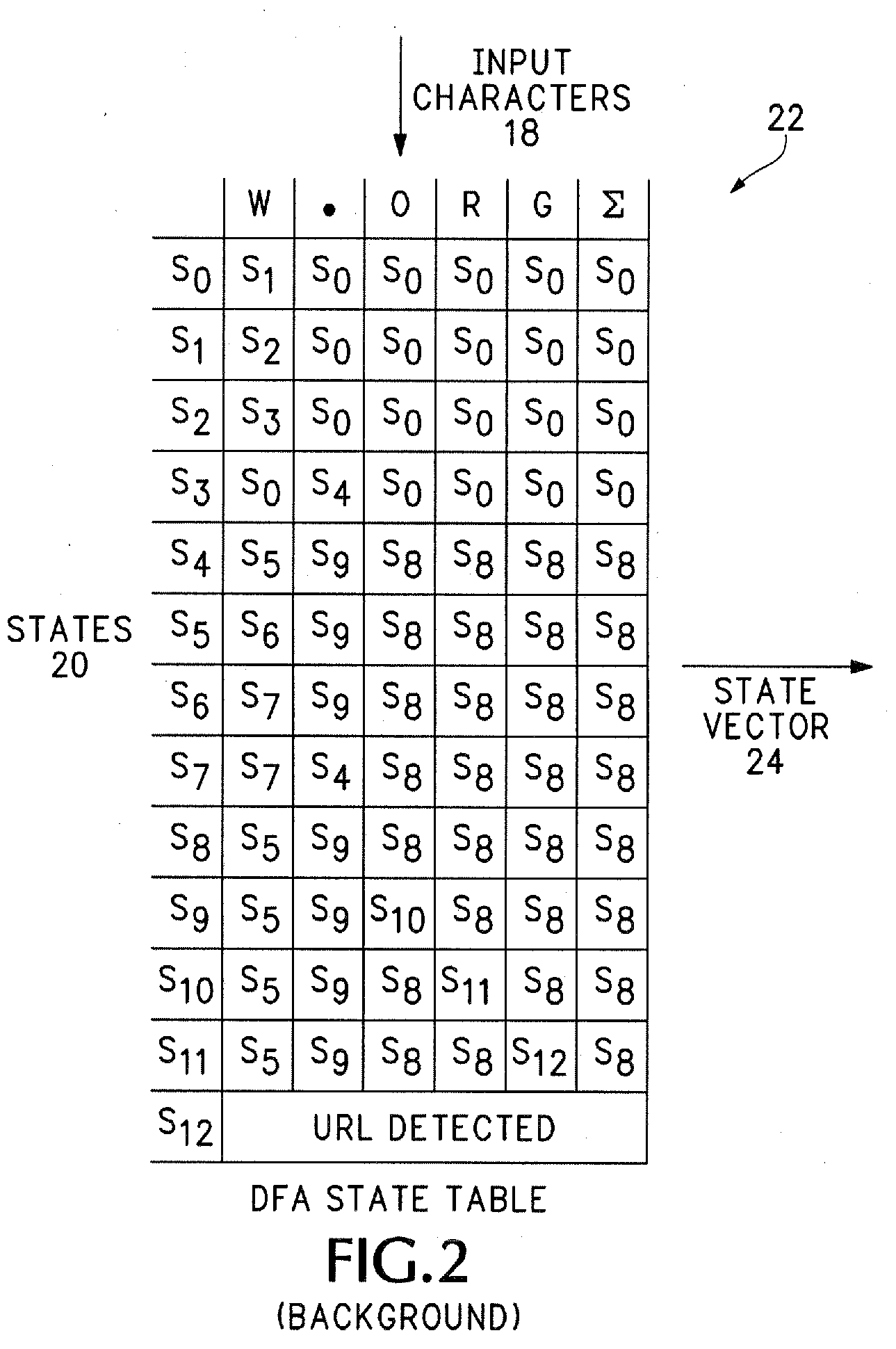
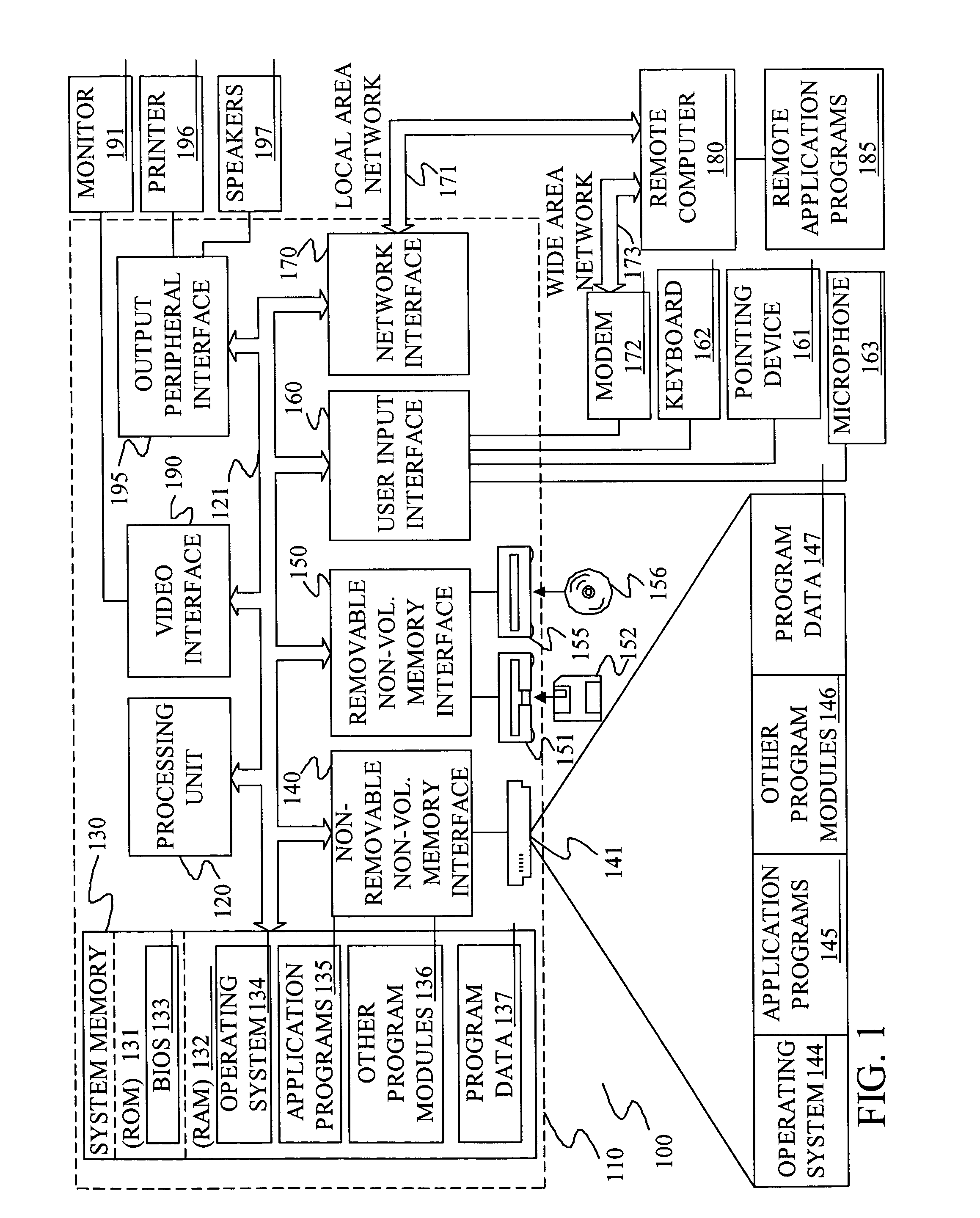
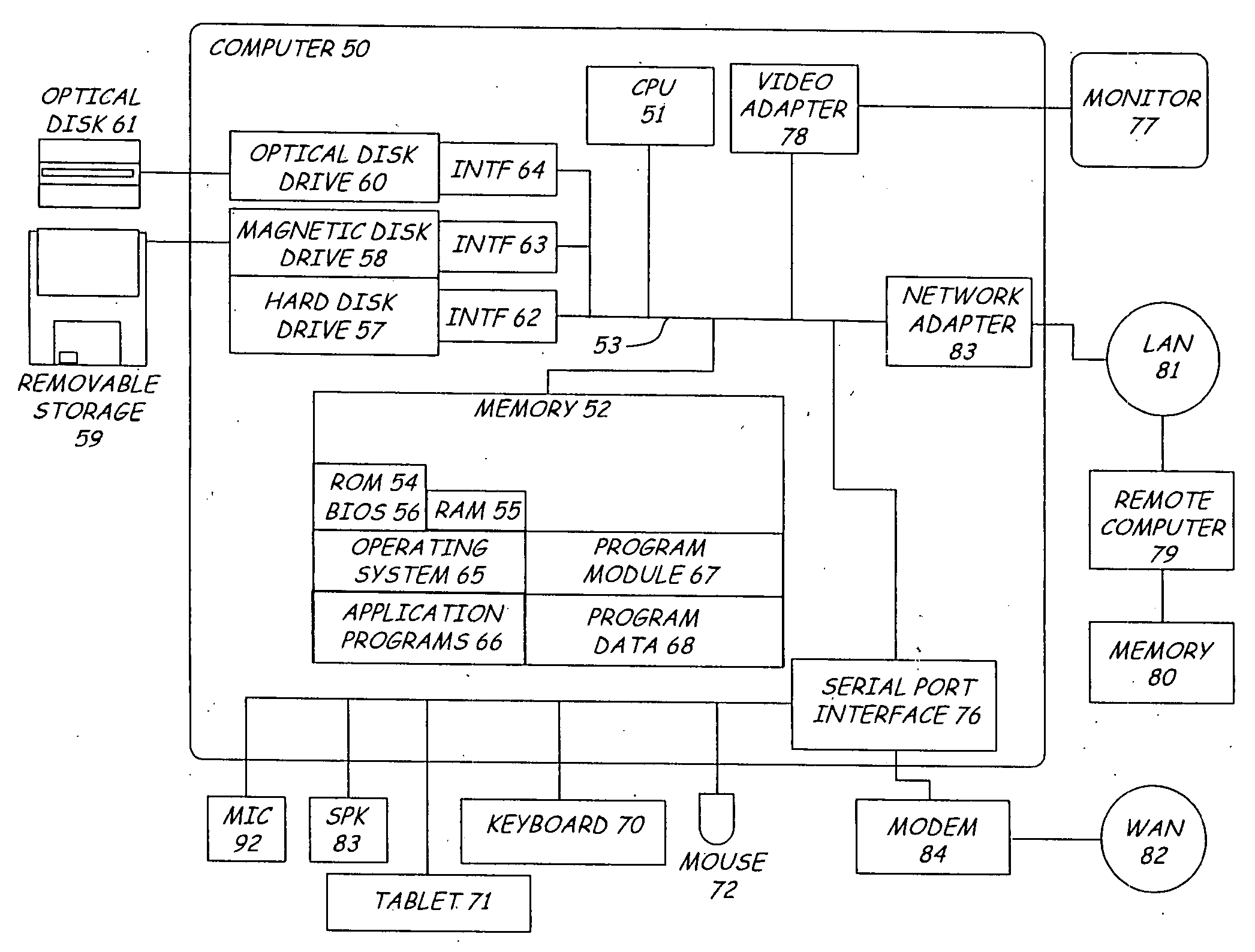
Patents
Literature
96 results about "Context-free grammar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
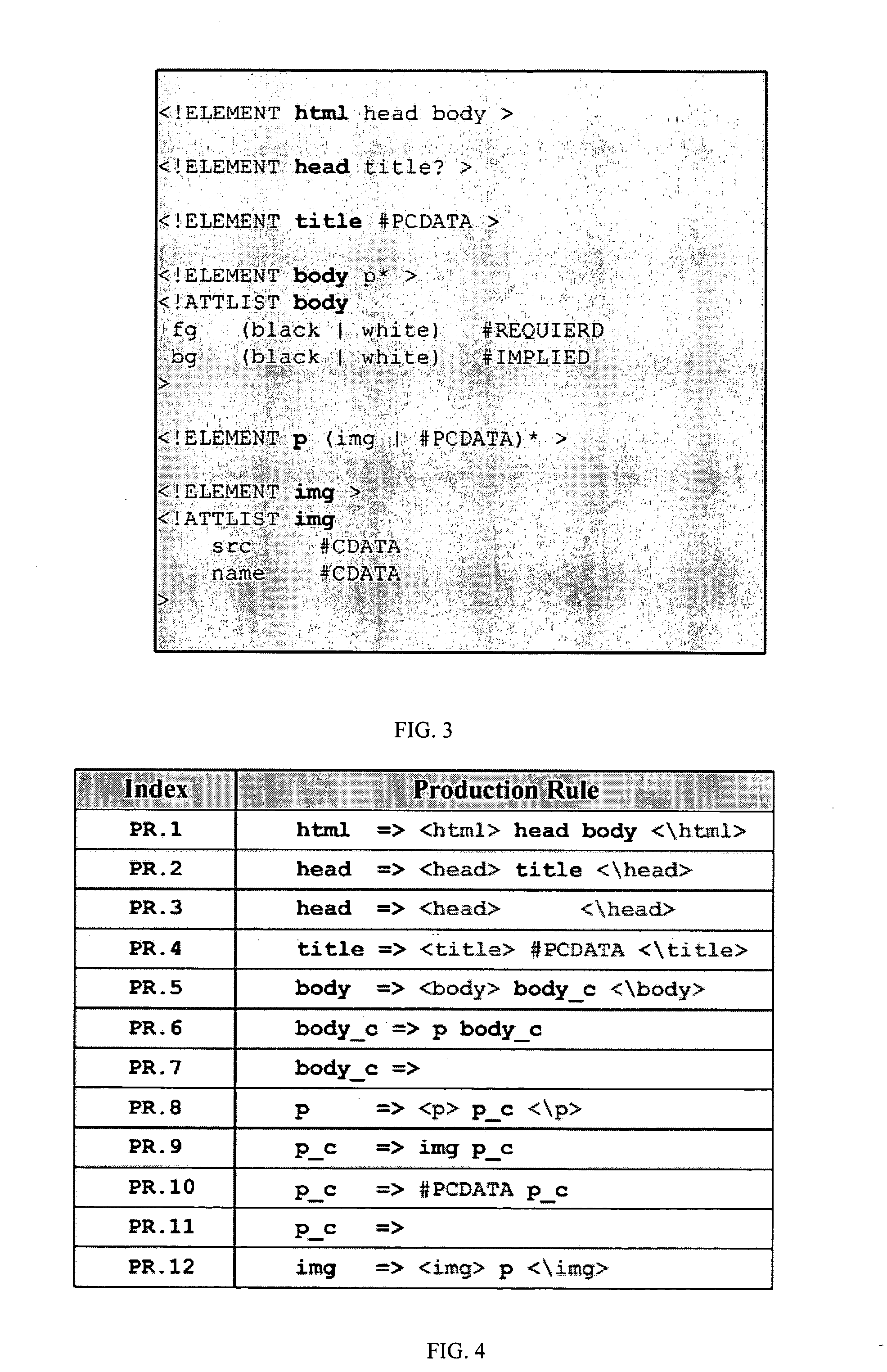
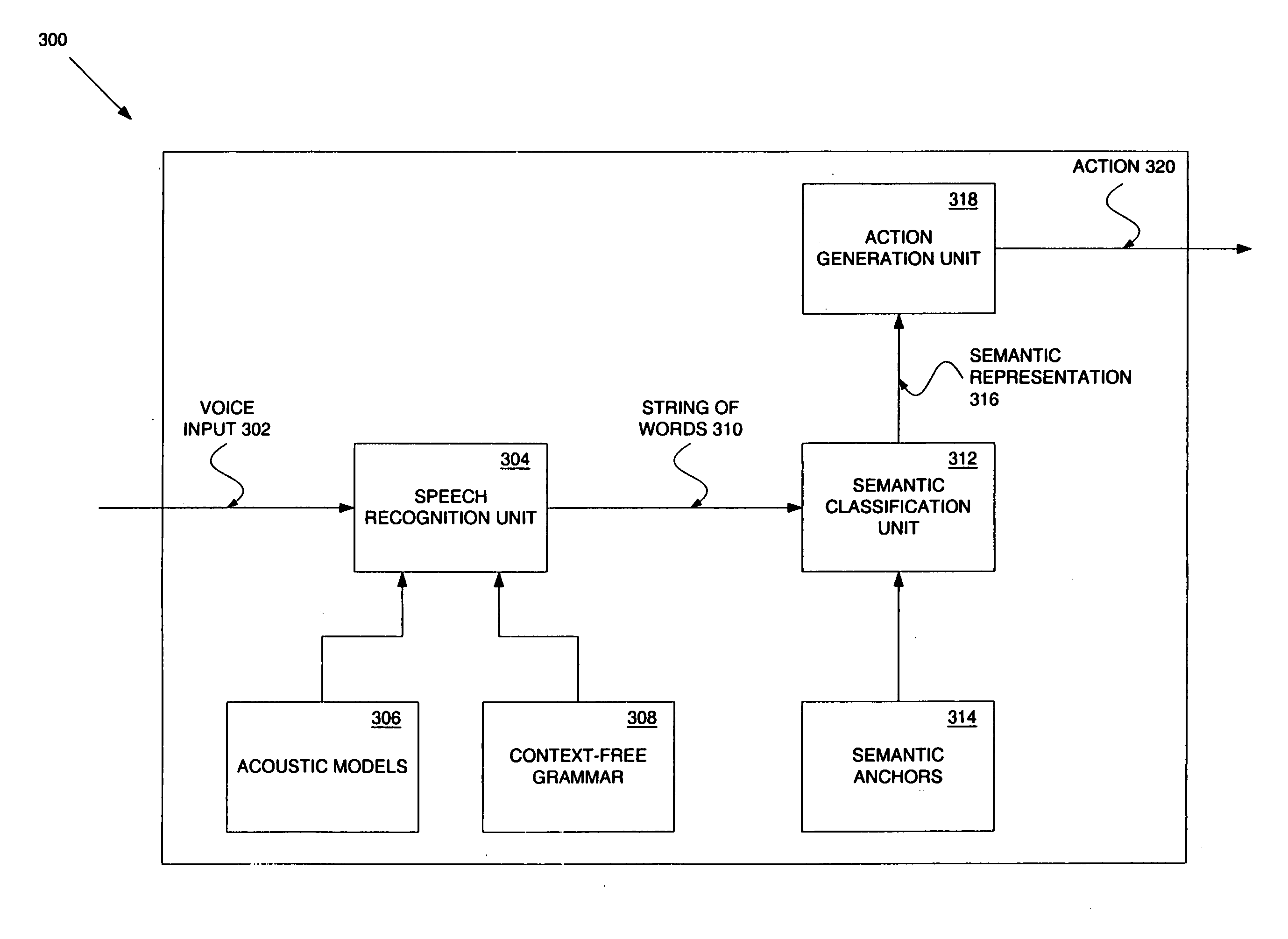
In formal language theory, a context-free grammar (CFG) is a certain type of formal grammar: a set of production rules that describe all possible strings in a given formal language. Production rules are simple replacements. For example, the rule A → α replaces A with α. There can be multiple replacement rules for any given value. For example, A → α A → β means that A can be replaced with either α or β.
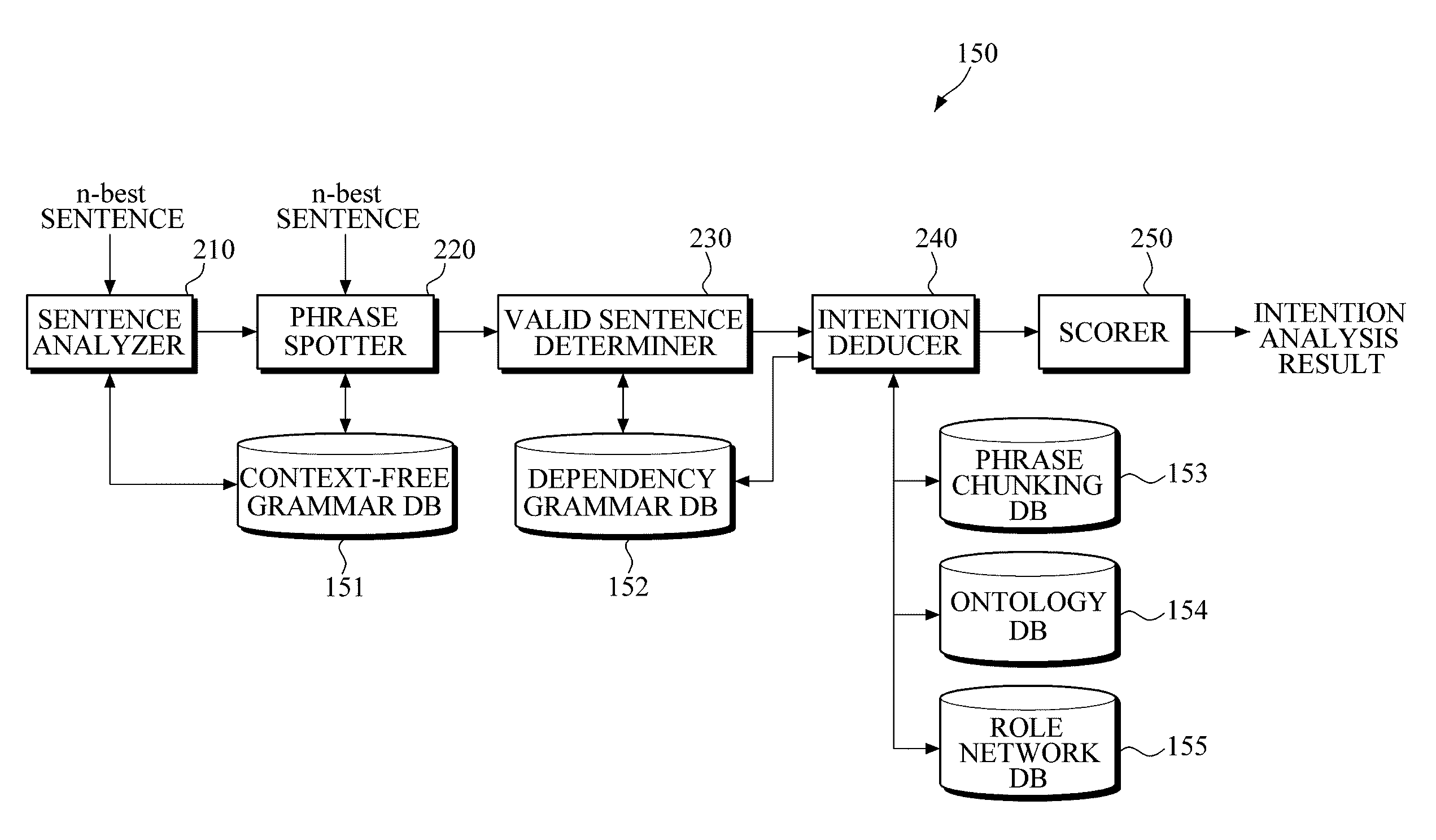
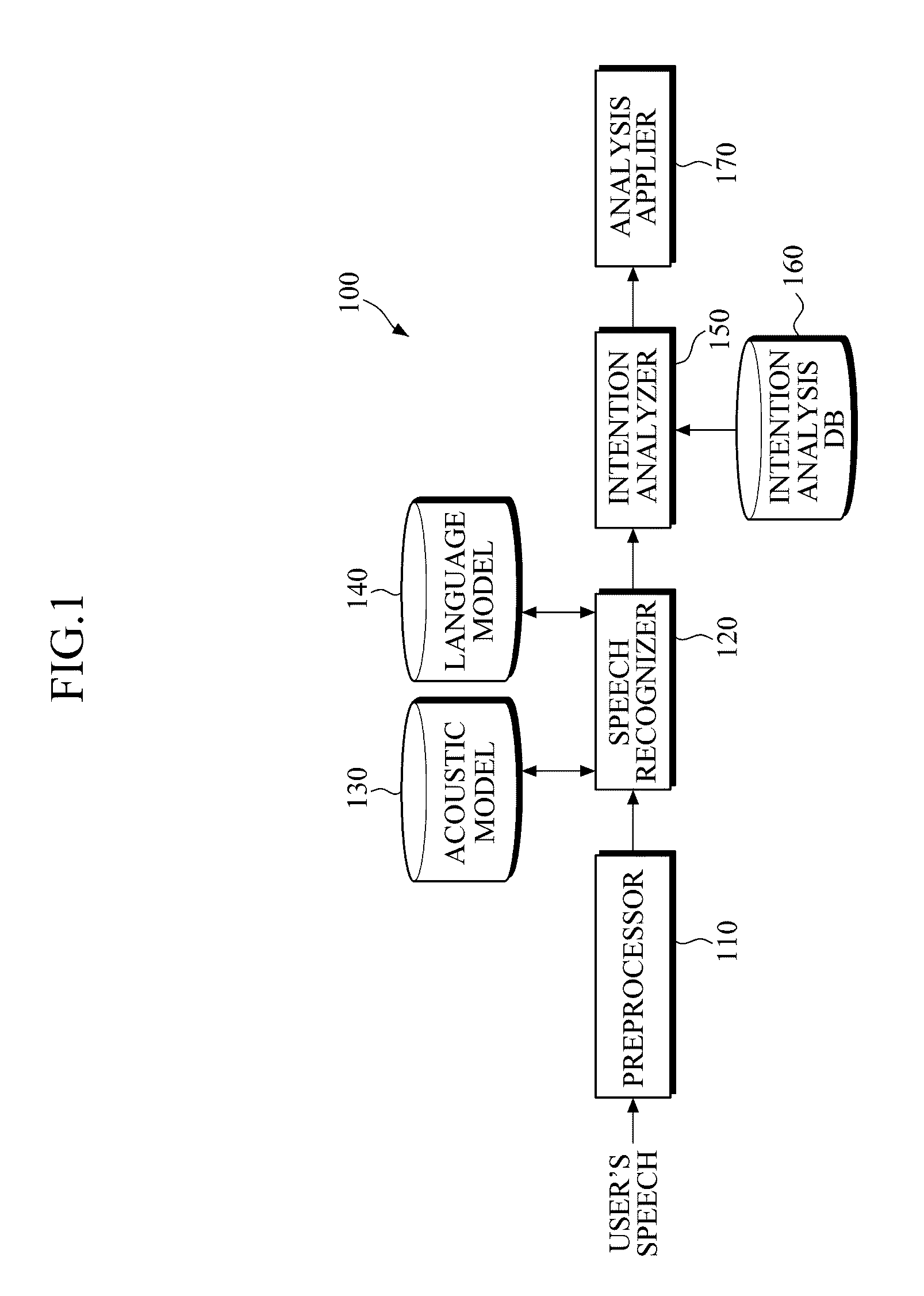
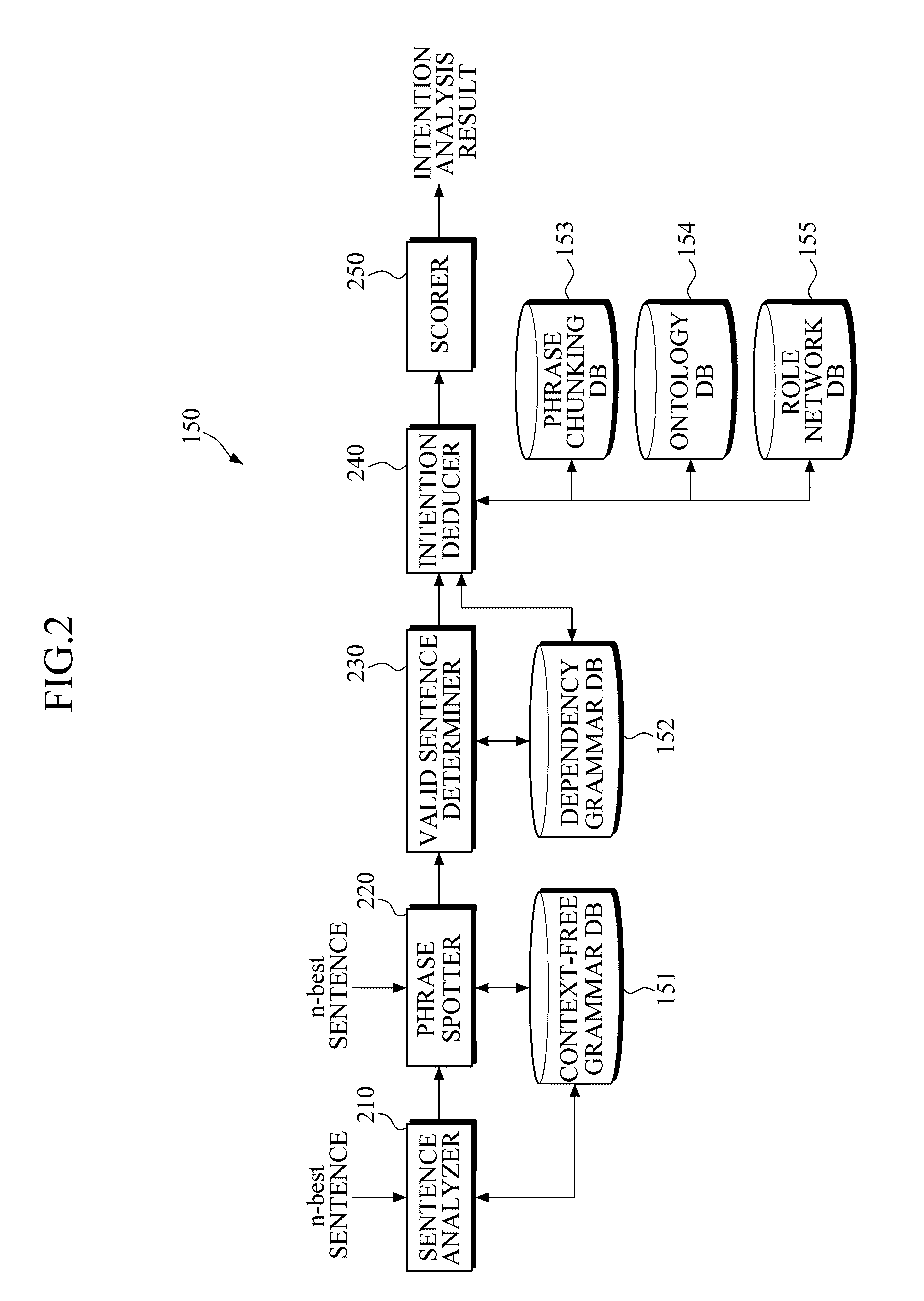
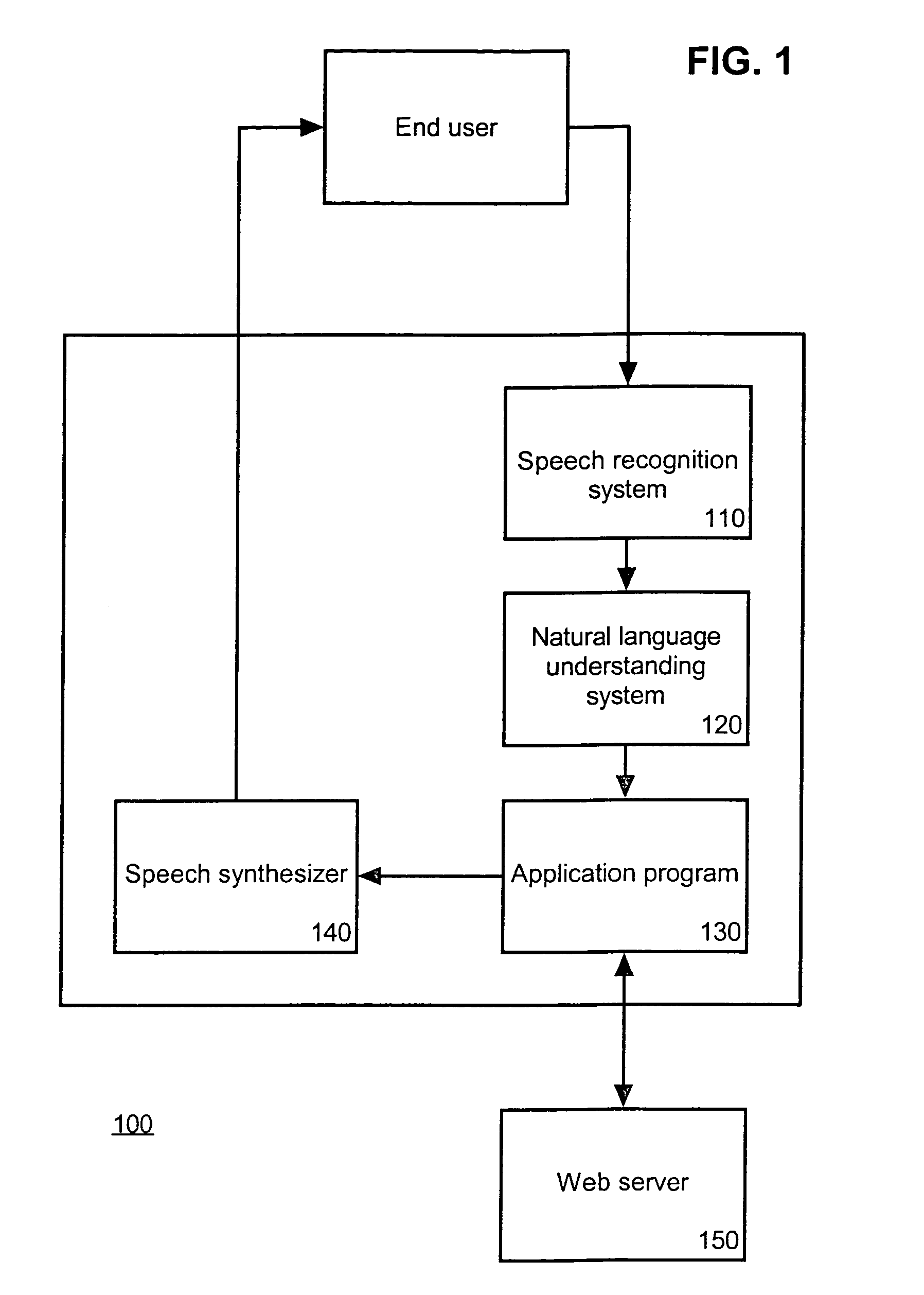
Apparatus and Method for Analyzing Intention
InactiveUS20110082688A1Natural language data processingSpeech recognitionSpeech soundSubvocal recognition
An apparatus and system for analyzing intention are provided. The apparatus for analyzing an intention applies a context-free grammar to each of one or more sentences in units of one or more phrases to perform phrase spotting on each sentence, thereby extending a recognition range for an out-of-grammar (OOG) expression. Meanwhile, the apparatus for analyzing an intention determines whether sentences that have undergone phrase spotting are grammatically valid by applying a dependency grammar to the sentences to filter an invalid sentence, and generates the intention analysis result of a valid sentence, thereby and grammatically and / or semantically verifying a sentence that has undergone speech recognition while extending a speech recognition range.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semantic object synchronous understanding implemented with speech application language tags
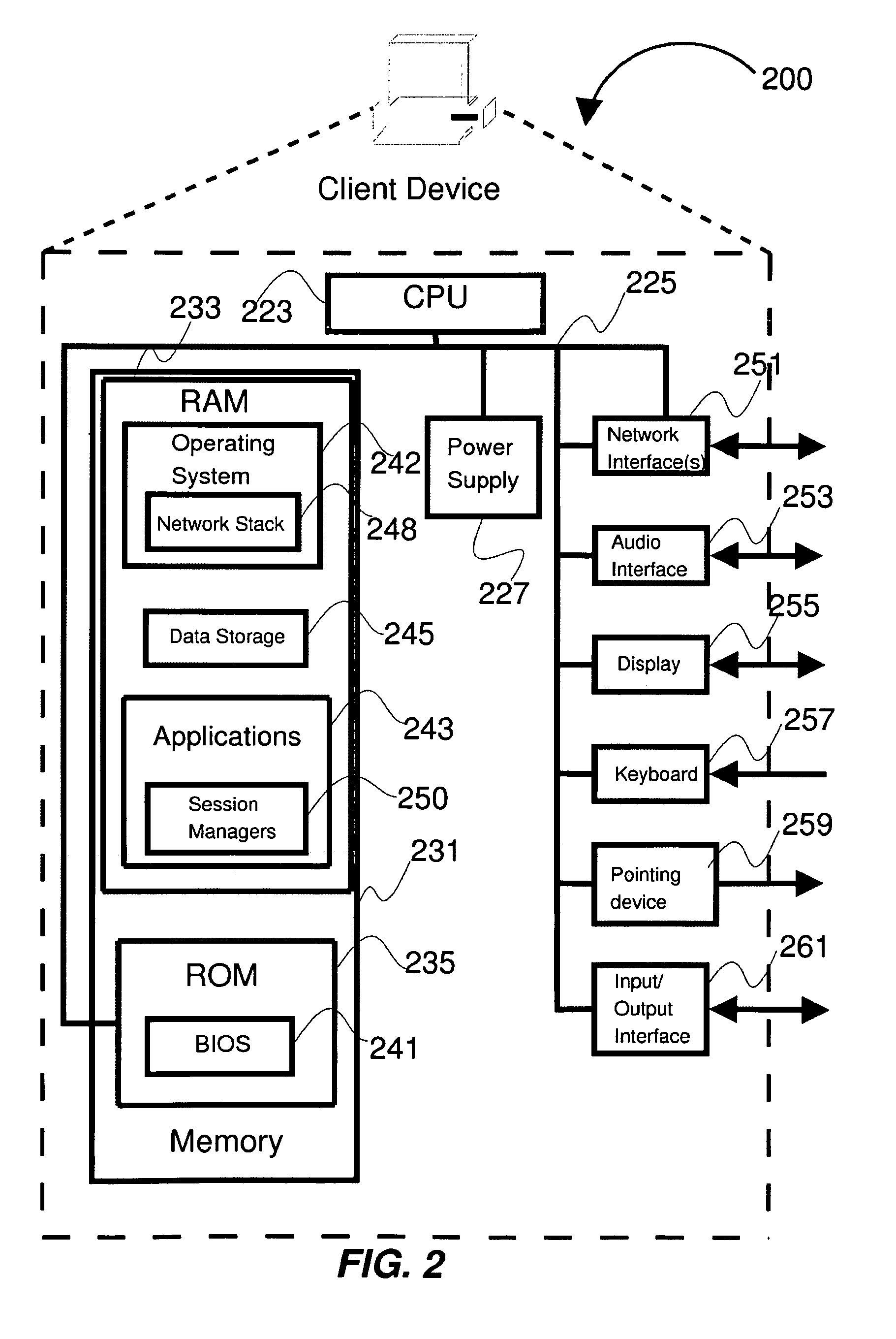
ActiveUS7200559B2Sound input/outputSpeech recognitionSpeech comprehensionApplication programming interface
A speech understanding system includes a language model comprising a combination of an N-gram language model and a context-free grammar language model. The language model stores information related to words and semantic information to be recognized. A module is adapted to receive input from a user and capture the input for processing. The module is further adapted to receive SALT application program interfaces pertaining to recognition of the input. The module is configured to process the SALT application program interfaces and the input to ascertain semantic information pertaining to a first portion of the input and output a semantic object comprising text and semantic information for the first portion by accessing the language model, wherein performing recognition and outputting the semantic object are performed while capturing continues for subsequent portions of the input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
