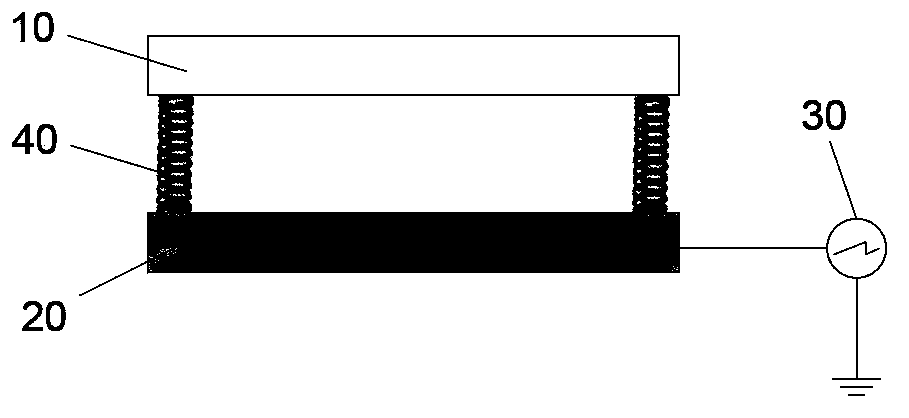
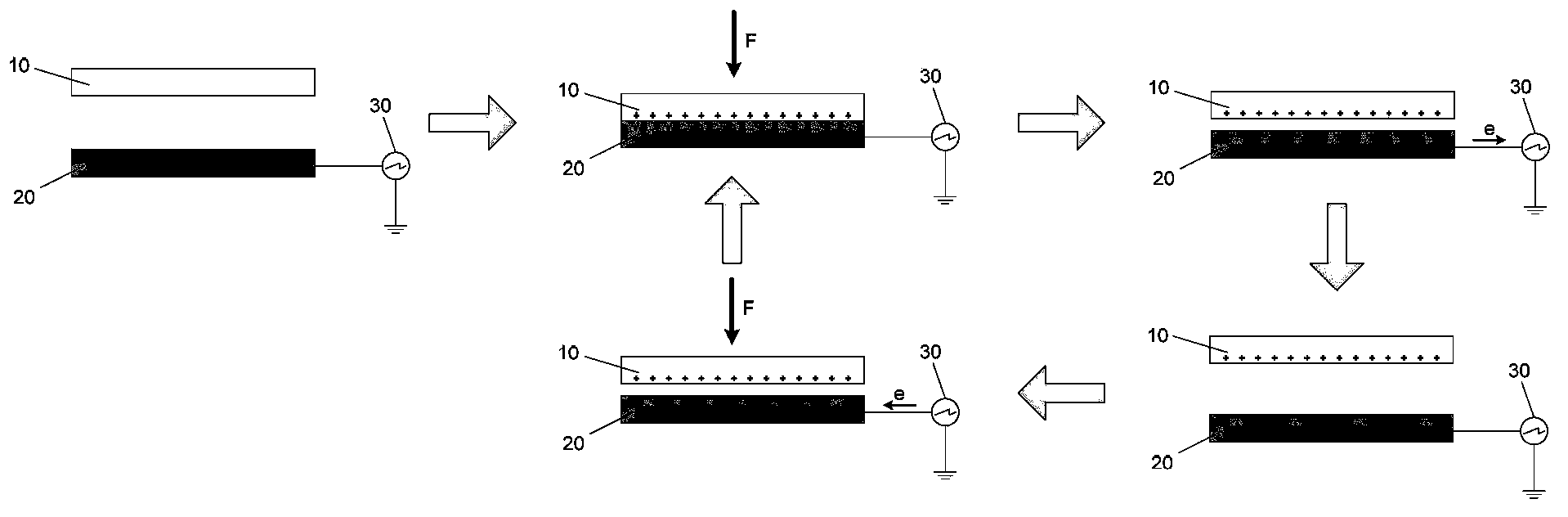
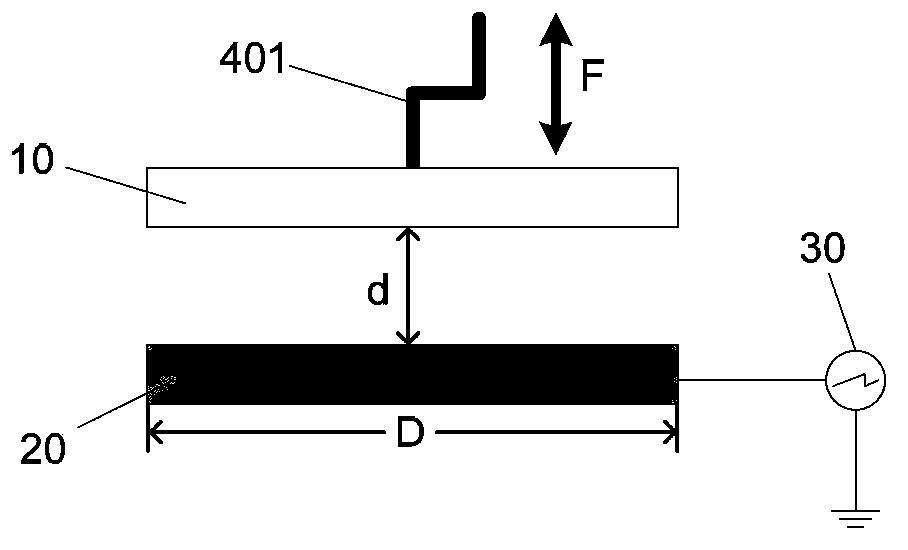
Patents
Literature
661 results about "Single electrode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sensor having electrode for determining the rate of flow of a fluid
InactiveUS6801041B2Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsTarget analysisAnalyte
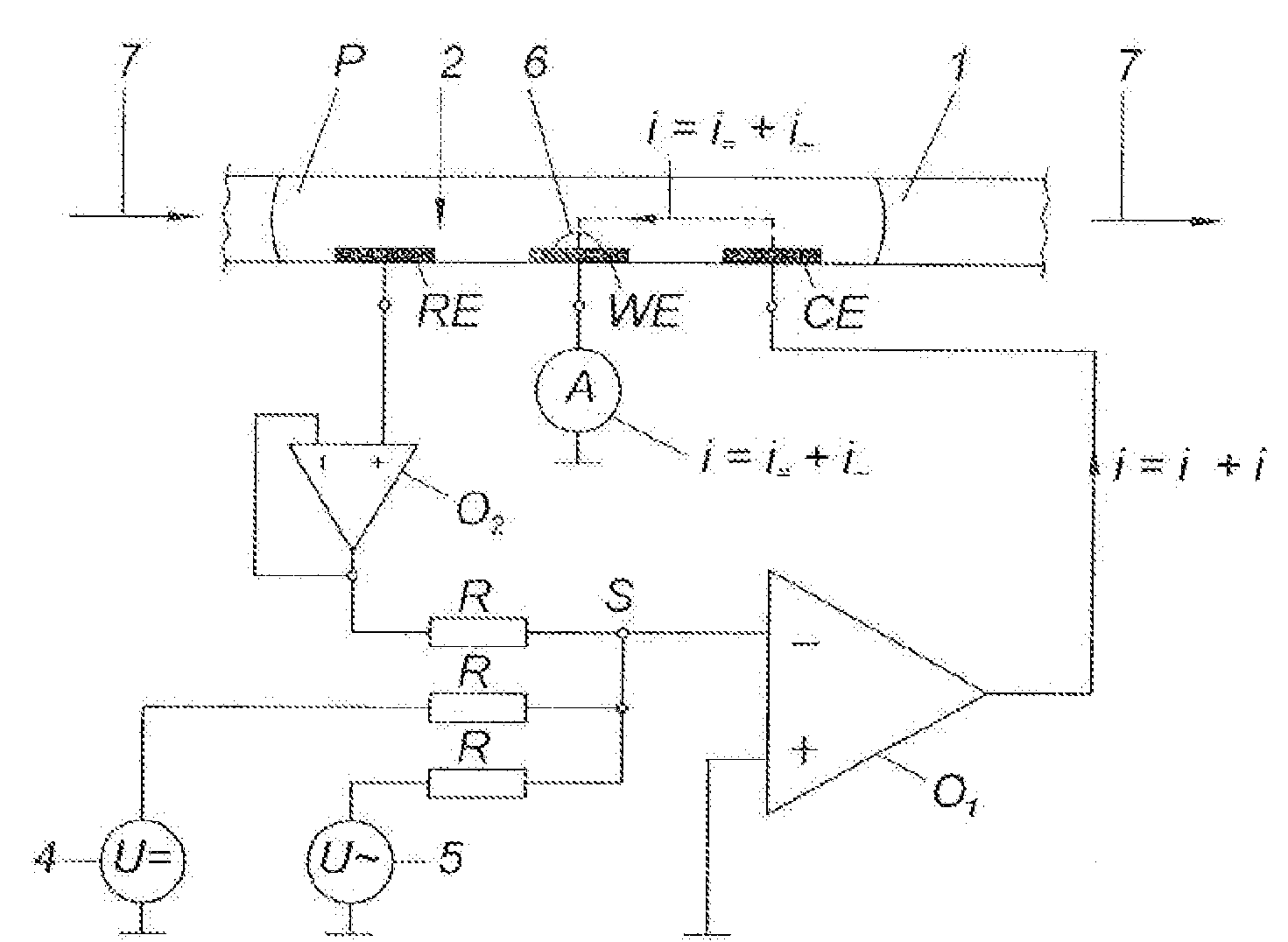
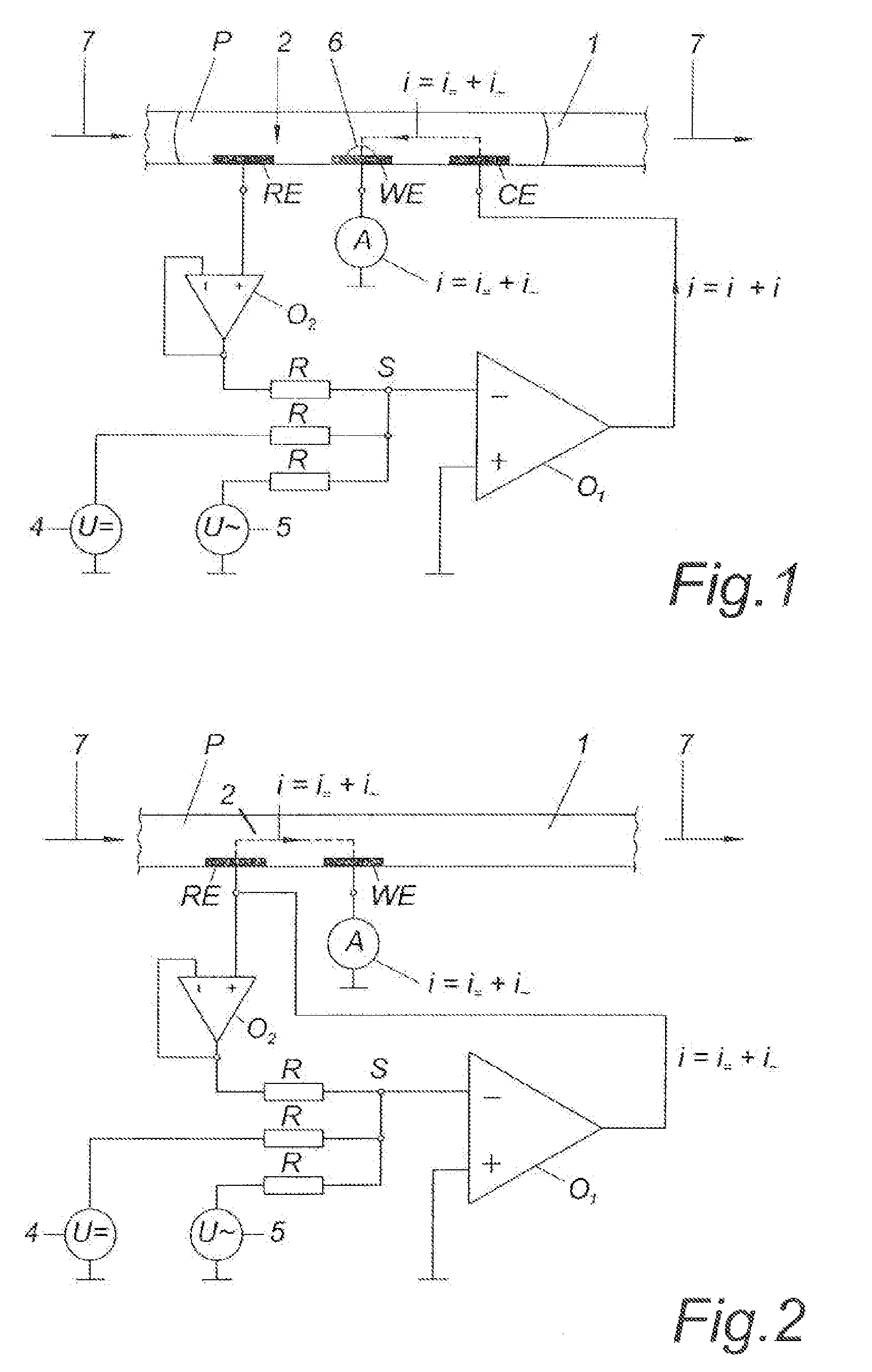
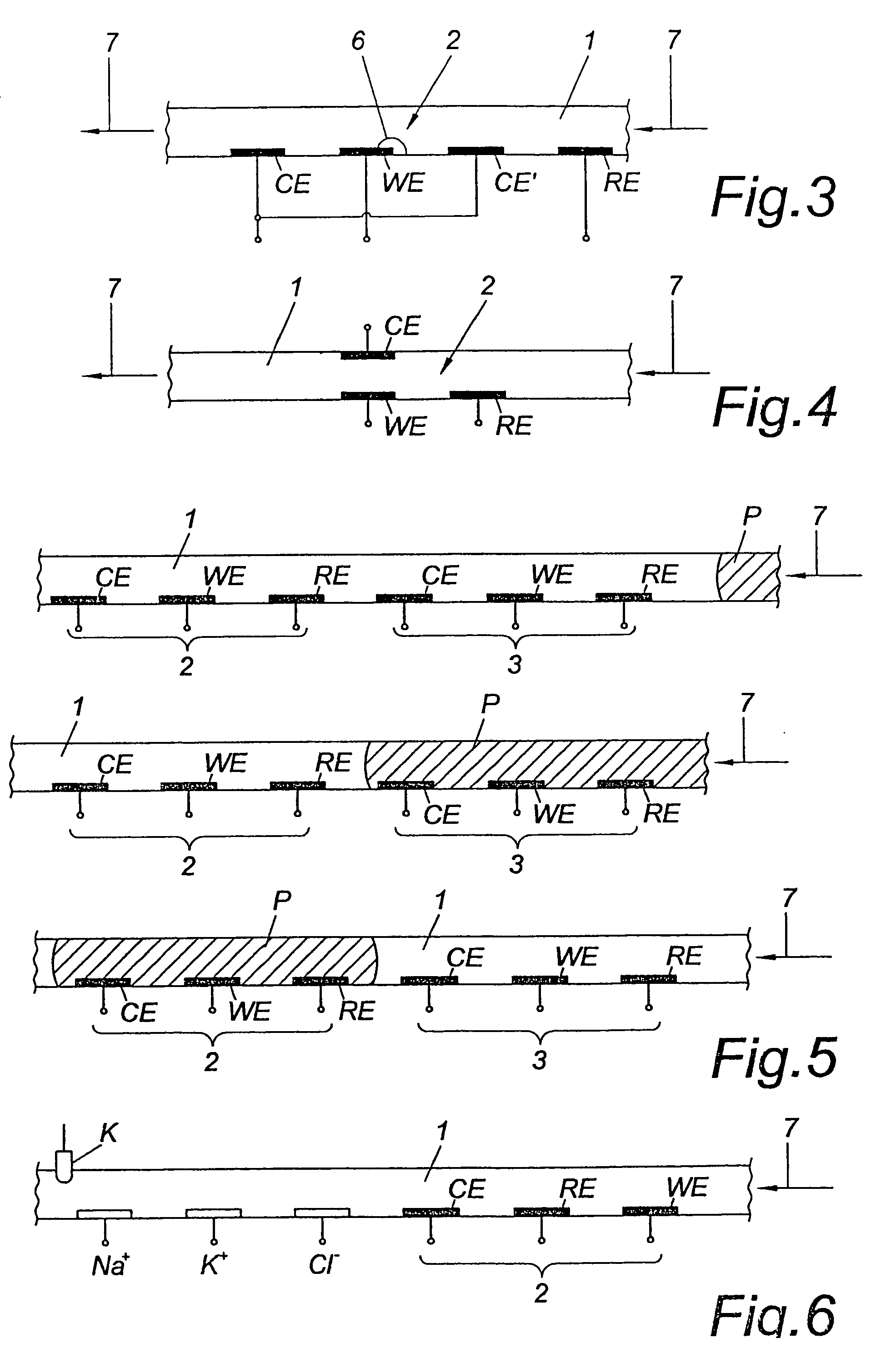
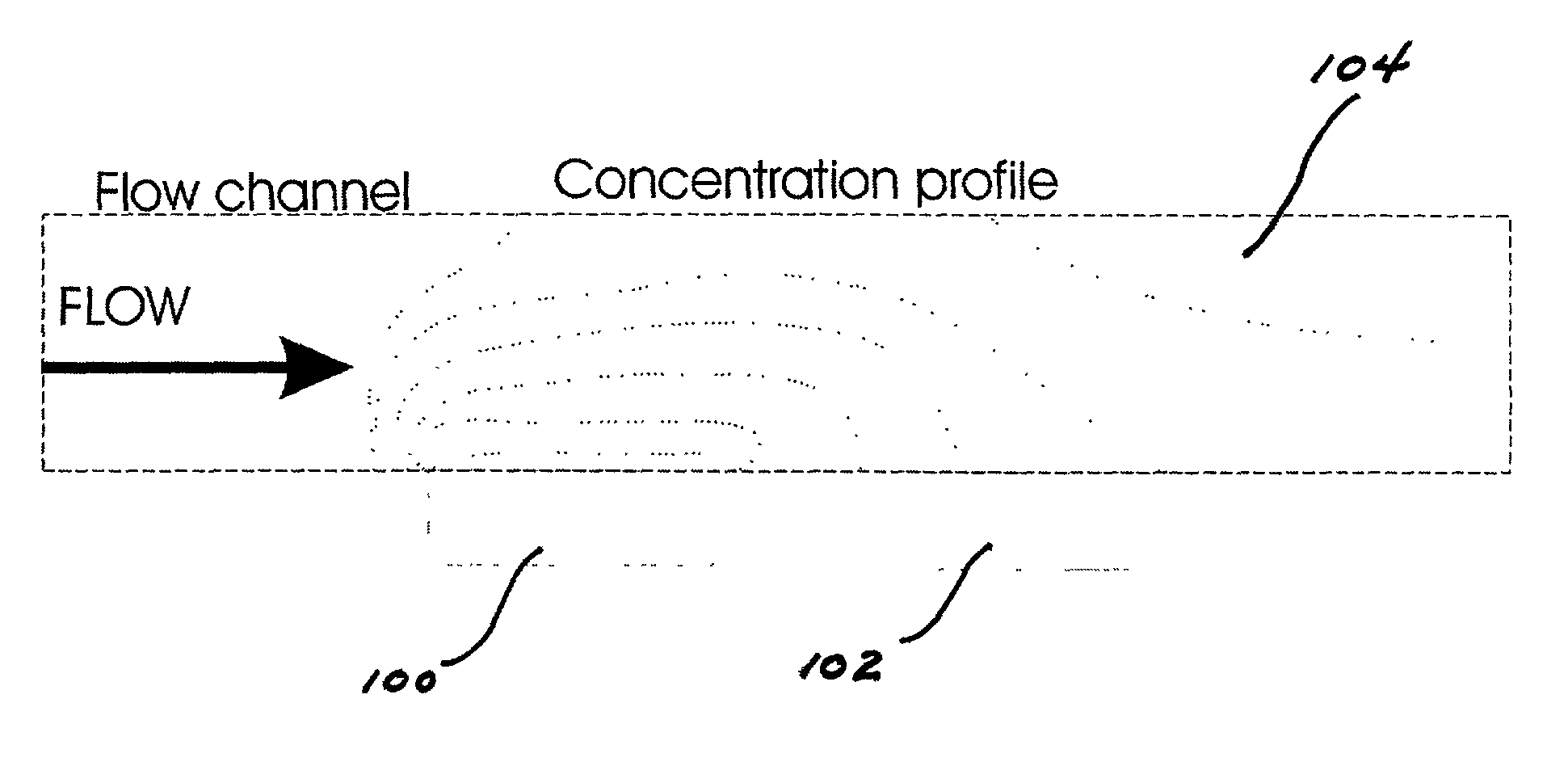
Sensors that are capable measuring the rate of flow of a fluid that passes over the electrodes of the sensor. In these sensors, an electrode, designated the flow rate-determining electrode, is used in conjunction with the conventional electrodes, e.g., the working electrode, the reference electrode, and the counter electrode, to determine the rate of flow of the fluid. In one aspect, this invention provides a sensor for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid when the sample flows continuously over the electrodes of the sensor, especially when the rate of flow of the sample is relatively low. In another aspect, this invention provides a method for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid, wherein the rate of flow of the sample varies during the period of time that the sensor is in place. In a preferred embodiment, the sensor employs four electrodes, namely, a working electrode, a reference electrode, a counter electrode, and a flow rate-determining electrode. Alternatively, a single electrode that performs both the function of the reference electrode and the function of the counter electrode can replace the reference electrode and the counter electrode. In addition, a dummy electrode or a blank electrode can be used to compensate for interference from electrochemically active species. The reagent(s) specific to the analyte of interest is required to be deposited on the working electrode.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Light emitting device
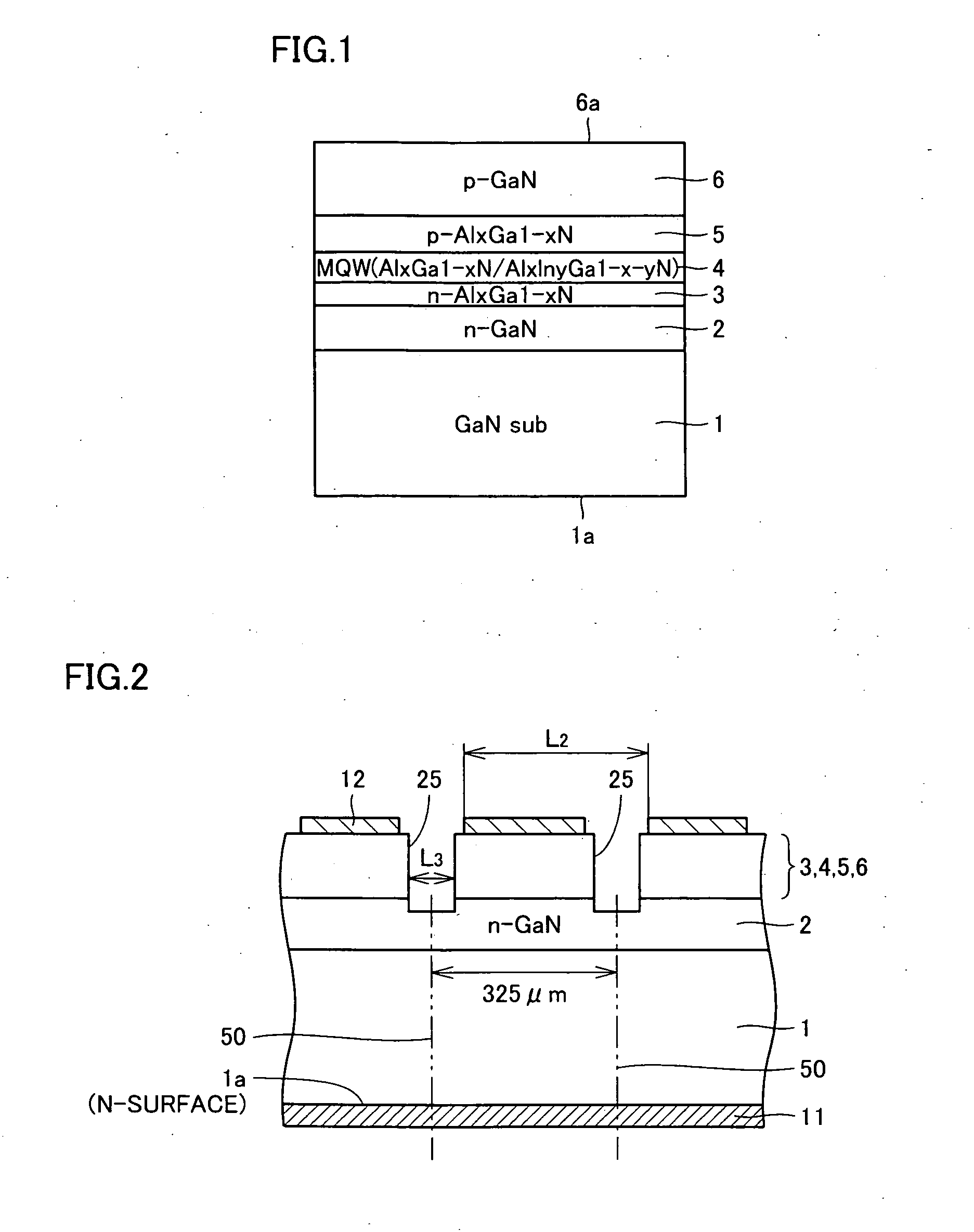
ActiveUS20050121688A1Simple configurationEasy to makeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight emissionSingle electrode
A light emitting device includes a nitride semiconductor substrate with a resistivity of 0.5 Ω·cm or less, an n-type nitride semiconductor layer and a p-type nitride semiconductor layer placed more distantly from the nitride semiconductor substrate than the n-type nitride semiconductor layer at a first main surface side of the nitride semiconductor substrate, and a light emitting layer placed between the n-type nitride semiconductor