Patents
Literature
285 results about "Logical expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
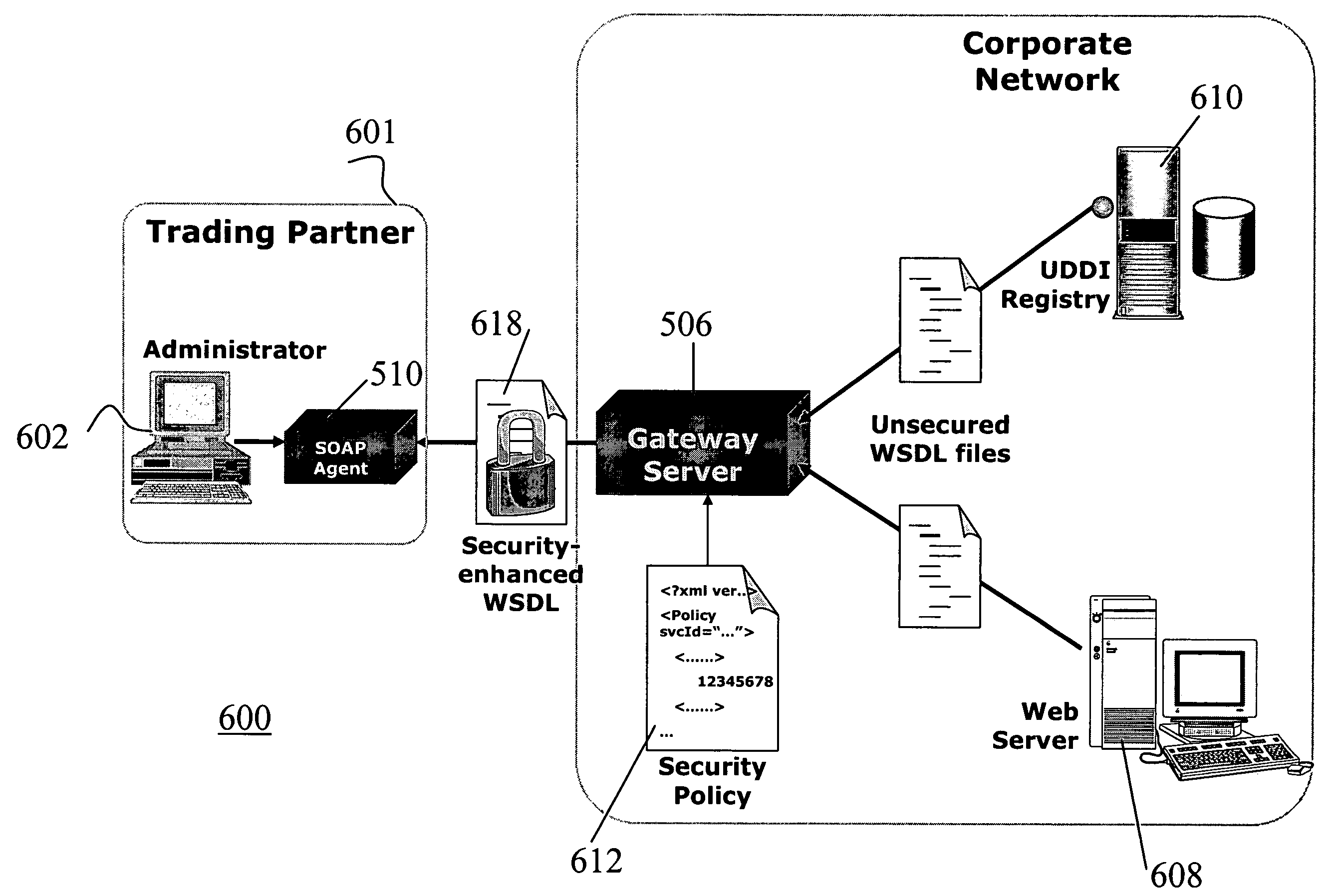
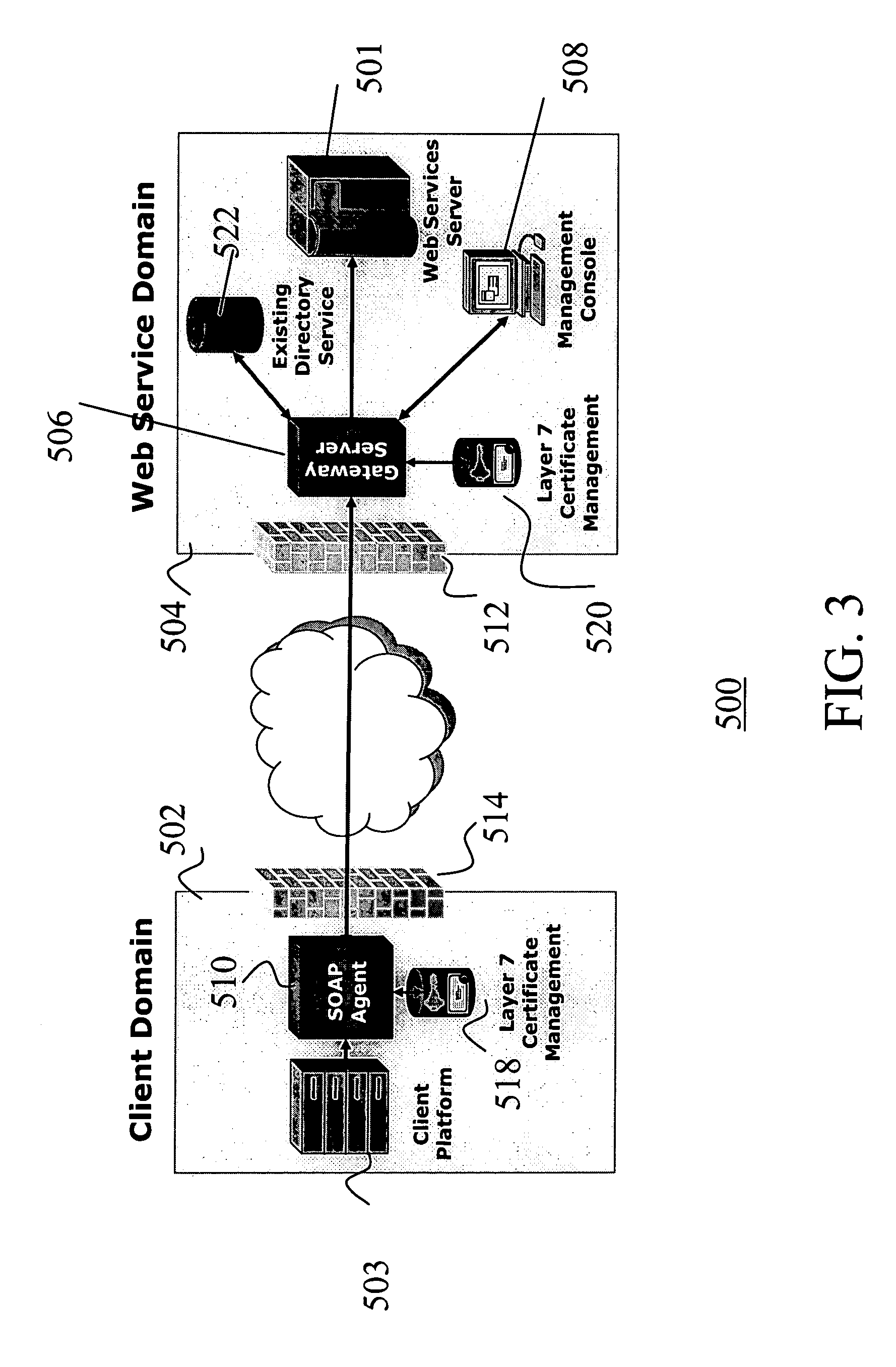
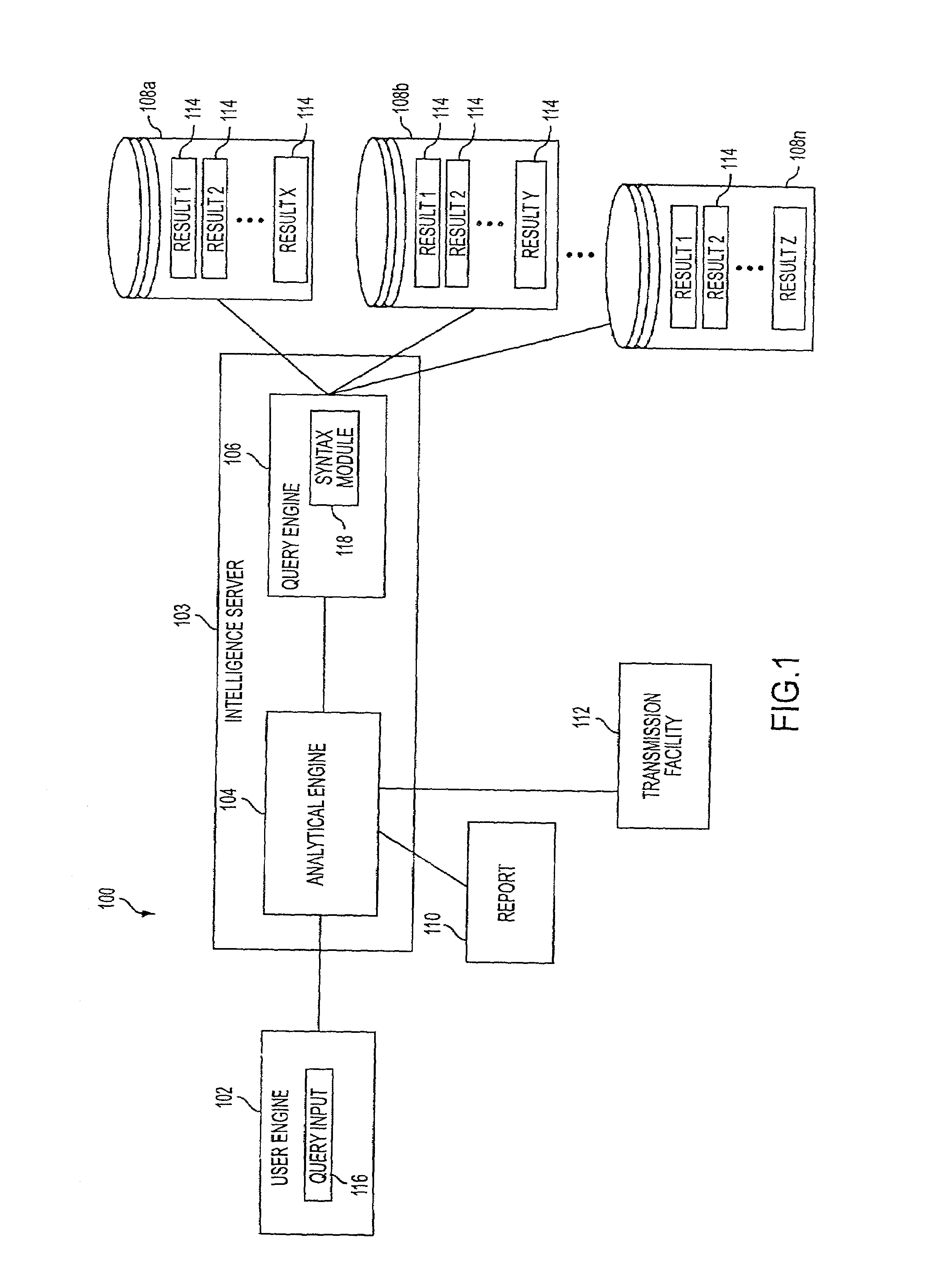
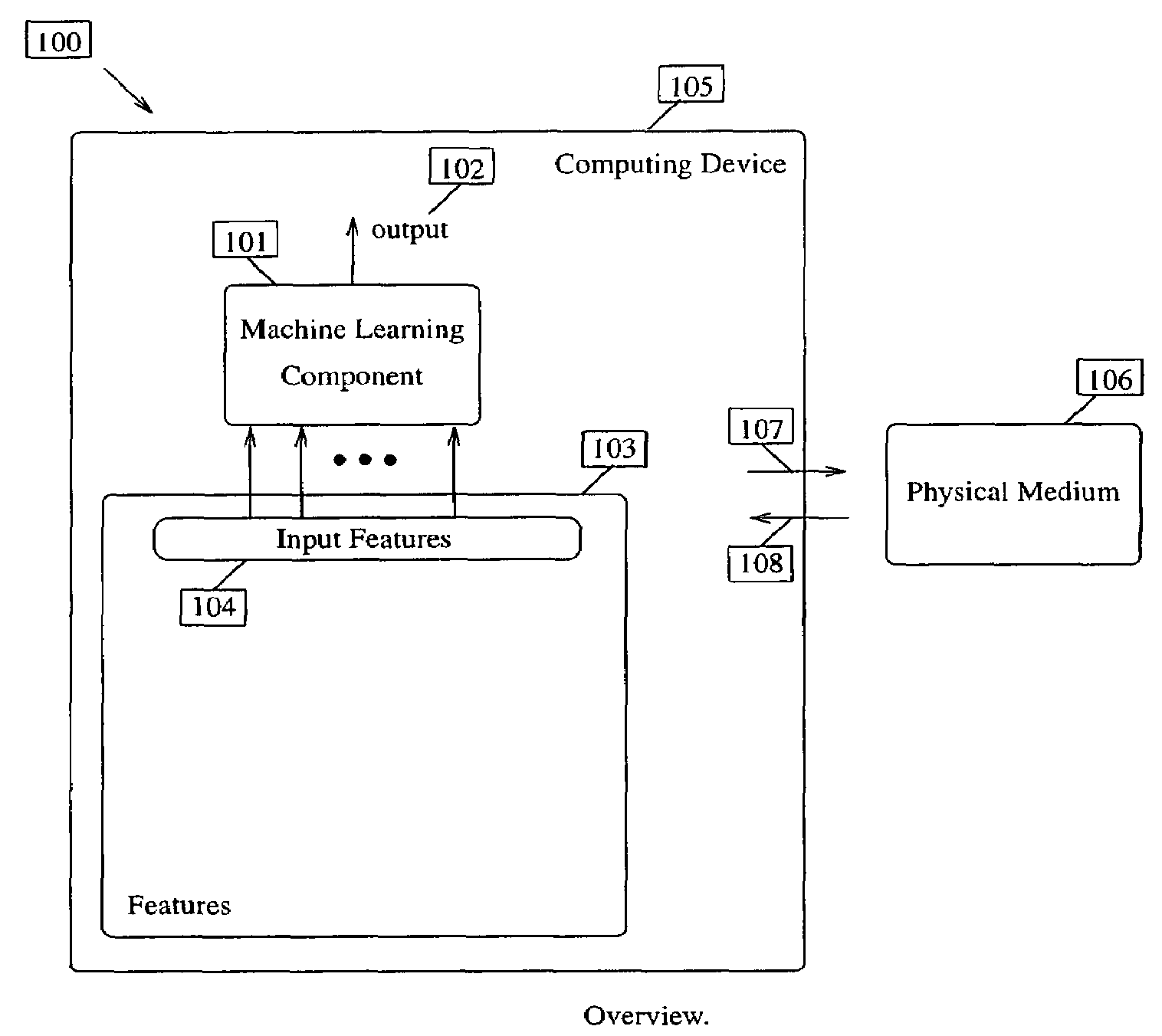
System and method securing web services
InactiveUS20050086197A1Easy and repeatable and reusable administrativeSpecial service provision for substationDigital data processing detailsWeb serviceClient-side
A method and system for securing web services on one or more server computers by one or more client computers, the computers connected to one or more networks through one or more network interfaces, each computer having one or more memories and one or more central processing units (CPUs), the system comprising one or more logical expressions that define constraints on one or more service releases; a gateway process receiving service request messages from one or more of the clients for i) identifying the service request message, ii) processing the service request message in accordance with one or more of the logical expressions associated with the requested service and iii) providing access to the requested service if the constraints are satisfied. The system includes an agent process associated with one or more the clients, for receiving service request messages from an associated client, the message destined for a requested service and applying to the received request message one or more of a subset of the logical expressions associated with the requested service for forwarding to the gateway process.
Owner:CA TECH INC
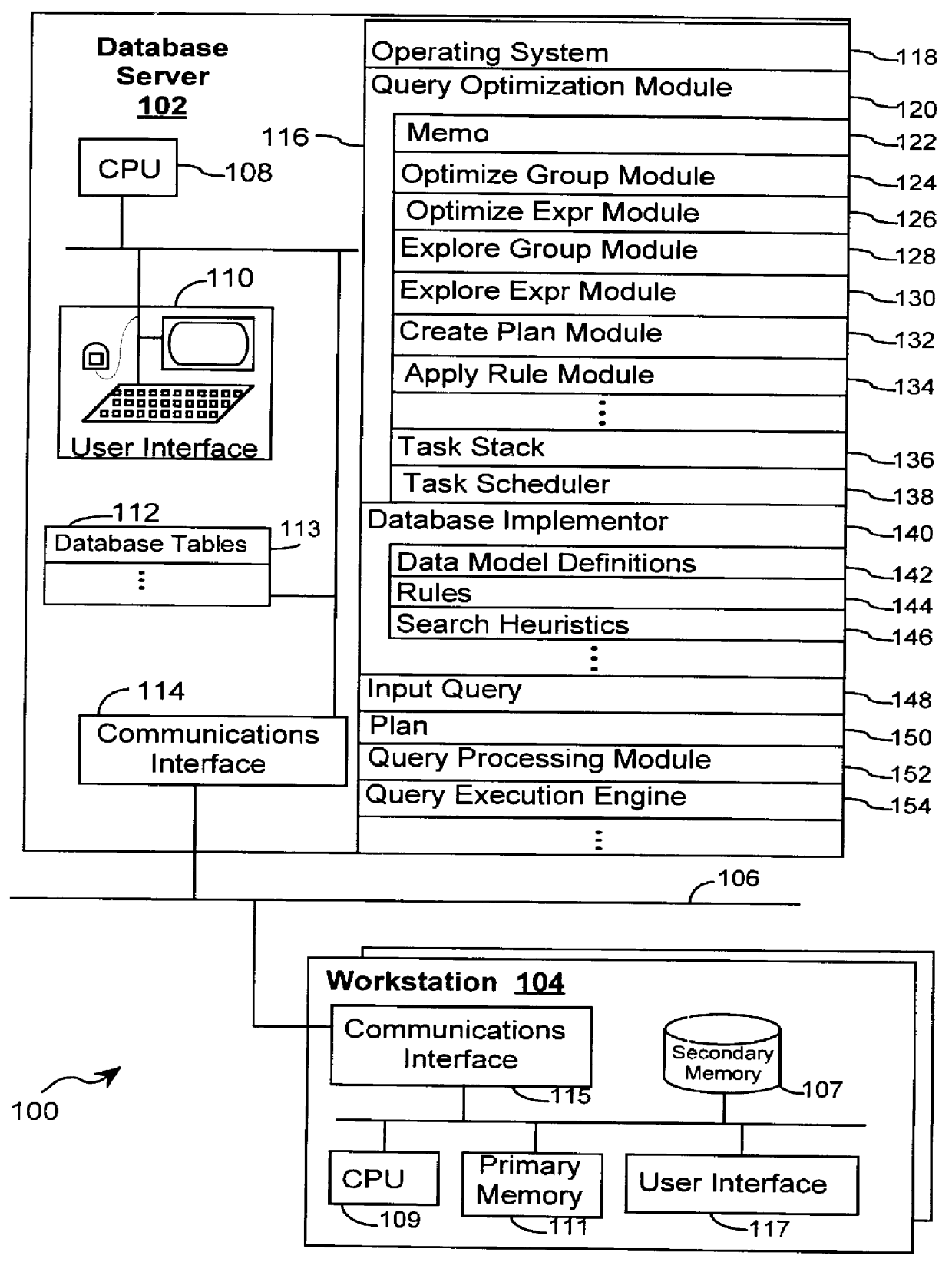
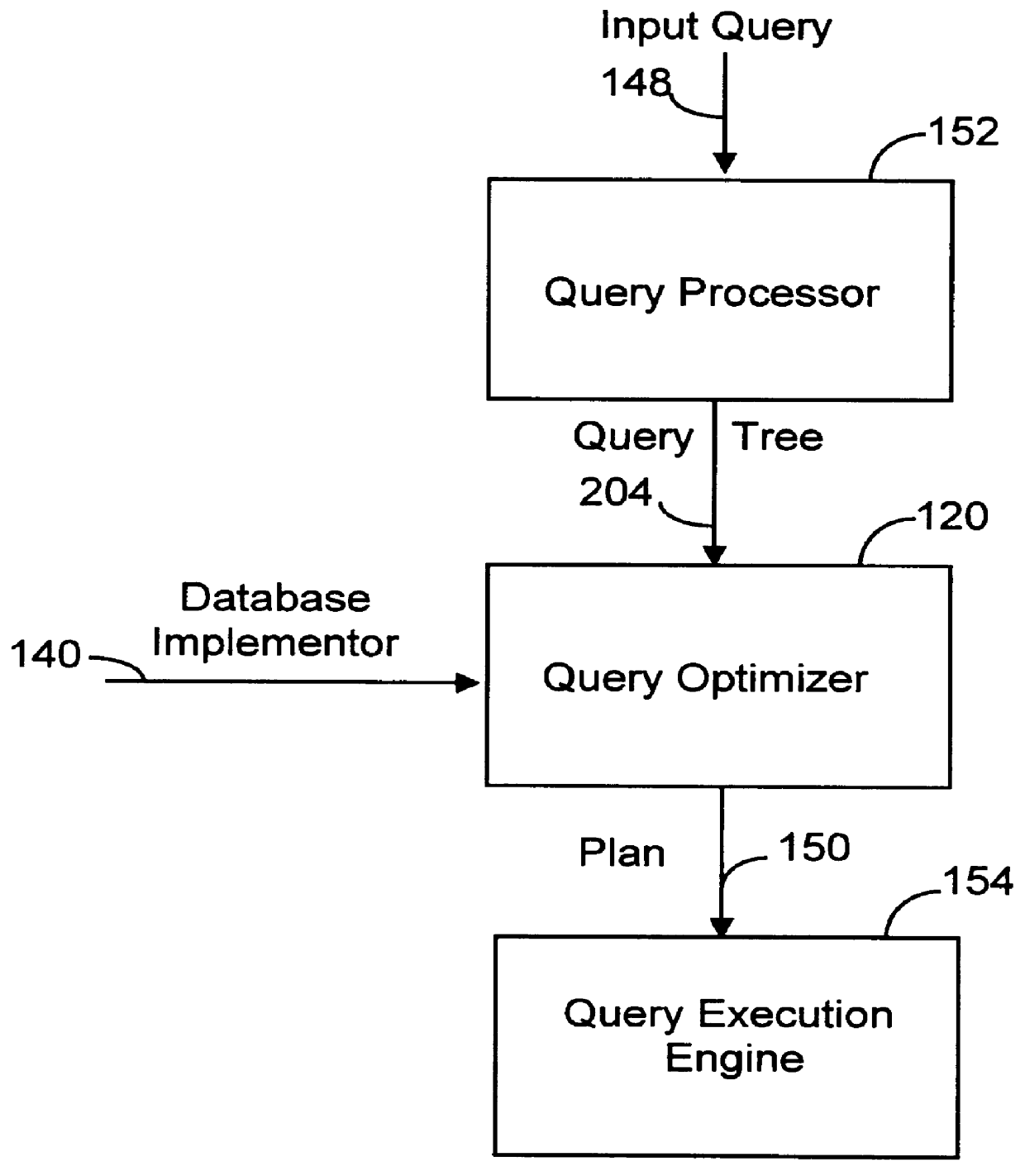
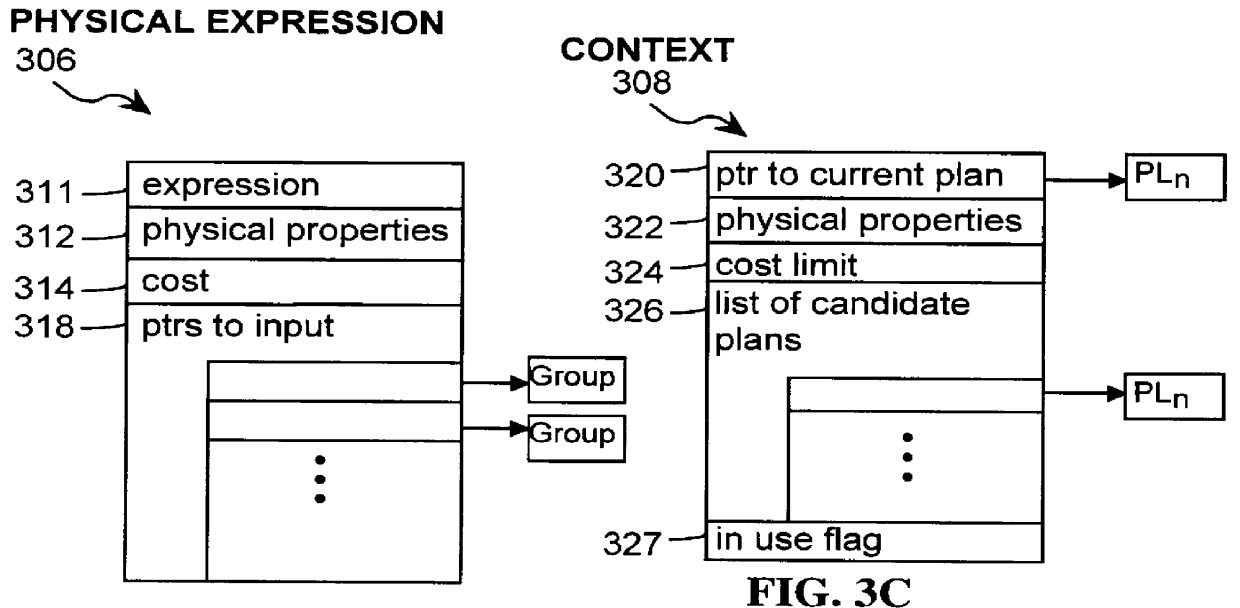
System and method for optimizing database queries with improved performance enhancements
InactiveUS6021405AEffective trackingEfficient searchDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsExecution planPerformance enhancement
A system and method for optimizing a database query with improved performance enhancements is herein disclosed. The database query consists of one or more logical expressions. Through the repeated application of one or more rules, the logical expressions are transformed into execution plans. The query optimizer partitions the database query into one or more subproblems with each subproblem consisting of one or more logical expressions. A plan is obtained for each subproblem with the plan for the database query including the plans for each subproblem. The query optimizer is cost-based and uses rules including transformation and implementation rules that are used to perform transformations on the logical expressions in a subproblem in order to produce a plan. The rules are classified into context-free and context-sensitive in order to avoid generating duplicate expressions. Context-free rules are applied once for each logical expression and context-sensitive rules are applied once for each logical expression for a particular optimization goal. In a preferred embodiment, the query optimizer performs several optimization passes over the database query in order to obtain an optimal plan. For each pass, if no optimal plan exists for the requested optimization goal, existing plans having the same optimization goal are utilized with each input reoptimized for a more cost effective plan.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
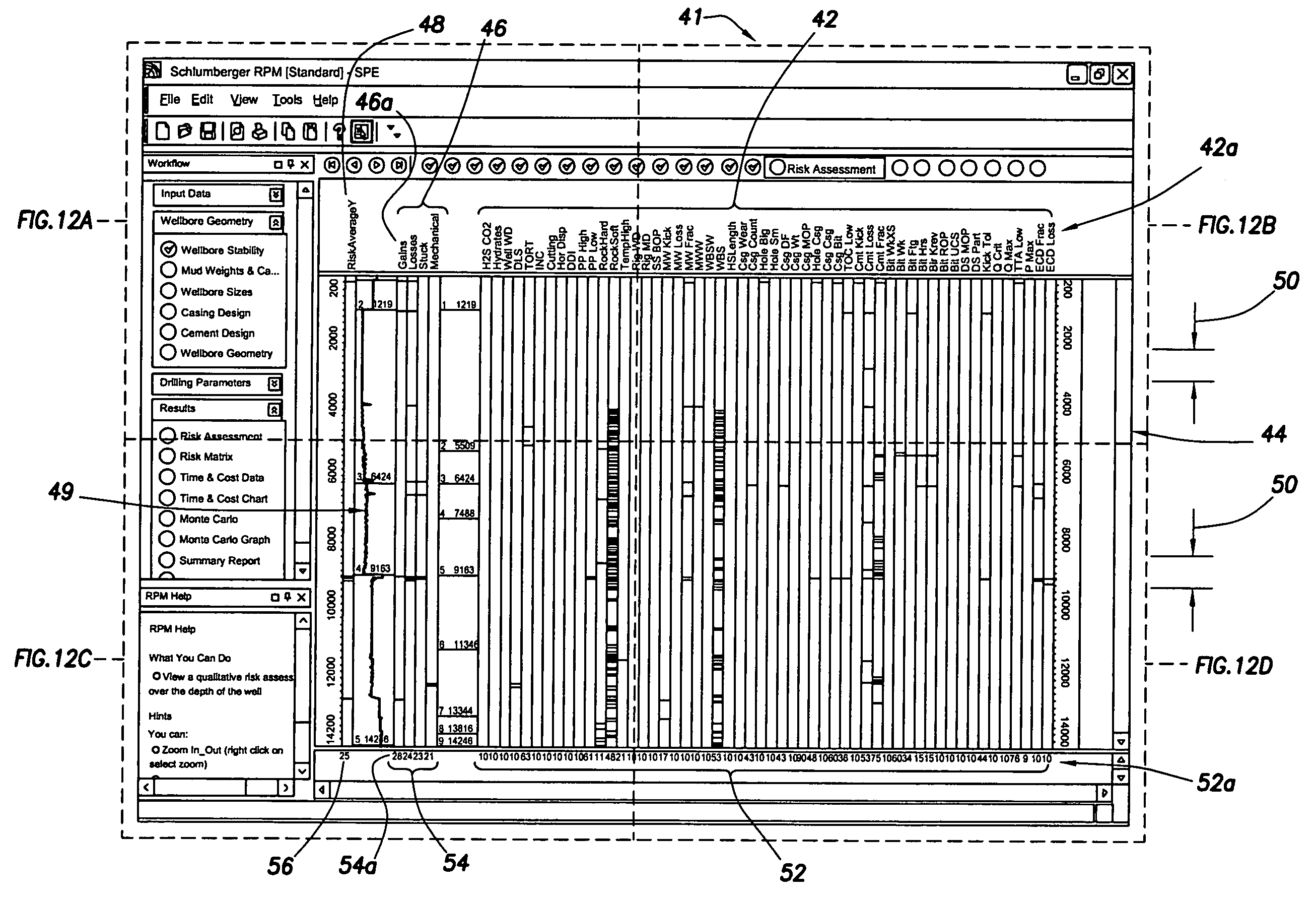
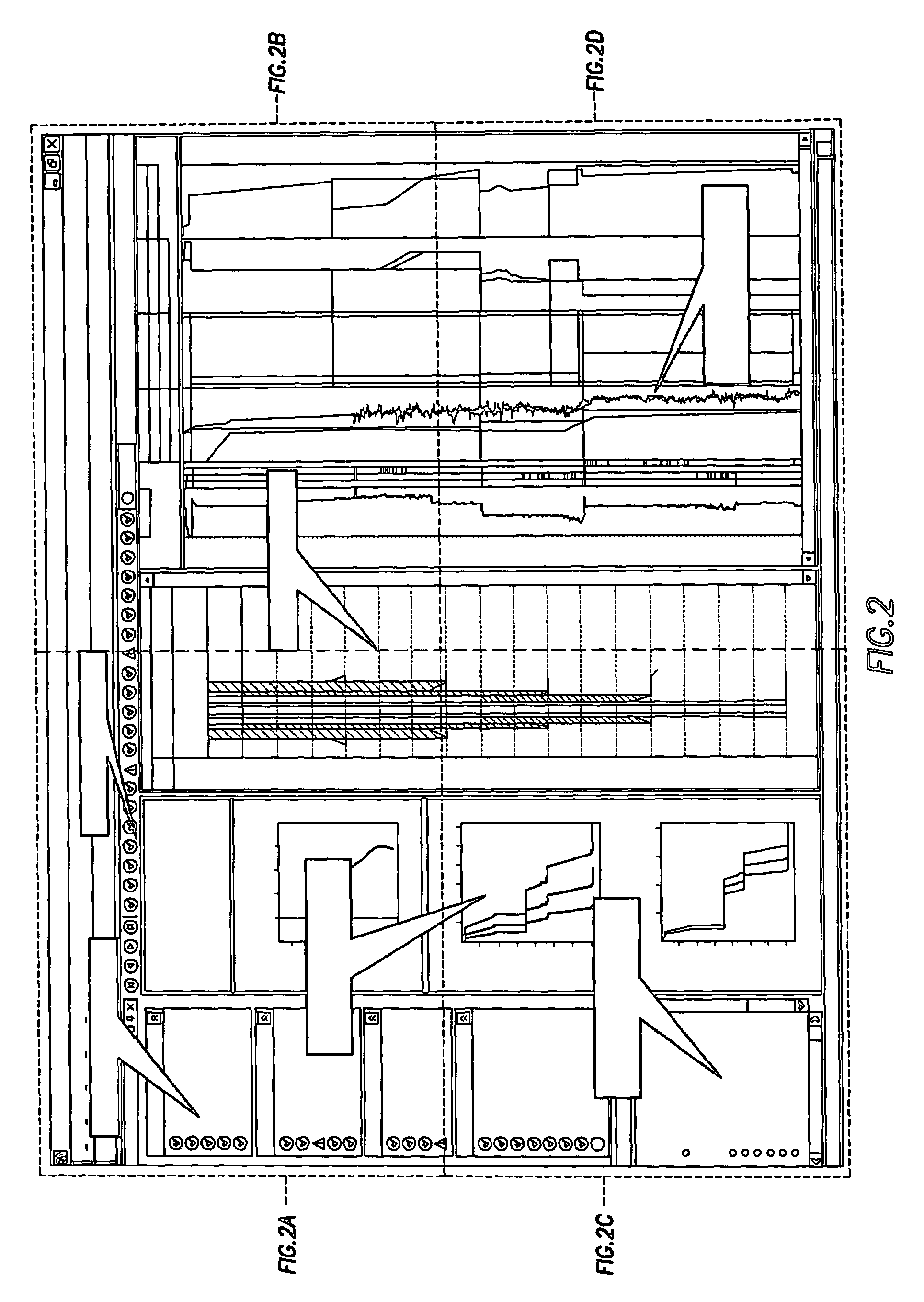
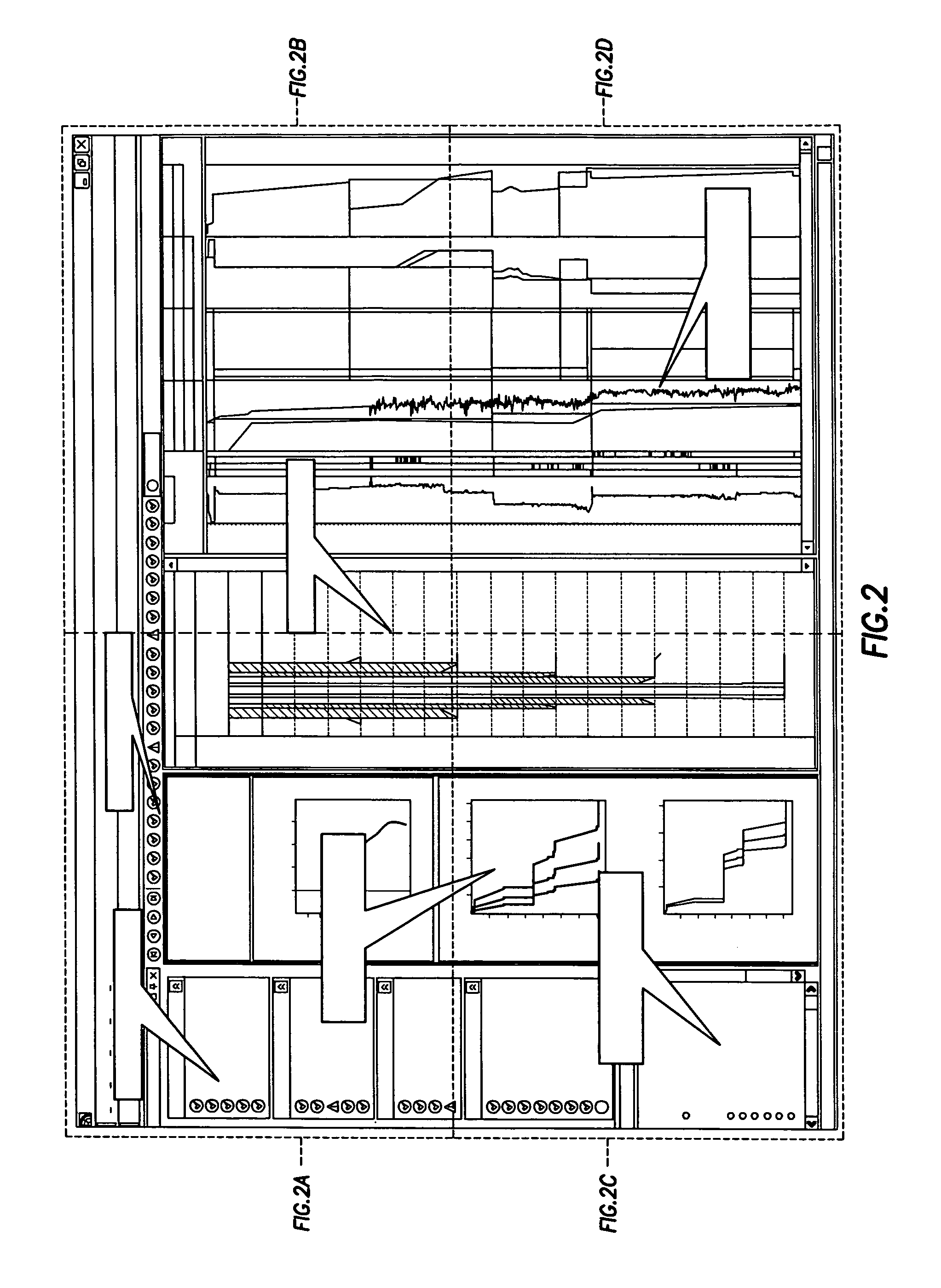
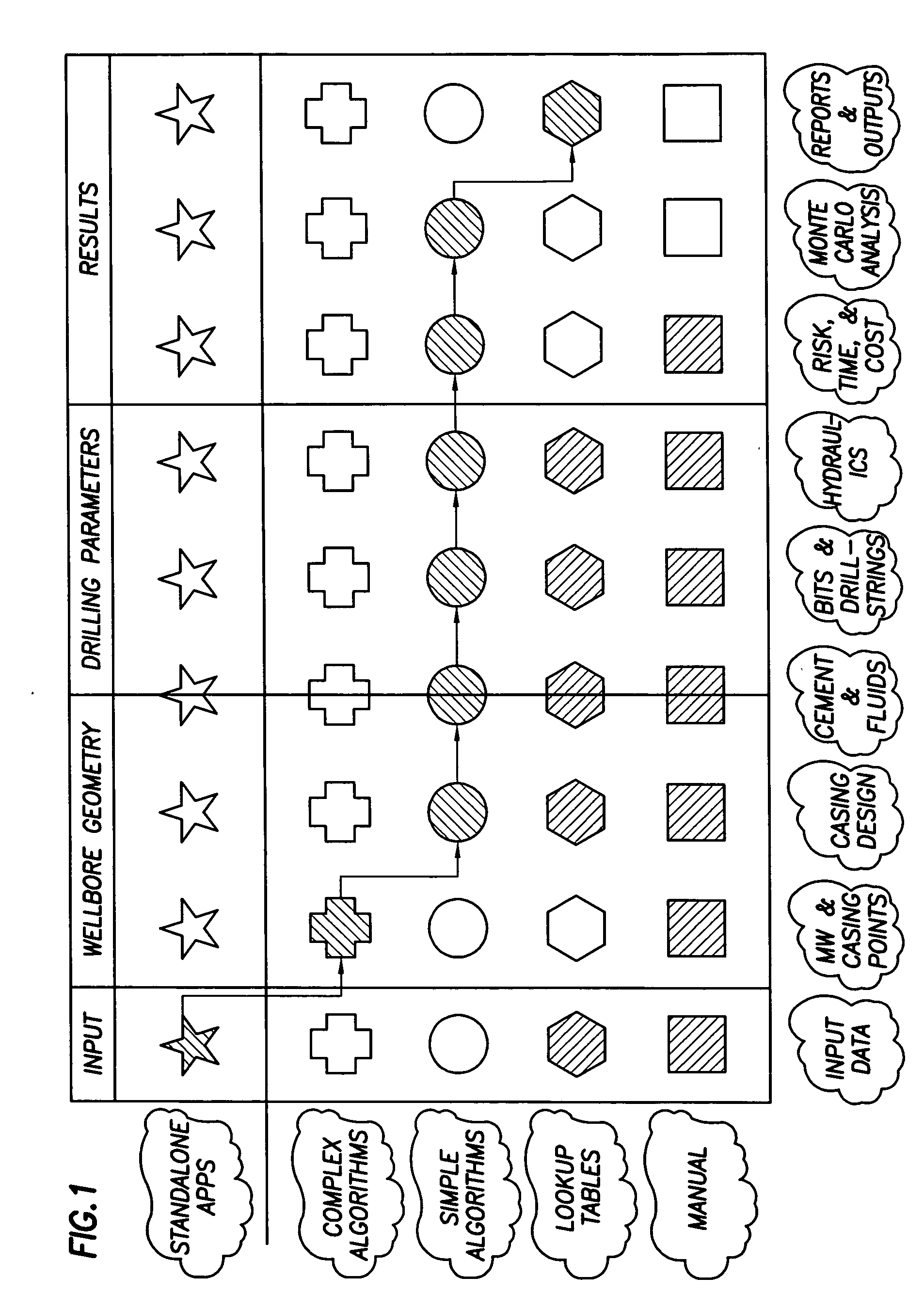
