Patents
Literature
46 results about "Cardiac rhythm disturbances" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
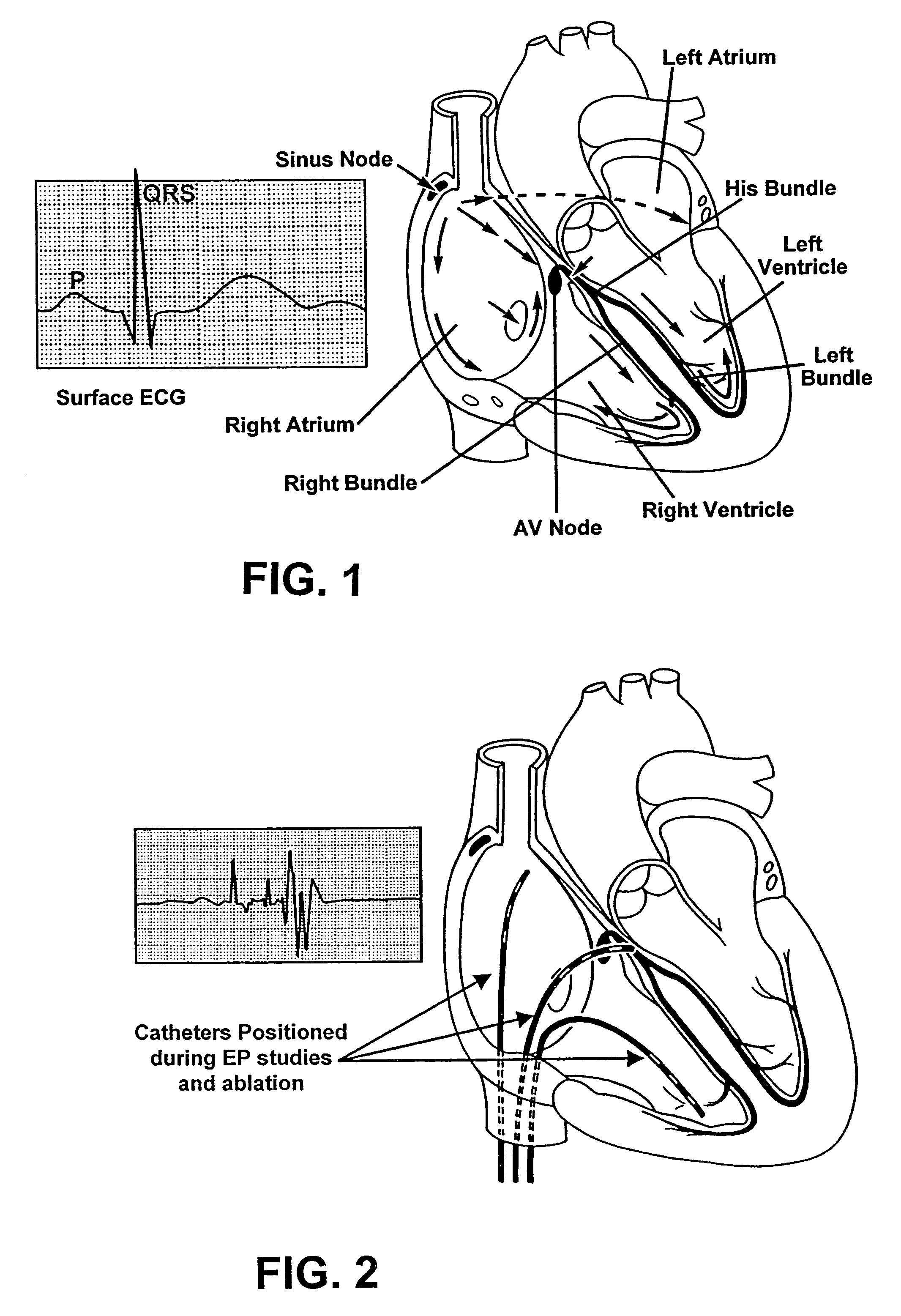
VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS Ventricular Tachycardia occurs when the pacemaking role of your heart is taken over by an area of the heart that typically is not involved in the process. Ventricular Fibrillation (Vfib) is one of the most serious cardiac rhythm disturbances.
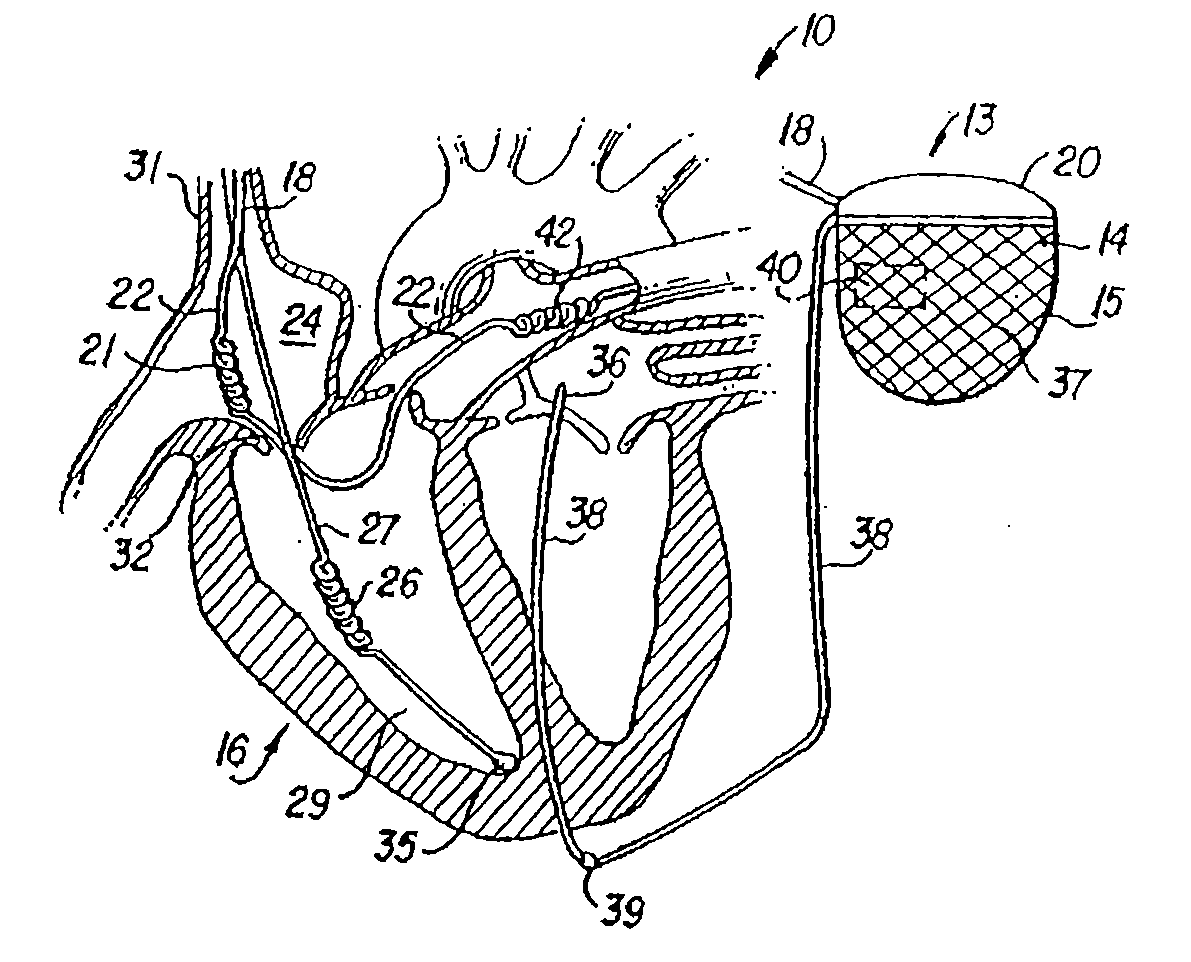
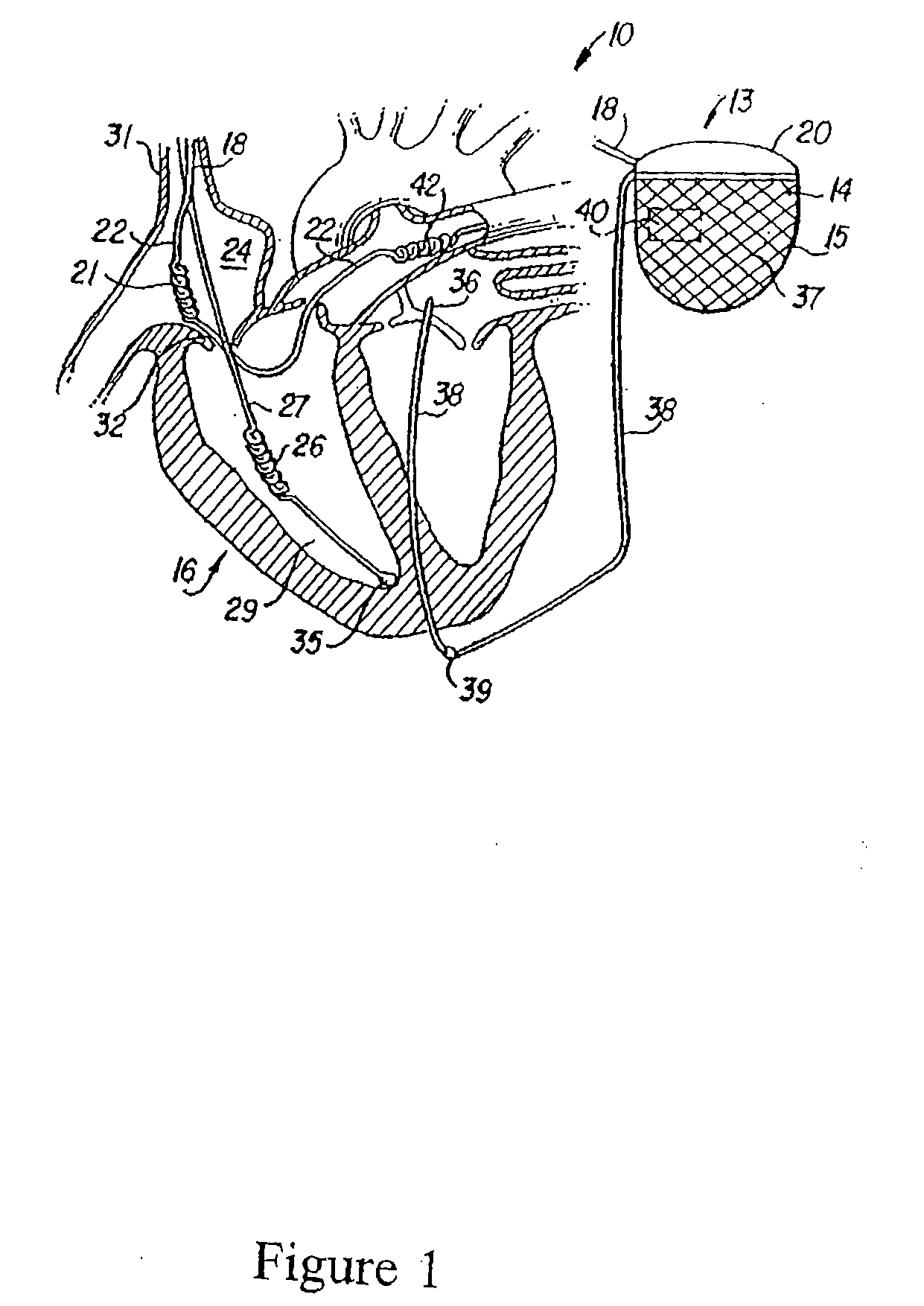
Methods and devices for repair or replacement of heart valves or adjacent tissue without the need for full cardiopulmonary support
ActiveUS20060074484A1Reduce in quantityEliminate needEar treatmentCannulasAortic dissectionVentricular aneurysm
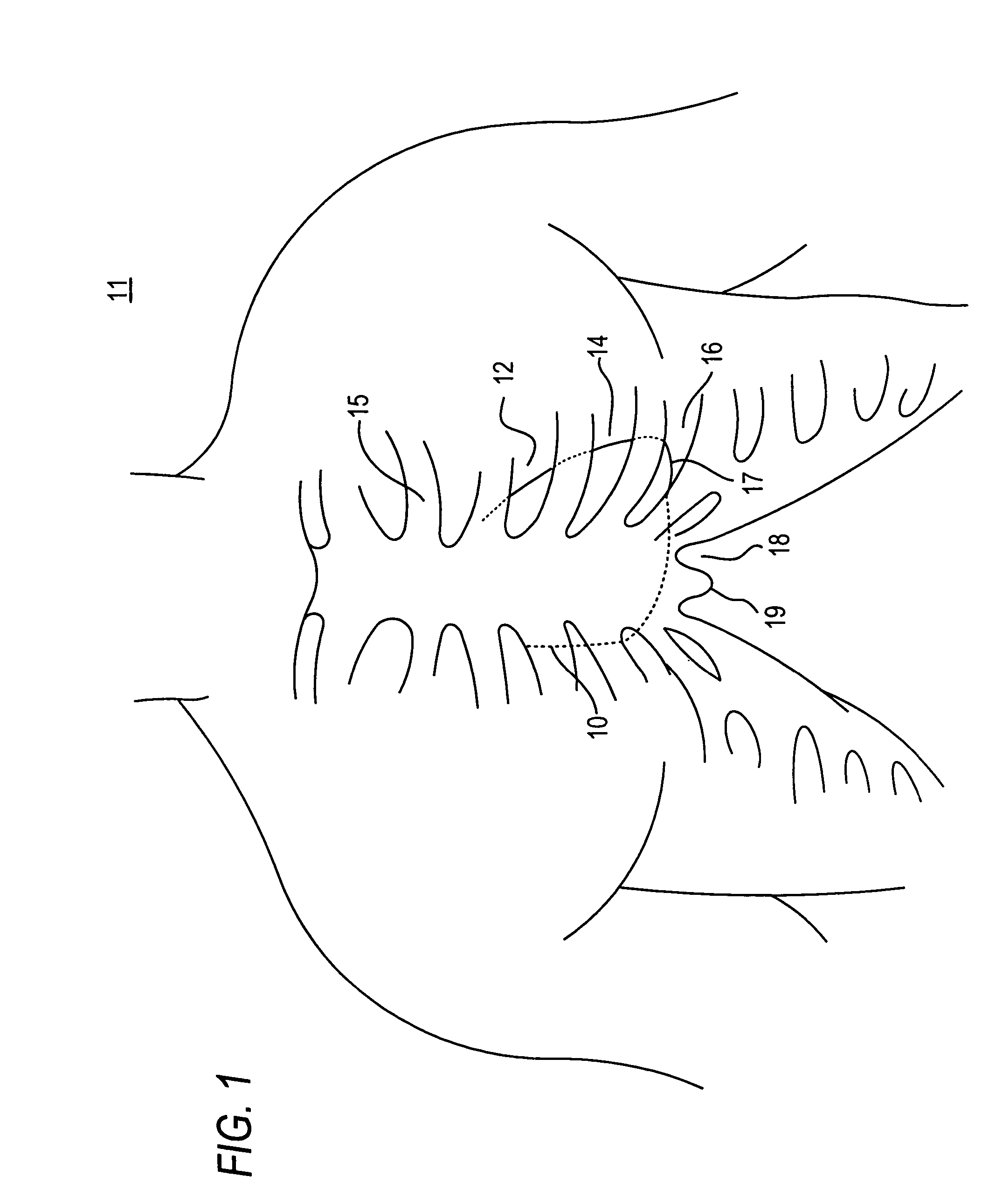
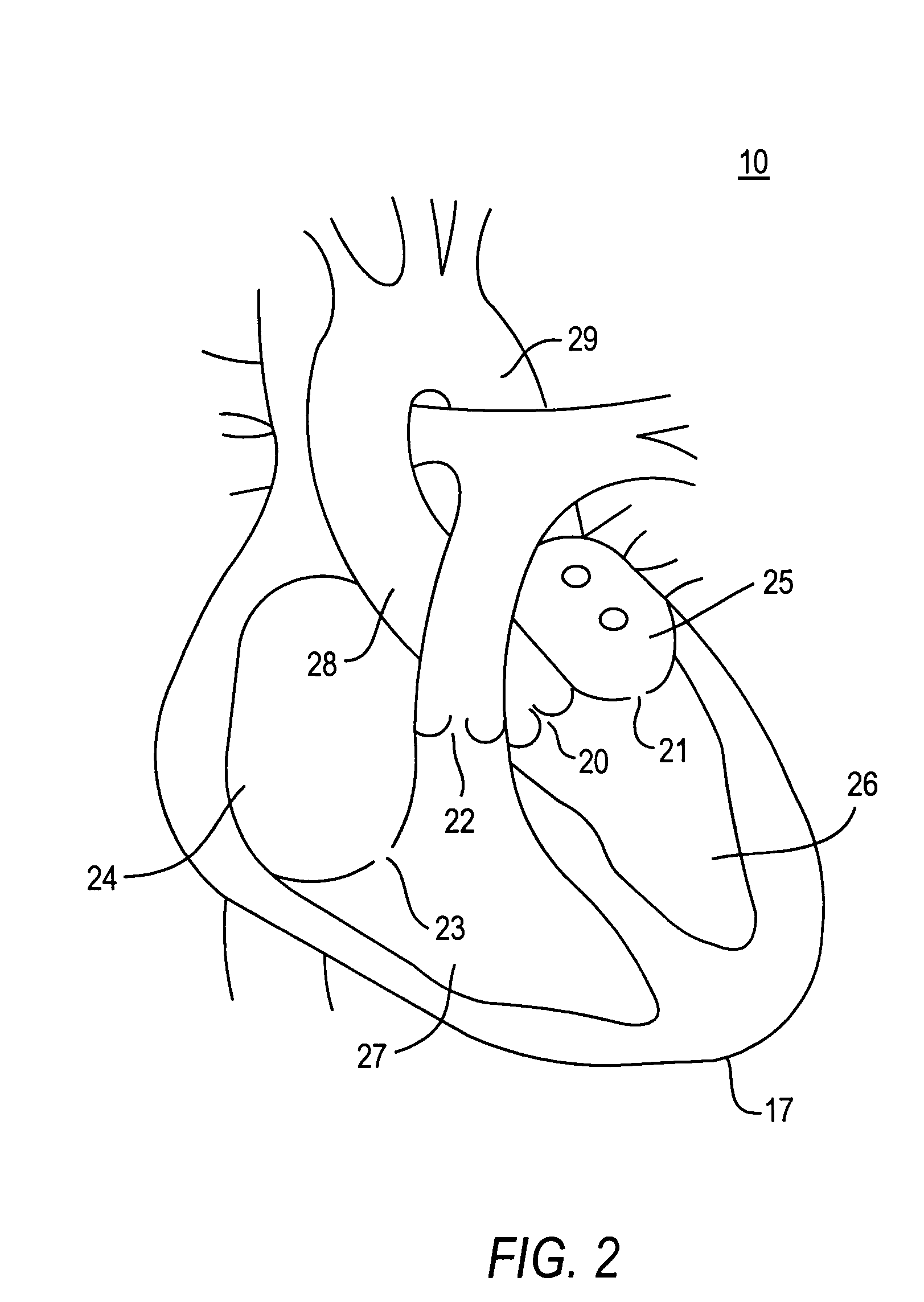
Methods and systems for endovascular, endocardiac, or endoluminal approaches to a patient's heart to perform surgical procedures that may be performed or used without requiring extracorporeal cardiopulmonary bypass. Furthermore, these procedures can be performed through a relatively small number of small incisions. These procedures may illustratively include heart valve implantation, heart valve repair, resection of a diseased heart valve, replacement of a heart valve, repair of a ventricular aneurysm, repair of an arrhythmia, repair of an aortic dissection, etc. Such minimally invasive procedures are preferably performed transapically (i.e., through the heart muscle at its left or right ventricular apex).
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Methods and devices for repair or replacement of heart valves or adjacent tissue without the need for full cardiopulmonary support
ActiveUS8182530B2Reduce in quantityEliminate needEar treatmentCannulasAortic dissectionVentricular aneurysm
Methods and systems for endovascular, endocardiac, or endoluminal approaches to a patient's heart to perform surgical procedures that may be performed or used without requiring extracorporeal cardiopulmonary bypass. Furthermore, these procedures can be performed through a relatively small number of small incisions. These procedures may illustratively include heart valve implantation, heart valve repair, resection of a diseased heart valve, replacement of a heart valve, repair of a ventricular aneurysm, repair of an arrhythmia, repair of an aortic dissection, etc. Such minimally invasive procedures are preferably performed transapically (i.e., through the heart muscle at its left or right ventricular apex).
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
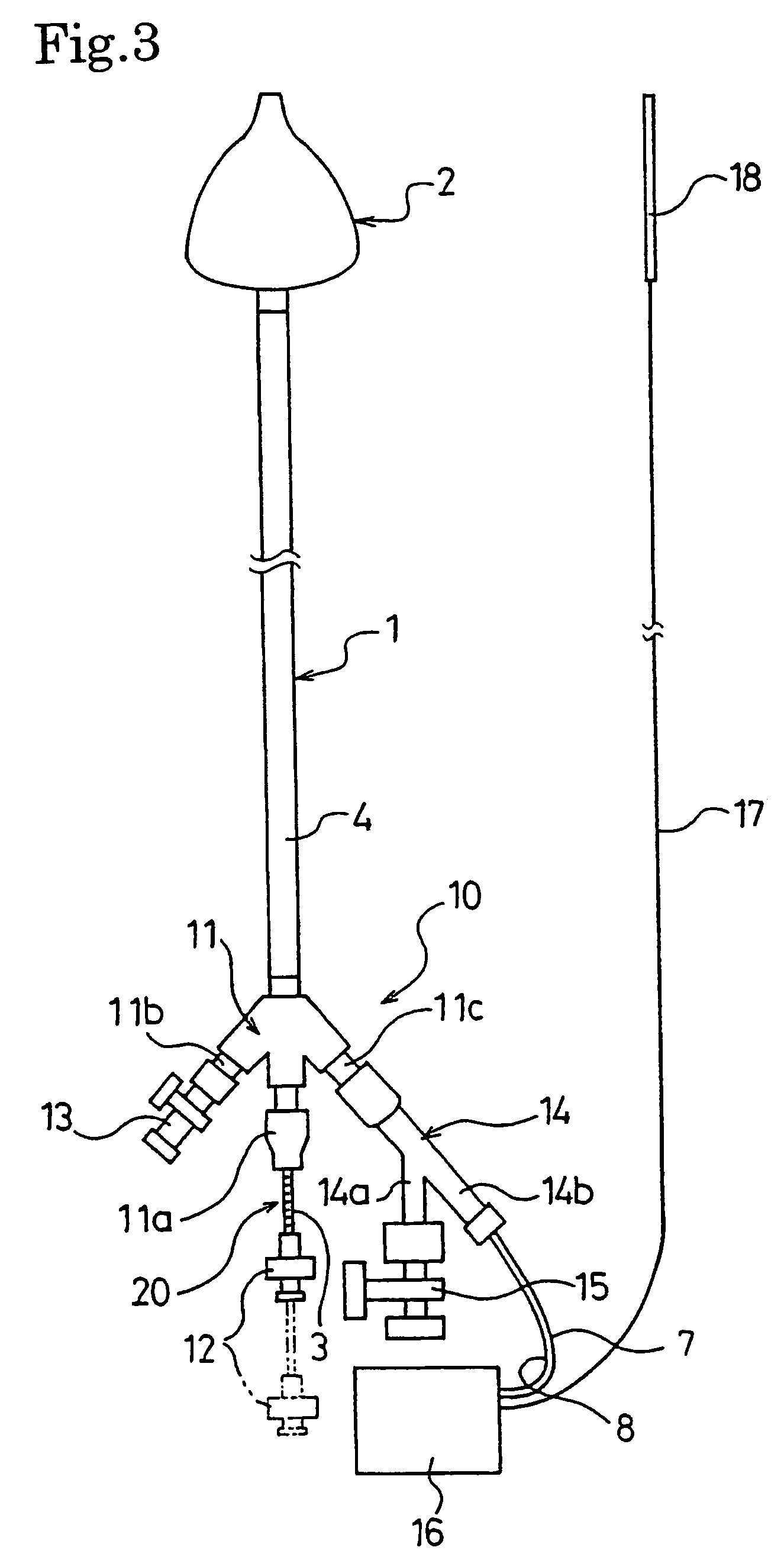
Catheter for treating of arrhythmia
ActiveUS7744594B2Improved ease of insertionHigh-frequency currentDilatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringFront edgeMotor shaft
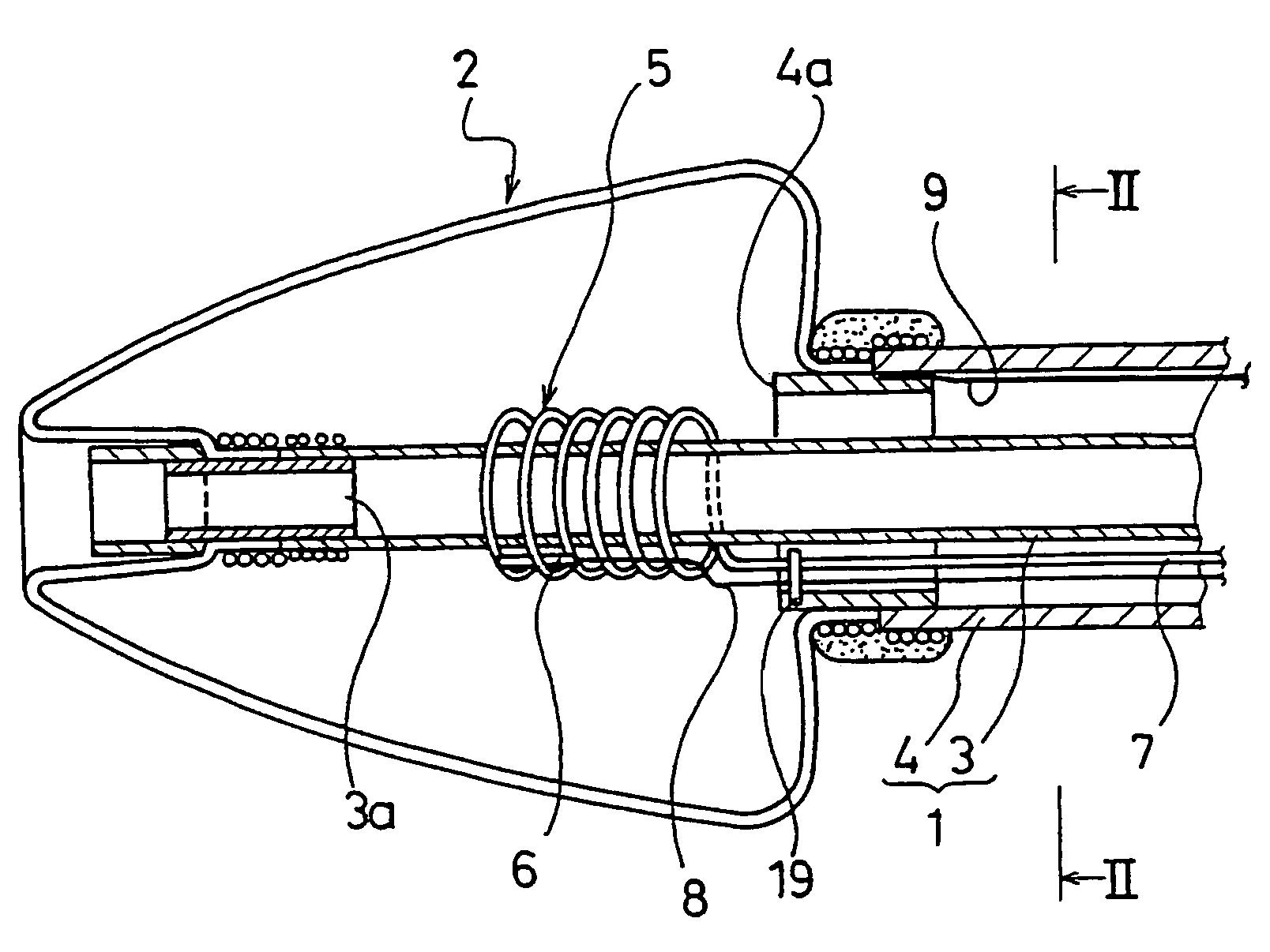
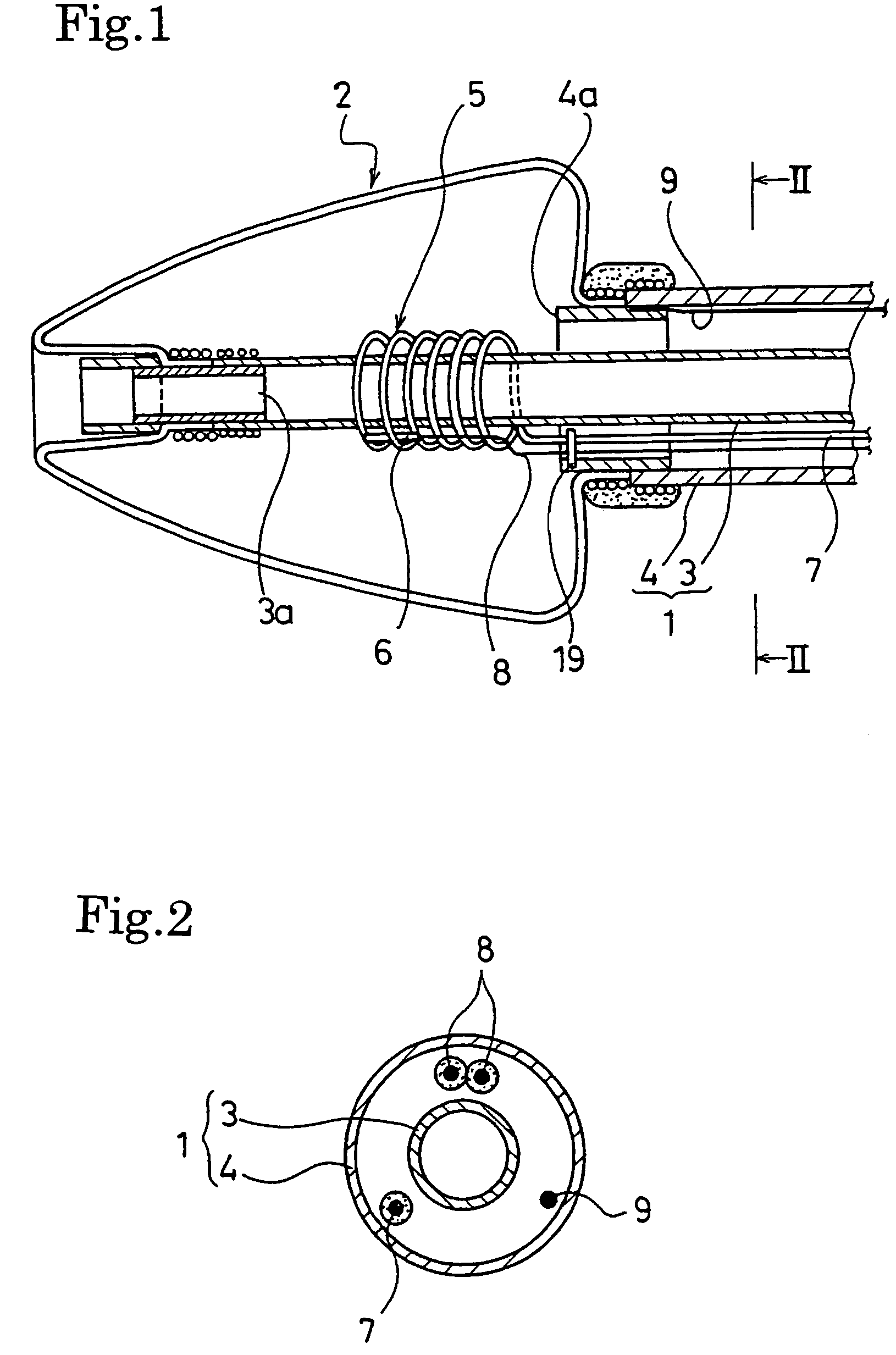
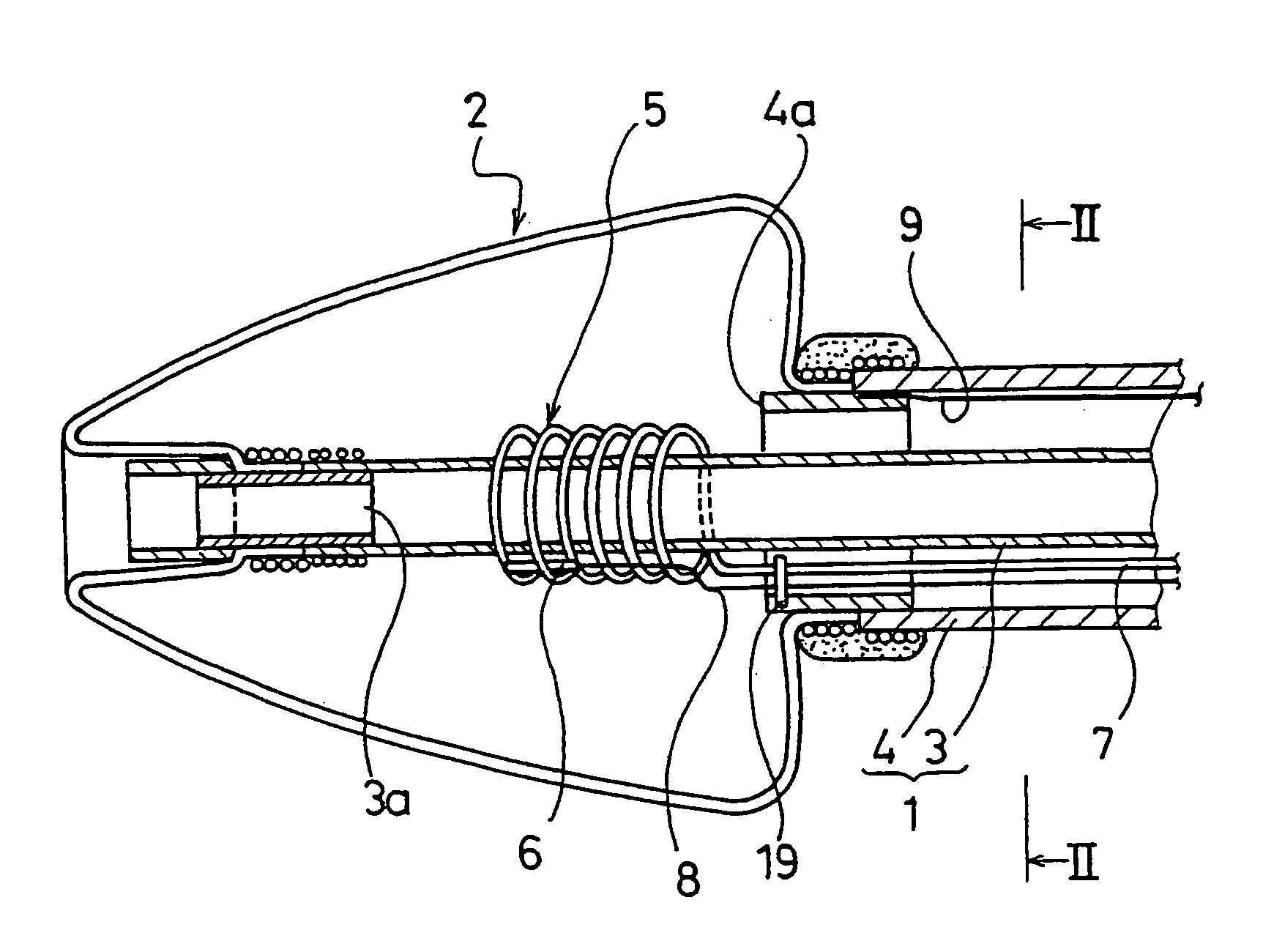
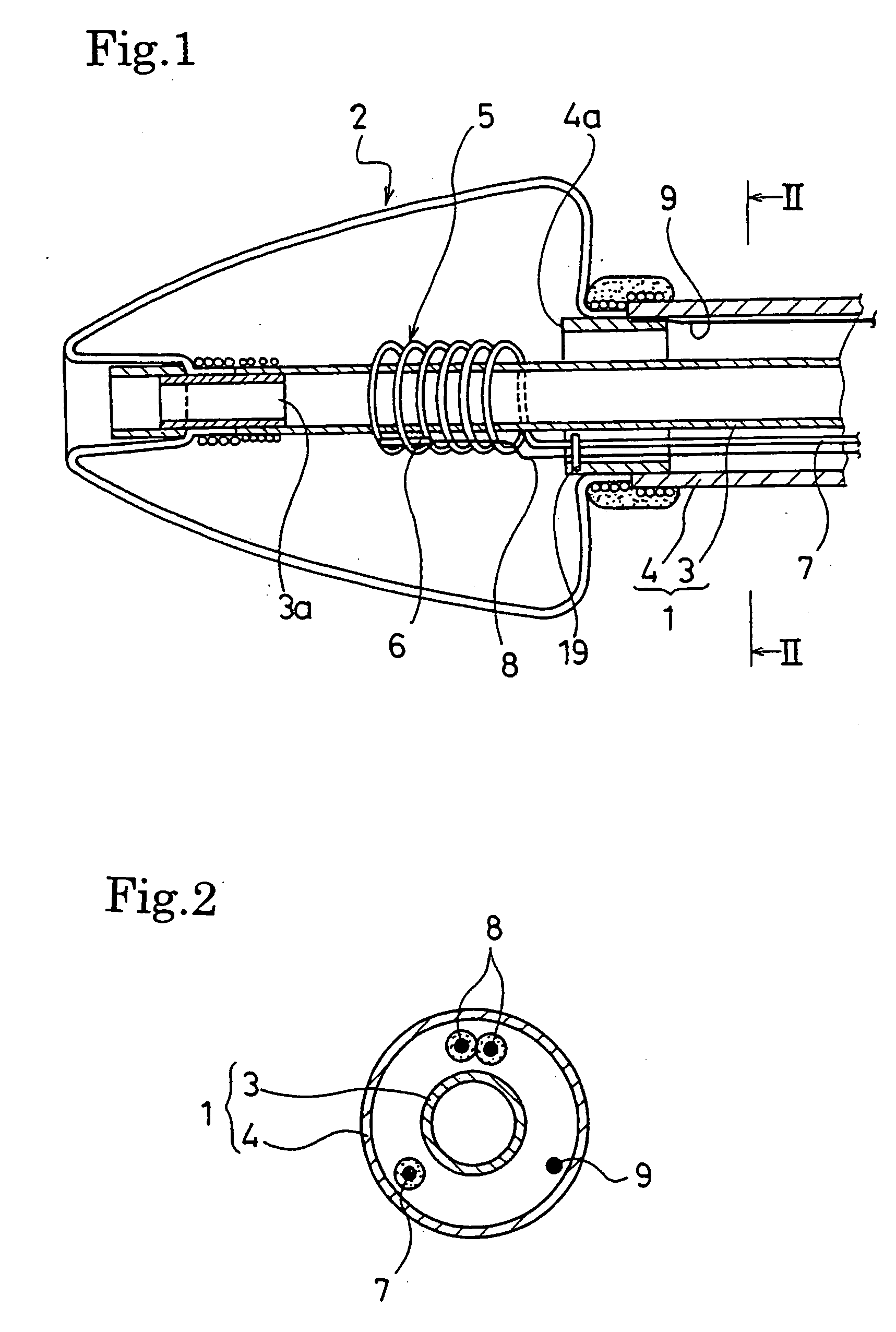
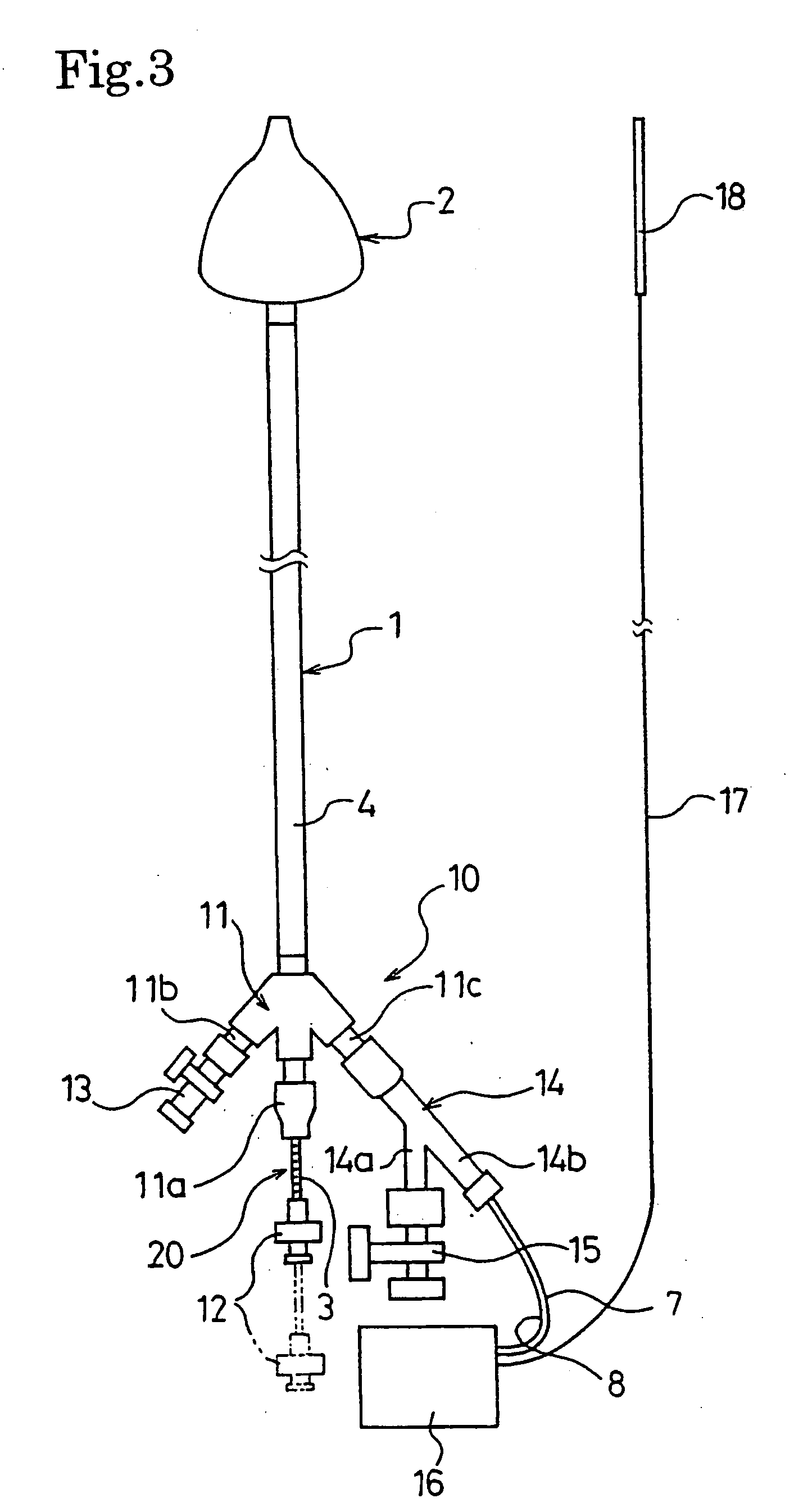
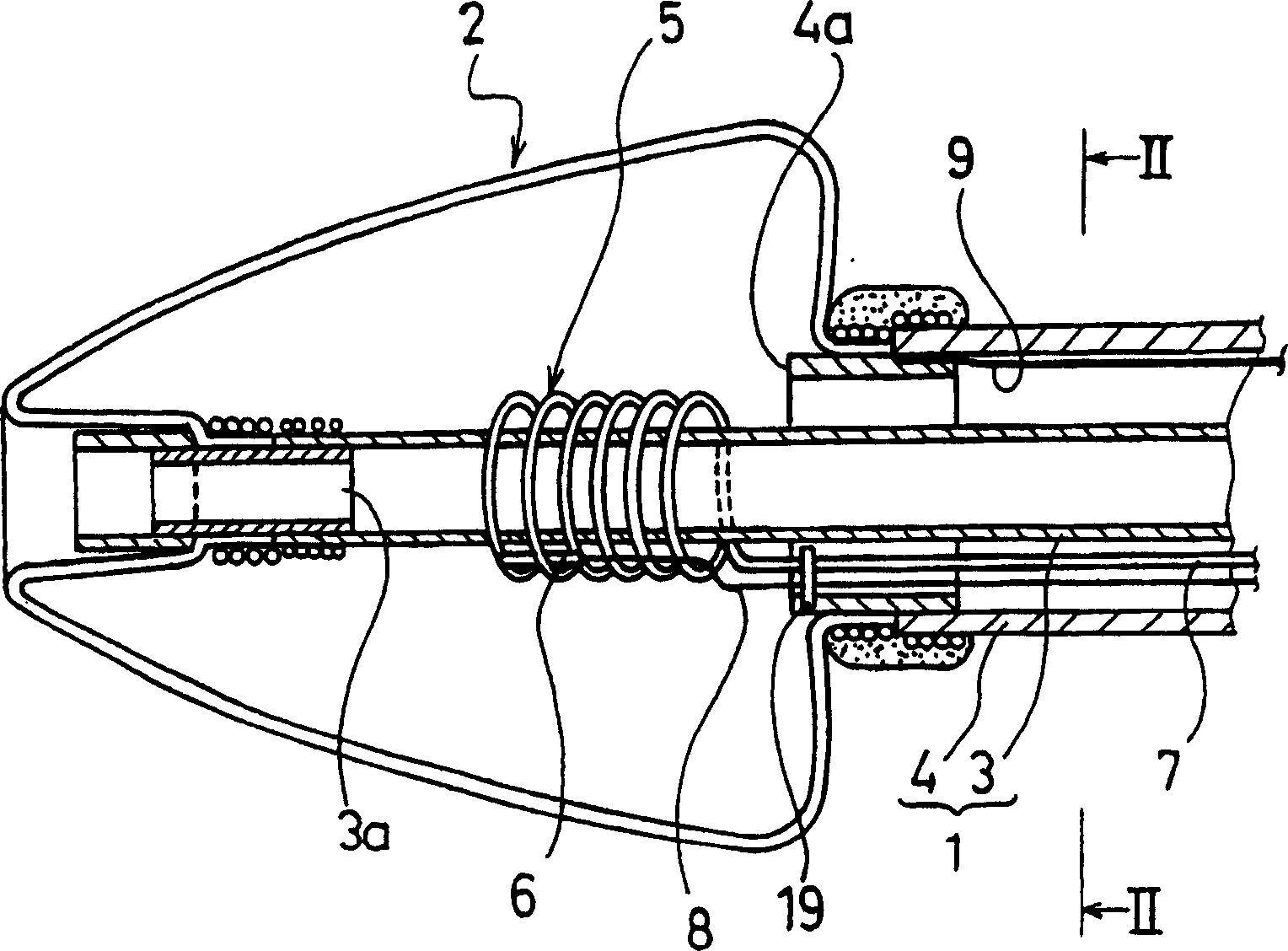
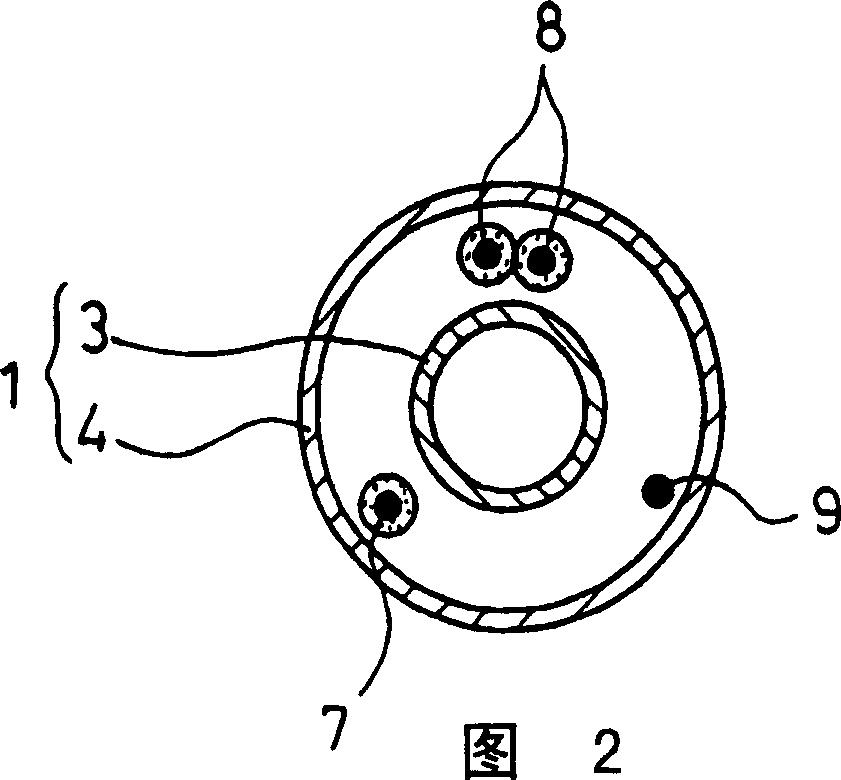