layer and the p-type nitride semiconductor layer, wherein one of the nitride semiconductor substrate and the p-type nitride semiconductor layer is mounted at the top side which emits light and the other is placed at the down side, and a single electrode is placed at the top side. Therefore, there is provided a light emitting device which has a simple configuration thereby making it easy to fabricate, can provide a high light emission efficiency for a long time period, and can be easily miniaturized.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Electric field proximity keyboards and detection systems
ActiveUS7145552B2High resolutionReduce complexityInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingDetector circuitsImage resolution
Owner:SOLECTRON
Stacked OLED display having improved efficiency
InactiveUS6903378B2Improved lifetimeImprove power efficiencyStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSingle electrode
An OLED device having a pixel, including a plurality of light transmissive filters; a first electrode layer defining a corresponding plurality of separately addressable electrodes; a first layer of white light emitting OLED material; a doped organic conductor layer; a second layer of white light emitting OLED material; and a second electrode layer defining a single electrode coextensive with the plurality of color filters.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Method and a device for monitoring a medical microsample in the flow measuring cell of an analyzer
ActiveUS7297241B2Reliable measurement resultsSimple designImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical impedanceSingle electrode
The invention relates to a method and device for the monitoring of a medical microsample in the flow measuring cell of an analyzer with regard to position and absence of bubbles by means of an alternating voltage applied to the measuring cell, the measuring cell being provided with a multitude of electrode systems placed one behind the other, each system comprising a number of single electrodes for measuring a substance contained in the microsample by means of a measurement voltage which essentially is a DC voltage. To monitor the exact position of the microsample and / or to detect air bubbles in the area of each electrode system, the alternating voltage and the measurement voltage are simultaneously and directly applied to the single electrodes of the corresponding electrode system, and the measured AC component respectively the measured impedance gives a measure for the position of the microsample and the absence of bubbles.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