Method and apparatus and program storage device adapted for visualization of qualitative and quantitative risk assessment based on technical wellbore design and earth properties
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
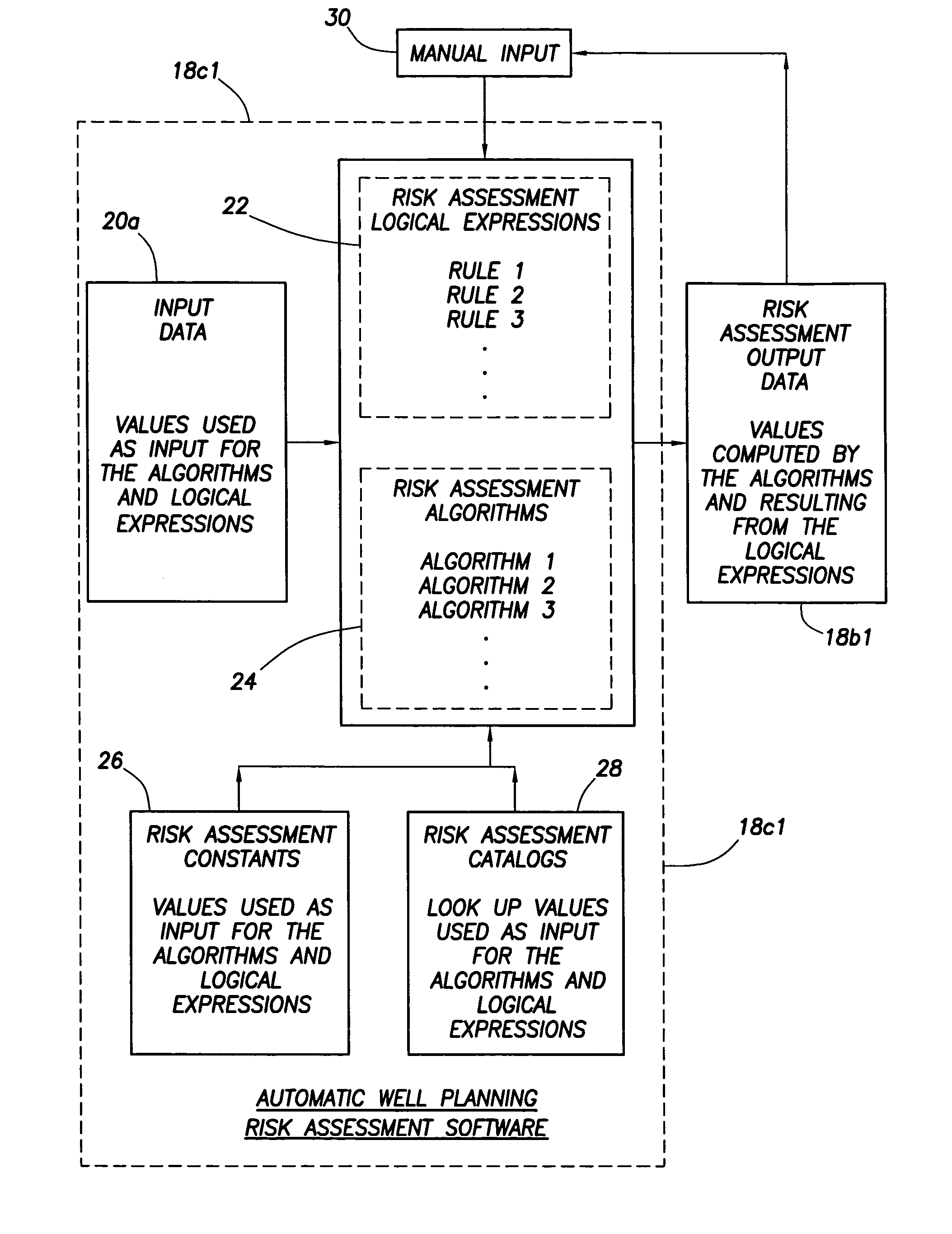
Method and apparatus and program storage device adapted for automatic qualitative and quantitative risk assessment based on technical wellbore design and earth properties
A Software System, known as an Automatic Well Planning Risk Assessment Software System, is adapted to determine and display risk information in response to a plurality of input data by: receiving the plurality of input data, the input data including a plurality of input data calculation results; comparing each calculation result of the plurality of input data calculation results with each logical expression of a plurality of logical expressions; ranking by the logical expression the calculation result; and generating a plurality of ranked risk values in response thereto, each of the plurality of ranked risk values representing an input data calculation result that has been ranked by the logical expression as either a high risk or a medium risk or a low risk; generating the risk information in response to the plurality of ranked risk values; and displaying the risk information.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
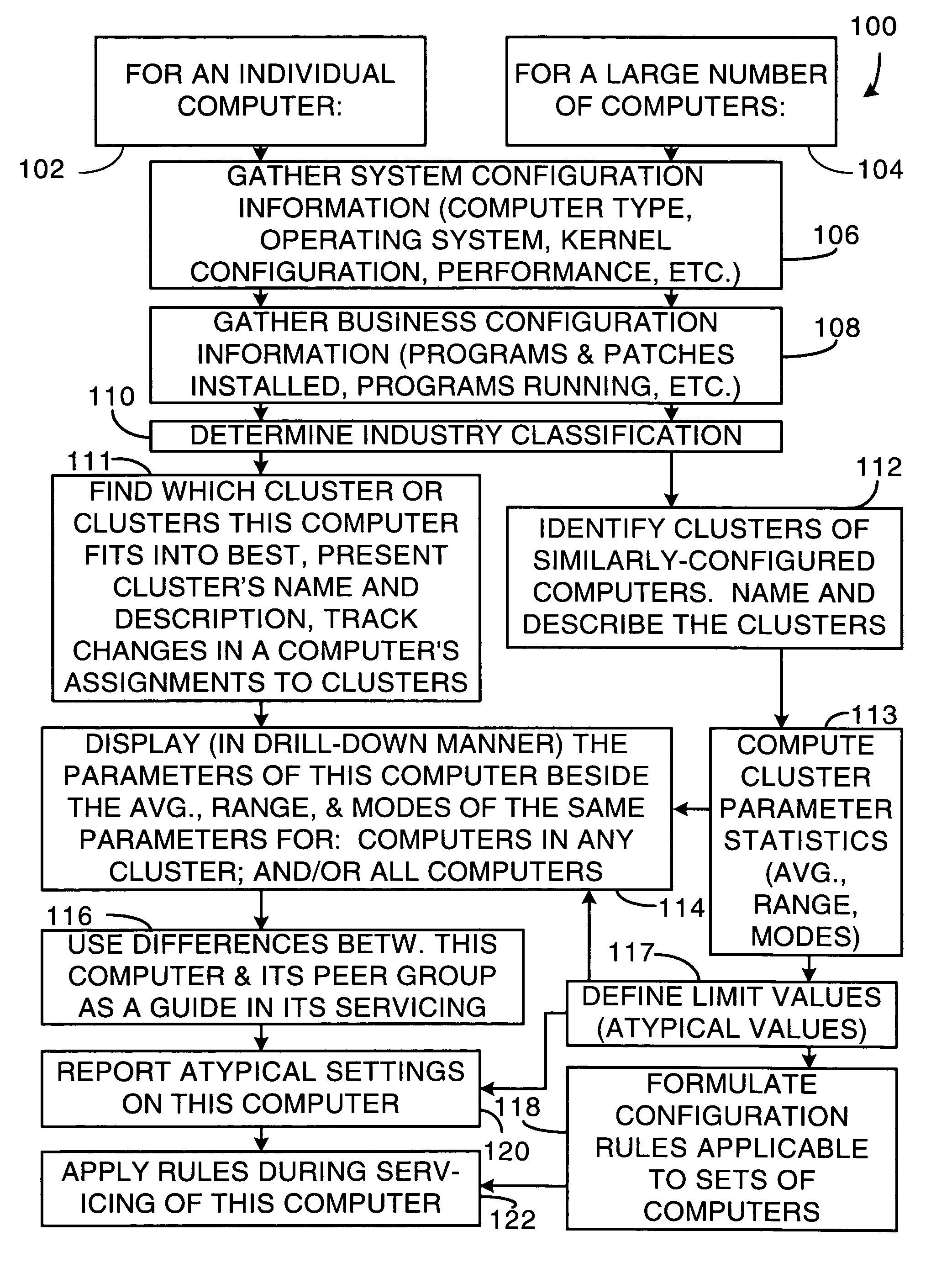
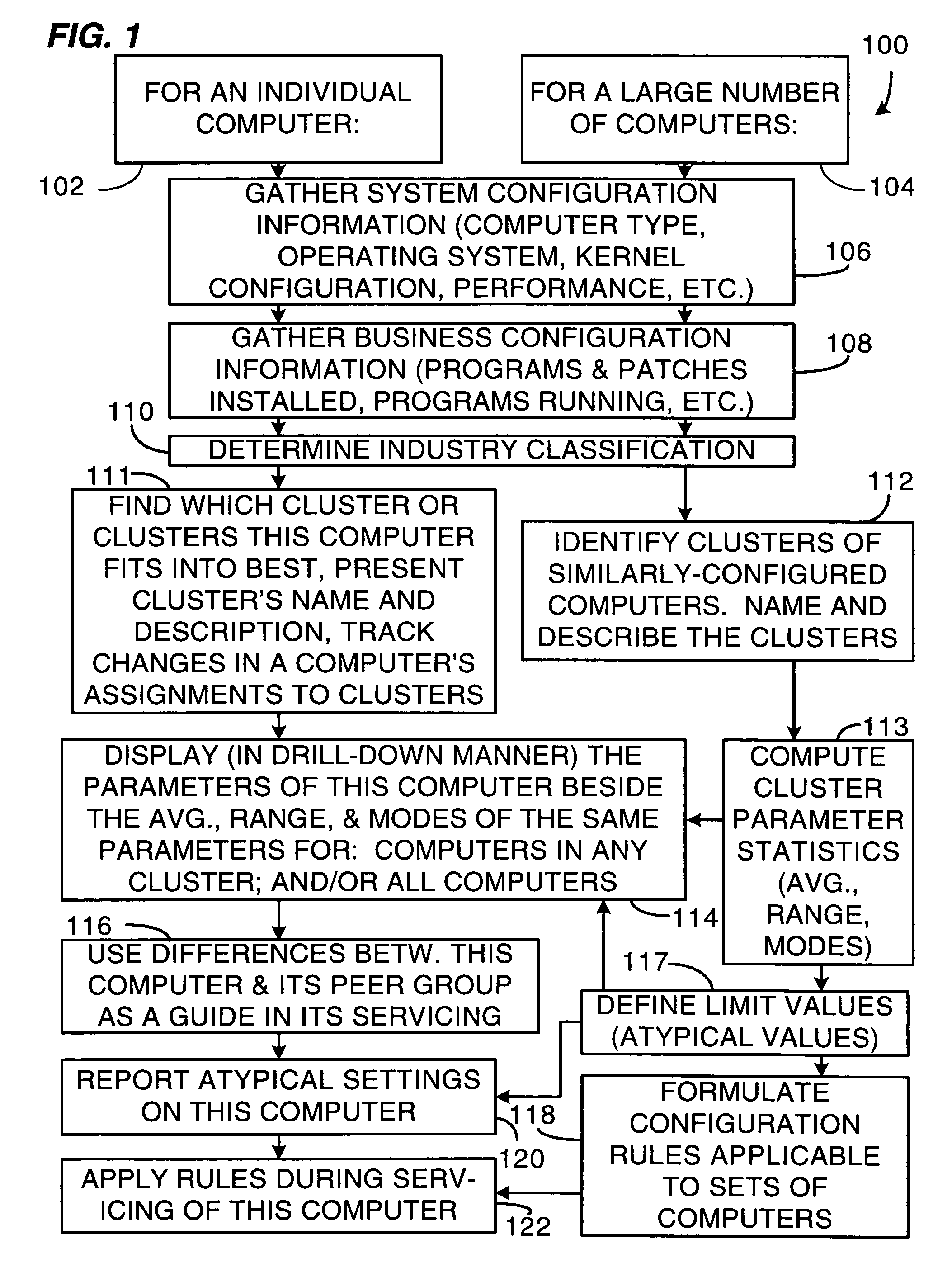
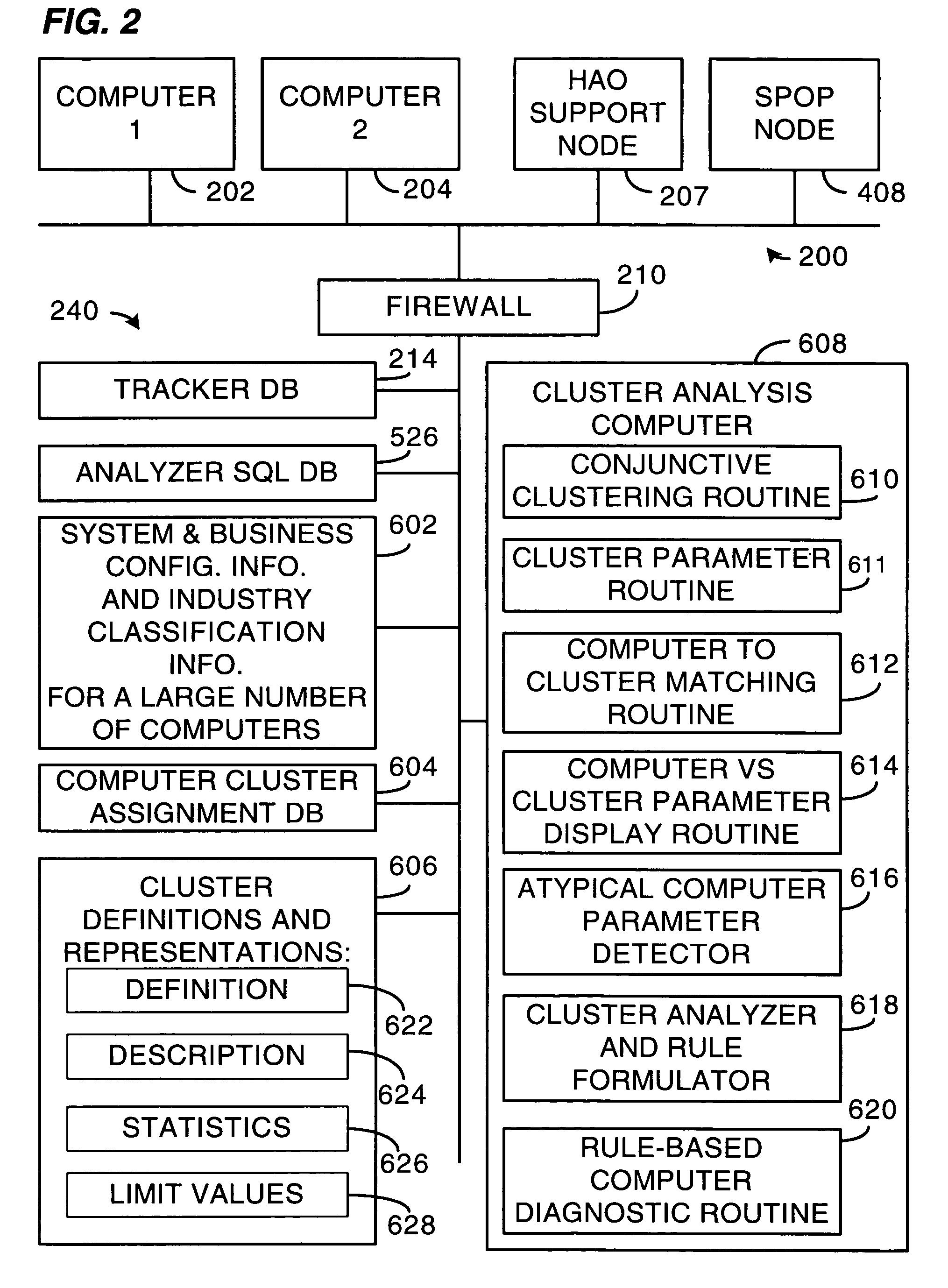
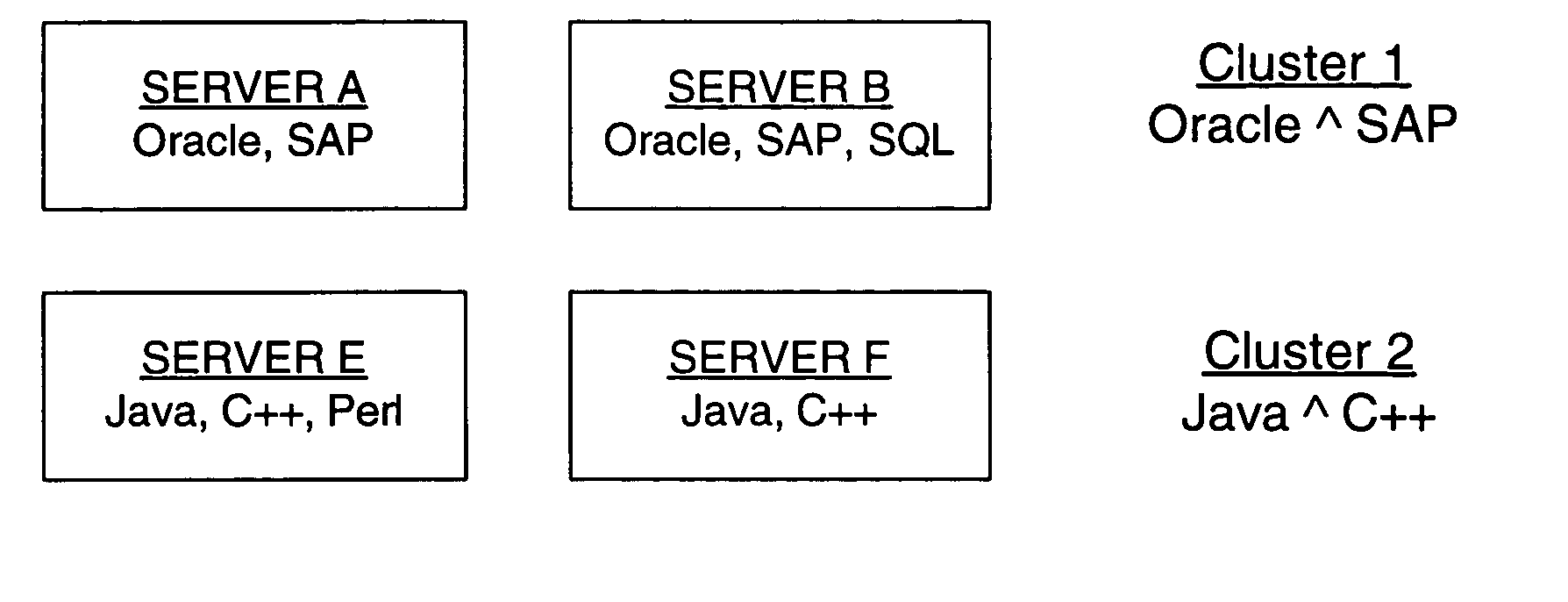
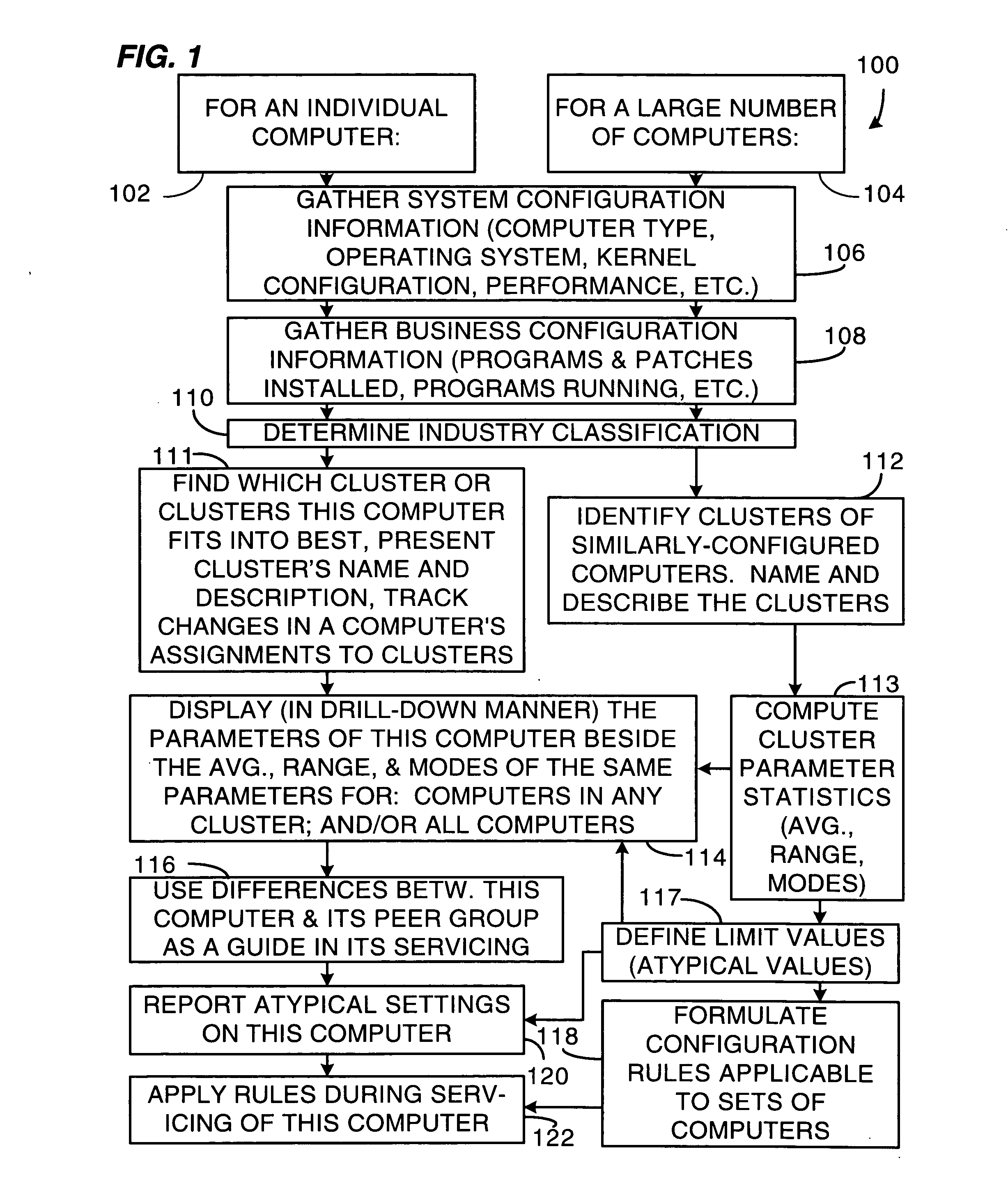
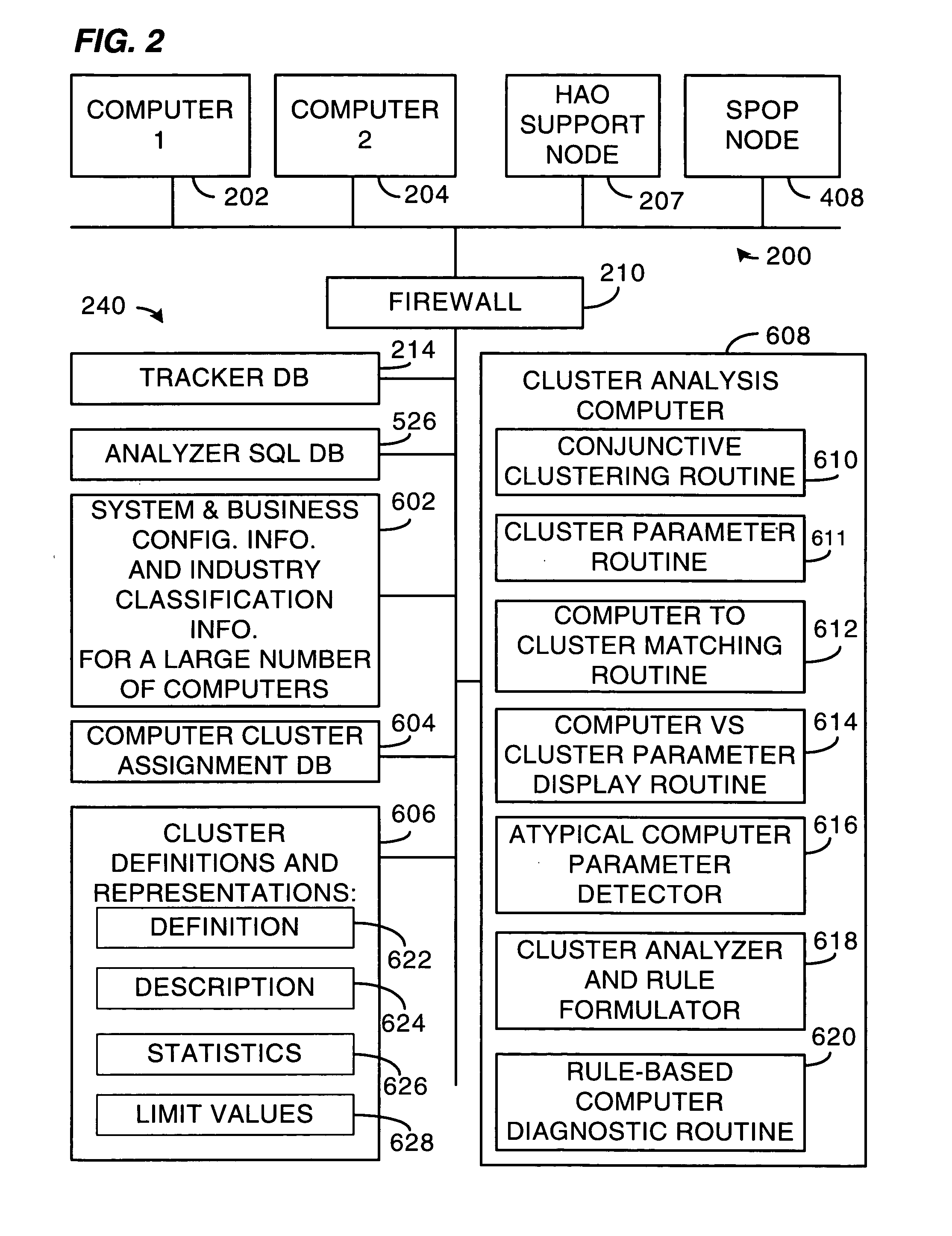
Method and system for clustering computers into peer groups and comparing individual computers to their peers
A method and system for identifying clusters of similarly-configured computers. The method, for example, comprises gathering system and business configuration information values from a set of computers. Next, at least a portion of the system and business configuration information values gathered from the set of computers is analyzed along with the numbers of computers that are configured in various ways. Then, using the result of the analysis as a guide, logical expressions of configuration information values are selected for use as definitions of one or more clusters of similarly-configured computers, the selection process generally maximizing the number of computers included within each cluster and also generally maximizing the number of configuration information value specifications included within the definition of each cluster. Then, for one or more clusters so defined and selected, one or more statistics or limit values are generated from one or more configuration information values or both gathered from the subset of computers included in the one or more clusters.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Systems and methods for custom grouping of data
InactiveUS6996569B1Improve filtering effectEasy to sortData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalGroup elementResult set
A system and method for creating a custom grouping of data in a database. A custom group object is created, a plurality of custom group elements are defined, each of the custom group elements being a subset of the custom group object and being defined by a different filter, each one of the different filters representing a logical expression of qualifications based on the data or a derived calculation of the data. Each of the different filters is resolved against the data or a subset of the data, and the plurality of custom group elements are grouped into a consolidated result set which in not naturally existing in the data structure.