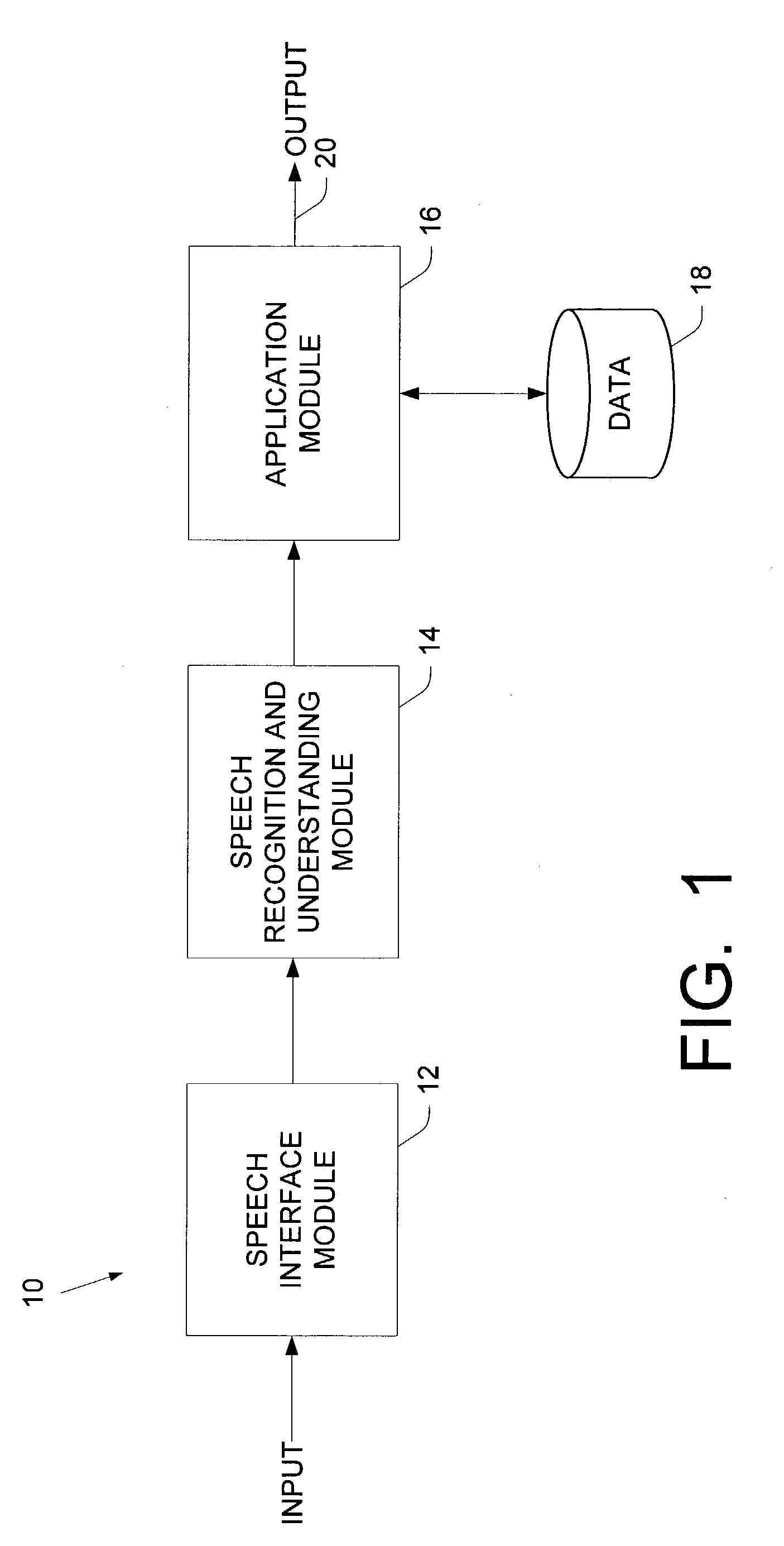
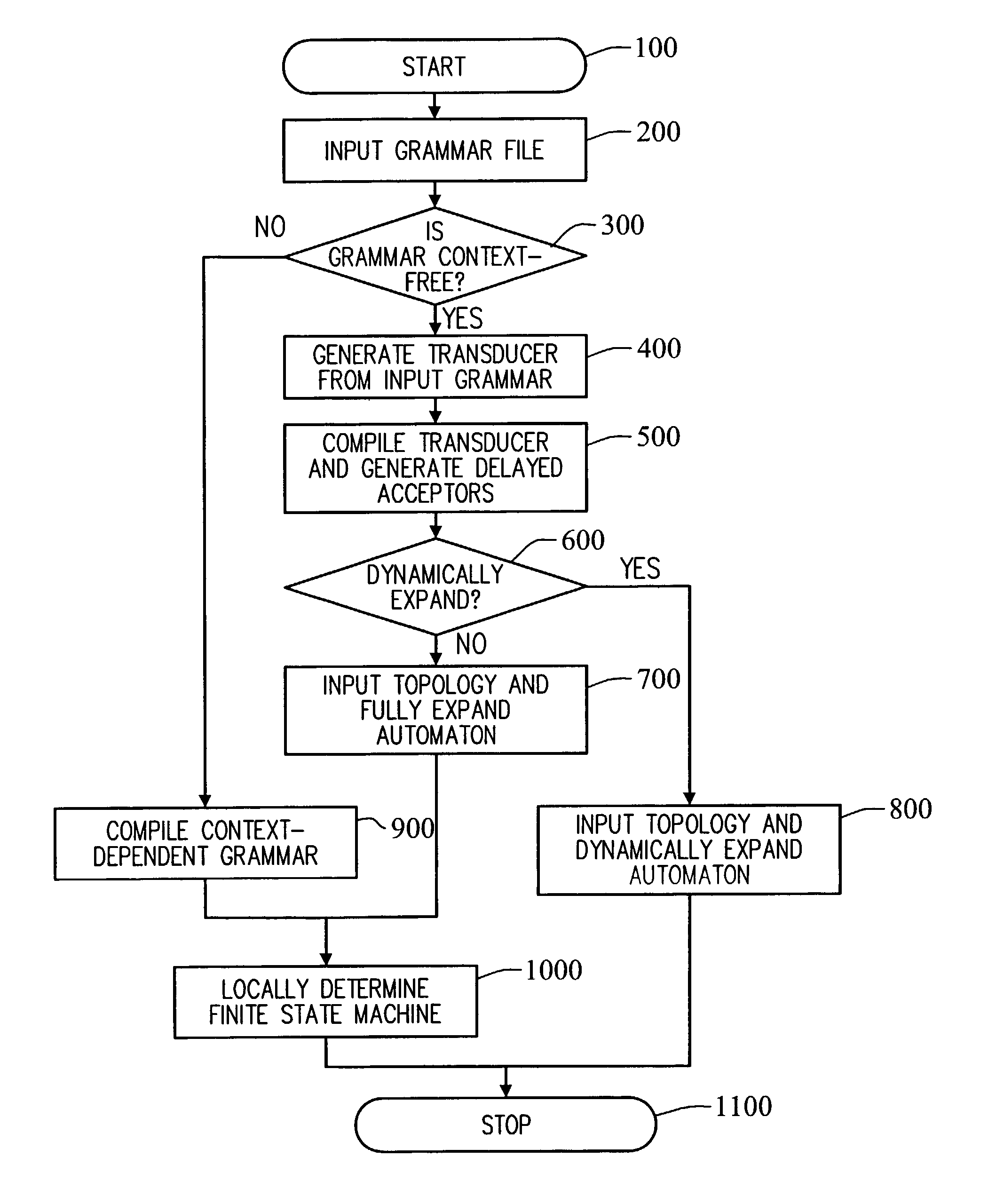
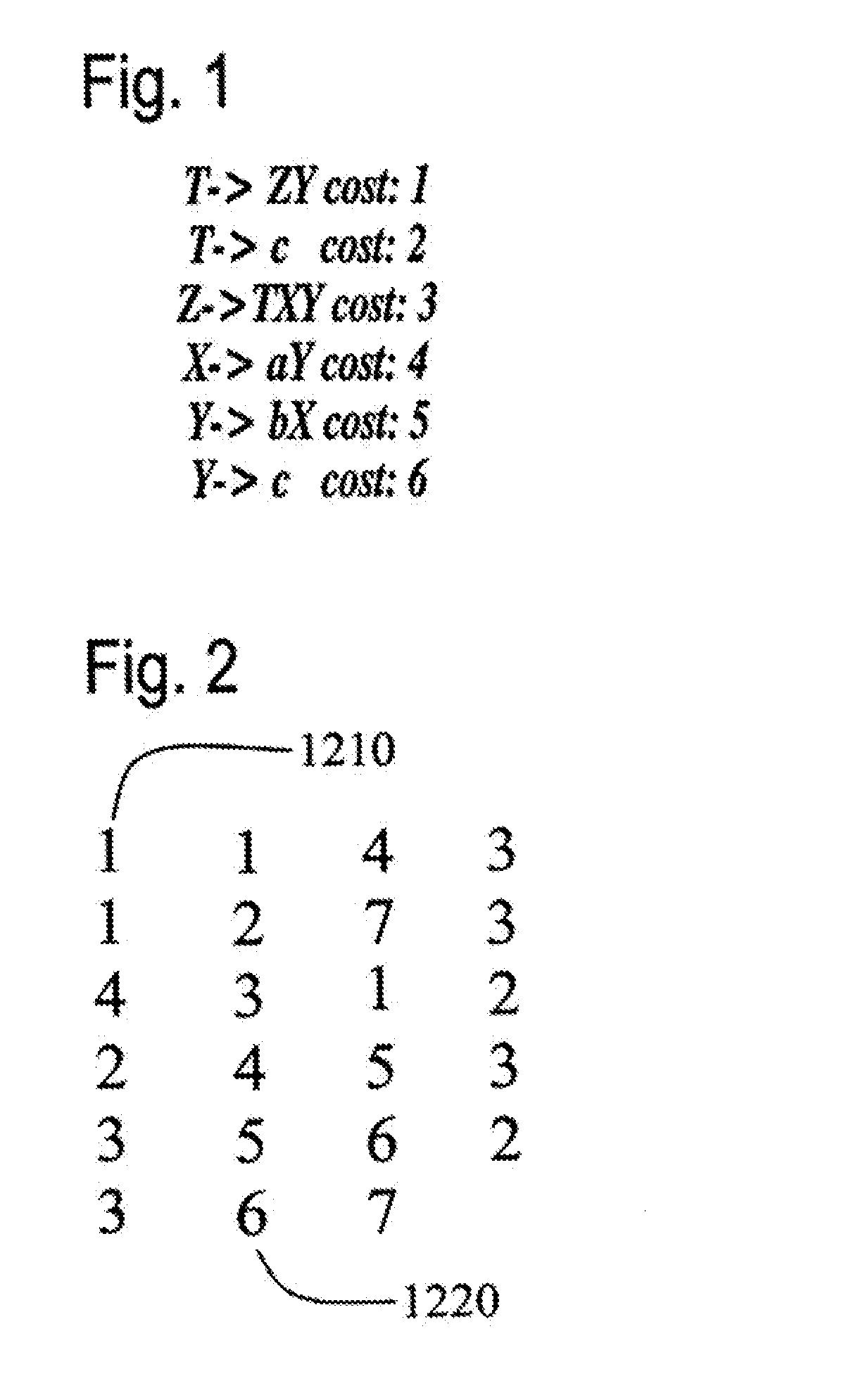
Systems and methods for generating weighted finite-state automata representing grammars
InactiveUS7181386B2Natural language analysisDigital data processing detailsFinite state transducerAutomaton
A context-free grammar can be represented by a weighted finite-state transducer. This representation can be used to efficiently compile that grammar into a weighted finite-state automaton that accepts the strings allowed by the grammar with the corresponding weights. The rules of a context-free grammar are input. A finite-state automaton is generated from the input rules. Strongly connected components of the finite-state automaton are identified. An automaton is generated for each strongly connected component. A topology that defines a number of states, and that uses active ones of the non-terminal symbols of the context-free grammar as the labels between those states, is defined. The topology is expanded by replacing a transition, and its beginning and end states, with the automaton that includes, as a state, the symbol used as the label on that transition. The topology can be fully expanded or dynamically expanded as required to recognize a particular input string.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
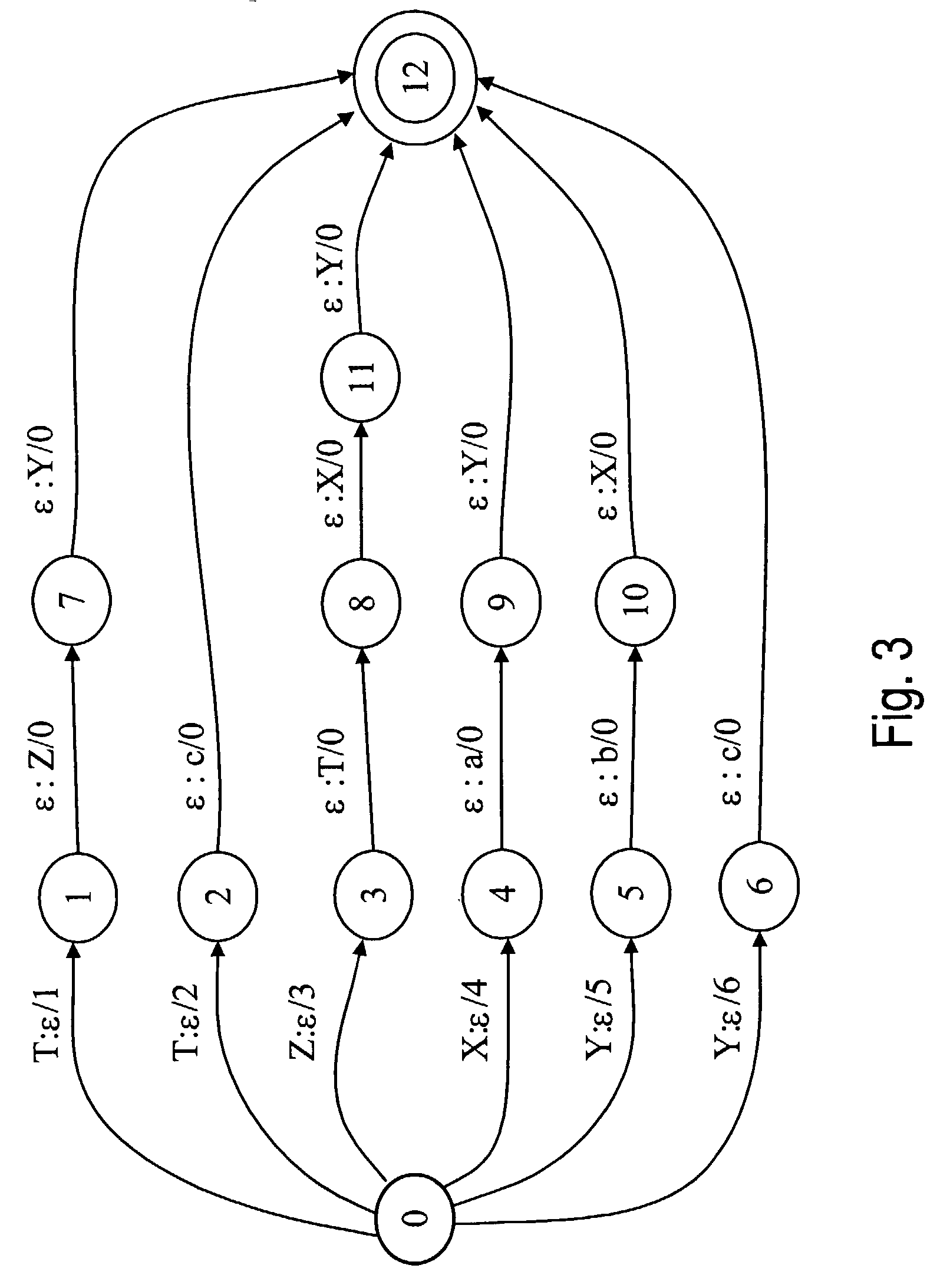
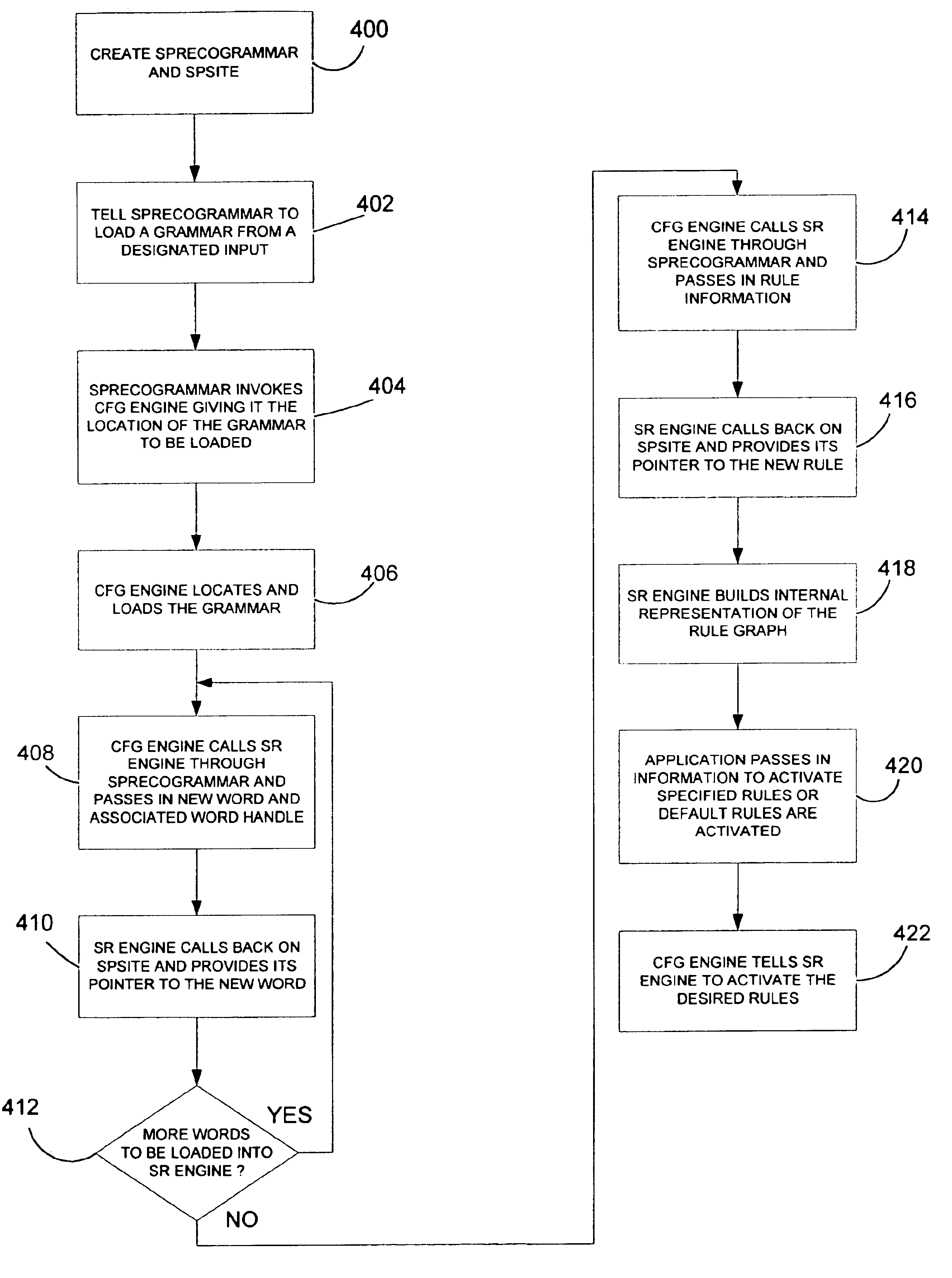
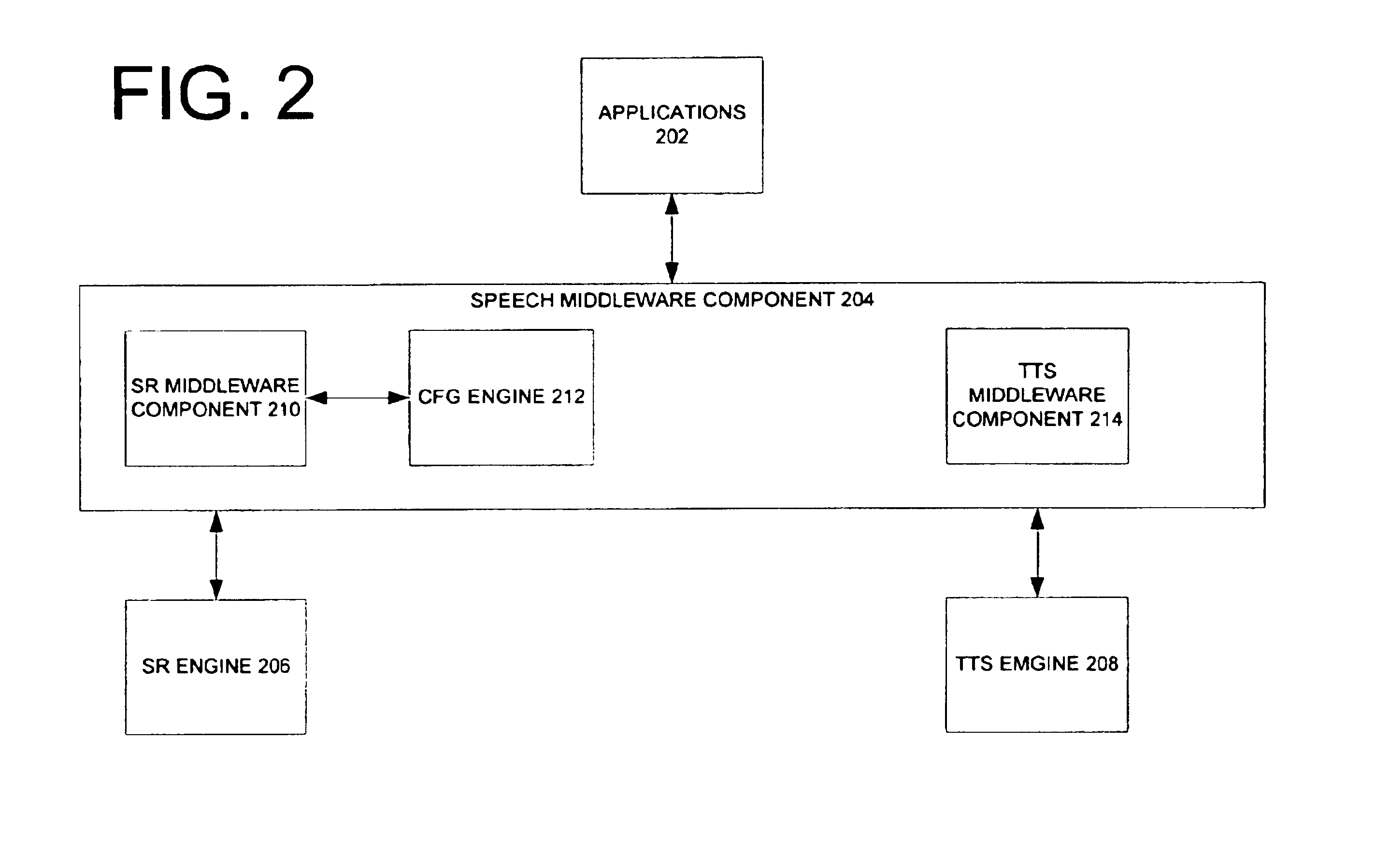
Context free grammar engine for speech recognition system
The present invention includes a context-free grammar (CFG) engine which communicates through an exposed interface with a speech recognition engine. The context-free grammar engine, in one illustrative embodiment, handles loading and unloading of grammars, as well as maintaining a desired activation state of the grammars which are loaded. Further, the CFG engine represents all loaded grammars, and their corresponding activation states, as a single grammar to the speech recognition engine.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
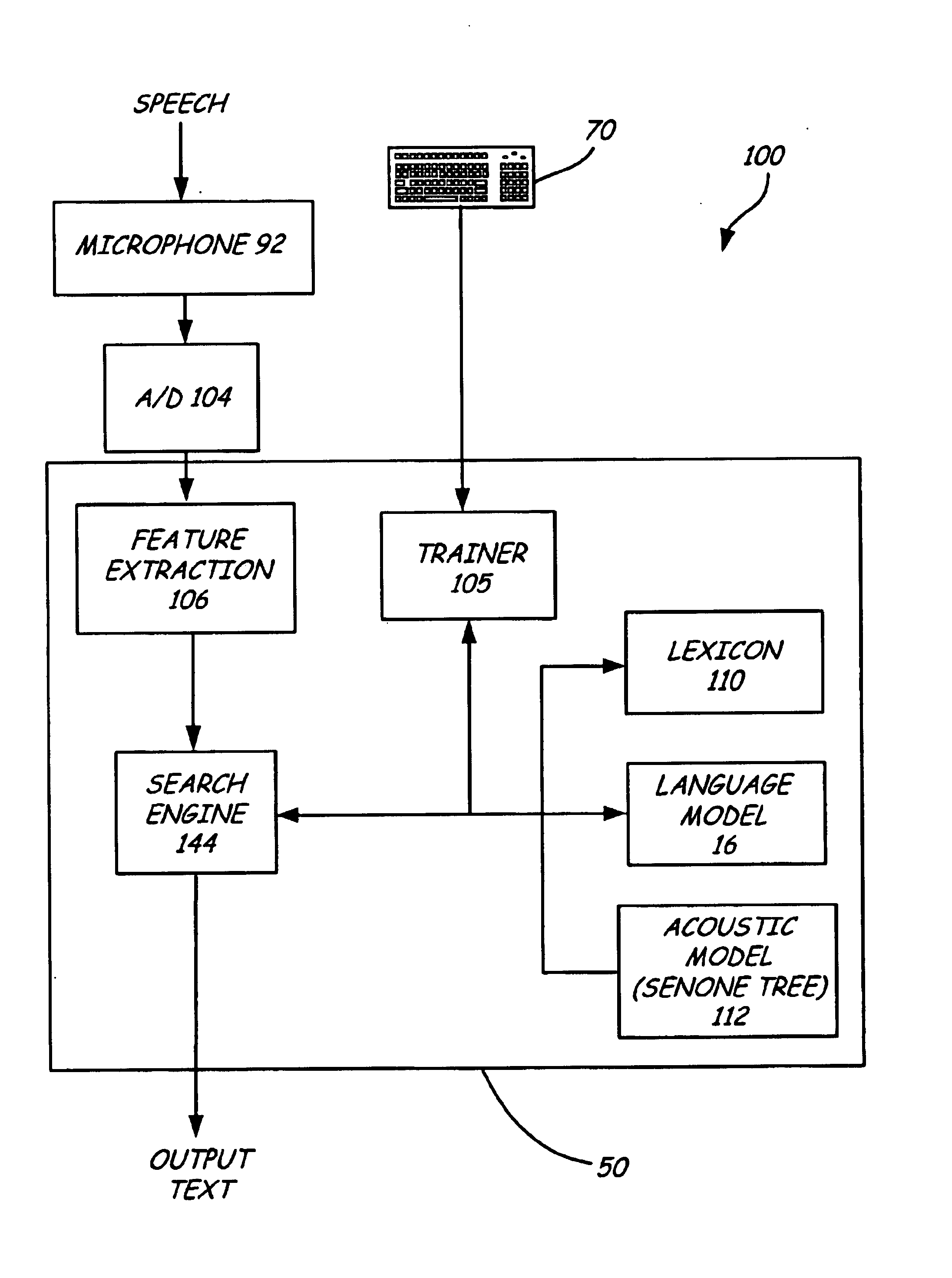
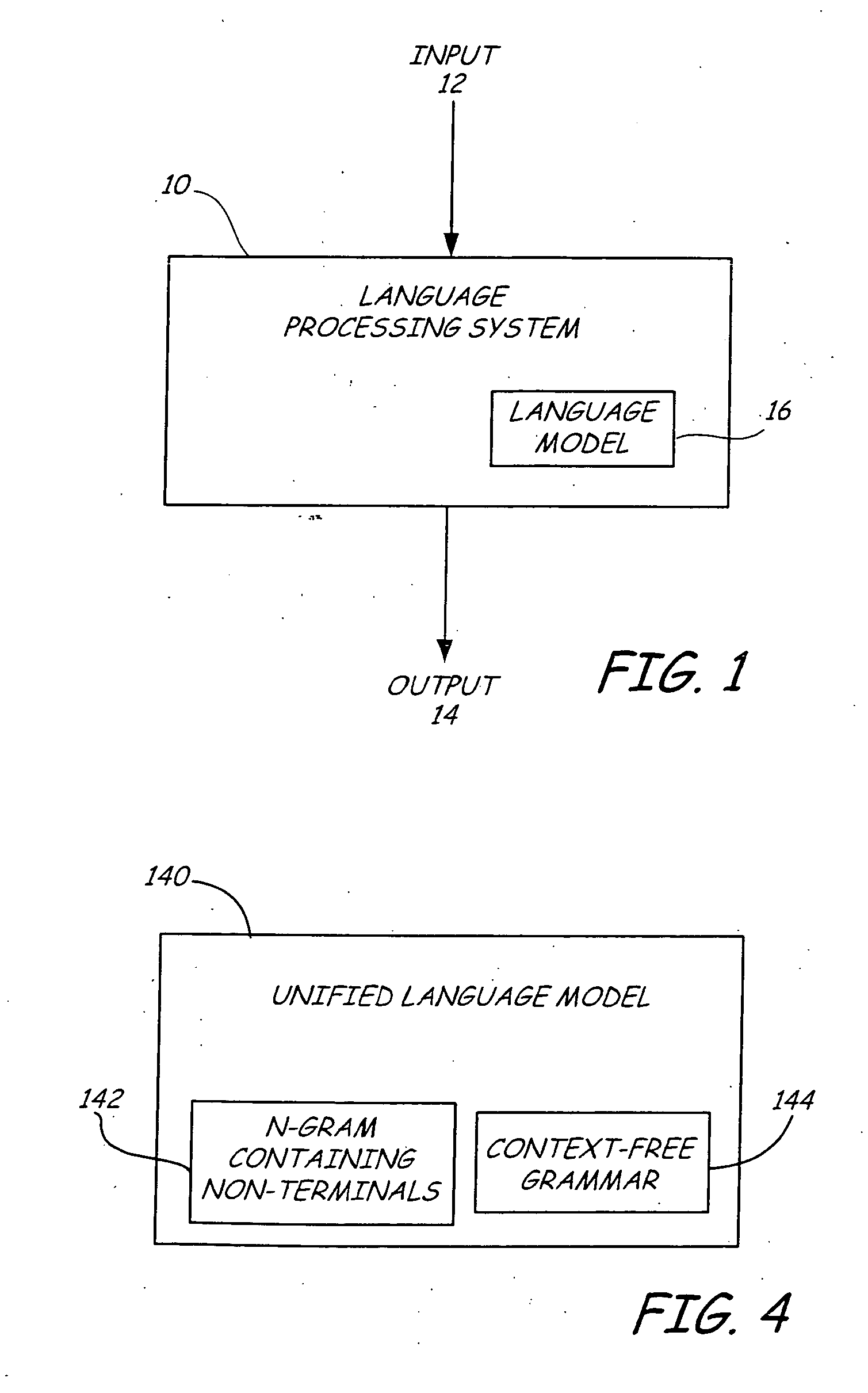
Creating a language model for a language processing system
InactiveUS7031908B1Speech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHuman languageContext-free grammar
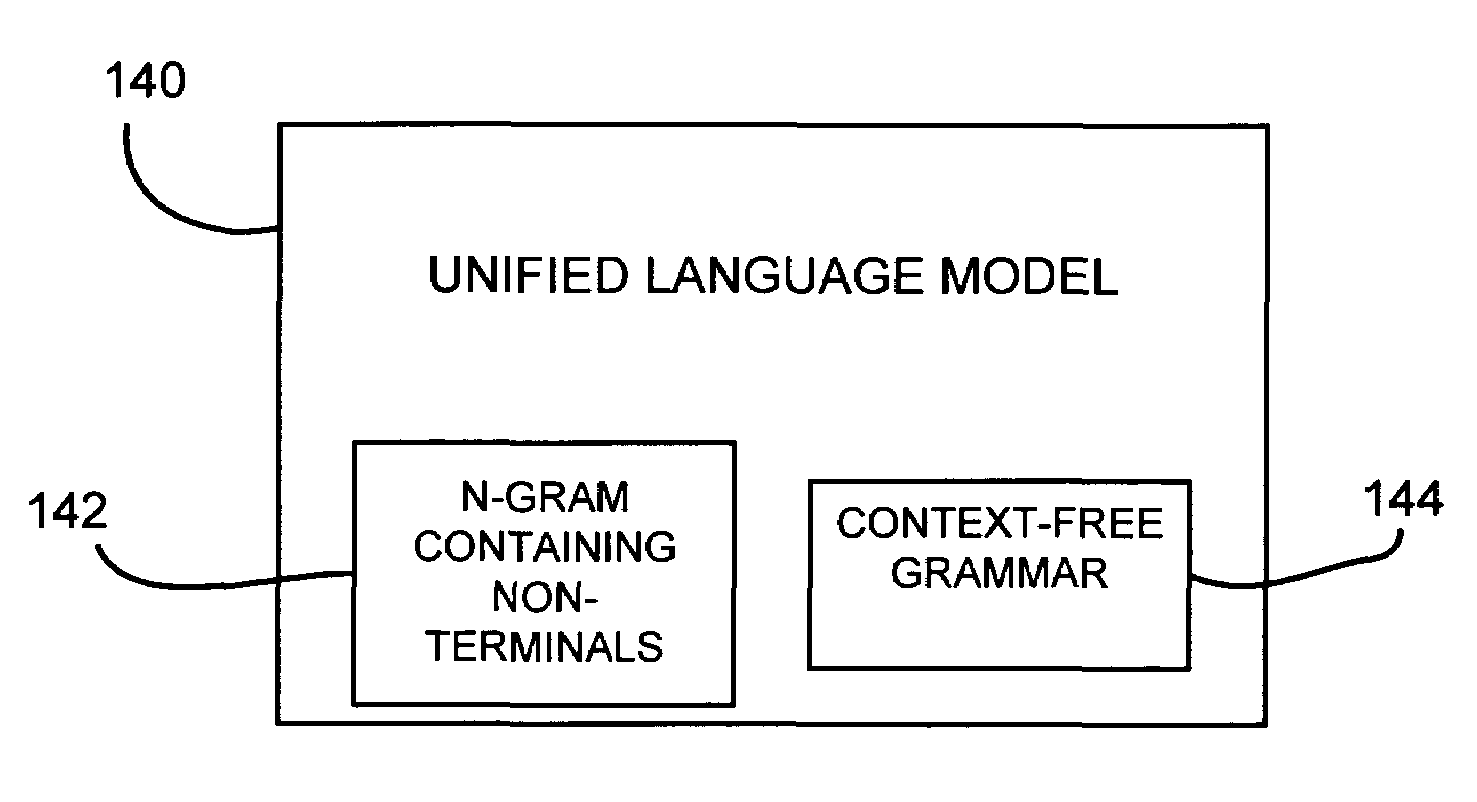
A method for creating a language model from a task-independent corpus is provided. In one embodiment, a task dependent unified language model is created. The unified language model includes a plurality of context-free grammars having non-terminals and a hybrid N-gram model having at least some of the same non-terminals embedded therein.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
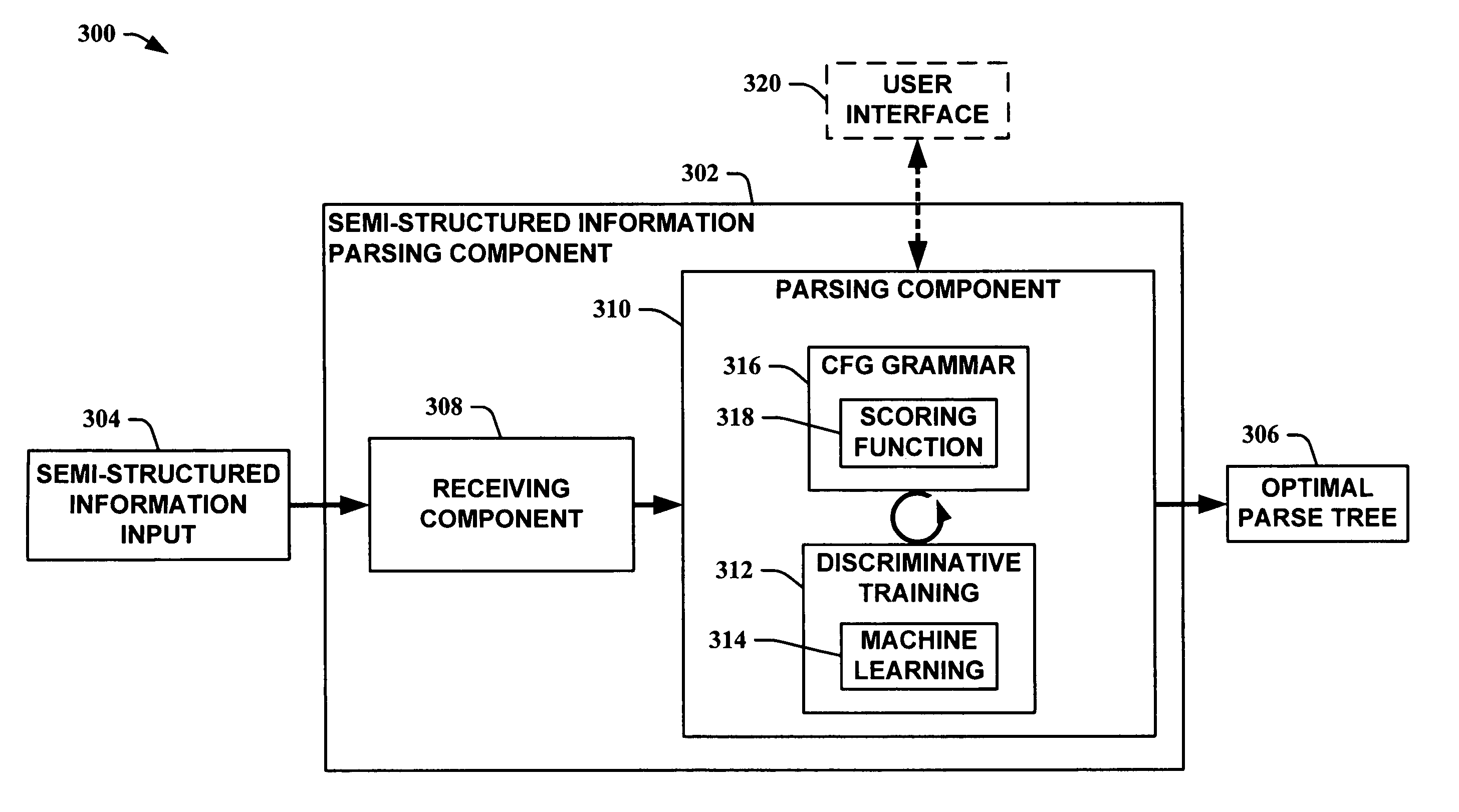
