Patents
Literature
50 results about "Datapath circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
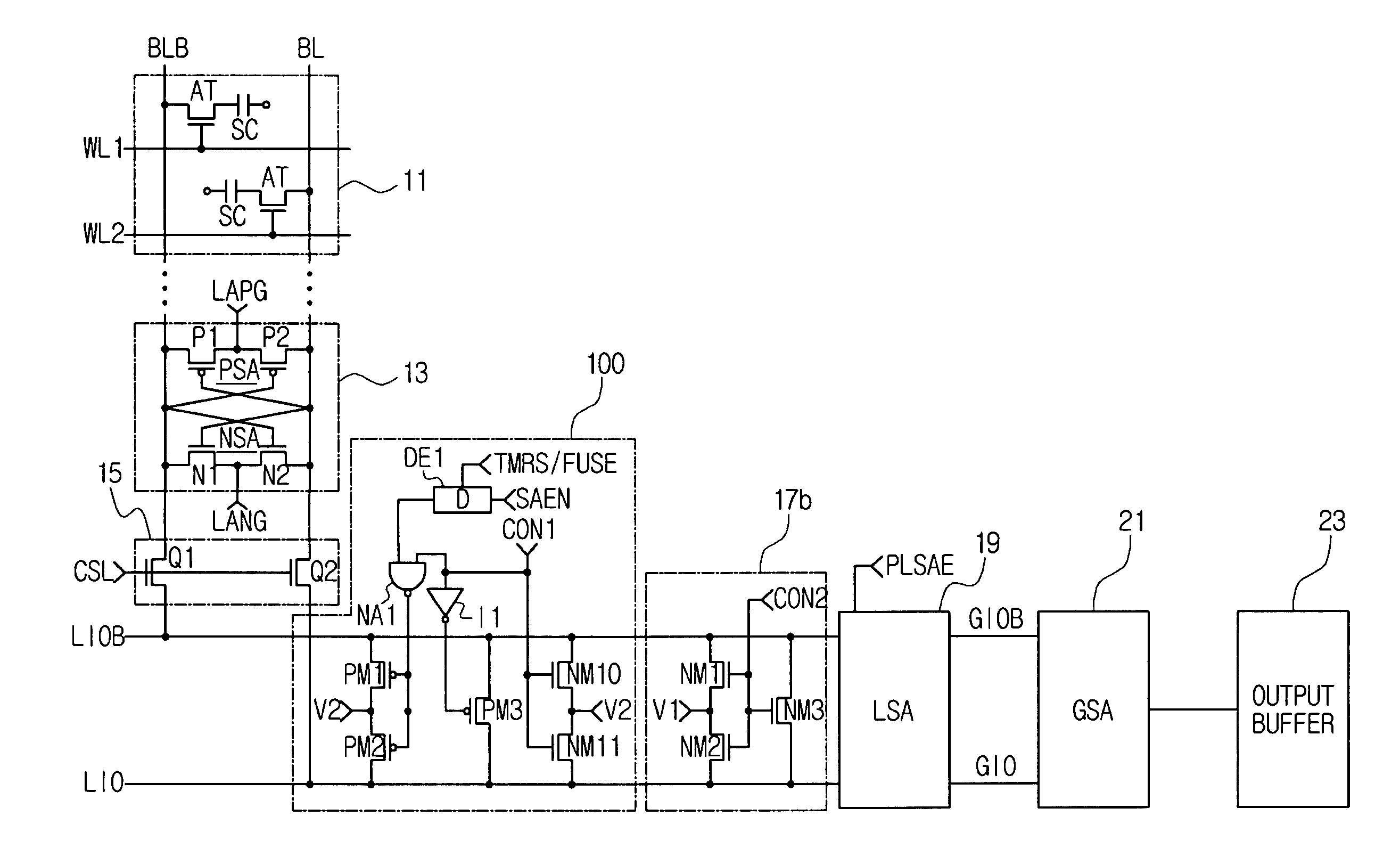
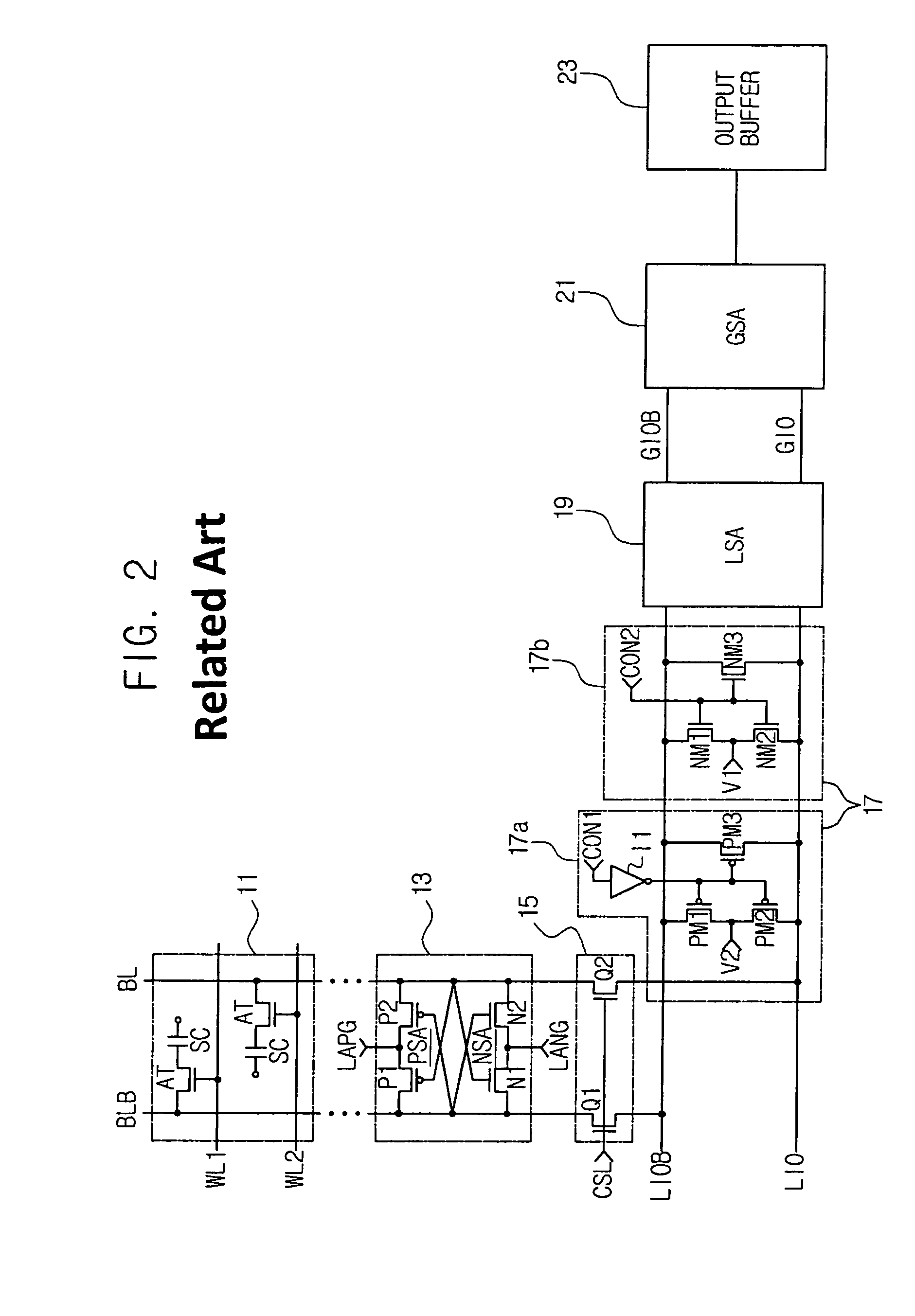
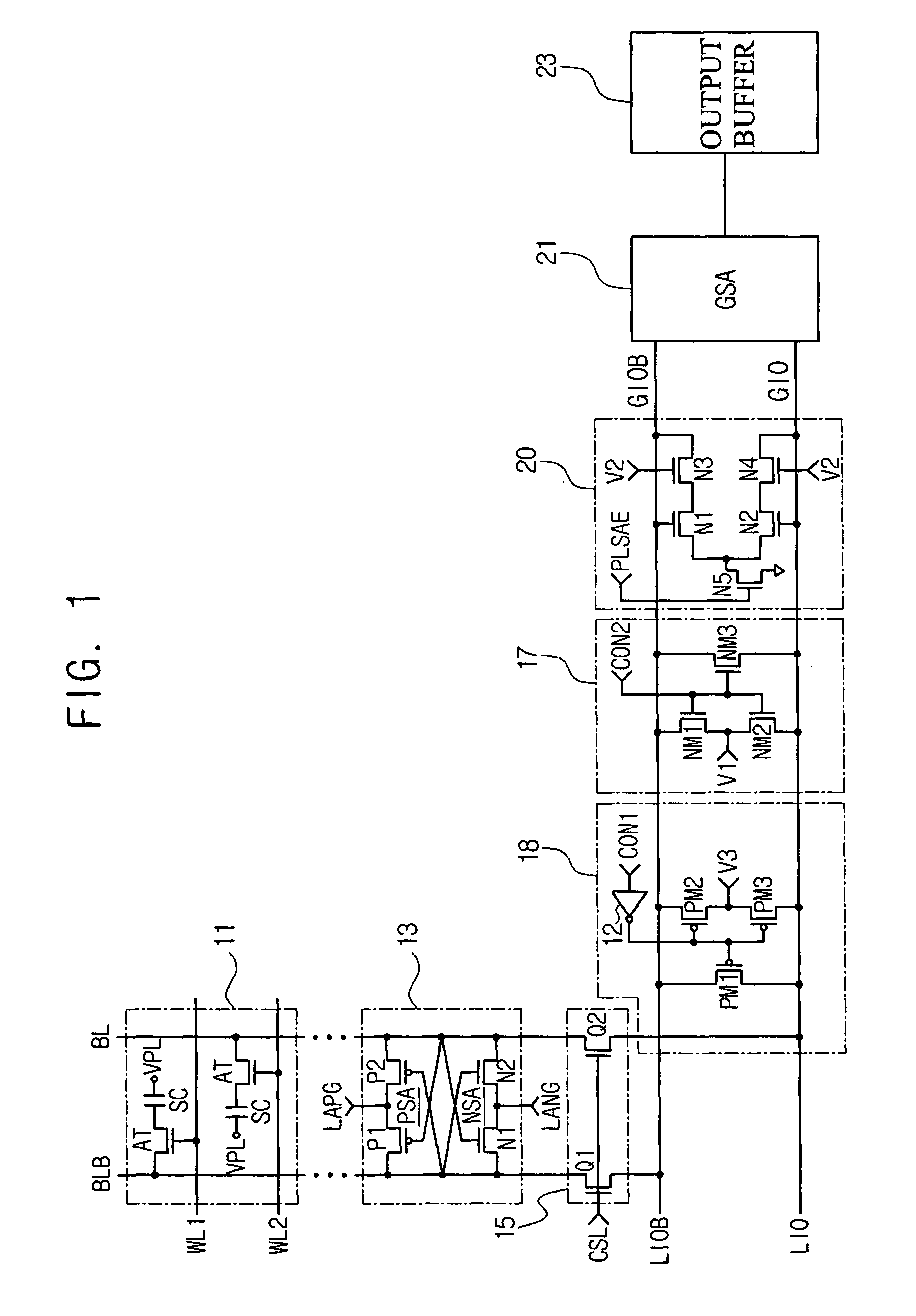
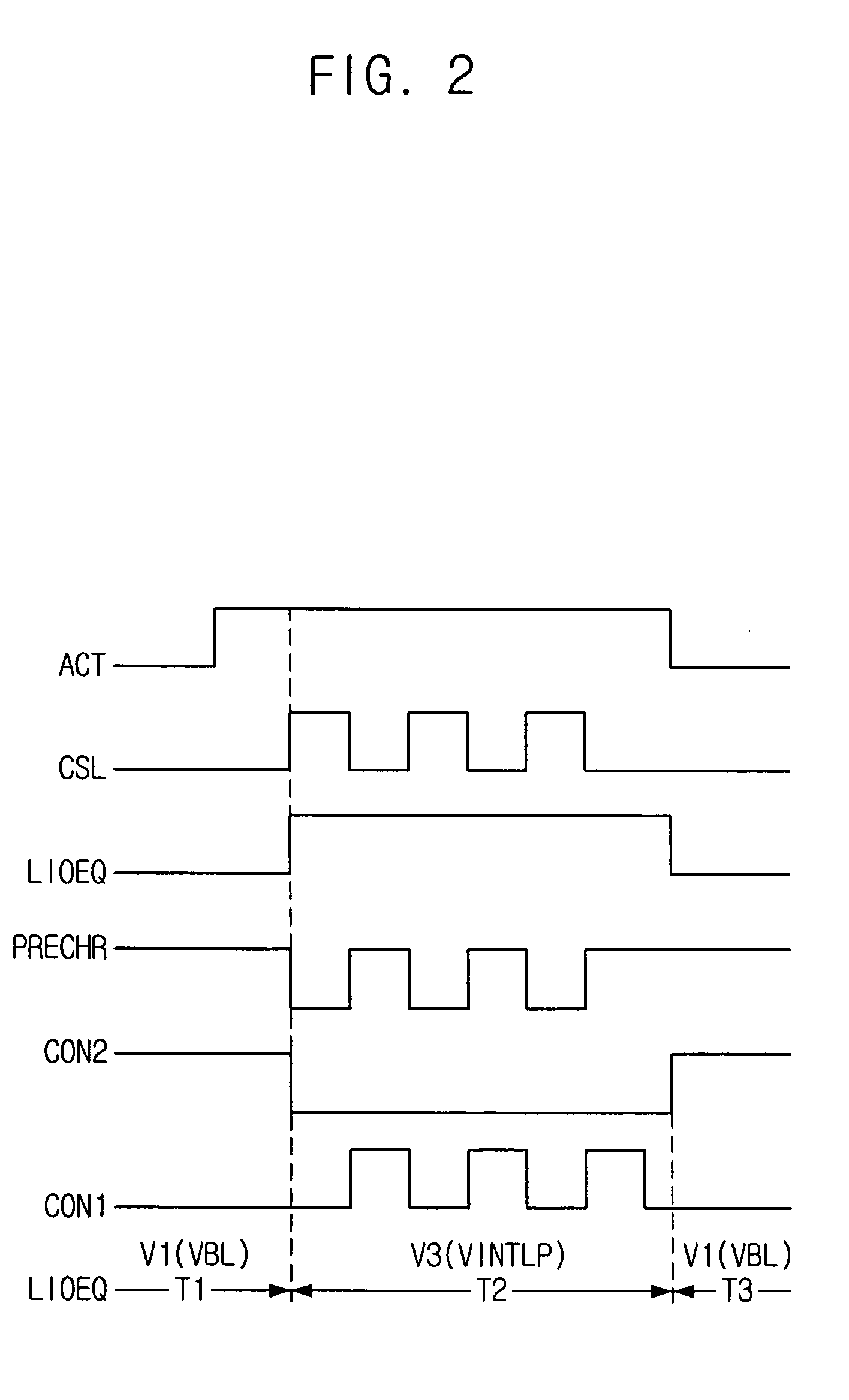
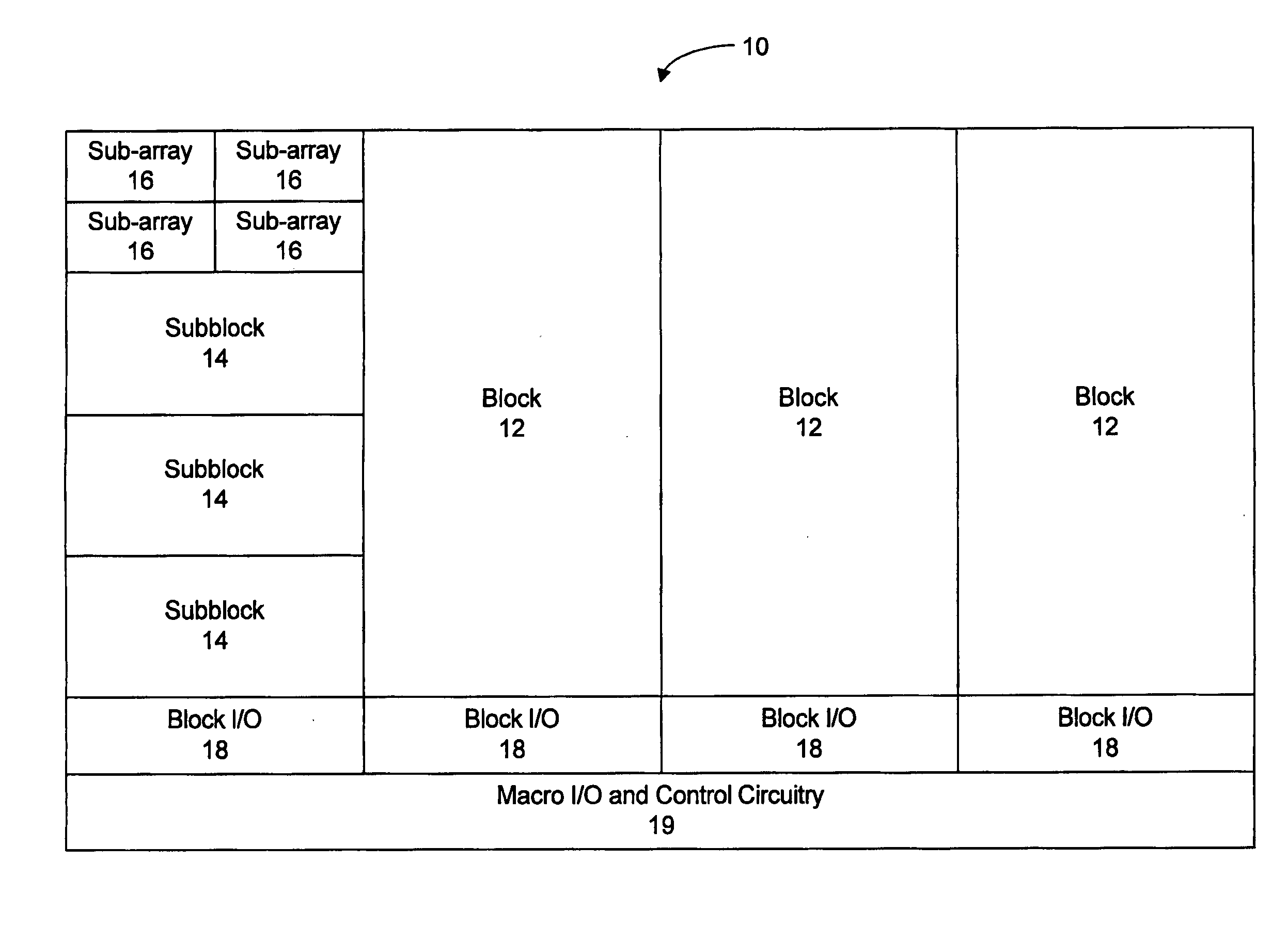
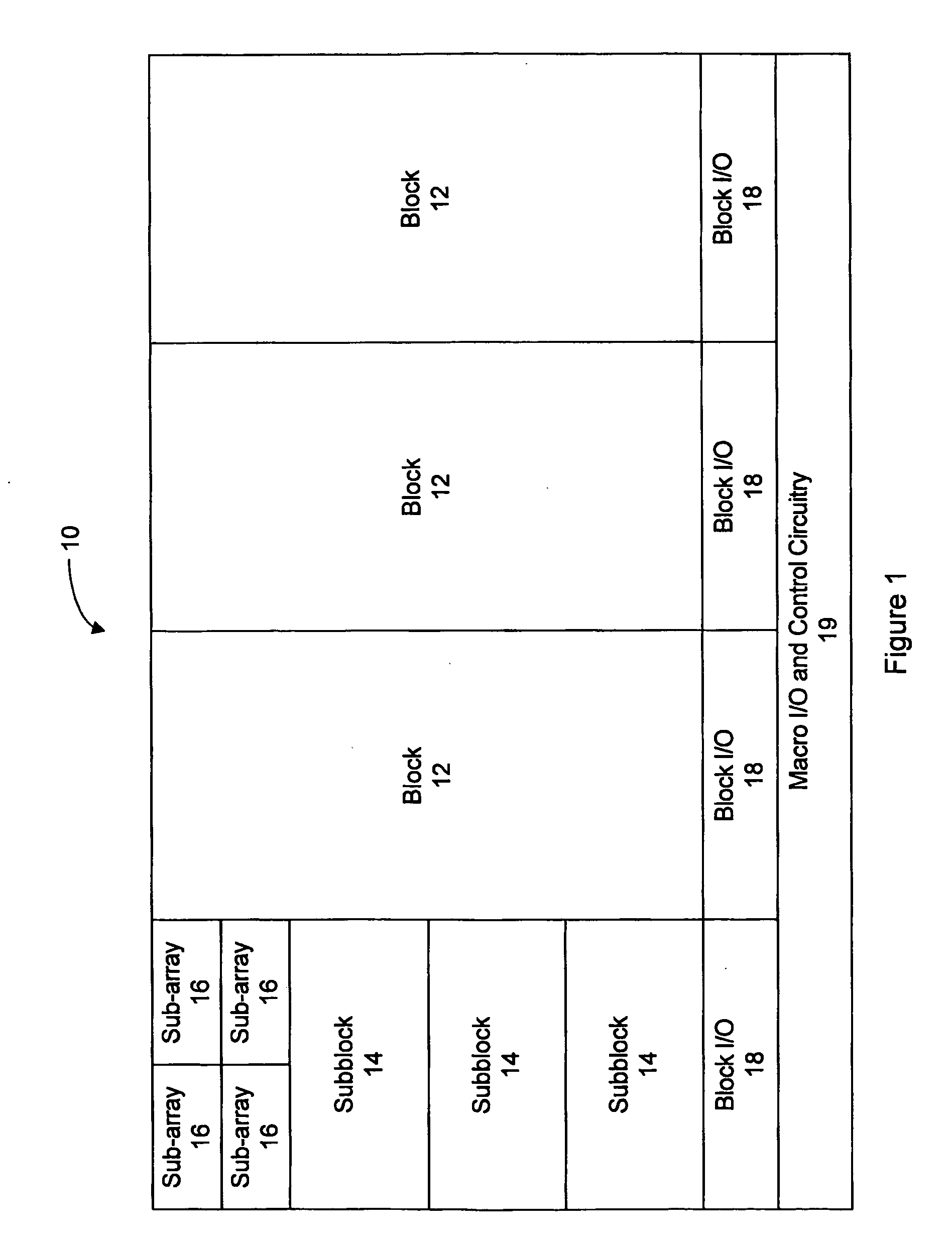
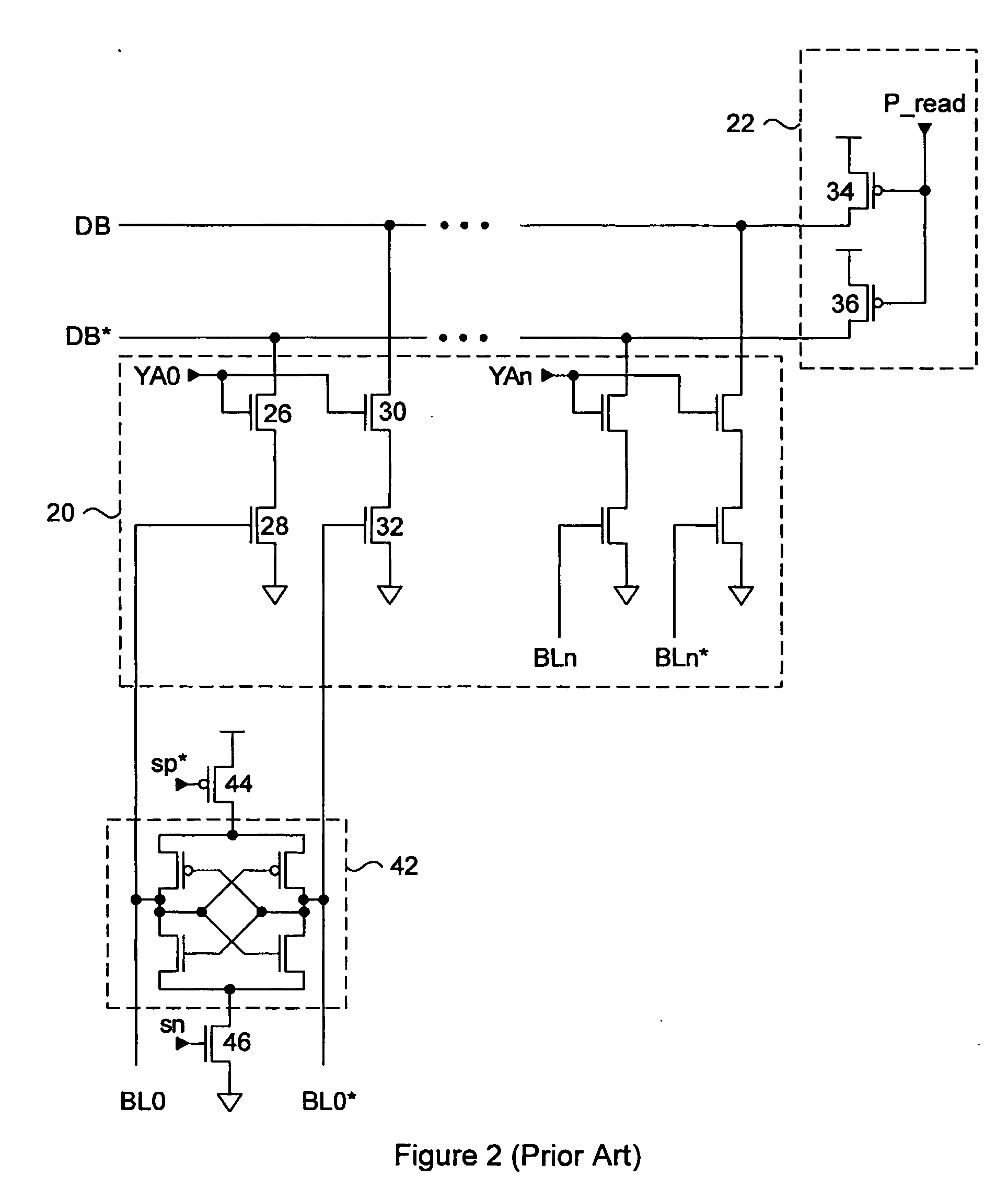
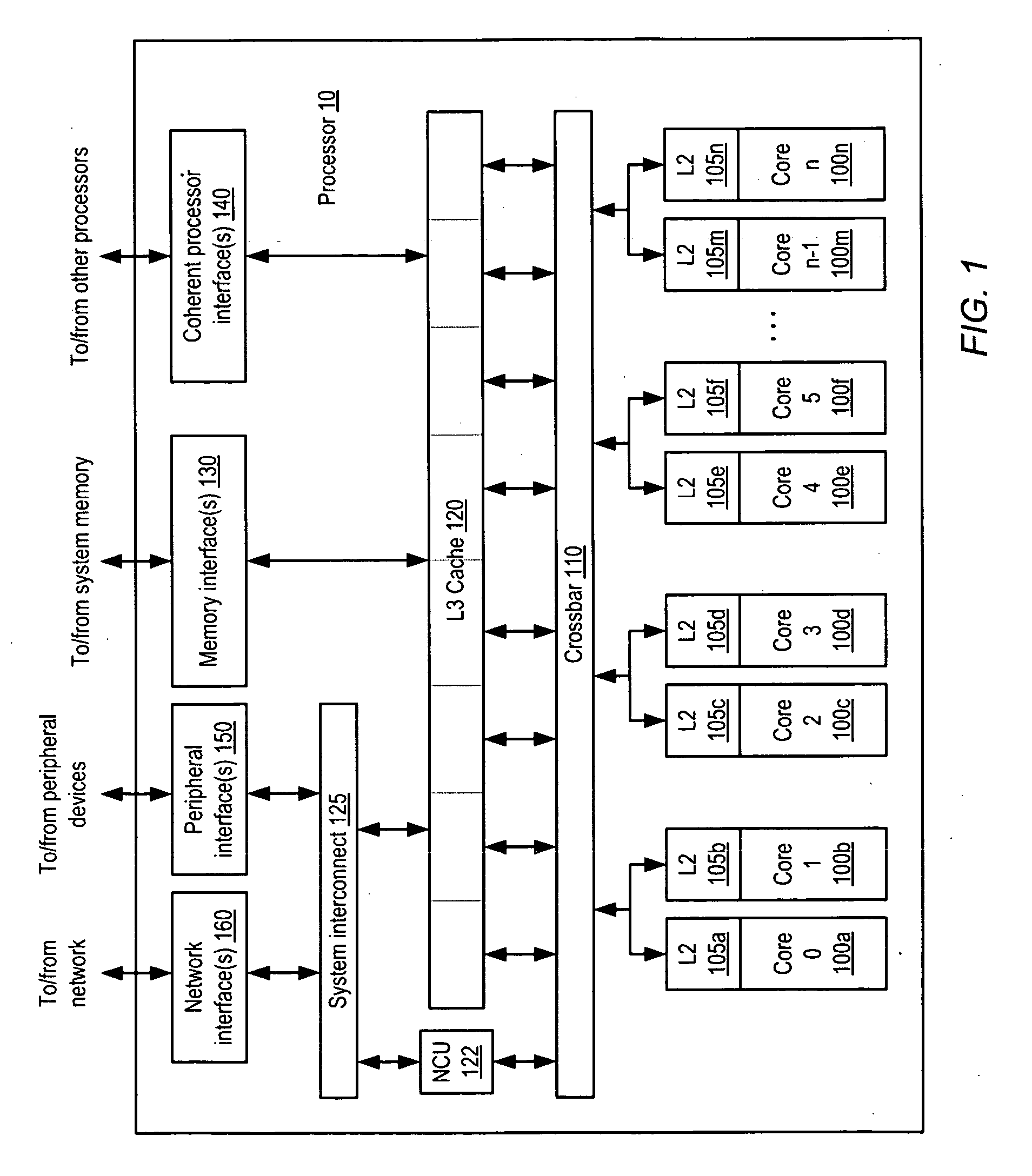
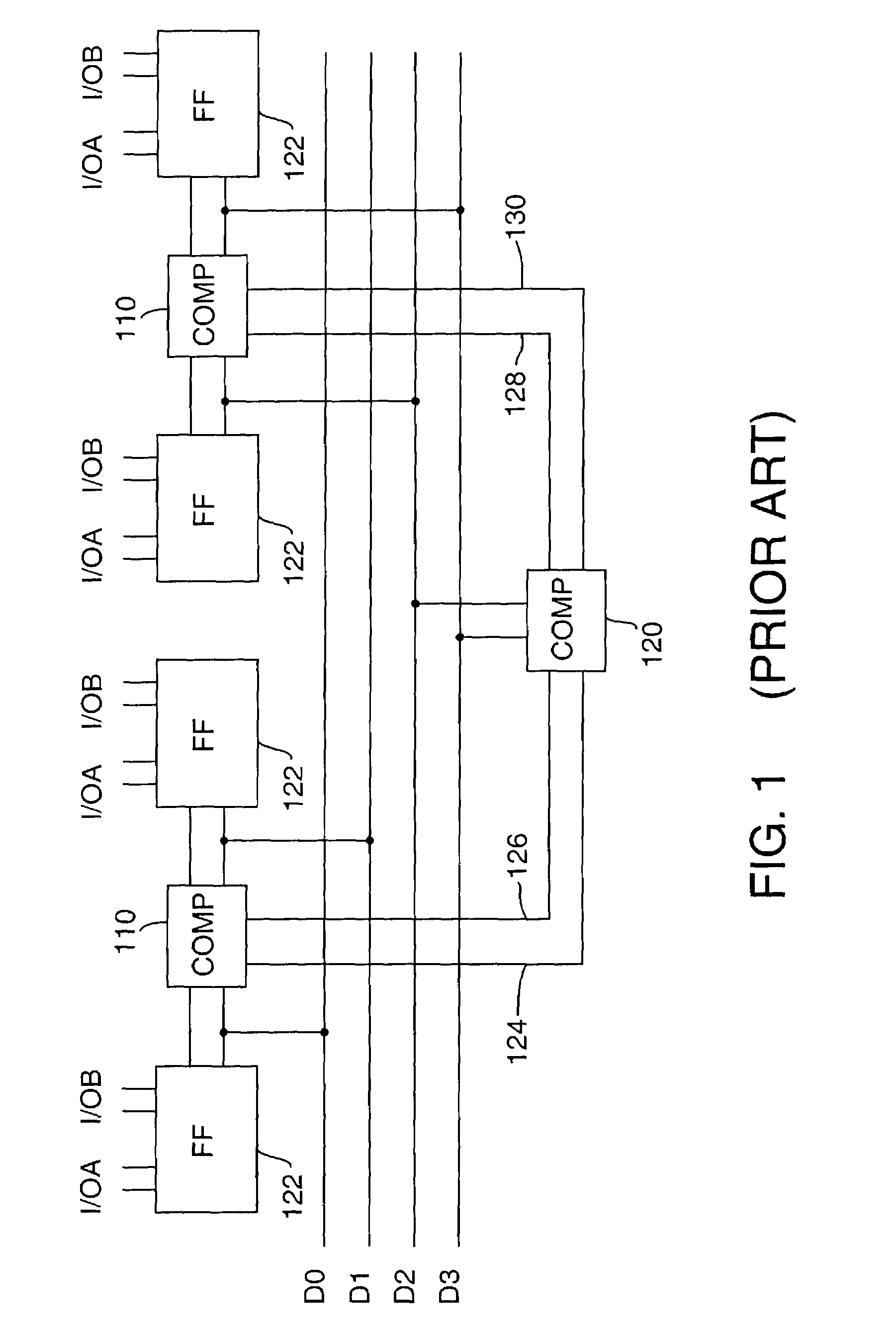
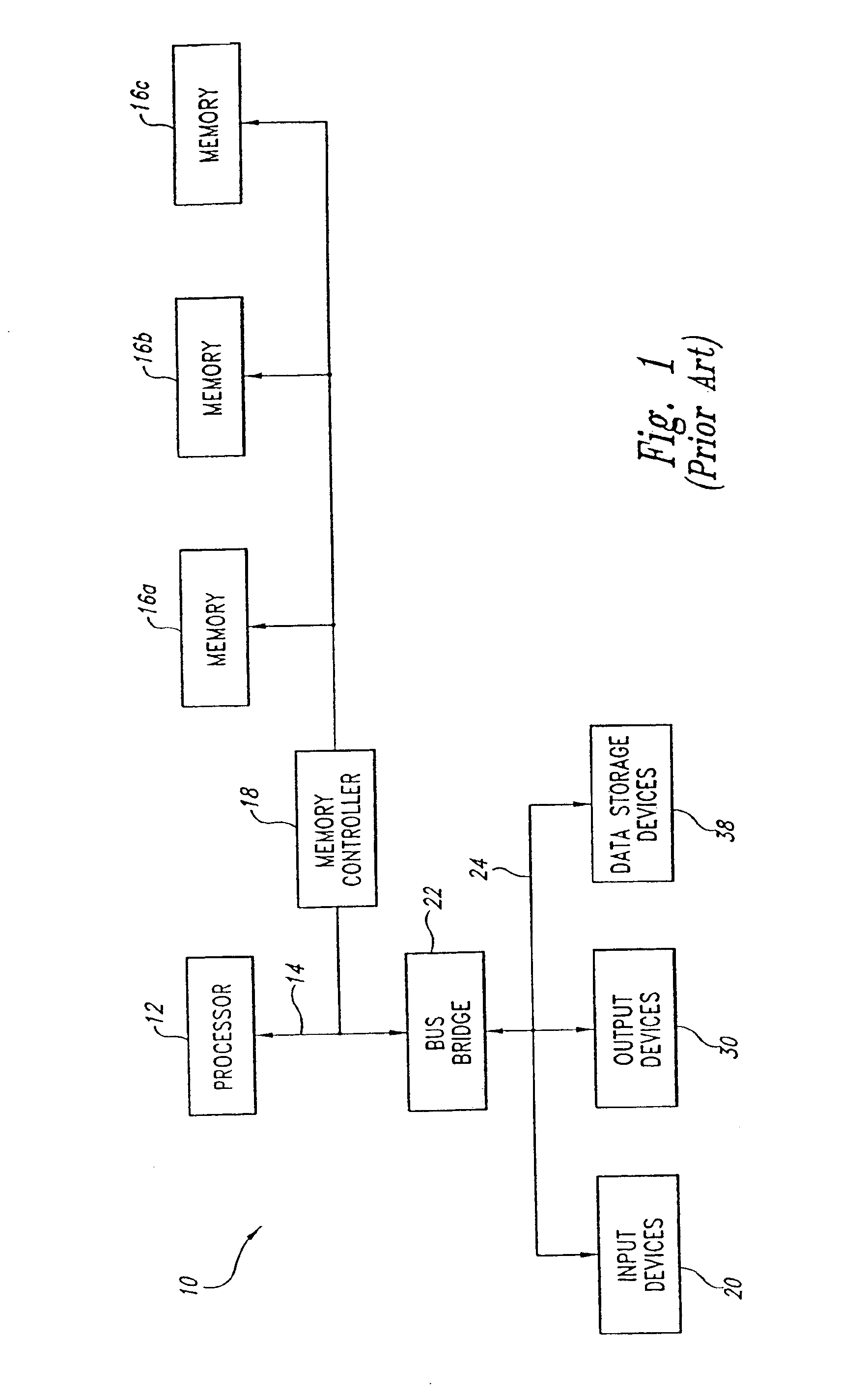
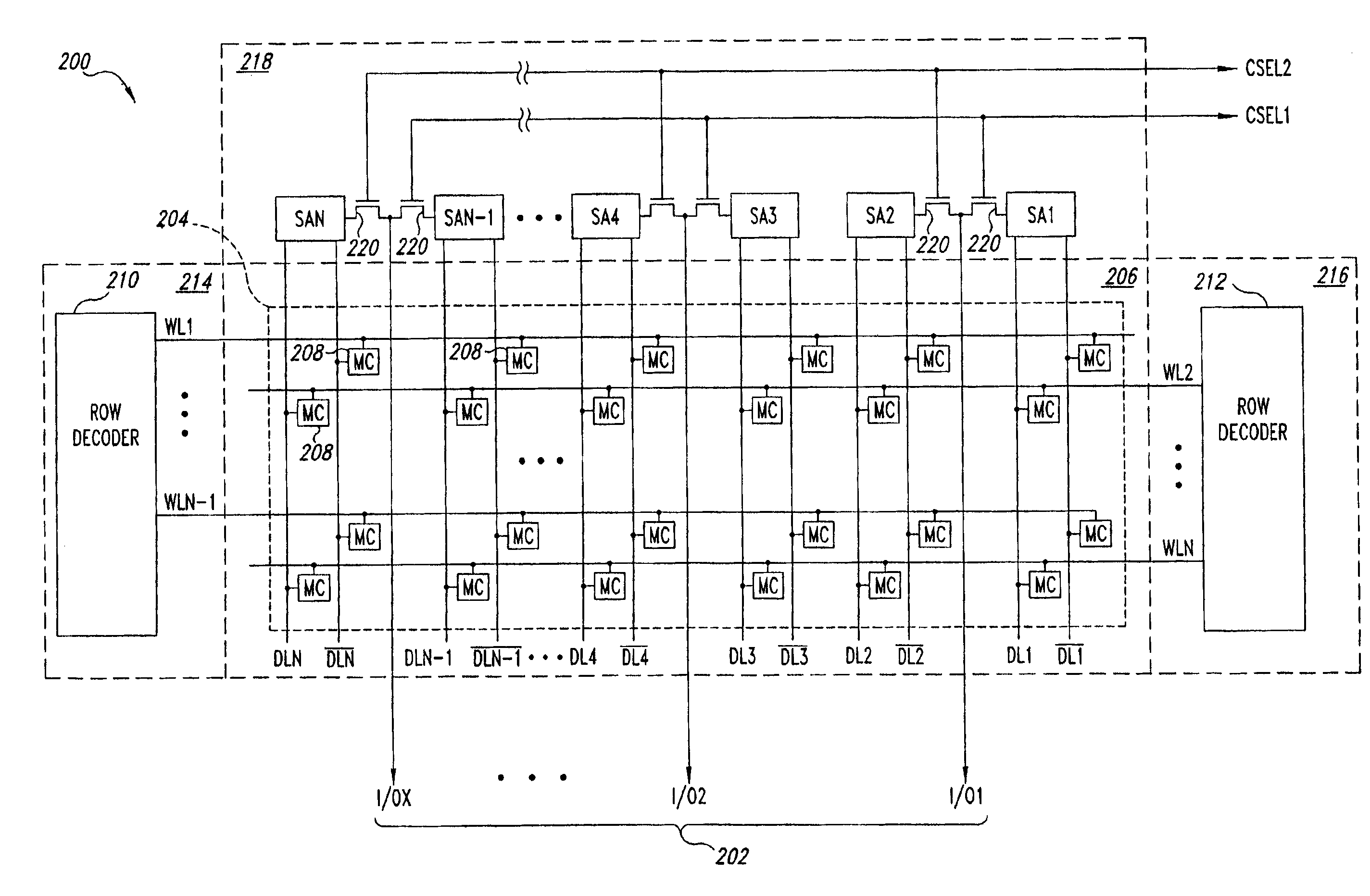
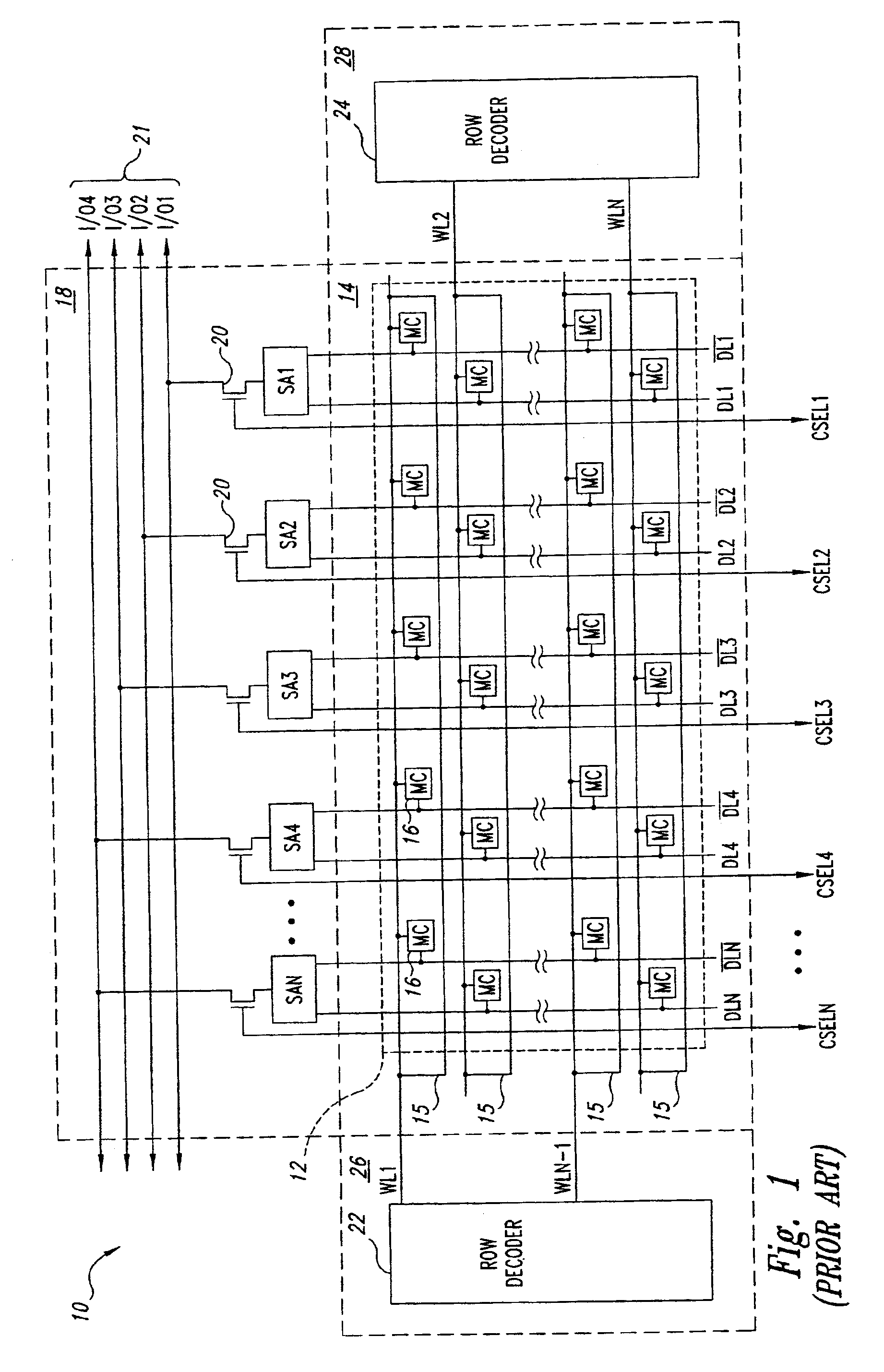
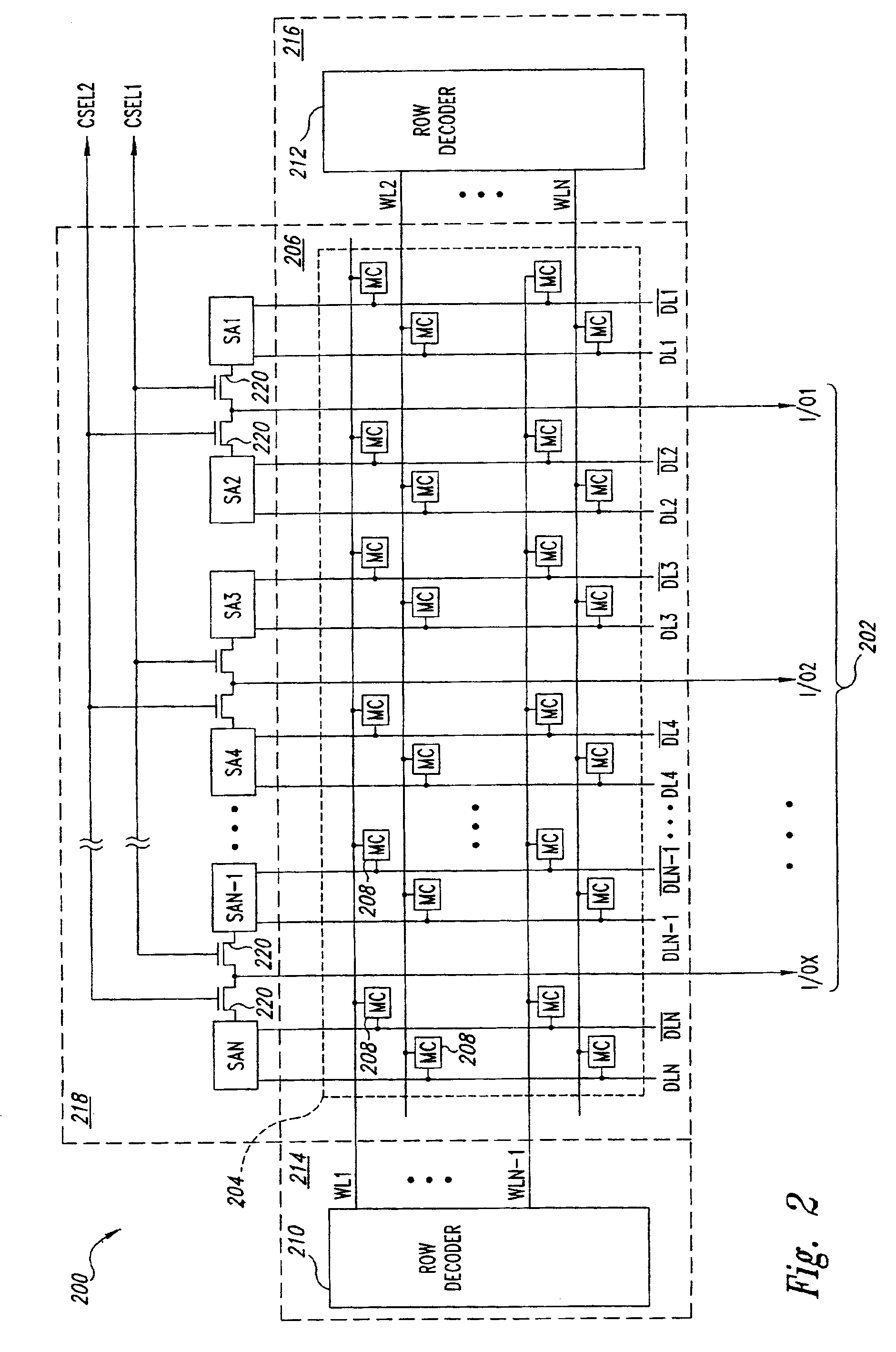
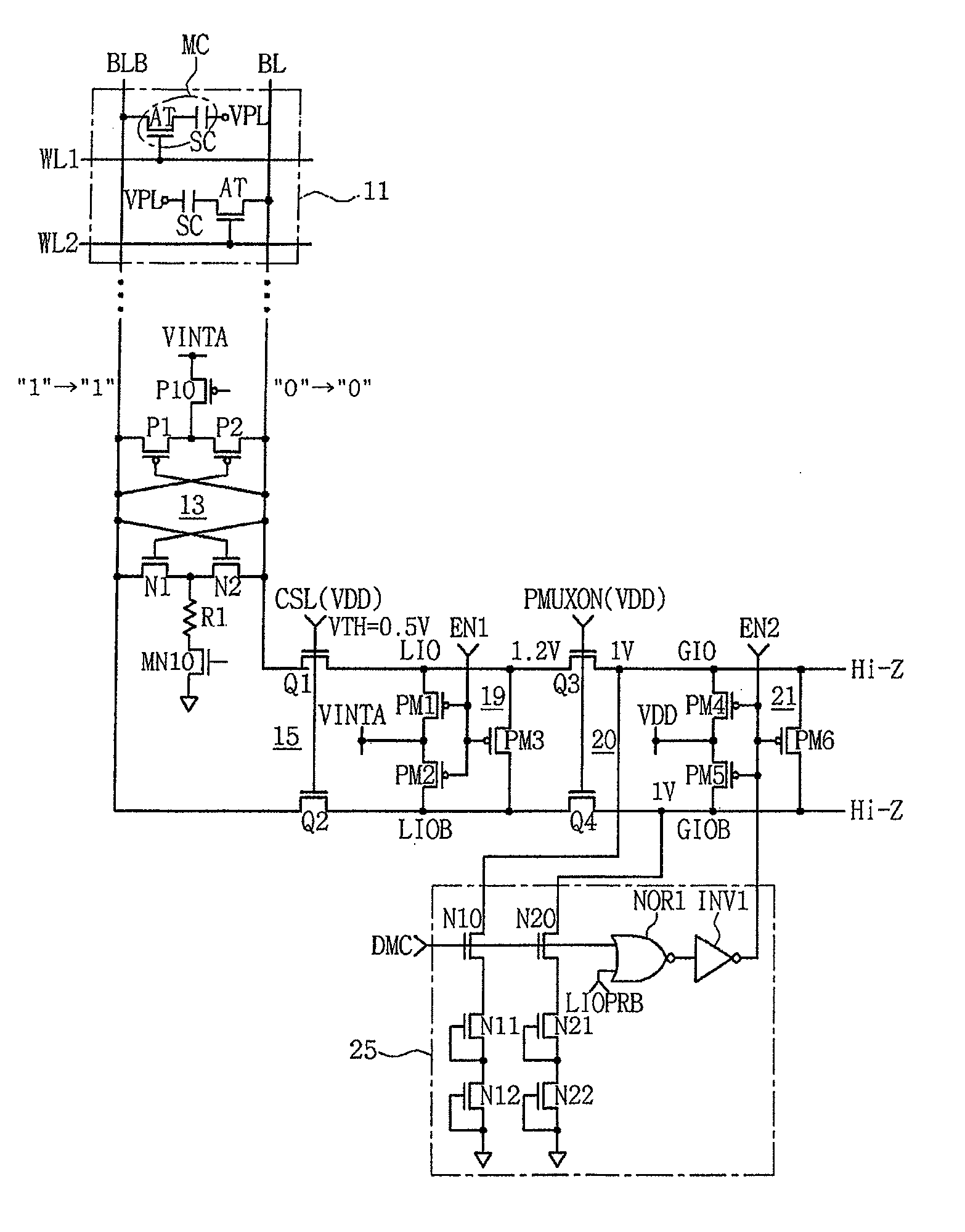
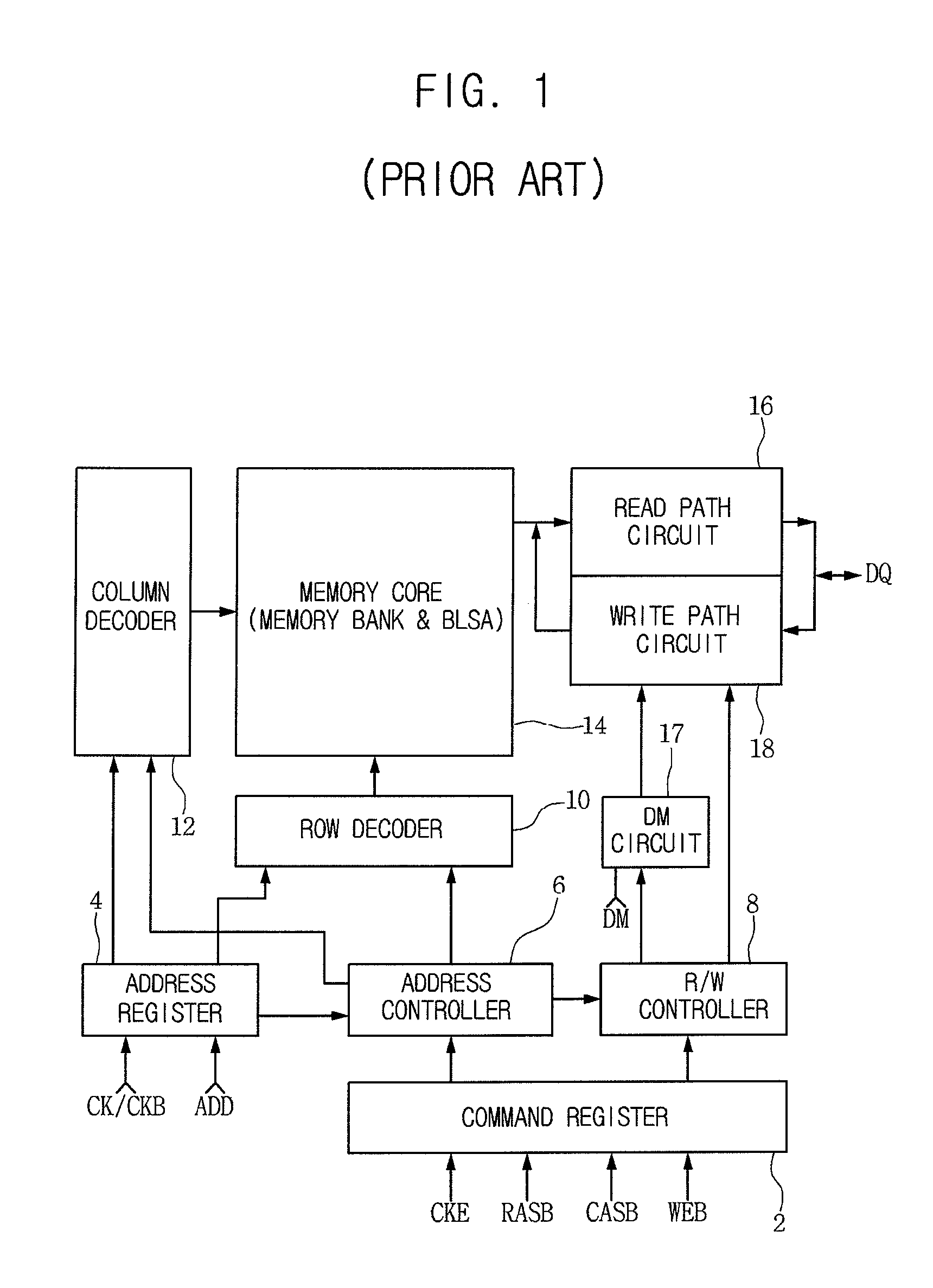
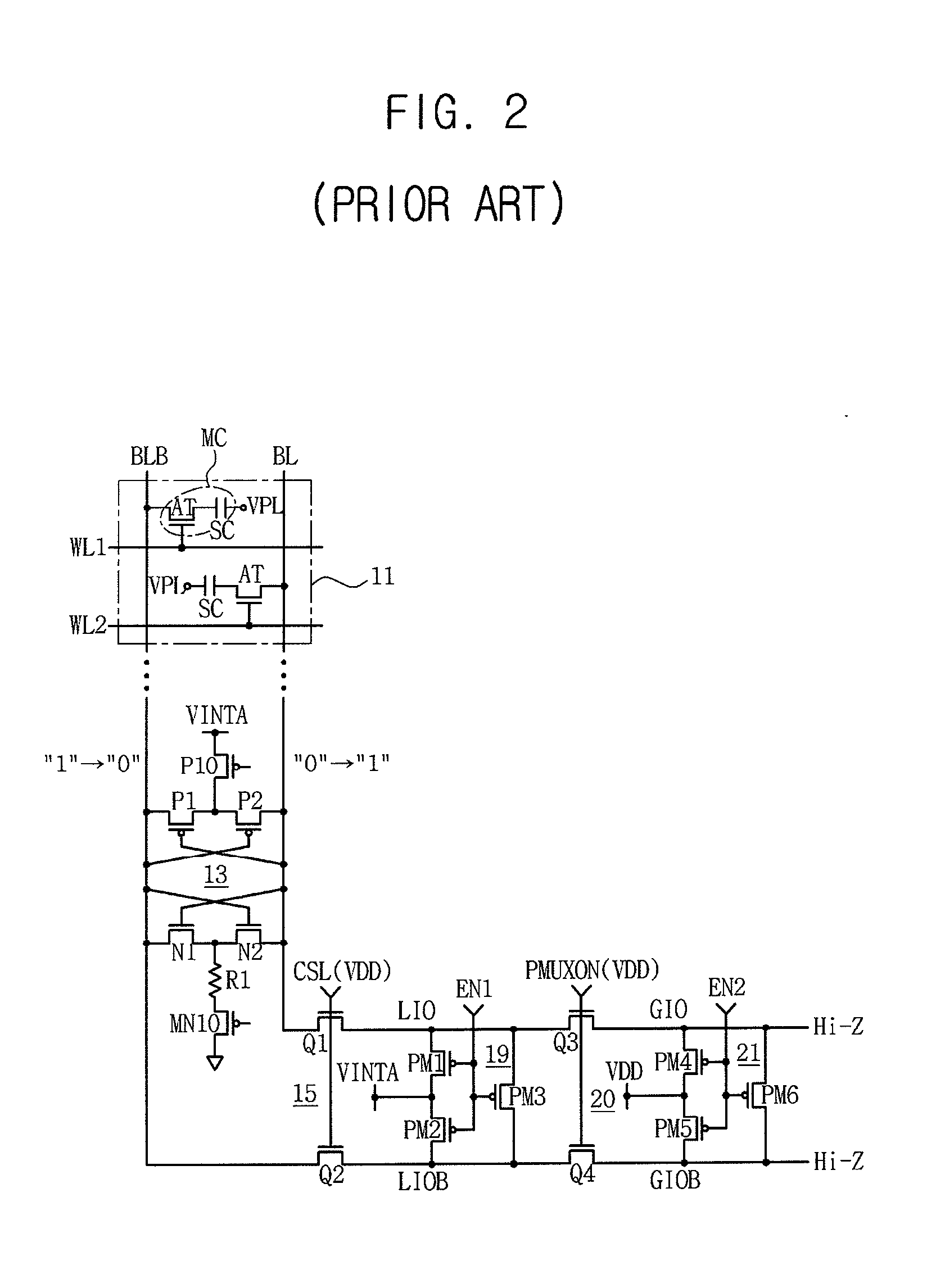
Semiconductor memory device adopting improved local input/output line precharging scheme
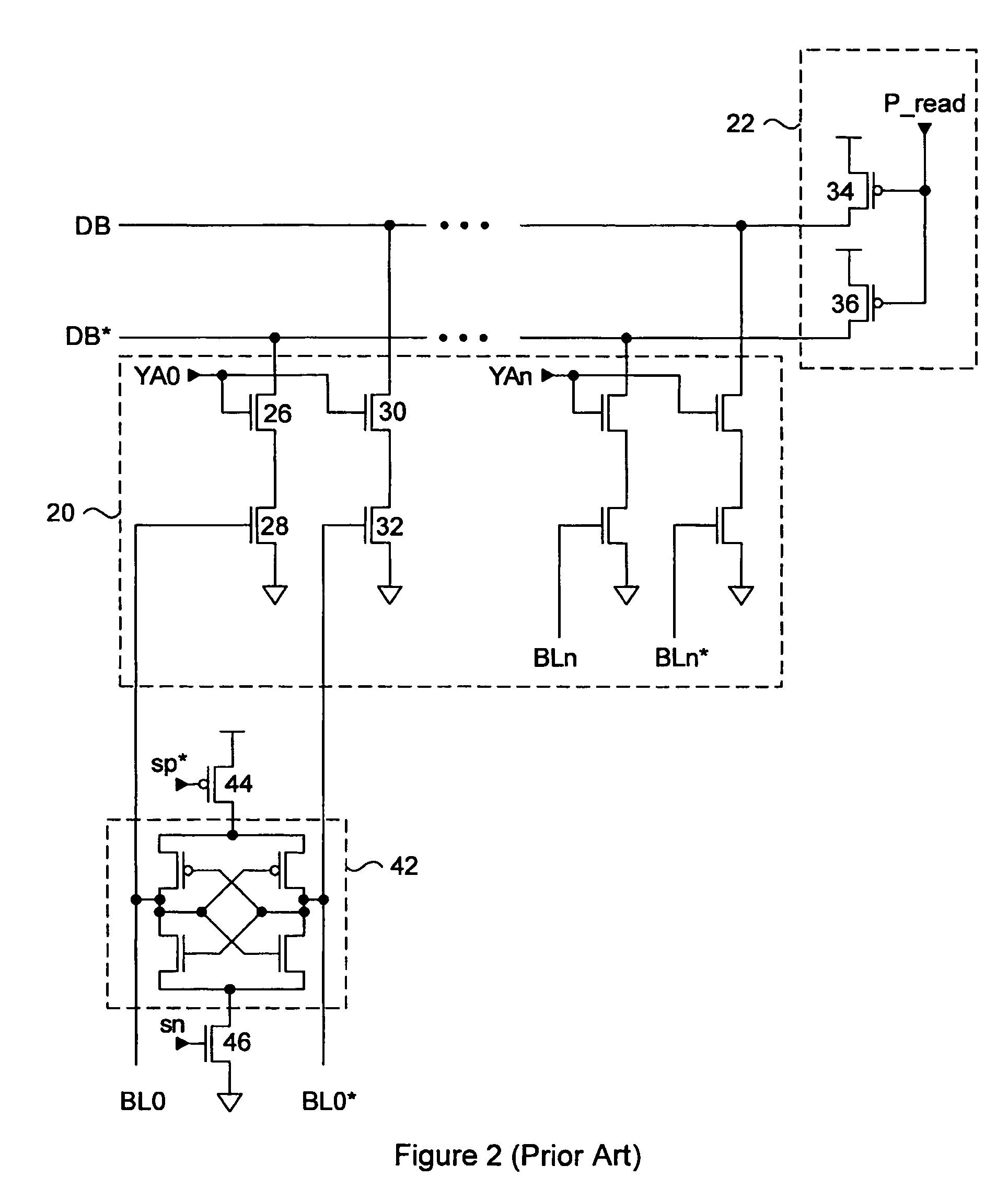
A semiconductor memory device capable of preventing or minimizing bit line disturbance and performing a low-voltage high-speed operation includes a read data path circuit including a bit line sense amplifier, a local input / output line sense amplifier, a column selecting unit to operationally connect bit lines connected to the bit line sense amplifier to local input / output lines connected to the local input / output line sense amplifier in response to a column selection signal, and a local input / output line precharging unit to precharge the pair of local input / output lines by a first precharging unit, equalizing the pair of local input / output lines by an equalizing unit, and to precharge the local input / output lines by a second precharging unit following an elapsed time after the bit line sense amplifier is activated, while the column selection is deactivated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
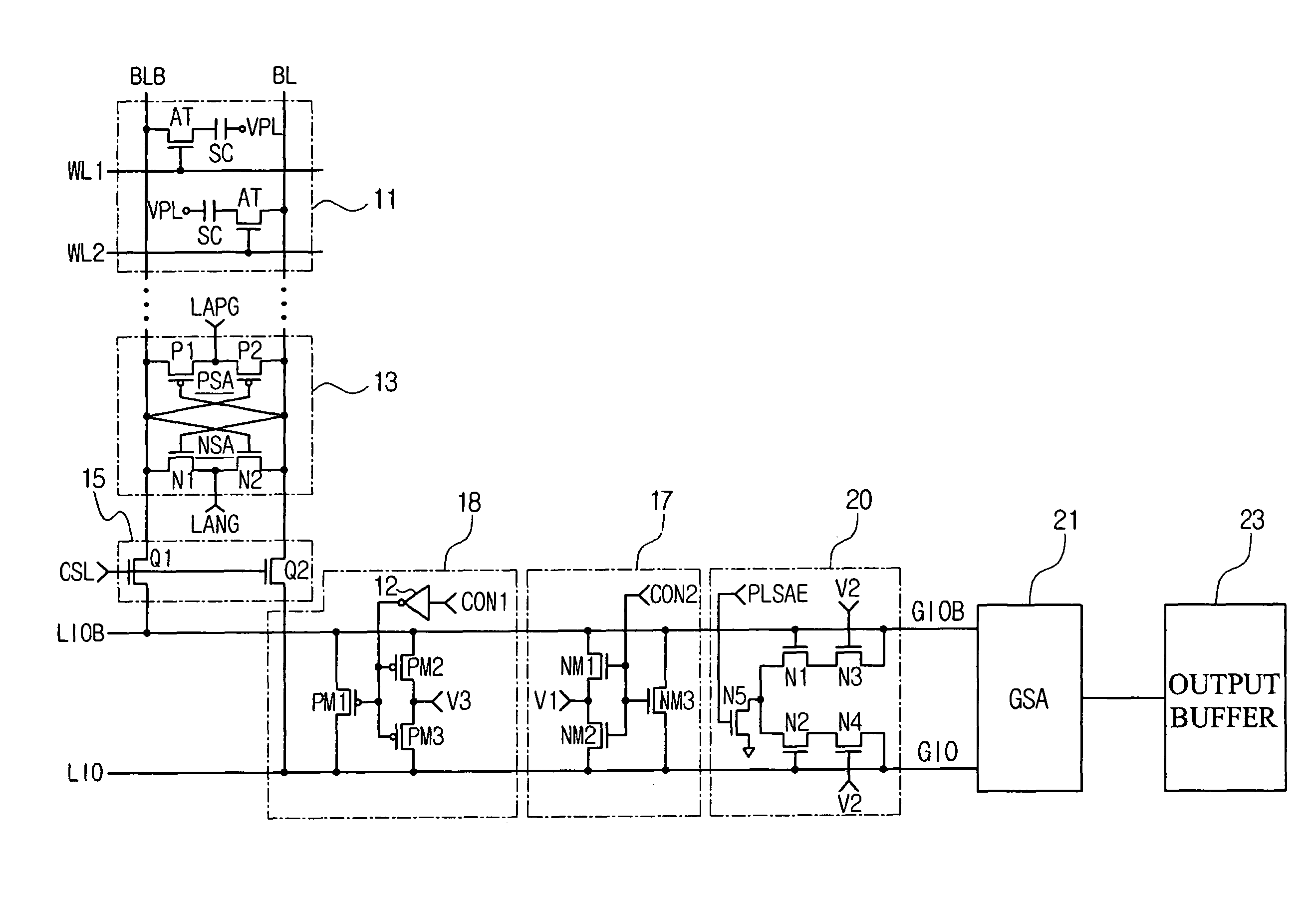
Semiconductor memory device having improved local input/output line precharge scheme
ActiveUS8213248B2Preventing bit line disturbanceRun at high speedDigital storageBit lineDatapath circuits
A data path circuit of a semiconductor memory device includes: a bit line sense amplifier driven by a first power supply voltage; a local input / output line sense amplifier; a column selecting unit operatively connecting a pair of bit lines connected to the bit line sense amplifier and a pair of local input / output lines connected to the local input / output line sense amplifier in response to a column selection signal; and a local input / output line precharge unit precharging the pair of local input / output lines with a second power supply voltage different from the first power supply voltage during a period for which the column selection signal is in an inactive state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