Owner:REPORTING TECH
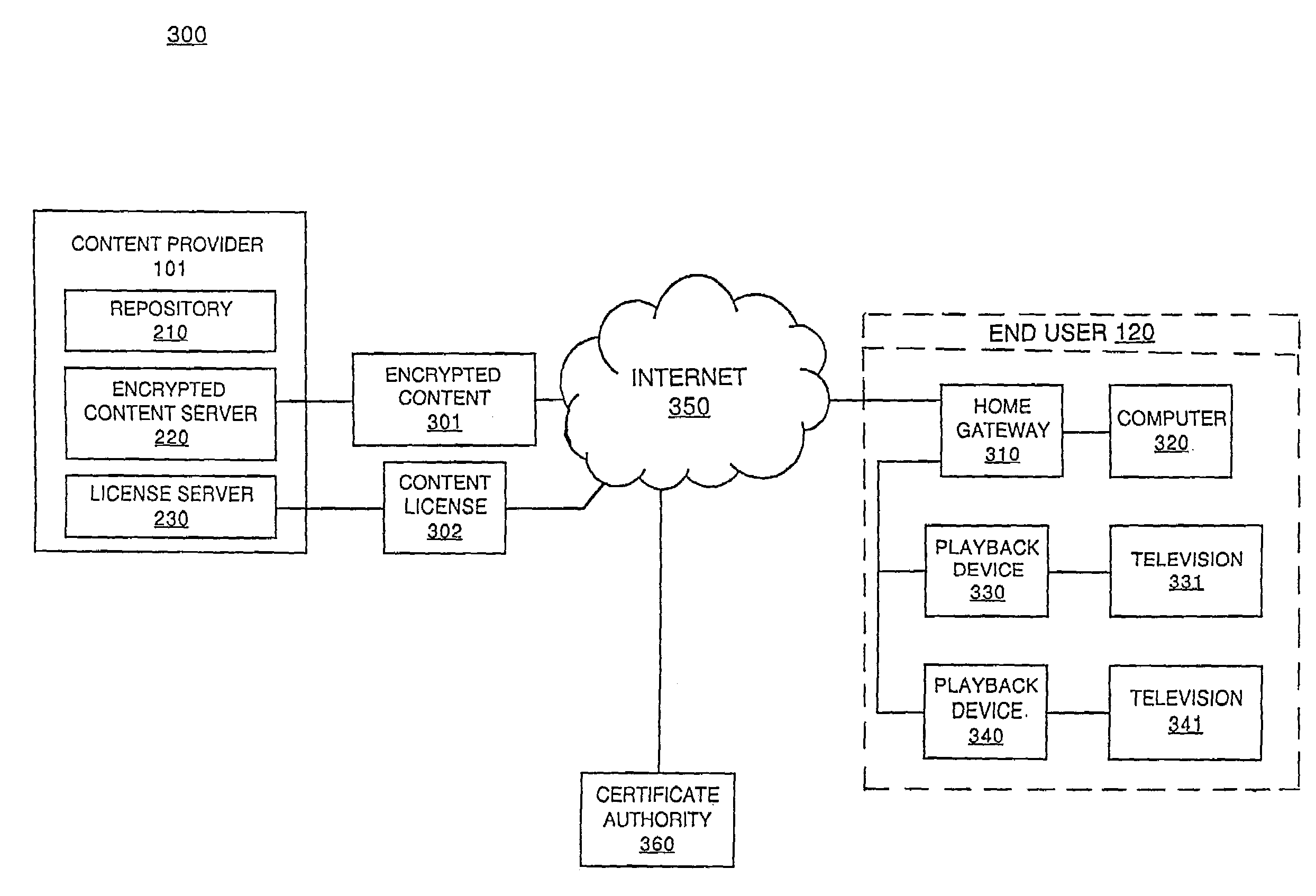
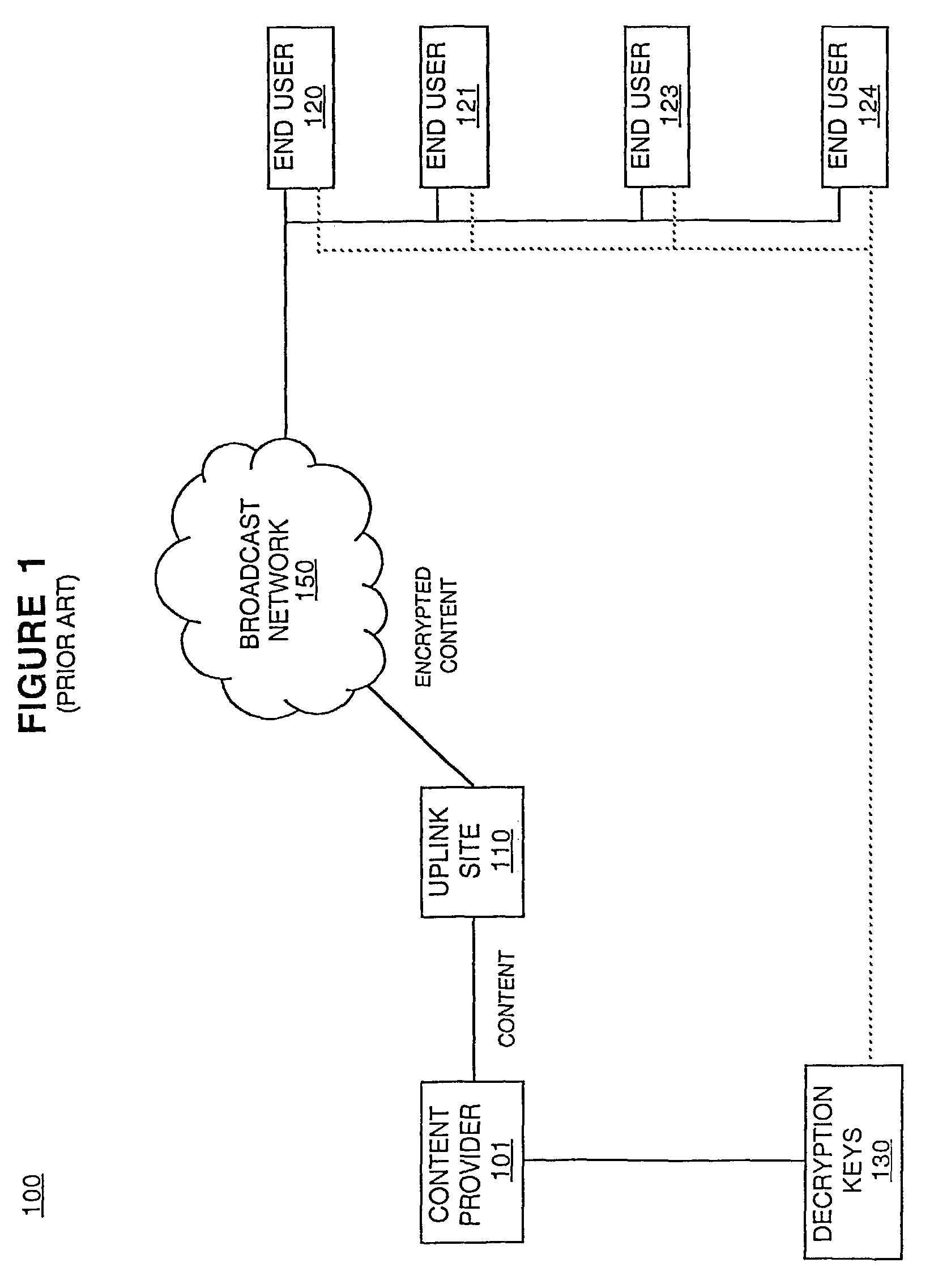
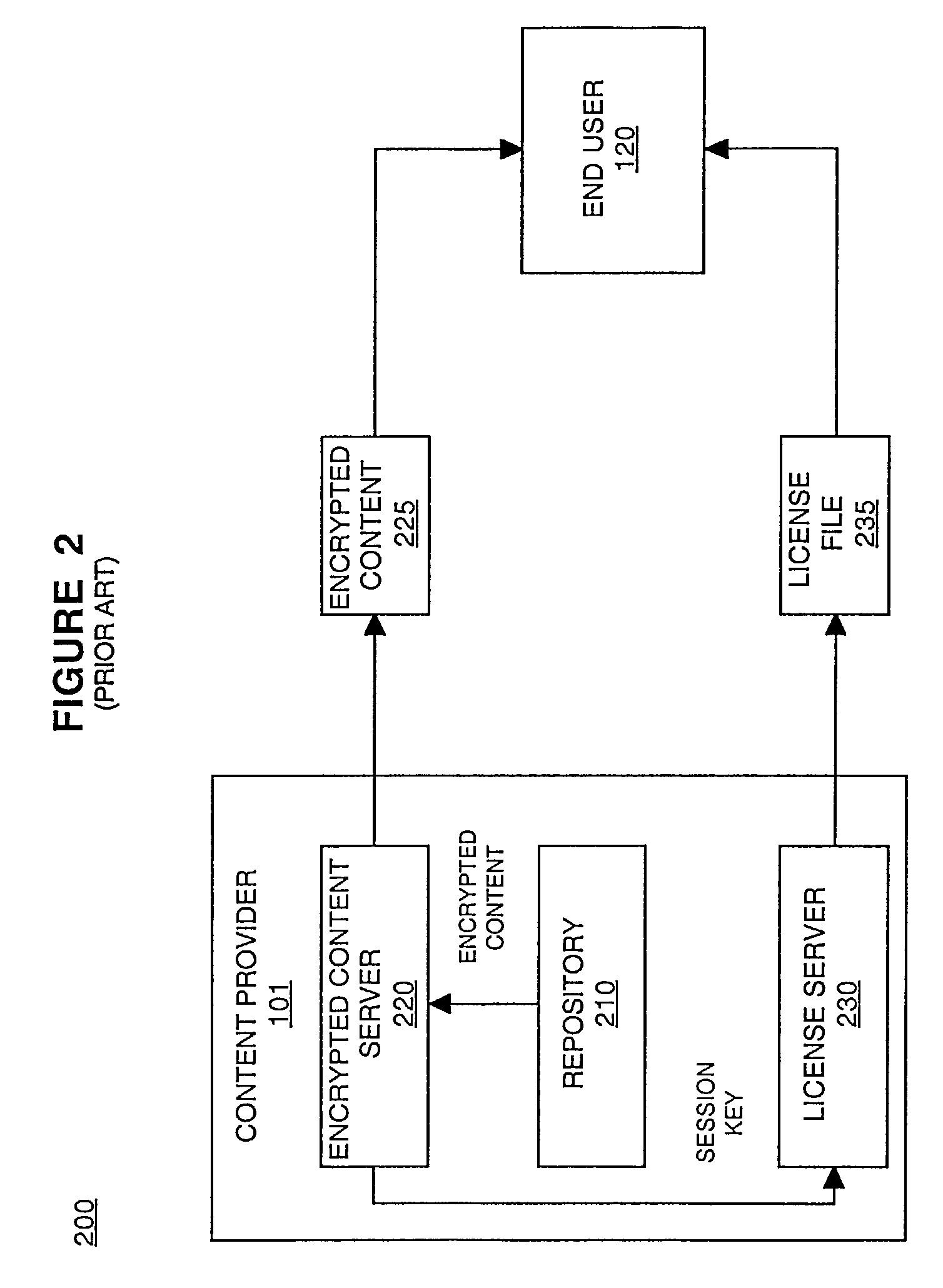
Method and system for implementing digital rights management
ActiveUS7278165B2Improve convenienceIncrease flexibilityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital contentNumber content
In one embodiment, a content license is created that defines parameters for accessing a piece of digital content. A first logical expression in the content license defines a plurality of playback devices that are authorized to access the piece of digital content. A second logical expression in the content license defines at least one time interval when the plurality of playback devices are authorized to access the piece of digital content. The content license is used to access the piece of digital content.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
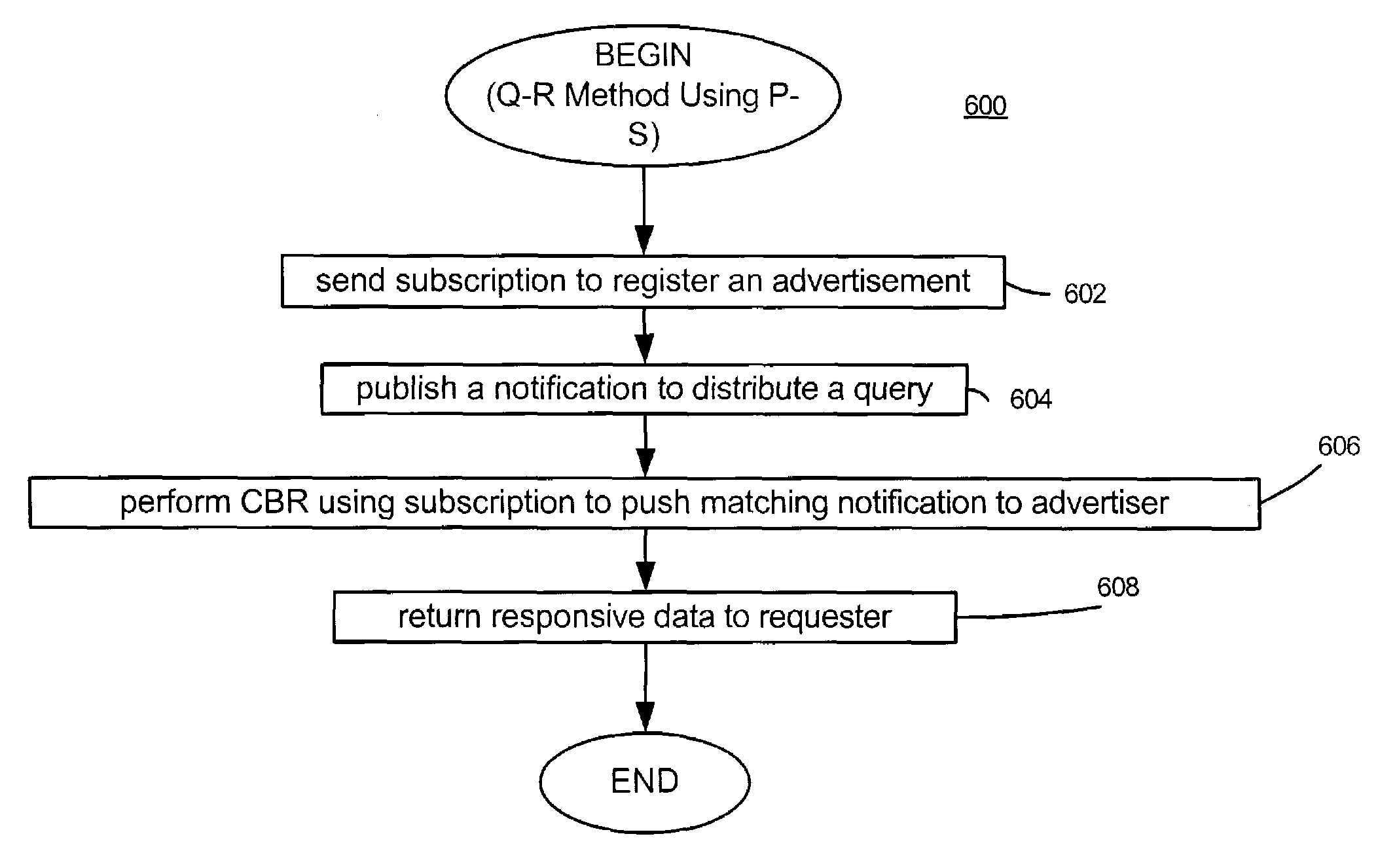
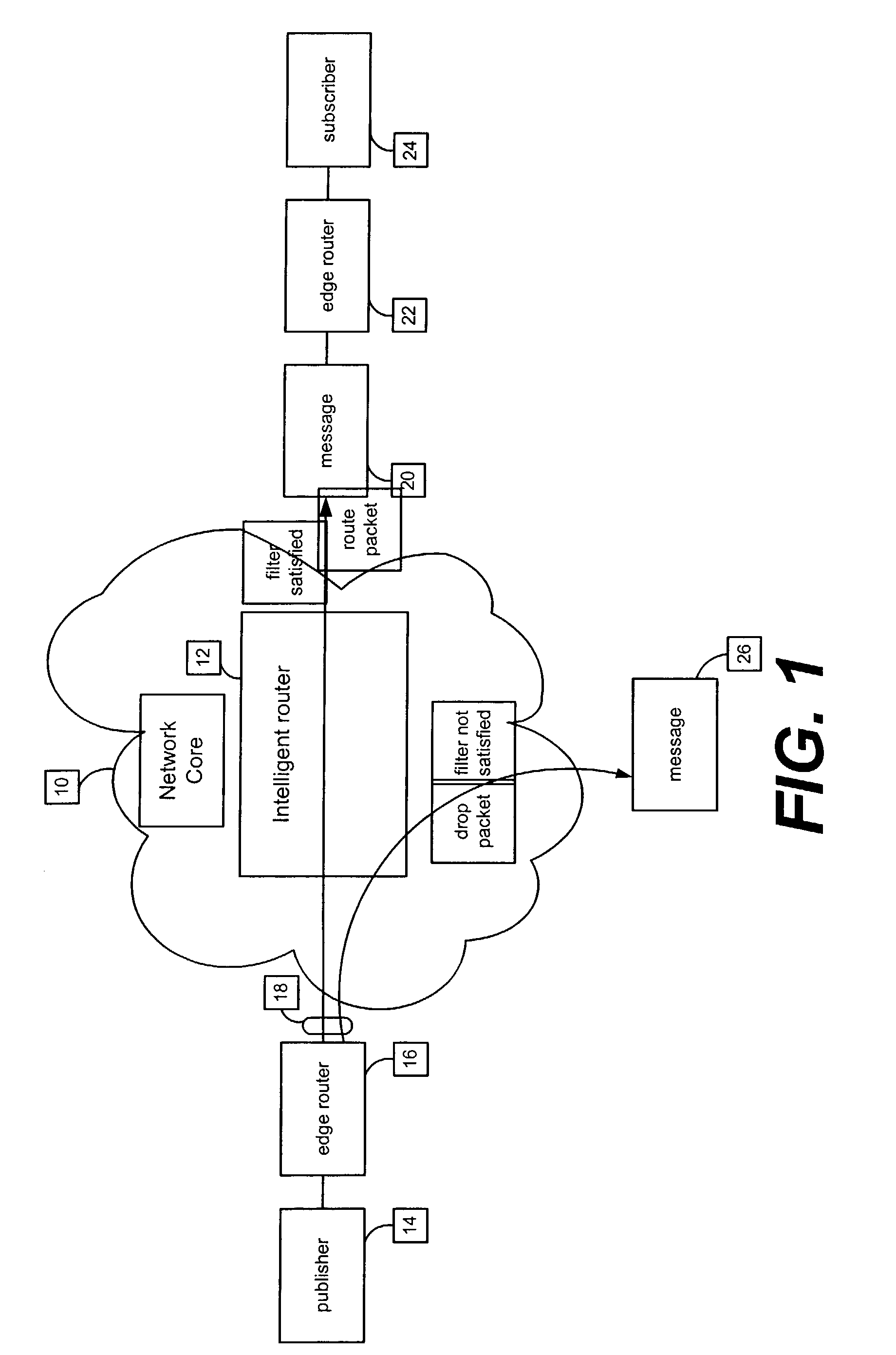
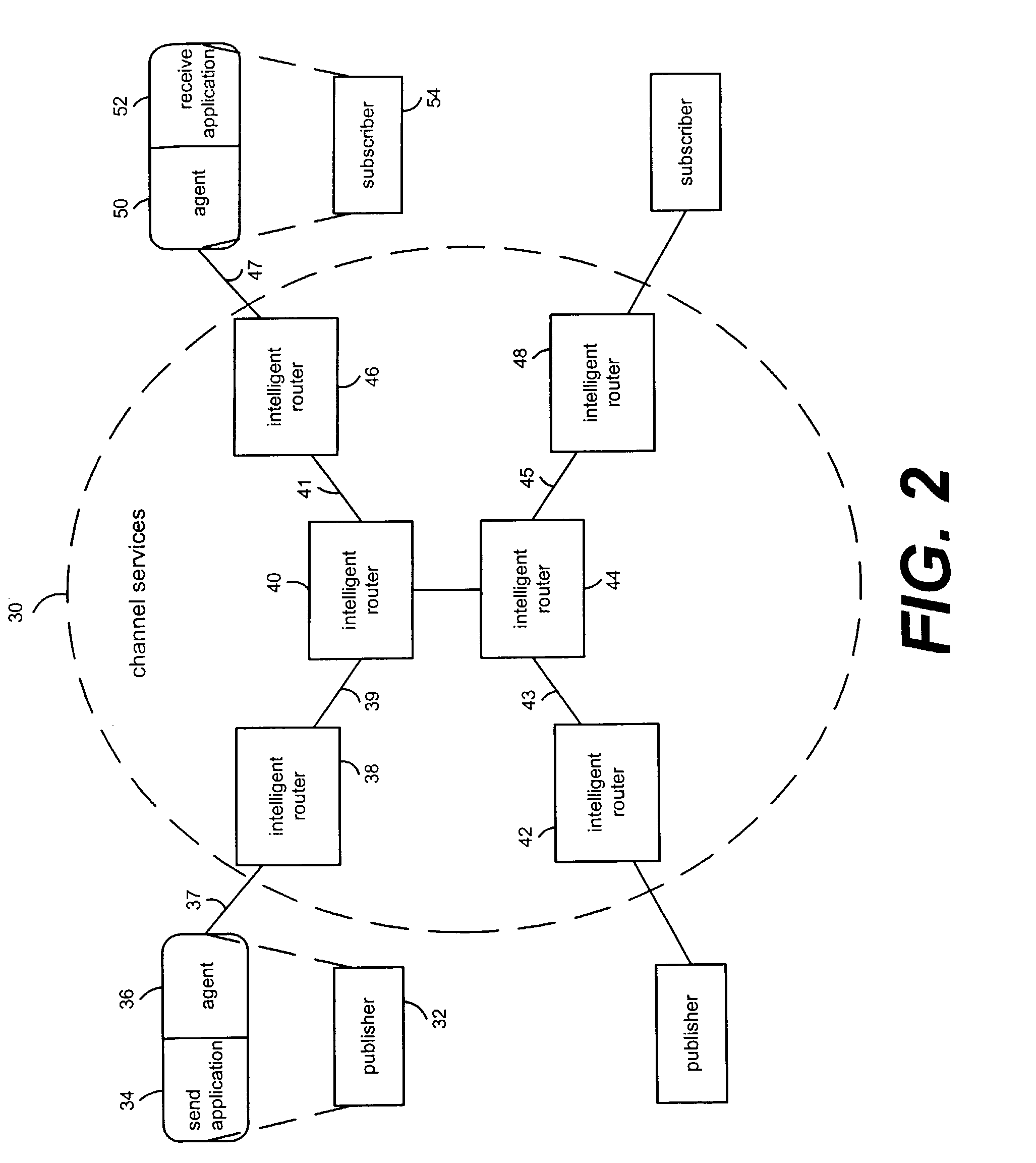
Method and apparatus for implementing query-response interactions in a publish-subscribe network
A method and apparatus provide for implementing query-response interactions on a publish-subscribe network. An advertisement relating to a data set and a query representing a logical expression are received. The advertisement is mapped to a corresponding subscription. The query is mapped to a corresponding notification. The subscription and the notification are used for implementing of the advertisement and the query in the network.