Extracting data from semi-structured information utilizing a discriminative context free grammar
InactiveUS20060245641A1Easy to extract dataImprovement in error reductionCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingDiscriminantContext independent
A discriminative grammar framework utilizing a machine learning algorithm is employed to facilitate in learning scoring functions for parsing of unstructured information. The framework includes a discriminative context free grammar that is trained based on features of an example input. The flexibility of the framework allows information features and / or features output by arbitrary processes to be utilized as the example input as well. Myopic inside scoring is circumvented in the parsing process because contextual information is utilized to facilitate scoring function training.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
XML parser
InactiveUS20060117307A1Easy to compressFacilitates top down parsingNatural language data processingProgram controlDocument type declarationMultiple context
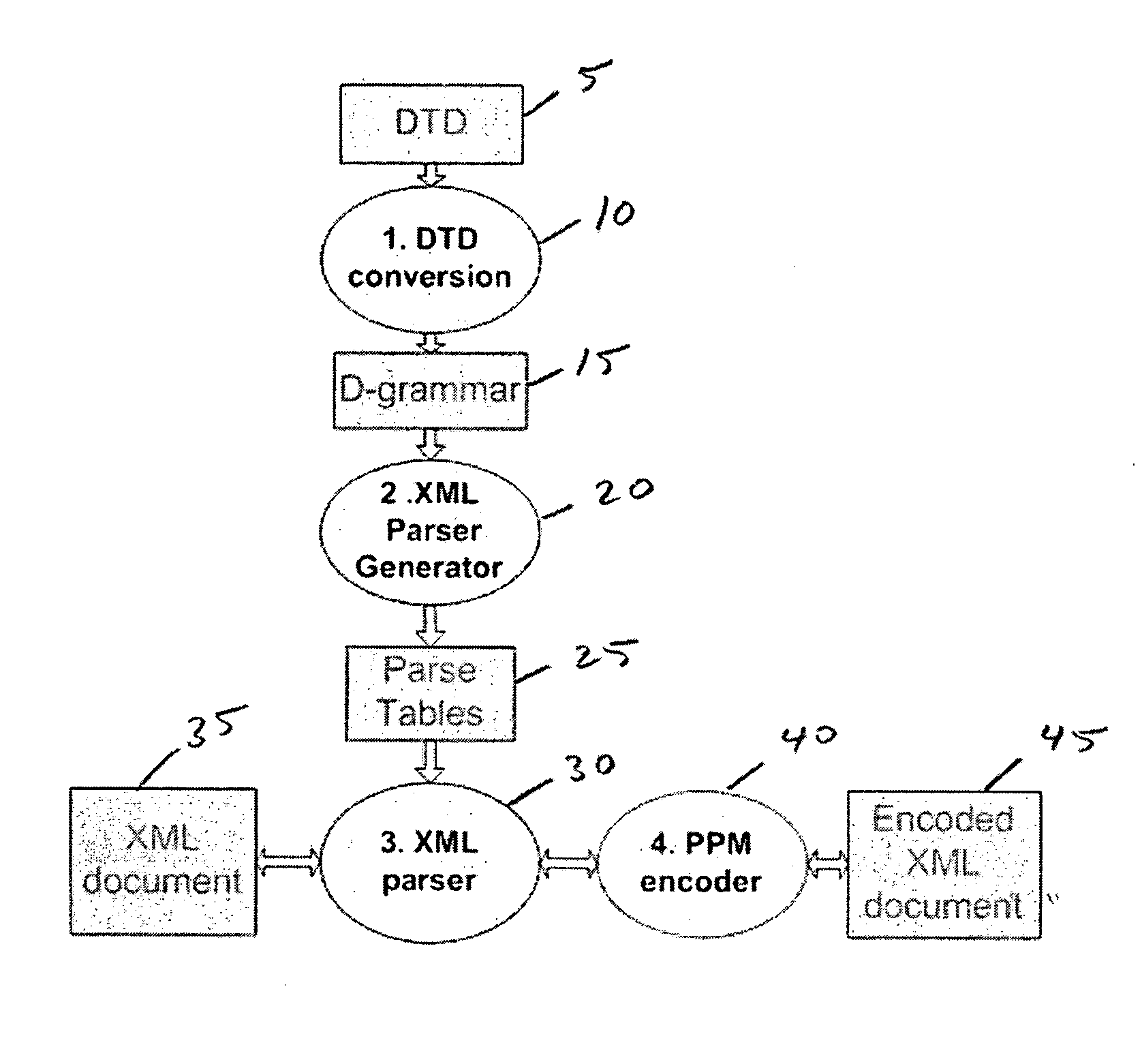
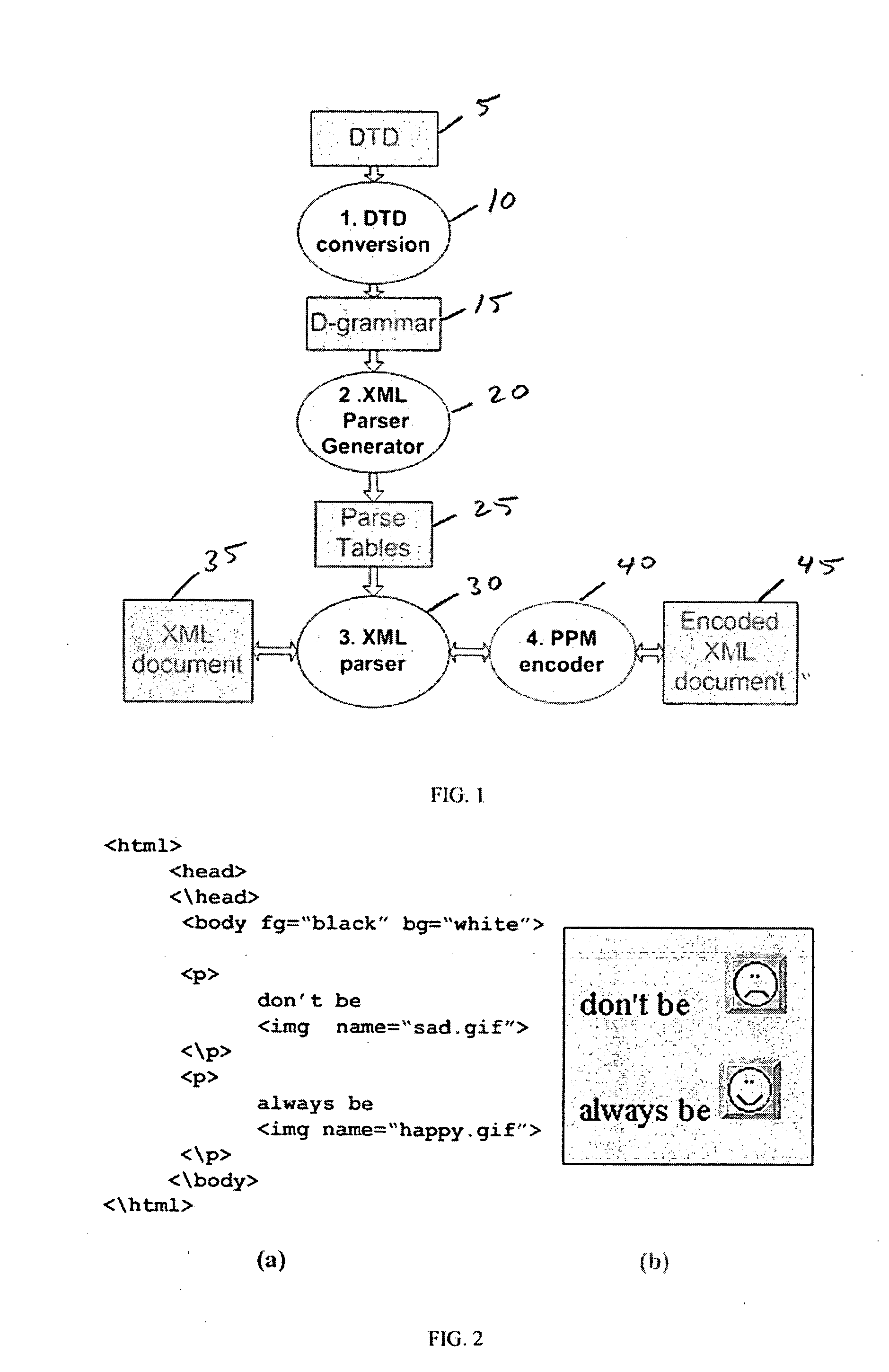
A method of generating a parser of a source code file that references a syntactic dictionary, a method of compressing the file, and apparatuses that use the methods. The syntactic dictionary is converted into a corresponding plurality of expressions, of a context-free grammar, that are a grammar of the source code. The parser is constructed from the expressions. The source code is compressed using the parser. Preferably, the grammar of the source code file is a D-grammar and the expressions are regular expressions. Preferably, the parser is a deterministic pushdown transducer. An important case of the present invention is that in which the source code is XML code and the syntactic dictionary is the document type declaration of the XML code. Apparatuses that use a parser of the present invention include compressors, decompressors, validators, converters, editors, network devices and end-user / hand-held devices.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
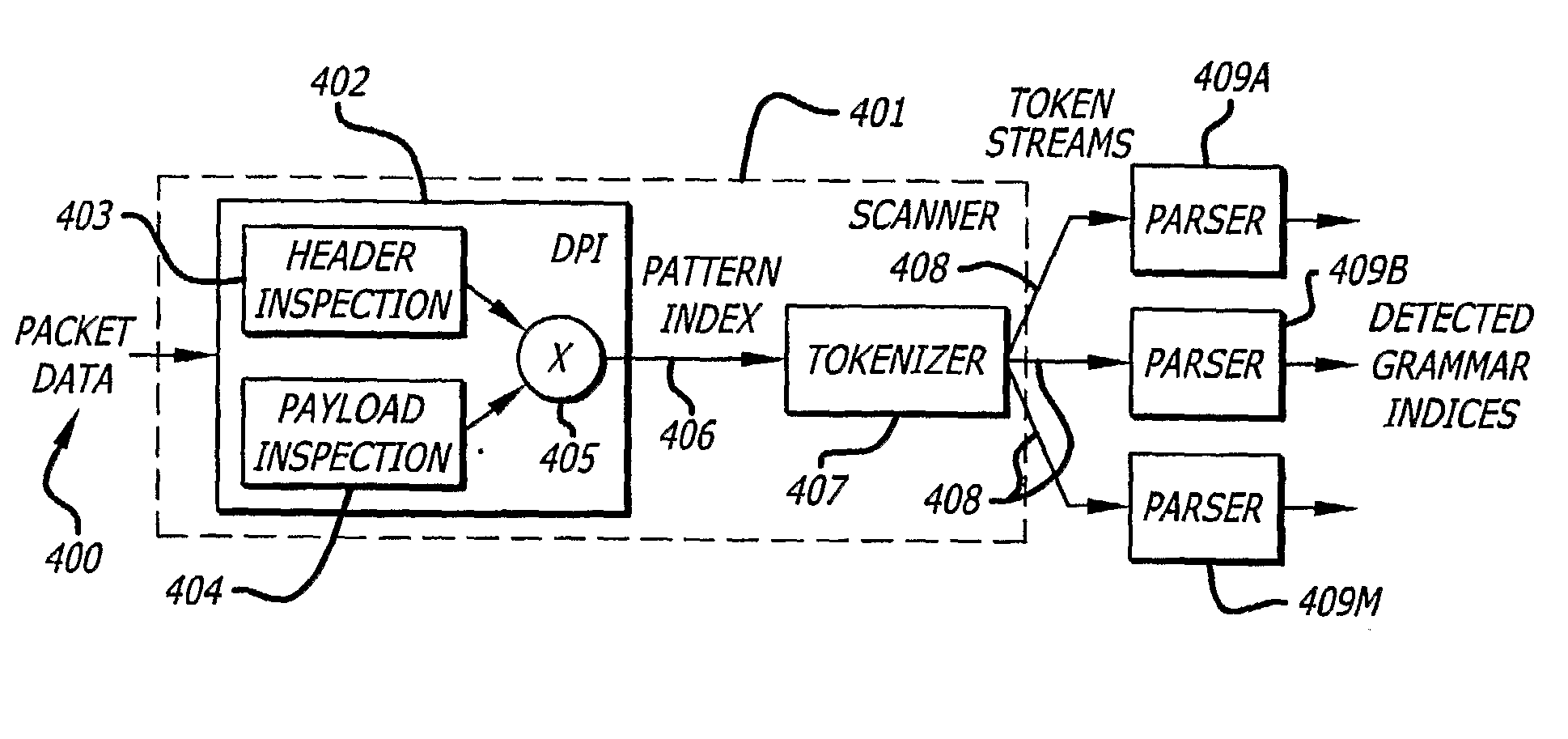
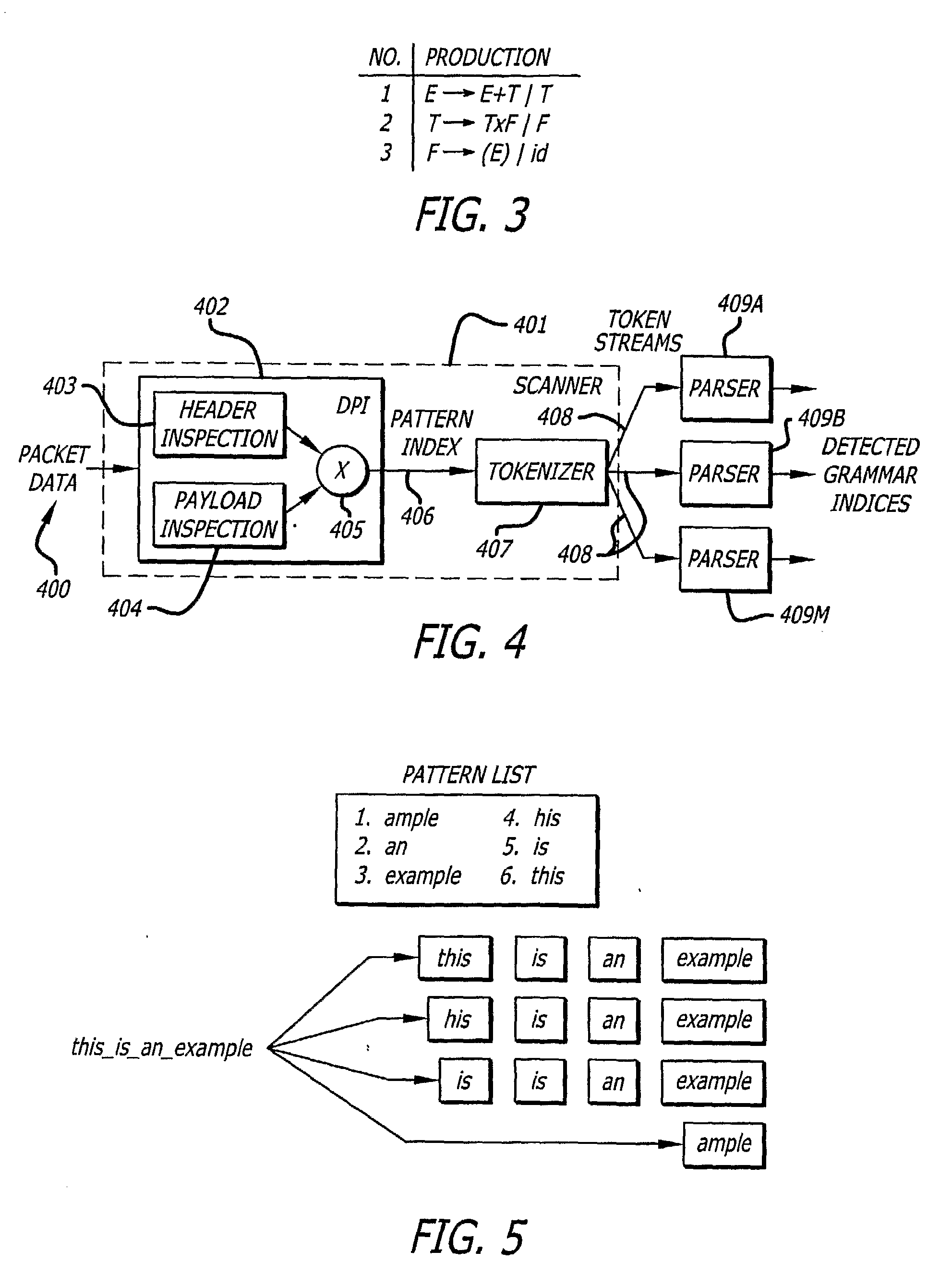
High-Performance Context-Free Parser for Polymorphic Malware Detection
The invention provides a method and apparatus for advanced network intrusion detection. The system uses deep packet inspection that can recognize languages described by context-free grammars. The system combines deep packet inspection with one or more grammar parsers (409A-409M). The invention can detect token streams (408) even when polymorphic. The system looks for tokens at multiple byte alignments and is capable of detecting multiple suspicious token streams (408). The invention is capable of detecting languages expressed in LL(I) or LR(I) grammar. The result is a system that can detect attacking code wherever it is located in the data stream (408).