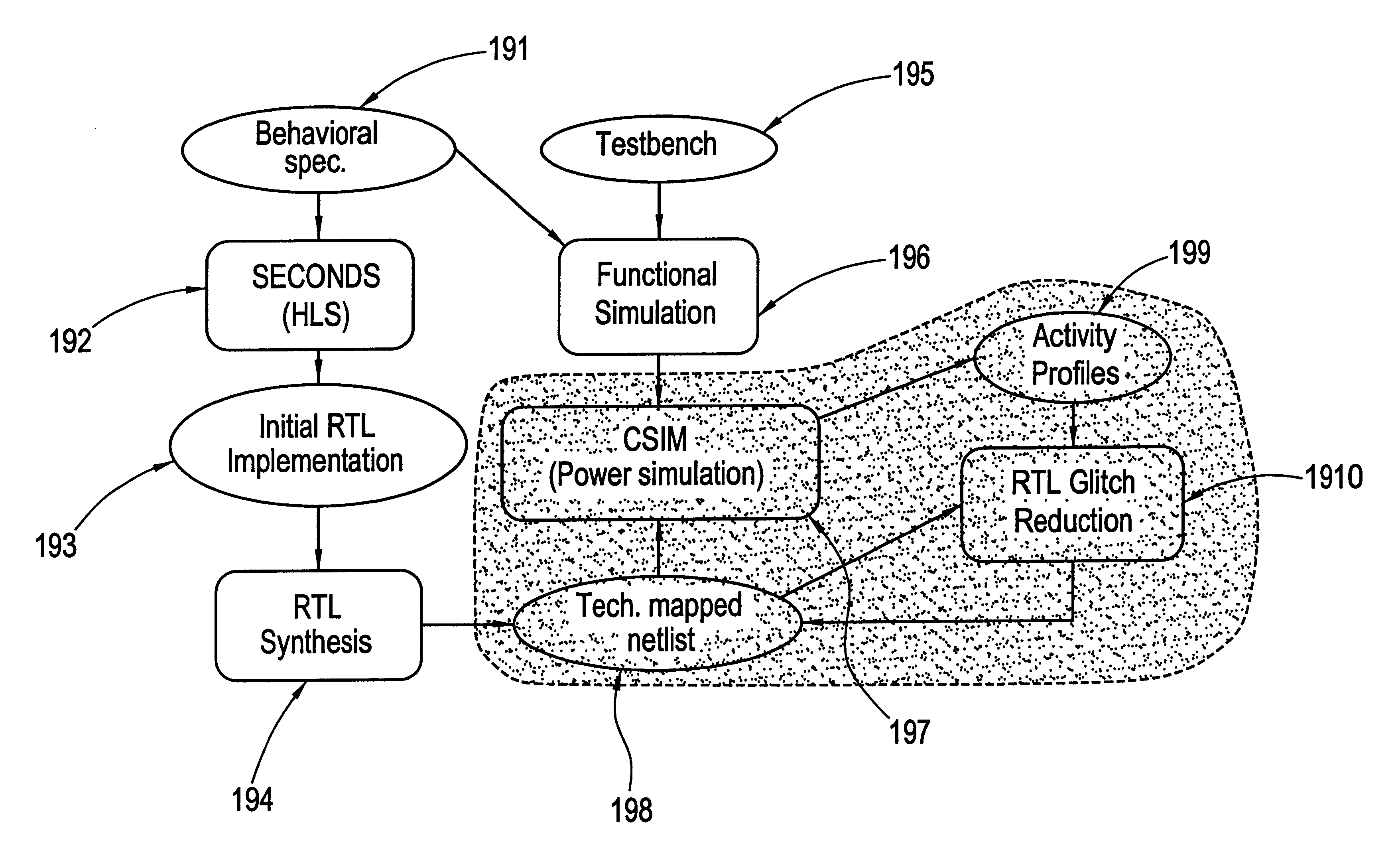
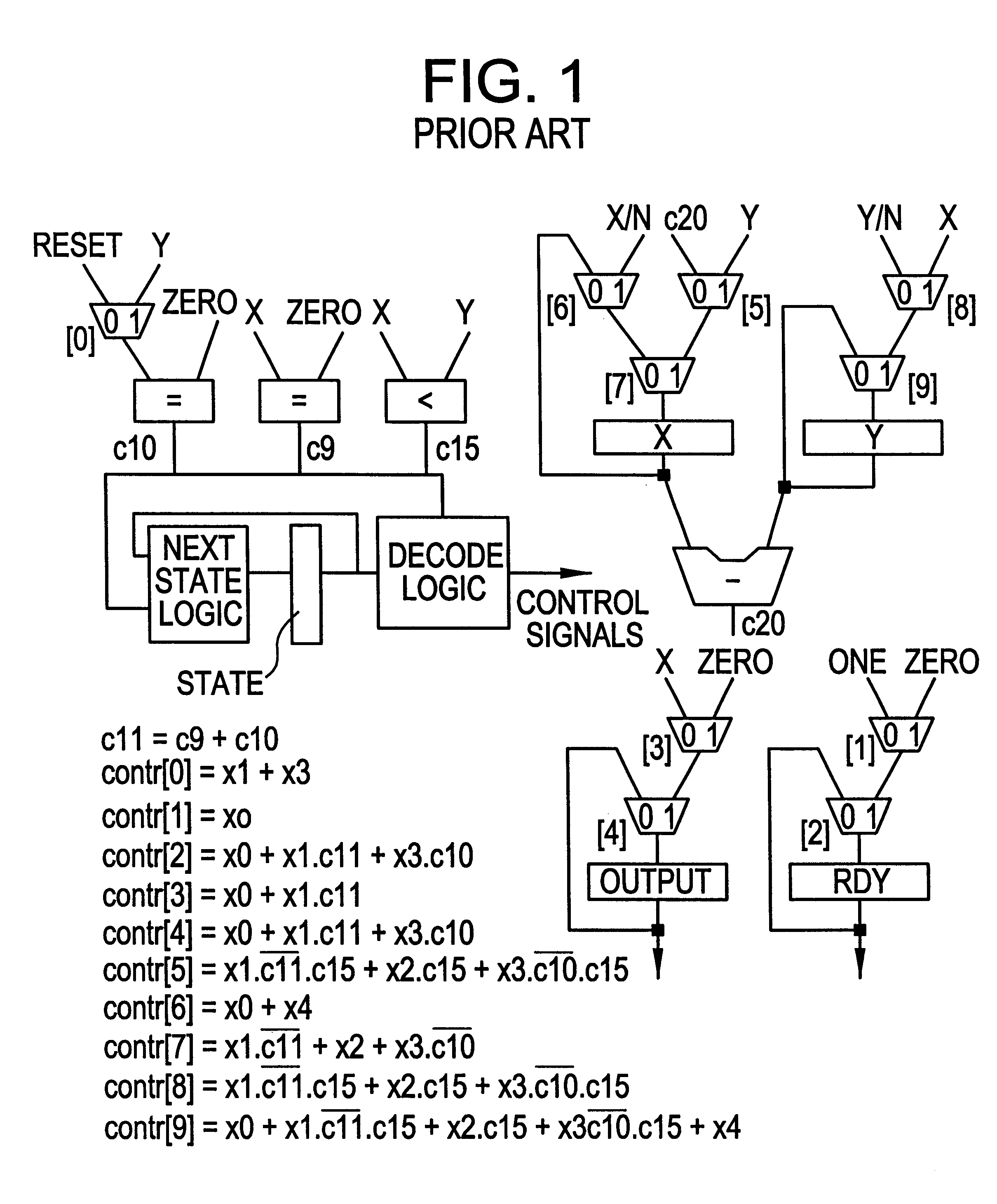
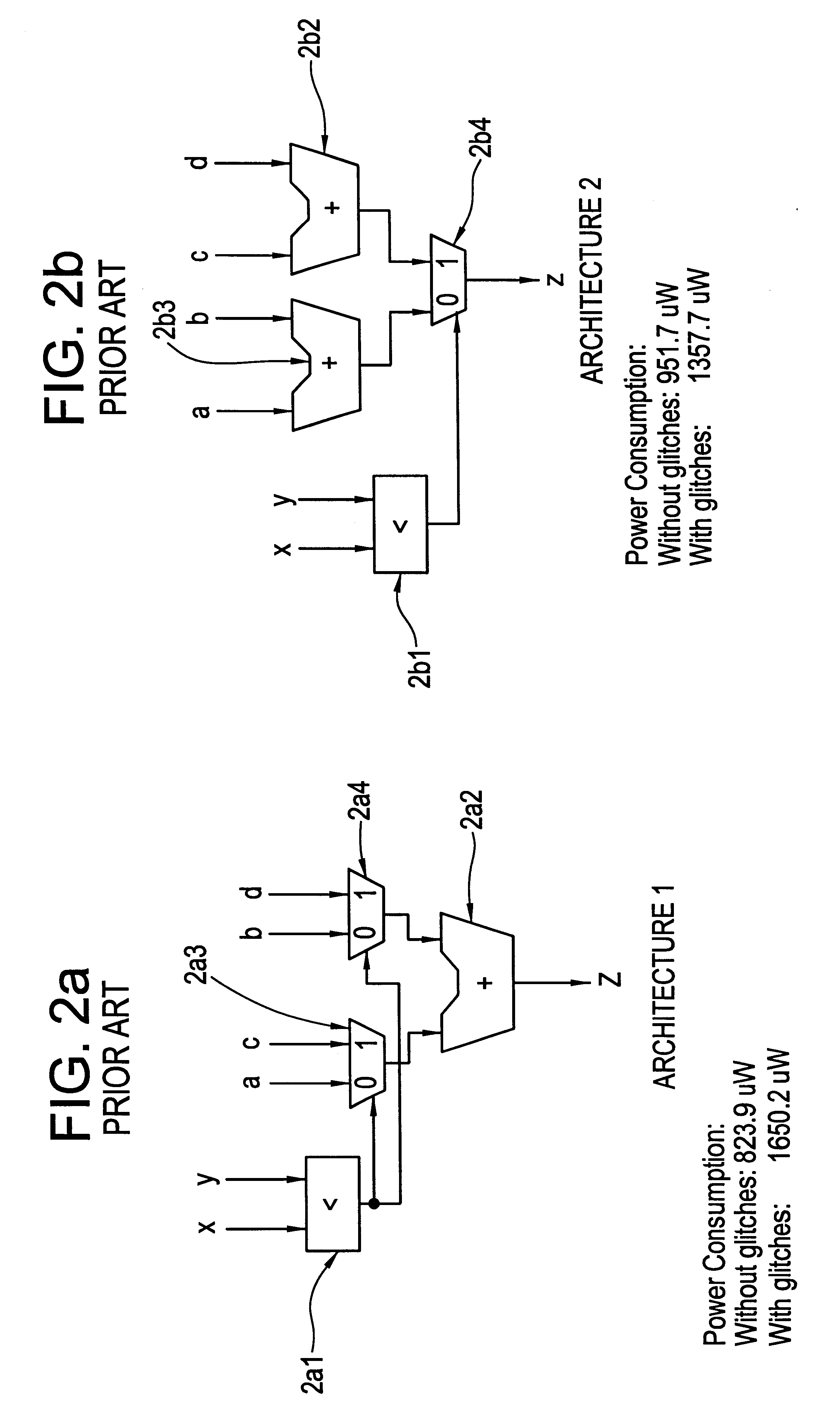
Register transfer level power optimization with emphasis on glitch analysis and reduction
InactiveUS6324679B1Reduce power consumptionLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital data processing detailsDatapath circuitsPathPing
A method and apparatus for design-for-low-power of register transfer level (RTL) controller / data path circuits that implement control-flow intensive specifications. The method of the invention focuses on multiplexer networks and registers which dominate the total circuit power consumption and reduces generation and propagation of glitches in both the control and data path parts of the circuit. Further the method reduces glitching power consumption by minimizing propagation of glitches in the RTL circuit through restructuring multiplexer networks (to enhance data correlations and eliminate glitchy control signals), clocking control signals, and inserting selective rising / falling delays, in order to kill the propagation of glitches from control as well as data signals. To reduce power consumption in registers, the clock inputs to registers are gated with conditions derived by an analysis of the RTL circuit, ensuring that glitches are not introduced on the clock signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
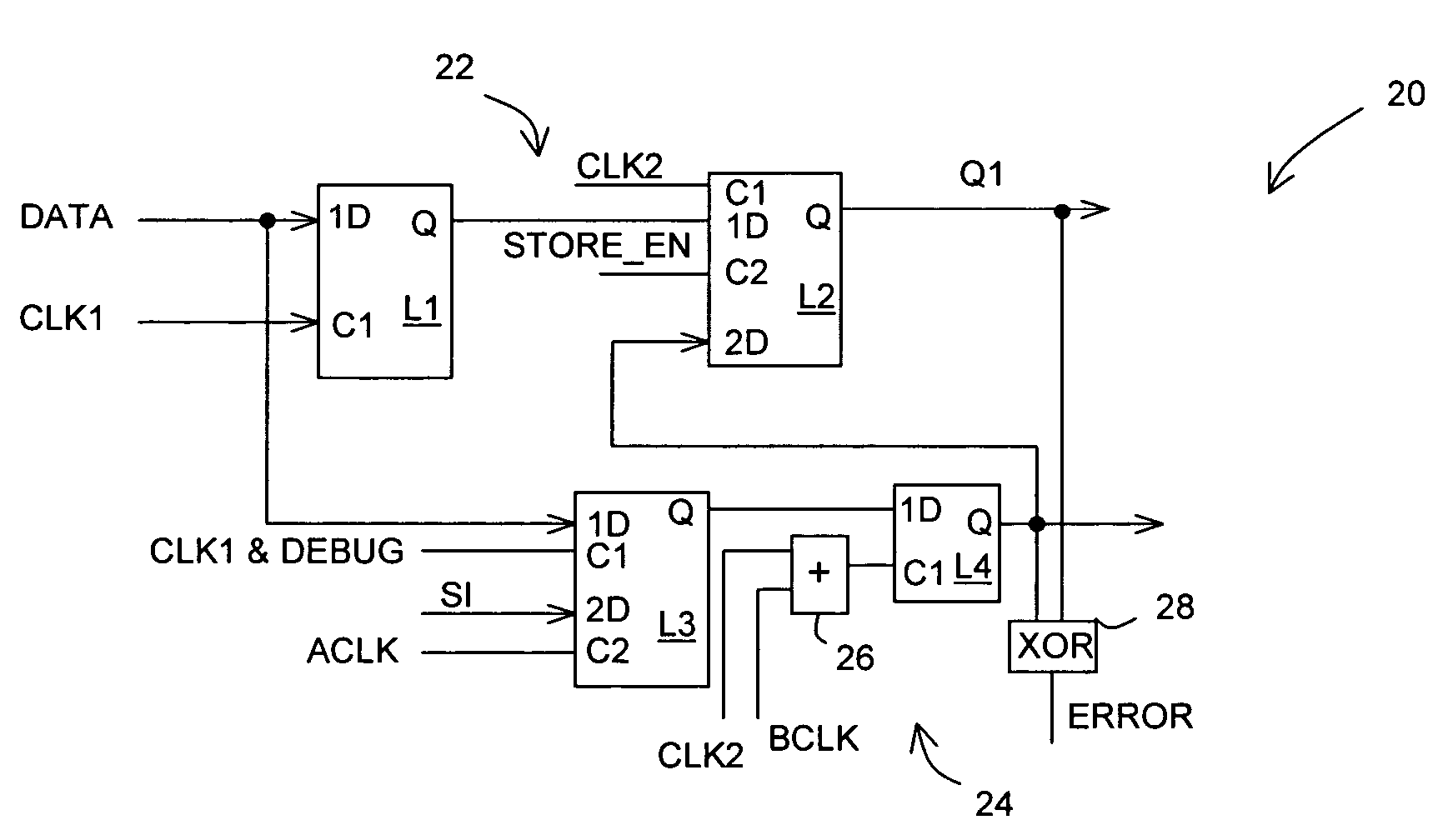
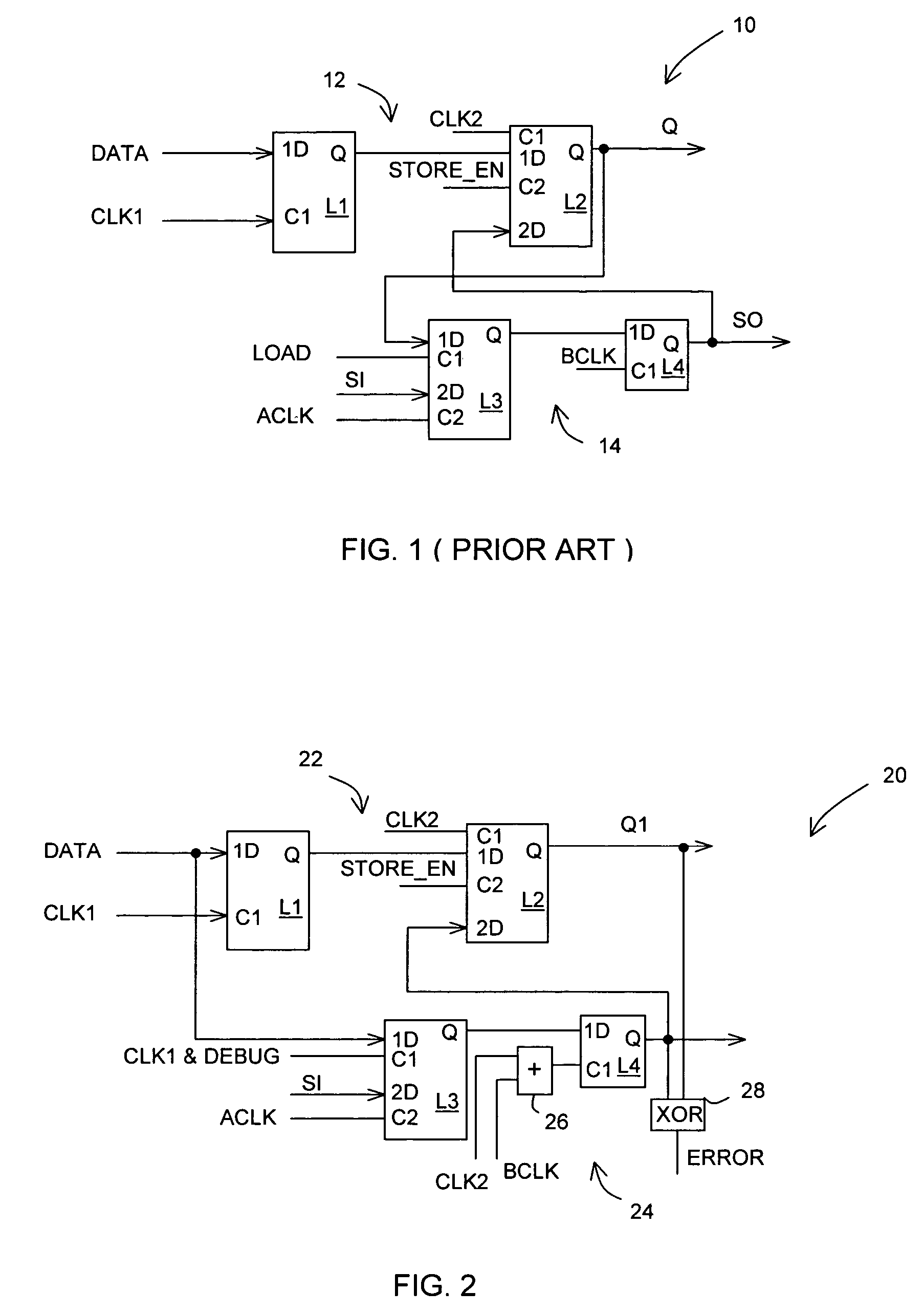
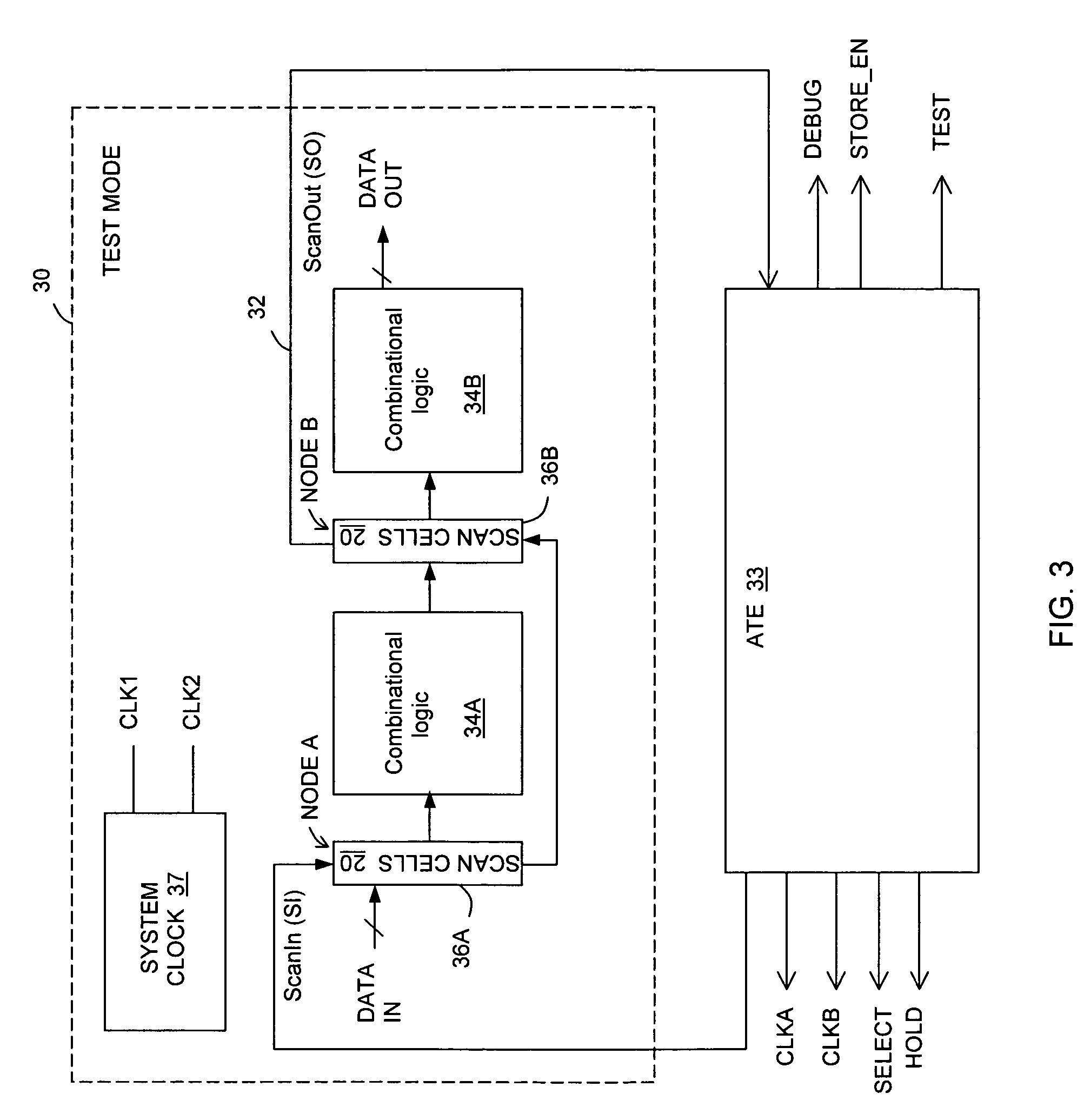
Error detecting circuit
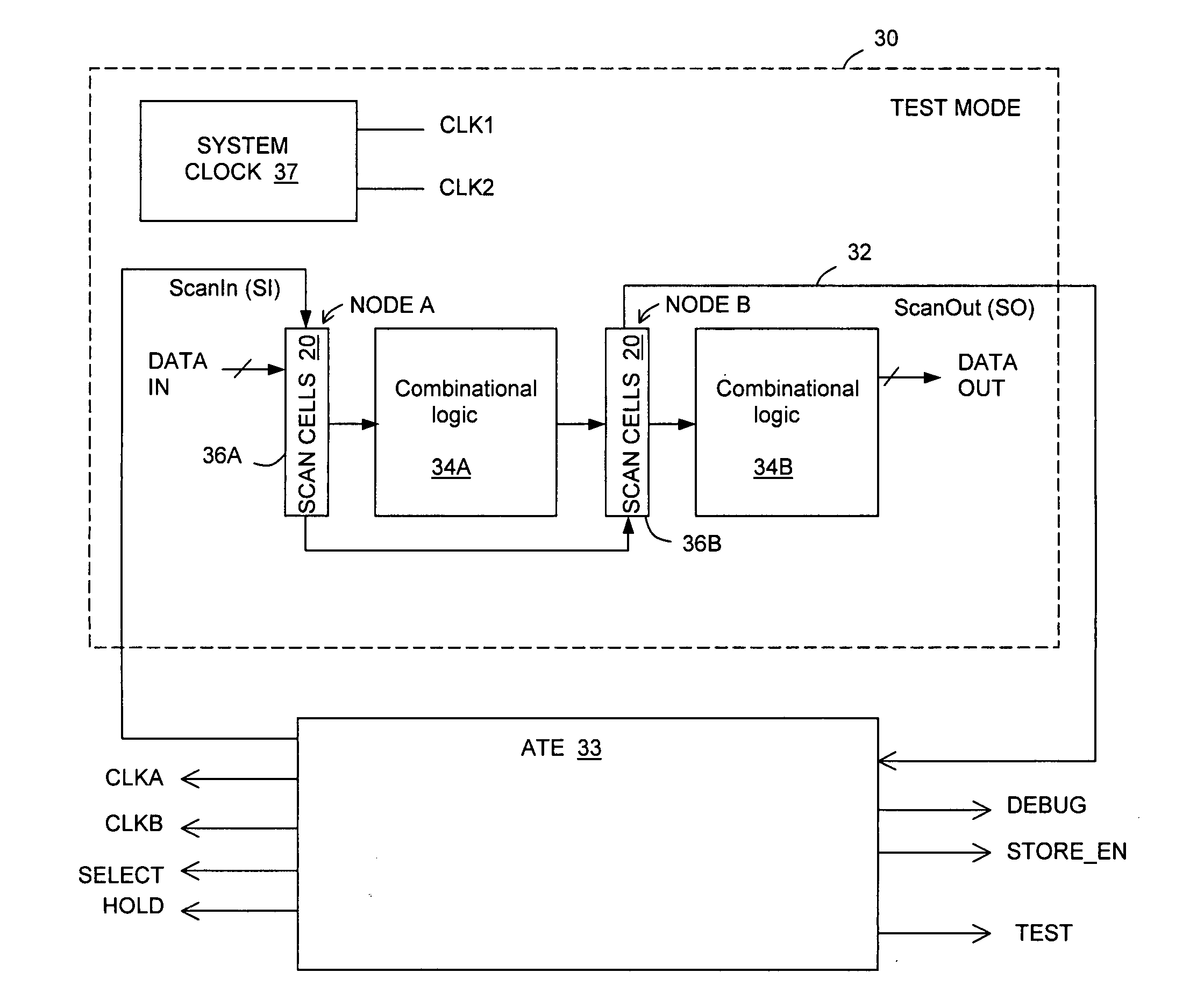
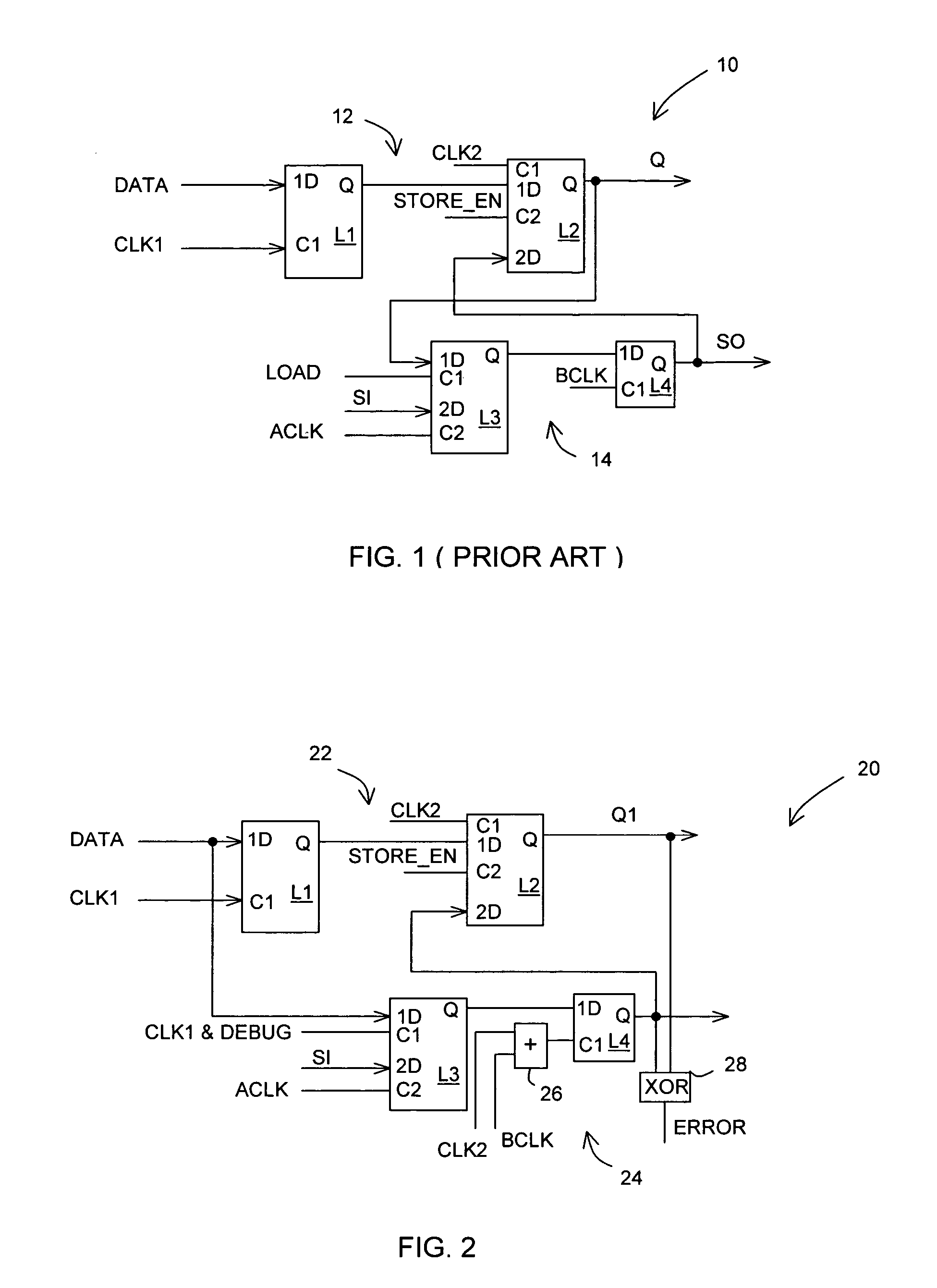
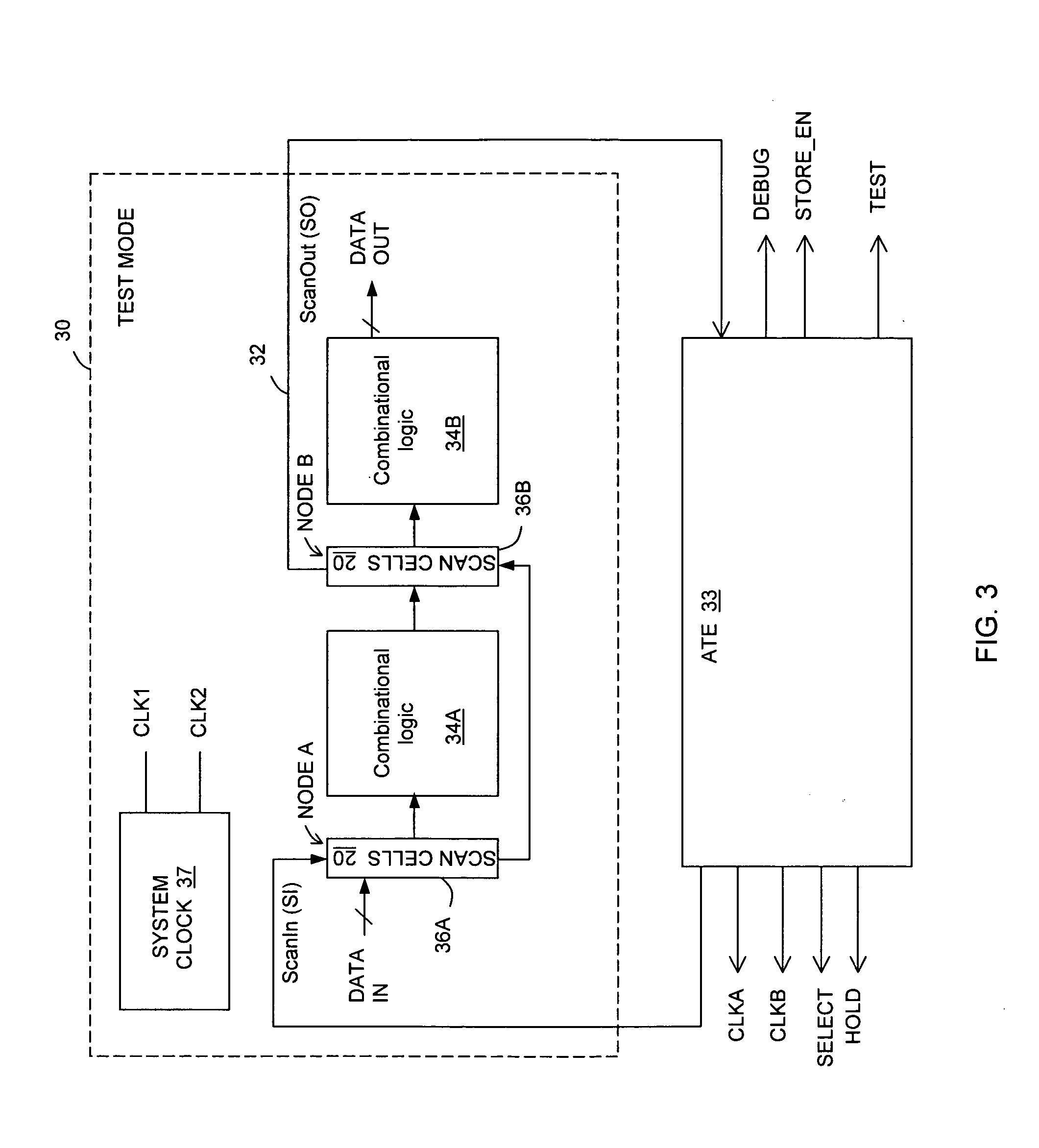
In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a datapath circuit to generate a data output signal in response to a data input signal and at least a first data clock signal; a shadow circuit, coupled to the datapath circuit, to generate a shadow output signal in response the data input signal and at least a second data clock signal during a functional mode of operation and to generate a scan-out signal in response to a scan-in signal and at least a first test clock signal during a test mode of operation; and an error detect circuit, coupled to the datapath and the shadow circuits, to generate an error signal in response to a mismatch between the data output signal and the shadow output signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Low power memory architecture
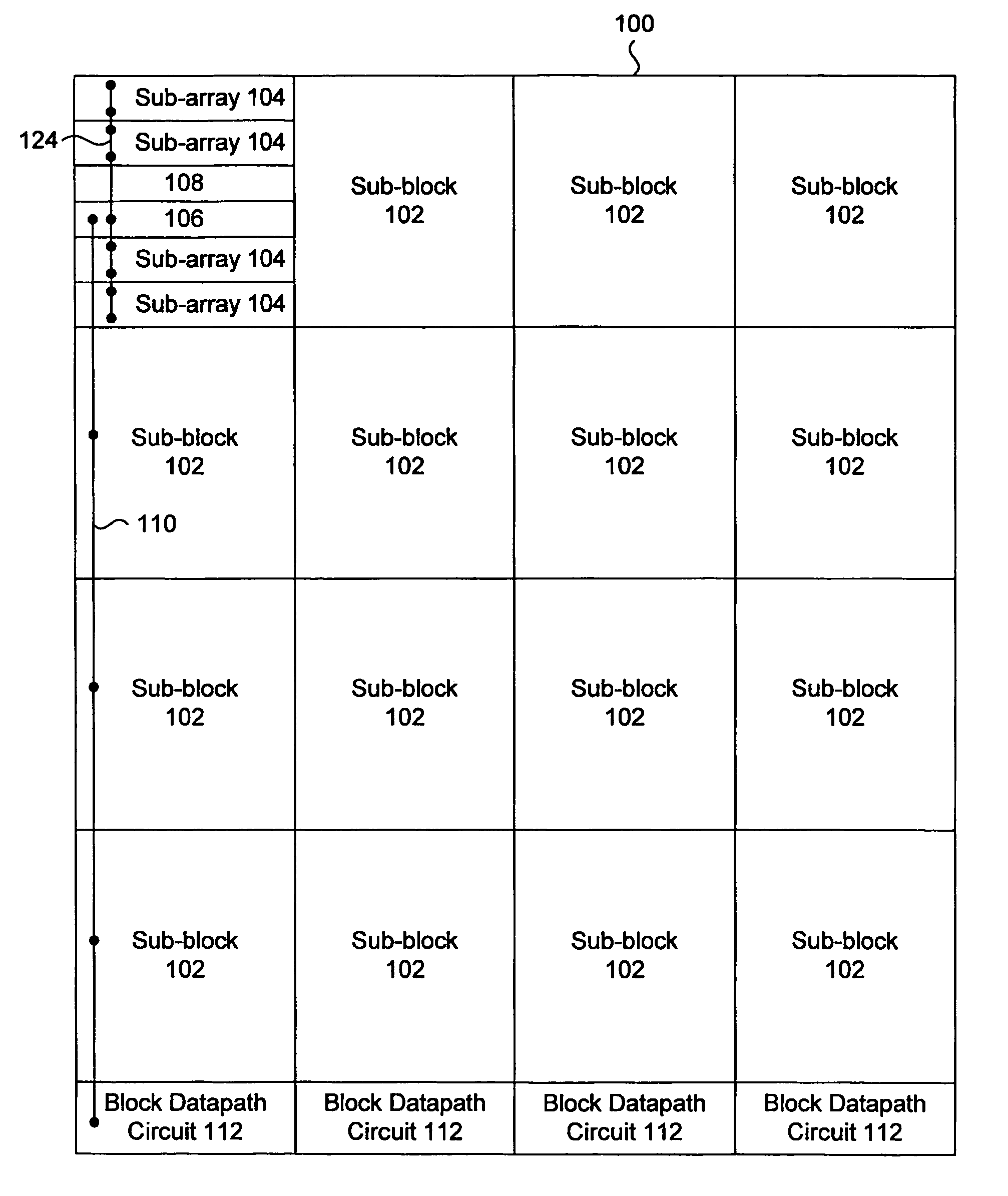
ActiveUS20070201295A1Minimizing current leakageMinimize current leakageDigital data processing detailsDigital storageDatapath circuitsPower grid
