Patents
Literature
567 results about "Tunneling field effect transistor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
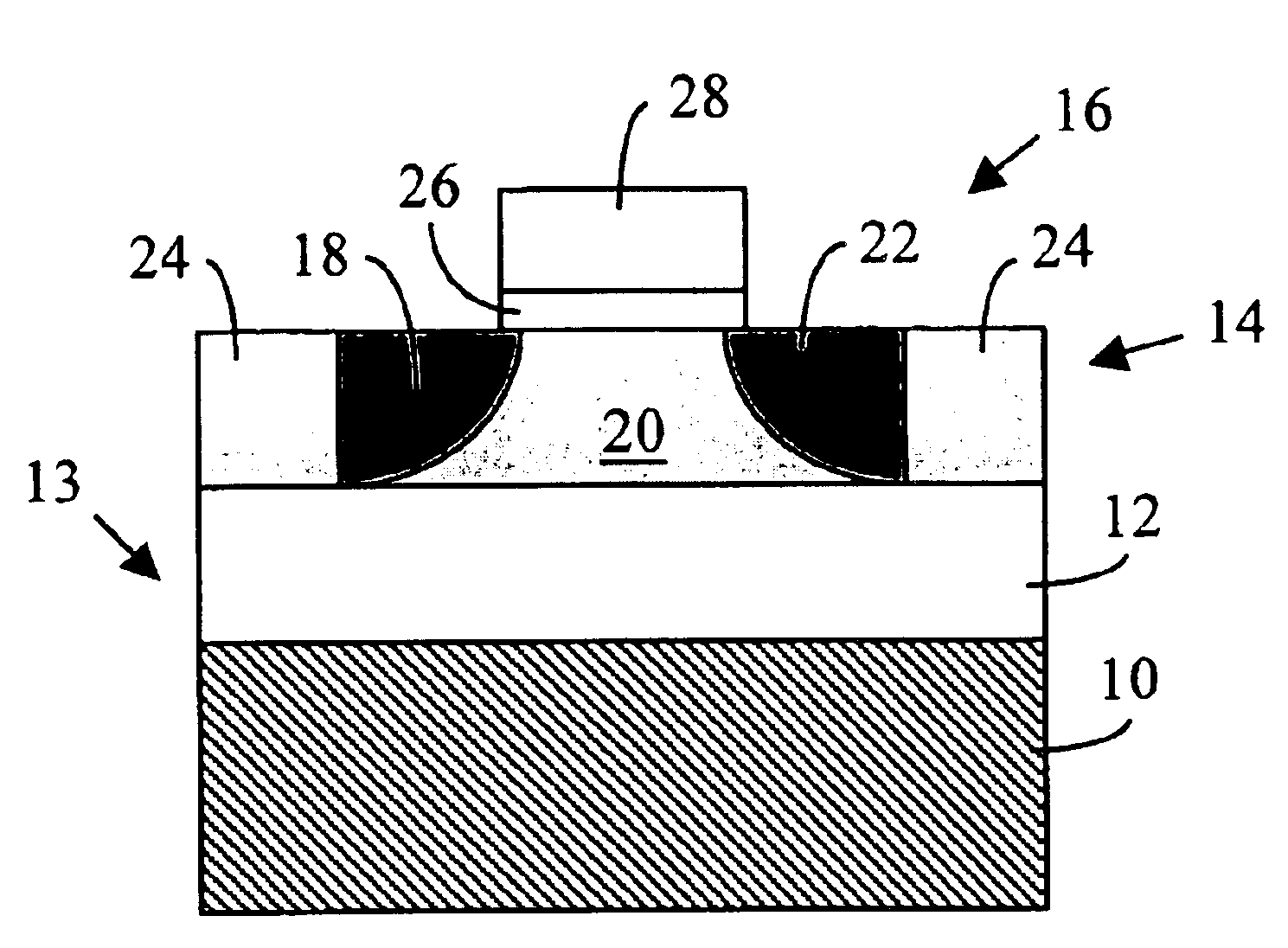
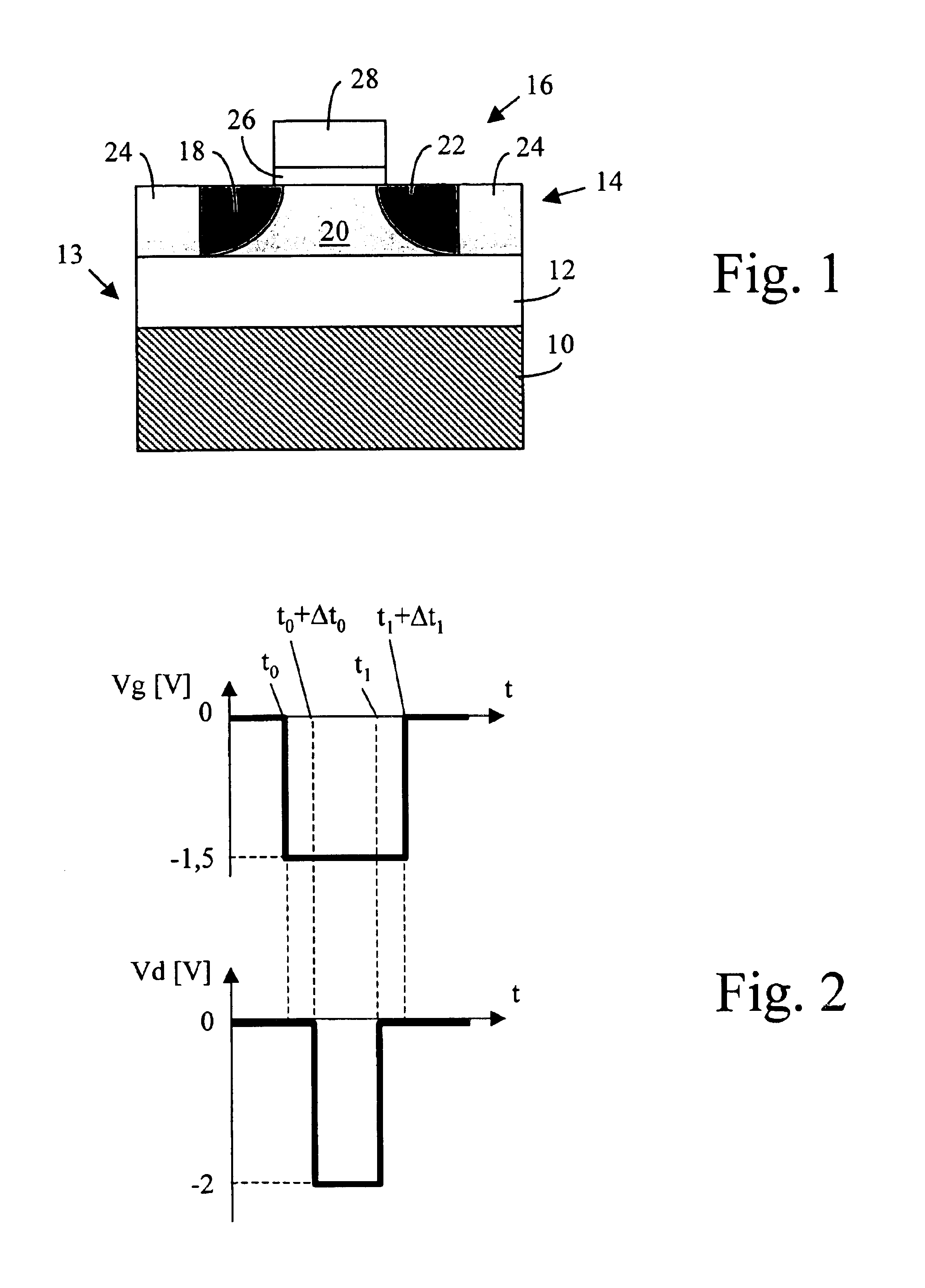
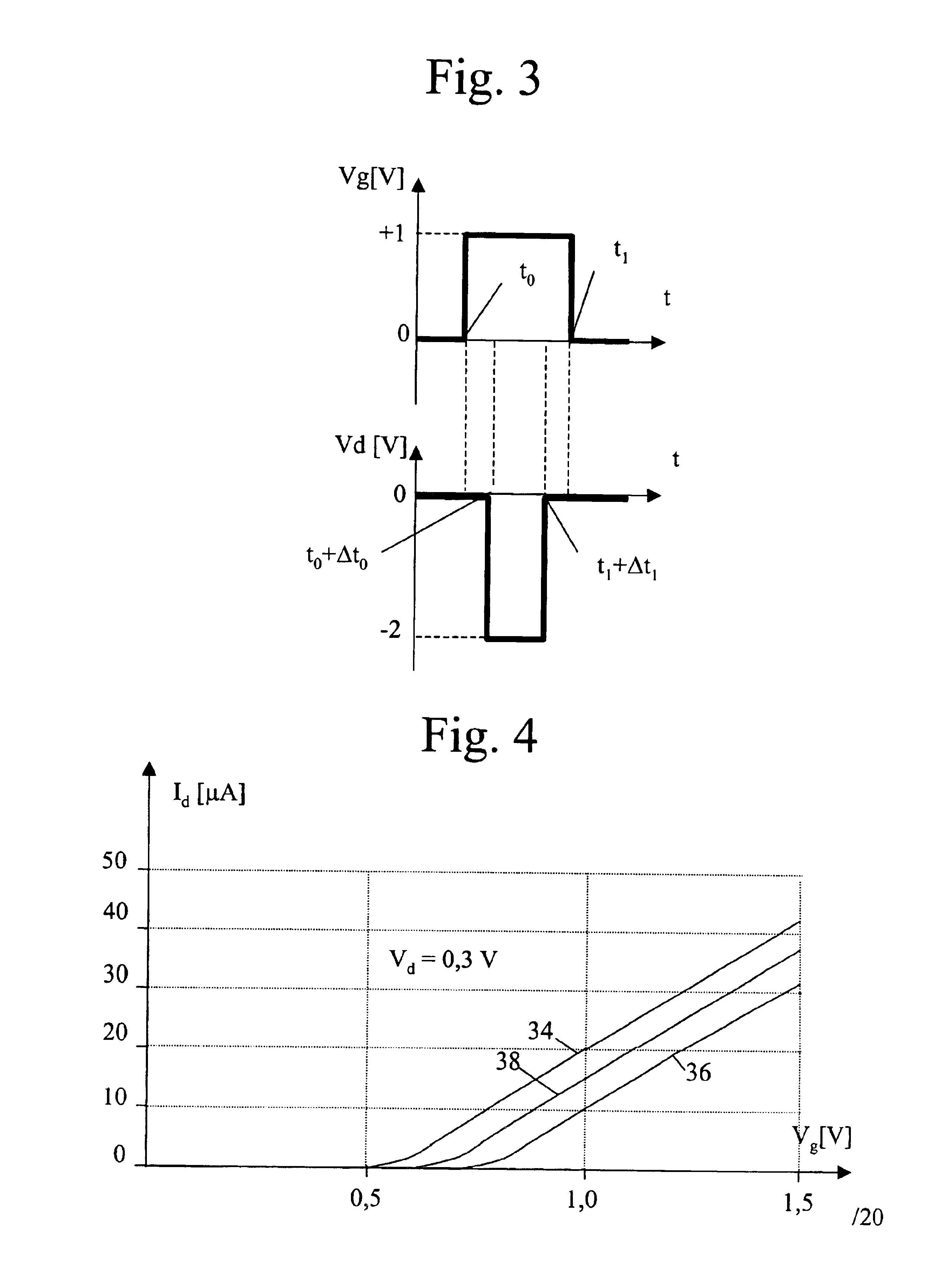
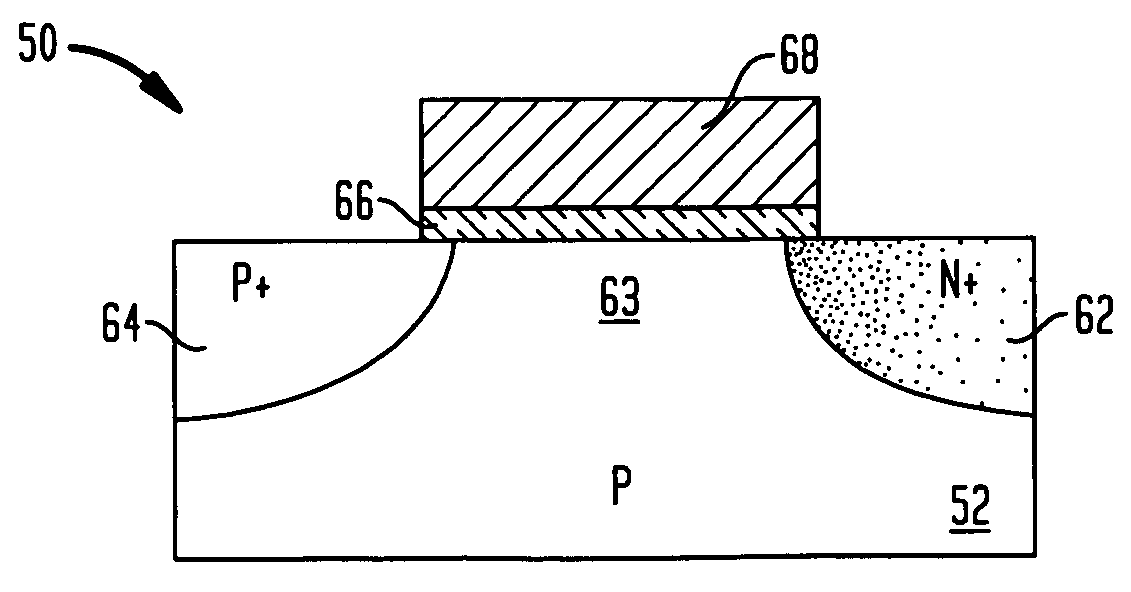
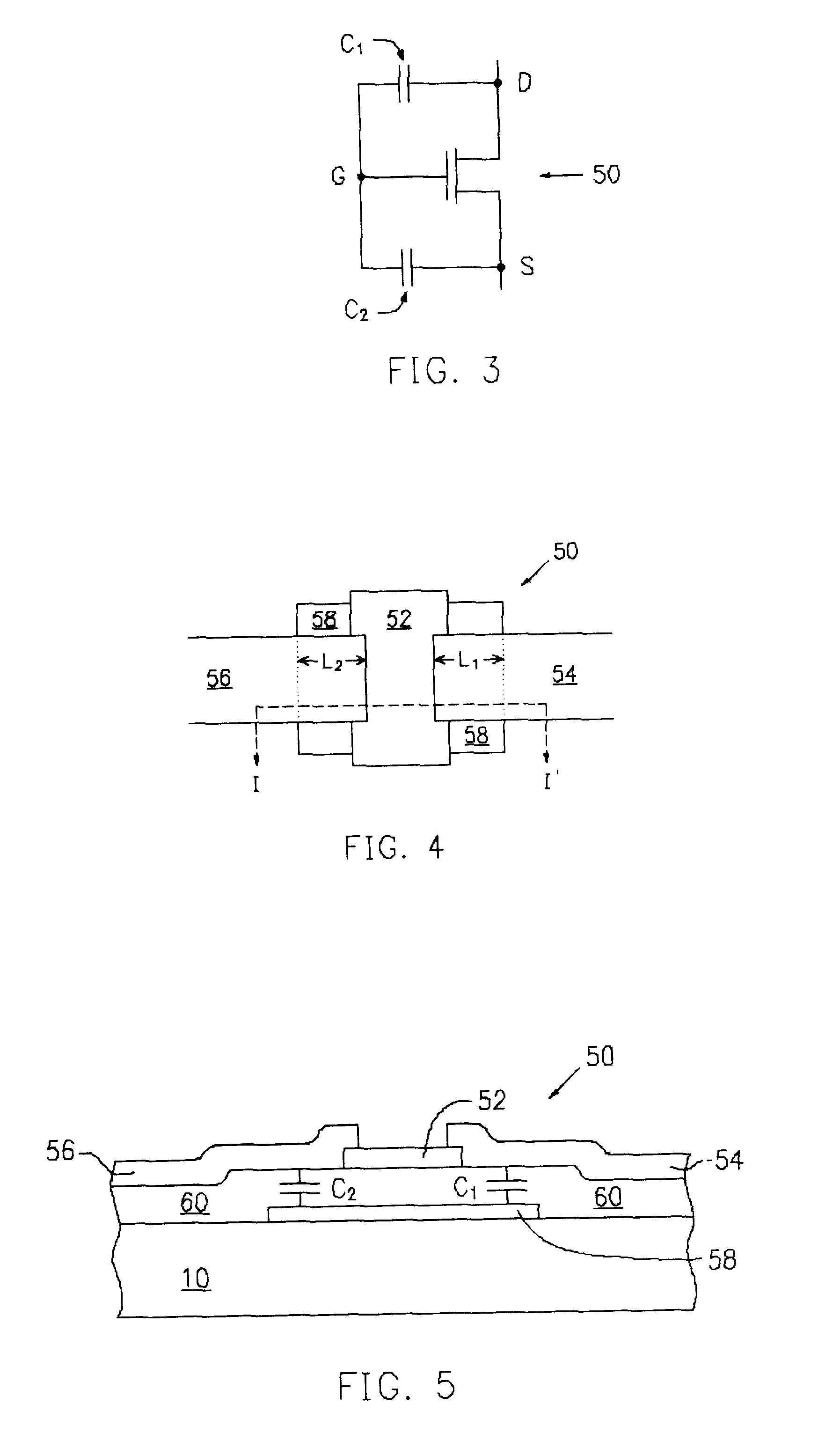
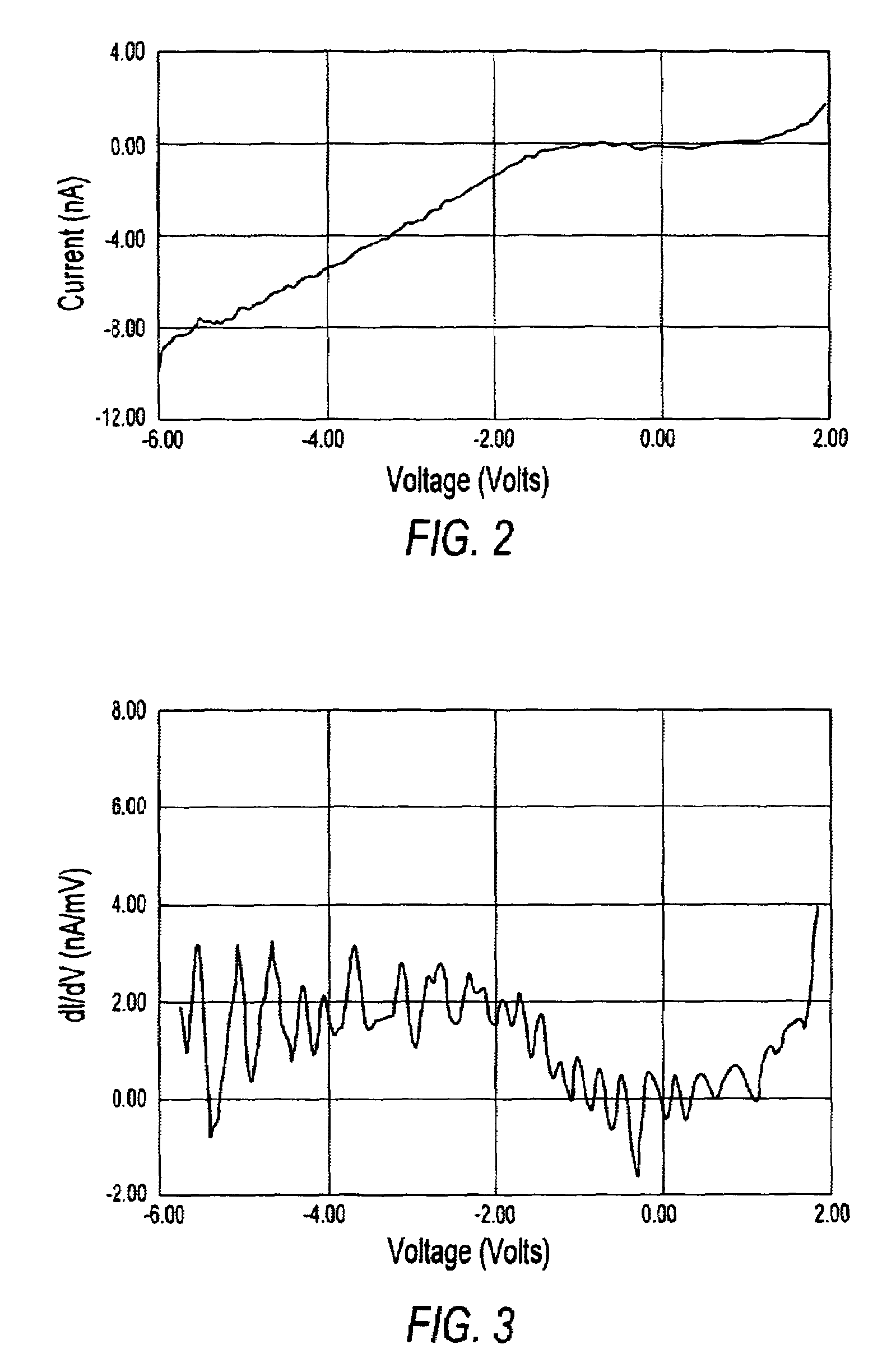
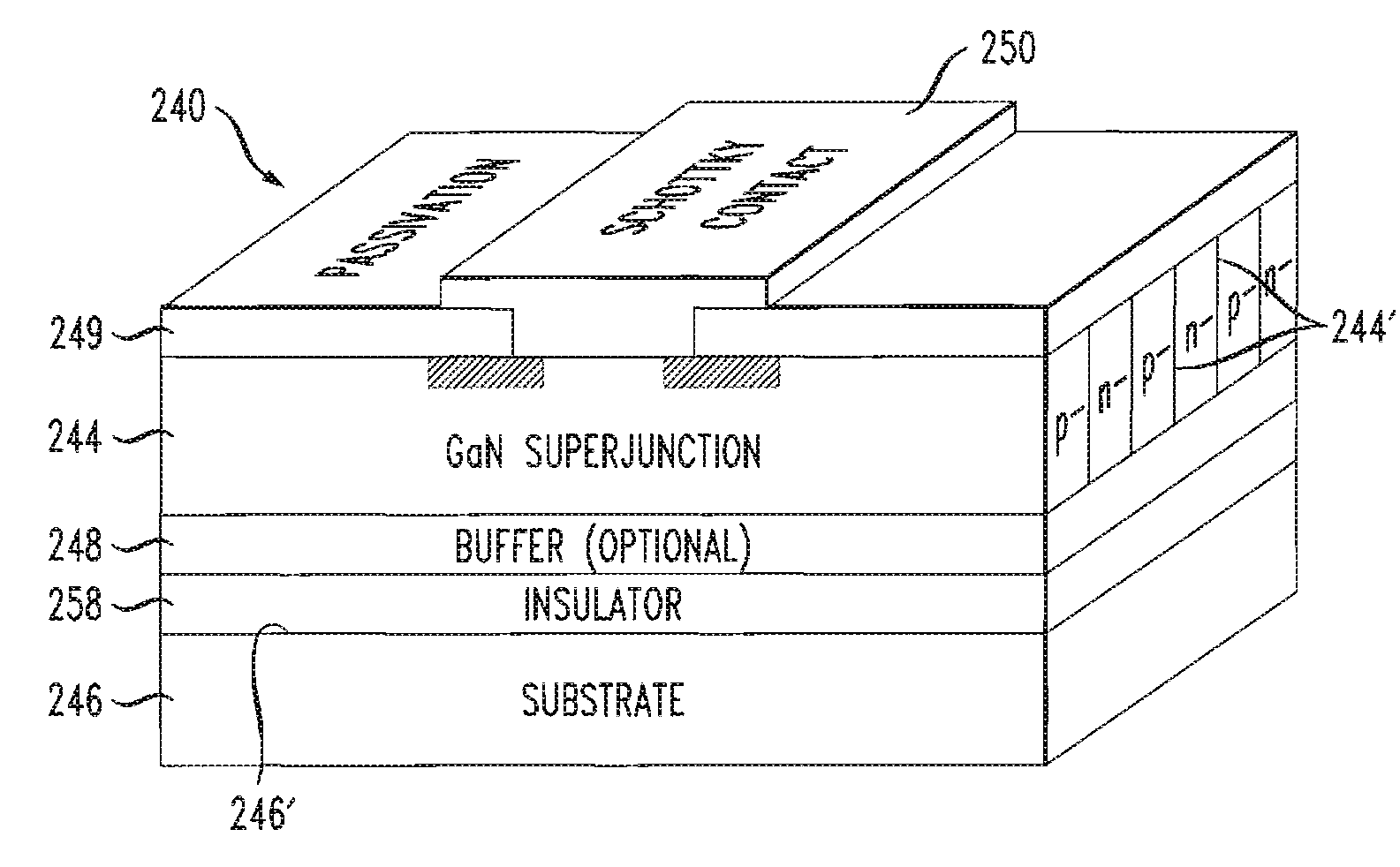
Tunneling field effect transistor (TFET) is a one type of upcoming emerging device. Generally, a MOSFET is used for low energy electronic devices. The structure of the tunneling field effect transistor is almost closer to the MOSFET, but, with different important switching mechanism.
