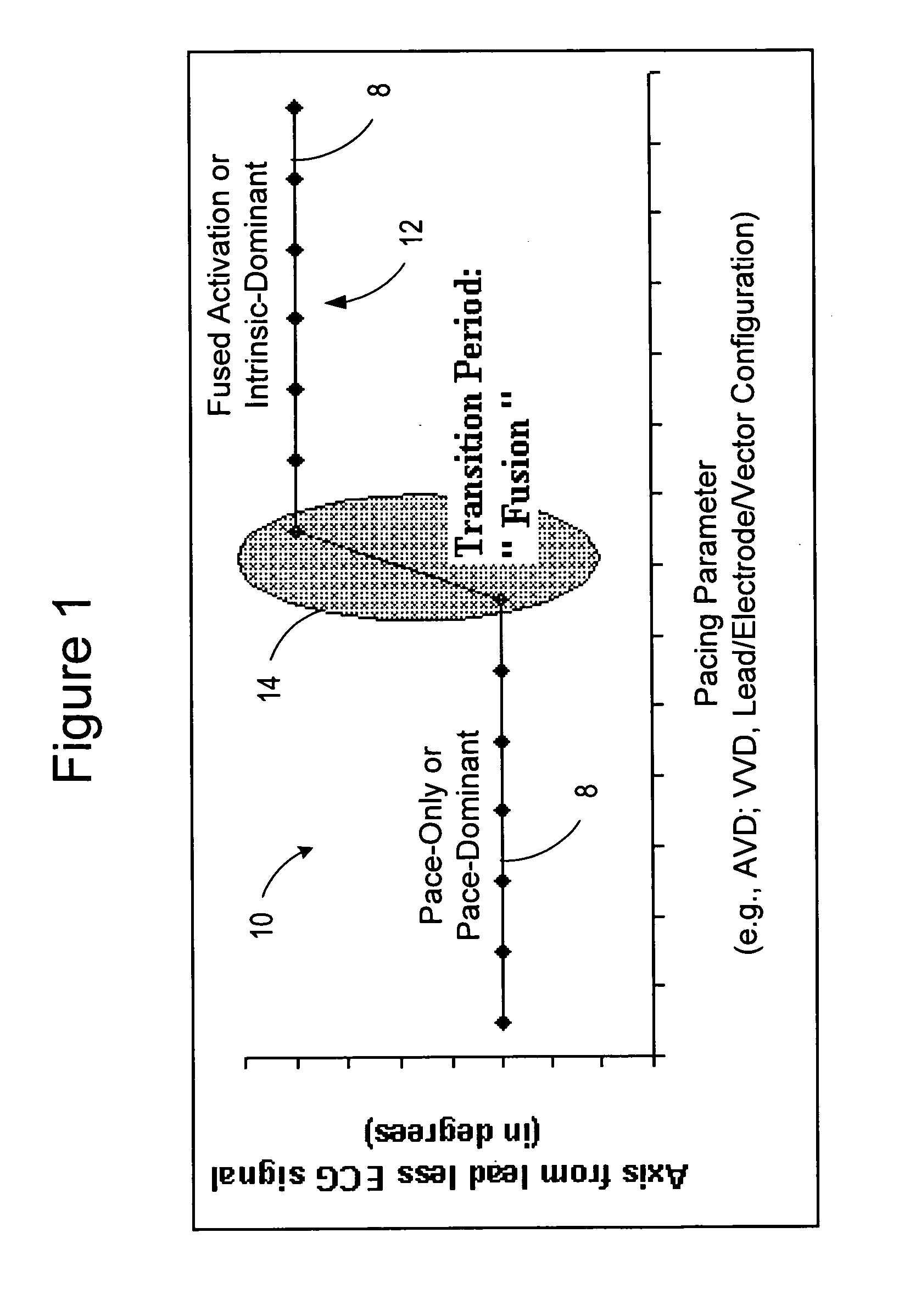
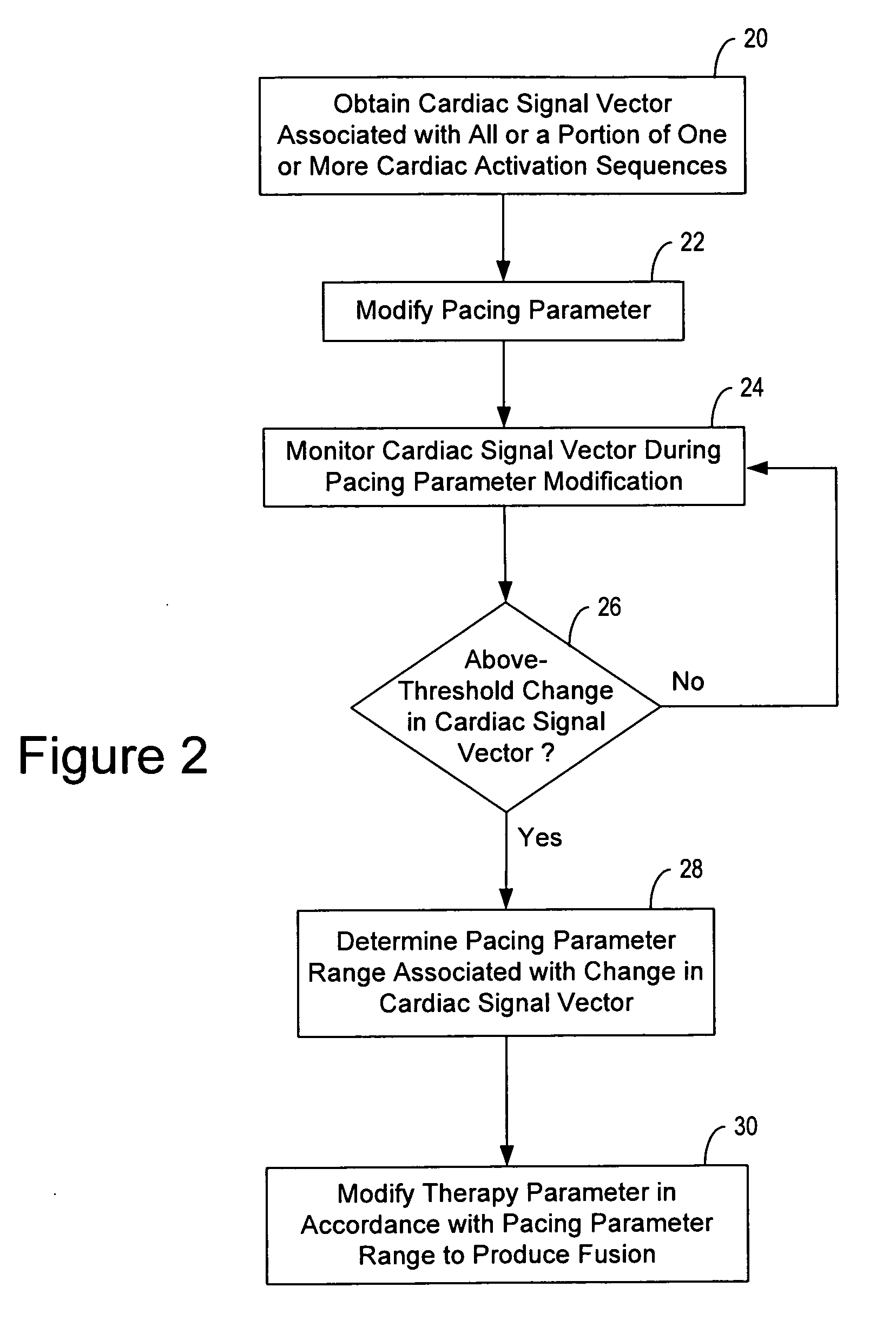
Cardiac resynchronization therapy optimization using cardiac activation sequence information
ActiveUS20080119903A1Improve pumping efficiencyConvenient treatmentElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsBiological activationInformation system
Systems and methods provide for pacing a heart to improve pumping efficiency of the heart, such as by producing a cardiac fusion response for patient's subject to cardiac resynchronization therapy. A pacing parameter, such as an A-V delay, V-V delay, lead / electrode configuration or vector, is adjusted and a cardiac signal vector representative of all or a portion of one or more cardiac activation sequences is monitored during pacing parameter adjustment. A change in a characteristic of the cardiac signal vector is detected in response to an adjusted pacing parameter, the change indicative of a cardiac fusion response. A pacing therapy may be delivered to produce the cardiac fusion response using the adjusted pacing parameter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
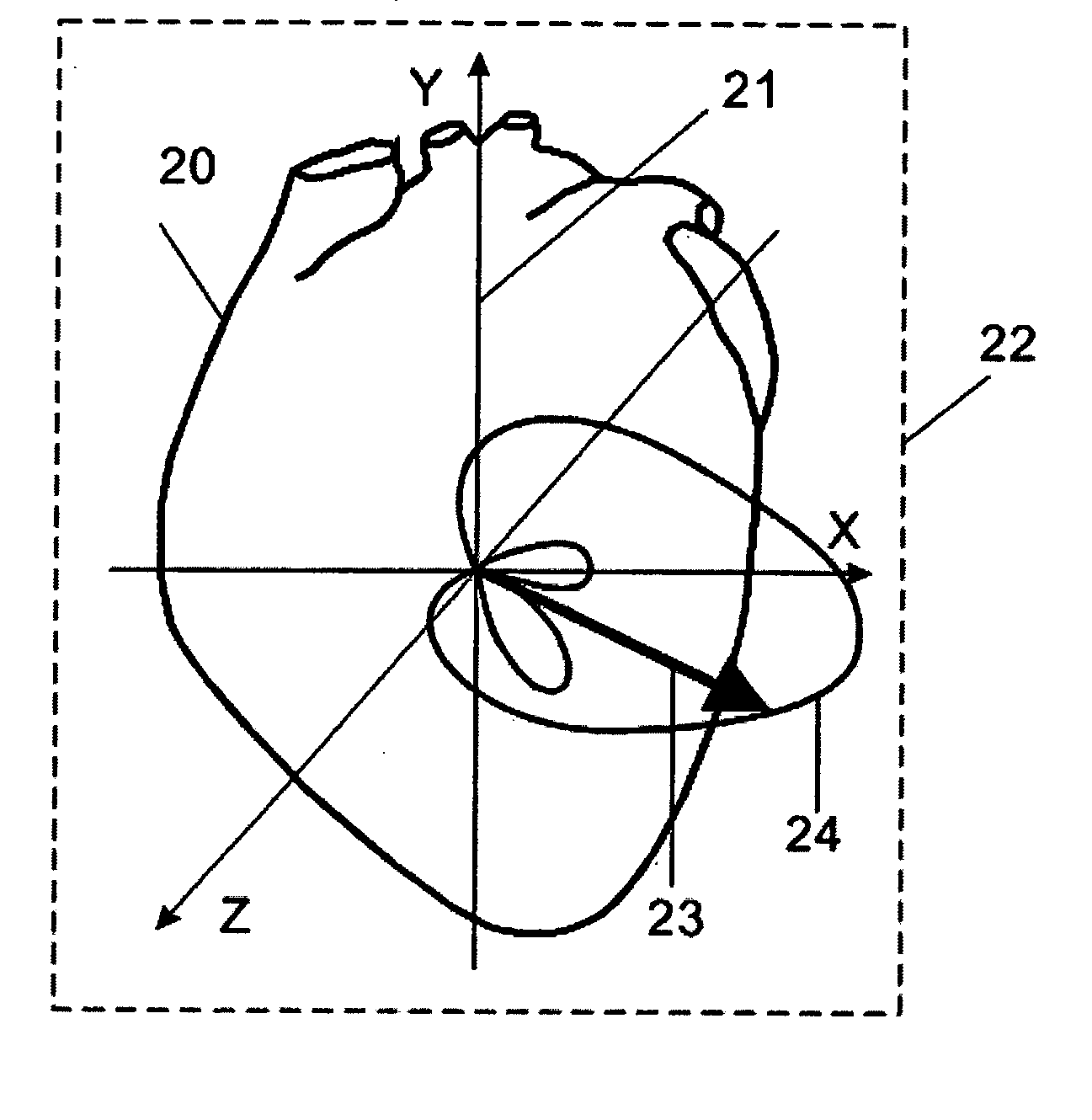