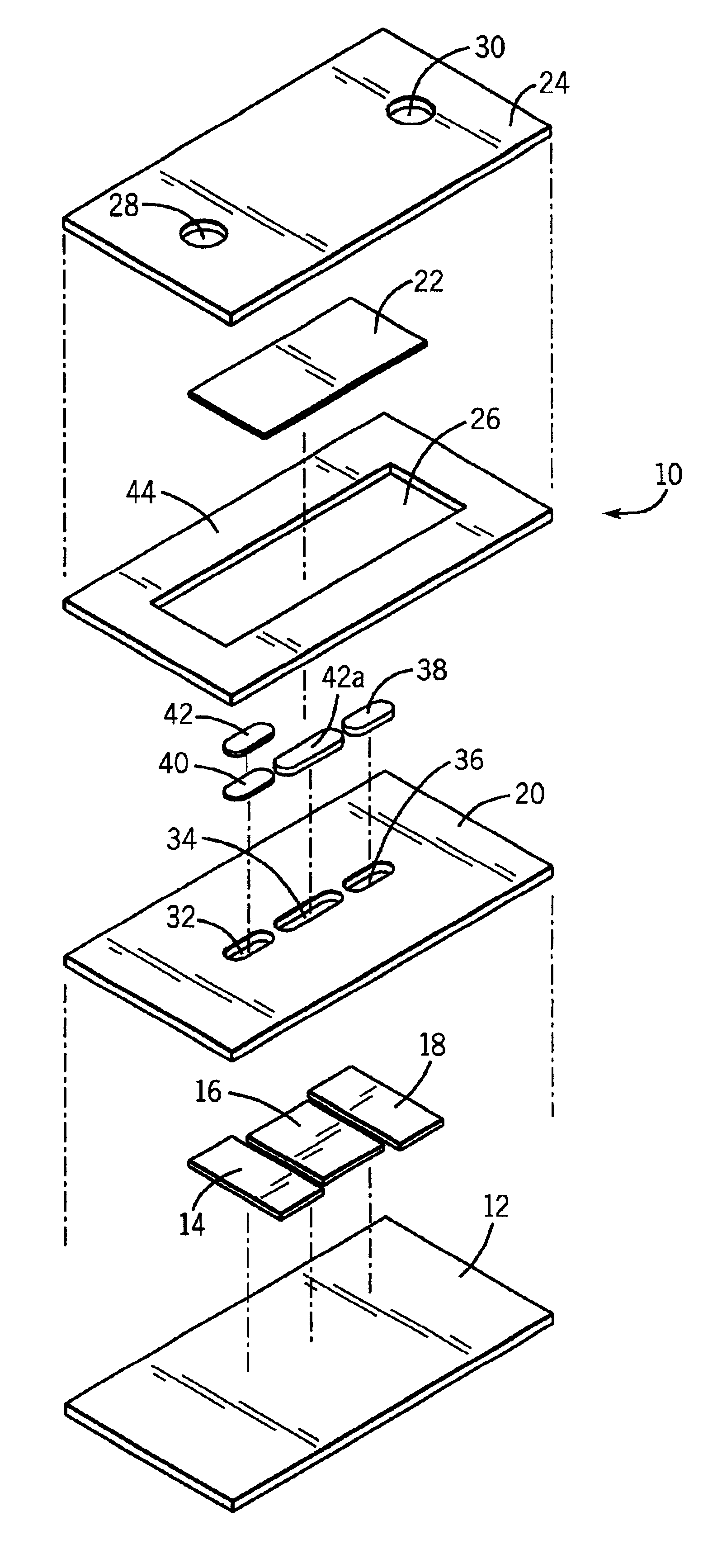
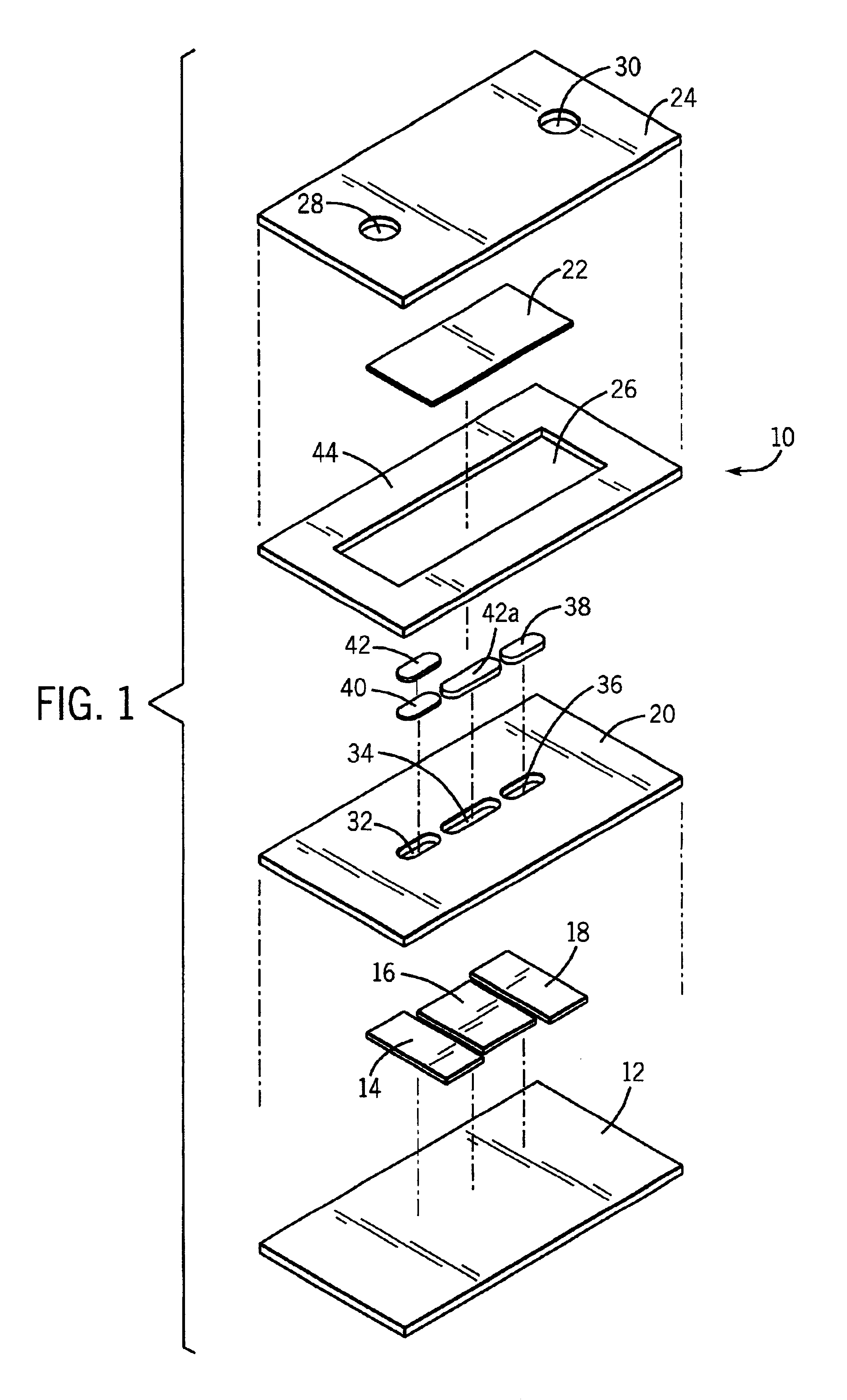
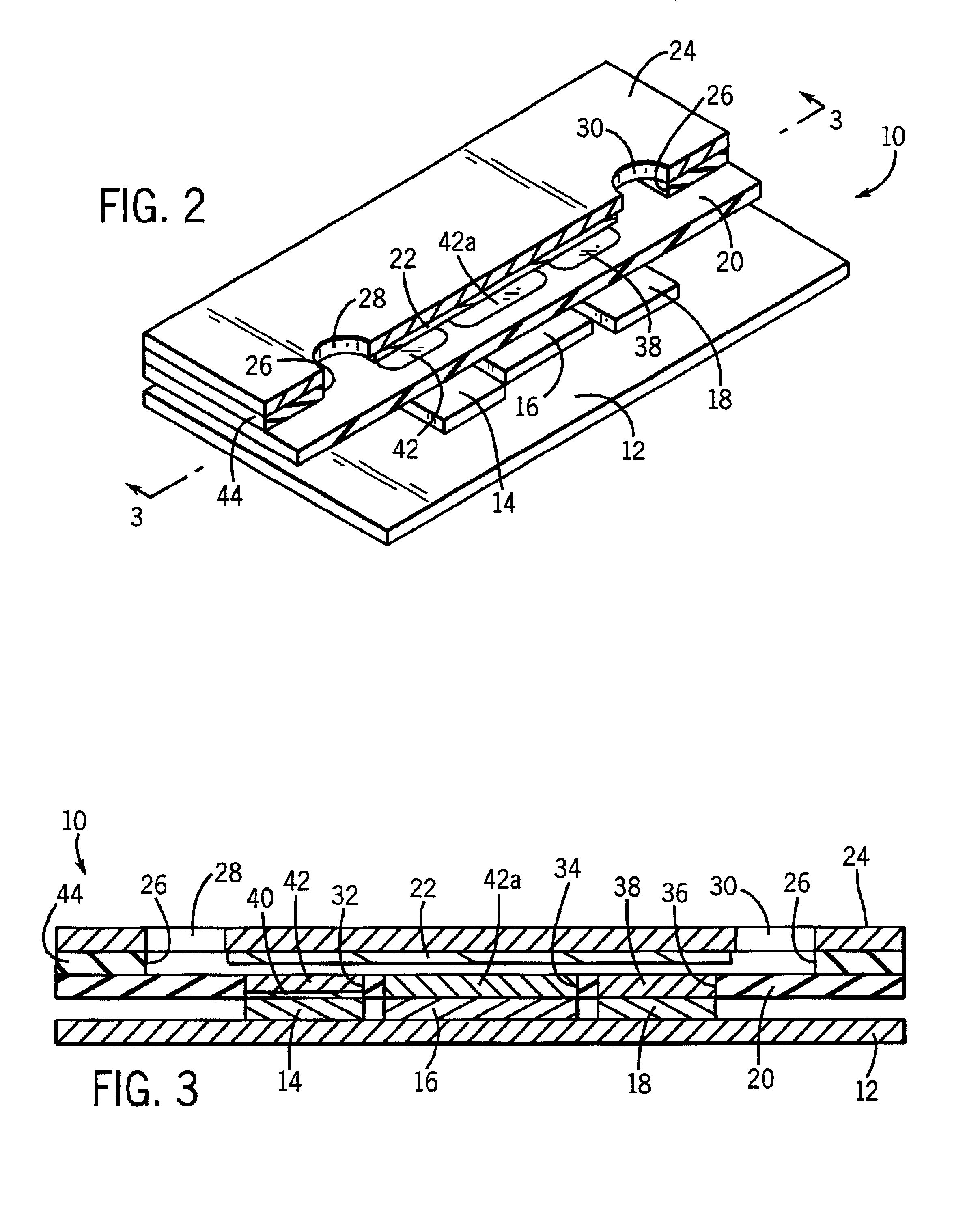
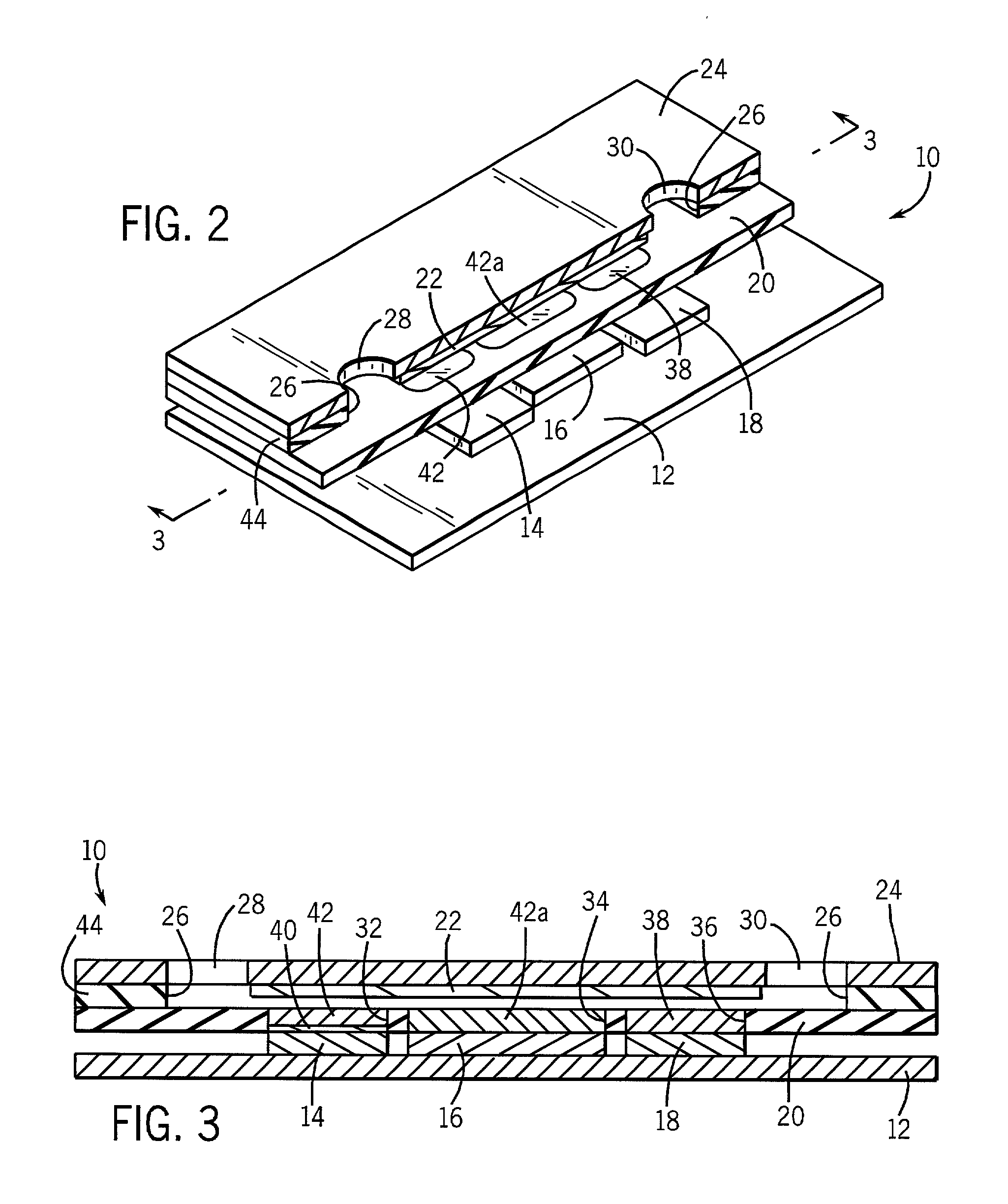
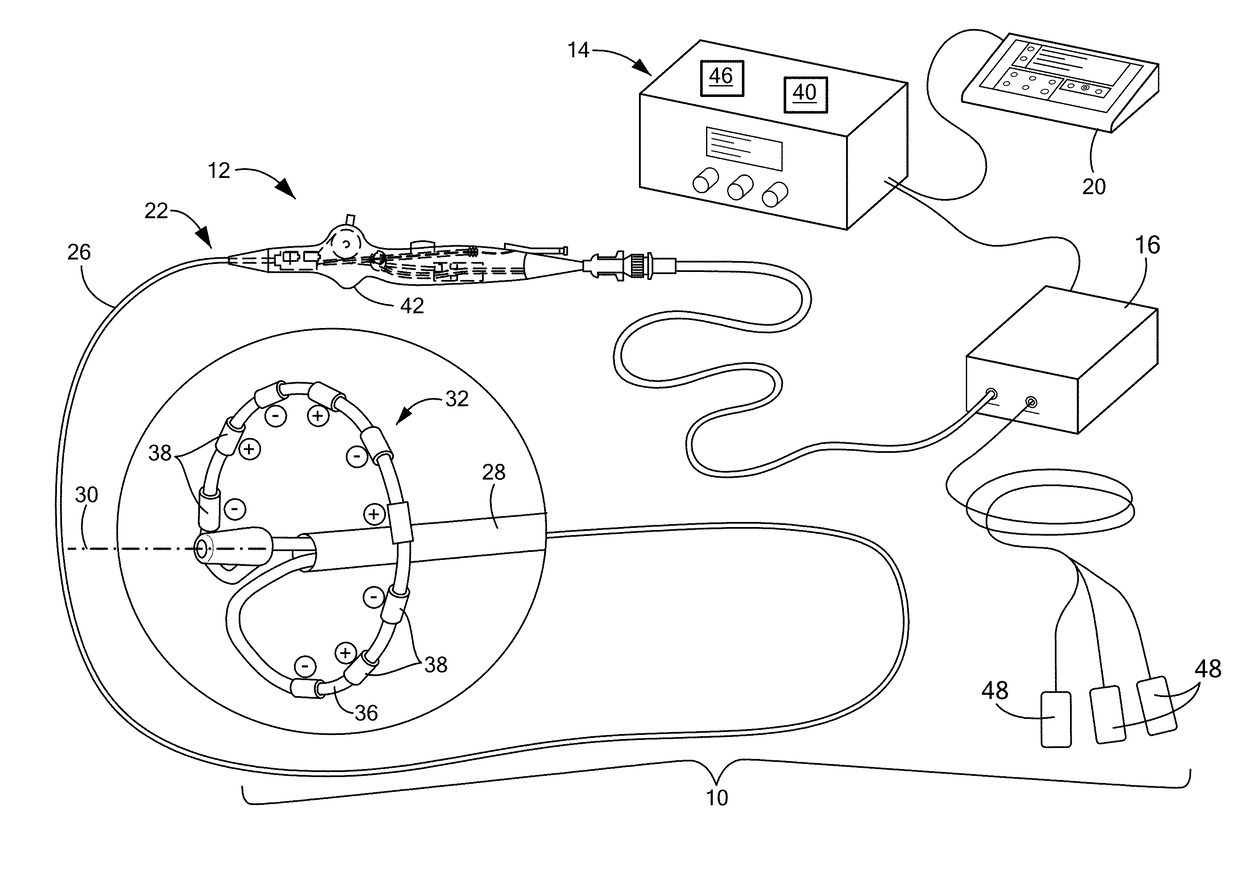
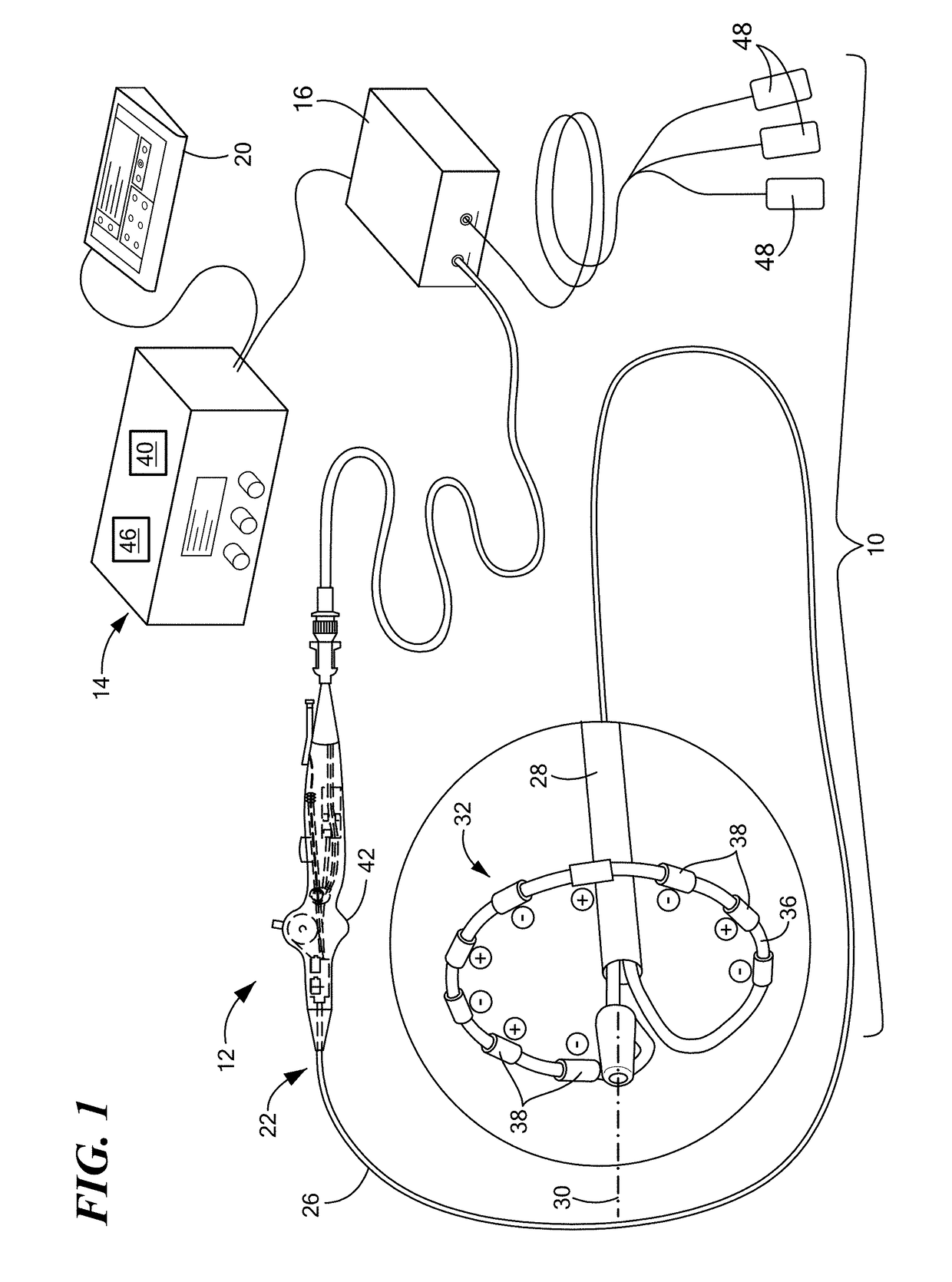
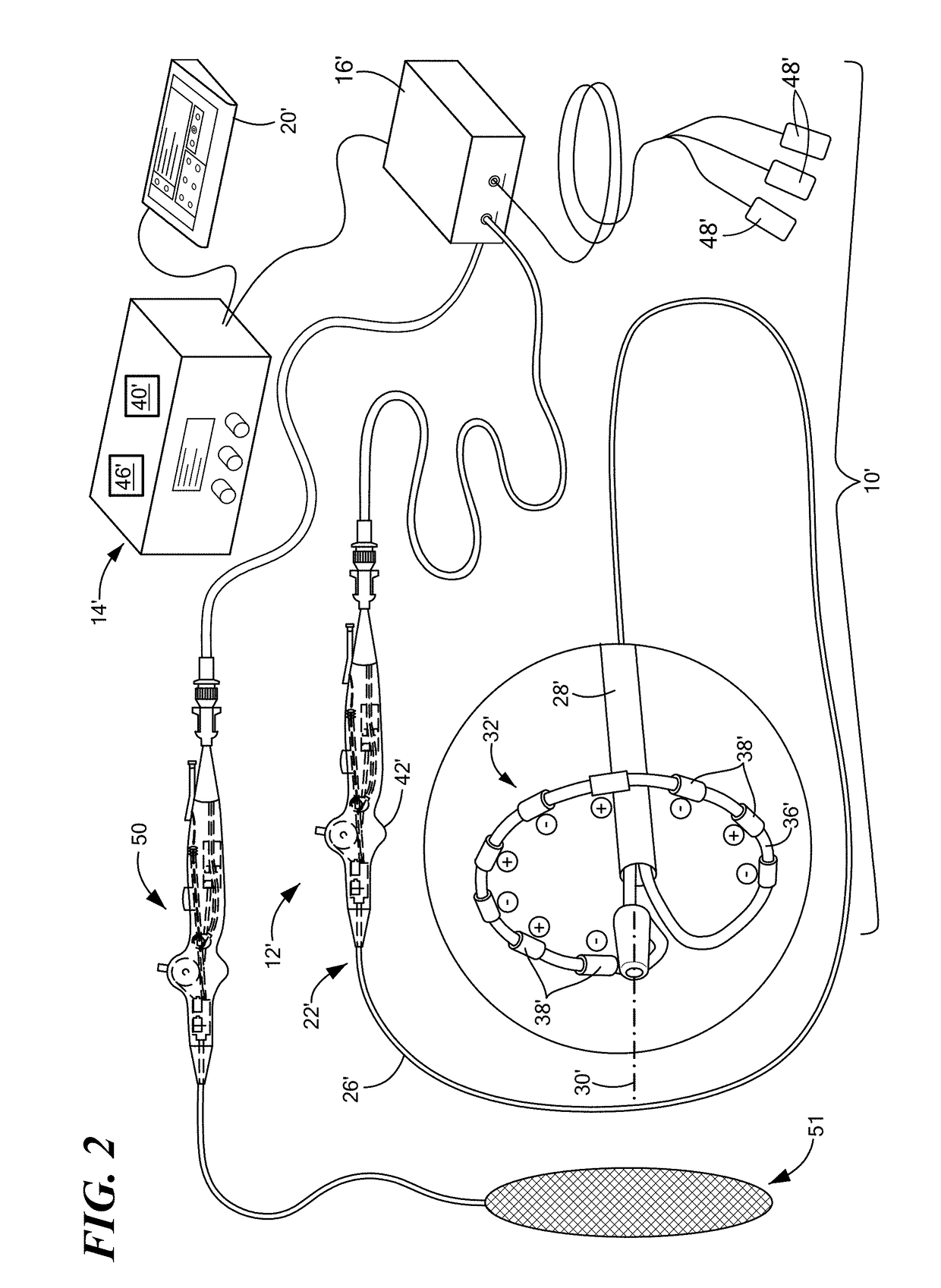
Method of mapping a plug in a mapping catheter
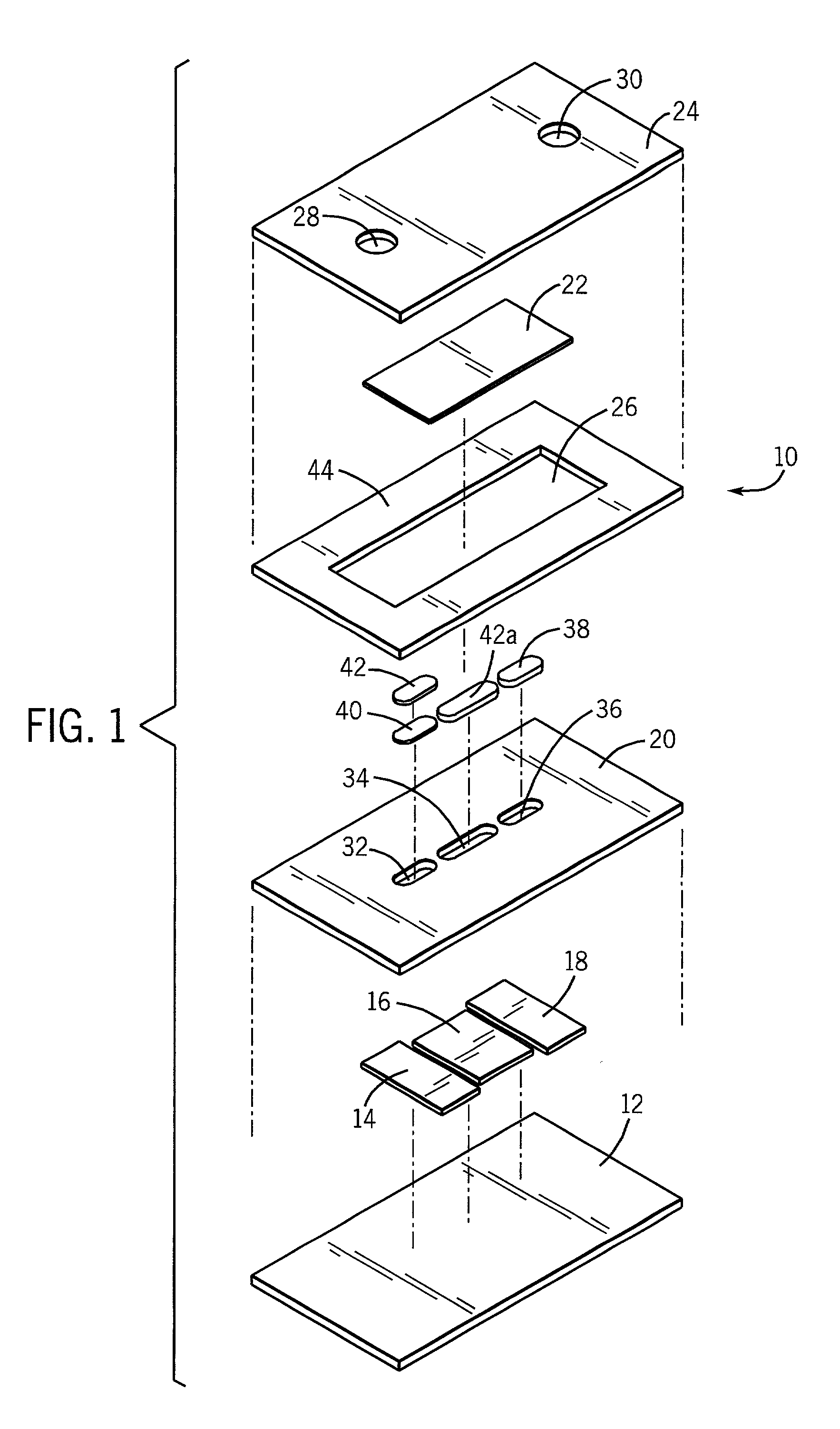
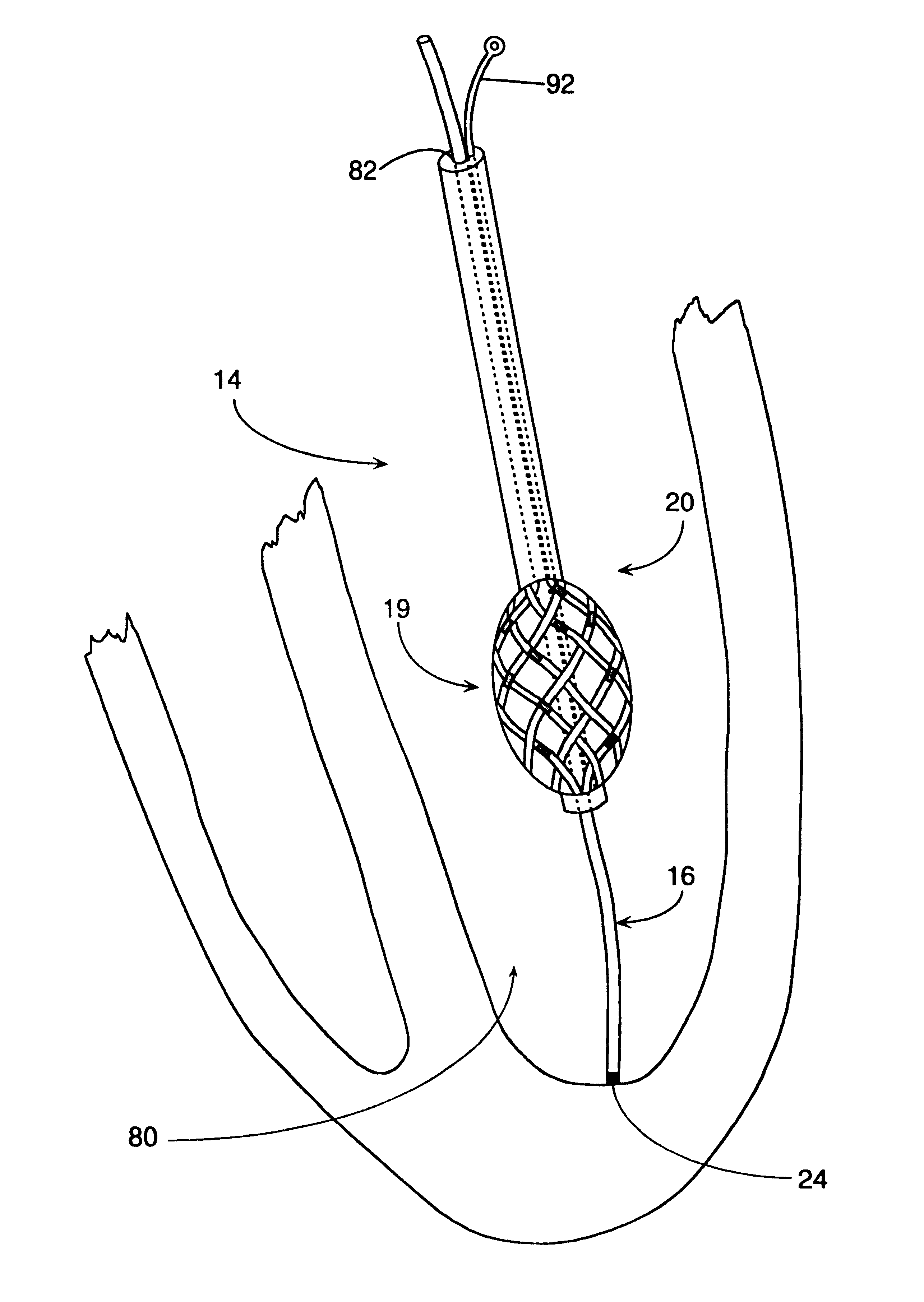
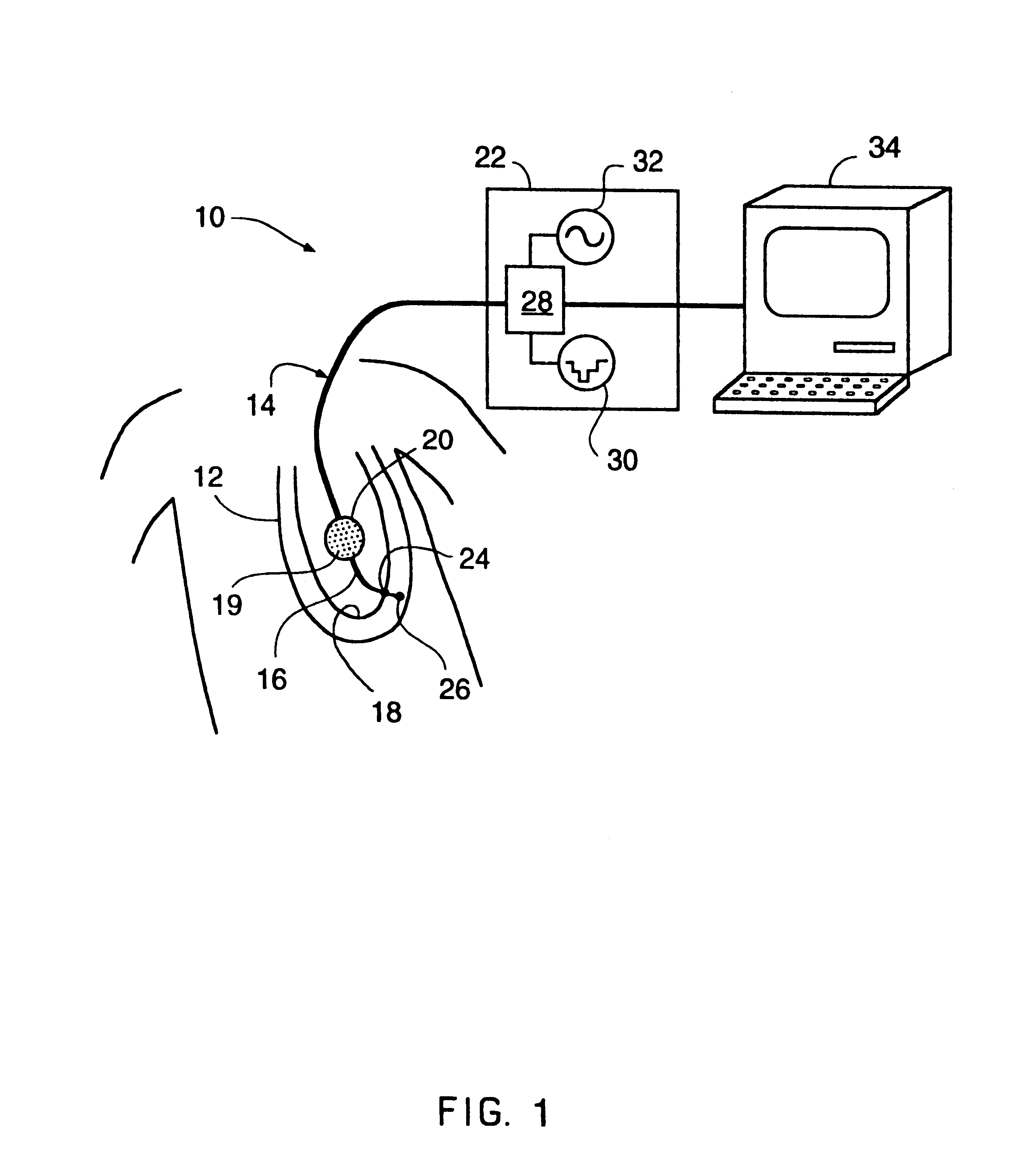
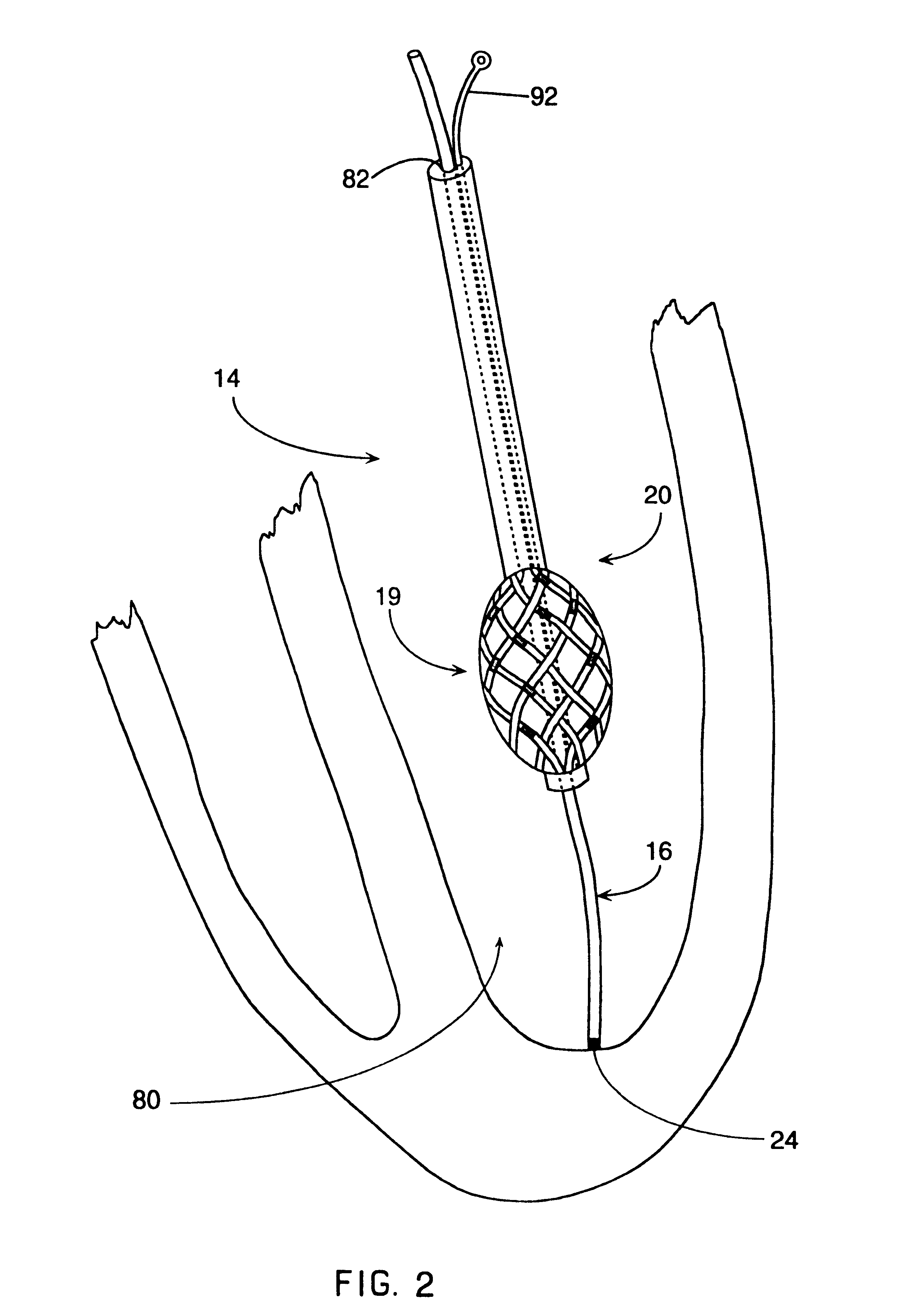
A method of constructing a mapping catheter is described where the catheter has numerous electrodes each associated with a single connection in a plug. The method consists of first arranging a plurality of wires in the desired relationship, with each of the wires running to a connection in a plug. Next, a single electrode is formed on each wire. Because it is often difficult to associate a particular connection with a particular plug, an electrical signal is then applied to a single one of the wires. The electrical signal can be applied to the connection or to the electrode. The electrical signal is then found among by examining either the electrodes or the connections, depending on which where the electrical signal was applied. Once the electrical signal is discovered, a map can be made between the connections and the electrodes.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Electric field proximity keyboards and detection systems
ActiveUS20050088416A1High resolutionReduce complexityInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingDetector circuitsSingle electrode
The invention is related to an electric field proximity detection system suitable for use as a touch sensitive keyboard or to be used in close proximity without direct contact. In an embodiment of a circuit useful in the system, an AC signal is coupled to a single electrode functioning as an antenna radiating an electric field through a high impedance circuit. A conductive object in close proximity disturbs the field causing a voltage change across nodes of the high impedance circuit that is compared by a detector circuit that generates a DC output indicating an object is close to the electrode. In another embodiment, the circuit couples to an analog multiplexer to control a plurality of electrodes. In another embodiment, a row and column address scheme coupling a plurality of electrodes and increases resolution without substantially increasing complexity. The circuits may be integrated in a semiconductor to reduce size and cost. The electric field proximity detection system extends to applications related to object detection such as remote sensing, motion detection and remote controls.
