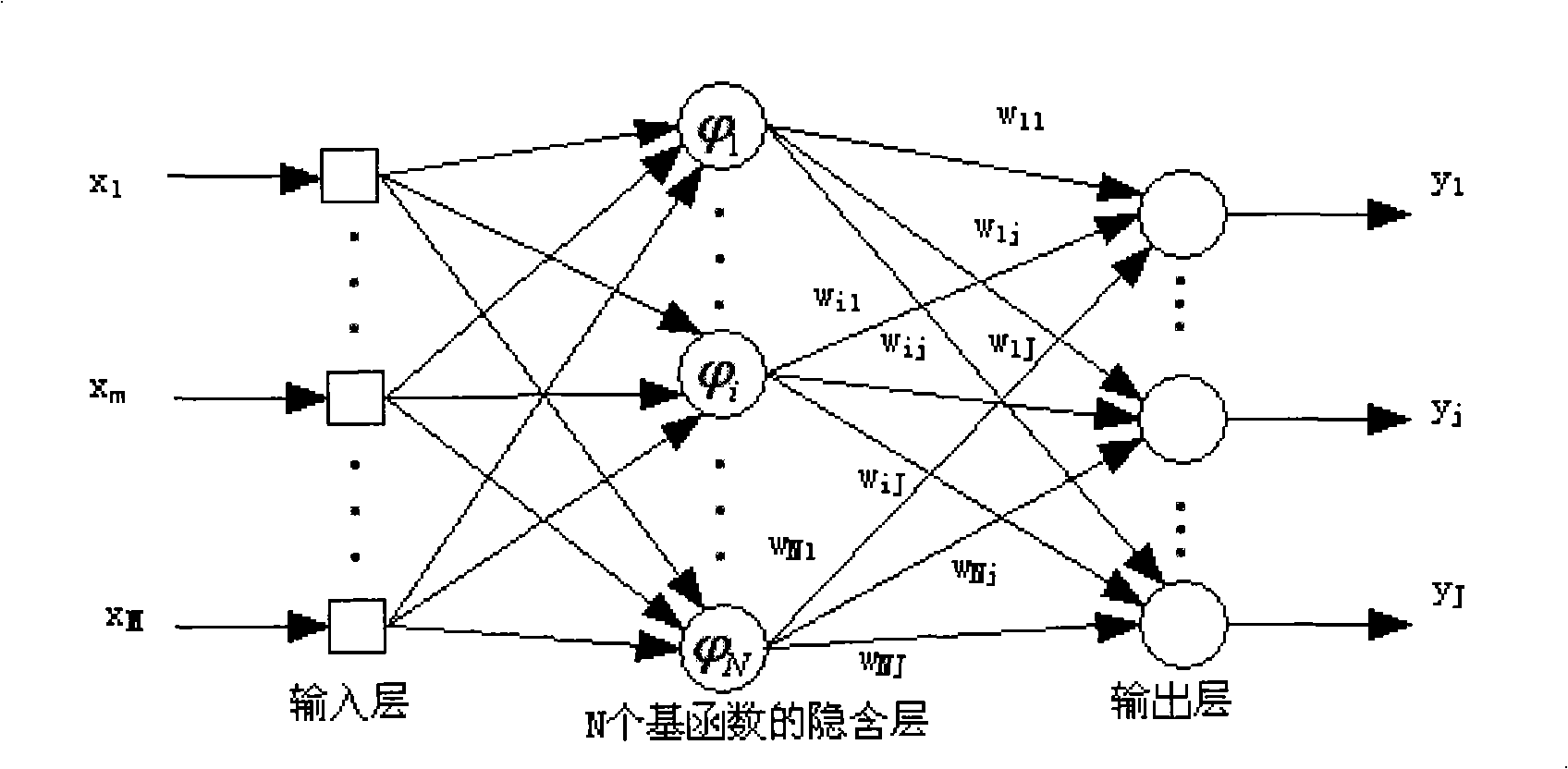
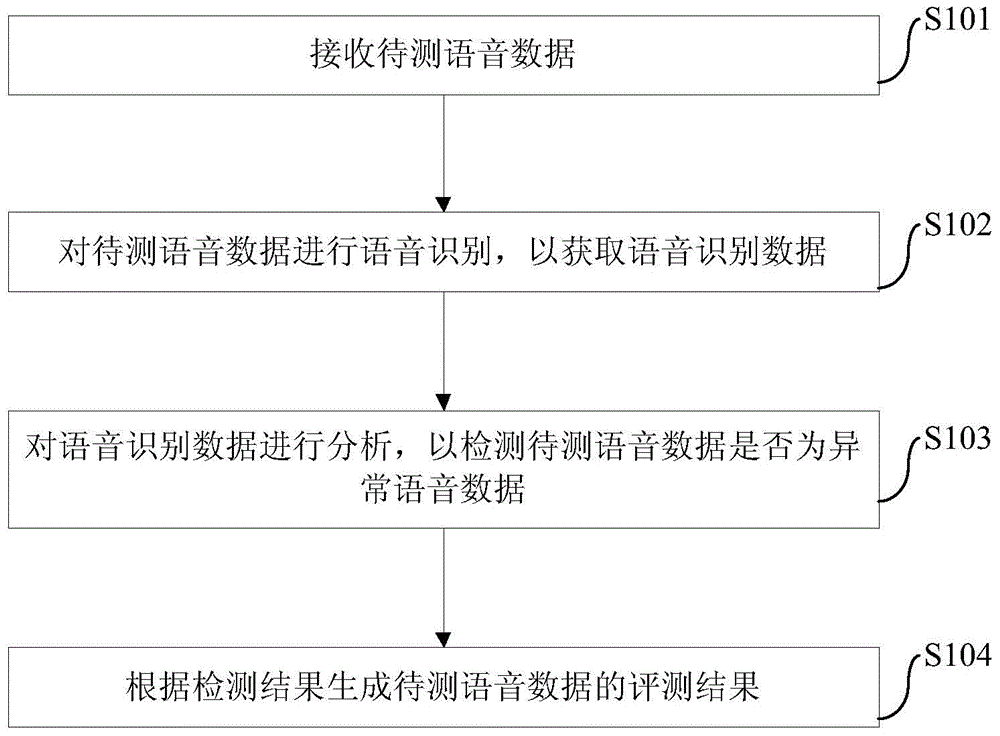
Patents
Literature
96 results about "Normal speech" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
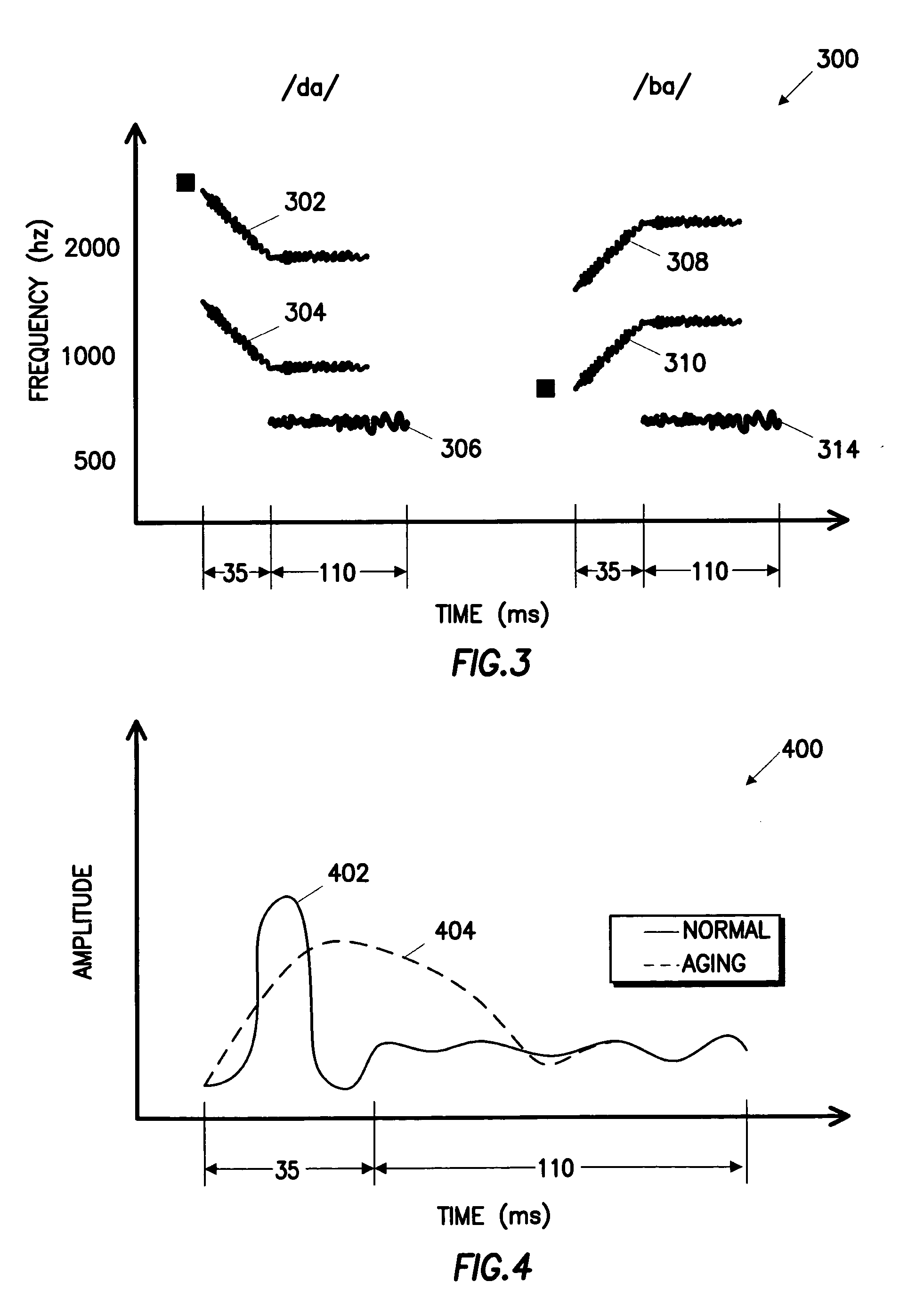
Normal speech between two people typically has a range of 50 to 60 decibels. When two people are speaking in a public place with background noise, normal speech is louder, around five extra decibels.
Method for adaptive training of listening and language comprehension using processed speech within an animated story
InactiveUS6364666B1Improve understandingMental therapiesElectrical appliancesLanguage understandingGraphics
A method for adaptively training a subject, using auditory processing of phonemes within command sentences, to improve the subject's listening comprehension, grammatical parsing, and serial memory is provided. The method utilizes a number of training installments, each designed for testing a particular aspect of the subject's language skills, all tied together by a common story. More specifically, installments are provided that narrate a story, test the subject's listening comprehension to the narrated story, test the subject's ability to grammatically parse increasingly difficult sentence structures, and test the subject's ability to select and manipulate graphical objects in response to auditory commands. Speech processing is used for the narration, as well as for commands within each test to allow the subject to more easily distinguish between similar sounding phonemes. As the subject improves his / her ability to correctly respond to the tests, the amount of processing applied to the commands is reduced, ultimately to the level of normal speech.
Owner:SCI LEARNING
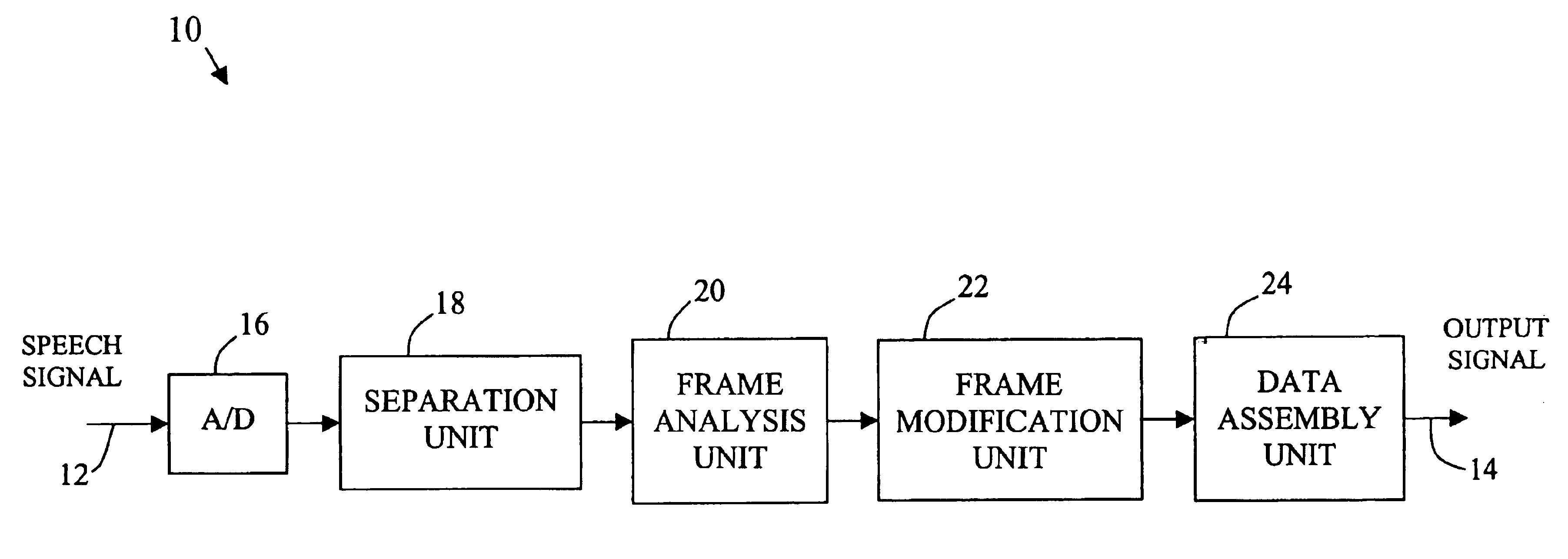
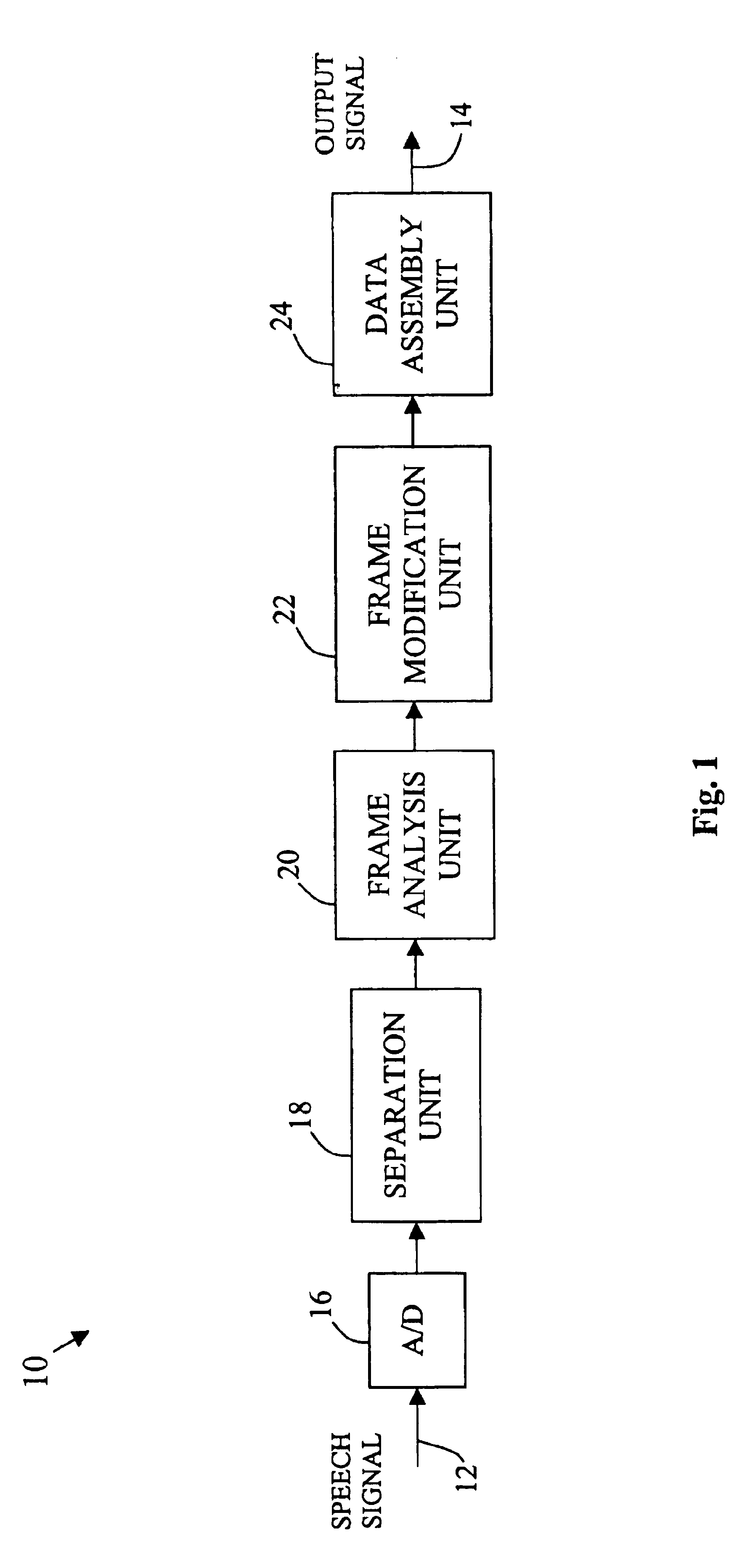
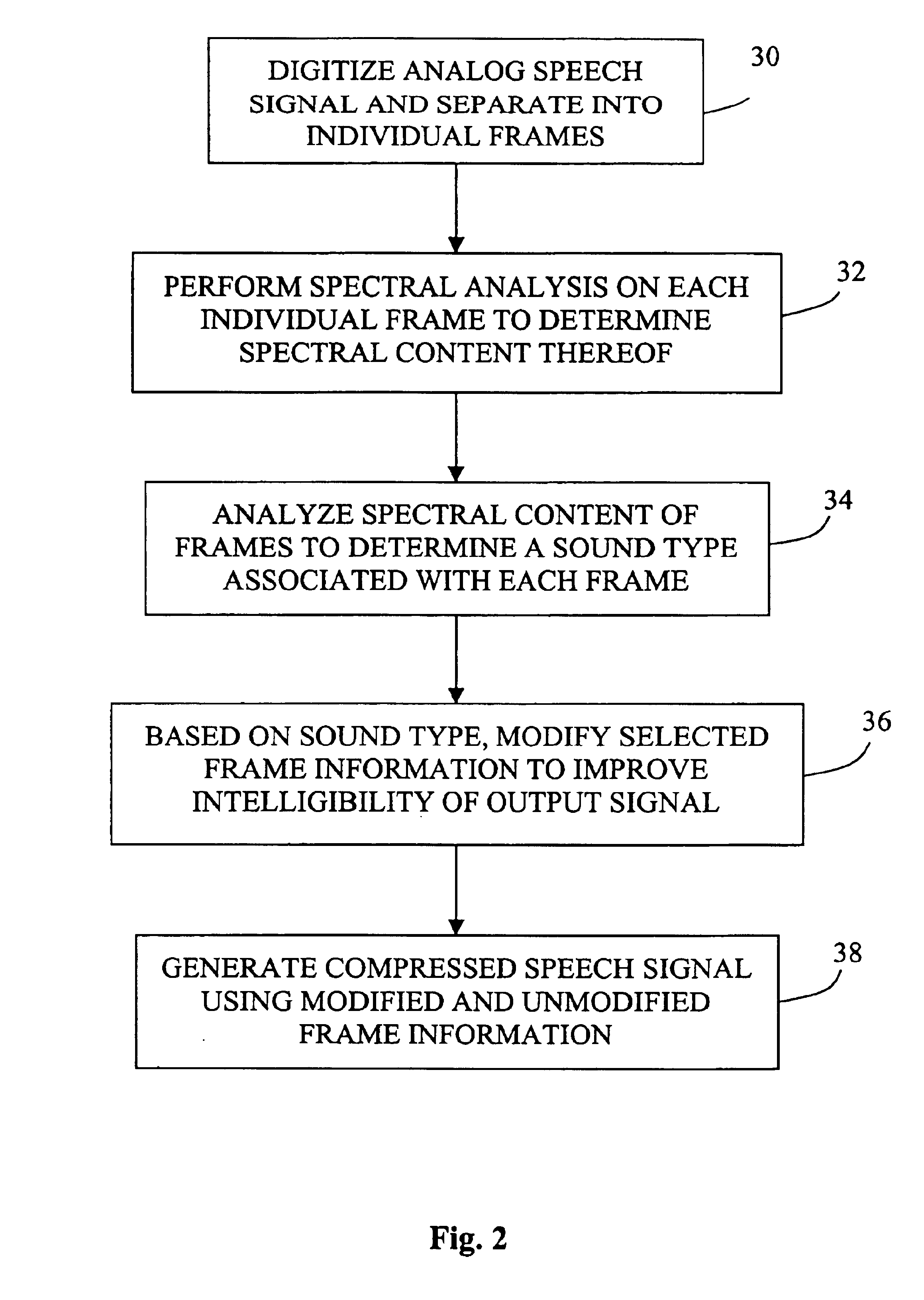
Method and apparatus for improving the intelligibility of digitally compressed speech
InactiveUS6889186B1Improve intelligibilityReduce the amplitudeSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisSystem identificationSpeech sound
A system for processing a speech signal to enhance signal intelligibility identifies portions of the speech signal that include sounds that typically present intelligibility problems and modifies those portions in an appropriate manner. First, the speech signal is divided into a plurality of time-based frames. Each of the frames is then analyzed to determine a sound type associated with the frame. Selected frames are then modified based on the sound type associated with the frame or with surrounding frames. For example, the amplitude of frames determined to include unvoiced plosive sounds may be boosted as these sounds are known to be important to intelligibility and are typically harder to hear than other sounds in normal speech. In a similar manner, the amplitudes of frames preceding such unvoiced plosive sounds can be reduced to better accentuate the plosive. Such techniques will make these sounds easier to distinguish upon subsequent playback.