Owner:CHO YOUNG H +1
Method and apparatus for embedding grammars in a natural language understanding (NLU) statistical parser
InactiveUS6983239B1Natural language data processingSpeech recognitionNatural language processingNatural language understanding
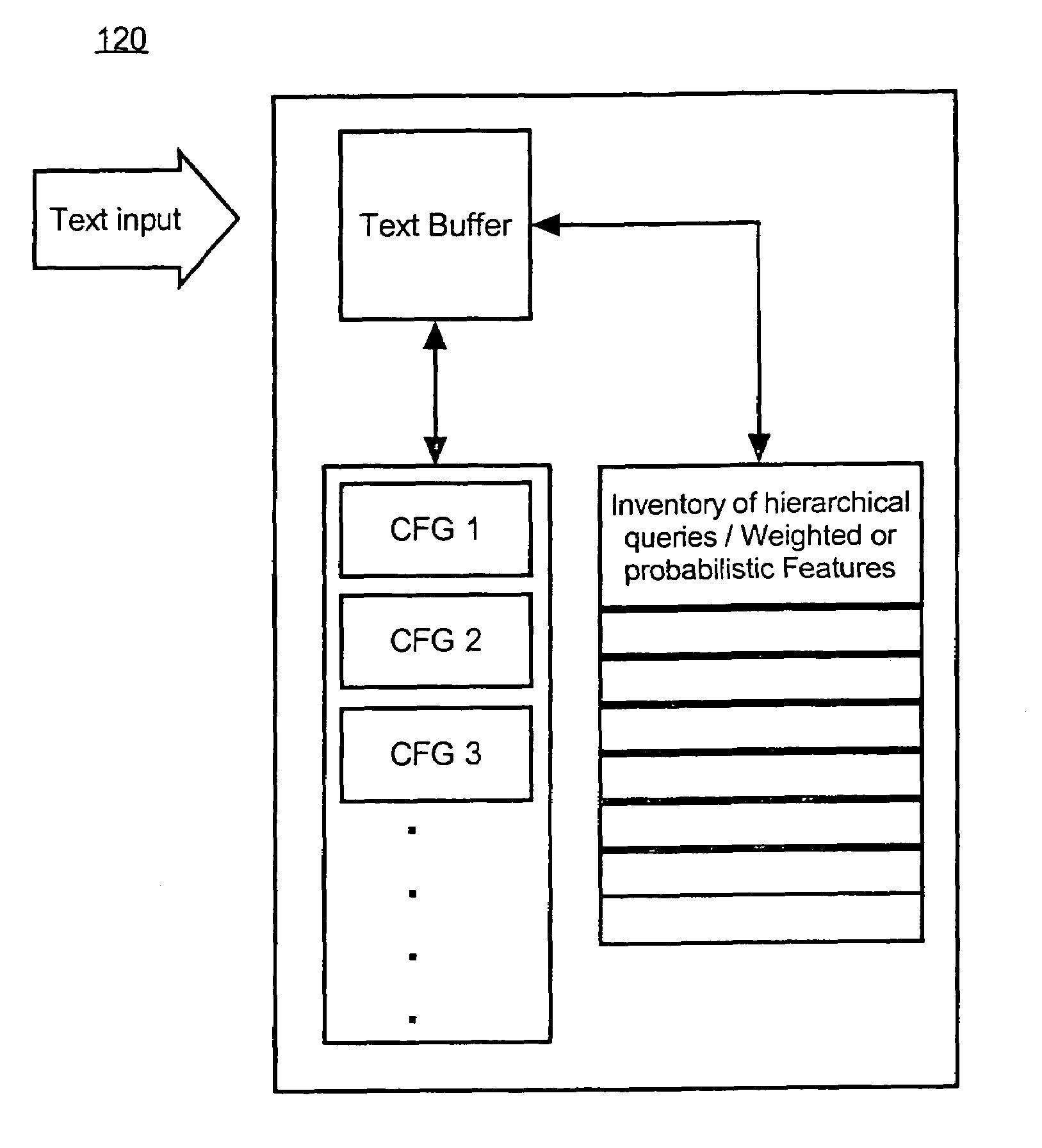
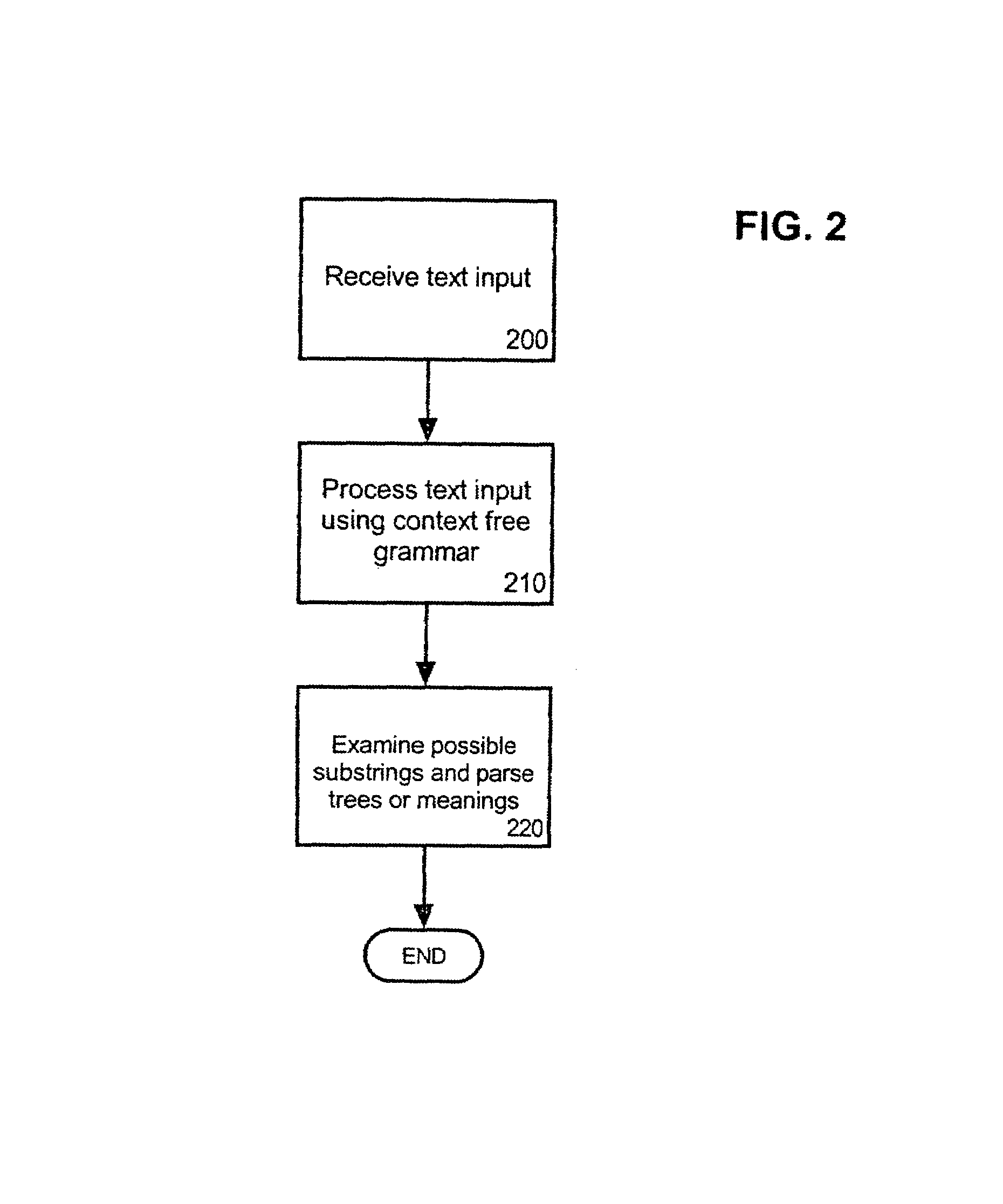
A method and system for use in a natural language understanding system for including grammars within a statistical parser. The method involves a series of steps. The invention receives a text input. The invention applies a first context free grammar to the text input to determine substrings and corresponding parse trees, wherein the substrings and corresponding parse trees further correspond to the first context free grammar. Additionally, the invention can examine each possible substring using an inventory of queries corresponding to the CFG.
Owner:IBM CORP
Adaptive Network Traffic Classification Using Historical Context
Adaptive network traffic classification using historical context. Network traffic may be monitored and classified by considering several attributes using packet filters, regular expressions, context-free grammars, rule sets, and / or protocol dissectors, among other means and by applying a variety of techniques such as signature matching and statistical analysis. Unlike static systems, the classification decisions may be reexamined from time to time or after subsequent processing determines that the traffic does not conform to the protocol specification corresponding to the classification decision. Historical context may be used to adjust the classification strategy for similar or related traffic.
Owner:EXTRAHOP NETWORKS
Adaptive network traffic classification using historical context
Adaptive network traffic classification using historical context. Network traffic may be monitored and classified by considering several attributes using packet filters, regular expressions, context-free grammars, rule sets, and / or protocol dissectors, among other means and by applying a variety of techniques such as signature matching and statistical analysis. Unlike static systems, the classification decisions may be reexamined from time to time or after subsequent processing determines that the traffic does not conform to the protocol specification corresponding to the classification decision. Historical context may be used to adjust the classification strategy for similar or related traffic.
Owner:EXTRAHOP NETWORKS
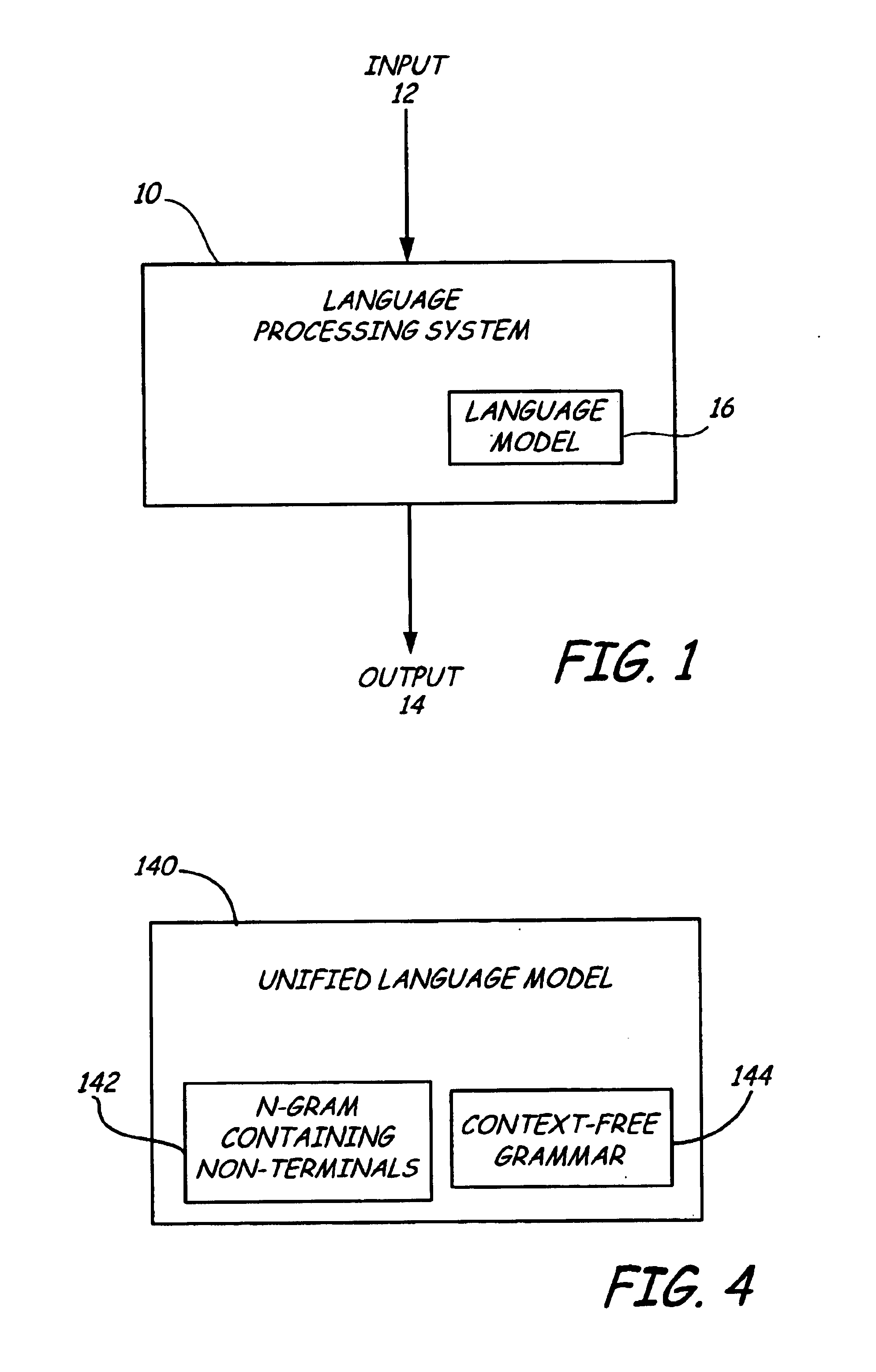
Use of a unified language model
A language processing system includes a unified language model. The unified language model comprises a plurality of context-free grammars having non-terminal tokens representing semantic or syntactic concepts and terminals, and an N-gram language model having non-terminal tokens. A language processing module capable of receiving an input signal indicative of language accesses the unified language model to recognize the language. The language processing module generates hypotheses for the received language as a function of words of the unified language model and / or provides an output signal indicative of the language and at least some of the semantic or syntactic concepts contained therein.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems, methods and computer program products for string analysis with security labels for vulnerability detection
InactiveUS7530107B1Suppress false detectionDetailed analysisMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionLocation detectionPre-condition
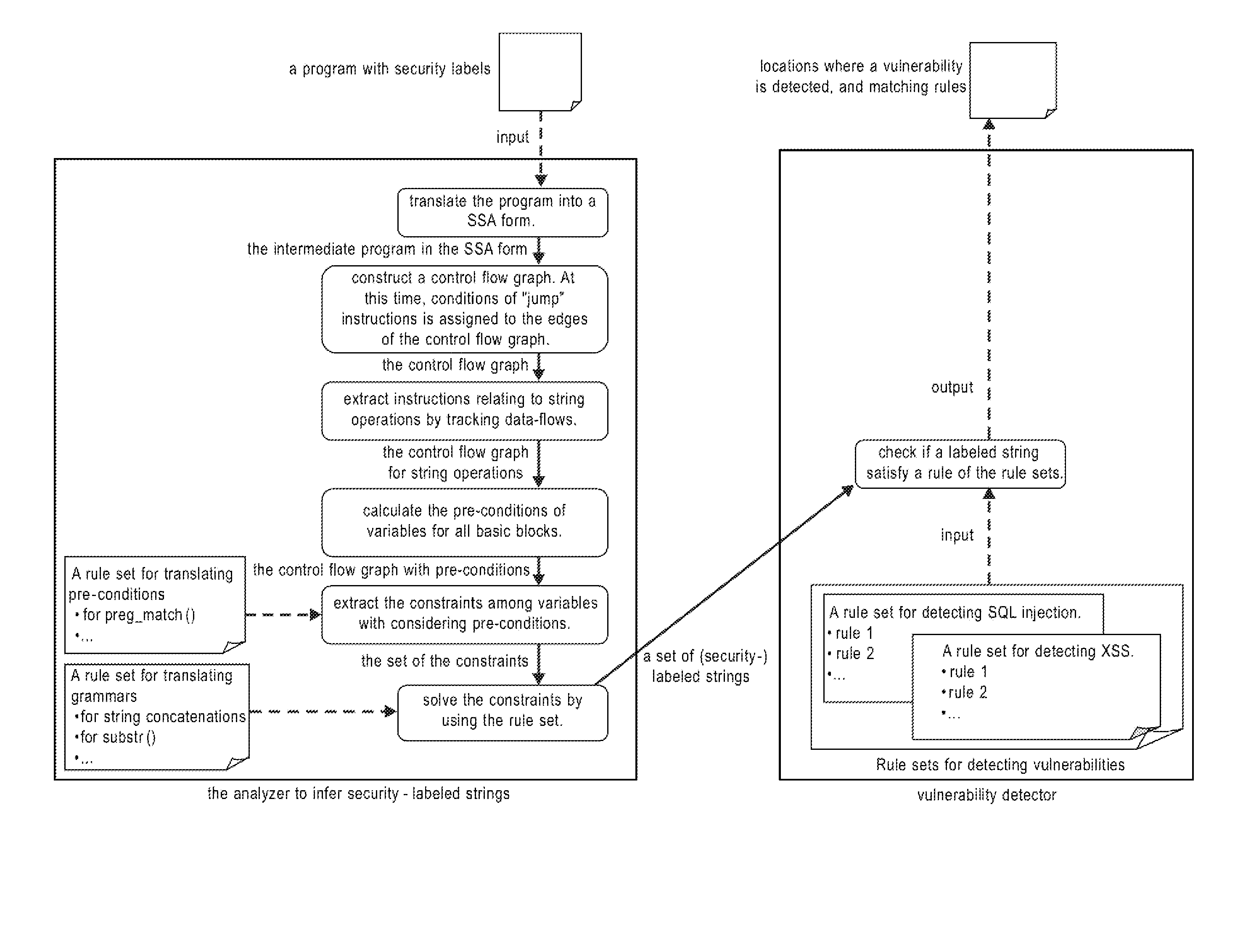
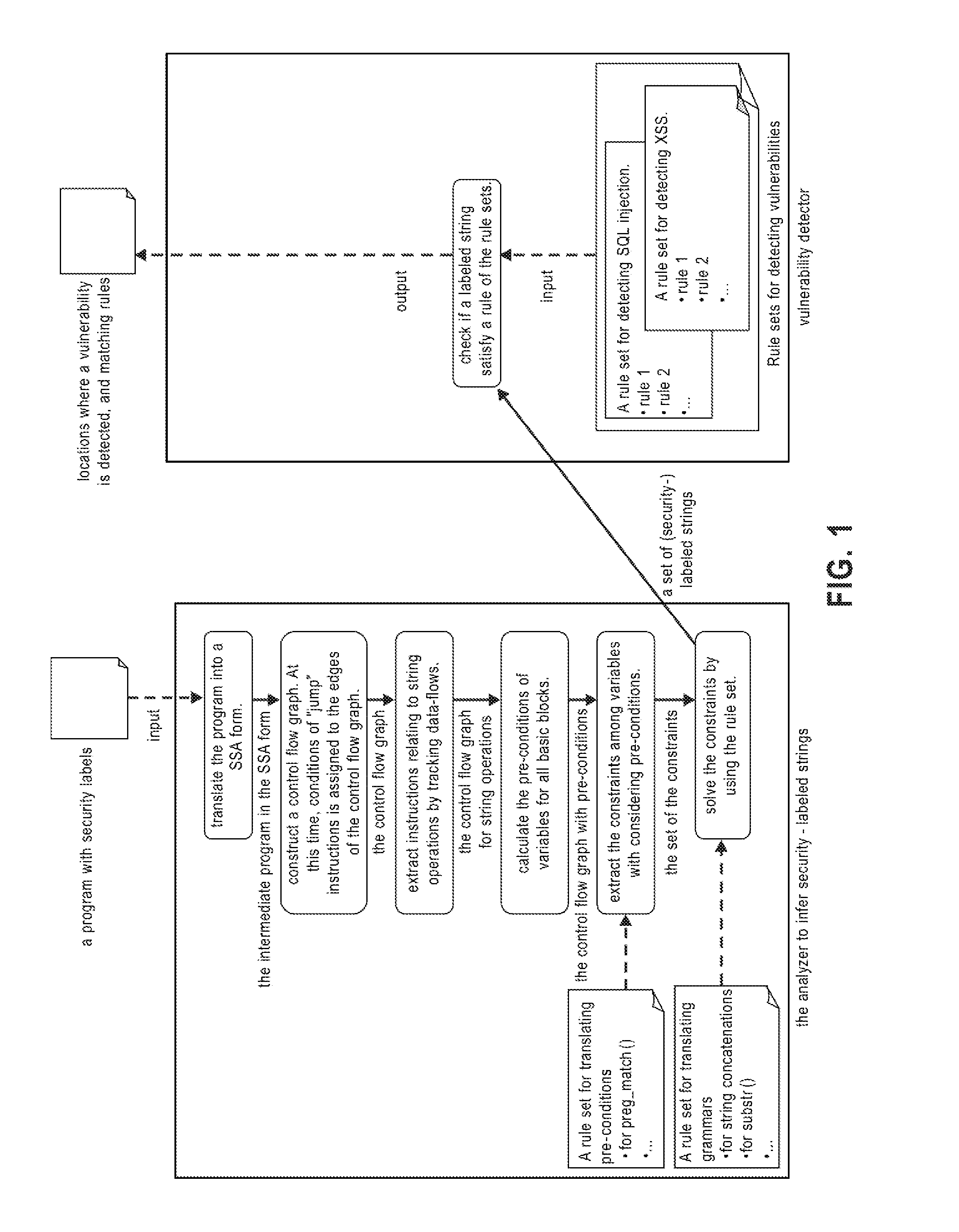
Systems, methods and computer program products for string analysis with security labels for vulnerability detection. Exemplary embodiments include a method in a computer system configured to analyze security-labeled strings and to detect vulnerability, the method including receiving a program with security labels, translating the program into a static single assignment form, constructing a control flow graph having basic blocks as nodes, extracting instructions relating to string functions and object variables, calculating pre-conditions of variables for the basic blocks, extracting constraints among the variables subject to a rule set for translating pre-conditions, solving the constraints and obtaining a set of strings that he object variables form as a context-free grammar to obtain a set of security-labeled strings, checking if the set of security-labeled strings satisfies a rule of the rule set for translating pre-conditions and identifying locations in the program where a vulnerability is detected.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for learning, recognizing and generalizing sequences