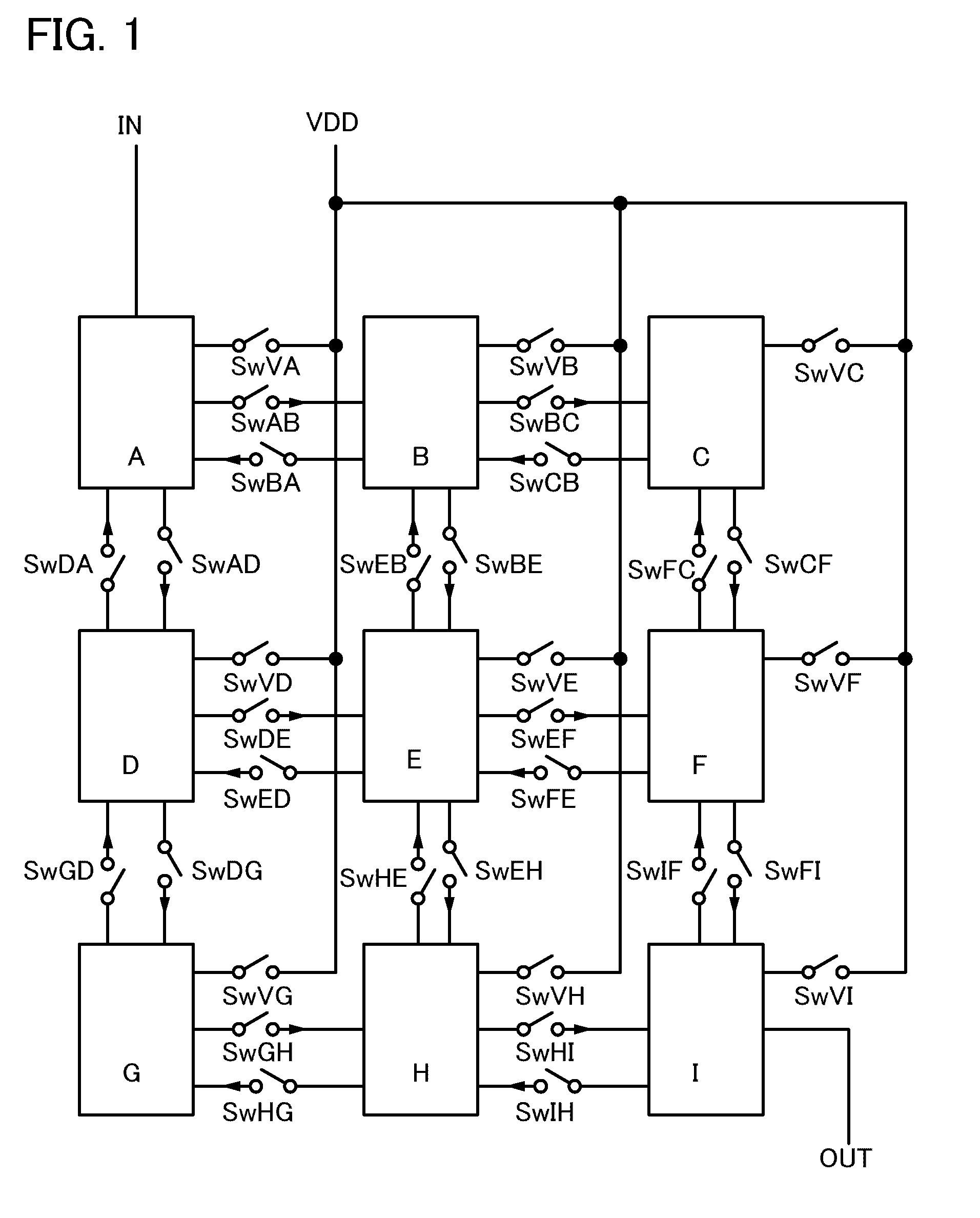
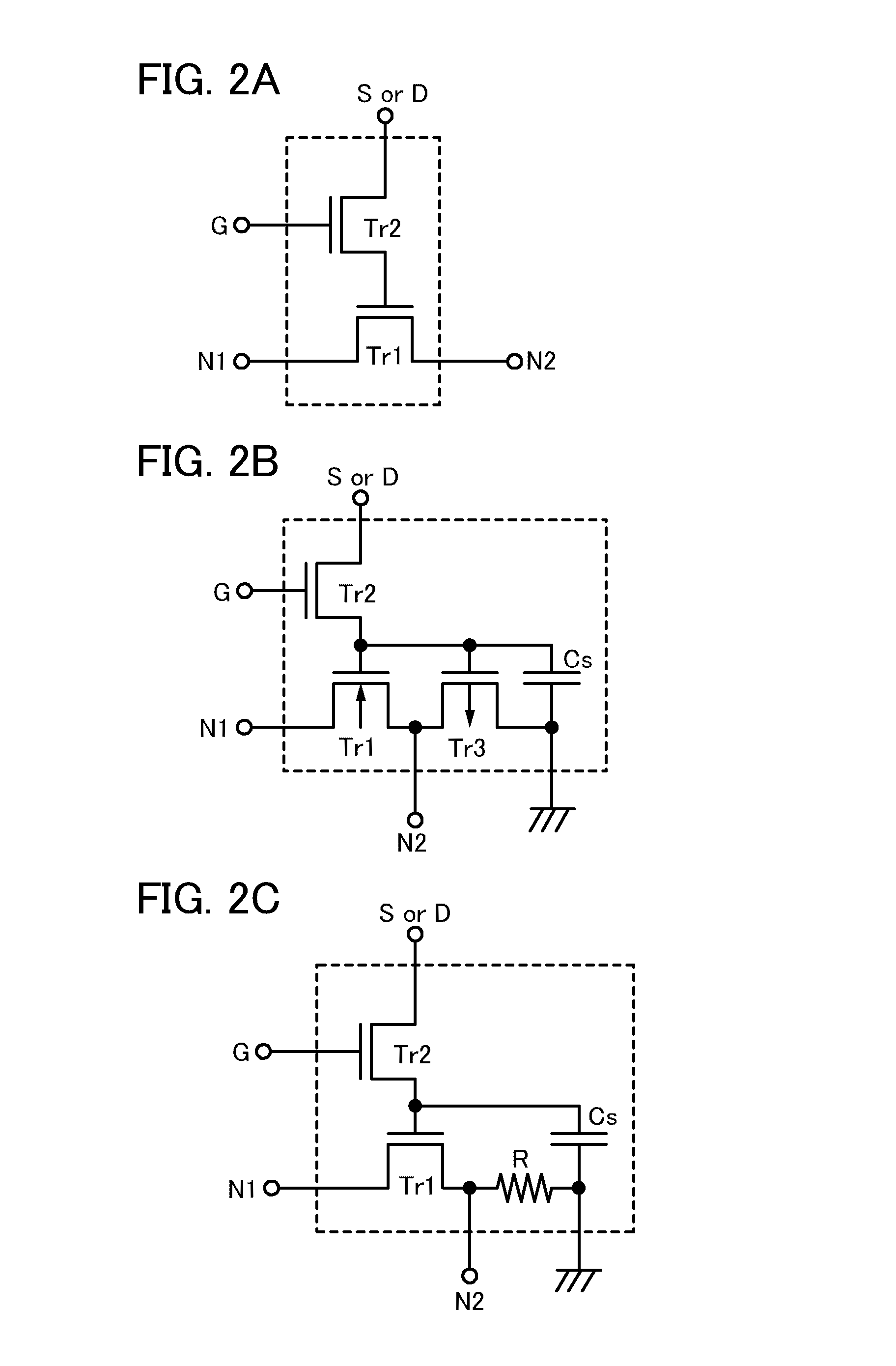
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS6925006B2Reduce in quantityImprove the level ofTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Heterojunction tunneling field effect transistors, and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070178650A1Increase currentEnhance junction currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeHeterojunctionDopant
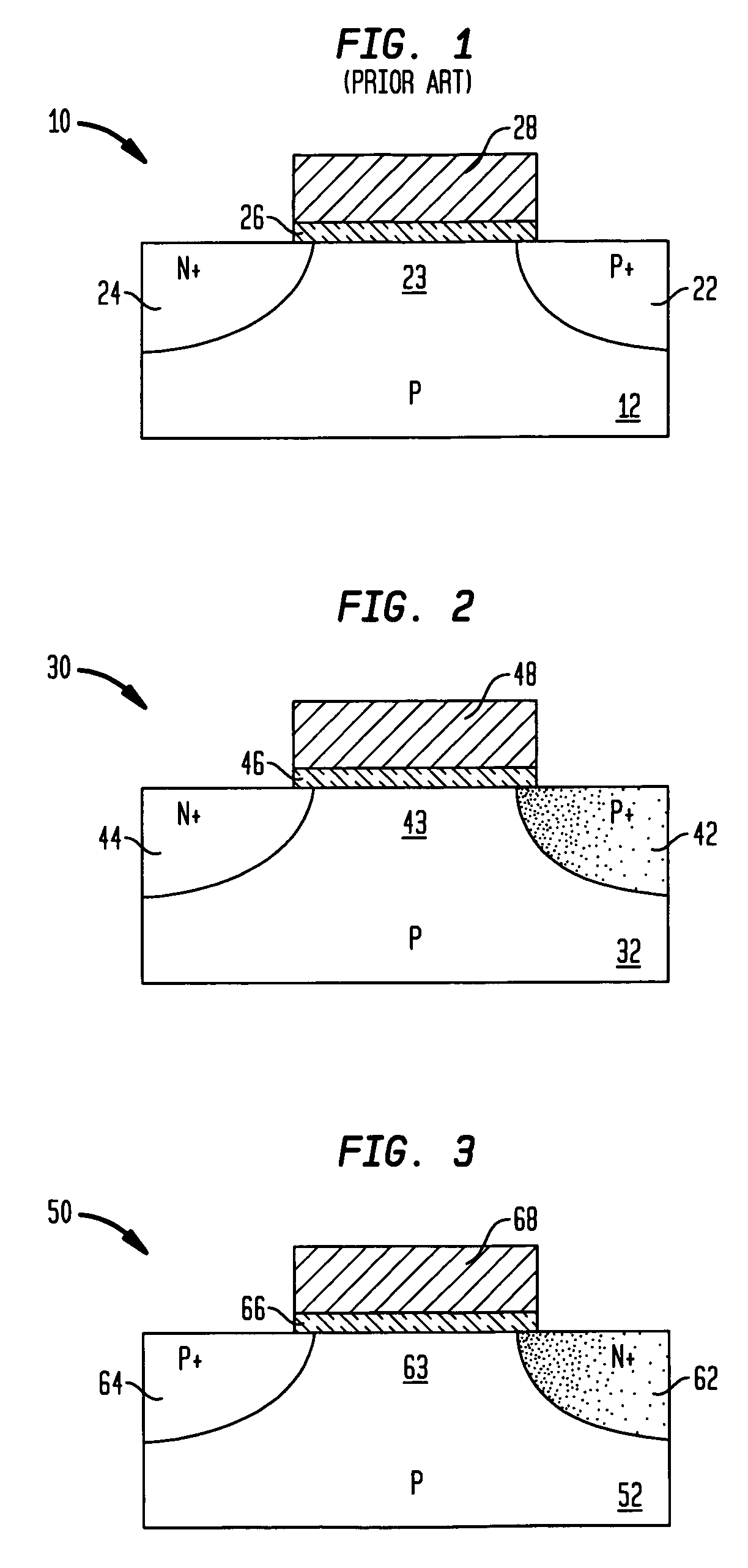
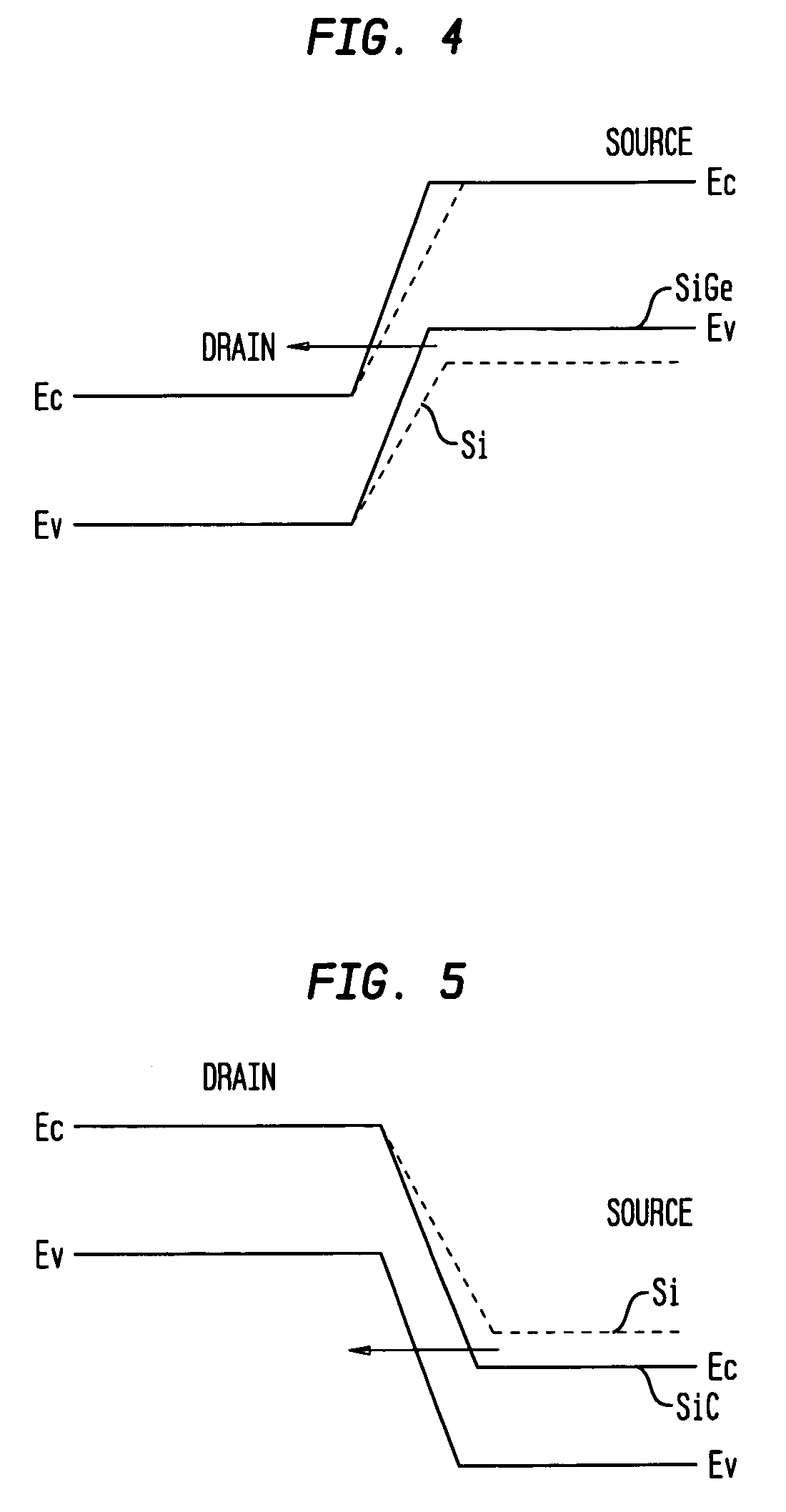
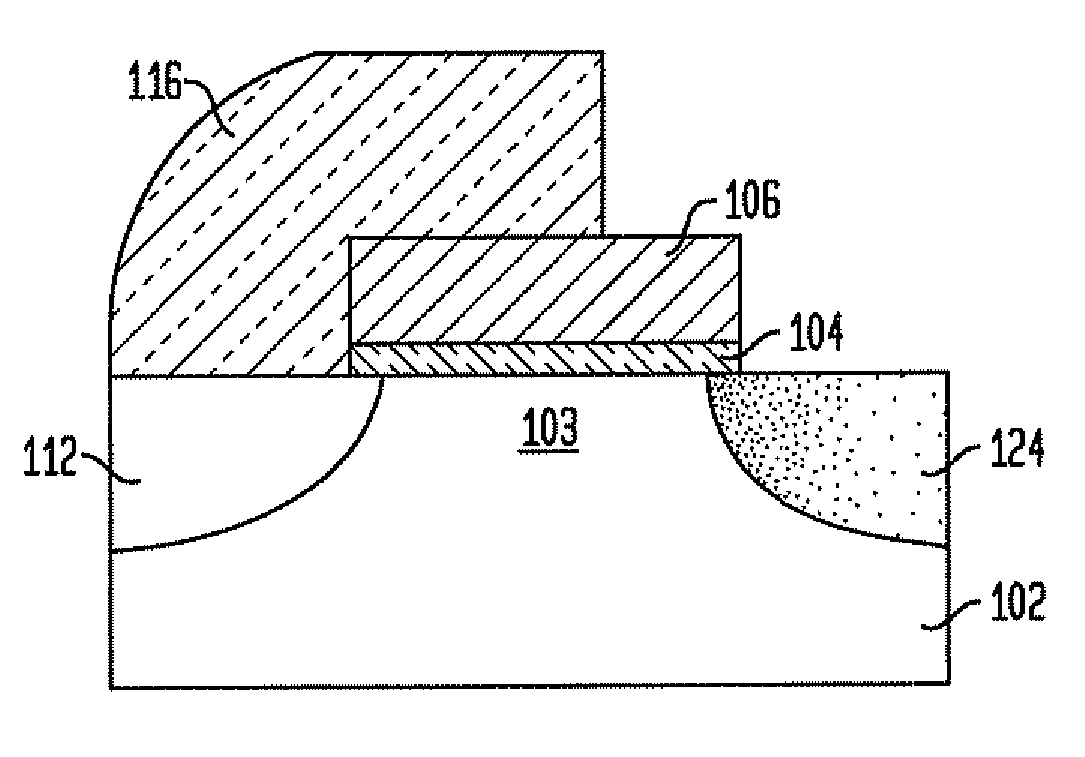
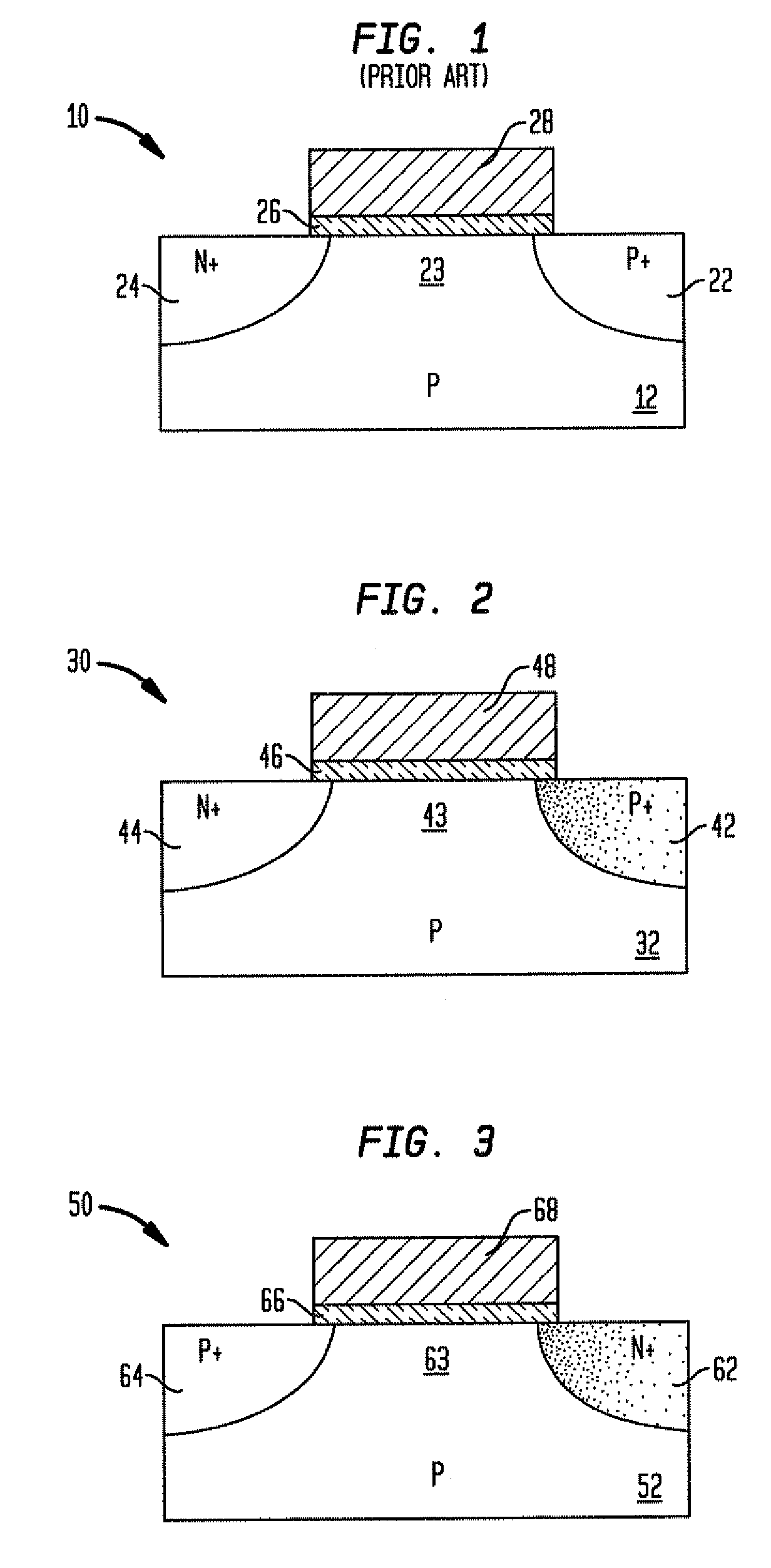
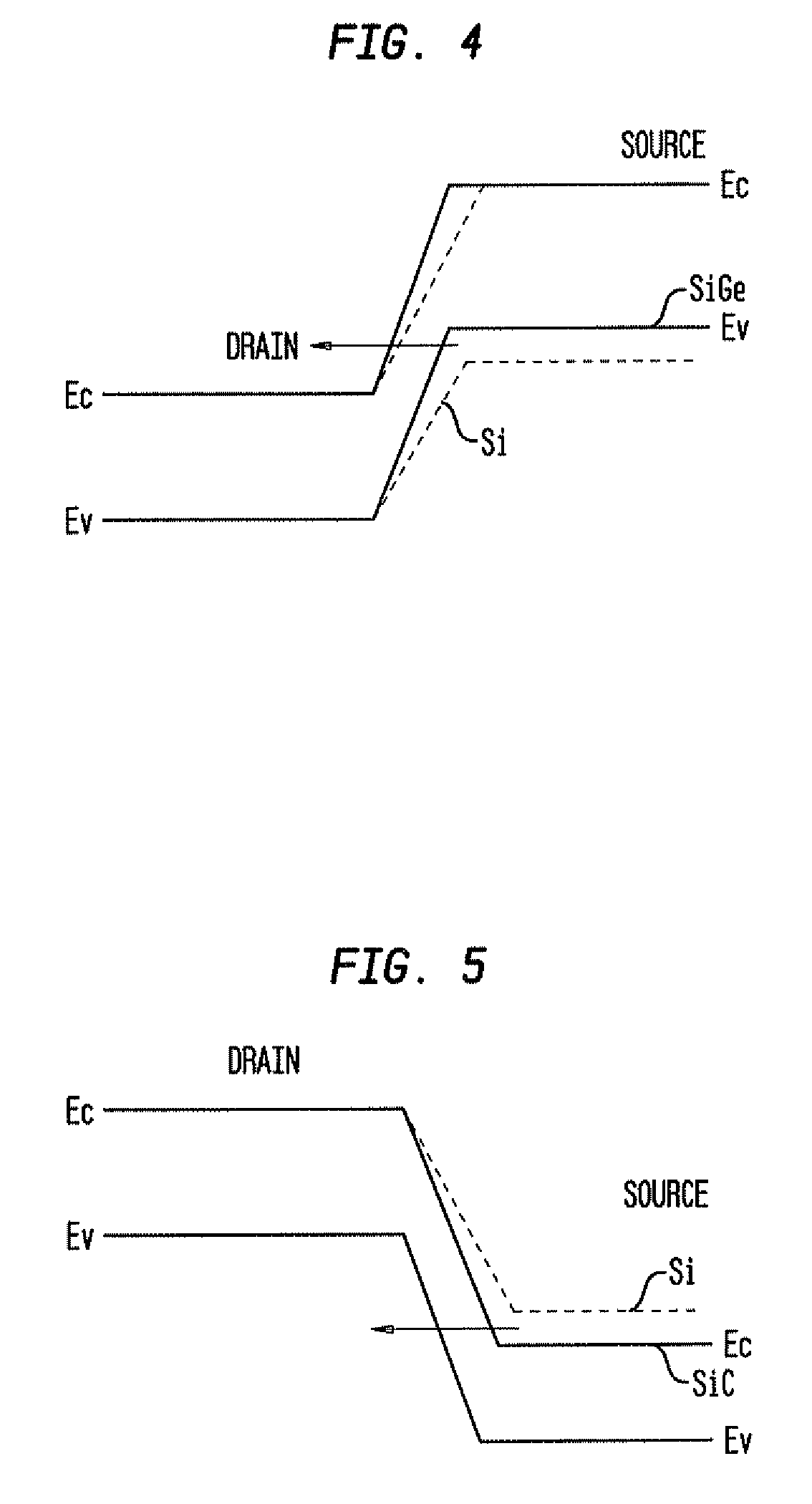
The present invention relates to a heterojunction tunneling effect transistor (TFET), which comprises spaced apart source and drain regions with a channel region located therebetween and a gate stack located over the channel region. The drain region comprises a first semiconductor material and is doped with a first dopant species of a first conductivity type. The source region comprises a second, different semiconductor material and is doped with a second dopant species of a second, different conductivity type. The gate stack comprises at least a gate dielectric and a gate conductor. When the heterojunction TFET is an n-channel TFET, the drain region comprises n-doped silicon, while the source region comprises p-doped silicon germanium. When the heterojunction TFET is a p-channel TFET, the drain region comprises p-doped silicon, while the source region comprises n-doped silicon carbide.