Owner:AVAYA INC
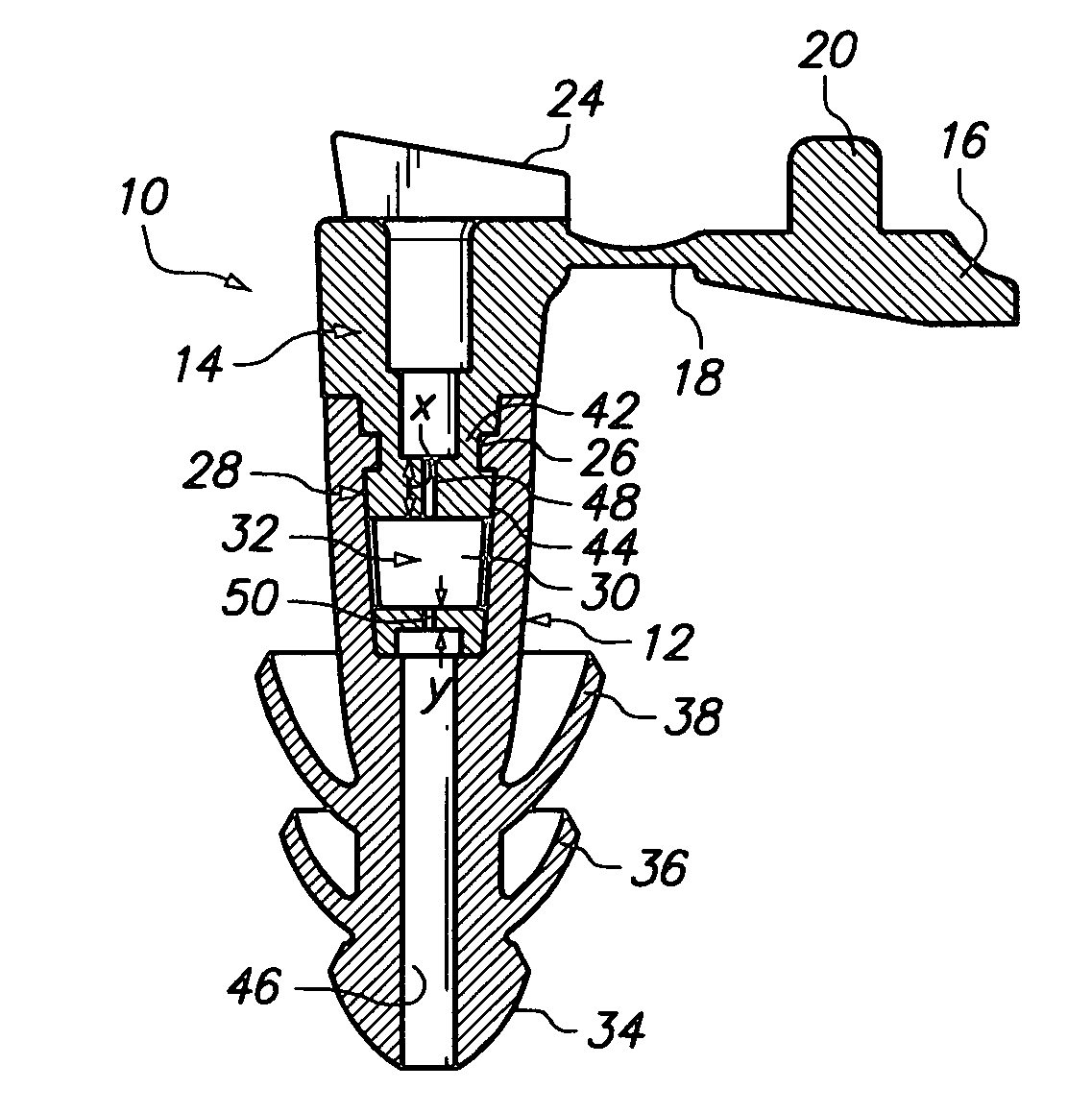
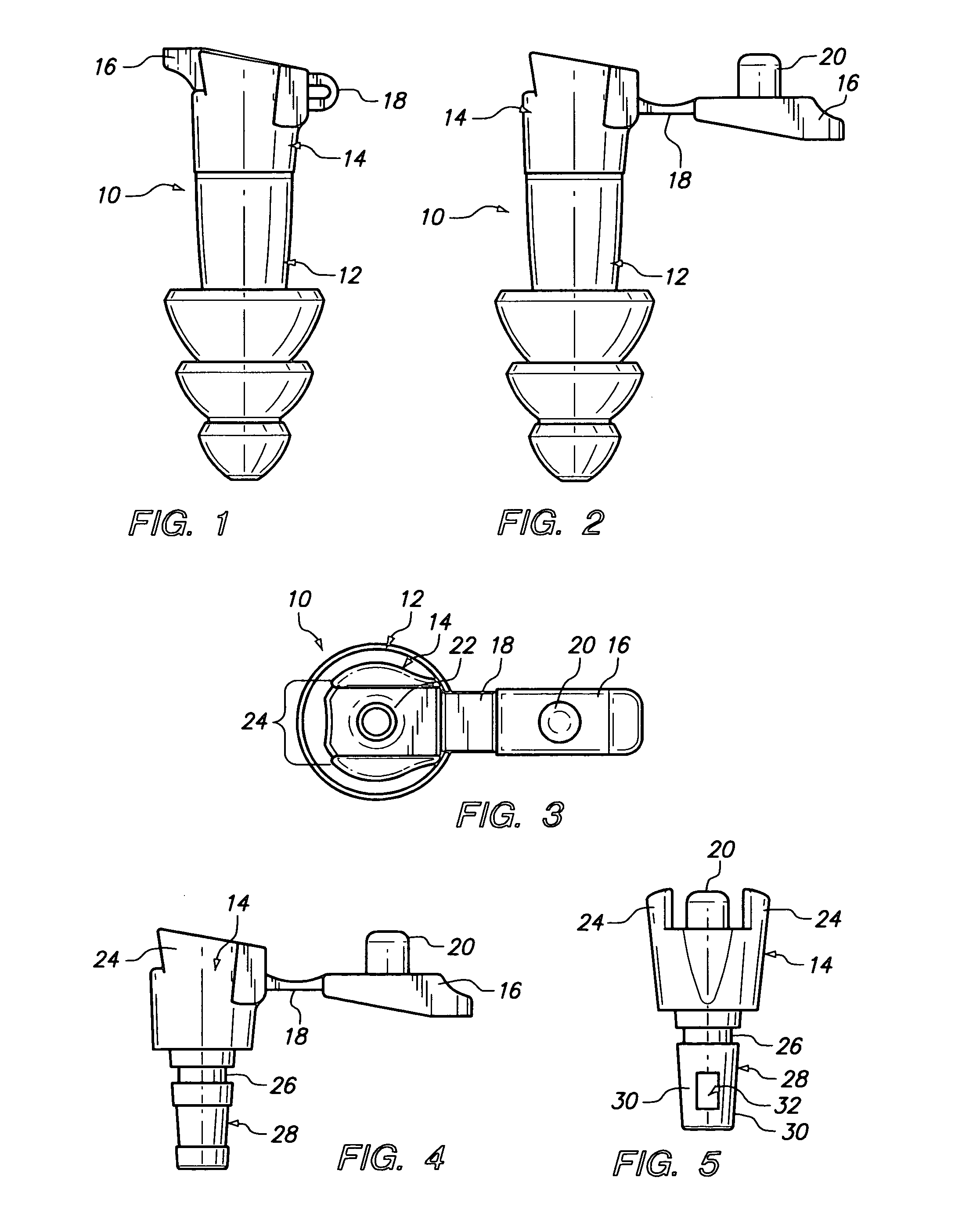
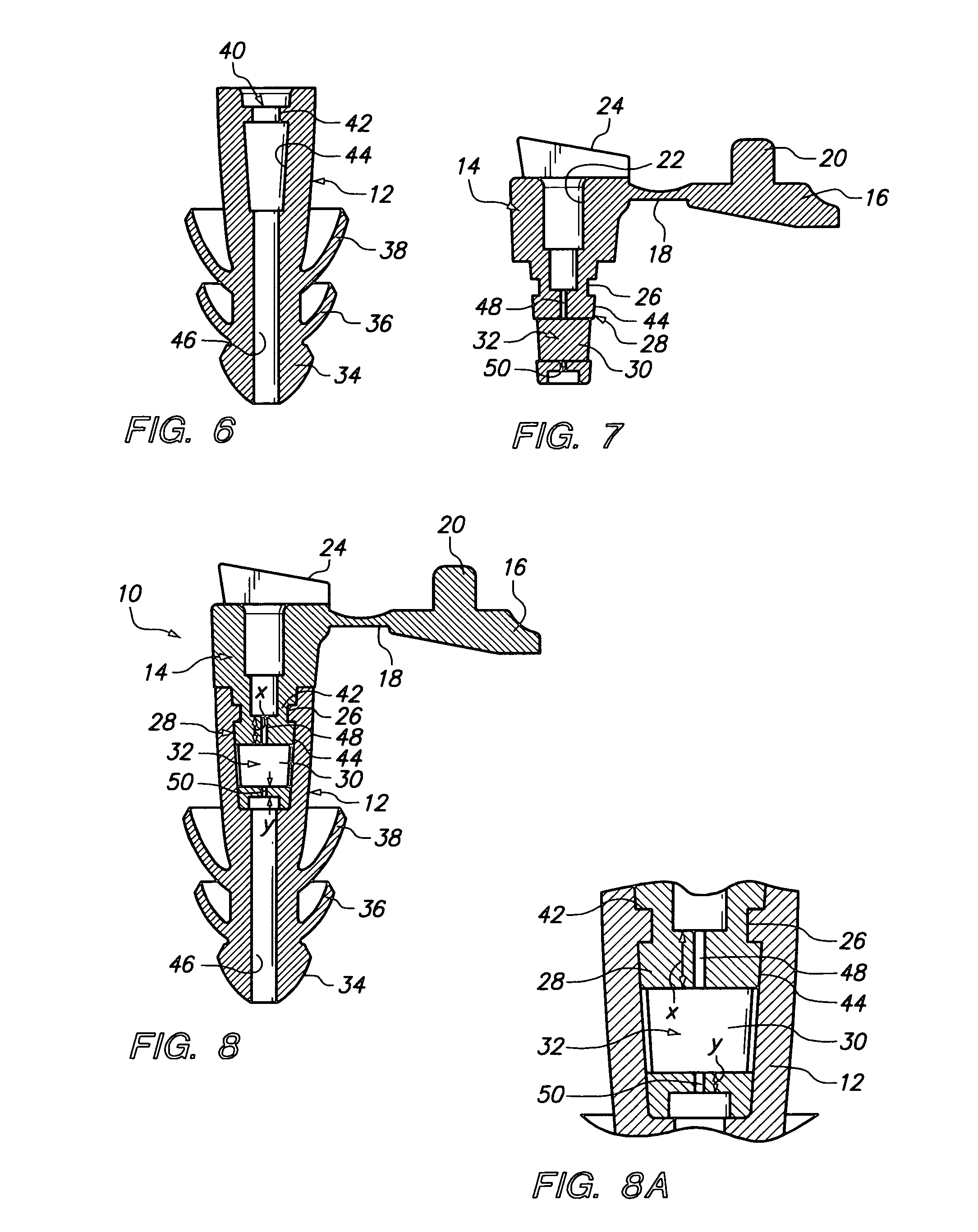
Dual mode impulse noise protecting earplug (D-182)
ActiveUS20100294285A1Eliminate deficienciesEasy constructionSubstation/switching arrangement detailsStethoscopeNormal speechUltrasound attenuation
A two piece dual mode earplug including an integrally molded elongated member having a nose end and an open rear end and a channel extending through the elongated member. An integrally molded insert member is formed with a base portion and a rod portion and with the rod portion seated within the open rear end of the elongated member. The insert member additionally includes an attenuation filter integrally molded as part of the rod portion and includes first and second openings located on each side of a chamber and with the size and length of the openings together with the chamber providing attenuation of impulse noise while allowing the passage of normal speech through the channel. The insert member also includes the base portion integrally molded to have a third opening larger than the first and second openings in the rod portion and with the first, second and third openings together forming a passageway through the insert member to the channel extending through the elongated member. The insert member further includes an integrally molded cap member and with the cap member having a plug portion of a size complementary to the third opening of the base member. The insertion of the plug portion into the third opening of the base portion seals off the third opening. The positioning of the cap member provides for the earplug being in a first mode of operation where the passageway is open and a second mode of operation where the passageway is closed.
Owner:MOLDEXMETRIC
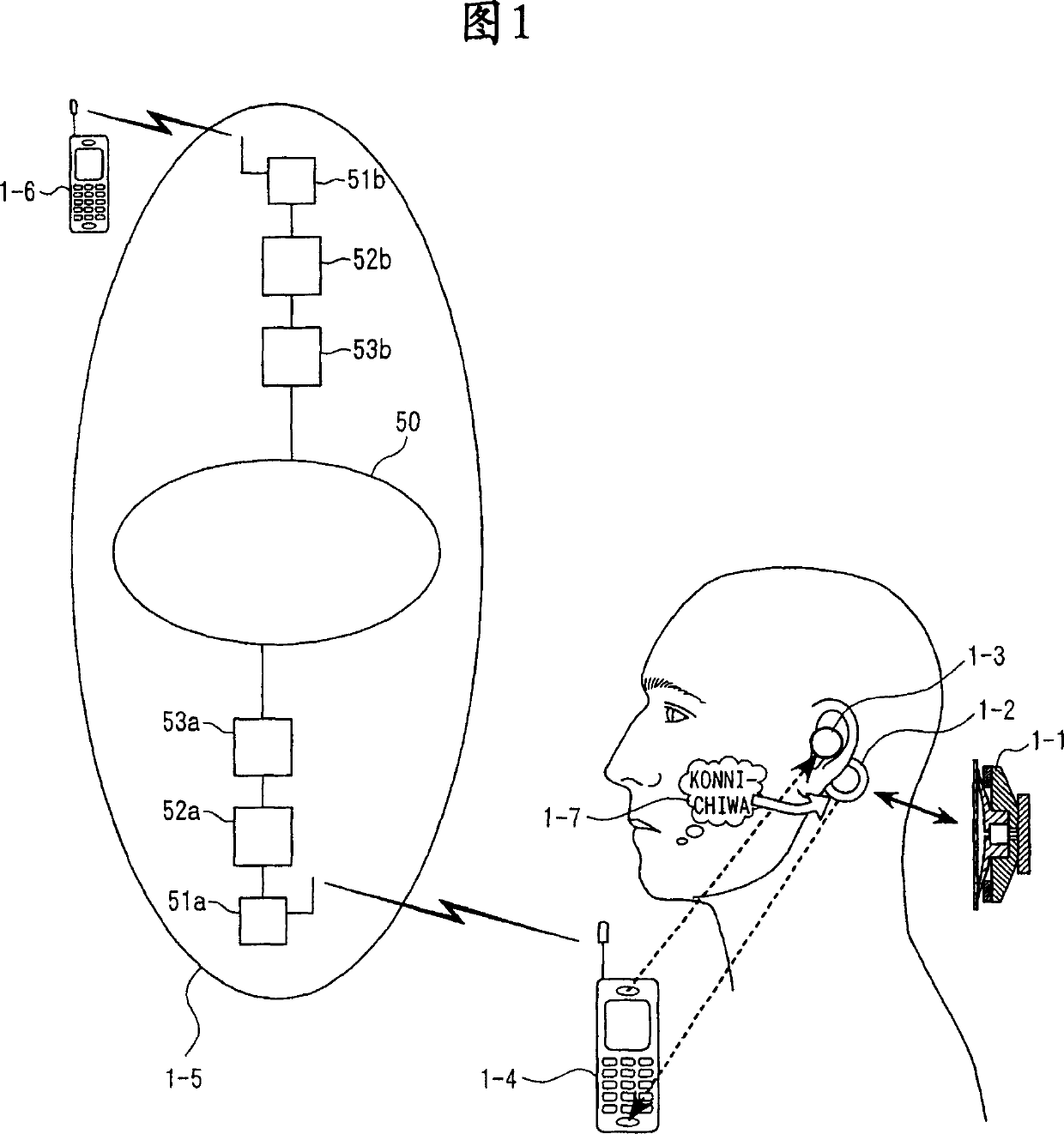
Microphone and communication interface system
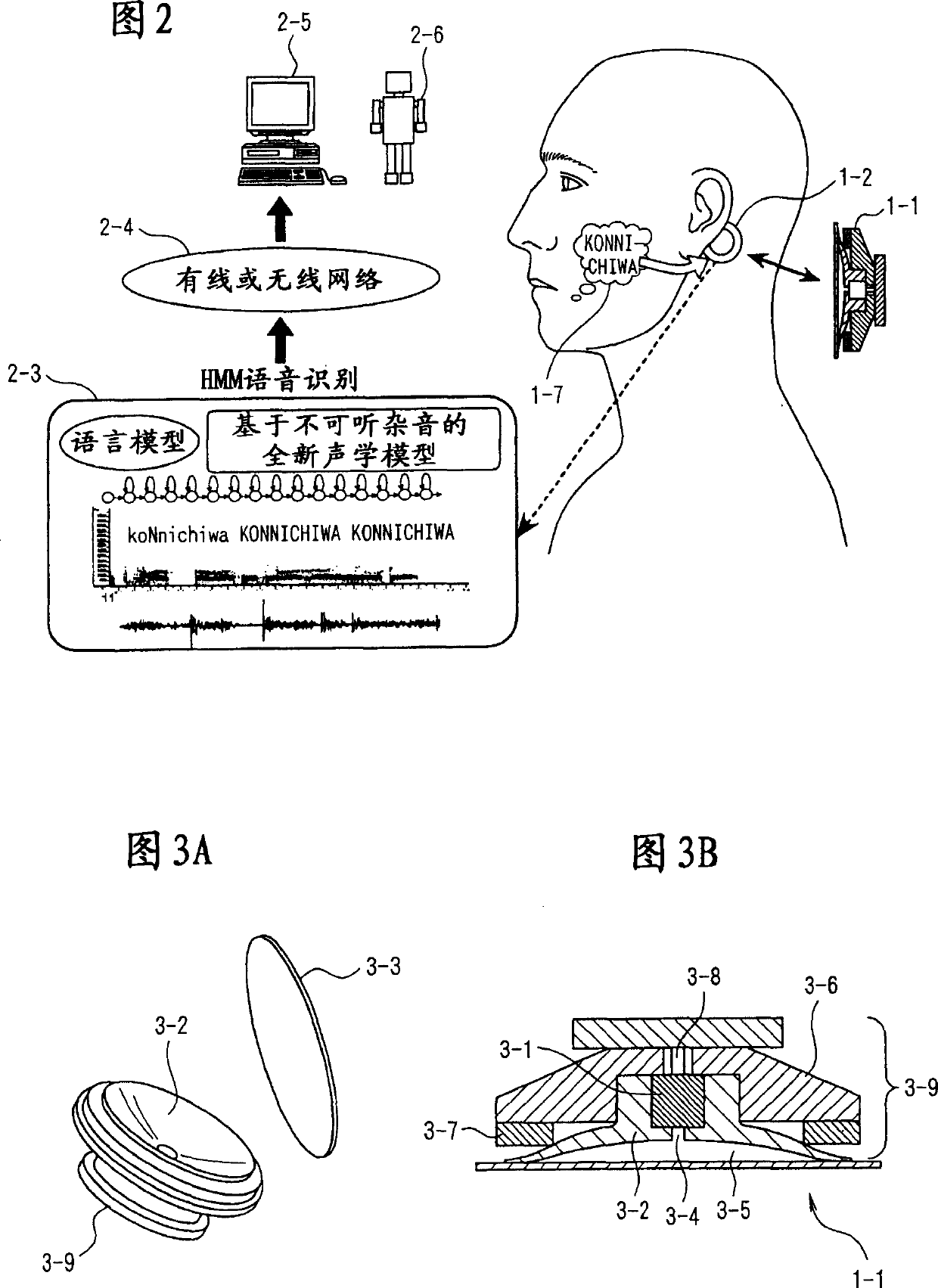
It is possible to improve a defect of an analysis object itself of a mobile telephone and speech recognition which is an air propagating normal speech taken from outside by a microphone and realize a new mobile terminal communication based on the human cultural habit in the personal mobile information terminal without requiring training. A stethoscope type microphone is mounted on a human skin surface so as to take a meat-propagating vibration sound of un-hearable murmur articulated by a speech act (mouth movement) without using vocal cord regular vibration. The meat-propagating vibration sound of the amplified non-hearable murmur is like a whisper and the whisper itself can be heard and understood by a human. Accordingly, it can be used for communication via a mobile telephone. Moreover, by making the meat-propagating vibration sound of the un-hearable murmur an object of analysis / parameterization, it is possible to realize a kind of soundless recognition as a new input method of a personal mobile information terminal.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method and system for obtaining stapedial reflexes in cochlear implant users using multiband stimuli
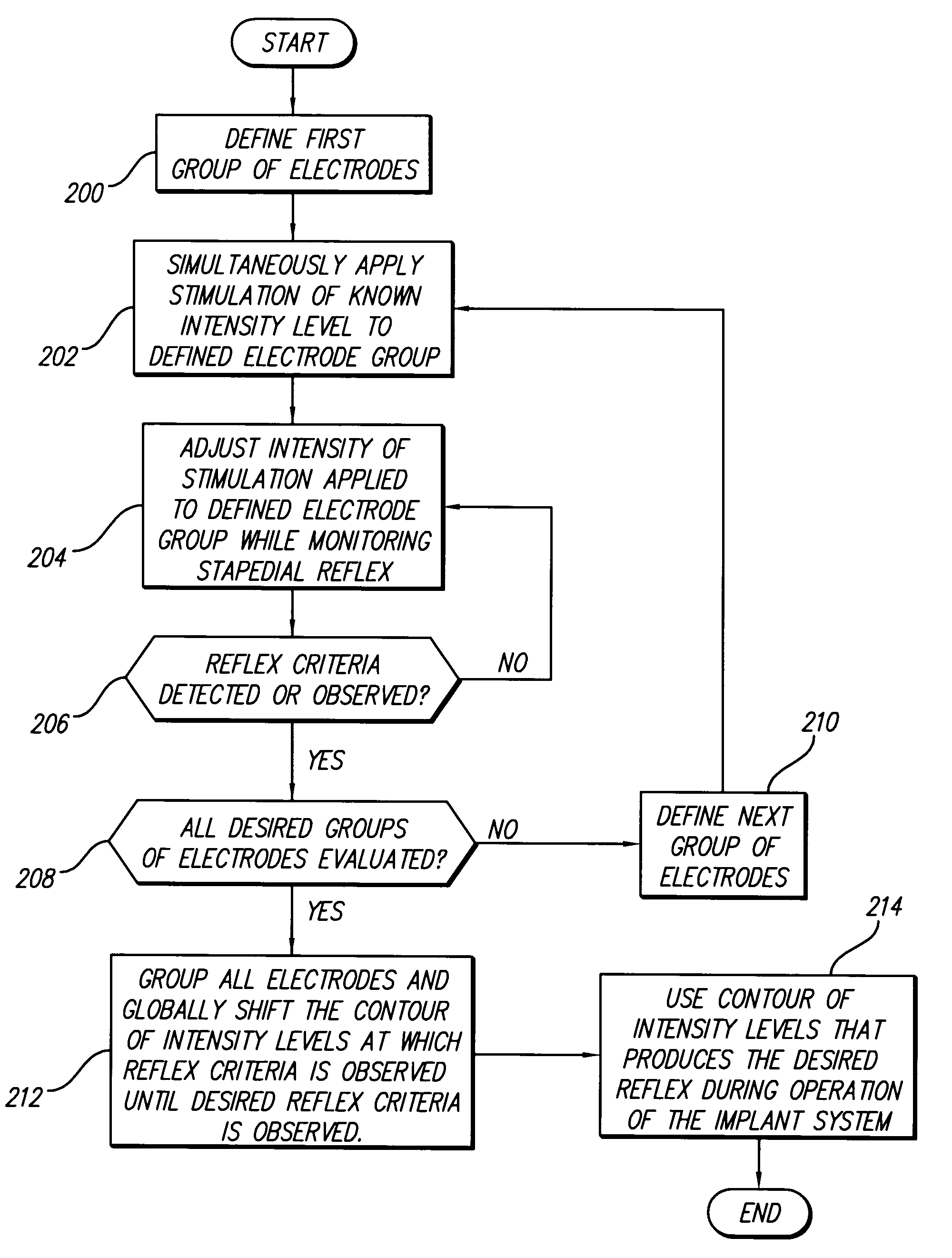