A memory architecture and circuits for minimizing current leakage in the memory array. Subdivisions of the memory array each have local power grids that can be selectively connected to power supplies, such that only an accessed subdivision will receive power to execute the memory access operation. The memory array can further include databuses which are precharged to one voltage during idle times and a second voltage during active read cycles, which reduces leakage current in datapath circuitry connected to the databuses within the memory array blocks.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
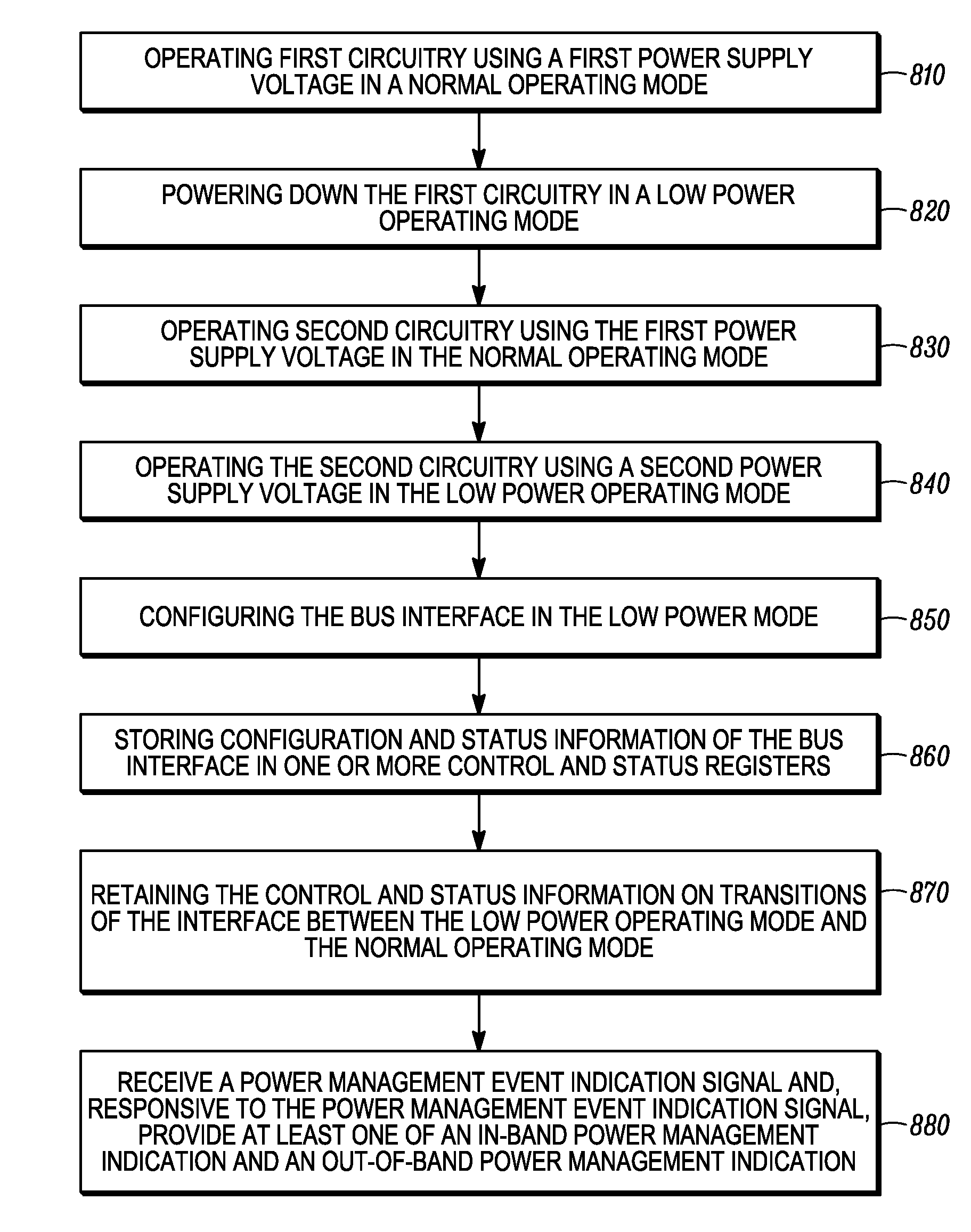
Method and apparatus for providing a bus interface with power management features
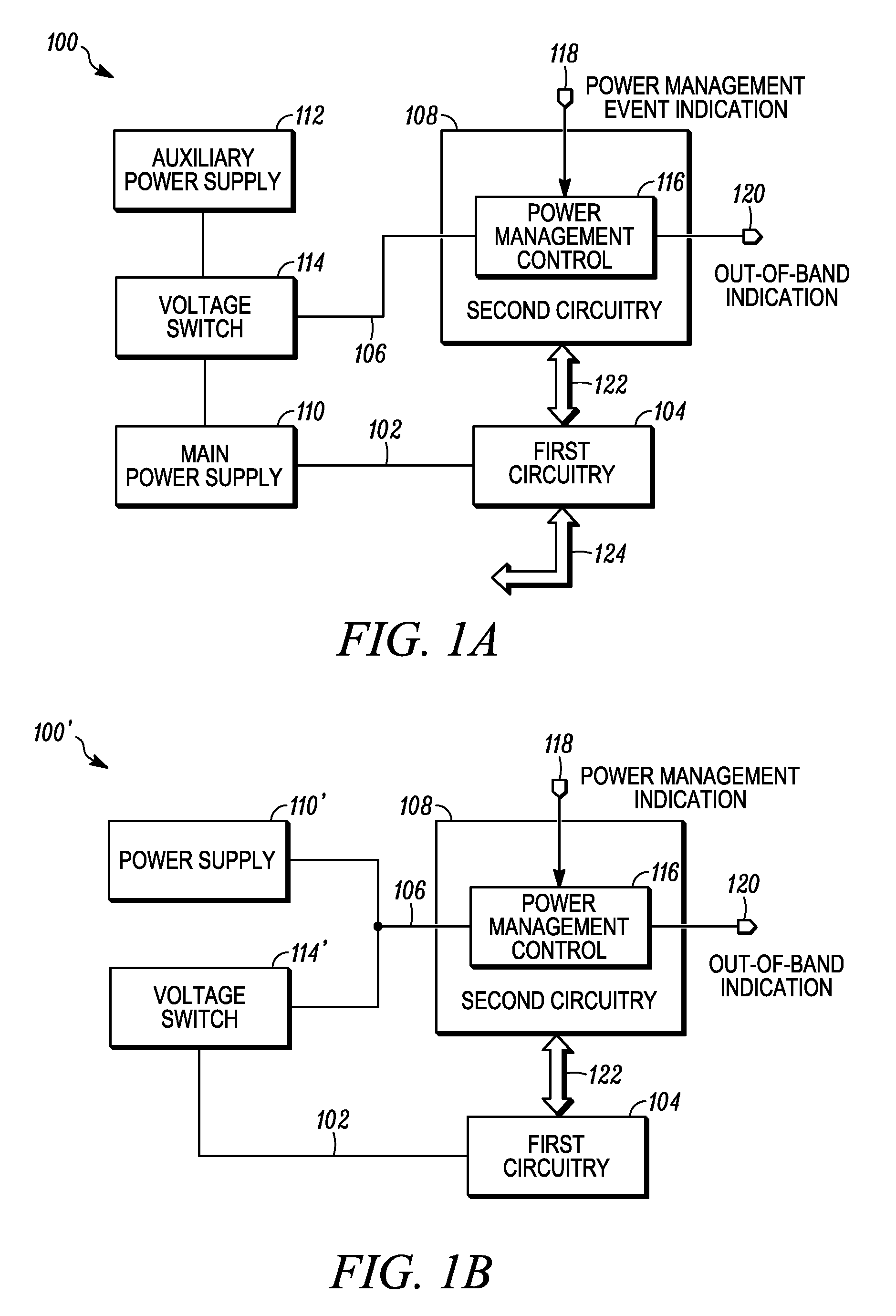
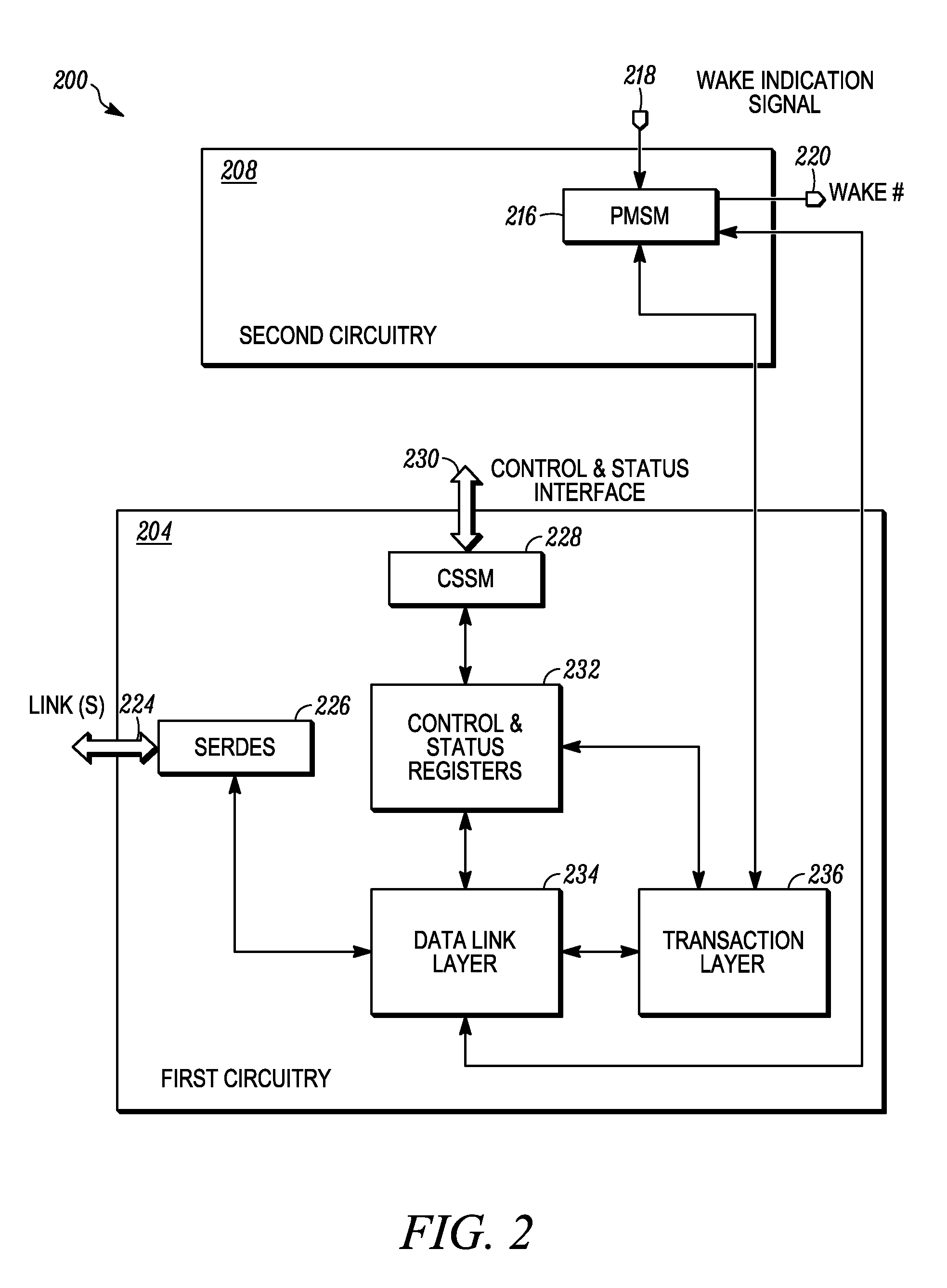
Methods and apparatus for providing a bus interface are disclosed. An example method for providing a bus interface includes operating first circuitry using a first power supply voltage in a normal operating mode, where the first circuitry includes at least a portion of datapath circuitry of the bus interface. The example method further includes powering down the first circuitry in a low power operating mode and operating second circuitry using the first power supply voltage in the normal operating mode. The example method also includes operating the second circuitry using a second power supply voltage in the low power operating mode. The second circuitry includes a power management control circuit adapted to receive a power management event indication signal. Responsive to the power management event indication signal, the control circuit provides at least one of an in-band power management indication and an out-of-band power management indication to one or more devices in a computing system. In the example method, the first and second power supply voltages may be provided by a single power supply or, alternatively, by multiple power supplies.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Error detecting circuit
In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a datapath circuit to generate a data output signal in response to a data input signal and at least a first data clock signal; a shadow circuit, coupled to the datapath circuit, to generate a shadow output signal in response the data input signal and at least a second data clock signal during a functional mode of operation and to generate a scan-out signal in response to a scan-in signal and at least a first test clock signal during a test mode of operation; and an error detect circuit, coupled to the datapath and the shadow circuits, to generate an error signal in response to a mismatch between the data output signal and the shadow output signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