Owner:IBM CORP
Capacitively coupled field effect transistors for electrostatic discharge protection in flat panel displays
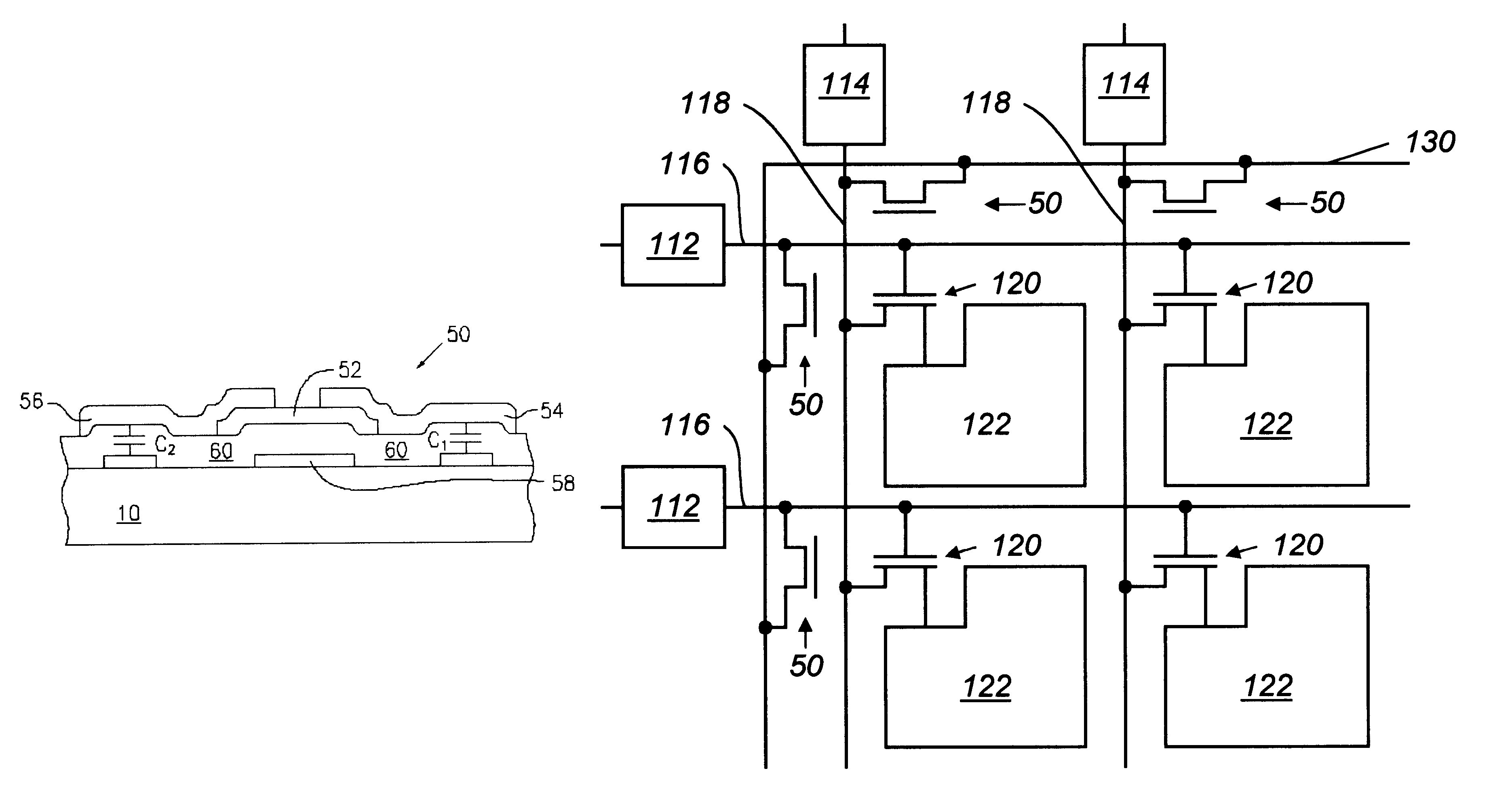
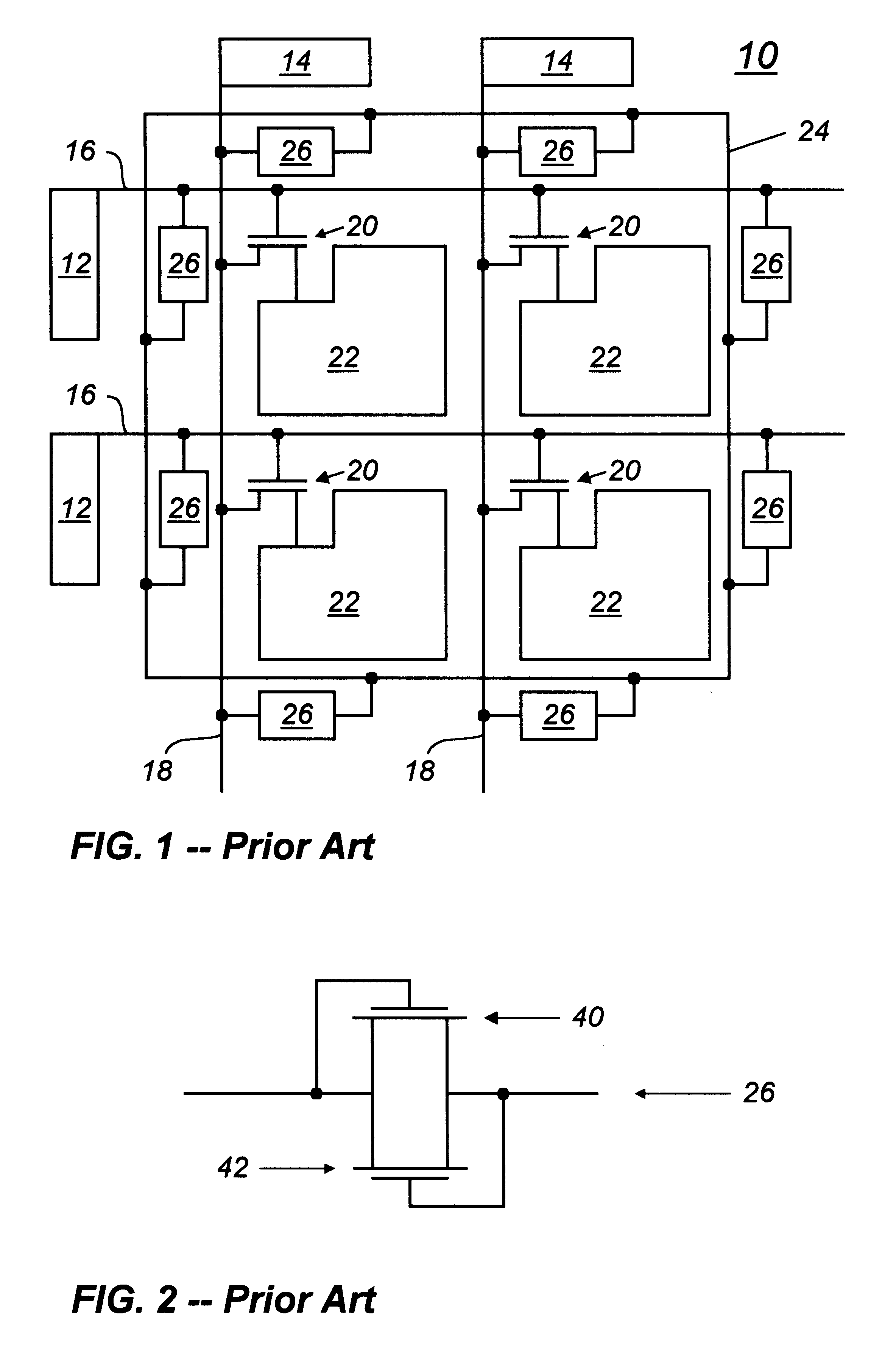
A flat panel display includes a plurality of parallel row select lines and a plurality of column drive lines, with the row select lines and the column drive lines intersecting to define a matrix of pixel locations. Signals are provided to contact pads located on the periphery of the display and the signals flow over the row select lines and the column drive lines to thin film transistors located adjacent a pixel electrode at each of the pixel locations. The signals provided to each thin film transistor cause the transistor to charge a corresponding pixel electrode to control a pixel of the display. ESD protection for the display comprises a guard ring adjacent the contact pads. Capacitively coupled field effect transistors (CCFETs) connect the row select lines to the guard ring and connect the column drive lines to the guard ring. A CCFET is formed as a thin film transistor and typically has a floating gate capacitively coupled to the drain and source of the thin film transistor.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
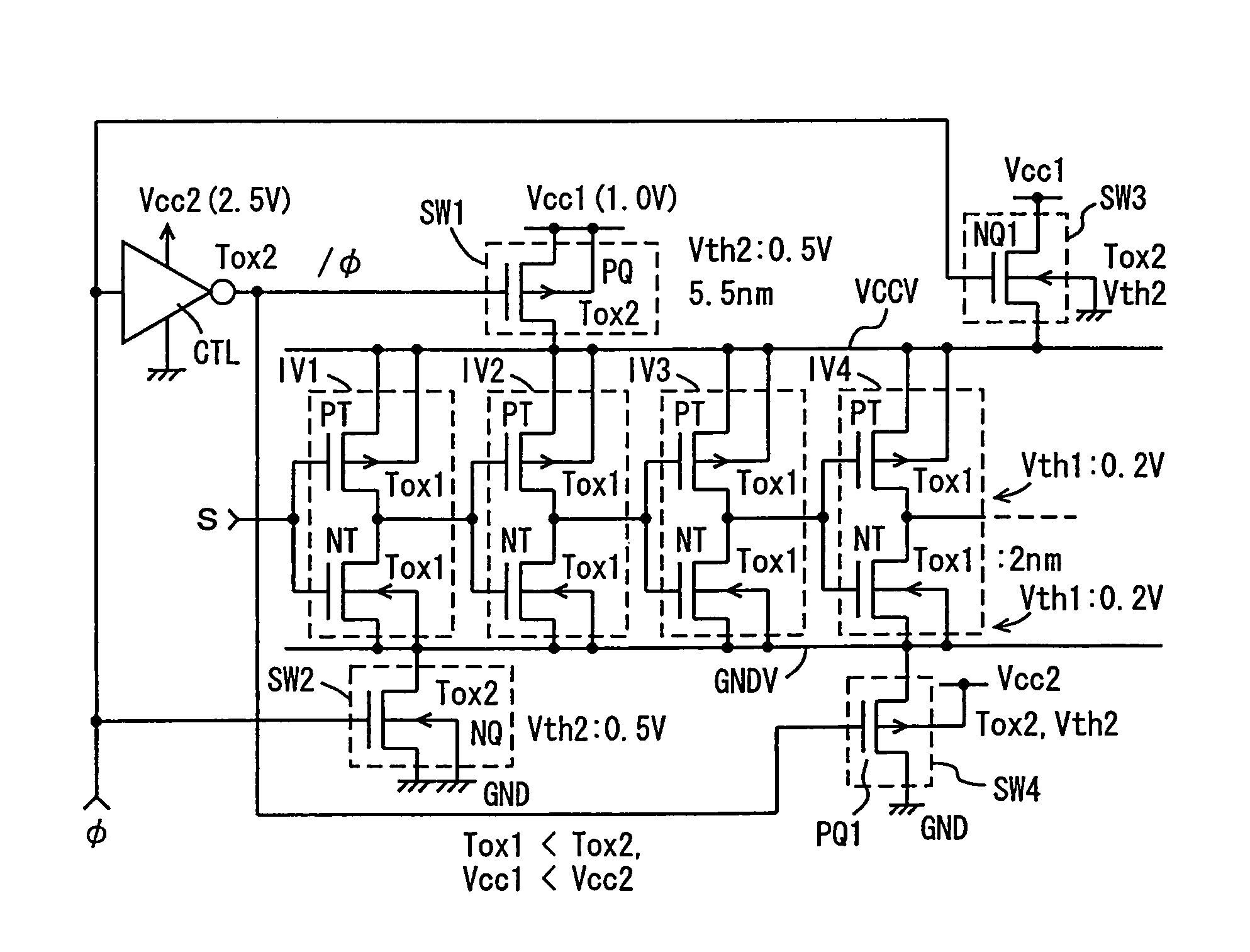
Low power consumption MIS semiconductor device
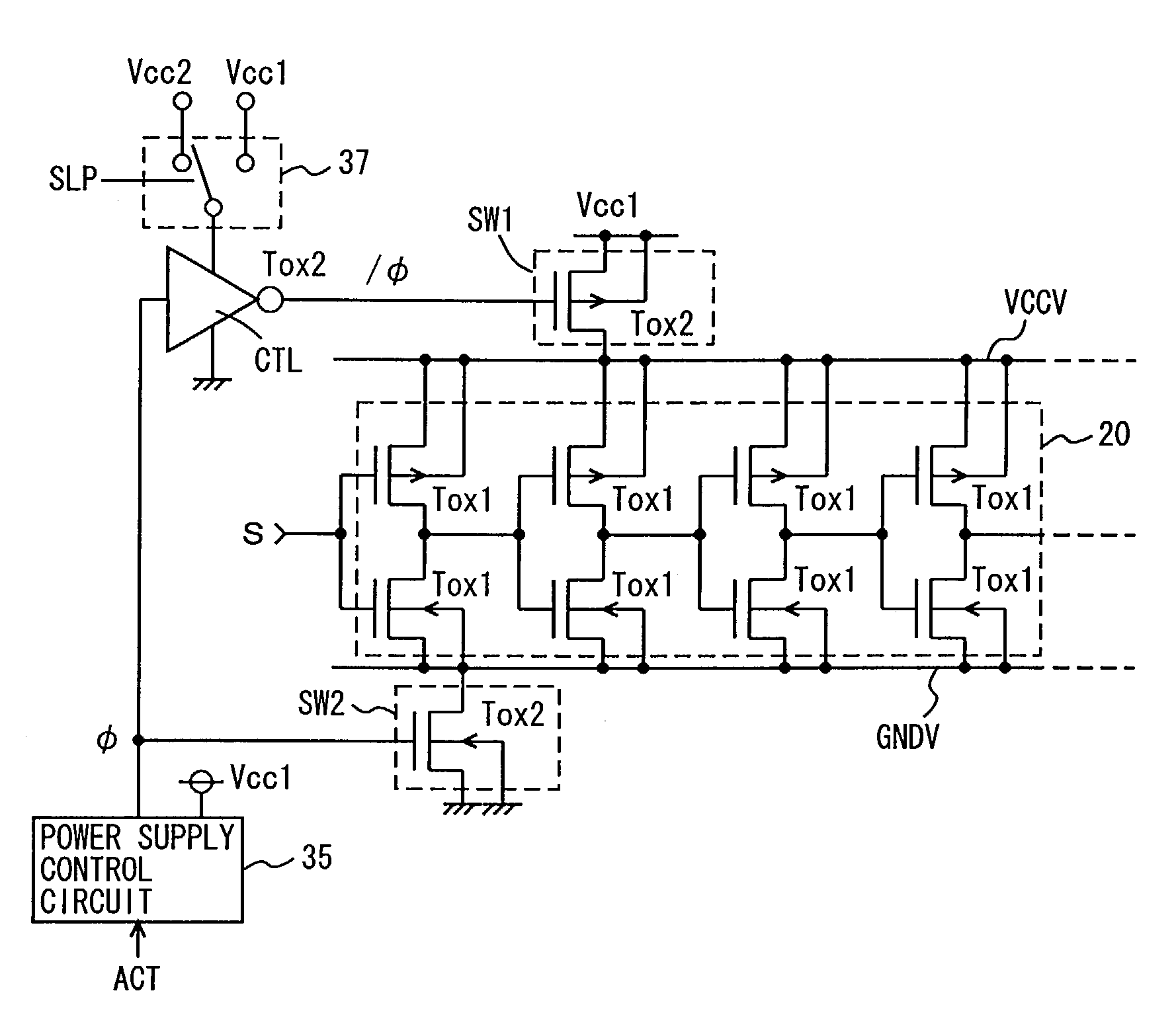
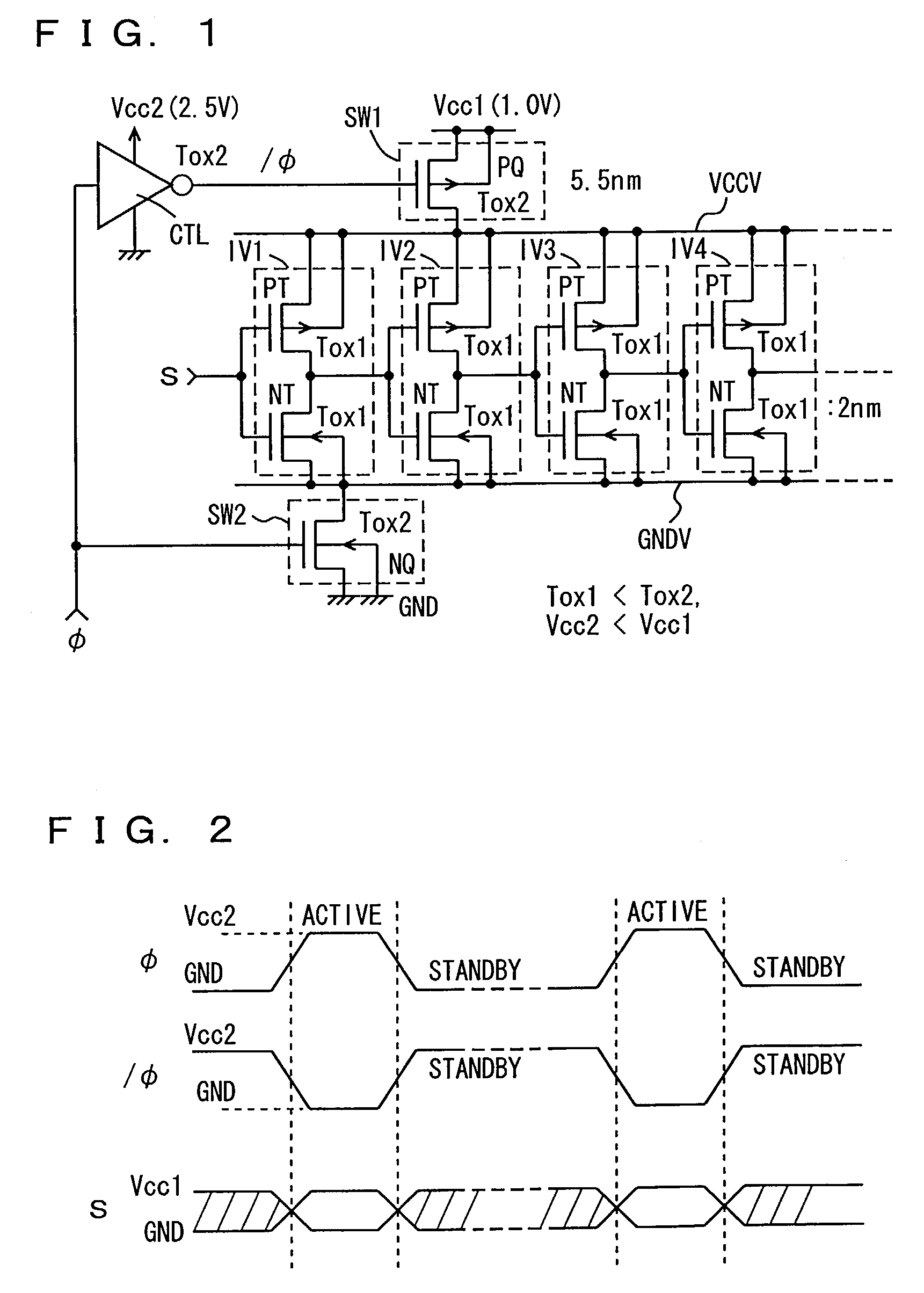
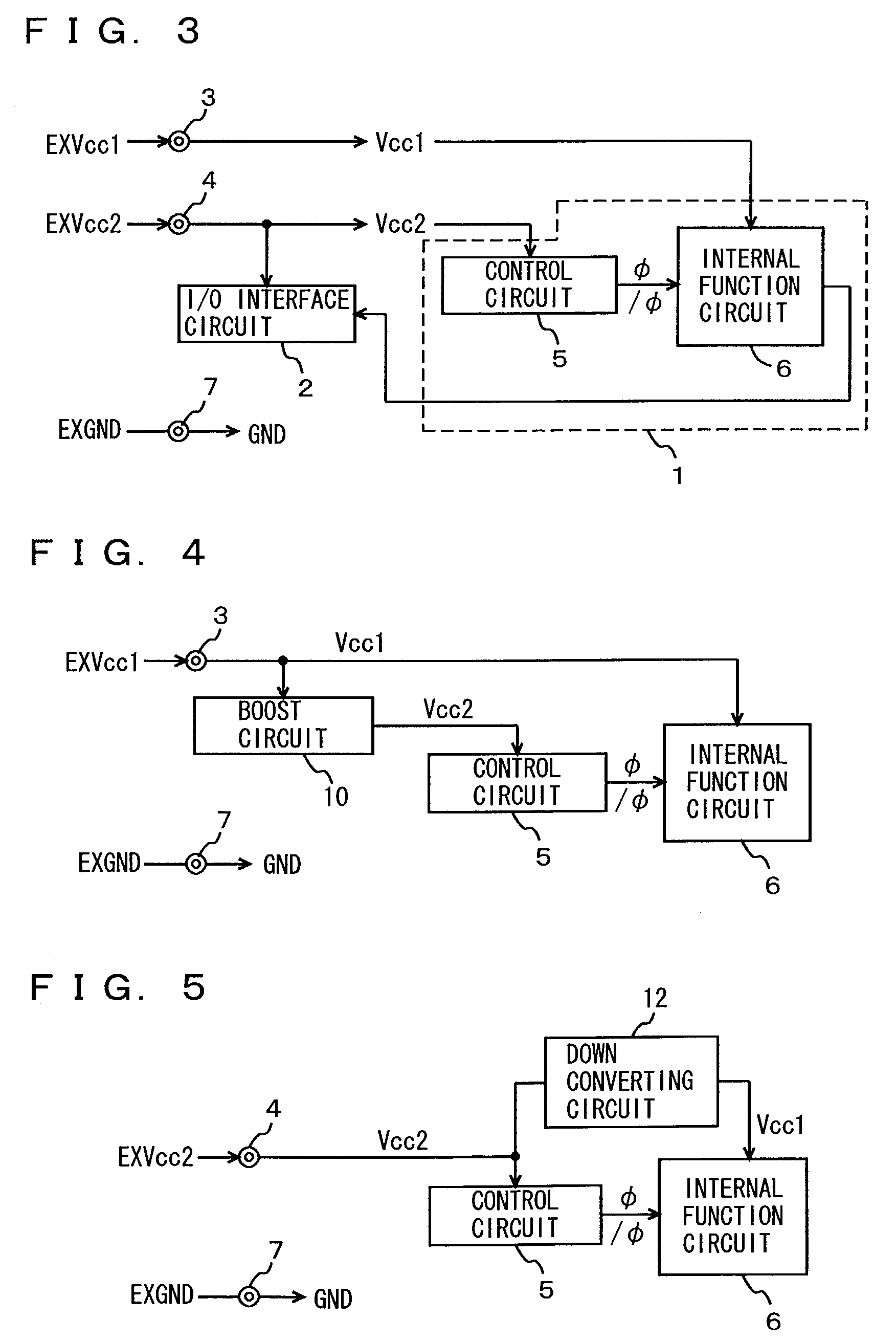
InactiveUS7042245B2Total current dropSimple circuit configurationTransistorReliability increasing modificationsCurrent consumptionLogic gate
A logic gate is constructed of an insulated gate field effect transistor (MIS transistor) having a thin gate insulation film. An operation power supply line to the logic gate is provided with an MIS transistor having a thick gate insulation film for switching the supply and stop of an operation power source voltage. A voltage of the gate of the power source switching transistor is made changing in an amplitude greater than an amplitude of an input and an output signal to the logic gate. Current consumption in a semiconductor device configured of MIS transistor of a thin gate insulation film can be reduced and an power source voltage thereof can be stabilized.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
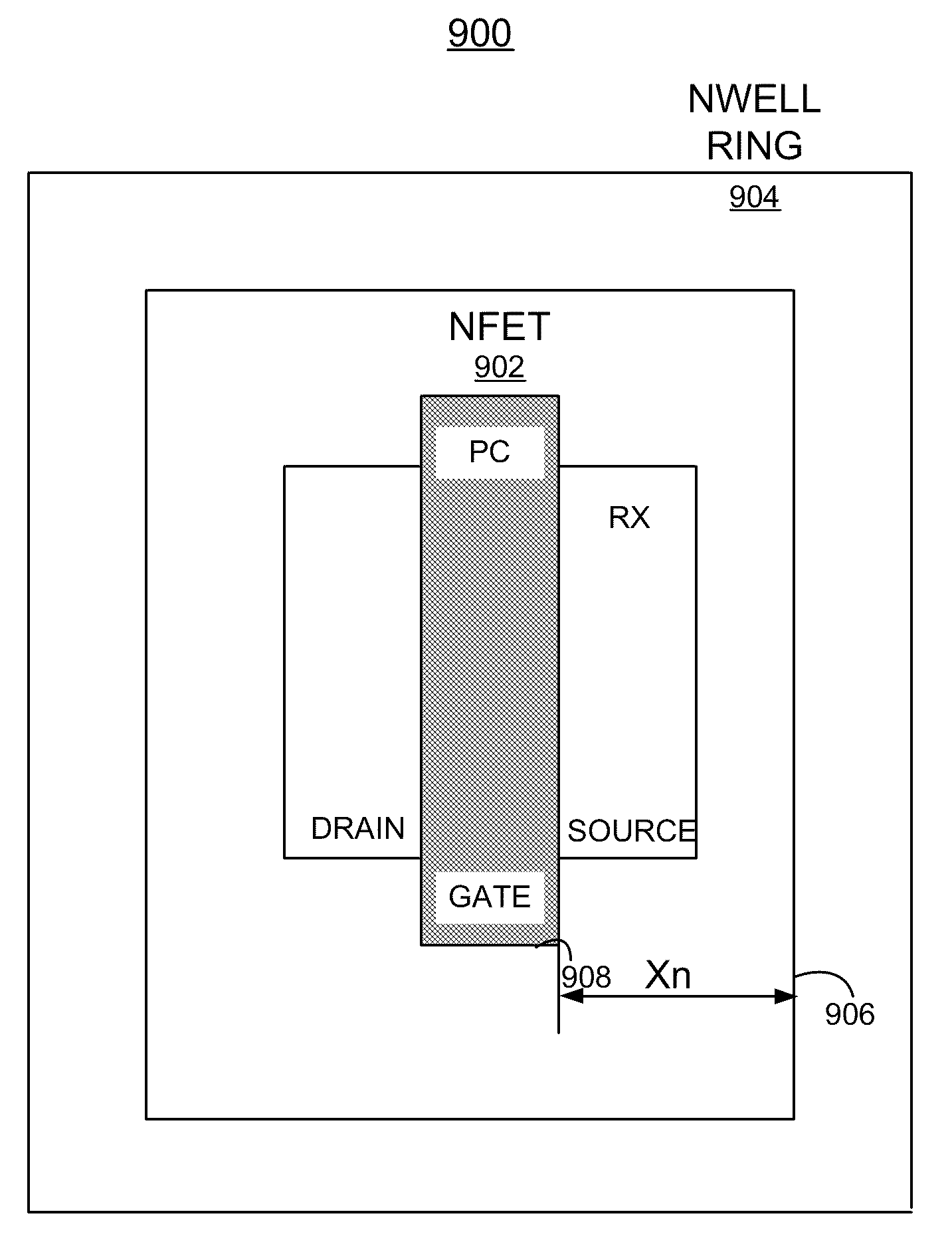
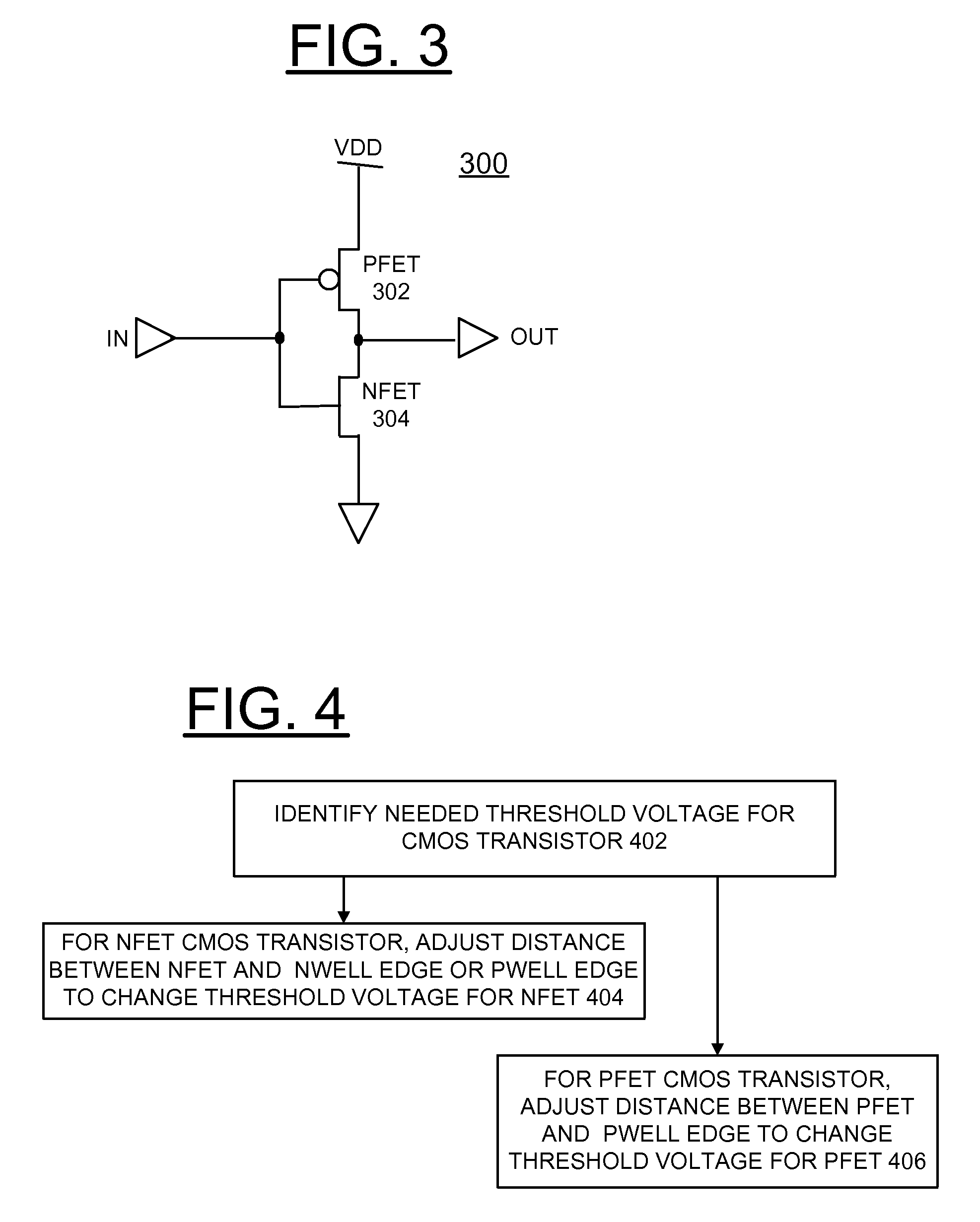
Implementing Variable Threshold Voltage Transistors
InactiveUS20100207182A1Overcome disadvantagesTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor chip
A circuit and method for implementing variable threshold voltage transistors in a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) semiconductor chip, and a design structure on which the subject circuit resides are provided. Variable threshold voltage transistors are provided utilizing the NWELL and PWELL proximity effects of the CMOS semiconductor chip without any additional mask steps. A distance between an adjacent field effect transistor (FET) and an NWELL edge or PWELL edge is adjusted to selectively provide a needed threshold voltage for the FET.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS8547753B2Improve versatilityReduce designPower reduction in field effect transistorsTransistorProgrammable logic deviceHemt circuits
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
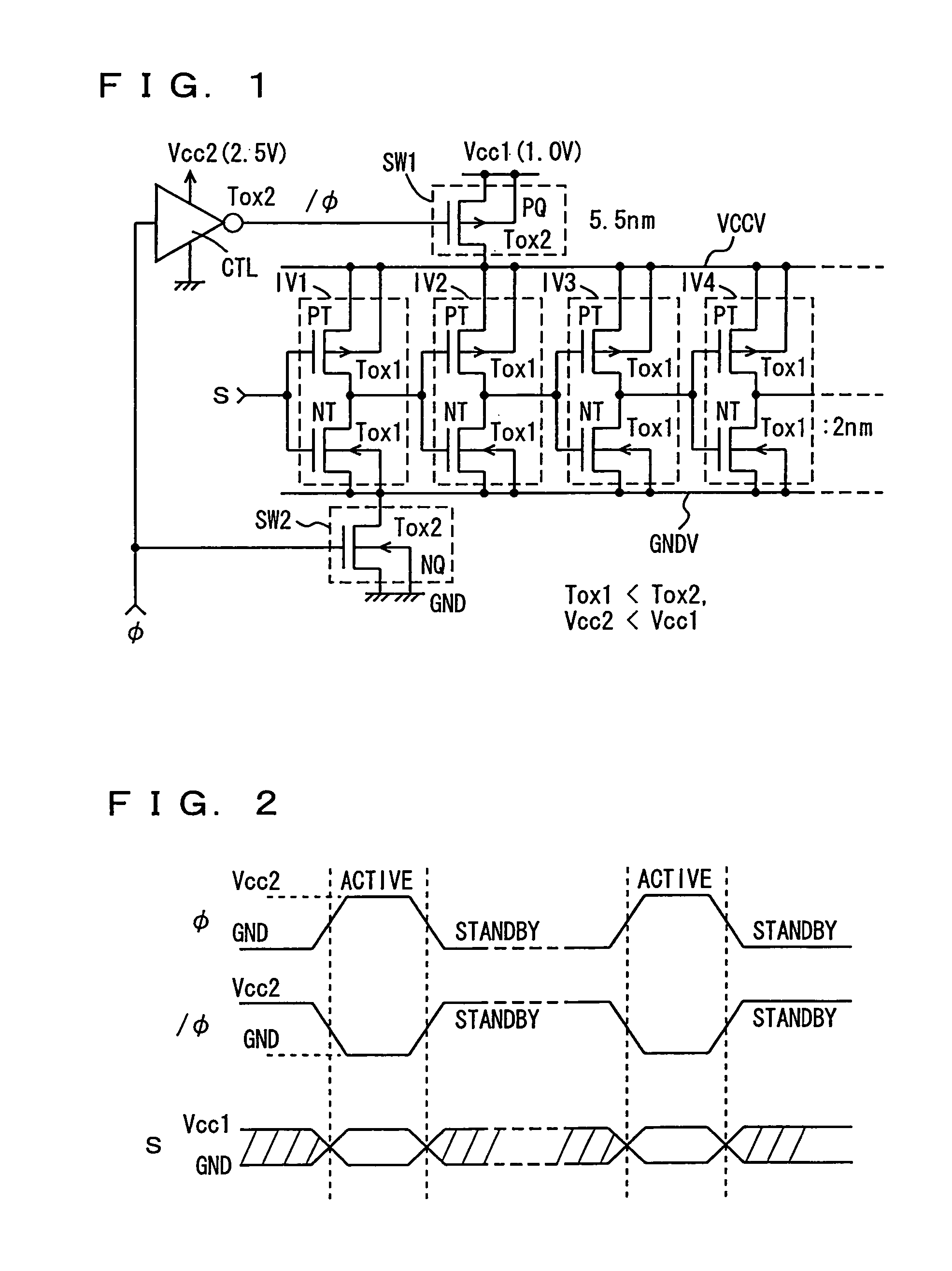
Low power consumption MIS semiconductor device
InactiveUS7355455B2Total current dropSimple circuit configurationTransistorReliability increasing modificationsCurrent consumptionLogic gate
A logic gate is constructed of an insulated gate field effect transistor (MIS transistor) having a thin gate insulation film. An operation power supply line to the logic gate is provided with an MIS transistor having a thick gate insulation film for switching the supply and stop of an operation power source voltage. A voltage of the gate of the power source switching transistor is made changing in an amplitude greater than an amplitude of an input and an output signal to the logic gate. Current consumption in a semiconductor device configured of MIS transistor of a thin gate insulation film can be reduced and an power source voltage thereof can be stabilized.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Active matrix oled voltage drive pixel circuit