A method and system for fitting a multichannel cochlear implant system to a patient increases the percentage of patients for which stapedial reflexes can be obtained, and increases the accuracy of predicting the “live speech” comfort levels of the patient's fitting programs from the stapedial reflex. Electrical stimuli are applied on multiple electrodes at “live speech” pulse rates. The neural excitation patterns elicited from such stimulation more closely resemble that which occurs when the system is subjected to normal speech patterns. By progressively setting threshold levels in bands, e.g., groups of electrodes, either overlapping or non-overlapping, as well as with a final check by globally adjusting the band obtained contour to the stapedial reflex, such values more closely resemble actual “live speech” program levels than those obtained with traditional methods. Further, broader excitation patterns produced by the activation of multiple electrodes increases the probability of obtaining reflex measurements where single electrode stimulation fails due to sparse neural survival.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
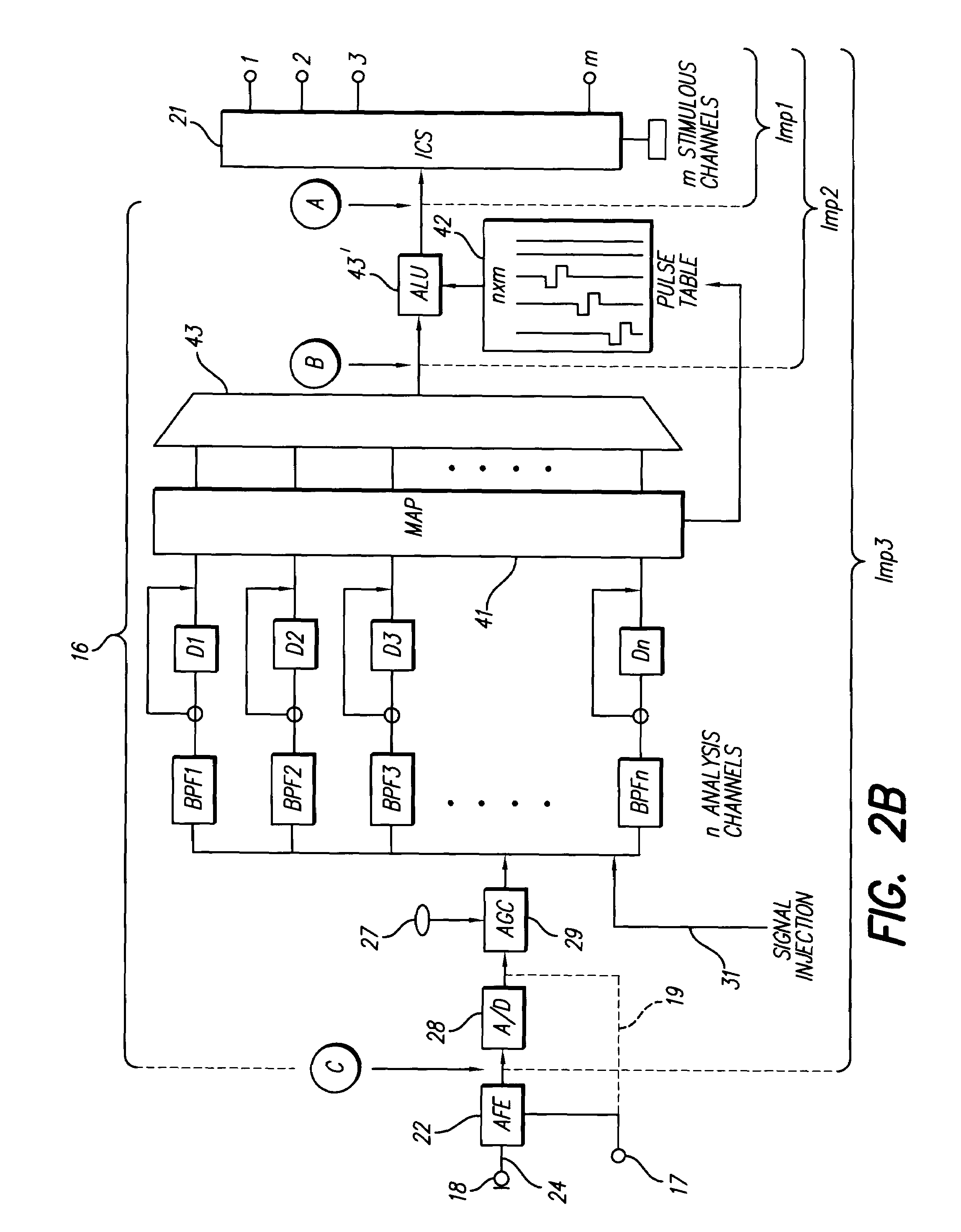
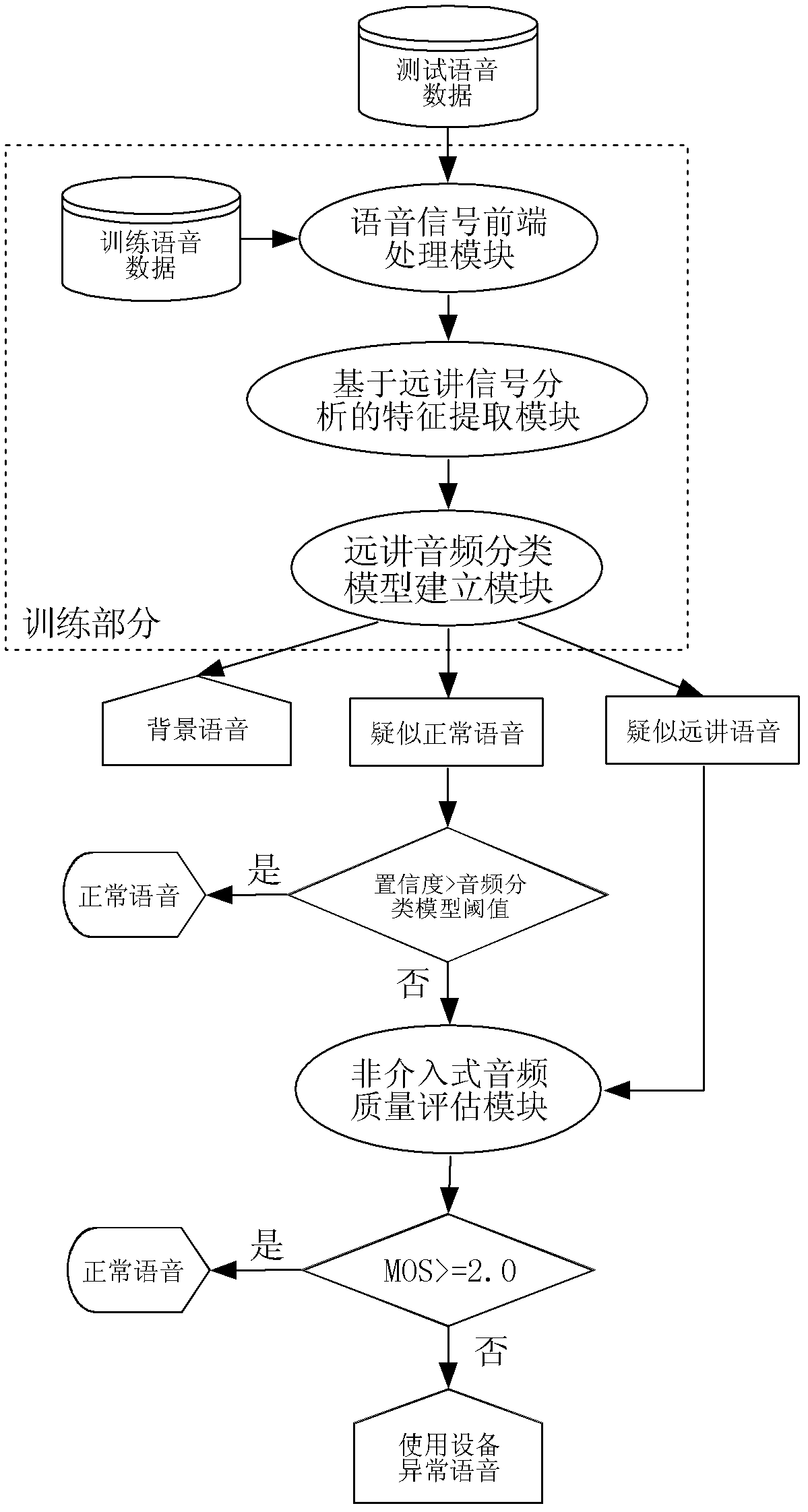
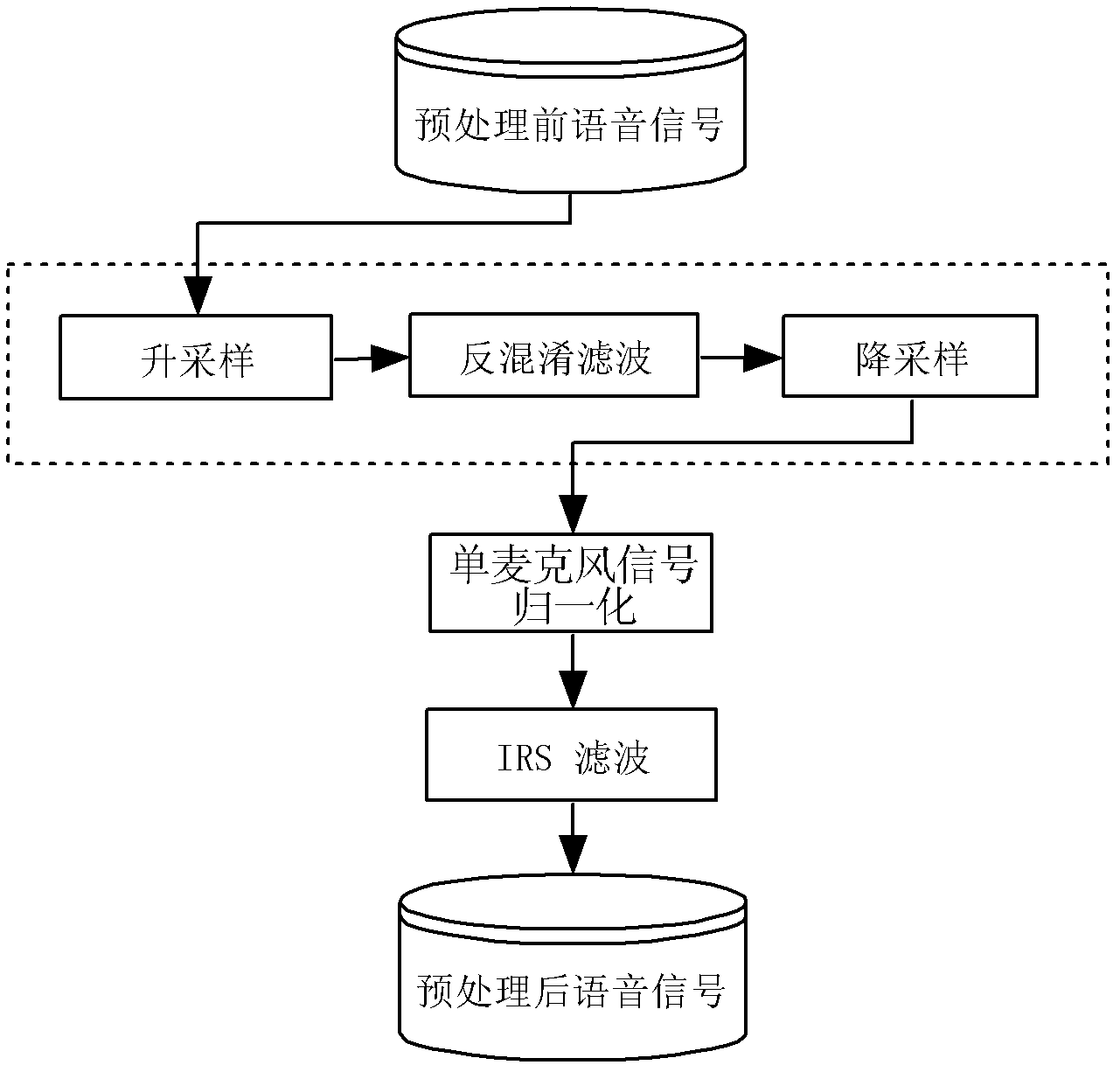
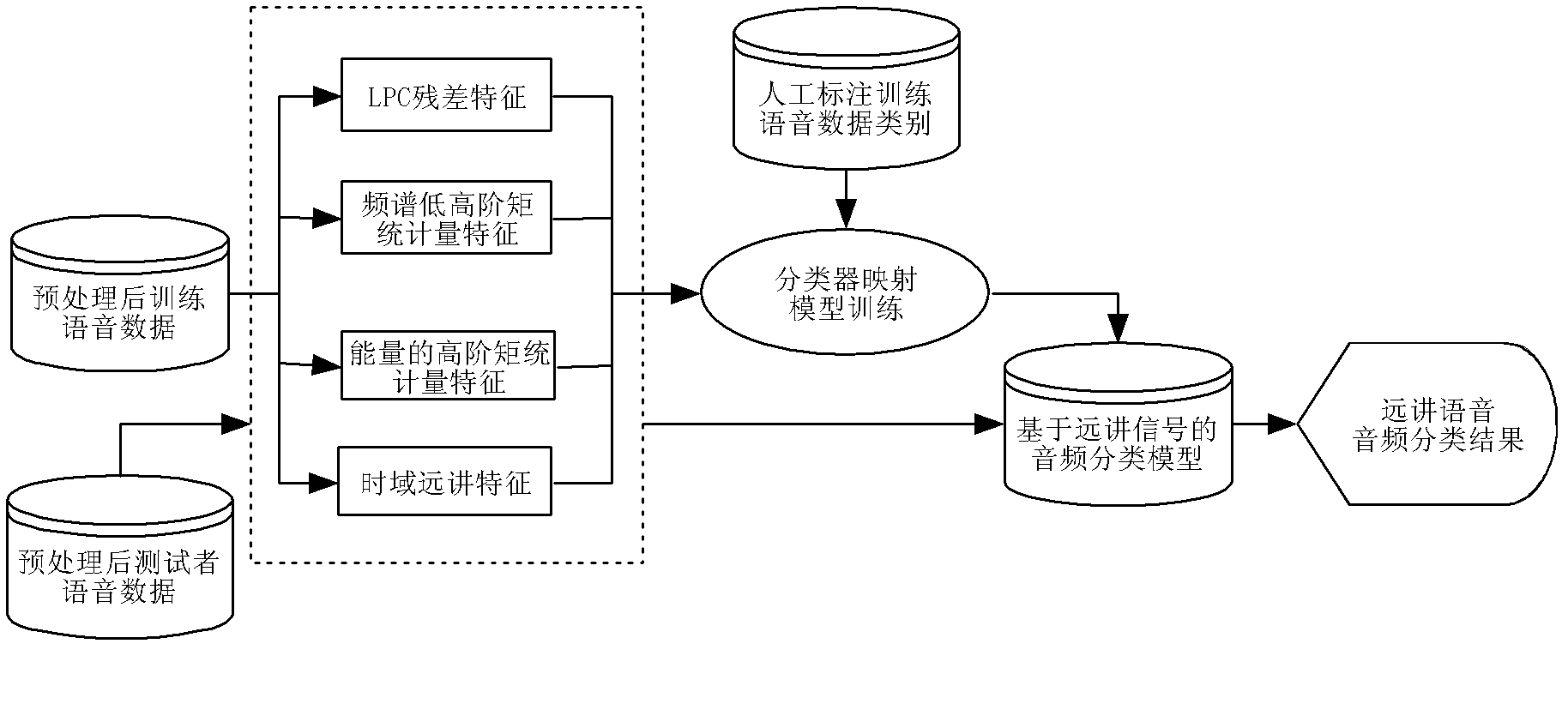
Method and system for detecting abnormal use of voice input equipment
ActiveCN102324229ATroubleshoot Voice Quality DiscrepanciesEnsure fairnessSpeech analysisSpoken languageCombined method
The invention discloses a method and system for detecting abnormal use of voice input equipment. A characteristic extracting mode which is more comprehensive to remote voice signal characteristics and closer to human perception is adopted in the invention so as to roughly judge background voice, normal voice and remote voice. On the basis of classification of audio signals, by adopting the combined method of a modern signal processing technology and a statistical machine learning theory, the problem of multiple limits on front-end voice input by a traditional method is overcome so that signal-level quality scoring is closer to human scoring. According to the invention, the difference problem of front-end input voice quality due to artificial use errors of the equipment in large-scale tests of spoken language is solved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
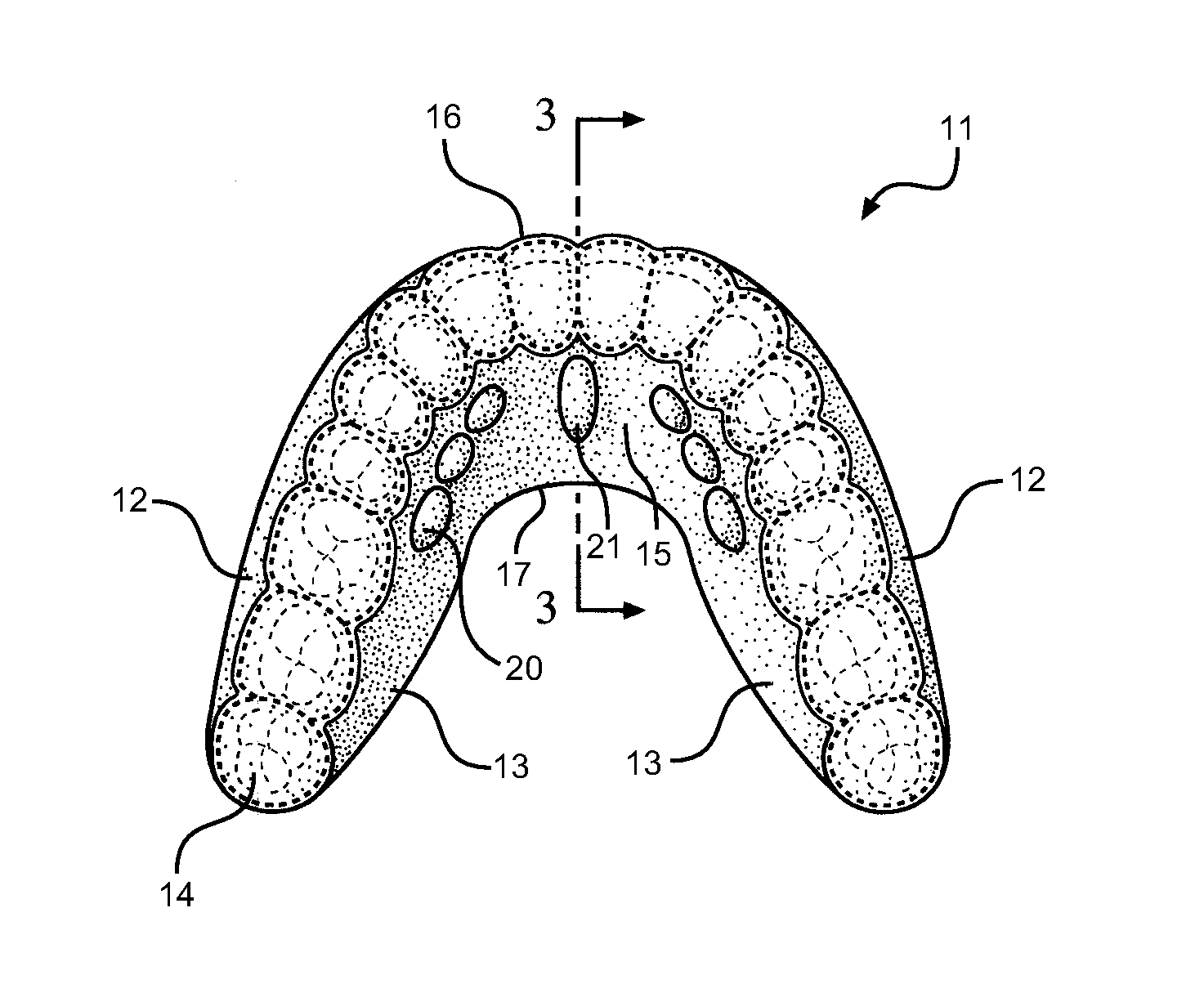
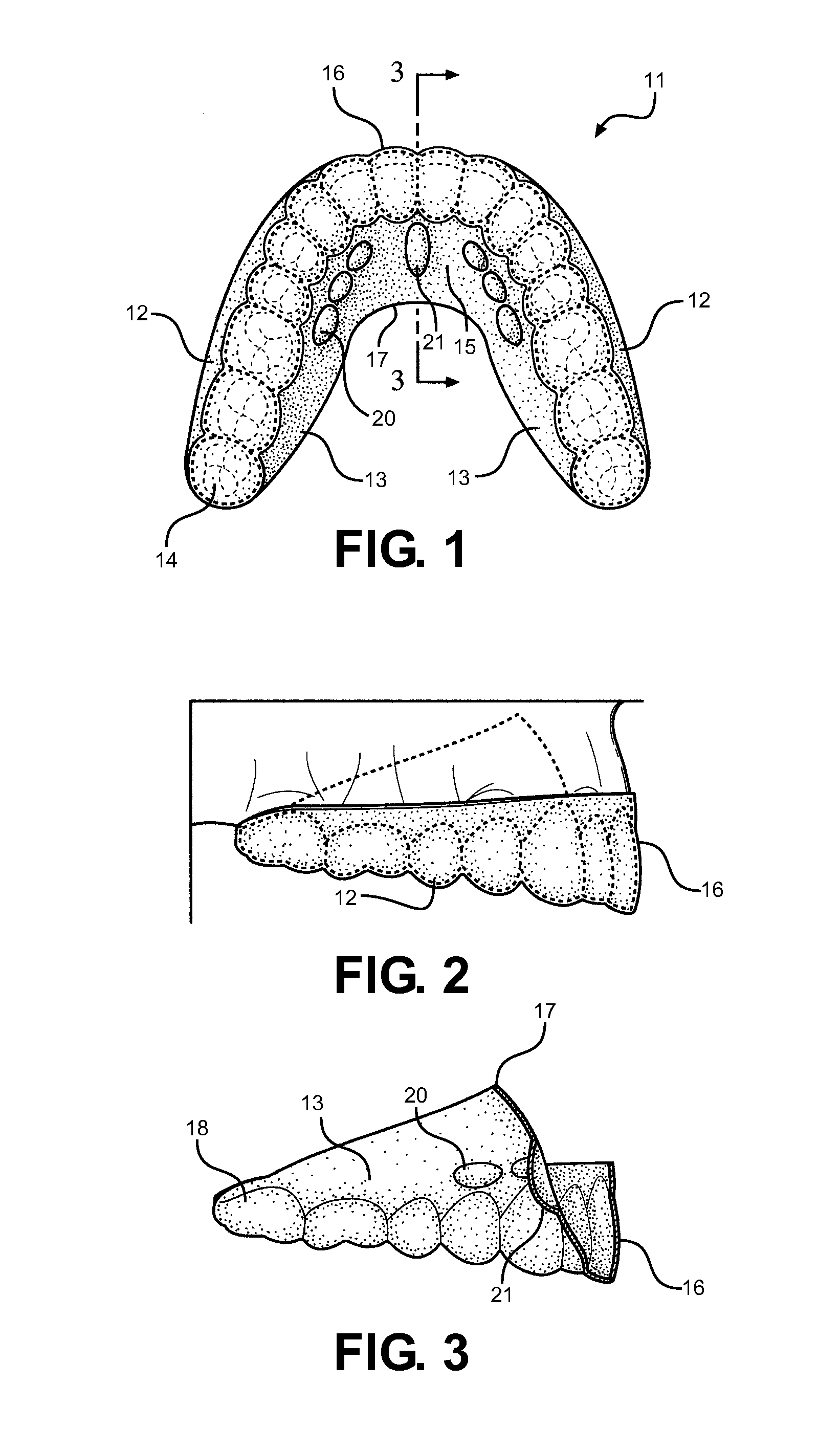
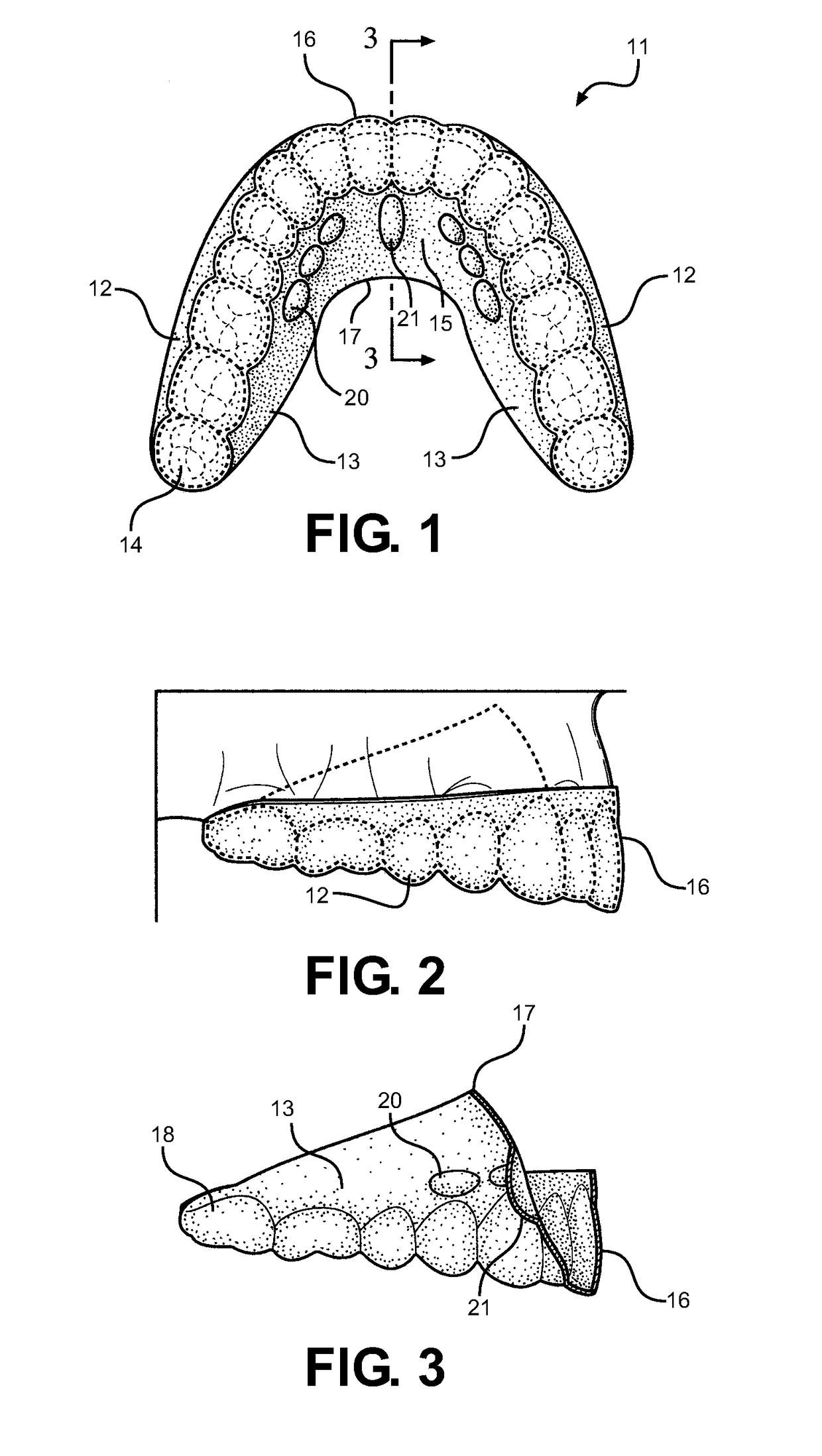
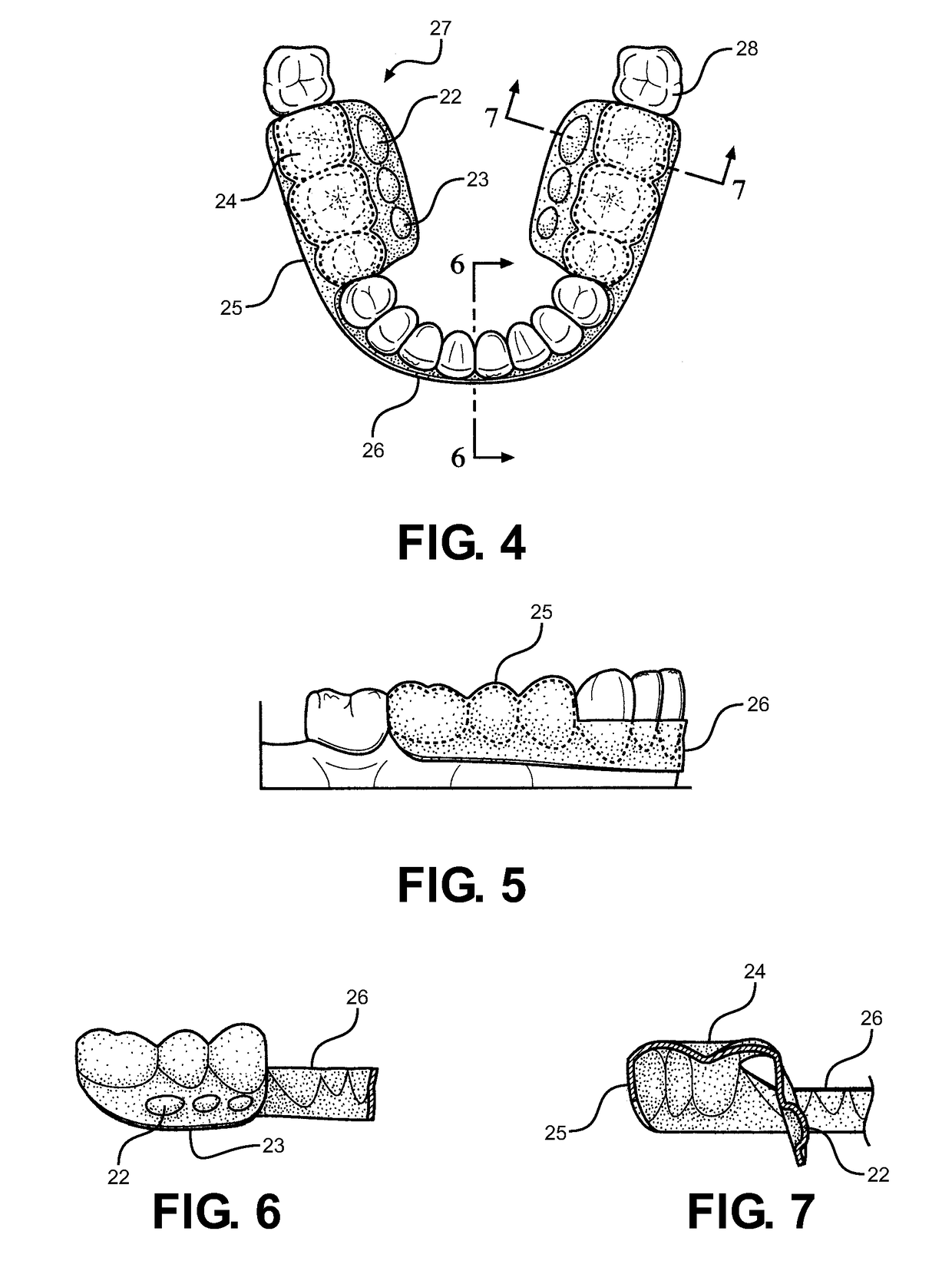
Method and Oral Appliance for Improving Air Intake and Reducing Bruxism
ActiveUS20130298916A1Alleviating numerous medical conditionImprove performanceSnoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesDiseaseThroat
Provided is a soft flexible oral appliance having protuberances that mimic naturally occurring dental Tori. An upper, palatial appliance and a lower, mandibular appliance may be used in conjunction or separately to alleviate a variety of disorders, improve facial tone, and increase physical performance. The appliances are lightweight, thin, and do not prohibit normal speech patterns when in use. Small protuberances are strategically molded along key surfaces of each appliance to stimulate nerves in the tongue and affect forward protrusion. Forward positioning of the tongue dilates the airways of the throat improving breathing while the use is sleeping, playing sports, or talking. It also reduces bruxing, or grinding of the teeth. A method is further provided, for adding protuberances to other types of oral appliances, thereby conferring some of the benefits listed above on appliances originally intended for other dental uses.
Owner:DENTAL CHOICE HLDG LLC
Applications of sub-audible speech recognition based upon electromyographic signals