A catheter for treating arrhythmia comprises a catheter shaft of a double-cylinder structure where an inner shaft is slidably inserted in an outer shaft, a balloon installed so as to straddle between the tip portion of the inner shaft and the tip portion of the outer shaft, a pair of high frequency current-carrying electrodes of which at least one electrode is provided inside the balloon, and a temperature sensor for monitoring the temperature in the balloon. The front edge portion of the balloon at least in a deflated state protrude from the tip portion of the inner shaft. Alternatively, a tube that is more flexible than the inner shaft is provided on the tip portion of the inner shaft.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
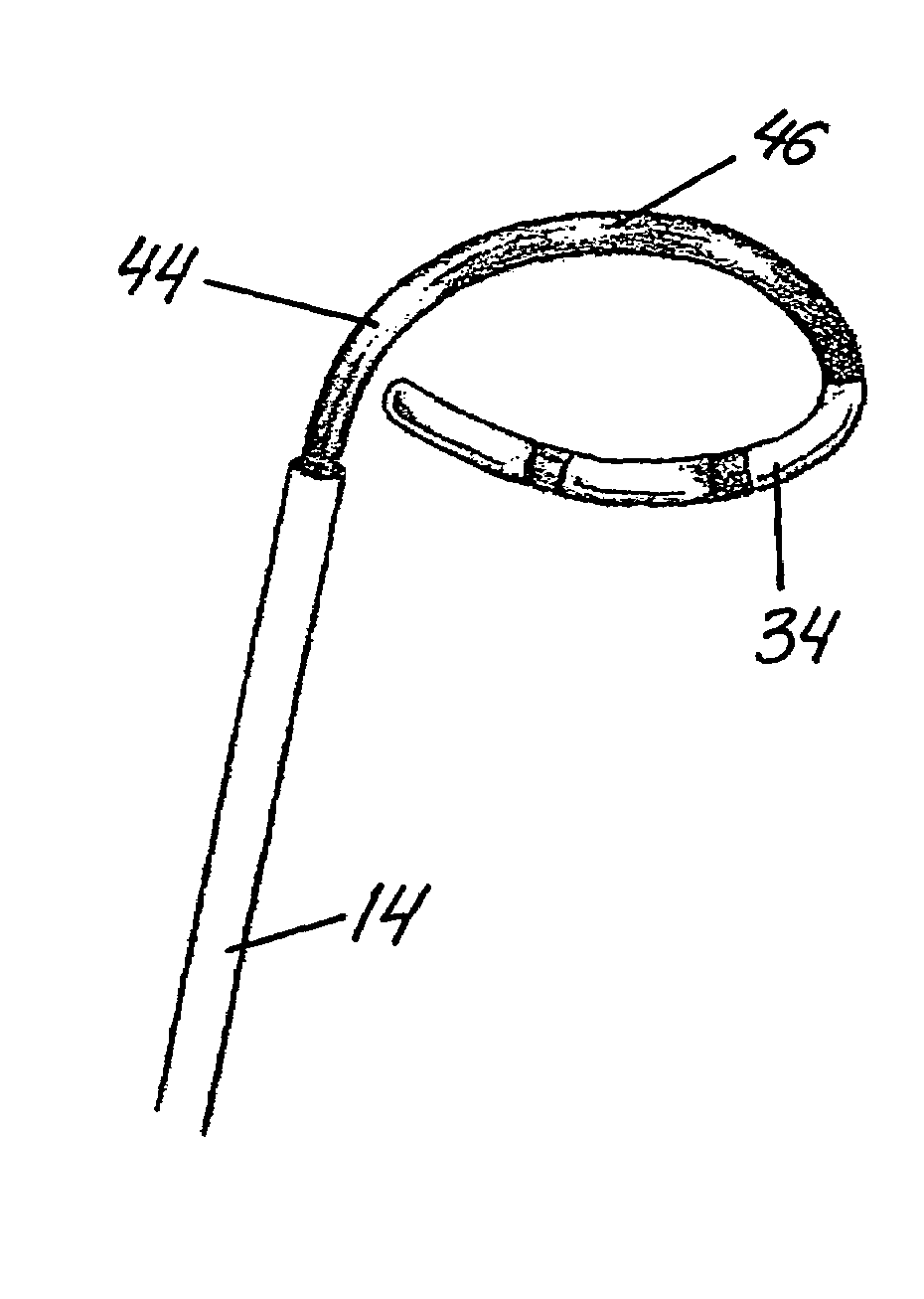
Catheter apparatus for treatment of heart arrhythmia
A catheter apparatus is provided for use in the treatment of heart arrhythmia having a catheter shaft, a mapping and ablation catheter disposed within the shaft, and a control mechanism coupled to both the shaft and catheter. The catheter shaft includes a main body and a coaxial tip section joined to the main body. The tip section can be rotated about a central axis and curved away from the central axis in a controlled manner. The mapping and ablation catheter can be extended outward from the catheter shaft where it is able to take the form of a pre-stressed curve. The control mechanism controls axial rotation of the tip section, the degree of deflection of the tip section and longitudinal movement of the mapping and ablation catheter with respect to the catheter shaft. Preferably, the mapping and ablation catheter forms a pre-stressed loop when it is fully extended from the catheter shaft.In another aspect of this invention, it provides a method for treatment of a heart arrhythmia having the steps of (1) obtaining cardiac image data from a medical imaging system, (2) creating a 3D model from this cardiac image data, (3) registering the 3D model to an interventional system, (4) positioning a catheter apparatus within a chamber of the heart, (5) displaying the catheter apparatus over the registered 3D model on the interventional system, (6) navigating the catheter apparatus within the heart guided by the registered 3D model, and (7) having the catheter apparatus ablate heart tissue at select locations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Catheter for treating irregular heart pulse
ActiveUS20050203597A1Insert smoothlyImproved ease of insertionDilatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac rhythm disturbancesFront edge
A catheter for treating arrhythmia comprises a catheter shaft of a double-cylinder structure where an inner shaft is slidably inserted in an outer shaft, a balloon installed so as to straddle between the tip portion of the inner shaft and the tip portion of the outer shaft, a pair of high frequency current-carrying electrodes of which at least one electrode is provided inside the balloon, and a temperature sensor for monitoring the temperature in the balloon. The front edge portion of the balloon at least in a deflated state protrude from the tip portion of the inner shaft. Alternatively, a tube that is more flexible than the inner shaft is provided on the tip portion of the inner shaft.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Automated Assessment Of Atrioventricular And Ventriculoatrial Conduction
ActiveUS20090143832A1Restore normal sinus rhythmHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaInappropriate shock
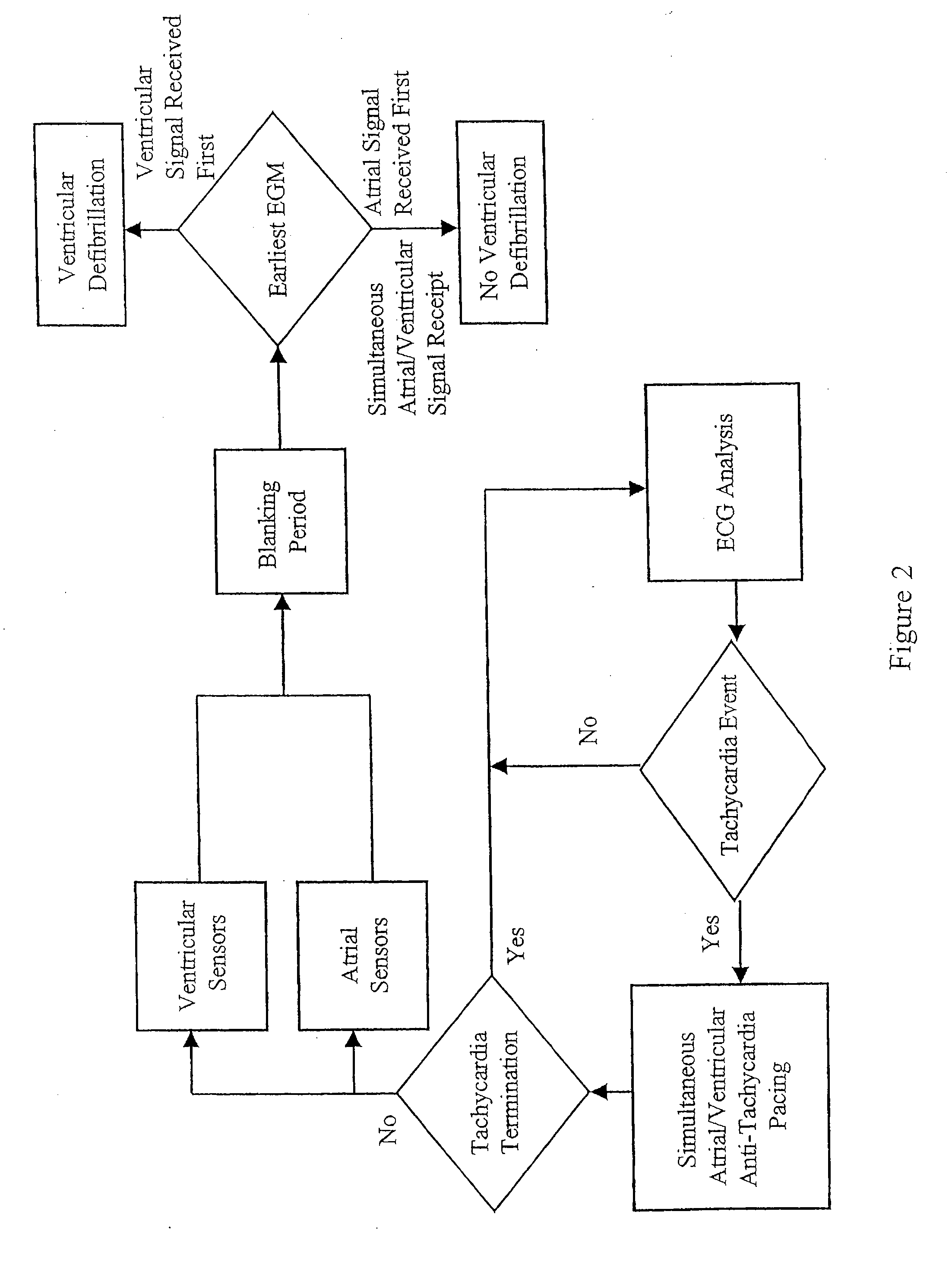
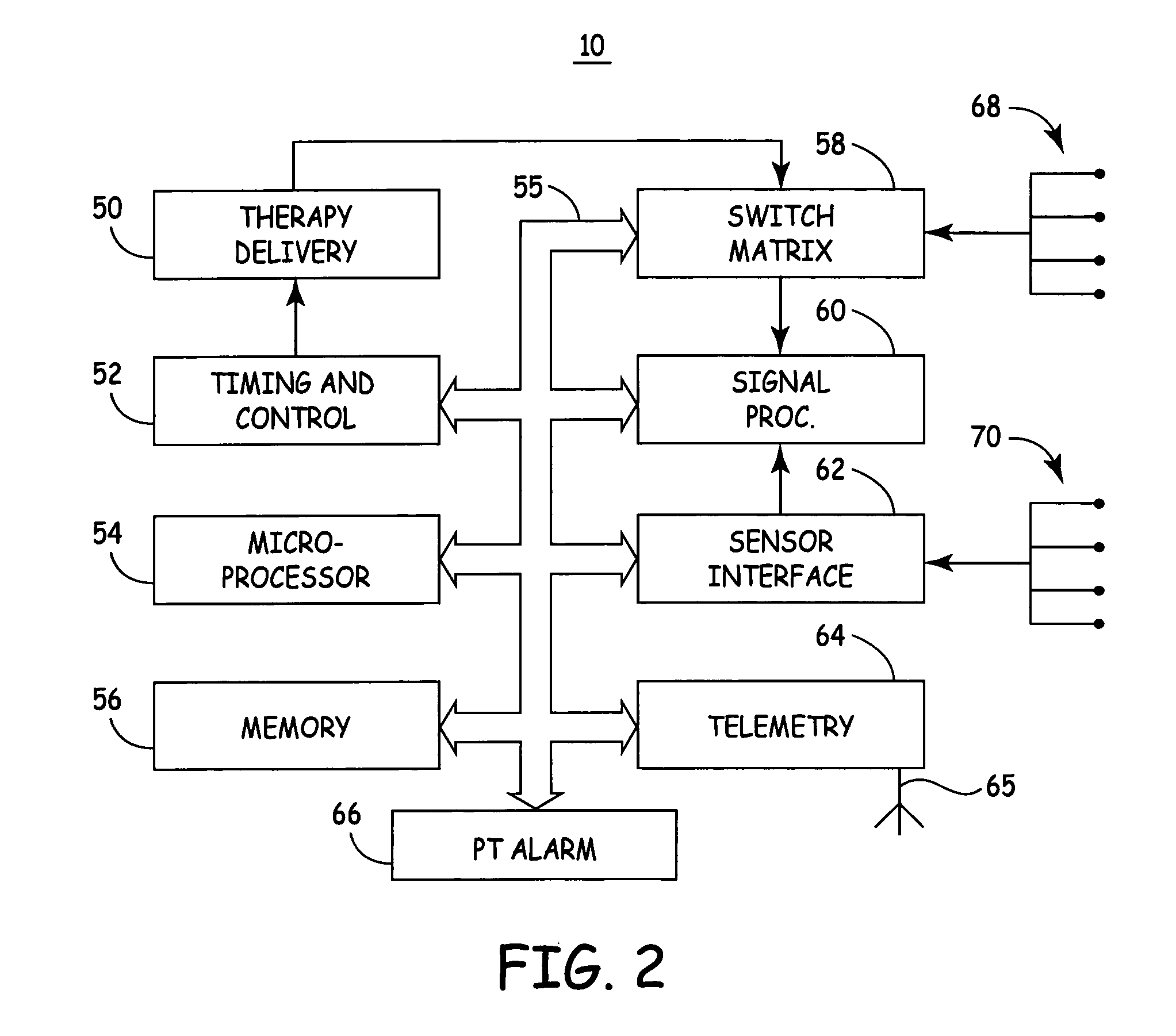
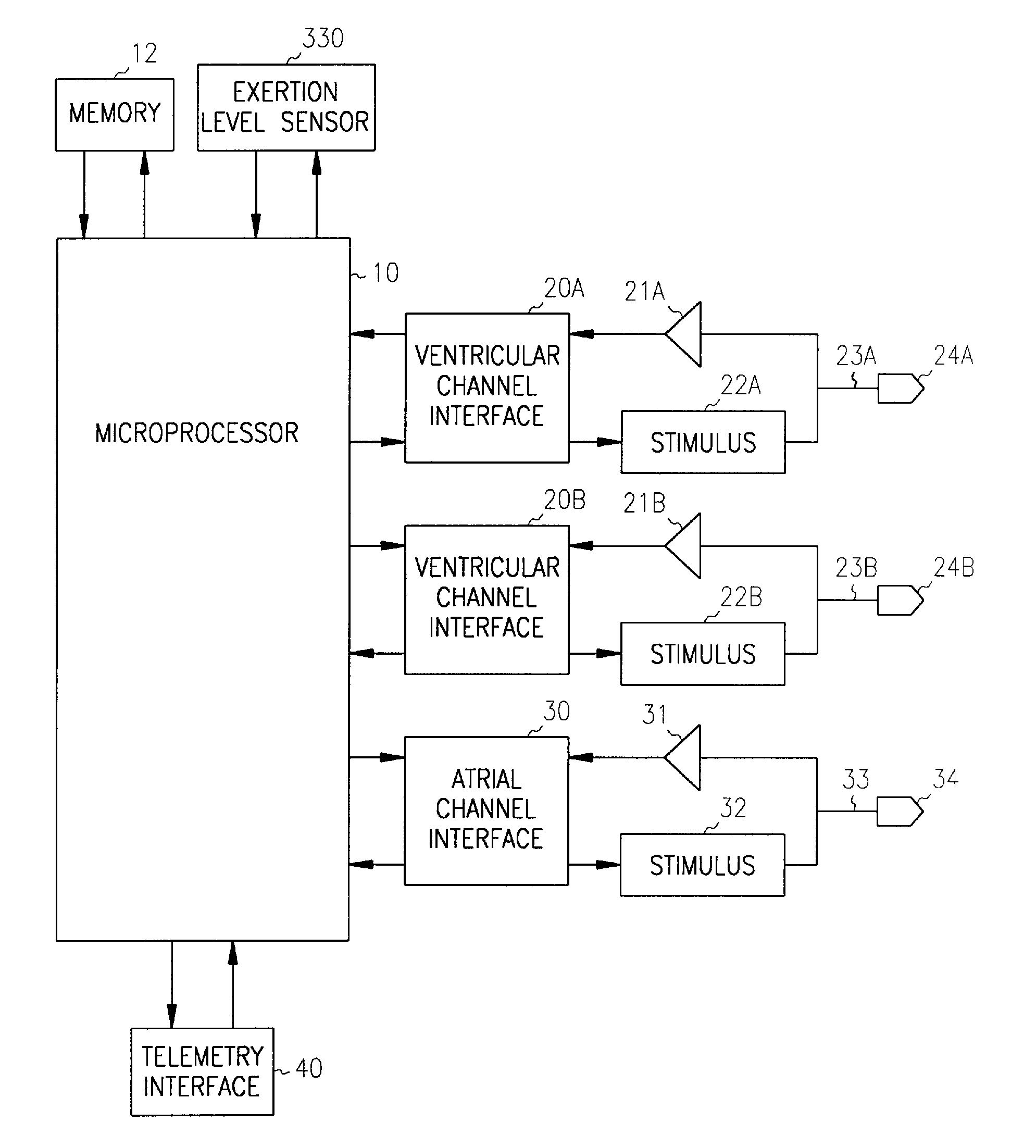