InactiveUS20070055662A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionData set
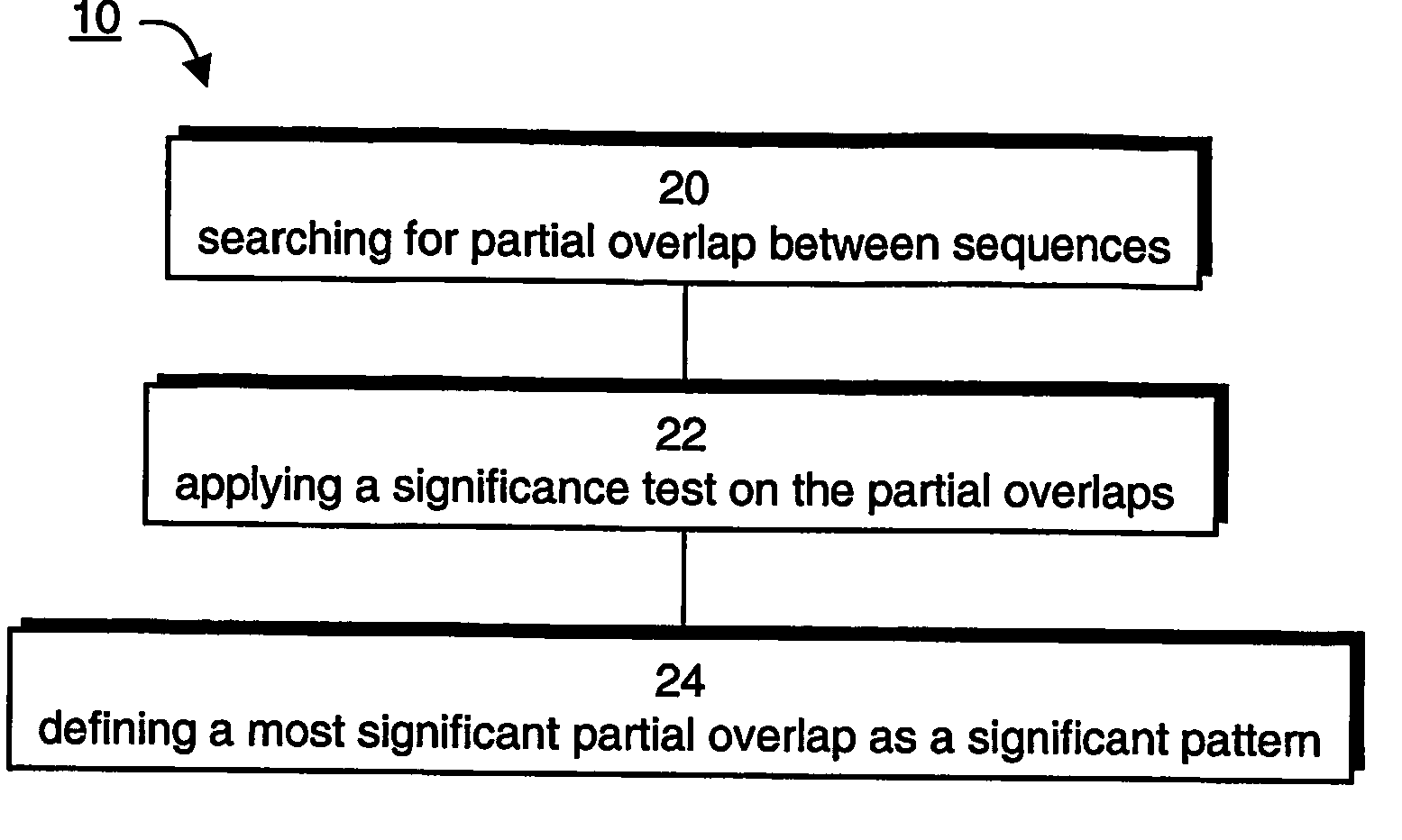
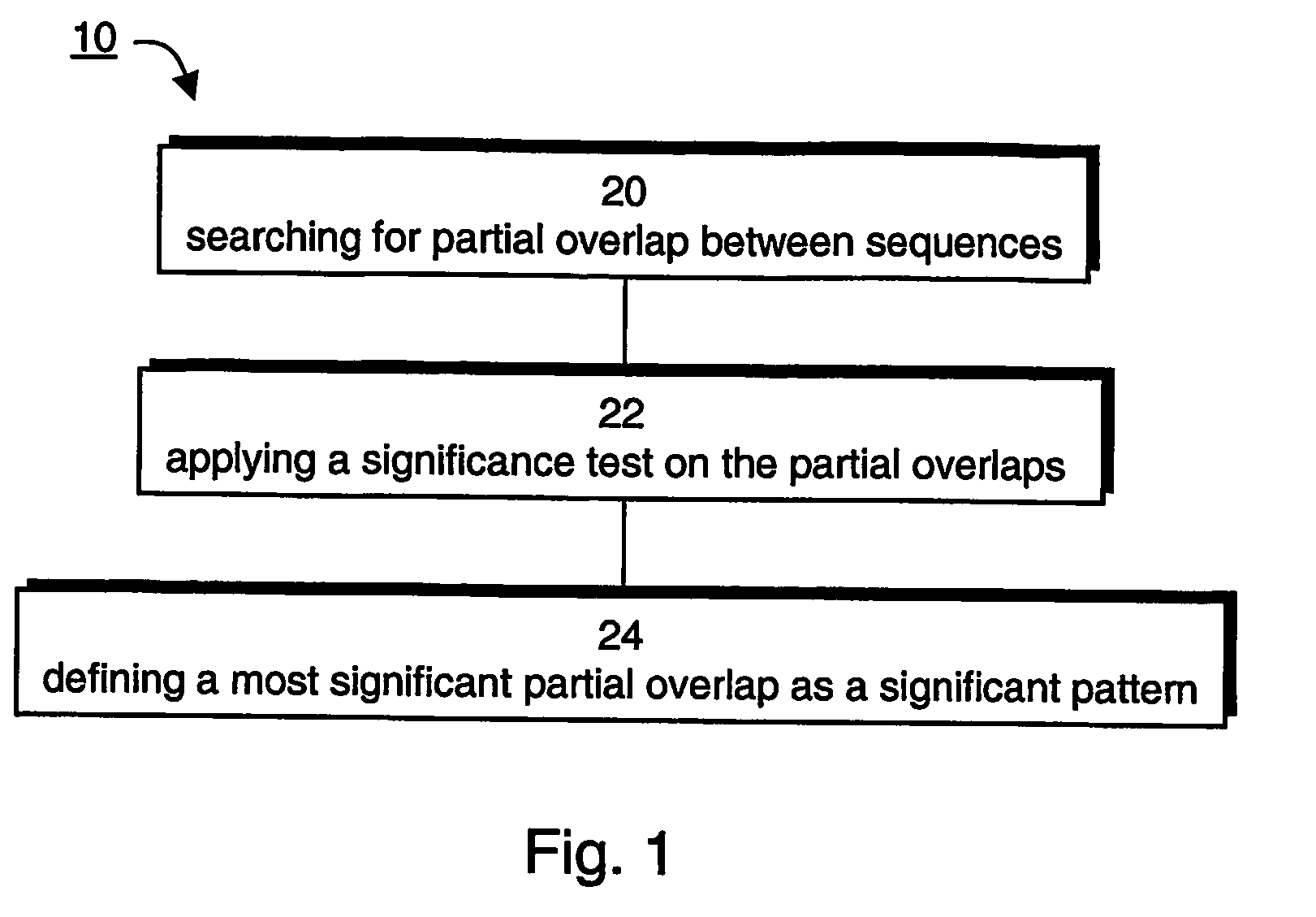
A method of generalizing a dataset having a plurality of sequences defined over a lexicon of tokens is provided. The method comprises: searching over the dataset for similarity sets, where each similarity set comprises a plurality of segments of size L having L−S common tokens and S uncommon tokens; and defining a plurality of equivalence classes corresponding to uncommon tokens of at least one similarity set. The method may further comprise a step in which a plurality of significant patterns are extracted, where each significant pattern corresponds to a most significant partial overlap between one sequence of the dataset and other sequences of the dataset. In one embodiment, a generalized dataset represented by a graph or a forest is constructed, and can be realized as a context-free grammar. The graph or forest can be used for generating sequences and / or testing grammatical structures.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Method and apparatus utilizing speech grammar rules written in a markup language
The present invention provides a method and apparatus that utilize a context-free grammar written in a markup language format. The markup language format provides a hierarchical format in which grammar structures are delimited within and defined by a set of tags. The markup language format also provides grammar switch tags that indicate a transitions from the context-free grammar to a dictation grammar or a text buffer grammar. In addition, the markup language format provides for the designation of code to be executed when particular grammar structures are recognized from a speech signal.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System for discovering data artifacts in an on-line data object
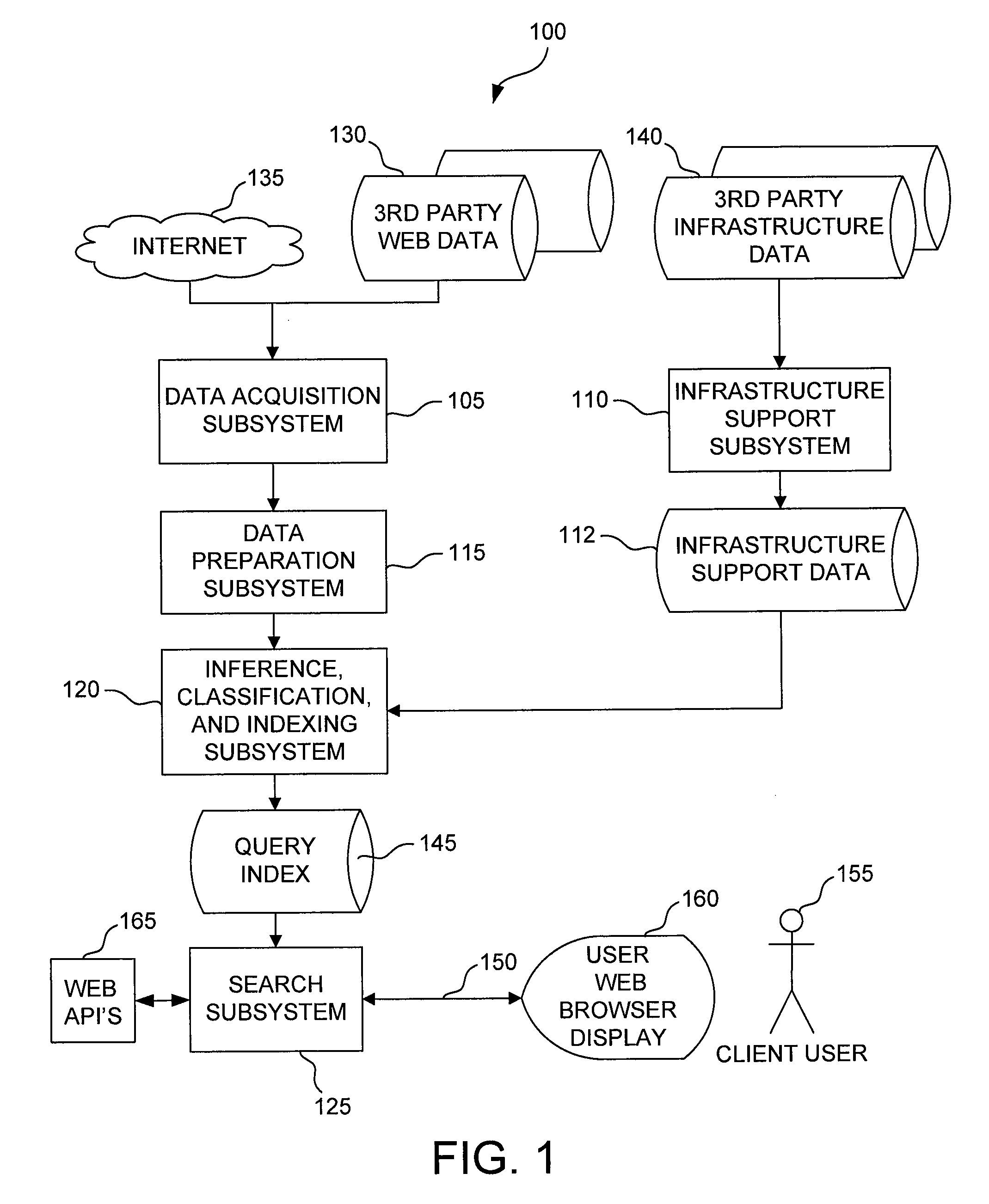
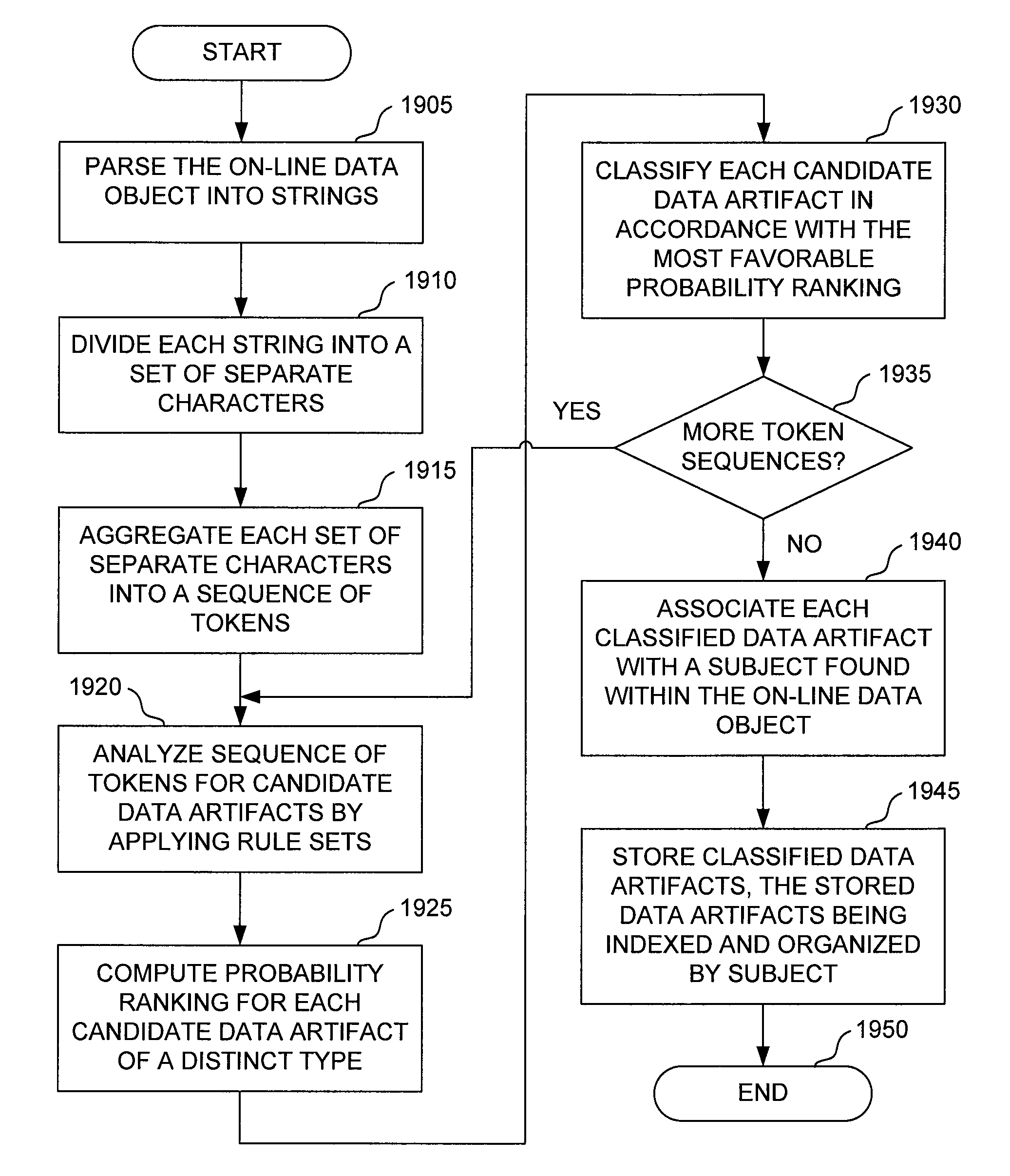
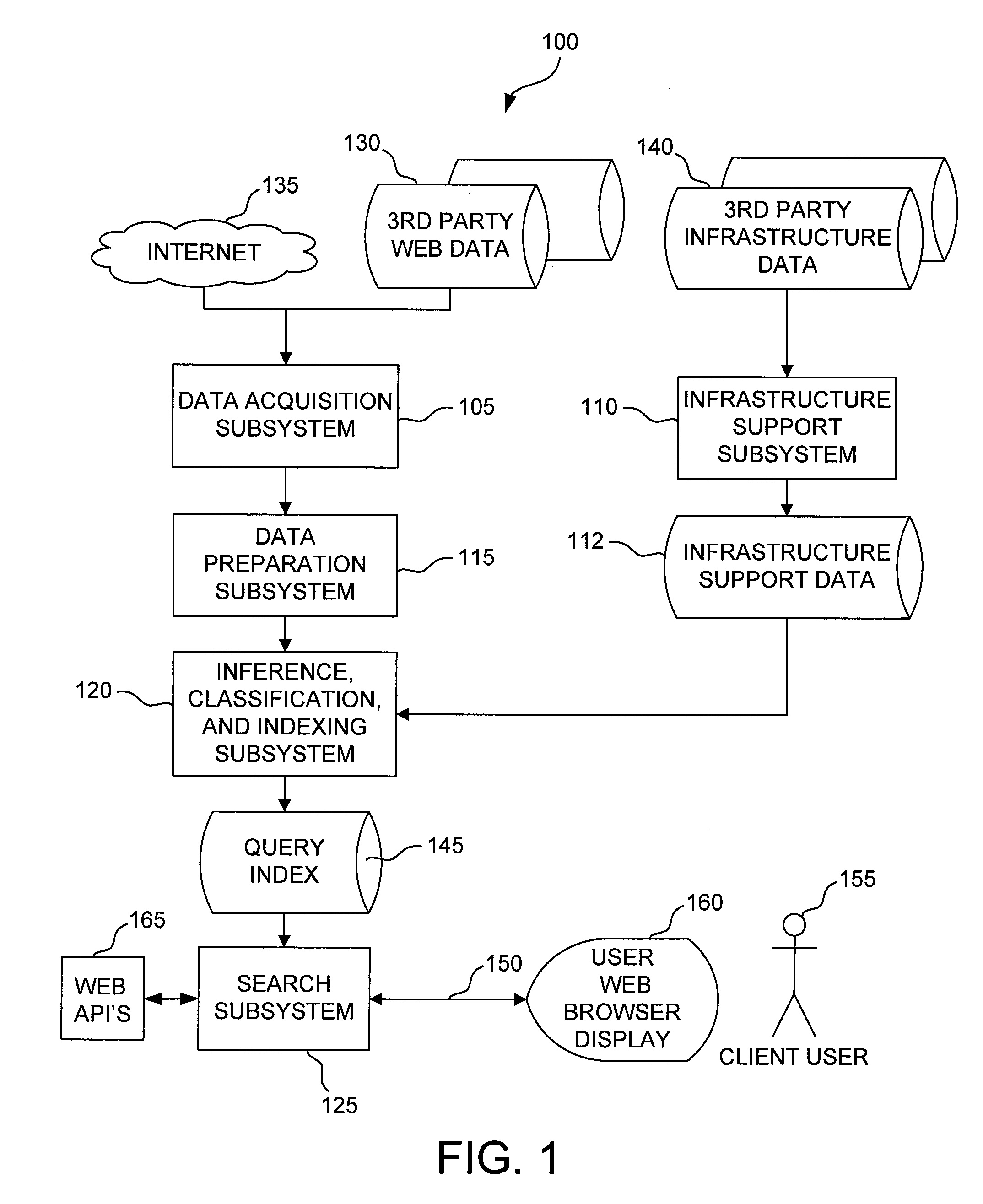
InactiveUS20080147642A1Web data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsContext-free grammarData objects
A system for discovering data artifacts in an on-line data object is described. One embodiment includes a data acquisition subsystem configured to parse the on-line data object into at least one string; a string pre-parser configured to divide each string into a set of separate characters; a lexical analyzer configured, for each set of separate characters, to aggregate the separate characters in that set of separate characters into a sequence of tokens, each token in the sequence of tokens being one of a word, a punctuation symbol, a HyperText-Markup-Language tag, and a number; a syntax analyzer configured, for each sequence of tokens during a first analysis phase, to determine, for each of a plurality of rule sets, whether the sequence of tokens includes one or more candidate data artifacts of a distinct type to which that rule set corresponds, each of the plurality of rule sets being adapted to discovery of the distinct type of data artifact to which that rule set corresponds, at least one rule set in the plurality of rule sets including a context-free grammar; compute, for each candidate data artifact of a distinct type, a probability ranking indicating a degree of likelihood that the candidate data artifact is a data artifact of that distinct type; and classify each candidate data artifact as a data artifact of the distinct type for which a most favorable probability ranking was computed for that candidate data artifact, the syntax analyzer being configured to associate with each classified data artifact a subject found within the on-line data object; and a storage subsystem including at least one data structure in which to store the classified data artifacts, the storage subsystem being configured to index and organize the classified data artifacts by subject for retrieval in response to a search query indicating a particular subject.
Owner:PROQUO
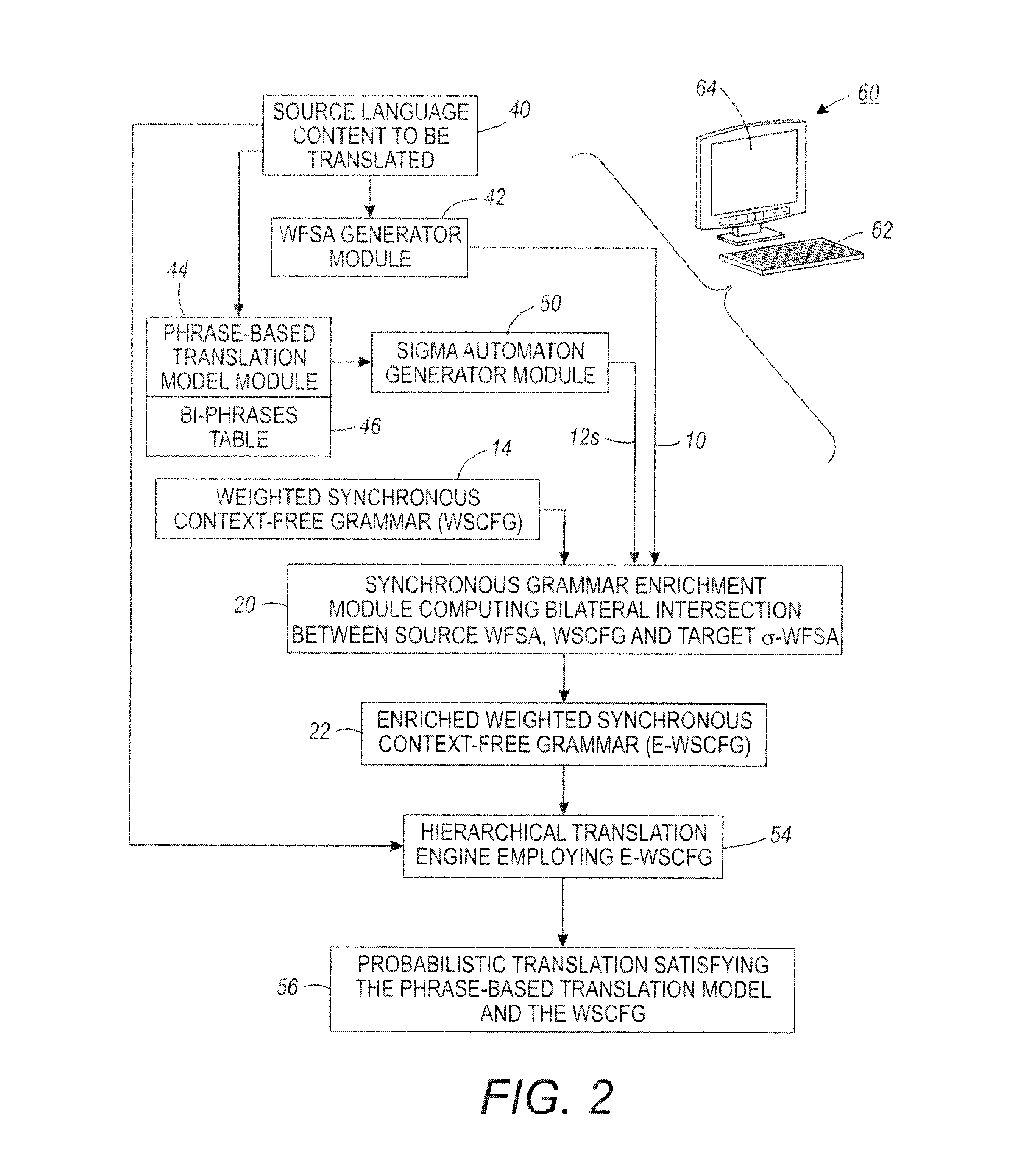
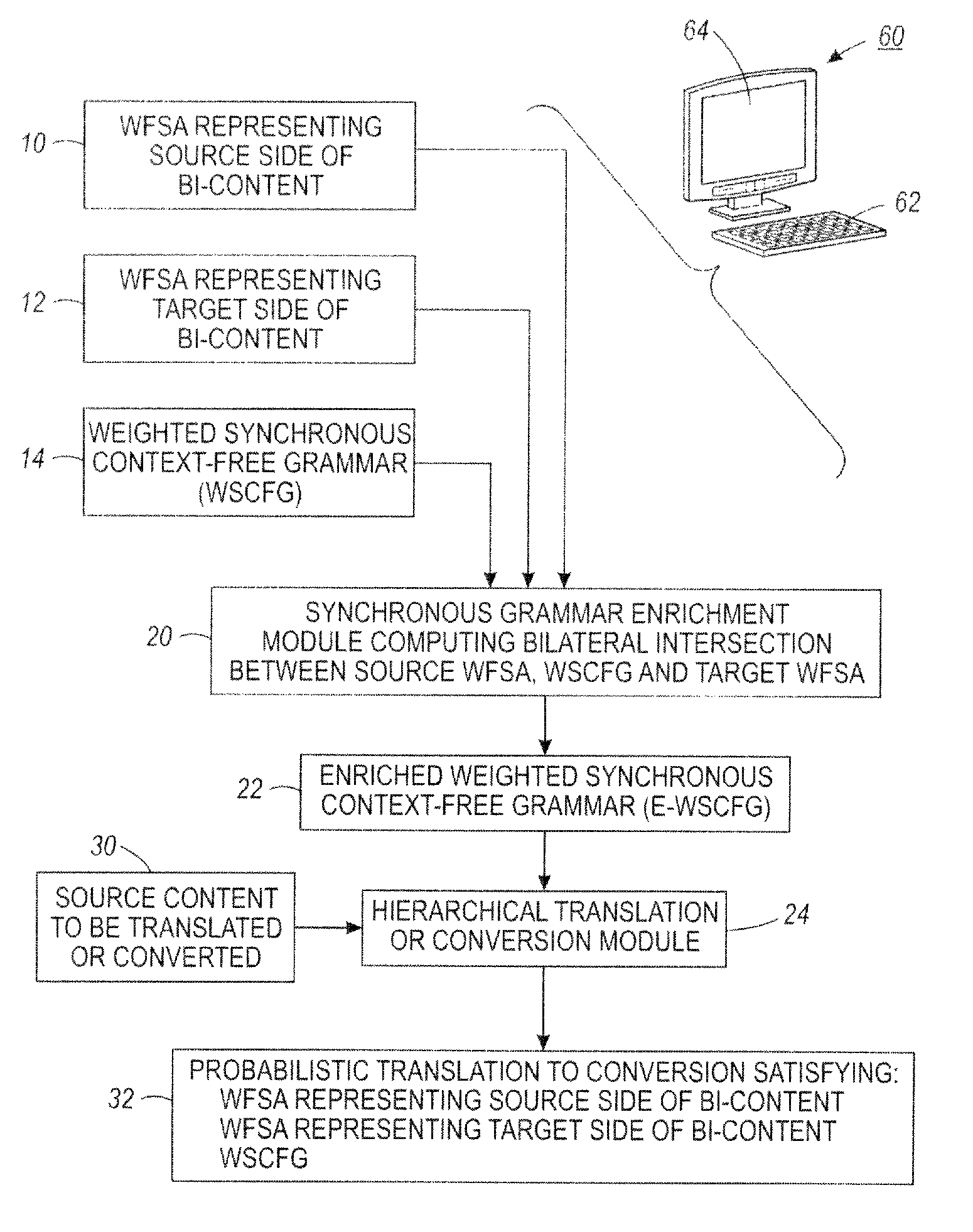
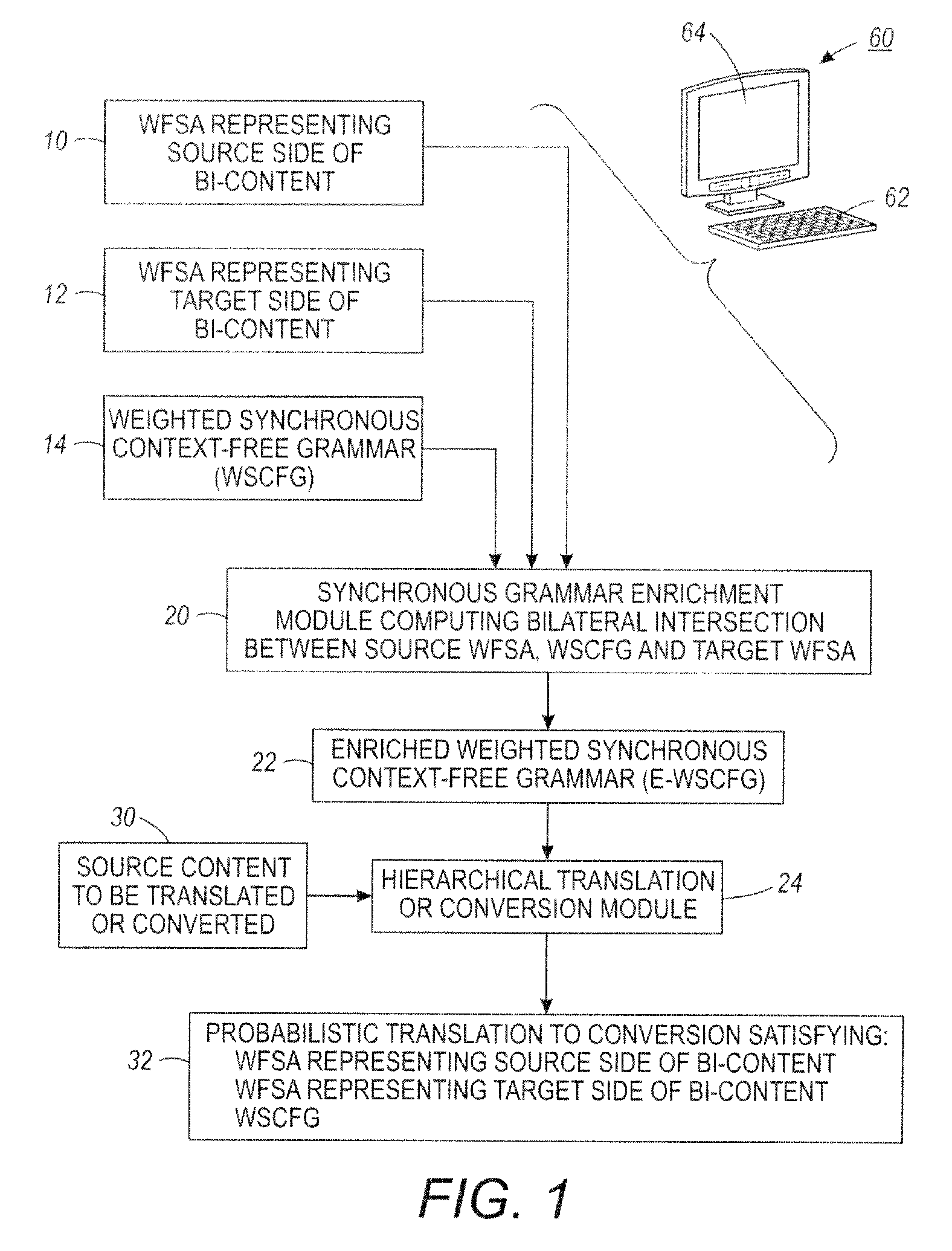
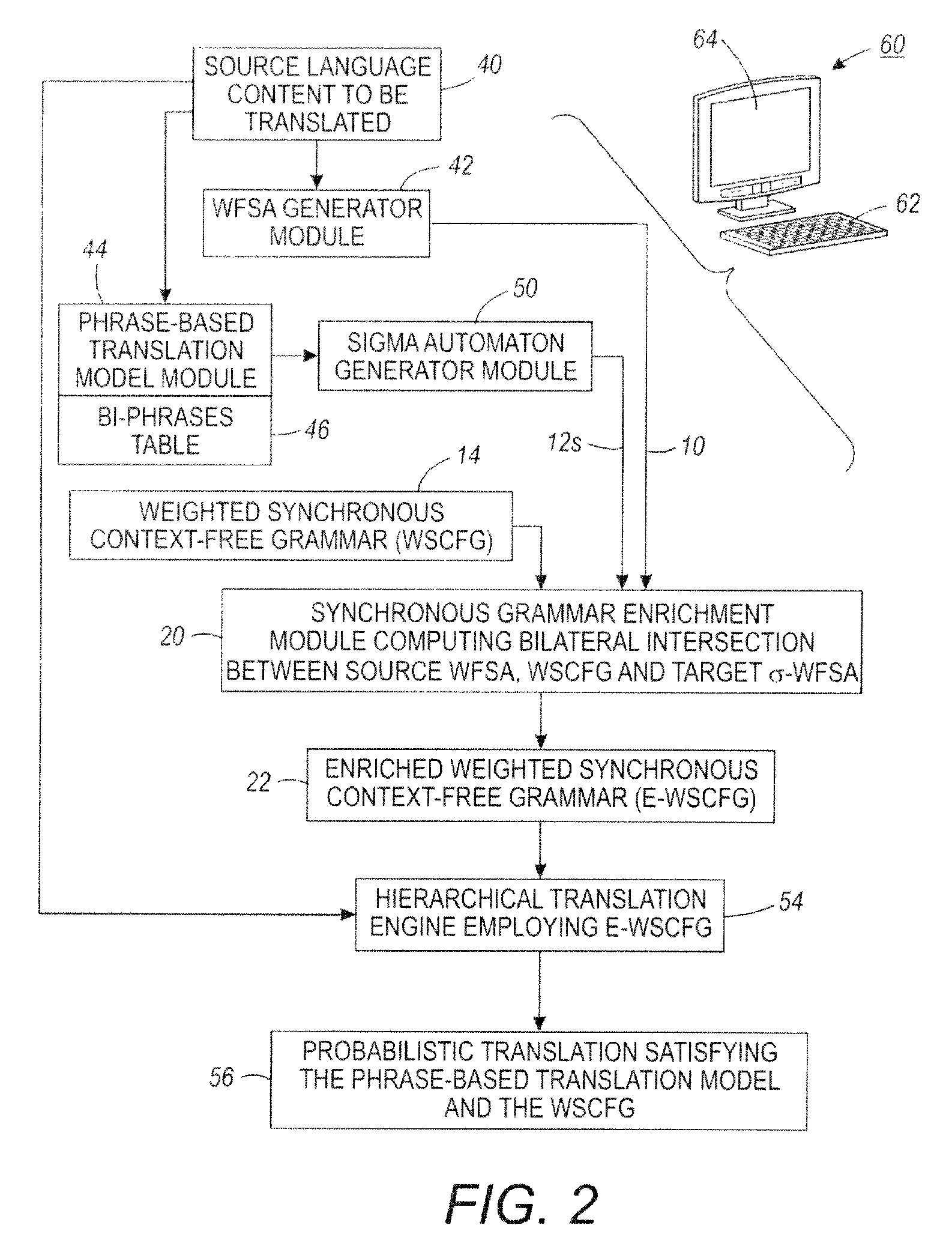
Translation system combining hierarchical and phrase-based models
InactiveUS20120041753A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsWeighted context-free grammarAutomaton
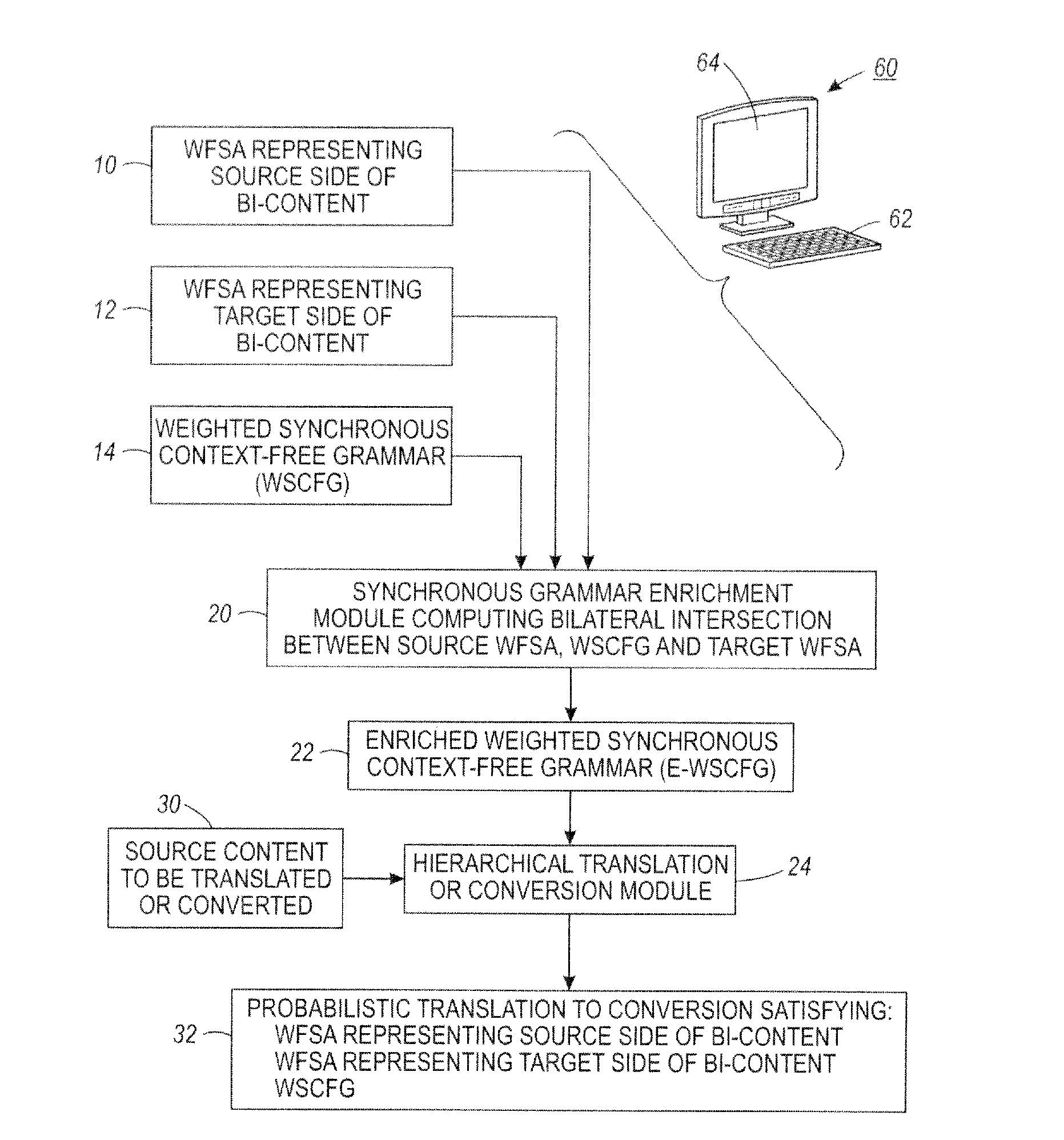
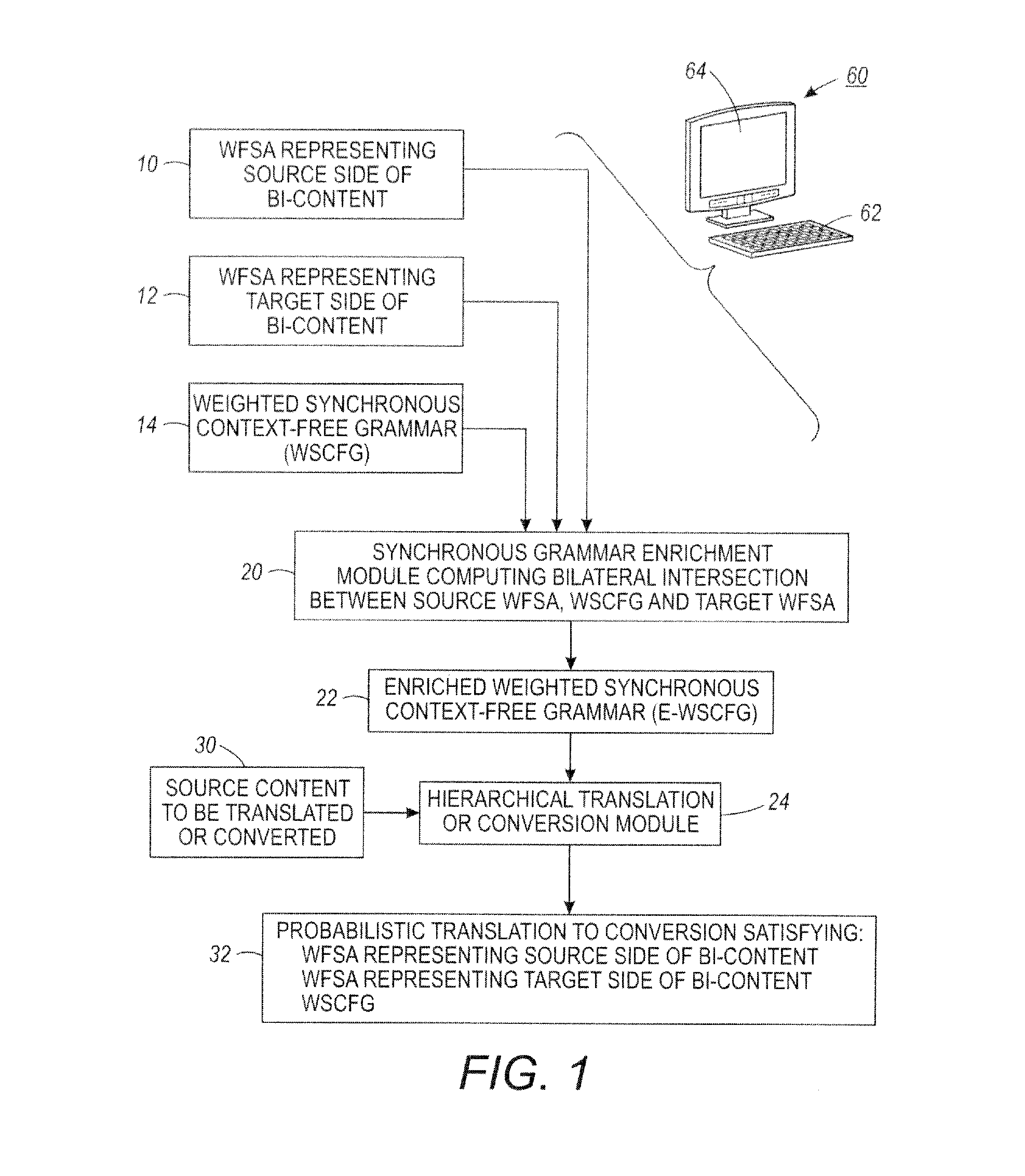