Method and system for generating electromyographic or sub-audible signals (“SAWPs”) and for transmitting and recognizing the SAWPs that represent the original words and / or phrases. The SAWPs may be generated in an environment that interferes excessively with normal speech or that requires stealth communications, and may be transmitted using encoded, enciphered or otherwise transformed signals that are less subject to signal distortion or degradation in the ambient environment.
Owner:NASA
Method for enhancing memory and cognition in aging adults
InactiveUS20060073452A1Improve “ noisy ” sensory representationShorten time constantElectrical appliancesTeaching apparatusCognition.knowledgeComputer science
A method on a computing device is provided for enhancing the memory and cognitive ability of an older adult by requiring the adult to differentiate between rapidly presented stimuli. The method utilizes a sequence of phonemes from a confusable pair which are systematically manipulated to make discrimination between the phonemes less difficult or more difficult based on the success of the adult. The manipulation includes processing of the consonant and vowel portions of the phonemes by emphasizing the portions, and / or by stretching the portions. Further processing includes separating the consonant and vowel portions by time intervals. As the adult improves in their auditory processing, the discriminations are made progressively more difficult by reducing the amount of processing to that of normal speech.
Owner:NEUROSCI SOLUTIONS CORP +1
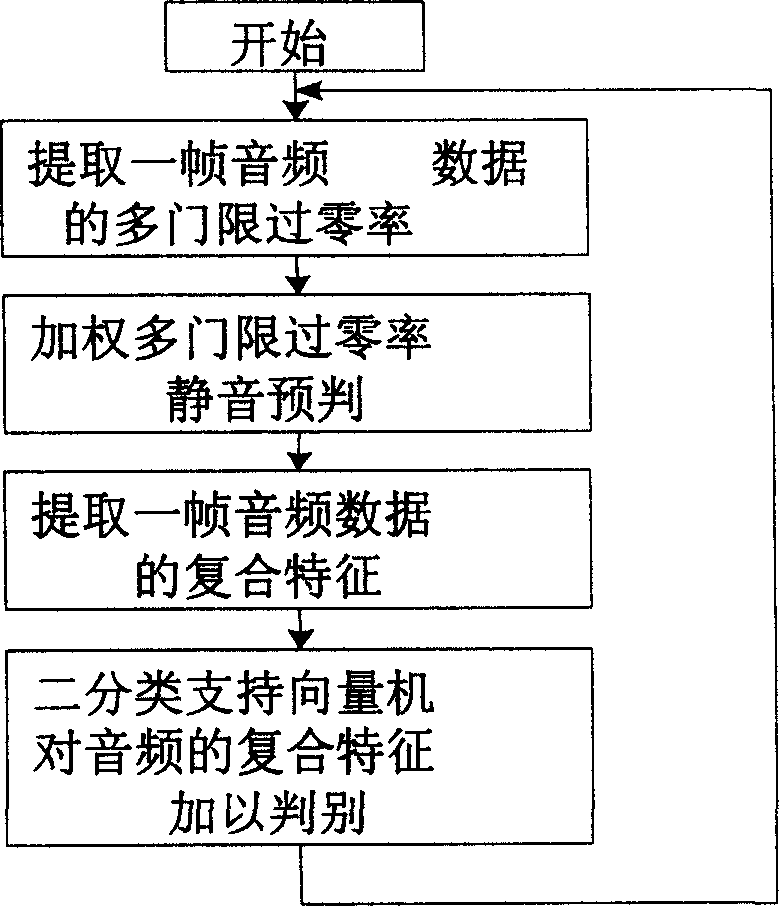
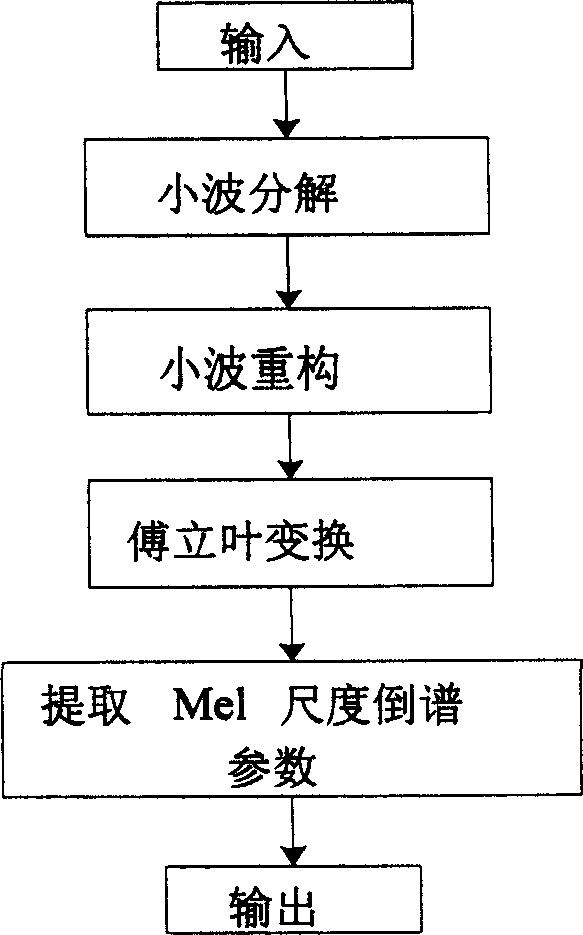
Mute detection method based on speech characteristic to jude
InactiveCN1835073AImprove classification effectImprove robustnessSpeech analysisSupport vector machineFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a voice characteristic identification-based silence detecting method, firstly extracting multi-threshold overzero rate of an audio data frame; pre-identify silence by weighting the multi-threshold overzero rate to identify obvious silence; extracting composite characteristic of an audio data frame, where the composite characteristic comprises overzero rate, short-time energy value, and variable resolution frequency spectrum-based Mel scale revere spectrum coefficient; using dichotomy support vector machine to identify the composite character of the audio frequency, one class normal voice and the other class silence. And the invention can raise success rate of silence detection and can identify some special voices, able to be widely applied to network voice talking, especially voice chatting and video meeting.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
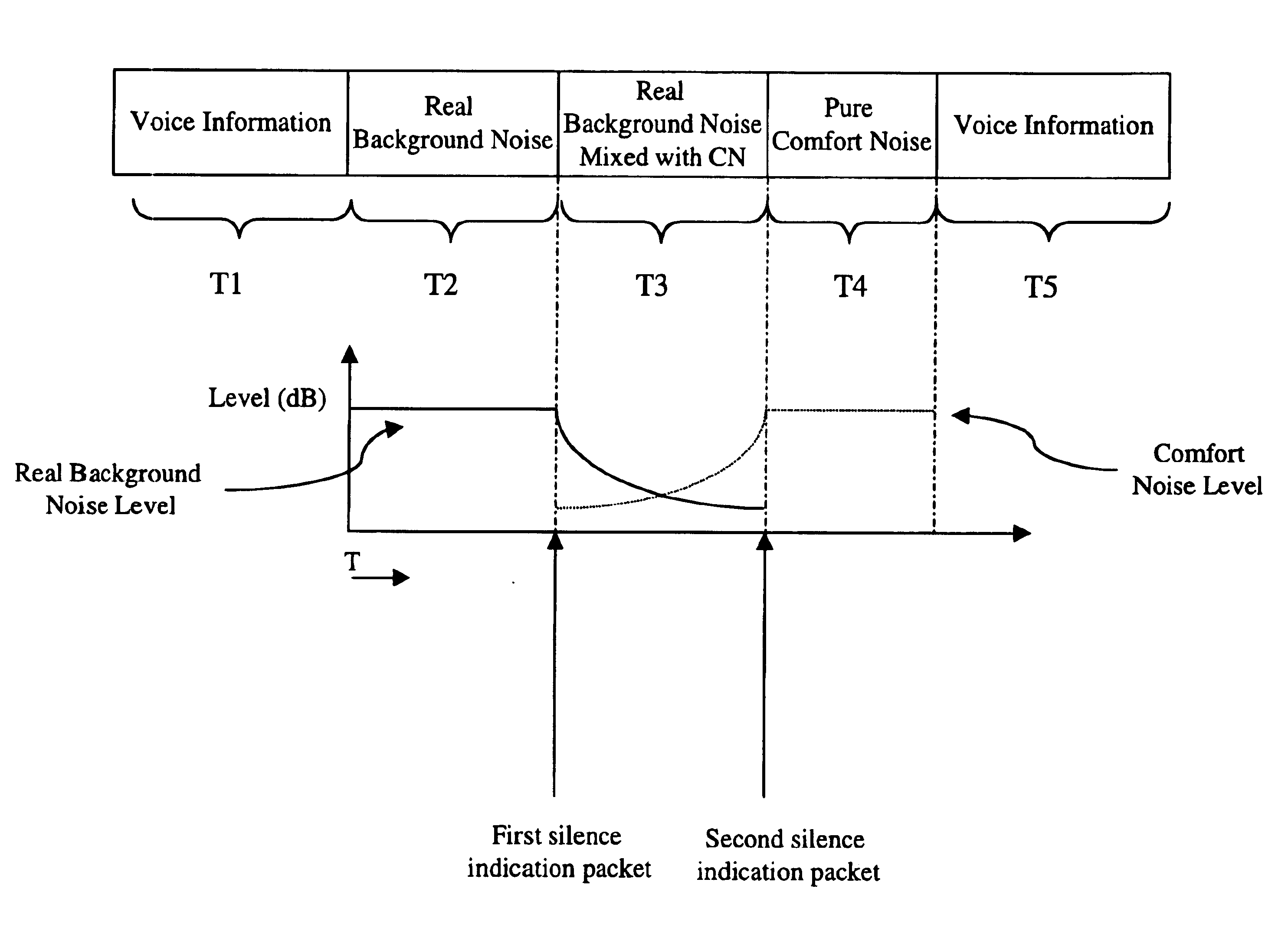
Method and apparatus for transitioning comfort noise in an IP-based telephony system
InactiveUS6873604B1Eliminating and minimizing transitionSatisfies needMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationUltrasound attenuationComfort noise
A method is disclosed, where the RX unit of an IP telephone waits for a first silence indication packet to be received. When the first silence indication packet is received, the RX begins attenuating incoming packets. The rate of attenuation may occur at a rate responsive to an indication provided by the TX unit. The RX unit also mixes comfort noise with the attenuated incoming packets. The RX unit the waits for a second silence indication packet to be received. When the second silence indication is received the RX unit mixes in comfort noise at a level responsive to an indication provided by the TX unit. The RX units then waits for voice packets to be received from the TX unit. When normal voice activity resumes, the RX unit stops the generation of comfort noise and begins playing voice packets again.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Data multiplexing for diversity operation