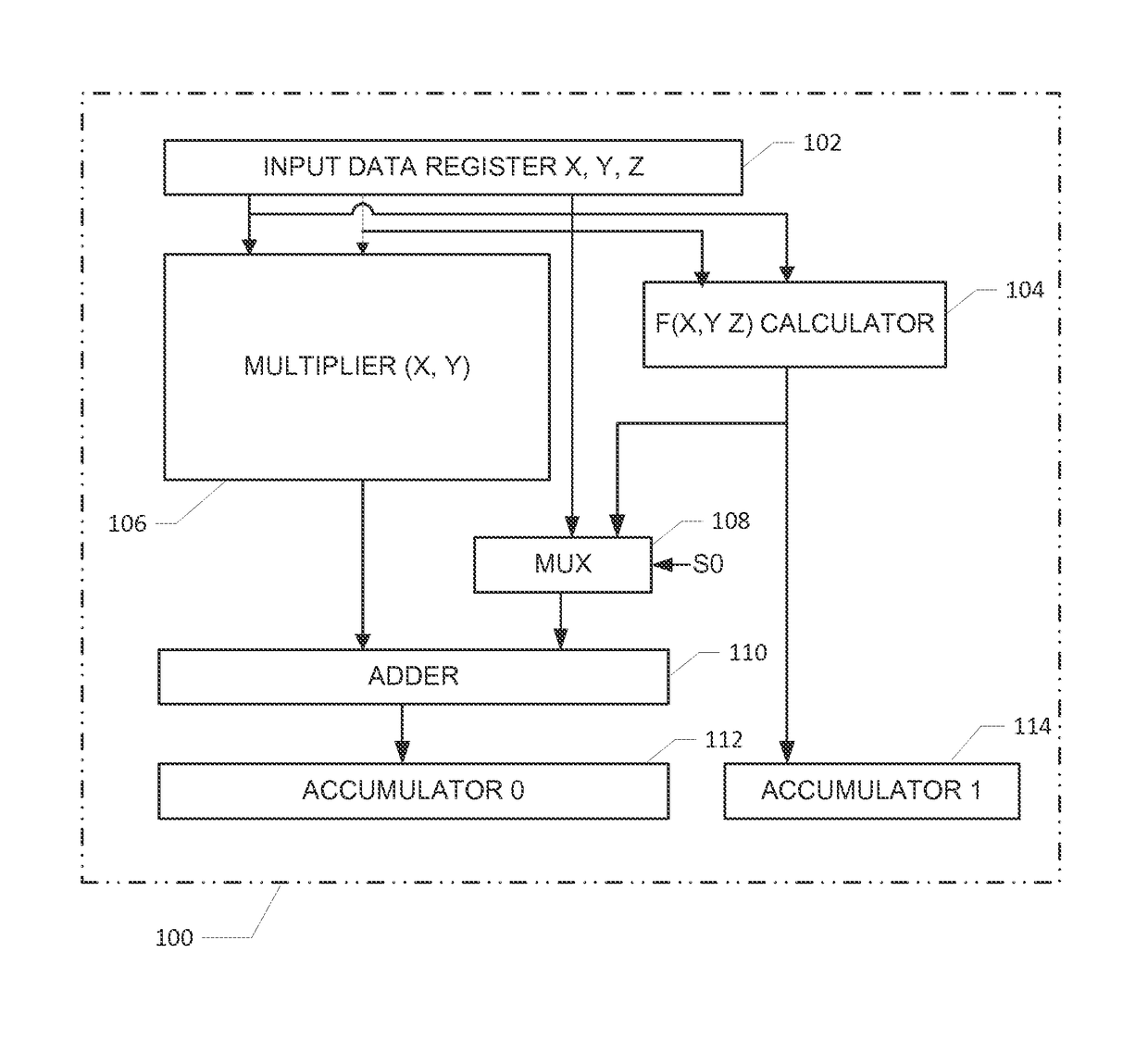
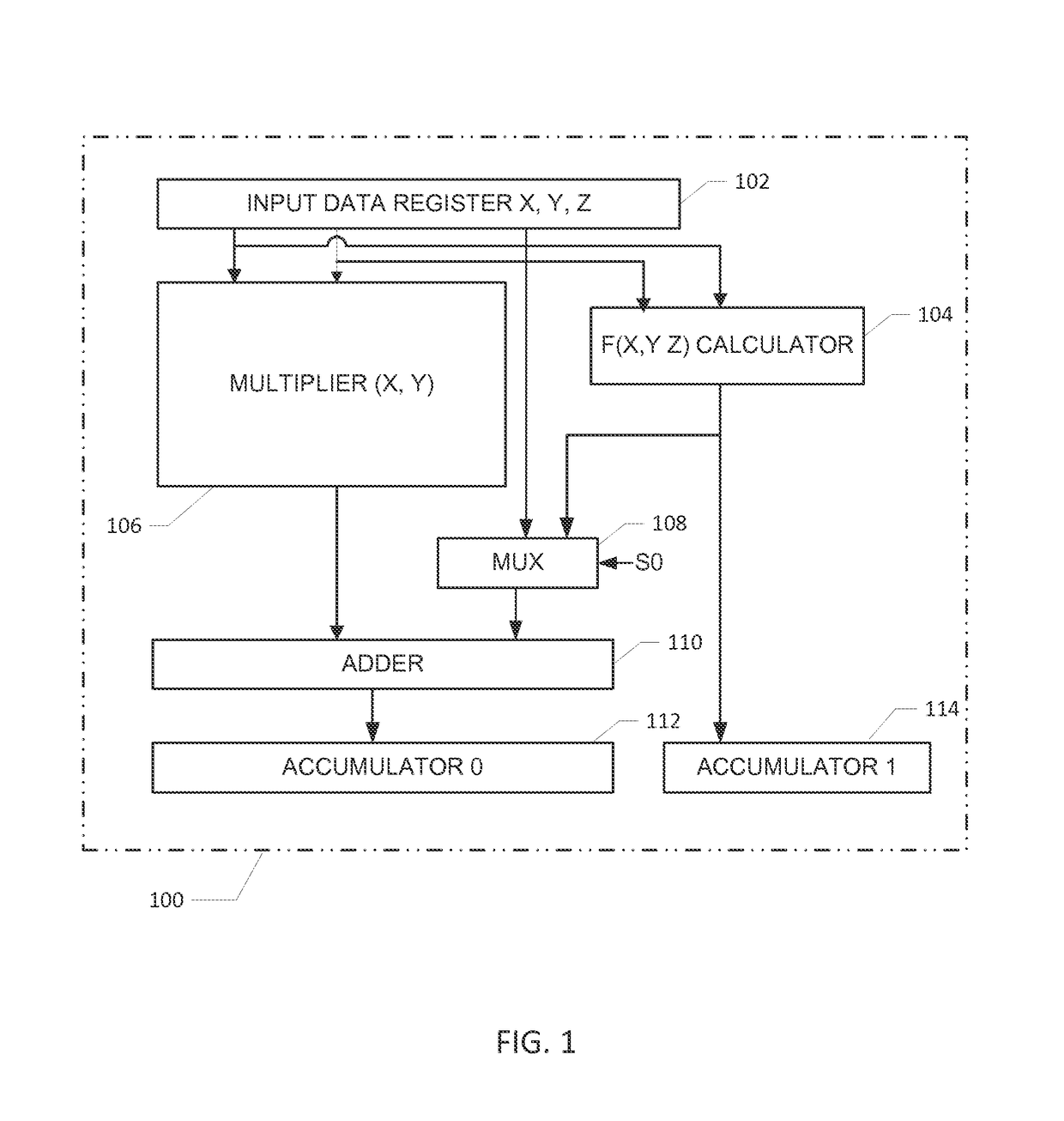
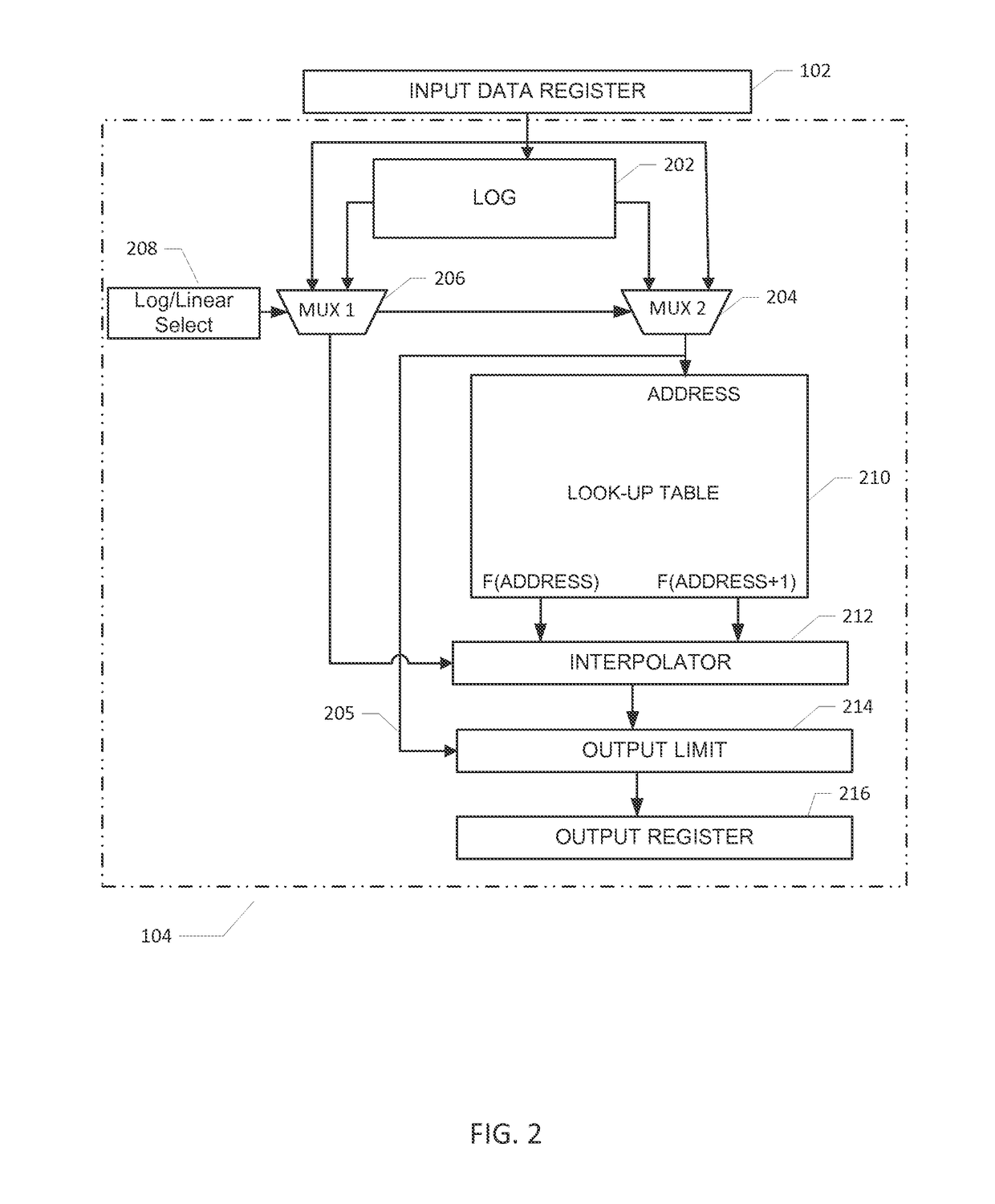
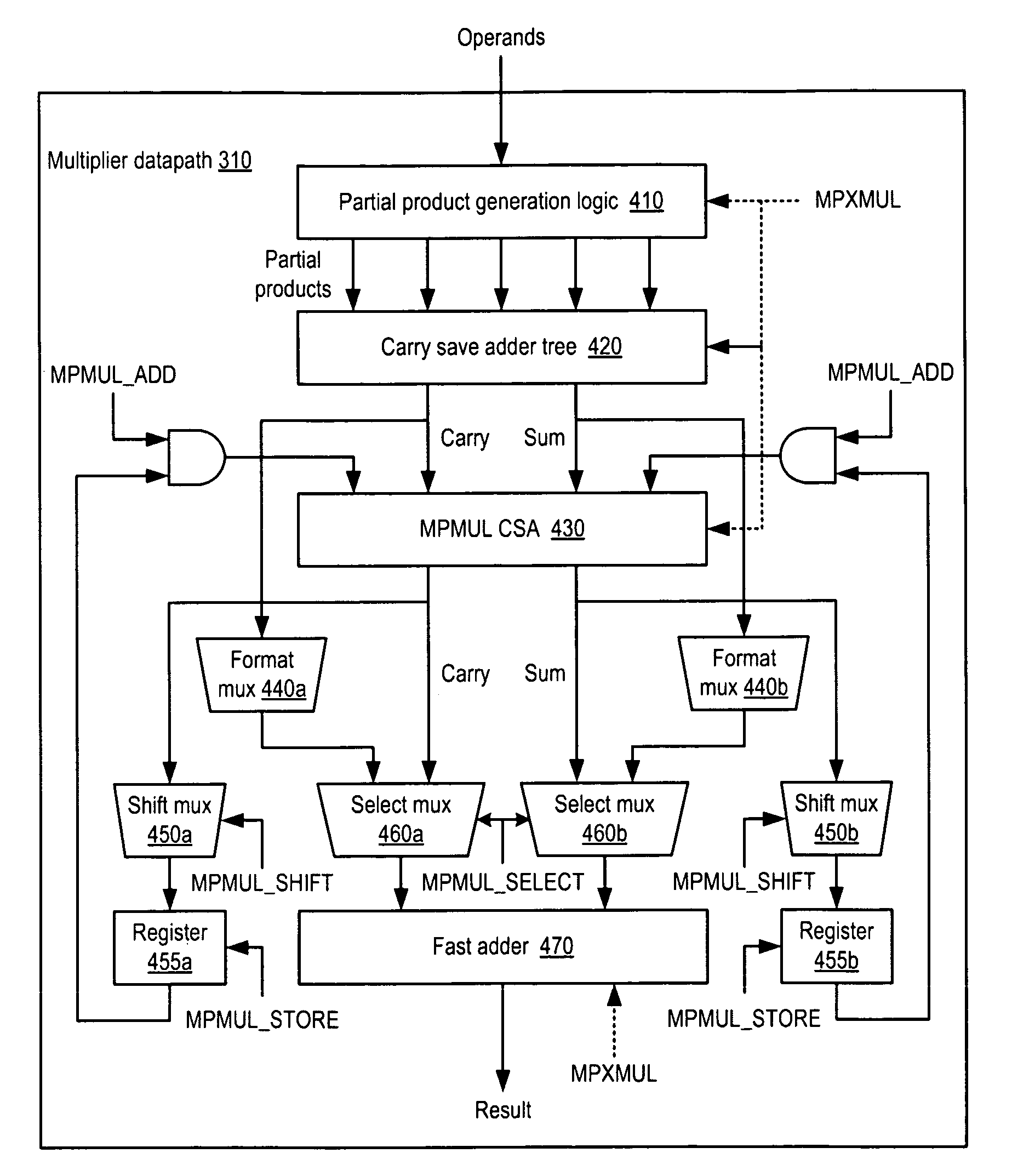
Datapath circuit for digital signal processors
ActiveUS20140067889A1Easy accessFast executionLogarithmic/exponential functionsDigital computer detailsDatapath circuitsComputer architecture
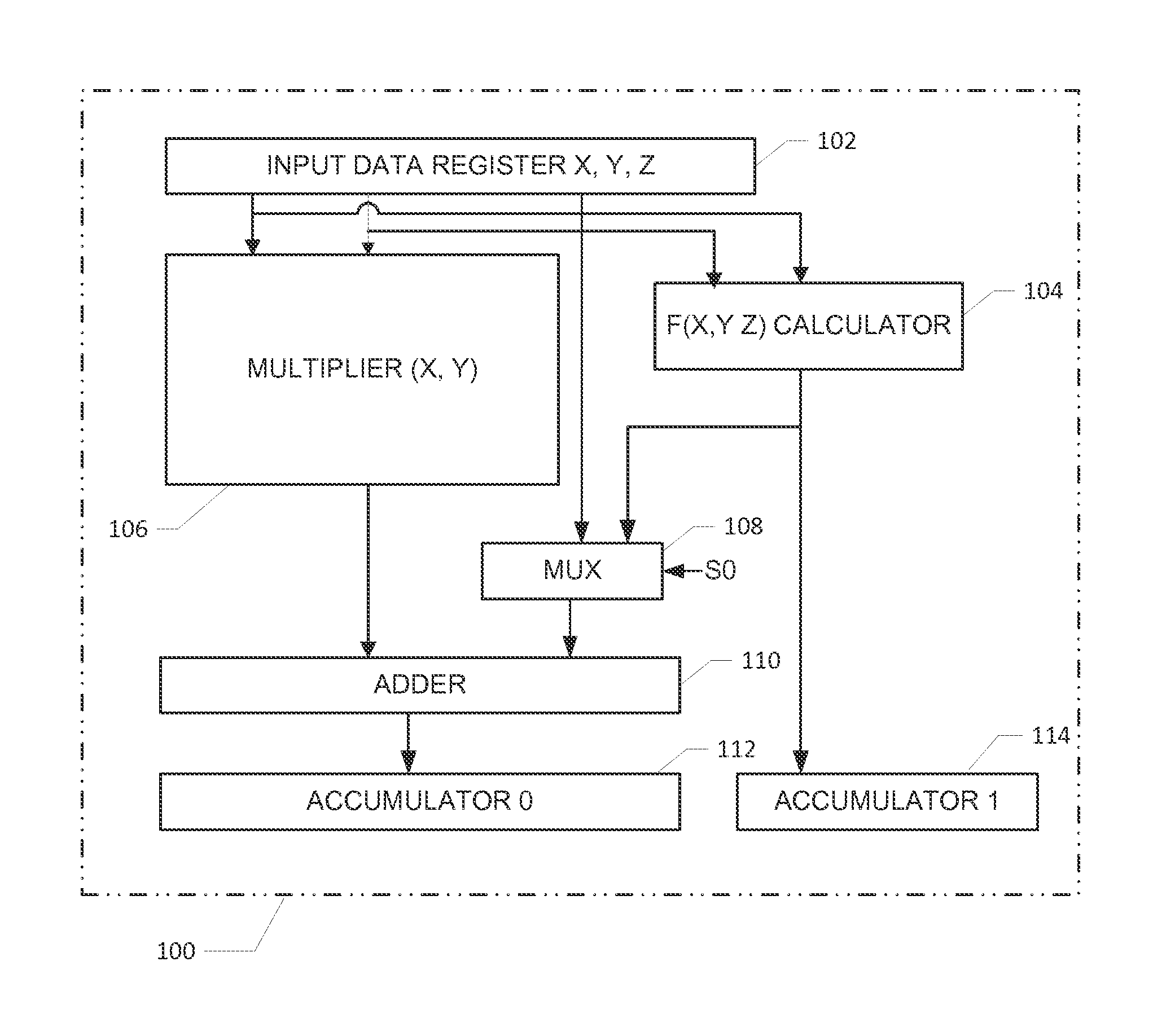
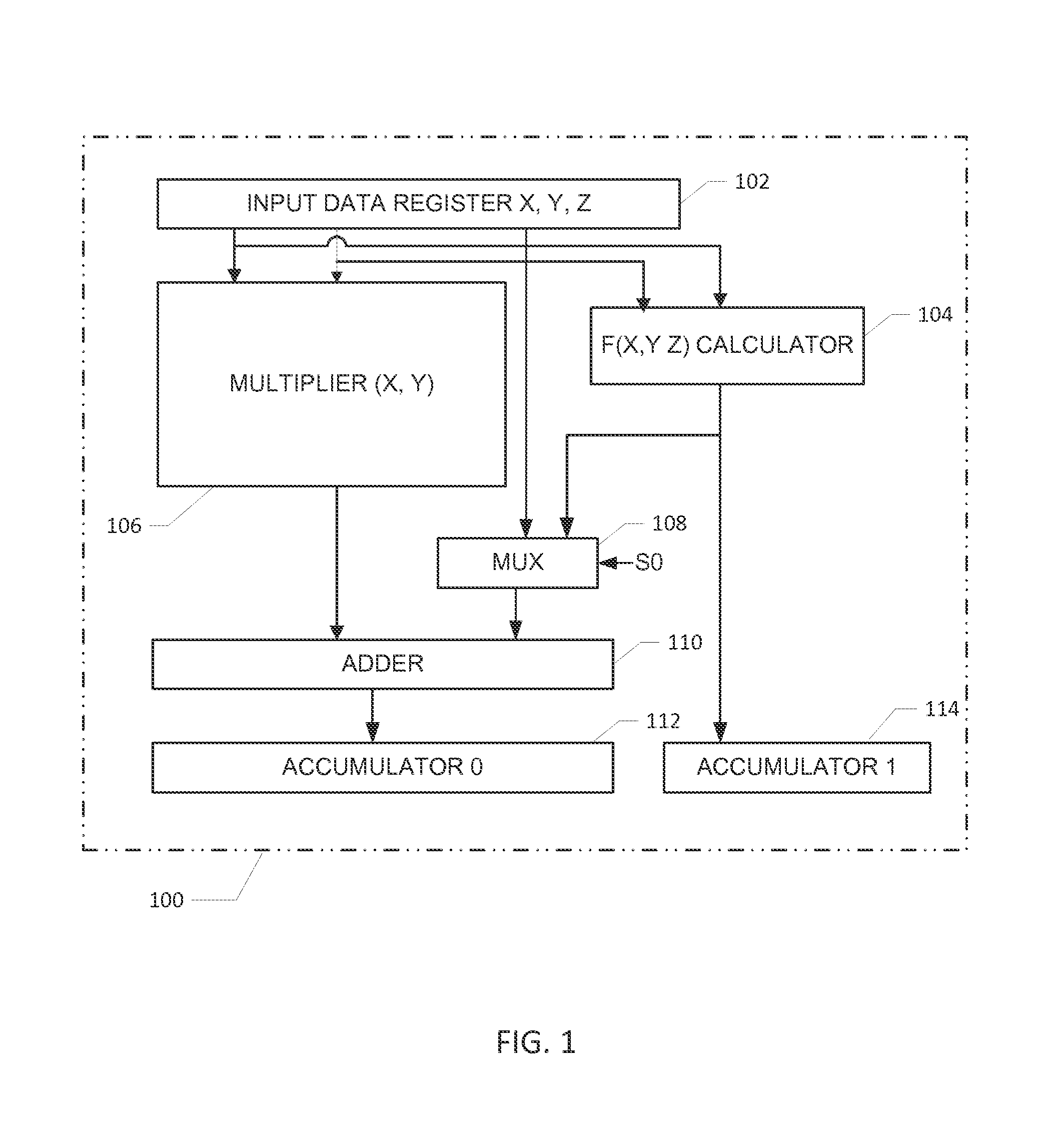
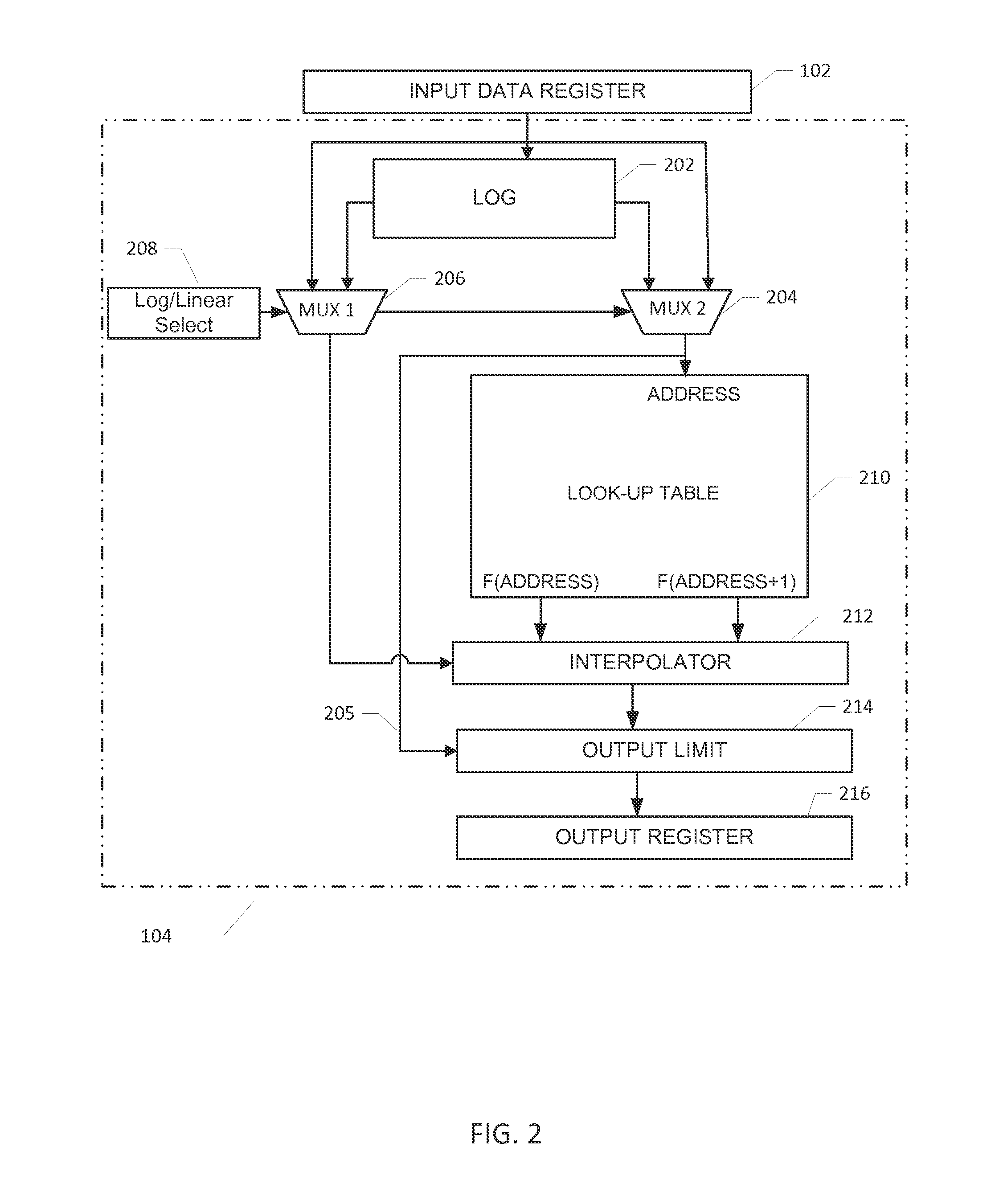
A datapath circuit may include a digital multiply and accumulate circuit (MAC) and a digital hardware calculator for parallel computation. The digital hardware calculator and the MAC may be coupled to an input memory element for receipt of input operands. The MAC may include a digital multiplier structure with partial product generators coupled to an adder to multiply a first and second input operands and generate a multiplication result. The digital hardware calculator may include a first look-up table coupled between a calculator input and a calculator output register. The first look-up table may include table entry values mapped to corresponding math function results in accordance with a first predetermined mathematical function. The digital hardware calculator may be configured to calculate, based on the first look-up table, a computationally hard mathematical function such as a logarithm function, an exponential function, a division function and a square root function.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Fused floating point datapath with correct rounding
ActiveUS9348557B1Improve efficiencySmall area consumptionComputation using non-contact making devicesDatapath circuitsSign bit
In accordance with some embodiments, a floating point number datapath circuitry, e.g., within an integrated circuit programmable logic device is provided. The datapath circuitry may be used for computing a rounded absolute value of a mantissa of a floating point number. The floating point datapath circuitry may have only a single adder stage for computing a rounded absolute value of a mantissa of the floating point number based on one or more bits of an unrounded mantissa of the floating point number. The unrounded and rounded mantissas may include a sign bit, a sticky bit, a round bit, and / or a least significant bit, and / or other bits. The unrounded mantissa may be in a format that includes negative numbers (e.g., 2's complement) and the rounded mantissa may be in a format that may include a portion of the floating point number represented as a positive number, (e.g., signed magnitude).