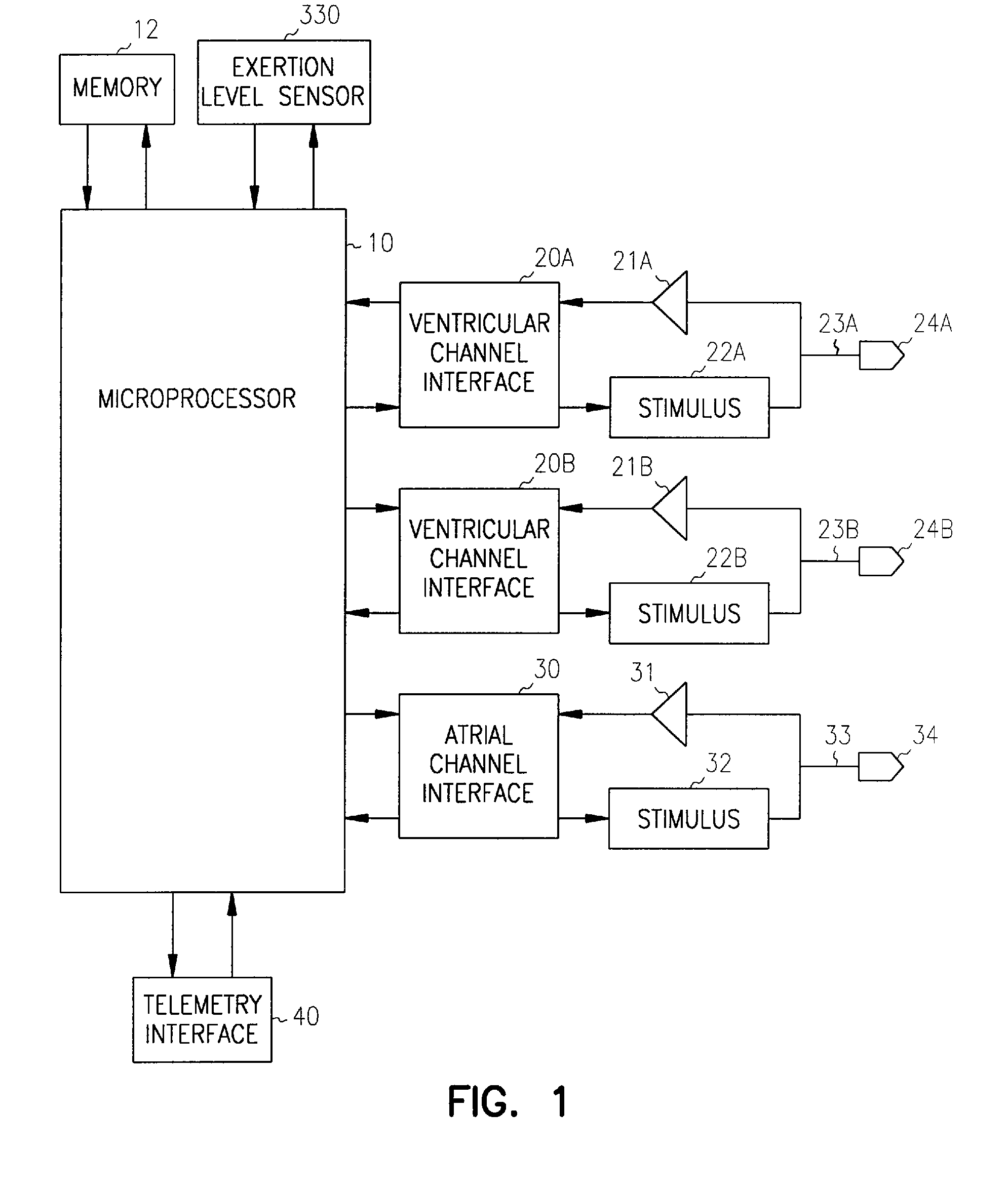
A method discriminates between ventricular arrhythmia and supraventricular arrhythmia by determining the direction of an electrical signal conducted through the atrioventricular node. An implantable cardiac defibrillator provides atrioventricular and ventriculoatrial pacing bursts to determine if an arrhythmia with a 1:1 atrial to ventricular relationship is due to ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia. This discrimination capability reduces the incidence of inappropriate shocks from dual-chamber implantable cardiac defibrillators to near zero and provides a method to differentially diagnose supraventricular tachycardia from ventricular tachycardia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
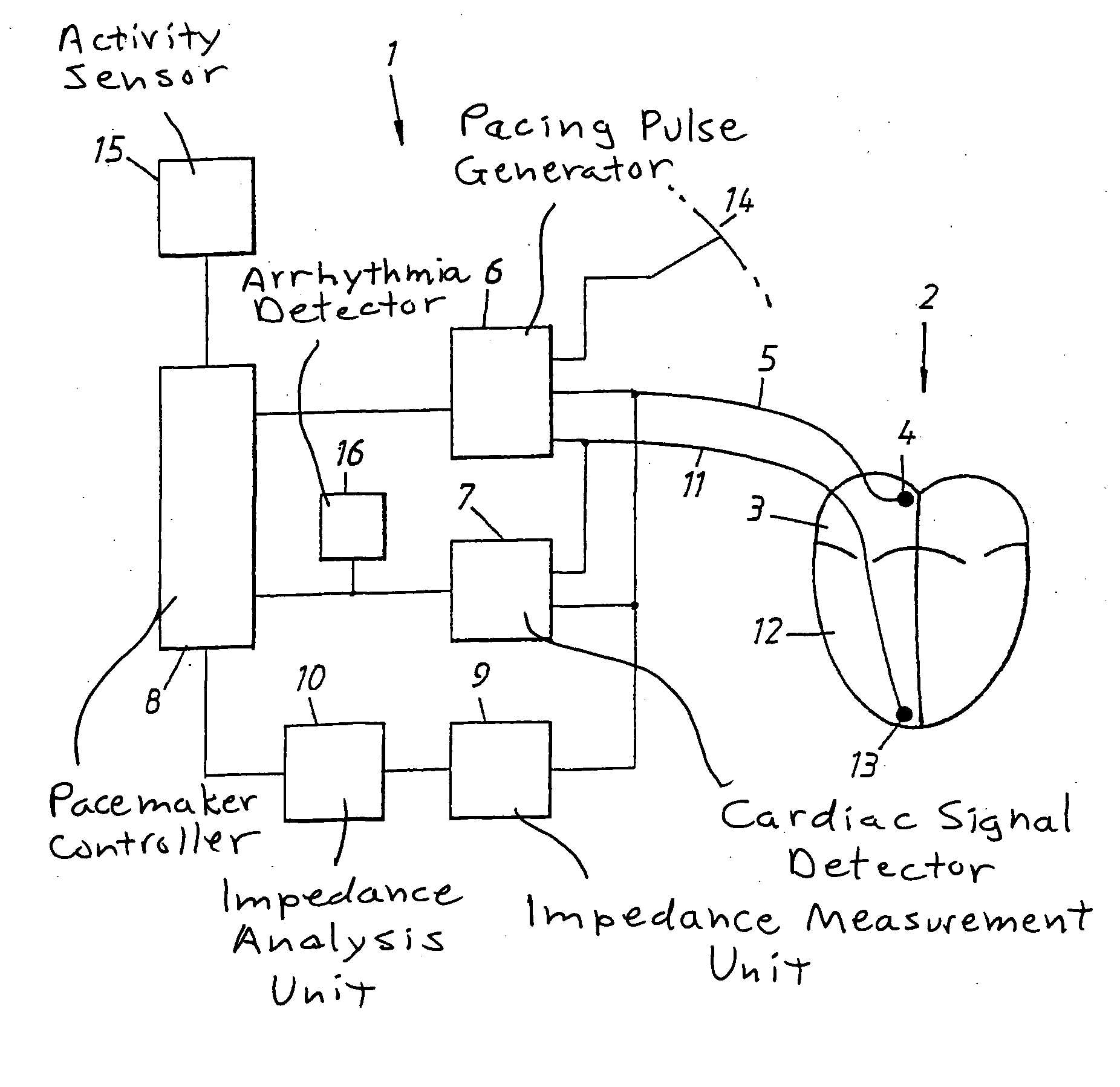
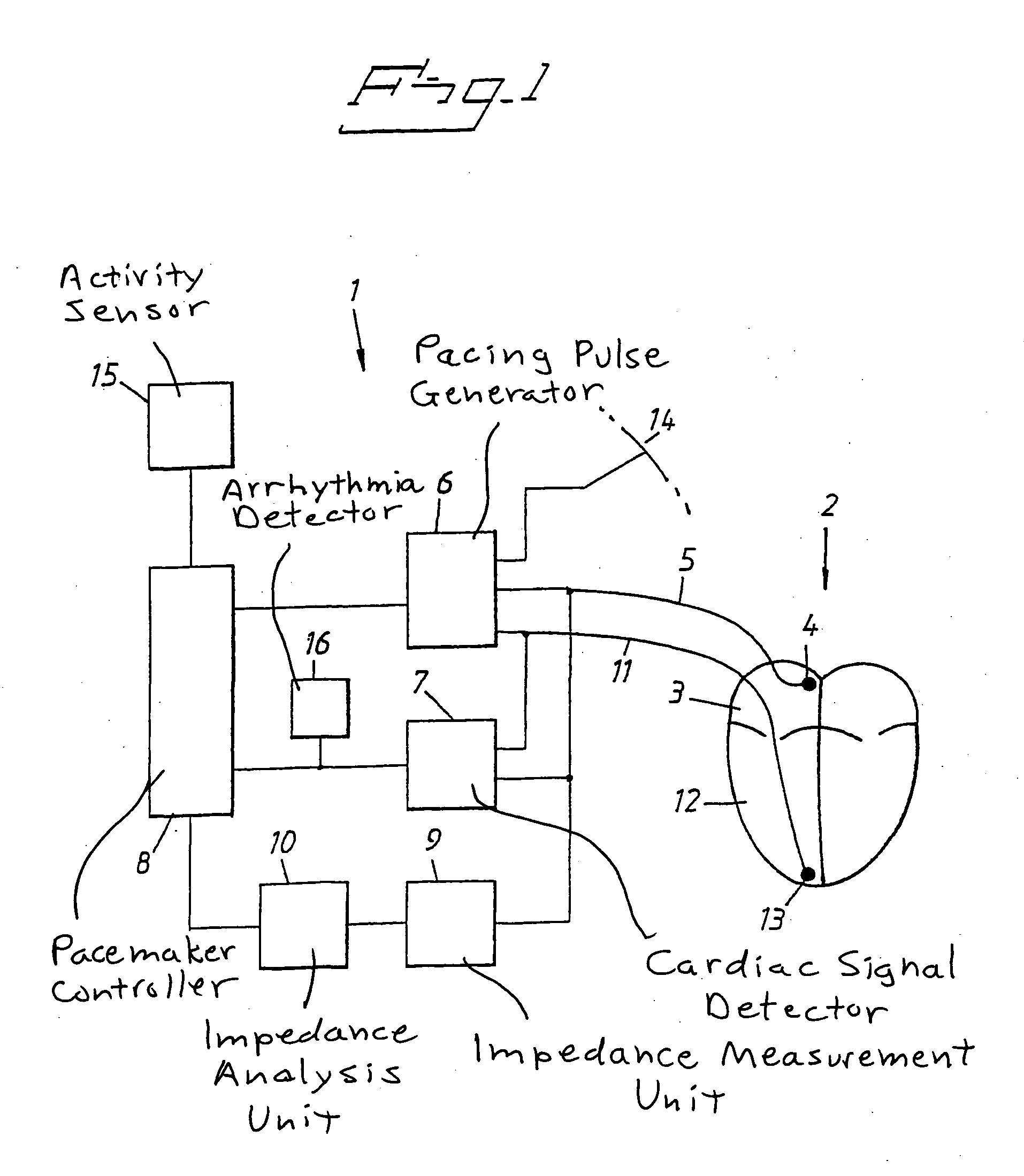
Heart stimulator detecting atrial arrhythmia by determing wall distension by impedance measuring
InactiveUS20060206157A1Limit atrial distensionEliminates atrial remodelingHeart stimulatorsAtrial cavityCardiac pacemaker electrode
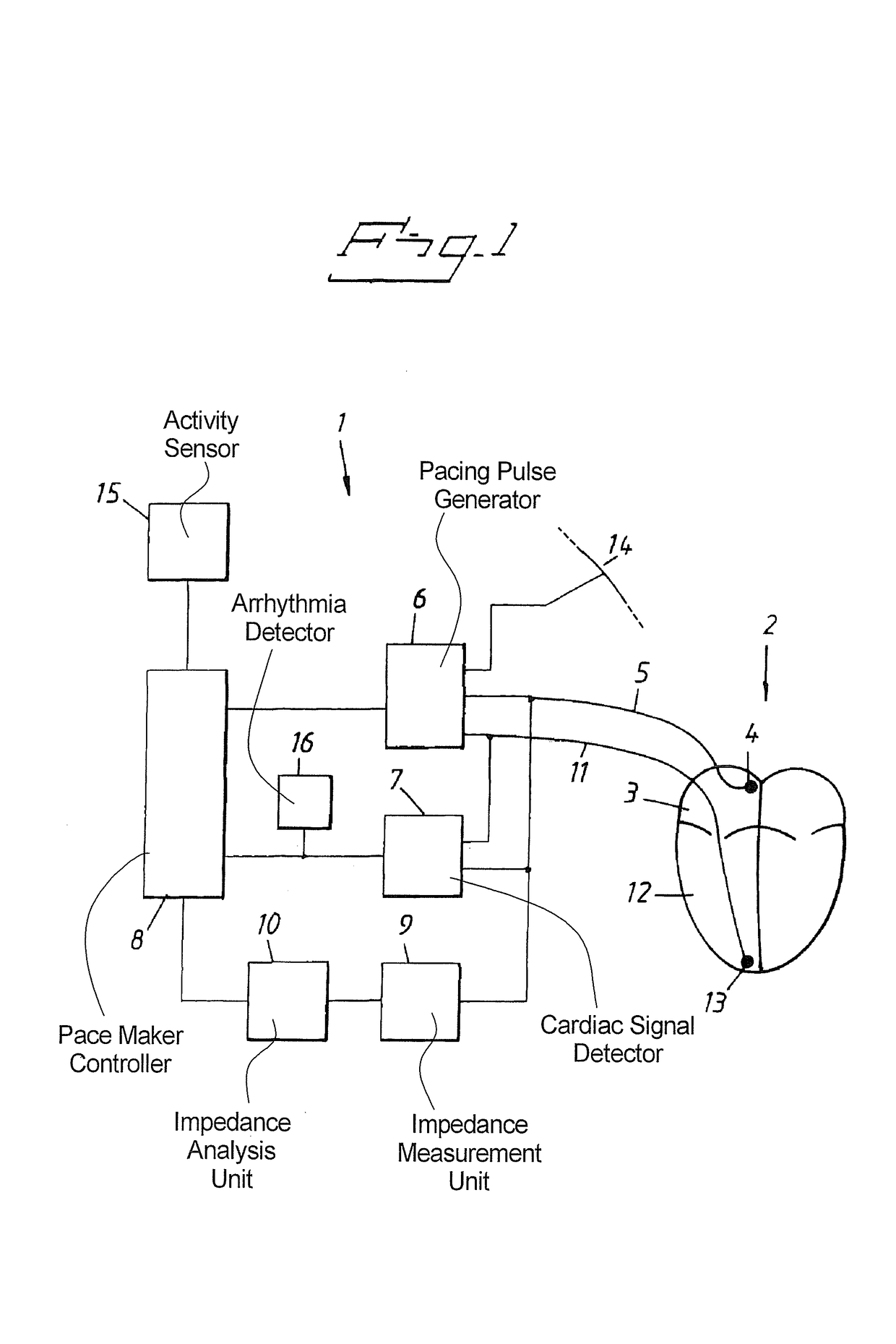
In an implantable pacemaker, pacing pulses are delivered to a ventricle in a P-wave synchronous mode as long as no atrial arrhythmia is detected, pacing pulses and a mode switch is made to deliver pacing pulses to the ventricle in a non-P-wave synchronous mode if atrial arrhythmia is detected. From an impedance signal measured in the atrium, atrial distention is determined and, in the non-P-wave synchronous mode, the delivery rate of the pacing pulses is increased to decrease the atrial distention during atrial arrhythmia.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
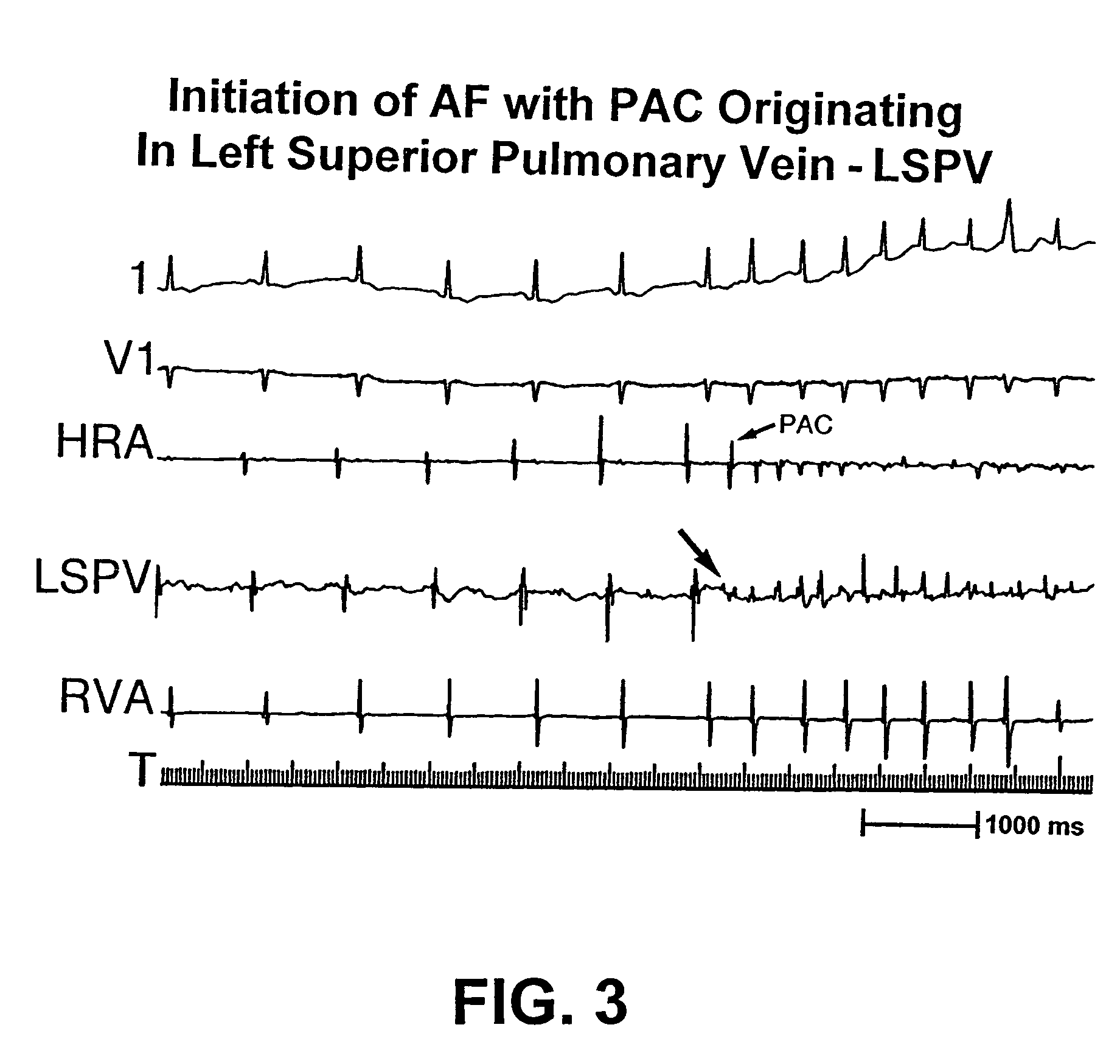
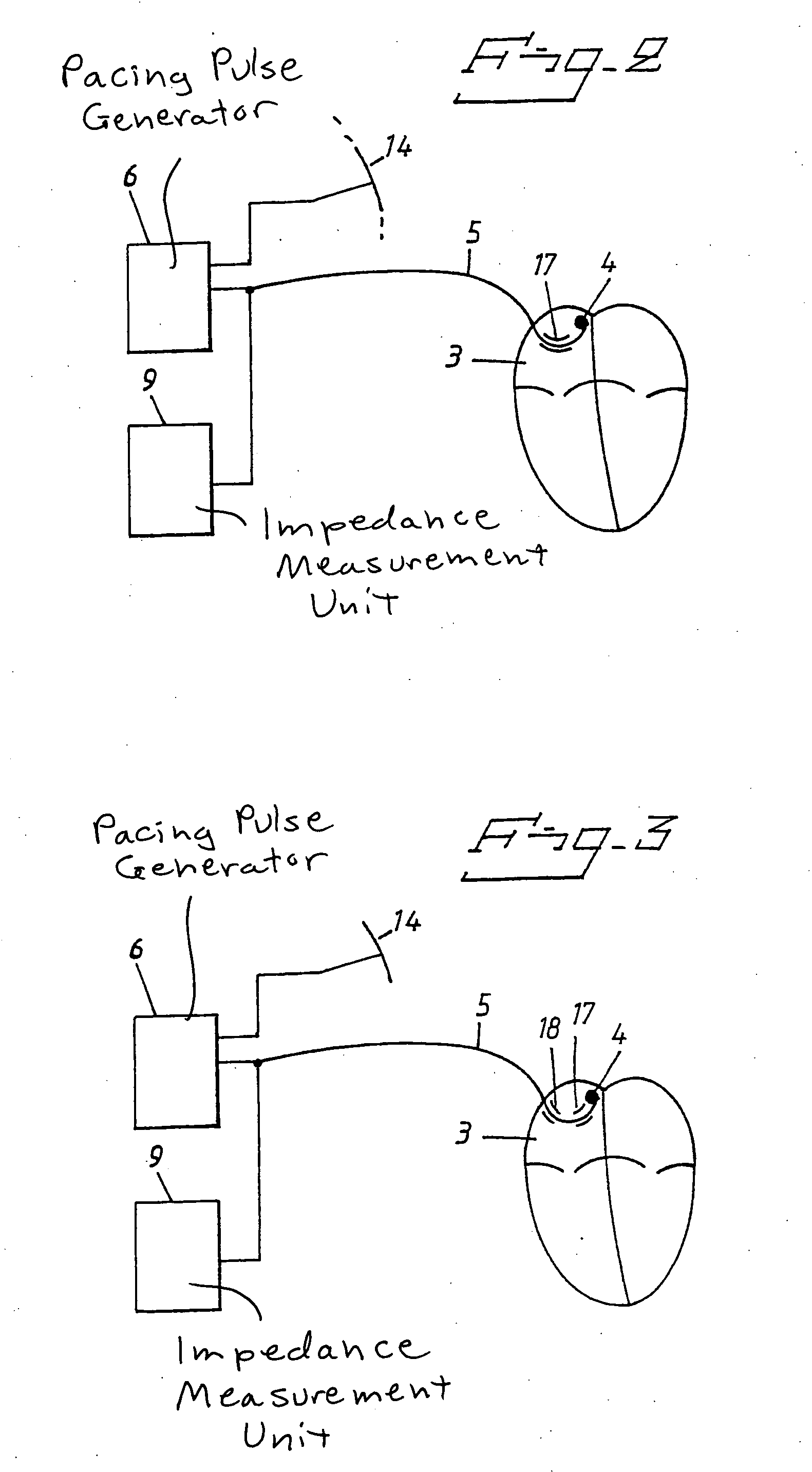
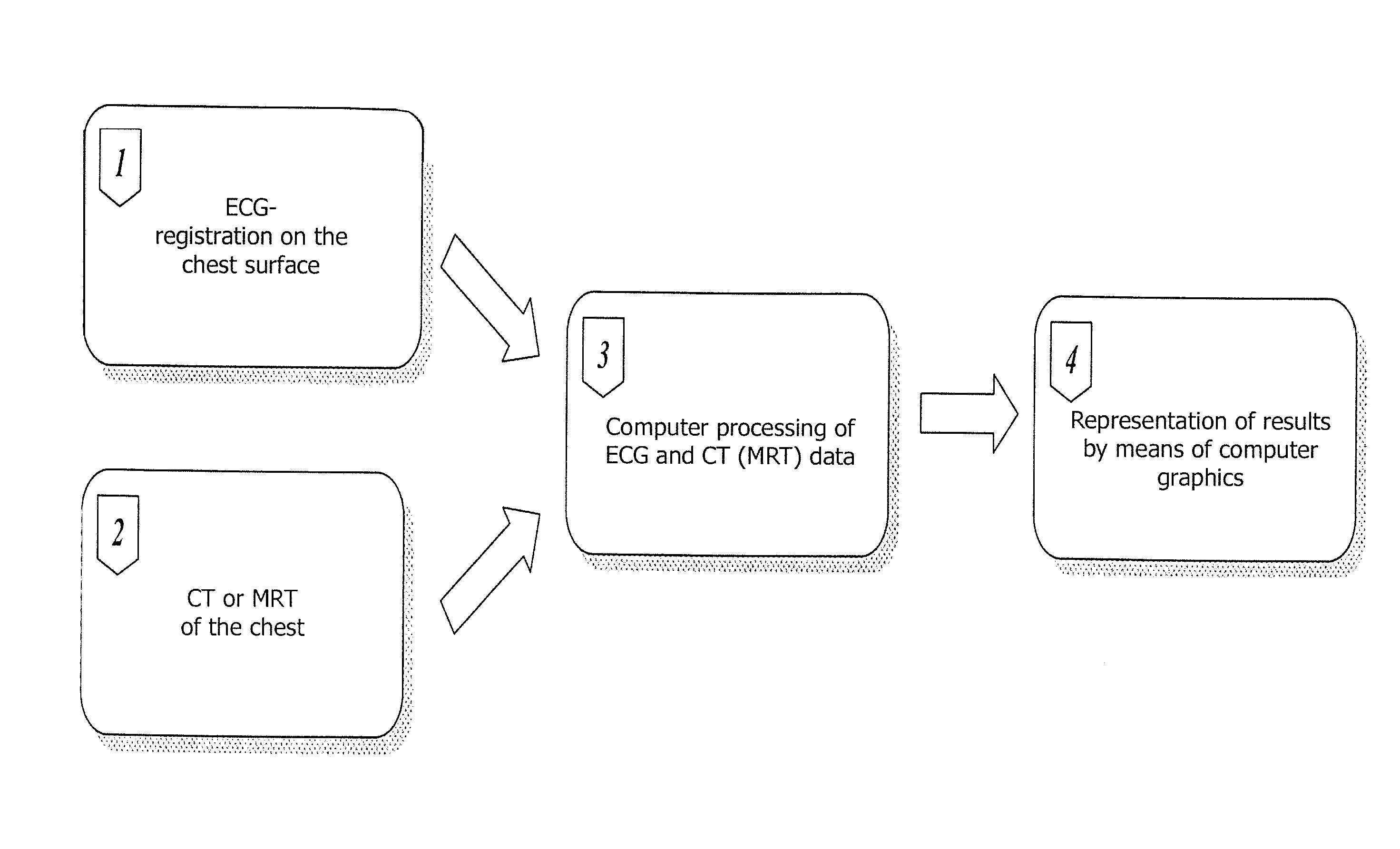
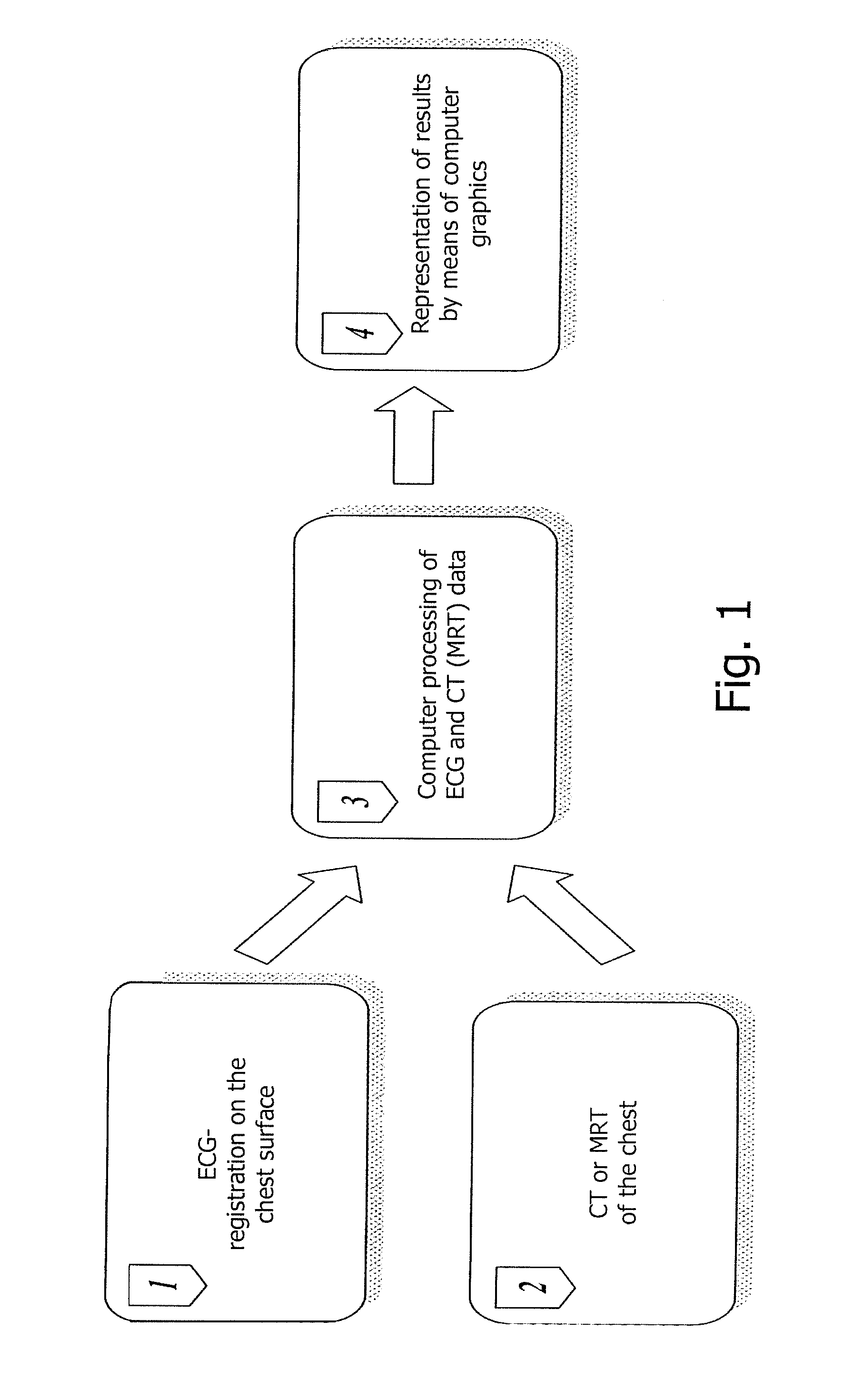
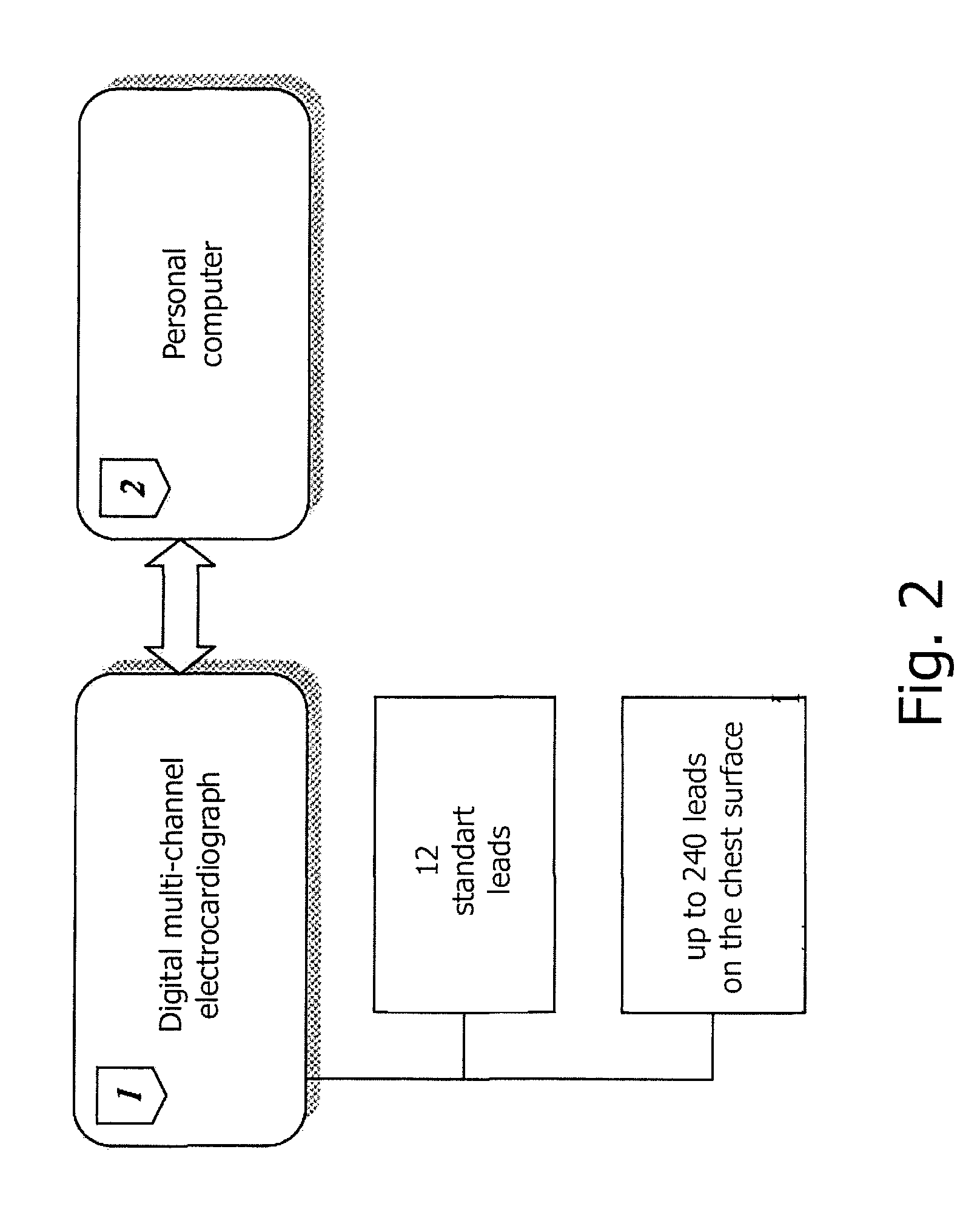
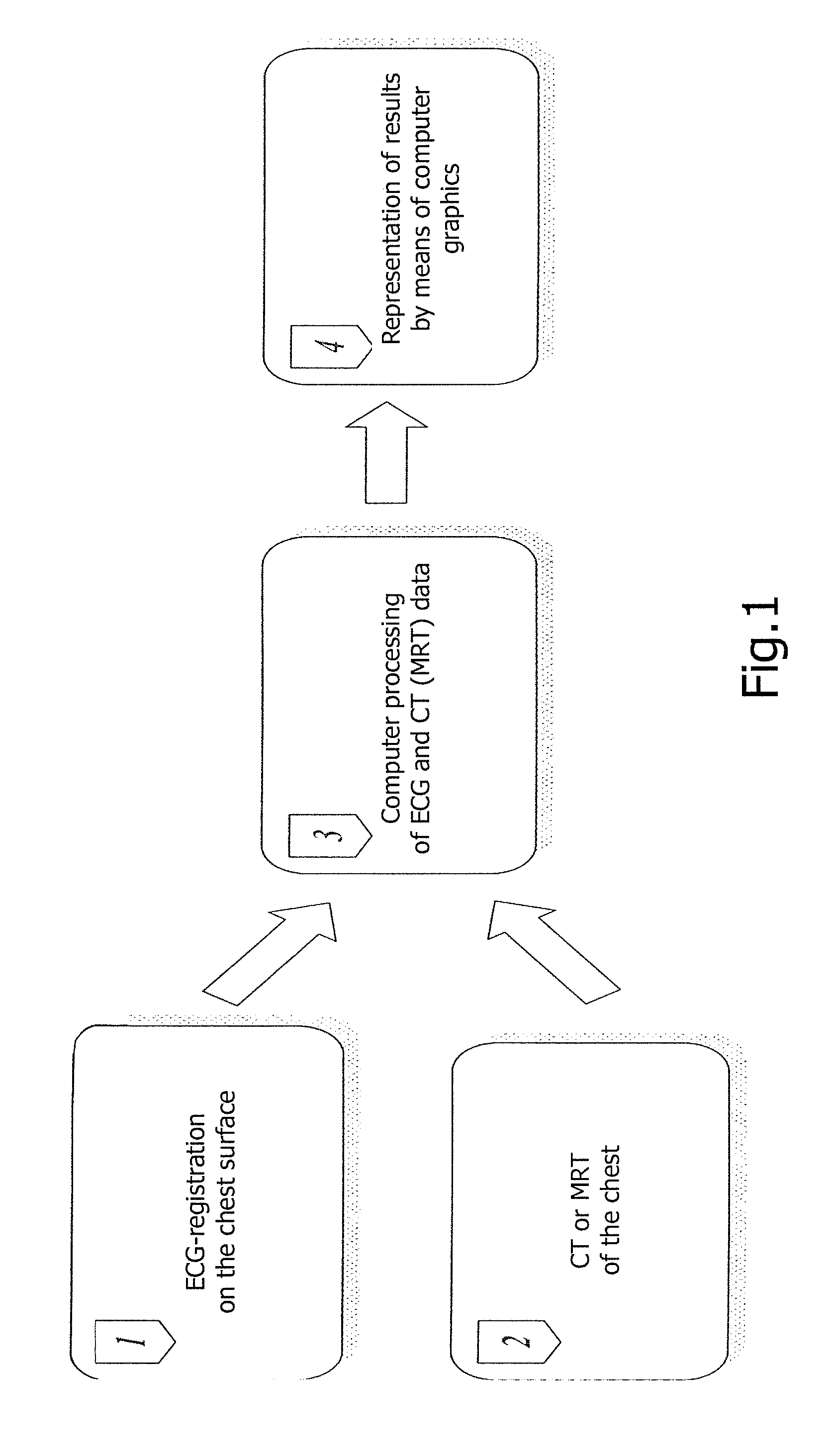
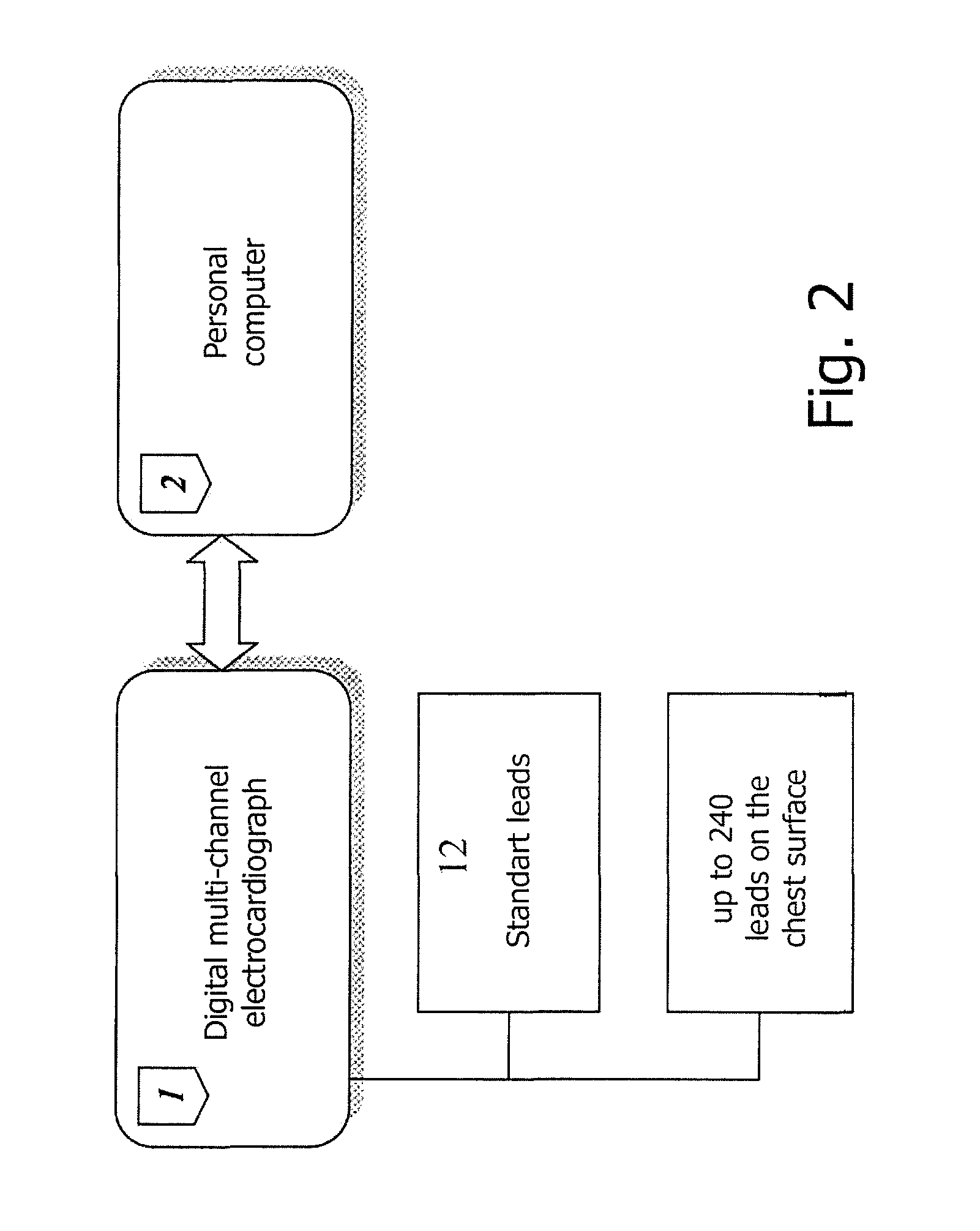
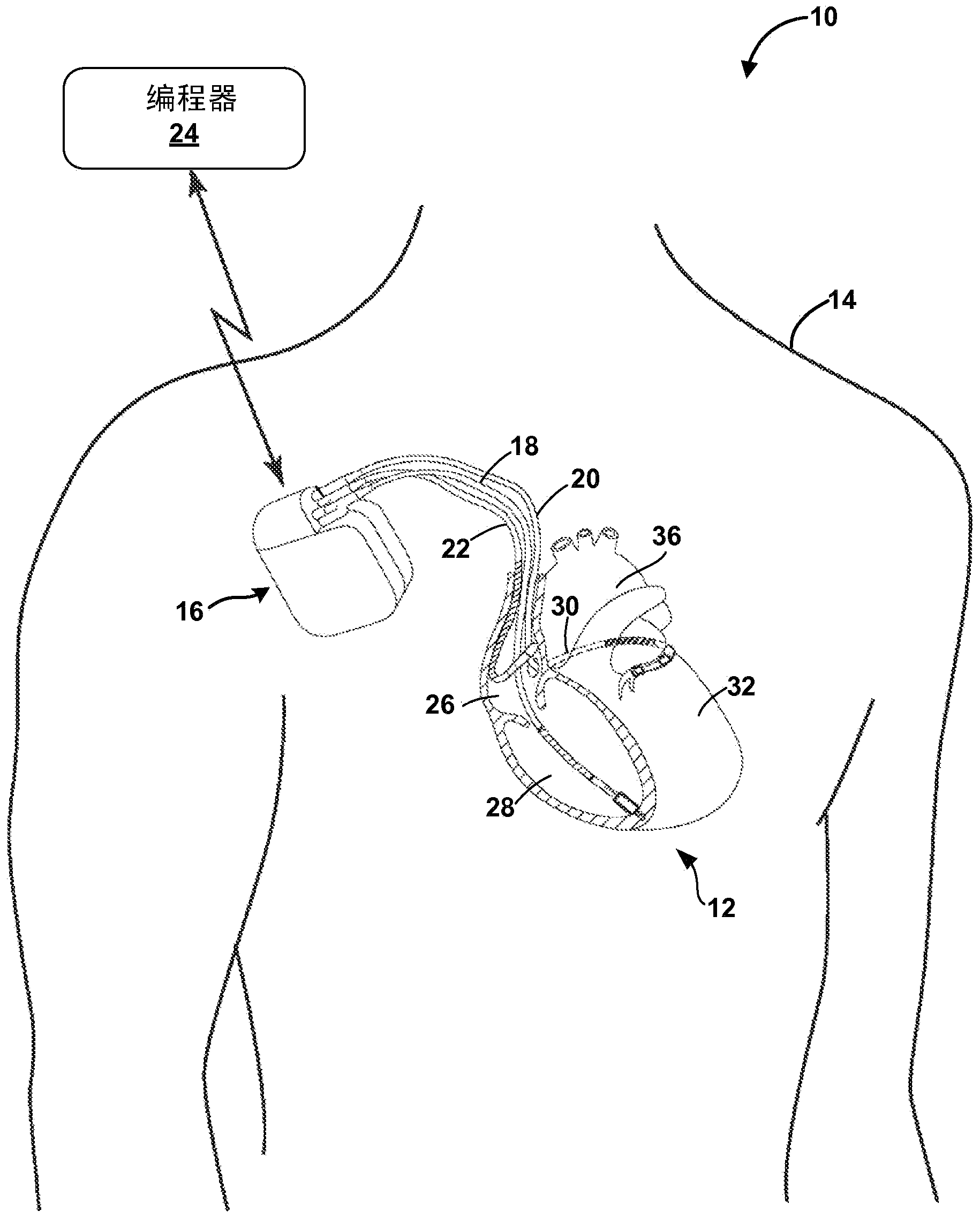
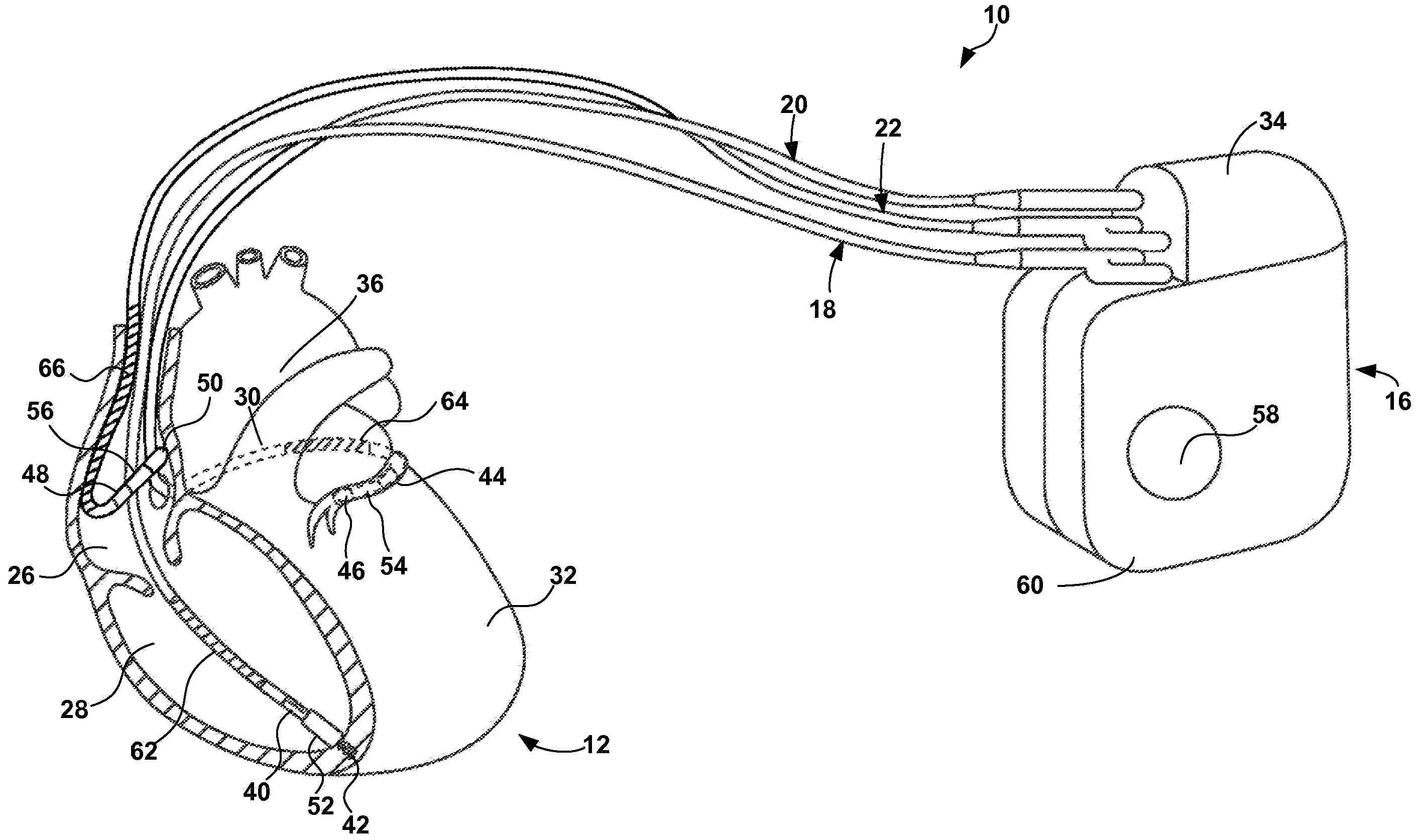
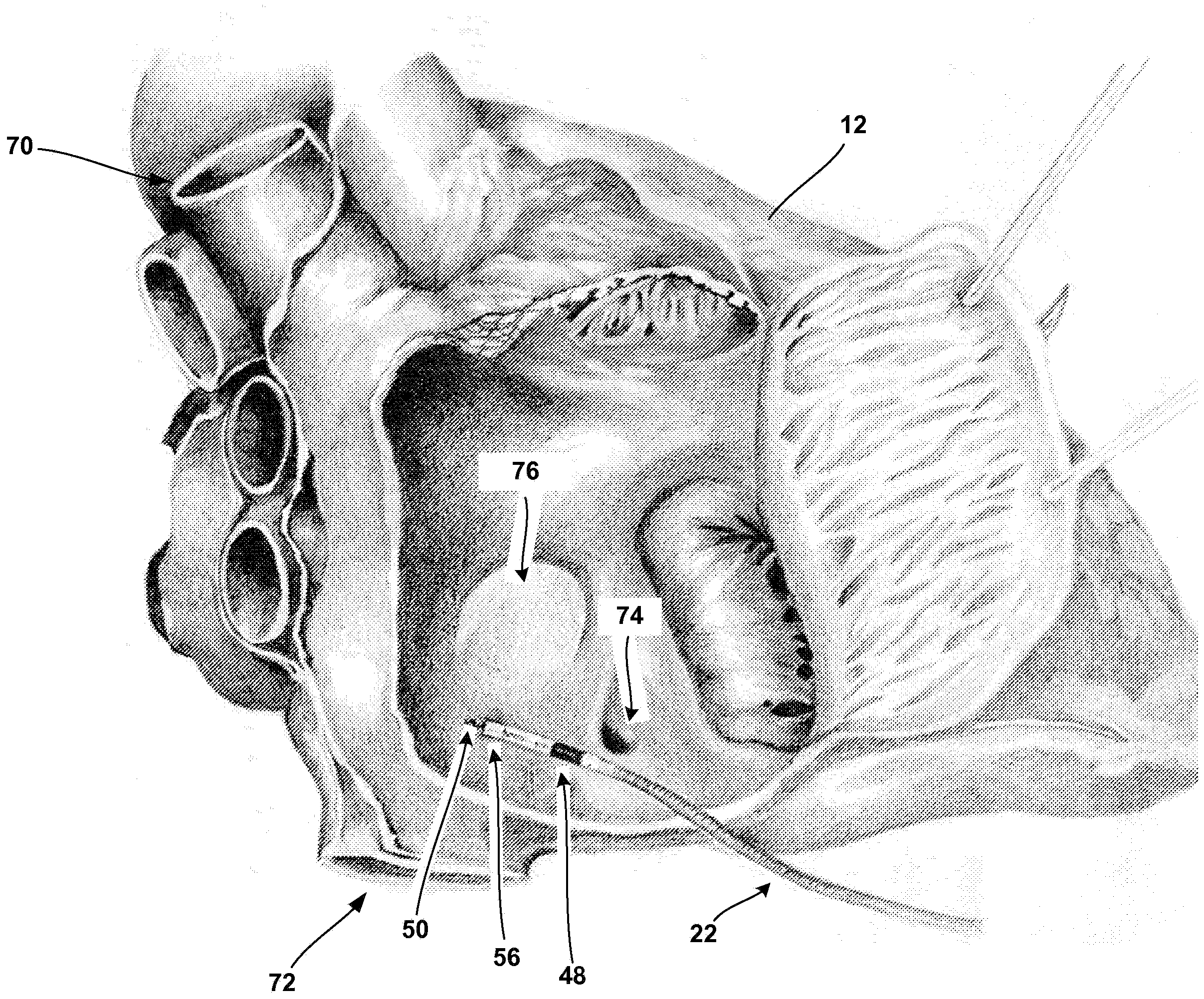
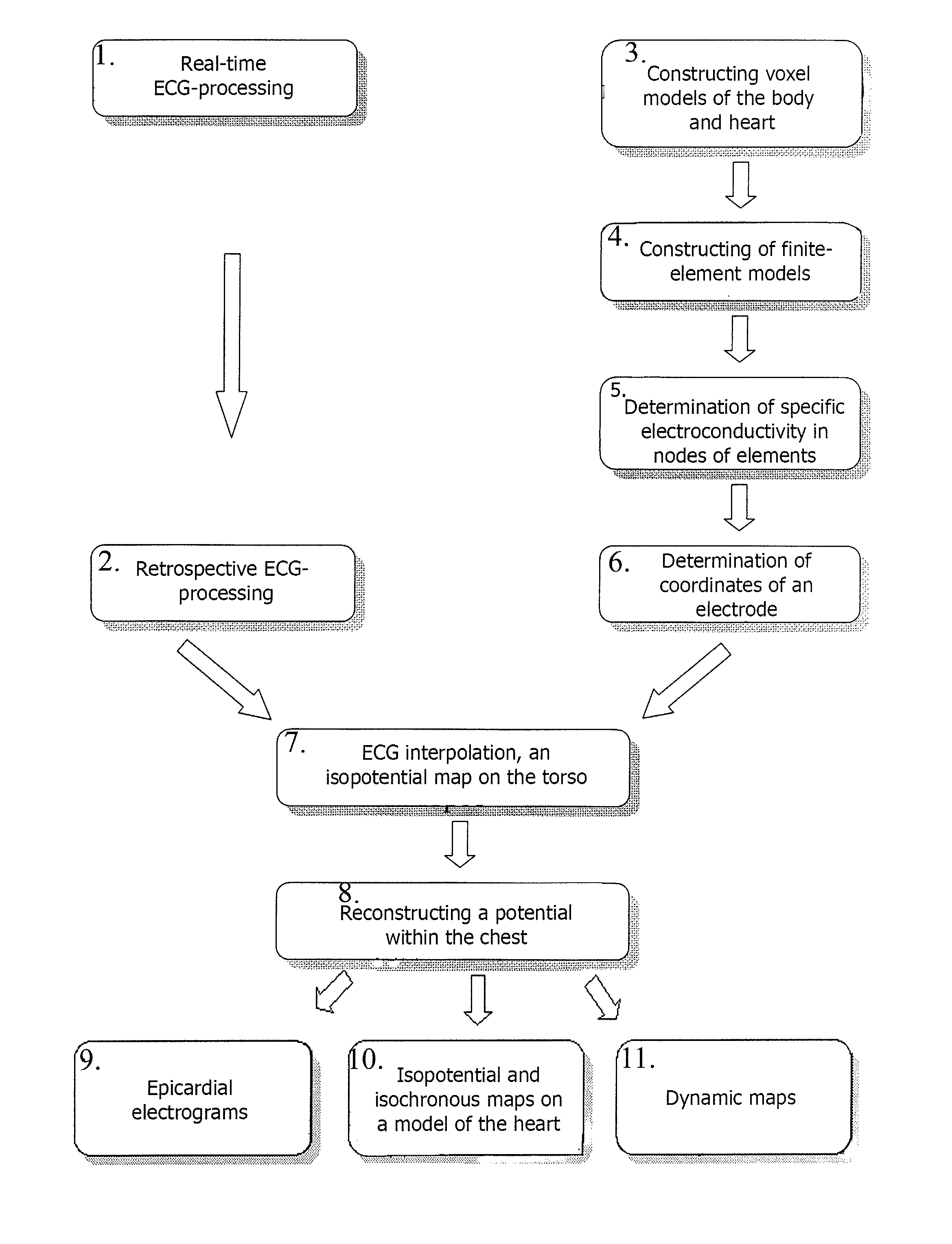
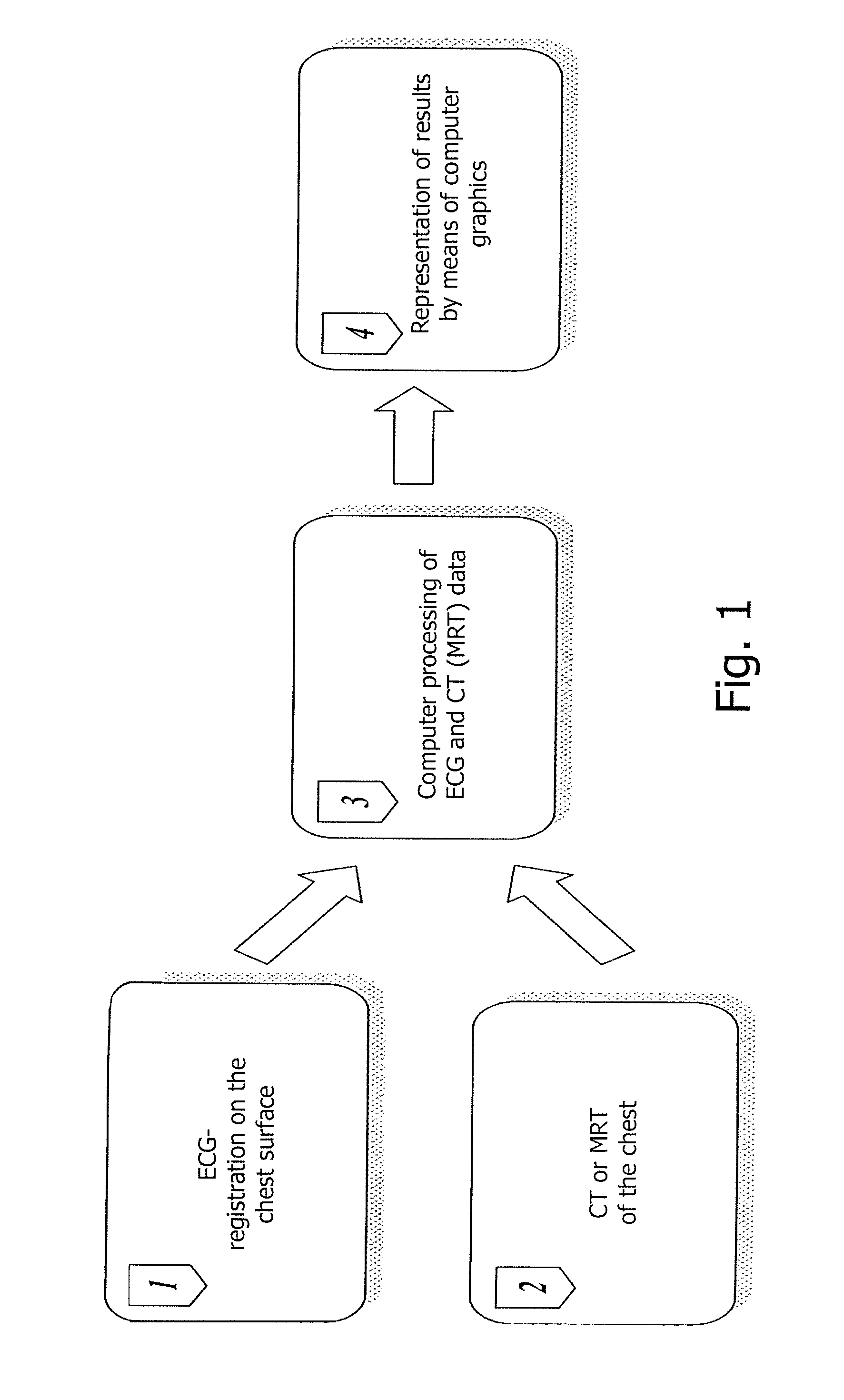
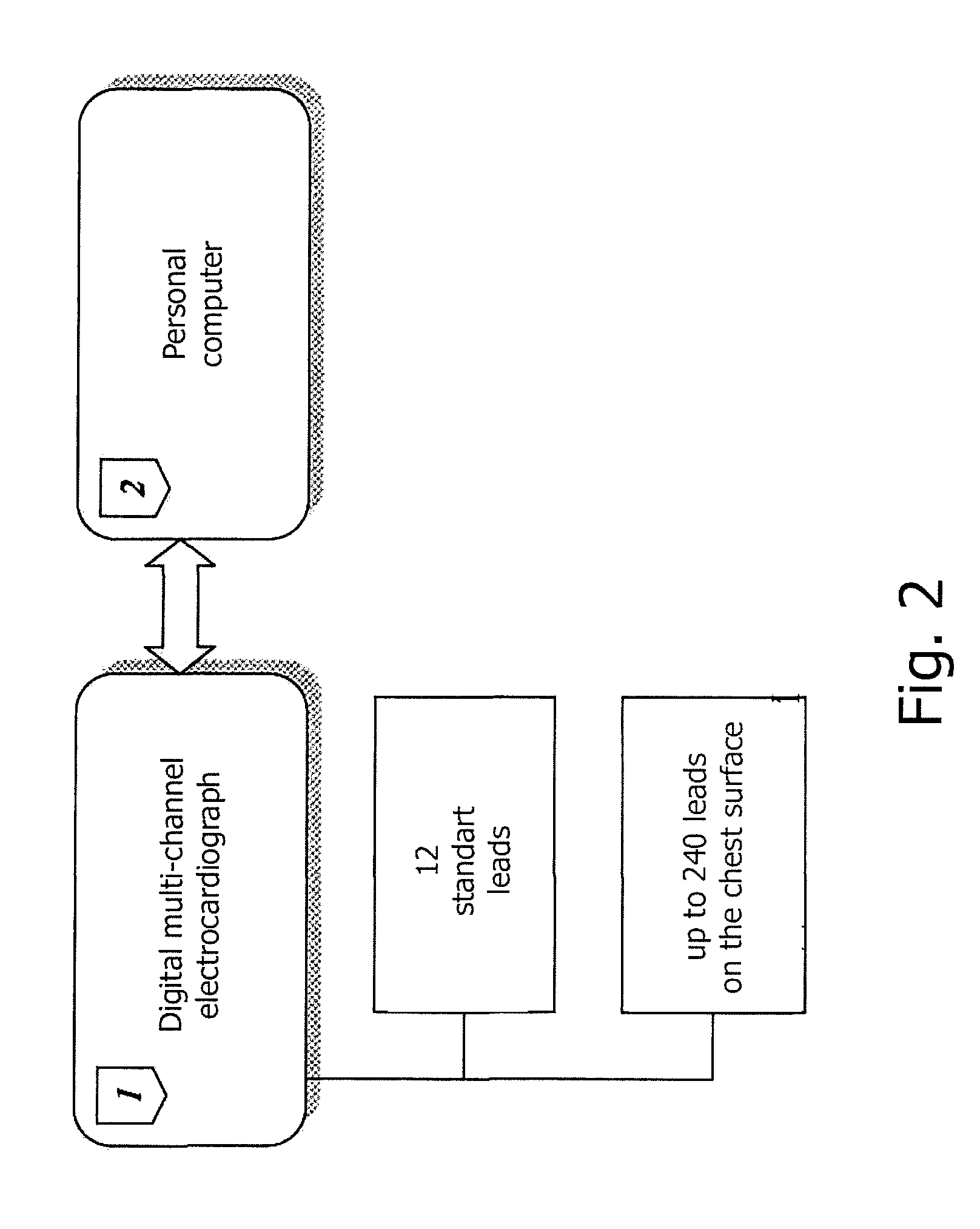
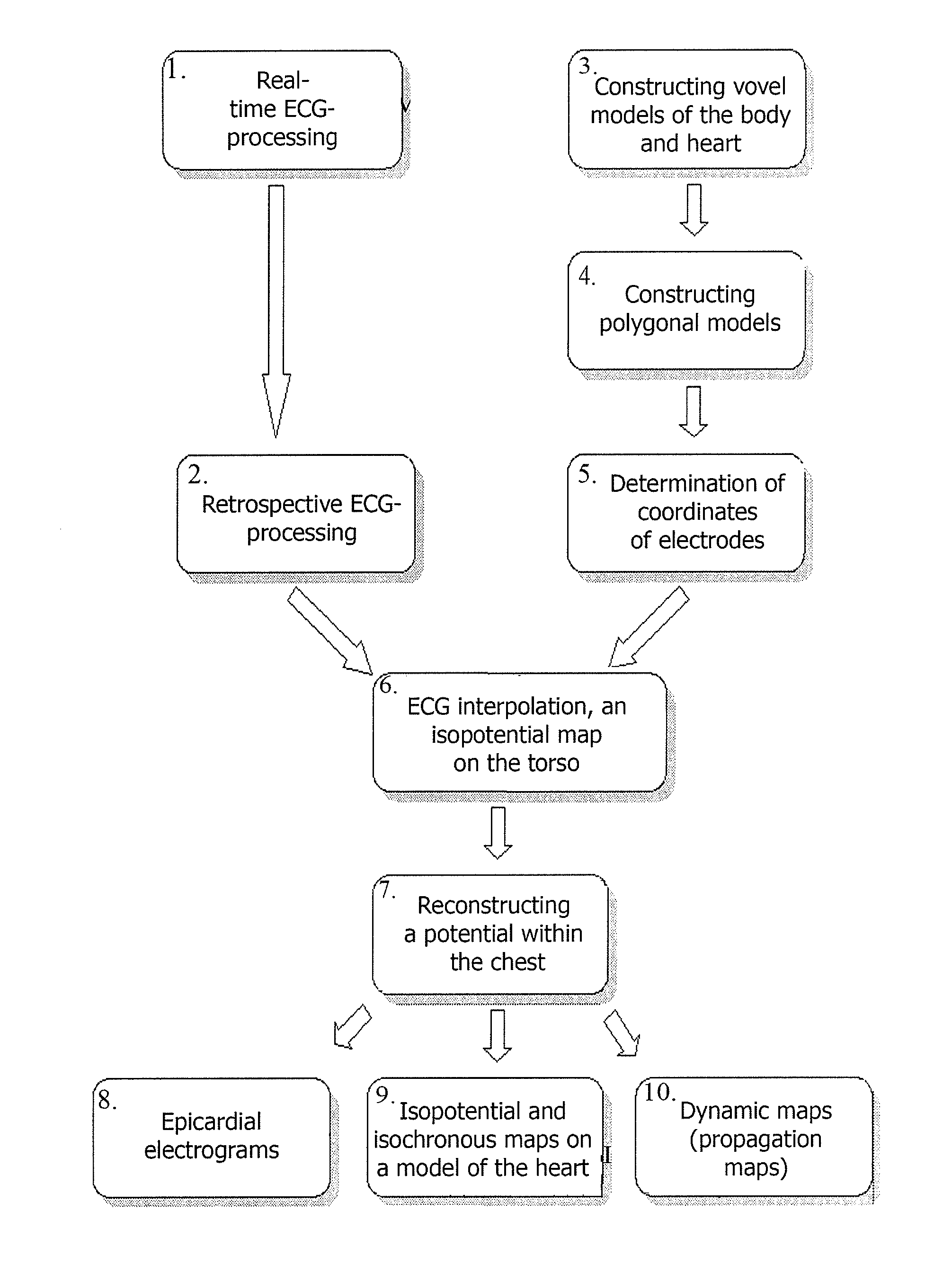
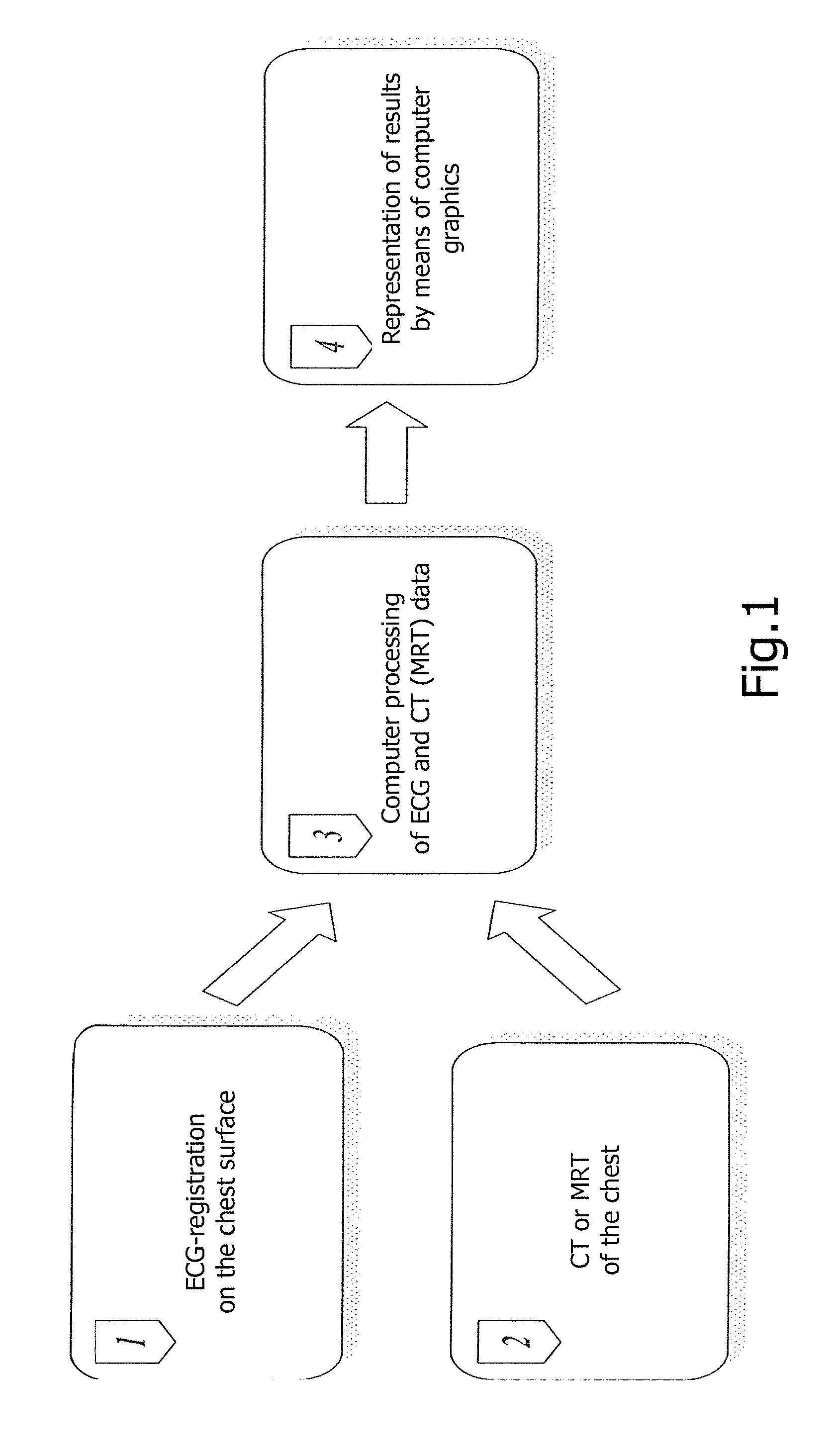
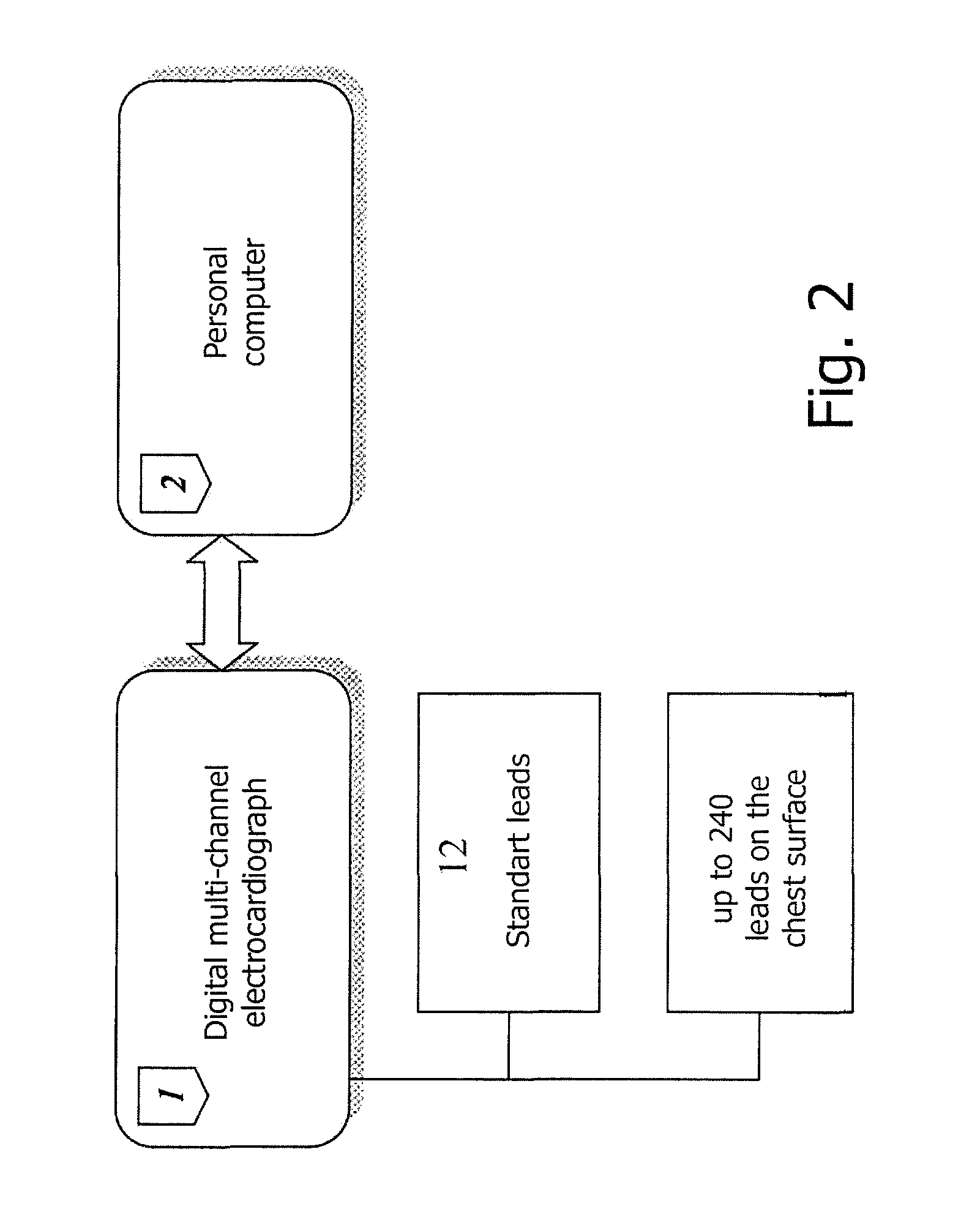
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, functional diagnosis and clinical electrophysiology of the heart. The invention consists in reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. Based on reconstructed electrograms, isopotential, isochronous maps on realistic models of the heart are constructed, the dynamics of the myocardium excitation is reconstructed and electrophysiological processes in the cardiac muscle are diagnosed. Application of the method allows one to improve the accuracy of non-invasive diagnosis of cardiac rhythm disturbances and other cardio-vascular diseases.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
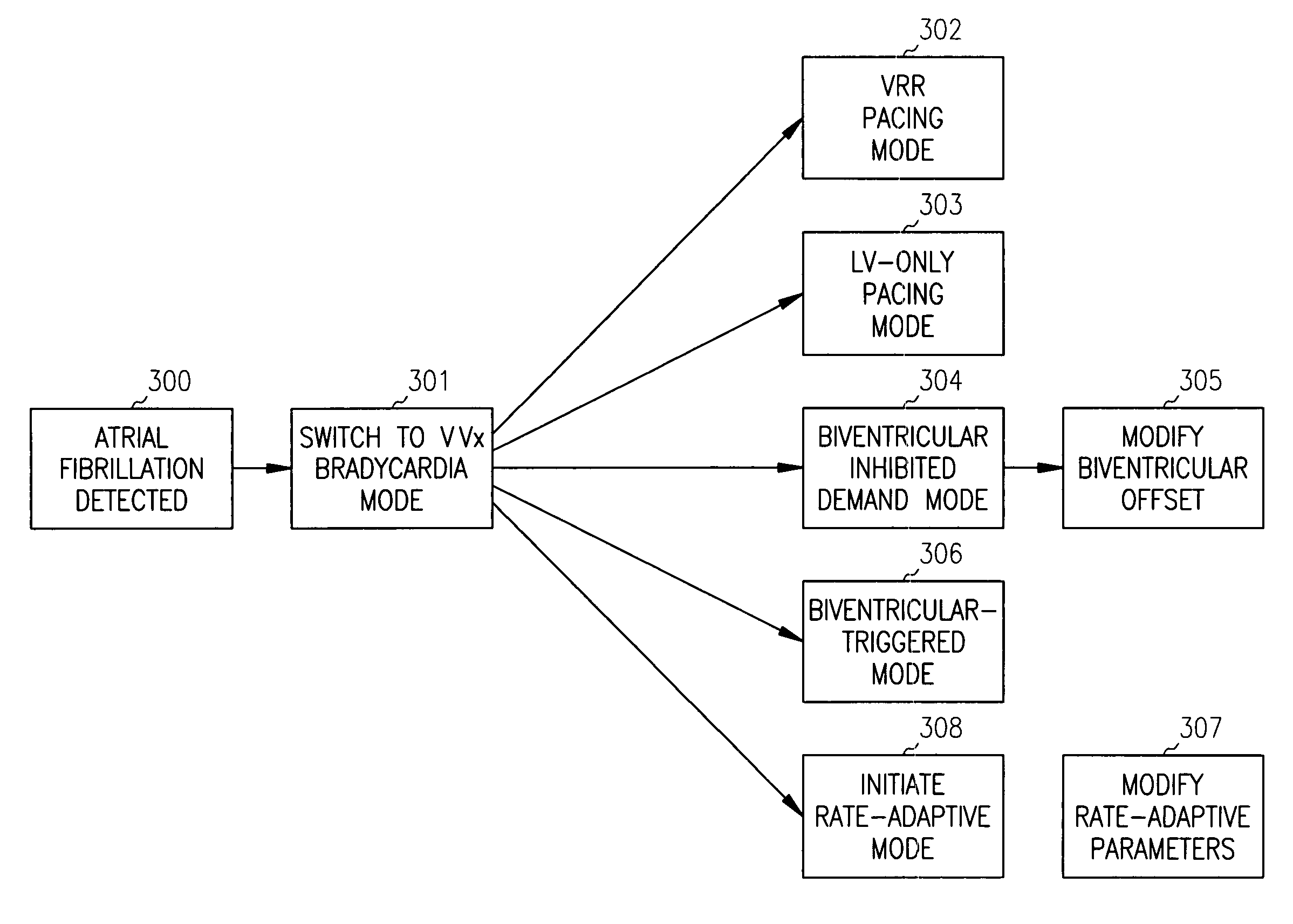
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS7142918B2Improve coordinationHigh outputHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCongestive heart failure chf