Owner:PRECACHE
Method and system for rapid evaluation of logical expressions
InactiveUS7636697B1Less gateRemove major bottleneckDigital computer detailsMachine learningTheoretical computer scienceLogical connective
Methods and systems capable of determining which subset of a set of logical expressions are true with relatively few evaluations of the primitives that, together with any standard logical connectives, make up the logical expressions. A plurality of directed acyclic graphs, each graph including at least one root node, at least one leaf node, and at least one non-leaf node associated with a leaf node. Each node is associated with a, possibly empty, subset of presumed to be true logical expressions. Each non-leaf node is associated with one of the primitives mentioned in any of the logical expressions. Edges are defined between two of the nodes, each edge being associated with a possible value, or range of possible values, of the primitive associated with the node at the tail of the edge. Paths are defined through each of the directed acyclic graphs from a root node to a leaf node by recursively following each edge corresponding to the current value of the primitive at a selected non-leaf node. Lastly, subsets of logical expressions associated with the nodes on the defined paths are collated to yield a subset of logical expressions that are true.
Owner:YEN WEI
Method and apparatus and program storage device adapted for automatic qualitative and quantitative risk assesssment based on technical wellbore design and earth properties
A Software System, known as an Automatic Well Planning Risk Assessment Software System, is adapted to determine and display risk information in response to a plurality of input data by: receiving the plurality of input data, the input data including a plurality of input data calculation results; comparing each calculation result of the plurality of input data calculation results with each logical expression of a plurality of logical expressions; ranking by the logical expression the calculation result; and generating a plurality of ranked risk values in response thereto, each of the plurality of ranked risk values representing an input data calculation result that has been ranked by the logical expression as either a high risk or a medium risk or a low risk; generating the risk information in response to the plurality of ranked risk values; and displaying the risk information.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
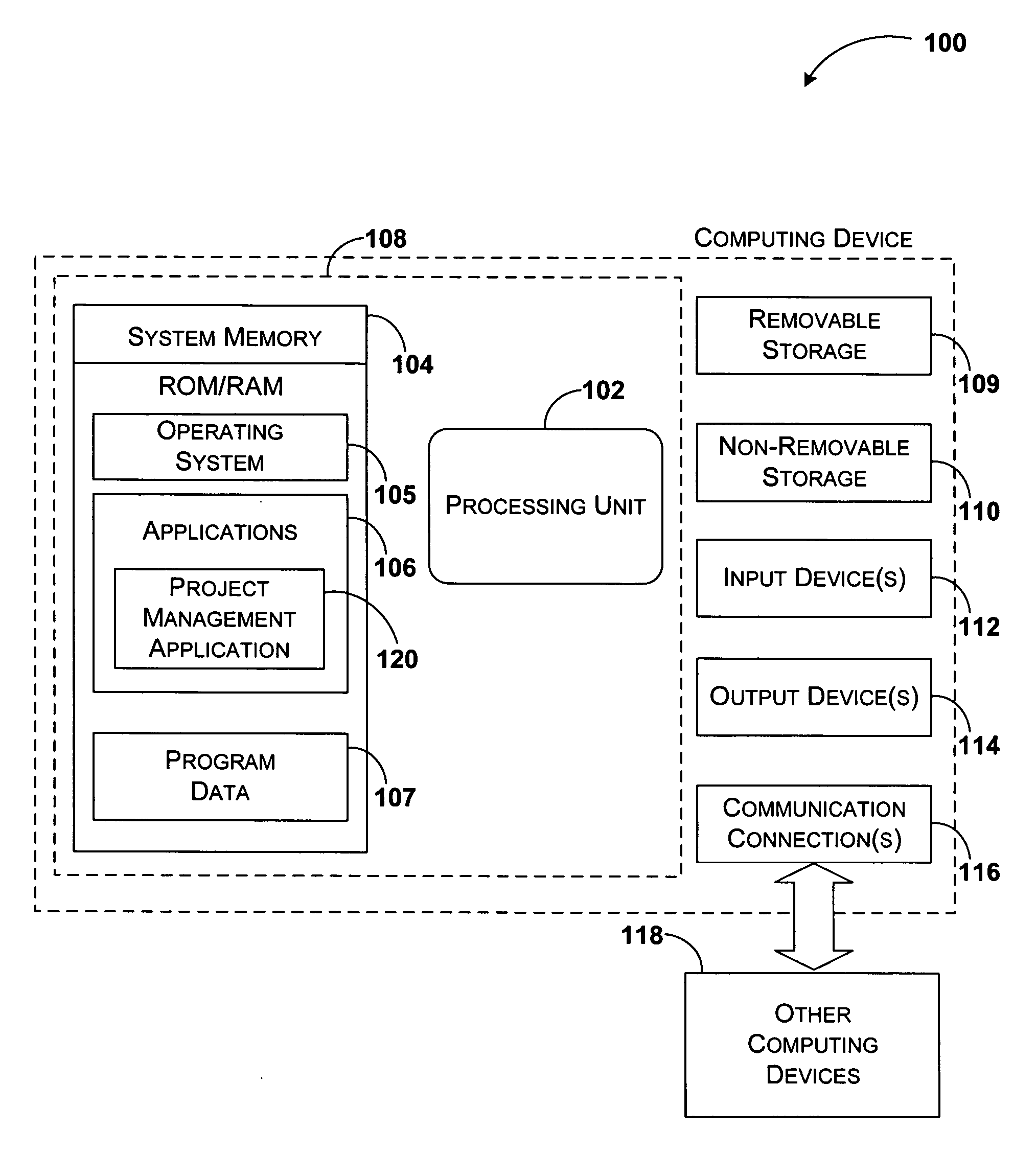
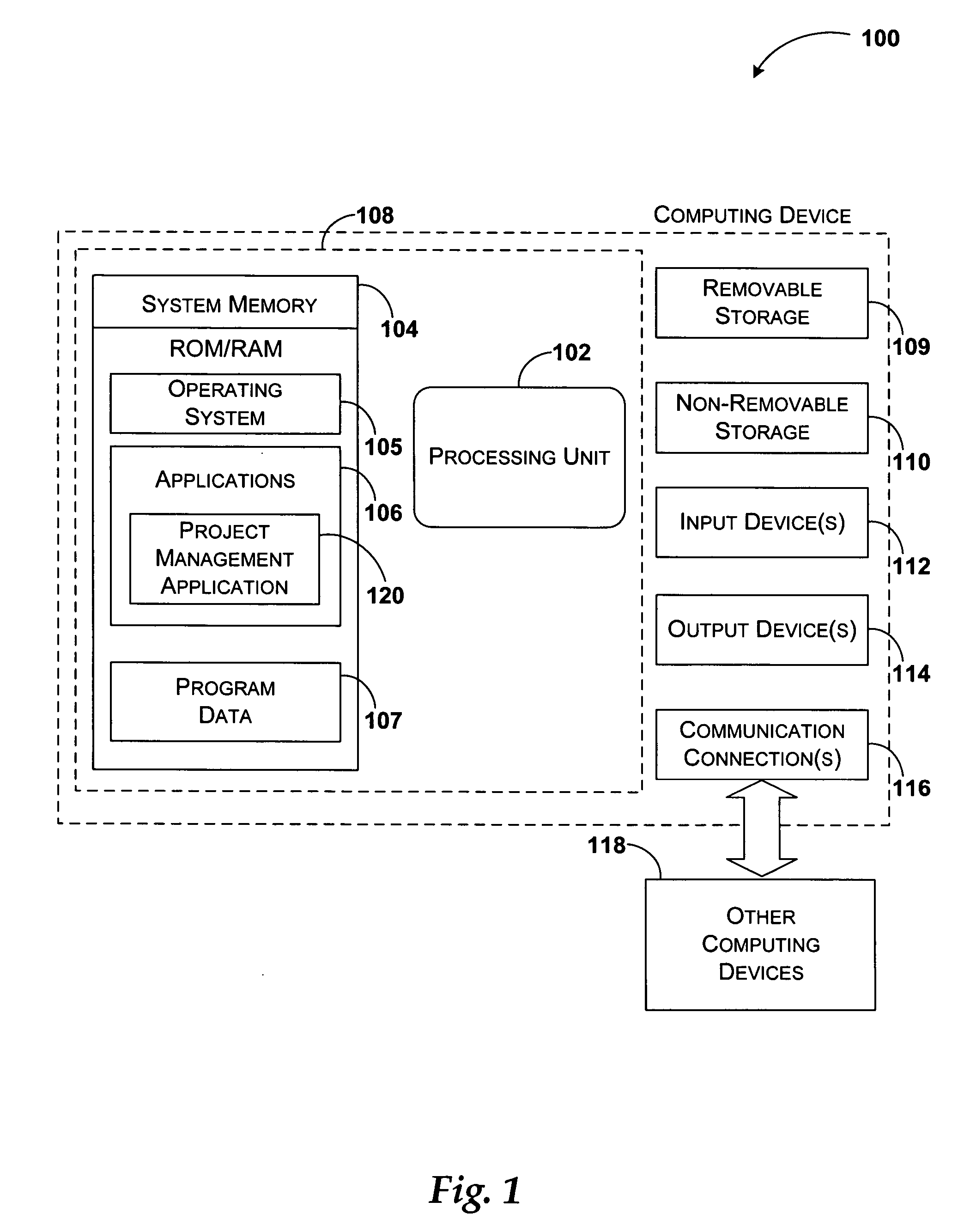
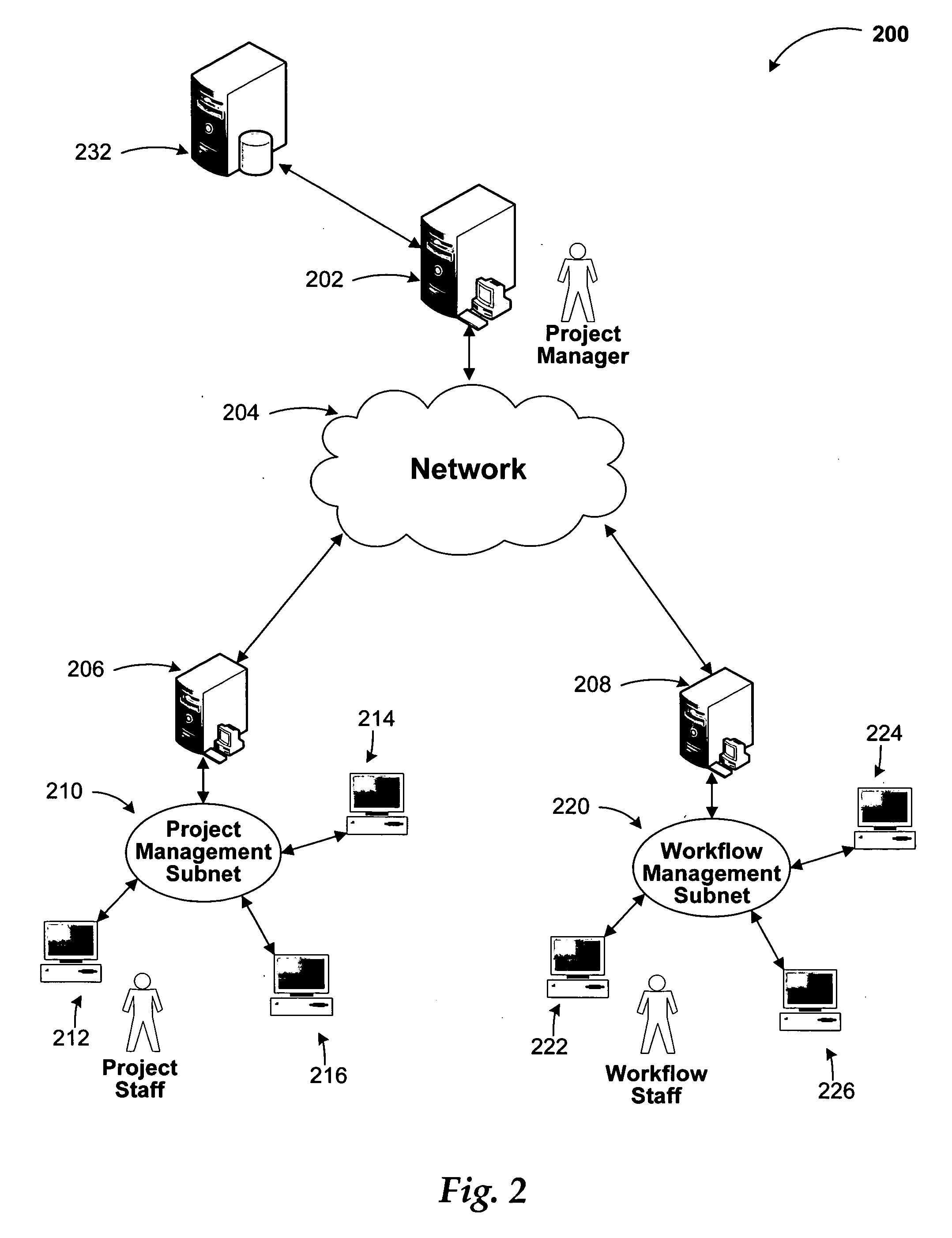
System and method for integrating workflow processes with a project management system
A project management system is integrated with a workflow engine to provide automatic coordination of project tasks and workflow processes. The workflow engine provides support for defining logical expressions that determine a path of execution for the defined workflow tasks. In addition to composition capabilities, the workflow engine may execute and track the defined processes. The project management system provides a platform for defining the project plan that includes tasks and resources. Tasks are annotated defining their behavior and implementation and exported to the workflow system. The workflow system substitutes project tasks with the appropriate workflow activities and provides feedback upon execution of the activities.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
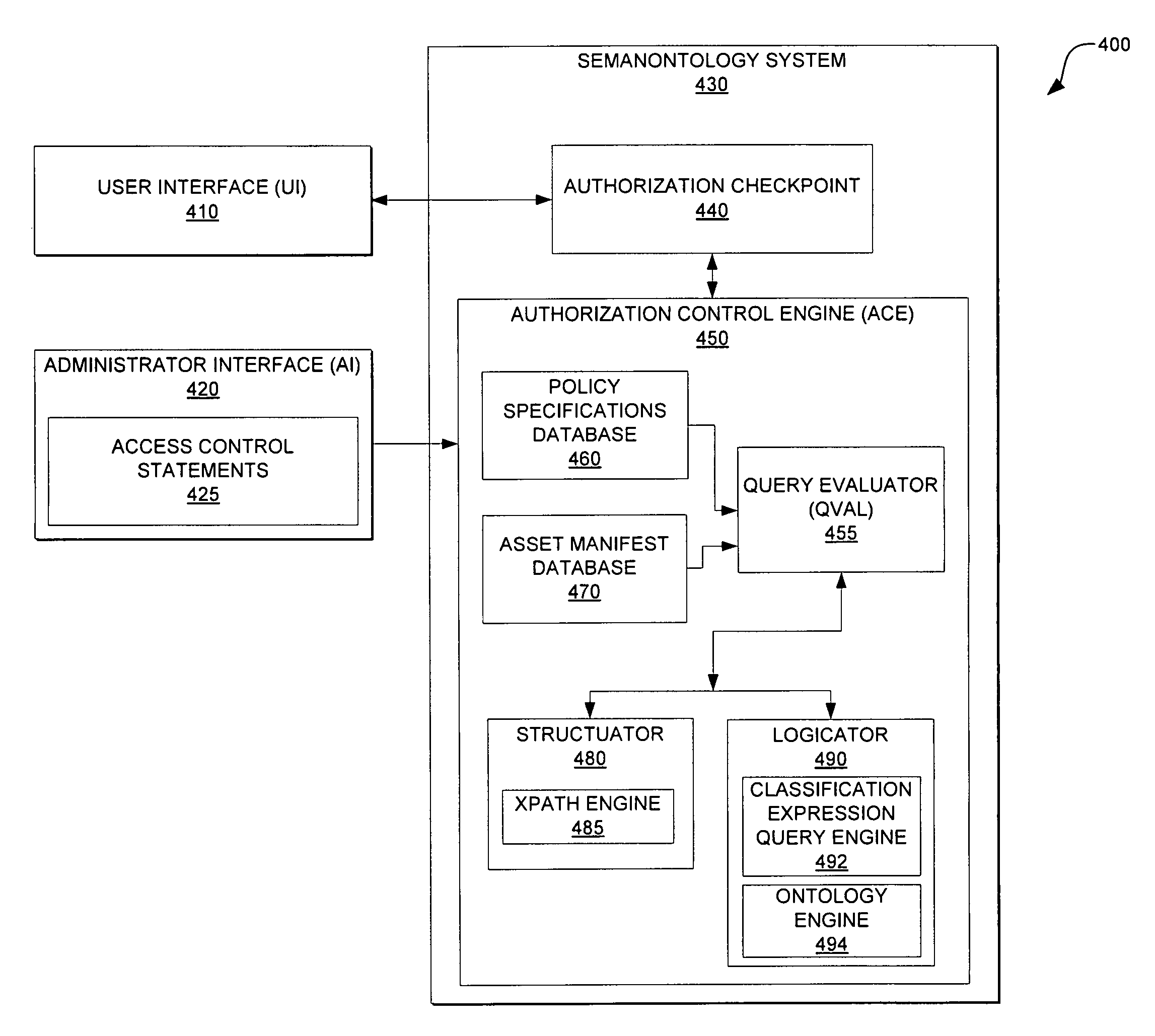
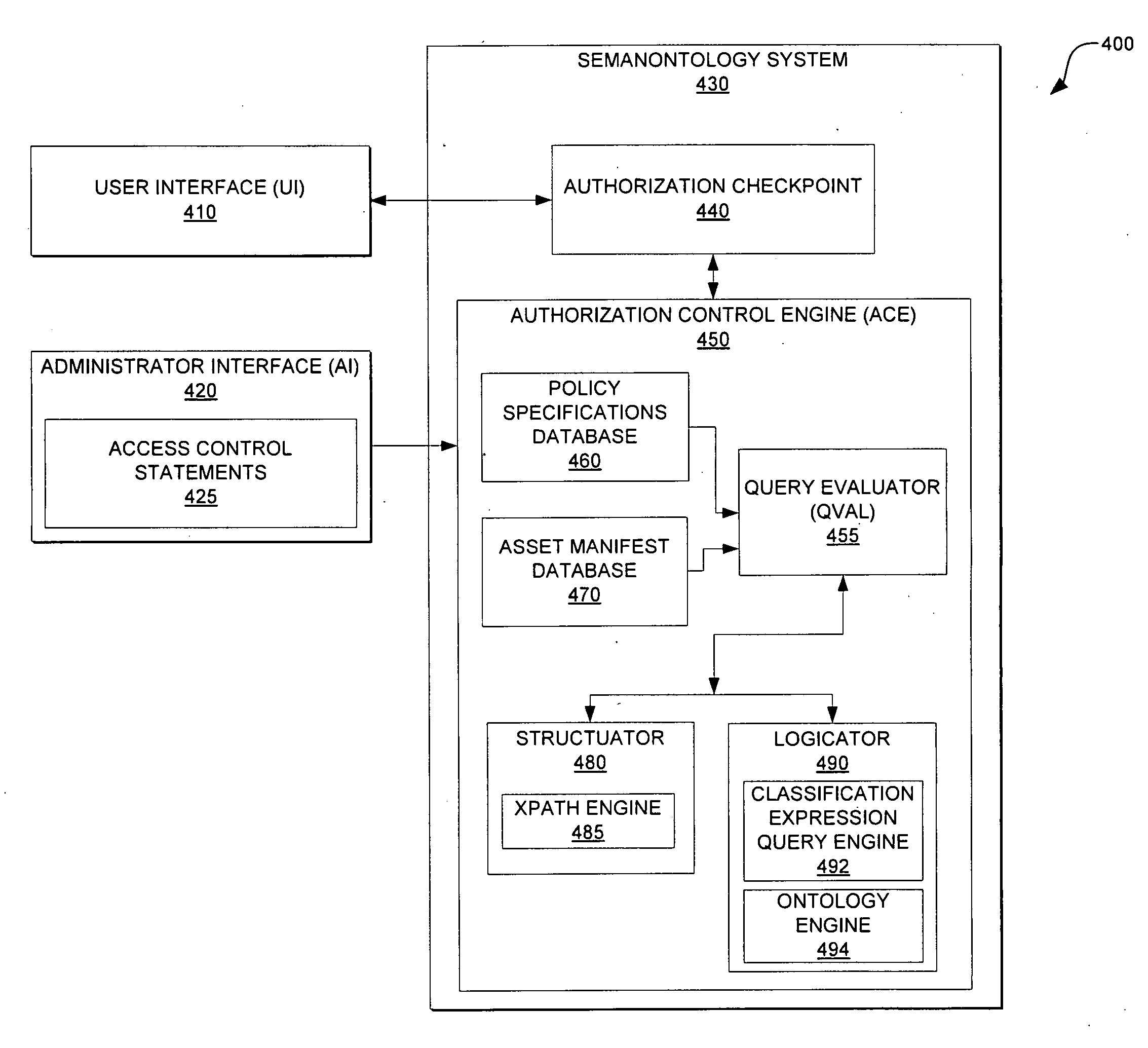
Using xpath and ontology engine in authorization control of assets and resources
InactiveUS8561100B2Easy to integrateDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSemanticsXPath
An embodiment defines access control allowing the expression of access control rules using ontology based semantics and references an ontology subset using XPath as the ontological expression. The access control rules or access criteria are defined by an access control statement and may be expressed using classification criteria and ontology classes. The access control statement comprises a structural description that is used to define an asset and a logical expression that may be used to express the classification criteria. The access control statement defines access policy for various assets.
Owner:IBM CORP
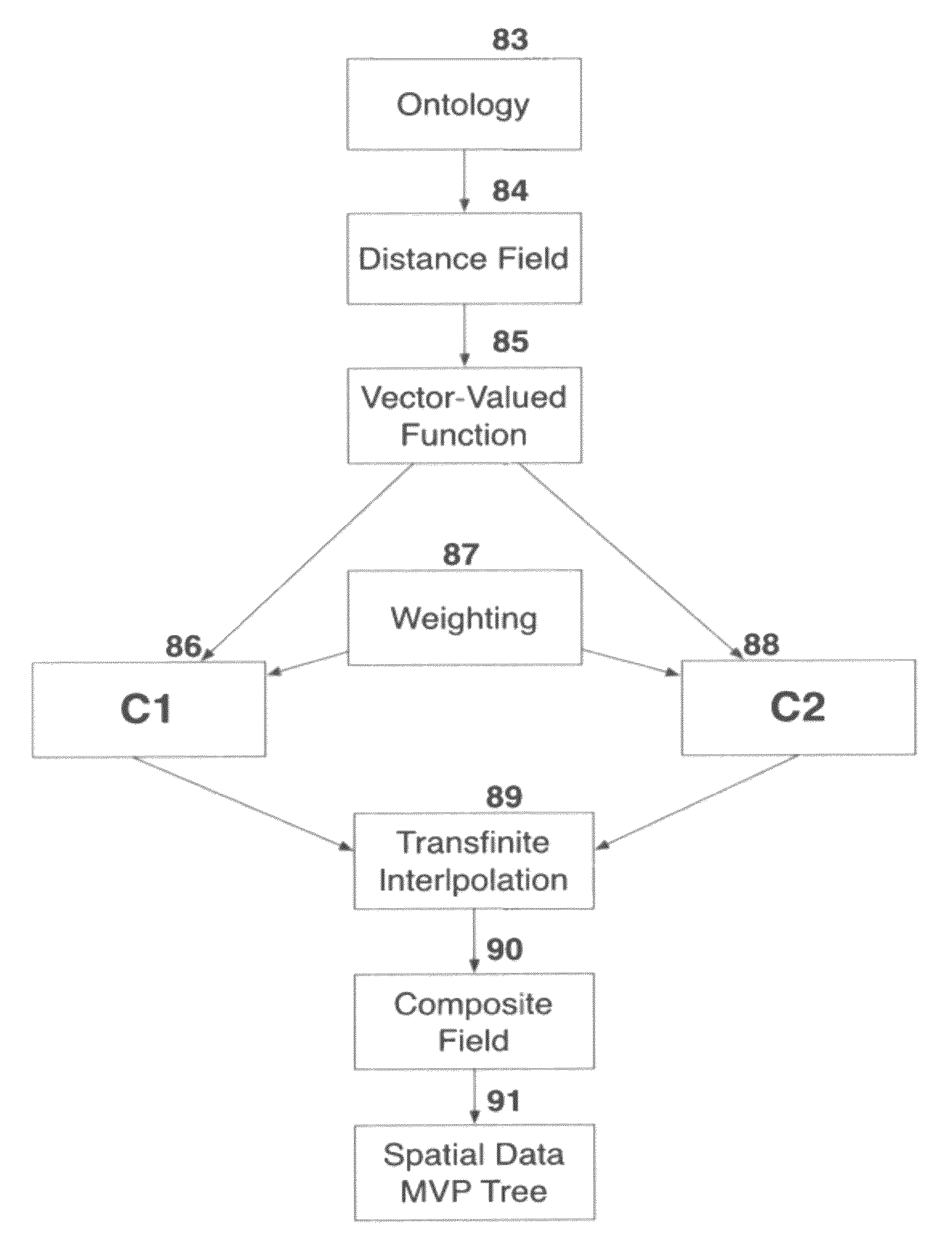
Relativistic concept measuring system for data clustering
ActiveUS20120233188A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheory of relativityData mining
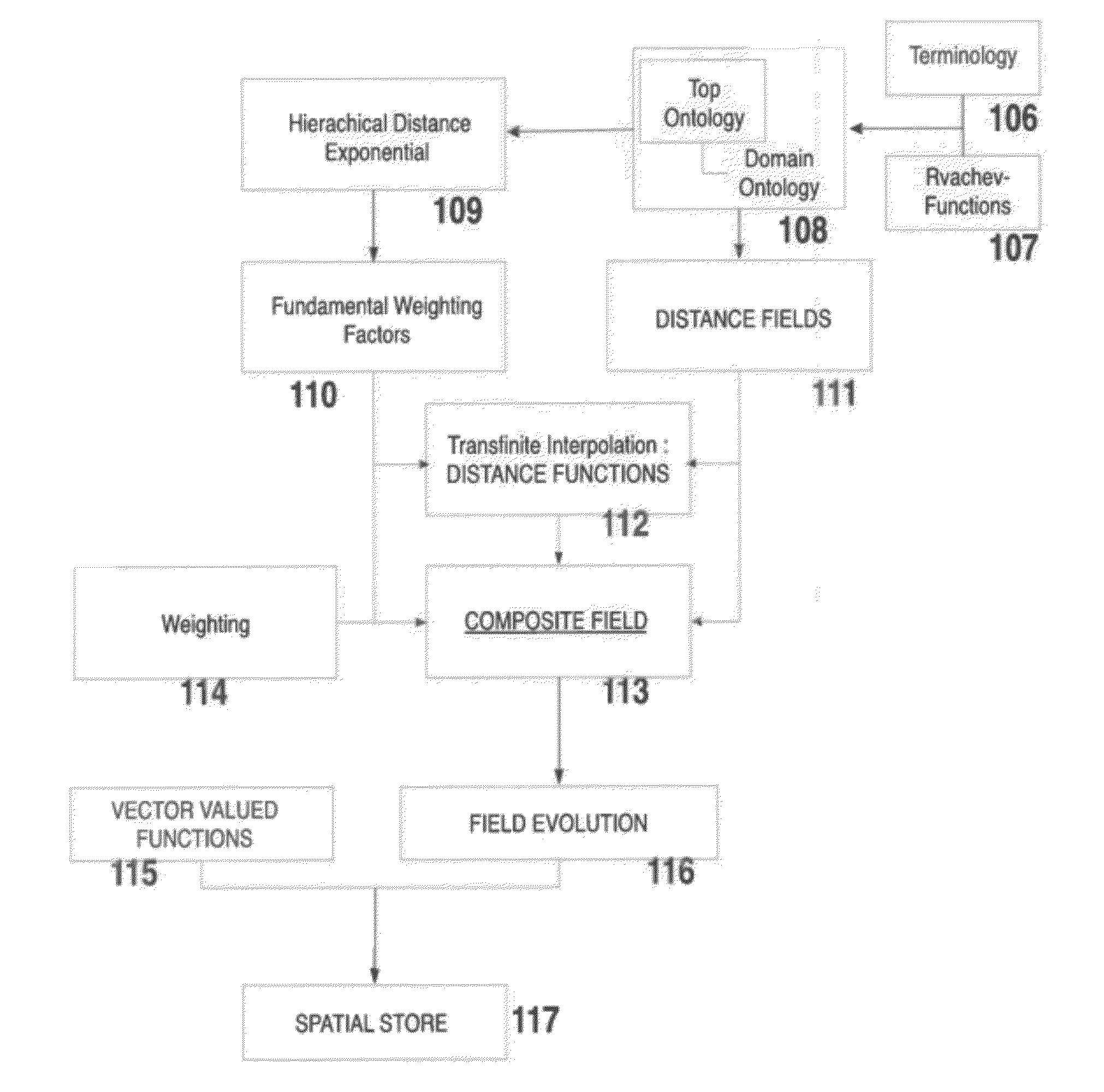
A method and apparatus for mapping concepts and attributes to distance fields via rvachev-functions. The steps including generating, for a plurality of objects, equations representing boundaries of attributes for each respective object, converting, for a plurality of objects, the equations into greater than or equal to zero type inequalities, generating, for a plurality of objects, a logical expression combining regions of space defined by the inequalities into a semantic entity, and substituting, for a plurality of objects, the logical expression with a corresponding rvachev-function such that the resulting rvachev-function is equal to 0 on a boundary of the semantic entity, greater then 0 inside a region of the semantic entity, and less then 0 outside the region of the semantic entity. Also included is the step of generating a composite rvachev-function representing logical statements corresponding to the plurality of objects using the respective rvachev-functions of the objects.