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
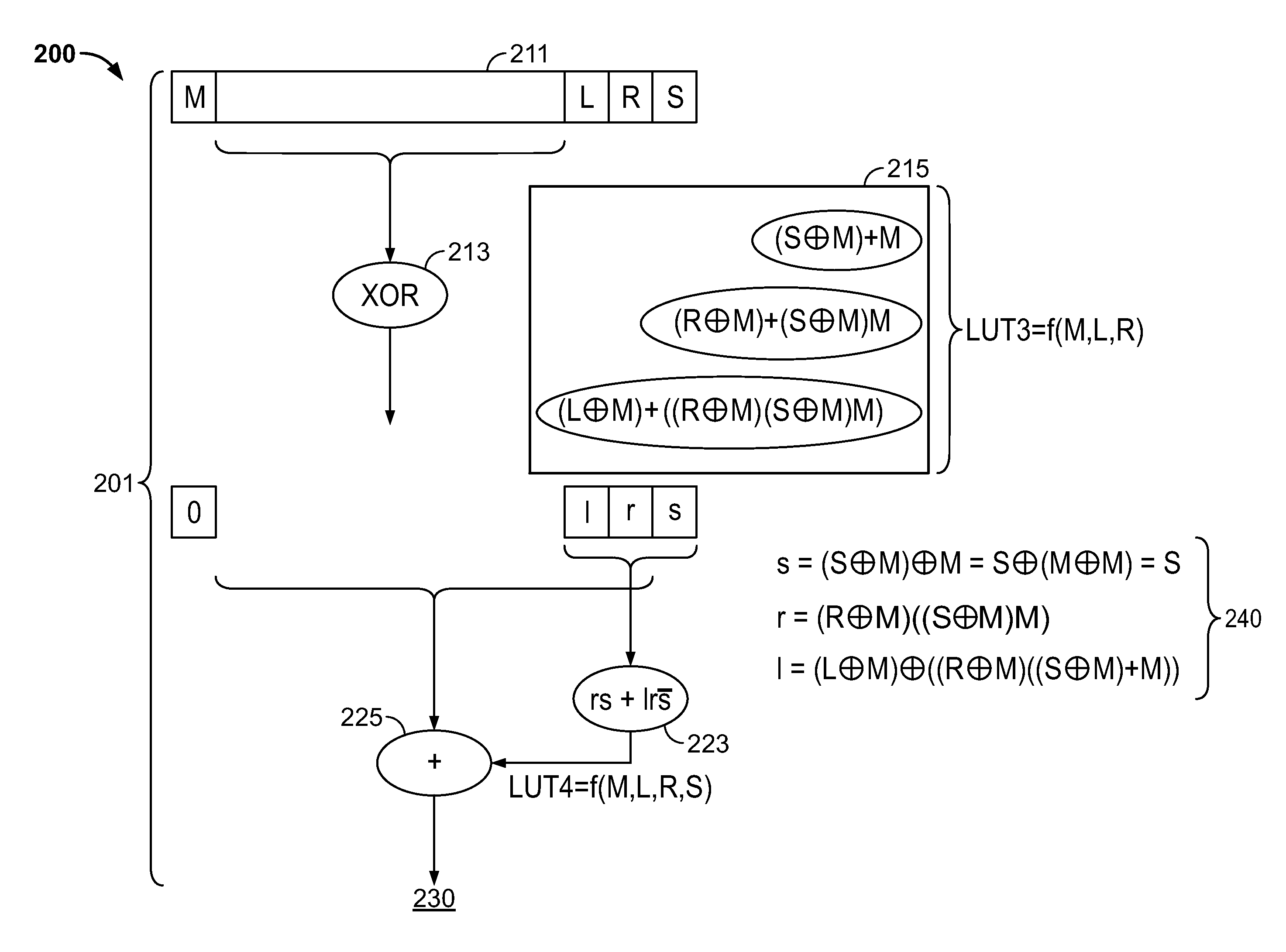
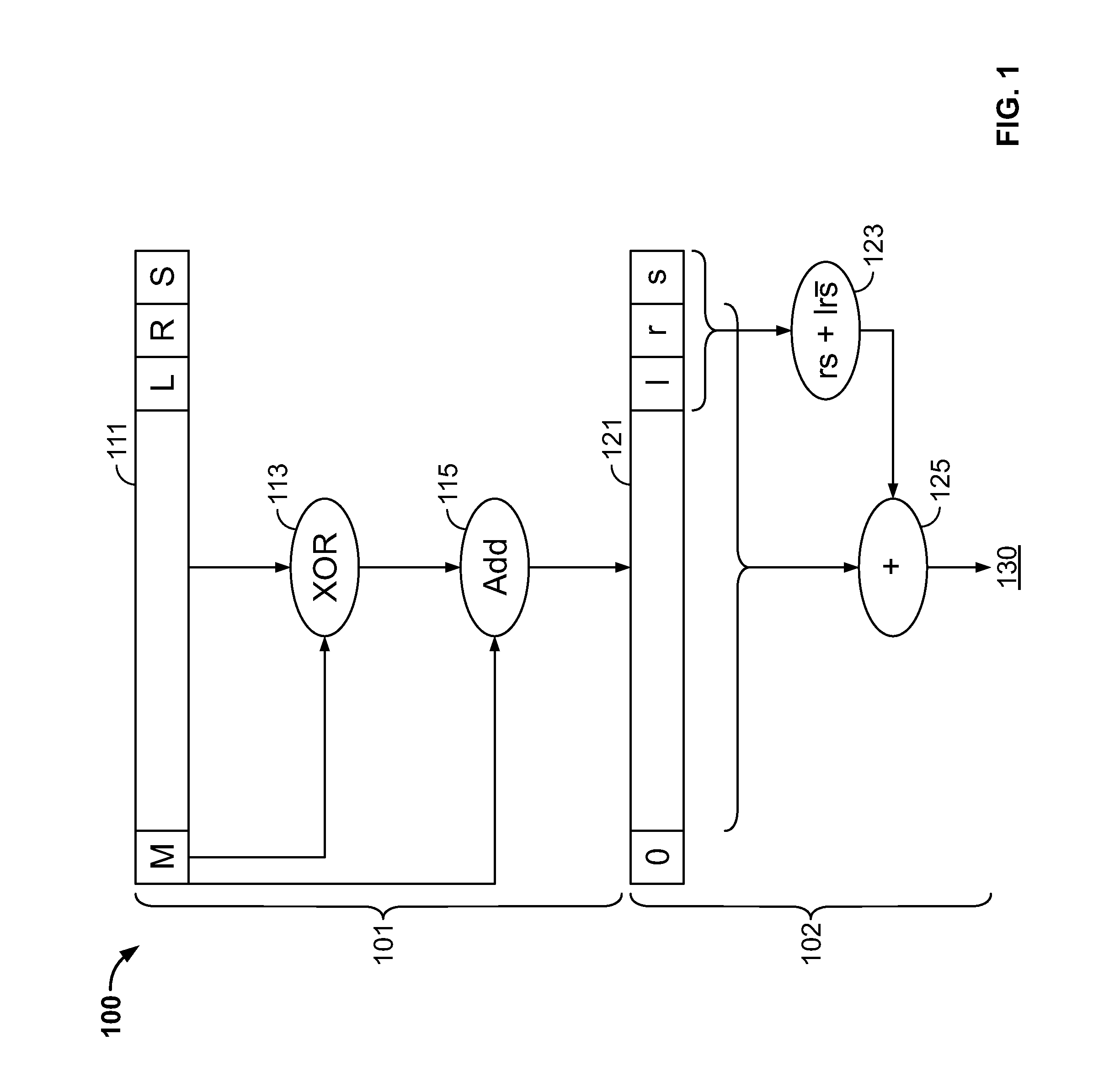
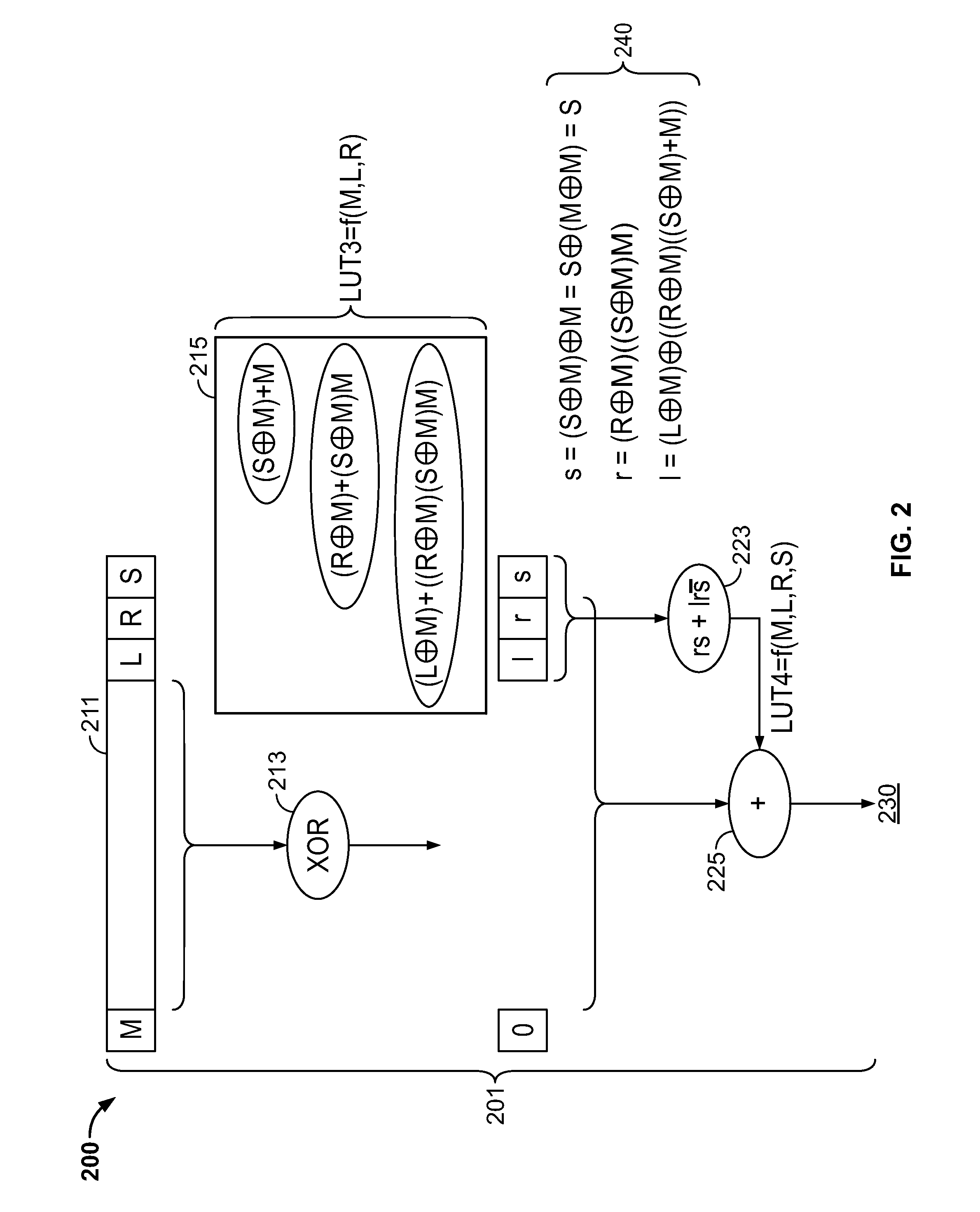
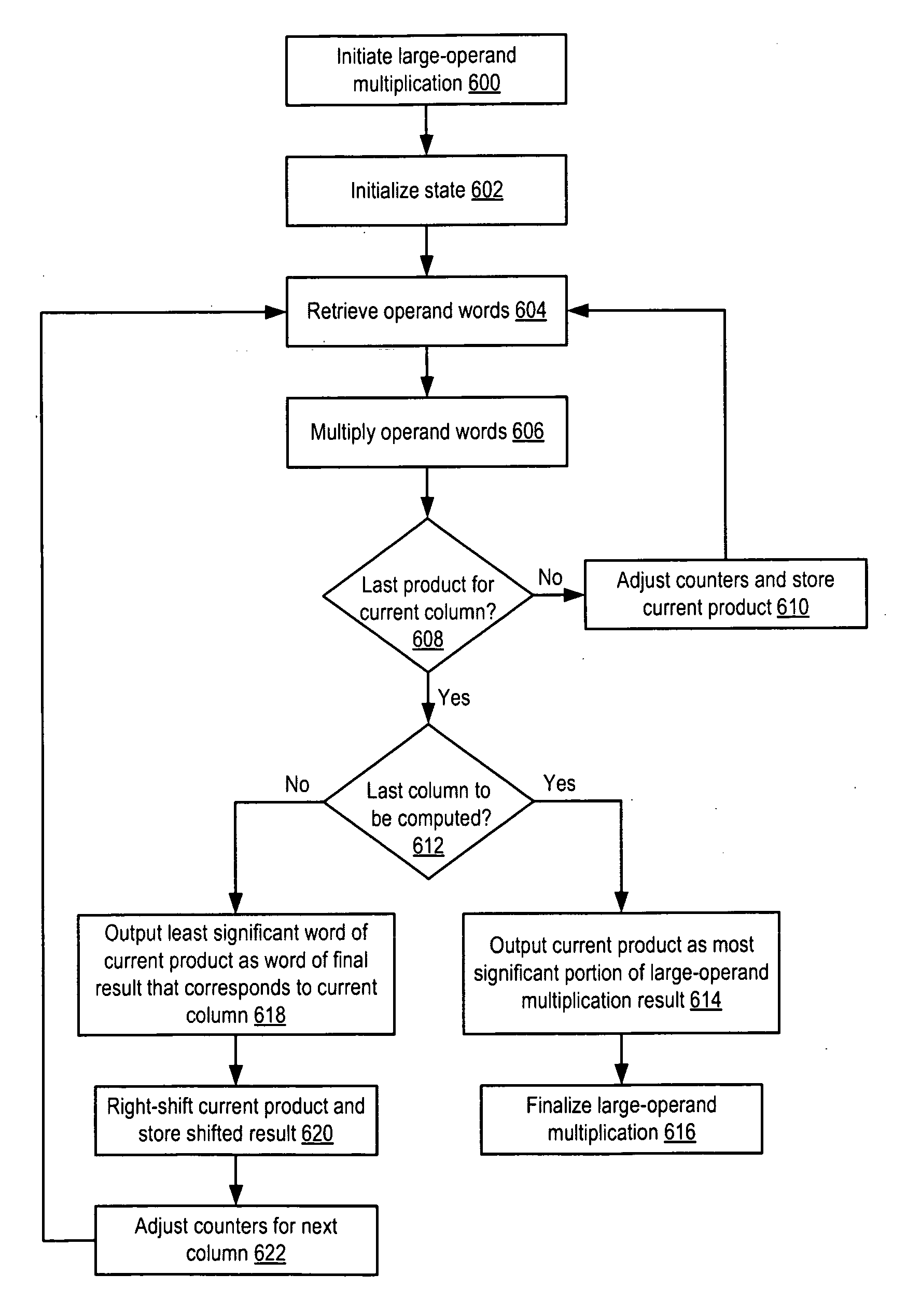
Processor and method for implementing instruction support for multiplication of large operands
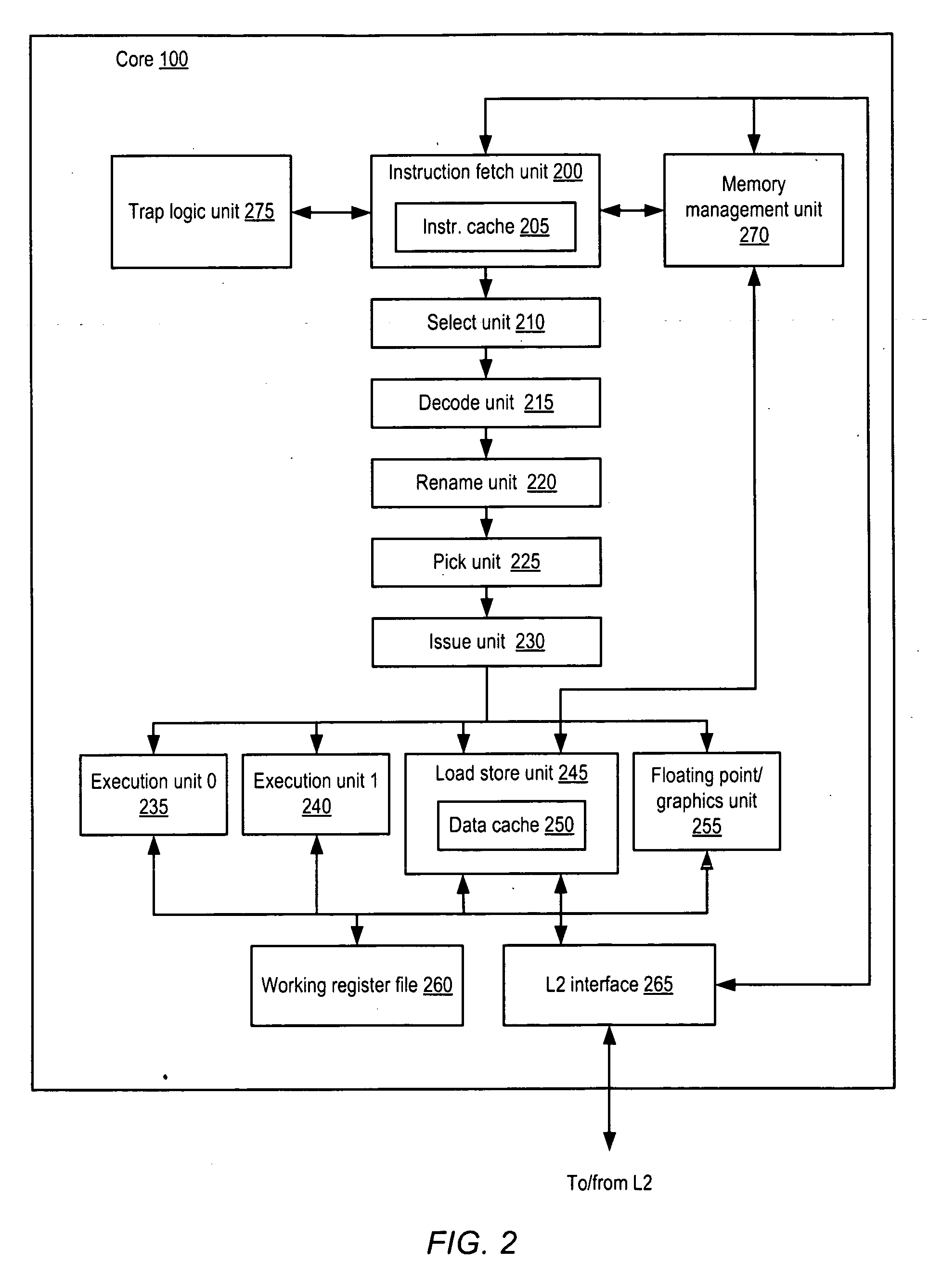
ActiveUS20100325188A1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesDatapath circuitsExecution unit
A processor including instruction support for implementing large-operand multiplication may issue, for execution, programmer-selectable instructions from a defined instruction set architecture (ISA). The processor may include an instruction execution unit comprising a hardware multiplier datapath circuit, where the hardware multiplier datapath circuit is configured to multiply operands having a maximum number of bits M. In response to receiving a single instance of a large-operand multiplication instruction defined within the ISA, wherein at least one of the operands of the large-operand multiplication instruction includes more than the maximum number of bits M, the instruction execution unit is configured to multiply operands of the large-operand multiplication instruction within the hardware multiplier datapath circuit to determine a result of the large-operand multiplication instruction without execution of programmer-selected instructions within the ISA other than the large-operand multiplication instruction.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
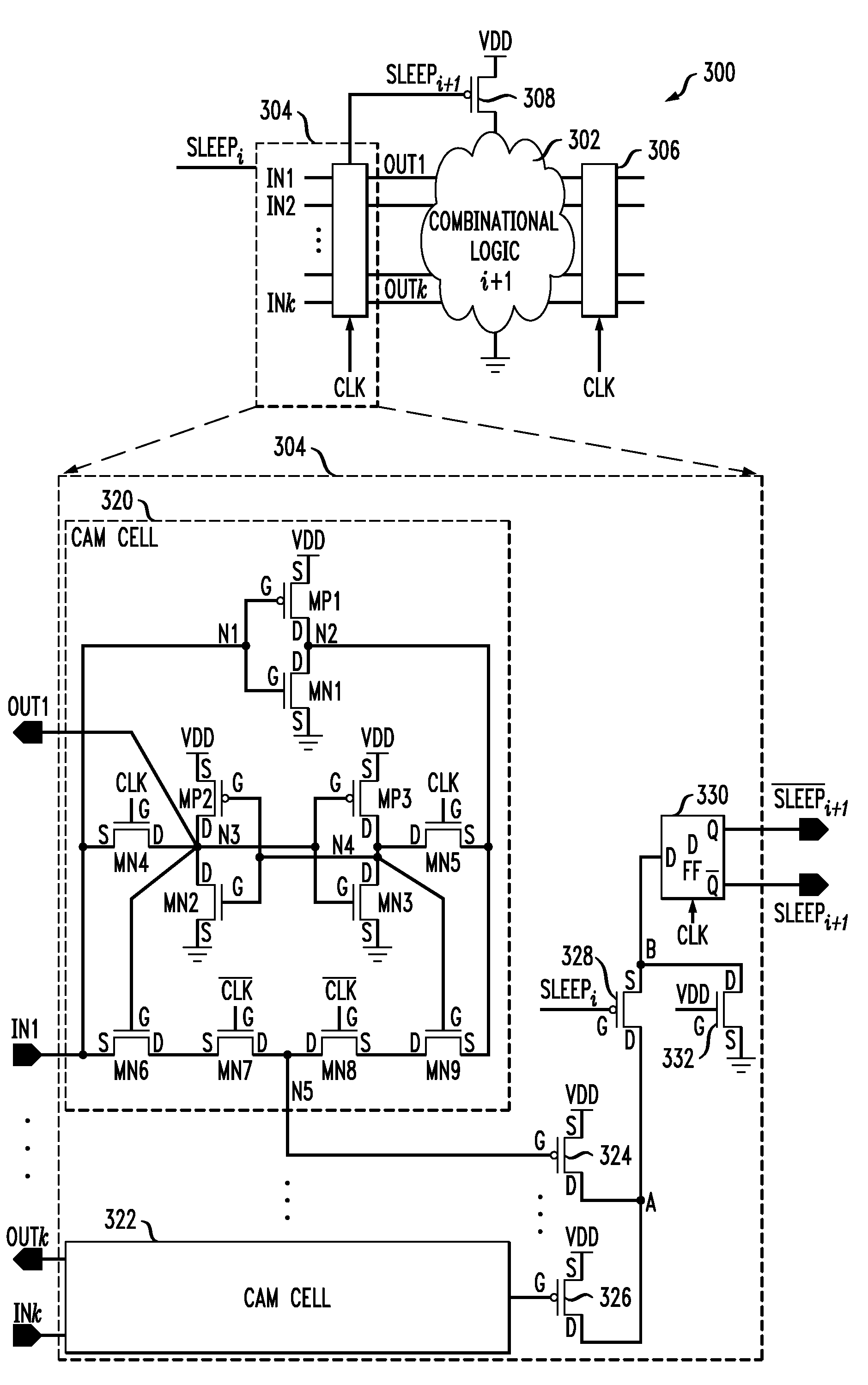
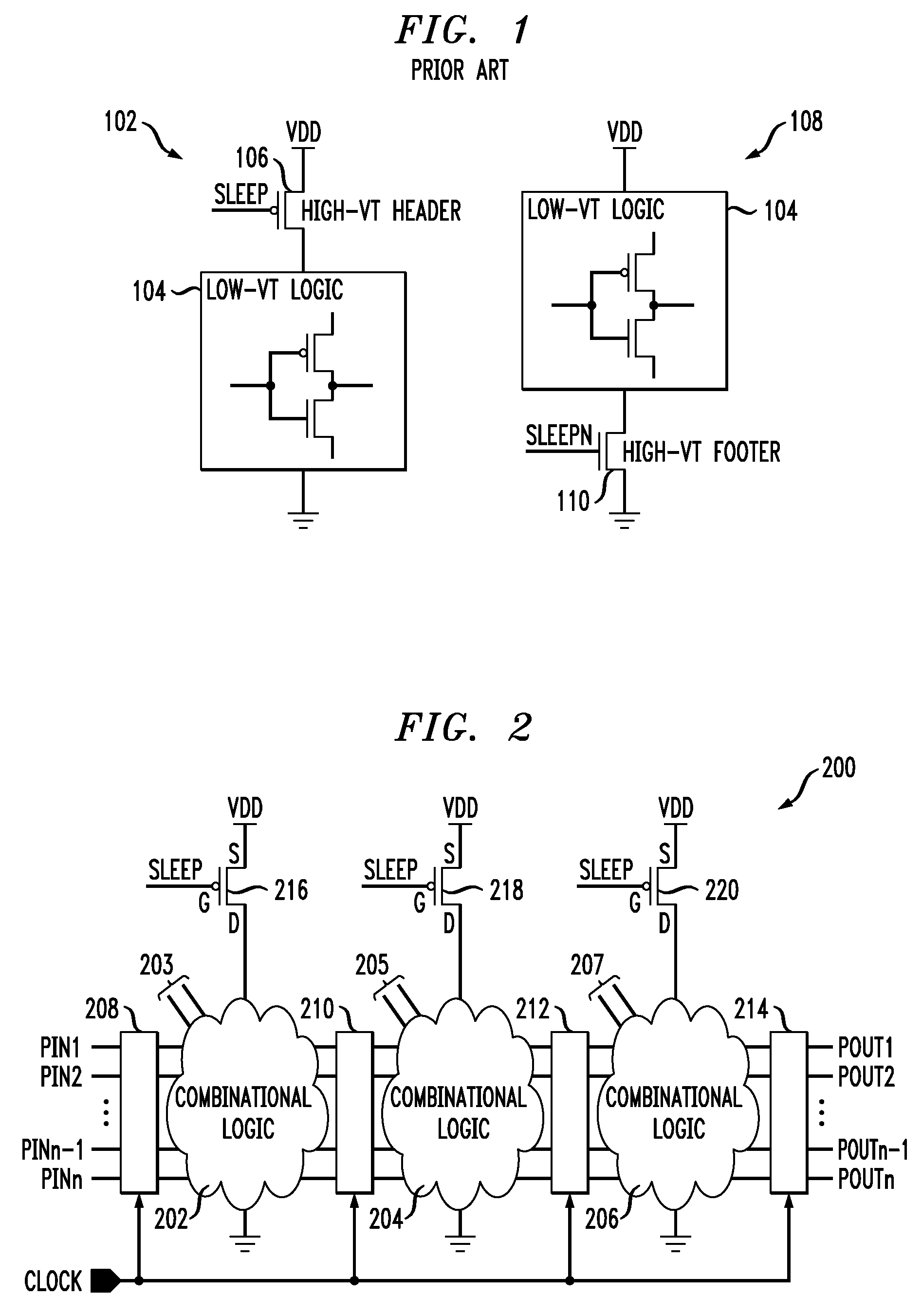
Fine-grained power management of synchronous and asynchronous datapath circuits
ActiveUS7511535B2Reliability increasing modificationsMajority/minority circuitsDatapath circuitsAsynchronous circuit
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
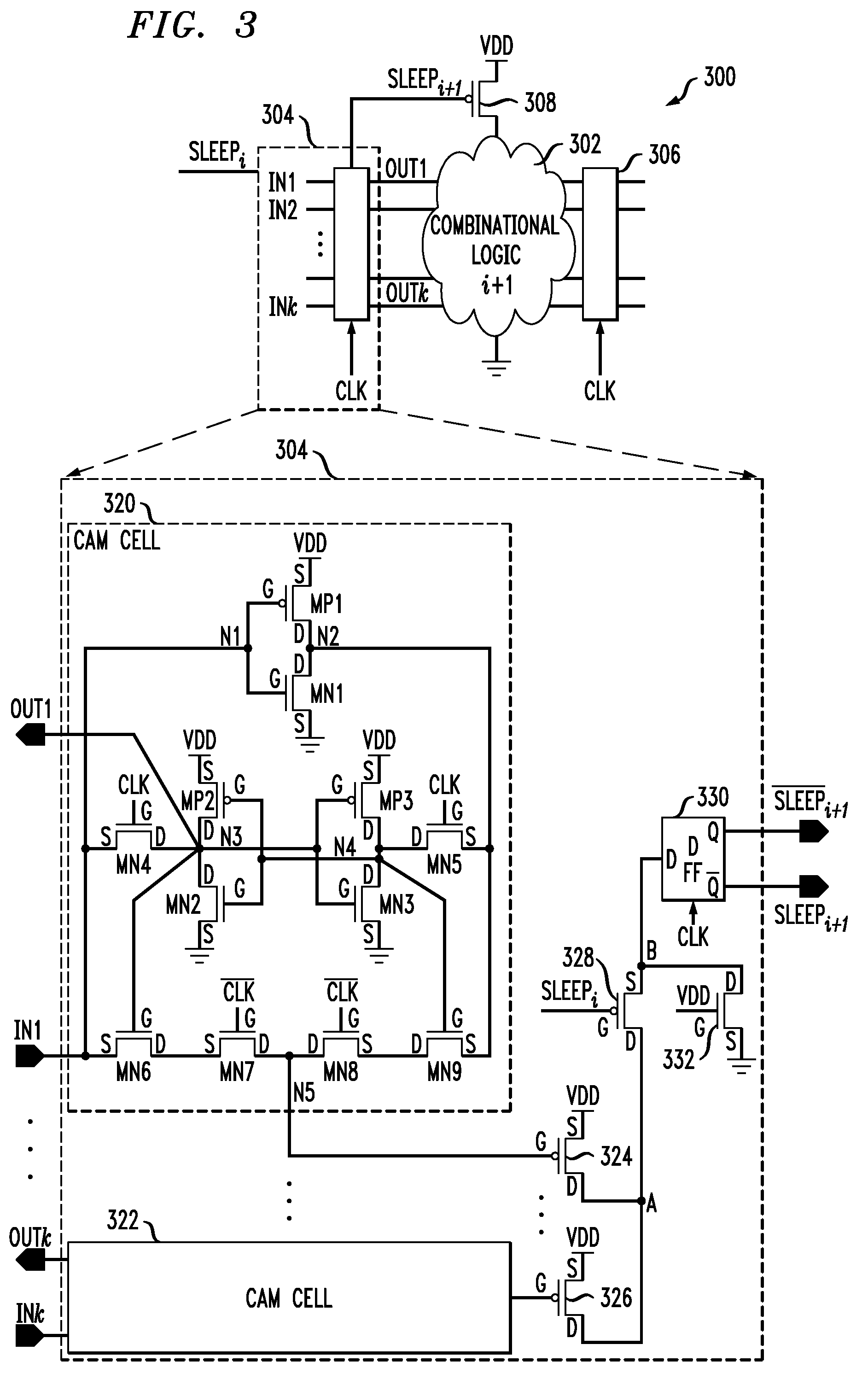
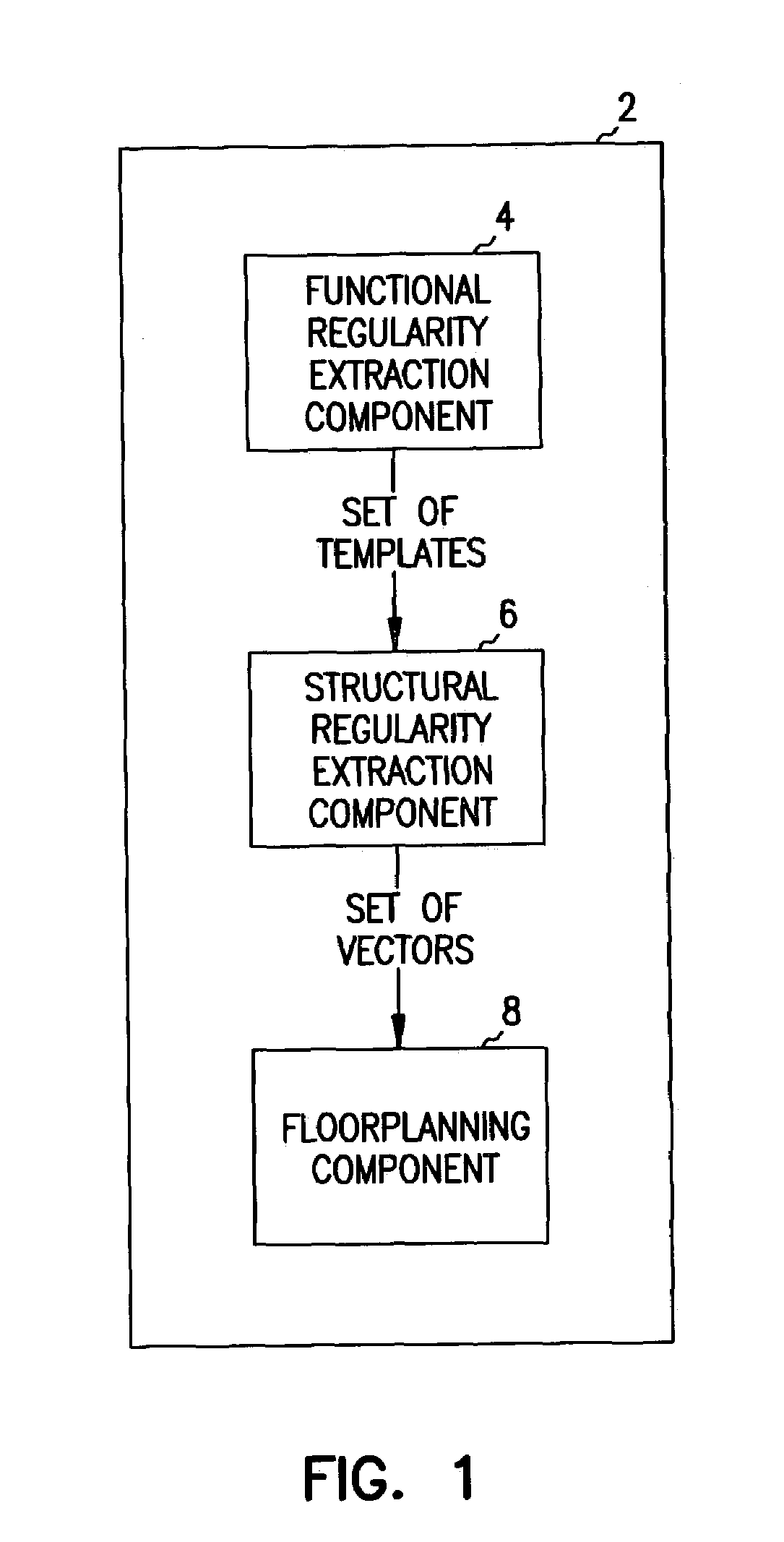
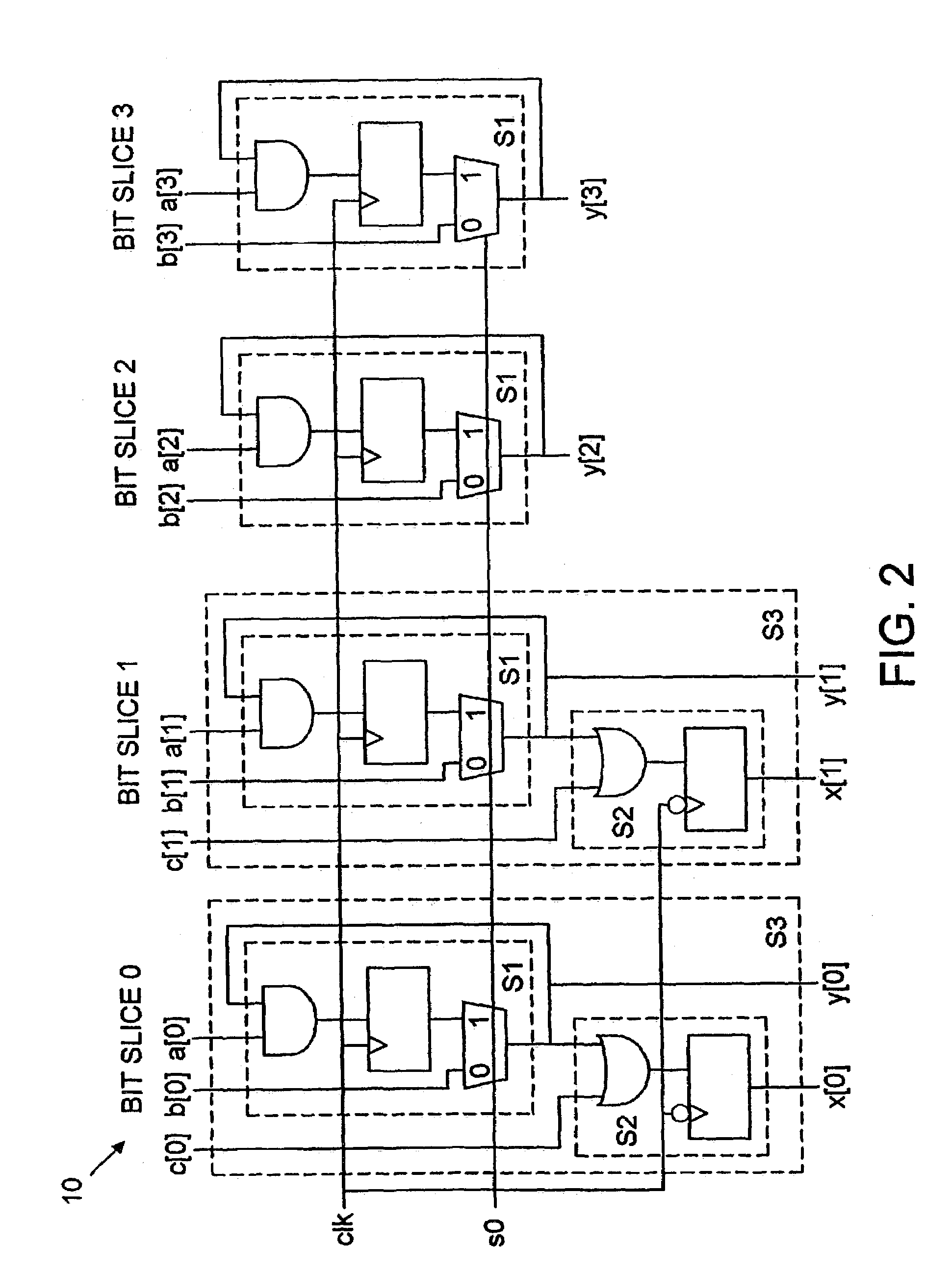
Structural regularity extraction and floorplanning in datapath circuits using vectors
InactiveUS7337418B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDatapath circuitsComputer Aided Design
In some embodiments, a computer-aided design system comprises a functional regularity extraction component, a structural regularity extraction component and a floorplanning component. The structural regularity extraction component provides a method to extract regularity for circuits (and in particular datapath circuits) based on the structural characteristics of a logic design. Some embodiments of the structural regularity extraction component automatically generate a set of vectors for the logic design. A vector is a group of template instances that are identical in function and in structure. The vectors generated by the structural regularity extraction component are used by a floorplanning component. The floorplanning component provides a method of generating a circuit layout from the set of vectors. In some embodiments, each vectors corresponds to a row in the circuit layout.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Datapath circuit for digital signal processors
ActiveUS9753695B2Fast executionLeveling precisionLogarithmic/exponential functionsComputation using non-denominational number representationDatapath circuitsDigital signal processing
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Memory data path circuit
InactiveUS7032143B1Improve scalabilityIncrease the compression ratioDigital storageDatapath circuitsNOR logic
A memory device with a data path circuit having support in the sense-amp region for compression testing of the device. The data path circuit uses NOR logic compression to provide a scalable design which may be extended to large circuits.