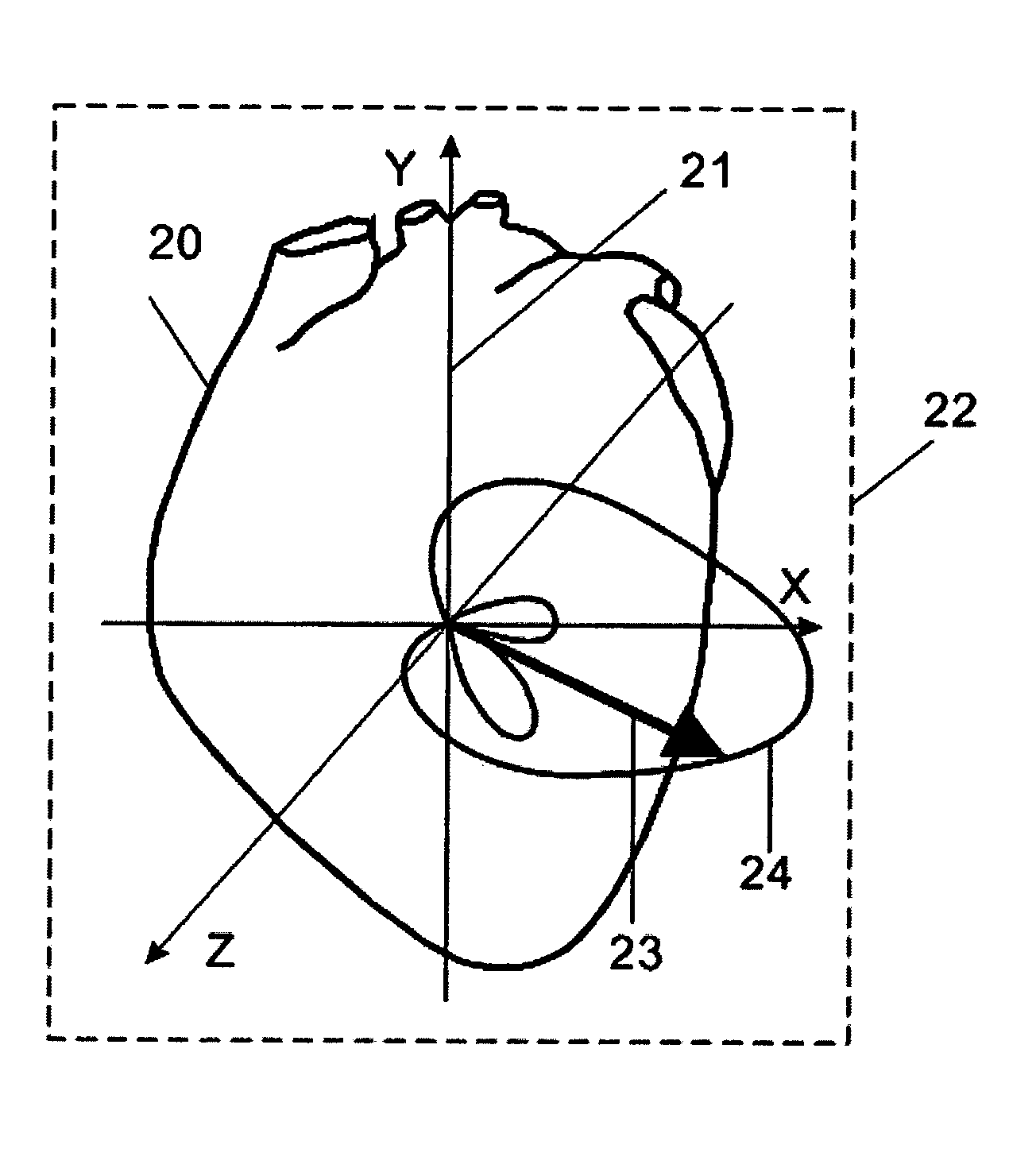
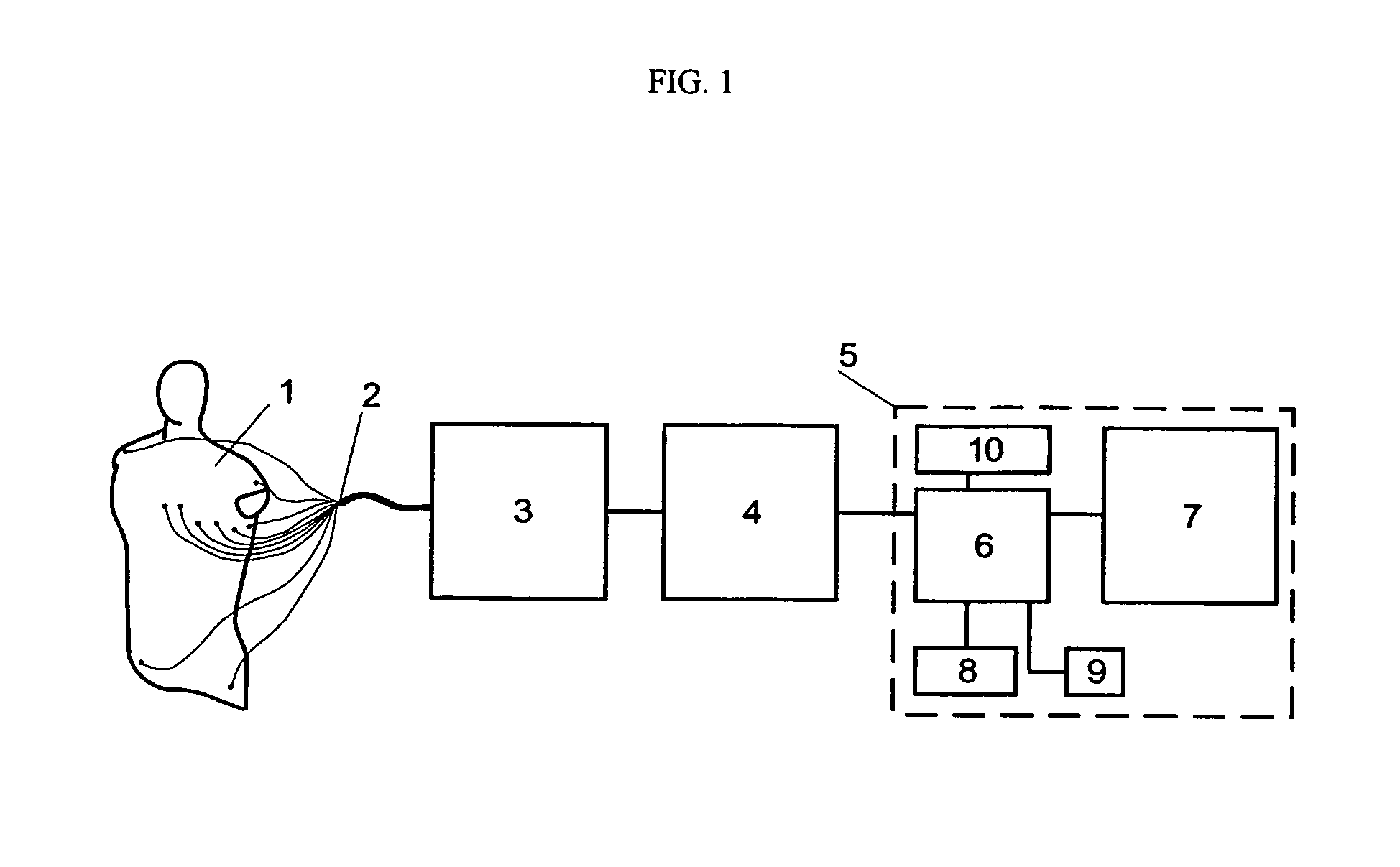
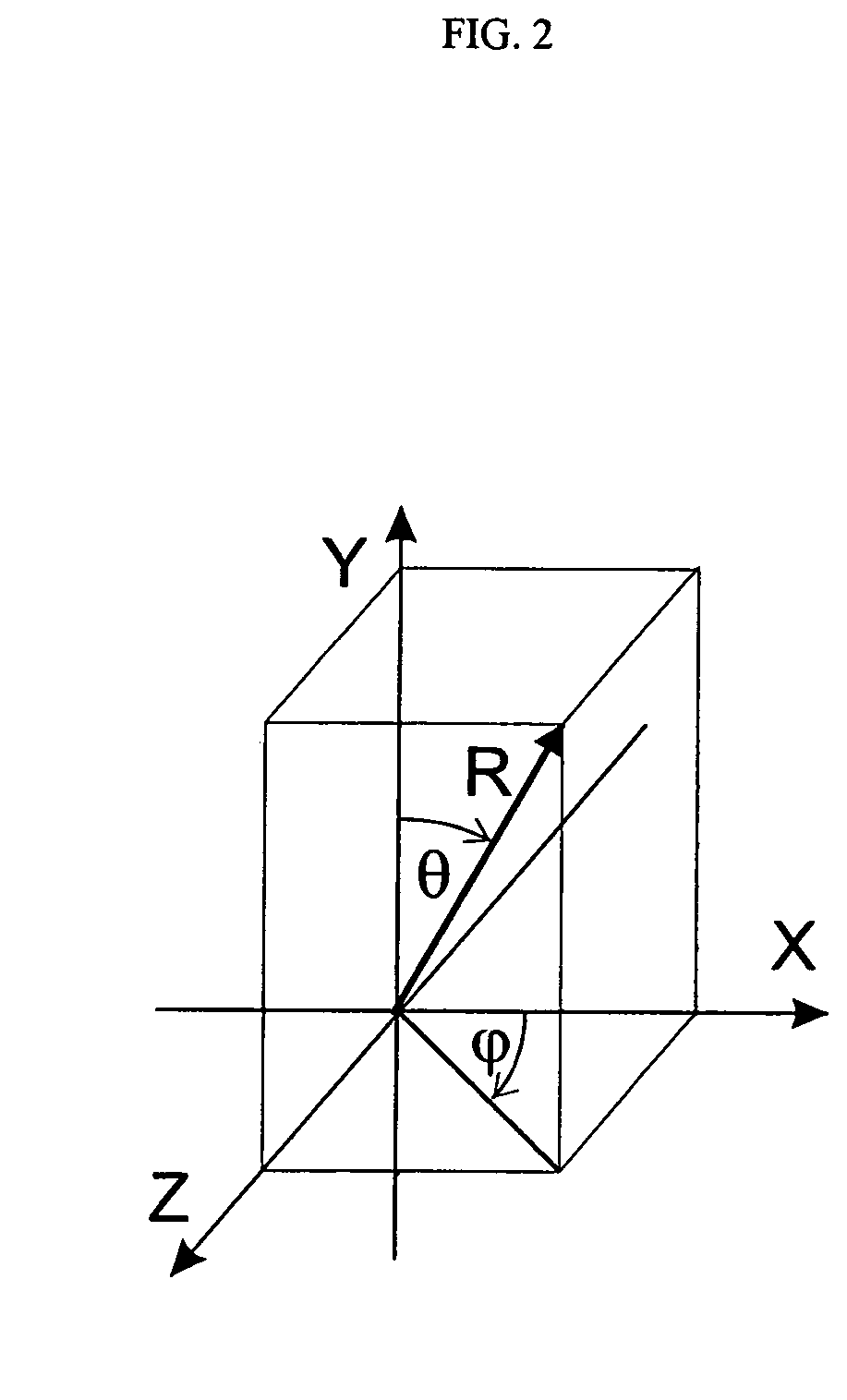
Device and procedure for visual three-dimensional presentation of ECG data
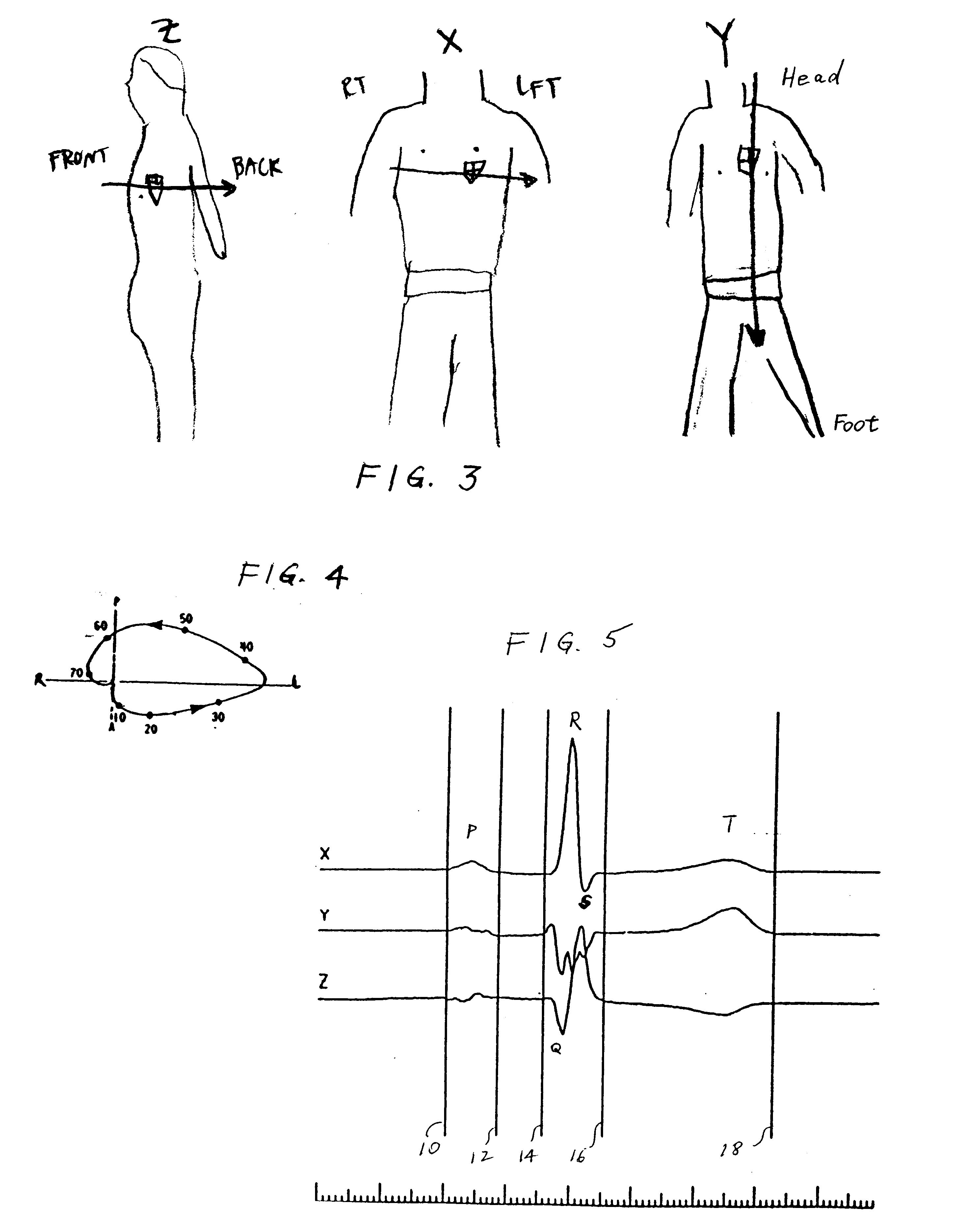
The invention relates to the analysis of ECG data by exploiting computerized three-dimensional spatial presentation of the measured data using the vector concept. A three-dimensional presentation of the human heart may be correlated with waveforms specific for standard ECG or derived ECG signals based on the dipole approximation of the heart electrical activity. The three-dimensional heart model may be rotated, and the ECG signals are interactively linked to the model. In the visualization process, different types of signal presentation may be used, including graphical presentation of the heart vector hodograph, graphical presentation of the signal waveform in an arbitrary chosen point on the heart, and graphical presentation of the map of equipotential lines on the heart in a chosen moment. Additional tools for analyzing ECG data are also provided which may be interactively used with the display tools.