A method for operating a cardiac pacemaker in which the mode of operation of the pacemaker is altered in response to detecting an episode of atrial tachycardia. In accordance with the invention, the pacemaker's pacing mode is altered in a manner that attempts to maintain hemodynamic stability during the atrial tachycardia. Such a mode switch is particularly applicable to pacemaker patients suffering from some degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
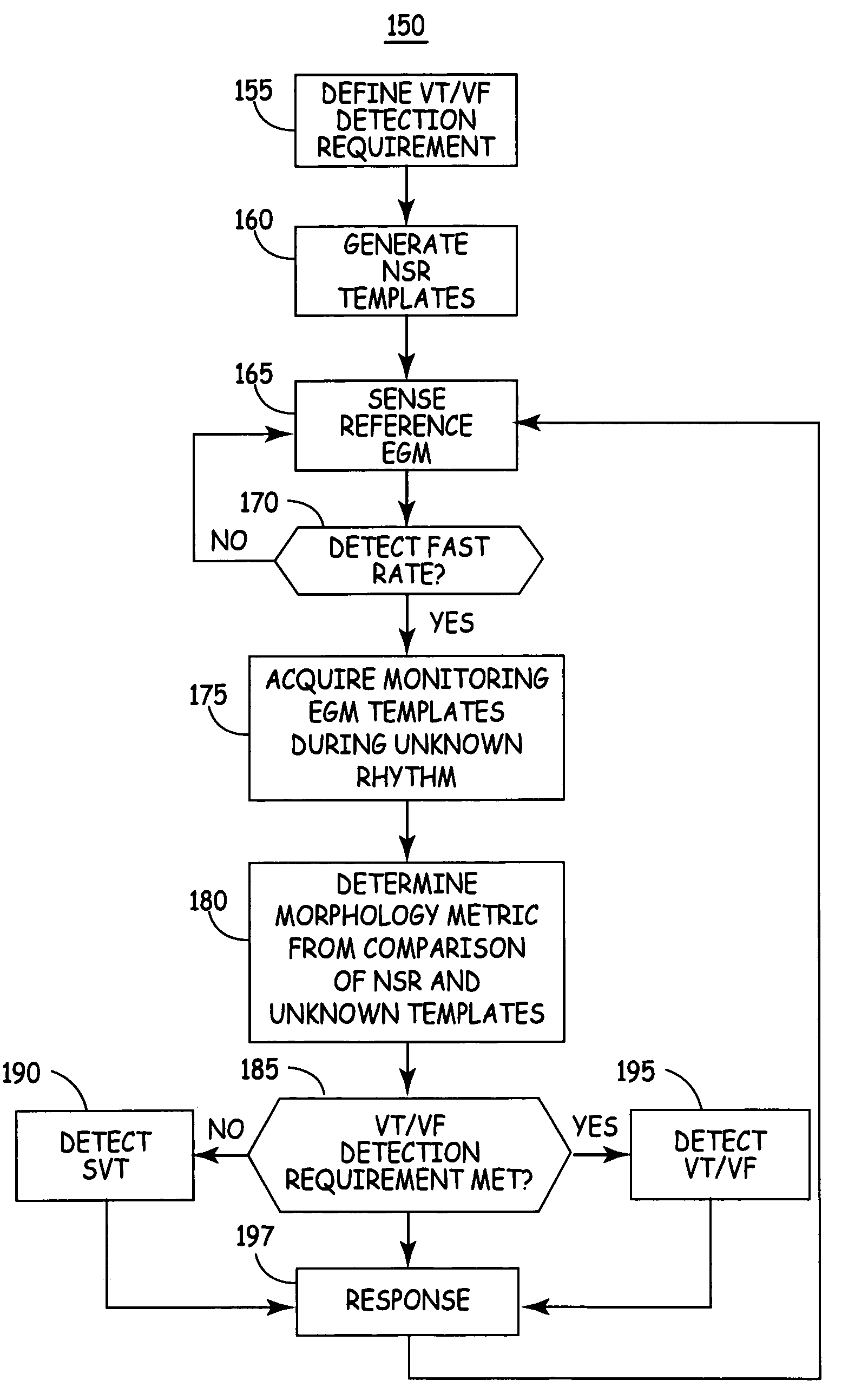
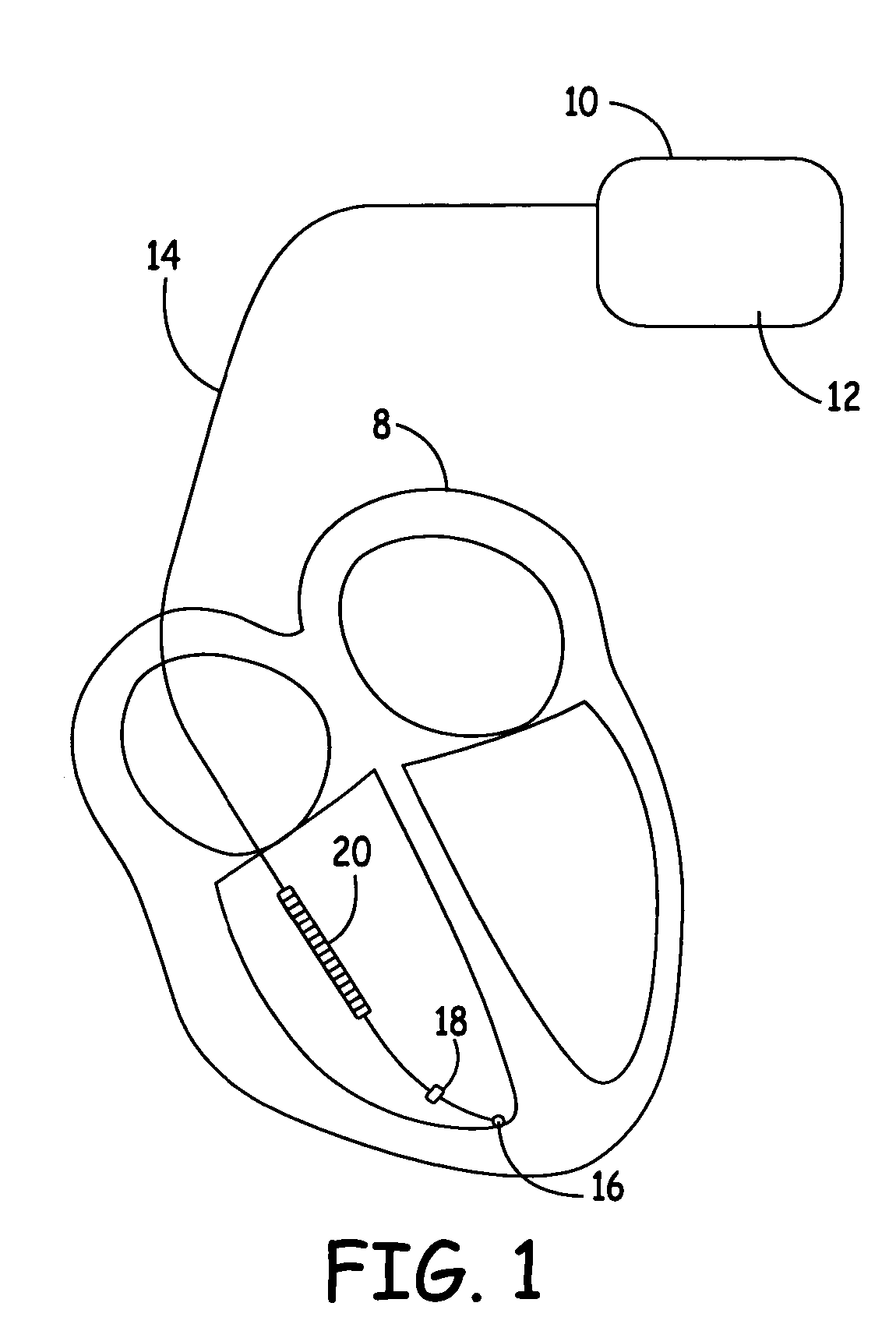
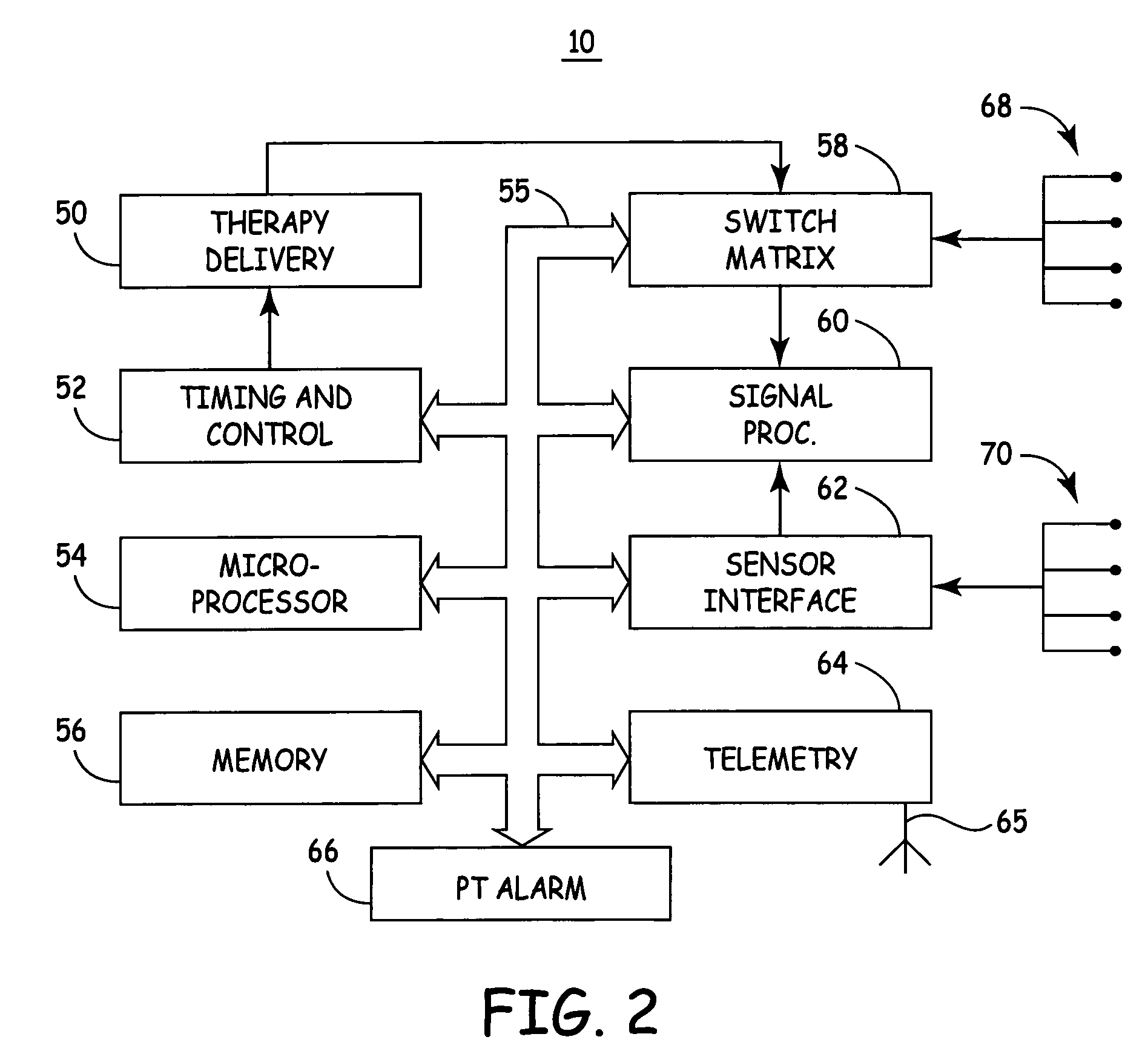
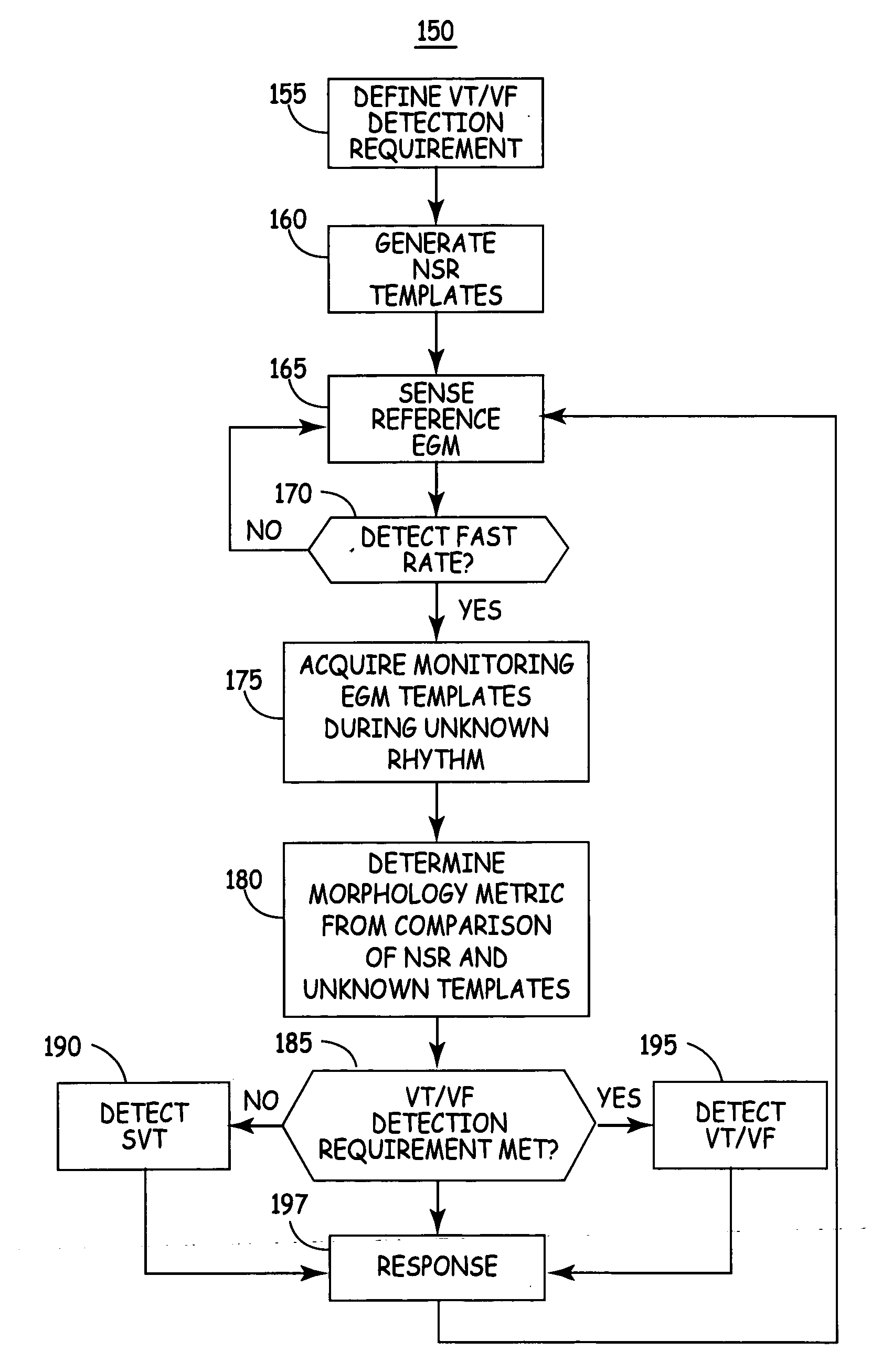
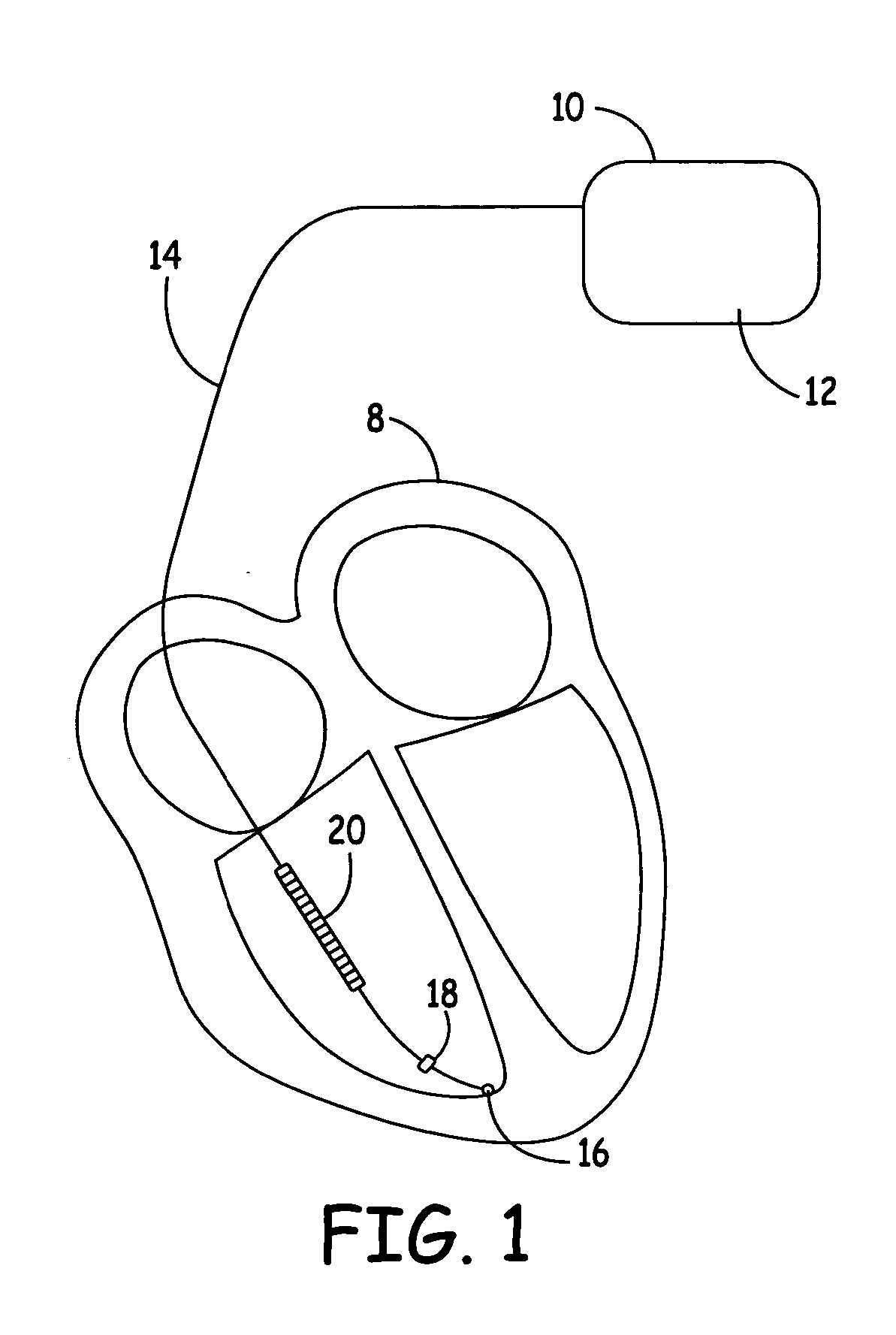
Method and apparatus for discriminating ventricular and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
A system and method are provided for discriminating supra-ventricular tachycardia (SVT) from ventricular tachycardia (VT). A monitoring EGM signal is acquired during a sensing window timed according to the time of R-wave detection on a reference EGM signal. A normal sinus rhythm (NSR) template is generated using the monitoring EGM signal during the time-referenced sensing window. During an unknown rhythm, the monitoring EGM signal sensed during the time-referenced sensing window is compared to the NSR template for use in computing a morphology metric. The morphology metric is compared to a VT / VF detection threshold for discriminating SVT from VT / VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for discriminating ventricular and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
A system and method are provided for discriminating supra-ventricular tachycardia (SVT) from ventricular tachycardia (VT). A monitoring EGM signal is acquired during a sensing window timed according to the time of R-wave detection on a reference EGM signal. A normal sinus rhythm (NSR) template is generated using the monitoring EGM signal during the time-referenced sensing window. During an unknown rhythm, the monitoring EGM signal sensed during the time-referenced sensing window is compared to the NSR template for use in computing a morphology metric. The morphology metric is compared to a VT / VF detection threshold for discriminating SVT from VT / VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Catheter for treating irregular heart pulse
A catheter for treating irregular heart pulse comprises a catheter shaft of a double-cylinder structure where an inner cylinder shaft is slidably inserted in an outer cylinder shaft, a balloon installed so as to straddle between the tip portion of the inner cylinder shaft and the tip portion of the outer cylinder shaft, a pair of high frequency current-carrying electrodes of which at least one electrode is provided inside the balloon, and a temperature sensor for monitoring the temperature in the balloon. The front edge portion of the balloon at least in a deflated state is projected to more forward than the tip portion of the inner cylinder shaft. Alternatively, a tube that is more flexible than the inner cylinder shaft is provided on the tip portion of the inner cylinder shaft.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
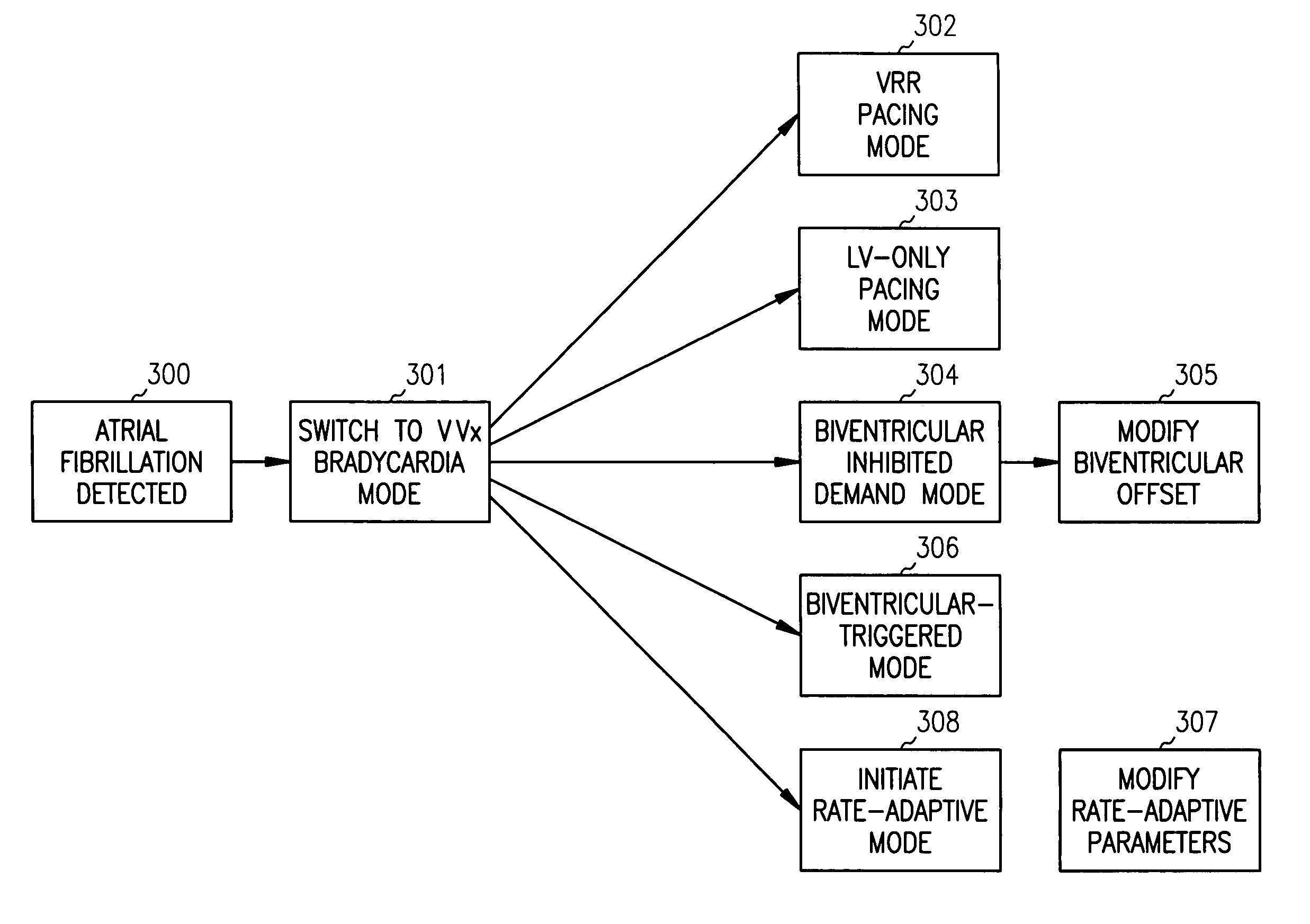
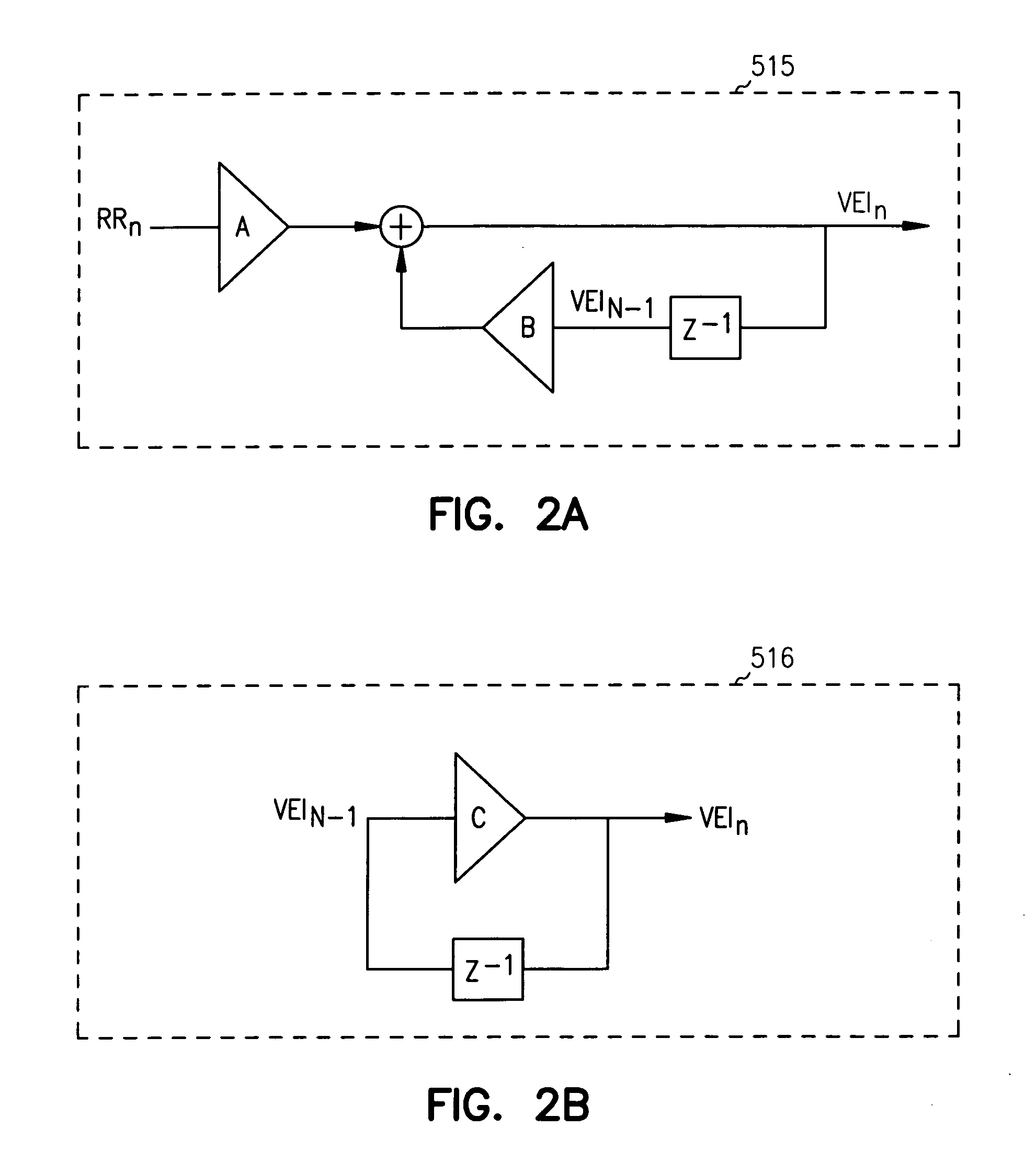
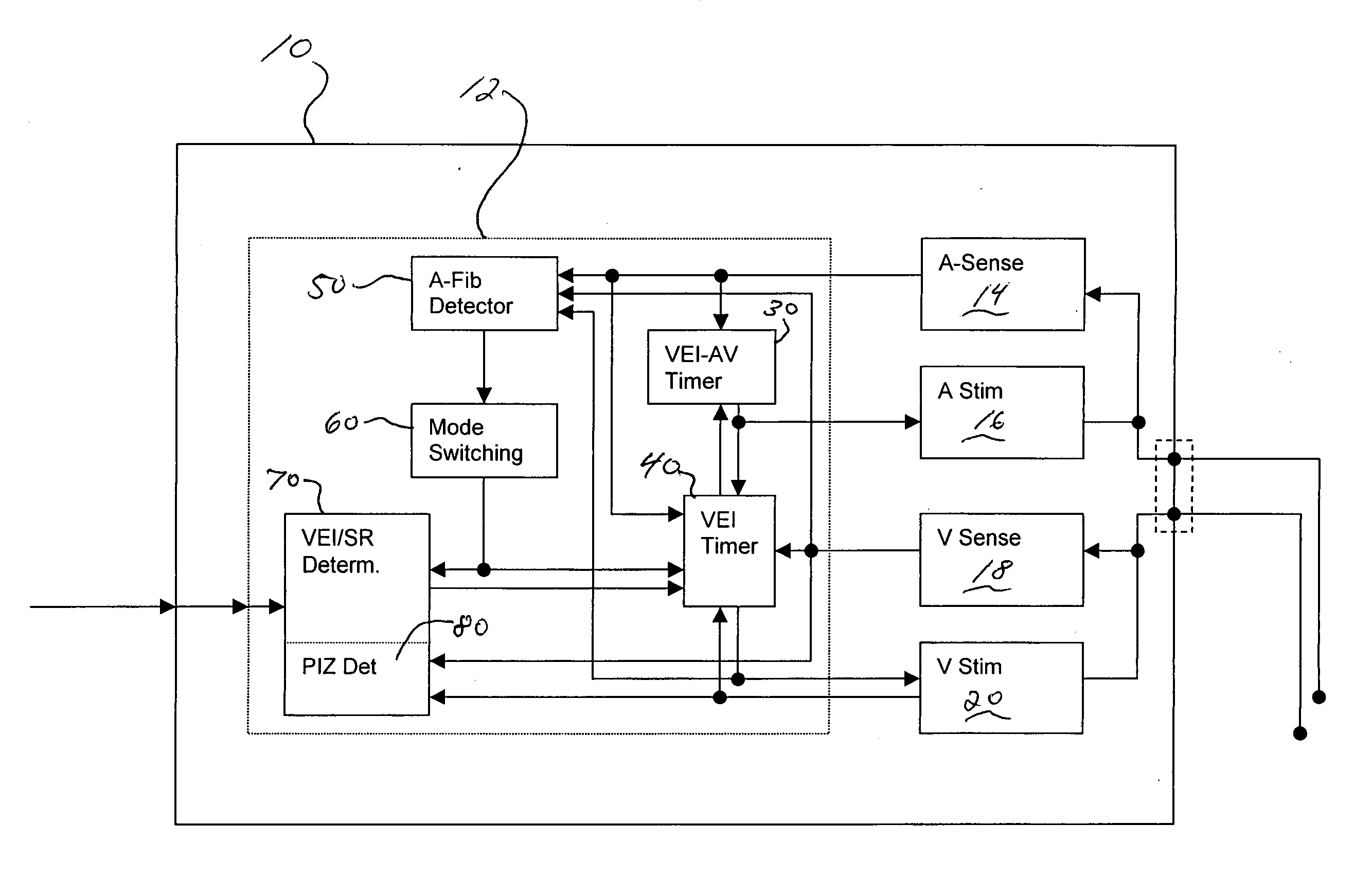
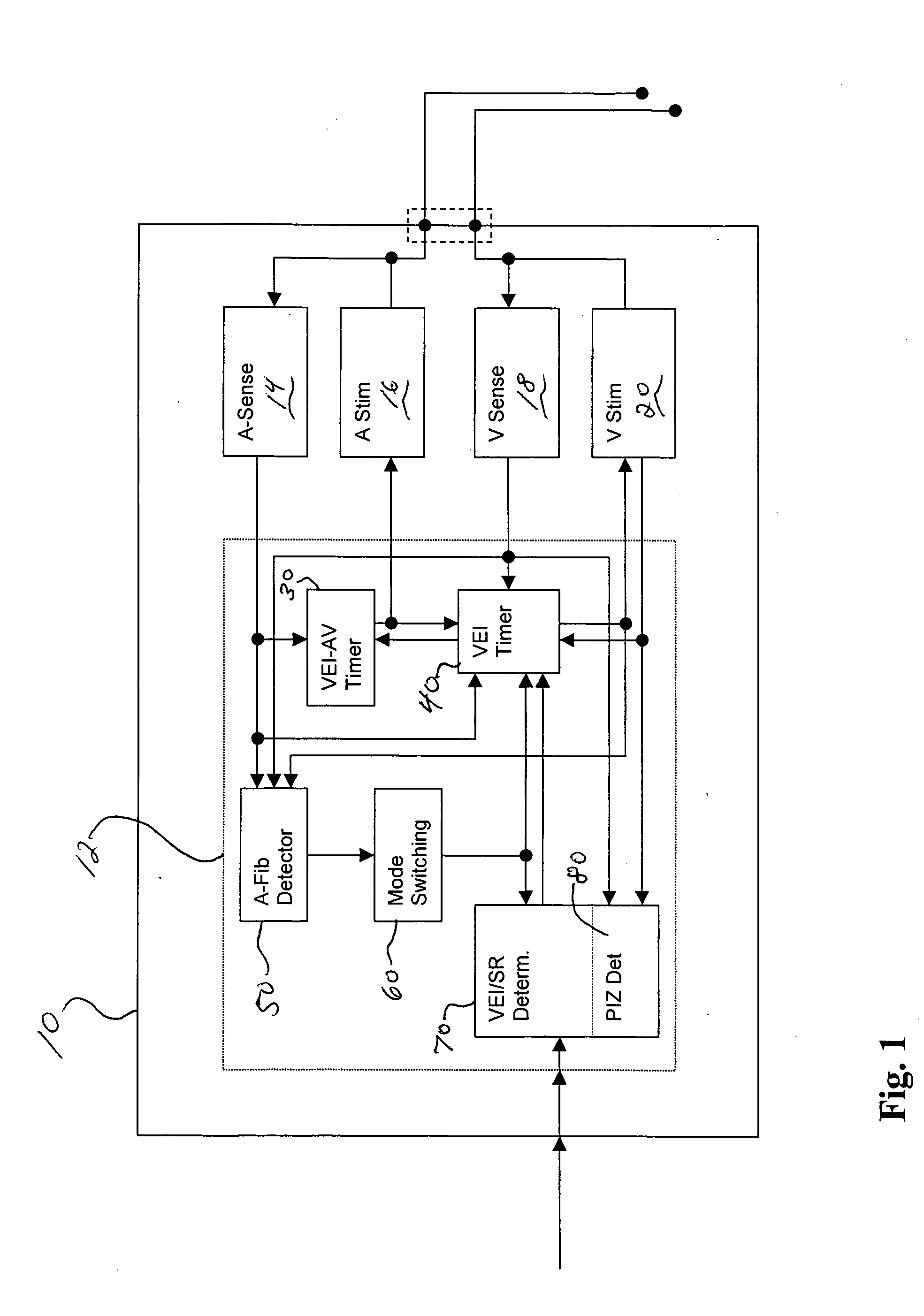
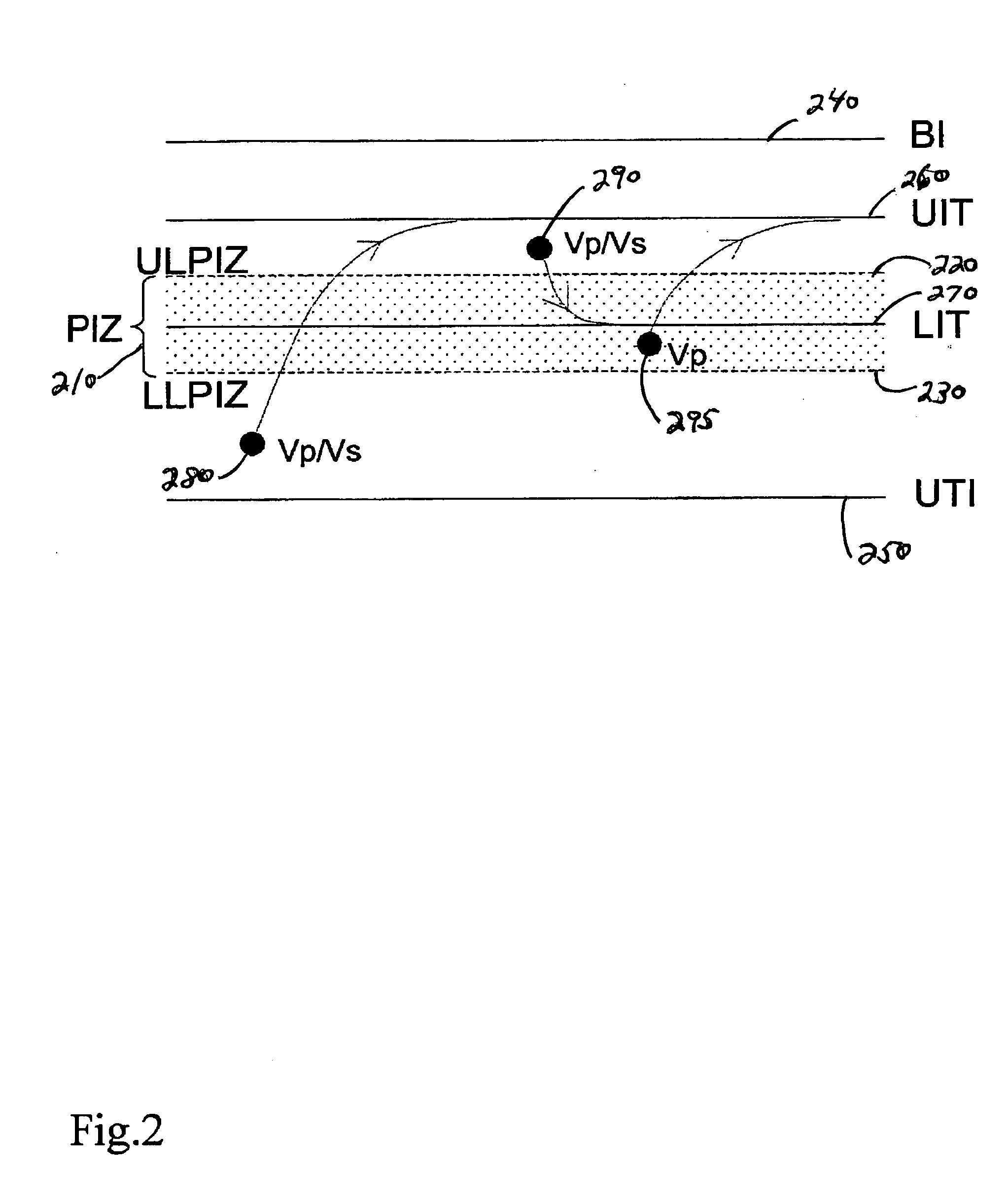
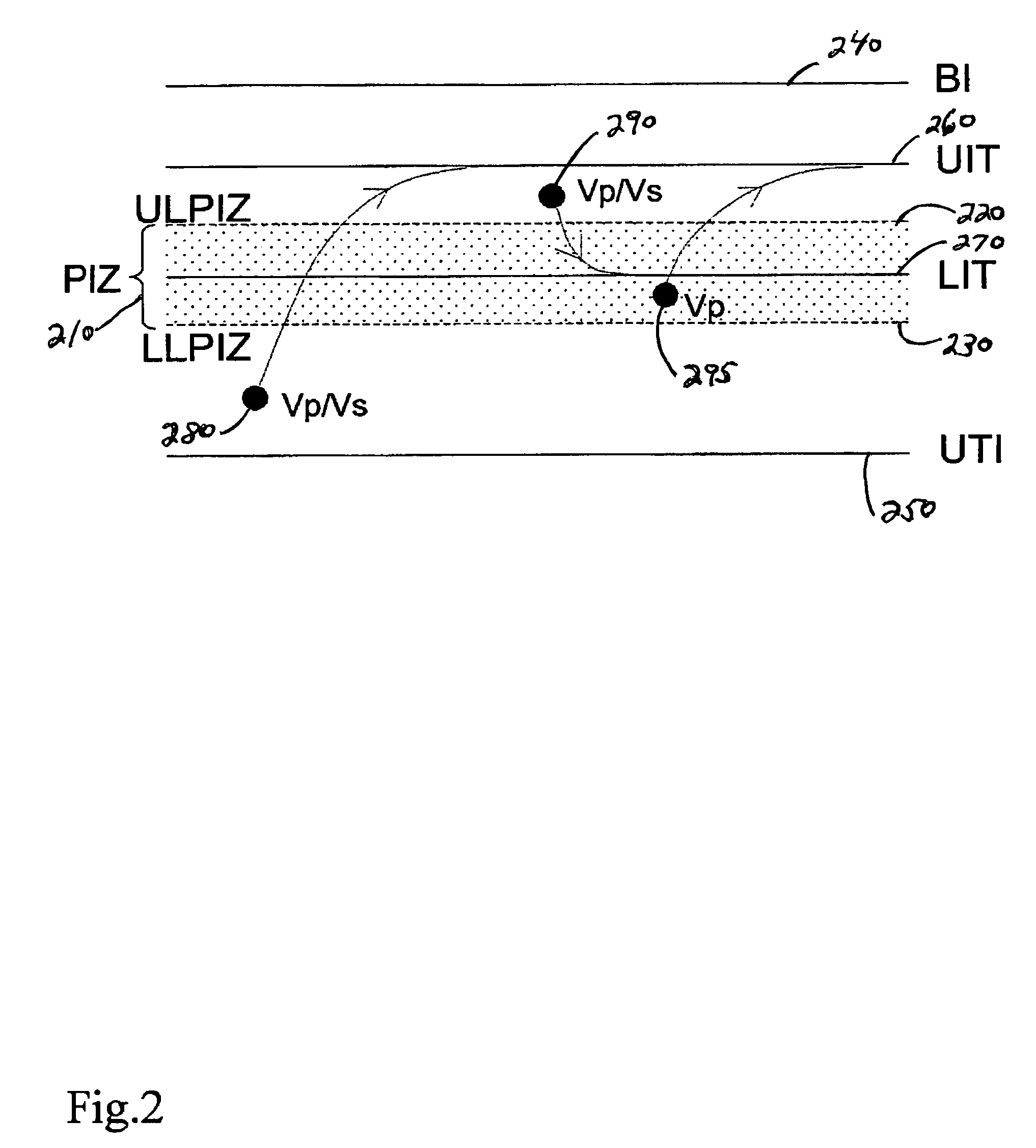
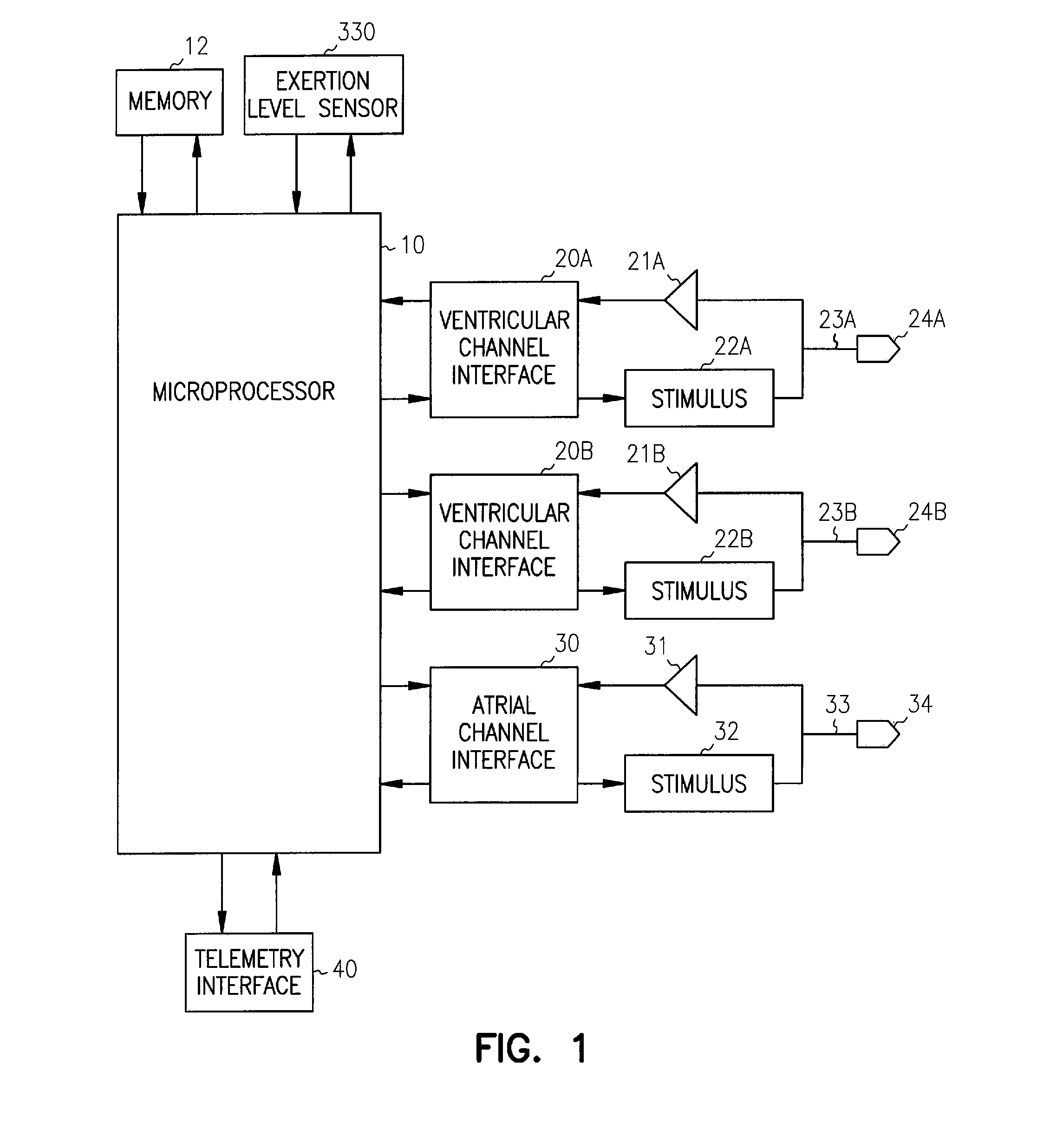
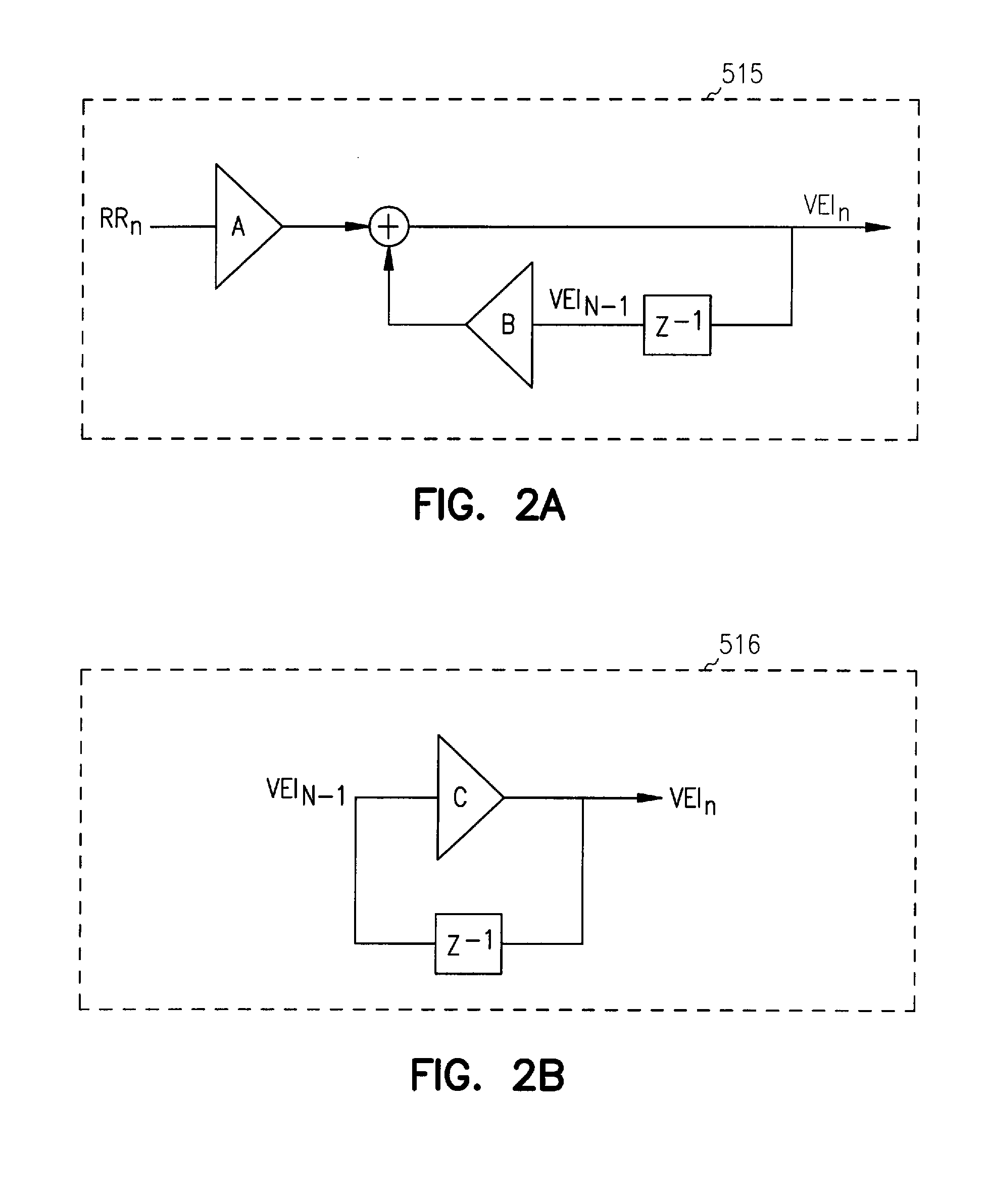
Adaptive ventricular rate smoothing during atrial fibrillation
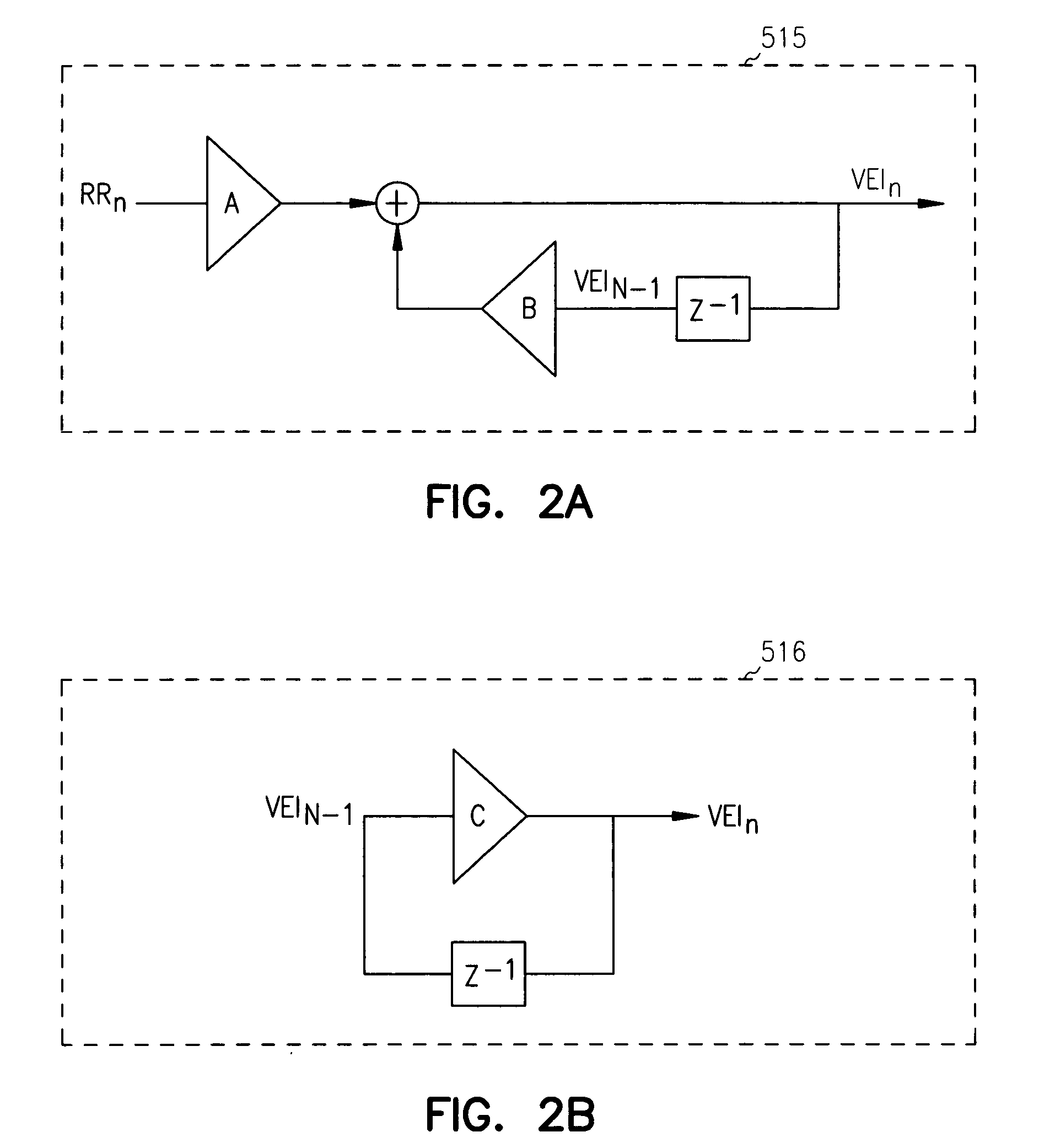