Owner:SOLECTRON
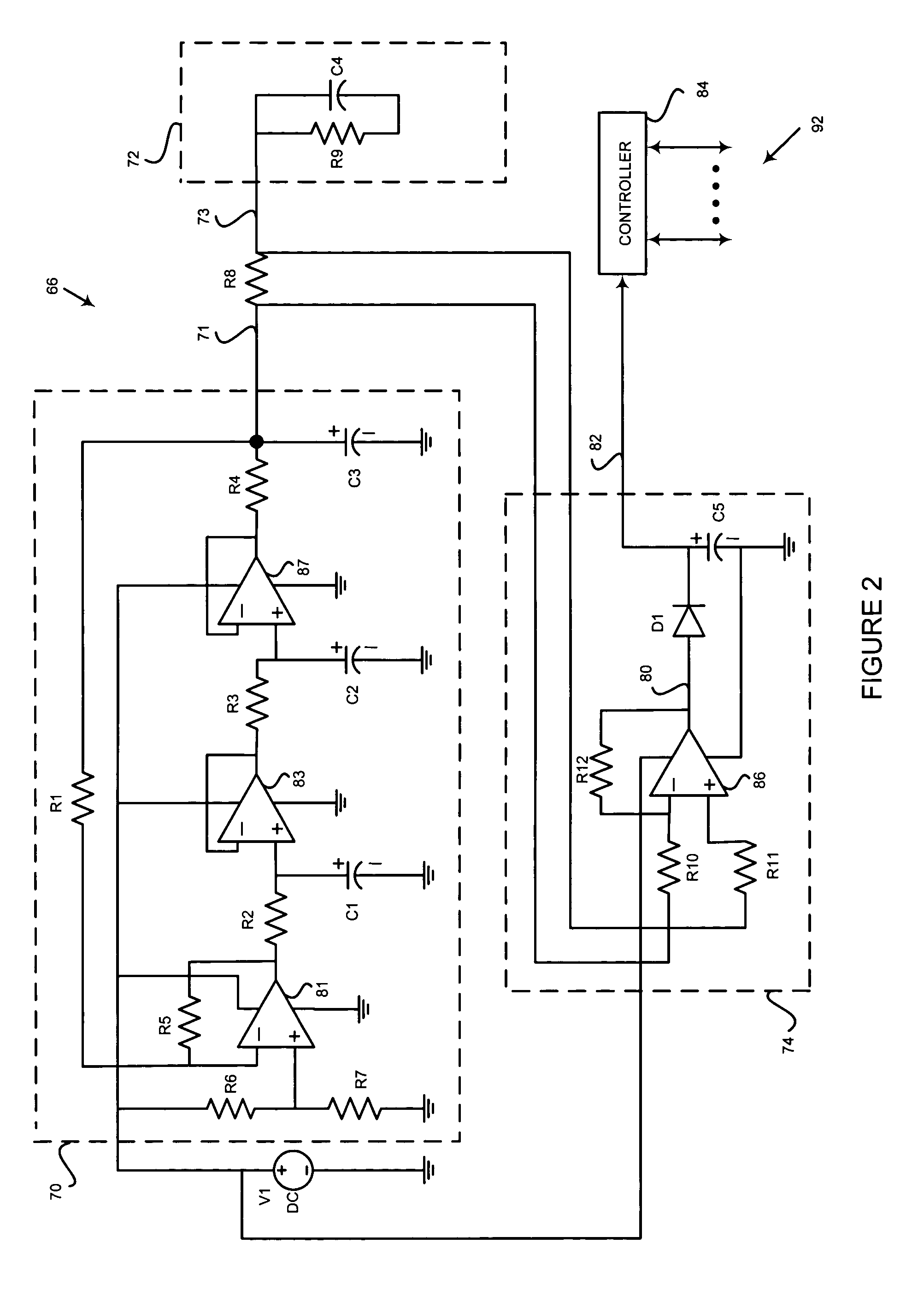
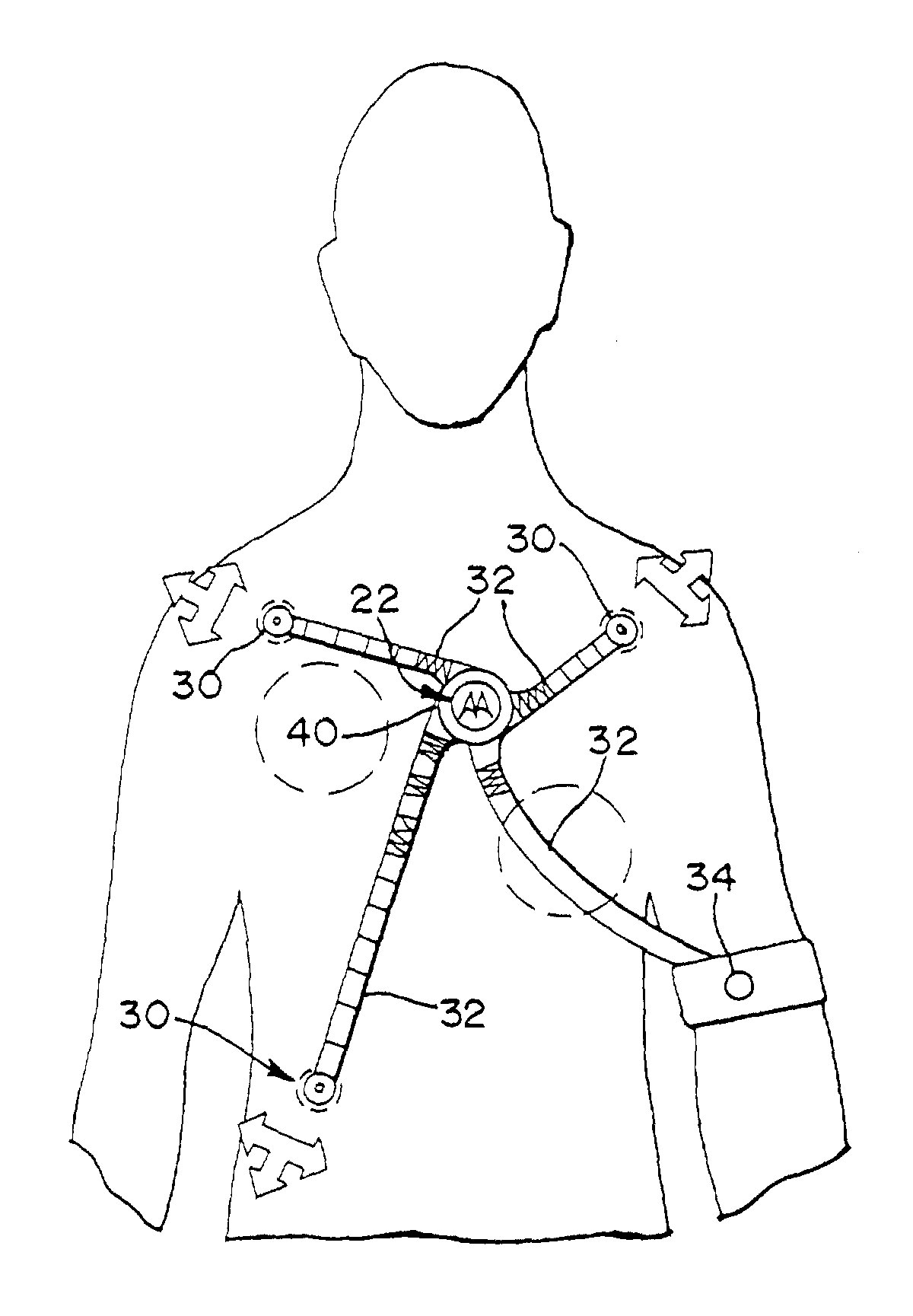
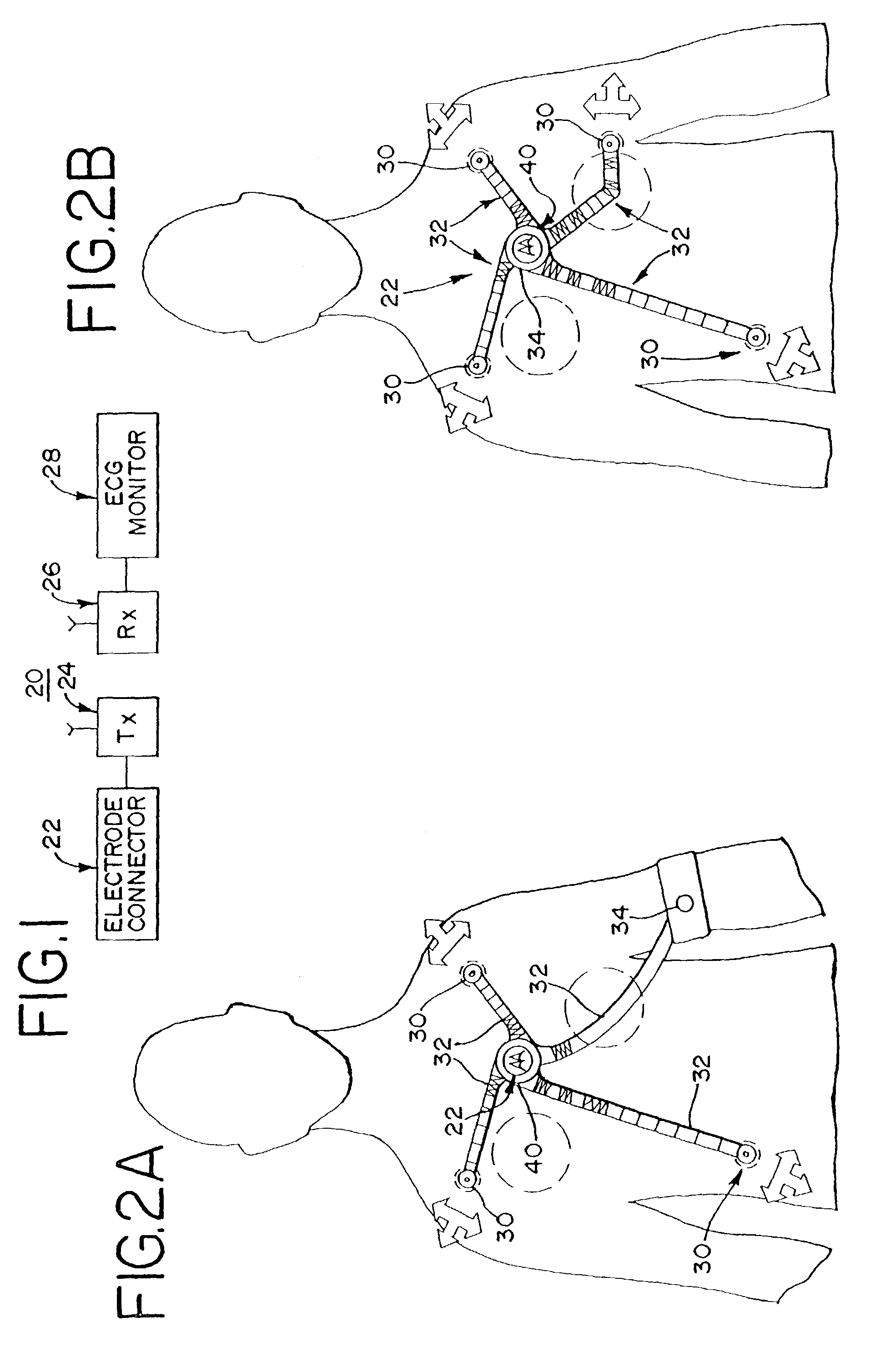
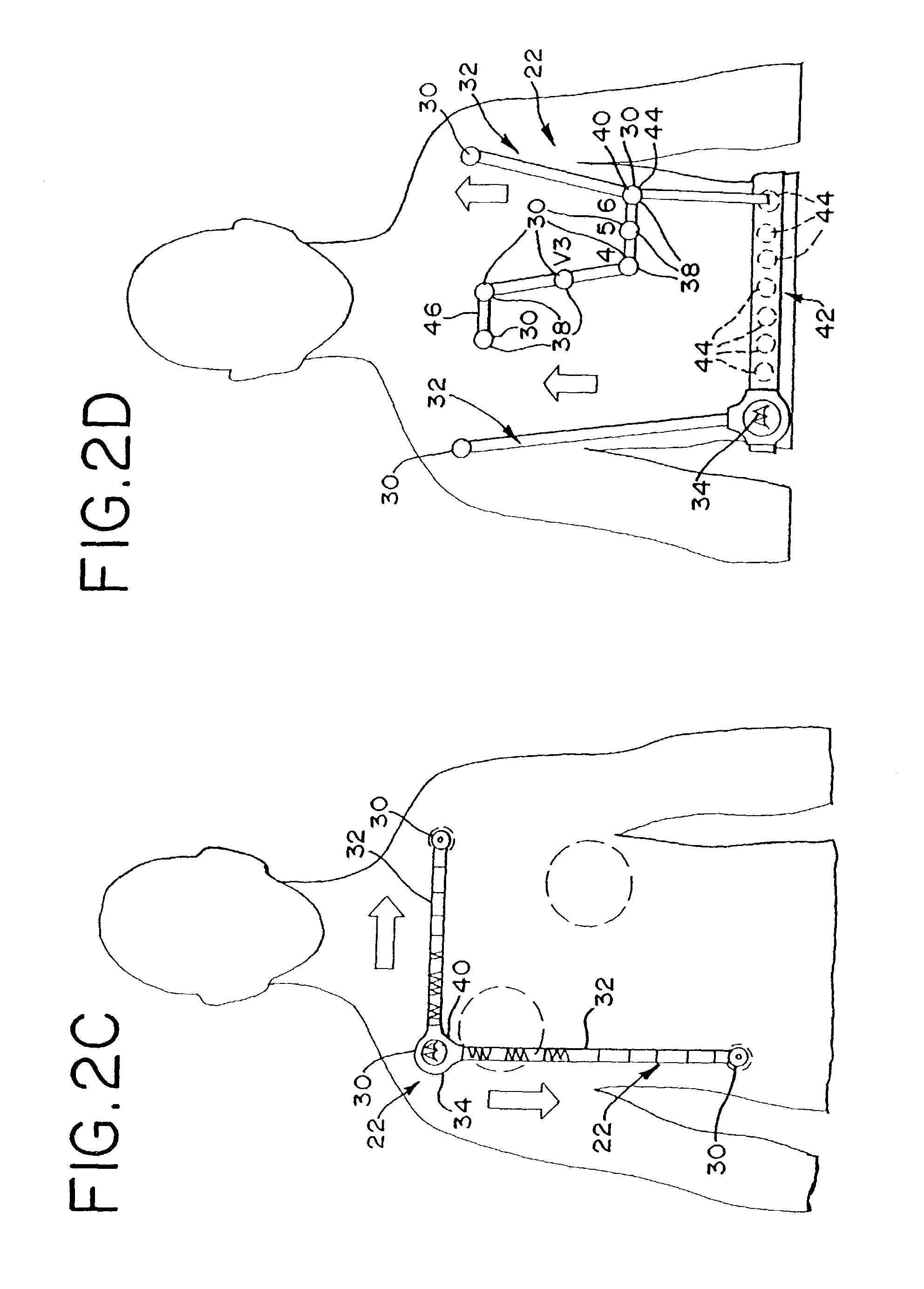
Wireless electrocardiograph system and method
A method and system for wireless ECG monitoring is provided. An electrode connector, transmitter and receiver operate with existing electrodes and ECG monitors. The electrode connector includes connectors for attaching to disposable or reusable single electrodes. The transmitter transmits the signals from the electrodes to the receiver. The receiver passes the electrode signals to the ECG monitor for processing. ECG monitors used with an electrical conductor, for example wire connections to electrodes, are connected with the receiver, avoiding the purchase of a new monitor. Any legacy ECG monitor, including different ECG monitors, connects with the receiver using the ECG monitor's lead-wires. The ECG monitor operates as if directly connected to the electrodes without the problems discussed above associated with wires running from the ECG monitor to the patient.
Owner:LIFESYNC
Multi-qubit tunable coupling architecture using fixed-frequency superconducting qubits
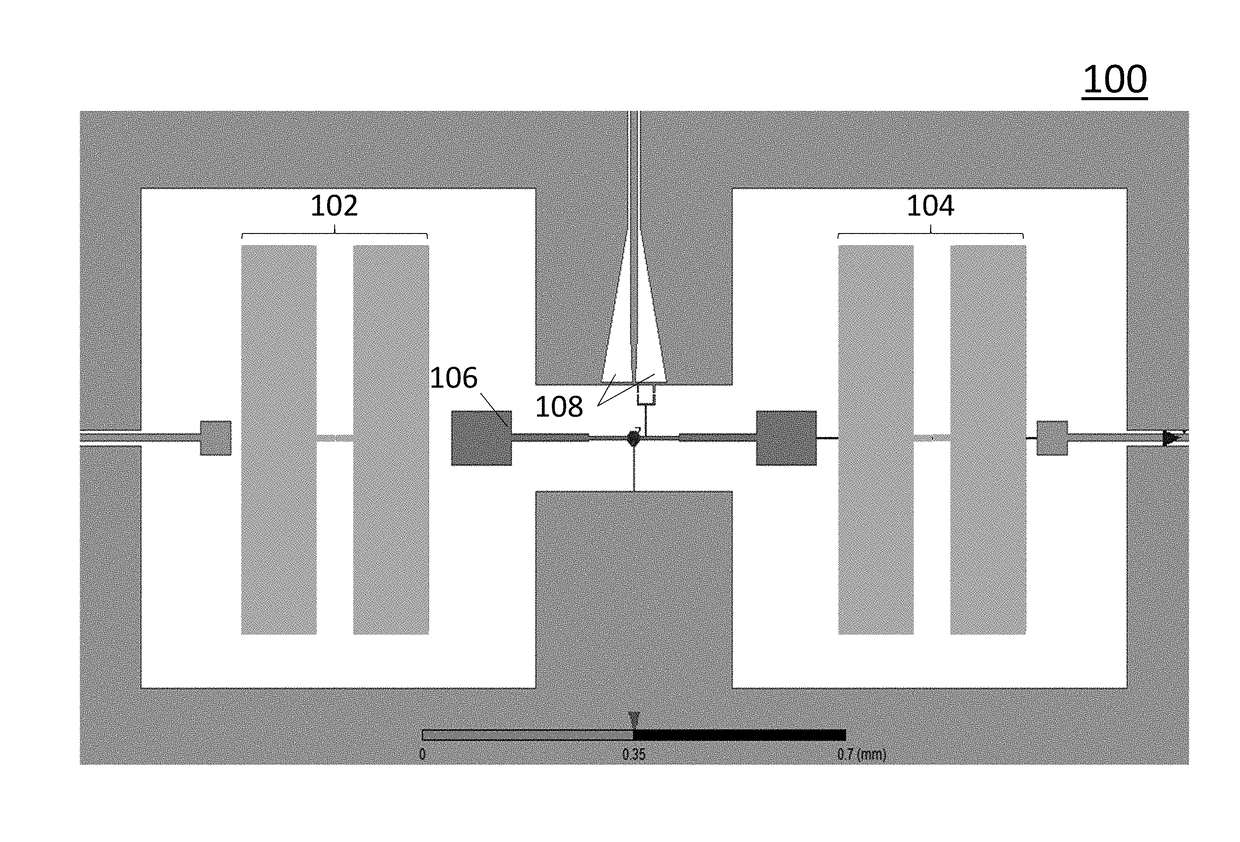
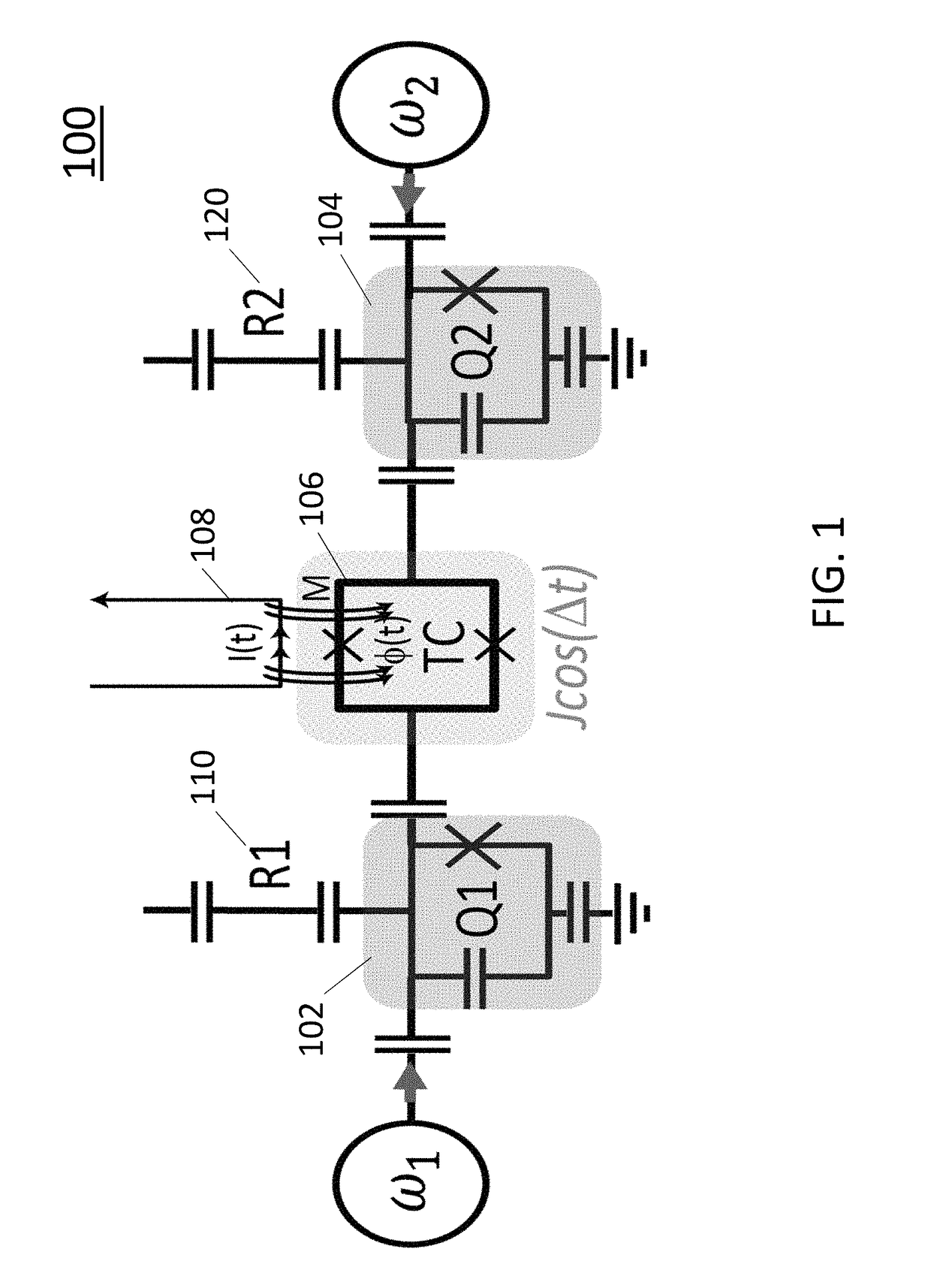
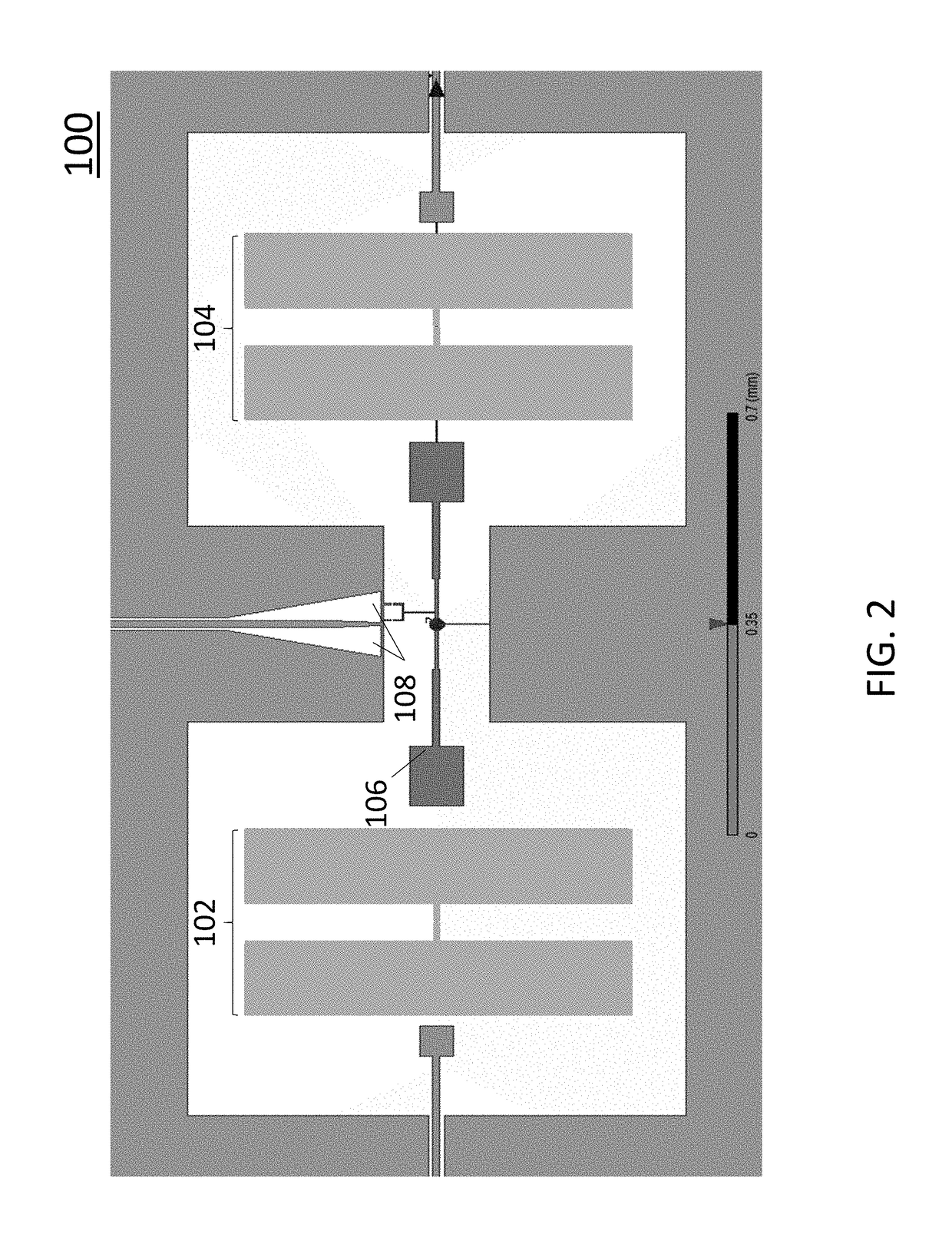
Various embodiments provide a coupling mechanism, method of activation and a square lattice. The coupling mechanism comprises two qubits and a tunable coupling qubit that activates an interaction between the two qubits by modulation of a frequency of the tunable coupling qubit. The tunable coupling qubit capacitively couples the two qubits. The tunable coupling qubit is modulated at a difference frequency of the two qubits. The difference frequency may be significantly larger than an anharmonicity of the two qubits. The tunable coupling qubit may be coupled to the two qubits by two electrodes separated by a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) loop having two Josephson junctions or by a single electrode with a SQUID loop coupling to ground. The SQUID loop is controlled by an inductively-coupled flux bias line positioned at the center of the tunable coupling qubit.