Owner:ERESTECH +1
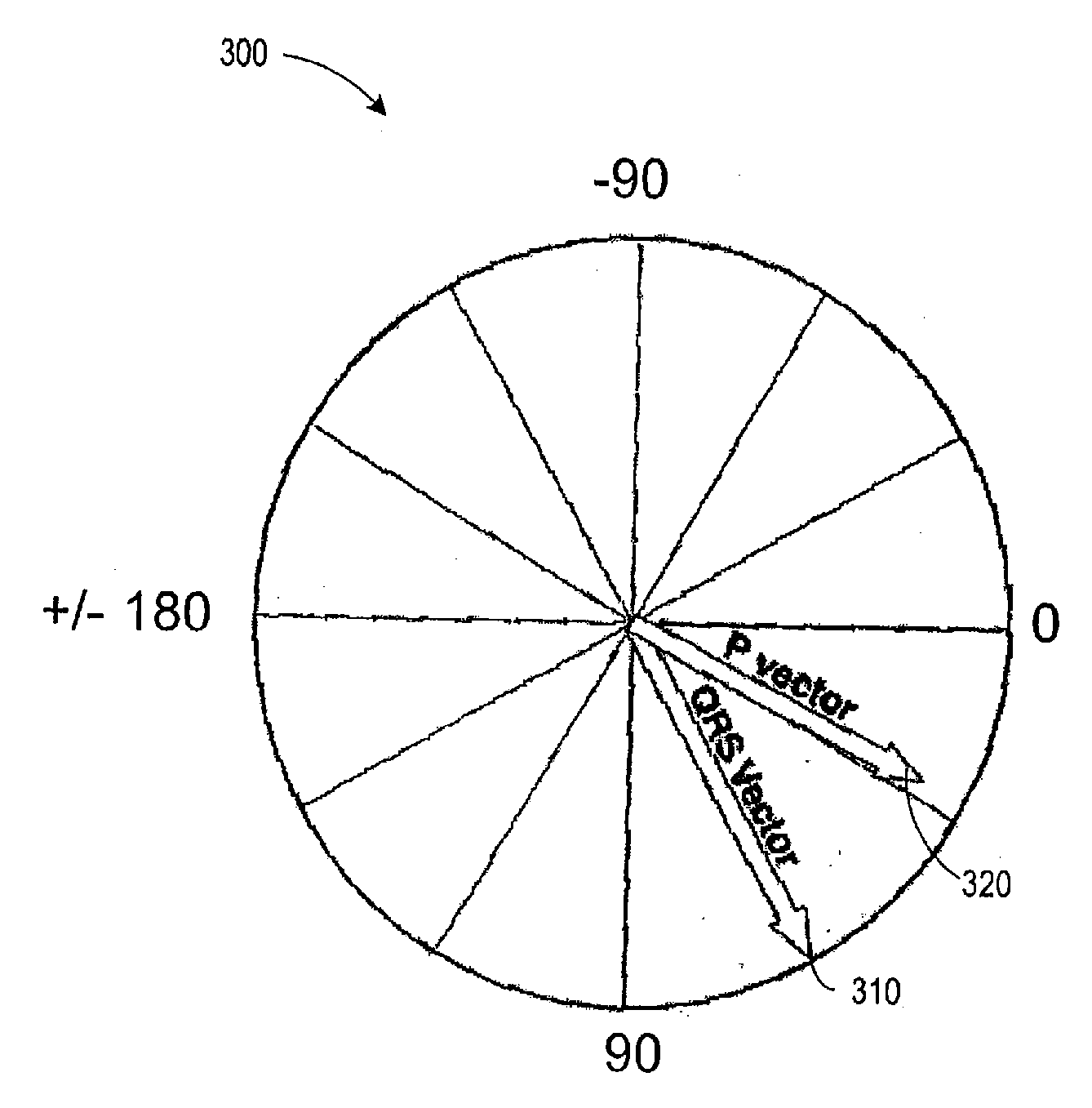
Three dimensional vector cardiograph and method for detecting and monitoring ischemic events
InactiveUS6884218B2Easy to analyzeGood techniqueElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesMaximum magnitudeT wave
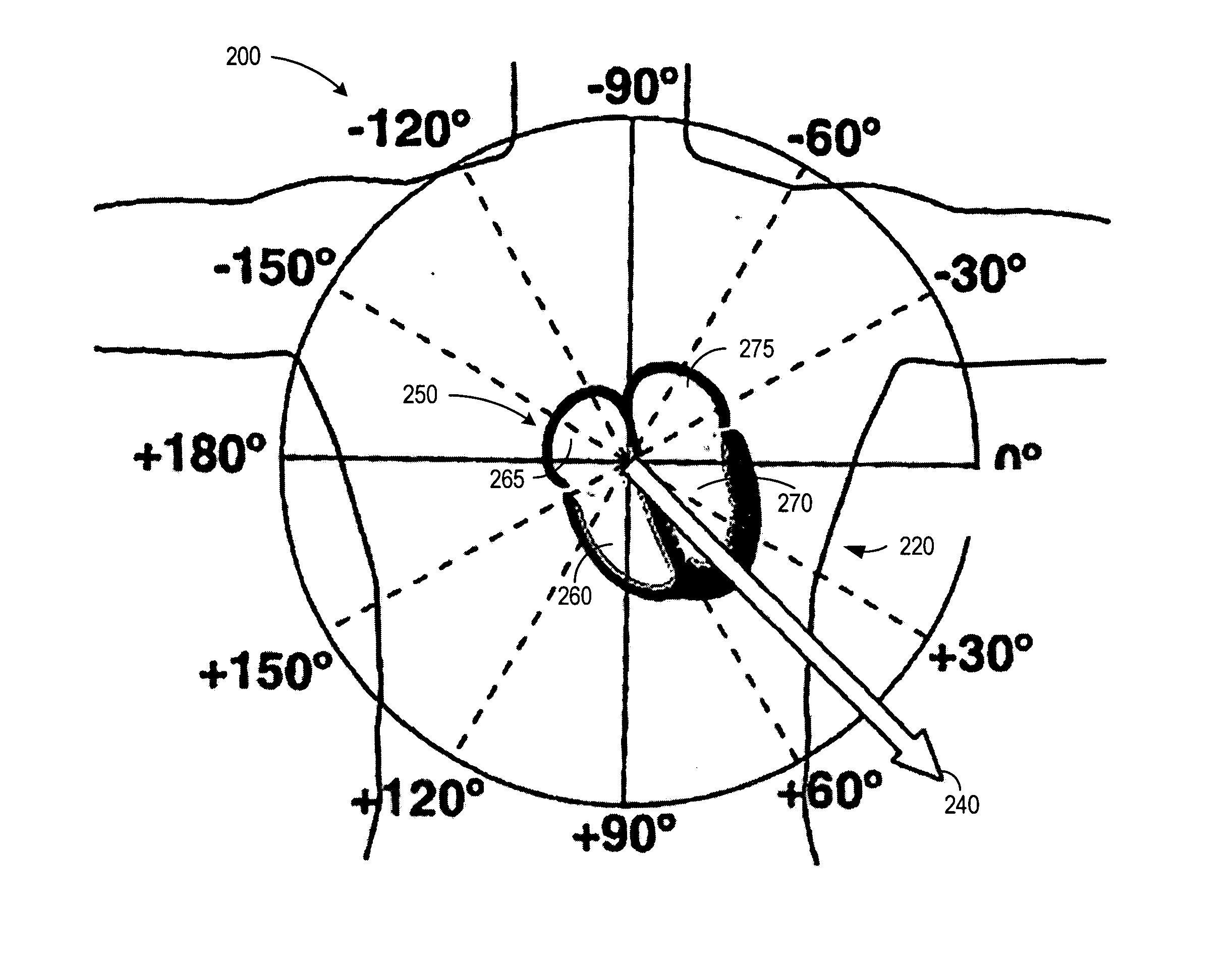
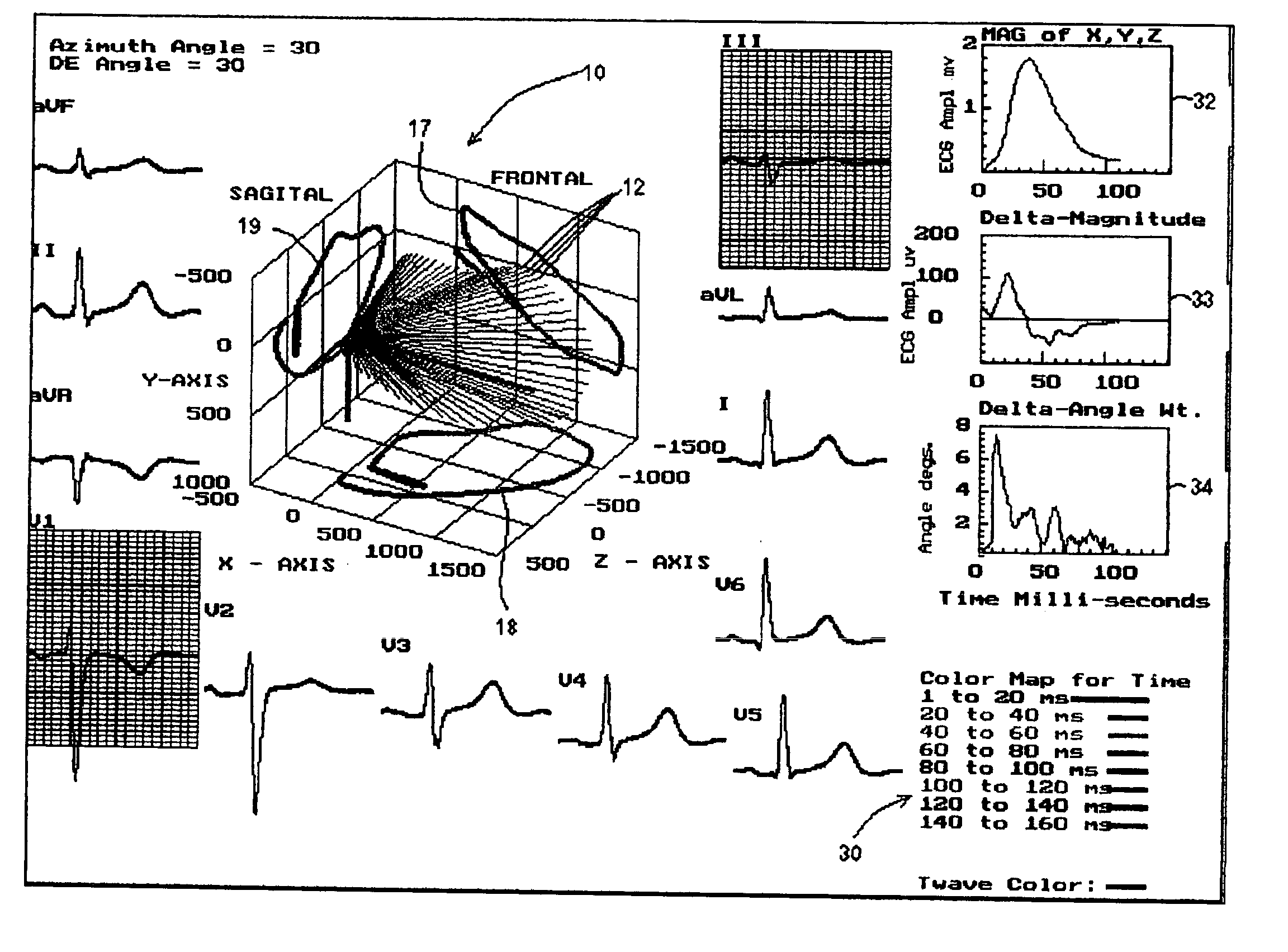
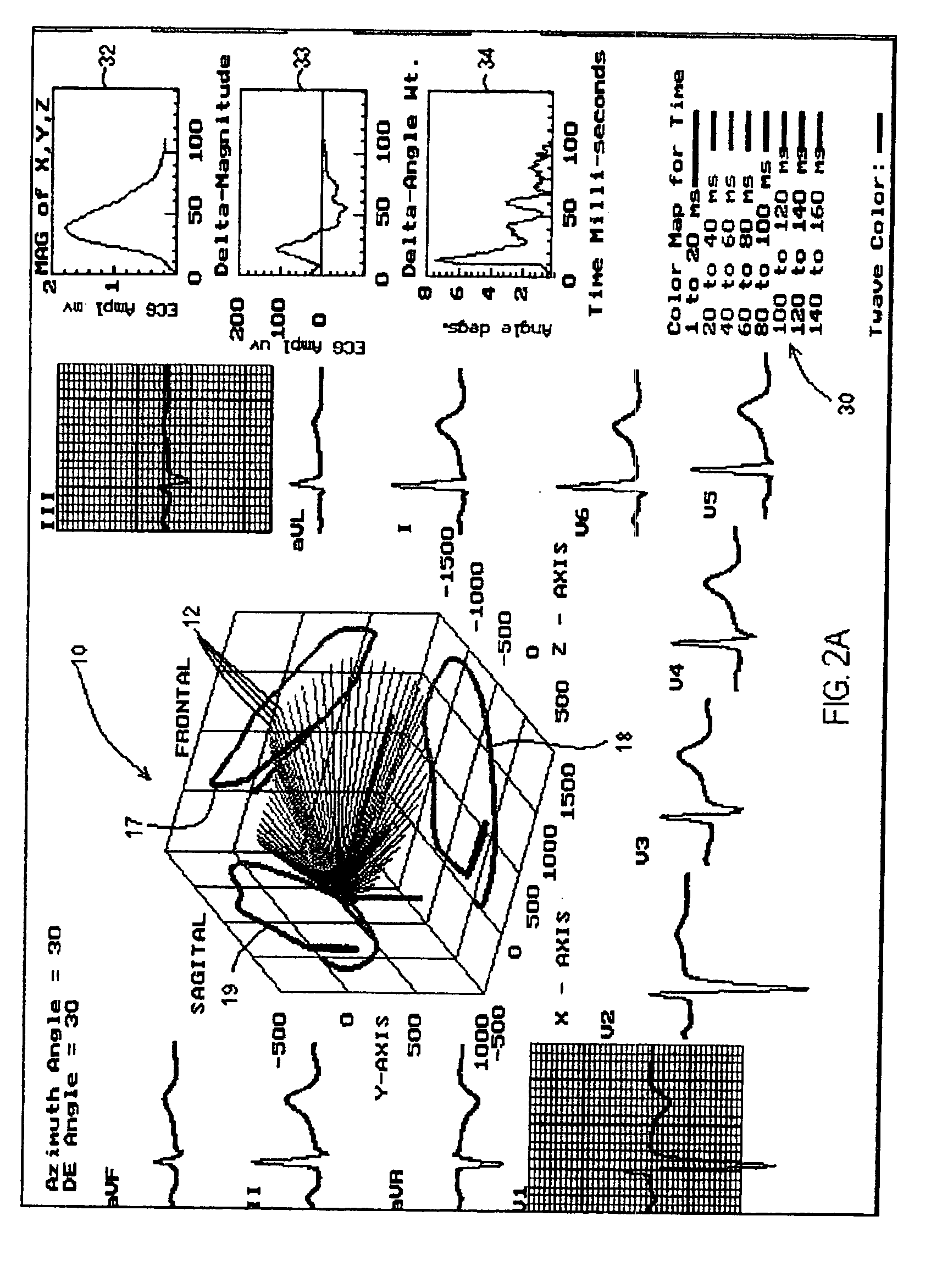
A method of determining an ischemic event includes the steps of: monitoring and storing an initial electrocardiogram vector signal (x, y, z) of a known non-ischemic condition over the QRS, ST and T wave intervals; calculating and storing a J-point of the vector signal and a maximum magnitude of a signal level over the T wave interval; monitoring a subsequent electrocardiogram vector signal over the QRS, ST and T wave intervals; measuring and storing the magnitude (Mag.) of the vector difference between a subsequent vector signal and the initial vector signal; measuring and storing the angle (Ang.) difference between a subsequent vector and the initial vector at points; regressing a line from points about 25 milliseconds prior to the J point and about 60 milliseconds after the J-point and determining the slope of the regression line and the deviation of the angle difference of the regression line; regressing a line from points about 100 milliseconds prior to the maximum magnitude of the signal level over the T wave interval and determining the slope of the regressing line and the deviation of the angle difference of the regression line; and comparing the slope and deviation of the lines from the J point and the T wave interval to a set of known values to determine the presence of an ischemic event.
Owner:ECG TECH CORP
Dual sensing for brady-tachy pacemaker/ICD
InactiveUS20070038253A1ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac activity
A system detects events related to cardiac activity. The system comprises a primary cardiac signal sensing circuit, at least one secondary cardiac signal sensing circuit having a higher sensitivity than the primary sensing circuit, and a controller circuit coupled to the primary and secondary cardiac signal sensing circuits. The controller circuit determines a rate of depolarization using the primary sensing circuit and detects tachyarrhythmia using the rate. The controller circuit also detects tachyarrhythmia using the secondary sensing circuit and also deems the tachyarrhythmia valid if the controller circuit detects the tachyarrhythmia using both the primary and secondary sensing circuit.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
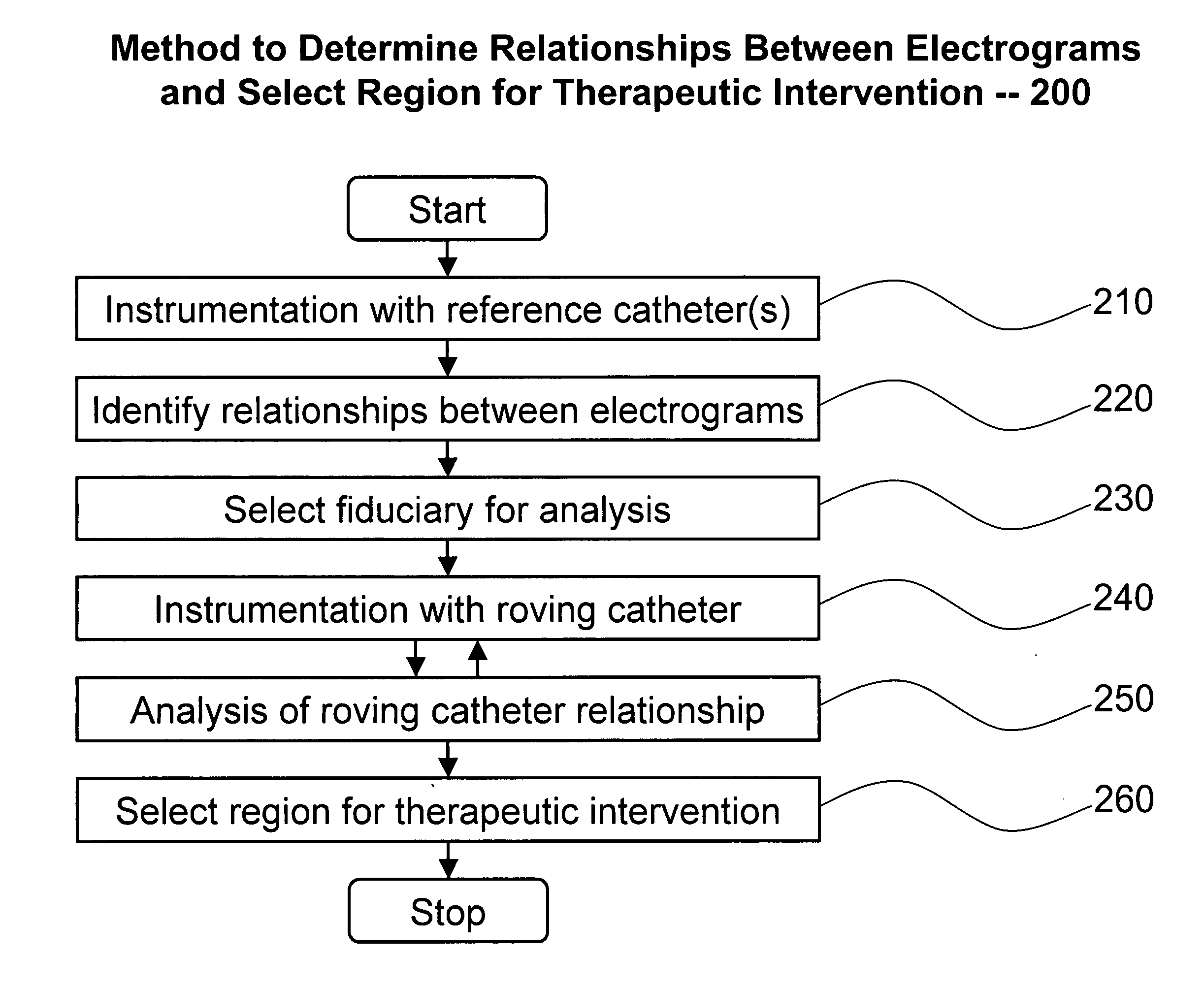
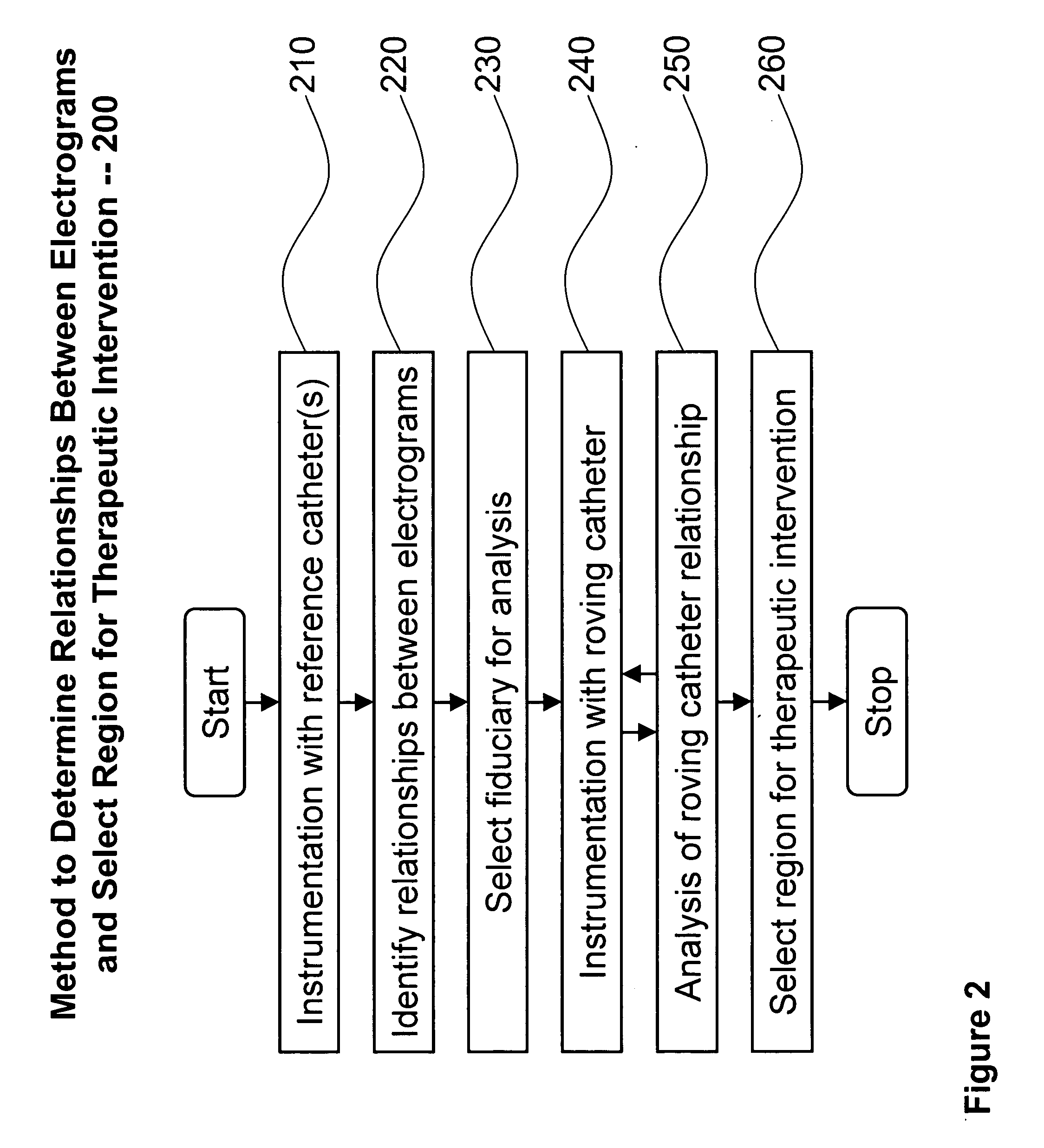
System and method for analysis of cardiac arrhythmia using timing and variability of relationships between elctrogram features
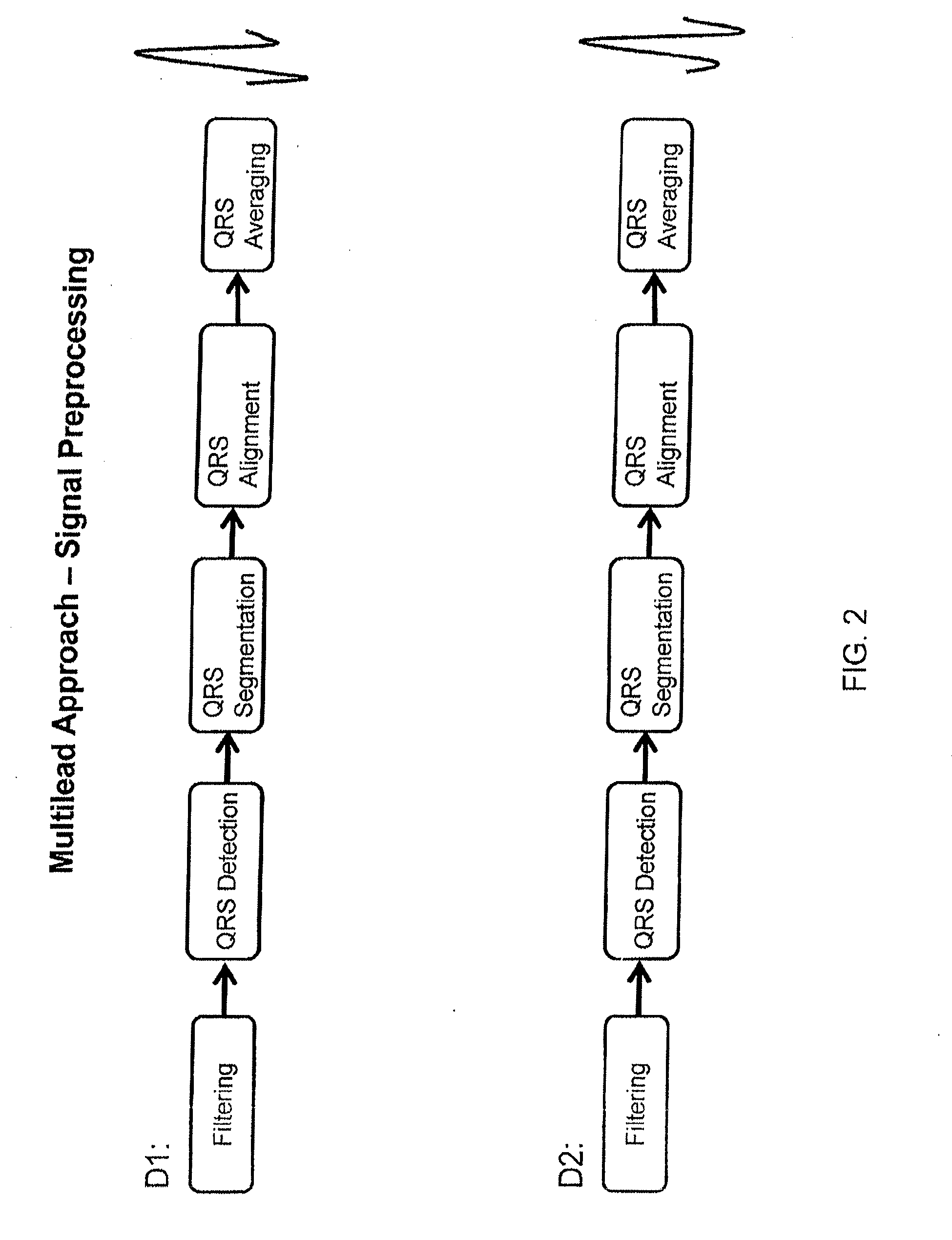