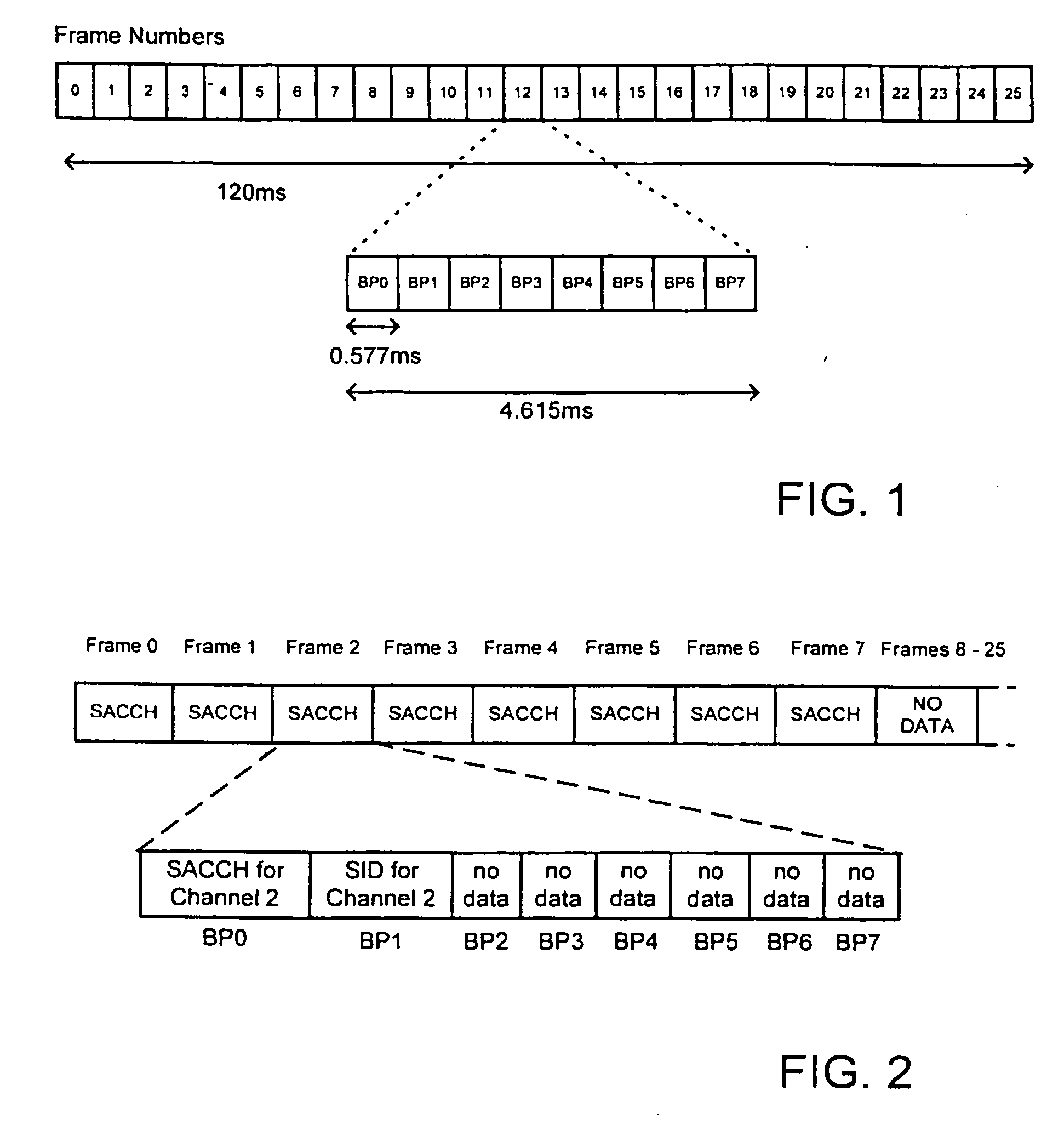
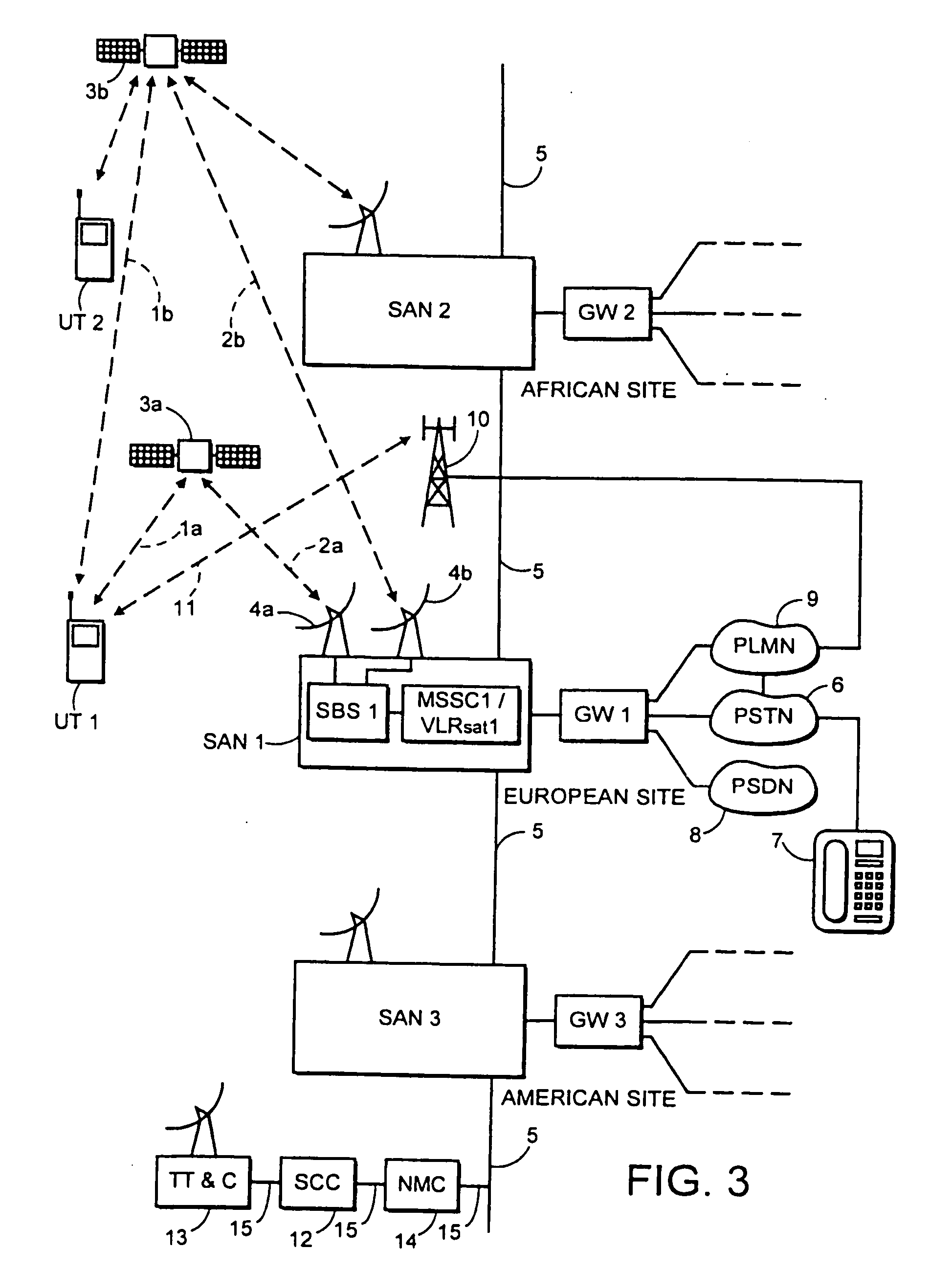
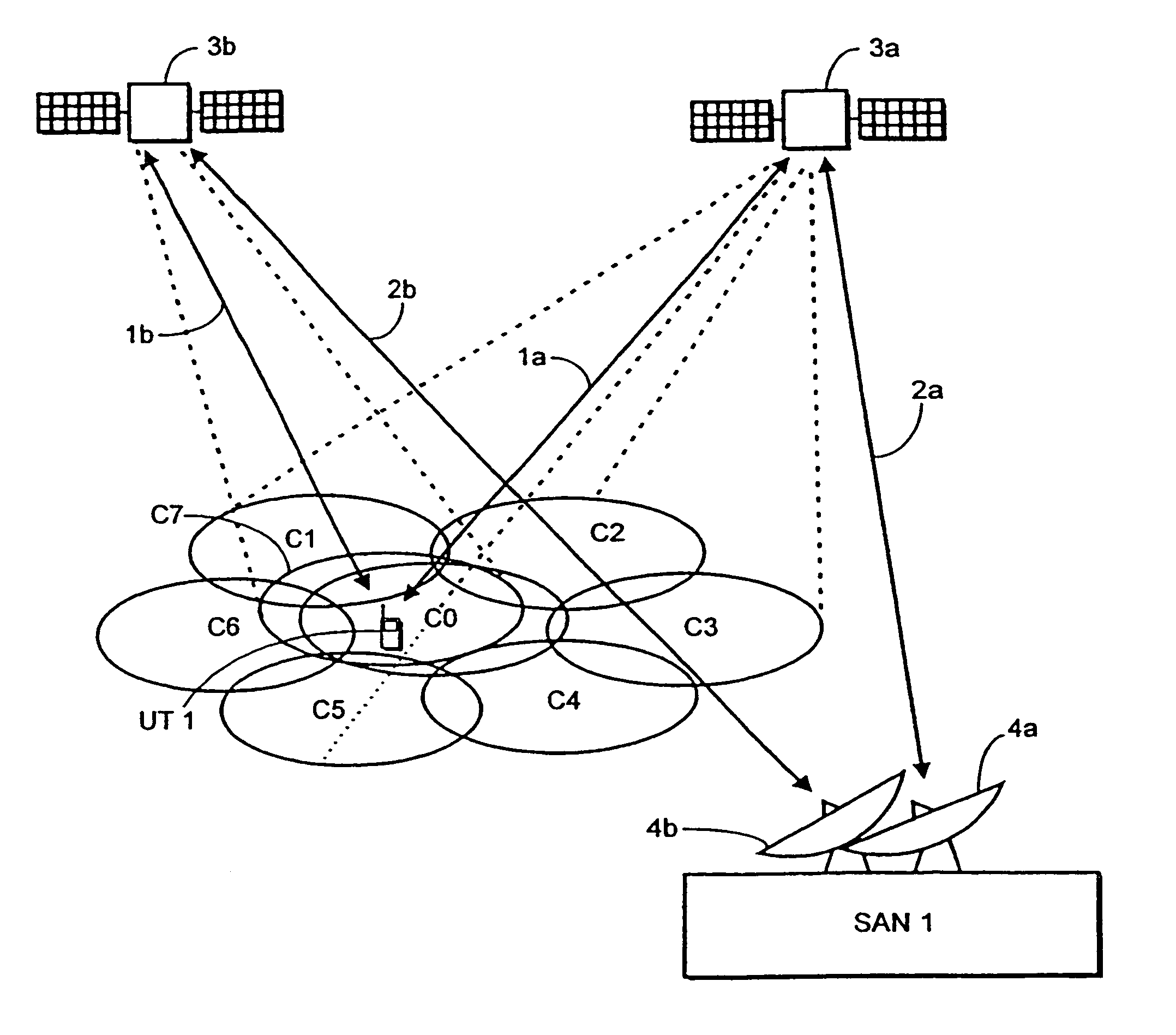
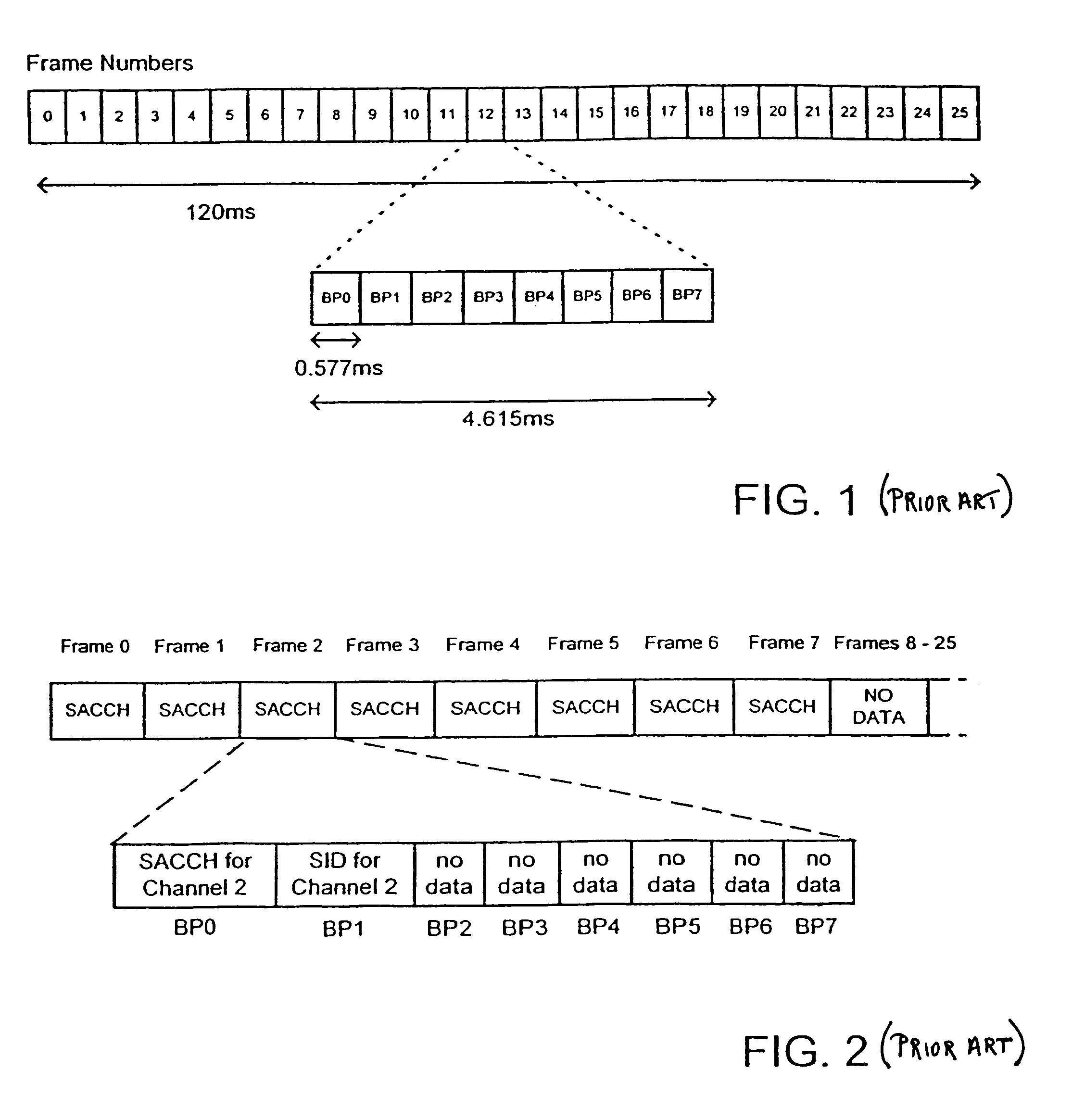
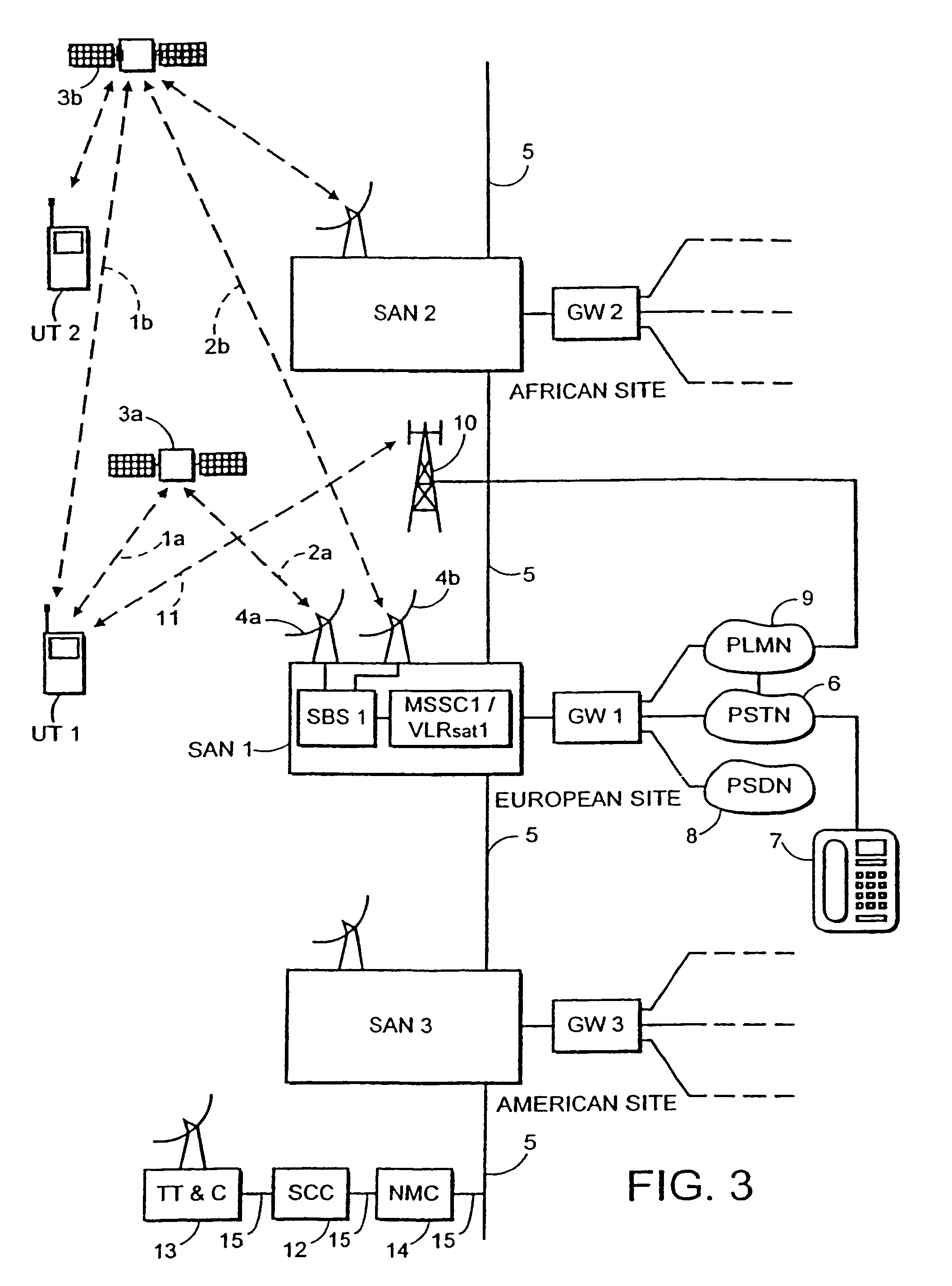
InactiveUS20070121537A1Minimize the numberAvoids high peak to mean valueRadio transmissionBurst transmissionPeak value
In a satellie mobile telecommunications system based on the GSM standard, and using a TDMA frame structure, discontinuous transmission (DTX) mode is used to take advantage of the substantial silences which occur during normal speech. In this mode, traffic channel (TCH) data is not sent, but control of the link between a ground station and a user terminal is maintained by sending control channel data bursts (SACCH) together with silence descriptor (SID) frames. To avoid high peak to mean values of transmission power at the satellite, the emission time of the bursts is controlled so as to be uniform over the available sending opportunities. Conventional techniques for doing this cannot be used in a system which includes diversity operation. Therefore, the burst transmission time at the ground station is set in dependence on a reference provided by the user terminal which is a modified version of the reference generated for contention resolution of random access requests.
Owner:ICO SERVICES LTD
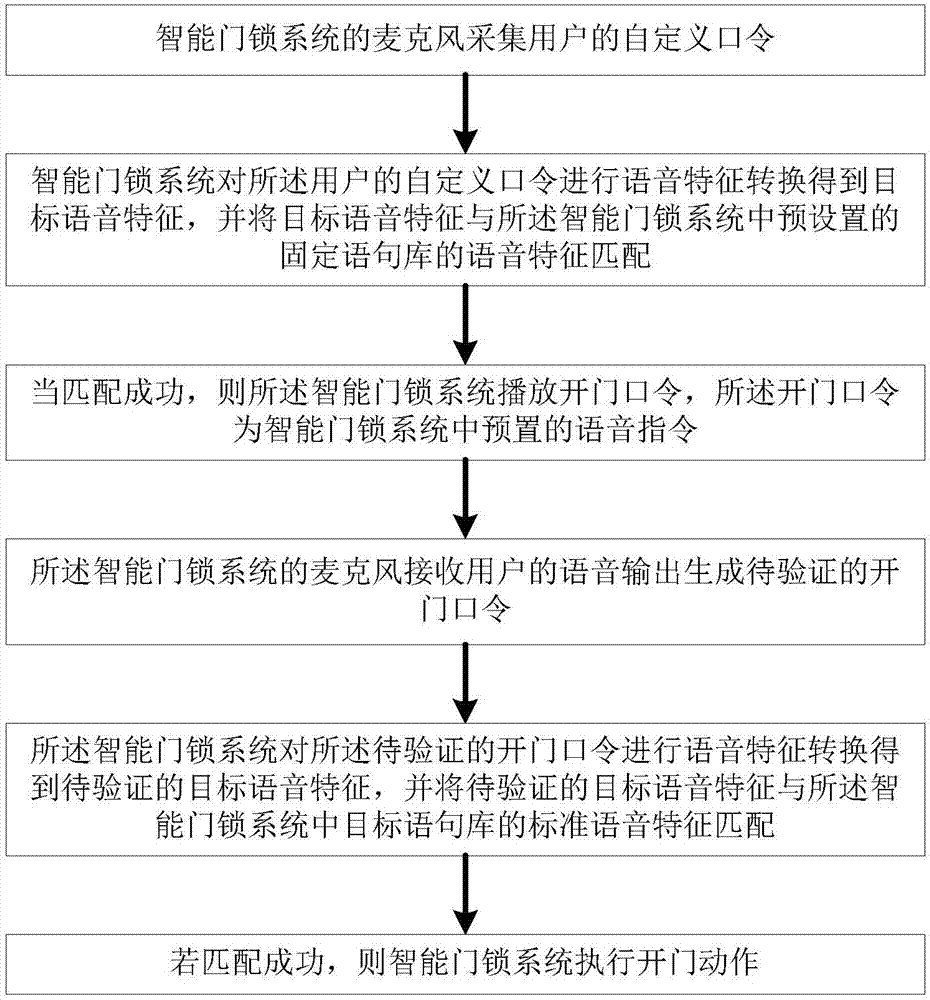
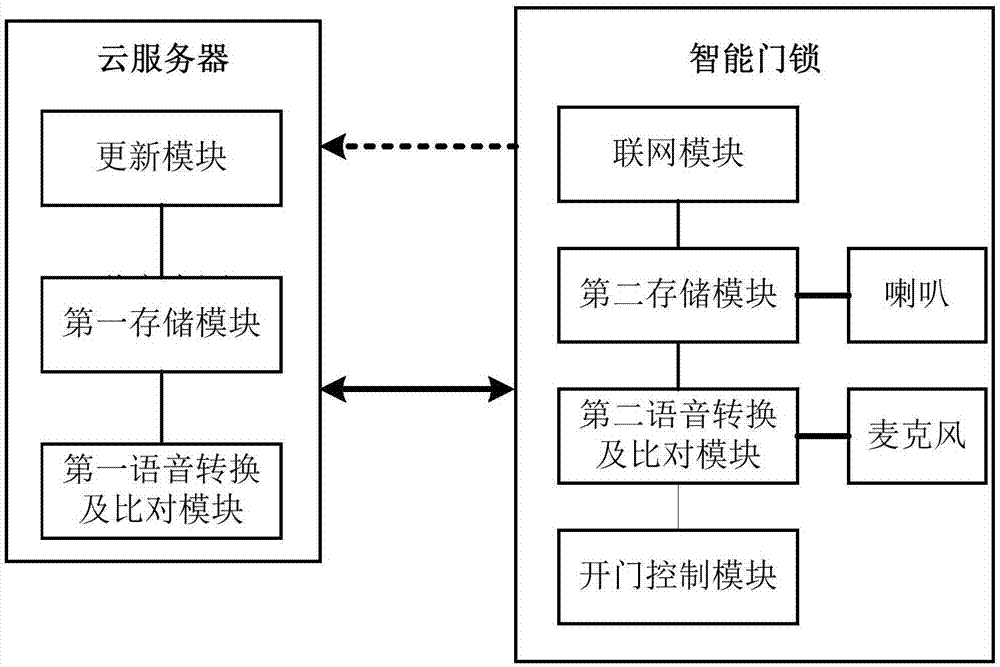
Speech recognition-based unlocking method, and intelligent door lock system thereof
The invention provides a speech recognition-based unlocking method. According to the speech recognition-based unlocking method, a user (keymaker) read a custom password and a random password at normal speech speed in the front of a door lock, secondary matching verifying is adopted, speed information of the user (keymaker) is collected by the intelligent door lock, speech characteristic extraction is carried out, the speech characteristics are compared with that of the user (keymaker) stored in a cloud server or speech characteristic local database, and cloud terminal can also be used for updating of the speech characteristic local database. The safety and convenience of intelligent door lock unlocking are improved greatly.
Owner:YUNDING NETWORK TECH BEIJING
Data multiplexing for diversity operation
InactiveUS7133377B1Minimize the numberAvoids high peak to mean valueTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionBurst transmissionPeak value
In a satellite mobile telecommunications system based on the GSM standard, and using a TDMA frame structure, discontinuous transmission (DTX) mode is used to take advantage of the substantial silences which occur during normal speech. In this mode, traffic channel (TCH) data is not sent, but control of the link between a ground station and a user terminal is maintained by sending control channel data bursts (SACCH) together with silence descriptor (SID) frames. To avoid high peak to mean values of transmission power at the satellite, the emission time of the bursts is controlled so as to be uniform over the available sending opportunities. Conventional techniques for doing this cannot be used in a system which includes diversity operation. Therefore, the burst transmission time at the ground station is set in dependence on a reference provided by the user terminal which is a modified version of the reference generated for contention resolution of random access requests.