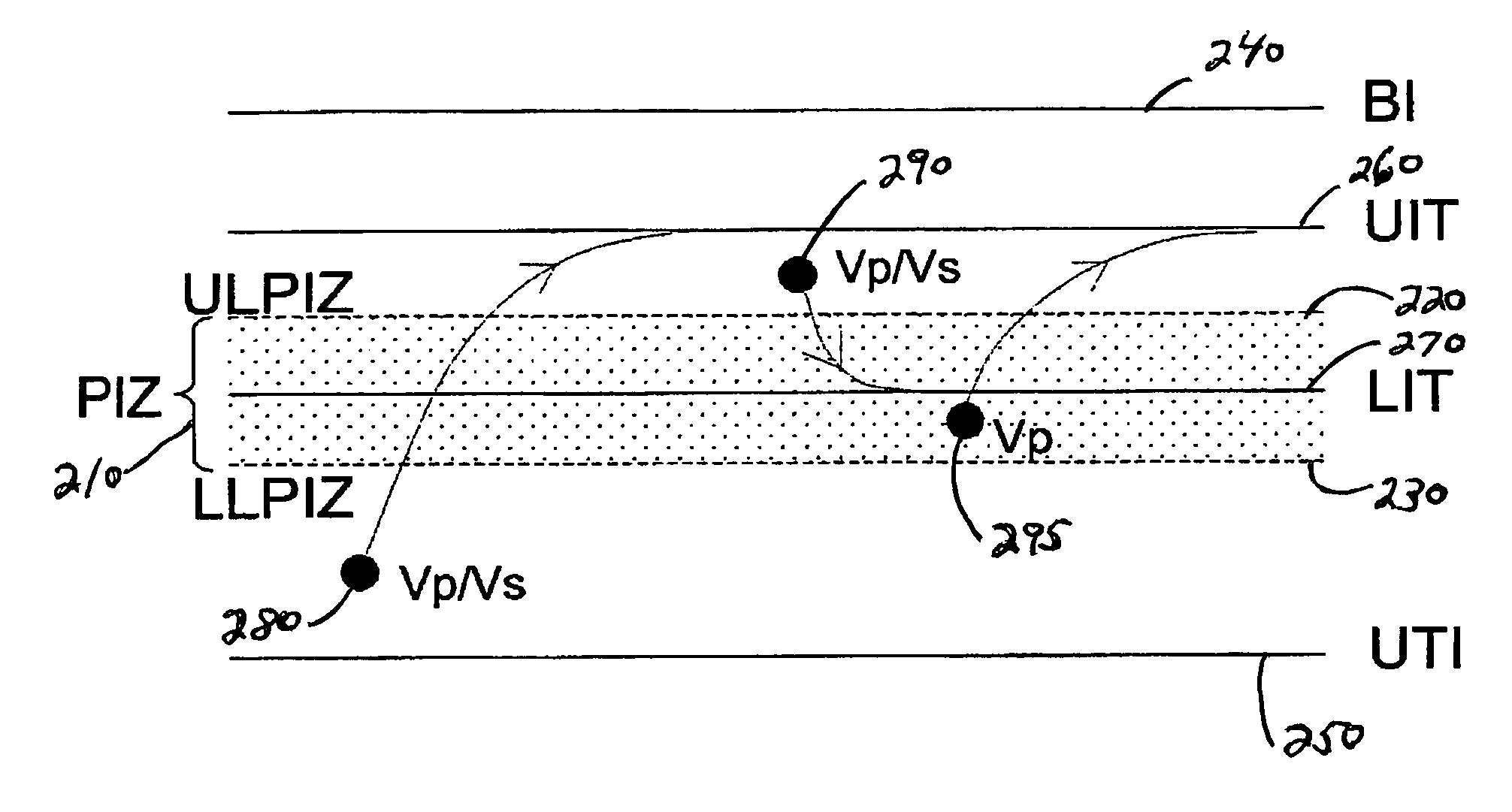
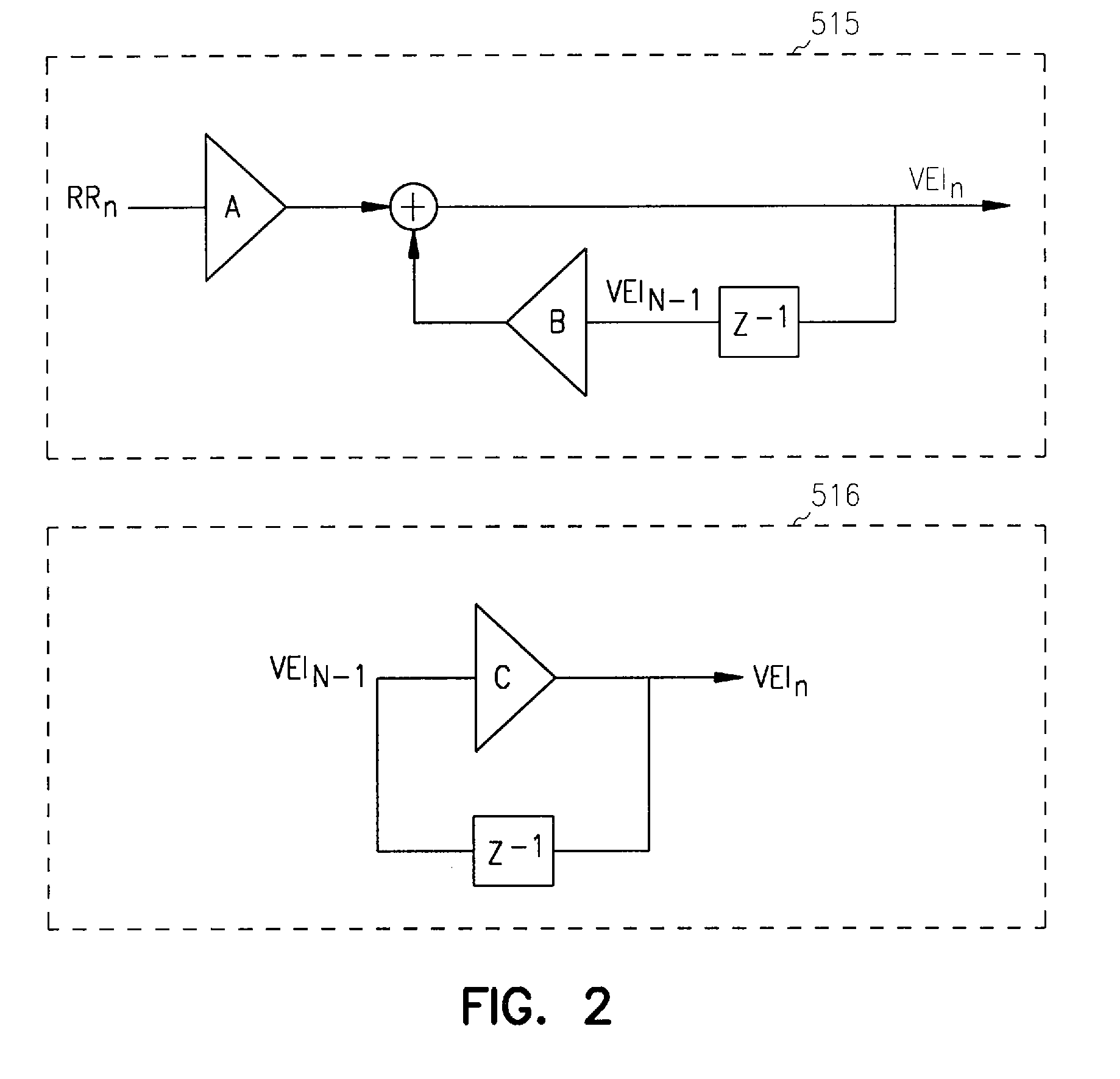
An implantable cardiac device is provided for adaptive ventricular rate smoothing during atrial fibrillation (AF). When AF is detected, the operation of the device is switched to non-atrial synchronized pacing mode such as DDI, DDIR, VDI, VDIR, VVI, or VVIR. The ventricular escape interval (VEI) is beat-by-beat modulated around a physiological interval zone (PIZ), which is determined by the pre-arrhythmia ventricular rate or the output of rate responsive sensor. The VEI remains unchanged if the preceding ventricular event is sensed and its RR interval is within the PIZ. Otherwise, the VEI is decreased asymptotically toward a lower interval threshold if the preceding RR interval is longer than the upper limit of the PIZ, or the VEI is increased asymptotically toward an upper interval threshold if the preceding RR interval is shorter than the upper limit of the PIZ. The step of incrementing or decrementing the VEI is adaptive to the absolute difference value between the preceding RR interval and the asymptotic interval threshold to ensure fast recovery of deviant RR interval toward the PIZ and to reduce the amount of high rate ventricular paces after a ventricular sense with very short coupling interval.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS7212860B2Improve coordinationIncrease cardiac outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCongestive heart failure chf
A method for operating a cardiac pacemaker in which the mode of operation of the pacemaker is altered in response to detecting an episode of atrial tachycardia. In accordance with the invention, the pacemaker's pacing mode is altered in a manner that attempts to maintain hemodynamic stability during the atrial tachycardia. Such a mode switch is particularly applicable to pacemaker patients suffering from some degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Adaptive ventricular rate smoothing during atrial fibrillation
An implantable cardiac device is provided for adaptive ventricular rate smoothing during atrial fibrillation (AF). When AF is detected, the operation of the device is switched to non-atrial synchronized pacing mode such as DDI, DDIR, VDI, VDIR, VVI, or VVIR. The ventricular escape interval (VEI) is beat-by-beat modulated around a physiological interval zone (PIZ), which is determined by the pre-arrhythmia ventricular rate or the output of rate responsive sensor. The VEI remains unchanged if the preceding ventricular event is sensed and its RR interval is within the PIZ. Otherwise, the VEI is decreased asymptotically toward a lower interval threshold if the preceding RR interval is longer than the upper limit of the PIZ, or the VEI is increased asymptotically toward an upper interval threshold if the preceding RR interval is shorter than the upper limit of the PIZ. The step of incrementing or decrementing the VEI is adaptive to the absolute difference value between the preceding RR interval and the asymptotic interval threshold to ensure fast recovery of deviant RR interval toward the PIZ and to reduce the amount of high rate ventricular paces after a ventricular sense with very short coupling interval.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Apparatus and method for ventricular rate regularization
InactiveUS7142915B2Less variabilityIncrease cardiac outputHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateBradycardia
A method and system for operating a cardiac rhythm management device which employs pacing therapy to regularize the ventricular rhythm. Such ventricular rate regularization may be employed with conventional bradycardia pacing, ventricular resynchronization therapy, or anti-tachyarrhythmia therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
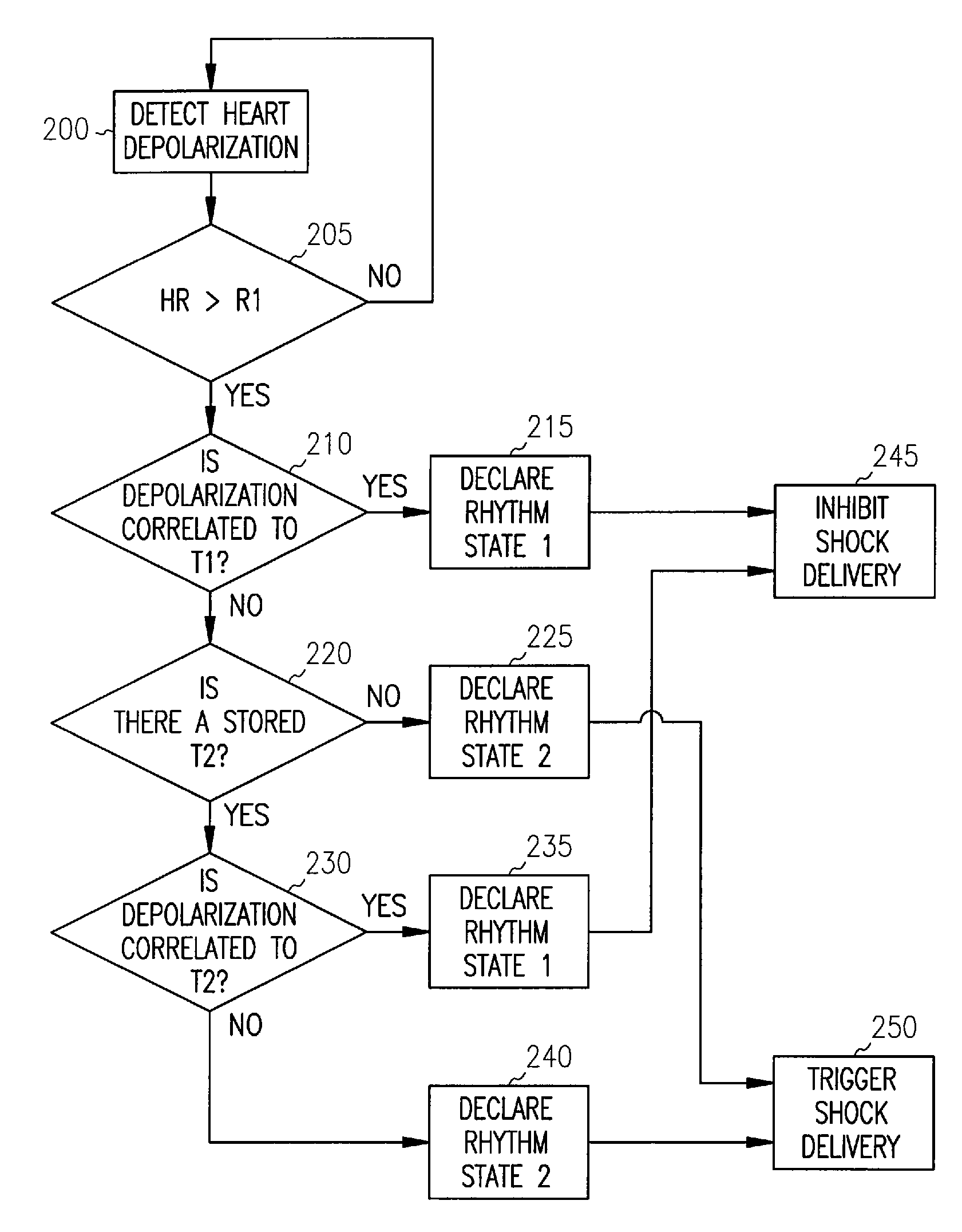
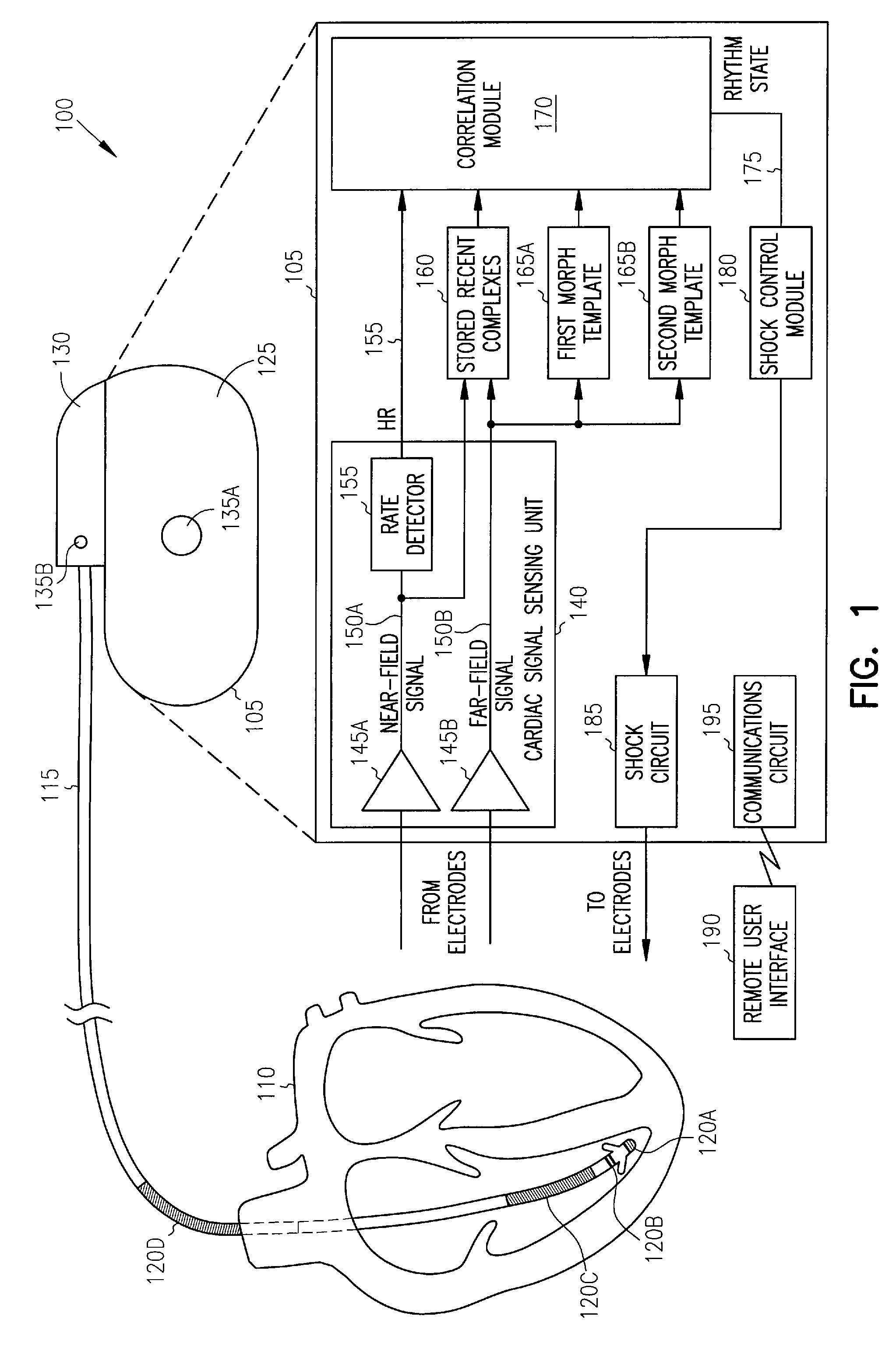
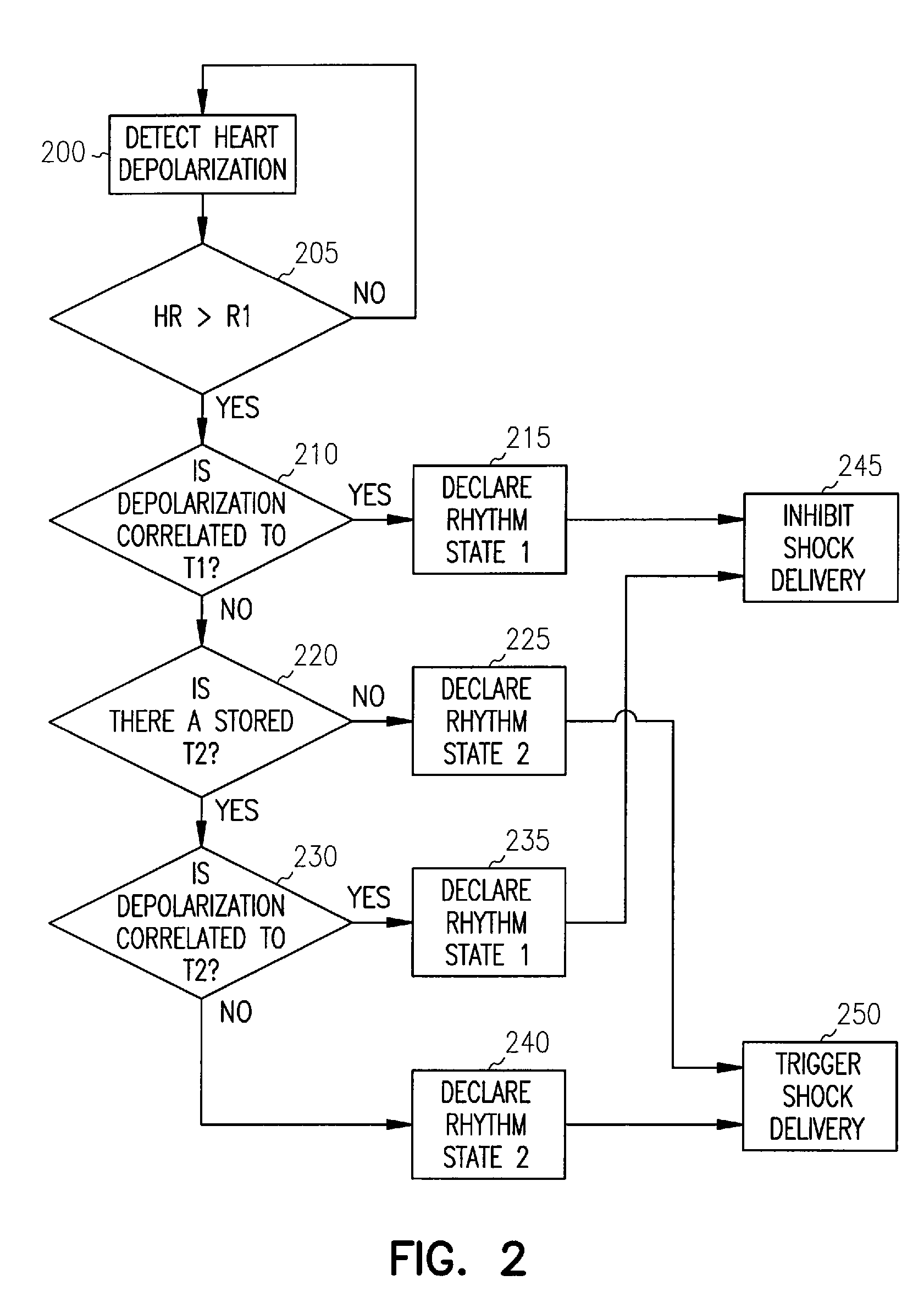
Cardiac rhythm management systems and methods using multiple morphology templates for discriminating between rhythms
InactiveUS7539536B2ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular TachyarrhythmiasActivity level
This document describes systems, devices, and methods that use multiple morphology templates for discriminating between rhythms, such as supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (SVTs) and ventricular tachyarrhythmias (VTs), for delivering a countershock in response to a VT episode, but withholding delivery of such a countershock in response to an SVT episode. In certain examples, the particular morphology used for storing morphological features is selected at least in part using a sensor-indicated activity level of a subject, or a metabolic need of the subject.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS20070288062A1Improve coordinationHigh outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsMedicineCardiac pacemaker electrode
A method for operating a cardiac pacemaker in which the mode of operation of the pacemaker is altered in response to detecting an episode of atrial tachycardia. In accordance with the invention, the pacemaker's pacing mode is altered in a manner that attempts to maintain hemodynamic stability during the atrial tachycardia. Such a mode switch is particularly applicable to pacemaker patients suffering from some degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
ActiveUS20110275921A1Improve accuracyIncrease ratingsElectrocardiographySensorsRadiologyVascular surgery
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, functional diagnosis and clinical electrophysiology of the heart. The invention consists in reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. An application of the method allows one to improve the accuracy of non-invasive diagnosis of cardiac rhythm disturbances and other cardio-vascular diseases.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
Prevention and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias
InactiveUS20110178014A1Promote recoveryLessen heart damagePeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsCardiac muscleGlucagon-like peptide-1
Compositions of the invention, including compounds that bind to a receptor for a glucagon-like peptide-1, an incretin, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), an exendin, or an agonist, an analog (preferably an agonist analog), a derivative, or a variant of any of aforementioned compounds, are used in the prevention and treatment of arrhythmias associated with cardiac ischemia, cardiac ischemia-perfusion and / or congestive heart failure. The invention relates to both the method and compositions for such treatment.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Av nodal stimulation during atrial tachyarrhythmia to prevent inappropriate therapy delivery