Owner:IBM CORP
Diagnostic device for remote sensing and transmitting biophysiological signals
InactiveUS20100042012A1Noise minimizationMaximize signalElectrocardiographySensorsSpatially resolvedWireless transmission
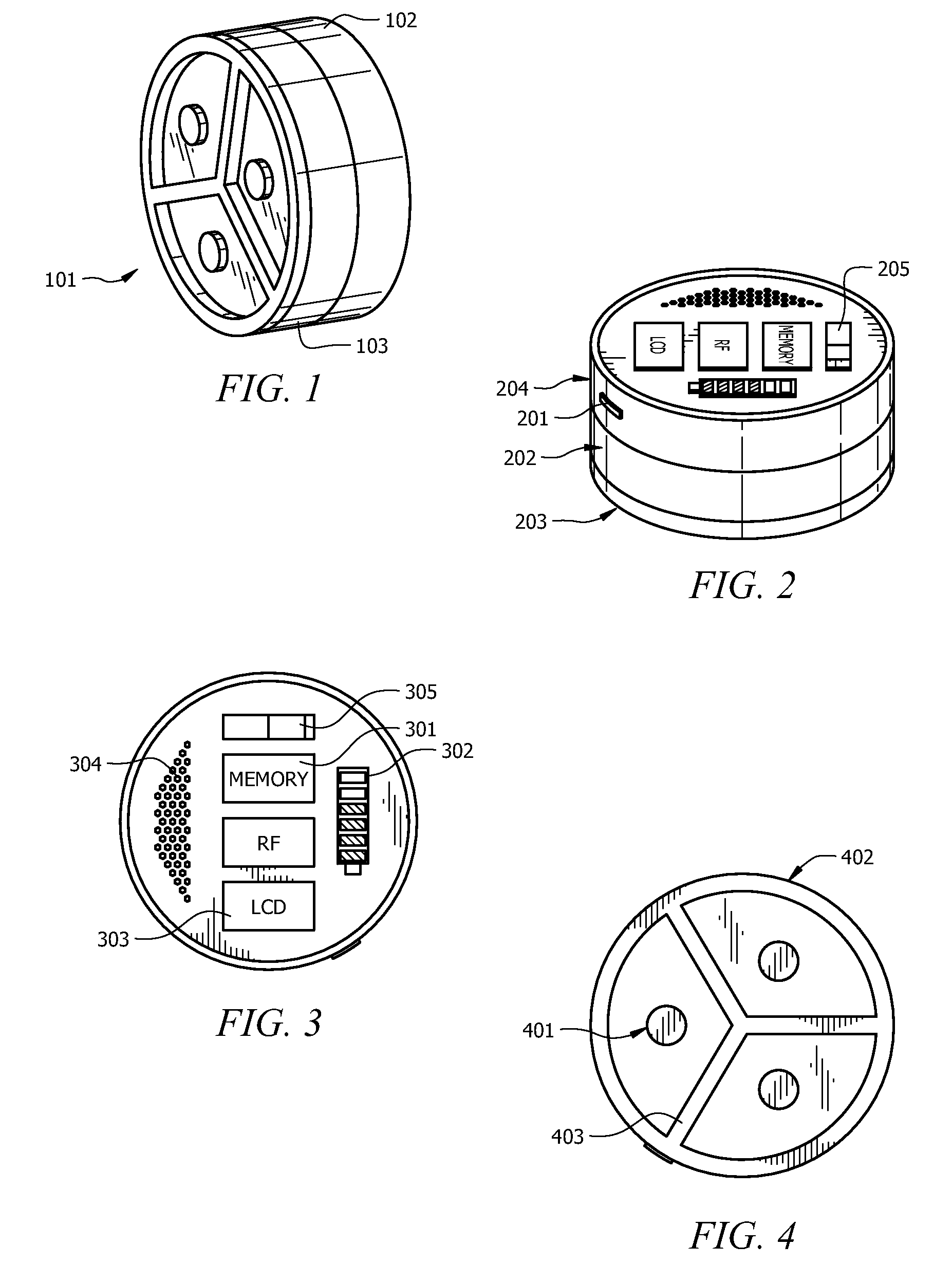
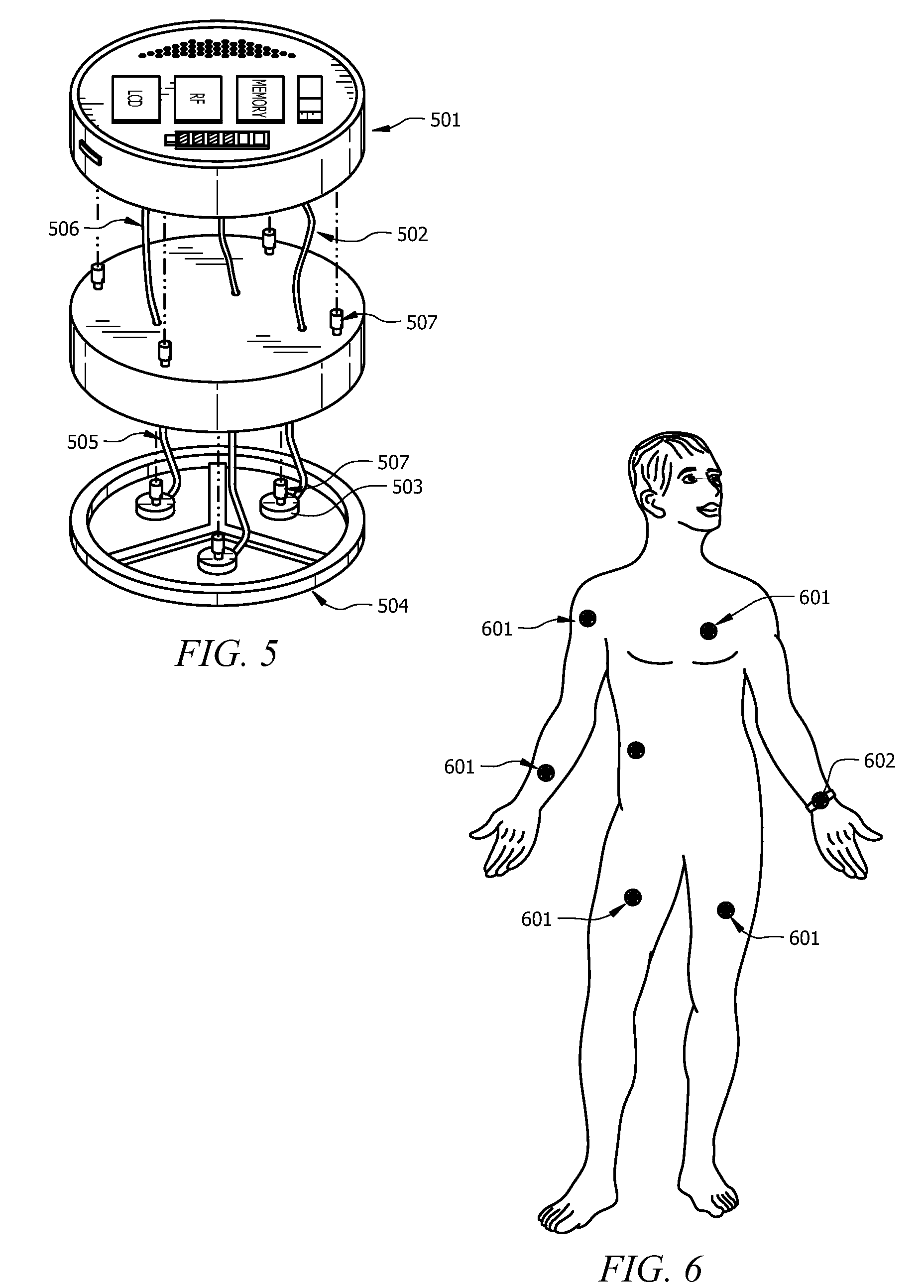
A diatrophic, bio-physiological interface is self-contained with onboard intensification, filtering, and signal processing and is wirelessly enabled (idio-electrode), with multiple sensory system for bio-physiological measurements, described herein utilizes spatially resolved potential profiles from a cluster of mini electrodes to form constituent sets comprising mini sensorial electrodes. The sets of sub electrodes containing the clusters are jointly optimized to attain measurable gradient of some diagnostic value. The present invention provides a distinct lead-free single electrode that is rotationally invariant with onboard Digital Signal Processor for arrhythmia detection, source encoding, and passive and active wireless transmission. Additionally, in one aspect of the present invention the lead-free idio-electrode bio-physiological adapter allows for utmost clinical operational freedom and dramatically obviates the needs for leads of any length that invariably encumber the acquisition and performance of electrocardiogram recordings of any sort.
Owner:ALHUSSINY KARIM
Sensor having electrode for determining the rate of flow of a fluid
InactiveUS20030214304A1Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementTarget analysisAnalyte
Sensors that are capable measuring the rate of flow of a fluid that passes over the electrodes of the sensor. In these sensors, an electrode, designated the flow rate-determining electrode, is used in conjunction with the conventional electrodes, e.g., the working electrode, the reference electrode, and the counter electrode, to determine the rate of flow of the fluid. In one aspect, this invention provides a sensor for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid when the sample flows continuously over the electrodes of the sensor, especially when the rate of flow of the sample is relatively low. In another aspect, this invention provides a method for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid, wherein the rate of flow of the sample varies during the period of time that the sensor is in place. In a preferred embodiment, the sensor employs four electrodes, namely, a working electrode, a reference electrode, a counter electrode, and a flow rate-determining electrode. Alternatively, a single electrode that performs both the function of the reference electrode and the function of the counter electrode can replace the reference electrode and the counter electrode. In addition, a dummy electrode or a blank electrode can be used to compensate for interference from electrochemically active species. The reagent(s) specific to the analyte of interest is required to be deposited on the working electrode.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Catheter electrodes for energy management
ActiveUS20180214202A1Improve efficacyImprove efficiencyElectrocardiographySurgical navigation systemsEngineeringActive electrode
Methods, systems, and devices for enhancing the efficiency and efficacy of energy delivery and tissue mapping. One system includes a treatment element having a plurality of electrodes and an energy generator that is configured to deliver electric energy pulses to the electrodes in a variety of patterns. For example, electrodes may be arranged in closely spaced pairs. The energy generator may deliver mapping energy to each electrode in each pair individually to map tissue and may deliver ablation energy to the electrodes in each pair together, such that each pair is treated like a single electrode, to deliver ablation energy, such as bipolar ablation energy between adjacent pairs. One system includes at least one concave electrode, the configuration of which concentrates the energy and drives it deeper into the tissue. One system includes neutral electrodes between active electrodes, the energy generator selectively coupling the neutral electrodes to alter the ablation pattern.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
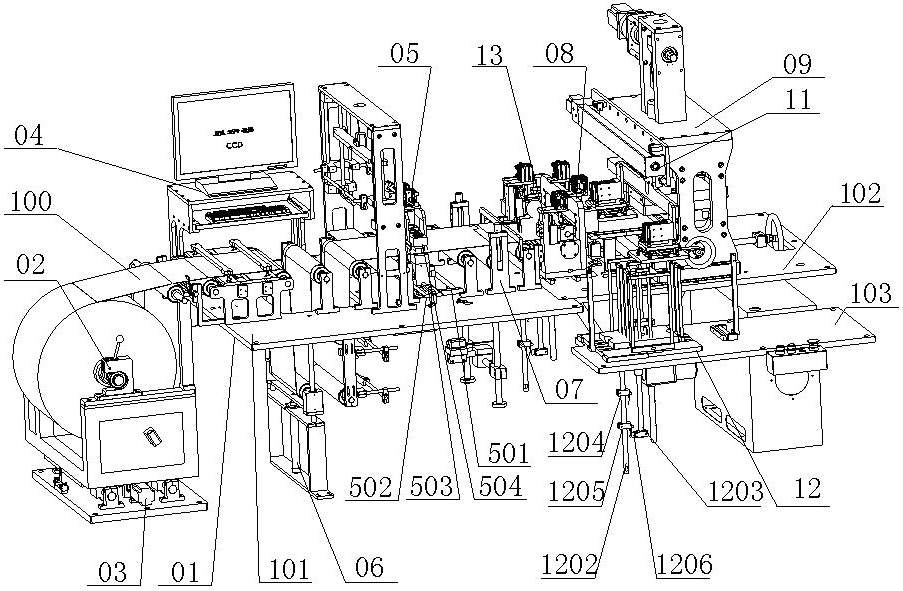
Electrode sheet forming machine
ActiveCN102306744AReduce manufacturing costExpanded range of specificationsElectrode manufacturing processesMetal-working feeding devicesPunchingAgricultural engineering
The present invention discloses an electrode sheet forming machine. The electrode sheet forming machine comprises a support mechanism, an unwinding mechanism, an unwinding rectification mechanism, an unwinding traction mechanism, a tension mechanism, a forming mechanism and a material collecting mechanism. The electrode sheet forming machine is characterized in that: the forming mechanism comprises a chamfer clipping mechanism, a constant length cutting mechanism and an electrode lug punching mechanism, wherein the chamfer clipping mechanism, the constant length cutting mechanism and the electrode lug punching mechanism are sequentially arranged on an electrode sheet belt in an unwinding direction; the chamfer clipping mechanism is provided for carrying out clipping for both sides of the electrode sheet belt to form the chamfer of each single electrode sheet, the constant length cutting mechanism is provided for carrying out constant length cutting for the electrode sheet belt to formthe single electrode sheet, the electrode lug punching mechanism is provided for punching the electrode lug of the single electrode sheet. Compare to the prior art, with the present invention, the die cost is saved.
Owner:深圳市和合自动化有限公司
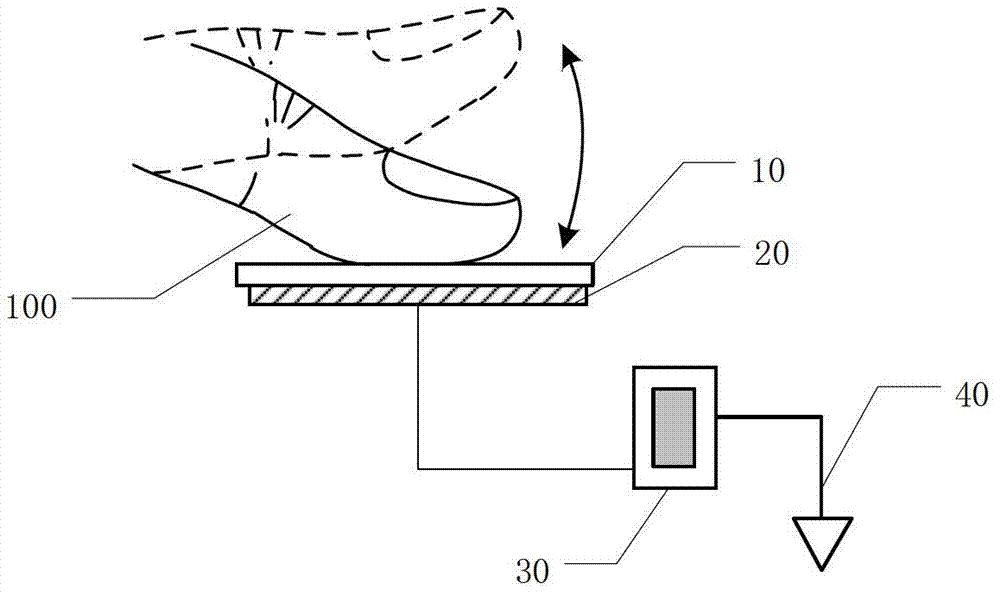
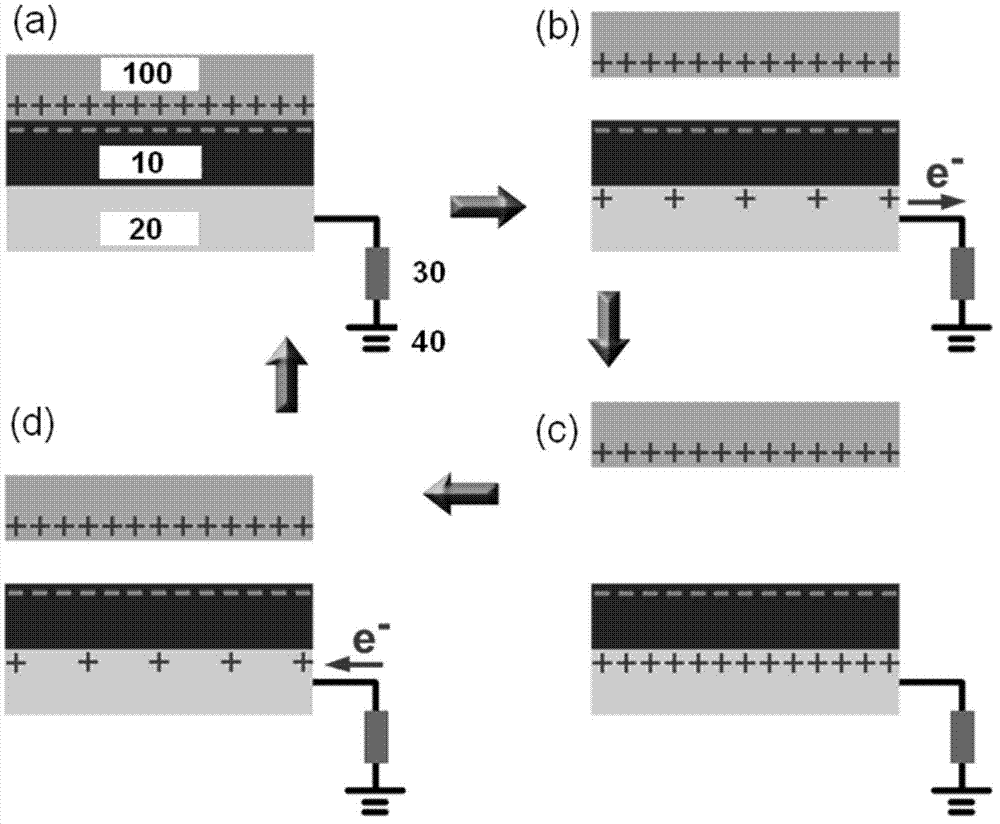
Single Electrode Triboelectric Generator
ActiveUS20140300248A1Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurementElectricitySingle electrode
A triboelectric generator includes a first contact charging member, a second contact charging member and an electrical load. The first contact charging member has a contact side and an opposite back side. The first contact charging member includes a material that has a first rating on a triboelectric series and also has a conductive aspect. The second contact charging member has a second rating on the triboelectric series, different from the first rating, and is configured to come into contact with the first contact layer and go out of contact with the first contact layer. The electrical load electrically is coupled to the first contact charging member and to a common voltage so that current will flow through the load after the second contact charging member comes into contact with the first contact charging member and then goes out of contact with the first contact charging member.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS7429981B2Reduce dependenceImprove display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display of the invention includes a plurality of pixels each of which has a liquid crystal layer and a plurality of electrodes for applying a voltage to the liquid crystal layer and which are arranged in a matrix of rows and columns, wherein: each of the plurality of pixels has a first sub-pixel and a second sub-pixel which can apply mutually different voltages to the liquid crystal layer, where the first sub-pixel has a higher brightness than the second sub-pixel in certain gradations; the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel each has: a liquid crystal capacitor formed by a counter electrode and a sub-pixel electrode opposing the counter electrode via the liquid crystal layer, and a storage capacitor formed by a storage capacitor electrode connected electrically to the sub-pixel electrode, an insulating layer, and a storage capacitor counter electrode opposing the storage capacitor electrode via the insulating layer; the counter electrode is a single electrode shared by the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel, and the storage capacitor counter electrodes of the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel are electrically independent of each other; and the storage capacitor counter electrode of the first sub-pixel in any of the plurality of pixels and the storage capacitor counter electrode of the second sub-pixel of a pixel adjacent to any of the pixels in the column direction are electrically independent of each other.