InactiveUS7167169B2Threshold voltage shift is minimizedQuick data voltage level chargingCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingSignal onActive matrix
There is provided a circuit for driving a current mode light modulating device. The circuit includes (a) a capacitor for storing a data voltage, (b) a field effect transistor (FET) controlled by a signal on a scan line, for coupling the data voltage from a signal line to the capacitor, and (c) a current source, controlled by the stored data voltage, for driving the device with current provided from a power line. The power line is in a plane that is geometrically parallel to a plane within which the scan line is located.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Cascode circuit and integrated circuit having it
ActiveUS7071786B2Increase powerImprove efficiencyTransistorHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceCascode
A cascode circuit includes a first field effect transistor which has a source terminal grounded, a second field effect transistor which has a source terminal connected to a drain terminal of the first field effect transistor, and a first capacitor connected between the source terminal of the first field effect transistor and a gate terminal of the second field effect transistor. The first field effect transistor and the second field effect transistor are cascode-connected successively. A capacitance value of the first capacitor is 0.01 to 10 times that between the gate and source terminals of the second field effect transistor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Magnetic memory device
ActiveUS6940747B1Digital storageSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The present invention provides a magnetic memory device. An embodiment of the present invention includes a magnetic memory cell that is switchable between two states offering electrical resistance which are detectible by a sense current though the magnetic memory cell. The device includes a field effect transistor (FET) arrangement which has a source and a drain. The source and the drain are connected by a connecting element which projects from a portion of the device and which has an electrical conductivity that varies in response to a gate voltage applied to the connecting element. The magnetic memory cell is in electrical communication with the connecting element so that at least a portion of the sense current is in use associated with a corresponding gate voltage and the FET arrangement amplifies at least a portion of the sense current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Carbon nanotube gate field effect transistor
The present invention generally relates to an apparatus and method of carbon nanotube (CNT) gate field effect transistor (FET), which is used to replace the current metal gate of transistor for decreasing the gate width greatly. The carbon nanotube has its own intrinsic characters of metal and semiconductor, so it can be the channel, connector or next-level gate of transistor. Furthermore, the transistor has the structure of exchangeable source and drain, and can be defined the specificity by outside wiring.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Silicide proximity structures for CMOS device performance improvements
A method for manufacturing an integrated circuit having a plurality of semiconductor devices including an n-type field effect transistor and a p-type field effect transistor on a semiconductor wafer by creating a spacer having a first width for the n-type field effect transistor and creating a spacer having a second width for the p-type field effect transistor, the first width being greater than the second width and depositing silicide material on the semiconductor wafer such that tensile mechanical stresses are formed within a channel of the n-type field effect transistor and compressive stresses are formed within a channel of the p-type field effect transistor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor structure including a high performance fet and a high voltage fet on a soi substrate