Owner:WALLER WILLIAM KENNETH
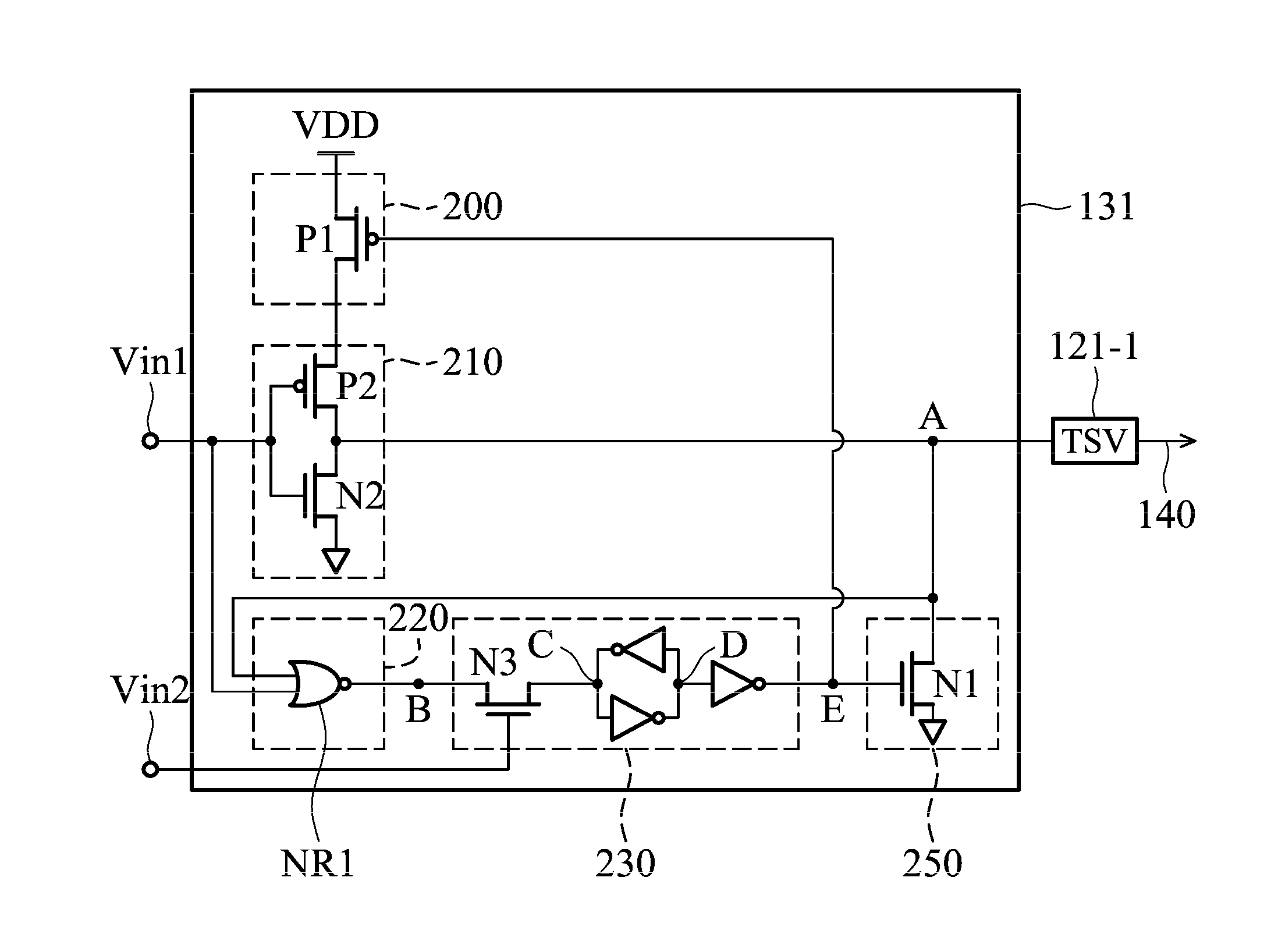
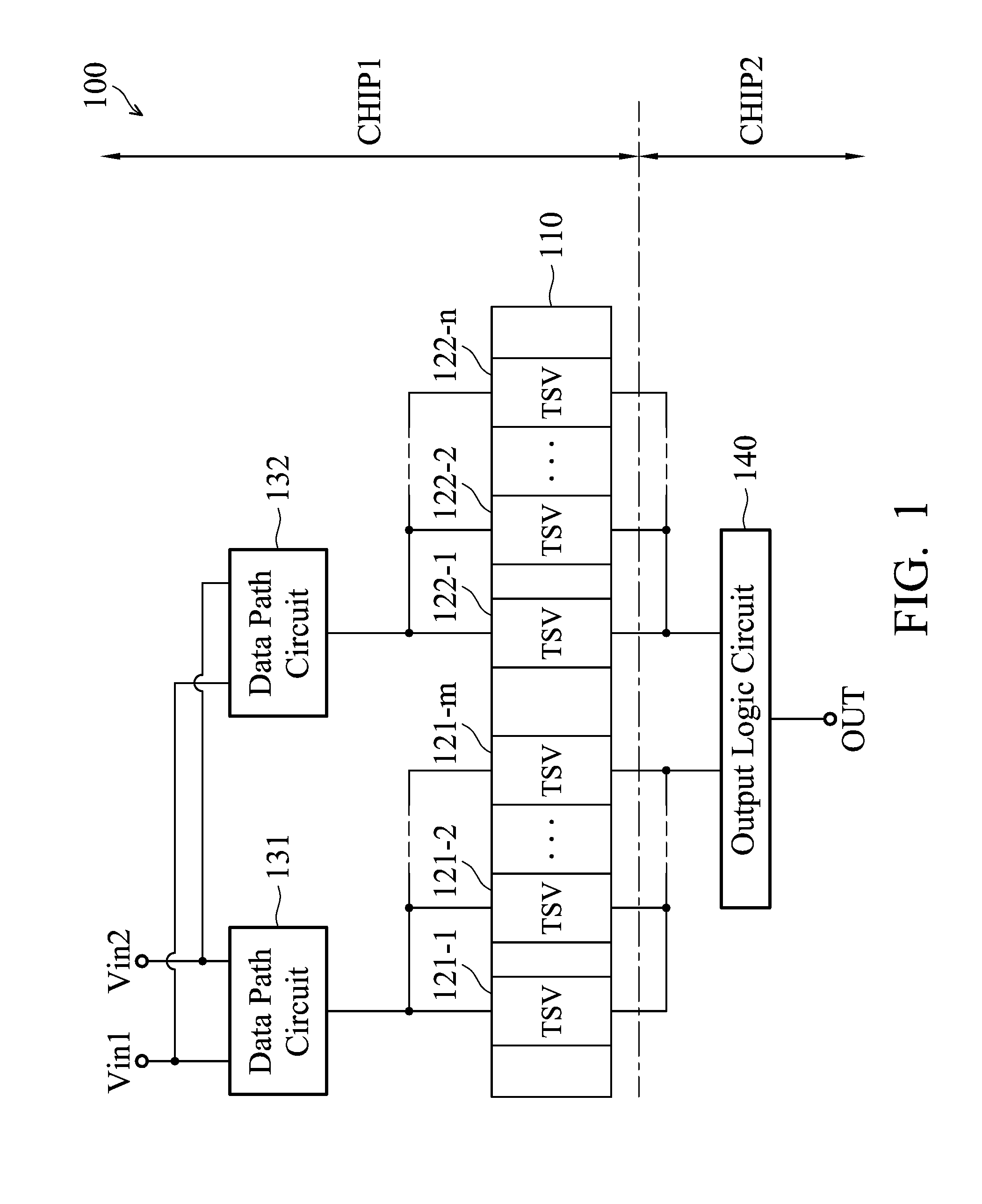
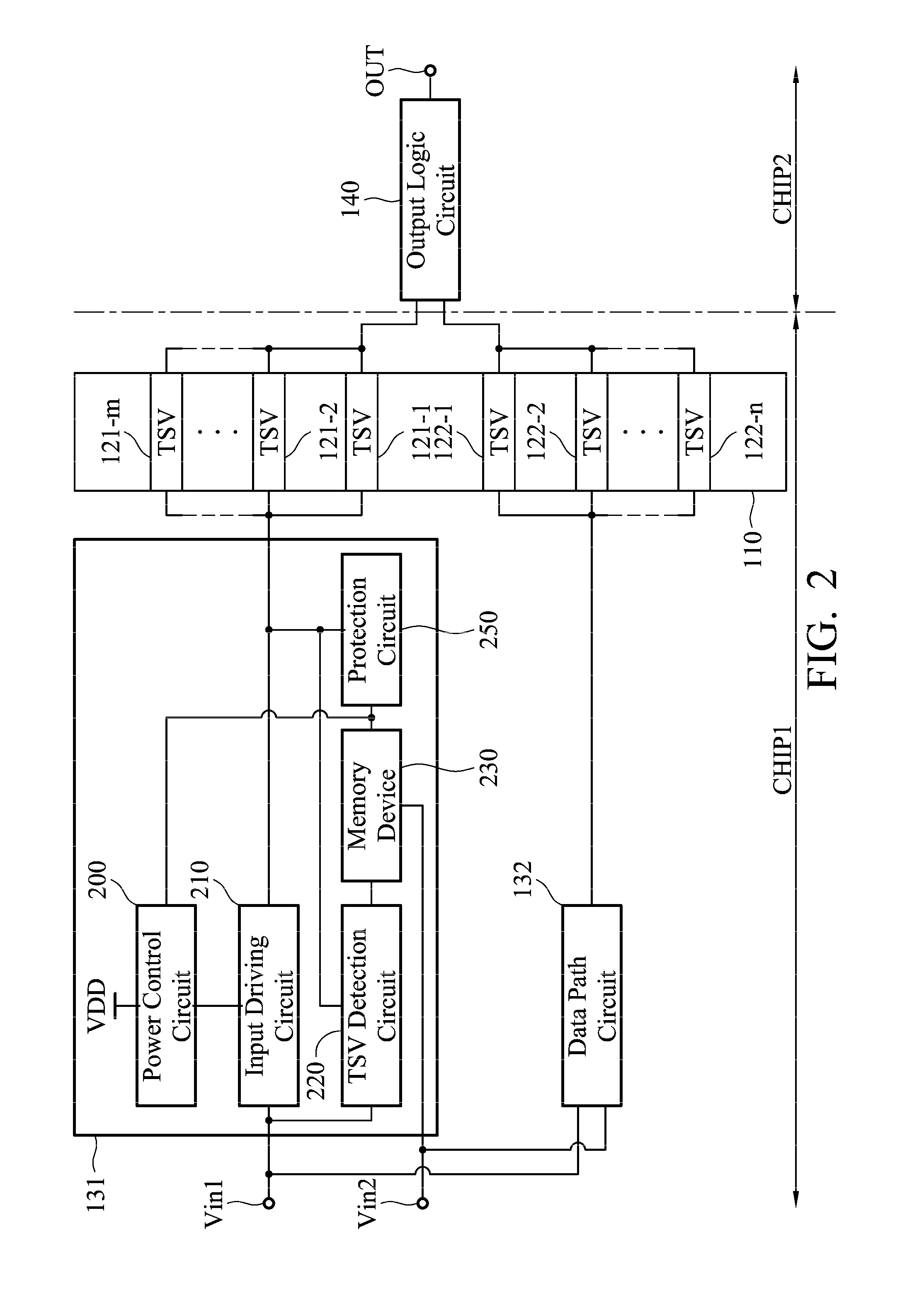
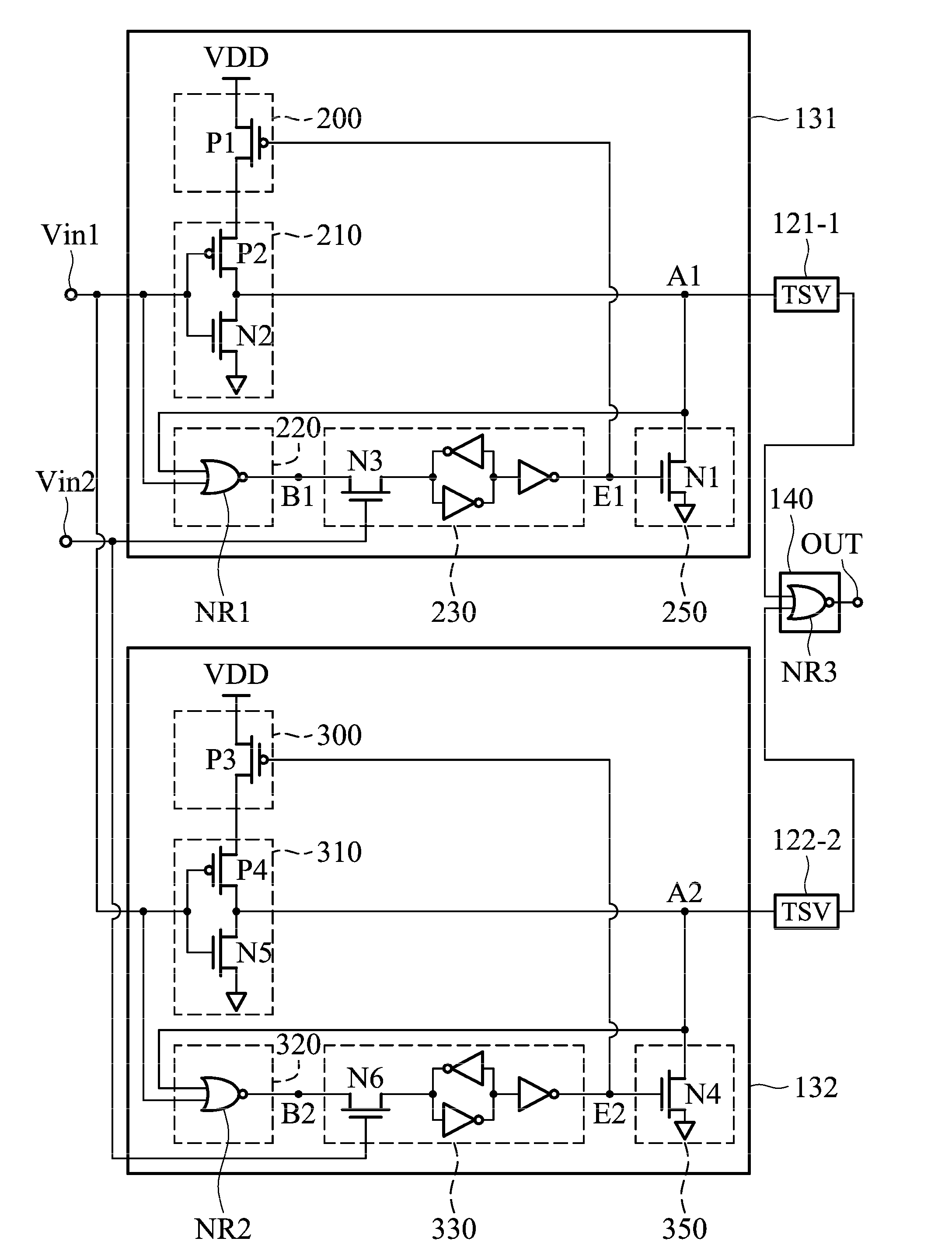
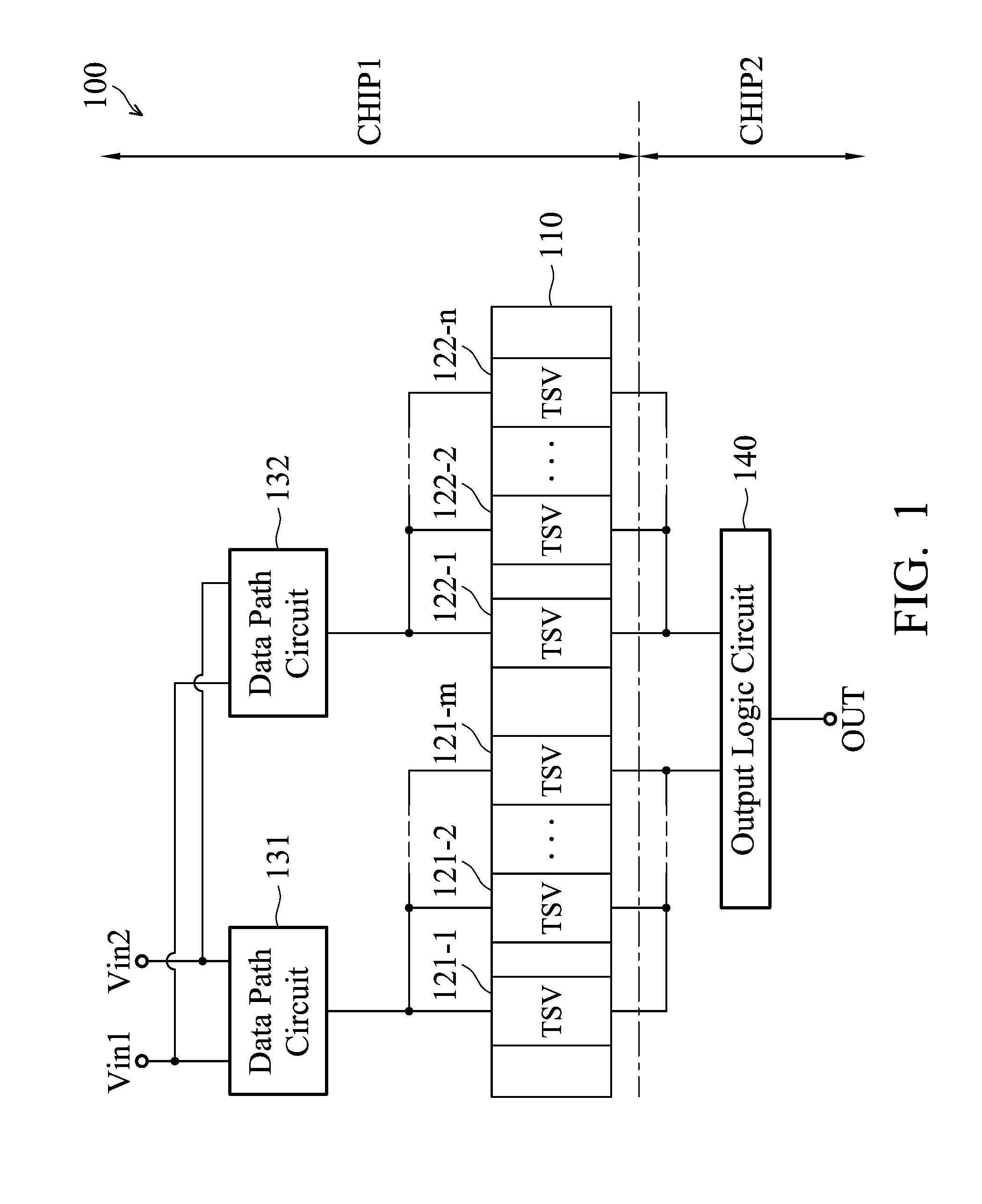
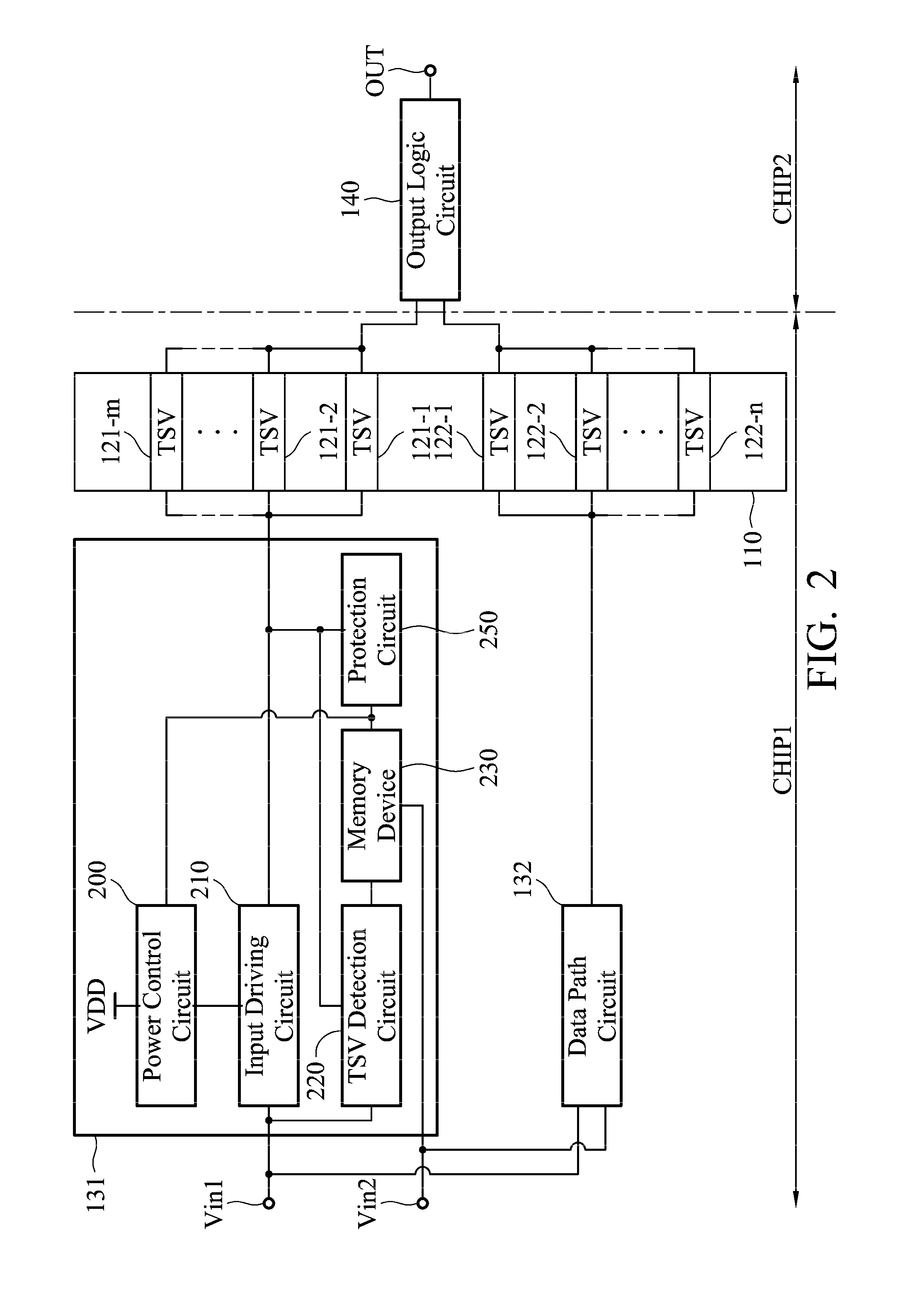
Through silicon via repair circuit of semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140340113A1Reliability increasing modificationsPower consumption reductionDatapath circuitsEngineering
TSV repair circuit of a semiconductor device includes a first chip, a second chip, at least two TSV, at least two data path circuits and an output logic circuit. Each data path circuit comprises an input driving circuit, a TSV detection circuit, a memory device, a protection circuit and a power control circuit. The TSV detection circuit detects a TSV status, the memory device keeps the TSV status, the protection circuit determines whether to pull a first end of the TSV to a ground voltage according to the TSV status, and the power control circuit prevents a leakage current of a power voltage from flowing through a substrate.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Processor and method for implementing instruction support for multiplication of large operands
ActiveUS8438208B2Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesDatapath circuitsExecution unit
A processor including instruction support for implementing large-operand multiplication may issue, for execution, programmer-selectable instructions from a defined instruction set architecture (ISA). The processor may include an instruction execution unit comprising a hardware multiplier datapath circuit, where the hardware multiplier datapath circuit is configured to multiply operands having a maximum number of bits M. In response to receiving a single instance of a large-operand multiplication instruction defined within the ISA, wherein at least one of the operands of the large-operand multiplication instruction includes more than the maximum number of bits M, the instruction execution unit is configured to multiply operands of the large-operand multiplication instruction within the hardware multiplier datapath circuit to determine a result of the large-operand multiplication instruction without execution of programmer-selected instructions within the ISA other than the large-operand multiplication instruction.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Low power memory architecture
ActiveUS7555659B2Minimizing current leakageMinimise currentVolume/mass flow measurementDigital storageDatapath circuitsComputer architecture
A memory architecture and circuits for minimizing current leakage in the memory array. Subdivisions of the memory array each have local power grids that can be selectively connected to power supplies, such that only an accessed subdivision will receive power to execute the memory access operation. The memory array can further include databuses which are precharged to one voltage during idle times and a second voltage during active read cycles, which reduces leakage current in datapath circuitry connected to the databuses within the memory array blocks.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
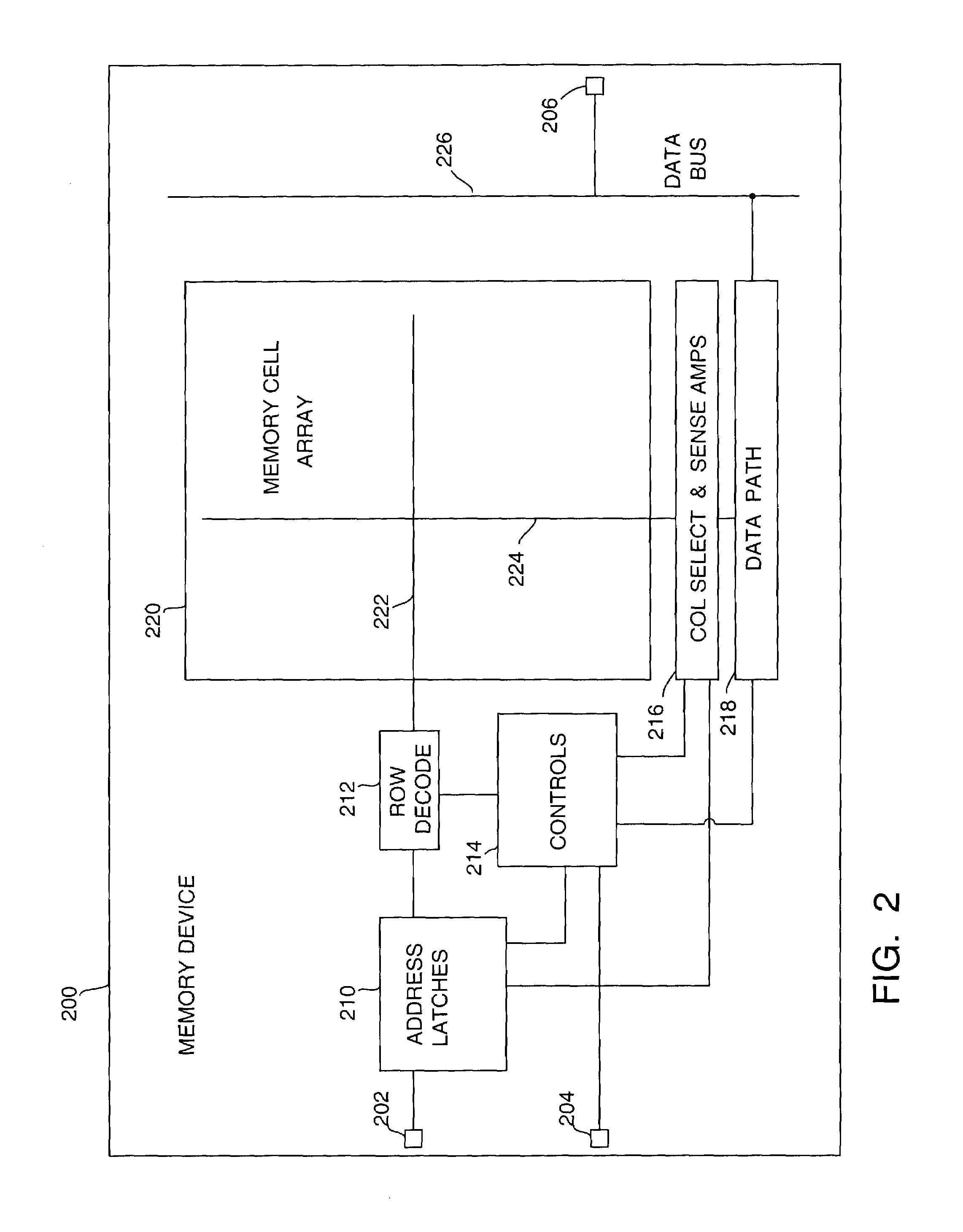
Methods and apparatus for reading memory device register data
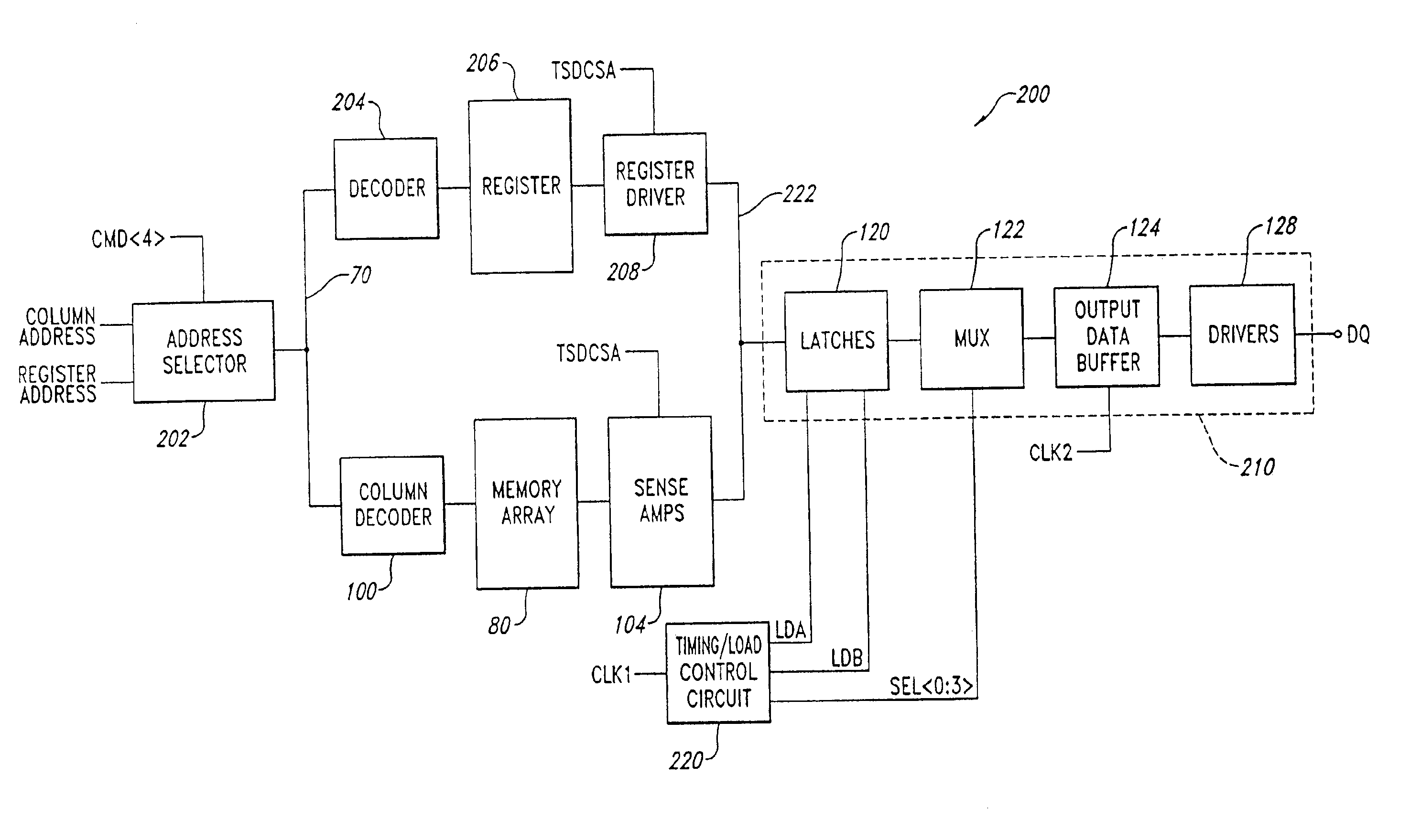
A methods and apparatus for reading register data from a memory device and outputting the register data to external data terminals of the memory device that outputs a first set of data bits from a memory array to the external terminals responsive to a first addressing signal. A register stores data, and outputs a second set of data bits responsive to a second addressing signal. A coupling circuit receives the second set of data bits, processes the data bits, and outputs a third set of data bits corresponding to the second set of data bits responsive to an enabling signal. A data path circuit that is coupled to the memory array to receive the first set of data bits is coupled to the coupling circuit to receive the third plurality of data bits, and to the external terminals. The data path circuit transmits the data bits received to the external terminals of the memory device.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
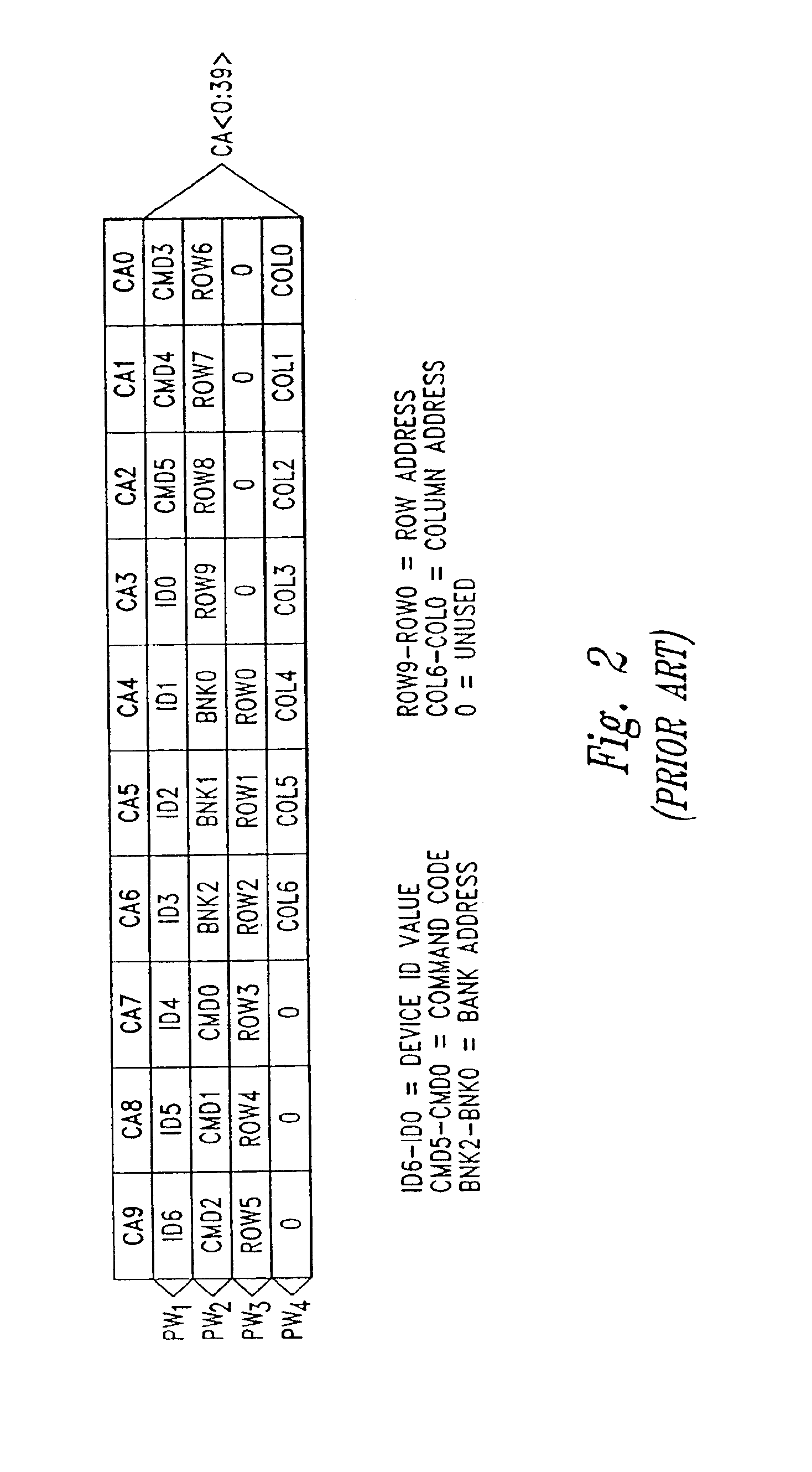
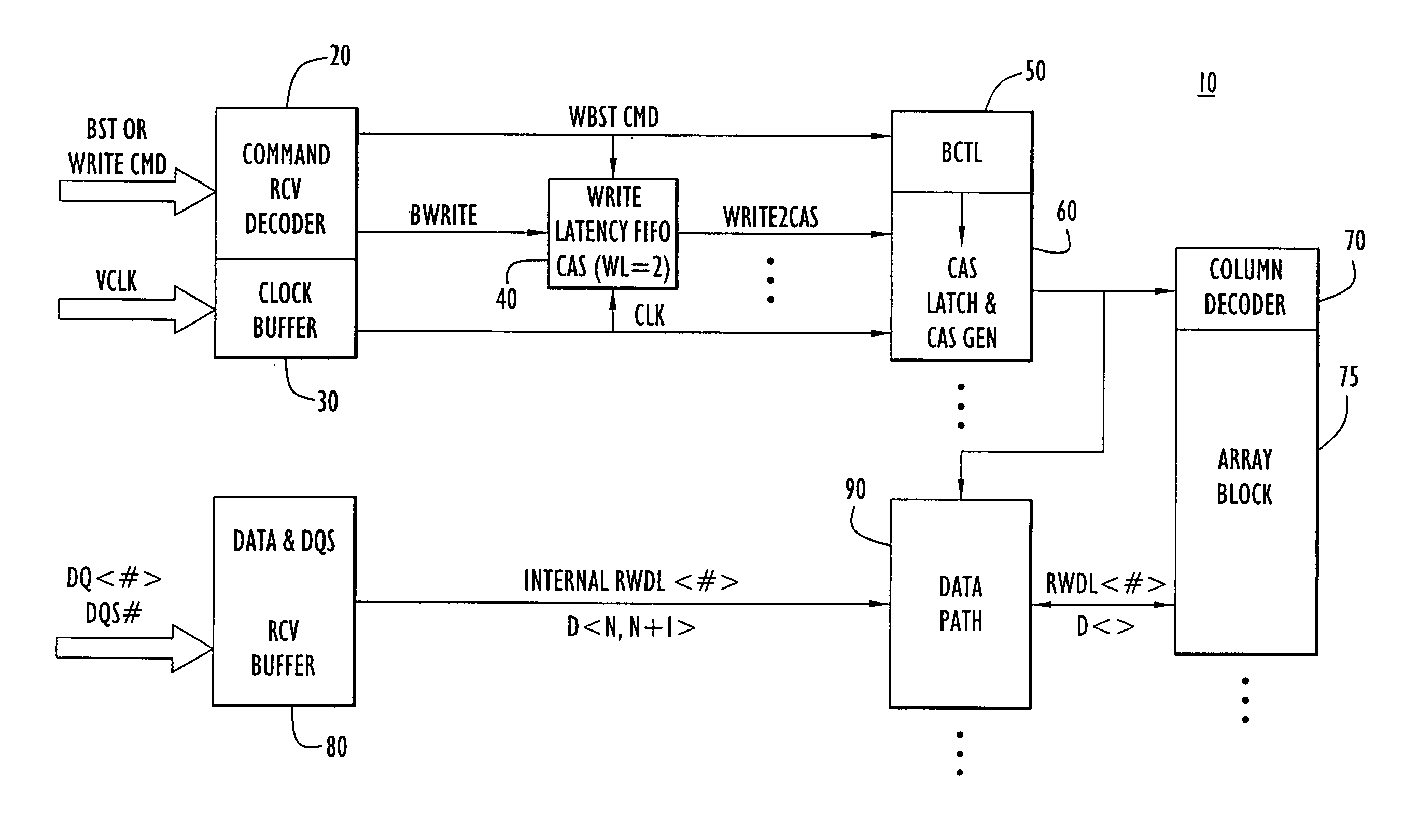
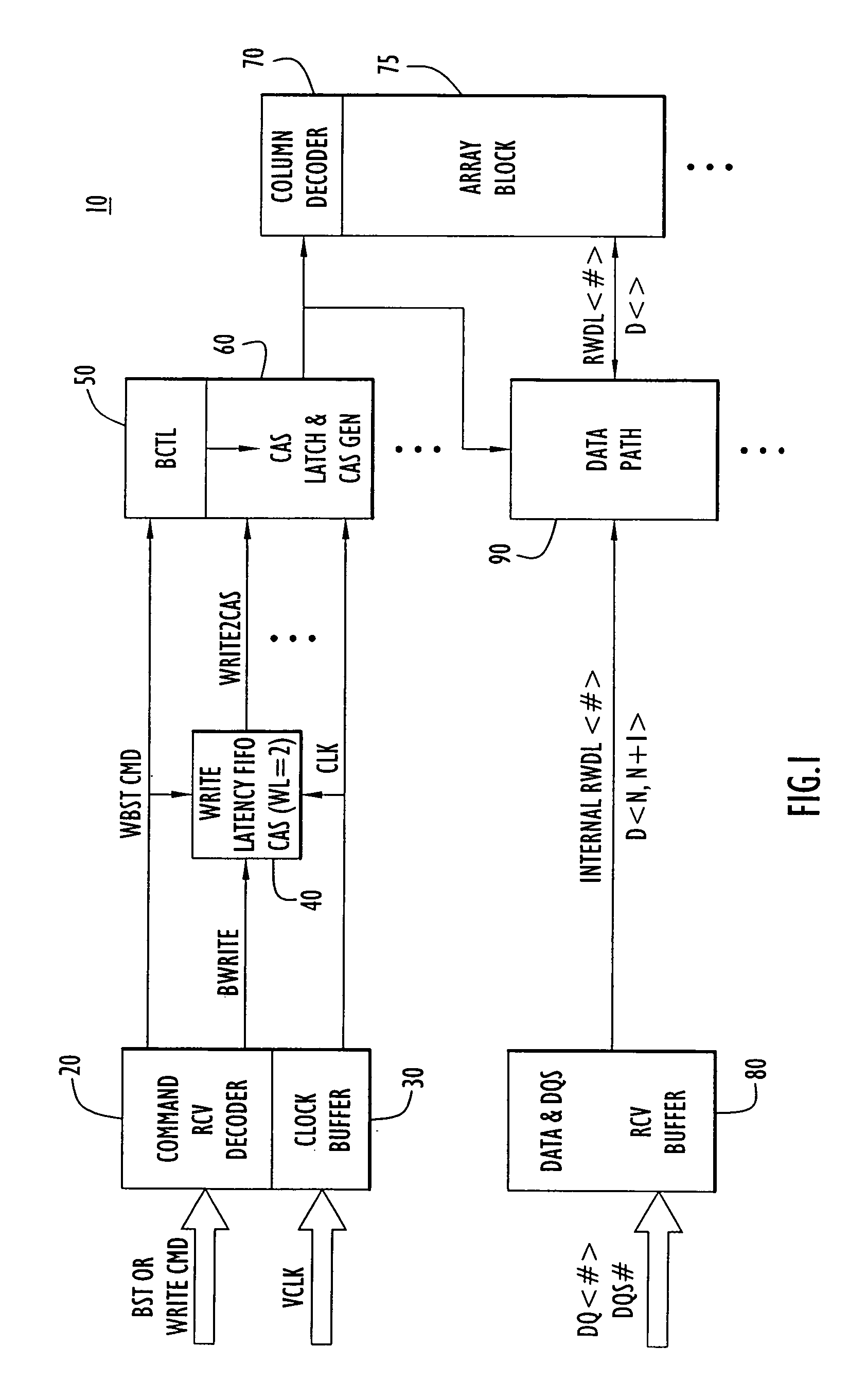
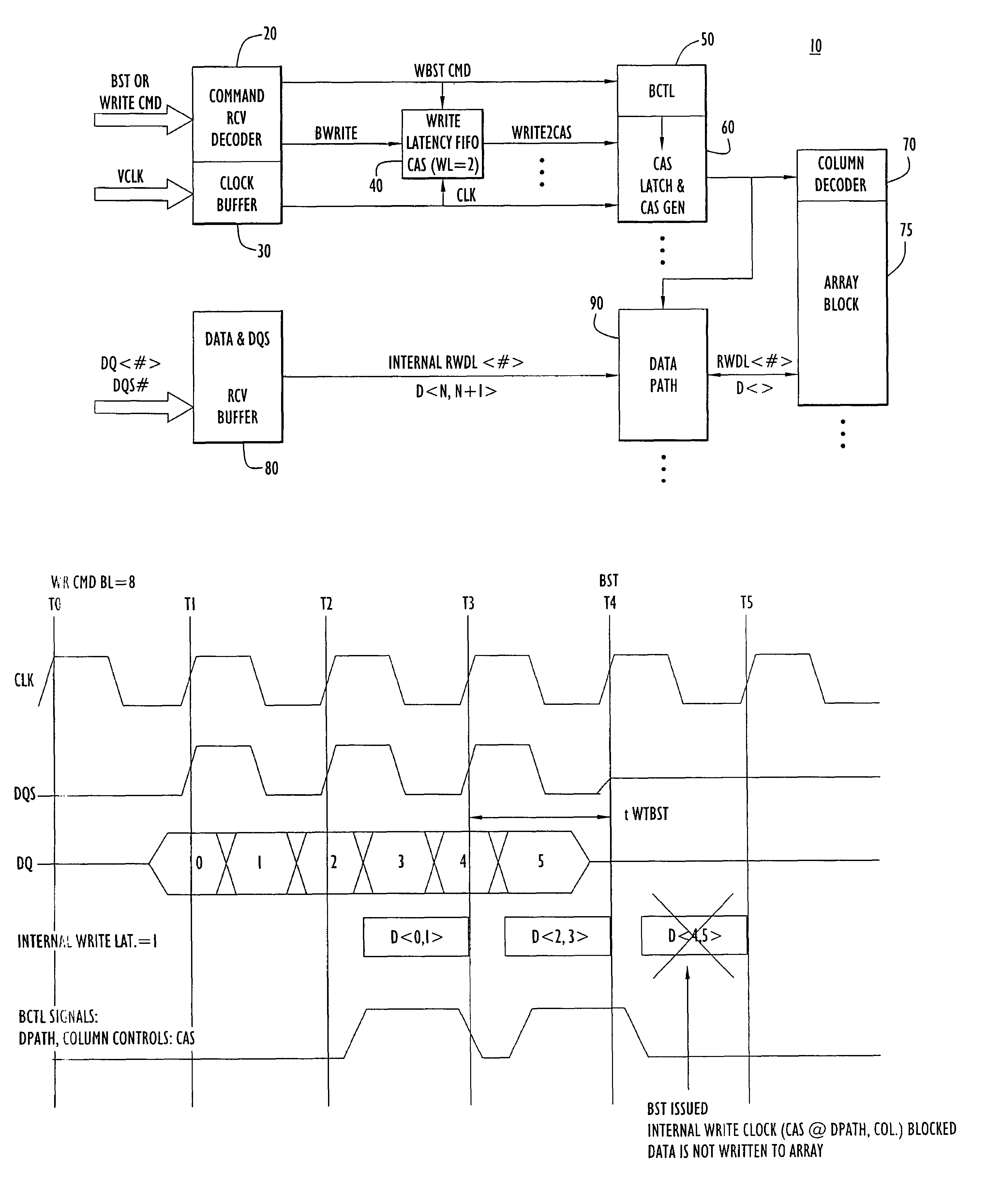
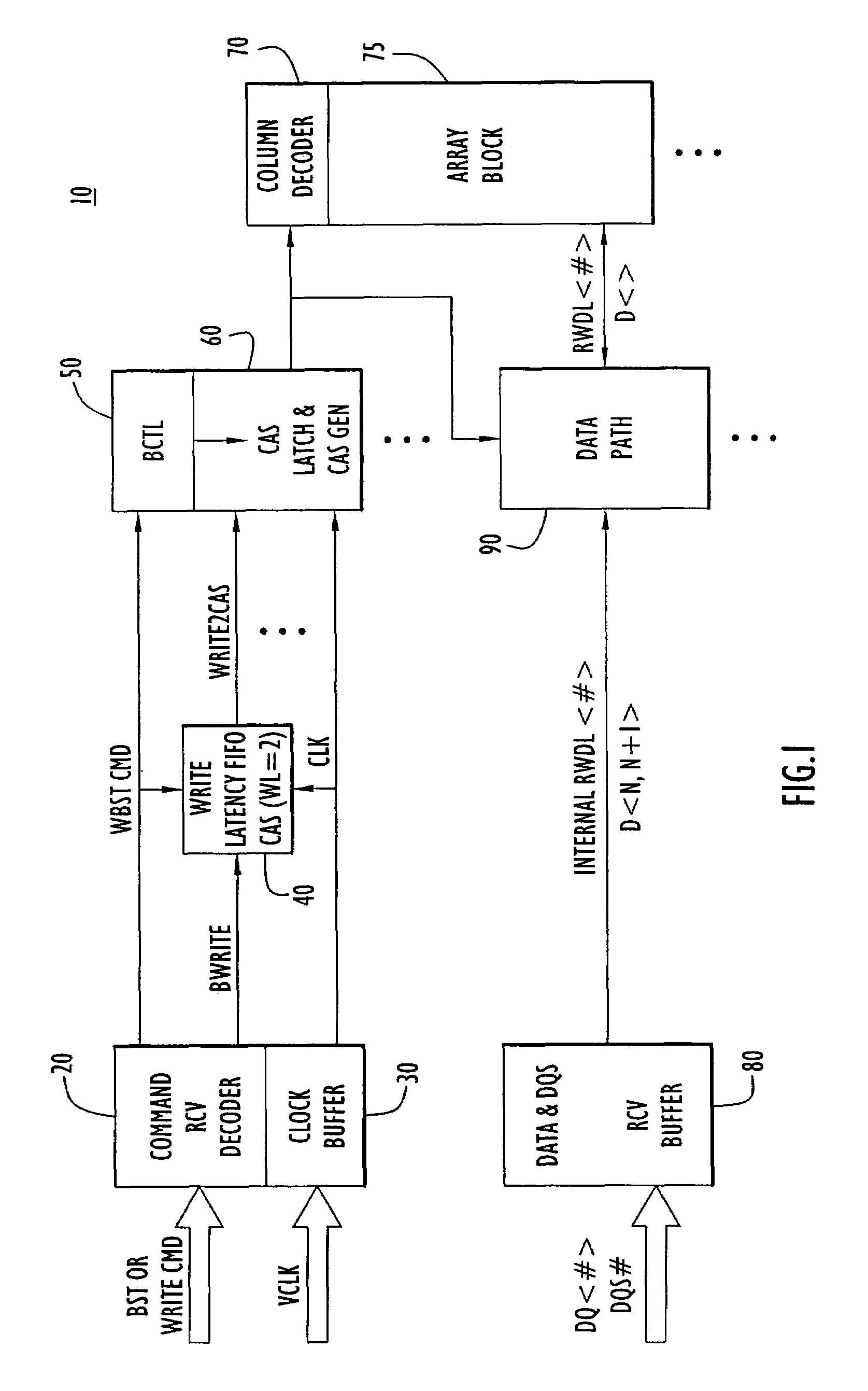
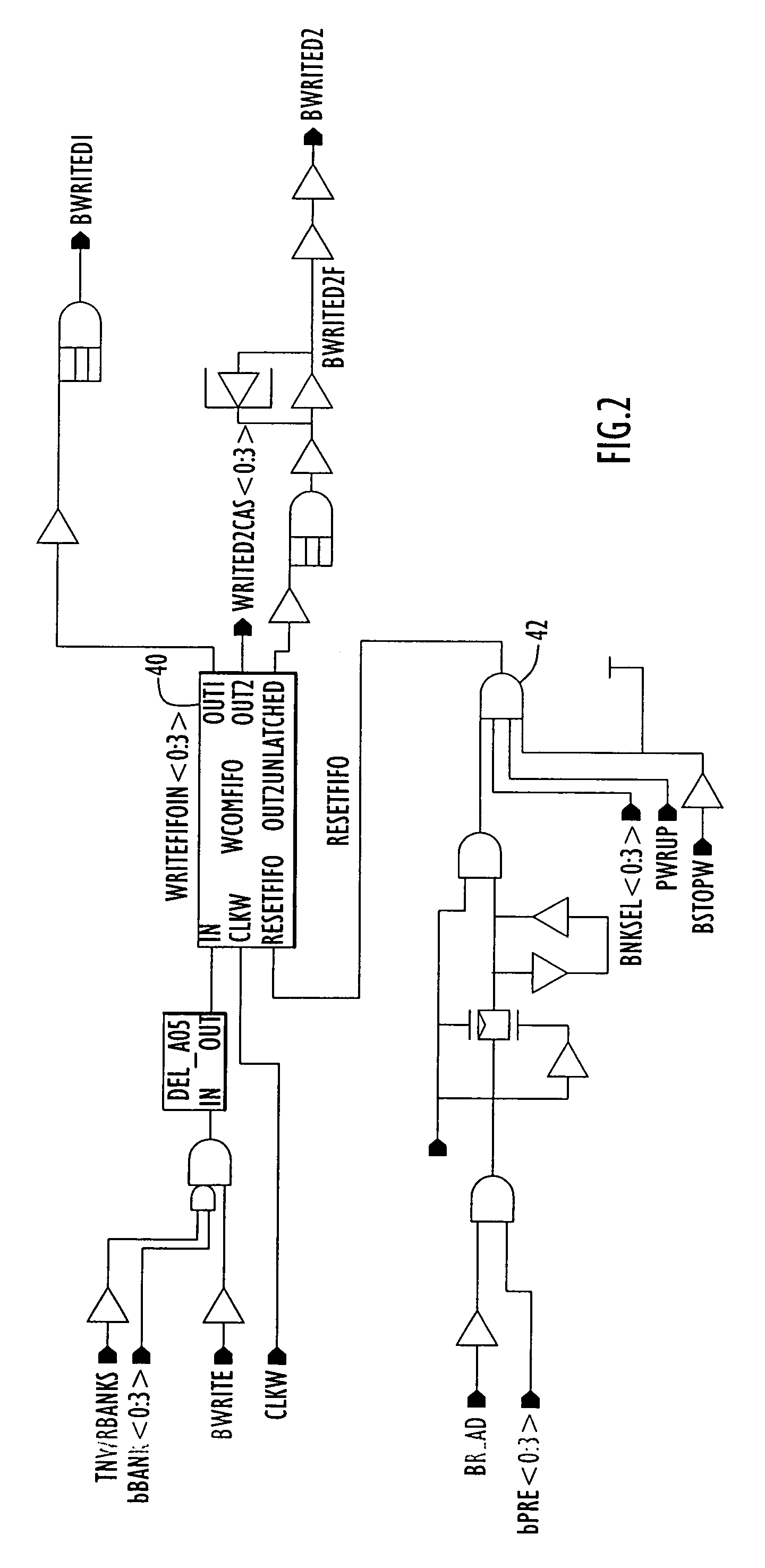
Write burst stop function in low power DDR sDRAM
A write burst stop command function is provided for a semiconductor memory device, and in particular for a memory device having a write latency, such as is common in a low power double data rate (DDR) dynamic random access memory (DRAM) device. In the memory device, when a write stop command is received, pulses that are generated for a column address strobe signal are terminated so that no further data already in the memory device is transferred into a memory array. When the write stop command is received at the beginning of a write operation prior to generation of the pulses in the column address strobe signal, a first-in first-out (FIFO) circuit is reset. The FIFO circuit is used to introduce a predetermined write latency to the write operation. The column address strobe signal is supplied to a column decoder associated with the memory array and to a data path circuit that transfers data to the memory array based on pulses in the column address strobe signal. In one embodiment, the pulses for the column address strobe signal are produced by a latch circuit based on a signal derived from the output of the write latency FIFO circuit and so an input to the latch is disabled in response to the write stop command to stop producing pulses for the column address strobe signal.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Fine-Grained Power Management of Synchronous and Asynchronous Datapath Circuits
