System and method for monitoring and diagnosing patient condition based on wireless sensor monitoring data
a wireless sensor and patient technology, applied in the field of system and method for monitoring and diagnosing patient condition based on wireless sensor monitoring data, can solve the problems of icds that can also have lead failures after being worn by patients, limiting factors of implantable devices, and other undesirable effects on the quality of life of patients, so as to improve the generation of ecg data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
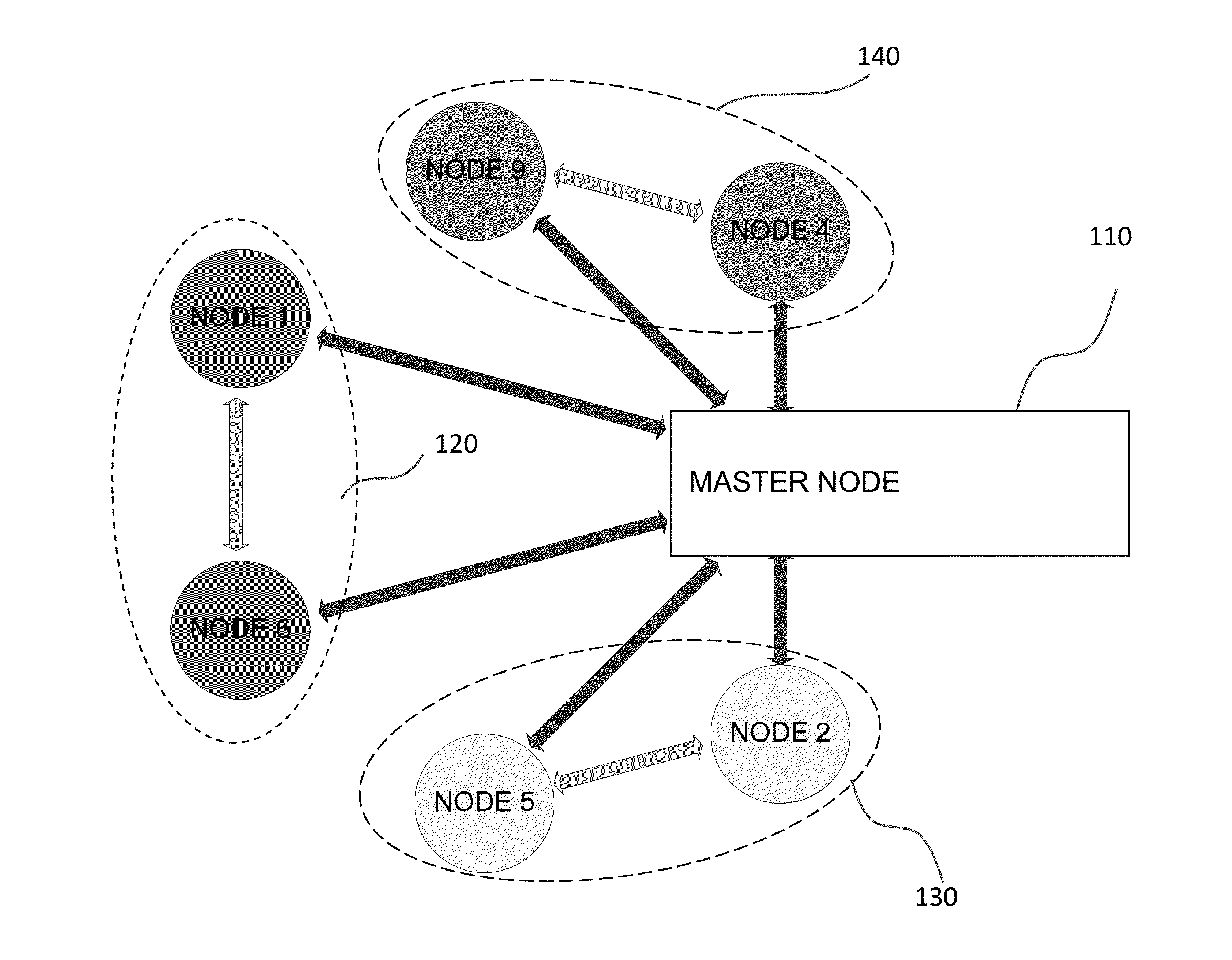
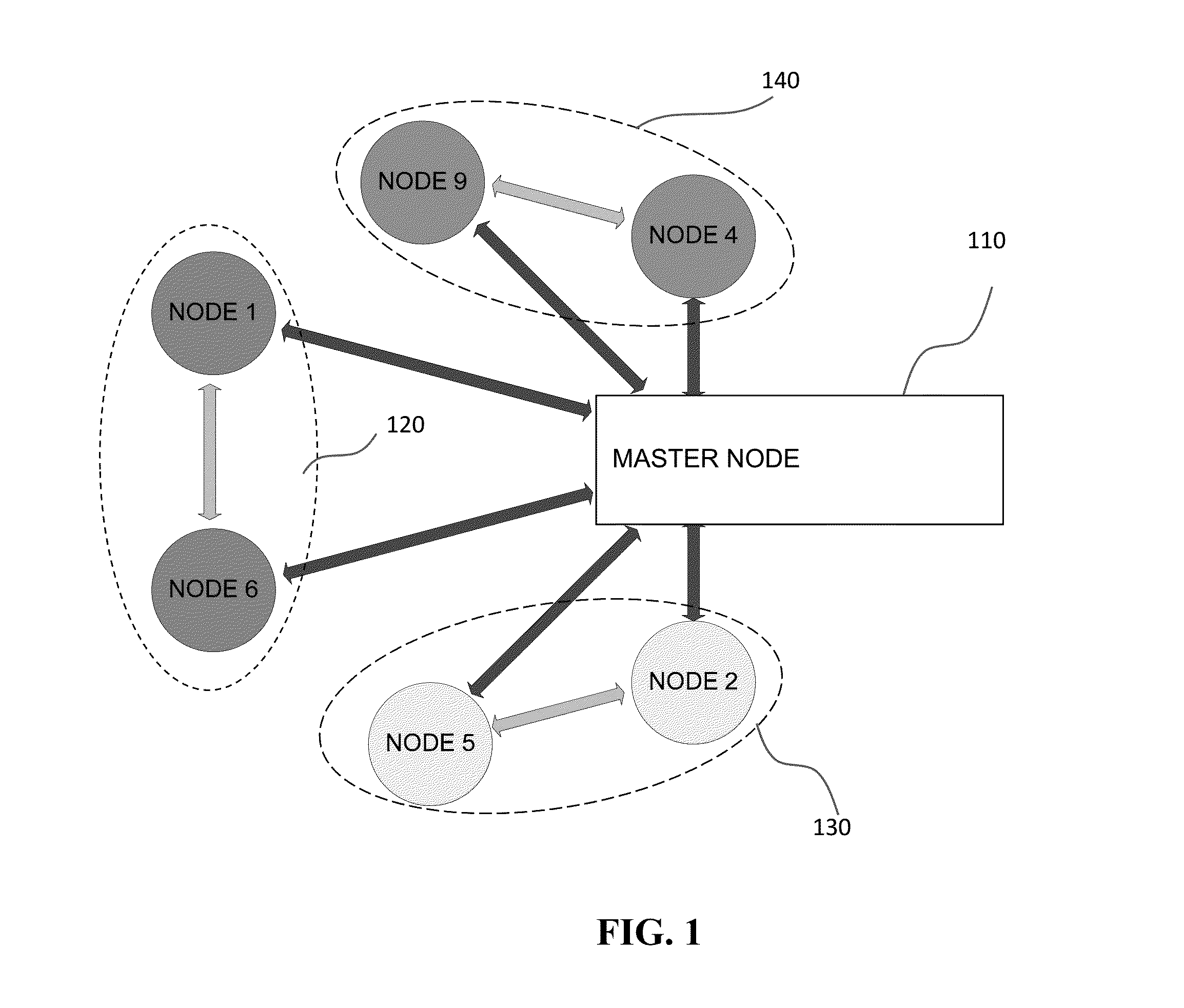
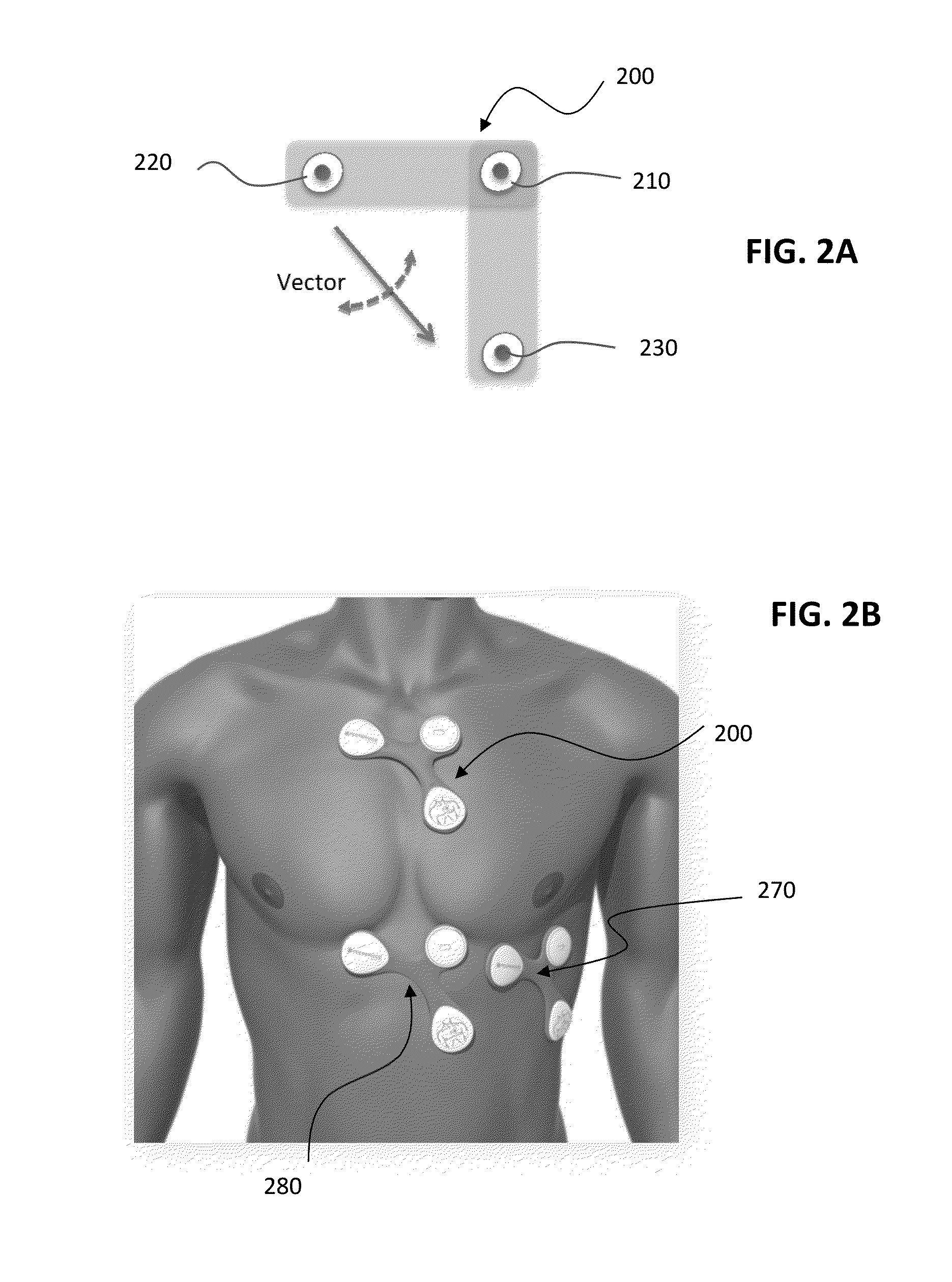
[0031]Certain embodiments of the present invention will now be discussed with reference to the aforementioned figures. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a system for managing healthcare for a subject (which used interchangeably herein with a “patient”). The system includes a plurality of wireless sensors suitable for attachment to the skin of a subject or implantable in the body of the subject. The plurality of wireless sensors can form a network. The type of network may utilize a routing topology include: star, mesh, pseudo-mesh network, or any other routing topology. Each of the sensors can include a sensing component configured to detect a signal corresponding to at least one physiological condition of the subject, and a communication component configured to wirelessly transmit the detected signal to either another wireless sensor or an external monitoring unit. The communication component of selected sensors can also be configured to receive and / or relay signals ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com