Memory device having a relatively wide data bus
a memory device and data bus technology, applied in the field of semiconductor memory, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of forming the dram b>10, limiting the speed of operation of the computer system, and complicating the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
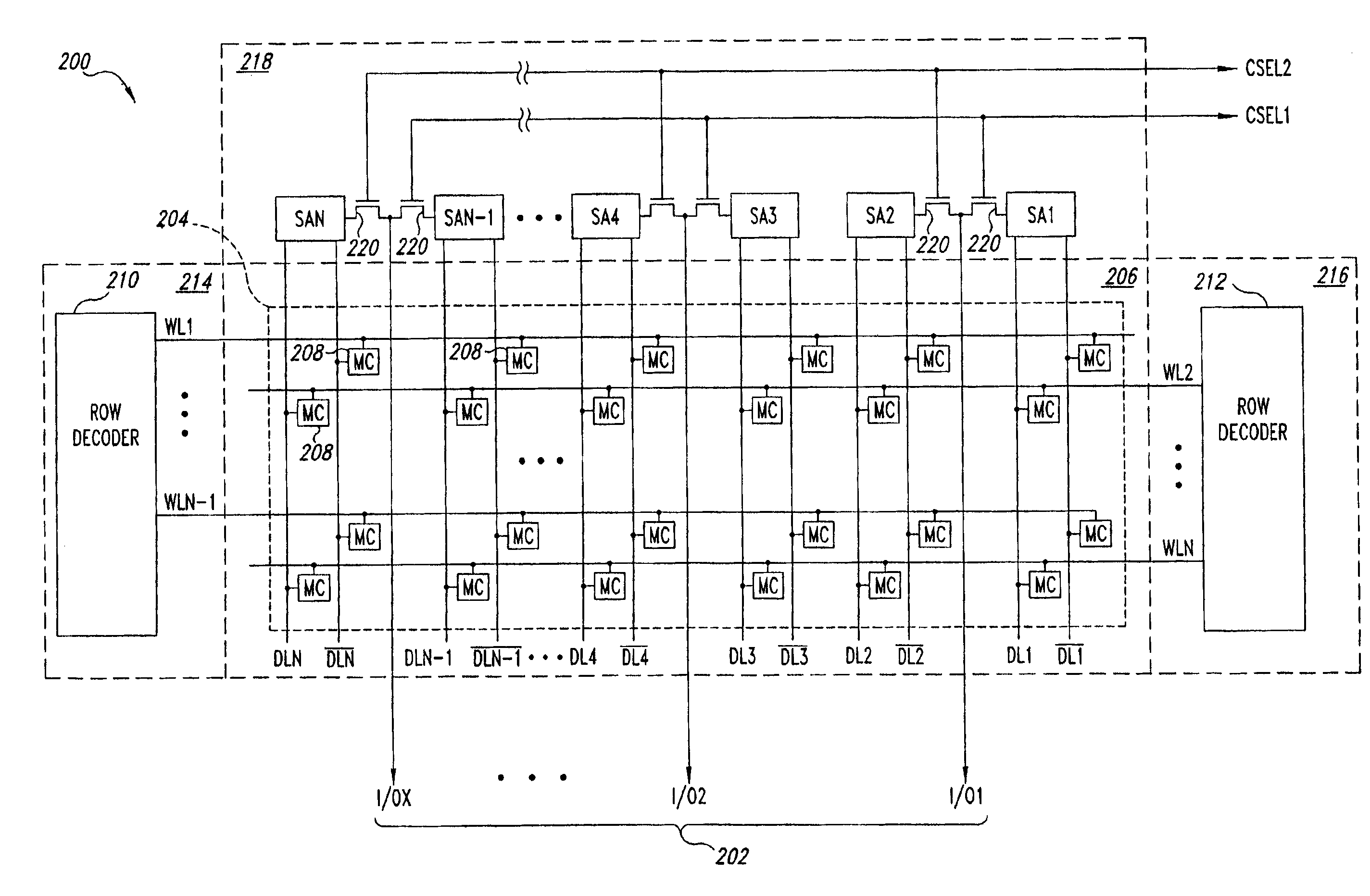
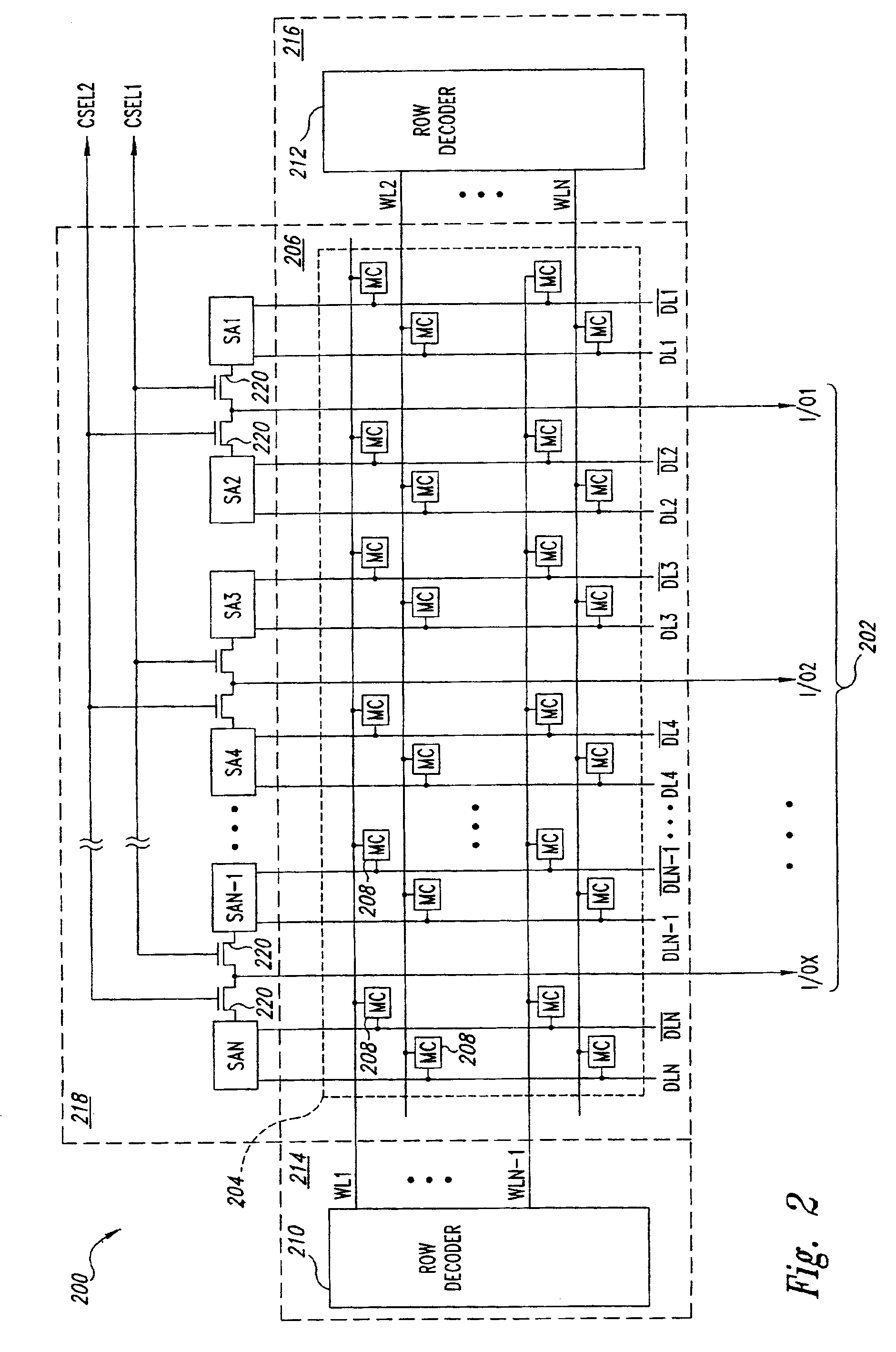
[0019]FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a portion of a DRAM 200 including a wide data path 202 according to one embodiment of the present invention. The wide data path 202 transfers a large block of data accessed in a memory-cell array 204, and may be formed without increasing the size of a semiconductor substrate in which the DRAM 200 is formed, and without requiring the formation of additional conductive layers, as will be explained in more detail below.
[0020]The DRAM 200 includes a memory-cell array 204 formed in an array region 206 of the semiconductor substrate in which the DRAM 200 is formed. The array 204 includes a plurality of memory cells 208 arranged in rows and columns. A plurality of word lines WL1-WLN are formed in a first conductive layer in the array region 206, and are disposed substantially perpendicular to the pairs of digit lines DL1, {overscore (DL1)}-DLN, {overscore (DLN)}. Typically, the first conductive layer is a polysilicon layer formed during fabrication of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com