ActiveCN103517734AHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationVentricular rateVentricular Tachyarrhythmias
The disclosure describes techniques for delivering electrical stimulation to decrease the ventricular rate response during an atrial tachyarrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation. AV nodal stimulation is employed during an atrial tachyarrhythmia episode with rapid ventricular conduction to distinguish ventricular tachyarrhythmia from supraventricular tachycardia and thereby prevent delivering inappropriate therapy to a patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, functional diagnosis and clinical electrophysiology of the heart. The invention consists in reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. Based on reconstructed electrograms, isopotential, isochronous maps on realistic models of the heart are constructed, the dynamics of the myocardium excitation is reconstructed and electrophysiological processes in the cardiac muscle are diagnosed. Application of the method allows one to improve the accuracy of non-invasive diagnosis of cardiac rhythm disturbances and other cardio-vascular diseases.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS7805192B2Improve coordinationHigh outputHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac pacemaker
A method for operating a cardiac pacemaker in which the mode of operation of the pacemaker is altered in response to detecting an episode of atrial tachycardia. In accordance with the invention, the pacemaker's pacing mode is altered in a manner that attempts to maintain hemodynamic stability during the atrial tachycardia. Such a mode switch is particularly applicable to pacemaker patients suffering from some degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Heart stimulator detecting atrial arrhythmia by determining wall distension by impedance measuring
InactiveUS7908002B2Limit distensionIncrease pressureHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeHeart atrium
In an implantable pacemaker, pacing pulses are delivered to a ventricle in a P-wave synchronous mode as long as no atrial arrhythmia is detected, pacing pulses and a mode switch is made to deliver pacing pulses to the ventricle in a non-P-wave synchronous mode if atrial arrhythmia is detected. From an impedance signal measured in the atrium, atrial distention is determined and, in the non-P-wave synchronous mode, the delivery rate of the pacing pulses is increased to decrease the atrial distention during atrial arrhythmia.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Traditional Chinese medicine active part composition for curing cardio and cerebral vascular disease and its preparing method
InactiveCN1425430AGood treatment effectMyocardial infarct size improvedUnknown materialsCardiovascular disorderClinical efficacySalvianolic acid B
The composition of Chinese medicine effective parts for treating cardiac and cerebral vascular diseases consists of general salvianolic acid and general astragalus saponin in certain ratio. The compound medicine has raised pharmacological effect and clinical curative effect and reduced impurity content. It may be prepared into various preparation forms. It is used in treating coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, myocardial ischemia, heart failure, arrhythmia, cerebral infarction and cerebral ischemia; and is safe, effective stable, controllable and convenient.