Described is a system and method for recording and receiving a plurality of electrograms, each electrogram corresponding to a region of a heart, wherein the electrograms are recorded substantially simultaneously. A plurality of fiducial markers are identified on a selected electrogram, wherein each fiducial marker marks a feature of interest in the first electrogram. Multiple segments of each of the plurality of electrograms are aligned with each segment temporally corresponding to each of the fiducial markers on the selected electrogram. The aligned segments of each of the plurality of electrograms are averaged resulting in an average electrogram for each of the plurality of electrograms. Features of interest are identified in each of the plurality of average electrograms and relationships are determined between features of interest in each of the plurality of average electrograms.
Owner:BULLINGA JOHN R
Rejection of noises caused by postural changes during acute myocardial infarction detection
A system comprising a processor that includes a cardiac signal vector module and an ischemia detection module. The cardiac signal vector module is configured to measure a first dominant vector corresponding to a direction and magnitude of maximum signal power of a first segment of at least one cardiac cycle of a subject and at least a second dominant vector corresponding to a direction and magnitude of maximum signal power of a second segment of the cardiac cycle from an electrical cardiac signal. The ischemia detection module is configured to measure a change in the first dominant vector, to form a difference by subtracting a measured change in the second dominant vector from a measured change in the first dominant vector, and to declare whether an ischemic event occurred using the difference.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Catheter with single axial sensors
ActiveUS8792962B2Easy to anchorElectrocardiographySurgical navigation systemsLocalization systemEngineering
A catheter has single axis sensors mounted directly along a portion of the catheter whose position / location is of interest. The magnetic based, single axis sensors are on a linear or nonlinear single axis sensor (SAS) assembly. The catheter includes a catheter body and a distal 2D or 3D configuration provided by a support member on which at least one, if not at least three single axis sensors, are mounted serially along a length of the support member. The magnetic-based sensor assembly may include at least one coil member wrapped on the support member, wherein the coil member is connected via a joint region to a respective cable member adapted to transmit a signal providing location information from the coil member to a mapping and localization system. The joint region provides strain relief adaptations to the at least one coil member and the respective cable member from detaching.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
System and Method for Generating Electrophysiology Maps
An electrophysiology map can be generated from a plurality of electrophysiology data points added automatically in response to defined inclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria can generally be grouped into two categories: location-based (e.g., velocity, distance moved, dwell time, and proximity) and rhythm-based (e.g., cycle length and EKG matching). As each electrophysiology data point is collected, it can be tested against one or more defined inclusion criteria, and added to the electrophysiology map when it satisfies all such criteria. Inclusion criteria can also be employed to generate the geometric model underlying the electrophysiology map.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Systems and methods for using electrophysiology properties for classifying arrhythmia sources