A first field effect transistor includes a gate dielectric and a gate electrode located over a first portion of a top semiconductor layer in a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate. A second field effect transistor includes a portion of a buried insulator layer and a source region and a drain region located underneath the buried insulator layer. In one embodiment, the gate electrode of the second field effect transistor is a remaining portion of the top semiconductor layer. In another embodiment, the gate electrode of the second field effect transistor is formed concurrently with the gate electrode of the first field effect transistor by deposition and patterning of a gate electrode layer. The first field effect transistor may be a high performance device and the second field effect transistor may be a high voltage device. A design structure for the semiconductor structure is also provided.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
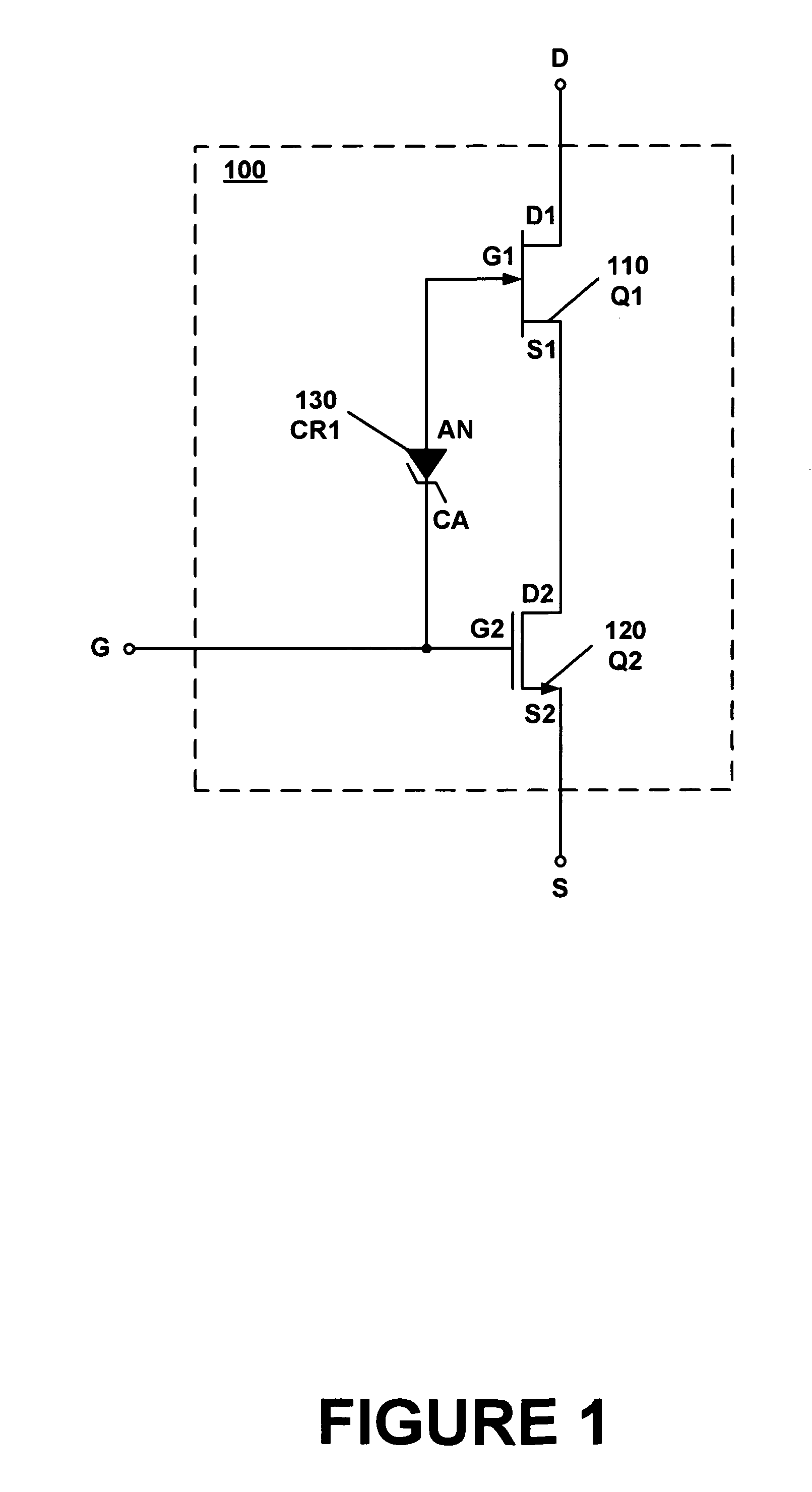
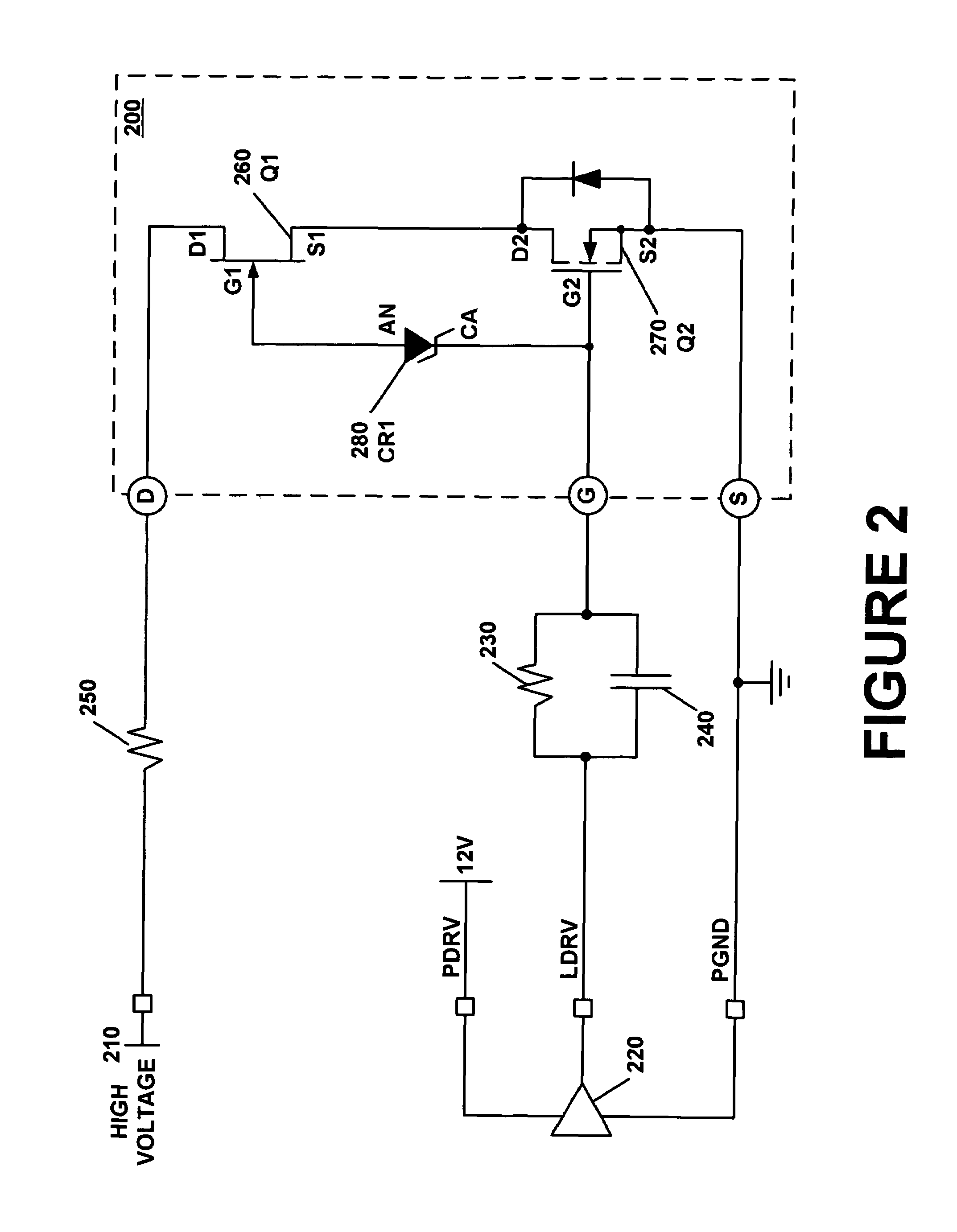
Composite field effect transistor
A composite field effect transistor, in accordance with one embodiment, includes a zener diode, a junction field effect transistor and a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor. A gate of the junction field effect transistor is coupled to an anode of the zener diode. A cathode of the zener diode is coupled to a gate of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor. A drain of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor is coupled to a source of the junction field effect transistor.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
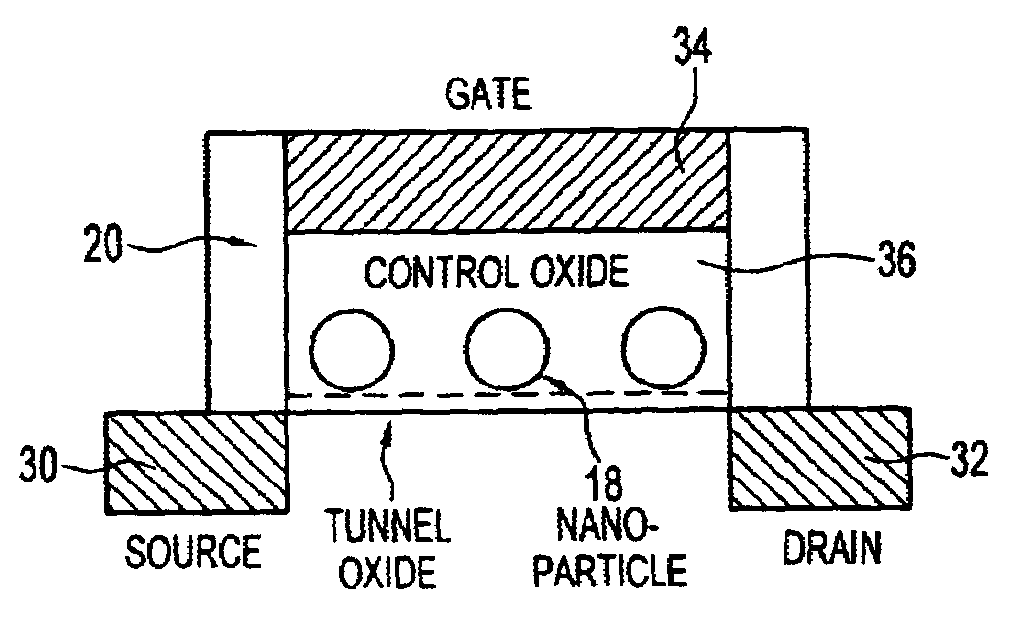
Silicon nanoparticle field effect transistor and transistor memory device
A silicon nanoparticle transistor and transistor memory device. The transistor of the invention has silicon nanoparticles, dimensioned on the order of 1 nm, in a gate area of a field effect transistor. The resulting transistor is a transistor in which single electron flow controls operation of the transistor. Room temperature operation is possible with the novel transistor structure by radiation assistance, with radiation being directed toward the silicon nanoparticles to create necessary holes in the quantum structure for the flow of an electron. The transistor of the invention also forms the basis for a memory device. The device is a flash memory device which will store electrical charge instead of magnetic effects.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Heterojunction tunneling field effect transistors, and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080050881A1Enhance junction currentEnhancing tunneling currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeHeterojunctionDopant
The present invention relates to a heterojunction tunneling effect transistor (TFET), which comprises spaced apart source and drain regions with a channel region located therebetween and a gate stack located over the channel region. The drain region comprises a first semiconductor material and is doped with a first dopant species of a first conductivity type. The source region comprises a second, different semiconductor material and is doped with a second dopant species of a second, different conductivity type. The gate stack comprises at least a gate dielectric and a gate conductor. When the heterojunction TFET is an n-channel TFET, the drain region comprises n-doped silicon, while the source region comprises p-doped silicon germanium. When the heterojunction TFET is a p-channel TFET, the drain region comprises p-doped silicon, while the source region comprises n-doped silicon carbide.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
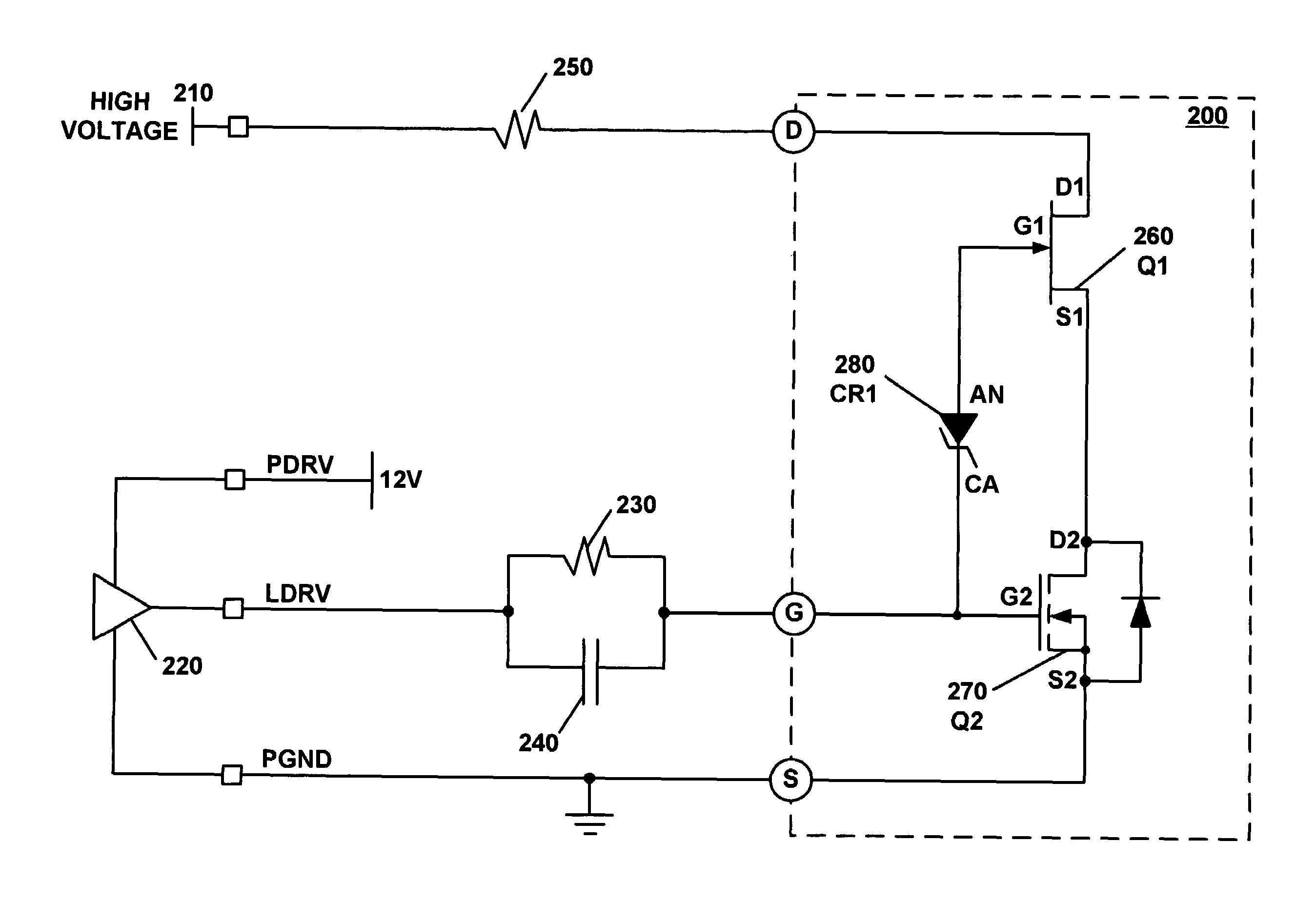
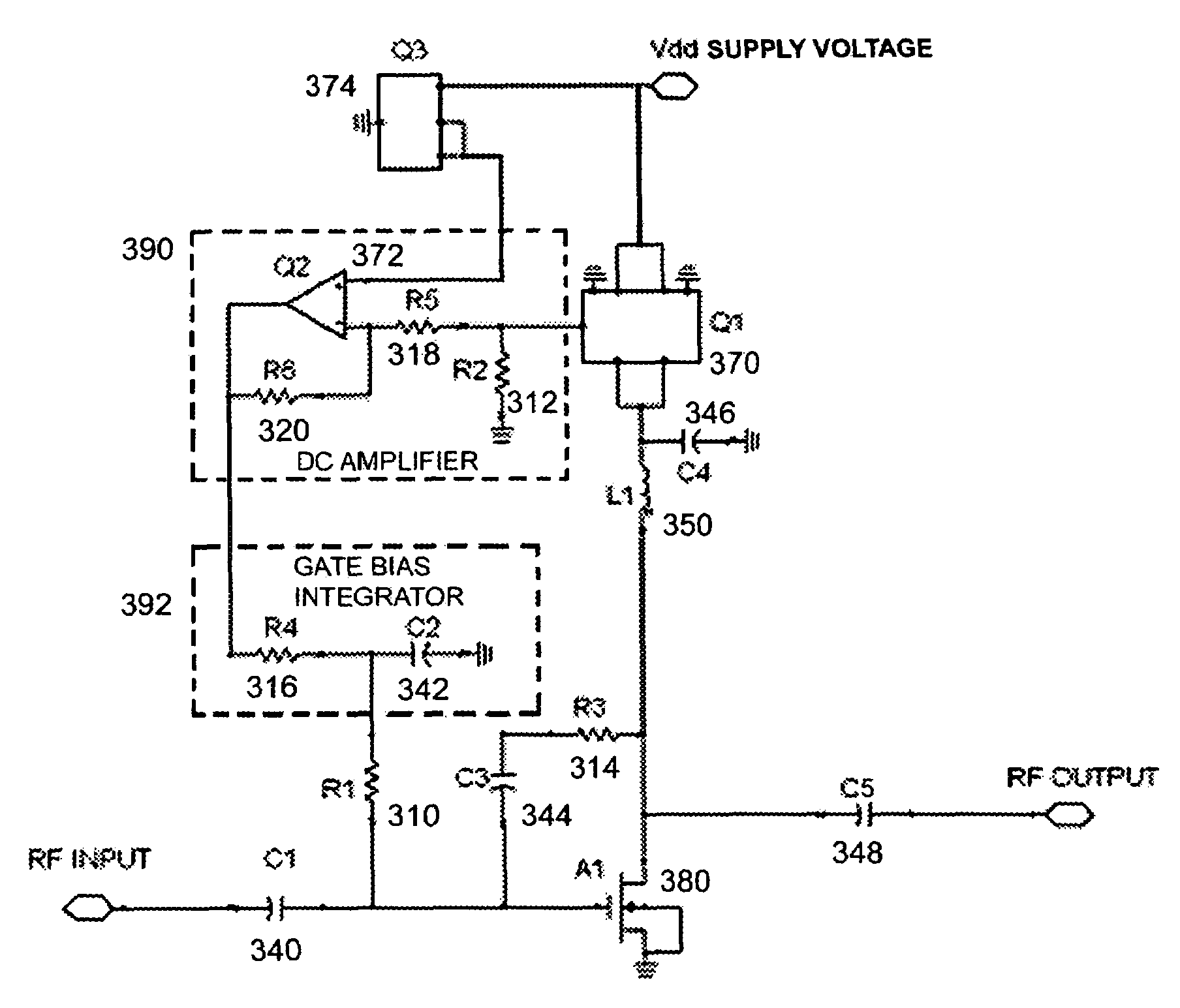
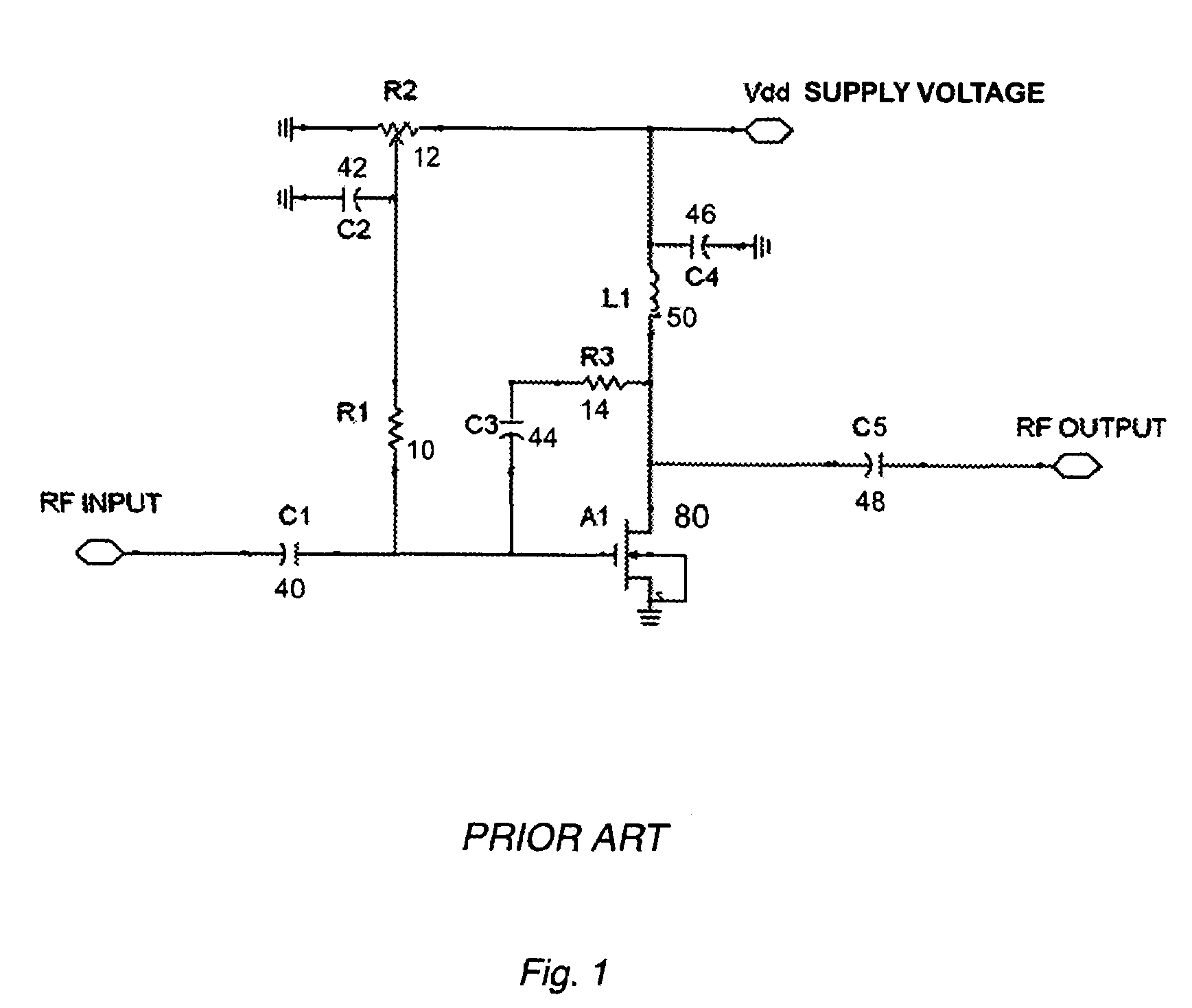
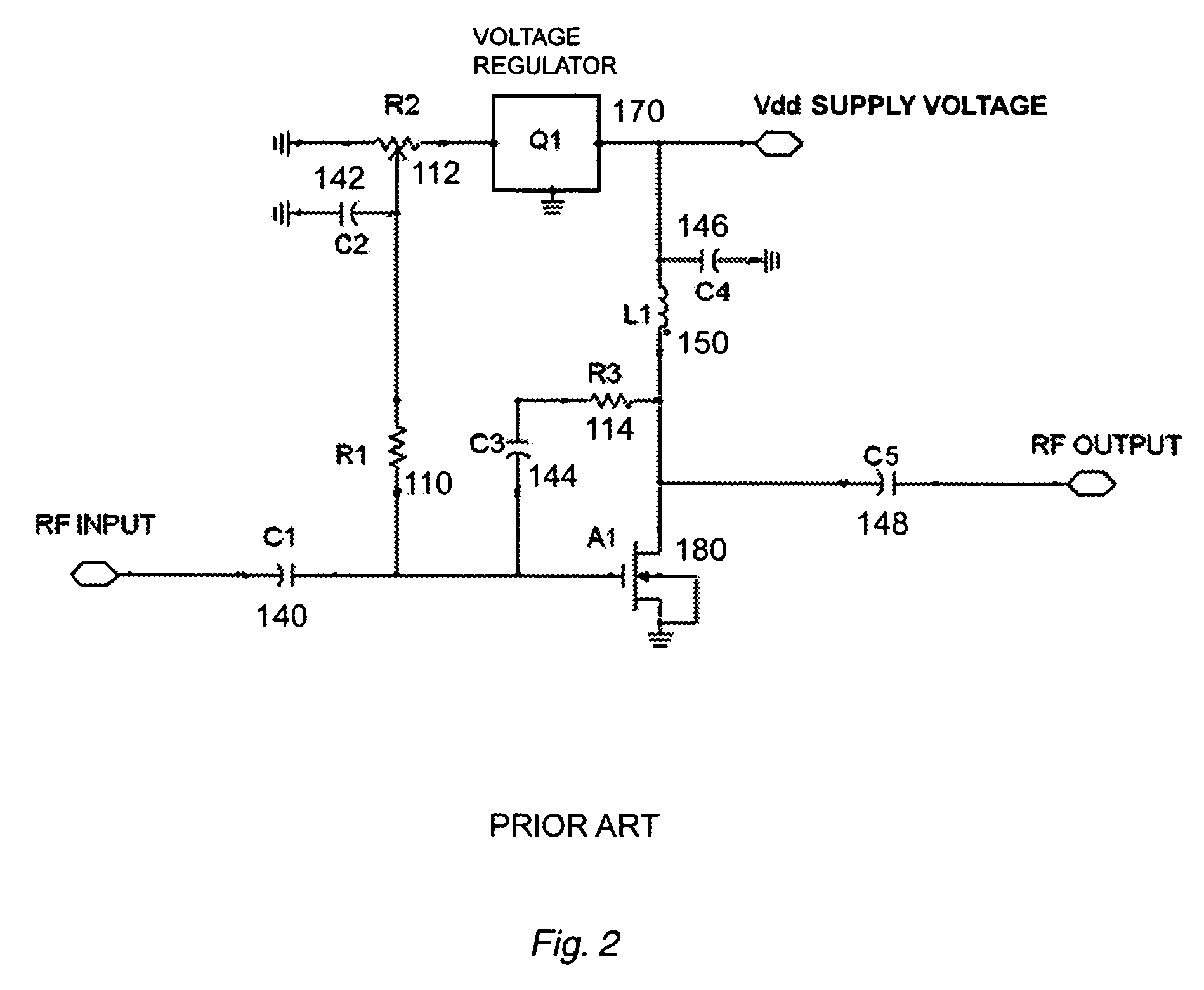
Automatic biasing and protection circuit for field effect transistor (FET) devices
ActiveUS7348854B1High power supply voltageHigh operating temperatureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlNegative feedbackIntegrator
A transistor biasing circuit is shown that utilizes a negative feedback loop control circuit to set the gate bias voltage in the output transistors of a power amplifier. This control circuit has a current sensor in series with the drain of the transistor, the current sensor output in turn feeding a dc signal into a dc amplifier, and the output of the dc amplifier driving a gate bias integrator which forms a dc control loop for maintaining the bias point. The output transistor is protected from excessive temperature and / or excessive power dissipation.