Owner:山东希尔康泰药业有限公司
Unit doses, aerosols, kits, and methods for treating heart conditions by pulmonary administration
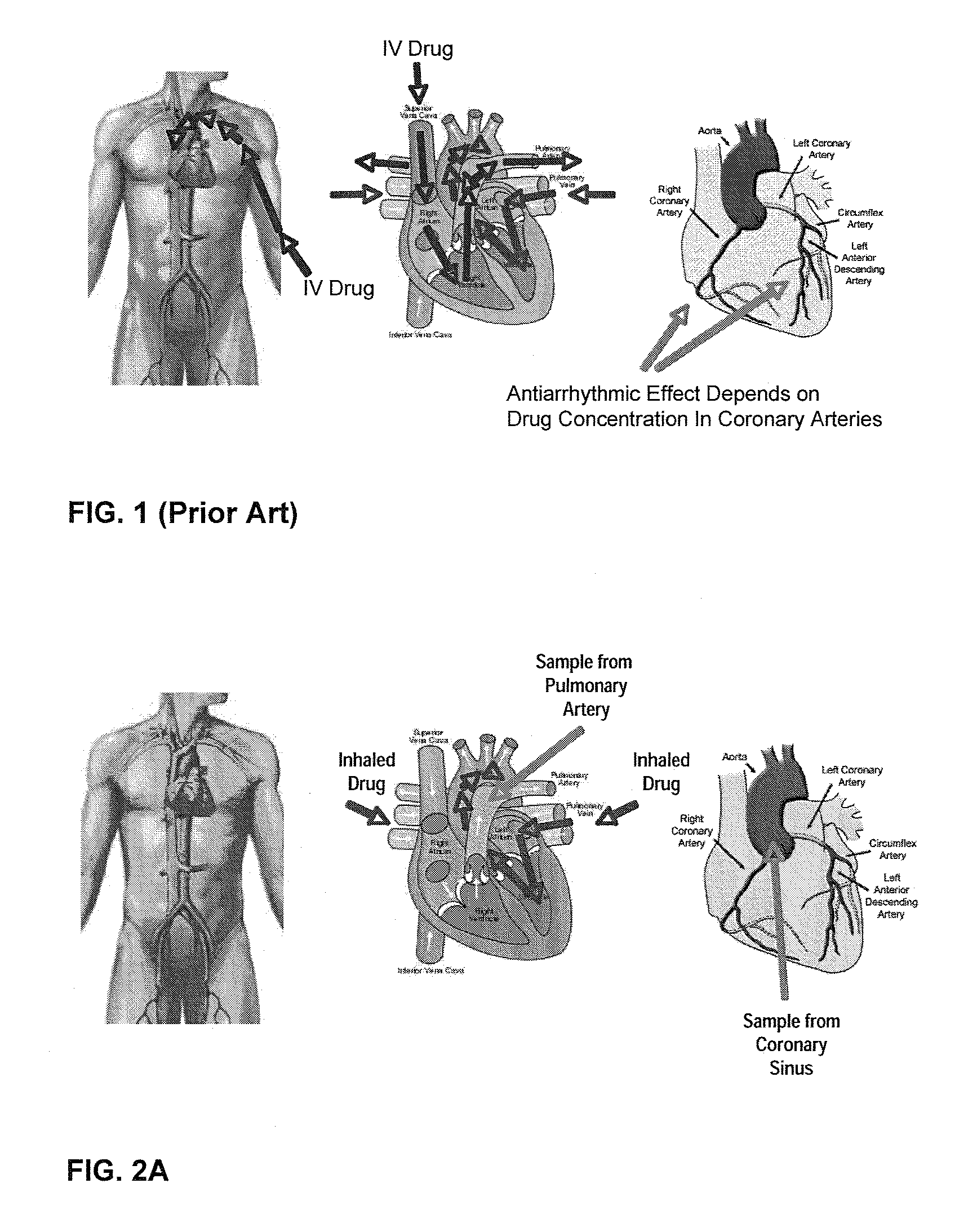
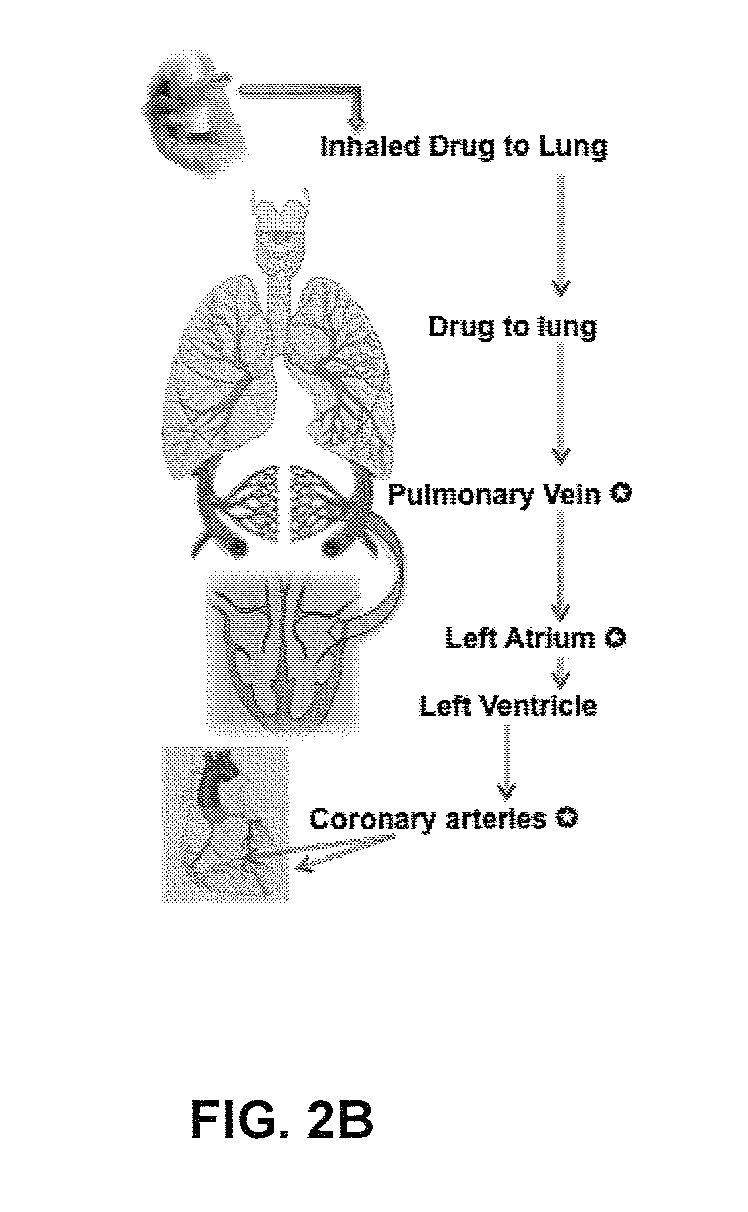
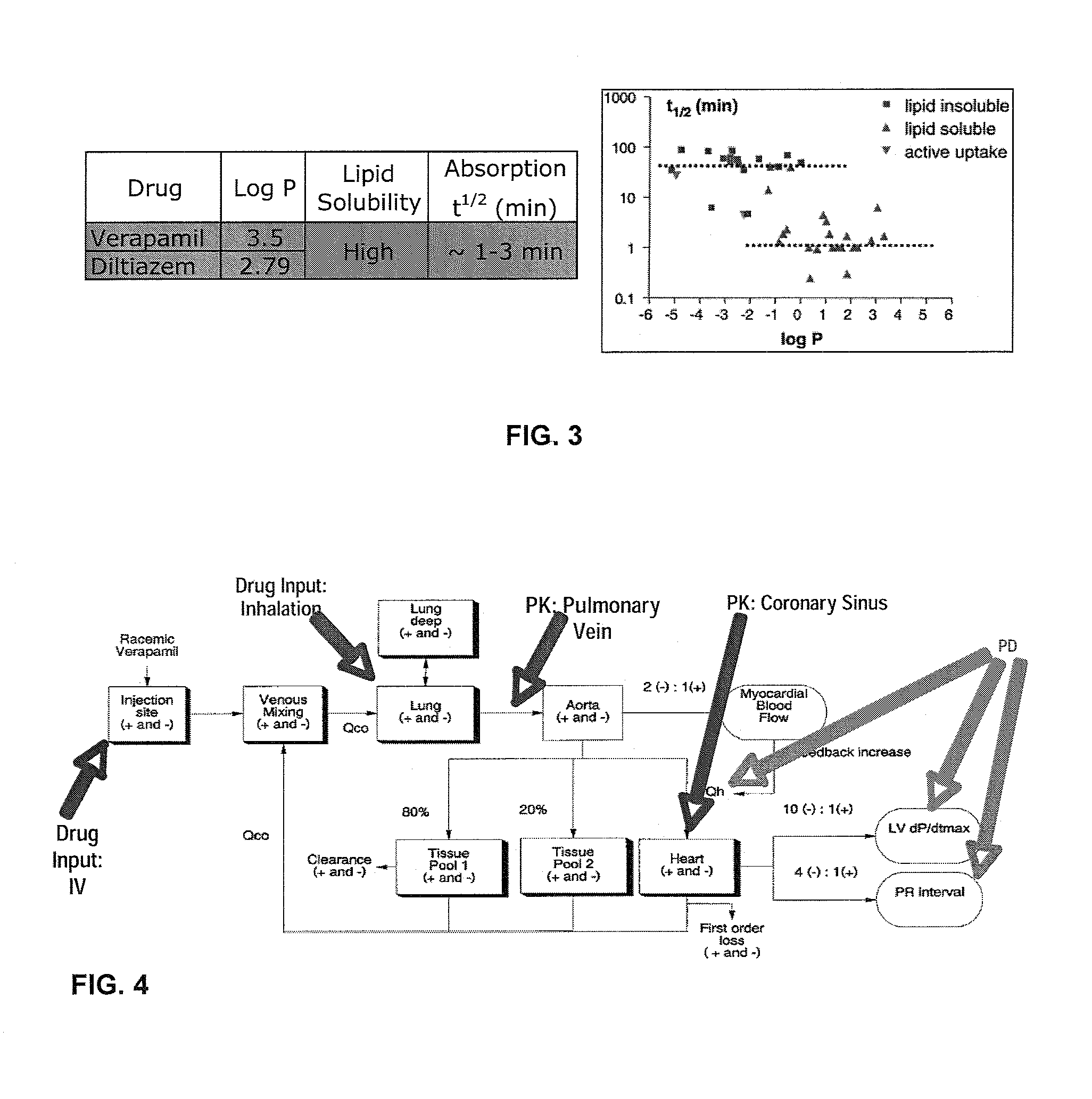
Methods of treating atrial arrhythmia include administering an effective amount of at least one antiarrhythmic pharmaceutical agent to a patient in need thereof, such that the at least one antiarrhythmic pharmaceutical agent first enters the heart through the pulmonary vein to the left atrium. Other methods of treating atrial arrhythmia include administering by inhalation an effective amount of at least one antiarrhythmic pharmaceutical agent to a patient in need thereof. An amount of the at least one antiarrhythmic pharmaceutical agent may peak in the coronary sinus of the heart at a time ranging from 10 seconds to 30 minutes from initiation of the administering. Unit doses, aerosols, and kits are also contemplated.
Owner:INCARDA THERAPEUTICS
Methods of treating a cardiac arrhythmia by thoracoscopic production of a Cox maze III lesion set
Methods of treating a subject for a cardiac arrhythmia are provided. Aspects of the methods include thoracoscopically producing a cardiac Cox maze III set of lesions in cardiac tissue of the subject in a manner sufficient to treat the subject for the cardiac arrhythmia.
Owner:ATRICURE
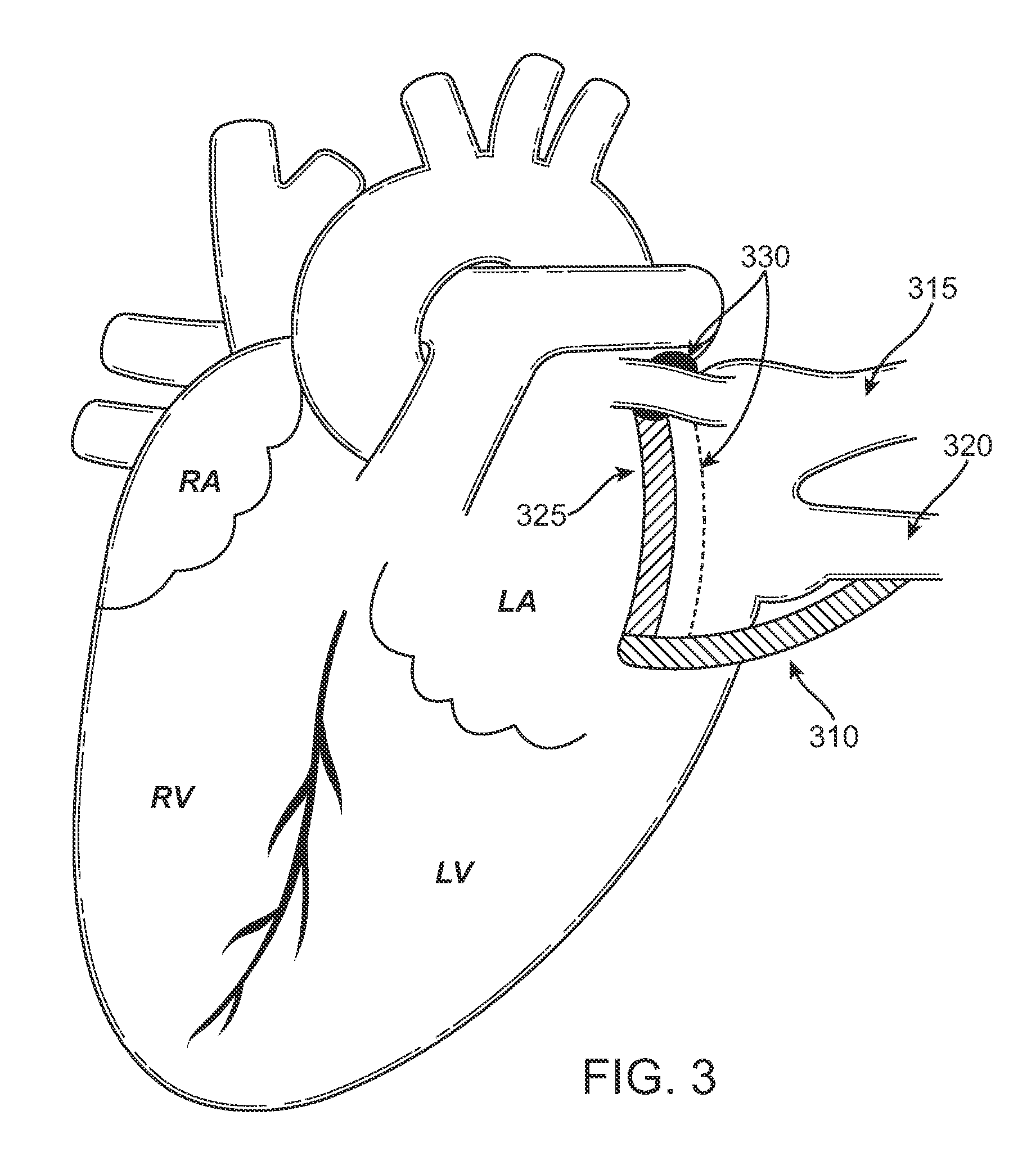
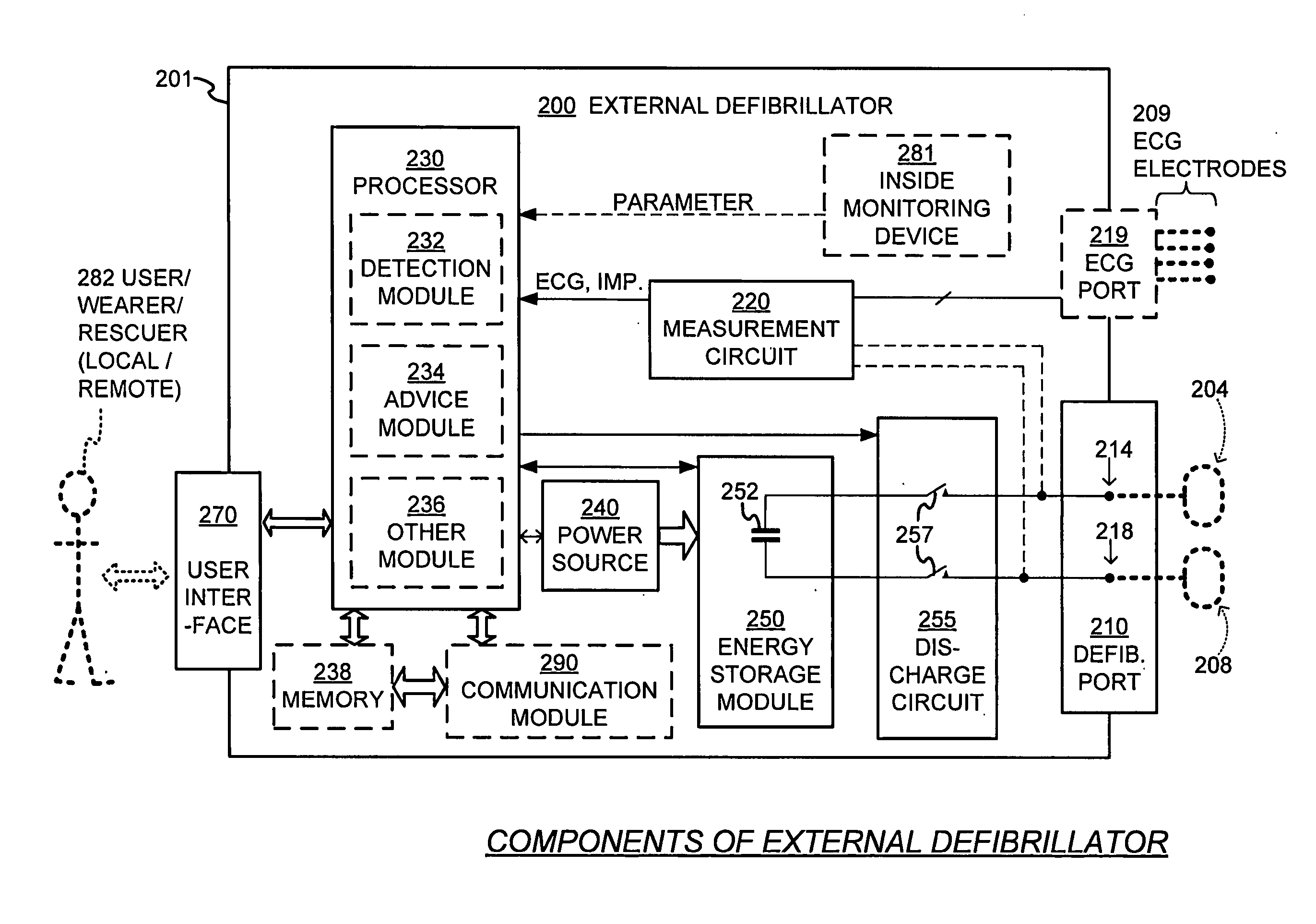
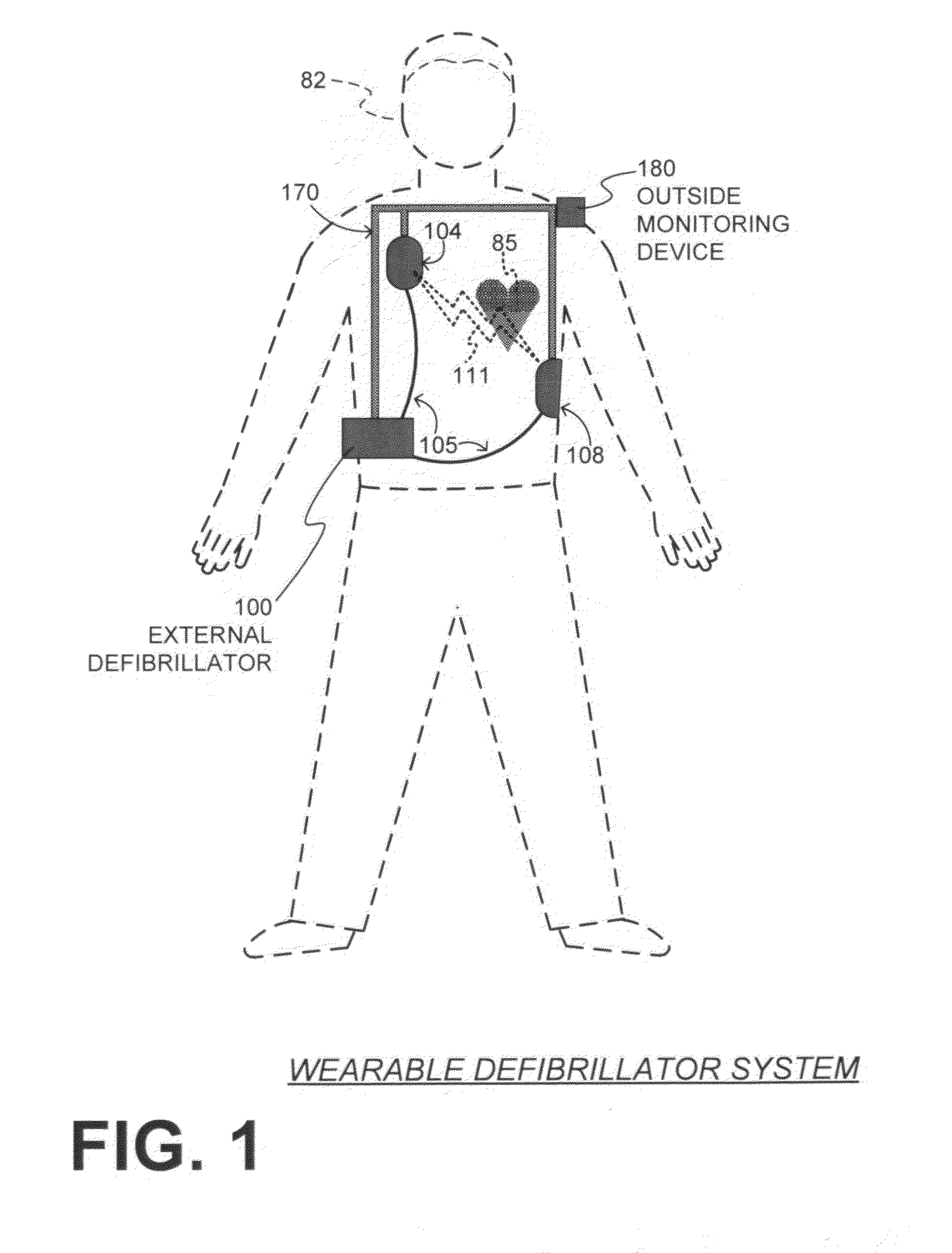
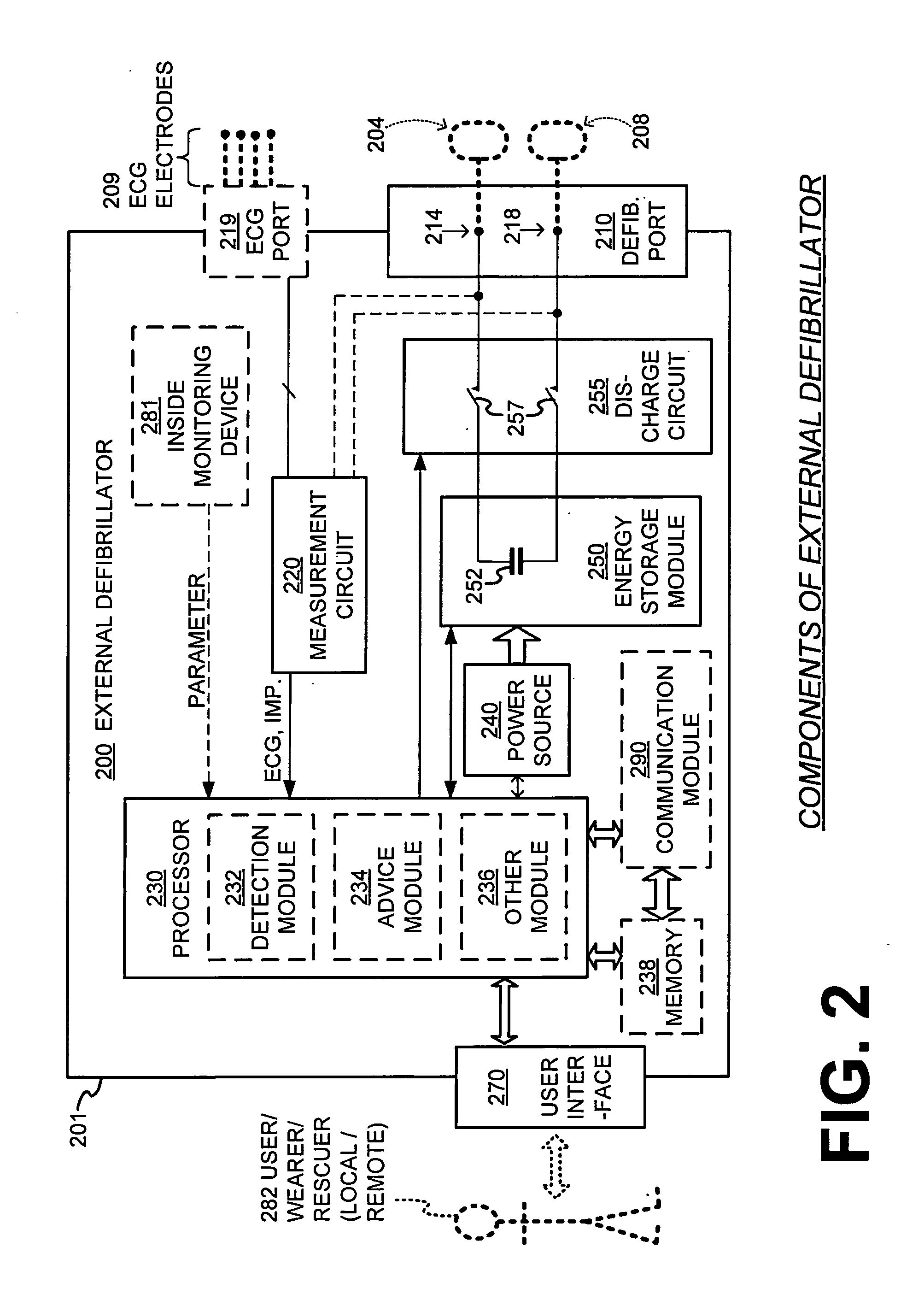
Wearable cardiac defibrillator system with Anti-bradyarrhythmia pacing & methods
ActiveUS20140088660A1Prevent the bradycardia from becoming worseHeart defibrillatorsBradycardiaConsciousness
In one embodiment, a wearable defibrillation system may sense whether its wearer meets an unconscious bradyarrhythmia condition that can be associated with becoming unconscious. Even though such a condition might not be helped with a defibrillation pulse, the wearable-defibrillation system may still administer pacing pulses to prevent the bradycardia from becoming worse, such as a sudden cardiac arrest. In some embodiments, the pacing pulses are administered at a frequency too slow for the patient to regain consciousness. An advantage is that, because the patient remains unconscious, he does not experience the sometimes severe discomfort due to the pacing pulses.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
ActiveUS8660639B2Improve accuracyIncrease ratingsElectrocardiographySensorsChest regionVascular surgery
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, functional diagnosis and clinical electrophysiology of the heart. The invention consists in reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. An application of the method allows one to improve the accuracy of non-invasive diagnosis of cardiac rhythm disturbances and other cardio-vascular diseases.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
Pyrolytic diterpenoid alkaloid compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111440112AExtended incubation periodReduce the incidence of ventricular tachycardia (VT)Organic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical drugAlkaloid
The invention provides a pyrolytic diterpenoid alkaloid compound shown as a formula I shown in the specification, or a salt, a stereoisomer or a solvate thereof, and a preparation method of the pyrolytic diterpenoid alkaloid compound. The invention also provides application of the compound or the salt thereof, the stereoisomer thereof or the solvate thereof in preparing medicines for preventing and / or treating ventricular premature beat, ventricular tachycardia and antiarrhythmia, and the clinical prospect is excellent.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com