ActiveUS20170049348A1Easy to identifyDiagnostic signal processingElectrocardiographyVelocity conductionCell electrophysiology
A method for determining electrophysiology properties of tissue comprising acquiring electrical signal data from a plurality of electrodes (130) of one or more catheters, determining at least one electrode clique from the plurality of adjacent electrodes (136), computing local conduction velocity vectors for the at least one electrode clique (138), determining at least one catheter orientation independent indicator from which to classify an arrhythmia source based on one or more of an angular dependence parameter associated with a flow field of the local velocity conduction vectors, an eccentricity parameter reflecting the uniformity of local conduction velocity, and divergence and curl-like sums or closed path integral parameters associated with the local velocity vectors, and displaying a rhythm classification responsive to catheter movement thereby facilitating identification of types and causes of arrhythmia disorders.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Determining locations of ganglia and plexi in the heart using complex fractionated atrial electrogram
Software and apparatus are provided to automatically detect and map ganglionated plexi that are found within areas of complex fractionated electrograms in cardiac chambers. Electrogram signal are analyzed to count the number of complexes whose amplitude and peak-to-peak intervals meet certain criteria. Functional maps indicating a spatial distribution of the ganglionated plexi and the relative numbers of complex fractionated electrograms are produced for display.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Device and procedure for visual three-dimensional presentation of ECG data
ActiveUS7266408B2Easy to useElectrocardiographyMedical report generationSignal waveThree-dimensional space
The invention relates to the analysis of ECG data by exploiting computerized three-dimensional spatial presentation of the measured data using the vector concept. A three-dimensional presentation of the human heart may be correlated with waveforms specific for standard ECG or derived ECG signals based on the dipole approximation of the heart electrical activity. The three-dimensional heart model may be rotated, and the ECG signals are interactively linked to the model. In the visualization process, different types of signal presentation may be used, including graphical presentation of the heart vector hodograph, graphical presentation of the signal waveform in an arbitrary chosen point on the heart, and graphical presentation of the map of equipotential lines on the heart in a chosen moment. Additional tools for analyzing ECG data are also provided which may be interactively used with the display tools.