Owner:SHARP KK
Video processing methods for improving visual acuity and/or perceived image resolution
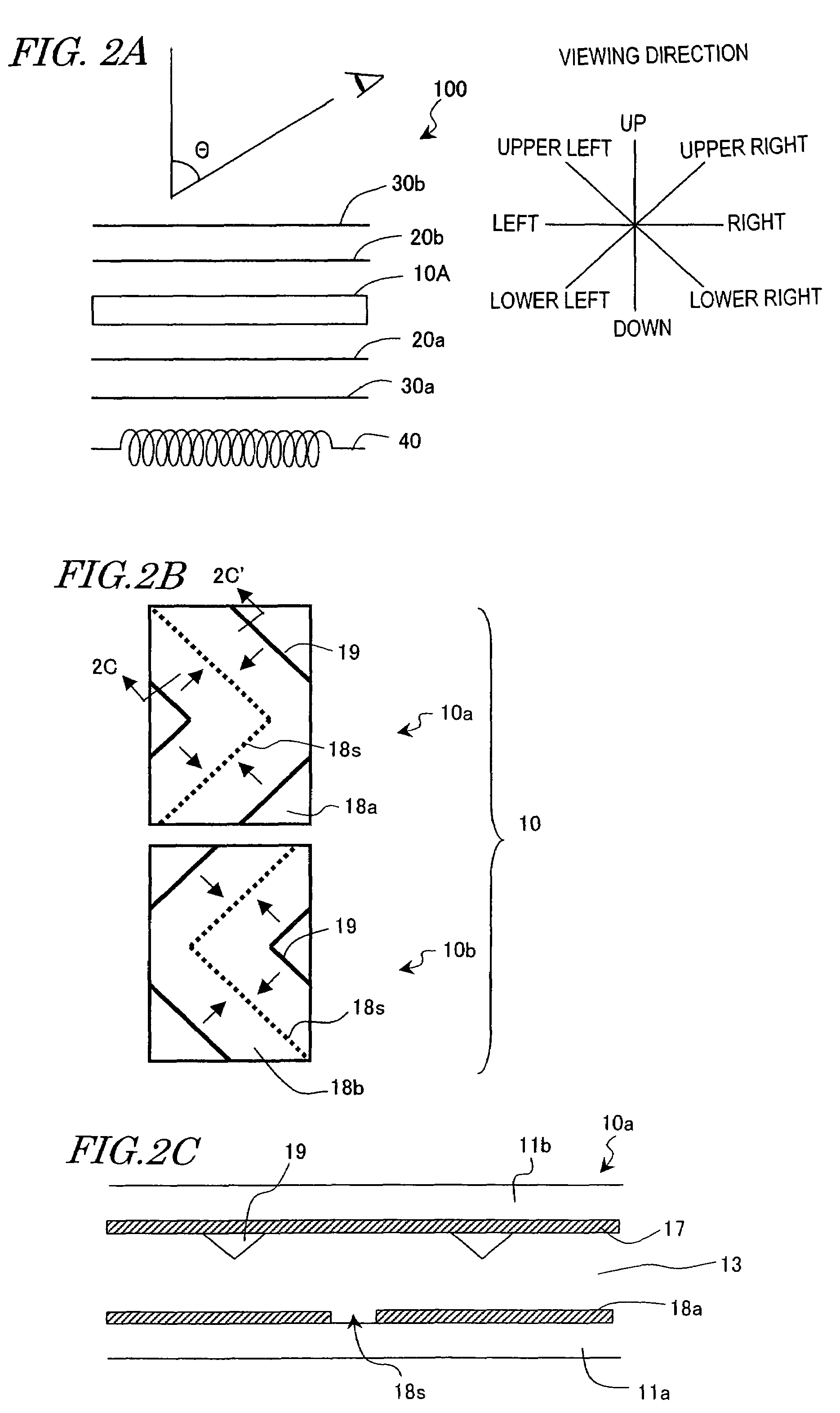
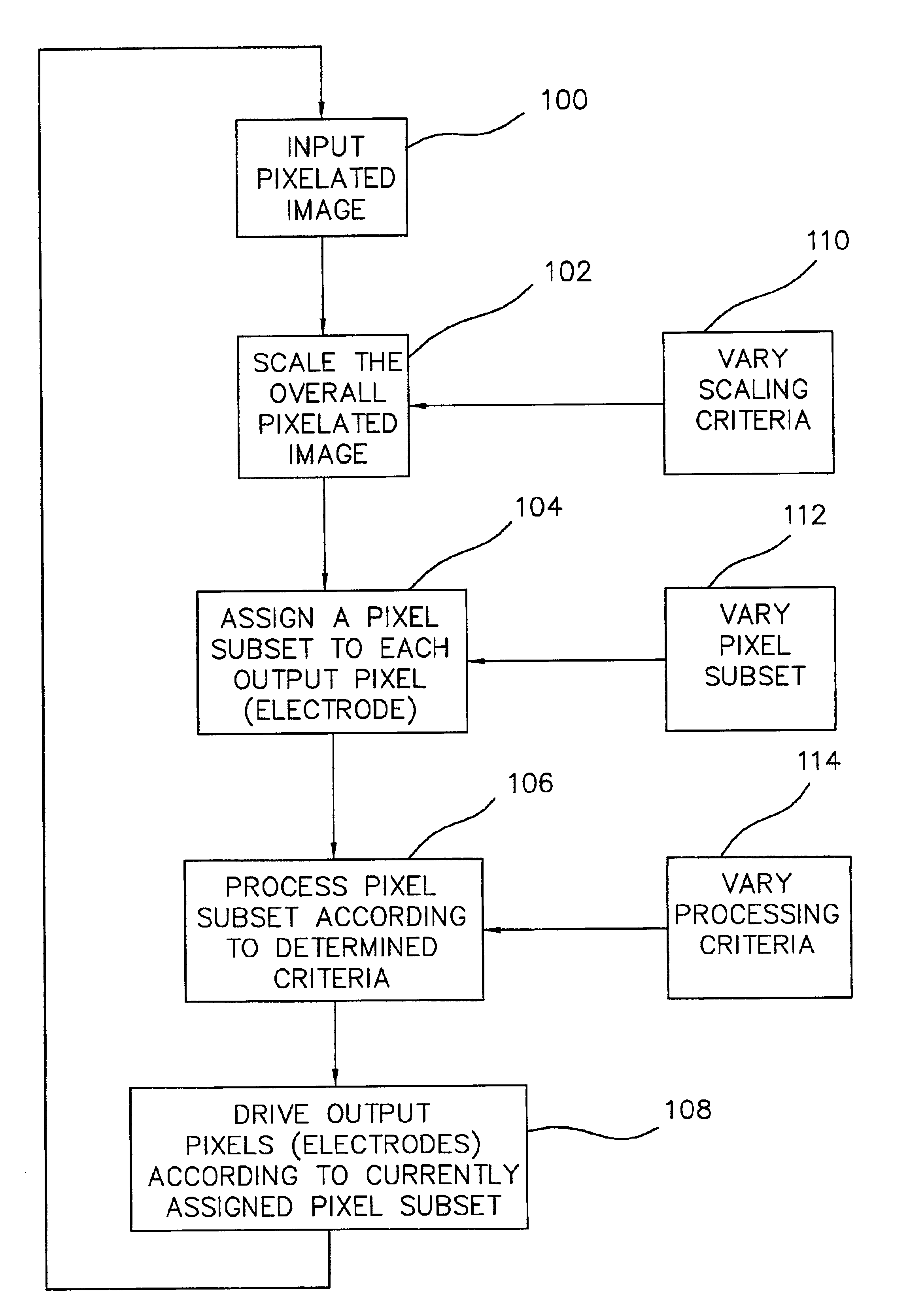
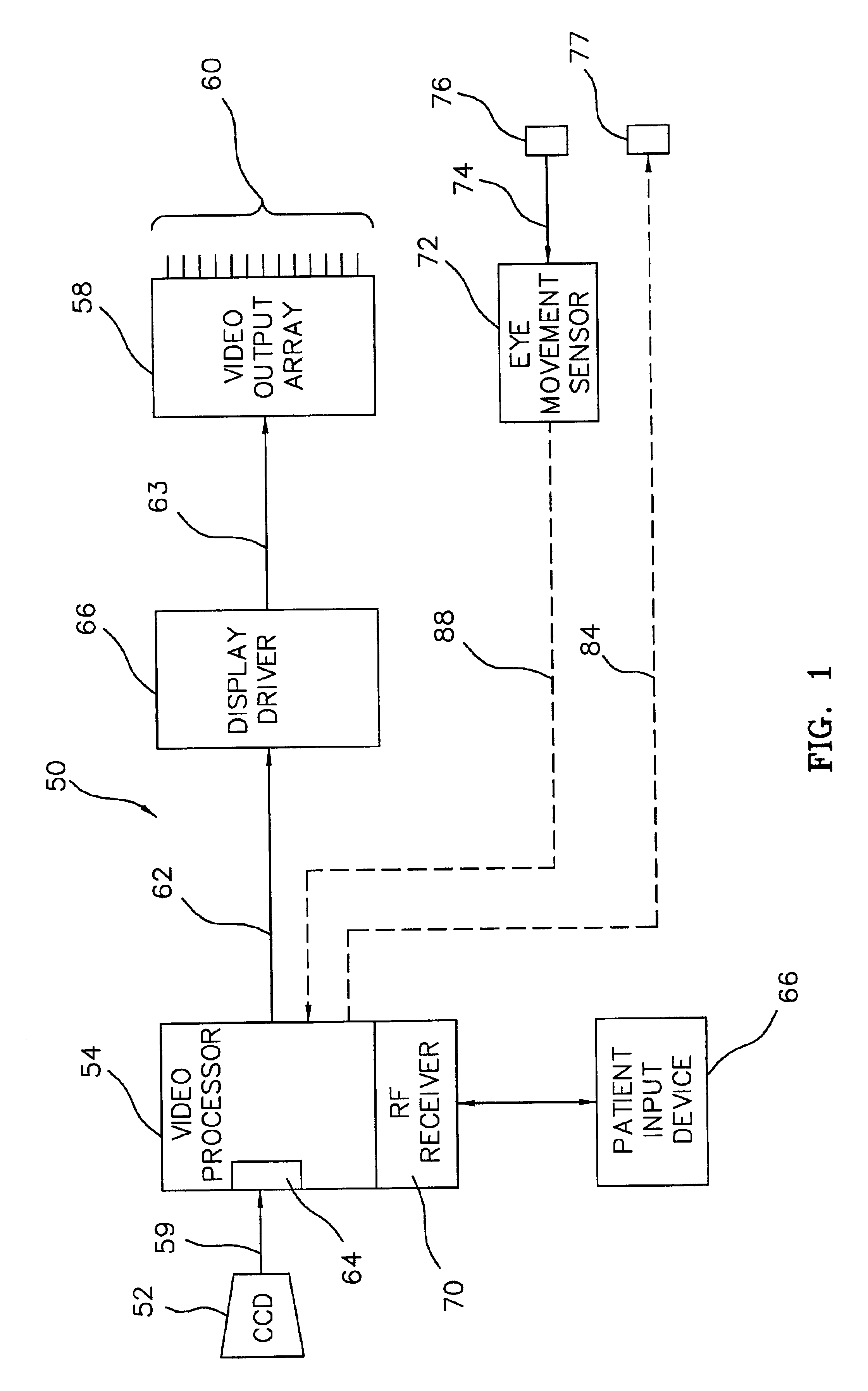
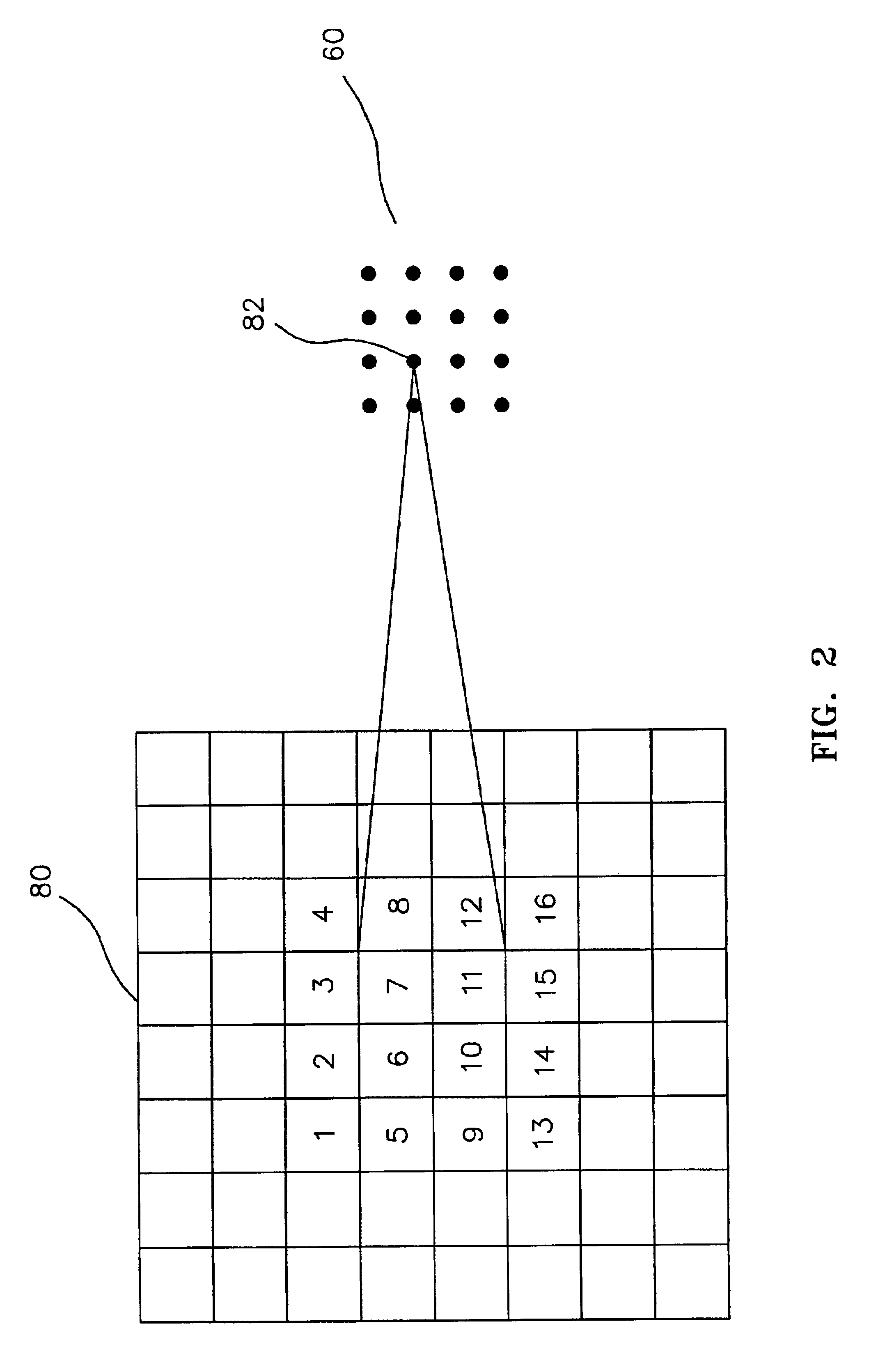
InactiveUS6920358B2Improve eyesightEliminate and severely degrade visionGeometric image transformationInternal electrodesVisually impairedRetinal Prosthesis
A method and apparatus for improving visual acuity when providing a visual image from a “high” resolution input device to a “low” resolution output device. The described invention is of particular use when the output device is an array of electrodes as part of a retinal prosthesis used to restore vision to a visually-impaired patient. In that various limitations may, within the foreseeable future, limit the density of such an electrode array (and thus the resolution of the output image), the present invention teaches techniques to assign processed pixel subsets of a higher resolution image to a single electrode. By varying the pixel subsets, e.g., by jittering, and / or altering the processing criteria, the perceived visual acuity may be further improved. Alternatively and additionally, such processing may be further extended to drive neighboring electrodes in combination to thus stimulate virtual electrode sites and thus further enhance visual acuity.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS
Biosensors having single reactant components immobilized over single electrodes and methods of making and using thereof
InactiveUS20050003396A1Promotes homogeneous mixingQuick analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementSingle electrodeBiosensor
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nickel cobaltate-graphene composite material and application and preparation method thereof
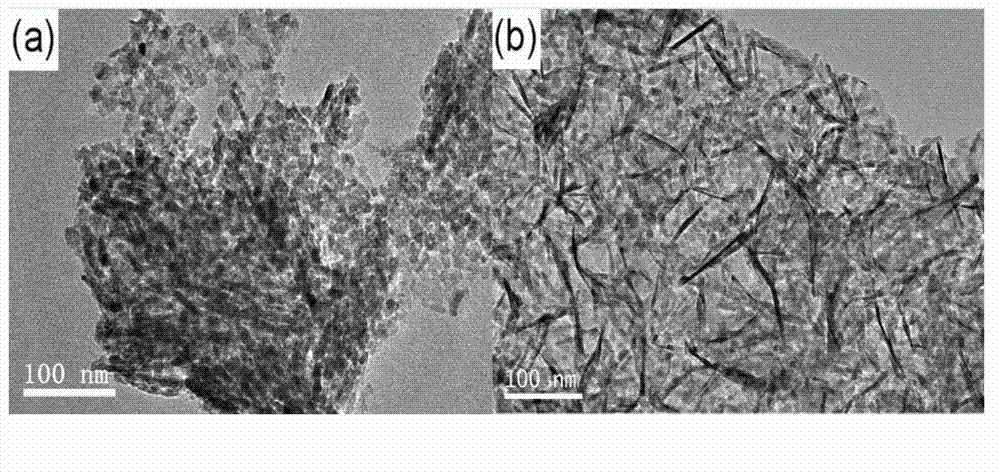
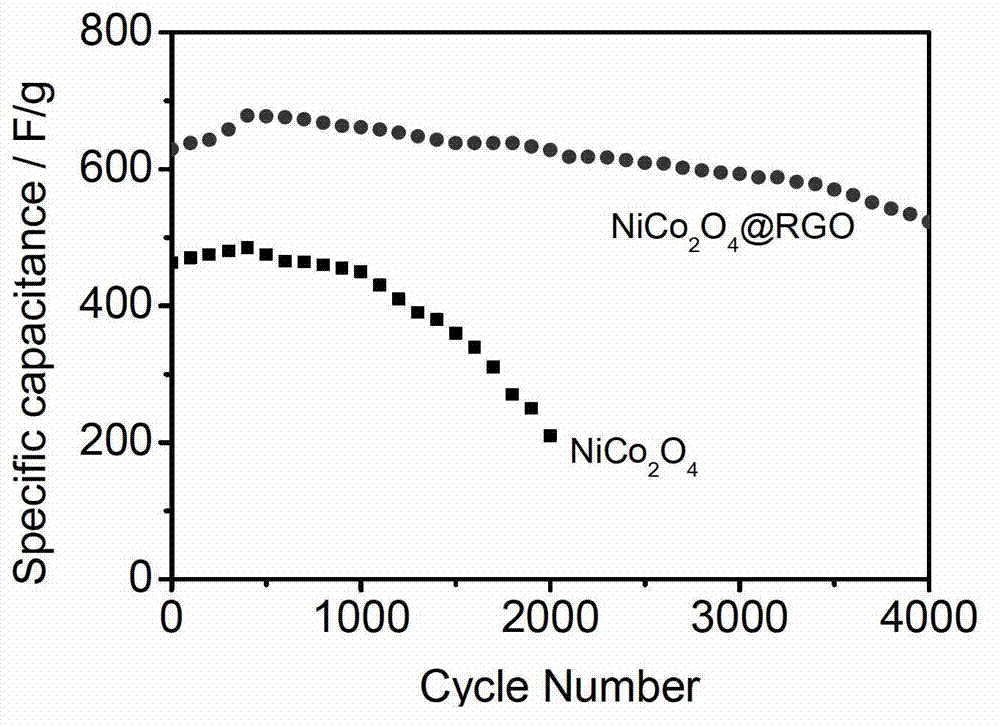
InactiveCN102891016ASmall sizeLarge specific surface areaElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitanceNickel salt
The invention relates to a nickel cobaltate-graphene composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material comprises graphene and nickel cobaltate, wherein nickel cobaltate nanowires are uniformly grown on a graphene sheet, the wire length of the nickel cobaltate nanowires is 50-300nm, and the wire width is 5-30nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking a graphene oxide water solution and a cobalt salt and nickel salt water solution which are dispersed in an ultrasonic manner, mixing, further adding a precipitator, uniformly stirring and mixing, transferring into a high-temperature reaction kettle, performing hydro-thermal reaction for a certain period of time, filtering, washing and drying an obtained product, and further performing thermal treatment so as to obtain the nickel cobaltate nanowire-graphene composite material. The nickel cobaltate nanowire-graphene composite material prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high single-electrode capacitance and good cycle performance, and is suitable for being used as an electrode material of a super-capacitor.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Fuel cell ordered porous nano-fiber single electrode, membrane electrode and preparation method
InactiveCN103413947AShorten the transmission distanceIncrease profitMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPorositySlurry
The invention discloses a fuel cell ordered porous nano-fiber single electrode, a membrane electrode and a preparation method. Polymer nano-fibers are deposited on one side of a gaseous diffusion material through an electro-spinning technology; metal nanoparticles with catalytic activity are deposited on the surfaces of the polymer nano-fibers by using magnetron sputtering and vacuum evaporation methods, or catalyst slurry is directly sprayed to one side of a nano-fiber thin film to form a porous single electrode; then two single electrodes and a layer of proton exchange membrane are combined into a three-in-one membrane electrode. The fuel cell ordered porous nano-fiber single electrode, the membrane electrode and the preparation method have the beneficial effects that the conventional micro-porous layer is substituted by the nano-fiber layer with high porosity and high specific surface area, prepared by electro-spinning, so that the catalytic activity area is increased and the three-phase reaction interface and the mass transfer are facilitated, and an active metal catalytic layer formed by magnetron sputtering and vacuum evaporation has high adhesion, is uniform in coating and has controllable thickness, so that the using amount of the active metal catalyst is reduced and the utilization rate of the catalyst is also greatly increased.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Biological membrane voltage estimator
InactiveUS6163719ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceExcitable cell
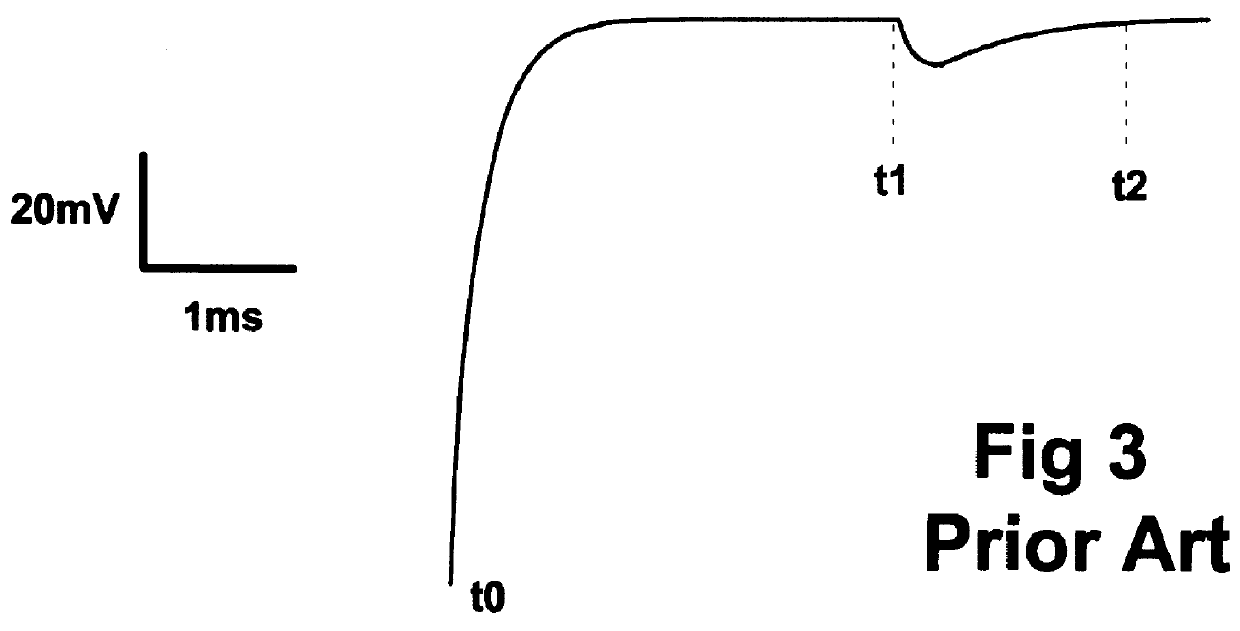
A method and apparatus for estimating the membrane voltage of a cell that is independent of cell conductance. This estimated voltage is used to implement stable, complete (100%) series resistance compensation for a single electrode voltage clamp amplifier, enabling the recording of rapid ionic currents in single, excitable cells.