Owner:SCI COMPONENTS
Field effect transistor, display element, image display device, and system
InactiveUS20110128275A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumPower flow
A field effect transistor includes a gate electrode to which a gate voltage is applied; a source electrode and a drain electrode for obtaining a current in response to the gate voltage; an active layer provided adjacent to the source electrode and the drain electrode and formed of an oxide semiconductor including magnesium and indium as major components; and a gate insulating layer provided between the gate electrode and the active layer.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method of forming a multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
ActiveUS20090209074A1Tailored drive currentIncrease width of deviceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentChannel width
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Breakdown voltage multiplying integration scheme
InactiveUS20130240893A1Improve breakdown voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesTerminal equipmentP channel
A circuit includes a first field effect transistor having a gate, a first drain-source terminal, and a second drain-source terminal; and a second field effect transistor having a gate, a first drain-source terminal, and a second drain-source terminal. The second field effect transistor and the first field effect transistor are of the same type, i.e., both n-channel transistors or both p-channel transistors. The second drain-source terminal of the first field effect transistor is coupled to the first drain-source terminal of the second field effect transistor; and the gate of the second field effect transistor is coupled to the first drain-source terminal of the second field effect transistor. The resulting three-terminal device can be substituted for a single field effect transistor that would otherwise suffer breakdown under proposed operating conditions.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
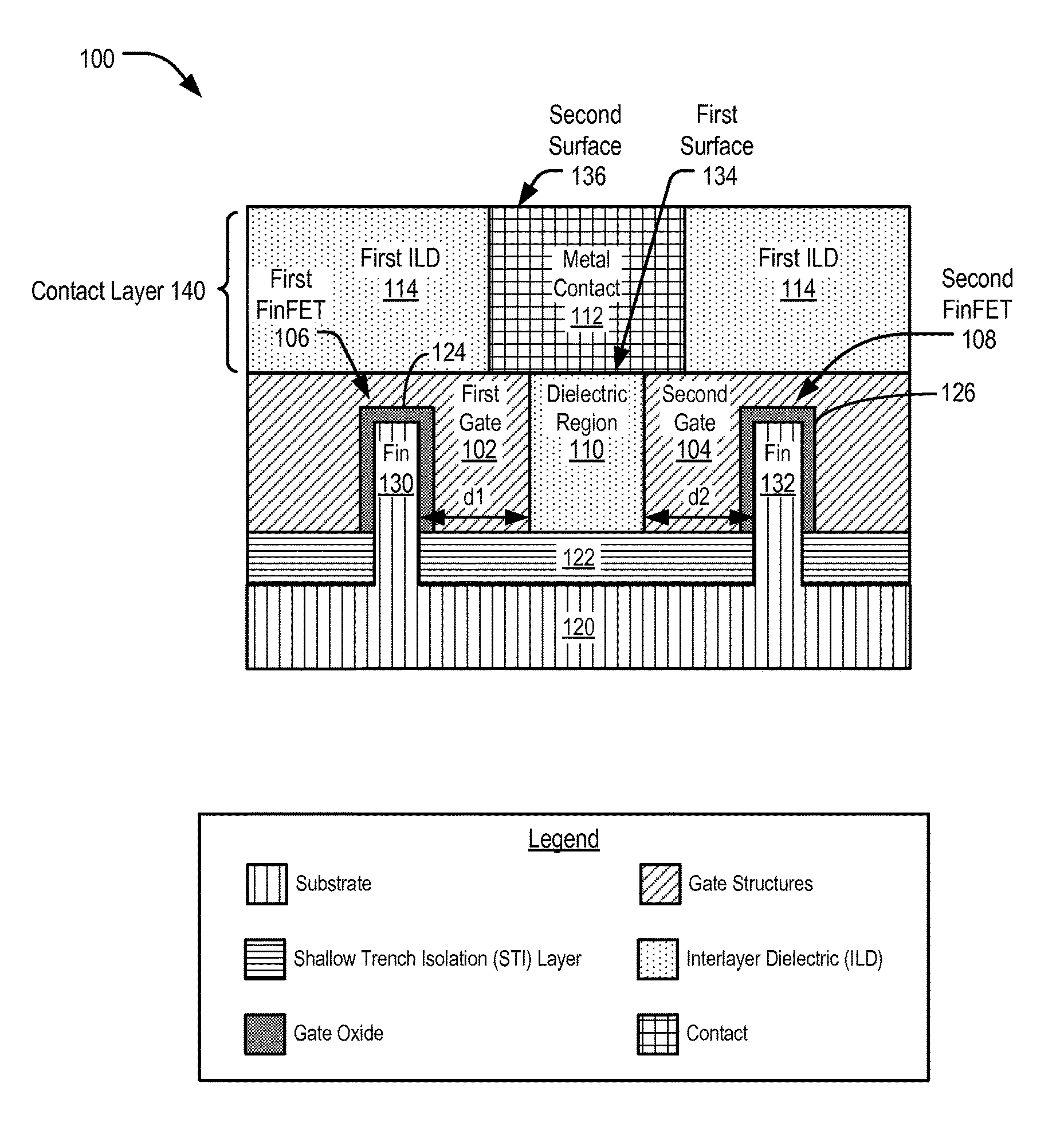
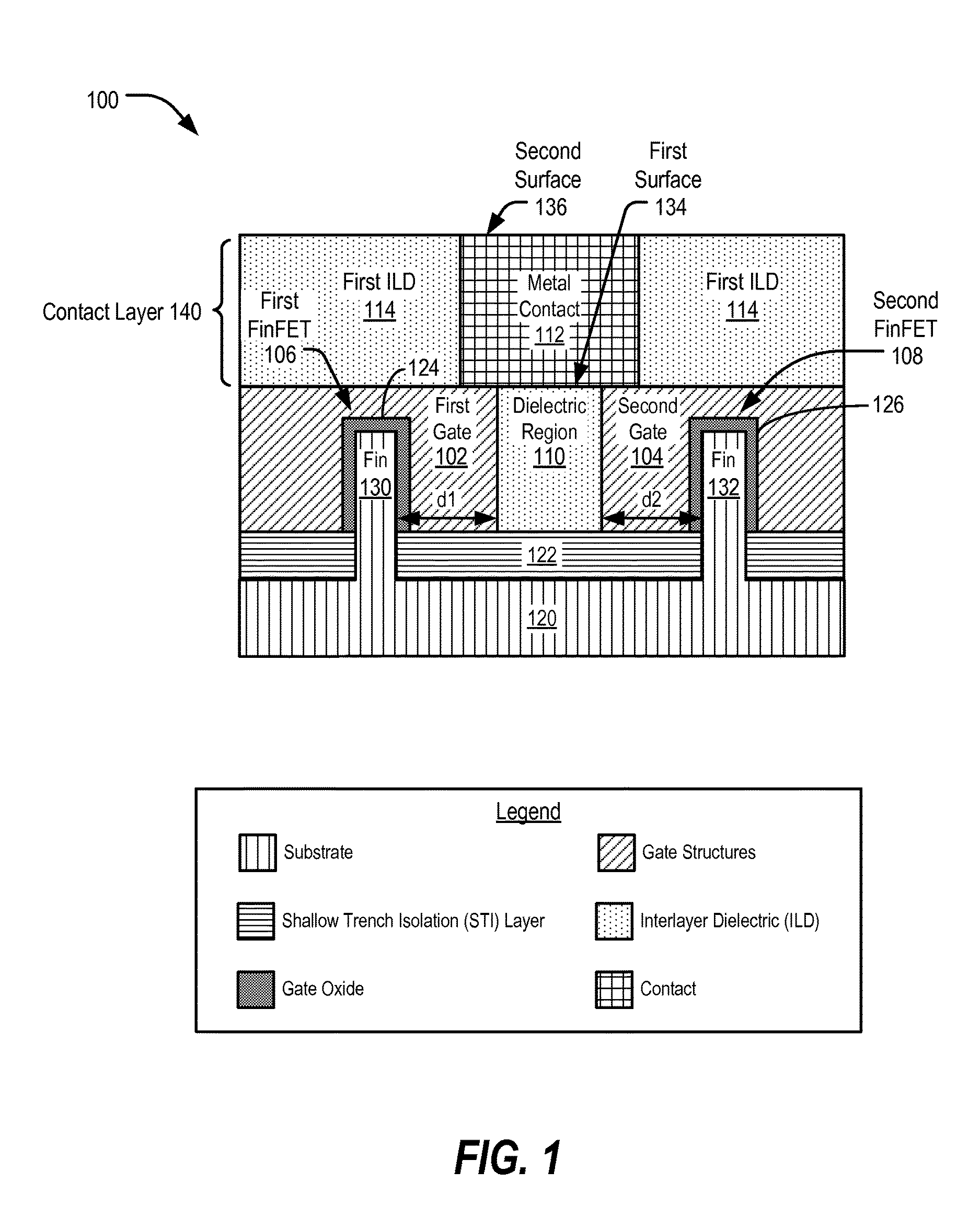
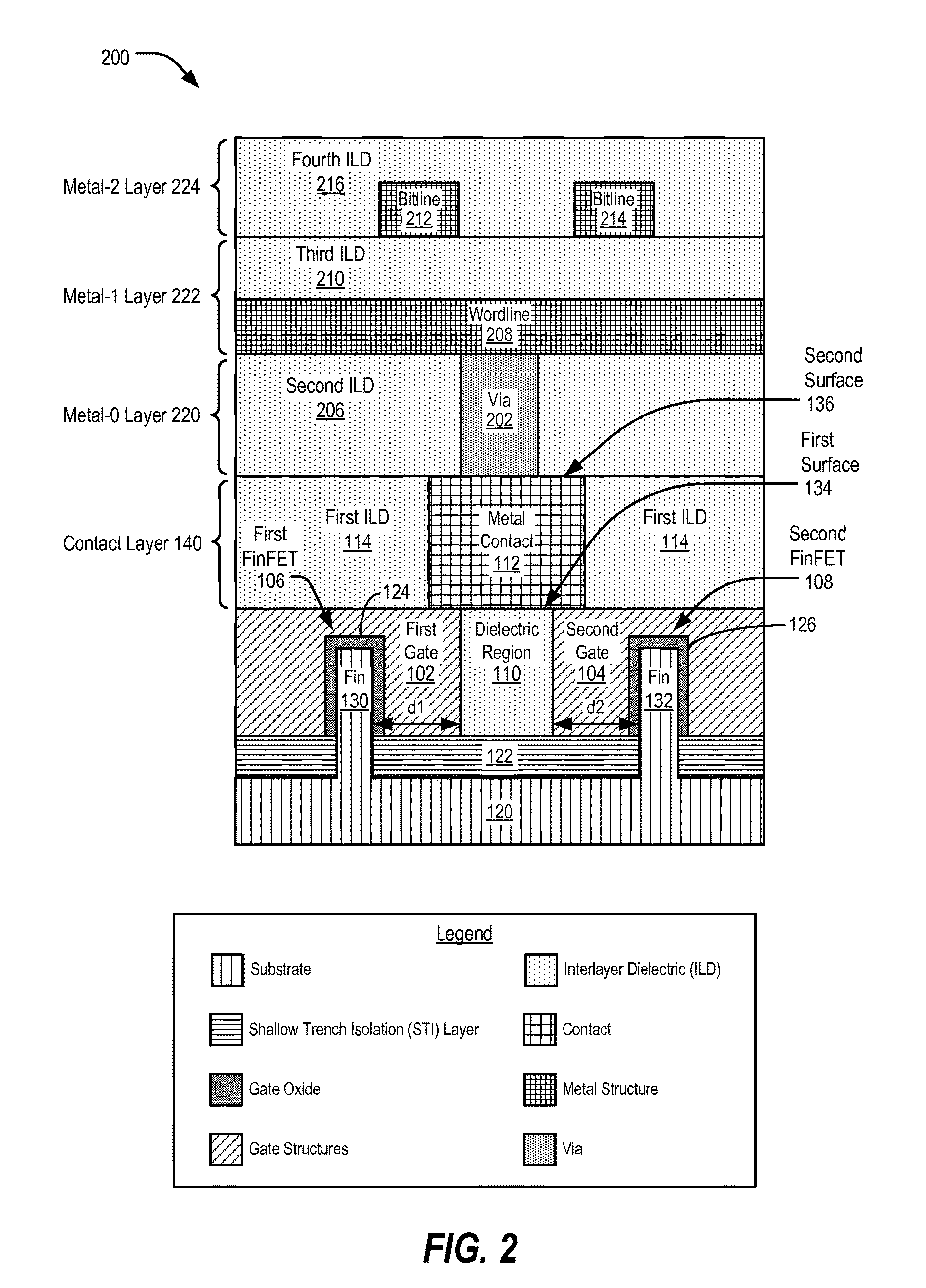
Structure and method for tunable memory cells including fin field effect transistors
In a particular aspect, an integrated circuit includes a first gate structure coupled to a first fin field effect transistor (FinFET) device. The integrated circuit includes a second gate structure coupled to a second FinFET device. The first gate structure and the second gate structure are separated by a dielectric region. The integrated circuit further includes a metal contact having a first surface that is in contact with the dielectric region, the first gate structure, and the second gate structure.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Fabrication technique for high frequency, high power group III nitride electronic devices