Owner:ERESTECH +1
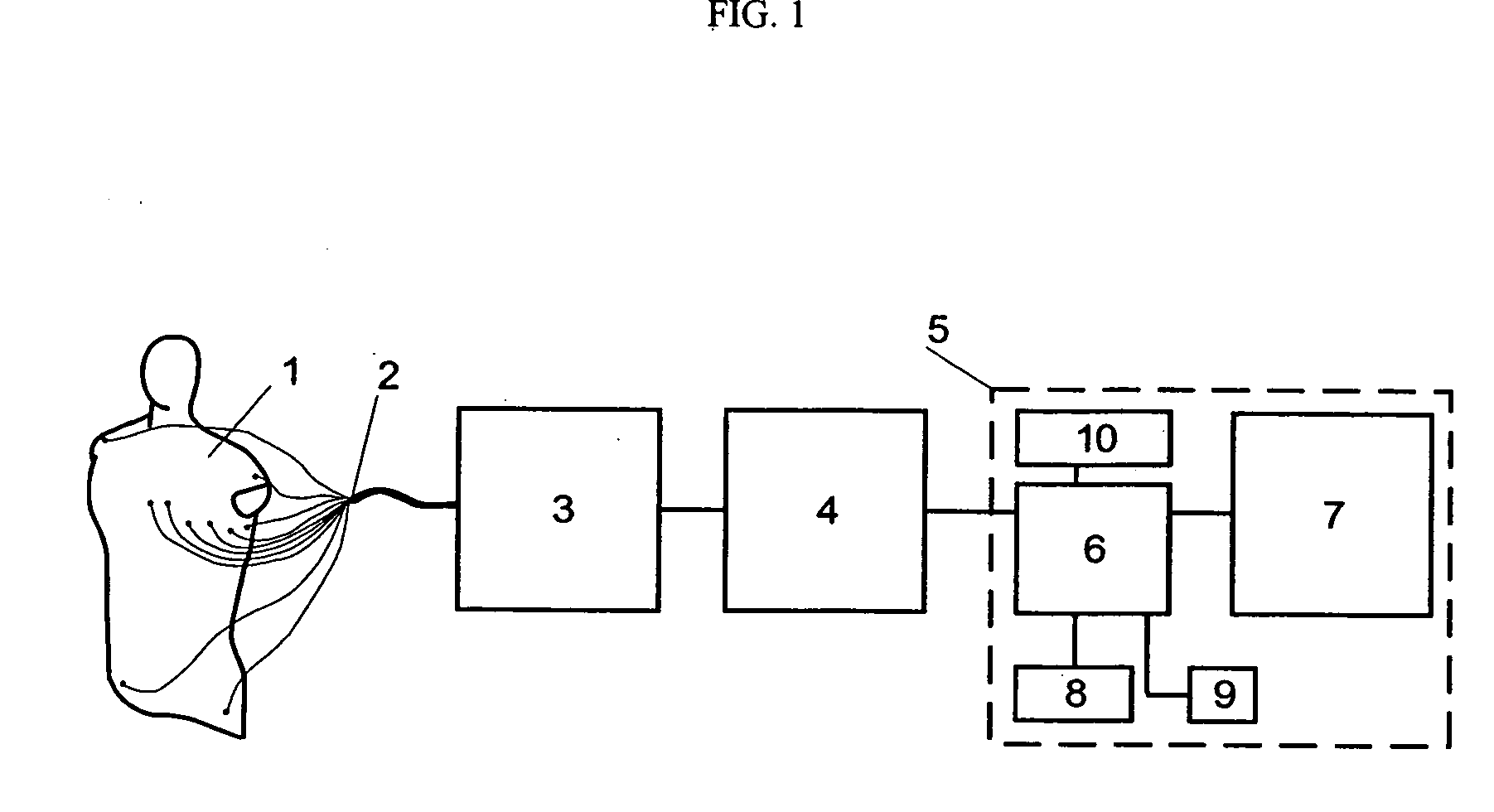
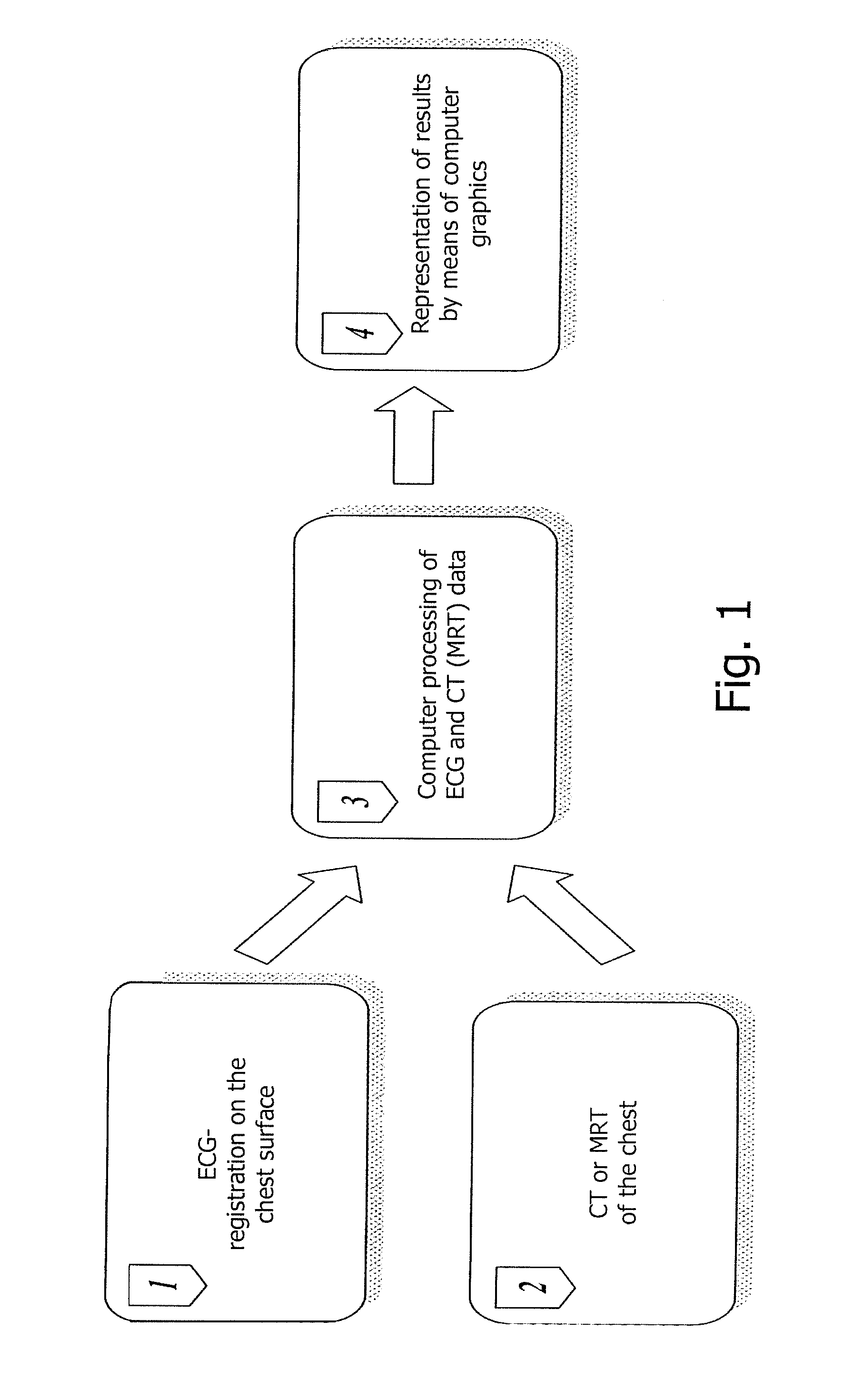
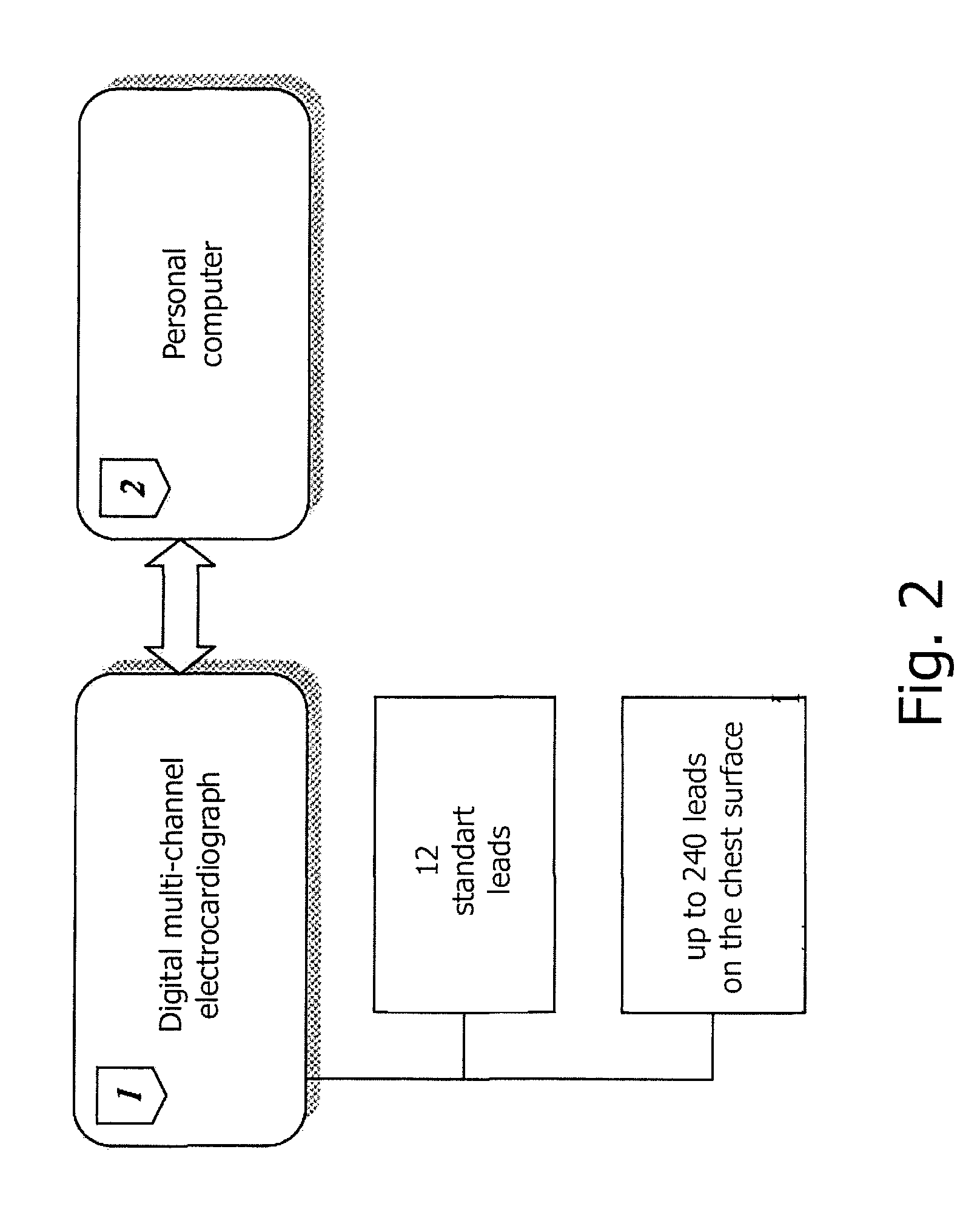
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
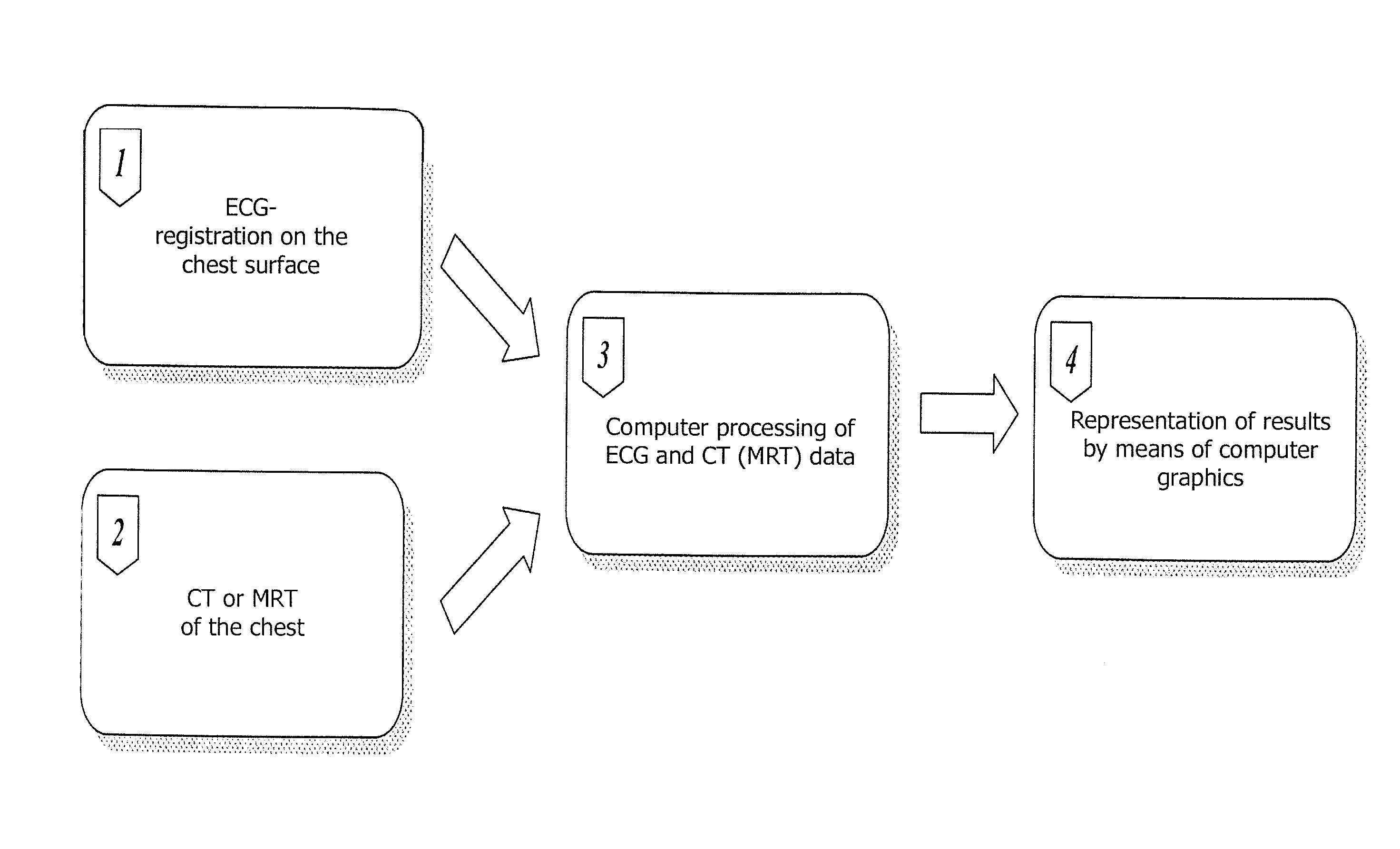
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, functional diagnosis and clinical electrophysiology of the heart. The invention consists in reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. Based on reconstructed electrograms, isopotential, isochronous maps on realistic models of the heart are constructed, the dynamics of the myocardium excitation is reconstructed and electrophysiological processes in the cardiac muscle are diagnosed. Application of the method allows one to improve the accuracy of non-invasive diagnosis of cardiac rhythm disturbances and other cardio-vascular diseases.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
System and method for monitoring and diagnosing patient condition based on wireless sensor monitoring data
InactiveUS20150238107A1Increase generationElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsLine sensorElectric signal
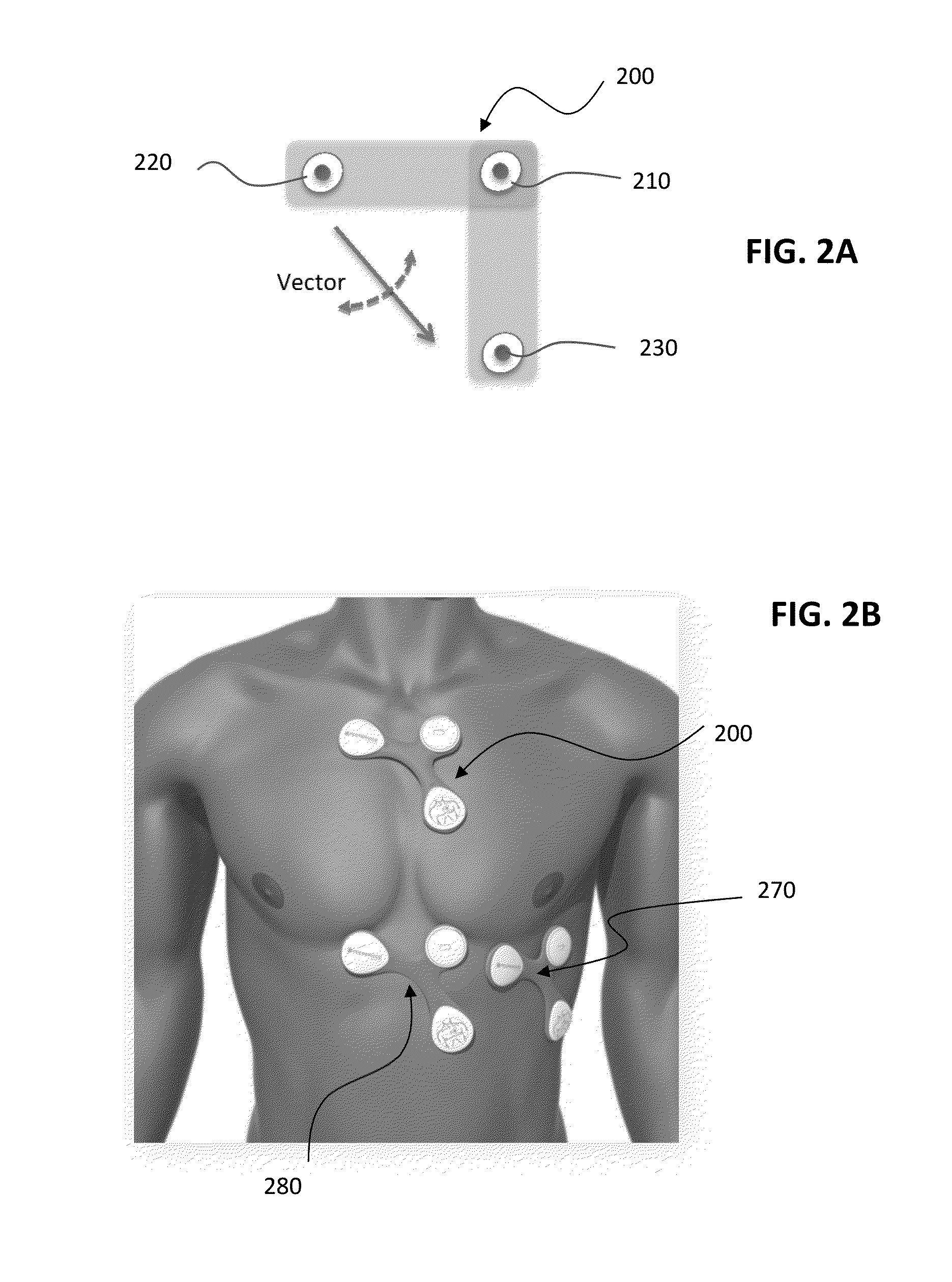
A system for detecting an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal of a subject includes a substrate that is placed on and adheres to the skin over the sternum of the subject. First, second and third electrodes are disposed on the substrate, each of which has an end for contacting a respective area of skin. Directional positioning from the second electrode to the first electrode is substantially perpendicular to directional positioning from the third electrode to the first electrode. A circuit on the first substrate is connected to the electrodes and generates a first ECG channel measuring a