A method comprises: receiving or generating bi-content including source content in a source language or format and corresponding target content in a target language or format, wherein the target language or format is different from the source language or format; generating a source weighted finite state automaton representing the source content of the bi-content; generating a target weighted finite state automaton representing the target content of the bi-content; and computing a bilateral intersection between (i) the source weighted finite state automaton, (ii) a synchronous weighted context-free grammar comprising synchronized grammars for the source language or format and the target language or format, and (iii) the target weighted finite state automaton to generate an enriched synchronous weighted context free grammar.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Translation system combining hierarchical and phrase-based models
InactiveUS8543374B2Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsWeighted context-free grammarAutomaton
A method comprises: receiving or generating bi-content including source content in a source language or format and corresponding target content in a target language or format, wherein the target language or format is different from the source language or format; generating a source weighted finite state automaton representing the source content of the bi-content; generating a target weighted finite state automaton representing the target content of the bi-content; and computing a bilateral intersection between (i) the source weighted finite state automaton, (ii) a synchronous weighted context-free grammar comprising synchronized grammars for the source language or format and the target language or format, and (iii) the target weighted finite state automaton to generate an enriched synchronous weighted context free grammar.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and apparatus to use semantic inference with speech recognition systems
InactiveUS20050038650A1Speech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSpoken languageContext independent
A method and apparatus to use semantic inference with speech recognition systems includes recognizing at least one spoken word, processing the spoken word using a context-free grammar, deriving an output from the context-free grammar, and translating the output to a predetermined command.
Owner:APPLE INC
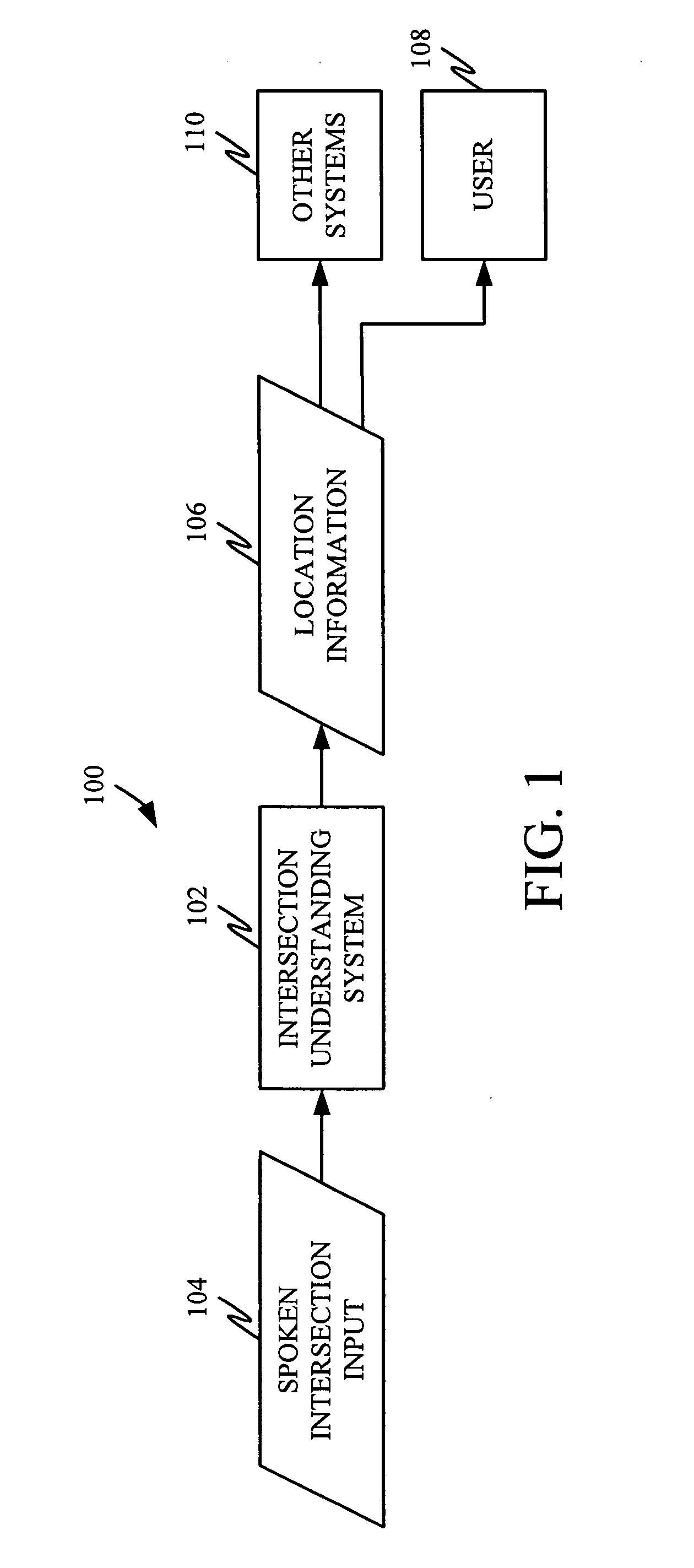
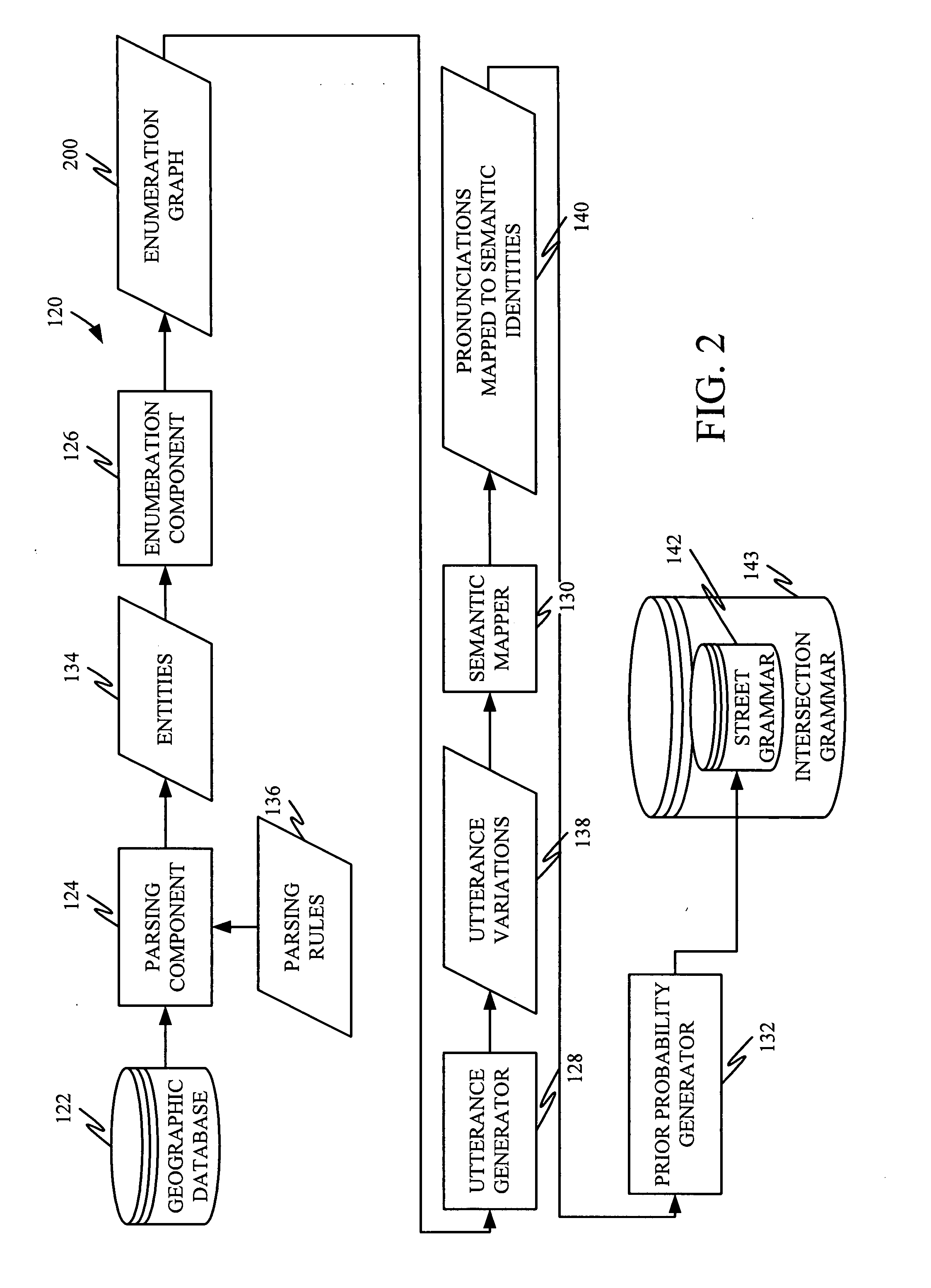
Understanding spoken location information based on intersections
ActiveUS20090037174A1Easy for userDisambiguation potentially much simplerSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPosition dependentSpeech input
In one embodiment, the present system recognizes a user's speech input using an automatically generated probabilistic context free grammar for street names that maps all pronunciation variations of a street name to a single canonical representation during recognition. A tokenizer expands the representation using position-dependent phonetic tokens and an intersection classifier classifies an intersection, despite the presence of recognition errors and incomplete street names.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
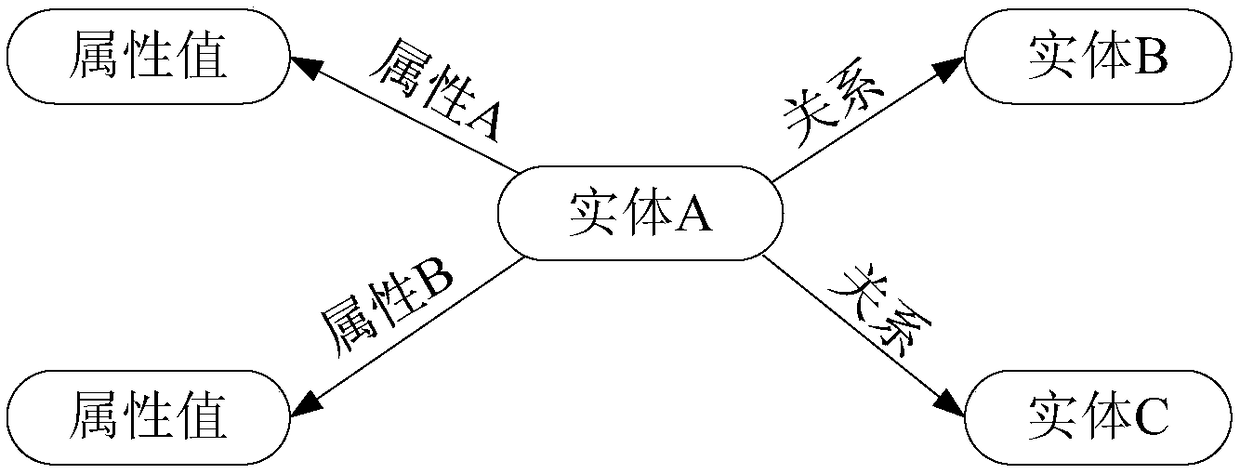
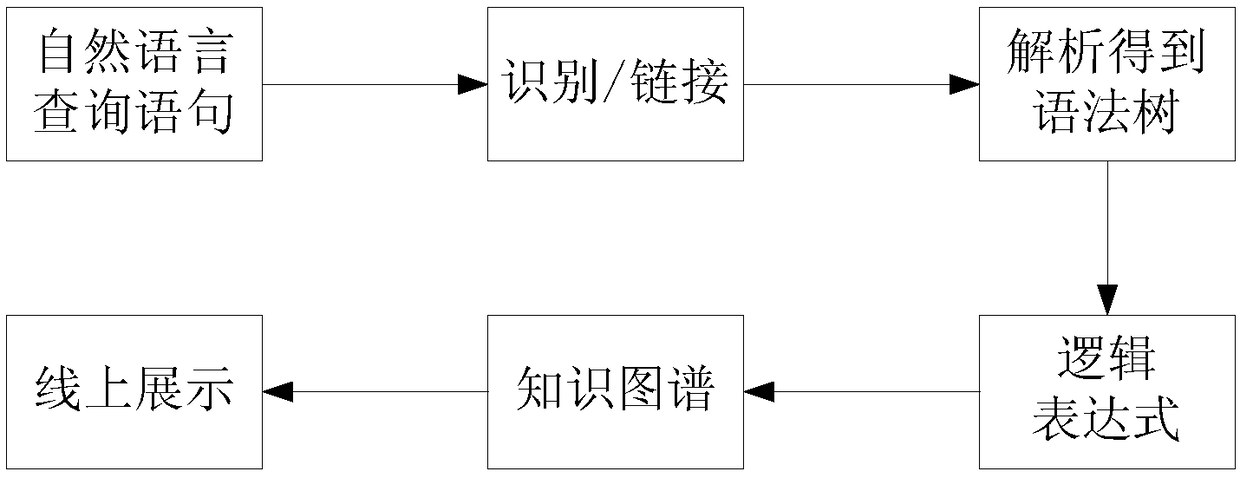
Question and answer method and apparatus based on knowledge map
InactiveCN108268580AAccurate Q&A resultsRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsUser inputQuestions and answers
The present invention provides a question and answer method and apparatus based on a knowledge map. The method comprises: obtaining a natural query statement input by a user, and identifying globallyunique identifiers GUIDs of entities in the natural query statement for the knowledge map, wherein the knowledge map comprises attributes and attribute values of entities and the relationship betweenthe entities; according to the context-free grammar rule, parsing the natural query statement into a syntax tree, and obtaining a logical expression corresponding to the natural query statement according to the syntax tree; generating a machine query statement corresponding to the knowledge map according to the logical expression and the GUIDs of the entities; and according to the machine query statement, querying a question and answer result corresponding to the machine query statement in the knowledge map, and feeding back the question and answer result to the user. According to embodimentsof the present invention, an accurate question and answer result can be obtained for the question and answer.