Owner:DISH NETWORK CORP
Method of converting whispered voice into normal voice based on radial group neutral network
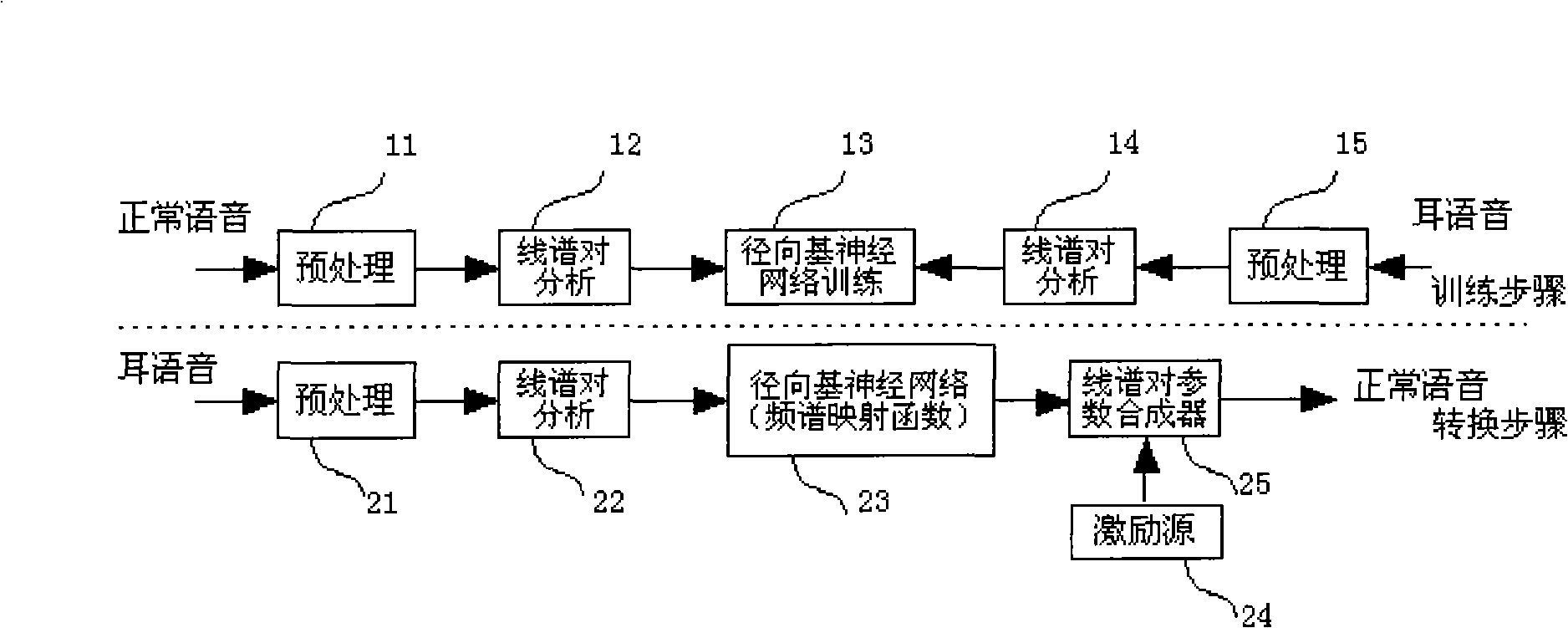
InactiveCN101527141AAchieve conversionFacilitate communicationSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumWhispered voice
The invention discloses a method of converting whispered voice into normal voice based on a radial group neutral network, which comprises two steps of training and converting: respectively extracting line spectrum pair parameters of the whispered voice and the normal voice when in training; seizing mapping relation of spectrum envelope of the whispered voice and the normal voice by using the radial group neutral network; preprocessing the whispered voice when in conversion and extracting the line spectrum pair parameters, converting the line spectrum pair parameters of the whispered voice by the trained radial group neutral network, at last generating a driving source of the voice by using basic frequency mean value of the voice as basic voice frequency, and converting into the normal voice by a line spectrum pair synthesizer. The whispered voice converted by the invention achieves better effect on the respects of intelligibility threshold and tone quality.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for modulating listener attention toward synthetic formant transition cues in speech stimuli for training
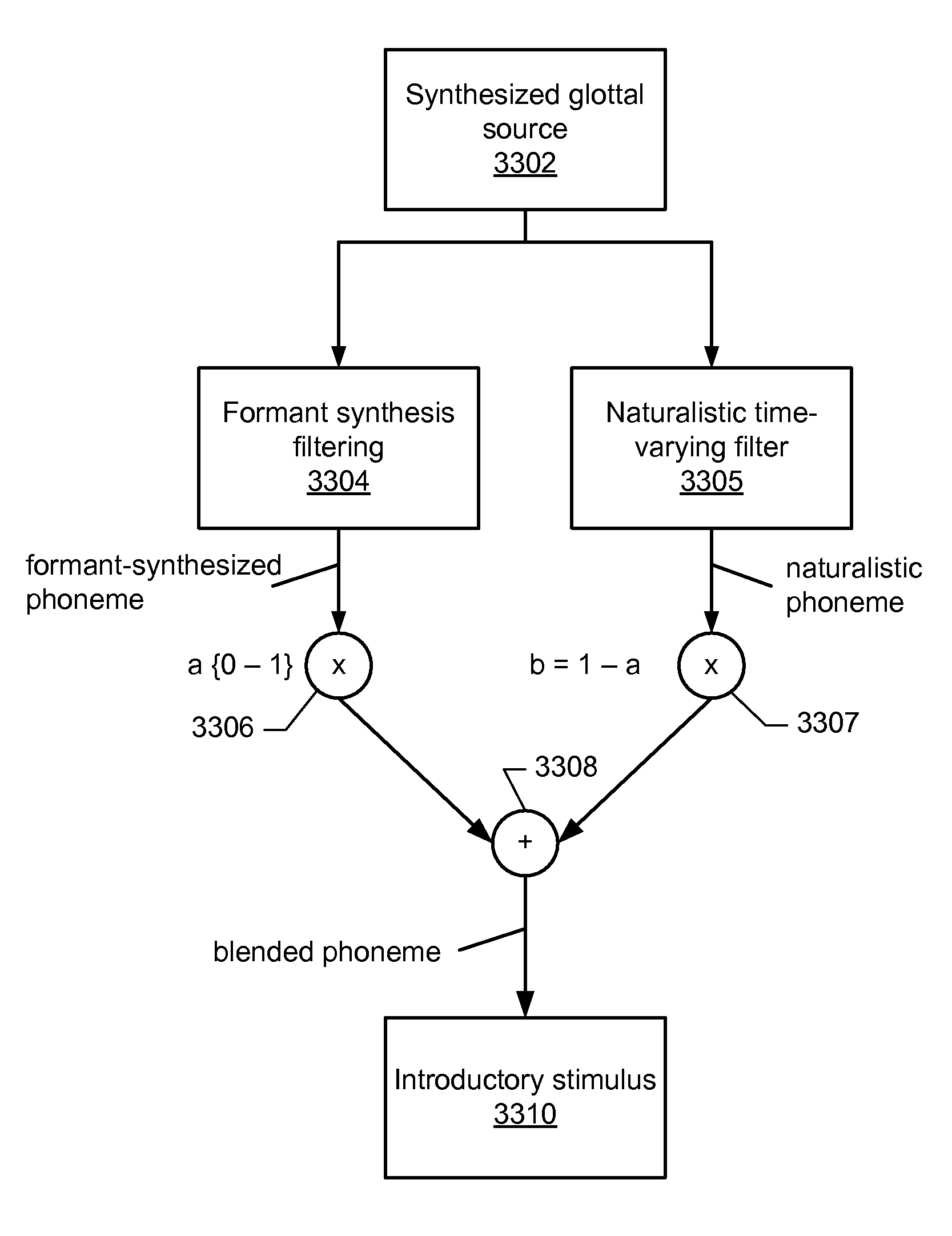
ActiveUS8210851B2Increase salienceImprove accuracyReadingElectrical appliancesSpeech soundNormal speech
A method on a computing device for enhancing the memory and cognitive ability of an older adult by requiring the adult to differentiate between rapidly presented stimuli. The method utilizes a sequence of phonemes from a confusable pair which are systematically manipulated to make discrimination between the phonemes less difficult or more difficult based on the success of the adult, such as processing the consonant and vowel portions of the phonemes by emphasizing the portions, stretching the portions, and / or separating the consonant and vowel portions by time intervals. As the adult improves in auditory processing, the discriminations are made progressively more difficult by reducing the amount of processing to that of normal speech. Introductory phonemes may each include a blend of a formant-synthesized phoneme and an acoustically naturalistic phoneme that substantially replicates the spectro-temporal aspects of a naturally produced phoneme, with the blends progressing from substantially natural-sounding to substantially formant-synthesized.
Owner:POSIT SCI CORP
Speech audiometry method based on auditory steady state response
ActiveCN103054587AGet rid of the influence of subjective factorsObjective and accurate audiometry resultsAudiometeringSensorsSpeech identificationSpeech audiometry
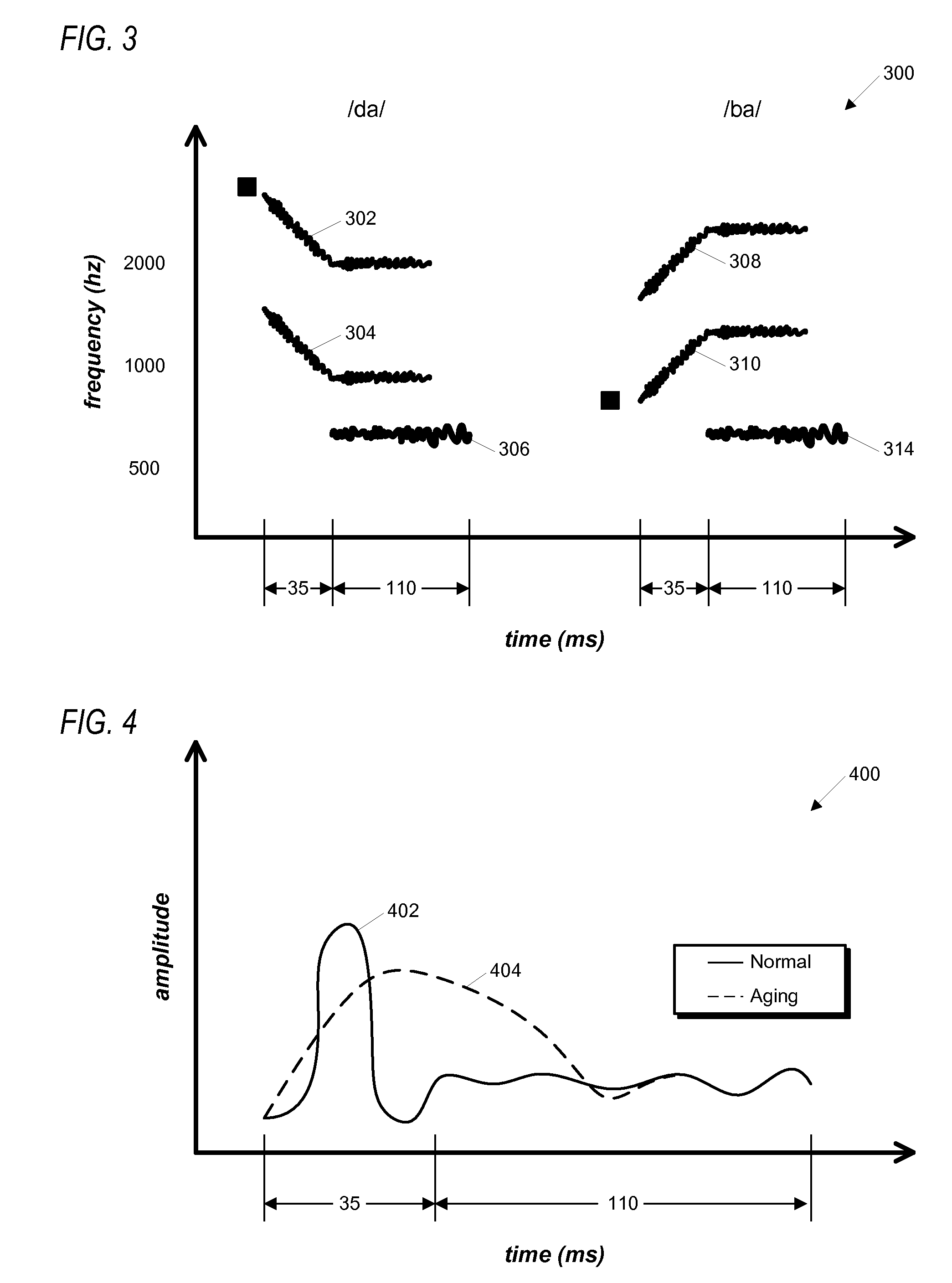
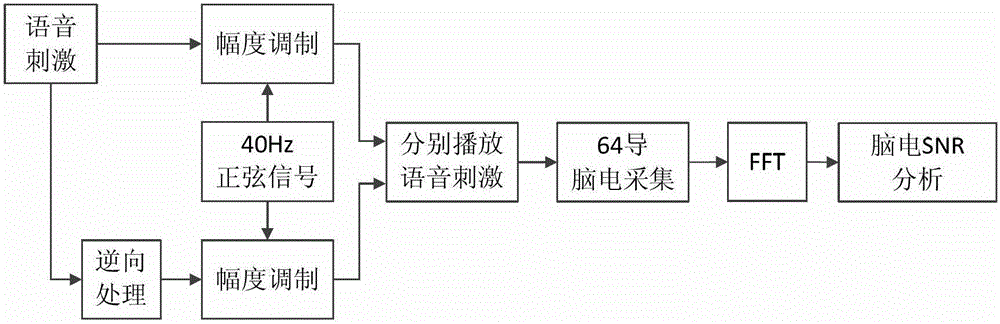
The invention relates to the technical field of neural engineering and speech audiometry field and particularly relates to a speech audiometry method based on auditory steady state response. The method comprises steps of generating modulating frequency on an electroencephalogram gamma section, which has audibility first voice stimulation and inaudibility second voice stimulation; simulating a testee by using the first voice stimulation and the second voice stimulation respectively, and recording electroencephalogram signals of the testee during the simulation; and according to electroencephalogram signals, analyzing the strength of the auditory steady state response, and determining whether the testee has the normal speech identification ability. By the aid of the method, the subject factor effect is avoided, the audiometry result can be obtained accurately and objectively, the method is quick and noninvasive, and the speech identification ability determination of the testee, differential diagnosis of deafness and treatment of deaf persons are facilitated.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Speech processing method, device and terminal
InactiveCN104599675AImprove experienceRemove and only remove background noiseSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumCommunication quality
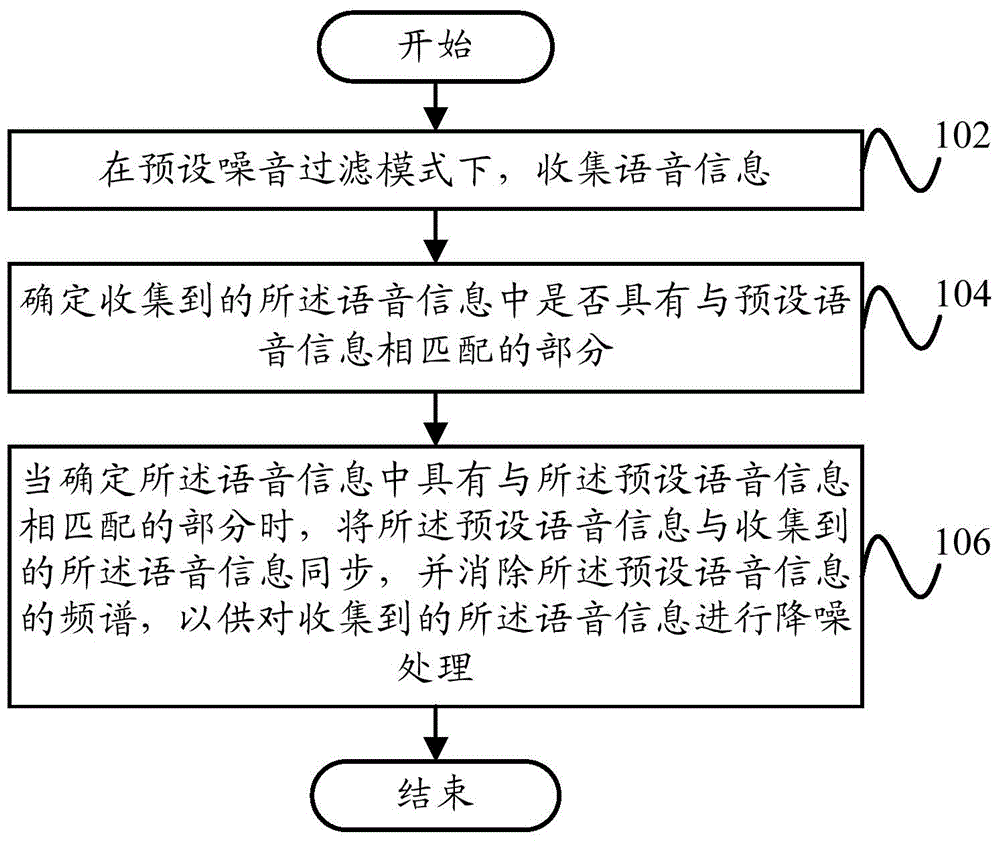
The invention provides a speech processing method, device and terminal. The method includes in a preset noise filtering mode, collecting speech information; determining whether the collected speech information contains the part matching with the preset speech information or not; if so, synchronizing the preset speech information with the collected speech information, and eliminating the spectrum of the preset speech information to perform noise reduction on the collected speech information. By the aid of the technical scheme, the background noise caused by the preset speech information can be eliminated only, the problem that normal speech except for noise produced by dual microphone noise reduction is eliminated is avoided, the noise eliminating accuracy and communication quality are improved, and the user's experience is improved.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
High-frequency cacophony processing method and analyzing method
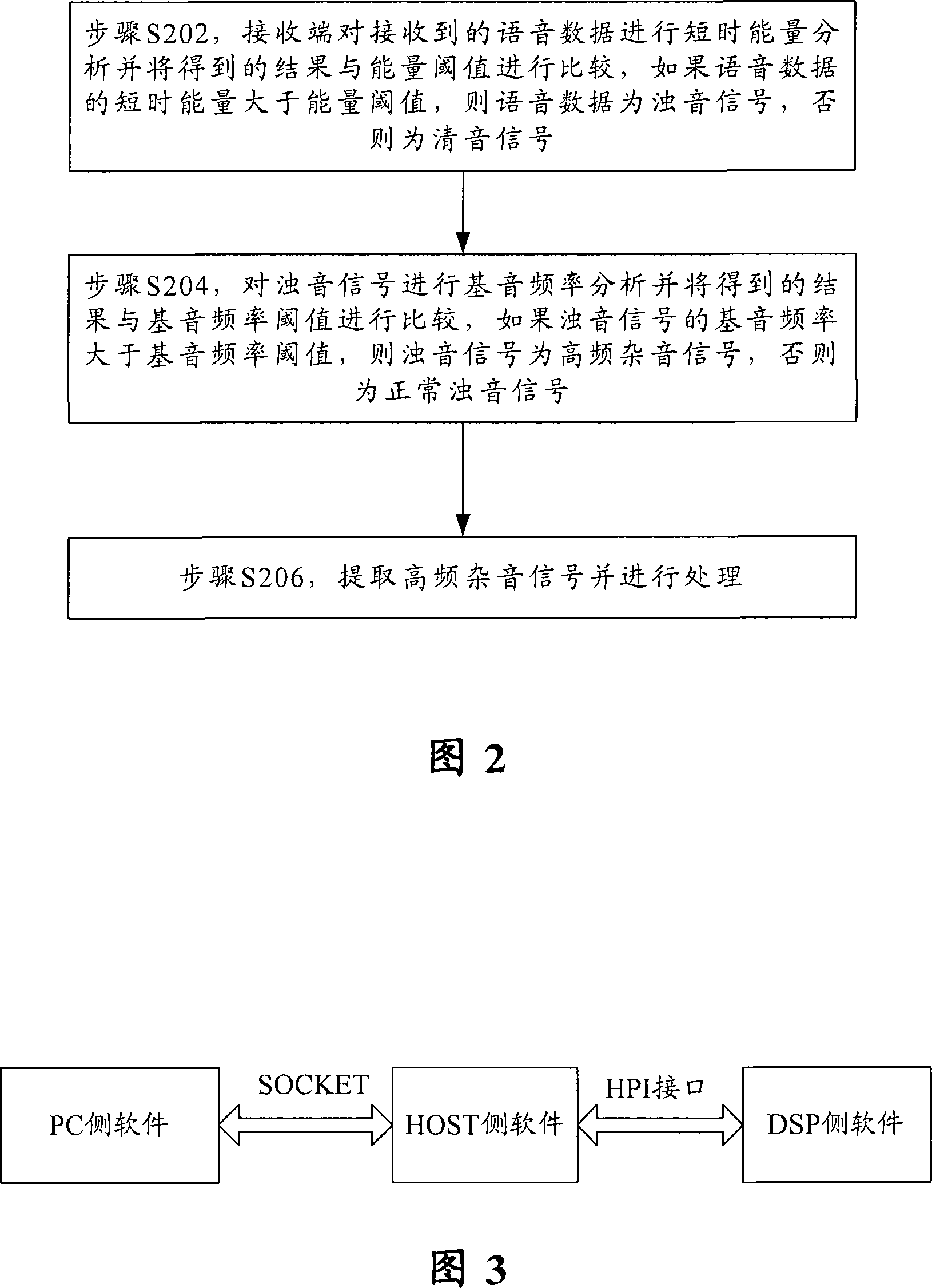
The invention provides a high-frequency cracks processing method which comprises that: the first step: a receiving terminal has a short-time energy analysis on received speech data; the short-time energy of the achieved speech data is compared with an energy threshold value; if the short-time energy of the speech data is greater than the energy threshold value, the speech data is a sonant signal, otherwise, the speech data is a surd signal; the second step: the sonant signal is processed by basetone frequency analysis and the basetone frequency of the received sonant signal is compared with a basetone frequency threshold value; if the basetone frequency of the sonant signal is greater than the basetone frequency threshold value, the sonant signal is a high-frequency cracks signal, otherwise, the sonant signal is a normal sonant signal; the third step: the judged high-frequency cracks signal is analyzed and processed. The invention also provides a high-frequency cracks analytical method. Through the high-frequency cracks processing method and the analytical method provided by the invention, the high-frequency cracks in the normal speech signal can be judged and data source is recorded, further the cause for producing the high-frequency cracks is analyzed, thereby solving the produced problems.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for modulating listener attention toward synthetic formant transition cues in speech stimuli for training
InactiveUS20070111173A1Increase salienceImprove accuracyElectrical appliancesTeaching apparatusFormantSpeech sound
A method on a computing device for enhancing the memory and cognitive ability of an older adult by requiring the adult to differentiate between rapidly presented stimuli. The method utilizes a sequence of phonemes from a confusable pair which are systematically manipulated to make discrimination between the phonemes less difficult or more difficult based on the success of the adult, such as processing the consonant and vowel portions of the phonemes by emphasizing the portions, stretching the portions, and / or separating the consonant and vowel portions by time intervals. As the adult improves in auditory processing, the discriminations are made progressively more difficult by reducing the amount of processing to that of normal speech. Introductory phonemes may each include a blend of a formant-synthesized phoneme and an acoustically naturalistic phoneme that substantially replicates the spectro-temporal aspects of a naturally produced phoneme, with the blends progressing from substantially natural-sounding to substantially formant-synthesized.