ActiveUS8476125B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesManufacturing technologyEtching
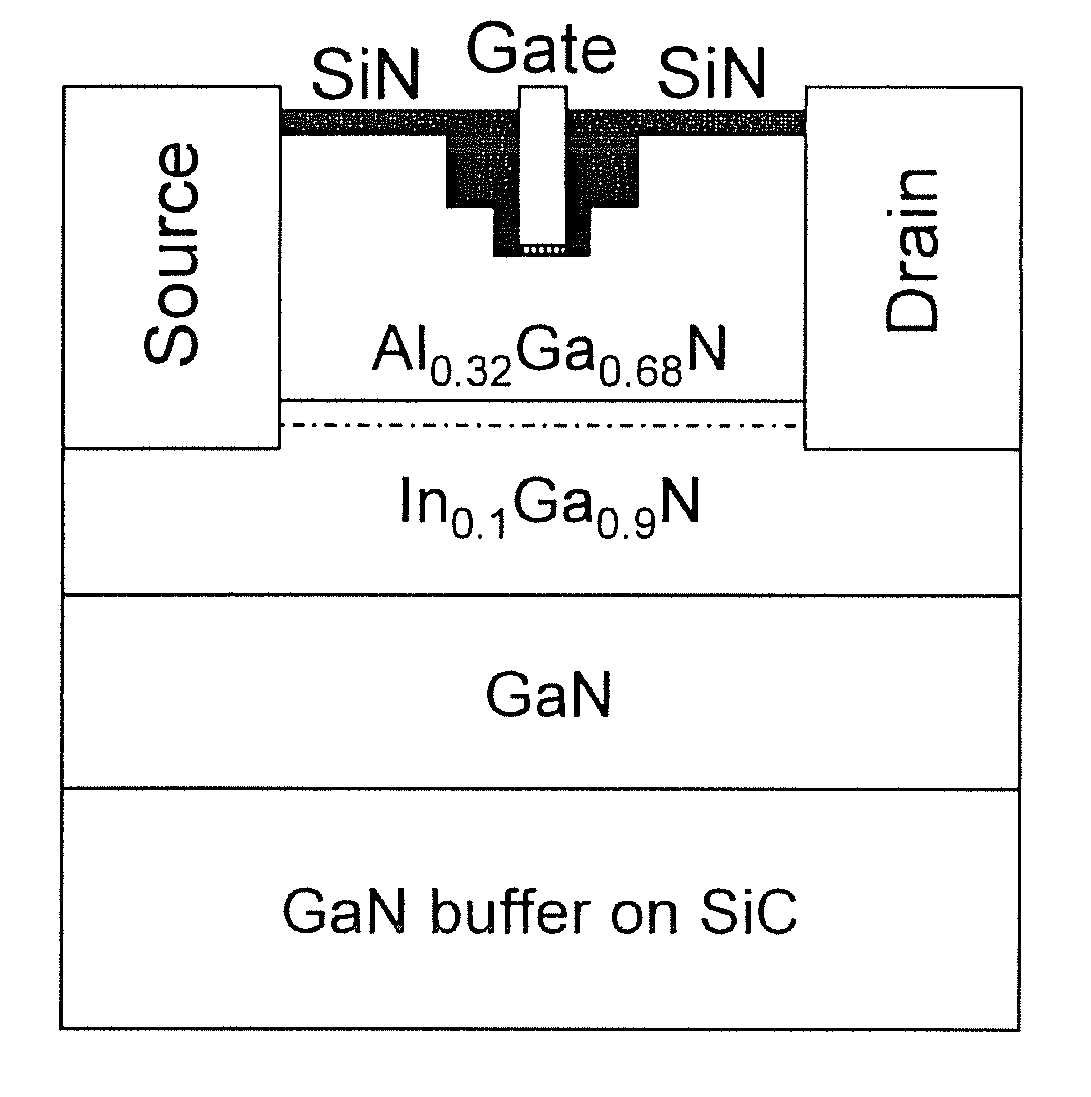
Fabrication methods of a high frequency (sub-micron gate length) operation of AlInGaN / InGaN / GaN MOS-DHFET, and the HFET device resulting from the fabrication methods, are generally disclosed. The method of forming the HFET device generally includes a novel double-recess etching and a pulsed deposition of an ultra-thin, high-quality silicon dioxide layer as the active gate-insulator. The methods of the present invention can be utilized to form any suitable field effect transistor (FET), and are particular suited for forming high electron mobility transistors (HEMT).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Method of forming a multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
ActiveUS8022478B2Increase widthEasy to tuneSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentEngineering
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
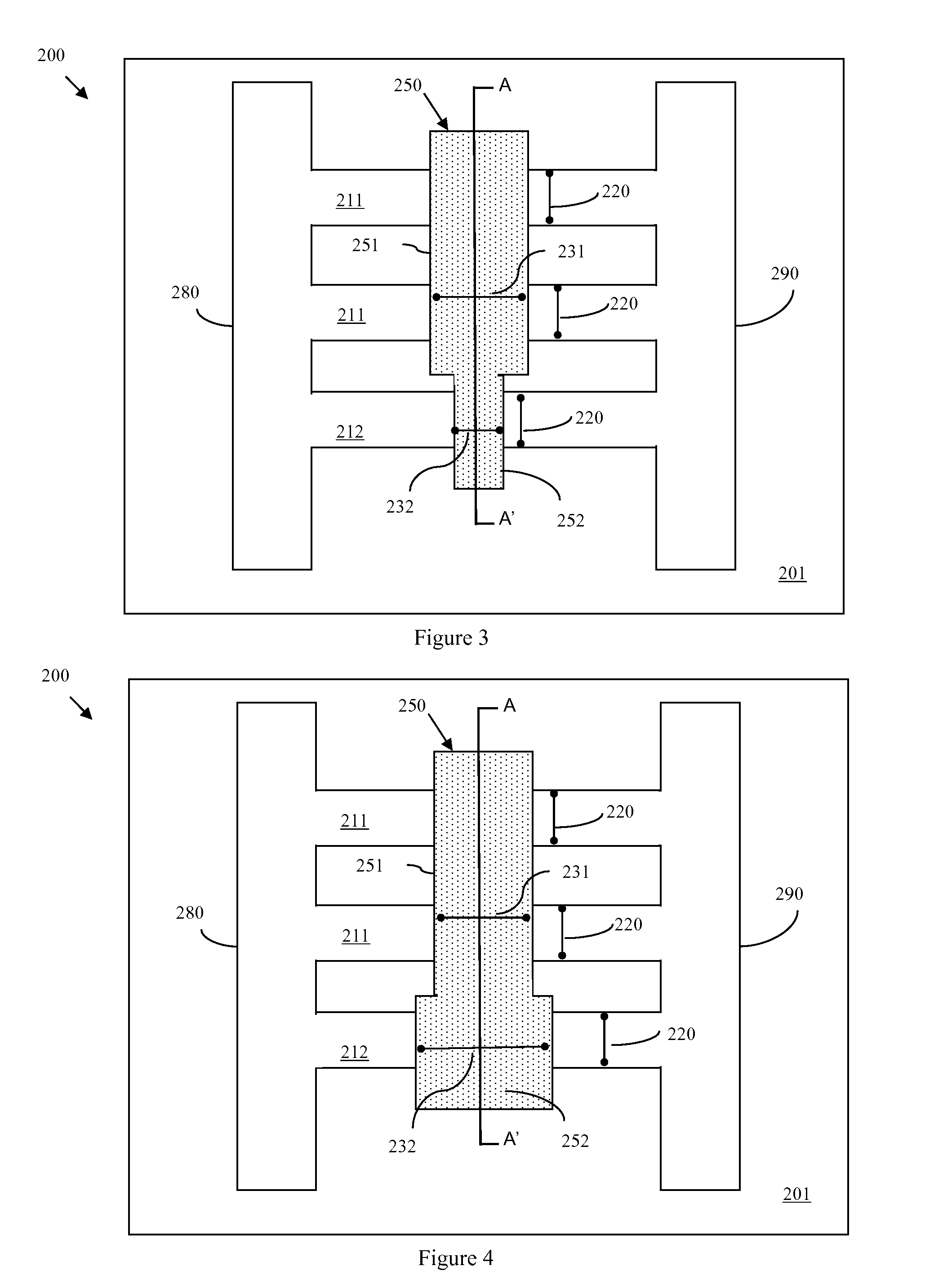
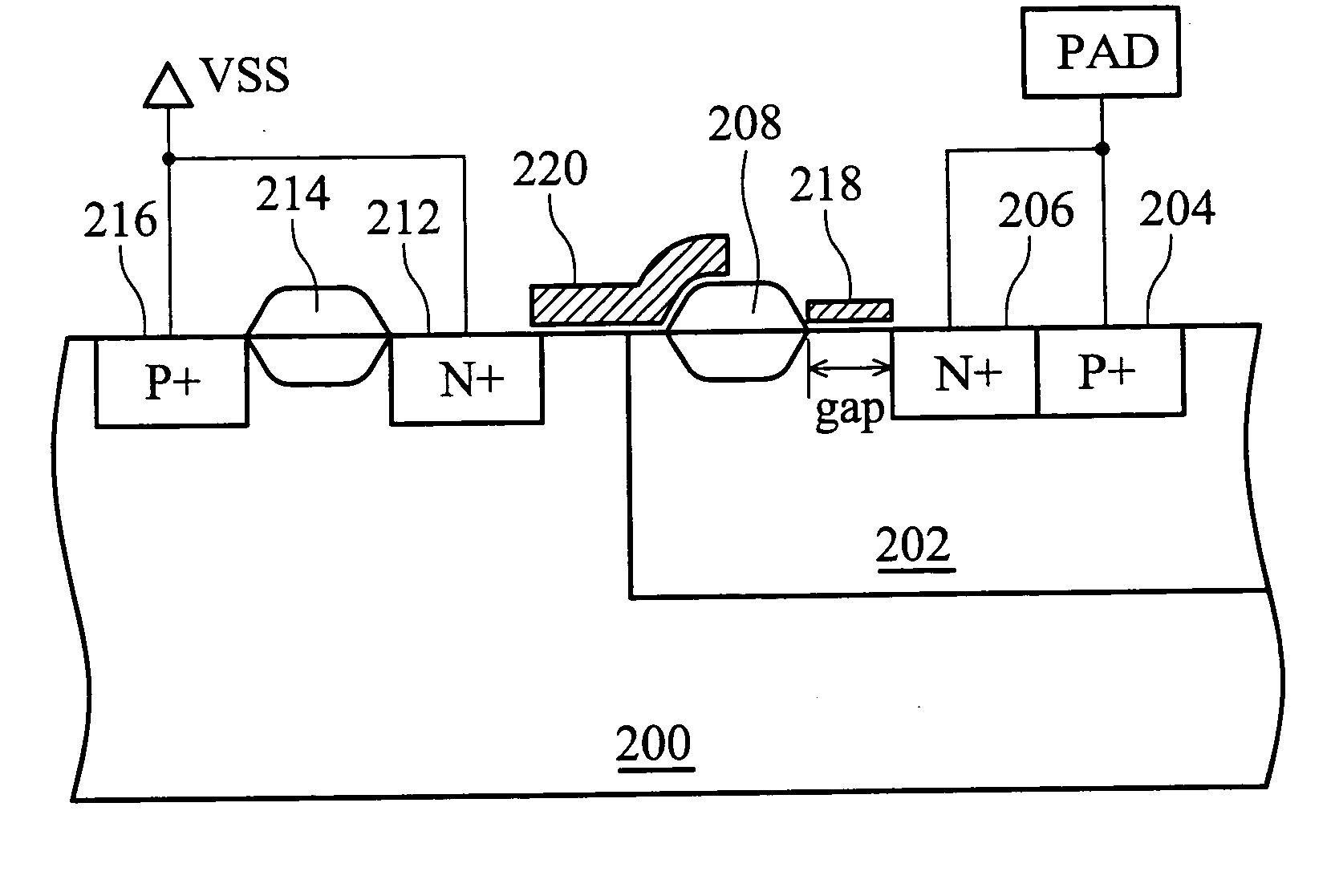
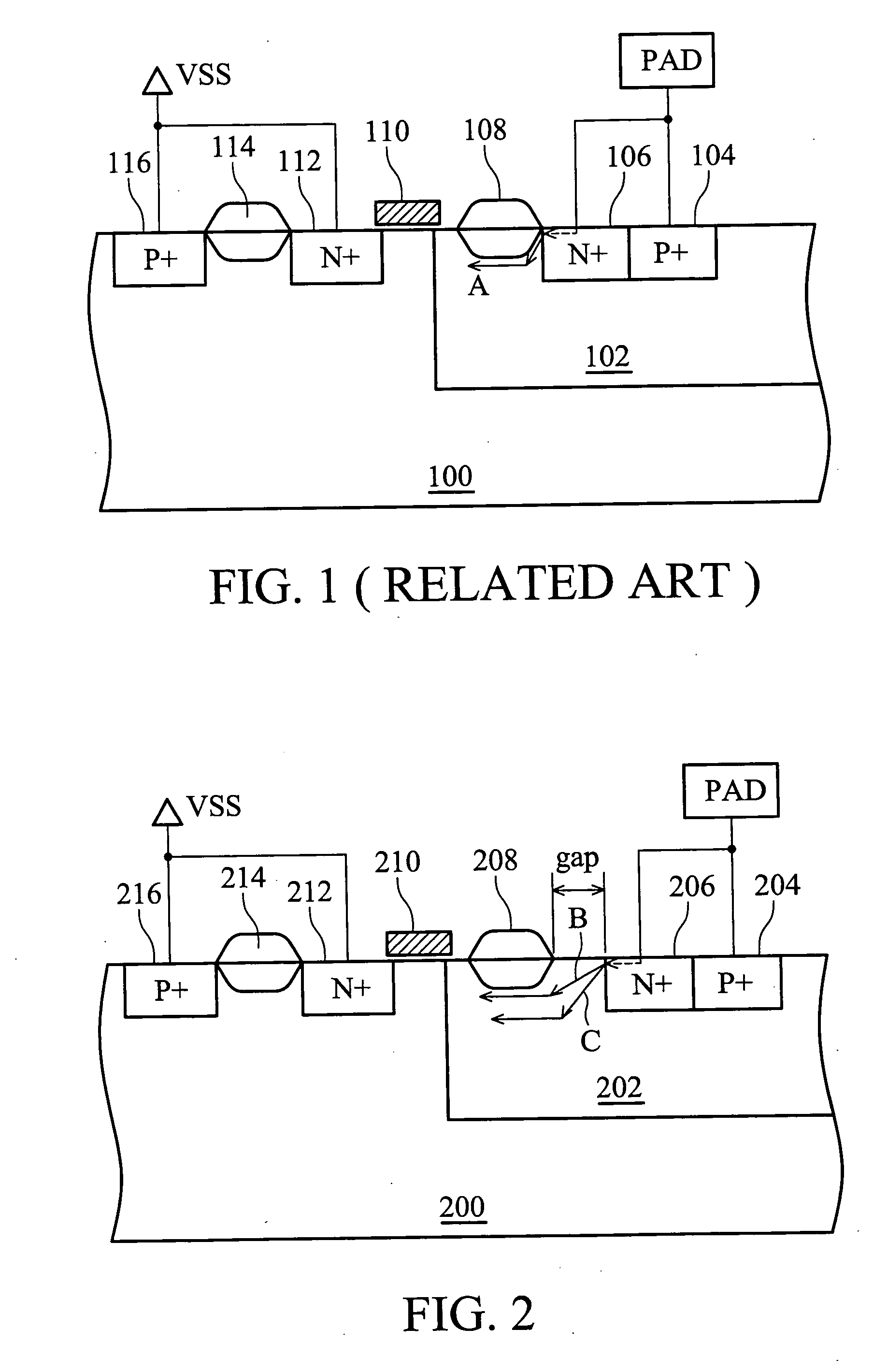
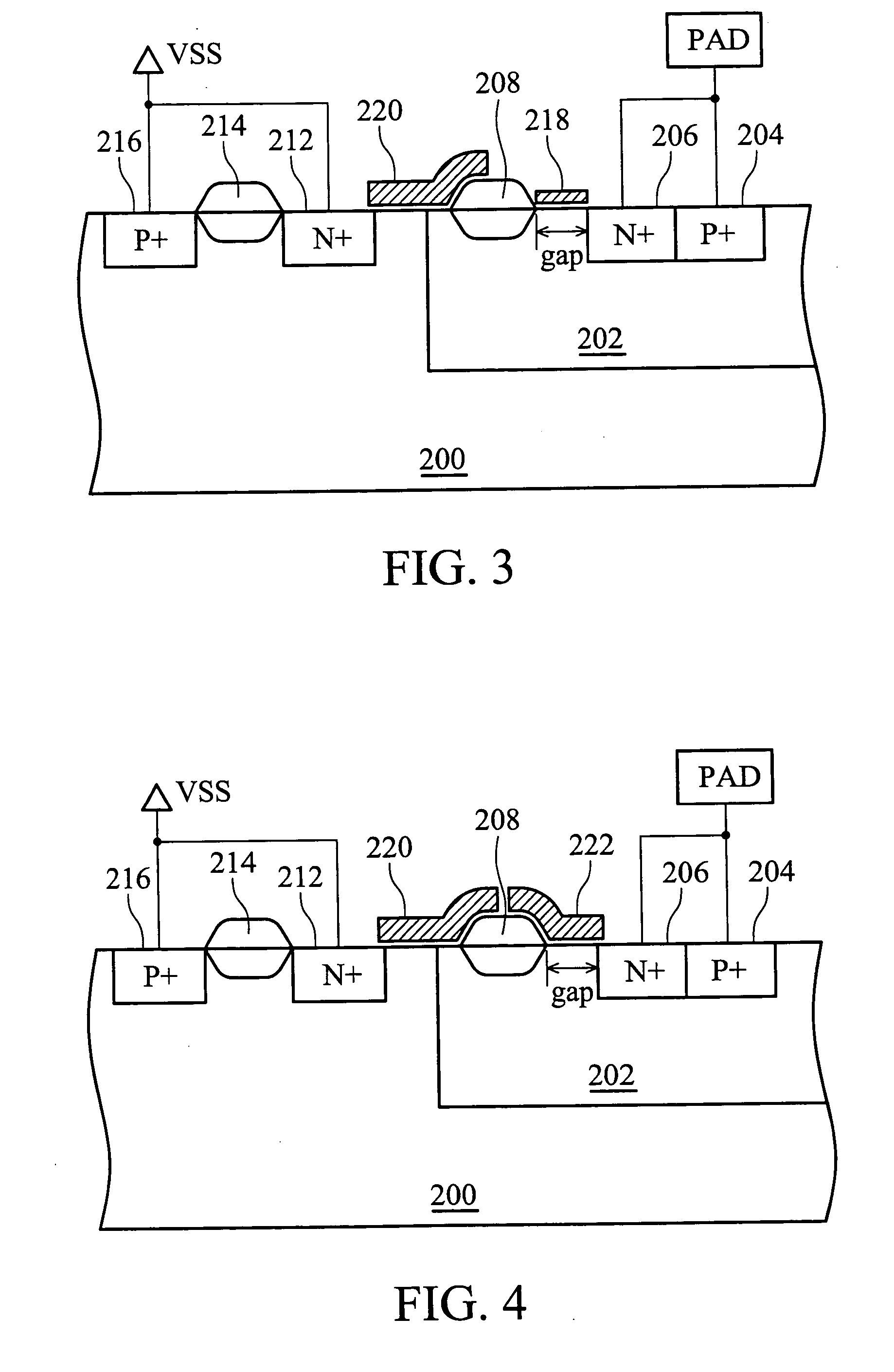
LDMOS transistor with improved ESD protection
An ESD protection device. The ESD protection device is incorporated with a gap structure in a laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) field effect transistor, isolating a doped region and a field oxide region. When a parasitical semiconductor controlled rectifier (SCR) of LDMOS is turned off, ESD current is discharged distributively through several discharge paths, avoiding ESD current focus in a signal narrow discharge path and the danger therefrom.
Owner:VANGUARD INTERNATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
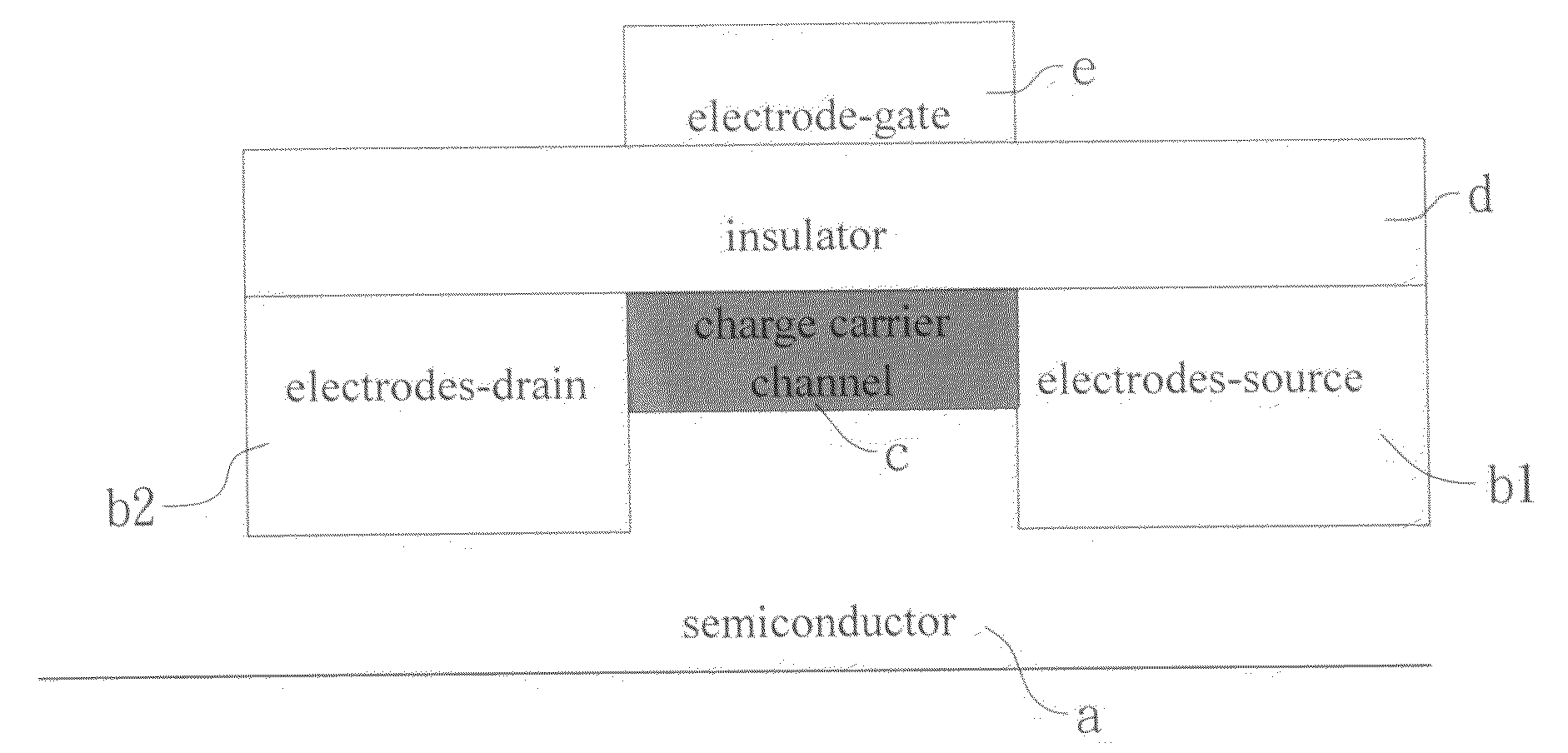
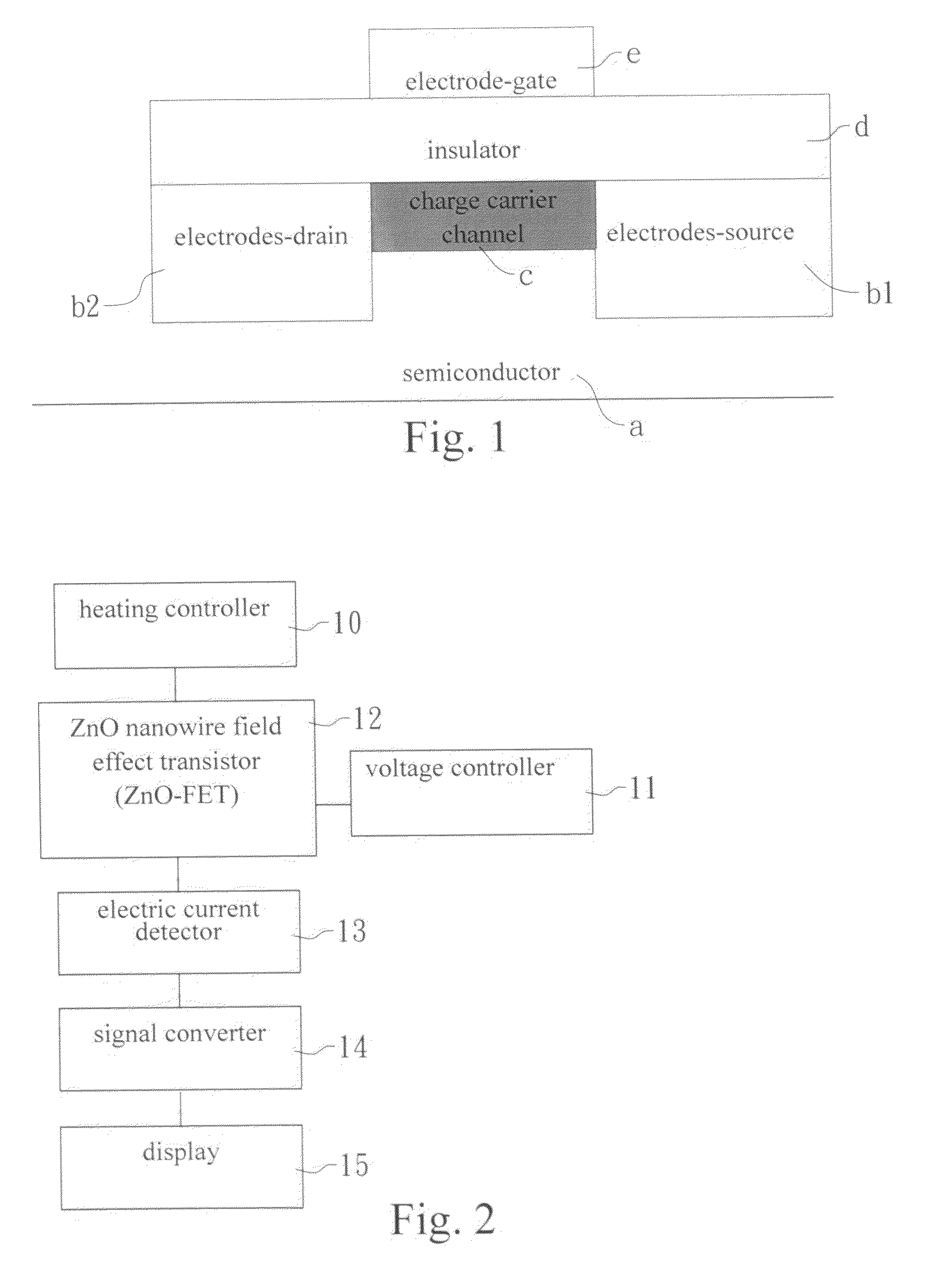
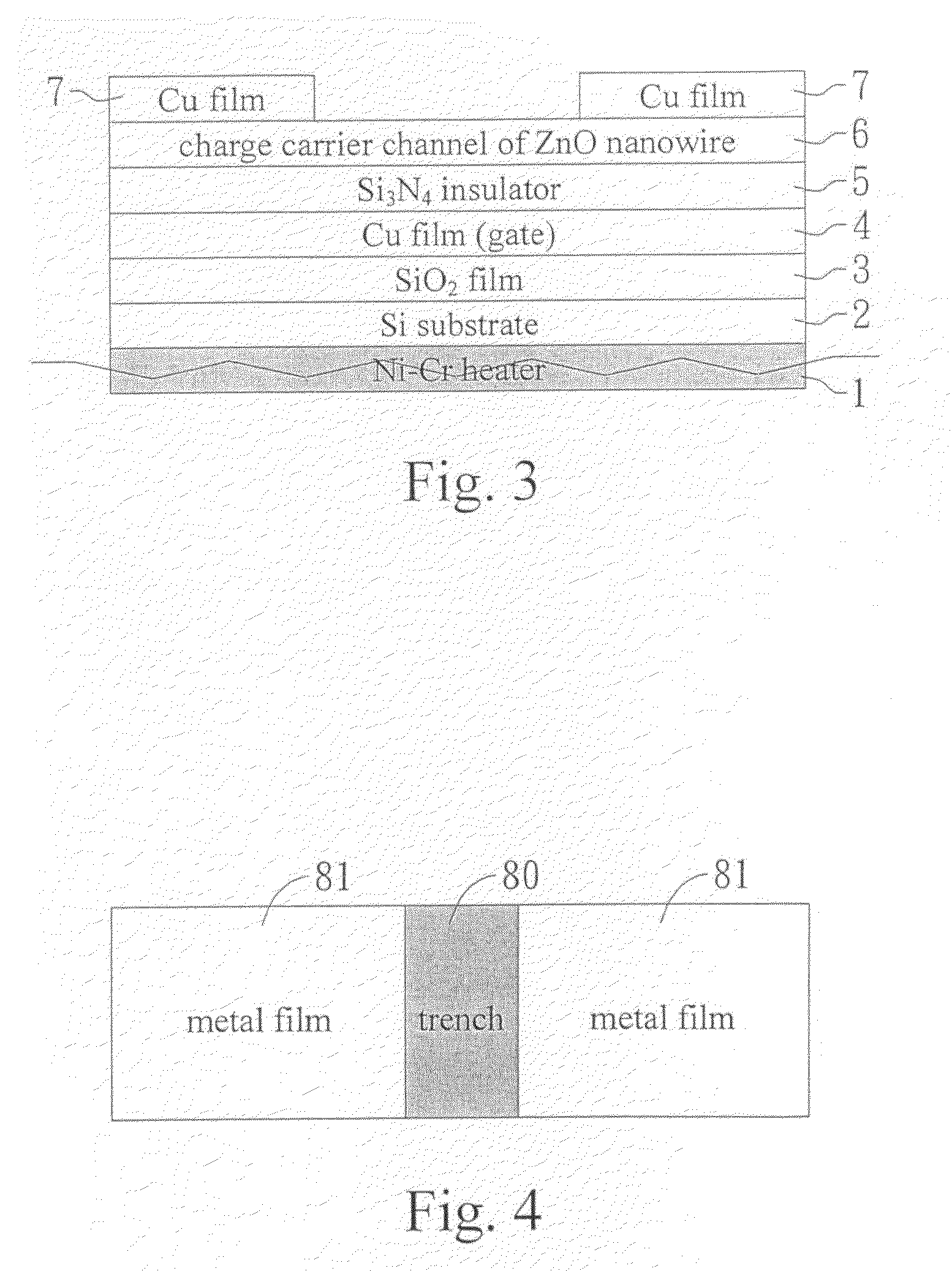
Gas sensor made of field effect transistor based on ZnO nanowires
InactiveUS20100050745A1Small sizeLight weightMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpecific gravity measurementMOSFETOrganic field-effect transistor
The present invention discloses a gas sensor made of field effect transistor based on ZnO nanowires (ZnO-FET) which operates according to the principle of metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) and has a charge carrier channel made of ZnO nanowires between source and drain. The gas sensor device disclosed in the present invention has three electrodes-gate, source and drain, so that it is different from the known gas sensor device which has only two electrodes-cathode and anode. The ZnO nanowires as charge channel in the gas sensor device of the present invention is an n-type semiconductor with high specific surface area, and its electric resistance can be controlled by the gate bias, so that the capability of the present device for sensing gas can be largely promoted.