Owner:ALIBABA (CHINA) CO LTD
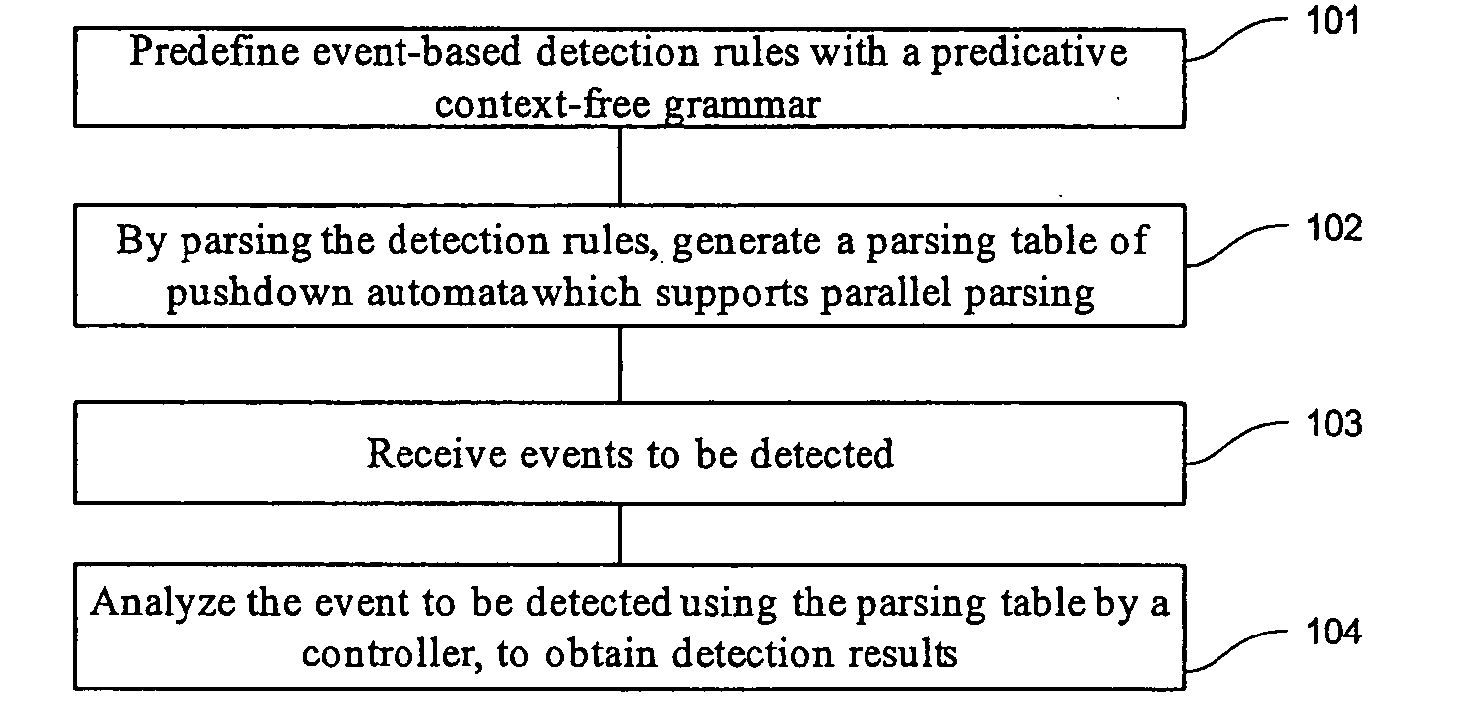
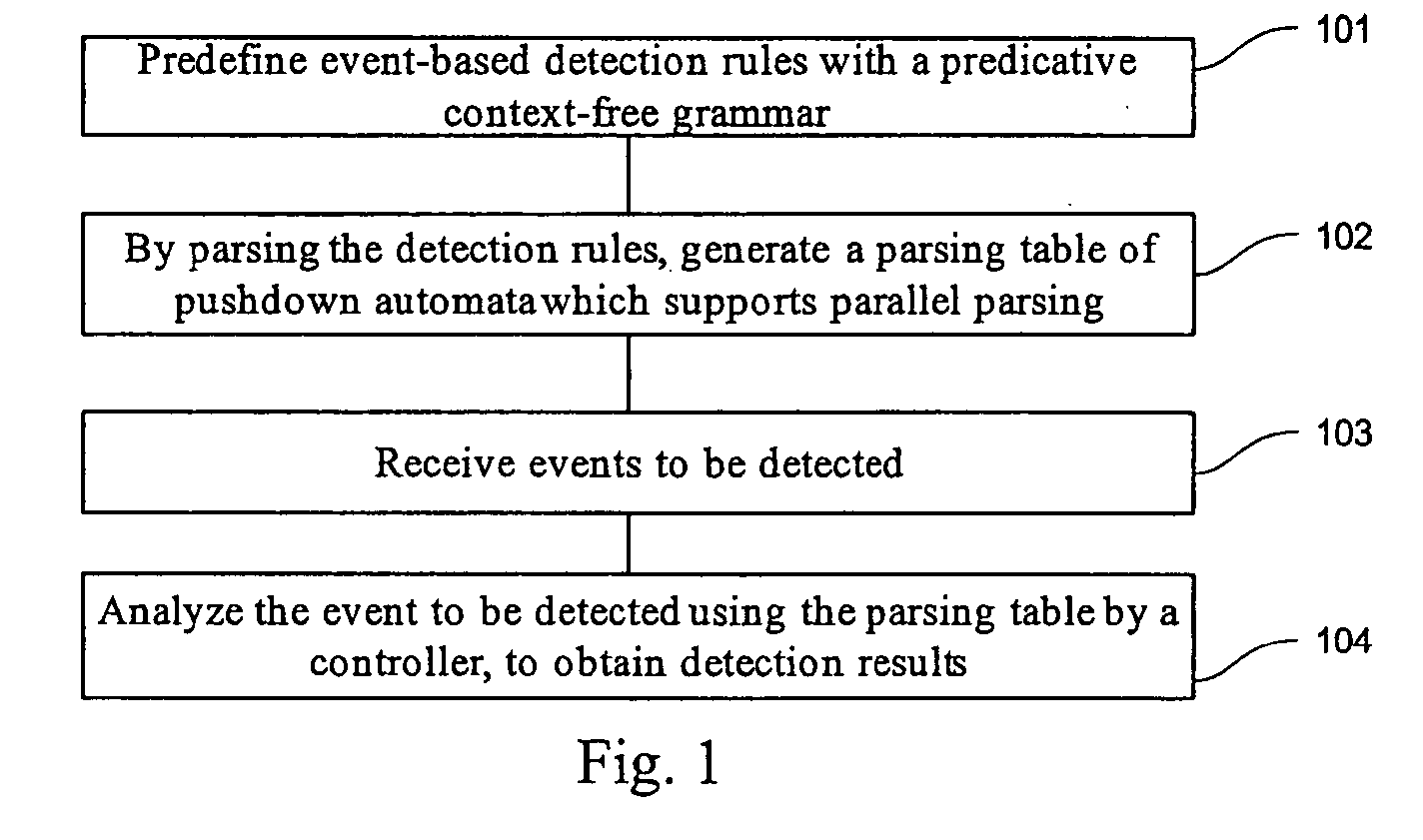
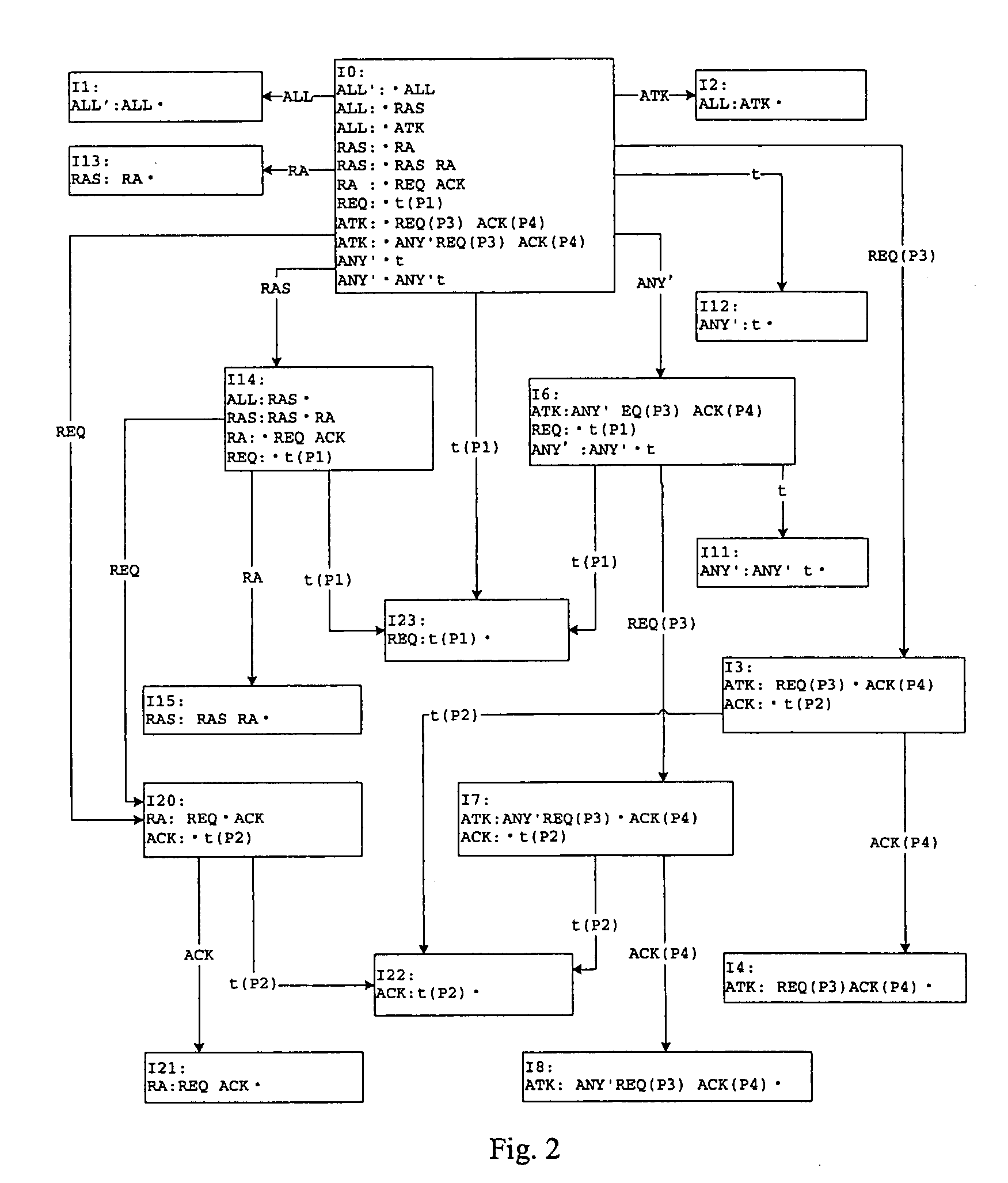
Event detection method
InactiveUS20080010680A1Improve acceleration performanceImprove efficiencyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionPushdown automatonAlgorithm
The embodiments of the present invention disclose an event detection method and device. The method includes: predefining event-based detection rules with a predicative context-free grammar; generating by parsing the detection rules a parsing table of pushdown automaton which supports parallel parsing; receiving an event to be detected; and analyzing by a controller the event to be detected according to the parsing table, to obtain a detection result. The present invention is especially applicable to detection of network attack events. The embodiments of the present invention detect the attacks with a predicative context-free grammar on the basis of events, and ensure a close combination of a protocol parsing process and an attack detection process, as well as a close combination of multiple attack detection rules, thus decreasing unnecessary calculations. In addition, with an optimized parallel pushdown automaton, the embodiments of the present invention can efficiently analyze the predicative context-free grammar. Consequently, besides hierarchical processing capability and state description capability, the embodiments of the present invention deliver high efficiency.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
Method for discovering data artifacts in an on-line data object
A method for discovering data artifacts in an on-line data object is described. One embodiment parses the on-line data object into at least one string; divides each string into a set of separate characters; for each set of separate characters, aggregates the separate characters in that set of separate characters into a sequence of tokens, each token in the sequence of tokens being one of a word, a punctuation symbol, a HyperText-Markup-Language tag, and a number; for each sequence of tokens during a first analysis phase, determines, for each of a plurality of rule sets, whether the sequence of tokens includes one or more candidate data artifacts of a distinct type to which that rule set corresponds, each of the plurality of rule sets being adapted to discovery of the distinct type of data artifact to which that rule set corresponds, at least one rule set in the plurality of rule sets including a context-free grammar; computes, for each candidate data artifact of a distinct type, a probability ranking indicating a degree of likelihood that the candidate data artifact is a data artifact of that distinct type; and classifies each candidate data artifact as a data artifact of the distinct type for which a most favorable probability ranking was computed for that candidate data artifact; associates with each classified data artifact a subject found within the on-line data object; and stores the classified data artifacts in a storage subsystem that includes at least one data structure, the classified data artifacts in the storage subsystem being indexed and organized by subject for retrieval in response to a search query indicating a particular subject.
Owner:PROQUO
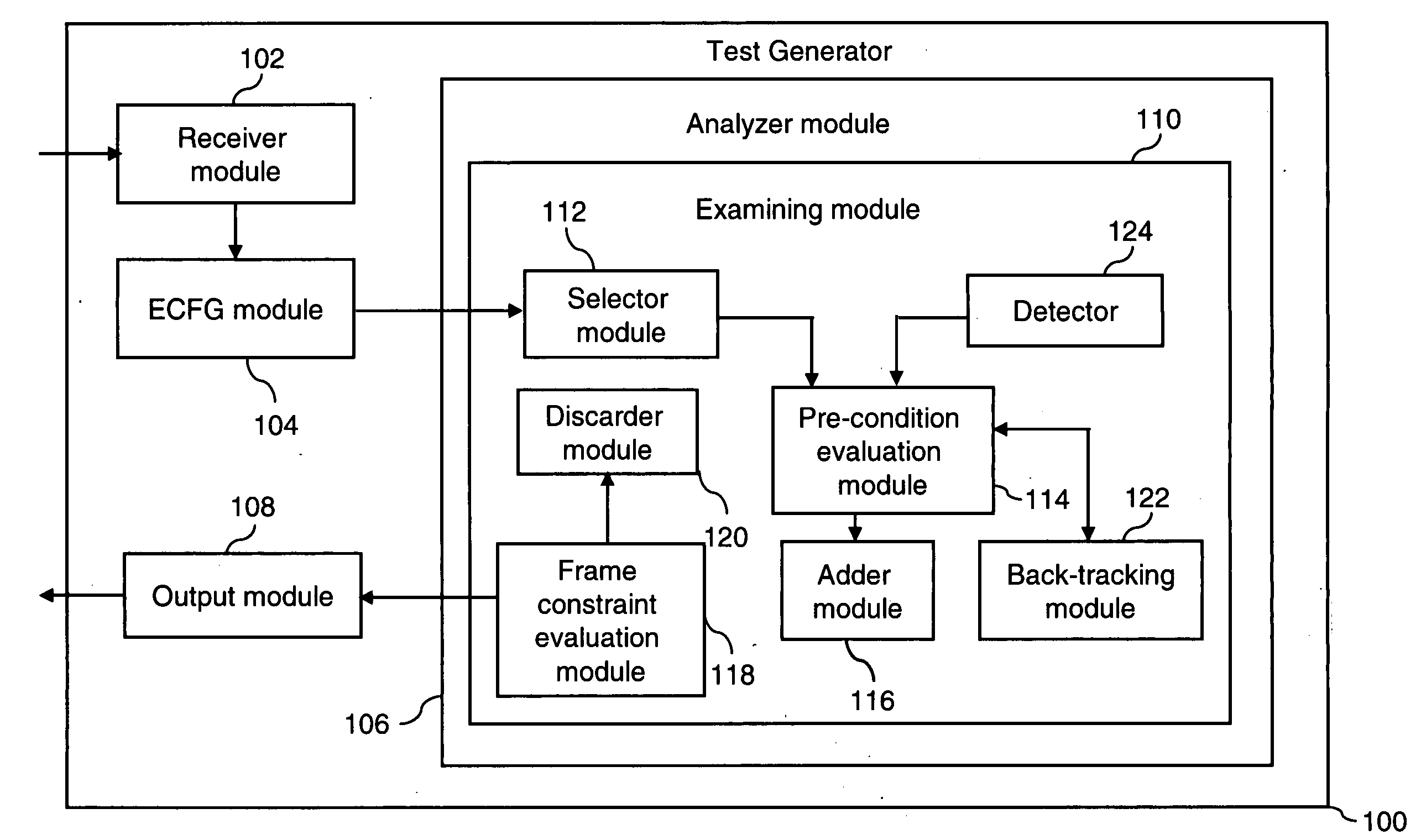
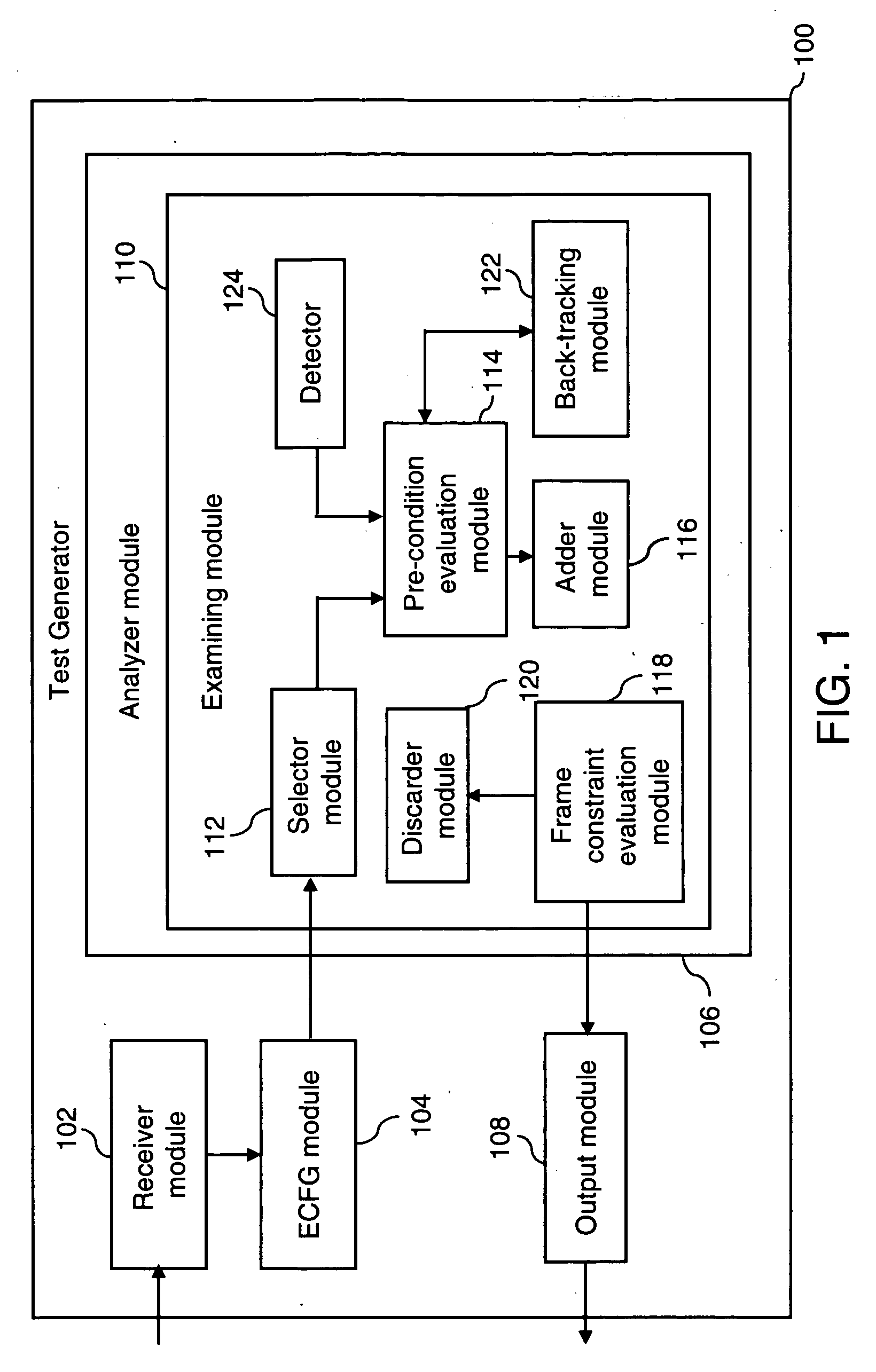
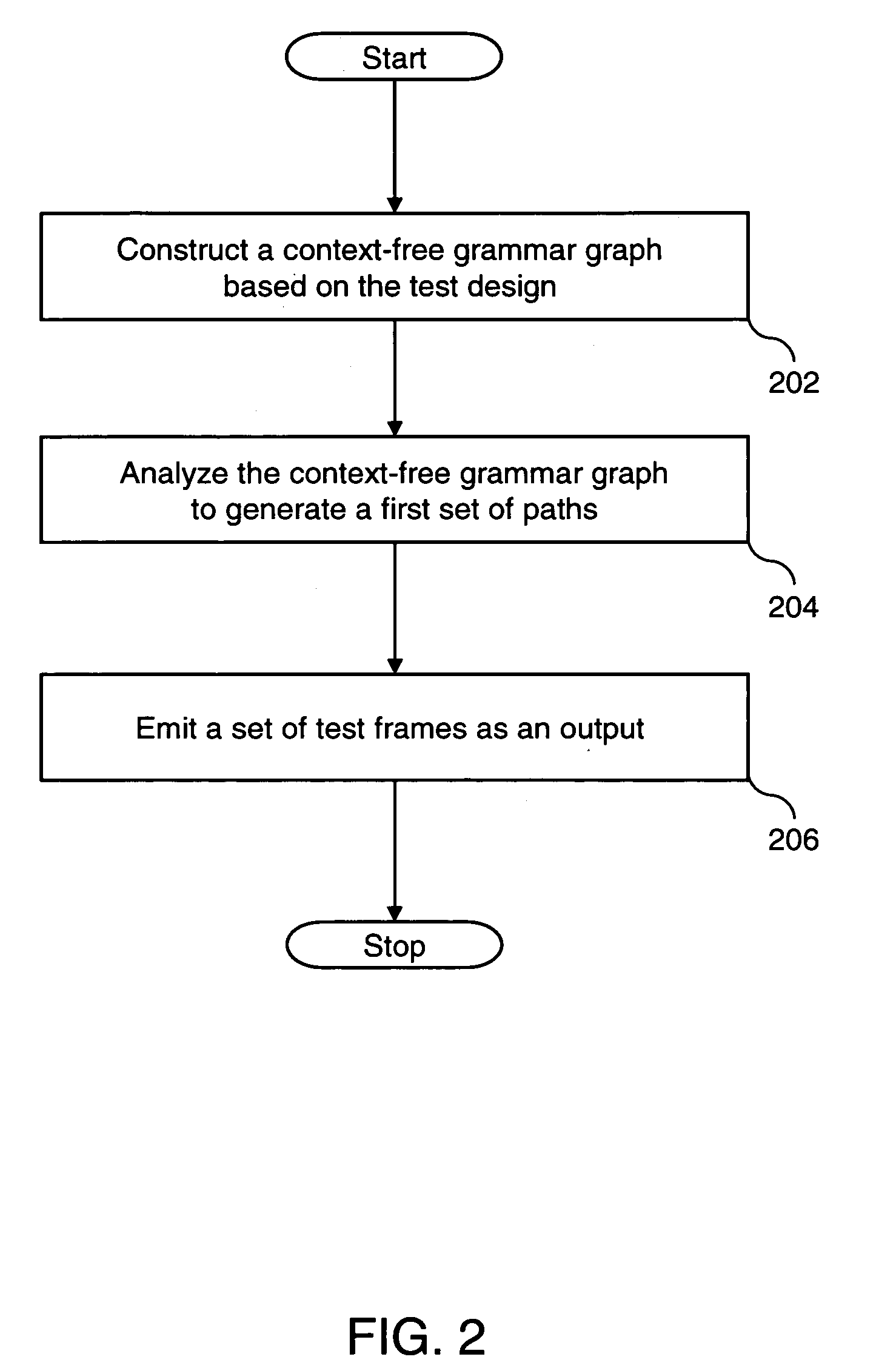
Path coverage criterion in specification-based testing based on an extended context-free grammar-based test specification model and a new test generation algorithm
InactiveUS20060214948A1Reduces frequent back-trackingError detection/correctionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTest designTest specification
A system and method for generating test frames in specification-based testing by using a path-coverage criterion is provided. The method includes receiving a test design as an input, and constructing a context-free grammar graph, based on the test design. The method further includes analyzing the context-free grammar graph to generate a first set of paths, and emitting a set of test frames as an output, based on the first set of paths.
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION SYSTEMS LTD
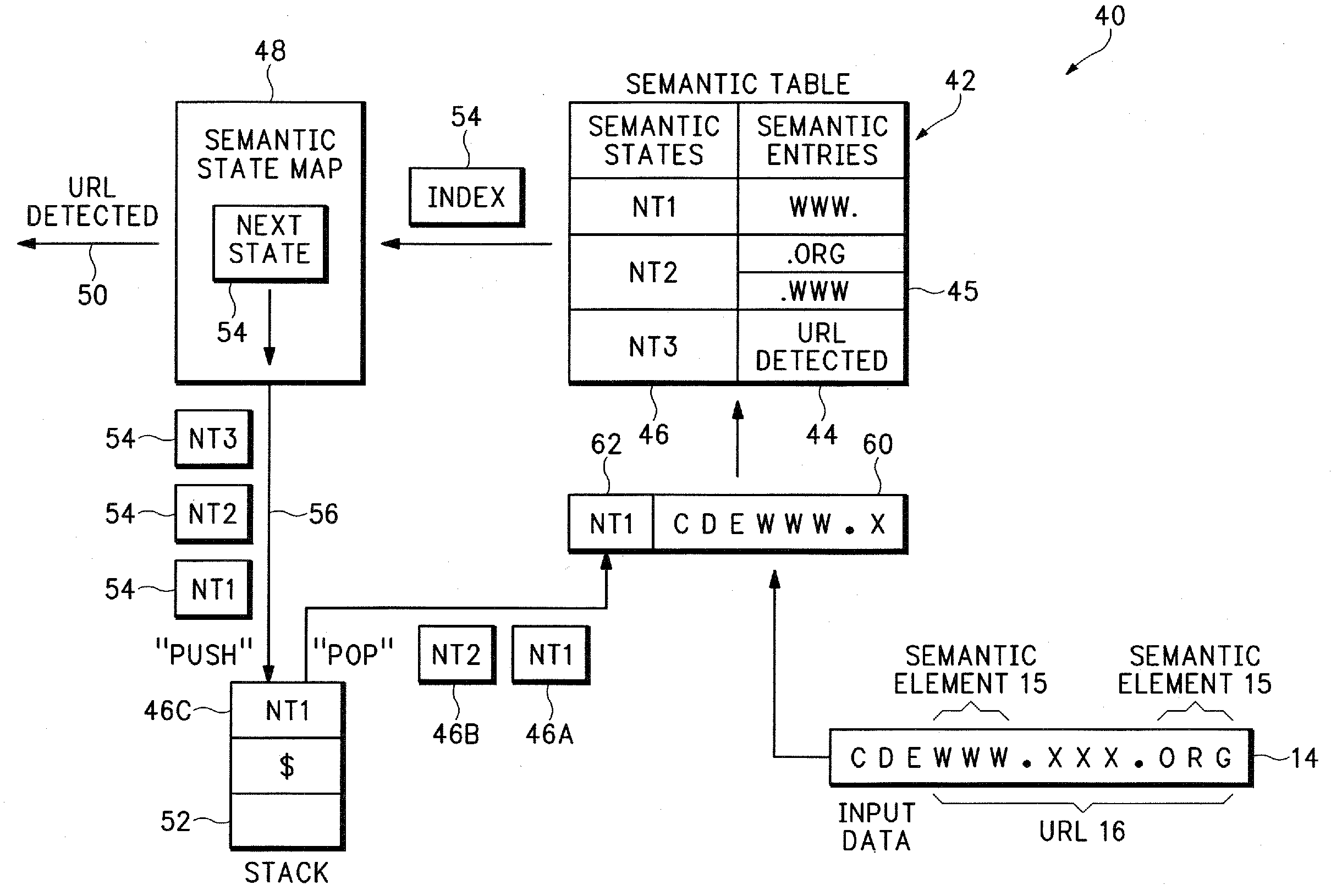
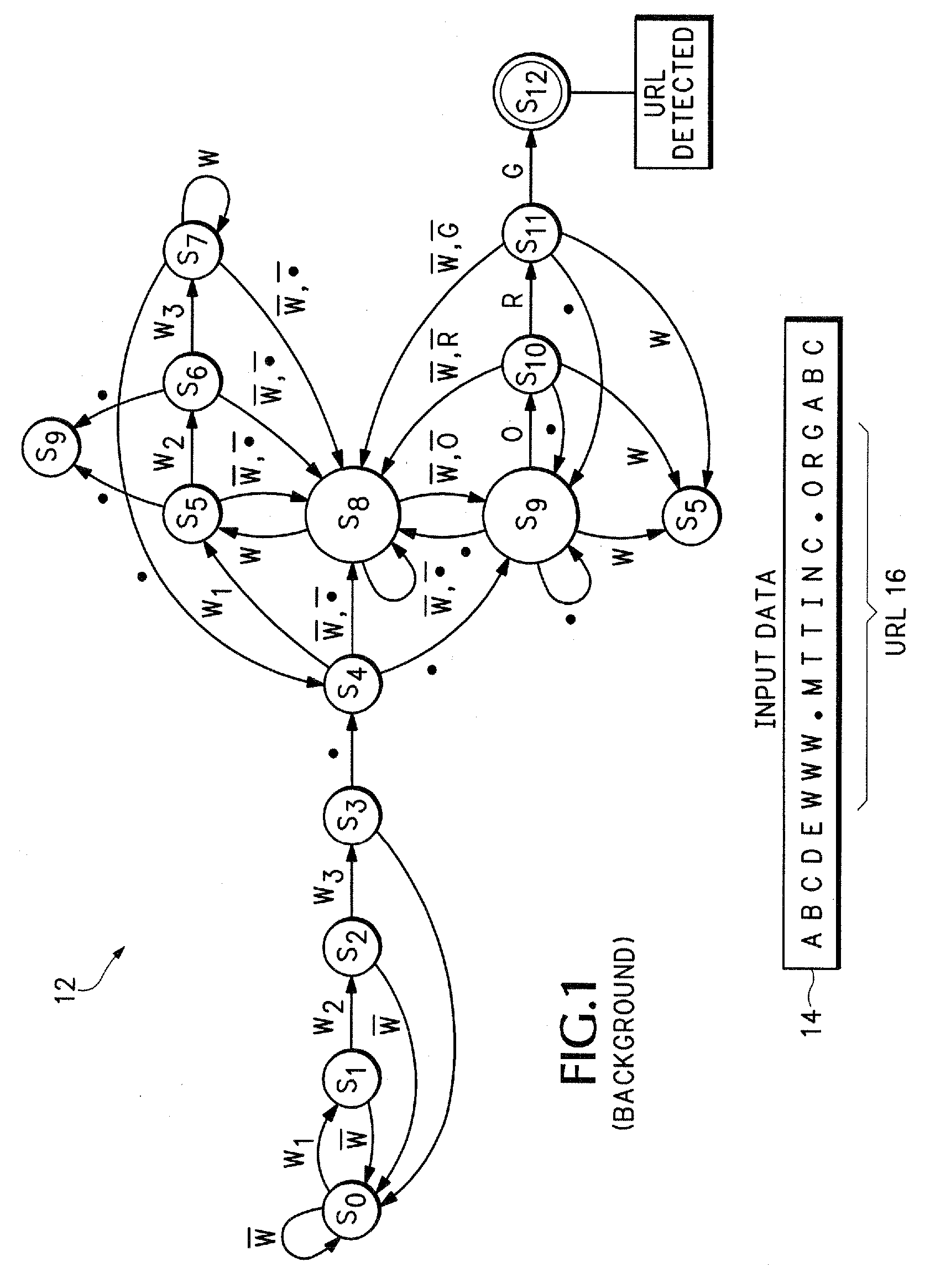
Method and apparatus for detecting semantic elements using a push down automaton
InactiveUS20060259508A1Small and more predictableSmaller and more predictable state tableDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData setPushdown automaton
A computer architecture uses a PushDown Automaton (PDA) and a Context Free Grammar (CFG) to process data. A PDA engine maintains semantic states that correspond to semantic elements in an input data set. The PDA engine does not have to maintain a new state for each new character in a target search string and typically only transitions to a new state when the entire semantic element is detected. The PDA engine can therefore use a smaller and more predictable state table than DFA algorithms. Transitions between the semantic states are managed using a stack that allows multiple semantic states to be represented by a single nested non-terminal symbol.