ActiveUS20080204124A1Reliability increasing modificationsMajority/minority circuitsDatapath circuitsControl power
A power management circuit is provided for controlling power dissipation in at least one combinational logic circuit. The power management circuit includes a detector operative to receive at least a first input signal to the combinational logic circuit and to detect a transition of the first input signal between a first logic state and a second logic state. The detector generates a control signal indicative of whether or not a transition of the first input signal has occurred. The power management circuit further includes a controller operative to receive the first control signal generated by the detector and to selectively disconnect the first combinational logic circuit from a power supply to the first combinational logic circuit when no logic transition of the first input signal is detected between a preceding computational cycle and a present computational cycle of the first combinational logic circuit, and to connect the first combinational logic circuit to the power supply when a logic transition of the first input signal is detected.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Memory device having a relatively wide data bus
An architecture for a wide data path in a memory device formed in a semiconductor substrate includes an array of memory cells is formed in an array region of the substrate, the array including a plurality of memory cells arranged in rows and columns. A plurality of complementary pairs of digit lines are formed in the array region from a first conductive layer, each complementary pair being coupled to a plurality of memory cells in an associated column. A plurality of word lines are formed in the array region from a second conductive layer, each word line being coupled to each memory cell in an associated row. A plurality of sense amplifiers are formed in a sense amplifier region of the substrate adjacent the array region, each sense amplifier being coupled to an associated pair of complementary digit lines. A plurality of input / output lines are disposed in a third conductive layer formed above the array region, each input / output line coupled to at least one of the sense amplifiers. At least one column select line is disposed in a portion of the third conductive layer formed above the sense-amplifier region, each column select line being coupled to at least some of the sense amplifiers. The memory device also includes a row address decoder, column address decoder, data path circuit, and control circuit that operate in response to signals applied on respective busses to transfer data to and from the memory device. The architecture may be used, for example, in packetized DRAMs, such as SLDRAMs, and in Embedded DRAMs.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Semiconductor memory device having a discharge path generator for global I/O lines
ActiveUS20100202189A1Minimizes problemReliablyRead-only memoriesDigital storageDatapath circuitsControl signal
A data path circuit includes a bit line sense amplifier, a local input / output line precharger connected to a local input / output line pair, a global input / output line precharger connected to a global input / output line pair, a column selector connecting a bit line pair connected to the bit line sense amplifier and the local input / output line pair to each other in response to a column selection signal, and a local input / output line selector connecting the local input / output line pair and the global input / output line pair to each other in response to a multiplexing control signal. A discharge path generator decreases the potential on the global input / output line pair down to a predetermined level in response to a data masking control signal which is activated earlier than the column selection signal during a data masking operation mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
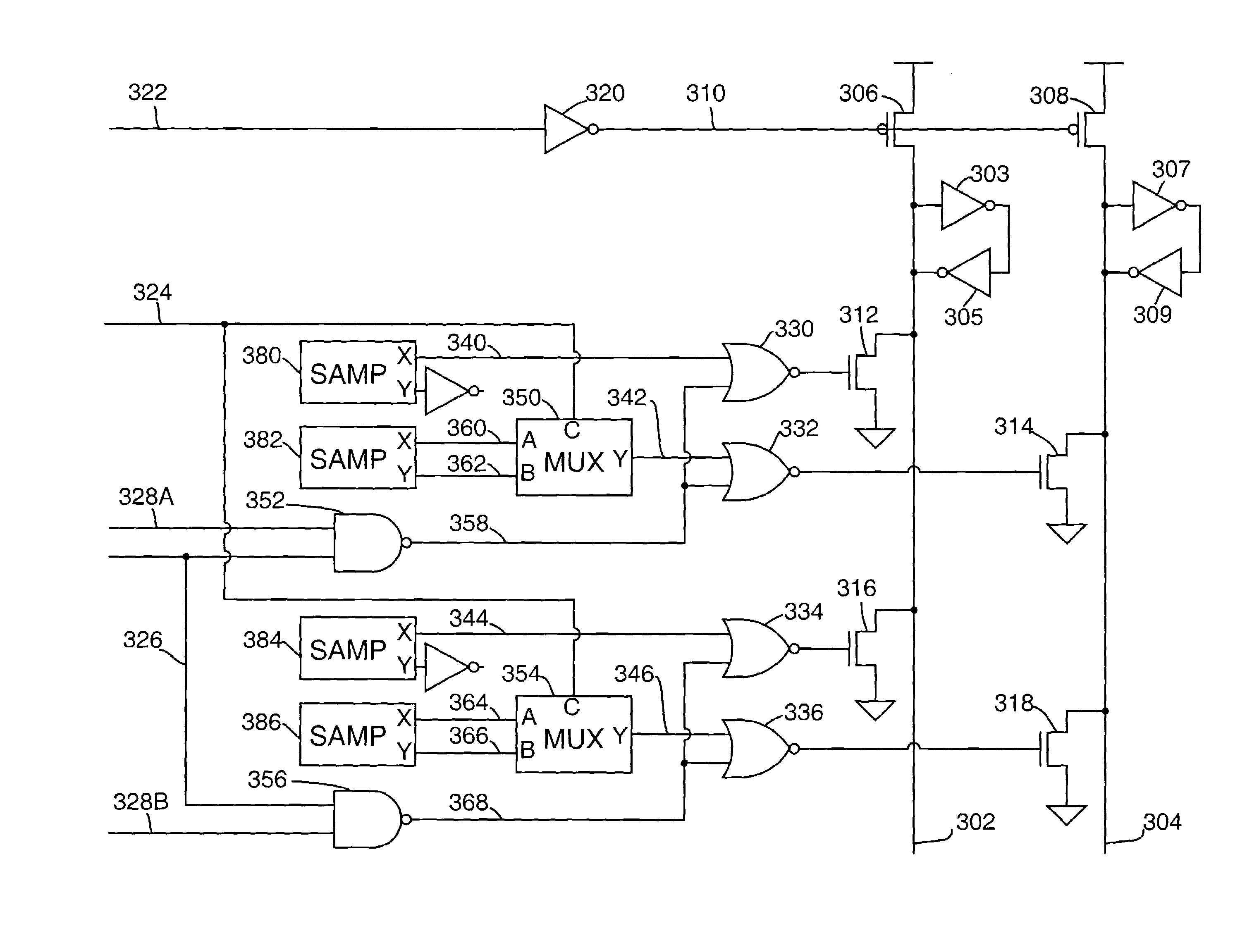
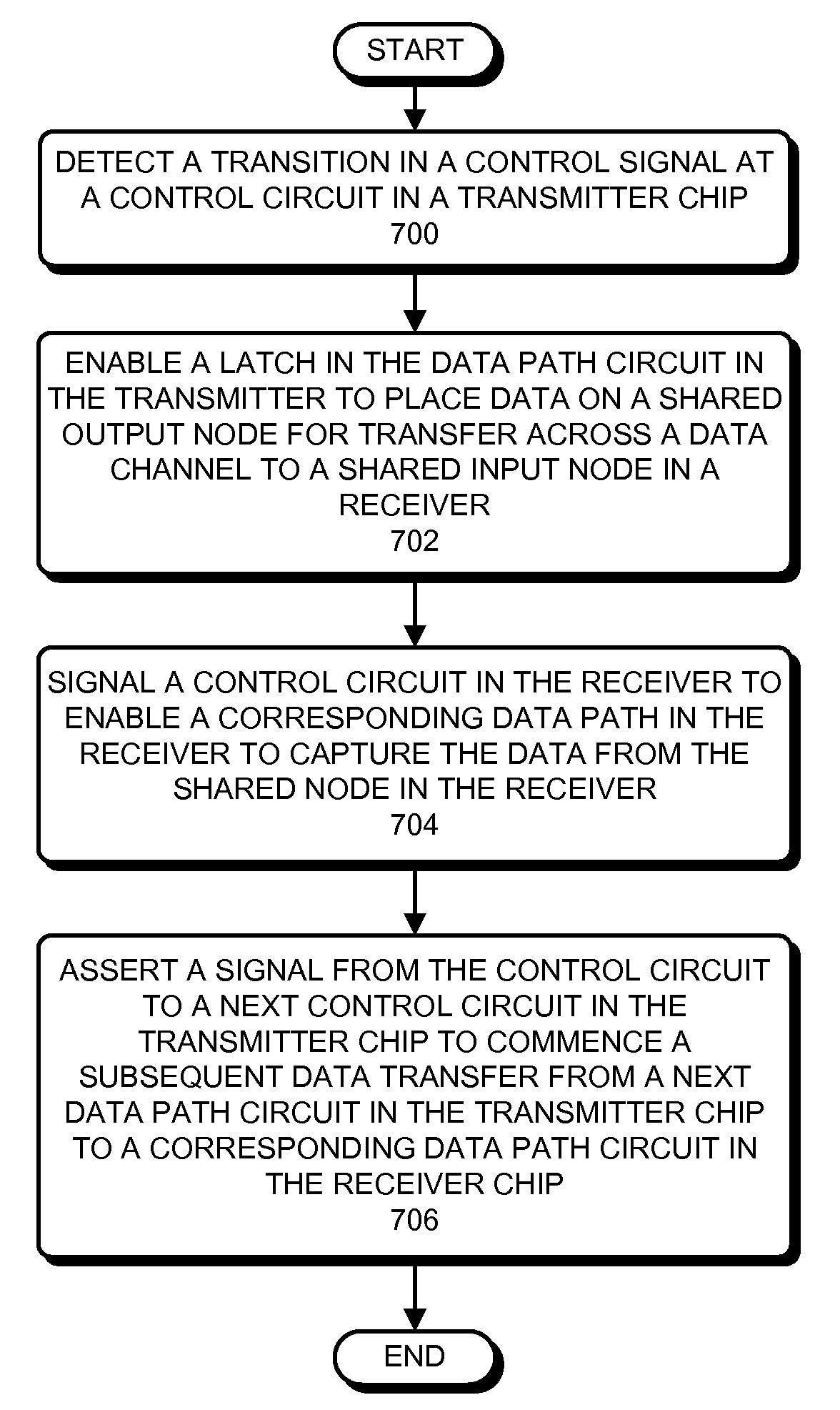
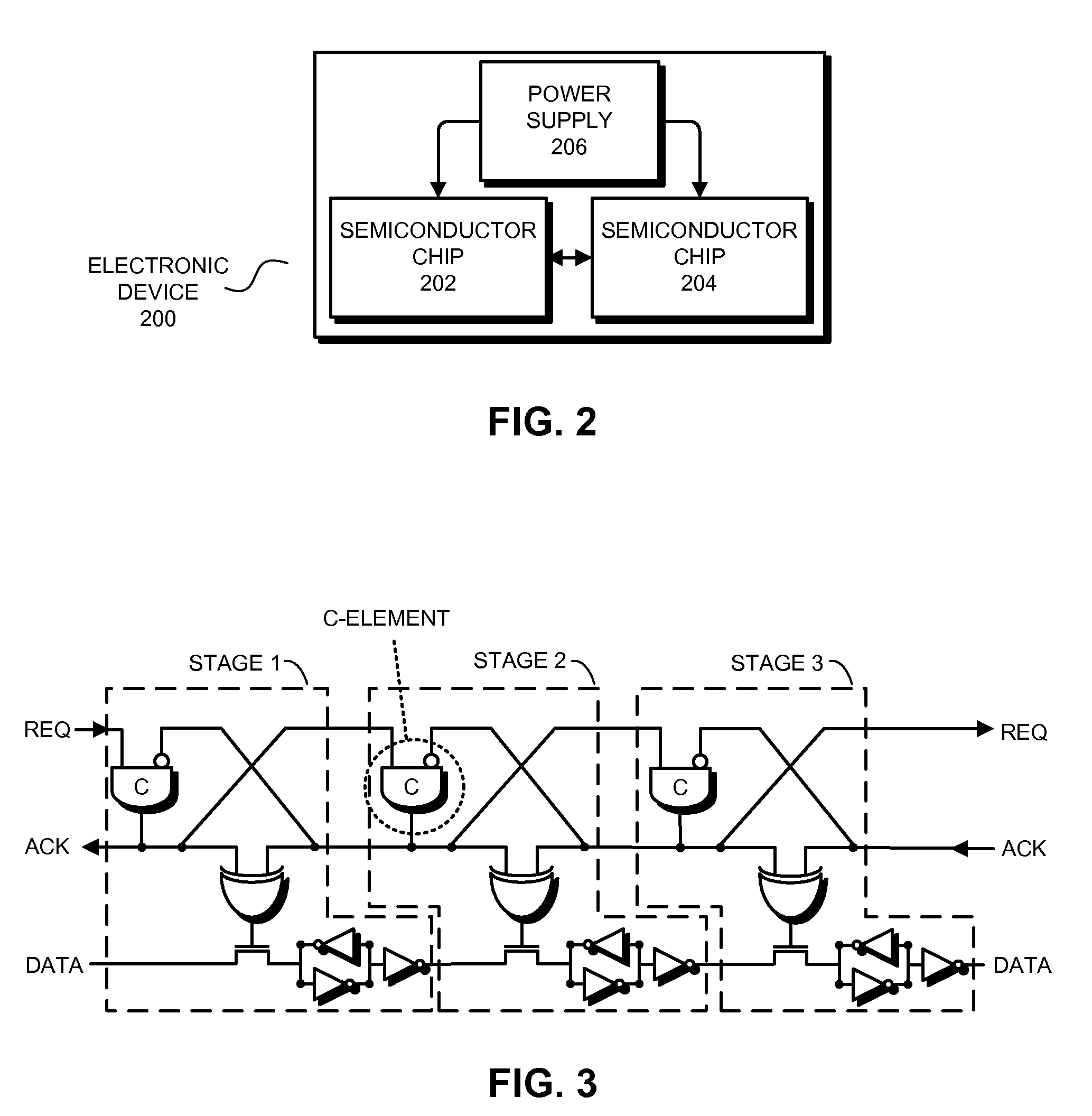
Communicating signals between semiconductor chips using round-robin-coupled micropipelines
ActiveUS20090086768A1Time-division multiplexGeneral purpose stored program computerDatapath circuitsControl signal
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system for transferring data between a receiver chip and a transmitter chip. The system includes a set of data path circuits in the transmitter chip and a set of data path circuits in the receiver chip coupled to a shared data channel. In addition, the system includes a set of asynchronous control circuits for controlling corresponding data path circuits in the transmitter chip and receiver chip. Upon detecting the transition of a control signal for an asynchronous control circuit in the transmitter chip, the asynchronous control circuit is configured to enable a transfer of data from the corresponding data path circuit in the transmitter chip across the data channel to a corresponding data path circuit in the receiver chip, and generate a control signal to cause a next asynchronous control circuit to commence the transfer of a data signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
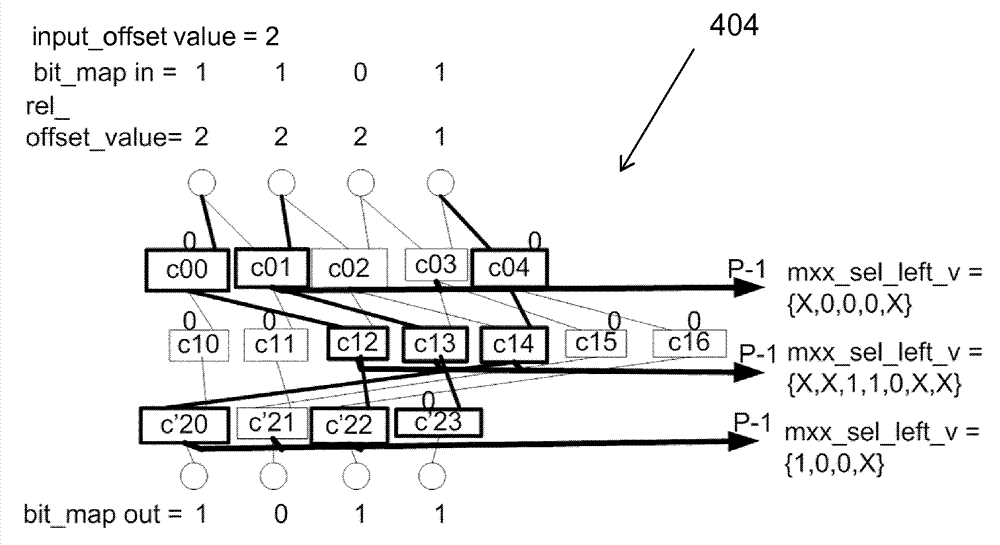
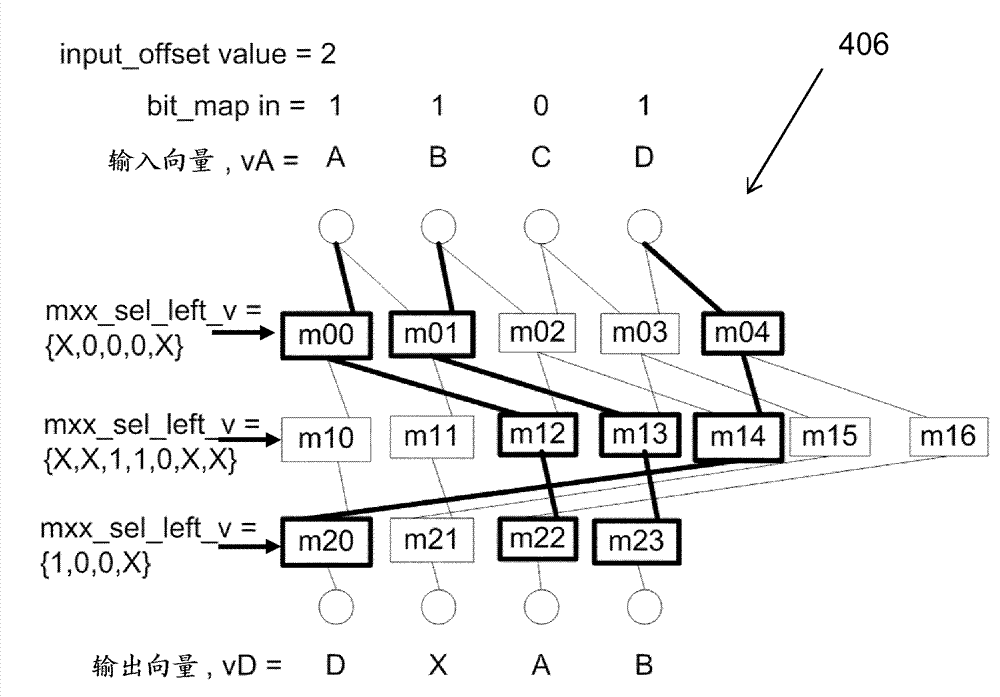
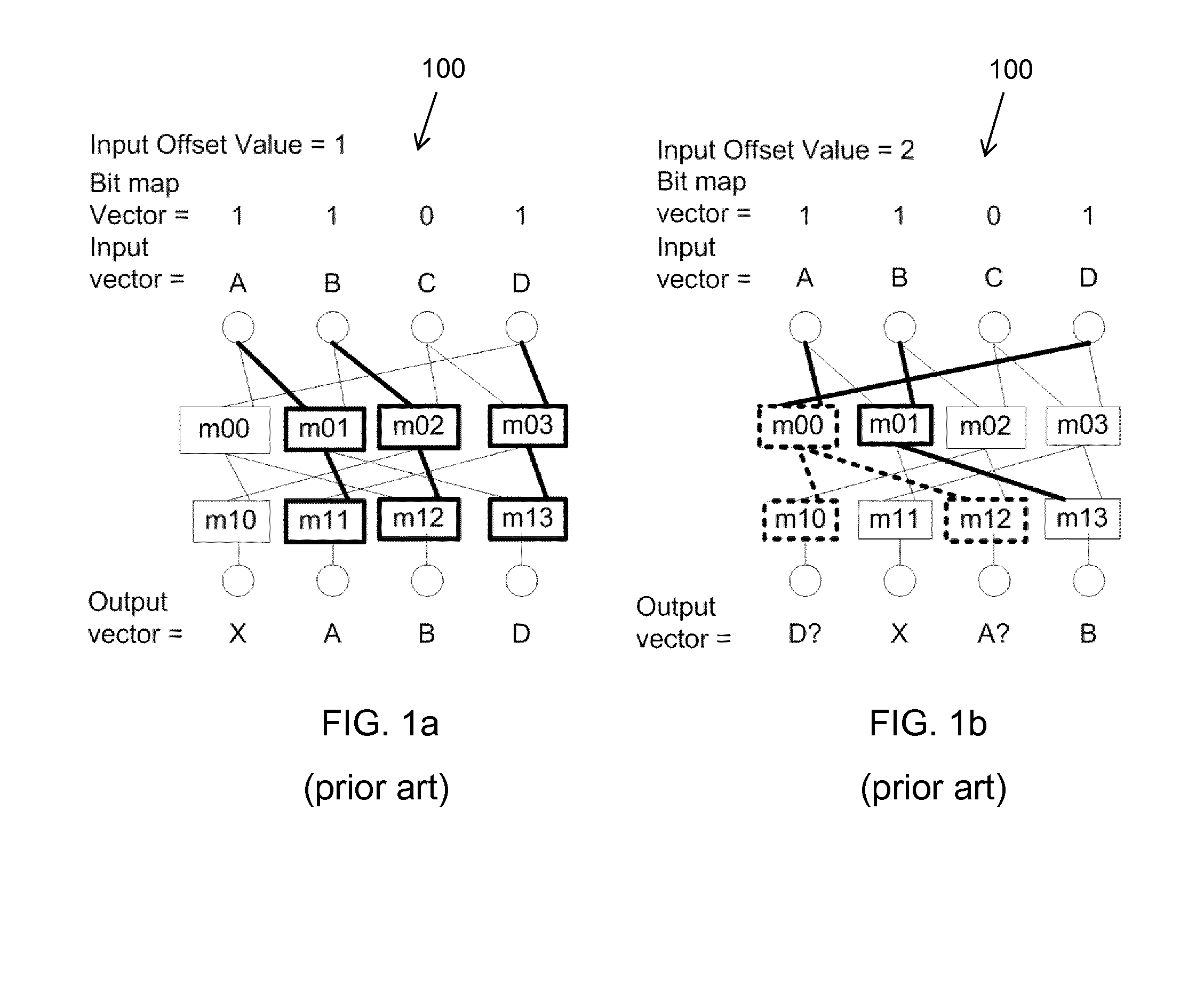
An element selection unit and a method therein
ActiveCN104756069AReduce configuration overheadEffective executionModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionDatapath circuitsPathPing