Owner:POSIT SCI CORP
Voice evaluation method and device
ActiveCN104464755AReduce the impactImprove accuracySpeech recognitionAbnormal voiceSpeech identification
The invention provides a voice evaluation method and device. The voice evaluation method comprises the steps that voice data to be tested are received; voice recognition is conducted on the voice data to be tested to obtain voice recognition data; the voice recognition data are analyzed to defect whether the voice recognition data are abnormal voice data or not, and an evaluation result of the voice data to be tested is generated according to a detection result. The voice evaluation method can detect and recognize abnormal voice, so that abnormal voice is deleted from the voice to be tested, the abnormal voice can not join evaluation of normal voice, influence of the abnormal voice on the evaluation result is greatly reduced, the accuracy of the evaluation result is improved, the evaluation requirement of a user is met, and user experience is improved.
Owner:IFLYTEK CO LTD
Method for modulating listener attention toward synthetic formant transition cues in speech stimuli for training
ActiveUS20070054249A1Improve “ noisy ” sensory representationShorten time constantReadingElectrical appliancesNormal speechConsonant
A method on a computing device for enhancing the memory and cognitive ability of an older adult by requiring the adult to differentiate between rapidly presented stimuli. The method utilizes a sequence of phonemes from a confusable pair which are systematically manipulated to make discrimination between the phonemes less difficult or more difficult based on the success of the adult, such as processing the consonant and vowel portions of the phonemes by emphasizing the portions, stretching the portions, and / or separating the consonant and vowel portions by time intervals. As the adult improves in auditory processing, the discriminations are made progressively more difficult by reducing the amount of processing to that of normal speech. Introductory phonemes may each include a blend of a formant-synthesized phoneme and an acoustically naturalistic phoneme that substantially replicates the spectro-temporal aspects of a naturally produced phoneme, with the blends progressing from substantially natural-sounding to substantially formant-synthesized.
Owner:POSIT SCI CORP
Electro-larynx
InactiveUS7212639B1Improve approximationFacilitates production of substantially natural sounding speechTracheaeElectric controllersFrequency spectrumGlottis
An improved electro-larynx includes a linear transducer and / or an improved waveform generator. The improved electro-larynx sets up a sound wave within the pharynx of the user which closely approximates a normal glottal excitation. The linear transducer preserves the harmonic structure of a glottal source wave generated by the waveform generator and translates it into a vibration. The transducer includes an armature assembly, suspension assembly, and coupler disk coupled together to move in concert. The armature assembly vibrates as a function of the desired and input glottal source wave, which in turn causes an immediate and corresponding vibration of the coupler disk. The suspension assembly constrains armature movement to one dimension and provides additional compliance. The coupler disk includes a substantially flat surface suitable for engaging the surface of a user's throat and vibrates as a linear function of the input glottal source wave. The improved waveform generator produces a relatively good approximation of an actual glottal source waveform by preferably deriving it from actual voice data and having the effects of the modulation of the vocal tract removed. As a result, the harmonic structure of the glottal source waveform has overtones which drift in frequency, similar to normal glottal excitations. The waveform generator also allows user adjustment of the pitch and amplitude of the glottal source wave and smoothes out any distortions caused by the process of obtaining the glottal data used to generate the glottal source wave. The waveform generator bolsters the frequency response at the high end of the spectrum to compensate for any roll-off, yielding a frequency response spectrum of about 20–5 Khz. The responsiveness of the linear transducer allows the glottal source wave's pitch, amplitude, and harmonic structure to be communicated through the coupler disk and realistic glottal source waves to be transduced into the user's pharynx, resulting in the production of substantially normal speech.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Defense method and device for speech recognition model based on CycleGAN
The invention discloses a defense method and device for a speech recognition model based on a CycleGAN. The defense method trains a CycleGAN model by utilizing an adversarial sample data set and a normal speech data set, GA-B generators in the model can perform denoising operation on the adversarial sample, and the normal sample is not influenced, and the normal sample is integrated into the speech recognition model to be used as a front-end processing device, so that the recognition precision of the speech recognition model is improved, the speech recognition model can resist the attack of the adversarial sample, and the robustness of the speech recognition model is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Sound quality adjusting apparatus and sound quality adjusting method
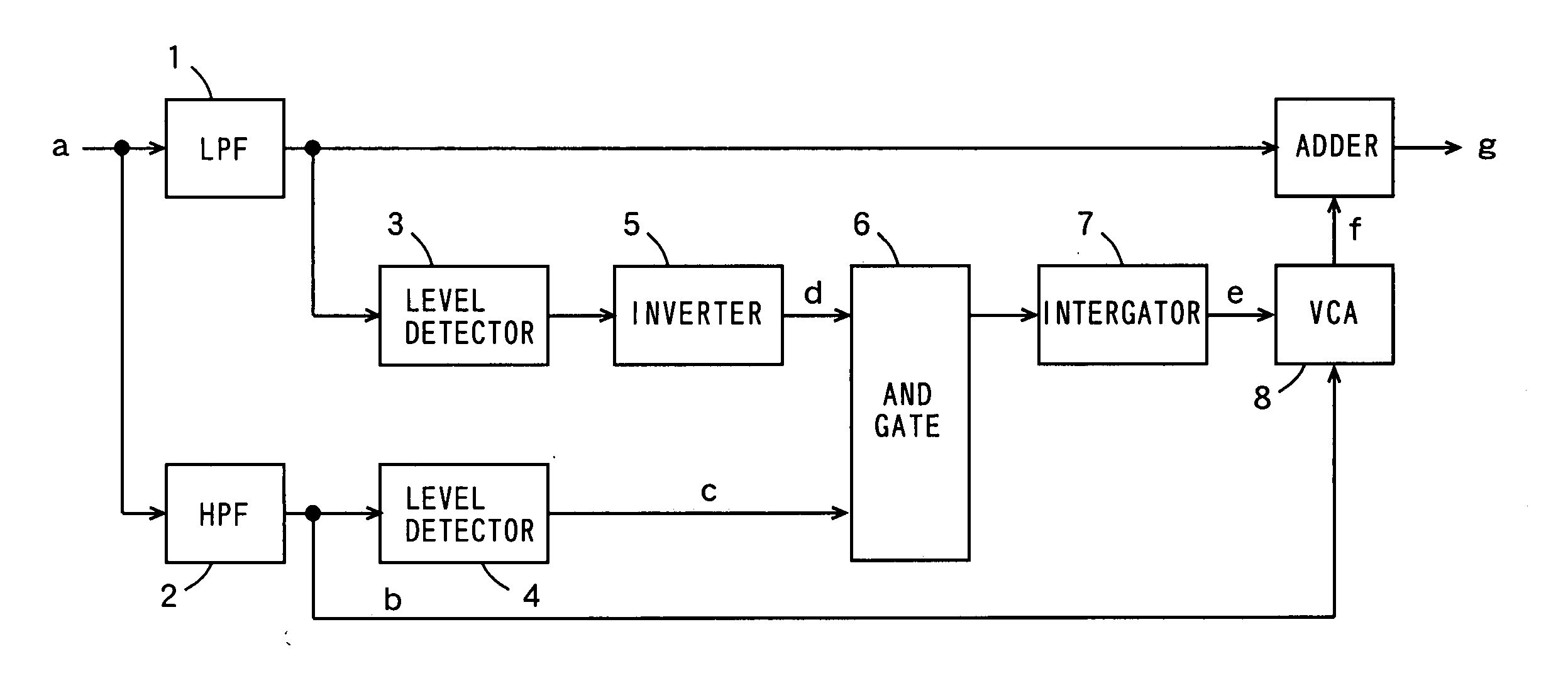
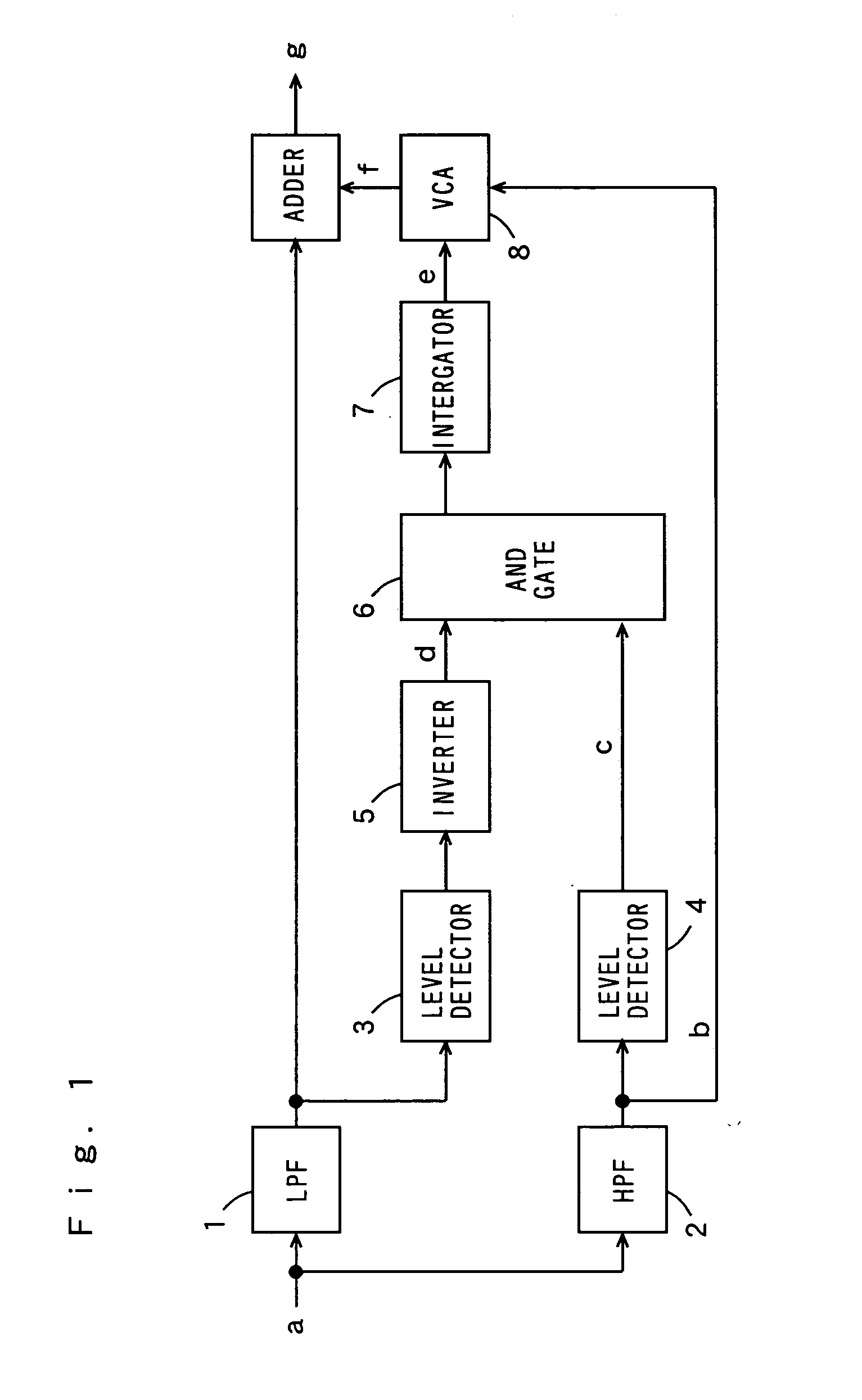
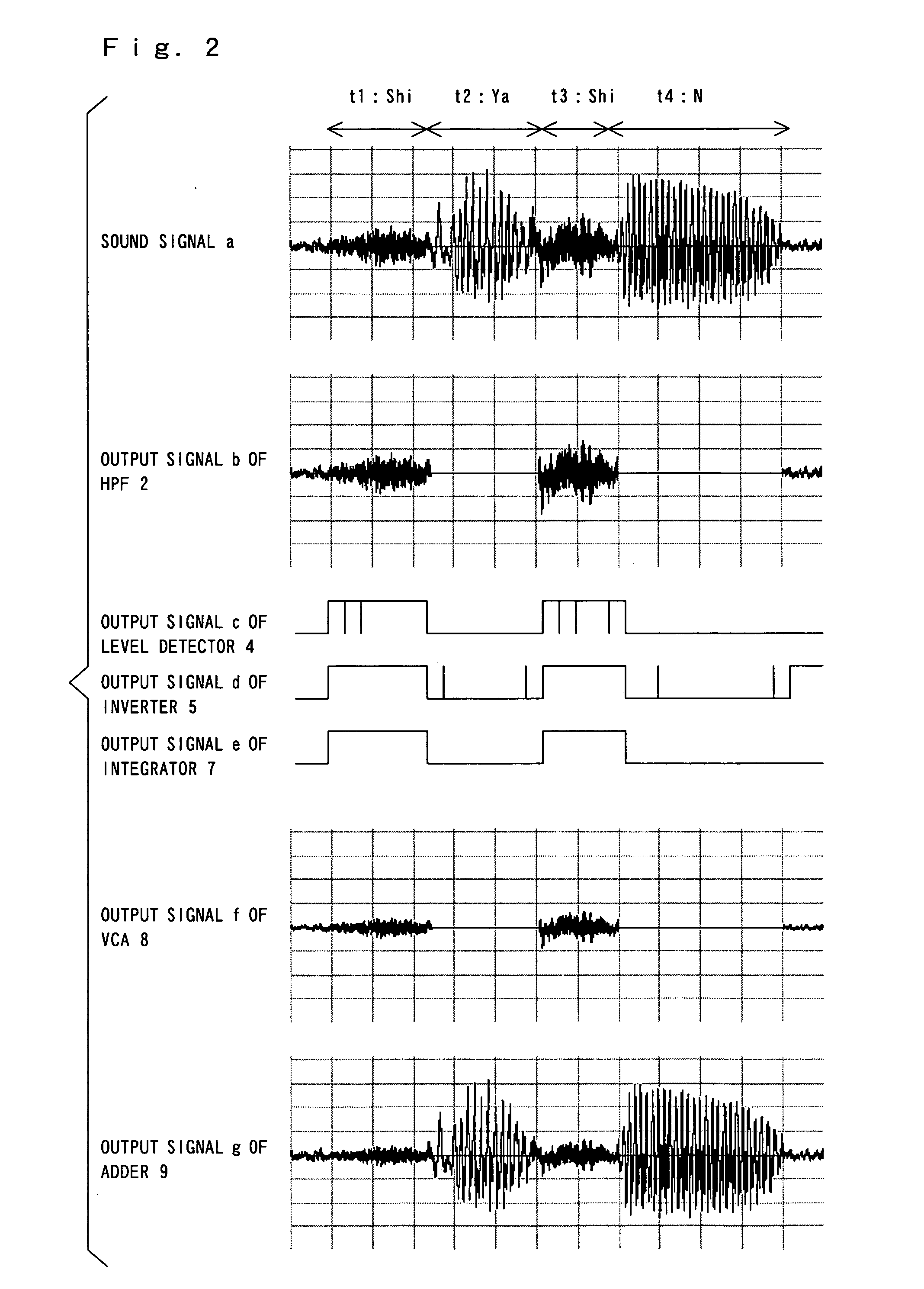
InactiveUS20060239472A1Reducing sibilantSpeech analysisAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlIntegratorEngineering
An LPF extracts a medium and low frequency component of an inputted sound signal. An HPF extracts a high and low frequency component in the inputted sound signal. One of the two level detectors determines whether the medium and low frequency component exists by detecting the level of an output signal of the LPF. The other level detector determines whether the high frequency component exists by detecting the level of an output signal of the HPF. An inverter inverts the level of an output signal of the one level detector. An AND gate operates an AND of an output signal of the inverter and an output signal of the other level detector. An integrator integrates an output signal of the AND gate. A VCA determines that the sound signal is a sibilant when the medium and low frequency component does not exist and when the high frequency component exists, and attenuates the level of the output signal of the HPF, while the VCA determines that the sound signal is a normal speech sound when the medium and low frequency component exist and outputs the output signal of the HPF without modification. An adder synthesizes the output signal of the LPF and the output signal of the VCA by addition.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
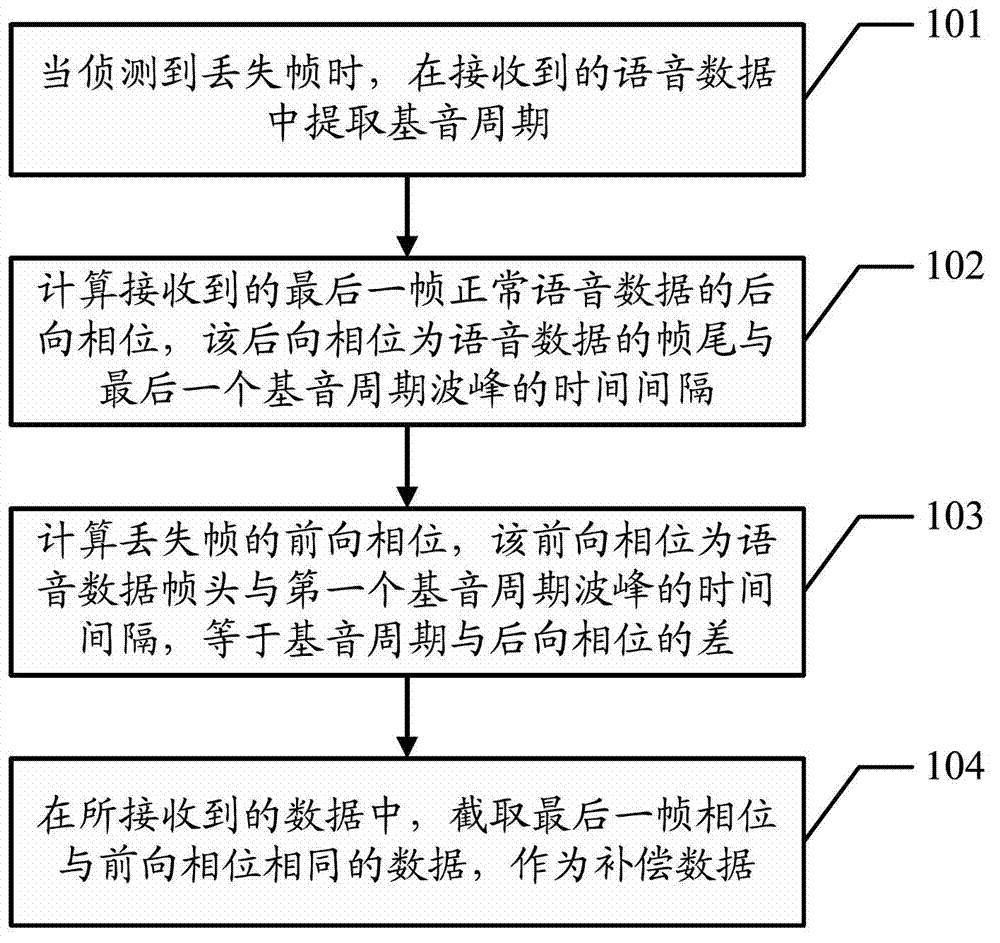
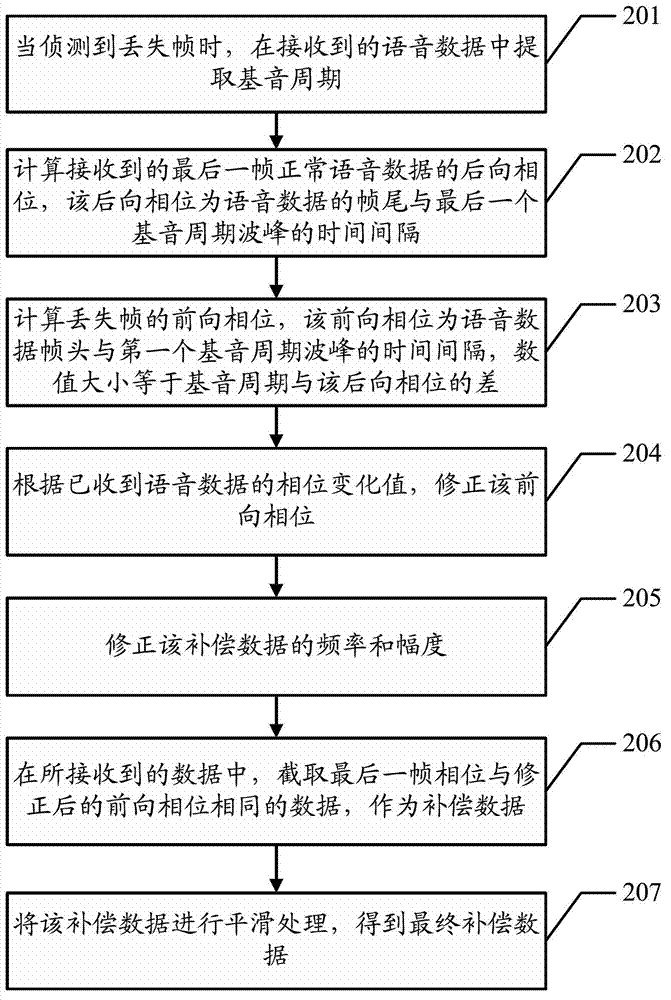
Speech data packet loss compensation method and device
ActiveCN102833037ASmall distortionNo delayError preventionSpeech analysisPacket lossComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses a speech data packet loss compensation method and device which are used for compensating for the lost speech data packet. The method comprises the following steps of: when the lost frame is detected, extracting the pitch period from the received speech data; calculating the backward phase of the received last frame of normal speech data; calculating the forward phase of the lost frame according to the backward phase; and capturing the last frame of data with the same phase as the forward phase from the received data as the compensation data.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
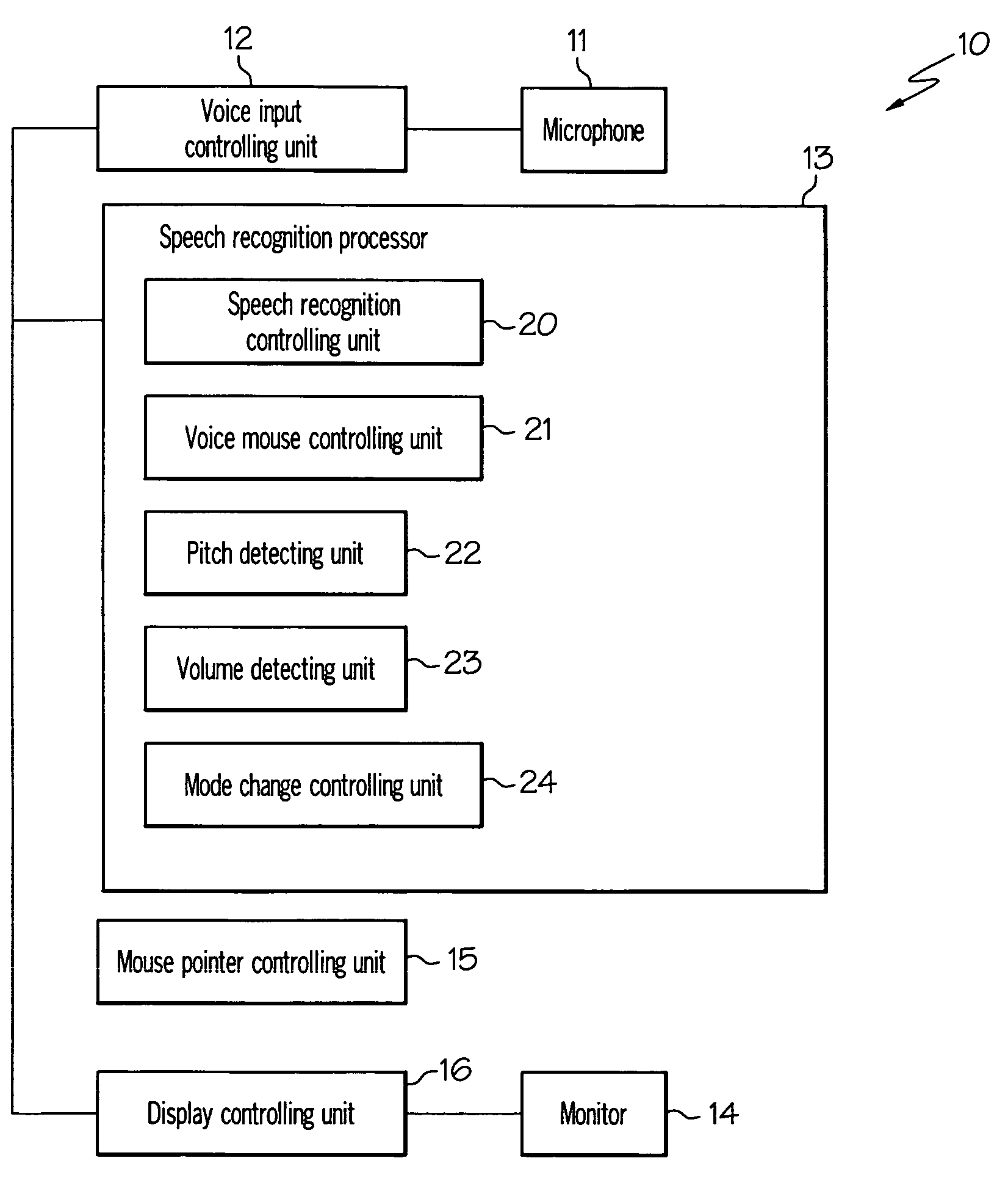
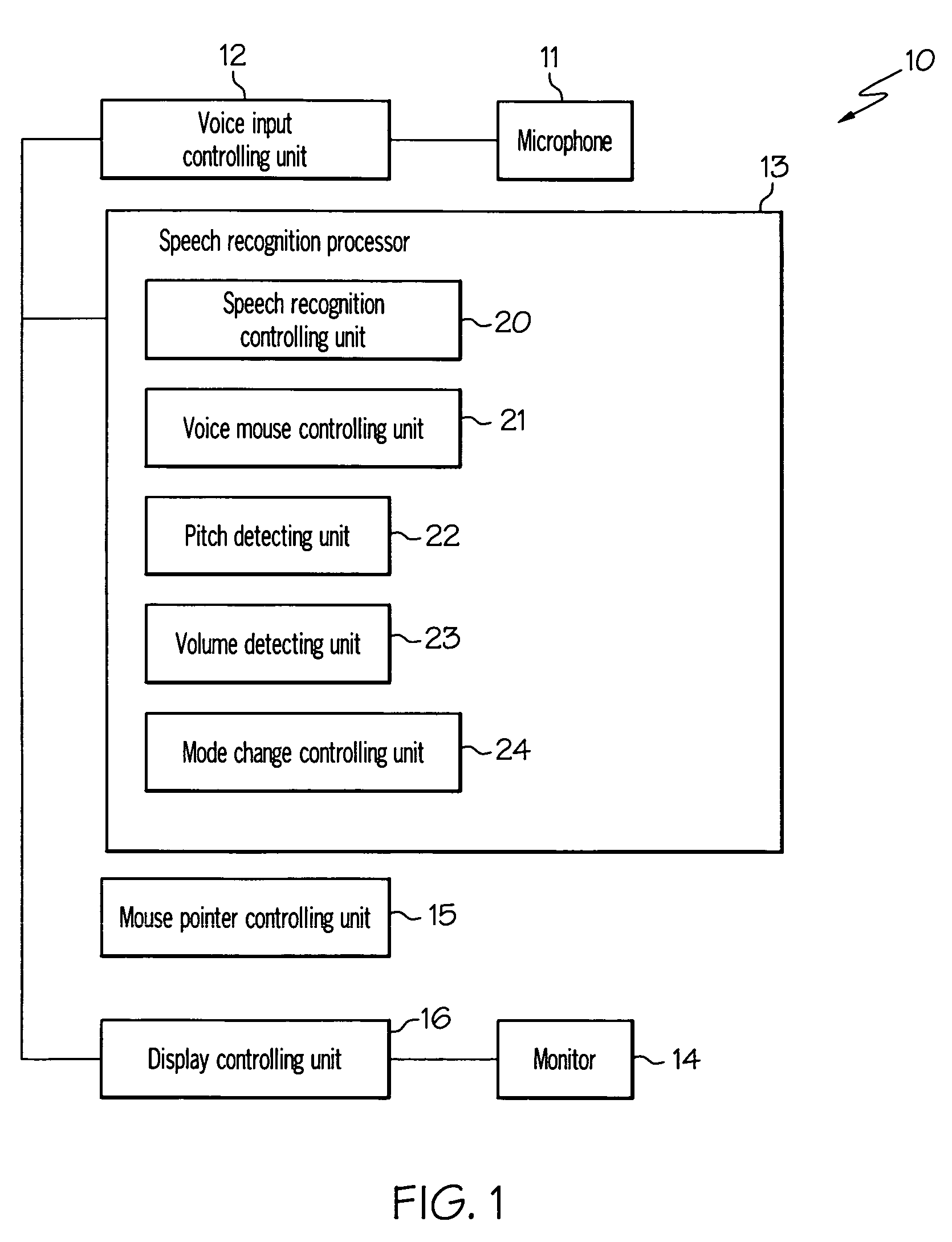
Computer, display control device, pointer position control method, and program
InactiveUS20080215335A1Input/output for user-computer interactionSpeech recognitionPosition controlSpeech sound
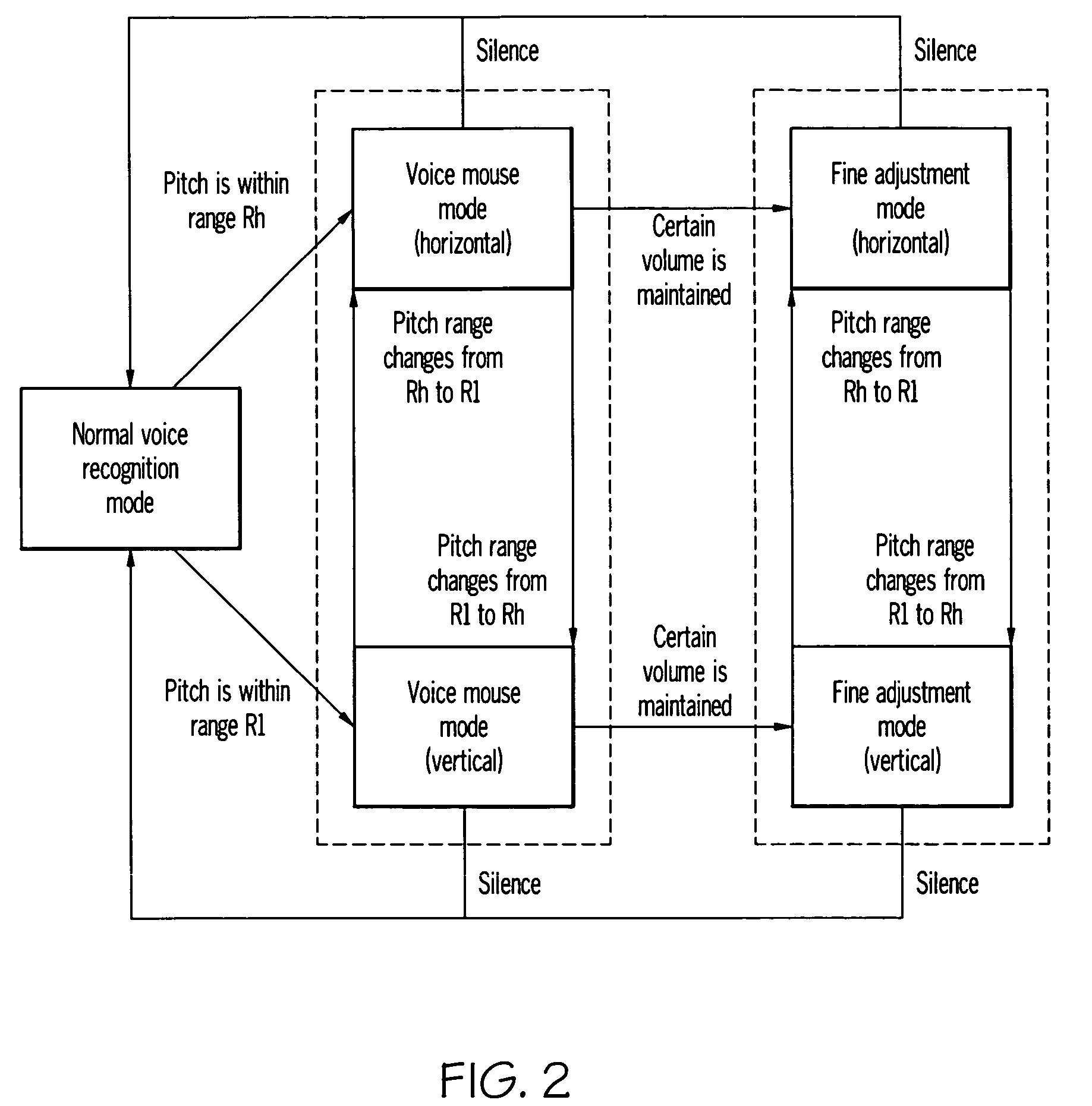
To provide a pointer position control method and the like for manipulating a pointer more easily. The user moves the pointer P two-dimensionally and perform click and other operations by using only “voice”—by varying the volume and pitch of produced voice without uttering any specific command. The user moves the pointer P by varying the volume and switches the travel direction of the pointer P by changing the pitch. Also, by stopping to vary the volume, the user can automatically enter a fine adjustment mode in which the user can make fine adjustments. Furthermore, the user can perform a click by stopping to produce voice suddenly and return to normal speech recognition mode by keeping silent.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Estimation method for fundamental frequency of Chinese whispered speech
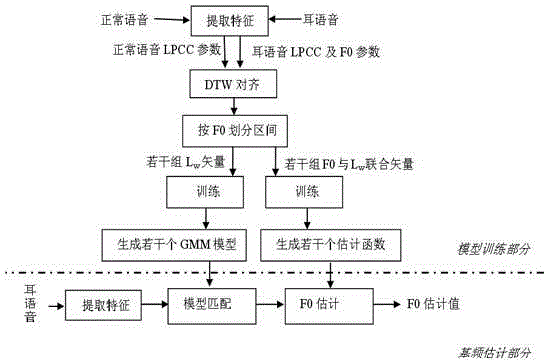
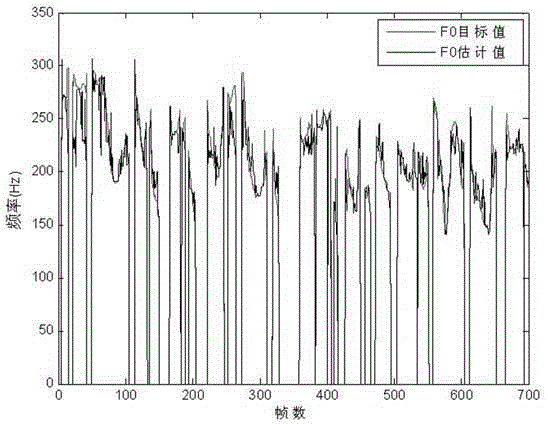
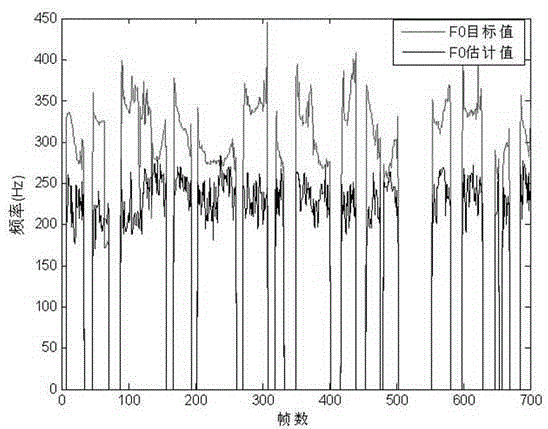
The invention discloses an estimation method for the fundamental frequency of Chinese whispered speech. The estimation method concretely includes the steps that a whispered speech and normal speech database uniform in linguistic data is set up; LPCC parameters Lw of whispered speech, LPCC parameters Ln of normal speech and fundamental frequency parameters F0 are extracted, and DTW alignment is carried out according to Lw and Ln; F0 of the normal speech is divided within the range of 100-300 Hz at the interval of 5 Hz, and forty intervals are generated in total; aligned vectors are assigned to all the intervals according to F0 values of the normal speech, all whispered speech LPCC vectors in each interval are trained to be a GMM model, the combined vectors formed by all the whispered speech LPCC vectors and the F0 parameters of the normal speech in the corresponding interval are trained be to a GMM model to obtain an estimation function, and forty estimation functions are obtained in total; the LPCC parameters of the whispered speech are extracted and matched with all the GMM models to search for the optimum matching model, and then the F0 values of the whispered speech are estimated according to the estimation function of the model. The fundamental frequency of the whispered speech can be estimated, and the difficulty, caused by the loss of fundamental frequency information, of the Chinese whispered speech is effectively overcome.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
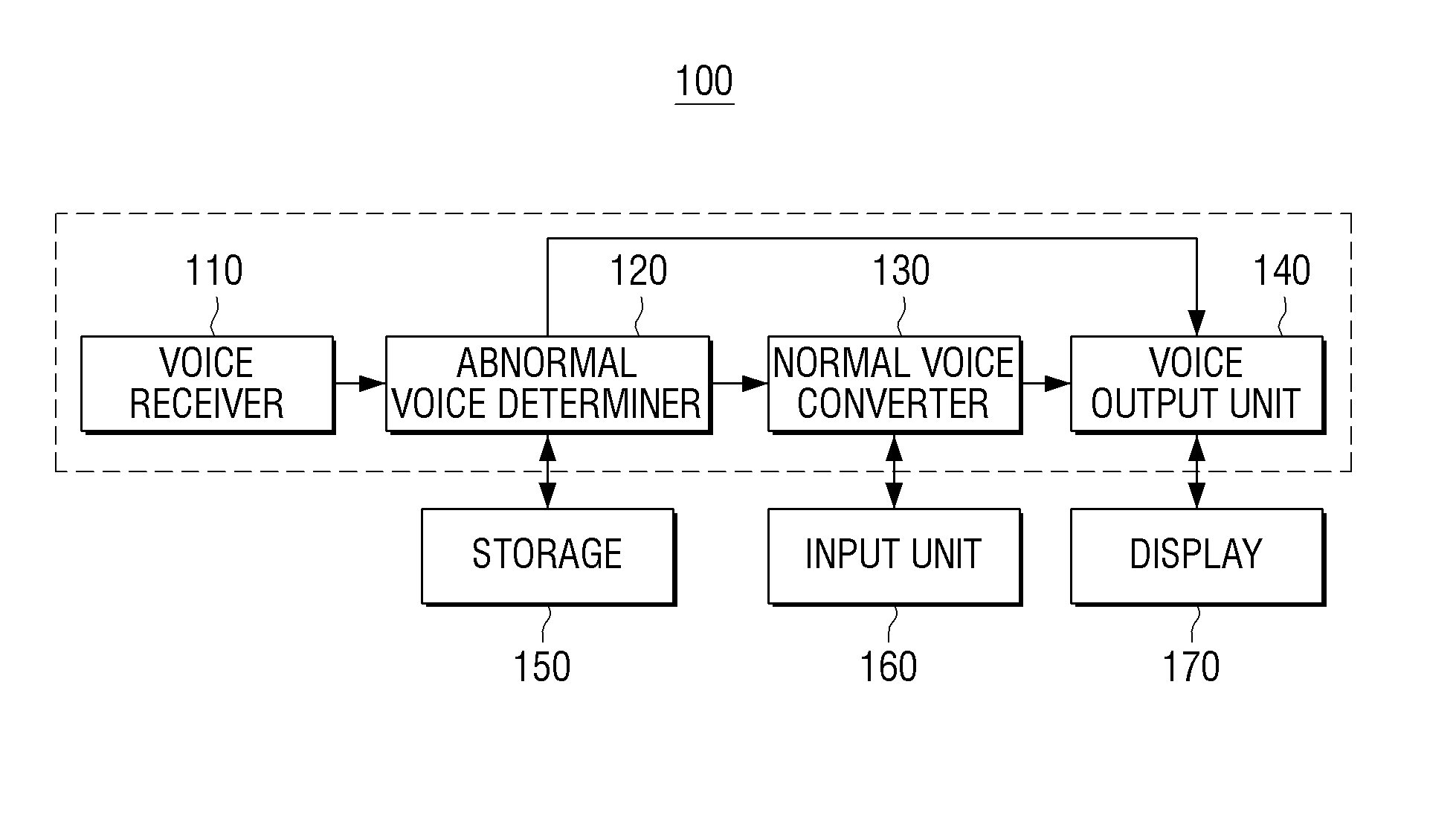
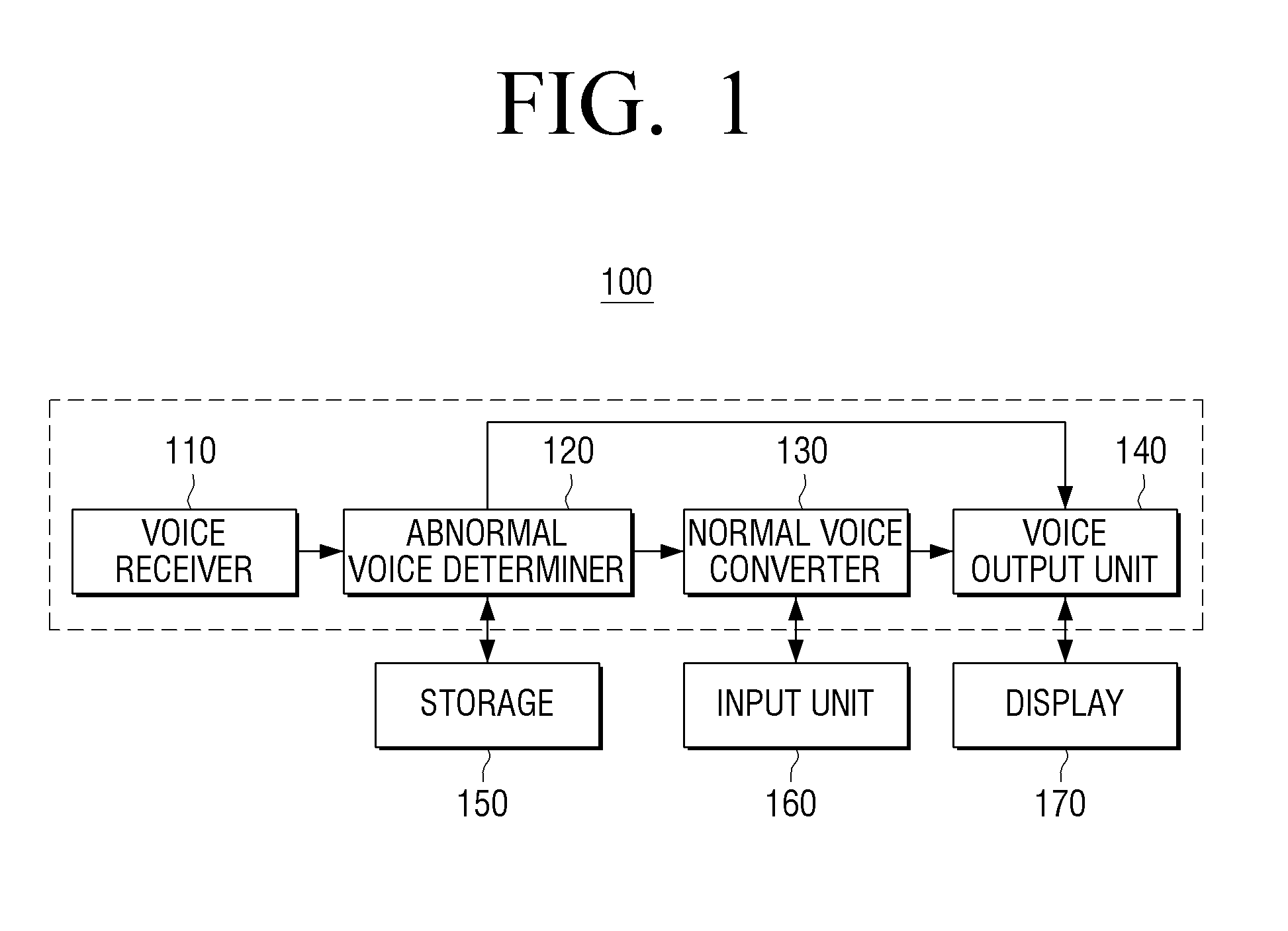
Voice converting apparatus and method for converting user voice thereof
A voice converting apparatus and a voice converting method are provided. The method of converting a voice using a voice converting apparatus including receiving a voice from a counterpart, analyzing the voice and determining whether the voice abnormal, converting the voice into a normal voice by adjusting a harmonic signal of the voice in response to determining that the voice is abnormal, and transmitting the normal voice.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and Oral Appliance for Improving Air Intake and Reducing Bruxism
ActiveUS20180207022A1Numerous medical conditionImprove performanceChiropractic devicesSnoring preventionDiseaseThroat
Provided is a soft flexible oral appliance having protuberances that mimic naturally occurring dental Tori. An upper, palatial appliance and a lower, mandibular appliance may be used in conjunction or separately to alleviate a variety of disorders, improve facial tone, and increase physical performance. The appliances are lightweight, thin, and do not prohibit normal speech patterns when in use Small protuberances are strategically molded along key surfaces of each appliance to stimulate nerves in the tongue and affect forward protrusion. Forward positioning of the tongue dilates the airways of the throat improving breathing while the use is sleeping, playing sports, or talking. It also reduces bruxing or grinding of the teeth. A method is further provided, for adding protuberances to other types of oral appliances, thereby conferring some of the benefits listed above on appliances originally intended for other dental uses.
Owner:DENTAL CHOICE HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com