difference in electric signals between the first electrode and the second electrode, and a second ECG channel measuring a difference in electric signals between the first electrode and the third electrode. A communication component on the substrate wirelessly transmits ECG information from the circuit to an external device.
Owner:PEERBRIDGE HEALTH
Robotic surgical system and method for diagnostic data mapping
ActiveUS20070185404A1Reduce exposureShorten the timeSurgical navigation systemsSurgical instrument detailsGraphicsDiagnostic data
A method of generating a diagnosis map of at least a portion of the heart includes inserting an electrode within the portion of a heart, robotically moving the electrode therein, measuring electrophysiology information at a point on the surface of the heart, associating the measured electrophysiology information with position information for the point on the surface of the heart, repeating the measuring and associating steps for a plurality of points on the surface of the heart, thereby generating a plurality of surface diagnostic data points, and generating the diagnosis map therefrom. The electrode may be moved within the heart randomly, pseudo-randomly, or according to one or more predetermined patterns. A three-dimensional model of the portion of the heart may be provided and presented as a graphical representation, either with or without information indicative of the measured electrophysiology information superimposed thereon.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method for generating three standard surface ECG leads derived from three electrodes contained in the mid-horizontal plane of the torso
A method for a 3-lead electrocardiographic (ECG) recording comprising three signal electrodes contained in the mid-horizontal plane of the human torso and the calculation of the standard leads I, II and III. Such electrodes are placed in-line as in a chest belt instead of the traditional positioning of electrodes in the upper and low parts of the frontal plane of the torso.
Owner:MISCZYNSKI DALE J +3
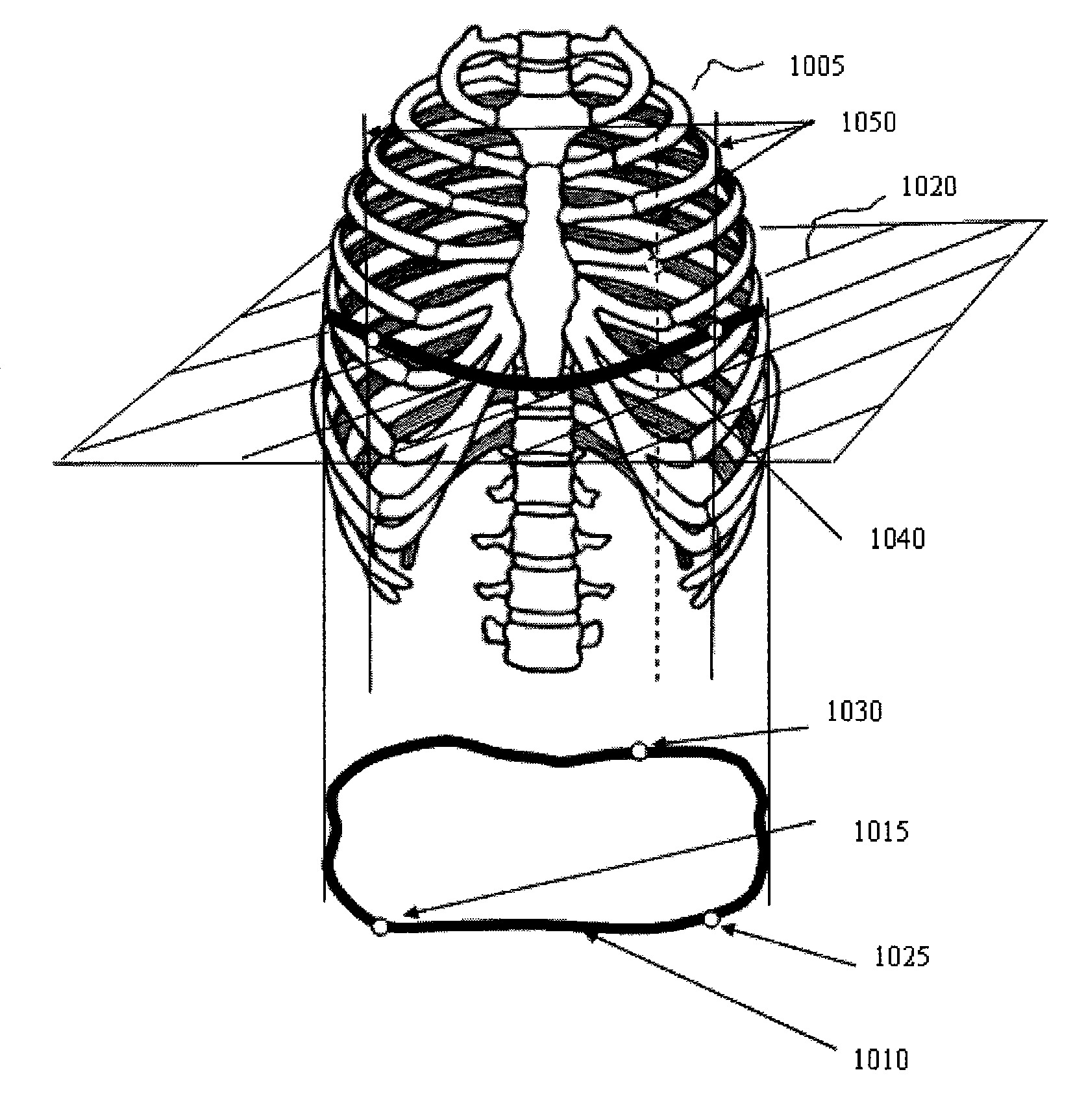
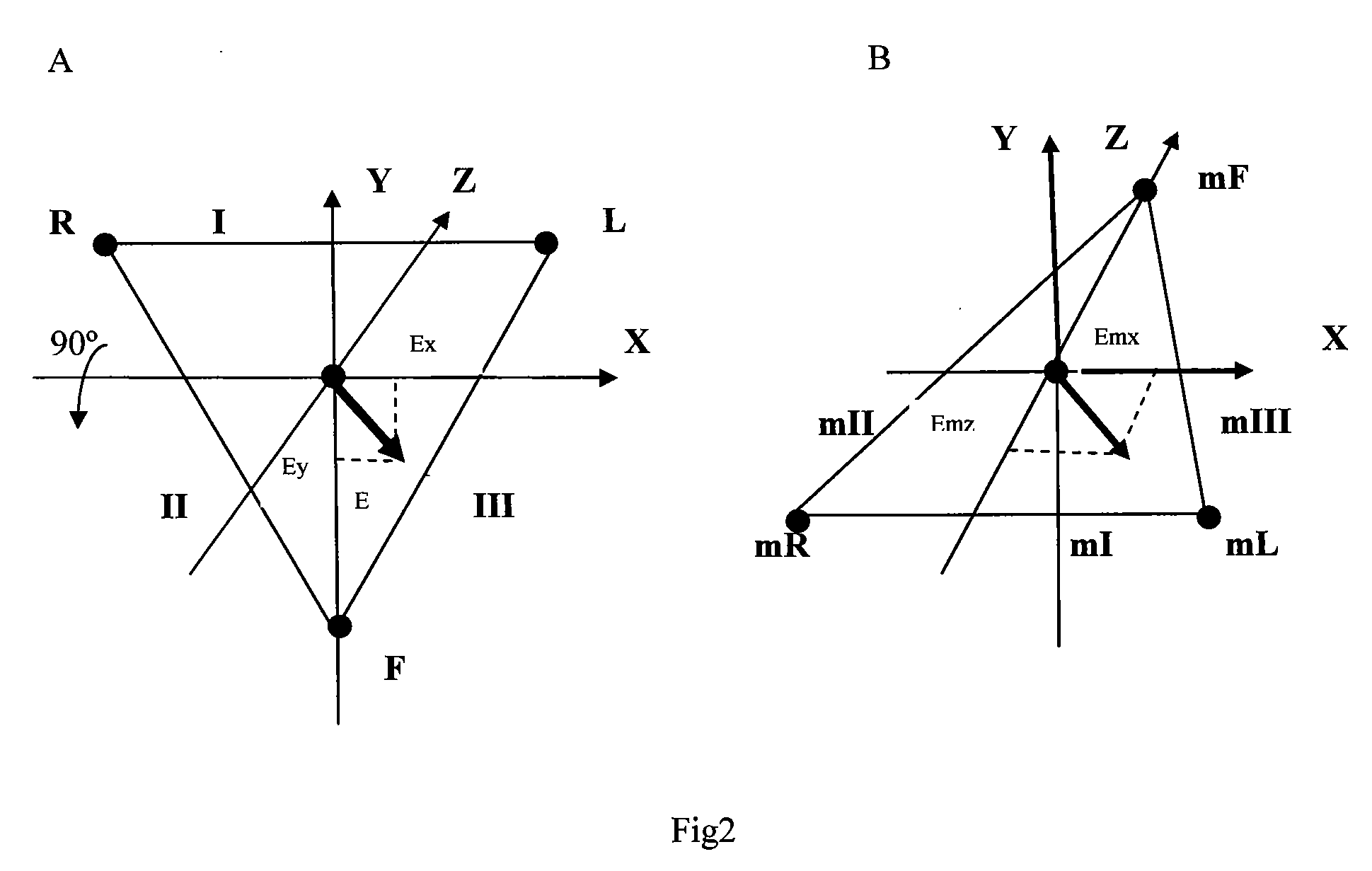
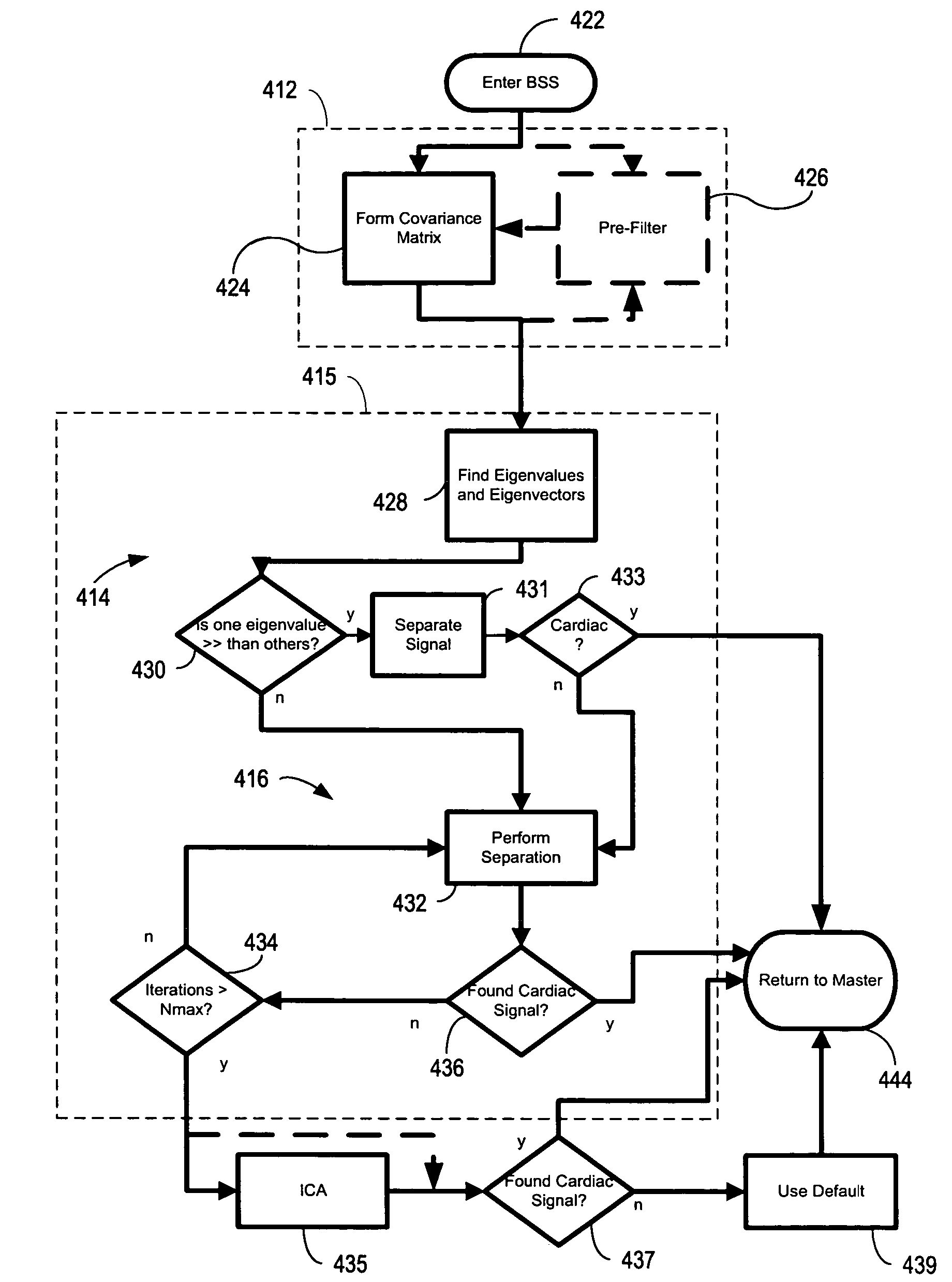
Automatic orientation determination for ECG measurements using multiple electrodes
InactiveUS7706866B2ElectrocardiographyCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisCardiac monitoring
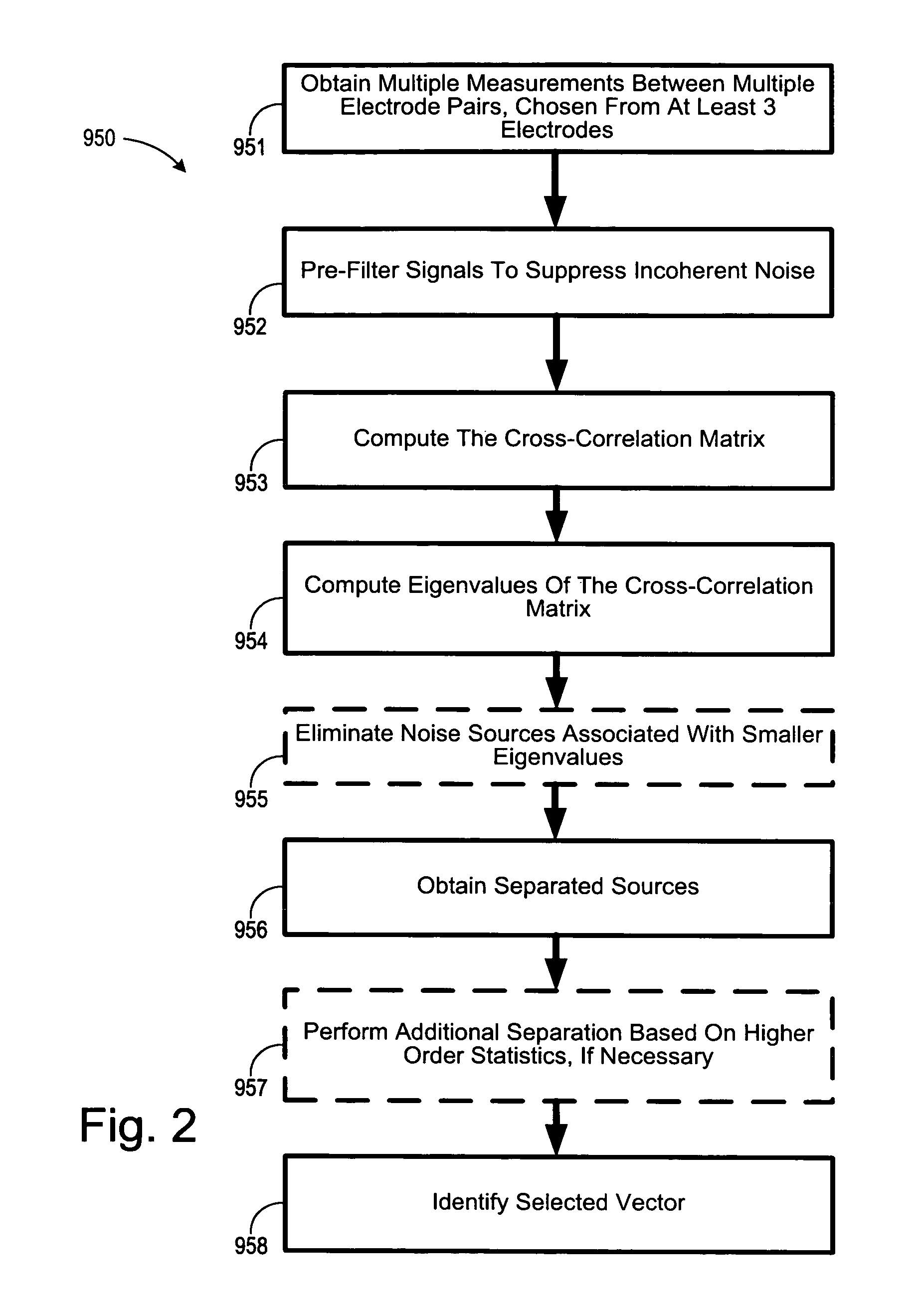
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems provide monitoring, defibrillation and / or pacing therapies. A signal processor receives a plurality of composite signals associated with a plurality of sources, separates a signal using a source separation algorithm, and identifies a cardiac signal using a selected vector. The signal processor may iteratively separate signals from the plurality of composite signals until the cardiac signal is identified. The selected vector may be updated if desired or necessary. A method of signal separation involves detecting a plurality of composite signals at a plurality of locations, separating a signal using source separation, and selecting a vector that provides a cardiac signal. The separation may include a principal component analysis and / or an independent component analysis. Vectors may be selected and updated based on changes of position and / or orientation of implanted components and changes in patient parameters such as patient condition, cardiac signal-to-noise ratio, and disease progression.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com