Owner:NAT FORMOSA UNIV
Field effect transistor with electric field and space-charge control contact
A group III nitride-based transistor capable of achieving terahertz-range cutoff and maximum frequencies of operation at relatively high drain voltages is provided. In an embodiment, two additional independently biased electrodes are used to control the electric field and space-charge close to the gate edges.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
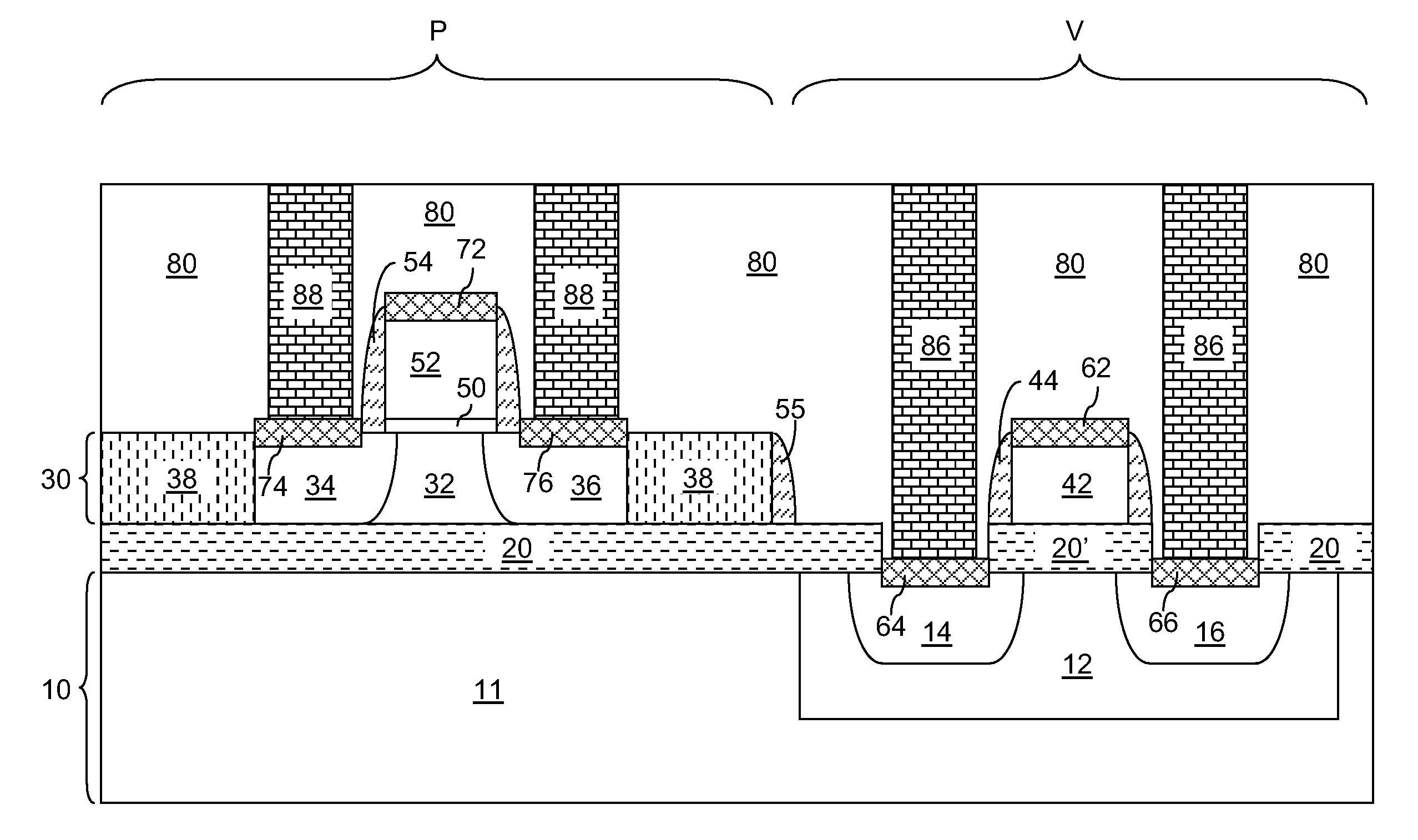
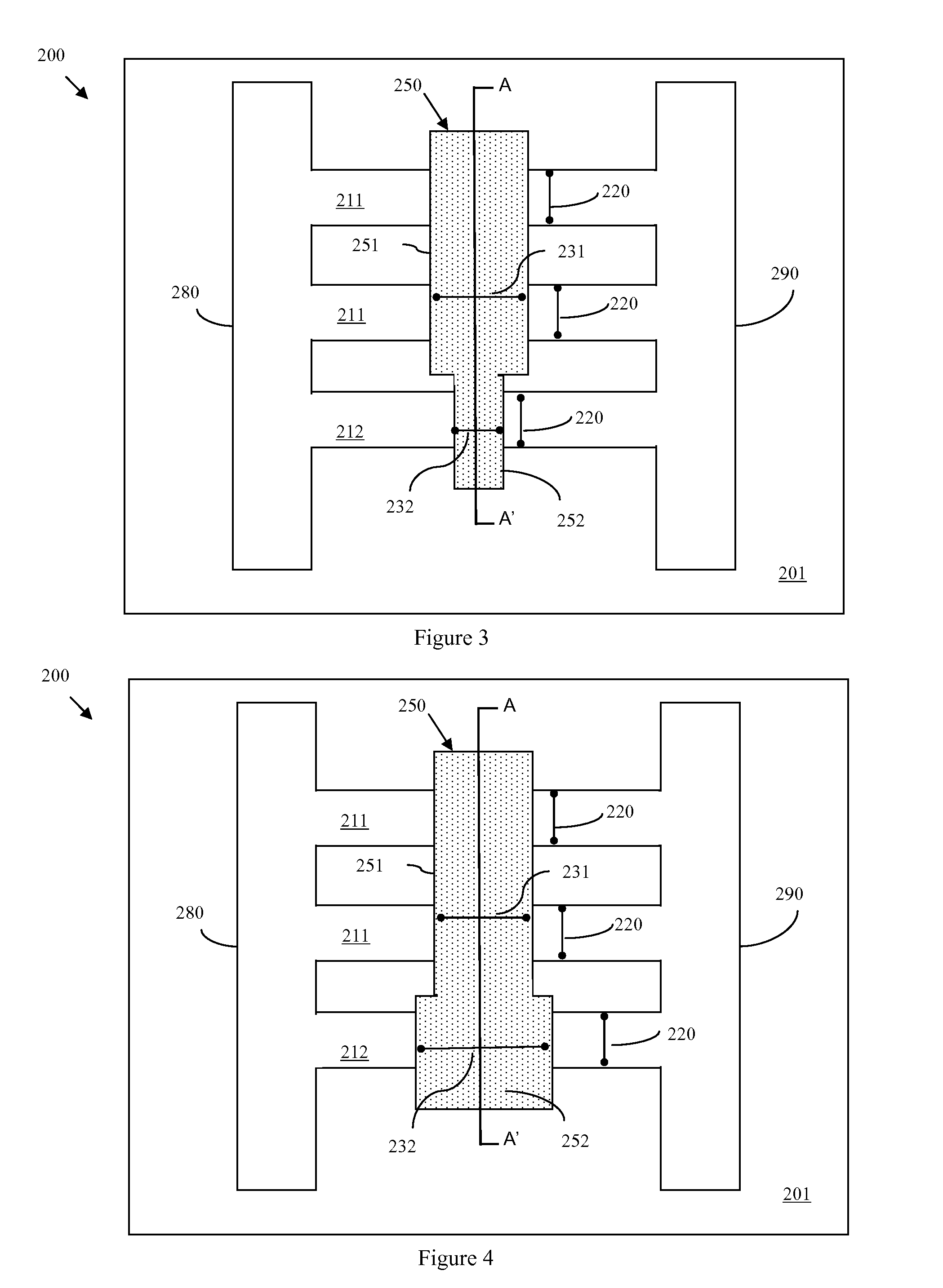
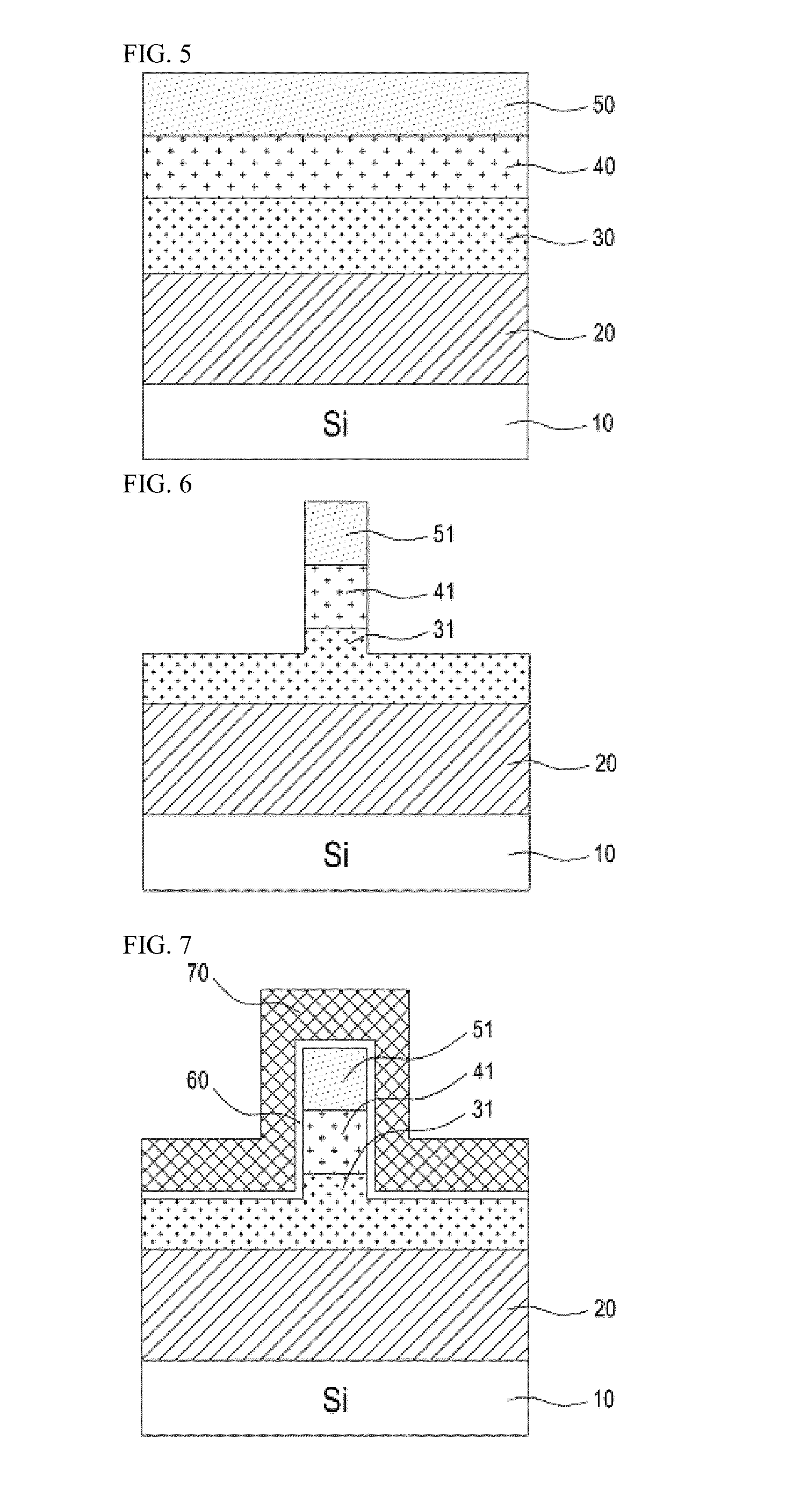
Compound tunneling field effect transistor integrated on silicon substrate and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20140291616A1High electron mobilityReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeField effectMaterials science
Compound tunneling field effect transistors integrated on a silicon substrate are provided with increased tunneling efficiency and an abrupt band slope by forming a source region with a material having a bandgap at least 0.4 electron volts (eV) narrower than that of silicon to increase a driving current (ON current) by forming a channel region with a material having almost no difference in lattice constant from a source region and having a high electron mobility at least 5 times higher than silicon. ON / OFF current ratio simultaneously is increased by forming a drain region with a material having a bandgap at least as wide as a channel region material to restrain OFF current. Tunneling field effect transistors having various threshold voltages according to circuit designs are formed easily by adding a specific material with an electron affinity less than a source region material when forming a channel region.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Coupled body contacts for SOI differential circuits
A silicon on insulator (SOI) CMOS circuit, macro and integrated circuit (IC) chip. The chip or macro may include be an SRAM in partially depleted (PD) SOI CMOS. Most field effect transistors (FETs) do not have body contacts. FETs otherwise exhibiting a sensitivity to history effects have body contacts. The body contact for each such FET is connected to at least one other body contact. A back bias voltage may be provided to selected FETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Grid controlled Schottky junction tunneling field effect transistor and forming method thereof
ActiveCN102142461AExcellent switching characteristicsExcellent high frequency characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
The invention provides a grid controlled Schottky junction tunneling field effect transistor, which comprises a substrate, a channel layer, a metal source region, a second semiconductor material layer, a drain region, step grid stacks and one-layer or multi-layer side walls, wherein the channel layer is formed on the substrate and made of a first semiconductor material, and the channel layer is provided with a channel region; the metal source region is formed in the channel layer and adjacent to the channel region, wherein the metal source region and the channel region form a Schottky junction; the second semiconductor material layer is formed on the first region of the channel layer; the drain region is formed in the second region of the second semiconductor material layer; the step gridstacks are formed on the third region of the channel layer and on the fourth region of the second semiconductor material layer; and the one-layer or multi-layer side walls are formed on two sides of the step grid stacks. The semiconductor structure provided by the invention has better switching property and high frequency property.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Integrated circuit structure incorporating stacked field effect transistors and method
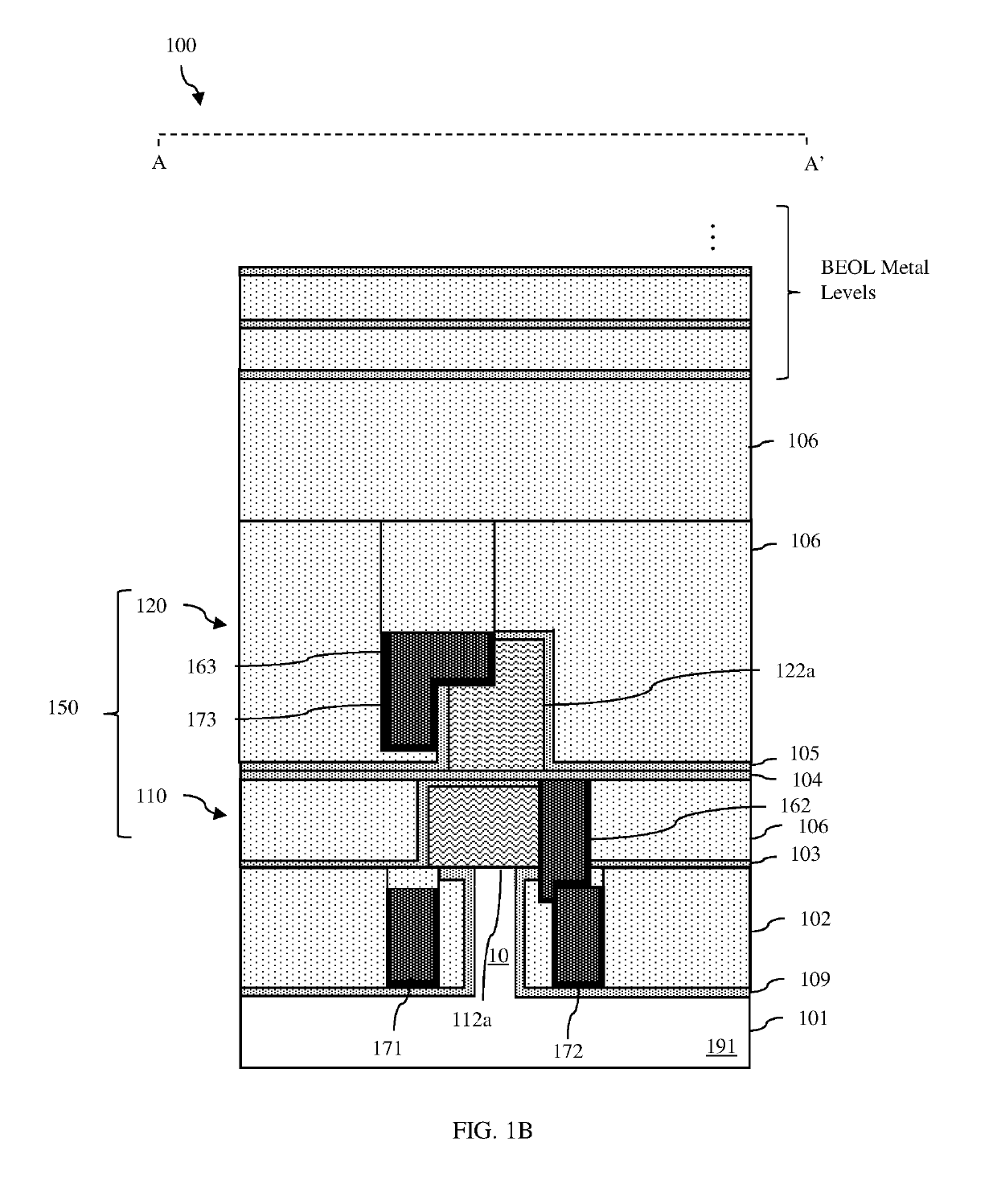
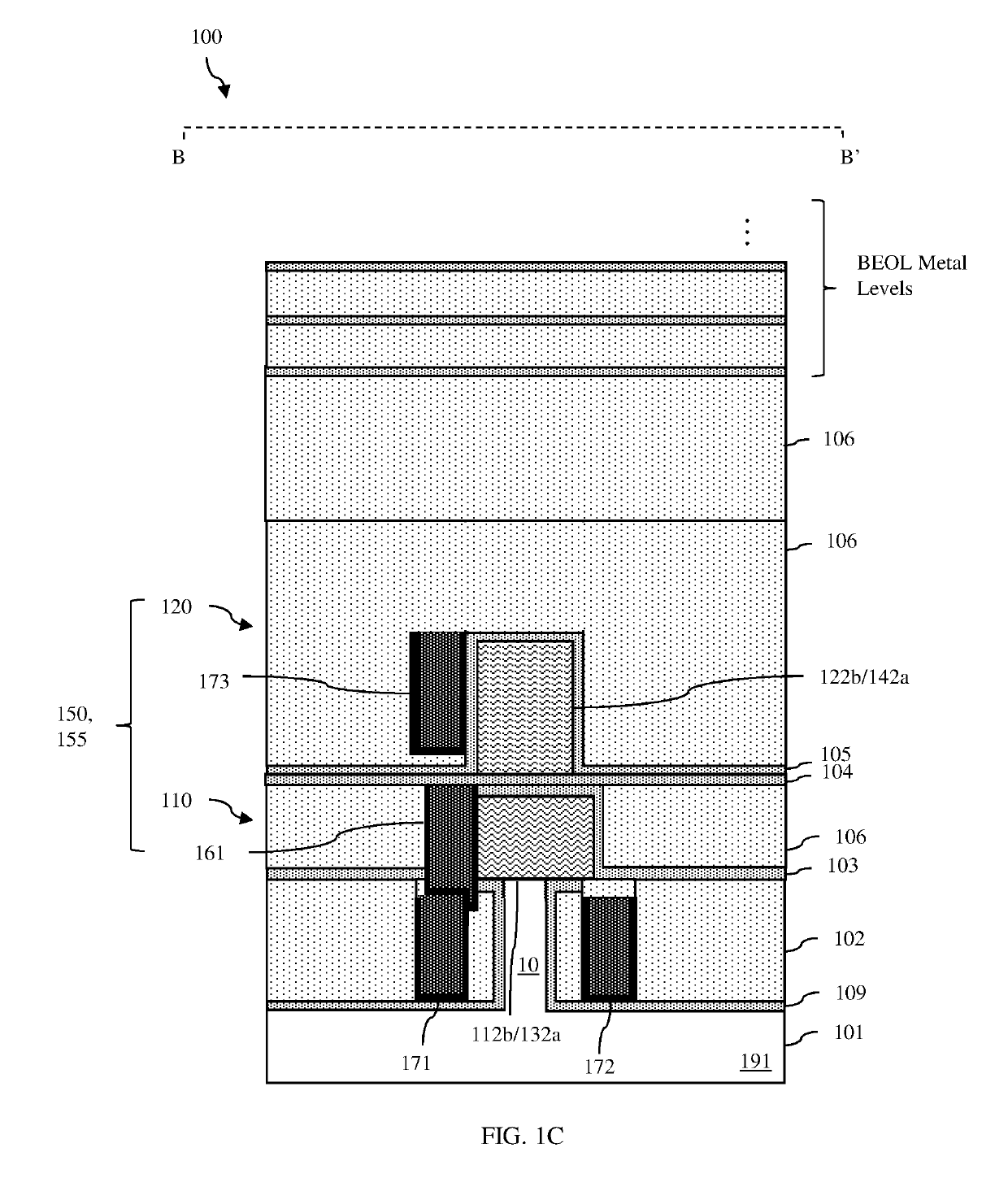
Disclosed are integrated circuit (IC) structure embodiments that incorporate stacked pair(s) of field effect transistors (FETs) (e.g., gate-all-around FETs), including a lower FET and an upper FET on the lower FET, and various metal components that enable power and / or signal connections to the source / drain regions of those FETs. The metal components can include first buried wire(s) within an isolation region in a level below the stacked pair and a first embedded contact that electrically connects a source / drain region of the lower FET to a first buried wire. Optionally, the metal components can also include second buried wire(s) in dielectric material at the same level as the upper FET and a second embedded contact that electrically connects a source / drain region of the upper FET to a second buried wire. Also disclosed are embodiments of a method of forming such IC structure embodiments.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com