Owner:ALEMBIC INSTR
Method and apparatus for addressing micro-components in a plasma display panel
InactiveUS6801001B2Sufficient resolutionManufactured very thinPoint-like light sourceStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceAlternative methods
An improved light-emitting display having a plurality of micro-components sandwiched between two substrates is disclosed. Each micro-component contains a gas or gas-mixture capable of ionization when a sufficiently large trigger voltage is supplied across the micro-component by up to two triggering electrodes and ionization can be maintain by a sustain voltage supplied by up to two sustain electrodes. The display is further divided into a plurality of panels that can be individually addressed in parallel, preferably directly through the back of the panels and can include voltage multiplying circuitry to decrease the power demands for addressing circuitry. Alternative methods of addressing the micro-components include the use of directed light and arrangements of electrodes to address multiple micro-components with a single electrode.
Owner:LEIDOS
Method of construction an endocardial mapping catheter
A method of constructing a mapping catheter is described where the catheter has numerous electrodes each associated with a single connection in a plug. The method consists of first arranging a plurality of wires in the desired relationship, with each of the wires running to a connection in a plug. Next, a single electrode is formed on each wire. Because it is often difficult to associate a particular connection with a particular plug, an electrical signal is then applied to a single one of the wires. The electrical signal can be applied to the connection or to the electrode. The electrical signal is then found among by examining either the electrodes or the connections, depending on which where the electrical signal was applied. Once the electrical signal is discovered, a map can be made between the connections and the electrodes.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
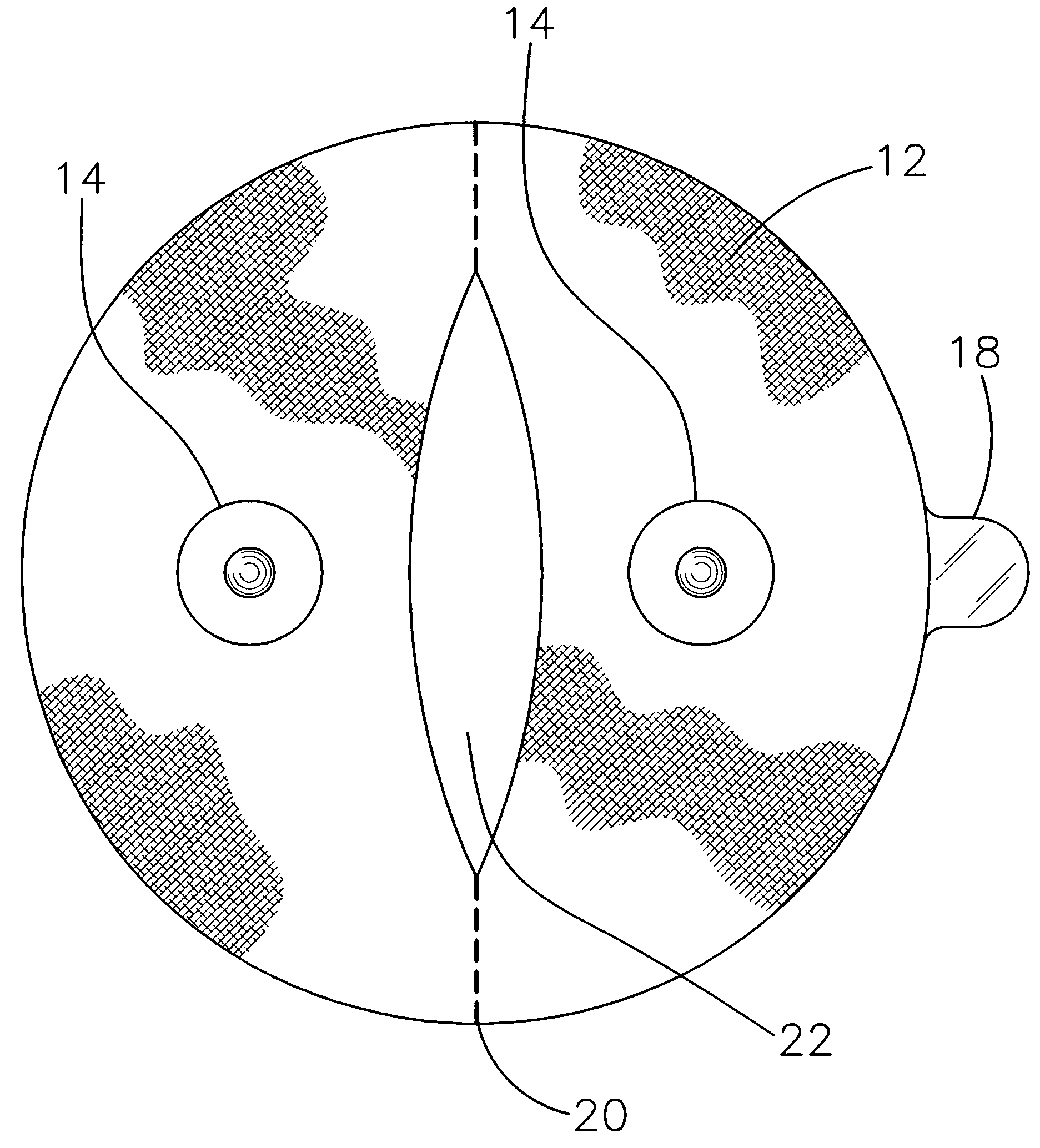
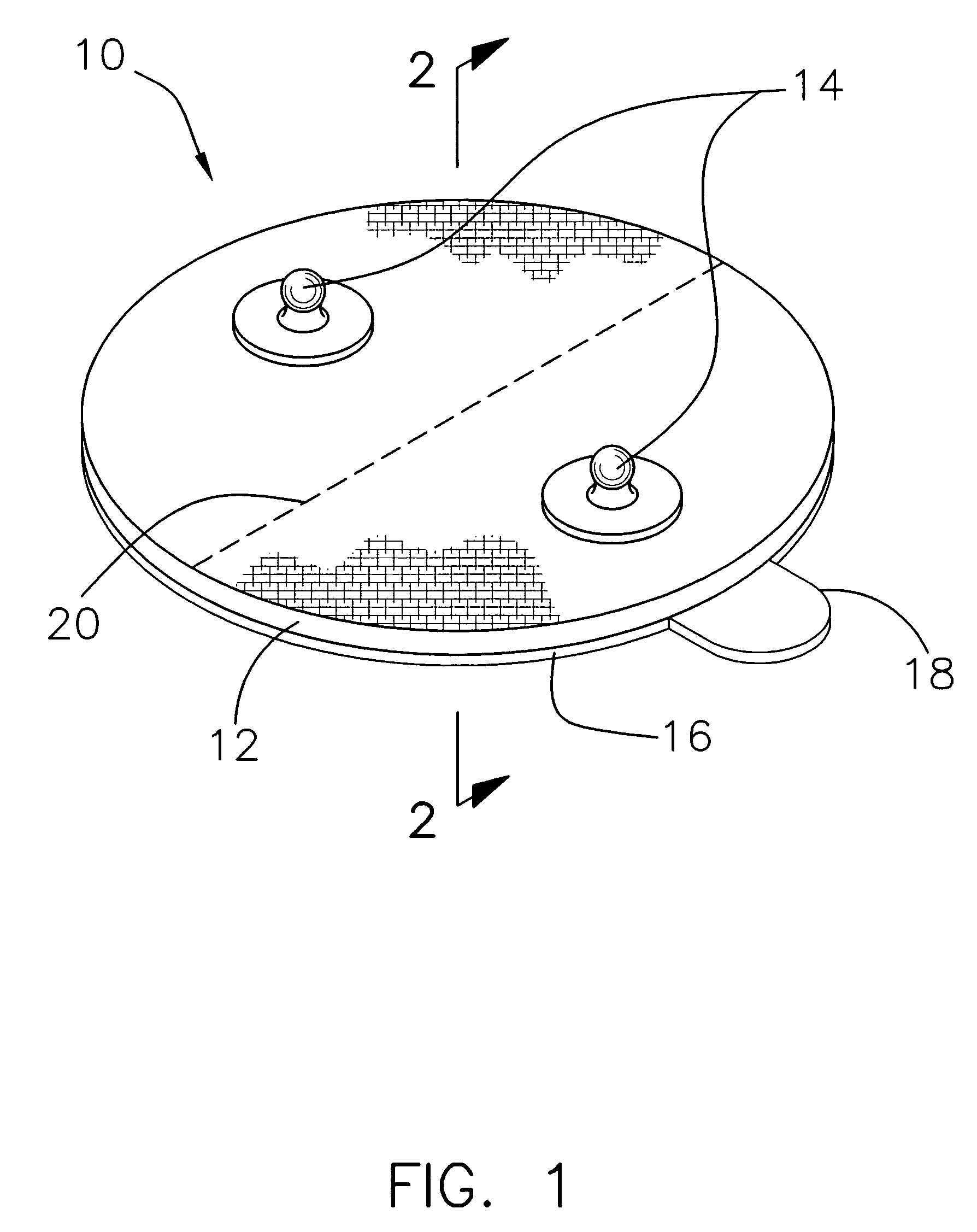
Single-electrode touch sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103777803AReal-timeRealize monitoringElectronic switchingFriction generatorsElectricityInteraction interface
The invention discloses a single-electrode touch sensor and a preparation method thereof. The single-electrode self-driven touch sensor is built due to the fact that a touch action applier and materials of a touch layer have different frictional electrical properties. When the touch action applier conducts touch-separation or sliding or other actions on the touch layer, an electric signal generation mechanism of the touch sensor will be triggered, and an electric signal is automatically output outwards, so that the touch actions are recorded and fed back, and the functions of the sensor are achieved. The single-electrode touch sensor can record the touch actions in real time, has the advantages of being low in cost, self-driven, simple in structure and the like, and has the quite wide application prospect in intelligent electronic devices and main-machine interaction interfaces.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
Multiple electrode assembly
InactiveUS7215989B1Quick connectionLess discomfortElectrocardiographySensorsElectricityElectrical connection
Multiple electrode assemblies provide an electrical connection between a patient's body and monitoring equipment. A multiple electrode assembly requires only half as many assemblies as a conventional single electrode assembly to attach a patient to multiple pieces of equipment. Less time is required to attach the patient to the monitoring equipment. There is less patient discomfort since fewer assemblies are attached to the patient. The placement of fewer assemblies also leads to a reduced cost. The assemblies can take on a number of different shapes and lead attachment configurations to accommodate a wide range of monitoring functions.
Owner:BURKS JONATHAN W
Method for preparing activated carbon material with humic acid as raw material and application of activated carbon material
InactiveCN103641117ALarge reservesLarge specific surface areaCarbon compoundsOther chemical processesCapacitancePotassium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for preparing activated carbon with humic acid as a raw material and an application of the activated carbon. The method comprises the steps of mixing industrial humic acid with an activating agent which is potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, zinc chloride, potassium carbonate or phosphoric acid uniformly to react under inert atmosphere protection for 1-5 hours; then cooling the product, washing the product in an acid solution until the pH value is 6-7 and drying the product, thus obtaining the activated carbon. The method is convenient to operate, is relatively low in energy consumption and is suitable for large-scale industrial production. The humic acid porous activated carbon material obtained by the method has a rich porous structure and a relatively big specific surface area, is used for preparing water purifiers or electrode materials of supercapacitors, and has methylene blue dye adsorption value of 600mg / g. Besides, the humic acid porous activated carbon material is used as the electrode material of a supercapacitor to assemble a high-performance supercapacitor. The specific capacitance of the activated carbon single electrode is 351Fg<-1>. Various test results show that the activated carbon is microporous-mesoporous composite carbon and has specific surface area of about 3200m<2> / g, the pore size distribution of the activated carbon is 1-5nm, and the pore volume of the activated carbon is about 2cm<3> / g.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