An element selection unit (200) and a method therein for vector element selection. The element selection unit comprises a selector control circuit (404) and a selector data path circuit (406), which data path circuit comprises a plurality of layers of multiplexers. The element selection unit further comprises a receiving circuit (401) configured to receive an instruction to perform a selection of elements from an input vector. The selector control circuit (404) is configured to generate a multiplexer control signal for each multiplexer based on a bit map and on a plurality of relative offset values. The data path circuit is configured to propagate the elements comprised in the input vector through the plurality of layers of multiplexers towards an output vector based on the generated multiplexer control signals. The data path circuit is further configured to write the propagated elements to enabled elements of the output vector.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Element Selection Unit and a Method Therein
ActiveUS20150124910A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionTransmission path divisionDigital computer detailsDatapath circuitsControl signal
An element selection unit (200) and a method therein for vector element selection. The element selection unit comprises a selector control circuit (404) and a selector data path circuit (406), which data path circuit comprises a plurality of layers of multiplexers. The element selection unit further comprises a receiving circuit (401) configured to receive an instruction to perform a selection of elements from an input vector. The selector control circuit (404) is configured to generate a multiplexer control signal for each multiplexer based on a bit map and on a plurality of relative offset values. The data path circuit is configured to propagate the elements comprised in the input vector through the plurality of layers of multiplexers towards an output vector based on the generated multiplexer control signals. The data path circuit is further configured to write the propagated elements to enabled elements of the output vector.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Through silicon via repair circuit of semiconductor device
ActiveUS9136843B2Reliability increasing modificationsPower consumption reductionDriver circuitDatapath circuits
TSV repair circuit of a semiconductor device includes a first chip, a second chip, at least two TSV, at least two data path circuits and an output logic circuit. Each data path circuit comprises an input driving circuit, a TSV detection circuit, a memory device, a protection circuit and a power control circuit. The TSV detection circuit detects a TSV status, the memory device keeps the TSV status, the protection circuit determines whether to pull a first end of the TSV to a ground voltage according to the TSV status, and the power control circuit prevents a leakage current of a power voltage from flowing through a substrate.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Write burst stop function in low power DDR sDRAM
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
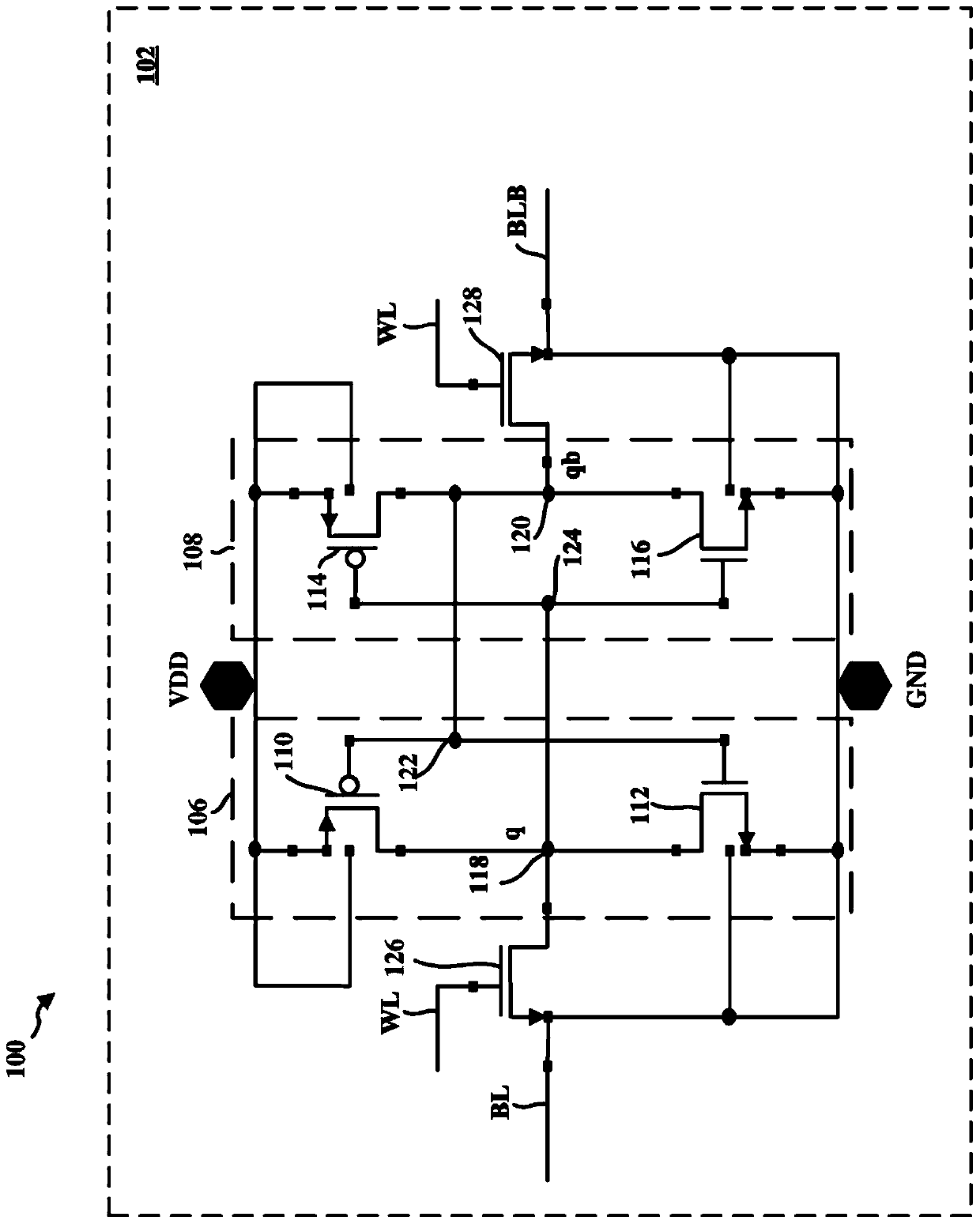
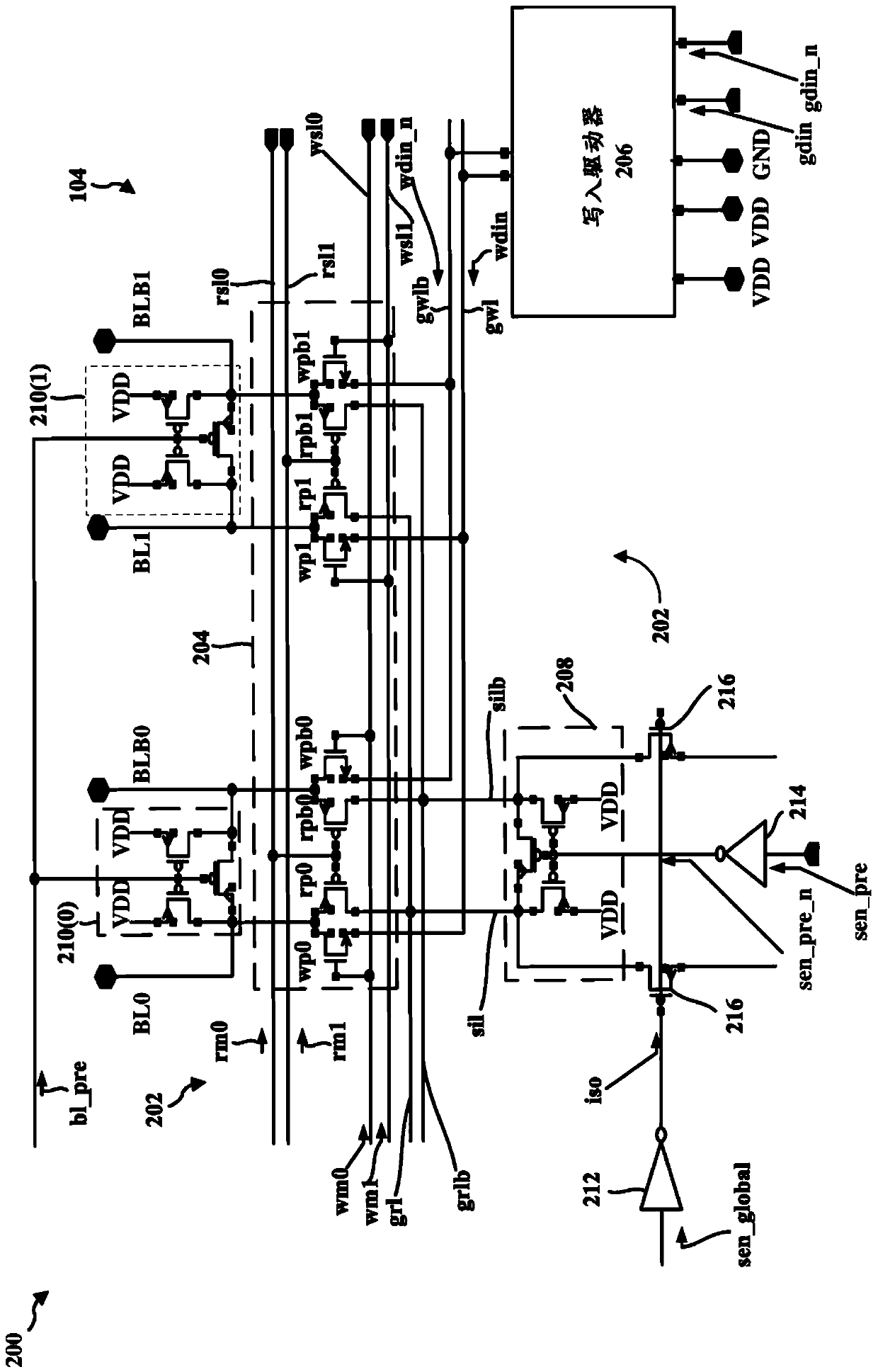
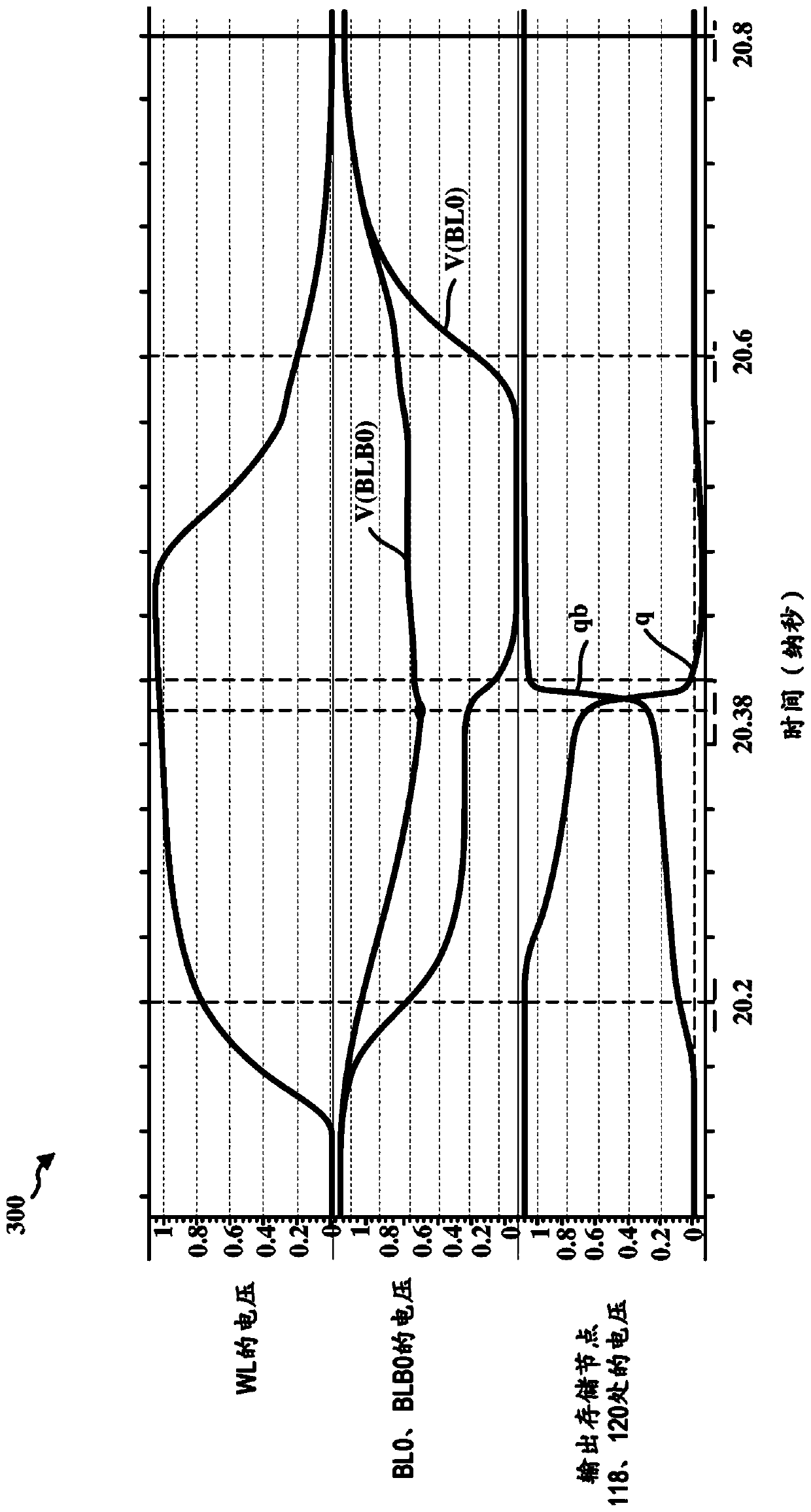
Area efficient write data path circuit for SRAM yield enhancement
PendingCN111164691AImprove reliabilityRaise the voltage differenceDigital storageDatapath circuitsCapacitance
A memory and method of performing a write operation in a memory are disclosed. In one aspect of the disclosure, the memory includes a memory cell, a pair of bit lines (BL; BLB) coupled to the memory cell, a multiplexer (404), and a pull-up circuit (418) coupled to the multiplexer. The multiplexer may be configured to select the pair of bit lines coupled to the memory cell during the write operation. To increase the write performance of the memory cell, the pull-up circuit is configured to select which of the pair of bit lines is a non zero bit line during the write operation and to clamp thenon-zero bit line through read pass transistors (rpO, rpbO) of the multiplexer to approximately a power rail voltage (VDD). Thus, the pull-up circuit (418) may increase the voltage difference betweenthe non-zero bit line and the zero bit line during the write operation and thus decrease the area and power consumed by a boost capacitance of a conventional write driver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
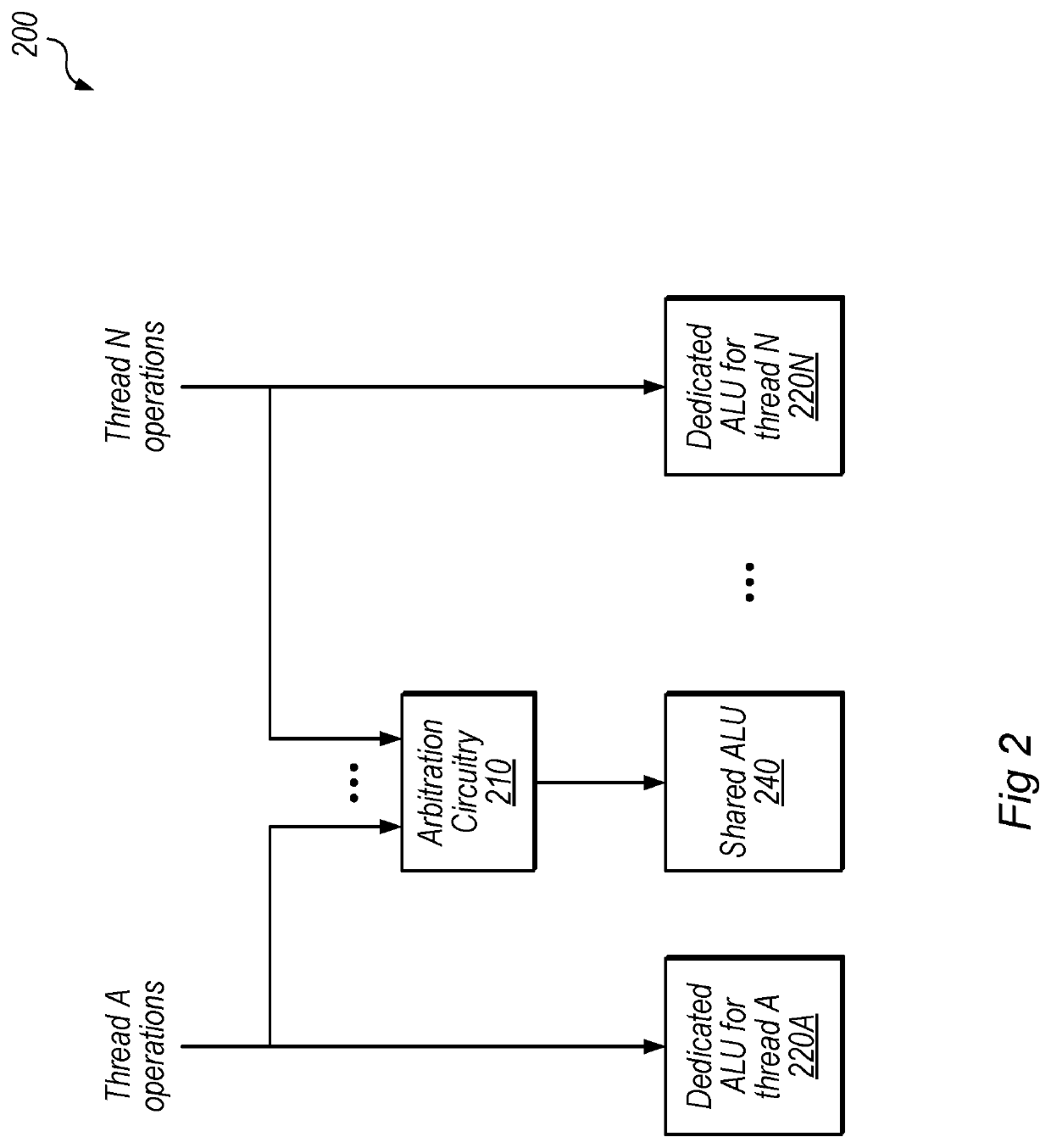
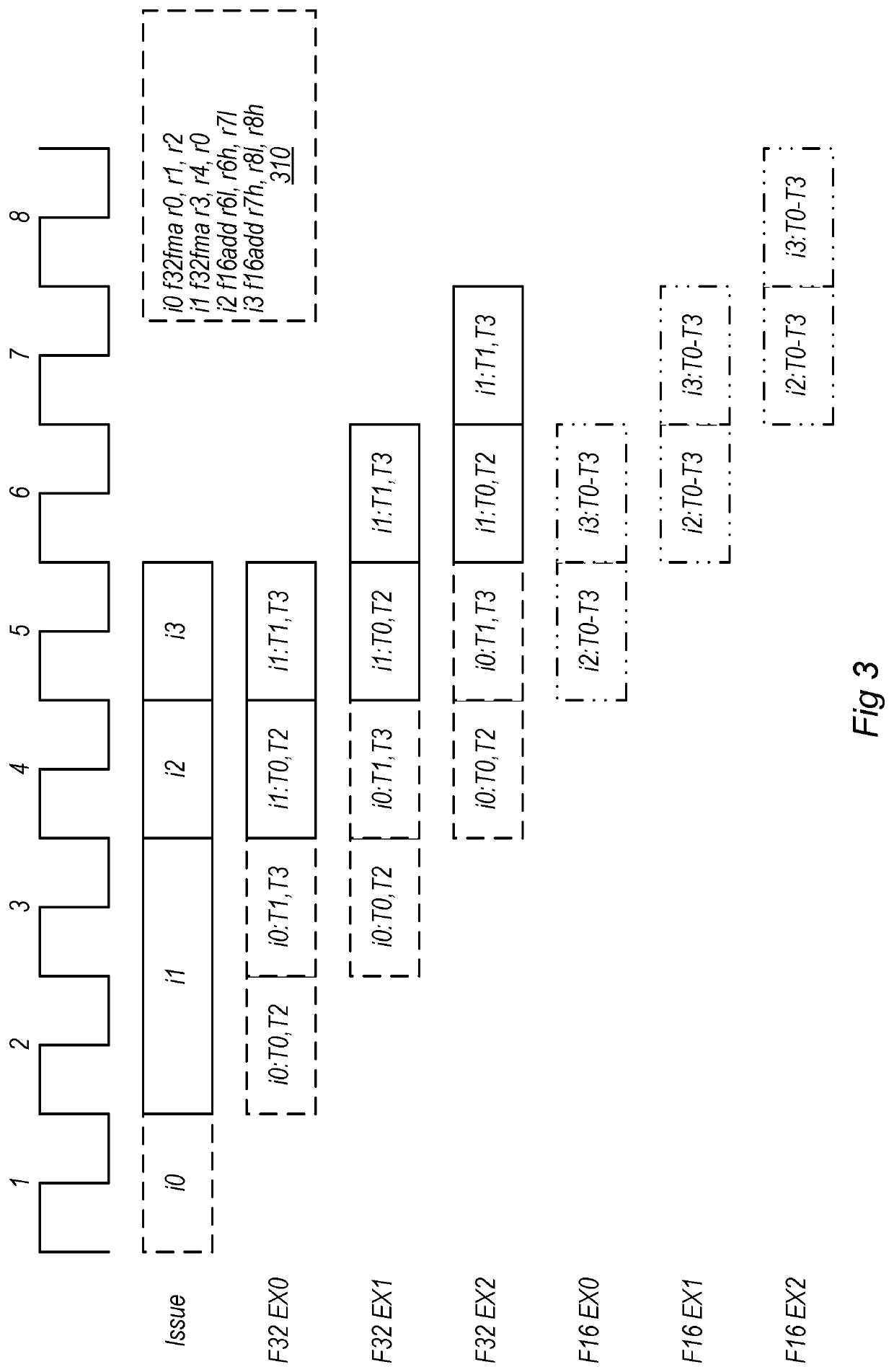
Techniques for ALU sharing between threads
ActiveUS10699366B1Concurrent instruction executionProcessor architectures/configurationDatapath circuitsArithmetic logic unit
Techniques are disclosed relating to sharing an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) between multiple threads. In some embodiments, the threads also have dedicated ALUs for other types of operations. In some embodiments, arbitration circuitry is configured to receive operations to be performed by the shared arithmetic logic unit from the set of threads and issue the received operations to the shared arithmetic logic unit. In some embodiments, the arbitration circuitry is configured to switch to a different one of the set of threads for each instruction issued to the shared arithmetic logic unit. In some embodiments, the shared ALU is configured to perform 32-bit operations and the dedicated ALUs are configured to perform the same operations using 16-bit precision. In some embodiments, the shared ALU is shared between two threads and is physically located adjacent to other datapath circuitry for the two threads.
Owner:APPLE INC
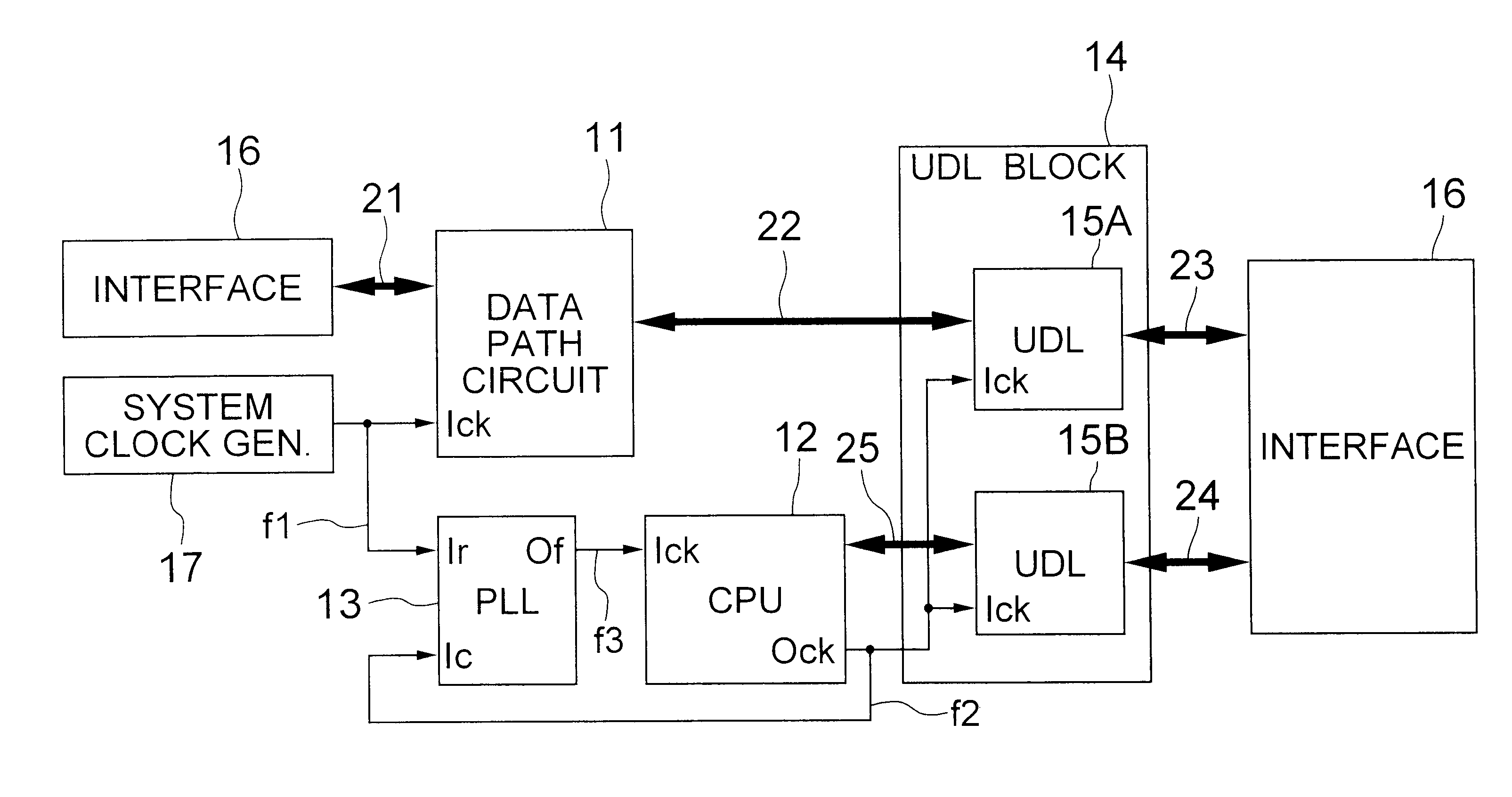
Synchronous signal processing system
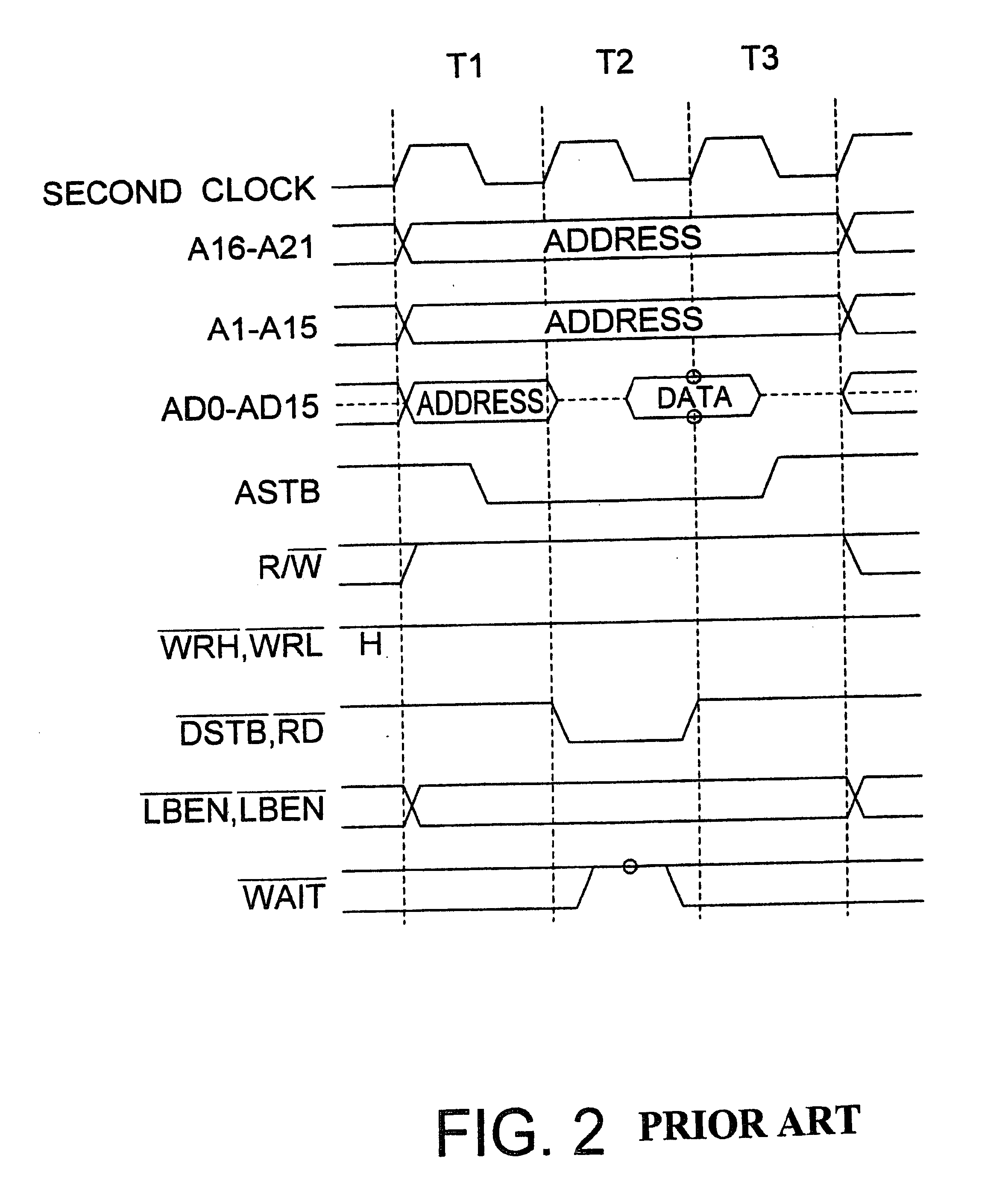
A signal processing system includes a PLL circuit for generating a first clock signal based on a system clock signal, a CPU for generating a second clock signal based on the first clock signal and operating with the second clock signal. The PLL circuit receives the second clock signal as a feed-back signal to deliver the first clock signal so that the phases of the second clock signal and the system clock signal coincide with each other. A data path circuit operates with the system clock signal and UDL circuit operates with the second clock signal, whereby the system can be handled as a synchronous circuit operating with the single system clock signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com