Owner:KYNDI
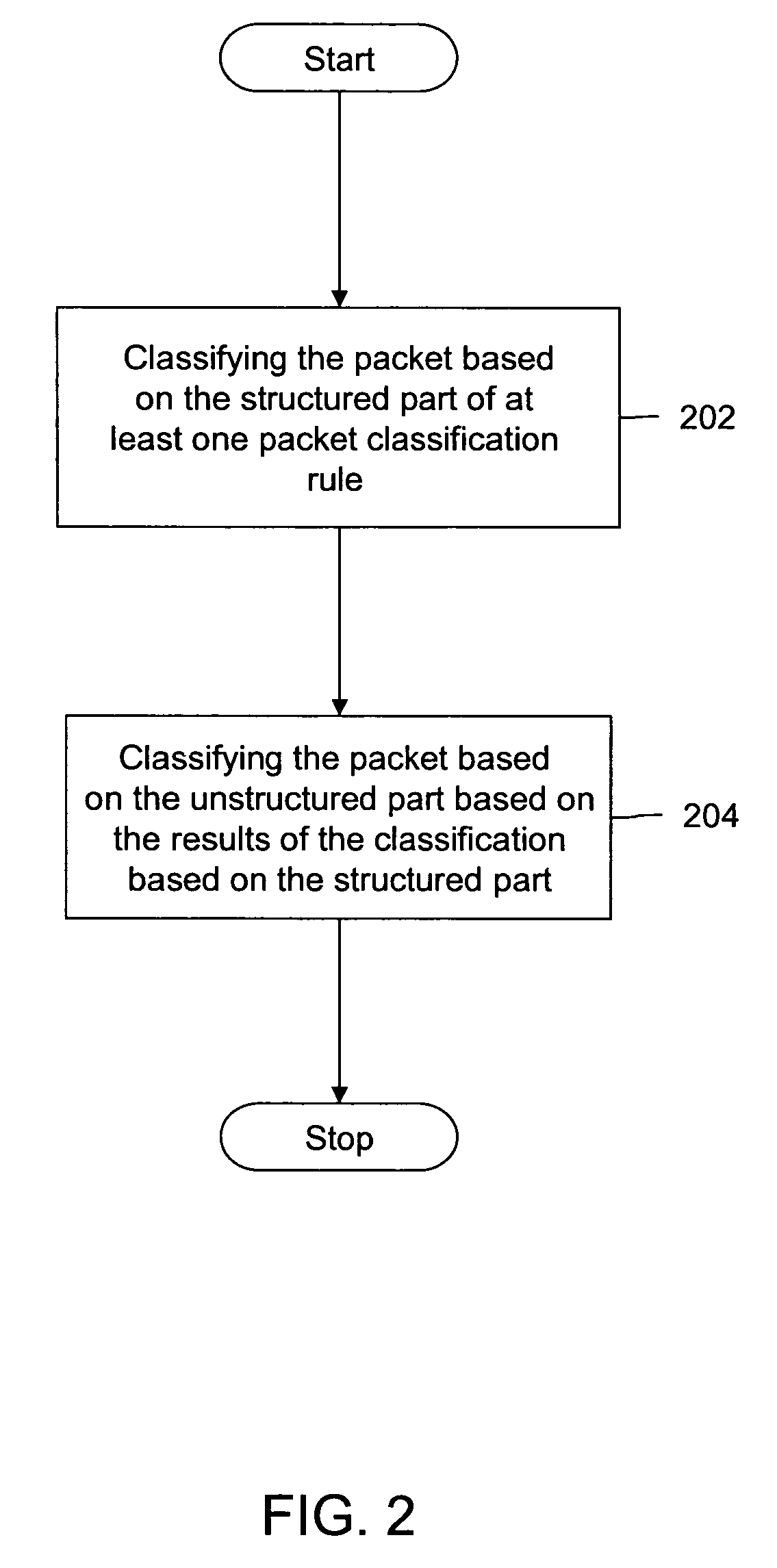
Method and system for classification of packets based on meta-rules
InactiveUS7474654B2Data switching by path configurationMemory systemsClassification methodsClassification rule
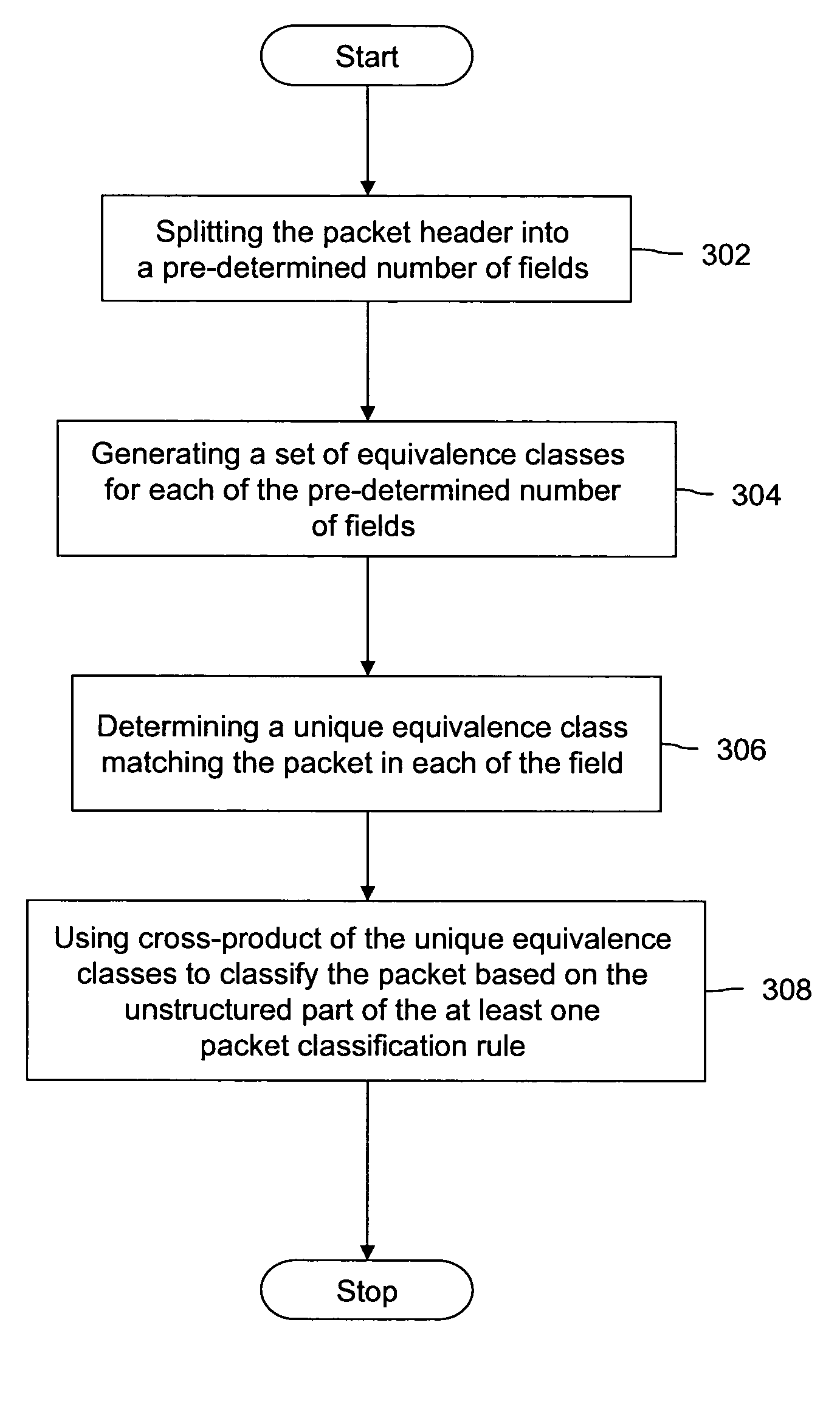
A method and apparatus for classification of packets is provided. The method includes classifying the packets based on the structured part of at least one packet classification rule, and classifying the packets based on the unstructured part of the at least one packet classification rule, the classification being done based on the structured classification results. The packet classification method provides a technique for splitting the n-dimensional space of the packet header fields into disjoint regions. The splitting is done such that all the packets falling into a region have the same packet classification result. The first packet falling into a region takes a longer time for classification, where the logical expression resulting from user-configured rule is solved. The classification of all subsequent packets falling into the same region gets accelerated and takes less time than the first packet to classify.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for clustering computers into peer groups and comparing individual computers to their peers
ActiveUS20050289071A1Maximizing numberDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringComputer clusterCollection system
A method and system for identifying clusters of similarly-configured computers. The method, for example, comprises gathering system and business configuration information values from a set of computers. Next, at least a portion of the system and business configuration information values gathered from the set of computers is analyzed along with the numbers of computers that are configured in various ways. Then, using the result of the analysis as a guide, logical expressions of configuration information values are selected for use as definitions of one or more clusters of similarly-configured computers, the selection process generally maximizing the number of computers included within each cluster and also generally maximizing the number of configuration information value specifications included within the definition of each cluster. Then, for one or more clusters so defined and selected, one or more statistics or limit values are generated from one or more configuration information values or both gathered from the subset of computers included in the one or more clusters.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
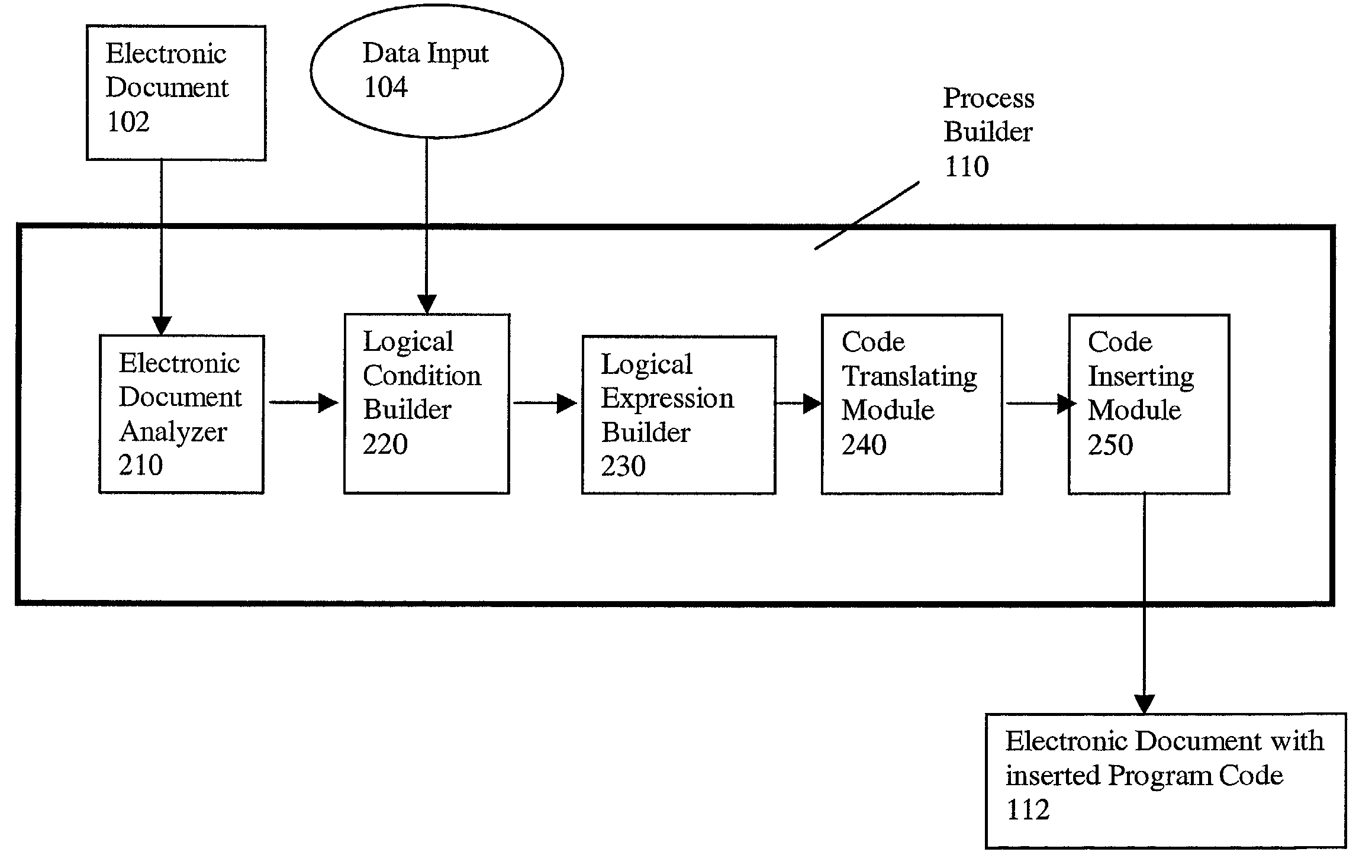
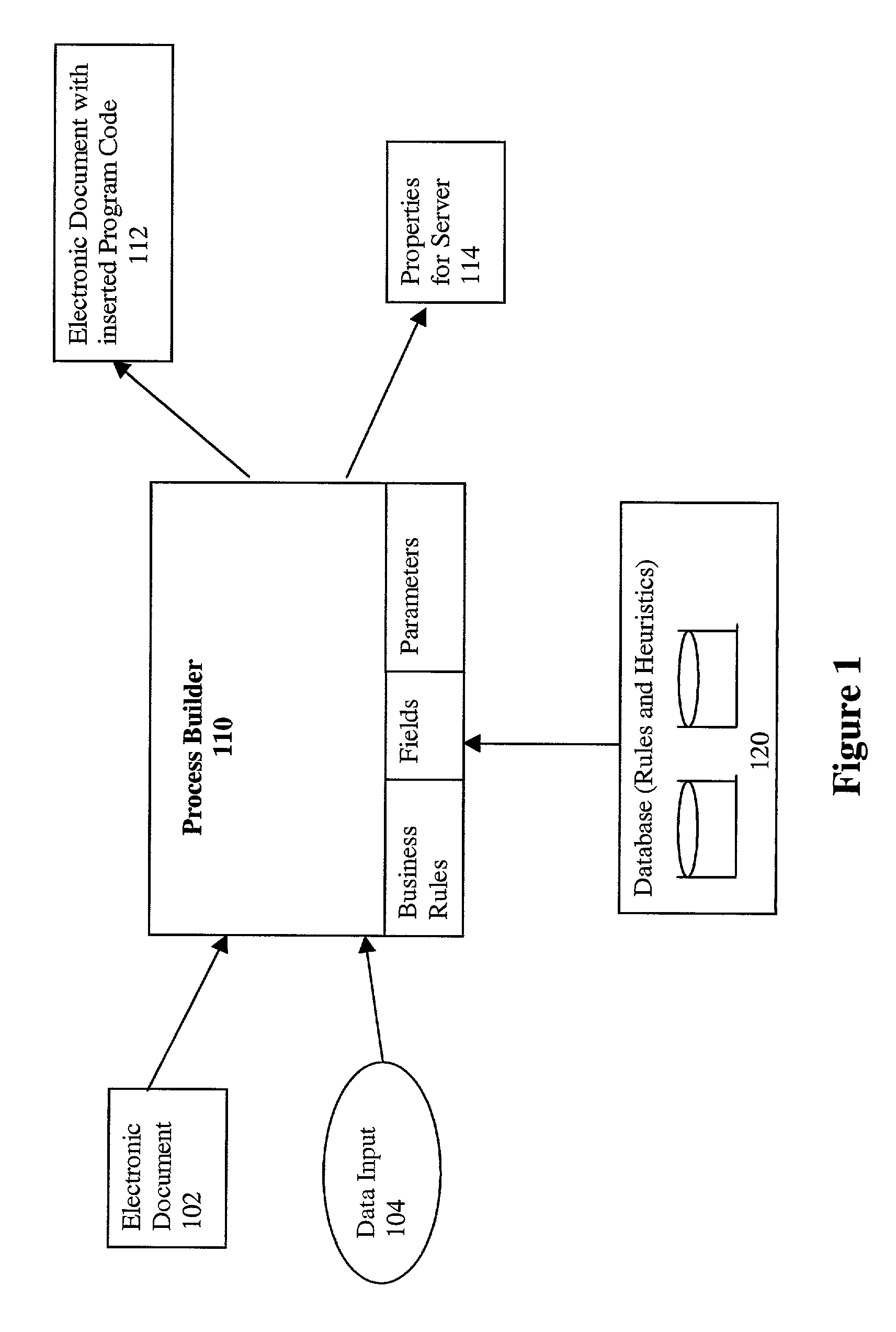
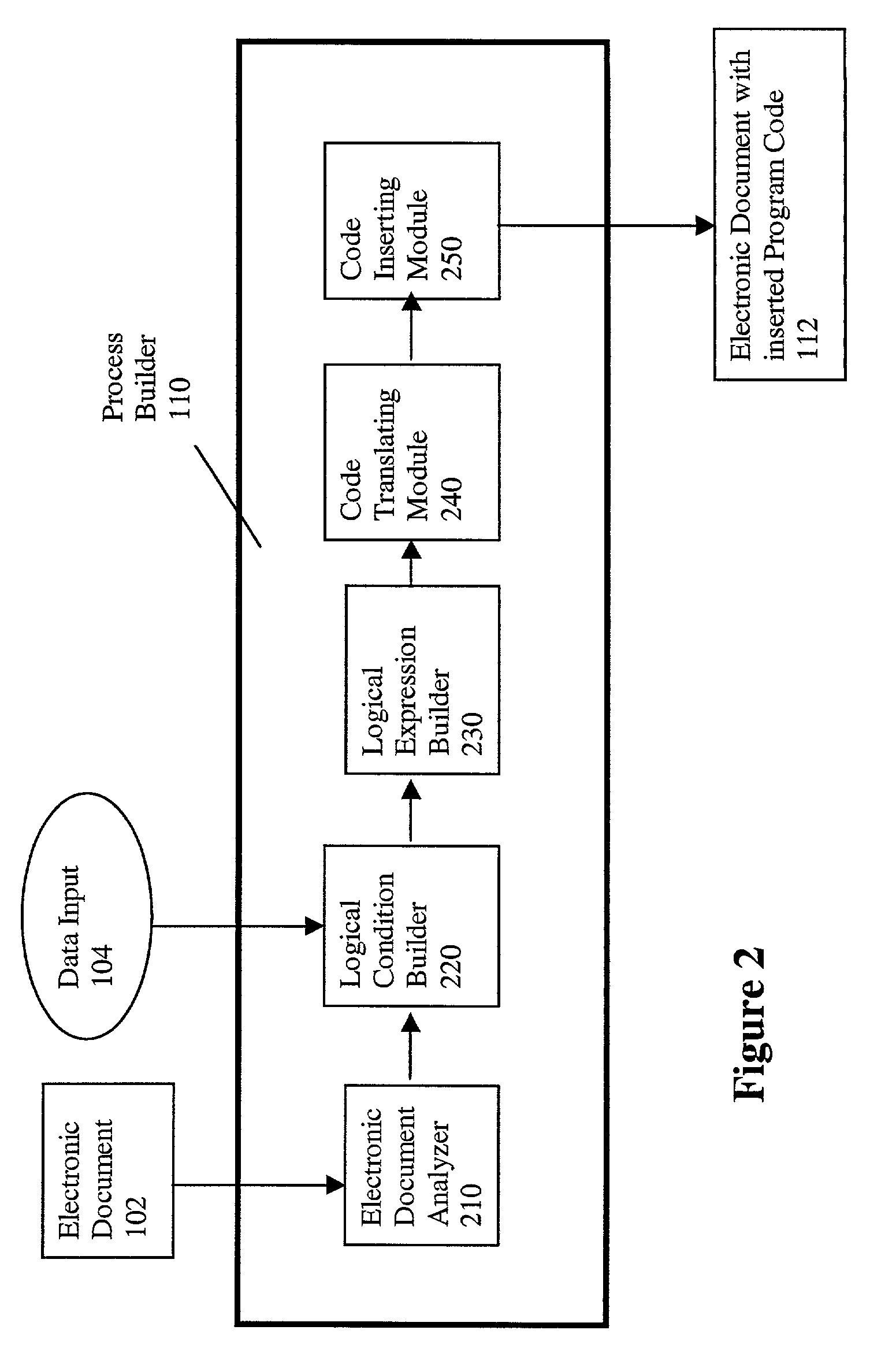
Process builder for a routable electronic document system and method for using the same
InactiveUS7103835B1Digital computer detailsNatural language data processingElectronic documentGraphics
A process builder for a system of routing electronic documents and a method for using the same are provided. The process builder receives an electronic document having programmable features. The process builder determines a number of attributes and form fields from the electronic document. Data input is received by the process builder from an electronic document author via a graphical user interface. The process builder defines logical conditions for one or more of the form fields and attributes based on the received data input, and combines the logical conditions into logical expressions. The process builder then translates the logical expressions into program code and inserts the generated program code into the electronic document.
Owner:MOVARIS
Distributed debugger environment
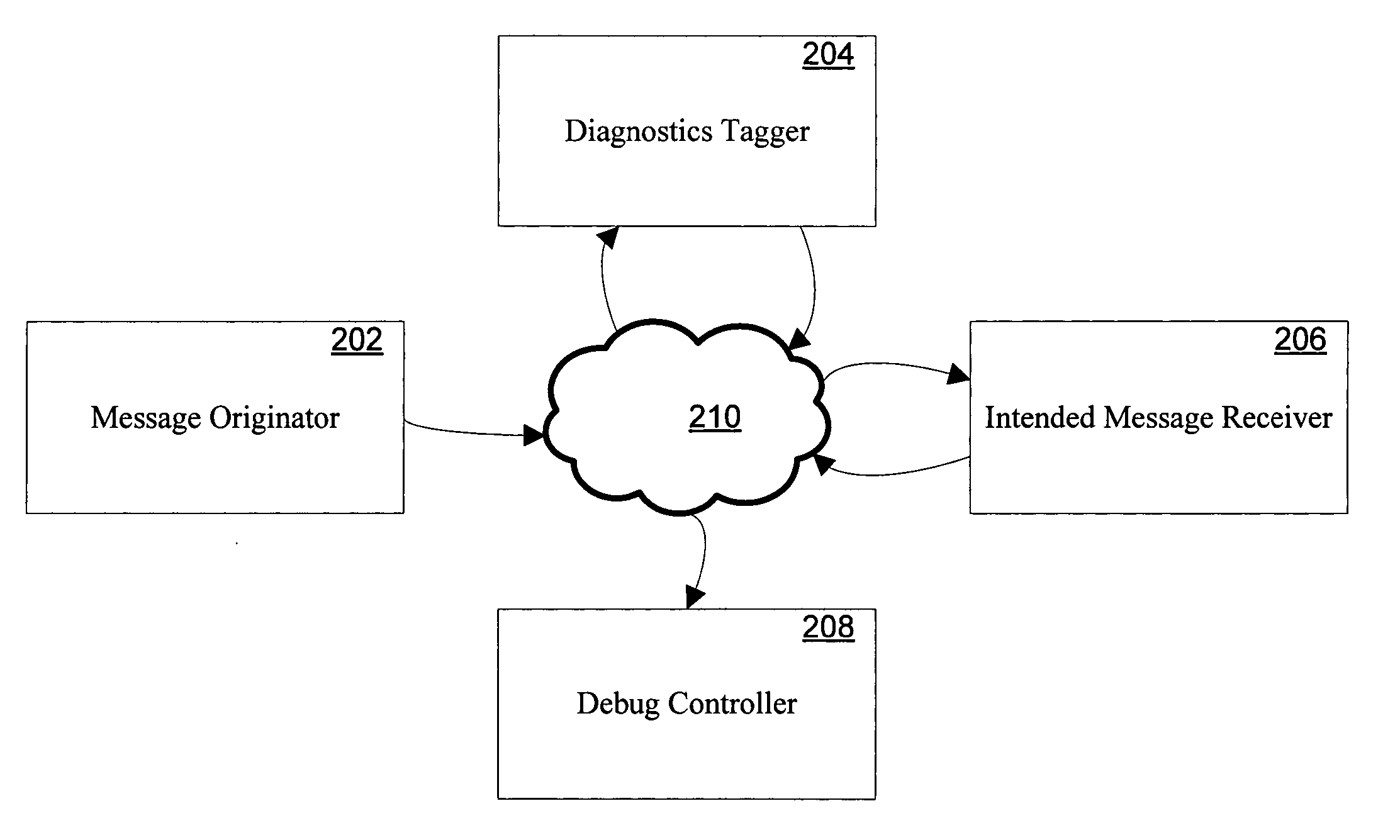
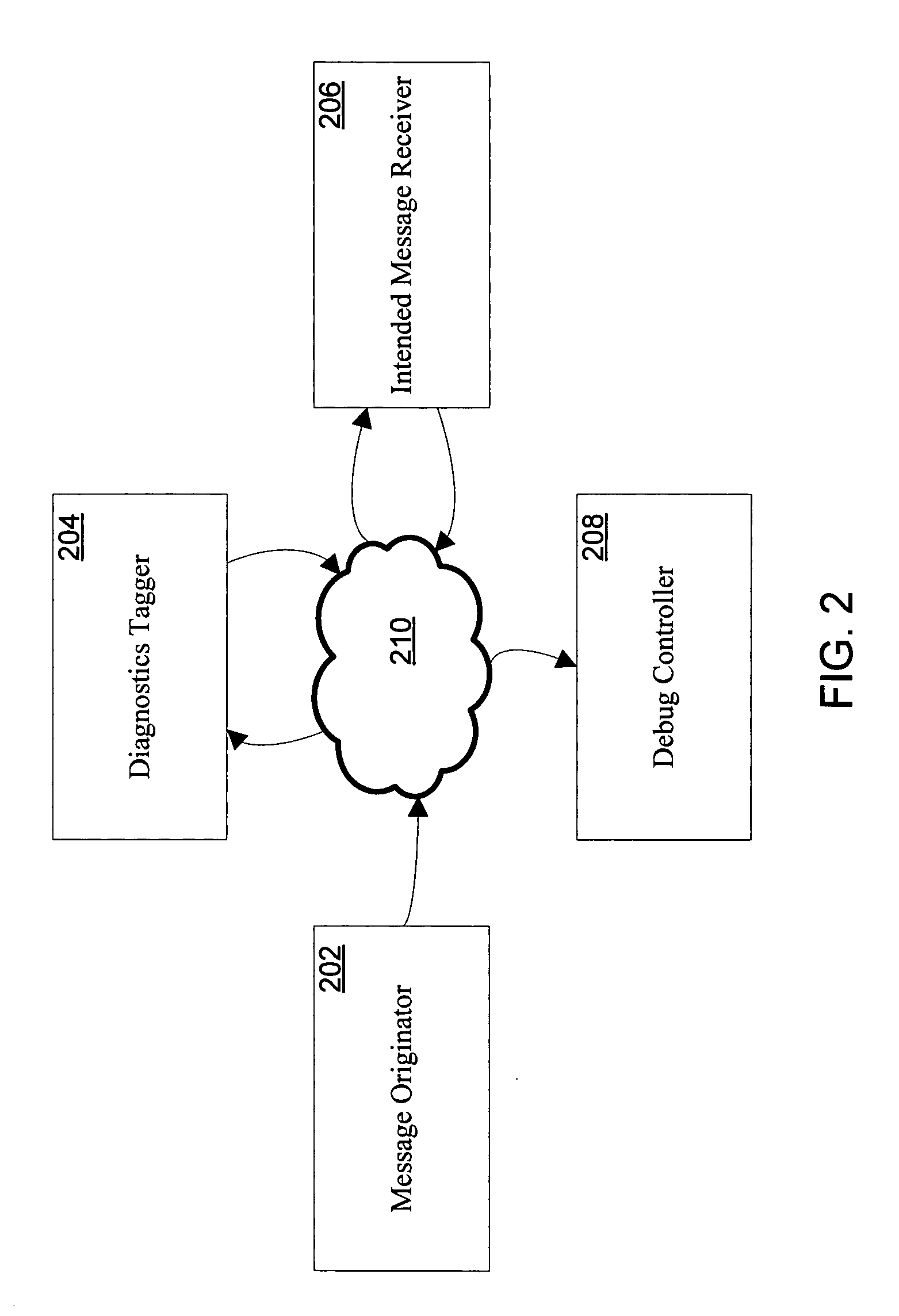
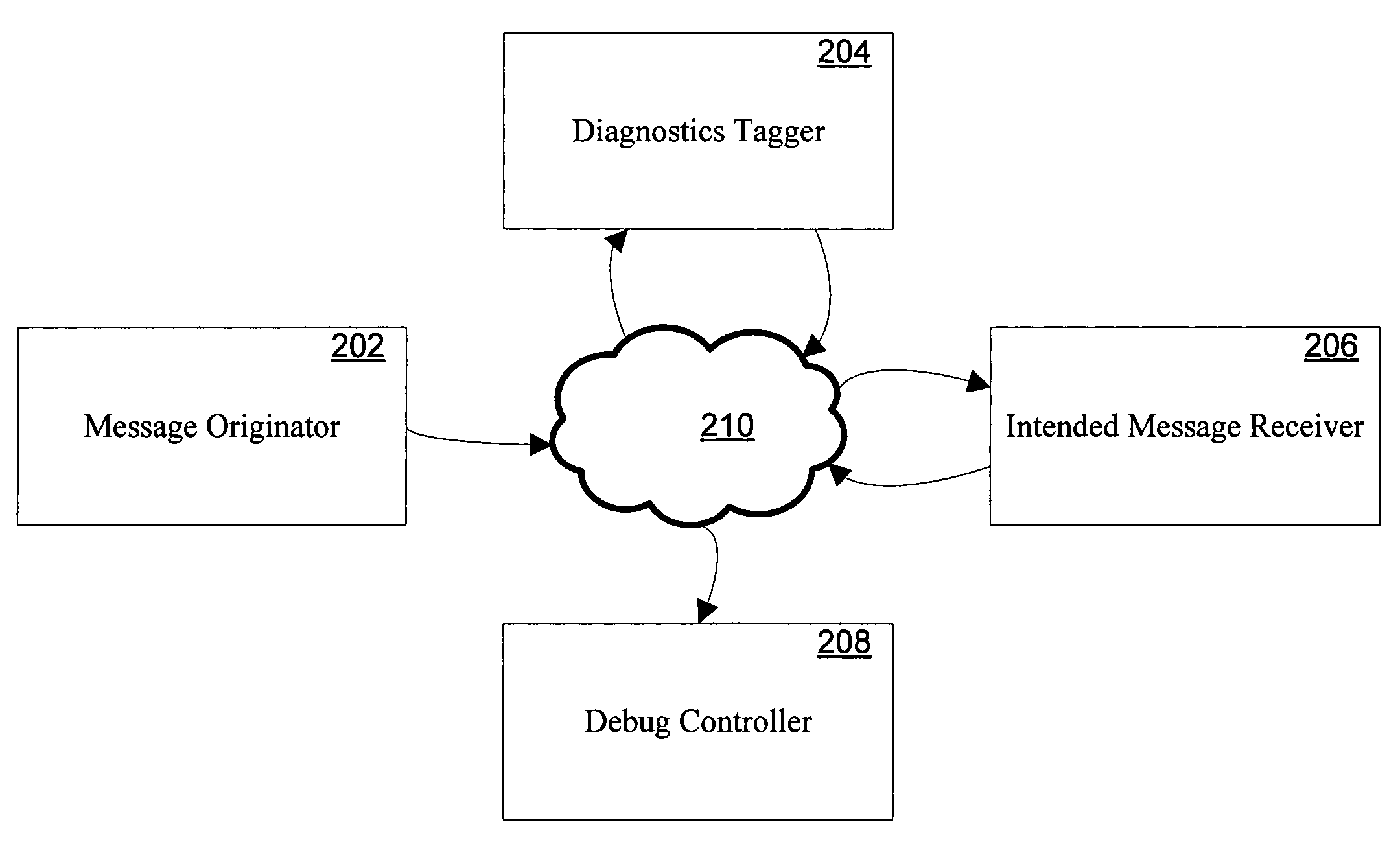
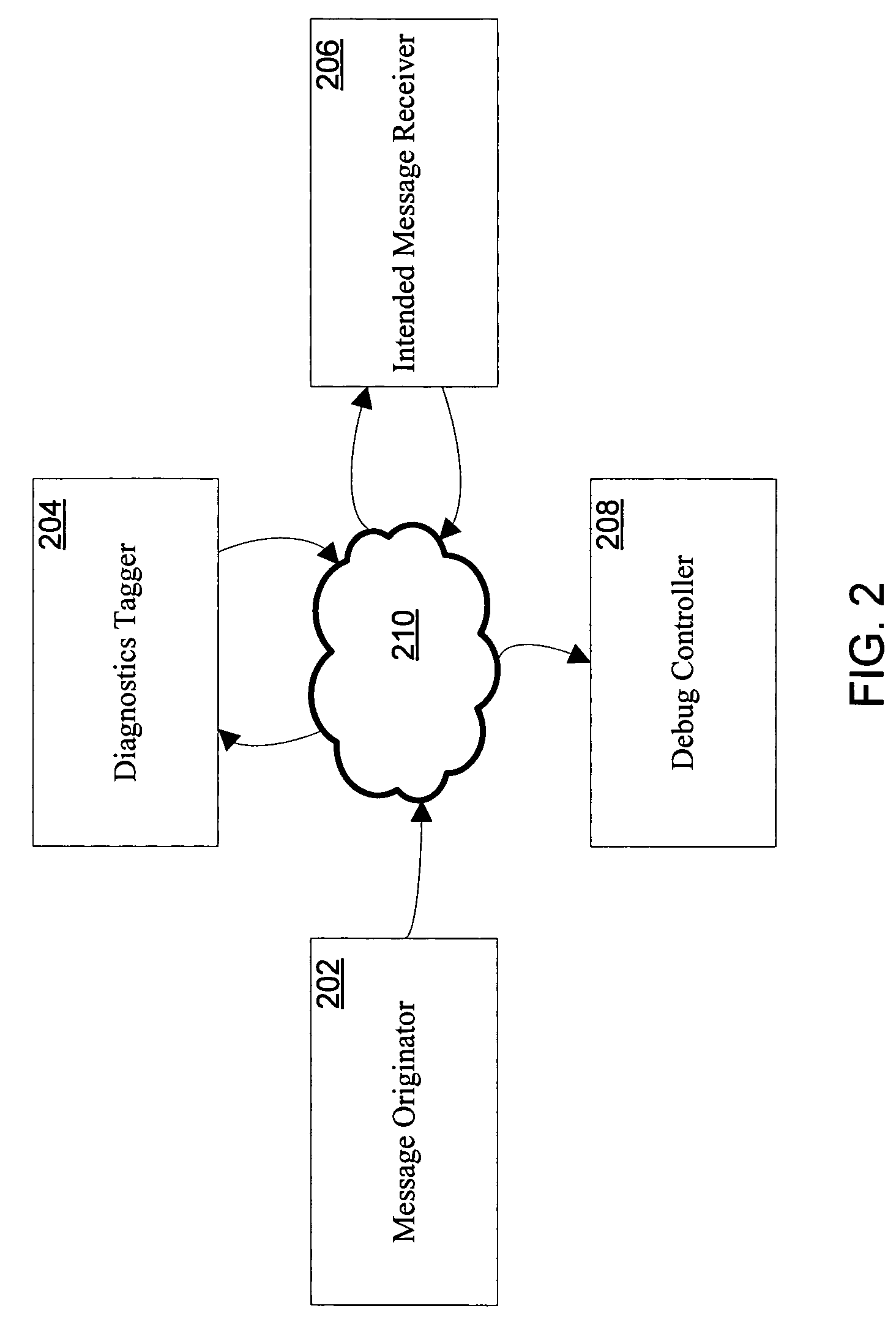
ActiveUS20060129988A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer hardwareMultiple criteria