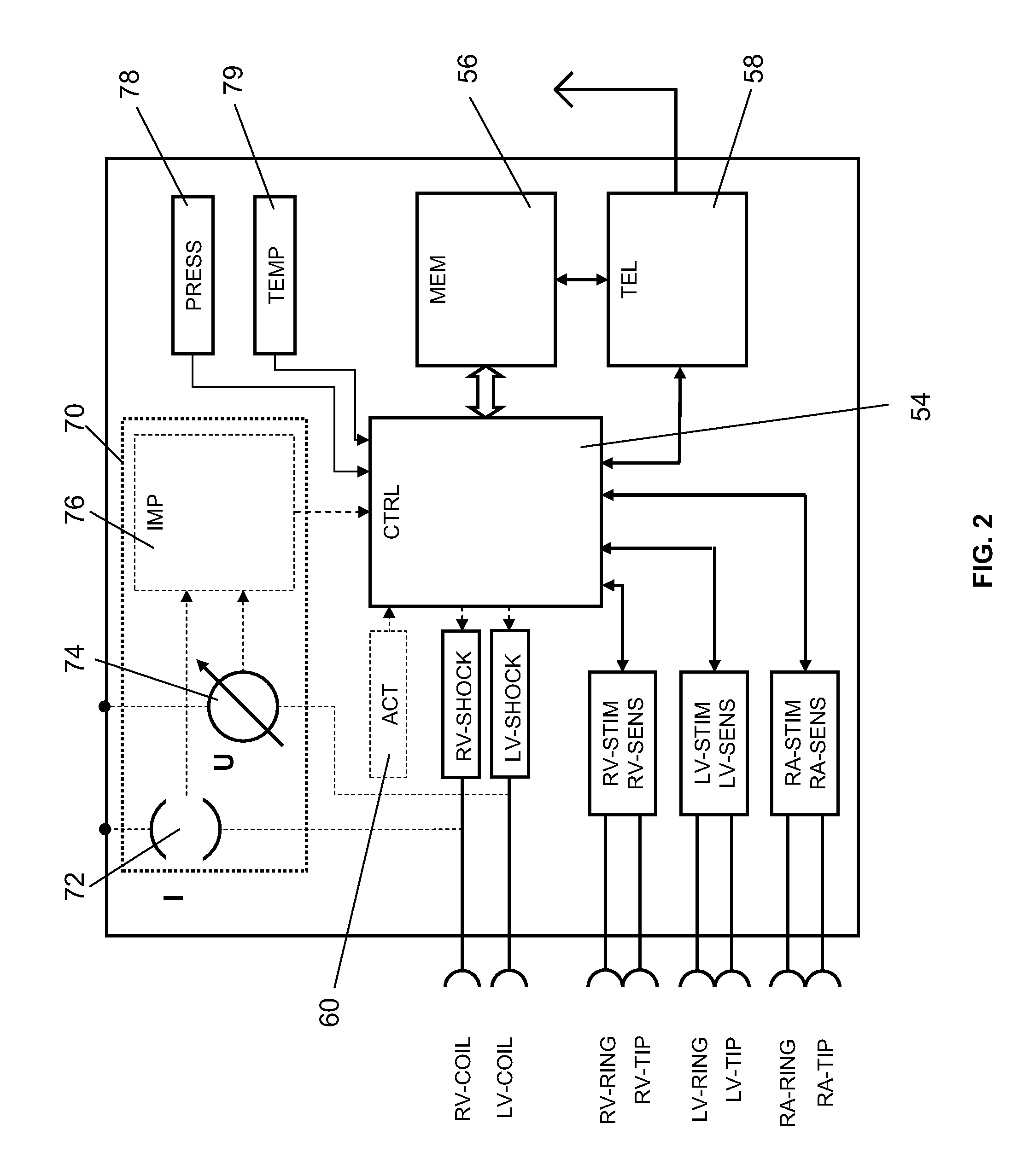
Switch polarity pacing to improve cardiac resynchronization therapy
InactiveUS20090240298A1Maximal improvement of cardiac functionSize is still affectedHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeCardiac muscle
The invention is directed to a heart stimulator for left-ventricular pacing comprising a left ventricular stimulation pulse generator connected or connectable to a single electrode lead for left ventricular stimulation having one or more electrodes for delivery of stimulation pulses to left ventricular myocardial heart tissue, said stimulation pulse generator being adapted to generate and deliver stimulation pulses of switchable polarity. The heart stimulator further comprises a control unit connected to the stimulation pulse generator for controlling the stimulation pulse generator and to trigger generation and delivery of stimulation pulses having a polarity controlled by said control unit, wherein the control unit is adapted to control said left ventricular stimulation pulse generator so as to deliver at least a pair of suprathreshold stimulation pulses of opposite polarity.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
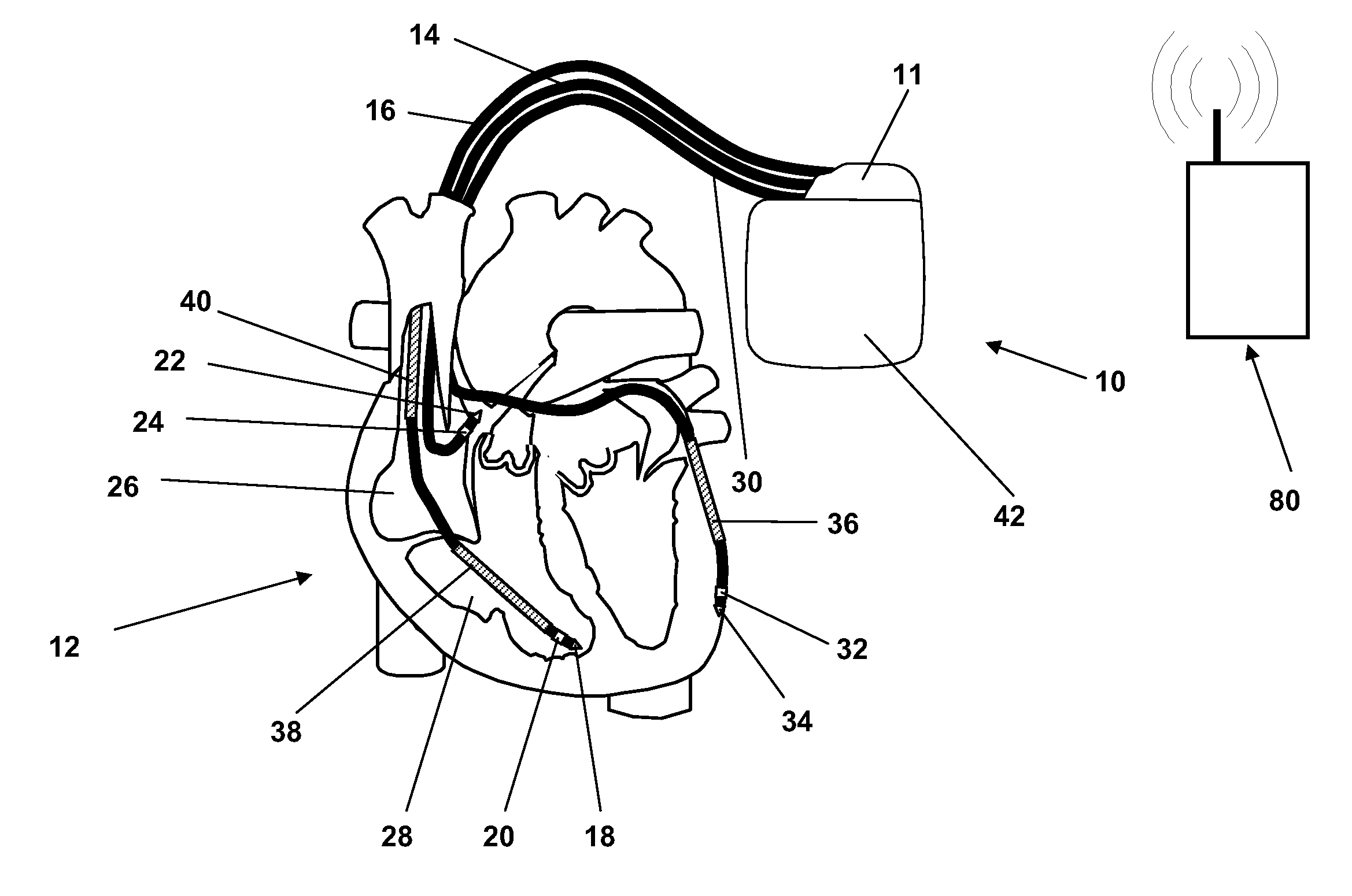
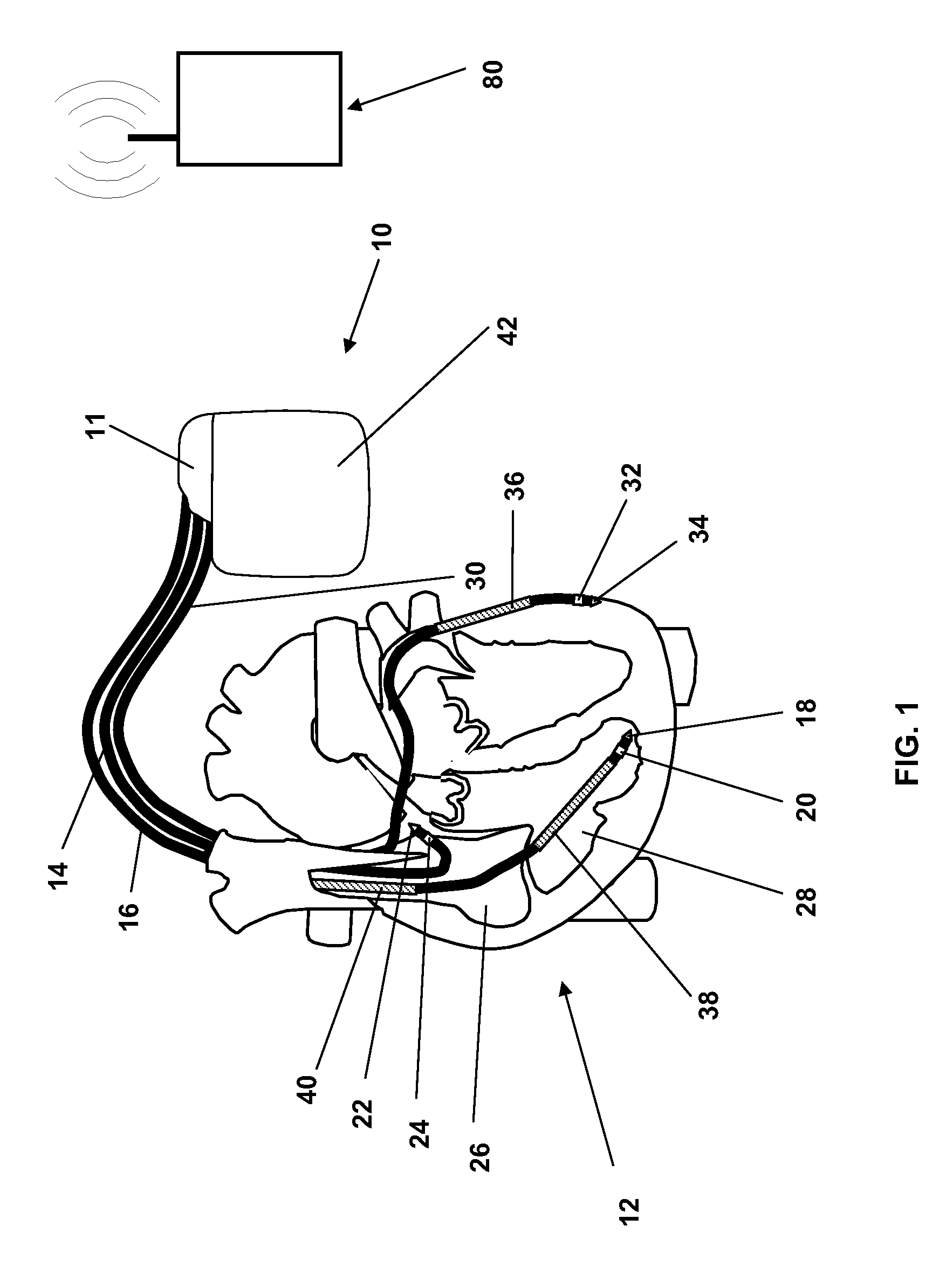
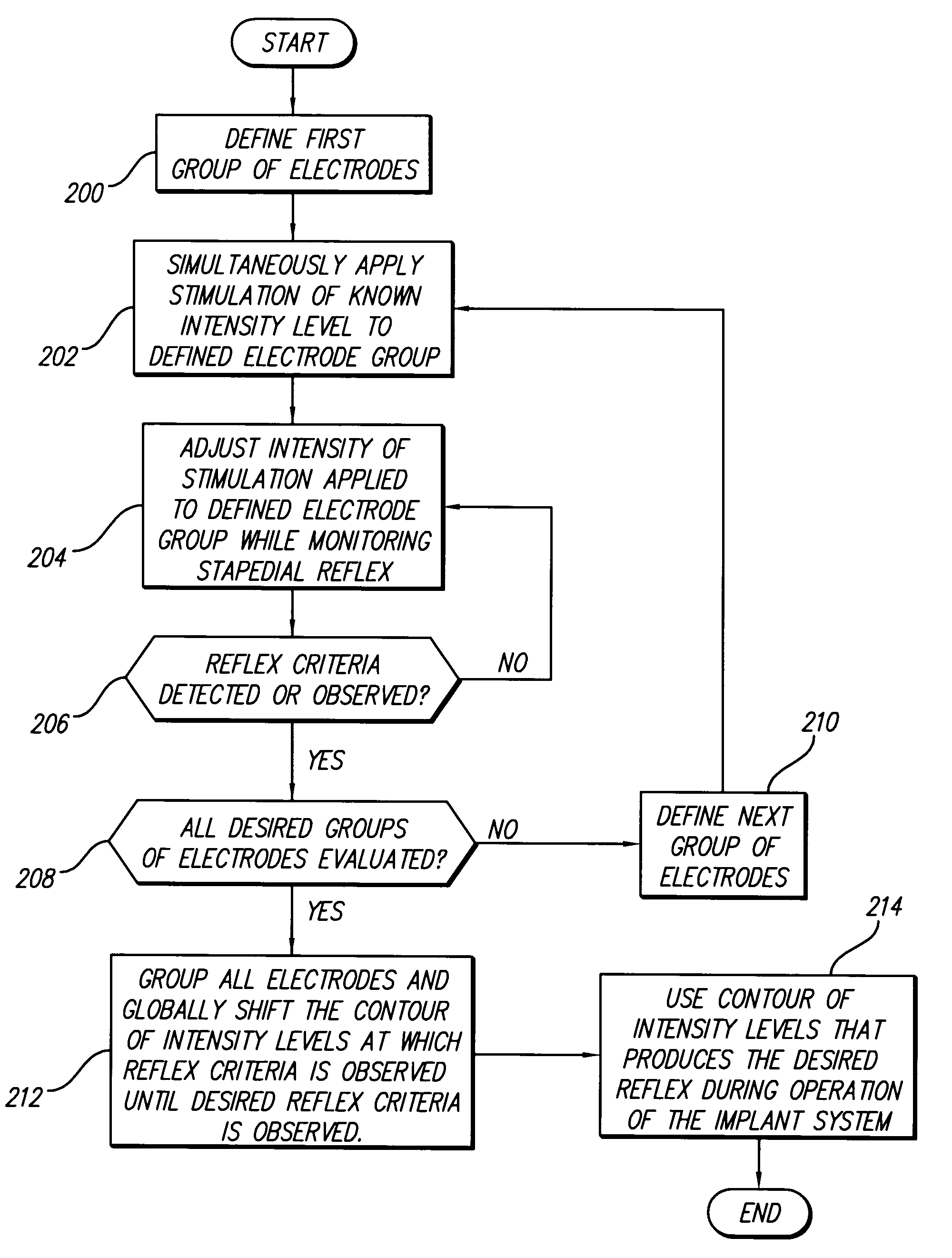
Method and system for obtaining stapedial reflexes in cochlear implant users using multiband stimuli
A method and system for fitting a multichannel cochlear implant system to a patient increases the percentage of patients for which stapedial reflexes can be obtained, and increases the accuracy of predicting the “live speech” comfort levels of the patient's fitting programs from the stapedial reflex. Electrical stimuli are applied on multiple electrodes at “live speech” pulse rates. The neural excitation patterns elicited from such stimulation more closely resemble that which occurs when the system is subjected to normal speech patterns. By progressively setting threshold levels in bands, e.g., groups of electrodes, either overlapping or non-overlapping, as well as with a final check by globally adjusting the band obtained contour to the stapedial reflex, such values more closely resemble actual “live speech” program levels than those obtained with traditional methods. Further, broader excitation patterns produced by the activation of multiple electrodes increases the probability of obtaining reflex measurements where single electrode stimulation fails due to sparse neural survival.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Amalgam of shielding and shielded energy pathways and other elements for single or multiple circuitries with common reference node
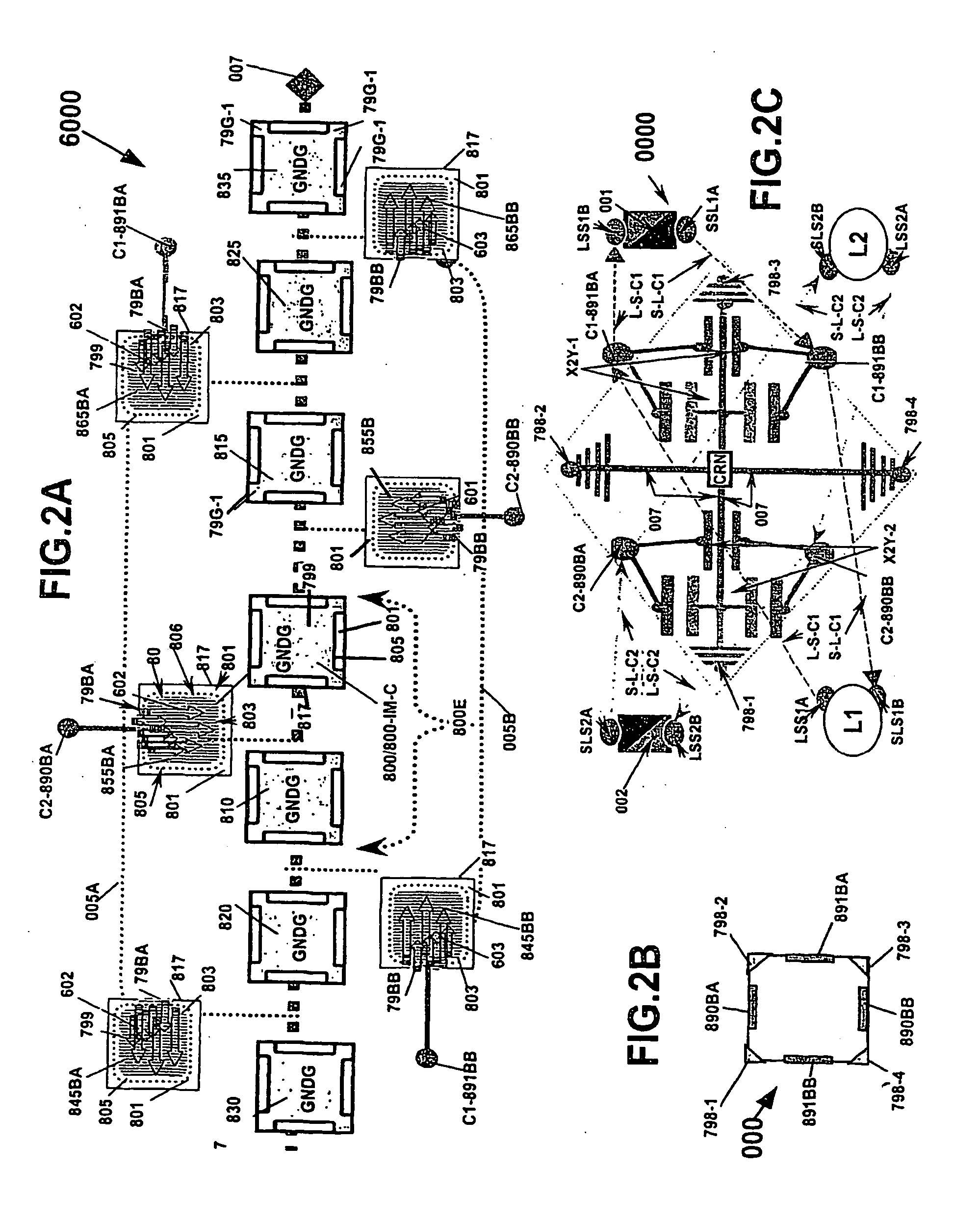
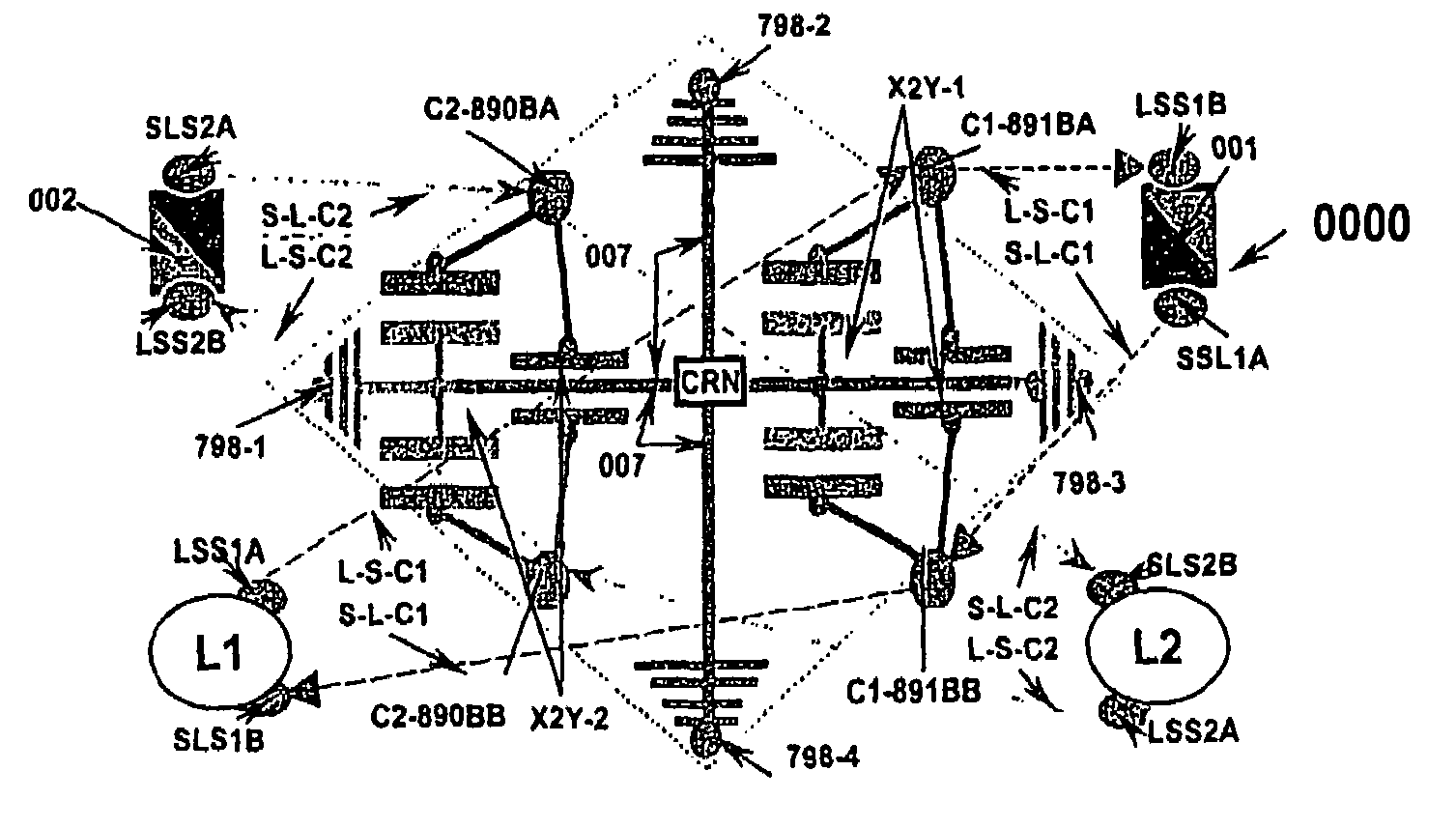
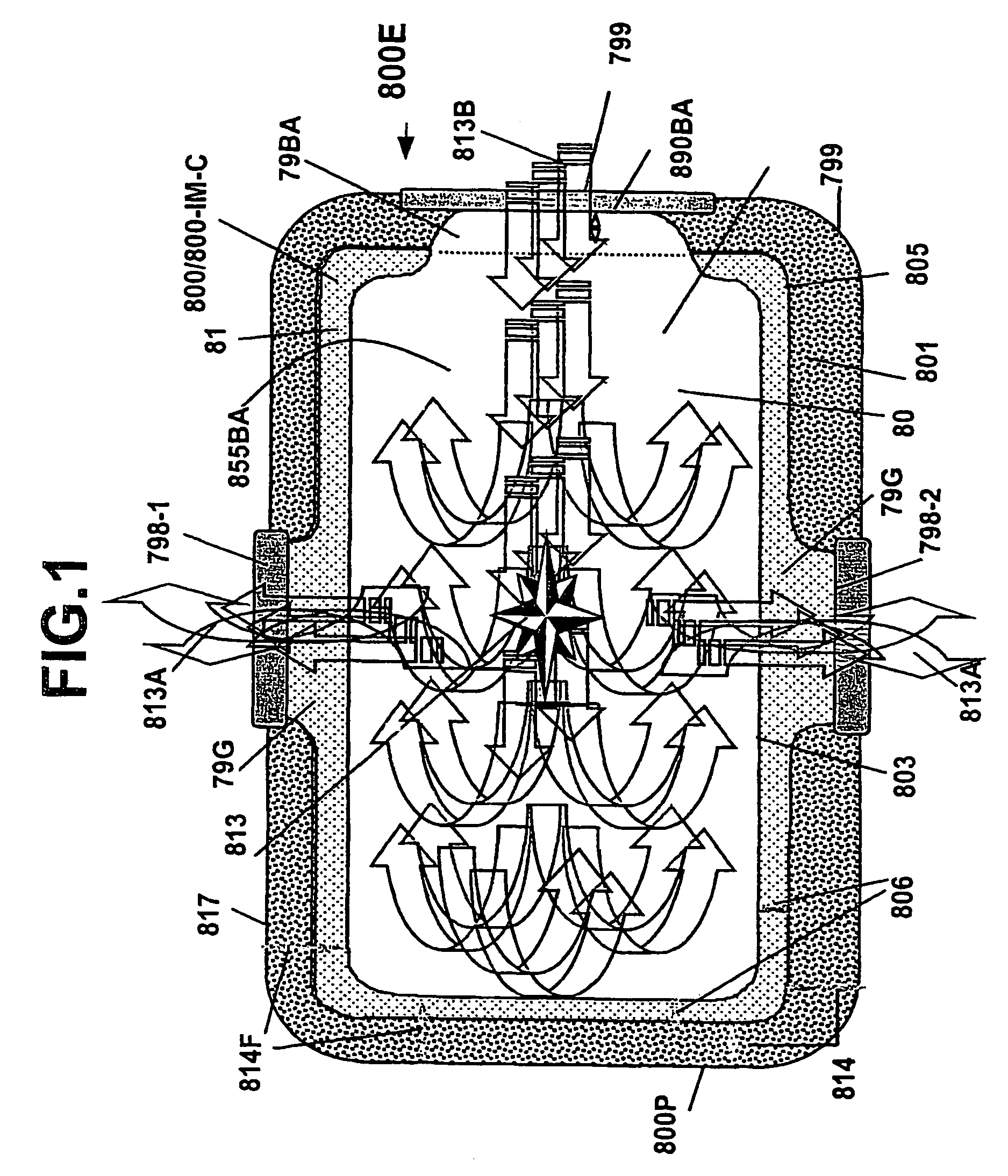
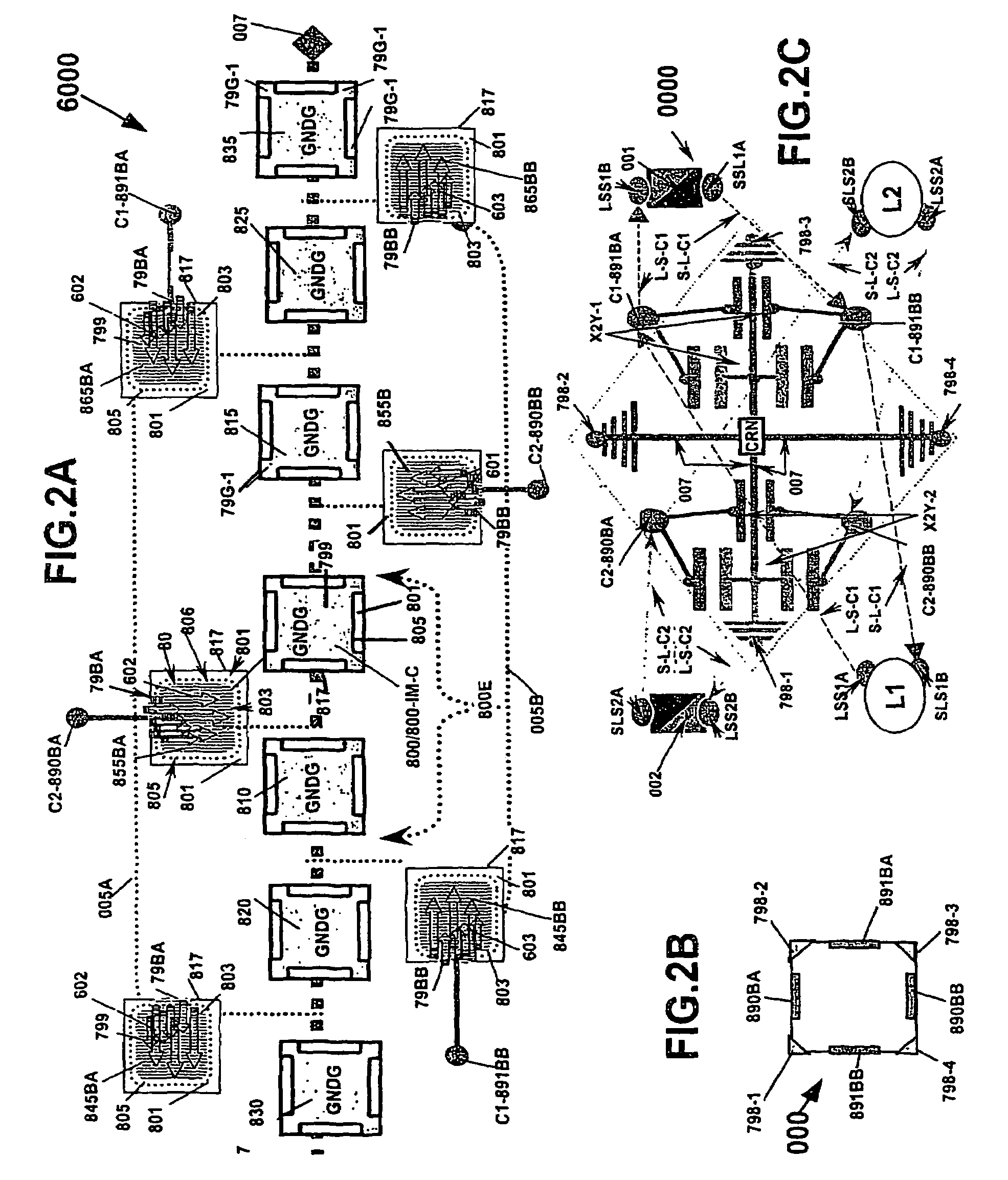
A predetermined single electrode shielding set for groupings of complementary electrodes that are operable to shield and that together are selectively formed or amalgamated into a predetermined sequential combination of commonly configured energy pathways operable for shielding various paired complementary electrodes and other predetermined elements that result in an electrode architecture practicable to provide multiple energy conditioning functions.
Owner:X2Y ATTENUATORS L L C
Amalgam of shielding and shielded energy pathways and other elements for single or multiple circuitries with common reference node
A predetermined single electrode shielding set for groupings of complementary electrodes that are operable to shield and that together are selectively formed or amalgamated into a predetermined sequential combination of commonly configured energy pathways operable for shielding various paired complementary electrodes and other predetermined elements that result in an electrode architecture practicable to provide multiple energy conditioning functions.
Owner:X2Y ATTENUATORS L L C
Single-electrode friction nanogenerator and generating method and self-driven tracking device
ActiveCN104242723AReduce manufacturing costFirmly connectedTransportation and packagingSynthetic resin layered productsElectricityNanogenerator
The invention discloses a single-electrode friction generator which is built according to the characteristic that polymer materials and metal materials have different friction electrical properties. A tracking system based on the generator is manufactured. According to the tracking system, a plurality of generator units form an array matrix. When an object moves on the tracking system, pressure acts on the generator, two layers of friction electrical materials forming the generator make contact, and therefore electrical signals are sent outwards. When the object gets away from the generator, the two layers of friction electrical materials forming the generator will be separated due to the action of elastic materials, and electrical signals are sent outwards as well. The tracking system based on the friction generator can track movement paths of some objects, and has the advantages of being low in cost, self-driven, simple in structure and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com