Owner:GIGAFIN NETWORKS
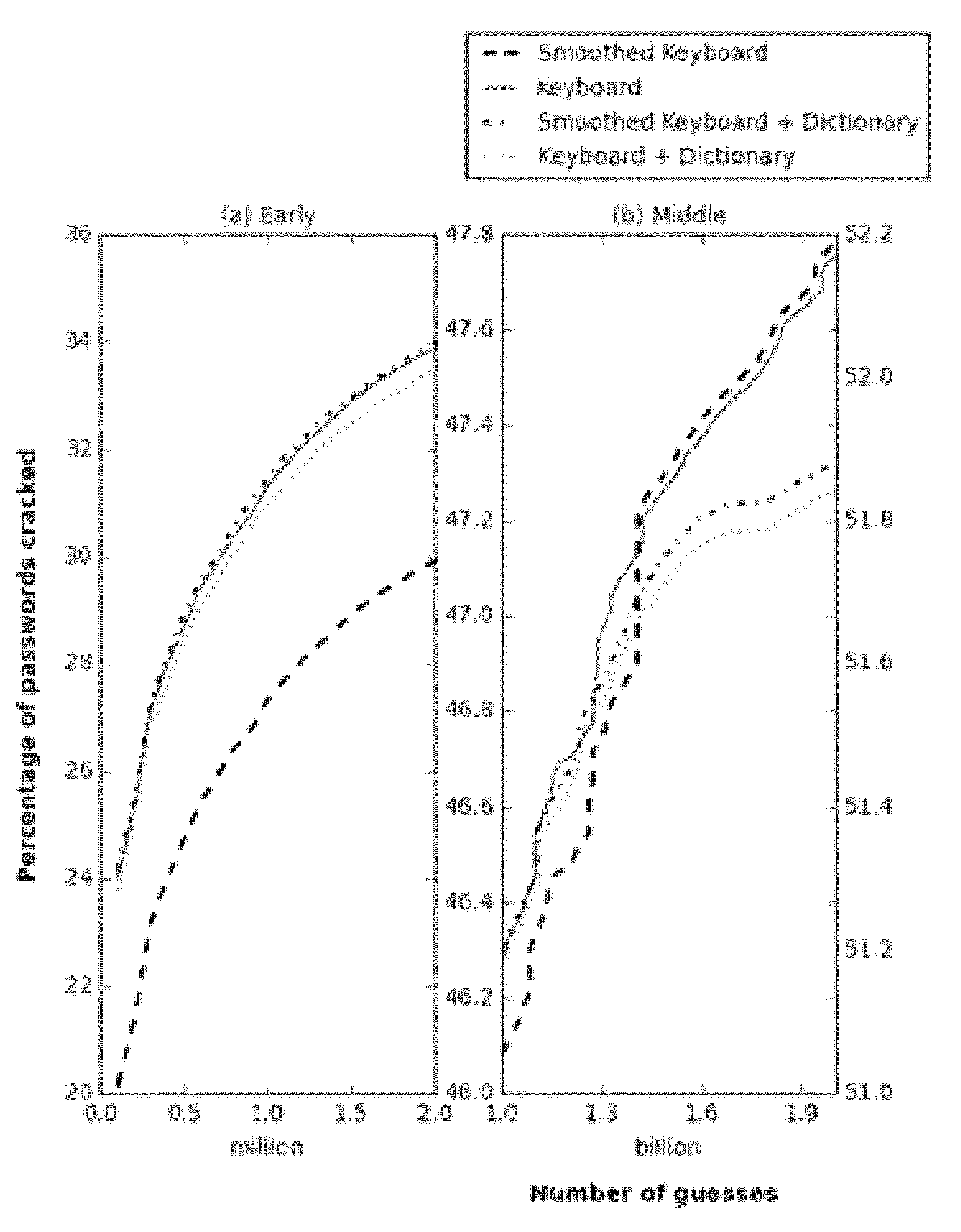
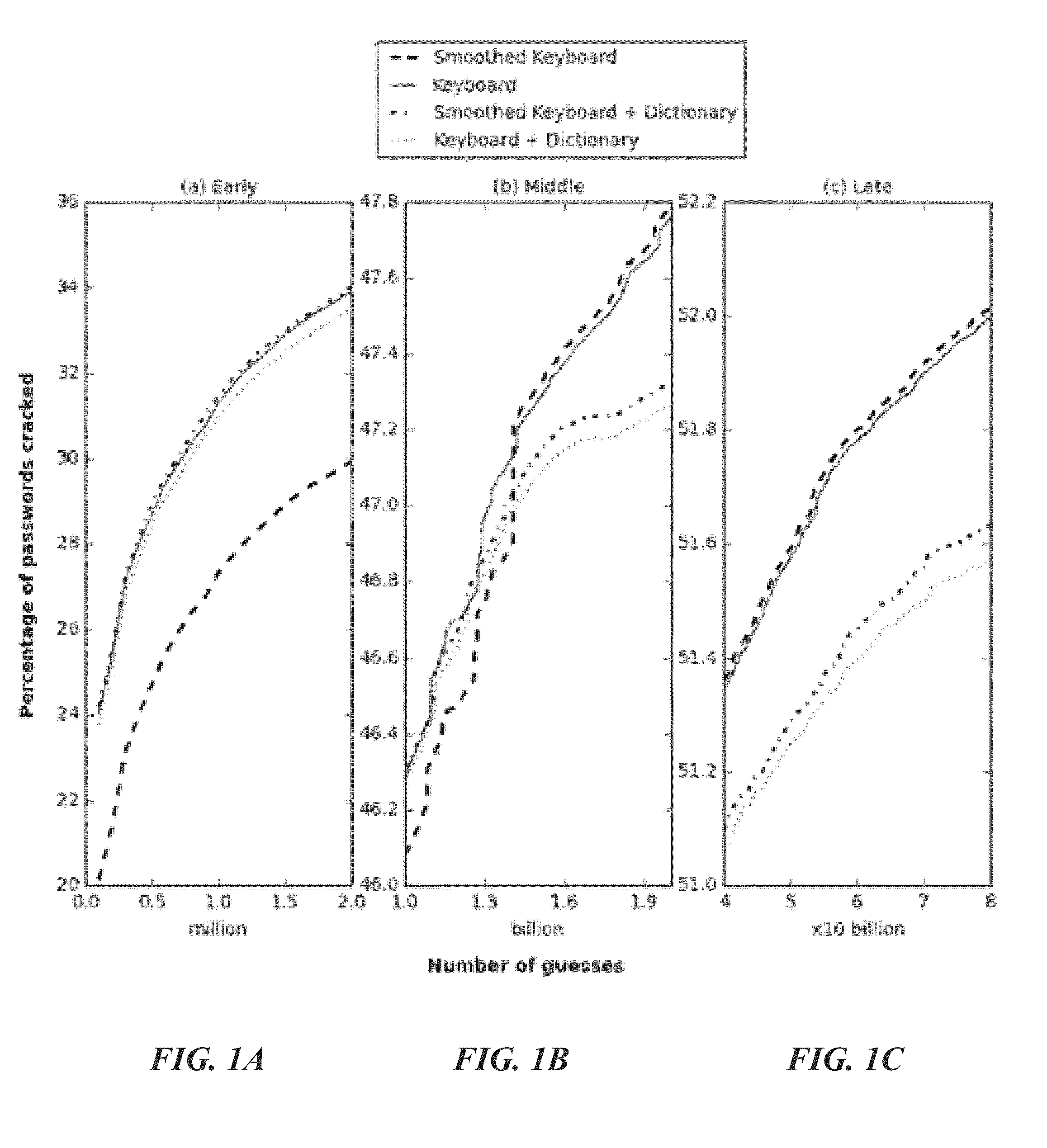
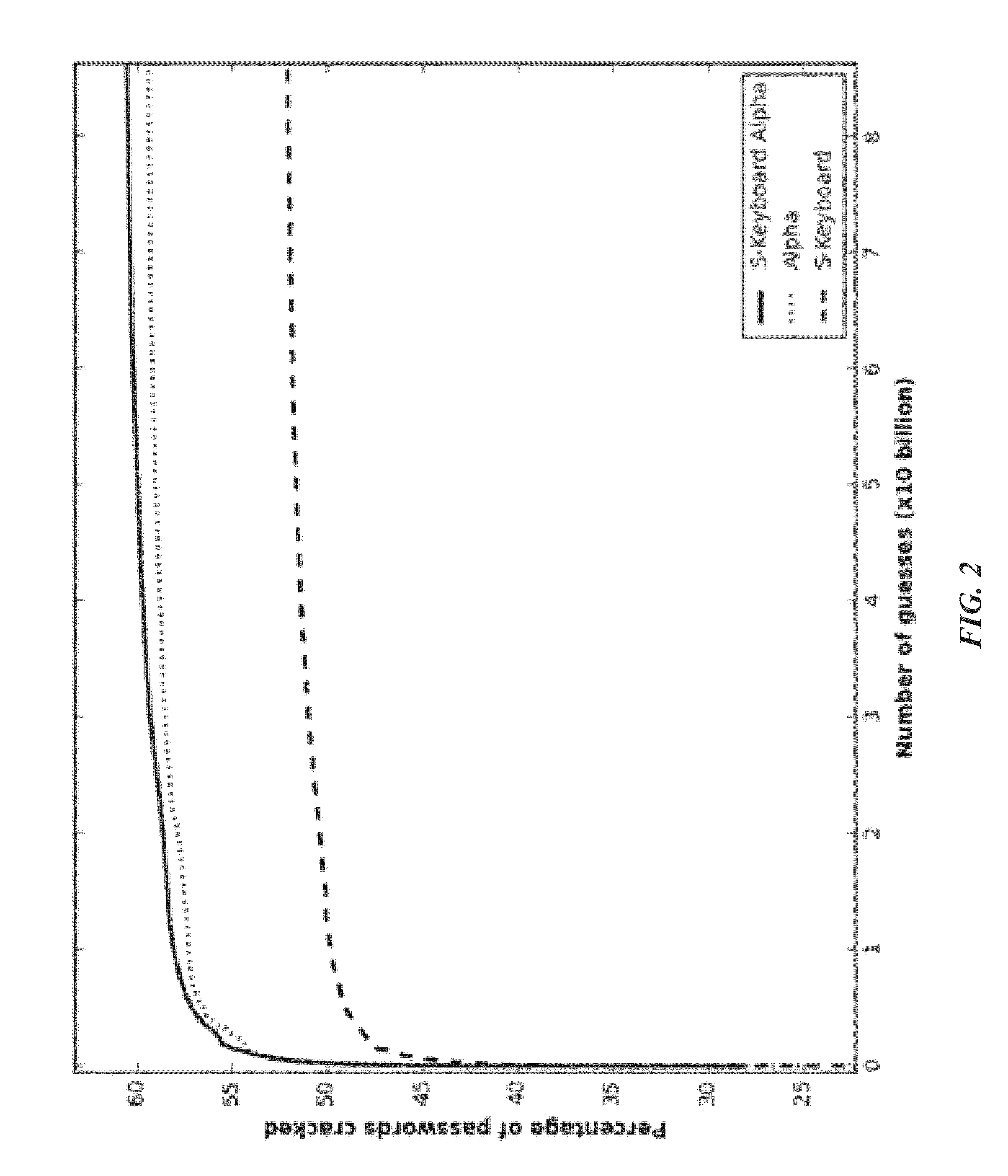
Probabilistic password cracking system
ActiveUS9438419B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data authenticationPasswordTheoretical computer science
System and methodology that utilizes keyboard patterns and alpha string patterns for password cracking. Keyboard patterns can be used as components of passwords, and the relevant shapes can extracted from these keyboard patterns and passwords. This keyboard information can be used to extend a probabilistic context-free grammar that can then be used to generate guesses containing keyboard patterns. Further, patterns in alpha strings, such as repeated words and multi-words, can be systematically learned using a training dictionary. This information can be used to extend the probabilistic context-free grammars which leads to generation of guesses based on the distribution of these patterns in the alpha strings, Keyboard patterns and alpha string patterns, individually and in combination, are shown herein to be effective for password cracking.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Unit selection module and method for Chinese text-to-speech synthesis
InactiveUS20060095264A1Prevent inappropriate unit generationAvoid it happening againSpecial data processing applicationsSpeech synthesisNatural language processingStructural distance
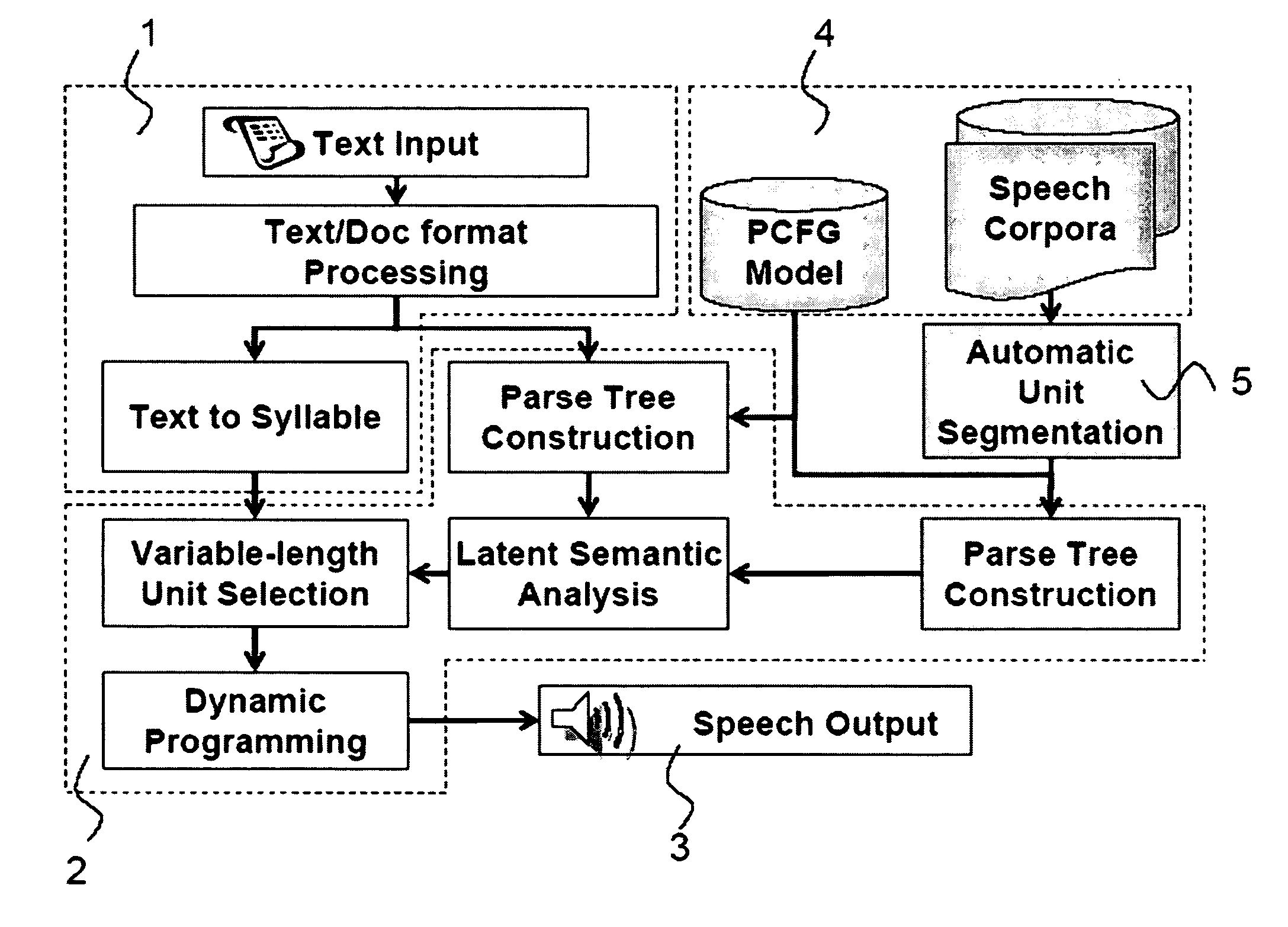
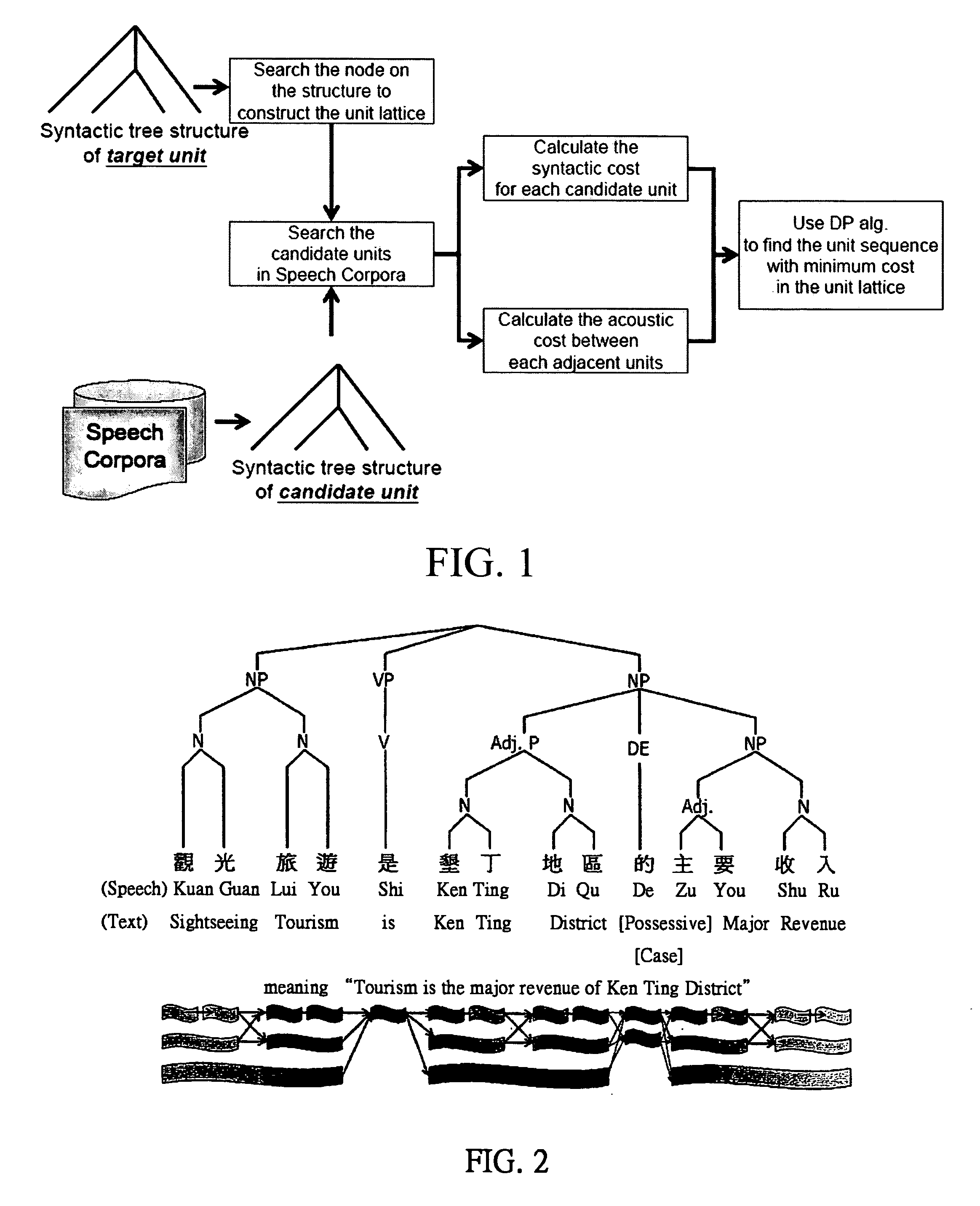
This invention relates to a unit selection module for Chinese Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesis, mainly comprising a probabilistic context free grammar (PCFG) parser, a latent semantic indexing (LSI) module, and a modified variable-length unit selection scheme; any Chinese sentence is firstly input and then parsed into a context-free grammar (CFG) by the PCFG parser; wherein there are several possible CFGs for every Chinese sentence, and the CFG (or the syntactic structure) with the highest probability is then taken as the best CFG (or the syntactic structure) of the Chinese sentence; the LSI module is then used to calculate the structural distance between all the candidate synthesis units and the target unit in a corpus; through the modified variable-length unit selection scheme, tagged with the dynamic programming algorithm, the units are searched to find the best synthesis unit concatenation sequence.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
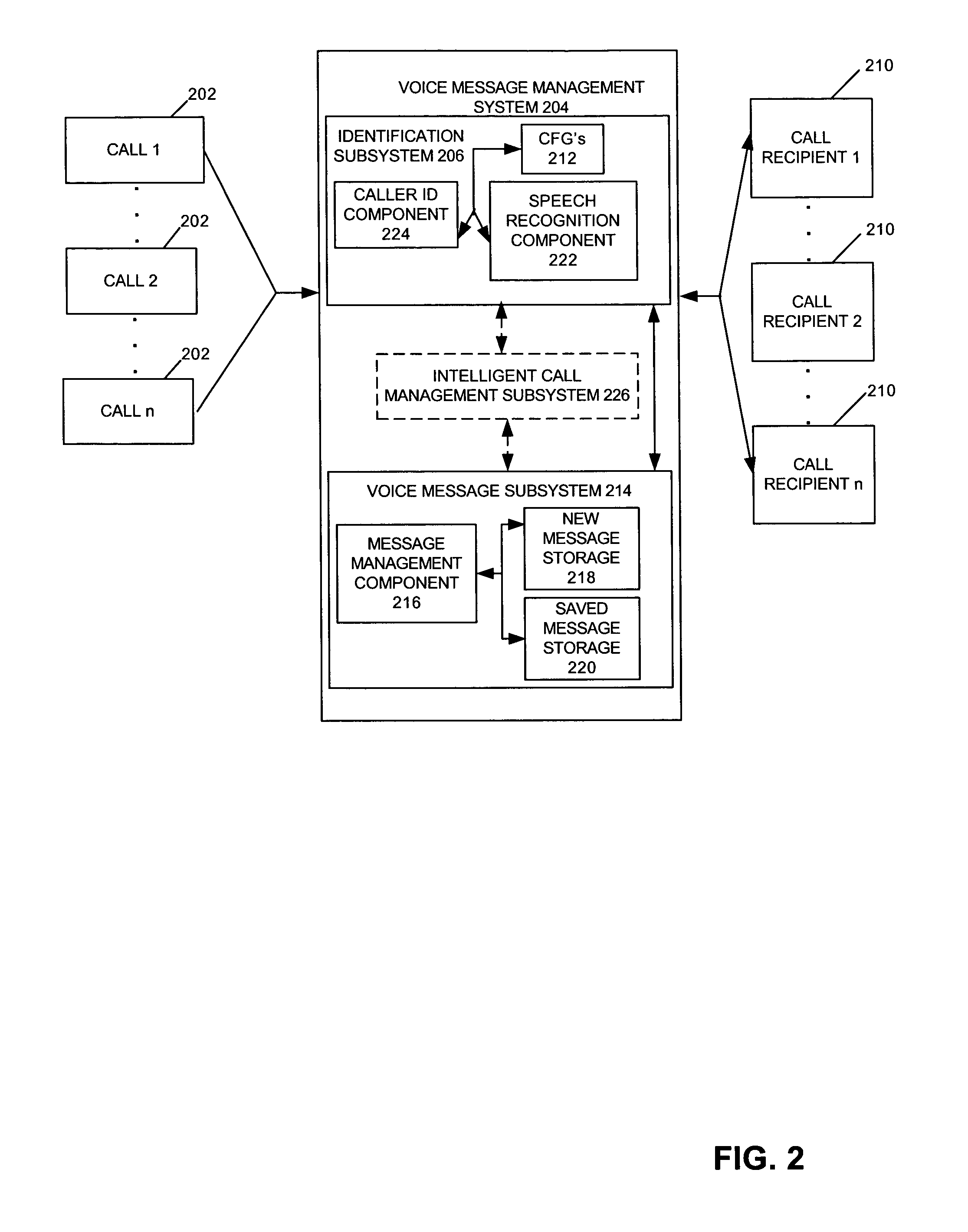
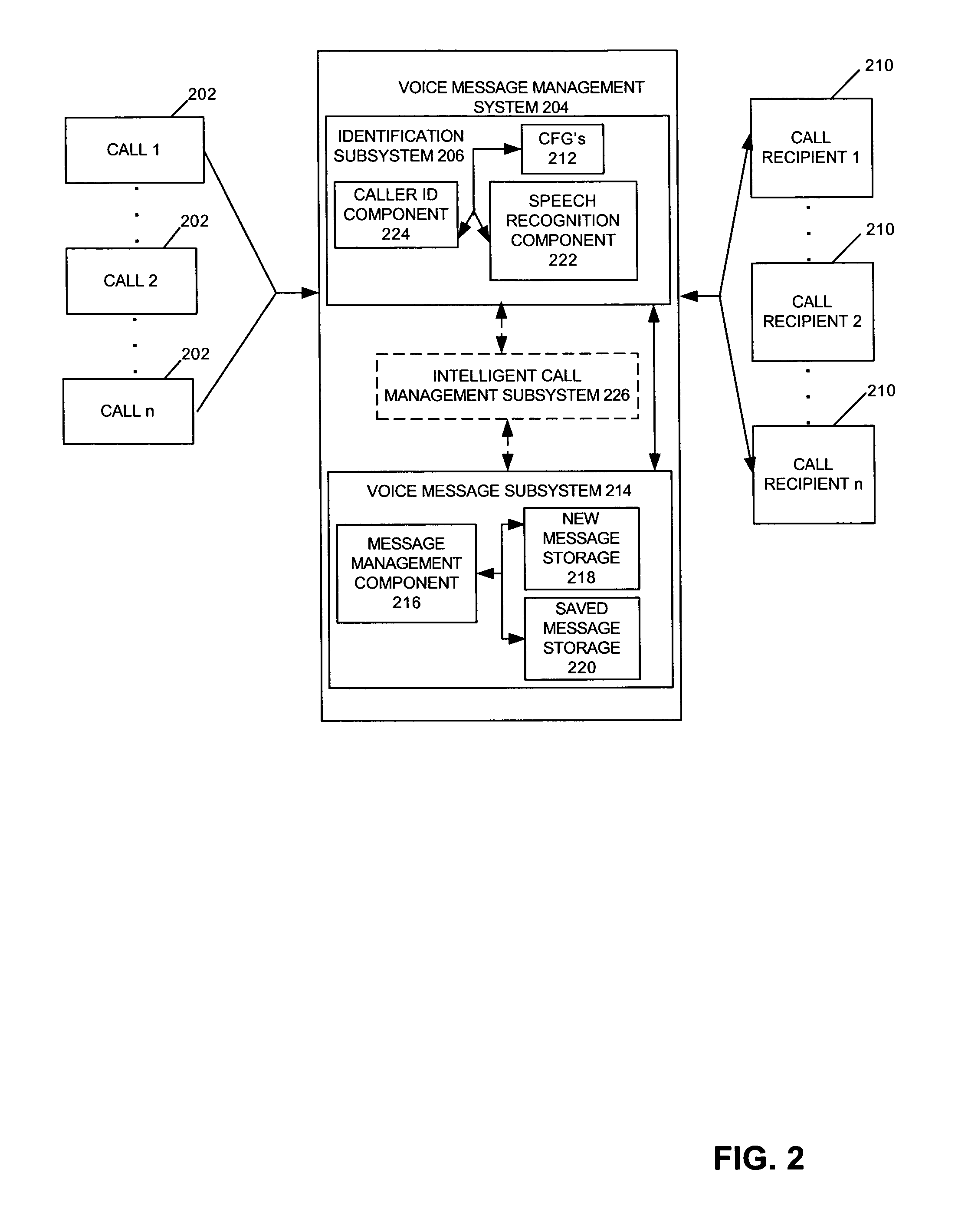
Speech recognition enhanced caller identification
InactiveUS7852993B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersPersonalizationHigh probability
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Use of a unified language model
InactiveUS20050080611A1Speech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsMultiple contextHypothesis
A language processing system includes a unified language model. The unified language model comprises a plurality of context-free grammars having non-terminal tokens representing semantic or syntactic concepts and terminals, and an N-gram language model having non-terminal tokens. A language processing module capable of receiving an input signal indicative of language accesses the unified language model to recognize the language. The language processing module generates hypotheses for the received language as a function of words of the unified language model and / or provides an output signal indicative of the language and at least some of the semantic or syntactic concepts contained therein.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Speech recognition enhanced caller identification
InactiveUS20050038648A1Special service for subscribersAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingPersonalizationHigh probability
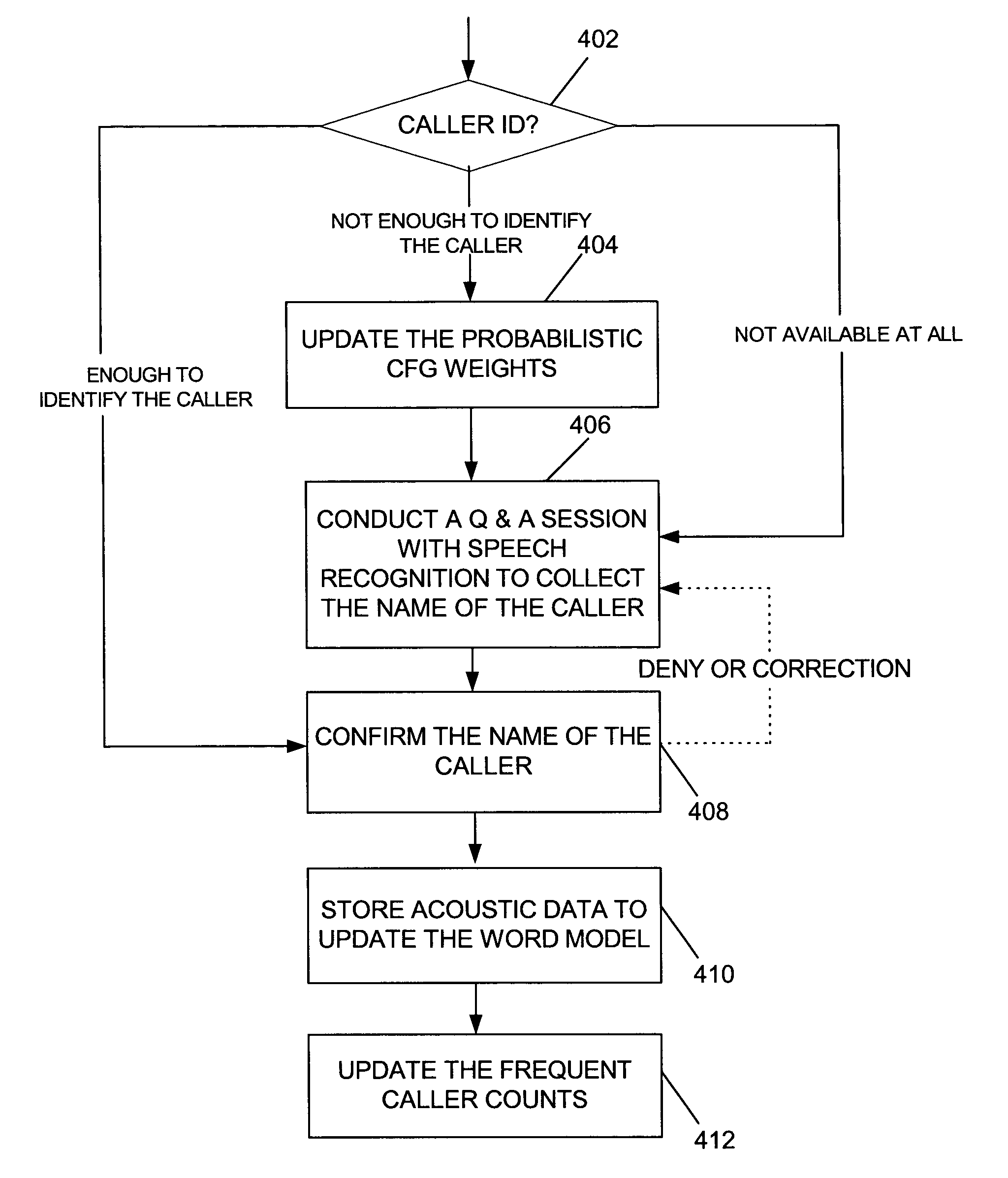
A process for collecting the identity of a telephone caller is disclosed. In one embodiment, a personalized Context Free Grammar (CFG) is created for each potential call recipient, and is configured to support identification of incoming callers utilizing voice recognition. Each CFG incorporates an indication of high probability callers and probability weights in each CFG are altered accordingly. When a recipient receives a call, the relevant CFG is applied in association with a voice recognition application to enable at least a preliminary identification of the caller. In accordance with another embodiment, the caller confirms identifications. In accordance with one embodiment, standard caller-ID functionality is utilized if possible at least to assist in the caller identification process. In accordance with still another embodiment, voice recognition enhanced caller identification is utilized to provide intelligent call routing functionality.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com