Systems and methods for providing distributed debugging in an extensible SOAP environment of asynchronous software web services are disclosed. Such a system may include a message originator, a diagnostics tagger, an intended message receiver, and a debug controller, which may communicate with one another via SOAP messages. The message originator originally puts the SOAP message onto the network. The diagnostics tagger modifies the SOAP message to include certain diagnostics elements that cause a breakpoint to be triggered. The intended message receiver eventually receives the message and is expected to trigger the breakpoint. The debug controller is a process that is called by the intended message receiver when a breakpoint is detected. The header of the SOAP message may include a security element and a diagnostics element. The diagnostics element may include one or more breakpoint elements. Each breakpoint element may include a debugging controller element, and one or more condition elements. Each condition element may include a logical expression. The intended message receiver determines whether the conditions are met. If the conditions are met, then the breakpoint is triggered.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
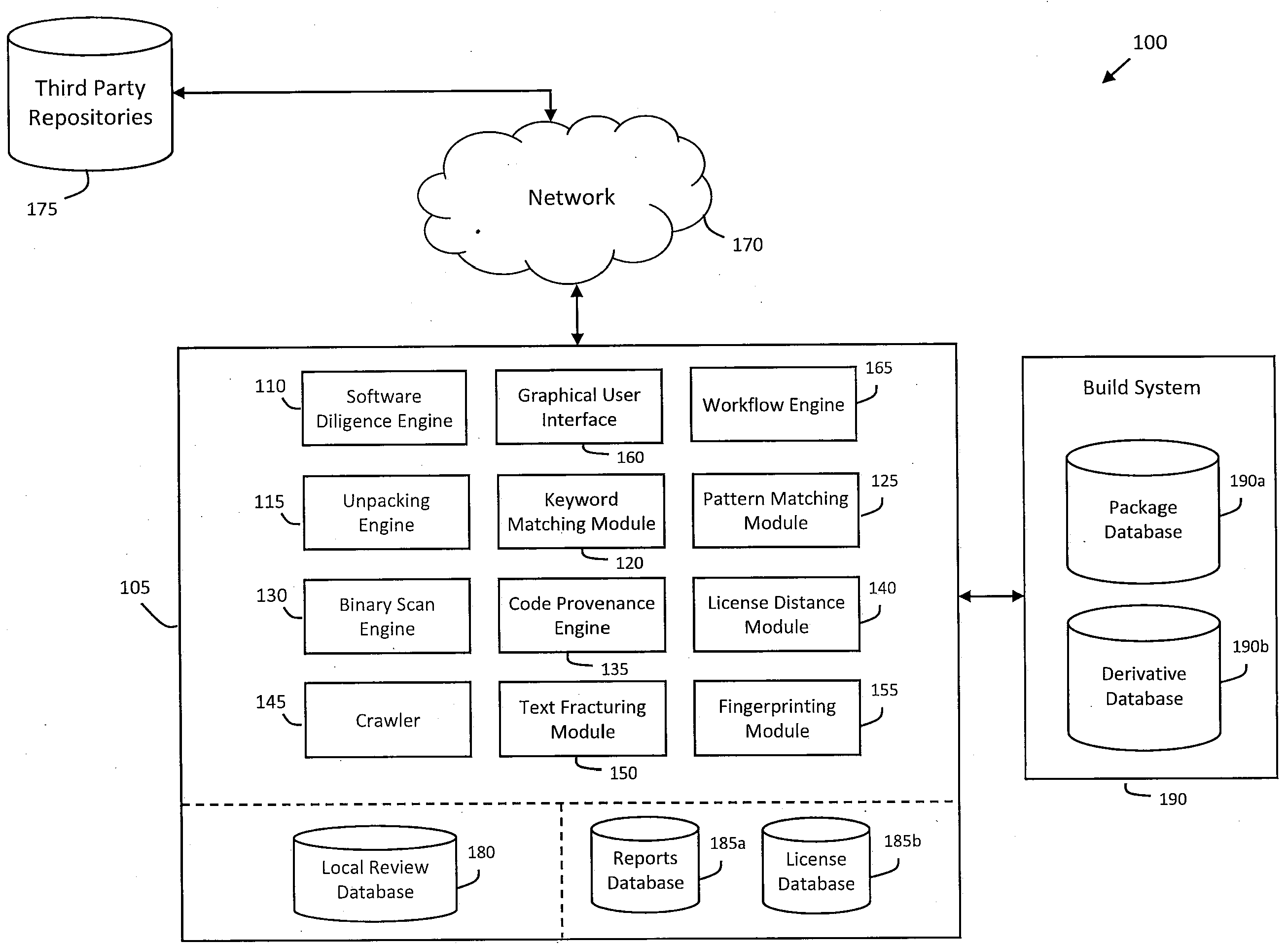
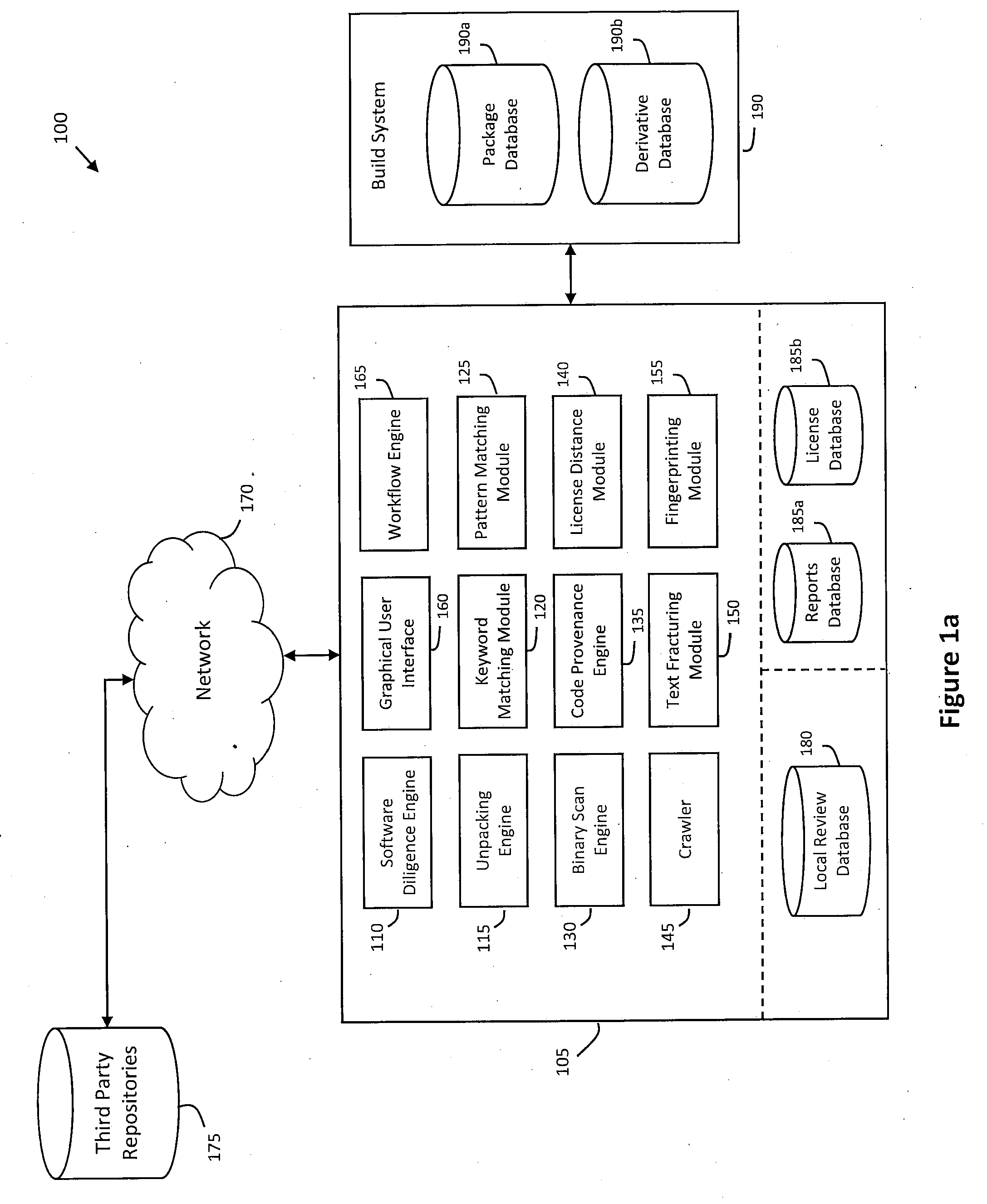
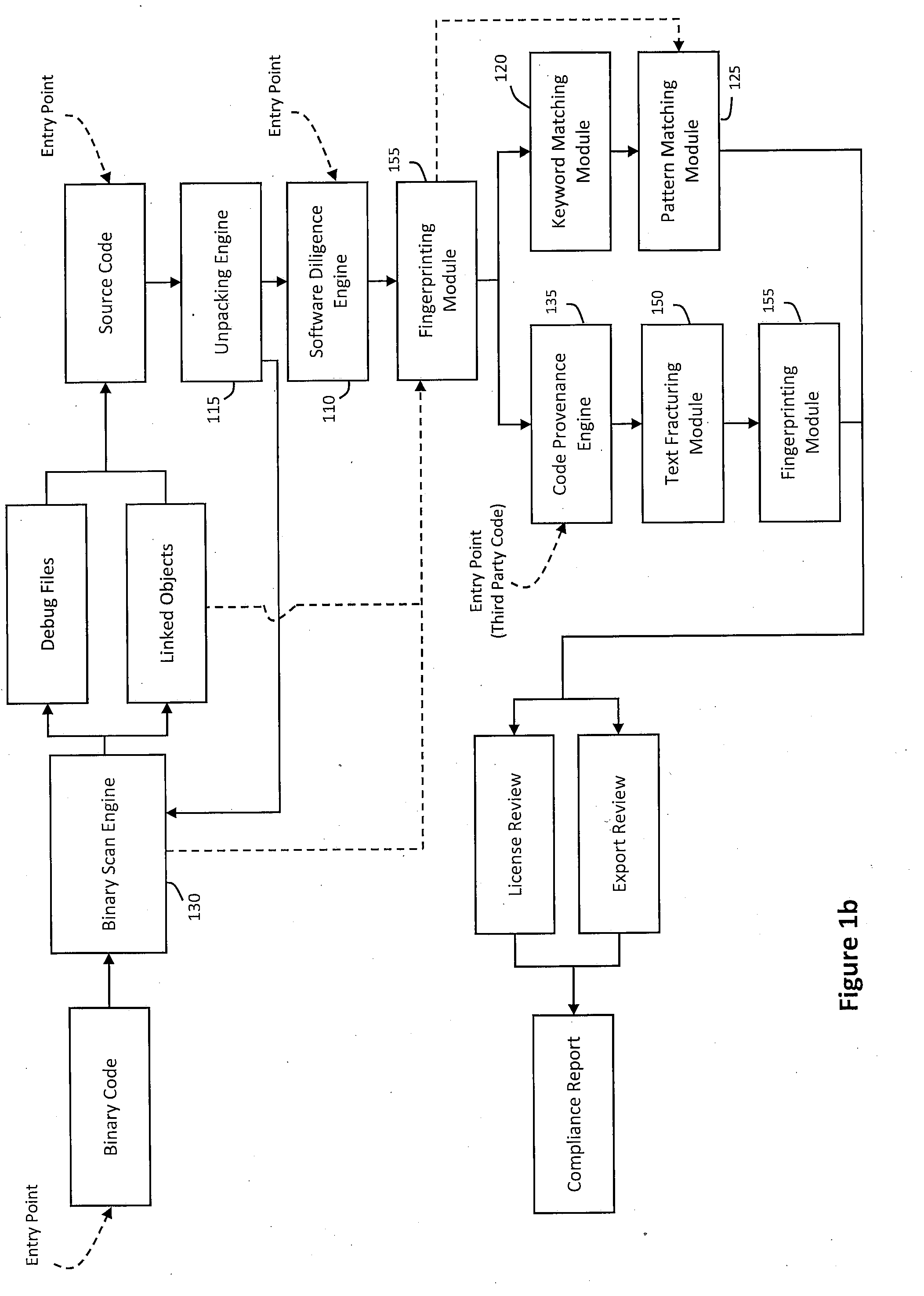
System and method for providing a license description syntax in a software due diligence system
ActiveUS20100185686A1Lack of precisionDigital data processing detailsProgram/content distribution protectionSoftware licenseGrammaticality
Described herein is a system and method for providing a condensed license description syntax for use in a software due diligence system. In particular, the license description syntax may employ a limited number of verifiable attributes to provide precision and lack of redundancy in describing various software licenses relevant to software due diligence. For example, the software due diligence system may identify licenses in software under review and invoke a compiler configured to perform various operations on the license description syntax to check for permissions and obligations associated with the identified licenses (e.g., name translation, operator translation, logical expression evaluation, etc.). Thus, the license description syntax may enable the license database to be established as a global public or private license database, in addition to providing licenses attributes useful in software due diligence review.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
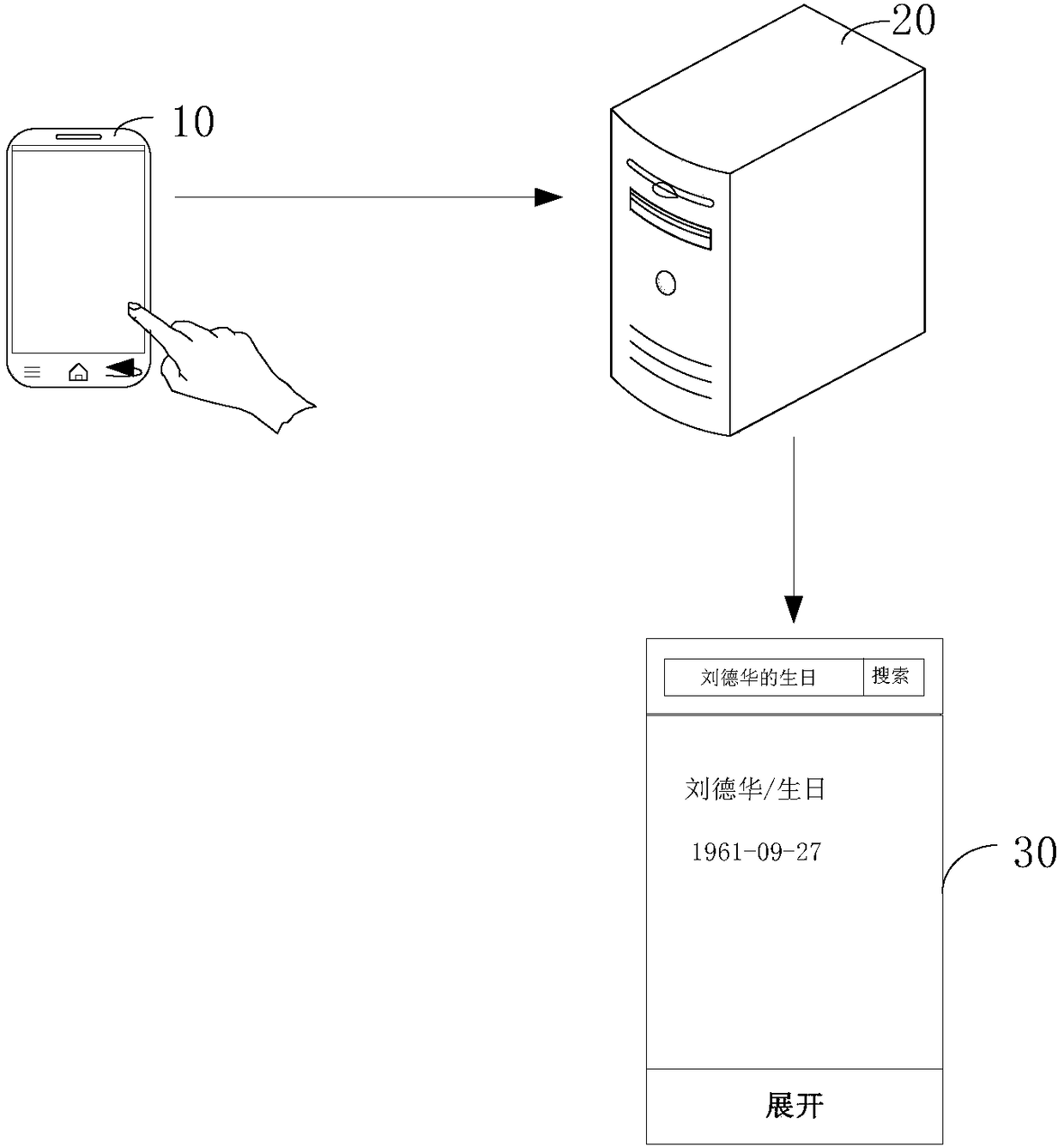
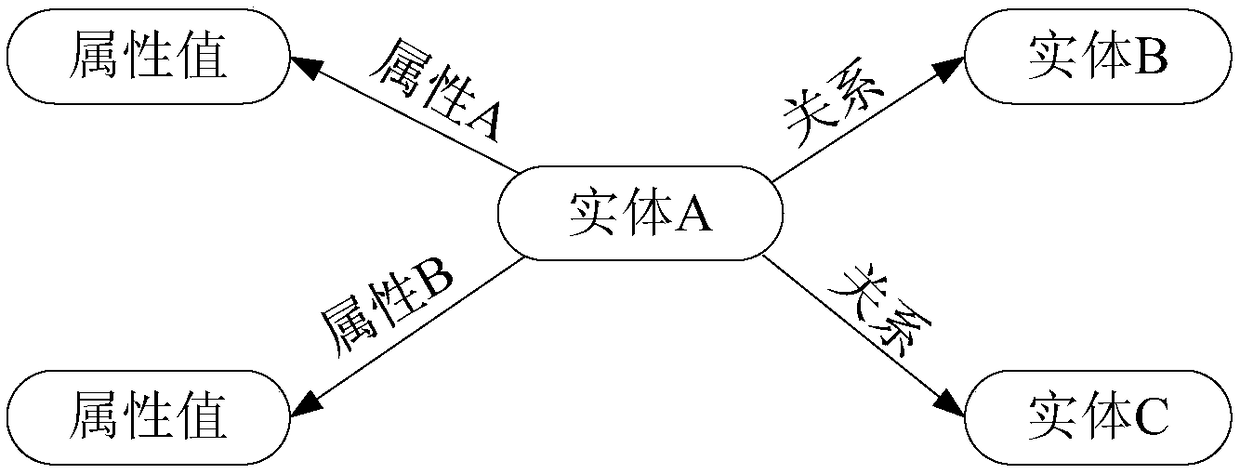
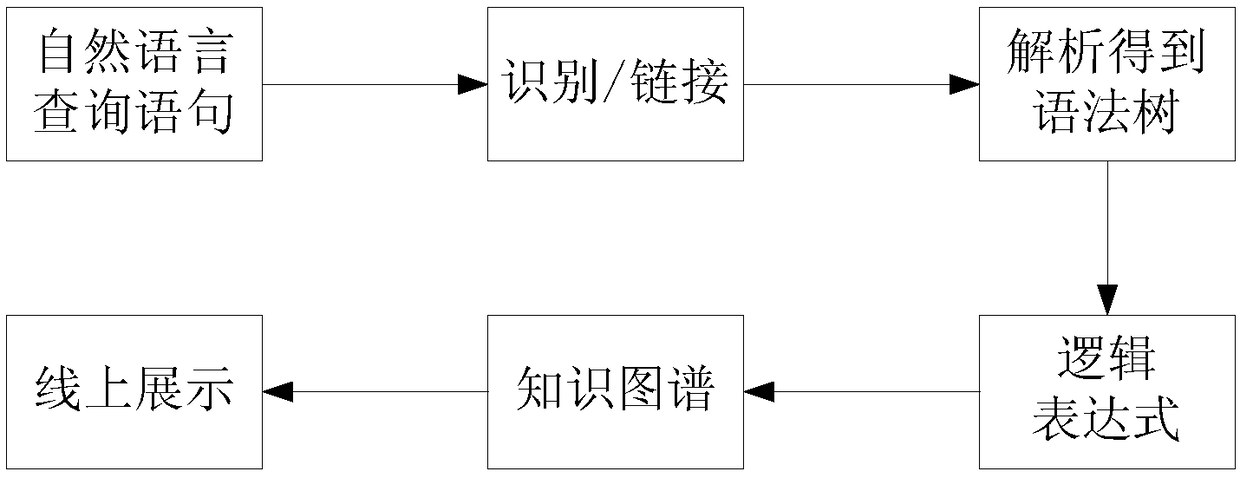
Question and answer method and apparatus based on knowledge map
InactiveCN108268580AAccurate Q&A resultsRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsUser inputQuestions and answers
The present invention provides a question and answer method and apparatus based on a knowledge map. The method comprises: obtaining a natural query statement input by a user, and identifying globallyunique identifiers GUIDs of entities in the natural query statement for the knowledge map, wherein the knowledge map comprises attributes and attribute values of entities and the relationship betweenthe entities; according to the context-free grammar rule, parsing the natural query statement into a syntax tree, and obtaining a logical expression corresponding to the natural query statement according to the syntax tree; generating a machine query statement corresponding to the knowledge map according to the logical expression and the GUIDs of the entities; and according to the machine query statement, querying a question and answer result corresponding to the machine query statement in the knowledge map, and feeding back the question and answer result to the user. According to embodimentsof the present invention, an accurate question and answer result can be obtained for the question and answer.
Owner:ALIBABA (CHINA) CO LTD
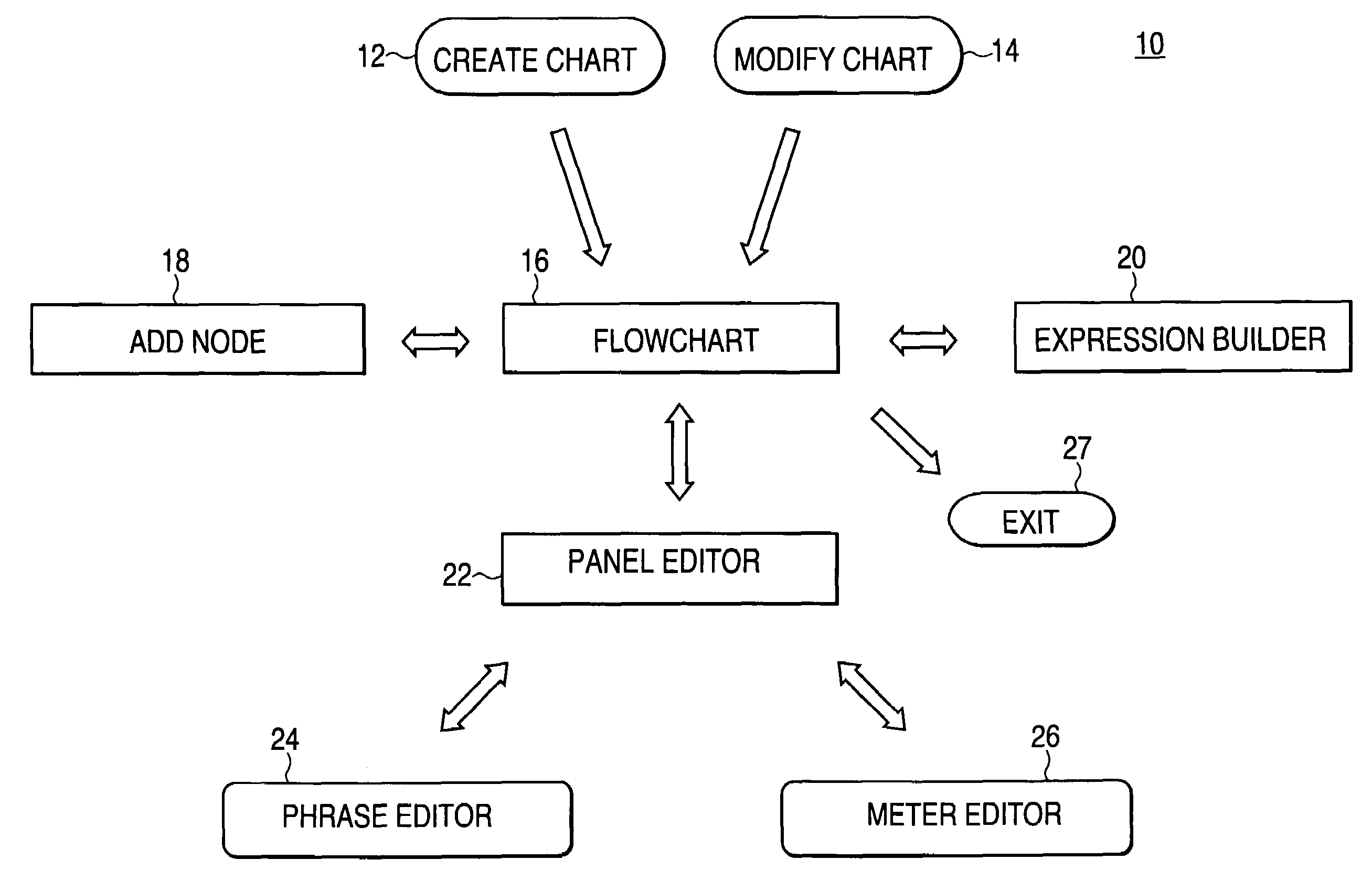
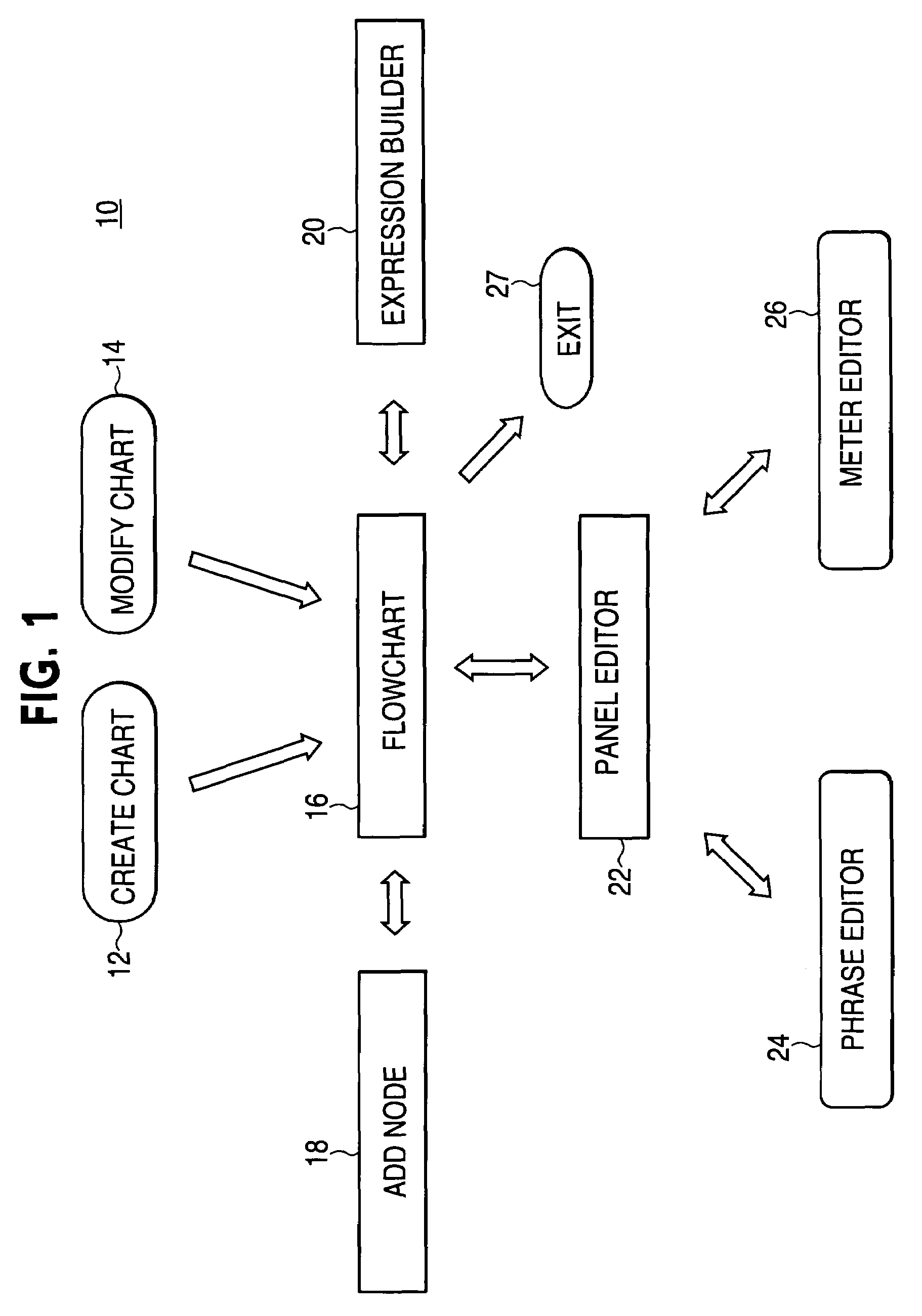
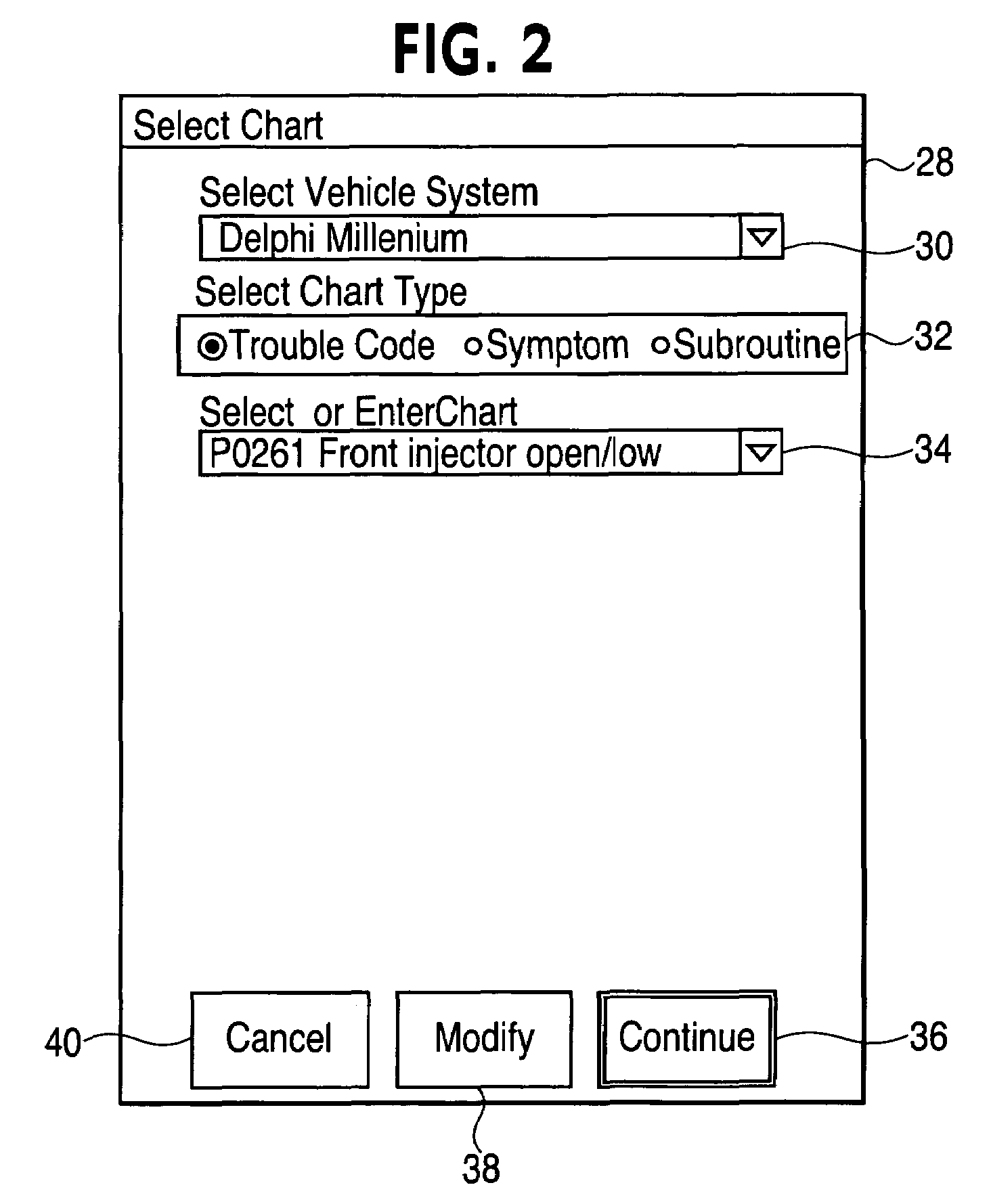
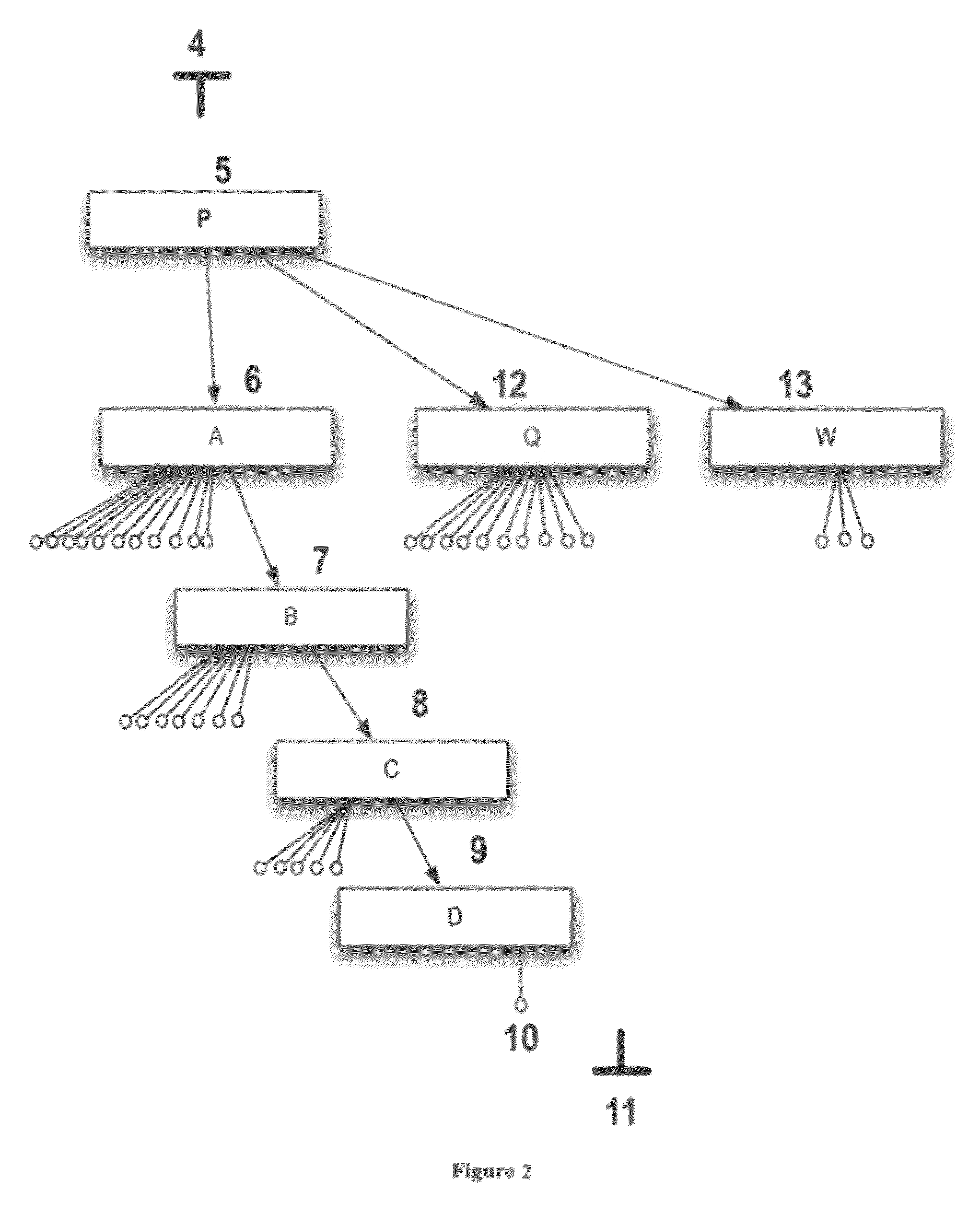
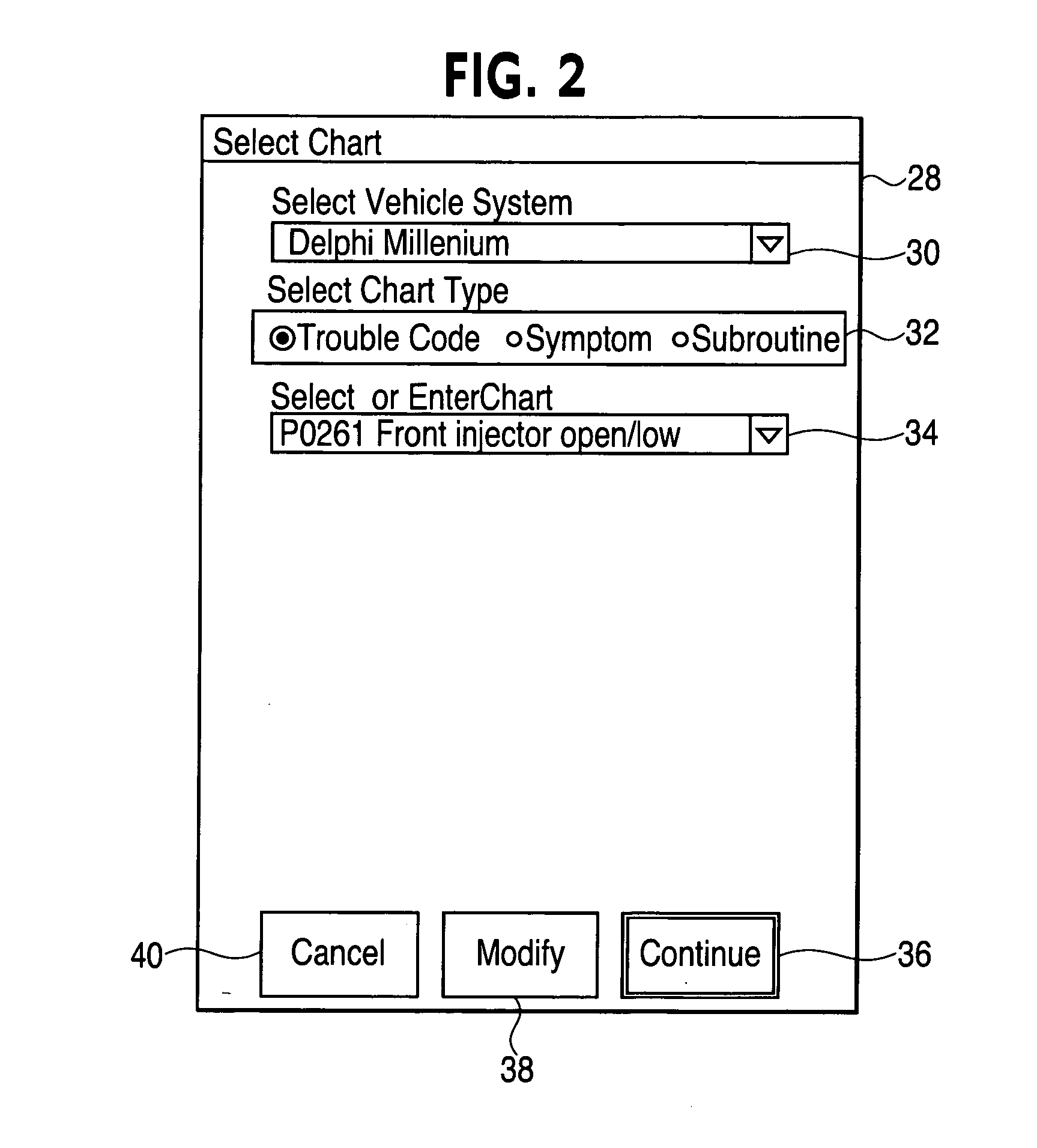
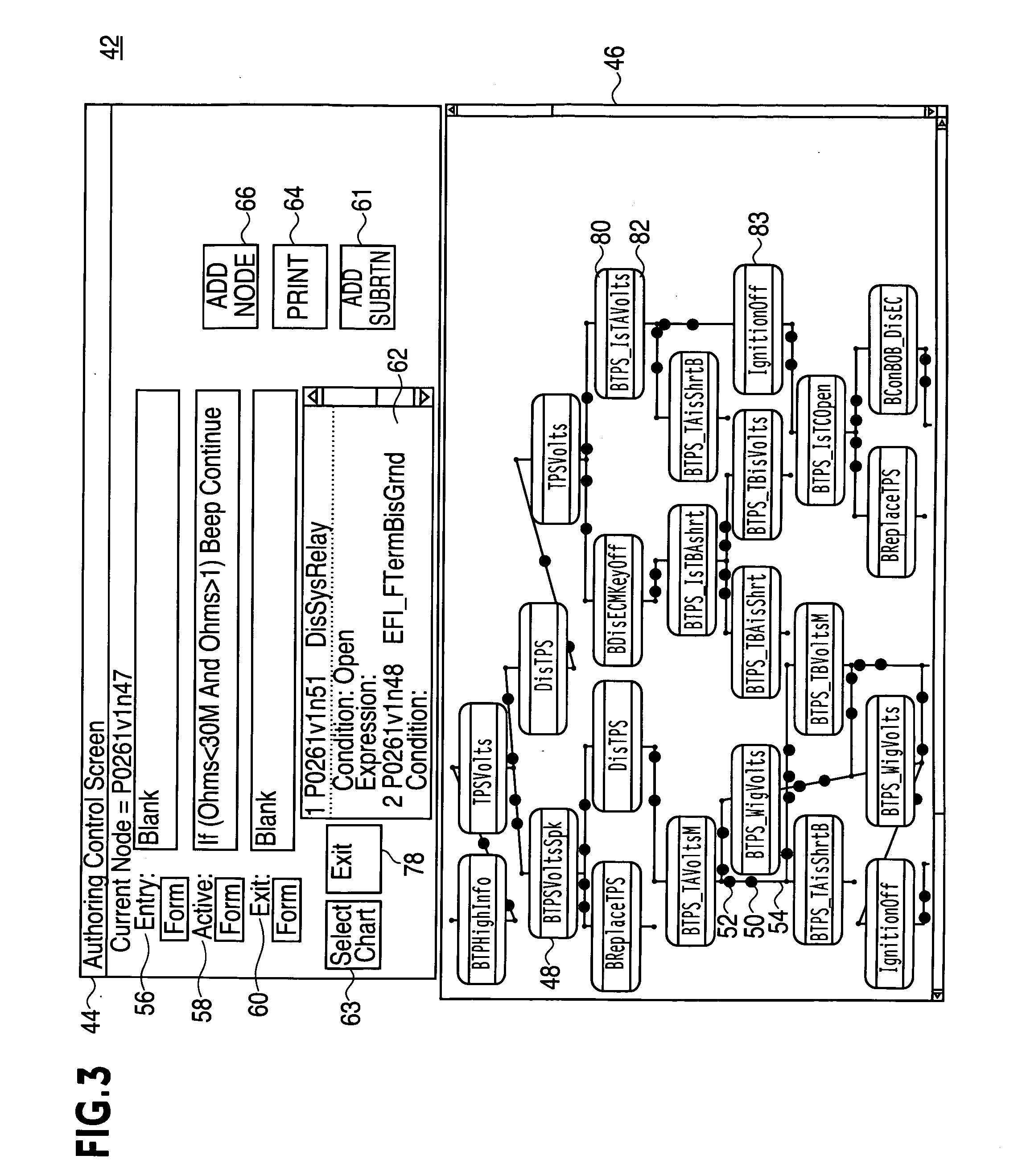
Authoring diagnostic test sequences apparatus and method
ActiveUS7216052B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceNuclear monitoringSoftware engineeringComputer programming
A vehicle diagnostic test sequence authoring module includes a flowchart display screen, an add node display screen, an expression builder display screen, a panel editor display screen, a phrase editor display screen, and a meter editor display screen. Each of the author module display screens include a combination of selectable fields, including editable text fields, dropdown menu fields, checkbox fields, selectable bullet fields, logical display buttons, and logical links, that facilitate development of diagnostic test sequences, represented by hierarchical flowcharts, by vehicle diagnostics experts who do not have substantial knowledge of a computer programming language. A flowchart includes multiple nodes, representing individual test steps, and branches that connect the nodes. Logical expressions based on vehicle test conditions determine the flow of the test sequence.
Owner:SPX CORP
Method of using xpath and ontology engine in authorization control of assets and resources
InactiveUS20100023997A1Easy to integrateDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSemanticsXPath
A method of defining access control. The method allows the expression of access control rules using ontology based semantics and references an ontology subset using XPath as the ontological expression. The access control rules or access criteria are defined by an access control statement and may be expressed using classification criteria and ontology classes. The access control statement comprises a structural description that is used to define an asset and a logical expression that may be used to express the classification criteria. The access control statement defines access policy for various assets.
Owner:IBM CORP
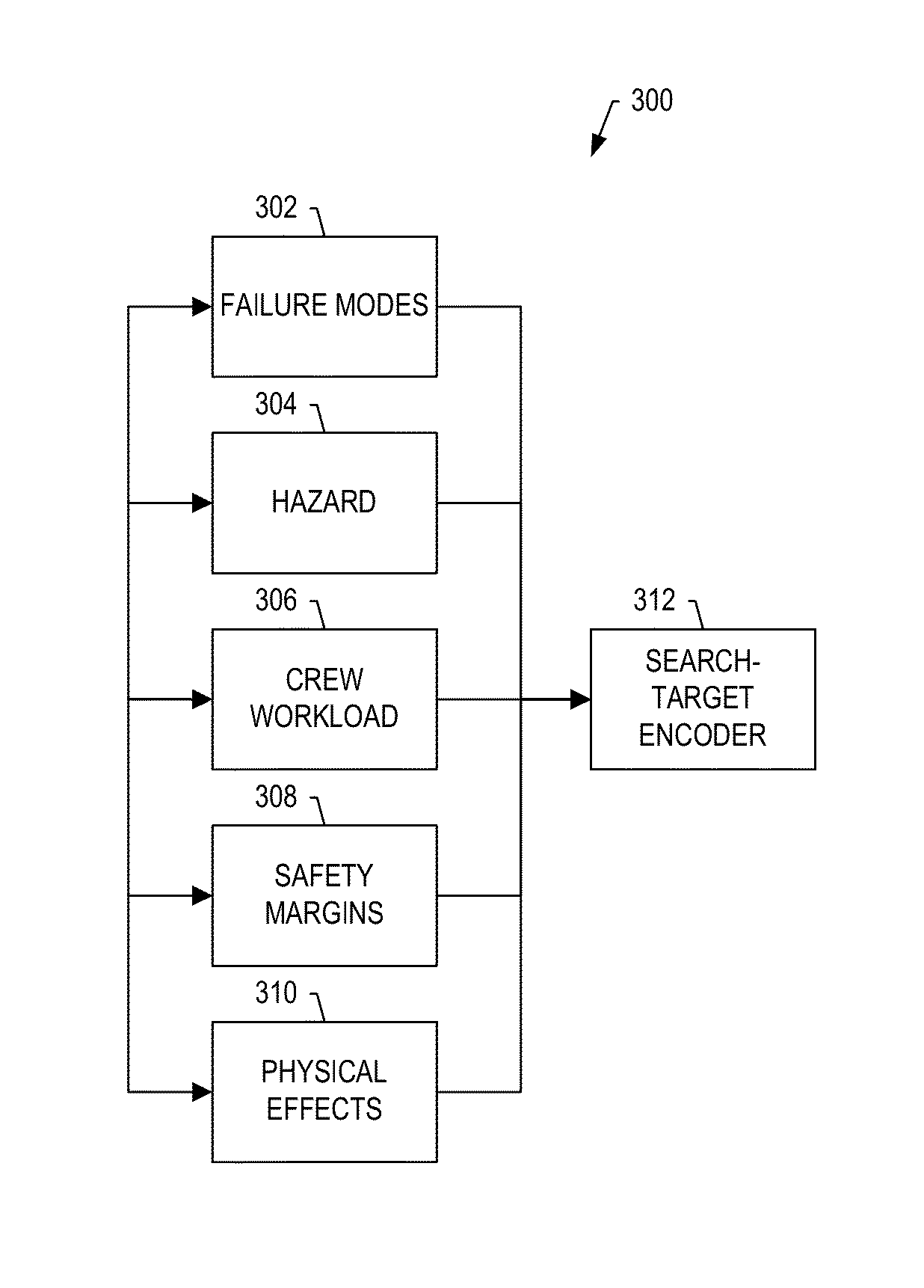
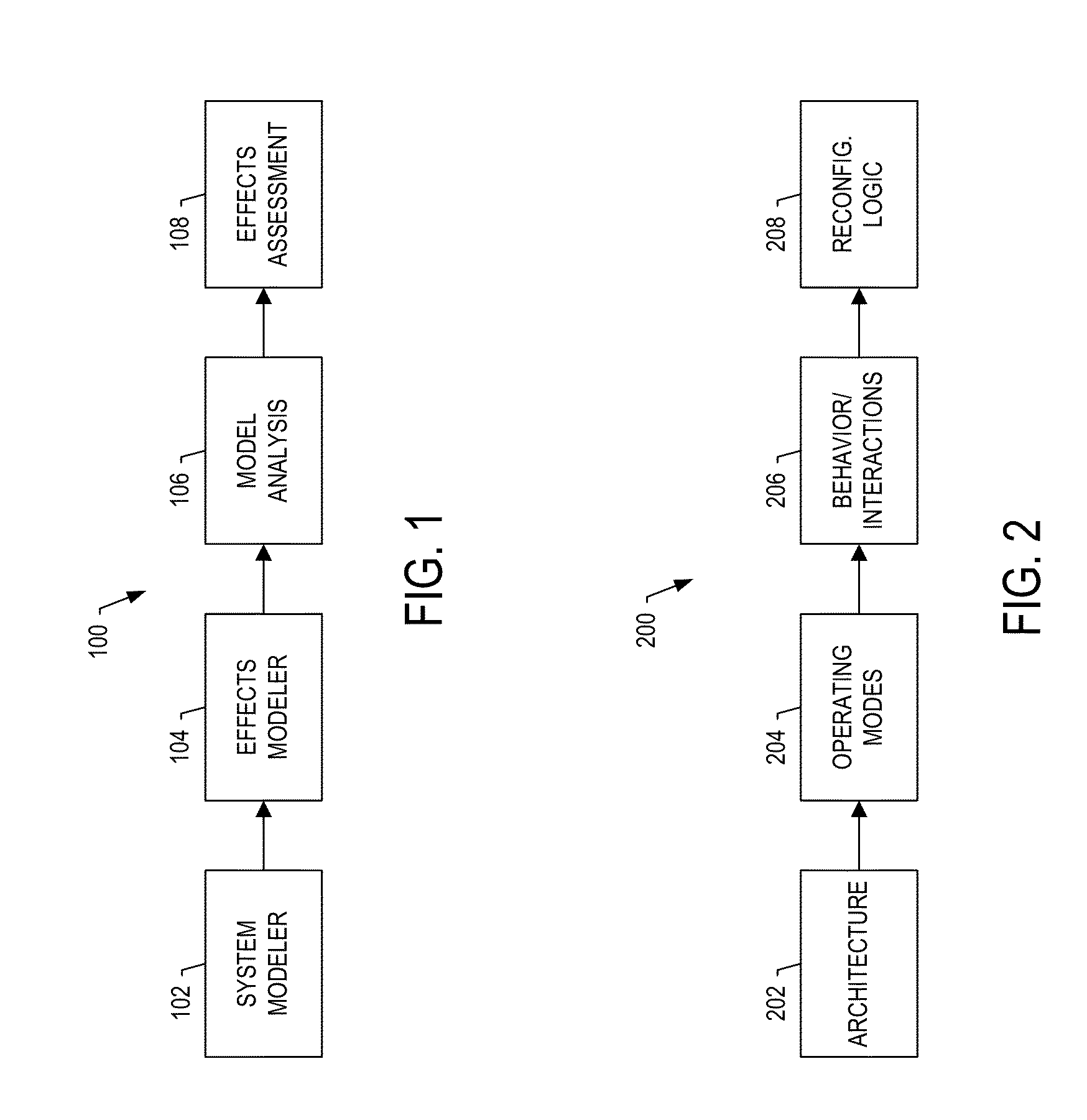
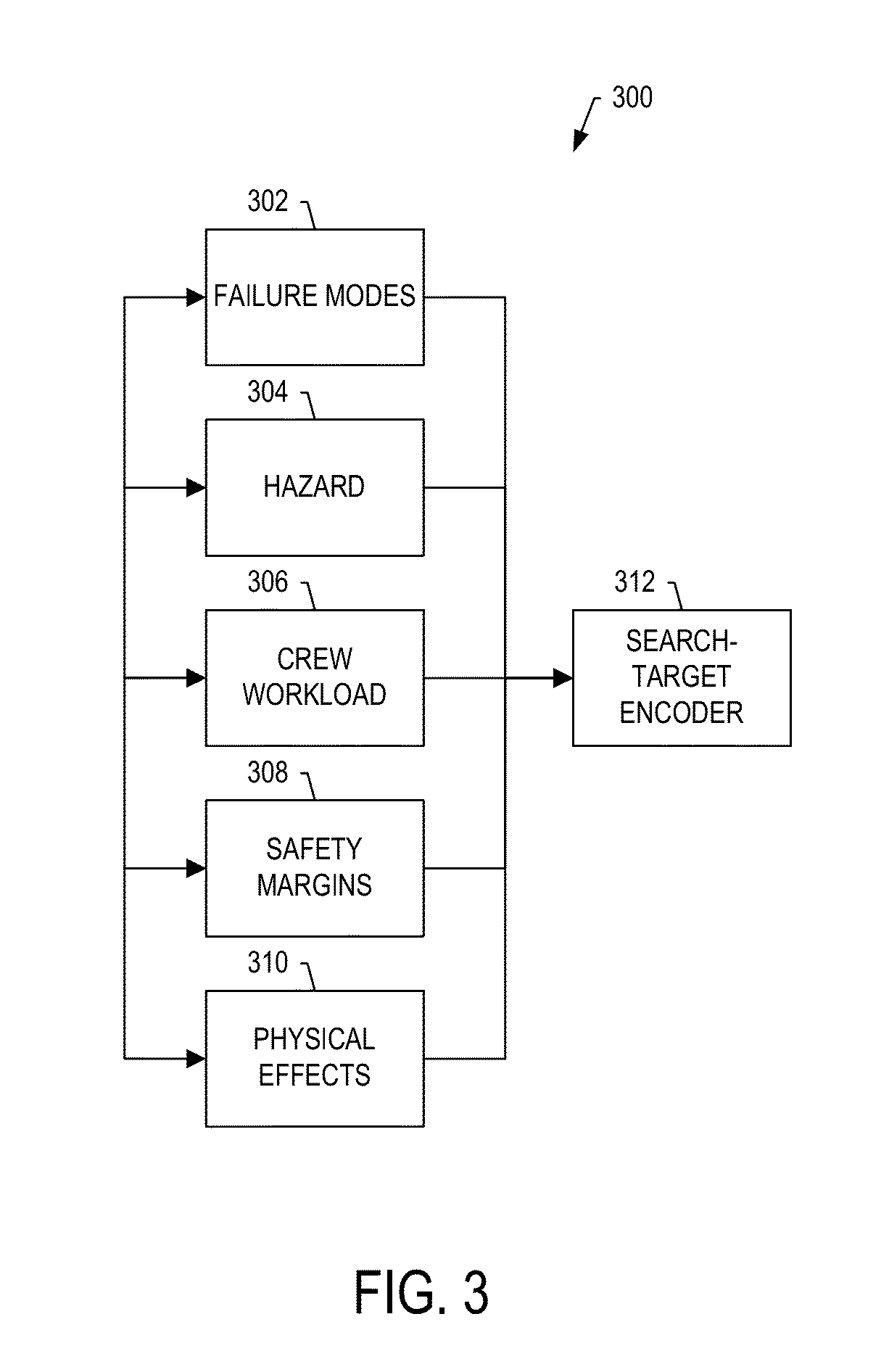
System and method for assessing cumulative effects of a failure
ActiveUS20150019187A1Ease of evaluationEasy to identifyTesting/monitoring control systemsDesign optimisation/simulationFailure analysisWorkload
A failure-effect validation system includes an effects modeler configured to develop a cumulative effects model for failure modes of the complex system, and by which a model of the complex system is extendible to form an extended complex-system model. The effects modeler is also configured to develop search targets each of which includes logical expressions of notable hazards and other factors that contribute to the cumulative effects, such as crew workload, safety margin and / or physiological effects. A model analysis system is configured to perform an automated analysis using the extended complex-system model and search targets, and in which the automated analysis includes a graph search of possible states of the extended complex-system model to locate search targets. And the effects assessment system is configured to selectively generate a layout of failure analysis data including at least a portion of the extended complex-system model and results of the automated analysis.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Relativistic concept measuring system for data clustering
ActiveUS8566321B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceTheory of relativity
A method and apparatus for mapping concepts and attributes to distance fields via rvachev-functions. The steps including generating, for a plurality of objects, equations representing boundaries of attributes for each respective object, converting, for a plurality of objects, the equations into greater than or equal to zero type inequalities, generating, for a plurality of objects, a logical expression combining regions of space defined by the inequalities into a semantic entity, and substituting, for a plurality of objects, the logical expression with a corresponding rvachev-function such that the resulting rvachev-function is equal to 0 on a boundary of the semantic entity, greater then 0 inside a region of the semantic entity, and less then 0 outside the region of the semantic entity. Also included is the step of generating a composite rvachev-function representing logical statements corresponding to the plurality of objects using the respective rvachev-functions of the objects.
Owner:KYNDI
Authoring diagnostic test sequences apparatus and method
A vehicle diagnostic test sequence authoring module includes a flowchart display screen, an add node display screen, an expression builder display screen, a panel editor display screen, a phrase editor display screen, and a meter editor display screen. Each of the author module display screens include a combination of selectable fields, including editable text fields, dropdown menu fields, checkbox fields, selectable bullet fields, logical display buttons, and logical links, that facilitate development of diagnostic test sequences, represented by hierarchical flowcharts, by vehicle diagnostics experts who do not have substantial knowledge of a computer programming language. A flowchart includes multiple nodes, representing individual test steps, and branches that connect the nodes. Logical expressions based on vehicle test conditions determine the flow of the test sequence.
Owner:SPX CORP
Mass spectrometric differentiation of tissue states
ActiveUS20060063145A1Easy to doMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpatially resolvedGray level
The invention relates to the determination and visualization of the spatial distribution of tissue states in histologic tissue sections on the basis of mass spectrometric signals acquired so as to be spatially resolved. The invention provides a method which determines the tissue state for the tissue spots as a state characteristic, which is calculated as a mathematical or logical expression from at least two mass signals of this tissue spot, and which indicates the tissue state as a gray-level or false-color image in one or two dimensions.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Distributed debugger environment
ActiveUS7634759B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware networkNetwork on
Systems and methods for providing distributed debugging in an extensible SOAP environment of asynchronous software web services are disclosed. Such a system may include a message originator, a diagnostics tagger, an intended message receiver, and a debug controller, which may communicate with one another via SOAP messages. The message originator originally puts the SOAP message onto the network. The diagnostics tagger modifies the SOAP message to include certain diagnostics elements that cause a breakpoint to be triggered. The intended message receiver eventually receives the message and is expected to trigger the breakpoint. The debug controller is a process that is called by the intended message receiver when a breakpoint is detected. The header of the SOAP message may include a security element and a diagnostics element. The diagnostics element may include one or more breakpoint elements. Each breakpoint element may include a debugging controller element, and one or more condition elements. Each condition element may include a logical expression. The intended message receiver determines whether the conditions are met. If the conditions are met, then the breakpoint is triggered.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
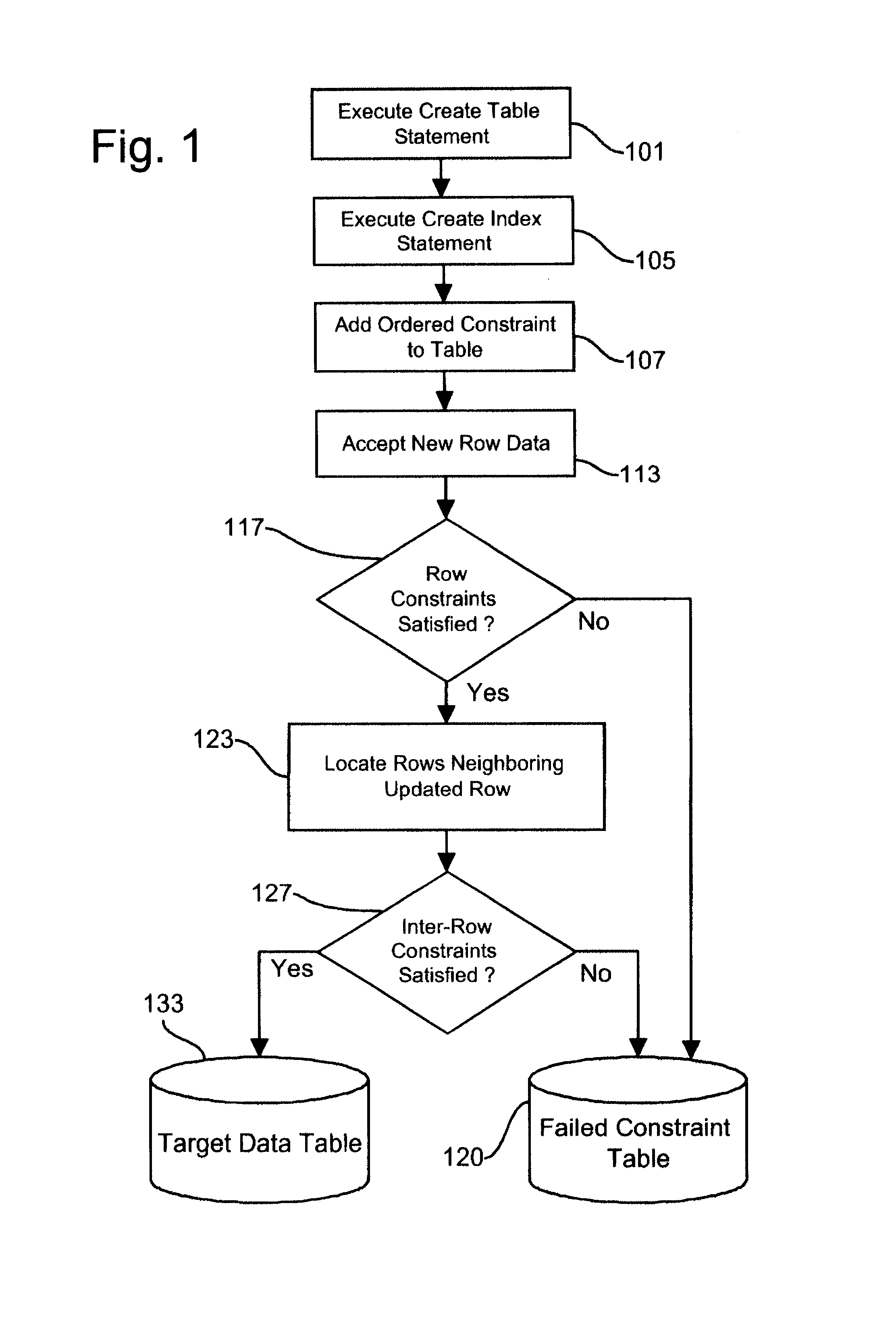
Generalized method for modeling complex ordered check constraints in a relational database system
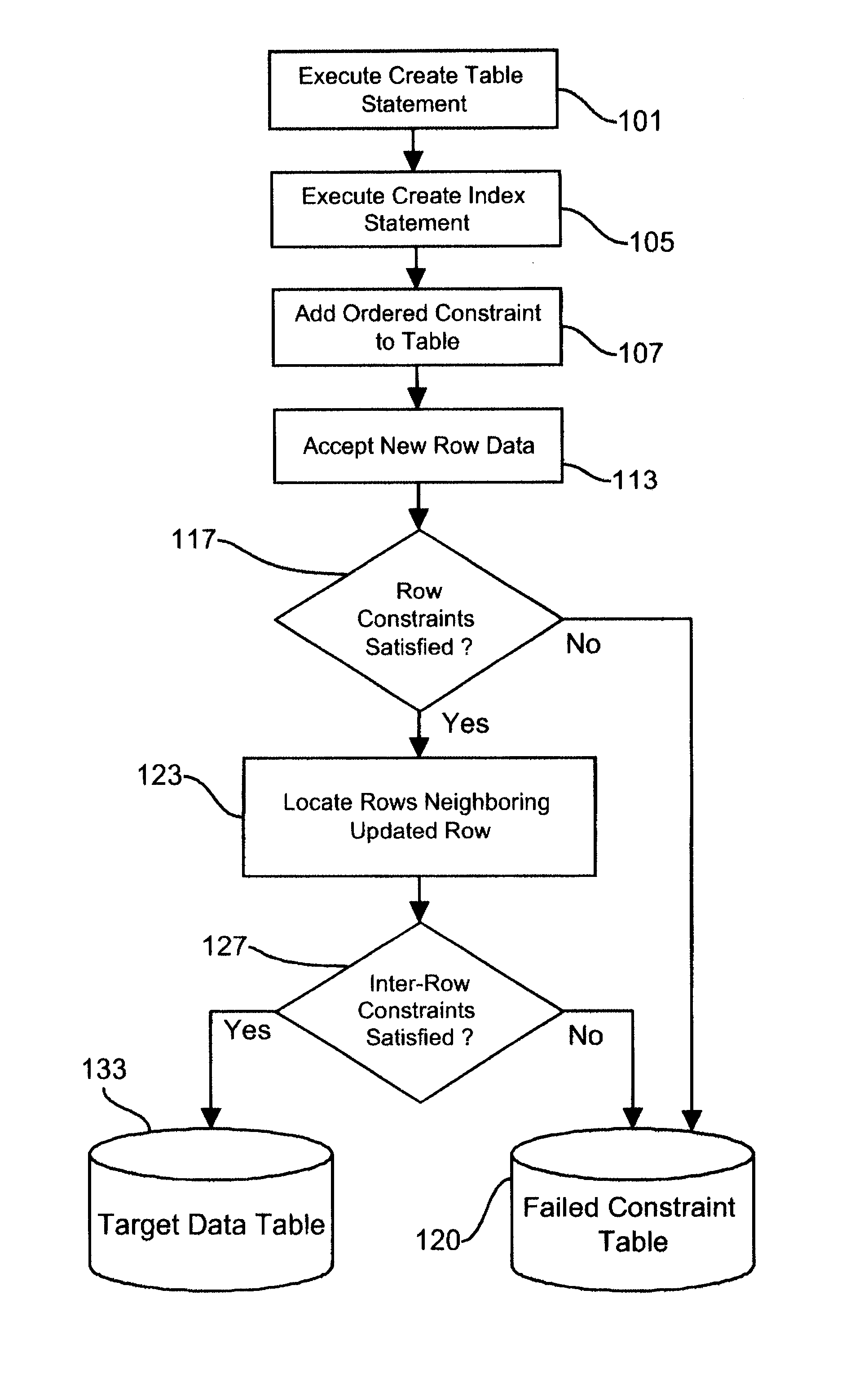
ActiveUS7328212B2Easy to specifyEfficiently enforcedData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsRelational databaseData value
A system for enabling a user of a relational database to define and enforce ordered check constraints to insure that defined logical relationships are maintained between data values in pairs of adjacent rows when adjacency is defined by some ordering of the data. These inter-row conditions, here called “ordered check constraints,” are expressed by a logical expressions which define a required relationship between the attributes of a given row and its adjacent row or rows. Arbitrarily complex expressions involving these sets of attributes can be formed to model the constraints of interest. These expressions can be created by the database in support of, for example, traditional primary key or uniqueness constraints, or they can be provided by the database user to model new more complex constraints such as a requirement that there be no gaps in a list of serial numbers. These constraints can then be efficiently supported in the presence of a b-tree or another ordered index structure by identifying any inserted, updated or deleted rows and evaluating the expression in the context of those rows and any associated adjacent rows. This approach is similar to that typically used in existing database systems to support primary key and uniqueness constraints, providing the user with the ability to model a much richer set of constraints using a generalized expression which extends and enhances the functionality of check constraints to permit relationships of data in different rows to be defined and enforced.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Mass spectrometric differentiation of tissue states
ActiveUS7873478B2Easy to doMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpatially resolvedGray level
The invention relates to the determination and visualization of the spatial distribution of tissue states in histologic tissue sections on the basis of mass spectrometric signals acquired so as to be spatially resolved. The invention provides a method which determines the tissue state for the tissue spots as a state characteristic, which is calculated as a mathematical or logical expression from at least two mass signals of this tissue spot, and which indicates the tissue state as a gray-level or false-color image in one or two dimensions.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
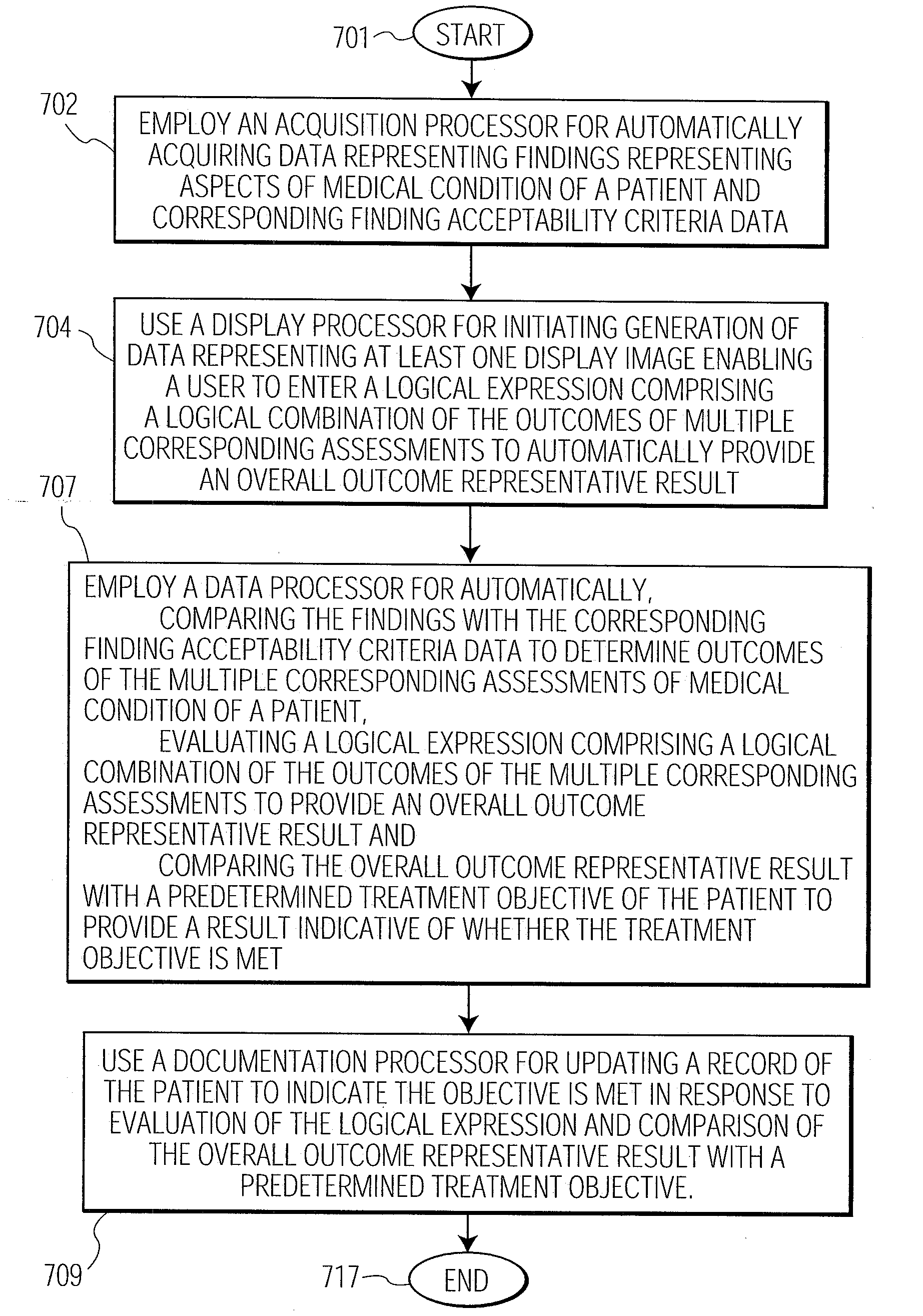
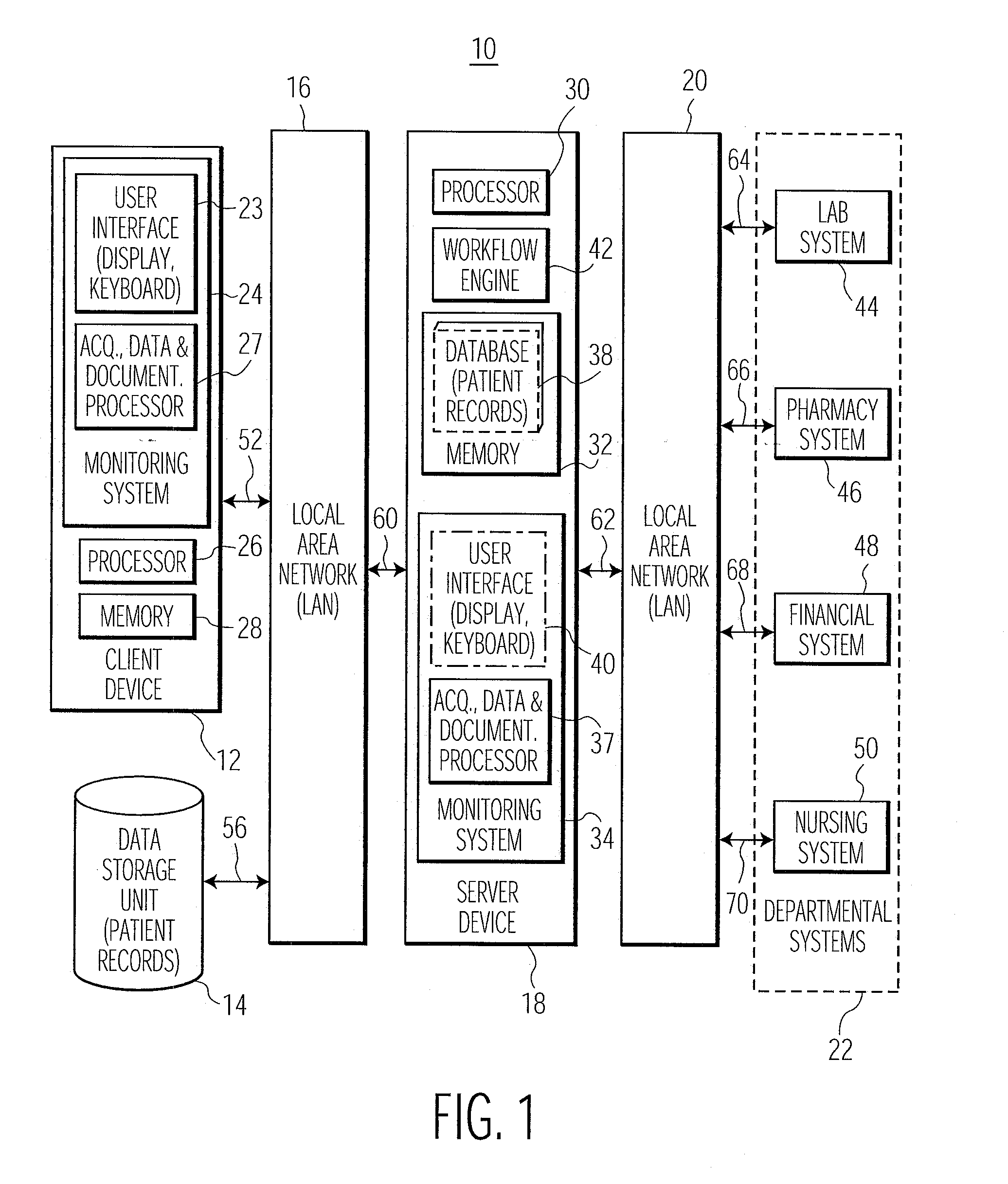
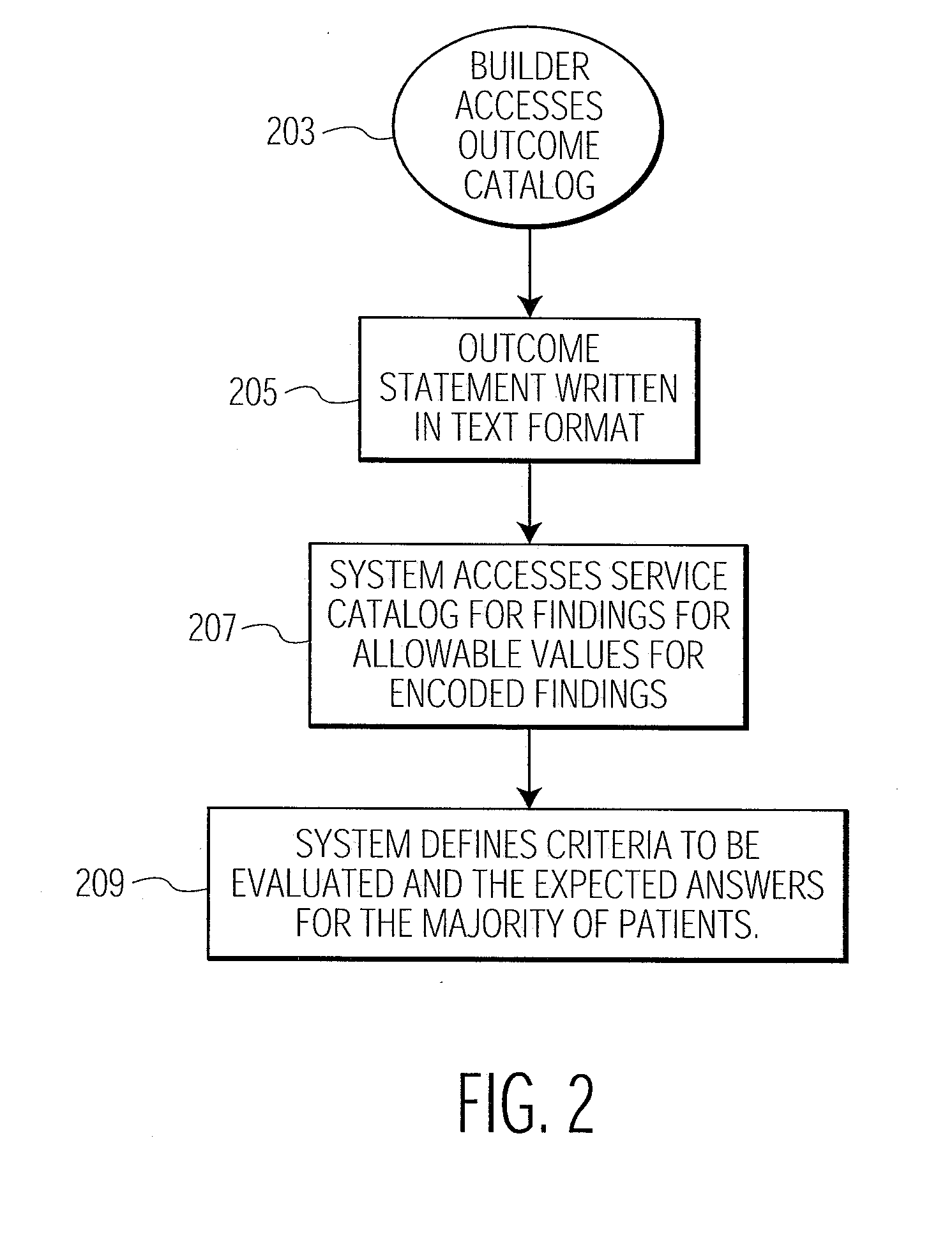
Automatic Patient Healthcare and Treatment Outcome Monitoring System
InactiveUS20070173702A1TherapiesMedical automated diagnosisDocumentation procedureLogical combination
A system generates criteria associating subjective narrative text describing a treatment outcome with acquired patient medical data and linking a narrative treatment outcome description to documented data during patient assessment documentation. A patient healthcare monitoring system includes an acquisition processor for automatically acquiring data representing outcomes of multiple corresponding assessments of medical condition of a patient. A data processor automatically evaluates a logical expression comprising a logical combination of the multiple corresponding assessments to provide an overall outcome representative result and compares the overall outcome representative result with a predetermined treatment objective of the patient to provide a result indicative of whether the treatment objective is met. A documentation processor updates a record of the patient to indicate the objective is met.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS HEALTH SERVICES CORPORAT
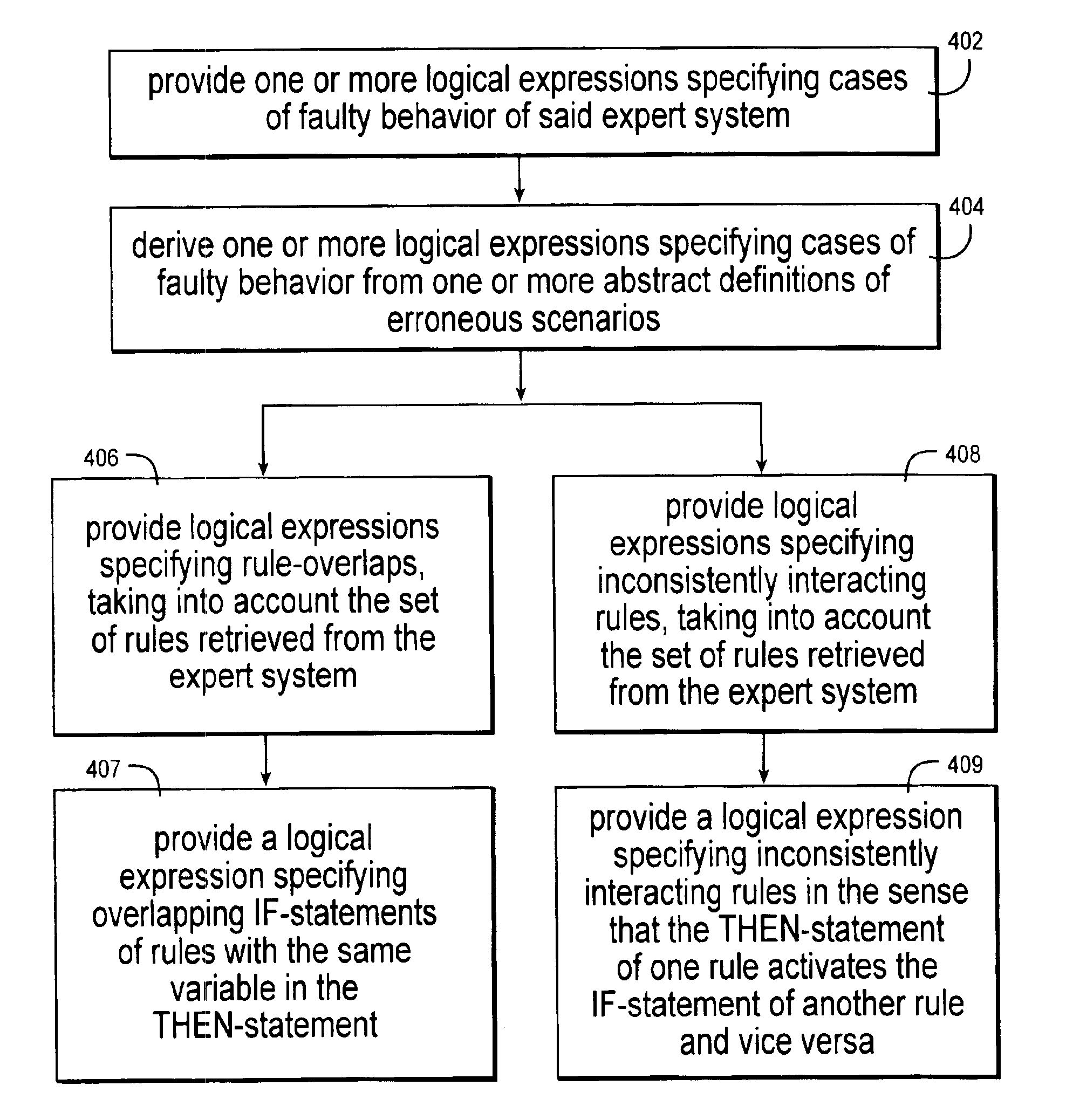
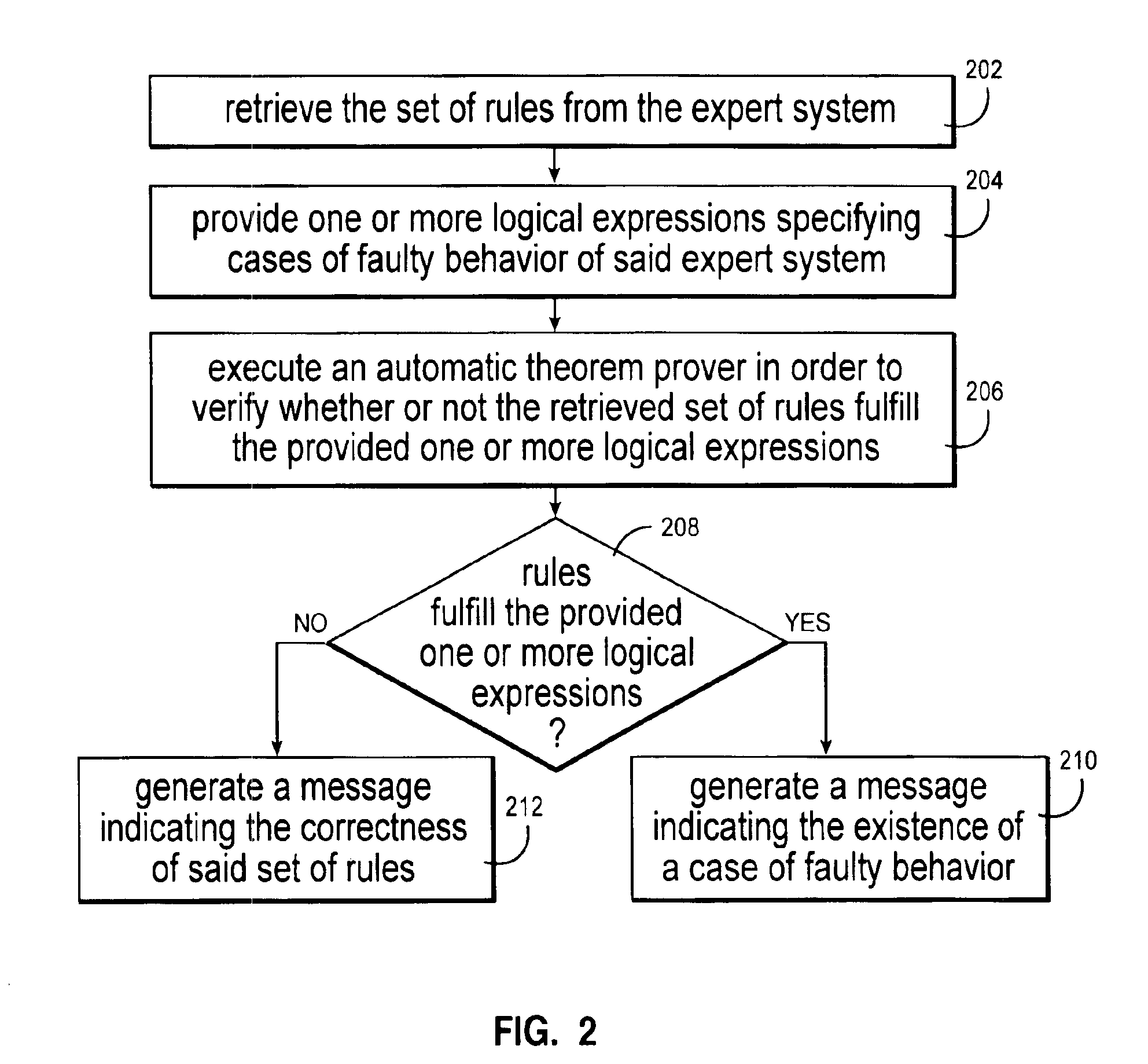
Loop detection in rule-based expert systems
InactiveUS6952690B2Easy to understandKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsRule based expert systemAlgorithm
This invention describes a method to verify non-looping properties of programs implemented as rule-based expert systems. Our method detects conditions under which the expert system enters erroneous infinite program loops, which lead to non-terminating or oscillating computations, or otherwise proves the absence of such conditions. Our automatic procedure also gives advice on how to correct these errors. The expert systems considered consist of condition-action rules (IF-THEN-statements), where the conditions are logical expressions (formulas of a propositional finite domain logic), and the actions modify the value of a single variable which in turn can be part of other logical expressions. There may be additional (external) variables not controlled by the expert system, and each rule may have an associated evaluation priority.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com